Patents
Literature
132 results about "Junction formation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
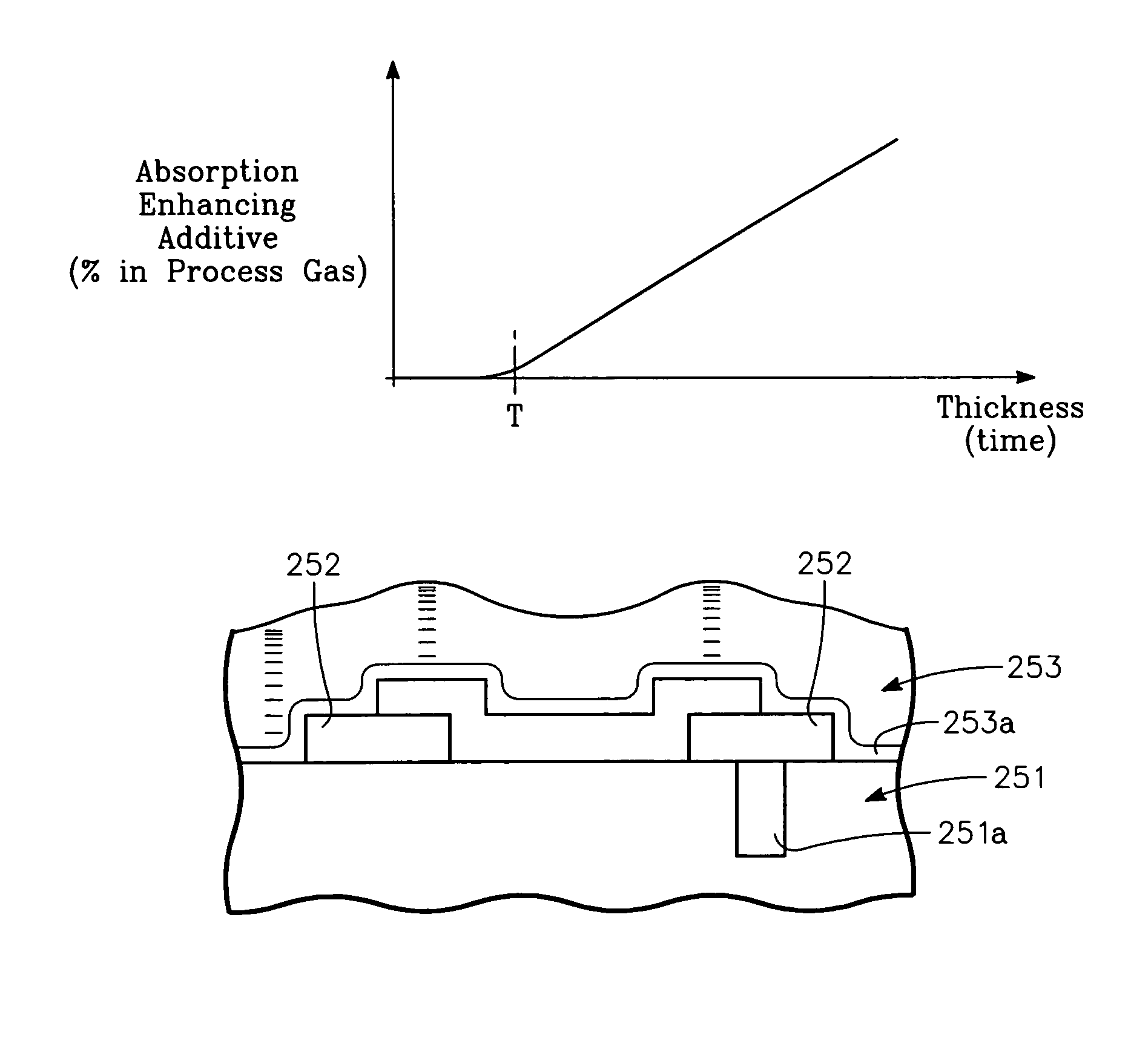
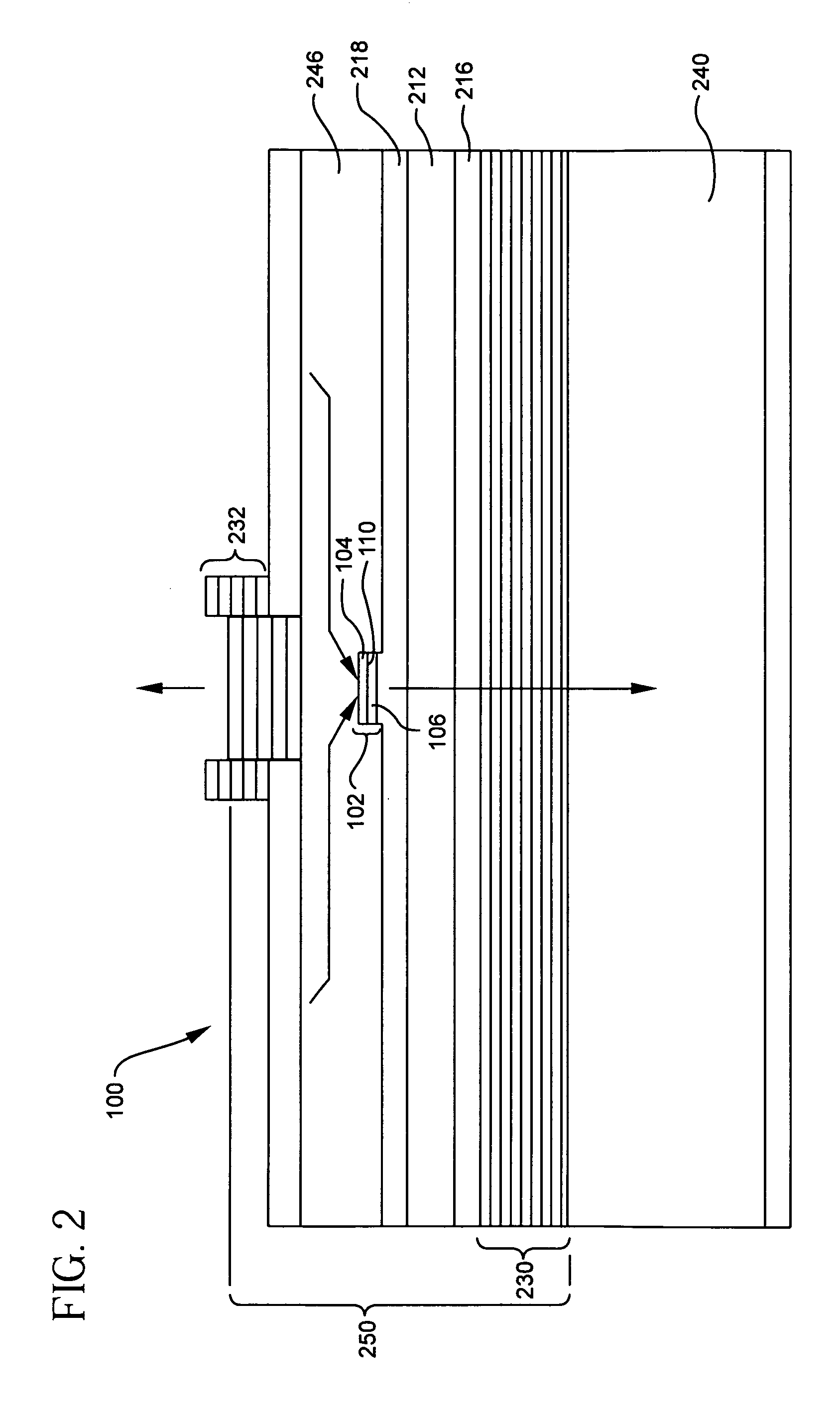
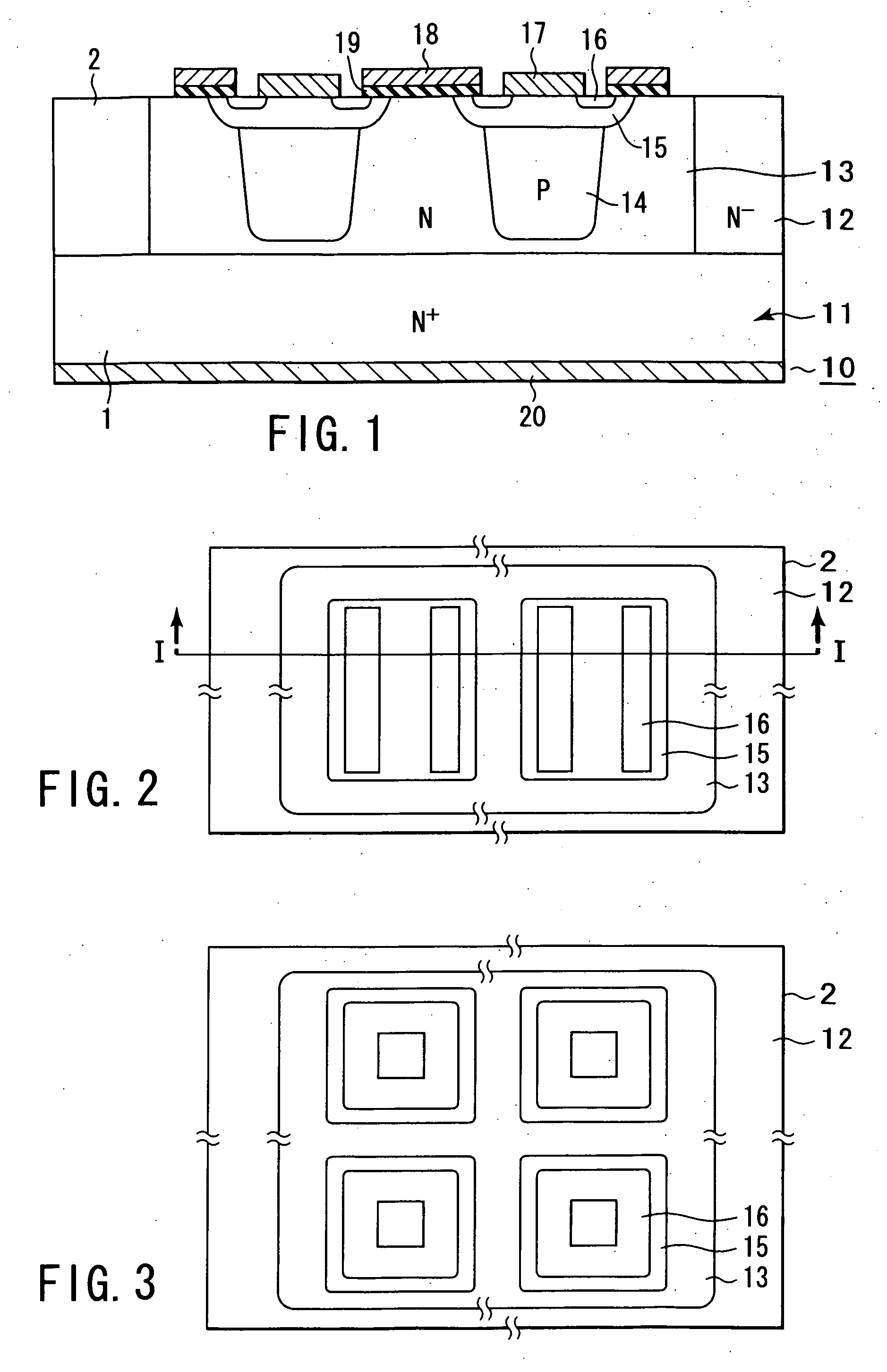
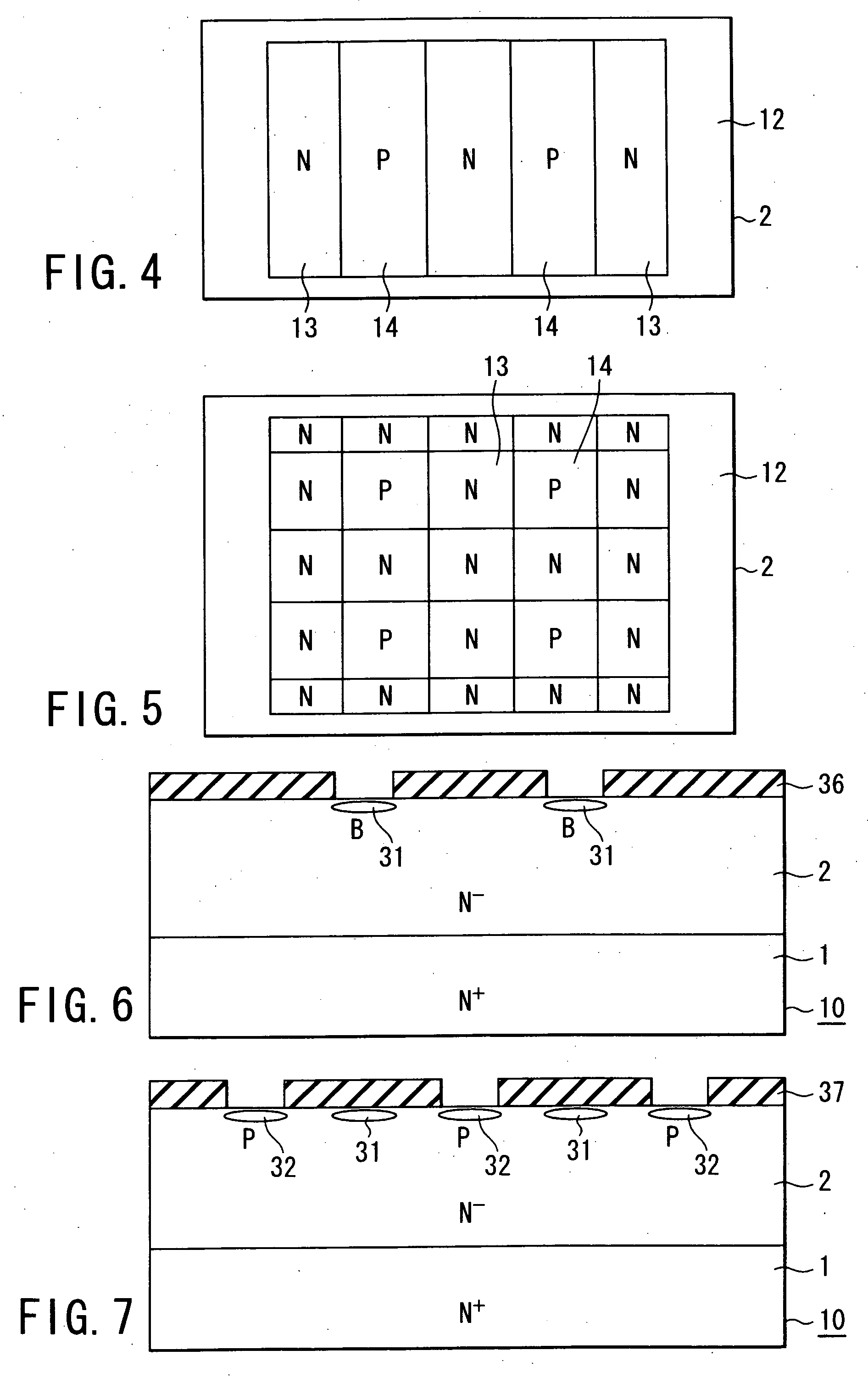
Semiconductor junction formation process including low temperature plasma deposition of an optical absorption layer and high speed optical annealing
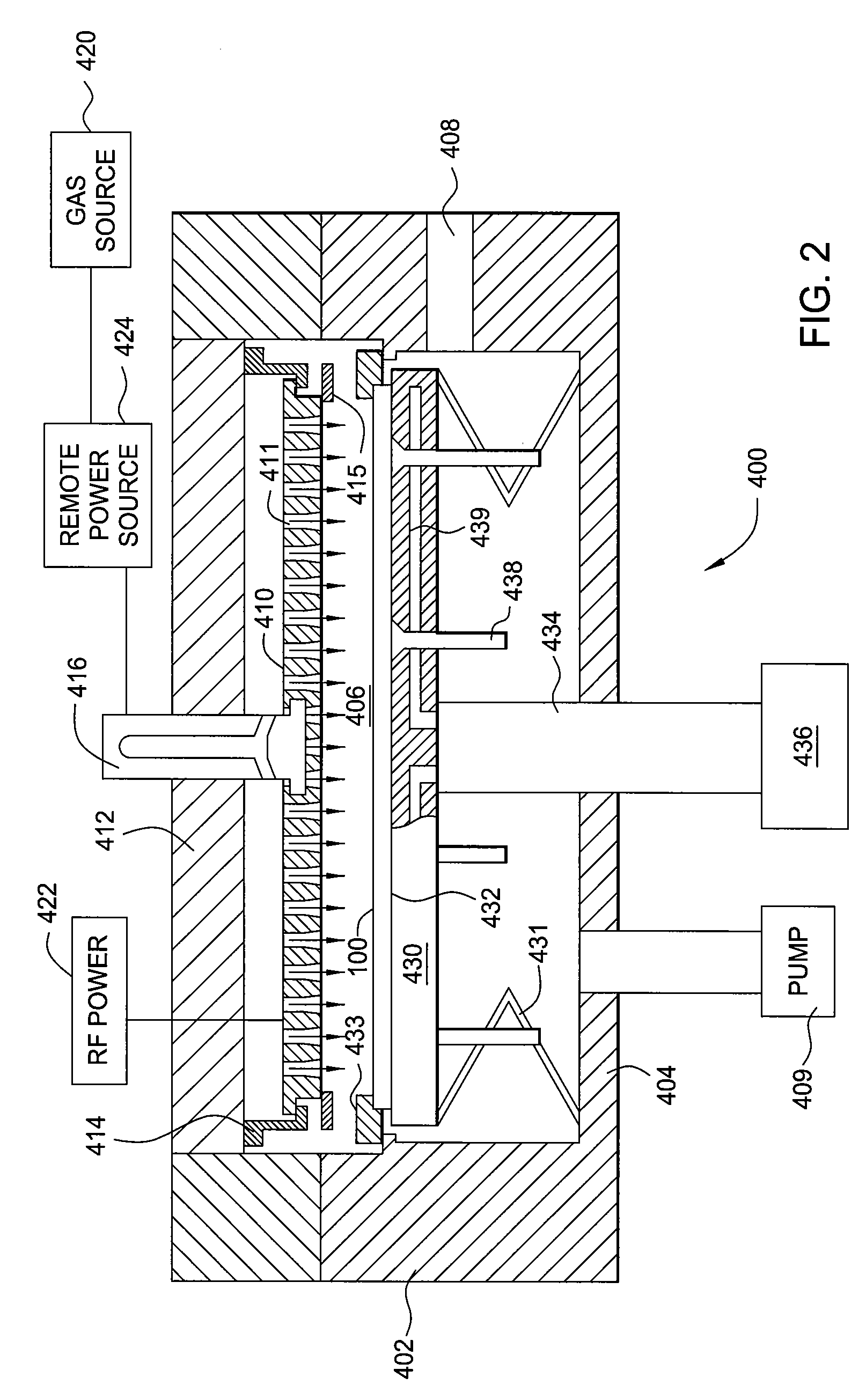
A method of forming semiconductor junctions in a semiconductor material of a workpiece includes ion implanting dopant impurities in selected regions of the semiconductor material, introducing an optical absorber material precursor gas into a chamber containing the workpiece, generating an RF oscillating toroidal plasma current in a reentrant path that includes a process zone overlying the workpiece by applying RF source power, so as to deposit a layer of an optical absorber material on the workpiece, and optically annealing the workpiece so as to activate dopant impurities in the semiconductor material.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
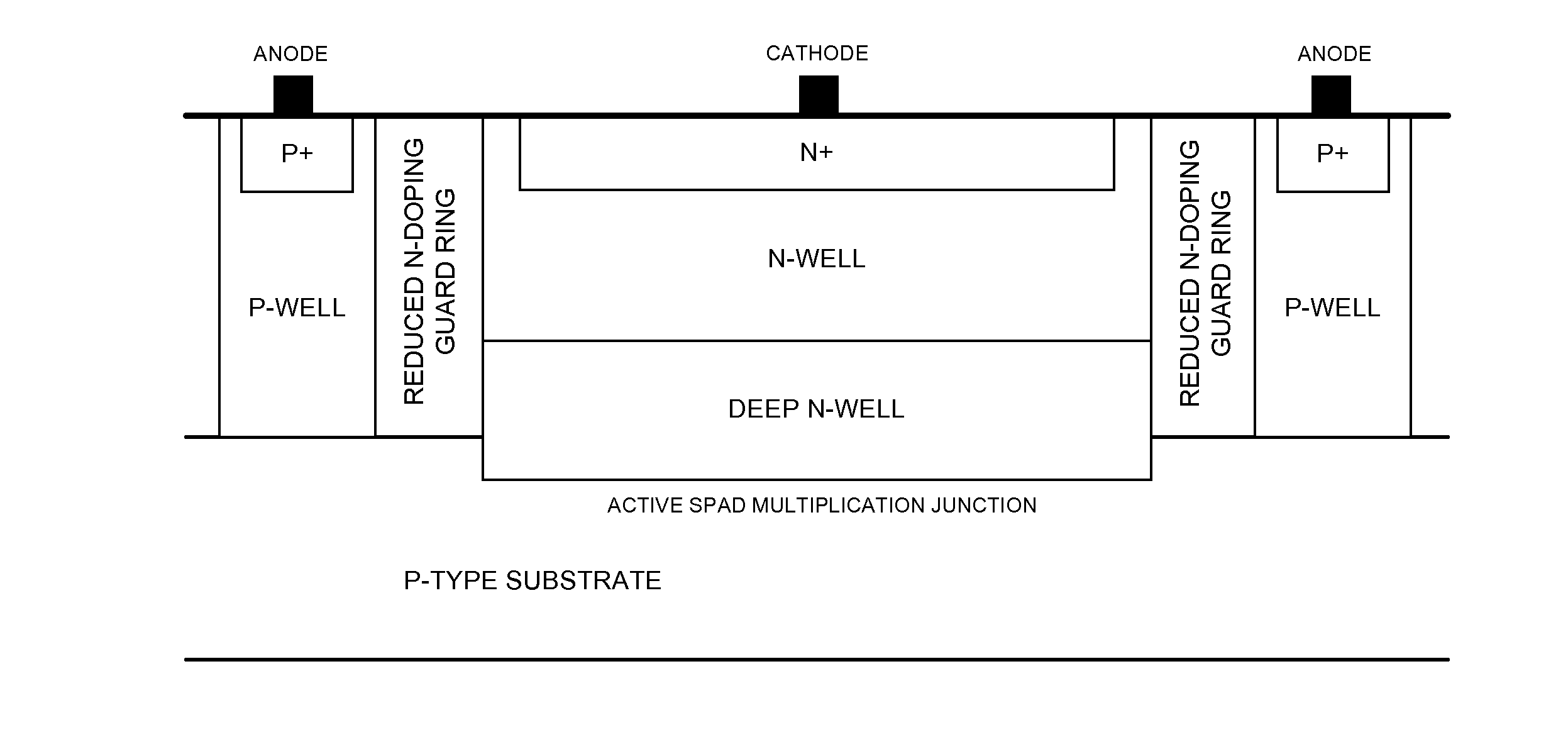
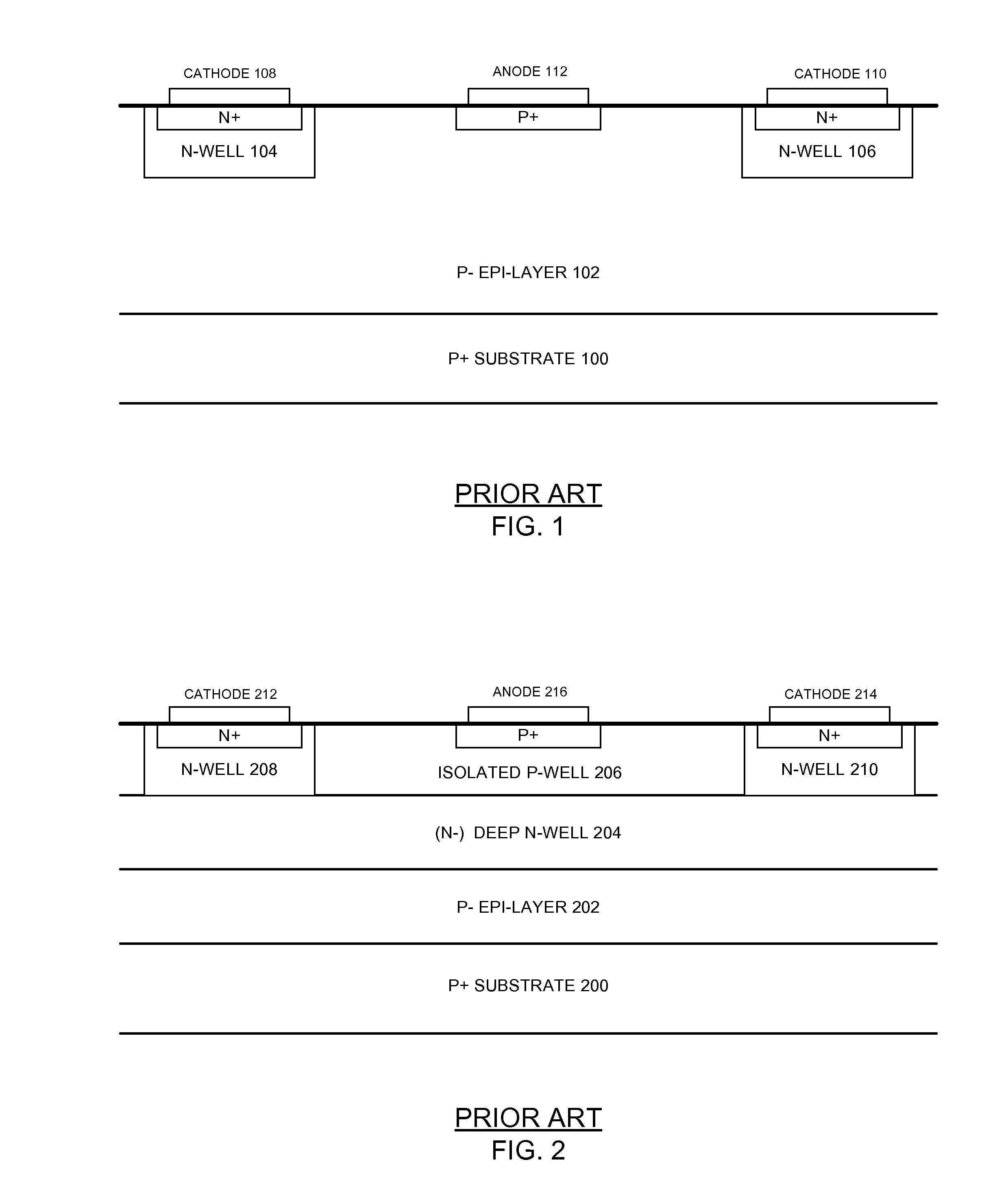
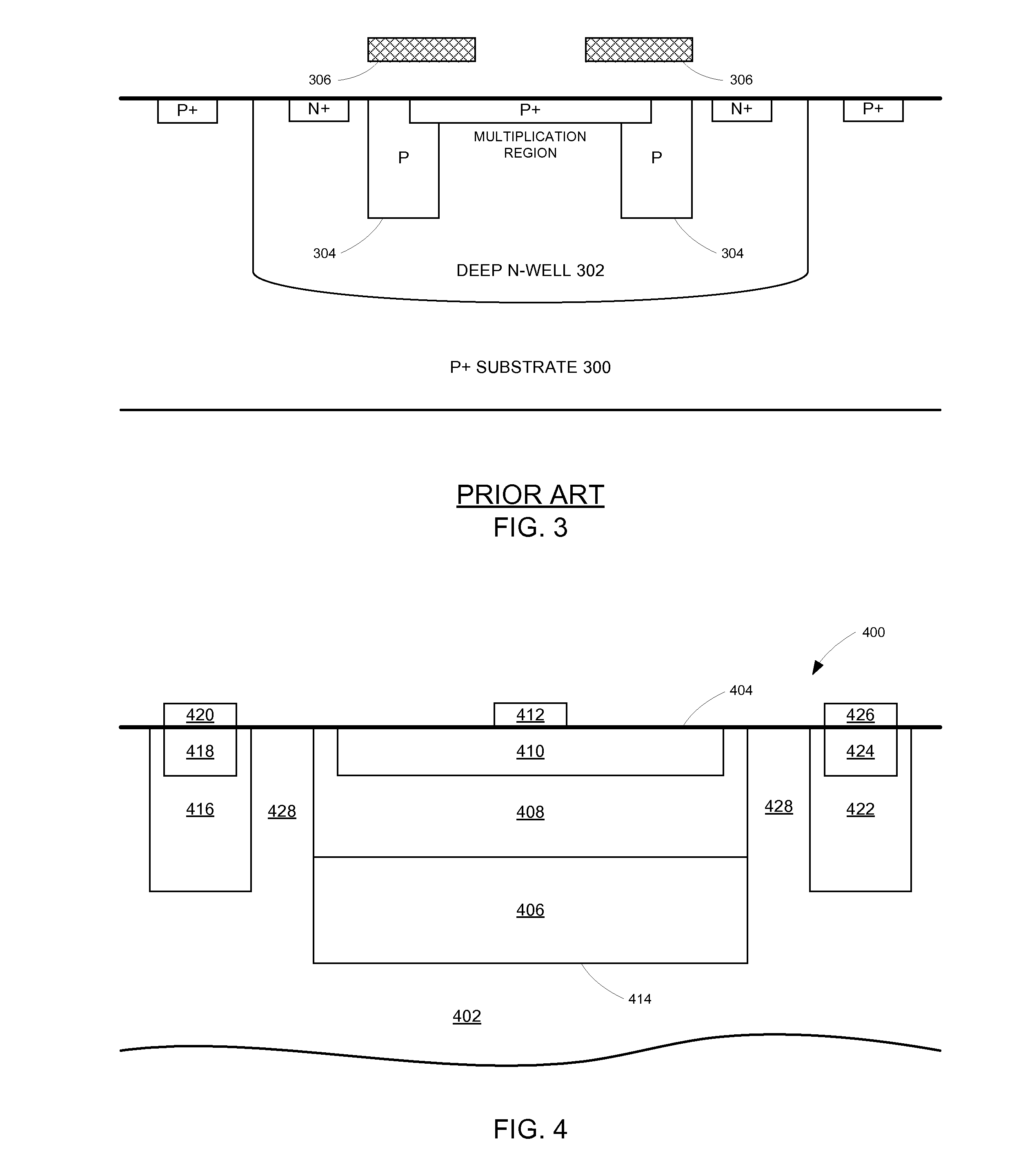
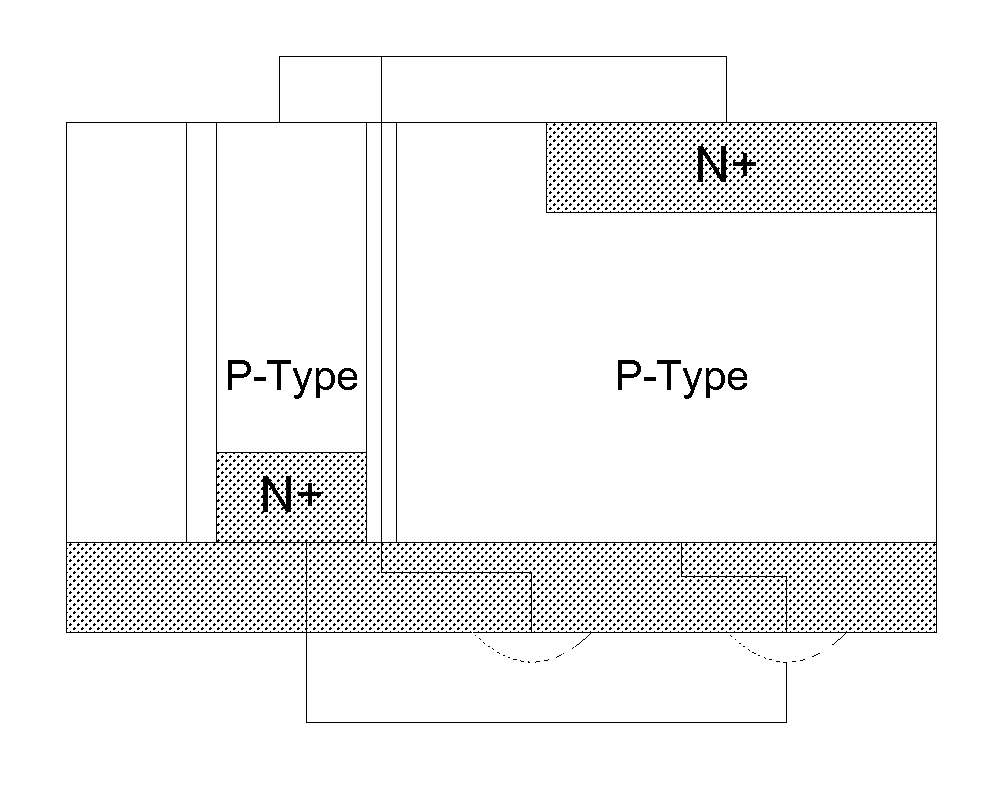
Single photon avalanche diode for CMOS circuits
ActiveUS20130193546A1Improves blue responseImproved broad spectrum sensitivityFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesCMOSSingle-photon avalanche diode
A single photon avalanche diode for use in a CMOS integrated circuit includes a deep n-well region formed above a p-type substrate and an n-well region formed above and in contact with the deep n-well region. A cathode contact is connected to the n-well region via a heavily doped n-type implant. A lightly doped region forms a guard ring around the n-well and deep n-well regions. A p-well region is adjacent to the lightly doped region. An anode contact is connected to the p-well region via a heavily doped p-type implant. The junction between the bottom of the deep n-well region and the substrate forms a multiplication region when an appropriate bias voltage is applied between the anode and cathode and the guard ring breakdown voltage is controlled with appropriate control of the lateral doping concentration gradient such that the breakdown voltage is higher than that of the multiplication region.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS RES & DEV +1
Thermal process for creation of an in-situ junction layer in CIGS
InactiveUS7319190B2Reduce the temperatureFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingJunction formationGrowth of photovoltaics
The present invention relates generally to the field of photovoltaics and more specifically to manufacturing thin-film solar cells using a thermal process. Specifically, a method is disclosed to manufacture a CIGS solar cell by an in-situ junction formation process.
