Patents
Literature
75 results about "Plasma current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
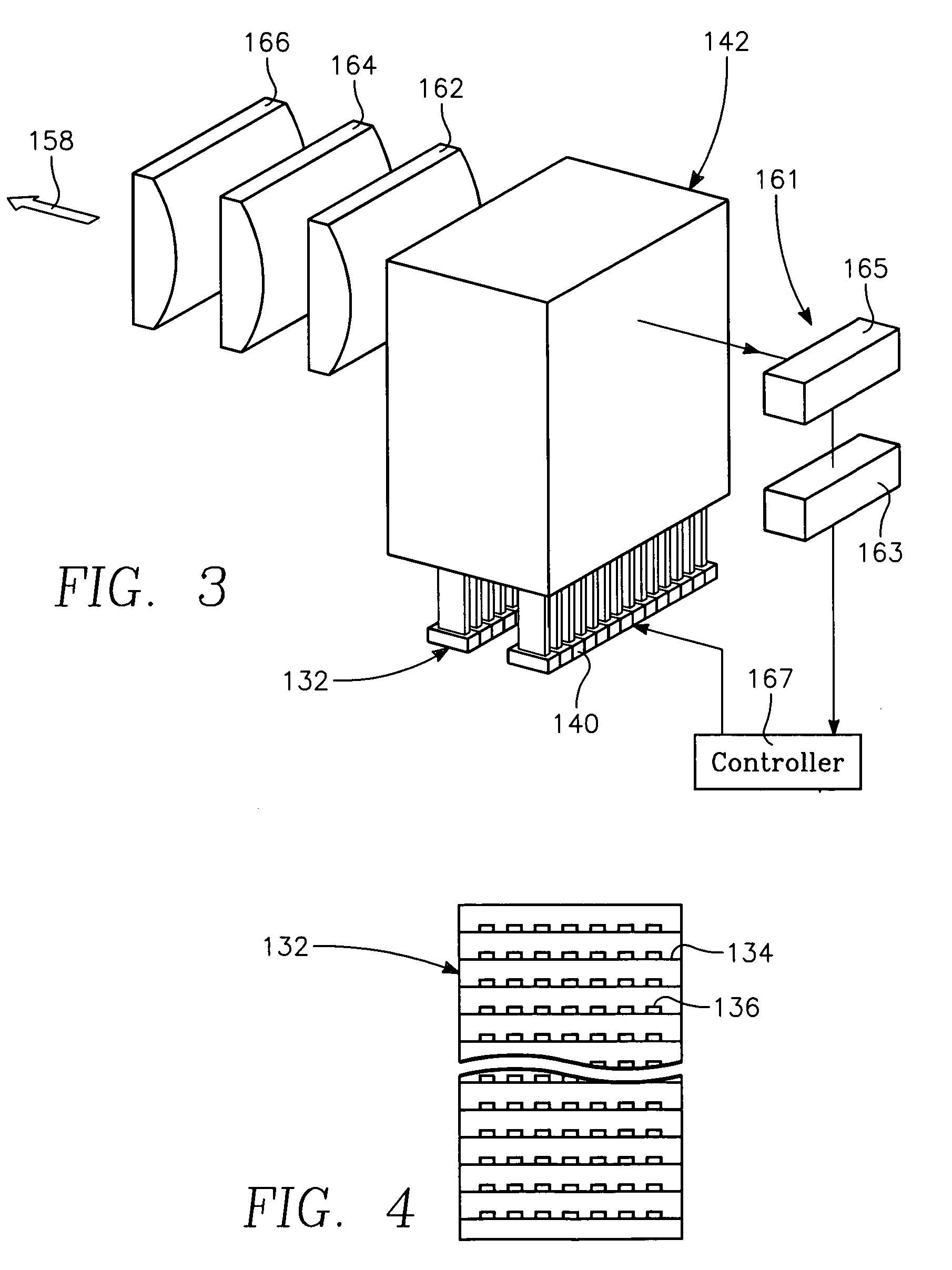
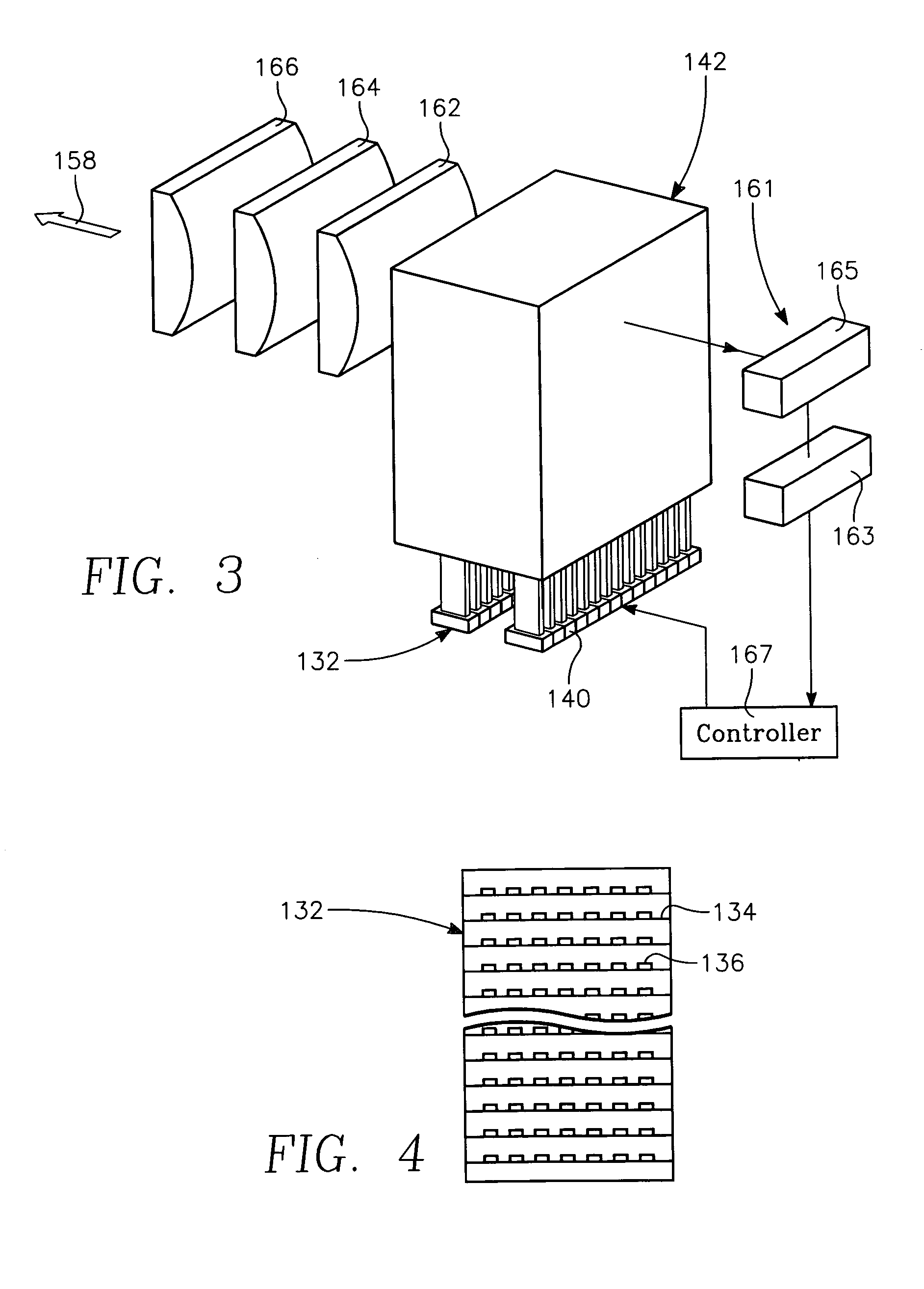
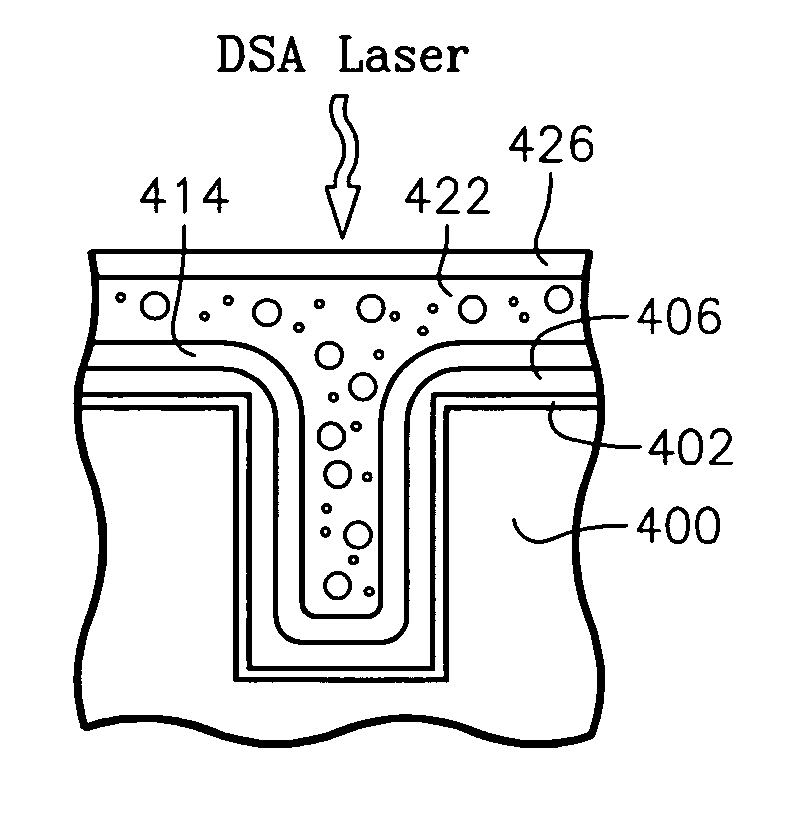
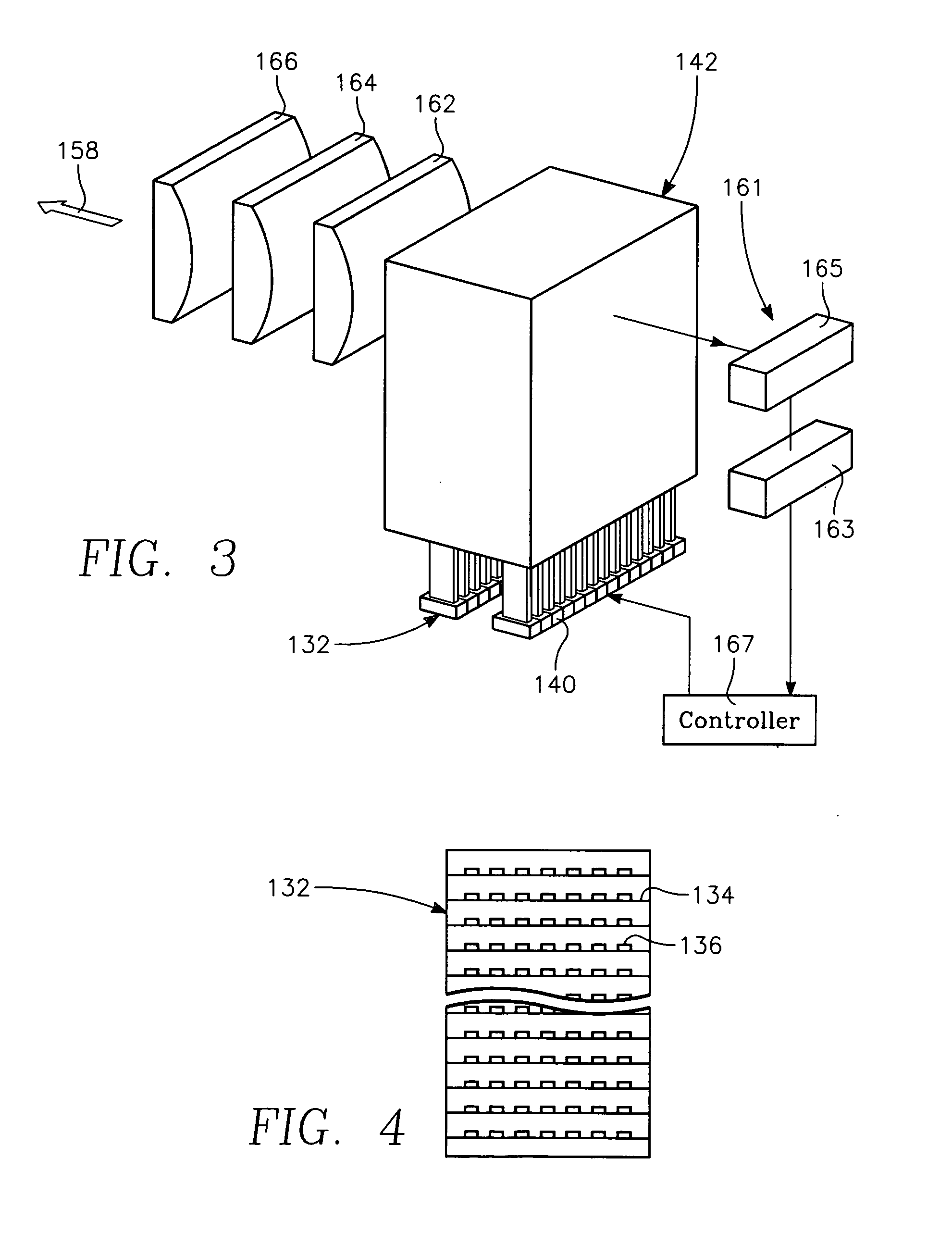
Semiconductor substrate process using a low temperature deposited carbon-containing hard mask
InactiveUS7323401B2Electric discharge tubesRadiation applicationsLow temperature depositionPlasma current
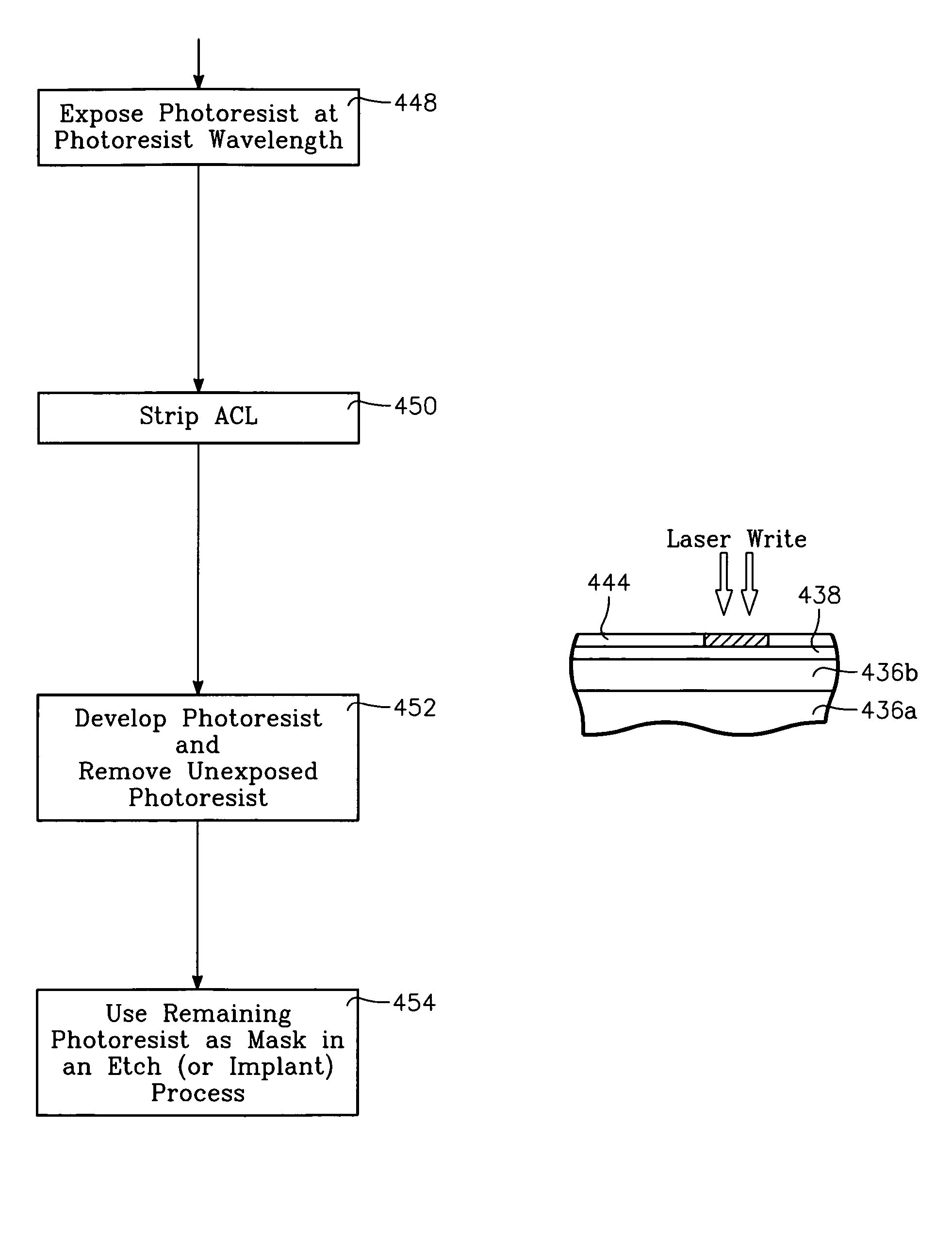
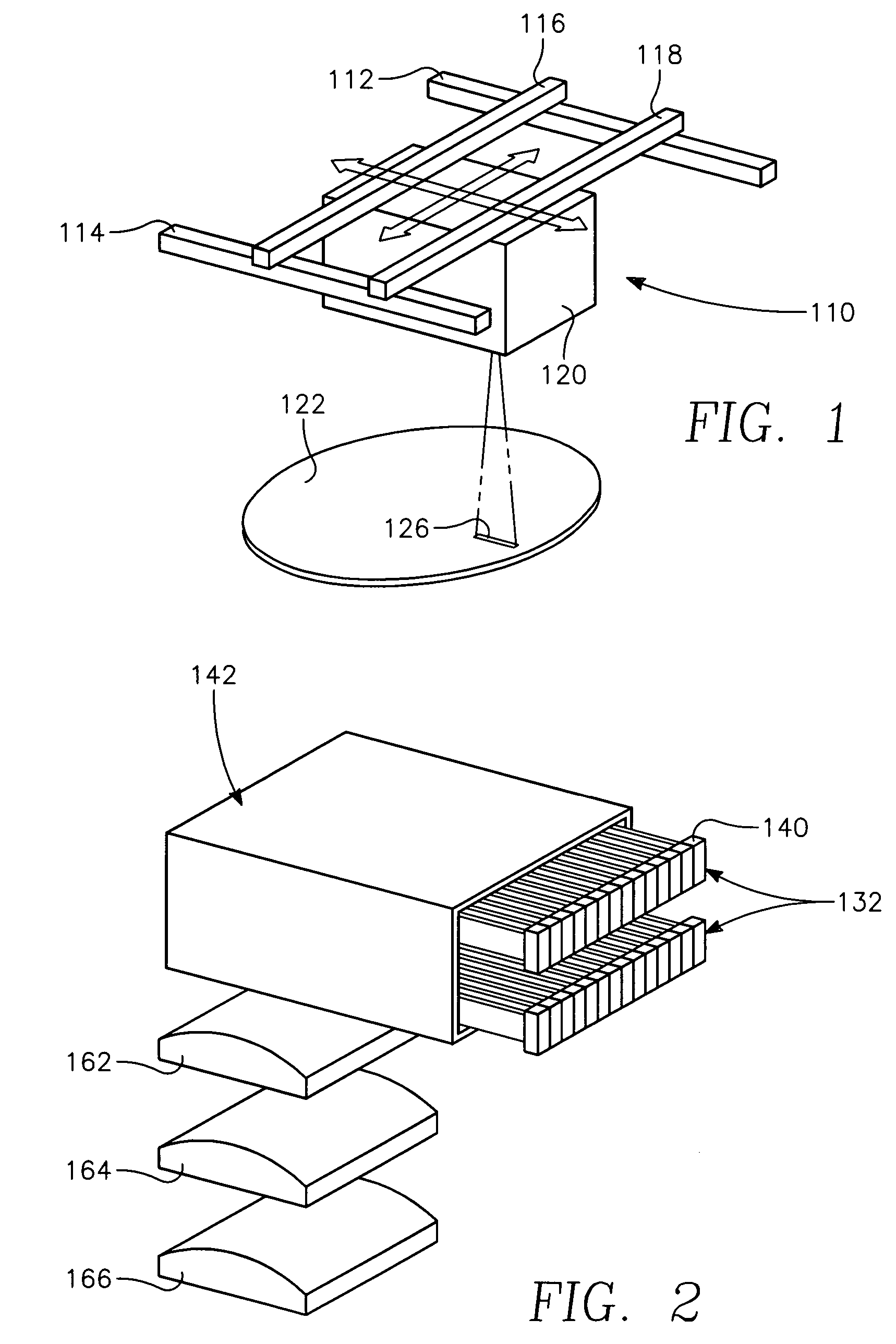
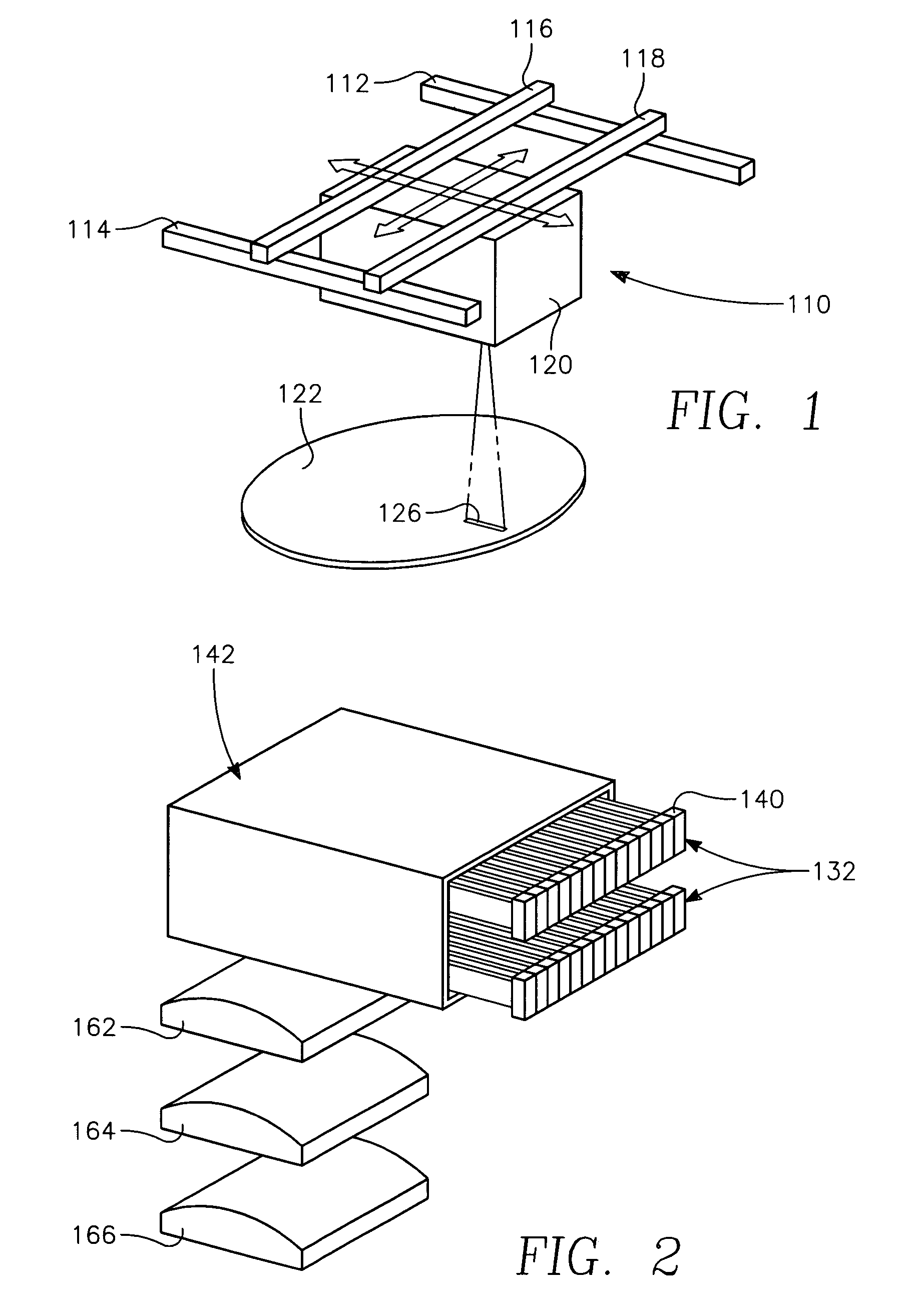
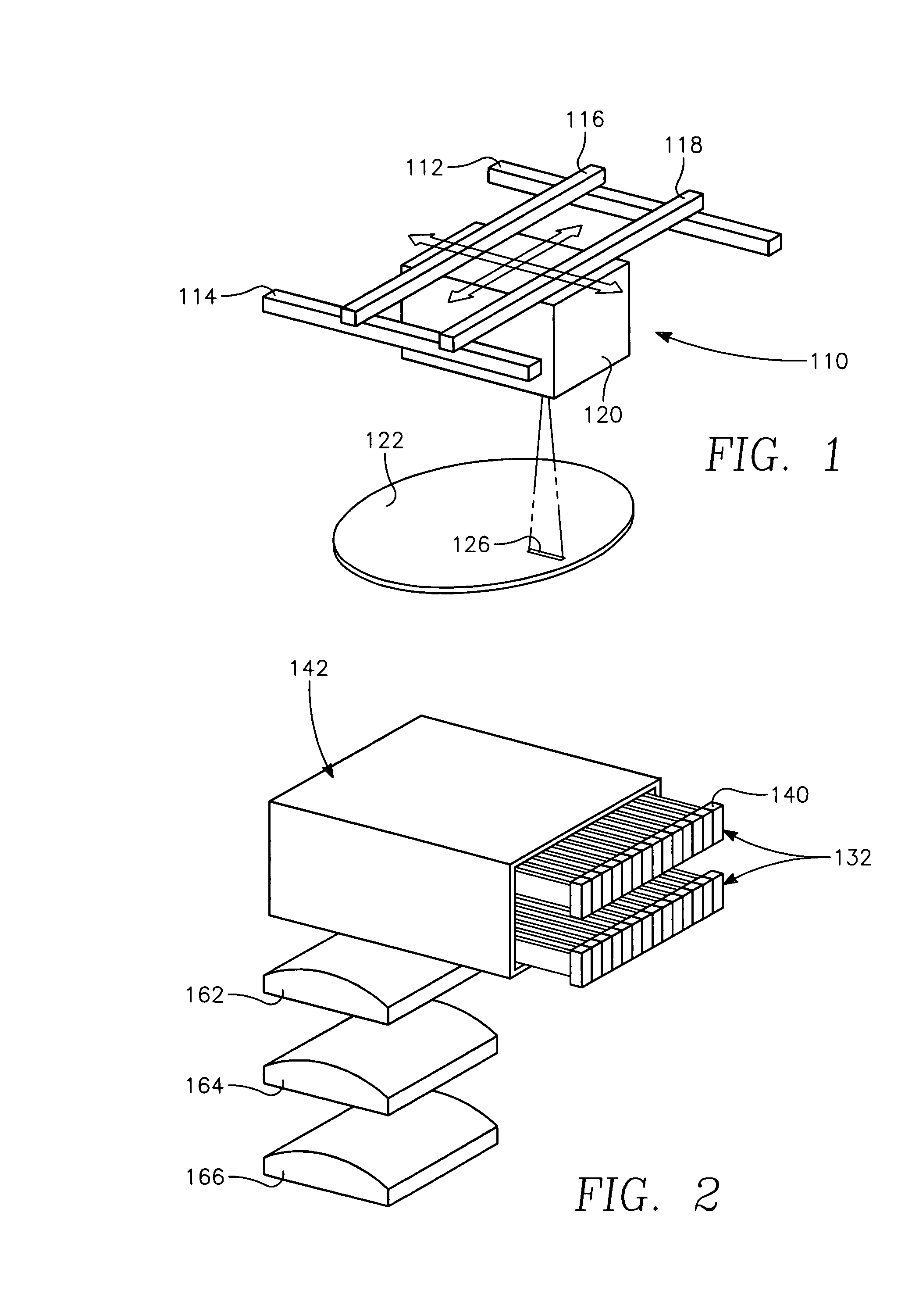
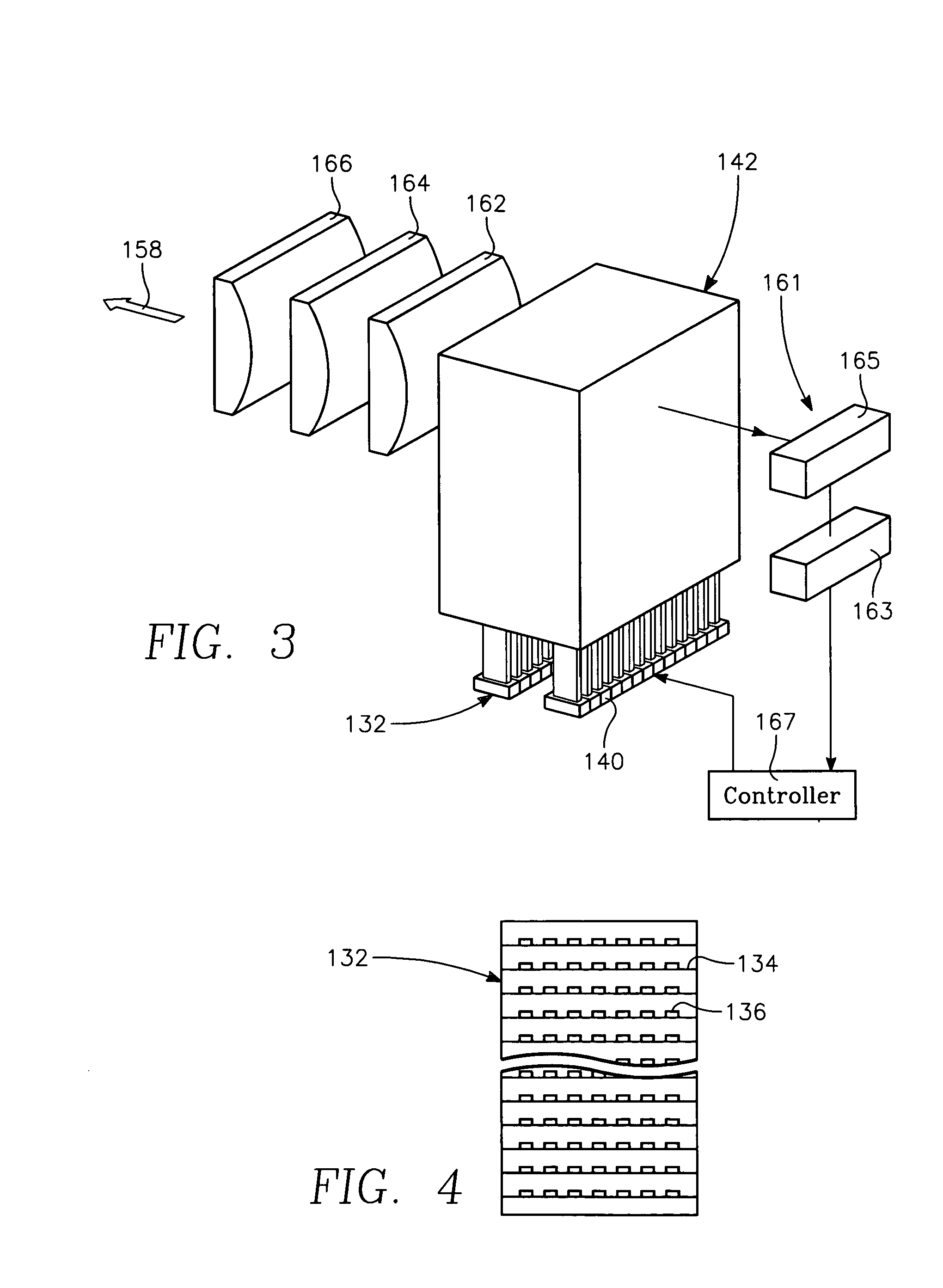
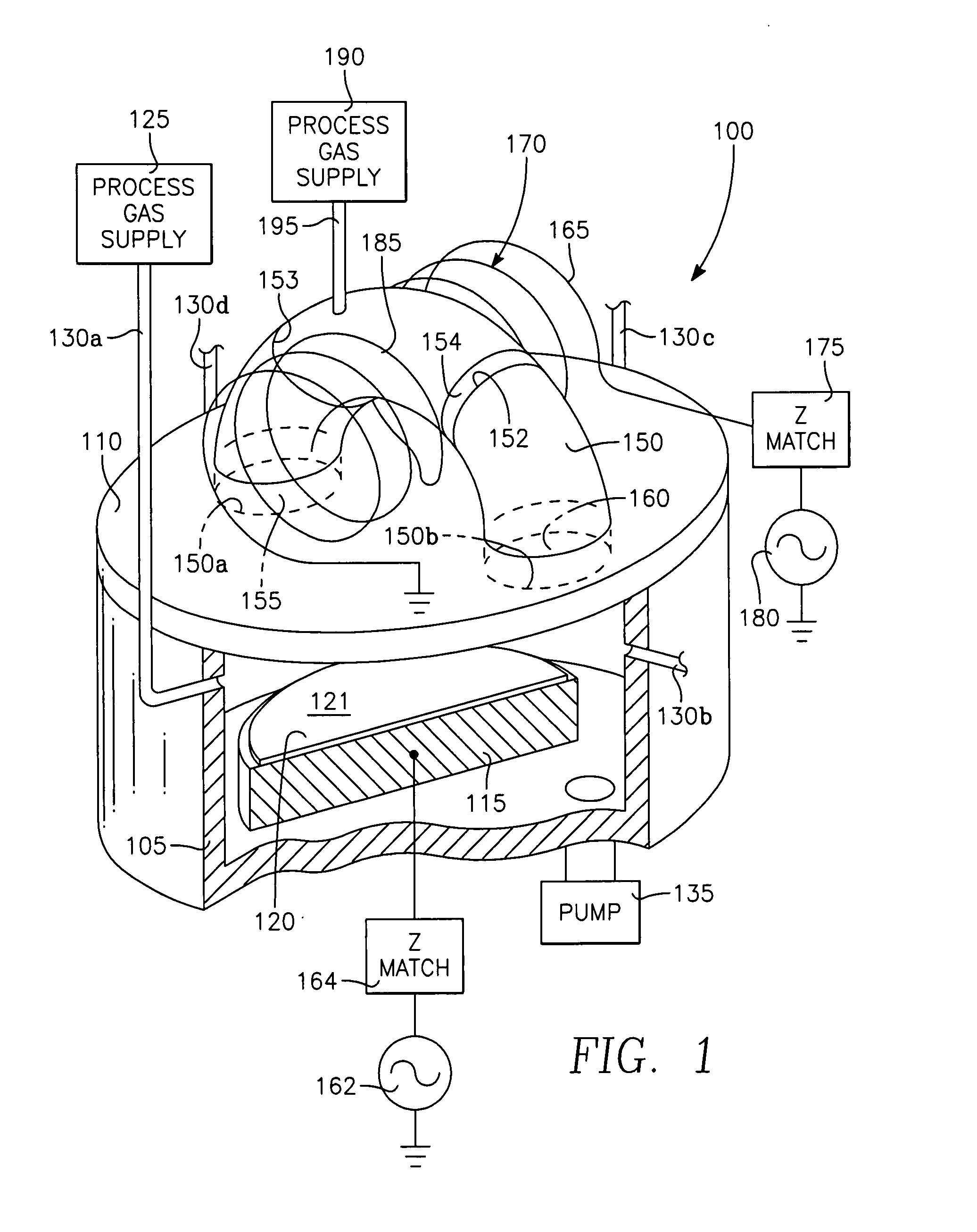
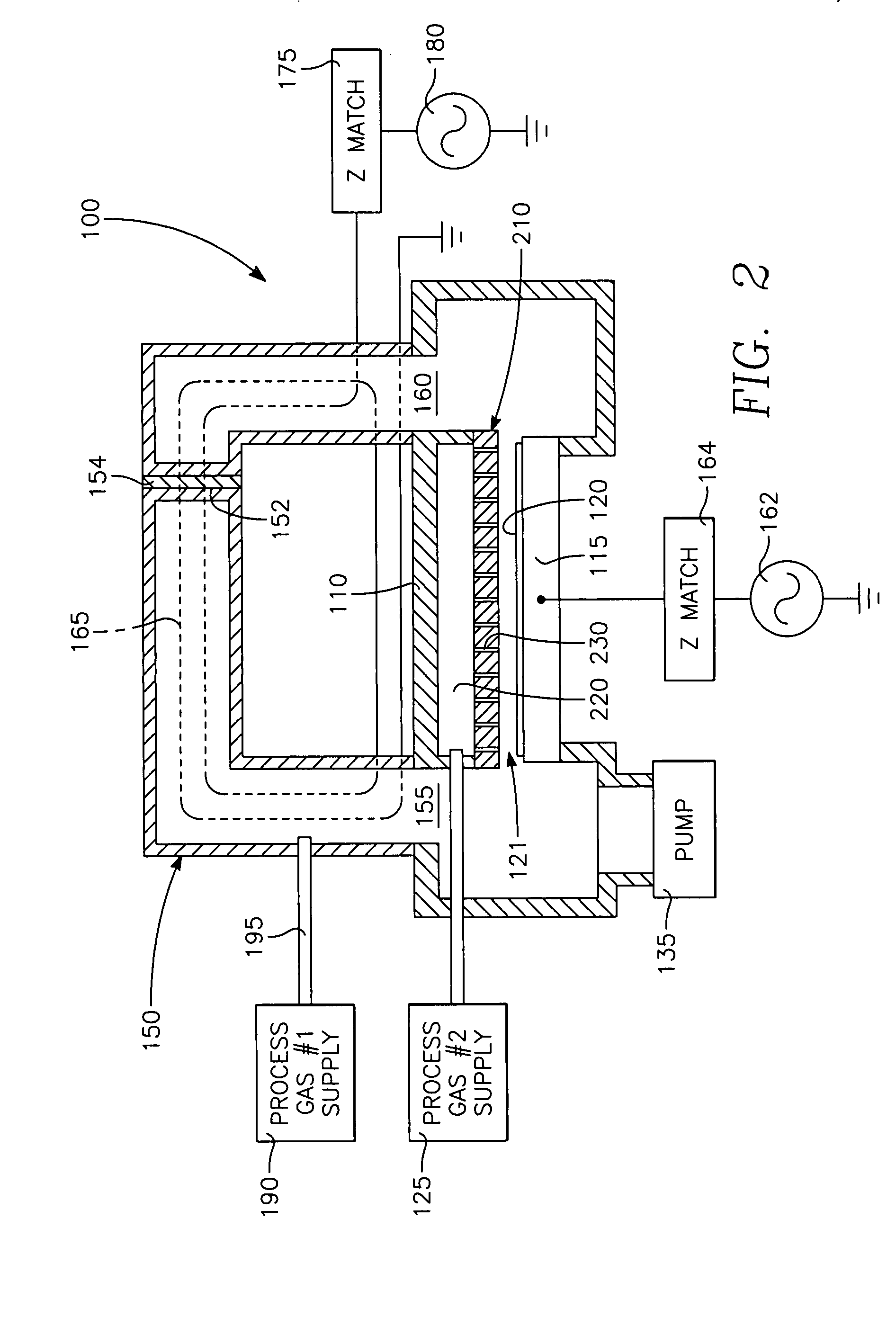
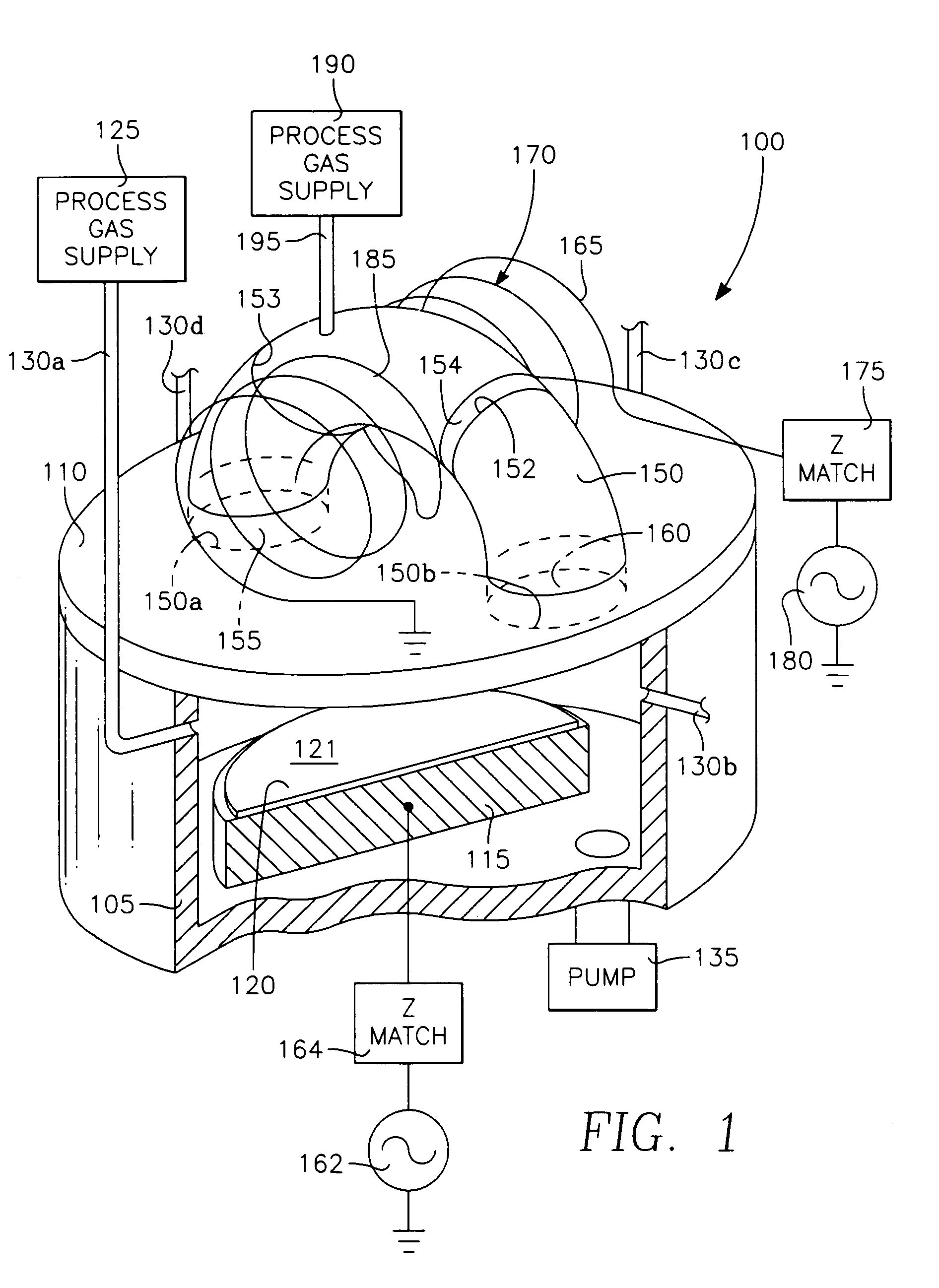
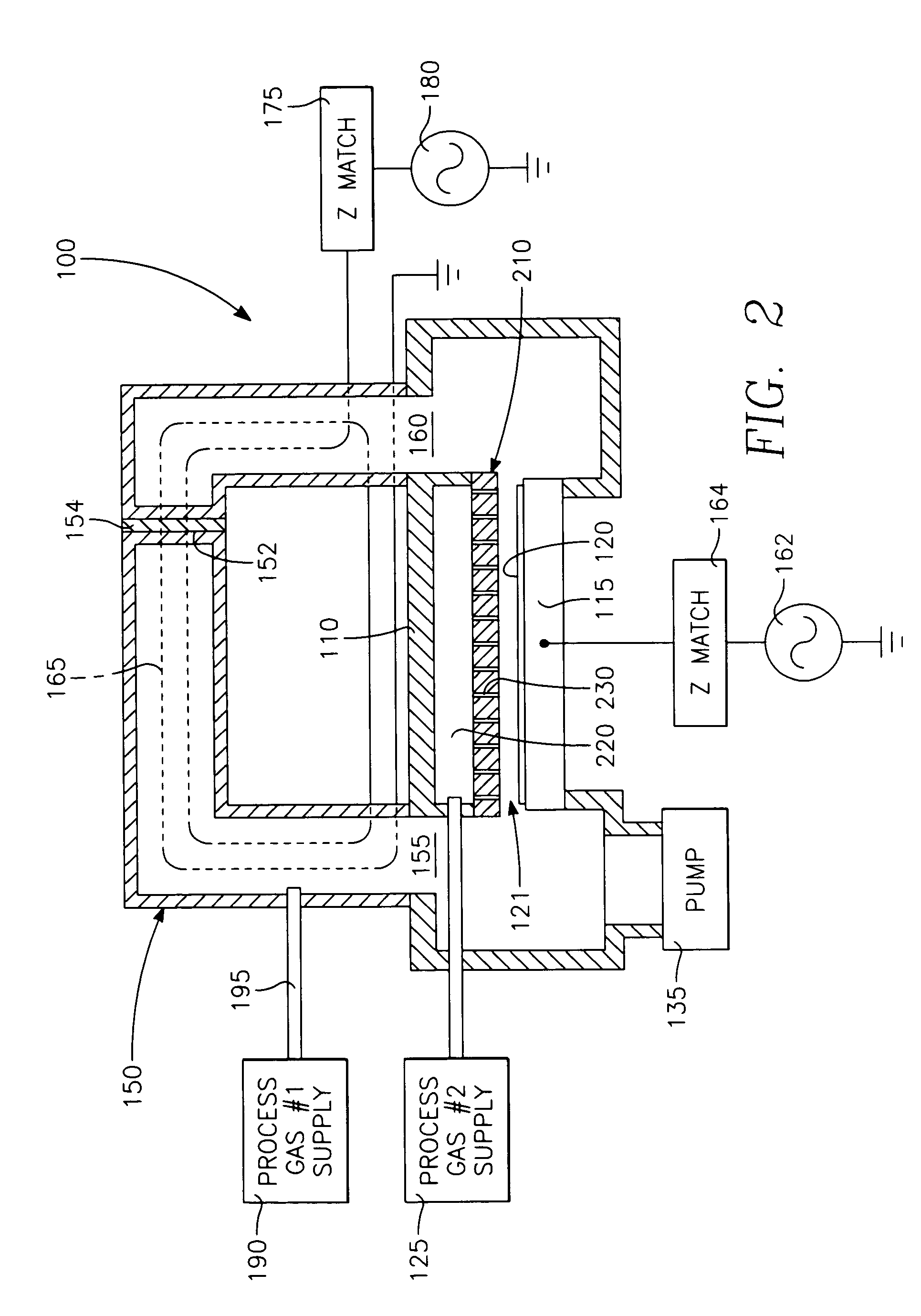
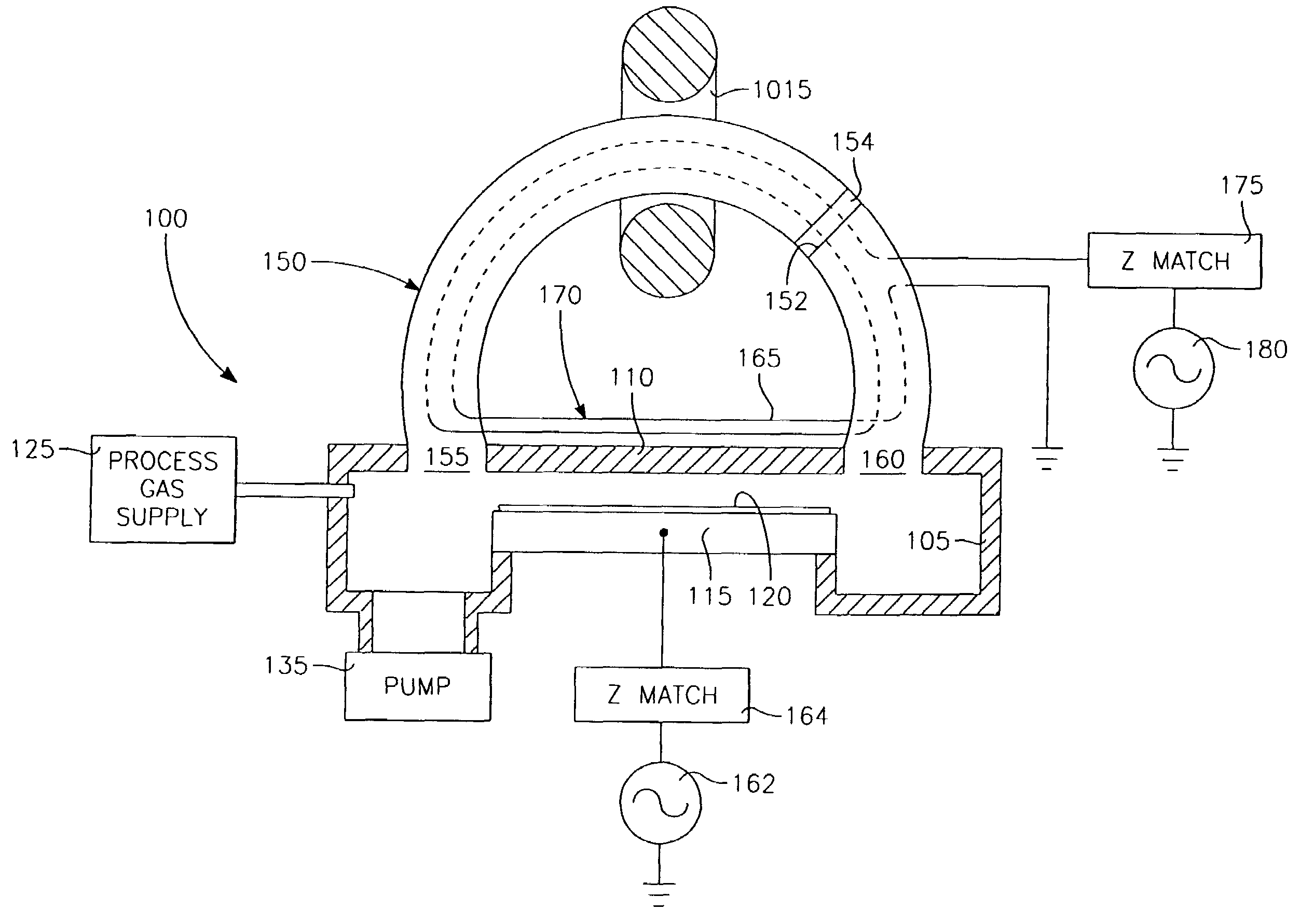
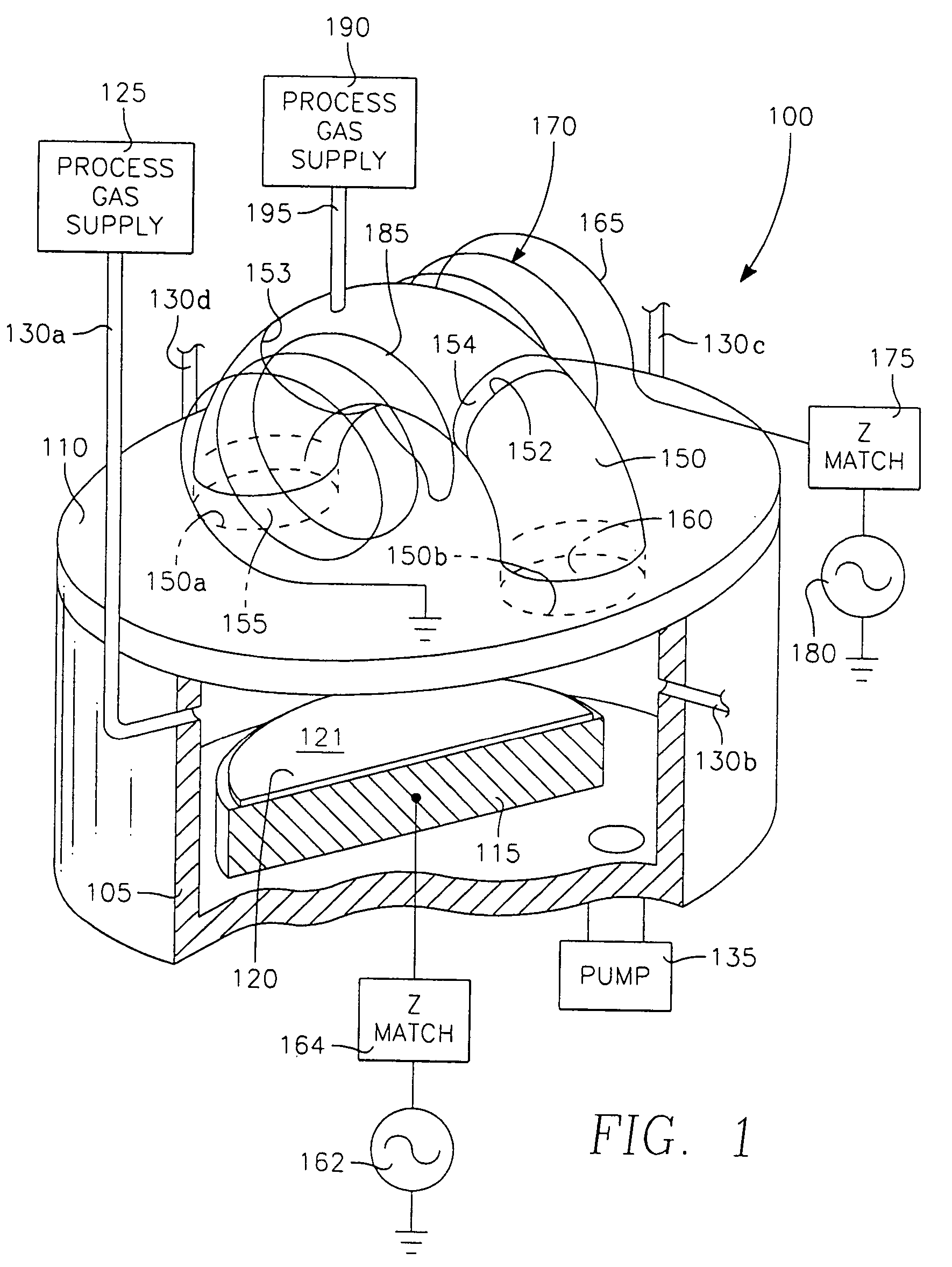
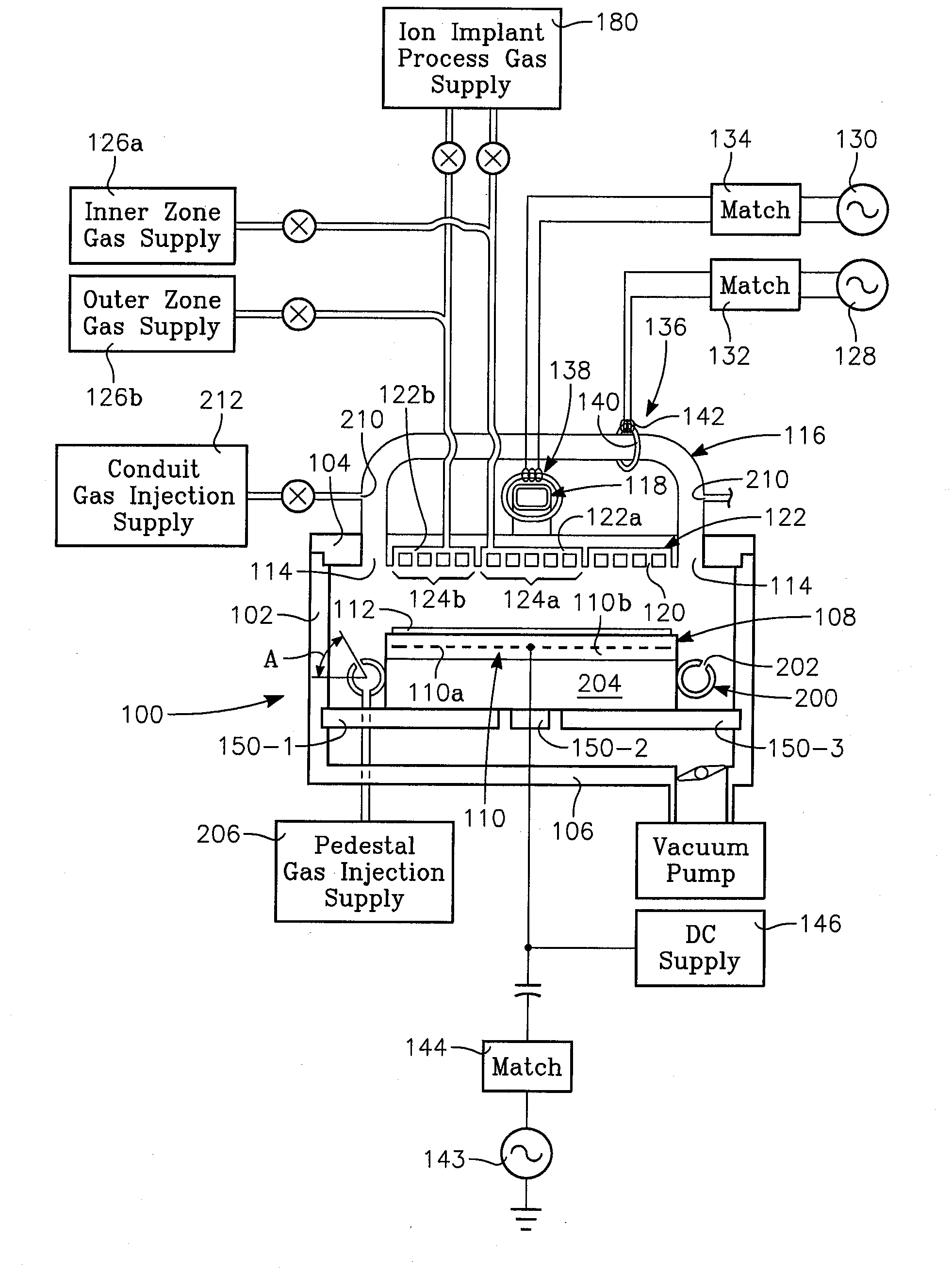
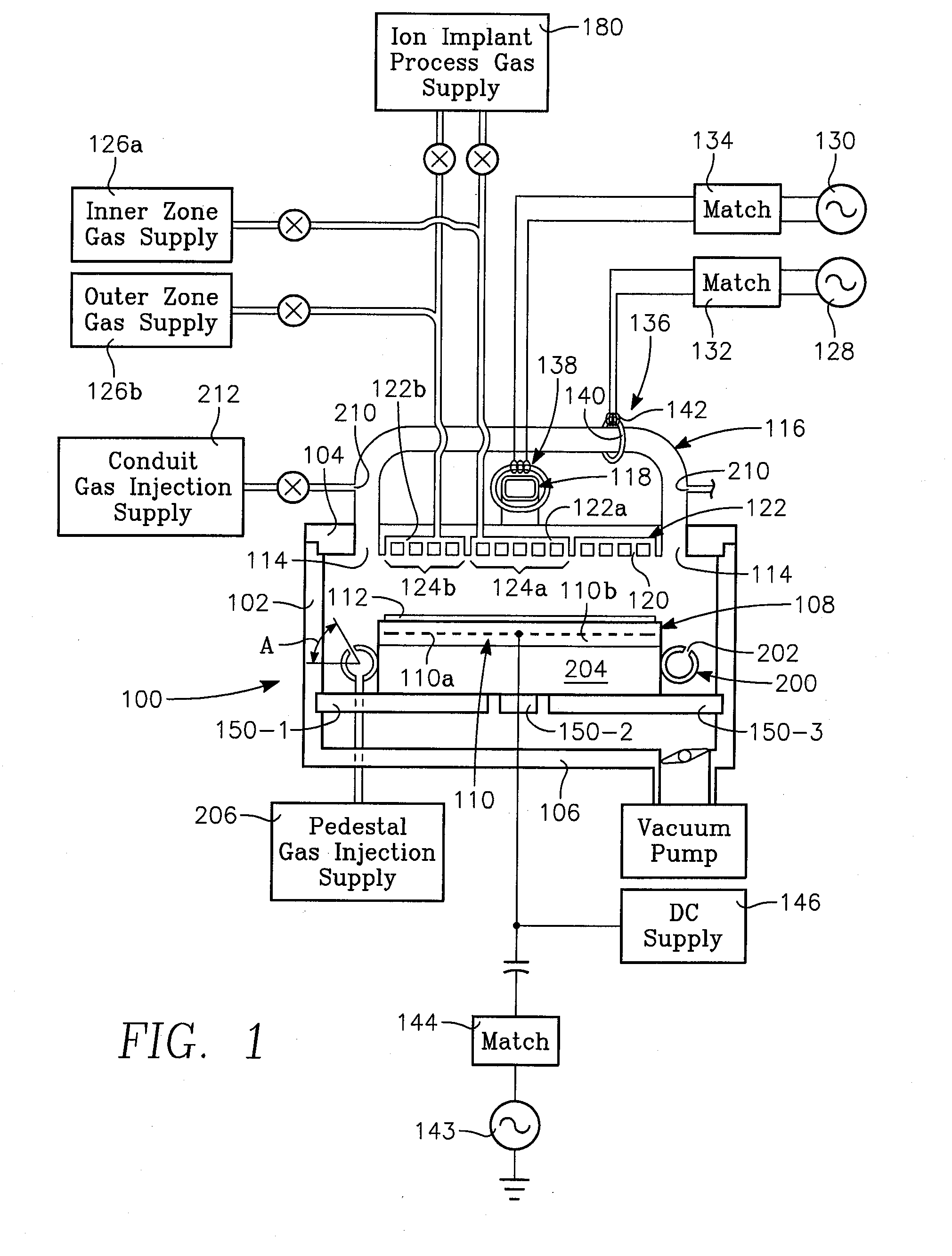
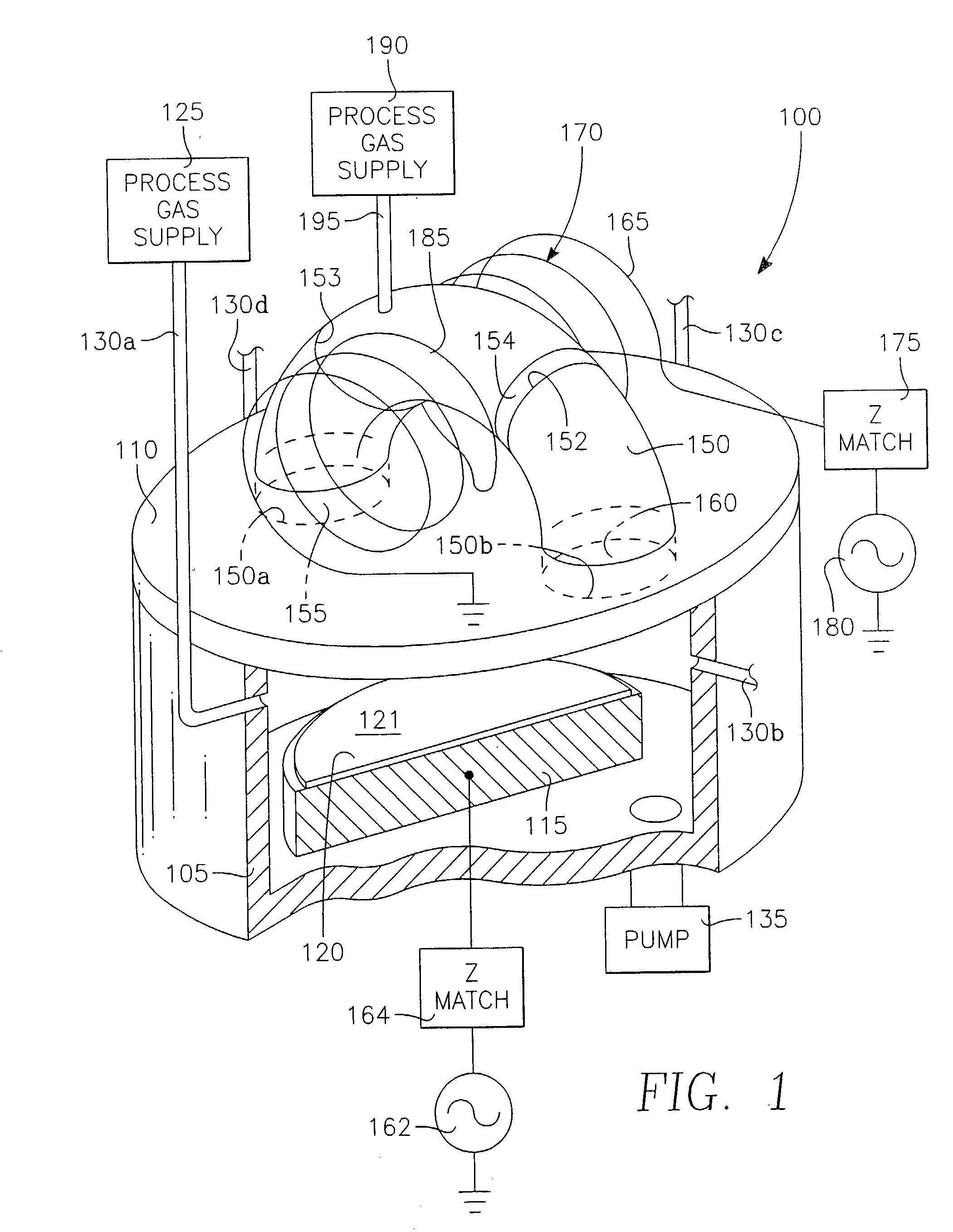
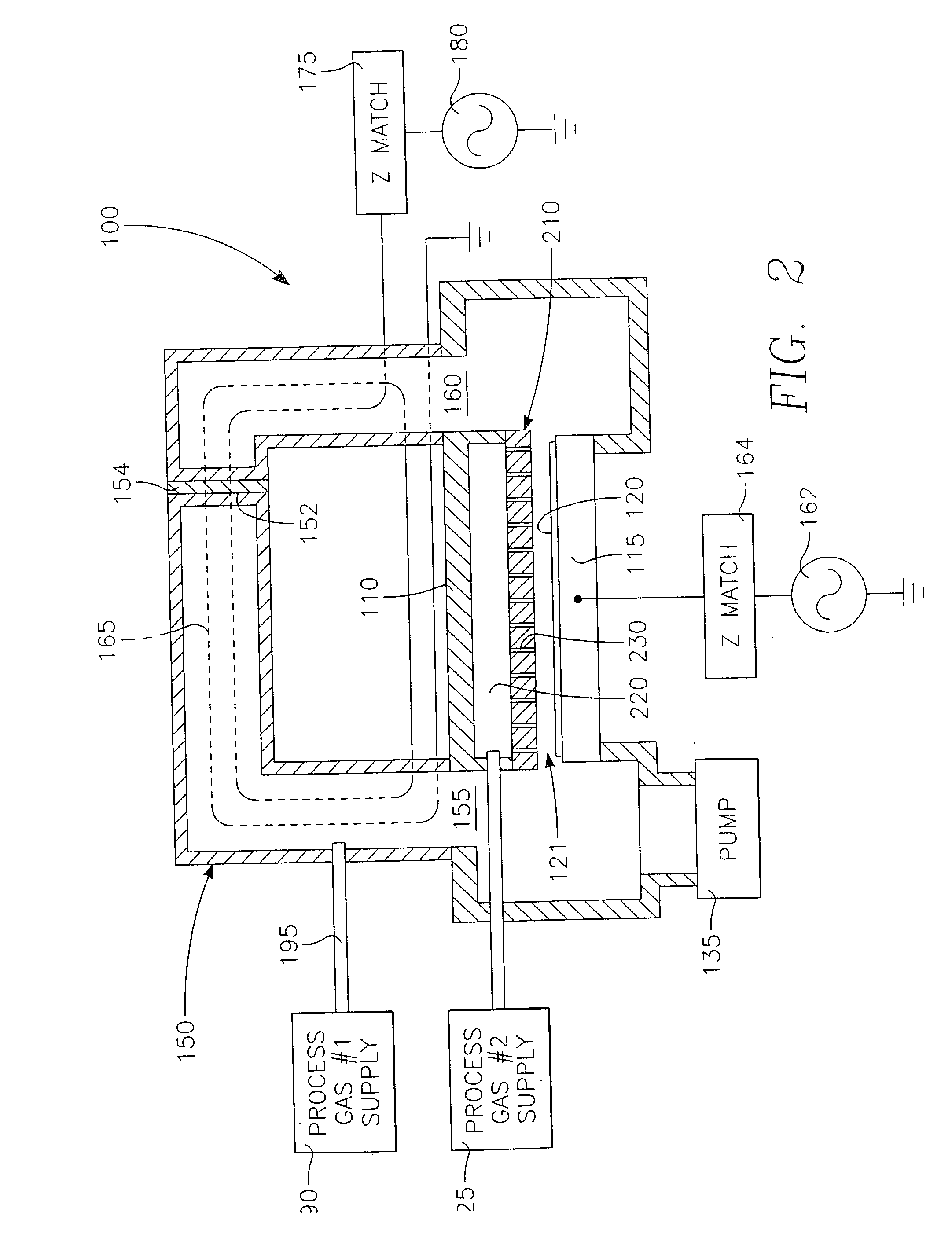
A method of processing a thin film structure on a semiconductor substrate using an optically writable mask includes placing the substrate in a reactor chamber, the substrate having on its surface a target layer to be etched in accordance with a predetermined pattern, and depositing a carbon-containing hard mask layer on the substrate by (a) introducing a carbon-containing process gas into the chamber, (b) generating a reentrant toroidal RF plasma current in a reentrant path that includes a process zone overlying the workpiece by coupling plasma RF source power to an external portion of the reentrant path, and (c) coupling RF plasma bias power or bias voltage to the workpiece. The method further includes photolithographically defining the predetermined pattern in the carbon-containing hard mask layer, and etching the target layer in the presence of the hard mask layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Low temperature plasma deposition process for carbon layer deposition
InactiveUS7312162B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingCarbon layerPlasma current
A method of depositing a carbon layer on a workpiece includes placing the workpiece in a reactor chamber, introducing a carbon-containing process gas into the chamber, generating a reentrant toroidal RF plasma current in a reentrant path that includes a process zone overlying the workpiece by coupling plasma RF source power to an external portion of the reentrant path, and coupling RF plasma bias power or bias voltage to the workpiece.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
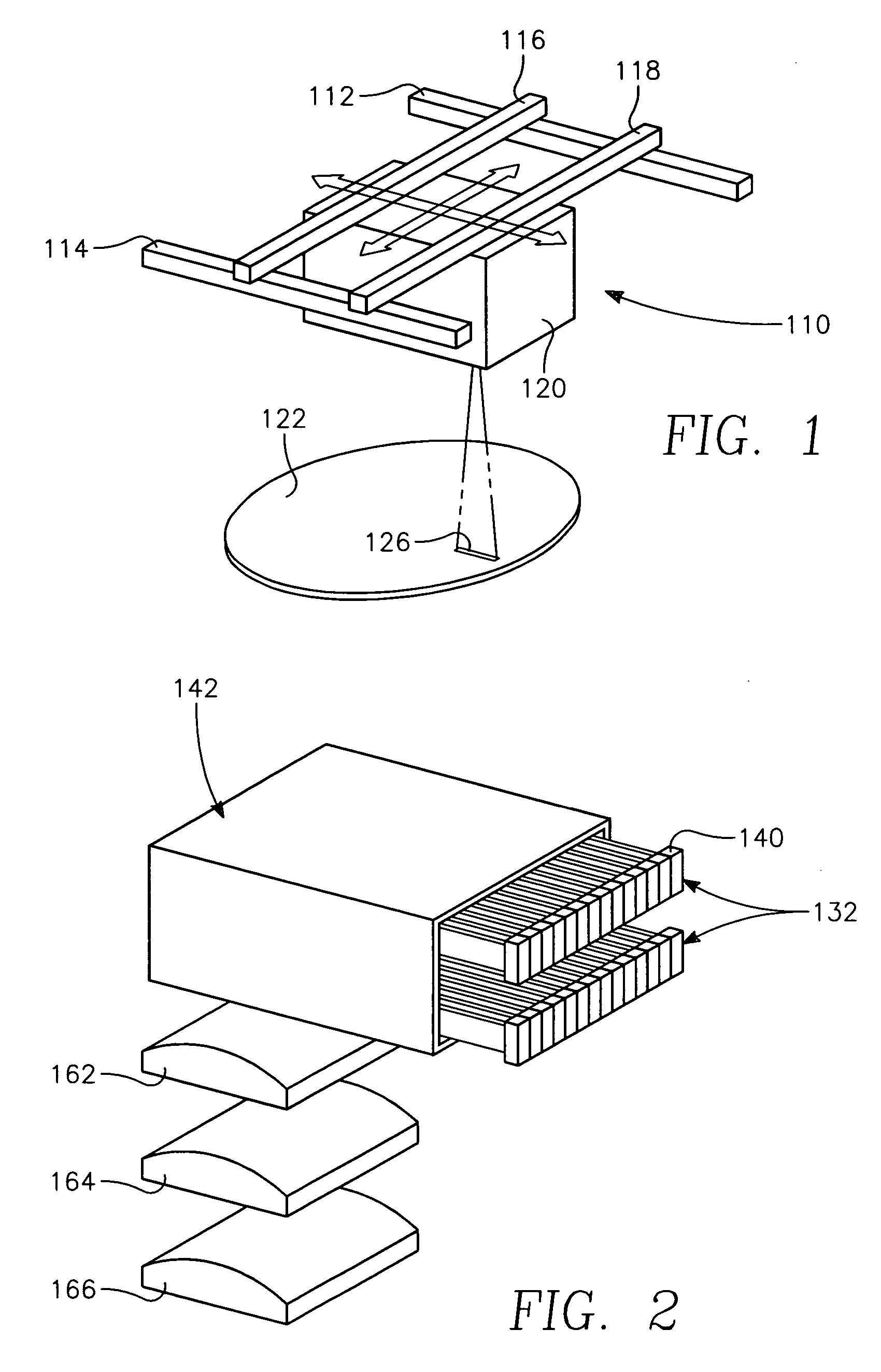
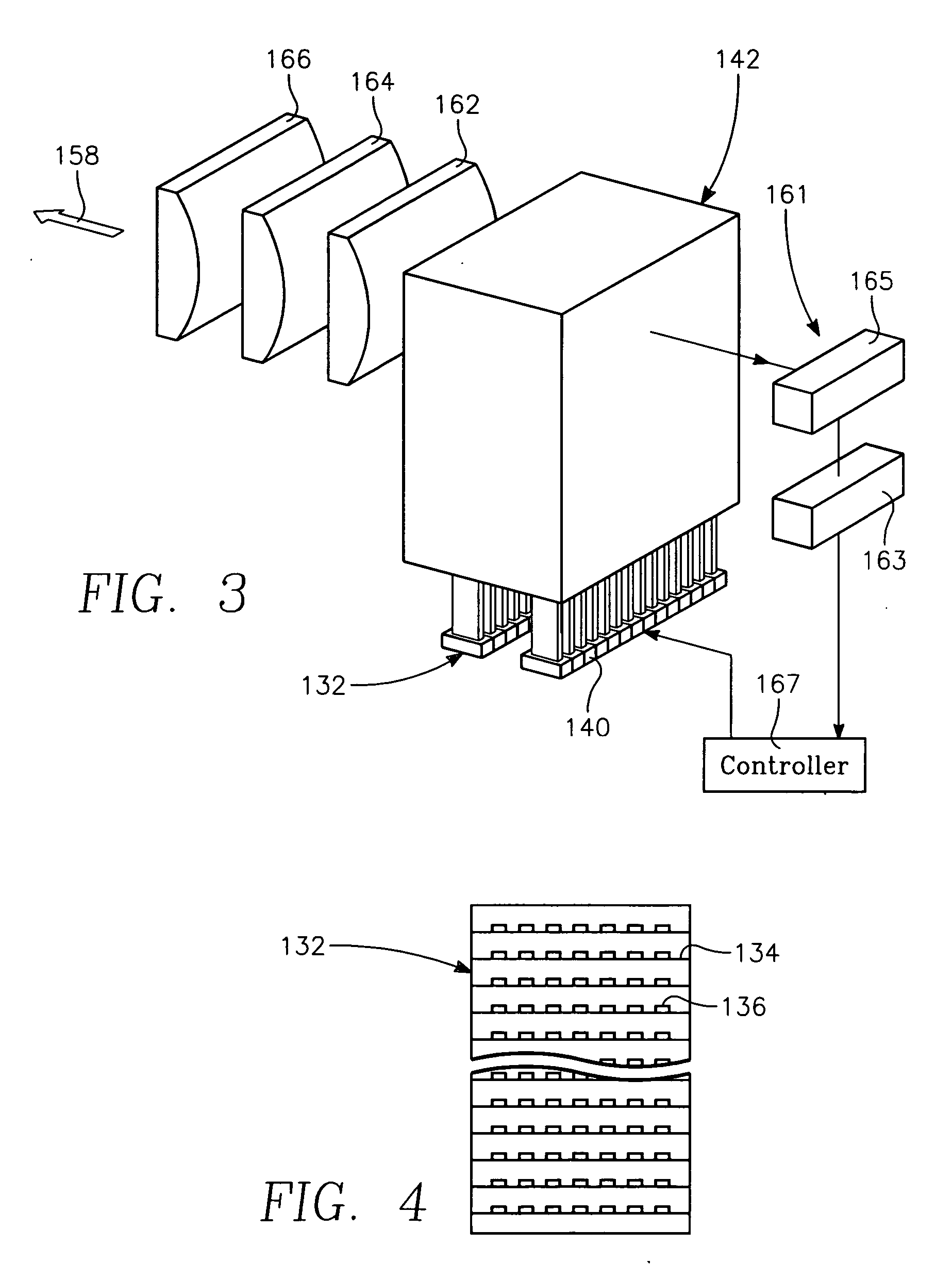
Copper conductor annealing process employing high speed optical annealing with a low temperature-deposited optical absorber layer
InactiveUS7335611B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesCopper conductorLow temperature deposition
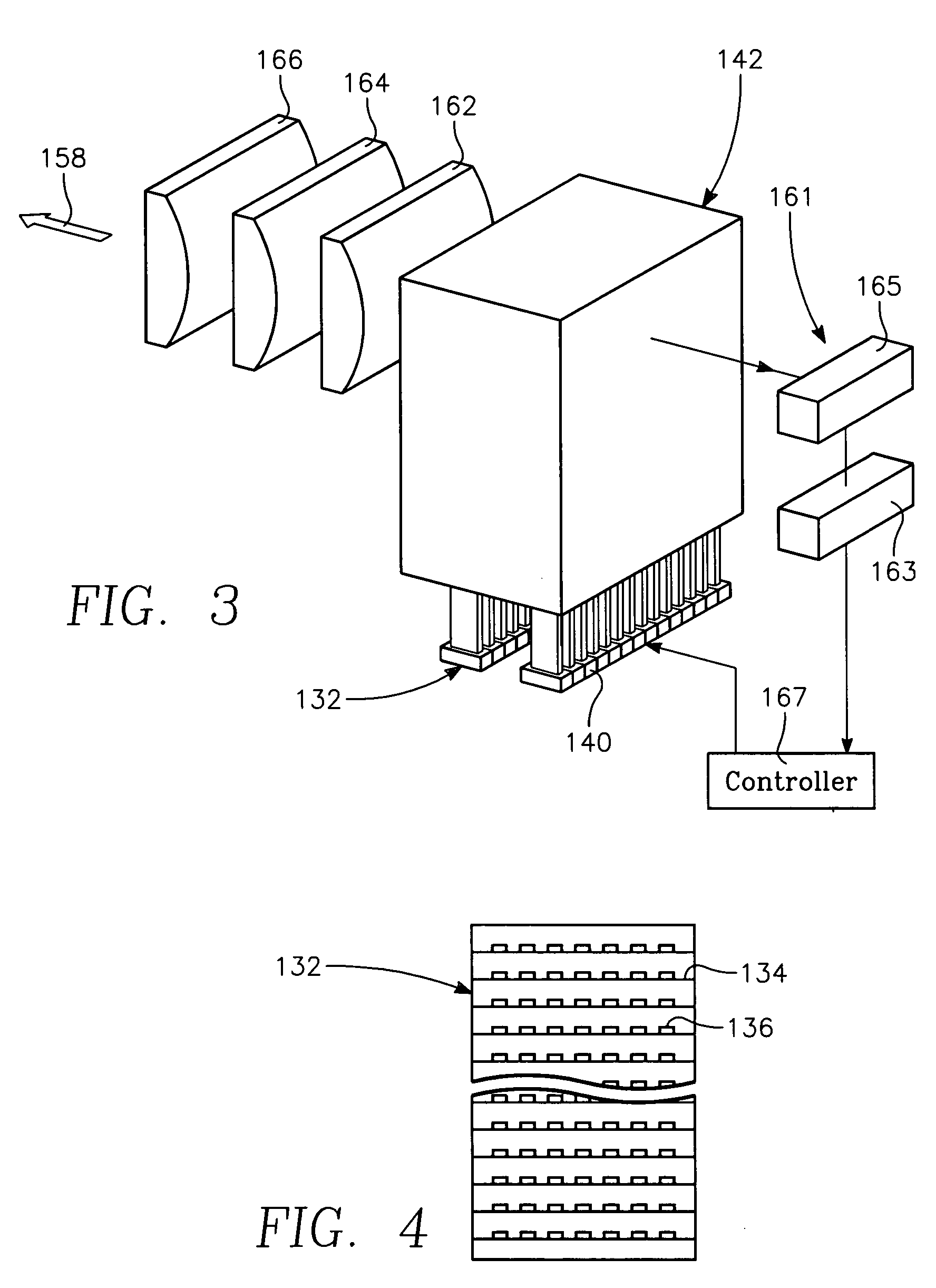
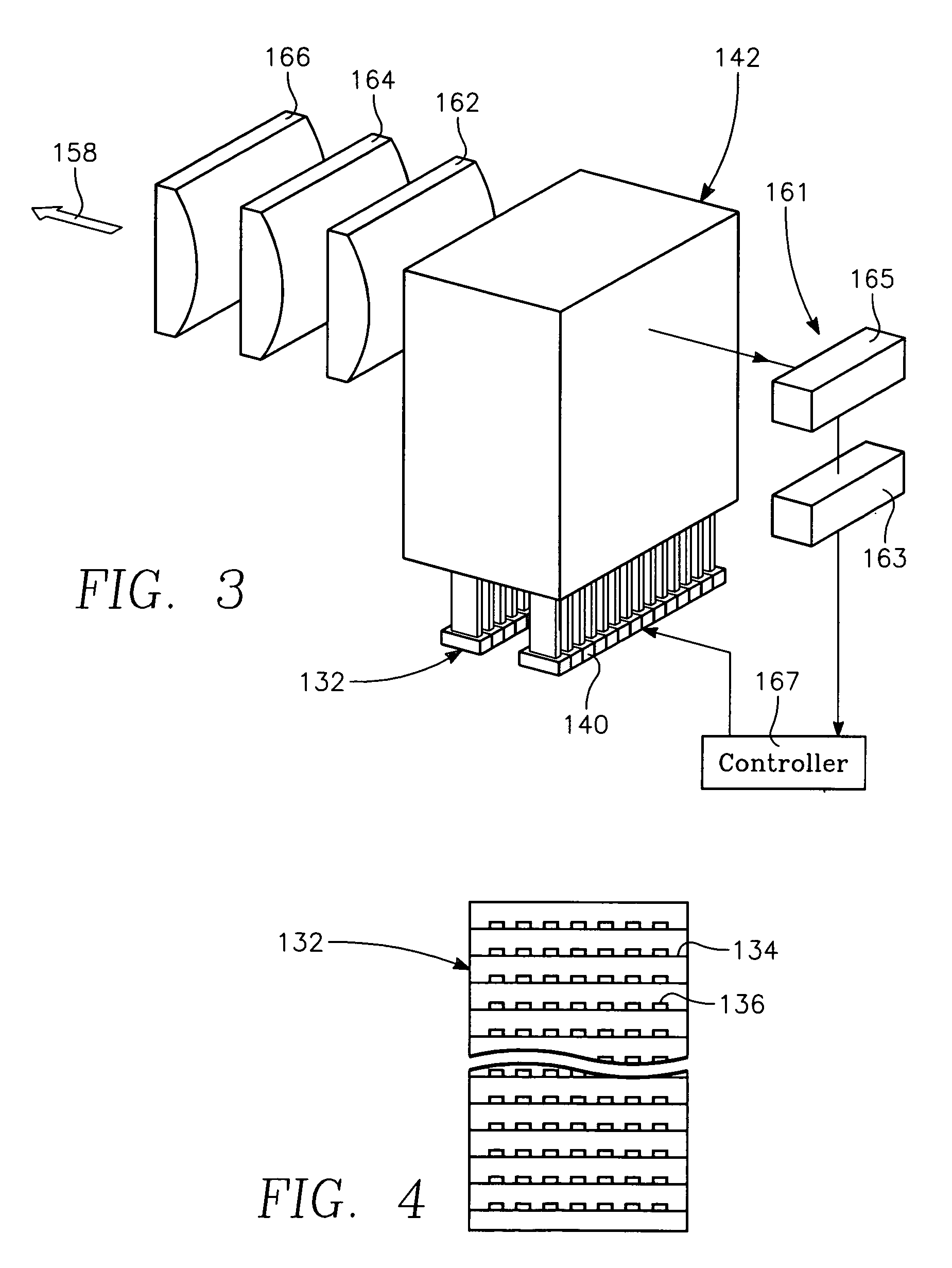
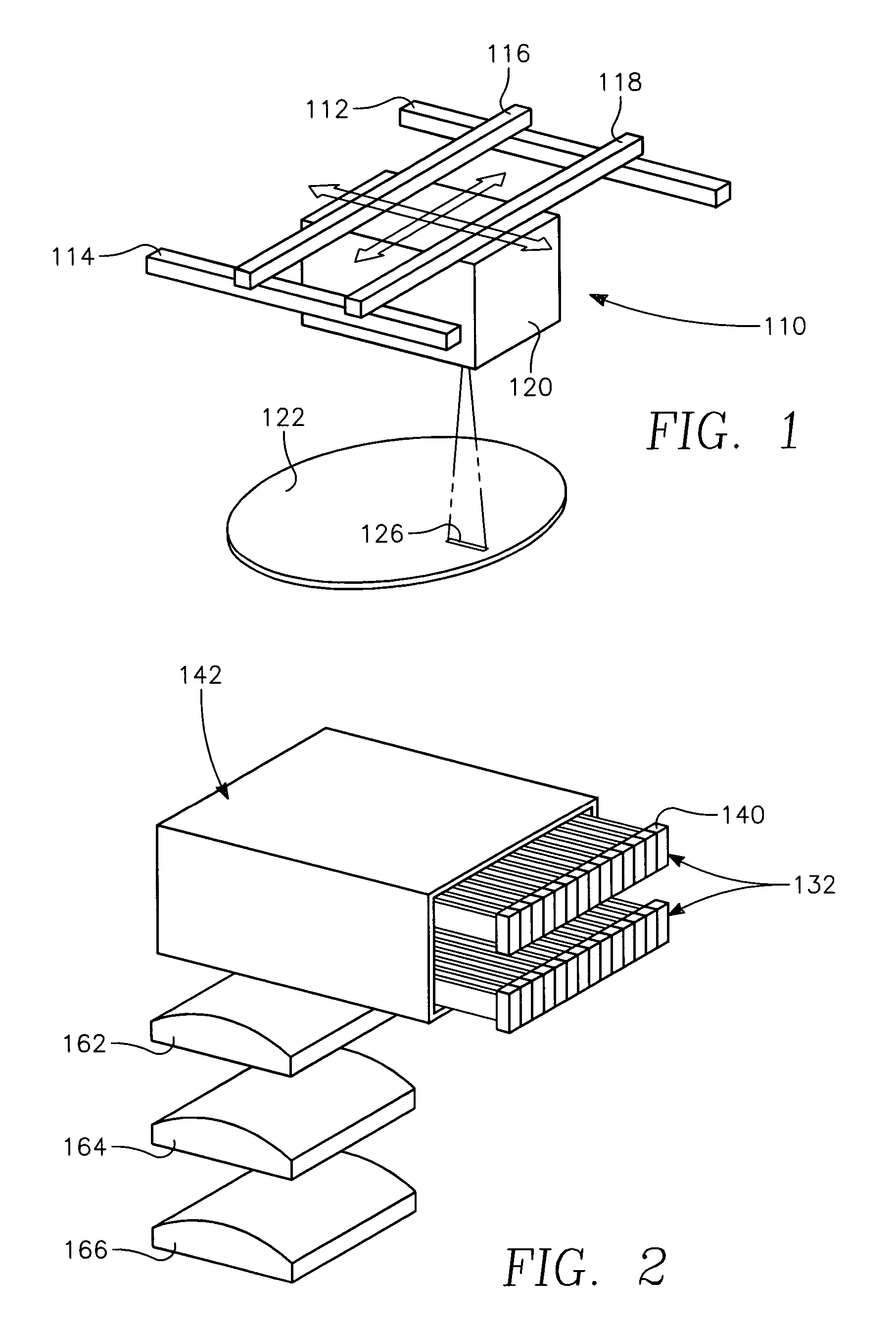
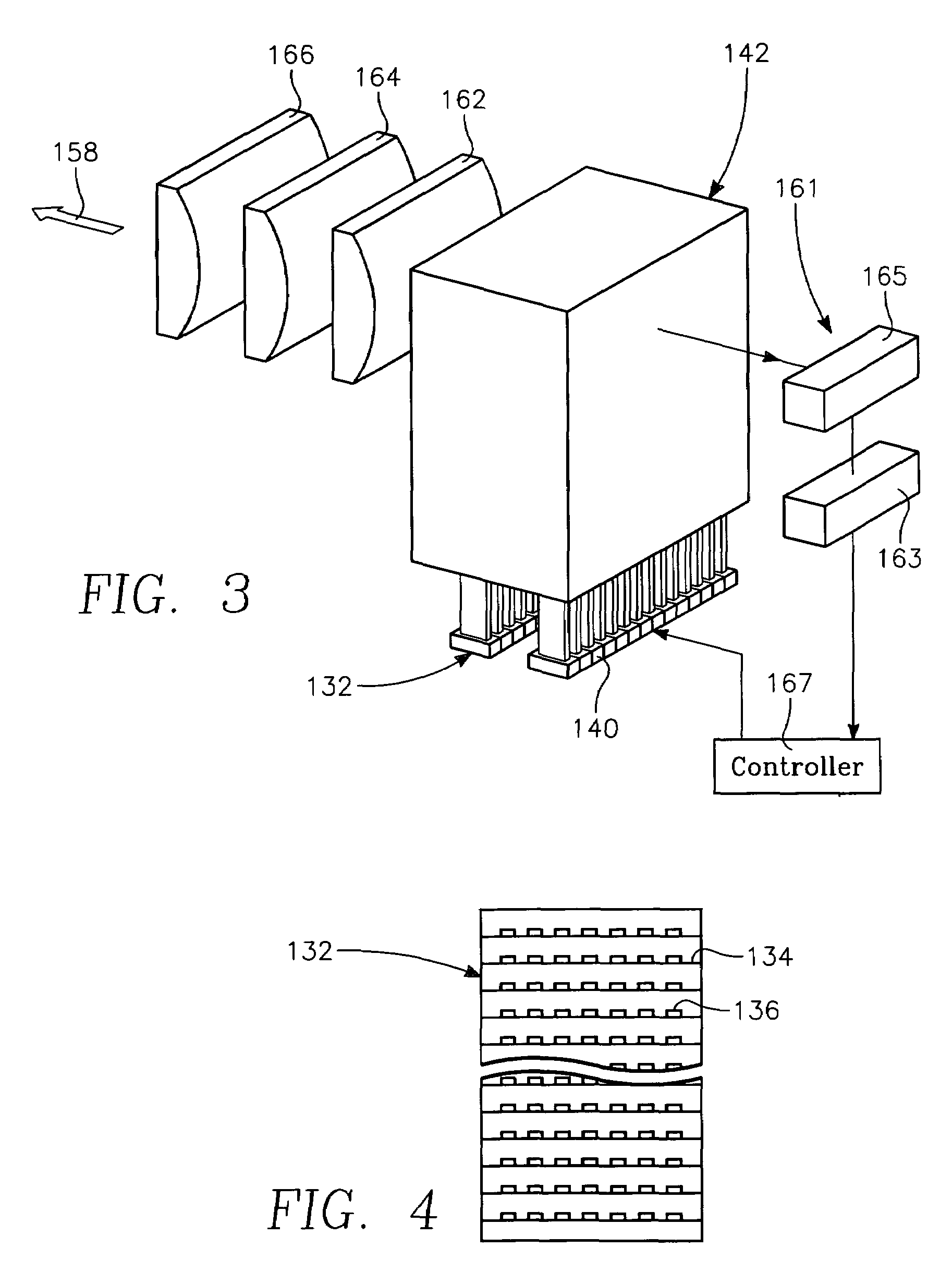
A method of forming a conductor in a thin film structure on a semiconductor substrate includes forming high aspect ratio openings in a base layer having vertical side walls, depositing a dielectric barrier layer comprising a dielectric compound of a barrier metal on the surfaces of the high aspect ratio openings including the vertical side walls, depositing a metal barrier layer comprising the barrier metal on the first barrier layer, depositing a main conductor species seed layer on the metal barrier layer and depositing a main conductor layer. The method further includes