Patents
Literature
65 results about "Stationary field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
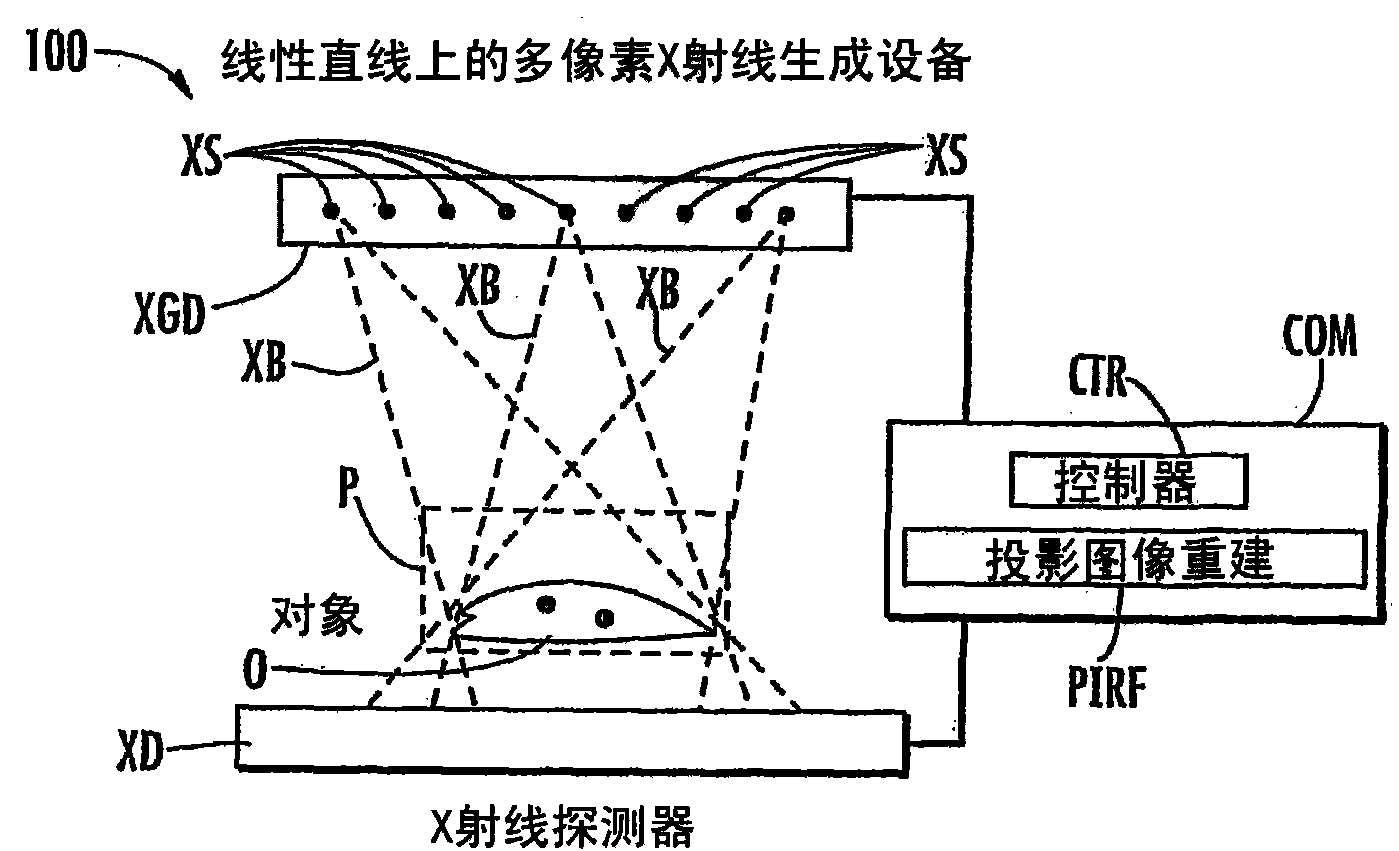
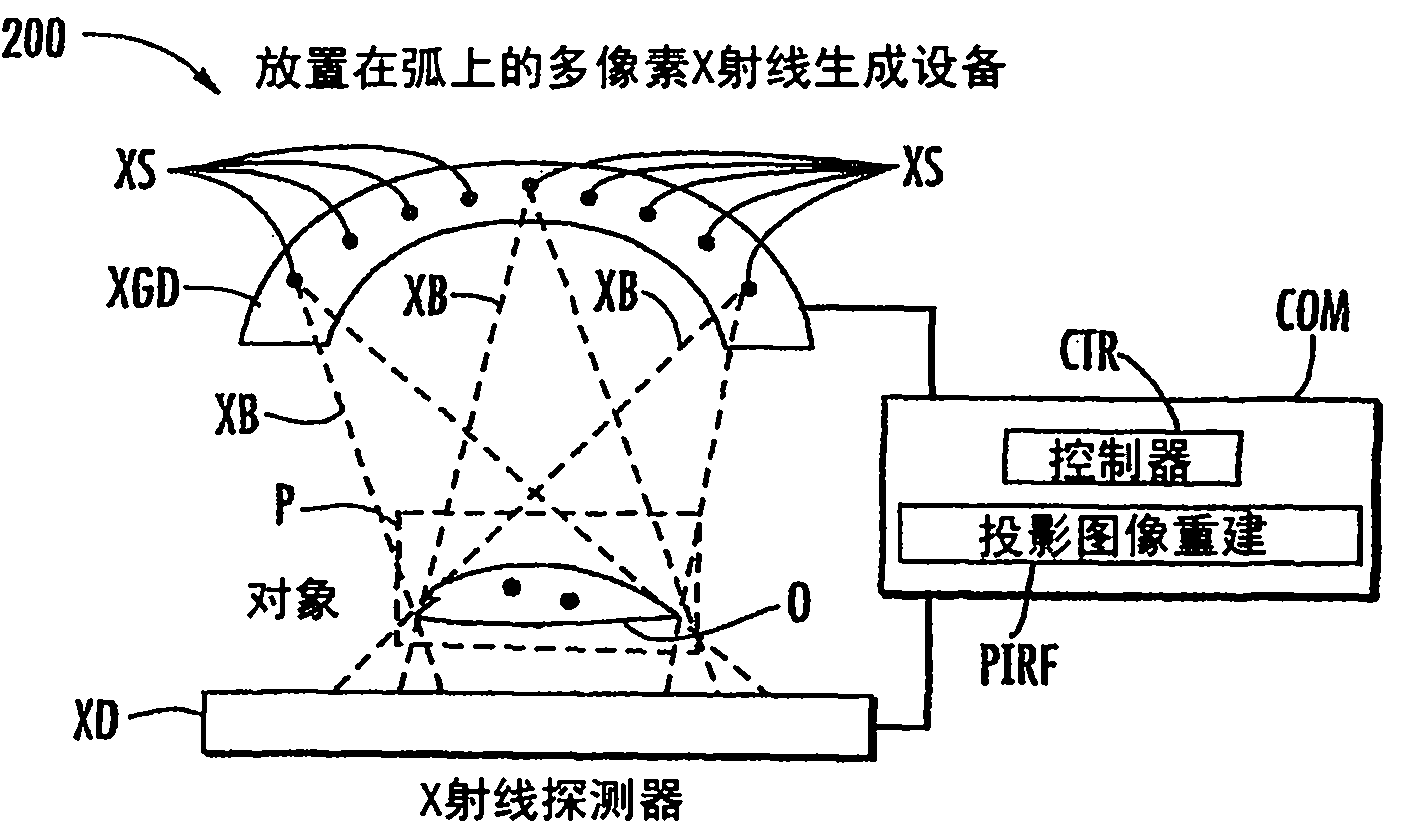
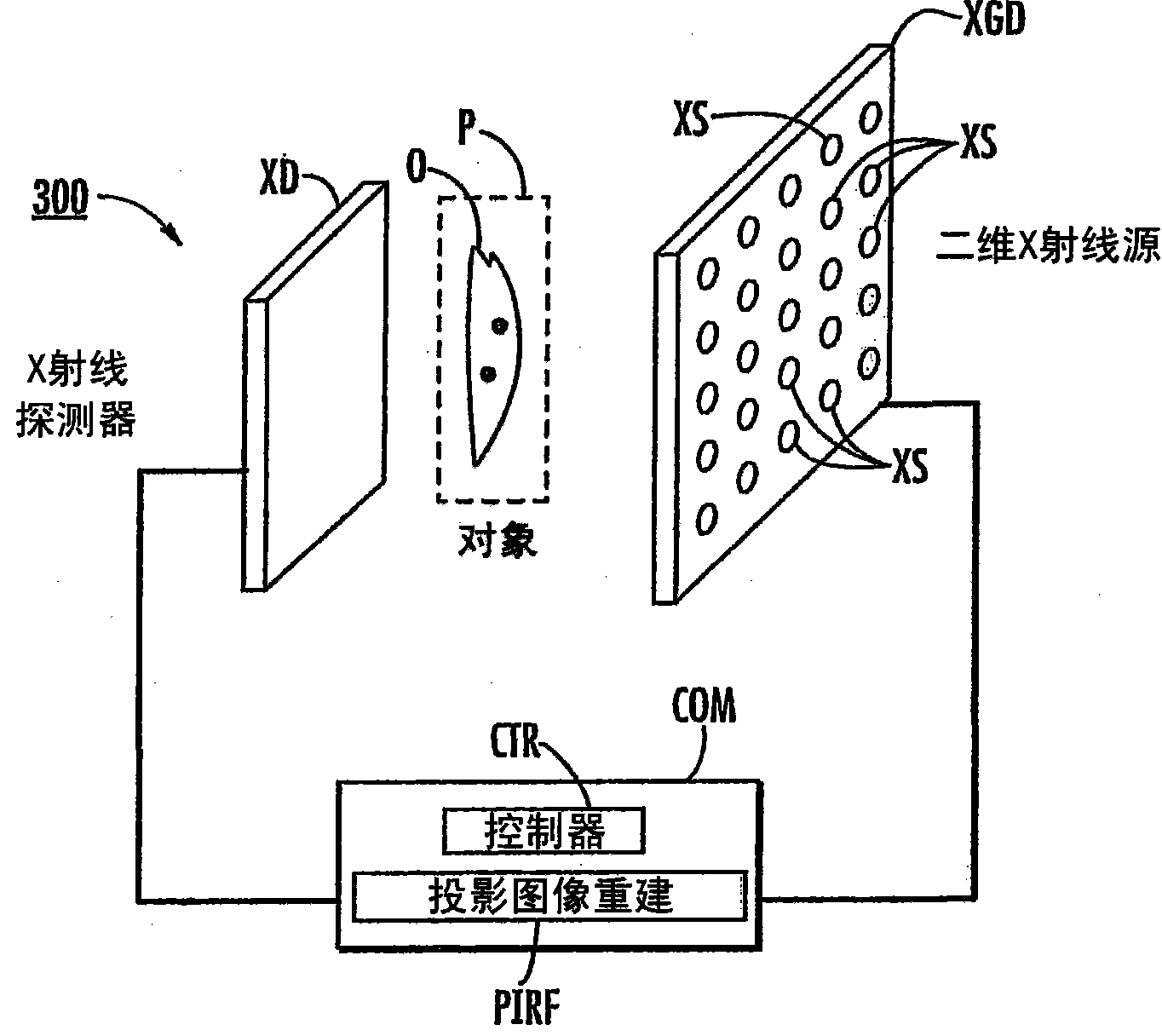
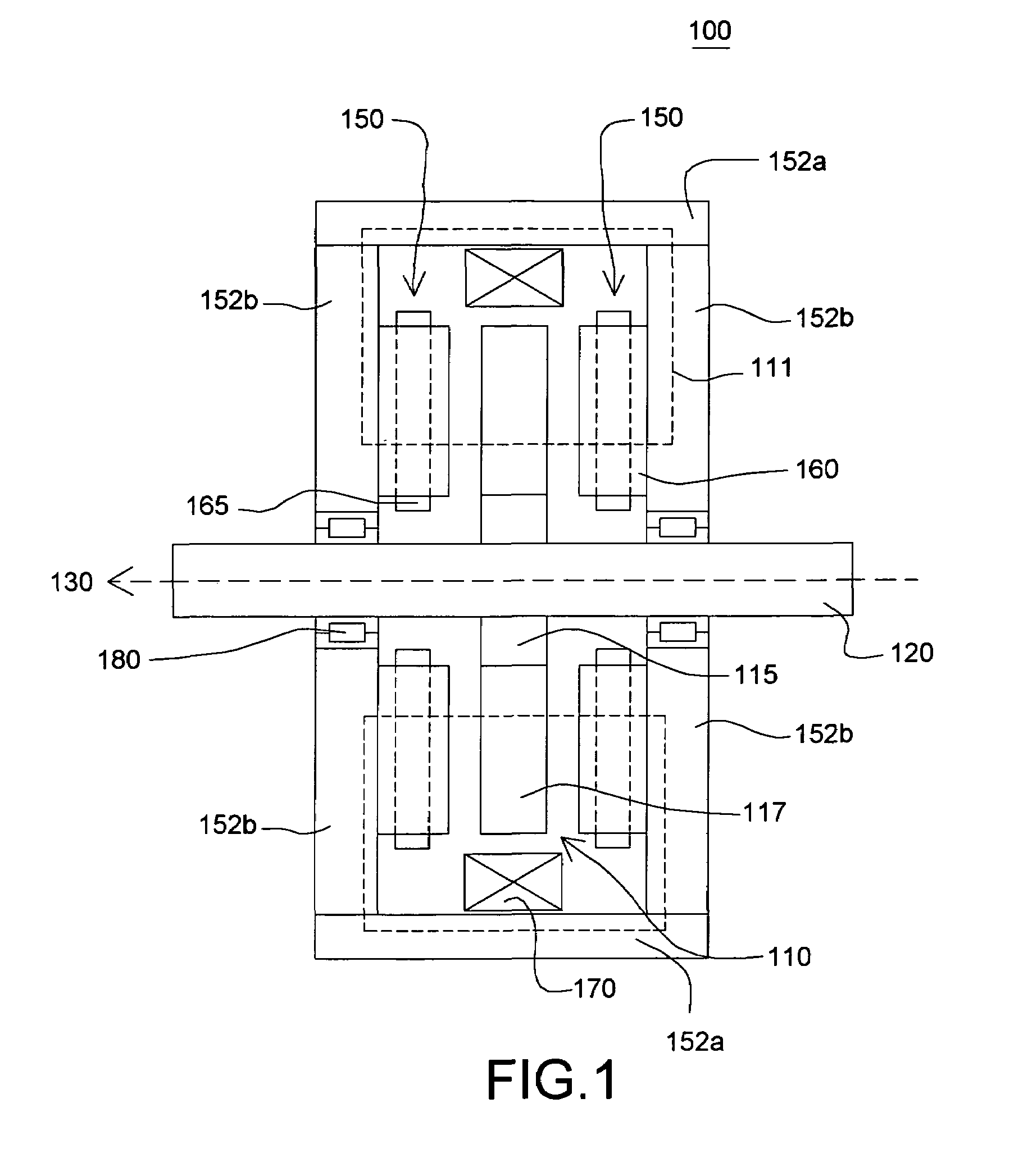
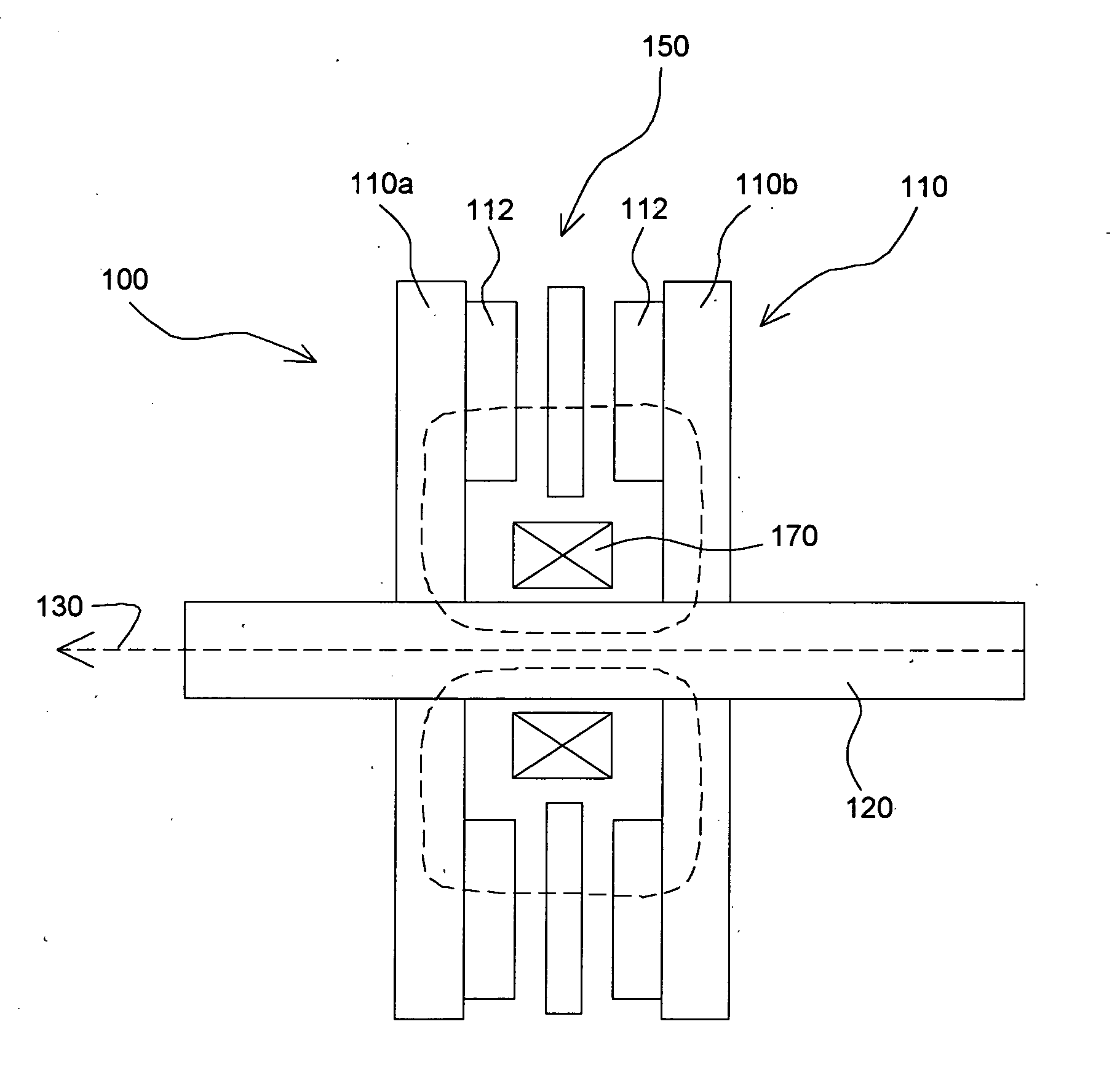
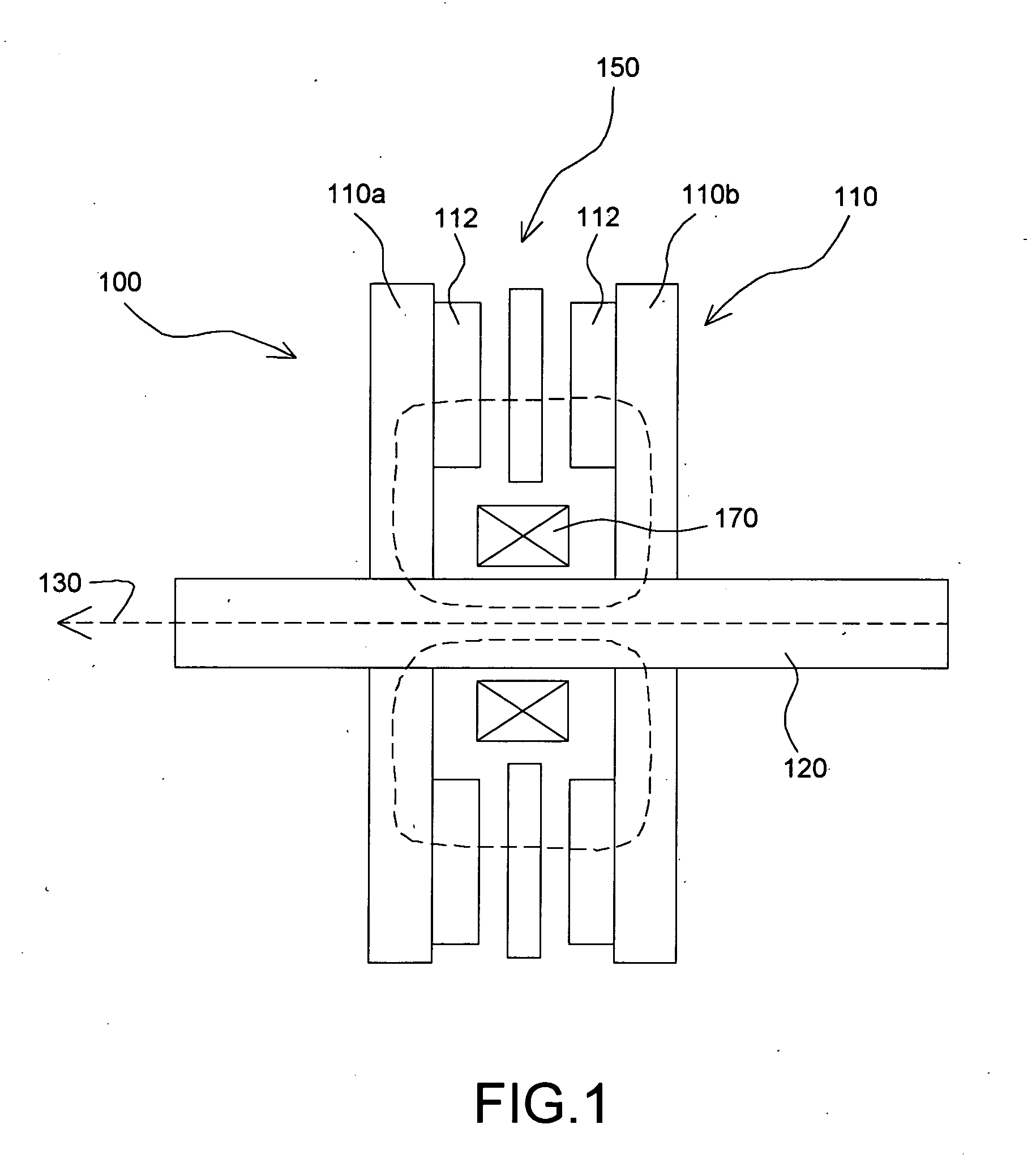
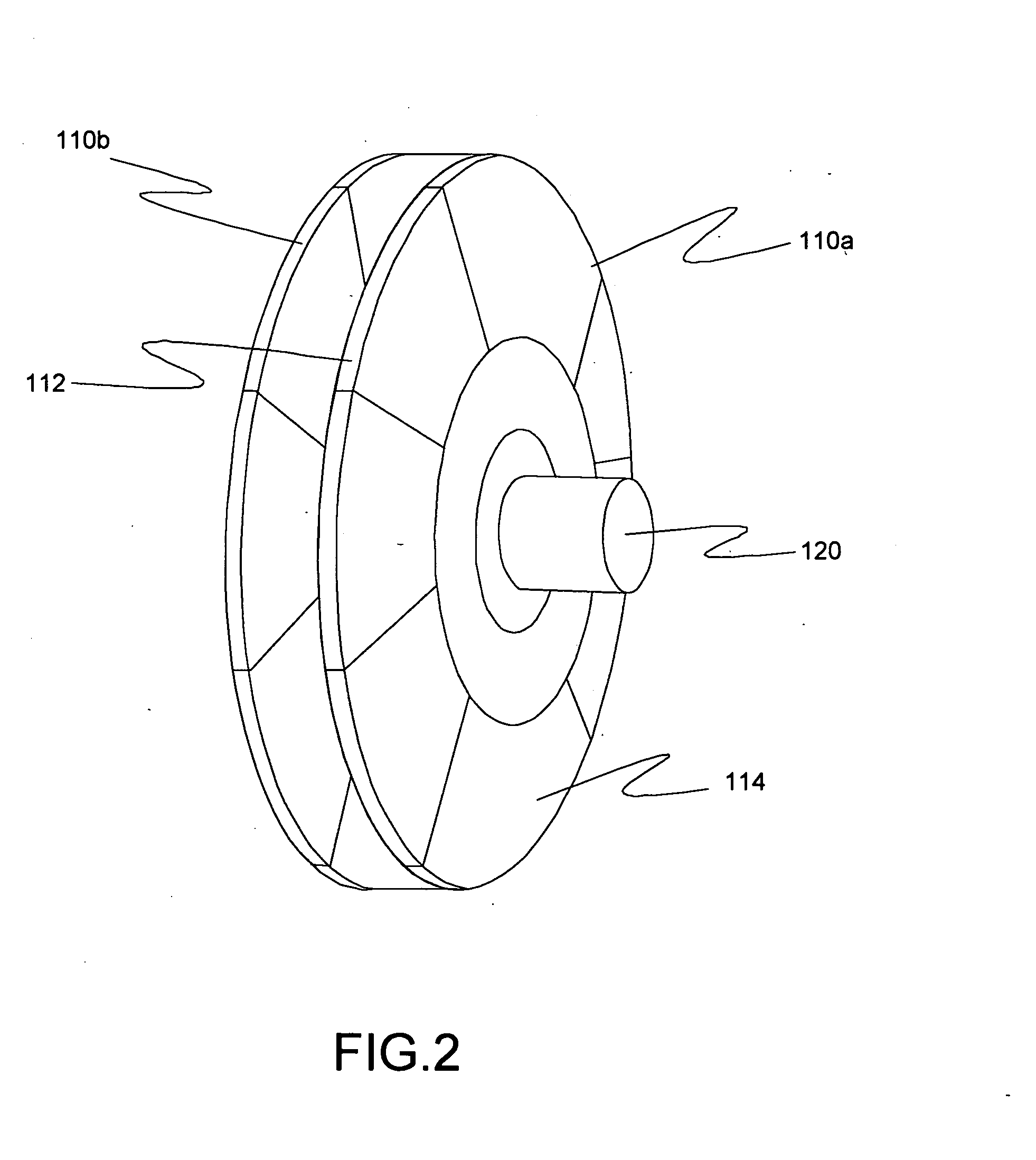
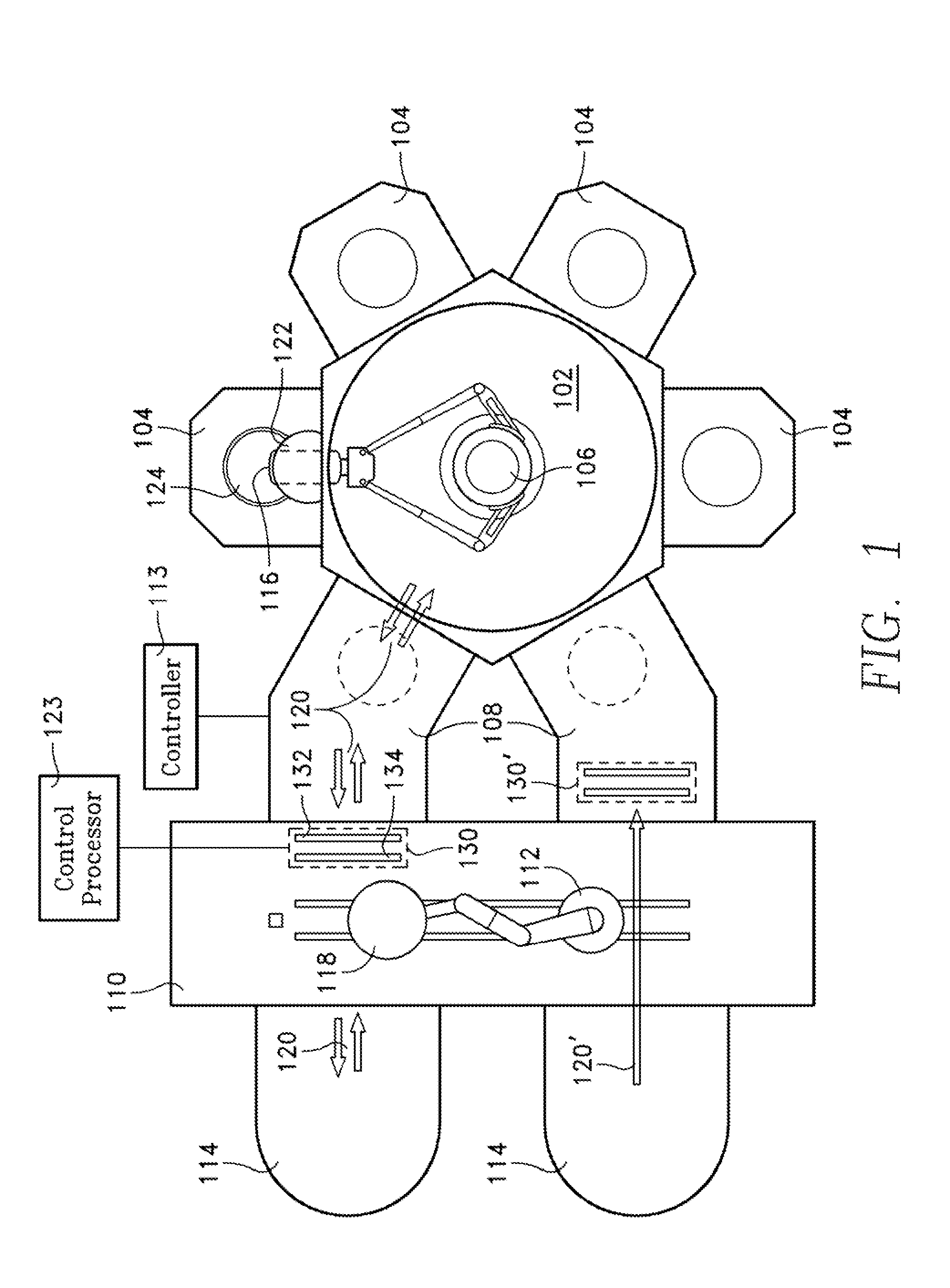
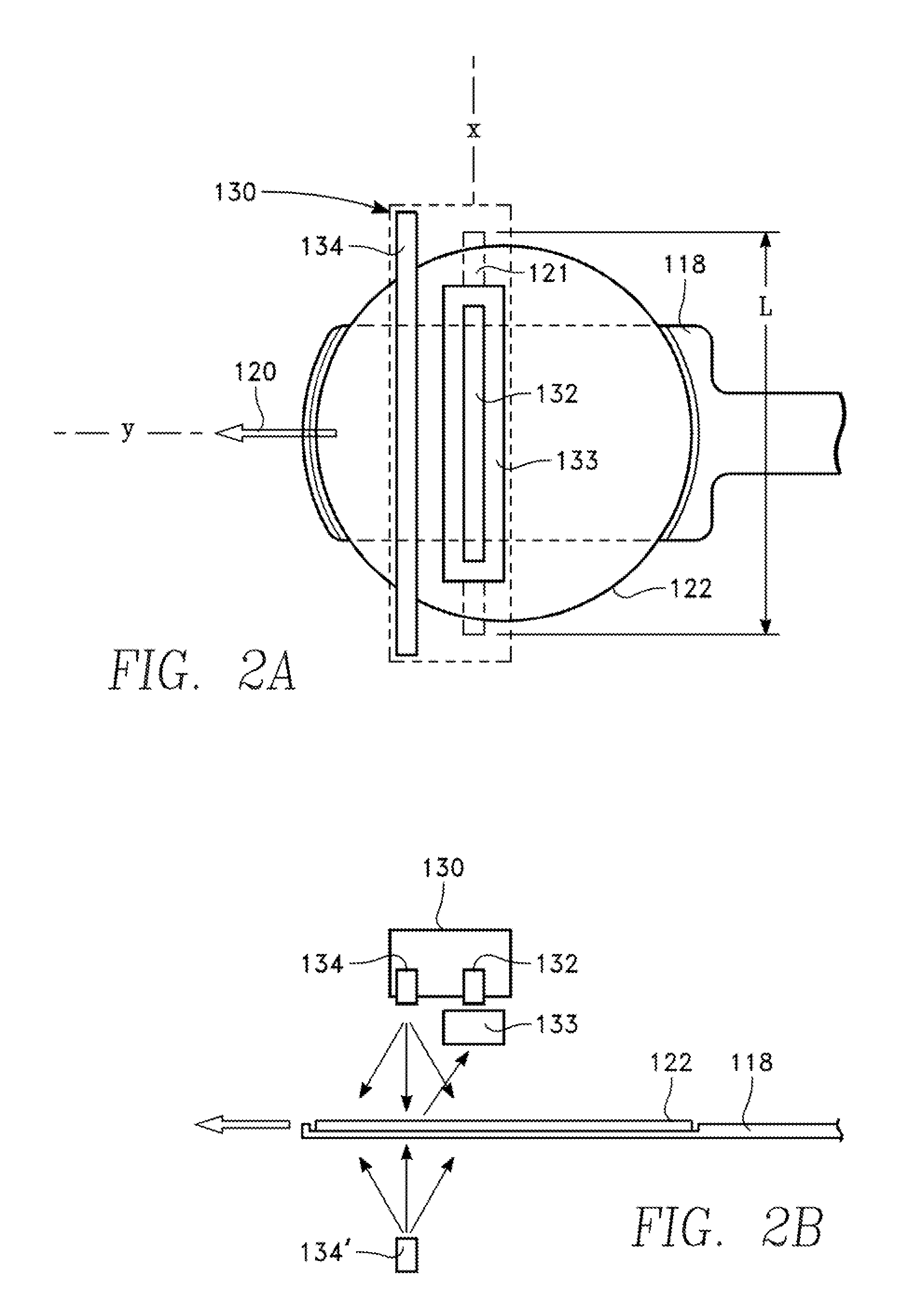
Stationary x-ray digital breast tomosynthesis systems and related methods
Stationary x-ray digital breast tomosynthesis systems and related methods are disclosed. According to one aspect, the subject matter described herein can include an x-ray tomosynthesis system having a plurality of stationary field emission x-ray sources configured to irradiate a location for positioning an object to be imaged with x-ray beams to generate projection images of the object. An x-ray detector can be configured to detect the projection images of the object. A projection image reconstruction function can be configured to reconstruct tomography images of the object based on the projection images of the object.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL +1
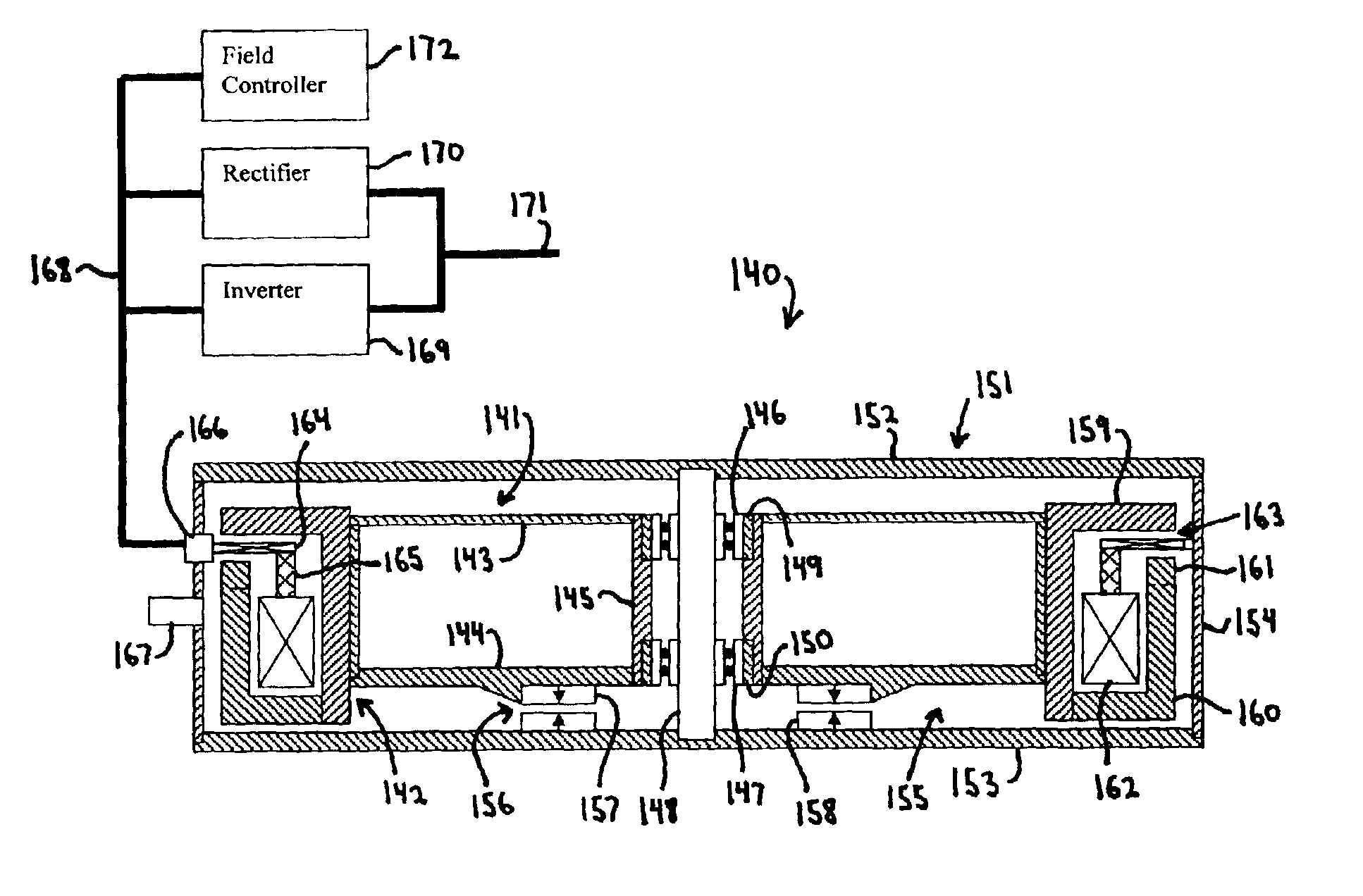
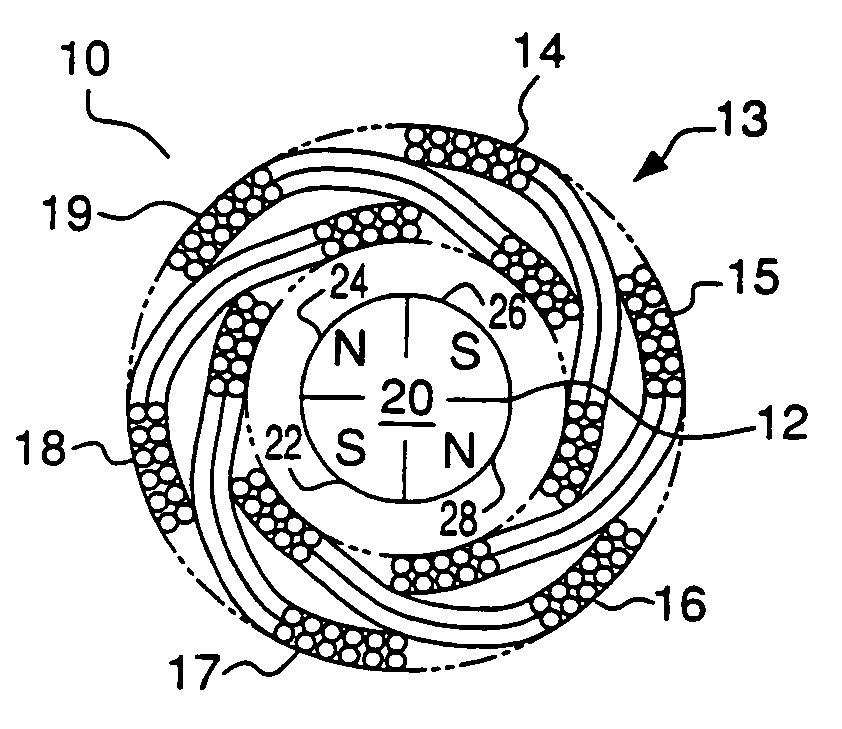
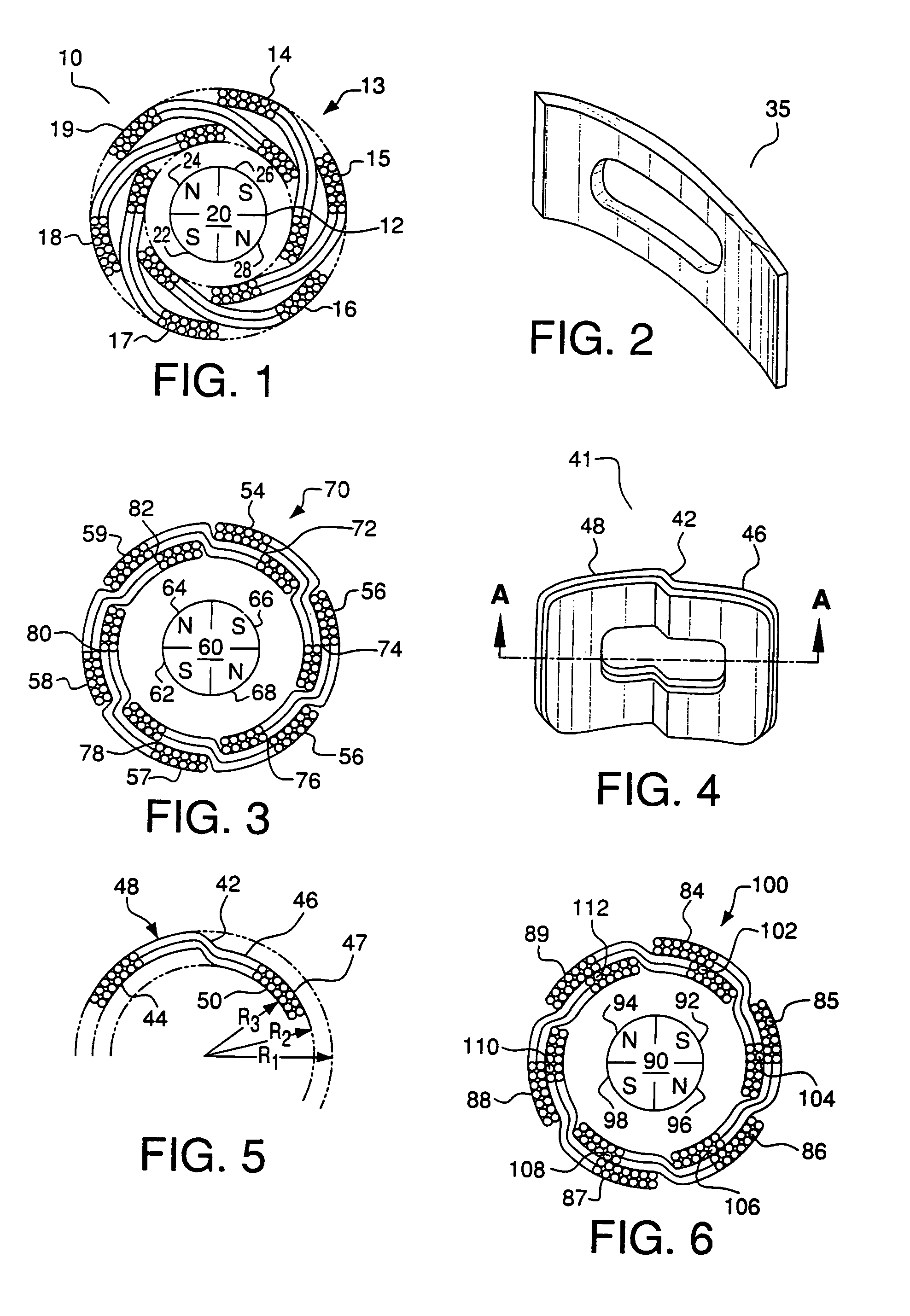
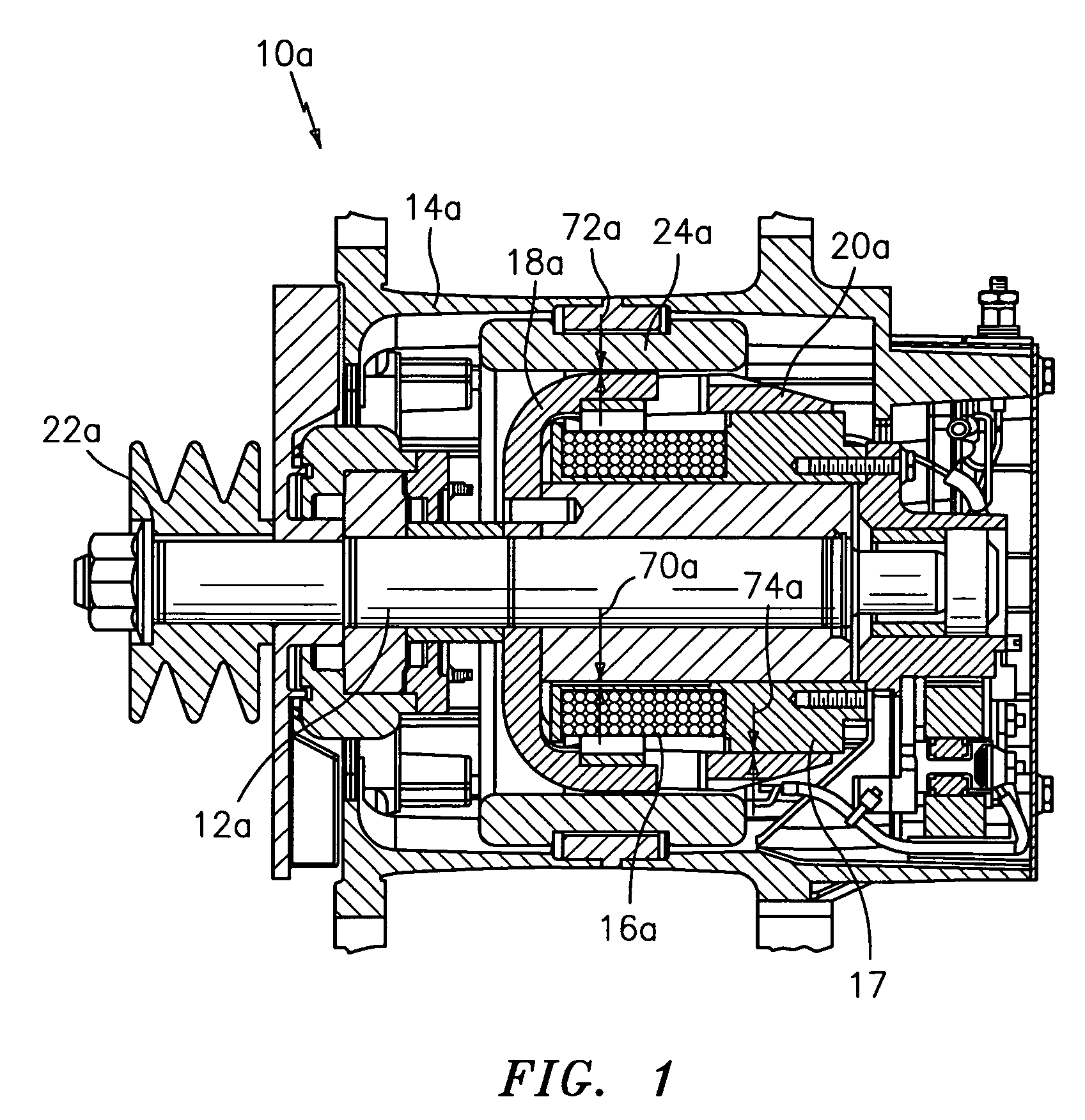
Light-weight high-power electrical machine
InactiveUS6891302B1High energyMotor/generator magnetic lossHybrid vehiclesWindingsAlternatorElectrical polarity
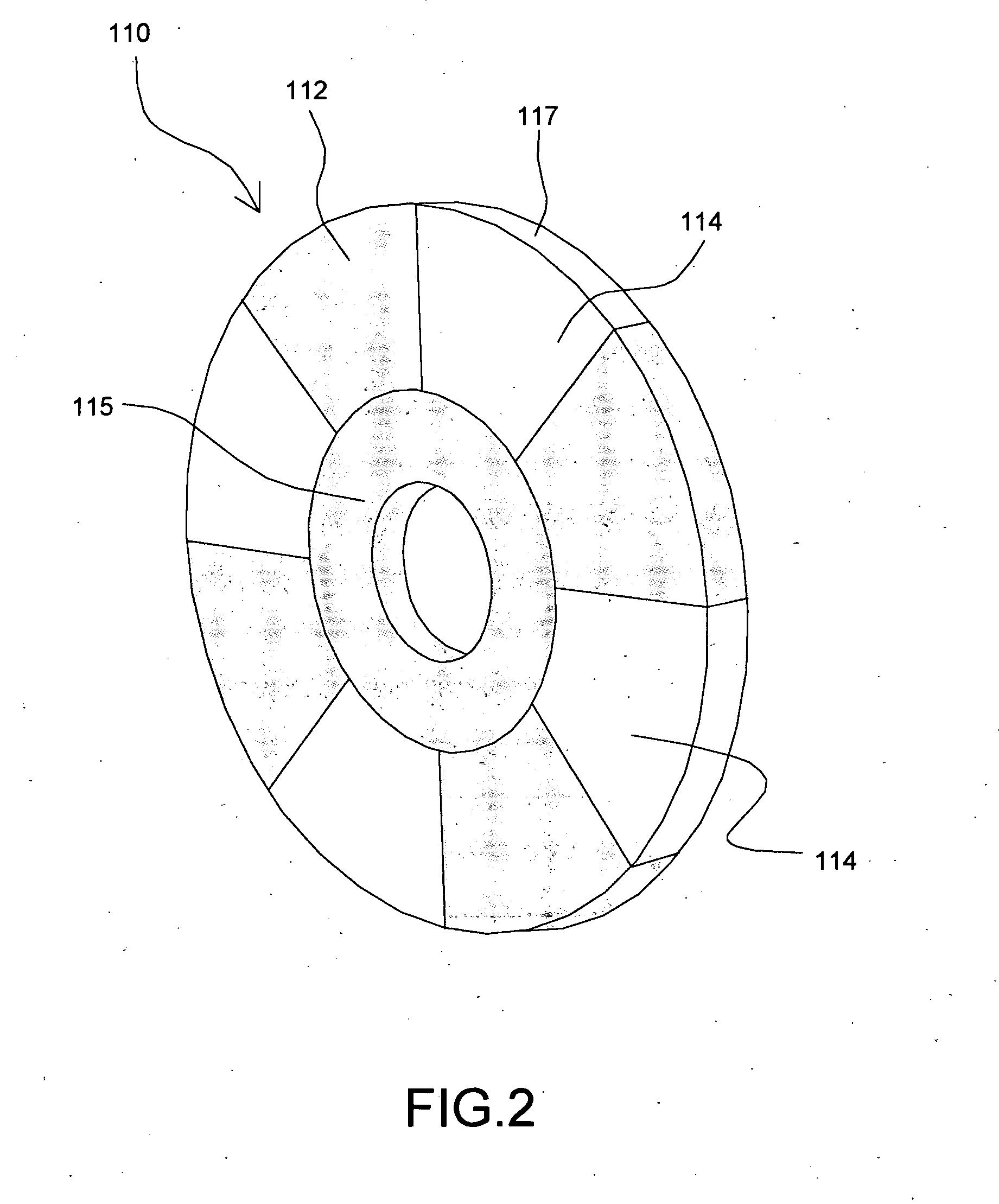
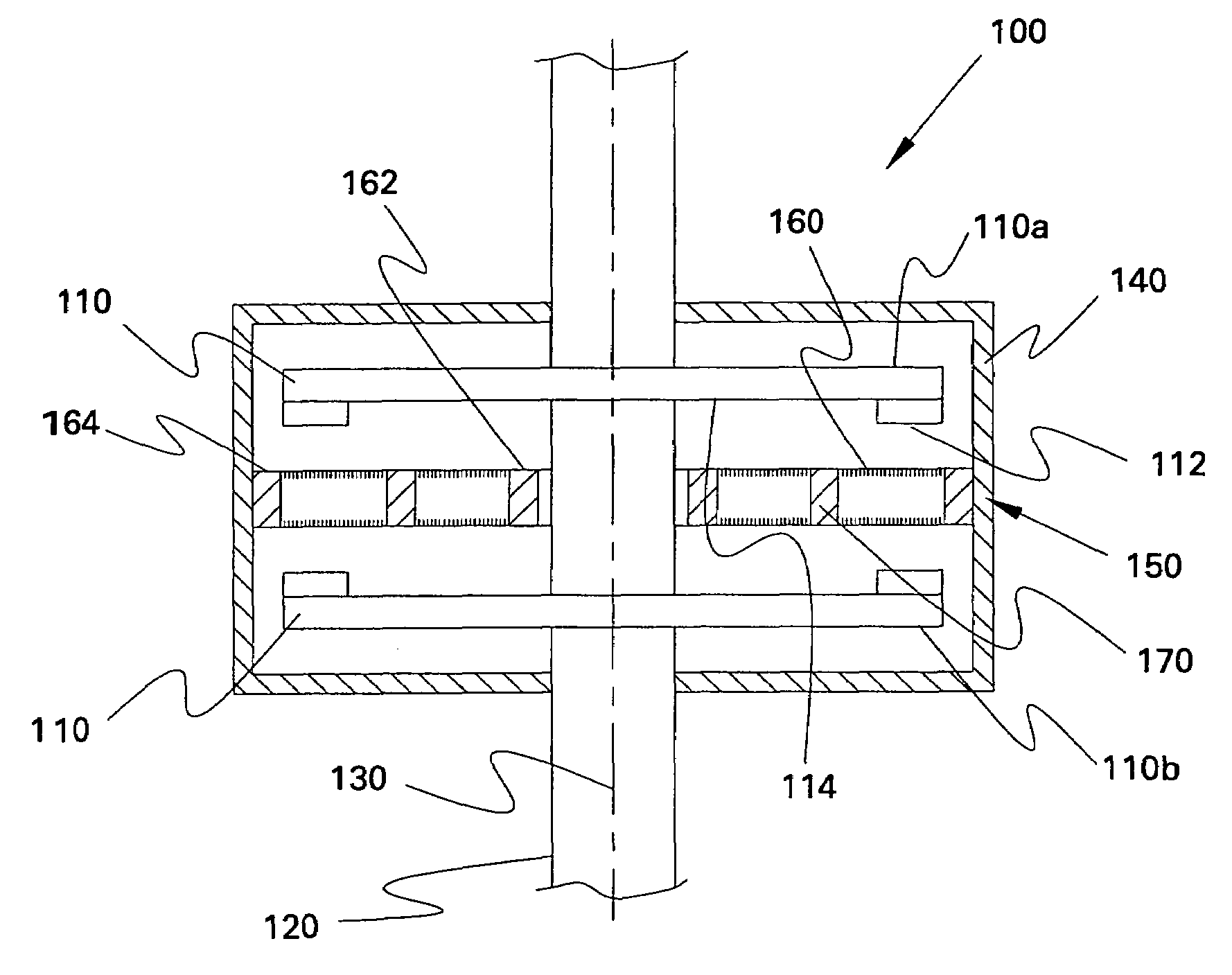
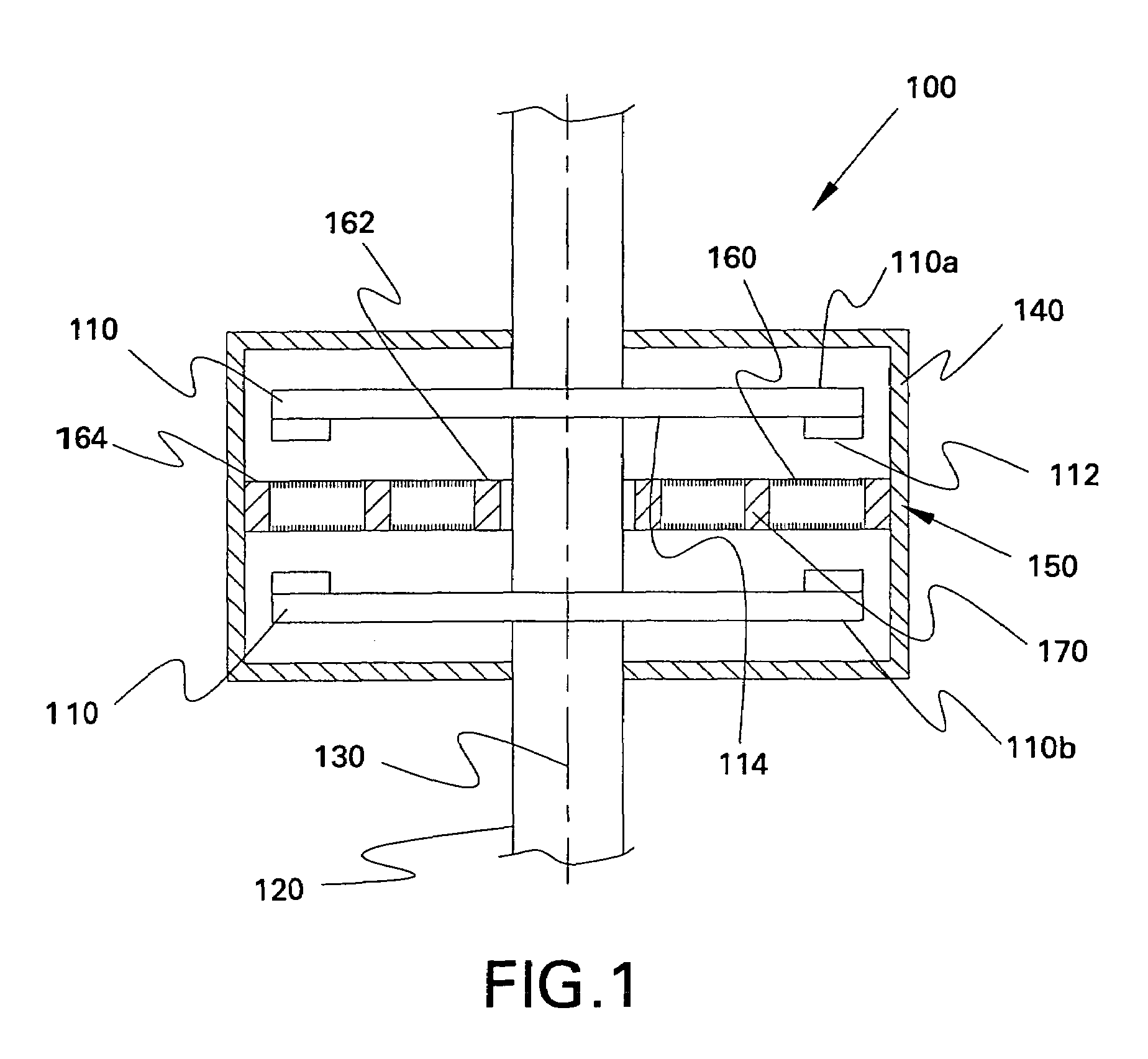
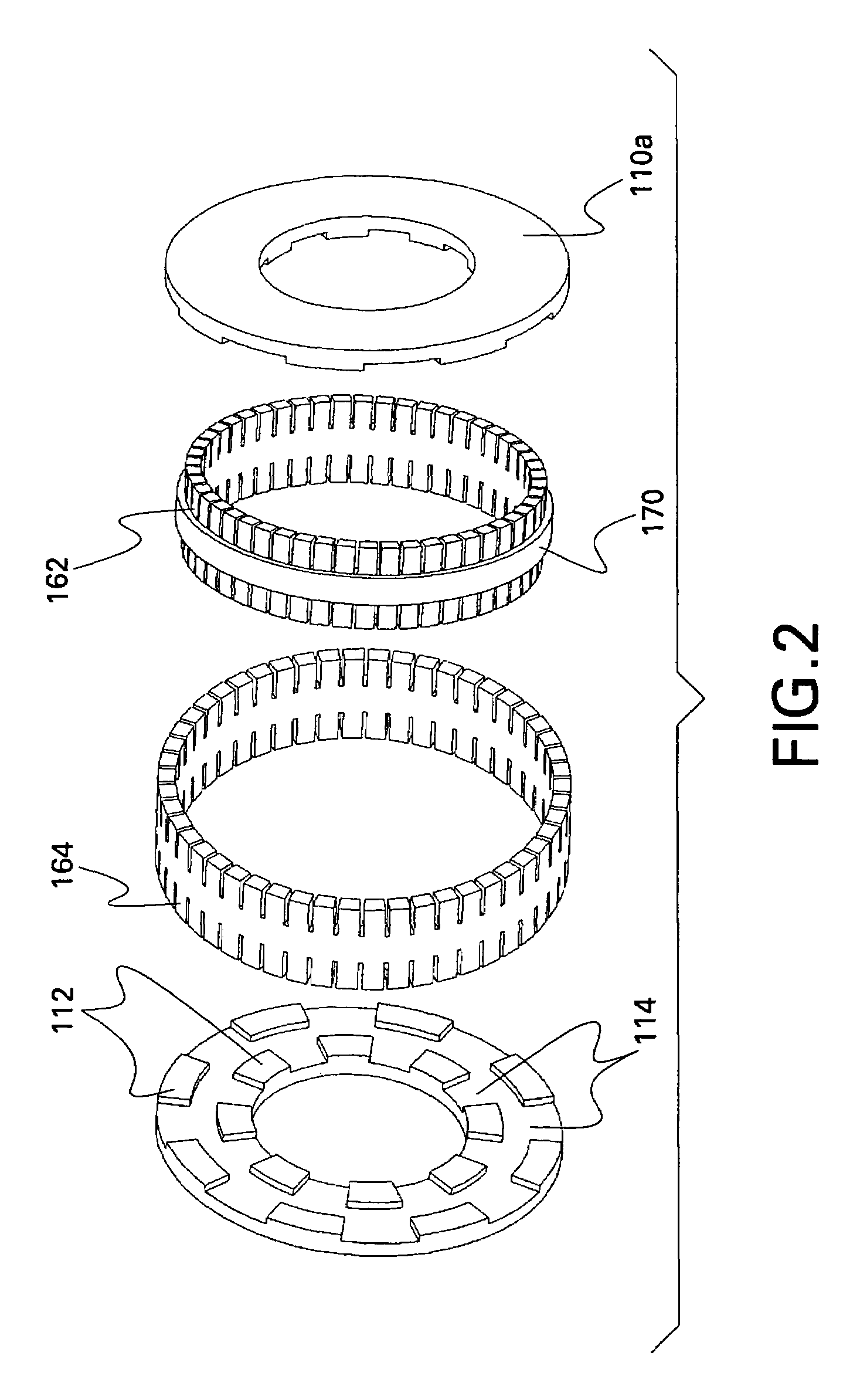
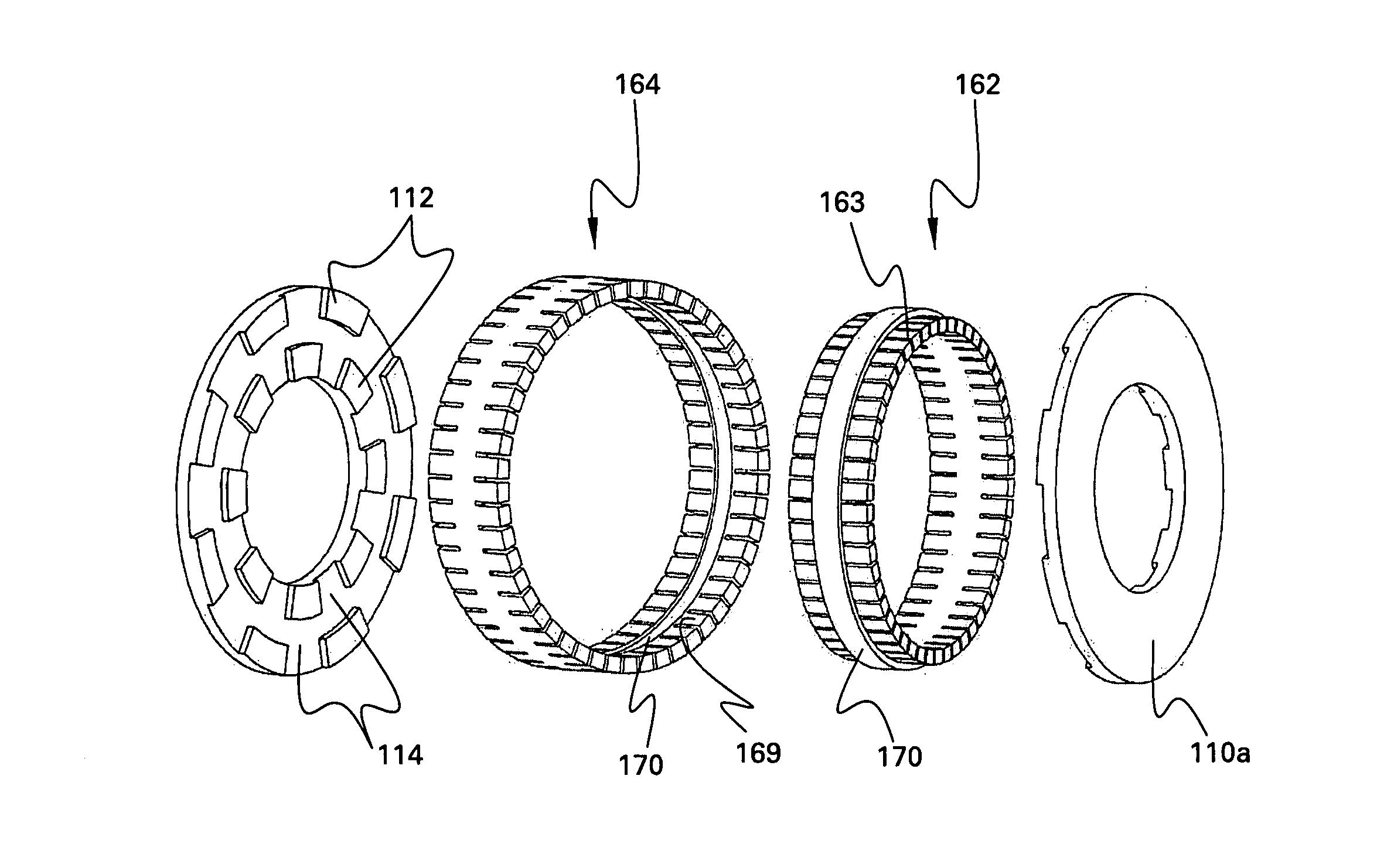
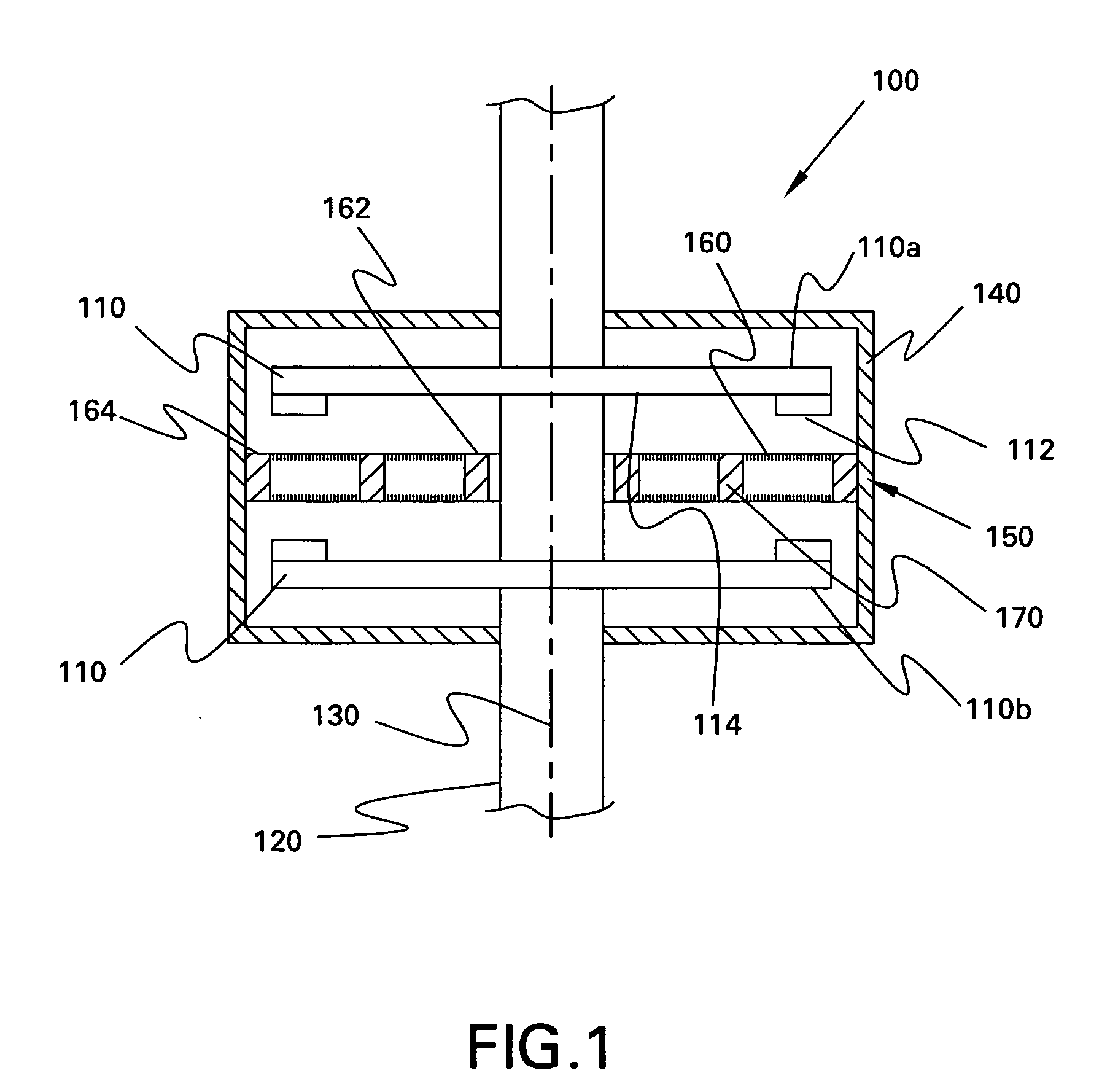
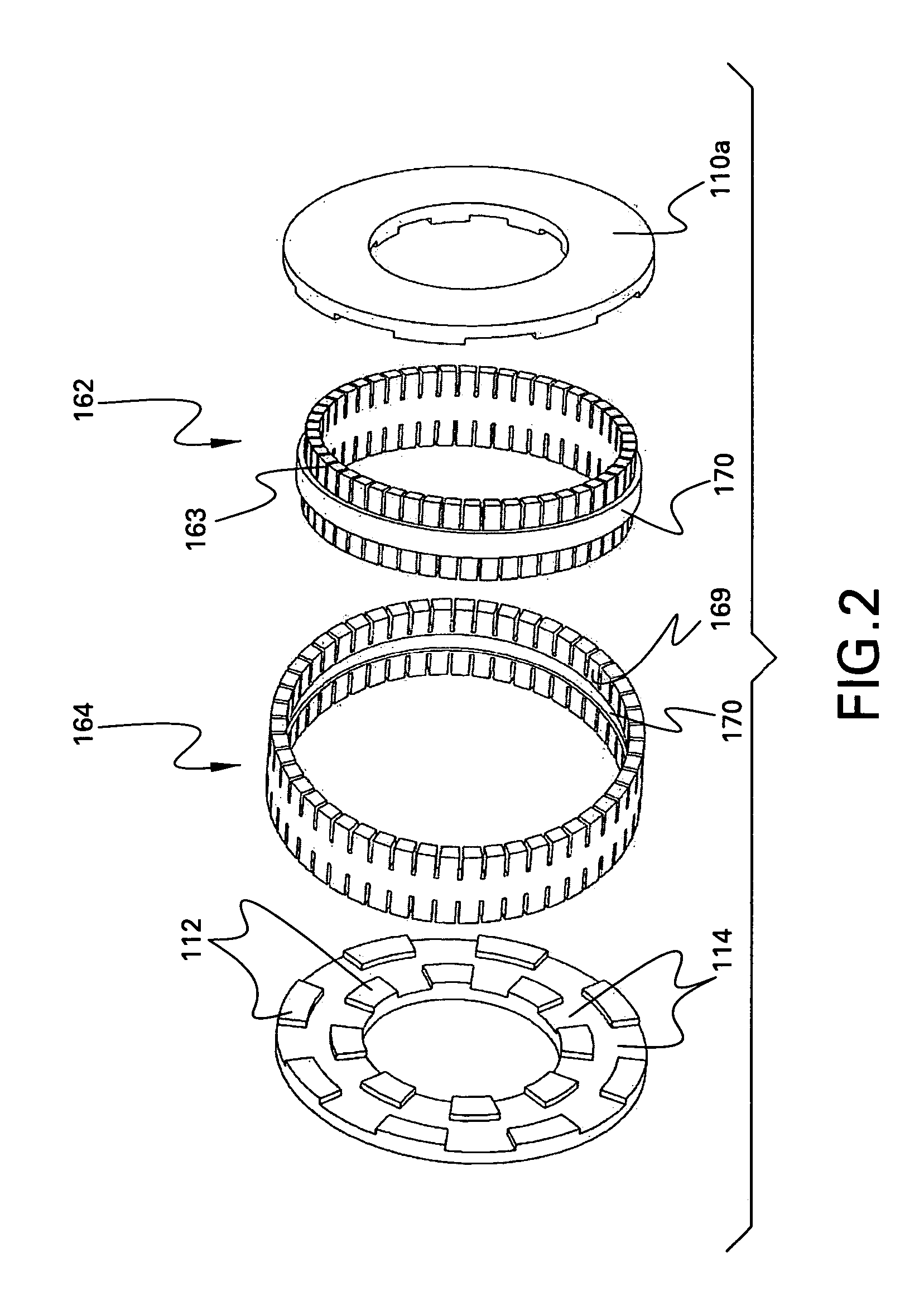
A brushless electrical machine, usable as a motor, generator, or alternator, has a rotor that is comprised of a rim portion and a substantially open center portion. The rim portion has a partially hollow core in which a stationary field coil is supported. Current to the field coil generates magnetic flux that circulates in a poloidal flux path in the rim, crossing a single magnetic air gap formed by the rim. Protrusions in the rim located around the circumference form poles all having the same polarity. As the rotor rotates, the flux exiting the poles passes through multiple stationary armature windings around the circumference that are located in the single air gap. An AC voltage is induced in the armature windings from rotation.
