Electric control zooming plane lens
A flat lens, electronically controlled zoom technology, applied in nonlinear optics, instruments, optics, etc., can solve problems such as dispersion and fixed focal length, and achieve the effect of high system light energy utilization, enhanced stability, and improved system integration.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
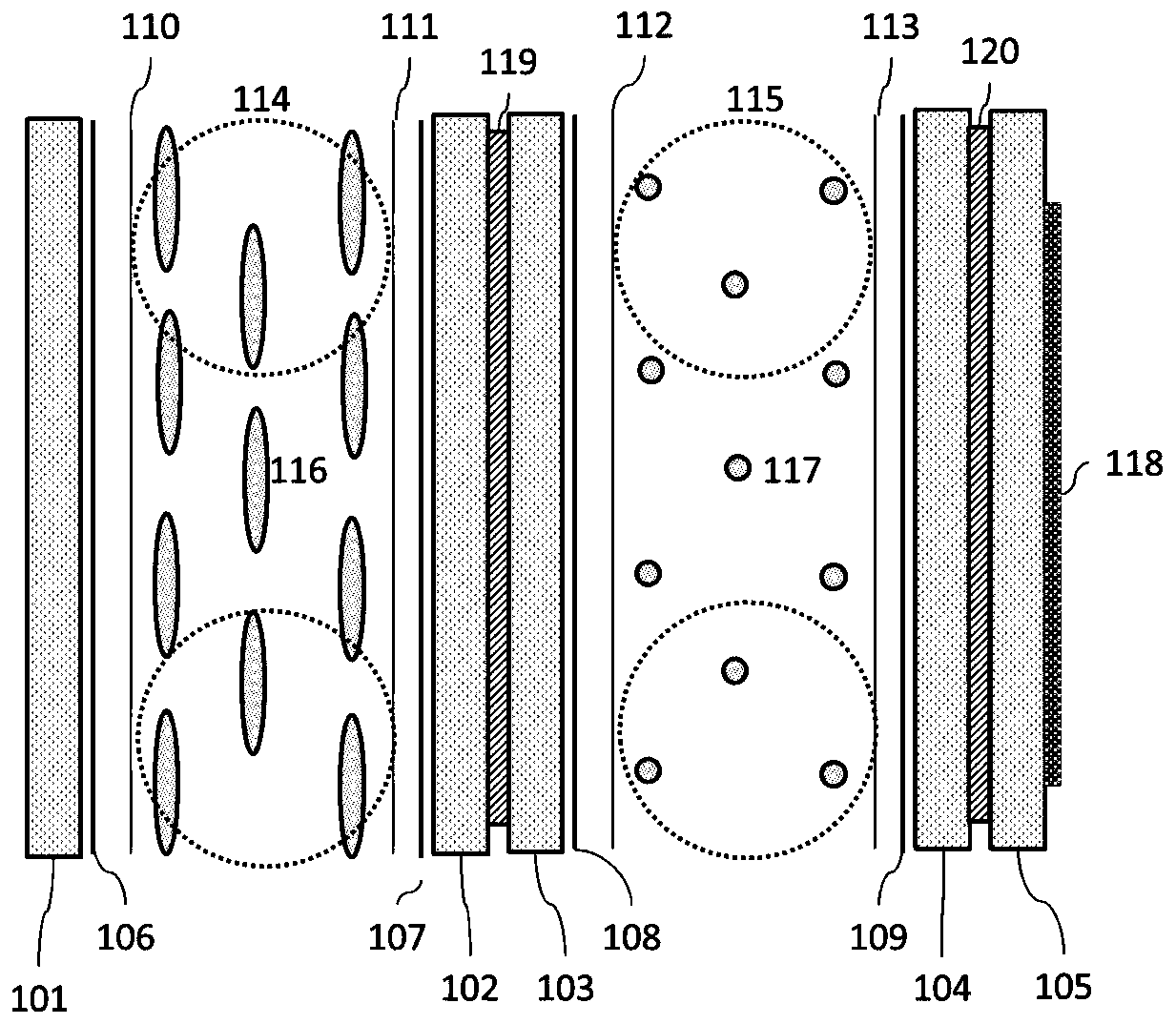
[0031] This embodiment provides an electronically controlled zoom plane lens, such as figure 1 As shown, it includes 5 glass substrates (the first glass substrate 101, the second glass substrate 102, the third glass substrate 103, the fourth glass substrate 104 and the fifth glass substrate 105), 4 transparent conductive layers (the first conductive film layer 106, second conductive film layer 107, third conductive film layer 108 and fourth conductive film layer 109), 4 alignment layers (first alignment layer 110, second alignment layer 111, third alignment layer 112 and fourth alignment layer Alignment layer 113), cell thickness control spacer (first spacer 114 and second spacer 115), liquid crystal layer (first liquid crystal layer 116 and second liquid crystal layer 117) and micro-nano structure layer (micro-nano structure layer 118 ) and glue layers (the first glue layer 119 and the second glue layer 120).
