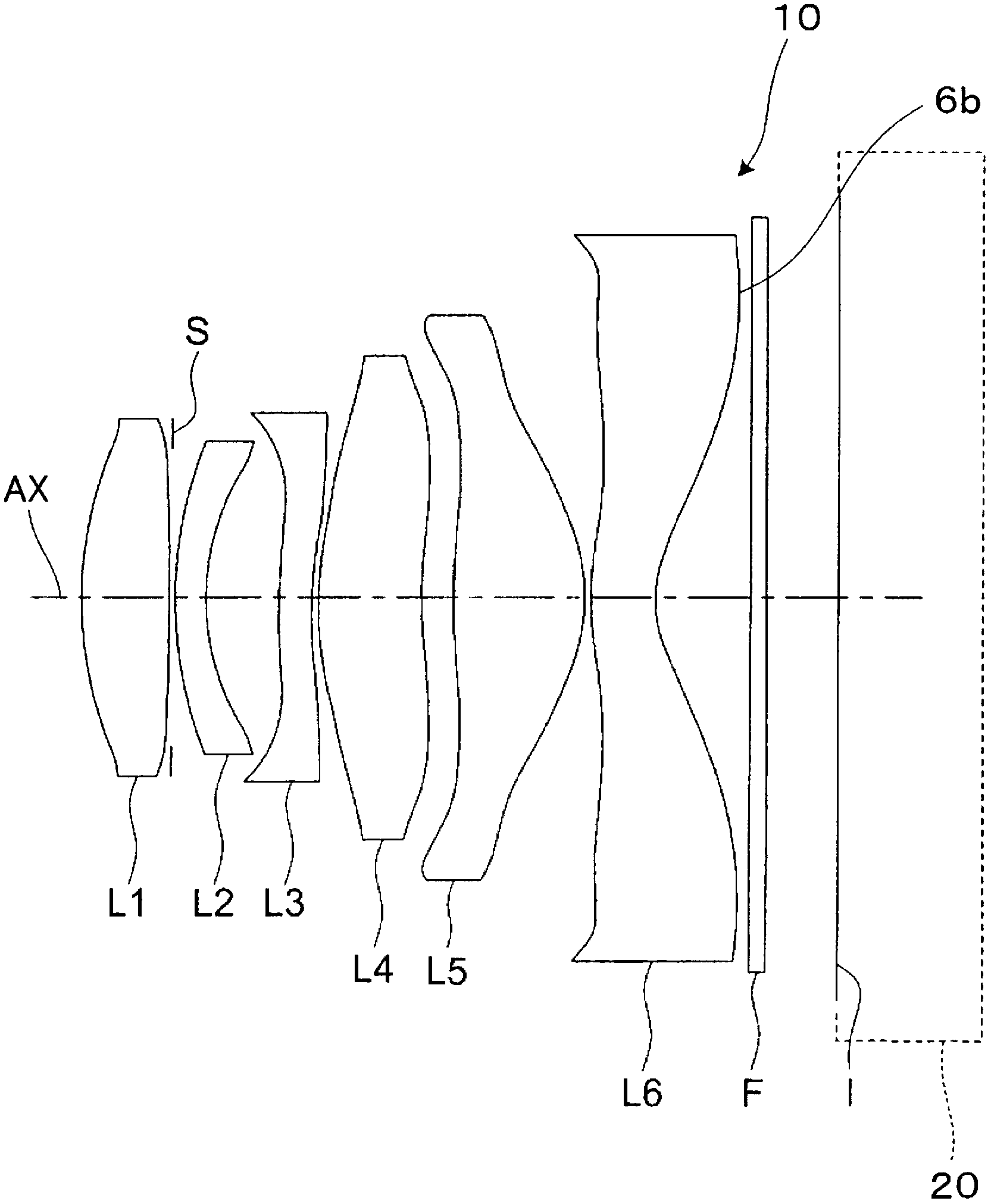
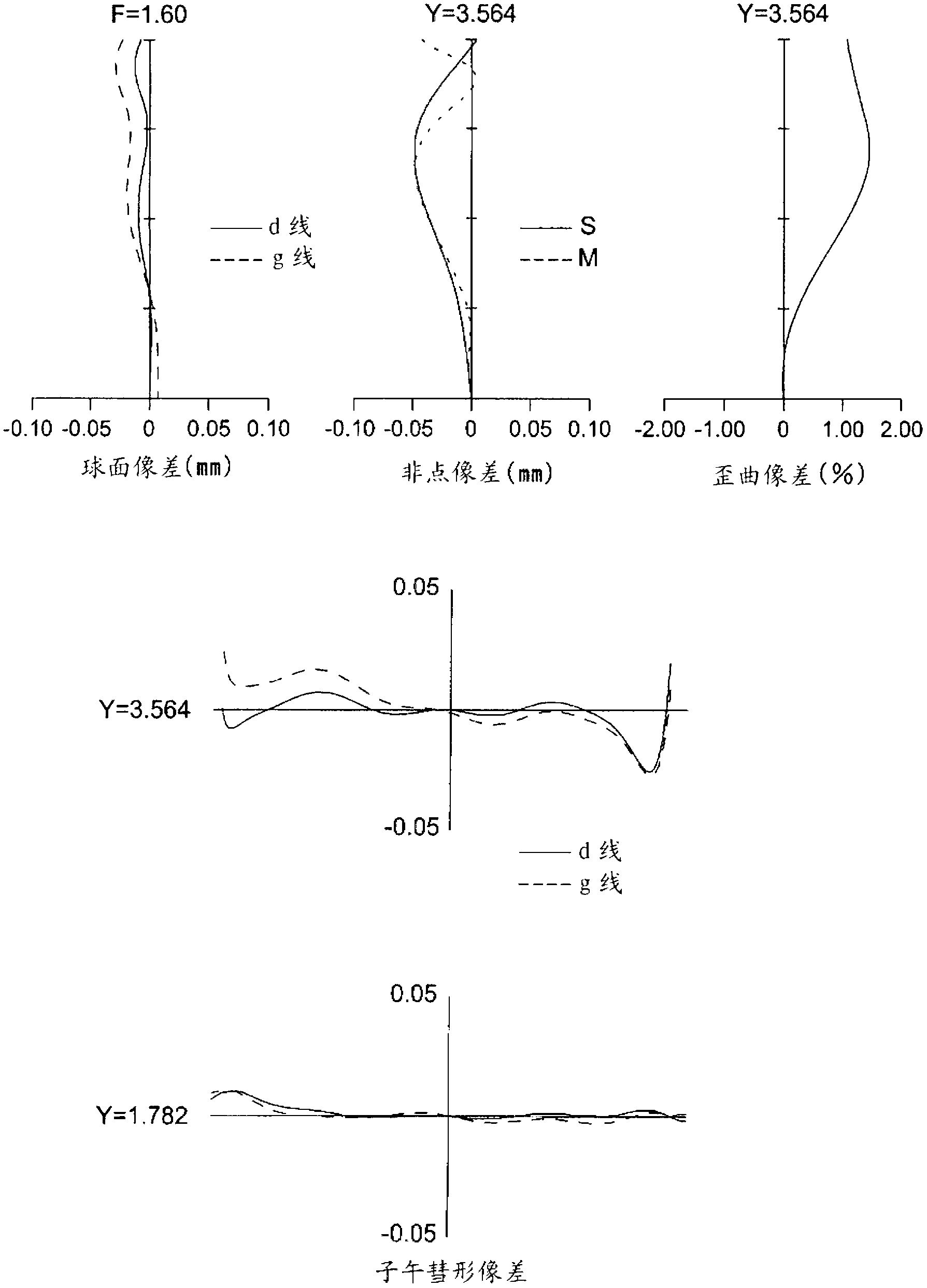
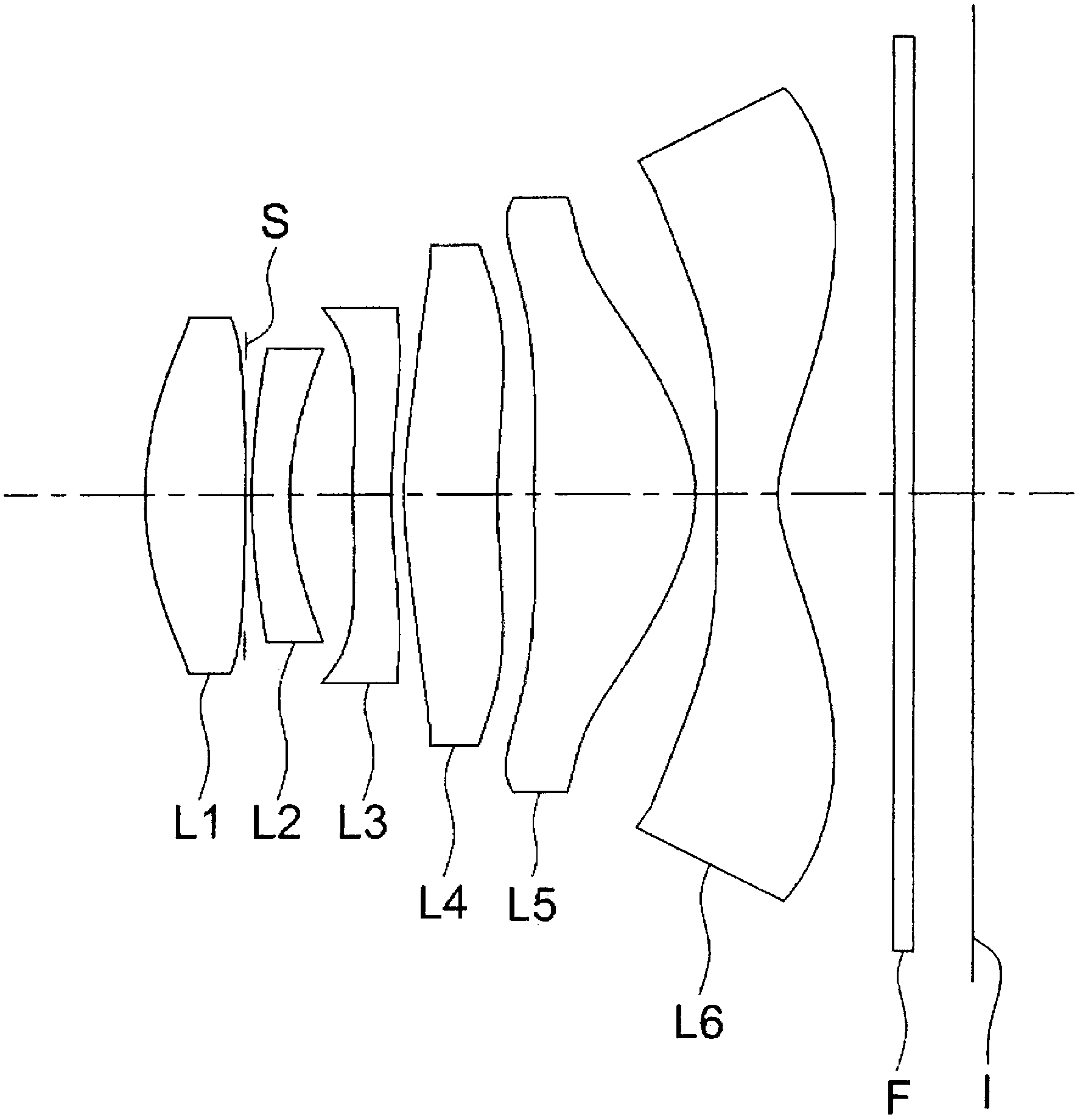
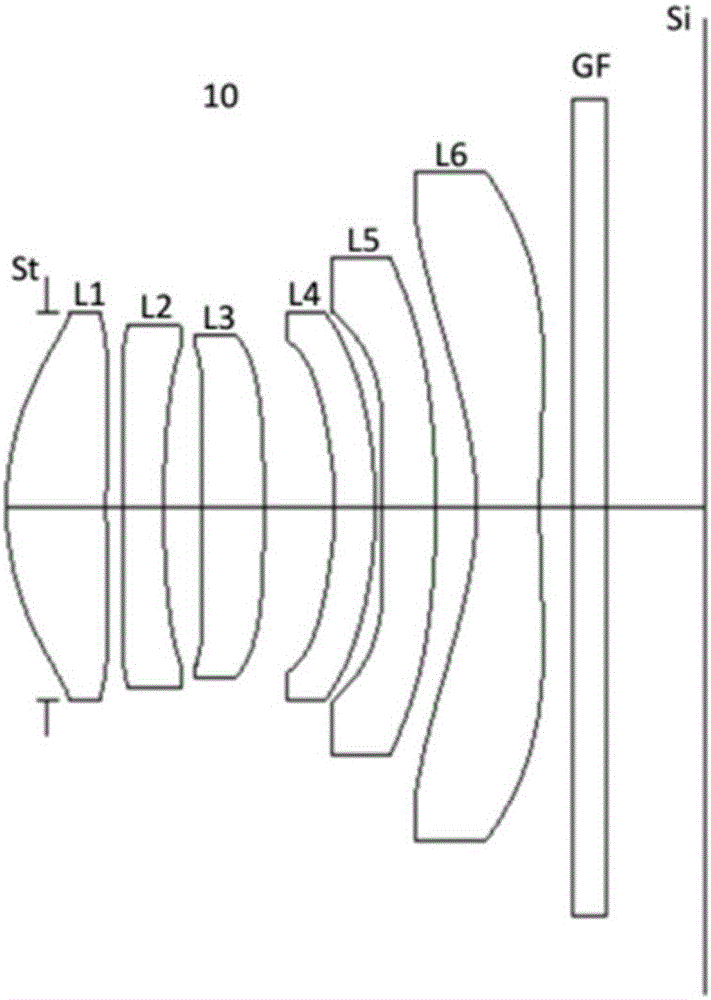
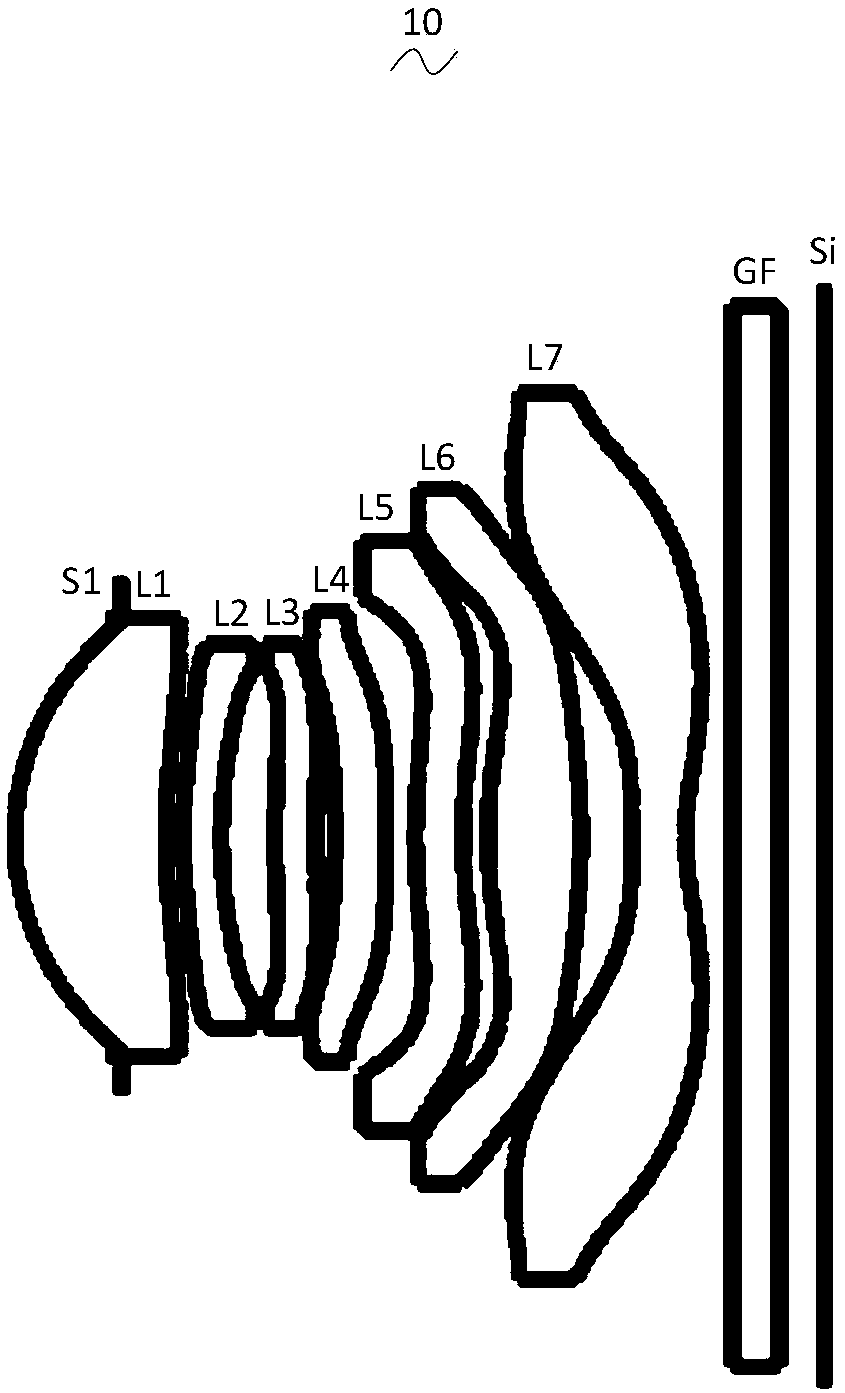
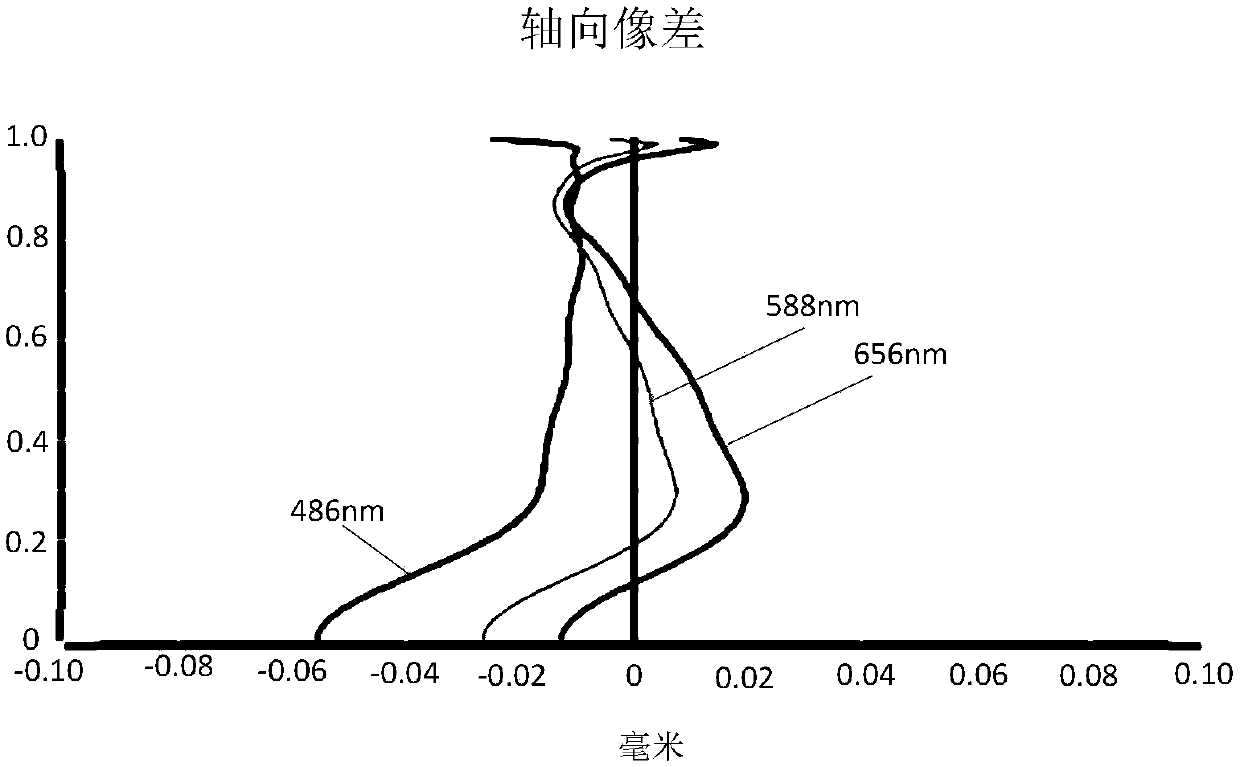
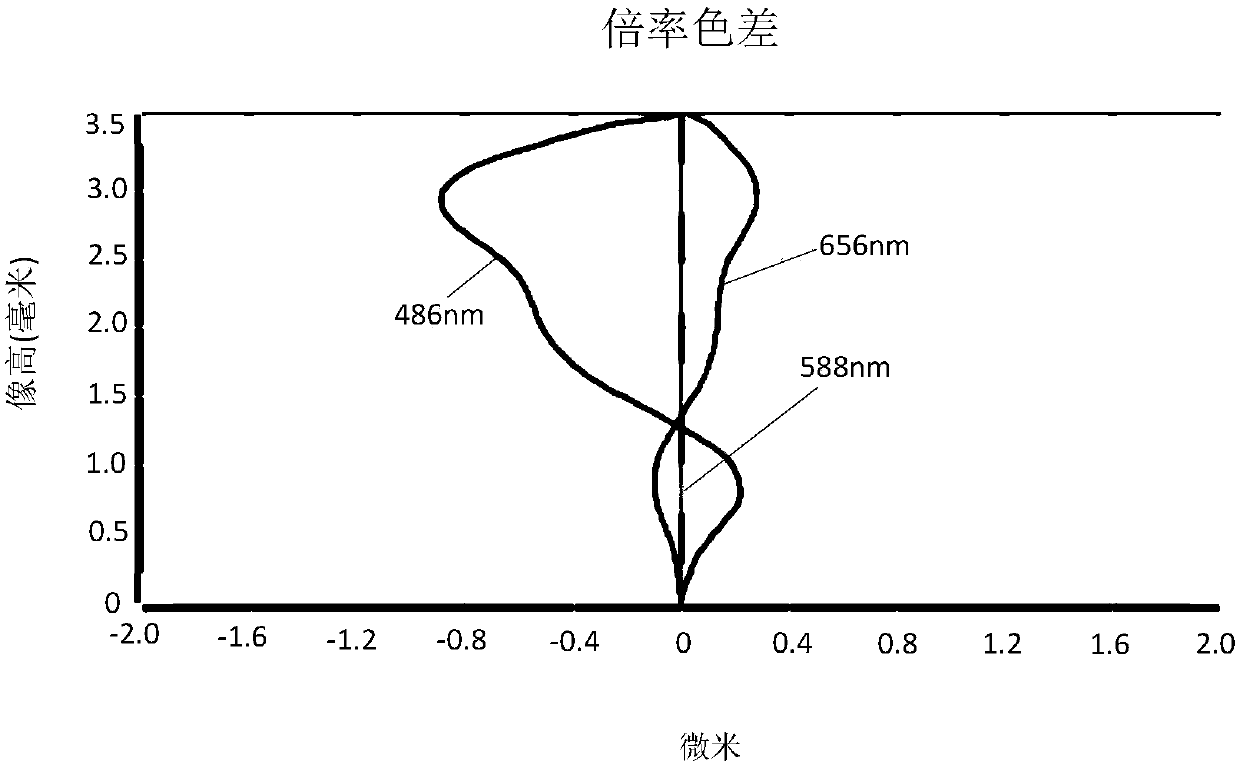
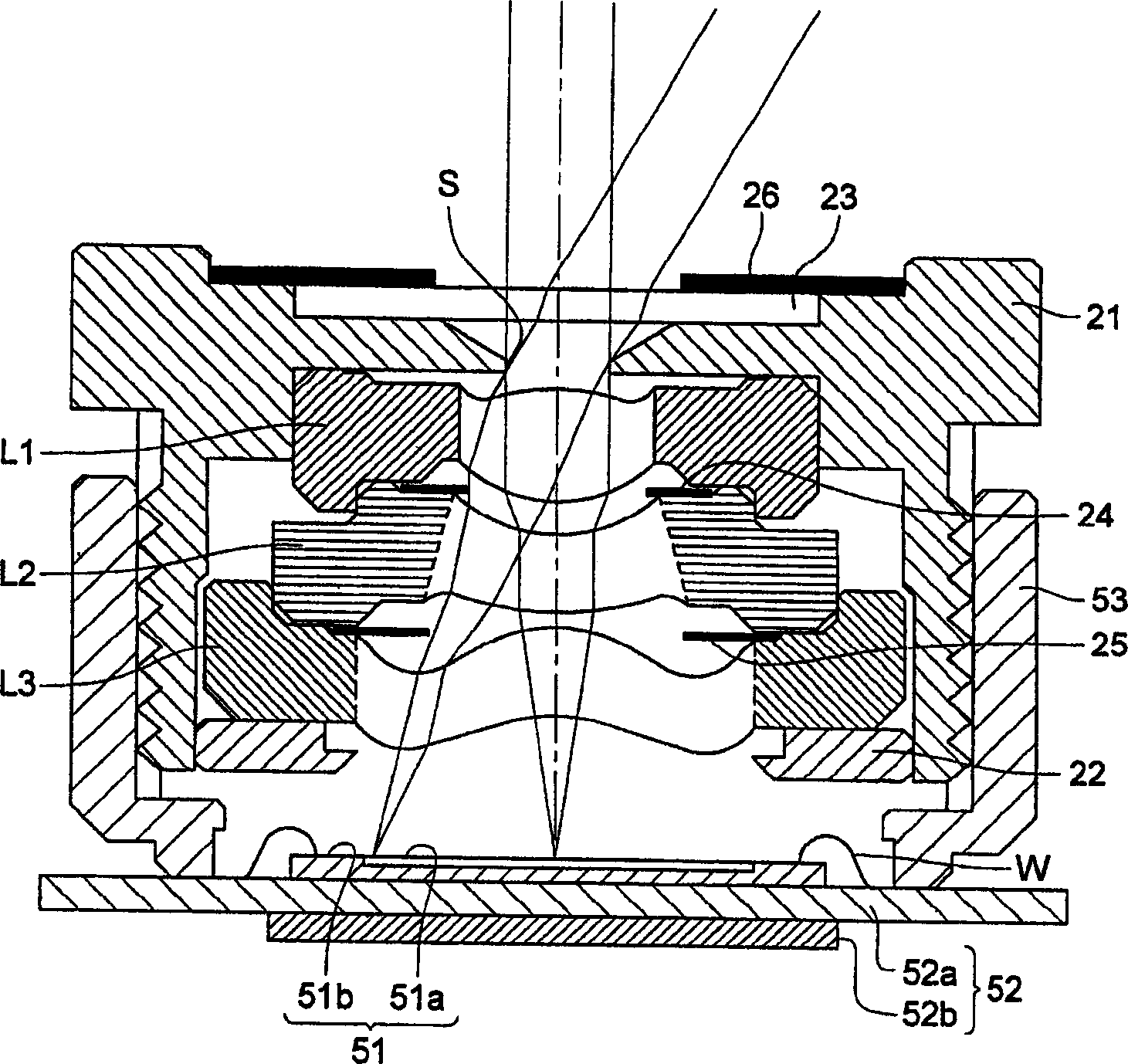
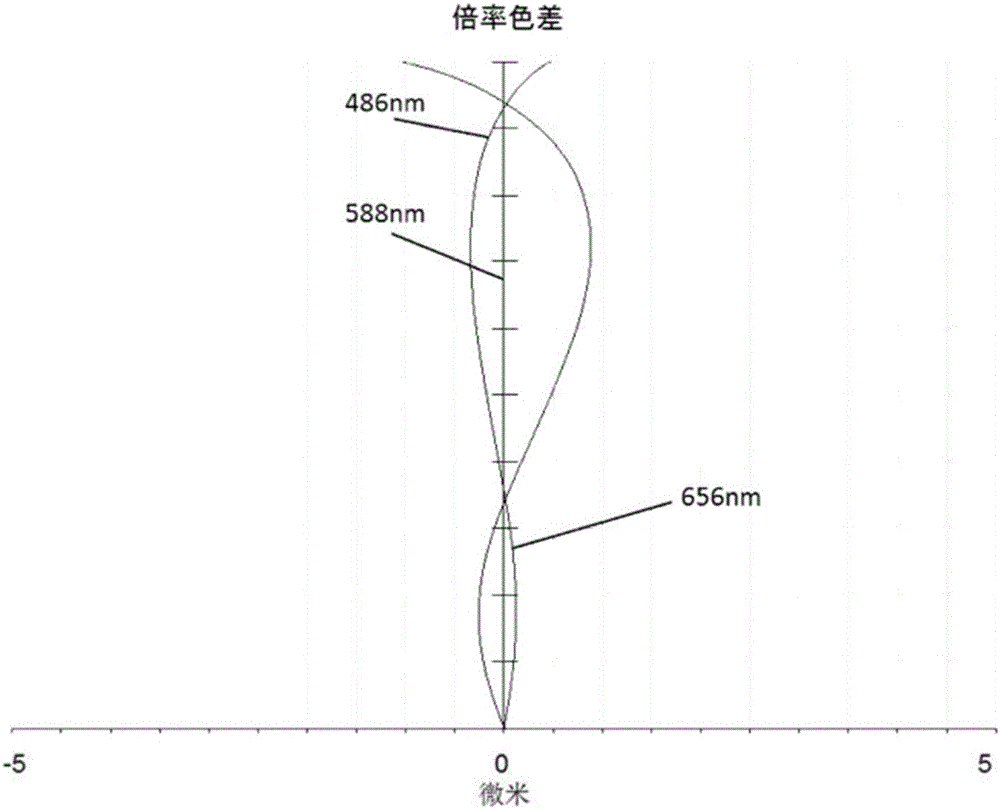
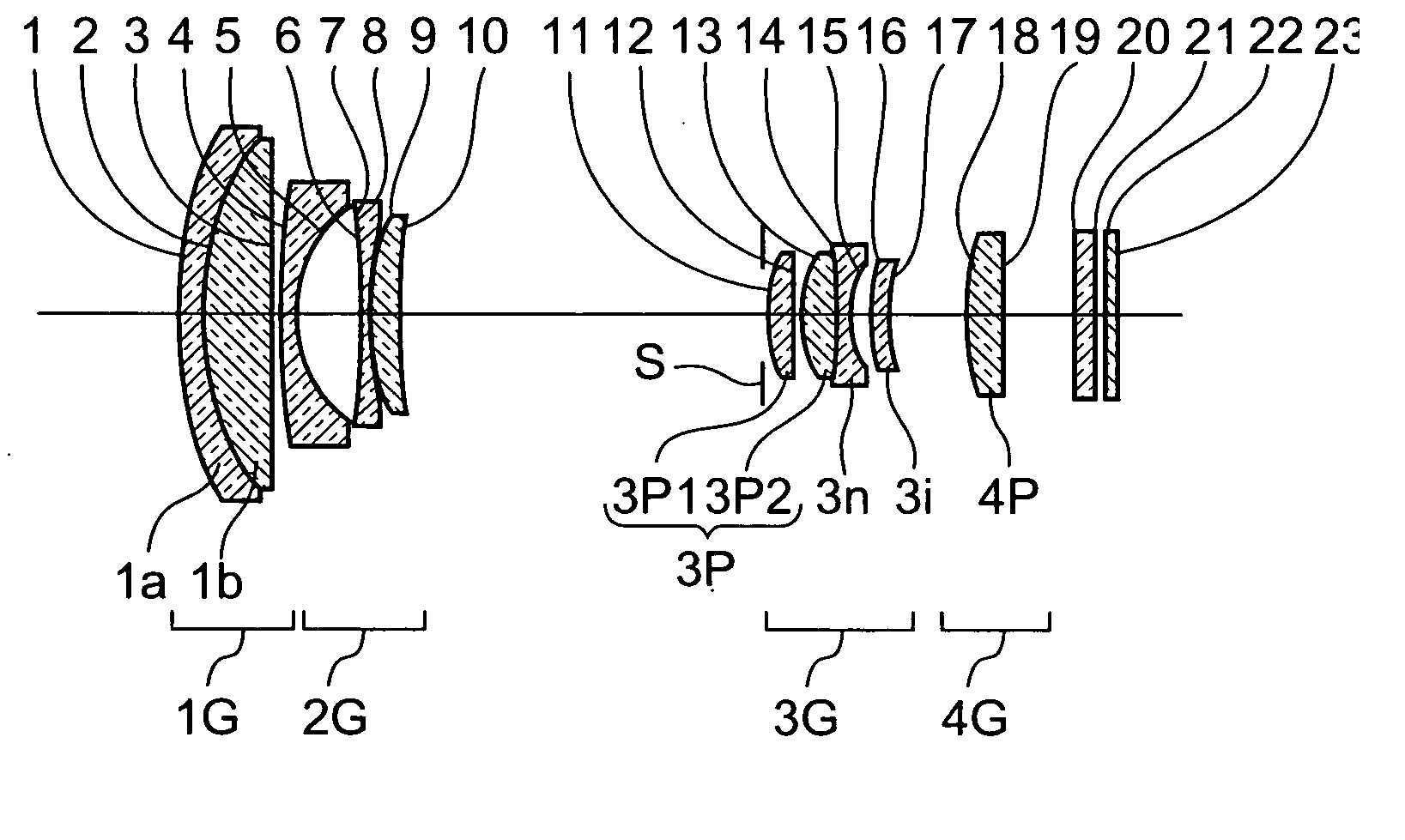
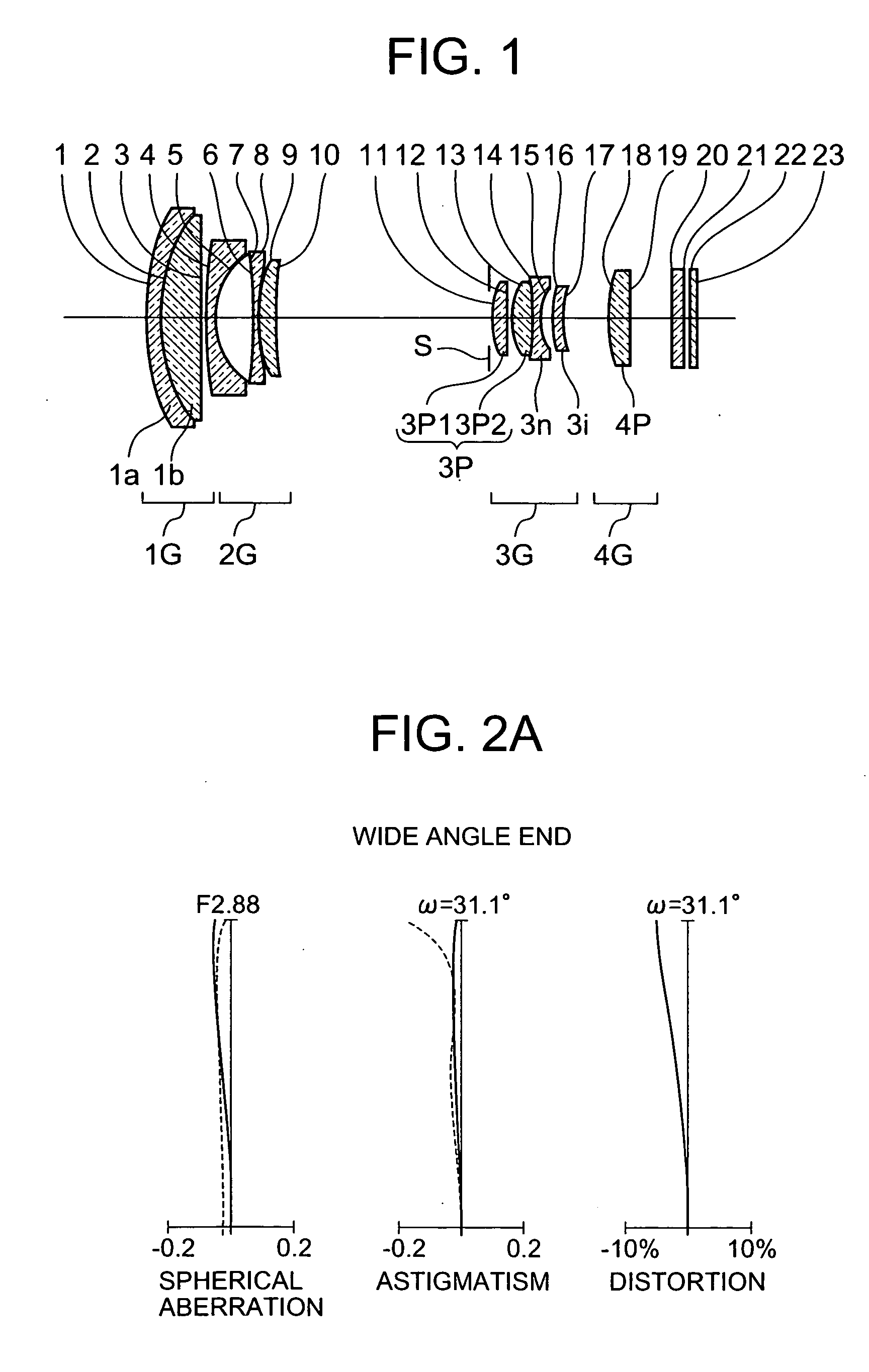
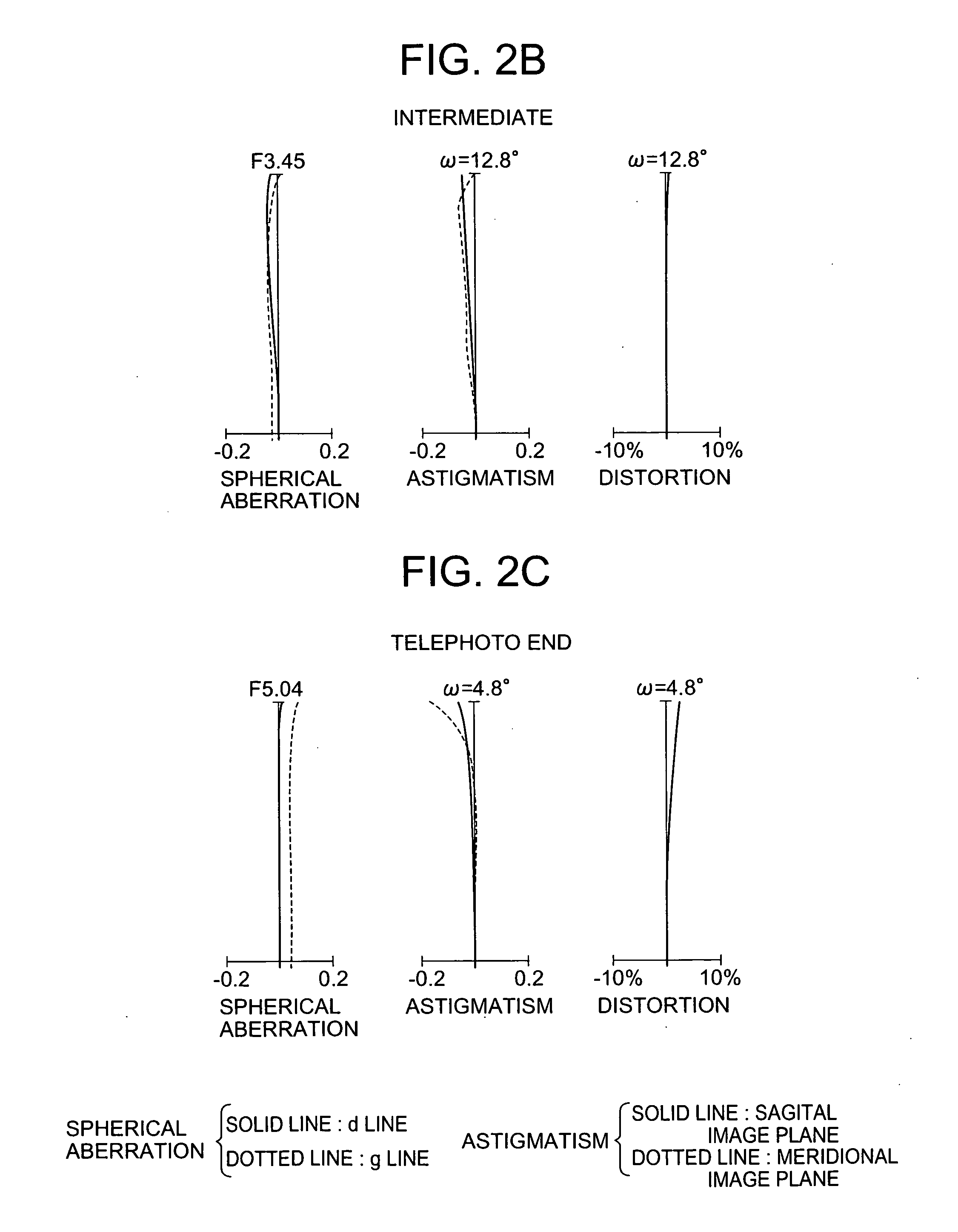
Patents
Literature
559 results about "Negative refraction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
