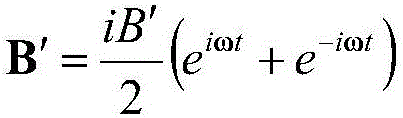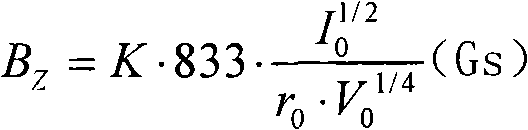Patents
Literature
278 results about "Transverse magnetic field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
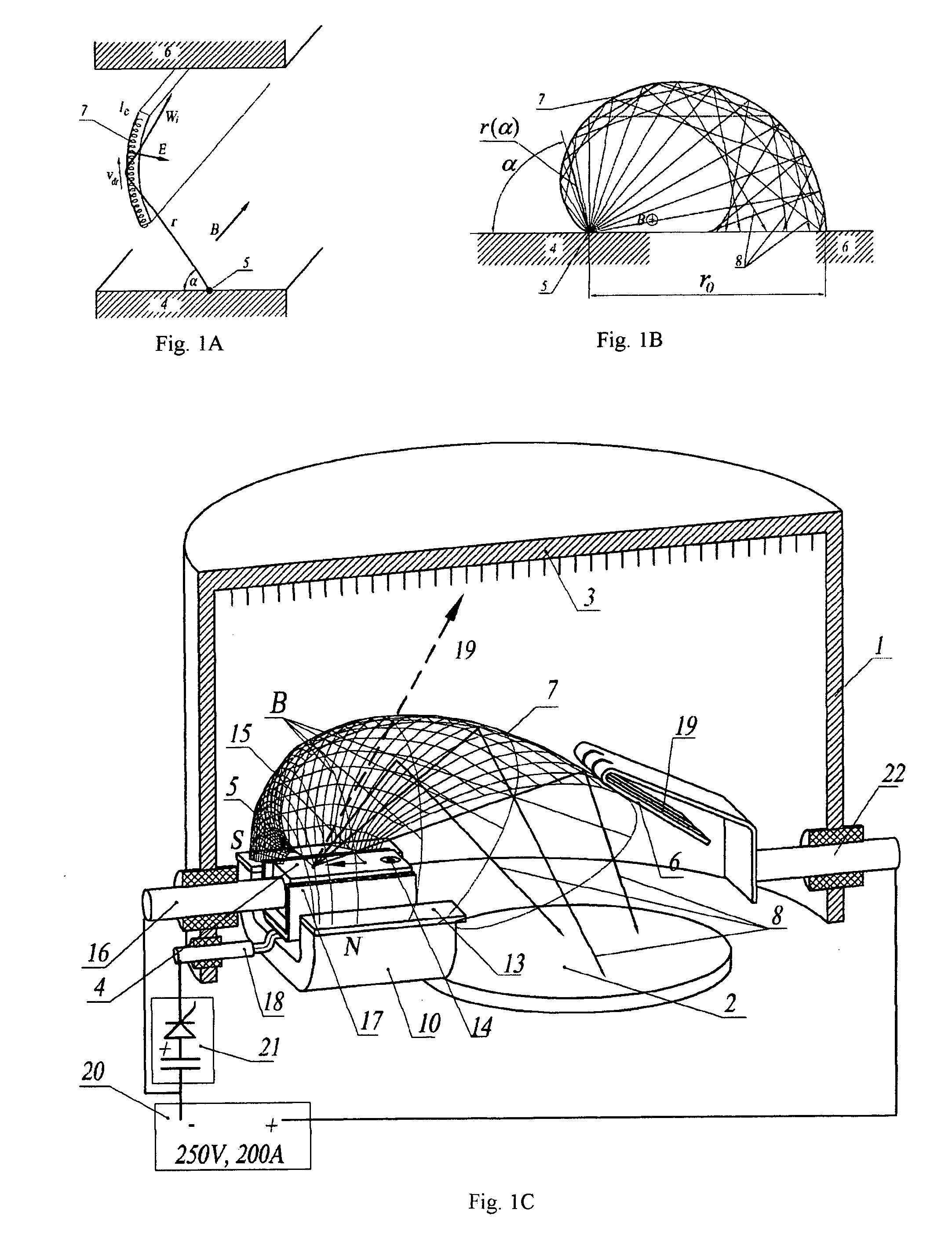
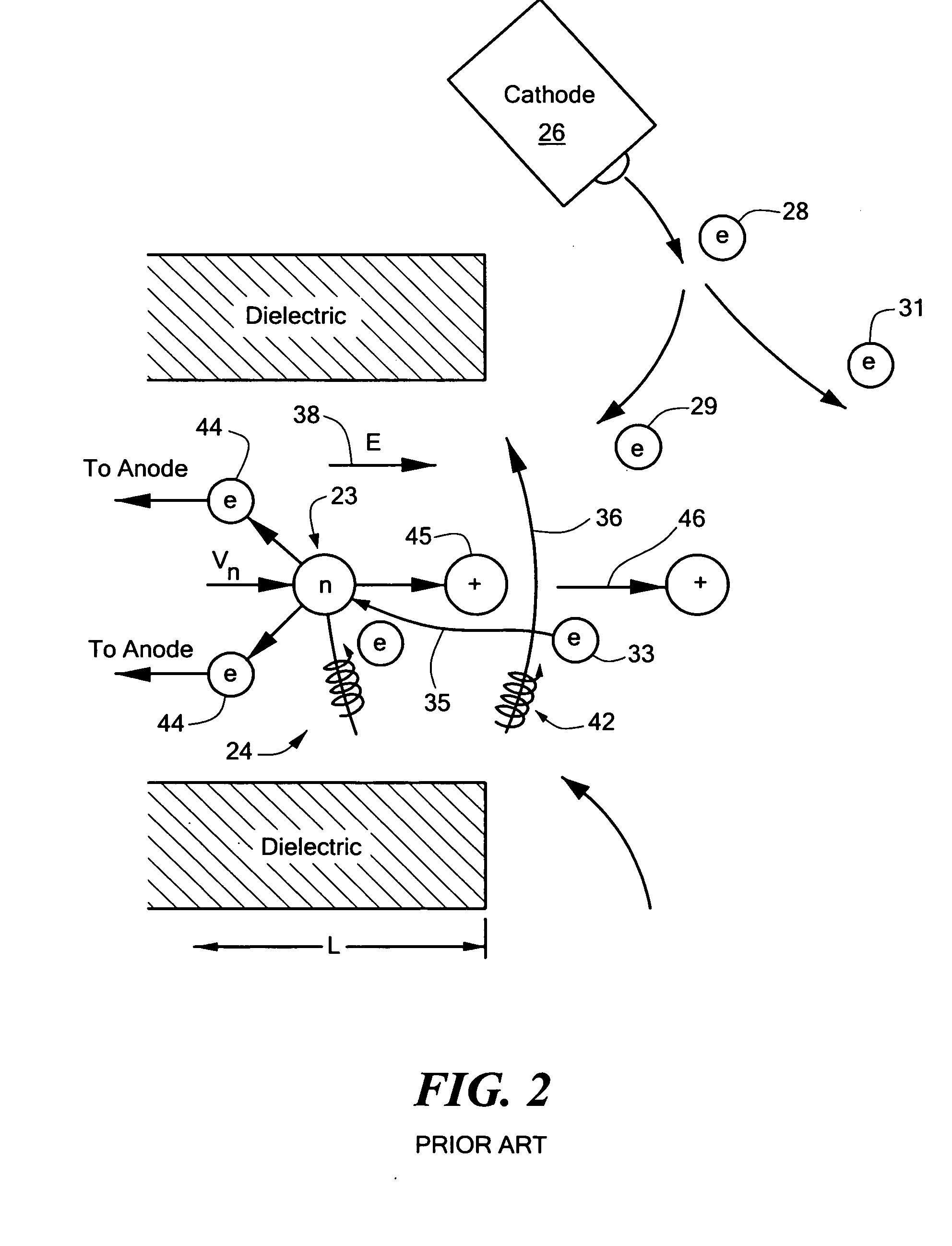
If an electric current flows through a conductor in a magnetic field, the magnetic field exerts a transverse force on the moving charge carriers which tends to push them to one side of the conductor.