Owner:DAYSTAR TECHNOLOGIES
Highly Conductive Shallow Junction Formation
InactiveUS20090224319A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingJunction formationPhysical chemistry
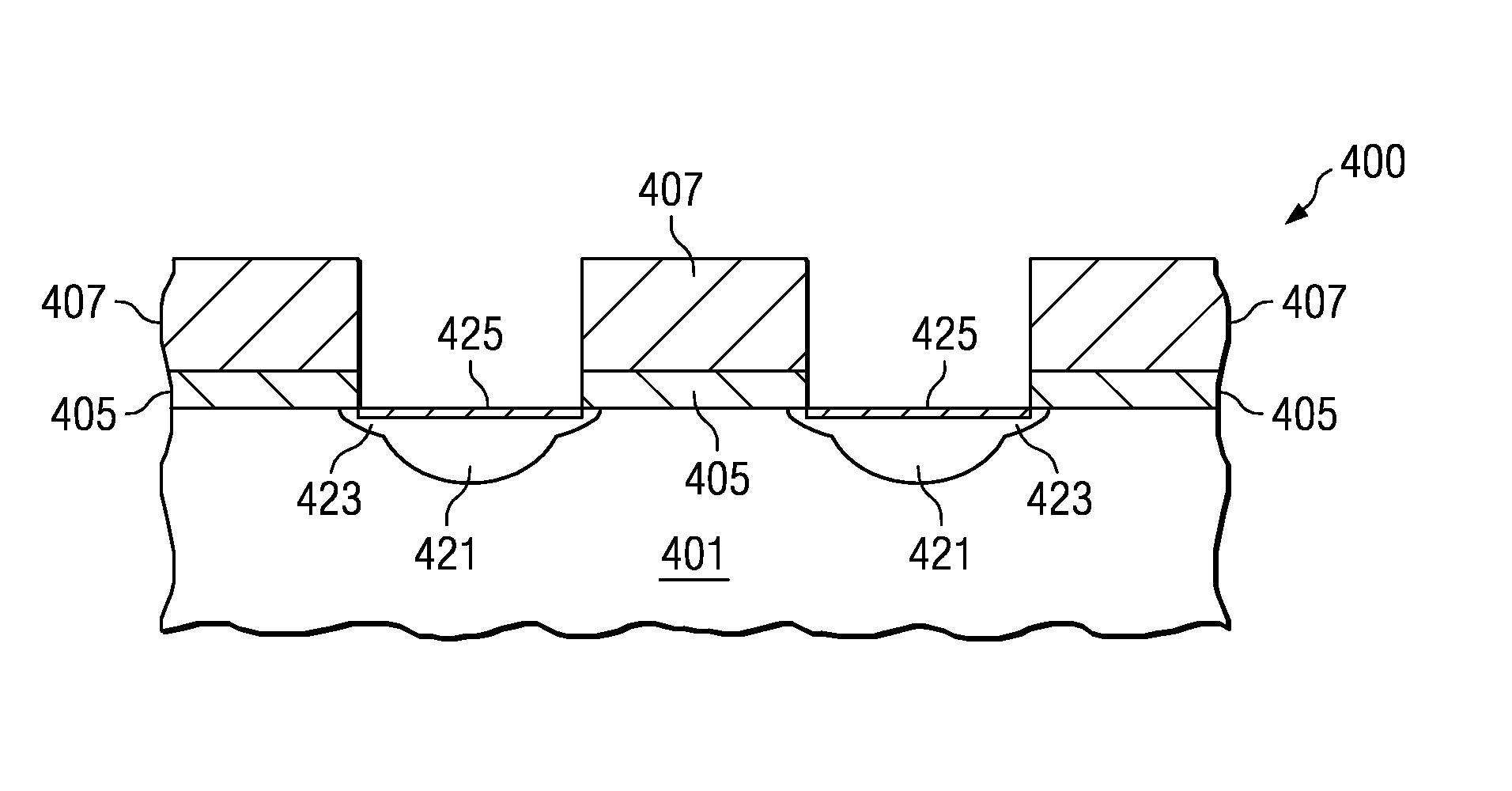
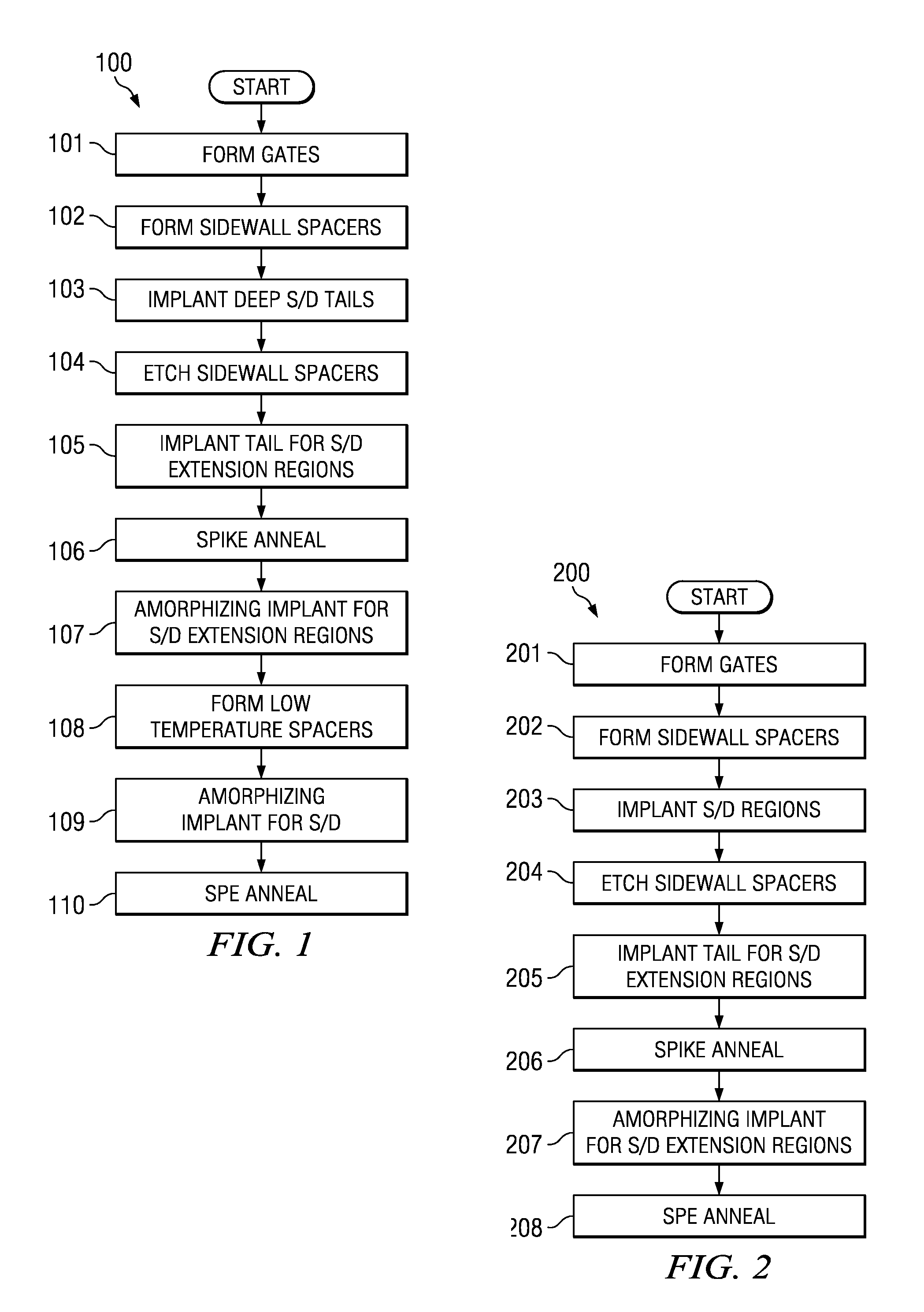
The invention relates to a method of forming a shallow junction. The method (100) comprises forming source / drain extension regions with a non-amorphizing tail implant (105) which is annealed conventionally (spike / RTP) and amorphizing implant which is re-grown epitaxially(SPER) (110). The non-amorphizing tail implant is generally annealed (106) before a doped amorphous layer for SPE is formed (107). SPE provides a high active dopant concentration in a shallow layer. The non-amorphizing tail implant (105) expands the source / drain extension region beyond the range dictated by the SPE-formed layer and keeps the depletion region of the P-N junction away from where end-of-range defects form during the SPE process. Thus, the SPE-formed layer primarily determines the conductivity of the junction while the tail implant determines the location of the depletion region. End-of-range defects form, but are not in a position to cause significant reverse bias leakage.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Thermal process for creation of an in-situ junction layer in CIGS
InactiveUS20060102230A1Reduce the temperatureFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingJunction formationEngineering
The present invention relates generally to the field of photovoltaics and more specifically to manufacturing thin-film solar cells using a thermal process. Specifically, a method is disclosed to manufacture a CIGS solar cell by an in-situ junction formation process.
Owner:DAYSTAR TECHNOLOGIES
Semiconductor device with reduced leakage current, and method of fabrication
InactiveUS20060118824A1Minimize current leakagePrevent leakageTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGallium nitrideElectron mobility
A high electron mobility transistor is disclosed which has a triple-layered main semiconductor region formed on a silicon substrate via a multilayered buffer region. The multilayered buffer region is in the form of alternations of an aluminum nitride layer and a gallium nitride layer. Whilst the aluminum nitride layers are of n-like conductivity, the gallium nitride layers are doped into p-type conductivity, with the consequent creation of pn junctions between the two kinds of buffer layers. Another pn junction is formed between one p-type gallium nitride layer and the adjoining n-like electron transit layer included in the main semiconductor region. The pn junctions serve for reduction of current leakage.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
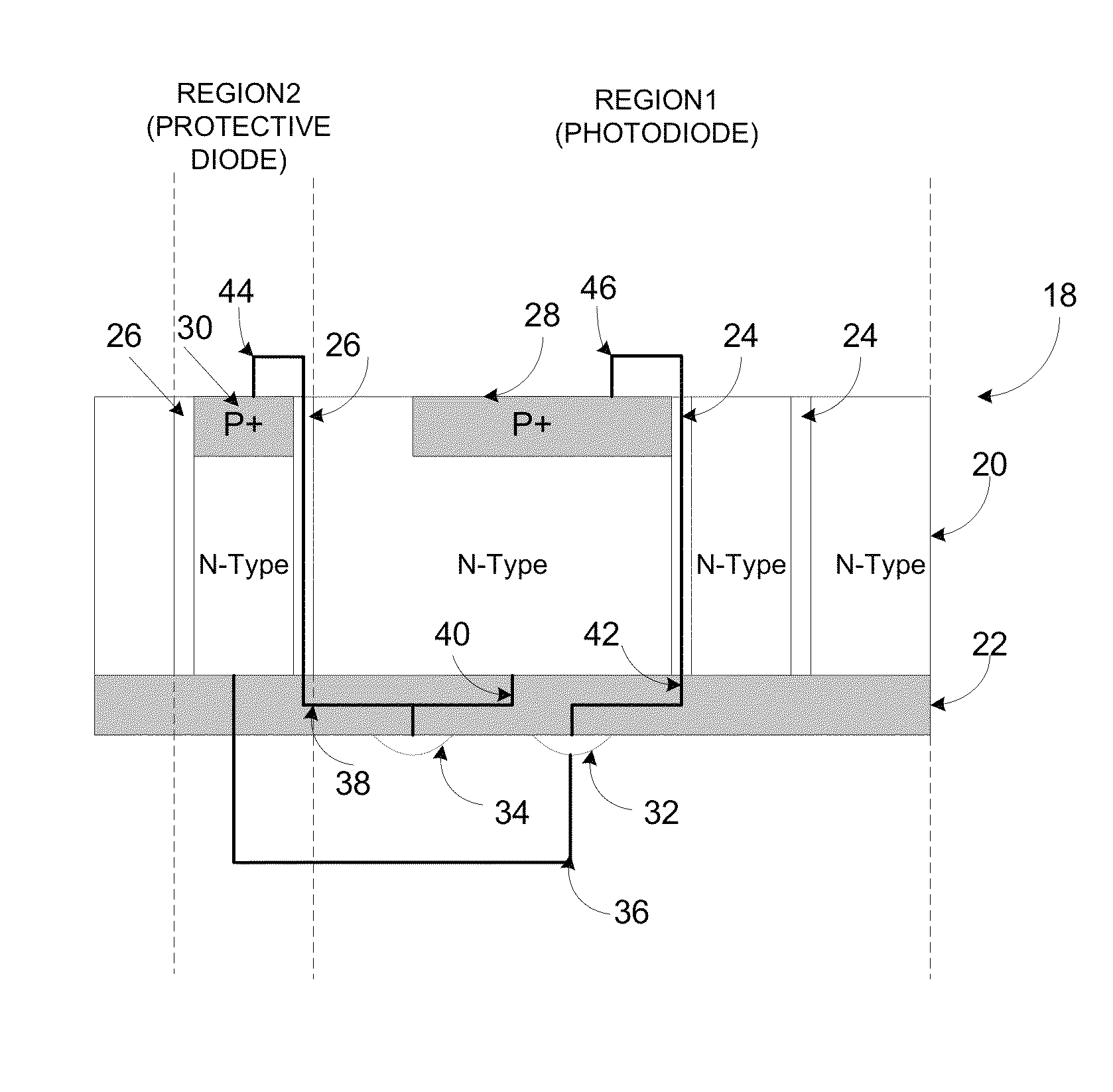
Electrical overstress protection using through-silicon-via (TSV)
ActiveUS8441104B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesJunction formationSemiconductor
A semiconductor device formed on a substrate includes a first diode junction formation, a second diode junction formation, and at least one through-silicon-via (TSV), in which a cathode and an anode of the first diode are cross-connected to an anode and cathode of the second diode through the at least one TSV for achieving electrical robustness in through-silicon-via based integrated circuits, including photosensitive devices and circuits for signal processing applications.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
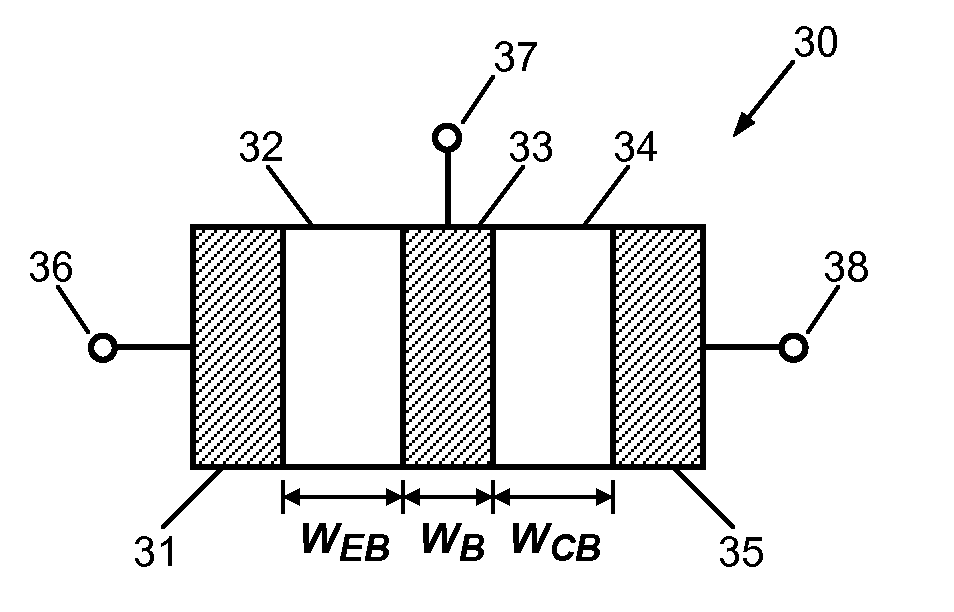
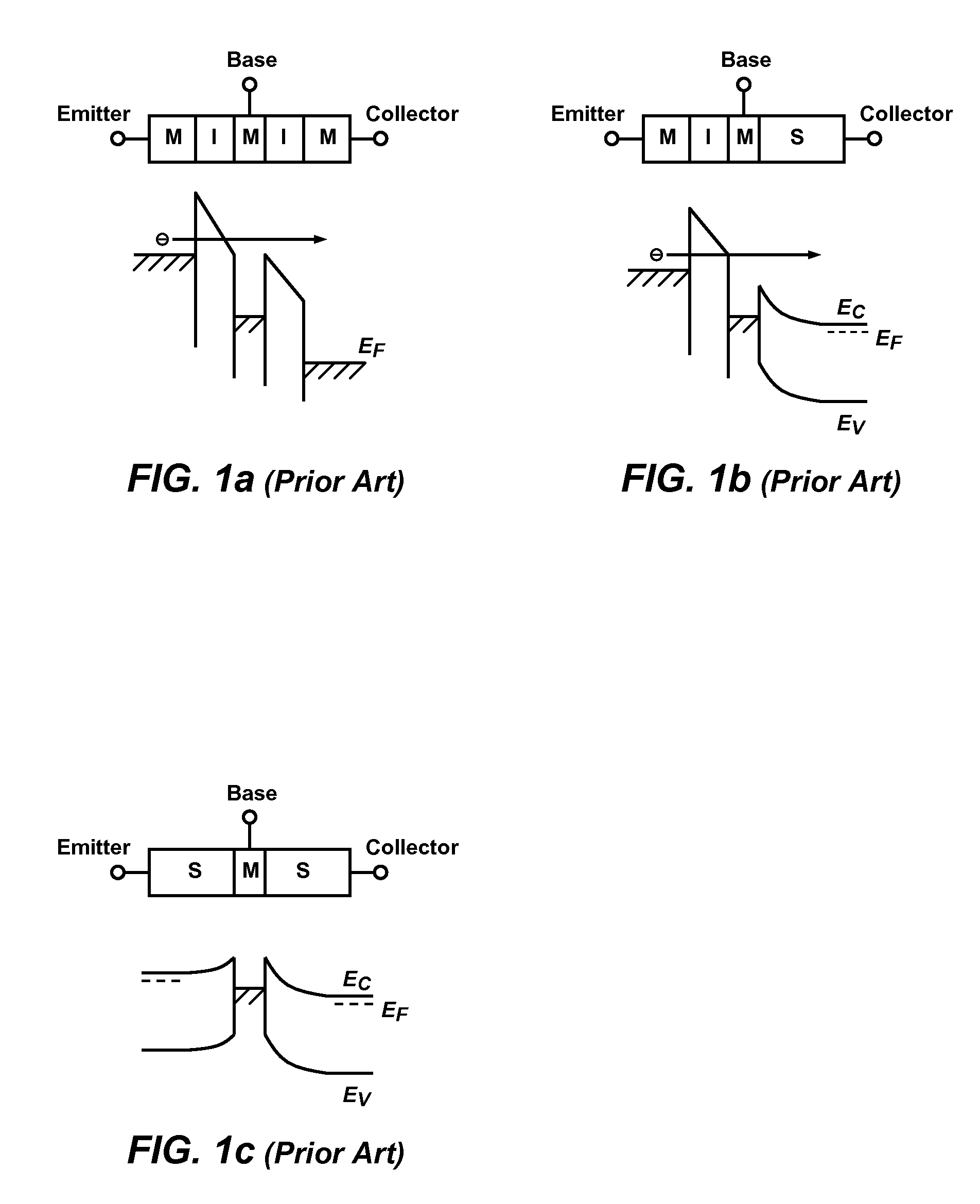
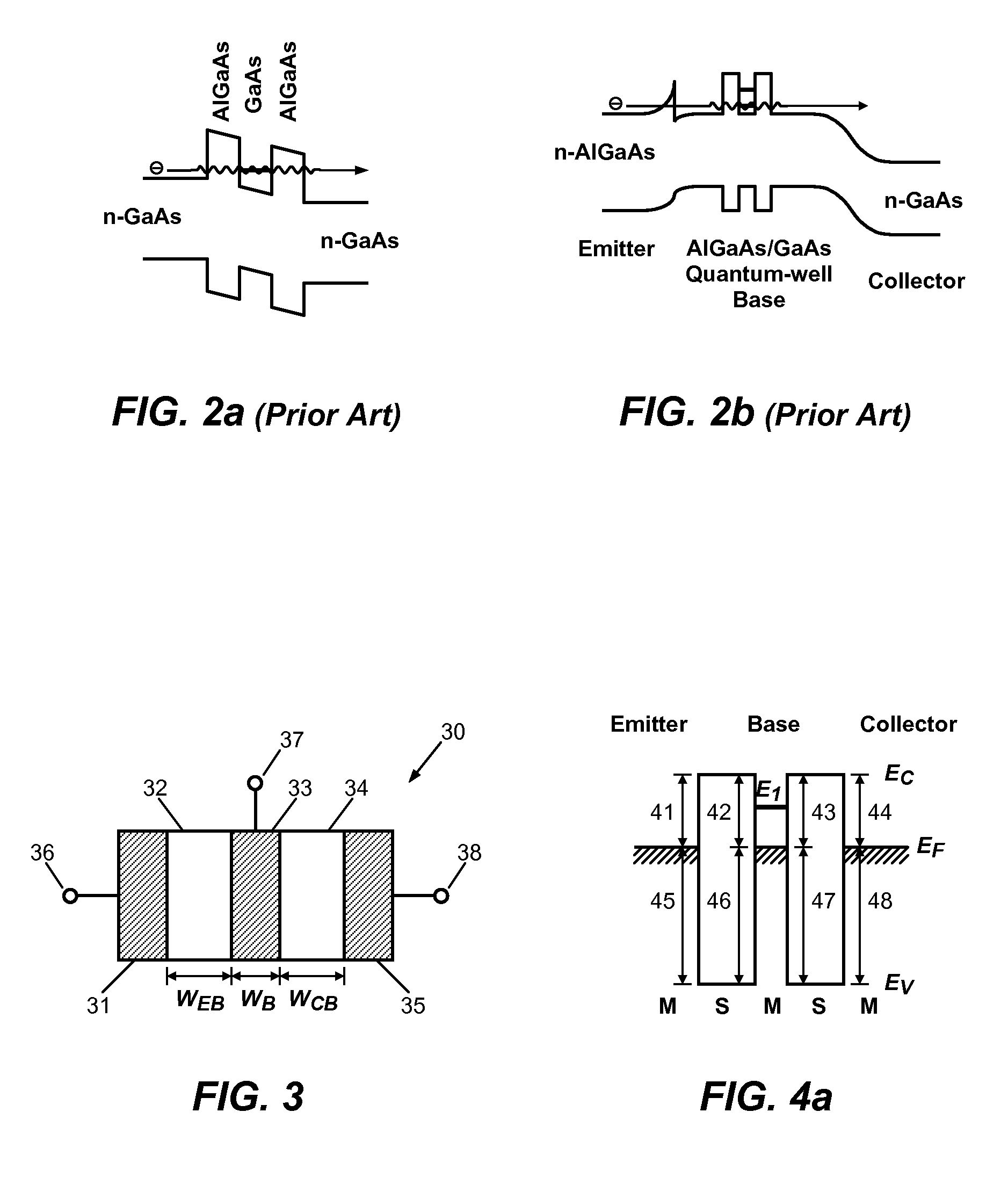
Schottky barrier quantum well resonant tunneling transistor
InactiveUS20100102298A1High speedReduce series resistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesQuantum wellSchottky barrier
A semiconductor transistor device includes one or more conductive base regions, a first semiconductor barrier region, a second semiconductor barrier region, a conductive emitter region, and a conductive collector region. The first semiconductor barrier region or the second semiconductor barrier region has a dimension smaller than 100 Å. A first Schottky barrier junction is formed at the interface of the first semiconductor barrier region and the one or more conductive base regions. A second Schottky barrier junction is formed at the interface of the second semiconductor barrier region and the one or more conductive base regions. A third Schottky barrier junction is formed at the interface of the conductive emitter region and the first semiconductor barrier region. A fourth Schottky barrier junction is formed at the interface of the conductive collector region and the second semiconductor barrier region.
