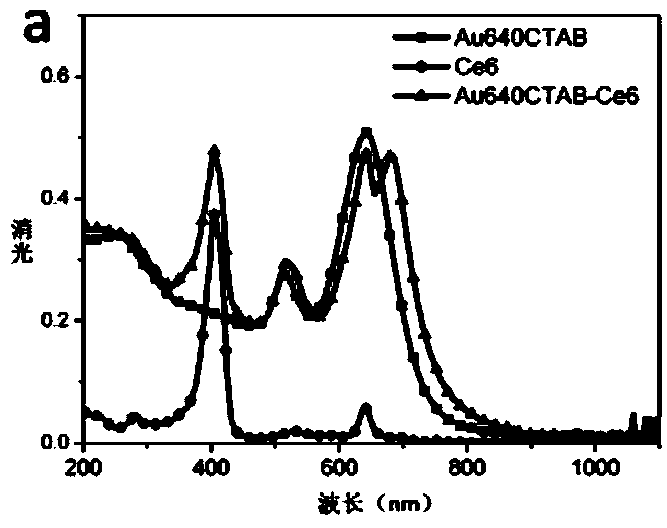
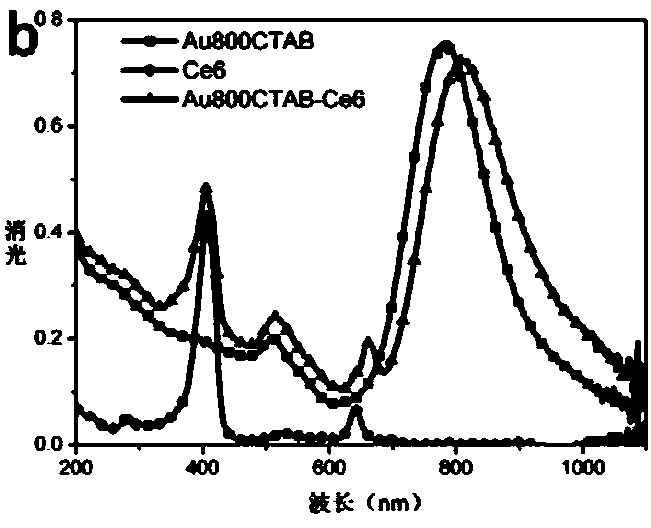
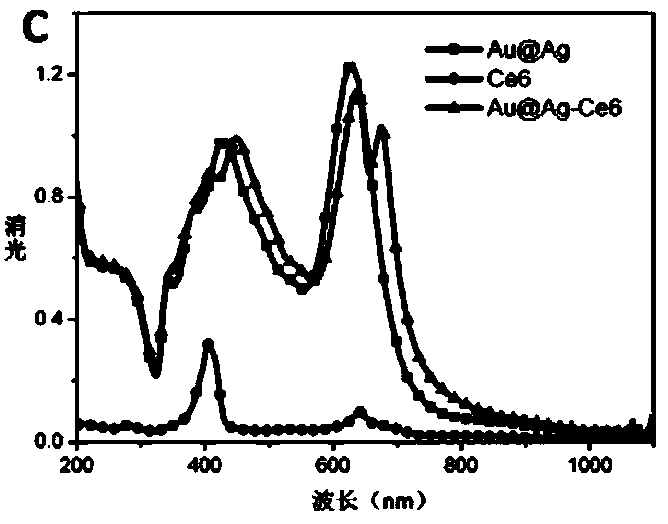
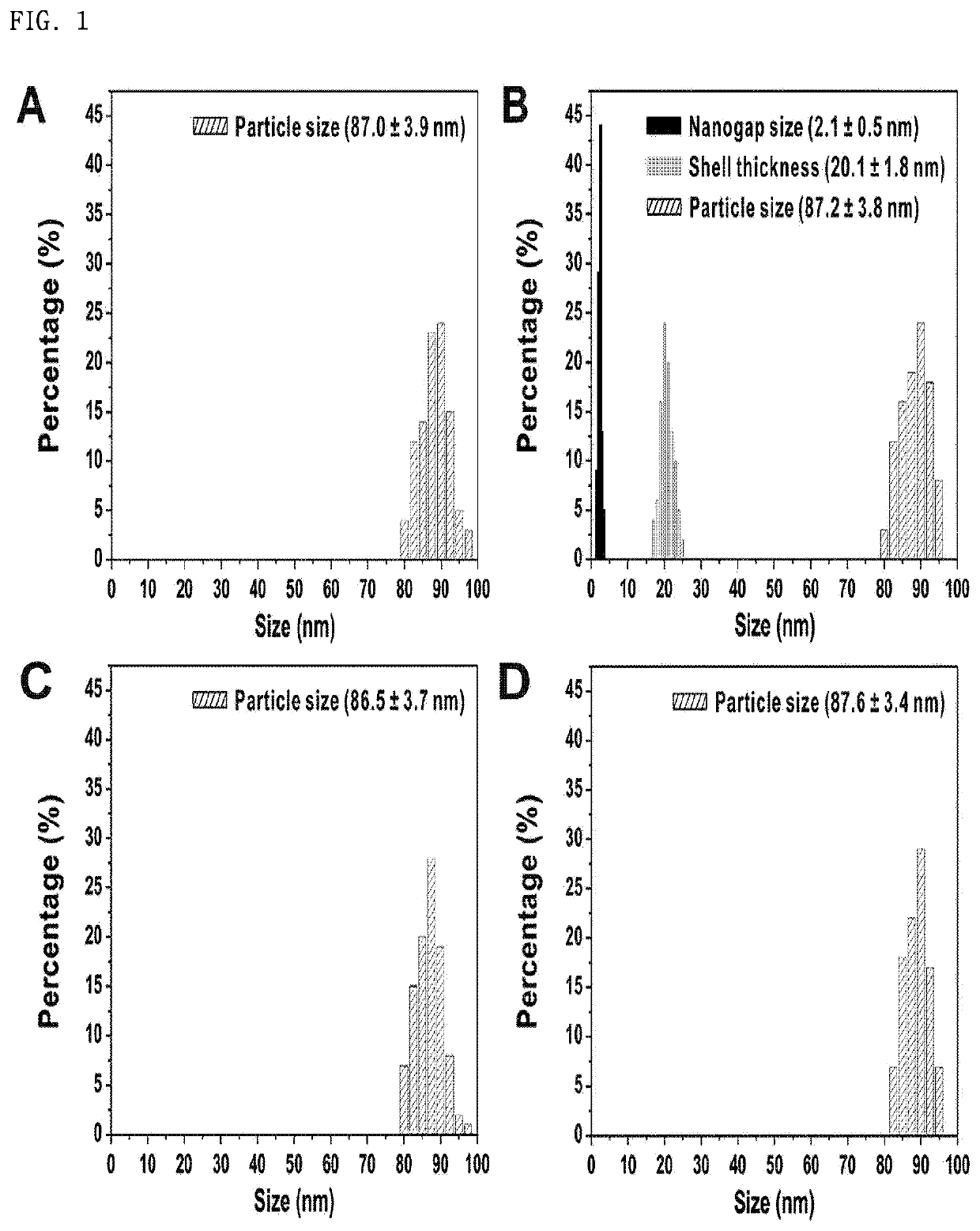
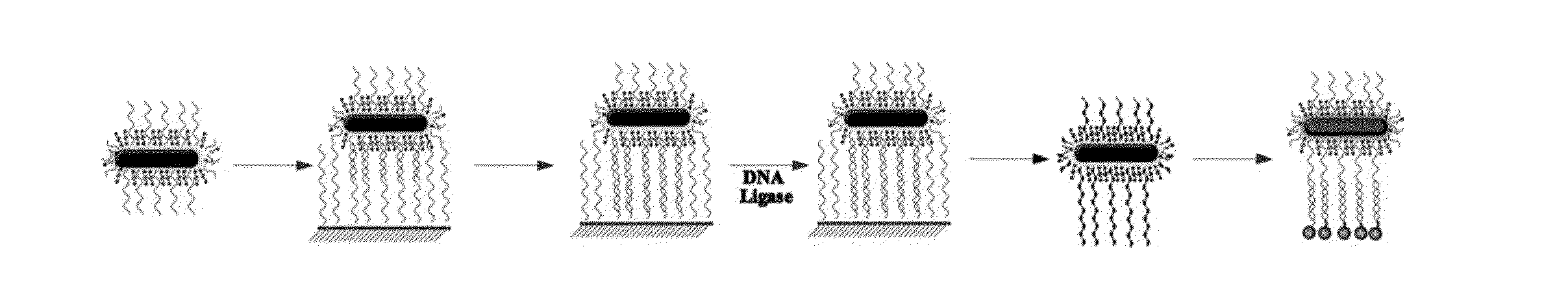Patents
Literature
46 results about "Plasmonic nanoparticles" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Plasmonic nanoparticles are particles whose electron density can couple with electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths that are far larger than the particle due to the nature of the dielectric-metal interface between the medium and the particles: unlike in a pure metal where there is a maximum limit on what size wavelength can be effectively coupled based on the material size.
Ultrasound delivery of nanoparticles
ActiveUS20140316387A1Substantial patient painSubstantial discomfortSonopheresisCosmetic preparationsPlasmonic nanoparticlesSkin tissue
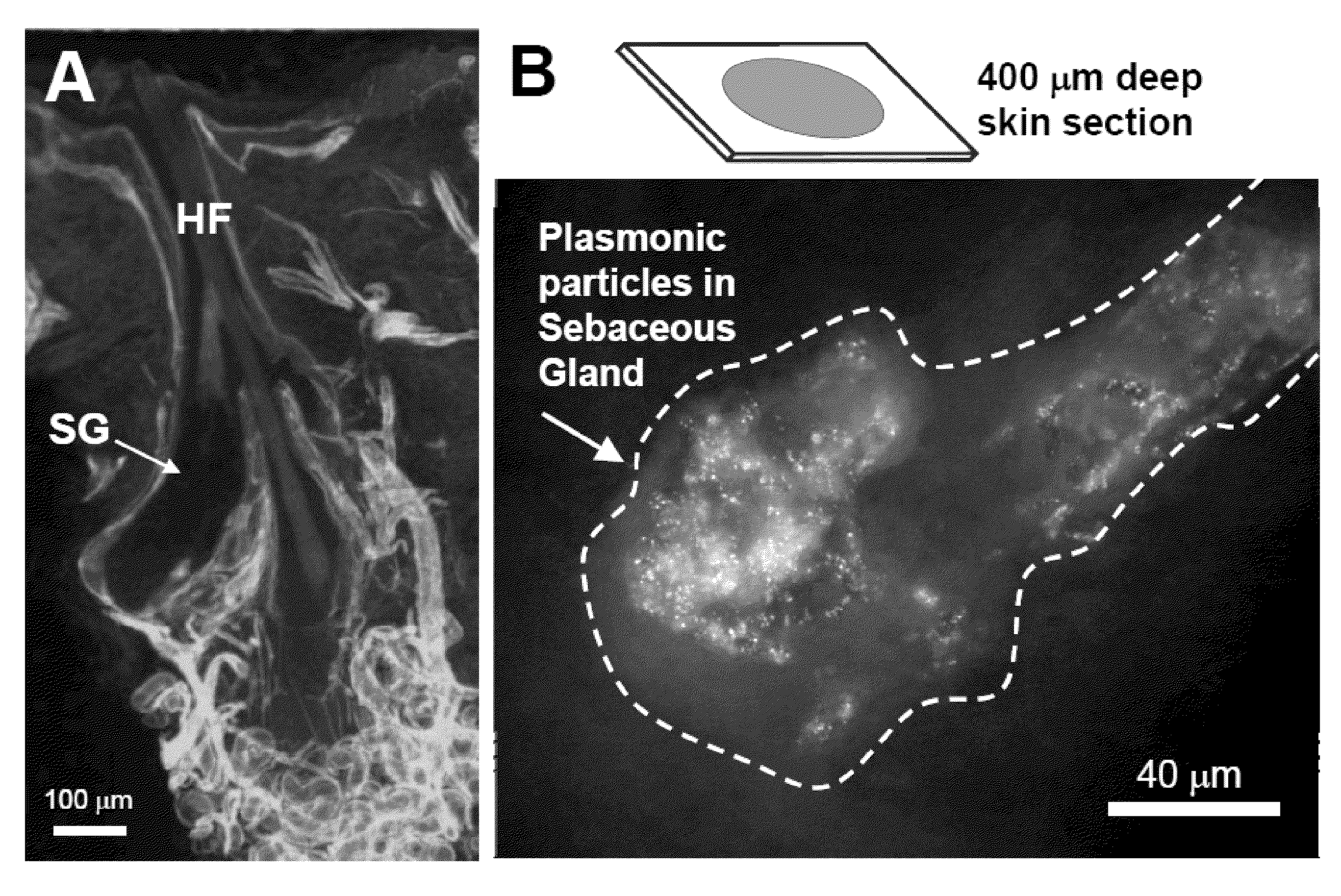
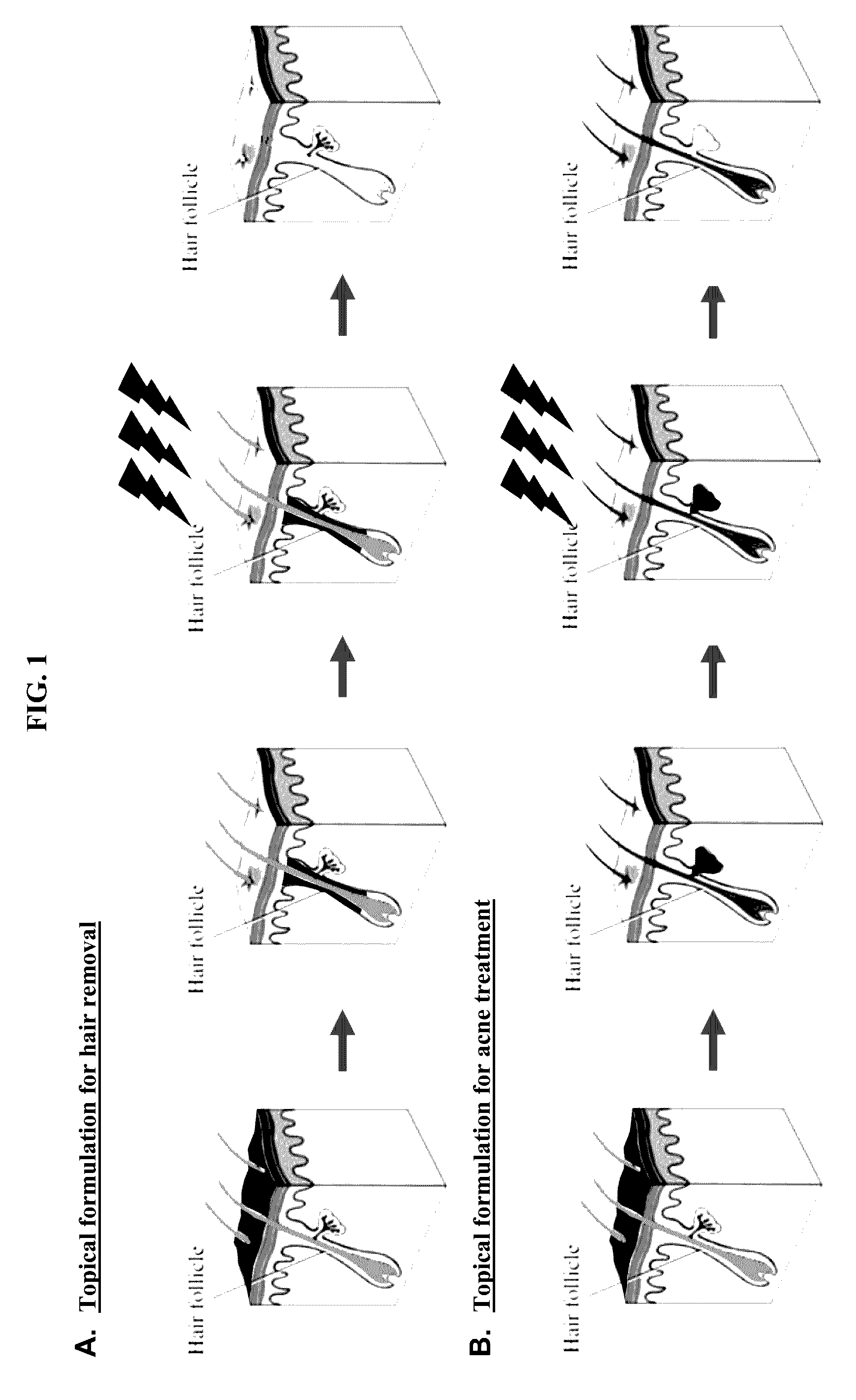
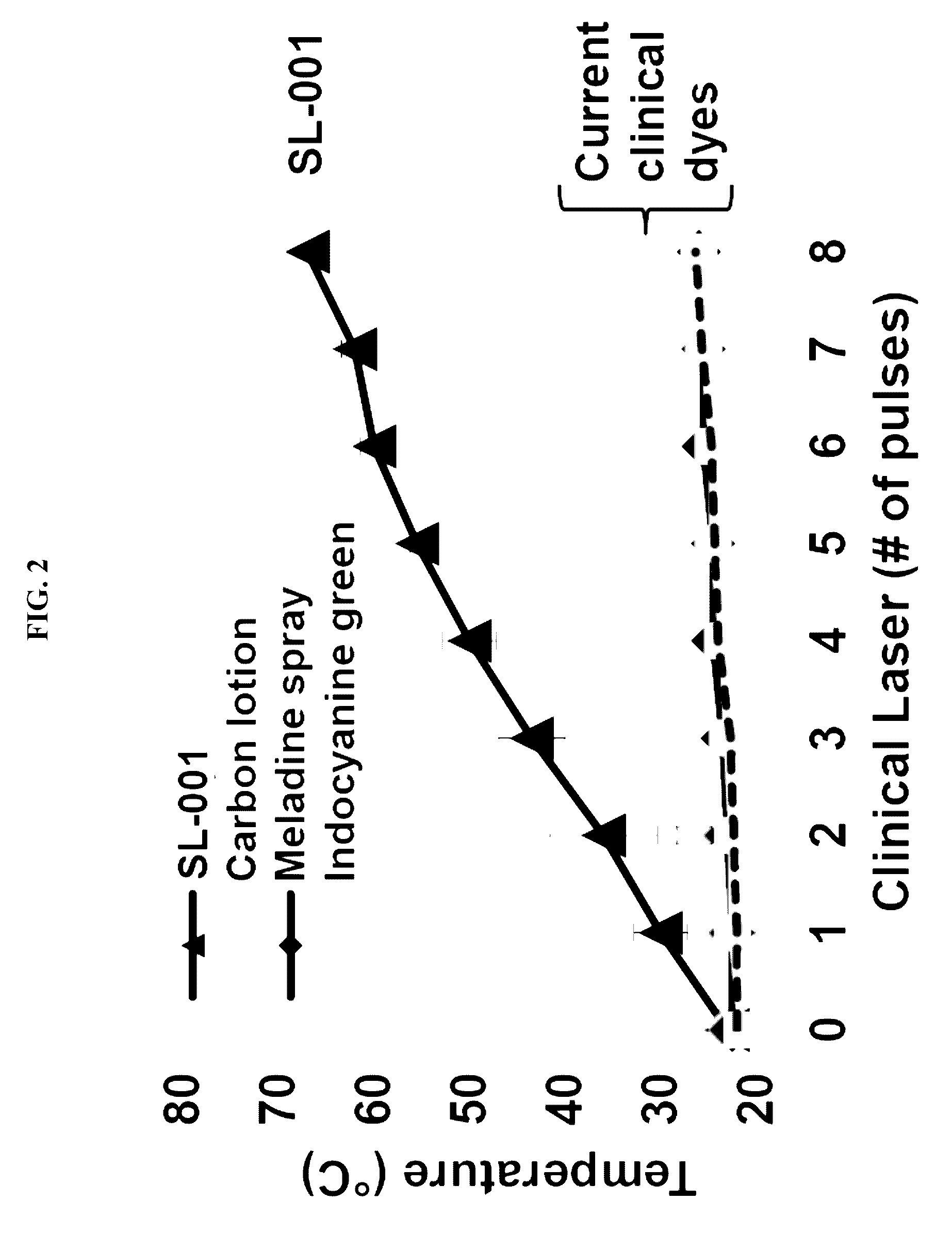
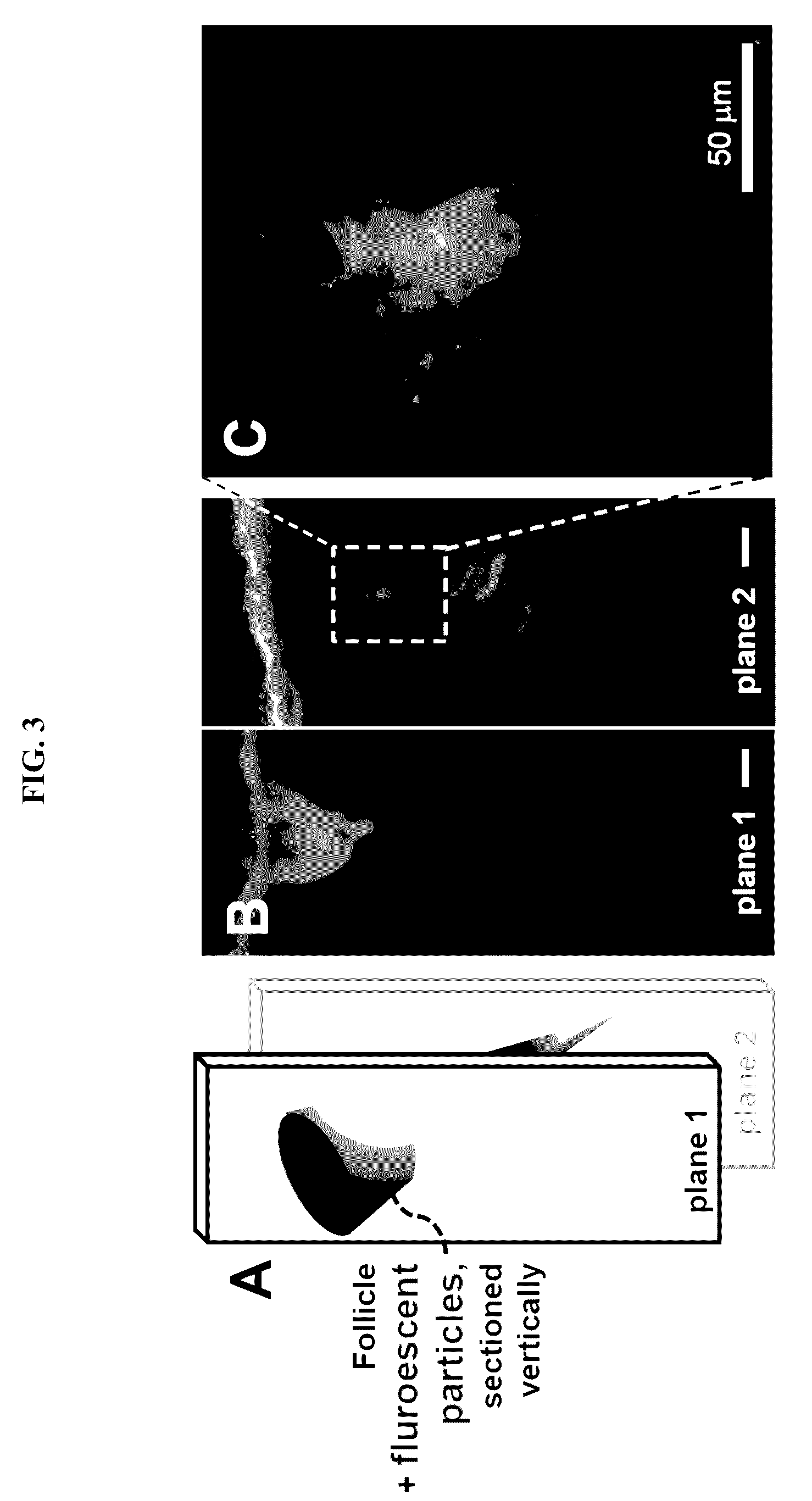
Enhanced delivery of compositions for treatment of skin tissue with photoactive plasmonic nanoparticles and light, with embodiments relating to delivery devices using, for example, ultrasound. Treatments are useful for cosmetic, diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
Owner:CORONADO AESTHETICS LLC
Porous SERS Analytical Devices and Methods of Detecting a Target Analyte
ActiveUS20130107254A1Avoid spreadingHigh complexityMaterial nanotechnologyRadiation pyrometryTarget analysisAnalyte
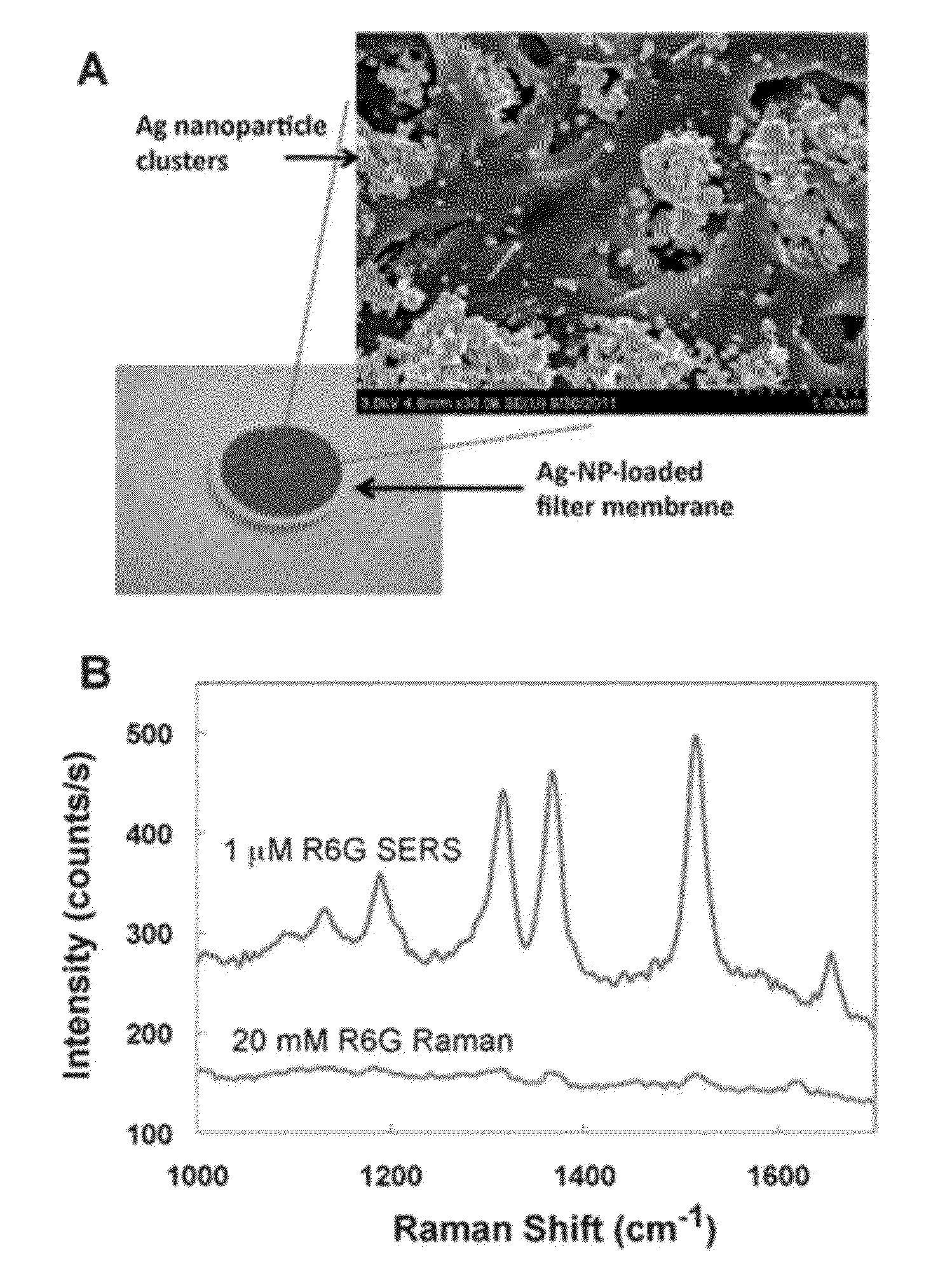
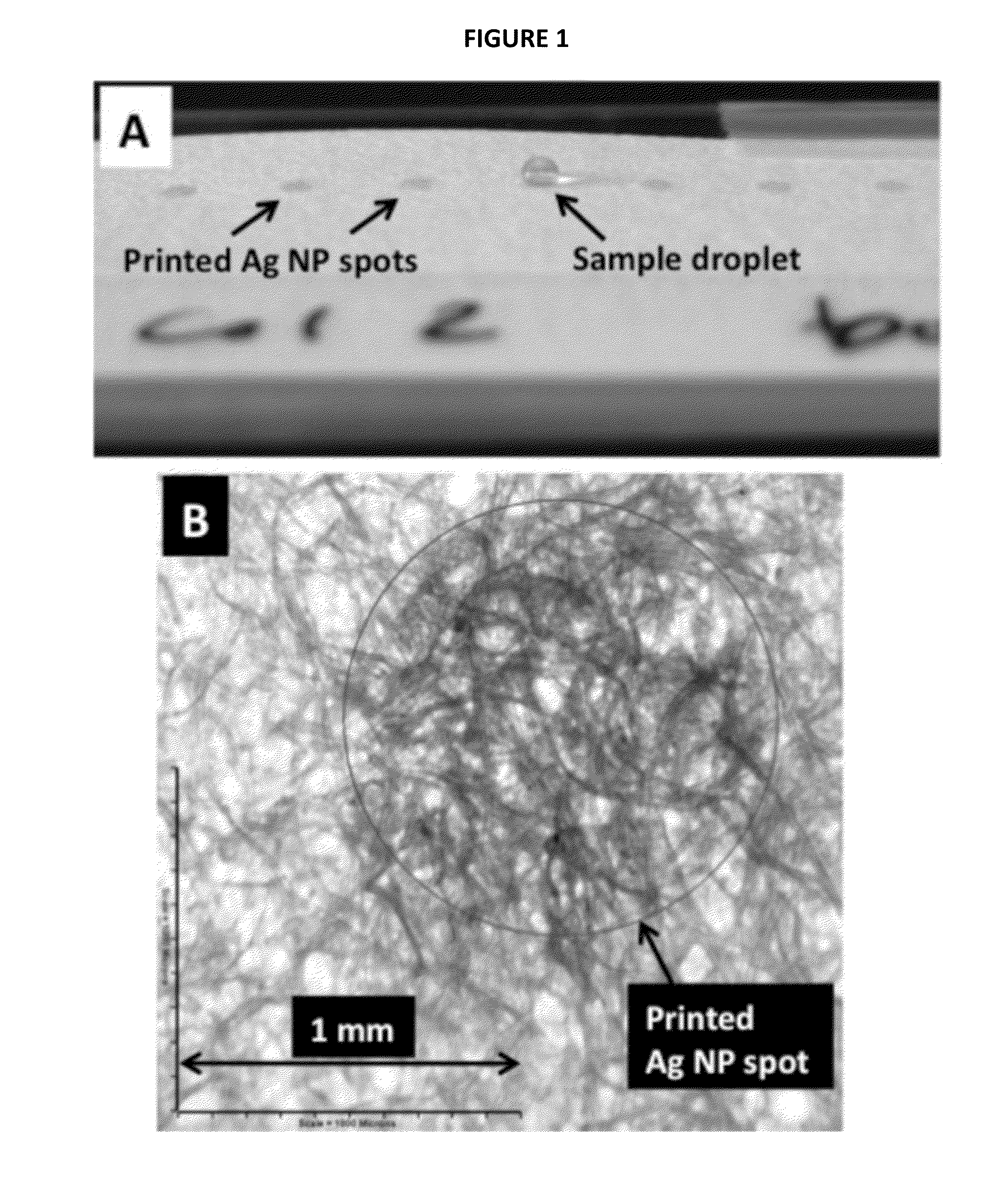
A surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) analytical device includes a substrate having a porous structure, and a plurality of plasmonic nanoparticles embedding in the porous structure and forming a sensing region. A method of detecting a target analyte in a sample includes contacting the sample with the substrate, whereby the target analyte, if present in the sample, is concentrated in the sensing matrix. The substrate may then be analyzed using SERS detection equipment.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
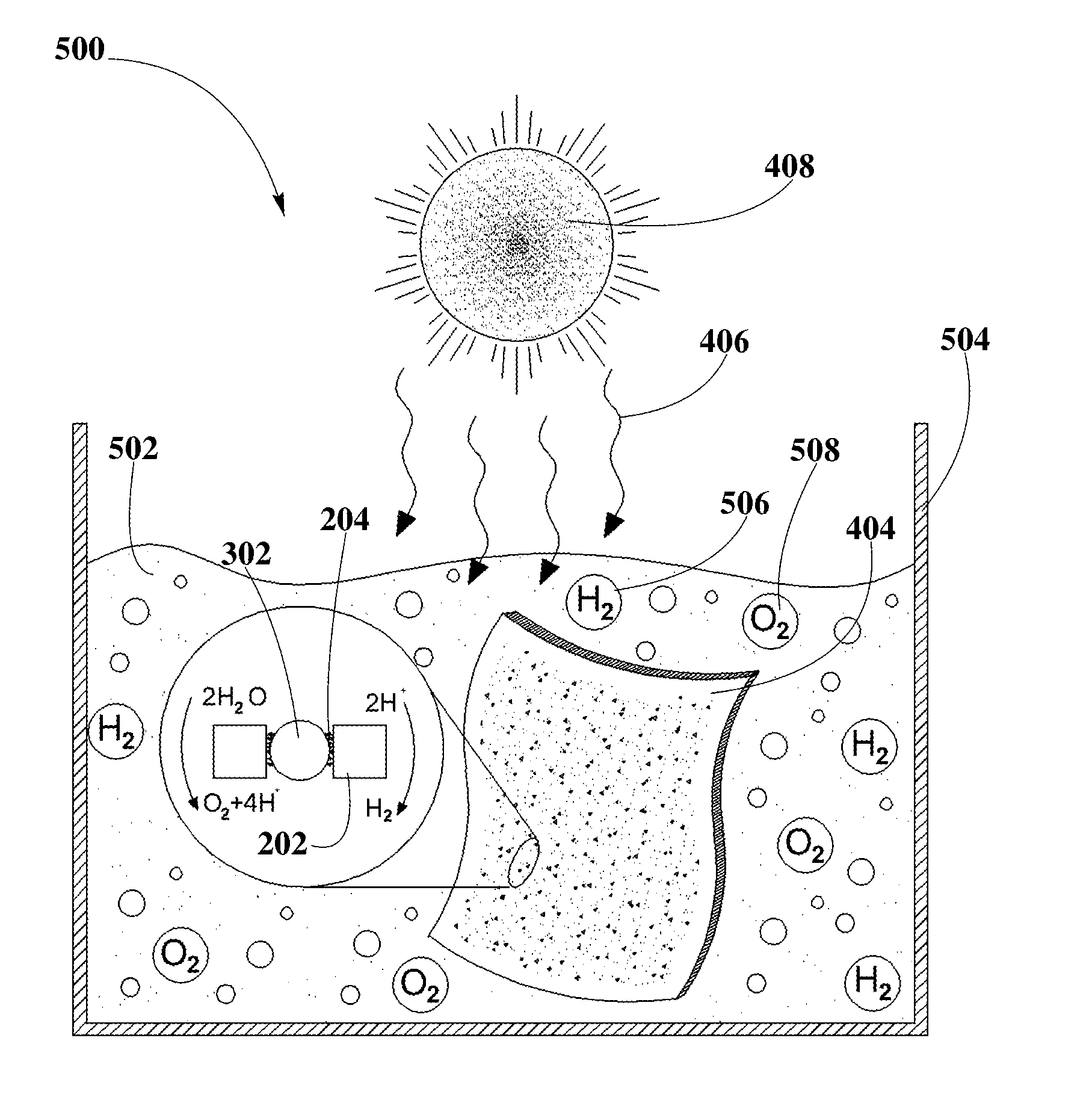
System for increasing efficiency of semiconductor photocatalysts employing a high surface area substrate
InactiveUS20140272623A1Speed up redox reactionHigh productHydrogenOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideSemiconductor nanocrystalsOxygen
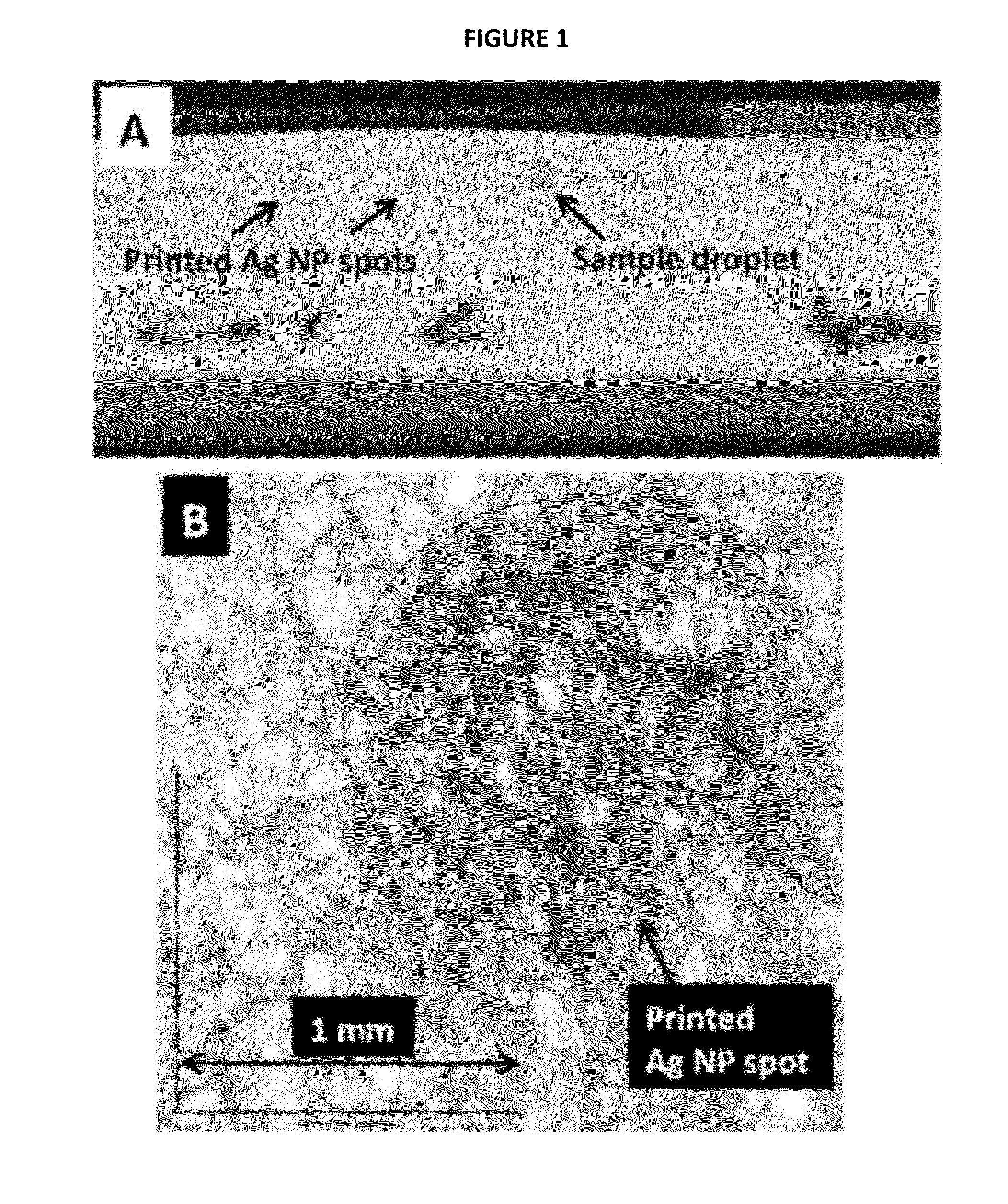
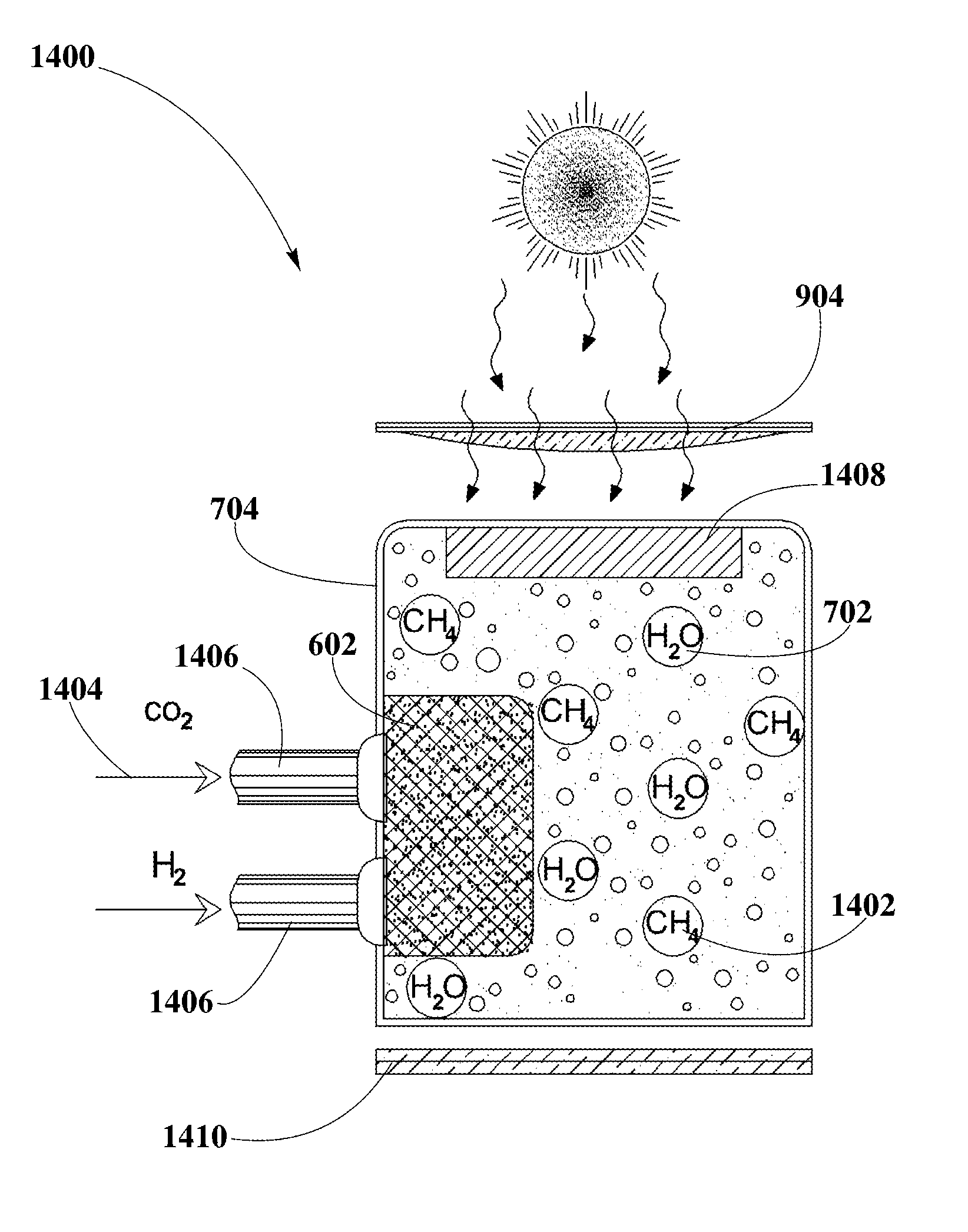
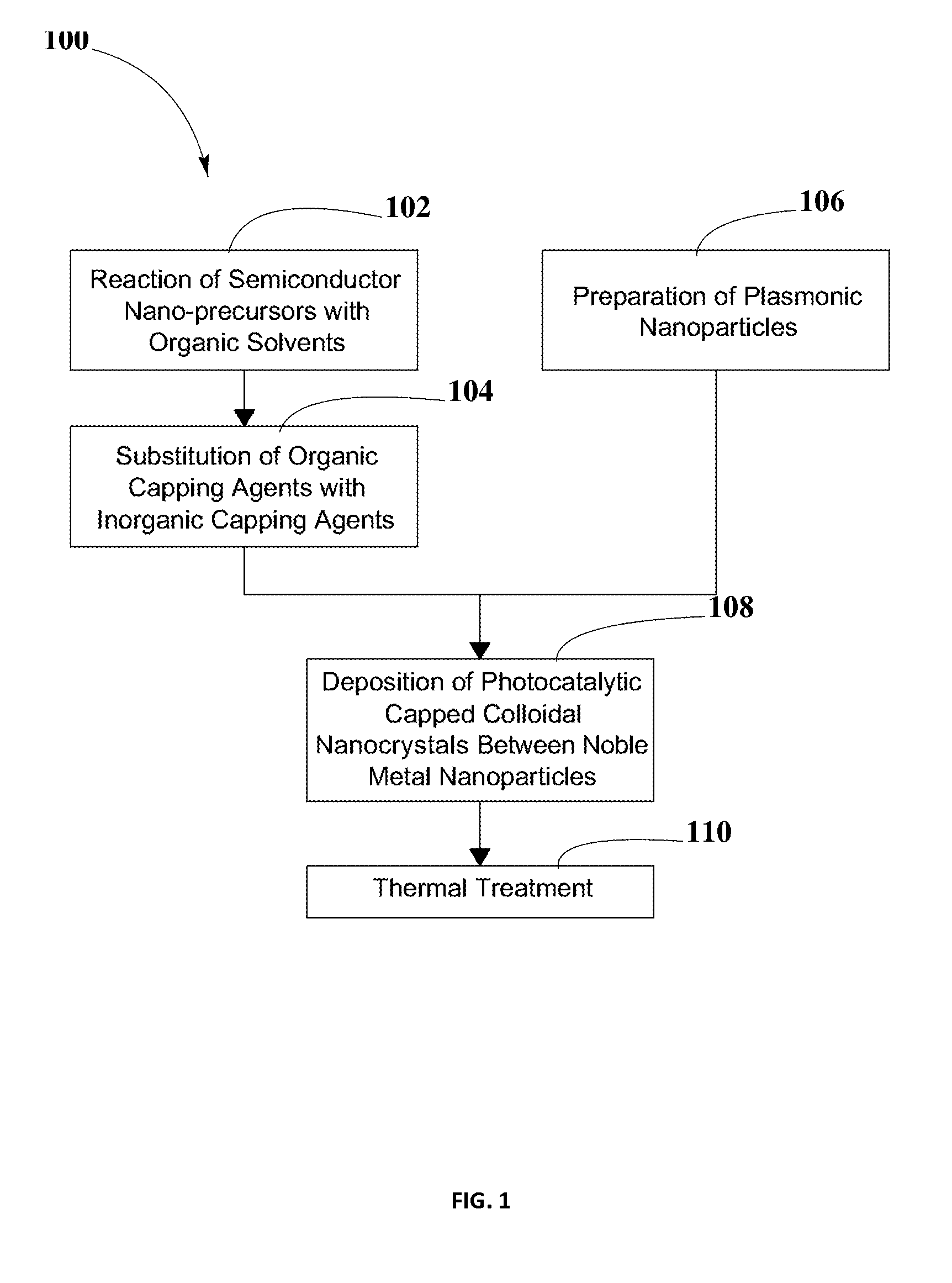