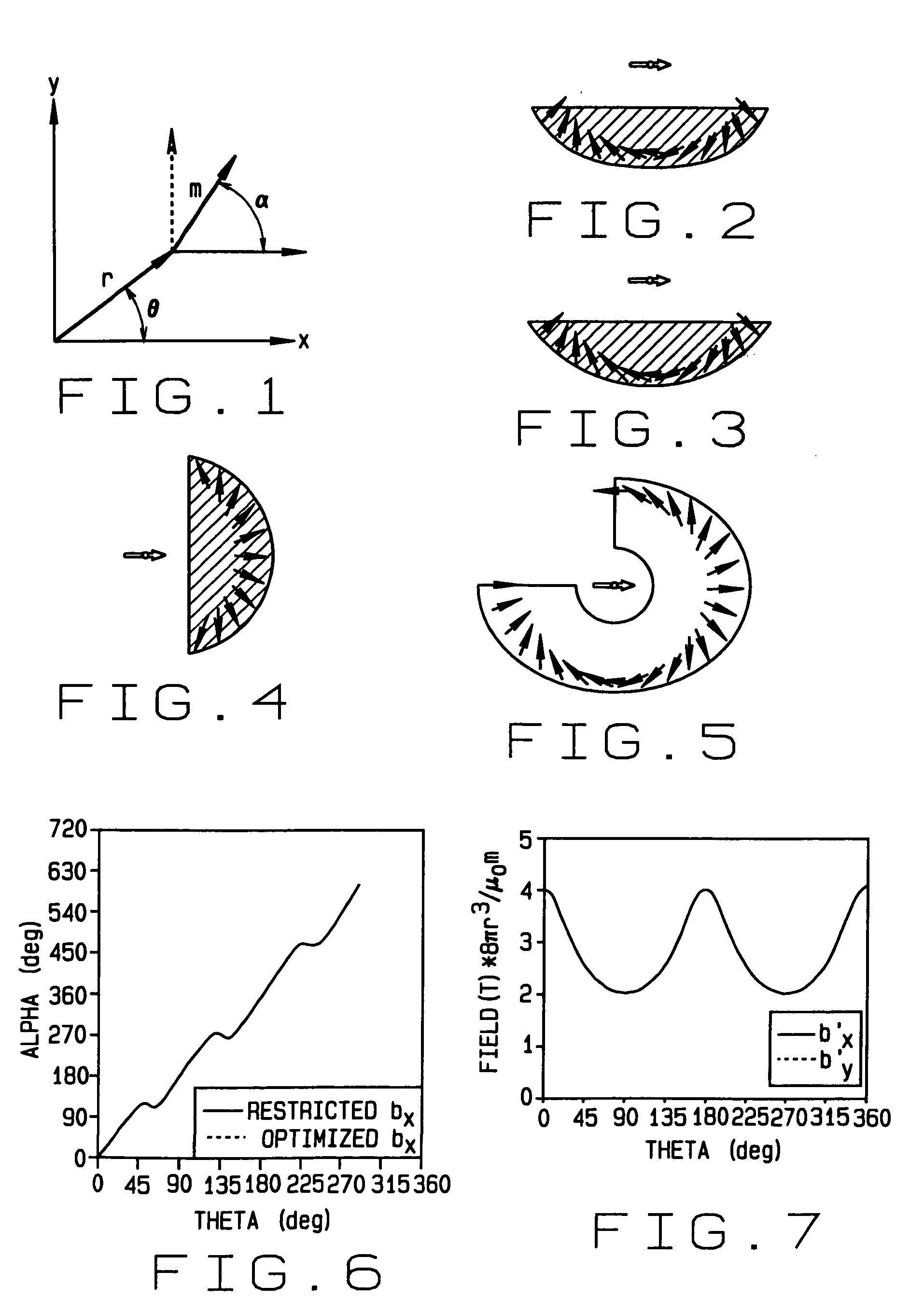
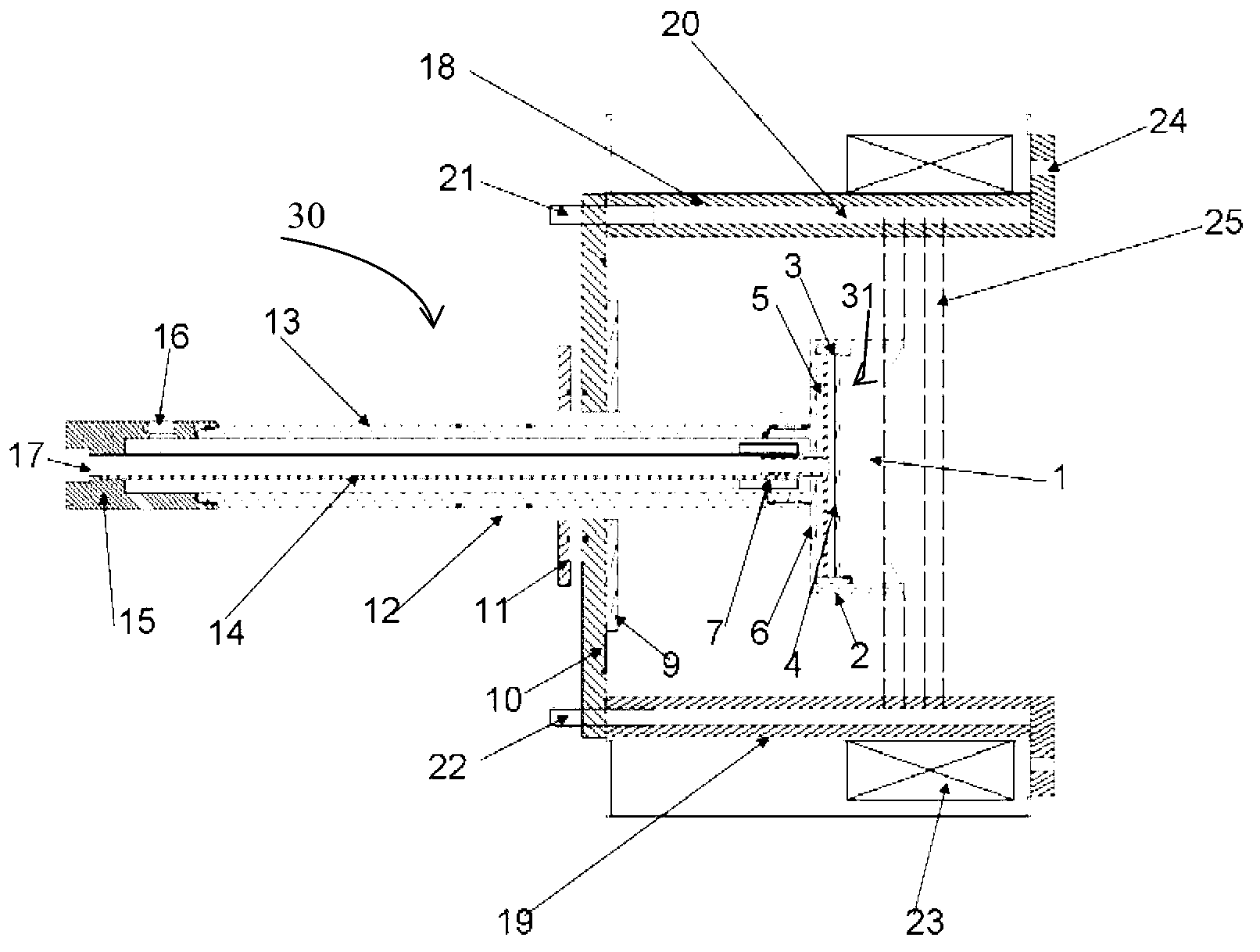
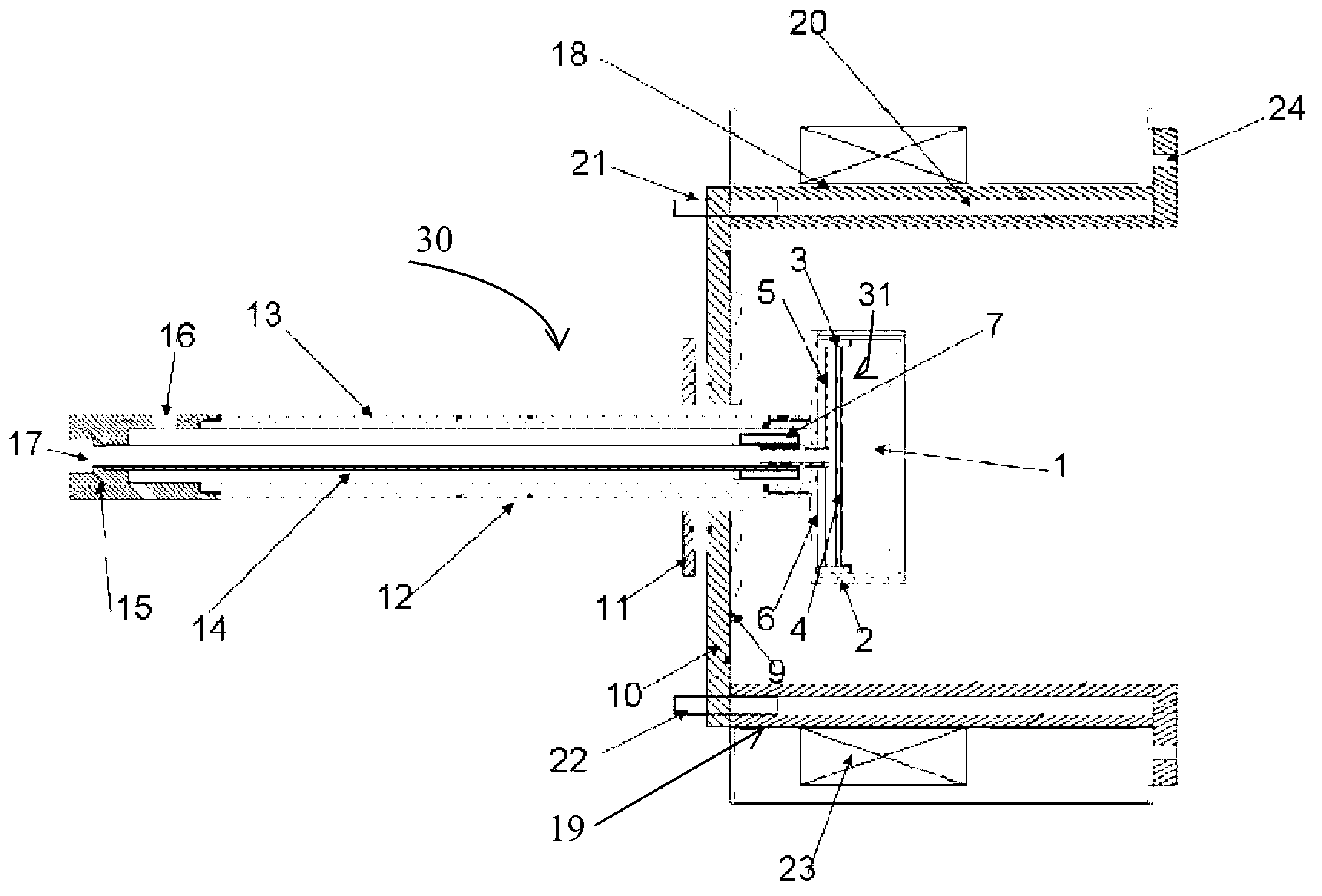
Magnets with varying magnetization direction and method of making such magnets
InactiveUS6940379B2Improve magnetic propertiesSmall sizePermanent magnetsDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetizationTransverse magnetic field
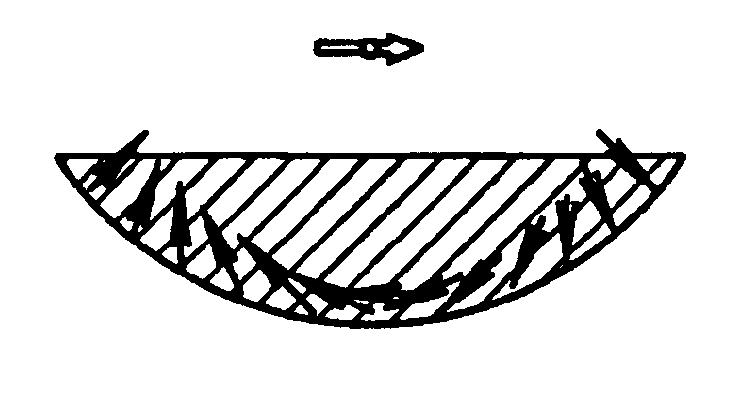
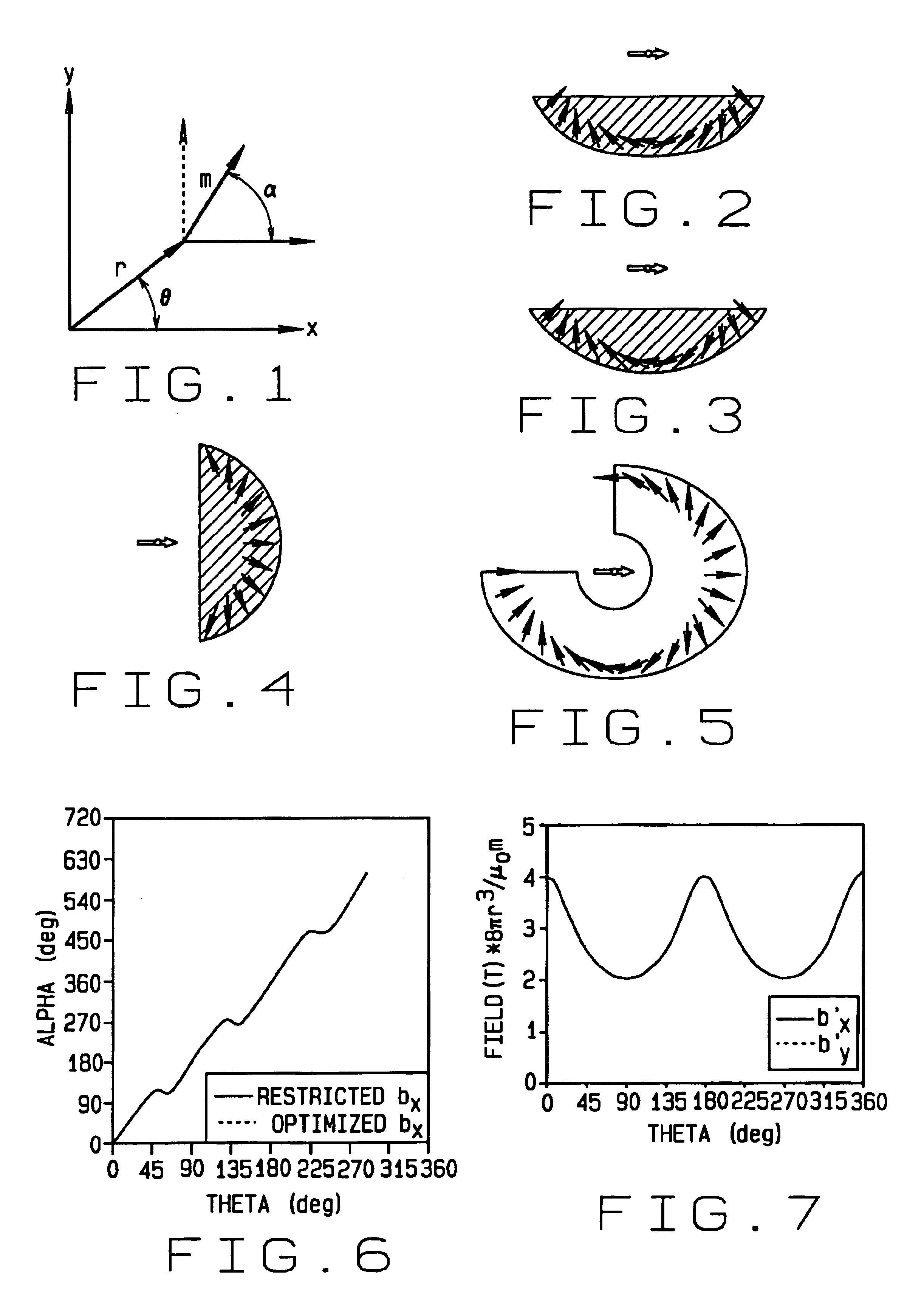
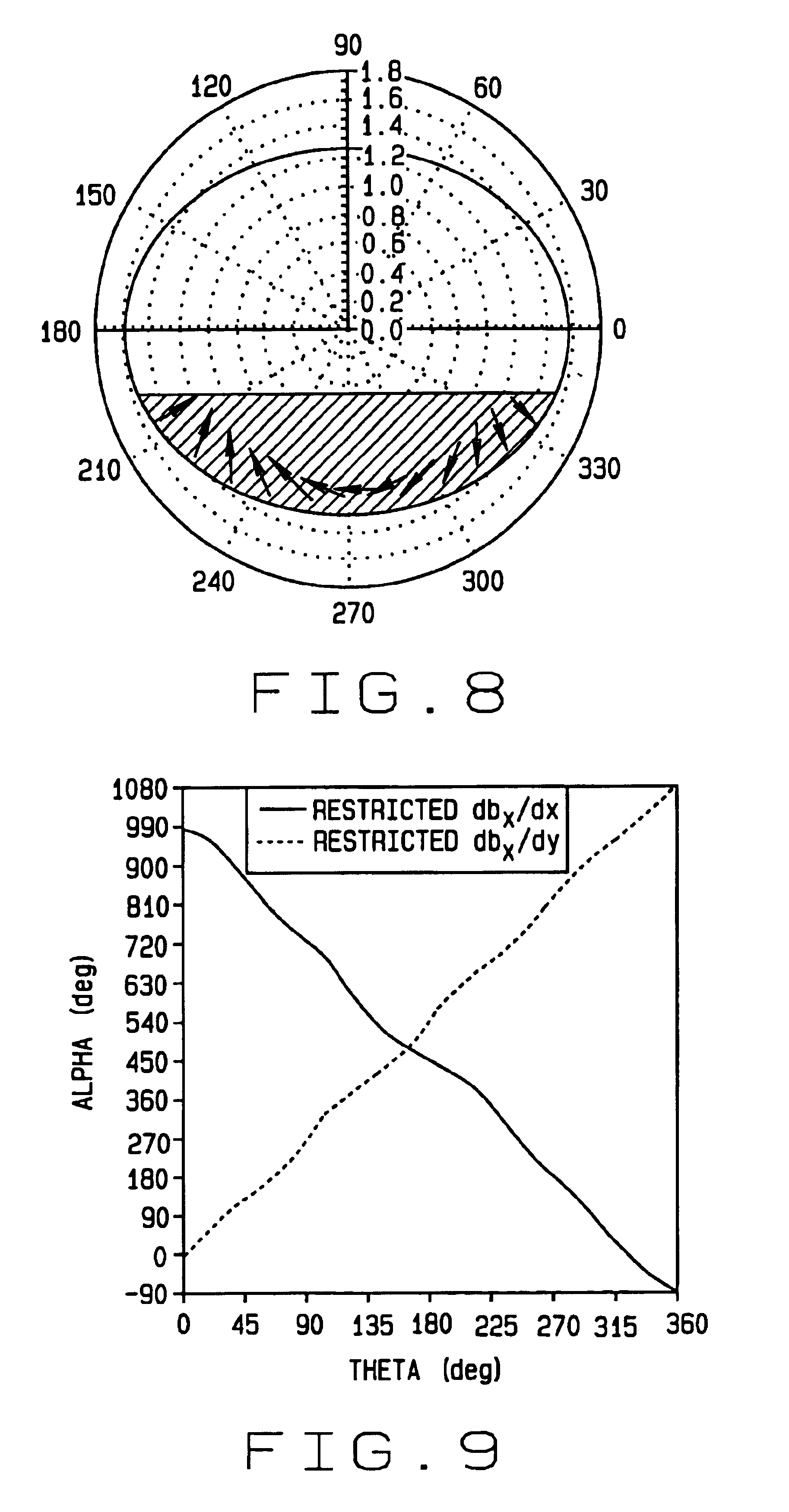
A permanent magnet in which the magnetization direction varies with location to optimize or restrict a magnetic field property in a selected direction at a selected point. The