Owner:WU KOUCHENG
P-channel silicon carbide mosfet
InactiveUS20100224886A1Solve low usageHigh avalanche breakdown toleranceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodeMOSFETDevice material
A second trench in each source electrode portion (Schottky diode portion) is formed to have a depth equal to or larger than the depth of a first trench in each gate electrode portion. The distance between the first and second trenches is set to be not longer than 10 μm. A source electrode is formed in the second trench and a Schottky junction is formed in the bottom portion of the second trench. In this manner, it is possible to provide a wide band gap semiconductor device which is small-sized, which has low on-resistance and low loss characteristic, in which electric field concentration into a gate insulating film is relaxed to suppress reduction of a withstand voltage, and which has high avalanche breakdown tolerance at turn-off time.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Doped ai paste for local alloyed junction formation with low contact resistance
InactiveUS20130255765A1Reduce carrier recombinationReduces cost-per-wattSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationJunction formationCharge carrier
Embodiments of the invention generally relate to solar cells having reduced carrier recombination and methods of forming the same. The solar cells have eutectic local contacts and passivation layers which reduce recombination by facilitating formation of a back surface field (BSF). A patterned aluminum back contact doped with a Group III element is disposed on the passivation layer for removing current form the solar cell. The methods of forming the solar cells include depositing a passivation layer including aluminum oxide and silicon nitride on a back surface of a solar cell, and then forming openings through the passivation layer. An aluminum back contact doped with a Group III element is disposed on the passivation layer in a pattern covering the holes, and thermally processed to form a silicon-aluminum eutectic within the openings.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
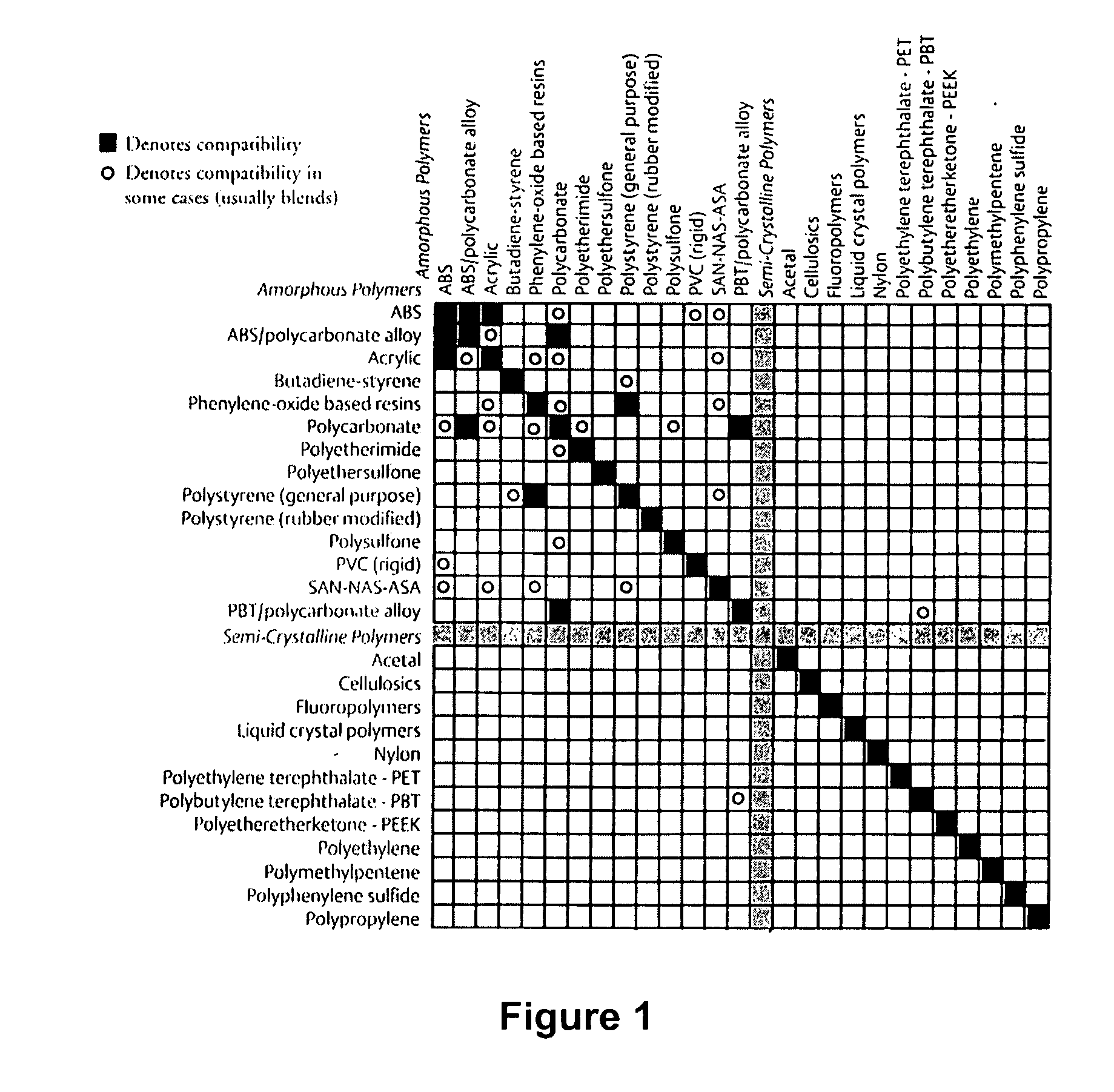
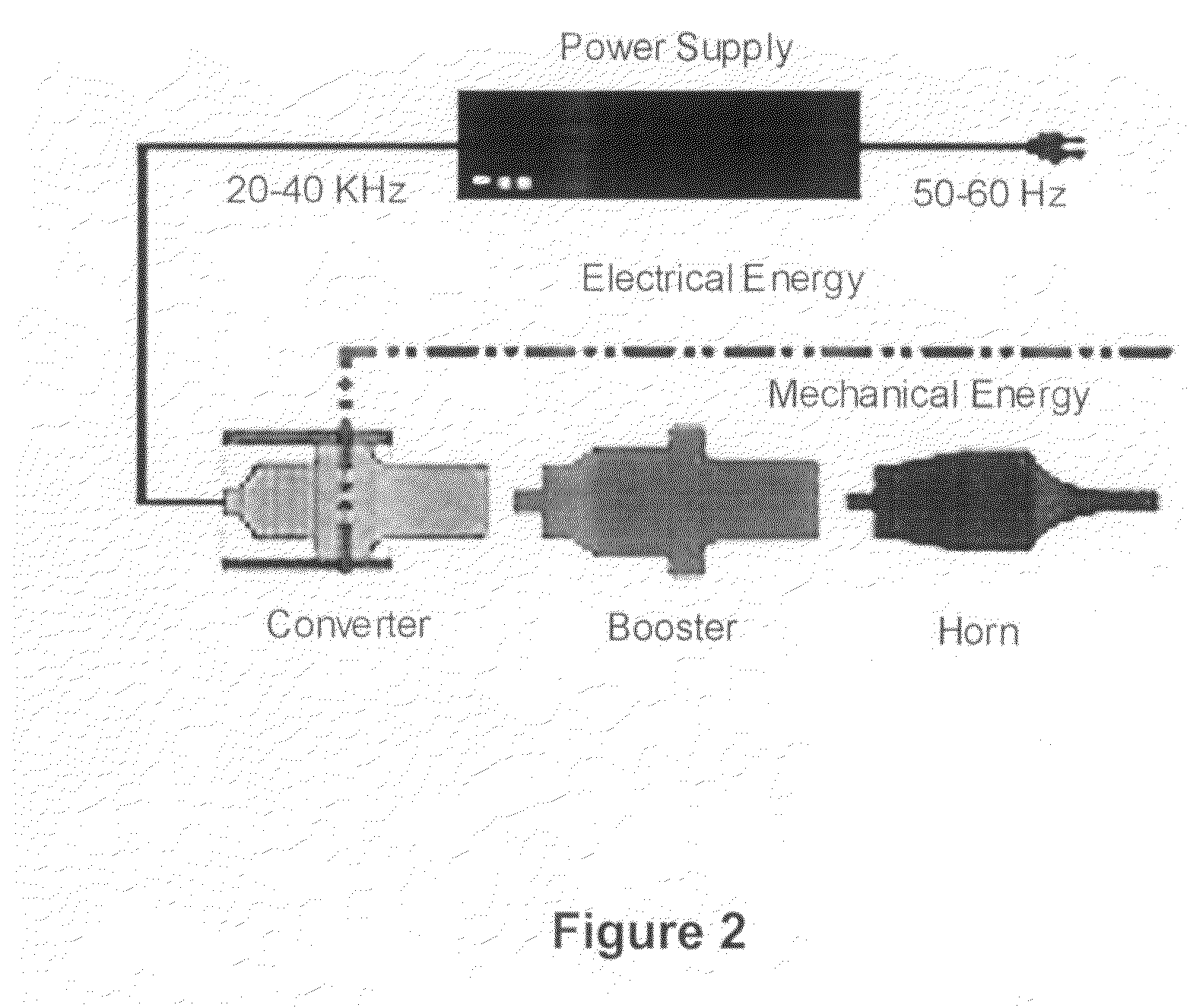
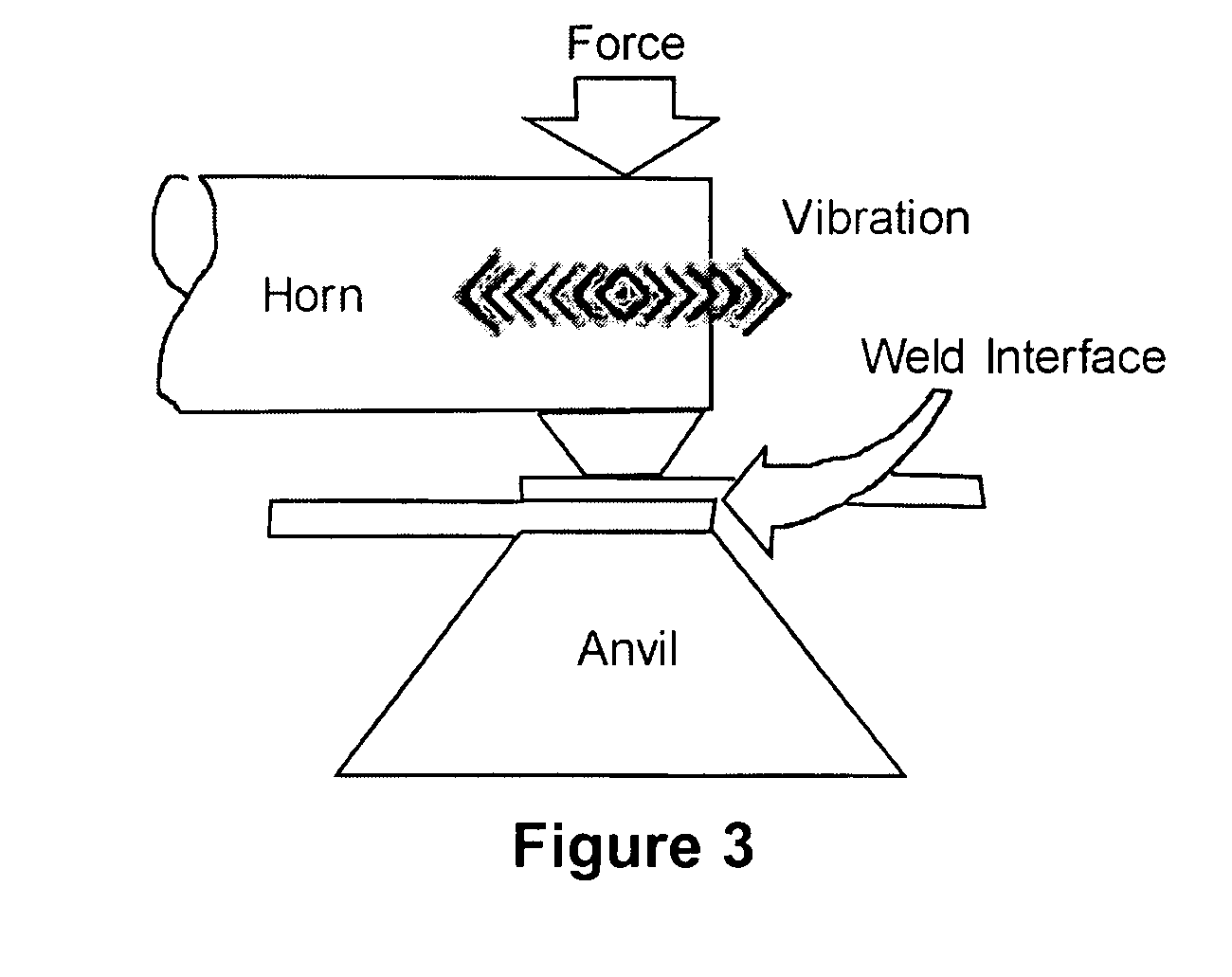
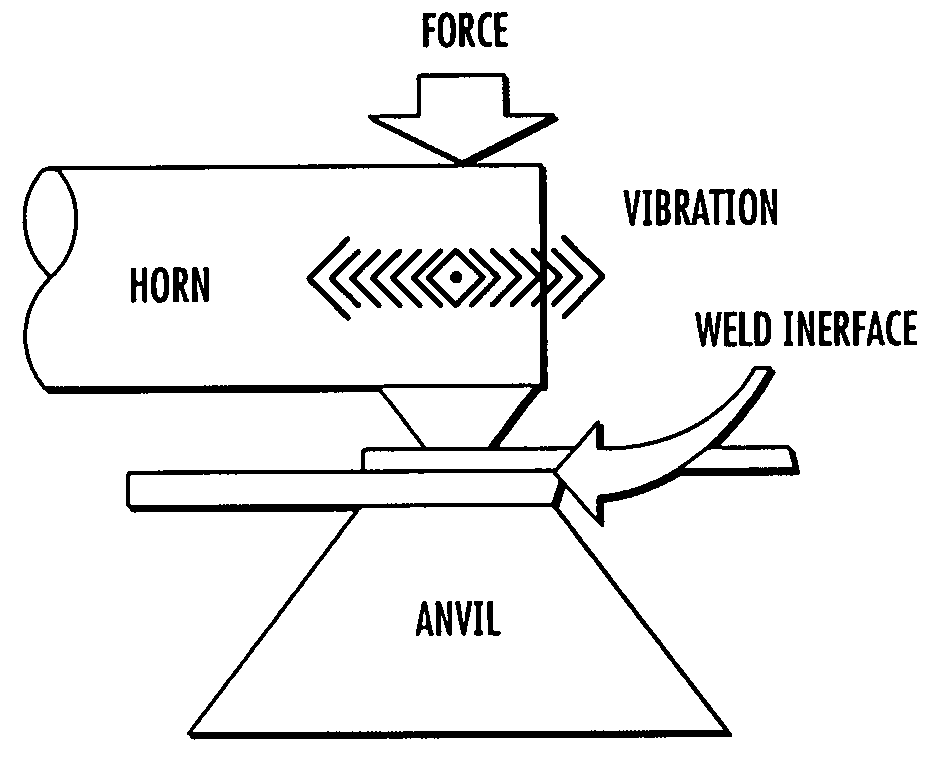
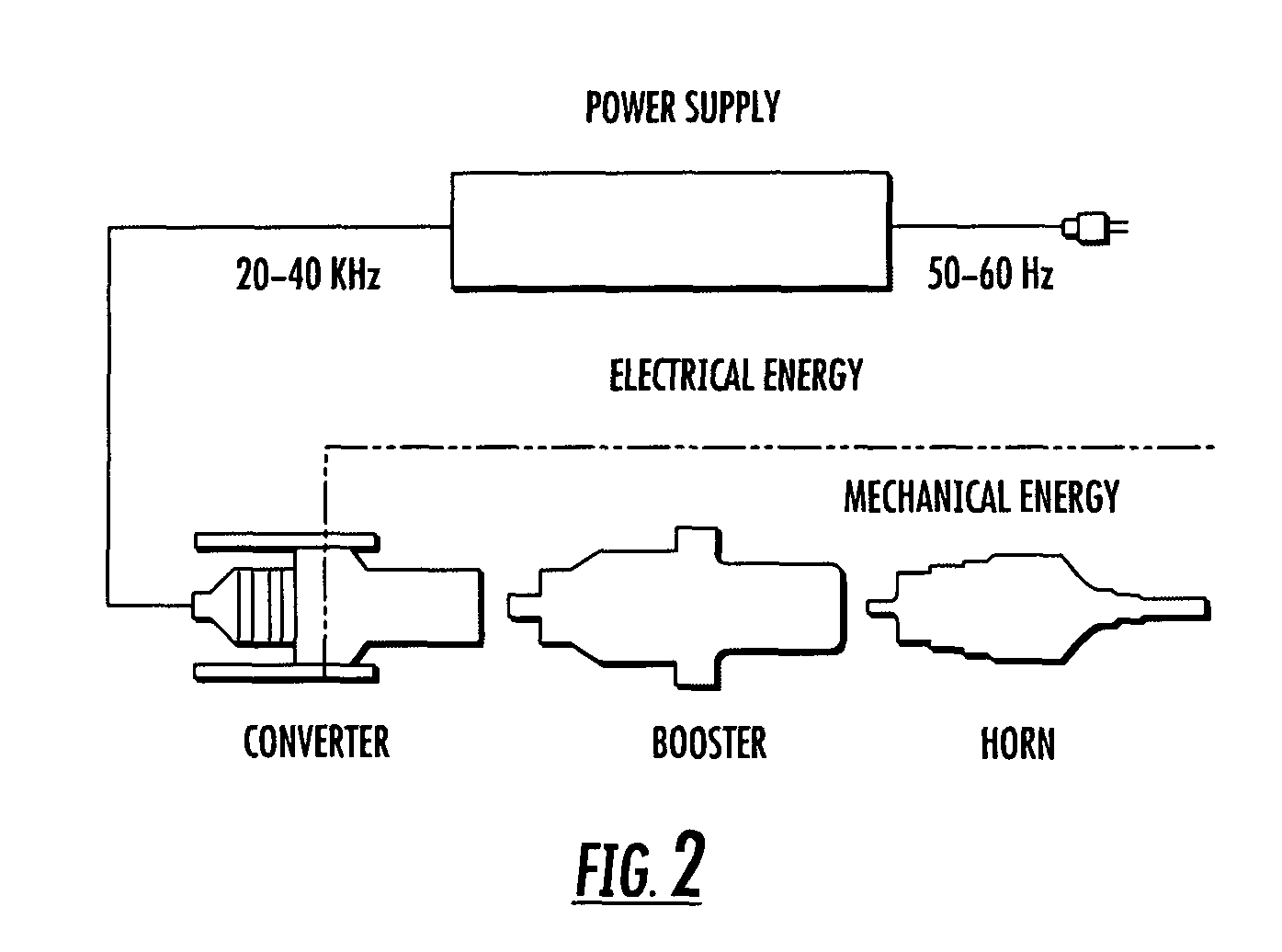
Adaptive continuous acoustic welding system for incompatible materials
InactiveUS20070257086A1Cooking-vessel materialsLamination ancillary operationsMaterial typeUltrasonic welding
A system and method are provided which enable the joining of two materials via ultrasonic welding, including materials normally considered incompatible in traditional ultrasonic welding techniques. The system permits ultrasonic welding of a first material to a second material, the second material including material types normally considered incompatible with the first material and includes an abrader for altering the surface of the material / s to be joined. A first pressure device is operative to vary the position of the abrader and thereby vary the abrasion applied to the materials. An ultrasonic source provides acoustic energy to a weld interface between the materials. A second pressure device is operative to vary the force applied to the interface between the materials while a sensor senses the weld interface temperature. A controller dynamically adjusts the acoustic energy of the ultrasonic source, the second pressure device, and at least one of the first pressure device and a temperature varying device during junction formation. The temperature varying device is operative to modify the temperature of the material / s being welded before abrasion and / or proximate the weld interface location. In this manner, the system enables a smooth, continuous junction to form at a predetermined rate.