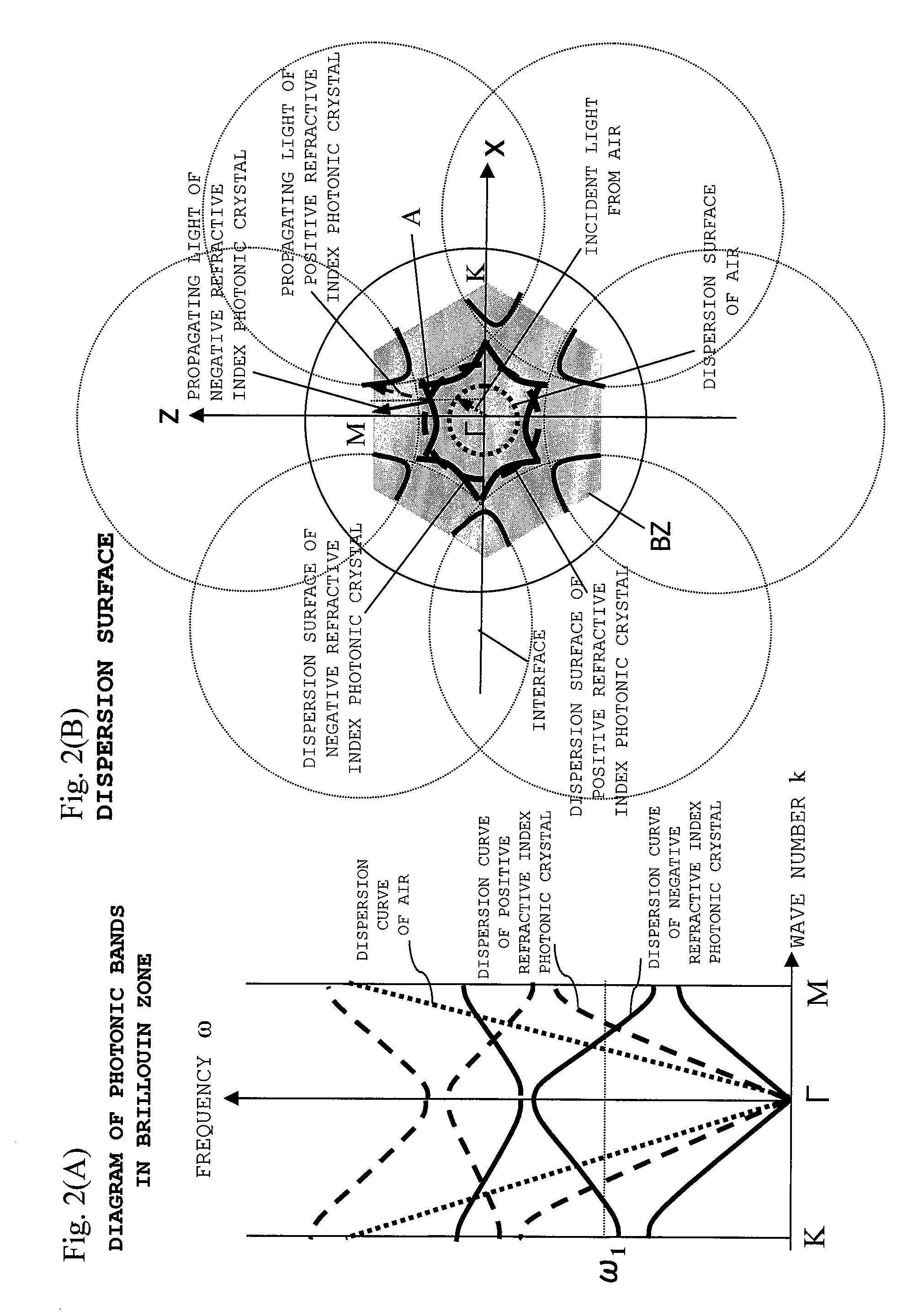
Negative refraction is the name for an electromagnetic phenomenon where light rays are refracted at an interface in the reverse sense to that normally expected. Such an effect can be obtained using a metamaterial which has been designed to achieve a negative value for both (electric) permittivity ε and (magnetic) permeability μ, as in such cases the material can be assigned a negative refractive index. Such materials are sometimes called "double negative" materials.
