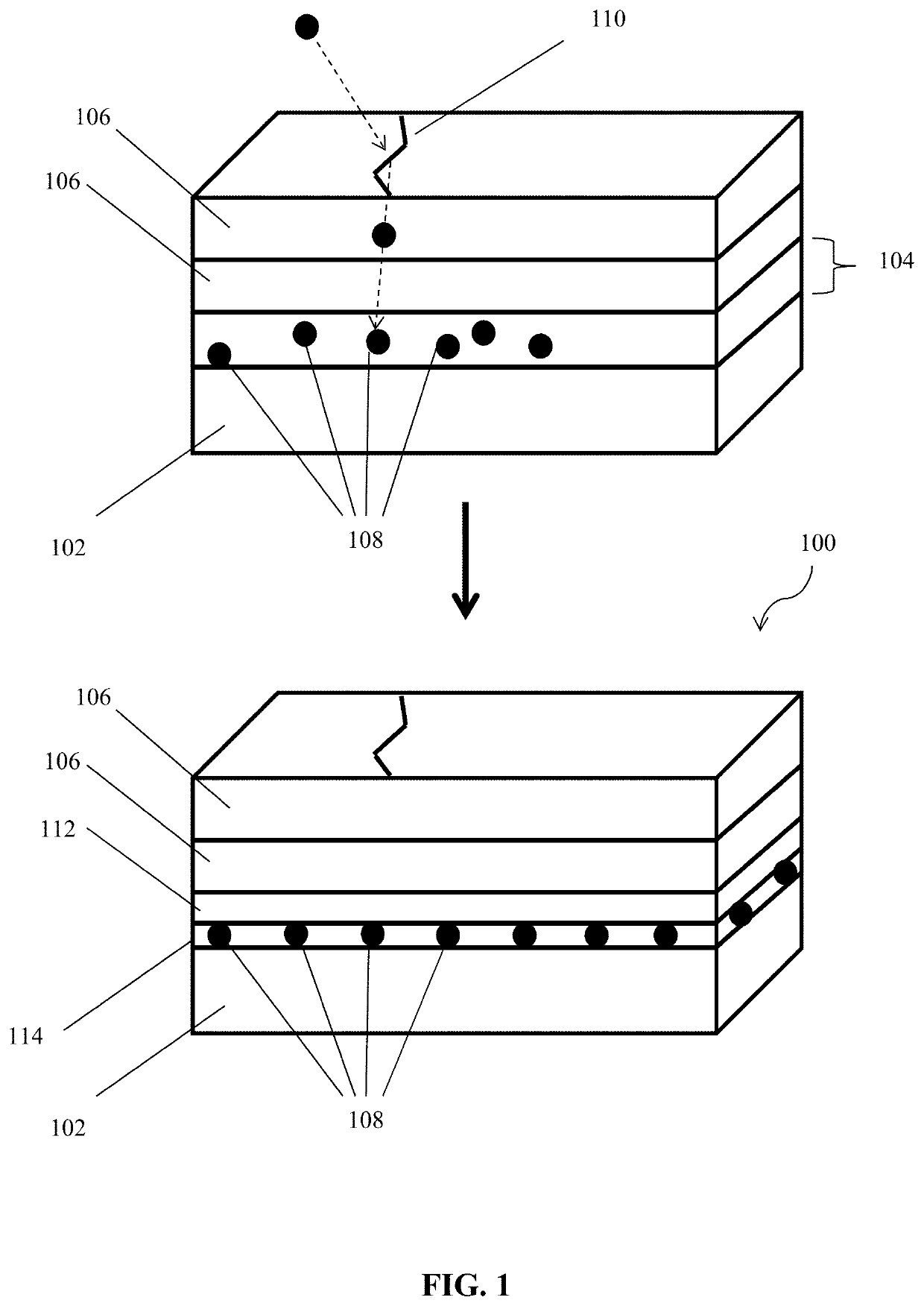
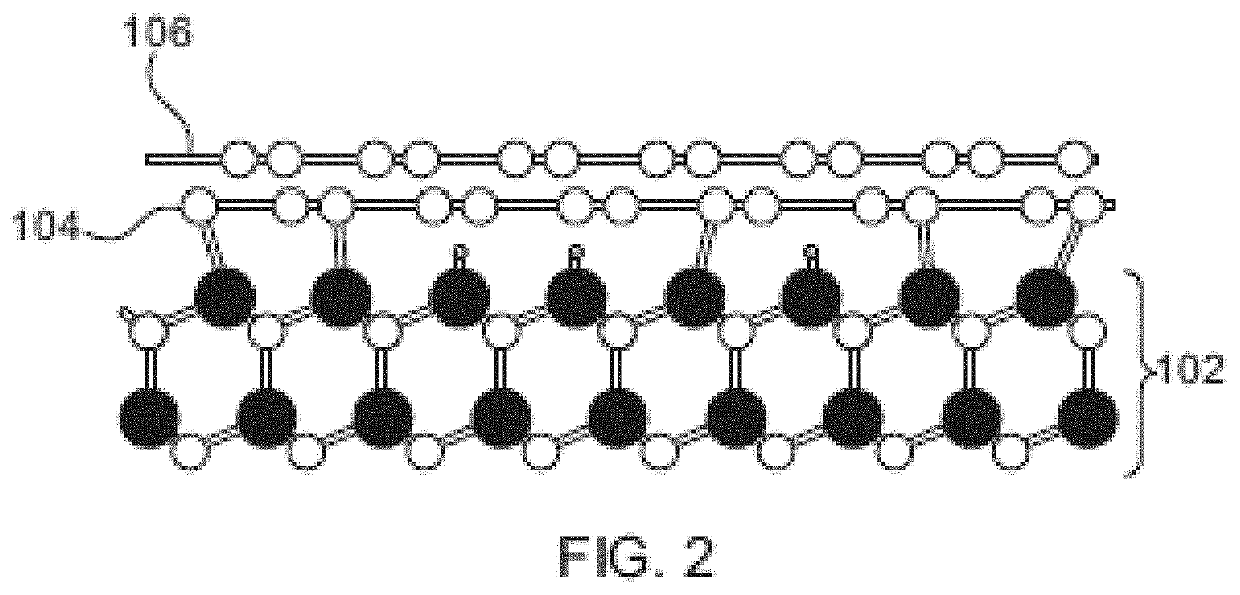
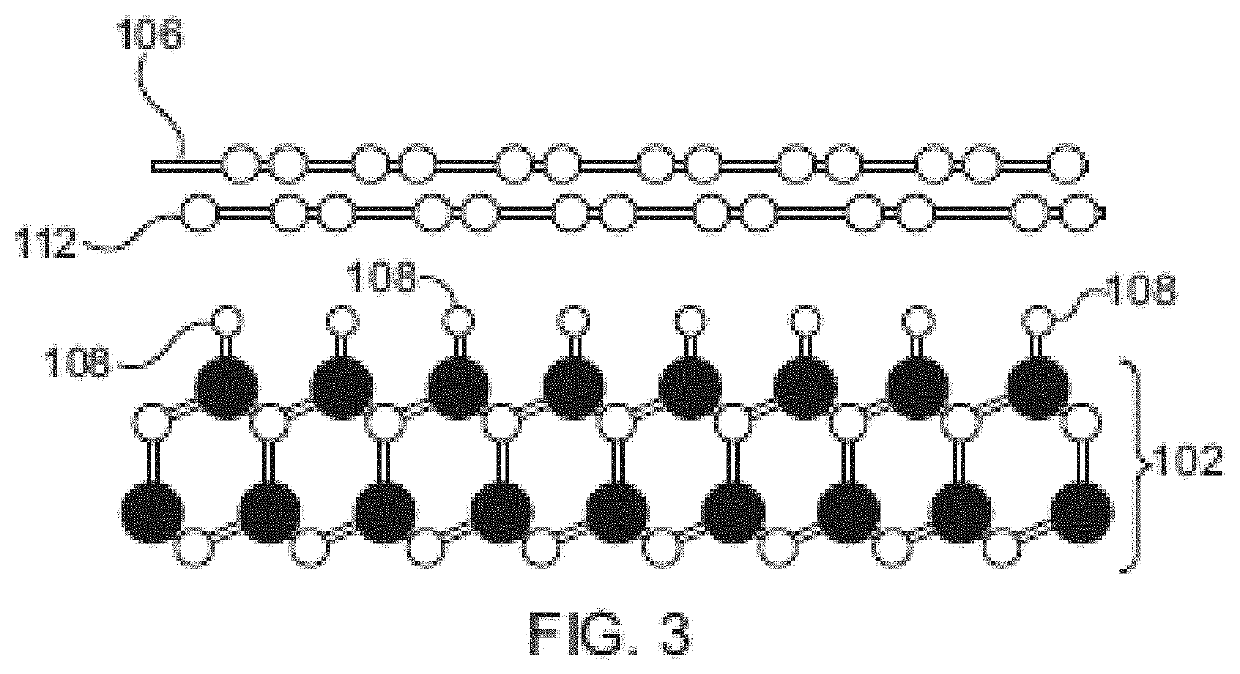
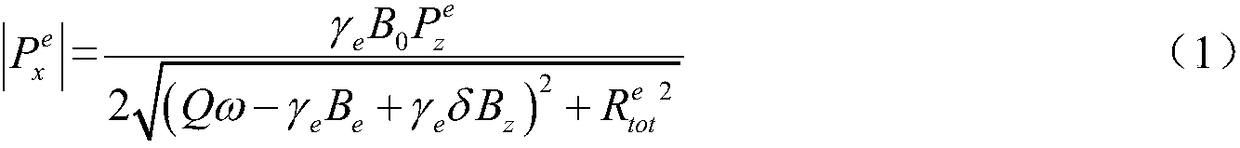Patents
Literature
32 results about "Electron resonance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
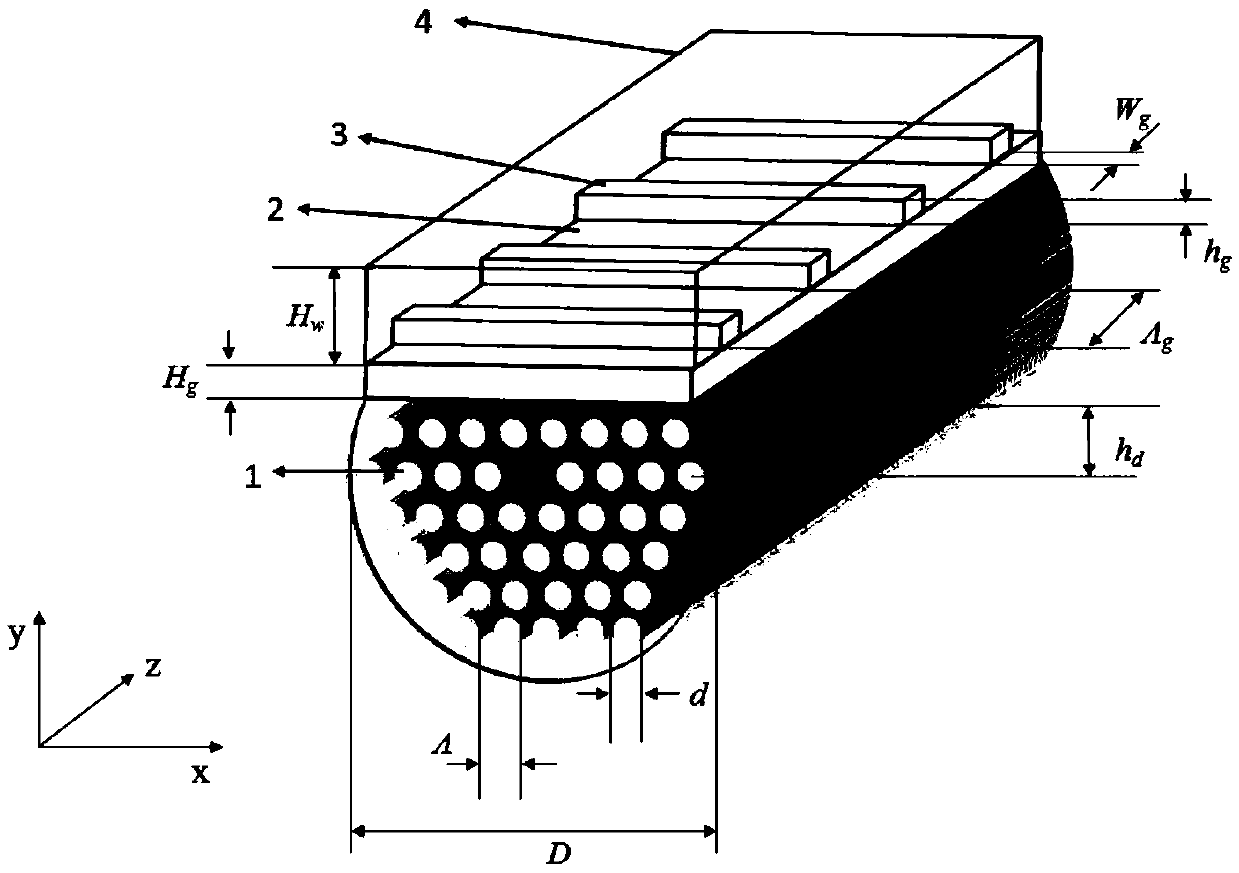
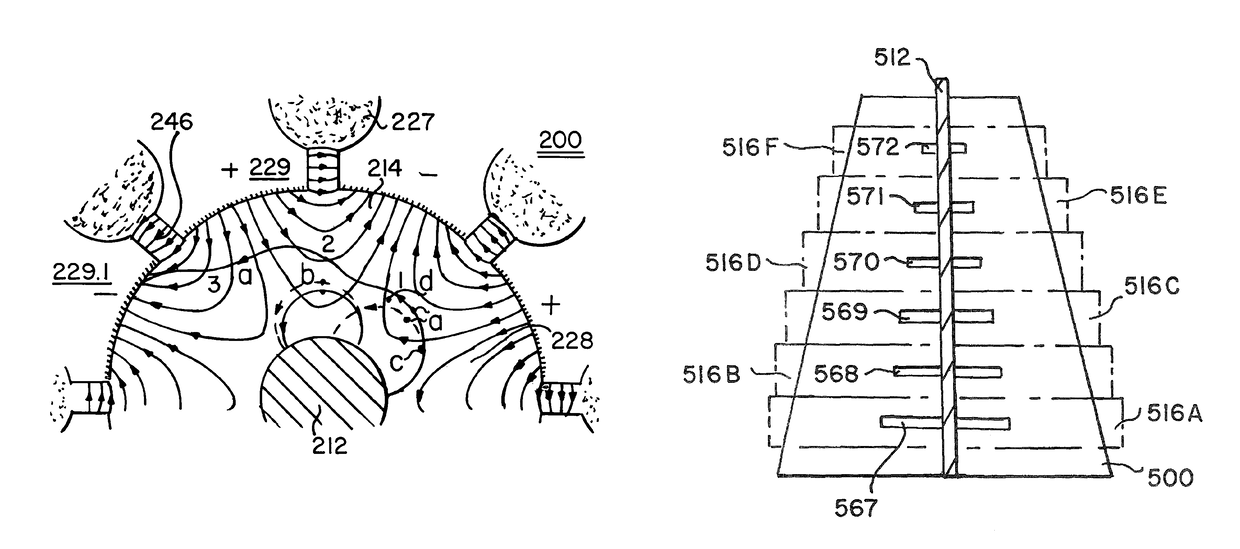
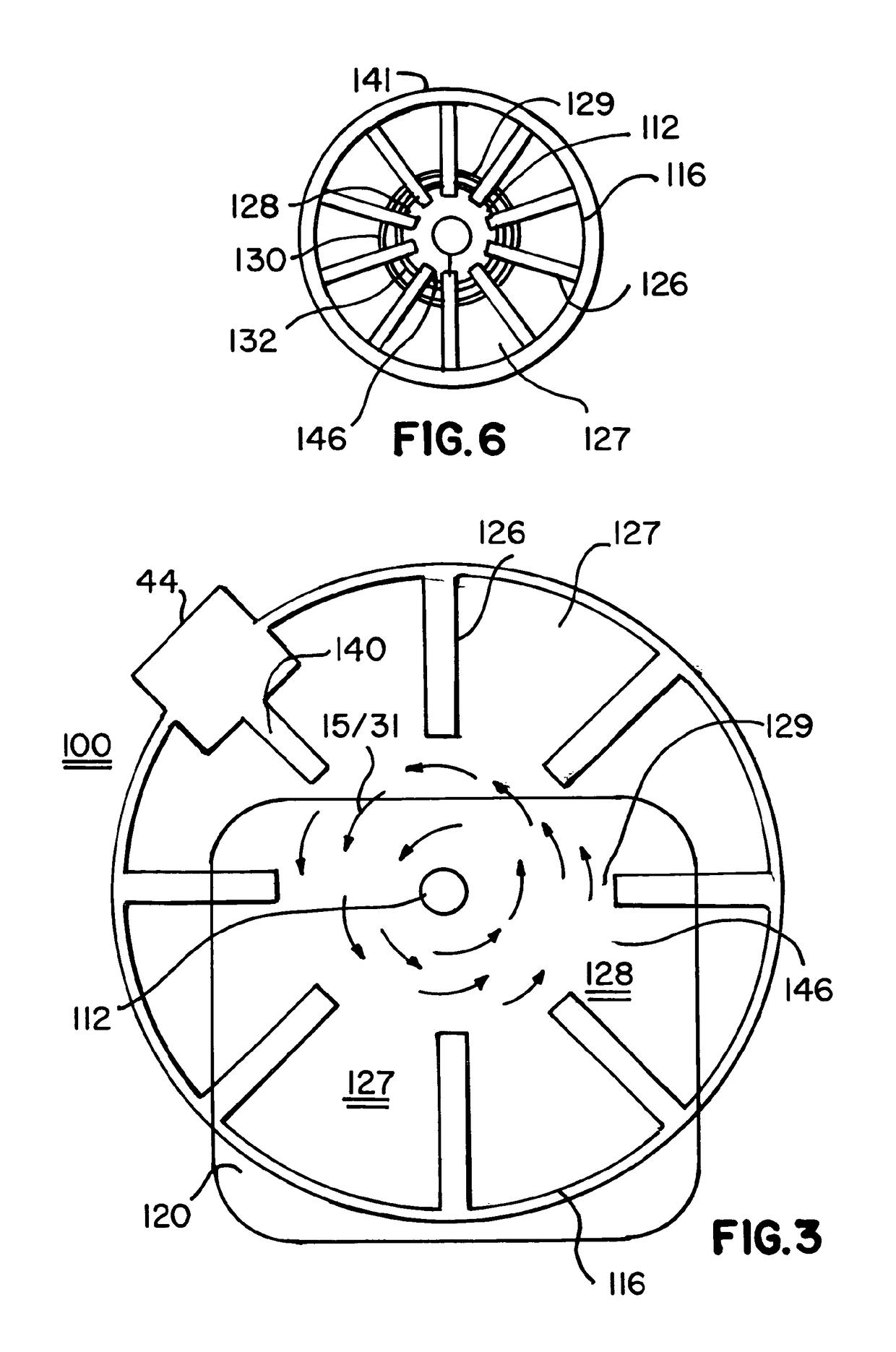
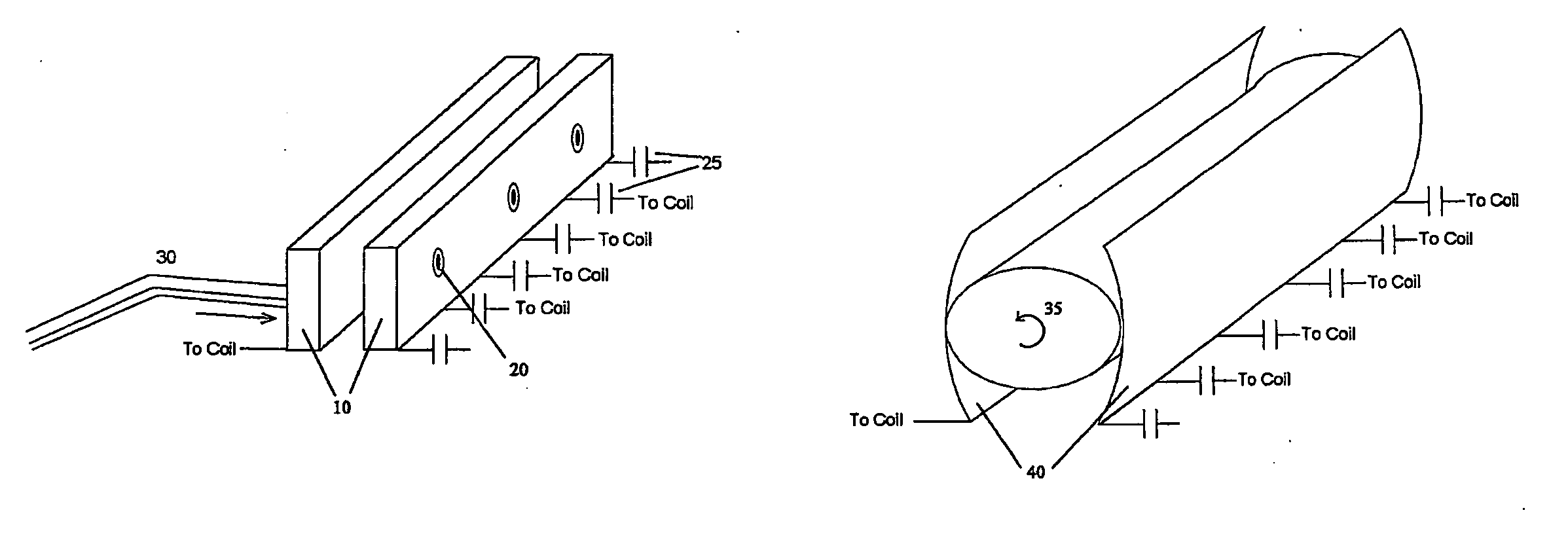
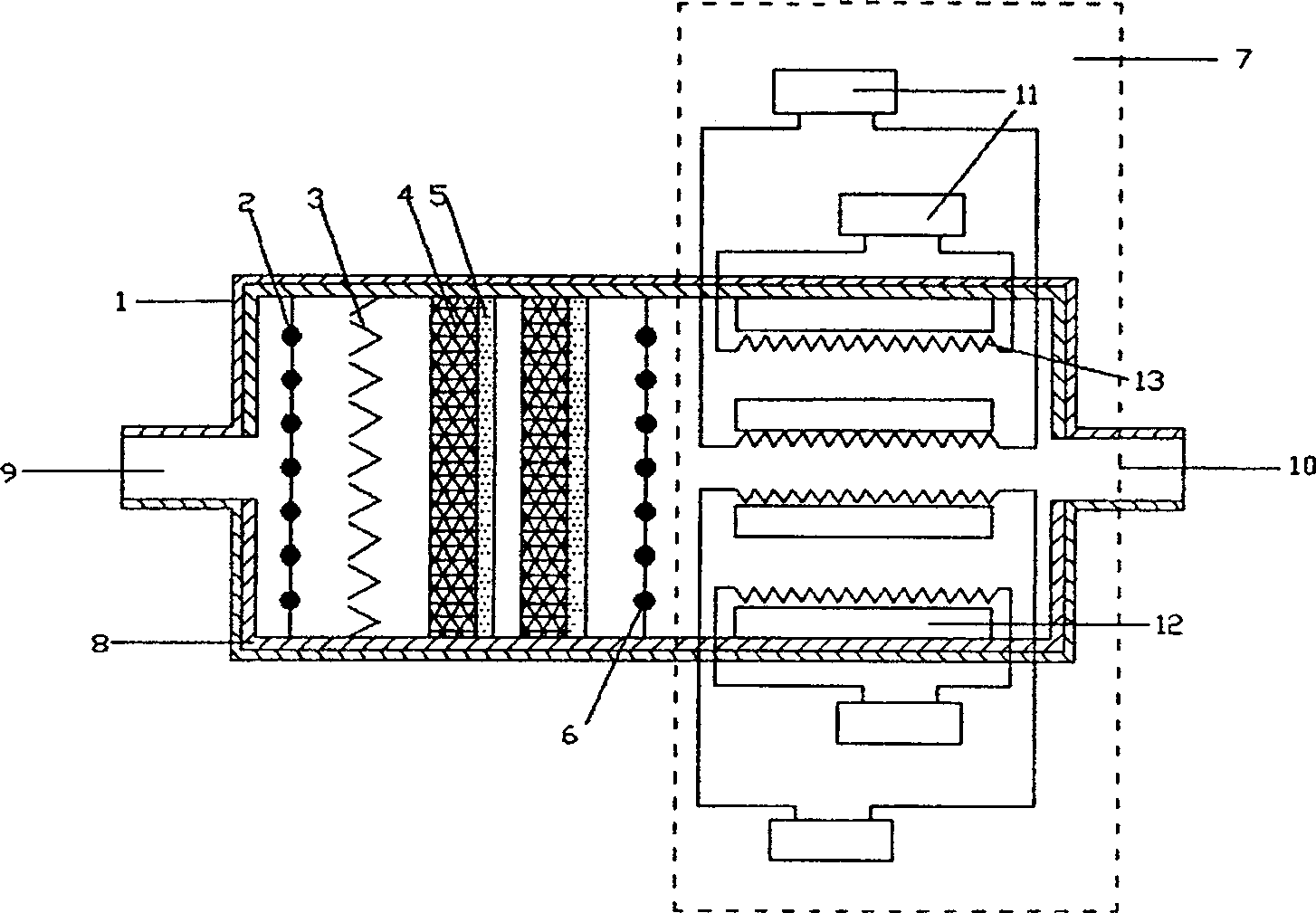
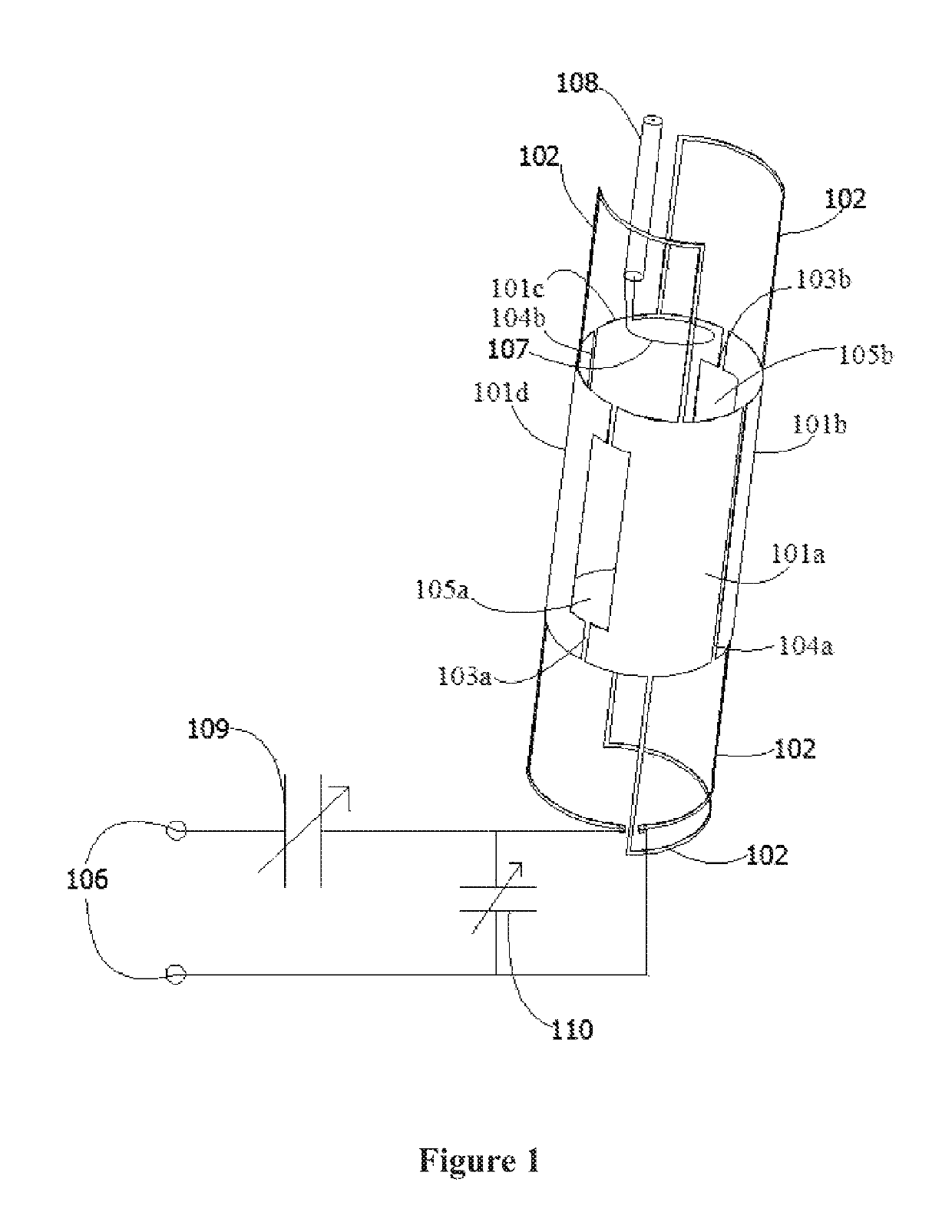
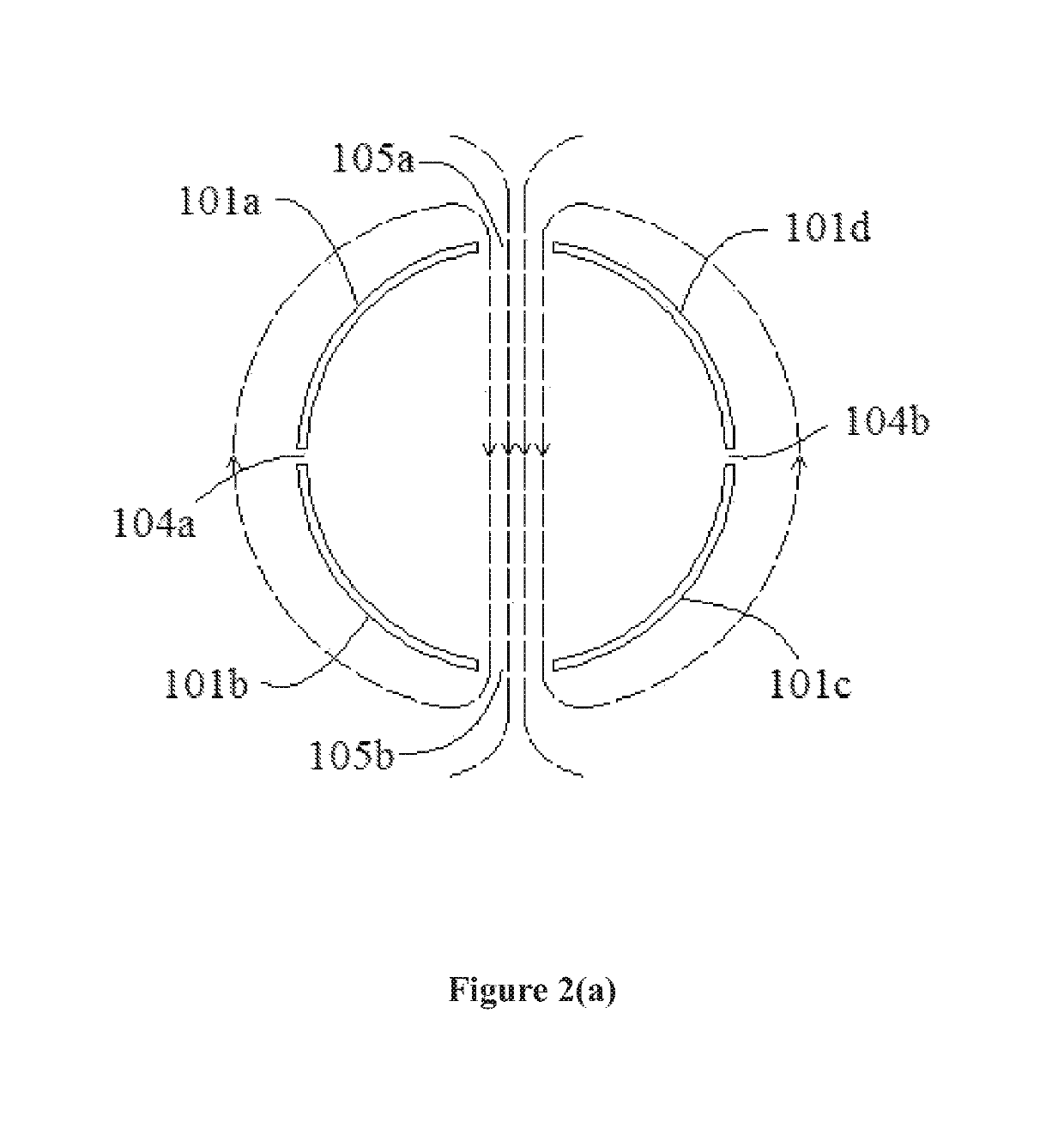
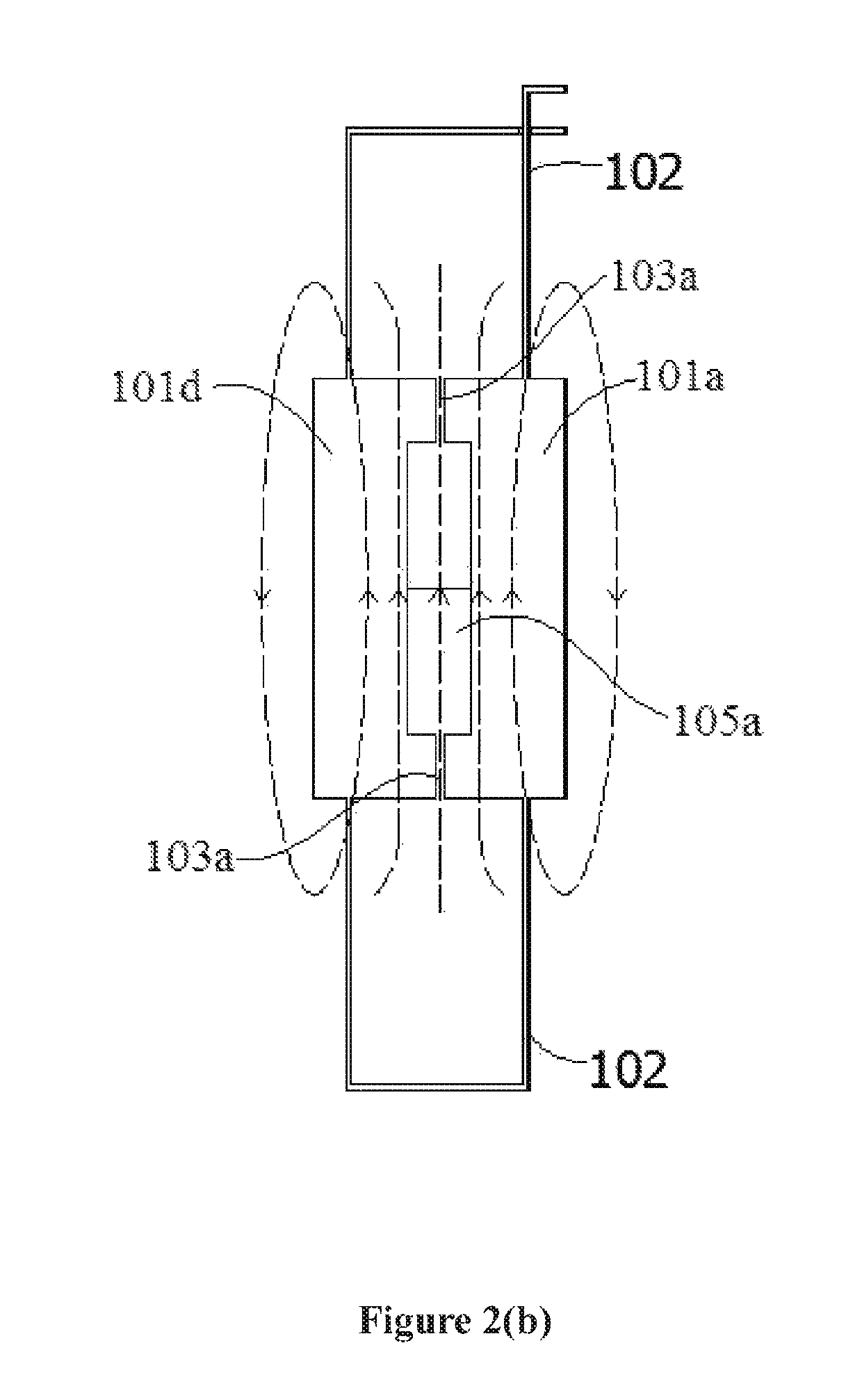
Transmit-receive coil system for nuclear quadrupole resonance signal detection in substances and components thereof
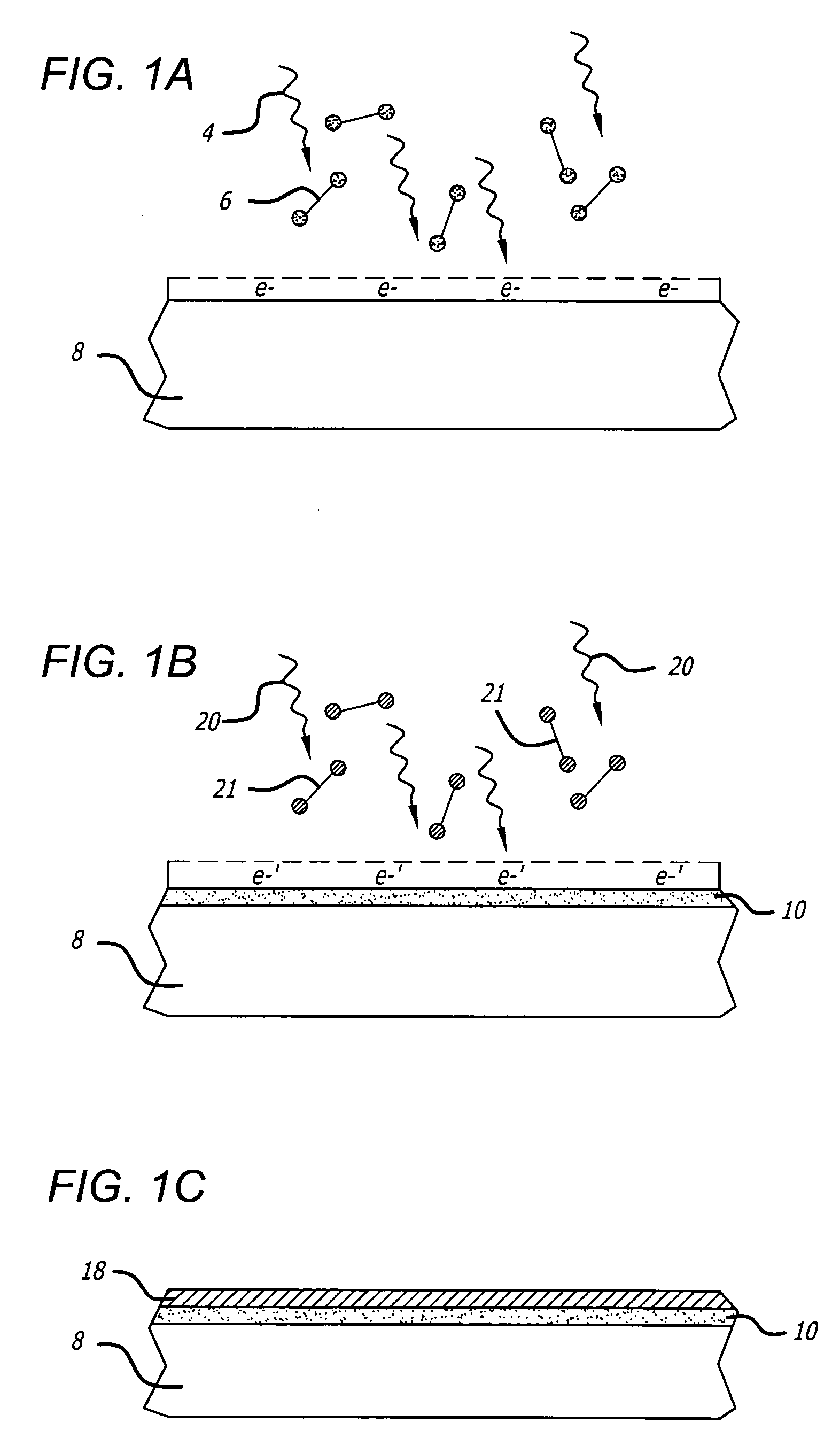
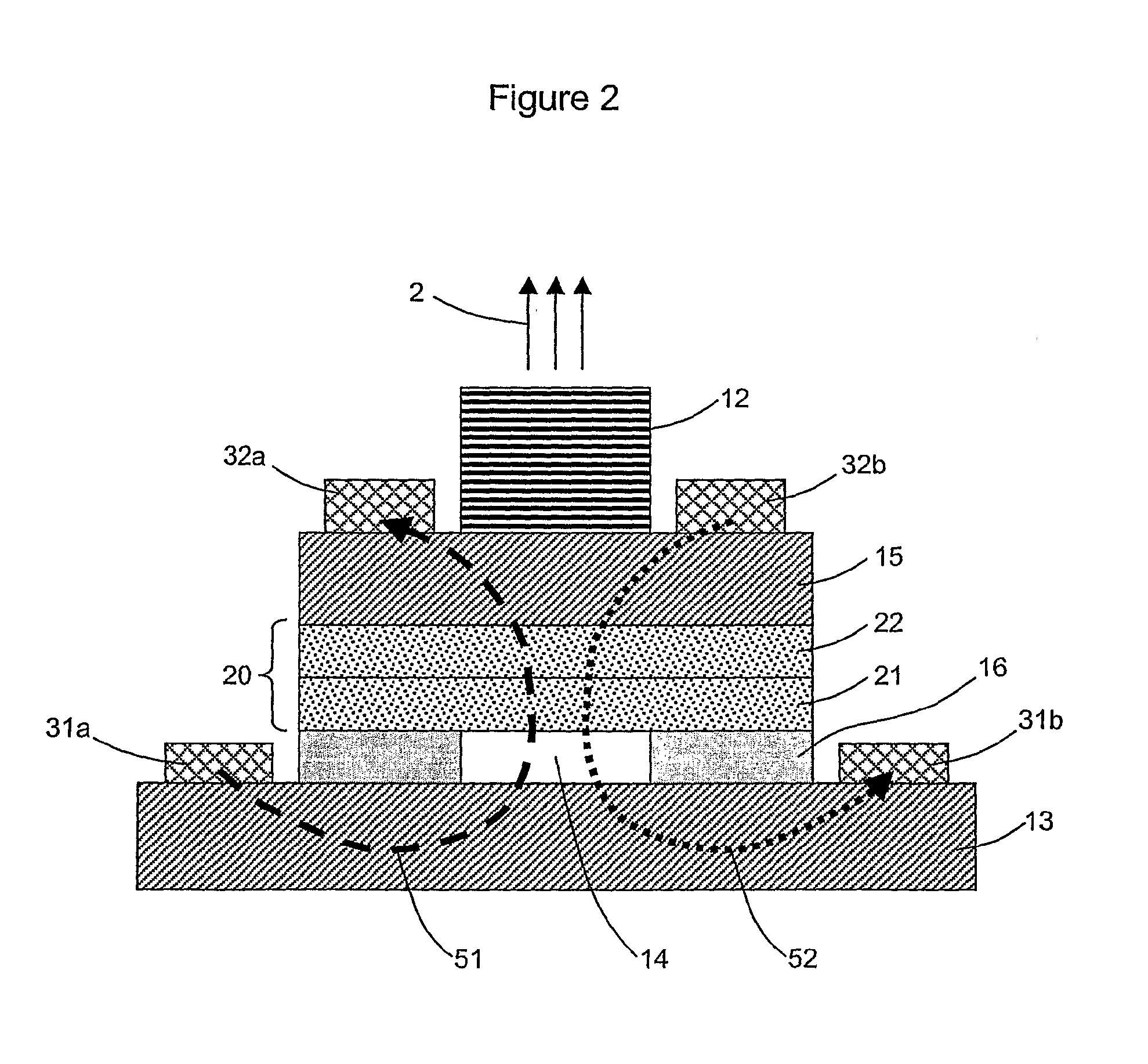
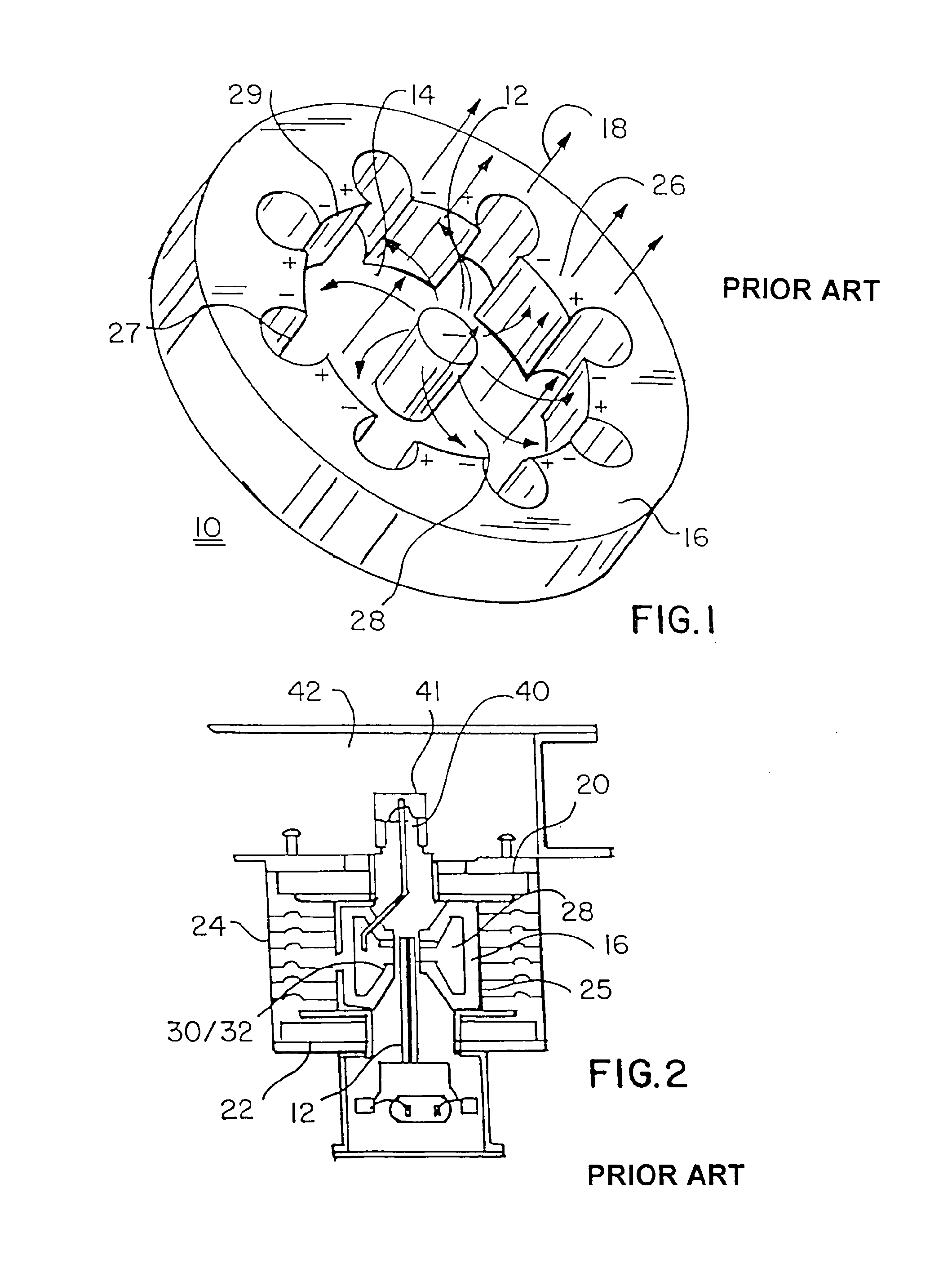
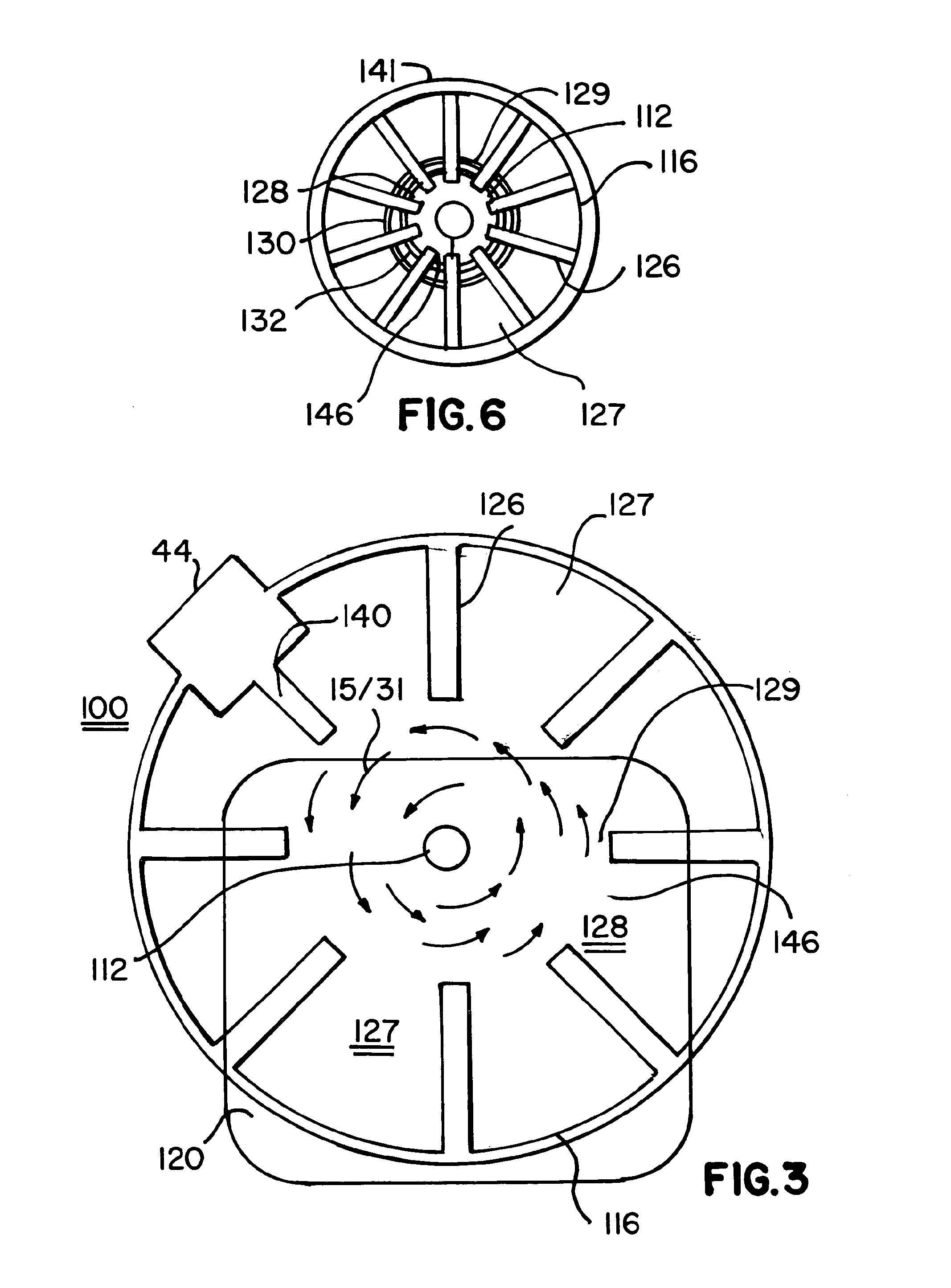
InactiveUS20050146331A1Avoid couplingImprove field uniformityLoop antennasElectric/magnetic detectionElectron resonanceNuclear quadrupole resonance
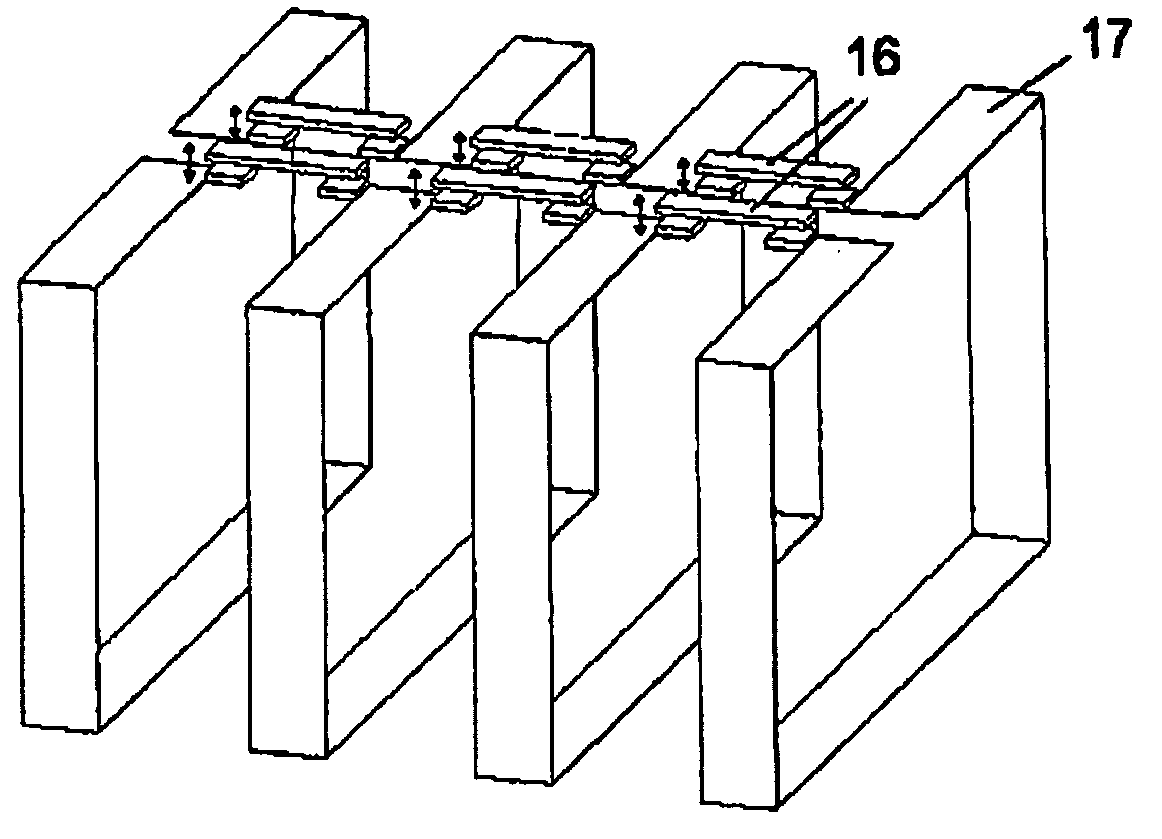
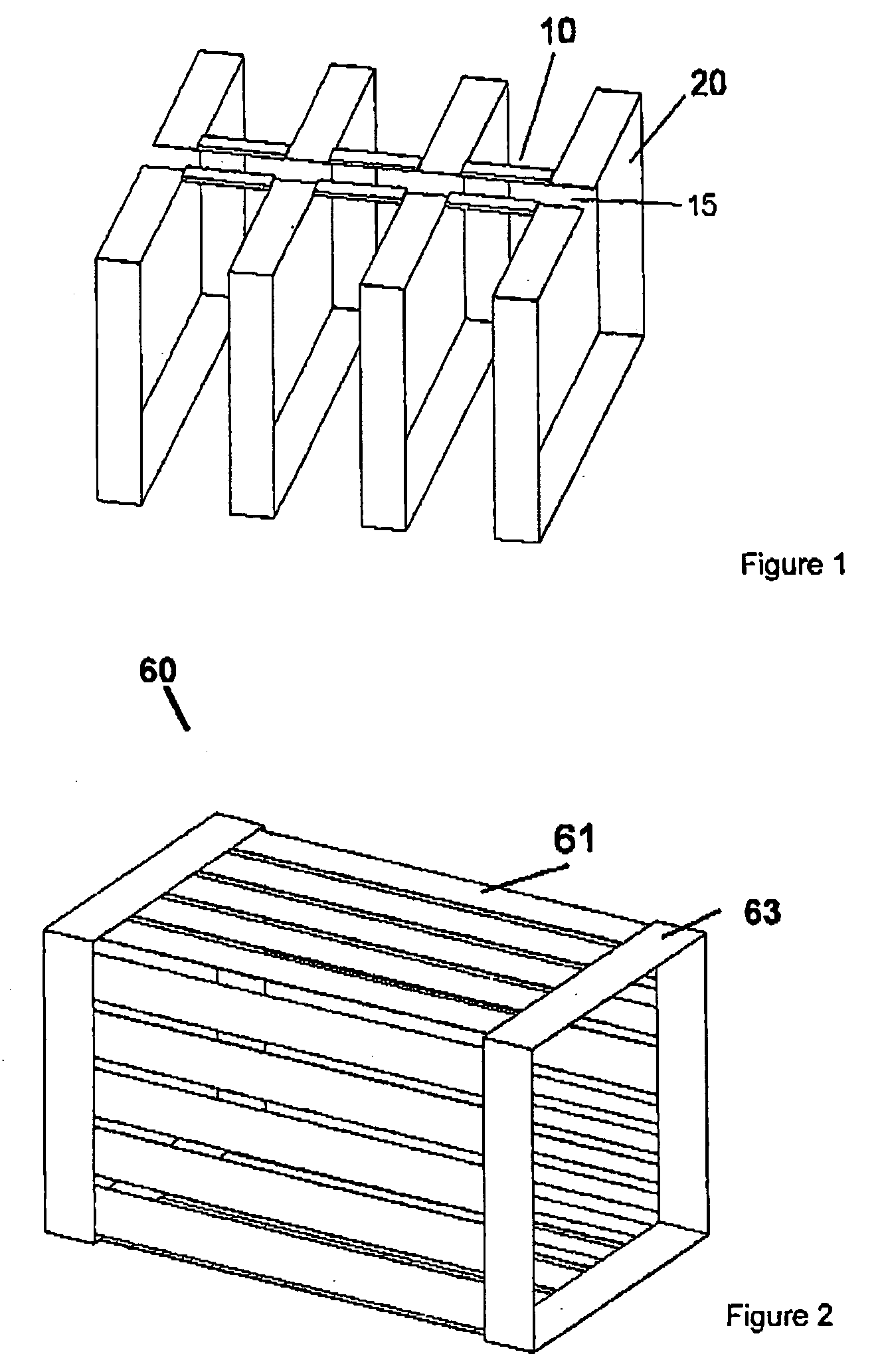
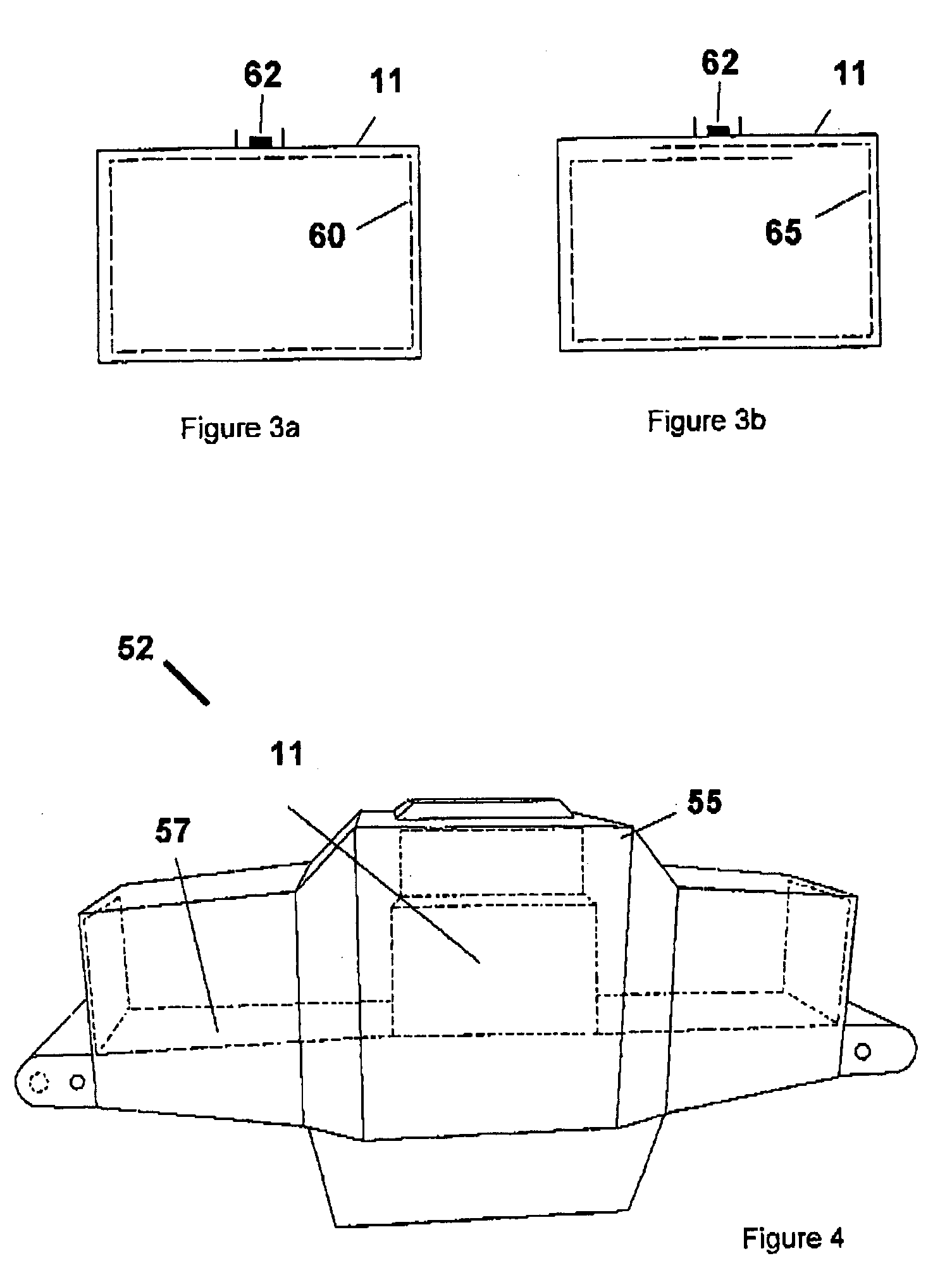
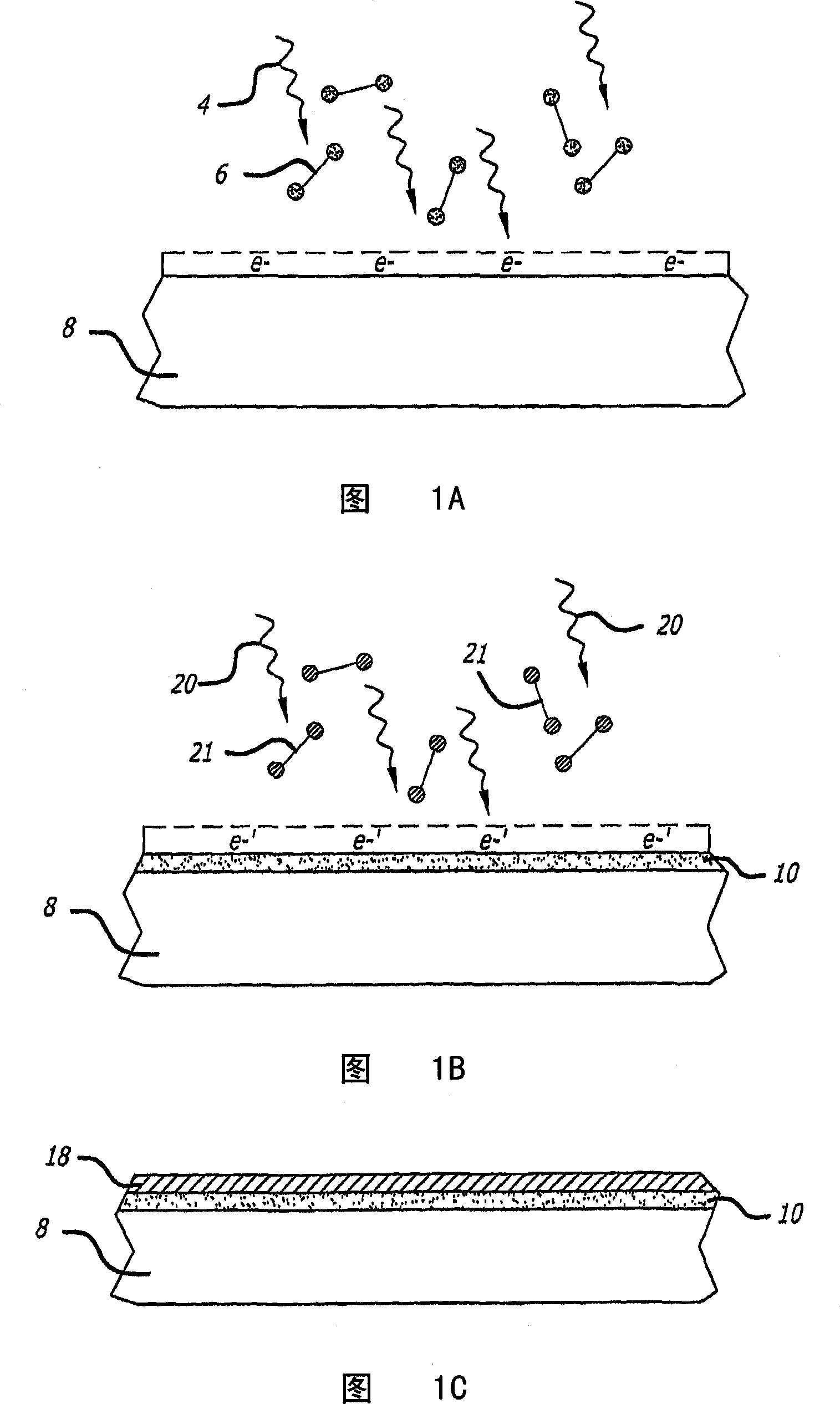
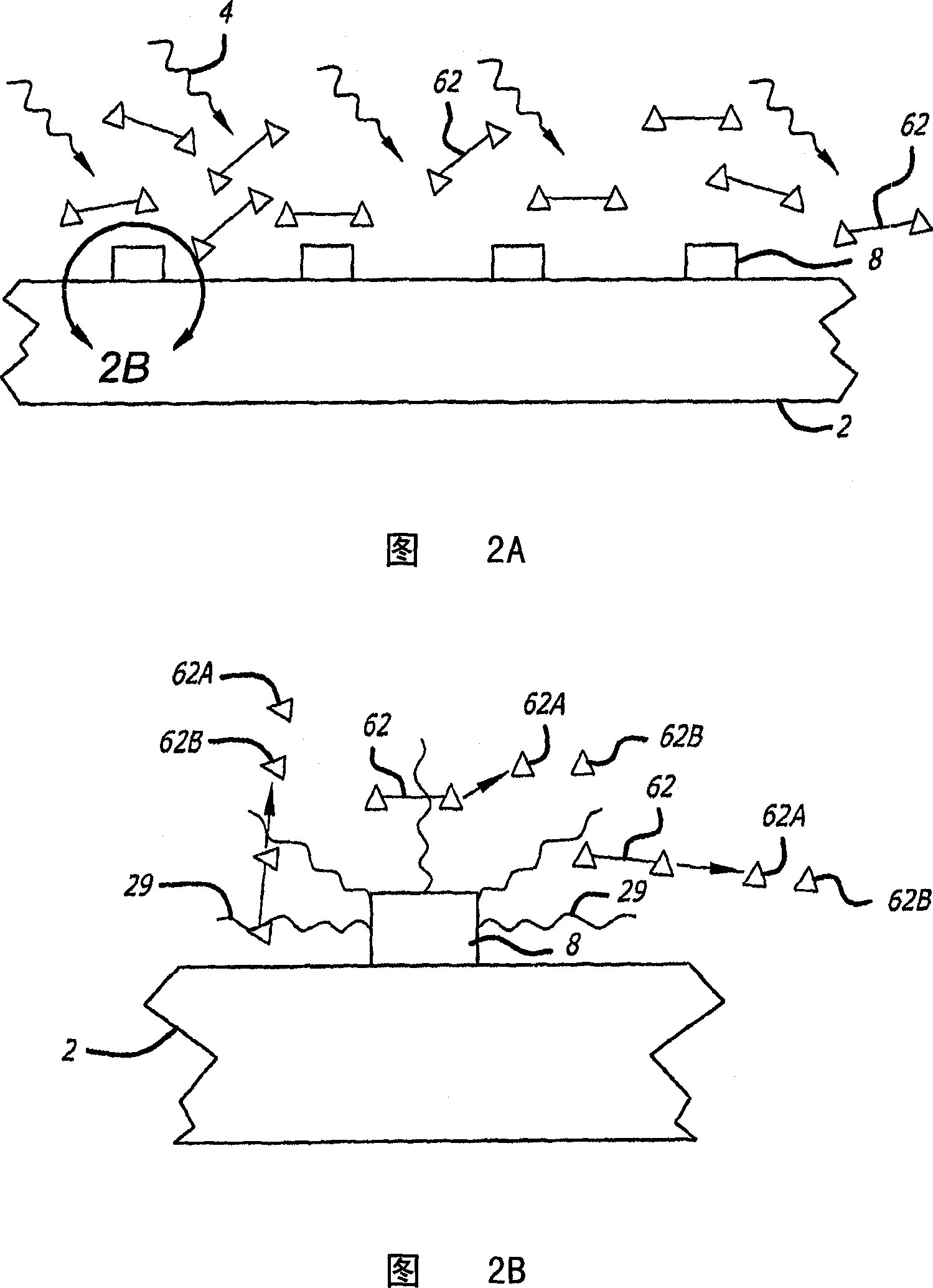
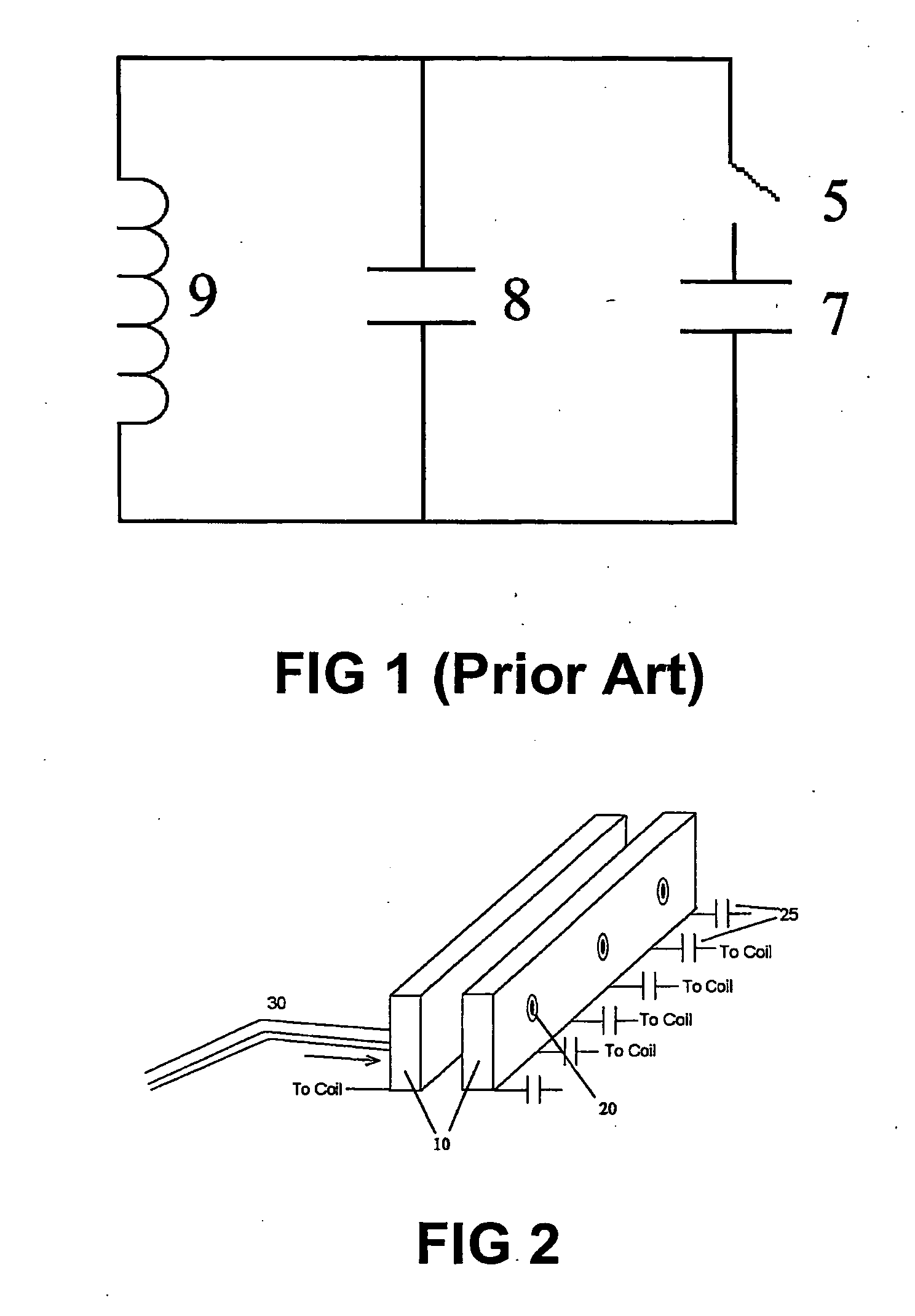
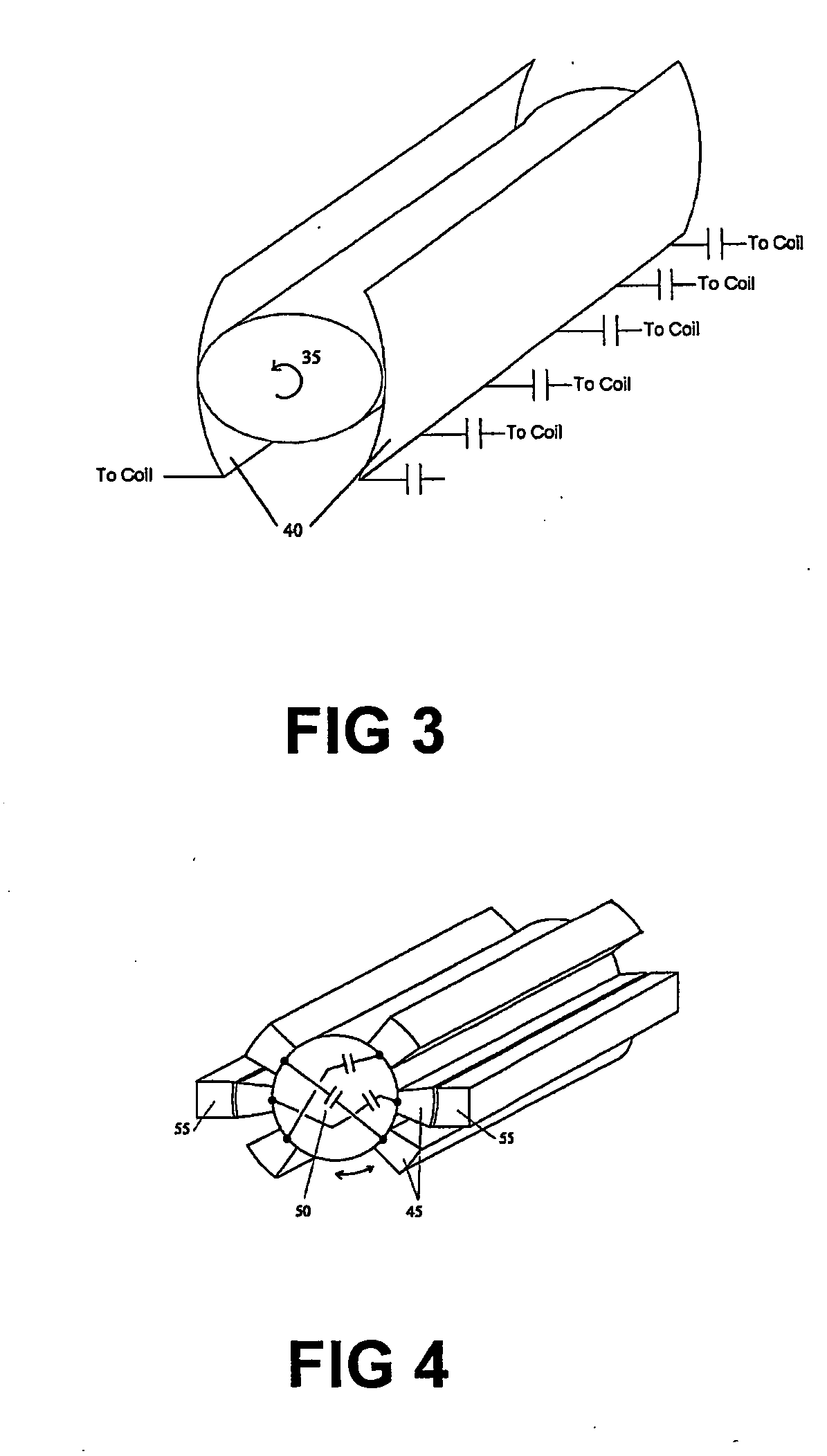
An antenna and shield apparatus for detecting phenomenal signals using nuclear and electronic resonance detection technology, comprising: a transmit and receive antenna, an electric field shield 60 and an outer shield 52. The antenna is a multiple parallel loop transmit-receive antenna forming a main coil assembly 11 having a plurality of loop segments 20 optionally interconnected by connectors in the form of conducting bars 10, relays 16, or nothing. The electric