Owner:REVOLUTION ELECTRIC MOTOR
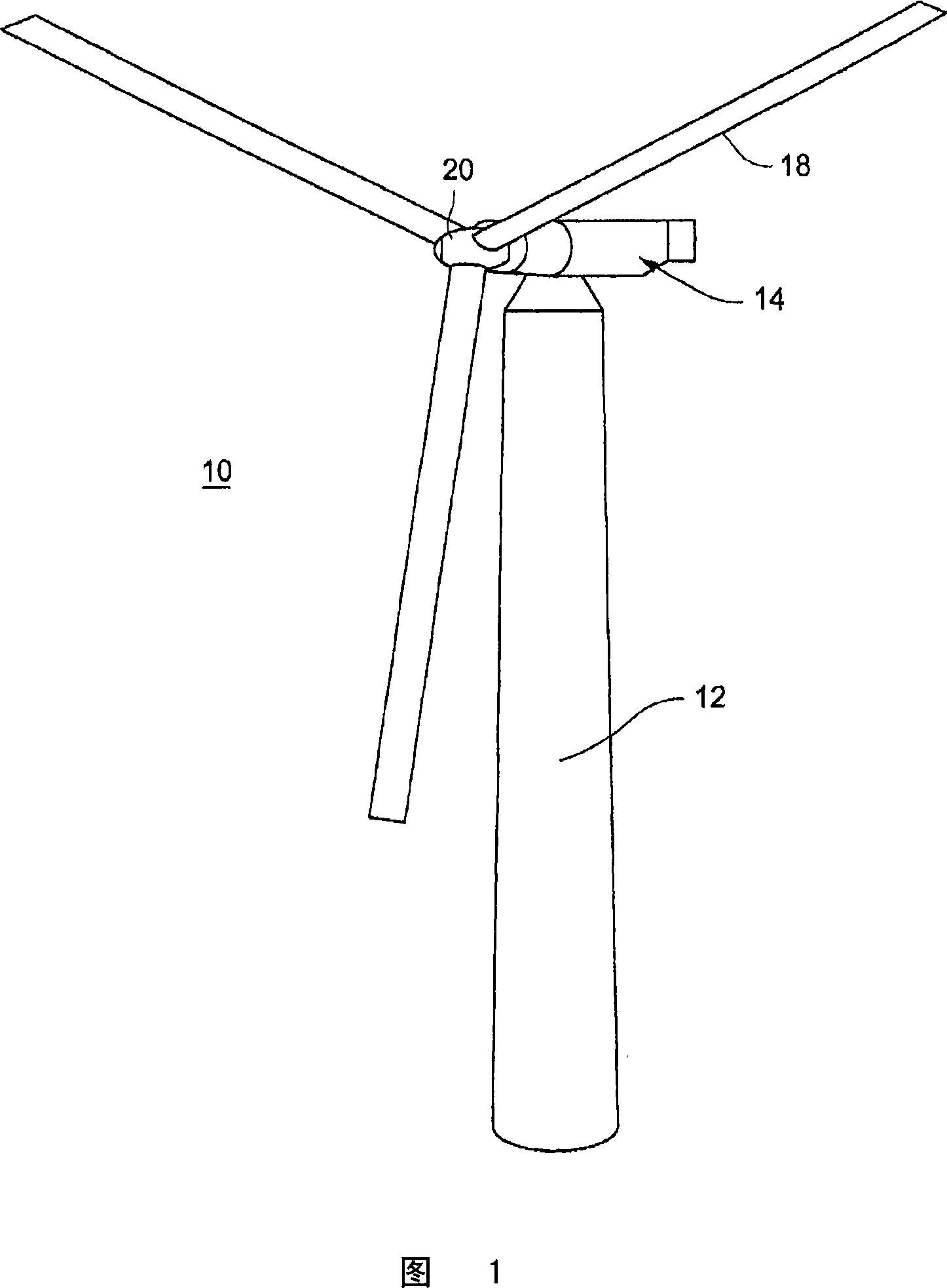
Method and apparatus for a superconducting generator driven by wind turbine
A generator including: an annular armature connectable to rotate with blades of a wind turbine; an annular stationary field winding assembly coaxial with the armature and separated by a gap from an inside surface of the armature, wherein the field winding include superconducting coils, and support structure connectable to an upper region of a tower of the wind turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Superconducting rotating machines with stationary field coils
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
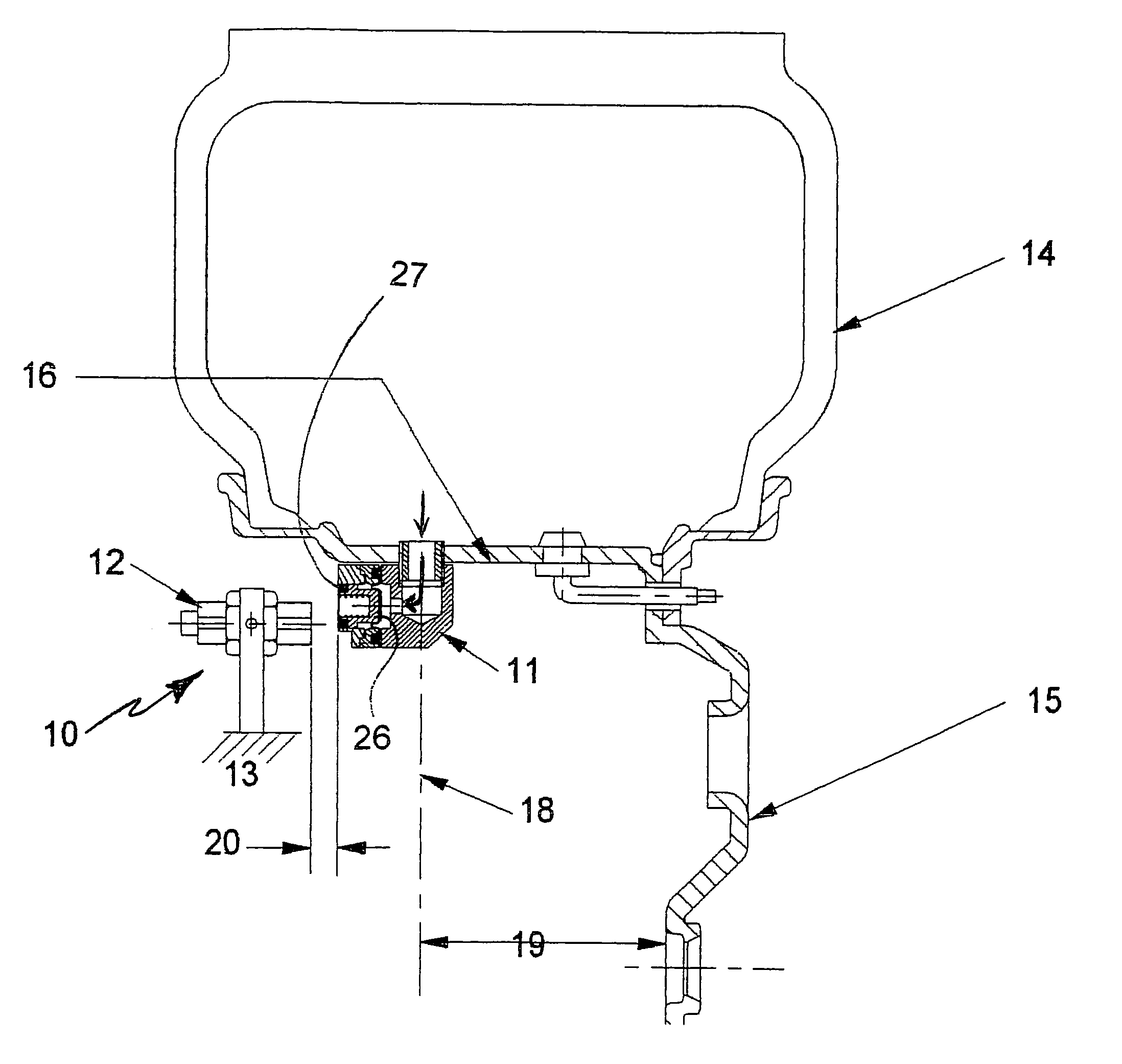
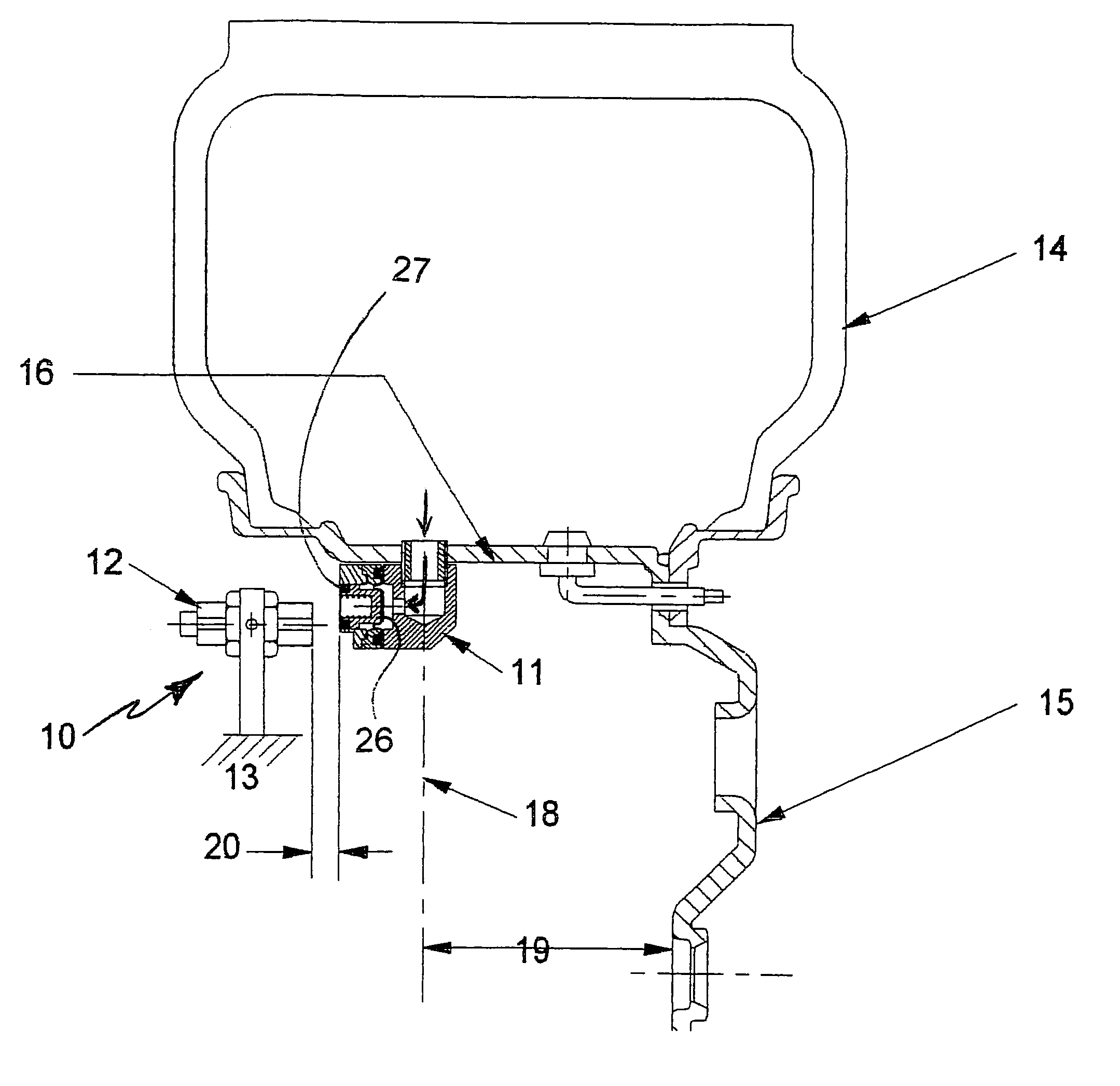
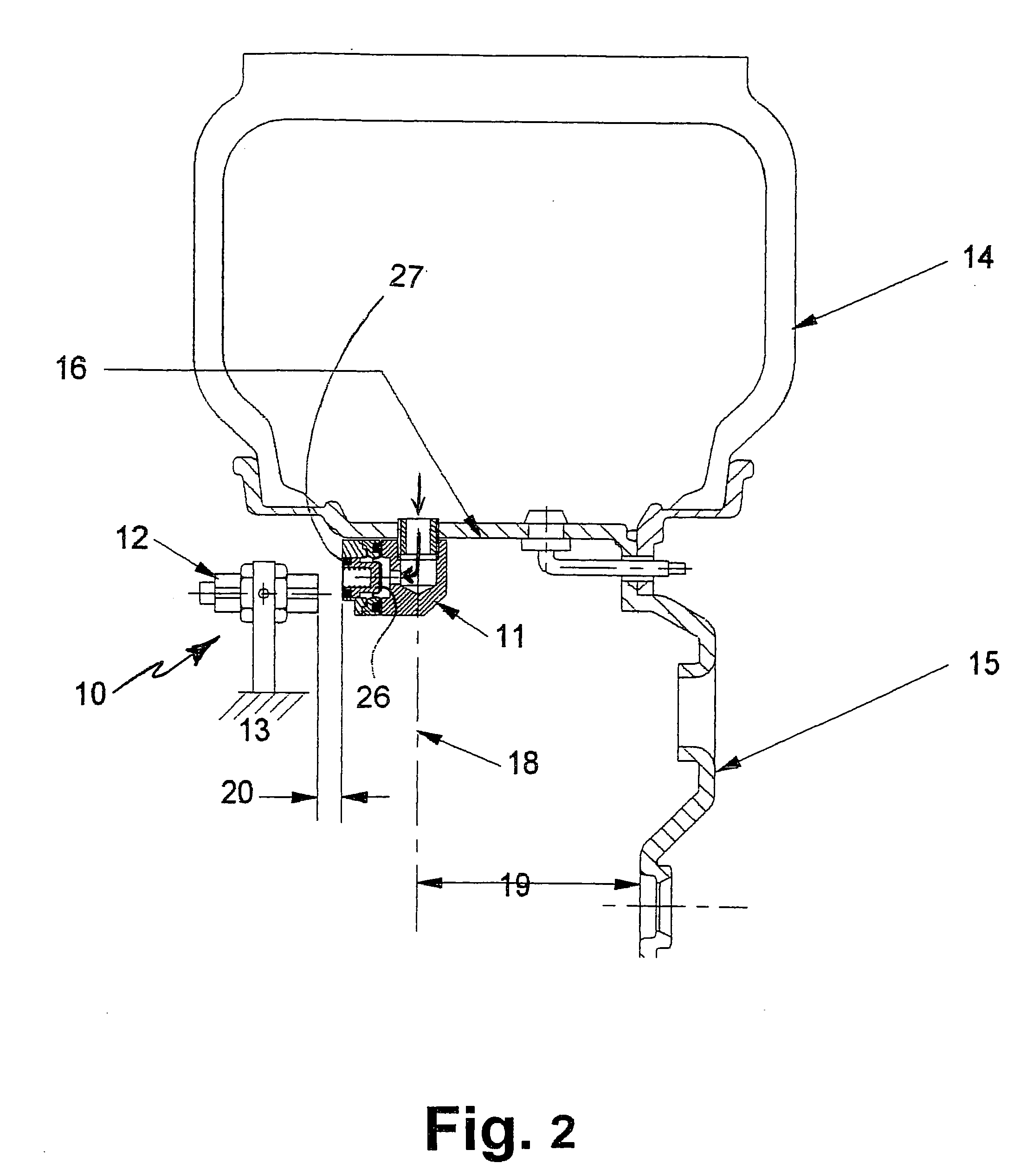
Tire pressure monitoring system and method of using same
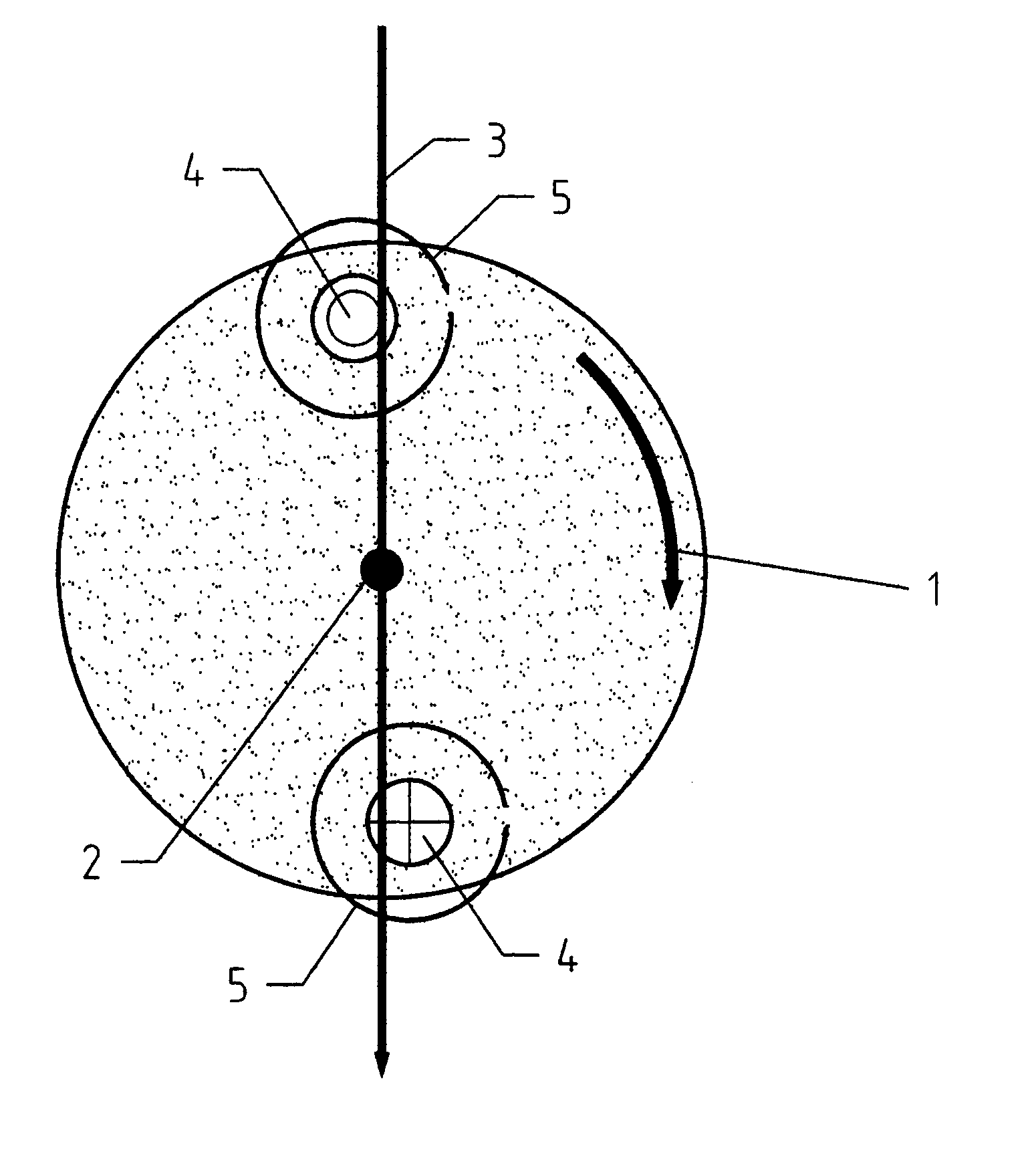
A tire pressure monitoring system (10) including a magnetic actuator (11) having an air pressure transducer therein for generating a signal proportional to the interior tire air pressure. The actuator (11) operates parallel to the axle to alleviate speed sensitivity. Magnetic actuator (11) communicates with a stationary field sensor (12) permanently mounted on the vehicle at a close proximity to the magnetic actuator (11). The magnetic actuator (11) rotates about the access with the wheel (15), and for every revolution of the wheel (15), comes in to close proximity to the sensor (12) at least once, and communicates information about the internal tire pressure to the driver.
Owner:ADVANCED DIGITAL COMPONENTS
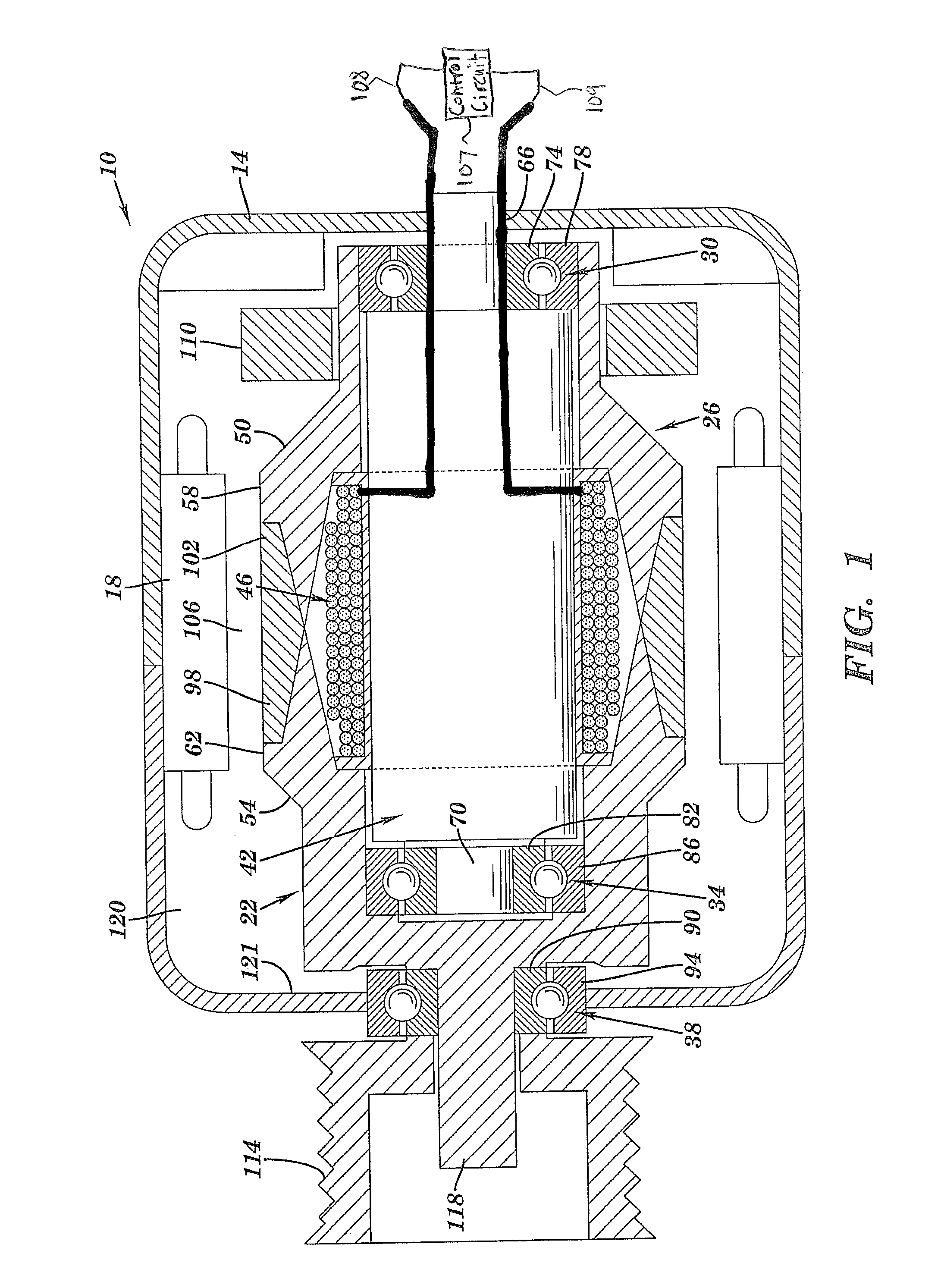
Superconducting rotating machines with stationary field coils
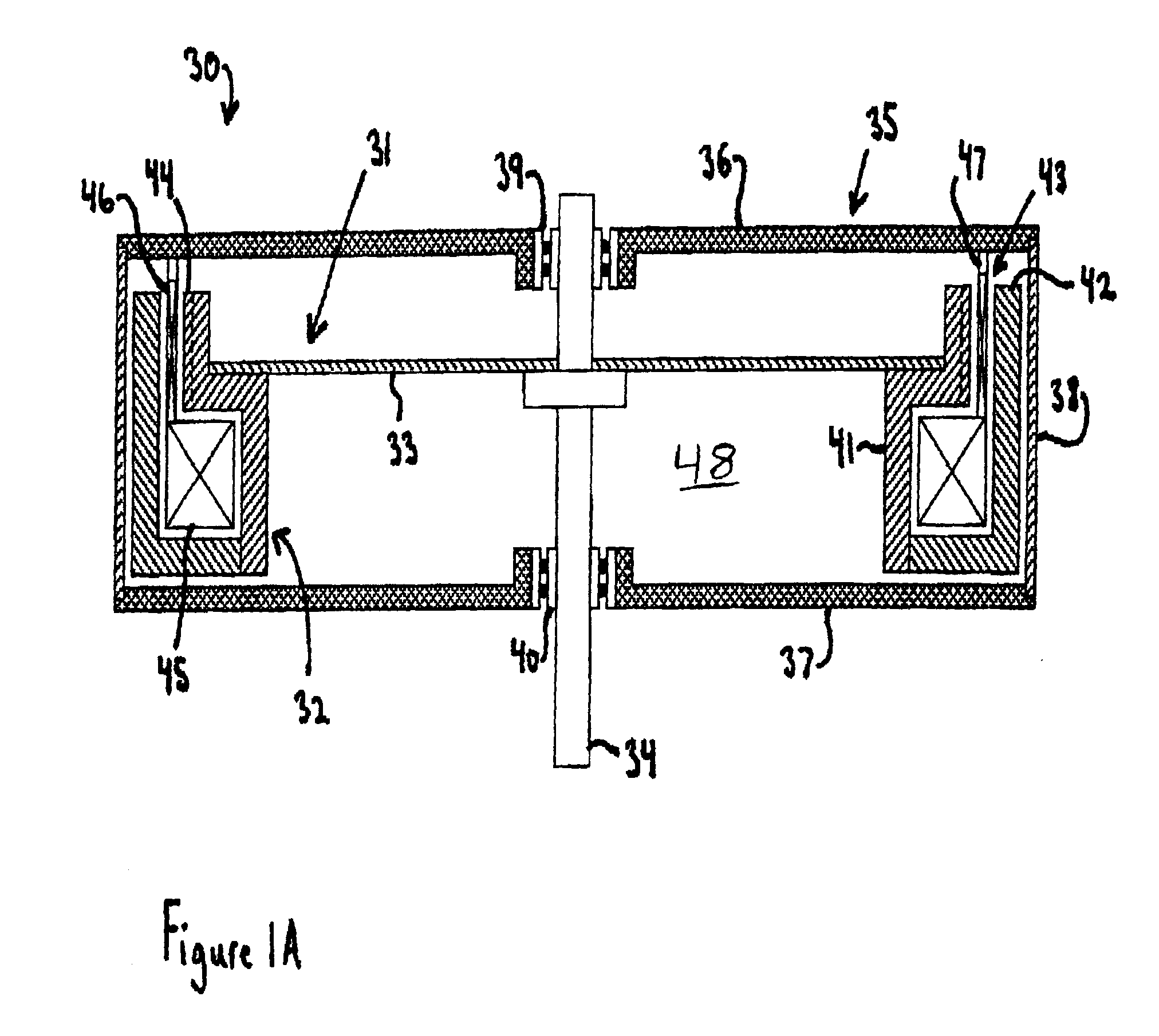
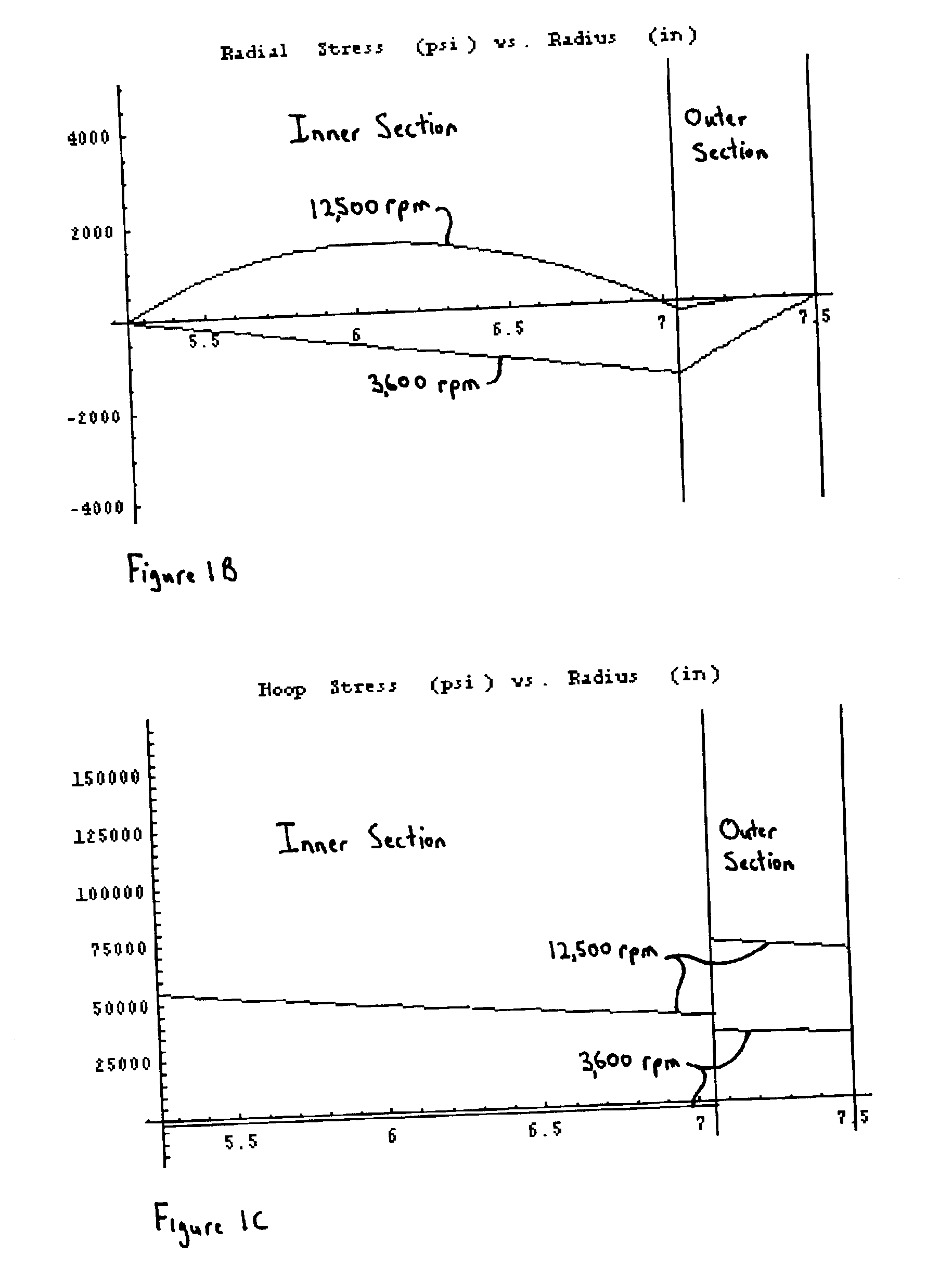
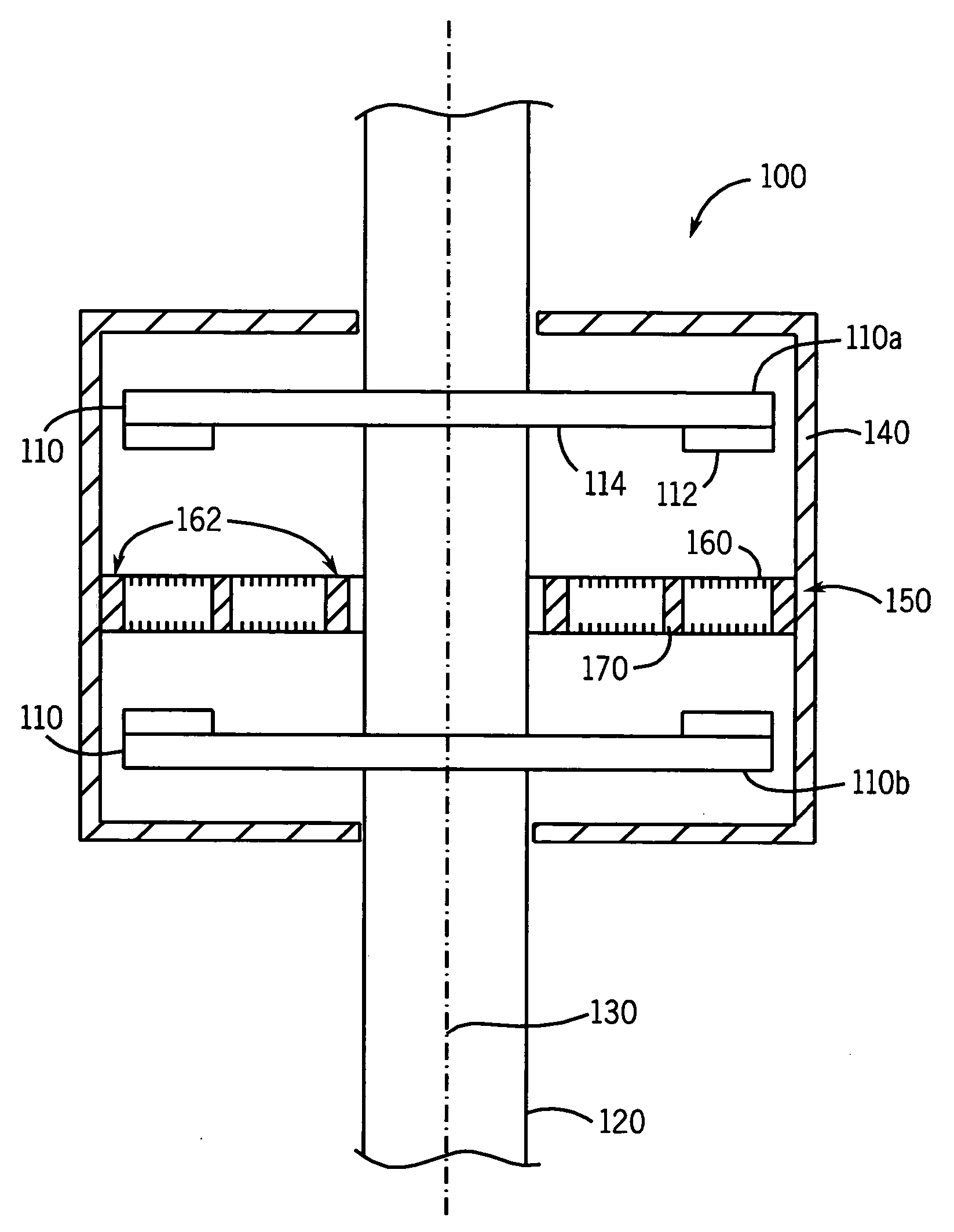
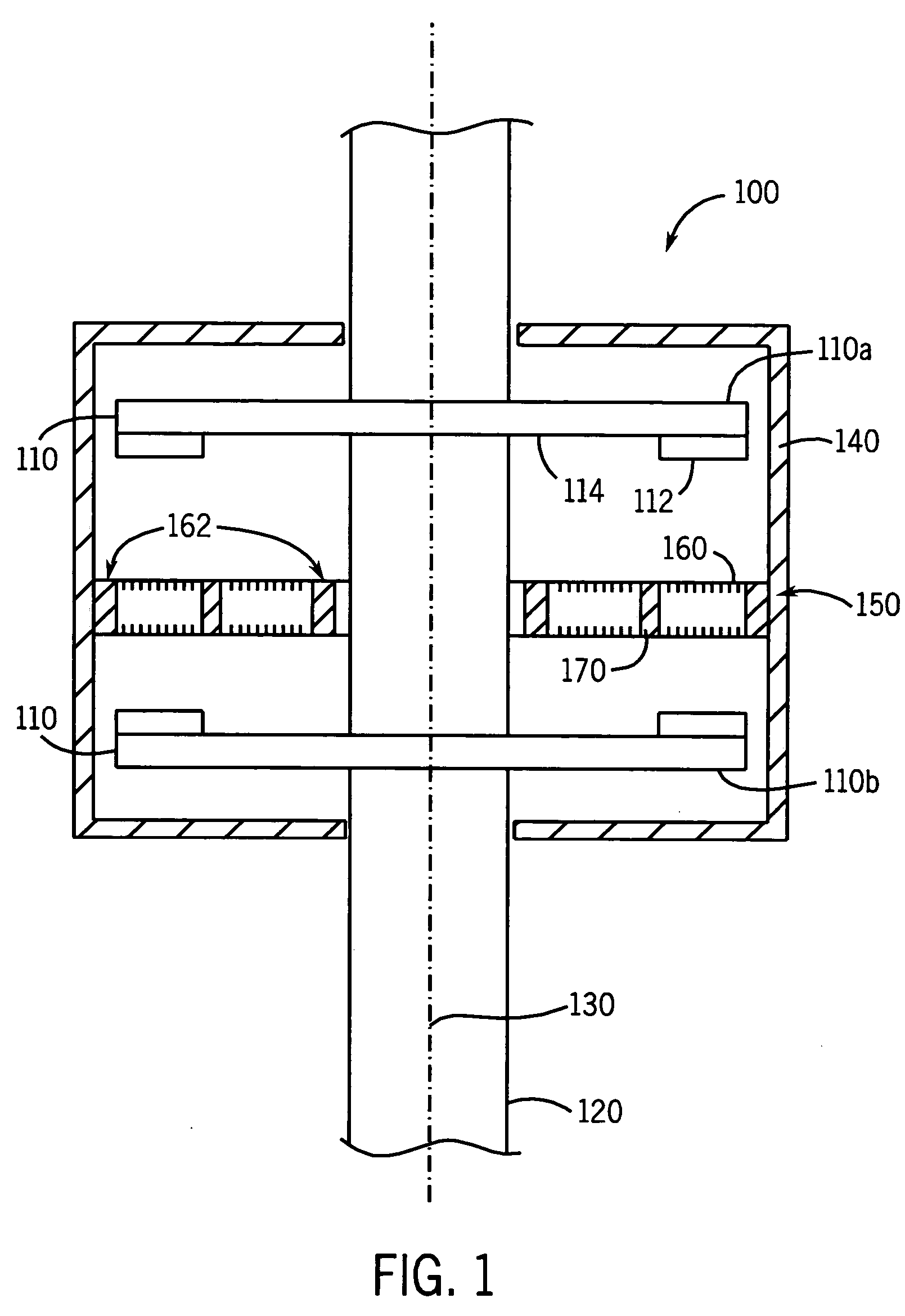
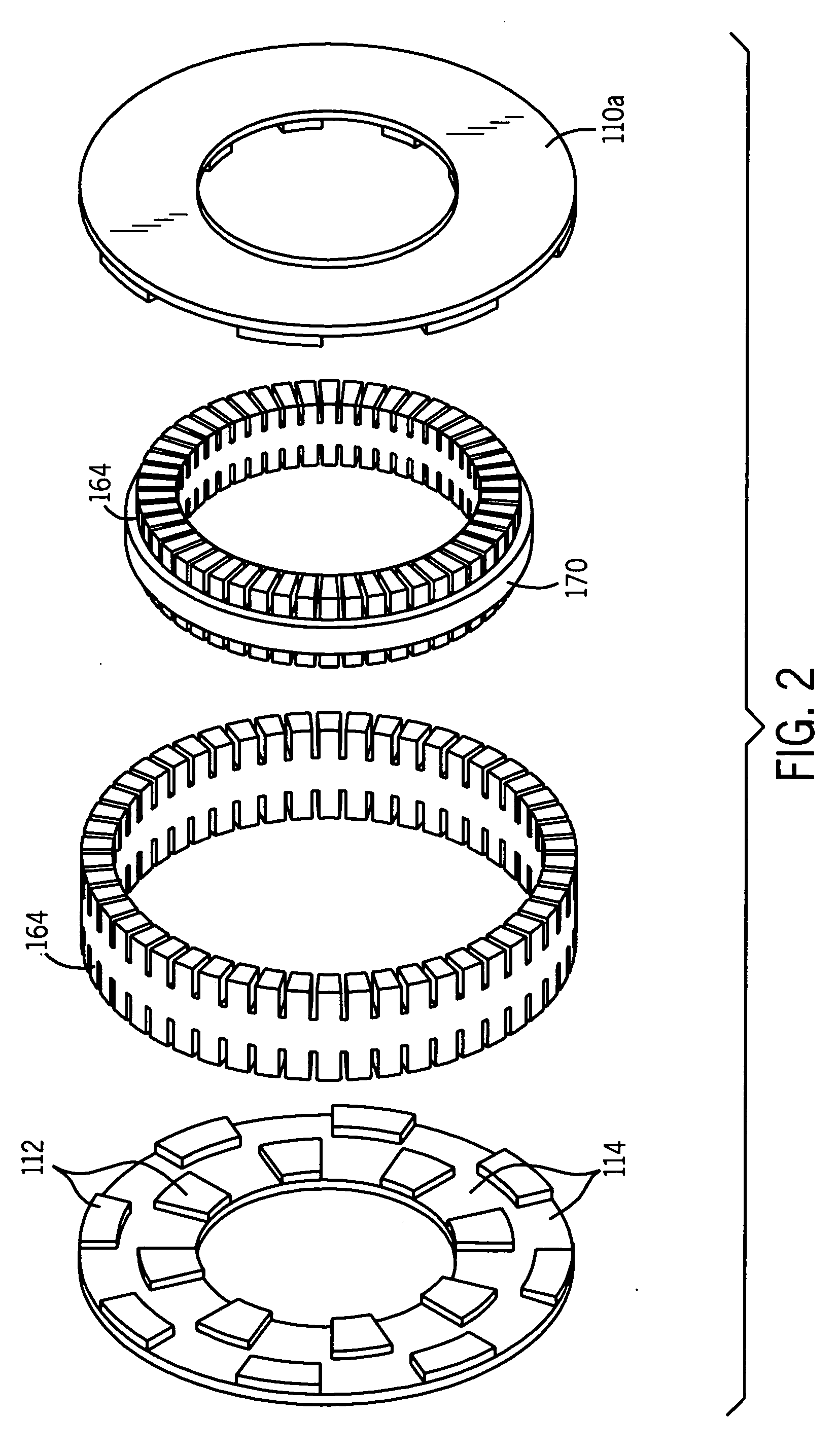