A system for energy production may include a photoactive material with photocatalytic capped colloidal nanocrystals (PCCN) and plasmonic nanoparticles over a high surface area gridded substrate for increasing light harvesting efficiency. The formation of PCCN may include a semiconductor nanocrystal synthesis and an exchange of organic capping agents with inorganic capping agents. Additionally, the PCCN may be deposited between the plasmonic nanoparticles, and may act as photocatalysts for redox reactions. The photoactive material may be used in a plurality of photocatalytic energy conversion applications such as water splitting or CO2 reduction. Higher light harvesting and energy conversion efficiency may be achieved by combining the plasmonic nanoparticles and PCCN over the high surface area gridded substrate. The system may also include elements necessary to collect, transfer and store hydrogen and oxygen, for subsequent transformation into electrical energy.
Owner:SUNPOWER TECH CORP
Plasmonic enhancement of whispering gallery mode biosensors
ActiveUS20120069331A1Reduce conductivityRadiation pyrometryMicrobiological testing/measurementWhispering galleryResonance
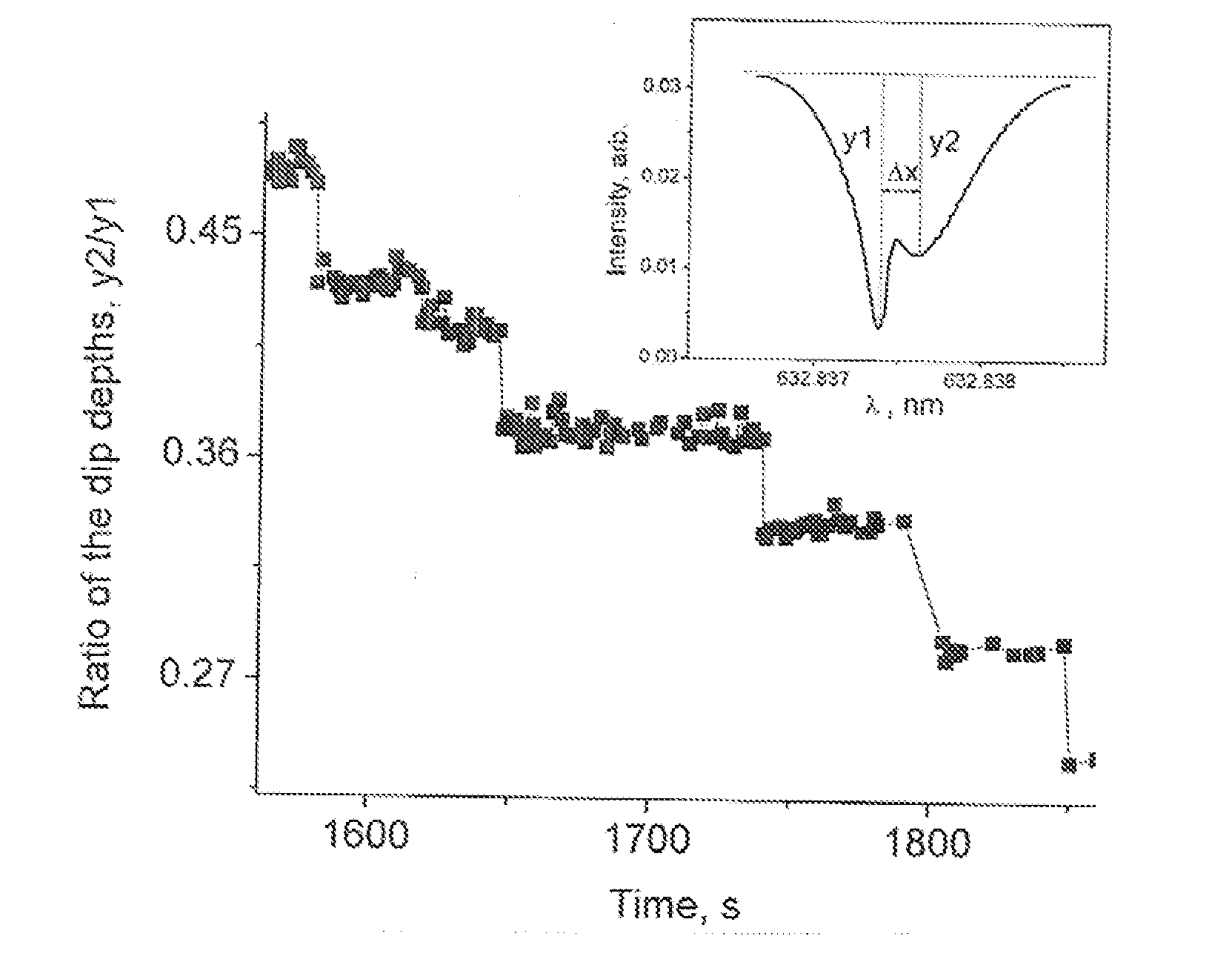
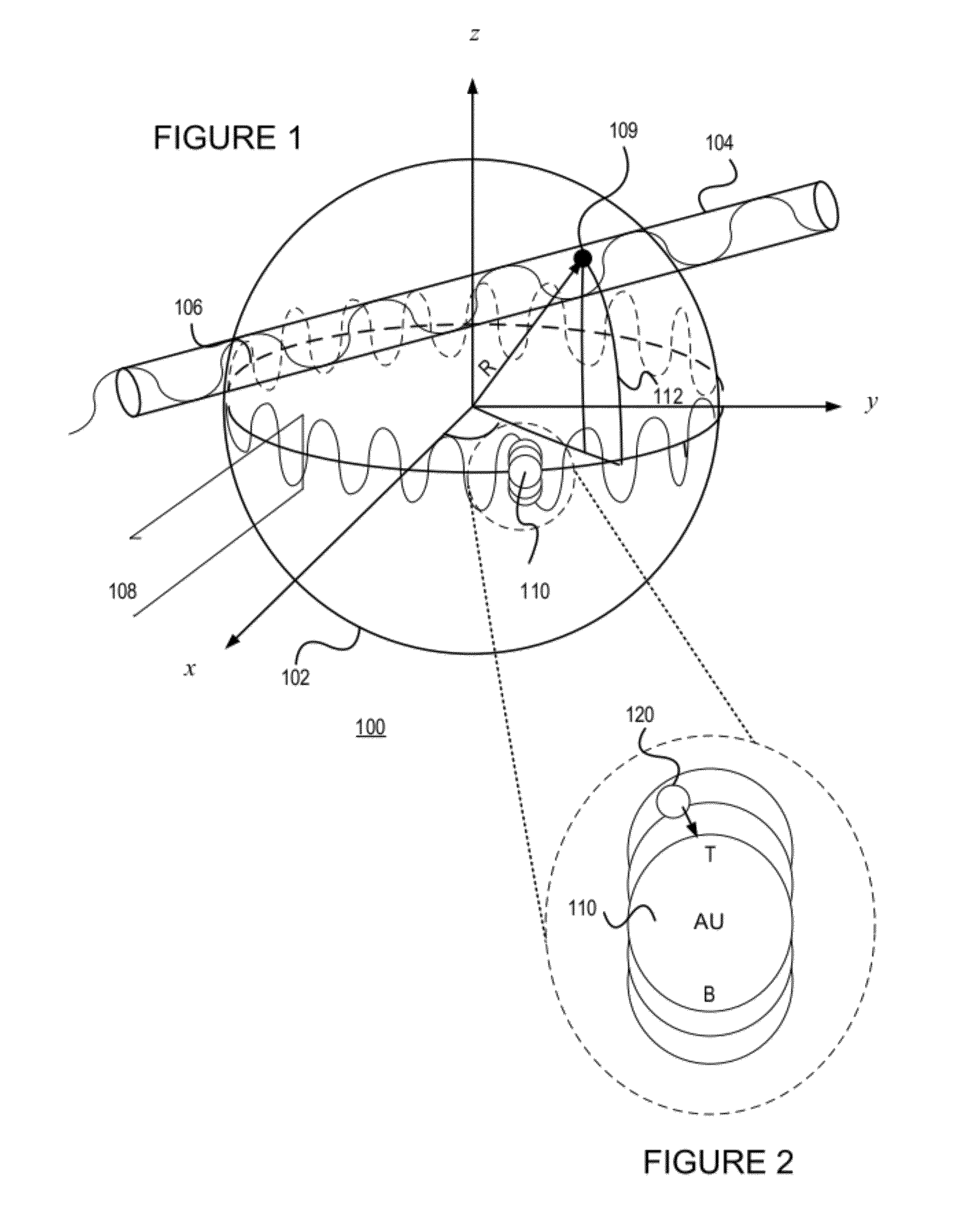
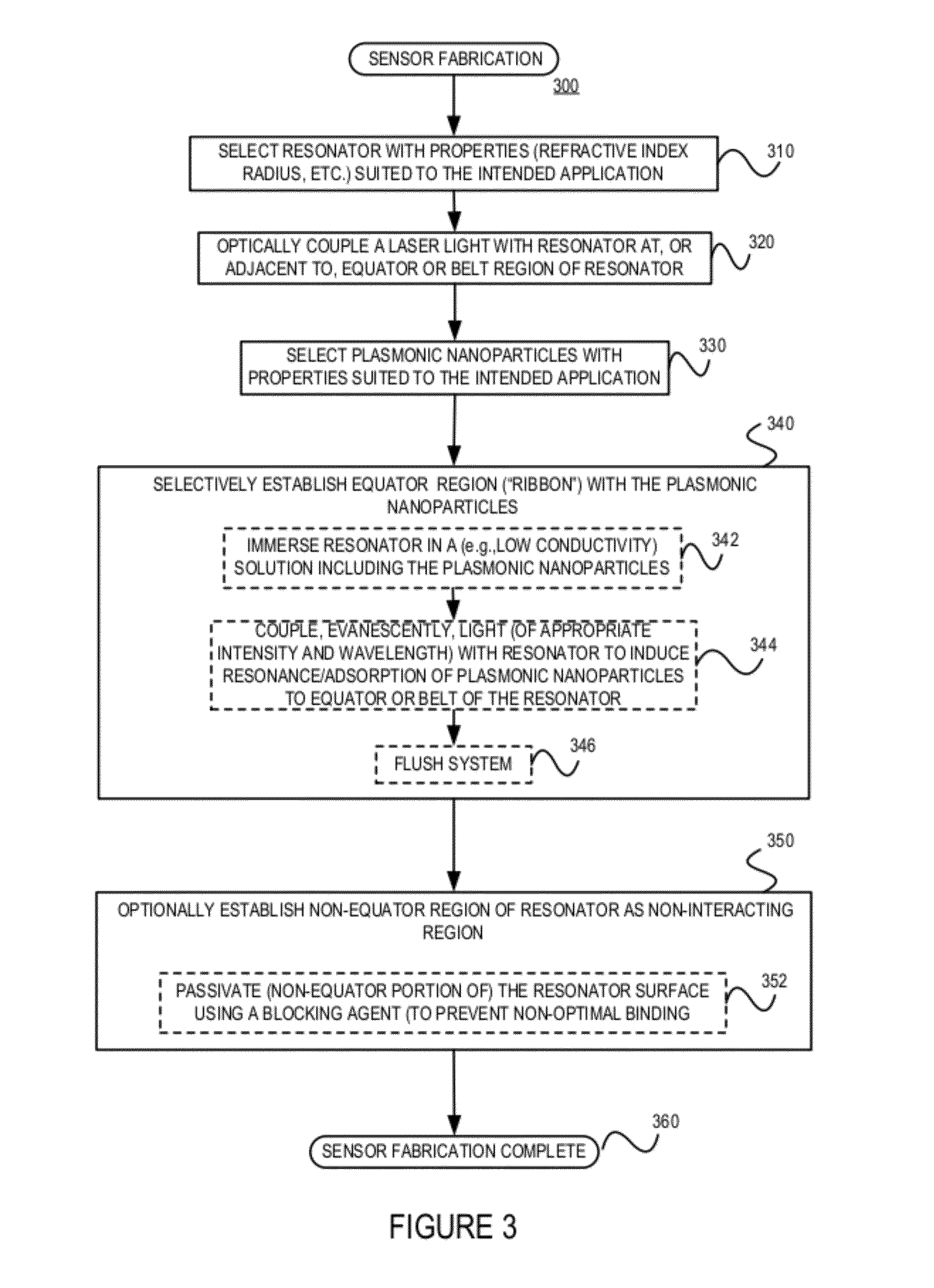
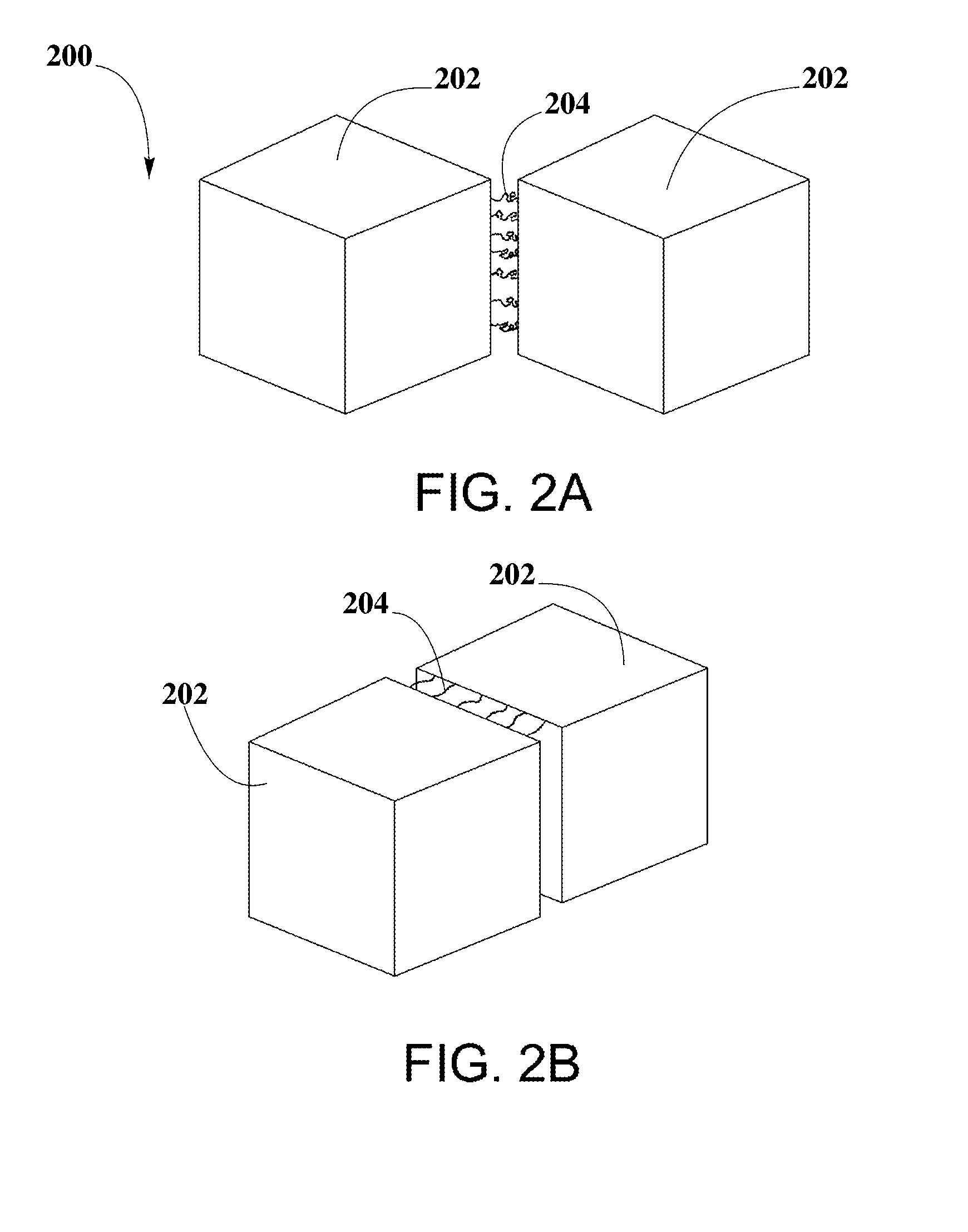
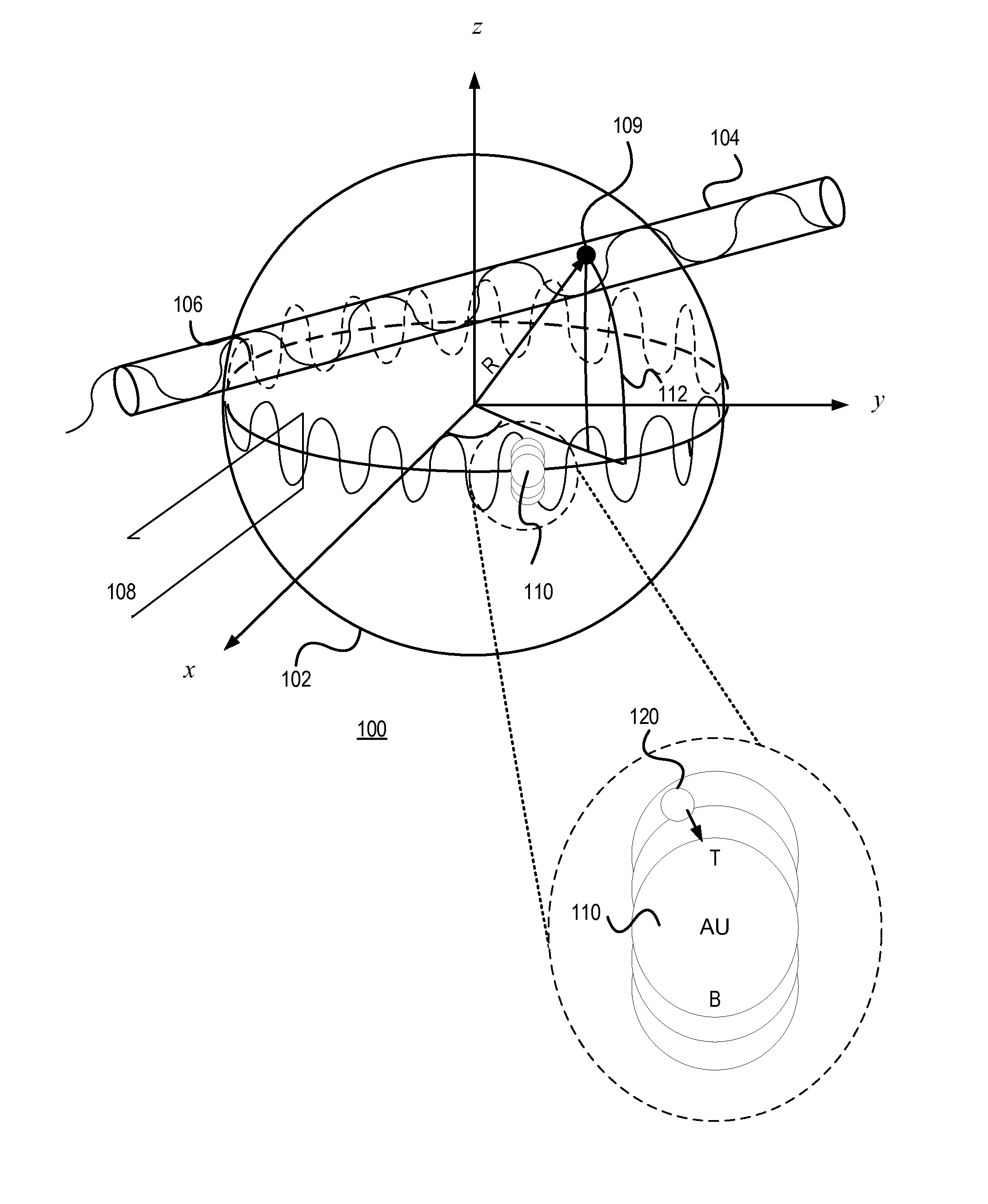
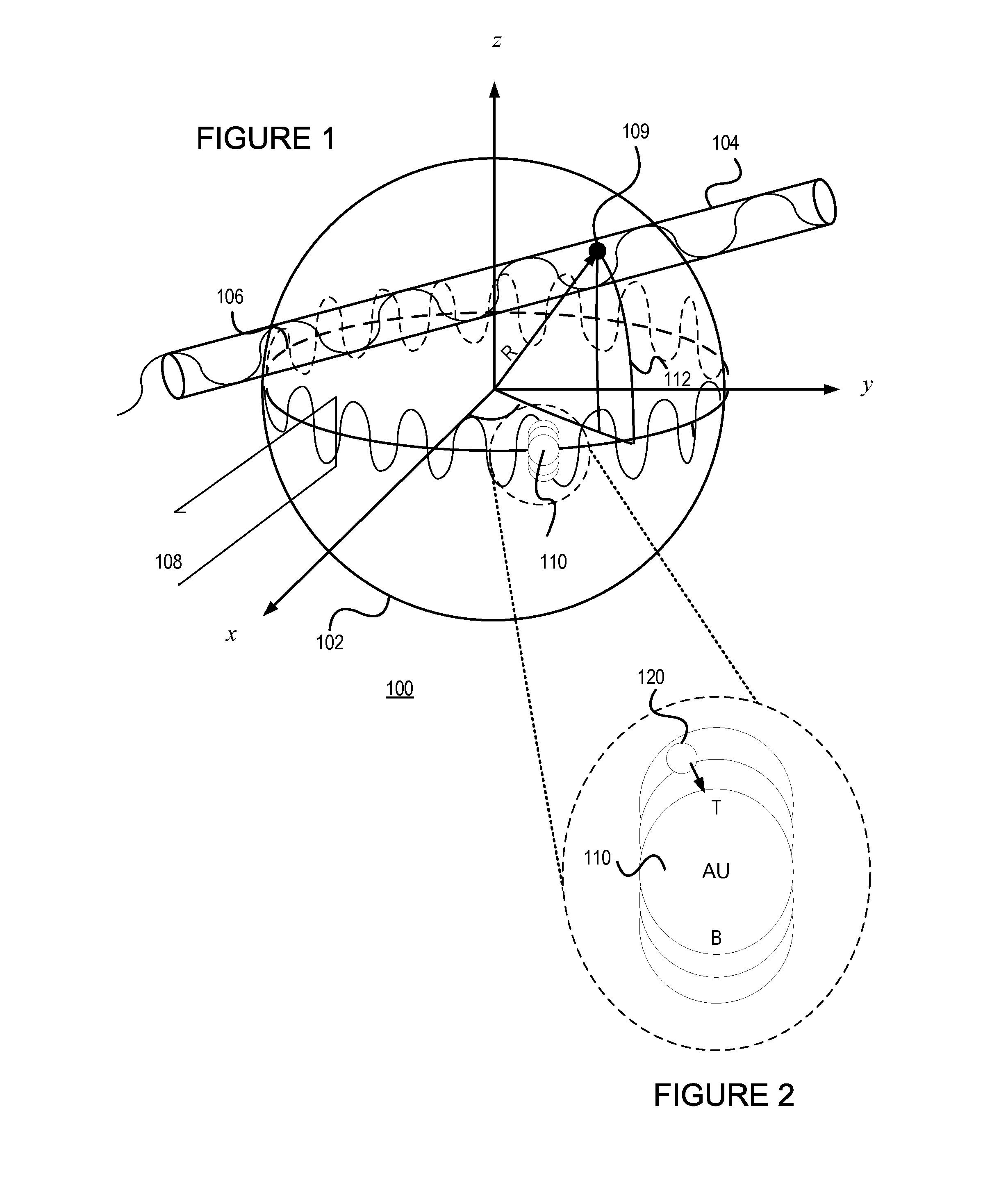
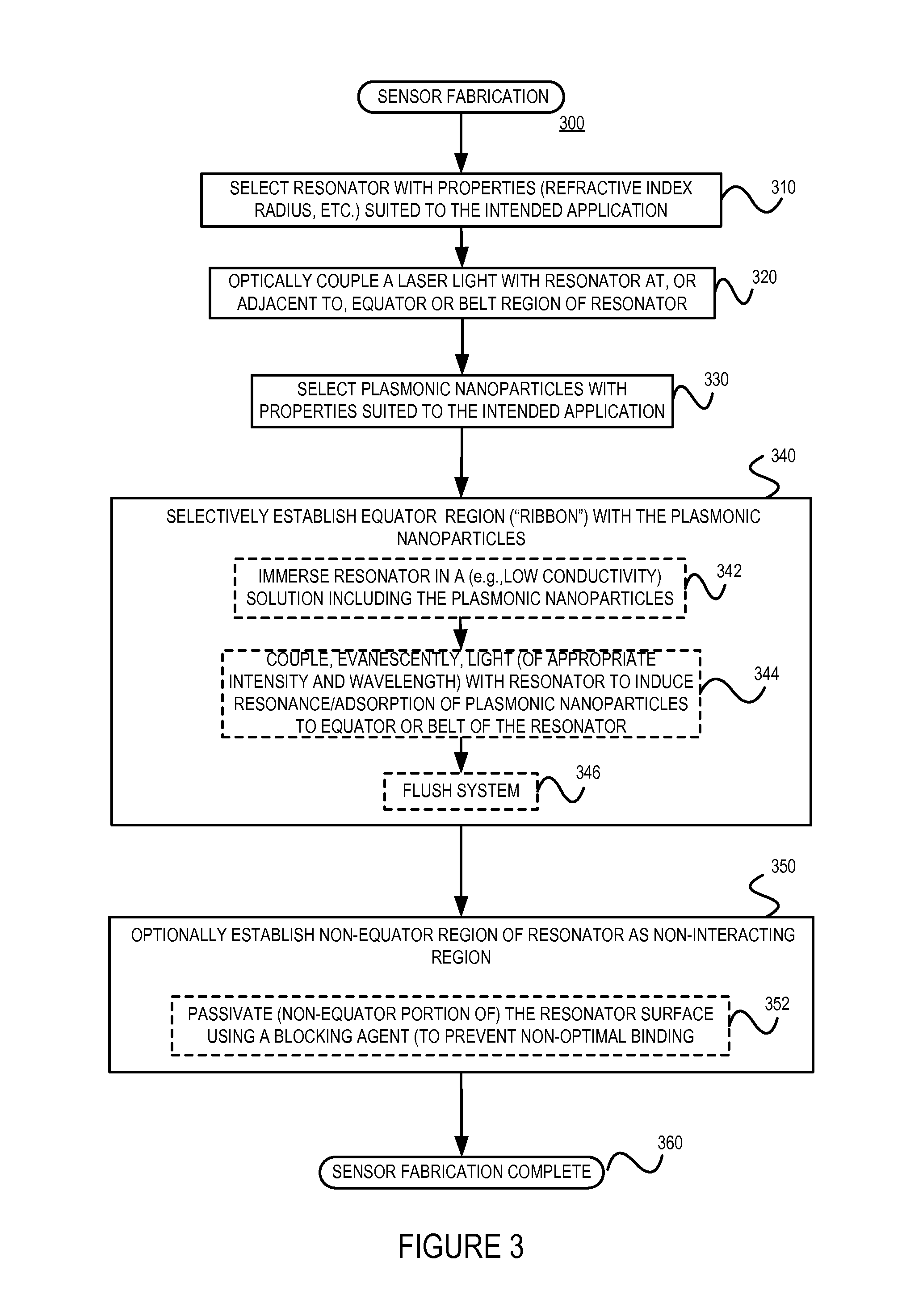
A sensor for determining the presence or concentration of a target entity in a medium is described, and includes (a) an optical waveguide; (b) a microresonator optically coupled with the optical waveguide such that light within the optical waveguide induces a resonant mode within the microresonator at an equator region (or a mode volume); and (c) at least one plasmonic nanoparticle adsorbed onto a surface area of the microresonator within the equator region (or the mode volume) such that light inducing a resonant mode within the microresonator also causes a plasmonic resonance in the at least one plasmonic nanoparticle. Detection methods for using such sensors are also described. Finally, methods, involving the use of carousel forces, for fabricating such sensors are also described.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
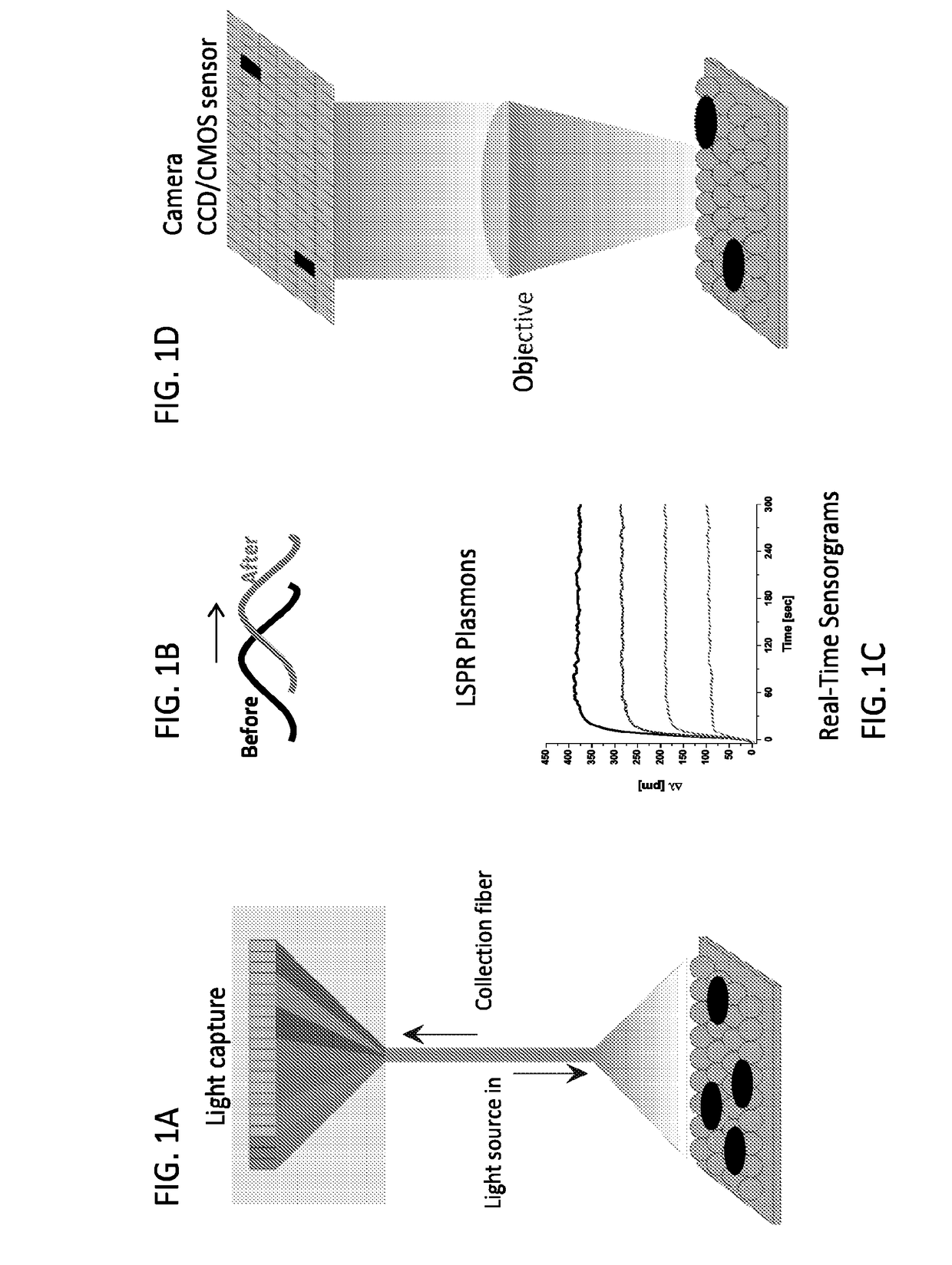
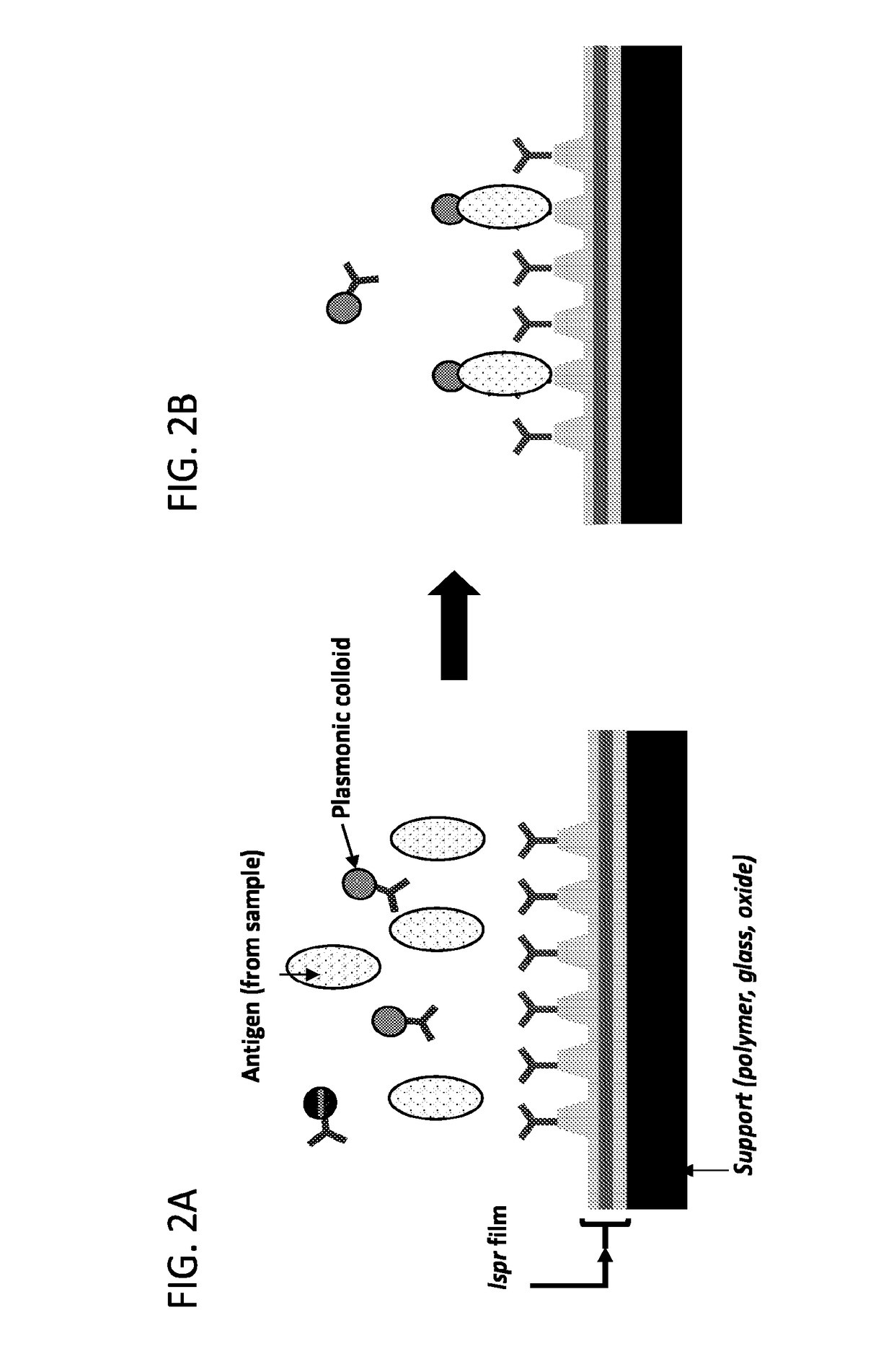
Plasmonic nanoparticles and lspr-based assays
InactiveUS20180299458A1Material nanotechnologyMaterial analysis by optical meansLower limitResonance
Compositions, methods, devices, and systems are described for performing single-step, homogenous, localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR)-based plasmonic assays having exceptional assay sensitivity and extremely low limits of detection (LODs). Ag / Au core / shell nanoparticles are described, which may be used with LSPR sensors to develop single-step, homogeneous, LSPR-based assays.
Owner:LAMDAGEN CORP
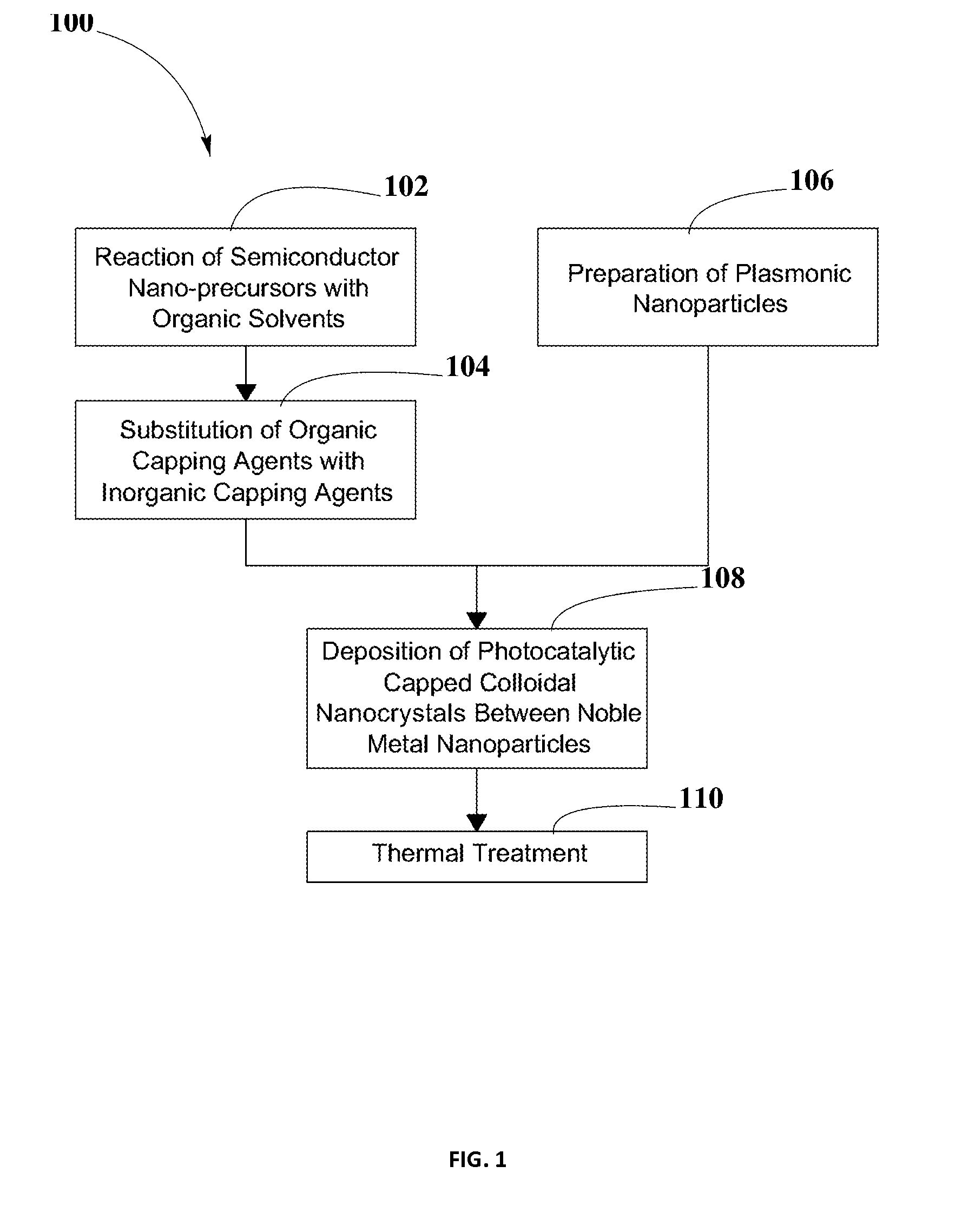
Method for Increasing Efficiency of Semiconductor Photocatalysts
InactiveUS20140262806A1Speed up redox reactionHigh productCellsHydrogenSemiconductor materialsWavelength