Owner:SWCE
Electrical overstress protection using through-silicon-via (TSV)
ActiveUS20130119502A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesJunction formationSemiconductor
A semiconductor device formed on a substrate includes a first diode junction formation, a second diode junction formation, and at least one through-silicon-via (TSV), in which a cathode and an anode of the first diode are cross-connected to an anode and cathode of the second diode through the at least one TSV for achieving electrical robustness in through-silicon-via based integrated circuits, including photosensitive devices and circuits for signal processing applications.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Method for predicting contributions of silicon interstitials to n-type dopant transient enhanced diffusion during a pn junction formation
ActiveUS7756687B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementAnalogue computers for electric apparatusDiffusionElectricity
A method for predicting the contribution of silicon interstitials to n-type dopant transient enhanced diffusion during a pn junction formation is disclosed. Initially, fundamental data for a set of microscopic processes that can occur during one or more material processing operations are obtained. The fundamental data are then utilized to build kinetic models for a set of reactions that contribute substantially to an evolution of n-type dopant concentration and electrical activities. The kinetic models are subsequently applied to a simulator to predict temporal and spatial evolutions of concentration and electrical activity profiles of the n-type dopants.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HLDG 40
Device for protecting an integrated circuit against overvoltages
ActiveUS20140036399A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesOvervoltageJunction formation
A device for protecting an integrated circuit against overvoltages, the device being formed inside and on top of a semiconductor substrate of a first conductivity type and including: a capacitor including a well of the second conductivity type penetrating into the substrate and trenches with insulated walls formed in the well and filled with a conductive material; and a zener diode formed by the junction between the substrate and the well.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
Adaptive continuous acoustic welding system for incompatible materials
InactiveUS7771551B2Cooking-vessel materialsLamination ancillary operationsMaterial typeJunction formation
A system and method are provided which enable the joining of two materials via ultrasonic welding, including materials normally considered incompatible in traditional ultrasonic welding techniques. The system permits ultrasonic welding of a first material to a second material, the second material including material types normally considered incompatible with the first material and includes an abrader for altering the surface of the material / s to be joined. A first pressure device is operative to vary the position of the abrader and thereby vary the abrasion applied to the materials. An ultrasonic source provides acoustic energy to a weld interface between the materials. A second pressure device is operative to vary the force applied to the interface between the materials while a sensor senses the weld interface temperature. A controller dynamically adjusts the acoustic energy of the ultrasonic source, the second pressure device, and at least one of the first pressure device and a temperature varying device during junction formation. The temperature varying device is operative to modify the temperature of the material / s being welded before abrasion and / or proximate the weld interface location. In this manner, the system enables a smooth, continuous junction to form at a predetermined rate.
Owner:SWCE
Symmetrical extension junction formation with low-k spacer and dual epitaxial process in finfet device
InactiveUS20160284820A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantJunction formation
A technique relates to a dual epitaxial process a device. A first spacer is disposed on a substrate, dummy gate, and hardmask. A first area extends in a first direction from the gate and a second area extends in an opposite direction. A doped intermediate spacer is disposed on the first spacer. A first region is opened on the substrate by removing first spacer and intermediate spacer at the first region. A first epitaxial layer is disposed in the first region. The intermediate spacer is removed from first area. A second spacer is disposed on the intermediate spacer. A second region is opened on the substrate by removing the first spacer, intermediate spacer, and second spacer. A second epitaxial layer is disposed in second region. The width of the second epitaxial layer is enlarged by annealing causing dopant in the intermediate spacer layer to flow into the second epitaxial layer.
Owner:IBM CORP
Tunnel junctions for long-wavelength VCSELs
ActiveUS6933539B1Excellent tunnel junctionDeleterious effectLaser detailsLaser active region structureLong wavelengthIndium
A tunnel junction device (102) with minimal hydrogen passivation of acceptors includes a p-type tunnel junction layer (106) of a first semiconductor material doped with carbon. The first semiconductor material includes aluminum, gallium, arsenic and antimony. An n-type tunnel junction layer (104) of a second semiconductor material includes indium, gallium, arsenic and one of aluminum and phosphorous. The junction between the p-type and an-type tunnel junction layers forms a tunnel junction (110).
Owner:THORLABS QUANTUM ELECTRONICS
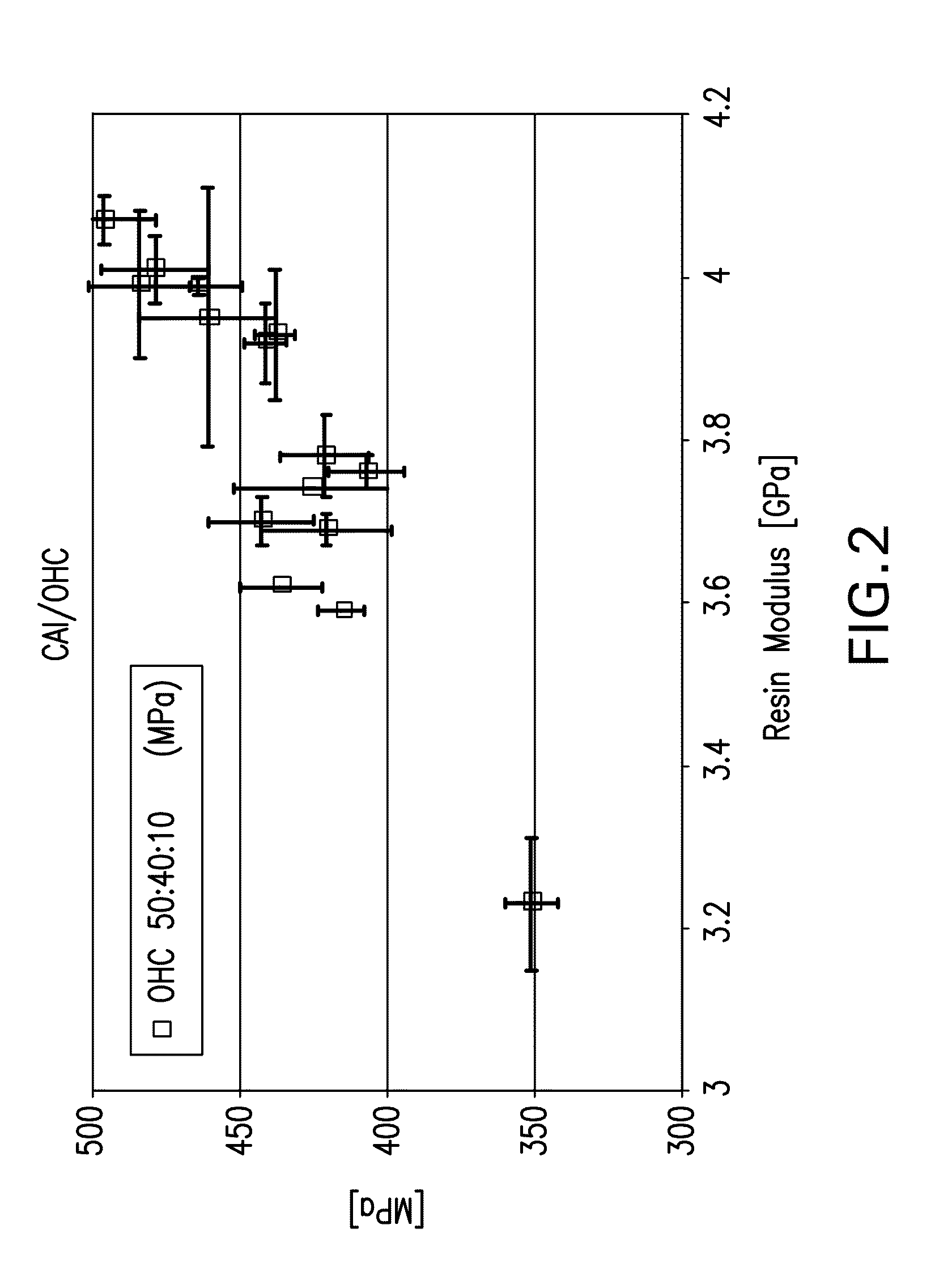
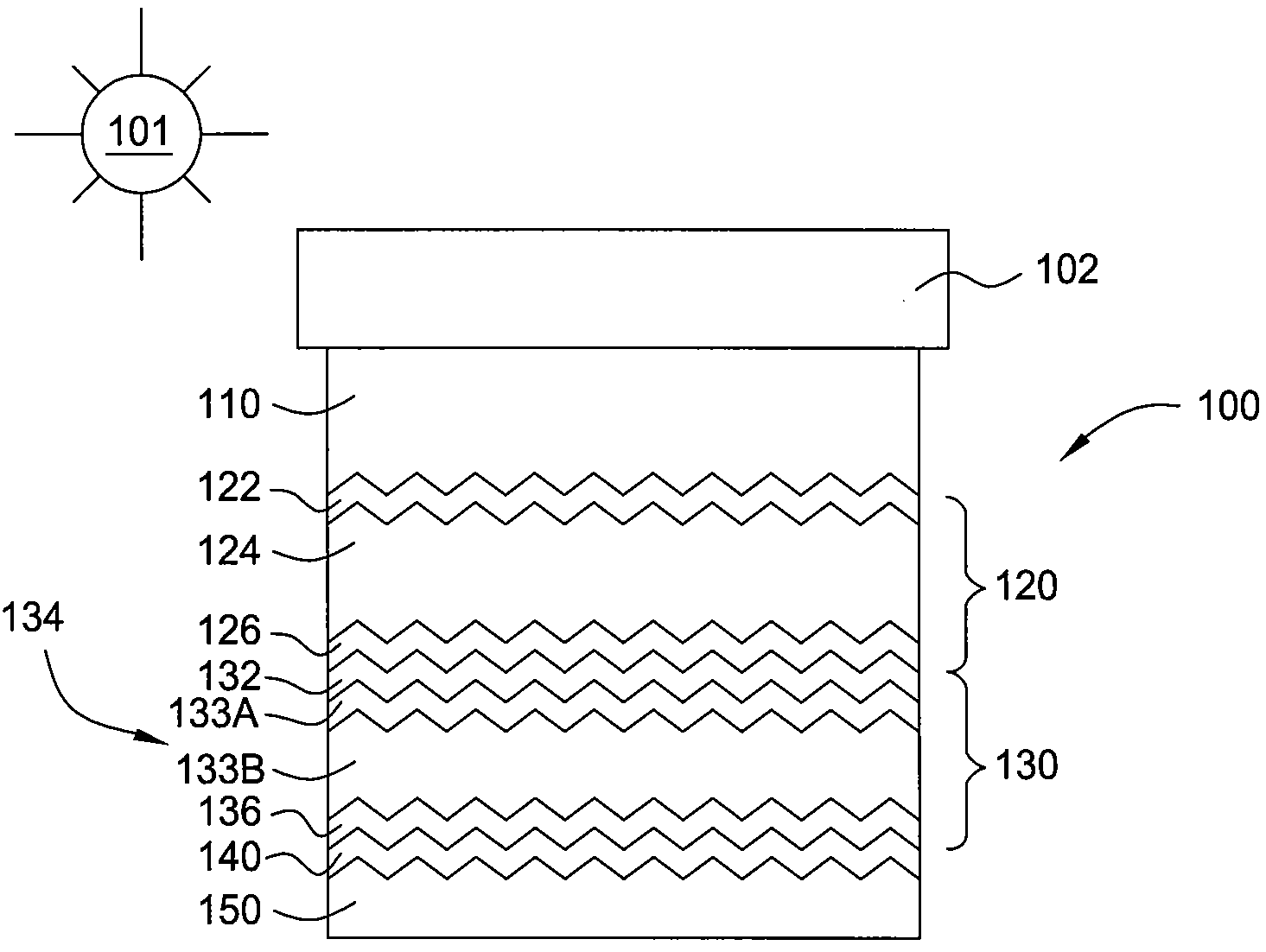
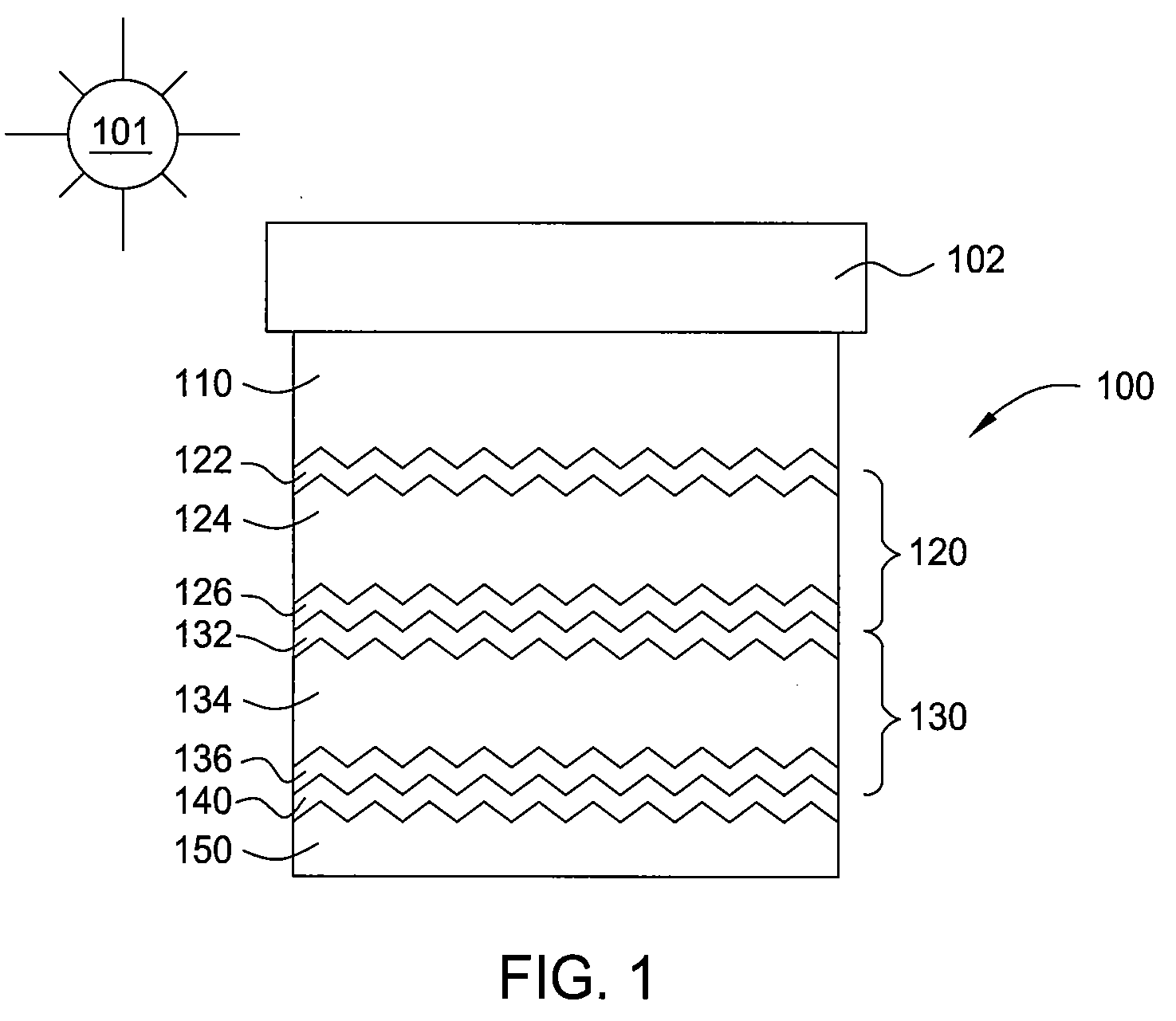
Composite materials and their use
ActiveUS8084120B2Synthetic resin layered productsGlass/slag layered productsDelaminationJunction formation
A composite material comprising the following components: (a) a first prepreg material with improved resistance to microbuckling and kinkband formation; and (b) a second prepreg material with improved resistance to delamination.
Owner:CYTEC TECH CORP
Intrinsic amorphous silicon layer
InactiveUS20090130827A1Electric discharge tubesFinal product manufactureJunction formationMicrocrystalline silicon
Embodiments of the present invention may include an improved thin film solar cell device that is formed by sequentially depositing an intrinsic amorphous silicon layer and an intrinsic microcrystalline silicon layer during the p-i-n or n-i-p junction formation process. Embodiments of the invention also generally provide a method and apparatus for forming the same. The present invention may be used to advantage to form other single junction, tandem junction, or multi-junction thin film solar cell devices.