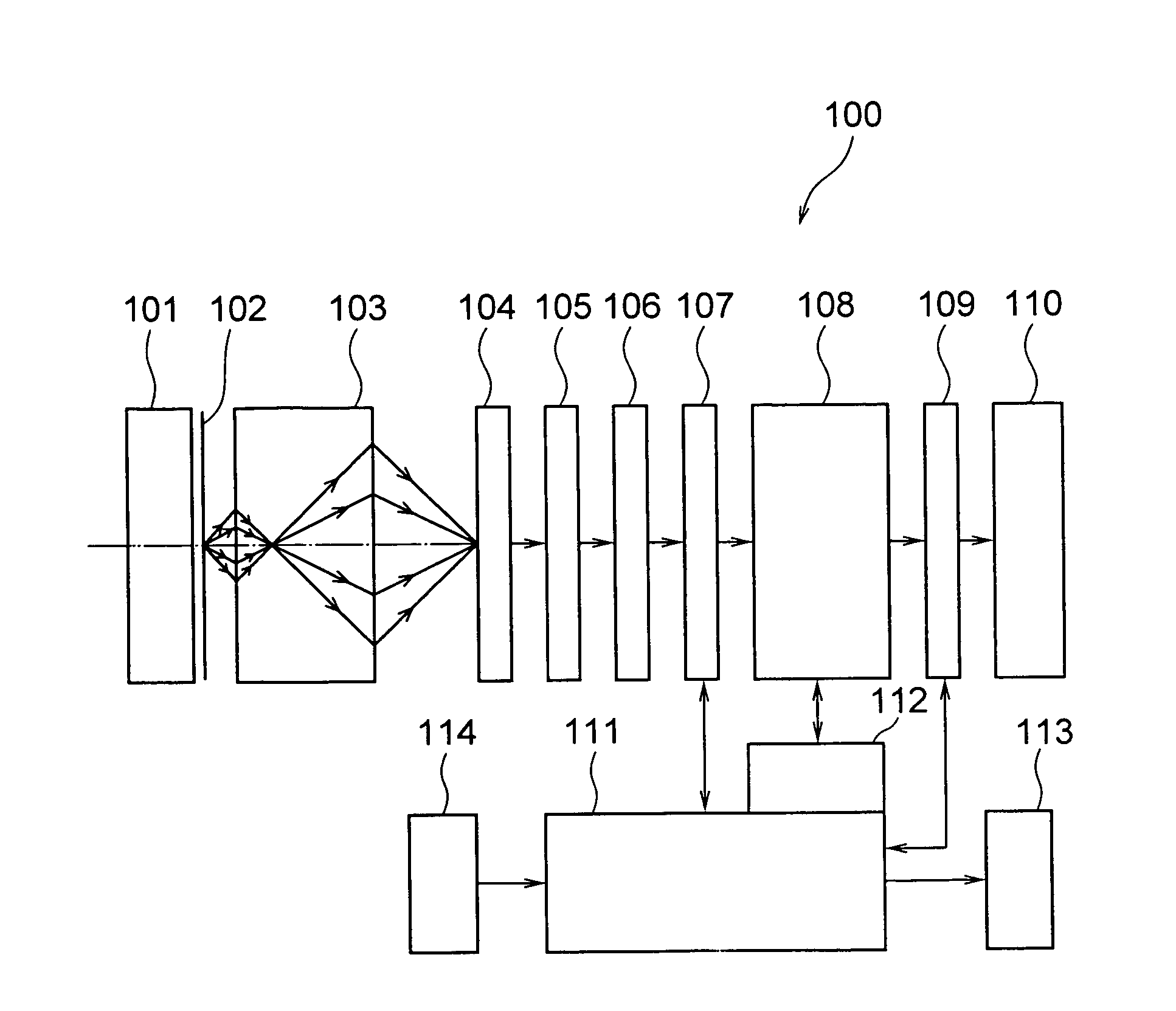
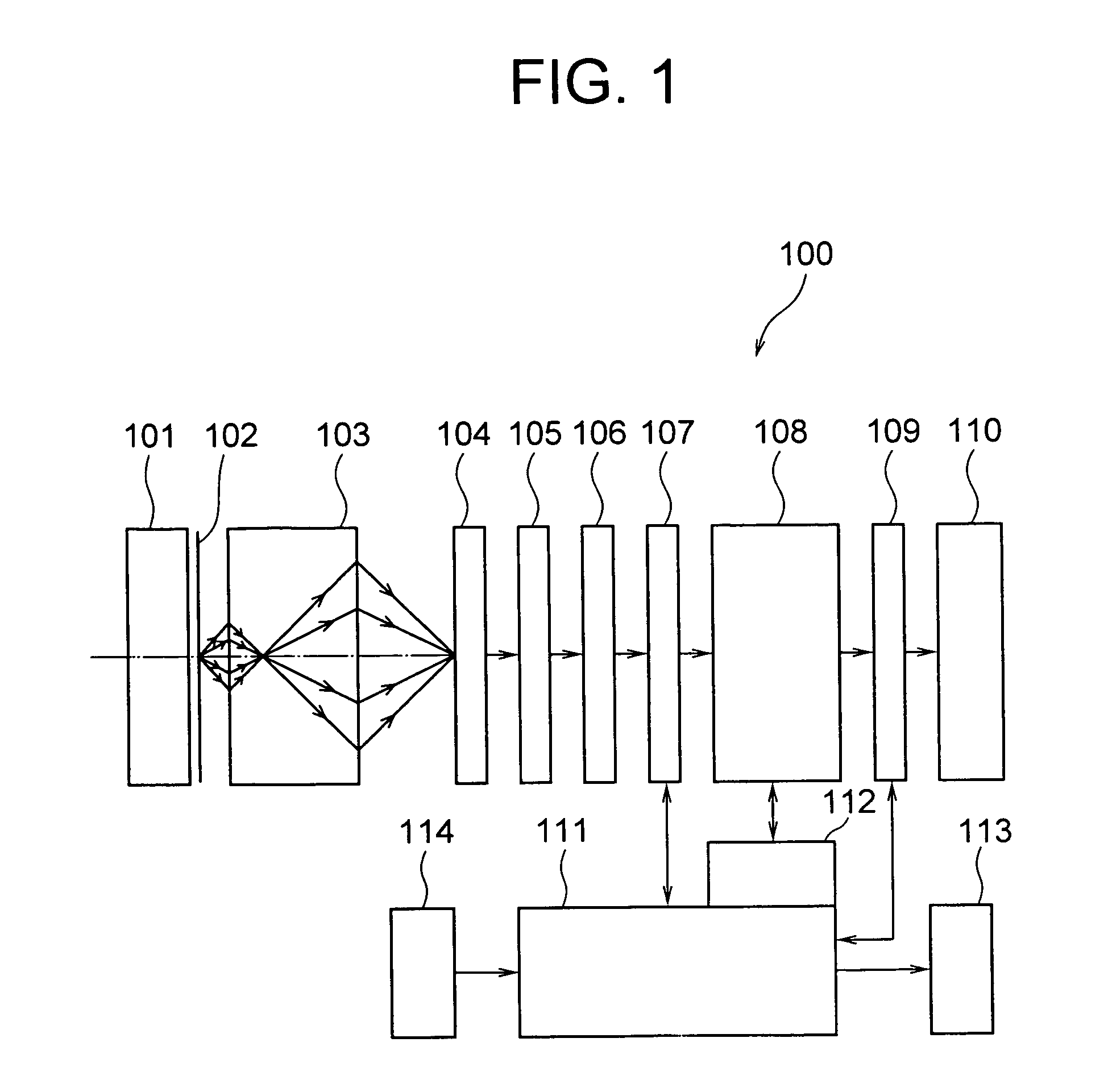
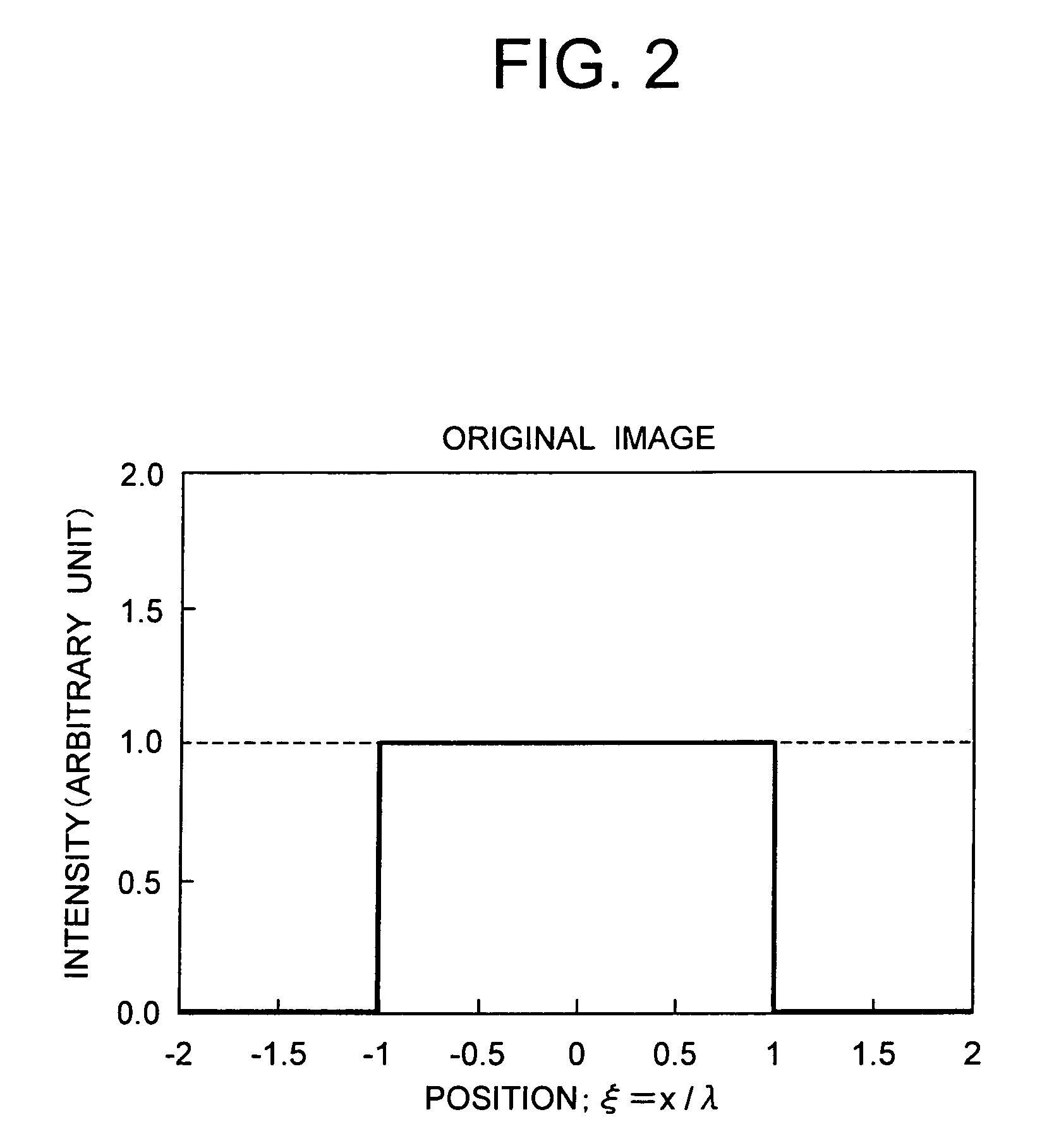
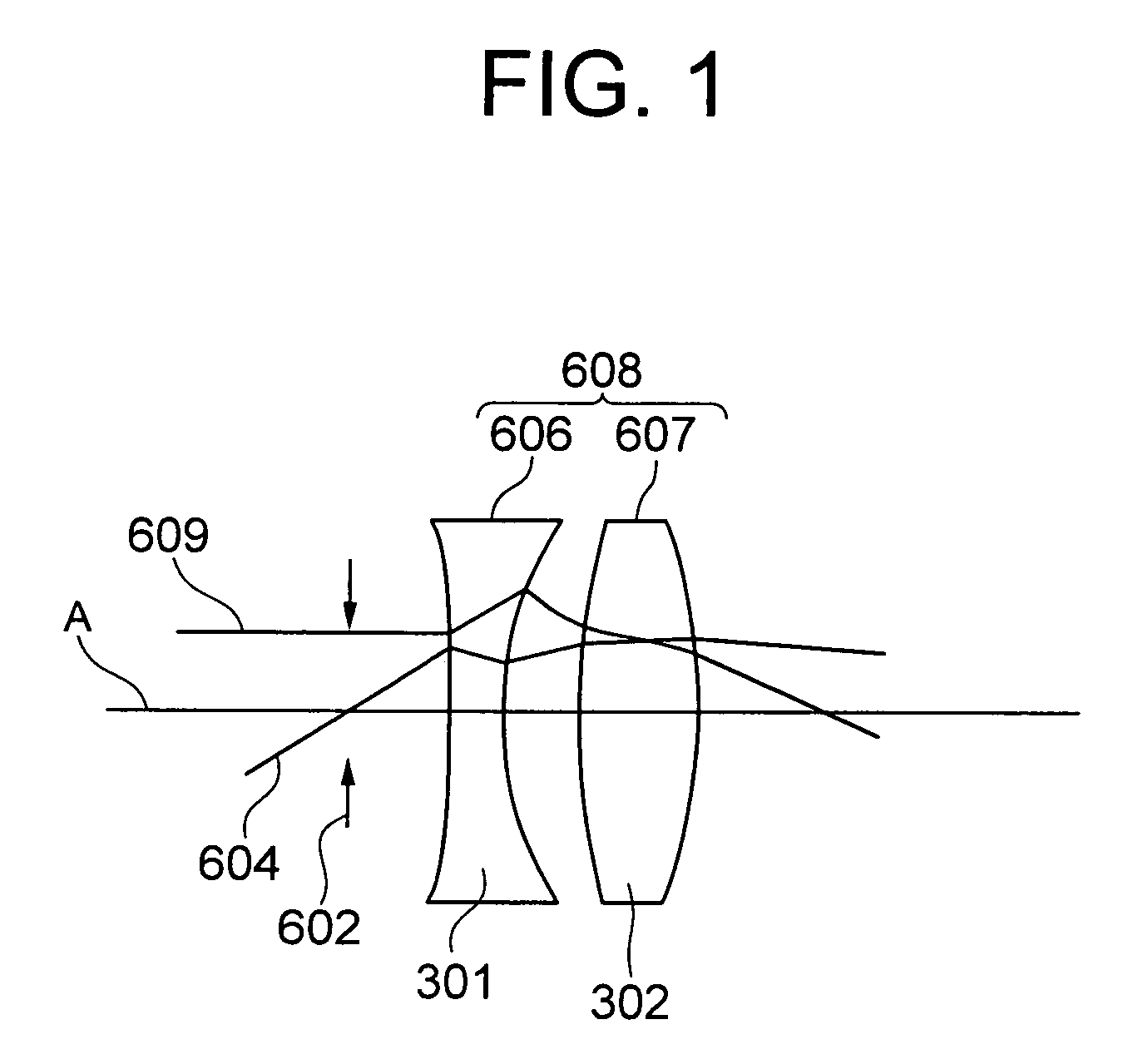
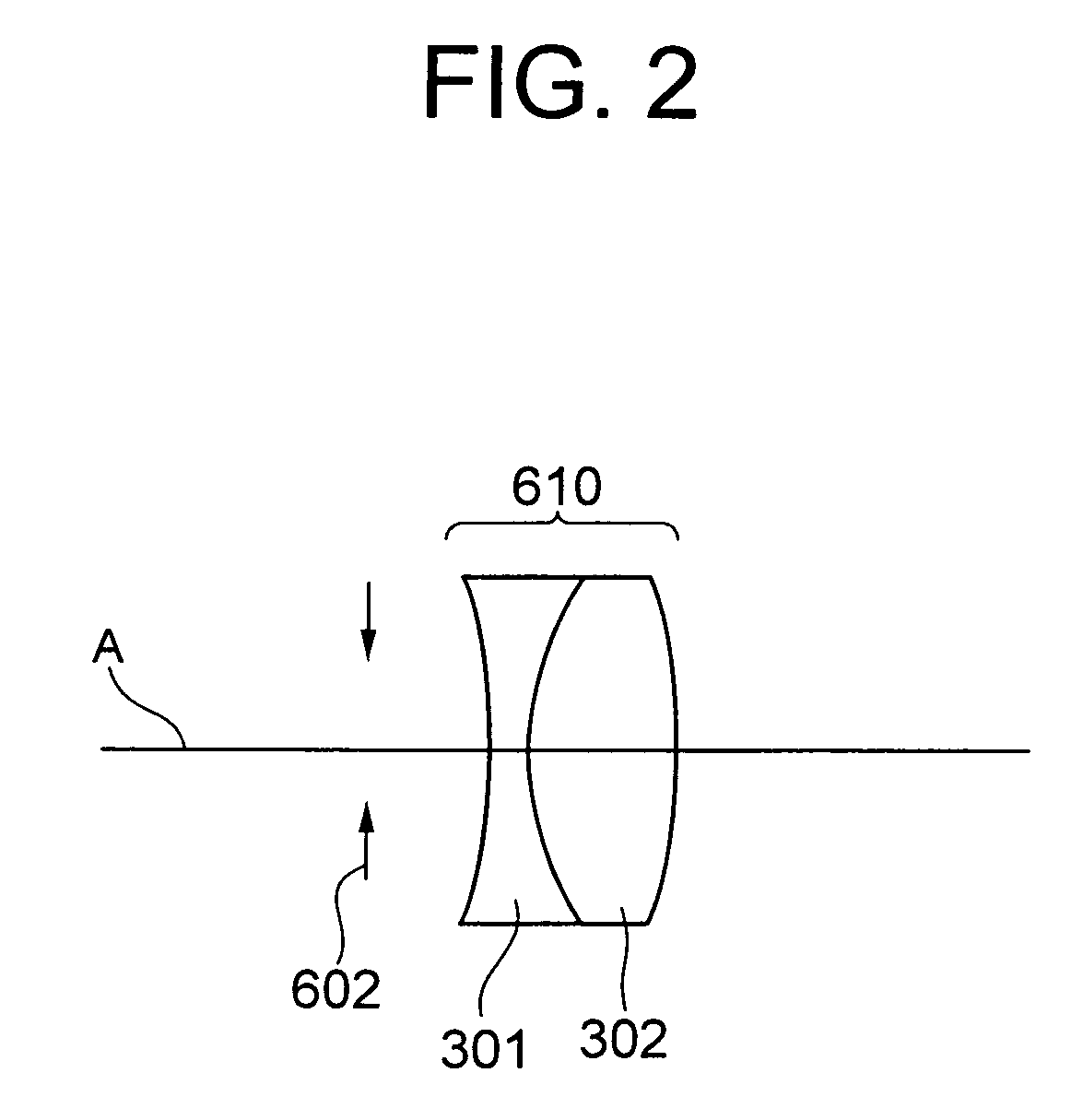
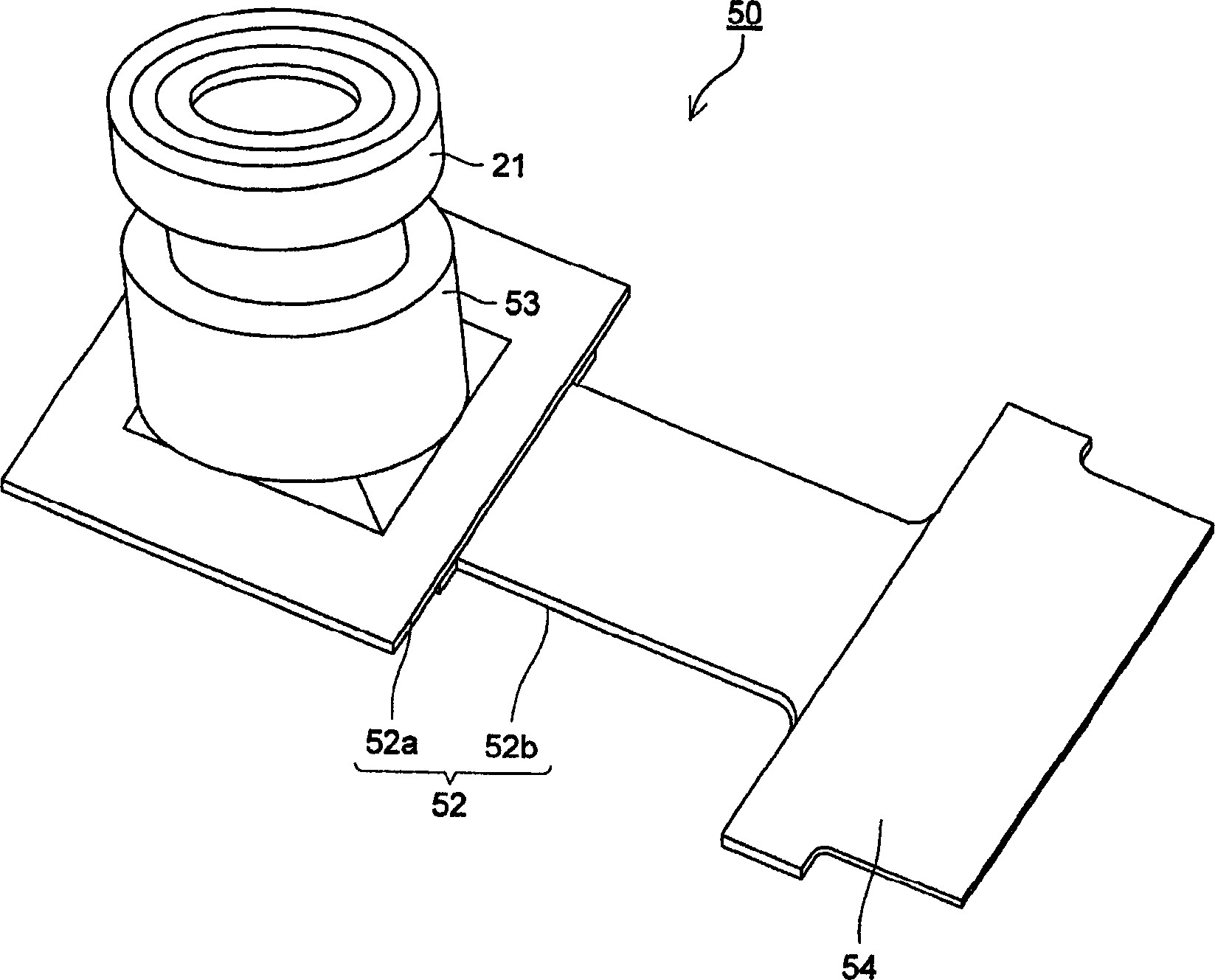
Medium exhibiting negative refraction, optical element, and optical system
InactiveUS20060171032A1Small thicknessPhotomechanical apparatusNanoopticsNegative refractionCarbon nanotube
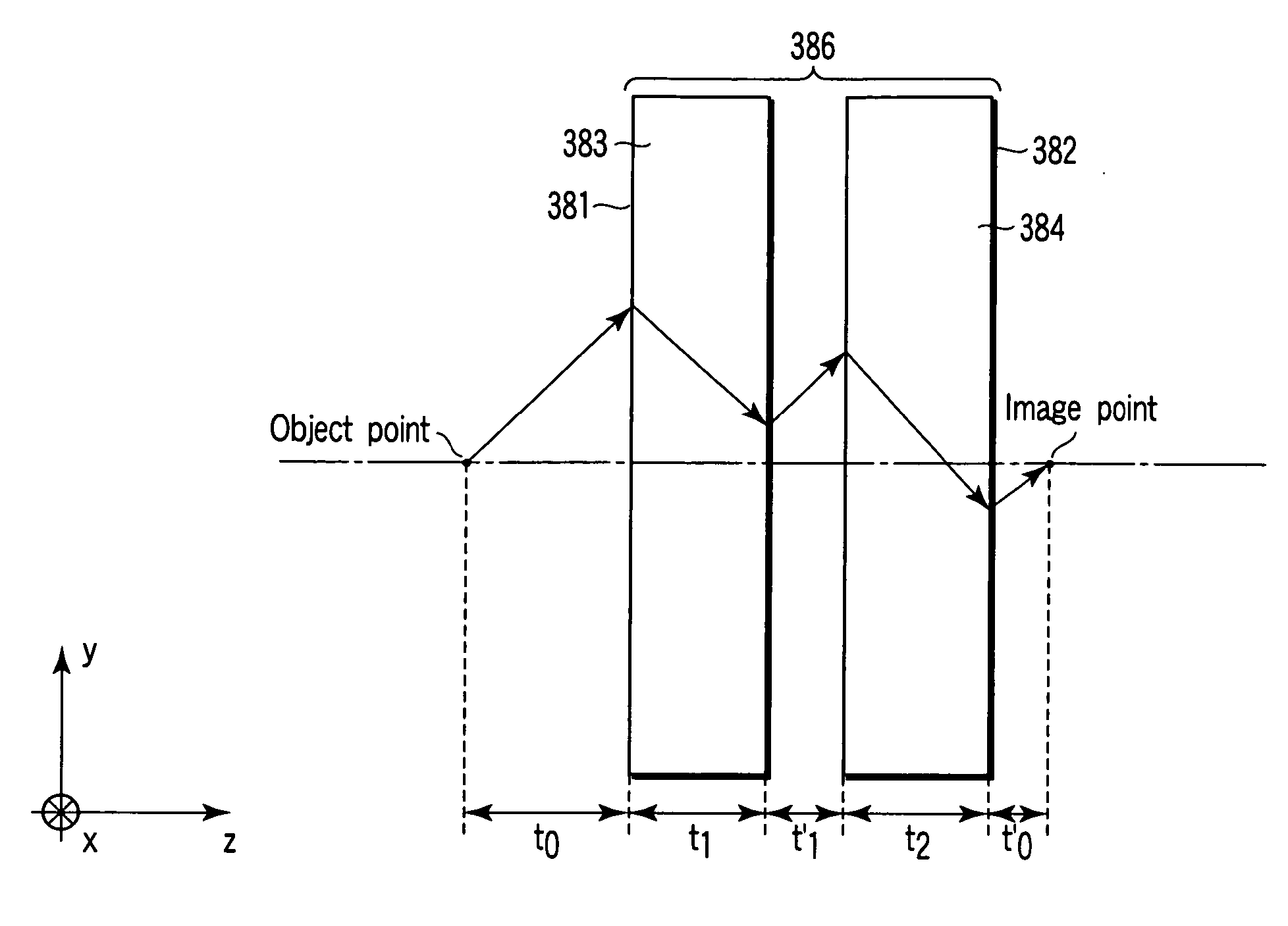
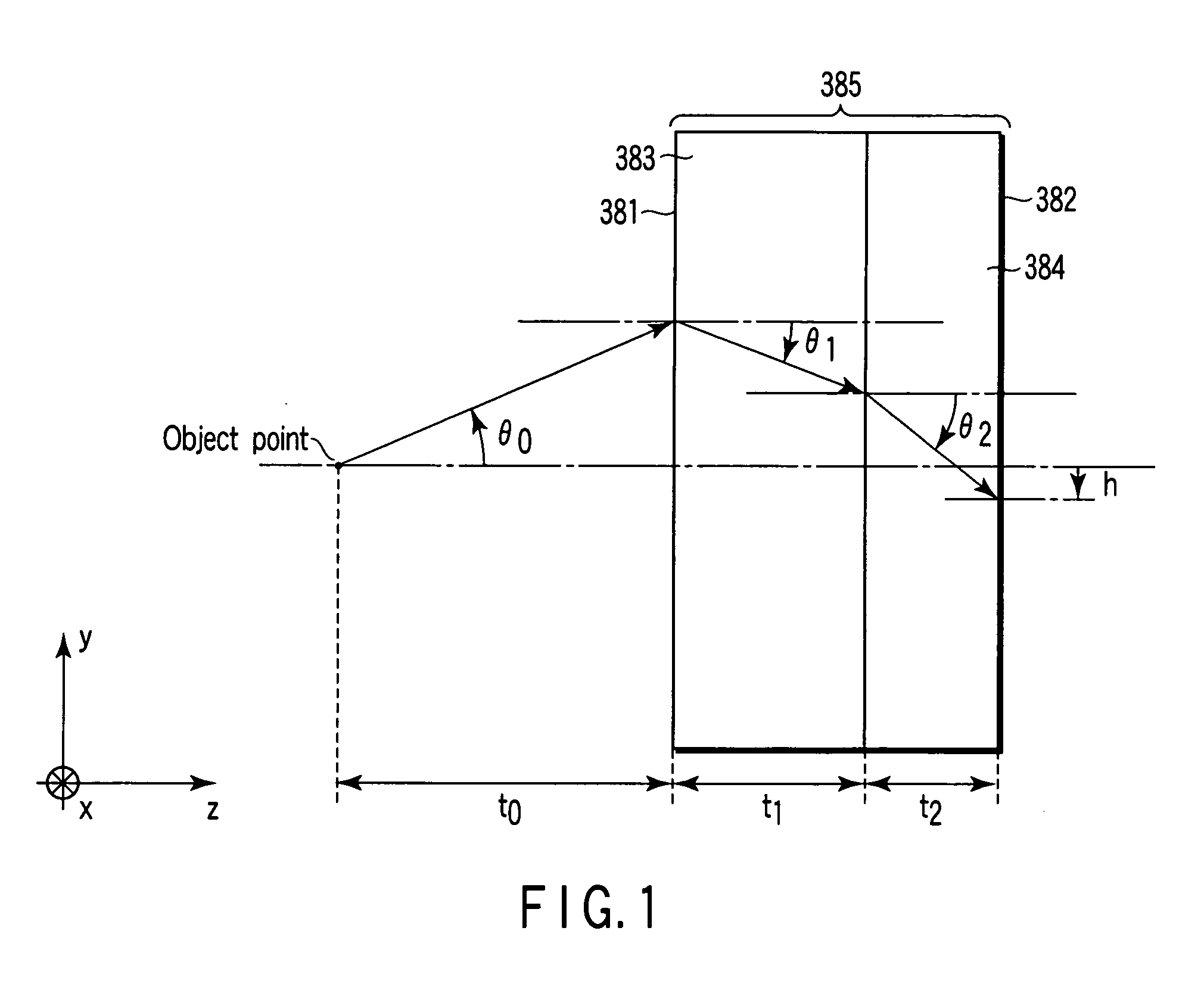
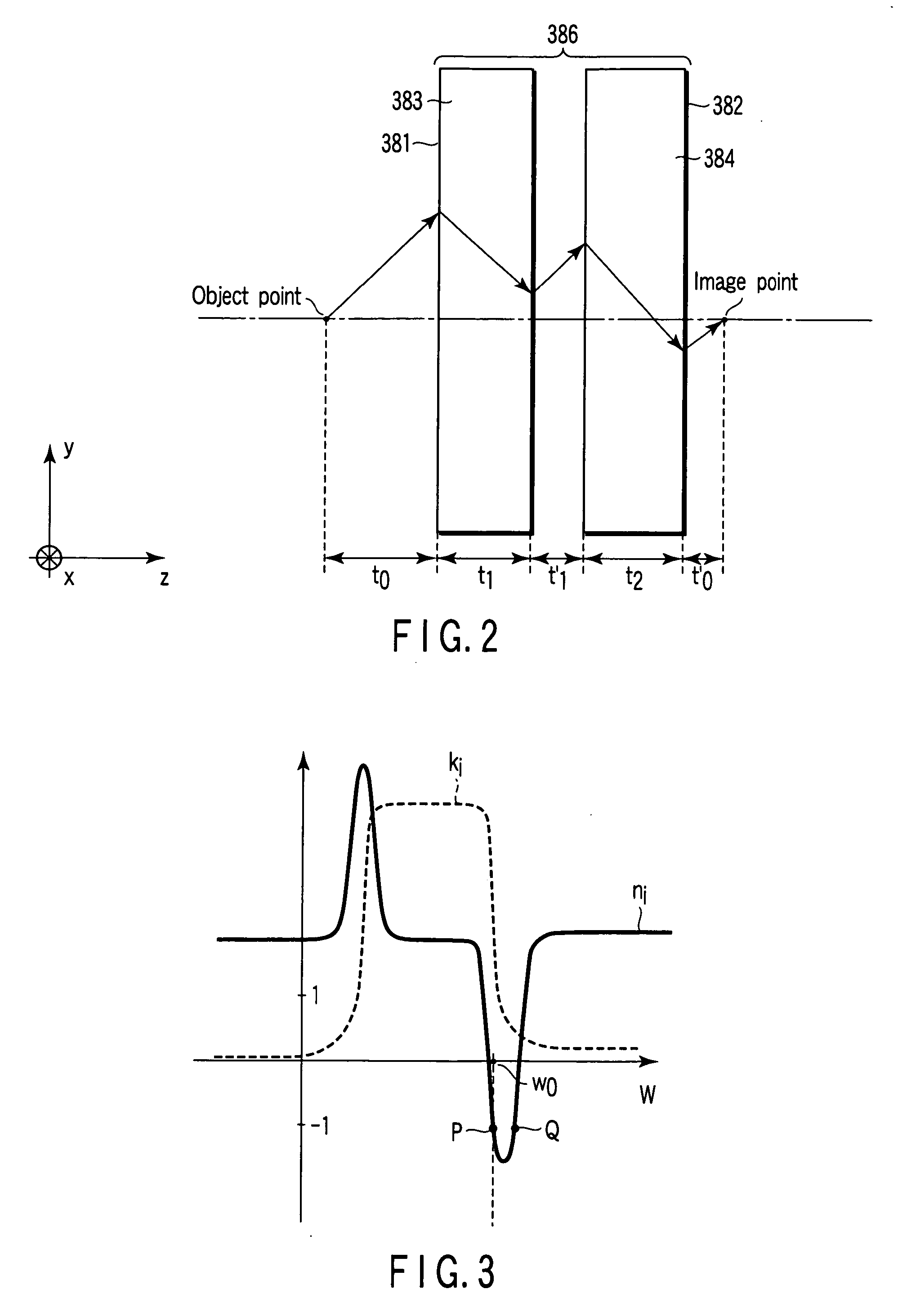
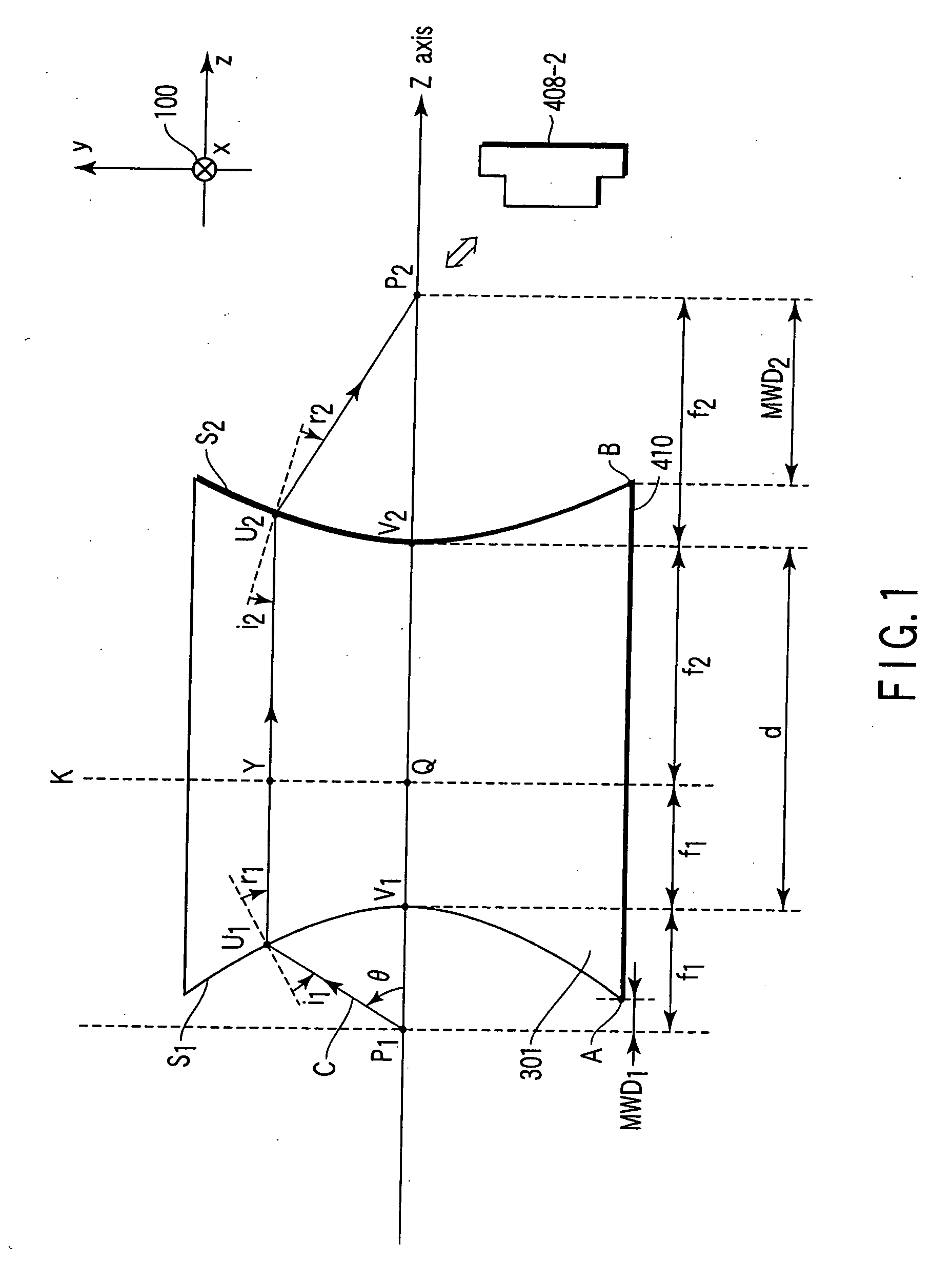
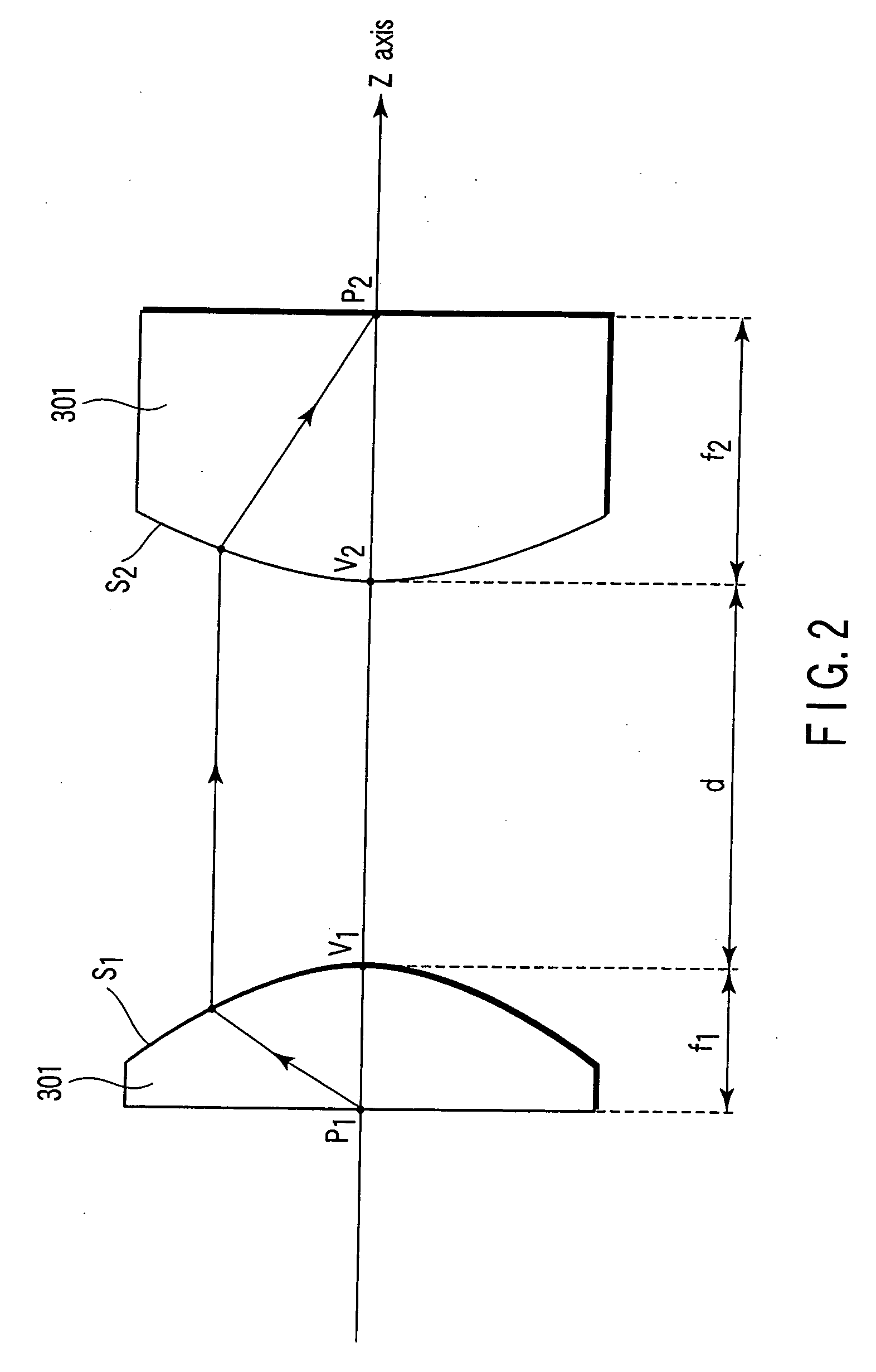
An optical element using a medium exhibiting negative refraction, a carbon nano tube being used for the medium exhibiting negative refraction, is disclosed. There is also disclosed an optical system having a plurality of optical elements each formed of a medium exhibiting negative refraction, wherein the plurality of optical elements includes optical elements having different chromatic dispersions.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Lens module with low chromatic aberration
InactiveUS20130044378A1Poor chromatic aberration correction propertyHigh chromatic aberration correction propertyMountingsLensNegative refractionCamera lens
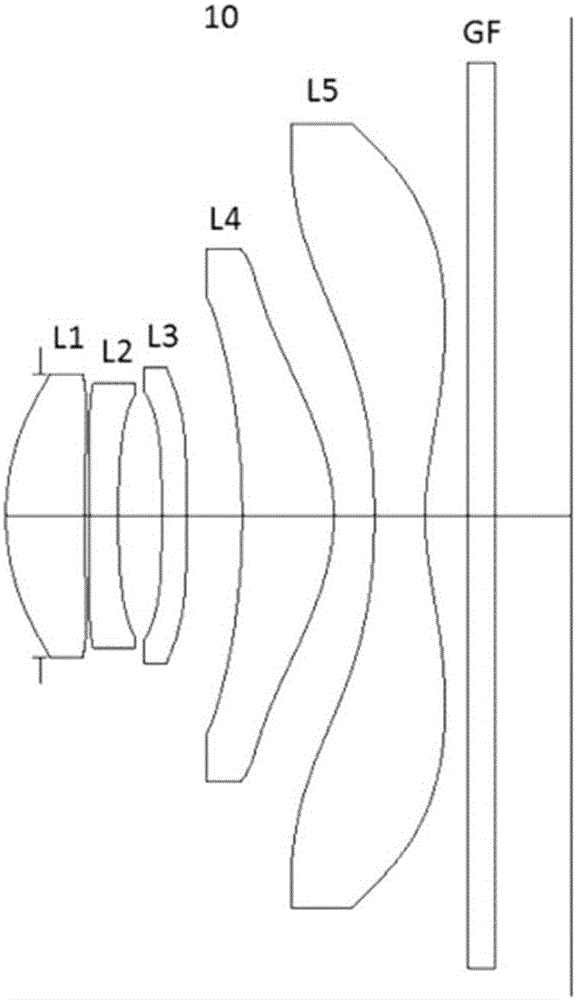
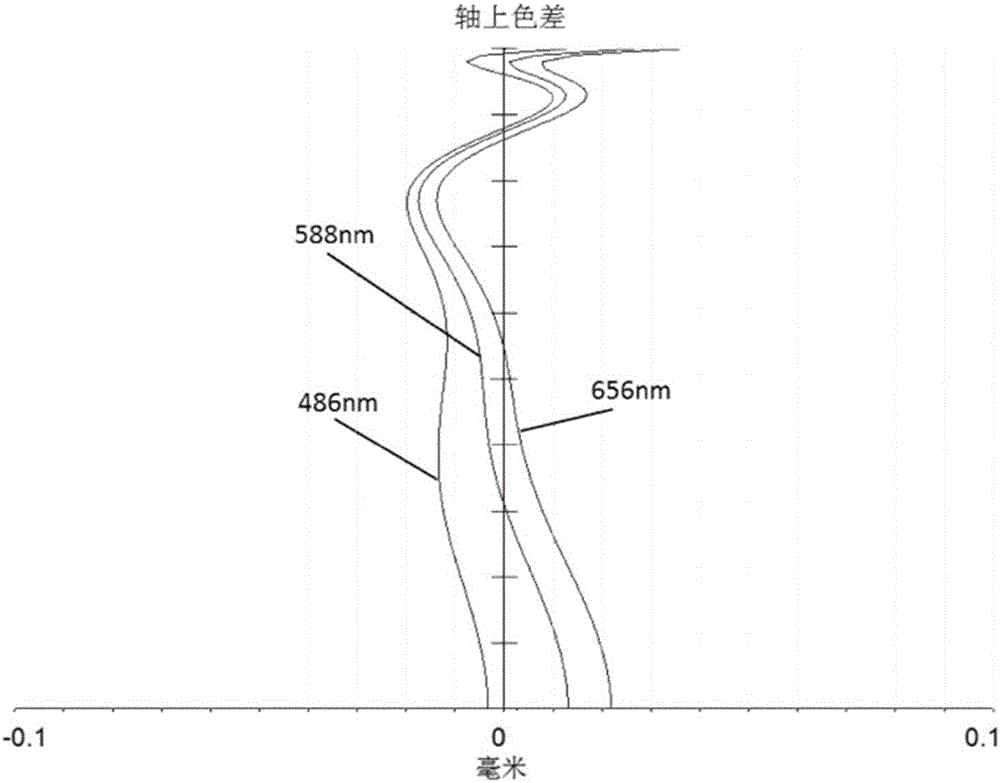
Provided is a lens module for imaging an object on an image plane. In the order from the object side to the image side of the lens module, the lens module includes a first lens made of glass and having positive refraction power, a second lens made of plastic and having negative refraction power, a aperture stopper, a third lens having positive refraction power, and a fourth lens having negative refraction power. The lens module satisfies the following formula: Vd1−Vd2≧35; wherein, Vd1 is the Abbe number of the first lens in d light and Vd2 is the Abbe number of the second lens in the d light.
Owner:FOSHAN PREMIER SCI & TECH CO LTD +1
Anisotropic metal-dielectric metamaterials for broadband all-angle negative refraction and superlens imaging
InactiveUS20090040132A1Easy to makeEasy to customizeLiquid surface applicatorsCoatingsNegative refractionDielectric matrix
A metamaterial comprises a plurality of metallic nanowires embedded in a dielectric matrix. The metamaterial composite media provide broadband all-angle negative refraction and flat lens, superlens and curved hyperlens imaging in specific spectral regions over a wide range of frequencies including, for example, from deep infrared to ultraviolet frequencies.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
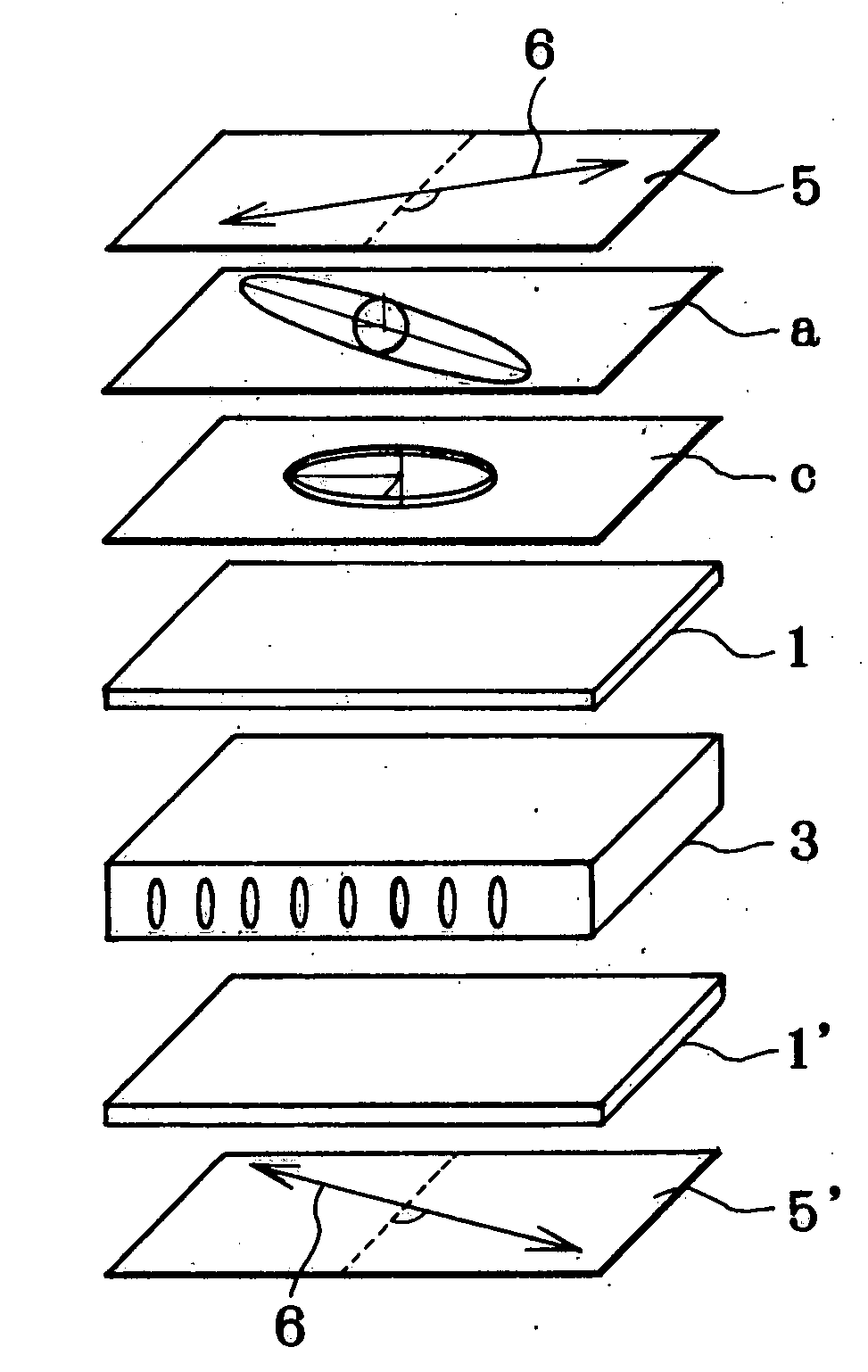
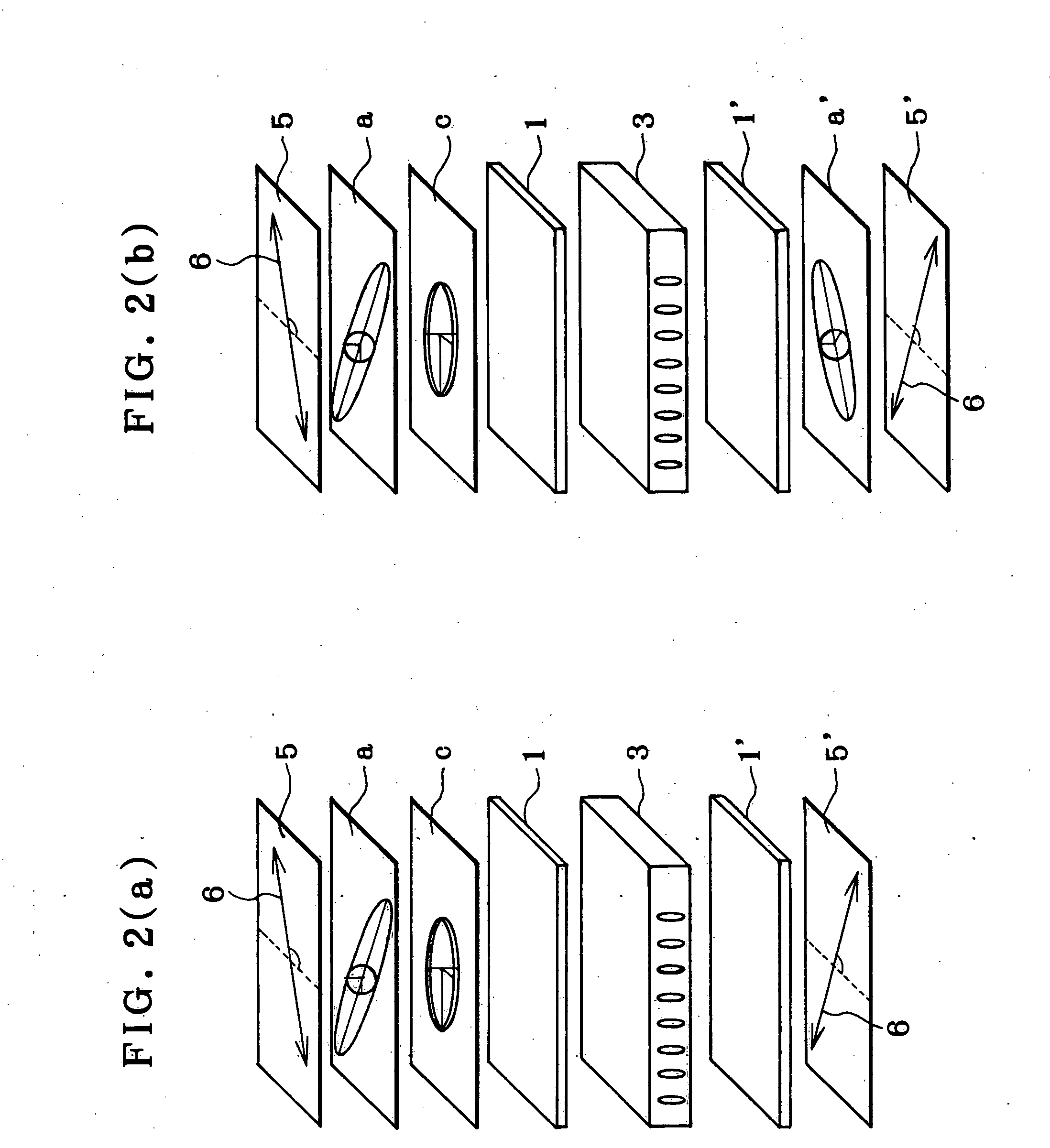
Liquid crystal display device and a method of manufacturing a viewing angle compensation film for the same