annealing the main conductor layer by (a) directing light from an array of continuous wave lasers into a line of light extending at least partially across the thin film structure, and (b) translating the line of light relative to the thin film structure in a direction transverse to the line of light. The method of Claim 1 further comprising, prior to the annealing step, depositing an amorphous carbon optical absorber layer on the main conductor layer. The step of depositing an amorphous carbon optical absorber layer includes introducing a carbon-containing process gas into a reactor chamber containing the substrate in a process zone of the reactor, applying RF source power to an external reentrant conduit of the reactor to generate a reentrant toroidal RF plasma current passing through the process zone and applying a bias voltage to the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Semiconductor junction formation process including low temperature plasma deposition of an optical absorption layer and high speed optical annealing
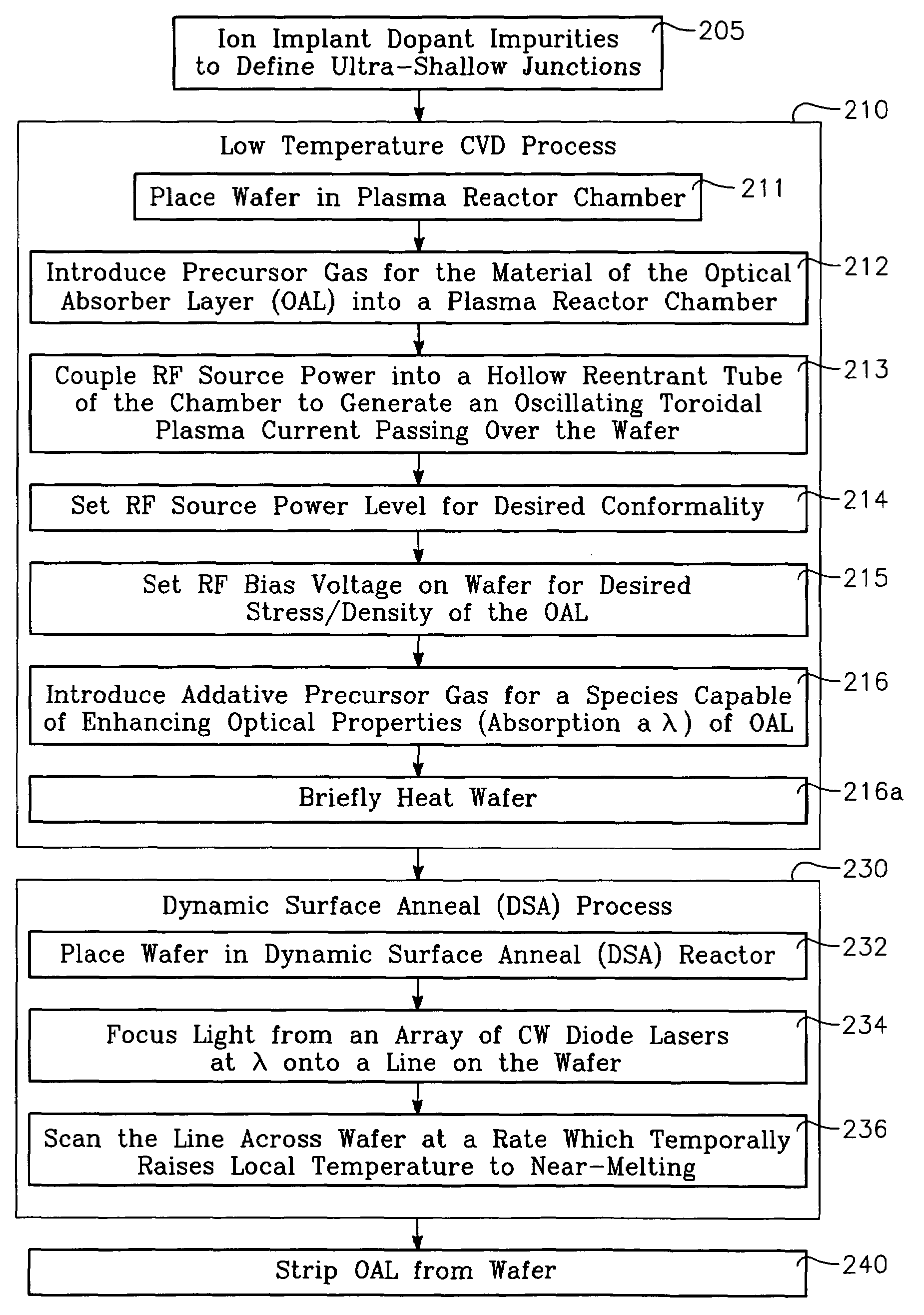
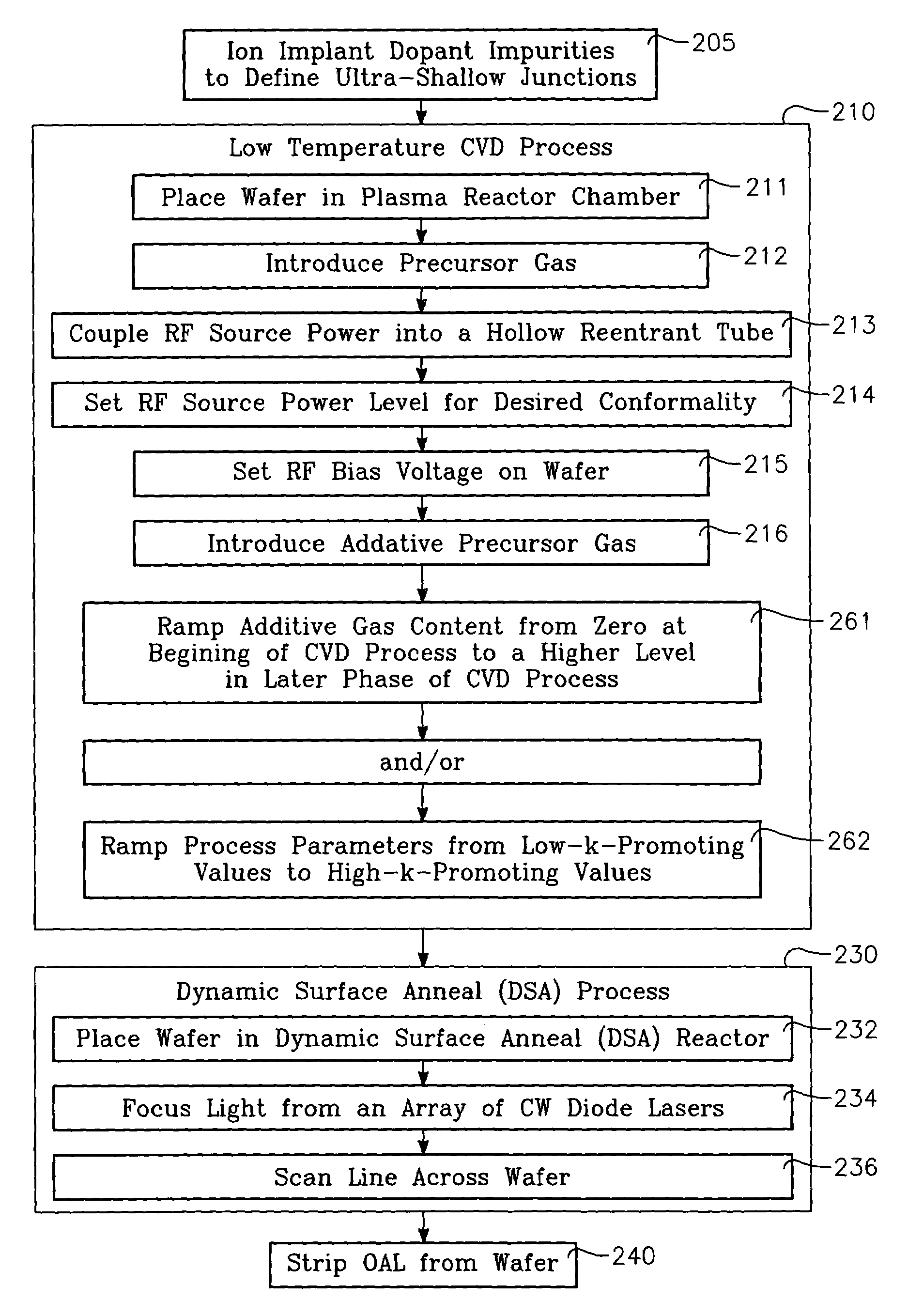
A method of forming semiconductor junctions in a semiconductor material of a workpiece includes ion implanting dopant impurities in selected regions of the semiconductor material, introducing an optical absorber material precursor gas into a chamber containing the workpiece, generating an RF oscillating toroidal plasma current in a reentrant path that includes a process zone overlying the workpiece by applying RF source power, so as to deposit a layer of an optical absorber material on the workpiece, and optically annealing the workpiece so as to activate dopant impurities in the semiconductor material.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Semiconductor substrate process using an optically writable carbon-containing mask
ActiveUS7429532B2Photomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlasma currentCoupling
A method of processing a thin film structure on a semiconductor substrate using an optically writable mask, the method includes placing the substrate in a reactor chamber, the substrate having on its surface a target layer to be exposed to a light source in accordance with a predetermined pattern, depositing an optically writable carbon-containing mask layer on the substrate by (a) introducing a carbon-containing process gas into the chamber, (b) generating a reentrant toroidal RF plasma current in a reentrant path that includes a process zone overlying the workpiece by coupling plasma RF source power to an external portion of the reentrant path, (c) coupling RF plasma bias power or bias voltage to the workpiece. The method further includes optically writing on the carbon-containing mask layer in accordance with the predetermined pattern with writing light of a characteristic suitable for transforming the transparency or opacity of the optically writable mask layer and exposing through the mask layer the target layer with reading light of a characteristic different from that of the writing light.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Low temperature plasma deposition process for carbon layer deposition
InactiveUS20060264060A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingCarbon layerPlasma current
A method of depositing a carbon layer on a workpiece includes placing the workpiece in a reactor chamber, introducing a carbon-containing process gas into the chamber, generating a reentrant toroidal RF plasma current in a reentrant path that includes a process zone overlying the workpiece by coupling plasma RF source power to an external portion of the reentrant path, and coupling RF plasma bias power or bias voltage to the workpiece.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Process for low temperature plasma deposition of an optical absorption layer and high speed optical annealing