field shield 60 comprises an inner sleeve of conducting material 60, 68 disposed on the inside of the coil assembly 11 for shielding the electric field emanating from the coil assembly 11 from the target volume circumscribed by the assembly. The outer shield 52 comprises a central screen portion 55, waveguides 57 at either end thereof and a sloping channel portion for interconnecting the two. The coil assembly 11 and the electric field shield 60 are housed within the outer shield 52.
Owner:QRSCI
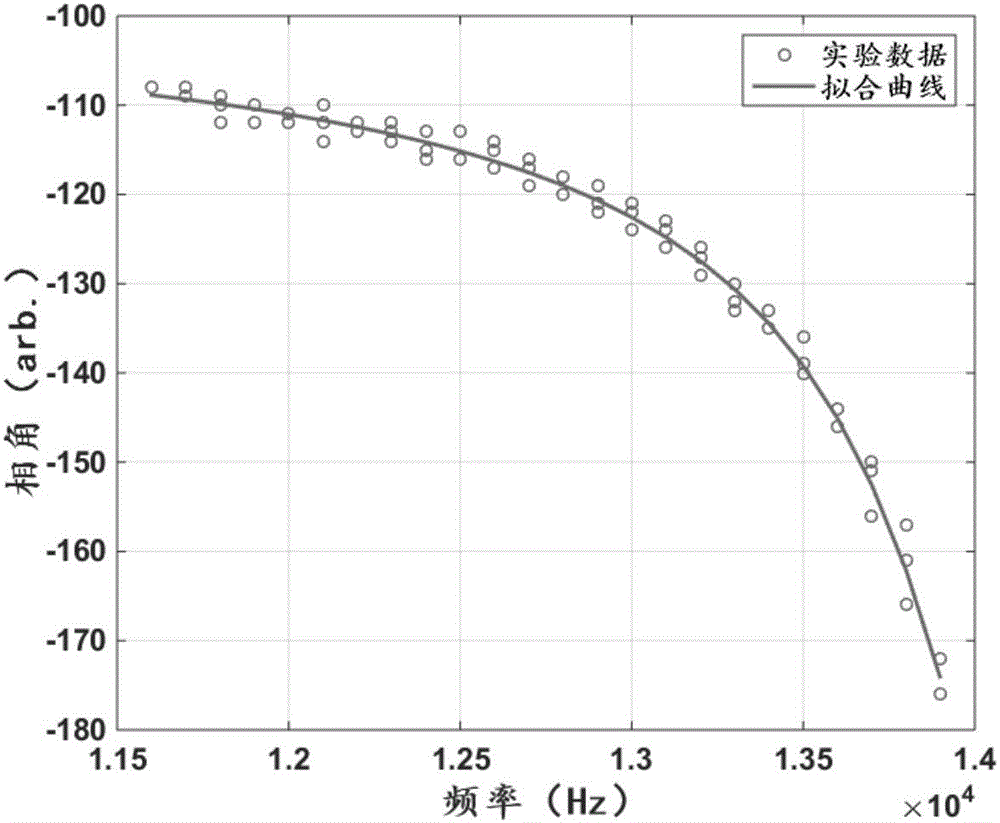
Method for measuring atomic transverse relaxation time based on electron resonance phase frequency analysis
InactiveCN106597338ASuppression of the effects of common coefficient fluctuationsExact transverse relaxation timeMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceAnalysis using electron paramagnetic resonanaceFrequency spectrumTransverse magnetic field
The invention discloses a method for measuring atomic transverse relaxation time based on an electron resonance phase frequency analysis. In a strong-background magnetic field with almost neglected residual magnetization in a magnetic shielding barrel, a swept-frequency signal that has a bandwidth covering a resonance curve and has an amplitude enabling the resonance curve to have a clear curve under low polarizability is applied in a horizontal direction; an optical swing angle signal of a magnetometer is detected and a spectral analysis is carried out on an outputted signal in a polar coordinate system to obtain a phase frequency response function of the magnetometer; the phase frequency response function is fitted to a corresponding theoretical phase frequency curve of the magnetometer to obtain atomic spinning transverse relaxation time. Because the