InactiveUS6853425B2Stable multi-domain structureWiden perspectivePolarising elementsNon-linear opticsNegative refractionLiquid-crystal display
A liquid crystal display (LCD) device include: first and second substrates, the first and second substrates having a plurality of pixels divided into at least two domains; a liquid crystal layer between the first and the second substrates, the liquid crystal layer having a different alignment direction in each domain; and first and second compensation films on outer surfaces of the first and second substrates, the first and second compensation films having a negative refractive anisotropy and having a triangle pattern.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Image capture lens
ActiveCN102985865ASmall outer diameterInhibition lossTelevision system detailsLensNegative refractionCamera lens
Provided is a six-layer configuration image capture lens that is compact and has adequate light at F2 or less, and wherein all aberrations are effectually corrected. In order from the object side, the image capture lens is configured of a first lens having a positive refraction and with a convex face oriented toward the object side; a second lens having a negative refraction and with a concave face oriented toward the imaging side; a third lens having either a positive or a negative refraction; a fourth lens having a positive refraction; a fifth lens having a positive refraction and with a convex face oriented toward the imaging side; and a sixth lens having a negative refraction and with a concave face oriented toward the imaging side. The imaging side face of the sixth lens further comprises an aspherical face shape, has an inflection point in a location other than a point of intersection with the optical axis, and satisfies the following formulae: ? d1 > 50, and ? d2 = 30, wherein ? d1 is the Abbe's number of the first lens, and ? d2 is the Abbe's number of the second lens.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Camera shooting optical lens
The present invention relates to the optical lens field, and discloses a camera shooting optical lens. The lens comprises from an object side to an image side in order: an aperture, a first lens with positive refraction power, a second lens with negative refraction power, a third lens with positive refraction power, a fourth lens with negative refraction power, a fifth lens with positive refraction power and a sixth lens with negative refraction power. The camera shooting optical lens satisfies the relation as follows: 0.70<f1 / f<0.80, 2.0<f2 / f< 1.8, 1.9<f3 / f<2.1, -2.6<f4 / f<-2.2, 0.8<f5 / f<1, -0.7< f6 / f <-0.5 and 1.9<f3 / f5<2.2. The camera shooting optical lens can satisfy the large aperture design requirement while shortening the optical total length and has good sensitivity appearance.
