Patents
Literature
88 results about "Nuclear quadrupole resonance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
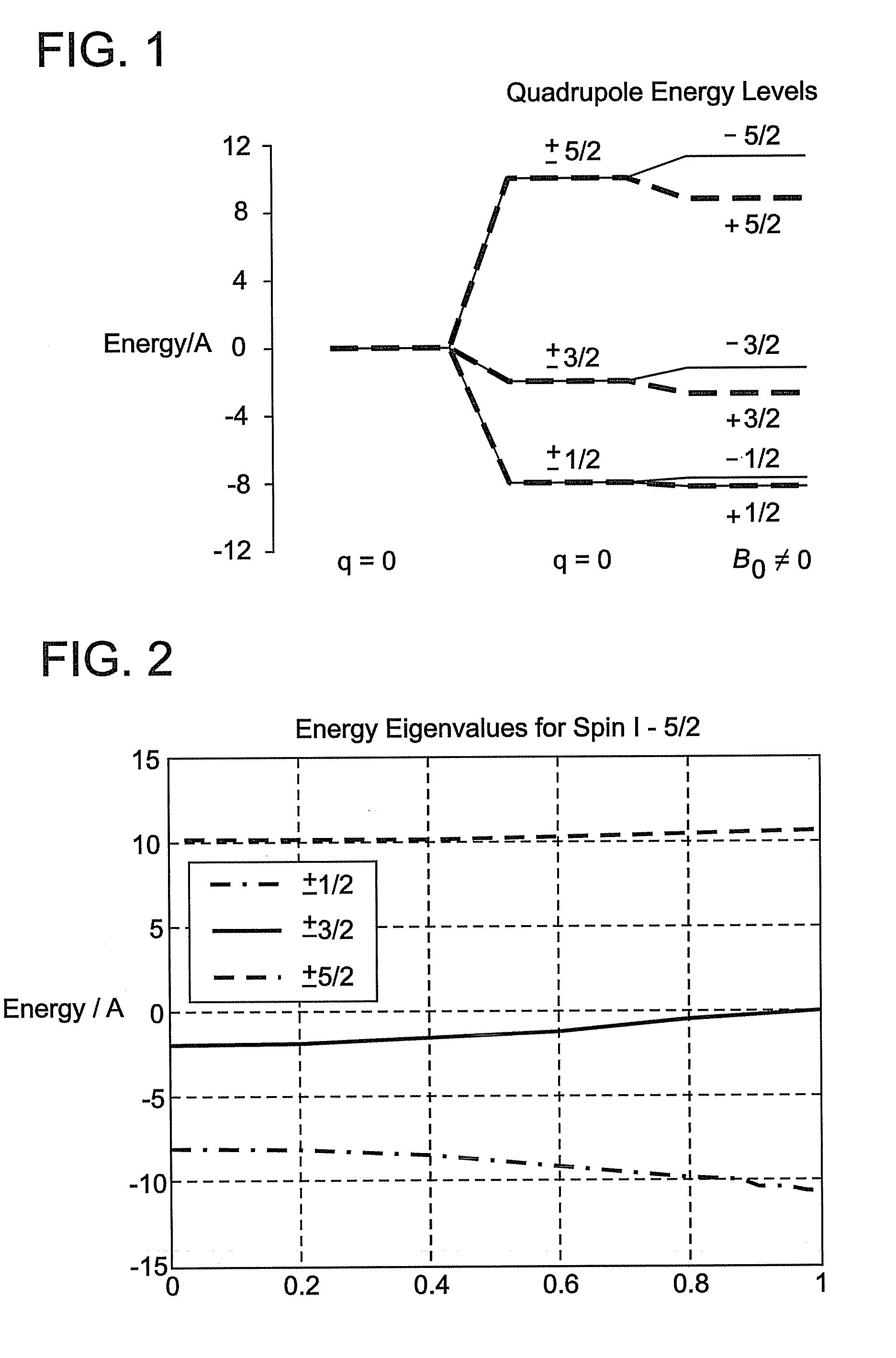
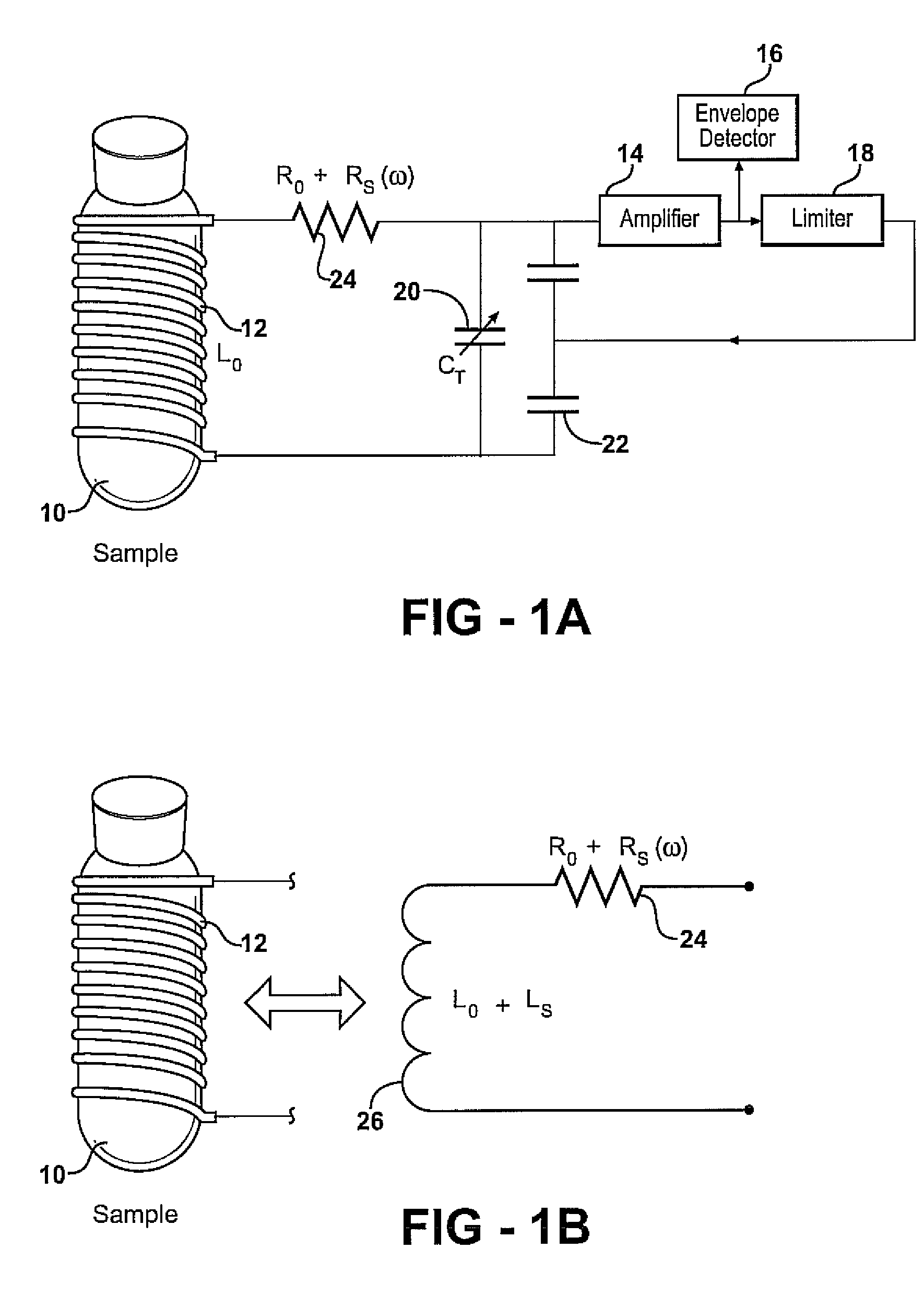
Nuclear quadrupole resonance spectroscopy or NQR is a chemical analysis technique related to nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). Unlike NMR, NQR transitions of nuclei can be detected in the absence of a magnetic field, and for this reason NQR spectroscopy is referred to as "zero Field NMR." The NQR resonance is mediated by the interaction of the electric field gradient (EFG) with the quadrupole moment of the nuclear charge distribution. Unlike NMR, NQR is applicable only to solids and not liquids, because in liquids the quadrupole moment averages out. Because the EFG at the location of a nucleus in a given substance is determined primarily by the valence electrons involved in the particular bond with other nearby nuclei, the NQR frequency at which transitions occur is unique for a given substance. A particular NQR frequency in a compound or crystal is proportional to the product of the nuclear quadrupole moment, a property of the nucleus, and the EFG in the neighborhood of the nucleus. It is this product which is termed the nuclear quadrupole coupling constant for a given isotope in a material and can be found in tables of known NQR transitions. In NMR, an analogous but not identical phenomenon is the coupling constant, which is also the result of an internuclear interaction between nuclei in the analyte.
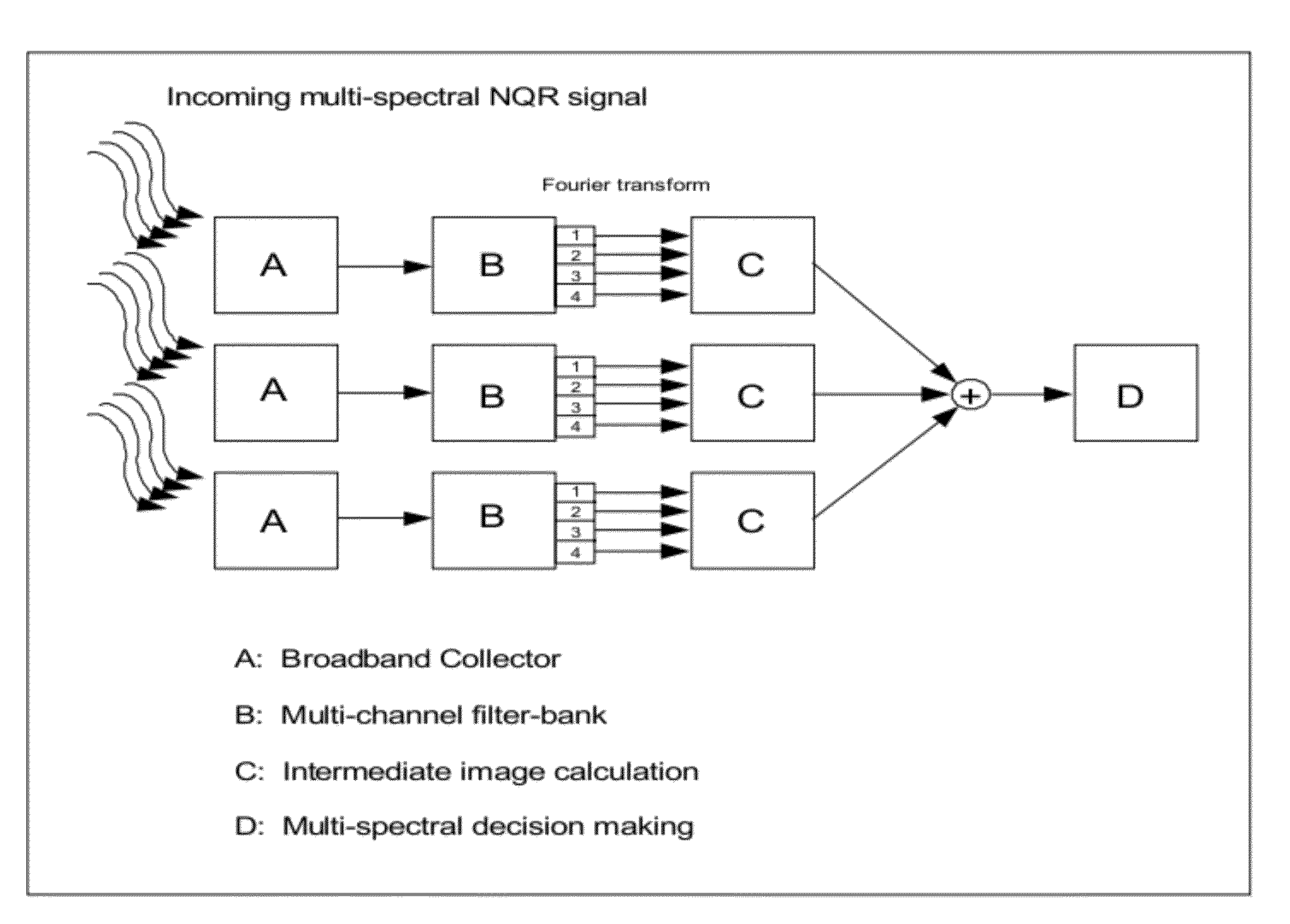
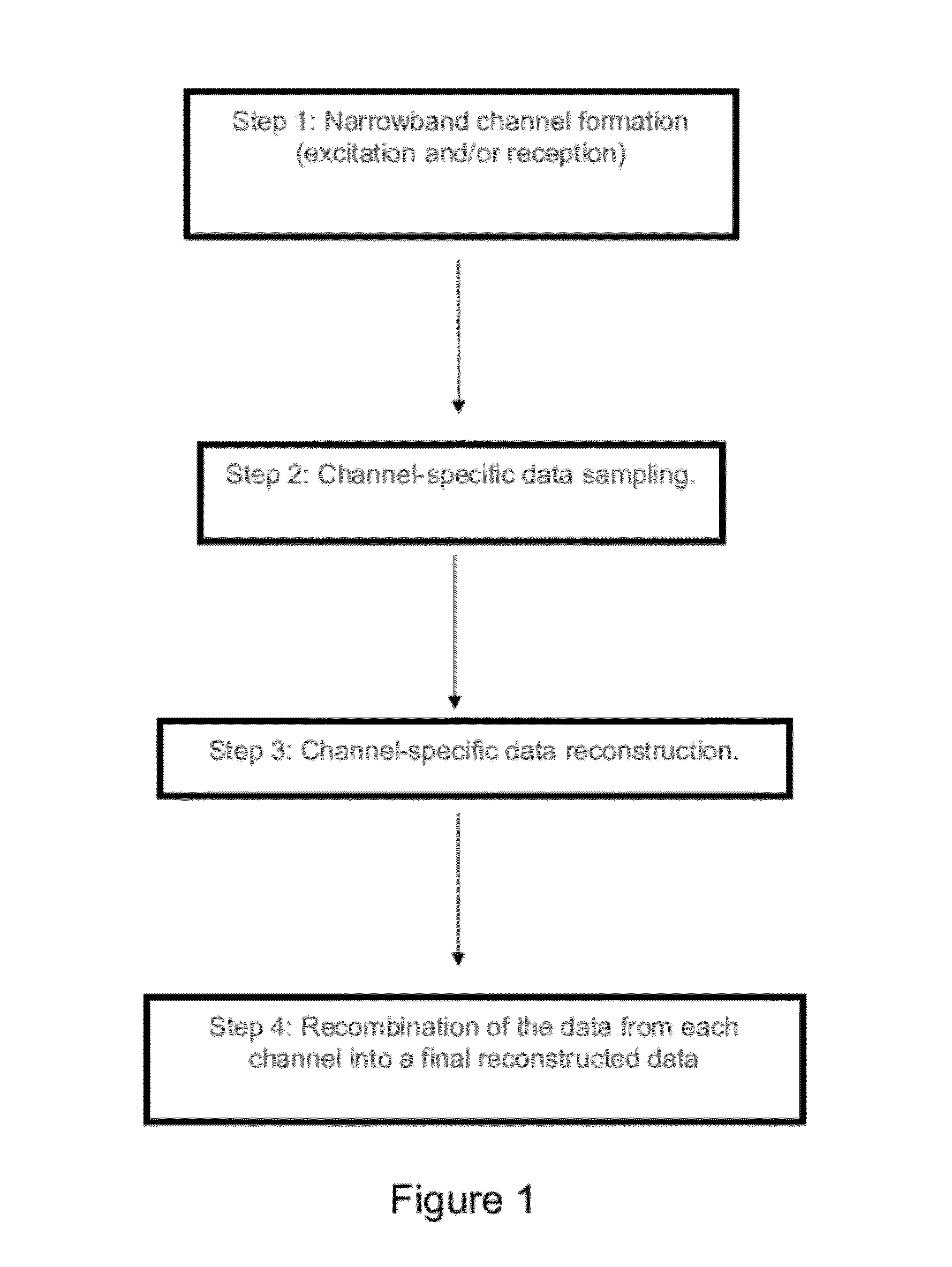
Noise Reduction Apparatus, Systems, and Methods
InactiveUS20090136104A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce noiseCharacter and pattern recognitionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsFrequency spectrumNoise reduction
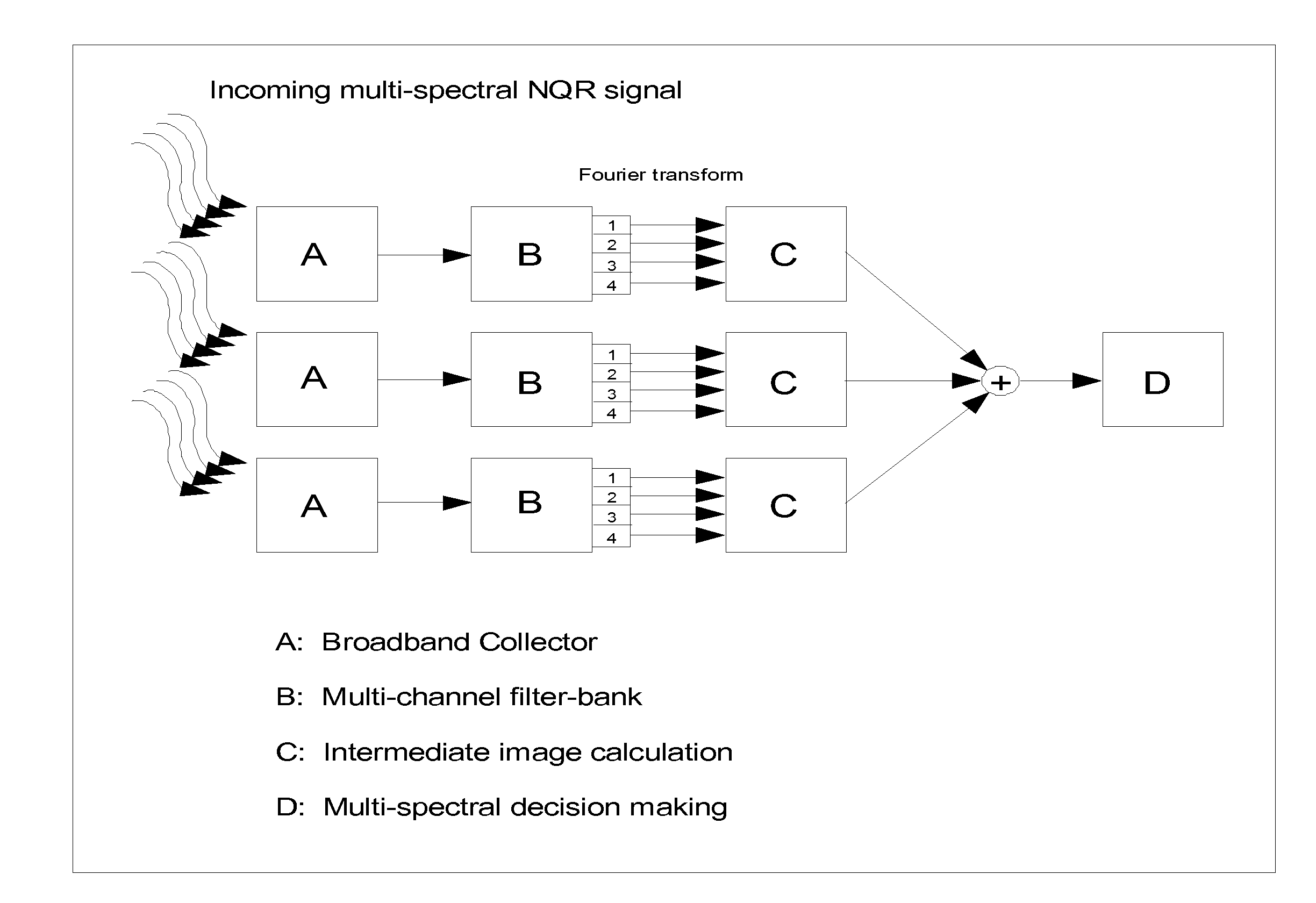
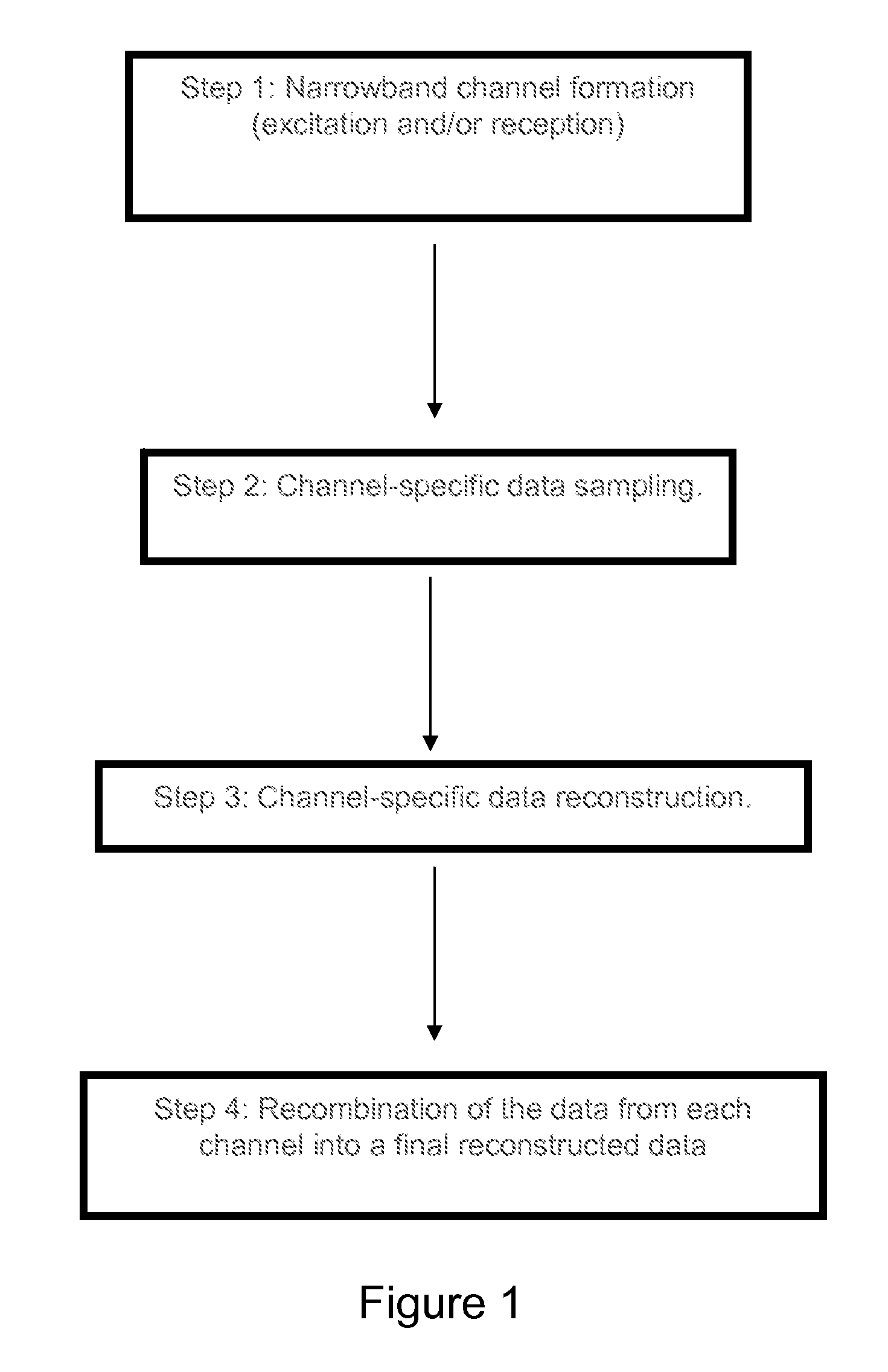
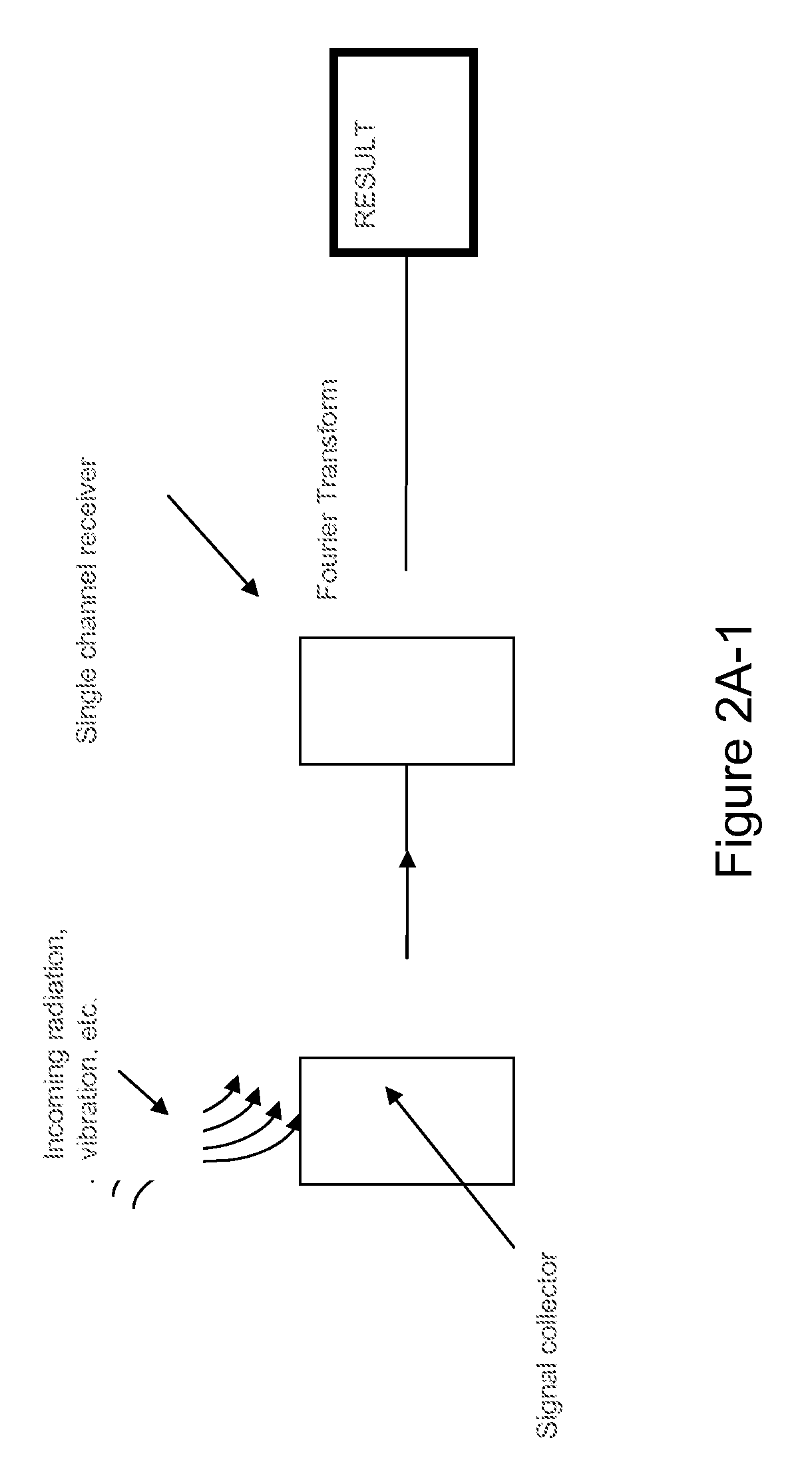
This document describes a general system for noise reduction, as well as a specific system for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Nuclear Quadrupole Resonance (NQR). The general system, which is called Calculated Readout by Spectral Parallelism (CRISP), involves reconstruction and recombination of frequency-limited broadband data using separate narrowband data channels to create images or signal profiles. A multi-channel CRISP system can perform this separation using (1) frequency tuned hardware, (2) a frequency filter-bank (or equivalent), or (3) a combination of implementations (1) and (2). This system significantly reduces what we call cross-frequency noise, thereby increasing signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR). A multi-channel CRISP system applicable to MRI and NQR are described.