phase angle is a result obtained by quotient processing of a spinning transverse component, the influence of common coefficient fluctuation is suppressed, so that the phase frequency signal expression is more stable by being compared with amplitude-frequency signal expression. Besides, the theoretical phase frequency curve is not affected by the magnetic induction intensity of the transverse magnetic field and the atomic spinning longitudinal relaxation time, so that complexity of data processing can be reduced. Moreover, a lorenz curve widening risk caused by the transverse magnetic field can be eliminated.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Conductive organic compound device, conductive liquid crystal device, and organic electroluminescence device
InactiveUS6858271B1Reduce power consumptionImprove carrier injection efficiencyLiquid crystal compositionsDischarge tube luminescnet screensTransport layerElectron resonance
A conductive organic compound device structure suitable for constituting an electronic device, such as an organic EL device, is formed by including a pair of oppositely spaced electrodes, and a carrier transporting layer disposed between the electrodes and in contact with one of the electrodes. The carrier transporting layer comprises a conductive organic compound having a π-electron resonance structure in its molecule. In the device, the π-electron resonance structure plane of the conductive organic compound in the carrier transporting layer is aligned substantially parallel to surfaces of the electrodes. The conductive organic compound is preferably a conductive liquid crystal, such as a discotic liquid crystal or a smectic liquid crystal, and a layer thereof is included in the device, preferably by vacuum deposition.