A method and composition for producing a photoactive material including photocatalytic capped colloidal nanocrystals (PCCN) and plasmonic nanoparticles are disclosed. The PCCN may include a semiconductor nanocrystal synthesis and an exchange of organic capping agents with inorganic capping agents. Additionally, the PCCN may be deposited between the plasmonic nanoparticles, and may act as photocatalysts for redox reactions. The photoactive material may be used in a plurality of photocatalytic energy conversion applications, such as water splitting and CO2 reduction. By combining different semiconductor materials for PCCN and plasmonic nanoparticles, and by changing their shapes and sizes, band gaps may be tuned to expand the range of wavelengths of sunlight usable by the photoactive material. Higher light harvesting and energy conversion efficiency may be achieved.
Owner:SUNPOWER TECH CORP
Plasmonic enhancement of whispering gallery mode biosensors
ActiveUS8493560B2Radiation pyrometryMicrobiological testing/measurementWhispering galleryEngineering
A sensor for determining the presence or concentration of a target entity in a medium is described, and includes (a) an optical waveguide; (b) a microresonator optically coupled with the optical waveguide such that light within the optical waveguide induces a resonant mode within the microresonator at an equator region (or a mode volume); and (c) at least one plasmonic nanoparticle adsorbed onto a surface area of the microresonator within the equator region (or the mode volume) such that light inducing a resonant mode within the microresonator also causes a plasmonic resonance in the at least one plasmonic nanoparticle. Detection methods for using such sensors are also described. Finally, methods, involving the use of carousel forces, for fabricating such sensors are also described.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Ultrasound delivery of nanoparticles
ActiveUS9572880B2Improve skinHigh energySonopheresisCosmetic preparationsPlasmonic nanoparticlesSkin tissue
Enhanced delivery of compositions for treatment of skin tissue with photoactive plasmonic nanoparticles and light, with embodiments relating to delivery devices using, for example, ultrasound. Treatments are useful for cosmetic, diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
Owner:CORONADO AESTHETICS LLC
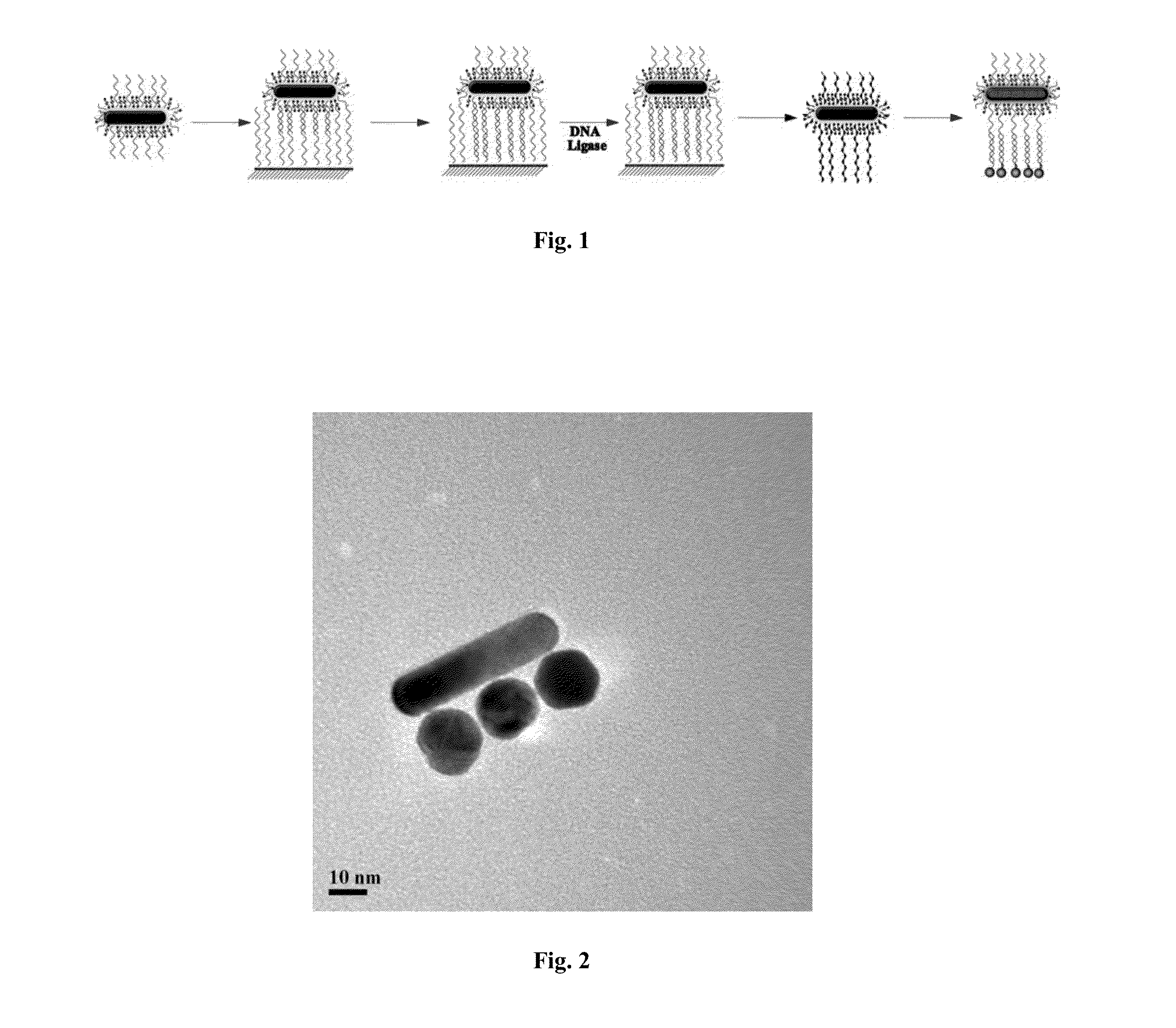
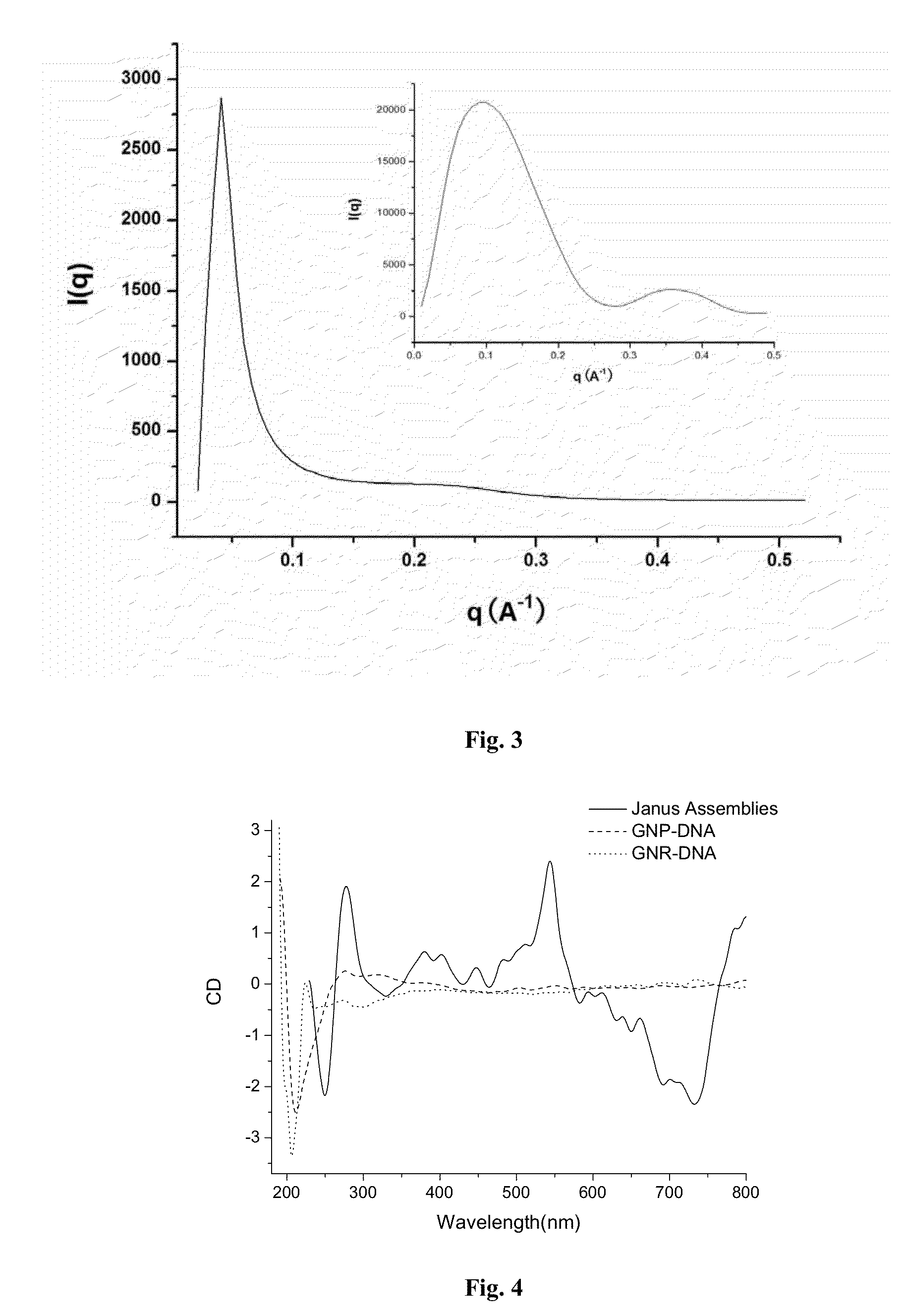
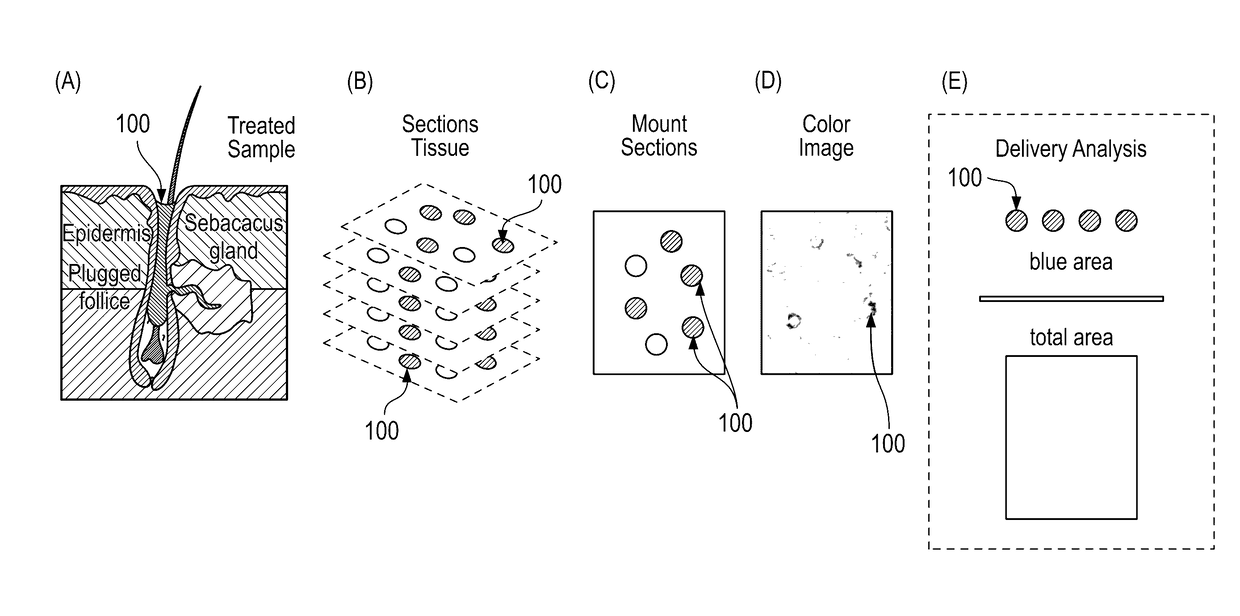
Collective chirality of binary plasmonic nanoparticles janus assemblies
InactiveUS20130071882A1Specific optical absorptionSugar derivativesNanoopticsGold nanorodPlasmonic nanoparticles
Multiple properties of plasmonic assemblies are determined by their geometrical organization. This patent focuses on the formation of Janus structure of the asymmetric assembly structure of the gold nanorods and gold nanoparticles. Chiral structure of gold nanorods and gold nanoparticles can be obtained through the characterization of optical spectra of the Janus structure. And it opens the door for the explanation of the mechanism of the chirality, plays a strong guiding role in the negative refractive material above and has good application prospects.