A method of processing a workpiece includes introducing an optical absorber material precursor gas into a chamber containing the workpiece, generating an RF oscillating toroidal plasma current in a reentrant path that includes a process zone overlying the workpiece by applying RF source power, so as to deposit a layer of an optical absorber material on the workpiece, and exposing the workpiece to optical radiation that is at least partially absorbed in the optical absorber layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Semiconductor substrate process using an optically writable carbon-containing mask
ActiveUS20070032082A1Photomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlasma currentCoupling
A method of processing a thin film structure on a semiconductor substrate using an optically writable mask, the method includes placing the substrate in a reactor chamber, the substrate having on its surface a target layer to be exposed to a light source in accordance with a predetermined pattern, depositing an optically writable carbon-containing mask layer on the substrate by (a) introducing a carbon-containing process gas into the chamber, (b) generating a reentrant toroidal RF plasma current in a reentrant path that includes a process zone overlying the workpiece by coupling plasma RF source power to an external portion of the reentrant path, (c) coupling RF plasma bias power or bias voltage to the workpiece. The method further includes optically writing on the carbon-containing mask layer in accordance with the predetermined pattern with writing light of a characteristic suitable for transforming the transparency or opacity of the optically writable mask layer and exposing through the mask layer the target layer with reading light of a characteristic different from that of the writing light.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Semiconductor substrate process using a low temperature deposited carbon-containing hard mask
InactiveUS20070032054A1Electric discharge tubesRadiation applicationsLow temperature depositionPlasma current
A method of processing a thin film structure on a semiconductor substrate using an optically writable mask includes placing the substrate in a reactor chamber, the substrate having on its surface a target layer to be etched in accordance with a predetermined pattern, and depositing a carbon-containing hard mask layer on the substrate by (a) introducing a carbon-containing process gas into the chamber, (b) generating a reentrant toroidal RF plasma current in a reentrant path that includes a process zone overlying the workpiece by coupling plasma RF source power to an external portion of the reentrant path, and (c) coupling RF plasma bias power or bias voltage to the workpiece. The method further includes photolithographically defining the predetermined pattern in the carbon-containing hard mask layer, and etching the target layer in the presence of the hard mask layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
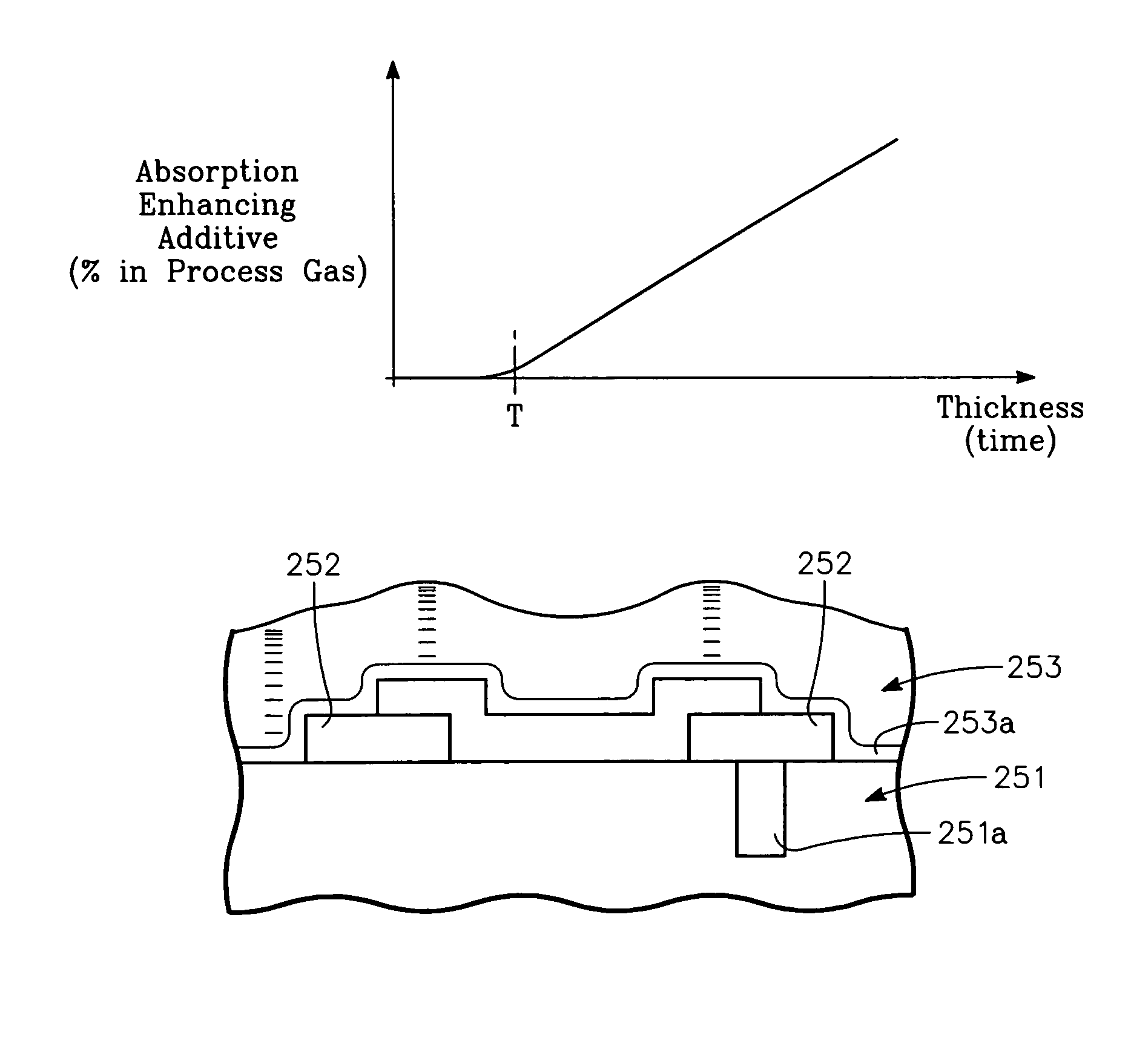
Low temperature CVD process with selected stress of the CVD layer on CMOS devices
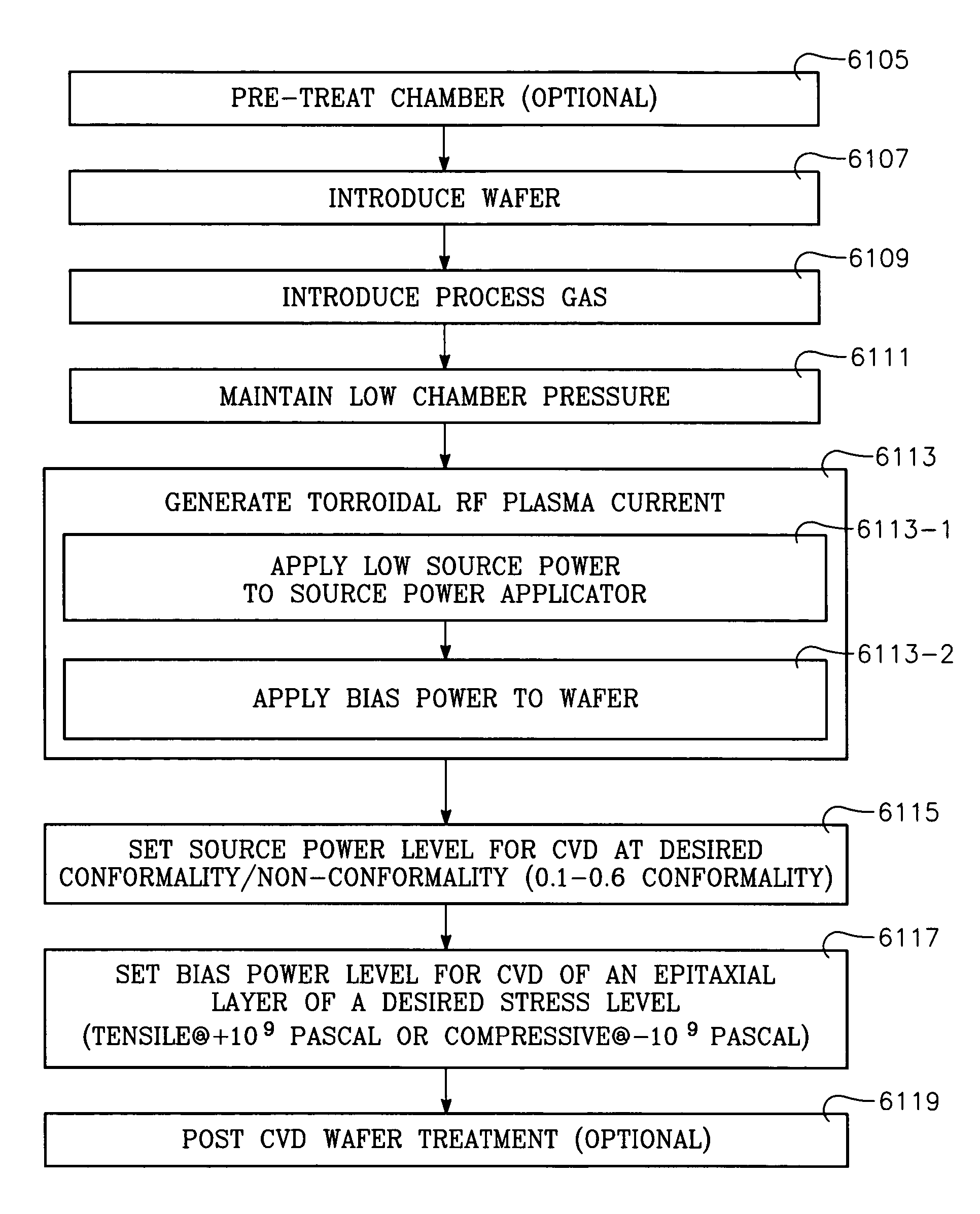