Owner:CANON KK
Electromagnetic control of chemical catalysis
ActiveUS20050202185A1Rapid coolingHigh degreeMaterial nanotechnologySolid state diffusion coatingChemical reactionElectron resonance
The present disclosure methods and systems that provide heat, via at least Photon-Electron resonance, also known as excitation, of at least a particle utilized, at least in part, to initiate and / or drive at least one catalytic chemical reaction. In some implementations, the particles are structures or metallic structures, such as nanostructures. The one or more metallic structures are heat at least as a result of interaction of incident electromagnetic radiation, having particular frequencies and / or frequency ranges, with delocalized surface electrons of the one or more particles. This provides a control of catalytic chemical reactions, via spatial and temporal control of generated heat, on the scale of nanometers as well as a method by which catalytic chemical reaction temperatures are provided.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Photo-catalytic Systems for Production of Hydrogen
InactiveUS20140342254A1Speed up redox reactionHigh productMaterial nanotechnologyOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideHydrogenPhoto catalytic
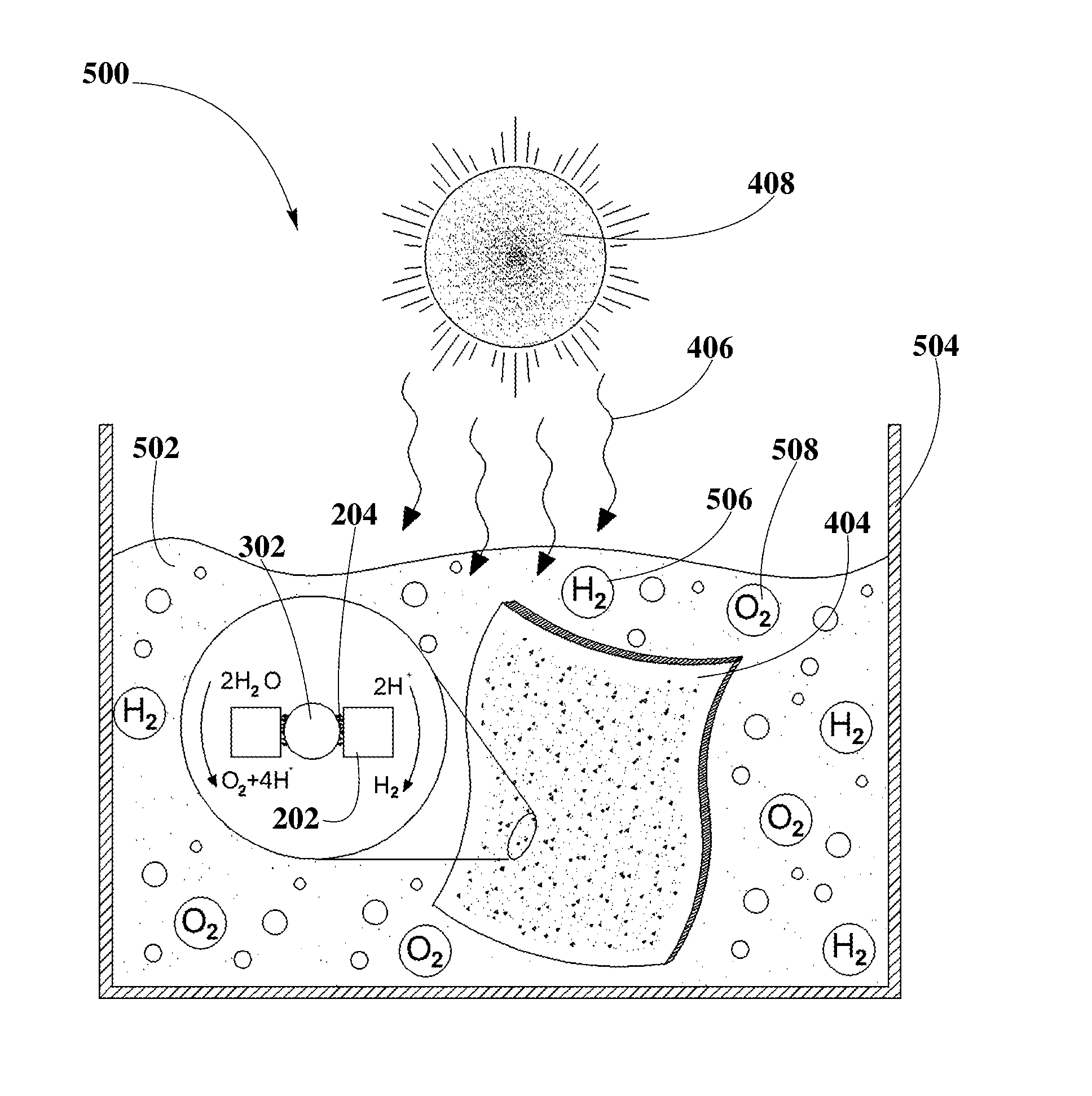
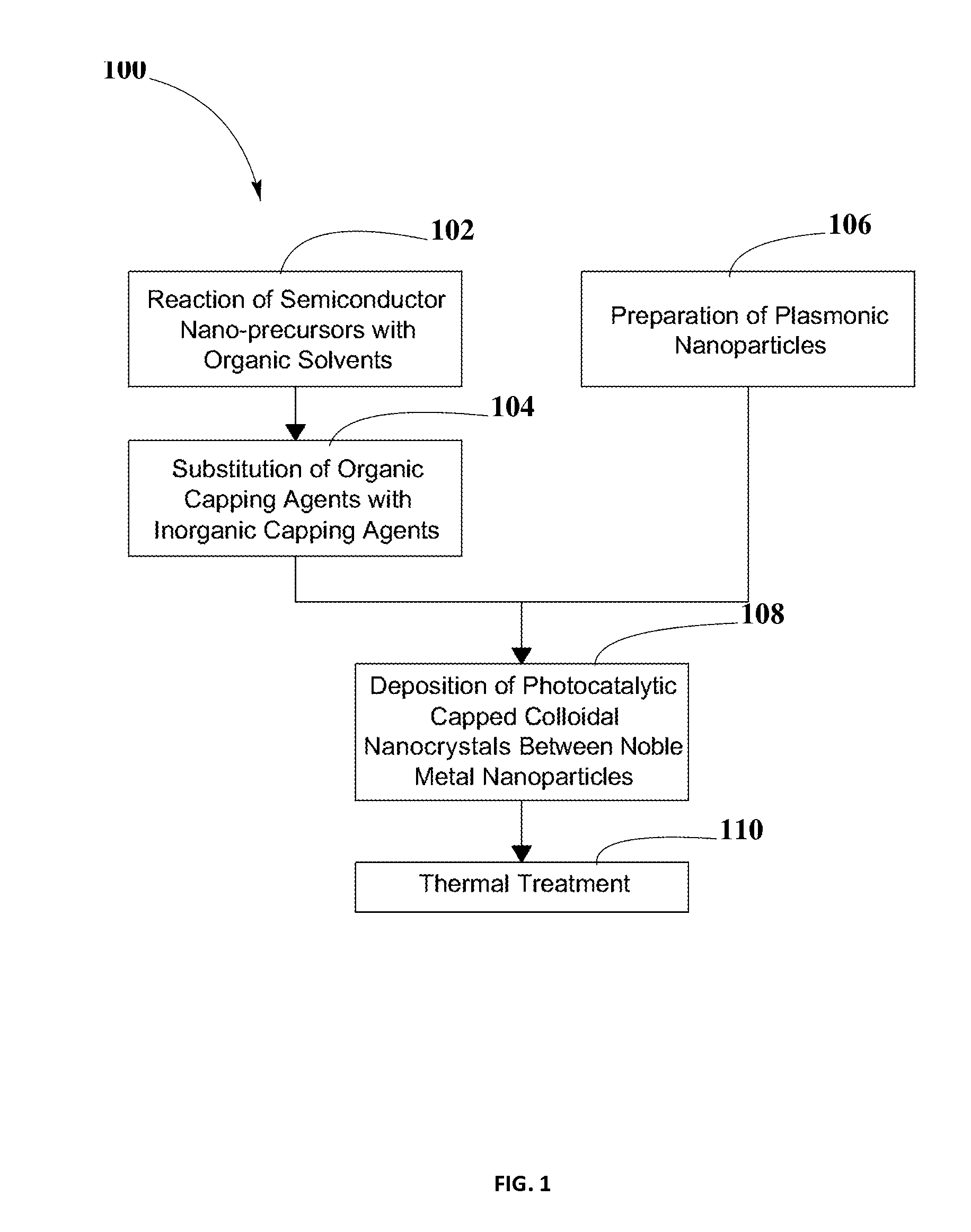
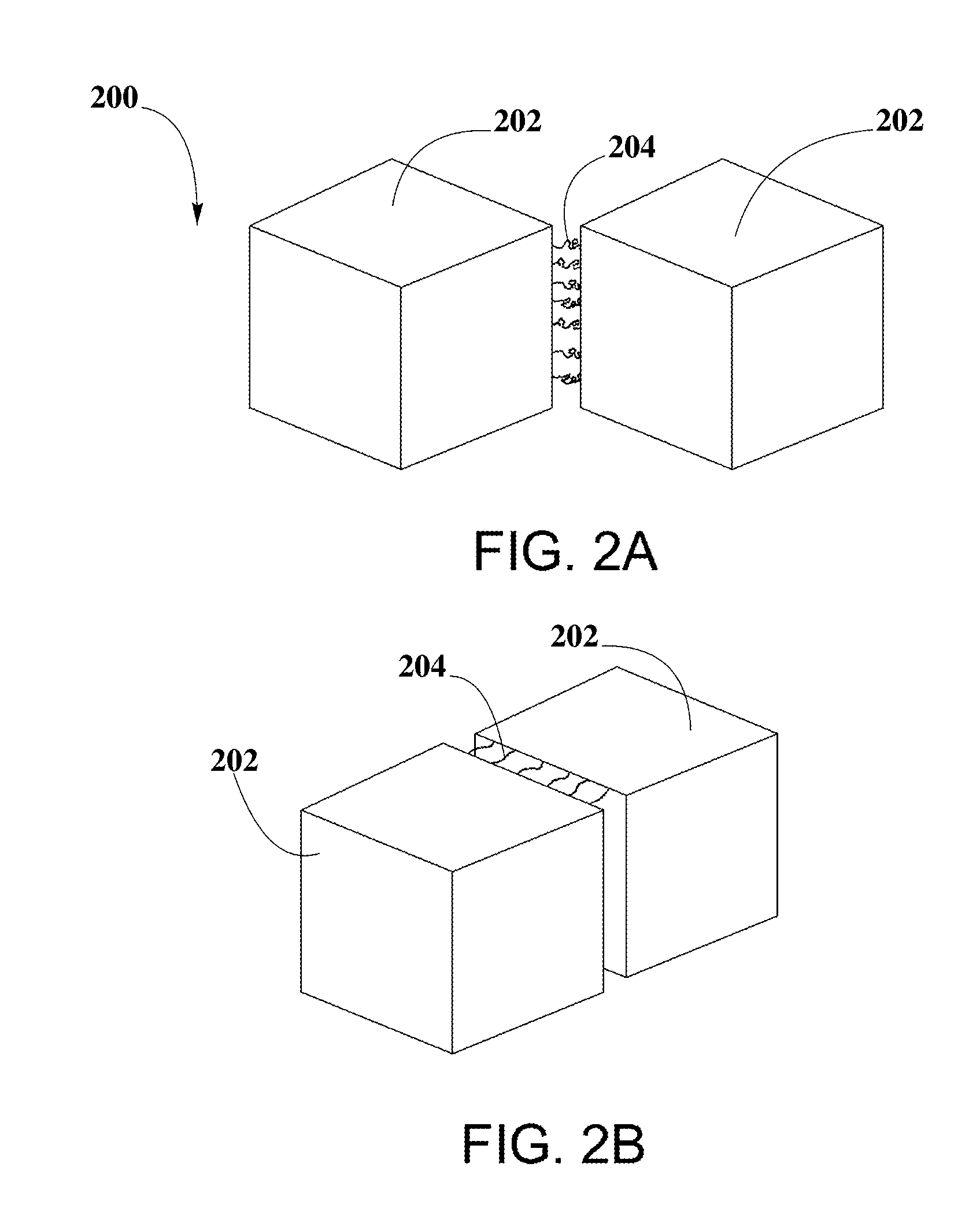
A system for splitting water and producing hydrogen for later use as an energy source may include the use of a photoactive material including PCCN and plasmonic nanoparticles. A method for producing the PCCN may include a semiconductor nanocrystal synthesis and an exchange of organic capping agents with inorganic capping agents. The PCCN may be deposited between the plasmonic nanoparticles and may act as photocatalysts for redox reactions. The photoactive material may be used in presence of water and sunlight to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. Production of charge carriers may be triggered by photo-excitation and enhanced by the rapid electron resonance from localized surface plasmon resonance of plasmonic nanoparticles. By combining different semiconductor materials for PCCN and plasmonic nanoparticles and by changing their shapes and sizes, band gaps may be tuned to expand the range of wavelengths of sunlight usable by the photoactive material. The system may include elements for collecting, transferring, and storing hydrogen and oxygen, for subsequent transformation into electrical energy.
Owner:SUNPOWER TECH CORP
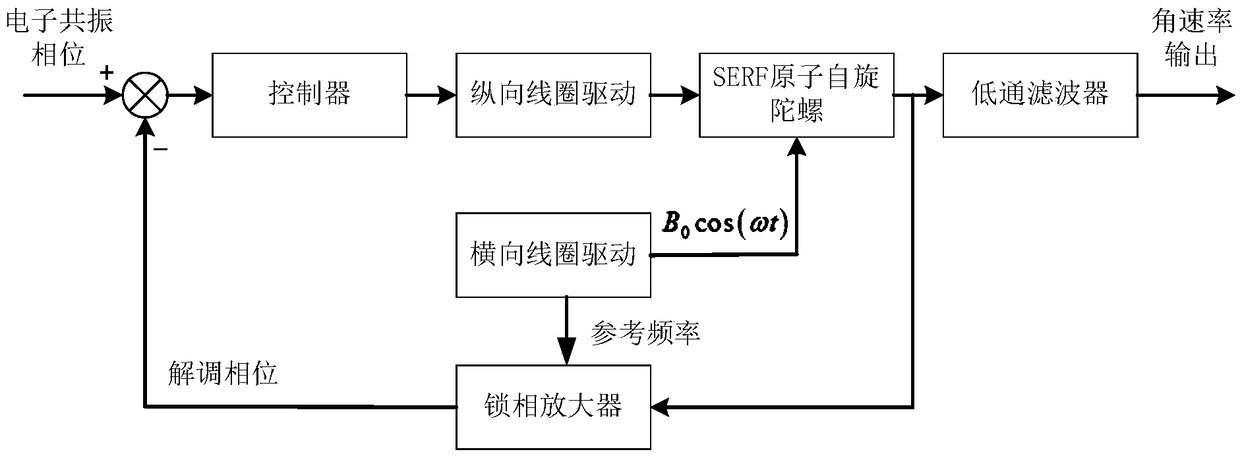
Closed-loop control method for nuclear-spin self-compensation point of SERF atomic-spin top
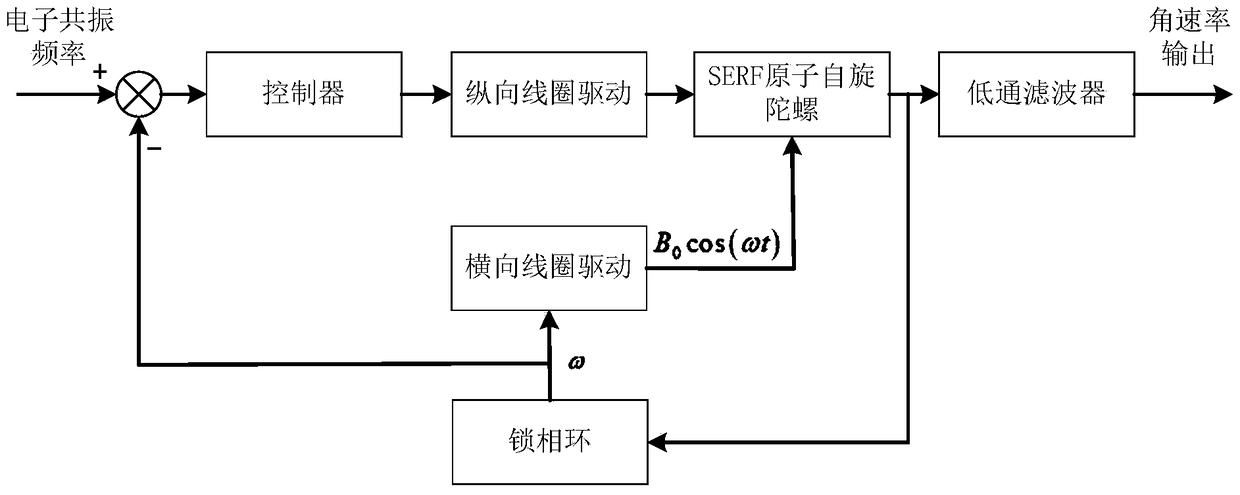
ActiveCN109373989AHigh precisionImprove Scale Factor LinearityTurn-sensitive devicesGyroscopeClosed loop
The invention discloses a closed-loop control method for a nuclear-spin self-compensation point of an SERF atomic-spin top. According to the method, an amplitude-frequency characteristic curve and a phase-frequency characteristic which respond to an alternating current magnetic field of a gyroscope are firstly measured, the resonant frequency and the resonant frequency phase position correspondingto an alkali metal electron resonance peak are found out, a longitudinal compensation offset magnetic field is dynamically adjusted in a frequency closed-loop manner or a phase position closed-loop manner, and the alkali metal electron resonance peak is controlled to be unchanged in real time, so that the longitudinal magnetic field sensed by alkali metal electrons is constant, and the closed-loop control of the nuclear-spin self-compensation point is realized. According to the method, the influence caused by the fluctuation of a longitudinal environmental magnetic field and an inert gas nucleon longitudinal magnetic field to the alkali metal electrons can be reduced, signal fluctuation and coupling errors during the measurement of double-shaft angular rate of the SERF atomic-spin top arerestrained, and the linearity degrees of precision and calibration factors of the gyroscope are increased.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Electromagnetic control of chemical catalysis
ActiveUS7998538B2High degreeFast decayMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic chemistryChemical reactionElectron resonance
The present disclosure relates to methods and systems that provide heat, via at least Photon-Electron resonance, also known as excitation, of at least a particle utilized, at least in part, to initiate and / or drive at least one catalytic chemical reaction. In some implementations, the particles are structures or metallic structures, such as nanostructures. The one or more metallic structures are heated at least as a result of interaction of incident electromagnetic radiation, having particular frequencies and / or frequency ranges, with delocalized surface electrons of the one or more particles. This provides a control of catalytic chemical reactions, via spatial and temporal control of generated heat, on the scale of nanometers as well as a method by which catalytic chemical reaction temperatures are provided.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Laser scanning electron resonance type carbon-hydrogen catalysis method and equipment
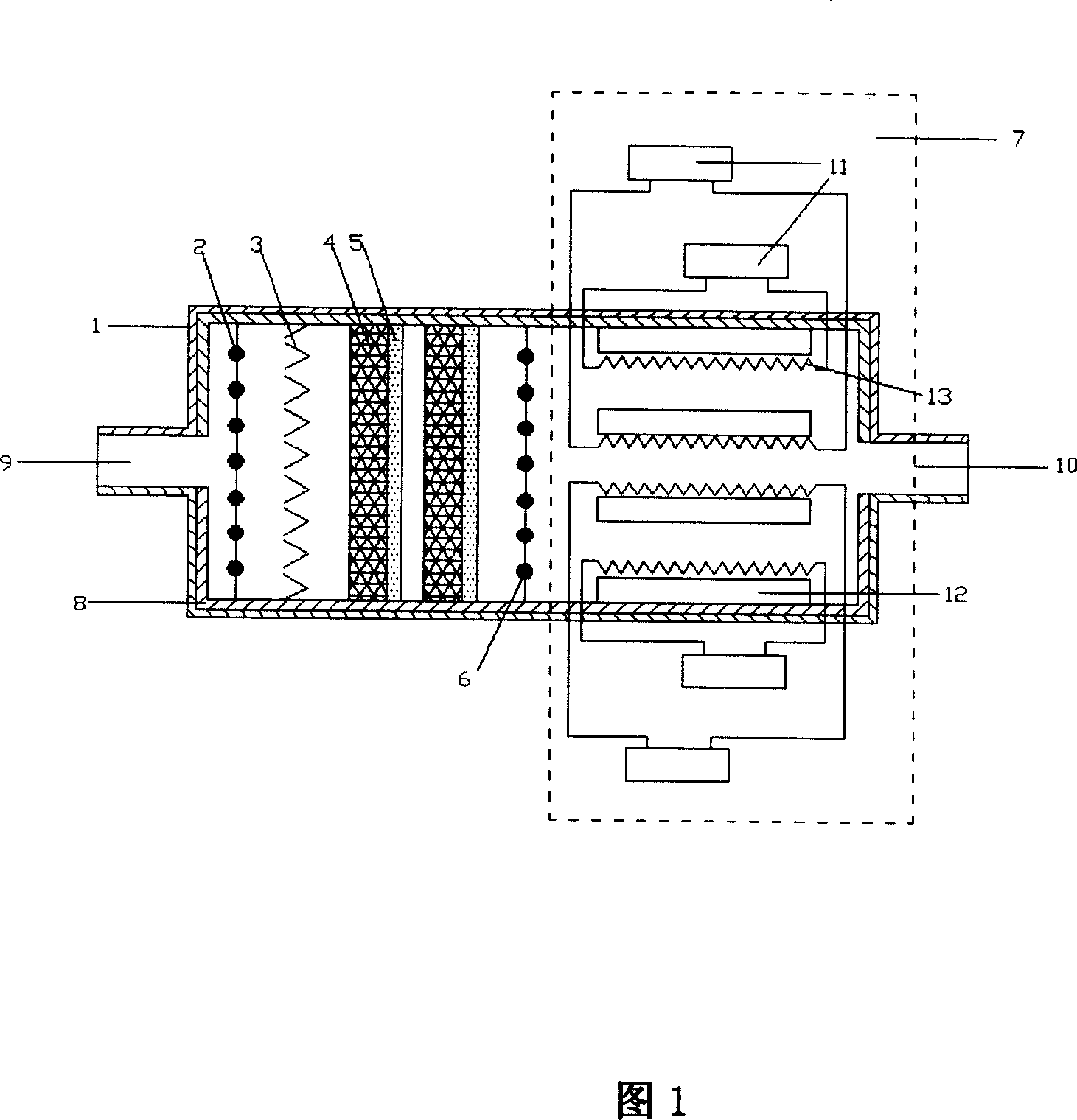
InactiveCN101008367ALiquid fuel feeder/distributionTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsMagnetic mediaLaser scanning
The invention relates to a laser scanning electric atom resonance carbon-hydrogen catalysis method and a relative device. The inventive carbon-hydrogen catalysis device comprises a frame, a laser radiation array, a dense metal network, and a nuclear magnetic resonance tunnel. The invention is characterized in that the liner of frame is arranged with an insulated layer; two ends of the frame are arranged with an inlet and an outlet; the frame is arranged with the first laser radiation array, a laser radiation reflected refraction plate, a dense metal network, the second laser radiation array and a nuclear magnetic resonance tunnel. The dense metal network is connected with high-frequency electricity. The dense metal network is contacted with ferrite particles. The invention can utilize the laser technique and ferrite technique into the treatment of carbon-hydrogen medium, and the magnetic medium generated by the abrasion between the copper network in high-frequency electromagnetic field and ferrite magnet vibration can release more energy in burnt, and the seal function of copper ion can improve the environment protection. The invention can be used in petrol device and gas device.