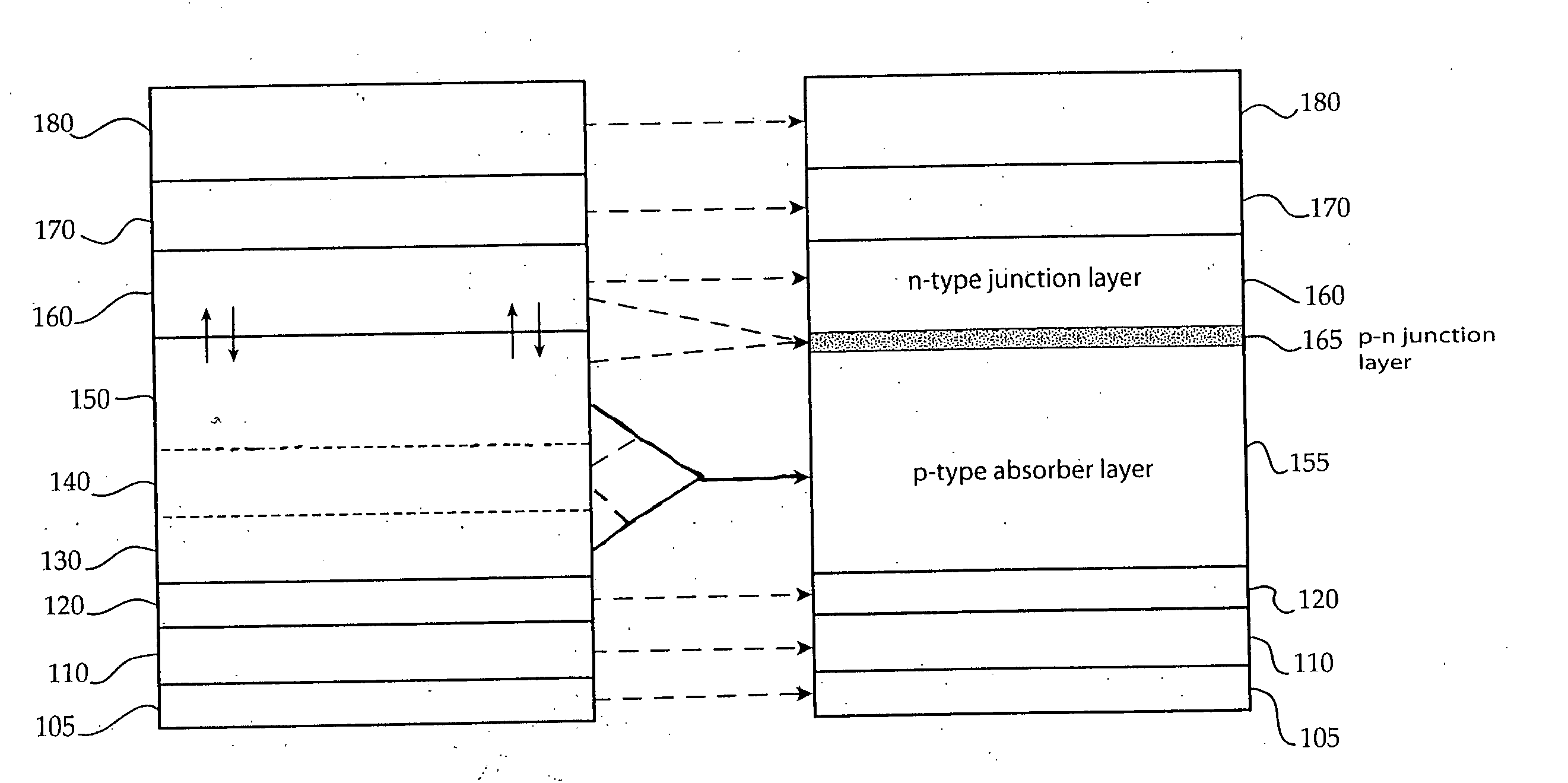
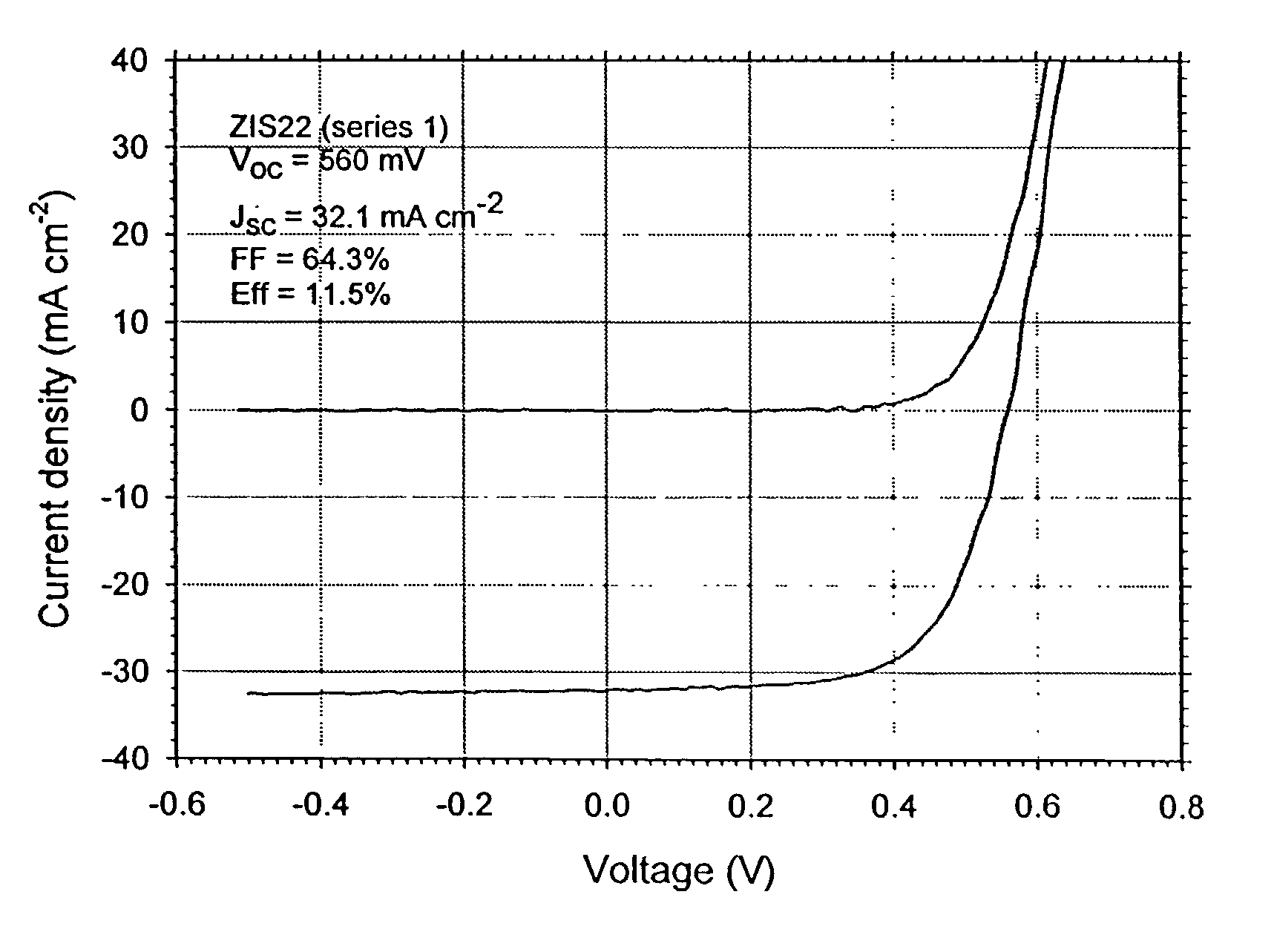
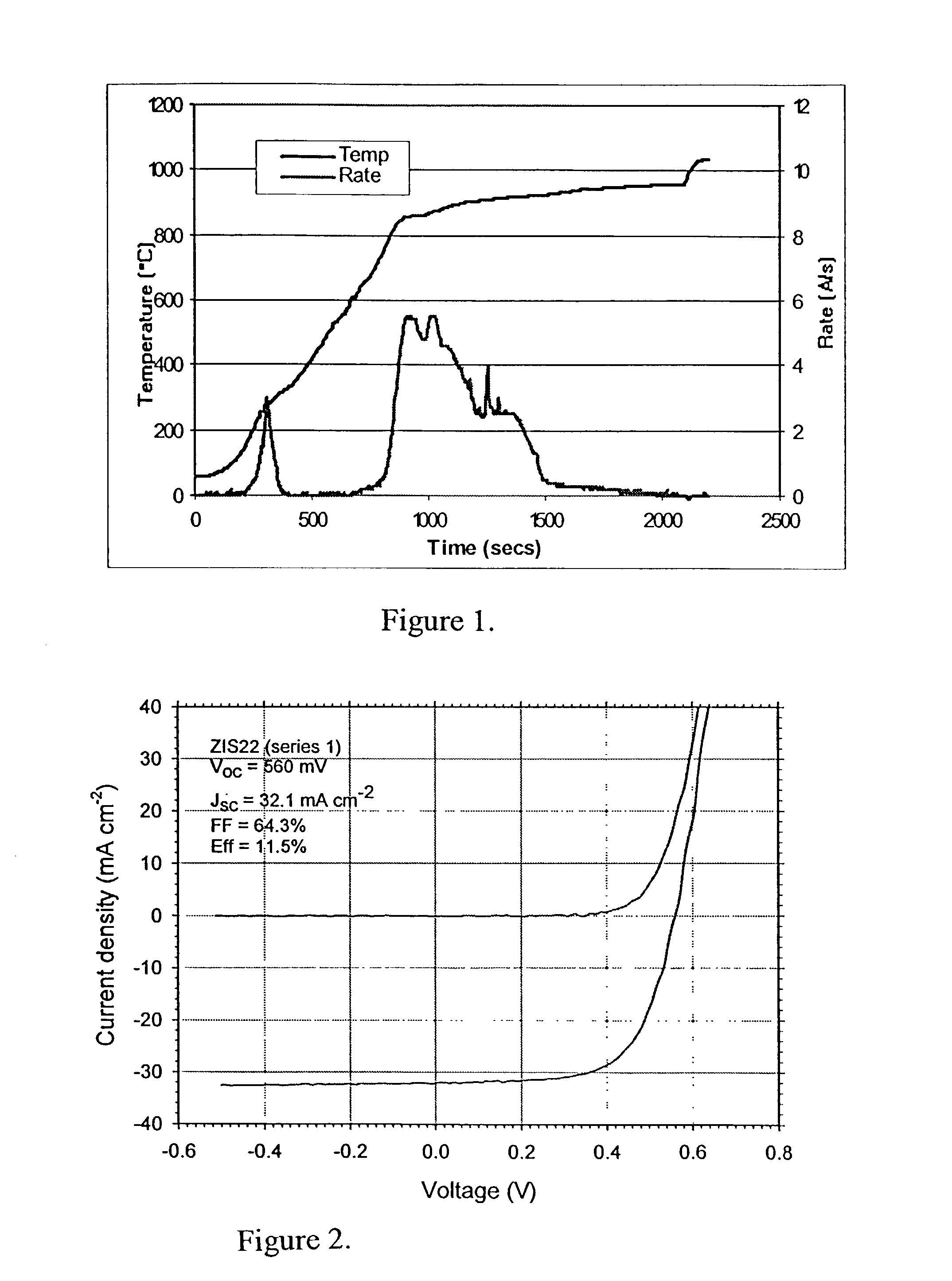
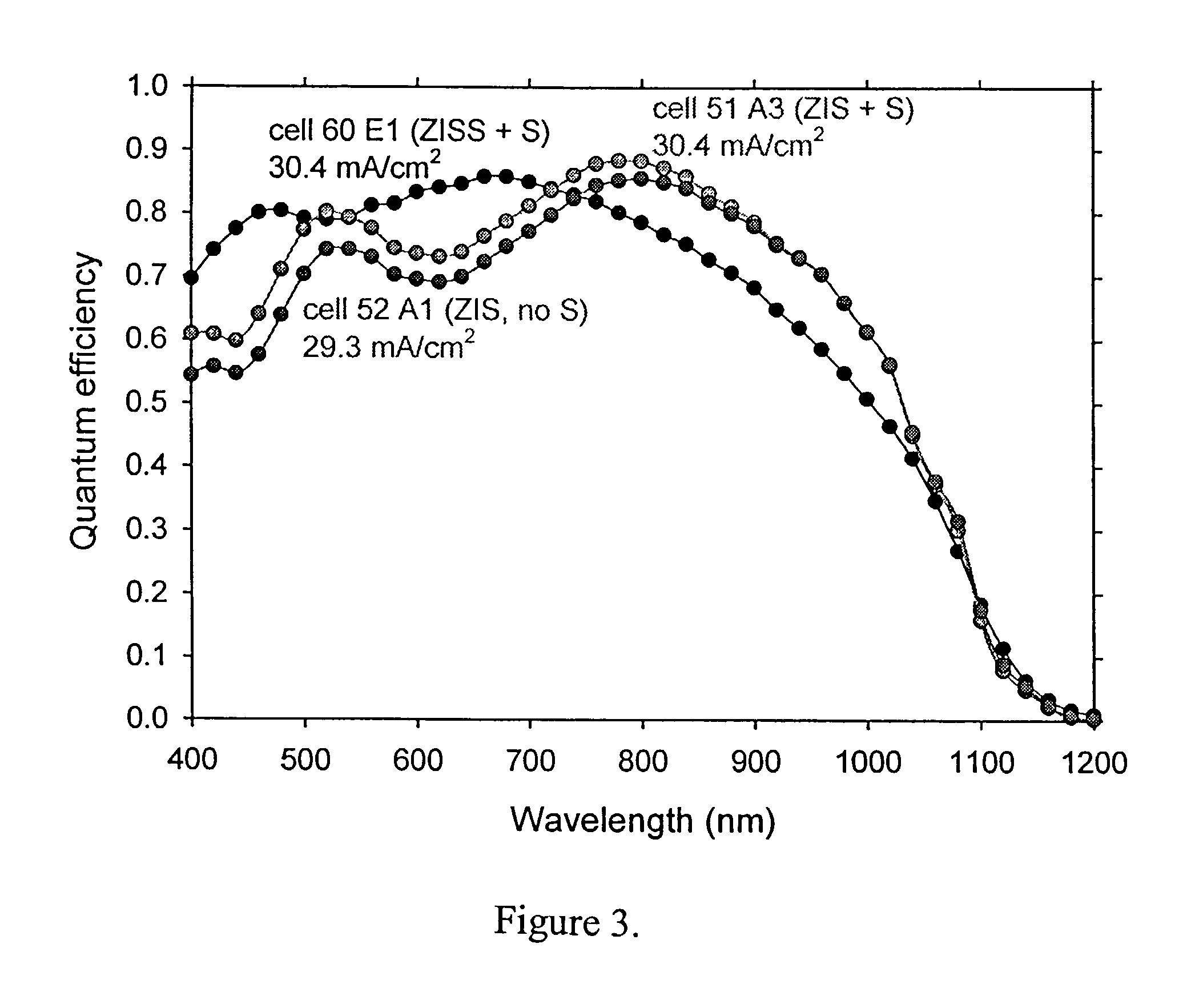
Method of junction formation for CIGS photovoltaic devices
InactiveUS7019208B2Simple processEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationSulfurThiourea
Sulfur is used to improve the performance of CIGS devices prepared by the evaporation of a single source ZIS type compound to form a buffer layer on the CIGS. The sulfur may be evaporated, or contained in the ZIS type material, or both. Vacuum evaporation apparatus of many types useful in the practice of the invention are known in the art. Other methods of delivery, such as sputtering, or application of a thiourea solution, may be substituted for evaporation.
Owner:NEW MILLENNIUM SOLAR EQUIP CORP
Non-equilibrium junction terminal structure for super-junction device
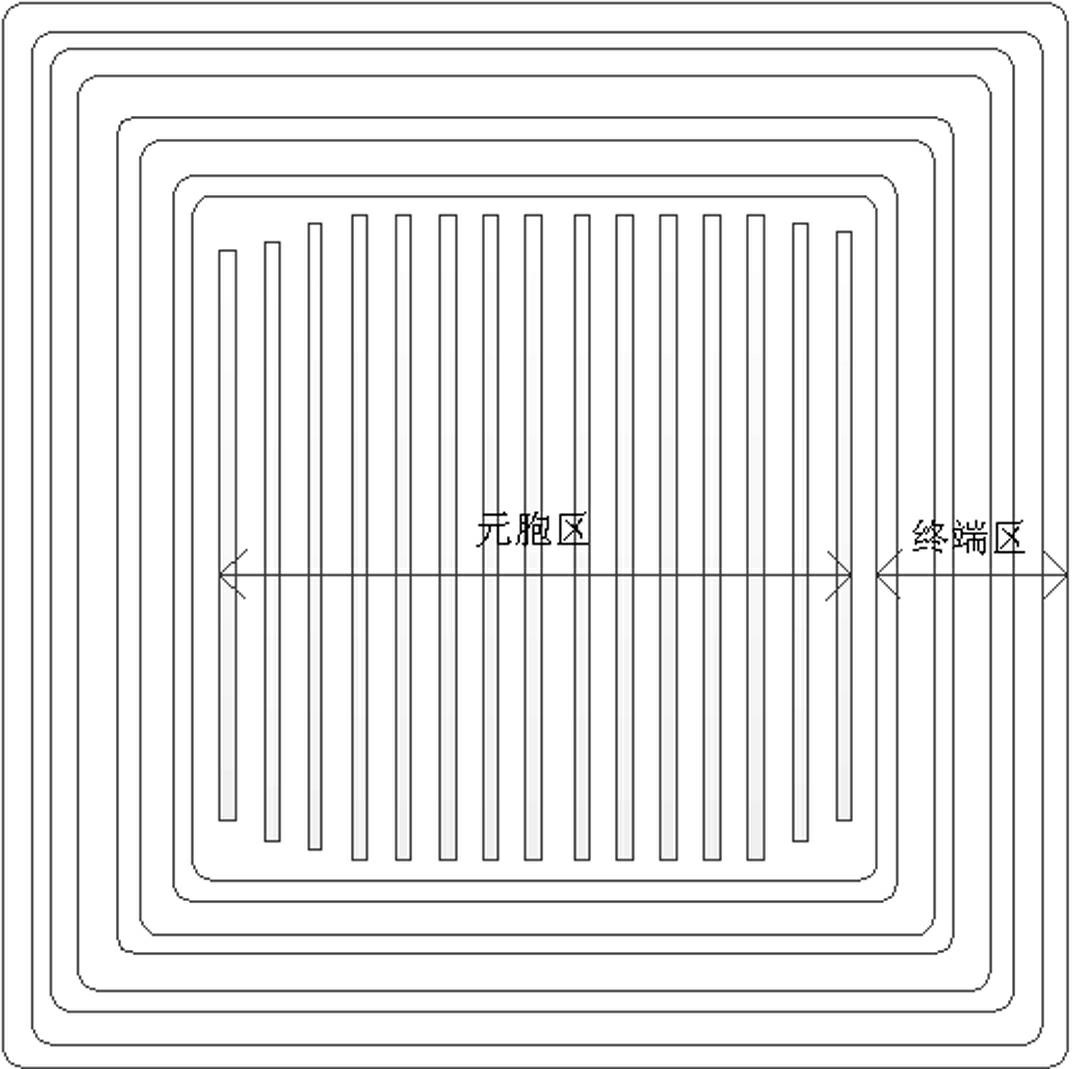
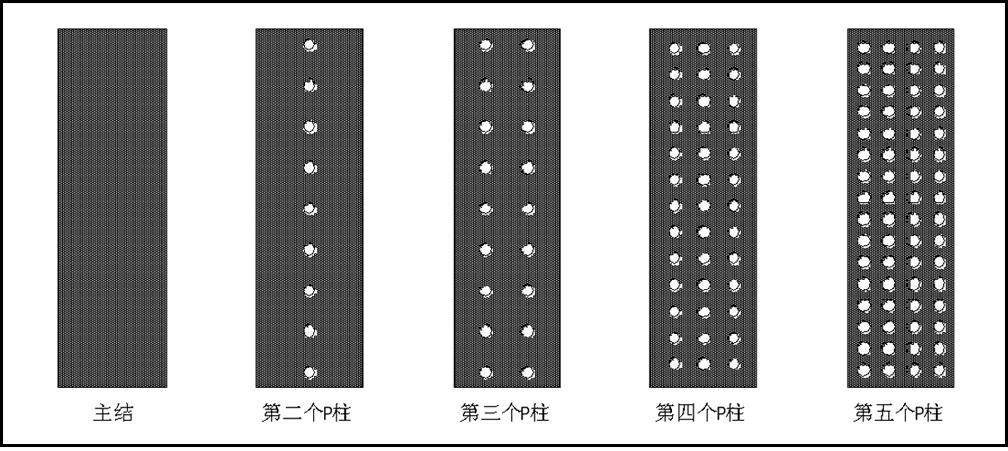
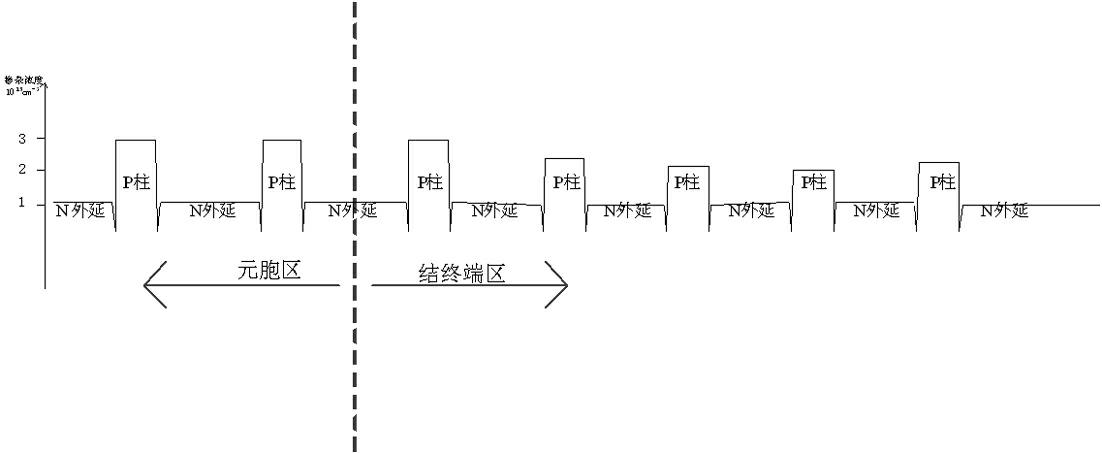
ActiveCN102694027AImproved breakdown voltage characteristicsLower on-resistanceSemiconductor devicesTerminal equipmentIon implantation
The invention relates to a non-equilibrium junction terminal architecture for a super-junction device. The junction terminal region of the terminal structure is provided with a plurality of uniform P pillars with different doping concentrations; the effective ion implantation area of the P pillars is correspondingly adjusted on the layout design according to the transverse electric field distribution conditions of all positions, so that the P pillars are completely exhausted when achieving the breakdown voltage; the ions are simultaneously implanted into all the P pillars under the masking of the mask sheet, thereby controlling the total amount of acceptor ions of all the P pillars in the junction terminal region; and after carrying out multiple extensions and multiple ion implantation processes, long-time high-temperature junction push is carried out to form several uniform P pillars with different doping concentrations. The invention can effectively improve the breakdown voltage characteristics of the junction terminal device, and has smaller junction terminal length, so that the total area of the device is reduced, thereby reducing the device conduction resistance on the same chip area.