A machine includes a rotatable rotor assembly having a number of salient poles. The machine further includes a stationary stator assembly having concentric inner and outer stators, at least one stationary superconducting field coil and at least one stator coil. The stationary superconducting field coil is disposed between the inner and outer stators and is mounted on at least one of the inner and outer stators. The stationary superconducting field coil and the salient poles are configured relative to each other, such that when the rotor assembly is rotated relative to the stator assembly around a predetermined axis, a rotating magnetic field is produced with an airgap flux direction substantially along the predetermined axis. The interaction between the stationary superconducting field coil and the rotating poles provides the only source of a time varying magnetic flux supplied to the stator coil.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Superconducting rotating machines with stationary field coils
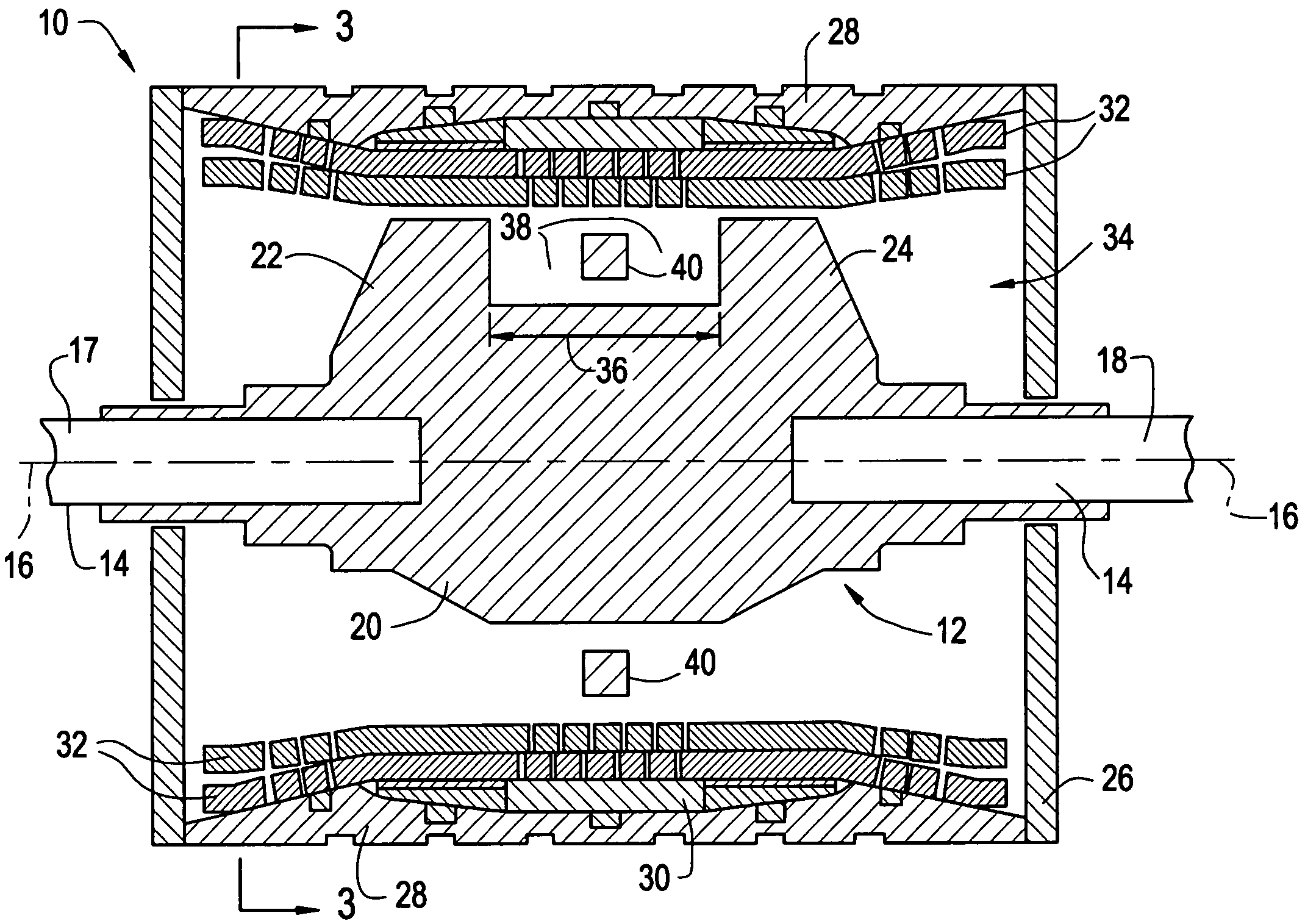
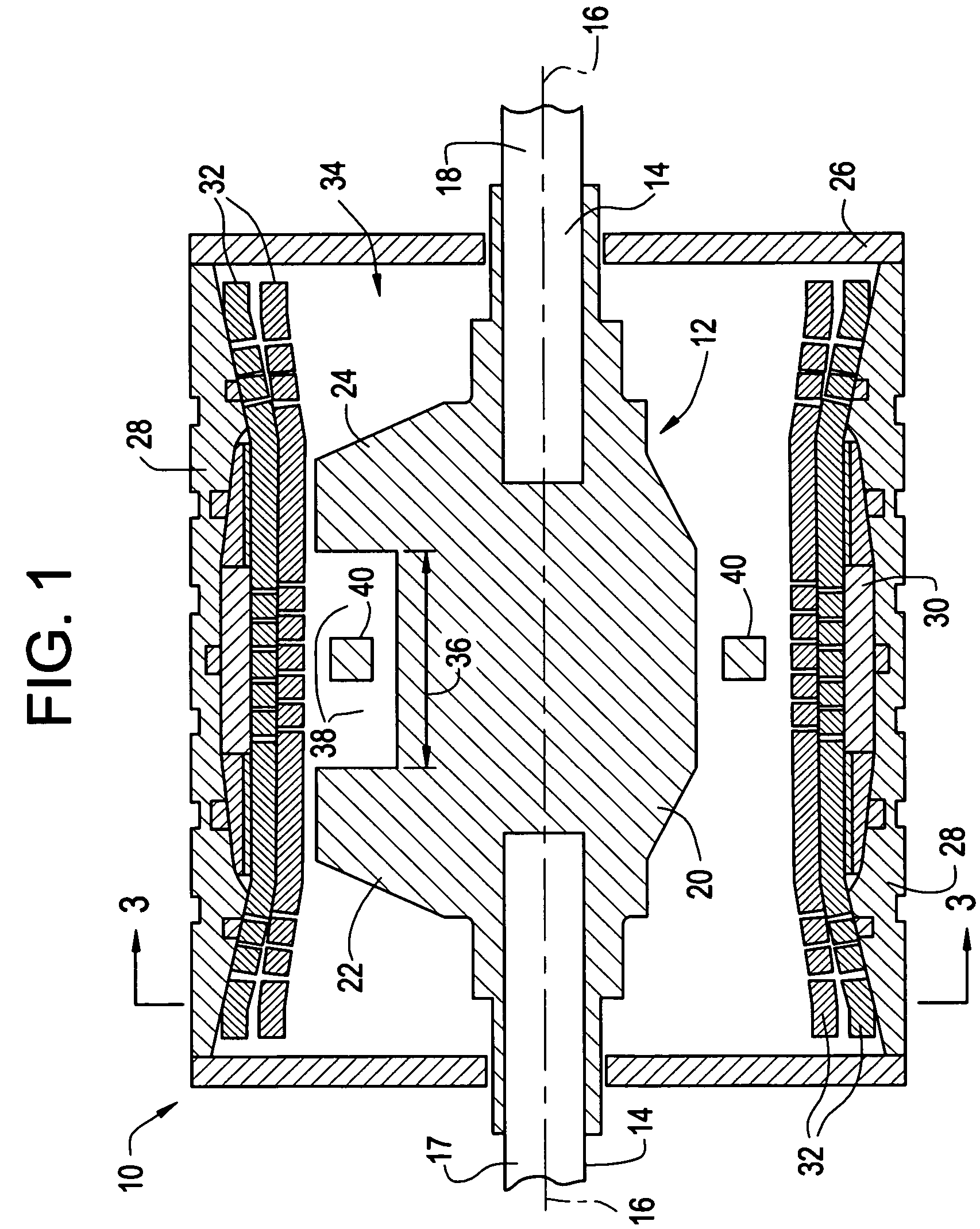
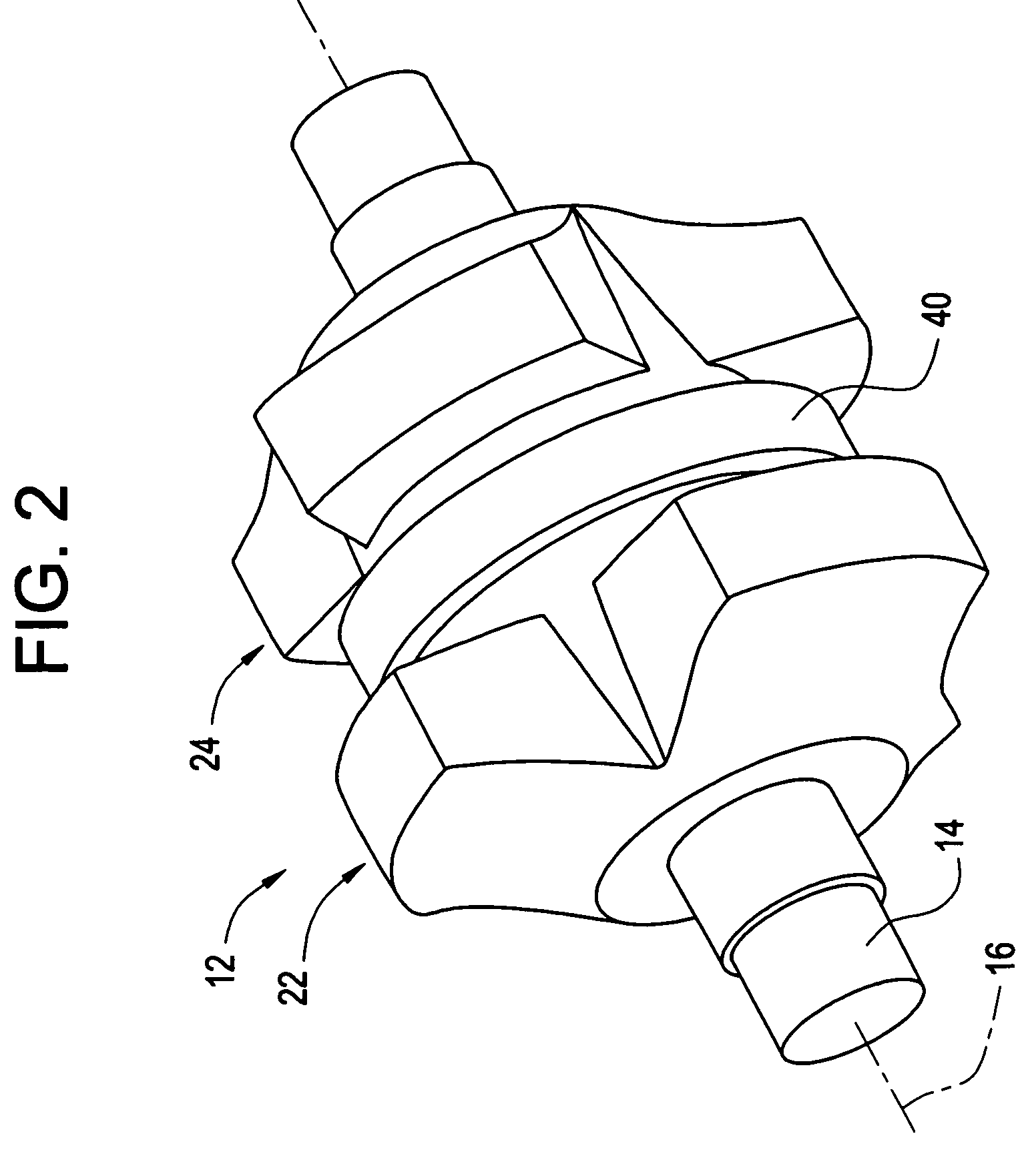
A machine includes a stator assembly that includes a stator yoke, a pair of armature coils mechanically coupled to the stator yoke, and a stationary superconducting field coil. The stator yoke comprises a magnetic material. The machine further includes a shaft rotatably mounted in the stator yoke, the shaft comprising a non-magnetic material. The machine further includes a rotor assembly rotationally engaged with the shaft. The rotor assembly includes a rotor disk extending between the armature coils, the rotor disk having an inner portion and an outer portion. The outer portion of the rotor disk includes a number of circumferentially-spaced, magnetic poles. The rotor disk is coupled to the shaft for rotation about the shaft and generation of a rotating permeance wave. The stationary superconducting field coil is disposed between the stator yoke and the rotor disk, and the stationary superconducting field coil is configured as a stationary magneto-motive force (MMF) source for the rotating permeance wave produced by the rotor assembly to produce a rotating magnetic field.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Superconducting rotating machines with stationary field coils and axial airgap flux