magnetic field property may be, for example, the transverse magnetic field, axial magnetic field, axial gradient of the transverse magnetic field, transverse gradient of the transverse magnetic field, axis gradient of the axial magnetic field, transverse gradient of the axial magnetic field, the product of the transverse magnetic field and the transverse gradient of the transverse magnetic field, the product of the transverse magnetic field and the axial gradient of the transverse magnetic field, the product of the axial magnetic field and the transverse gradient of the axial magnetic field, or the product of the axial magnetic field and the axial gradient of the axial magnetic field. The magnet may be formed of one or more segments in which the magnetization direction varies smoothly and continuously, or the magnet may be formed of a plurality of segments in which the magnetization direction is constant. A method of making and using such magnets is also disclosed.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
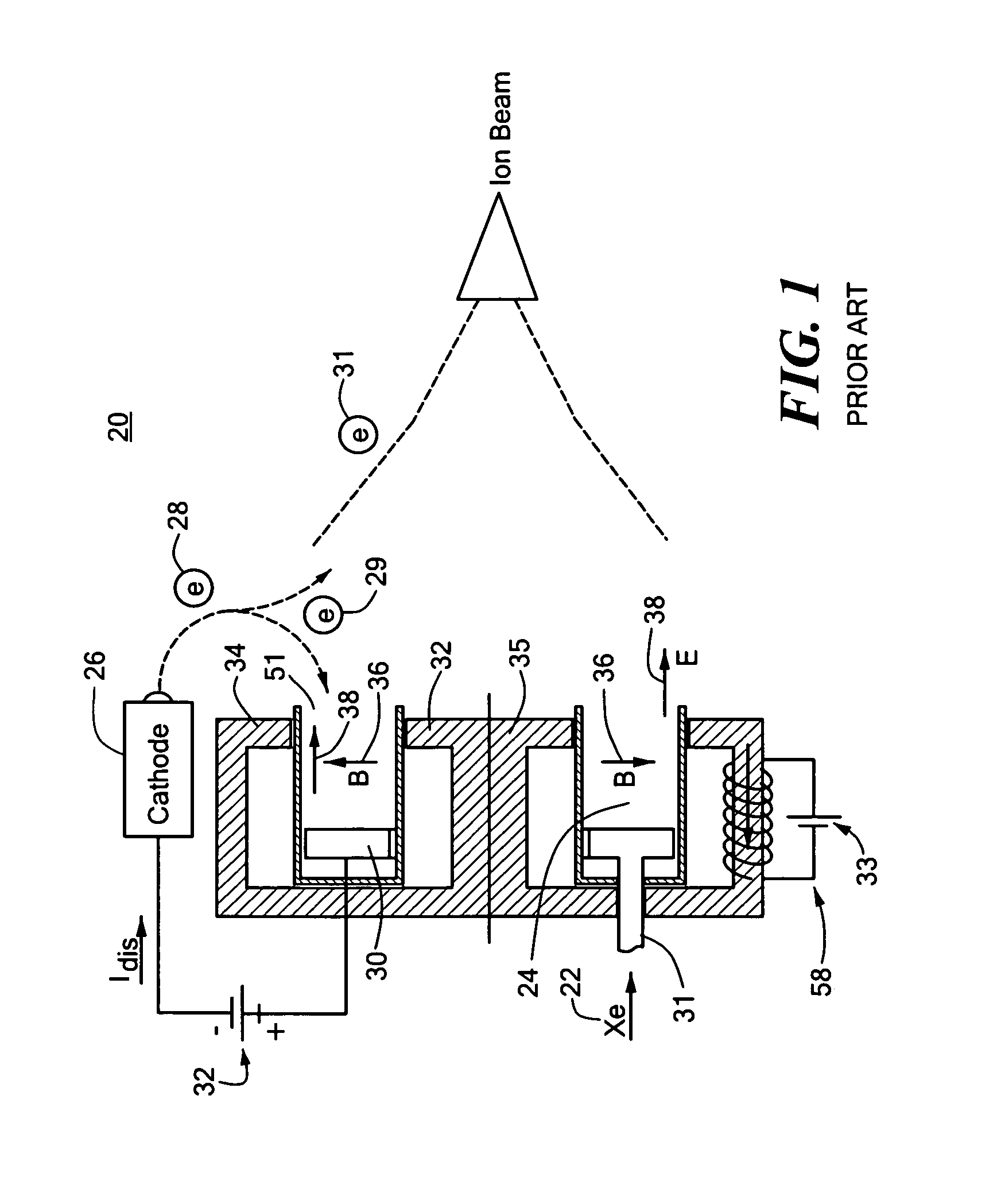
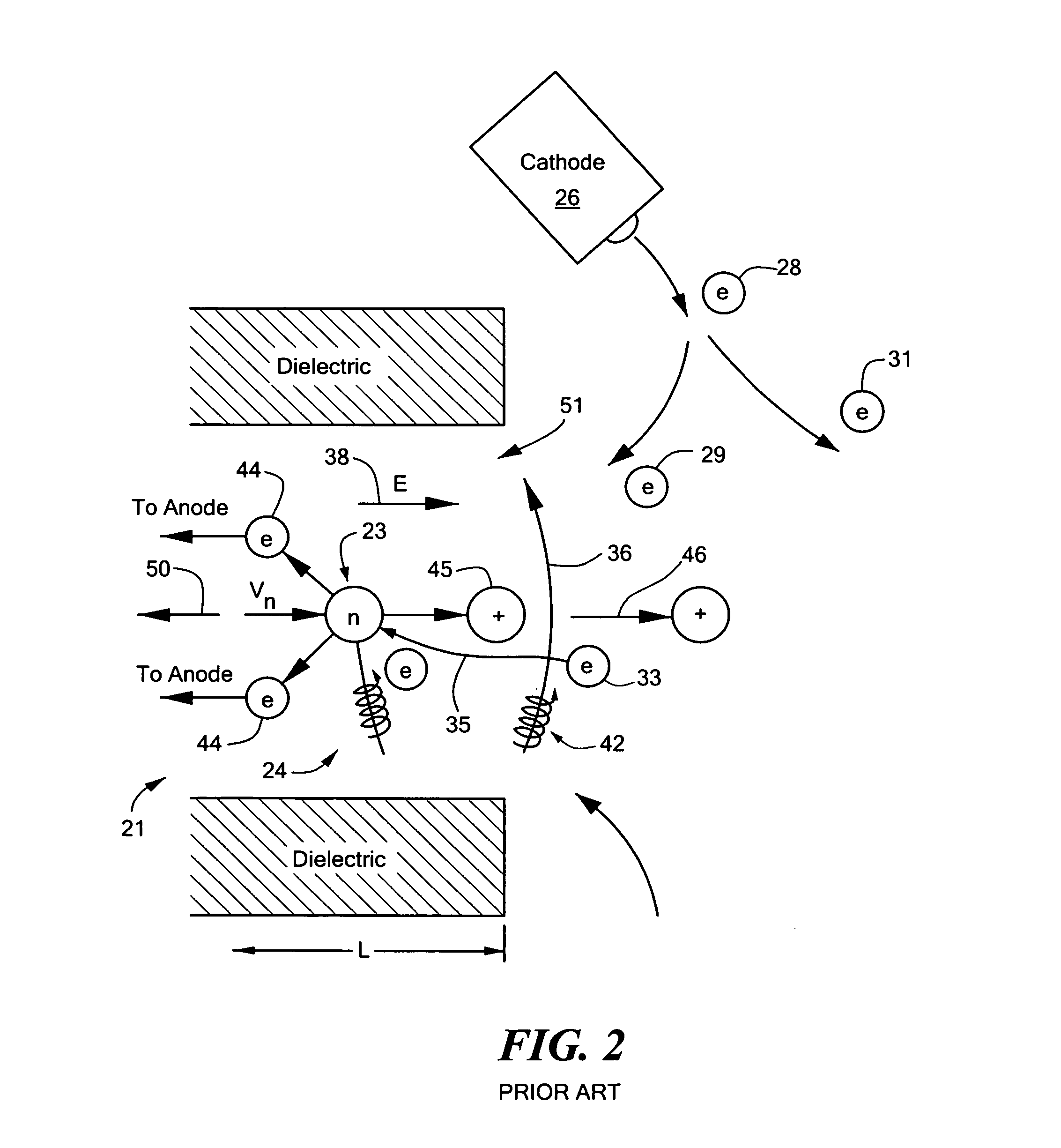
Combined radio frequency and hall effect ion source and plasma accelerator system
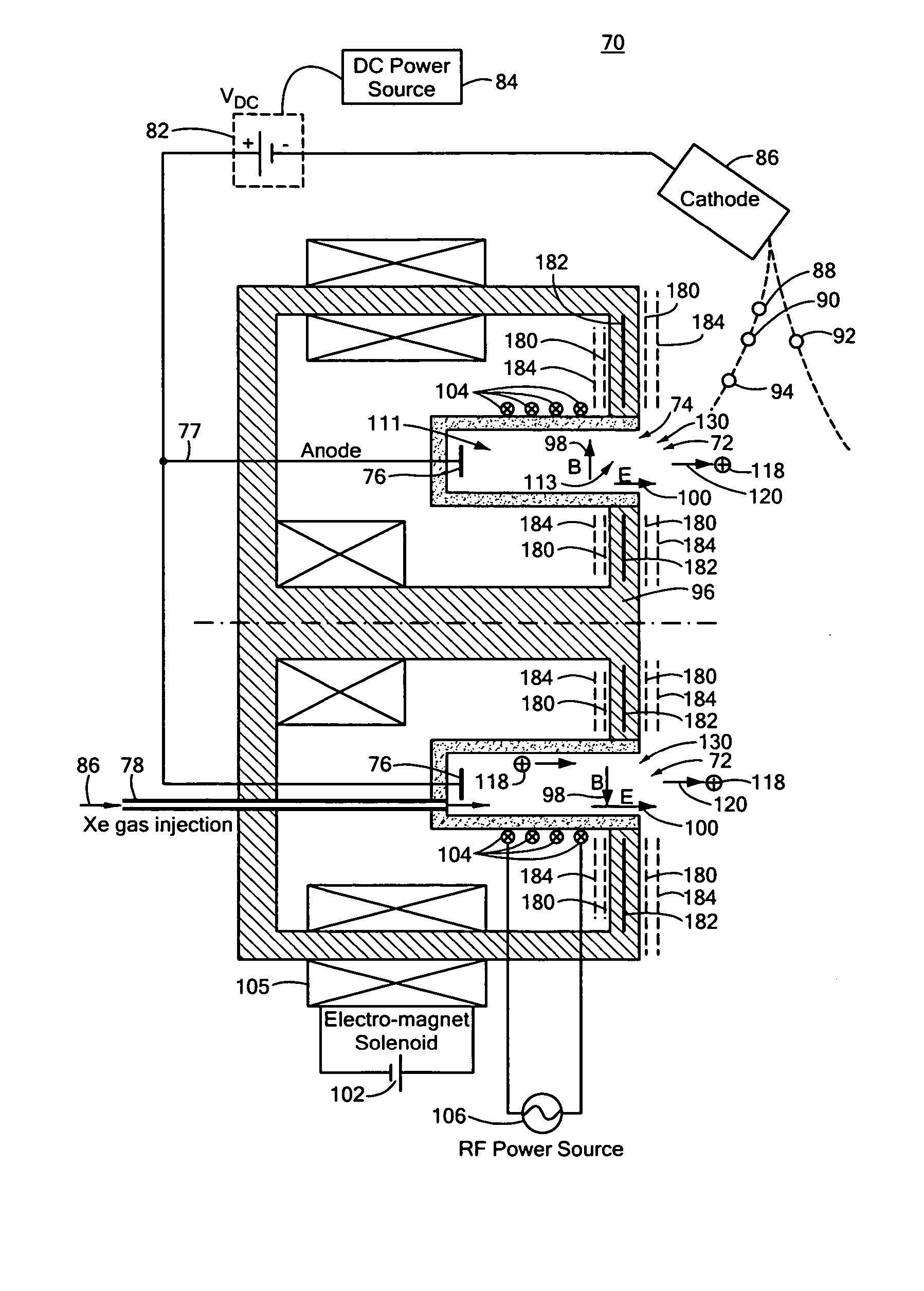
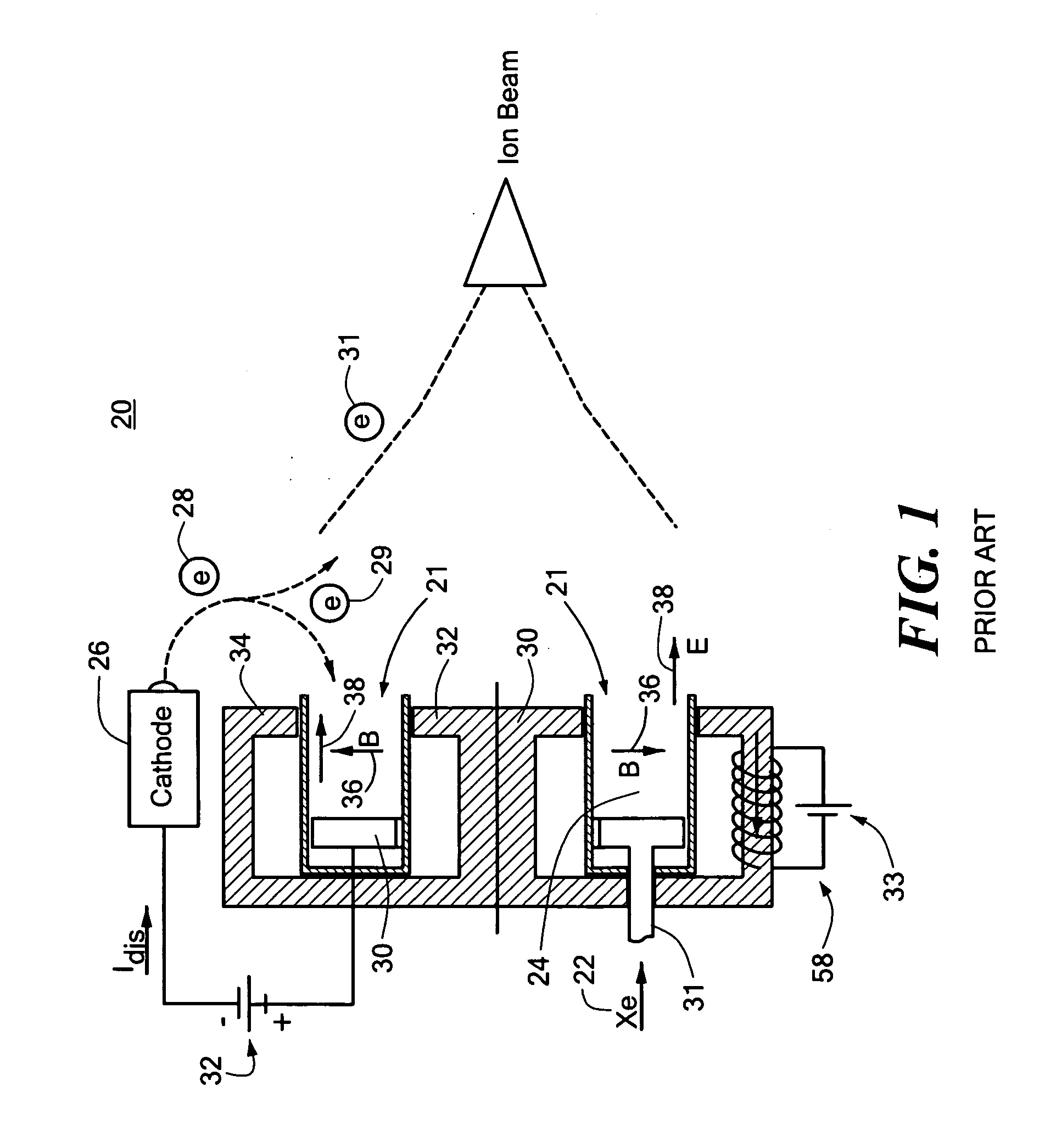
ActiveUS20060284562A1Improve efficiencyEliminate needLaser detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansTransverse magnetic fieldElectrical impedance
This invention features a combined radio frequency (RF) and Hall Effect ion source and plasma accelerator system including a plasma accelerator having an anode and a discharge zone, the plasma accelerator for providing plasma discharge. A gas distributor introduces a gas into the plasma accelerator. A cathode emits electrons attracted to the anode for ionizing the gas and neutralizing ion flux emitted from the plasma accelerator. An electrical circuit coupled between the anode and the cathode having a DC power source provides DC voltage. A magnetic circuit structure including a magnetic field source establishes a transverse magnetic field in the plasma accelerator that creates an impedance to the flow of the electrons toward the anode to enhance ionization of the gas to create plasma and which in combination with the electric circuit establishes an axial electric field in the plasma accelerator. An RF power source provides RF power to at least one electrode disposed about and / or inside the plasma accelerator that induces current for ionizing the gas to create the plasma such that the axial electric field accelerates ions through the plasma accelerator to provide ion flux.
