Patents
Literature
194 results about "Superlens" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
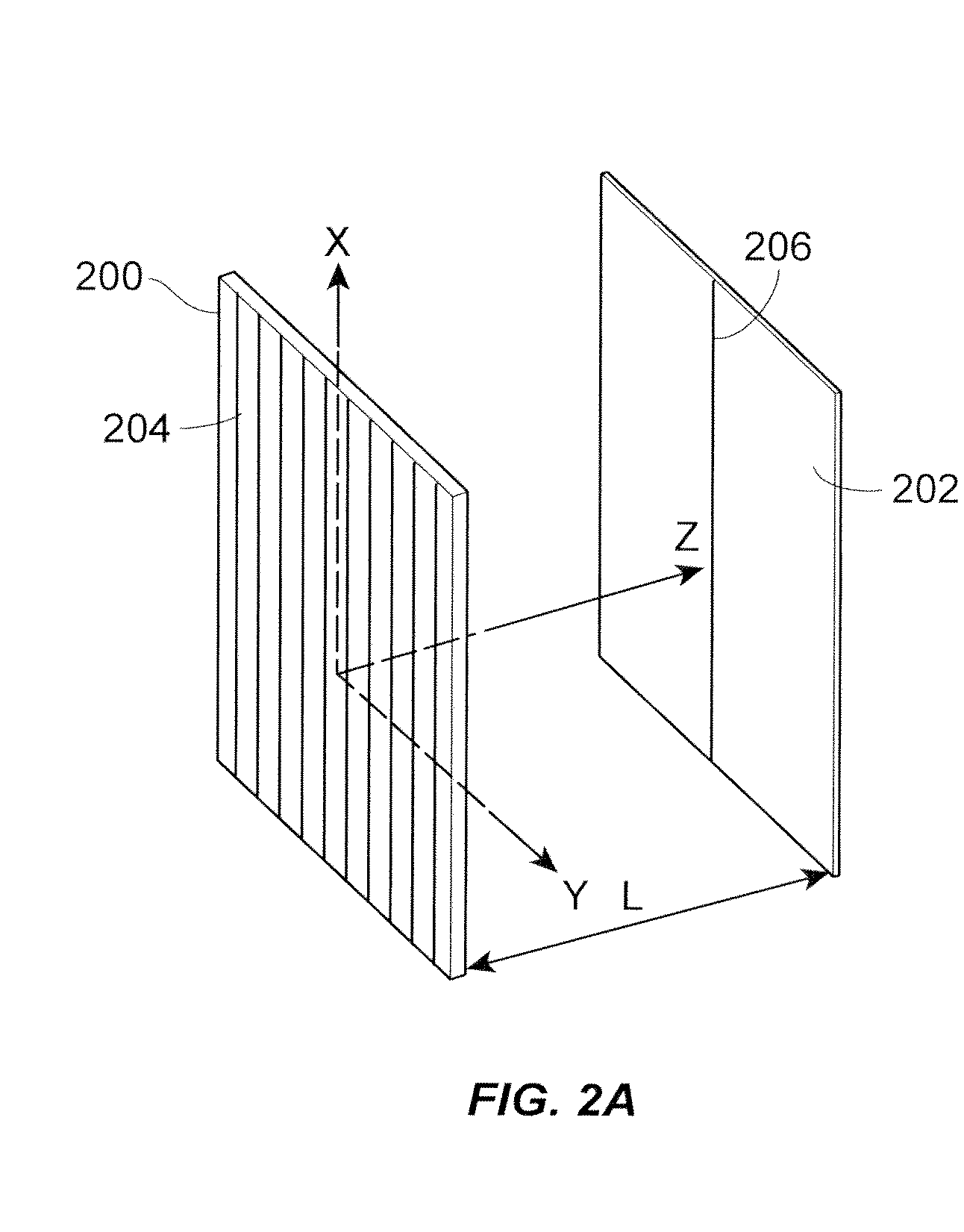
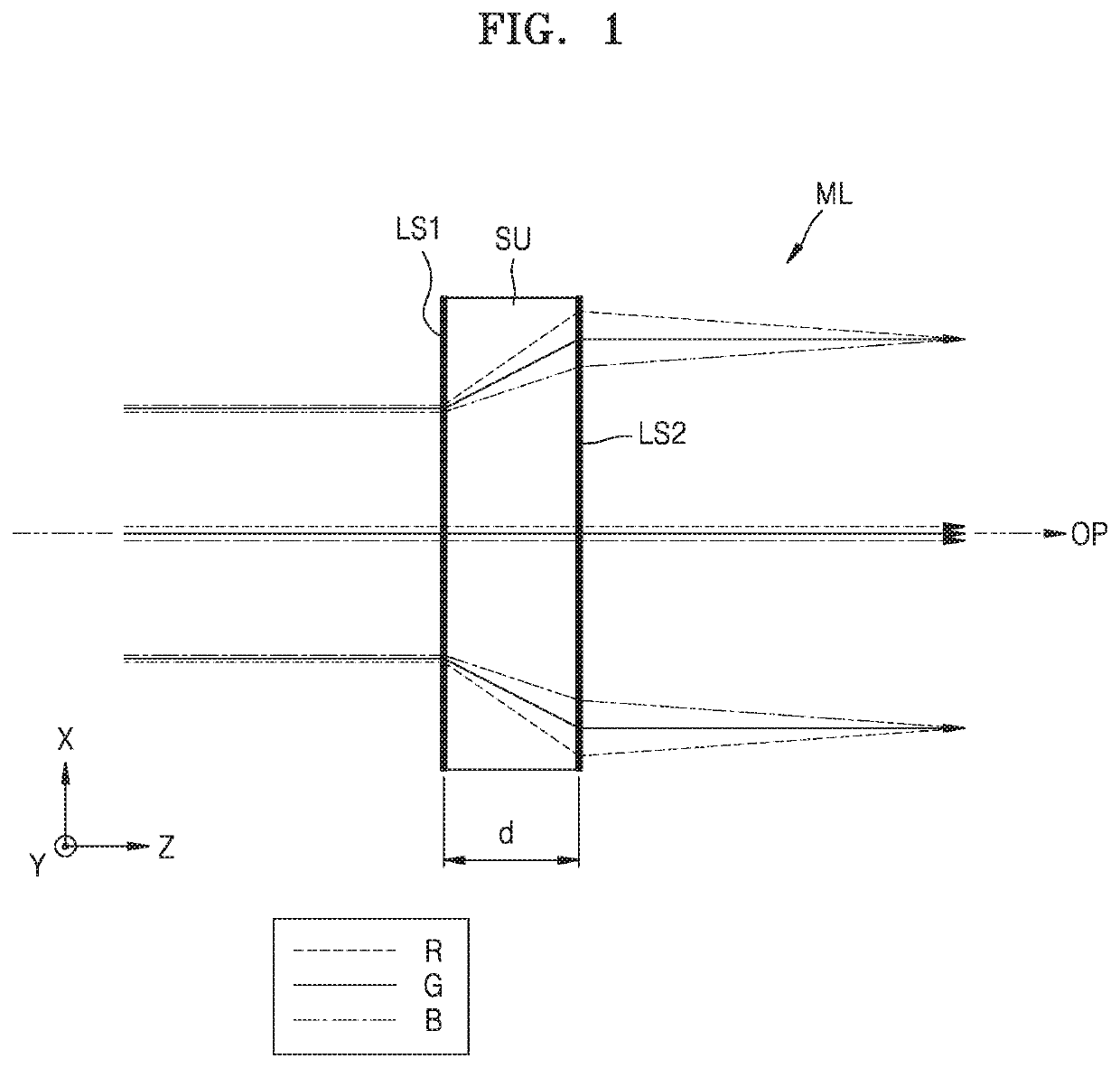
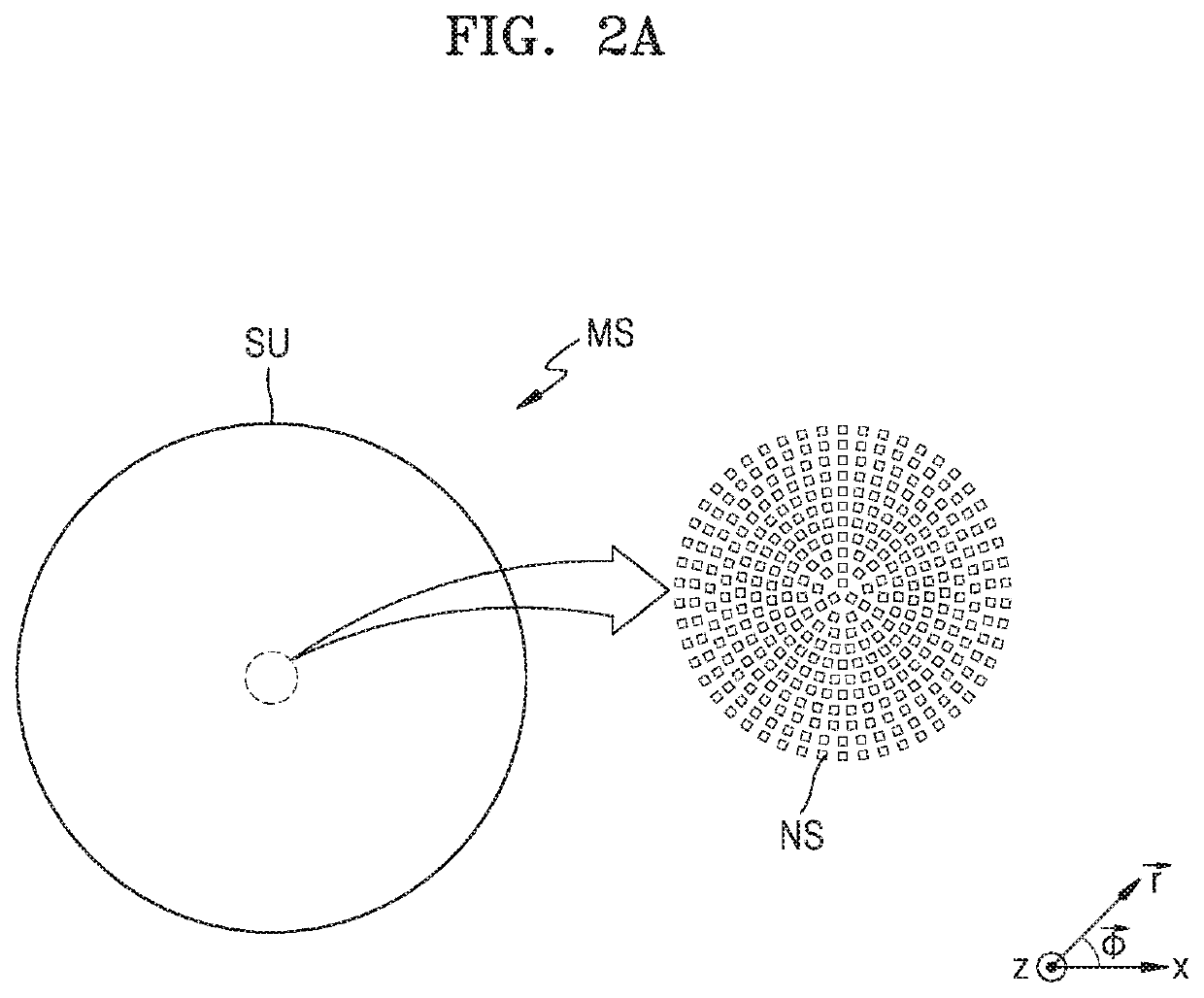
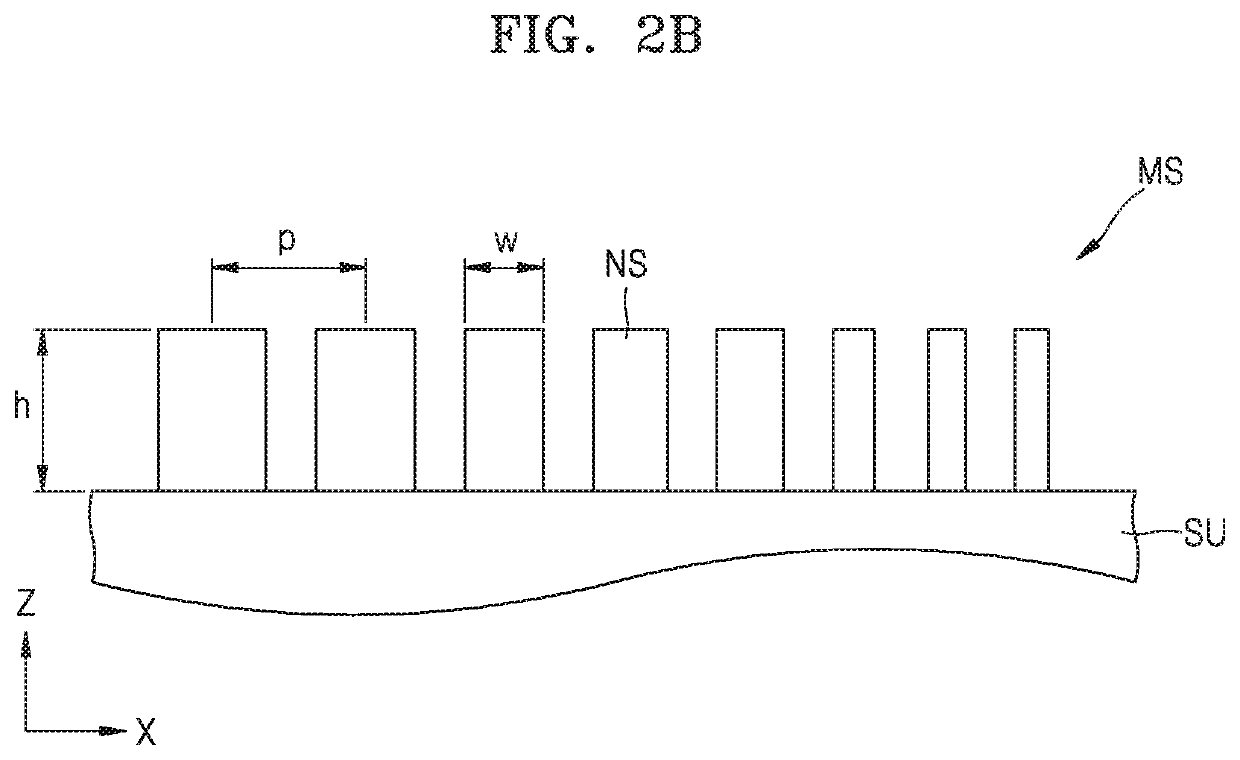
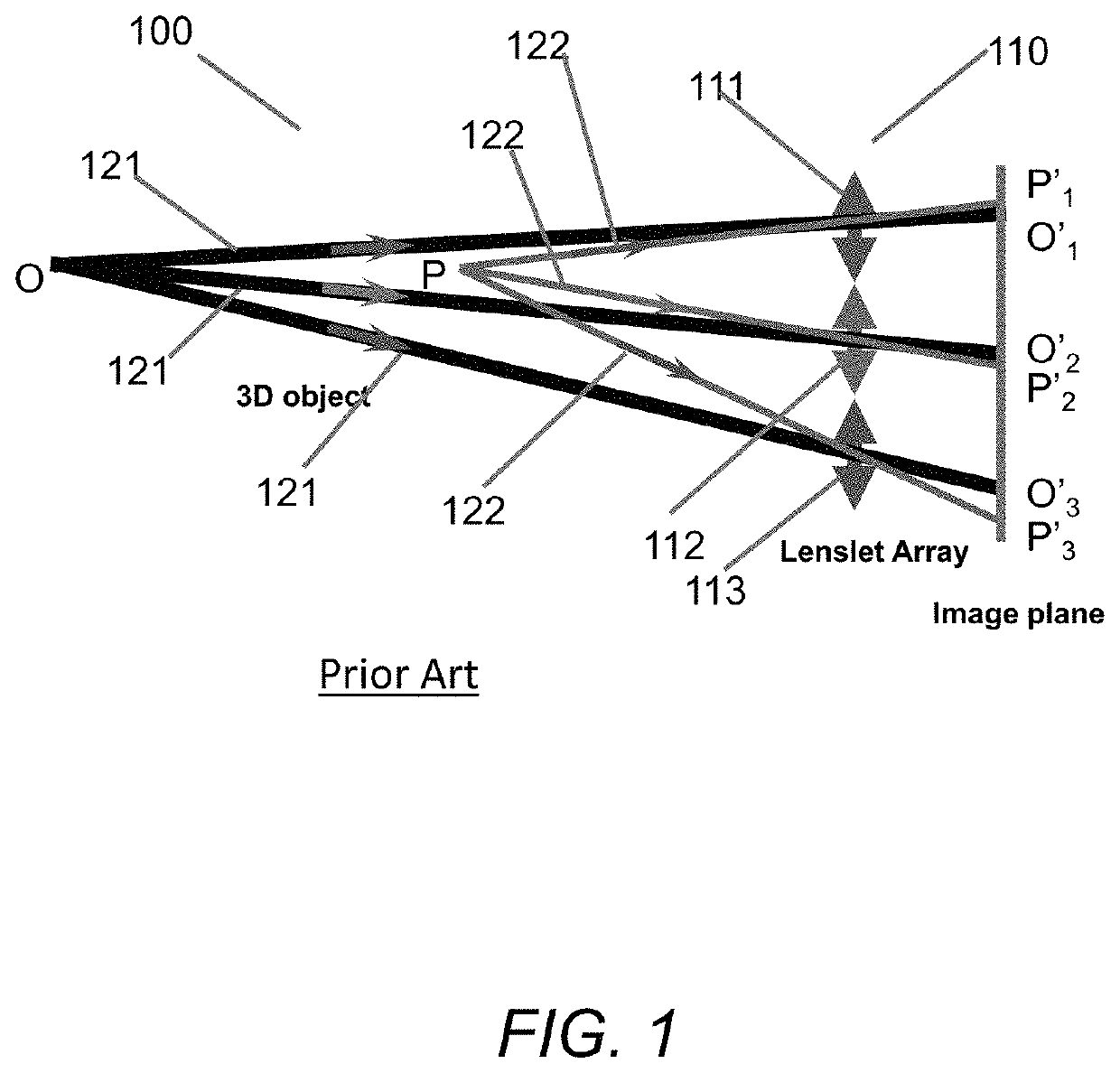
A superlens, or super lens, is a lens which uses metamaterials to go beyond the diffraction limit. The diffraction limit is a feature of conventional lenses and microscopes that limits the fineness of their resolution. Many lens designs have been proposed that go beyond the diffraction limit in some way, but constraints and obstacles face each of them.