Device-enhancing coatings are deposited on CMOS devices by successively masking with photoresist each one of the sets of N-channel and P-channel devices while unmasking or leaving unmasked the other set, and after each step of successively masking one of the sets of devices, carrying out low temperature CVD steps with a toroidal RF plasma current while applying an RF plasma bias voltage. The temperature of the workpiece is held below a threshold photoresist removal temperature. The RF bias voltage is held at a level at which the coating is deposited with a first stress when the unmasked set consists of the P-channel devices and with a second stress when the unmasked set consists of N-channel devices.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Copper conductor annealing process employing high speed optical annealing with a low temperature-deposited optical absorber layer
InactiveUS20070032095A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesCopper conductorEngineering
A method of forming a conductor in a thin film structure on a semiconductor substrate includes forming high aspect ratio openings in a base layer having vertical side walls, depositing a dielectric barrier layer comprising a dielectric compound of a barrier metal on the surfaces of the high aspect ratio openings including the vertical side walls, depositing a metal barrier layer comprising the barrier metal on the first barrier layer, depositing a main conductor species seed layer on the metal barrier layer and depositing a main conductor layer. The method further includes annealing the main conductor layer by (a) directing light from an array of continuous wave lasers into a line of light extending at least partially across the thin film structure, and (b) translating the line of light relative to the thin film structure in a direction transverse to the line of light. The method of Claim 1 further comprising, prior to the annealing step, depositing an amorphous carbon optical absorber layer on the main conductor layer. The step of depositing an amorphous carbon optical absorber layer includes introducing a carbon-containing process gas into a reactor chamber containing the substrate in a process zone of the reactor, applying RF source power to an external reentrant conduit of the reactor to generate a reentrant toroidal RF plasma current passing through the process zone and applying a bias voltage to the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
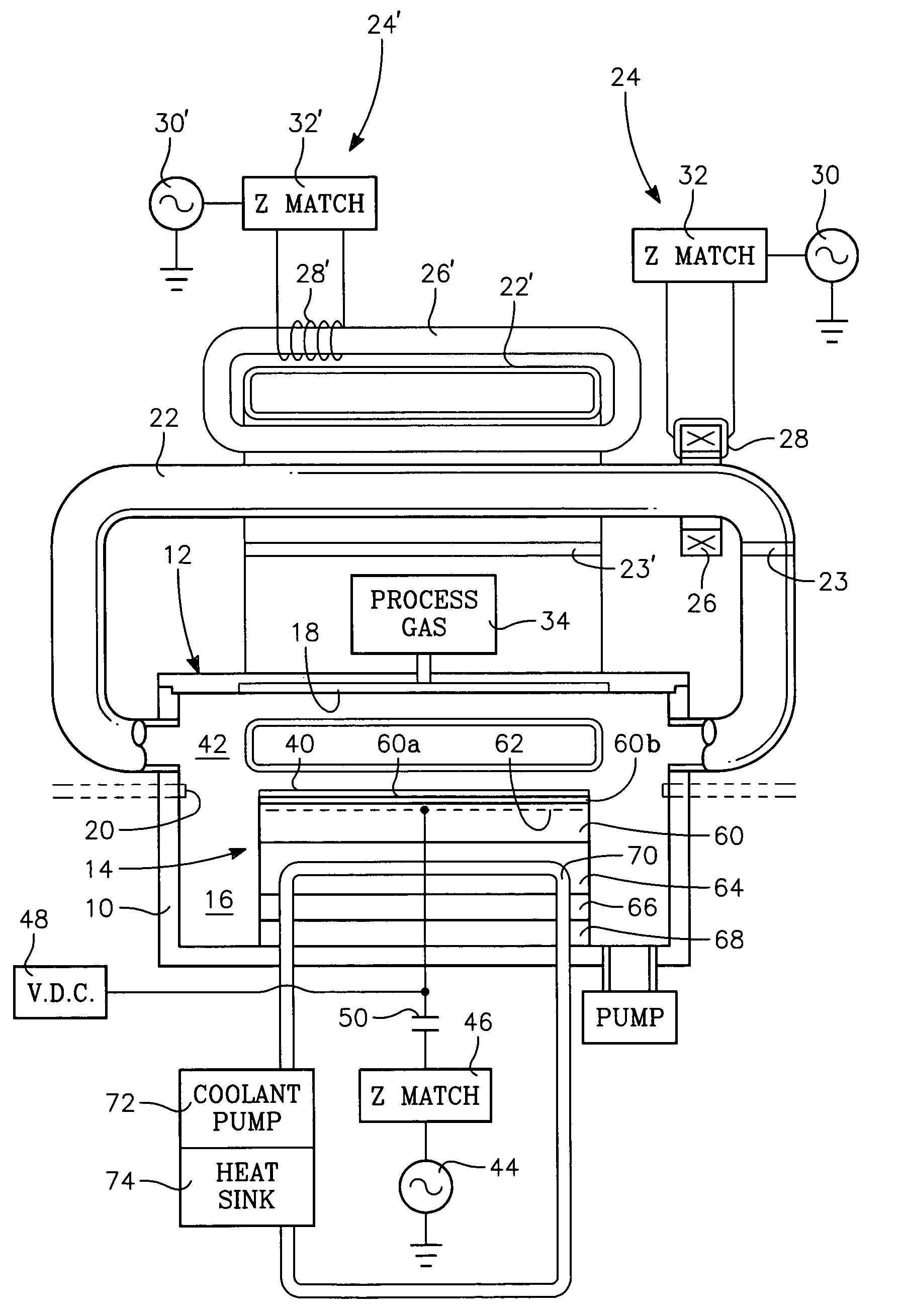
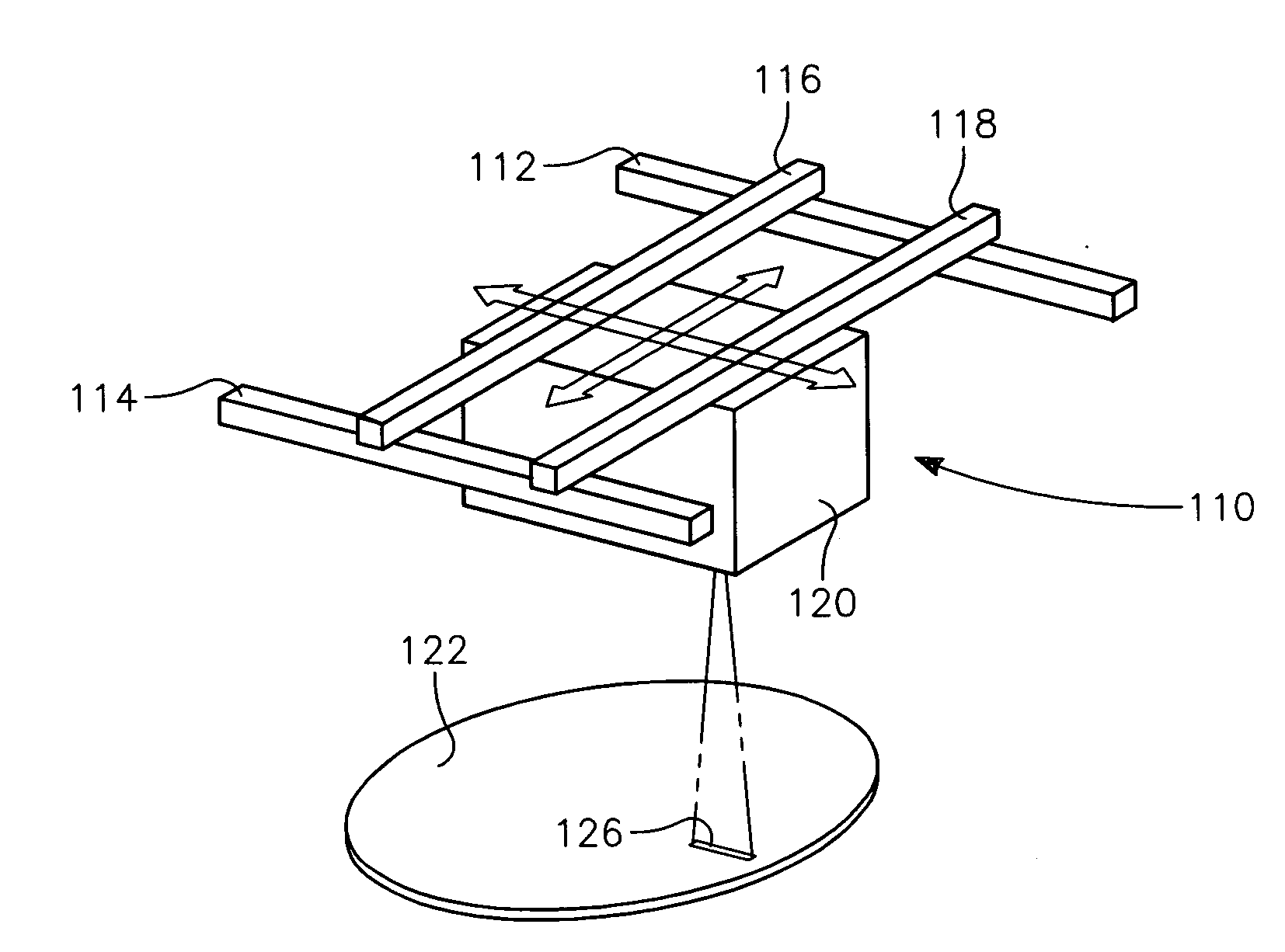
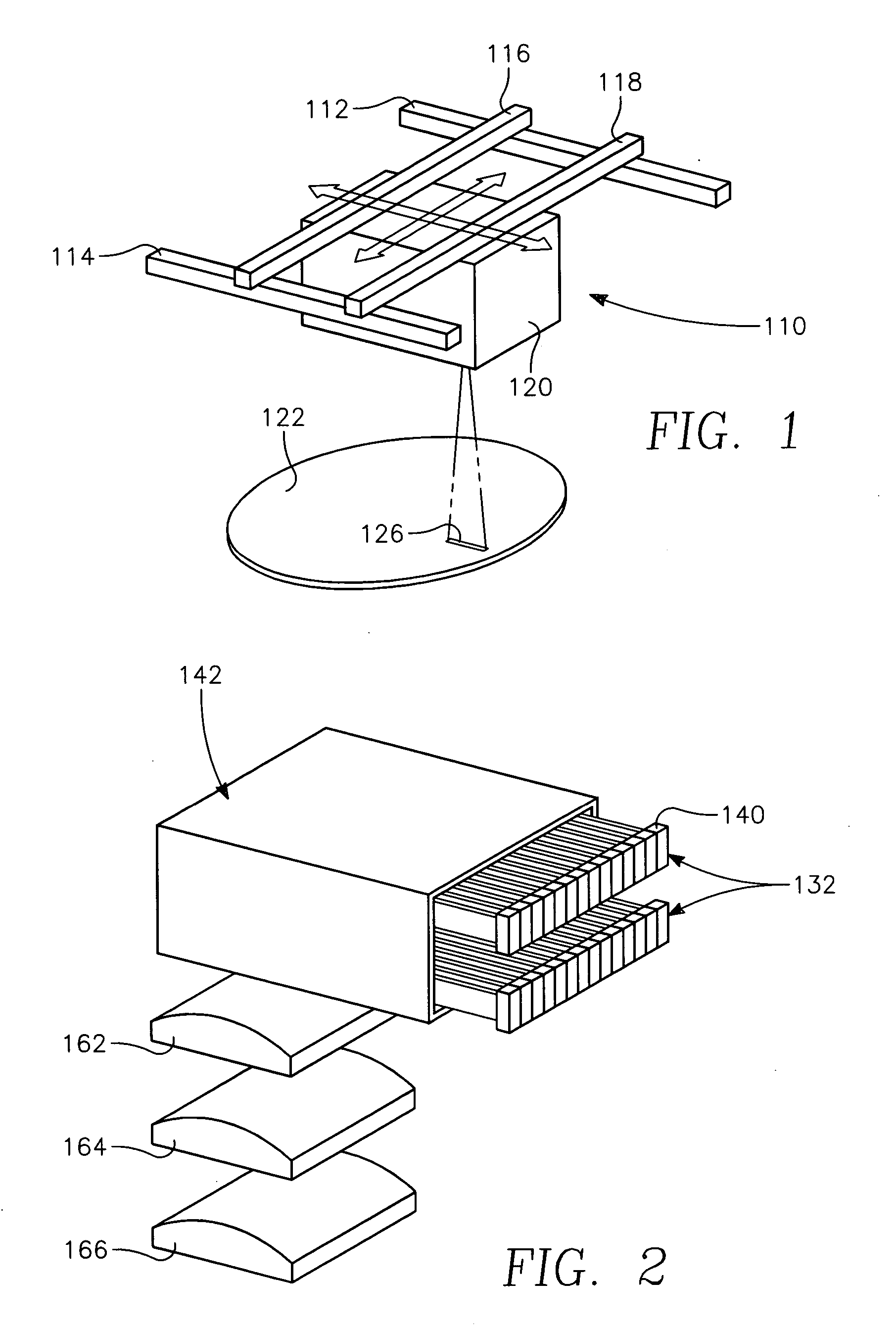
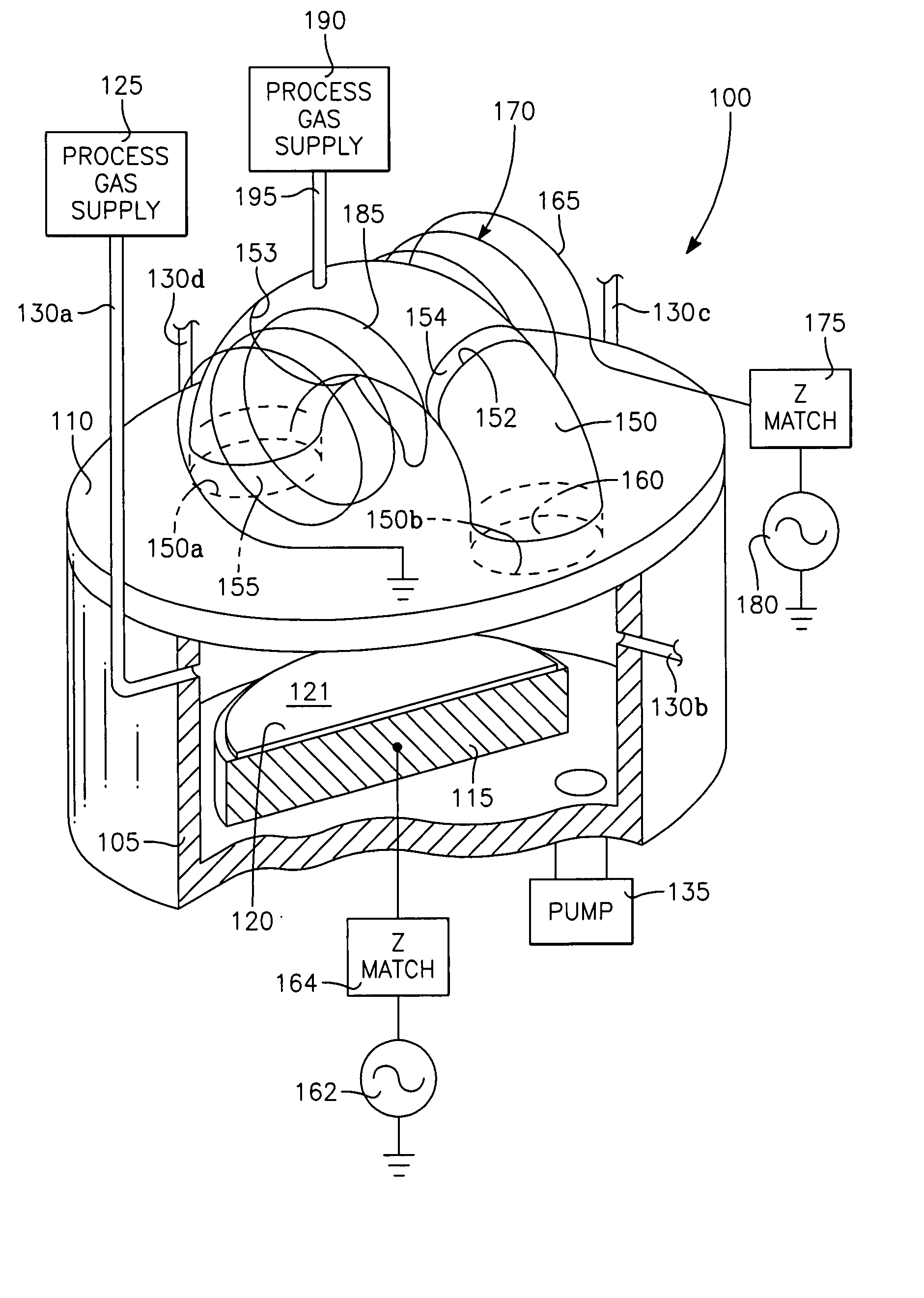
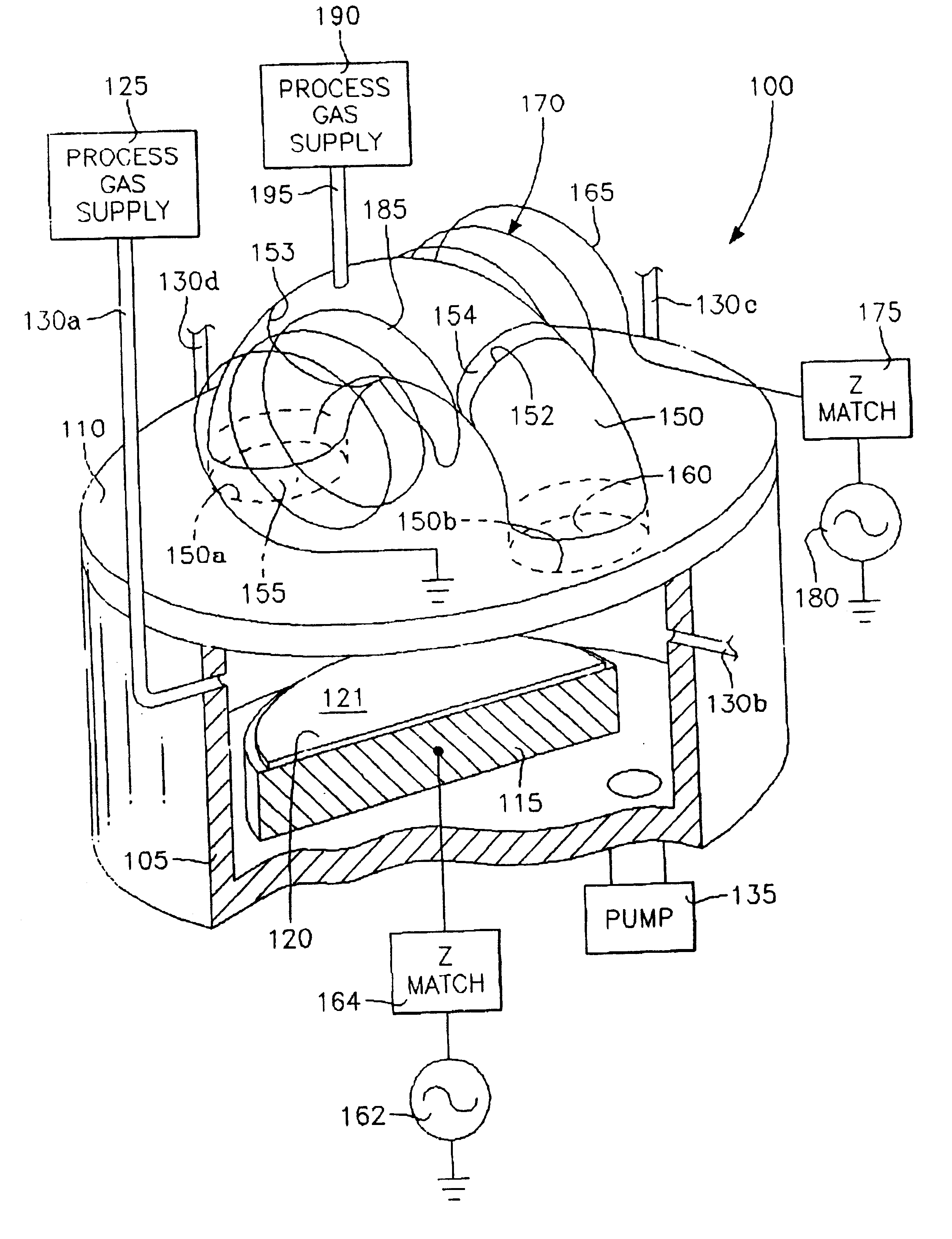
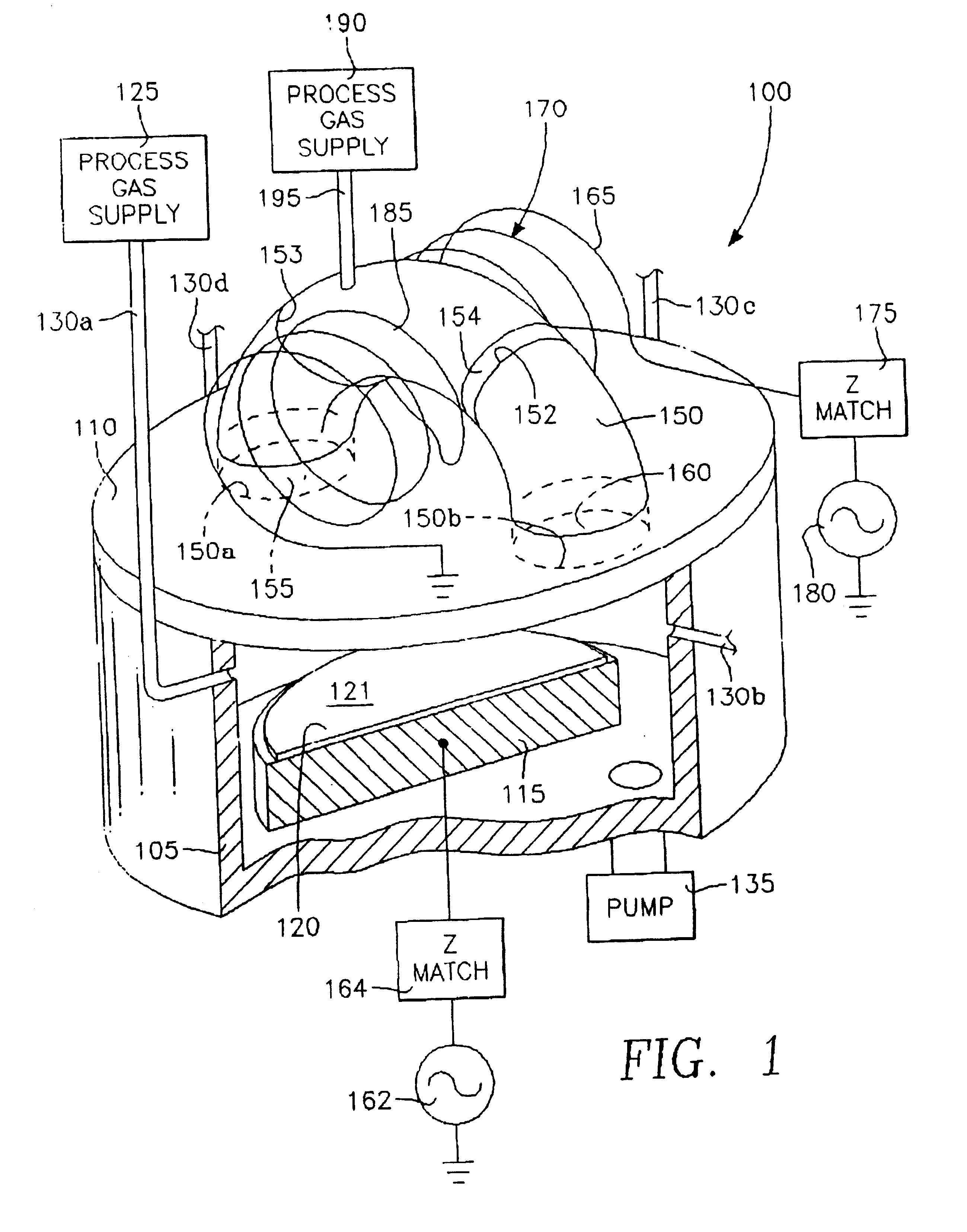
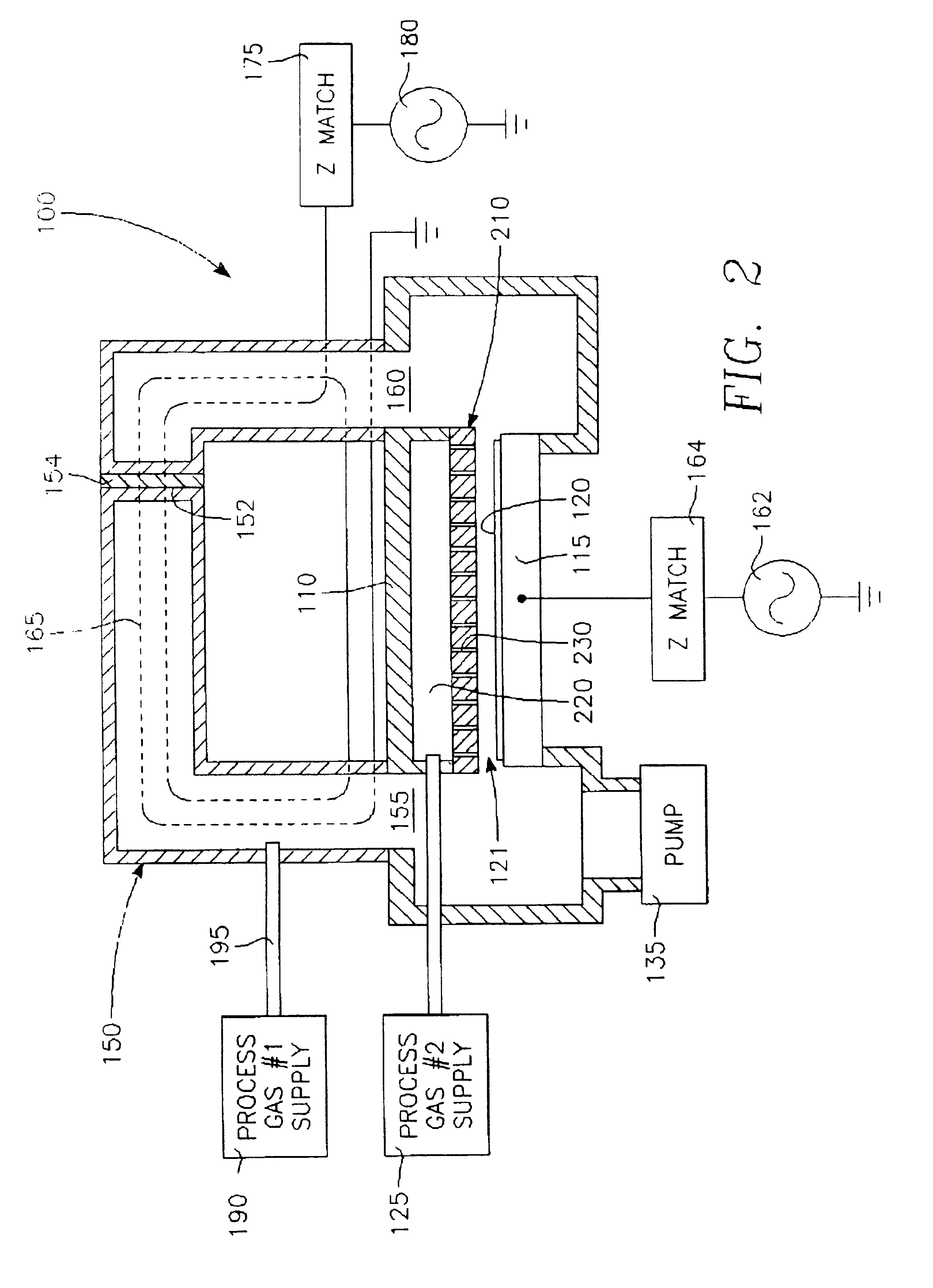
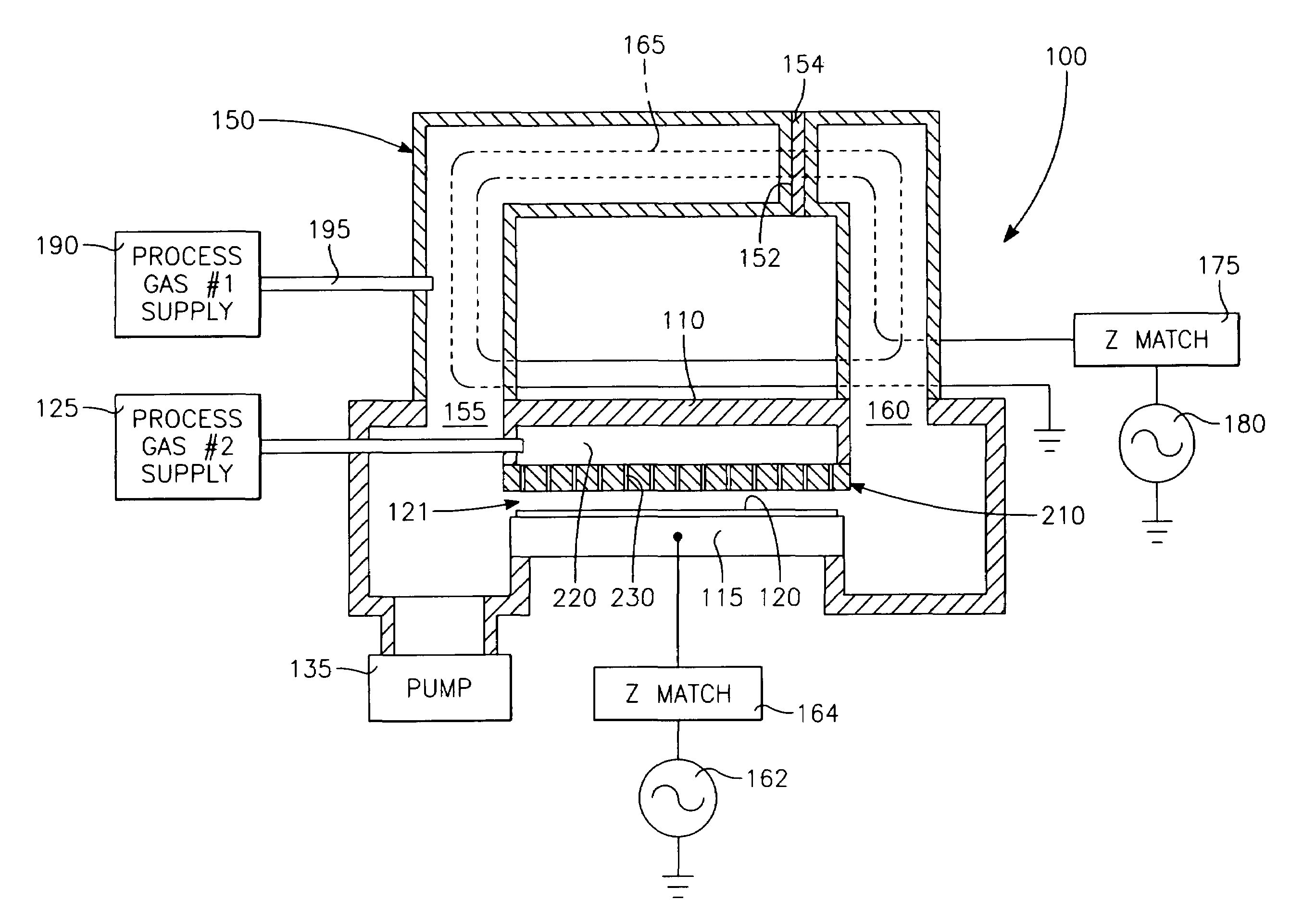
Method of processing a workpiece using an externally excited torroidal plasma source
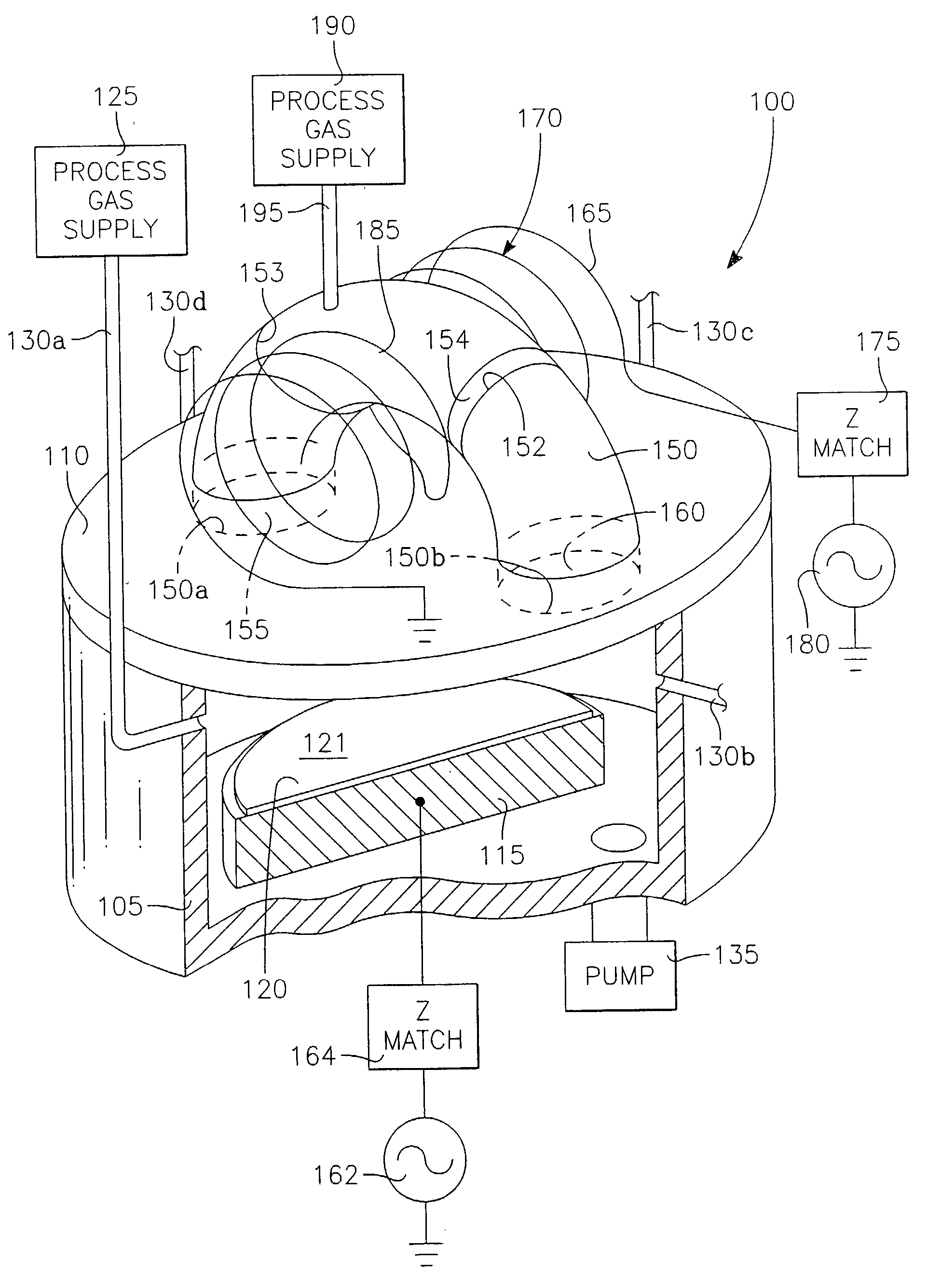
InactiveUS6410449B1Increase ion densityIncrease plasma densityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlasma currentIon density
A method of processing a workpiece in a plasma reactor includes establishing a torroidal path for a plasma current to flow that passes near and transverse to the surface of said workpiece, maintaining a plasma current in the torroidal path by applying RF power to a portion of the torroidal path away from the surface of the workpiece, and increasing the ion density of the plasma current in the vicinity of the workpiece by constricting the area of a portion of the torroidal path overlying the workpiece.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
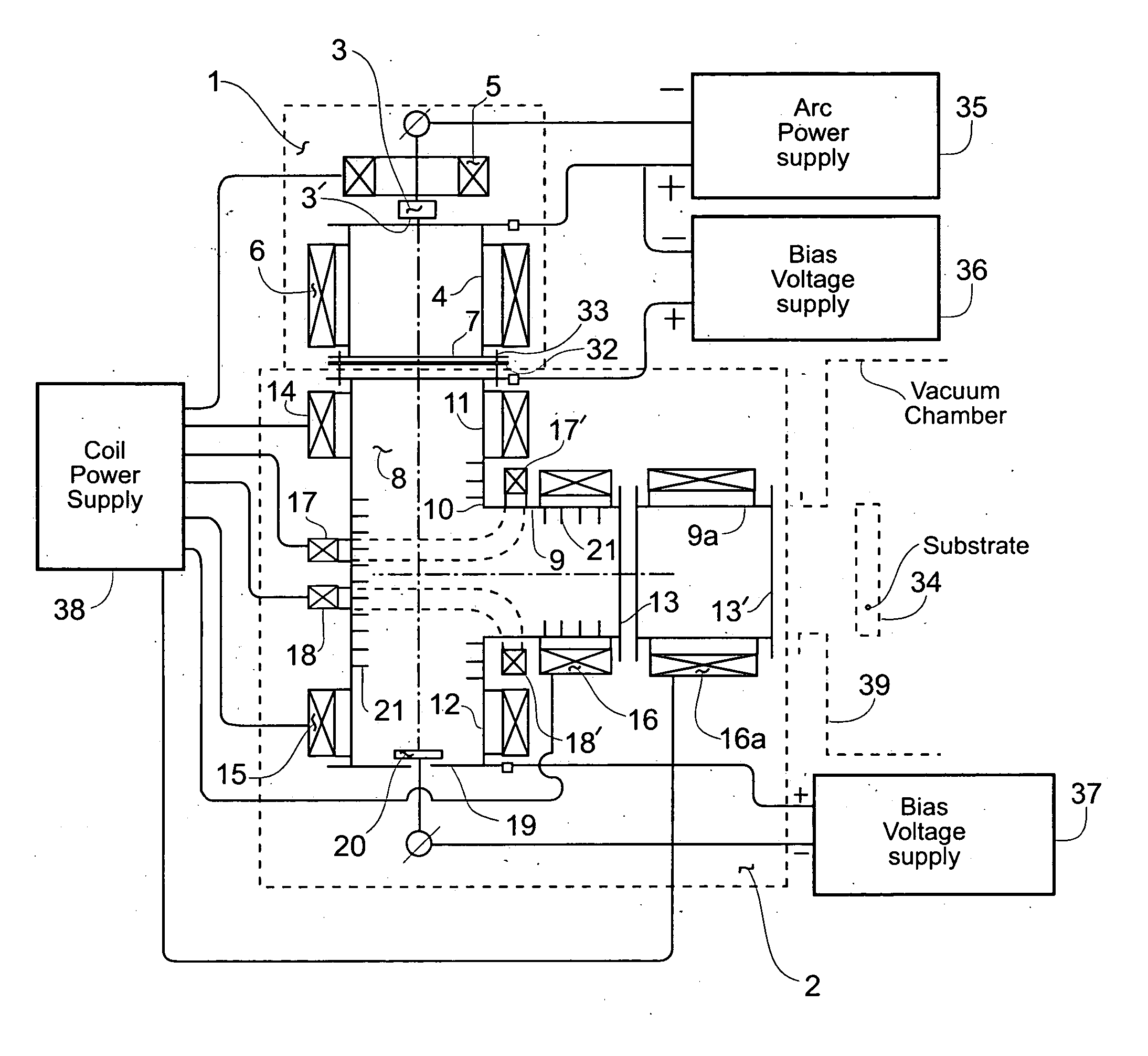
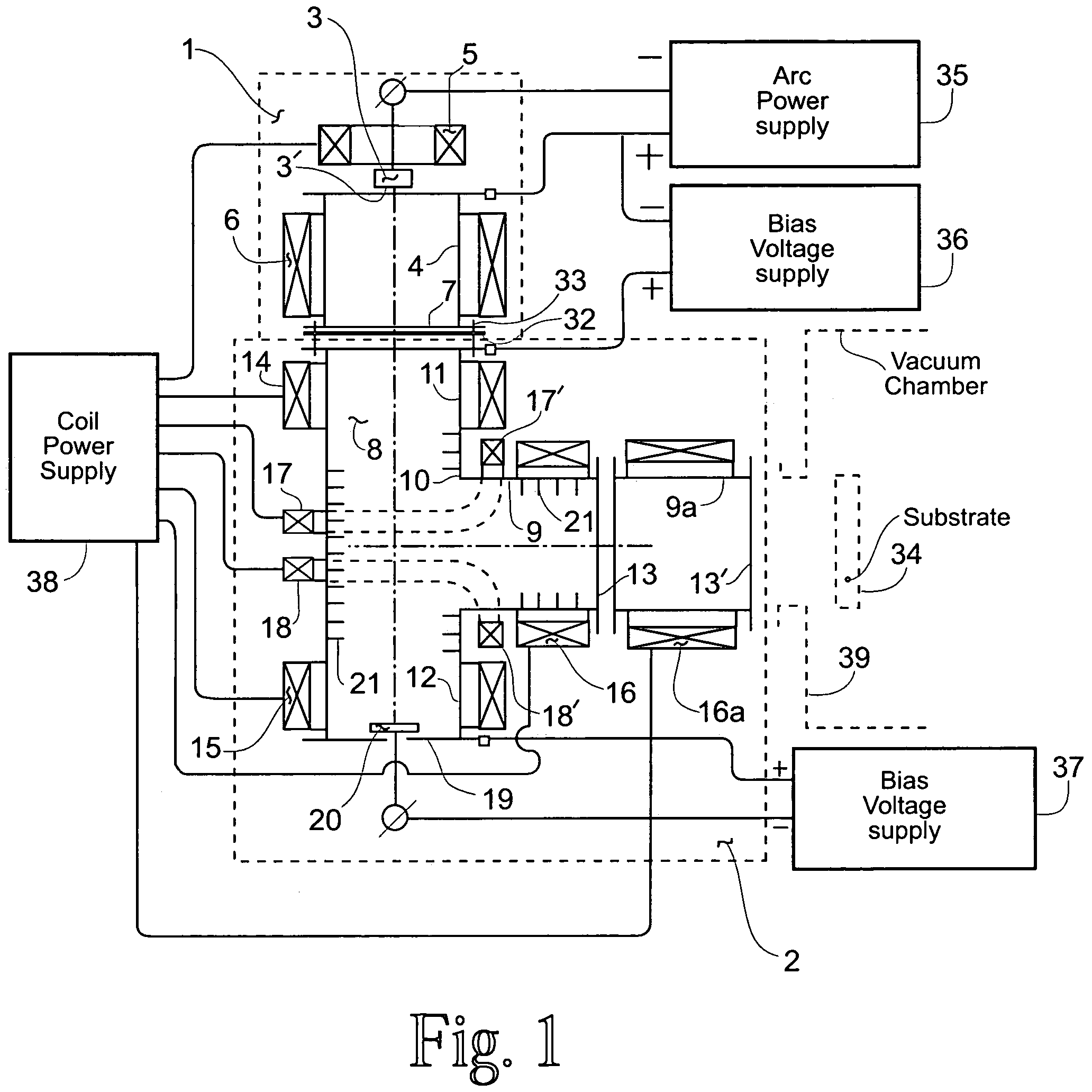
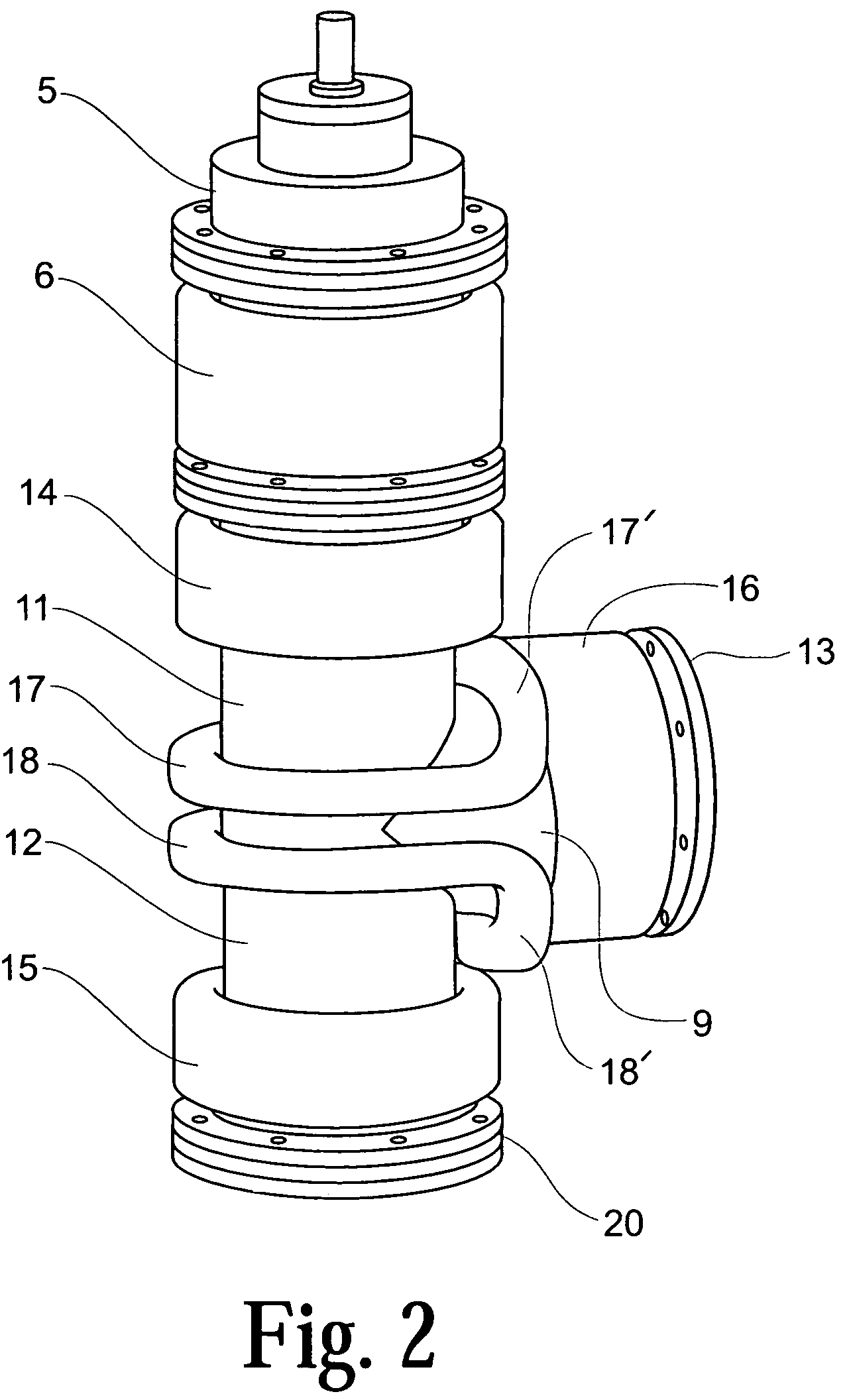
Filtered cathodic-arc plasma source
InactiveUS20070187229A1Reduction in kinetic ion energyImprove ion transmission efficiencyCellsElectric discharge tubesPlasma currentMagnetic flux