Owner:北京万国智谷知识产权代理有限公司
Light emitting system according to a polariton mode with electrical injection of quantum wells
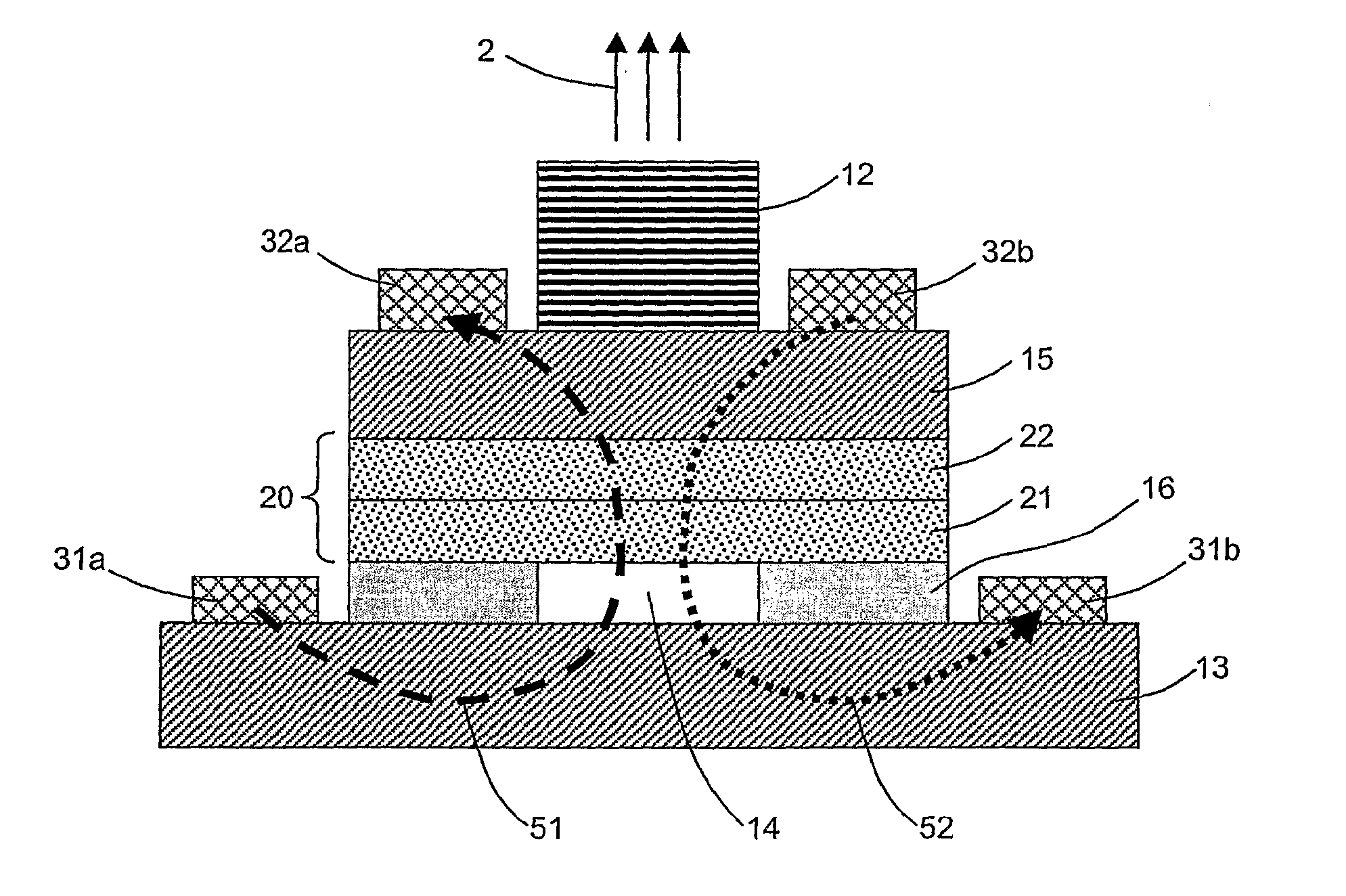
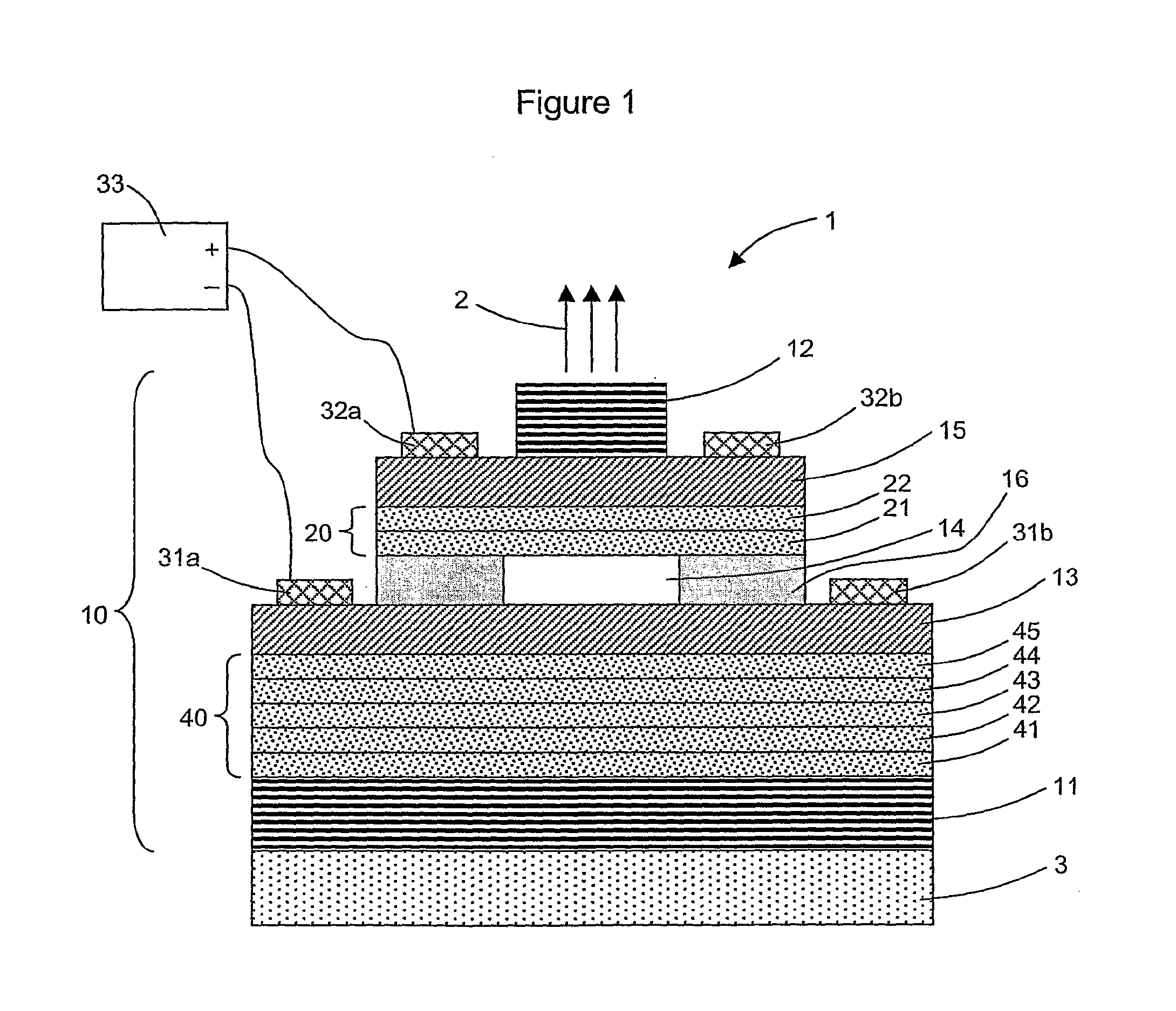
ActiveUS20110261851A1Lower average energyObtain goodLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionOptical cavityElectron resonance
A light (2) emitting system (1) includes an optical cavity (10) having at least one optical mode and including at least one transmissive reflector (12), a first set (20) of quantum wells (21, 22) and elements (31, 32, 33) of electrical injection of the quantum wells of the first set. The quantum wells of the first set are arranged so that at least one of their electronic resonances is a strong coupling regime with an optical mode of the optical cavity and emits a light according to a mixed exciton-polariton mode. The optical cavity further includes a second set (40) of quantum wells (41, 42, 43, 44, 45) arranged outside of the direct range of the elements of electrical injection and arranged in relation to the quantum wells of the first set so that at least one of their electronic resonances is in a strong coupling regime with the mixed exciton-polariton mode of the optical cavity.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
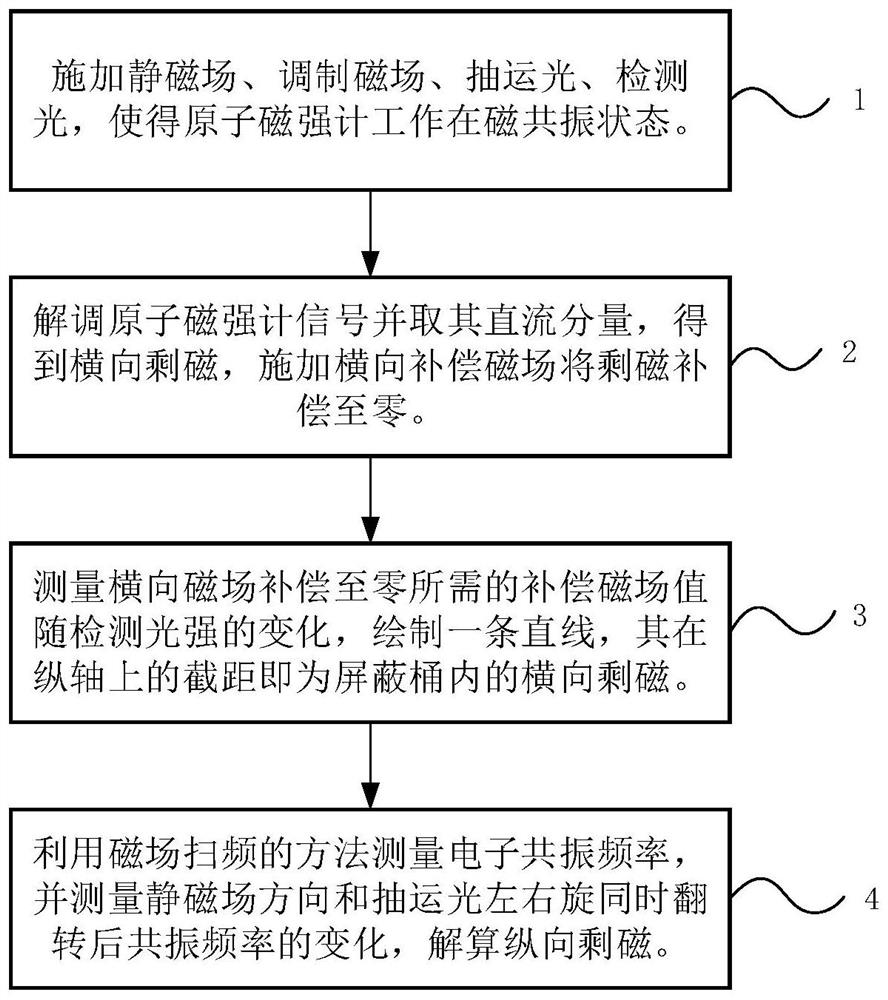
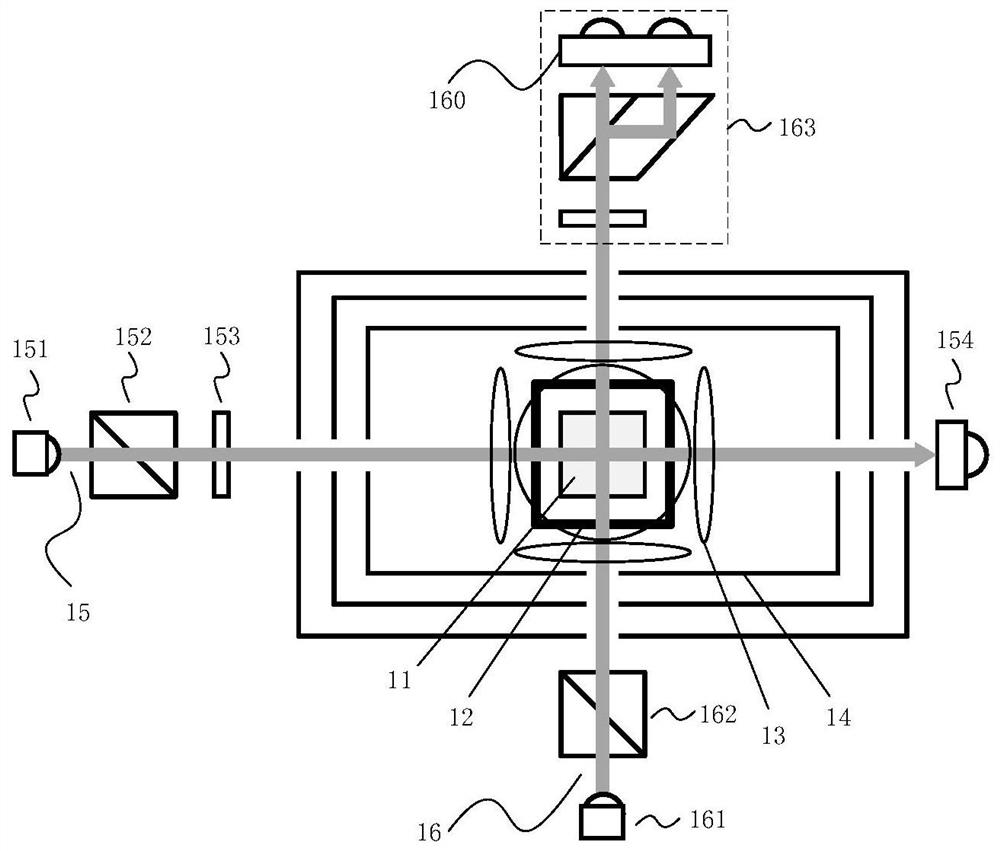
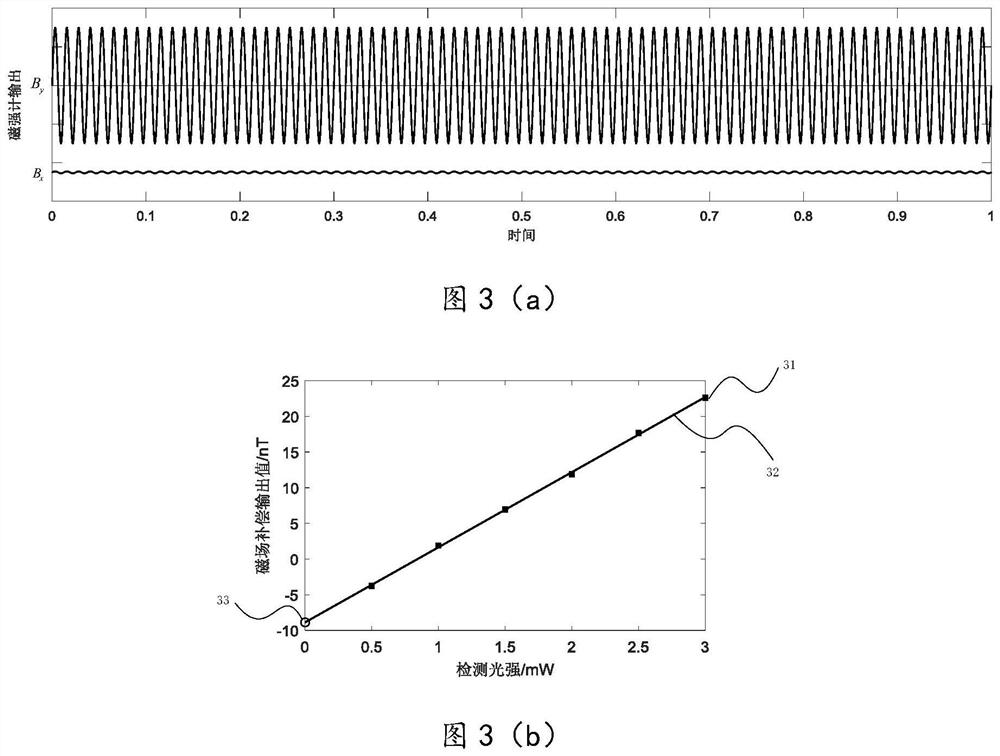
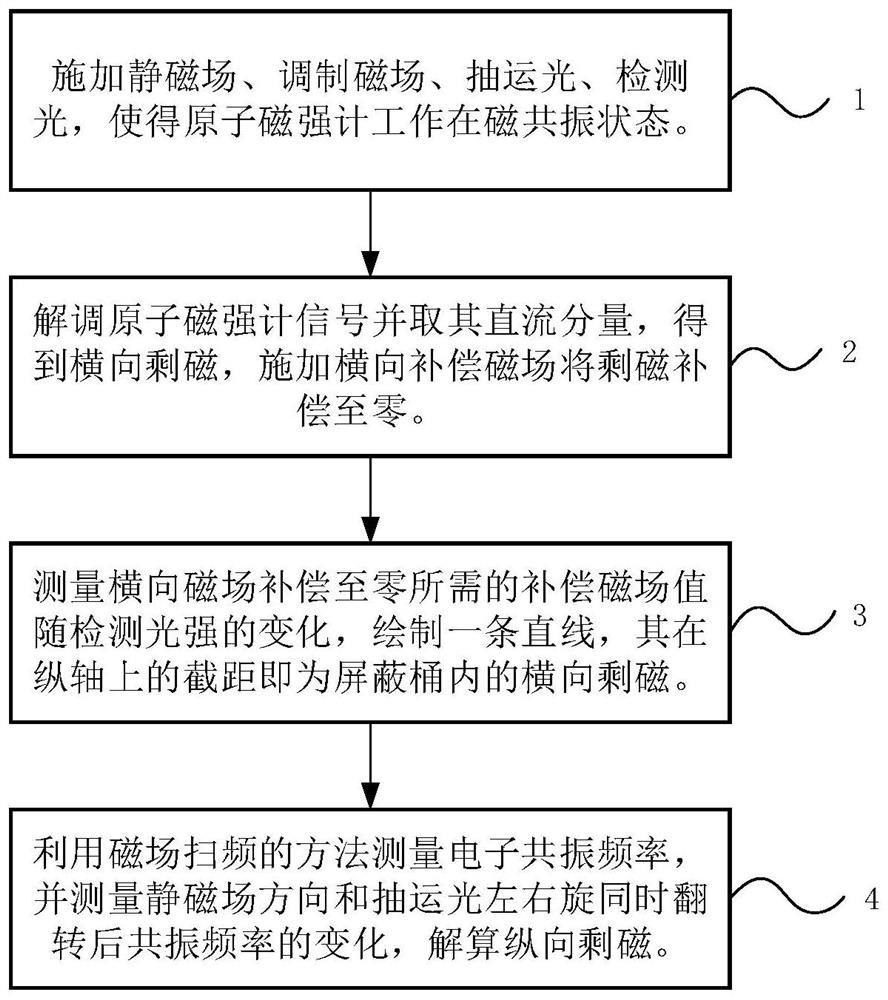
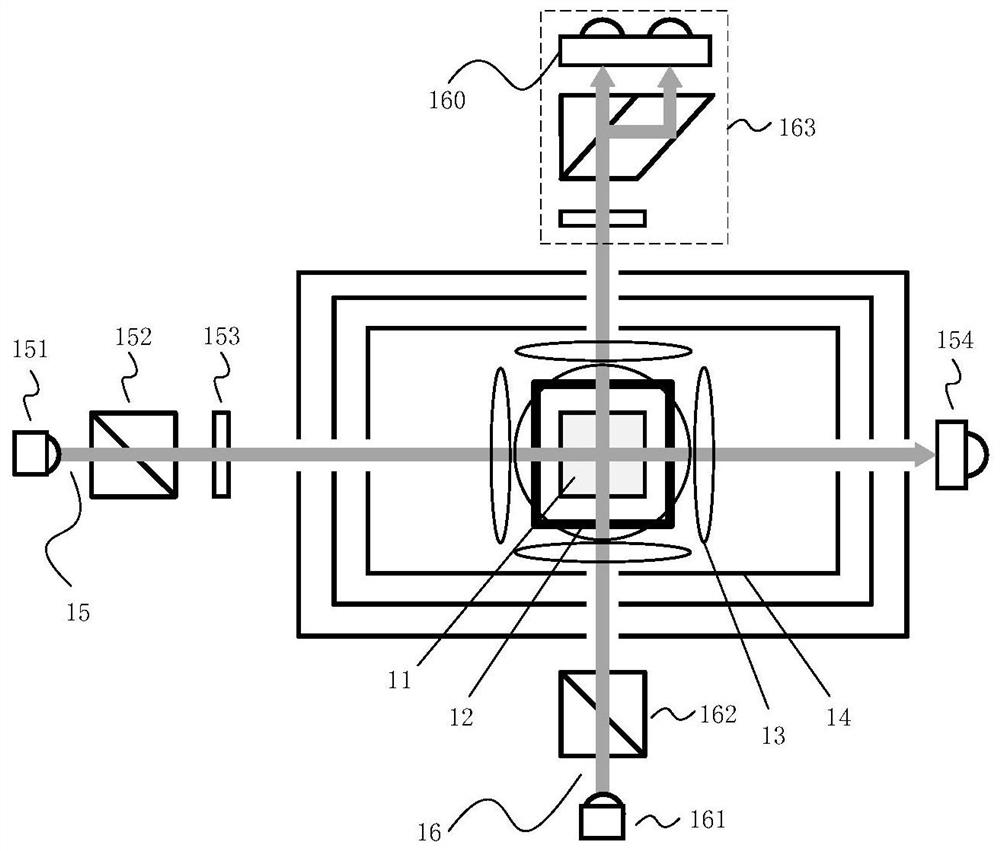
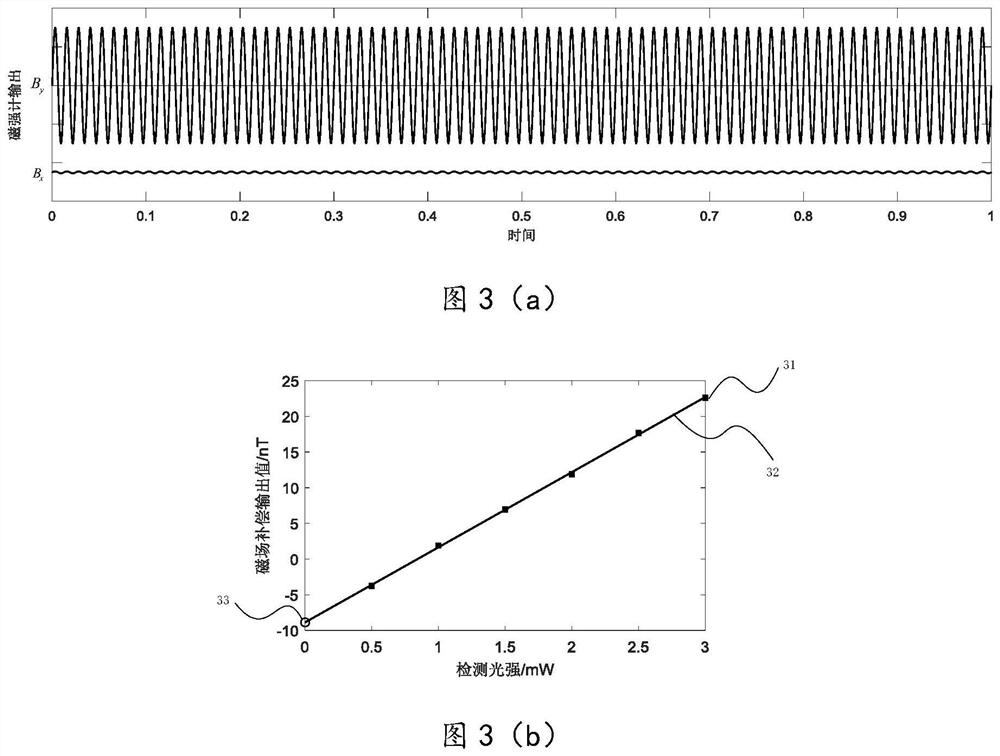
Method for measuring residual magnetism in shielding barrel based on in-situ magnetometer
The invention discloses a method for measuring residual magnetism in a shielding barrel based on an in-situ magnetometer, and is suitable for testing the residual magnetism in the shielding barrel of an atomic sensor. The method comprises the steps of firstly, applying a static magnetic field, a modulation magnetic field, pumping light and detection light to enable an atom magnetometer to work in a magnetic resonance state; demodulating a magnetometer signal, extracting a direct-current component of the magnetometer signal by using a low-pass filter to obtain the residual magnetism in the transverse direction, namely the direction perpendicular to a static magnetic field, and applying a direct-current compensation magnetic field in the transverse direction to compensate the residual magnetism to zero; and carrying out residual magnetism measurement and compensation under different detection light intensities, so that it is found that the output value of a compensation magnetic field linearly changes along with the detection light intensities, and the intercept of a straight line on a longitudinal axis is the value of the transverse actual residual magnetism after light frequency shift is eliminated. The electronic resonance frequency is measured by using a magnetic field frequency sweeping method, and the change of the resonance frequency after the static magnetic field direction and the left and right rotation of the pumping light are turned at the same time is measured, and the longitudinal actual residual magnetism can be obtained by dividing the change by two times of the alkali metal gyromagnetic ratio. According to the present invention, an external sensor is not needed, and the design of the atom sensor is greatly facilitated.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Magnetic field sensor based on photonic crystal fiber and optical grating and measurement method
ActiveCN107807338AHigh strengthEnhanced interactionWater resource assessmentMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesResonance wavelengthParticle physics
The invention provides a magnetic field sensor based on a photonic crystal fiber and an optical grating and a measurement method. The magnetic field sensor consists of the D-shaped photonic crystal fiber, a nanogold layer, the nano optical grating and magnetofluid film, wherein the nanogold layer is coupled to the axially extending smooth surface of the D-shaped photonic crystal fiber, the nano optical grating is inscribed on the nanogold layer, the magnetofluid film covers the nano optical grating, and the structures of the D-shaped photonic crystal fiber and the nano optical grating improvethe intensity of evanescent waves. The refractive index of a magnetofluid changes with the change of magnetic field intensity, free electrons on the surface of the nanogold layer produce absorbing peaks through resonance, their resonant wavelengths offset, magnetic field sensing measurement is achieved by observing the offset process of the resonant wavelengths, a surface plasmon resonance principle is adopted, and the problem of poor linearity of an optical fiber magnetic field sensor prepared by utilizing magnetofluid refraction index characteristics is solved only analyzing the resonance relation of the magnetofluid and the nanogold layer and the more obvious linear relation between the absorbing peaks and magnetic fields.