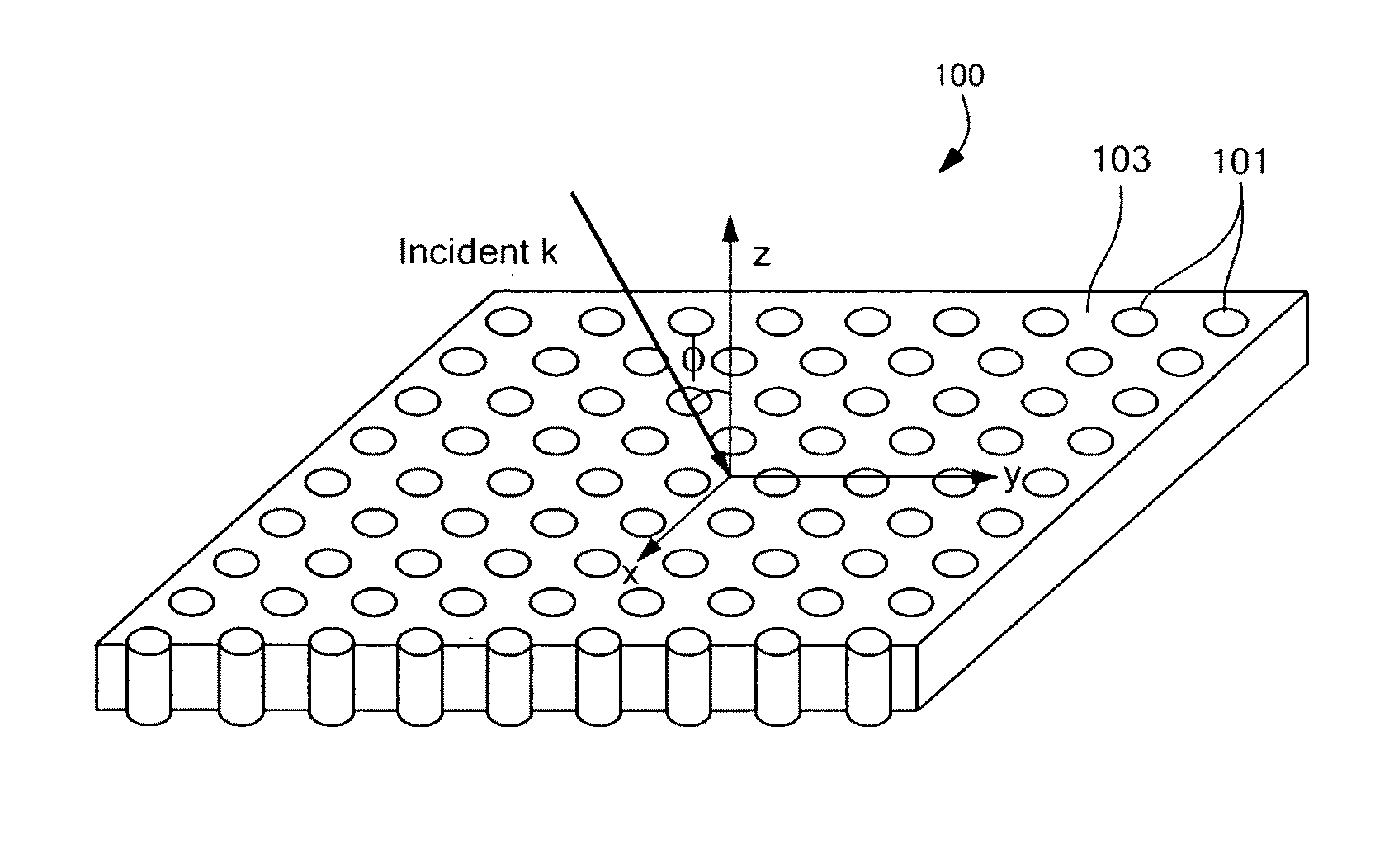
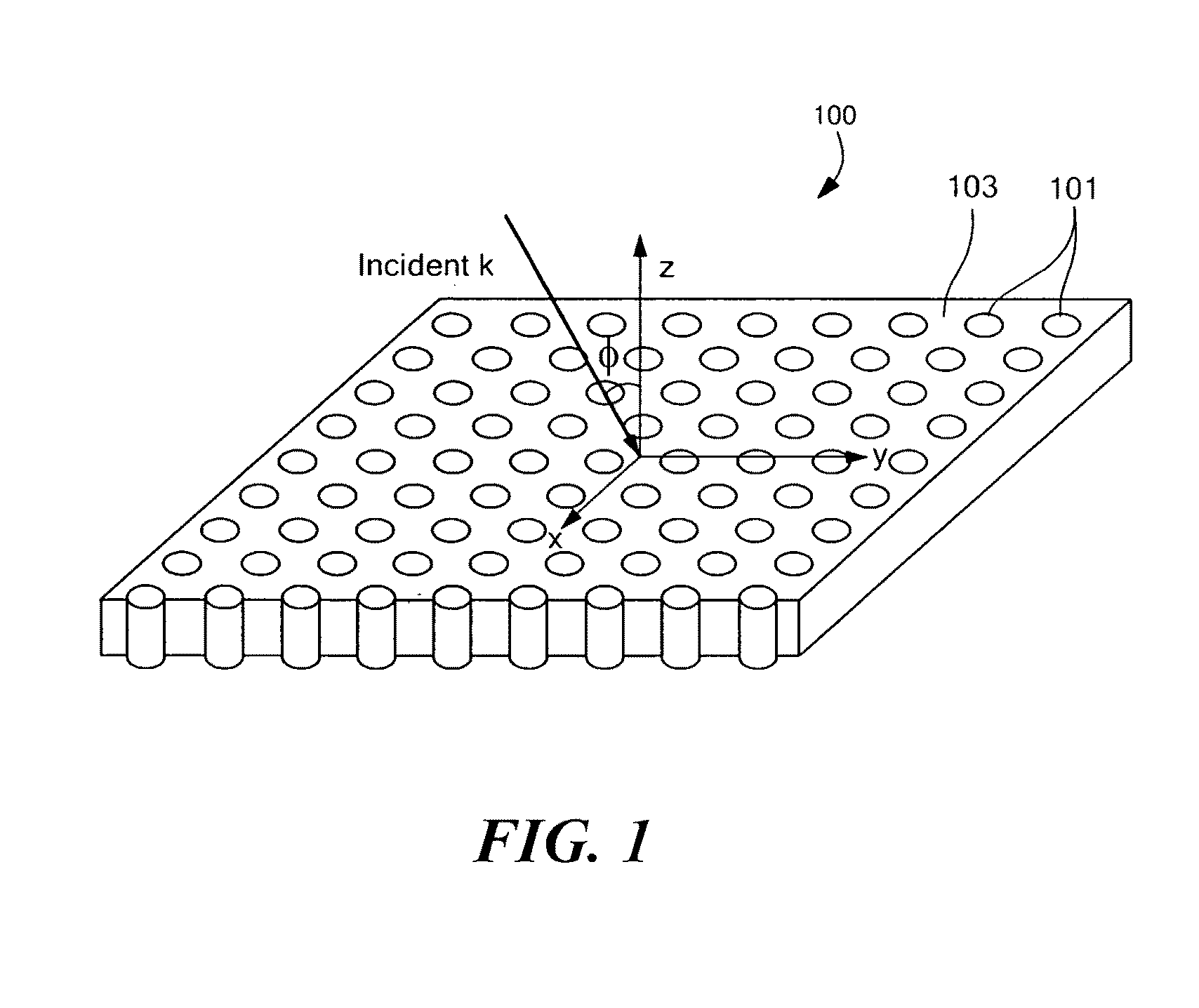
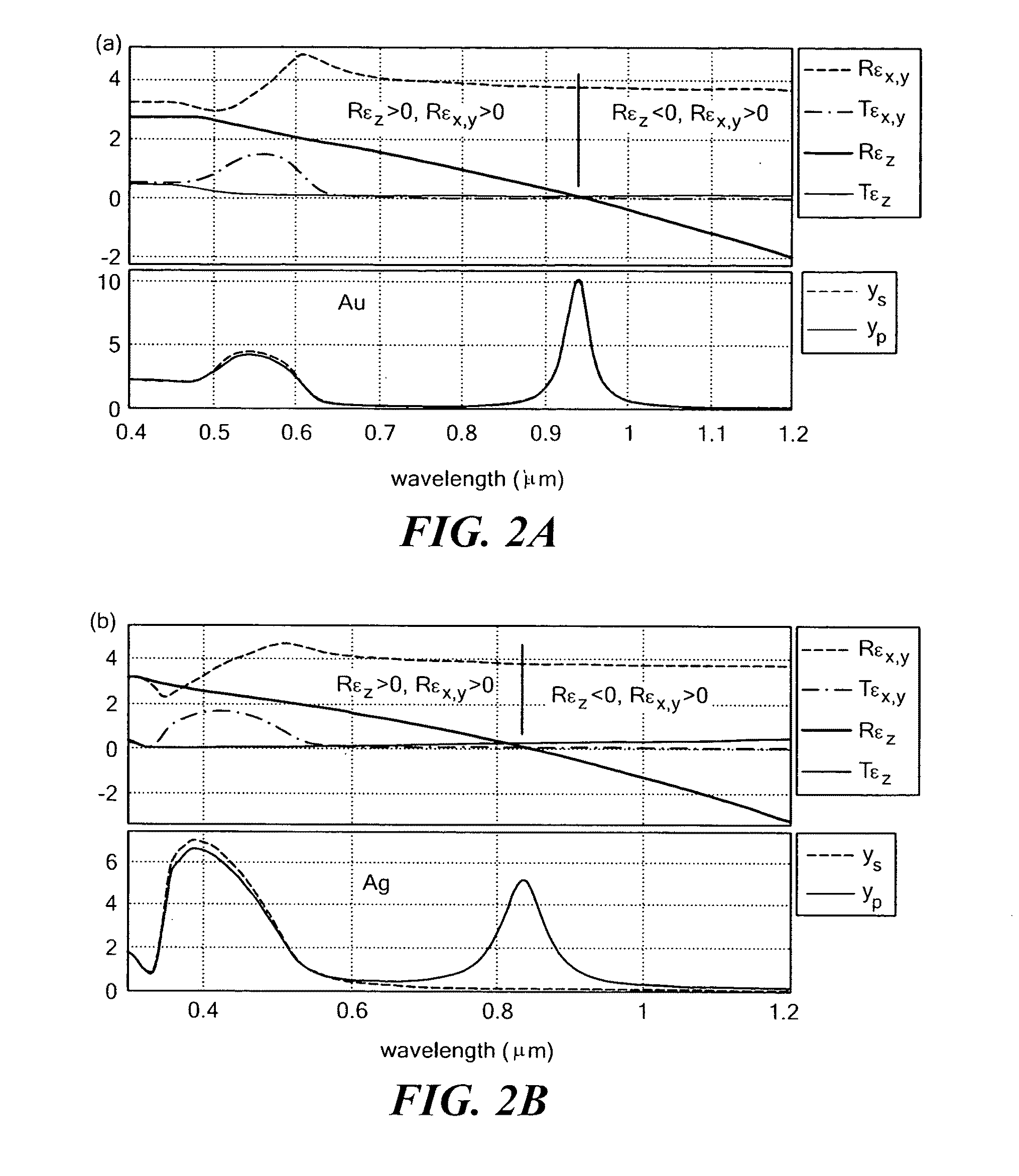
Anisotropic metal-dielectric metamaterials for broadband all-angle negative refraction and superlens imaging
InactiveUS20090040132A1Easy to makeEasy to customizeLiquid surface applicatorsCoatingsNegative refractionDielectric matrix
A metamaterial comprises a plurality of metallic nanowires embedded in a dielectric matrix. The metamaterial composite media provide broadband all-angle negative refraction and flat lens, superlens and curved hyperlens imaging in specific spectral regions over a wide range of frequencies including, for example, from deep infrared to ultraviolet frequencies.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
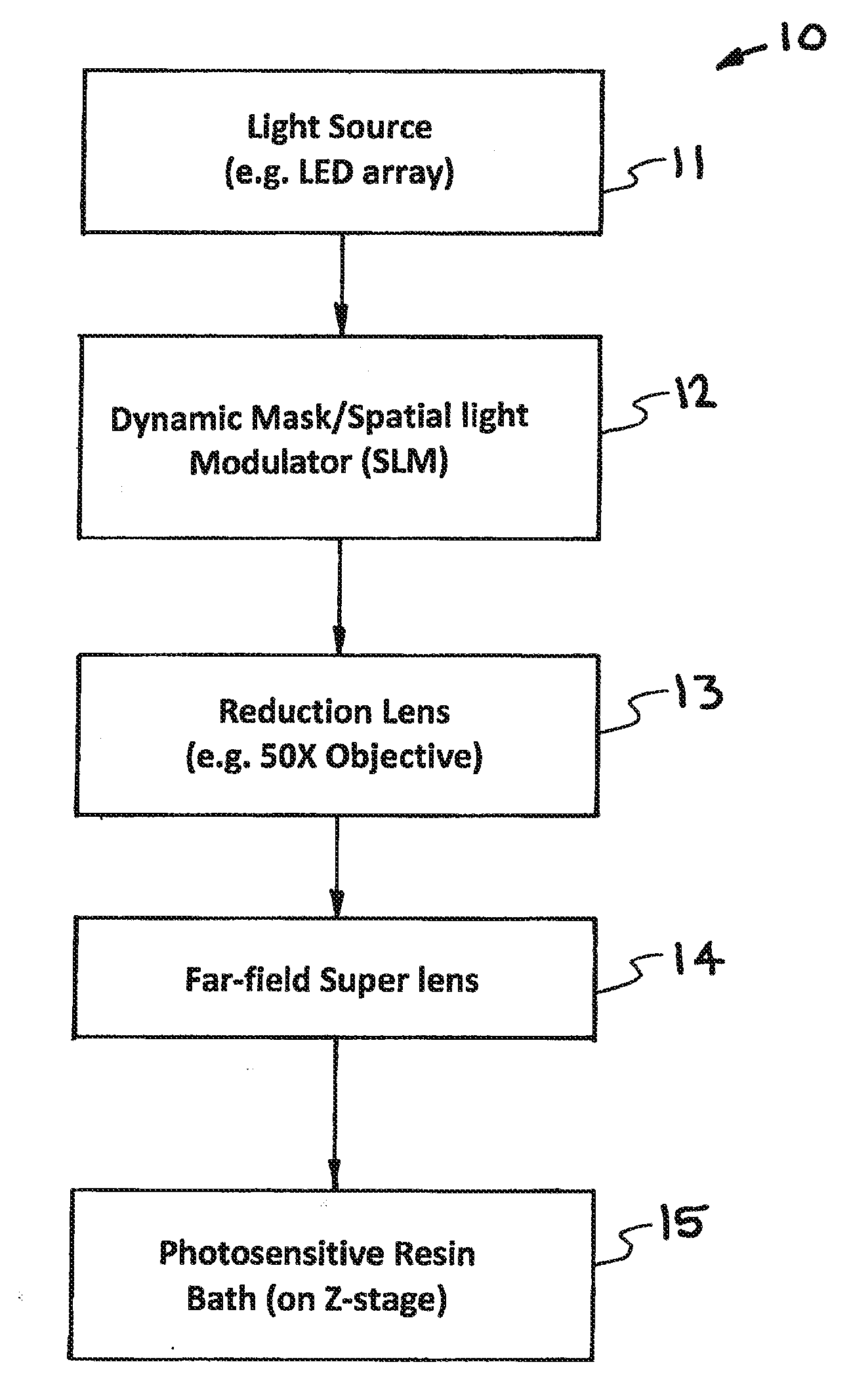
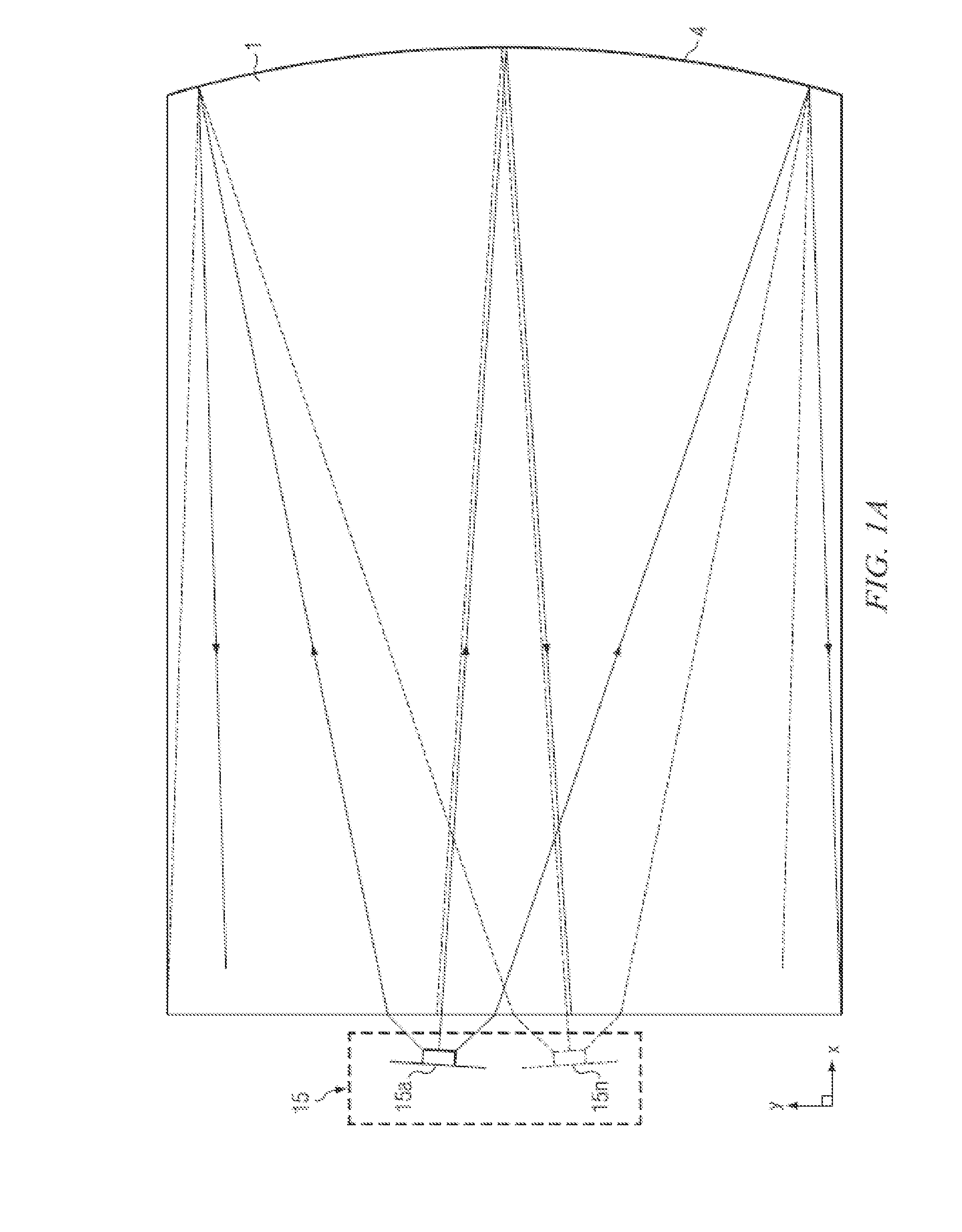
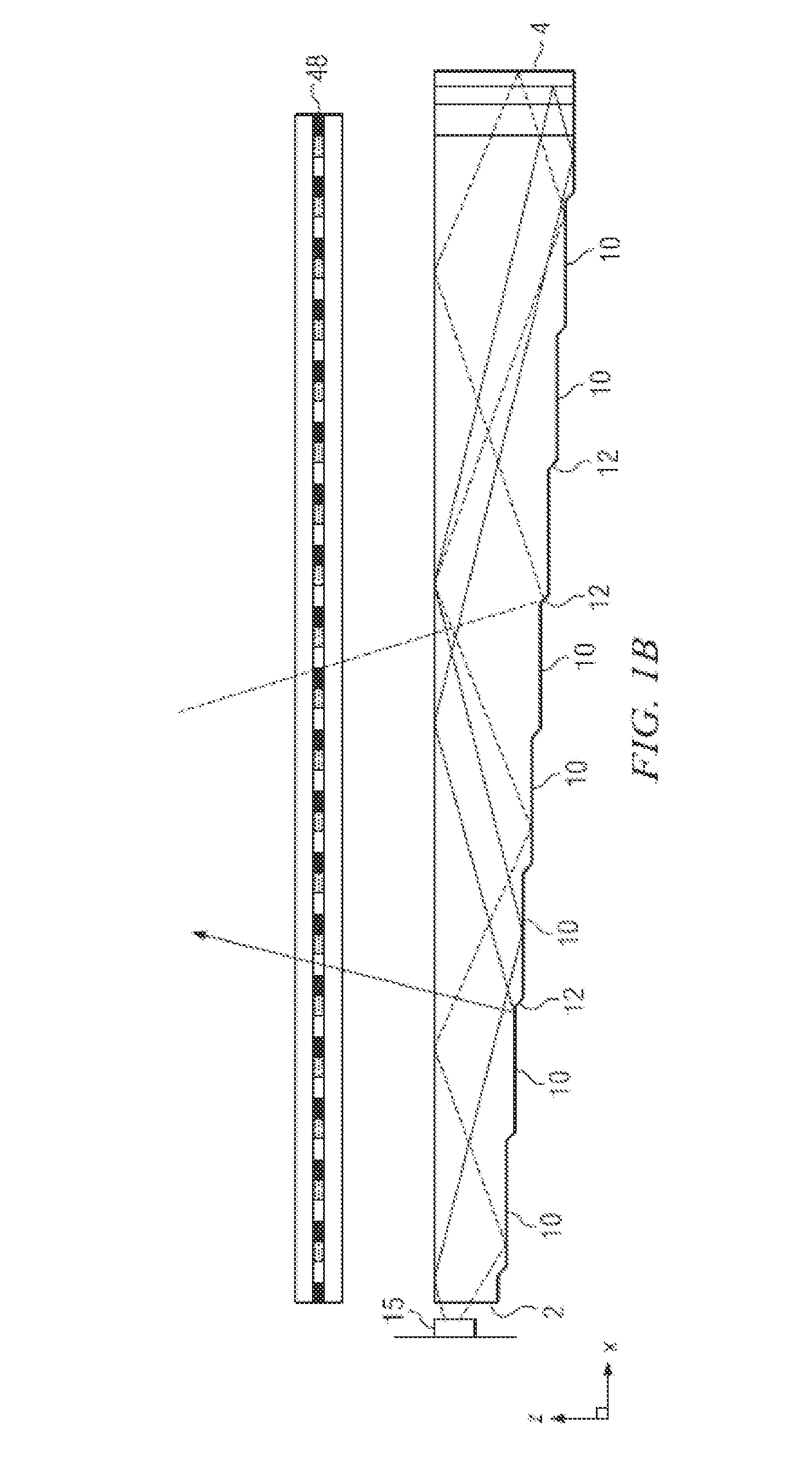
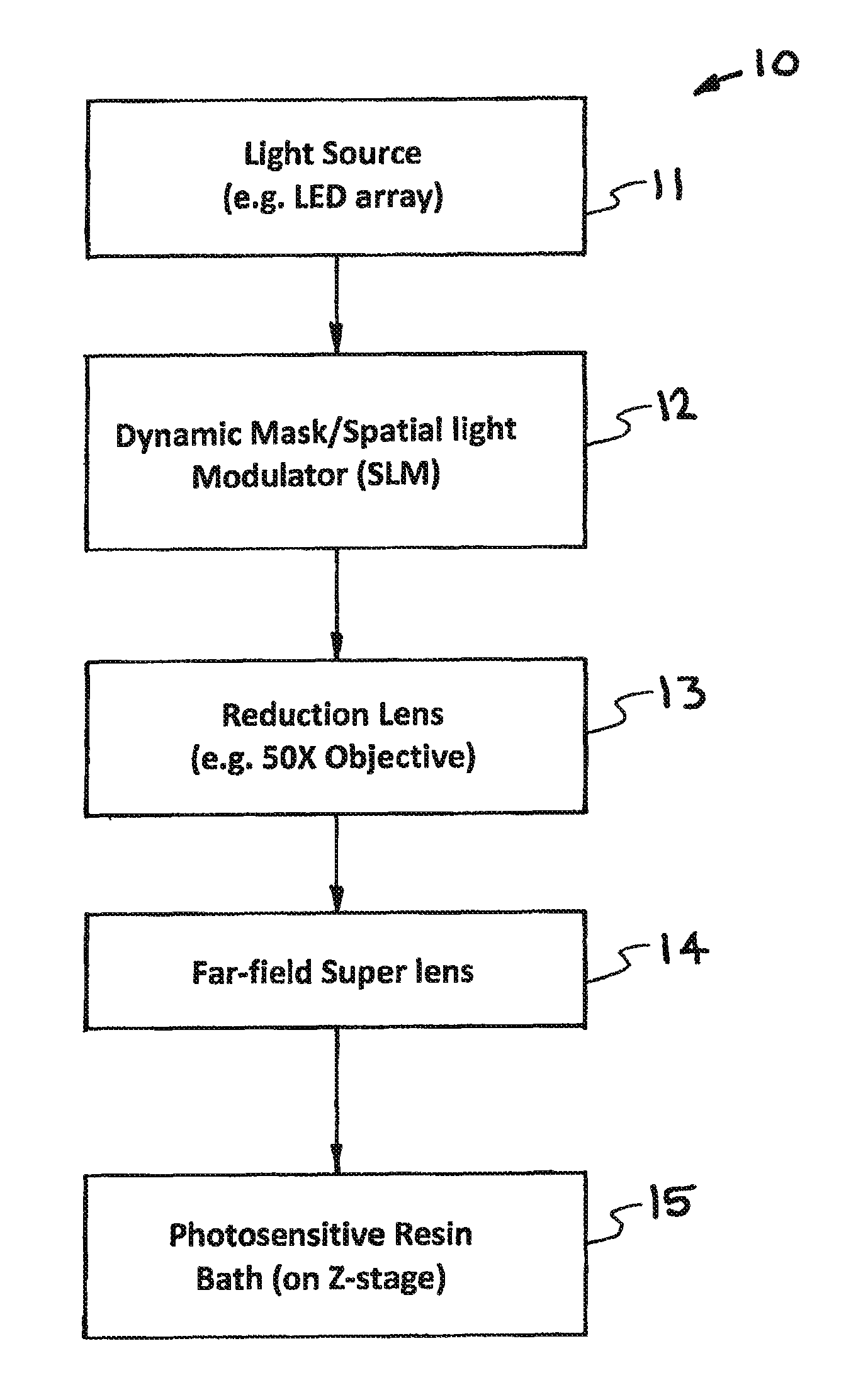
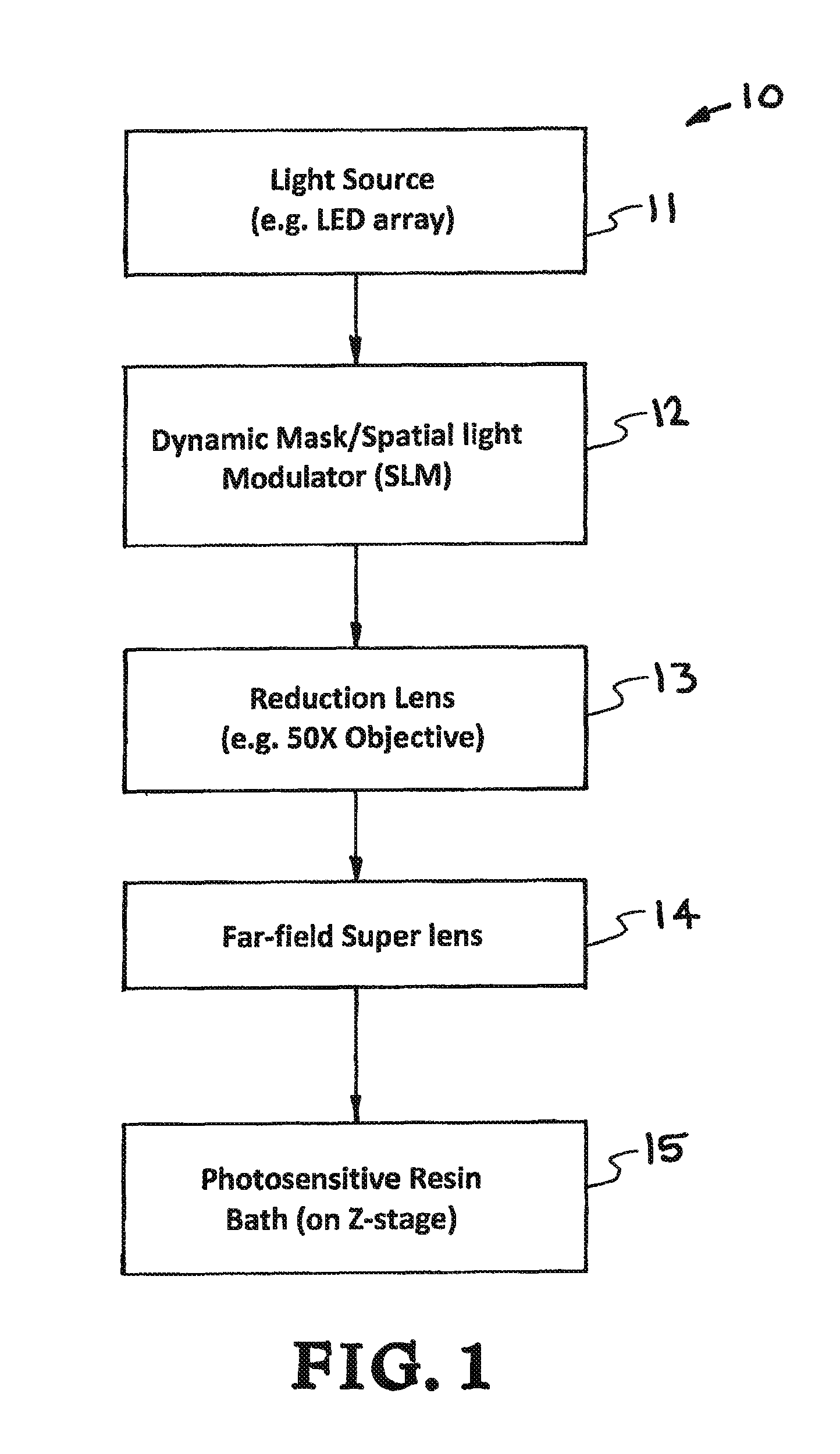
High Resolution Projection Micro Stereolithography System And Method
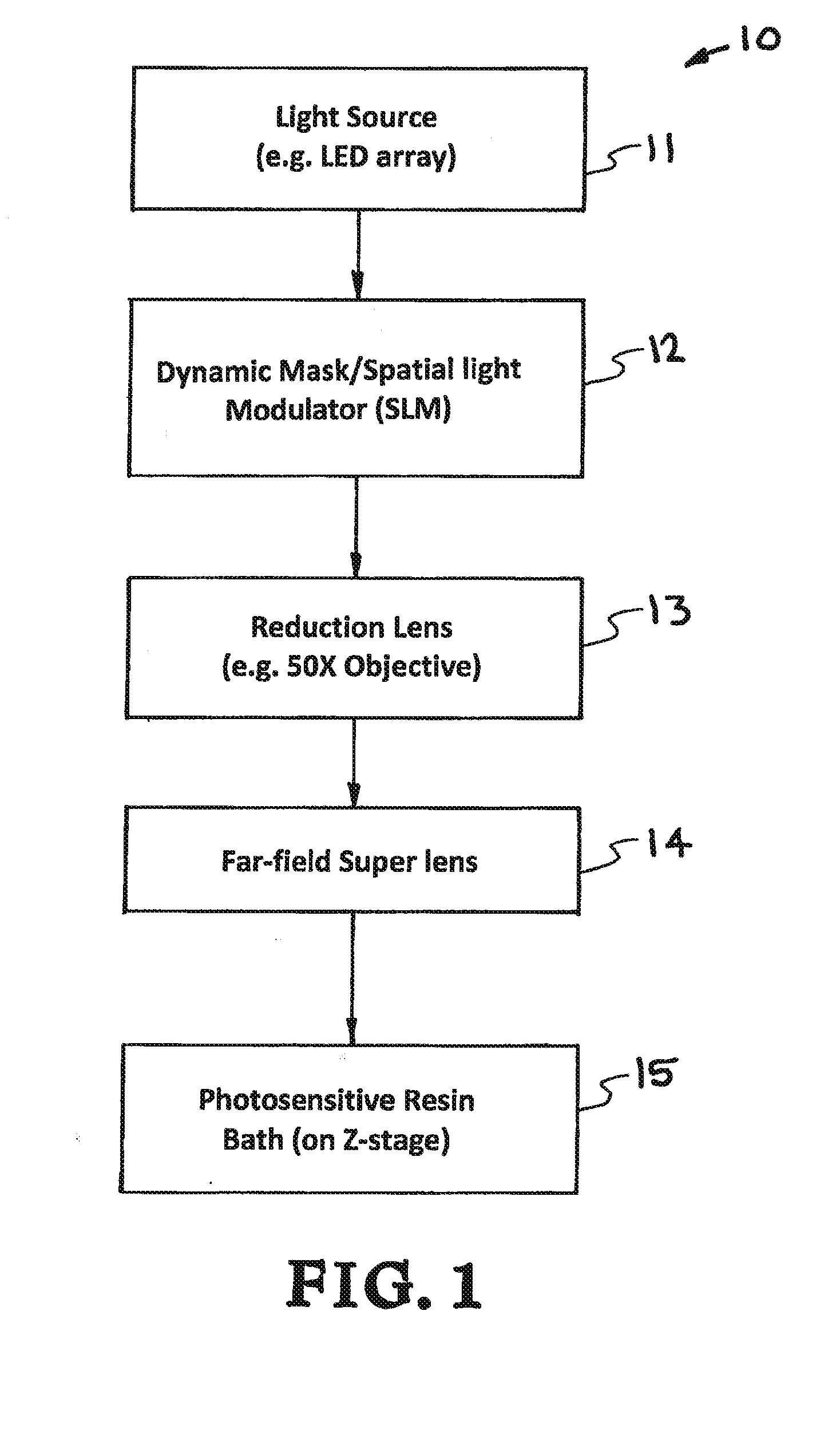
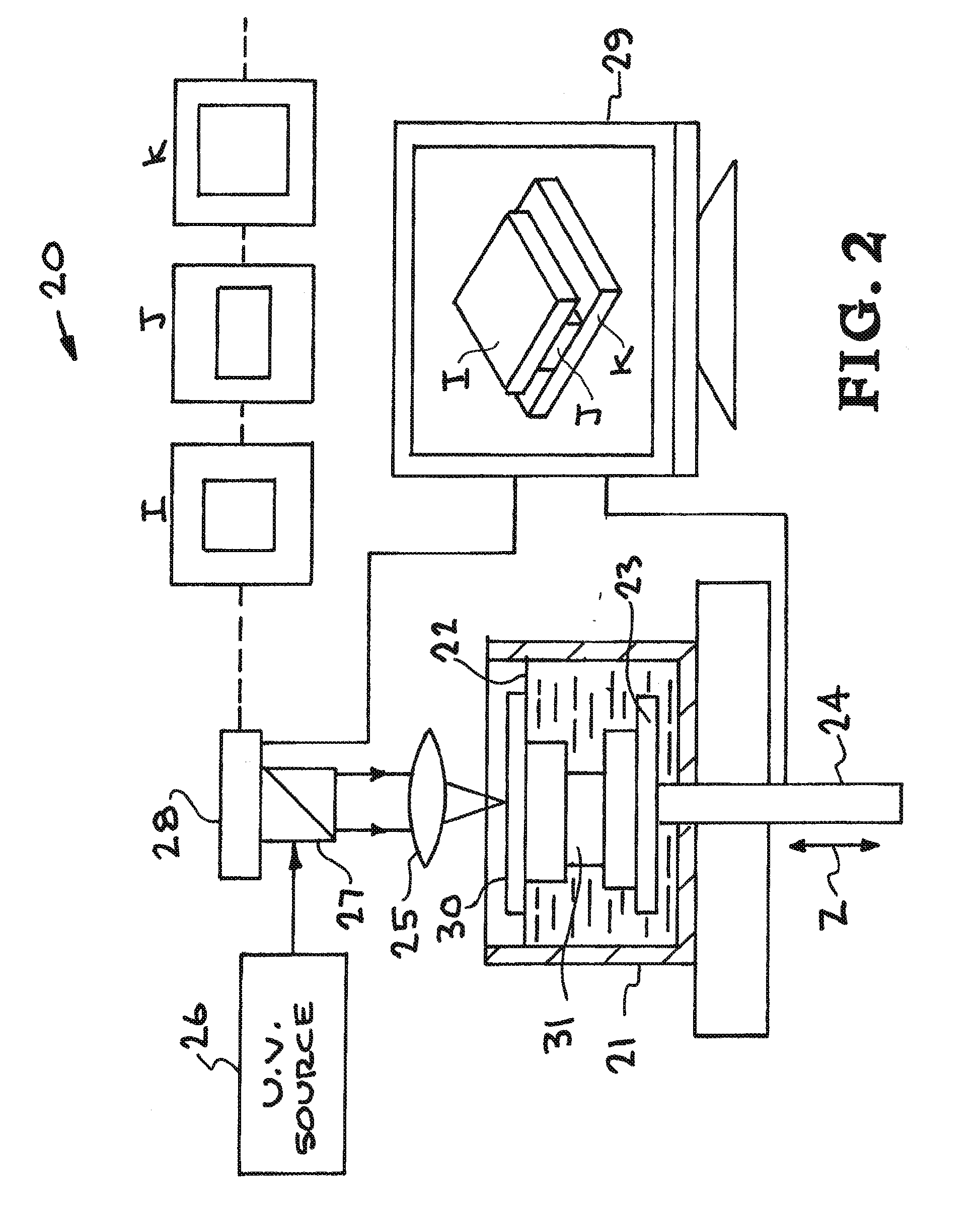
ActiveUS20150309473A1Increase amplitudeNegative index of refractionAdditive manufacturing apparatusPhotomechanical apparatusSpatial light modulatorCombined use
A high-resolution PμSL system and method incorporating one or more of the following features with a standard PμSL system using a SLM projected digital image to form components in a stereolithographic bath: a far-field superlens for producing sub-diffraction-limited features, multiple spatial light modulators (SLM) to generate spatially-controlled three-dimensional interference holograms with nanoscale features, and the integration of microfluidic components into the resin bath of a PμSL system to fabricate microstructures of different materials.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Apparatus for Sub-Wavelength Near-Field Focusing of Electromagnetic Waves
ActiveUS20090303154A1Radiation/particle handlingElectrode and associated part arrangementsGratingElectromagnetic radiation