Owner:ARJAE SPECTRAL ENTERPRISES
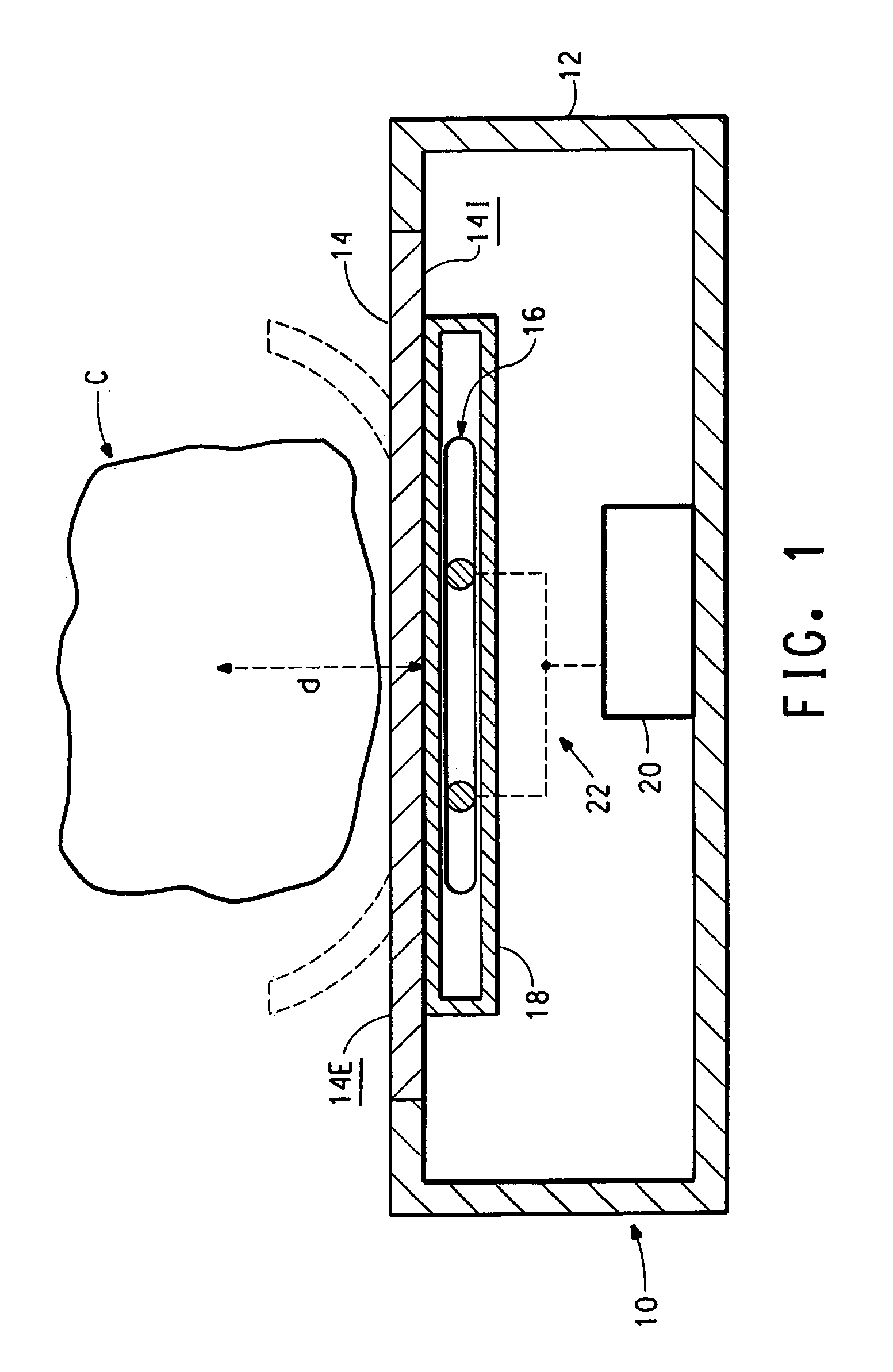
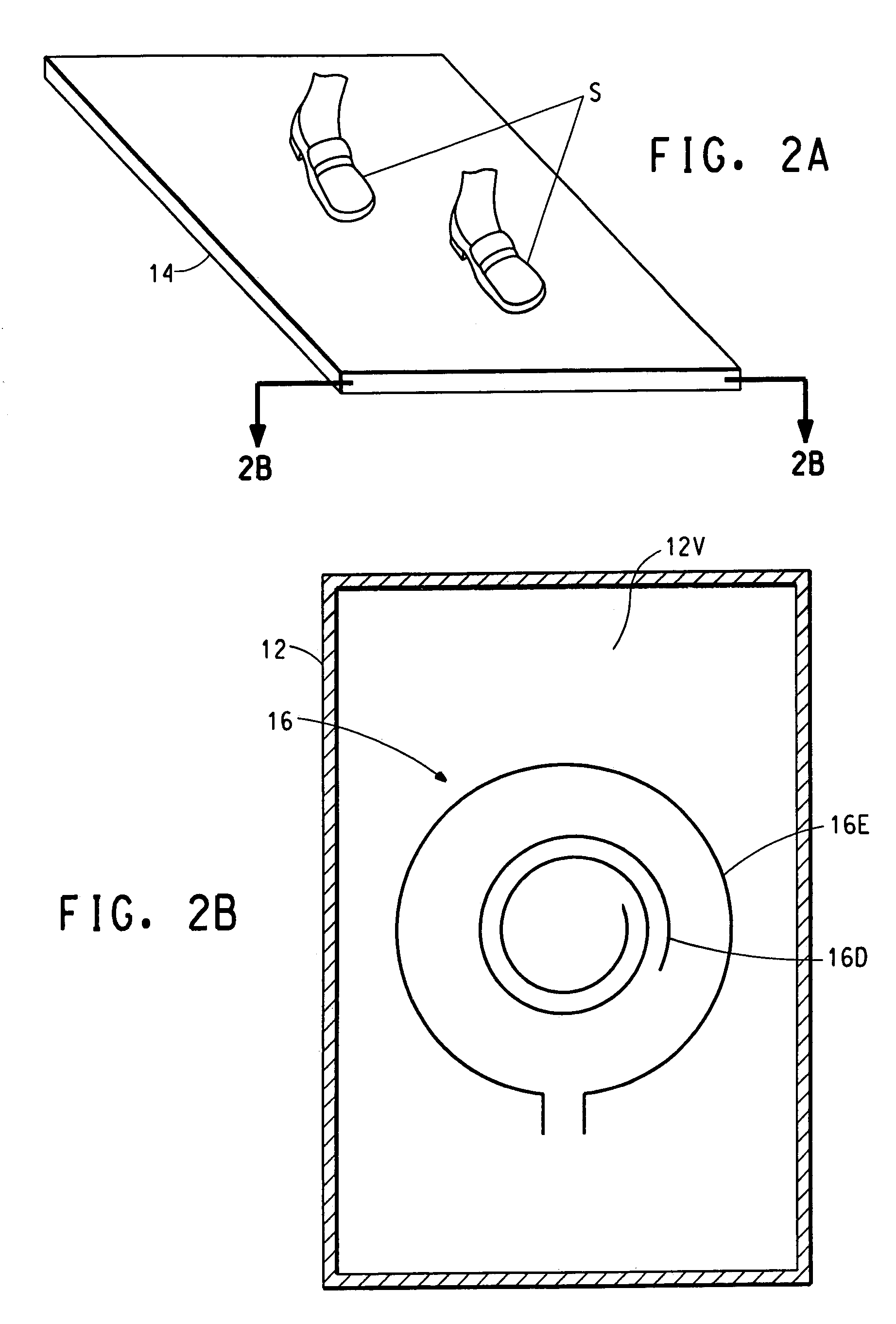
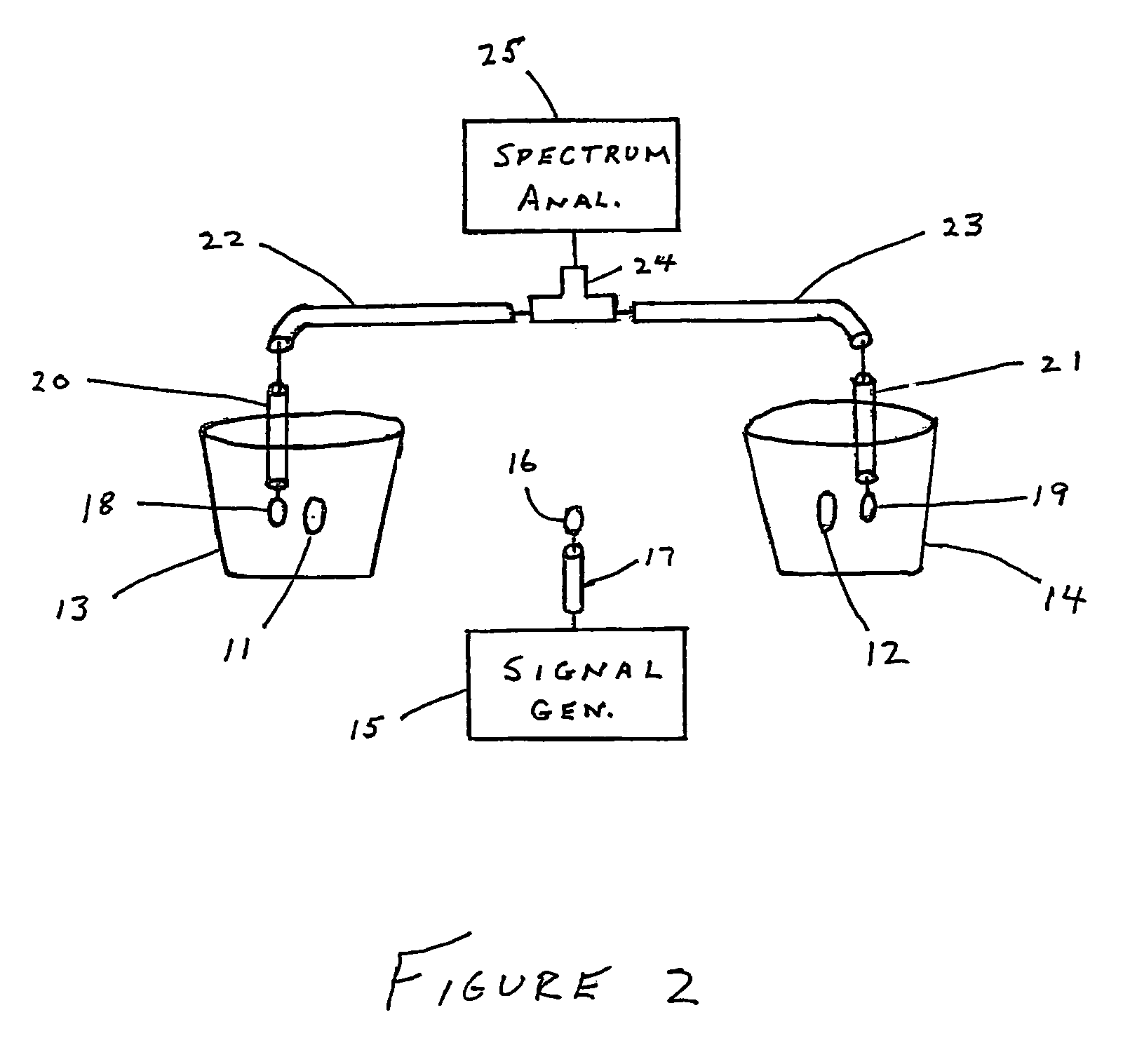
Detection of contraband using nuclear quadrupole resonance
InactiveUS7106058B2Efficient detectionMaterial analysis by using resonanceDetection using electromagnetic wavesNuclear quadrupole resonanceNuclear physics
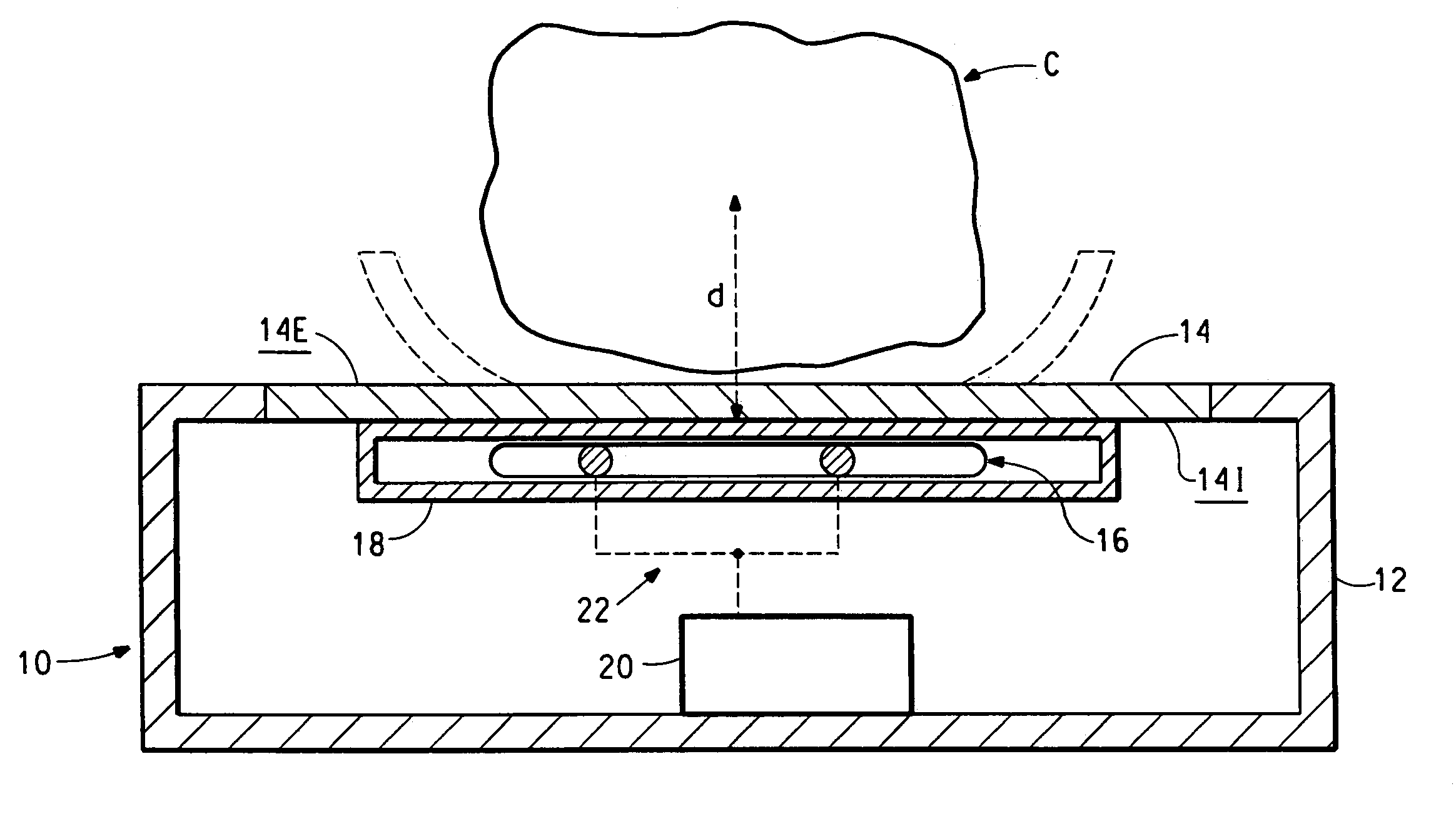
This invention relates to the use of a nuclear quadrupole resonance detection system for detecting contraband, wherein the detection system comprises a container with a detection panel and at least one coil for exciting and detecting the nuclear quadrupole resonance frequencies of a contraband source placed near an outer side of the detection panel.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
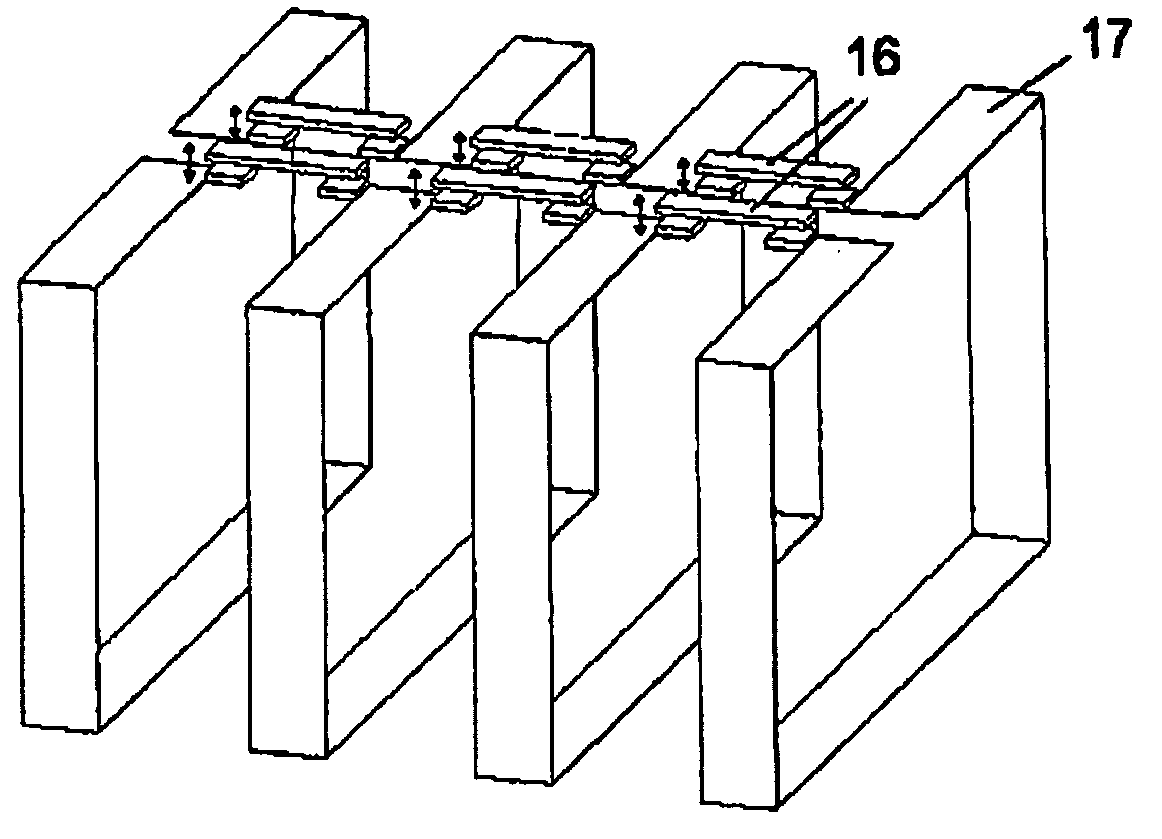
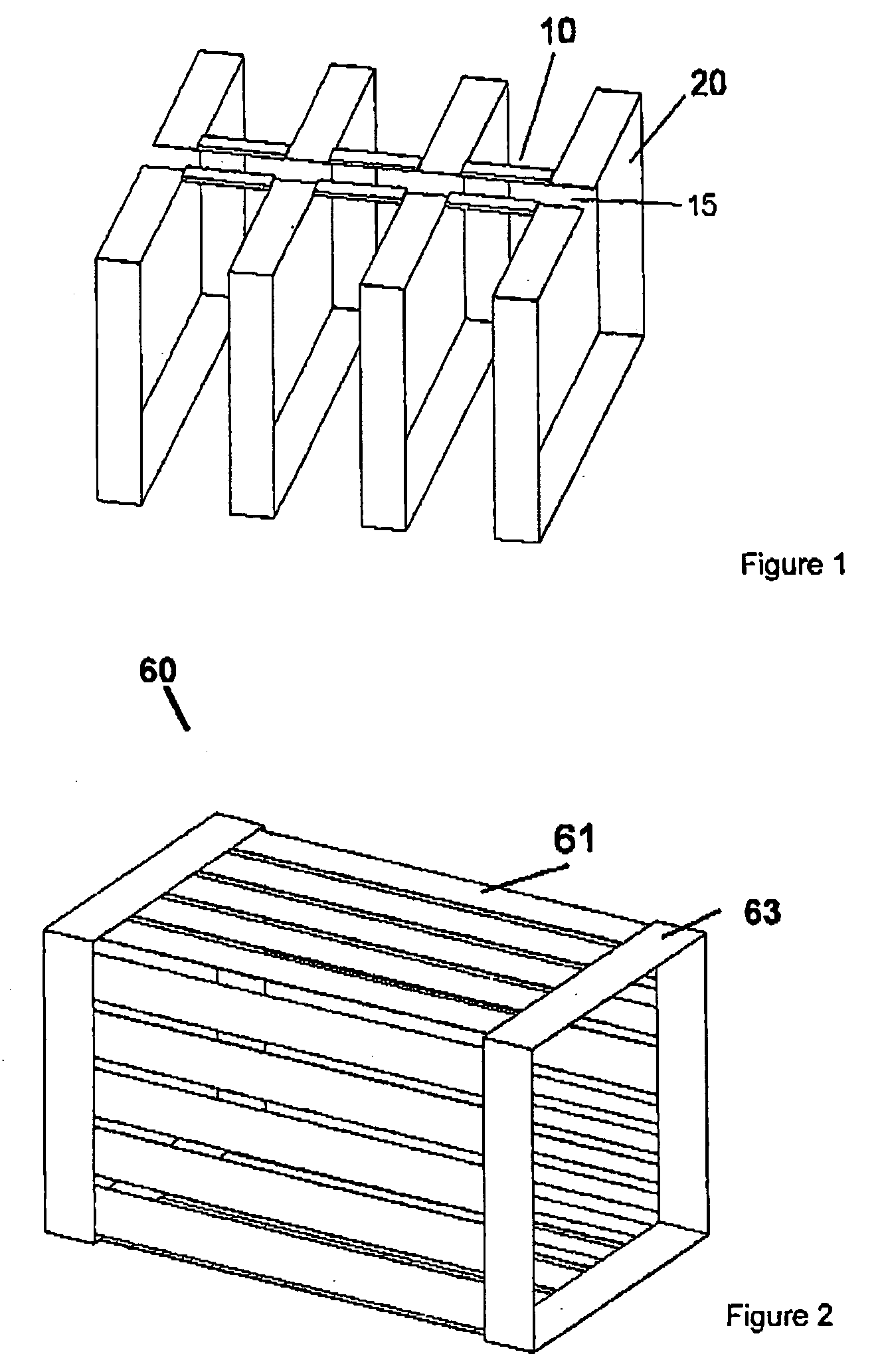
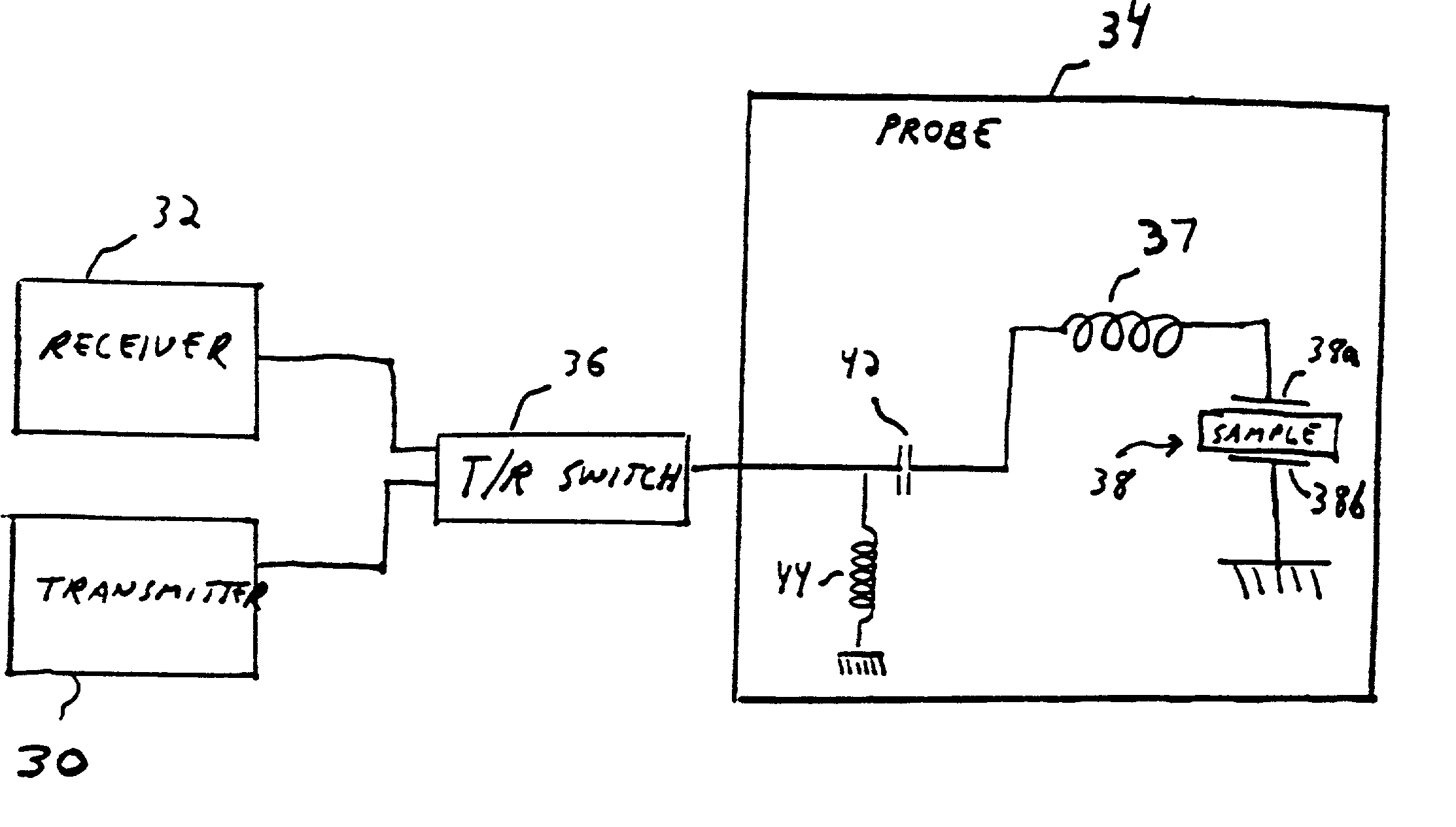
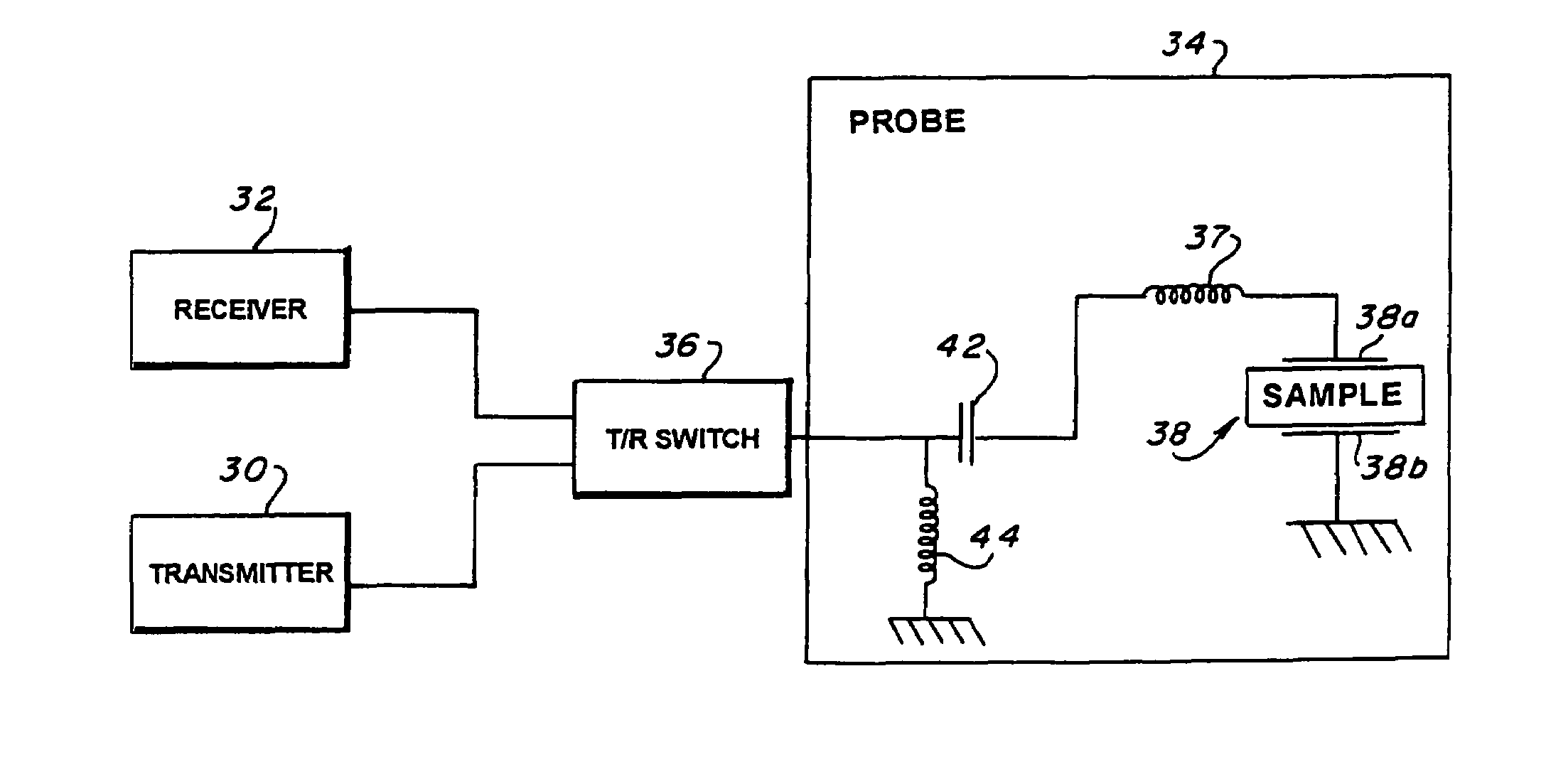
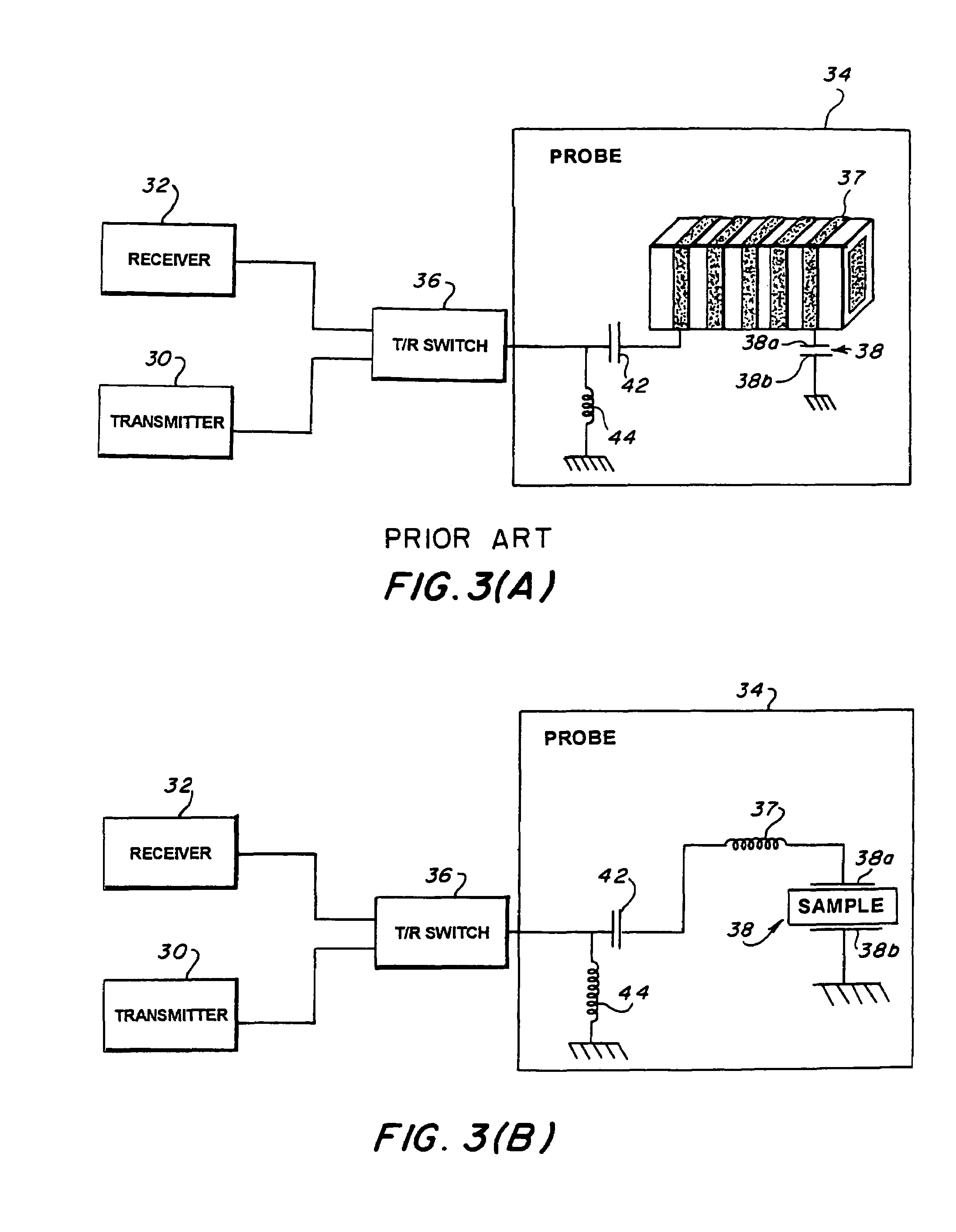
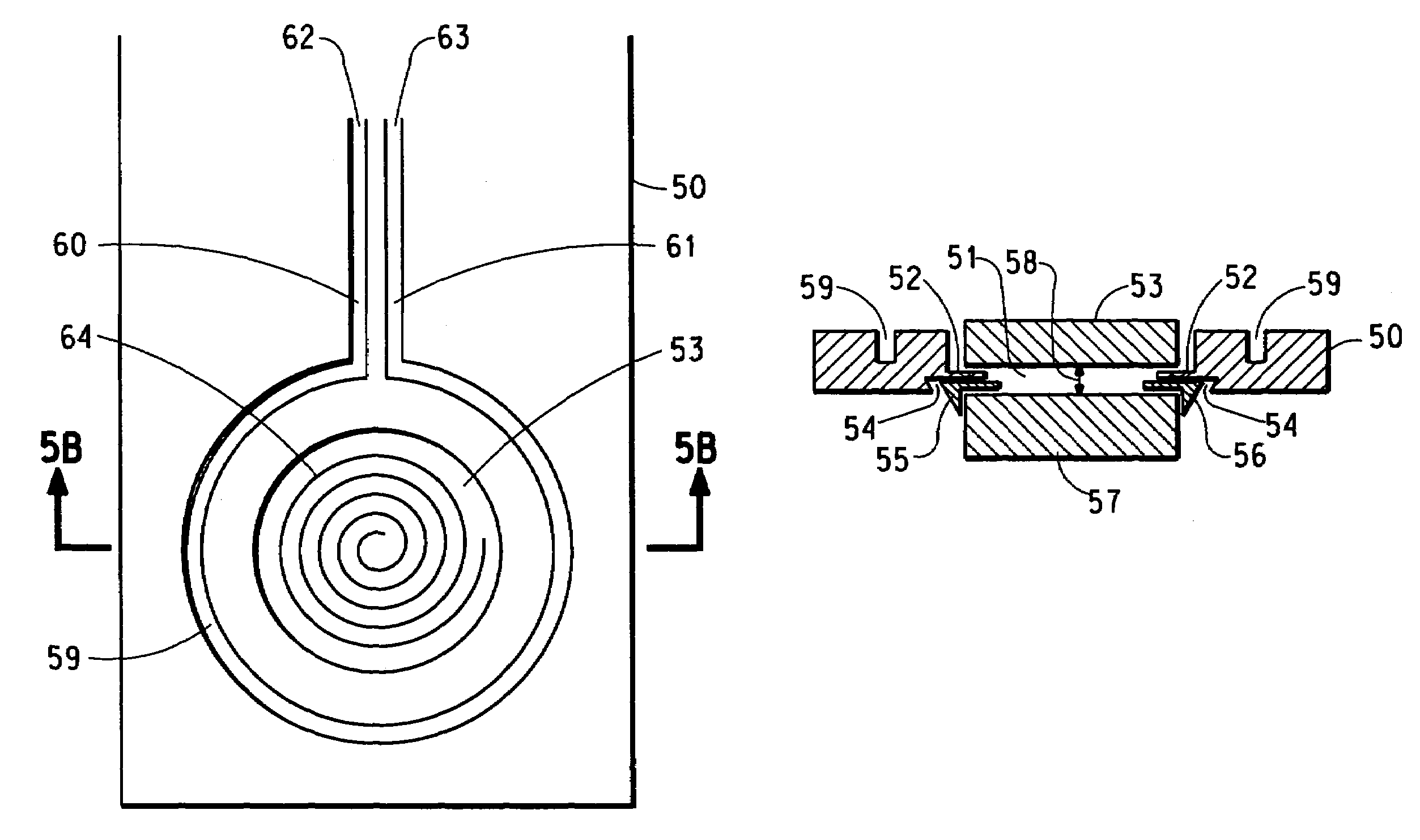
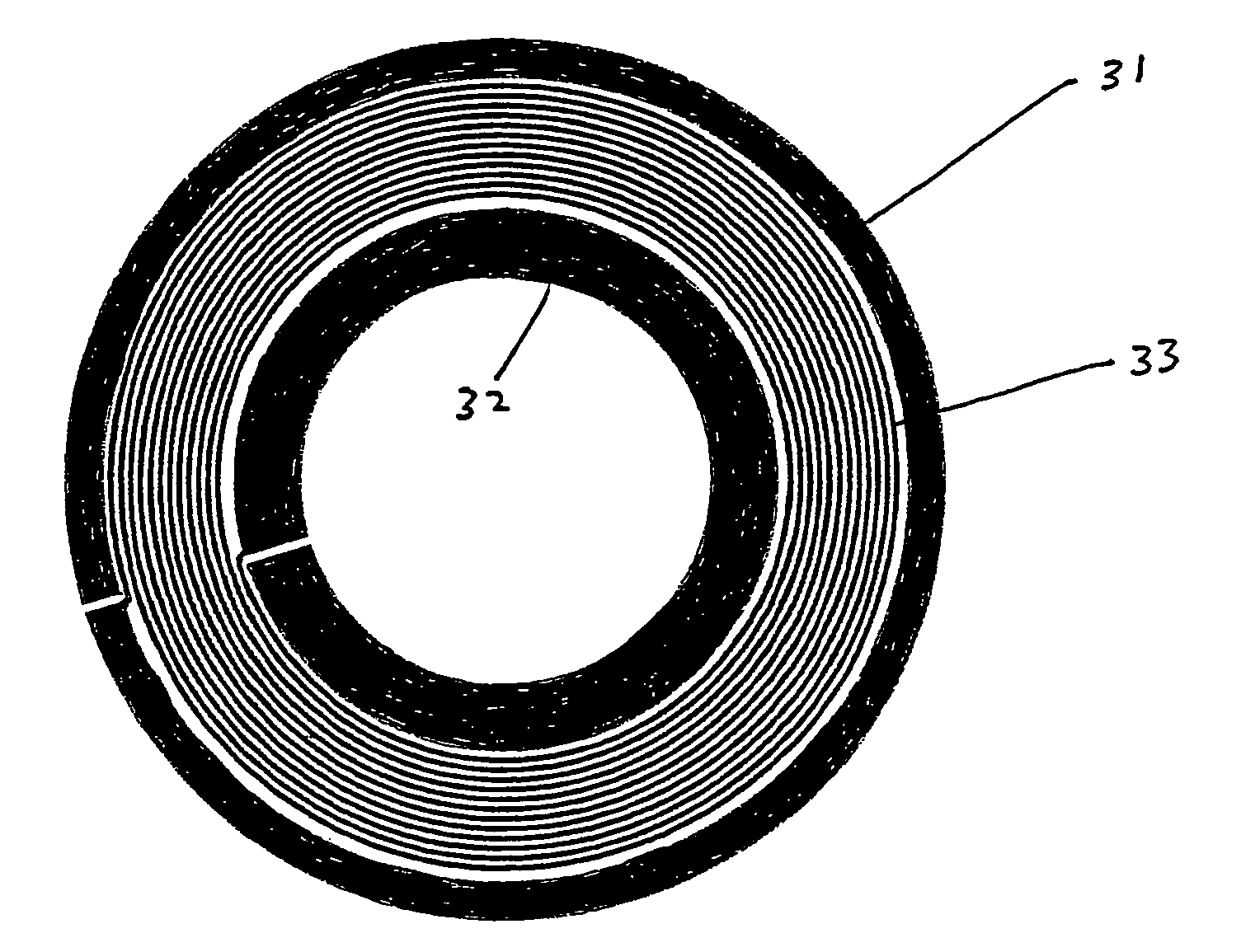
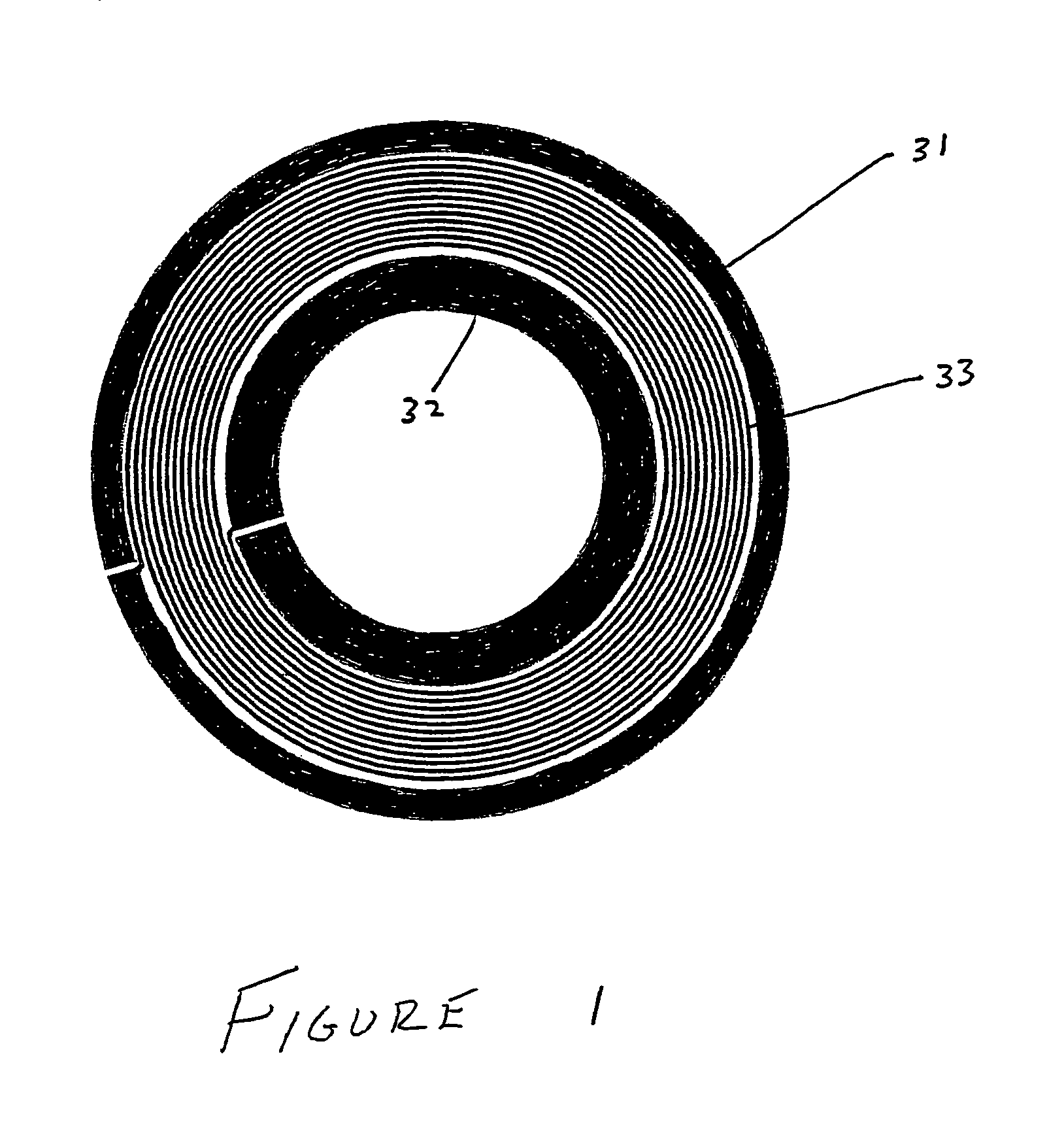
Transmit-receive coil system for nuclear quadrupole resonance signal detection in substances and components thereof
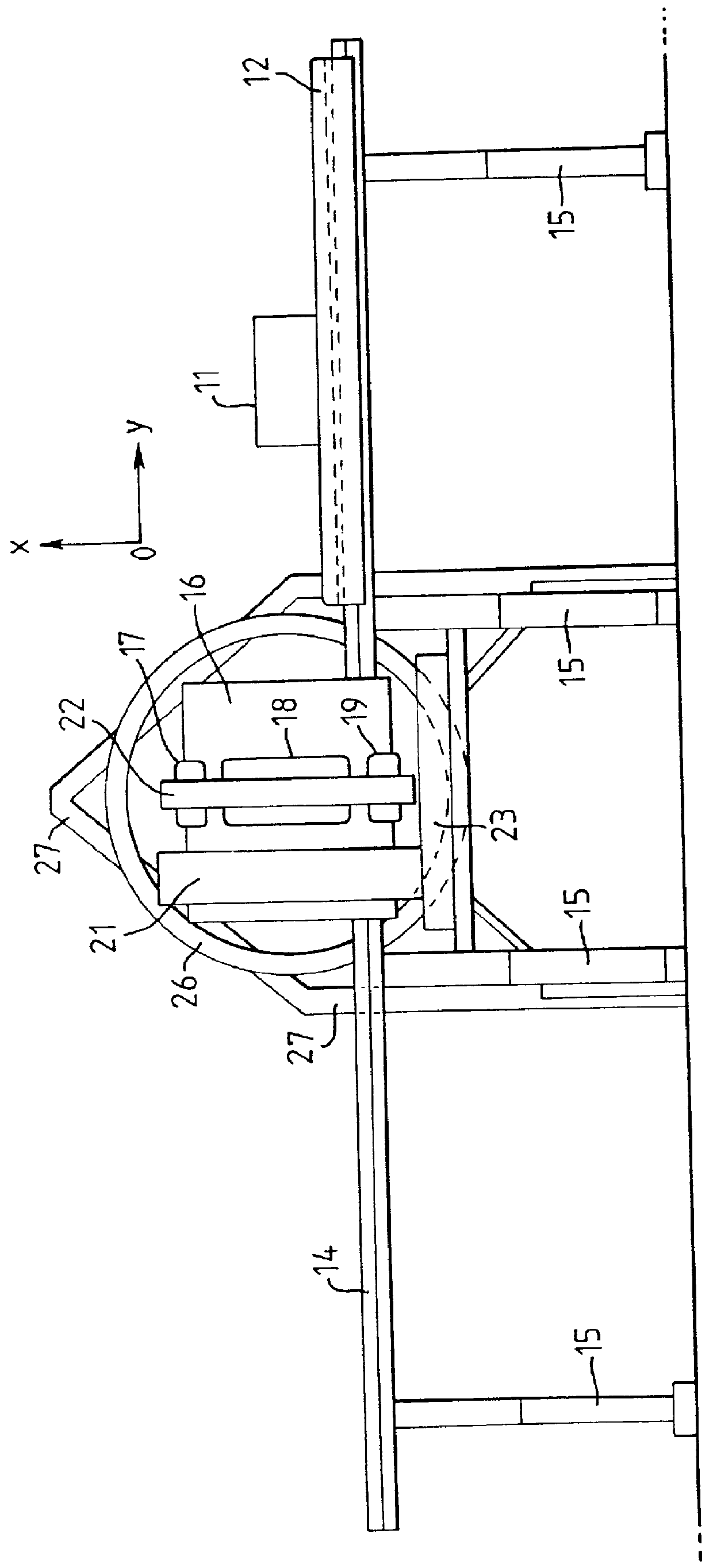
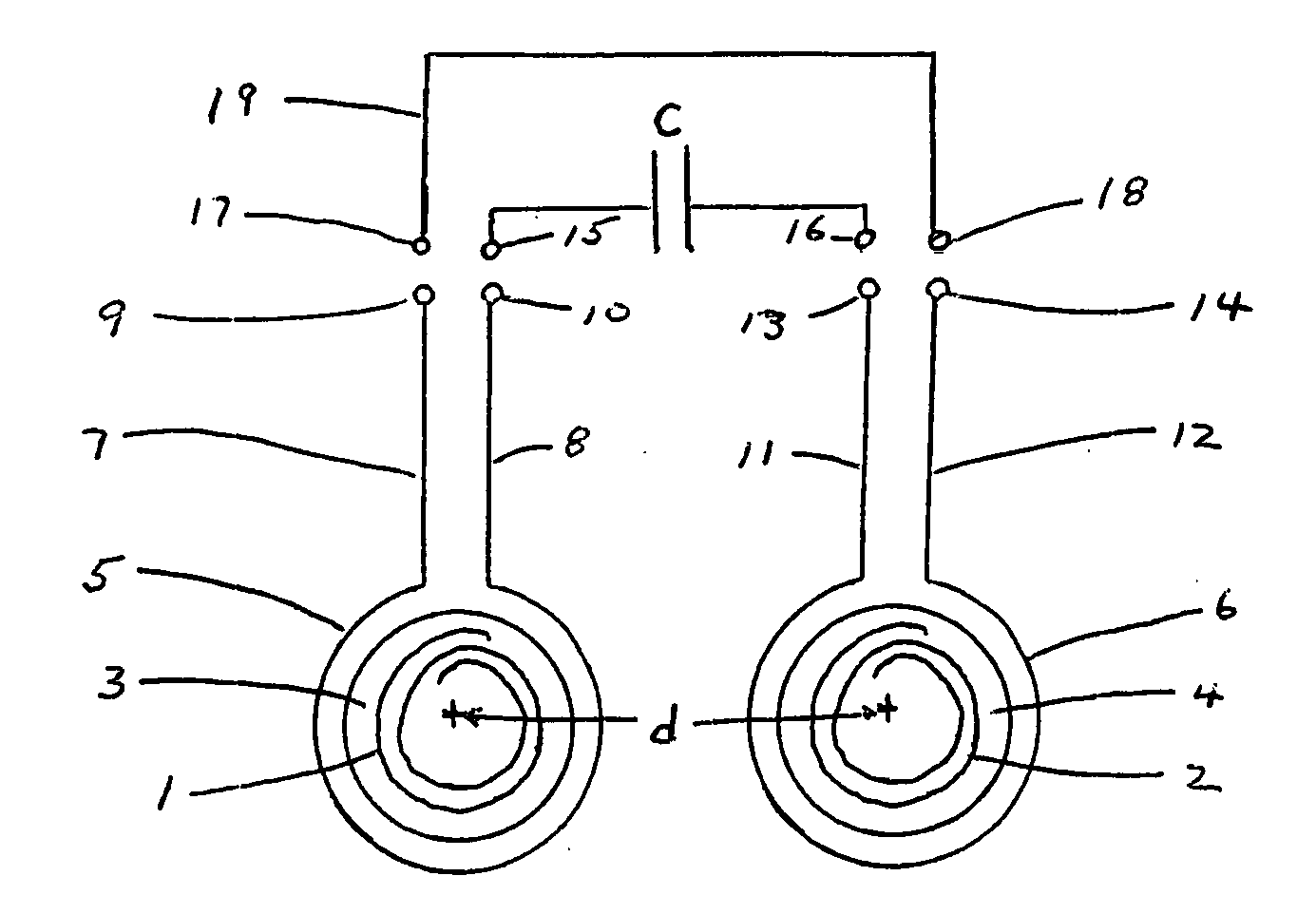
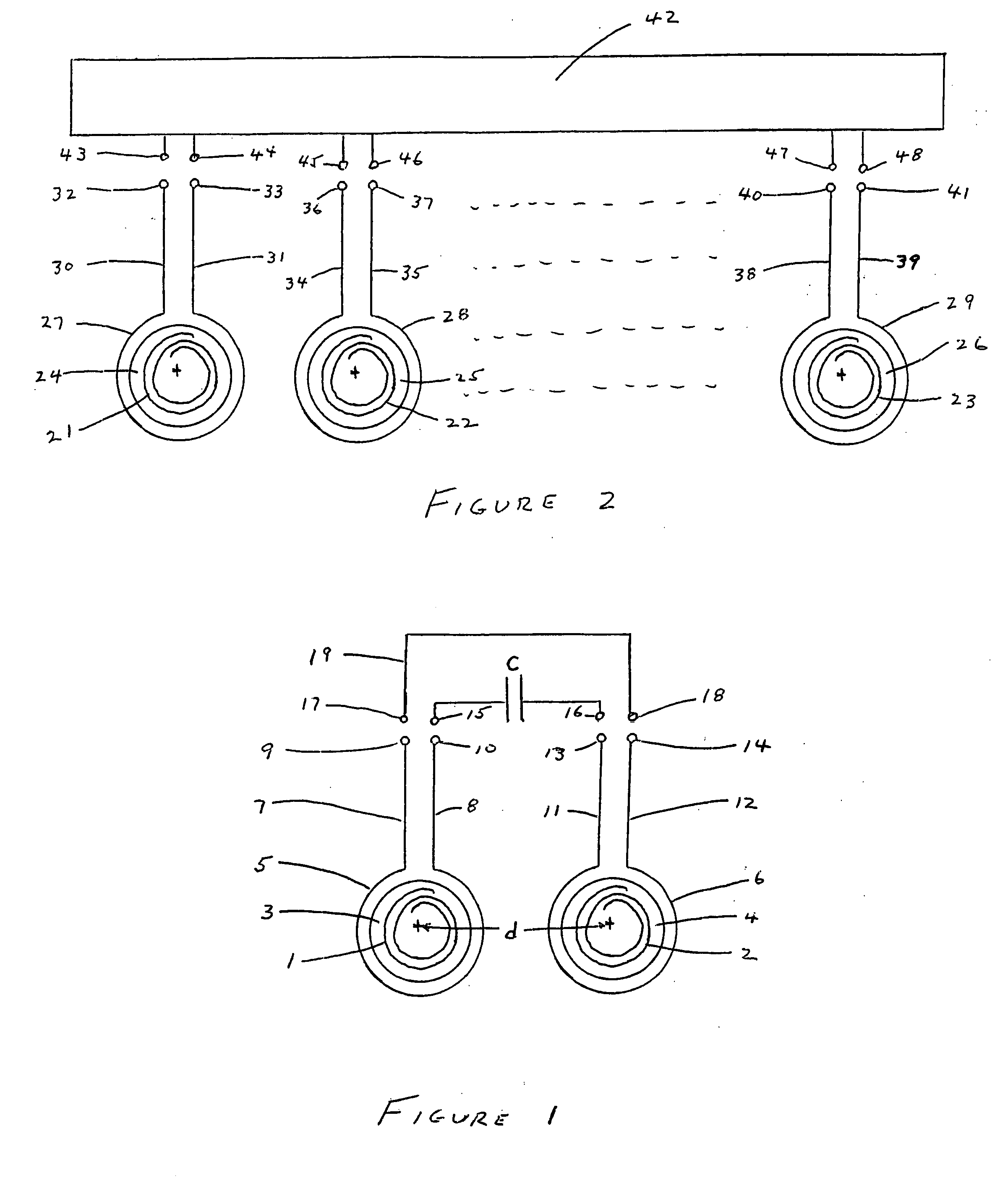
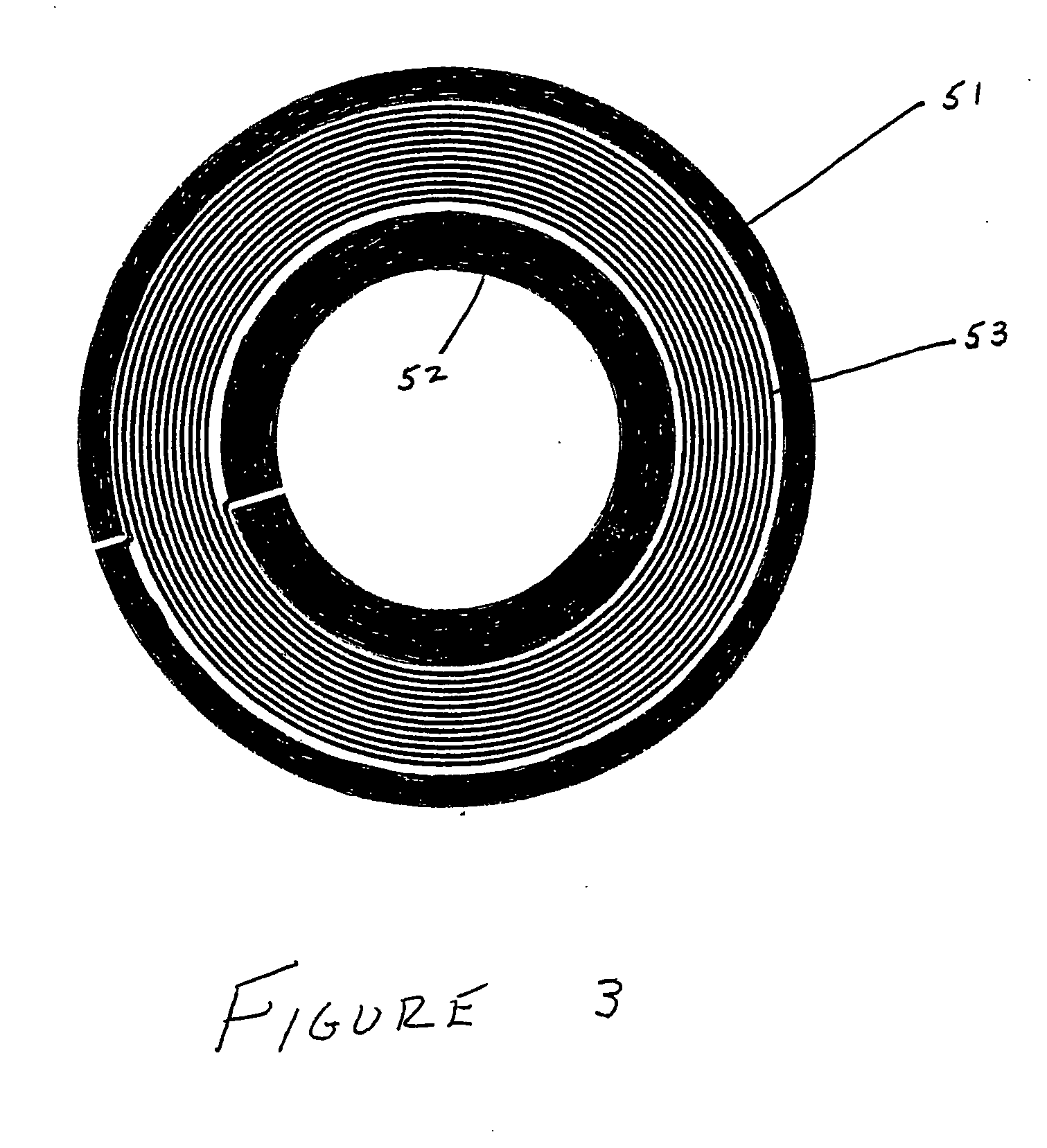
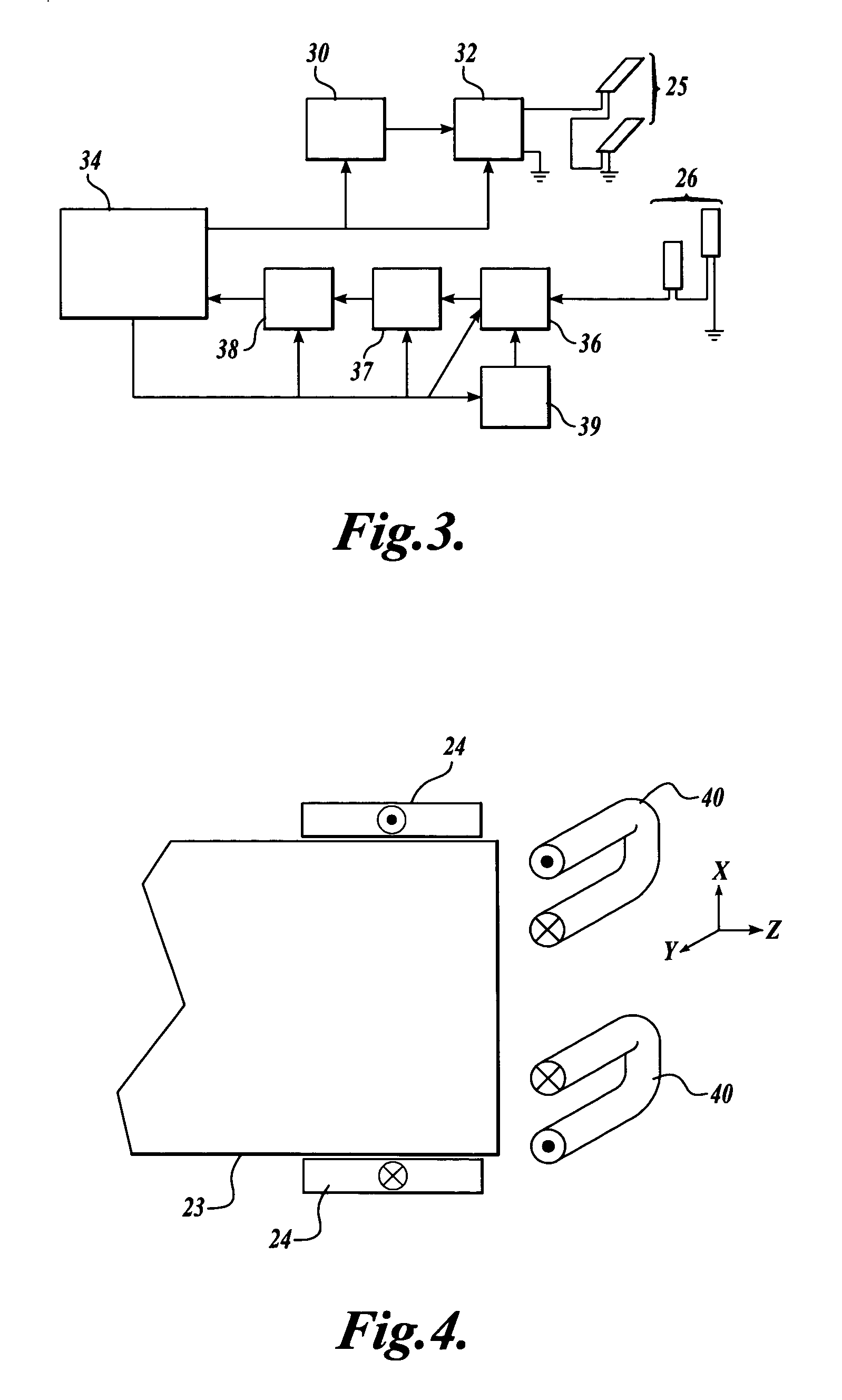
InactiveUS20050146331A1Avoid couplingImprove field uniformityLoop antennasElectric/magnetic detectionElectron resonanceNuclear quadrupole resonance
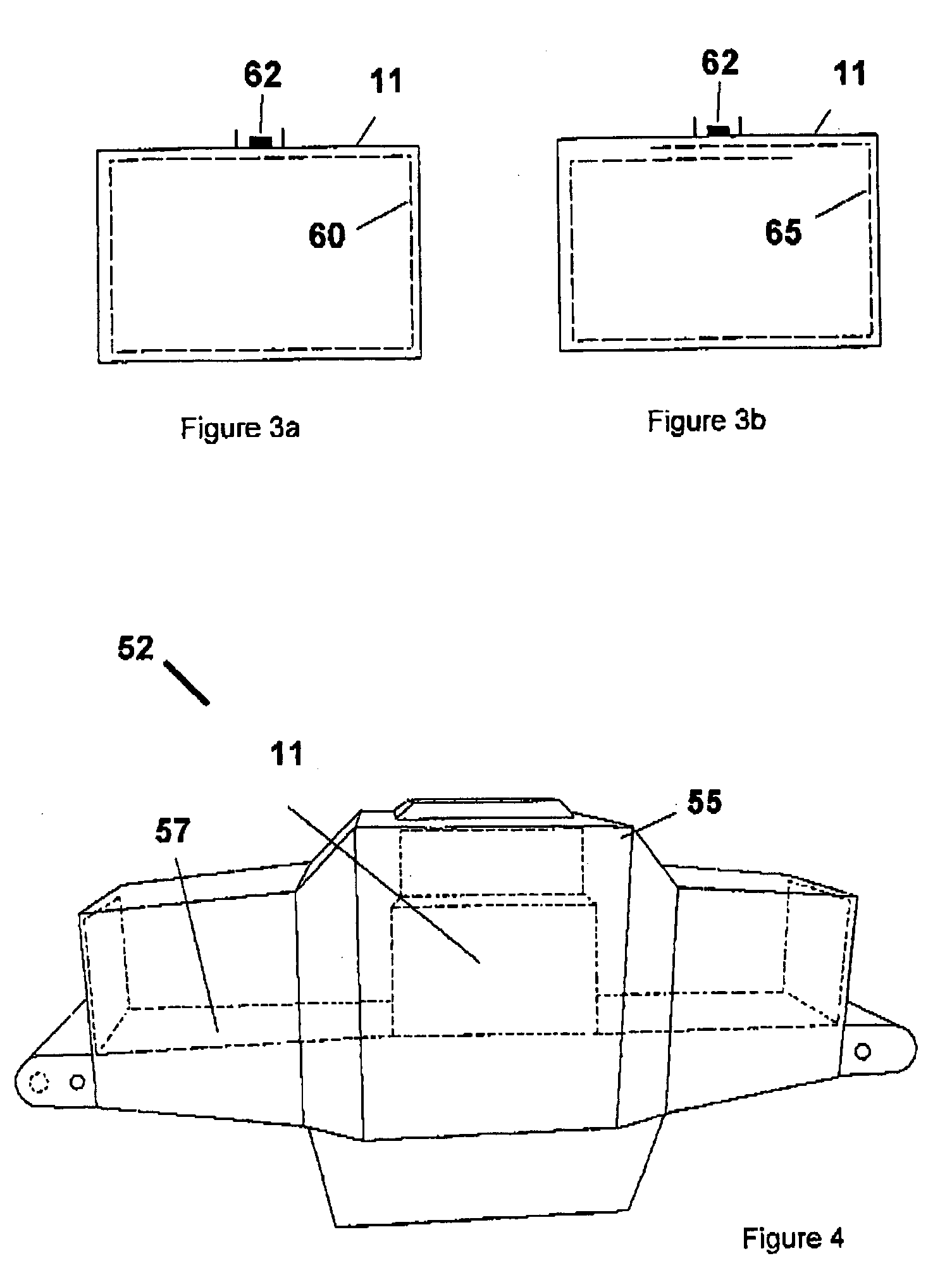
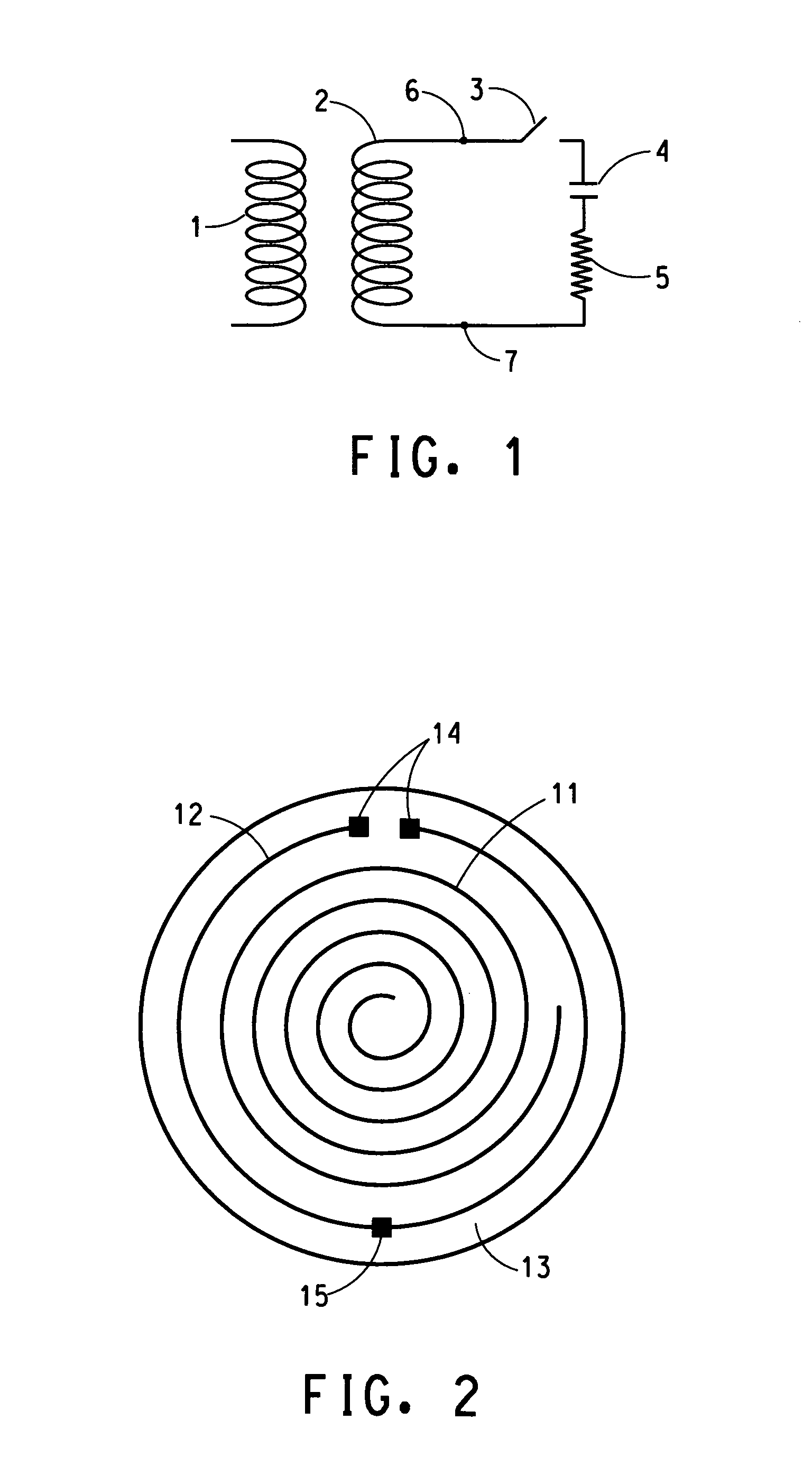
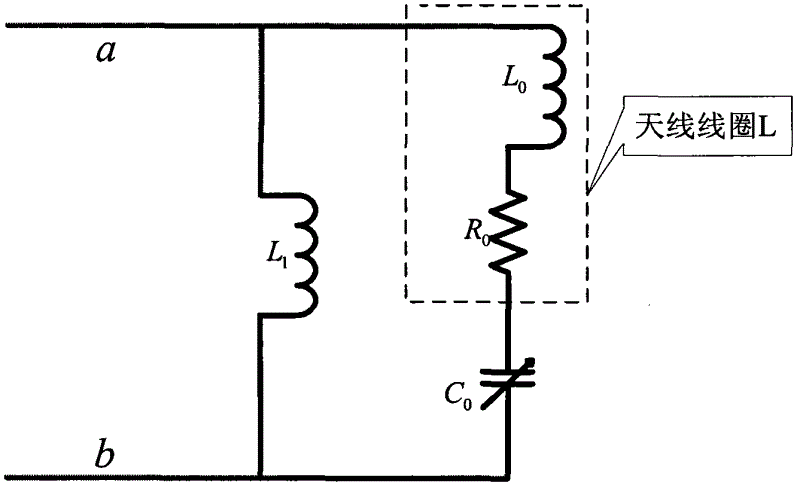
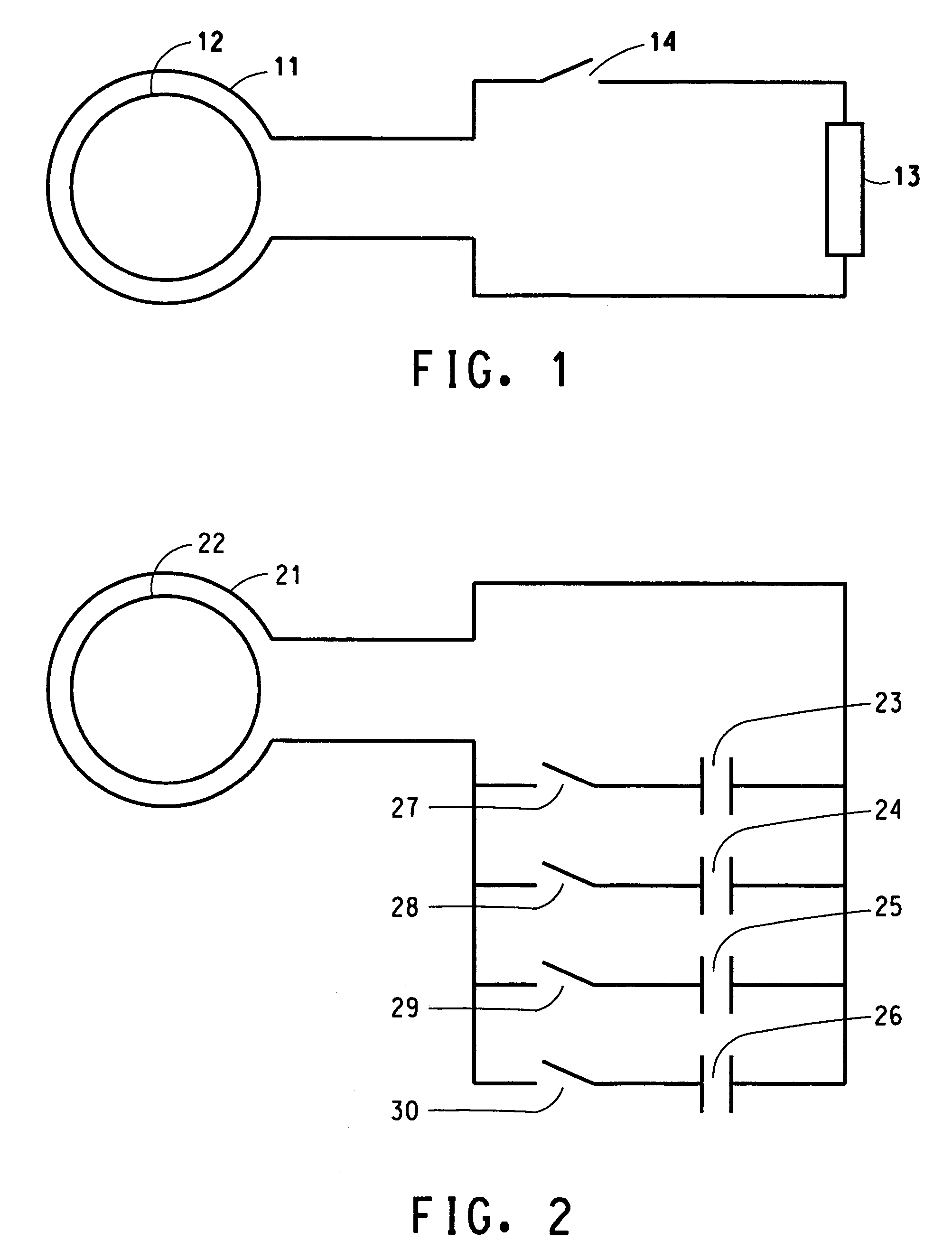
An antenna and shield apparatus for detecting phenomenal signals using nuclear and electronic resonance detection technology, comprising: a transmit and receive antenna, an electric field shield 60 and an outer shield 52. The antenna is a multiple parallel loop transmit-receive antenna forming a main coil assembly 11 having