Owner:SHENYANG JIANZHU UNIVERSITY
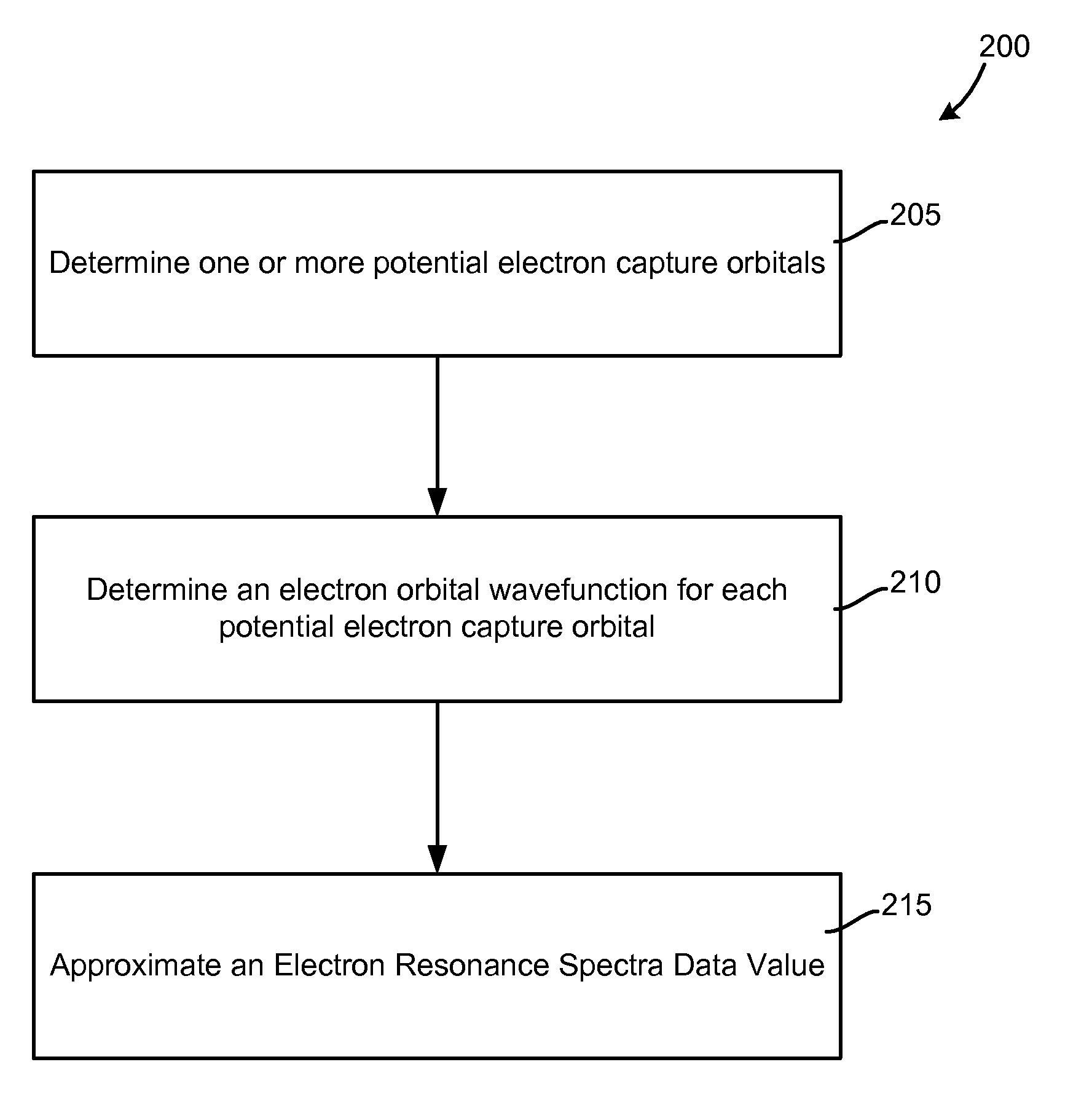
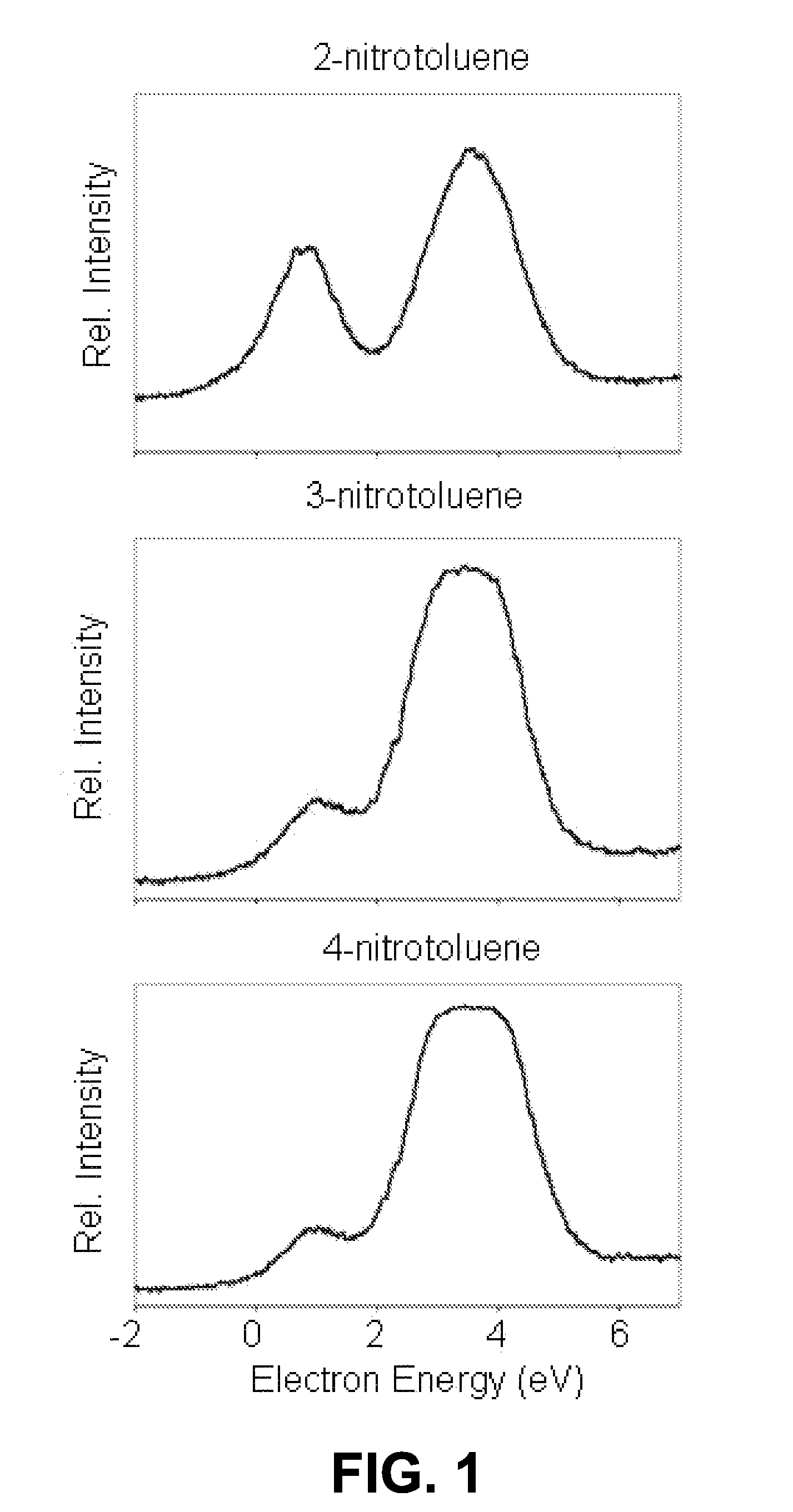
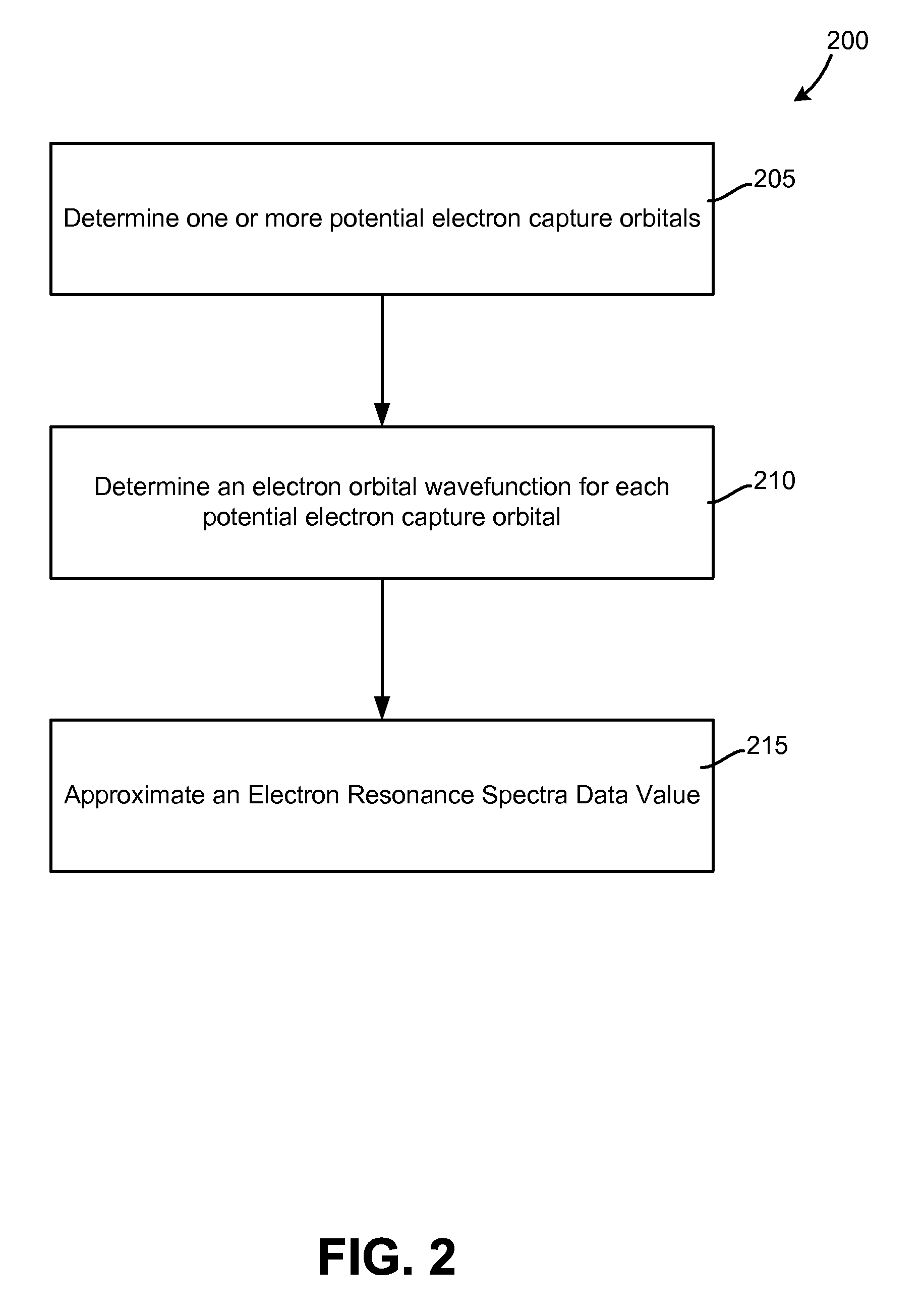
Molecular identification and electron resonance system and method
InactiveUS7570055B1Analysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceAnalysis using electron paramagnetic resonanaceMolecular identificationElectron orbital
A method of calculating an electron resonance spectra data value for each of one or more chemical constituents. In one embodiment, one or more potential electron capture orbitals is identified for each of the one or more chemical constituents; an electron orbital wavefunction is determined for each of the one or more potential electron capture Orbitals; and a theoretical electron resonance spectra data value is generated for each of the one or more chemical constituents. In another embodiment, a theoretical electron resonance spectra data value may be used to identify an unknown chemical constituent.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF VERMONT
A diamond film flat field emission cathode and method for making same
InactiveCN1567506AImplement injectionReduce compoundingDischarge tube/lamp detailsCold cathode manufactureElectron injectionMetal silicide
The invention belongs to a diamond film planar field emission cathode applied to plate display and its making method. It includes: a substrate, where a measuring metal electrode is deposited on one surface of the substrate and a measuring lead wire is connected with them; there is a diamond film layer on the other surface of the substrate; a metal silicide transition layer is situated between the substrate and diamond film layer. Its making method includes: firstly making a metal silicide transition layer on one surface of the substrate; then adopting various traditional methods to grow a diamond film on the metal silicide, because it is difficult in directly growing diamond film on the metal silicide, normally nucleating at bias voltage and then growing the diamond film; adopting spurting or depositing process to deposit 300-1000 nm thick Au electrode on the other surface of the substrate. The metal silicide transition layer provides two interface barriers tunneled by electron resonance, thus realizing high-density electron injection. And the making method is easy to spread.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System For Generation Of Useful Electrical Power From Isotopic Emissions
ActiveUS20140035435A1Safe and cost-effectiveTransit-tube cathodesGenerators/motorsElectricityHigh energy
Particles emitted by radio-isotopic by-products of nuclear fission are used as a power source at the cathode of a magnetron system. Particles include high energy electrons having a large associated EMF. In the system a radial electrical vector E, between the cathode and anode, interacts with an axial magnetic vector B vector to produce an E×B force that rotates the particles about the system axis. These emissions are within a set range of velocities. The angular velocity and geometry of a rotating field, known as a space charge wheel (SCW), may be modulated by an external RF inputs to cavities of an anode block and the use of concentric biasing grids between the cathode and anode block. The SCW induces LC values into cavities of the anode, exciting them and producing electrons resonance which may be used to generate power.
Owner:WEBER DAVID
Method for improving photo-thermal excitation micro-cantilever beam vibration energy conversion efficiency by using local plasmon structure
InactiveCN106949914AImprove energy conversion efficiencyImprove light-mechanical energy conversion efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologyConverting sensor output opticallyOptical power meterLight energy
A method for improving photo-thermal excitation micro-cantilever beam vibration energy conversion efficiency by using a local plasmon structure comprises steps of: preparing the local plasmon structure on the micro-cantilever beam and acquiring a vibration signal emitted by photo-excited micro-cantilever beam vibration. The metal nanoparticles convert the absorbed light energy into the kinetic energy of electron resonance, and further convert the kinetic energy into the vibration energy of the lattices by means of the scattering of the lattices on electrons. The metal nanoparticles can also increase the effective mass of the micro-cantilever beam so as to increase the quality factor of the micro-cantilever beam, thereby improving the detection accuracy and the resolution of a micro-cantilever beam sensor. In addition, the micro-cantilever beam combining the plasmon can also be used as an optical power meter with excellent performance to achieve a limit of detection up to pm / nW. The method solves the low vibration efficiency of the photo-excited micro-cantilever beam, is simple and convenient, and has a great practical value to the development and application of the photo-excited micro-cantilever beam vibration.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
System for generation of useful electrical power from isotopic emissions
Particles emitted by radio-isotopic by-products of nuclear fission are used as a power source at the cathode of a magnetron system. Particles include high energy electrons having a large associated EMF. In the system a radial electrical vector E, between the cathode and anode, interacts with an axial magnetic vector B vector to produce an E×B force that rotates the particles about the system axis. These emissions are within a set range of velocities. The angular velocity and geometry of a rotating field, known as a space charge wheel (SCW), may be modulated by an external RF inputs to cavities of an anode block and the use of concentric biasing grids between the cathode and anode block. The SCW induces LC values into cavities of the anode, exciting them and producing electrons resonance which may be used to generate power.
Owner:WEBER DAVID
Electromagnetic control of chemical catalysis
InactiveCN101090990AMaterial nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsChemical reactionElectron resonance
Owner:莱斯利・格林歌德 +2
Microwave ultraviolet lamp based on electron cyclotron resonance principle
InactiveCN104576296ASolve the problem of poor UV curing effectImprove luminous efficiencyGas discharge lamp detailsResonant cavityStart time
The invention relates to a microwave ultraviolet lamp based on an electron cyclotron resonance principle, and belongs to the field of microwave electrodeless lightening technology. The microwave ultraviolet lamp based on the electron cyclotron resonance principle is used for solving the problems in the prior art that the starting time of the middle portion of a microwave ultraviolet lamp is long and the luminous efficiency is low. According to the microwave ultraviolet lamp based on the electron cyclotron resonance principle, a modulator tube ia arranged on a microwave resonant cavity which is formed by a reflector and a metal shielding net, a permanent magnet is arranged on the outside surface of the reflector, and the permanent magnet and the modulator tube are arranged on the same straight line. A feed inlet is formed in the reflector, the microwave emanated from a magnetron enters the reflector through an incentive cavity of the magnetron and the feed inlet, a constant magnetic field is generated around the modulator tube by the permanent magnet when the microwave enters the reflector, the coupling of the constant magnetic field and the microwave entering the reflector enables the middle portion inside the modulator tube to generate an electronic resonant acceleration, so that the middle portion of the modulator tube can be started in a relatively short time, and the problems that the starting time of the middle portion of the microwave ultraviolet lamp is long and the luminous efficiency is low and the like are solved. The microwave ultraviolet lamp based on the electron cyclotron resonance principle can be utilized in the fields of the ultraviolet sterilization, the fluorescence excitation, and the relevant ultraviolet curing and the like.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
D-type double-core photonic crystal fiber double-parameter plasma sensor
PendingCN113640251APrevent oxidationImprove tolerancePhase-affecting property measurementsThermometers using physical/chemical changesResonance wavelengthMetal membrane
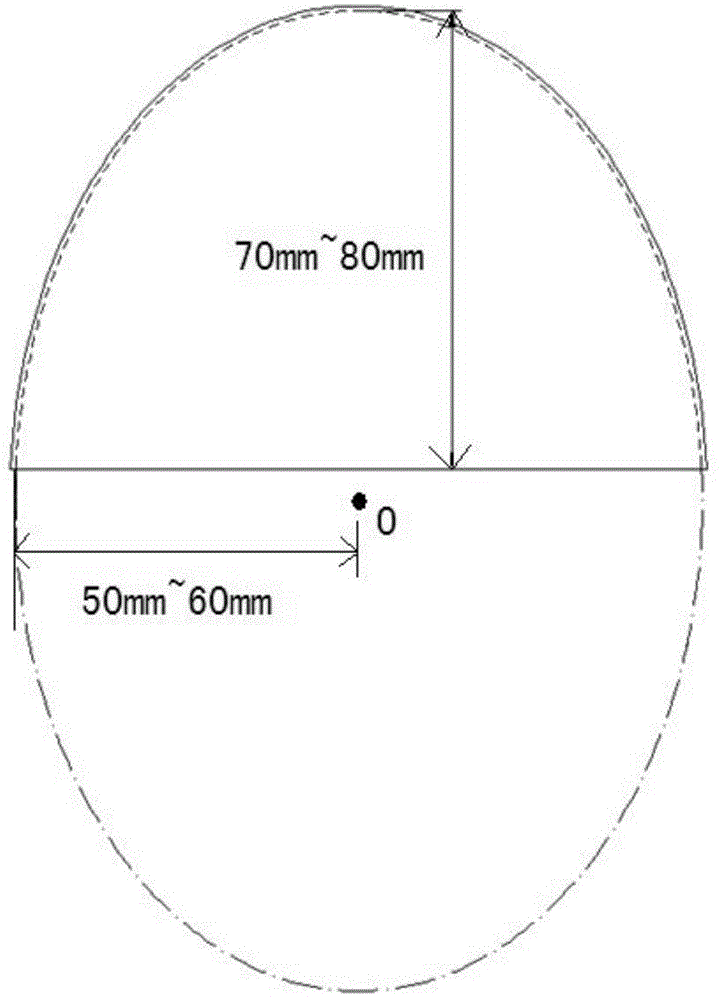
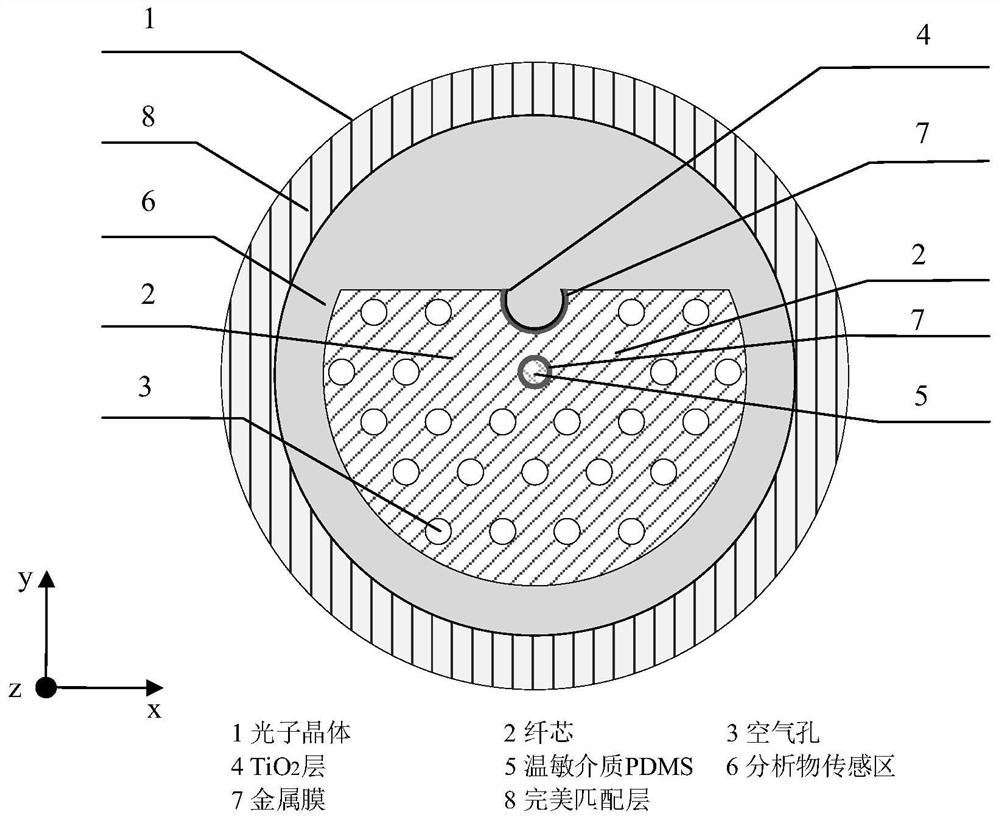
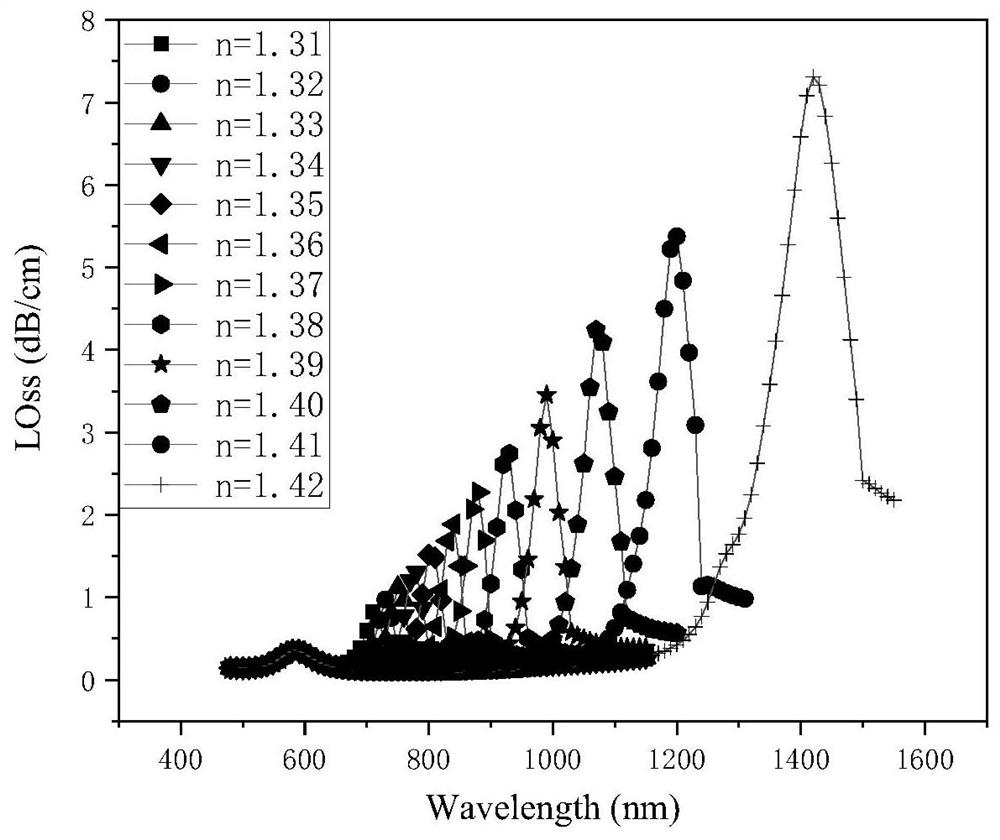
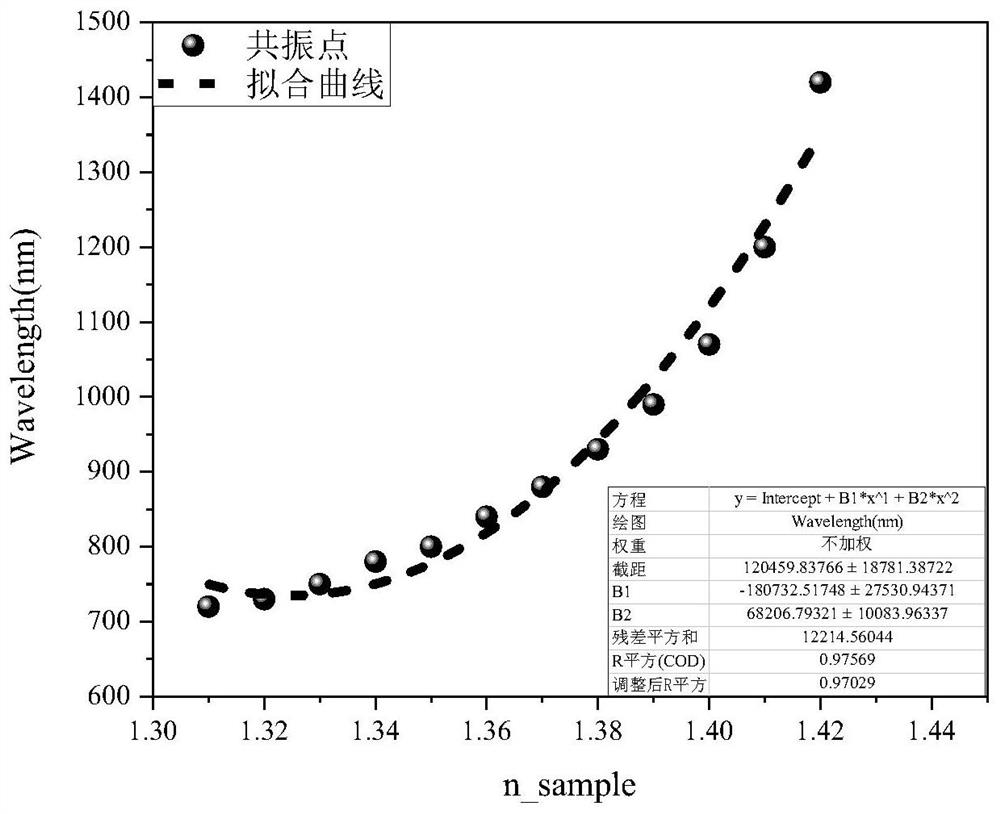
The invention provides a D-type double-core photonic crystal fiber double-parameter plasma sensor. An optical fiber SPR sensor comprises a D-type photonic crystal optical fiber with an open annular channel and a curved side wall; a fiber core, an air hole, a metal film, a TiO2 layer, a temperature-sensitive medium, a liquid analyte and a perfect matching layer are comprised. The photonic crystal fiber is formed by arranging a fiber core of the photonic crystal fiber and air holes with the same size, a substrate material is quartz, one air hole in the middle of the fiber core is filled with a temperature-sensitive medium PDMS, and the outer ring thereof is coated with a metal film; and the metal film and the TiO2 layer are arranged on an open annular plane. The refractive index of the temperature-sensitive medium changes along with the change of the temperature, meanwhile, free electrons on the surface of a nanogold layer resonate to generate an absorption peak, the resonant wavelength of the absorption peak deviates, the temperature sensing measurement is realized by observing the deviation process of the resonant wavelength, and the surface plasmon resonance principle is adopted. The sensor is high in sensitivity, wide in detection range and high in corrosion resistance.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
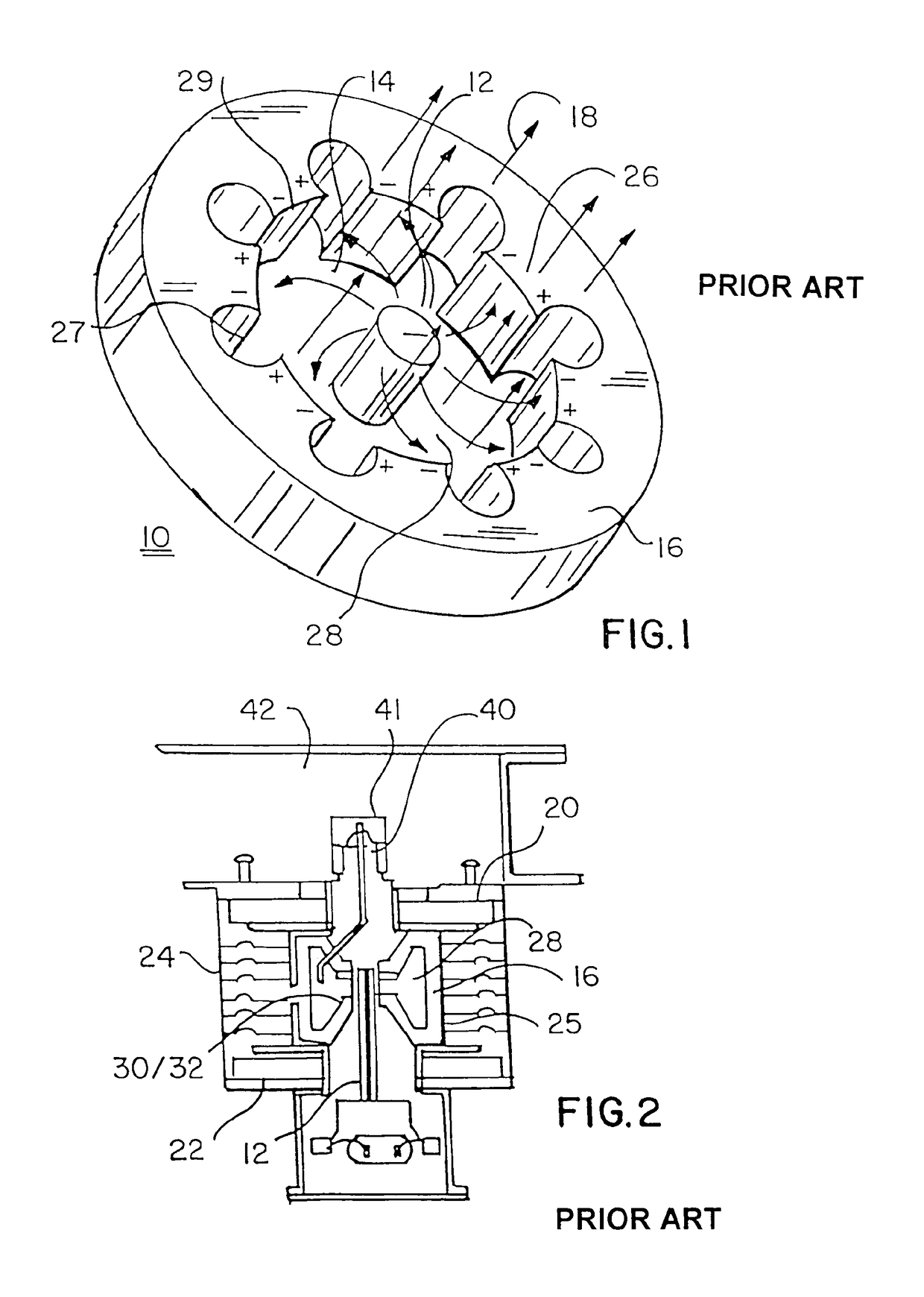
Low esr switch for nuclear resonance measurements
InactiveUS20060091886A1Lower resistanceIncrease the Q of the systemMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceMaterial analysis by using resonanceElectricityElectron resonance
A low equivalent series resistance (ESR) switch for selectively adding to a coil-capacitor circuit of a nuclear or electron resonance system. The switch comprises a pair of physically and electrically contacting members having mutually large contact surface areas. The members are movable between a quiescent position where the contact surface areas are separated by a small distance and an active position where the contact surface areas are brought into physical and electrical contact to connect into the coil-capacitor circuit.