[0032] Among them, the first glass substrate 101, the second gla...
Embodiment 2
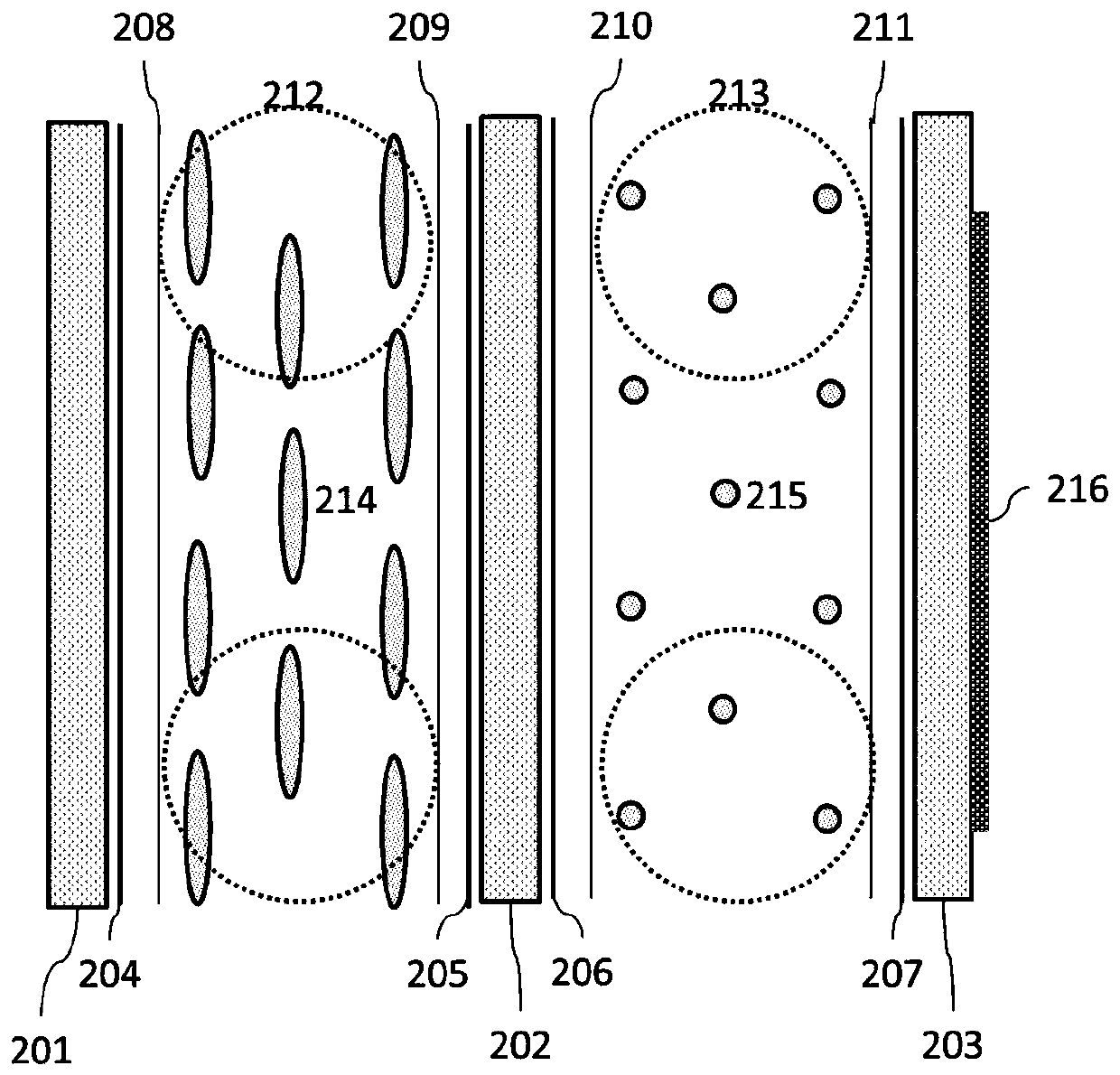
[0037] This embodiment provides an electronically controlled zoom plane lens, such as figure 2 As shown, it includes three glass substrates (the first glass substrate 201, the second glass substrate 202 and the third glass substrate 203), four transparent conductive layers (the first conductive film layer 204, the second conductive film layer 205, the third Conductive film layer 206 and fourth conductive film layer 207), four alignment layers (first alignment layer 208, second alignment layer 209, third alignment layer 210 and fourth alignment layer 211), two cell thickness control spacers (the first spacer 212 and the second spacer 213), two liquid crystal layers (the first liquid crystal layer 214 and the second liquid crystal layer 215) and one micro-nano structure layer (micro-nano structure layer 216). This structure is similar to the structure of the electronically controlled zoom plane lens provided in Example 1, except that in order to reduce the thickness of the lens...