Owner:XIAN LONTEN RENEWABLE ENERGY TECH +1
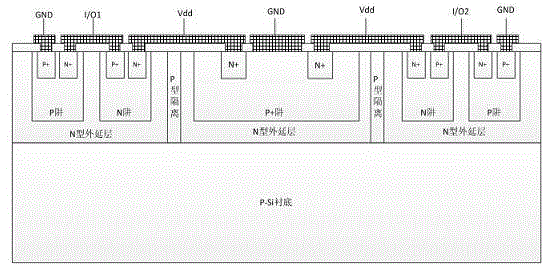
SOI base-based low-leakage and low-capacitance TVS array and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105489612AReduce parasitic capacitanceSuppress interferenceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingState of artParasitic capacitance
The invention relates to an SOI base-based low-leakage and low-capacitance TVS array and a preparation method thereof. The SOI base-based low-leakage and low-capacitance TVS array comprises an n-type SOI base, a p+ region, an n+ region, a p region, a silicon nitride isolator and an electrode, wherein the n-type SOI base is formed by a three-layer structure of an Si substrate, an SiO<2> layer and an n-type Si layer; and highly doped PN junctions are formed on P-type and / N-type SI substrates through diffusion or ion implantation to form a PN junction region and a central TVS region. Compared with a TVS device in the prior art, according to the SOI base-based low-leakage and low-capacitance TVS array, the stray capacitance and the leakage current of the device are effectively reduced; the power consumption of the device is reduced; and the performance of the device is further improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGYUAN WAYON MICROELECTRONICS
Tunnel junctions for long-wavelength vcsels
ActiveUS20050253164A1Good junctionDeleterious effectLaser detailsLaser active region structureIndiumSemiconductor materials
A tunnel junction device (102) with minimal hydrogen passivation of acceptors includes a p-type tunnel junction layer (106) of a first semiconductor material doped with carbon. The first semiconductor material includes aluminum, gallium, arsenic and antimony. An n-type tunnel junction layer (104) of a second semiconductor material includes indium, gallium, arsenic and one of aluminum and phosphorous. The junction between the p-type and an-type tunnel junction layers forms a tunnel junction (110).
Owner:THORLABS QUANTUM ELECTRONICS
Preparation method of P-type crystal silicon double-sided cell
InactiveCN103646992AIncrease power generationIncrease profitFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingJunction formationPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a preparation method of a P-type crystal silicon double-sided cell. The preparation method comprises the following steps of felting and chemical cleaning, PN junction formation, antireflection film deposition performed on two sides, film splitting performed on a back surface, cell positive and negative pole preparation and sintering. Compared with the prior art, and according to the preparation method of the P-type crystal silicon double-sided cell of the invention, only one-time doping is required, and therefore, a preparation process can be simpler; and original processes such as frequent high-temperature doping and mask manufacture can be avoided, and therefore, preparation steps can be simplified, and preparation cost can be saved. The double-sided cell prepared by using the preparation method provided by the technical schemes of the invention can fully utilize scattered light of sunlight on the ground, and therefore, the utilization rate of the sunlight can be improved, power generation amount of the cell can be increased.
Owner:ALTUSVIA ENERGY TAICANG
Heterojunction solar cell and interfacing processing method and preparing technology thereof
InactiveCN103762276AEnhanced built-in electric fieldReduce recombination lossPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionJunction formation
The invention discloses a heterojunction solar cell and an interfacing processing method and preparing technology thereof. According to the interface processing method of the heterojunction solar cell, in the preparing technology of the heterojunction solar cell, highly doping processing is conducted on the front surface of a crystalline silicon wafer with the ion implantation technology or the diffusion technology so that a heavy doped layer can be formed on the front surface of the crystalline silicon wafer, and then the Fermi level of the surface of the crystalline silicon water of the heterojunction solar cell is changed and an built-in electric field is enhanced. According to the method, the built-in electric field of the substrate interface of crystalline silicon can be enhanced, separation and conveyance of current carriers on the border of a depletion region can be promoted more effectively, film / crystalline silicon abrupt junction formation is facilitated, the width of a depletion layer on the base region of the crystalline silicone is reduced, light absorption efficiency is improved, recombination losses of the current carriers are reduced, and the voltage characteristic of a heterojunction efficient battery is improved.
Owner:TRINA SOLAR CO LTD
Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETS) used in ink-jet head chips and method for making the same
A MOSFET and the method for fabricating them are disclosed to make the inkjet head chips. The MOSFET has the scaled-down junction formation for the source and drain. Using a lower temperature process and interlayer dielectric, the source and drain dopants can not be diffused deeply due to high-temperature driver-in. The contact holes of the drain are provided with plugs of refractory material to avoid spiking between the metal and silicon. This achieves the requirement of high-density devices on the print head chip.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES II
Semiconductor device having vertical metal insulator semiconductor transistors having plural spatially overlapping regions of different conductivity type
InactiveUS20060145290A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesImpurity diffusionDevice material
A semiconductor device includes a diffusion area formed in a semiconductor layer of a first conductive type. The diffusion area comprises first and second impurity diffusion areas of the first and second conductive types, respectively. The diffusion area has a first and second areas which are defined by an impurity concentration of the first and second impurity diffusion areas. A junction between the first and second area is formed in a portion in which the first and second impurity diffusion areas overlap each other. A period of the impurity concentration, in a planar direction of the semiconductor layer, of the first or second area is smaller than the maximum width, in the planar direction of the semiconductor layer, of the first and second impurity diffusion areas constituting the first or second area.
Owner:OKUMURA HIDEKI +6
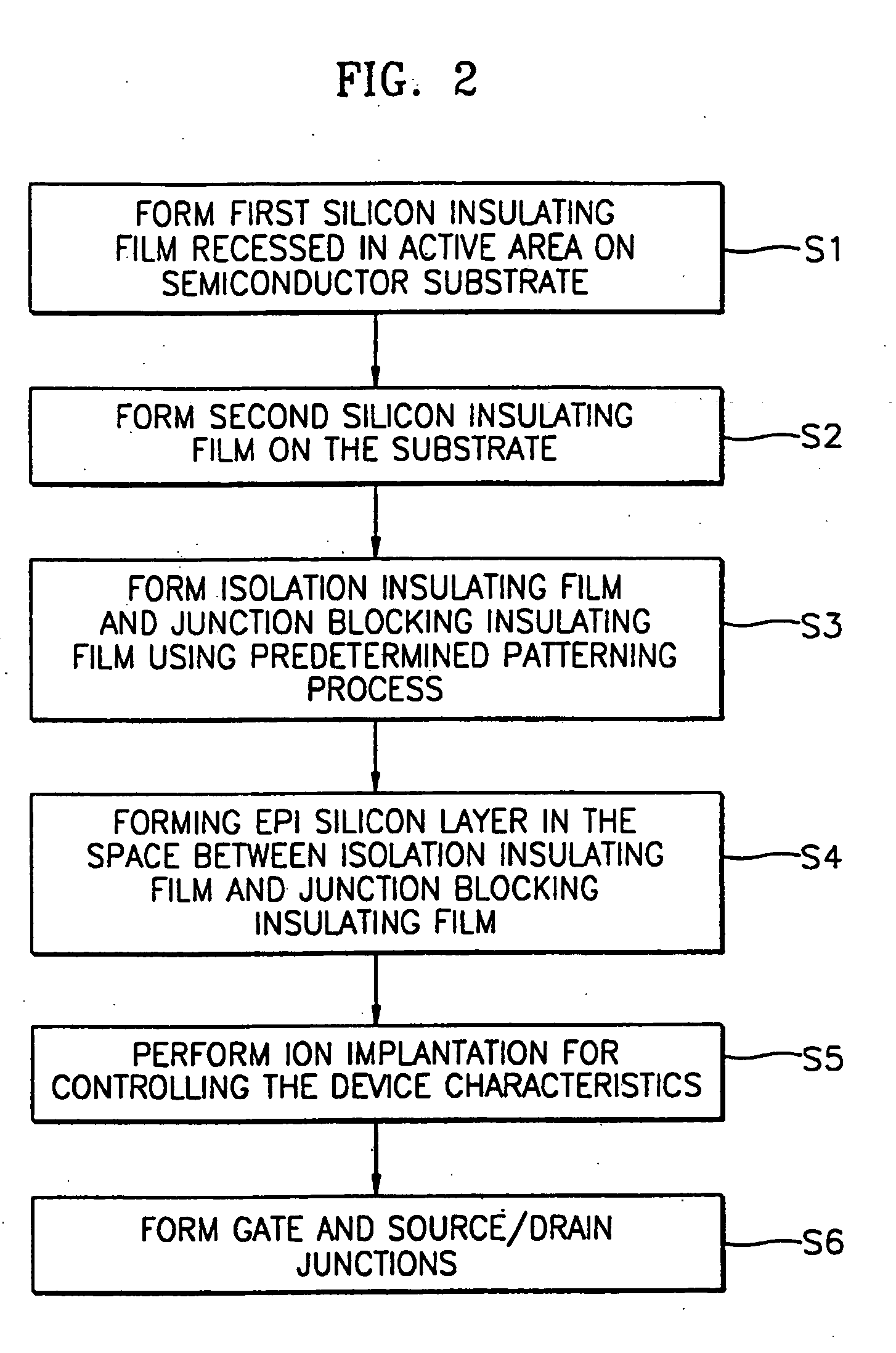
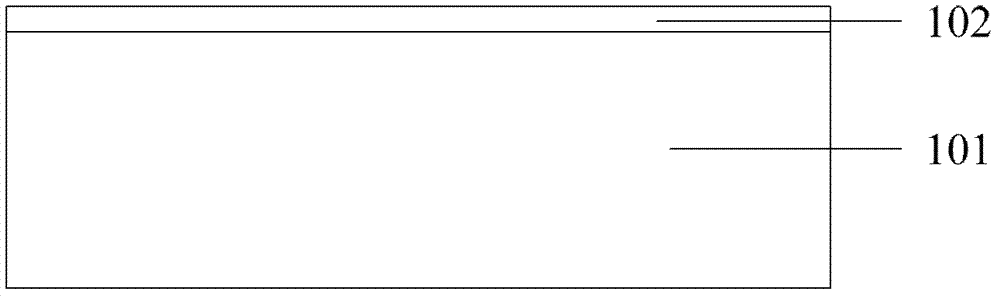
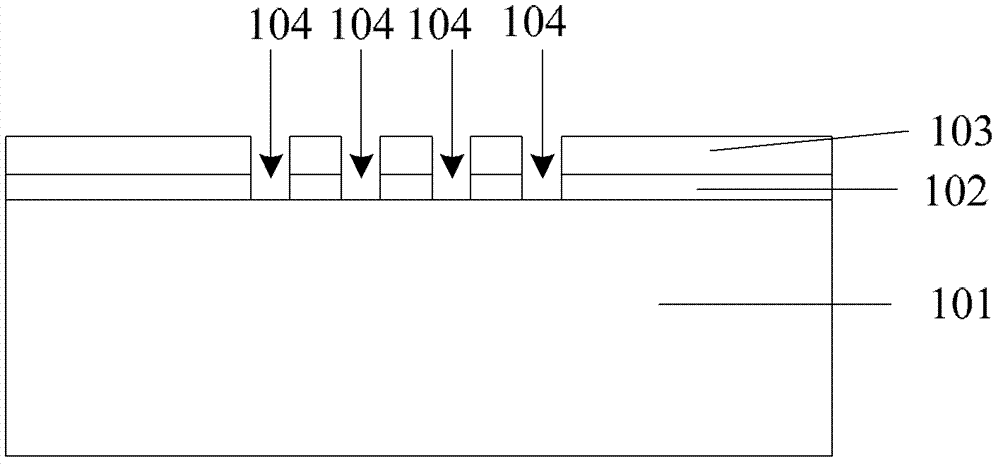
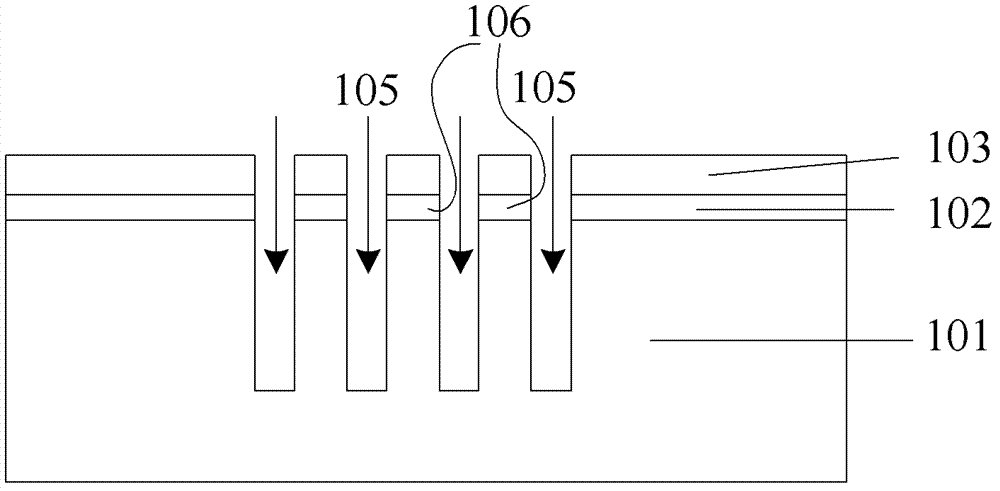
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050064640A1Reduction in design ruleDistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialGate stack
Provided are a semiconductor device and a method for manufacturing the semiconductor device. The semiconductor device includes an isolation insulating film, an epitaxial silicon layer, a junction blocking insulating film, a gate stack, and source and drain junctions. The isolation insulating film is formed on a semiconductor substrate to define an active area. The epitaxial silicon layer is formed in the active area of the semiconductor substrate and surrounded by the isolation insulating film. The junction blocking insulating film is formed in the epitaxial silicon layer. The gate stack is formed over the epitaxial silicon layer so that the junction blocking insulating film is buried under approximately the center of the gate stack. The source and drain junctions are formed adjacent the sidewalls of the gate stack. Accordingly, a short circuit between source / drain junctions in a bulk area caused by the unwanted diffusion of the junctions can be prevented.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High-density and embedded-type capacitor and manufacturing method of the same
ActiveCN103094068AIncrease capacitance densityIncrease the effective areaSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCapacitanceHigh density
An embodiment of the invention discloses a high-density and embedded-type capacitor and a manufacturing method of the high density and embedded-type capacitor. The method comprises providing a base with a body layer and an etching barrier layer, forming a plurality of grooves with good verticality and high depth-to-width ratios, doping body layer materials of the bottom side walls of the groove and body layer materials between adjacent groove to get a doping area of the capacitor in order to form a three-dimensional PN junction on the contact regions of the body layer and a doping region, and forming a first electrode and a second electrode of the capacitor, wherein the polarities of the first electrode and the second electrode are opposite, and are electrically insulated, the first electrode is placed on two sides of the doping area or the periphery of the doping area, and the second electrode is placed on the surface of the doping area. Because the dielectric layer of the capacitor is made of three-dimensional grooves, the effective area of the dielectric layer is much larger than of a dielectric layer of an ordinary capacitor. Therefore, capacitance density of the capacitor is improved, and the capacitor can simultaneously satisfy requirements of low frequency decoupling and high frequency decoupling.