Owner:AAC OPTICS SOLUTIONS PTE LTD
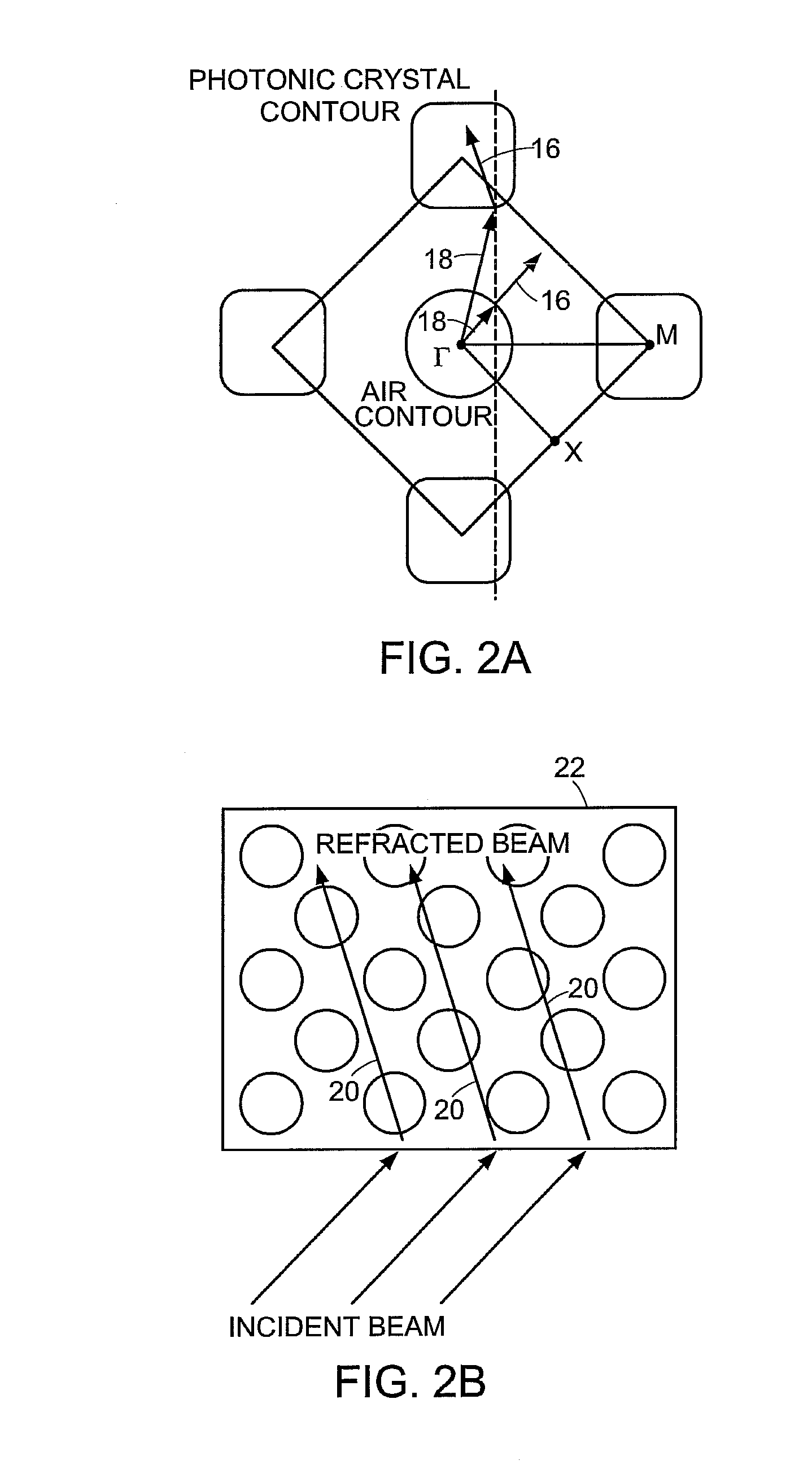
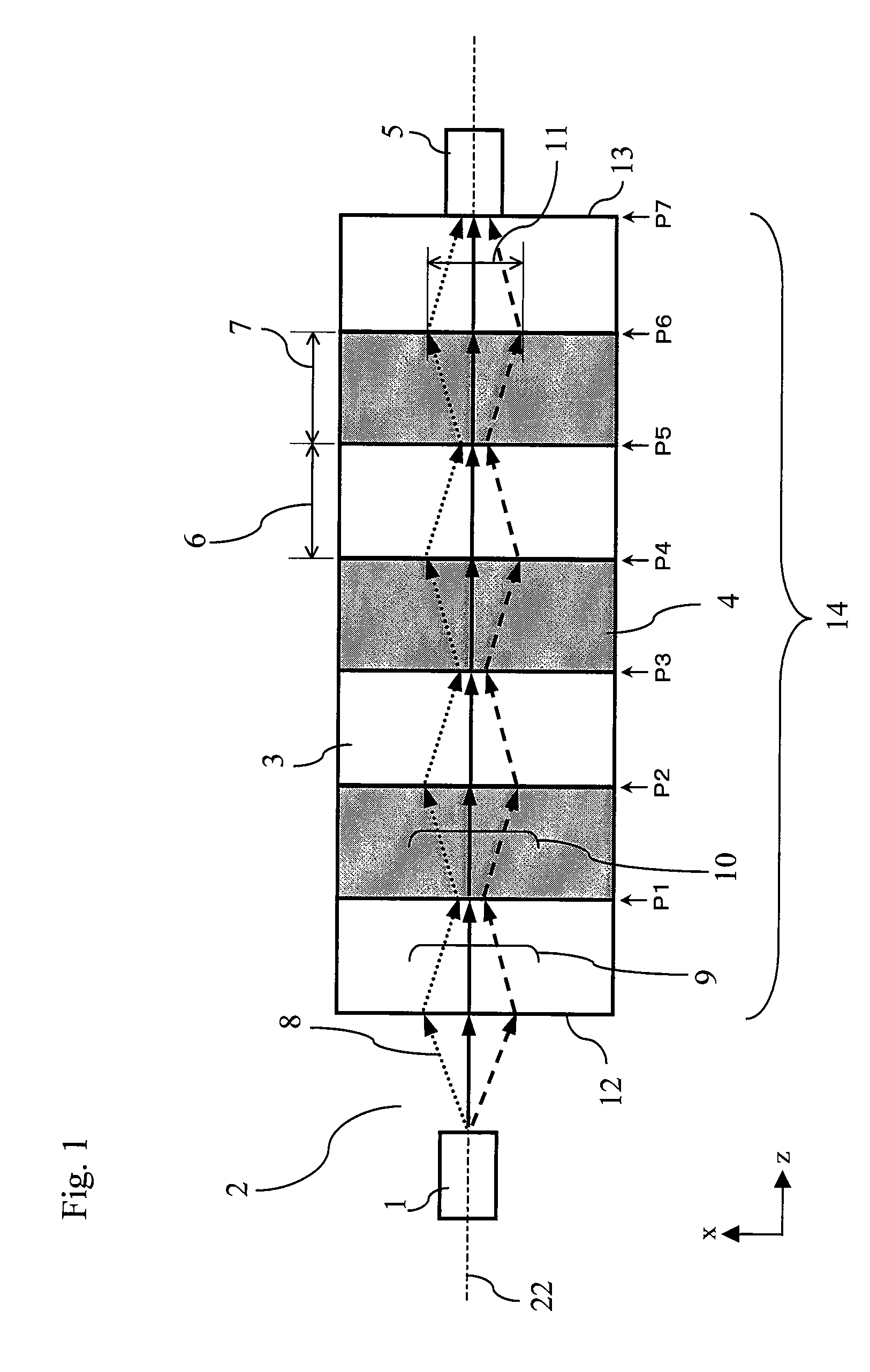
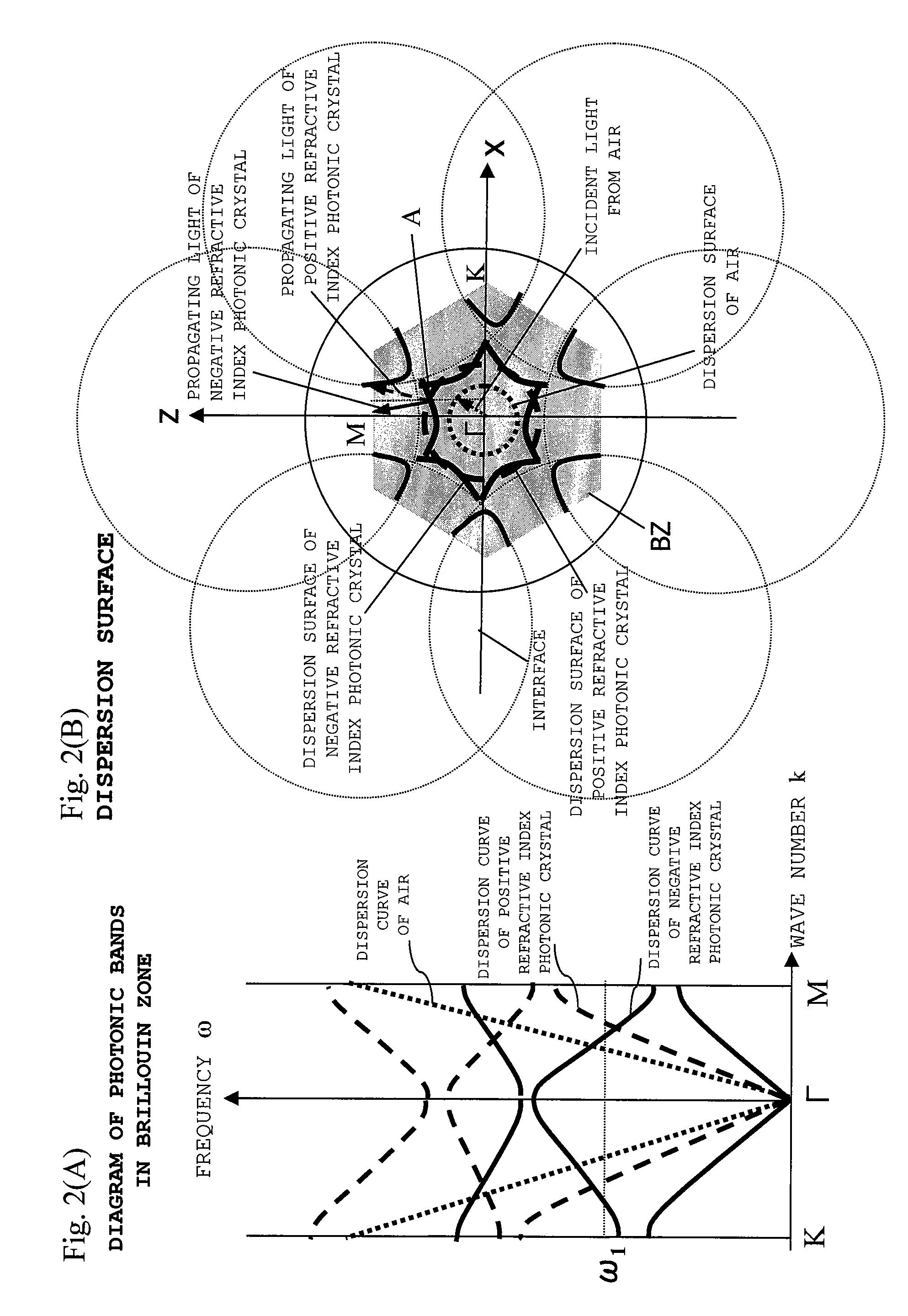
Photonic crystal exhibiting negative refraction without requiring a negative effective index
InactiveUS7339539B2Small sizeNanoopticsOptical waveguide light guideNegative refractionPhotonic crystal
A periodic electromagnetic medium is disclosed that includes a surface that provides an interface with an ambient medium and a periodic structure that provides negative refraction within the medium of an incident electromagnetic field incident on the surface. In various embodiments the incident electromagnetic field is within a range of frequencies, the medium may include dielectric or metallic material, and has either a positive or negative effective index.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Camera lens
The invention discloses a camera lens. From the object side to the image side, the camera lens sequentially comprises a first lens with positive refraction power a convex object side surface, a second lens, a third lens, a fourth lens, a fourth lens with a concave object side surface, a fifth lens with positive refraction power, a sixth lens, and a seventh lens with negative refraction power; the camera lens also comprises a diaphragm arranged between an object to be shot and a second lens. The camera lens meets relation expressions of TTL / Img H<2.4 and 1.5<CTl / CT2<4, wherein TTL is the total length of the camera lens, Img H is a half of the diameter of the effective pixel area of the camera lens on an imaging surface, CT1 is the central thickness of the first lens, and CT2 is the central thickness of the second lens. Meeting the expressions above, the camera lens has the advantages of wide field angle (wide angle), miniaturization, high imaging quality and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SUNNY OPTICAL CO LTD
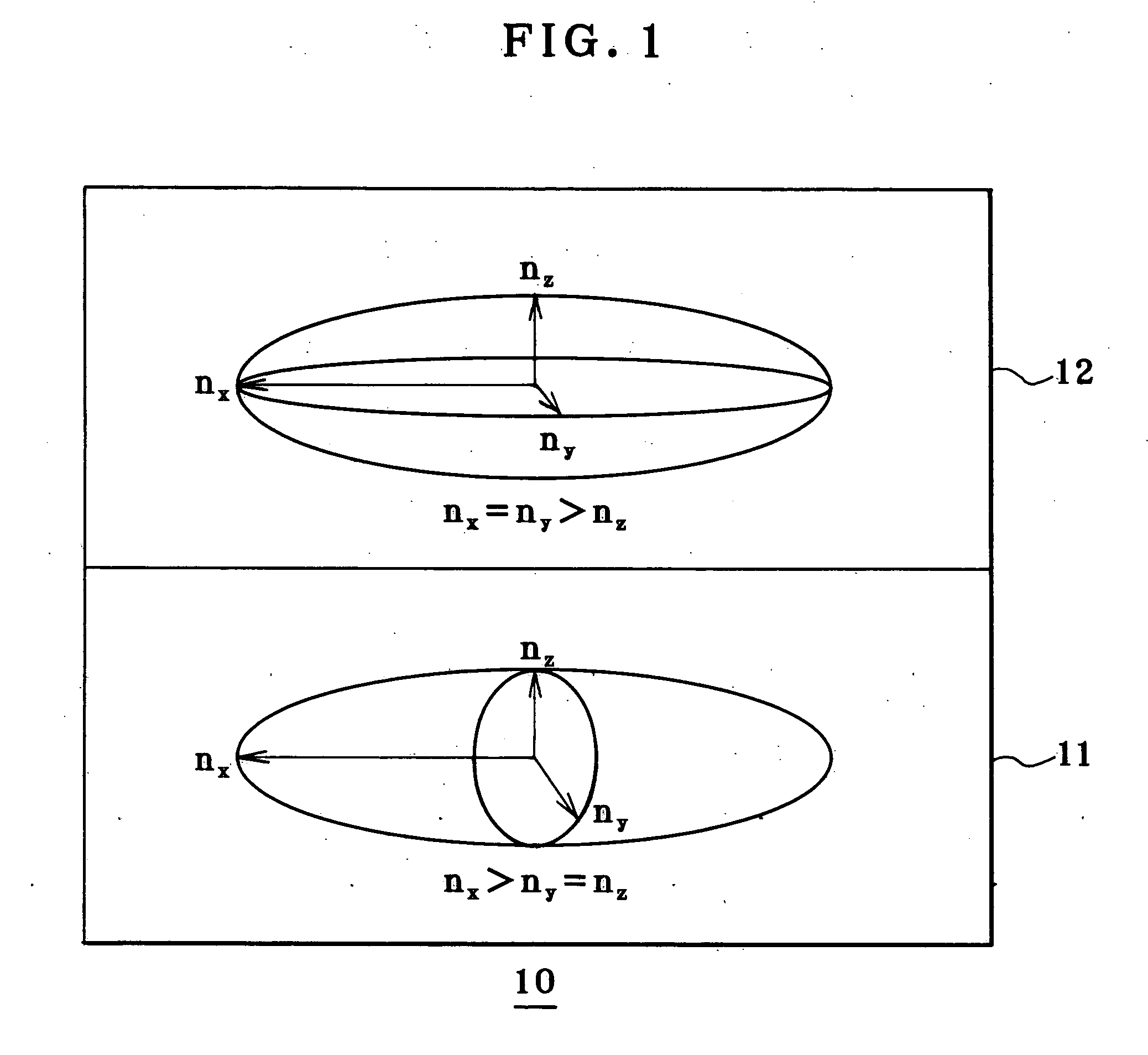
Laminated retardation layer, its fabrication process, and liquid crystal display incorporating the same
InactiveUS20050062917A1Widen perspectiveHigh color reproductionPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsManufacturing technologyPhase difference
The invention relates to a liquid crystal display that incorporates a laminated retardation layer 10 comprising a combination of a negative C-plate having a specific chromatic dispersion and a positive A-plate having a specific chromatic dispersion, used to improve the viewing angle characteristics thereof, thereby presenting high-contrast images with high color reproducibility yet with neither interference variations nor color shifts. The laminated retardation layer 10 is obtained by lamination of a retardation layer 11 having positive index anisotropy and an optical axis in a layer plane and a retardation layer 12 having negative index anisotropy and an optical axis in a normal direction to a layer plane. A stretched polymer film having inverse chromatic dispersion that causes retardation defined by an optical path difference between extraordinary light and ordinary light to become small as wavelength becomes short is used as the retardation layer 11 having positive index anisotropy and an optical axis in a layer plane, and a coating layer having normal chromatic dispersion that causes retardation defined by an optical path difference between extraordinary light and ordinary light to become large as wavelength becomes short is used as the retardation layer 12 having negative index anisotropy and an optical axis in a normal direction to a layer plane.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
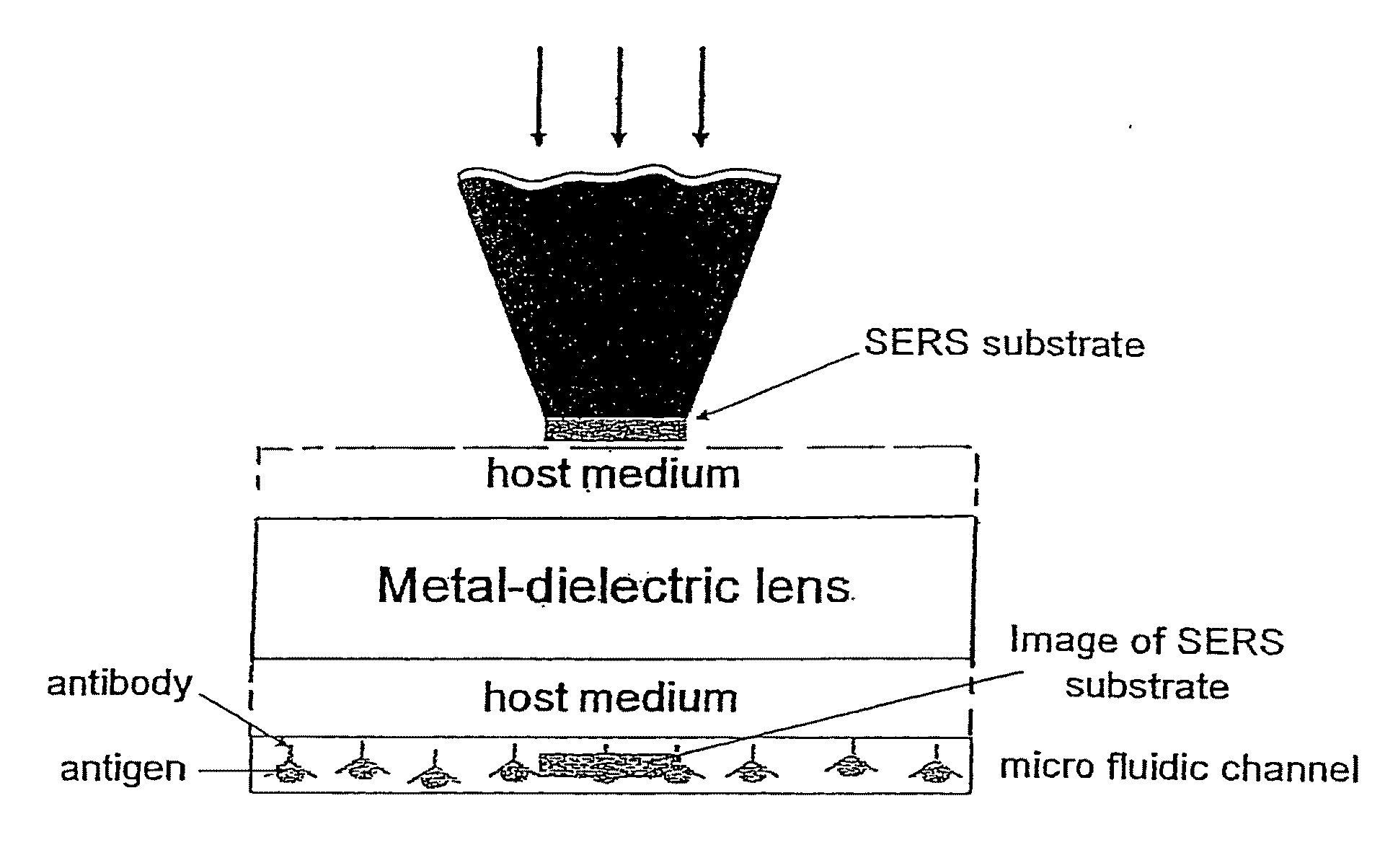
Near field super lens employing tunable negative index materials
ActiveUS20100134898A1High resolutionFast and accurate calculationNanoopticsMicroscopesCamera lensBio molecules
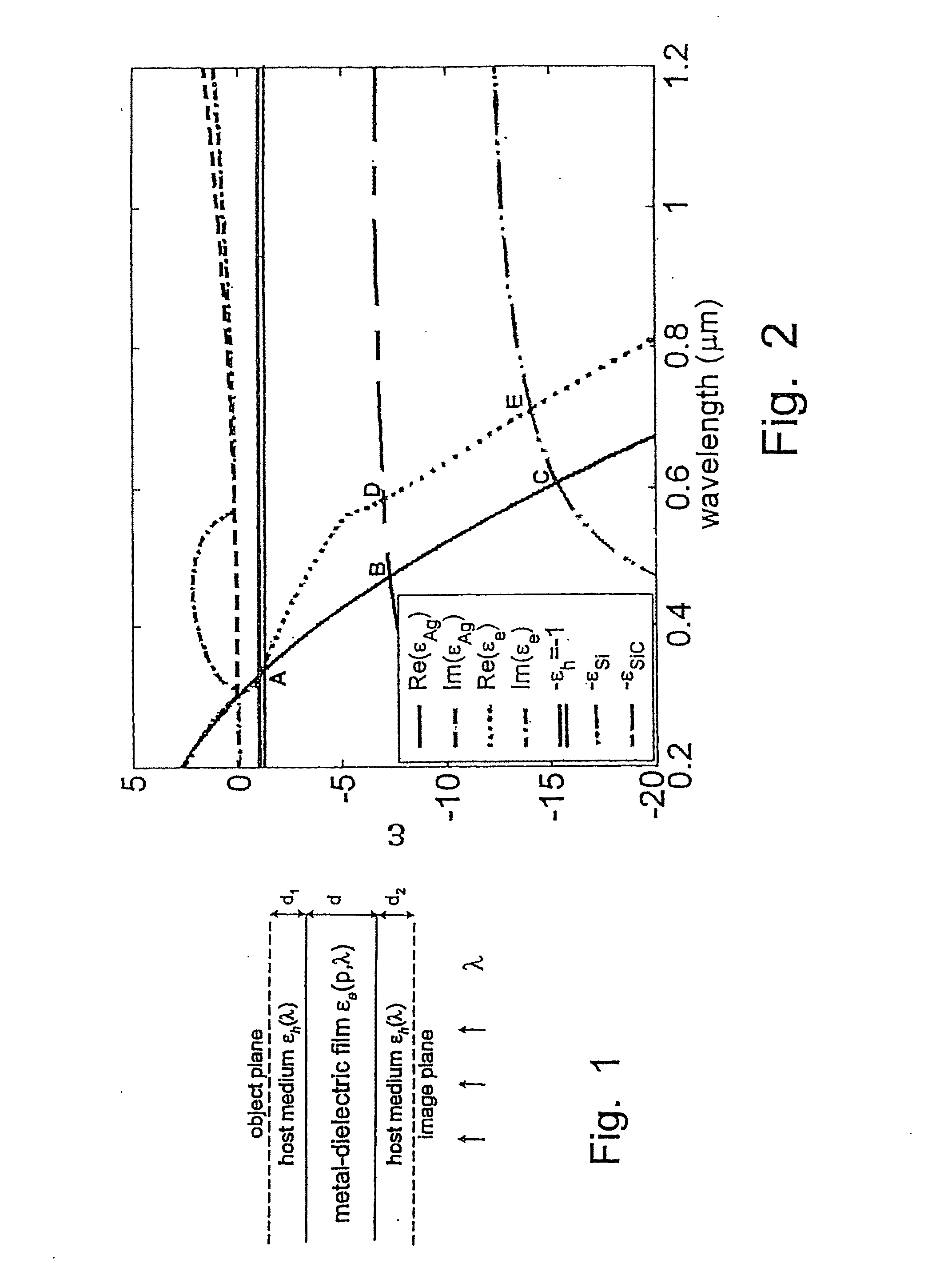
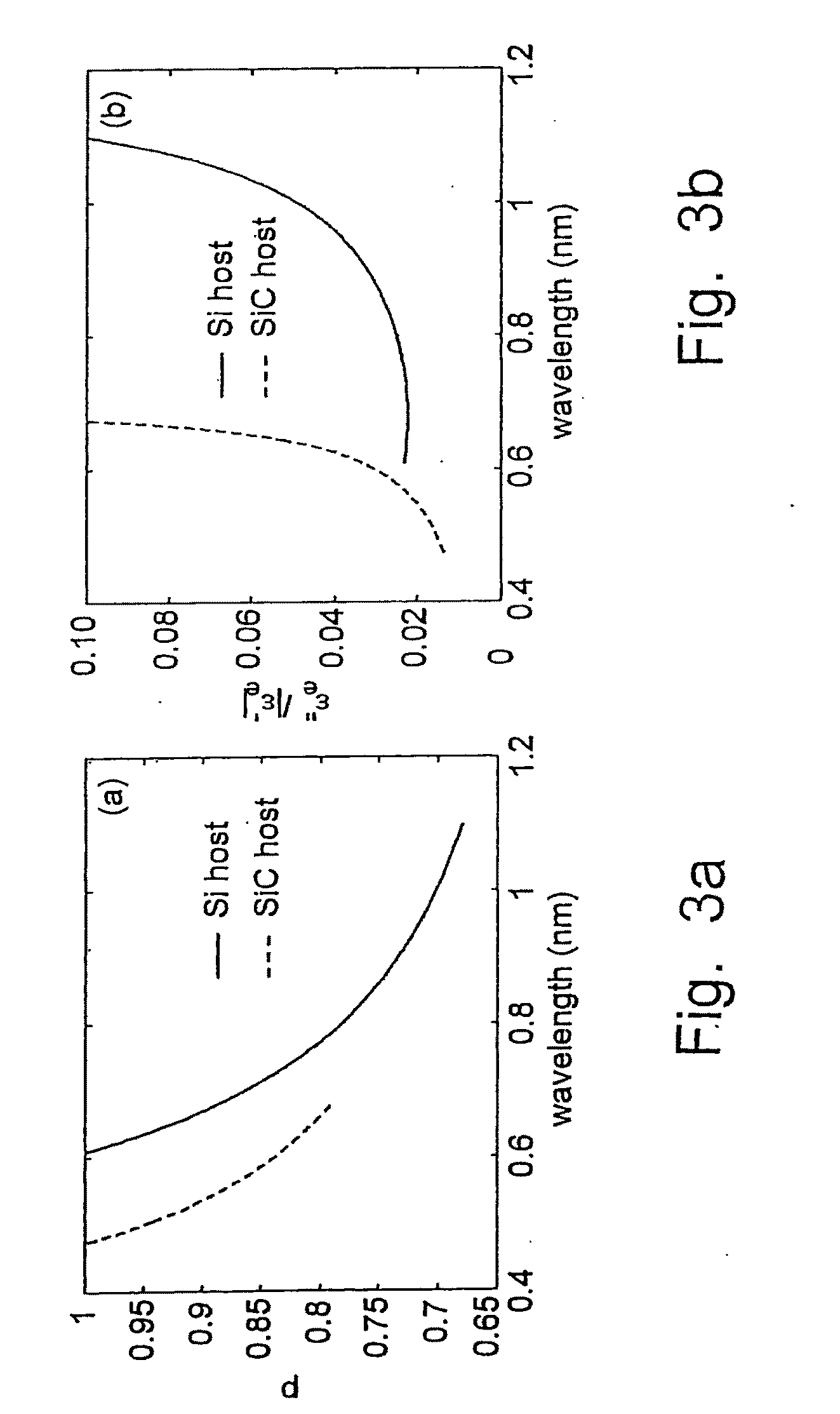
A tunable super-lens (TSL) for nanoscale optical sensing and imaging of bio-molecules and nano-manufacturing utilizes negative-index materials (NIMs) that operate in the visible or near infrared light. The NIMs can create a lens that will perform sub-wavelength imaging, enhanced resolution imaging, or flat lens imaging. This new TSL covers two different operation scales. For short distances between the object and its image, a near-field super-lens (NFSL) can create or enhance images of objects located at distances much less than the wavelength of light. For the far-zone, negative values are necessary for both the permittivity ε a permeability μ. While well-structured periodic meta-materials, which require delicate design and precise fabrication, can be used, metal-dielectric composites are also candidates for NIMs in the optical range. The negative-refraction in the composite films can be made by using frequency-selective photomodification.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Optical transmission device and light-receiving module
InactiveUS20070201805A1Easy to makeLarge caliberNanoopticsOptical waveguide light guideNegative refractionLight beam
An optical transmission device is provided with a first optical member having a negative refraction angle with respect to an incident angle of a beam and a second optical member having a positive refraction angle with respect to the incident angle, wherein the first and second optical members are arranged one each or more in tandem alternatively.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Reflex, magnifying optical system