A filtered cathodic-arc plasma source of lower plasma losses and higher output plasma current to input current efficiency is disclosed. Plasma filtering is accomplished in a right angle bend magnetic filter arranged to include the effects of at least three added magnetic coils located at the right angle bend of the filter path. These magnetic coils and other filter attributes, including an array of transverse fins and a magnetic cusp trap in the filter path, achieve desirable magnetic flux paths, lower plasma collision losses and reduced undesired particle output from the plasma filter. Multiple cathode sources, multiple plasma output ports, Larmour radius influence, equipotential magnetic flux lines and electron / ion interaction considerations are also included in the plasma source. Application of the plasma source to film coating processes is included.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
Semiconductor on insulator vertical transistor fabrication and doping process
InactiveUS7294563B2Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantPlasma current
A process for conformally doping through the vertical and horizontal surfaces of a 3-dimensional vertical transistor in a semiconductor-on-insulator structure employs an RF oscillating torroidal plasma current to perform either conformal ion implantation, or conformal deposition of a dopant-containing film which can then be heated to drive the dopants into the transistor. Some embodiments employ both conformal ion implantation and conformal deposition of dopant containing films, and in those embodiments in which the dopant containing film is a pure dopant, the ion implantation and film deposition can be performed simultaneously.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Very low temperature CVD process with independently variable conformality, stress and composition of the CVD layer
A low temperature process for depositing a coating containing any of silicon, nitrogen, hydrogen or oxygen on a workpiece includes placing the workpiece in a reactor chamber facing a processing region of the chamber, introducing a process gas containing any of silicon, nitrogen, hydrogen or oxygen into the reactor chamber, generating a torroidal RF plasma current in a reentrant path through the processing region by applying RF plasma source power at an HF frequency on the order of about 10 MHz to a portion of a reentrant conduit external of the chamber and forming a portion of the reentrant path, applying RF plasma bias power at an LF frequency on the order of one or a few MHz to the workpiece, and maintaining the temperature of the workpiece under about 100 degrees C.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
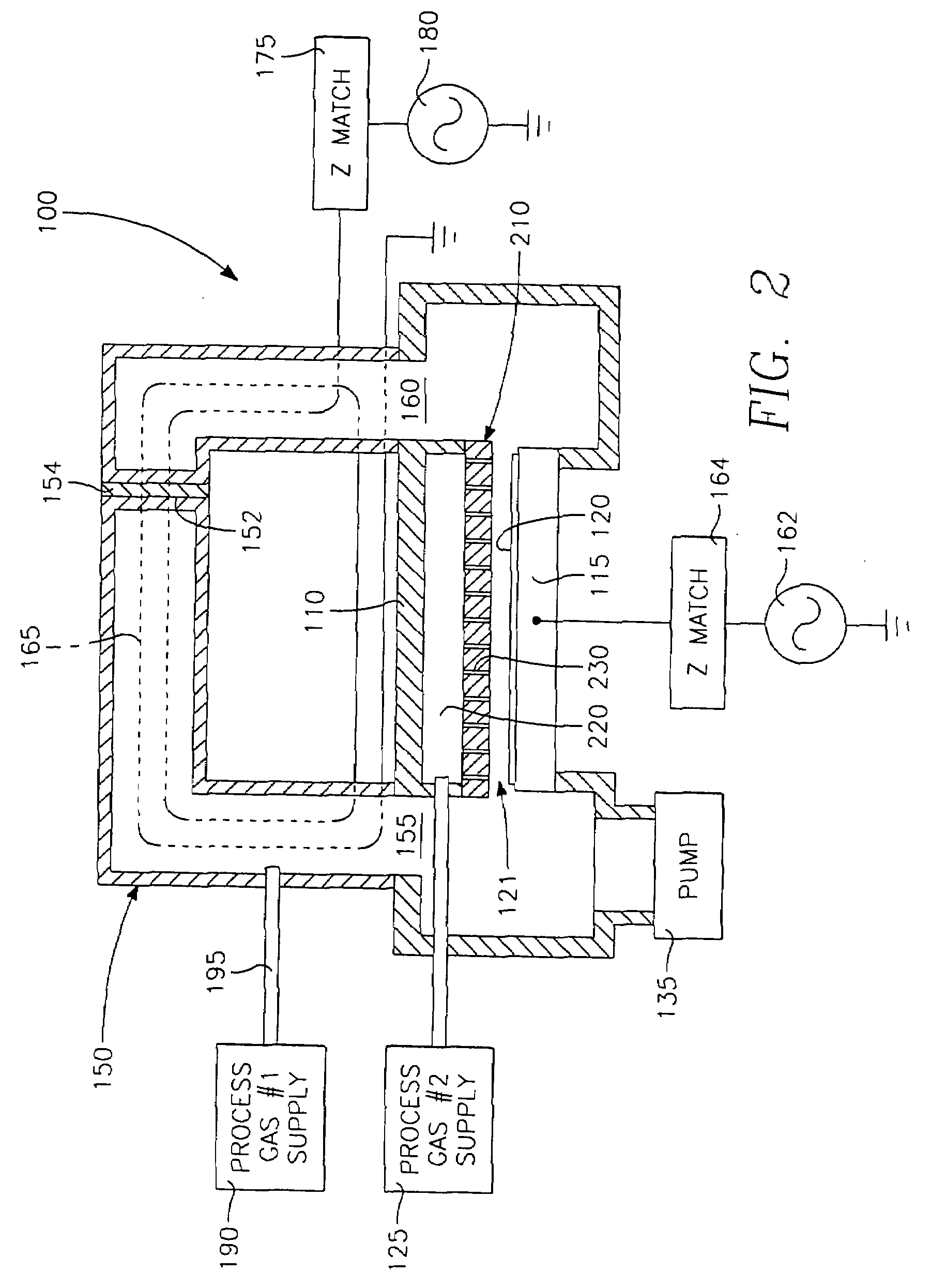
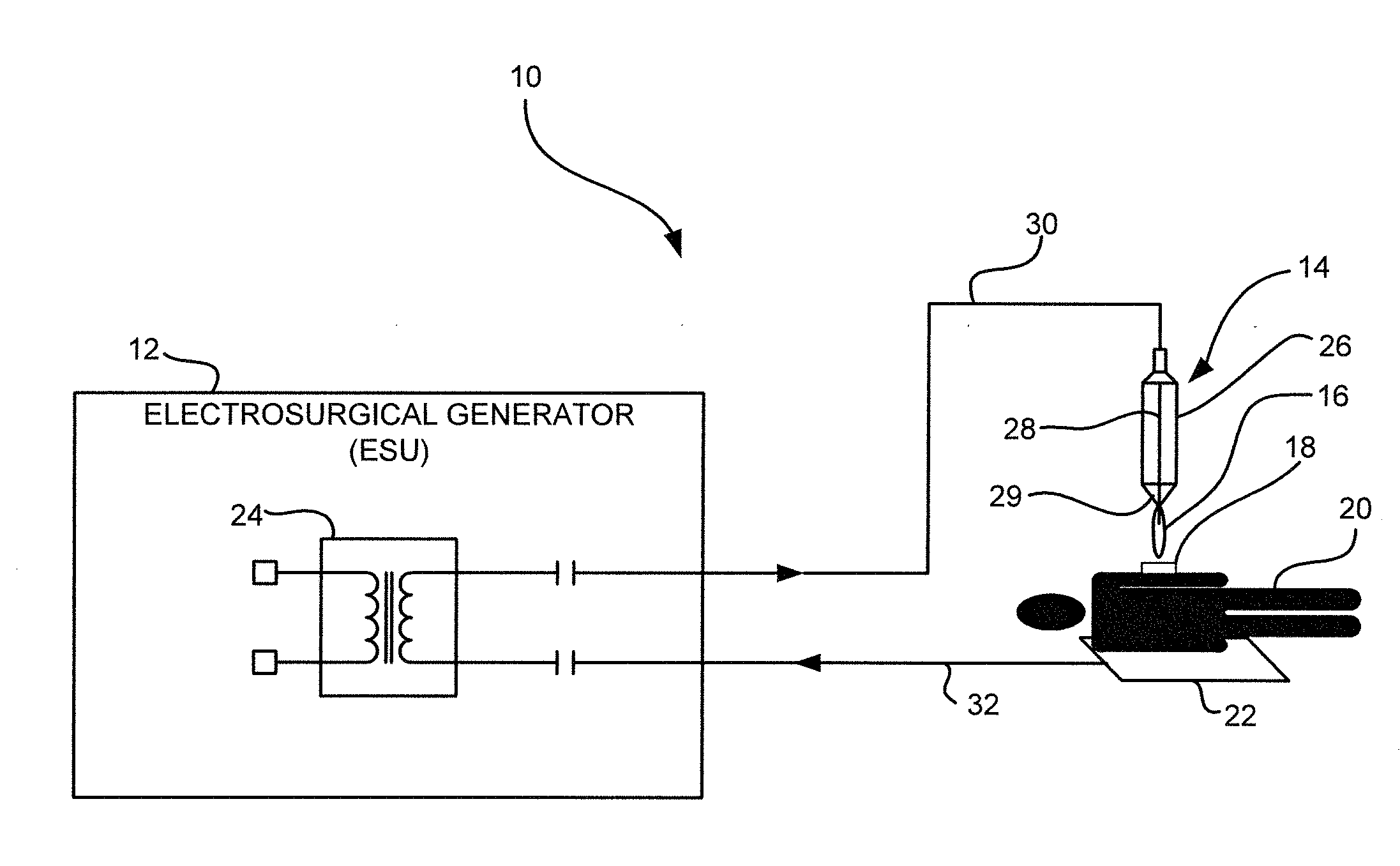
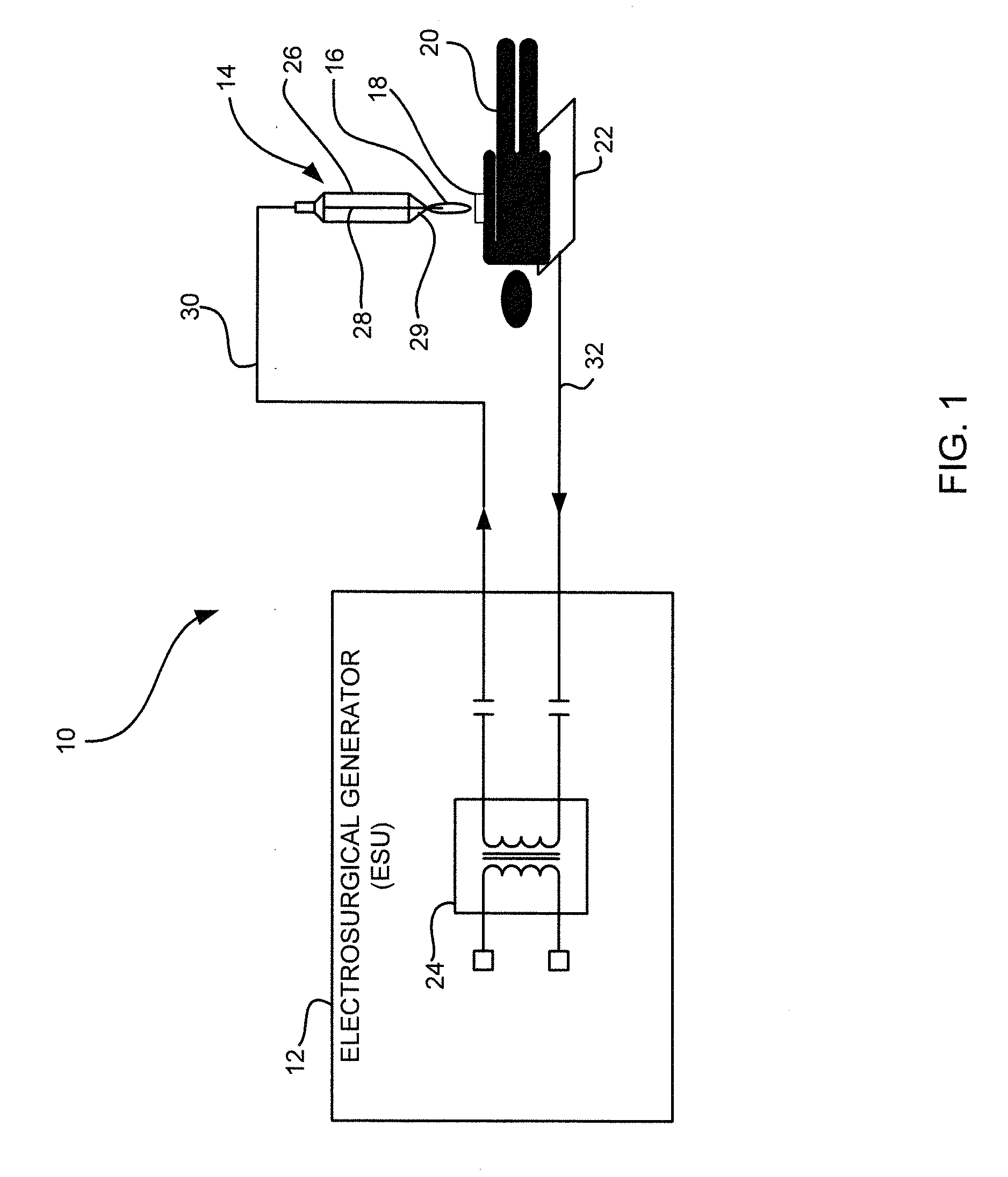
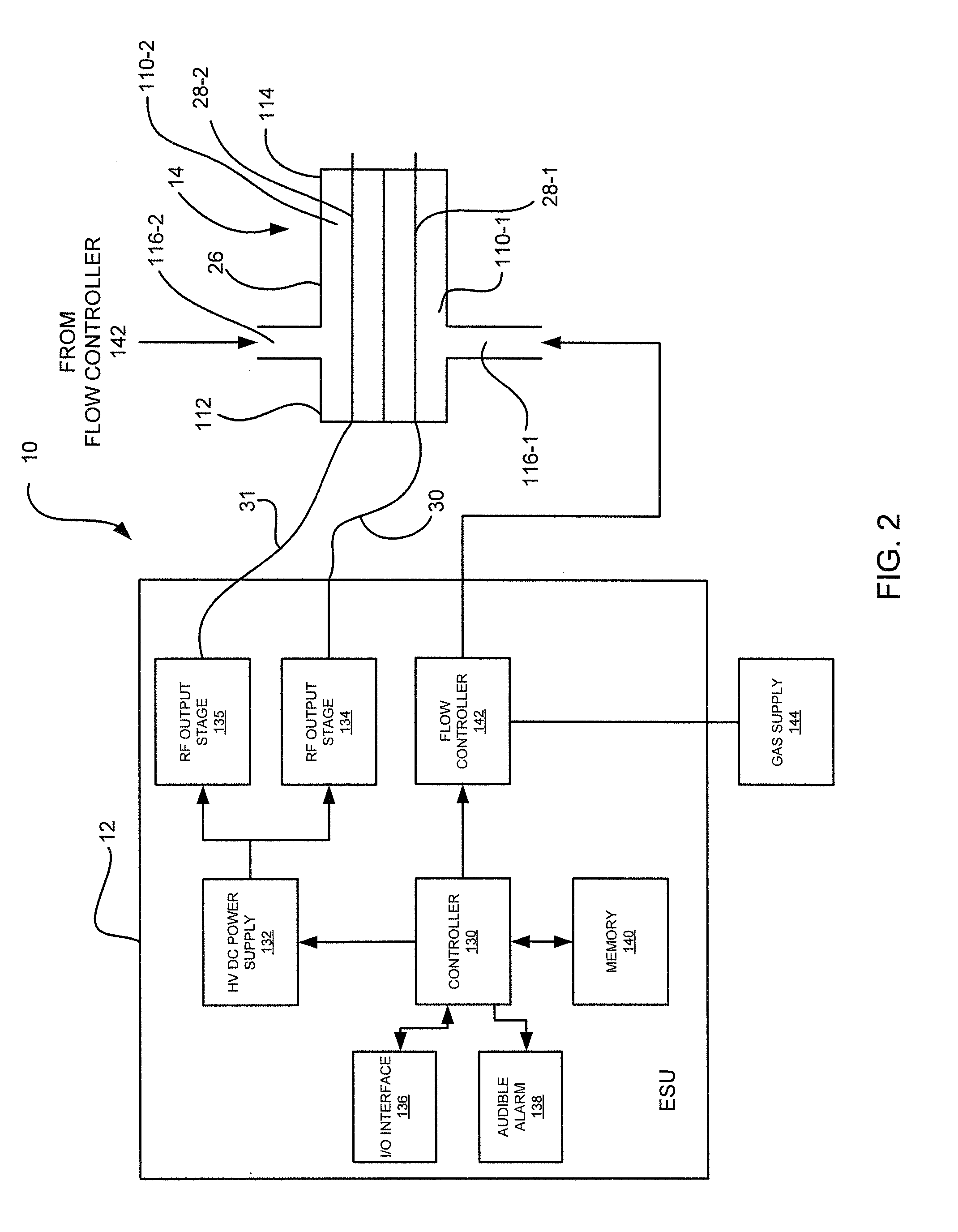
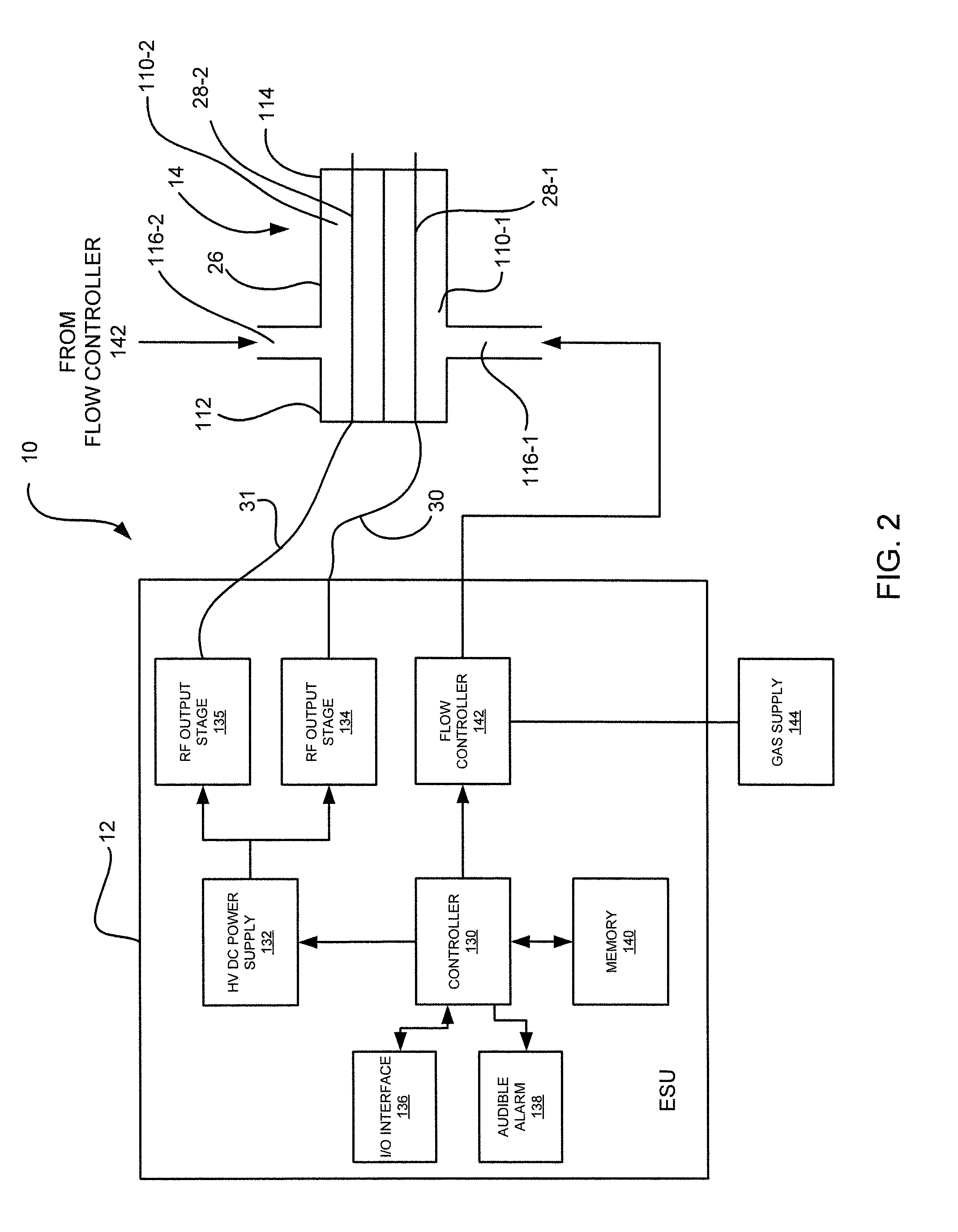
Electrosurgical apparatus to generate a dual plasma stream and method thereof
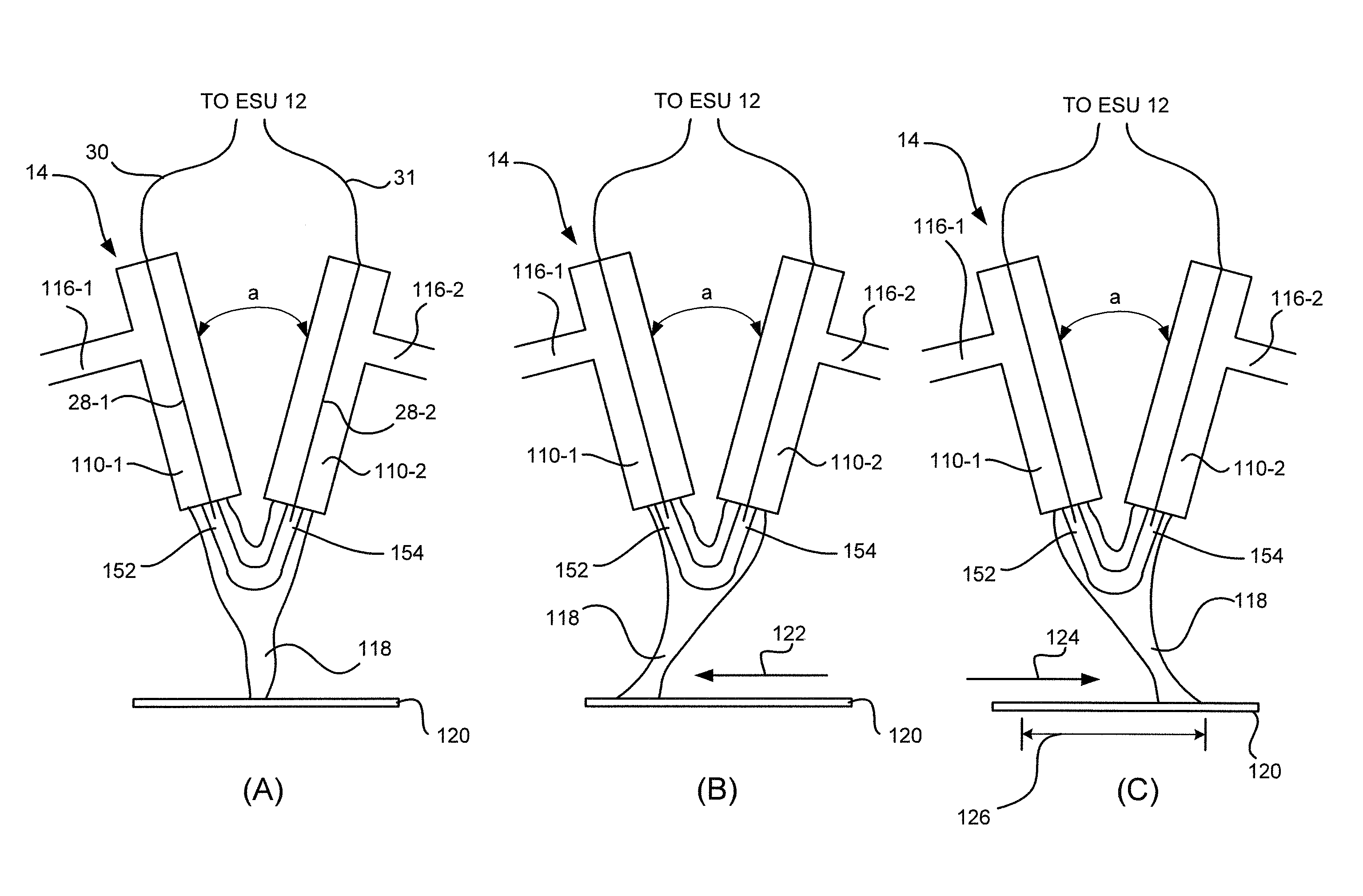
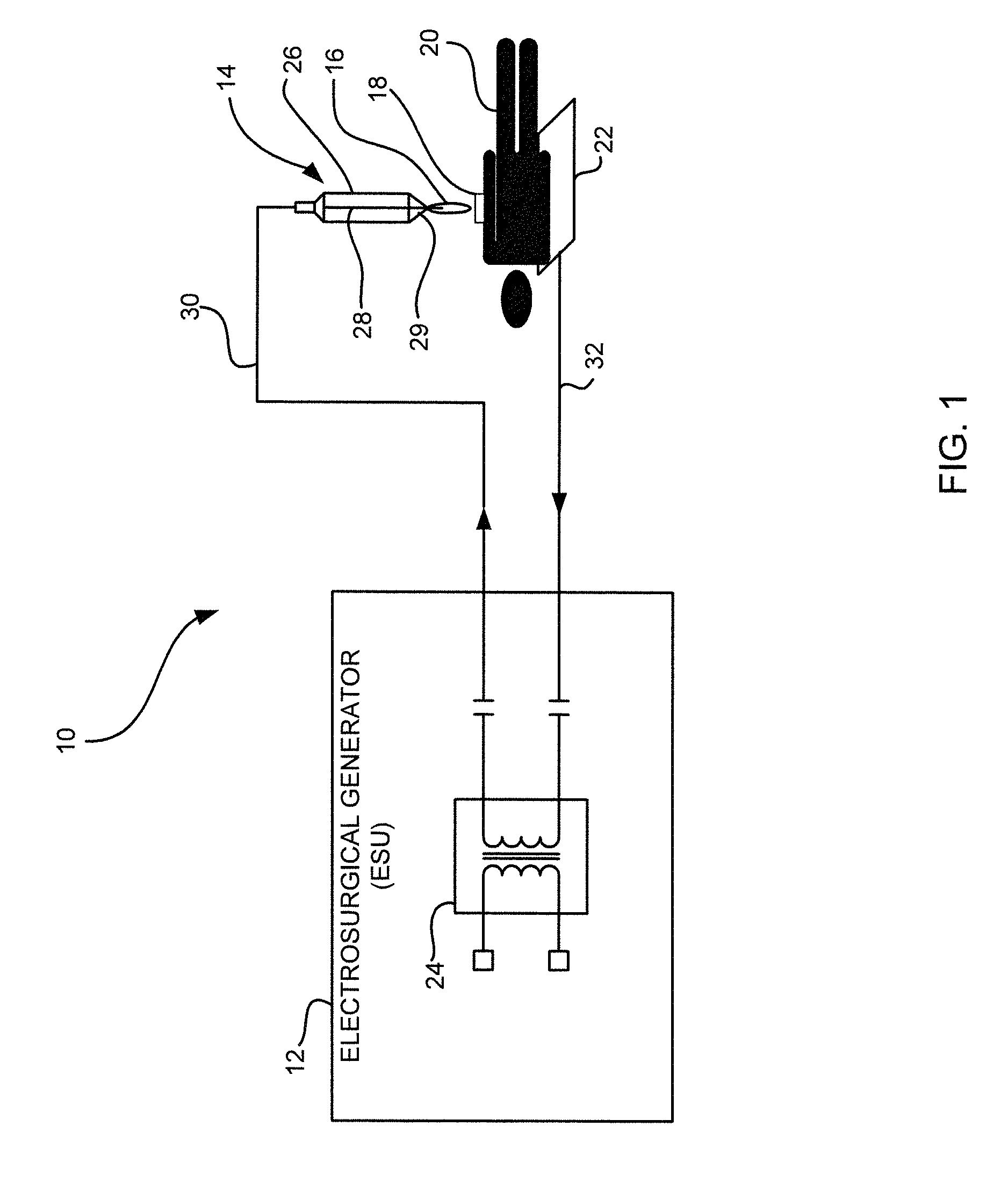
ActiveUS20110184408A1Small equivalent capacitanceGood effectSurgical instruments for heatingPlasma currentElectrosurgery
The present disclosure relates to an electrosurgical apparatus to generate a dual plasma stream to perform electrosurgery on a surgical site on a patient. The apparatus and method of the present disclosure generates a hot gas jet to a surgical site by generating two plasma beams that are electrically up to 180 degrees out of phase from each other. Since each beam uses the other beam to establish plasma currents at a load, the combined dual plasma stream can be used on non-conductive surfaces, e.g., a tissue at the surgical site. Furthermore, by applying different flow rates to the plasma beams, various scanning effects by the hot gas jet can be achieved.
Owner:BOVIE MEDICAL CORPORATION
Plasma immersion ion implantation with highly uniform chamber seasoning process for a toroidal source reactor