a plurality of loop segments 20 optionally interconnected by connectors in the form of conducting bars 10, relays 16, or nothing. The electric field shield 60 comprises an inner sleeve of conducting material 60, 68 disposed on the inside of the coil assembly 11 for shielding the electric field emanating from the coil assembly 11 from the target volume circumscribed by the assembly. The outer shield 52 comprises a central screen portion 55, waveguides 57 at either end thereof and a sloping channel portion for interconnecting the two. The coil assembly 11 and the electric field shield 60 are housed within the outer shield 52.
Owner:QRSCI
Frequency detection system comprising circuitry for adjusting the resonance frequency of a high temperature superconductor self-resonant coil
InactiveUS20060012371A1Magnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesElectric/magnetic detectionElectrical conductorResonance
The use of a circuit to adjust the resonance frequency of a high temperature superconductor self-resonant transmit, receive, or transmit and receive coil results in improved performance. The circuit is useful in a frequency detection system, especially in a nuclear quadrupole resonance detection system.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Method and apparatus for detecting a target material in a sample by pre-screening the sample for piezoelectric resonance
InactiveUS6956476B2Quick checkMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesResonant frequencyElectricityNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A method and apparatus for screening samples to determine which samples include a target material. Generally, the samples are pre-screened to determine which of the samples have a piezoelectric resonance when irradiated with an electric field, to thereby indicate the presence of the target material. The samples that have the piezoelectric resonance are then further screened by a different process to confirm the presence of the target material. For example, samples that have the piezoelectric resonance are further screened