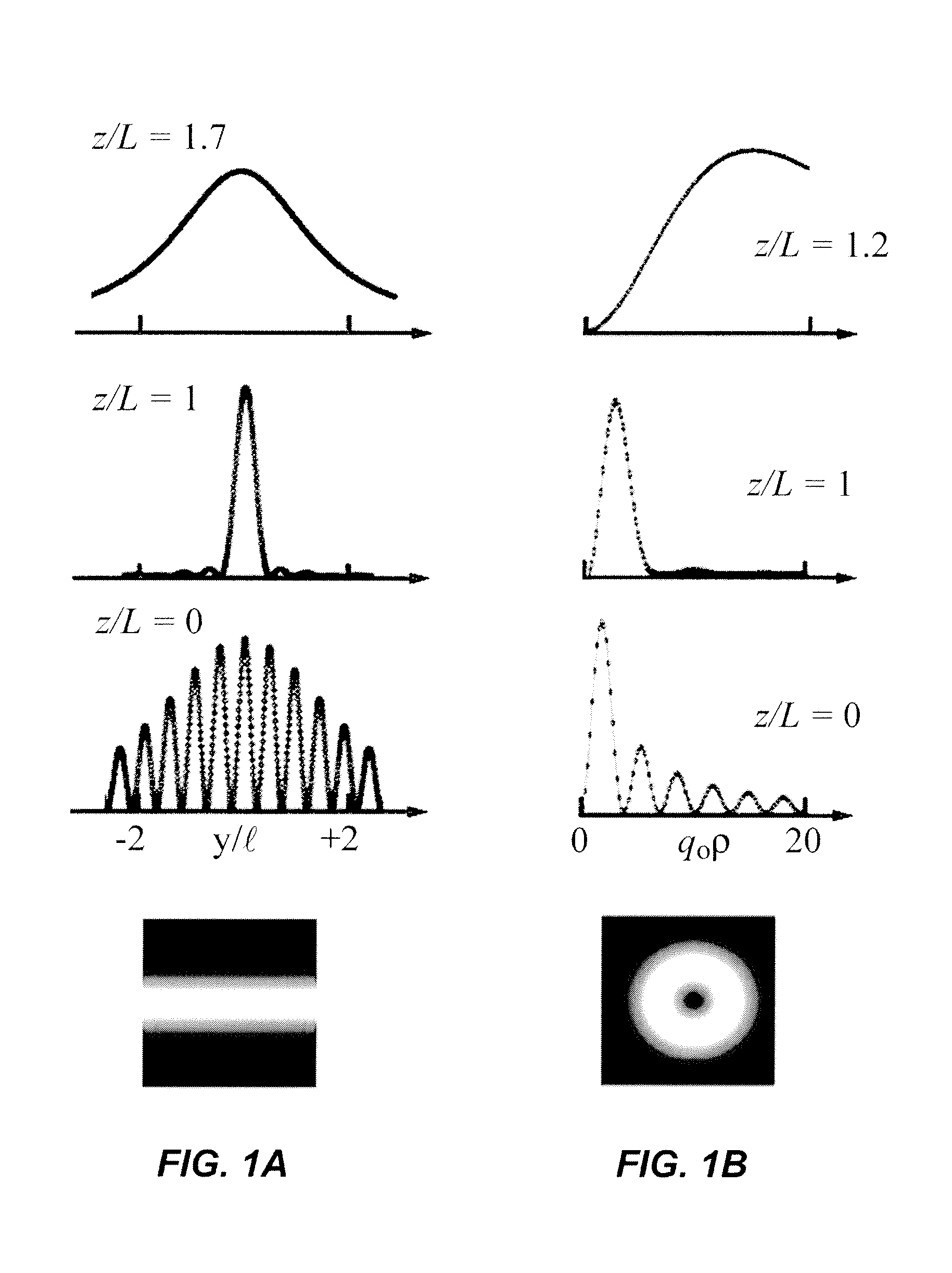
Planar sub-wavelength structures provide superlensing, i.e., electromagnetic focusing beyond the diffraction limit. The planar structures use diffraction to force the input field to converge to a spot on the focal plane. The sub-wavelength patterned structures manipulate the output wave in such a manner as to form a sub-wavelength focus in the near field. In some examples, the sub-wavelength structures may be linear grating-like structures that can focus electromagnetic radiation to lines of arbitrarily small sub-wavelength dimension, or two dimensional grating-like structures and Bessel (azimuthally symmetric) structures that can focus to spots of arbitrarily small sub-wavelength dimensions. The particular pattern for the sub-wavelength structures may be derived from the desired focus. Some examples describe sub-wavelength structures that have been implemented to focus microwave radiation to sub-wavelength dimensions in the near field.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
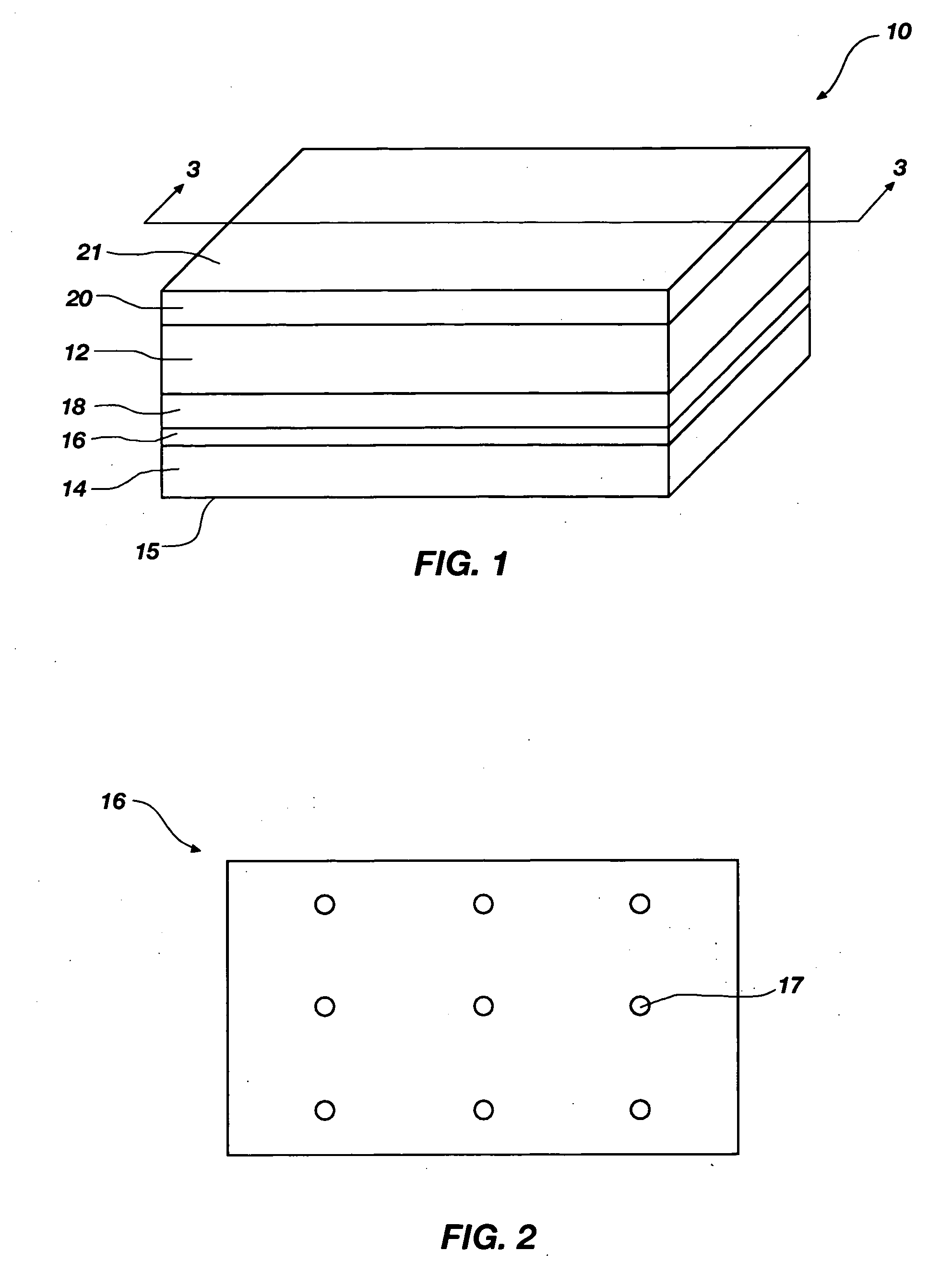
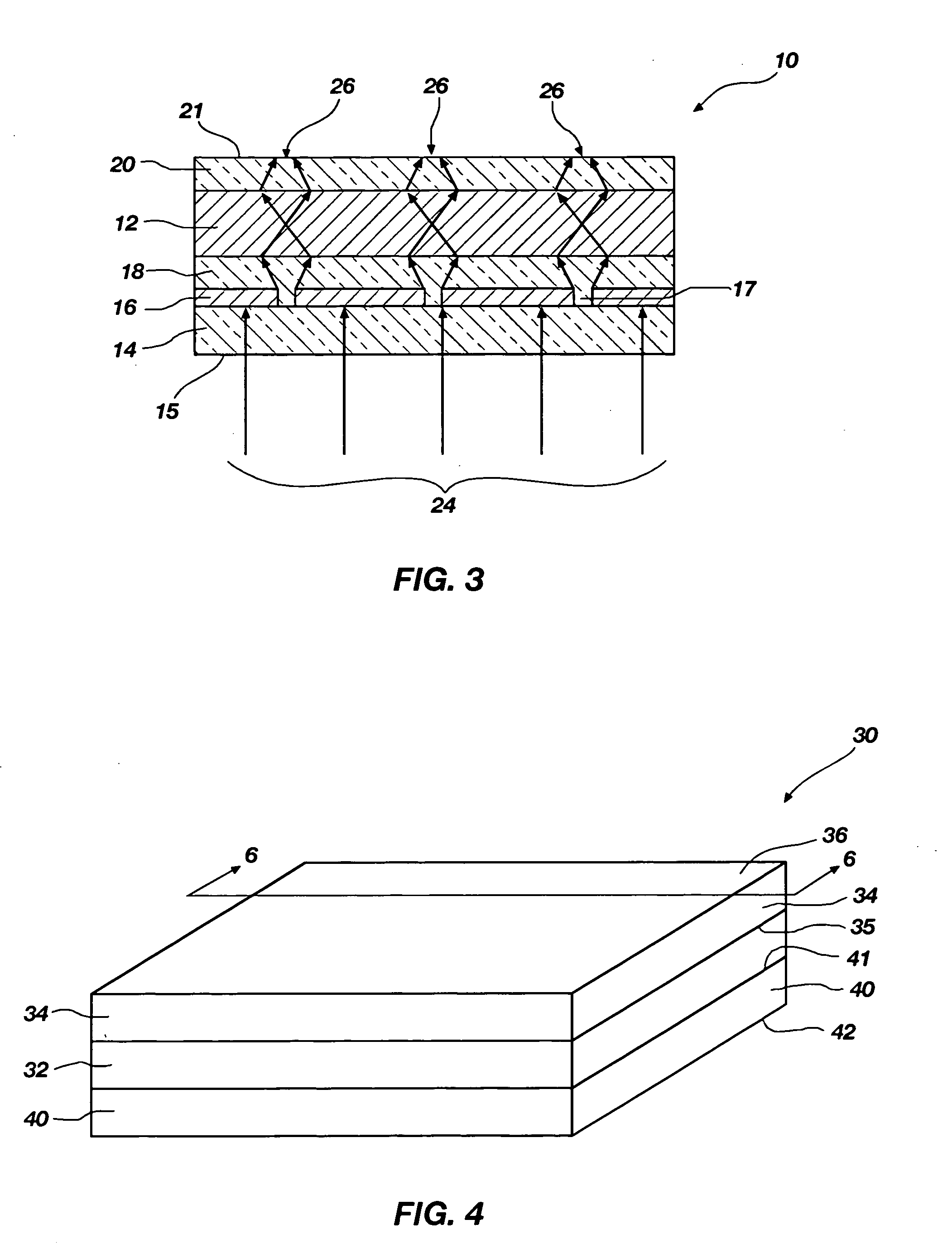
Superlens and a method for making the same
ActiveUS7643719B1Small sizeIndependent controlCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideEngineeringHorizontal and vertical
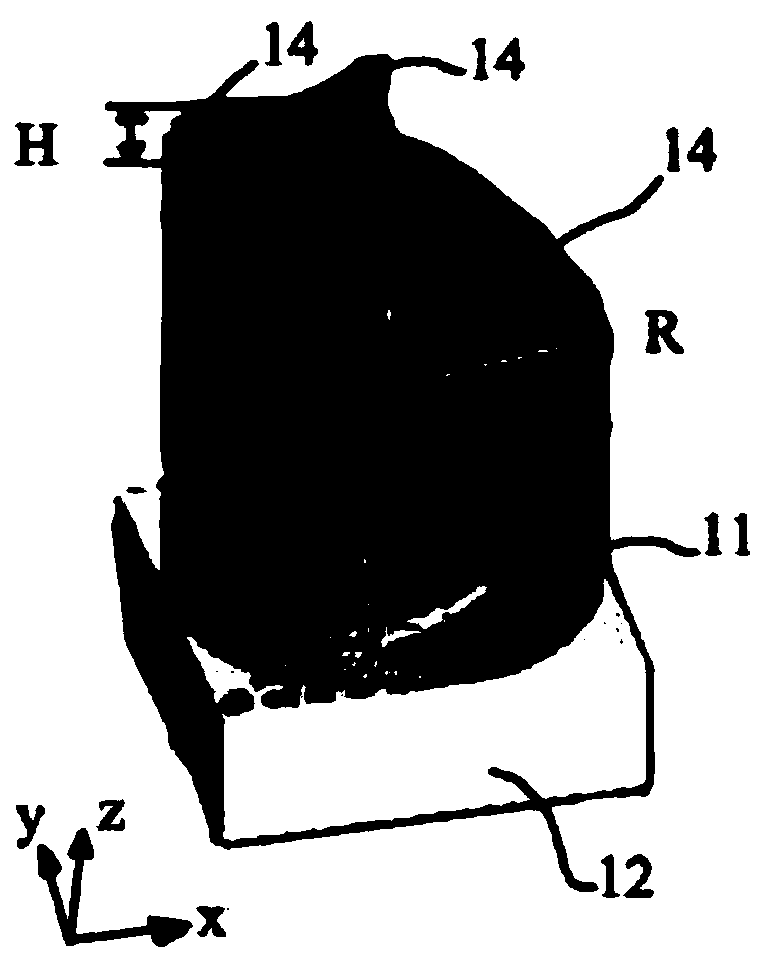
A superlens for controlling the size and the phase of an electromagnetic beam that passes through it, and a method for independently controlling the horizontal and vertical focusing of the electromagnetic beam using the superlens is provided. The superlens comprises a vertically GRIN multi-layer structure with one or more horizontally curved sidewalls. The vertical focusing is controlled by varying the longitudinal thickness of the multi-layer structure. The horizontal focusing is controlled by varying the profile and the radius of curvature of the horizontally curved sidewalls. Varying the thickness and radius of curvature is done by etching. Also provided is a method for making the superlens.