InactiveUS20080286982A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlasma currentPlasma-immersion ion implantation
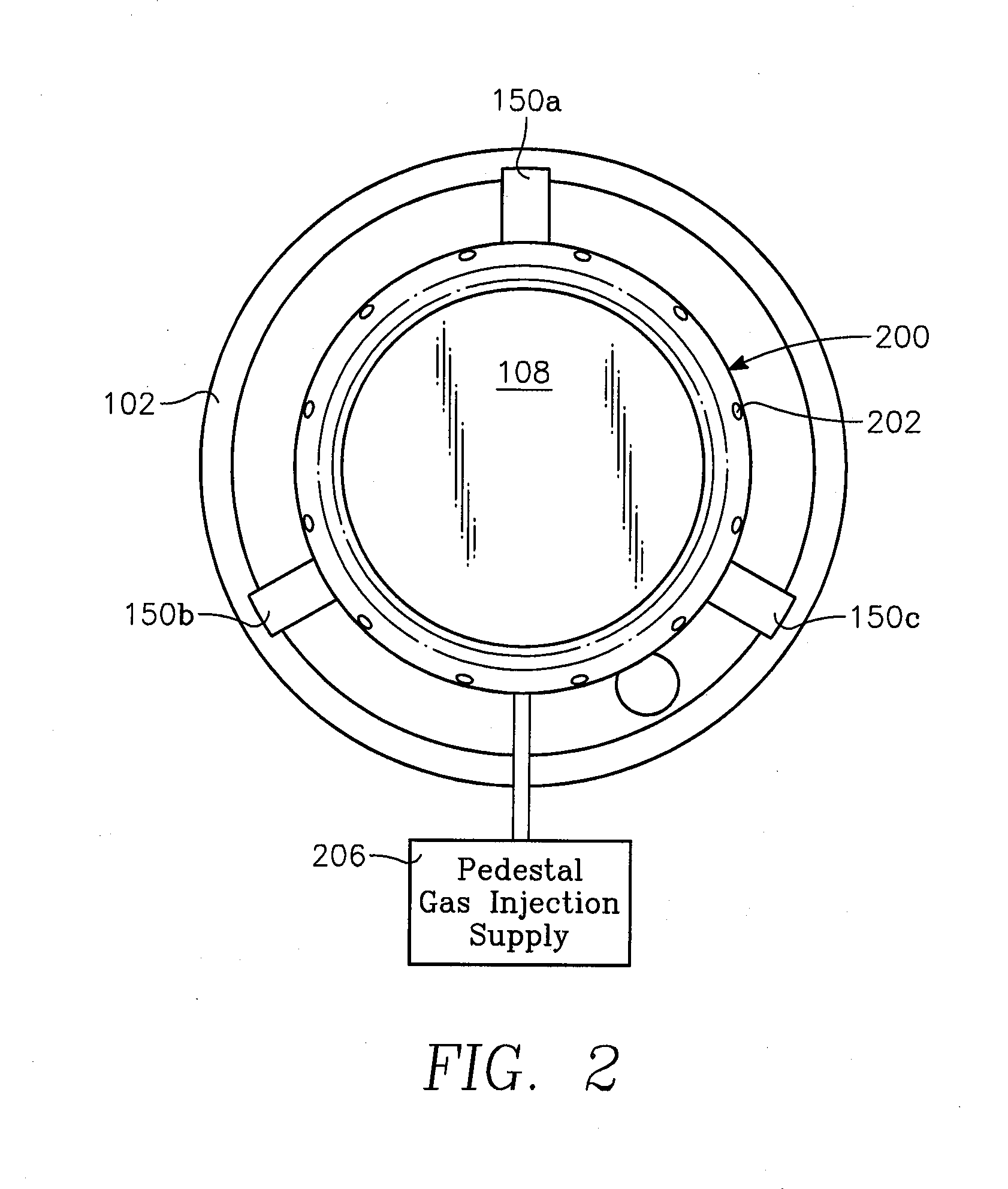
A method is provided for performing plasma immersion ion implantation with a highly uniform seasoning film on the interior of a reactor chamber having a ceiling and a cylindrical side wall and a wafer support pedestal facing the ceiling. The method includes providing a gas distribution ring with plural gas injection orifices on a periphery of a wafer support pedestal, the orifices facing radially outwardly from the wafer support pedestal. Silicon-containing gas is introduced through the gas distribution orifices of the ring to establish a radially outward flow pattern of the silicon-containing gas. The reactor includes pairs of conduit ports in the ceiling adjacent the side wall at opposing sides thereof and respective external conduits generally spanning the diameter of the chamber and coupled to respective pairs of the ports. The method further includes injecting oxygen gas through the conduit ports into the chamber to establish an axially downward flow pattern of oxygen gas in the chamber. RF power is coupled into the interior of each of the conduits to generate a toroidal plasma current of SixOy species passing through the chamber to deposit a seasoning layer of a SixOy material on surfaces within the chamber, while leaving the pedestal without a wafer so as to expose a wafer support surface of the pedestal.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
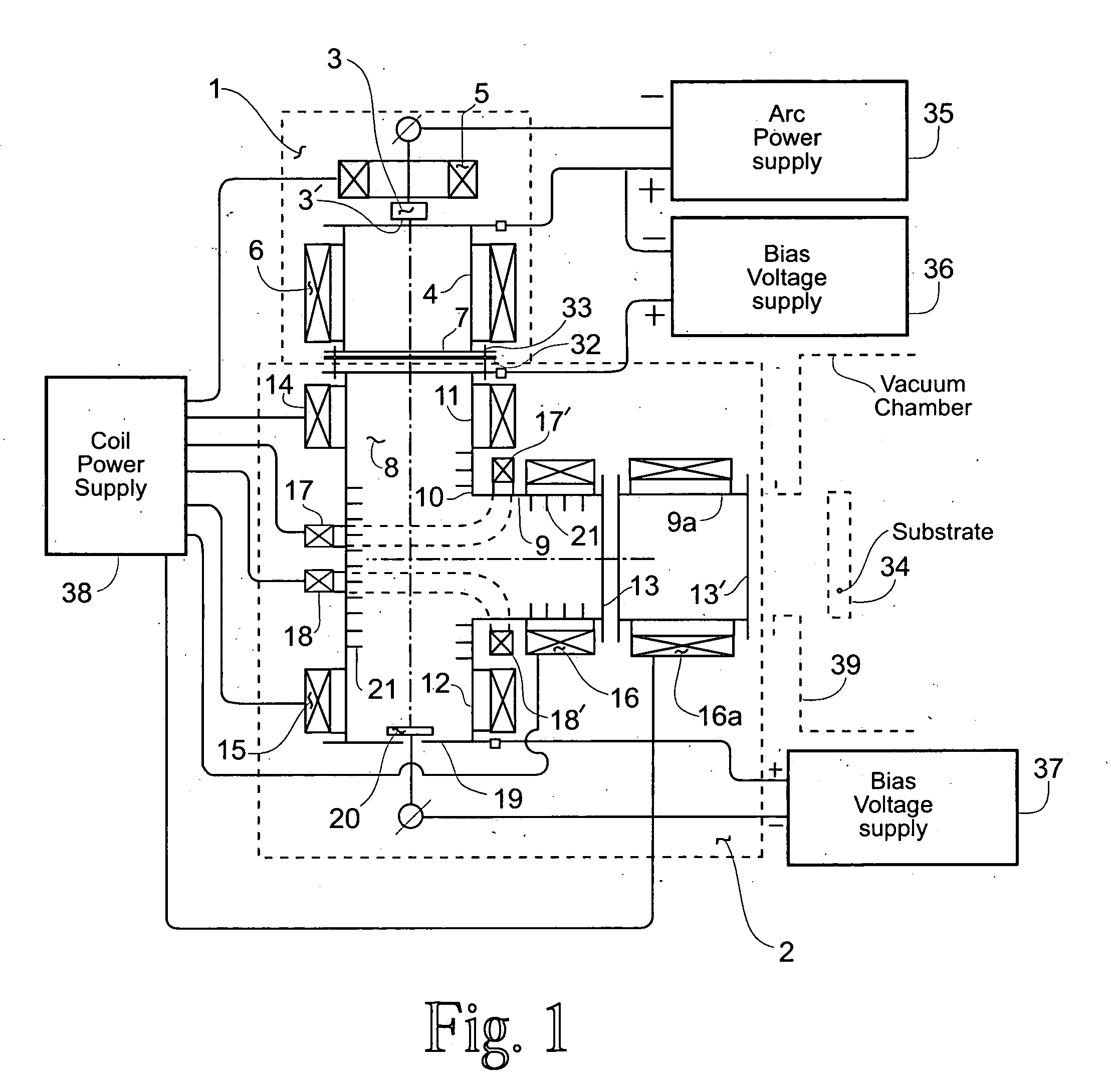
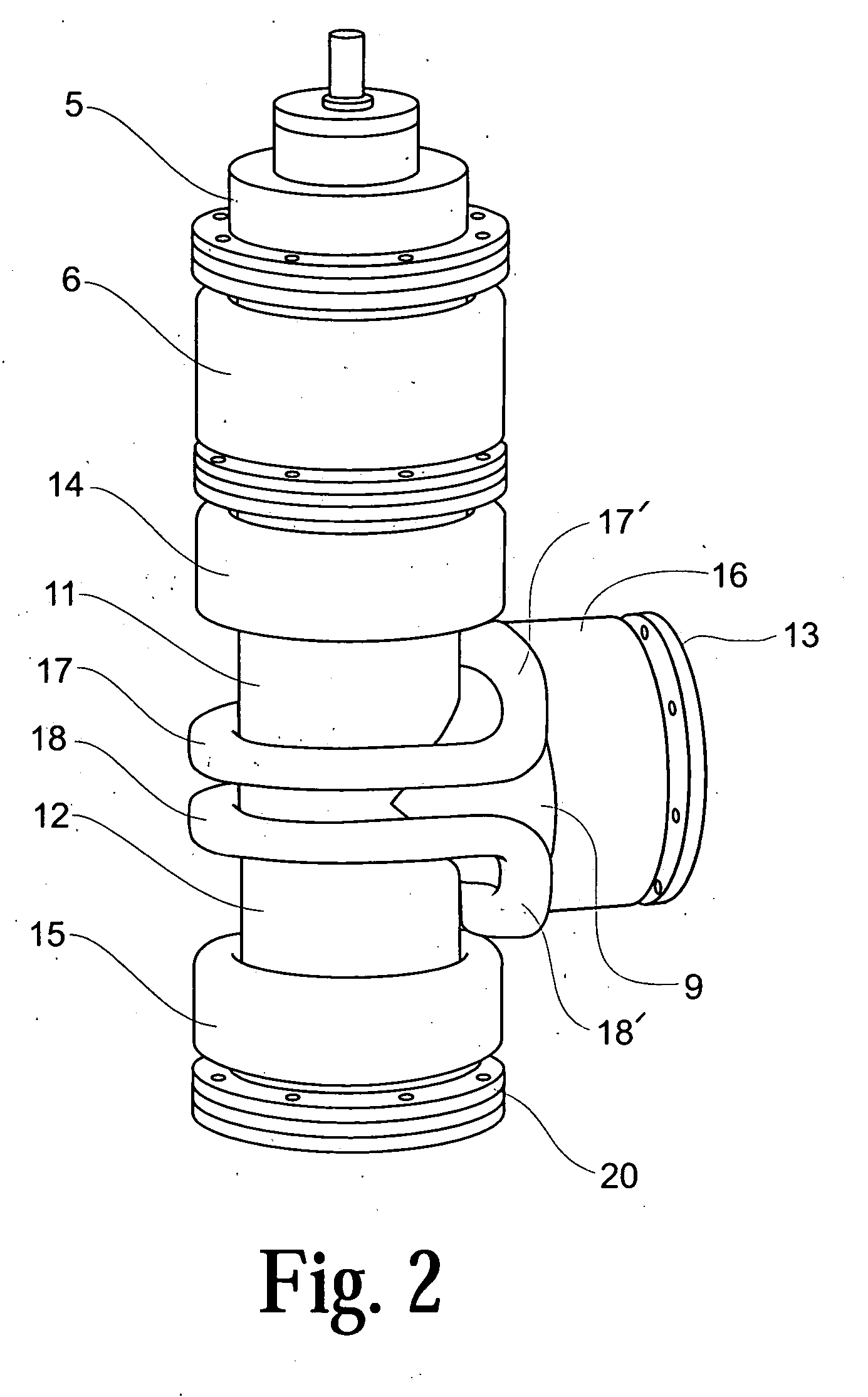
Externally excited torroidal plasma source with magnetic control of ion distribution
InactiveUS20030226641A1Short separation distanceSmall separationElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlasma currentIon distribution
A plasma reactor is described that includes a vacuum chamber defined by an enclosure including a side wall and a workpiece support pedestal within the chamber defining a processing region overlying said pedestal. The chamber has at least a first pair of ports near opposing sides of said processing region and a first external reentrant tube is connected at respective ends thereof to the pair of ports. The reactor further includes a process gas injection apparatus (such as a gas distribution plate) and an RF power applicator coupled to the reentrant tube for applying plasma source power to process gases within the tube to produce a reentrant torroidal plasma current through the first tube and across said processing region. A magnet controls radial distribution of plasma ion density in the processing region, the magnet having an elongate pole piece defining a pole piece axis intersecting the processing region.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Electrosurgical apparatus to generate a dual plasma stream and method thereof
ActiveUS8795265B2Small equivalent capacitanceGood effectSurgical instruments for heatingPlasma currentElectrosurgery
The present disclosure relates to an electrosurgical apparatus to generate a dual plasma stream to perform electrosurgery on a surgical site on a patient. The apparatus and method of the present disclosure generates a hot gas jet to a surgical site by generating two plasma beams that are electrically up to 180 degrees out of phase from each other. Since each beam uses the other beam to establish plasma currents at a load, the combined dual plasma stream can be used on non-conductive surfaces, e.g., a tissue at the surgical site. Furthermore, by applying different flow rates to the plasma beams, various scanning effects by the hot gas jet can be achieved.
