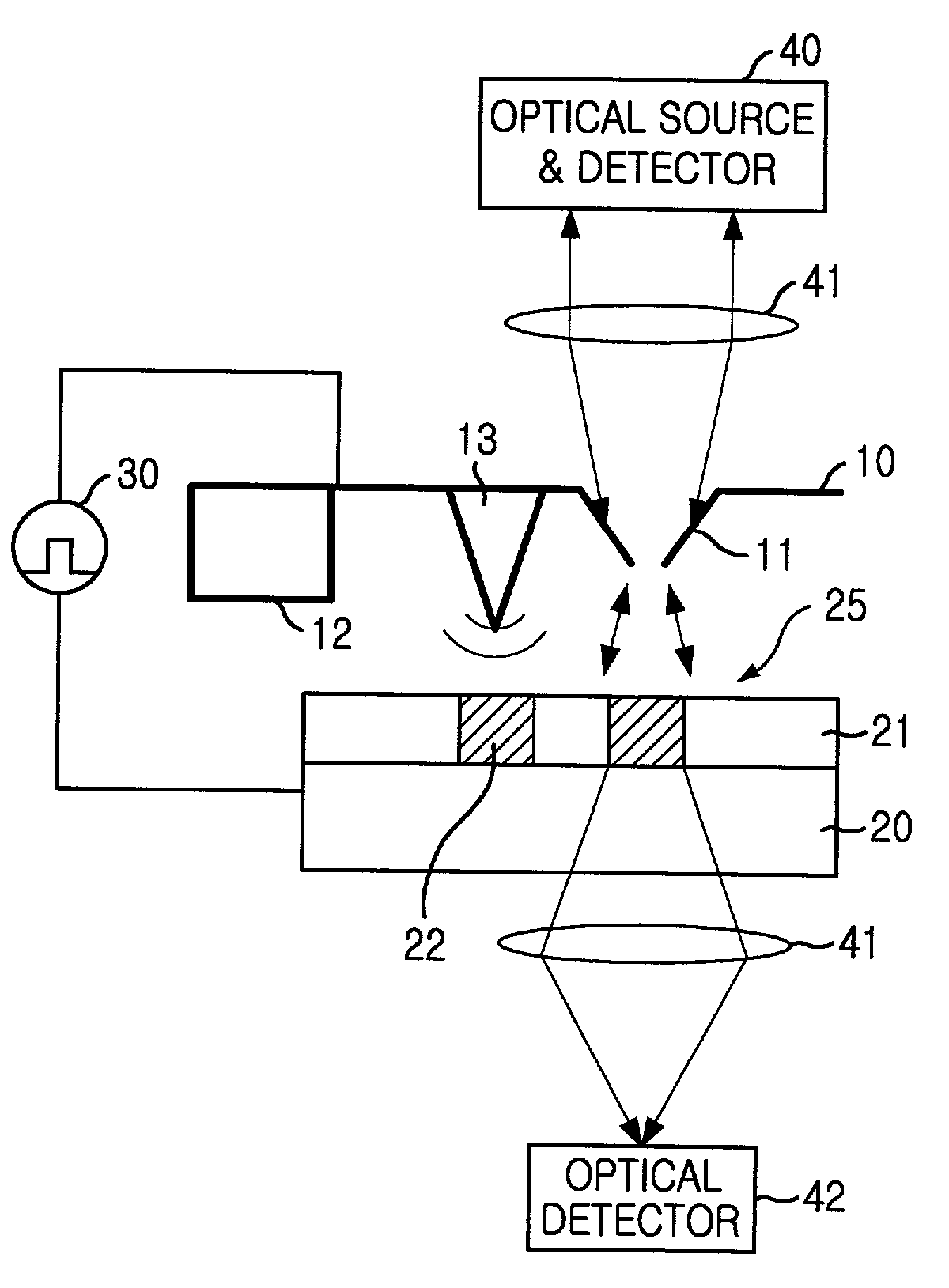
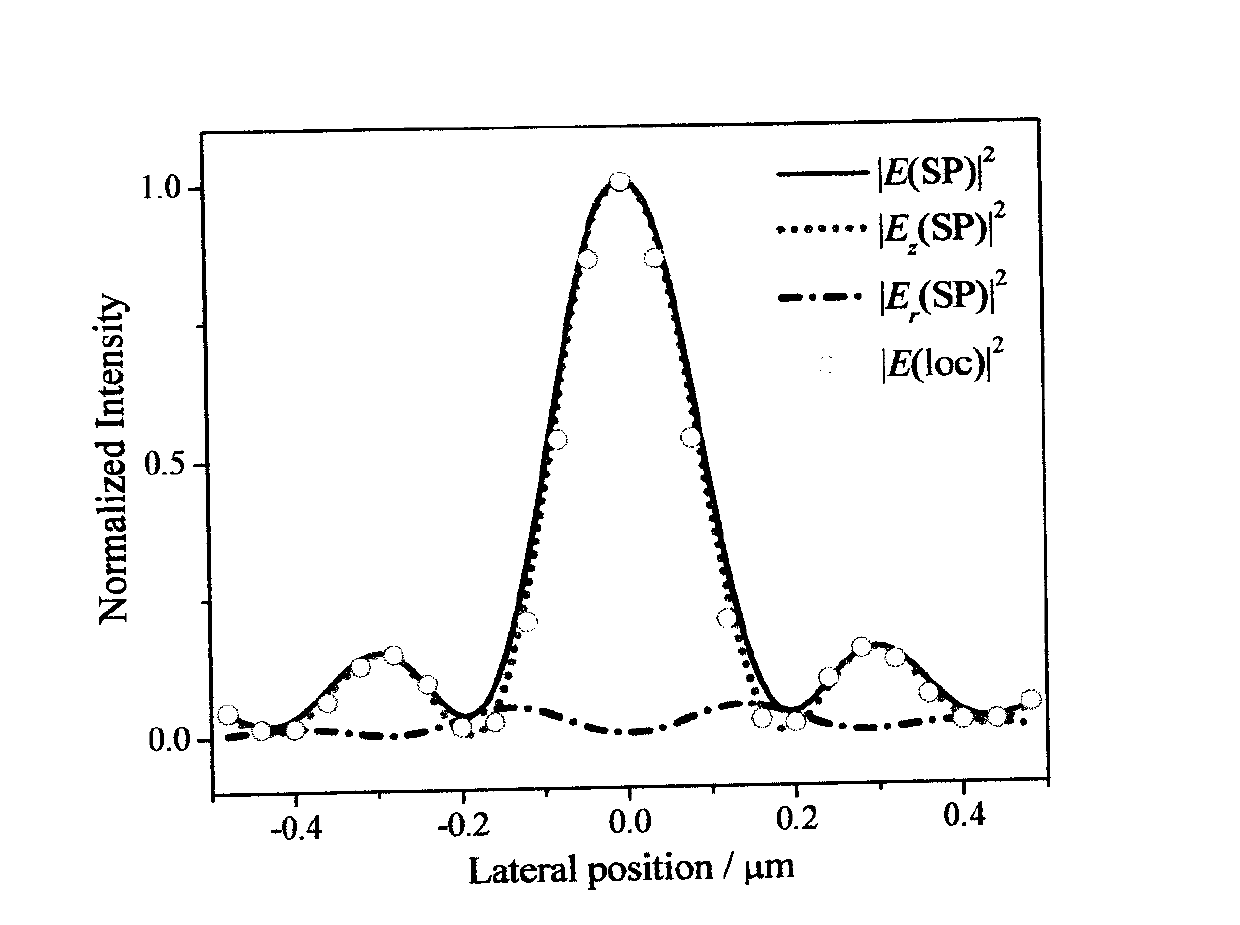
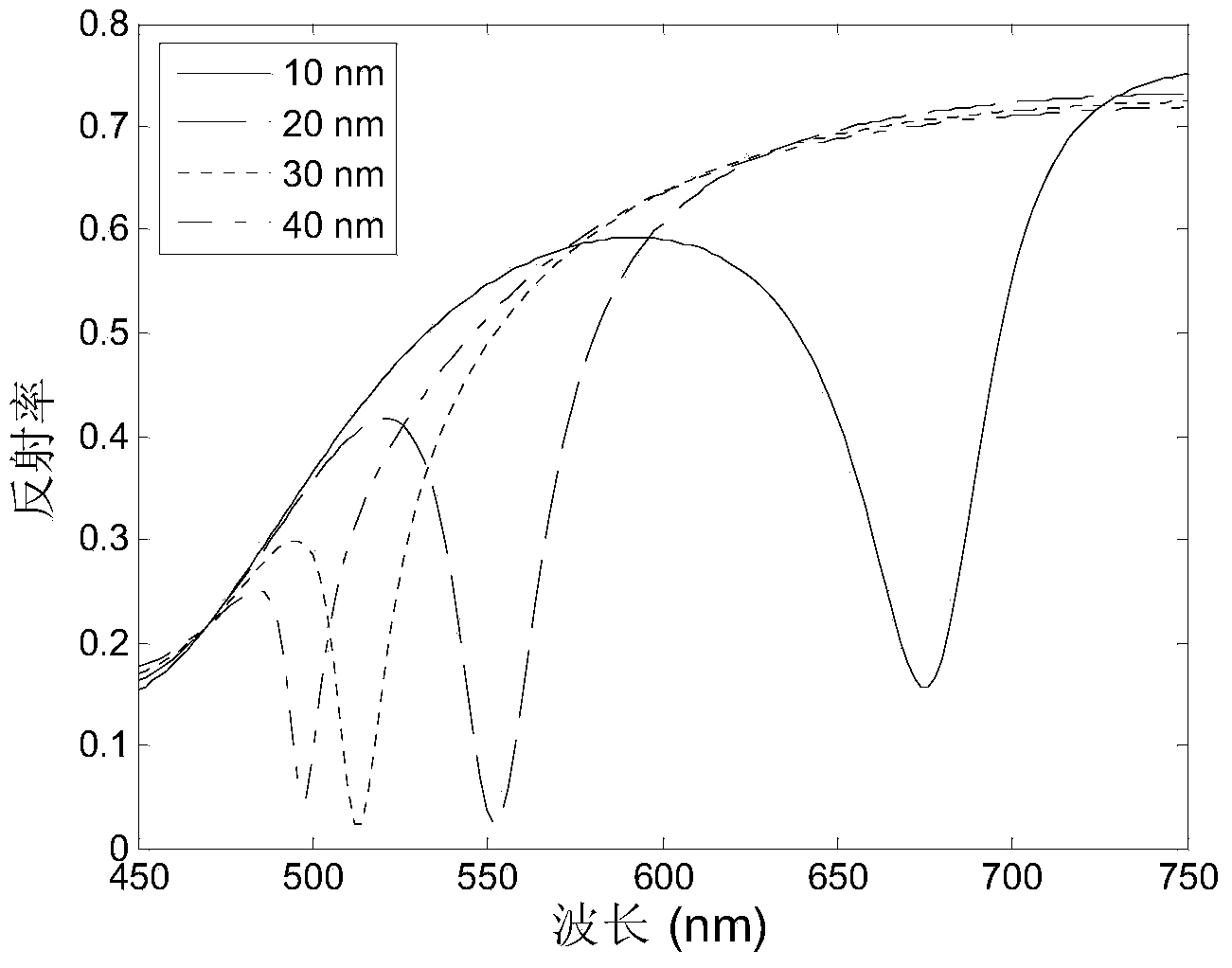
Patents
Literature
34 results about "Near-field optics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Near-field optics is that branch of optics that considers configurations that depend on the passage of light to, from, through, or near an element with subwavelength features, and the coupling of that light to a second element located a subwavelength distance from the first. The barrier of spatial resolution imposed by the very nature of light itself in conventional optical microscopy contributed significantly to the development of near-field optical devices, most notably the near-field scanning optical microscope, or NSOM.