Owner:QRSCI
A method for measuring residual magnetism in shielded barrels based on in-situ magnetometer
A method for measuring residual magnetism in shielded barrels based on an in-situ magnetometer is suitable for testing the residual magnetism in shielded barrels of atomic sensors. First, apply a static magnetic field, modulate the magnetic field, pump light, and detect light to make the atomic magnetometer work in the magnetic resonance state; demodulate the magnetometer signal, extract its DC component with a low-pass filter, and obtain the horizontal or vertical static For the remanence in the magnetic field direction, apply a DC compensation magnetic field in the transverse direction to compensate the remanence to zero; carry out the remanence measurement and compensation under different detection light intensities, and find that the output value of the compensation magnetic field changes linearly with the detection light intensity, and the straight line is on the vertical axis. The intercept above is the value of the actual lateral remanence after excluding the optical frequency shift; the electronic resonance frequency is measured by the method of magnetic field sweep, and the change of the resonance frequency after the direction of the static magnetic field and the left-right rotation of the pump light are simultaneously reversed, divided by Twice the alkali metal gyromagnetic ratio can get the actual longitudinal remanence. The invention does not need to use an external sensor, which greatly facilitates the design of the atomic sensor.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for Detecting Analyte and System for Detecting Analyte
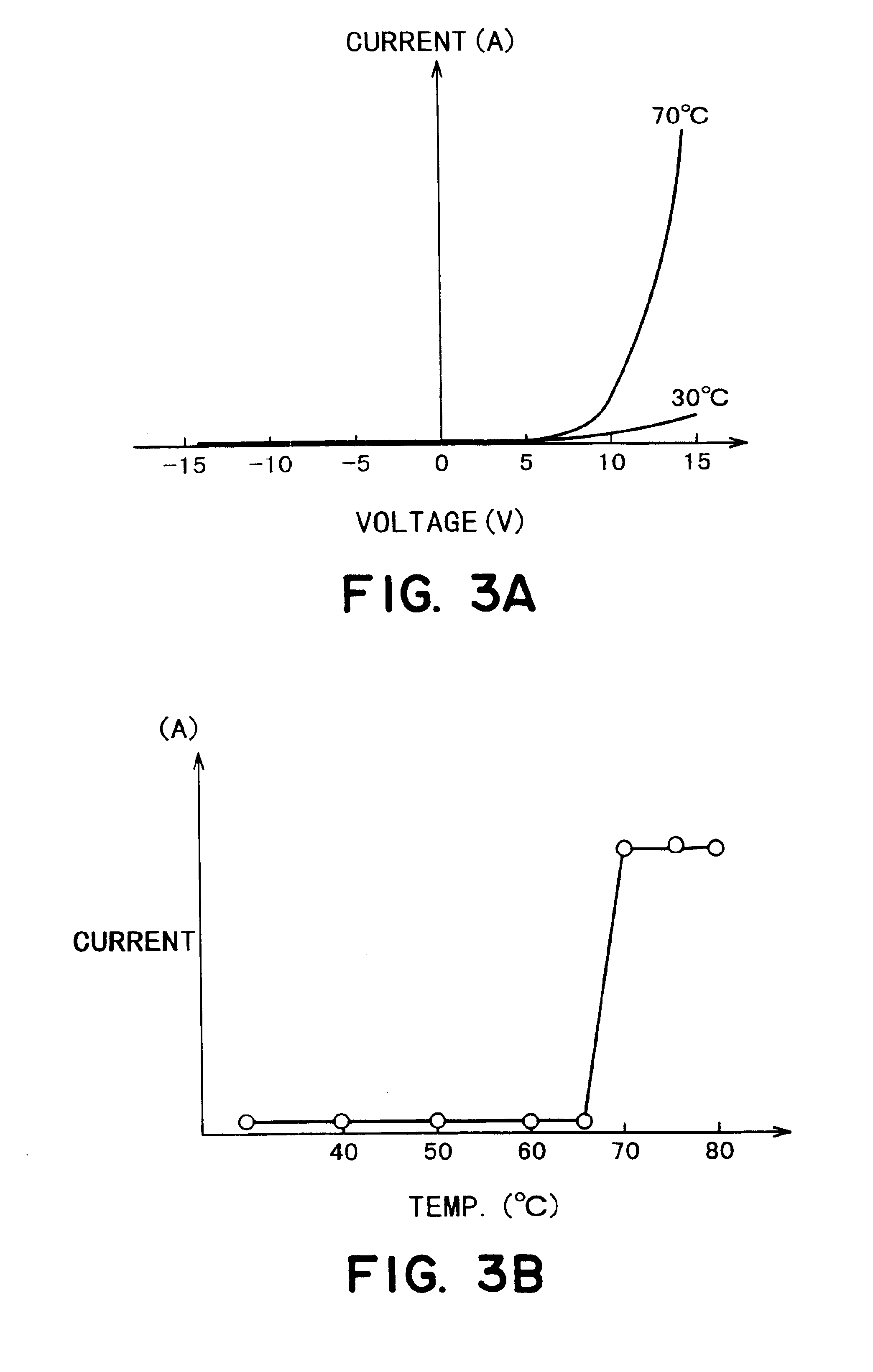
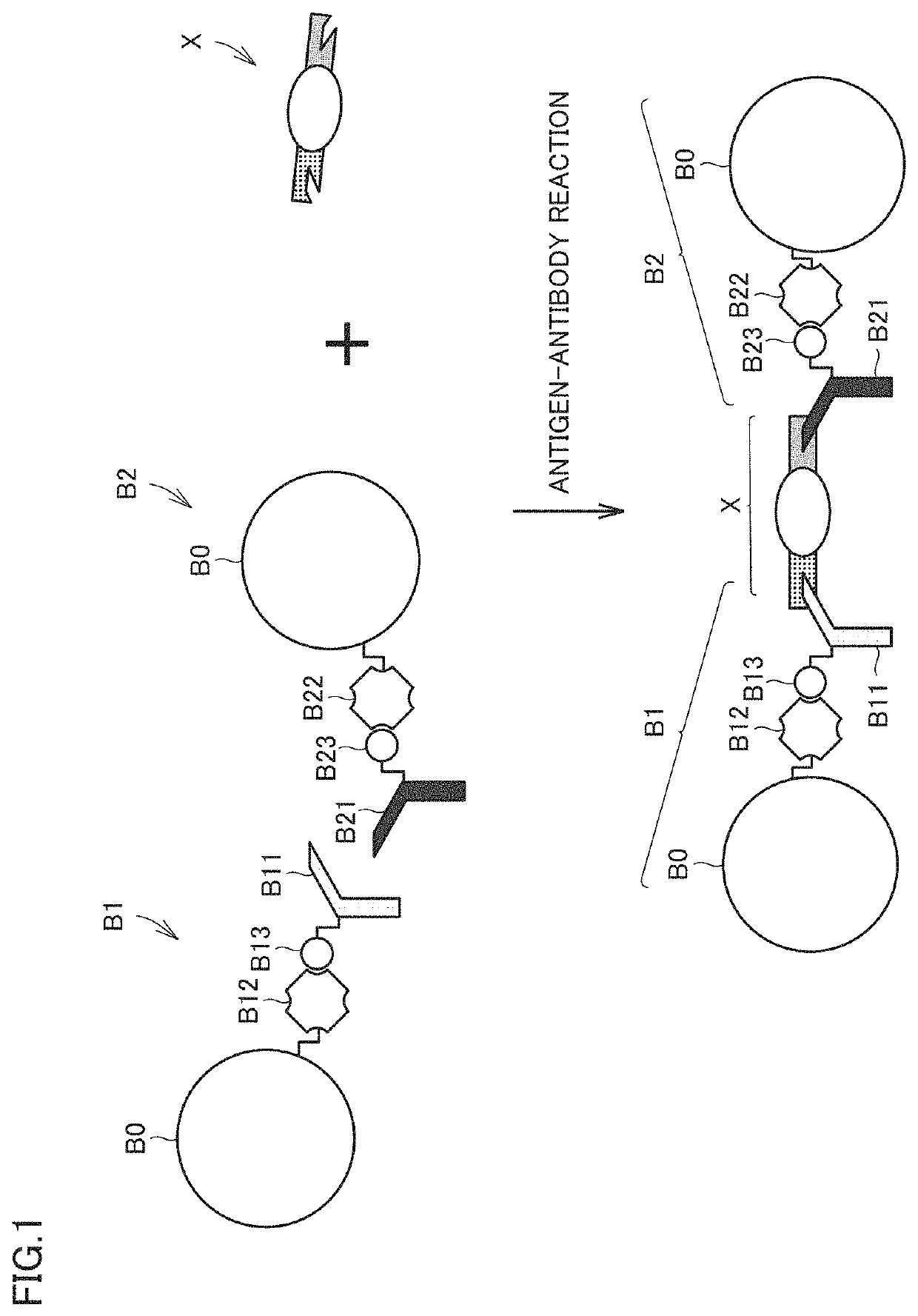
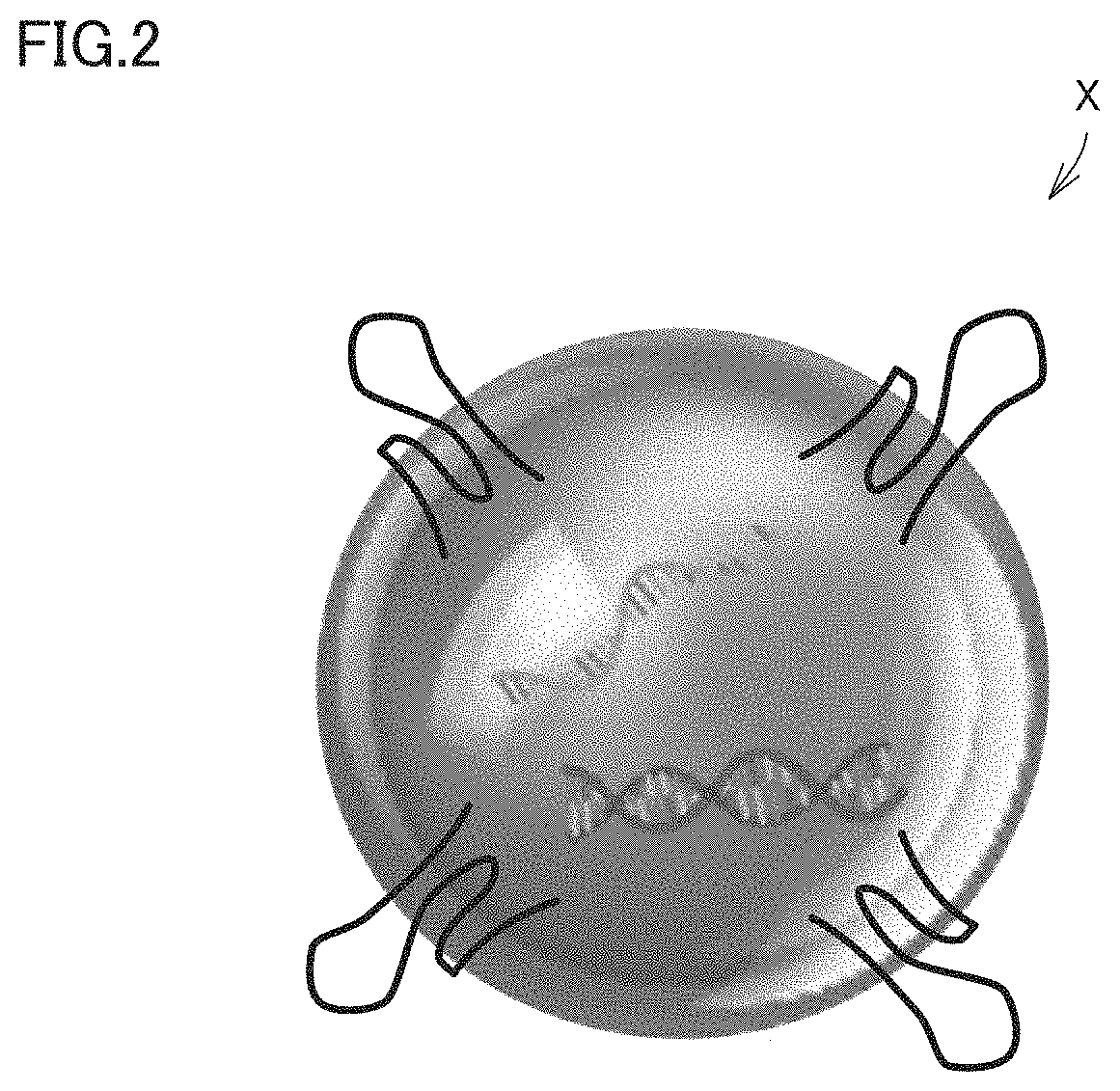
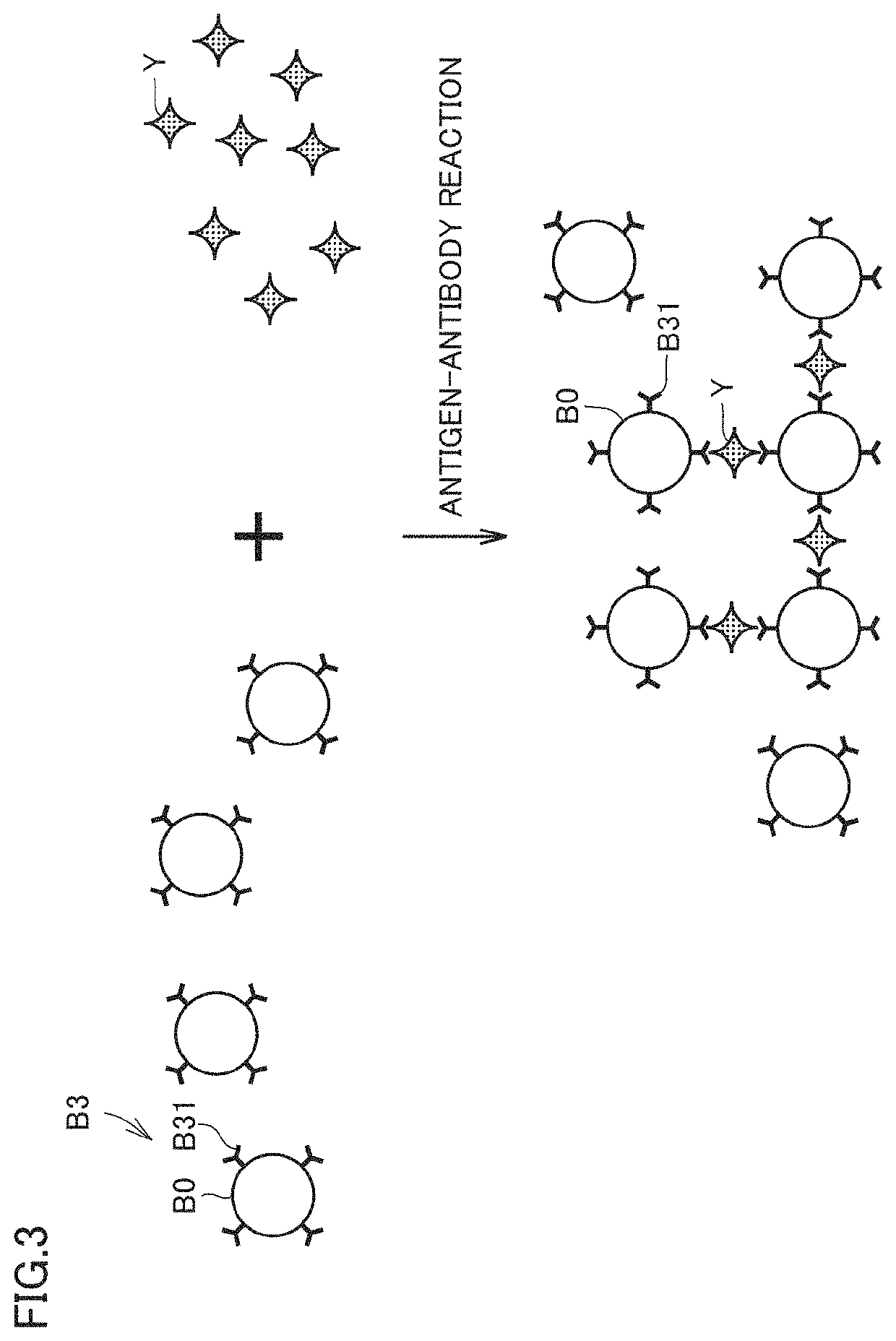
PendingUS20220326249A1Avoid splittingQuick checkLaboratory glasswaresBiological testingAnalytePhoto irradiation
A method for detecting an analyte includes first to third steps. The first step is distributing a sample containing a bead modified with a host molecule that is specifically bound to the analyte in a microchannel using a syringe pump. The second step is irradiating the sample with non-resonant light that is light outside a wavelength range of electronic resonance of the bead. The third step is detecting the analyte based on a signal from a camera that receives the light from the sample.
Owner:PUBLIC UNIVERSITY CORPORATION OSAKA CITY UNIVERSITY
Non-contact charging device and non-contact charging method
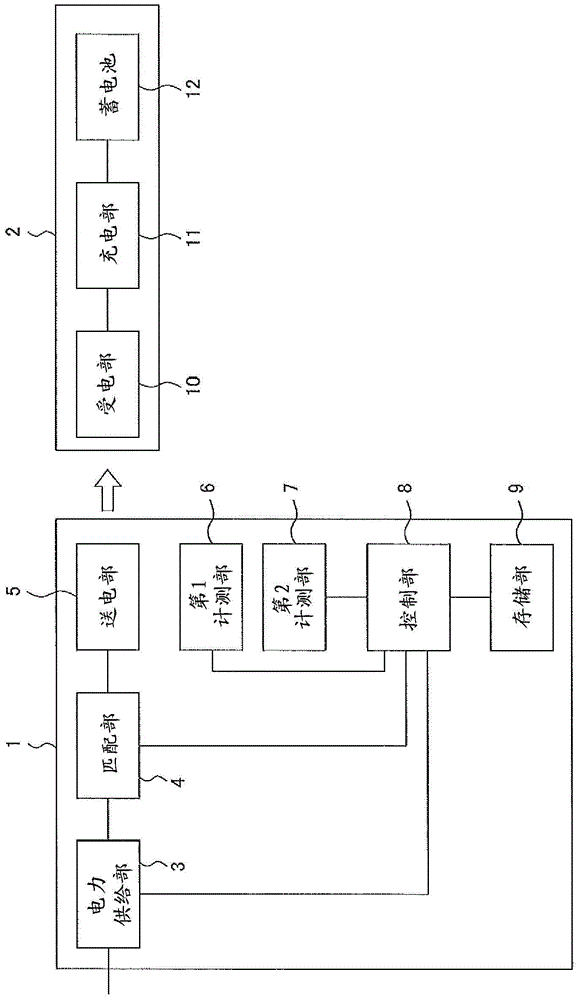
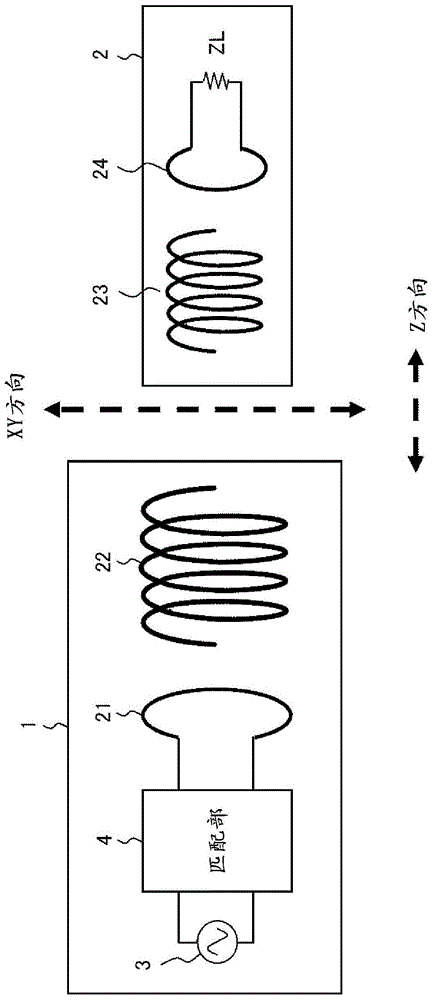
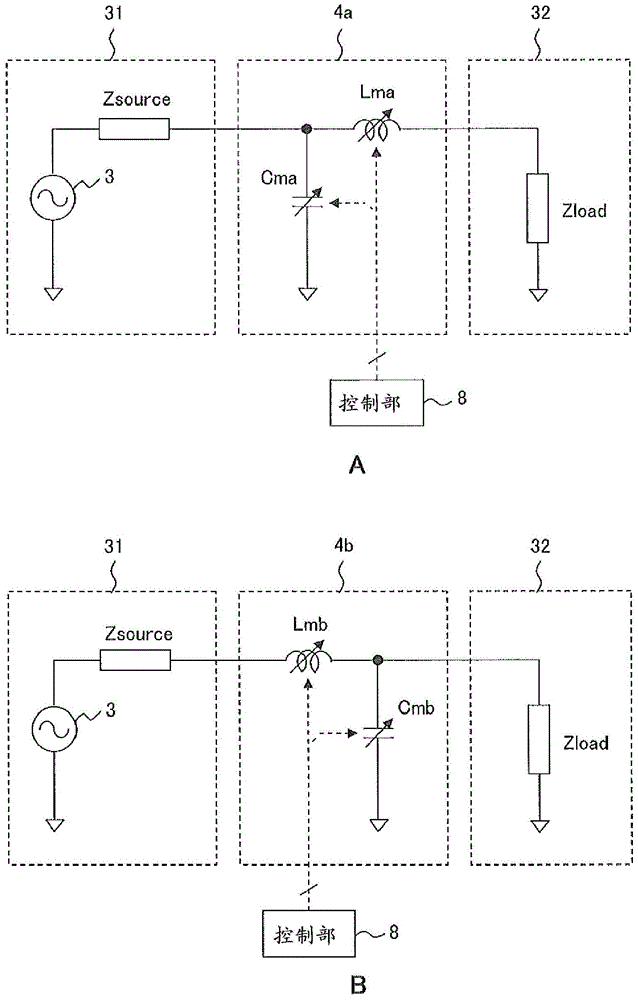
ActiveCN103988389BSuppress reflected powerMultiple-port networksCharging stationsCapacitanceElectricity
The invention provides a non-contact charging device and a non-contact charging method. The non-contact charging device uses variable information for changing the inductance and capacitance of the matching part associated with the first distance and the second distance, in order to adjust the impedance of the power supply system that supplies AC power and The impedance matching of the power transmission and reception system having the power transmission unit and the power reception device changes the inductance and capacitance of the matching unit, where the first distance represents the distance between the center point of the power transmission resonant coil and the center point of the power reception resonant coil The length of the line segment connecting the positions, the second distance is the distance between the surface having the power transmitting resonant coil and the surface having the power receiving resonant coil, and the matching part is used to make the impedance of the power supply system The impedance matching of the sending and receiving power system varies with the relative position of the electric resonant coil.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Laser scanning electron resonance type carbon-hydrogen catalysis method and equipment
InactiveCN100507255CLiquid fuel feeder/distributionTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsInsulation layerLaser scanning
A laser-scanning electric atom-resonating hydrocarbon-catalyzing method and a device thereof are disclosed. The device comprises a housing (1), a laser radiation array, a wire mesh having big mesh count, and a nuclear magnetic resonance passage. An insulation layer (8) is lined in the housing, an inlet (9) and an outlet (10) are provided at the both ends of the housing. A first laser radiation array (2), a laser radiation refraction-reflection sheet (3) , a wire mesh (4) having big mesh count, a second laser radiation array (6) and the nuclear magnetic resonance passage (7) are provided in the housing. The wire mesh having big mesh count is connected with the electricity of high frequency and is provided with ferrite particle.