Owner:WANG LIBING +3
Ultrasound delivery of nanoparticles
Owner:CORONADO AESTHETICS LLC +1
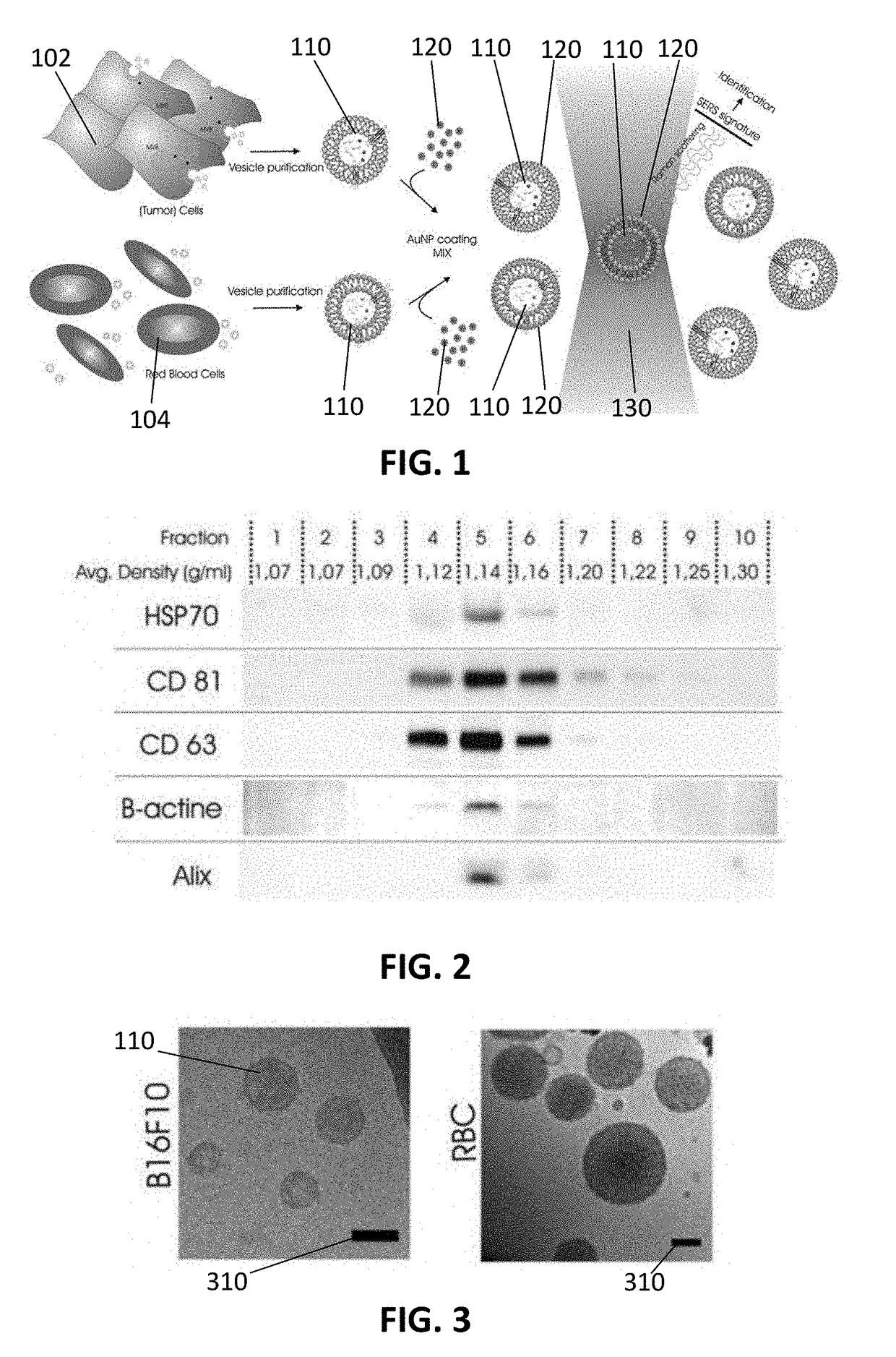
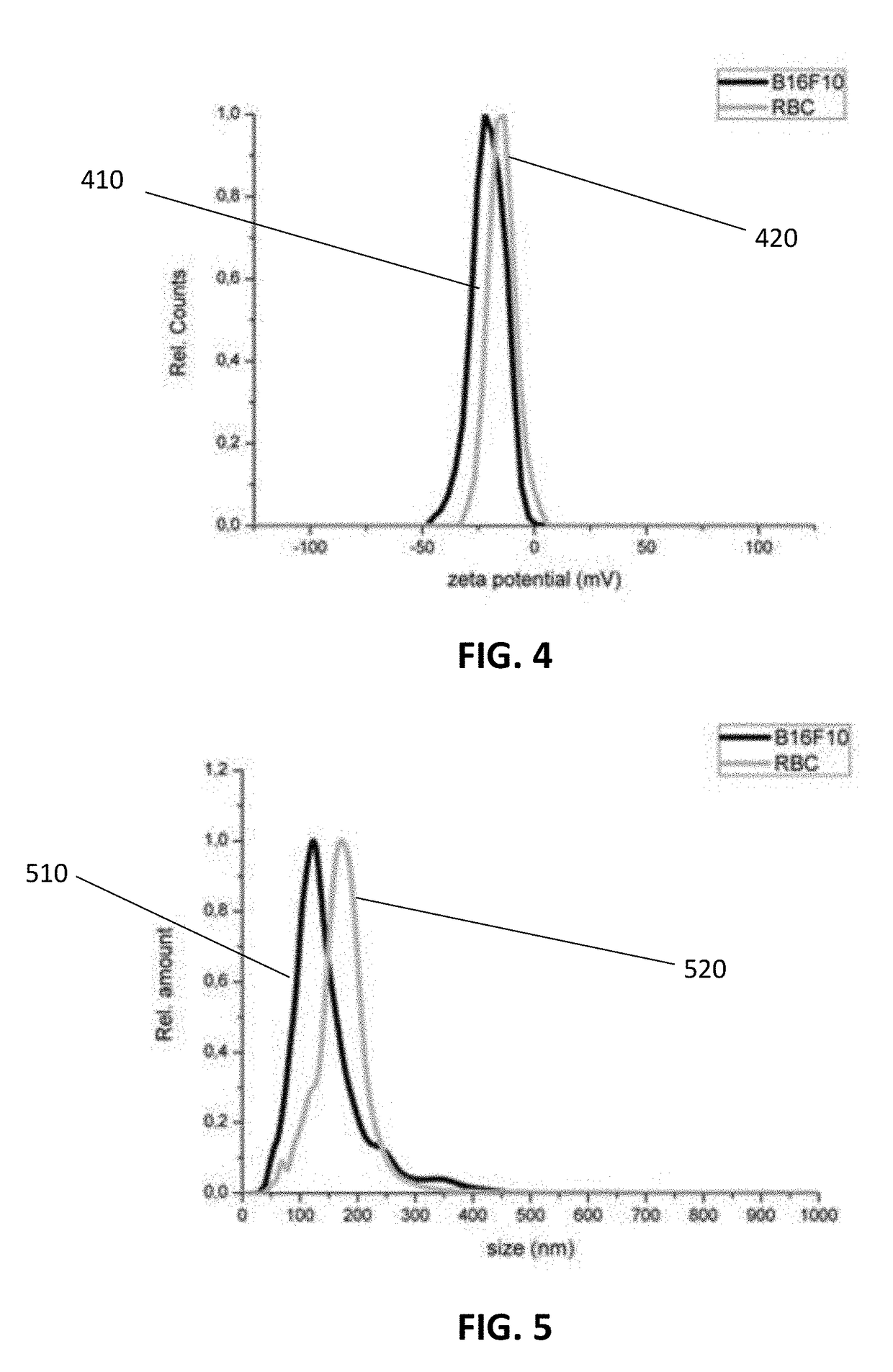
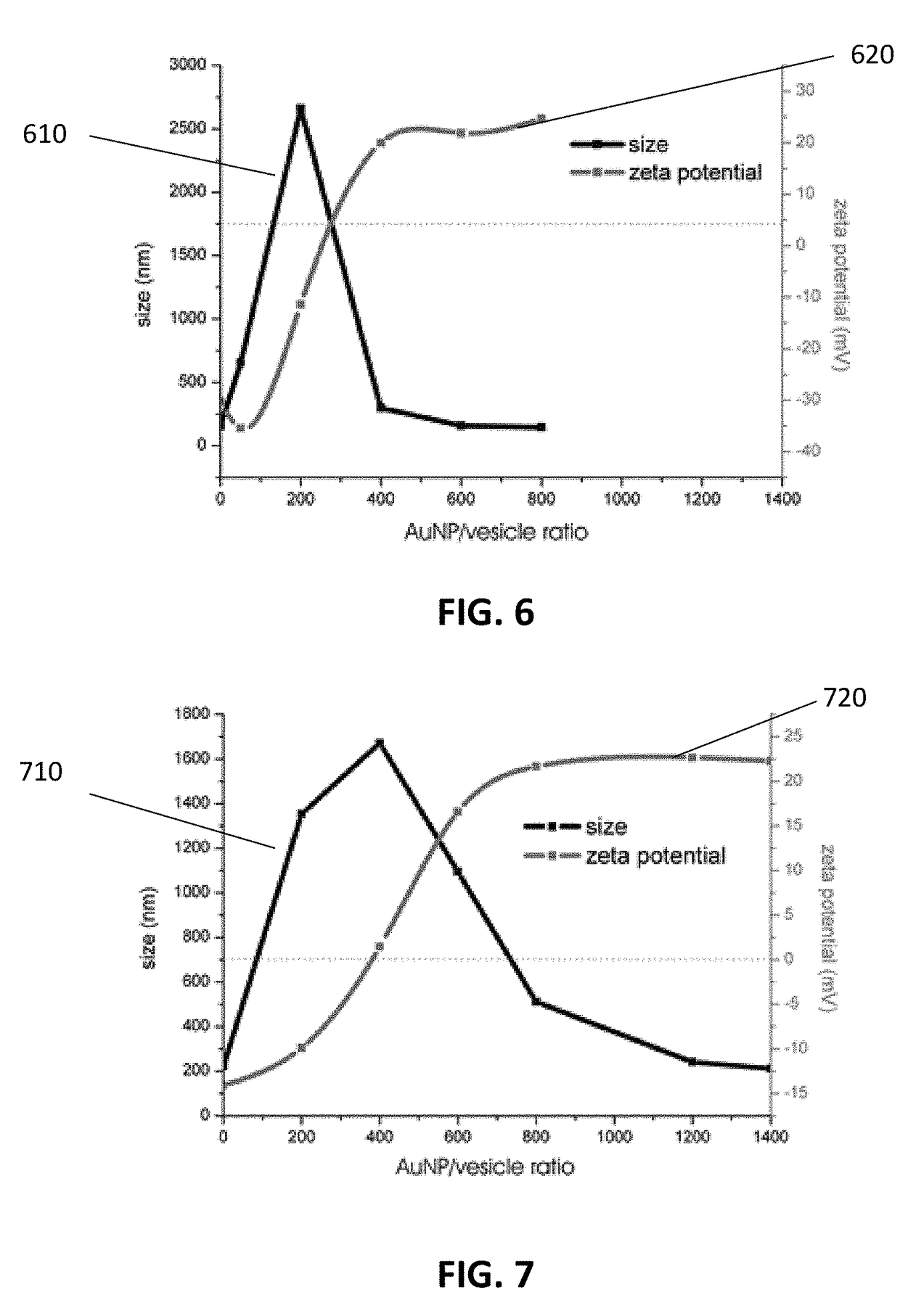
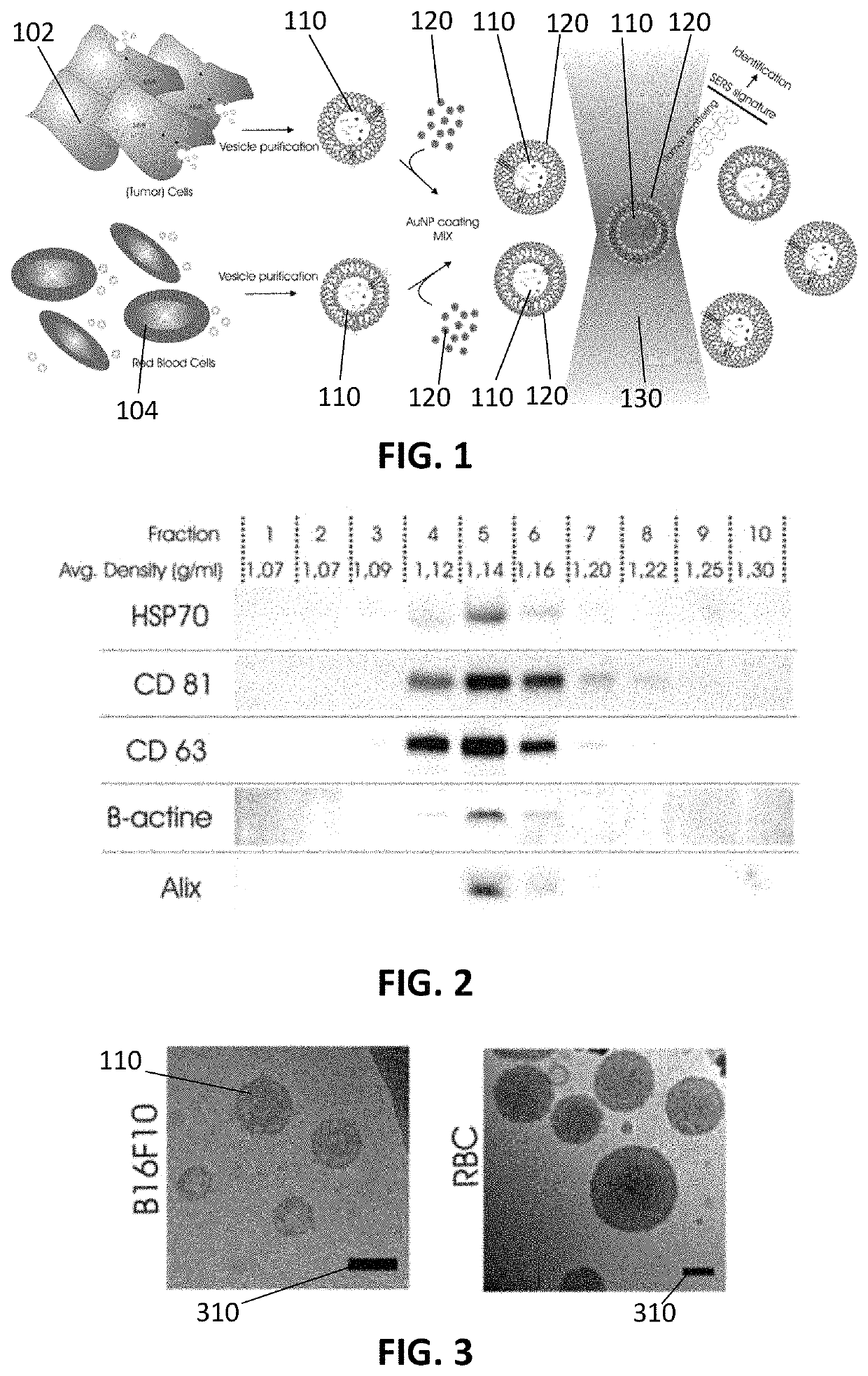
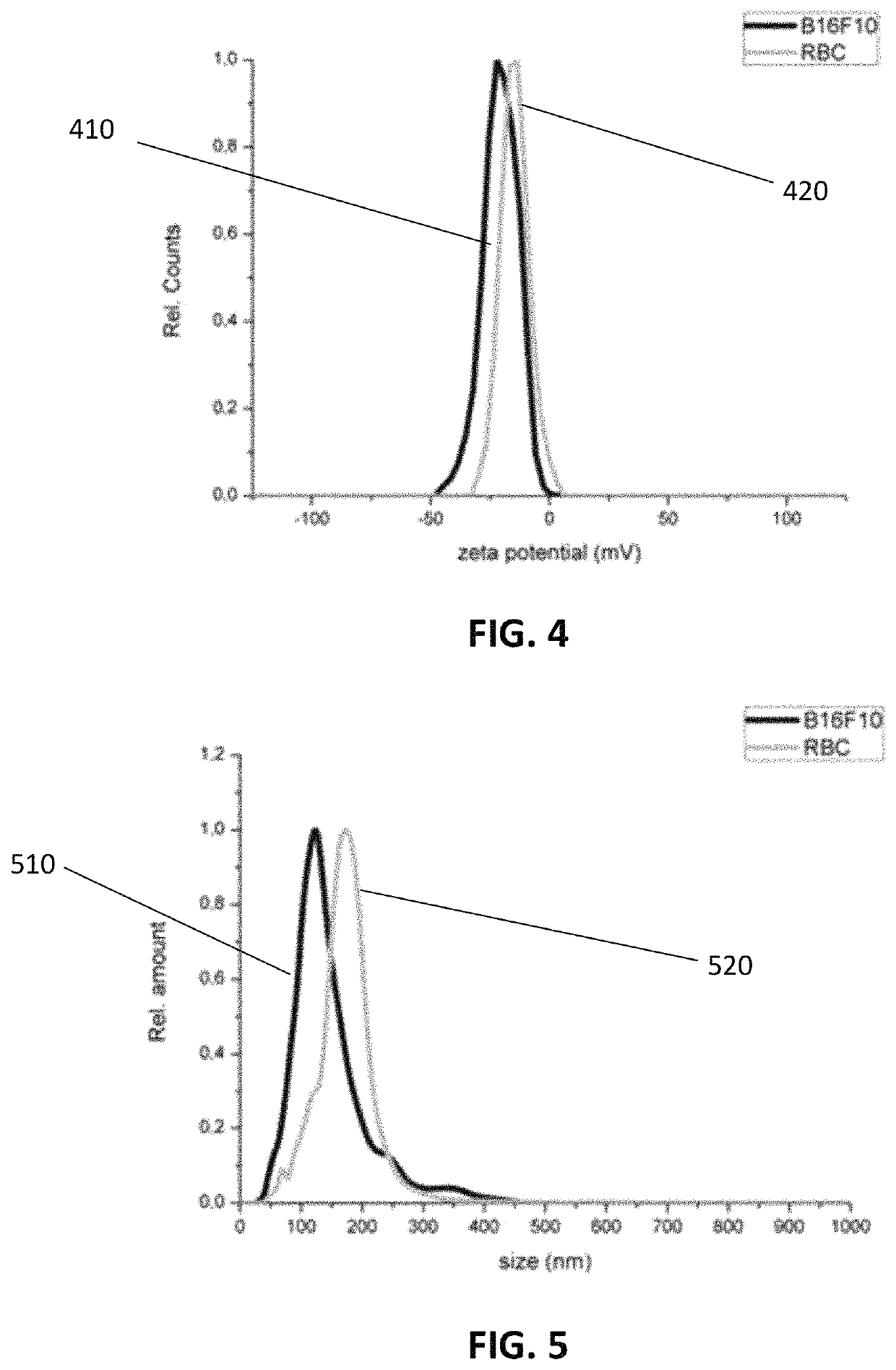
Method and system for characterizing extracellular vesicles
ActiveUS20180372730A1Well representedRaman scatteringDisease diagnosisSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopyVesicle/vacuole
A method for characterizing extracellular vesicles at an individual level is described. It comprises obtaining a sample comprising extracellular vesicles to be characterized and functionalizing the extracellular vesicles with plasmonic nanoparticles or a plasmonic coating. The method further comprises irradiating the individual extracellular vesicles with a laser beam and detecting a surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy signal from said individual extracellular vesicle.
Owner:UNIV GENT
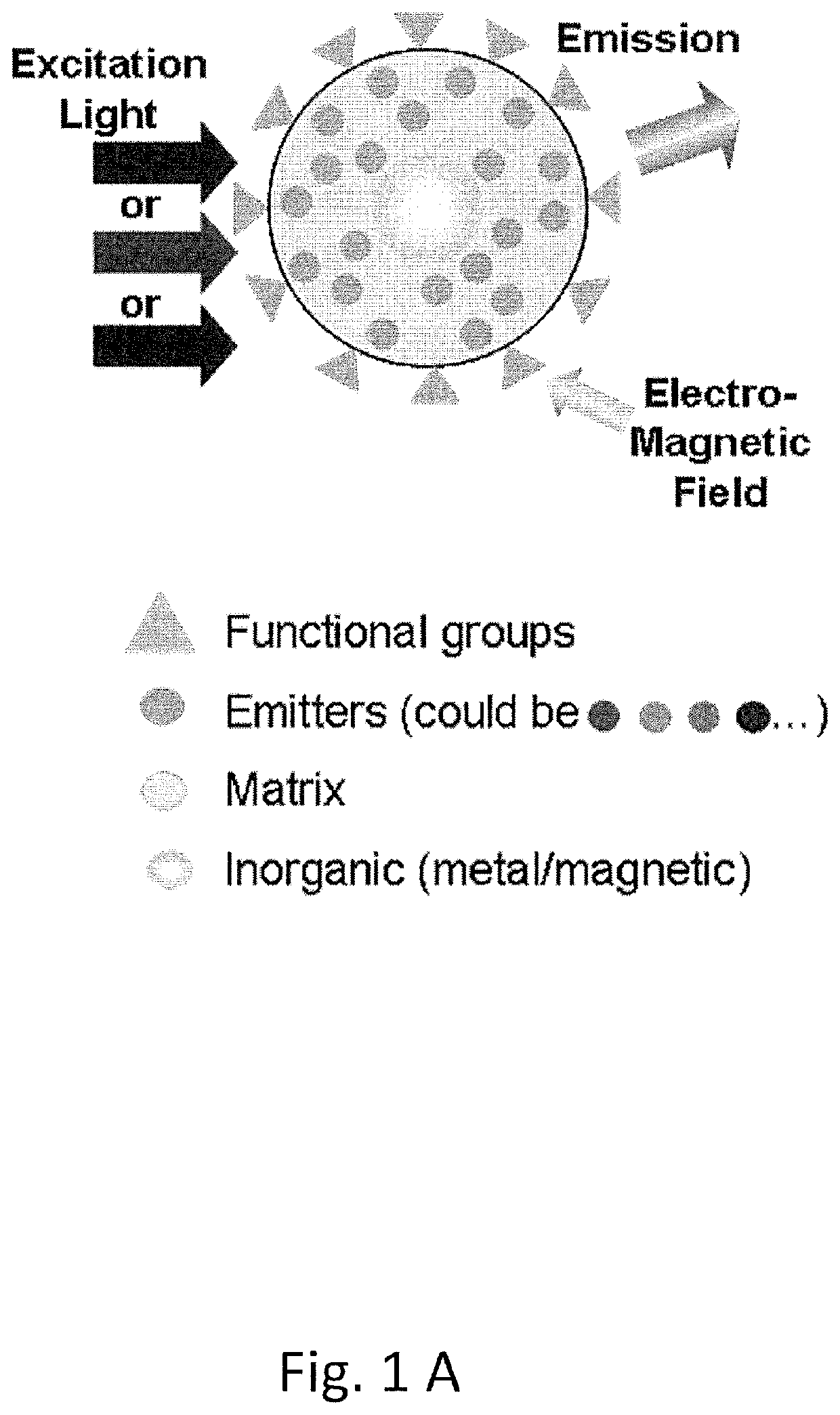
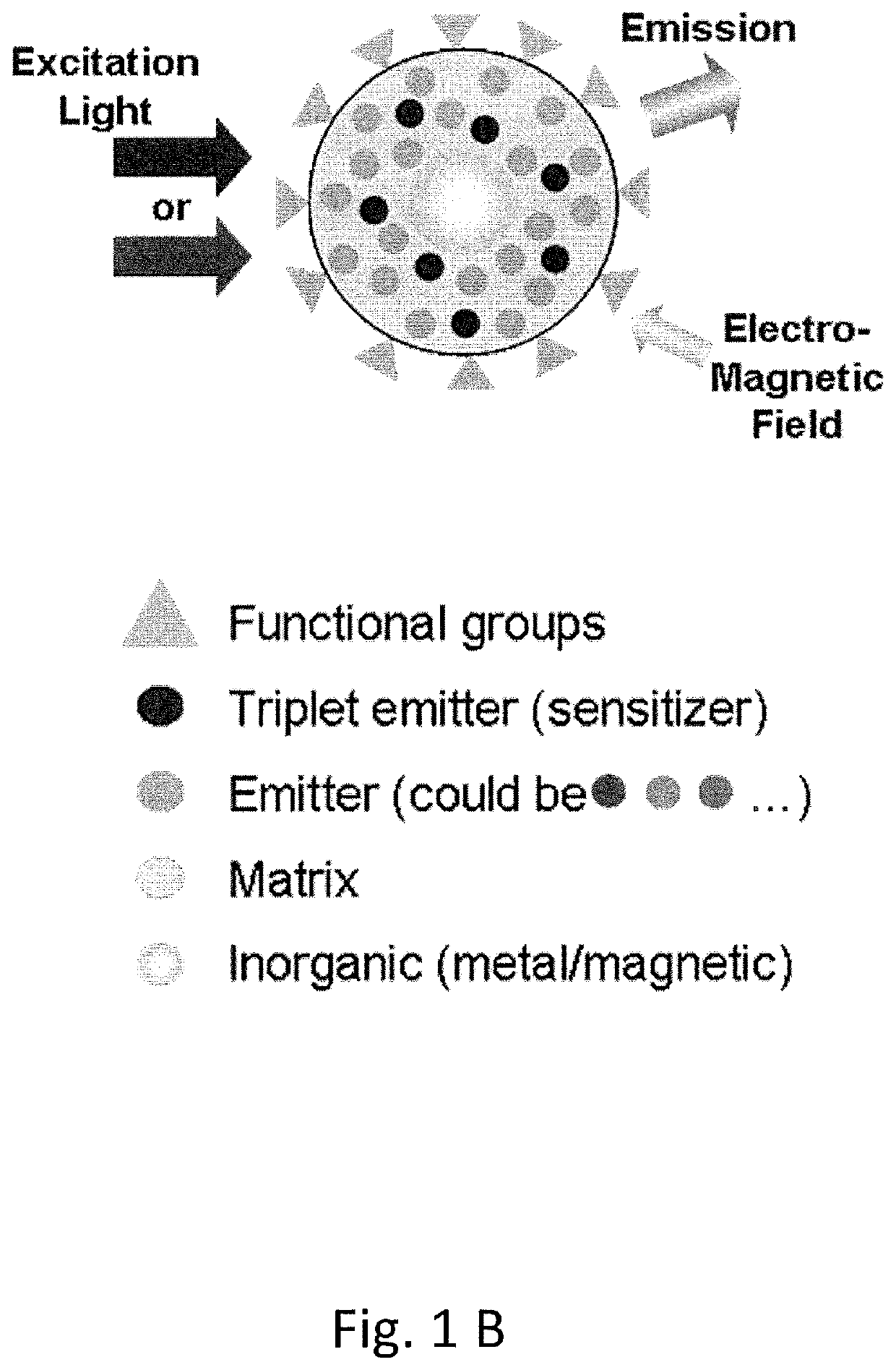
Polymeric organic nanoparticles with enhanced emission
ActiveUS20190085237A1Improve light resistanceMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsMetal particlePhoton upconversion
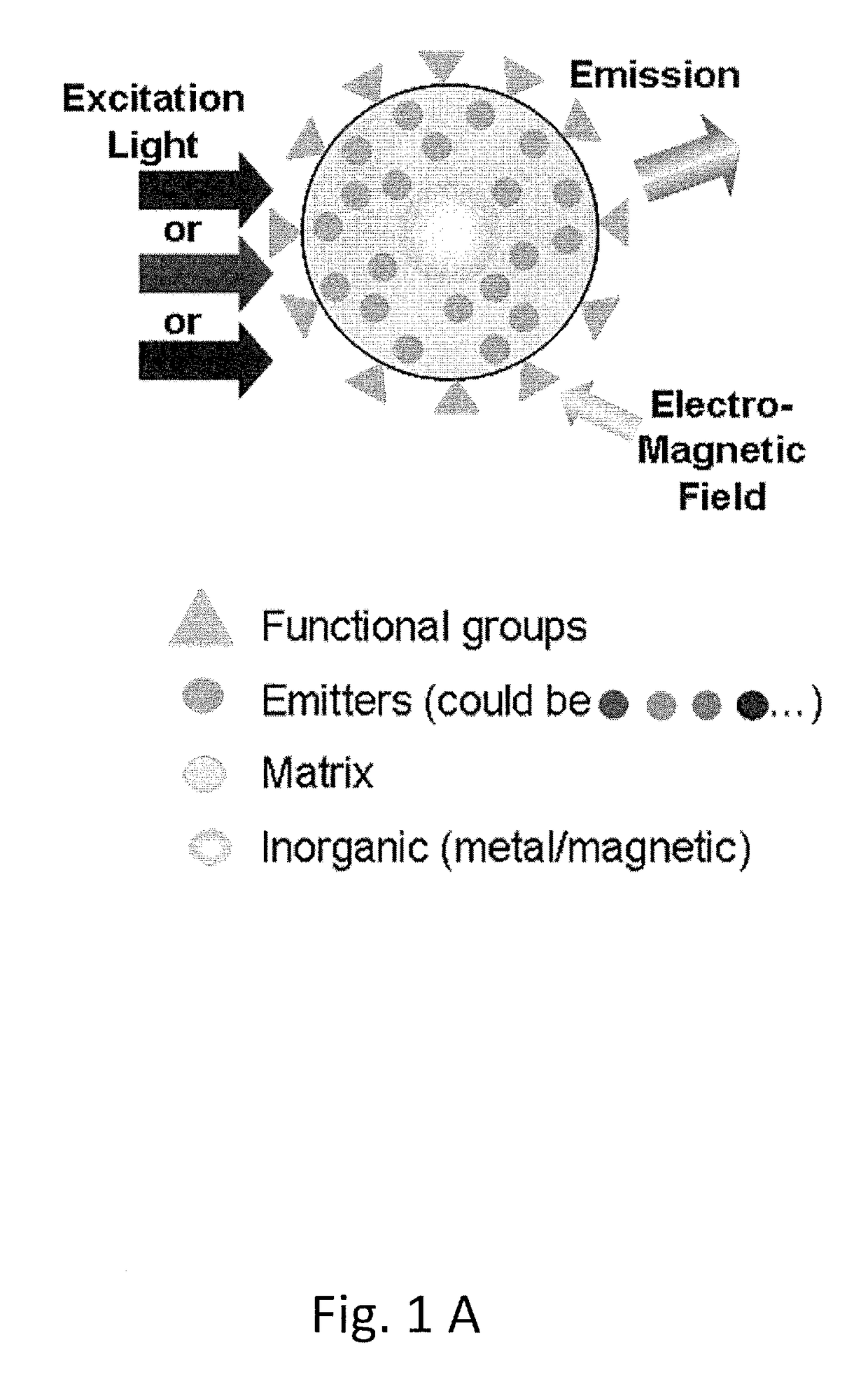
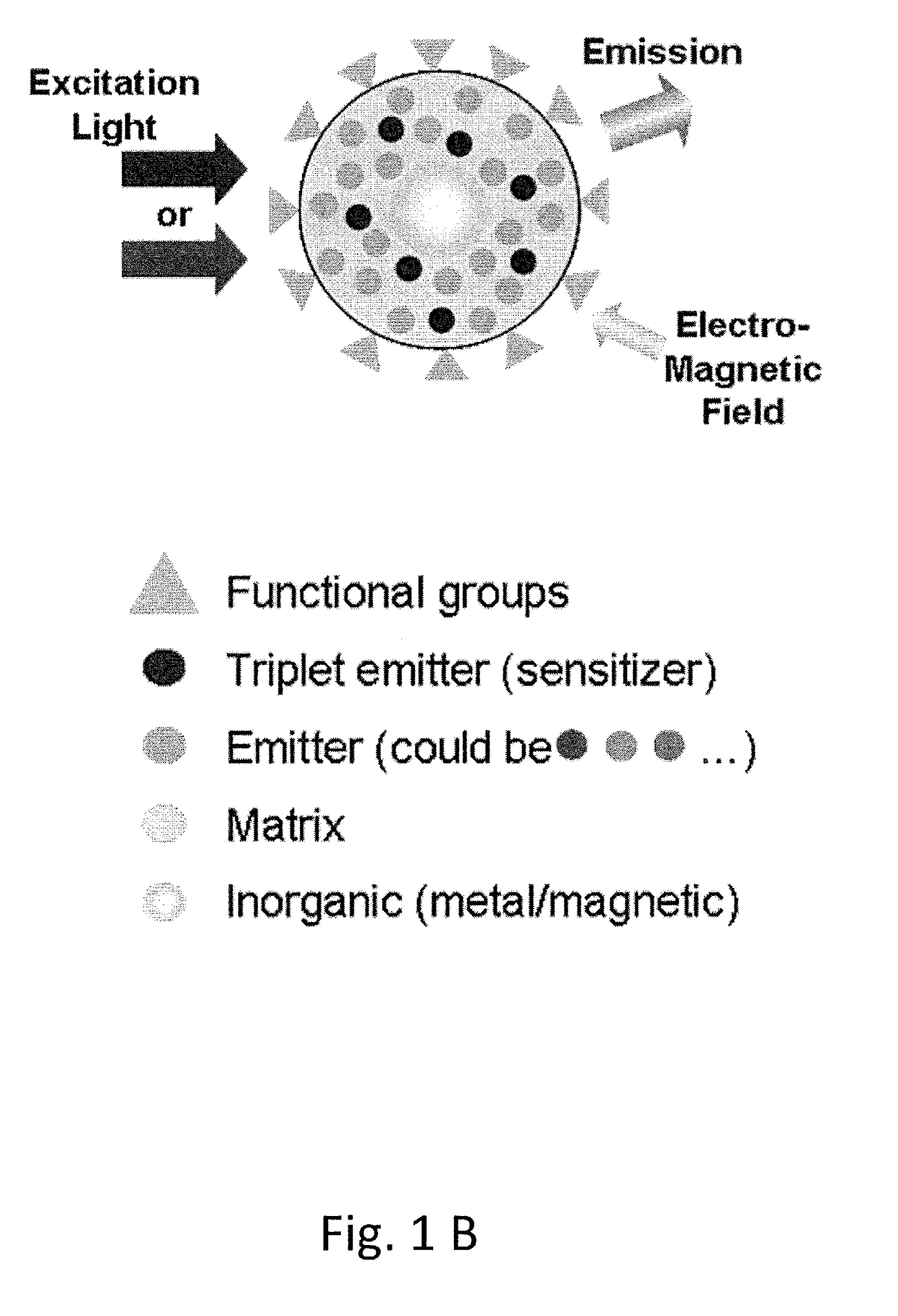
The present disclosure relates to luminescent including photon up-conversion nanoparticles. These nanoparticles dude a polymeric organic matrix, at least one light emitter distributed within this matrix, a stabilizing agent, and at least one metal particle enclosed within the matrix, wherein the metal particles are plasmonic nanoparticles. The present disclosure further relates to methods of manufacture and to uses of such nanoparticles.