Owner:HO SENG TIONG
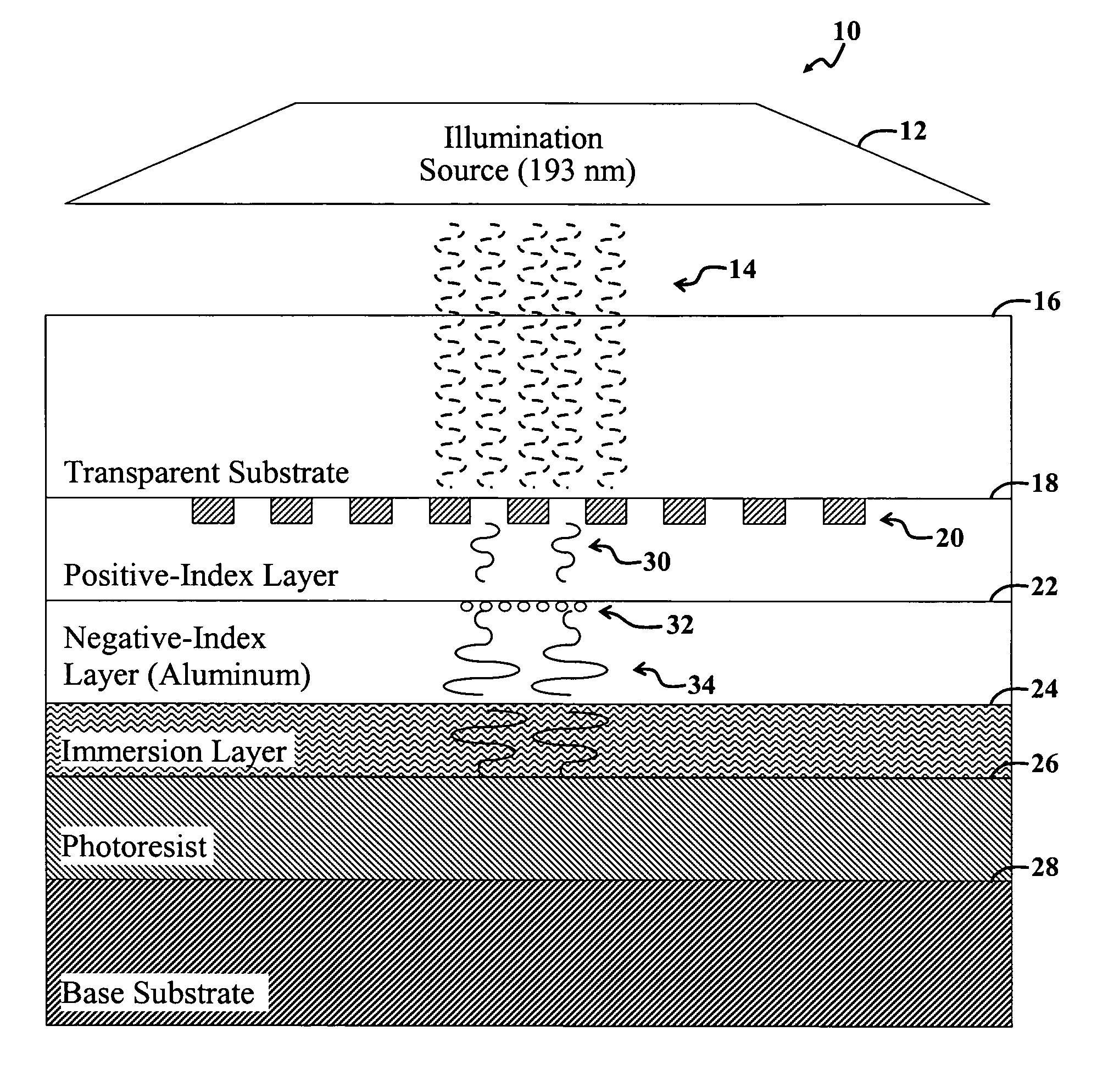
Photolithographic systems and methods for producing sub-diffraction-limited features
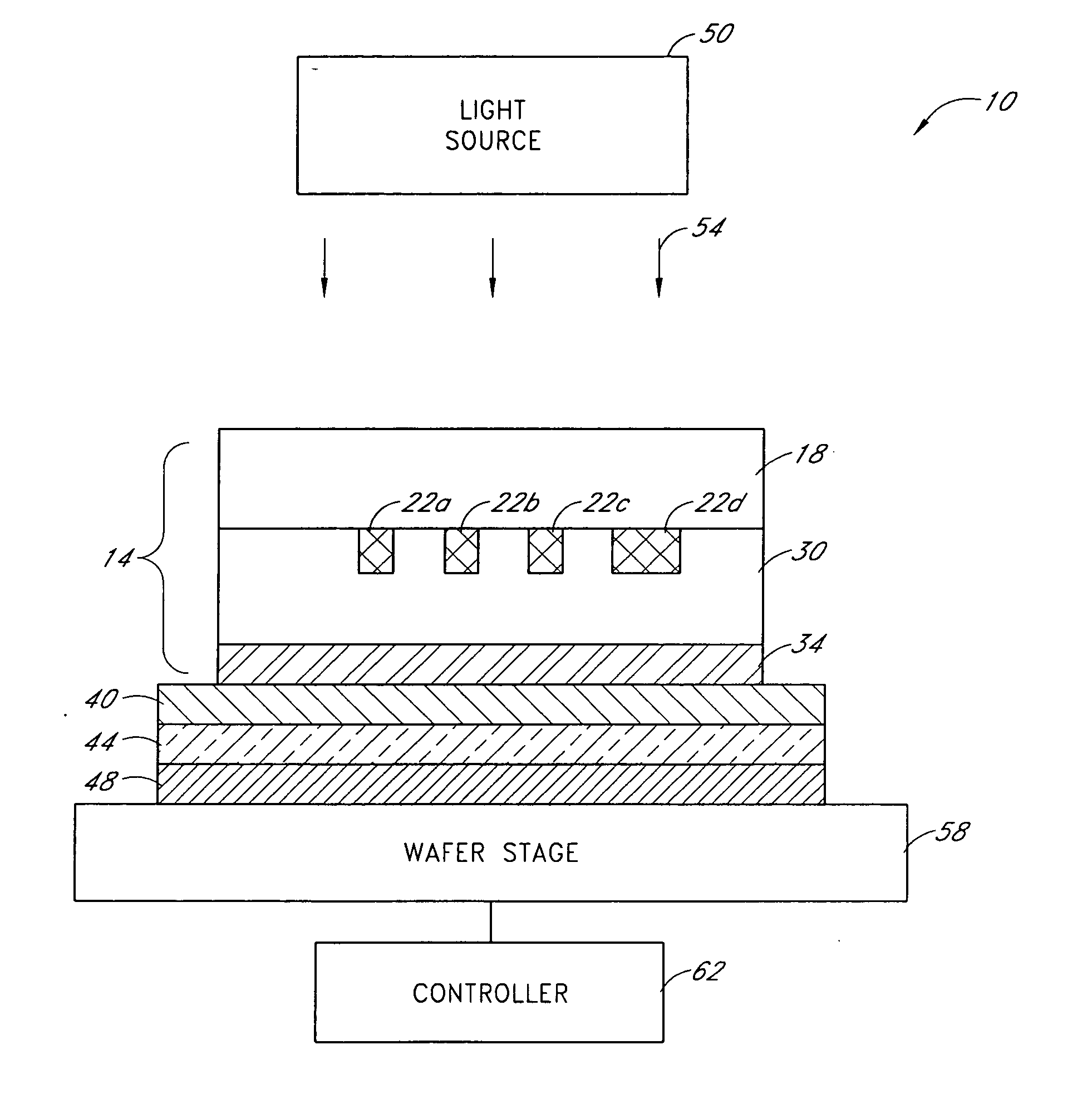
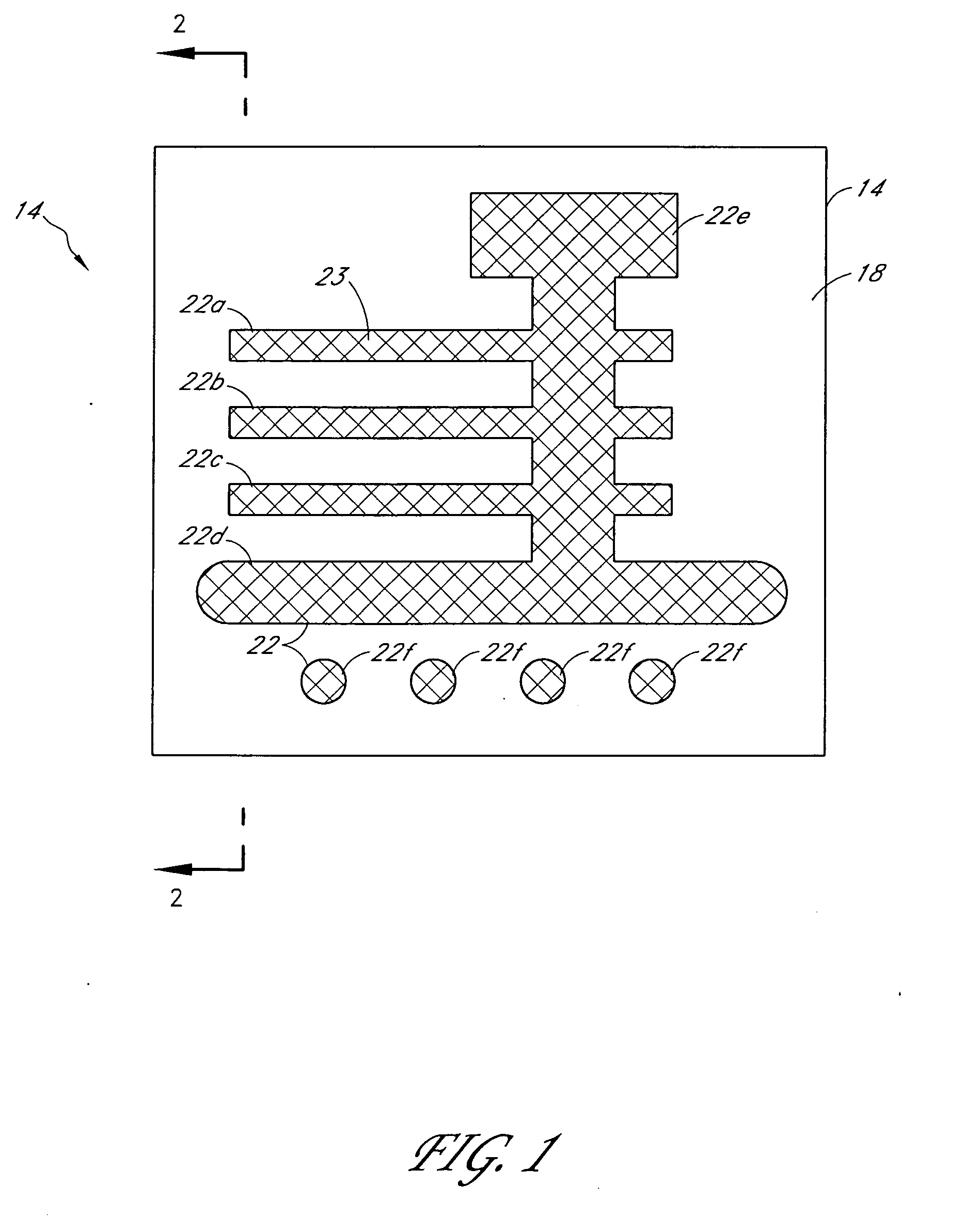
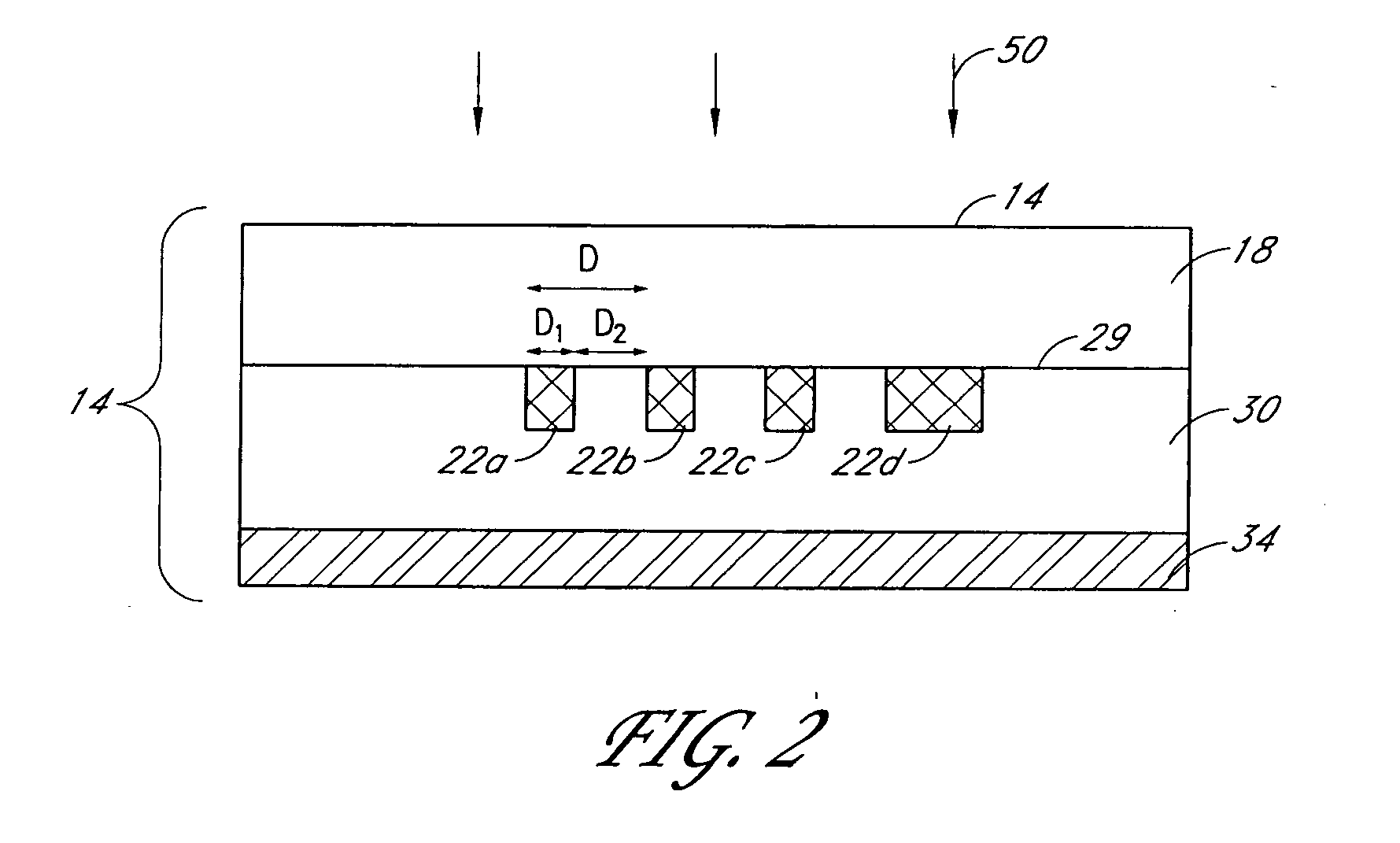
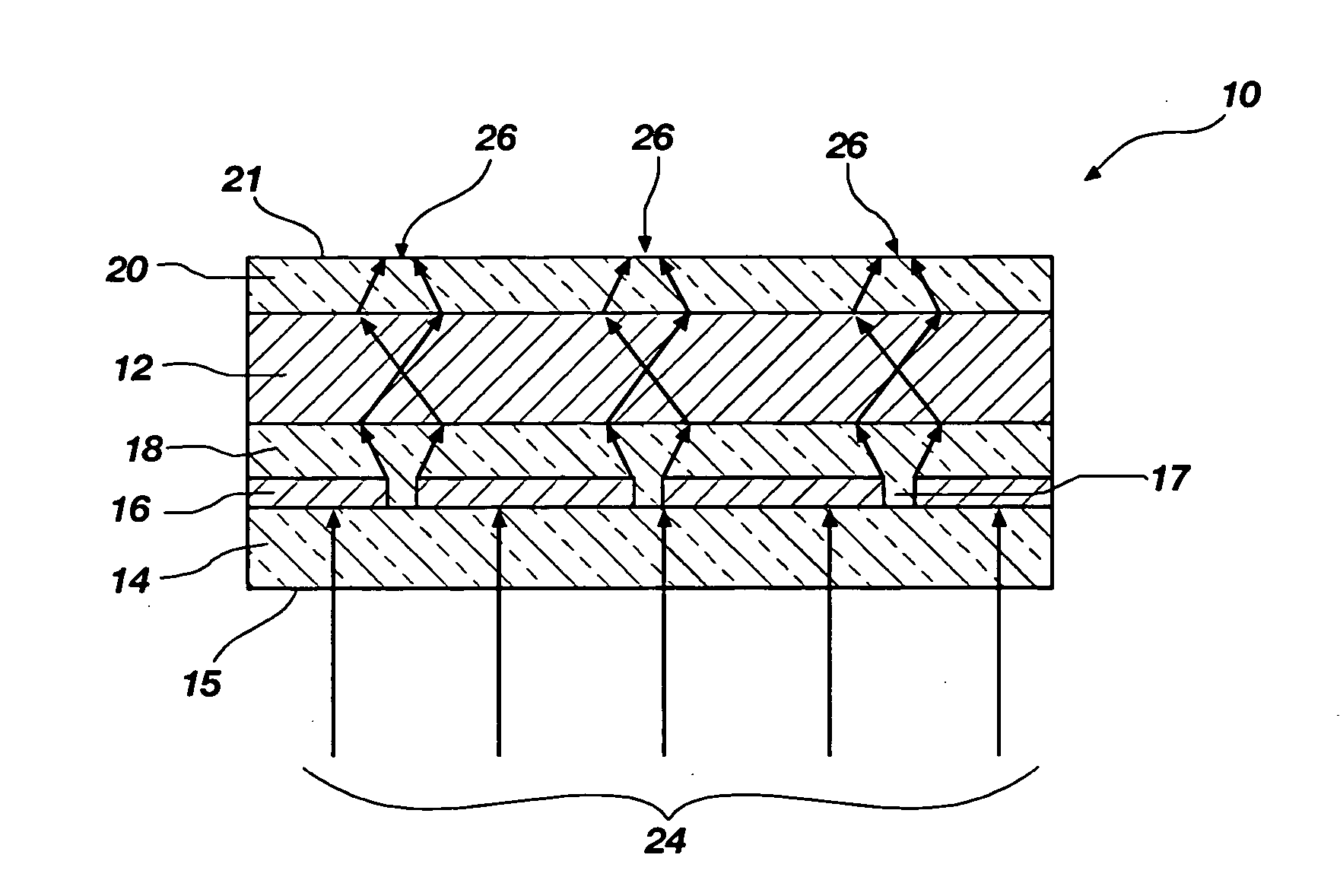
ActiveUS7538858B2Protect normal useNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface plasmonPhotoresist
Systems and methods for near-field photolithography utilize surface plasmon resonances to enable imaging of pattern features that exceed the diffraction limit. An example near-field photolithography system includes a plasmon superlens template including a plurality of opaque features to be imaged onto photosensitive material and a metal plasmon superlens. The opaque features and the metal superlens are separated by a polymer spacer layer. Light propagates through the superlens template to form an image of the opaque features on the other side of the superlens. An intermediary layer including solid or liquid material is interposed between the superlens and a photoresist-coated semiconductor wafer to reduce damage resulting from contact between the superlens template and the photoresist-coated semiconductor wafer.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
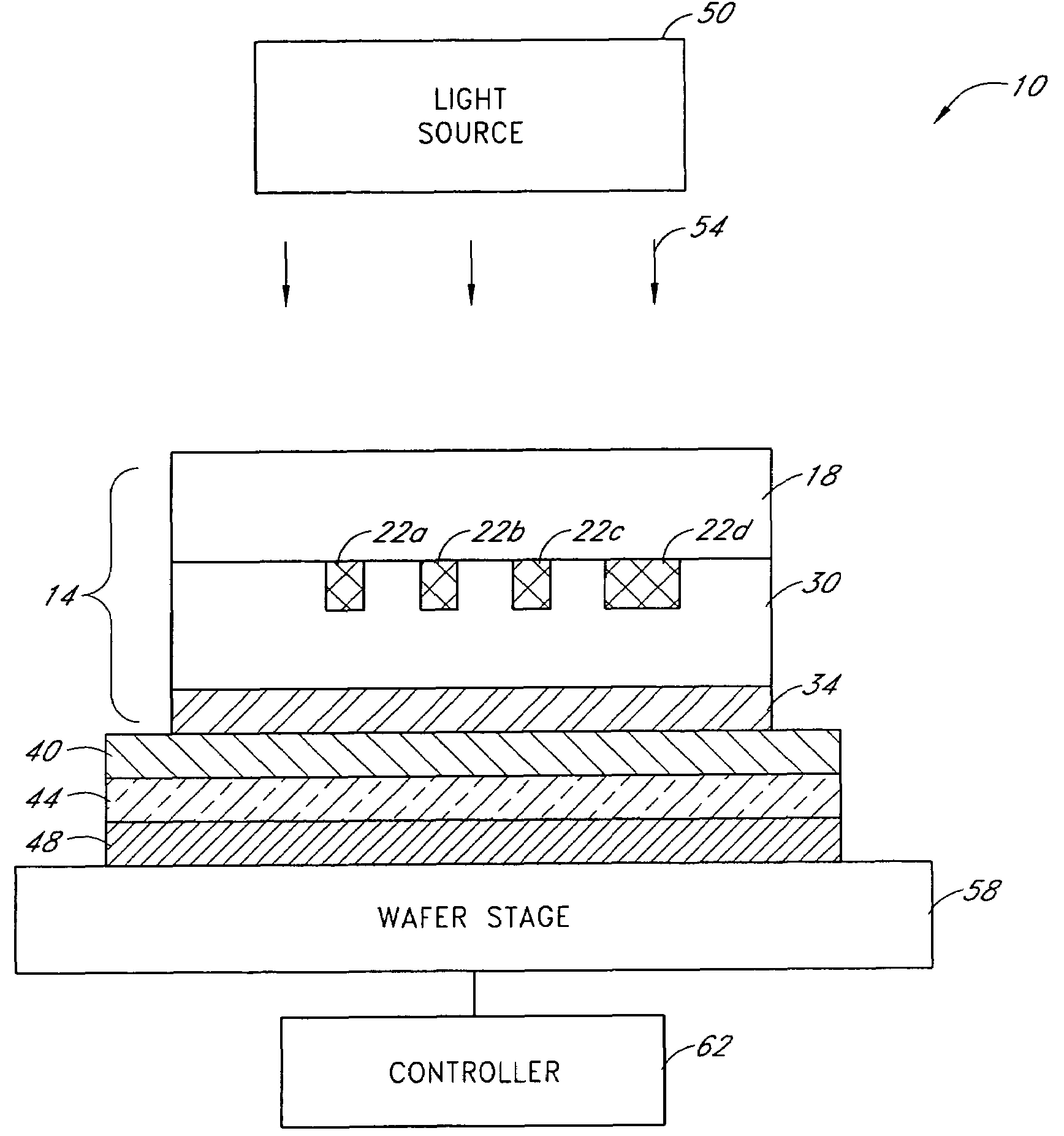
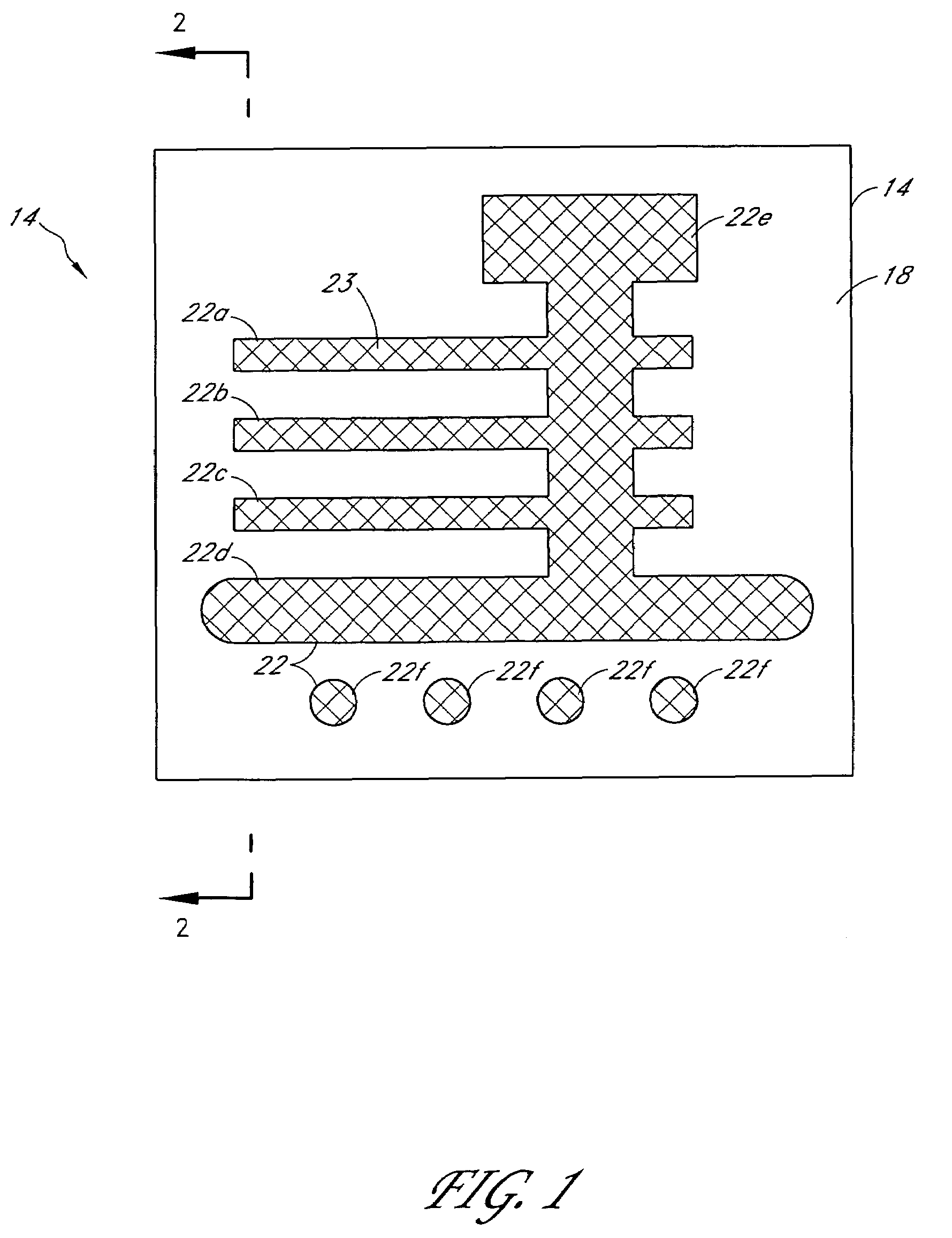