Owner:NAT CENT FOR ADVANCED PACKAGING
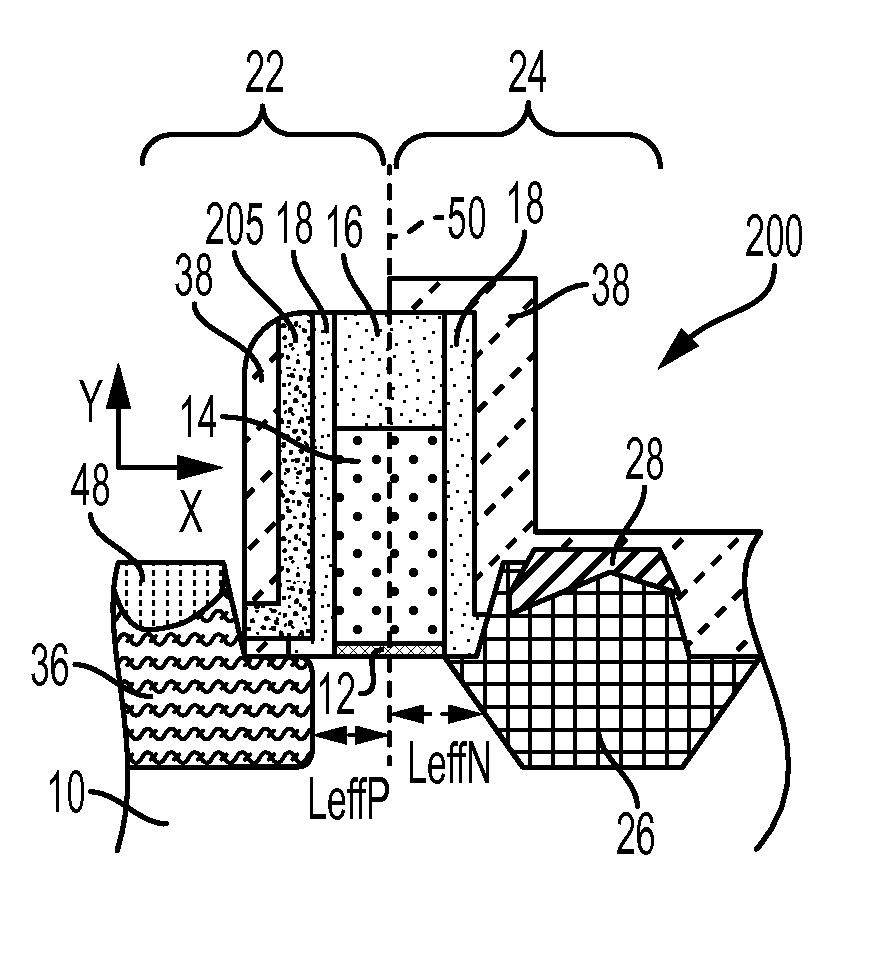
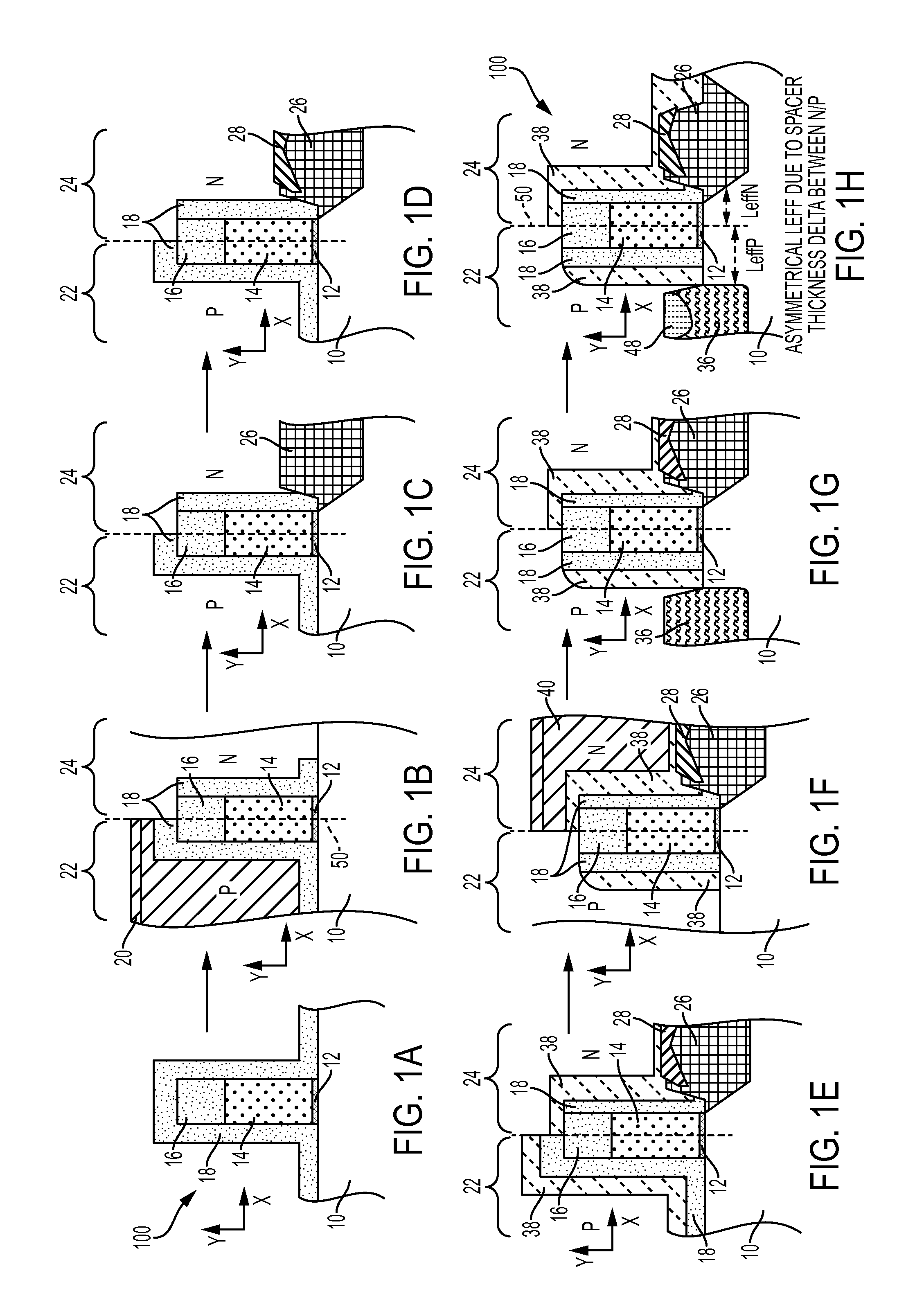
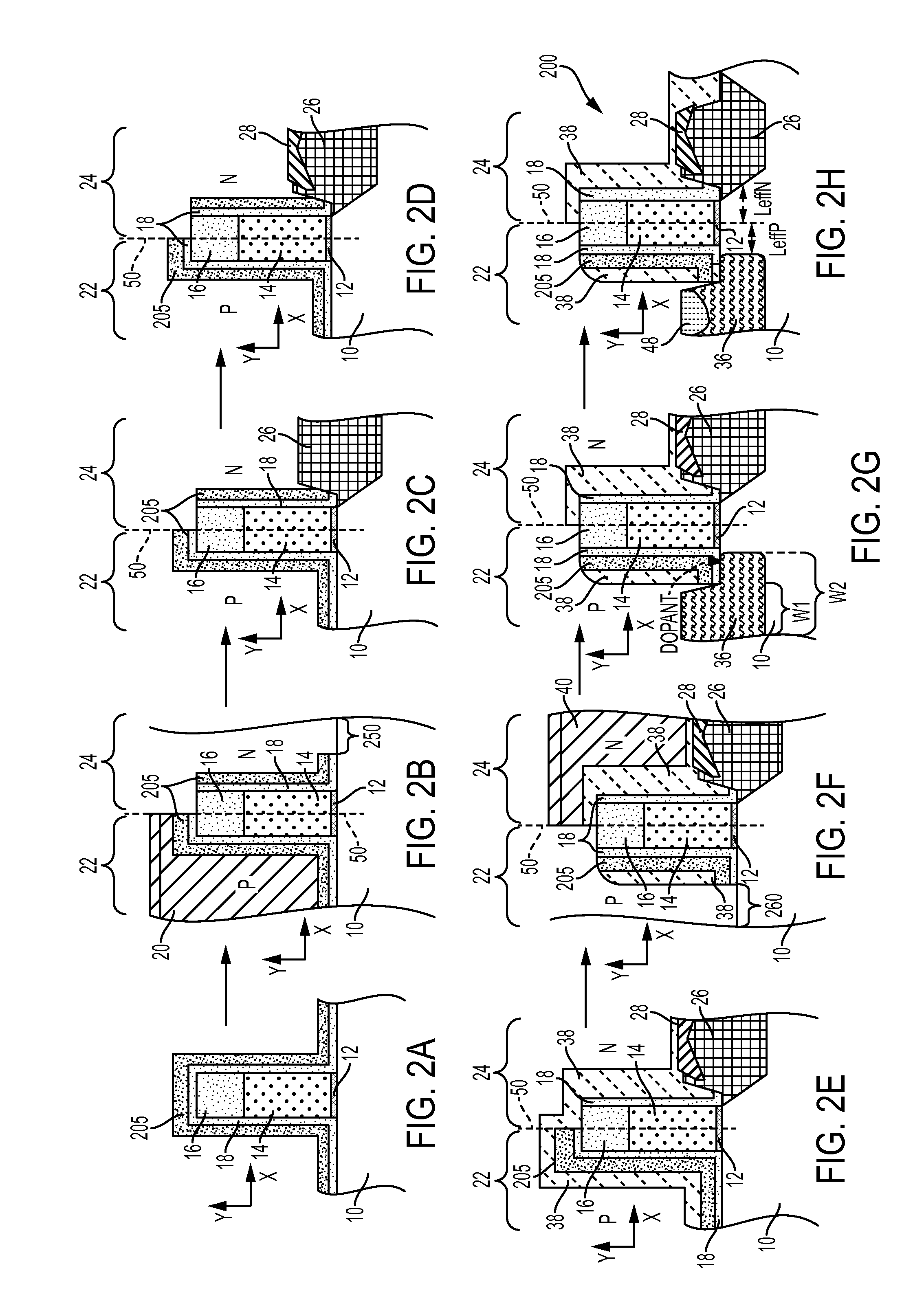
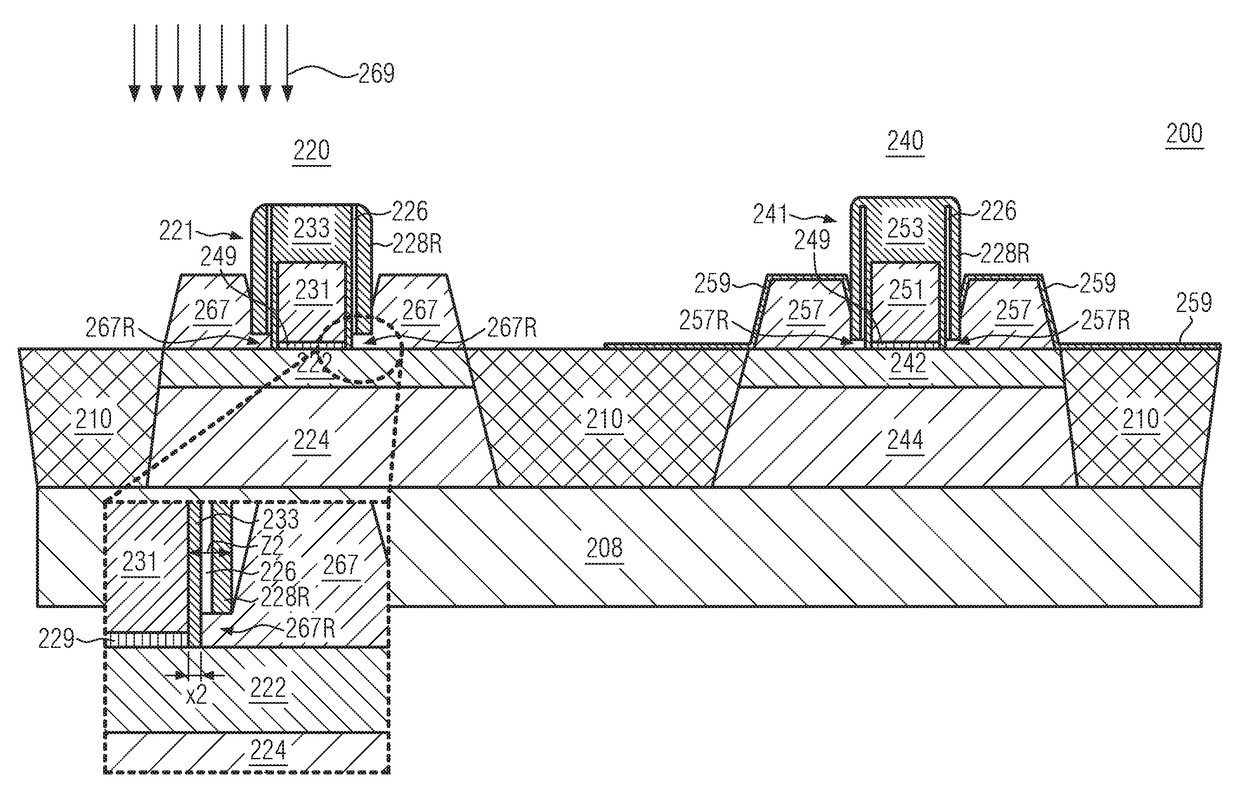
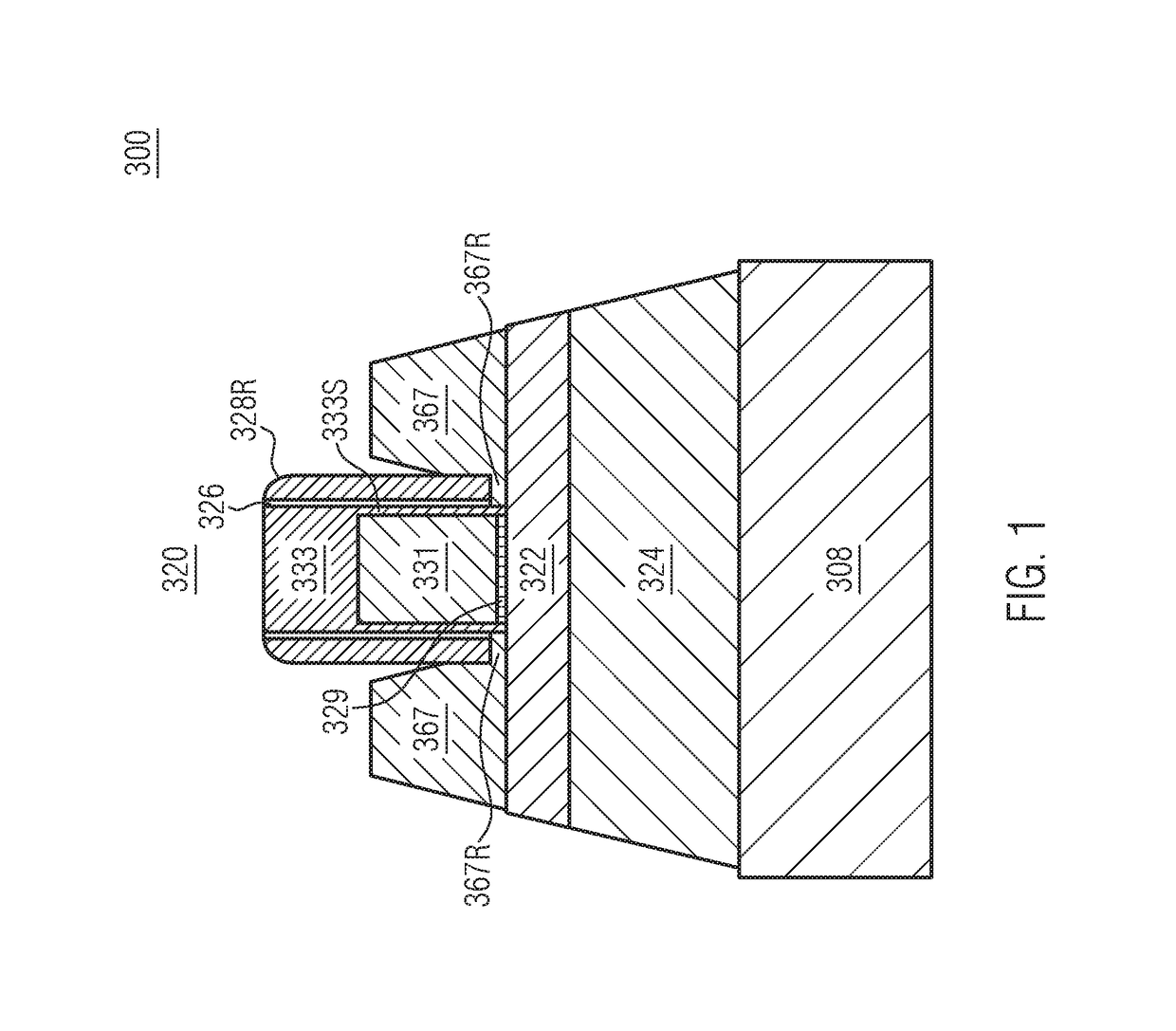
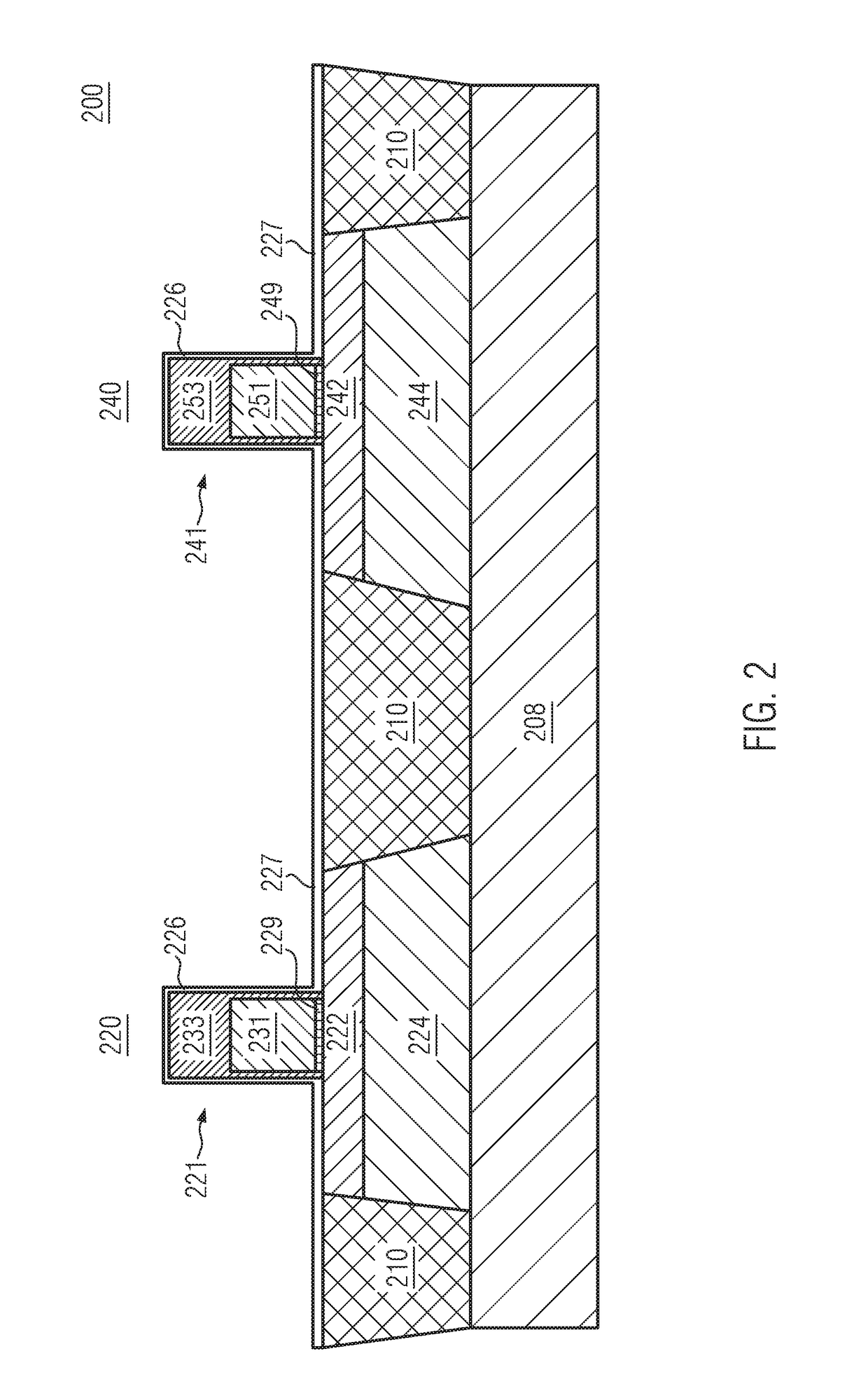
Junction formation with reduced CEFF for 22NM FDSOI devices
ActiveUS9634088B1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingJunction formationSemiconductor
A method of forming a semiconductor device is disclosed including providing a silicon-on-insulator substrate comprising a semiconductor bulk substrate, a buried oxide layer formed on the semiconductor bulk substrate and a semiconductor layer formed on the buried oxide layer, and forming a transistor device on the silicon-on-insulator substrate including providing a gate structure on the semiconductor layer having a gate electrode and a first cap layer on the gate electrode, growing an oxide liner on the transistor device having a first part covering the gate structure and a second part covering the semiconductor layer, forming a second cap layer on the oxide liner, at least partially removing the second part of the oxide liner underneath the second cap layer and the first part of the oxide liner, and epitaxially forming raised source / drain regions on the semiconductor layer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com