Owner:SONY CORP
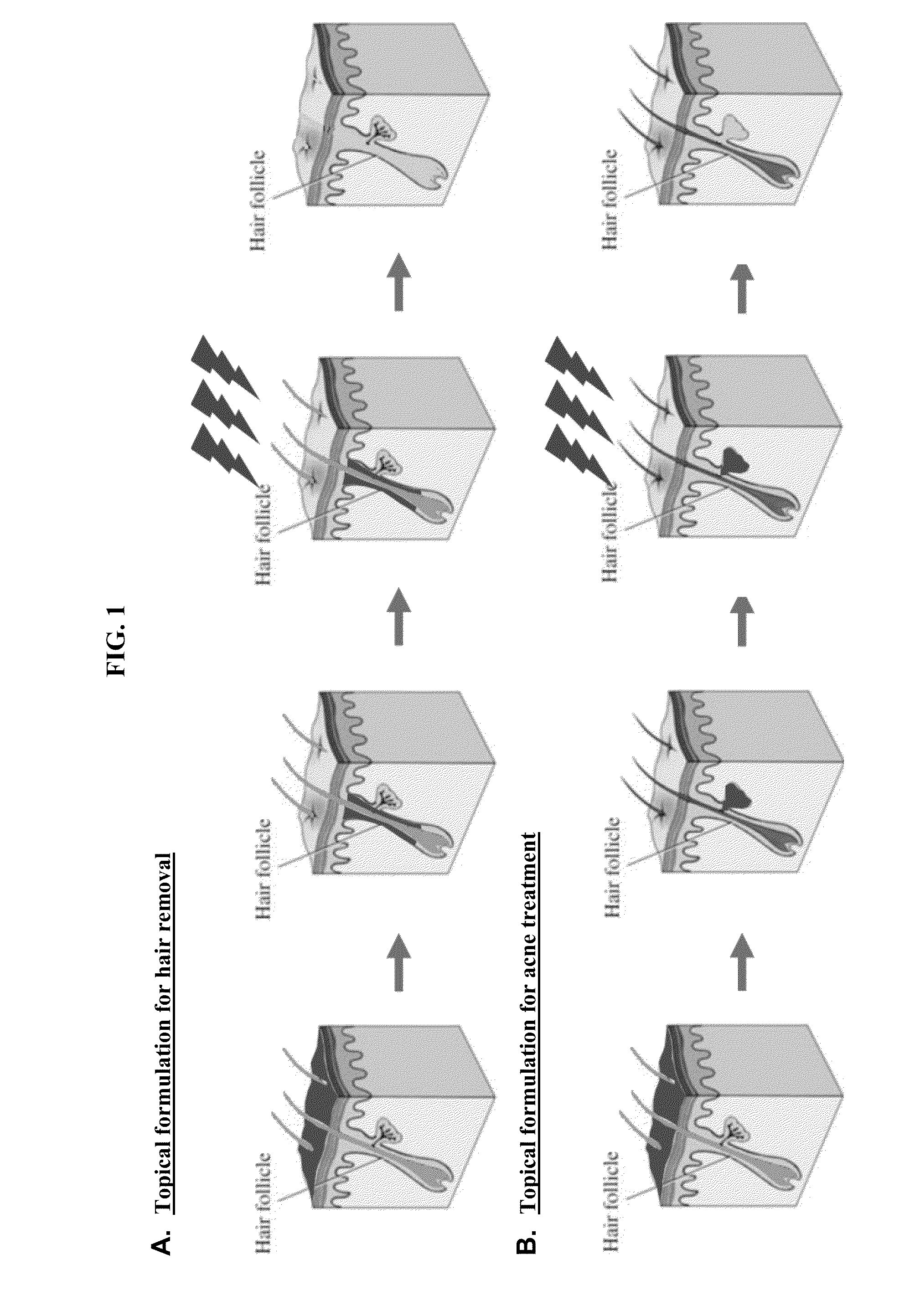
Methods of treating skin conditions using plasmonic nanoparticles
PendingUS20180325594A1Achieve therapeutic effectPromote recombinationPowder deliveryCosmetic preparationsMedicineSurface plasmon
Methods, and materials useful in such methods, of treating certain skin conditions are described. In brief, the methods impregnate portions of the skin needing treatment with plasmonic materials. Thereafter, surface plasmons are generated on the surface of these plasmonic materials by irradiating the treated skin with near infrared light that is absorbed by the plasmonic materials in the skin.
Owner:CORONADO AESTHETICS LLC
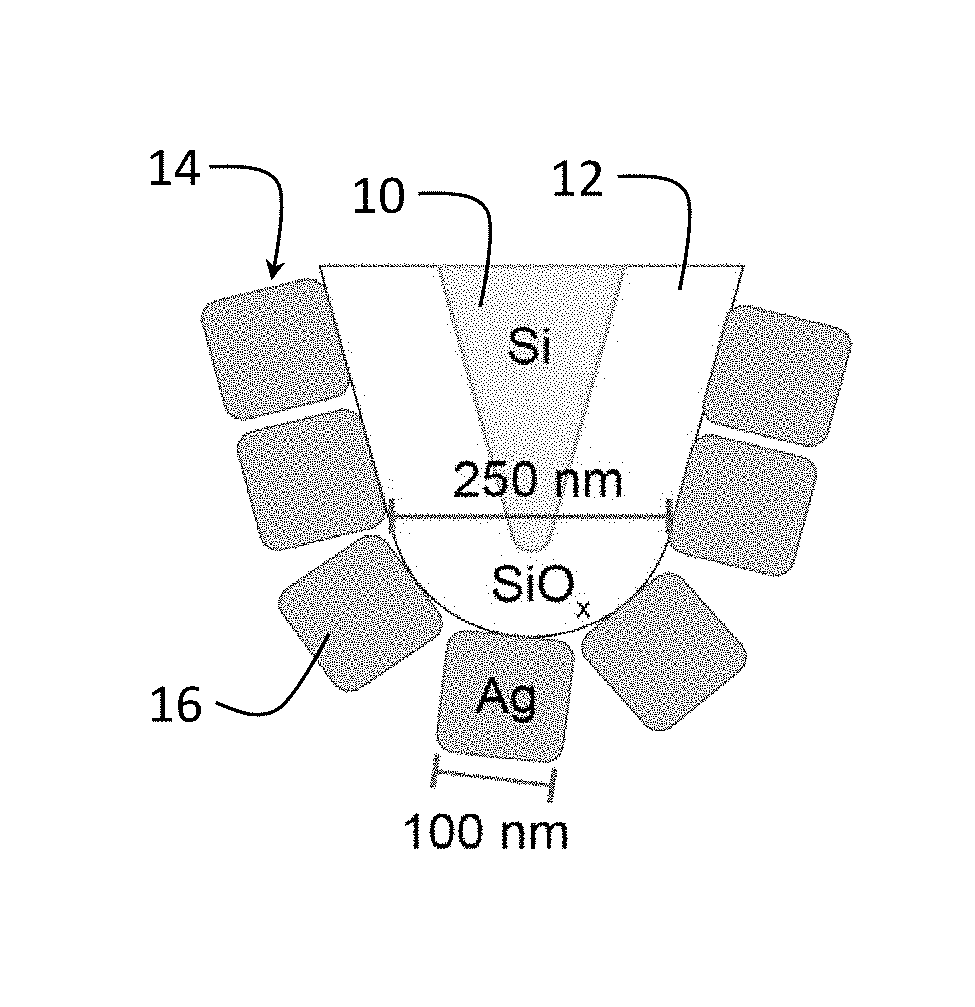
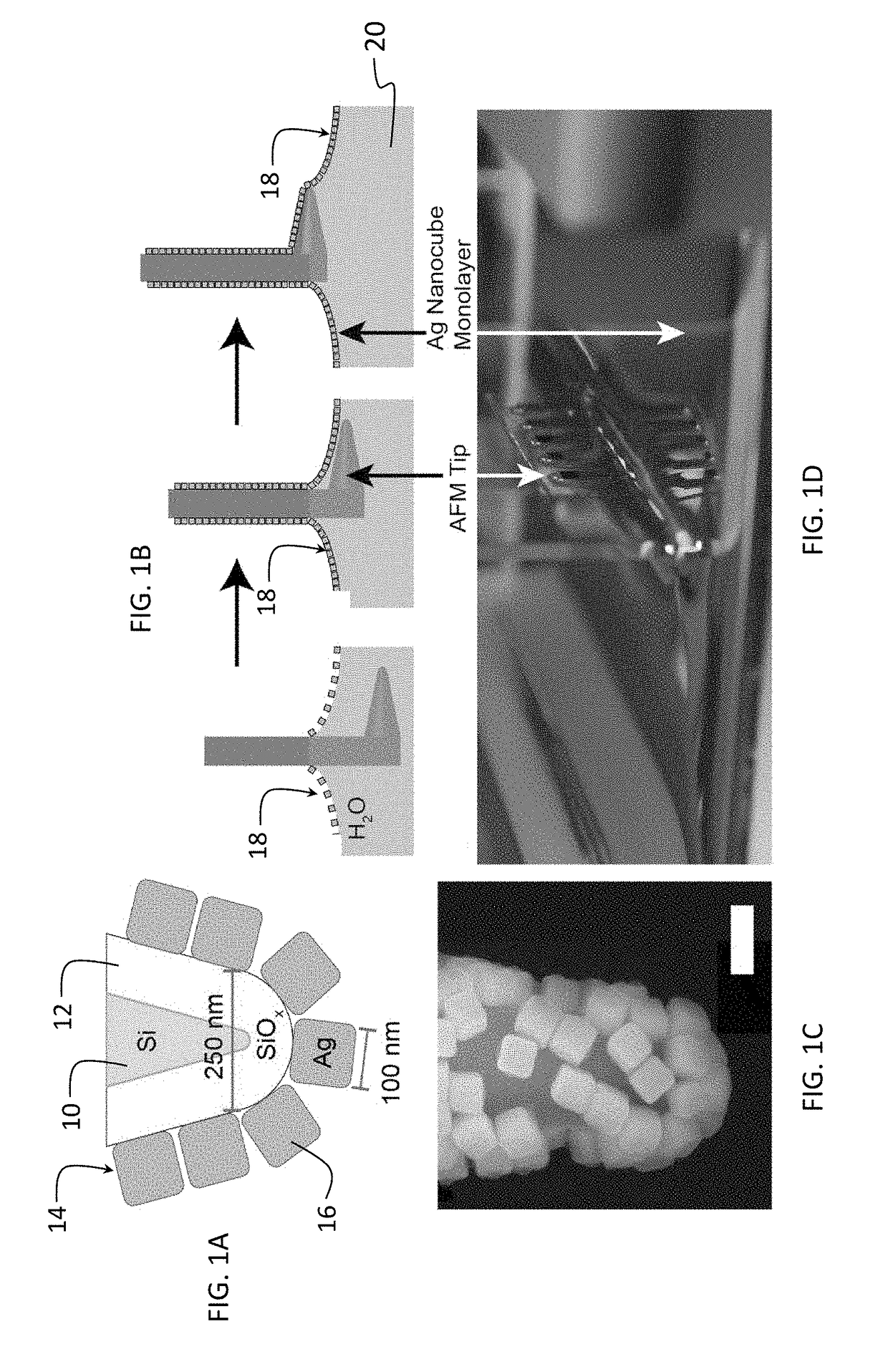
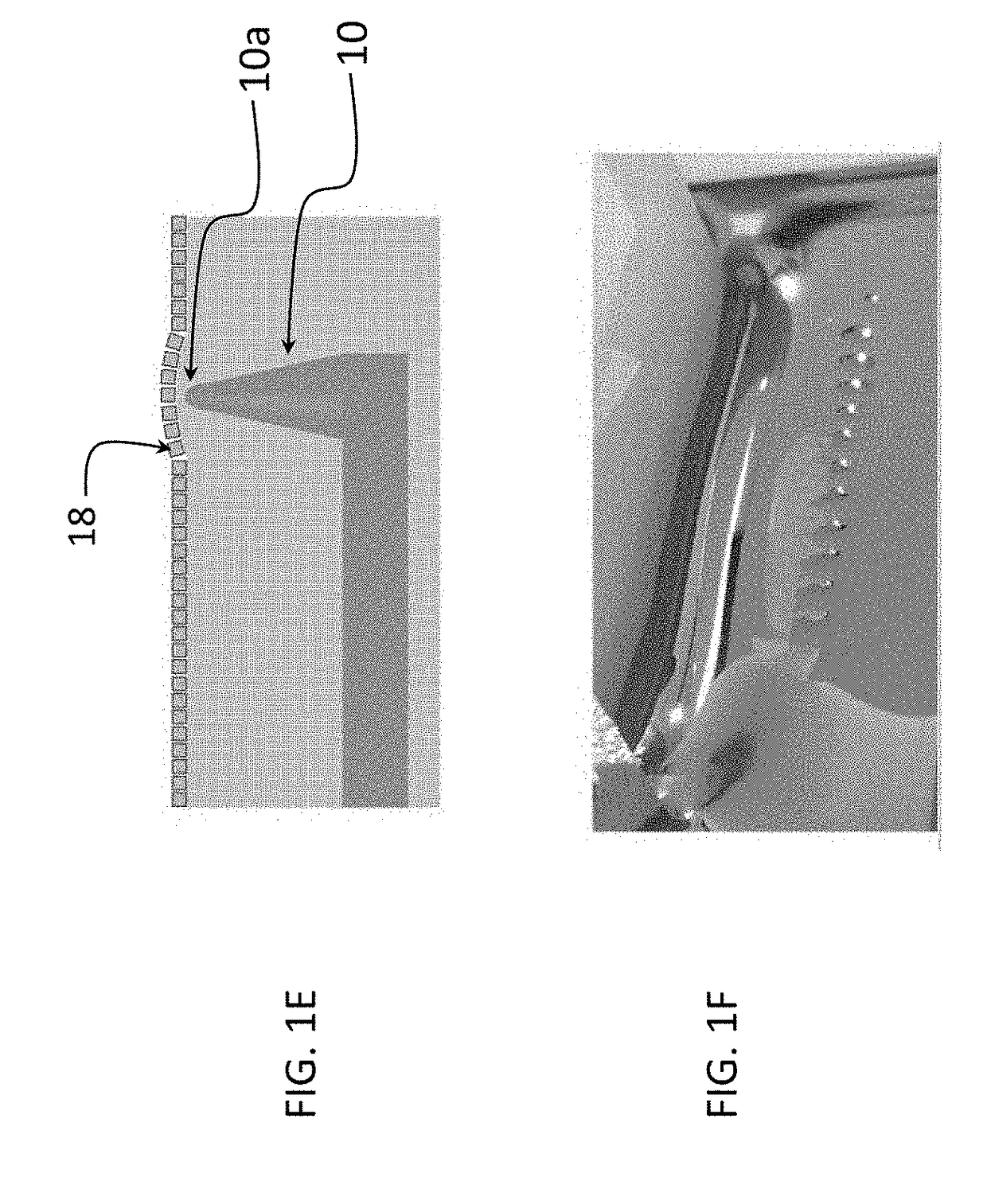
Nanoantenna scanning probe tip, and fabrication methods
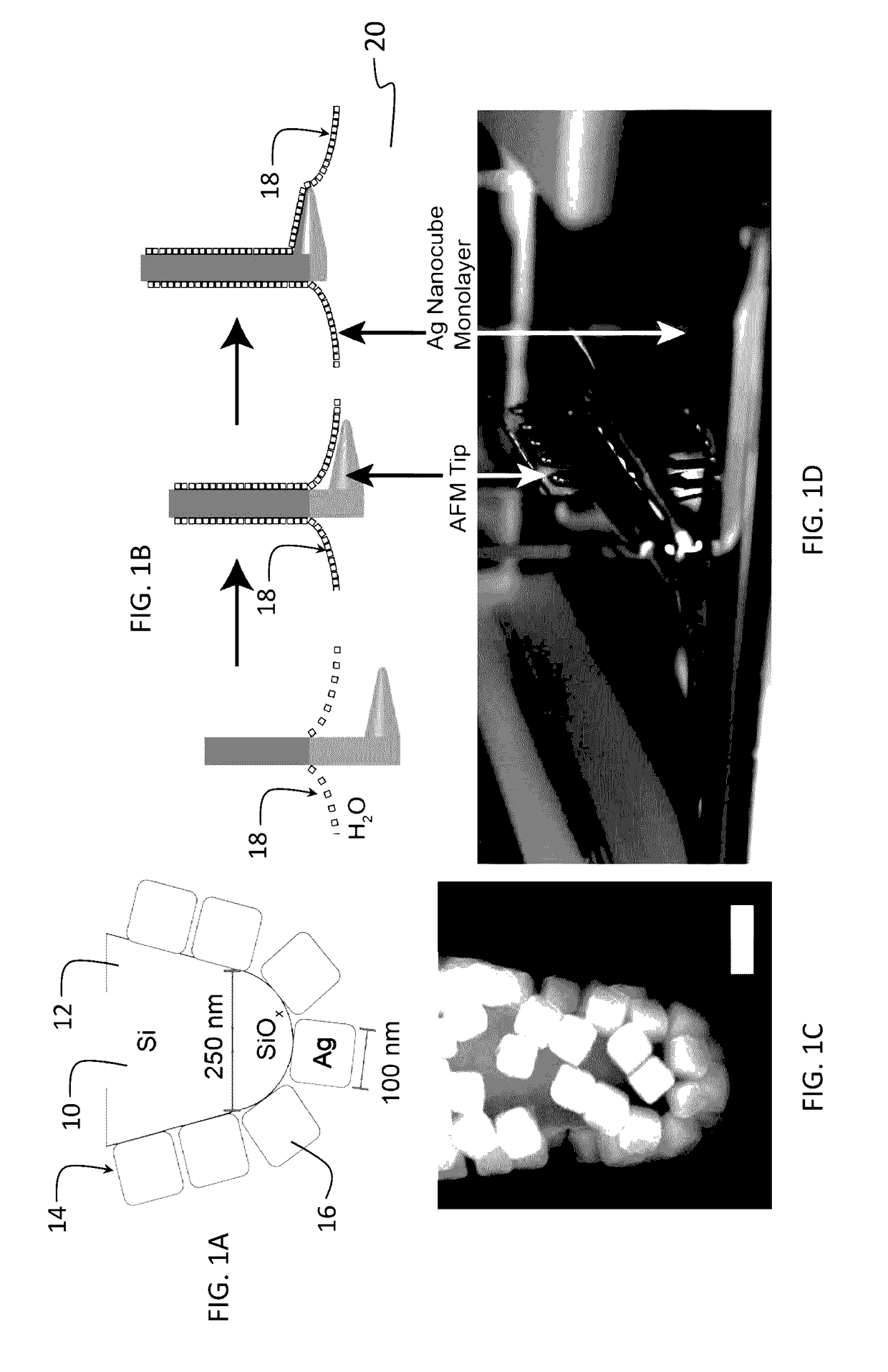
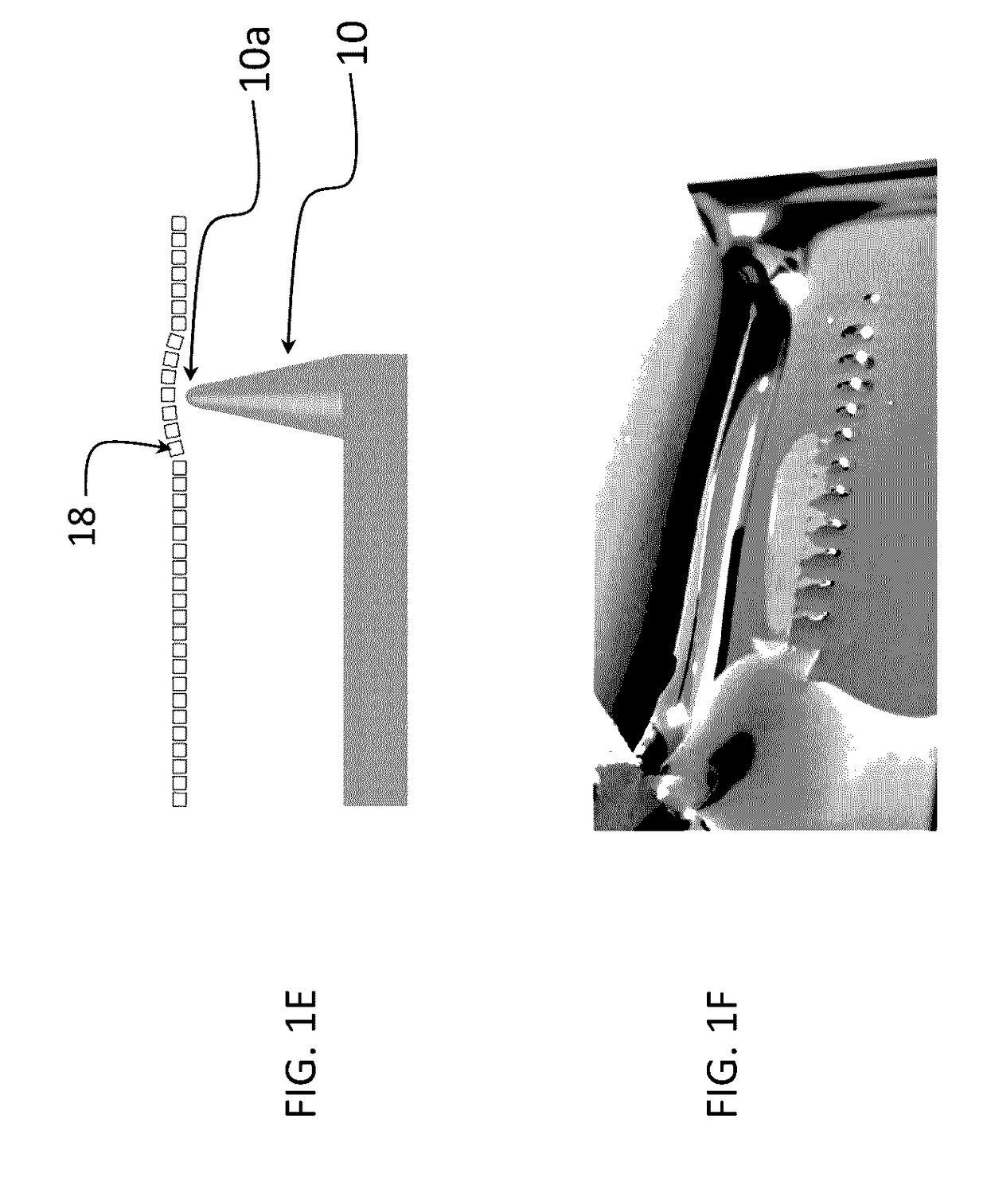
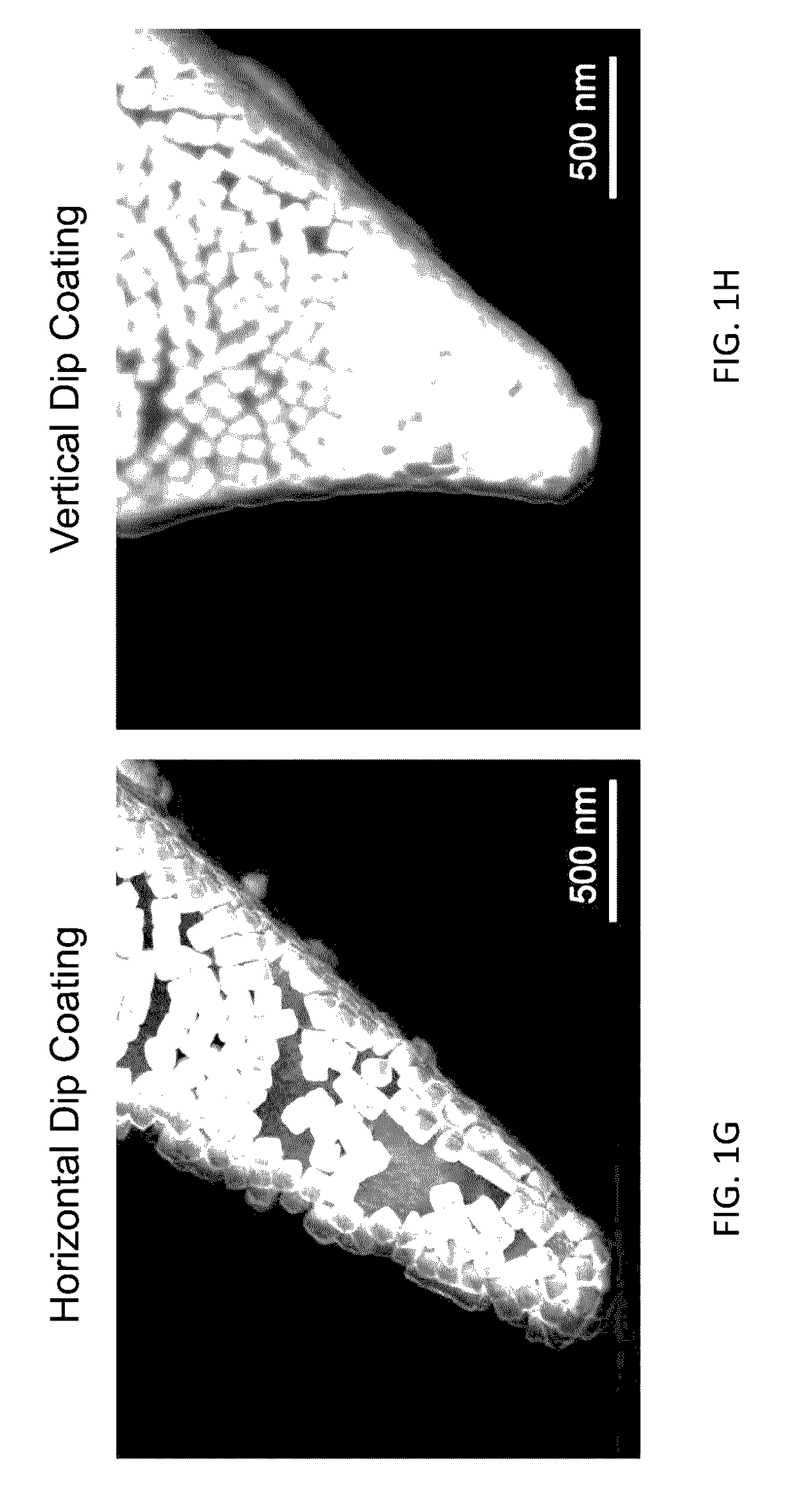
The invention provides a nanoantenna scanning probe tip for microscropy or spectroscopy. The nanoantenna scanning probe tip includes a sharp probe tip covered with a contiguous film of predetermined sized and shaped plasmonic nanoparticles. A method for forming the nanoantenna scanning probe tip by trapping nanoparticles having a predetermined size and shape at a liquid surface using surface tension, forming a uniform and organized monolayer film on the liquid surface, and then transferring portions of the film to a sharp probe tip. In preferred embodiments, the sharp probe tip is one of a conductive STM (scanning tunneling microscopy) tip, a tuning fork tip or an AFM (atomic force microscopy) tip. The sharp tip can be blunted with an oxide layer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Porous SERS analytical devices and methods of detecting a target analyte
ActiveUS9255843B2Reduce high costIncreasing sensitivity and sophistication of SERS-basedMaterial nanotechnologyRadiation pyrometryTarget analysisAnalyte
A surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) analytical device includes a substrate having a porous structure, and a plurality of plasmonic nanoparticles embedding in the porous structure and forming a sensing region. A method of detecting a target analyte in a sample includes contacting the sample with the substrate, whereby the target analyte, if present in the sample, is concentrated in the sensing matrix. The substrate may then be analyzed using SERS detection equipment.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Plasmonic nanoparticles with hidden chiroptical activity
InactiveUS20170184497A1Polarisation-affecting propertiesVacuum evaporation coatingFluorescenceMolecular size
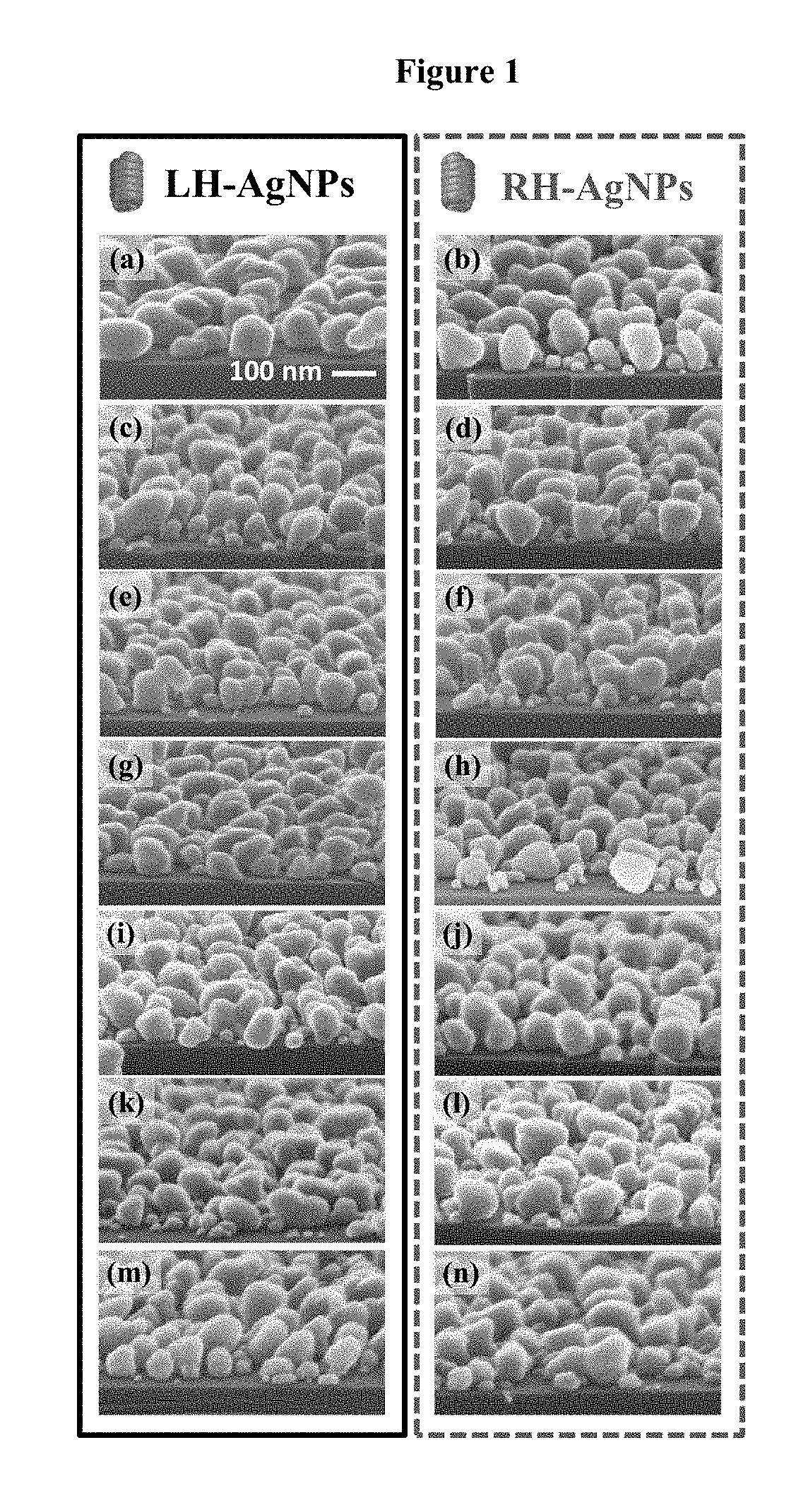
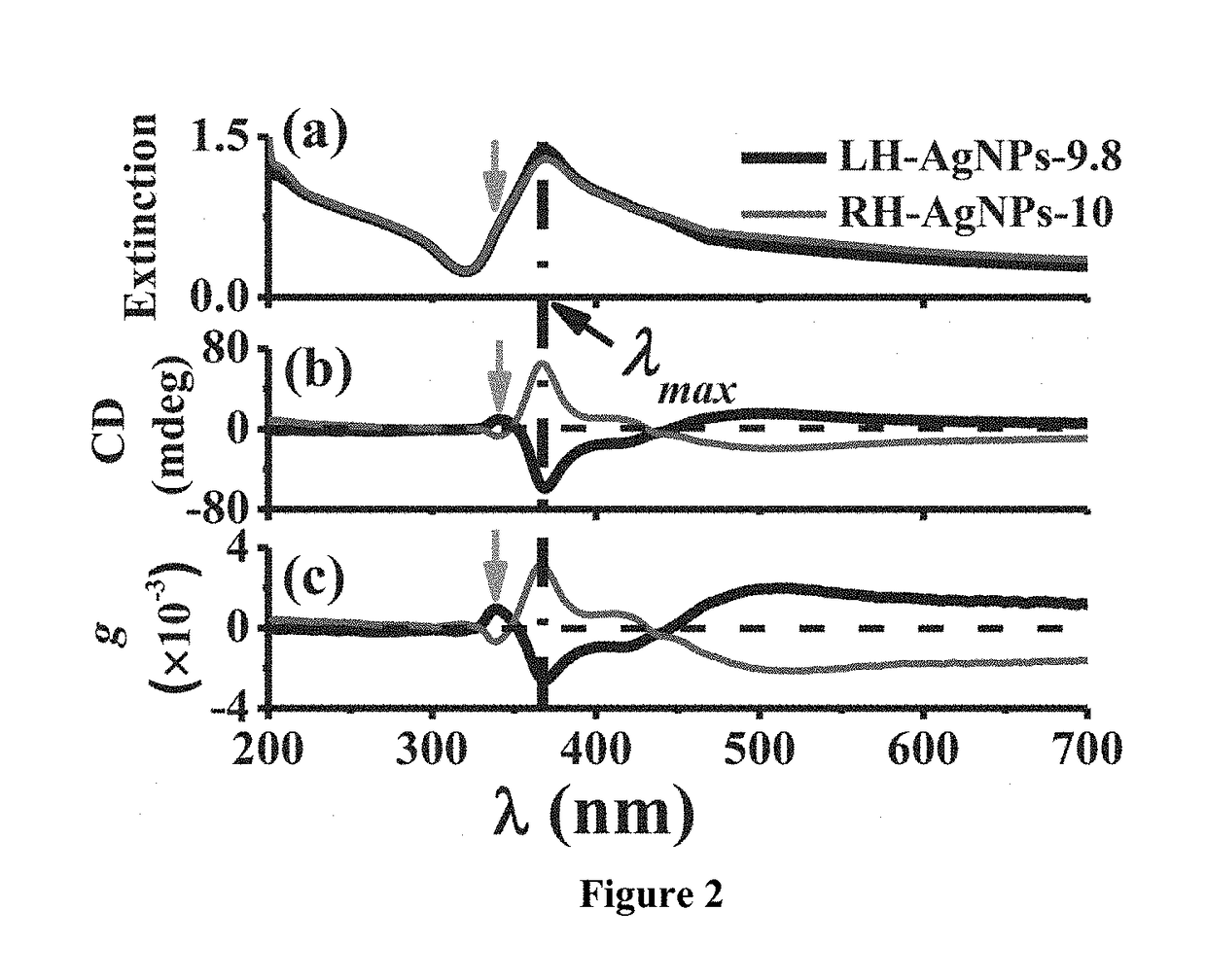
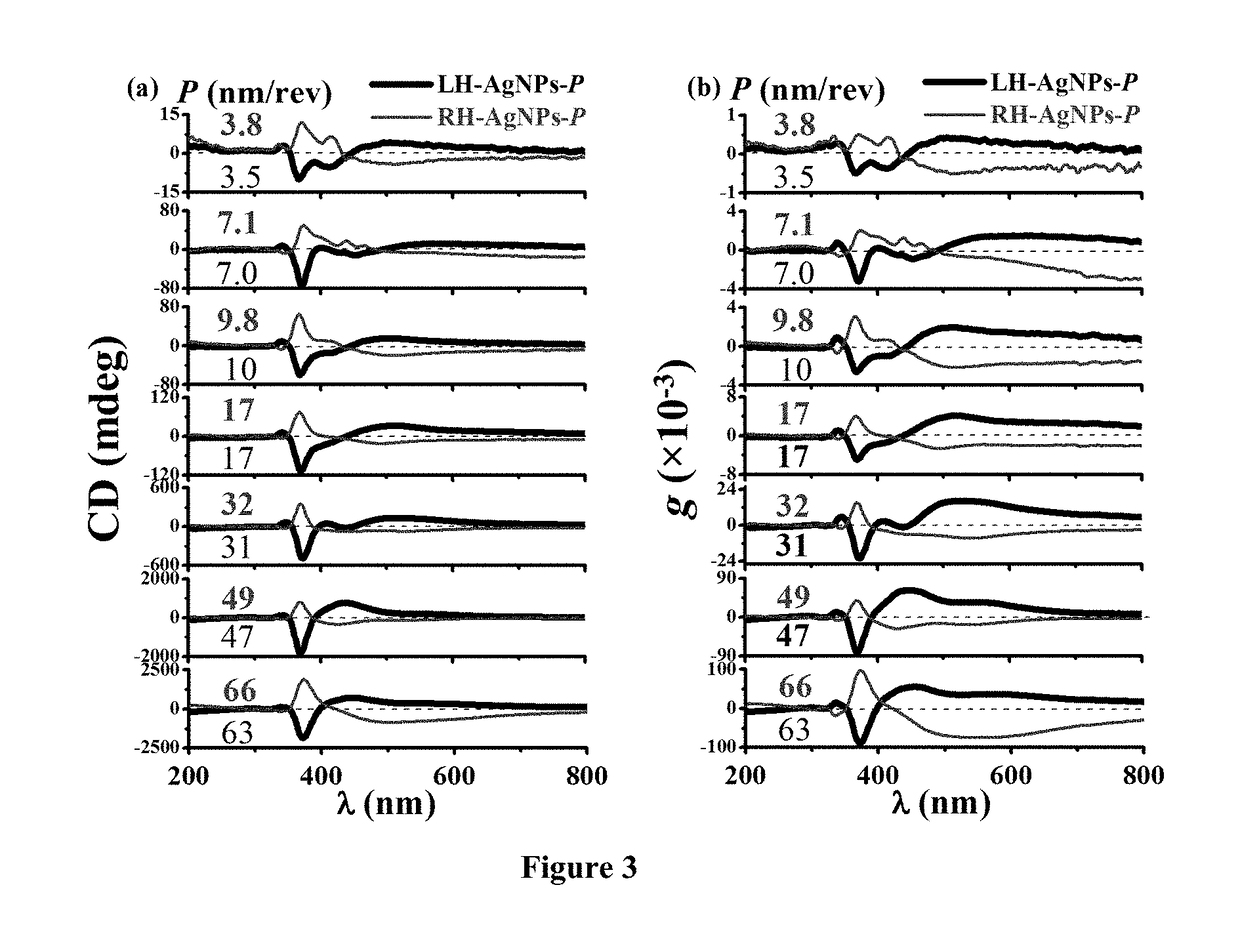
A method is presented to minimize the helical pitch (P) of chiroplasmonic nanostructures to the molecular size-comparable scale. In particular, chiroplasmonic nanostructures can be used to induce plasmonic chirality via chirality transfer and used for chirality-related primary applications such as chiral sensing. In one aspect, there is provided a chiroptically active plasmonic nanoparticle with a helical pitch (P) less than its wire diameter (d) produced via a glancing angle deposition (GLAD) process.
Owner:HONG KONG BAPTIST UNIV
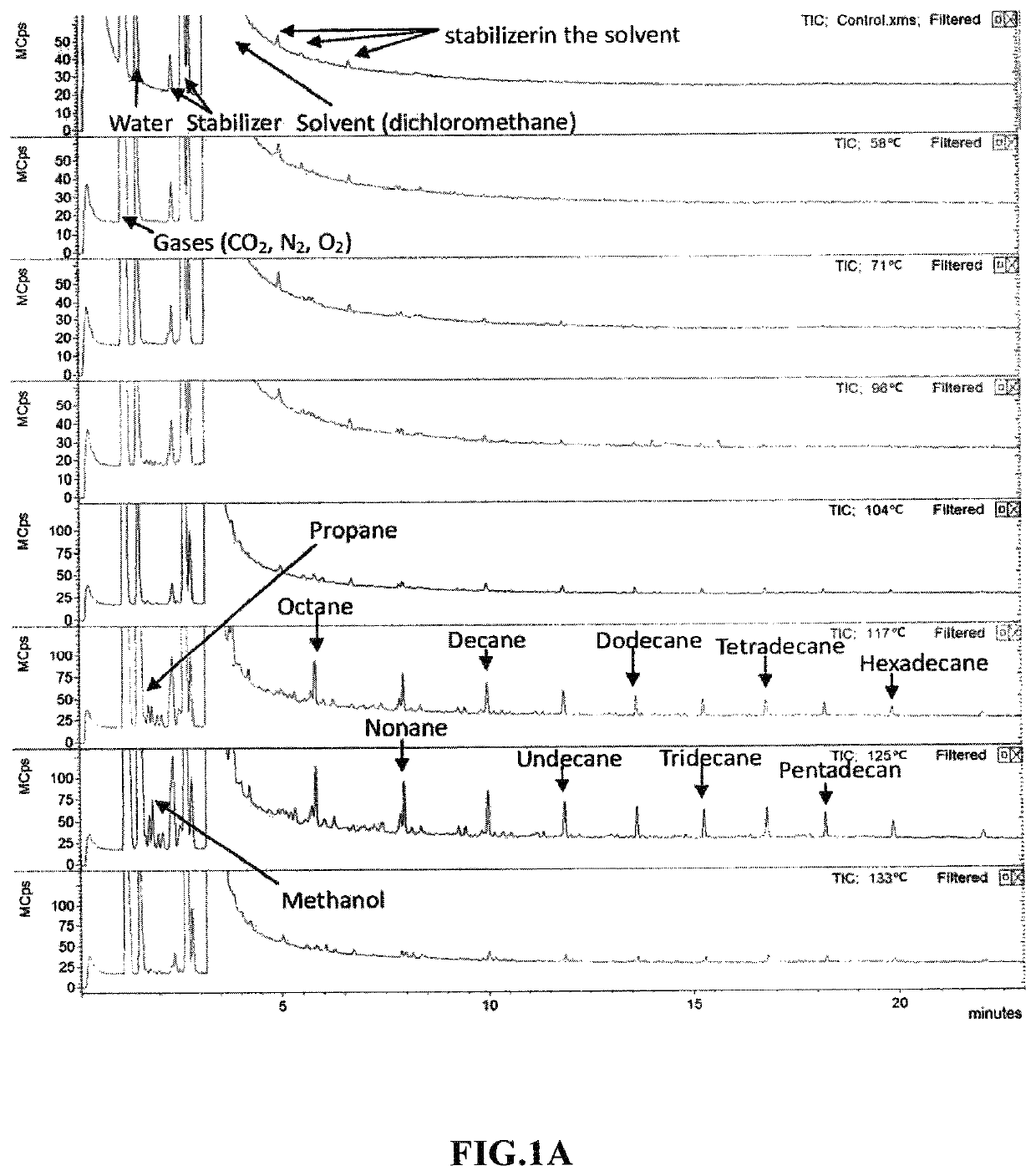
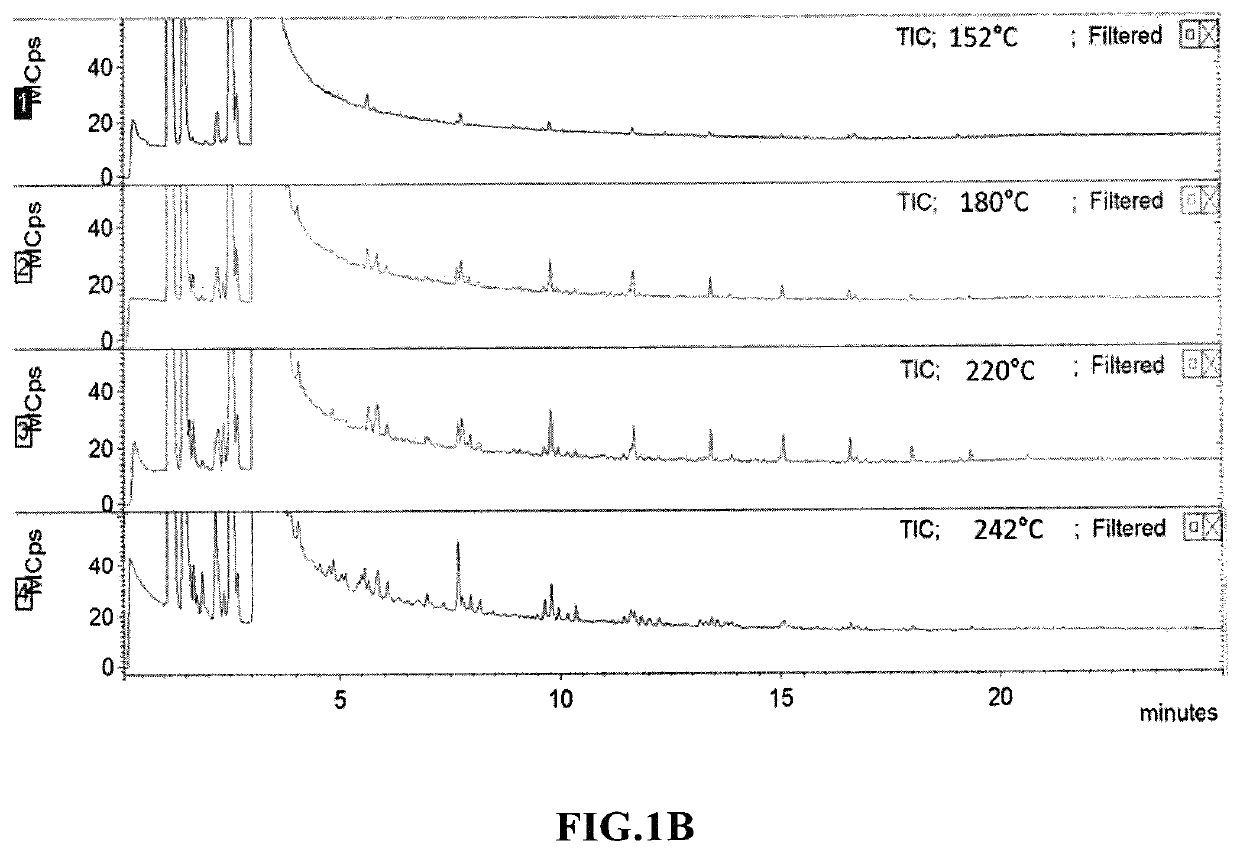
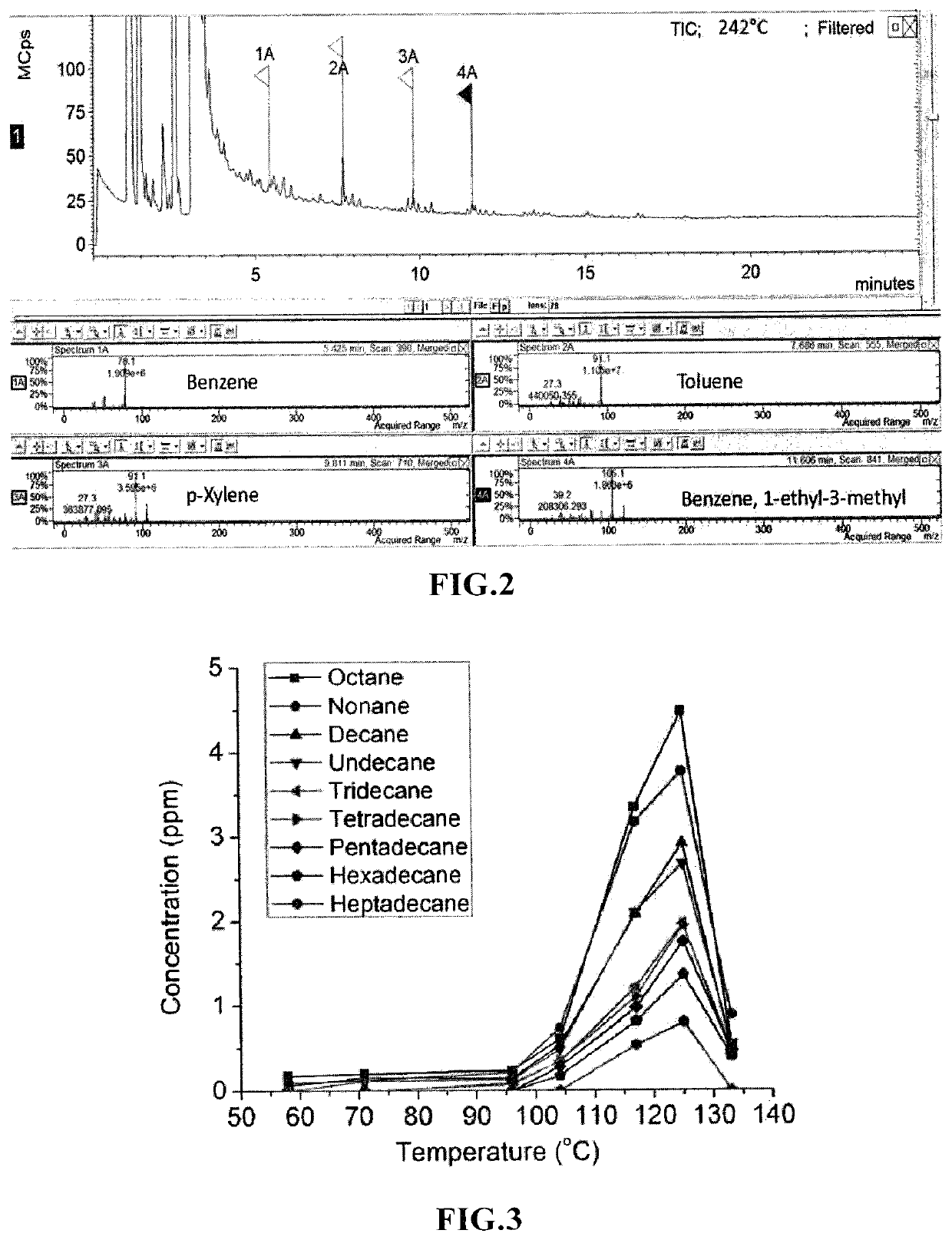
Plasmonic Nanoparticle Catalysts and Methods for Producing Long-Chain Hydrocarbon Molecules
ActiveUS20190046966A1Material nanotechnologyHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsMolecular compositionLight irradiation
A plasmonic nanoparticle catalyst for producing hydrocarbon molecules by light irradiation, which comprises at least one plasmonic provider and at least one catalytic property provider, wherein the plasmonic provider and the catalytic property provider are in contact with each other or have distance less than 200 nm, and molecular composition of the hydrocarbon molecules produced by light irradiation is temperature-dependent. And a method for producing hydrocarbon molecules by light irradiation utilizing the plasmonic nanoparticle catalyst.