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Superconducting rotating machines with stationary field coils
InactiveUS20060028085A1Improved performance characteristicsIncreased torque densitySynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsStator coilStationary field
A machine includes a rotatable rotor assembly having a number of salient poles. The machine further includes a stationary stator assembly having concentric inner and outer stators, at least one stationary superconducting field coil and at least one stator coil. The stationary superconducting field coil is disposed between the inner and outer stators and is mounted on at least one of the inner and outer stators. The stationary superconducting field coil and the salient poles are configured relative to each other, such that when the rotor assembly is rotated relative to the stator assembly around a predetermined axis, a rotating magnetic field is produced with an airgap flux direction substantially along the predetermined axis. The interaction between the stationary superconducting field coil and the rotating poles provides the only source of a time varying magnetic flux supplied to the stator coil.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Rotating plasma current drive
InactiveUS20050249324A1Electric discharge tubesNuclear energy generationRotational axisElectrode Contact
The present invention includes electromagnetic methods and apparatus to form a sustained direct current loop in a conductive fluid such as plasma for applications including gas discharge arc lamps and fusion confinement systems. The current loop is driven by rotating plasma within a stationary magnetic field perpendicular to the axis of rotation. Polyphase rotating electric or magnetic fields drive the plasma rotation, and the interaction between the rotating plasma and the stationary field forms and sustains the current loop. Plasma cooling and contamination are minimized since, unlike conventional direct current drive methods and apparatus, no electrodes contact the plasma.
Owner:MEACHAM GEORGE BEVAN KIRBY
Organic white light emitting diode in tiny cavity type
InactiveCN1728413AHigh luminous intensityImprove luminous efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLuminous intensityHole transport layer