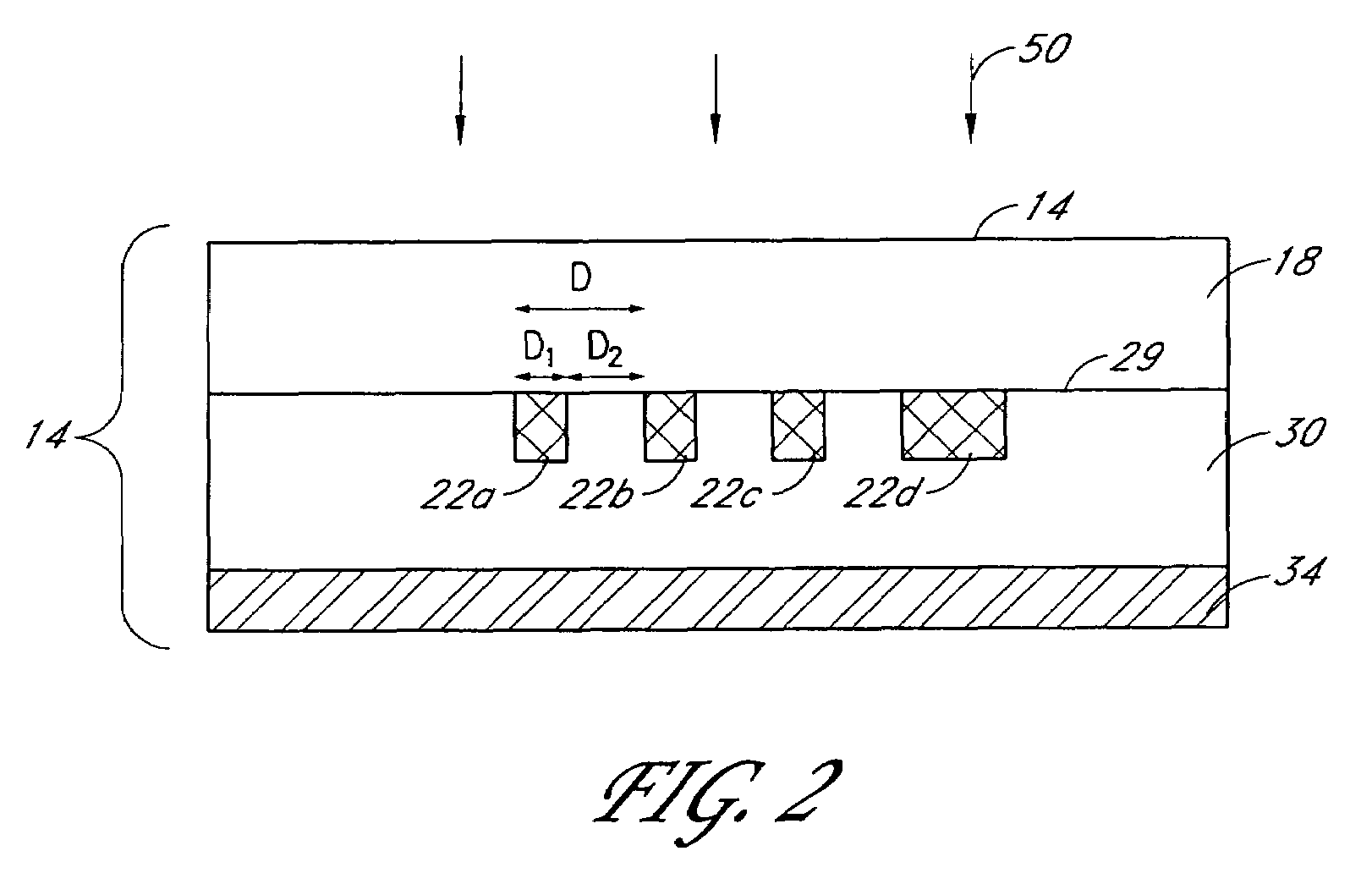
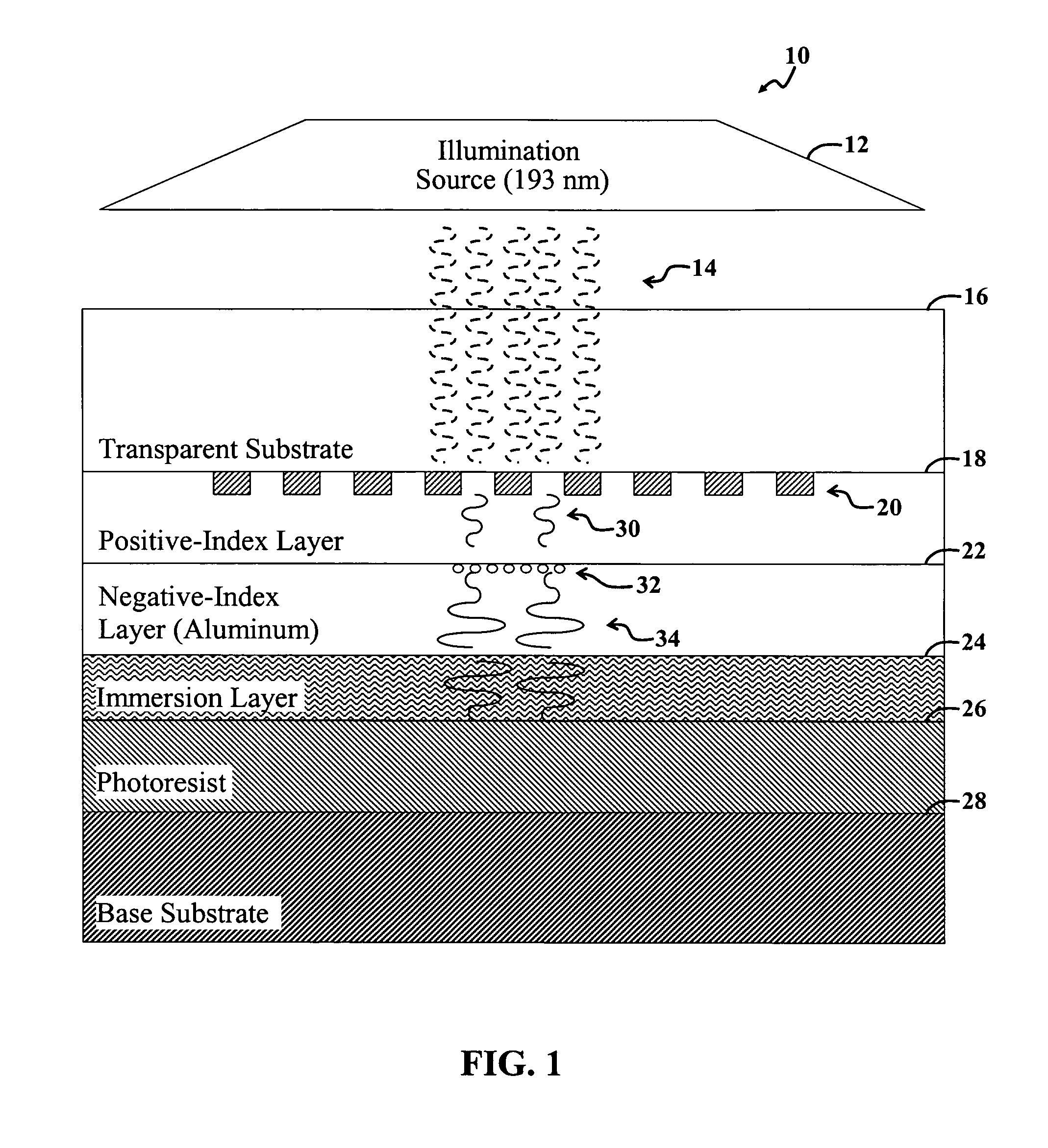
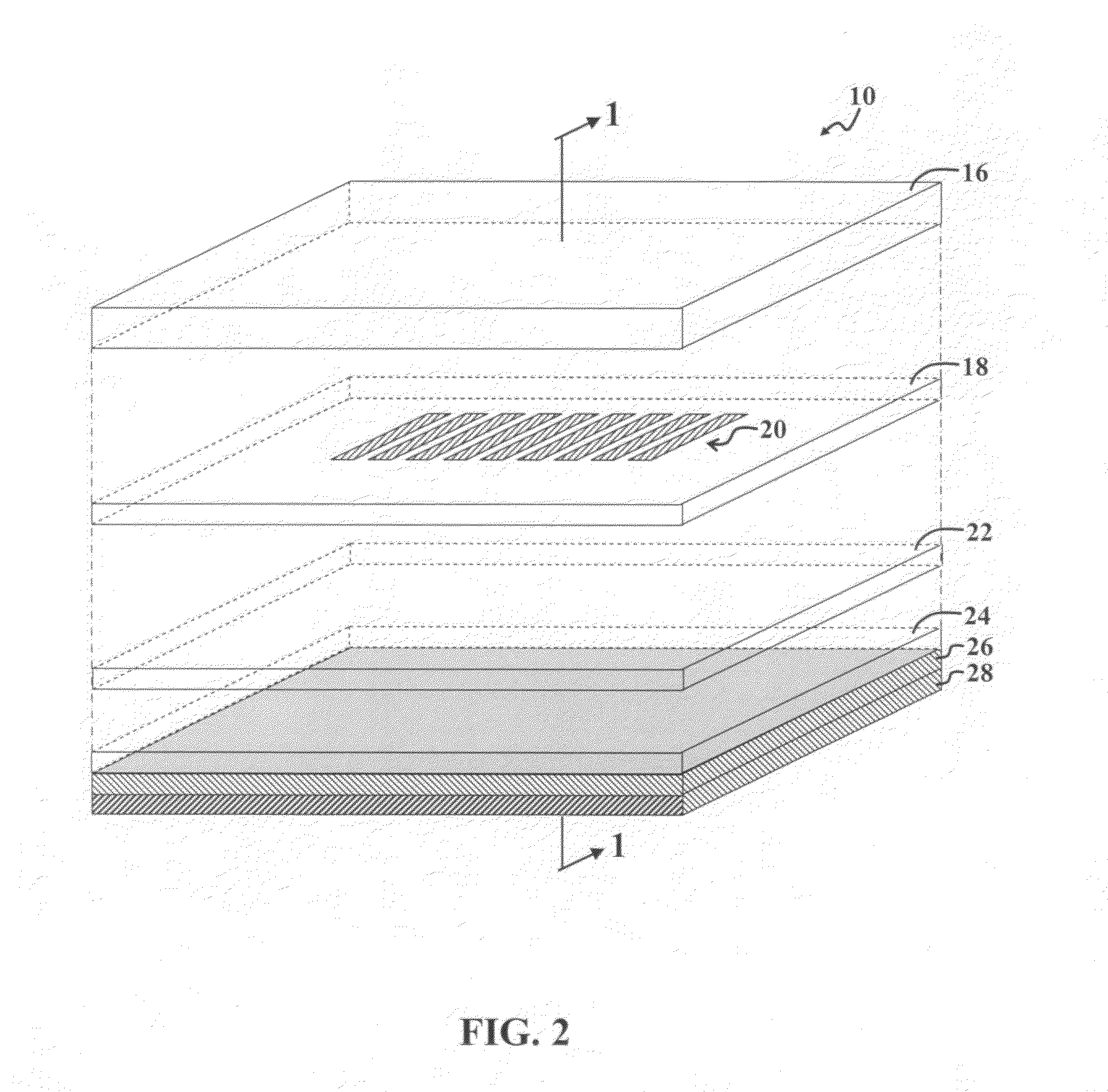
Superlens and lithography systems and methods using same
InactiveUS20100033701A1Improve performanceInnovative designPhotomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentLithographic artistNanoparticle
A superlens that includes, in one example embodiment, a positive-index material adjacent to a negative-index material, wherein the negative-index material includes aluminum. In a more specific embodiment, the positive-index material includes a dielectric layer, such as Poly(Methyl MethAcrylate) (PMMA), which is less than 50 nanometers thick. The negative-index material includes a smoothed aluminum layer less than 50 nanometers thick. The aluminum layer is disposed on the dielectric layer or vice versa, forming a superlens comprising the aluminum layer and the dielectric layer. In another embodiment, the superlens further includes plural aluminum layers separated by one or more layers of positive-index material. A mask is adjacent to the positive-index material. The mask may include one or more features that extend into a transparent substrate. The mask is positioned so that the positive-index material separates the mask from the smoothed aluminum layer. In an illustrative embodiment, the superlens is adapted for use with thermal lithography using nanoparticles.