Miniature array spectral filter based on metallic surface plasma excimer
InactiveCN101256246AWide range of choicesPerformance indicators unchangedOptical filtersEtchingMedical diagnosis
The invention discloses a minitype array filter based on metal surface plasma excimer. A plurality of array units are provided on an optical substrate, a sub-wavelength hairline is set between the array units and a plurality of linear grid grooves of incidence plane, or emergence plane or incidence plane and emergence plane which are symmetrically distributed are set at the two sides of the sub-wavelength hairline in a space, wherein the distance of the linear grid groove is same to the width thereof. The invention has features: simple technique, compactness, and can be connected with the LED, photosensitive detection, optical imaging sensor to form a variety of filters and imaging spectrometer of sub-wavelength, with high resolution, high integrity and wide application foreground in photo etching, high density data storage, near-field optics, space exploration, and medical diagnosis. The minitype array filter can be used in microwave, infrared and visible light band.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Apparatus for recording and reproducing high-density information using multi-functional probe
InactiveUS20020080709A1Shorten the timeImprove data transfer rateNanoinformaticsPhotometryComing outHigh density
In the apparatus for recording and reproducing high-density information using a multi-functional probe, media is locally heated not only by near-field optics come out of an aperture and but also by current induced from an end of an conducting cantilever, to record information and thereby increase a recording speed. The apparatus and method for recording and reproducing the high-density information using the multi-functional probe includes a conducting cantilever, in which a cantilever stage and a near-field optical aperture probe are formed in one body, the media is locally heated not only by the near-field optics from a near-field optical aperture probe but also by the current induced from the probe to the media or induced from the probe itself, and then the information is recorded; and an optical detector for reproducing the recorded information with a reflectivity of light come out of the near-field optical aperture probe or a transmission onto the media.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Long-wavelength scanning near-field microscopic analysis system
The invention provides a long-wavelength scanning near-field microscopic analysis system. The long-wavelength scanning near-field microscopic analysis system integrates broadband long-wavelength and single-frequency THz waves, utilizes a scanning probe to integrate a variable electric field, a variable magnetic field and a variable temperature field, fills the technical blank of long-wavelength wave bands in the near-field microscopy field, enables a near-field optic microscopic technology to be linked with a near-field microwave microscopic technology and provides an all-around sample physical property testing tool for scientific research persons.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Near-field polarized light scanning probe microscope
ActiveCN105588954AImprove signal-to-noise ratioScanning probe microscopyBeam splitterScanning Hall probe microscope
The invention relates to a near-field polarized light scanning probe microscope having a near-field optics detecting optical path in which a bundle of linearly polarized lights emitted from an He-Ne laser successively pass a quarter-wave plate A, a beam splitter, an objective lens A, and a probe to an objective table to form a near-field optics generation optical path. The reflected lights reflected from the probe successively pass the objective lens A, the beam splitter, a quarter-wave plate B, a Glan-Taylor prism, and the objective lens and are received by a photoelectric receiver to an image display system. The near-field polarized light scanning probe microscope can effectively inhibit a far-field background light and improves the signal to noise ratio of a near-field light, and the spatial resolution is less than 10 nanometers.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Surface plasma longitudinal field scanning near-field optic microscope device and detection method
InactiveCN103105511AReduce distractionsImprove reliabilityScanning probe microscopyHigh numerical apertureNear-field optics
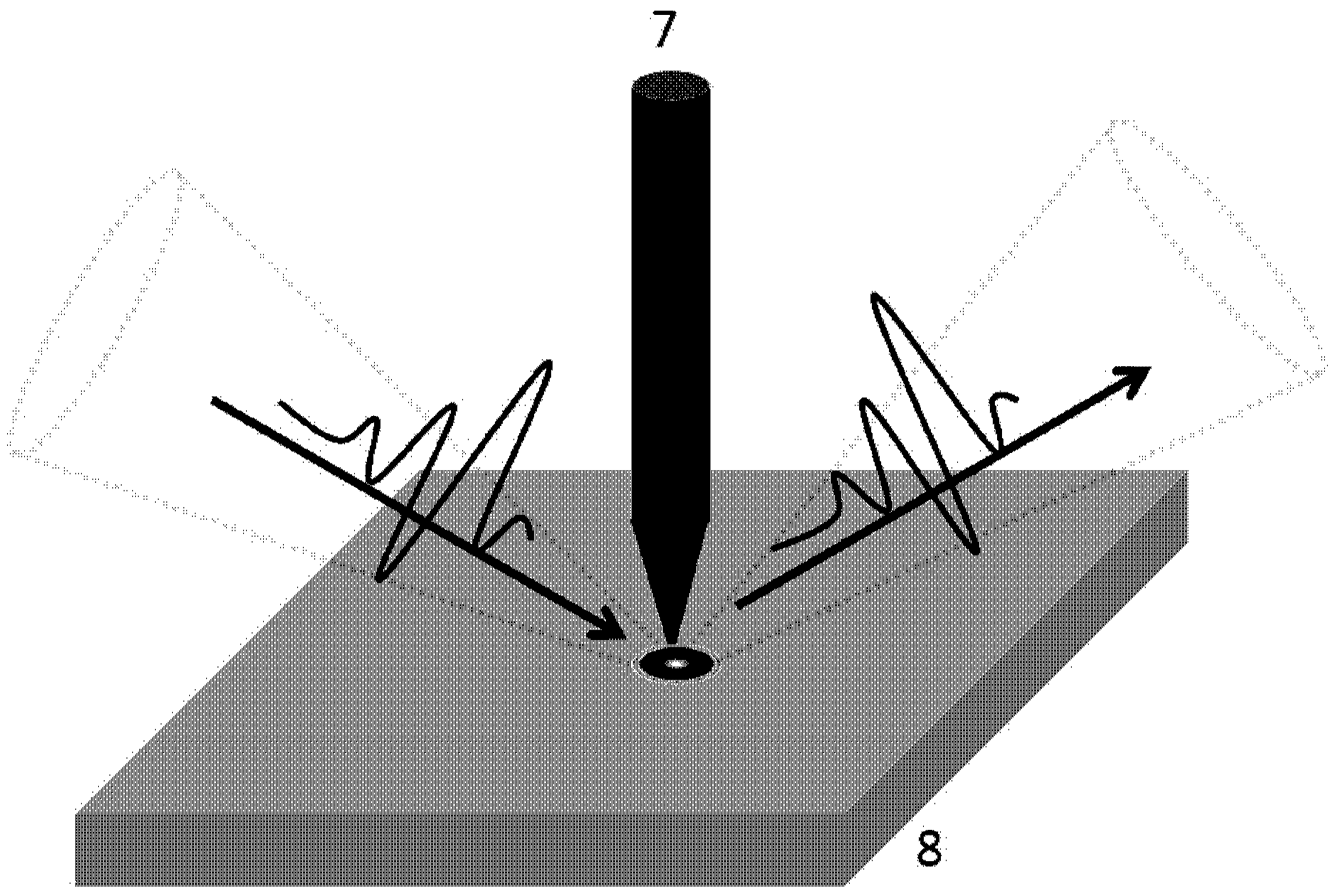
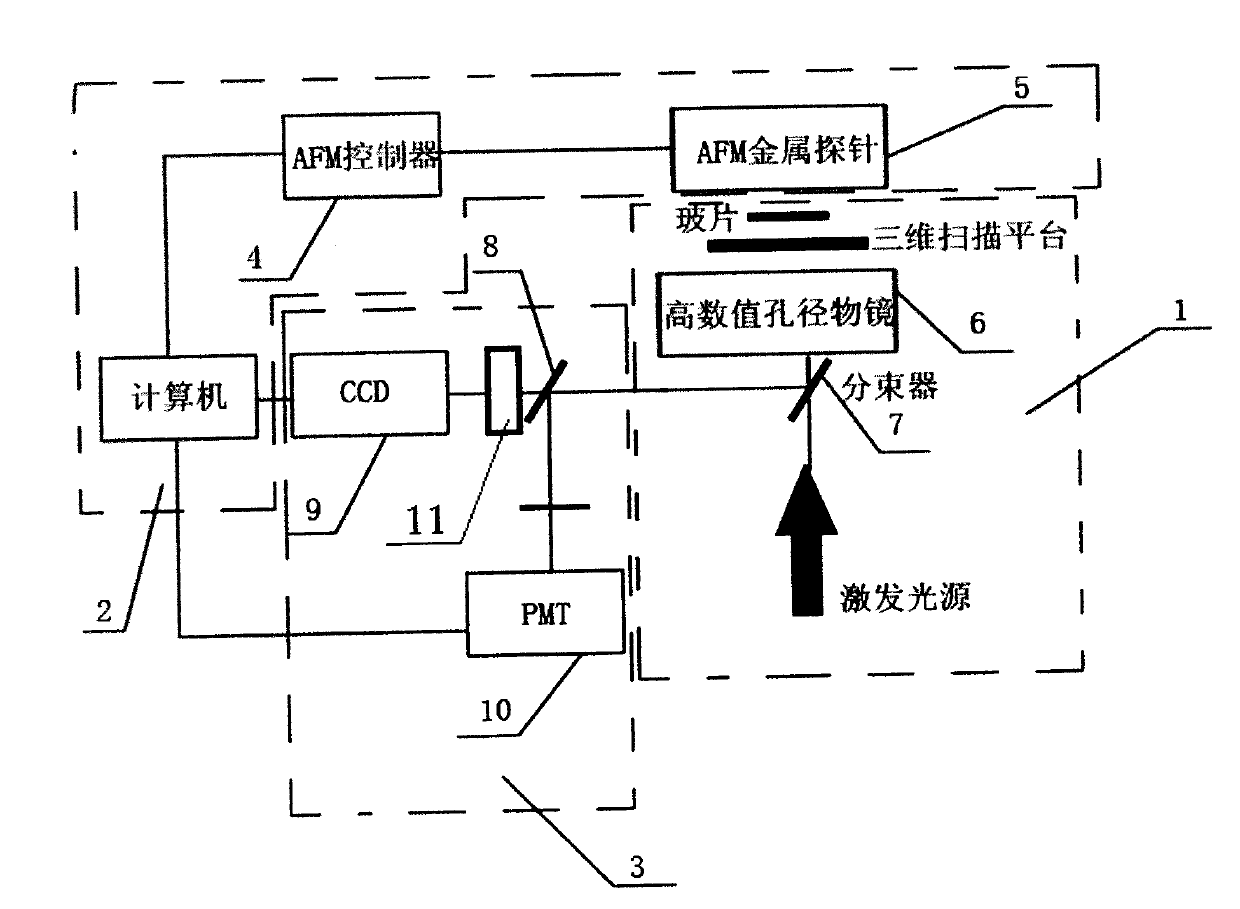
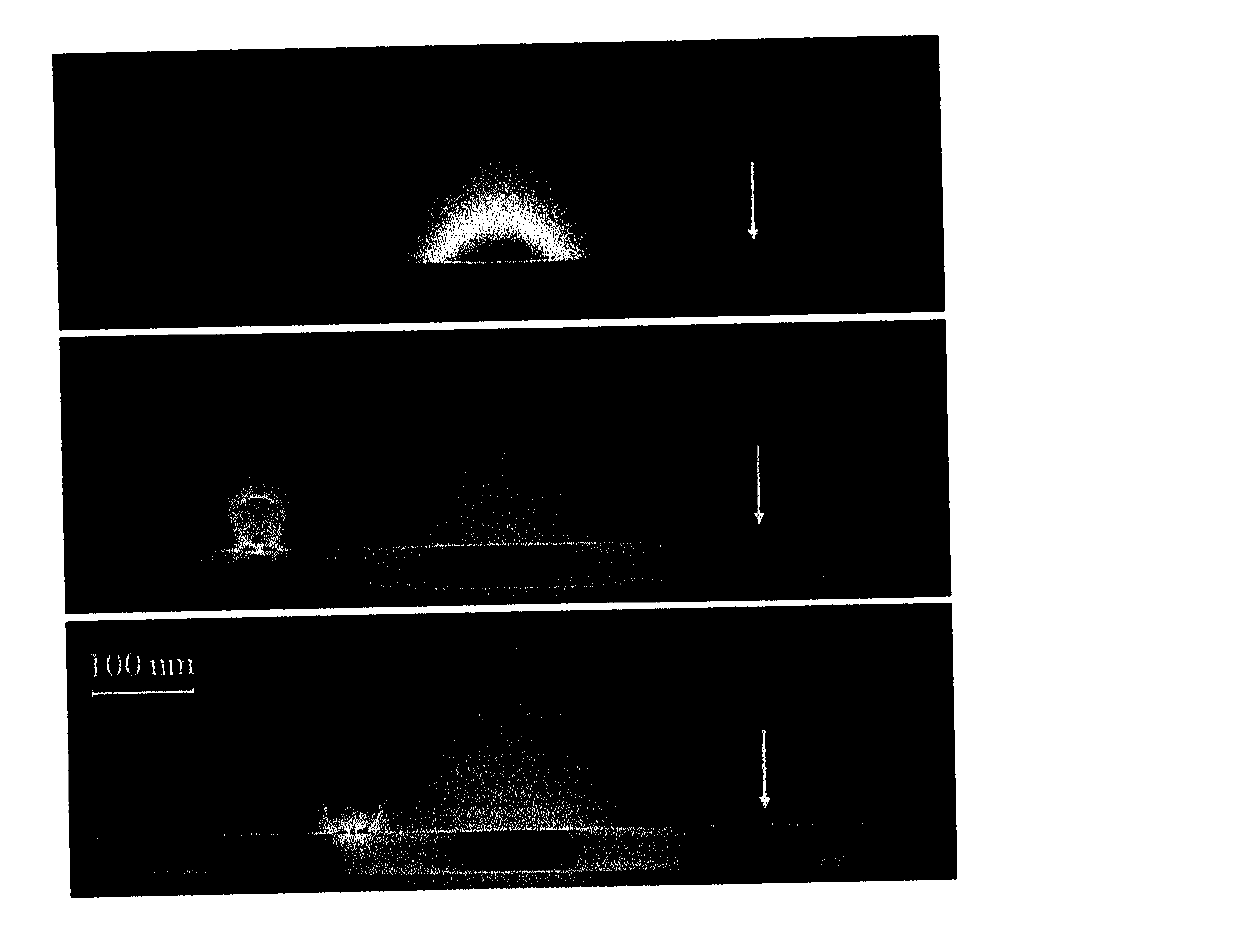
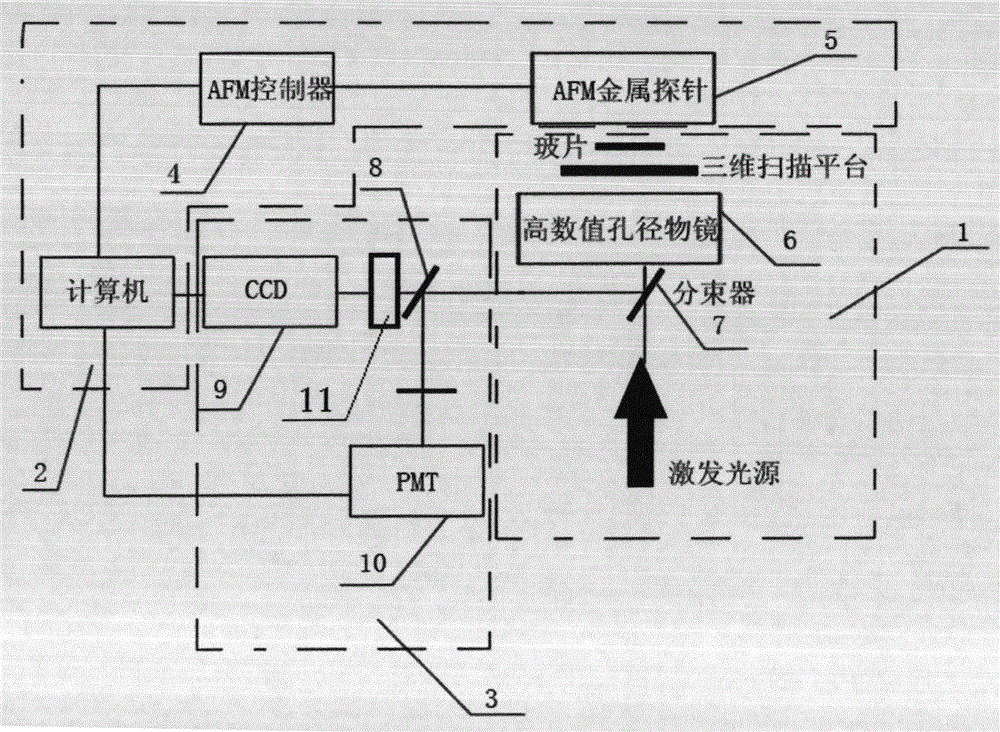
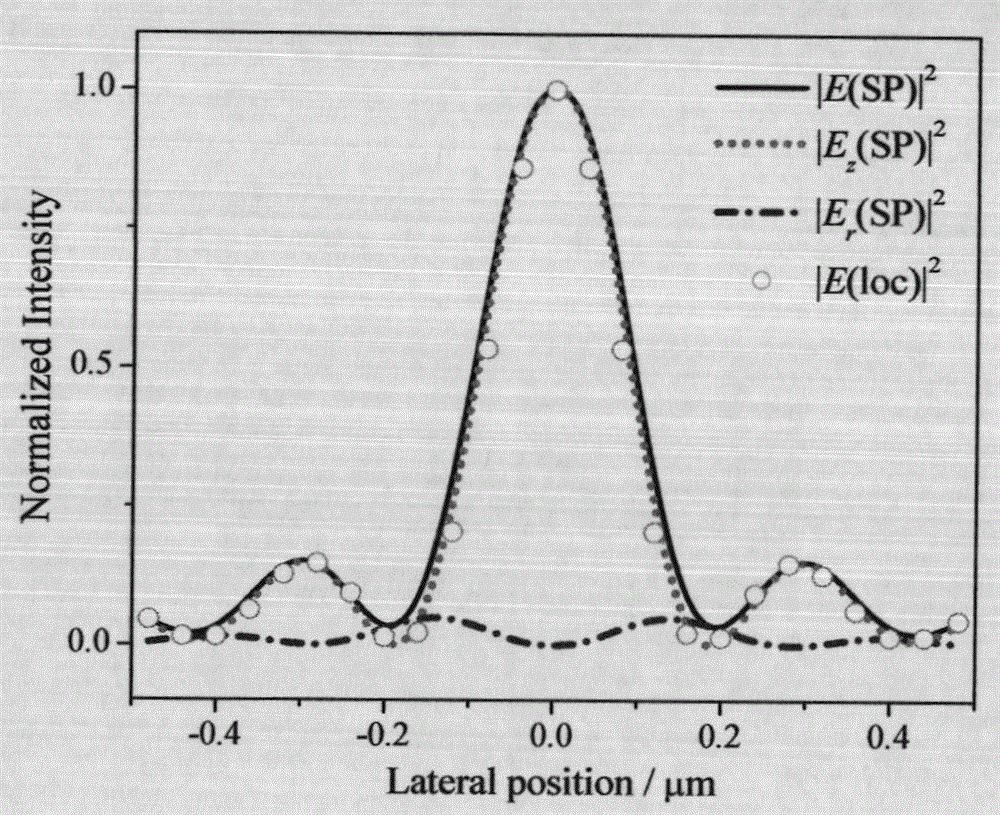
The invention provides a surface plasma longitudinal field scanning near-field optic microscope device and a detection method. The device is provided with a surface plasma excitation unit (1). After being focused through a high numerical aperture objective lens (6), incident light excites an SPP field on an interface of a metal membrane and air, raman signals and the SPP field interfere each other to form a stationary field of the SPP field around a focus, a scanning control unit (2) can achieve three-dimensional scanning and positioning for an atomic force microscope (AFM) metal probe (5) by means of an AFM controller (4), and a detection unit (3) achieves three-dimensional measurement and analysis for a longitudinal field component of a surface plasma field.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Negative refraction artificial material based on iron-clad
ActiveCN101424758AReduce lossEasy to manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingPhotomechanical apparatusGratingPhotoresist