The invention solves issues of color purity of white color, stability of color and luminous efficiency. The disclosed diode includes substrate, Bragg reflection mirror, anode, hole transport layer, luminous layer, cavity barrier layer, electron transport layer, and cathode. Through structure of micro cavity, changing luminous characters of broadband of organic material, the invention realizes irradiance in two modes of resonance in visible range, making match of spectrum generate white light. Since luminous layer is positioned near to antinode of stationary field intensity in two modes of resonance in micro cavity, luminous intensities in two modes are enhanced, and luminous efficiency is increased. Under condition of not changing length of cavity, adjusting relative position of luminous layer changes relative luminous intensities between two modes to optimize color purity. Features are: stable white light and raised luminous efficiency.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and apparatus for a superconducting generator driven by wind turbine
A generator including: an annular armature connectable to rotate with blades of a wind turbine; an annular stationary field winding assembly coaxial with the armature and separated by a gap from an inside surface of the armature, wherein the field winding include superconducting coils, and support structure connectable to an upper region of a tower of the wind turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC RENOVABLES ESPANA SL
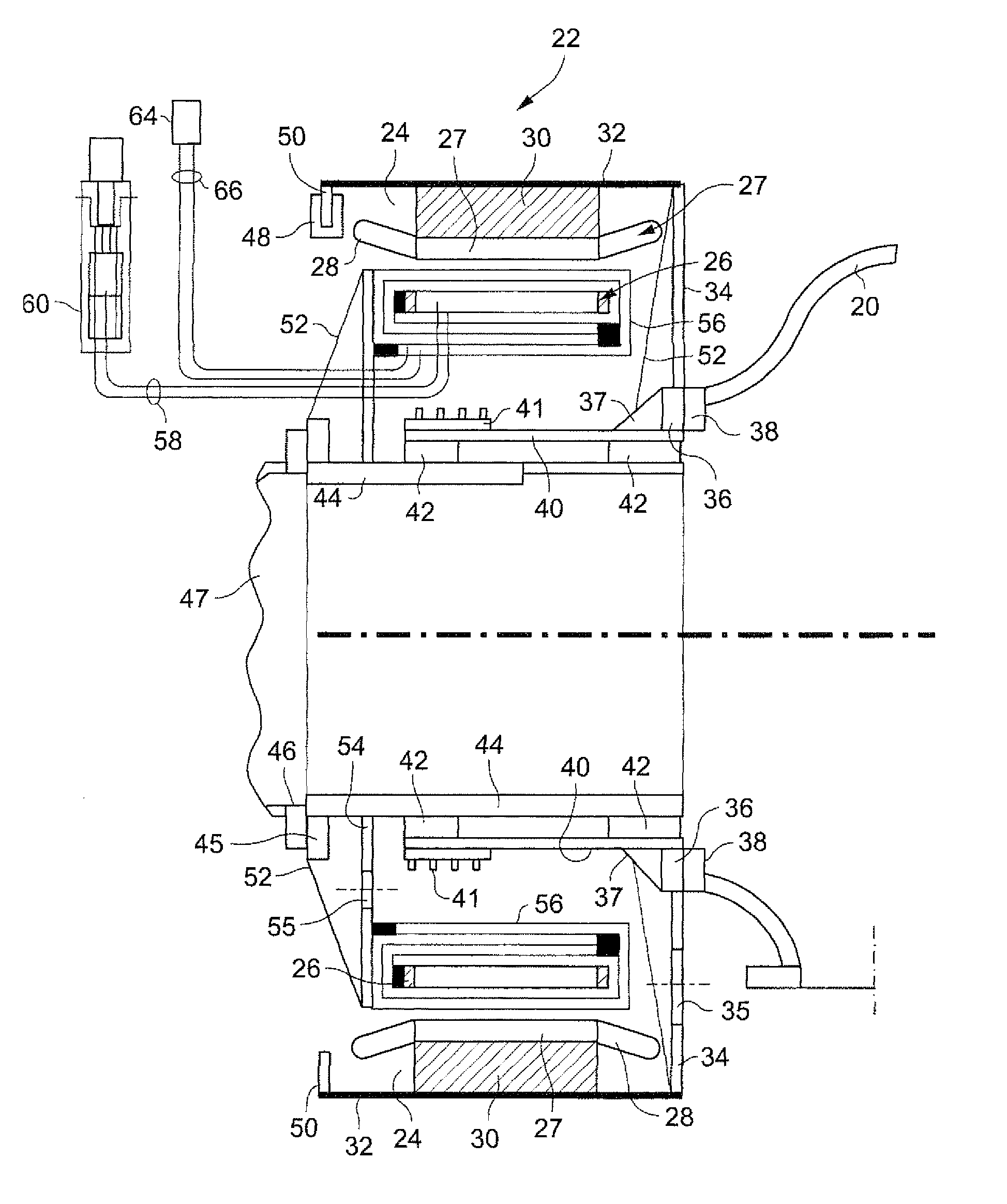
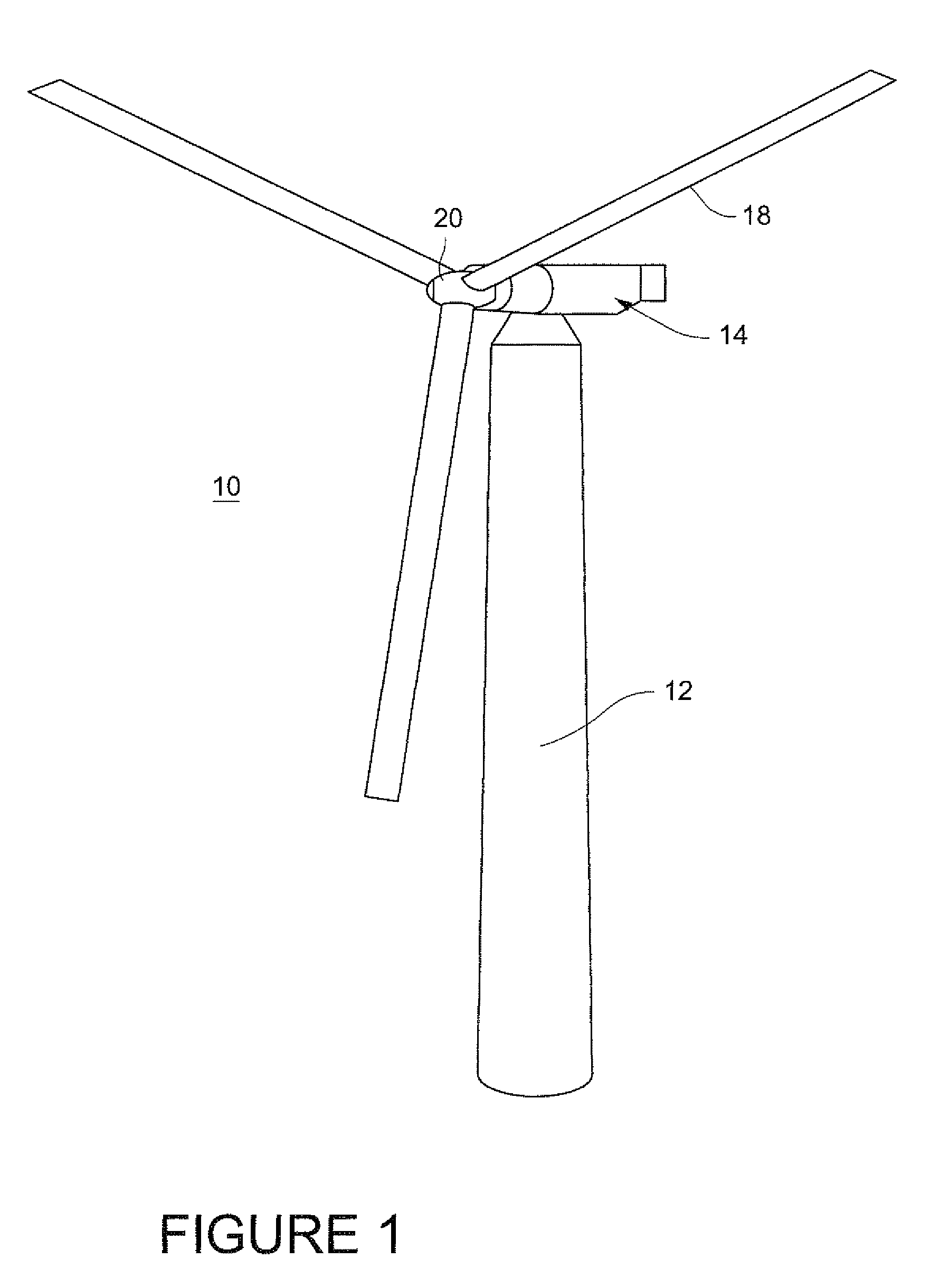
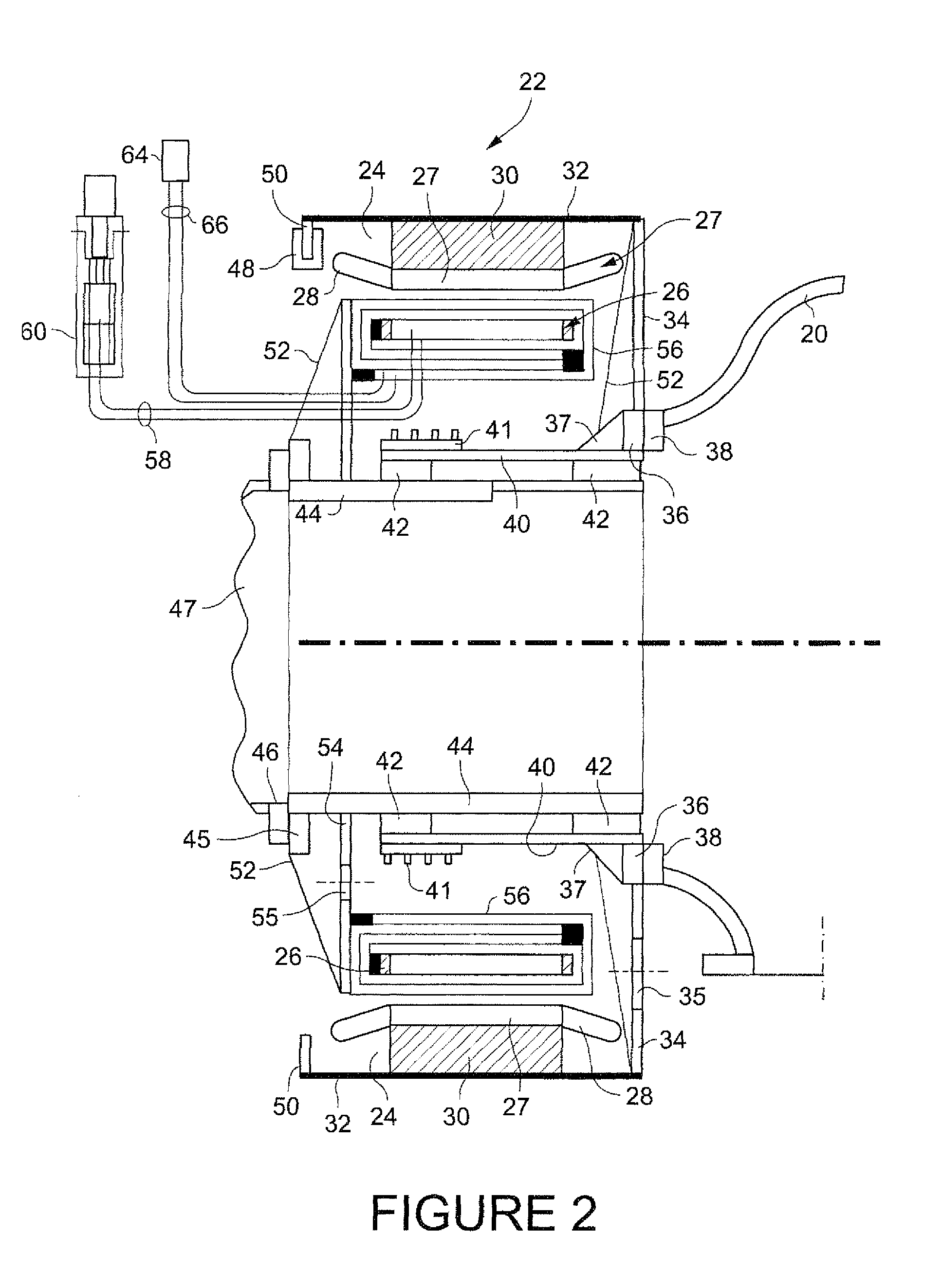
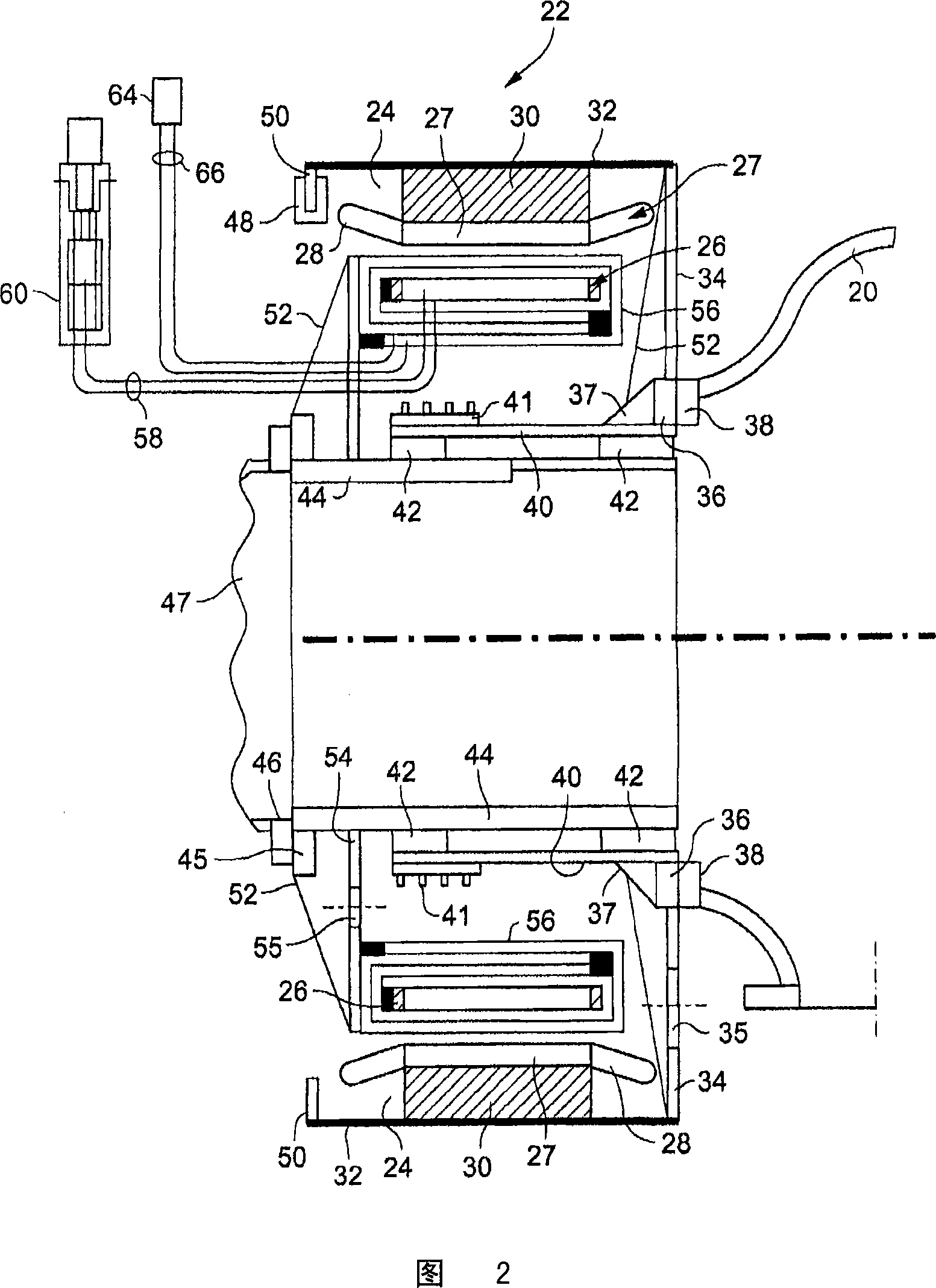
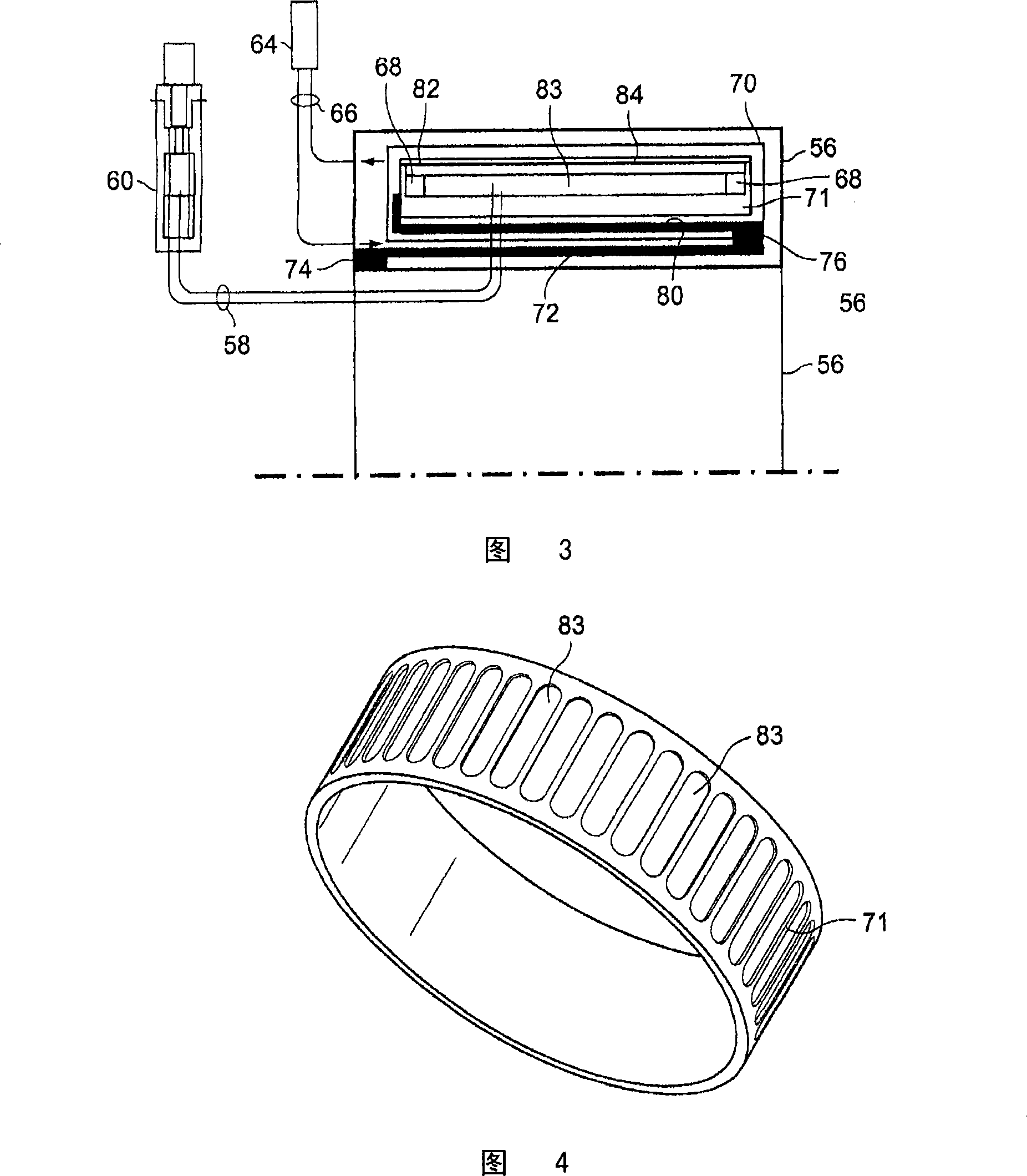
Method and apparatus for a superconducting generator driven by wind turbine
The invention provides a generator (22) including: an annular armature (24) connectable to rotate with blades (18) of a wind turbine (10); an annular stationary field winding assembly (26) coaxial with the armature and separated by a gap from an inside surface of the armature, wherein the field winding include superconducting coils (68), and support structure connectable to an upper region of a tower (12) of the wind turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC RENOVABLES ESPANA SL