for a specific nuclear quadrupole resonance (NQR), a specific nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) or a specific visual characteristic, to confirm the presence of the target material in the sample. The apparatus and method can be used, for example, to search luggage at ports of entry for the presence of cocaine hydrochloride or heroin hydrochloride.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Detection of contraband using nuclear quadrupole resonance
InactiveUS20050122109A1Efficient detectionMaterial analysis by using resonanceDetection using electromagnetic wavesNuclear physicsNuclear quadrupole resonance
This invention relates to the use of a nuclear quadrupole resonance detection system for detecting contraband, wherein the detection system comprises a container with a detection panel and at least one coil for exciting and detecting the nuclear quadrupole resonance frequencies of a contraband source placed near an outer side of the detection panel.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Noise reduction apparatus, systems, and methods
InactiveUS8232799B2Reduce scan timeReduce data noiseCharacter and pattern recognitionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsFrequency spectrumNoise reduction
This document describes a general system for noise reduction, as well as a specific system for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Nuclear Quadrupole Resonance (NQR). The general system, which is called Calculated Readout by Spectral Parallelism (CRISP), involves reconstruction and recombination of frequency-limited broadband data using separate narrowband data channels to create images or signal profiles. A multi-channel CRISP system can perform this separation using (1) frequency tuned hardware, (2) a frequency filter-bank (or equivalent), or (3) a combination of implementations (1) and (2). This system significantly reduces what we call cross-frequency noise, thereby increasing signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR). A multi-channel CRISP system applicable to MRI and NQR are described.