The invention relates to a negative refraction artificial material based on a metal covering layer, which comprises the following steps that (1) a quartz basal piece is selected, the surface of the quartz basal piece is polished, and then, a high-purity SiO2 film is evaporated and plated on the surface of the quartz basal piece; (2) the surface of a high-purity SiO2 film is evaporated and plated with a chrome film, and a layer of photoresist is evenly coated on the high-purity SiO2 film; (3) an electron beam photoetching method is adopted, and a medium grating structure is prepared on the photoresist; (4) a wet etching technology is adopted, the photoresist is used as a mask, and the exposed chrome film is etched; (5) a dry etching technology is adopted, the chrome film is used as the mask, the medium grating structure is etched on the high-purity SiO2 film, and the chrome film is removed; (6) a vacuum evaporation technology is adopted, a metal layer is evaporated and plated on the SiO2 grating structure, the thickness of the metal layer is h, and the negative refraction artificial material based on the metal covering layer is completely prepared. The invention has the advantages of convenient preparation, little single-layer consumption and signal-layer normal incidence and has a wide application prospect in the fields of magnetic resonance, near field optics, stealth materials, and the like.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of producing photon scanning tunneling microscope probe with optical fiber and Indium-Tin-oxide
InactiveCN1805061AImprove conductivityGood light transmissionDecorative surface effectsSurface/boundary effectFiberIndium
The invention discloses a method for using light guide fiber and indium stannic oxide to make the optical scanning channel microscope probe. The method comprises: choosing the optical fiber, preparing for the buffer solution, chemical etching the optical fiber, evaporated depositing the mental conductive film, etching removing the optical fiber push-button metal membrane, magnetron sputtering depositing the ITO film, connecting the pivot-end and the base. The optical scanning channel microscope probe can be sued in scanning channel microscope, light quantum scanning channel microscope and scanning near-field optics microscope and so on.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Long-focal-depth and deep-sub-wavelength-focused one-dimensional photonic crystal flat cone mirror for column vector beams
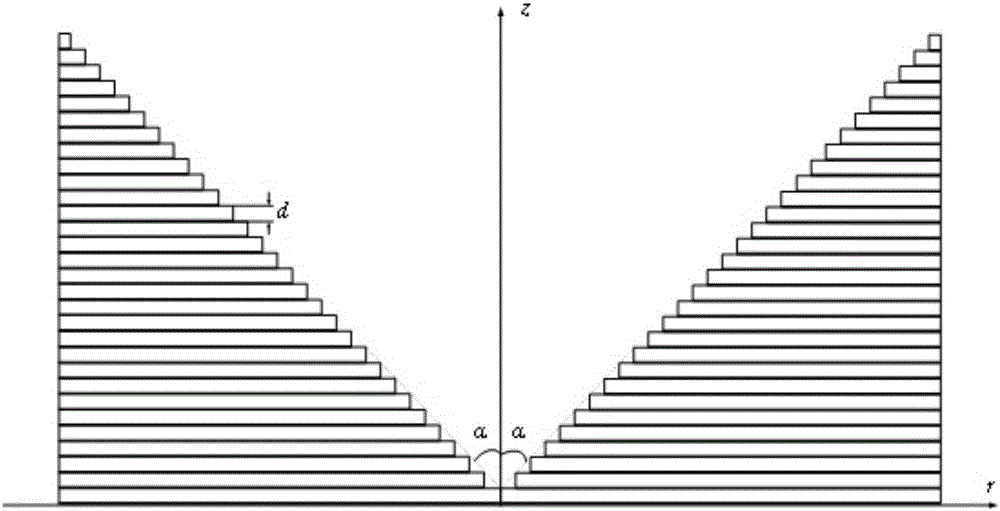
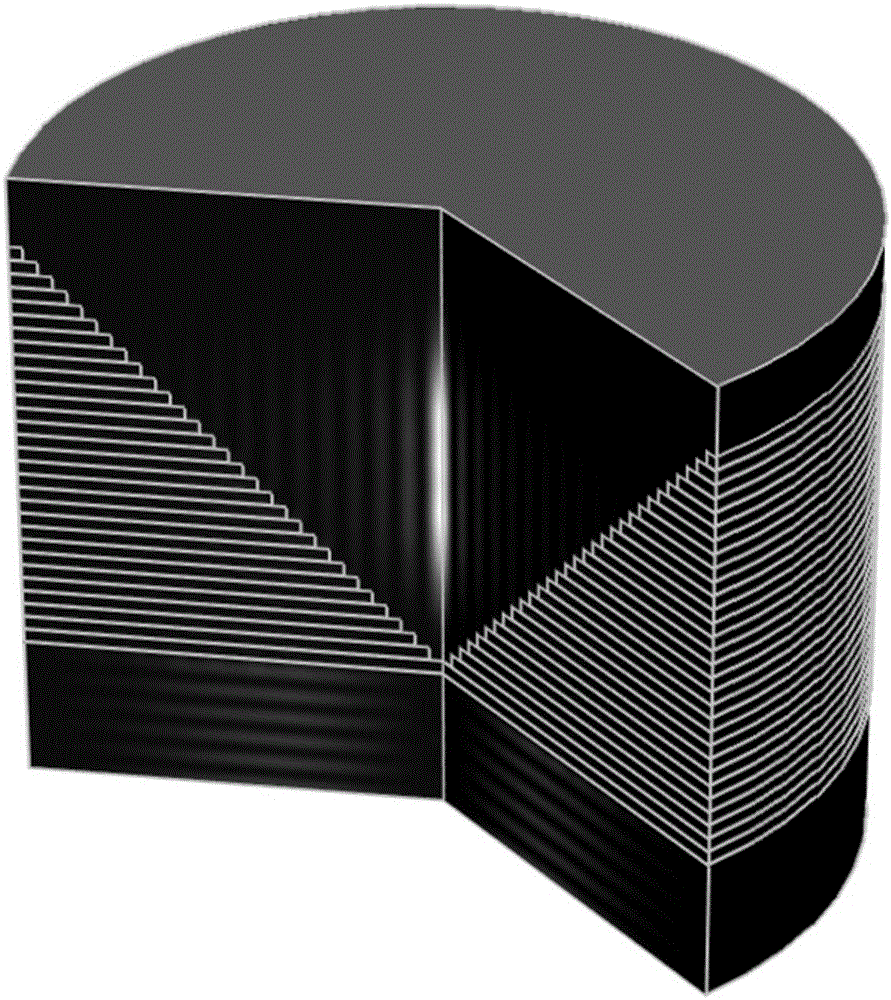
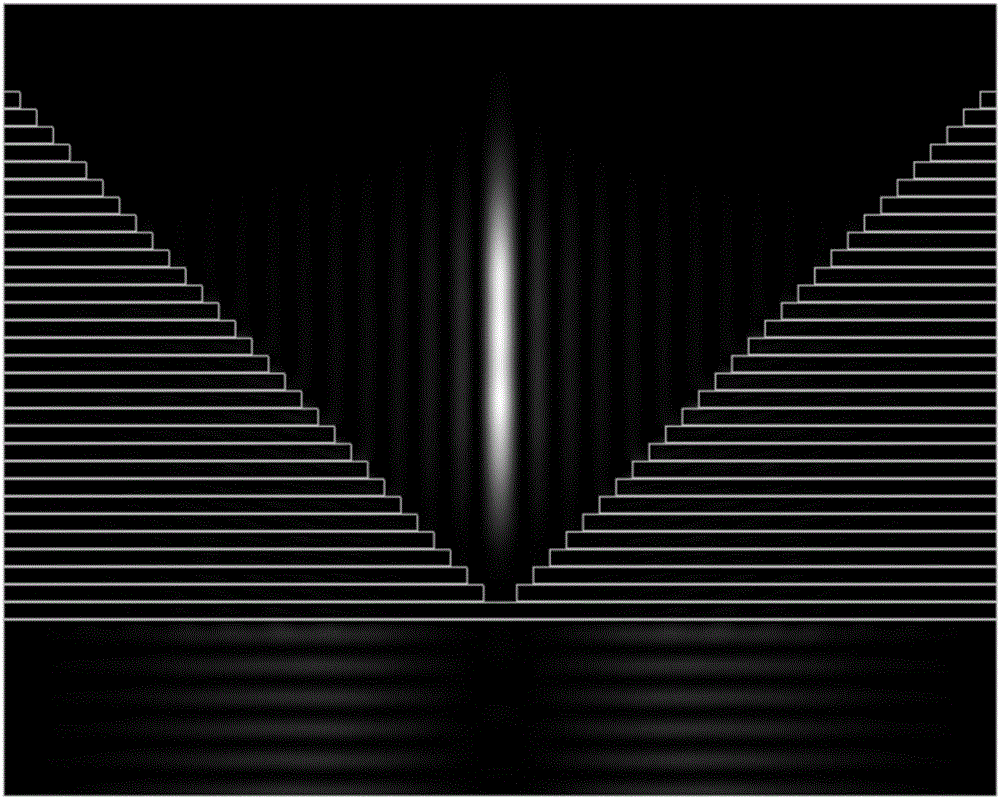
The invention discloses a long-focal-depth and deep-sub-wavelength-focused one-dimensional photonic crystal flat cone mirror for column vector beams. The one-dimensional photonic crystal flat cone mirror is composed of one-dimensional photonic crystals formed through the alternate arrangement of a material A and a material B. The emitting surface of the flat cone mirror is in the form of an inverted cone-shaped surface. The inverted cone-shaped surface is not a continuous cone-shaped surface, wherein circular rings of fixed thickness are stacked up to form the inverted cone-shaped surface, with one cycle (d) of the photonic crystals as one unit and the internal diameters of the circular rings being gradually and equivalently increased from bottom to top. The inner sides of the circular rings are in the form of a vertical wall, and the connecting line of the vertex angles of the circular rings is at an included angle relative to the horizontal plane. By means of the flat cone mirror, radially polarized beams and rotatably polarized beams are focused at the same time, so that light needle-shaped focuses and light pipe-shaped focuses that are uniformly distributed in the longitudinal field can be respectively obtained. Through changing the structural parameters of photonic crystals, the wide-band focusing is realized. Meanwhile, through stretching out or drawing back the flat cone mirror, the length of the focal depth can be controlled. The flat cone mirror is simple in structure, and simple and convenient in design process. The structure of the flat cone mirror can be easily prepared. Therefore, the flat cone mirror is good in application prospect in the fields of near-field optics, laser processing, medical science and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for realizing two-dimensional cold atom surface optic lattices by circular aperture array
The invention discloses a method for realizing two-dimensional cold atom surface optic lattices by a circular aperture array and relates to the field of neutral cold atom laser imprison and cold atom optic lattices. The method is implemented by a laser source system, a focusing lens, a beam expanding lens, a sub-wavelength circular aperture array, two-dimensional cold atom surface optic lattices, magneto-optical trap atom optic viscose, an atom detector, a laser, a wave chopper, another focusing lens, an optical fiber and a computer system on the basis of near-field optic diffraction of the sub-wavelength circular aperture array. Laser light irradiates on the horizontally arranged sub-wavelength circular aperture and diffracts through the same, local reinforcing near optical fields distributed periodically are generated, and neutral cold atoms loaded can be effectively imprisoned, and two-dimensional cold atom surface optic lattices are realized. The method for realizing two-dimensional cold atom surface optic lattices can realize surface optic lattices of neutral cold atoms of different types, lattice constant is adjustable, principle is simple, operation is convenient, and application range is wide.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Apparatus and method for atomic force, near-field scanning optical microscopy
InactiveUS20150338627A1High refractive indexCladded optical fibreOptical articlesNear-field opticsRefractive index
A near-field optic has a high refractive index waveguide with a planar far field facet more than half of a wavelength across for coupling propagating light and a near field facet with the near field zone of the waveguide supporting only the fundamental optical mode in each polarization. A tapered waveguide section extends from the near field facet to transform the fundamental optical mode. A cantilever supports the tapered waveguide section.