Owner:LEE HYESOG +2
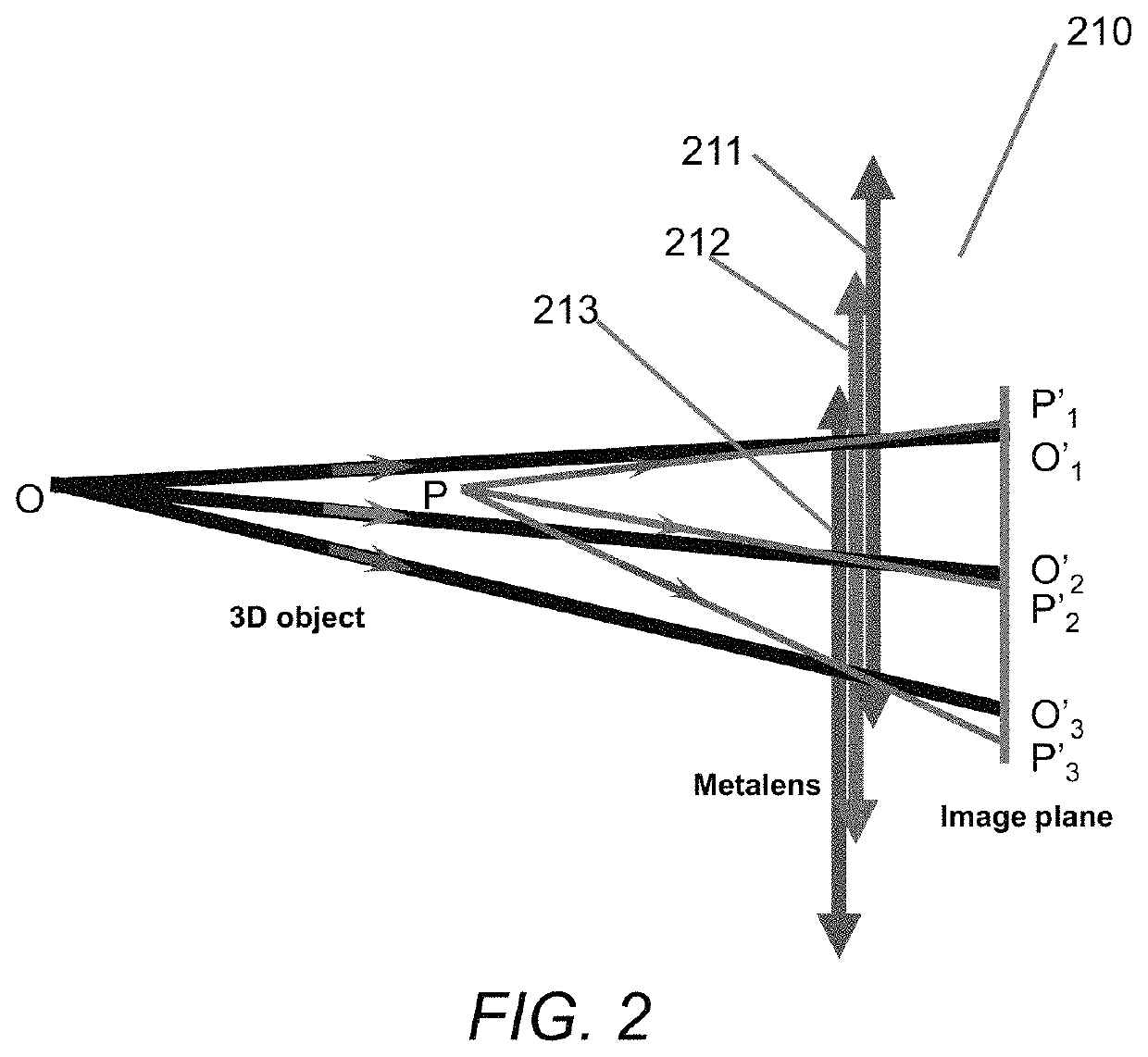
Metalens for light field imaging
Compound eyes of insects are great optical system for imaging and sensing by the nature creator, which is an unsurpassed challenge due to its precision and small size. Here, we use meta-lens consisting of GaN nano-antenna to open the fascinating doorway to full-color achromatic light field imaging and sensing. A 60×60 multi-channels meta-lens array is used for effectively capturing multi-dimensional optical information including image and depth. Based on this, the multi-dimensional light field imaging and sensing of a moving object is capable to be experimentally implemented. Our system presents a diffraction-limit resolution of 1.95 micrometer via observing the standard resolution test chart under white light illumination. This is the first mimic optical light field imaging and sensing system of insect compound eye, which has potential applications in micro robotic vision, non-men vehicle sensing, virtual and augmented reality, etc.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Method for constructing dynamic multifocal superlens based on medium and graphene
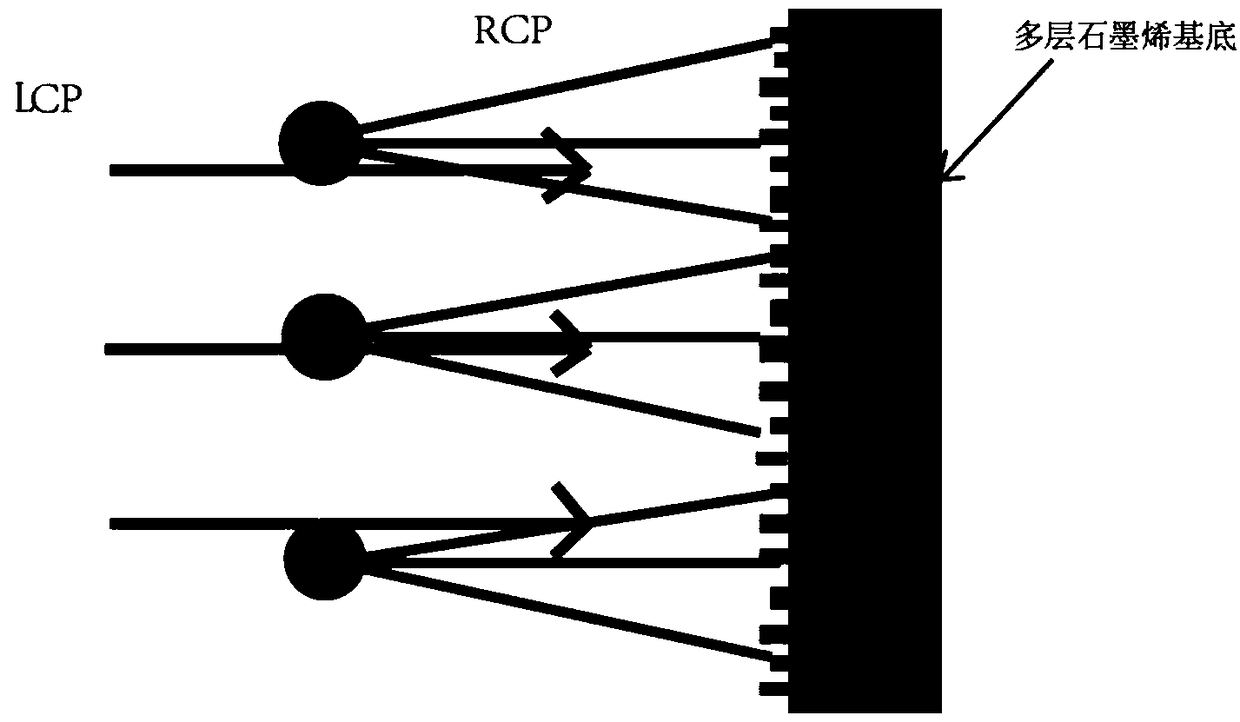
The invention discloses a method for constructing a dynamic multifocal superlens based on a medium and graphene. The method includes the following steps that: (1) as for incident light of different wavelengths, phase gradient distribution on a medium metasurface within an infrared wavelength range of 0.7 micron to 500 microns is calculated according to positional relations between focuses and wavelengths; (2) different periodic structures are designed for each center wavelength, specific phase values are determined according to the phase gradient distribution and Pancharatnam-Berry phases; (3)height-determined columnar structures are designed as the basic units of the medium metasurface, and then, a corresponding concrete realization structure and rotation direction are designed; and (4)according to a substrate part, multilayer graphene is adopted to form a reflection type focusing lens, and the Fermi level of the graphene can be changed such the position of a focusing point can be dynamically adjusted. According to the method of the invention, the dynamic multifocal reflective lens is realized through the medium metasurface and the multilayer graphene structure. The method has the advantages of high-efficiency focusing function, ultra-wideband performance, dynamic adjustment, easiness in integration and the like.
Owner:GUILIN G LINK TECH
Dual-beam super-resolution focusing method by utilizing meta-material lens
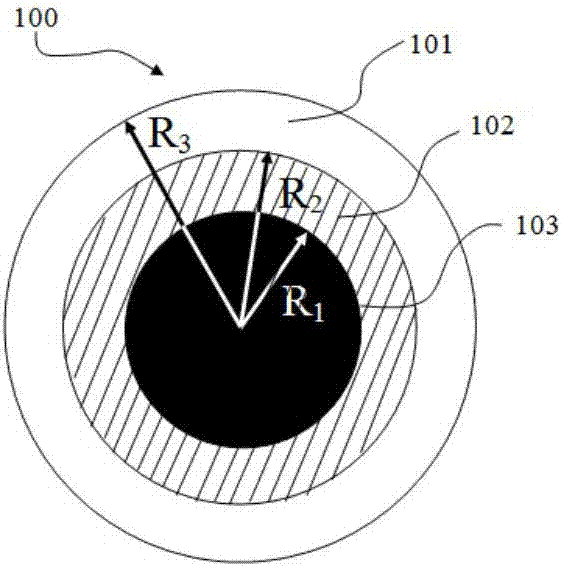
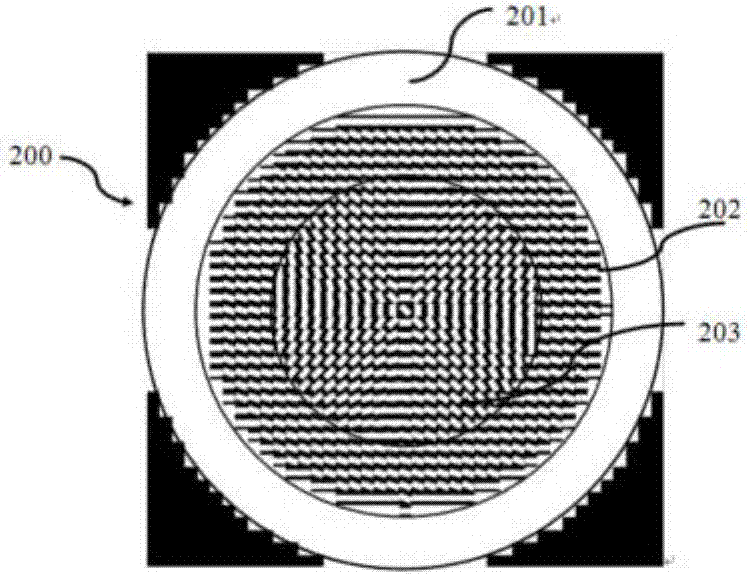
The invention discloses a dual-beam super-resolution focusing method by utilizing a meta-material lens. A circular-subregion disc-type superlens and a circular-subregion optical filter are prepared, wherein the disc-type superlens and the optical filter each comprises a disc, an inner circular ring portion and an outer circular ring portion; the outer circular ring portions are respectively made of transparent substrate material; and the radius of each circular subregion of the optical filter and the number of the subregions are same with those of the circular-subregion superlens, and accurate coaxial alignment is realized, thereby realizing dual-beam super-resolution focusing. The method enables the circular-subregion meta-material lens and the circular subregion optical filter to be combined, and is used for dual-beam super-resolution photoetching, dual-beam super-resolution high-density optical data storage and dual-beam super-resolution fluorescence imaging. The method is high in integration level, small in size, thin in thickness and light in weight; and aberrations and chromatic aberrations can be better than those of existing high-quality objective lenses or a single free-form lens.
Owner:唐山斯腾光电科技有限公司
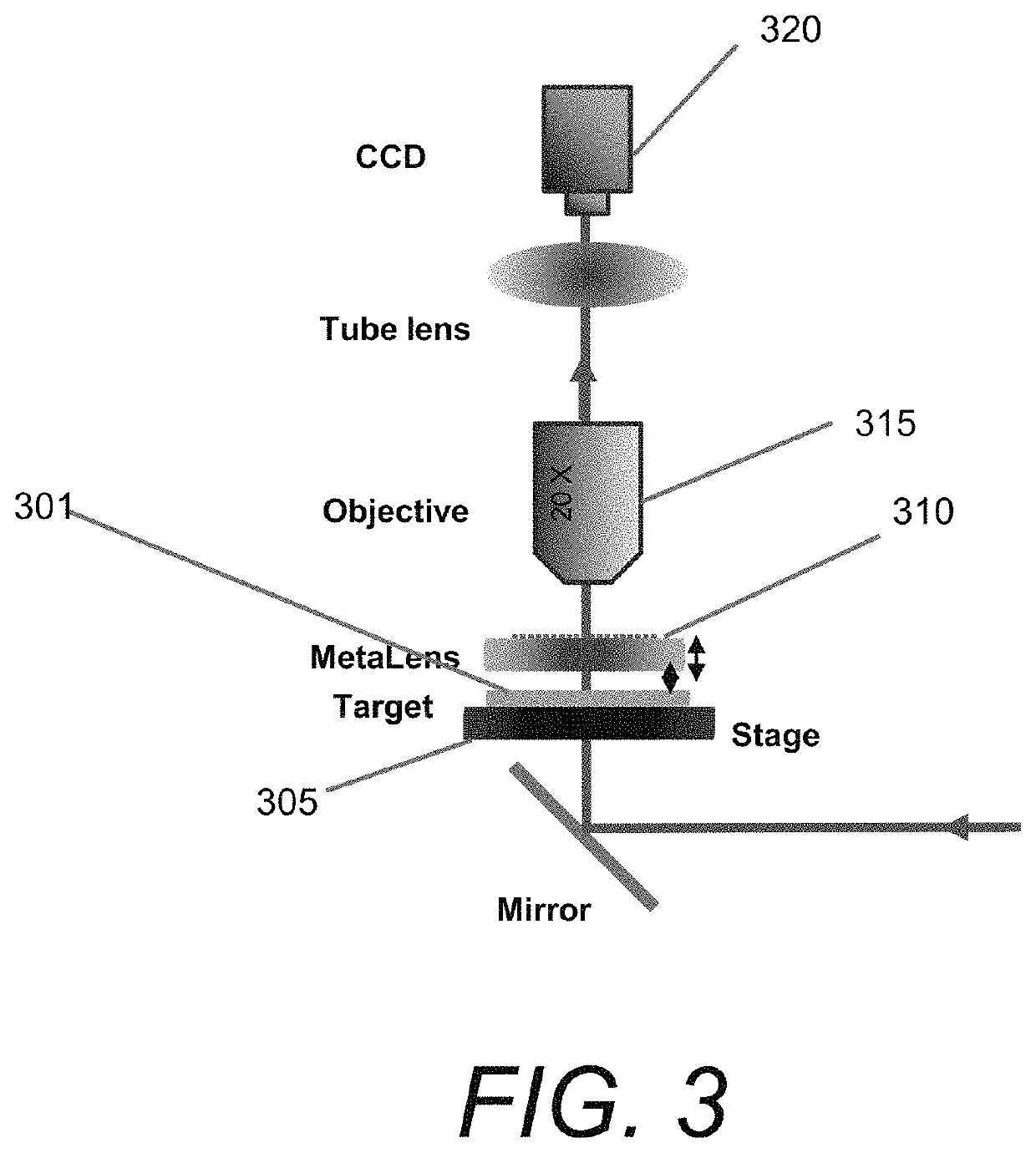
Super-surface microscope and preparation method thereof, and optical path measurement system
ActiveCN110007451ANo spherical aberrationSimple structureVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingMicrometerOperability
The invention provides a super-surface microscope, a preparation method thereof and a light path measurement system, the preparation method adopts a titanium dioxide super-surface to prepare the super-surface microscope consisting of two super-lenses with different focal lengths and diameters of up to 100 micrometers, and the invention also provides the light path measurement system. Compared withthe prior art, the super lens has no spherical aberration; the structure is simple, the lens is composed of two simple planar super lenses, and no extra lens group needs to be added; the size is verysmall, the diameter can reach 100 micrometers, and integration is facilitated; according to the preparation method, conventional reagents and instruments are adopted, the steps are easy to implement,and operability is high; the optical path measuring system is simple and quick, and can quickly measure the finished product of the super-surface microscope.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Multilayered meta lens and optical apparatus including the same
A meta-lens includes a first layer that is arranged on a substrate and that includes a plurality of first nanostructures and a second layer including a plurality of second nanostructures separately arranged from the first nanostructures. The meta-lens may focus light of a plurality of wavelengths or light of a wide wavelength bandwidth due to the arrangement of the nanostructures in a multilayer structure.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Photolithographic systems and methods for producing sub-diffraction-limited features
ActiveUS20070159617A1Protect normal useNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface plasmonPhotoresist
Systems and methods for near-field photolithography utilize surface plasmon resonances to enable imaging of pattern features that exceed the diffraction limit. An example near-field photolithography system comprises a plasmon superlens template comprising a plurality of opaque features to be imaged onto photosensitive material and a metal plasmon superlens. The opaque features and the metal superlens are separated by a polymer spacer layer. Light propagates through the superlens template to form an image of the opaque features on the other side of the superlens. An intermediary layer comprising solid or liquid material is interposed between the superlens and a photoresist-coated semiconductor wafer to reduce damage resulting from contact between the superlens template and the photoresist-coated semiconductor wafer.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Superlens component for directional display
ActiveUS20140177032A1Thin structureIncrease the areaMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesDirect illuminationLight beam
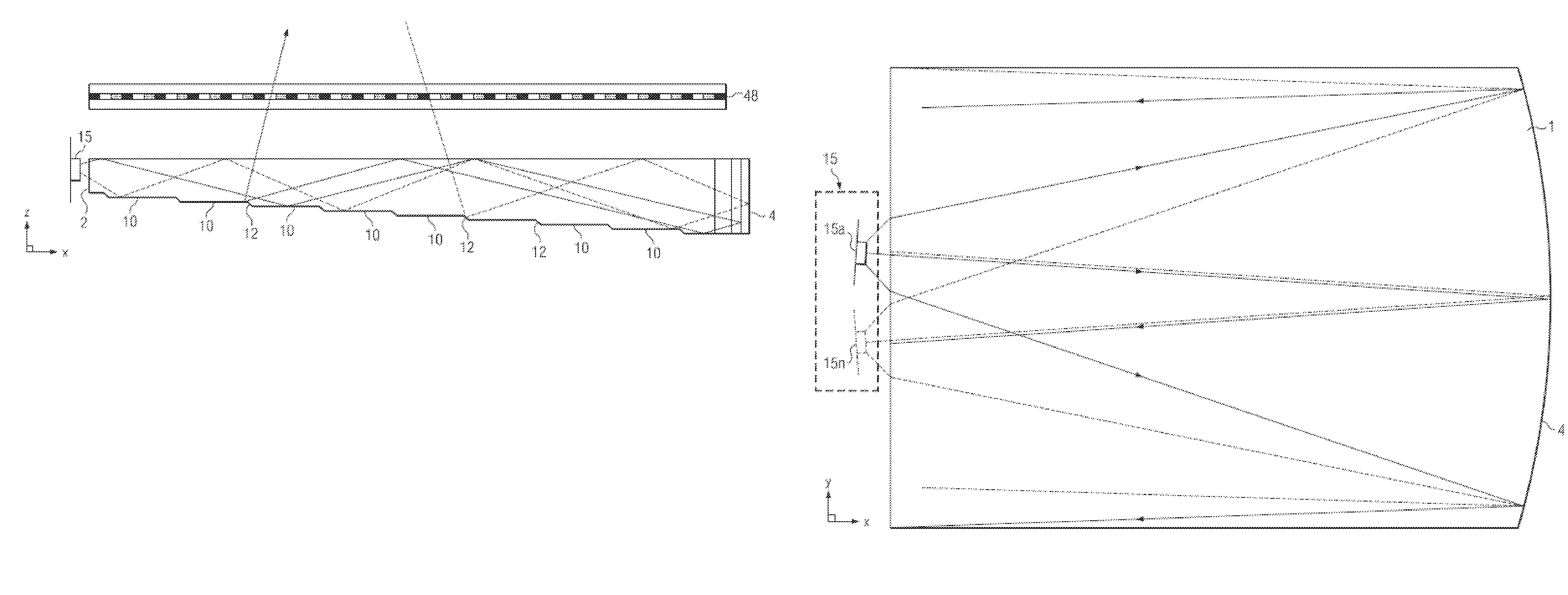
Disclosed is an imaging directional backlight apparatus comprising a waveguide, a light source array, and a further optical element for providing large area directed illumination from localized light sources. The imaging directional backlight may comprise a stepped waveguide that may include a stepped structure, in which the steps may further include extraction features optically hidden to guided light, propagating in a first forward direction. Returning light propagating in a second backward direction may be refracted, diffracted, or reflected by the features to provide discrete illumination beams exiting from the top surface of the waveguide. Viewing windows are formed through imaging individual light sources. The further optical element may comprise a superlens comprising first and second aligned lens arrays that may be arranged to modify the output viewing windows to achieve enhanced window imaging from the directional backlight.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
High resolution projection micro stereolithography system and method
ActiveUS9492969B2Increase amplitudeNegative index of refractionAdditive manufacturing apparatusHolographic optical componentsSpatial light modulatorCombined use
A high-resolution PμSL system and method incorporating one or more of the following features with a standard PμSL system using a SLM projected digital image to form components in a stereolithographic bath: a far-field superlens for producing sub-diffraction-limited features, multiple spatial light modulators (SLM) to generate spatially-controlled three-dimensional interference holograms with nanoscale features, and the integration of microfluidic components into the resin bath of a PμSL system to fabricate microstructures of different materials.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Meta-lens and optical apparatus including the same
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Device for realizing super-lens zooming based on polarization state regulation and control, zooming method and application
ActiveCN111338156APolarization modulation zoom functionSimple designFocusing aidsOptical elementsEngineeringPolarizer
The invention provides a device for realizing super-lens zooming based on polarization state regulation and control. The device comprises a light source, a linear polarizing film, a quarter-wave plate, a polarization regulation and control super-lens and a photosensitive camera, wherein the polarization regulation and control super lens is arranged behind the linear polaroid and the quarter-wave plate, and the quarter-wave plate is rotated to obtain incident light in different polarization states to be gathered at different positions of an image space to realize zooming. The invention also provides a zooming method and application of the device. The device is simple in structure, small in size, compatible with a semiconductor process and easy to integrate and produce on a large scale. Theinvention provides a new means and method for biomedical detection, material analysis, chiral evolution research and the like which are sensitive to circularly polarized light.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Meta-lens and optical apparatus including the same
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Electric control zooming plane lens
PendingCN111103739AWith electronically controlled non-mechanical zoom functionAchieve imagingNon-linear opticsElectrical field strengthElectric control
The invention discloses an electric control zooming plane lens which comprises a first electric control zooming liquid crystal lens, a second electric control zooming liquid crystal lens and a super lens with a fixed focal length which are cascaded. In a state of not applying an electric field, the arrangement direction of molecules in the first liquid crystal layer of the first liquid crystal lens is parallel to the overall mirror surface direction of the first liquid crystal lens, the arrangement direction of the molecules in the second liquid crystal layer of the second liquid crystal lensis parallel to the overall mirror surface direction of the second liquid crystal lens, and the arrangement directions of the molecules in the first liquid crystal layer and the molecules in the secondliquid crystal layer are perpendicular to each other. The electric field is applied to the first liquid crystal layer and the second liquid crystal layer respectively, and the molecular arrangement state of the first liquid crystal layer and the second liquid crystal layer is adjusted by adjusting the electric field intensity. The plane lens is the super lens with a fixed focal length. The planarlens group has an electric control zooming function and is insensitive to polarization based on the combination of the liquid crystal lens and the super lens which are arranged in a cascaded manner,a high-quality imaging effect is achieved and the practical application of the planar lens technology is promoted.