Owner:ARJAE SPECTRAL ENTERPRISES
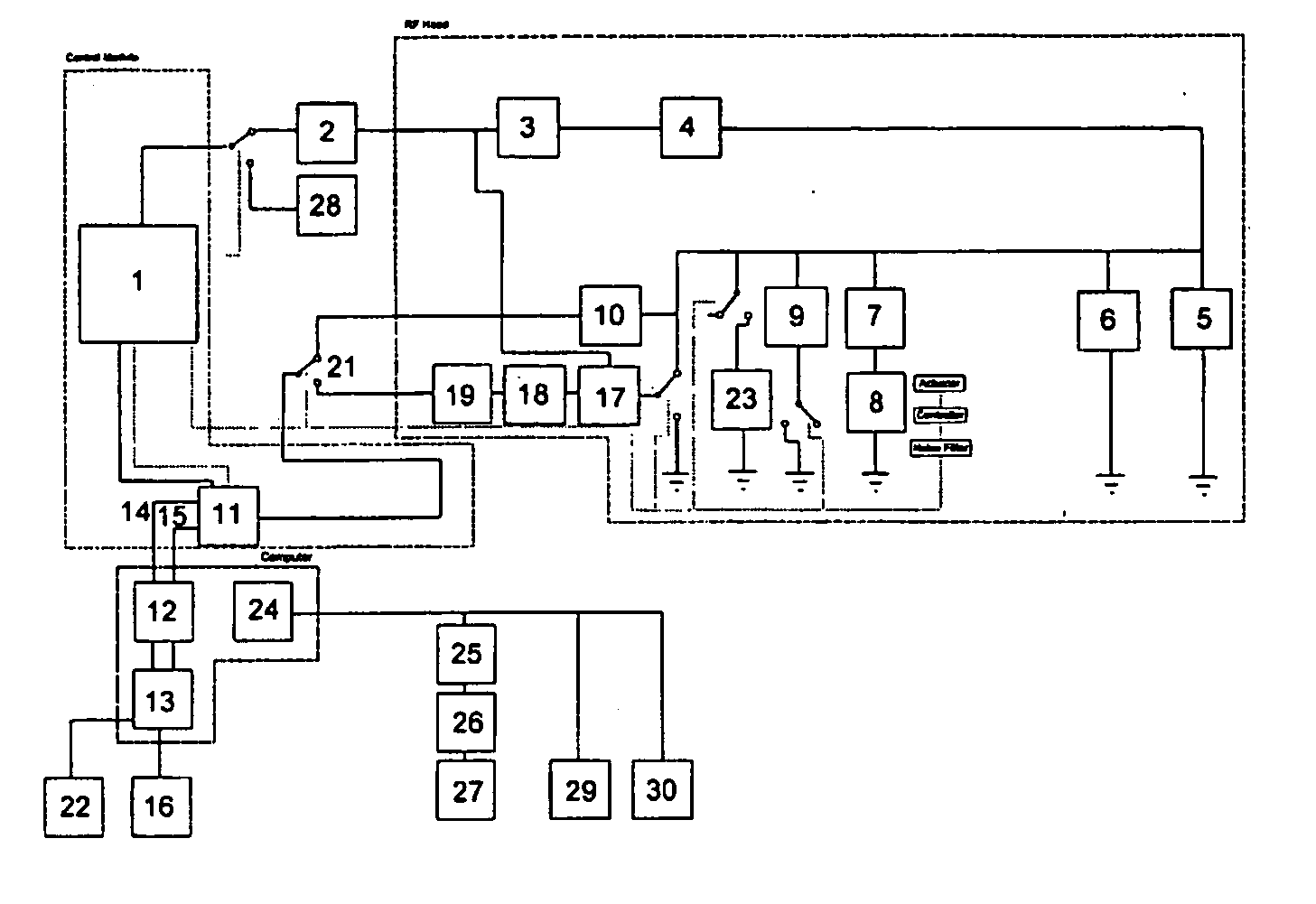
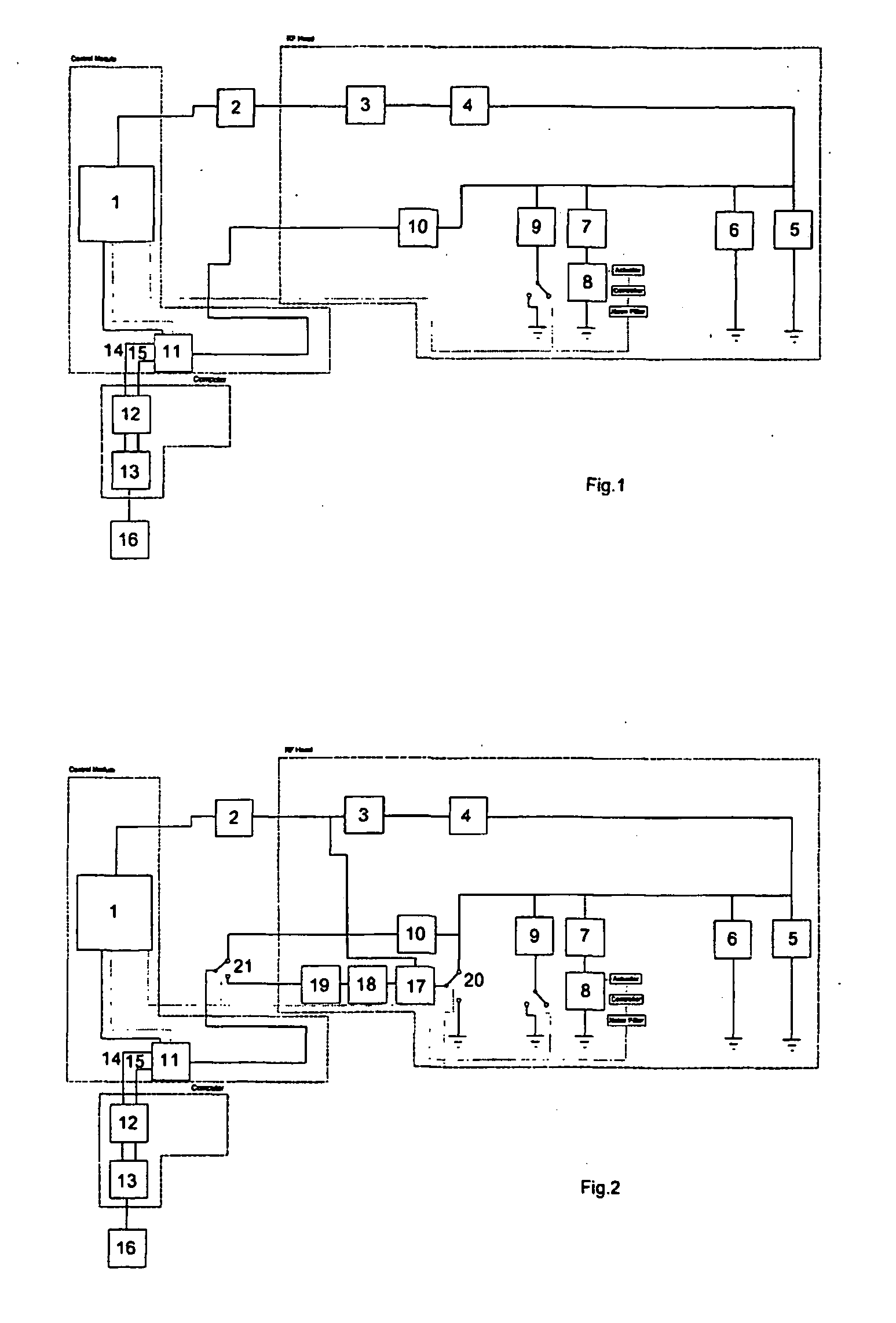
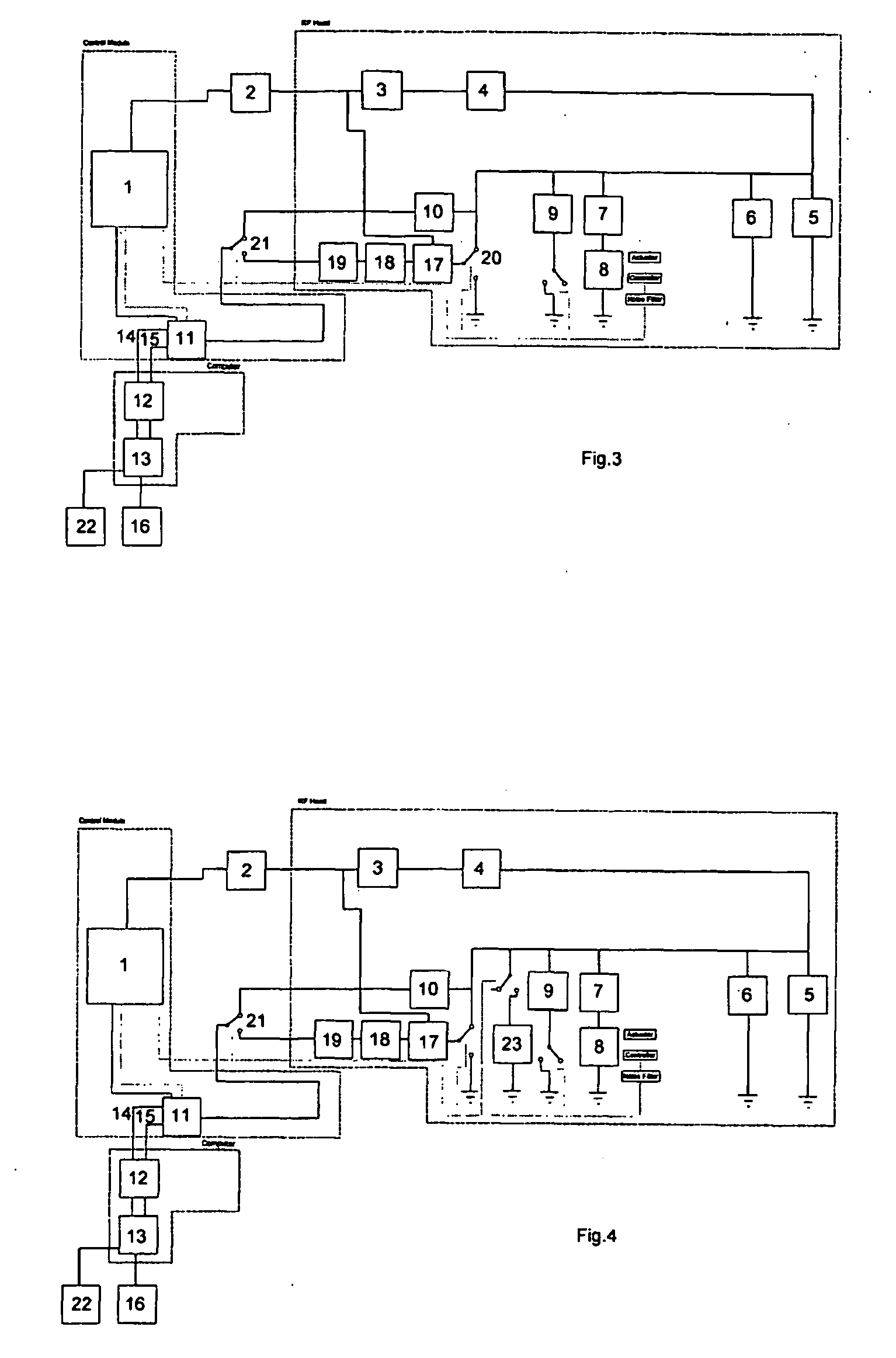
Methods and apparatus for NQR testing
InactiveUS6100688AEasy to distinguishImprove signal-to-noise ratioThermometerDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic field gradientResonance
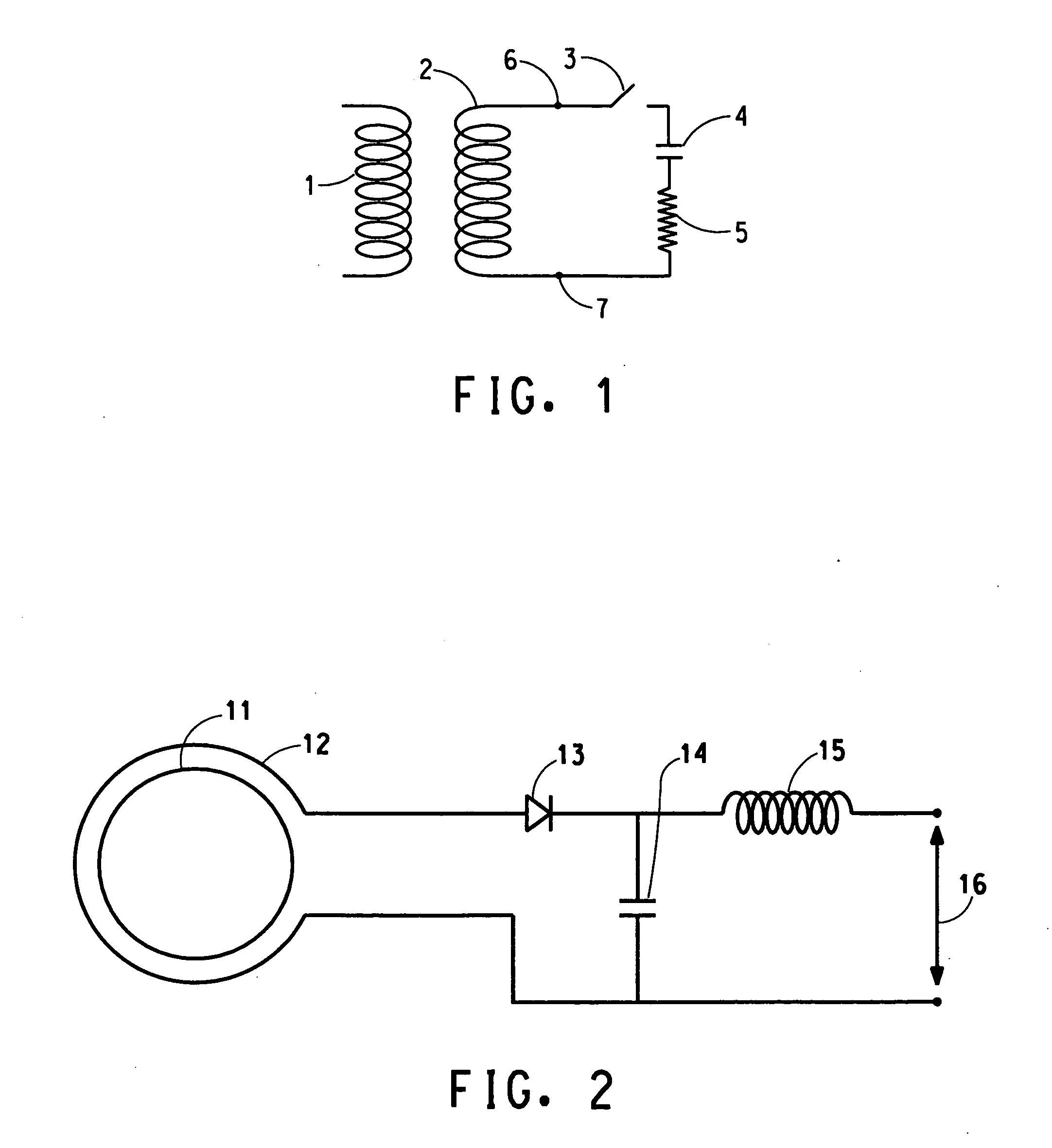
A method and apparatus for imaging within a sample space an object containing quadrupolar nuclei comprises irradiating the object to excite nuclear quadrupole resonance, applying to the object a magnetic field gradient having a profile Bo(x) such that the square of the profile (Bo(x))2 varies linearly with distance (x), detecting resonance response signals from the nuclei, and deriving an image from the response signals. A method of and apparatus for nuclear quadrupole resonance testing an object, and a method of and apparatus for detecting the presence of a particular substance containing a given species of quadrupolar nucleus, are also disclosed.
Owner:BTG INT LTD
Continuous wave nuclear quadrupole resonance spectrometer
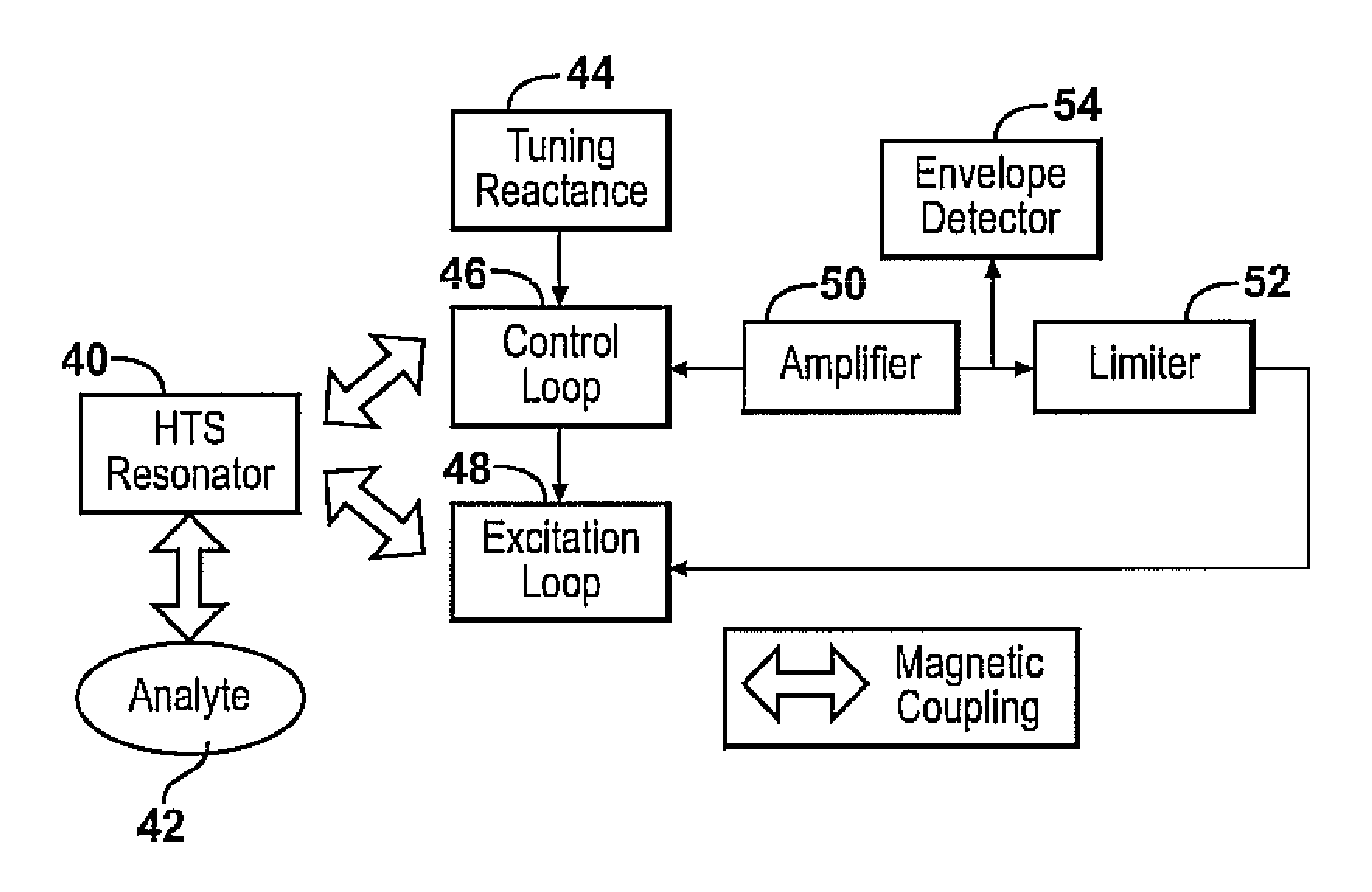
InactiveUS20090039884A1Less estimation errorEasy to implementElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceAnalyteResonance
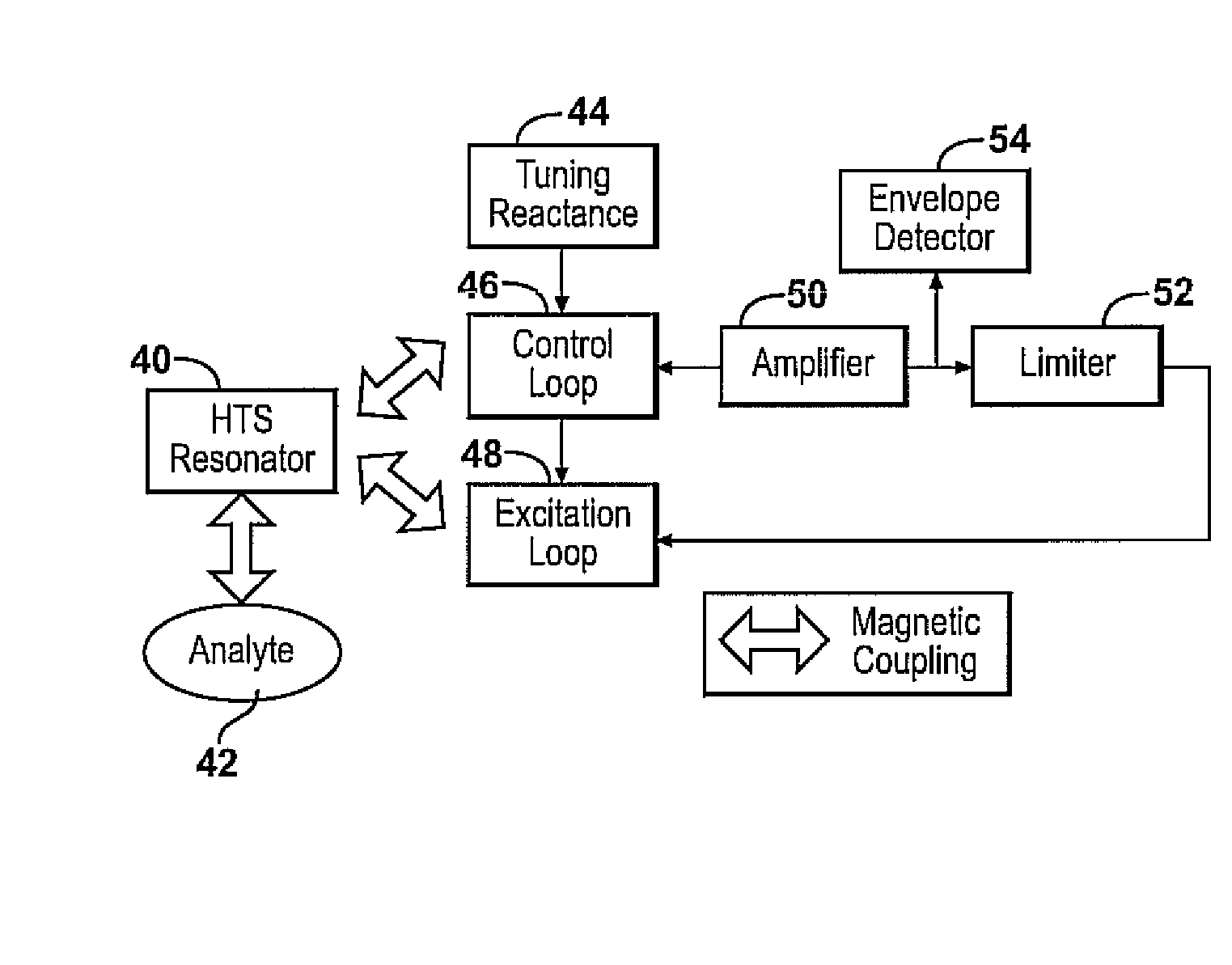
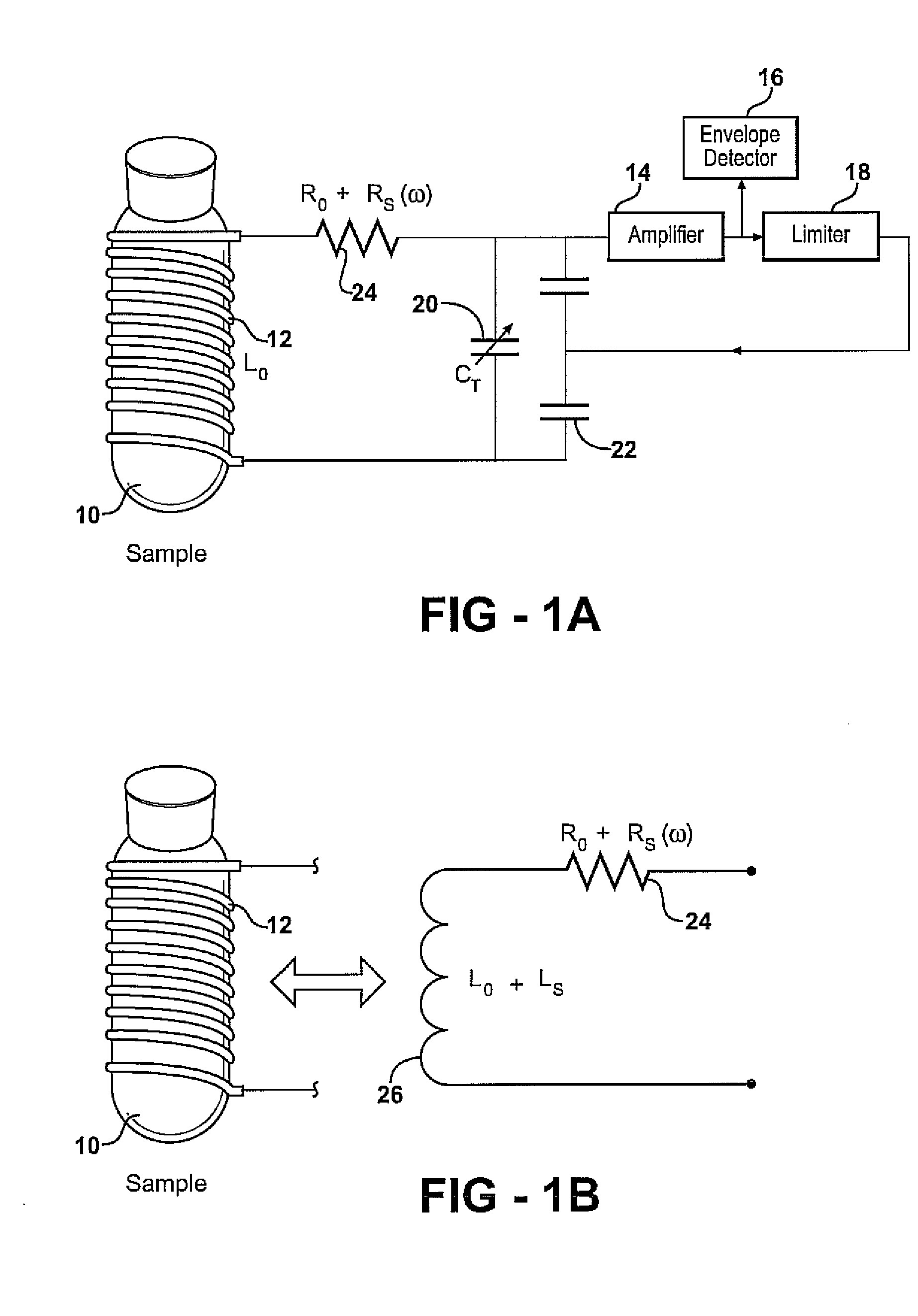
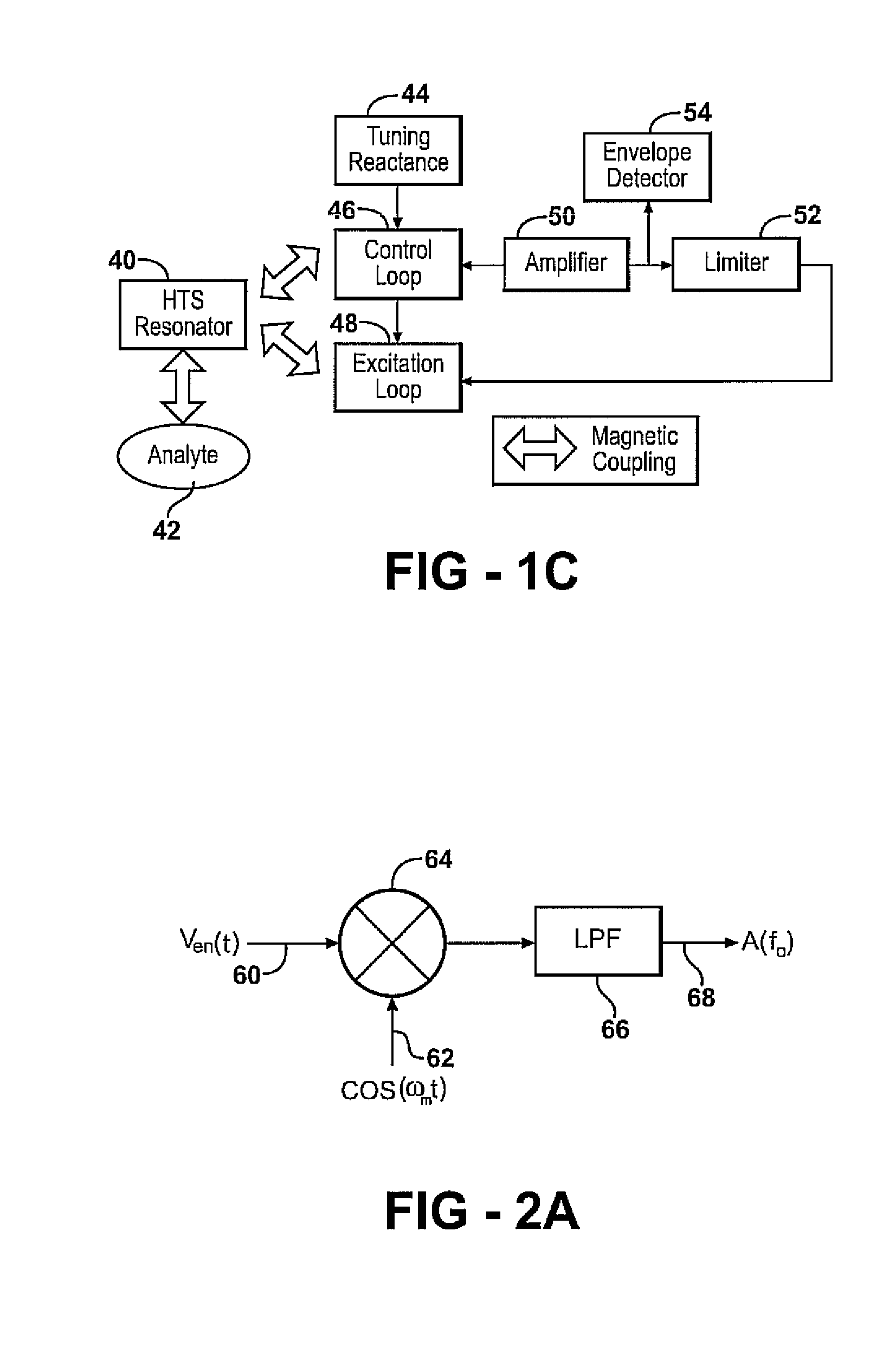
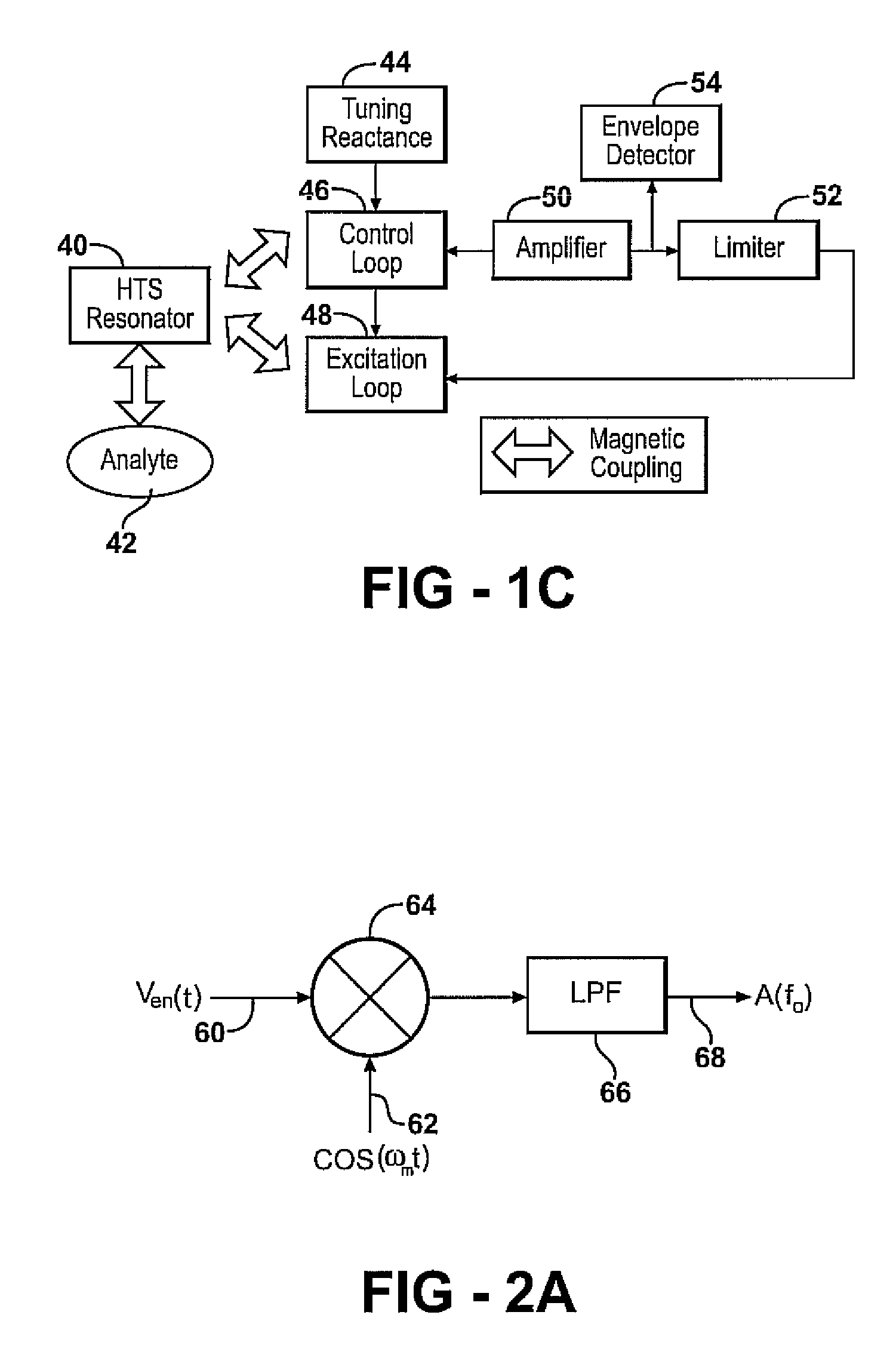
Apparatus and methods for locating a nuclear quadrupole resonance are described. In an example method, a search frequency is adjusted using a blind search until a resonance absorption of an analyte is detected, and then an extremum seeking search to be used to locate an extremum frequency.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Decoupling high temperature superconductor sensor arrays in nuclear quadrupole resonance detection systems
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Q-damping of a high temperature superconductor self-resonant coil in a nuclear quadrupole resonance detection system
InactiveUS20060082368A1Useful in detectionMaterial analysis by using resonanceDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceElectrical conductorHigh-temperature superconductivity
The use of a high temperature superconductor single loop or coil in the Q-damping circuit for a high temperature superconductor transmit, receive, or transmit and receive self-resonant coil in a nuclear quadrupole resonance system results in improved performance of the nuclear quadrupole resonance detection system.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Use of two or more sensors to detect different nuclear quadrupole resonance signals of a target compound
InactiveUS20050206382A1Improving the reliability of the identification of a target compoundImprove performanceElectric/magnetic detectionMaterial analysis by using resonanceHigh pressureNuclear quadrupole resonance
The use of two or more sensors tuned to at least two different nuclear quadrupole resonance frequencies of a target compound to detect the different nuclear quadrupole resonance signals greatly reduces the chance of misidentification, and thereby improves nuclear quadrupole resonance detection system performance.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Q-damping of a high temperature superconductor self-resonant coil in a nuclear quadropole detection system
InactiveUS20050140371A1Television system detailsSelective content distributionElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical conductor