Owner:MULTIPROBE
Double-frequency tunable magnetic resonance artificial compound material based on asymmetric metal grating structure
ActiveCN101386984AAchieve magnetic resonanceReduce lossVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingNon symmetricElectron-beam lithography
The invention provides a double-frequency adjustable magnetic resonance artificial composite material based on a non-symmetric metal grating structure, which is characterized in that the material is produced through the following steps: selecting a quartz substrate and polishing the surface of the quartz substrate; evaporating a SiO2 film on the surface of the quartz substrate; evaporating a chromium film on the surface of the SiO2 film; coating a photoresist layer on the chromium film; preparing a medium grating structure on the photoresist by electron beam lithography method; eroding and exposing the chromium film by using the photoresist as a mask by wet etching technology; etching the medium grating structure on the SiO2 film by using the chromium film as a mask by dry etching technology, and removing the chromium film; laterally depositing a metal layer with the thickness of h on one side of the SiO2 grating structure by lateral vacuum deposition technology, similarly, depositing a metal layer with the same thickness on the other side of the SiO2 grating structure, thereby forming an n-shaped metal structure with the top thickness of 2h and the side wall width of h to complete the production of the double-frequency adjustable magnetic resonance artificial composite material based on the non-symmetric metal grating structure. The method has the characteristics of simple and convenient production, small monolayer consumption, monolayer normal incidence and double frequency, and has revelatory significance and great application prospect in magnetic resonance, near-field optics, camouflage materials and other fields.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High precision nanometer clearance detection structure and method on basis of surface plasma resonance
ActiveCN103968770ARealize high-precision measurementRealize dynamic detectionUsing optical meansBeam splitterNear-field optics
The invention provides a high precision nanometer clearance detection structure and method on the basis of surface plasma resonance, and belongs to the technical field of nanooptics. The high precision nanometer clearance detection structure and method on the basis of the surface plasma resonance can solve the problems that measuring precision is low and dynamic measurement cannot be carried out in the prior art. Light output by a light source enters a beam splitter through a collimating mirror and a broadband polarizer; the transmission light passing through the beam splitter interacts with the nanometer clearance detection structure and a substrate and then is reflected to the beam splitter; the light enters a spectrum detector after being reflected by the beam splitter and converged by a lens, the detector transmits obtained data through detection to a computer, clearance values are obtained through the processing of the computer, and the detection of the nanometer clearance is achieved. According to the high precision nanometer clearance detection structure and method on the basis of the surface plasma resonance, the method of spectrum detection is adopted to achieve high precision dynamic detection of a nanometer level clearance, a brand new testing technology is provided for the field of nanometer machining and nanometer measuring, and hopefully, the high precision nanometer clearance detection structure and method on the basis of the surface plasma resonance can play an important role in multiple fields including near-field optics and near-field physics.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
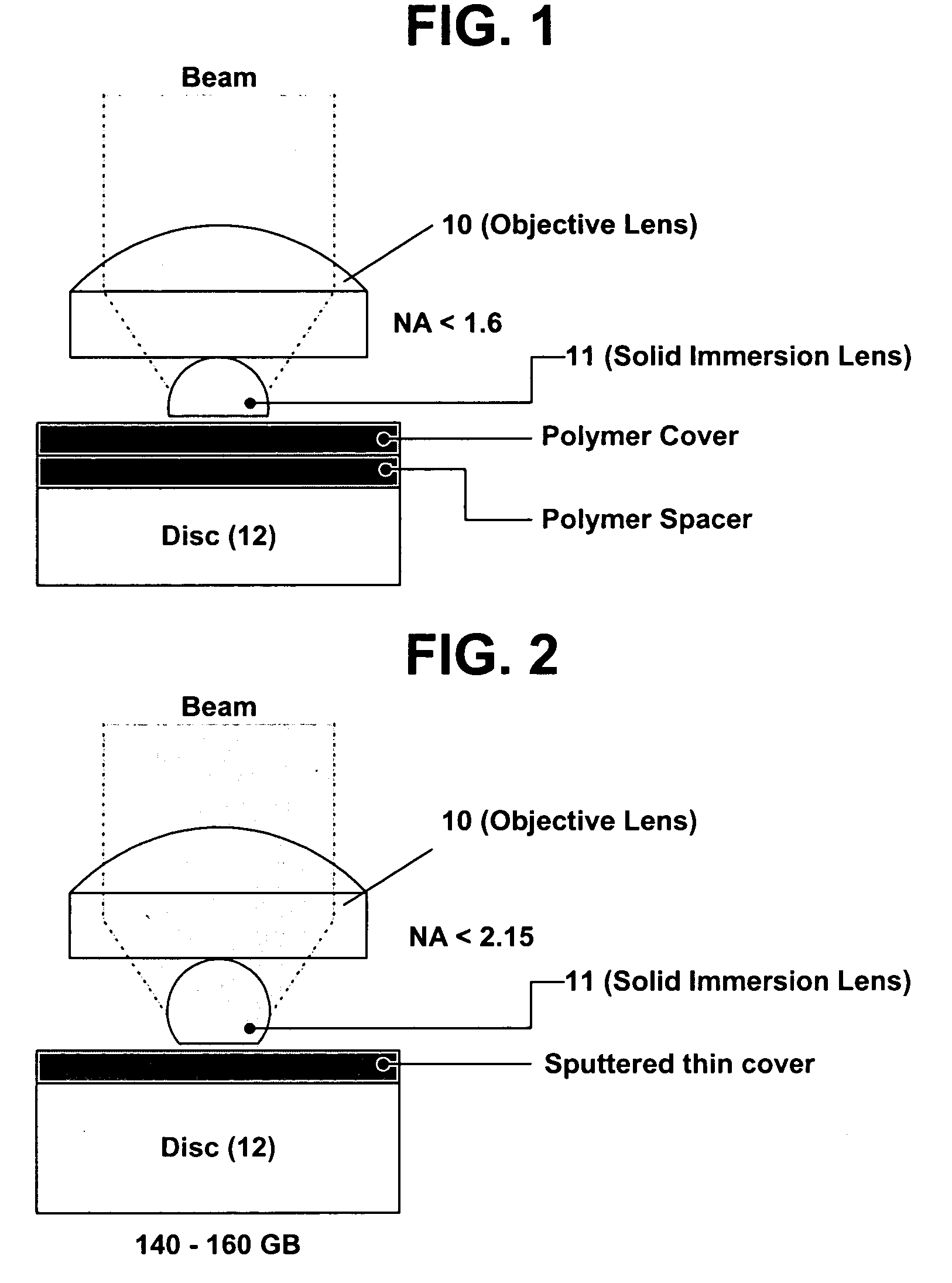
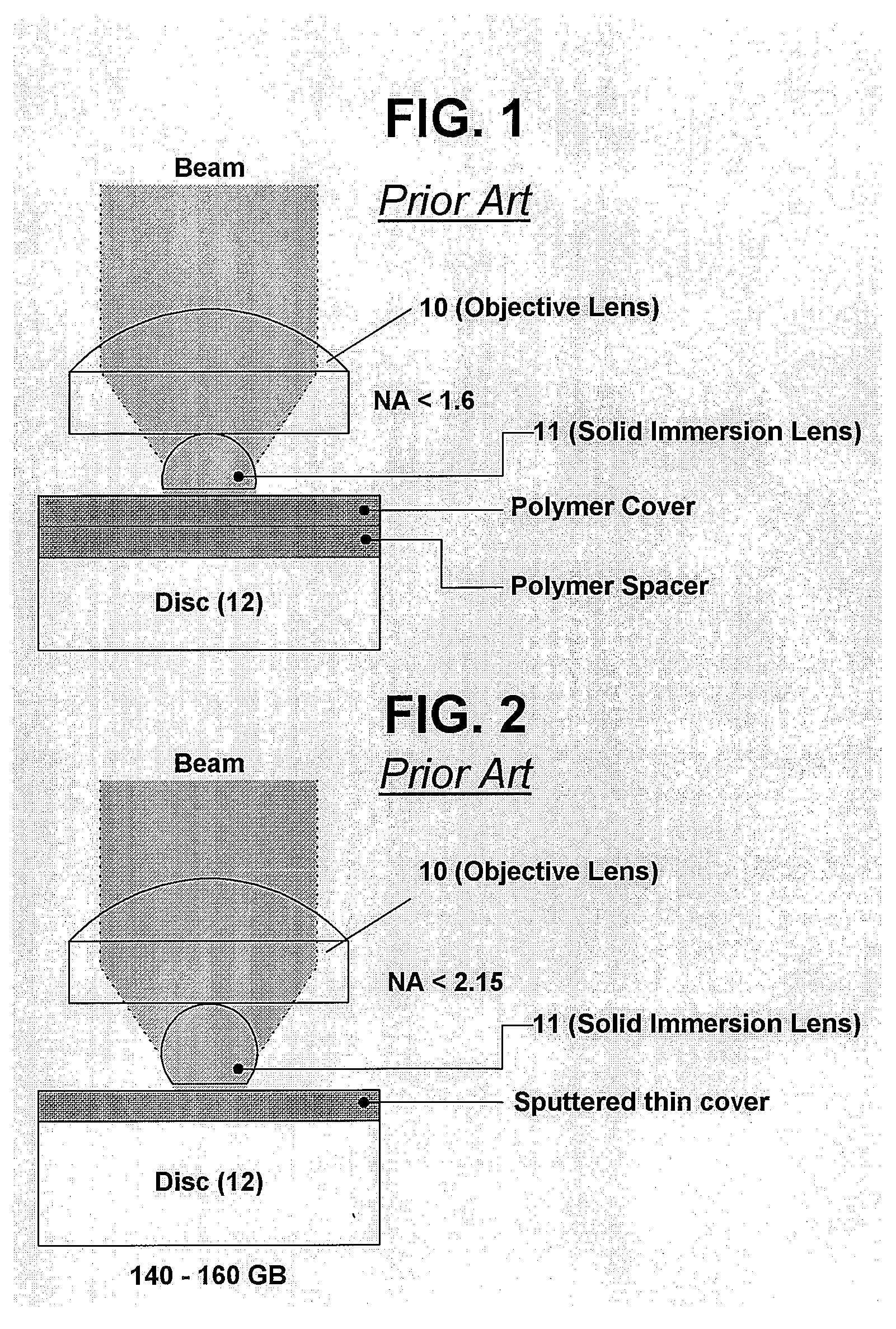
Parallel access data storage system using a combination of VCSEL arrays and an integrated solid immersion lens array
A digital reading and / or writing system and method for reading and / or digital data recorded on a digital recording medium. The system includes a first array having a plurality of near-field solid immersion optical lenses and a second array having a plurality organic micro-cavity lasers with the capability of light intensity modulation. The first array being positioned with respect to the second array such that each near-field optical lens of the first array is associated with at least one organic micro-cavity laser in the second array wherein each of the plurality of organic micro-cavity lasers with the capability of light intensity modulation providing light to its associated near-field solid immersion optical lens that is used for reading digital data on the digital recording medium. An device is provided for modulation of the laser light beams and a sensor for capturing reflected light from the medium that passes through the array of near-field optics so as to obtain the digital data from the digital recording medium.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
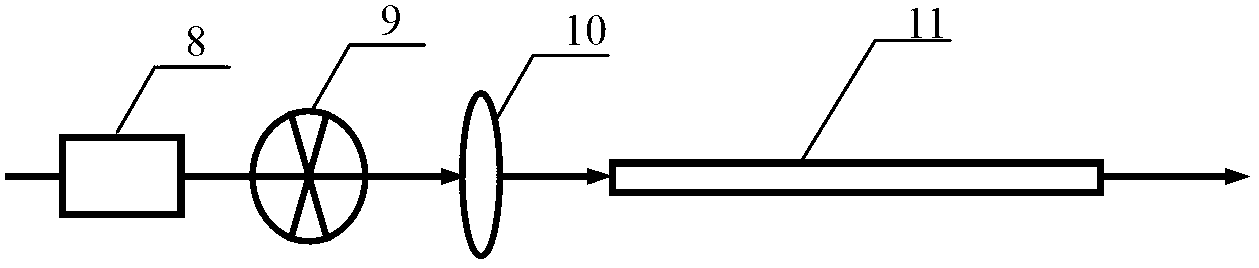