Owner:北京万国智谷知识产权代理有限公司
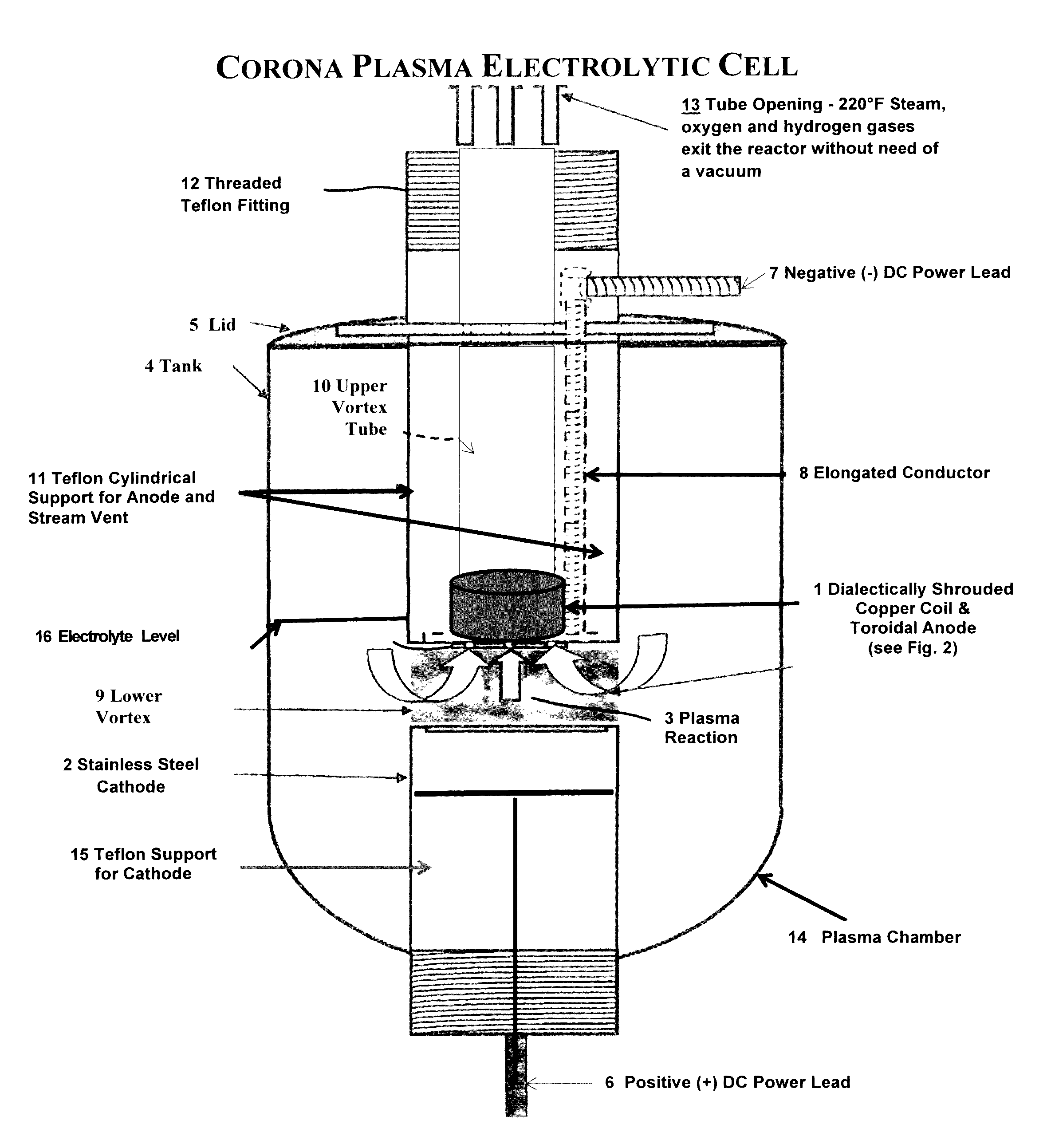
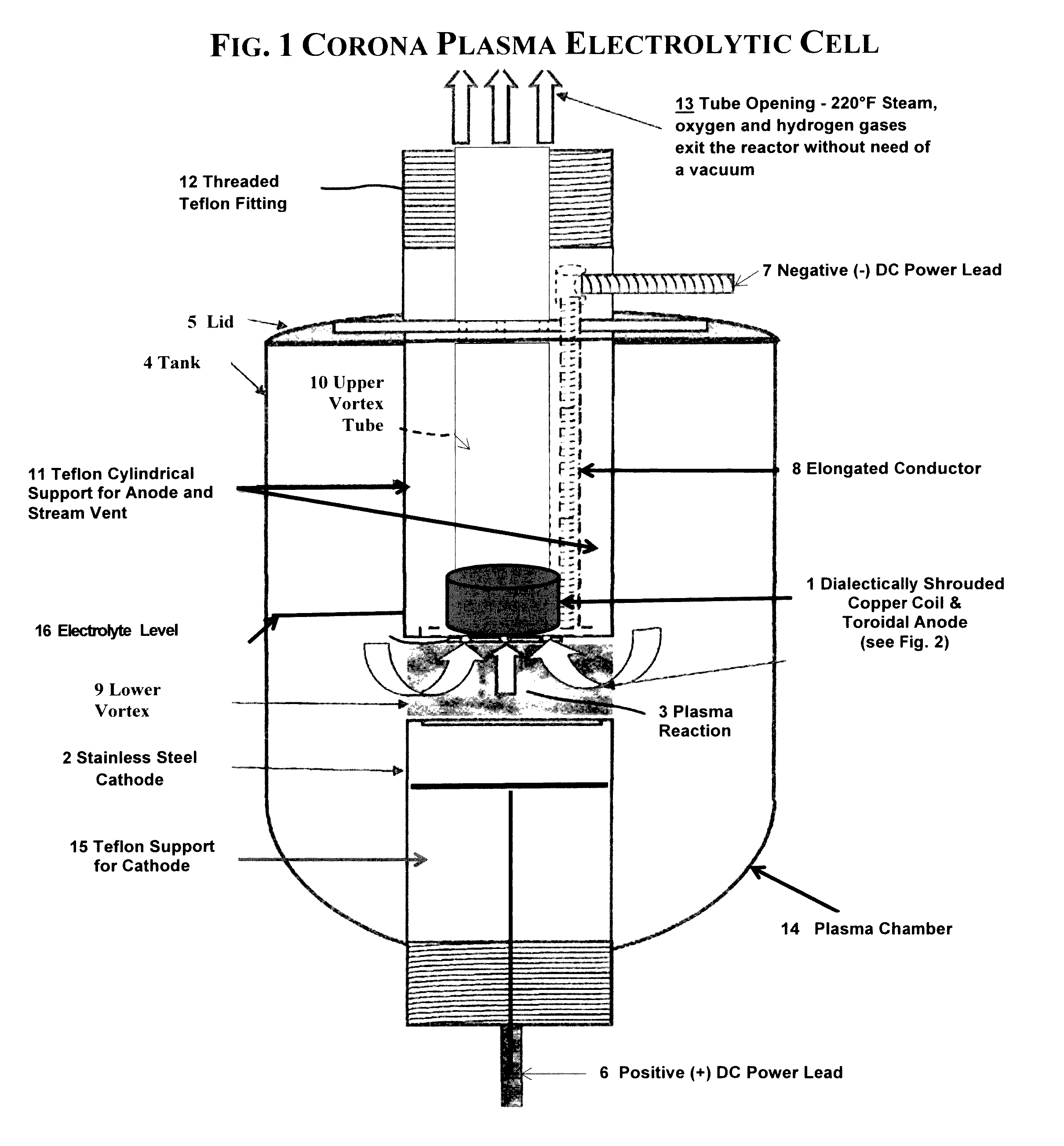
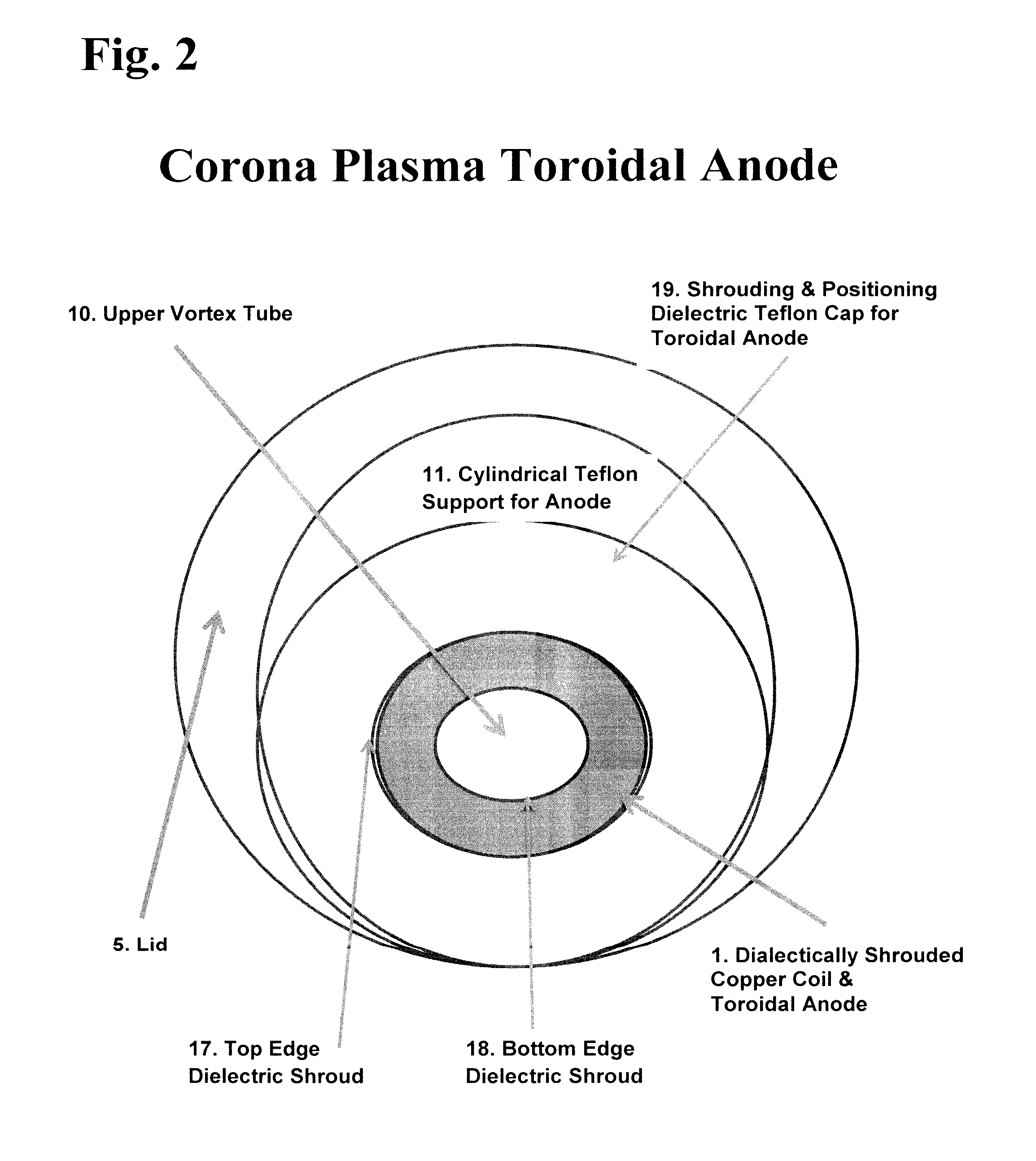
Electrolytic cell for heating electrolyte by a glow plasma field in the electrolyte
An apparatus and method for generating a Contact Glow Plasma Discharge in an electrolyte such as 7% K2CO3. A Shrouded Toroidal Anode is partially submerged in the electrolyte directly above a Flat Torus Cathode (totally submerged in the electrolyte), spaced approximately 50 mm apart, and the two electrodes are arranged in a concentric manner. A potential difference is applied from the cathode to the anode causing gas to be formed on the cathode. This is followed by a contact glow plasma being formed on the surface of the cathode and electromagnetically confined by a Spheromark formed by the configuration of the electrodes. This confinement of the plasma prevents a plasma arc from consuming the anode, which in turn allows for the application of 12,000 Watts and the occurrence of “non-linear electron resonance heating”. The effects of nonlinear series resonance increase the total power dissipation by factors of 2-5 for low pressure capacitive plasmas. Thus explaining the 303% efficiency obtained with this apparatus.
Owner:CORONA PLASMA SYST
Graphene Hybrids for Biological and Chemical Sensing
PendingUS20220178831A1Easy to controlImprove material performancePolycrystalline material growthGrapheneOptical propertyElectron resonance
Embodiments relate to a layered material (having a substrate, at least a buffer layer, with zero or more growth layers) that has been intercalated via a process that decouples (physically and electronically) the buffer layer from the substrate, thereby resulting in the creation of few-atom thick metal layers that exhibit a range of optical properties, including plasmonic or electronic resonance, that enables superior optical (e.g. Raman) detection of molecules.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
A diamond film flat field emission cathode and method for making same
InactiveCN100390921CImplement injectionReduce compoundingDischarge tube/lamp detailsCold cathode manufactureElectron injectionMetal silicide
The invention belongs to a diamond film planar field emission cathode applied to plate display and its making method. It includes: a substrate, where a measuring metal electrode is deposited on one surface of the substrate and a measuring lead wire is connected with them; there is a diamond film layer on the other surface of the substrate; a metal silicide transition layer is situated between the substrate and diamond film layer. Its making method includes: firstly making a metal silicide transition layer on one surface of the substrate; then adopting various traditional methods to grow a diamond film on the metal silicide, because it is difficult in directly growing diamond film on the metal silicide, normally nucleating at bias voltage and then growing the diamond film; adopting spurting or depositing process to deposit 300-1000 nm thick Au electrode on the other surface of the substrate. The metal silicide transition layer provides two interface barriers tunneled by electron resonance, thus realizing high-density electron injection. And the making method is easy to spread.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Electron-nuclear double resonance resonator
ActiveUS10340578B2High detection sensitivityImprove fill factorMeasurements using double resonanceMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceElectron nuclear double resonanceElectron resonance
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
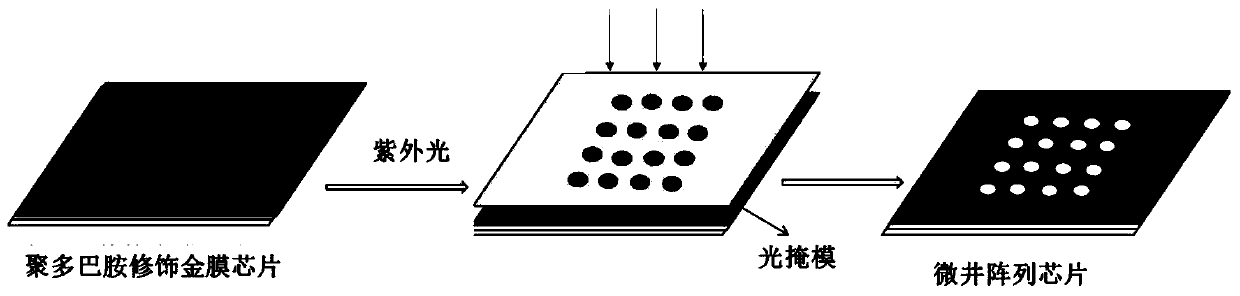
Preparation method of micro-well structure SPRi chip and product and application thereof
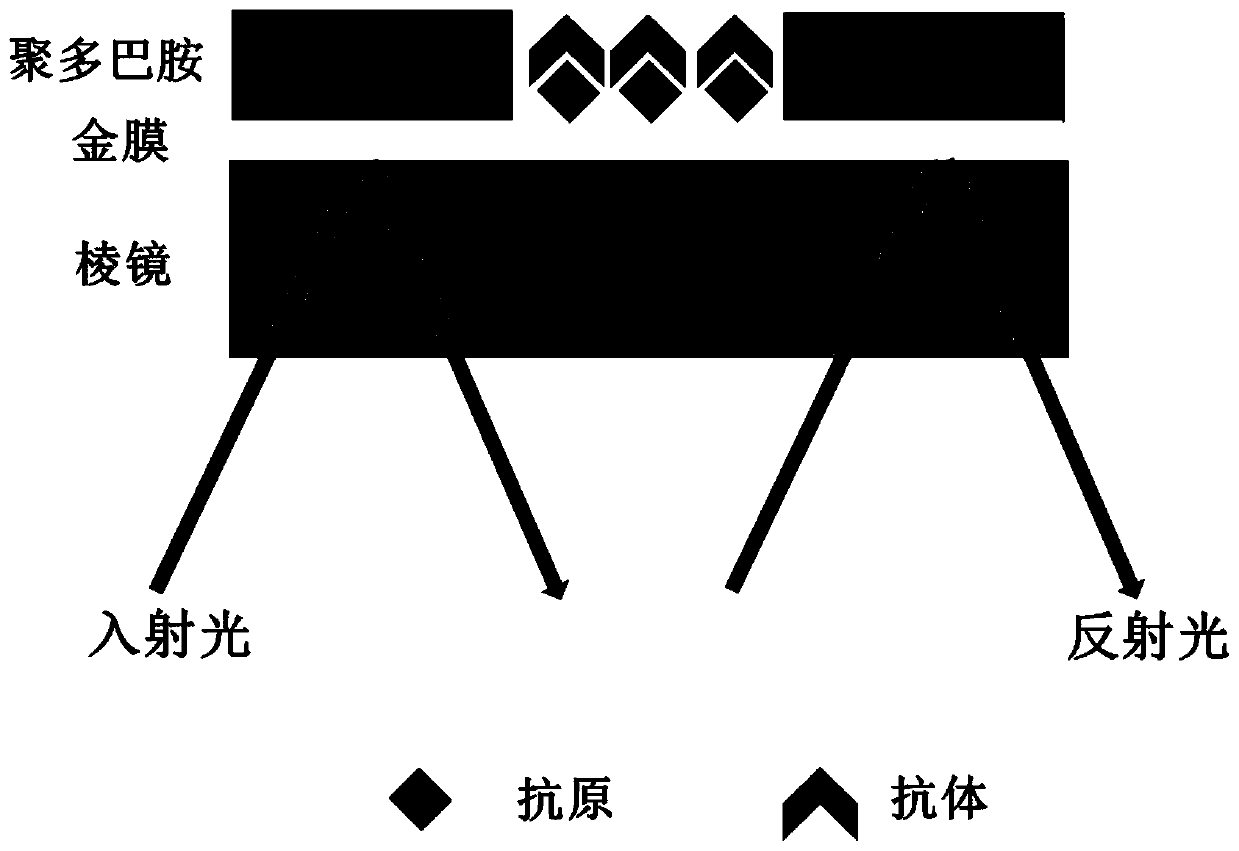
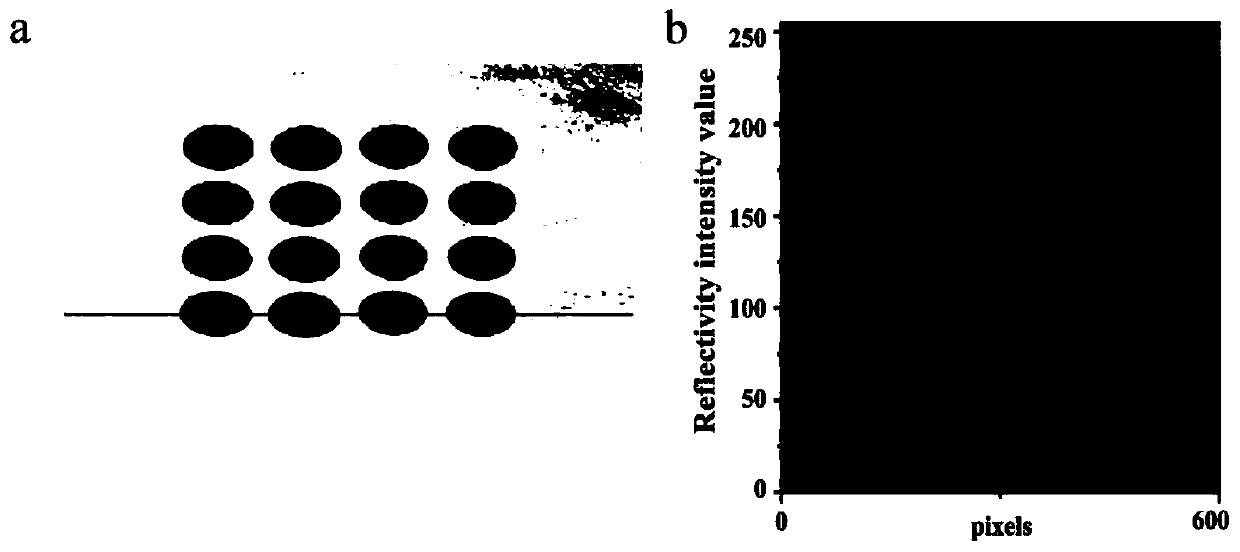
ActiveCN110702642AEasy extractionEasy to analyzeMaterial analysis by optical meansDot matrixElectron resonance
The invention relates to a preparation method of a micro-well structure SPRi chip, a product and application thereof, and belongs to the field of biological detection. The preparation method comprisesthe following steps: firstly, growing a polydopamine film with the thickness of 15-100 nm on a gold film chip, and then placing a mask to form the micro-well structure SPRi chip under the irradiationof ultraviolet light. Efficient SPRi multi-component detection and parallel analysis can be realized, surface electron resonance waves are converged in a detection area (micro-well), the SPRi detection intrinsic sensitivity of the area is improved, meanwhile, background signals are reduced, in addition, a micro-array dot matrix with a clear area is further constructed, and extraction and analysisof detection signals are facilitated.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Shock absorber and manufacturing method of shock absorber
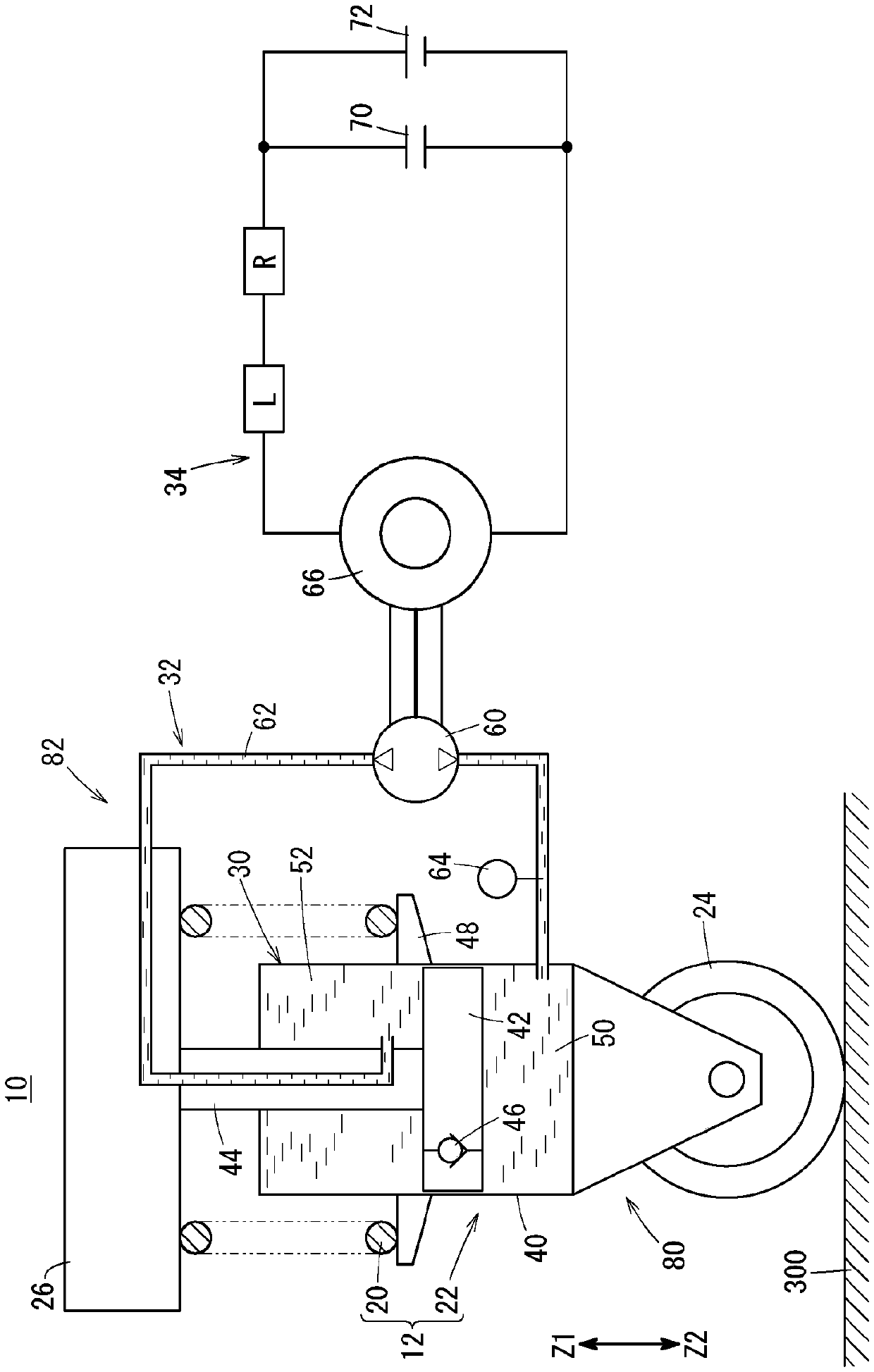
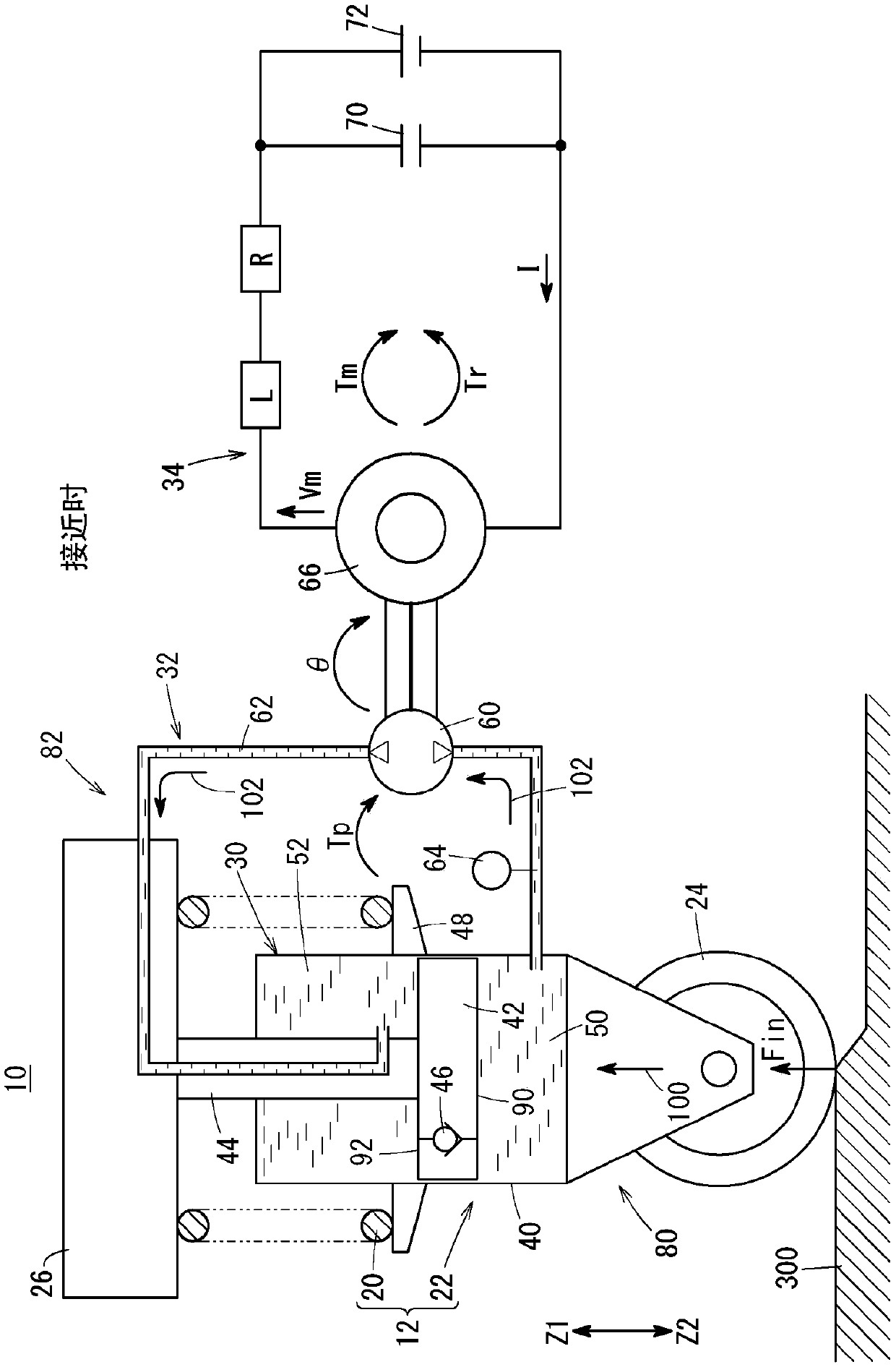
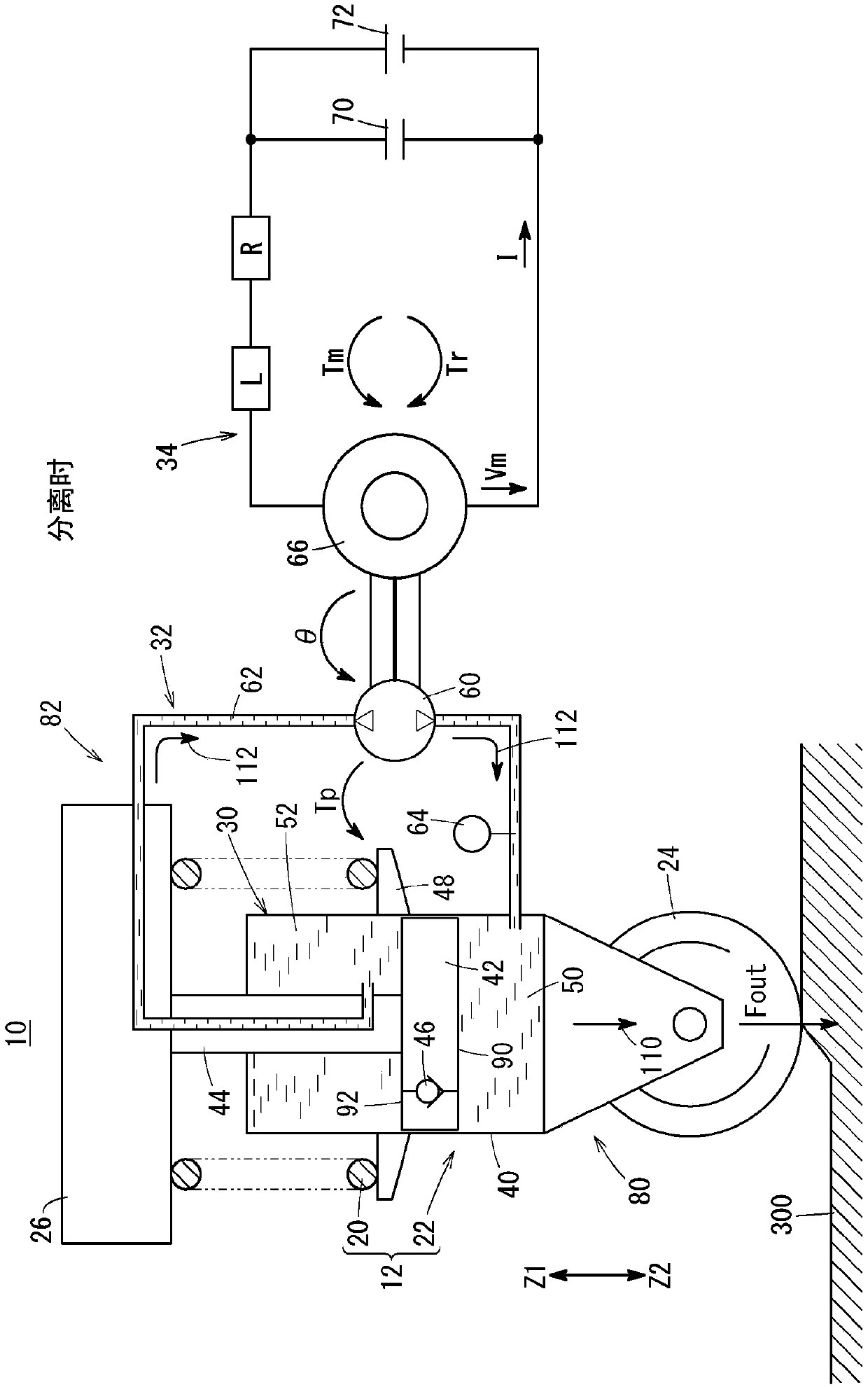
InactiveCN106795937BHave an effectSpringsSprings/dampers functional characteristicsElectricityCapacitance
The present invention provides a shock absorber capable of improving energy efficiency for attenuating input vibration corresponding to an unsprung resonance frequency and a sprung resonance frequency, and a method of manufacturing the shock absorber. In the shock absorber (22), the electrical resonance frequency determined according to the inductance (L) of the electromagnetic motor (66) and the capacity (C) of the capacitor (70) is set within ±20% of the unsprung resonance frequency, thereby In addition to suppressing the input vibration corresponding to the unsprung resonance frequency, the input vibration corresponding to the sprung resonance frequency is also passively suppressed.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com