The use of a bias controlled diode in the Q-damping circuit of a high temperature superconductor transmit, receive, or transmit and receive self-resonant coil in a nuclear quadrupole resonance detection system results in improved performance. The diode is operated with a forward bias such that the diode is resistive with a resistance of about 10 to about 1000 ohms.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method and apparatus for detecting a target material in a sample by pre-screening the sample for piezoelectric resonance
InactiveUS7132942B1Quick checkAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonancePiezoelectric resonance
A method and apparatus for screening samples to determine which samples include a target material. Generally, the samples are pre-screened to determine which of the samples have a piezoelectric resonance when irradiated with an electric field, to thereby indicate the presence of the target material. The samples that have the piezoelectric resonance are then further screened by a different process to confirm the presence of the target material. For example, samples that have the piezoelectric resonance are further screened for a specific nuclear quadrupole resonance (NQR), a specific nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) or a specific visual characteristic, to confirm the presence of the target material in the sample. The apparatus and method can be used, for example, to search luggage at ports of entry for the presence of cocaine hydrochloride or heroin hydrochloride.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
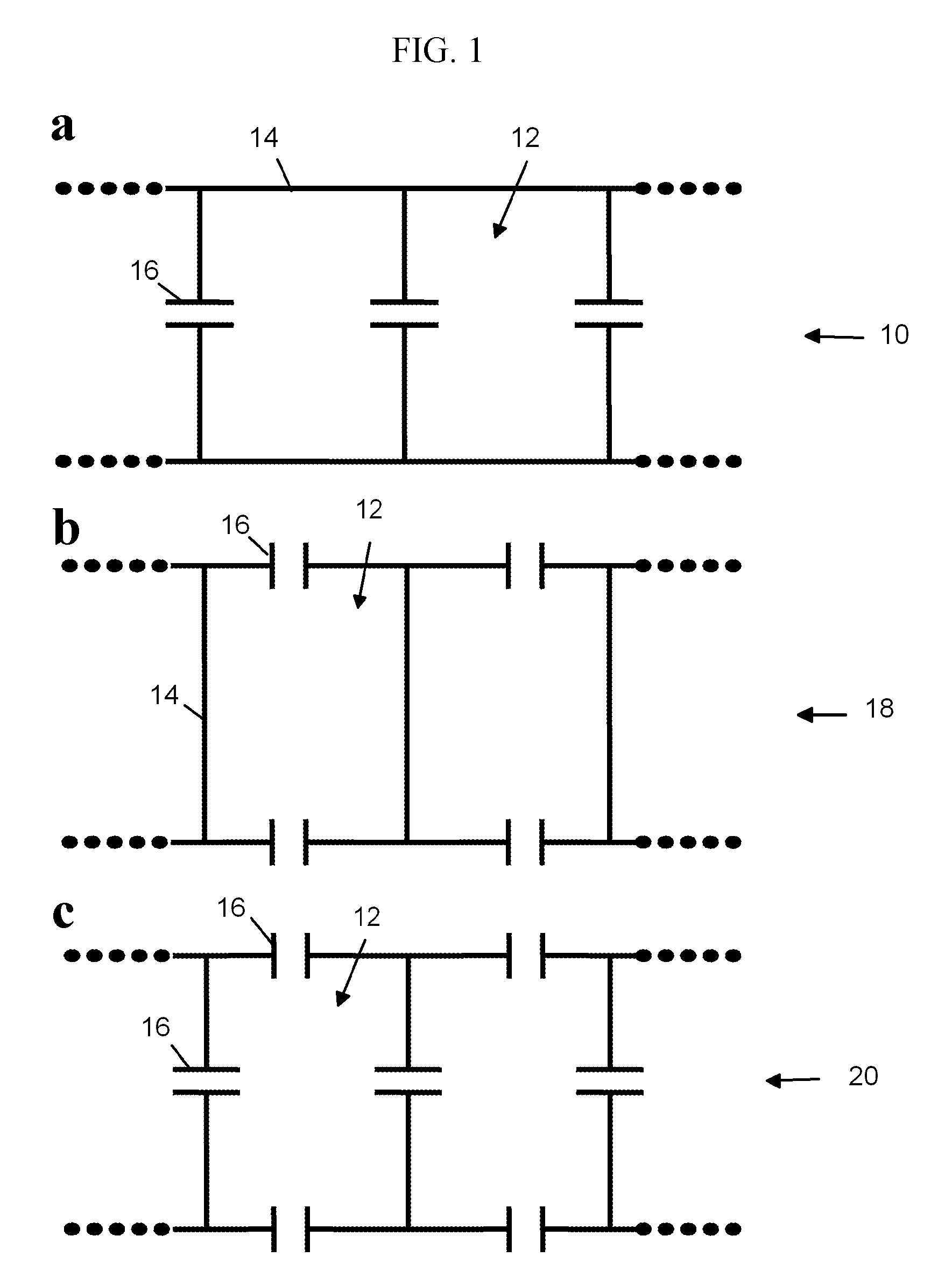
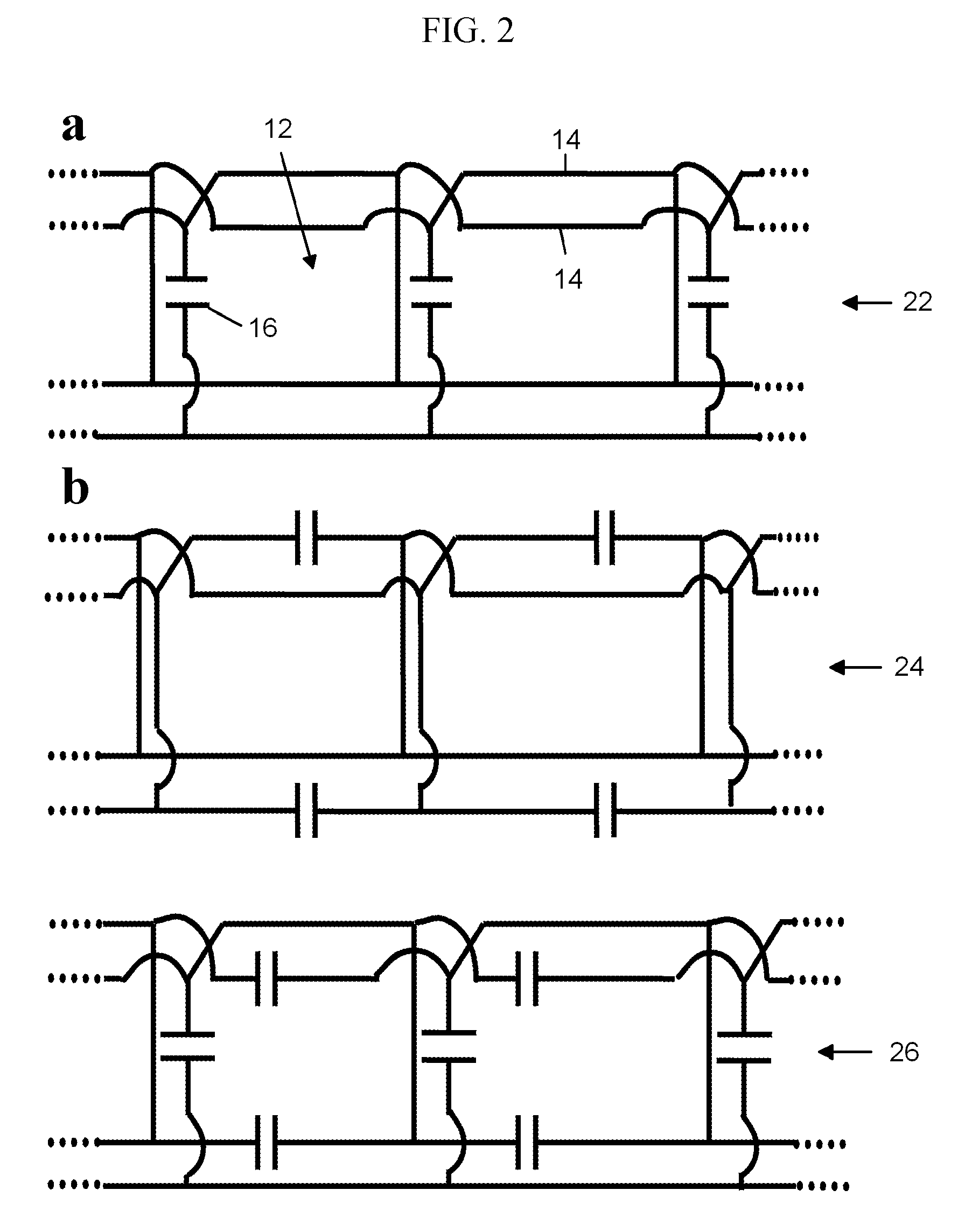
Open-Shape Noise-Resilient Multi-Frequency Sensors
InactiveUS20070096731A1Maximum efficiencyMaximal sensitivityMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionEnvironmental noiseEngineering
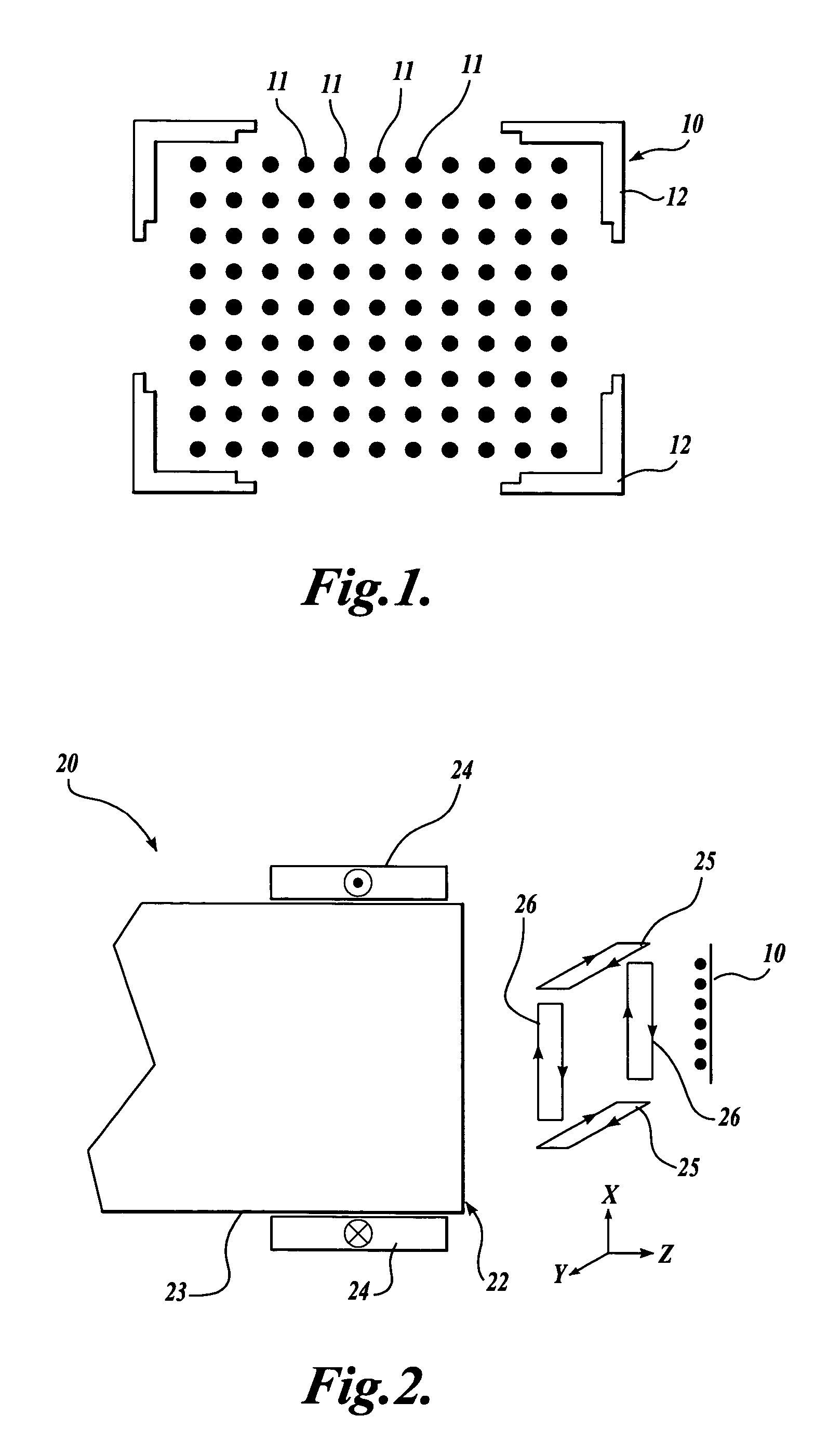
A series of open-shape nuclear quadrupole resonance (NQR) sensors having environmental noise resilience and a capability for simultaneous independent multi-frequency operation is disclosed. The sensors are multimodal birdcage or TEM-type structures made from single-turn or multi-turn interconnected windows or magnetically coupled elements having uniform distributions of the amplitudes of the corresponding radiofrequency magnetic fields along their surfaces. The phases of these fields change in a cyclical fashion, such that the interference signals are picked up with opposite phases by different parts of the sensors and are, therefore, cancelled out. The devices may have a planar or a curved shape and may or may not be shielded on one side. Planar unshielded sensors may be used to simultaneously detect signals from objects positioned on both of their sides.
Owner:SPINLOCK SRL +1
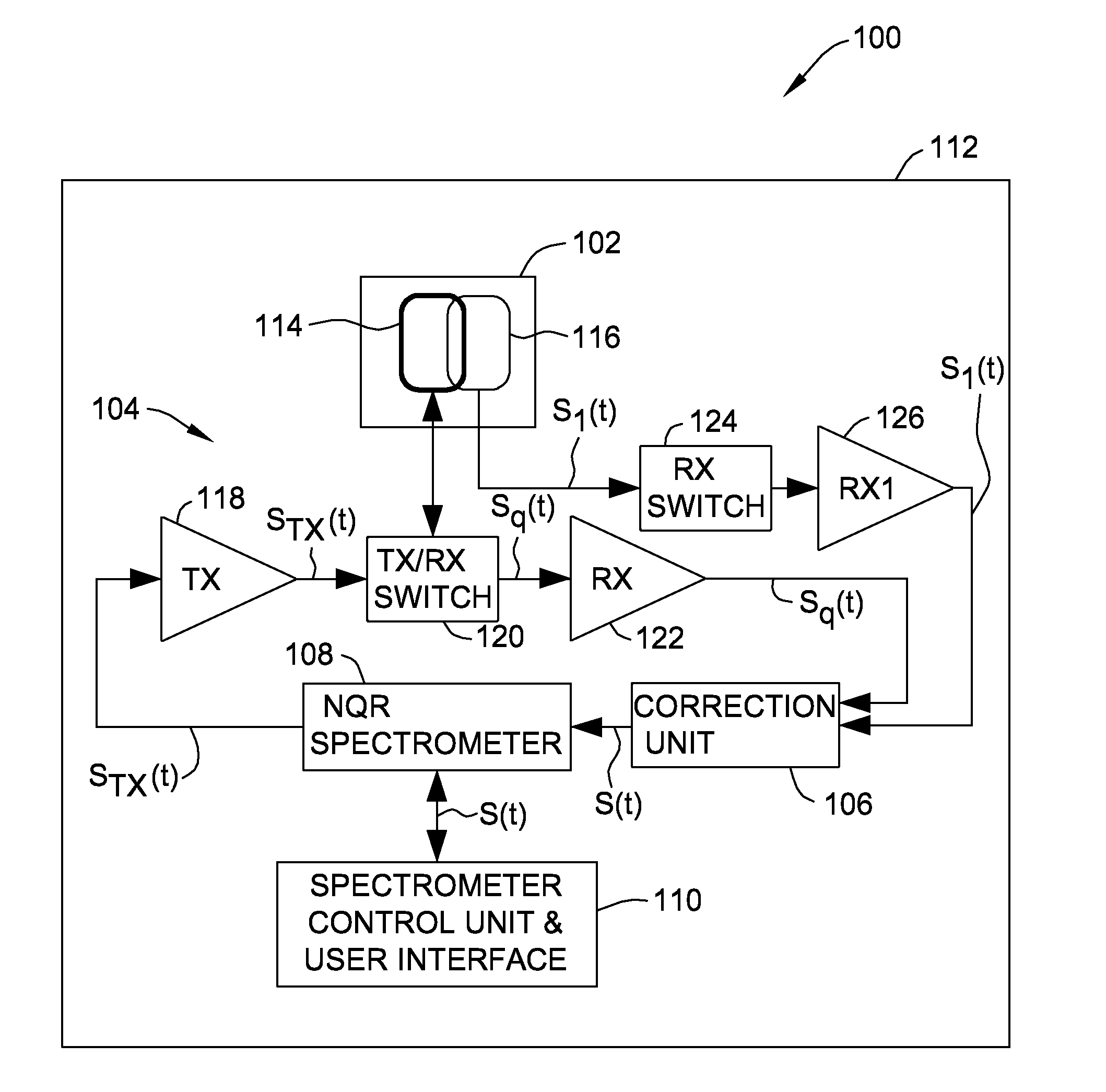
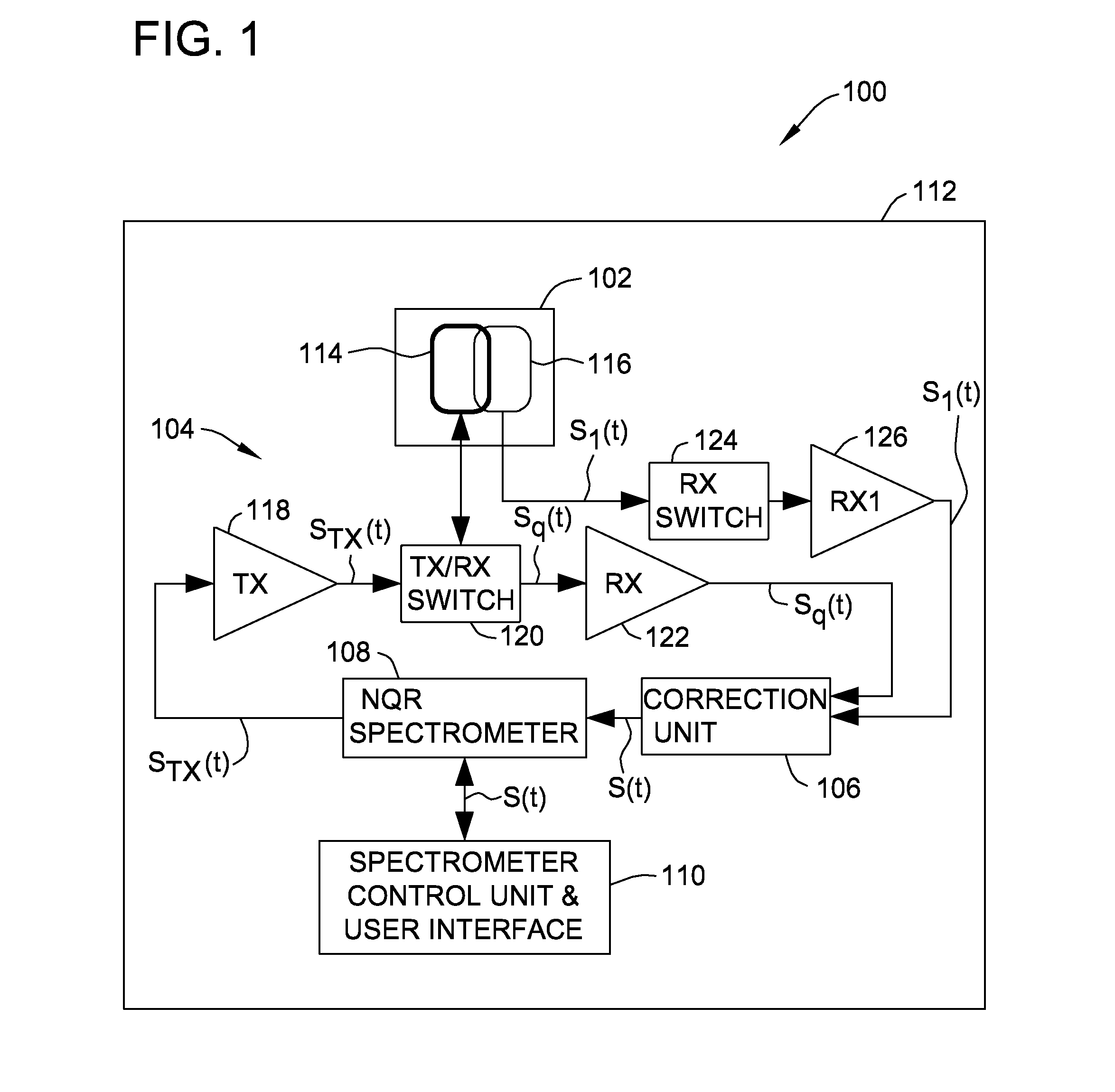
Nuclear quadrupole resonance system and method of using the same
ActiveUS20140070810A1Reduce componentsMaterial analysis by using resonanceElectric/magnetic detectionEngineeringNuclear quadrupole resonance
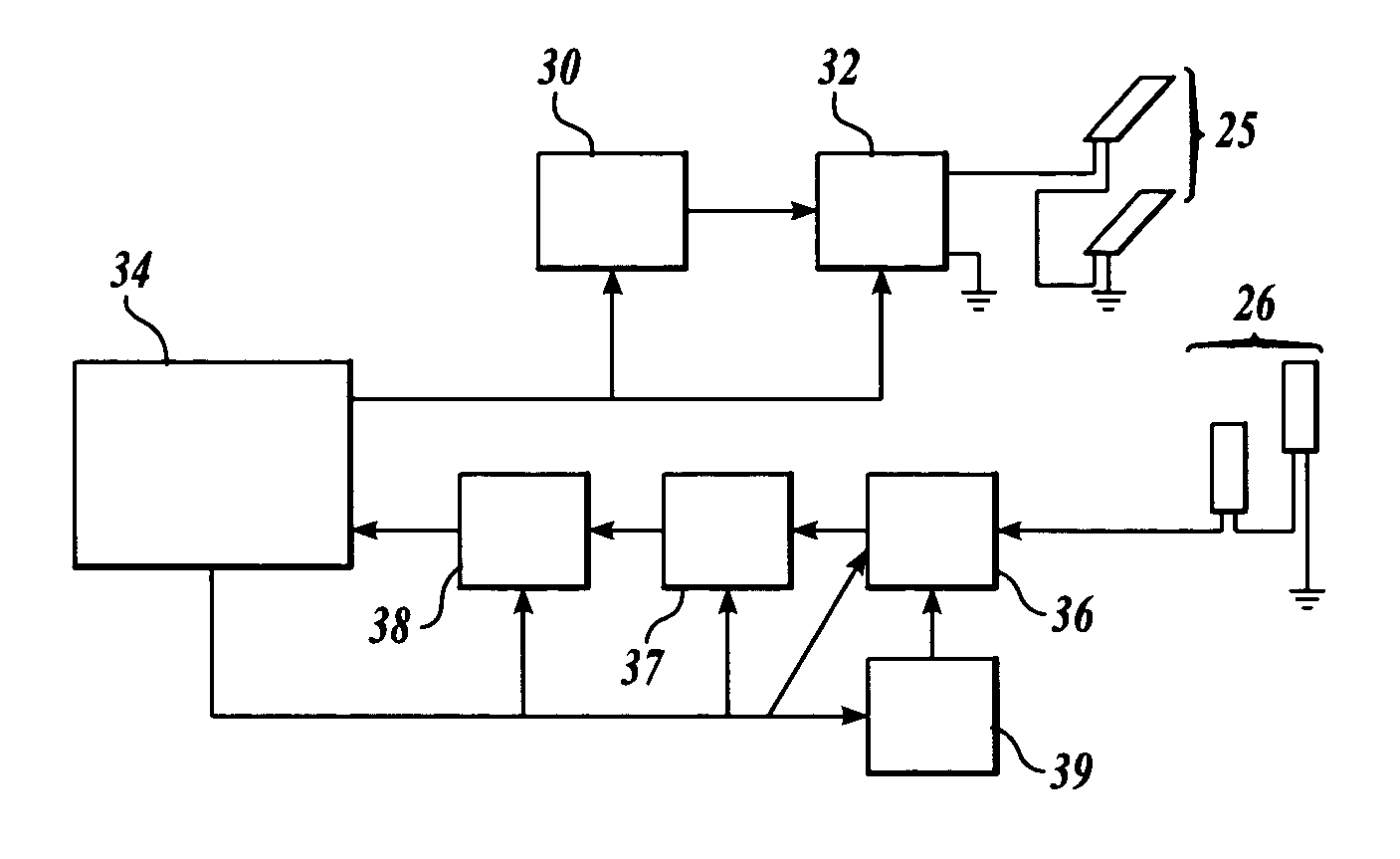
A nuclear quadrupole resonance (NQR) sensor assembly includes an active sensor coil configured to transmit radiofrequency (RF) signals to an object of interest and receive return RF signals from the object of interest to generate sensor signals substantially representative of the return signals. The at least one reference coil is configured to receive environmental RF signals to generate reference signals at least partially representative of the environmental RF signals. The at least one reference coil is co-located with the active sensor coil. The active sensor coil and the at least one reference coil are in communication with a correction unit configured to remove interference components from the sensor signals using the reference signals.