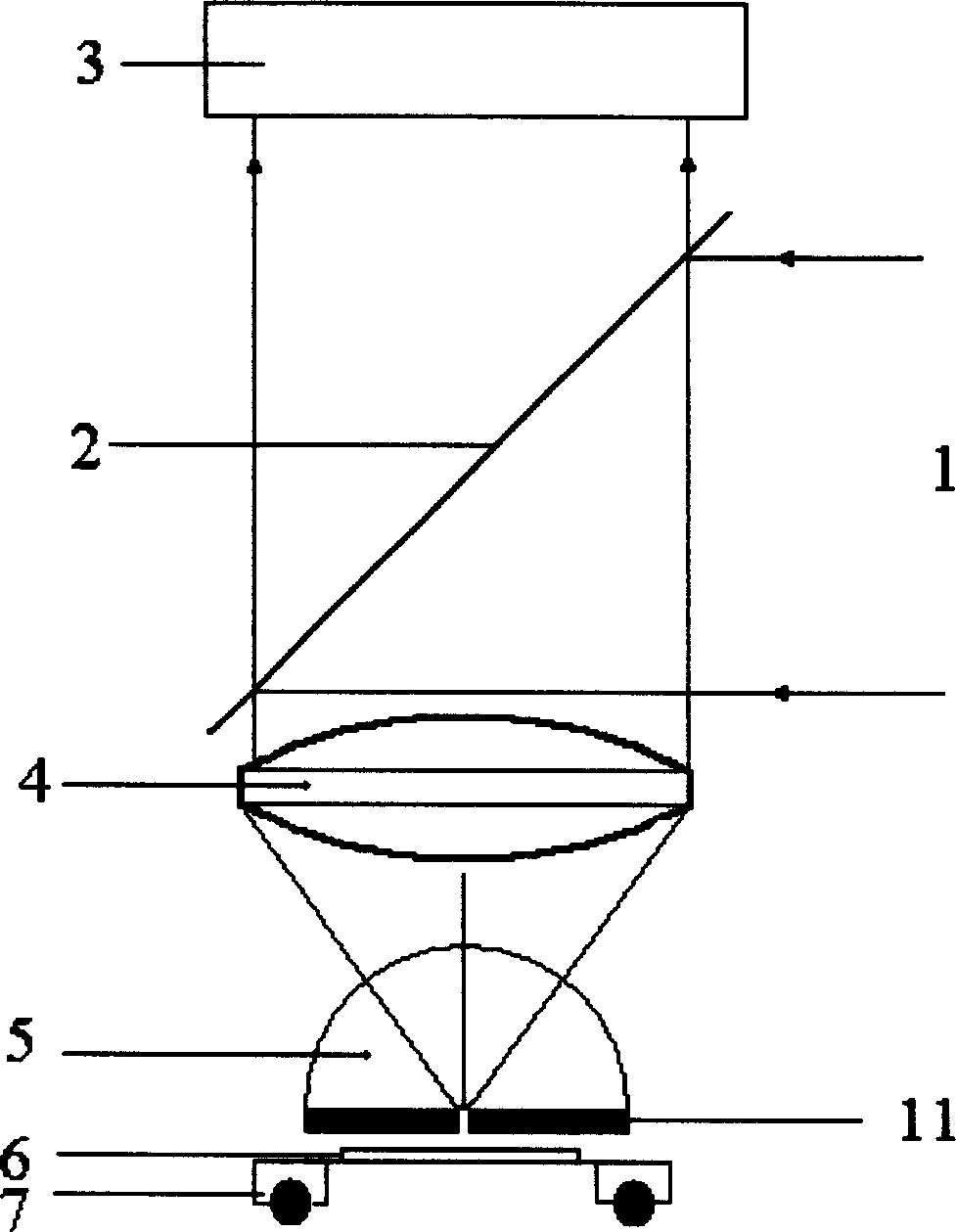
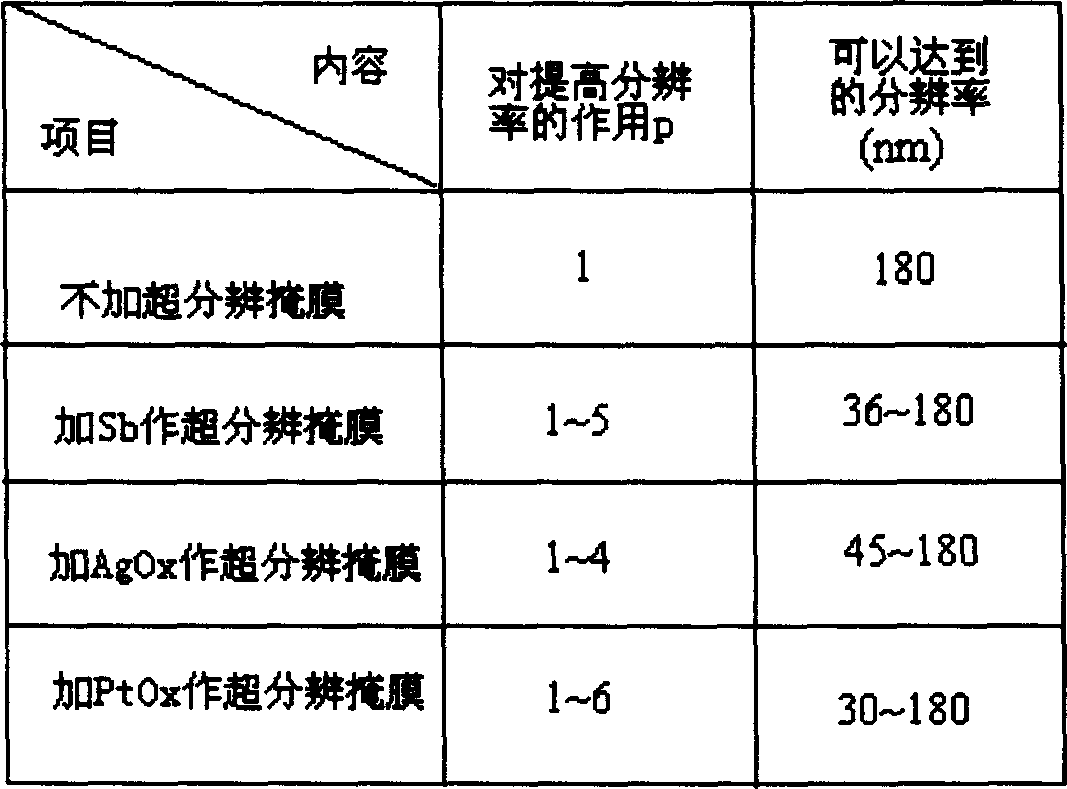
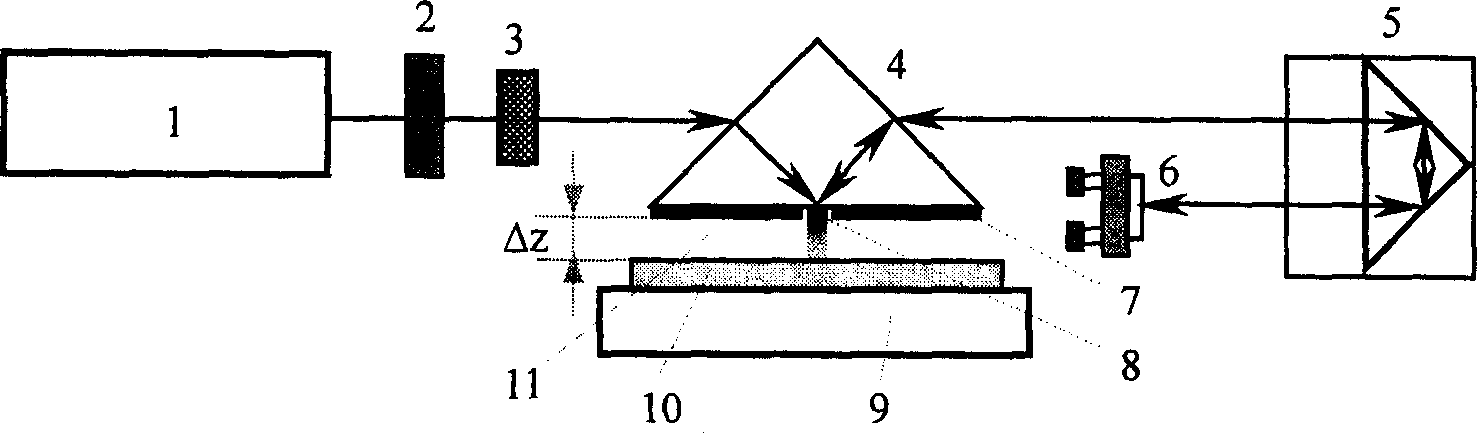
Near field optic microscope
InactiveCN1588156AEnhanced couplingOvercome immobilitySurface/boundary effectMicroscopesImage resolutionNear-field optics
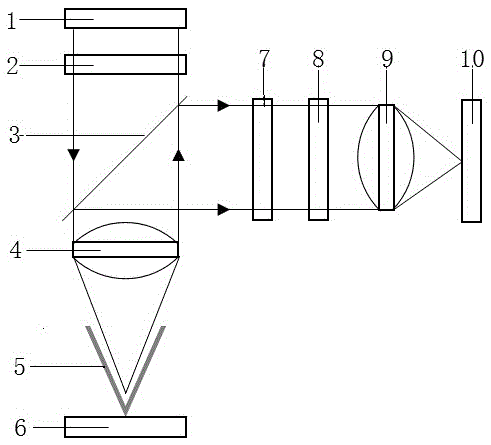
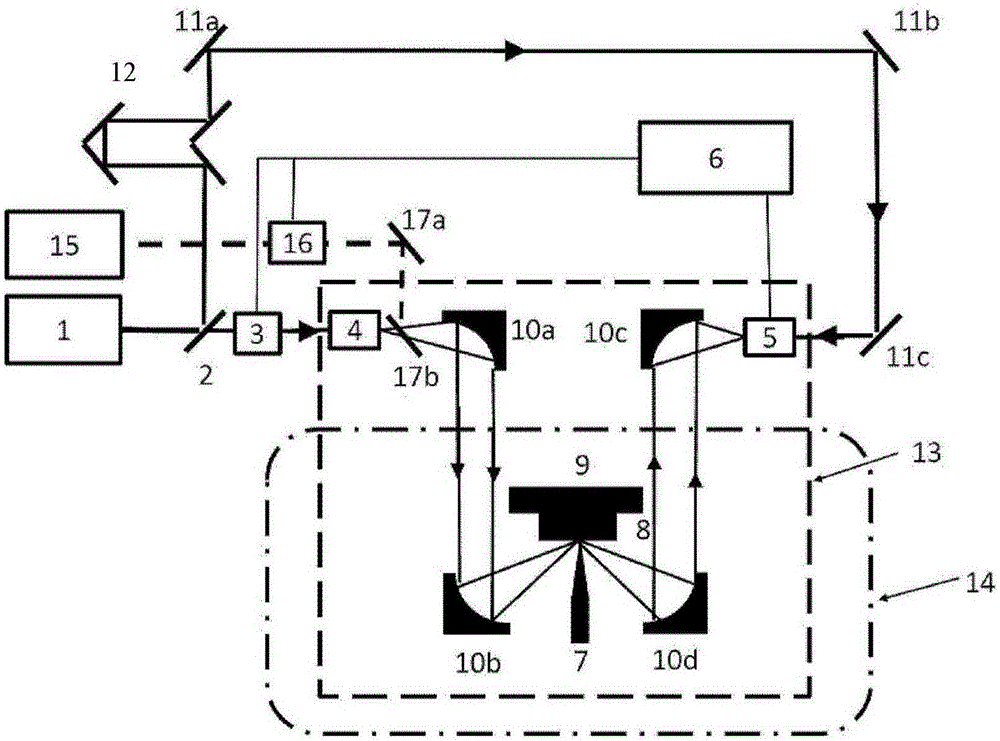
The invention is a near field optical microscope which includes a laser beam, its character lies in: its structure is: semi-reflect and semitransparent mirror is arranged on the advancing direction of the laser beam and form an angle of 45 degrees to the laser beam, on the light shaft vertical to the laser beam and penetrating the semi-reflection and semitransparent mirror, a detector is arranged above the semi-reflection and semitransparent mirror coaxially, a gathering lens, semi-sphere solid immersing lens, sample and sample frame are arranged under the semi-reflection and semitransparent mirror, the lower surface of the solid immersing lens are plated with a layer of mask layer and the super-resolution mask layer is on the focus plane of the gathering lens, the sample is on the sample frame. The resolution of the microscope is higher and it is adjustable.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
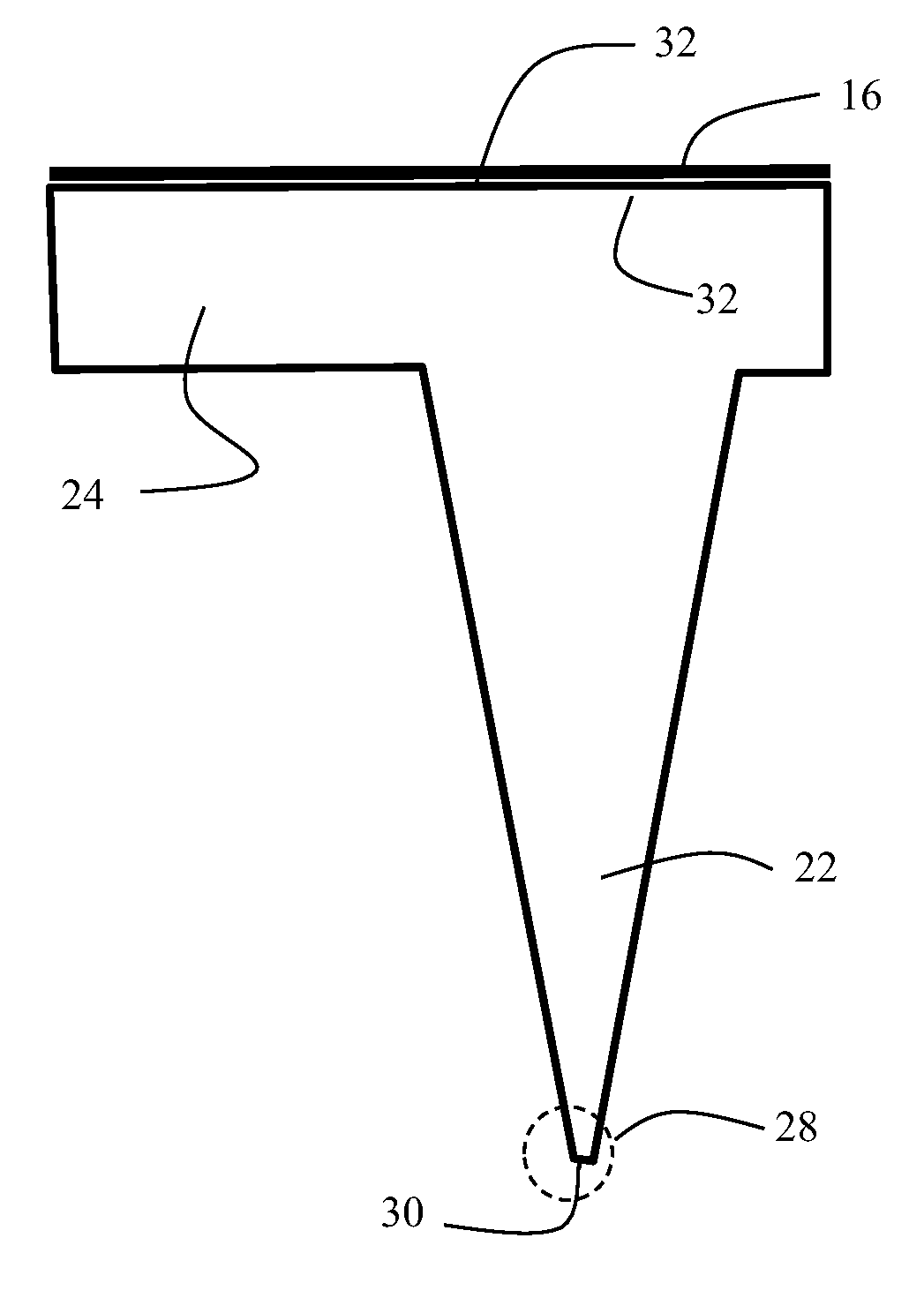
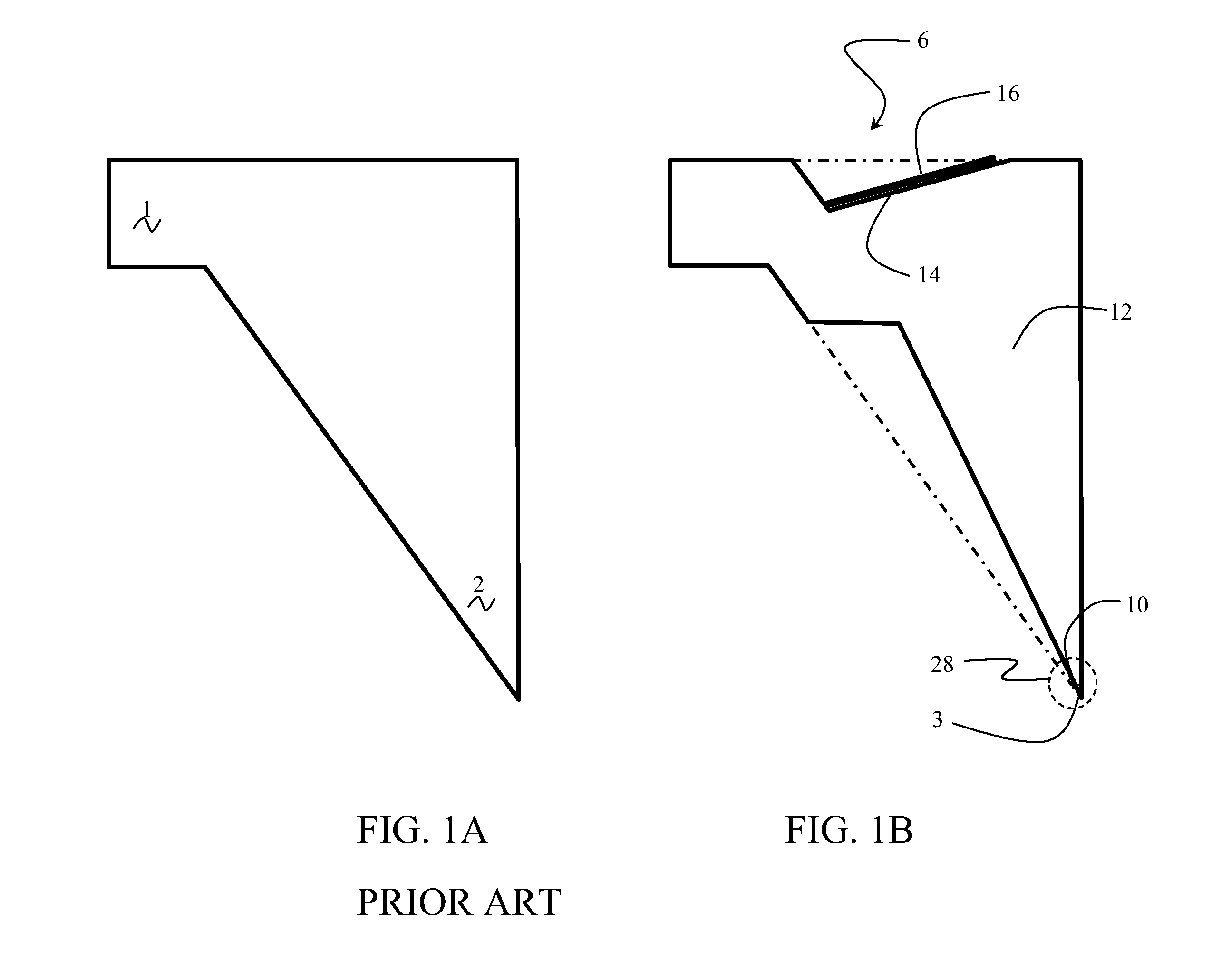
An inclined silicon pinpoint and a manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN106610439AMeet the needs of real-time observationEasy to prepareScanning probe microscopyNear-field opticsPyramid
The invention discloses an inclined silicon pinpoint and a manufacturing method thereof. The pinpoint is a triangular pyramid and has a first inclined surface, a second inclined surface, a third inclined surface and a bottom surface, and the angles between at least two of the first inclined surface, the second inclined surface and the third inclined surface and the bottom surface are not equal. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: forming a first and a second inclined surface of the inclined silicon pinpoint by applying an isotropic etching process on a silicon wafer; then providing protective layers on the first and second inclined surfaces; and afterwards, processing the silicon wafer with an etching process to form a third inclined surface to obtain a target product. The invention provides the inclined silicon pinpoint which is different from traditional silicon pinpoints and can satisfy demands of near-field optics for real time observation; the manufacturing method is simple; the raw materials are cheap and easily available; the inclined silicon pinpoint is suitable for large scale production; and a new path is provided for popularization and application of pinpoints.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Scanning near-field photoacoustic microscopic imager
InactiveCN110261315ARealize real-time detectionRich relevant informationAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by optical meansSonificationSynchronous control
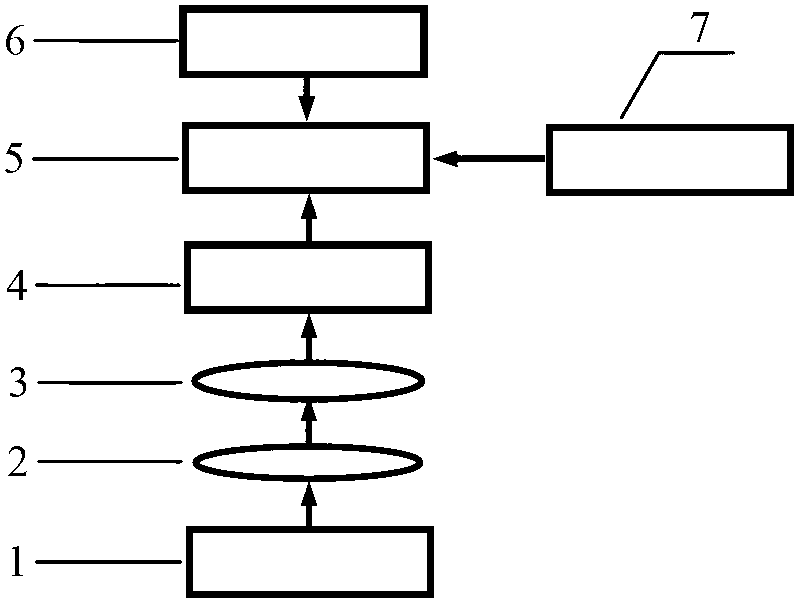
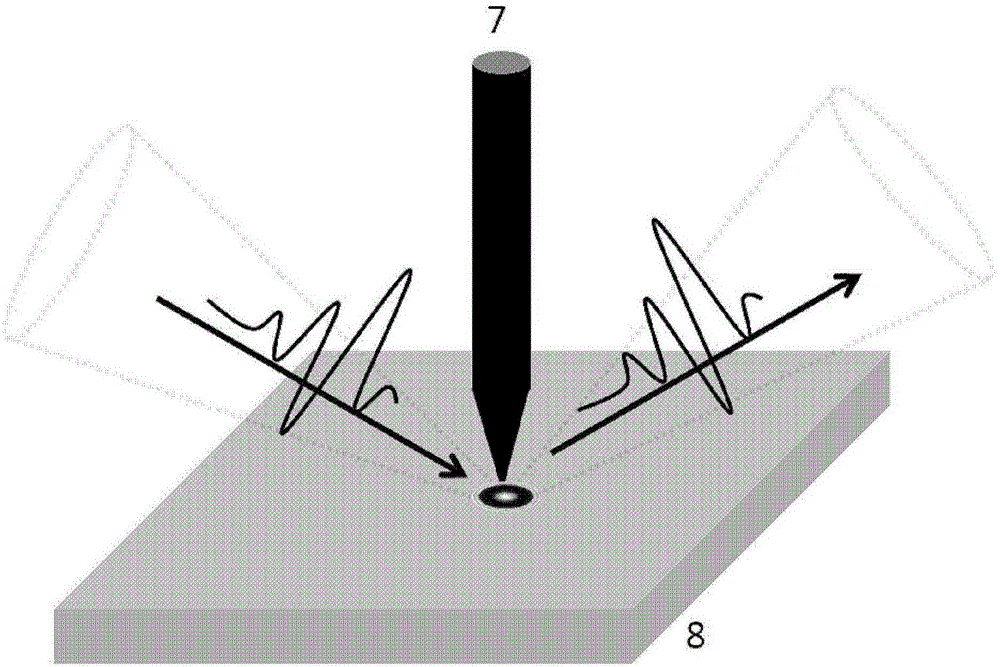
The invention relates to a scanning near-field photoacoustic microscopic imager, which is used for realizing near-field optics and photoacoustic simultaneous and real-time detection. The scanning near-field photoacoustic microscopic imager comprises a light emitting module, a signal acquisition system, a scanning control module, a timing control module and a signal analysis imaging module, wherein the light emitting module comprises a multi-wavelength pulsed light source, an optical path collimation and focusing subsystem and a near-field optical probe which are arranged in sequence along an optical path; the signal acquisition system comprises a near-field light receiving module, an ultrasonic receiving module and a signal acquisition subsystem; the scanning control module is used for enabling light pulses to move on a sample surface to realize scanning; the timing control module is used for synchronously controlling the pulsed light source to emit the light pulses, the near-field optical probe to receive a light signal, the ultrasonic receiving module to receive a photoacoustic signal and the scanning control module to perform scanning synchronously; and the signal analysis imaging module is used for acquiring a near-field optical image of the sample surface and a near-field photoacoustic image inside the sample. Compared with the prior art, the scanning near-field photoacoustic microscopic imager has the advantages of being capable of near-field optics and photoacoustic simultaneous and real-time detection, being rich in information, satisfying various needs and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV +1
Near-field optics-based scanning microsphere lens super-resolution microscope and imaging method thereof
InactiveCN108445262ARealize optical super-resolution large-scale scanning imagingEasy to controlScanning probe microscopyMicrosphereNear-field optics