Owner:BEIJING GUANGHE NEW ENERGY TECH CO LTD
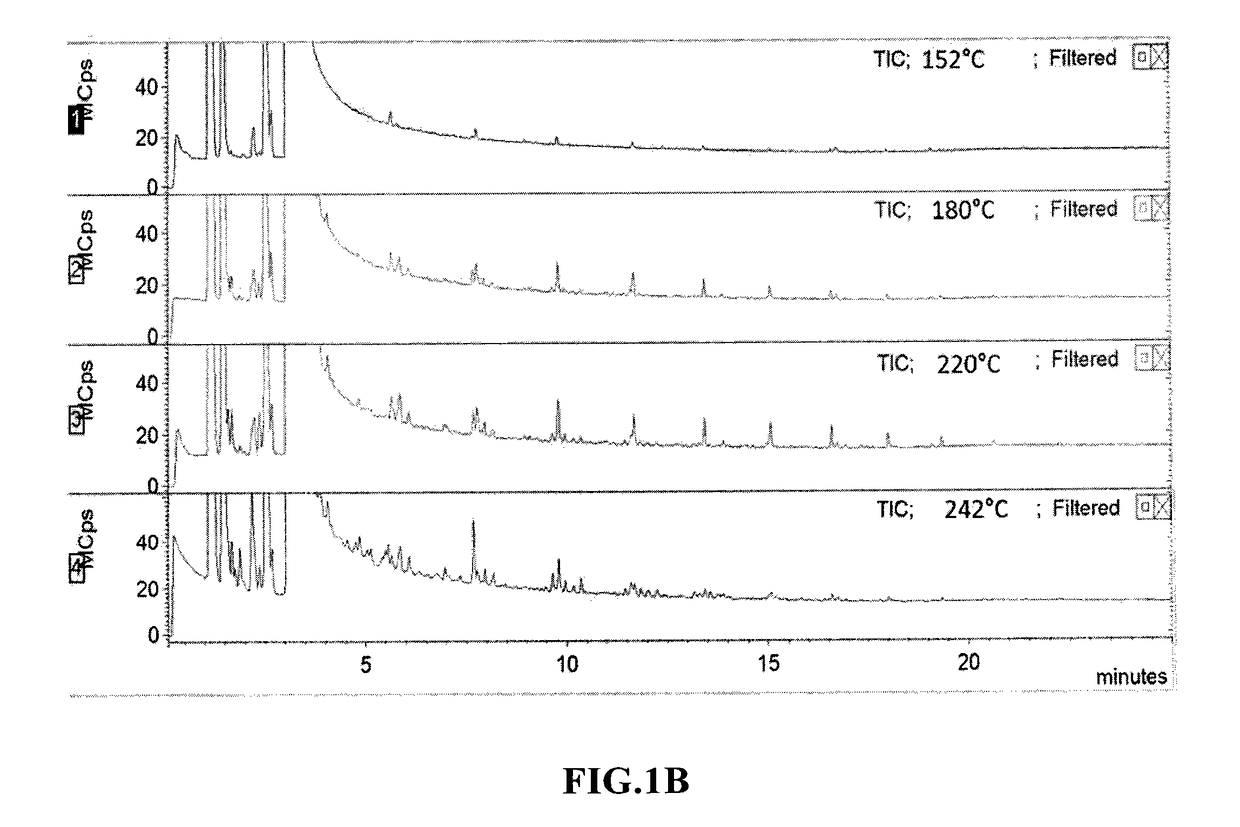
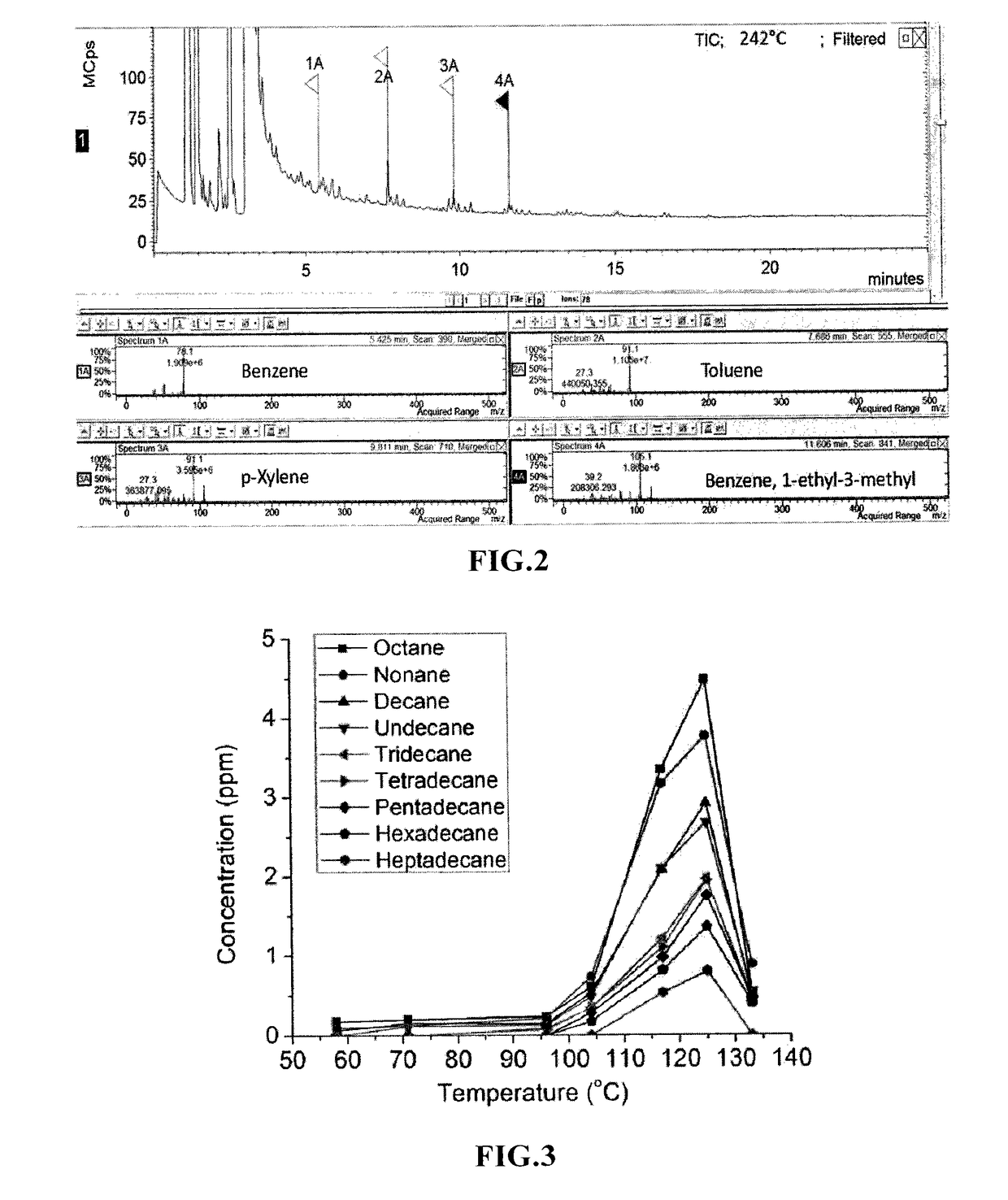
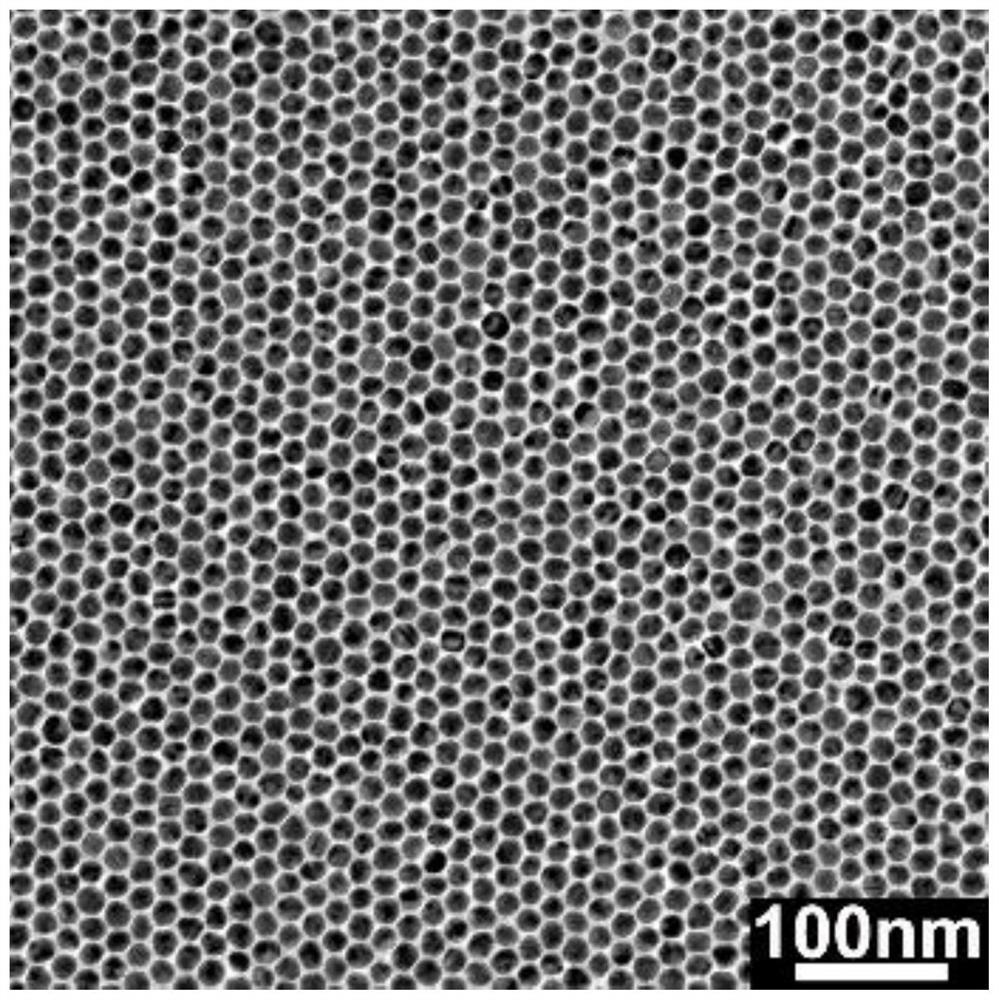
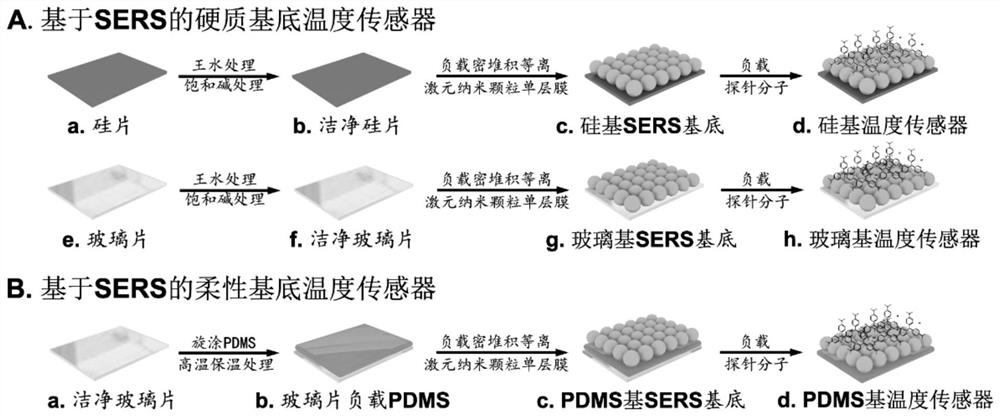
A method for accurate temperature detection based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering effect
ActiveCN112683419BThermometers using physical/chemical changesPhysical chemistryPlasmonic nanoparticles
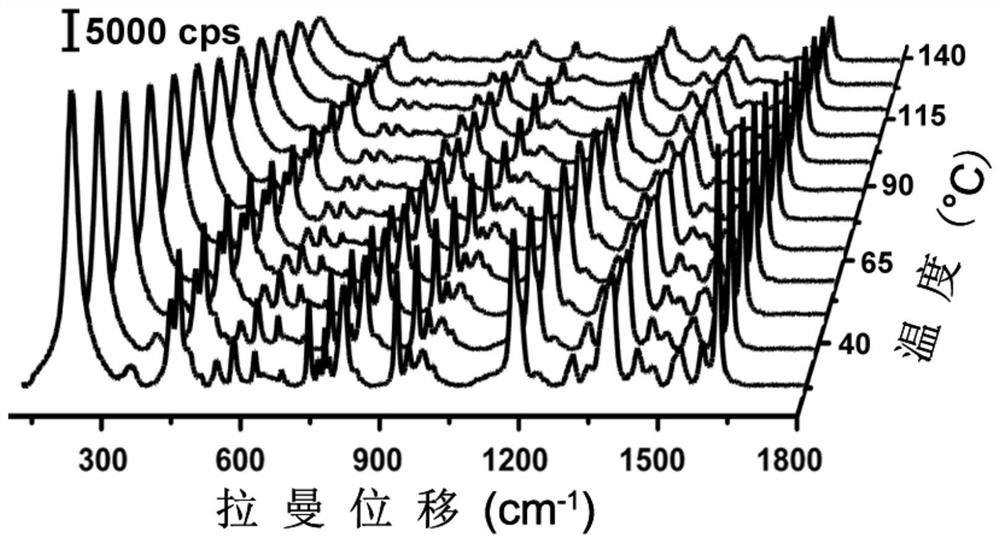
A method for accurately detecting temperature based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering effect, comprising the following steps: (1) loading a plasmonic nanoparticle monolayer film on a support substrate; (2) soaking the monolayer film substrate in a probe In the molecular solution, it is dried to make a hard substrate temperature sensor or a flexible substrate temperature sensor; (3) The hard substrate temperature sensor or flexible substrate temperature sensor is placed under a gradient working temperature to collect the Raman spectrum of its surface, and the characteristic temperature is established. and the standard curve between the corresponding characteristic peak intensity; (4) place the hard substrate temperature sensor or flexible substrate temperature sensor in the detection range, collect the Raman spectrum of its surface, read the characteristic peak intensity and the temperature The standard curve comparison of the interval can realize the detection of unknown ambient temperature. The invention is simple to operate, and can realize reproducible, high-stability and high-precision temperature detection based on the temperature-dependent SERS effect of the plasmonic nanoparticle monolayer film.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Polymeric organic nanoparticles with enhanced emission
ActiveUS11230663B2Improve light resistanceMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsNanoparti clesPhoton upconversion
Owner:SONY CORP
Nanoantenna scanning probe tip, and fabrication methods
The invention provides a nanoantenna scanning probe tip for microscropy or spectroscopy. The nanoantenna scanning probe tip includes a sharp probe tip covered with a contiguous film of predetermined sized and shaped plasmonic nanoparticles. A method for forming the nanoantenna scanning probe tip by trapping nanoparticles having a predetermined size and shape at a liquid surface using surface tension, forming a uniform and organized monolayer film on the liquid surface, and then transferring portions of the film to a sharp probe tip. In preferred embodiments, the sharp probe tip is one of a conductive STM (scanning tunneling microscopy) tip, a tuning fork tip or an AFM (atomic force microscopy) tip. The sharp tip can be blunted with an oxide layer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
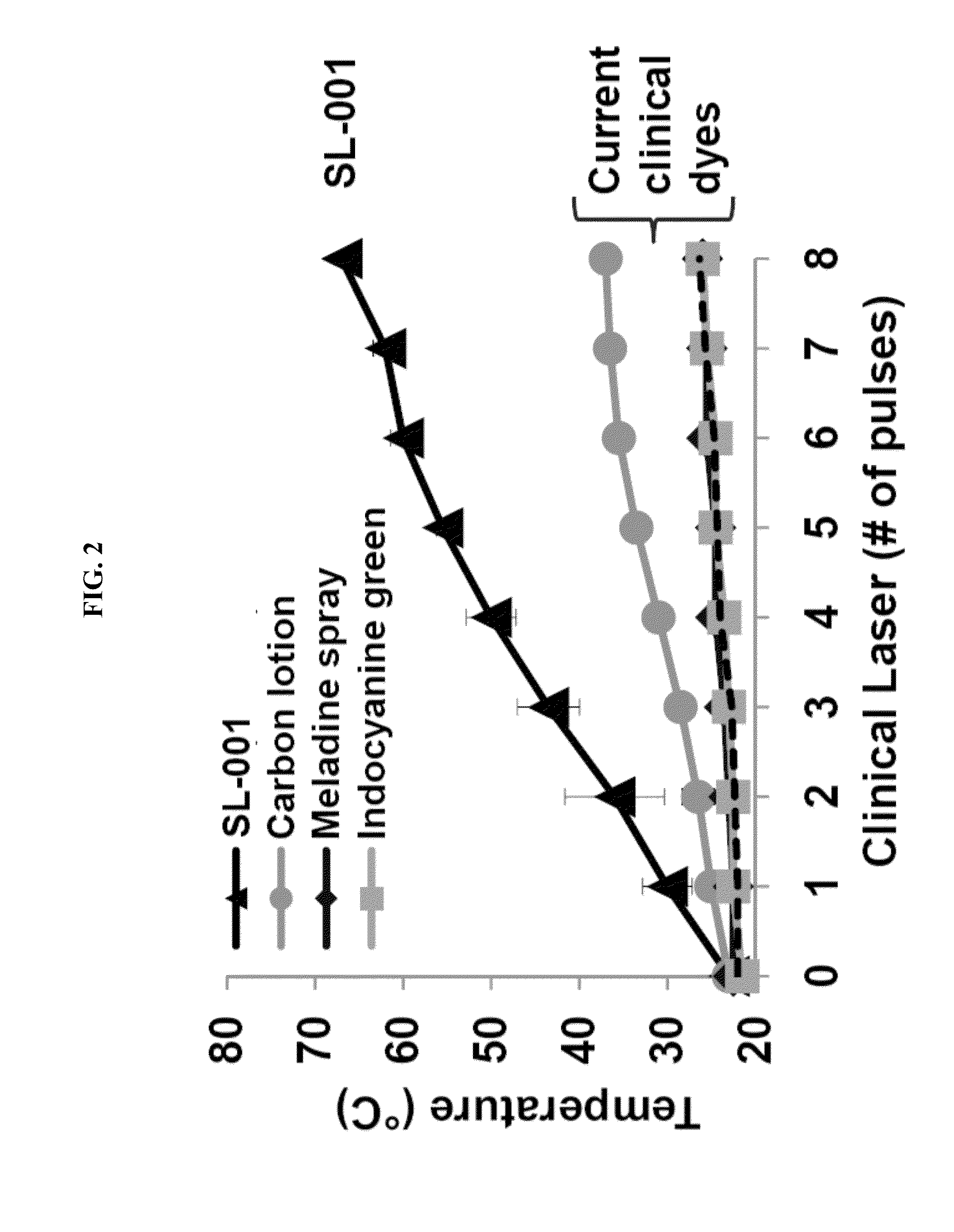
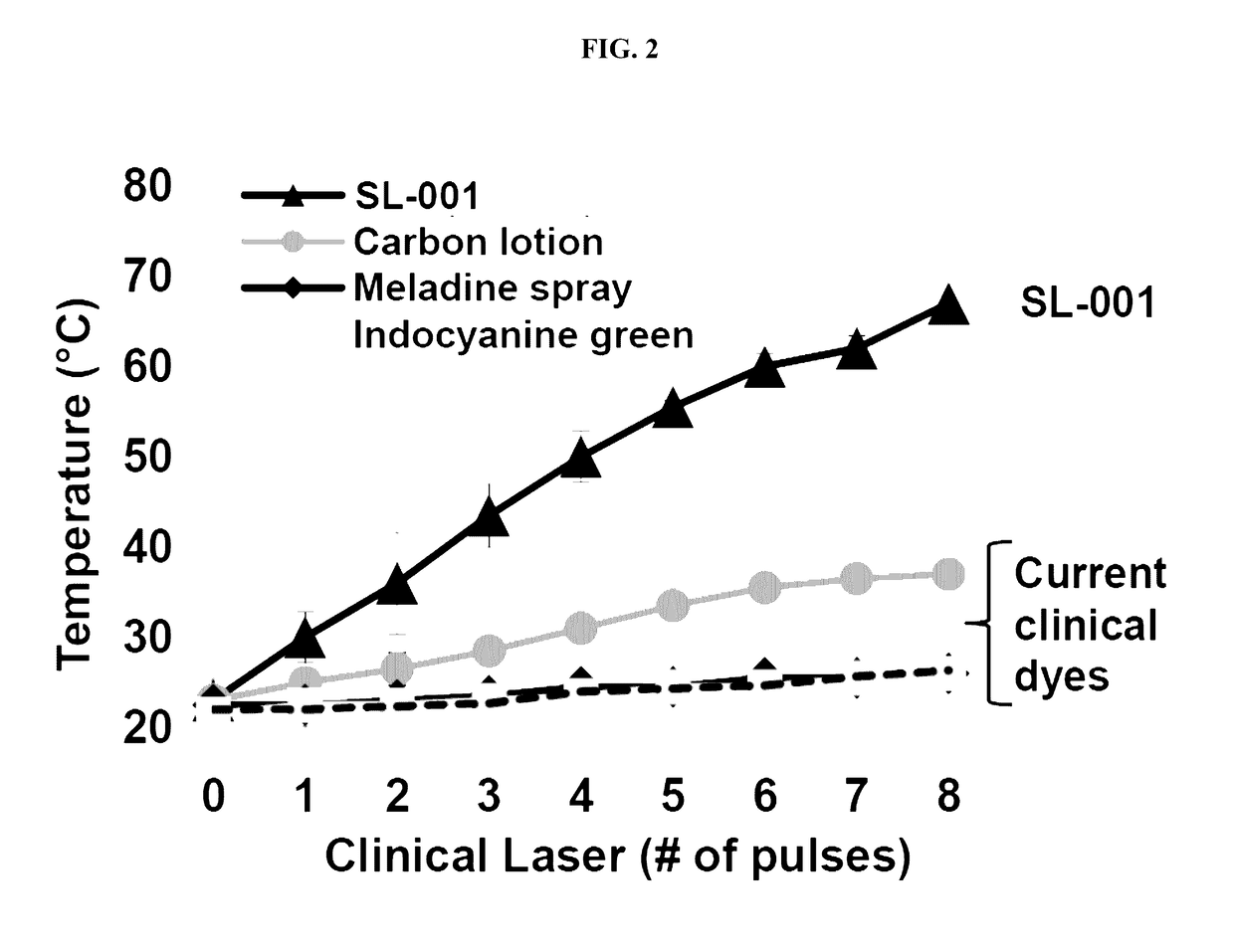
Titanium nitride plasmonic nanoparticles for clinical therapeutic applications
InactiveUS20200054752A1Easy to controlPowder deliveryEnergy modified materialsTitanium nitrideNanoparti cles
Disclosed herein are nanoparticle-based plasmonic solutions to therapeutic applications employing titanium nitride (TiN) and other non-stoichiometric compounds as the plasmonic material. Current solutions are suboptimal because they require complex shapes, large particle sizes, and a narrow range of sizes, in order to achieve plasmonic resonances in the biological window. The nanoparticles discloses herein provide plasmonic resonances occurring in the biological window even with small sizes, simple shapes, and better size dispersion restrictions. Local heating efficiencies of such nanoparticles outperform currently used Au and transition metal nanoparticles. The use of smaller particles with simpler shapes and better heating efficiencies allows better diffusion properties into tumor regions, larger penetration depth of light into the biological tissue, and the ability to use excitation light of less power.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Method and system for characterizing extracellular vesicles
ActiveUS10746730B2Well representedRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringExtracellular vesicleSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
A method for characterizing extracellular vesicles at an individual level is described. It comprises obtaining a sample comprising extracellular vesicles to be characterized and functionalizing the extracellular vesicles with plasmonic nanoparticles or a plasmonic coating. The method further comprises irradiating the individual extracellular vesicles with a laser beam and detecting a surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy signal from said individual extracellular vesicle.
Owner:UNIV GENT
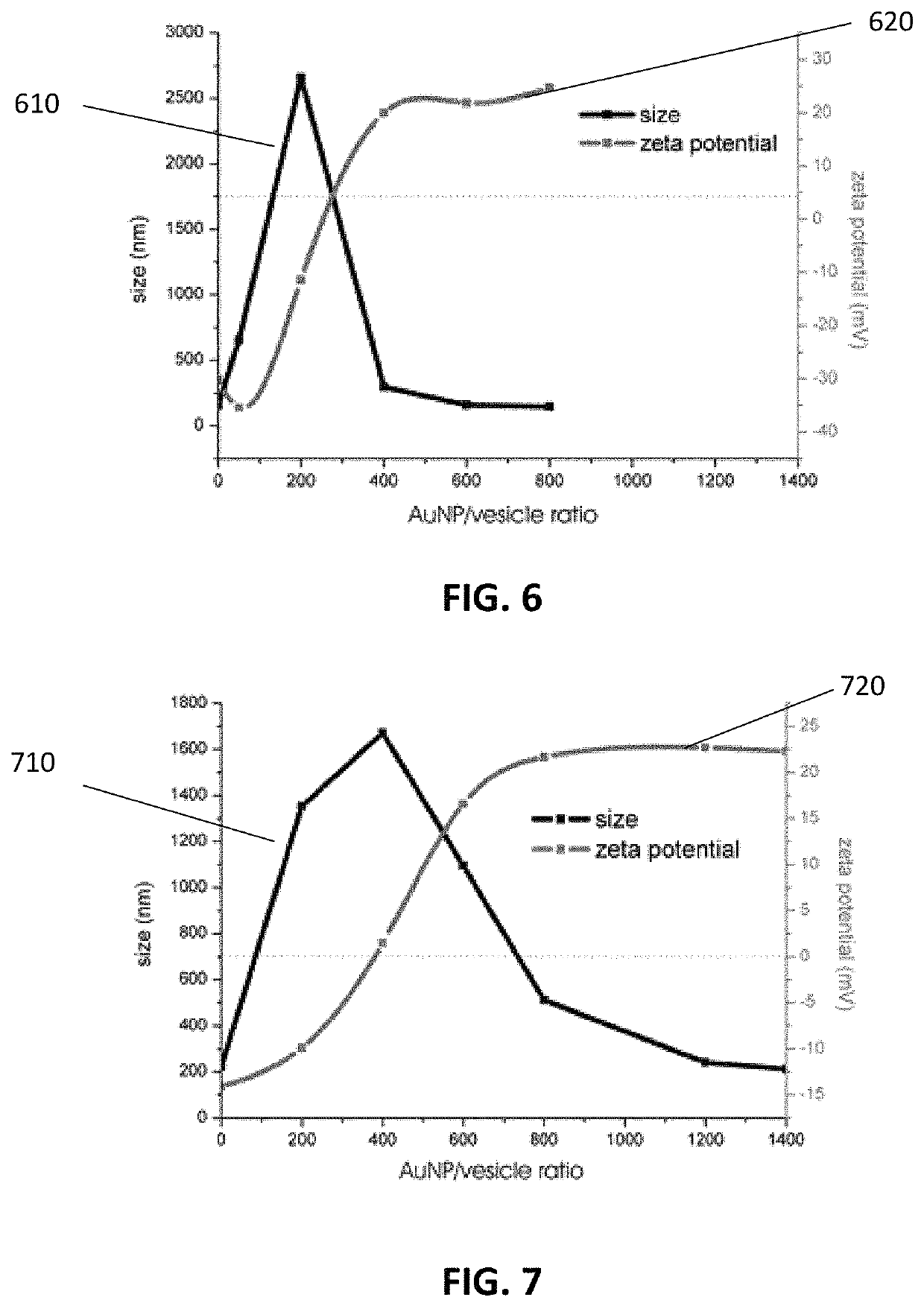
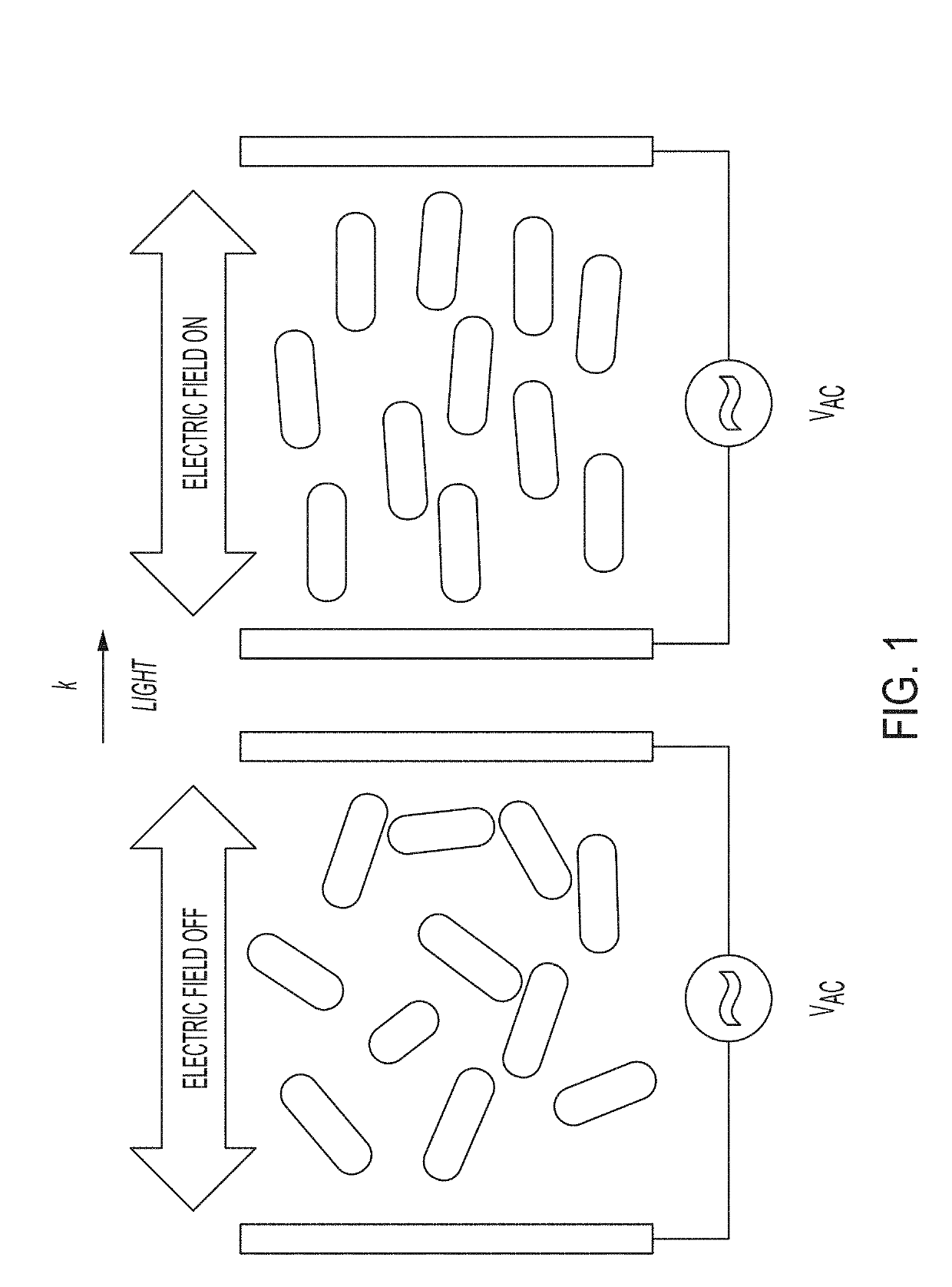
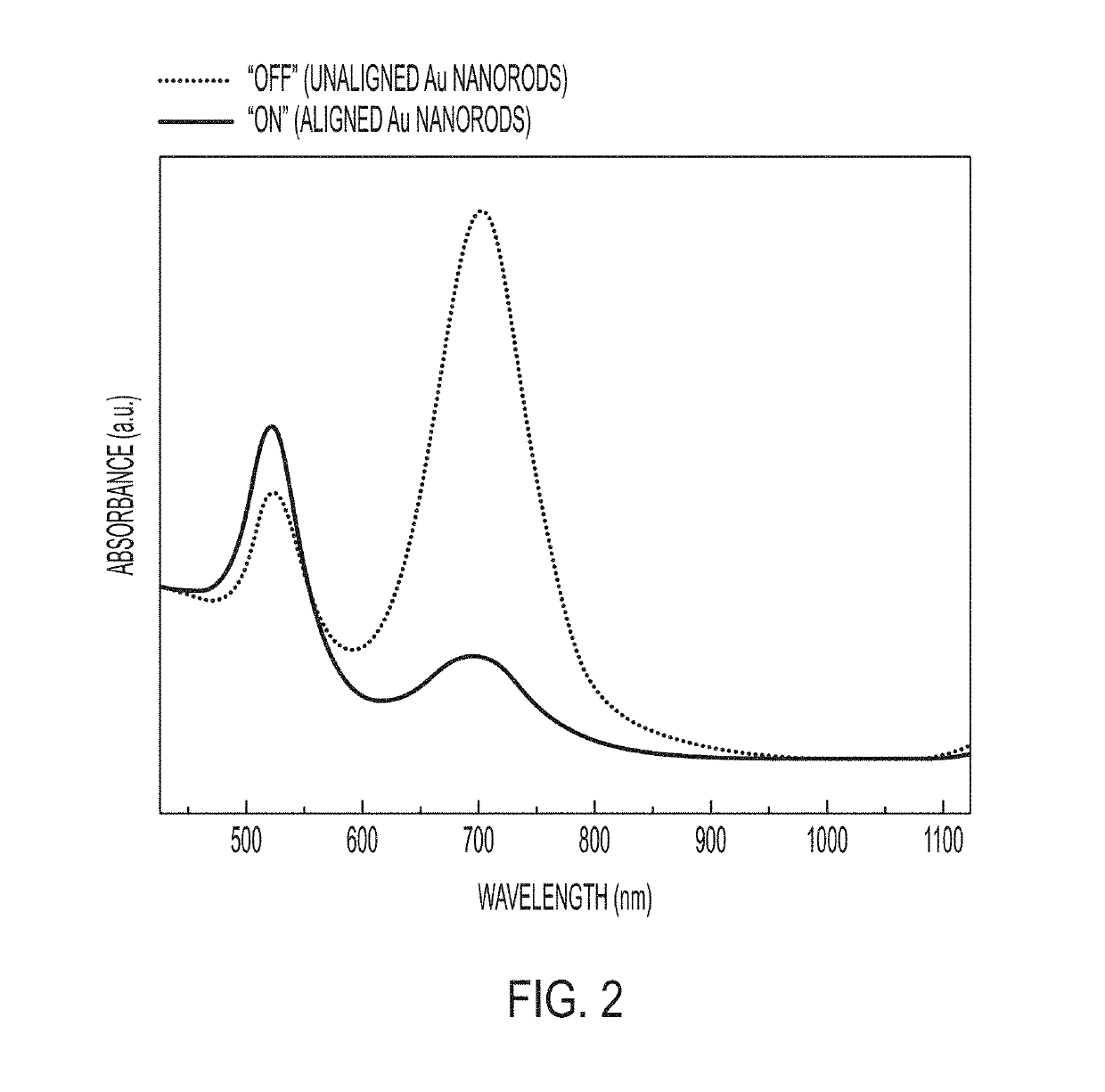
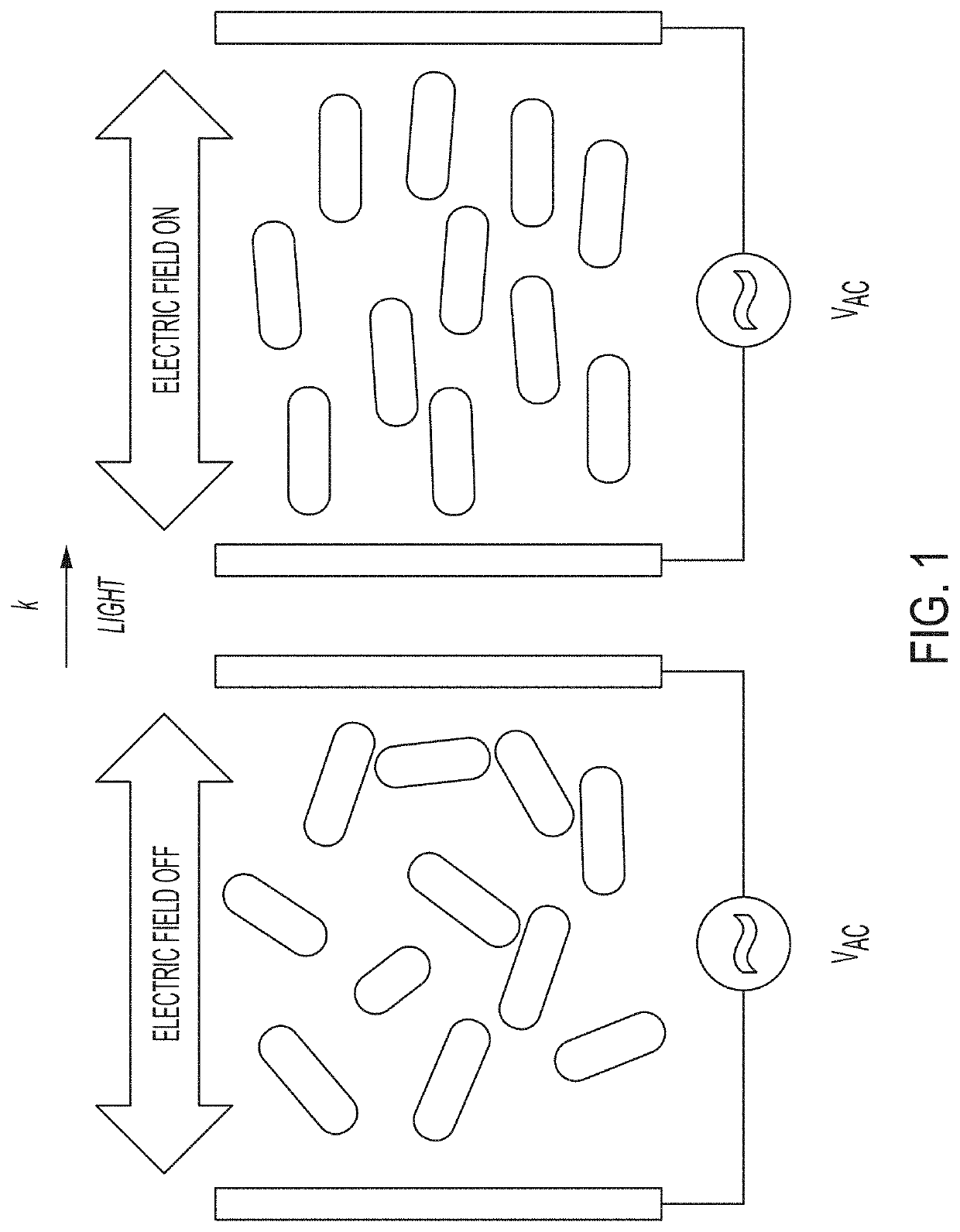
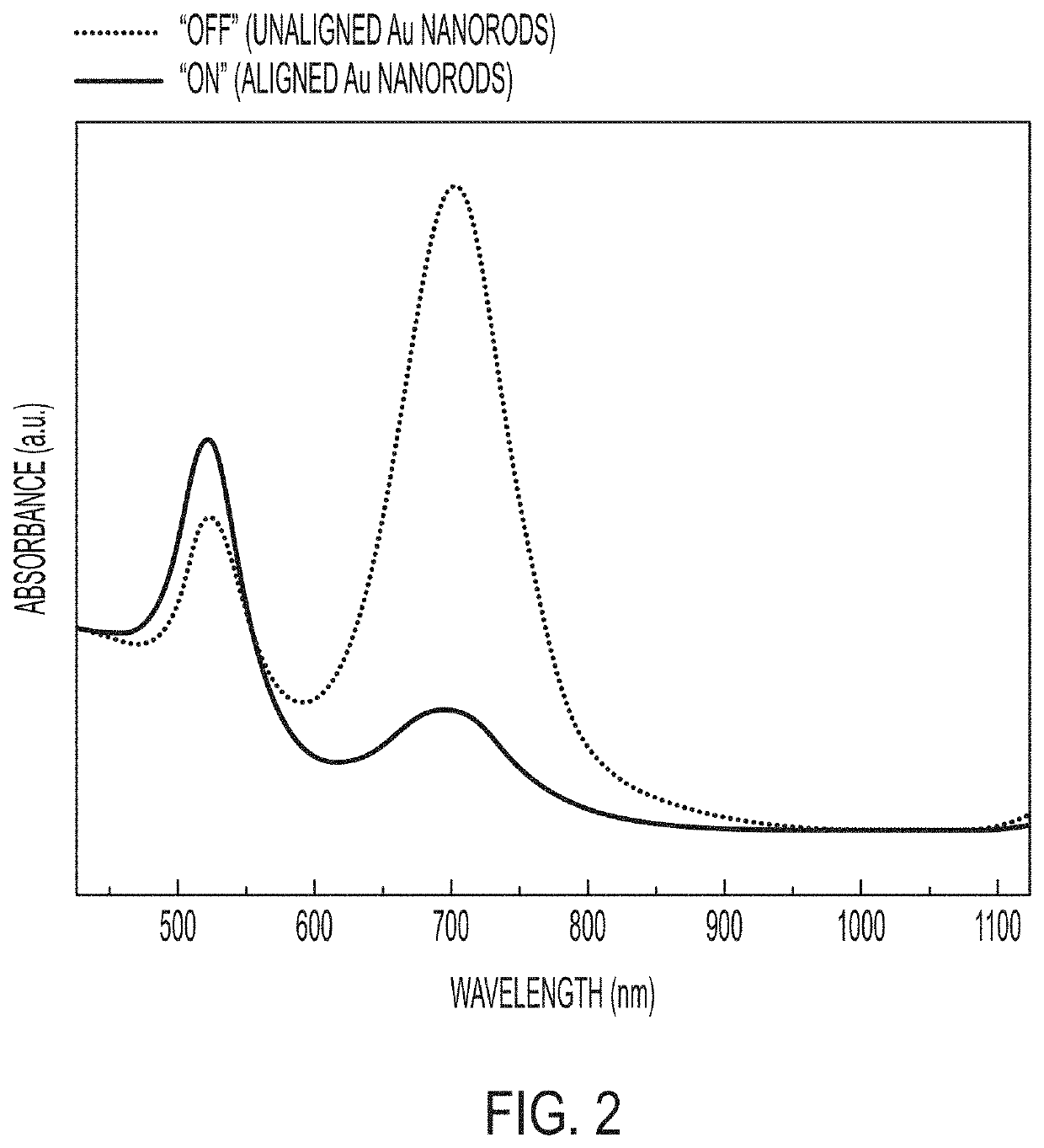
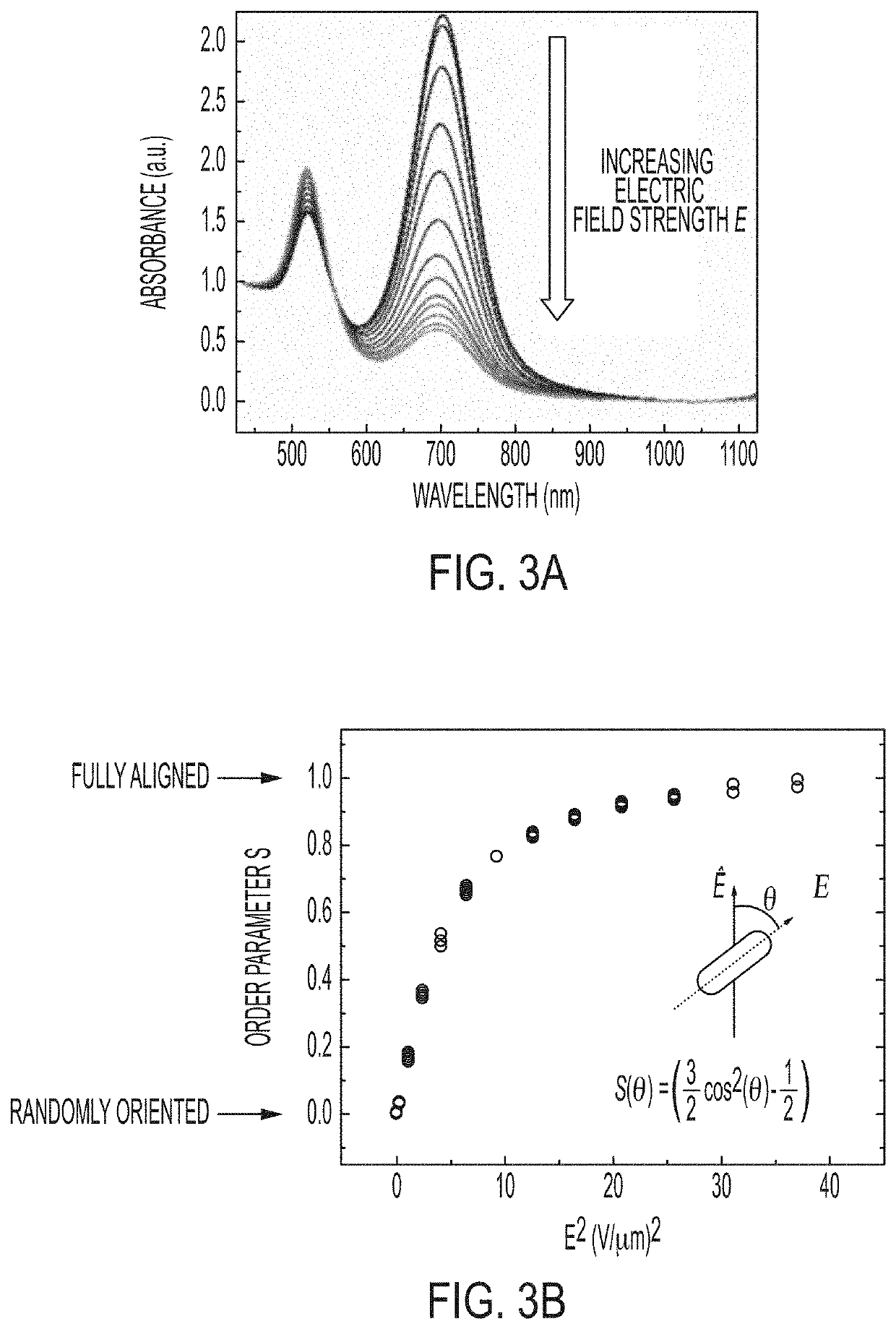
Plasmonic Nanoparticles as Pixels and Sub-Microsecond Switches
ActiveUS20190113824A1Controlling chromaticityControlling luminanceActive medium shape and constructionNon-linear opticsUltra fastPlasmonic nanoparticles
Application of an electric field to nanorods can control their alignment, thus providing techniques for ultra-fast switching and optical modulators, for example those that might serve as display indicators.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Exciton-plasmon coupling system, its construction method and method for enhancing singlet oxygen generation of photosensitizer by using the coupling system
ActiveCN106139145BEnhanced SkippingGood treatment effectEnergy modified materialsTransportation and packagingPhotosensSinglet oxygen