Owner:INST OF FLUID PHYSICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Meta lens and optical apparatus including the same
A meta lens includes a first lens surface, and a second lens surface provided opposite to the first lens surface, wherein at least one of the first lens surface and the second lens surface is a metasurface including a plurality of nanostructures having a sub-wavelength dimension that is less than a central wavelength λ0 in an operation wavelength band of the meta lens, and wherein a deflection property of the first lens surface and a deflection property of the second lens surface based on positions of incident light are opposite to each other in at least some regions of each of the first lens surface and the second lens surface.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Light-field imaging using a gradient metasurface optical element
Embodiments of 3D imaging systems that use a multifunctional, nano structured metalens to replace the conventional microlens array in light field imaging are disclosed. The optical focusing properties of the metalenses provided by gradient metasurface optical elements. The gradient metasurfaces allow the properties of the elements of the metalens array to be changed by tuning the gradient metasurfaces.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
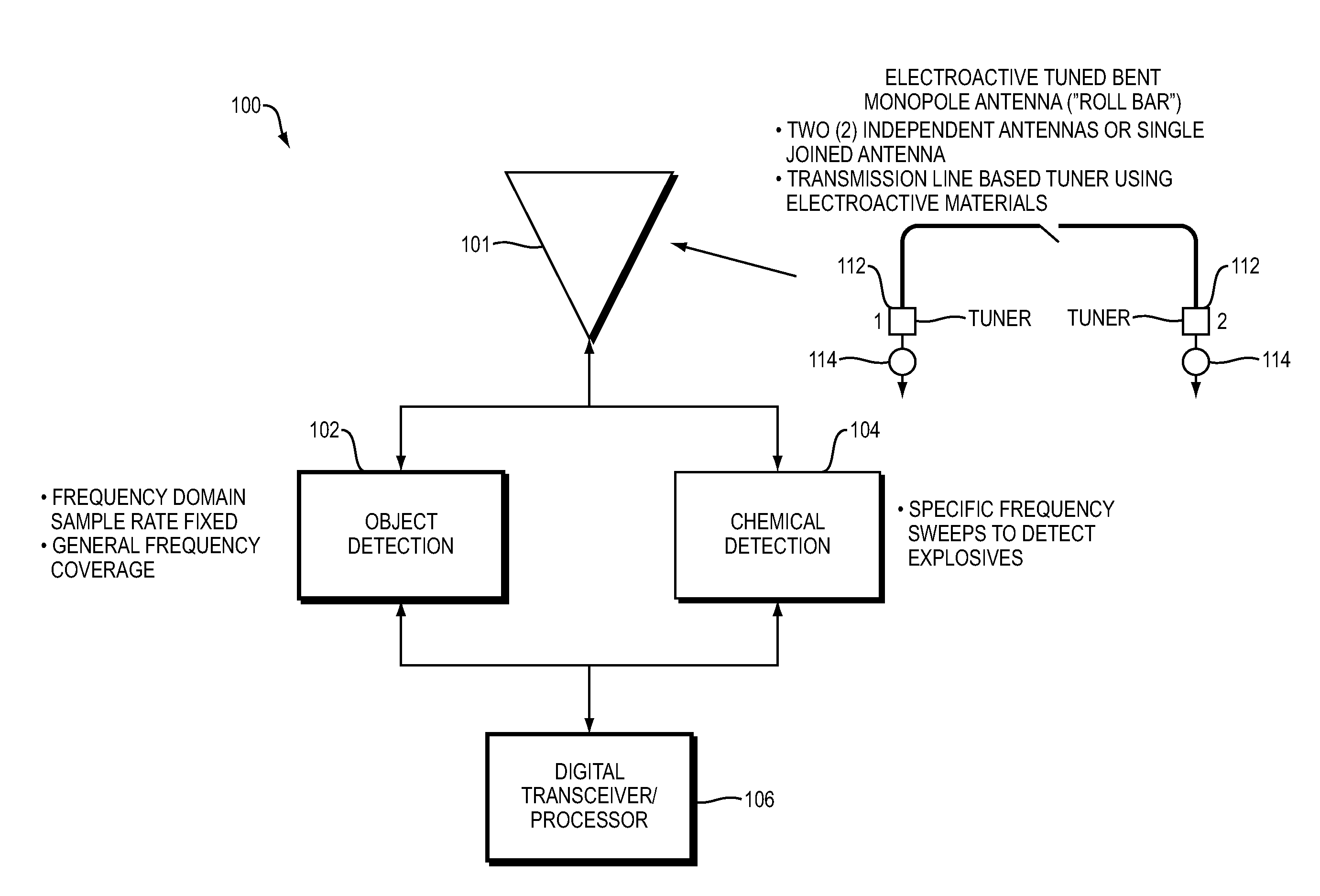
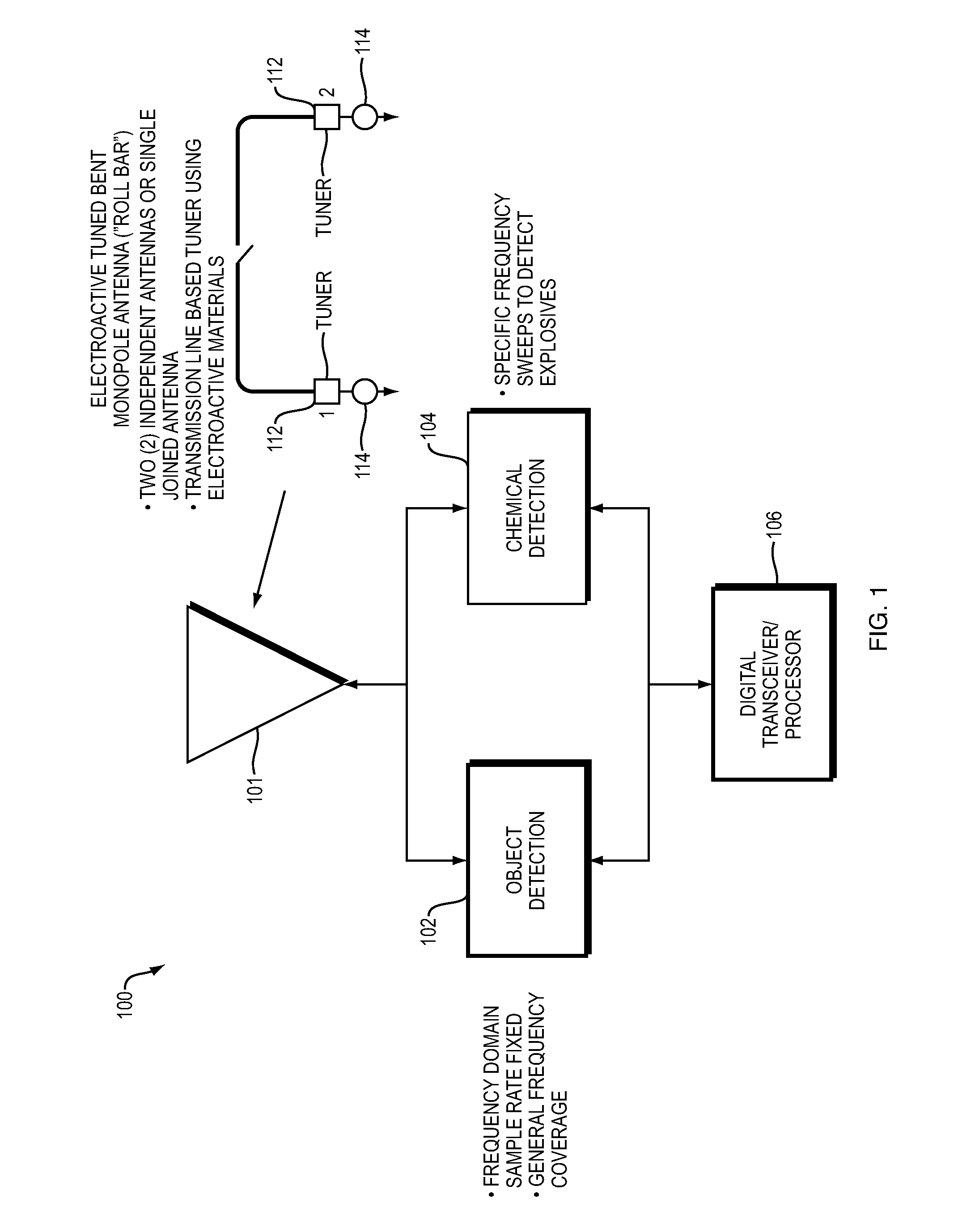
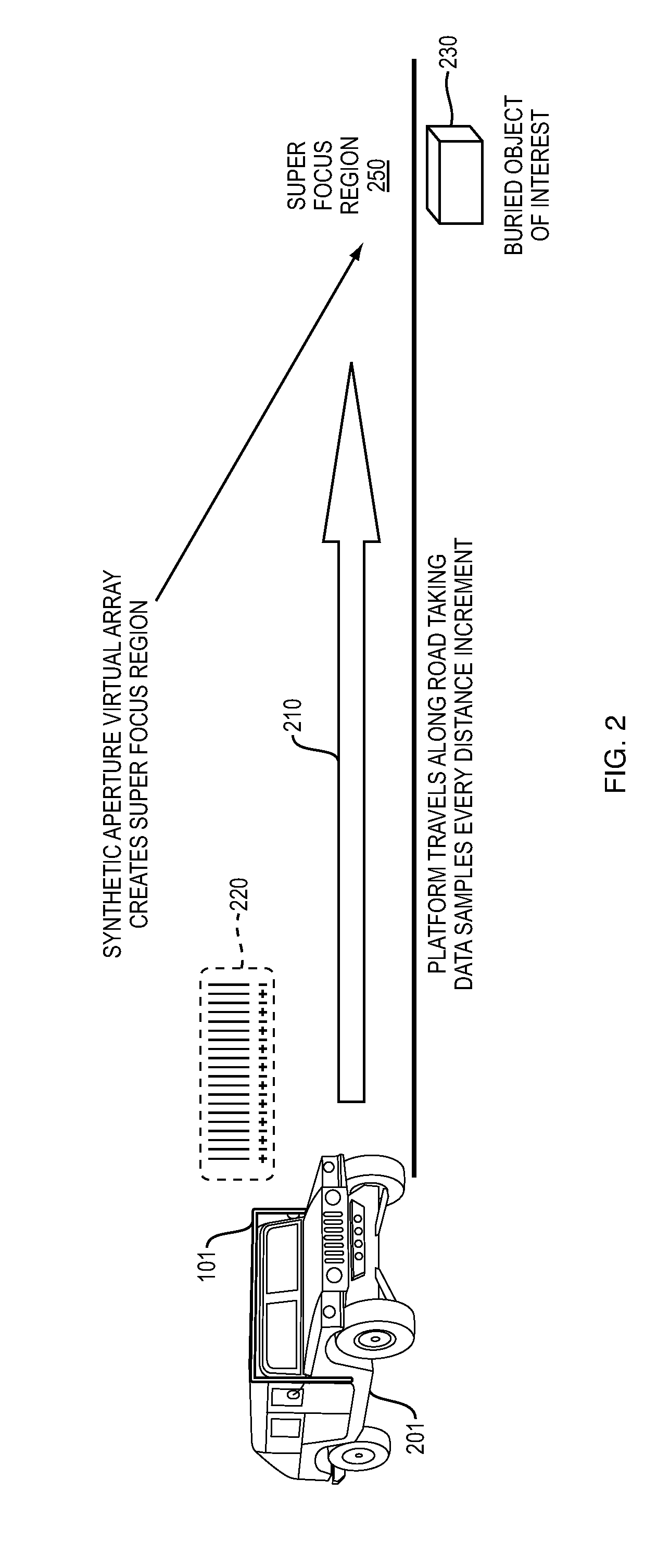
Near field subwavelength focusing synthetic aperture radar with chemical detection mode
InactiveUS20140152486A1Save livesImprove securityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture sonarRadar
Detection of objects such as a buried explosive device while operating from a moving platform using a radio frequency emission system having two modes. An electromagnetic wave emission and detection system operates in a first mode to locate objects of interest and in a second mode to determine if an object contains explosive materials. In the first mode, the emission and detection system preferably operates as a subwavelength focusing, wideband, superlens using a near field super gain synthetic aperture continuous wave (CW) swept radar. In the second mode the system preferably enabled after detection of an object in the first mode, uses chemical detection methods such as Nuclear Quadrupole Resonance (NQR).
Owner:AMI RES & DEV
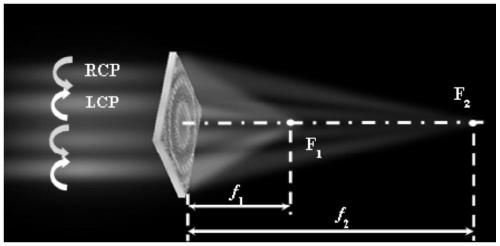
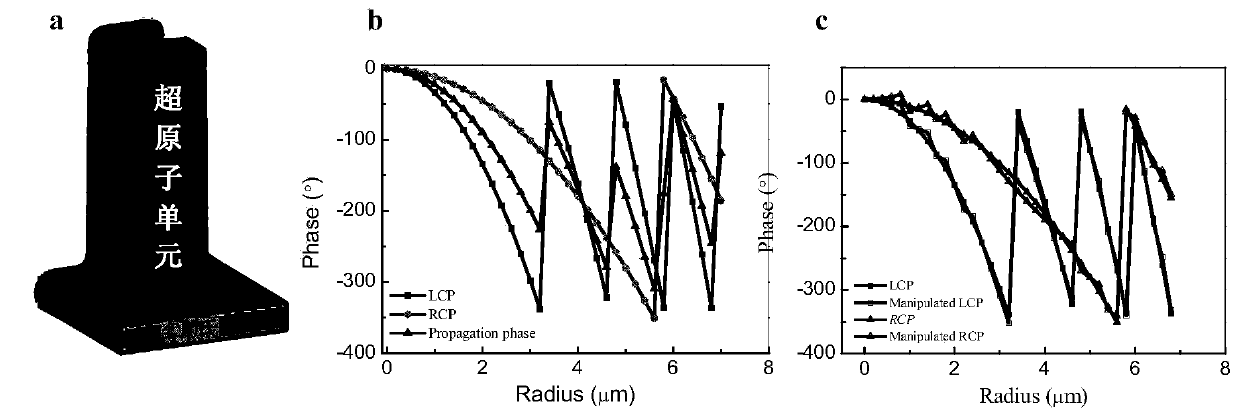
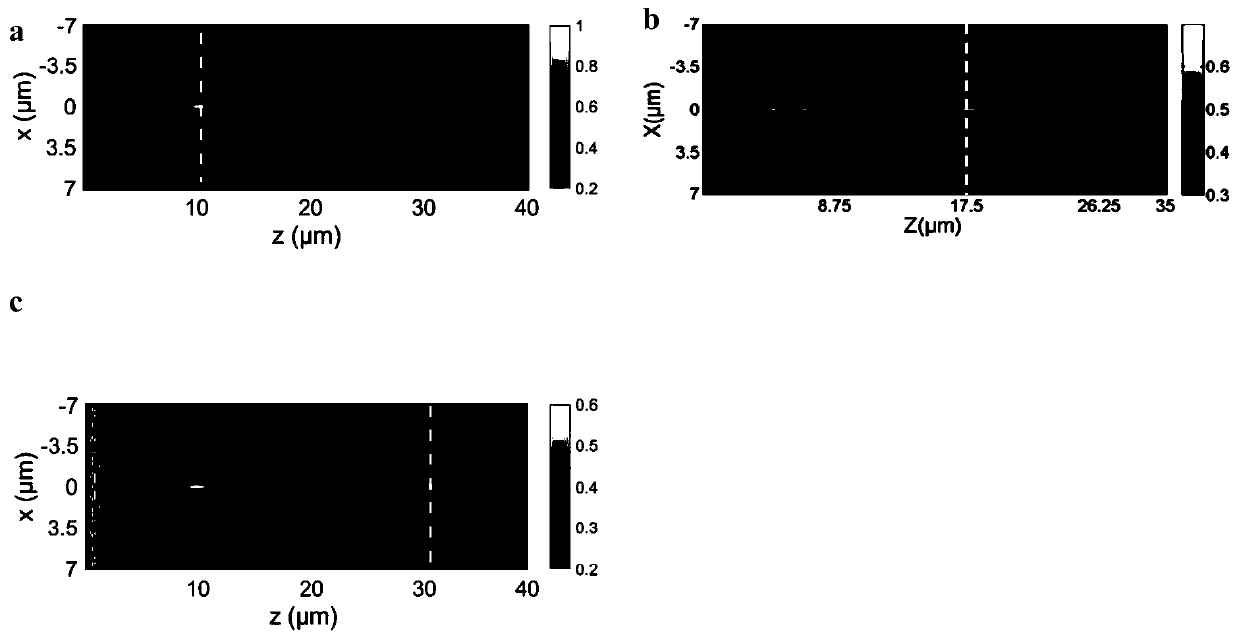
Circular polarization dichroic super lens and light path system comprising same
The invention discloses a circular polarization dichroic super lens and a light path system comprising the same. The super lens comprises a substrate and a surface structure; the surface structure comprises a metal layer and a plurality of spiral surface structures arranged in an array, the metal layer is formed on the spiral surface structures, and the plurality of spiral surface structures are arranged on the substrate. The range of the rotation angle of the plurality of spiral surface structures along the radial direction is 0-360 degrees, and the phase of the left-handed circularly polarized light and the right-handed circularly polarized light passing through the super lens can realize full-phase delay. The super lens of the embodiment of the invention can provide a new idea for realizing the combined function of focusing imaging and circular dichroism for a single device, and has great application prospect in the aspects of chiral sensing measurement, imaging, display, biologicaldetection and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Multifunctional super-lens array and optical system
ActiveCN111025671AWith dispersion spectroscopicWith focused spectrumOptical elementsFresnel lensDetector array
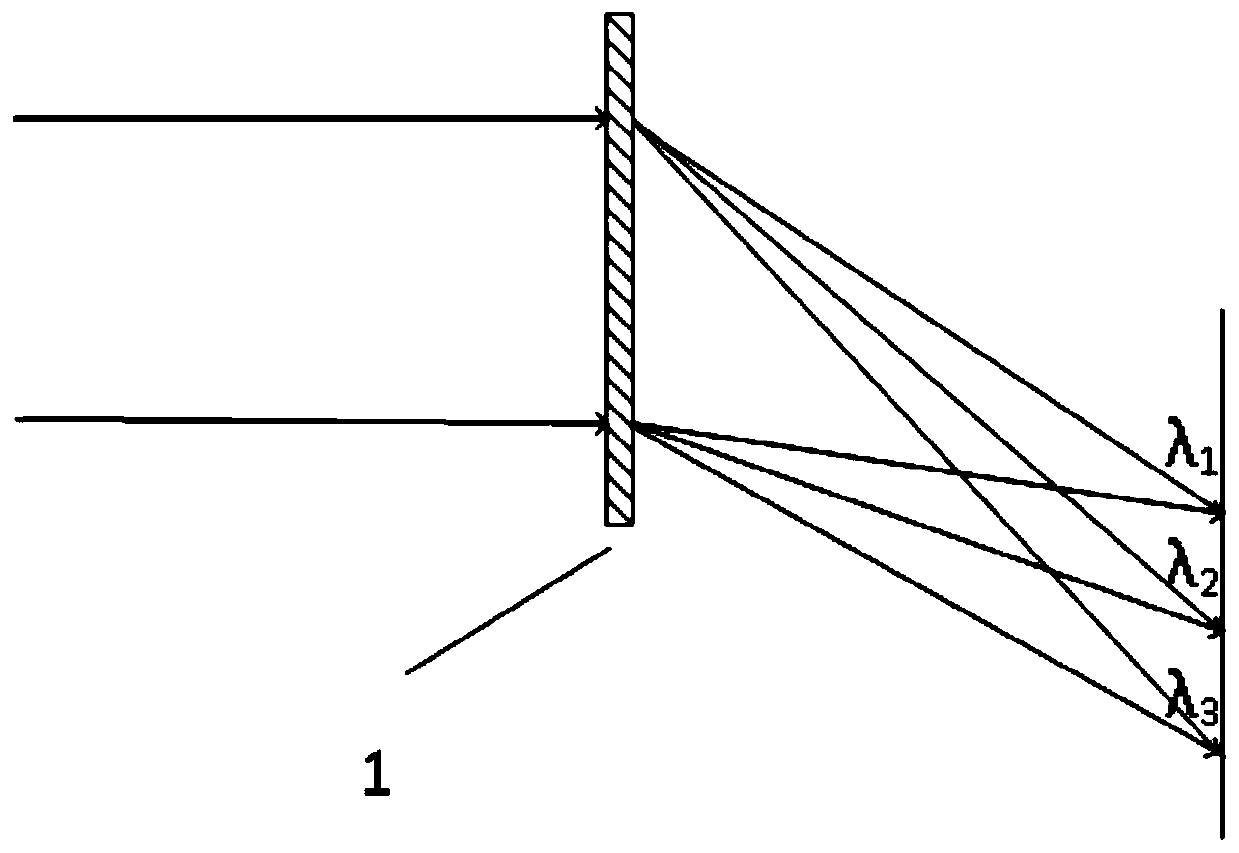
The invention relates to the field of optics, in particular to a super-lens, and specifically relates to a multifunctional super-lens array and an optical system thereof. The multifunctional super lens array comprises n tightly arranged super-lens units formed on a same substrate, wherein n is a positive integer larger than 1, each super lens unit is provided with an off-axis Fresnel lens structure and a plane super-lens structure, the plane super-lens structures are used for focusing incident light waves, and the off-axis Fresnel lens structures are used for achieving light splitting of lightwaves with different wavelengths; the optical system comprises the multifunctional super-lens array, a photon integration loop and a detector array. According to the invention, the off-axis Fresnel lens and the plane super-lens are combined together, and the functions of the off-axis Fresnel lens and the plane super-lens are fused, so that a light splitting phase is introduced into the plane super-lens, light wave focusing can be realized, light splitting of light waves with different wavelengths can also be realized, and the multifunctional super-lens with dispersive light splitting and focusing spectrums is formed.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
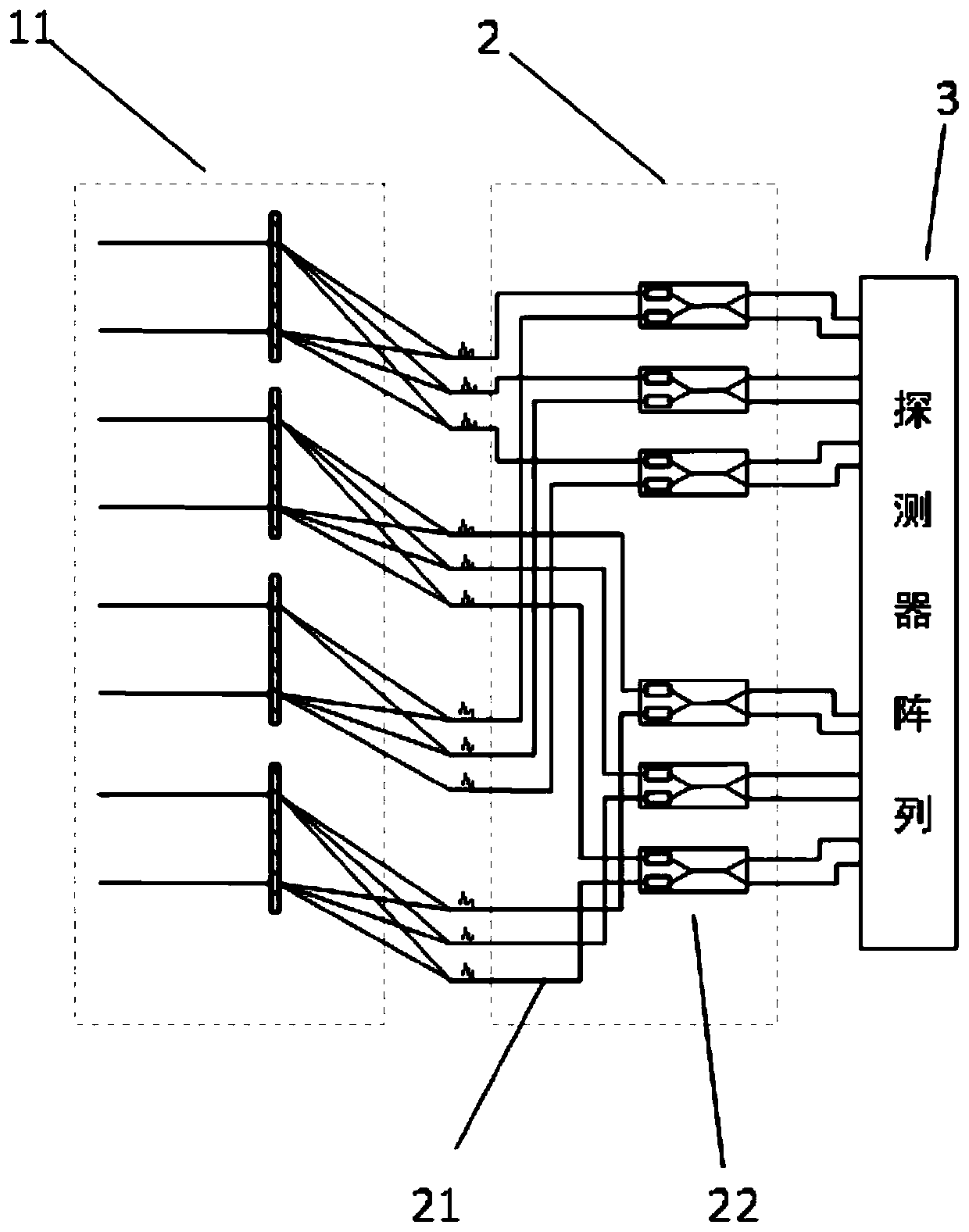
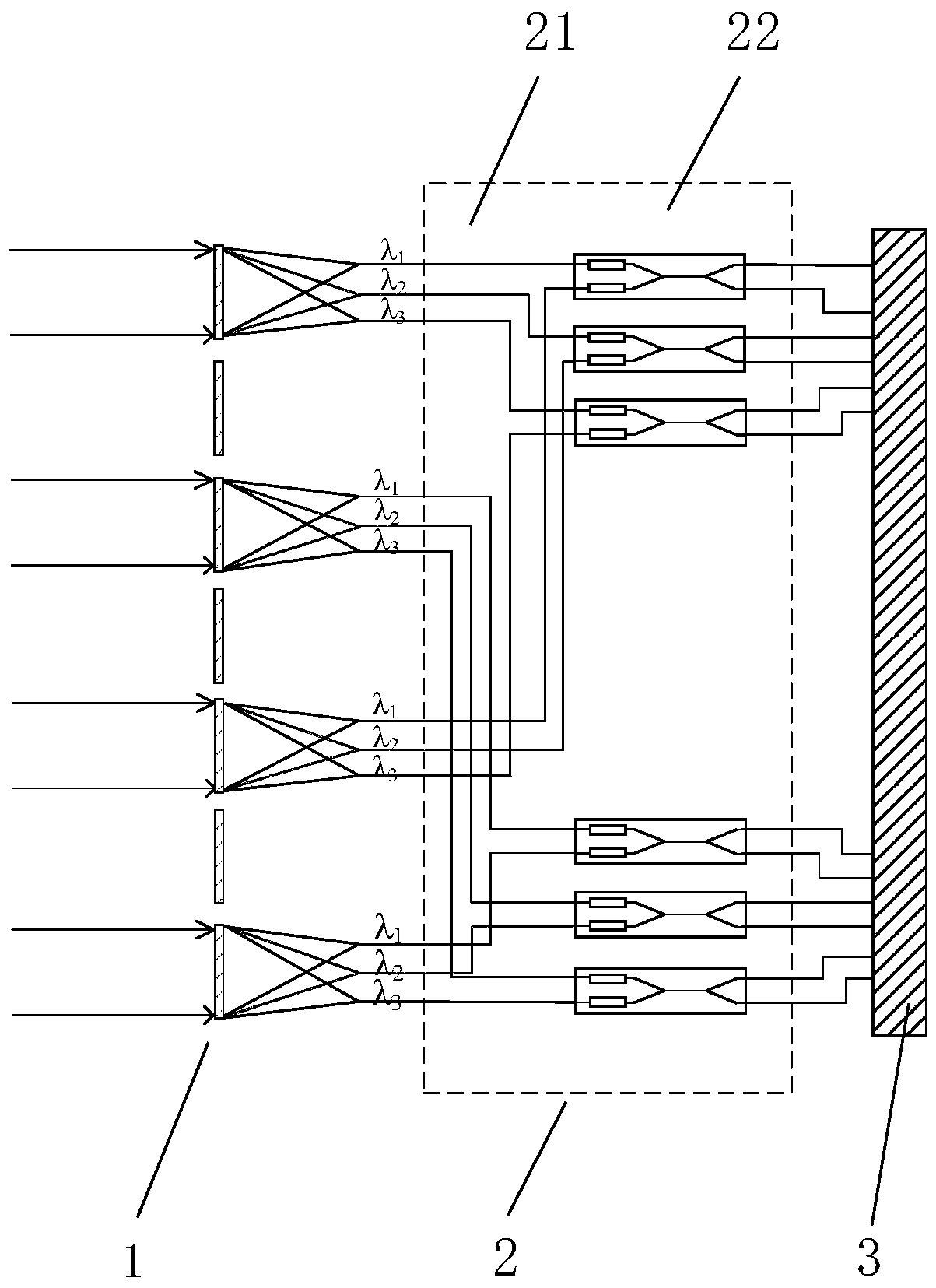
Planar photoelectric detection system based on super-lens array
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical imaging, and provides a planar photoelectric detection system based on a super-lens array, and the system comprises a radial planar super-lens array which consists of a plurality of planar super-lenses sequentially arranged along an optical path, a photon integration loop, and an information processing module. The planar super-lens array is used for splitting incident light into a plurality of narrow-band light beams and focusing the narrow-band light beams; the photon integration loop is used for receiving incident light passing throughthe planar super-lens array and carrying out phase adjustment on the incident light to meet interference conditions; and the information processing module is used for restoring the image based on theinterference image generated by the photon integration loop to obtain a high-resolution image. The system does not need to use a large number of grating beam splitters for light splitting, the scale of a photon integration loop is reduced, the overall structure is compact, and the integration level is high; meanwhile, loss is reduced, and the energy utilization rate is high; furthermore, the sizeand the weight of the remote sensing load can be greatly reduced.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Raman and hyper-rman excitation using superlensing