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
Receive system for high q antennas in nqr and a method of detecting substances
InactiveUS20060033499A1Rapidly removing energyHigh phase stabilityElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRElectricityAudio power amplifier
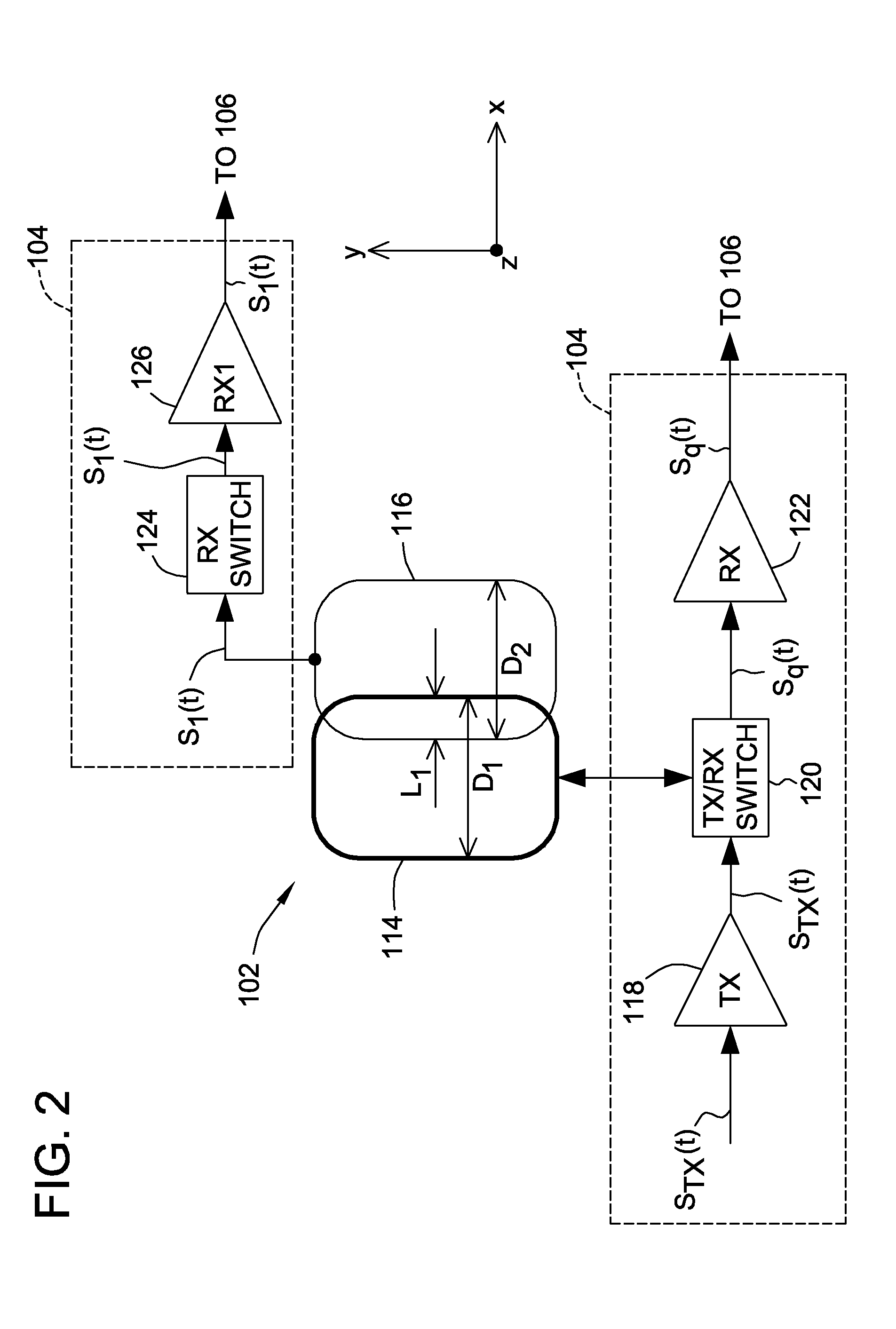
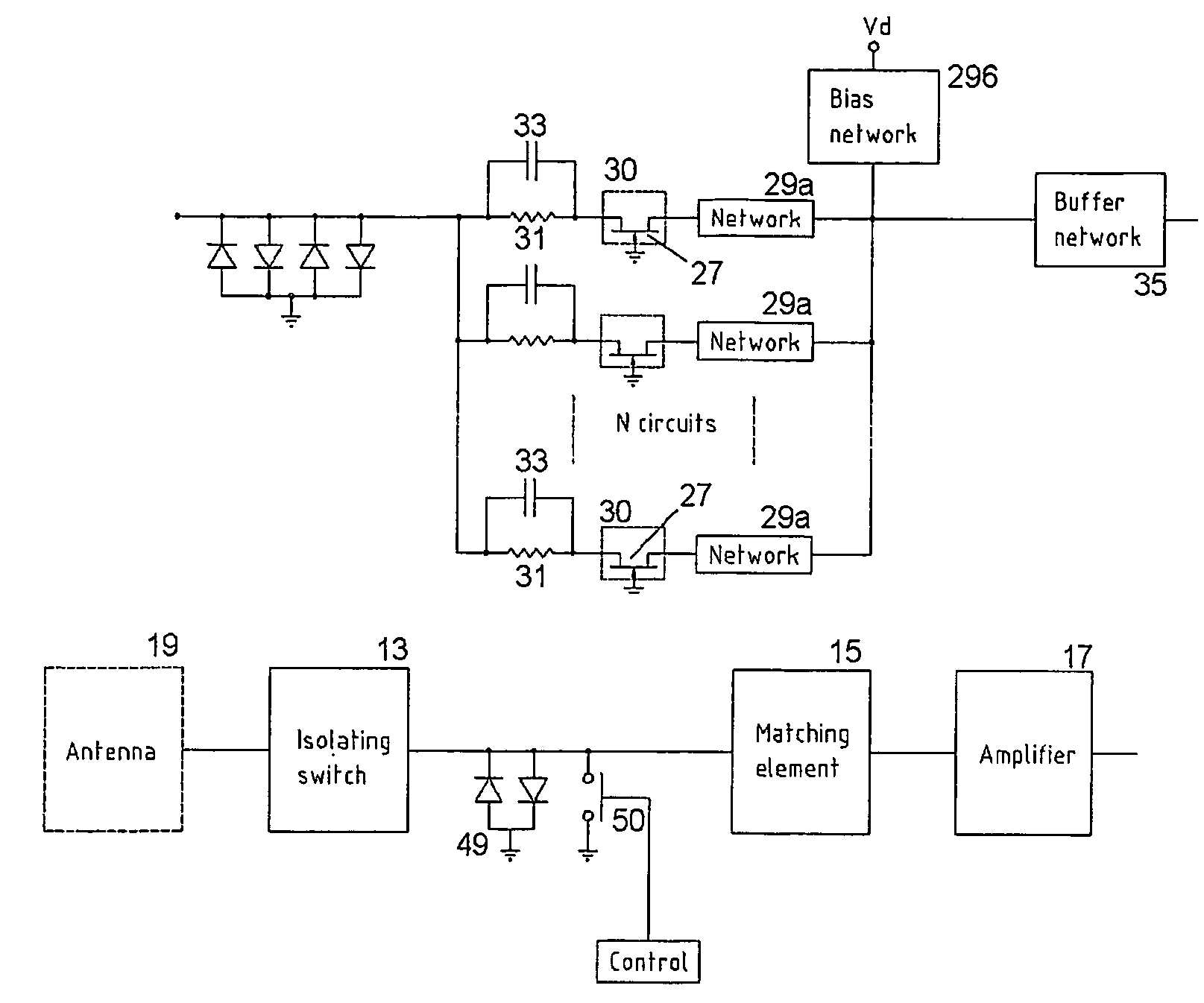
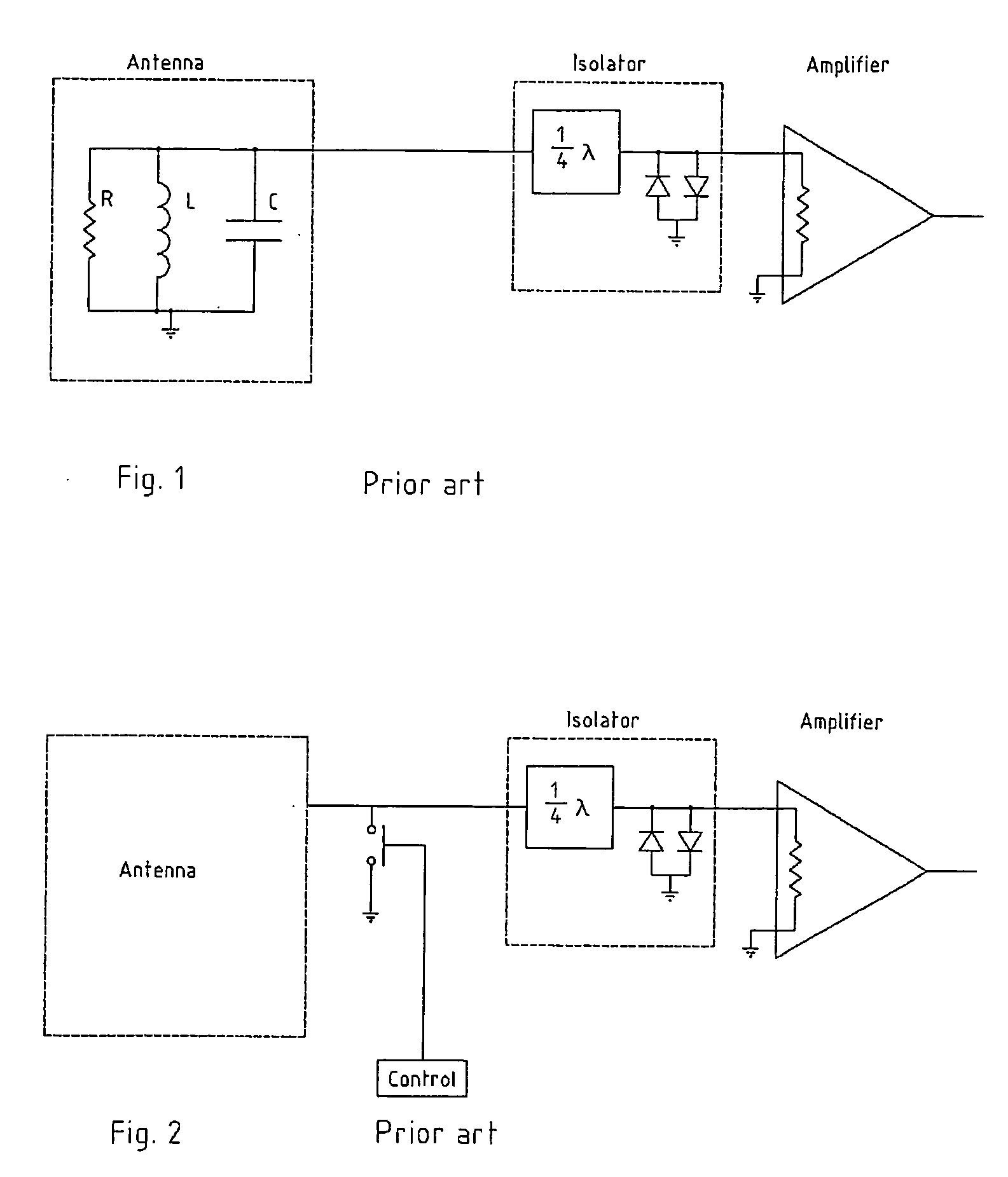
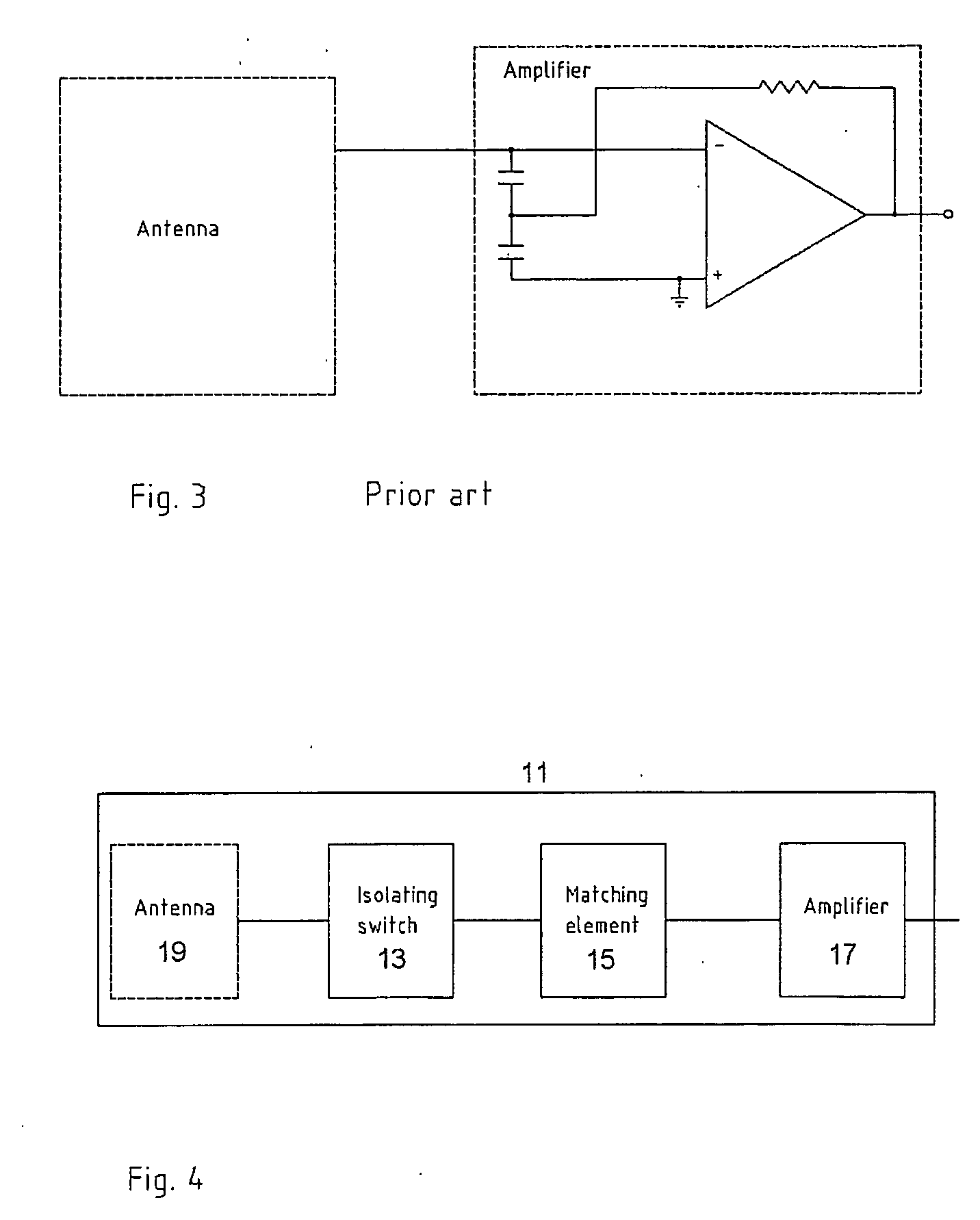
A receiving system (11) for connection to an antenna arrangement (19) for detecting response signals from a substance having quadrupolar nuclei excited so as to produce nuclear quadrupole resonance in certain of the quadrupolar nuclei. A method for receiving a response signal via the antennae arrangement (19) is also described. The receiving system (11) includes an amplifier (17) to amplify the received response signal from the antenna arrangement (19) for subsequent processing, a matching section (15) to match the amplifier (17) to the antenna (19), and an isolating switch (13) to isolate the antenna from the receiving system (11). The matching section (15) noise matches the receiving system (11) to the antenna (19) during a receiving period to reduce the Q factor of the antenna without significantly degrading the signal to noise ratio. The isolating switch (13) isolates the receiving system (11) from the antenna (19) during a transmitting period when an excitation signal is transmitted by the antenna (19) to irradiate the substance. It also electrically connects the receiving system (11) to the antenna during the receiving period immediately after the transmitting period.
Owner:QRSCI
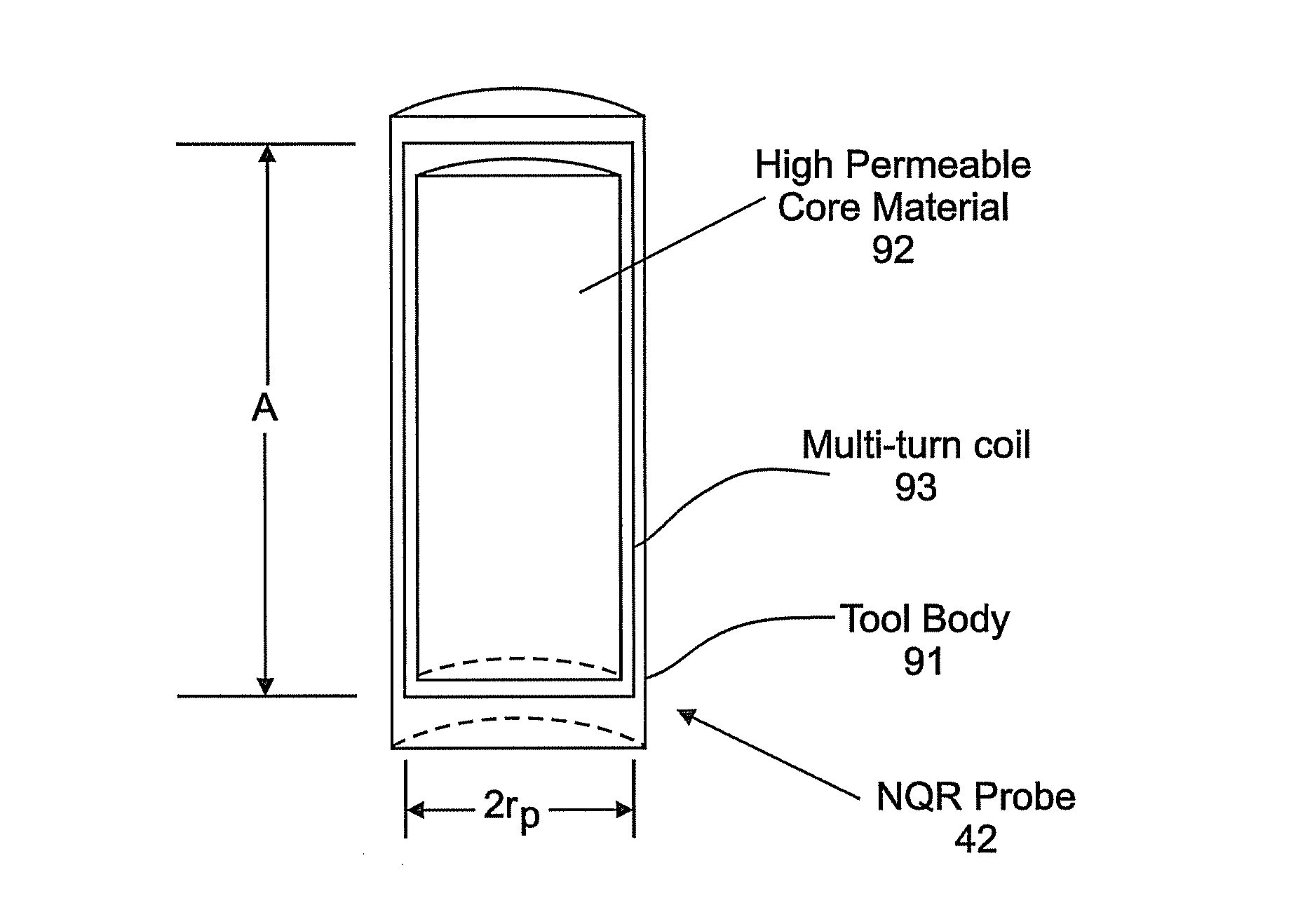
Nuclear quadrupole resonance logging tool and methods for imaging therewith
ActiveUS20080224696A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMagnetic measurementsCouplingNuclear quadrupole resonance
An instrument for investigating properties of an earth formation includes a body housing a nuclear quadrupole resonance (NQR) probe, the probe having at least one coil wound around a core material and an electronics coupling, the body being adapted for insertion into a wellbore within the earth formation. A method and computer program product are provided.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
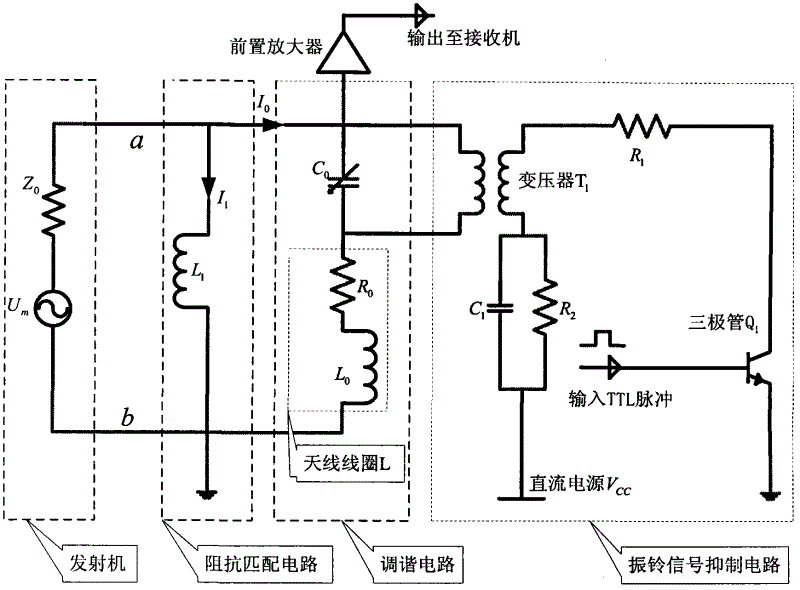
Low frequency tuning antenna applicable to explosive detection
InactiveCN102624411AMultiple-port networksAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceStopped workResonance
The invention discloses a low frequency tuning antenna applicable to explosive detection, which comprises a high Q-value tuning circuit, an impedance matching circuit and a ringing signal suppression circuit. The high Q-value tuning circuit receives radio frequency pulse containing characteristic frequency of a sample to be tested and output from a high-power transmitter. The impedance matching circuit is used for turning complex impedance of the high Q-value tuning circuit into 50 ohm, and a phase is 0. The ringing signal suppression circuit has effects that when the transmitter works, Q value of the circuit is high, and the antenna ringing signal suppression circuit does not work; and when the transmitter stops working, the Q value of the circuit is low, and residual energy stored in an antenna coil is consumed as soon as possible through the antenna ringing signal suppression circuit. Therefore, time from closing the transmitter to opening a receiver is shortened, the Q value of the circuit is high during a nuclear quadrupole resonance (NQR) signal receiving period, and detecting sensitivity on weak NQR signals is improved, namely a process that the Q value of a resonance circuit becomes smaller then bigger in a detection process is required.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Use of two or more sensors in a nuclear quadrupole resonance detection system to improve signal-to-noise ratio
InactiveUS7265550B2Magnetic property measurementsMaterial analysis by using resonanceSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Nuclear quadrupole resonance
The use of two or more sensors tuned to the same nuclear quadrupole resonance frequency and detecting the nuclear quadrupole resonance signal results in improved signal-to-noise ratio and therefore improved nuclear quadrupole resonance detection system performance.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Scanner for nuclear quadrupole resonance measurements and method therefor
InactiveUS20060012366A1Sufficient protectionCombat magnetoacoustic ringingMaterial analysis by using resonanceDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceAudio power amplifierPulse sequence
An NQR scanner for detecting the presence of a substance containing quadrupole nuclei within an object. A pulse generating means (1) generates pulse sequences that are used to irradiate the object in a pulsed magnetic field at a requisite NQR frequency for the substance to be detected. A high power RF transmit amplifier (2) amplifies the signal to produce sufficient magnetic field strength to irradiate a scan volume within which the object is disposed for detection purposes and cause an NQR transition to a detectable level within the substance if present within the object. A method for detecting the presence of a substance containing quadrupole nuclei within an object is also described
Owner:QRSCI
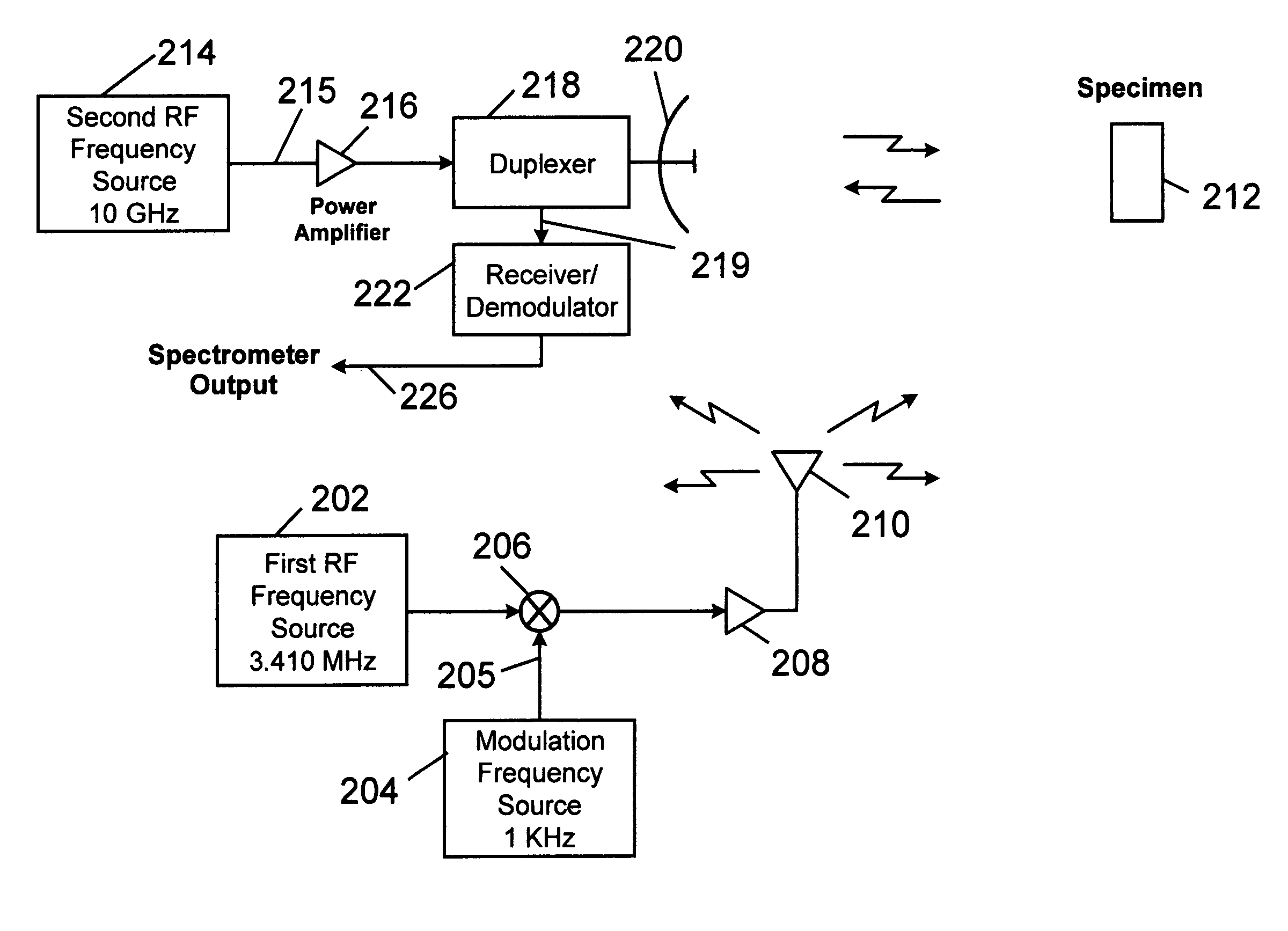
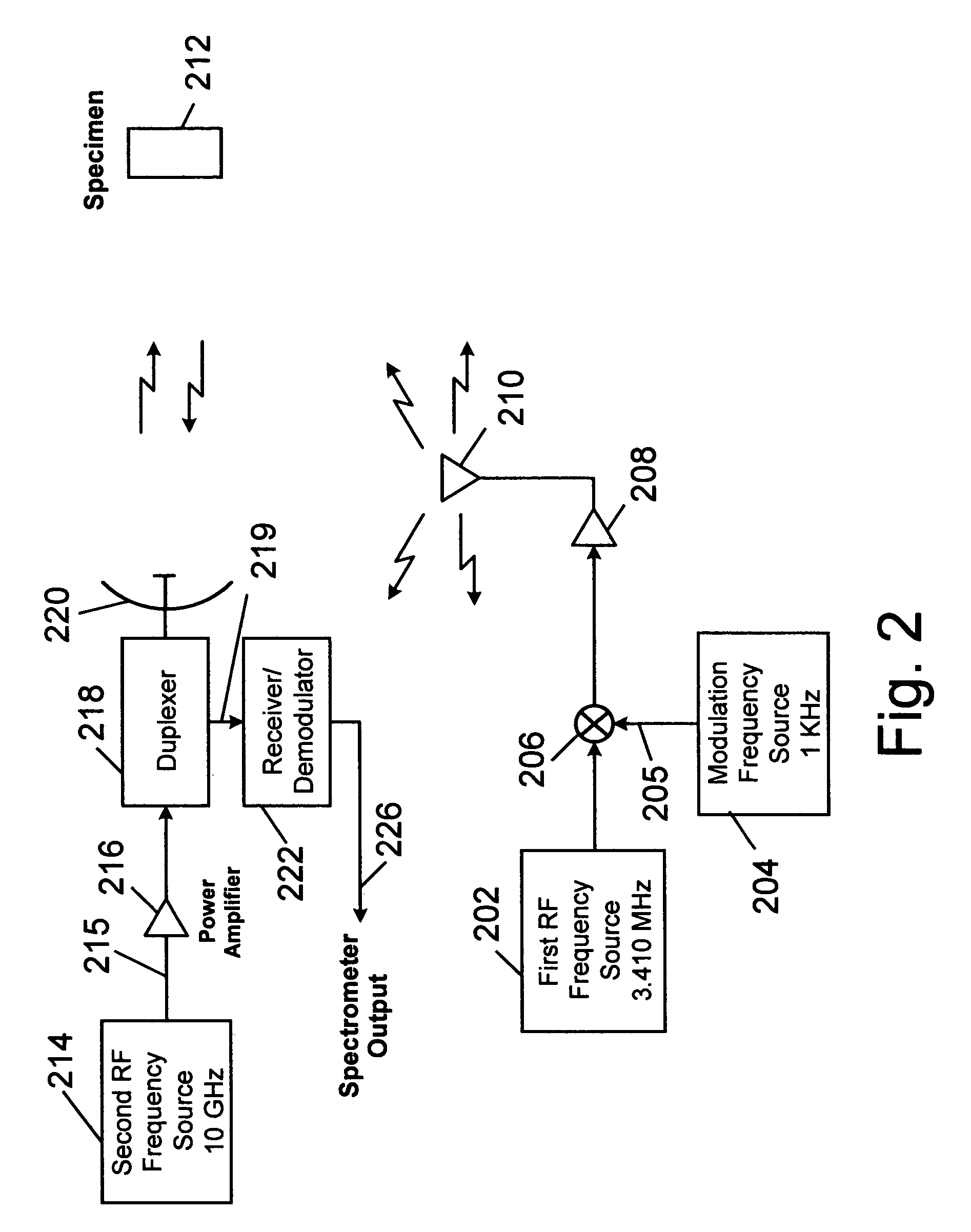
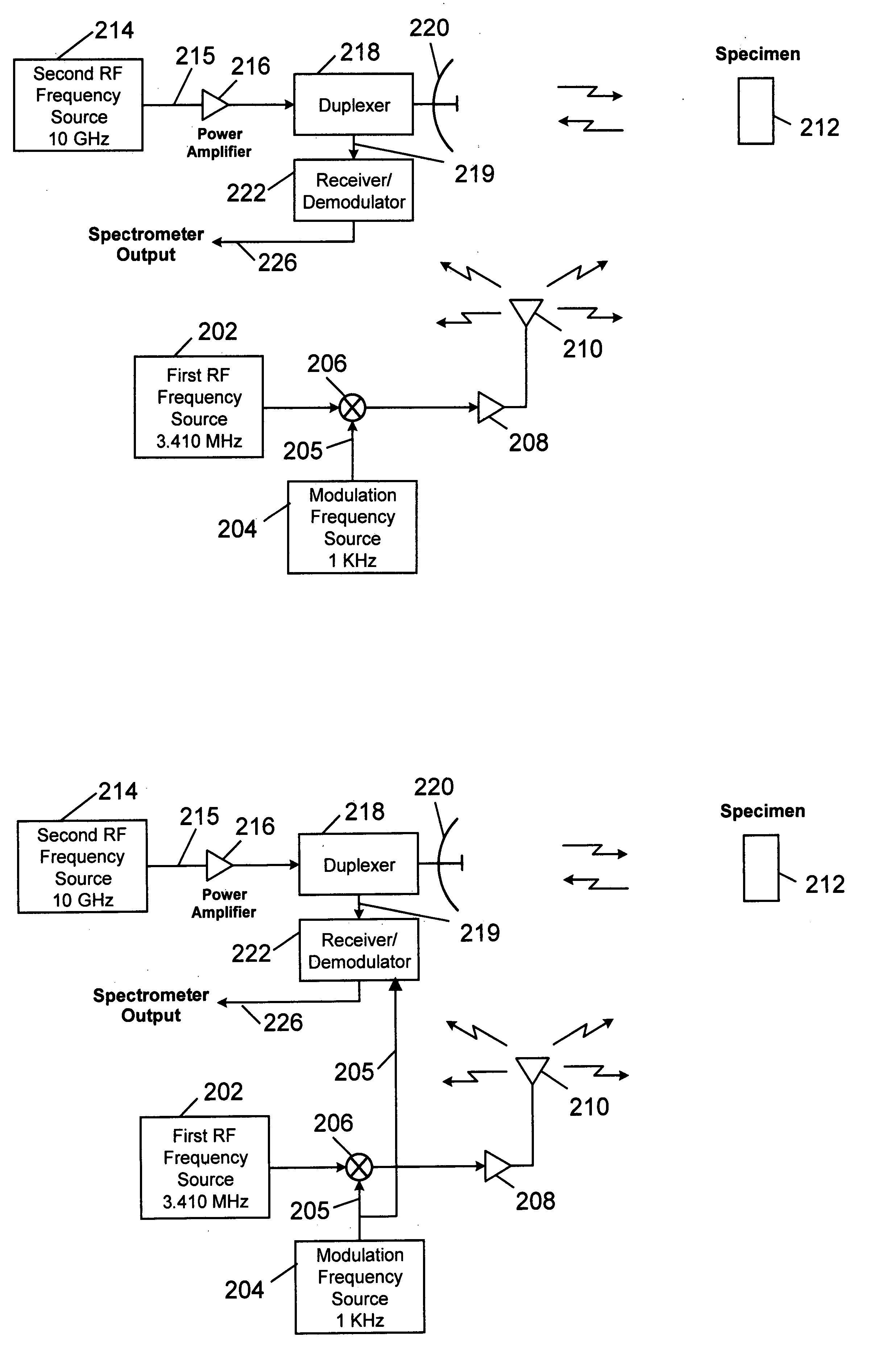
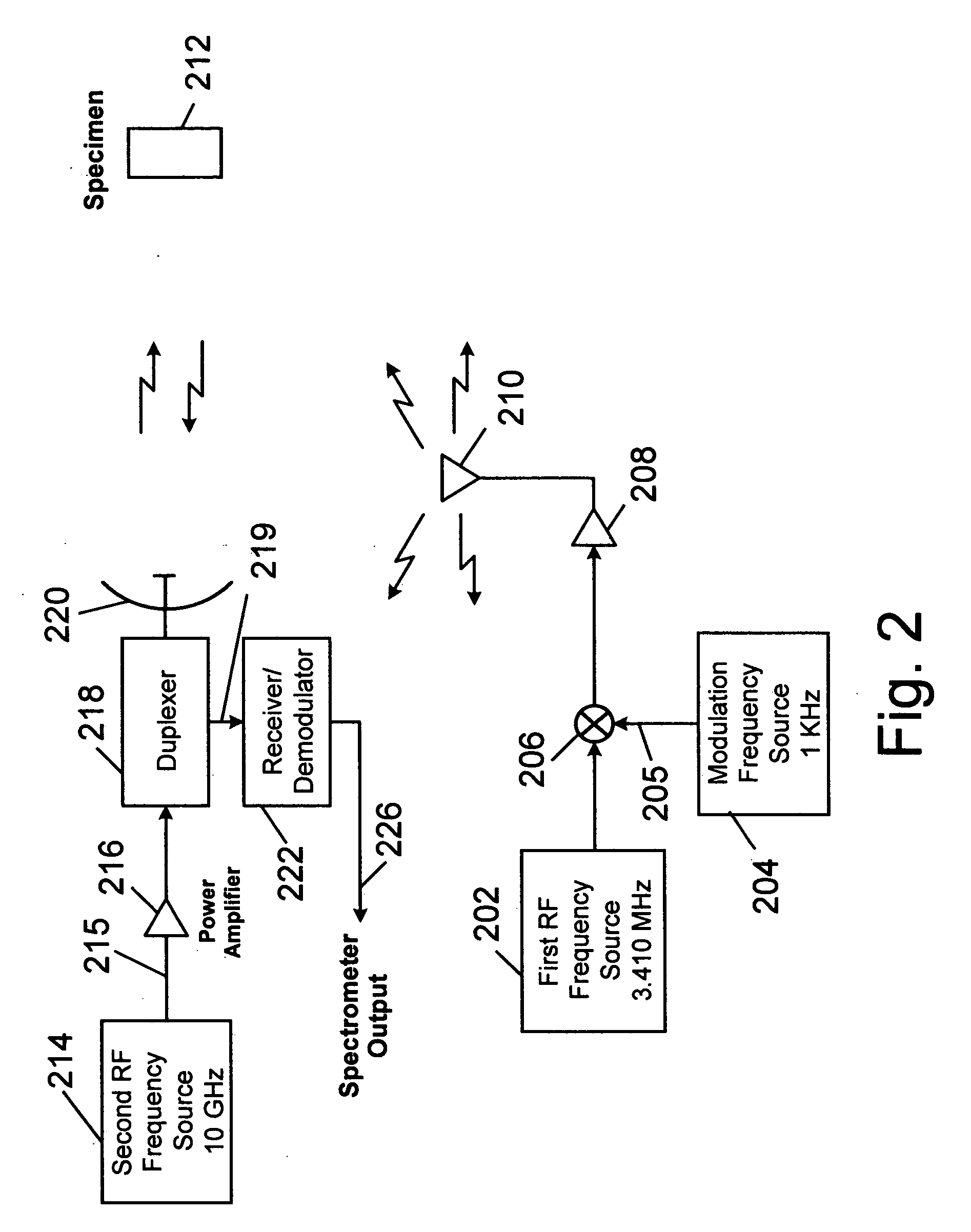
Parametric nuclear quadrupole resonance spectroscopy system and method
A system and method for probing a specimen to determine one or more components by utilizing a first signal to excite the specimen at a nuclear quadrupole resonant frequency and observing changes in a specimen property. One exemplary property may be dielectric constant. Another exemplary property may be magnetic permeability. In one embodiment, the first signal is unmodulated and a second signal is observed for the presence of modulation at the frequency of the first signal. Alternatively, the first signal may be modulated and the second signal may be observed for the presence of the modulation. A system is disclosed wherein the specimen is excited using the first frequency and a radar at the second frequency is used to observe changes in radar reflectivity of the specimen due to the excitation.
Owner:CEDAR RIDGE RES
Frequency detection system comprising circuitry for adjusting the resonance frequency of a high temperature superconductor self-resonant coil
InactiveUS7332910B2Magnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesElectric/magnetic detectionElectrical conductorResonance