Owner:BOVIE MEDICAL CORPORATION
Rotating plasma current drive
InactiveUS20050249324A1Electric discharge tubesNuclear energy generationRotational axisElectrode Contact
The present invention includes electromagnetic methods and apparatus to form a sustained direct current loop in a conductive fluid such as plasma for applications including gas discharge arc lamps and fusion confinement systems. The current loop is driven by rotating plasma within a stationary magnetic field perpendicular to the axis of rotation. Polyphase rotating electric or magnetic fields drive the plasma rotation, and the interaction between the rotating plasma and the stationary field forms and sustains the current loop. Plasma cooling and contamination are minimized since, unlike conventional direct current drive methods and apparatus, no electrodes contact the plasma.
Owner:MEACHAM GEORGE BEVAN KIRBY
Compact fusion reactor
InactiveCN103081021ANuclear energy generationDirect voltage acceleratorsNuclear fusionPlasma confinement
A compact nuclear fusion reactor for use as a neutron source is described. The reactor comprises a toroidal plasma chamber (34) and a plasma confinement system (31) arranged to generate a magnetic field for confining a plasma in the plasma chamber (34). The plasma confinement system (31) is configured so that a major radius of the confined plasma is 0.75 m or less. The reactor is configure to operate with a plasma current of 2 MA or less. The magnetic field includes a toroidal component of 5 T or less. Despite these low values, the reactor can generate a neutron output of 1 MW or more.
Owner:TOKAMAK ENERGY
Efficient compact fusion reactor
An efficient compact nuclear fusion reactor for use as a neutron source or energy source is described. The reactor comprises a toroidal plasma chamber and a plasma confinement system arranged to generate a magnetic field for confining a plasma in the chamber. The plasma confinement system is configured so that a major radius of the confined plasma is 1.5m or less. The toroidal magnetic field is operated 5T or less and the plasma current is 5 MA or less. Despite this, [Alpha]-particles generated are confined in the plasma.
Owner:TOKAMAK ENERGY
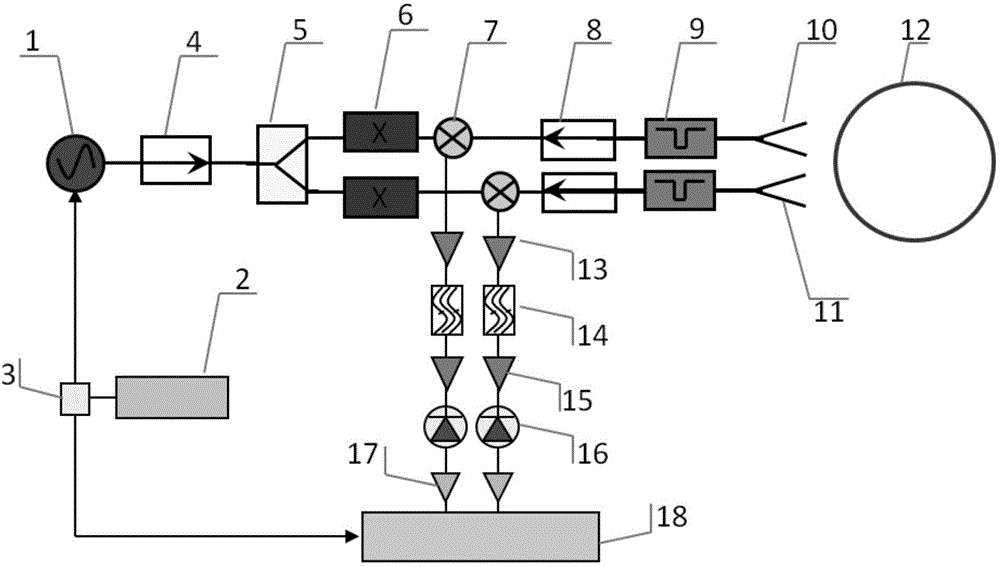
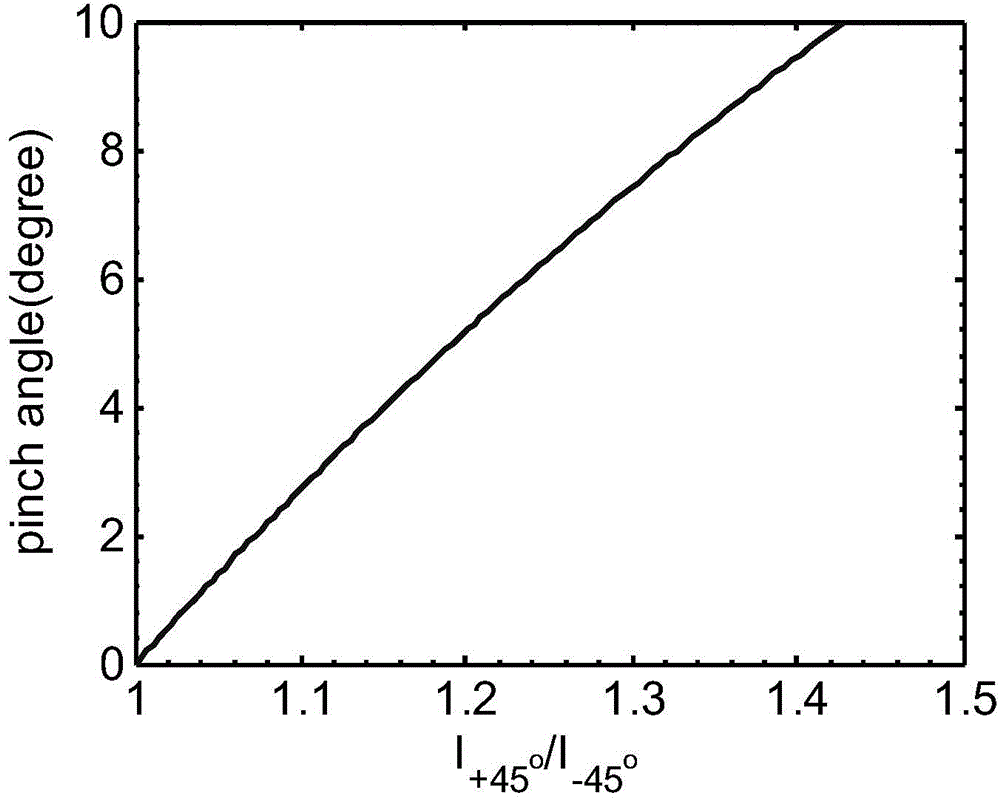
Polarized electron cyclotron emission (ECE) diagnosis system for measuring plasma current distribution
The present invention belongs to the nuclear fusion plasma diagnosis field, in particular relates to a polarized ECE diagnosis system for measuring the plasma current distribution and the safety factor distribution. The system is composed of a frequency sweep source, a signal generator, a frequency multiplier, a mixer, an isolator, a polarized antenna system, an intermediate frequency system, a demodulation system, a video amplification system, a data acquisition and analysis system and the like. By measuring a polarized distribution ratio of the ECE, a pitch angle of the magnetic field distribution, the plasma current distribution and the safety factor q distribution are obtained. According to the present invention, by utilizing the basic properties of an X mold and an O mold of an ECE wave and by two antenna channels, the intensity ratio of the ECE waves of different angles is measured, and the pitch angle of the magnetic field distribution is obtained, and further the current distribution and the safety factor distribution are obtained. The measurement of the system is not influenced by the external conditions, such as the plasma heating, etc., to be the passive measurement, so that the data of the current distribution and the safety factor distribution can be obtained at any time.
Owner:SOUTHWESTERN INST OF PHYSICS
Method for controlling TOKMAK discharge low noise wave power mode
InactiveCN1925061AQuick protectionFast shutdownComputer controlNuclear energy generationLow noiseKlystron
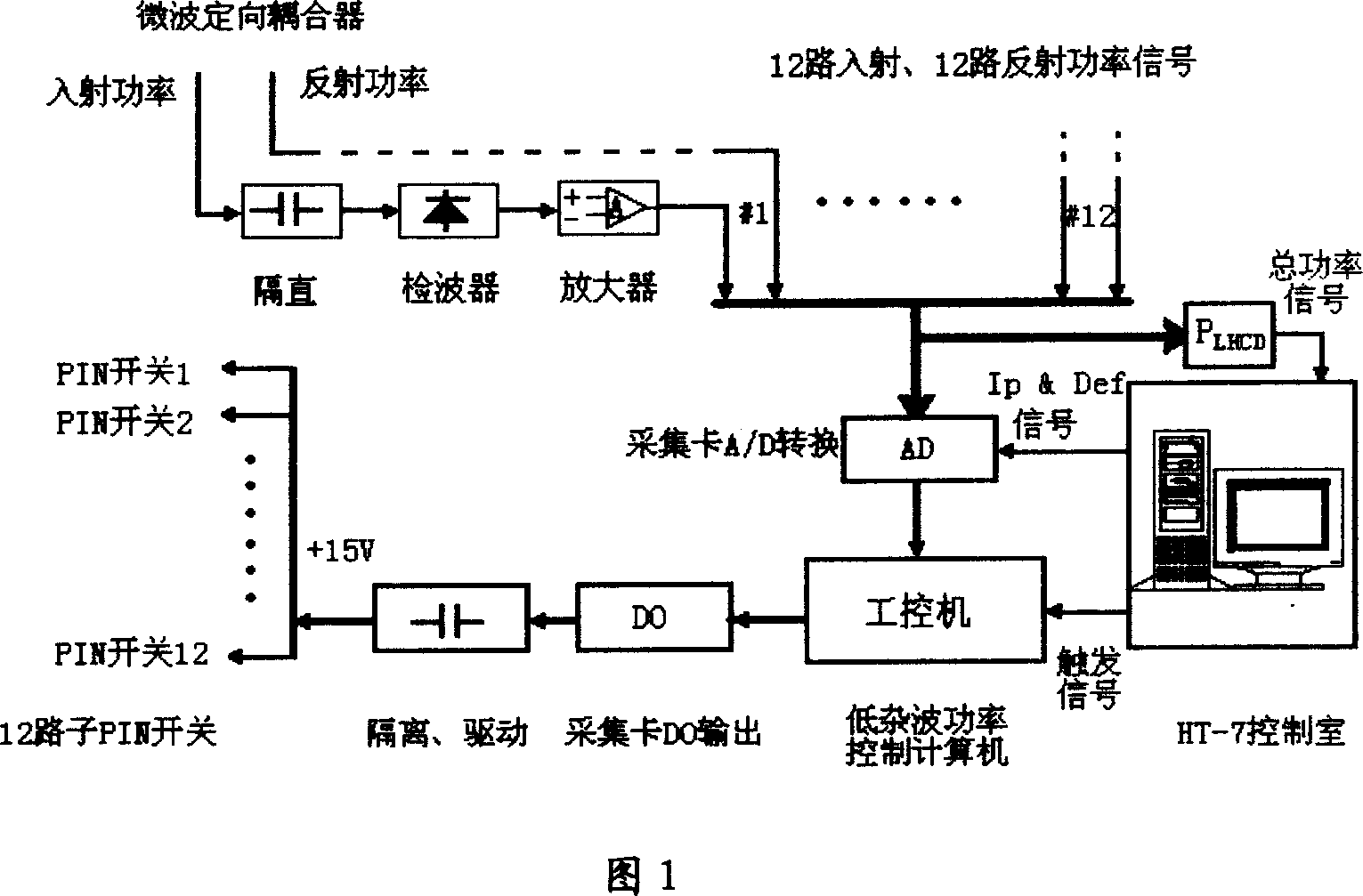
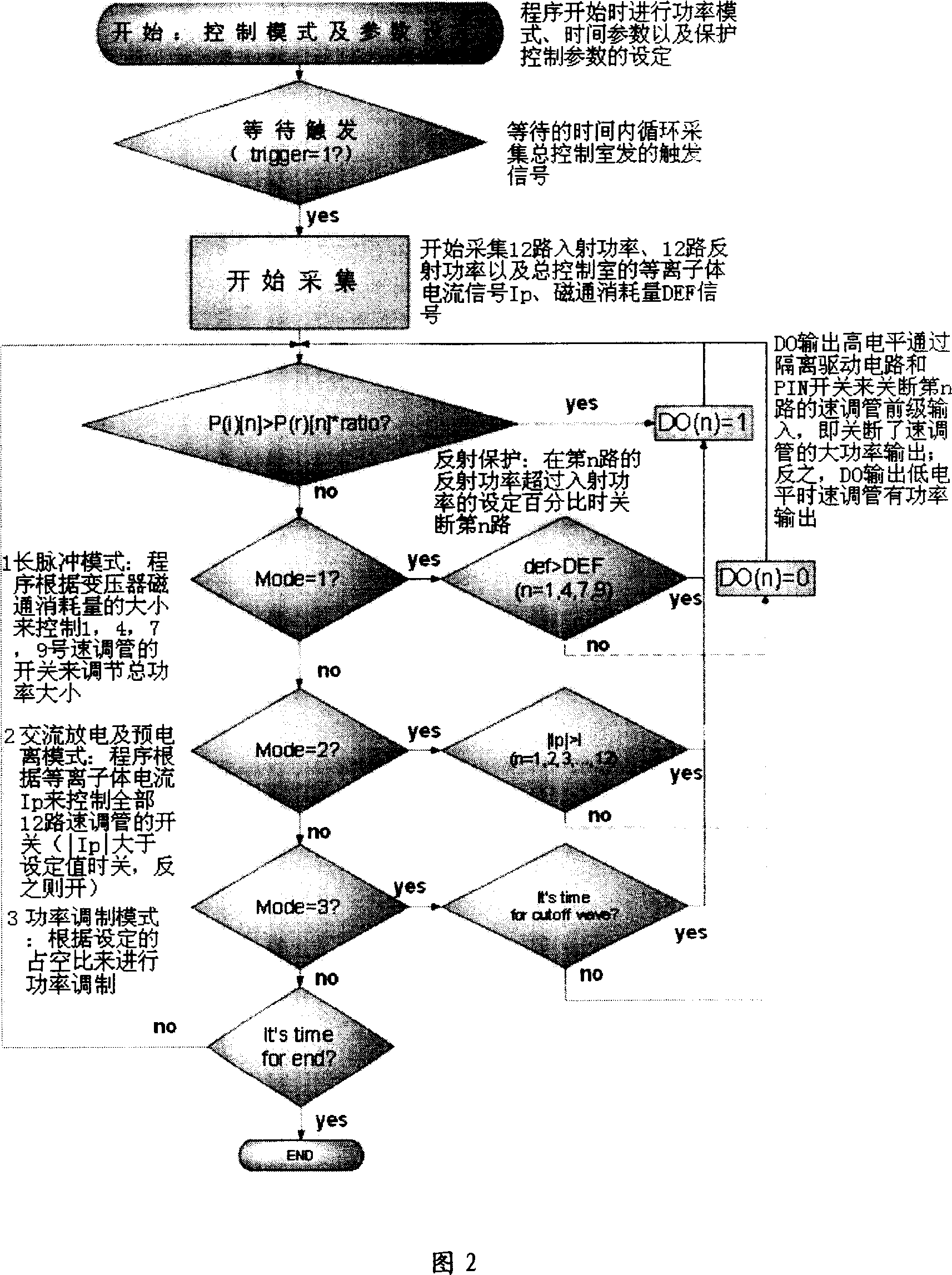
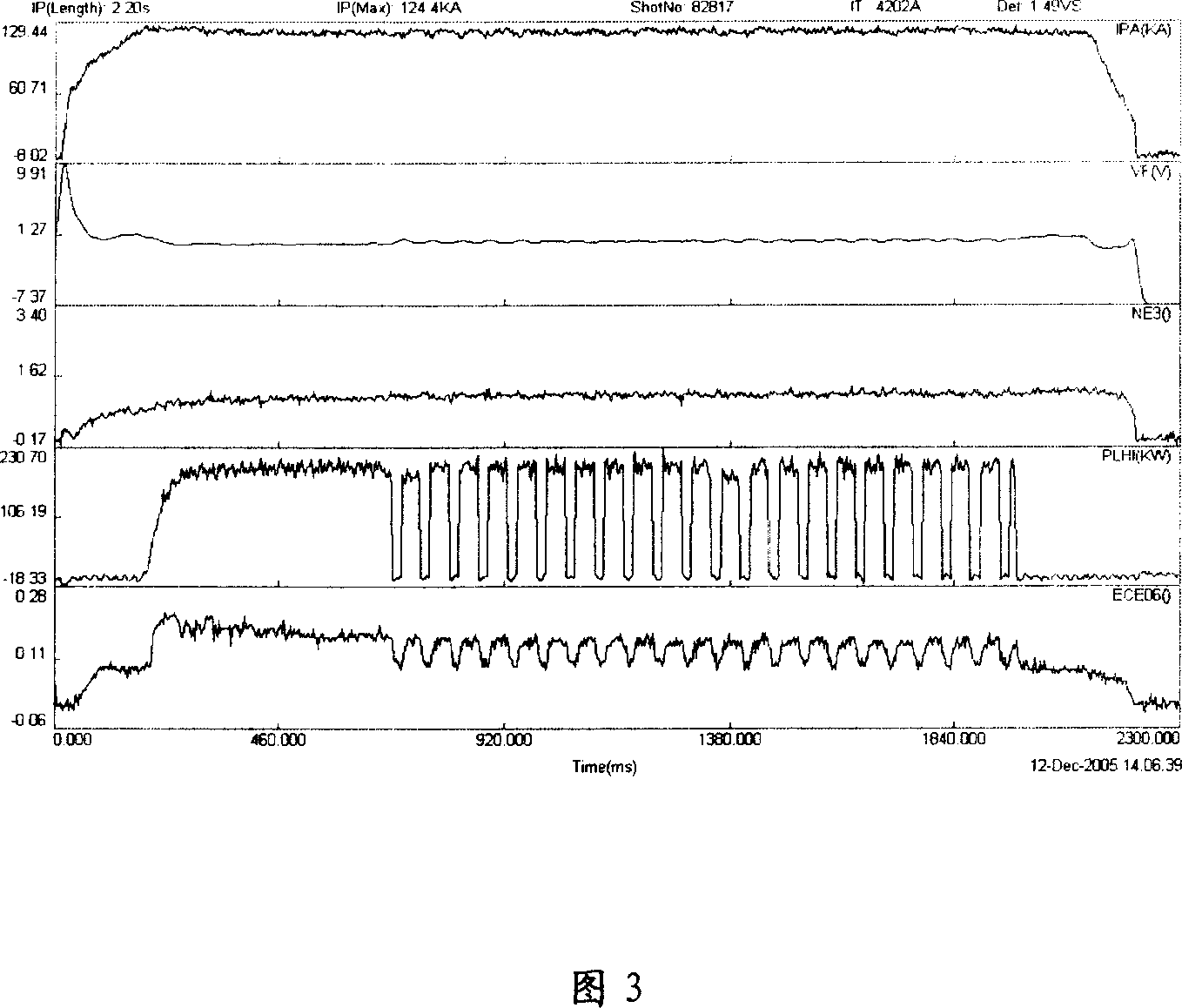
This invention discloses one TOKMAK discharging clutter power mode control method, which controls low clutter front degree of power through computer to control klystron output to realize needed microwave power mode. The incidence power and reflection power microwave signal and plasma current signal Ip and transducer flux consumption signals Def control the output level of Do according to needs of control modes to control DC blocking drive circuit and to control each sub circuit PIN switch to realize clutter power output in different modes.
Owner:INST OF PLASMA PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Filtered cathodic-arc plasma source
InactiveUS7381311B2Improve ion transmission efficiencyQuality improvementCellsElectric discharge tubesPlasma currentMagnetic flux
A filtered cathodic-arc plasma source of lower plasma losses and higher output plasma current to input current efficiency is disclosed. Plasma filtering is accomplished in a right angle bend magnetic filter arranged to include the effects of at least three added magnetic coils located at the right angle bend of the filter path. These magnetic coils and other filter attributes, including an array of transverse fins and a magnetic cusp trap in the filter path, achieve desirable magnetic flux paths, lower plasma collision losses and reduced undesired particle output from the plasma filter. Multiple cathode sources, multiple plasma output ports, Larmour radius influence, equipotential magnetic flux lines and electron / ion interaction considerations are also included in the plasma source. Application of the plasma source to film coating processes is included.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
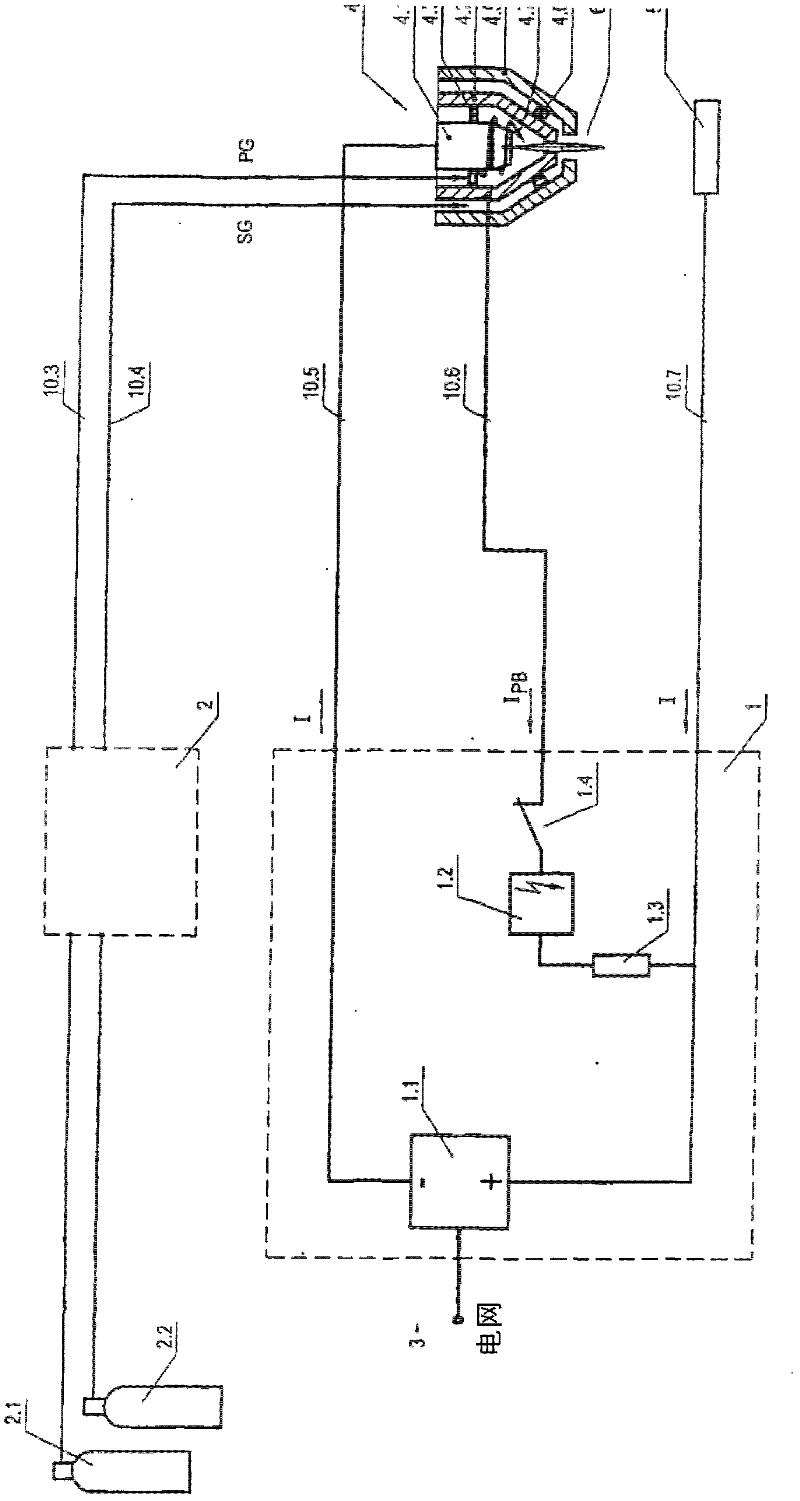
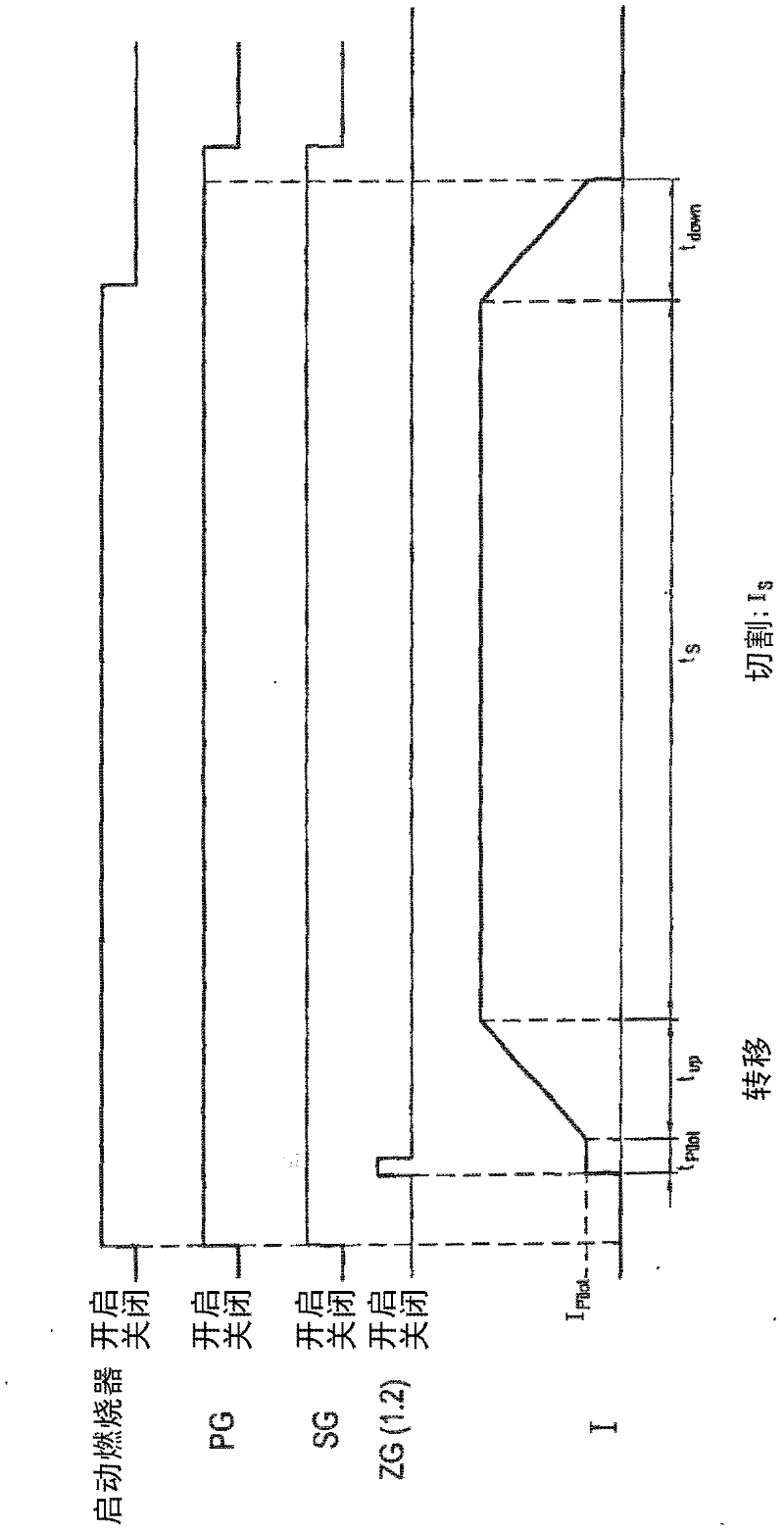
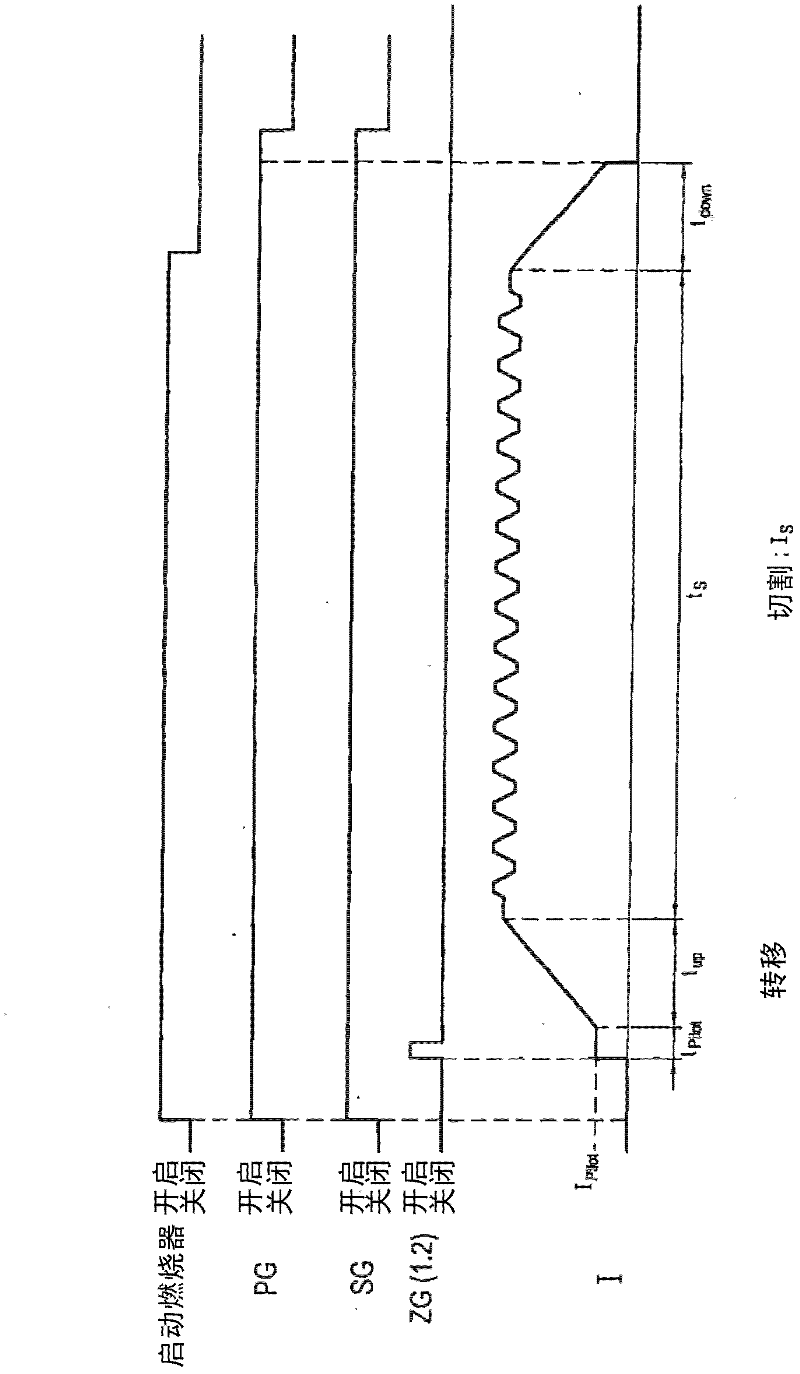
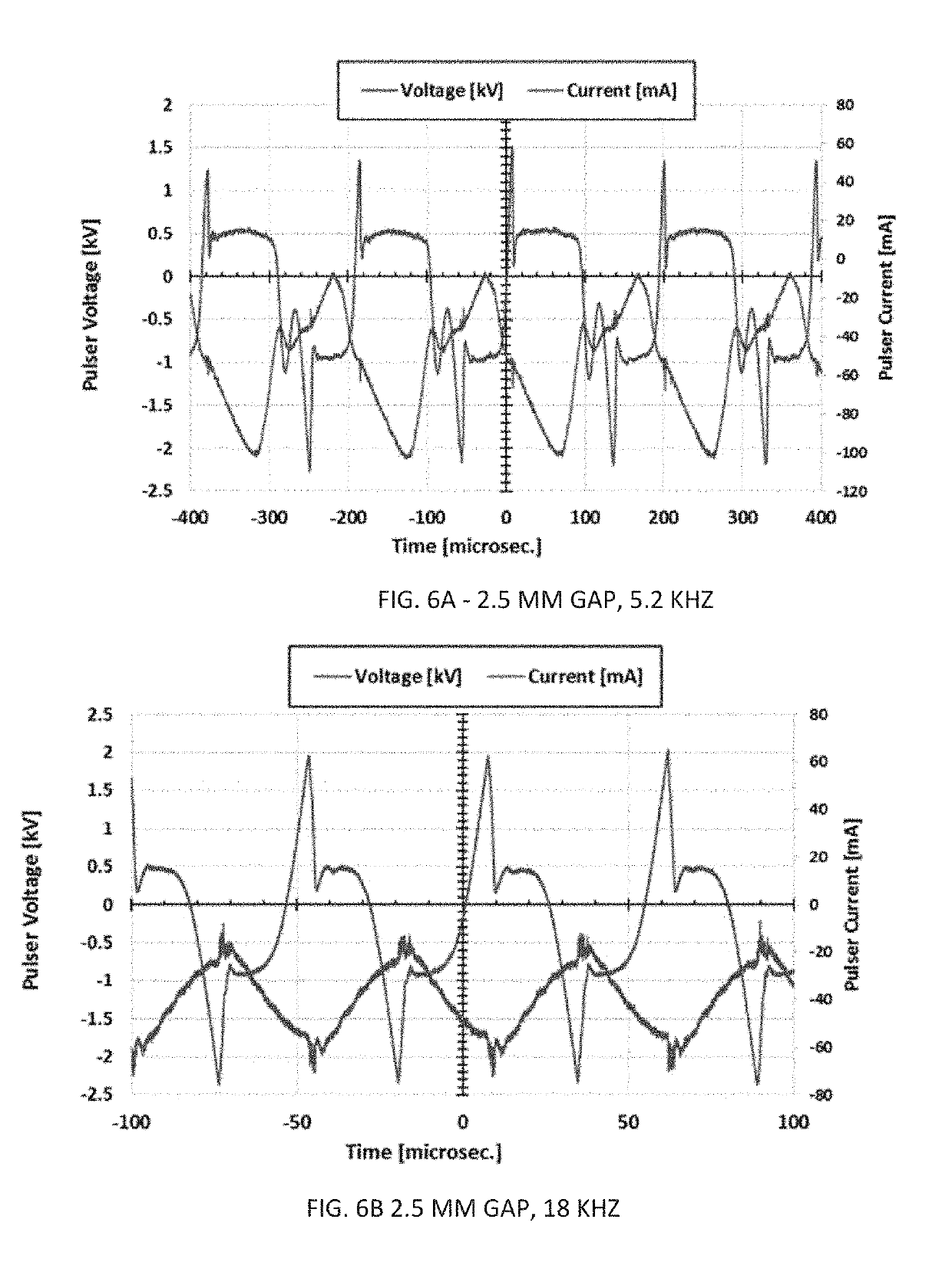
Method for plasma-cutting a workpiece by means of a plasma-cutting system and pulsating current
The invention relates to a method for plasma-cutting a workpiece by means of a plasma-cutting system, which comprises a plasma current source and a plasma torch, which has an electrode and a nozzle, which has a small distance from the electrode at a lower end of the plasma torch in order to form a plasma chamber therebetween, characterized in that a current I produced by the plasma current source and flowing through the plasma torch is brought to pulsation in a targeted or controlled manner at an arbitrary frequency f in the range of 30 Hz to 500 Hz, preferably 35 Hz to 500 Hz, especially preferably 55 Hz to 400 Hz, at least during a partial time period of the plasma-cutting process, or a current I produced by the plasma current source and flowing through the plasma torch is brought to pulsation in a targeted or controlled manner at an arbitrary frequency f in the range of 0.1 Hz to 30 Hz, preferably 0.1 Hz to 29 Hz, especially preferably 0.1 Hz to 20 Hz, at least during a partial time period of the plasma-cutting process.