Raman-enhancing structures include a layer of dielectric material, a superlens configured to focus electromagnetic radiation having a wavelength greater than about 100 nanometers to a two-dimensional focal area having linear dimensions less than about 100 nanometers on a surface of the layer of dielectric material, and at least two nanoparticles comprising a Raman-enhancing material disposed proximate the focal area. Additional Raman-enhancing structures include a layer of dielectric material, a layer of conductive material, and at least two nanoparticles comprising a Raman-enhancing material disposed on a second, opposite surface of the layer of dielectric material. The layer of conductive material has a plurality of apertures therethrough that are arranged in a two-dimensional array. Methods for conducting Raman spectroscopy are performed using such structures and systems.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Focal length adjustable terahertz graphene metasurface lens and design method
ActiveCN110133876AImprove efficiencyHigh transmission outputNon-linear opticsHigh numerical apertureGraphite
The invention relates to a focal length adjustable terahertz graphene metasurface lens and a design method, and belongs to the field of novel artificial electromagnetic materials and terahertz scienceand technology. The metasurface lens comprises three layers of structures, which are a metal gate layer, a dielectric layer and a graphene micro-structure layer in sequence, wherein a bias voltage control device is arranged between a graphene microstructure and a metal gate, and is used for changing the conductivity of graphene. By changing an arrangement sequence of units, the focal length of the metasurface lens can be moved and kept still along with a bias voltage. Dynamic regulation of a focal point of the lens can be realized, and the focal length of the lens is not sensitive to the material characteristics of the graphene, so that different application requirements can be met; and meanwhile, the metasurface lens has the advantages of high numerical aperture, transmission type, highefficiency, compact structure and the like.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
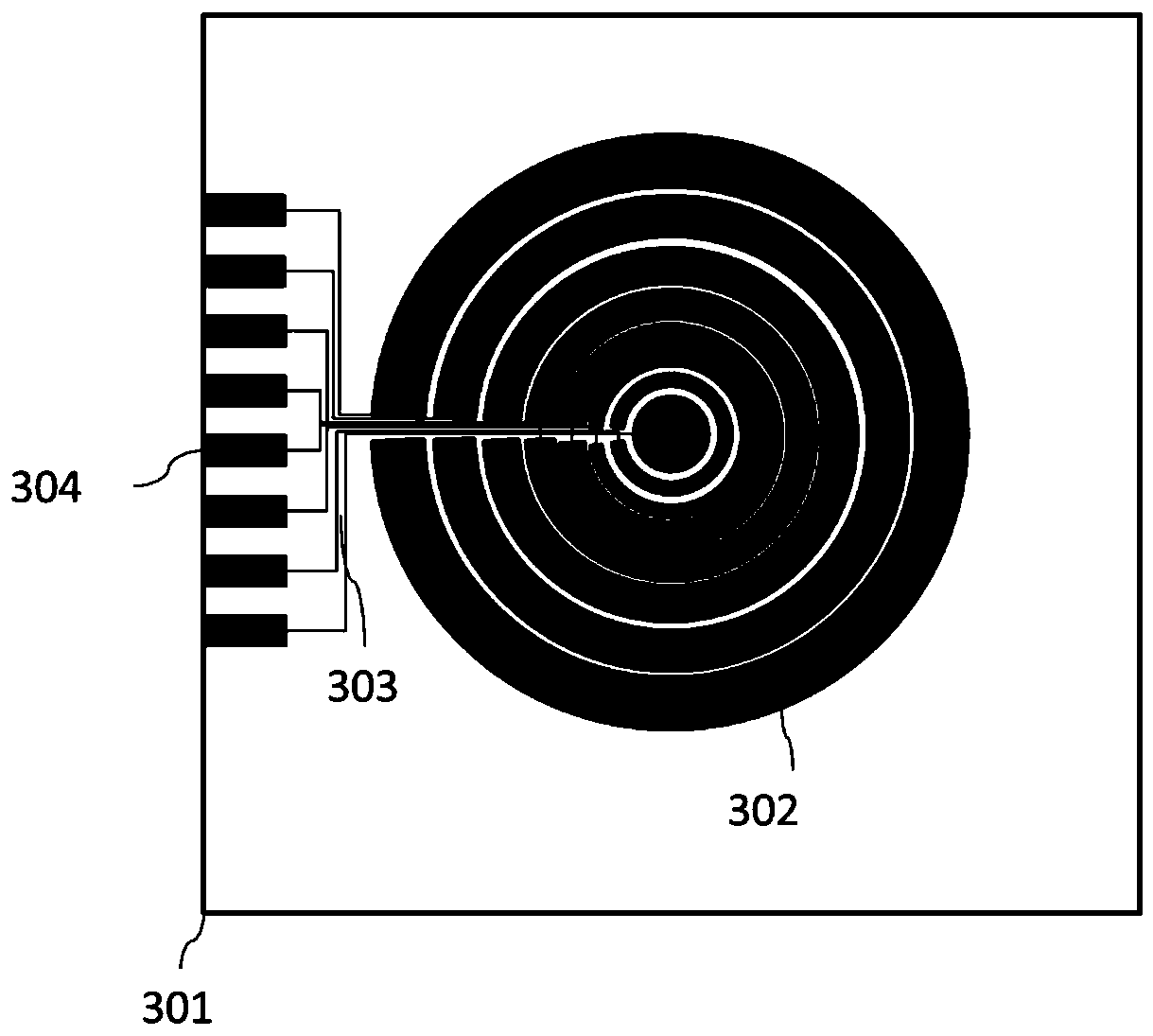
Superlens based on artificial electromagnetic structure in nuclear magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveCN102349831ASimple preparation processStructurally scalableDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCapacitanceEngineering
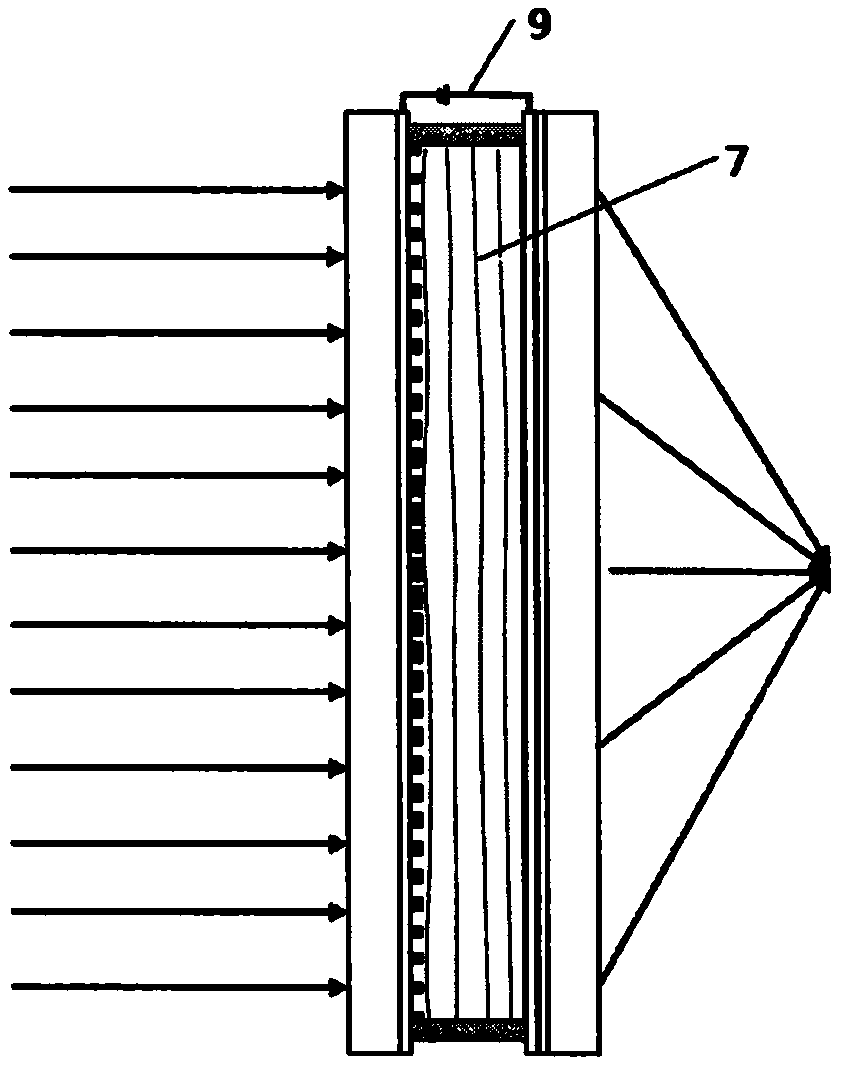
The invention relates to a superlens based on an artificial electromagnetic structure. Traditional equipment restricts the operating frequency and operating bandwidth of electromagnetic superlenses. The superlens comprises an inner fixed ring, an outer fixed ring and a plurality of resonance units, wherein the resonance units are vertically arranged between the inner fixed ring and the outer fixed ring; the inner and outer fixed rings are concentrically arranged; the plurality of resonance units are uniformly distributed with the circle center as the center; each resonance unit comprises an elongated FR-4 substrate, a plurality of LC loop resonance units and a plurality of nonmagnetic load capacitors; the LC loop resonance units are transversely and longitudinally distributed on the elongated FR-4 substrate uniformly; each LC loop resonance unit corresponds to a nonmagnetic load capacitor; and the nonmagnetic load capacitors are mounted at the openings of the LC loop resonance units. The superlens has the following beneficial effects: the manufacturing process is simple and the structure is extensile; and high spatial resolution and signal to noise ratio can be realized by introducing the resonance unit structures to the conventional nuclear magnetic resonance imaging equipment.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Intermediate infrared polarization independent broadband achromatic super lens and construction method thereof
The invention relates to an intermediate infrared polarization independent broadband achromatic super lens and a construction method thereof. The super lens comprises a substrate and a unit structurearranged on the substrate; the phase change of the unit structure is linearly changed along with the angular frequency of incident light; the unit structure is used for adjusting the phase of the incident light of the super lens. According to the intermediate infrared polarization independent broadband achromatic super lens and the construction method thereof of the invention,the unit structure ofwhich the phase changes linearly along with the angular frequency of the incident light is arranged on the substrate, so that hyperbolic phase distribution is obtained on the surface of the super lens, a focusing effect is achieved; the focusing performance of the super lens is not sensitive to the frequency of the incident light, so that a broadband achromatic effect is achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Variable-focus super lens based on polymer network liquid crystal and preparation method
The invention provides a variable-focus super lens based on polymer network liquid crystal and a preparation method. The variable-focus super lens comprises a first substrate layer, a super-lens layer, a polymer network liquid crystal layer and a second substrate layer which are sequentially arranged in the direction of an incident light path, wherein the first substrate layer comprises a first base and a first conductive layer located on a side face, facing the second substrate layer, of the first base, the super-lens layer comprises a plurality of nano resonance units which are periodicallydistributed according to a sequence, the super-lens layer is formed on the first conductive layer, the polymer network liquid crystal layer comprises polymer network liquid crystal filled between thesuper-lens layer and the second substrate layer, the second substrate layer comprises a second base, a second conductive layer located on a side face, facing the first substrate layer, of the second base, and a liquid crystal alignment layer formed on the second conductive layer. Based on combination of the liquid crystal material and a super lens, the function of the variable-focus super lens isrealized, and the application range of the super lens is expanded.
Owner:CHINA WEAPON EQUIP RES INST
Meta lens and optical apparatus including the same
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com