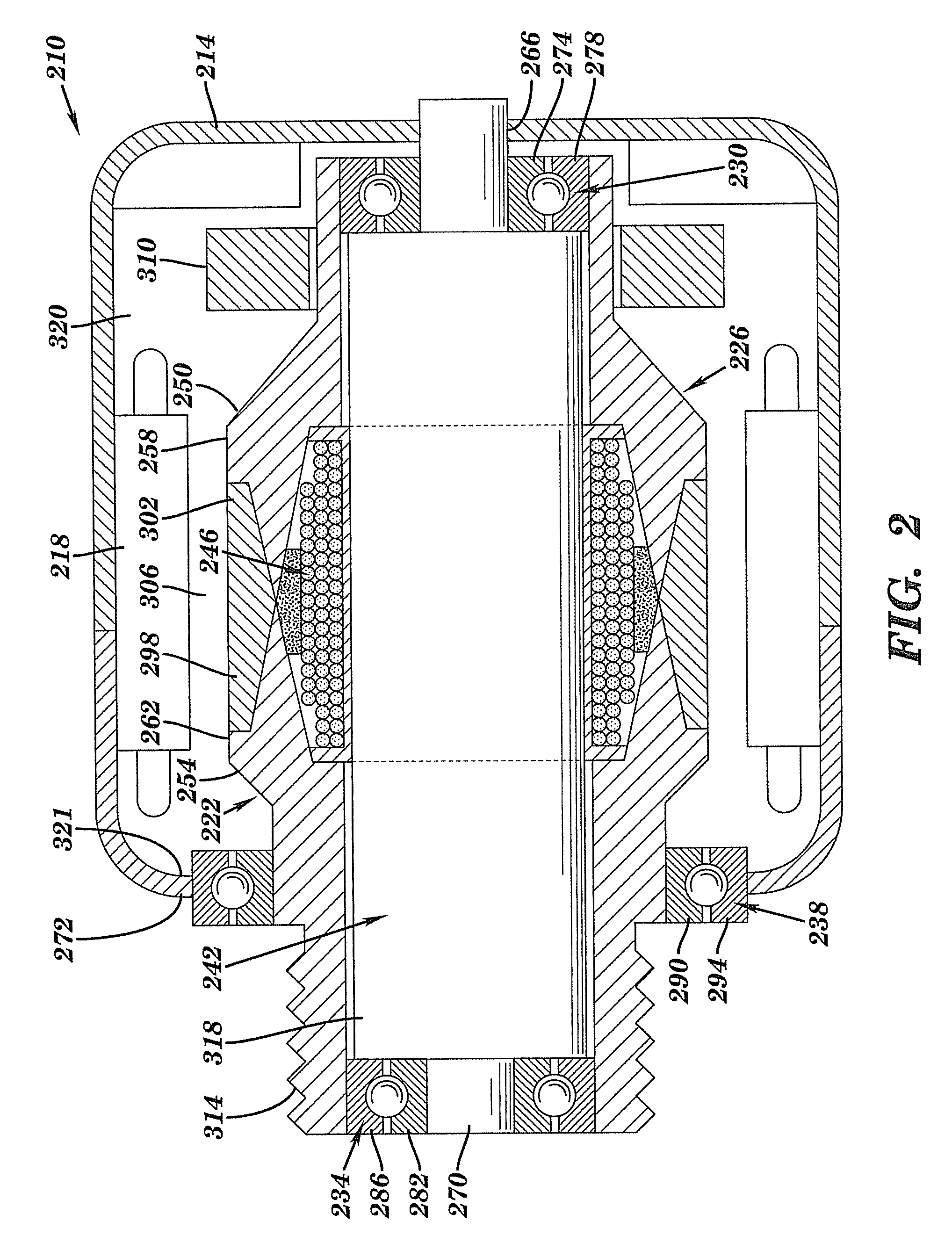
Superconducting rotating machines with stationary field coils
A machine includes a stator assembly that includes a stator yoke, a pair of armature coils mechanically coupled to the stator yoke, and a stationary superconducting field coil. The stator yoke comprises a magnetic material. The machine further includes a shaft rotatably mounted in the stator yoke, the shaft comprising a non-magnetic material. The machine further includes a rotor assembly rotationally engaged with the shaft. The rotor assembly includes a rotor disk extending between the armature coils, the rotor disk having an inner portion and an outer portion. The outer portion of the rotor disk includes a number of circumferentially-spaced, magnetic poles. The rotor disk is coupled to the shaft for rotation about the shaft and generation of a rotating permeance wave. The stationary superconducting field coil is disposed between the stator yoke and the rotor disk, and the stationary superconducting field coil is configured as a stationary magneto-motive force (MMF) source for the rotating permeance wave produced by the rotor assembly to produce a rotating magnetic field.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
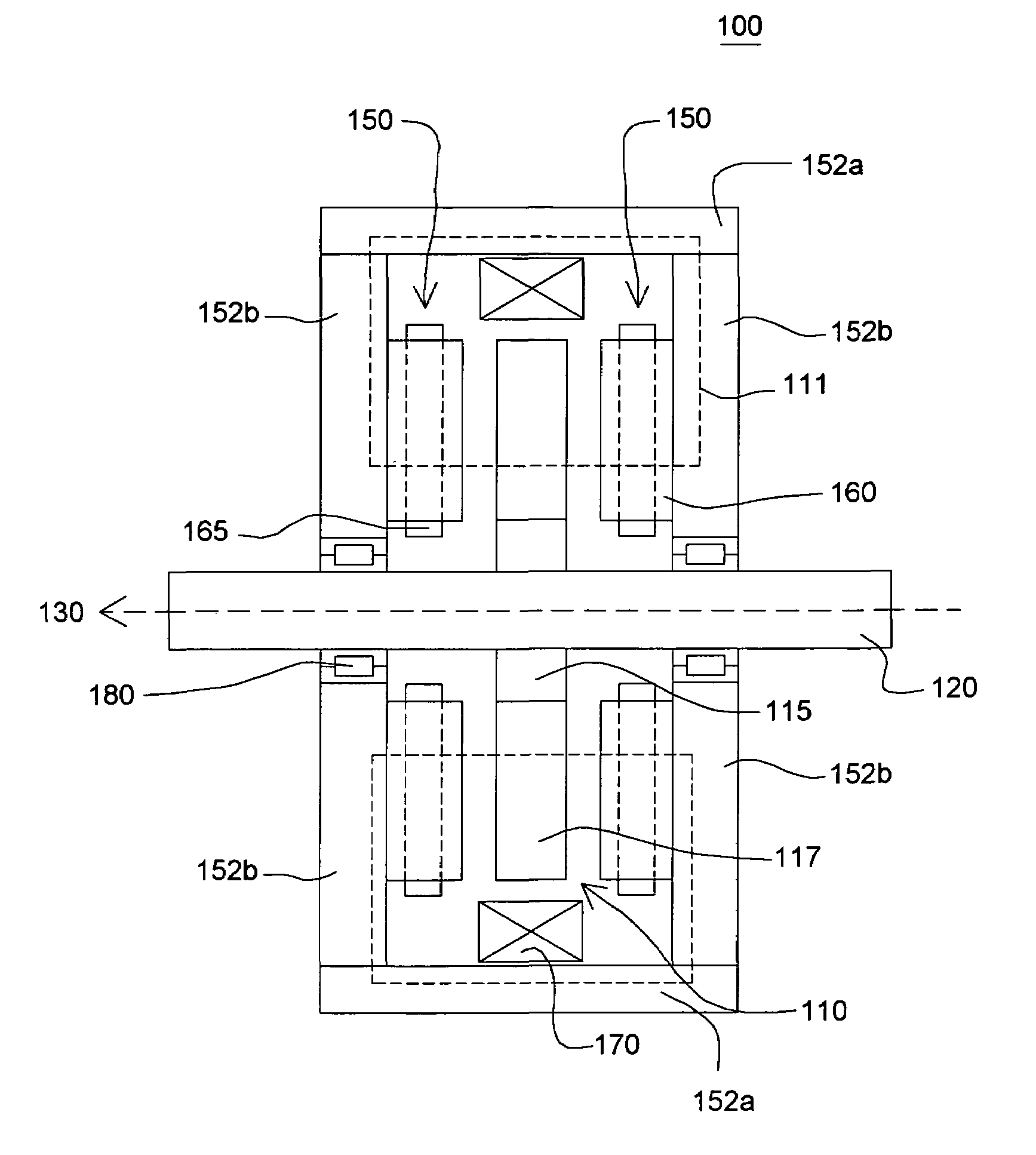
High speed motor coils
InactiveUS7061153B1Reduce gapSmall sizeSynchronous generatorsWindingsCentre of rotationStationary field
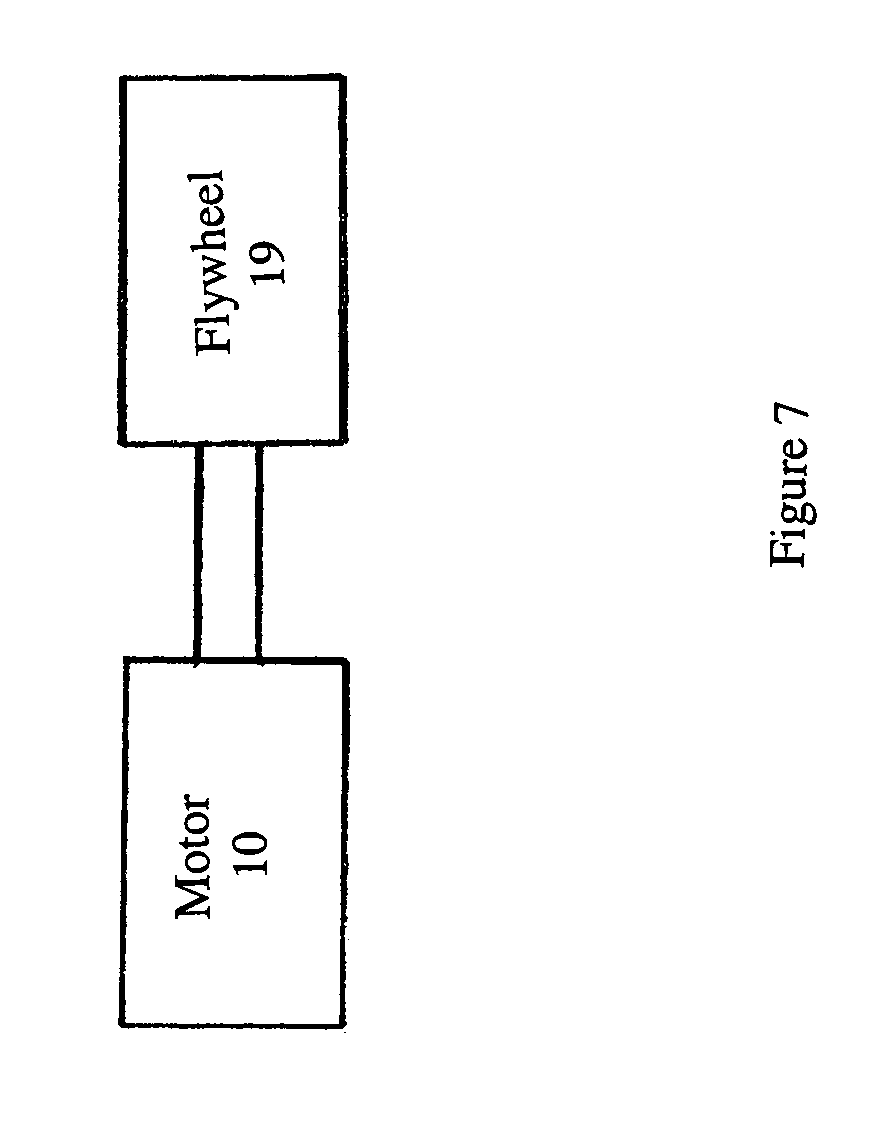
An electric motor may include a plurality of stationary field coils. The field coils are disposed so that they are overlap and are nested with adjacent field coils. A portion of each coil is disposed above a portion of an adjacent coil, and a portion of each coil is disposed beneath another adjacent coil. The average radial distance of the coils from the rotational center of the motor rotor is substantially the same. This arrangement of coils facilitates rotation of the rotor at relatively high speed for applications such as flywheel storage batteries because it reduces or eliminates variations in the torque produced by the coils. In an embodiment, the coils are bent so that they are nested. By bending the coils, the coils overlap and the air gap within the motor is minimized.
