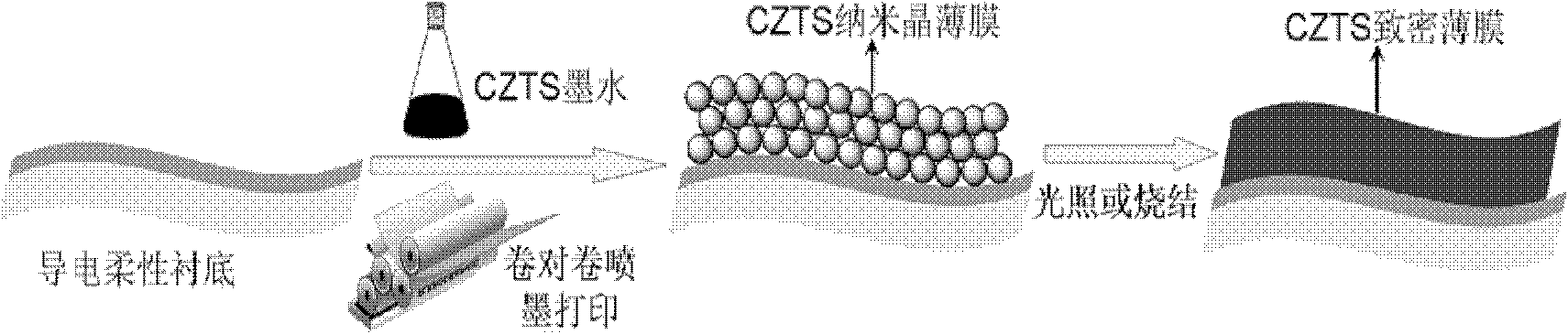
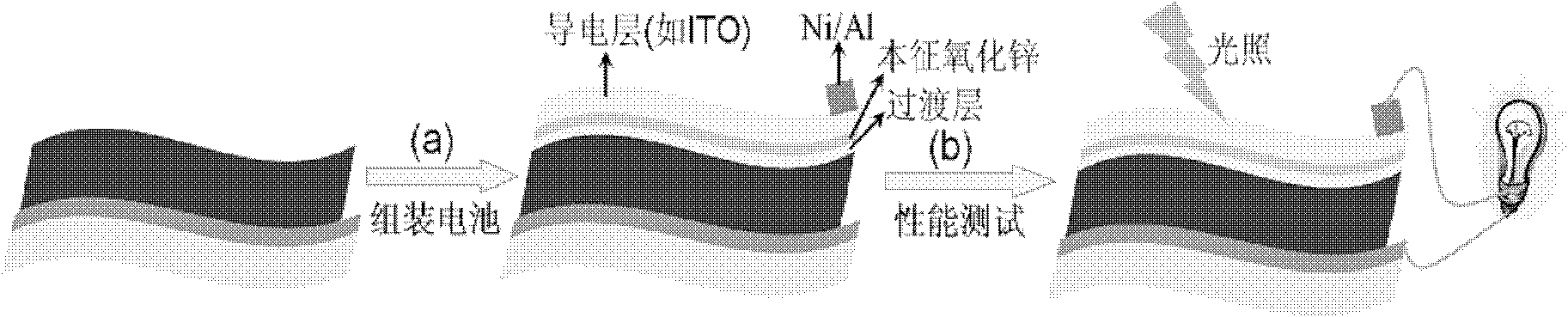
Method for preparing Cu2ZnSnS4 nanocrystalline thin-film solar cell
A technology of solar cells and nanocrystals, applied in the direction of nanotechnology, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of limiting battery applications, Cd poisonous, easy to explode, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing weight, cheap price, and reducing environmental pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] 1. Preparation of flexible substrate
[0033] Firstly, flexible aluminum foil is selected as the substrate, and then ultrasonically cleaned with ethanol and deionized water to remove surface oil stains, and then a layer of metal molybdenum is coated by magnetron sputtering to prepare a flexible substrate.
[0034] 2. Hydrophilic Cu 2 ZnSnS 4 Preparation of nanocrystals
[0035] Synthesis of hydrophobic Cu in the first step 2 ZnSnS 4 Nanocrystalline: Dissolve 0.35mmol copper acetylacetonate, 0.3mmol zinc acetylacetonate, and 0.25mmol tin acetylacetonate in 15mL oleylamine solution, then pass nitrogen into the oleylamine solution, raise the temperature to 120°C to remove water; then raise the temperature to 300°C ℃, inject 5mL oleylamine solution containing 1mmol sulfur, react for 30 minutes, cool and centrifuge to obtain Cu 2 ZnSnS 4 Nanocrystalline. 1mmol Cu 2 ZnSnS 4 The nanocrystals were dispersed in a blend solution of 25mL water / 25mL ethanol / 50mL cyclohexan...
Embodiment 2
[0043] 1. Preparation of flexible substrate
[0044] Firstly, a flexible copper foil is selected as the substrate, and then ultrasonically cleaned with ethanol and deionized water to remove surface oil stains, and then a layer of metal molybdenum is plated by magnetron sputtering to prepare a flexible substrate.
[0045] 2. Hydrophilic Cu 2 ZnSnS 4 Preparation of nanocrystals
[0046] 20 mL of n-heptane was used as the oil phase, bis(2-ethylhexyl) sodium sulfosuccinate was used as the surfactant, and 2 mL of aqueous solution was added to prepare an inverse microemulsion system, which was divided into two parts. The first aqueous solution contained 0.35 mmol of copper acetate, 0.3 mmol of zinc acetate and 0.25 mmol of tin acetate, and the second aqueous solution contained 1 mmol of thioacetamide. Stir the two inverse microemulsion systems separately for about 1 h to obtain a very clear colorless solution, then mix them and stir for 20 min. The mixture was transferred to a h...
Embodiment 3
[0054] 1. Preparation of flexible substrate
[0055] Firstly, a flexible aluminum foil is selected as the substrate, and then ultrasonically cleaned with ethanol and deionized water to remove surface oil stains, and then a layer of metal molybdenum is coated by magnetron sputtering to prepare a flexible substrate.
[0056] 2. Hydrophilic Cu 2 ZnSnS 4 Preparation of nanocrystals
[0057] (A) Weigh 0.35mmol CuCl 2 2H 2 O, 0.3 mmol ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 0.25 mmol SnCl 2 2H 2 O, put in a round bottom flask, add 10mL ethylene glycol, stir, and dissolve each substance. (B) Weigh 5mmol of Na 2 S, dissolved in 10mL ethylene glycol, ultrasonically dissolved. Pour B into A with stirring, continue to stir for half an hour, transfer to a high-pressure reactor, 220 ° C, 24 hours. After the reaction, centrifuge. to get Cu 2 ZnSnS 4 , redispersed in 50mL ethanol solution for later use.
[0058] 3. Cu 2 ZnSnS 4 Fabrication of Nanocrystalline Dense Films
[0059] Take 5mL Cu in the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com