The invention discloses a scanning microsphere lens super-resolution microscope based on near-field optics used for a liquid environment. The scanning microsphere lens super-resolution microscope includes an optical microscope, a microsphere lens, a container, a glass tube probe, a sampling electrode, a grounding electrode, a DC power supply, current amplifier, a real-time feedback and scanning controller, and a pre-adjustment displacement table and a scanning table that can move in three-dimensional directions, a positive electrode of the DC power supply and the sampling electrode are connected with a corresponding end of the current amplifier separately, the glass tube probe includes a straight section connected with a pre-adjustment displacement table and a slant section connected withthe straight section, the bottom end of the slant section is provided with a needle tip part, the sampling electrode is arranged in the glass tube probe, the microsphere lens is arranged in the needle tip part of the slant section, and the vertex of the microsphere lens is almost the same position as the bottom of the microsphere lens. The scanning microsphere lens super-resolution microscope based on near-field optics is mainly used in the fields of life science and the like which require nanoscale super-resolution real-time dynamic observation and operation in a liquid environment.
Owner:苏州显纳精密仪器有限公司
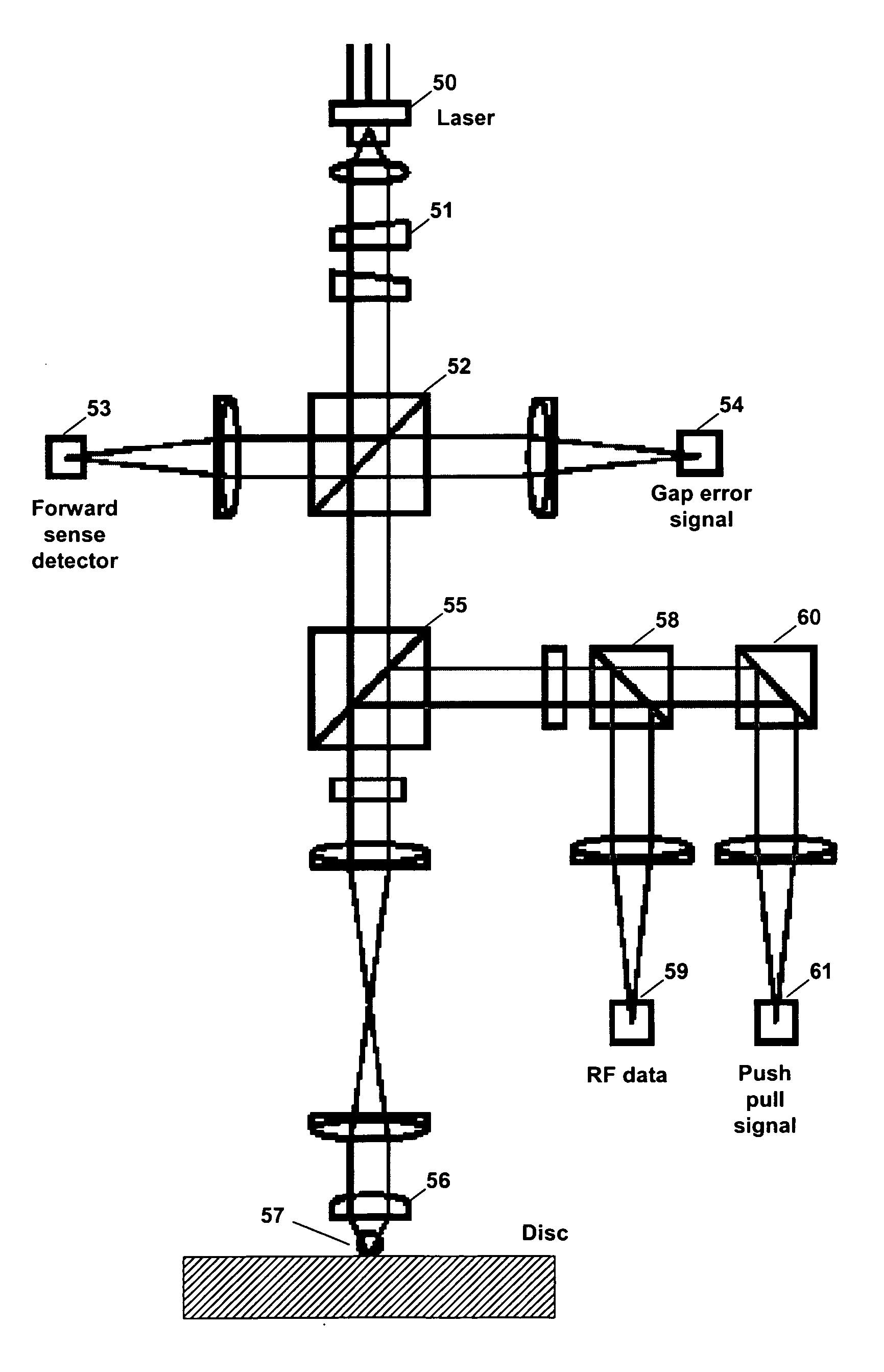
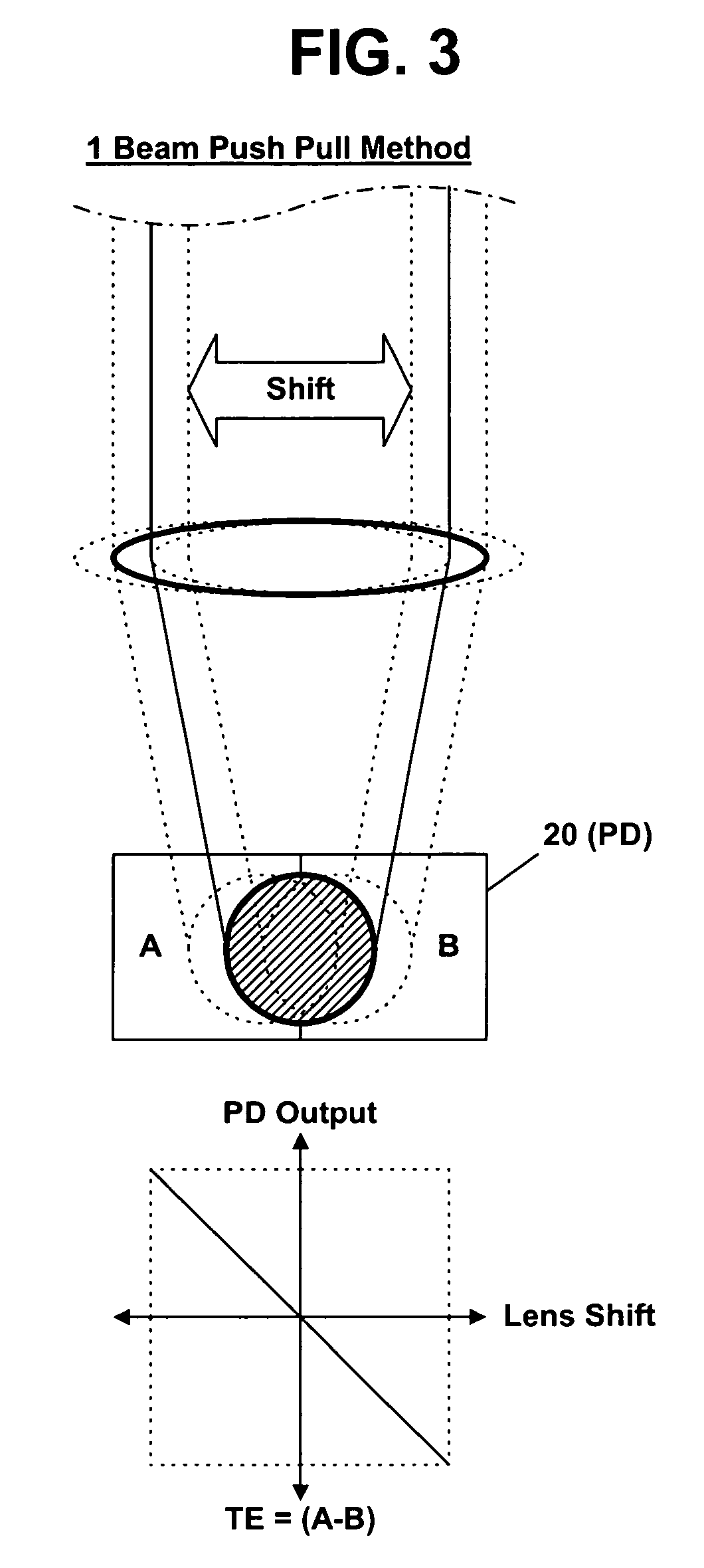
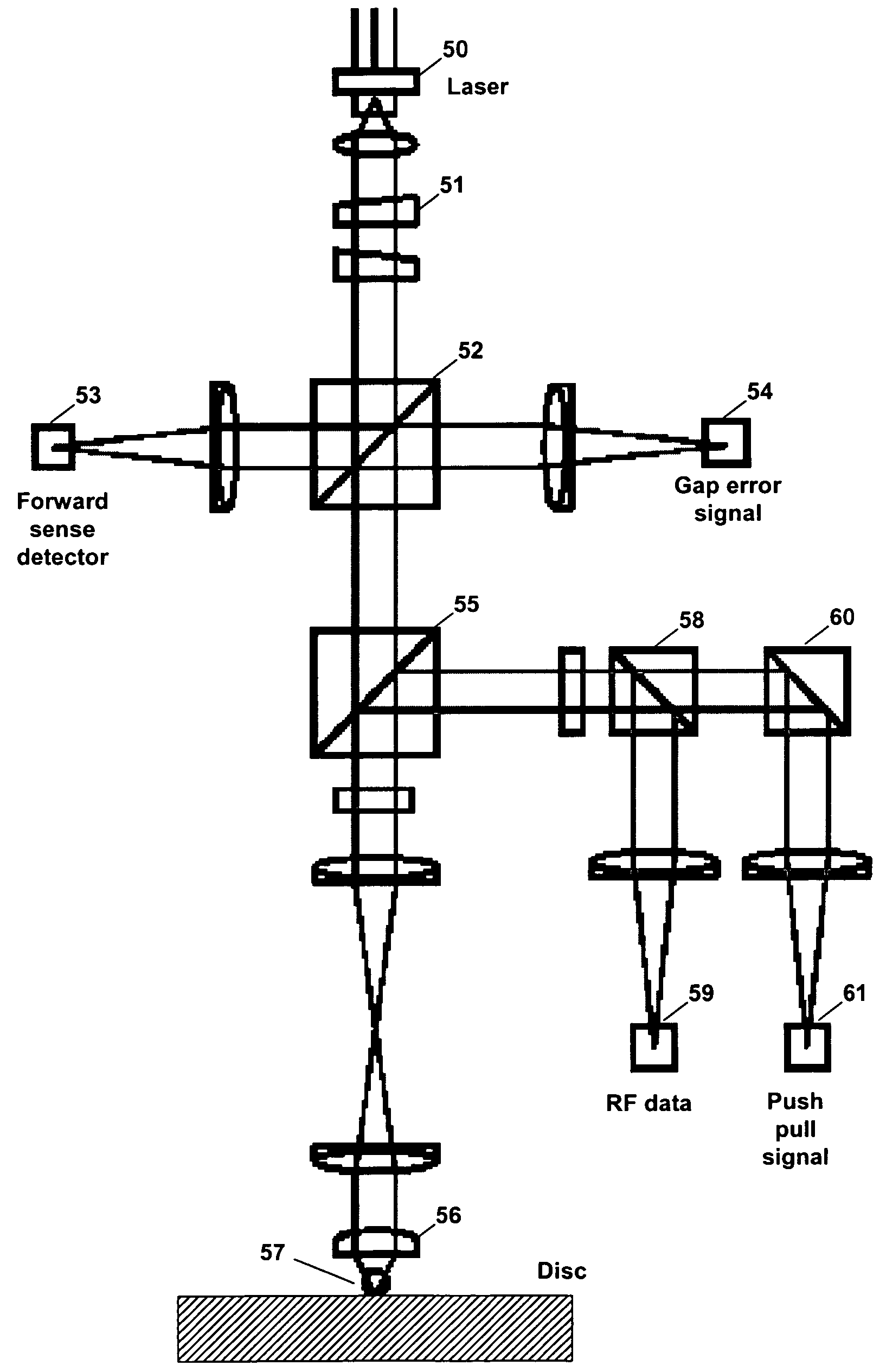
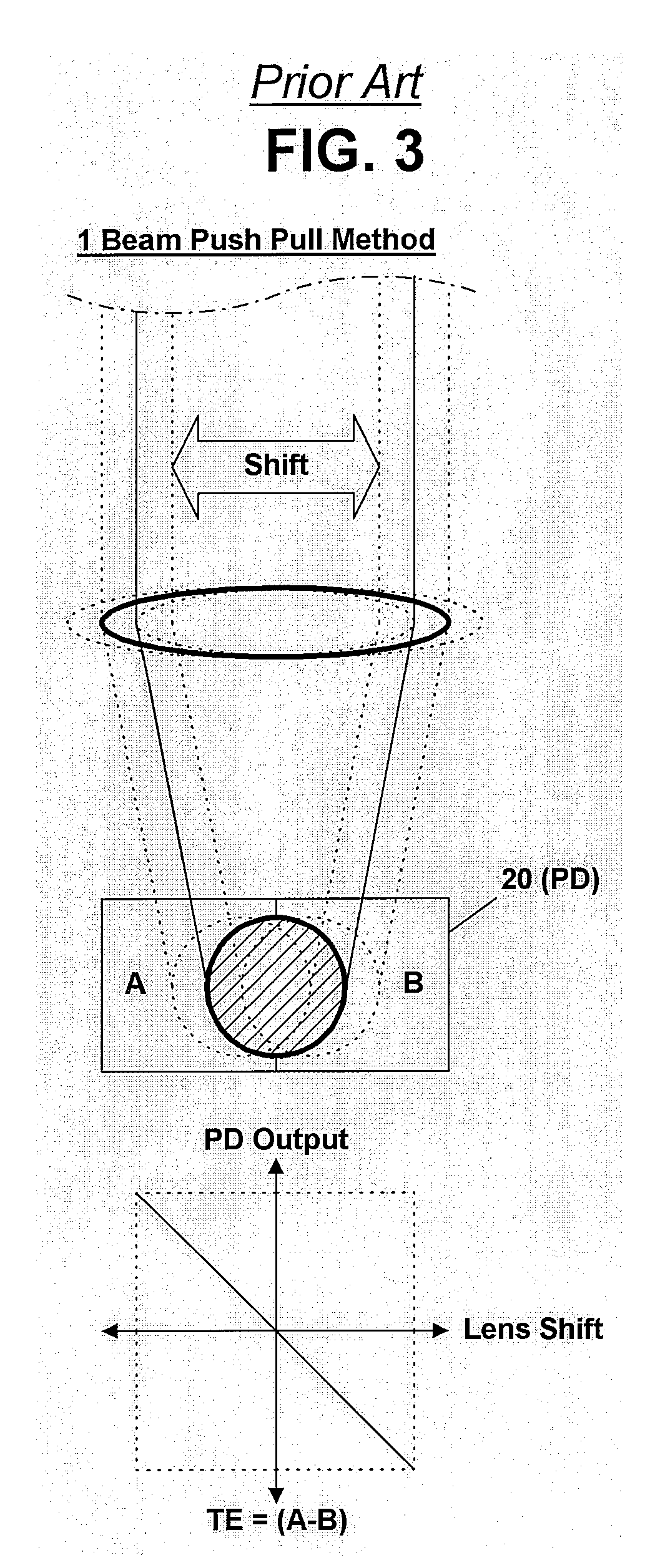
Apparatus and method for controlling tracking servo in near field optics
InactiveUS20060133231A1Improve performanceCombination recordingRecord information storageNear-field opticsPush pull
Disclosed are an apparatus and a method for controlling a tracking servo in a near field optics. Gap error signals are detected in a divided state, and a push pull signal is compensated based on the detected gap error signals. A photo detector detecting the gap error signals is divided into two areas such that movement of an image formed on the photo detector can be detected. The push pull signal is compensated by subtracting a value proportional to a difference value between the two gap error signals detected in the photo detector. The difference value between the two gap error signals is proportional to a dc offset component included in the push pull signal. Accordingly, it is possible to simply remove a dc offset included in a push pull signal without largely modifying the near field optics, so that it is possible to exactly perform a tracking servo operation.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
A high-precision nano-gap detection structure and method based on surface plasmon resonance
ActiveCN103968770BRealize high-precision measurementRealize dynamic detectionUsing optical meansBeam splitterNano structuring
The invention provides a high precision nanometer clearance detection structure and method on the basis of surface plasma resonance, and belongs to the technical field of nanooptics. The high precision nanometer clearance detection structure and method on the basis of the surface plasma resonance can solve the problems that measuring precision is low and dynamic measurement cannot be carried out in the prior art. Light output by a light source enters a beam splitter through a collimating mirror and a broadband polarizer; the transmission light passing through the beam splitter interacts with the nanometer clearance detection structure and a substrate and then is reflected to the beam splitter; the light enters a spectrum detector after being reflected by the beam splitter and converged by a lens, the detector transmits obtained data through detection to a computer, clearance values are obtained through the processing of the computer, and the detection of the nanometer clearance is achieved. According to the high precision nanometer clearance detection structure and method on the basis of the surface plasma resonance, the method of spectrum detection is adopted to achieve high precision dynamic detection of a nanometer level clearance, a brand new testing technology is provided for the field of nanometer machining and nanometer measuring, and hopefully, the high precision nanometer clearance detection structure and method on the basis of the surface plasma resonance can play an important role in multiple fields including near-field optics and near-field physics.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
One-dimensional metal photonic crystal cylindrical symmetric vector beam focusing plano-concave mirror
The invention discloses a one-dimensional metallic photonic crystal plano-concave mirror for cylindrical symmetrical vectorial light beam focusing, and relates to the field of light field regulation in sub-wavelength photonics. The plano-concave mirror is composed of a one-dimensional metallic photonic crystal with metallic layers and dielectric layers arranged periodically and alternatively, and along the periodic photonic direction of the photonic crystal, one side is a plane while the other side is a hemispherical concave surface. By making full use of negative refraction properties and simultaneous orthogonal polarized light regulation capacity of the photonic crystal, the structure can effectively focus radial and spiral polarized light, and sizes of focused light spots reach sub-wavelength magnitude. In other words, by the structure, sub-wavelength focusing of cylindrical symmetrical vectorial light beams of any polarization component can be realized. By changes on constituent materials and structural parameters, focusing effect can be realized within broadband. The plano-concave mirror is simple in constituent material, easy for designing parameters and structurally easy to produce, and has good application prospects in the fields of near-field optics, quantum optics and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Surface plasmon longitudinal field scanning near-field optical microscope device and detection method