Owner:AFS TRINITY POWER CORP
Superconducting rotating machines with stationary field coils and axial airgap flux
A machine, such as a motor or generator, includes a rotatable rotor assembly comprising a plurality of salient poles and a stationary stator assembly comprising a superconducting field coil. The superconducting field coil and the salient poles are configured relative to each other such when the rotor assembly is rotated relative to the stator assembly around a predetermined axis, a rotating magnetic field is produced with an airgap flux direction substantially along the predetermined axis.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Superconducting rotating machines with stationary field coils
A machine includes a shaft adapted to rotate about a longitudinal axis and formed of a magnetic material and a rotor assembly rotationally engaged with the shaft The rotor assembly includes a pair of rotor disks comprising a magnetic material, each of the rotor disks having a number of magnetic poles, the magnetic poles being spaced apart circumferentially. The rotor disks are coupled to the shaft for rotation about the shaft and generation of a rotating permeance wave. The machine further includes a stator assembly that includes a magnetic core stator disposed between the rotor disks, a number of armature windings supported on the magnetic core stator, and a stationary superconducting field coil disposed between the magnetic core stator and the shaft. The stationary superconducting field coil is configured as a stationary magneto-motive force (MMF) source for the rotating permeance wave produced by the rotor assembly to produce a rotating magnetic field.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Brushless electric machine with stator with cascaded end loops
ActiveUS7687954B2Synchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsBrushless motorsElectrical conductor
Disclosed herein is a brushless electric machine comprising, a housing, a stationary field coil, a shaft, a bearing, a pole segment, and a stator. The stator including a core having a plurality of core slots that extend between a first and a second end of the stator core. The stator also including a winding with a plurality of phases, each of the phases having at least one conductor having a plurality of substantially straight segments disposed in the core slots. The straight segments are alternately connected at the first and the second ends of the stator core by a plurality of end loop segments. A section of at least one of the conductors including three consecutive end loop segments and two straight segments, is formed from a single continuous conductor, and one of the core slots houses a plurality of the straight segments arranged in at least one radial row.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
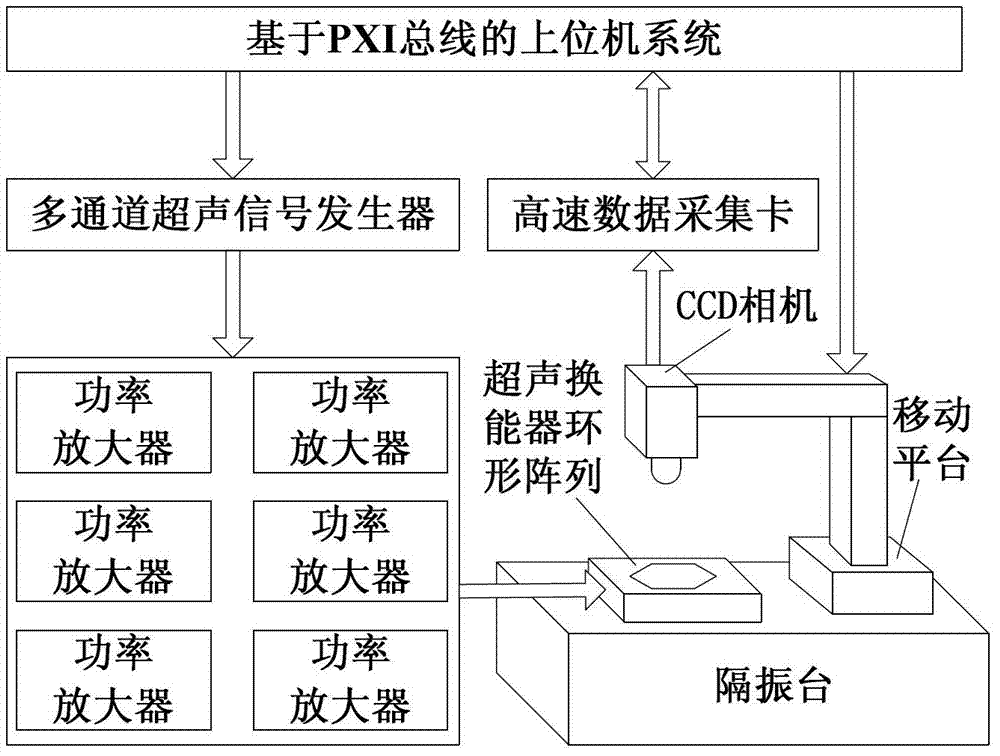
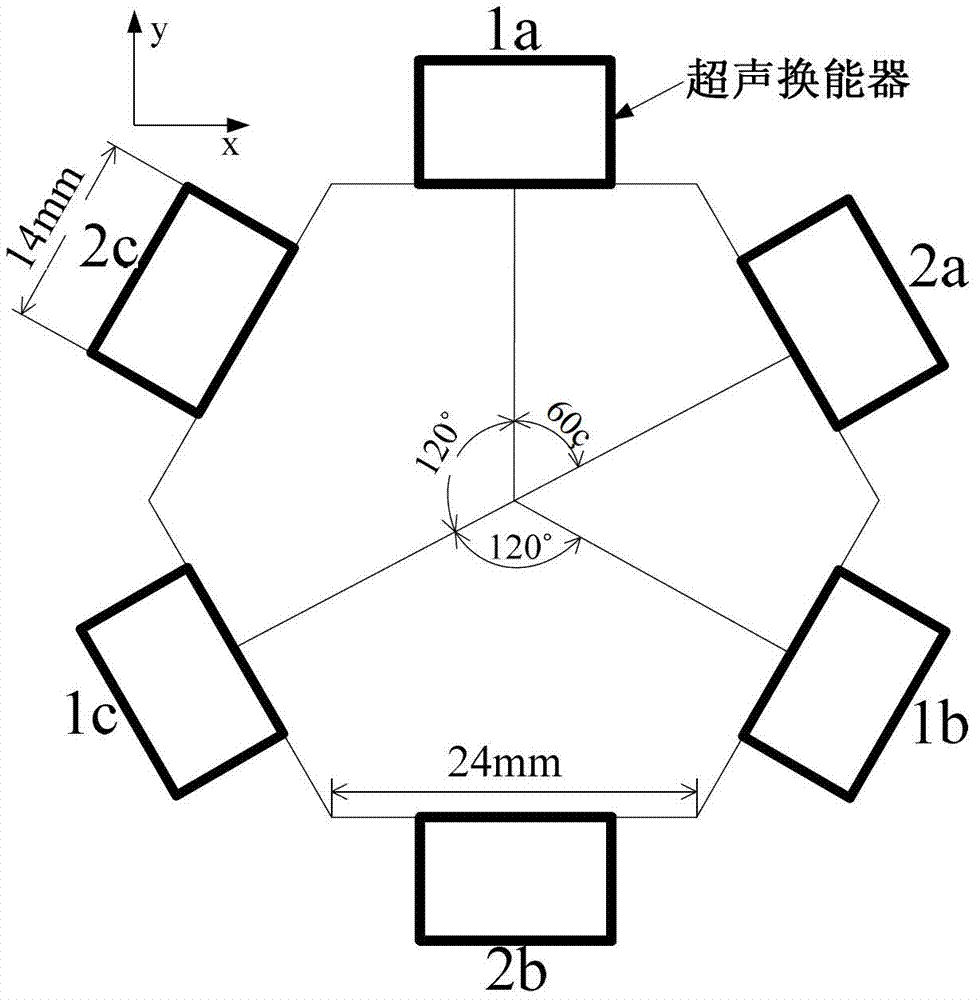
Method for compositely controlling micro-mechanical component by ultrasonic radiation force and moment
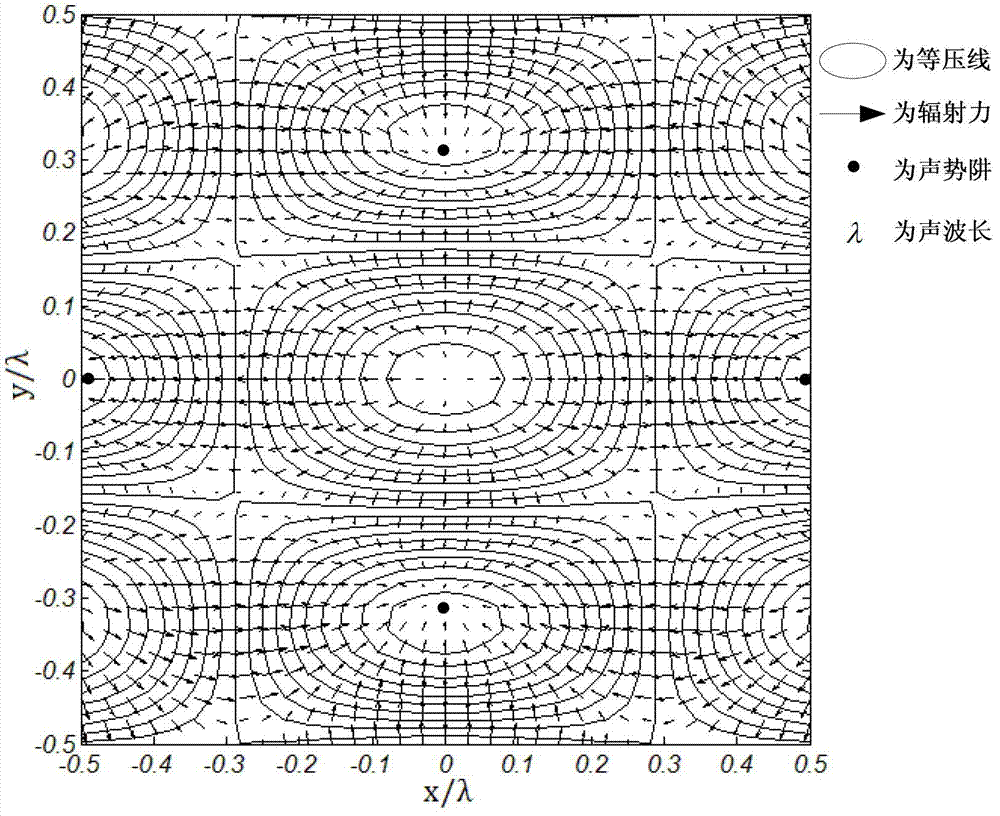
InactiveCN103043598ACapture implementationRealize transmissionDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingMomentumMechanical components
The invention discloses a method for compositely controlling a micro-mechanical component by ultrasonic radiation force and moment. Six planar ultrasonic transducers are applied and divided into two groups; only one group of ultrasonic transducers can be used to work at the same time; three beams of planar ultrasonic waves are superposed to synthesize a two-dimensional stationary field; the micro-component is captured in a momentum trap by the ultrasonic radiation force; the two-dimensional stationary field rotates by rapidly switching the two groups of ultrasonic transducers to work, and the position and orientation of the momentum trap are changed; and the micro-component is transmitted and rotates at the same time under the common action of the ultrasonic radiation force and moment. By virtue of a high-speed microscopic camera system, the front and back positions of the micro-component are calibrated, the phases of the ultrasonic transducers are adjusted, the micro-component is transmitted back to the original position, and thus the micro-component just rotates. The method has wide application prospect in high-tech areas of manufacturing and assembling of complicated and fine micro electro mechanical systems, cell biological engineering and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
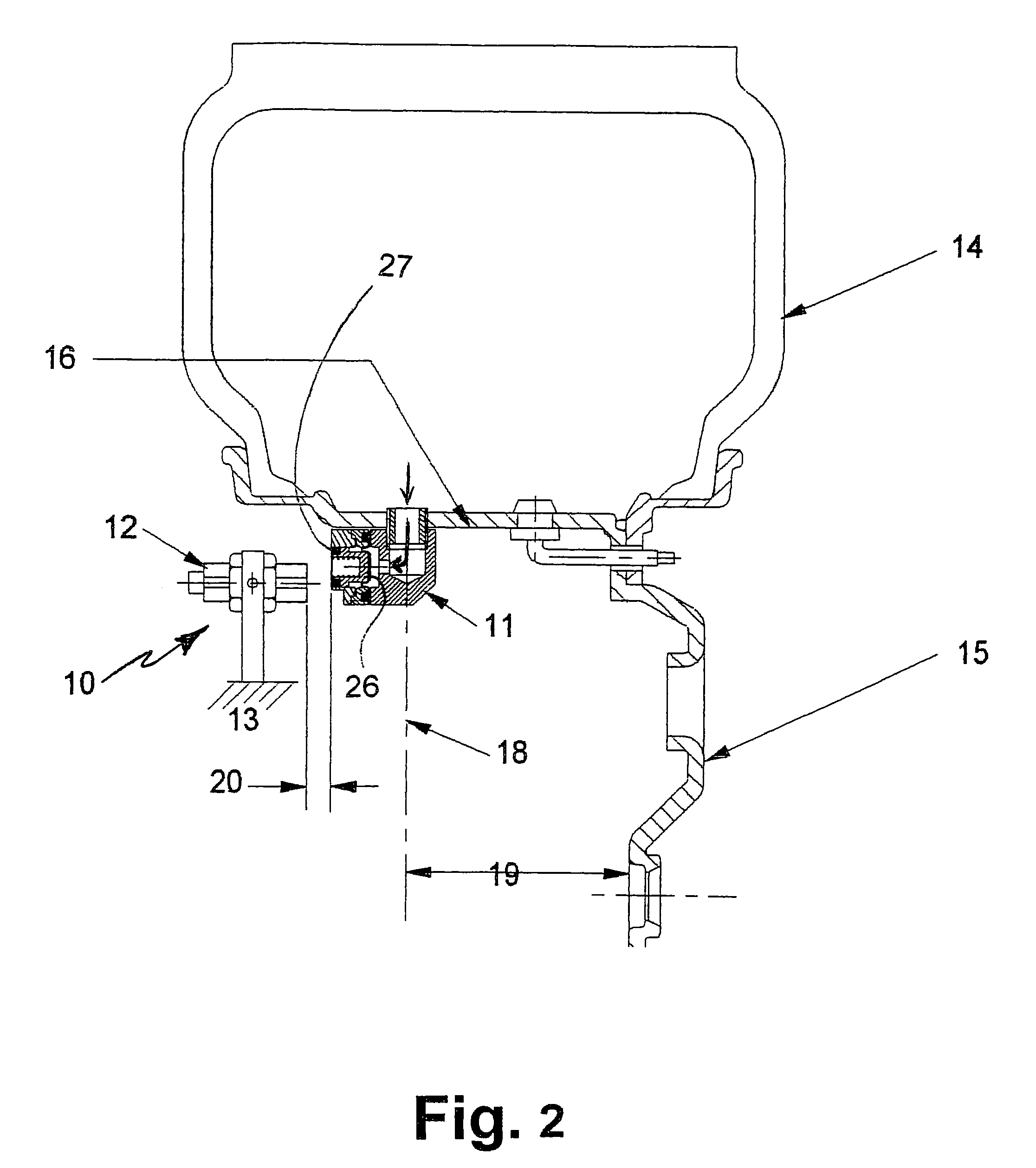
Tire pressure monitoring system and method of using same
A tire pressure monitoring system (10) including a magnetic actuator (11) having an air pressure transducer therein for generating a signal proportional to the interior tire air pressure. The actuator (11) operates parallel to the axle to alleviate speed sensitivity. Magnetic actuator (11) communicates with a stationary field sensor (12) permanently mounted on the vehicle at a close proximity to the magnetic actuator (11). The magnetic actuator (11) rotates about the access with the wheel (15), and for every revolution of the wheel (15), comes in to close proximity to the sensor (12) at least once, and communicates information about the internal tire pressure to the driver.
Owner:ADVANCED DIGITAL COMPONENTS
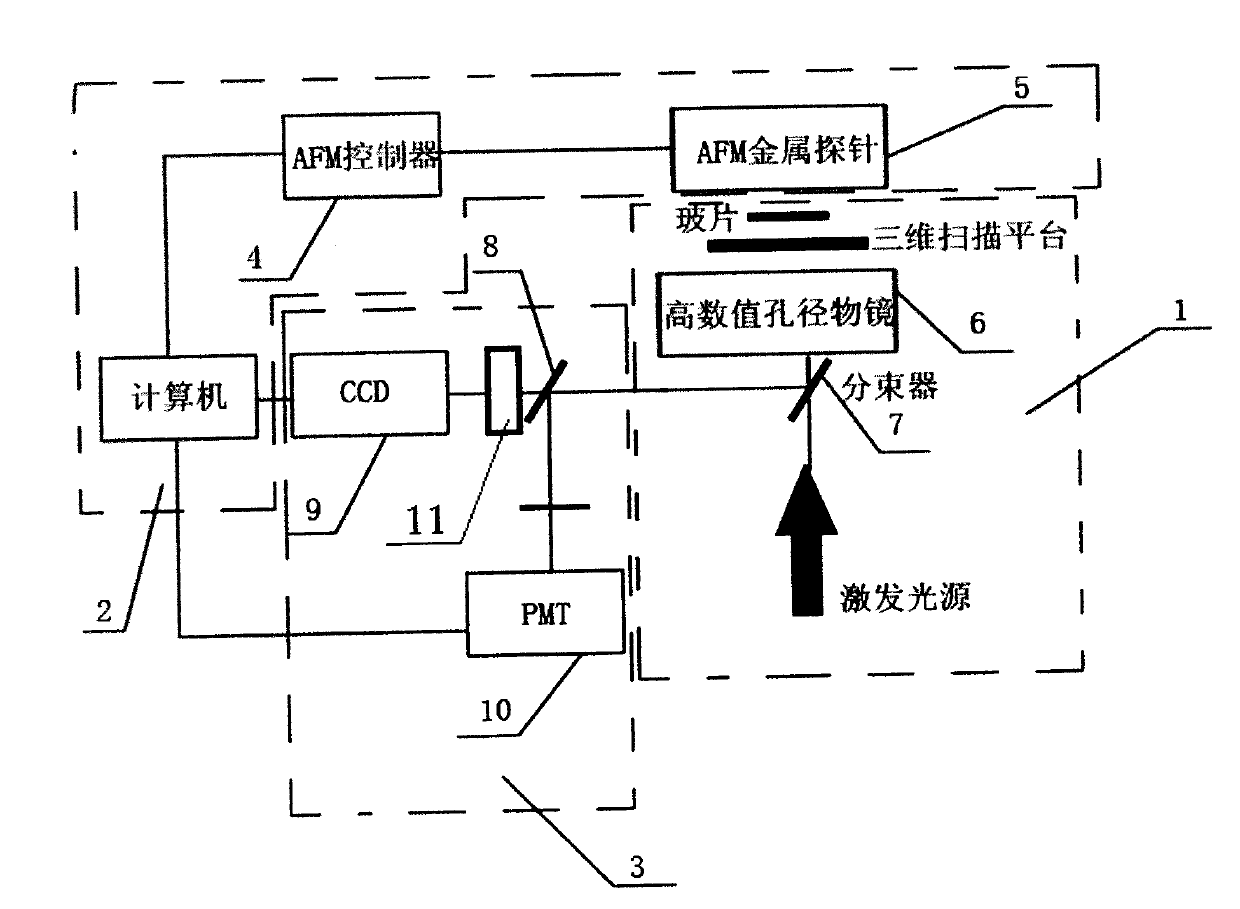
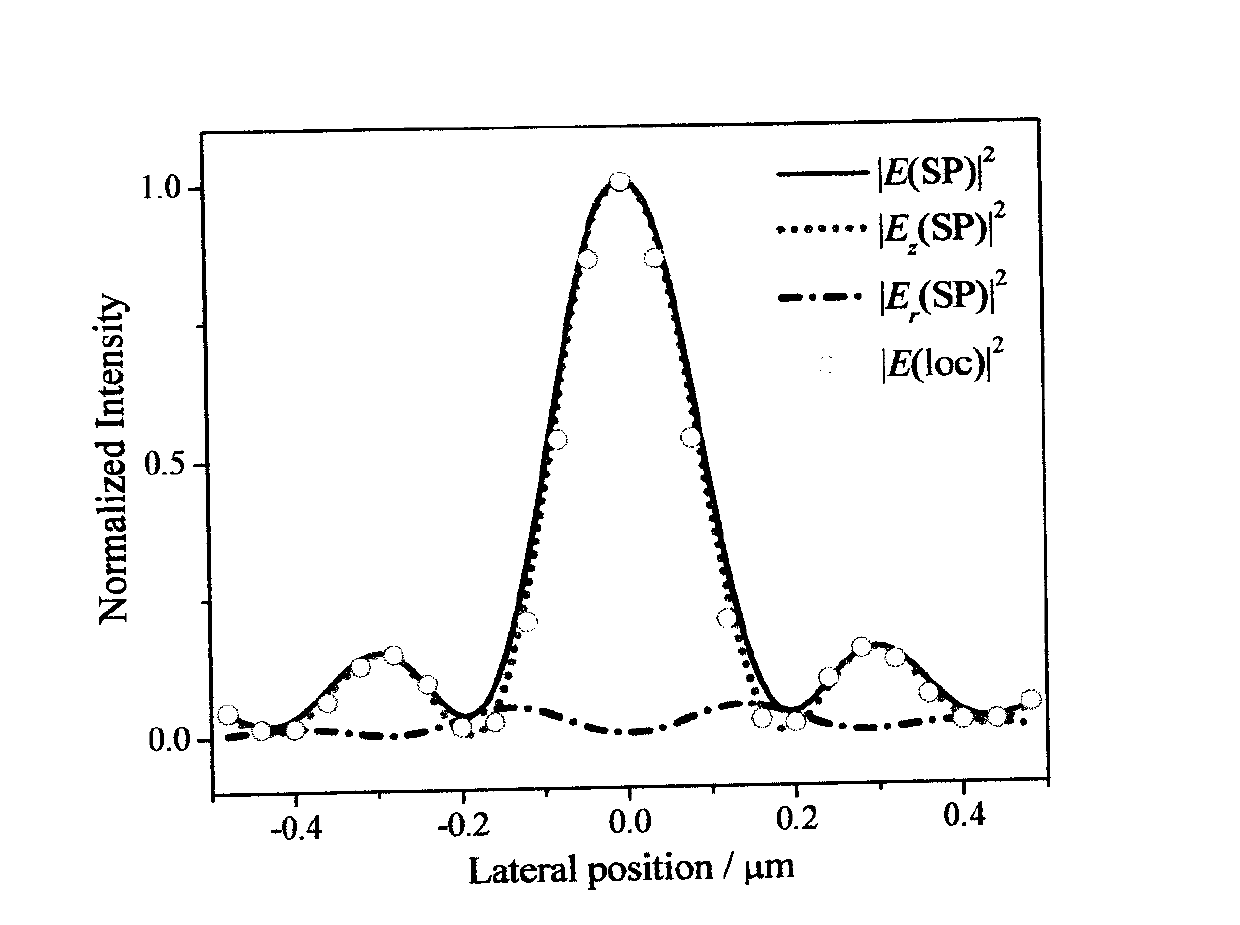
Surface plasma longitudinal field scanning near-field optic microscope device and detection method
InactiveCN103105511AReduce distractionsImprove reliabilityScanning probe microscopyHigh numerical apertureNear-field optics
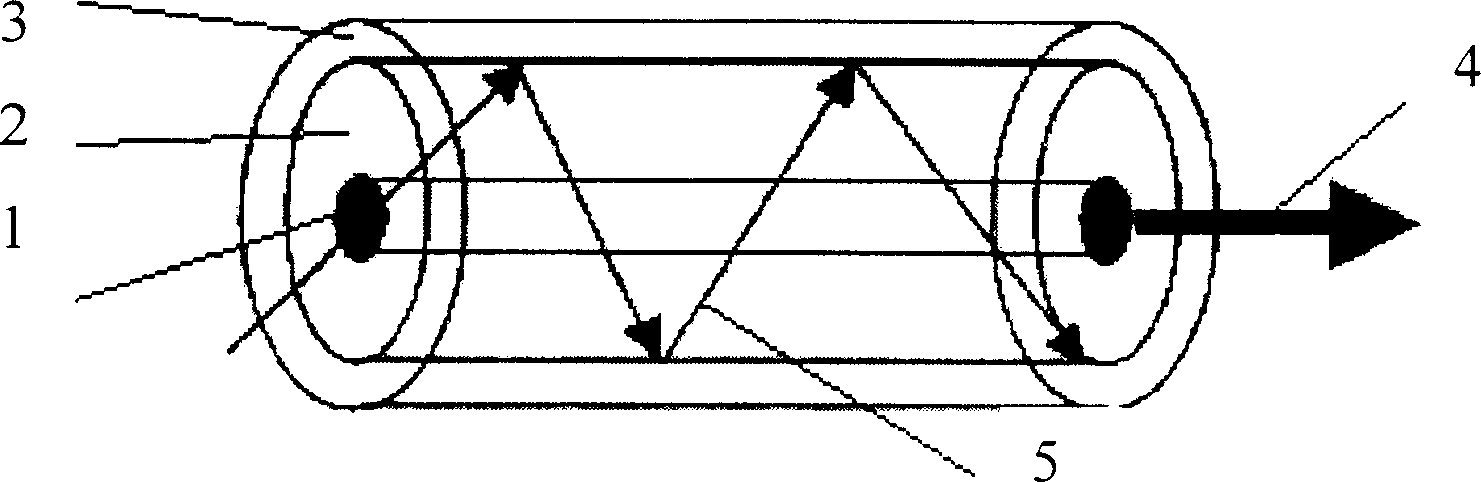
The invention provides a surface plasma longitudinal field scanning near-field optic microscope device and a detection method. The device is provided with a surface plasma excitation unit (1). After being focused through a high numerical aperture objective lens (6), incident light excites an SPP field on an interface of a metal membrane and air, raman signals and the SPP field interfere each other to form a stationary field of the SPP field around a focus, a scanning control unit (2) can achieve three-dimensional scanning and positioning for an atomic force microscope (AFM) metal probe (5) by means of an AFM controller (4), and a detection unit (3) achieves three-dimensional measurement and analysis for a longitudinal field component of a surface plasma field.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for imaging workpiece surfaces at high robot transfer speeds with correction of motion-induced distortion
A method is provided for imaging a workpiece by capturing successive frames of an elongate stationary field of view transverse to a workpiece transit path of a robot, while the workpiece is transported by the robot. The robot transit path is illuminated with an elongate illumination pattern transverse to the transit path to obtain a workpiece image of successive frames. Motion-induced image distortion is corrected by computing respective correct locations of respective ones of the frames along the transit path.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
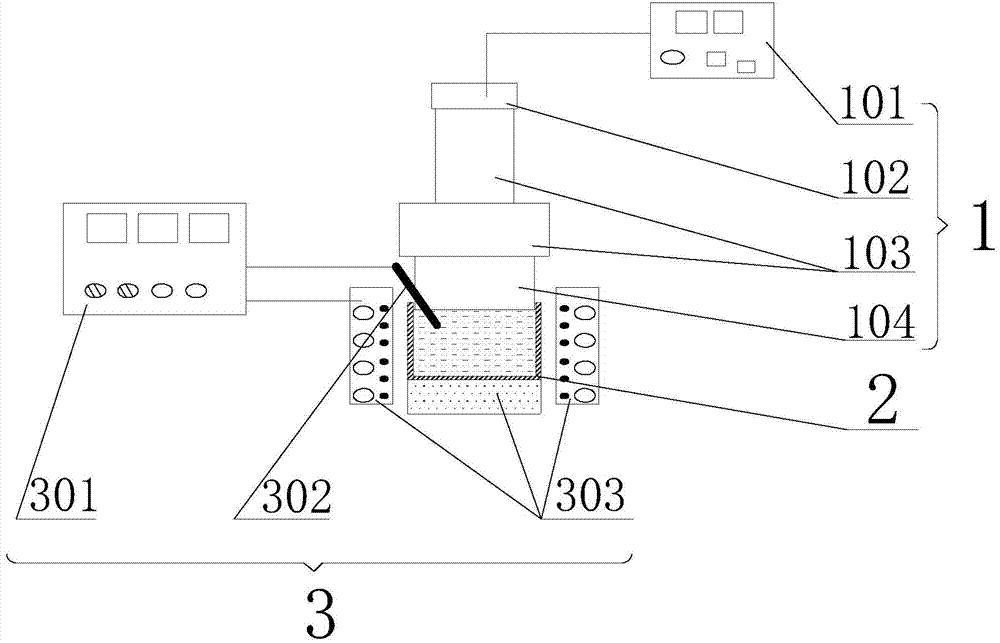
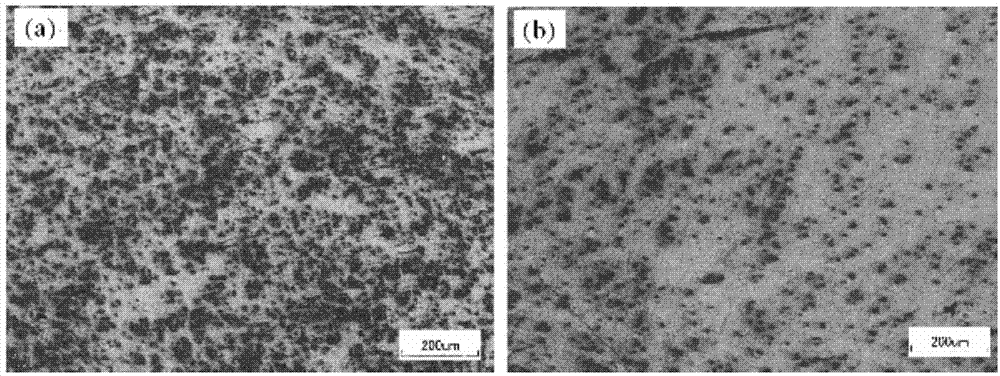
As cast condition large gradient material preparation method and utilization device thereof
The invention belongs to the field of materials, in particular to an as cast condition large gradient material preparation method and a utilization device thereof. The large gradient material preparation method comprises the steps of selecting alloy materials with semi-solid temperature ranges, heating the alloy materials and enabling the alloy materials to be completely melted so as to obtain alloy melt; feeding 6-60% of enhanced phase particles into the alloy melt, and then applying ultrasonic vibration on the alloy melt and the enhanced phase particles; reducing the temperature of the alloy melt to the alloy semi-solid temperature range, and enabling the solid fraction in the solid-liquid mixture to be 6-61%; after applying ultrasonic stationary fields on the solid-liquid mixture for 2-1200s, cooling the solid-liquid mixture, and obtaining the as cast condition large gradient material after solidification. According to the as cast condition large gradient material preparation method, the enhanced phase particles and the alloy melt are mixed evenly, the viscosity of the alloy melt is adjusted, and the motion resistance of the enhanced phase particles in the alloy melt is increased, so that gradient distribution of the enhanced phase particles in a large range of the alloy material can be achieved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for imaging workpiece surfaces at high robot transfer speeds with reduction or prevention of motion-induced distortion