The use of a circuit to adjust the resonance frequency of a high temperature superconductor self-resonant transmit, receive, or transmit and receive coil results in improved performance. The circuit is useful in a frequency detection system, especially in a nuclear quadrupole resonance detection system.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Method and system for producing and reading labels based on magnetic resonance techniques
ActiveUS20070075865A1Electric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceResonance
The invention provides a method and system for labeling items, wherein the labels contain digital information and can be read when desired. The coding of the labels is done by choosing specifically engineered nano-particles, micro-particles, or liquid material in the form of “ink.” The particles are designed to contain materials with distinguishable NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) or NQR (Nuclear quadrupole resonance) frequencies and are combined in sets to encode digital information. The NMR / NQR label particle sets are printed on the item to be labeled, or on a label substrate which is then attached to the item to be labeled. In one embodiment, the printed NMR / NQR label consists of an array of spots, each of which may encode one or more digital characters. These spots can be detected and the digital information in the label can be read using a suitable magnetic resonance detector.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
Interference canceller applied to detecting core quadrupole moment resonance signal
InactiveCN102608663AGood for interference suppressionEasy to filterDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceAcoustic wave reradiationInterference cancellerMain channel
The invention discloses an interference canceller applied to detecting a core quadrupole moment resonance signal. The interference canceller comprises a main channel, an auxiliary channel, a space domain interference canceling treatment module between the main channel and the auxiliary channel, and a time domain interference canceling module in the main channel. A master control computer generates an exciting pulse sequence, and the exciting pulse sequence is loaded to a main antenna coil to excite a sample to be detected through a signal generator and a high-power transmitter; an NQR (nuclear quadrupole resonance) signal obtained by excitation is received in the main channel through the main antenna coil, and meanwhile, the space domain interference is received in the auxiliary channel through an auxiliary antenna coil; signals in the main channel and the auxiliary channel enter a space domain interference canceling treatment process through a preamplifier, an analog receiver, A / D (analog to digital) and signal preprocessing, and finally a processing result is transmitted to the master control computer. A double-channel explosive detection system scheme is benefit to suppressing the interference in a space domain; and moreover, a space-time adaptive processing method is firstly adopted to suppress the interference aiming at a double receiving channel explosive detection system.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Continuous wave nuclear quadrupole resonance spectrometer
InactiveUS7768262B2Quick checkUseful SNRMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionAnalyteResonance
Apparatus and methods for locating a nuclear quadrupole resonance are described. In an example method, a search frequency is adjusted using a blind search until a resonance absorption of an analyte is detected, and then an extremum seeking search to be used to locate an extremum frequency.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Method for biological identification using high temperature superconductor enhanced nuclear quadrupole resonance
InactiveUS7148684B2Measurements using NMRDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceHigh-temperature superconductivityElectrical conductor
This invention relates to a method for identifying biological agents using high temperature superconductor enhanced nuclear quadrupole resonance. The targeted biological agents are attached to functionalized nanoparticles and the quadrupole nuclei in these nanoparticles are detected by the nuclear quadrupole resonance detection system.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
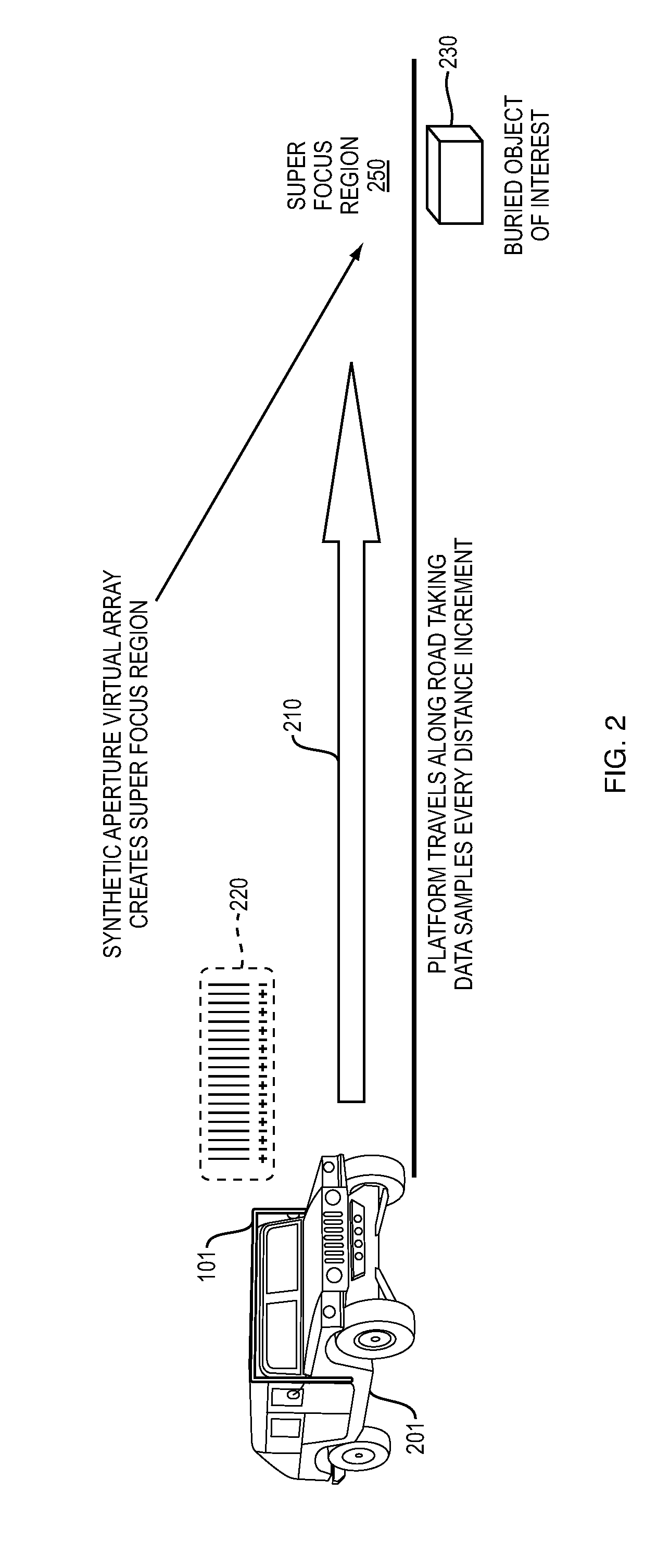
Near field subwavelength focusing synthetic aperture radar with chemical detection mode
InactiveUS20140152486A1Save livesImprove securityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture sonarRadar
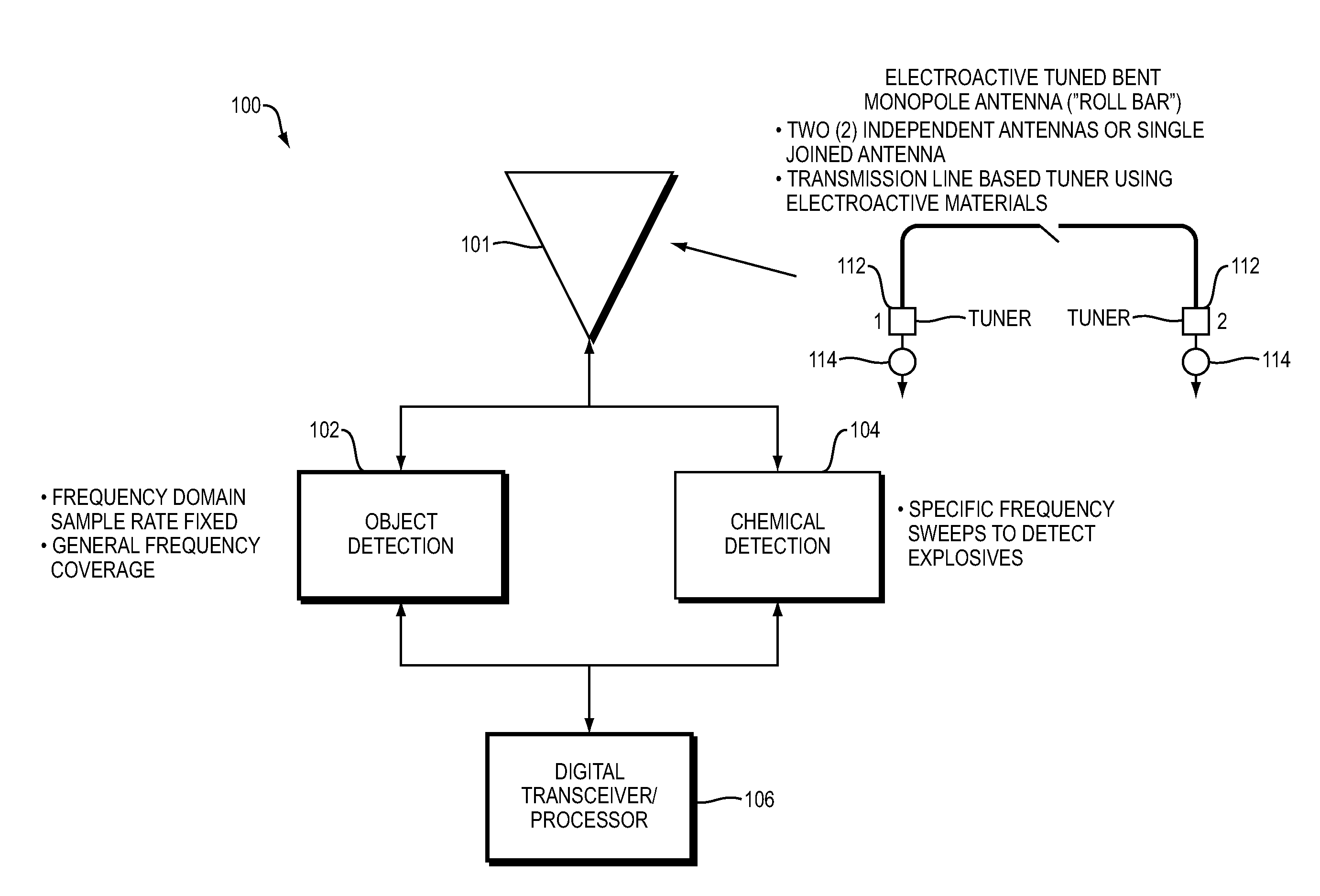
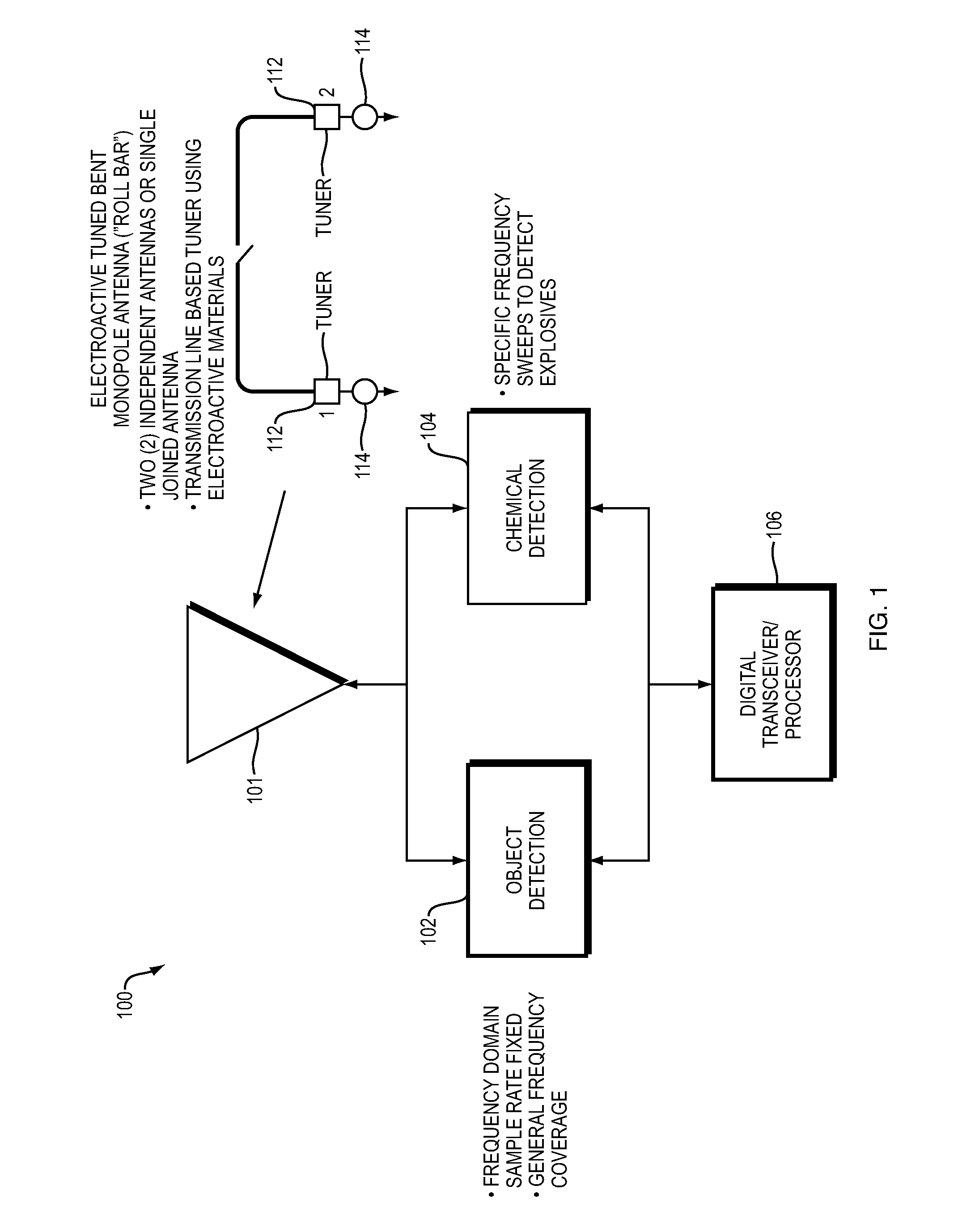
Detection of objects such as a buried explosive device while operating from a moving platform using a radio frequency emission system having two modes. An electromagnetic wave emission and detection system operates in a first mode to locate objects of interest and in a second mode to determine if an object contains explosive materials. In the first mode, the emission and detection system preferably operates as a subwavelength focusing, wideband, superlens using a near field super gain synthetic aperture continuous wave (CW) swept radar. In the second mode the system preferably enabled after detection of an object in the first mode, uses chemical detection methods such as Nuclear Quadrupole Resonance (NQR).
Owner:AMI RES & DEV
Use of two or more sensors in a nuclear quadrupole resonance detection system to improve signal-to-noise ratio
InactiveUS20070176600A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioDetection performanceMagnetic property measurementsMaterial analysis by using resonanceSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Nuclear quadrupole resonance
The use of two or more sensors tuned to the same nuclear quadrupole resonance frequency and detecting the nuclear quadrupole resonance signal results in improved signal-to-noise ratio and therefore improved nuclear quadrupole resonance detection system performance.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Parametric Nuclear Quadrupole Resonance spectroscopy system and method
A system and method for probing a specimen to determine one or more components by utilizing a first signal to excite the specimen at a nuclear quadrupole resonant frequency and observing changes in a specimen property. One exemplary property may be dielectric constant. Another exemplary property may be magnetic permeability. In one embodiment, the first signal is unmodulated and a second signal is observed for the presence of modulation at the frequency of the first signal. Alternatively, the first signal may be modulated and the second signal may be observed for the presence of the modulation. A system is disclosed wherein the specimen is excited using the first frequency and a radar at the second frequency is used to observe changes in radar reflectivity of the specimen due to the excitation.
Owner:CEDAR RIDGE RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com