InactiveUS20090225438A1Deterioration and variation is preventedReduce error sensitivityOptical elementsReflexPrism
A first lens group in a reflex, magnifying optical system includes sequentially from the side of an object, a first lens that has a negative refractive power and is a meniscus lens having a concave aspect facing toward an image, an optical element (prism) that refracts an optical path, a second lens having a negative refractive power and a concave aspect facing toward the object, and a third lens having a positive refractive power. A portion of an image-side aspect of the first lens abuts a plane of incidence of the optical element. A portion of an object-side aspect of the second lens abuts a plane of transmission of the optical element.
Owner:TAMRON
Image detection method and image detecting apparatus
InactiveUS7411736B2Enhancement of evanescent waves is reducedGood effectNanoopticsCharacter and pattern recognitionNegative refractionImage detection
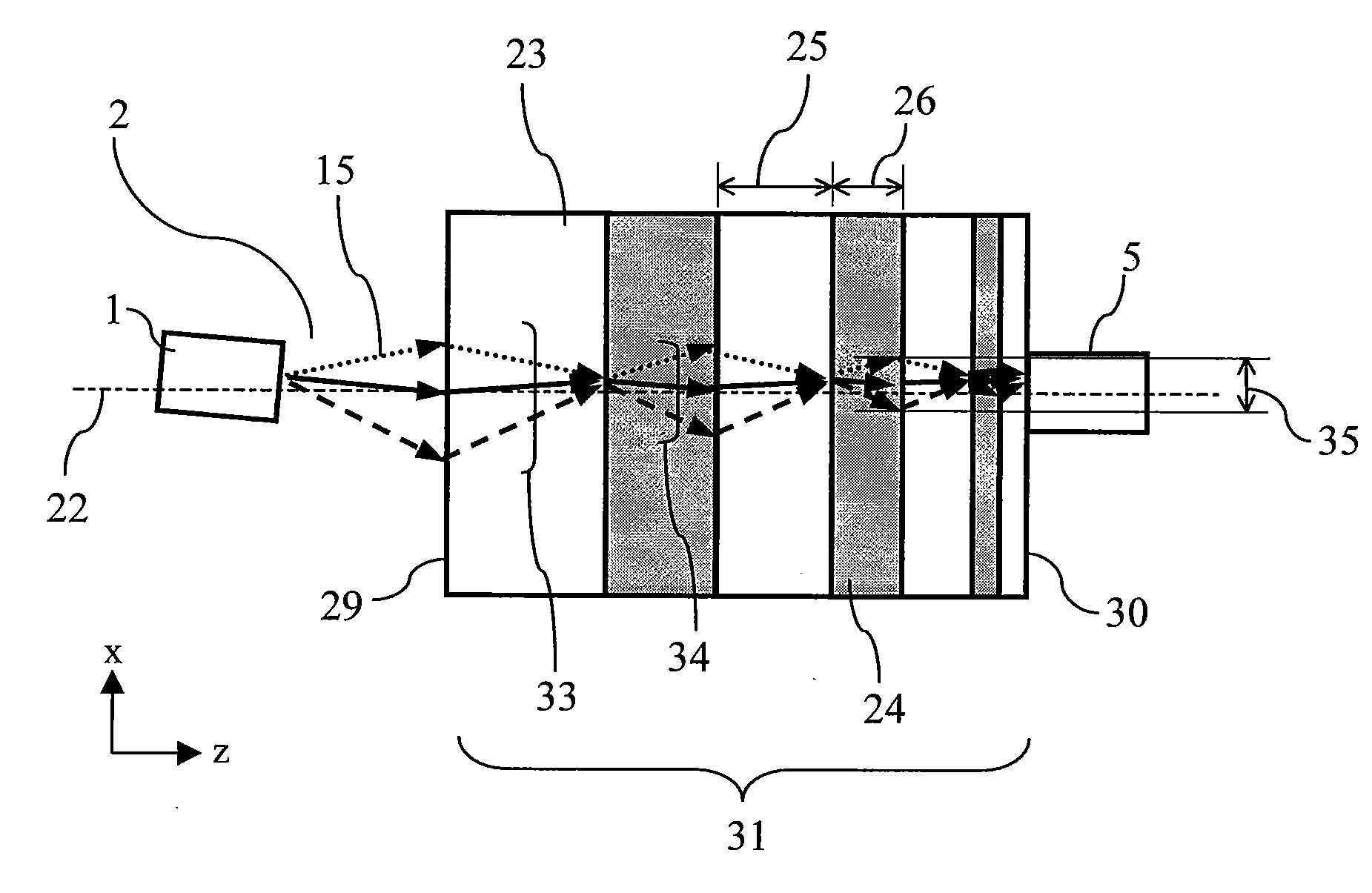
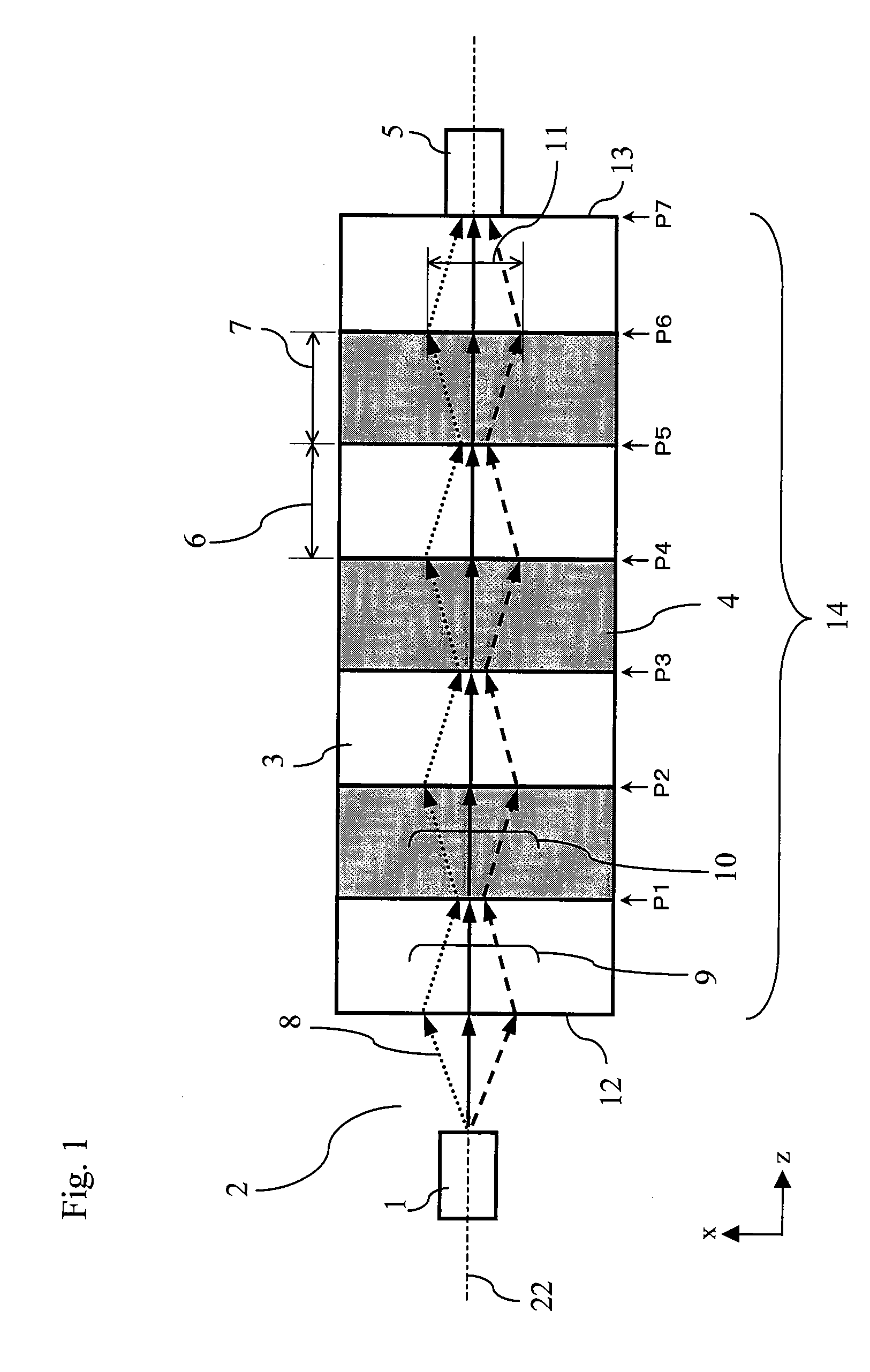
An image detection method includes steps of transferring image information in which, information of an object image on a sample (object plane) is transferred to a detection plane (image plane) of an imaging element via an optical system which includes a negative refraction lens formed of a material exhibiting negative refraction, detecting image in which, image-plane image information transferred to the detection plane (image plane) of the imaging device is detected optically, and calculation processing in which, for the image-plane image information which is detected, information of the object image is calculated by performing a calculation processing based on optical characteristics of the optical system.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Optical transmission device and light-receiving module
InactiveUS7554741B2Easy to makeLarge caliberNanoopticsOptical waveguide light guideNegative refractionAngle of incidence
An optical transmission device is provided with a first optical member having a negative refraction angle with respect to an incident angle of a beam and a second optical member having a positive refraction angle with respect to the incident angle, wherein the first and second optical members are arranged one each or more in tandem alternatively.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
3D interactive lens
ActiveCN104166220AHigh resolutionLarge resolution under the premise of high resolutionOptical elementsNegative refractionMicro imaging
The invention provides a 3D interactive lens. A micro imaging lens system formed by five groups of lenses is arranged. The 3D interactive lens comprises a first lens, a second lens, a third lens, a fourth lens, a fifth lens from an object side to an image side successively. The first lens has a negative refraction power and the objective side is a convex surface; the second lens has positive fraction power and the image side of the second lens is a convex surface; the third lens has a negative refraction power and the image side of the third lens is a concave surface; the fourth lens has a positive refraction power and the image side of the fourth lens is a convex surface; and the fifth lens has a negative refraction power and the object side of the fifth lens is a convex surface and the image side is a concave surface. The lens meets the relations: 0<(R3+R4) / (R3-R4)<1.2, and 7<T12 / T23<25, wherein R3 and R4 respectively indicate curvature radiuses of the object side and the image side of the second lens, T12 indicates a distance between the first lens and the second lens at the optical axis, and the T23 indicates the distance between the second lens and the third lens at the optical axis. According to the invention, On the basis of configuration of the lens, advantages of small aperture and miniaturization and the like can be realized on the premise that wide angle and high resolution ratio are guaranteed. Meanwhile, the heat difference can be effectively eliminated and distortion can be well corrected.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SUNNY OPTICAL CO LTD
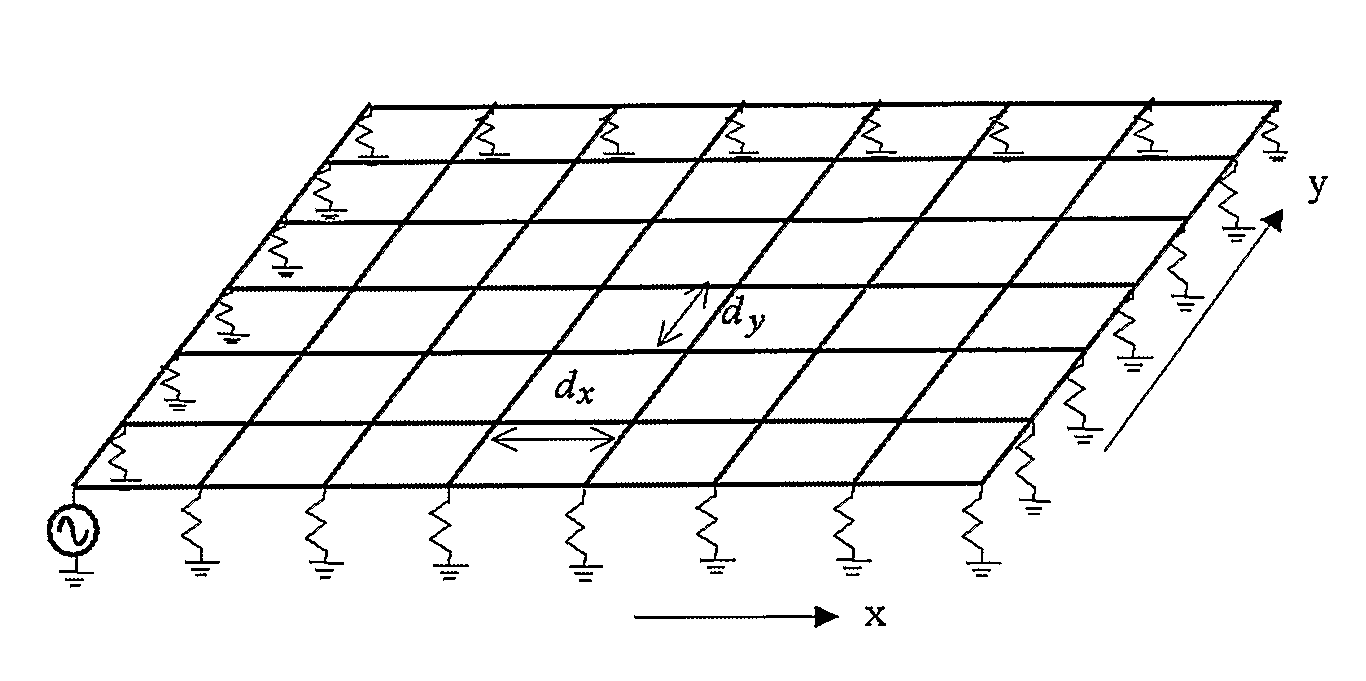
Negative-Refraction Metamaterials Using Continuous Metallic Grids Over Ground for Controlling and Guiding Electromagnetic Radiation
InactiveUS20080204164A1Easy and less-costly to manufactureMultiple-port networksHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionNegative refractionElectromagnetic radiation
For the cost effective implementation of negative-index refraction, an anisotropic hyperbolic planar metamaterial comprising a first set of substantially parallel, unloaded and coplanar transmission lines, said first set being spaced with a periodicity dy a second set of substantially parallel, unloaded and coplanar transmission lines, said second set being spaced with a periodicity dx, further being coplanar and substantially orthogonal with said first set of transmission lines, wherein the periodicities of said first set and second set of transmission lines being governed by the relationship βx(fr)dx+βy(fr)dy=2π, where: βx and βy are the intrinsic propagation constants of electromagnetic waves of frequency fr propagating along the first and second set of transmission lines, respectively.