ActiveUS20110199477A1Prevention and reduction of motion-induced imageImage enhancementImage analysisConsecutive frameStationary field
A method is provided for imaging a workpiece by capturing successive frames of an elongate stationary field of view transverse to a workpiece transit path of a robot, while the workpiece is transported by the robot. The robot transit path is illuminated with an elongate illumination pattern transverse to the transit path to obtain a workpiece image of successive frames. Motion-induced image distortion is prevented or reduced adjusting the camera frame rate in real time in proportion to changes in robot velocity profile of the workpiece along the transit path.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
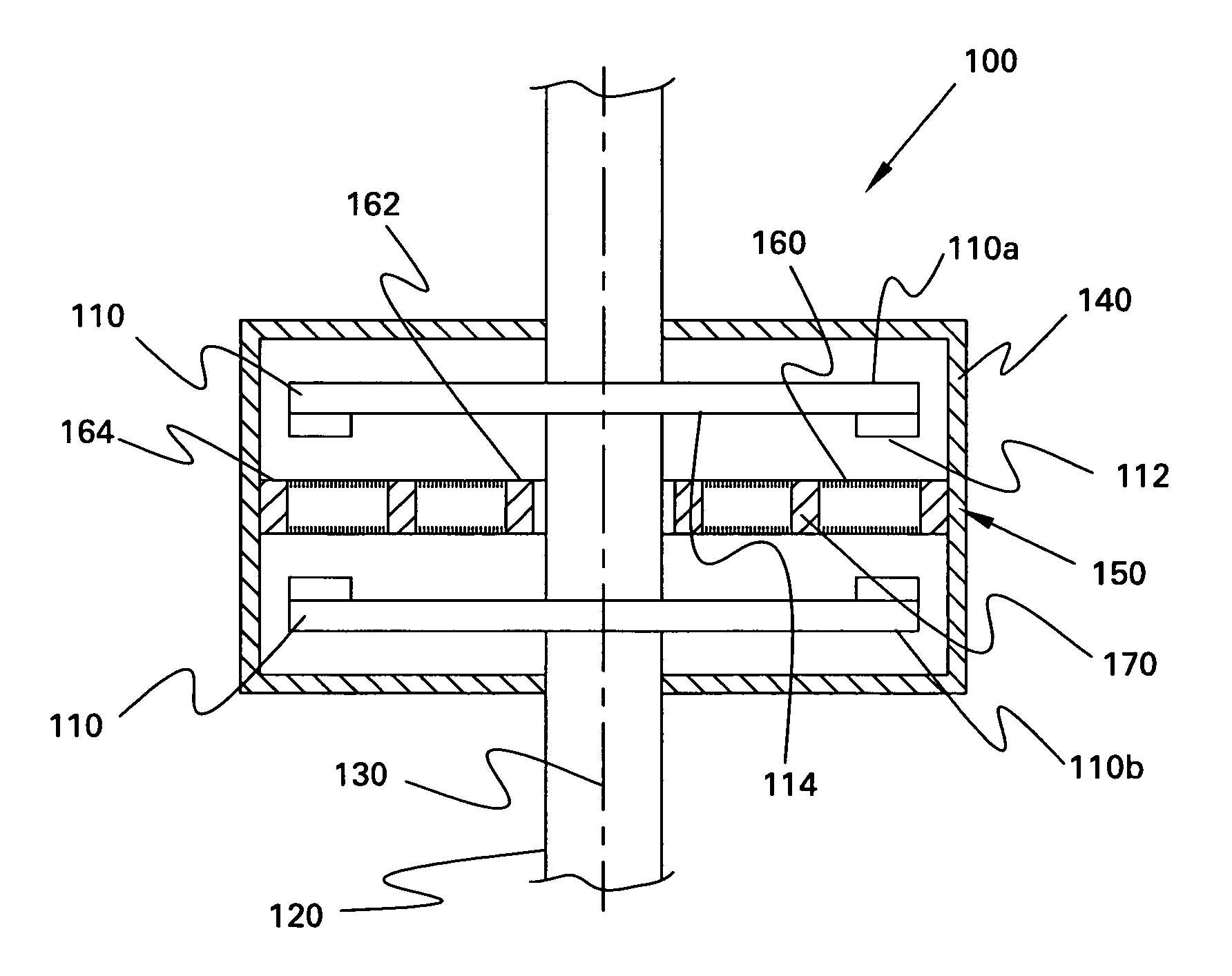
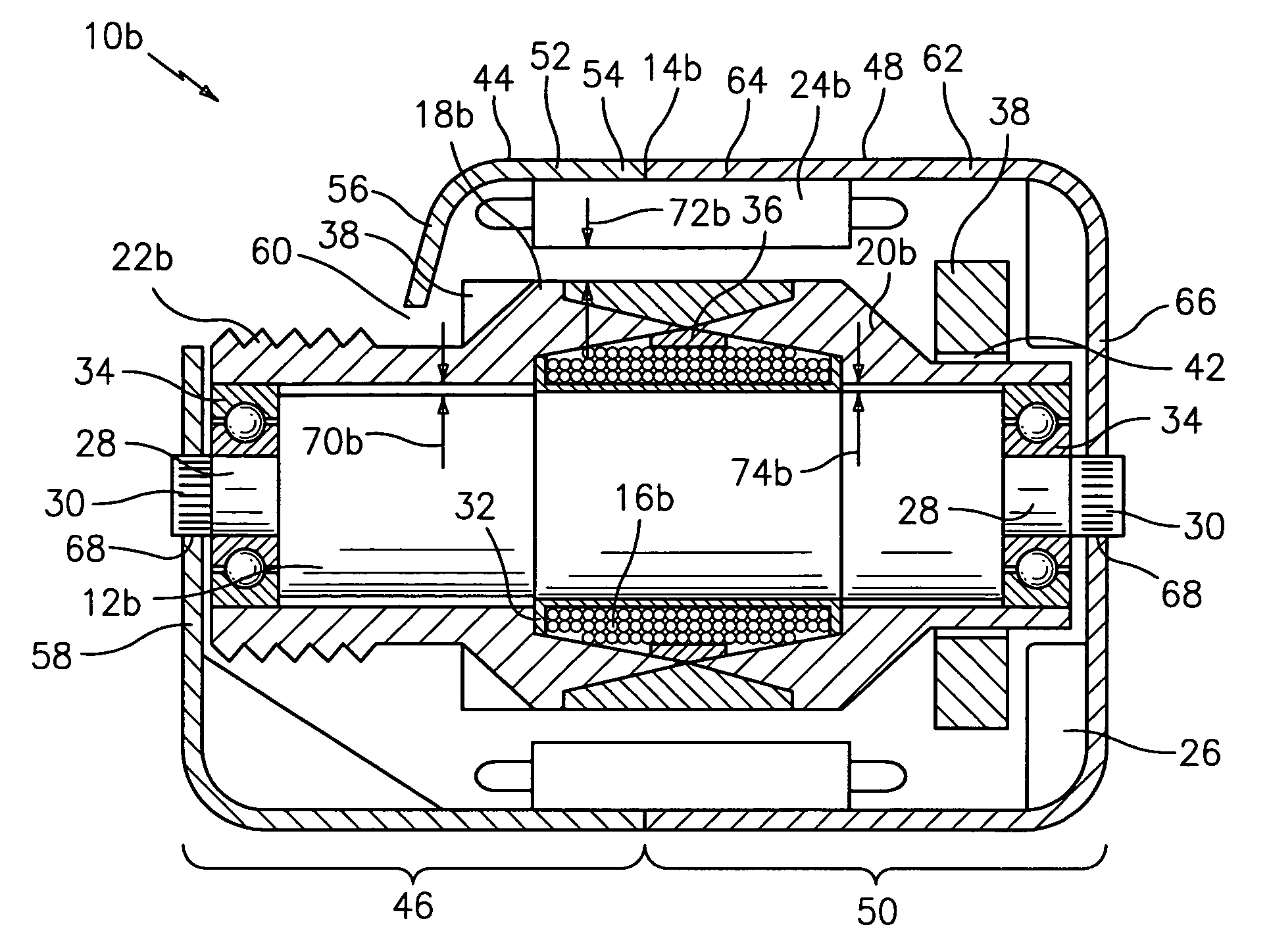
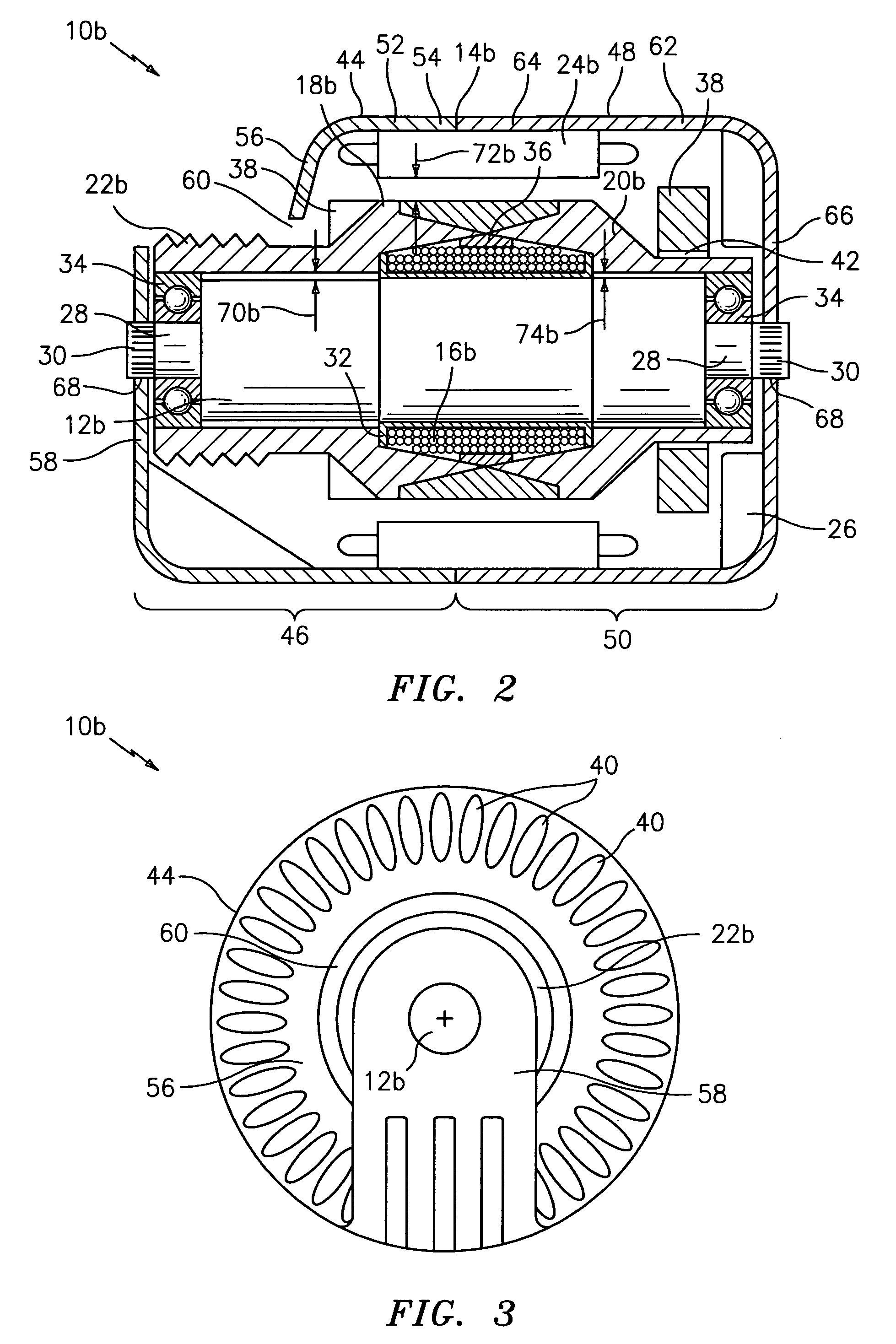
Rotational coupling device with wear compensation structure
ActiveUS20100116616A1Extended service lifeAxially engaging brakesMagnetically actuated clutchesElectrical conductorEngineering
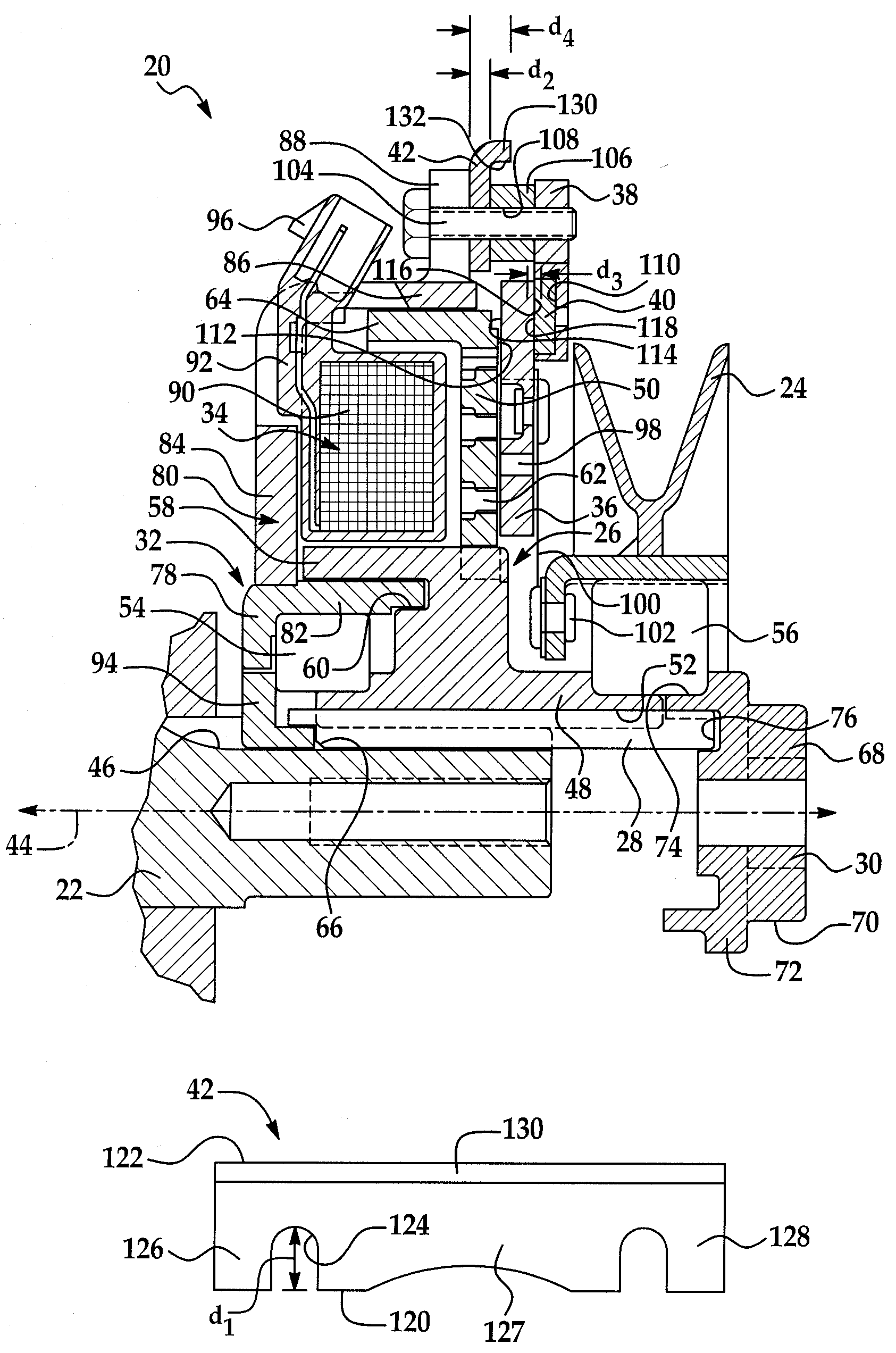
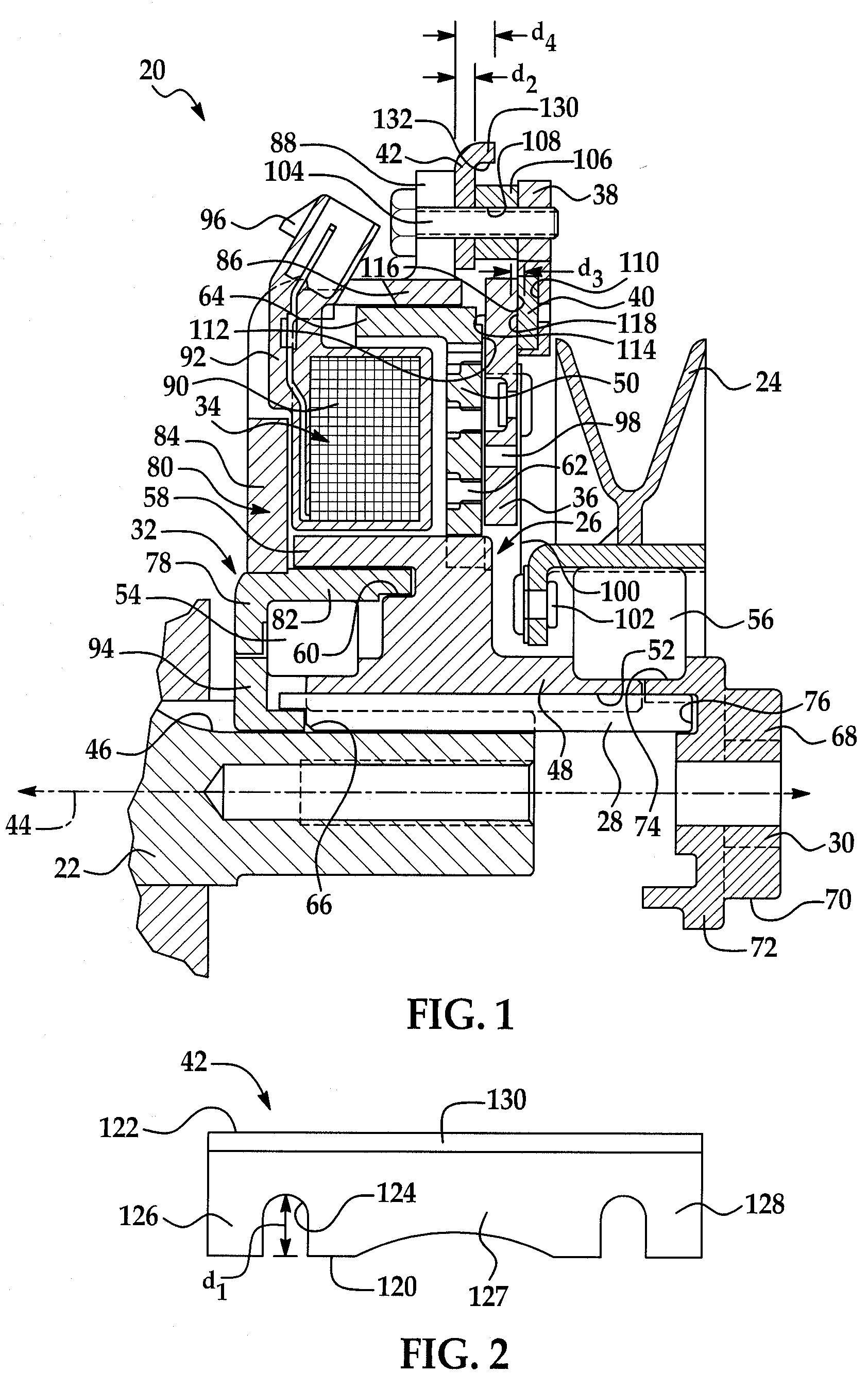
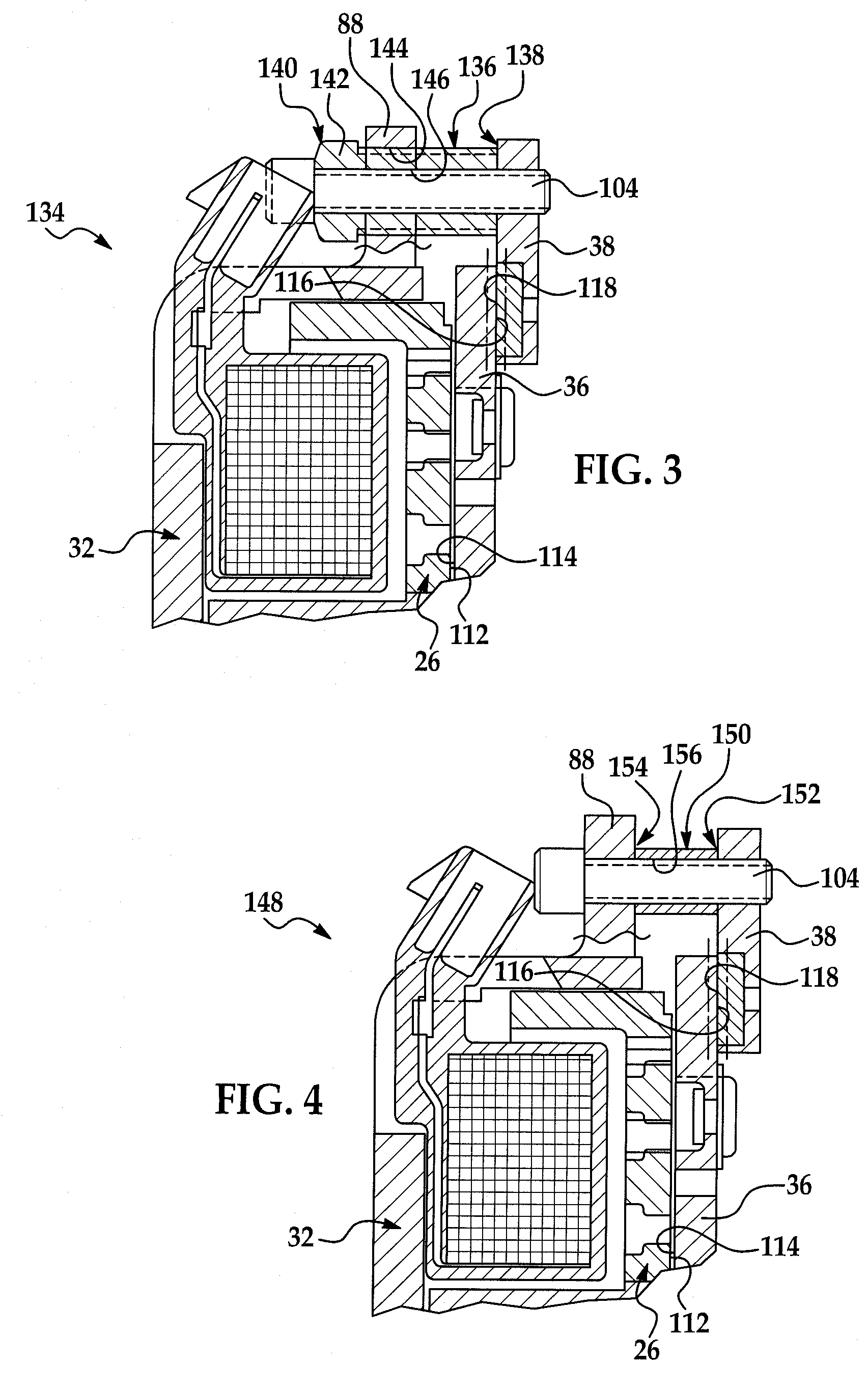
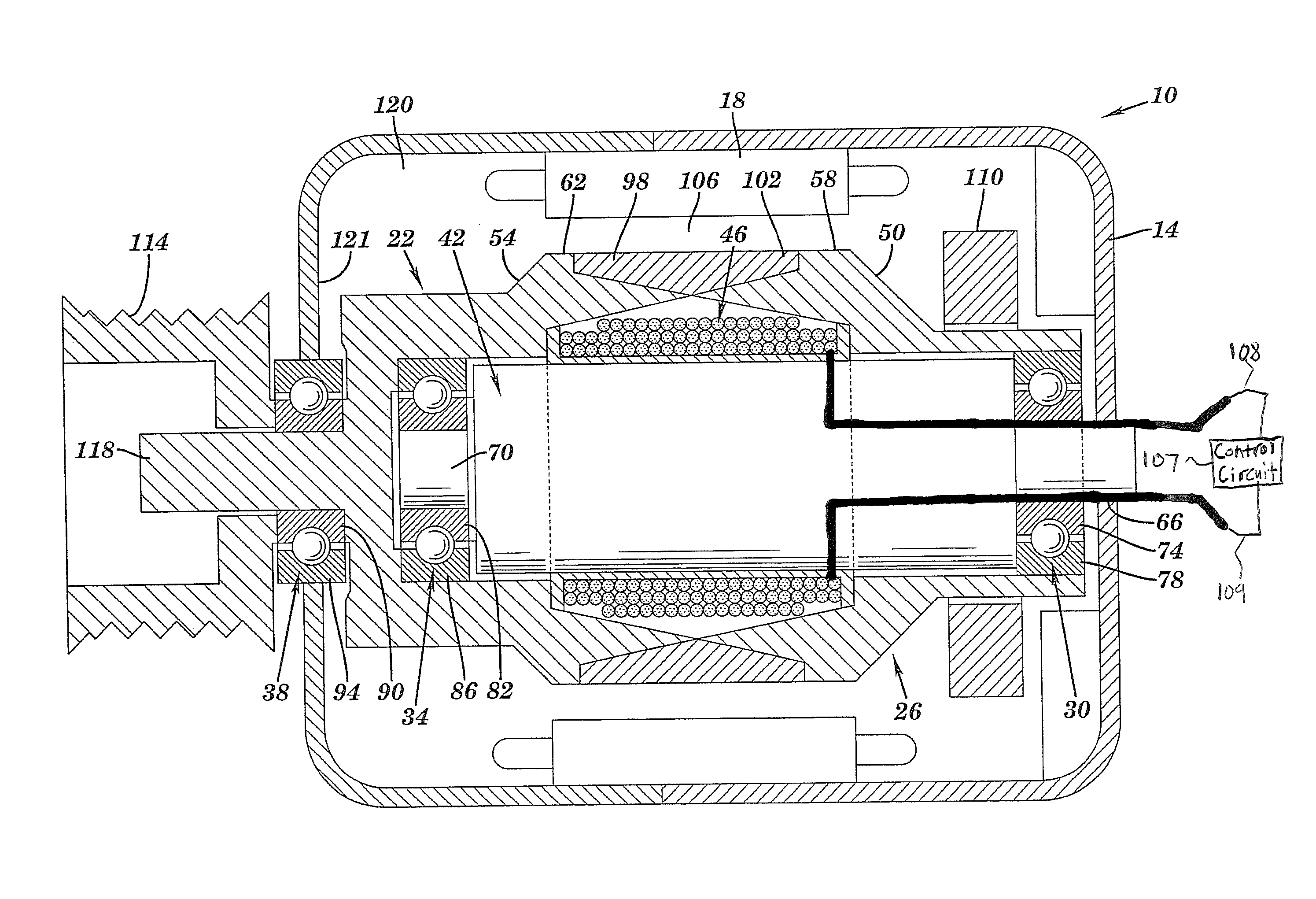
A rotational coupling device for use as a clutch and / or brake is provided having structure to compensate for wear on braking surfaces. The device includes an armature coupled to an output member and movable between positions of engagement with a rotor and a brake plate. The brake plate is coupled to a stationary field shell that houses a conductor on one side of the rotor opposite the armature and brake plate. The brake plate is axially spaced from the field shell and a removable shim or adjustable spacer is disposed between the brake plate and the field shell. Removal of the shim or adjustment of the spacer permit movement of the brake plate towards the field shell to compensate for wear in the clutch and / or brake engagement surfaces of the device.
Owner:WARNER ELECTRIC TECH
Brushless electric machine with stationary shaft and method of making same
Disclosed herein is an electric machine. The electric machine includes, a housing defining an internal volume, a stationary shaft fixedly attached to the housing, a stationary field coil attached to the shaft, a pole assembly rotatable about the shaft, and a pulley fixedly attached to the pole assembly being positioned externally of the internal volume.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
Anti-drifting pneumatic atomizer capable of regulating and controlling particle size of fog drops on line and control method
PendingCN108114822AReduce loadReduce power consumptionSpray nozzlesLiquid spraying apparatusPressure amplitudeWave field
The invention relates to an anti-drifting pneumatic atomizer capable of regulating and controlling the particle size of fog drops on line and a control method thereof. The atomizer comprises an atomizer body and a fan-shaped atomizing cavity; the atomizer body is composed of a chemical liquid flow guide cavity, a gas flow guide cavity and an electromagnetic flow valve; the rear part of the chemical liquid flow guide cavity is connected to the electromagnetic flow valve; the front part of the chemical liquid flow guide cavity is provided with a fan-shaped nozzle; the gas flow guide cavity is ahollow cone and wraps the outer side of the chemical liquid flow guide cavity; a plurality of circular gas outlets with different gas outlet angles are formed in the front part of the gas flow guide cavity and are distributed around the fan-shaped nozzle. According to the atomizer, a pneumatic atomizing mode is adopted to carry out primary atomizing on chemical liquid by means of crossed gas flow,in addition, the gas flow and the chemical liquid flow are adjusted independently, and therefore different gas-liquid mixing ratios are dynamically achieved, and the requirements for the anti-drifting capability and the penetrating capability of the fog drops are met; and meanwhile, the pressure amplitude of an ultrasonic stationary field in the fan-shaped atomizing cavity is adjusted on line, ultrasonic secondary atomizing is carried out on the fog drops, and therefore on-line dynamic regulation and control over the particle size of the fog drops are realized, and the atomizing uniformity isimproved.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Rotational coupling device with wear compensation structure
ActiveUS8123012B2Extended service lifeAxially engaging brakesMagnetically actuated clutchesElectrical conductorStationary field
A rotational coupling device for use as a clutch, a brake, or a combination clutch and brake is provided having structure to compensate for wear on braking surfaces. The device includes an armature coupled to an output member and movable between positions of engagement with a rotor and a brake plate. The brake plate is coupled to a stationary field shell that houses a conductor on one side of the rotor opposite the armature and brake plate. The brake plate is axially spaced from the field shell and a removable shim or adjustable spacer is disposed between the brake plate and the field shell. Removal of the shim or adjustment of the spacer permit movement of the brake plate towards the field shell to compensate for wear in any of the clutch or brake engagement surfaces of the device.
Owner:WARNER ELECTRIC TECH
Superconducting homopolar inductor alternator for power applications
InactiveUS7732966B2Efficient propulsion technologiesMachines/enginesElectric power systemMechanical energy
A portable power system has a turbine engine generating mechanical energy. A homopolar electrical machine receives this energy. The homopolar electrical machine has a single stationary superconducting field coil configured to create a magnetic field. A homopolar rotor is configured to rotate within the magnetic field such that a rotating magnetic field is created in a stationary winding by interaction of the rotating permeance wave produced by the homopolar rotor and the magnetic field produced by the single stationary field coil. The homopolar electrical machine is configured as a generator and produces electrical power for the portable power system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Acoustic optical Q-regulating method for two-clad optical-fiber laser and apparatus
InactiveCN1710482ALow insertion lossIncreased waveguide transmission lossActive medium materialActive medium shape and constructionUltrasonic sensorDouble-clad fiber
In the method, quartz optical fiber of doubly coated fiber laser is as acoustooptic medium directly. Stationary field of sound wave or traveling wave field is formed in the medium so as to form phase grating. Deflection of transmitting direction of oscillated laser occurred caused by diffraction under effect of the phase grating is as a leaking wave. The leaking wave prevents forming oscillated laser. Thus, laser of optical fiber is in state of low Q value. When traveling wave field is disappeared, laser is in state of high Q value. The device includes a radio frequency excited ultrasonic transducer, medium for sound propagation, sound reflection interface or body of sound absorption. The medium for sound propagation is placed between the said transducer and the said interface or body of sound absorption. The doubly coated fiber is in medium for sound propagation. Advantages are: acoustooptic Q switch is realized in coated fiber directly so as to lower insertion loss.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com