InactiveCN103105511BReduce distractionsImprove reliabilityScanning probe microscopyHigh numerical apertureNear-field optics
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Long-wavelength scanning near-field microanalysis system
The invention provides a long-wavelength scanning near-field microscopic analysis system. The long-wavelength scanning near-field microscopic analysis system integrates broadband long-wavelength and single-frequency THz waves, utilizes a scanning probe to integrate a variable electric field, a variable magnetic field and a variable temperature field, fills the technical blank of long-wavelength wave bands in the near-field microscopy field, enables a near-field optic microscopic technology to be linked with a near-field microwave microscopic technology and provides an all-around sample physical property testing tool for scientific research persons.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Apparatus and method for controlling tracking servo in near field optics
InactiveUS7656765B2Stable trackingCombination recordingRecord information storageNear-field opticsPush pull
Disclosed are an apparatus and a method for controlling a tracking servo in a near field optics. Gap error signals are detected in a divided state, and a push pull signal is compensated based on the detected gap error signals. A photo detector detecting the gap error signals is divided into two areas such that movement of an image formed on the photo detector can be detected. The push pull signal is compensated by subtracting a value proportional to a difference value between the two gap error signals detected in the photo detector. The difference value between the two gap error signals is proportional to a dc offset component included in the push pull signal. Accordingly, it is possible to simply remove a dc offset included in a push pull signal without largely modifying the near field optics, so that it is possible to exactly perform a tracking servo operation.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Selective micro processing method and system for near field optic virtual light probe
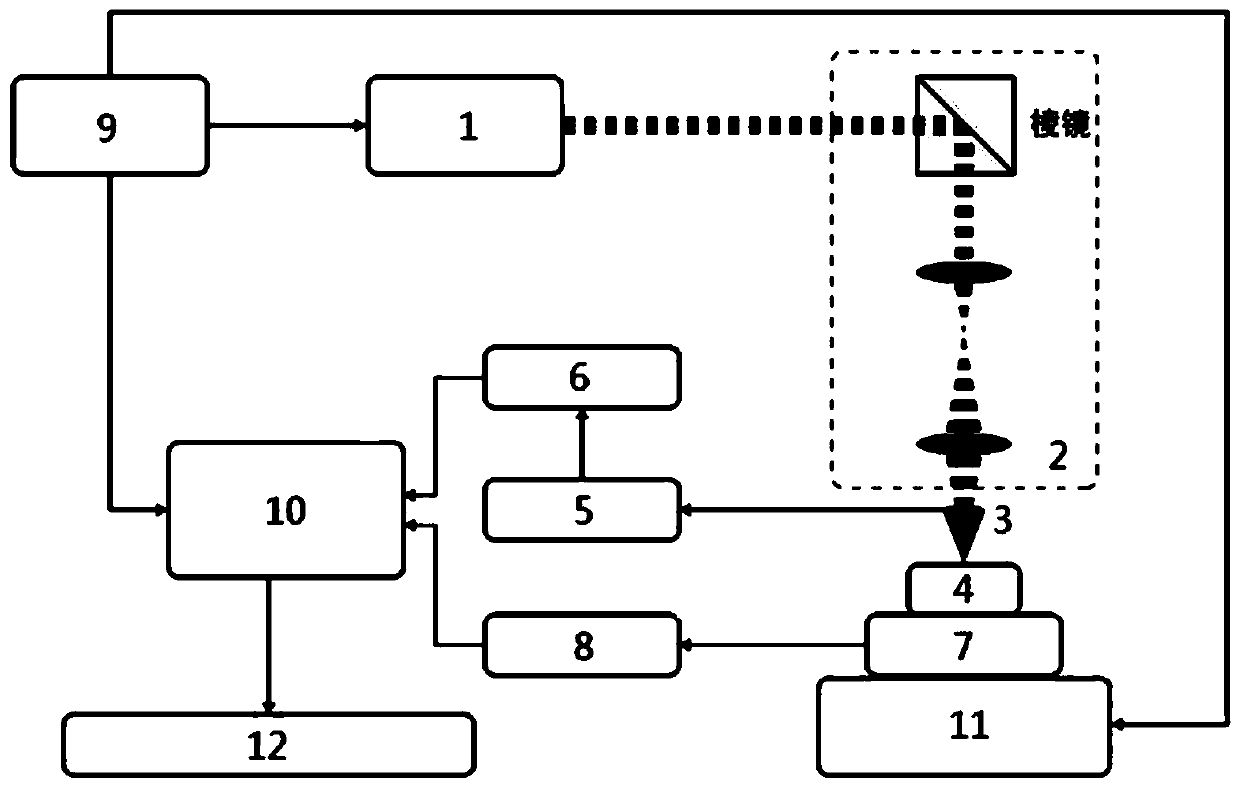
InactiveCN1899748AImprove lighting efficiencyImplementation conditions are easy to meetLaser beam welding apparatusOptical elementsTotal internal reflectionNear-field optics
The present invention is selective micro machining method and system for different materials with near field optical virtual light probe. The present invention proposes selective micro machining with near field optical virtual light probe in nanometer size and provides one designed micro machining system. After the laser beam the laser emits after passing through the light filter and the polarizer is incidenced to the triangular prism, the refracted laser beam may be total internally reflected and the reflected laser beam out of the other side of the triangular prism is made to pass through the optical delayer and reflected by the reflector to the bottom of the triangular prism along the original path to form the virtual light probe. The material to be machined is set in certain distance below the bottom of the triangular prism for micro machining with the virtual light probe while being micro shifted with some miniature stage. The present invention has raised micro machining precision.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Thermo-writing and magnetic-reading record medium having high-density and system thereof
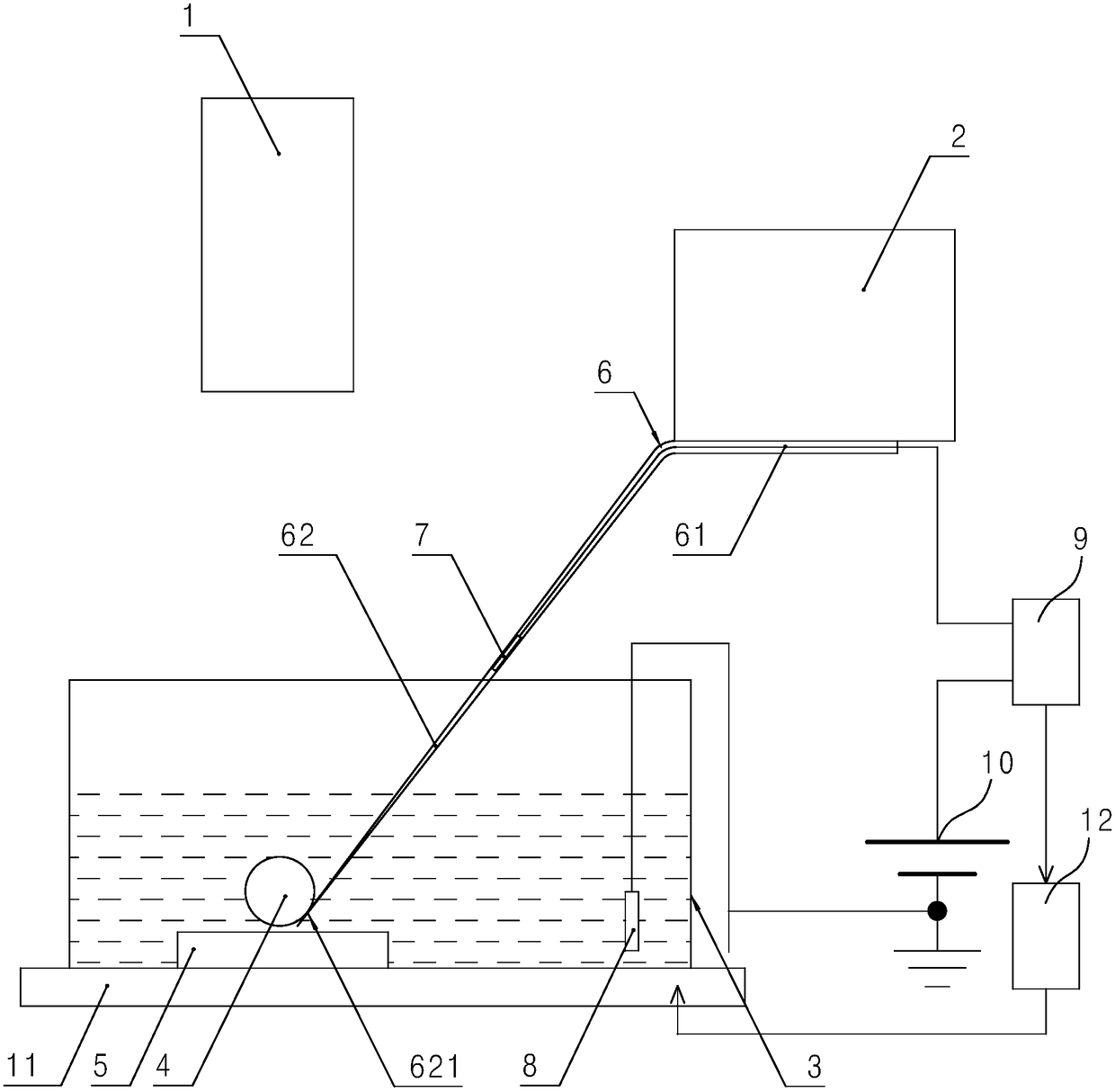
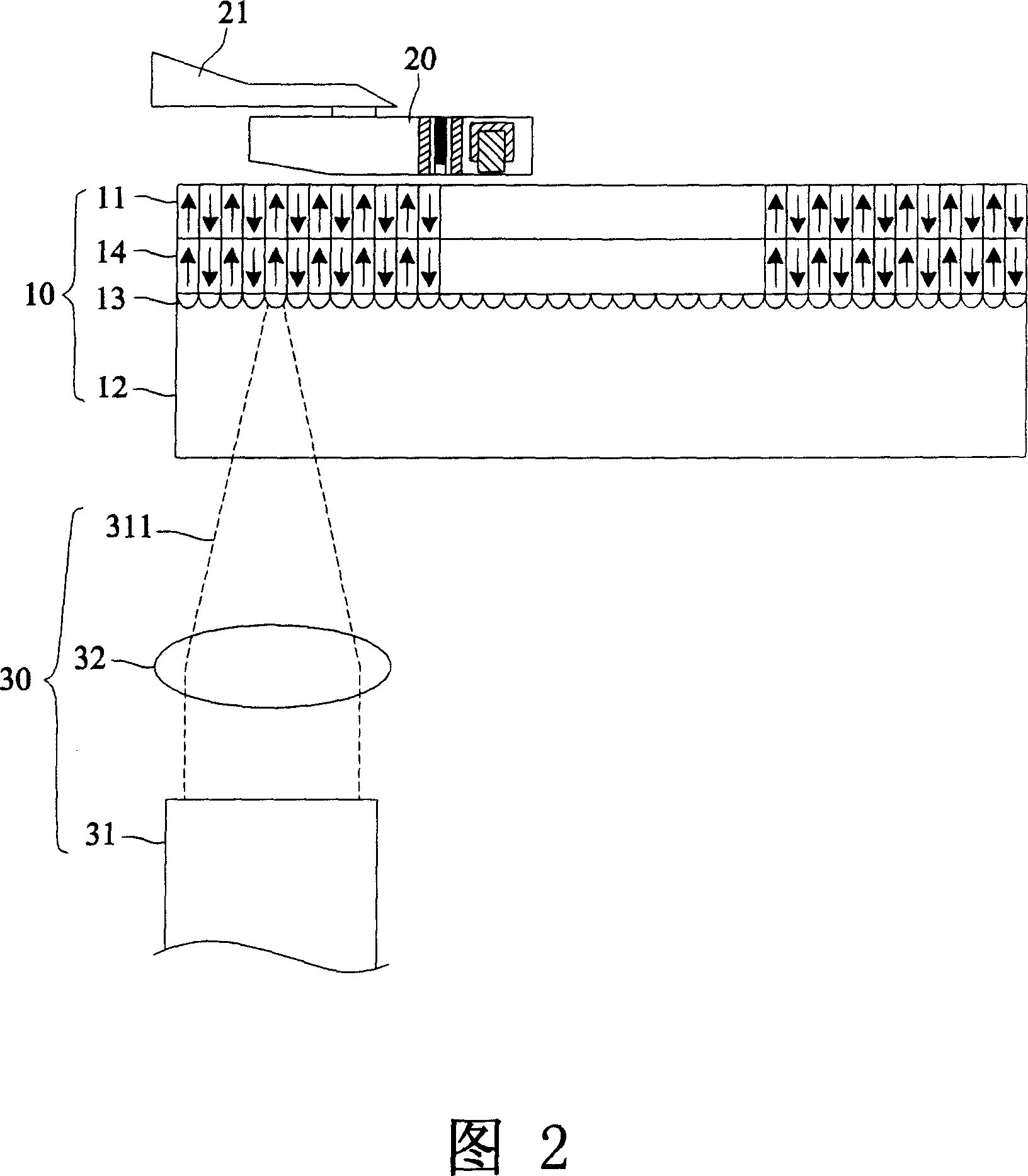
This invention relates to a heat-writing recorder medium and its system, which reads the materials through near-field optical laser writing-in data through magnetic resistance head. The recording media comprises the following: one baseboard; one recording layer formed on side of the baseboard; multiple micro round column lens formed between the baseboard and the recording layer to generate the near-field optics effect and reduce the light point size when writing in the recording layer.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Near-field optical device based on nano antenna enhancement effect and manufacturing method thereof
PendingCN114778474ASimple preparation processImprove stabilityNanoopticsNanosensorsRefractive indexIr absorption