Owner:KJELLBERG FINSTERWALDE PLASMA & MASCH GMBH
Welding gun pose-variable closed geometric component GMAW added material manufacturing method
InactiveCN106513931AFirmly connectedQuality improvementArc welding apparatusMetal working apparatusPlasma currentEngineering
The invention provides a welding gun pose-variable closed geometric component GMAW added material manufacturing method. A closed geometric component consists of multiple layers of single-way thin-wall pieces connected end to end; an angle between the growth direction of a forming layer and a projection thereof on a substrate plane is smaller than and equal to 90 degrees; the method adopts a method for controlling the arc starting and quenching end joint quantity of the forming layer to improve the forming quality in the end-to-end connecting place; in the forming process, a welding gun gesture is adjusted to enable a welding gun to always point to the growth direction of the forming layer; and the generated arc force and plasma current force direction is parallel to the growth direction of the forming layer, so that the improvement of the stability of a molten pool of the forming layer is facilitated, and the large-dip-angle growth of the forming layer is realized. The method effectively overcomes the difficulties of weak forming quality of the end-to-end connecting place of the closed geometric component and low inclined surface forming capacity, is simple in operation, and is easy to realize automation of the GMAW added material manufacturing process.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Arc suppression device and arc suppression method
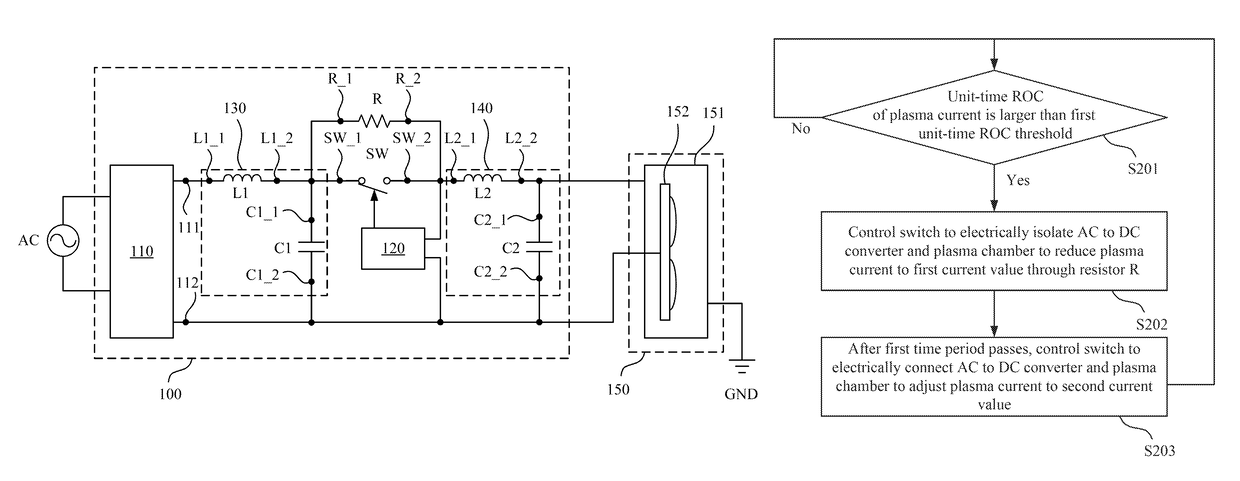
ActiveUS10111315B1Arc eliminationElectric discharge tubesElectric lighting sourcesElectricityPower flow
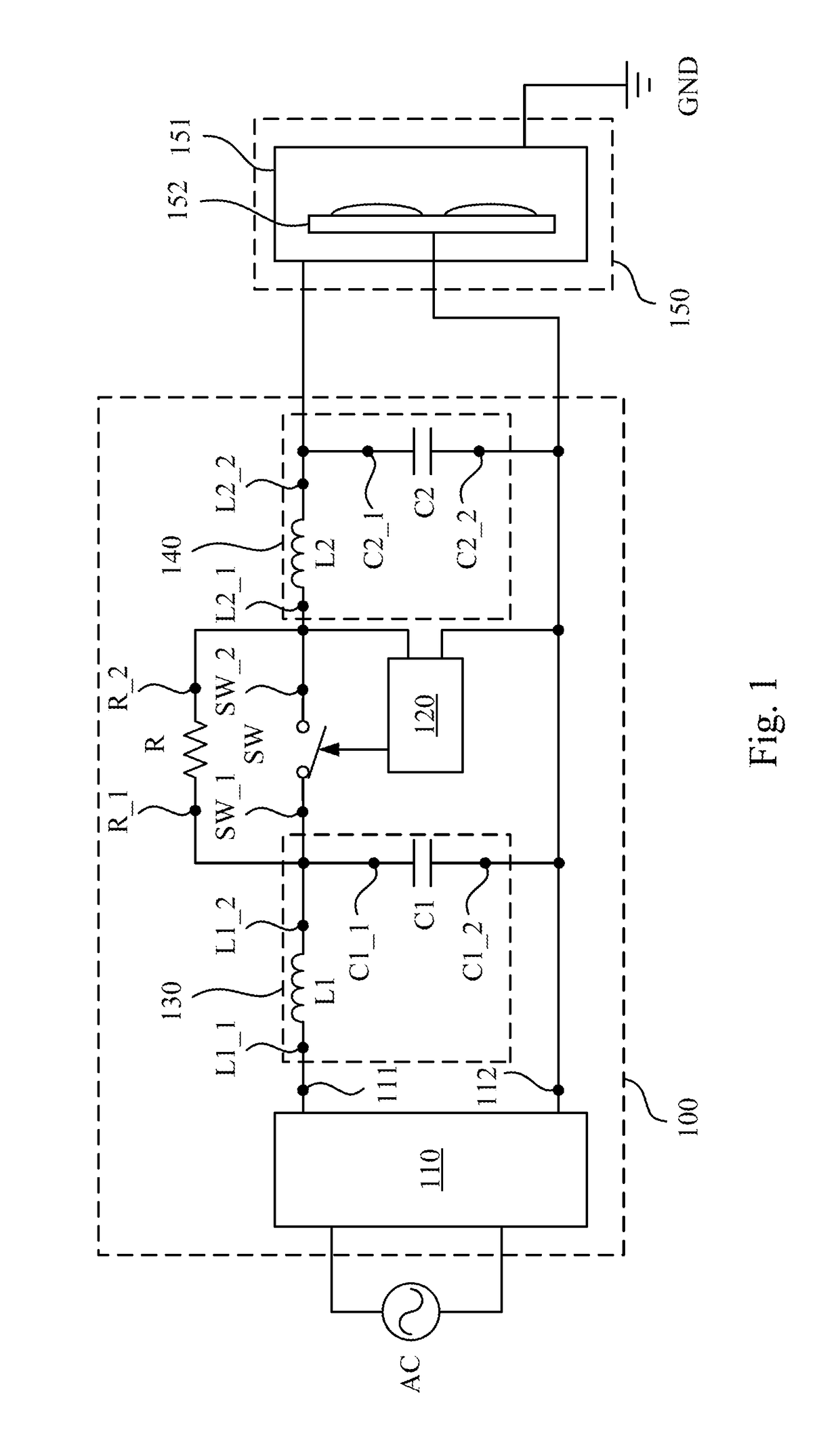
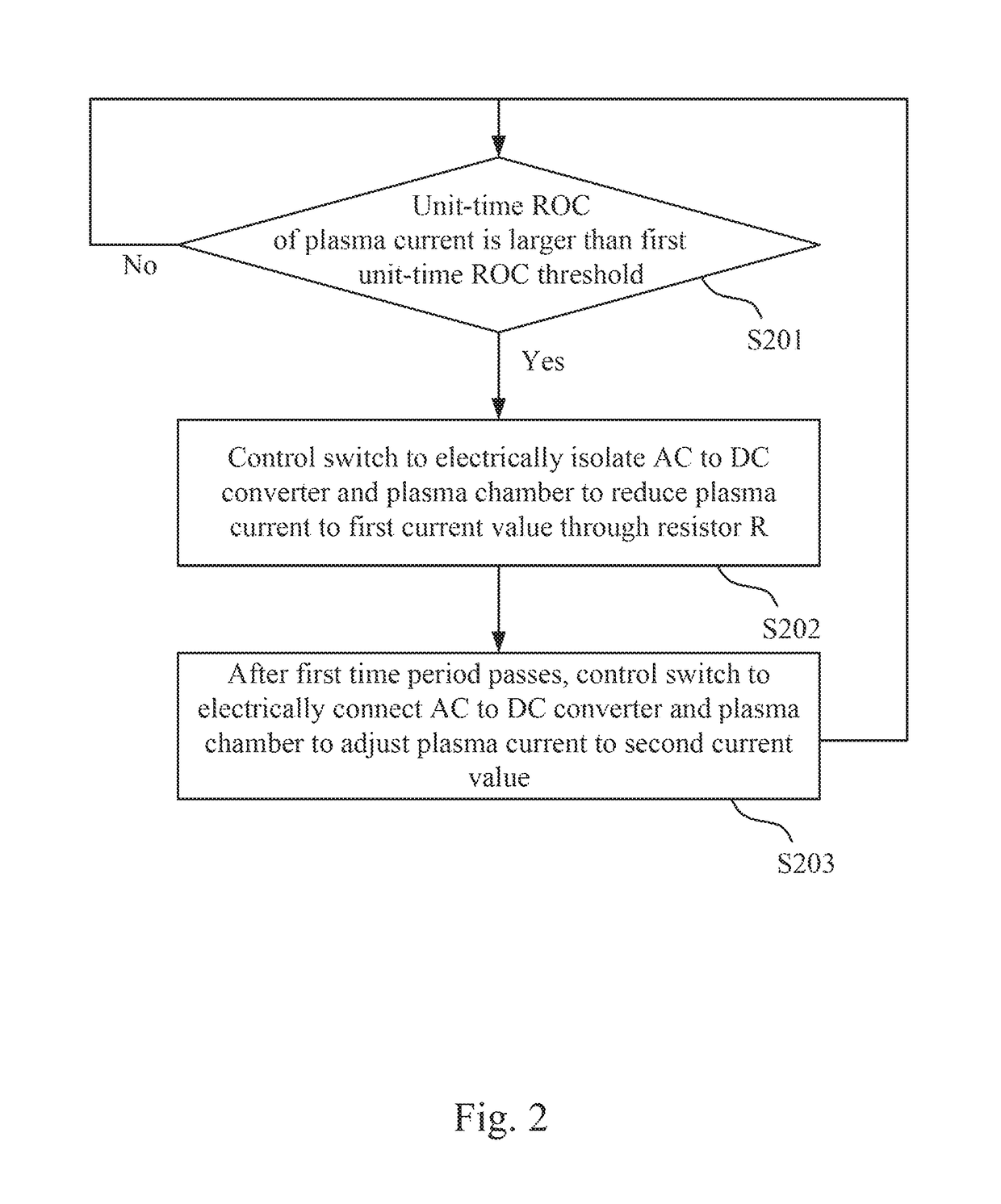
An arc suppression device includes an AC to DC converter, a switch, a resistor and a controller. The switch is coupled between the AC to DC converter and a plasma chamber. The resistor is coupled in parallel with the switch. The AC to DC converter is configured to convert an AC voltage into a DC voltage for providing to the plasma chamber. The controller is configured to detect a unit-time rate of change (ROC) of a plasma current received by the plasma chamber. When the controller determines that the unit-time ROC of the plasma current is larger than a first unit-time ROC threshold, the controller controls the switch to electrically isolate the AC to DC converter and the plasma chamber to reduce the plasma current to a first current value through the resistor.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
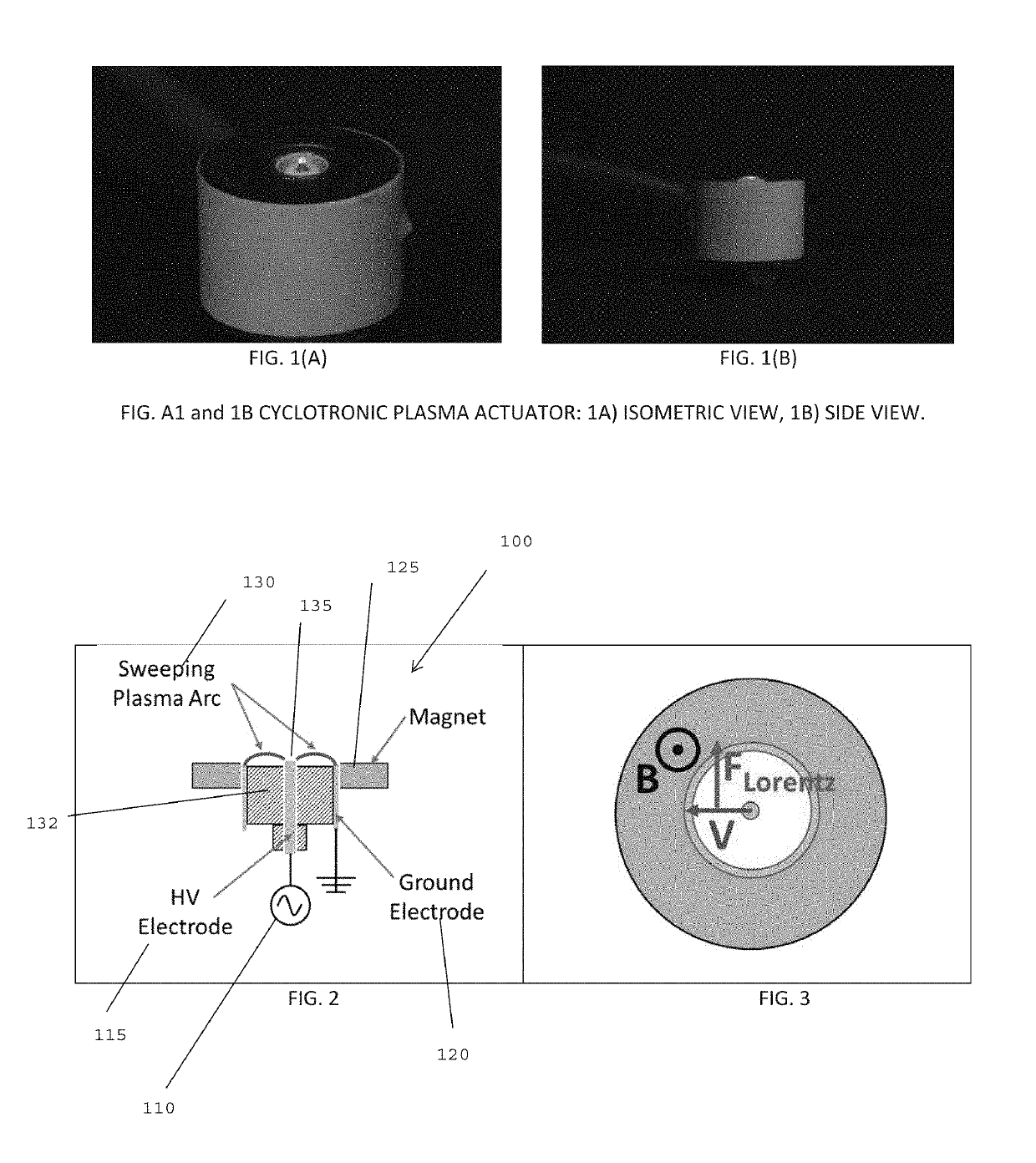
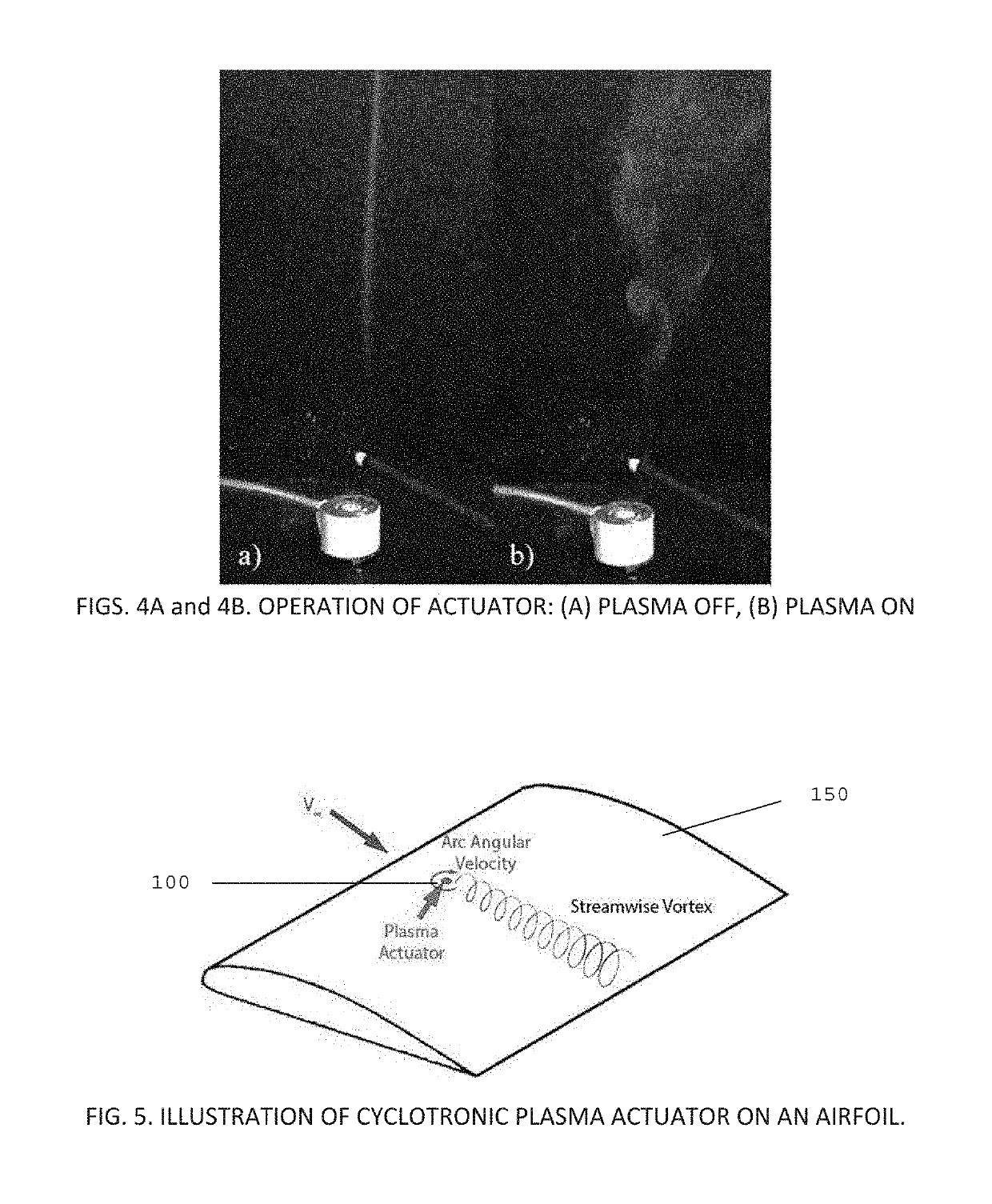
Cyclotronic plasma actuator with arc-magnet for active flow control
Owner:CU AEROSPACE +1
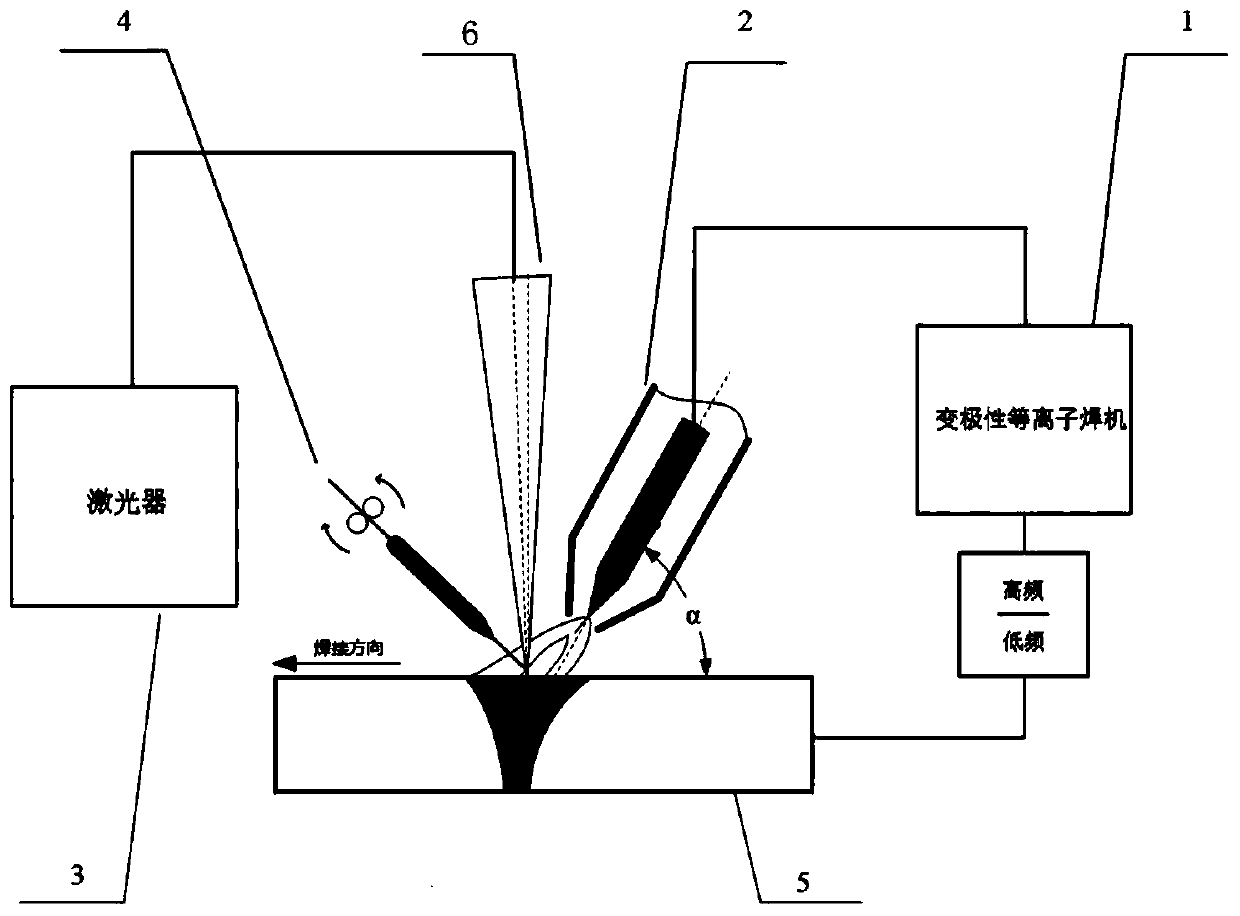
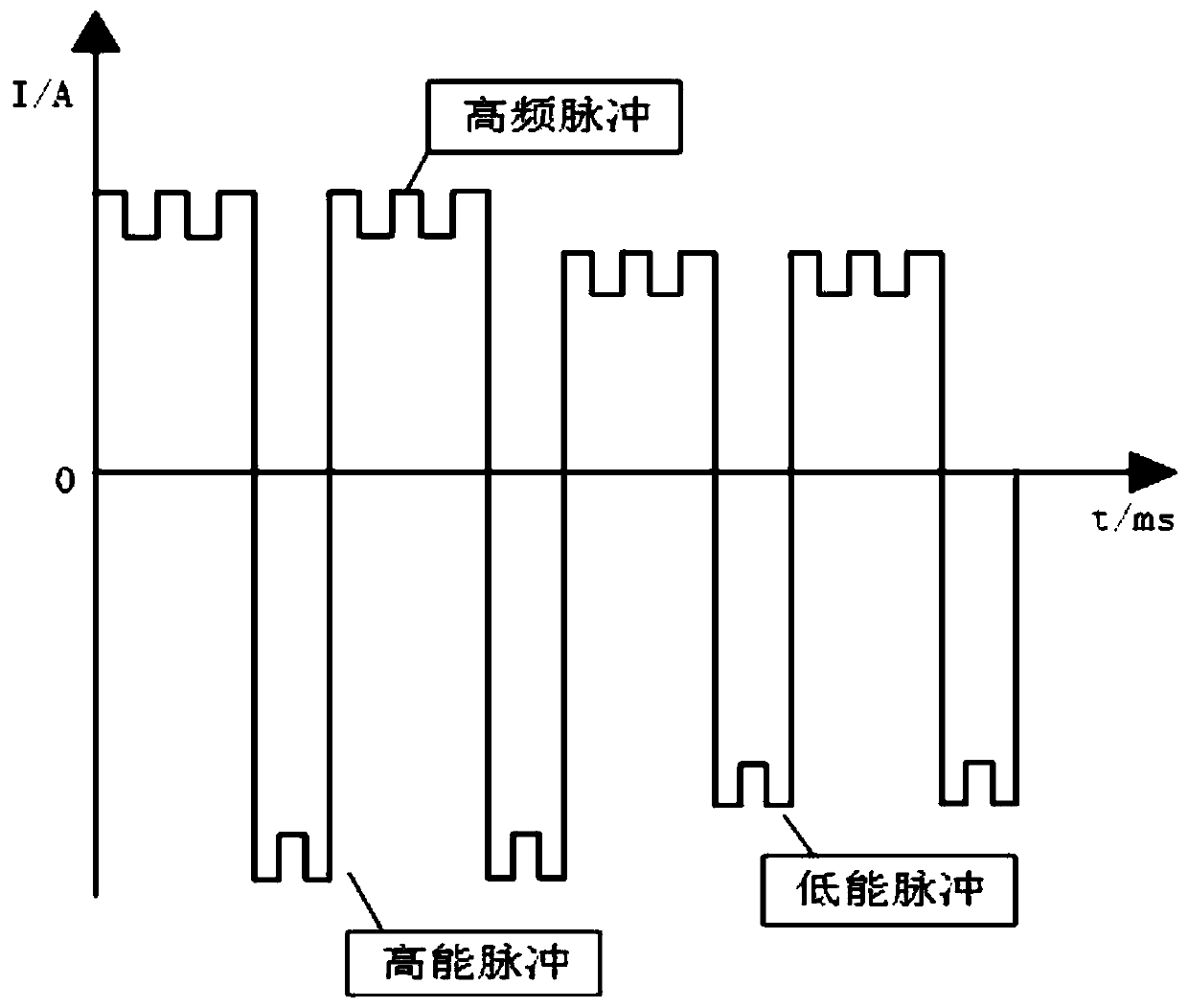
Laser-electric arc compound welding method suitable for high strength aluminum alloy downward welding
PendingCN110587138AImprove welding qualityBeautiful shapeWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser beam welding apparatusLaser beamsPlasma arc welding
The invention relates to a laser-electric arc compound welding method suitable for high strength aluminum alloy downward welding. By adopting a compound welding process of combining dipulse variable polarity plasma arc welding with laser welding, high, intermediate and low frequencies of pulse variable polarity plasma arc pulse currents are controllable by means of control: the high frequency pulse frequency is 200-1000 Hz, the low frequency pulse frequency is 1-5 Hz, and the power frequency is 40 Hz; the welding process parameters are as follows: the plasma current is 160-220 A, the electricarc voltage is 21-30 V, the arc height is 5-6 mm, the plasma welding gun angle is 45-60 degrees, and high purity argon protection is carried out; the laser power is 1.5-2.5 kw, the laser defocusing amount is -5-5 mm, and the laser beam is 5-10 degrees inclining to the side of the welding gun; and the electric arc is in front of the laser beam, the separation distance from light to tungsten is 3-6mm, and the welding speed is 480-1040 mm / min. The laser-electric arc compound welding method can reduce weld heat input and improve the welding efficiency.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com