Embodiment 3
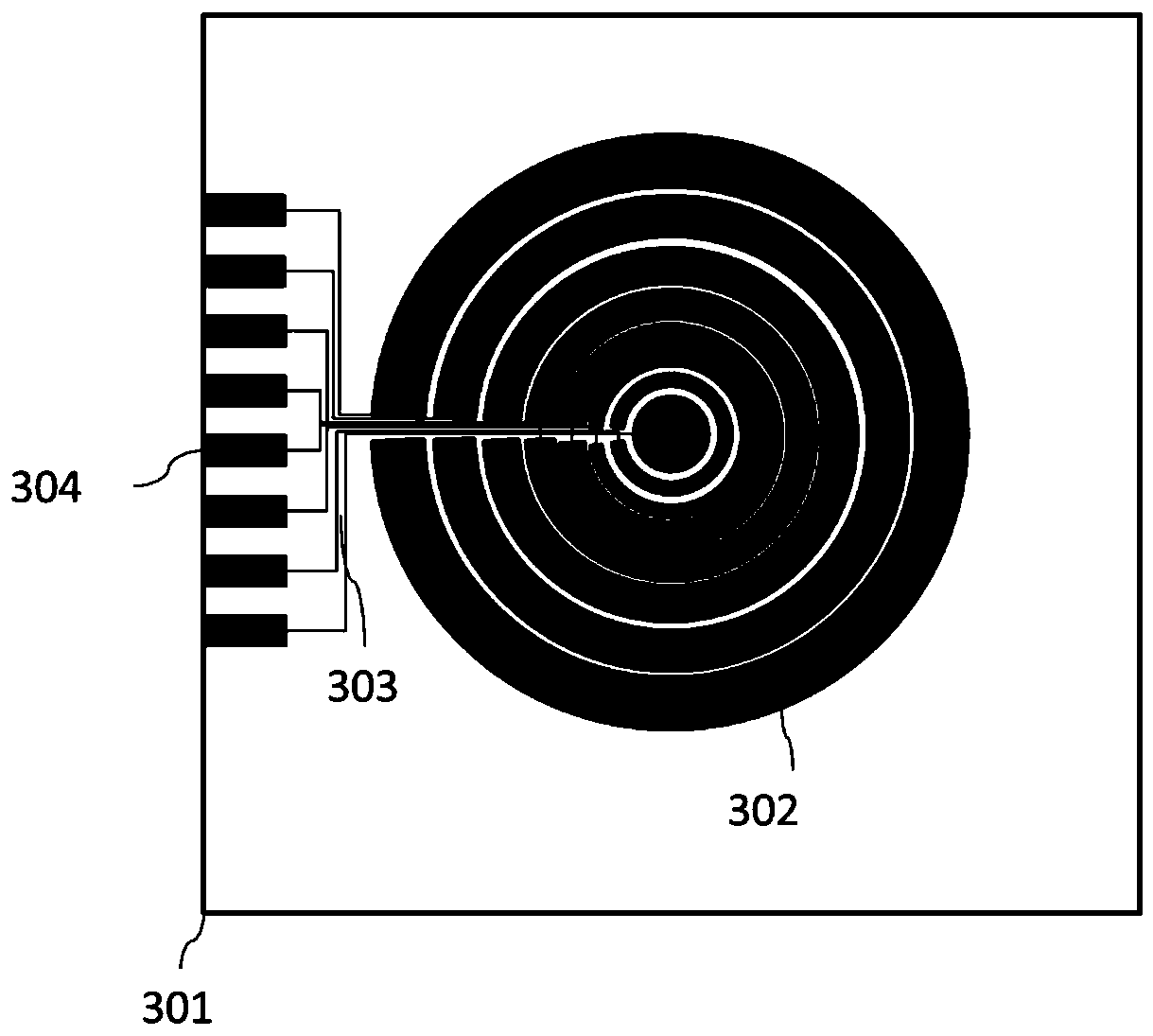
[0039] Further improvement on the basis of Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2, the independent electrode structure of the liquid crystal lens is as follows image 3 As shown, include a glass substrate 301 (the glass substrate here refers to the first glass substrate 101 and the third glass substrate 103 for embodiment 1); refers to the first glass substrate 201 and the second glass substrate 202 for embodiment 2— side panel), a plurality of concentric diffractive ring electrodes 302 for independent delay control, electrode terminals 304 for connecting the driving circuit, and transparent conductive leads 303 connecting the independent ring electrodes 302 with the electrode terminals 304. The width of the ring electrode 302 is comprehensively designed according to parameters such as the design focal length of the liquid crystal lens, the thickness of the liquid crystal layer, and the birefringence difference. The transparent conductive lead 303 is as thin as possible under the premi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com