The invention relates to an exciton-plasma coupling system, its construction method and a method for enhancing the generation of singlet oxygen of a photosensitizer by utilizing the coupling system. The exciton-plasmon coupling system of the present invention is a core-shell structure formed by the adsorption of photosensitizer excitons and plasmonic nanoparticles, and the LSPR absorption peak of the plasmonic nanoparticles covers the excitation of the photosensitizer in the visible region. sub-absorption peaks. The method of the invention includes selecting the peak position and concentration of the plasmonic nanoparticle, the type and concentration of the charged substance, and the peak position and concentration of the photosensitizer to form a stable coupling system. Measure the singlet oxygen yield of the product by electron spin resonance technology, and determine that the coupling effect is the main factor for enhancing the singlet oxygen yield of the photosensitizer through the measurement of Raman spectroscopy. The results show that the exciton-plasmon coupling of the present invention The system has a higher singlet oxygen yield than the uncoupled system.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Plasmonic nanoparticles with intra-nanogap produced by dealloying, method for preparing the same and use thereof
PendingUS20210023626A1Easy to useUniform thicknessMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingAlloyNanoparti cles
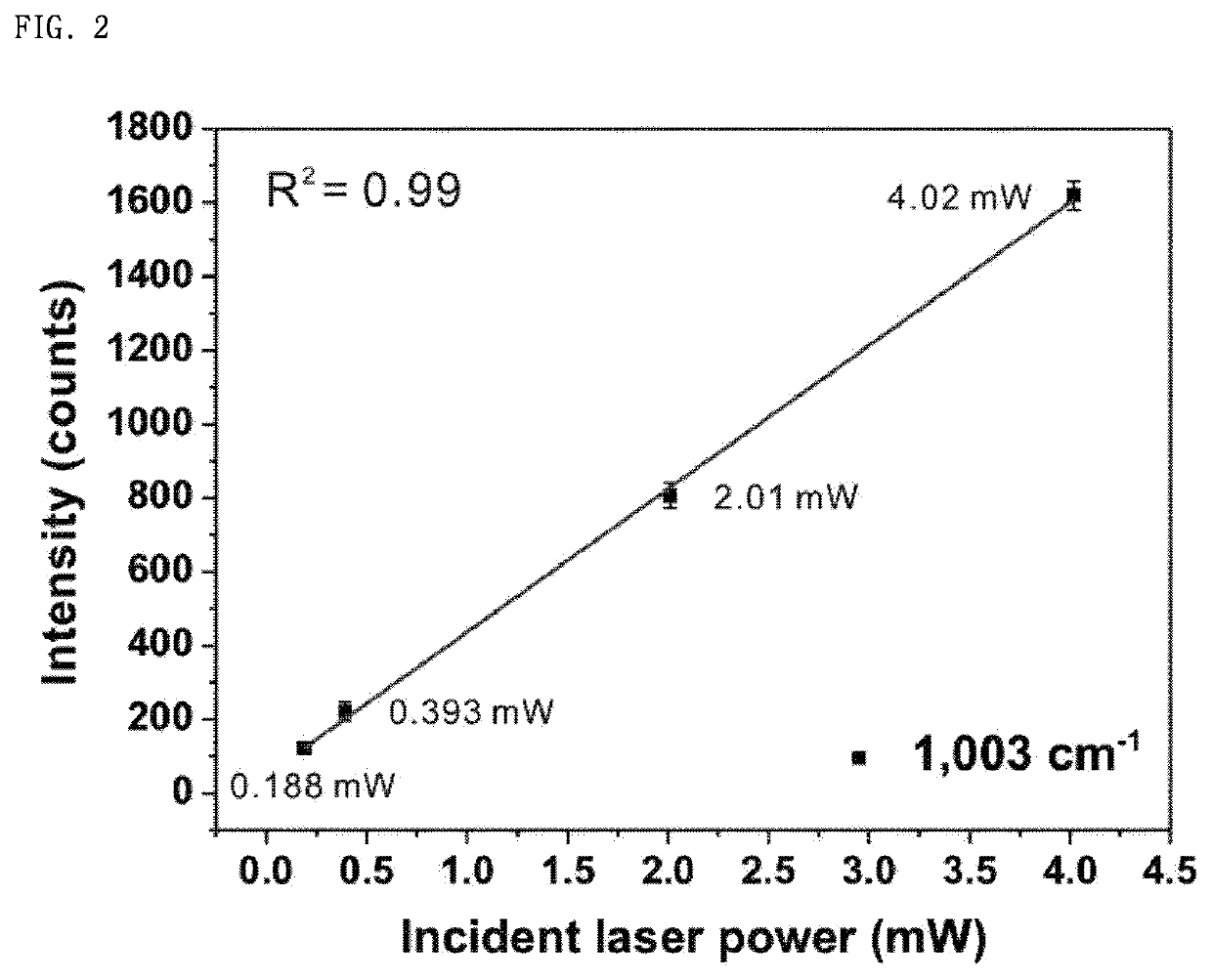
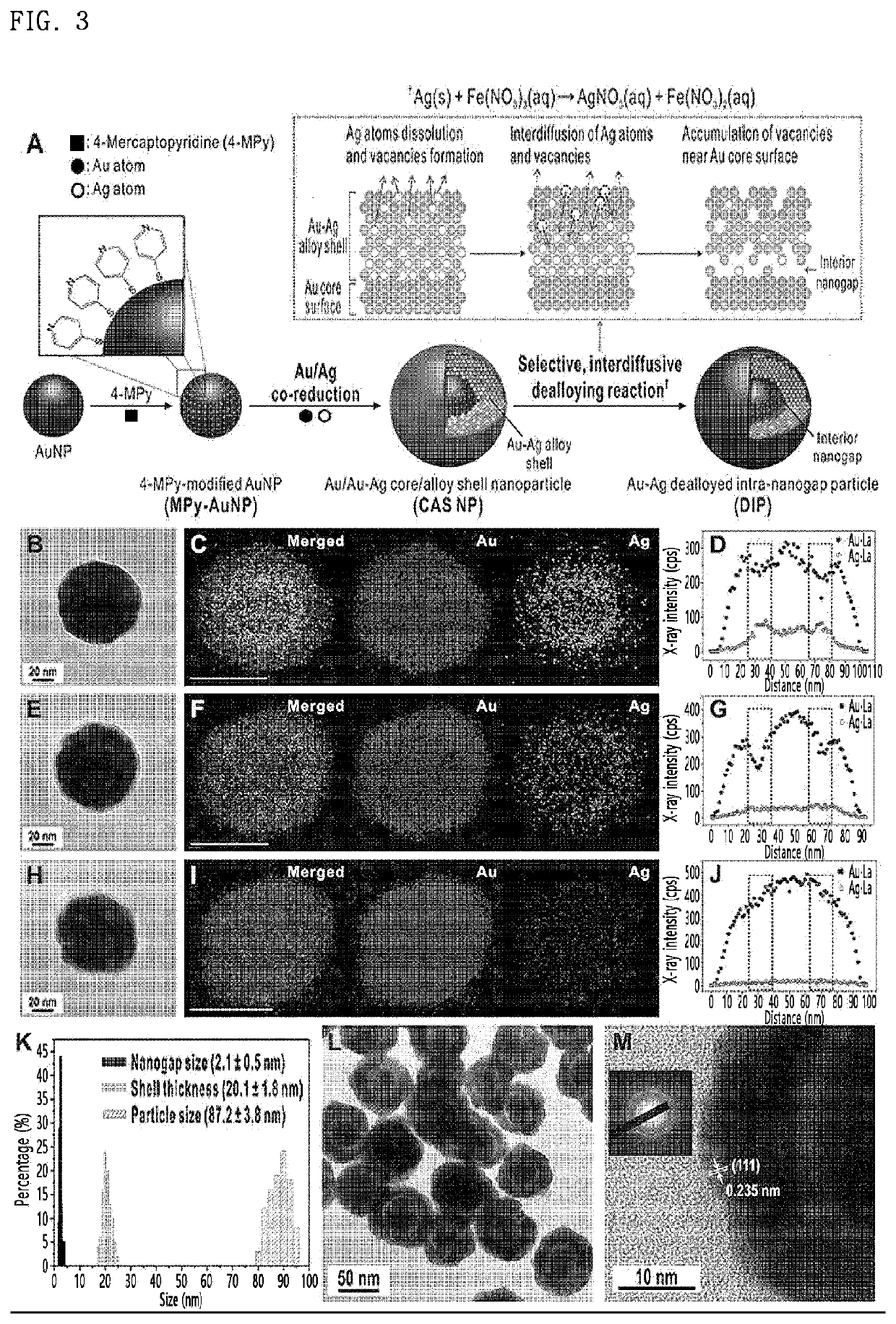
The present invention relates to a method for preparing a core-gap-shell nanoparticle having an average height of 0.1 nm to 10 nm, in which a Raman-active material is disposed between a core and a shell, and more specifically, to a method for preparing a core-gap-shell nanoparticle, which comprises introducing a shell made of an alloy of a second metal and a third metal, on the core particles of the first metal, the surface of which is modified with a Raman-active material; selectively removing the second metal by treating with a second metal etchant, followed by dealloying; the core-gap-shell nanoparticle prepared by the above method comprising a Raman-active material disposed in the gap, and uses of the core-gap-shell nanoparticle for biosensing and / or bioimaging.
Owner:BIONANO HEALTH GUARD RES CENT +1
Method for optical opening of the blood-brain barrier
PendingUS20210252151A1Powder deliveryGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsPlasmonic nanoparticlesBlood–brain barrier
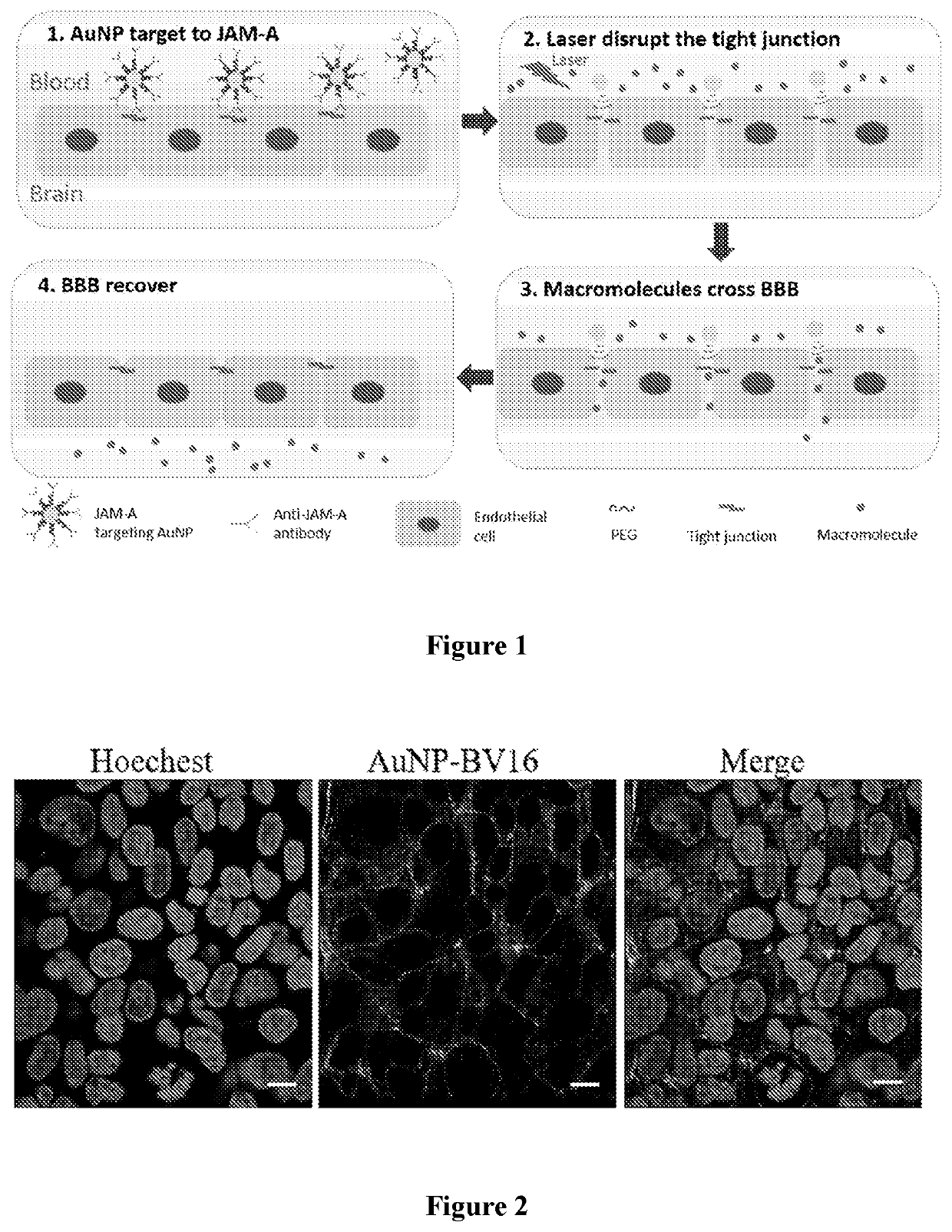
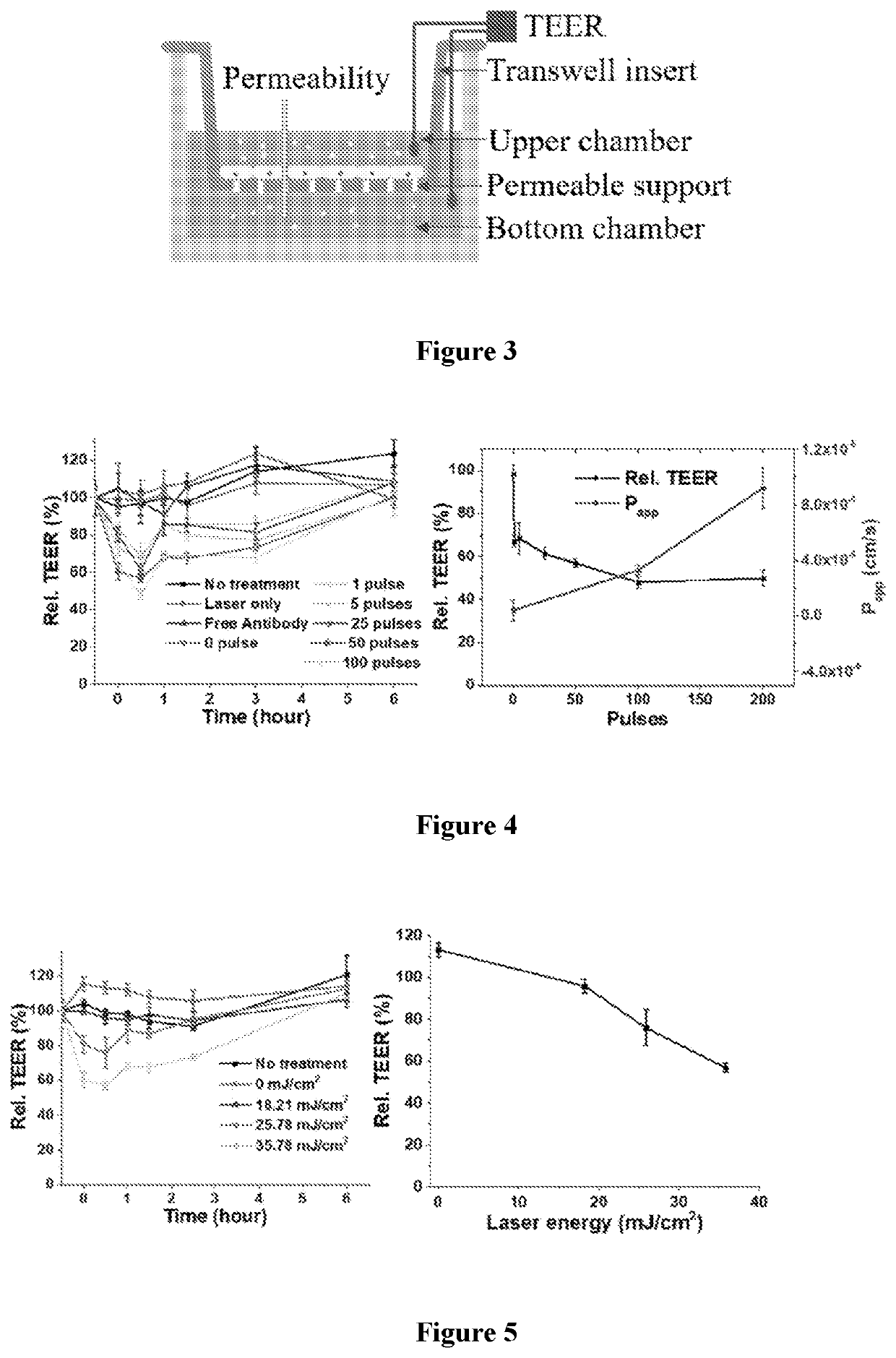
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) excludes most drugs and poses a significant challenge to treat brain diseases. Current methods for BBB opening yield modest outcomes in clinical applications due to safety and toxicity. This disclosure relates to methods of optically opening the BBB by laser excitation of tight-junction targeted nanoparticles to induce BBB transient opening. The excitation of plasmonic nanoparticles produces localized effects such as nanoscale heating and photomechanical force leading to BBB transiently opening to allow macromolecules across it. The safe and predictable platform for brain drug delivery will improve therapies for brain disease such as cancers, infections and neurologic disorders.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Shape tunable plasmonic nanoparticles
ActiveUS9588124B2Energy modified materialsTransportation and packagingMolecular imagingPlasmonic nanoparticles
Noble metal nanoparticles and methods of their use are provided. Certain aspects provided solid noble metal nanoparticles tuned to the near infrared. The disclosed nanoparticles can be used in molecular imaging, diagnosis, and treatment. Methods for imaging cells are also provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Plasmonic nanoparticle catalysts and methods for producing long-chain hydrocarbon molecules
ActiveUS10926252B2Material nanotechnologyHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsLight irradiationPtru catalyst
A plasmonic nanoparticle catalyst for producing hydrocarbon molecules by light irradiation, which comprises at least one plasmonic provider and at least one catalytic property provider, wherein the plasmonic provider and the catalytic property provider are in contact with each other or have distance less than 200 nm, and molecular composition of the hydrocarbon molecules produced by light irradiation is temperature-dependent. And a method for producing hydrocarbon molecules by light irradiation utilizing the plasmonic nanoparticle catalyst.
Owner:BEIJING GUANGHE NEW ENERGY TECH CO LTD
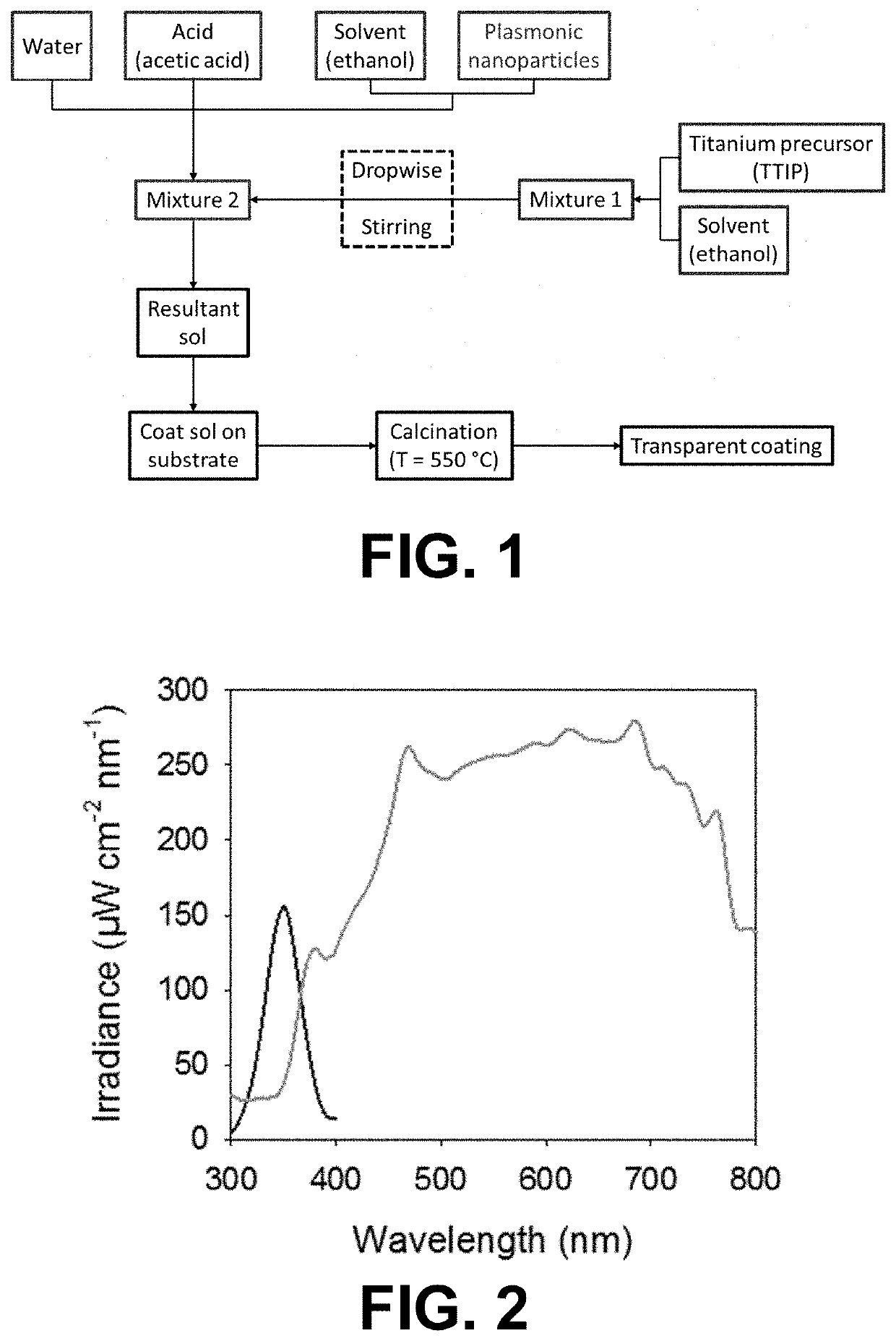
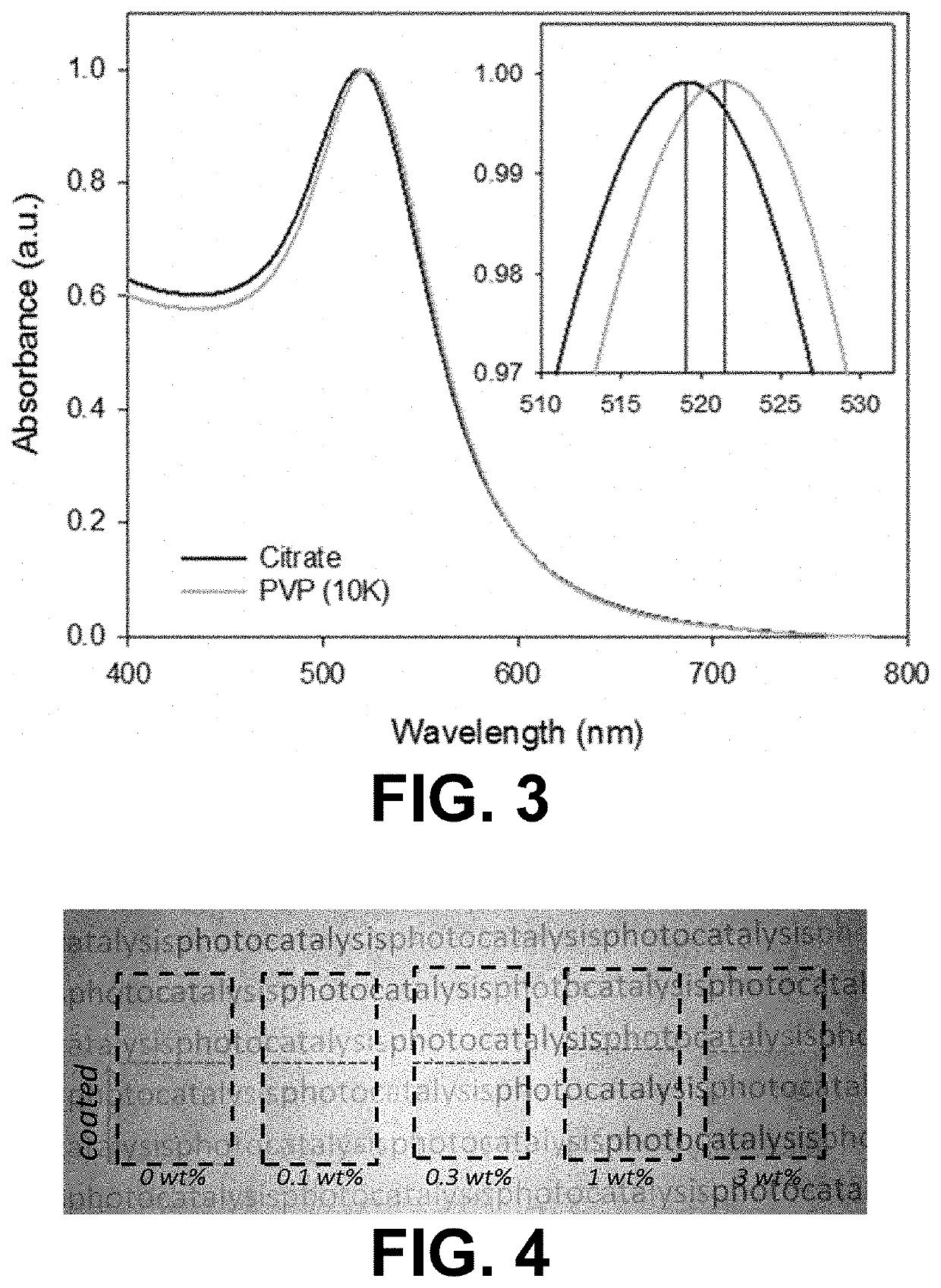
Self-cleaning coating
PendingUS20200347246A1Less recombination eventImproves bothCoatingsOptical elementsPhoto catalysisPlasmonic nanoparticles
A method for forming a self-cleaning coating, comprises providing a first dispersion comprising plasmonic nanoparticles by suspending plasmonic nanoparticles in an organic medium and providing a second dispersion comprising a precursor of a photocatalytic matrix in an organic medium. The method further comprises forming a mixture of the first and second dispersion and coating the mixture on a surface. The method also comprises calcining the coated mixture.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ANTWERP
Plasmonic nanoparticles as pixels and sub-microsecond switches
ActiveUS10606145B2Controlling chromaticityControlling luminanceActive medium shape and constructionNon-linear opticsEngineeringPlasmonic nanoparticles
Application of an electric field to nanorods can control their alignment, thus providing techniques for ultra-fast switching and optical modulators, for example those that might serve as display indicators.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com