The invention discloses a near-field optical device based on a nanometer antenna enhancement effect and a manufacturing method of the near-field optical device, and provides the near-field optical device based on the nanometer antenna enhancement effect in order to solve the problems of low sensitivity and low signal-to-noise ratio caused by the adoption of a low-refractive-index organic nanometer material representing the thickness of a molecular layer in the prior art. Comprising a substrate and a phonon excimer resonance excitation crystal film with a local electromagnetic enhancement structure, and further discloses a manufacturing method of the near-field optical device based on the nano-antenna enhancement effect, the manufacturing method comprises the following steps: firstly, depositing the crystal film on the substrate, then spin-coating photoresist on the crystal film, patterning the photoresist, then coating a chromium metal layer on the photoresist, and finally forming the nano-antenna enhancement effect on the chromium metal layer, thereby obtaining the near-field optical device based on the nano-antenna enhancement effect. And finally, stripping the metal layer and the residual adhesive. The manufacturing process is simple and good in stability; the local electromagnetic enhancement structure forms an extremely strong electromagnetic enhancement'hot spot ', can promote weak near-field infrared absorption response of an object to be tested, and improves the test sensitivity and the signal-to-noise ratio of the nanometer Fourier transform infrared spectrum.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Dual frequency adjustable magnetic resonance artificial composite material based on asymmetric metal grating structure
ActiveCN100588742CAchieve magnetic resonanceReduce lossVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingNon symmetricElectron-beam lithography
The invention provides a double-frequency adjustable magnetic resonance artificial composite material based on a non-symmetric metal grating structure, which is characterized in that the material is produced through the following steps: selecting a quartz substrate and polishing the surface of the quartz substrate; evaporating a SiO2 film on the surface of the quartz substrate; evaporating a chromium film on the surface of the SiO2 film; coating a photoresist layer on the chromium film; preparing a medium grating structure on the photoresist by electron beam lithography method; eroding and exposing the chromium film by using the photoresist as a mask by wet etching technology; etching the medium grating structure on the SiO2 film by using the chromium film as a mask by dry etching technology, and removing the chromium film; laterally depositing a metal layer with the thickness of h on one side of the SiO2 grating structure by lateral vacuum deposition technology, similarly, depositinga metal layer with the same thickness on the other side of the SiO2 grating structure, thereby forming an n-shaped metal structure with the top thickness of 2h and the side wall width of h to completethe production of the double-frequency adjustable magnetic resonance artificial composite material based on the non-symmetric metal grating structure. The method has the characteristics of simple andconvenient production, small monolayer consumption, monolayer normal incidence and double frequency, and has revelatory significance and great application prospect in magnetic resonance, near-field optics, camouflage materials and other fields.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Selective micro processing method and system for near field optic virtual light probe
InactiveCN100448592CImprove lighting efficiencyImplementation conditions are easy to meetLaser beam welding apparatusOptical elementsAngle of incidenceEngineering
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
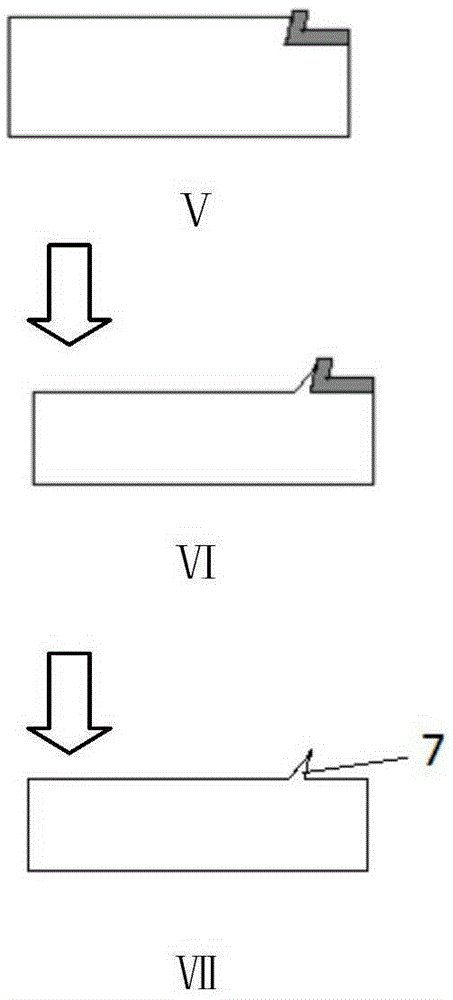
Inclined silicon needle point and its manufacturing method
ActiveCN106610439BMeet the needs of real-time observationEasy to prepareScanning probe microscopyNear-field opticsPyramid
The invention discloses an inclined silicon needle point and a manufacturing method thereof. The needle tip is a triangular pyramid and has a first inclined surface, a second inclined surface, a third inclined surface and a bottom surface, and at least two of the first inclined surface, the second inclined surface and the third inclined surface are connected to the bottom surface angles are not equal. The manufacturing method comprises: using an isotropic etching process to process and form the first and second inclined surfaces of the inclined silicon needle tip on the silicon wafer, then setting a protective layer on the first and second inclined surfaces, and then The etching process is used to process and form the third inclined surface on the silicon wafer, so as to obtain the target product. The invention provides an inclined silicon needle tip different from the traditional silicon needle tip, which can meet the demand of near-field optics for real-time observation, and has a simple manufacturing method, cheap and easy-to-obtain raw materials, and is suitable for large-scale production. The promotion and application of it provides a new path.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com