Owner:ONTARIO CENTS OF EXCELLENCE
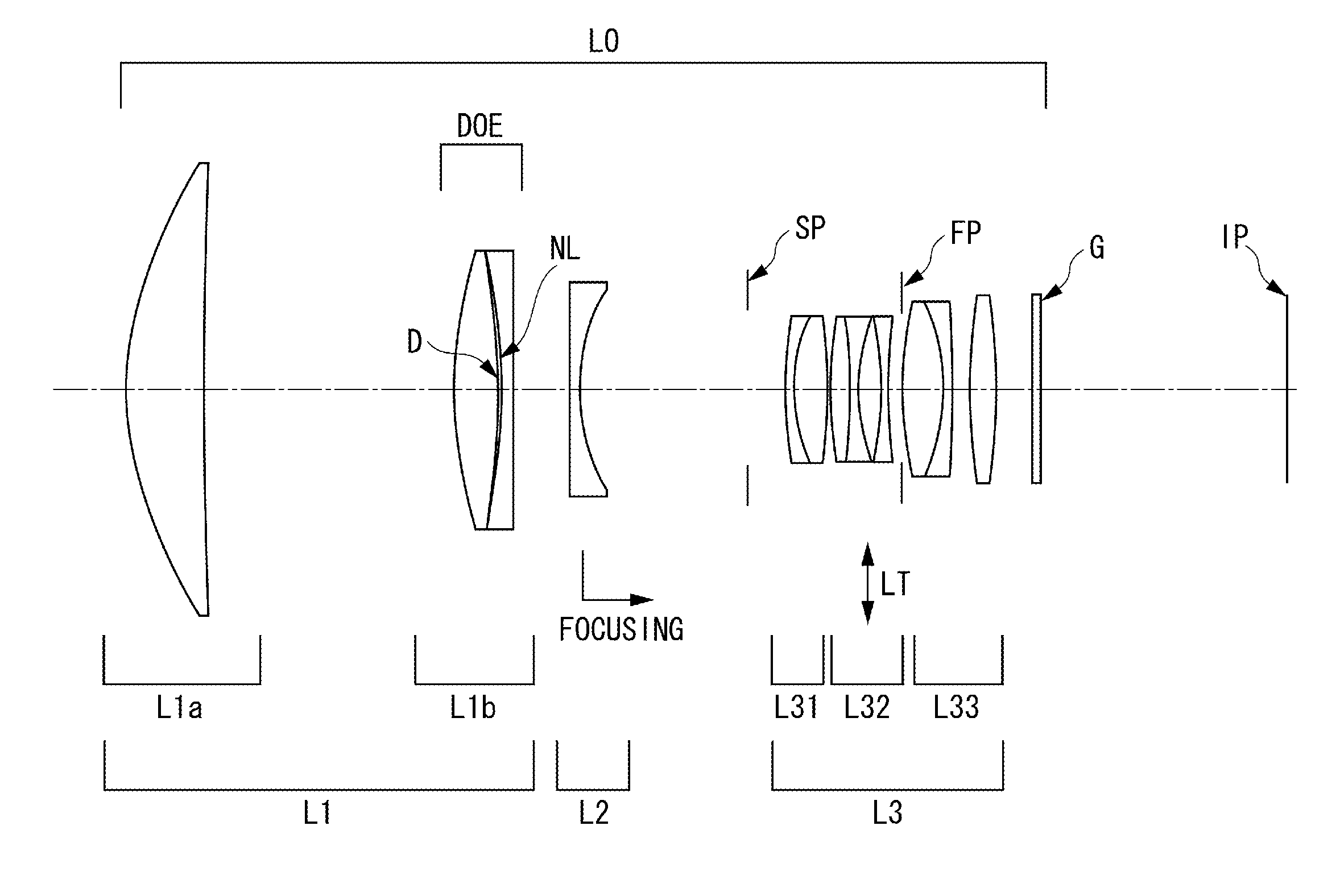
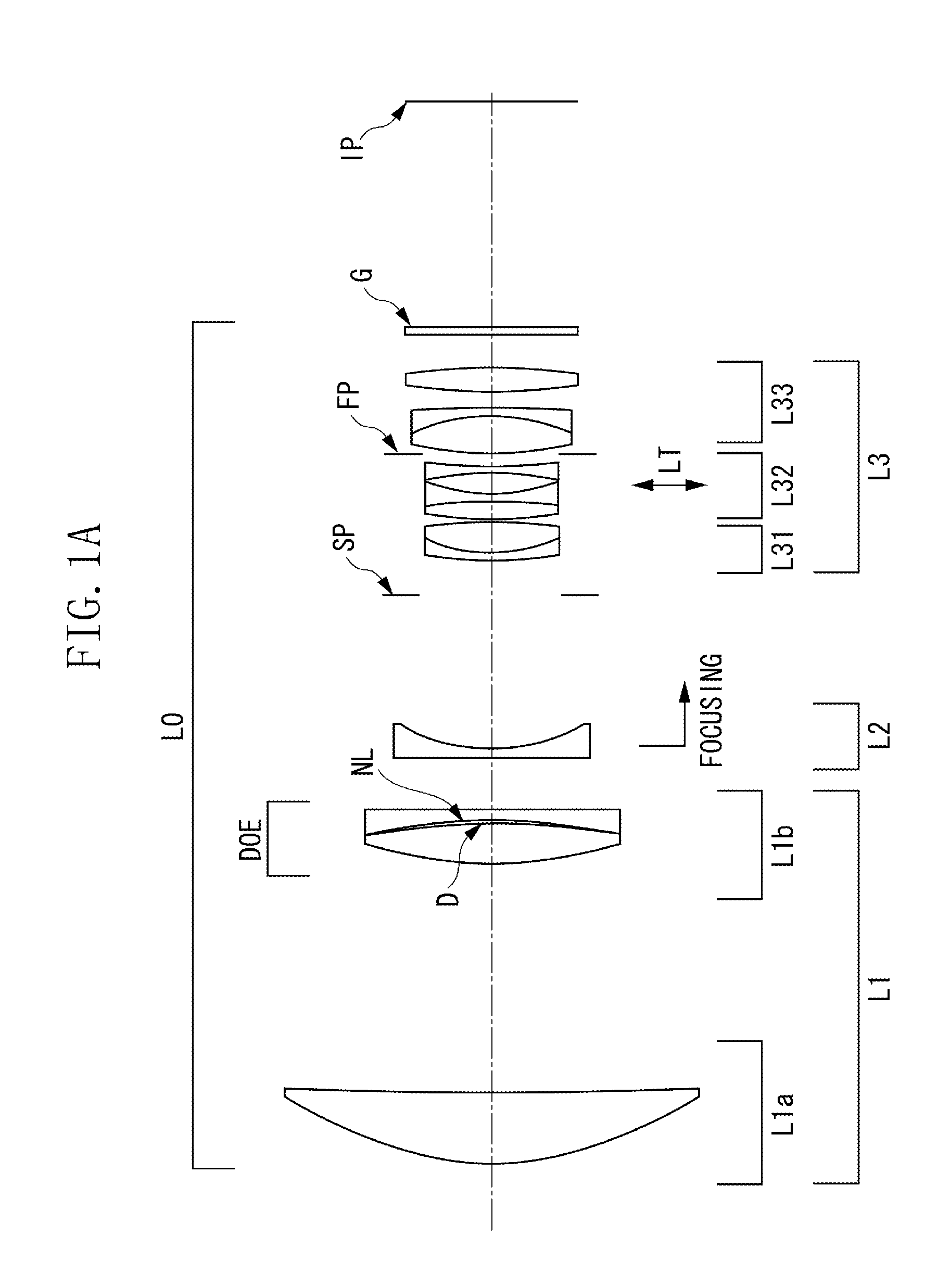
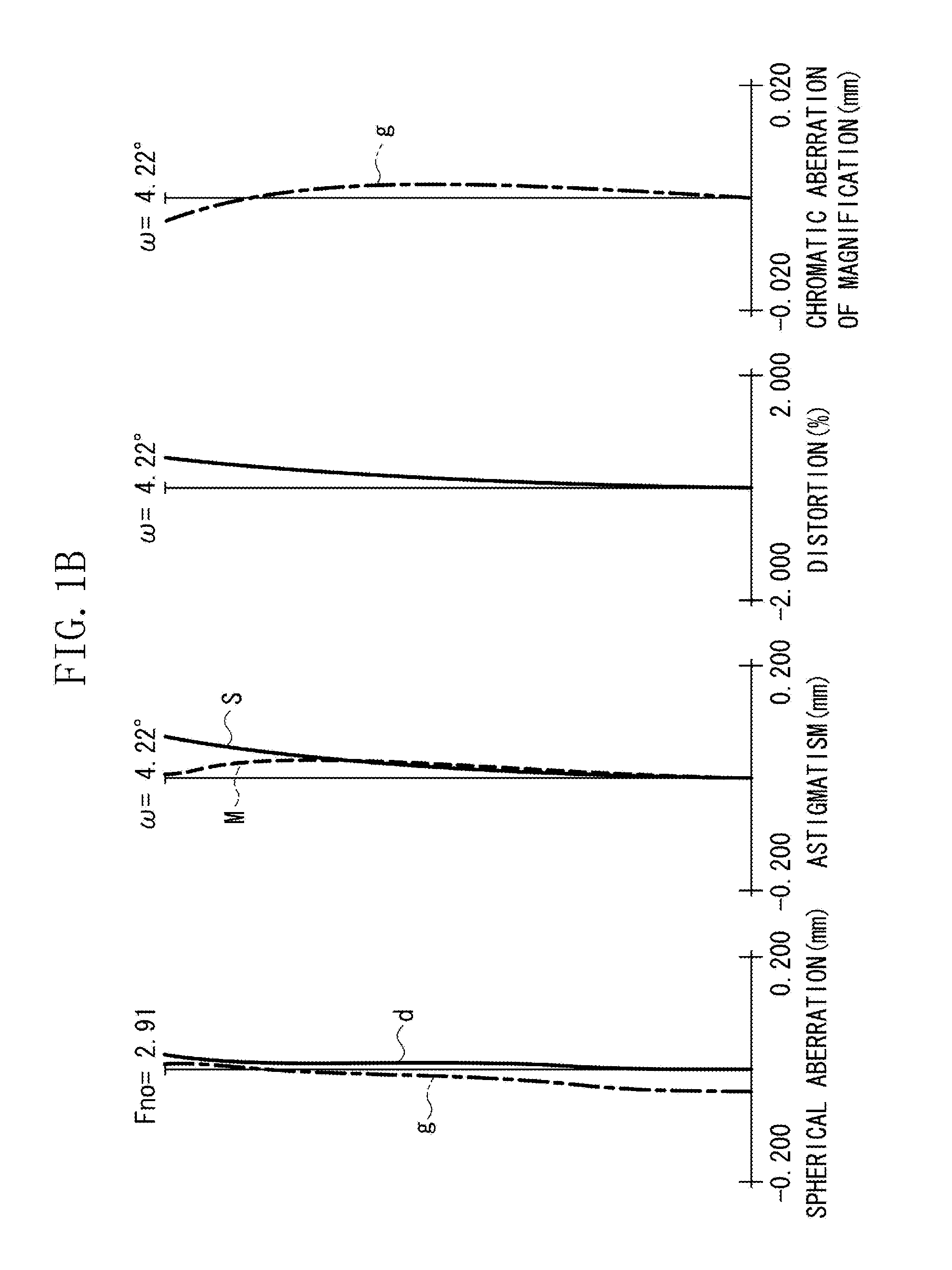
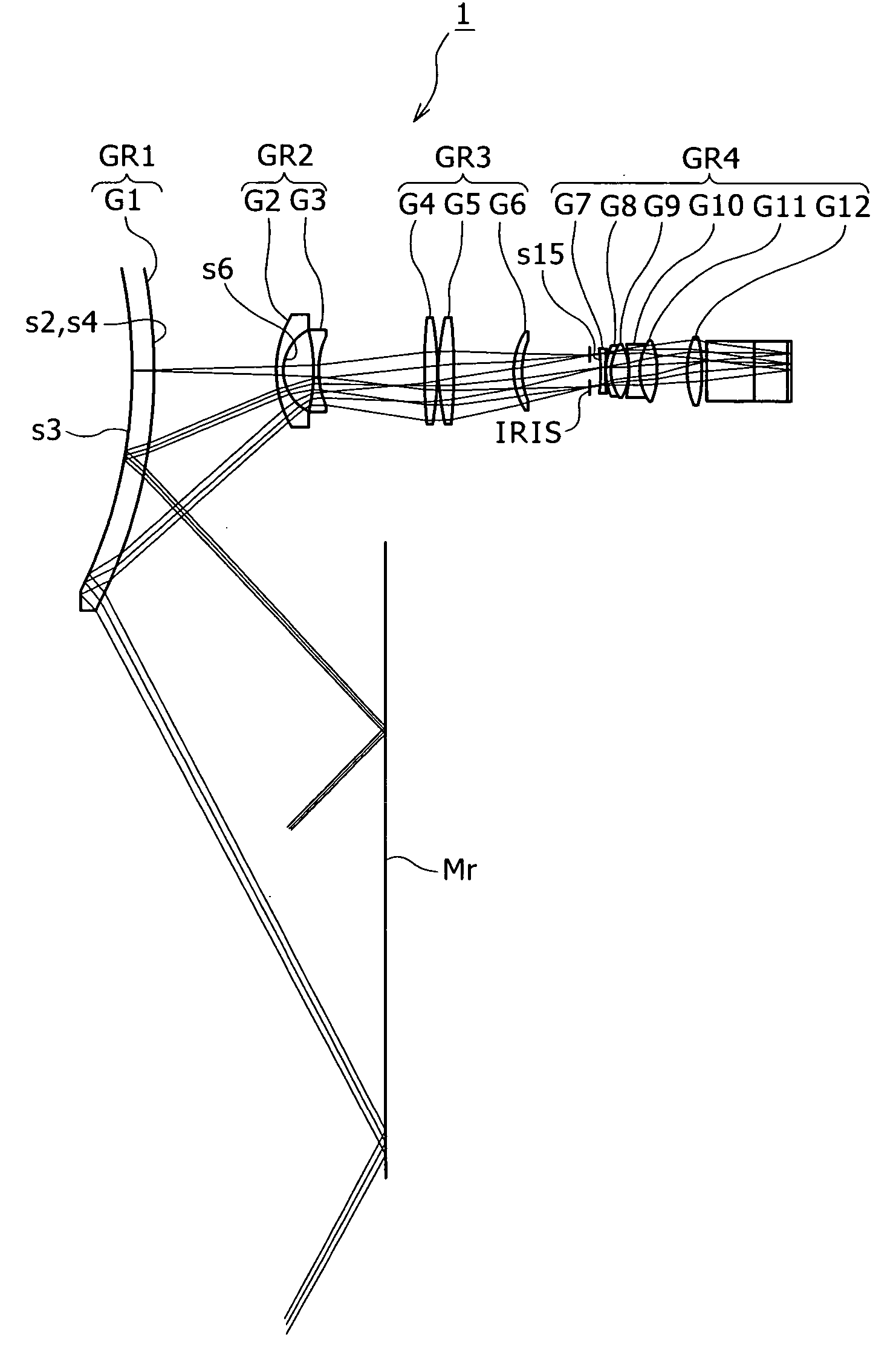
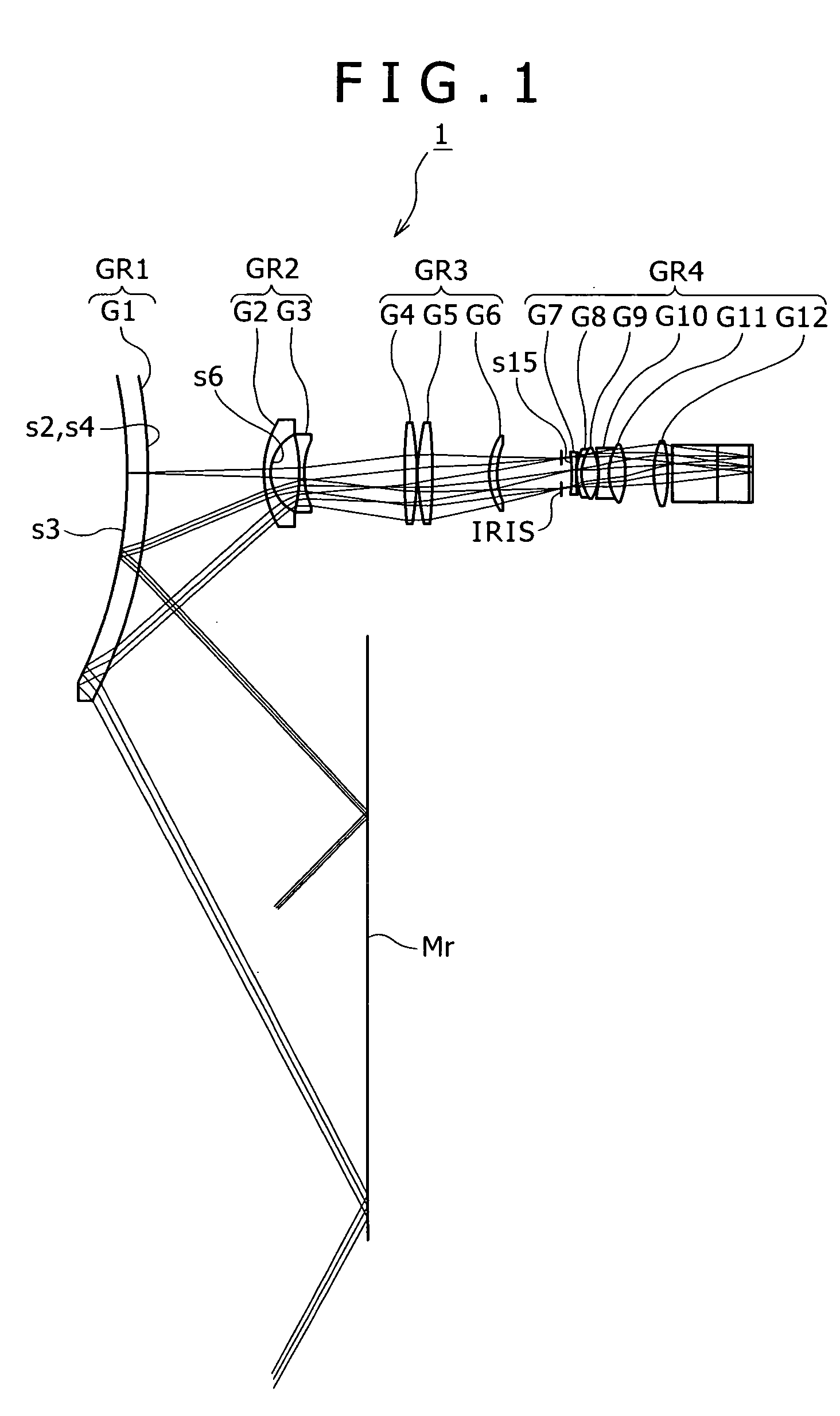
Photographic optical system and image pickup apparatus having the same
A photographic optical system includes, in order from an object side to an image side, a first lens unit having a positive refractive power, a second lens unit having a positive or negative refractive power, and a third lens unit having a positive or negative refractive power, focusing being performed by moving the second lens unit, wherein at least one diffractive optical element and at least one optical element made of solid material are provided closer to the object side than a position where a paraxial chief ray intersects an optical axis, and wherein a focal length obtained by only a diffraction component of the diffractive optical element, a focal length of the optical element made of solid material, a focal length of the first lens unit, and a relative anomalous partial dispersion of a material forming the optical element made of solid material are appropriately set.
Owner:CANON KK
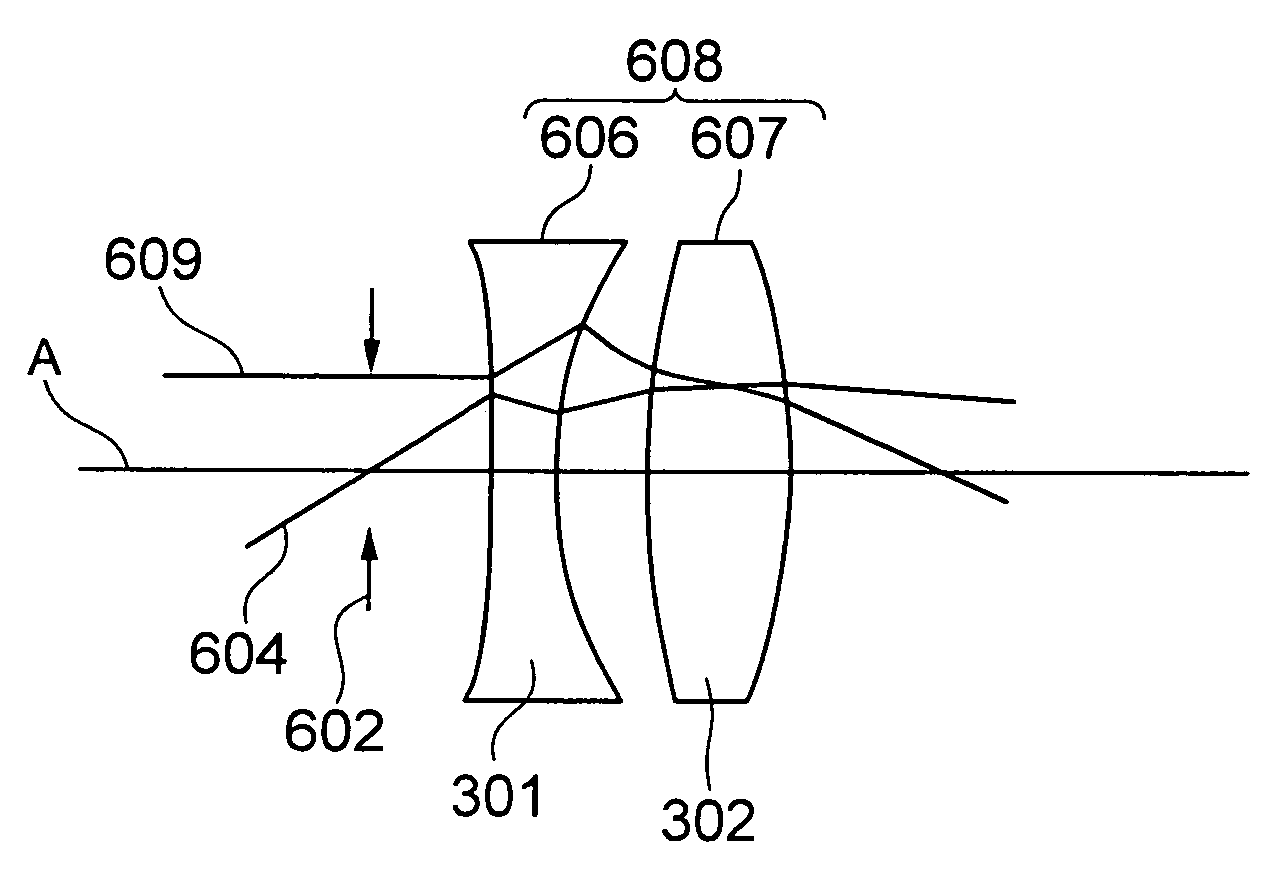
Lens system and optical apparatus
A lens system includes a first lens which is formed of a medium exhibiting negative refraction, and a second lens having a positive refractive index. Accordingly, it is possible to provide a lens system in which a negative refractive index medium for which a curvature of field is reduced. Moreover, it is also possible to have a lens system in which a lens having a positive focal length and a lens having a positive focal length, which is made of a positive refractive index medium, are combined.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
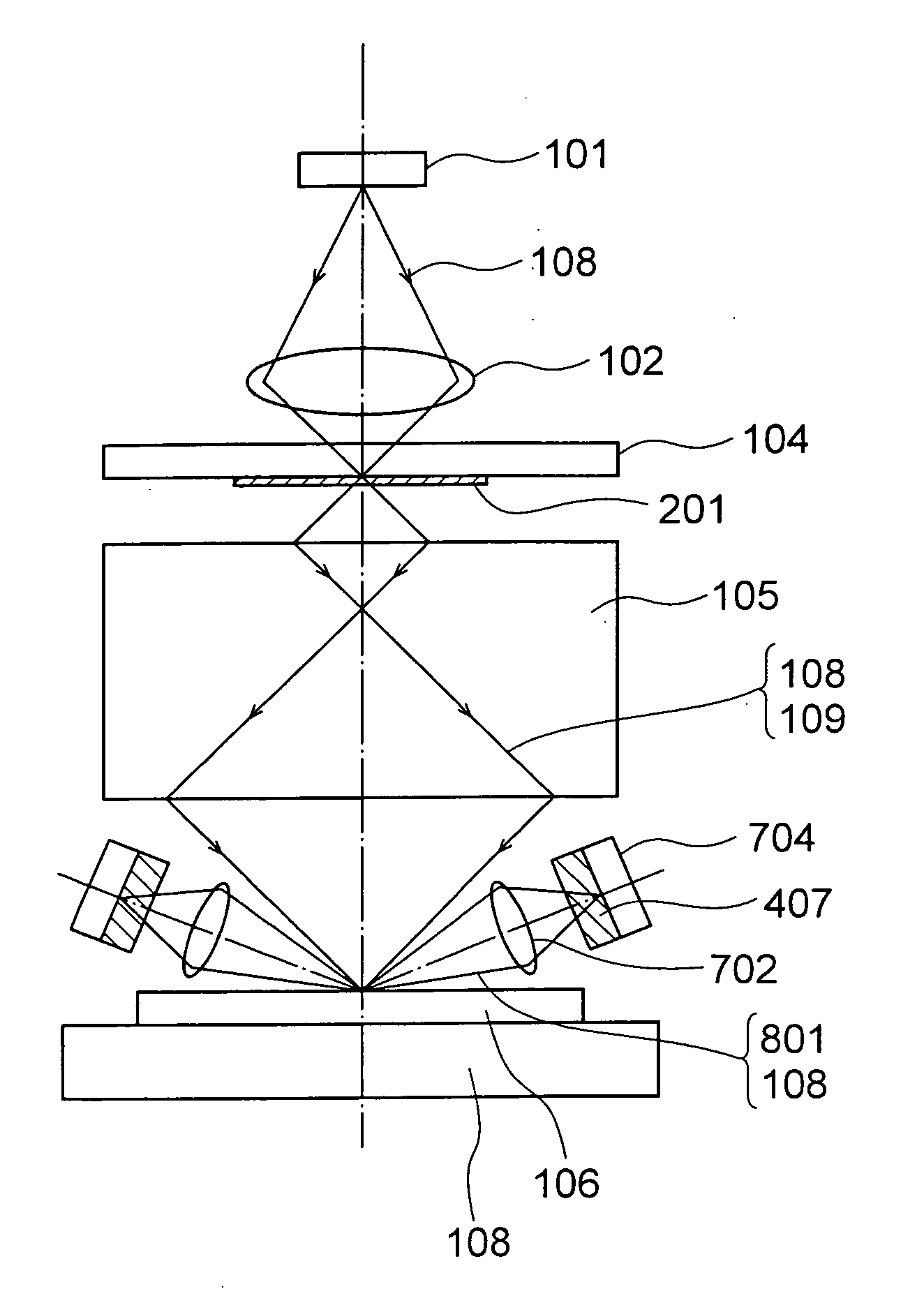
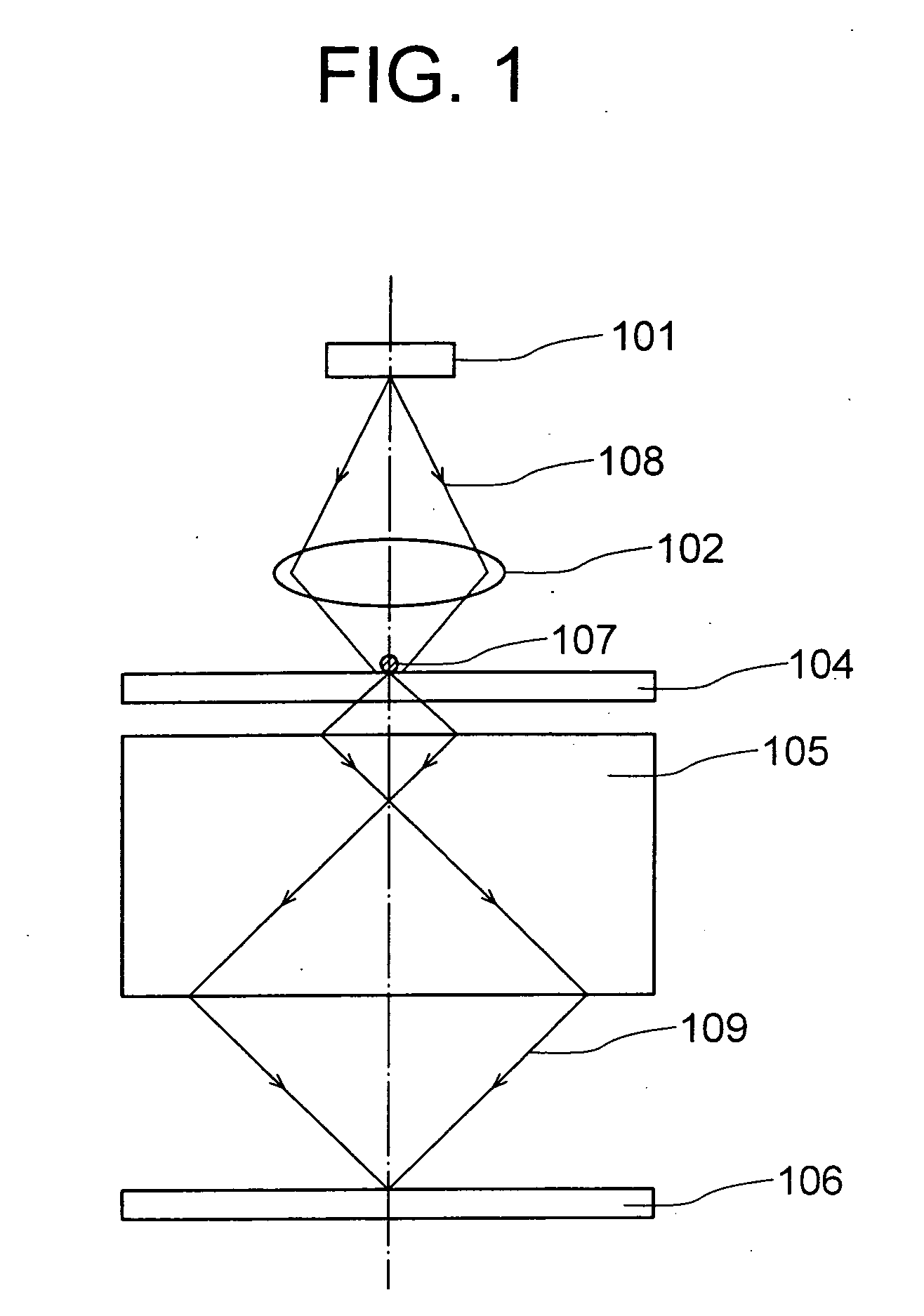
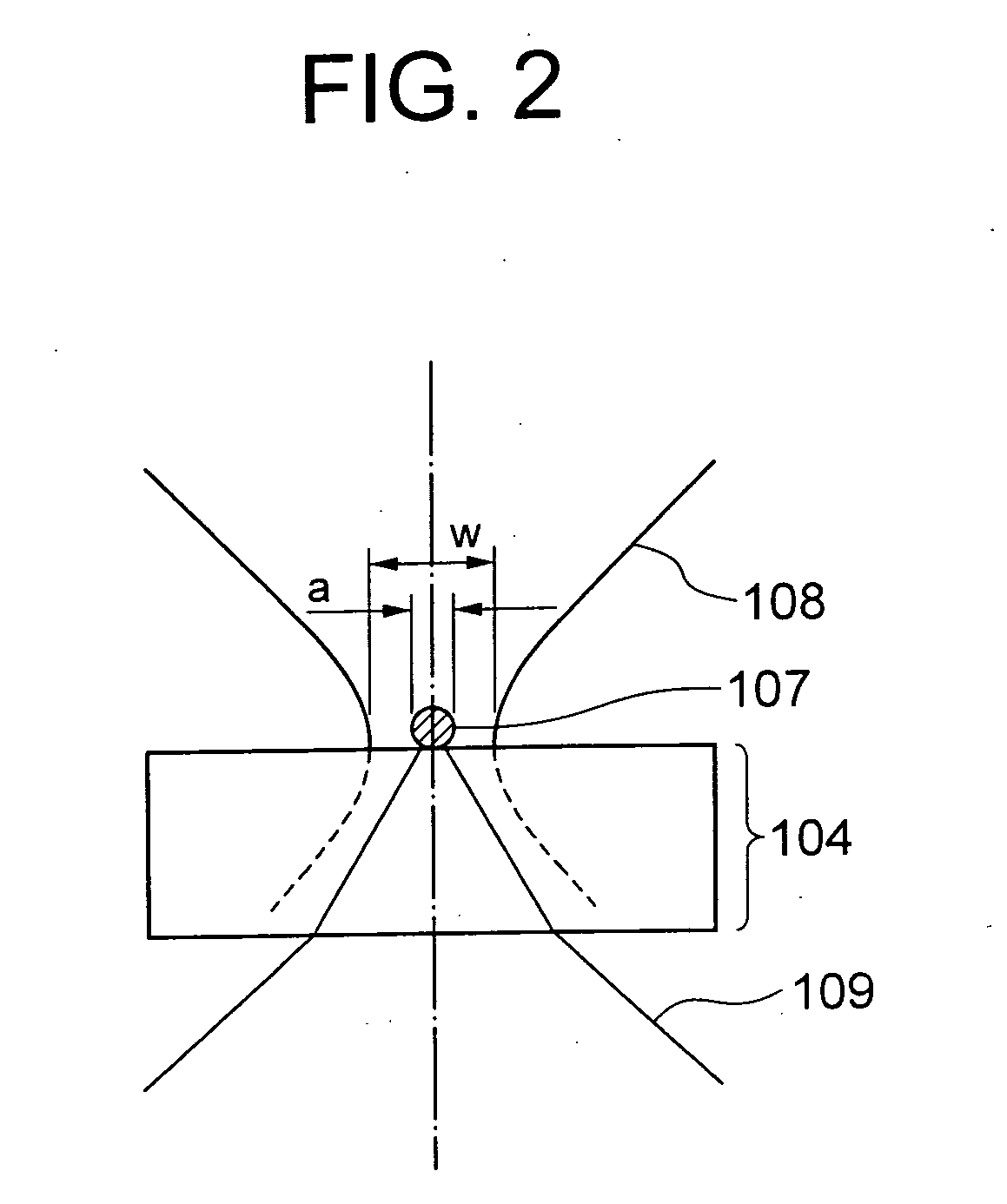
Lighting system, method of lighting, and scanning optical microscope
InactiveUS20100002291A1Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesNegative refractionFluorescence
Light emitter excitation light (108) of a wavelength λ1 emitted by a light source (101) is collected on a light emitter (107) by a collective lens (102). The light emitter (107) is held on a substrate (104), and emits fluorescent light of a wavelength λ2 when the light emitter excitation light (108) of the wavelength λ1 is irradiated. A diameter of the light emitter (107) being formed to be smaller than the wavelength λ2, this fluorescent light includes evanescent waves, and advances through the substrate (104) as an object illuminating light (109) having the light emitter (107) as a point light source. A negative refraction lens (105) is disposed such that an image of the light emitter (107) is formed on a surface of an object 106, and accordingly, not only a propagating-light component included but also a evanescent-wave component in the object illuminating light (109) is also collected simultaneously, and a minute beam spot of a size almost same as of the light emitter (107) is formed on the surface of the object (106).
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Zoom lens and imaging apparatus
InactiveUS7312934B2Increase in sizeGood compensationOptical elementsNegative refractionImaging equipment
Disclosed is a zoom lens which is composed of a plurality of groups of lenses and which varies the power thereof by changing inter-group spacings. The zoom lens is configured such that: the last group of lenses that is located at the end of an image space and is negatively refractive is held stationary in optical-axis directions during variation of the power of the zoom lens, and includes a front group of negative lenses and a rear group of positive lenses; and the rear group of positive lenses or part of the rear group of positive lenses (hereinafter, referred to as a group of blur compensation lenses) is movable in directions orthogonal to the optical axis of the zoom lens. In this configuration, the group of blur compensation lenses is moved in the directions orthogonal to the optical axis in order to shift an image.
Owner:SONY CORP
Camera optical lens
The invention relates to the field of optical lenses, and discloses a camera optical lens. The camera optical lens sequentially comprises, form the object side to the image side, a diaphragm, a firstlens with positive refraction force, a second lens with negative refraction force, a third lens with positive refraction force, a fourth lens with negative refraction force, a fifth lens with negativerefraction force, a sixth lens with positive refraction force, and a seventh lens with negative refraction force. The focal distance of the first lens is f1, the focal distance of the second lens isf2, the abbe number of the first lens is v1, and the abbe number of the second number is v2, wherein v1 / v2 is no less than 3.00 and no more than 4.20, and f2 / f1 is no less than -21.00 and no more than-5.00. The camera optical lens has good optical performance and can meet design requirements of a large diaphragm and being ultrathin.
Owner:AAC OPTICS (CHANGZHOU) CO LTD
Image trapping lens, image trapper, and image trapping unit
InactiveCN1447144AImprove image qualityRadiation controlled devicesOptical elementsNegative refractionOphthalmology
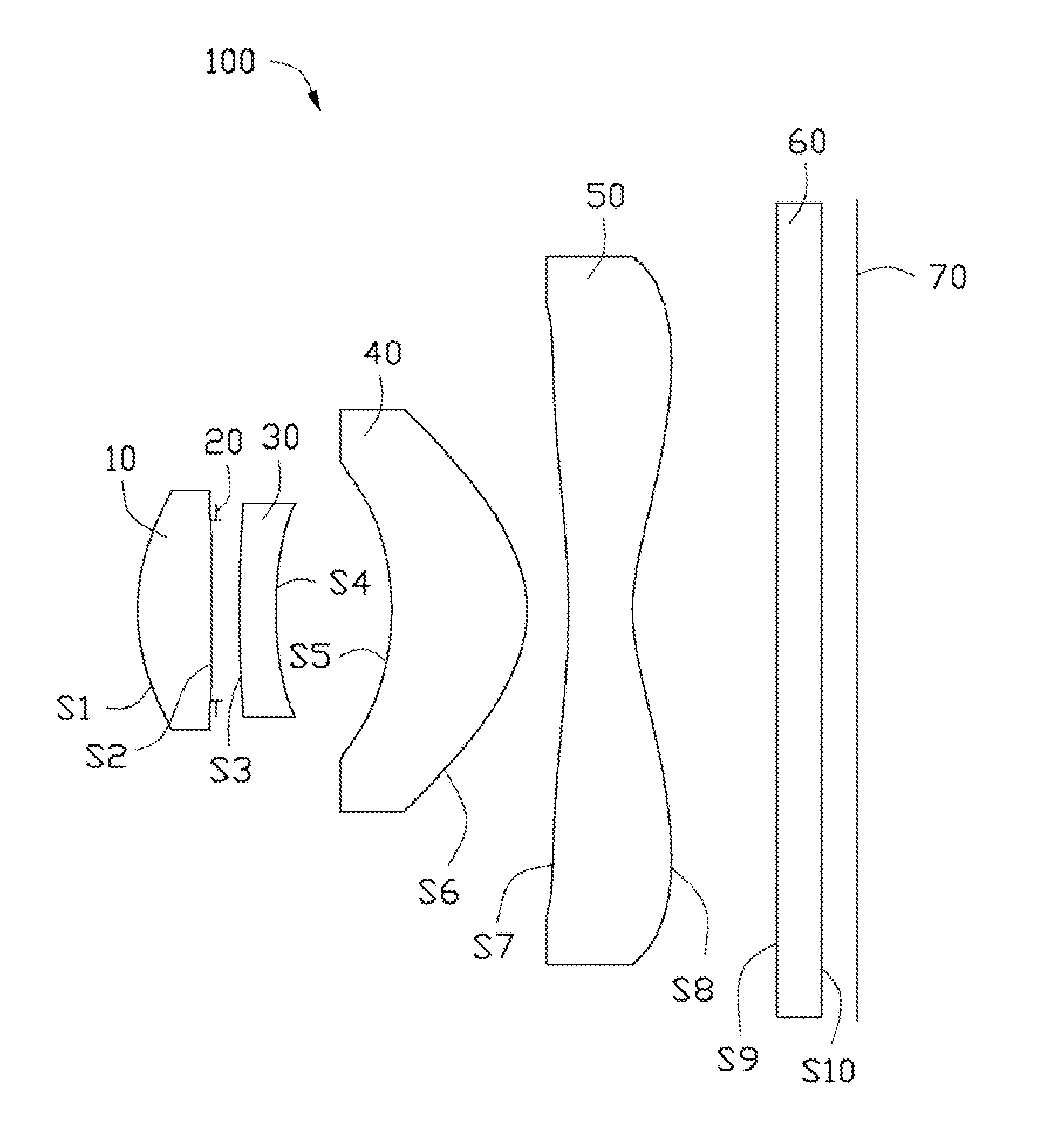
An image capturing lens to capture an image of an object is provided with an aperture diaphragm having an aperture through which an image is captured; a first lens having a positive refracting power, wherein both surfaces of the first lens are shaped in a convex form; a second lens having a negative refracting power, wherein an object-side surface of the second lens is shaped a concave form; and a third lens which is a meniscus lens whose convex surface faces toward the object side; wherein the aperture diaphragm, the firs lens, the second lens and the third lens are aligned in this order from the object side. <IMAGE>
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Projection optical system and image projection apparatus
InactiveUS20050200974A1Small sizeGood performanceBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsOptical elementsProjection opticsConcave surface
A projection optical system and an image projection apparatus that are small in size and can achieve projection with a wide angle while a good image forming performance is assured includes a first lens group having a negative refracting power and a second lens group also having a negative refracting power. The first and second lens groups are arranged in order from the projection side. The first lens group includes a negative meniscus lens that has a concave surface directed to the projection side and formed as an aspherical reflecting surface.
Owner:SONY CORP
Underwater sub-wavelength resolution ratio three-dimensional imaging method
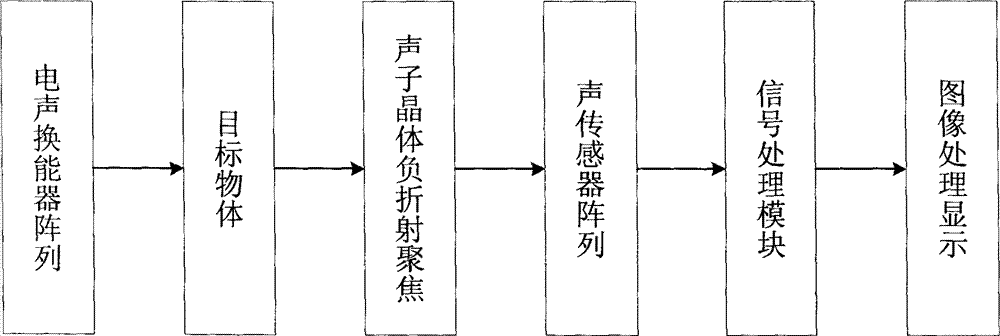
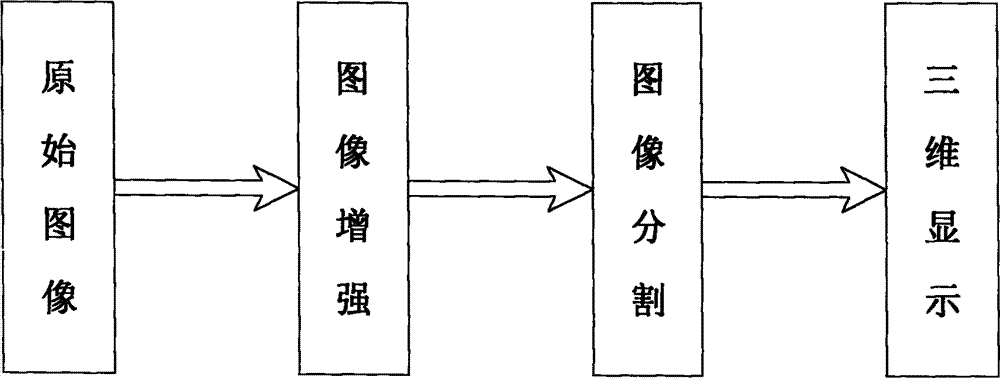
InactiveCN102928844ASimple structureAchieving identifiabilityAcoustic wave reradiationSound imageImage segmentation
The invention discloses an underwater sub-wavelength resolution ratio three-dimensional imaging method. The underwater sub-wavelength resolution ratio three-dimensional imaging method includes the following steps: (1) a sound signal is emitted; (2) acoustic lens wave beams are formed; (3) the sound signal is received and adjusted; (4) an image is processed and displayed. A two dimensional datum is obtained according to an imaging rule of an acoustic lens, a distance datum is obtained by utilizing an emission time and a receiving time, and a three dimensional underwater sound datum is obtained by combining with an electric signal received by a underwater sound sensor. The three dimensional underwater sound image datum undergoes image enhancement and image segmentation and a three dimensional image of a target is achieved by use of an open-sourcing visualization program library visualization toolkit (VTK). A reflected sound wave is focused through the acoustic lens and forms the wave beam. Hardware circuits of a normal imaging system are greatly reduced. A sub-wavelength image is achieved due to the characteristic of negative refraction of a phonon crystal. The novel underwater sound sensor with a mesoscopic pressure resistance is utilized, the underwater sound sensor responds to an underwater sound signal well, and a faint underwater signal can be effectively transformed.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Lens and optical system
A lens has a convex or concave shaped smooth non-spherical surface or non-circular curve which is formed of a medium indicating negative refraction.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Camera shooting optical lens
The present invention relates to the optical lens field, and discloses a camera shooting optical lens. The lens comprises from an object side to an image side in order: an aperture, a first lens with positive refraction power, a second lens with negative refraction power, a third lens with negative refraction power, a fourth lens with positive refraction power and a fifth lens with negative refraction power. The camera shooting optical lens satisfies the relation as follows: 0.70<f1 / f<0.80, 2.0<f2 / f< 1.7, 14<f3 / f< 10, 0.59<f4 / f<0.62, 0.52<f5 / f< 0.48, 1.09<(f3 f4) / (f3+f4)<1.12 and other relations. The camera shooting optical lens can satisfy the low TTL and the large aperture design requirement and has good sensitivity appearance.
Owner:AAC OPTICS SOLUTIONS PTE LTD
Zoom lens
ActiveUS20050134971A1Broaden your optionsImprove the correction effectDiffraction gratingsNegative refractionMagnification
In a zoom lens of this invention, a first lens group having a positive refraction power, a second lens group having a negative refraction power, a third lens group having a positive refraction power, and a fourth lens group having a positive refraction power are arranged sequentially from an object side toward an image side, and the magnification is changed from the wide angle end of the zoom lens to the telephoto end thereof, and vice versa, by varying each distance between each pair of the first to the fourth lens groups. The first lens group includes a positive lens and a negative lens. The third lens group includes at least a positive lens and a negative lens arranged sequentially from the object side toward the image side. At least the positive lens of the third lens group is a spherical lens. That lens of the third lens group which is located closest to the image side is a lens having an aspherical surface on at least one surface thereof.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Photonic Crystal Devices Using Negative Refraction
Negative refraction in photonic crystals and diffraction grating is used to design plano-concave lenses to focus plane waves. Microwave experiments are carried out to demonstrate negative refraction and the performance of these lenses. Demonstration of negative refraction of visible light is also performed for the grism. These lenses can be used in optical circuits, astronomical applications, etc.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Optical lens group used for image photographing, image capture device and electronic device
The invention discloses an optical lens group used for image photographing, an image capture device and an electronic device. The optical lens group used for image photographing comprises a first lens, a second lens, a third lens, a fourth lens, a fifth lens, a sixth lens and a seventh lens which are arranged from an object side to an image side in turn. The first lens has positive refraction power, and the position, which is near the optical axis, of the object side surface of the first lens is a convex surface. The second lens has a negative refraction power. At least one surface of the object side surface and the image side surface of the sixth lens is an aspheric surface, and at least one surface includes at least one point of inflexion. The object side surface and the image side surface of the seventh lens are aspheric surfaces. When the specific condition is met, the optical lens group used for image photographing is enabled to have a telescope function and an aberration reducing function and effectively control the total length so as to achieve the requirement of micromation. The invention also discloses an image capture device having the optical lens group used for image photographing and an electronic device having the image capture device.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Apochromatically corrected microscope objective
A microscope objective with high aperture, large object field and apochromatic correction in the wavelength range from ultraviolet to infrared. The microscope objective includes, starting from the object level: a first group of lenses with overall positive refraction power, including a cemented group with positive-negative refraction power effect, made out of one of two lenses, and of a further lens with positive refraction power, a second group of lenses with positive refraction power, including three cemented lenses, a third group of lenses with negative refraction power, including three cemented lenses, in which the side that faces the image plane is convex, a fourth group of lenses, consisting of a lens with positive refraction power and a cemented group of two lenses with positive-negative refraction power, and a fifth group of lenses, including two lenses in a cemented group with negative-positive refraction power.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com