Owner:BUSEK
Magnets with varying magnetization direction and method of making such magnets
InactiveUS20060061445A1Maximize selected magnetic propertyReduces opportunity of interferenceDiagnosticsPermanent magnetsMagnetizationTransverse magnetic field
A permanent magnet in which the magnetization direction varies with location to optimize or restrict a magnetic field property in a selected direction at a selected point. The magnetic field property may be, for example, the transverse magnetic field, axial magnetic field, axial gradient of the transverse magnetic field, transverse gradient of the transverse magnetic field, axis gradient of the axial magnetic field, transverse gradient of the axial magnetic field, the product of the transverse magnetic field and the transverse gradient of the transverse magnetic field, the product of the transverse magnetic field and the axial gradient of the transverse magnetic field, the product of the axial magnetic field and the transverse gradient of the axial magnetic field, or the product of the axial magnetic field and the axial gradient of the axial magnetic field. The magnet may be formed of one or more segments in which the magnetization direction varies smoothly and continuously, or the magnet may be formed of a plurality of segments in which the magnetization direction is constant. A method of making and using such magnets is also disclosed.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
Method and apparatus for directional resistivity measurement while drilling
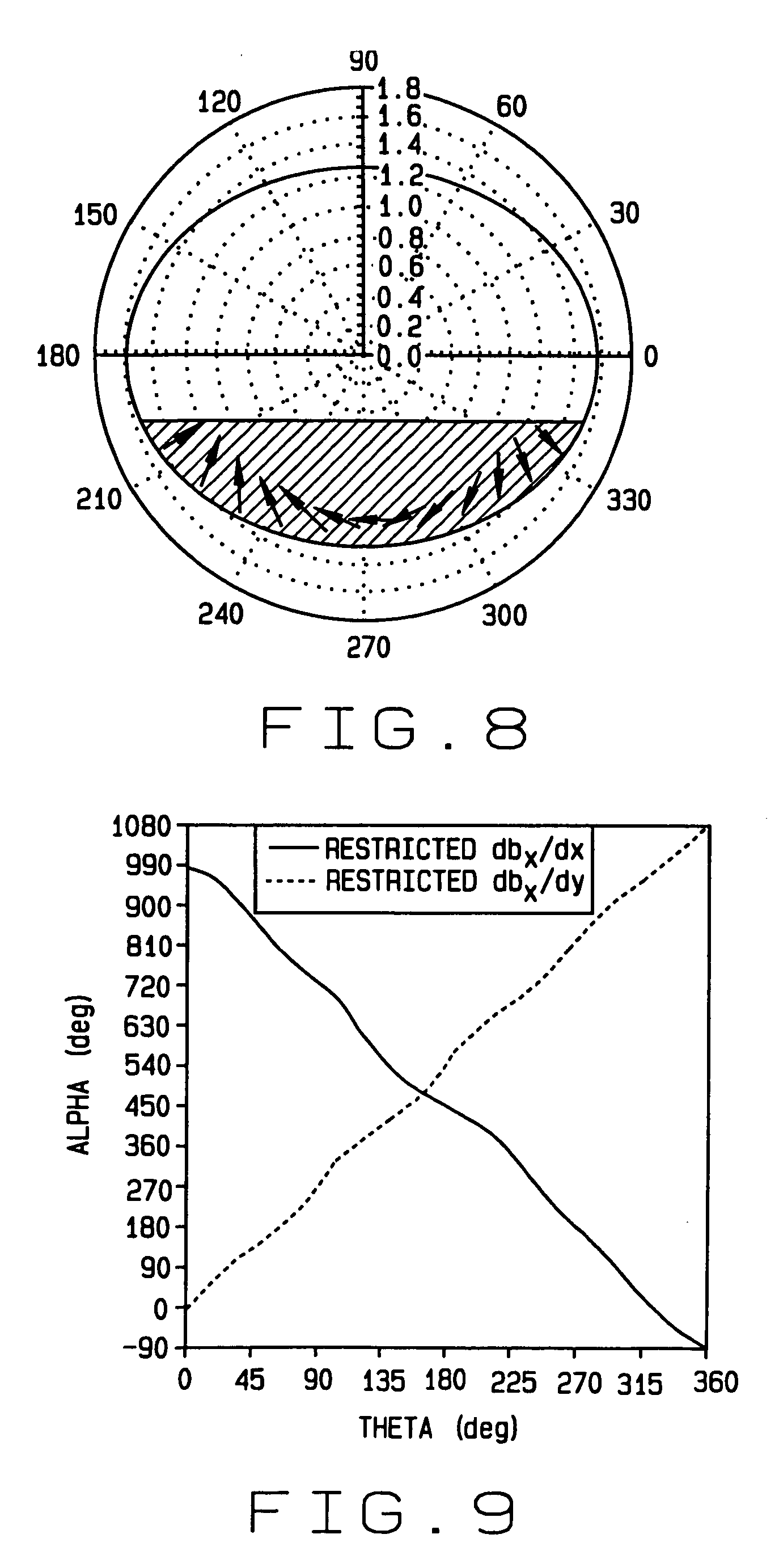
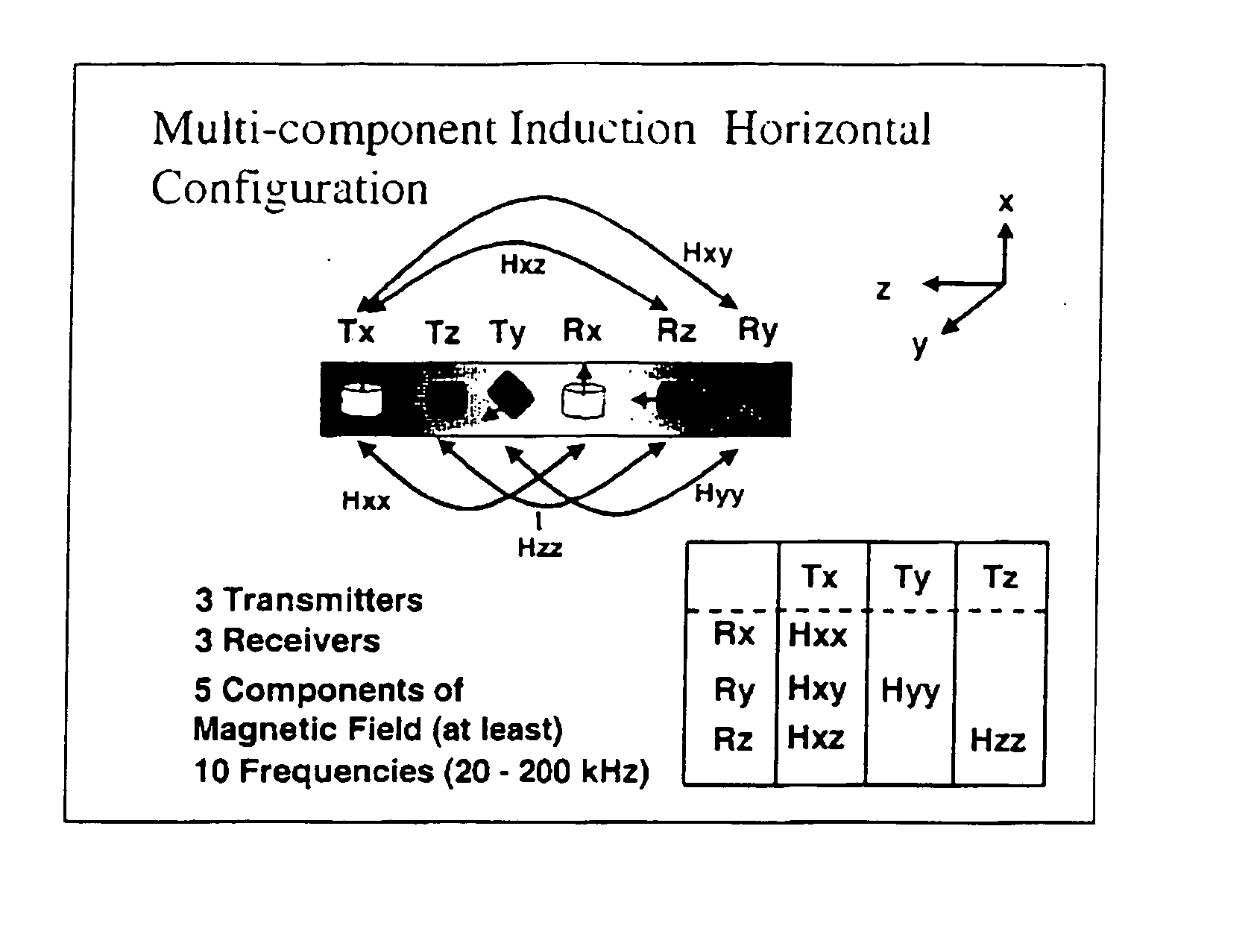
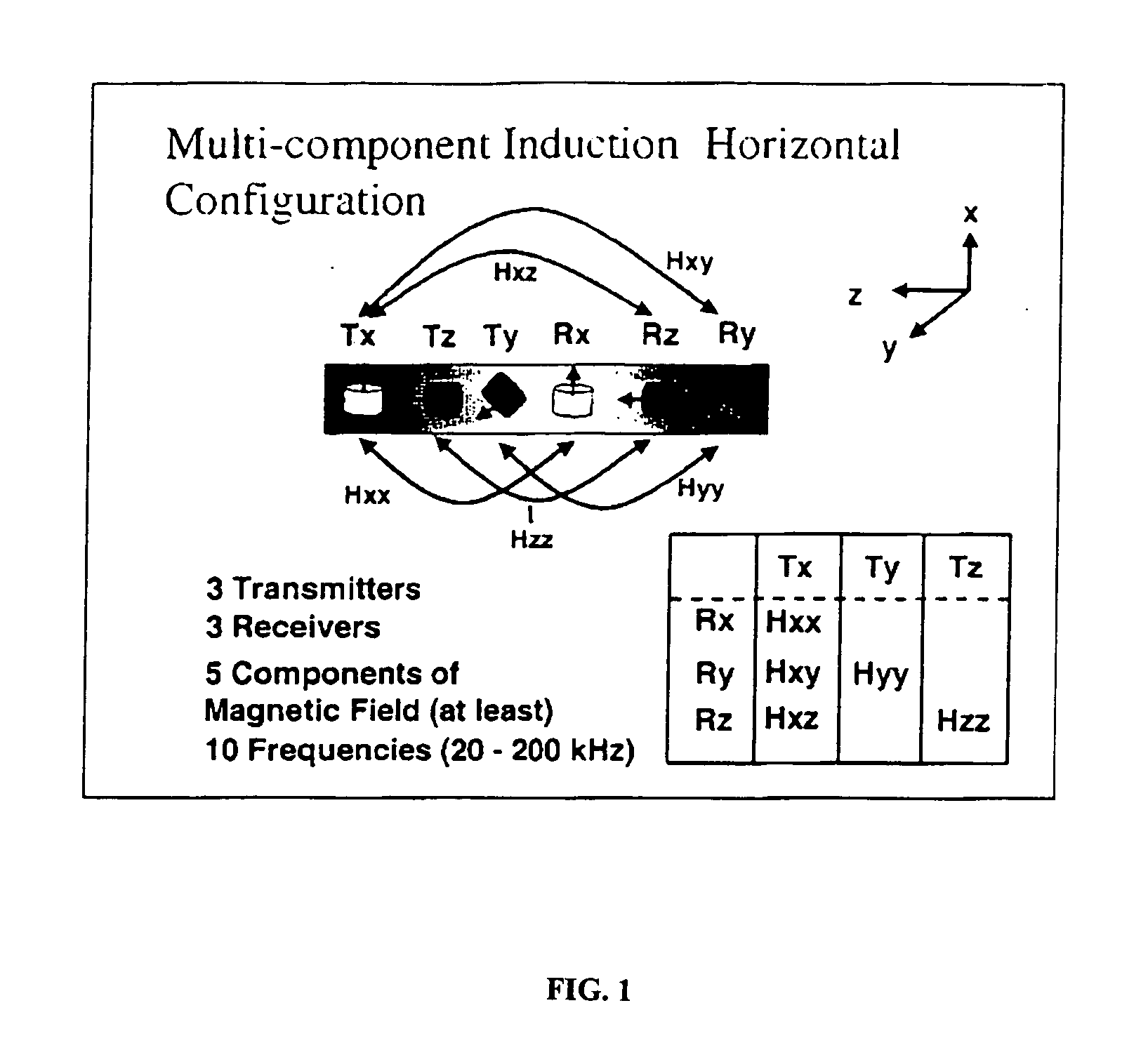
ActiveUS20040113626A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAcoustic wave reradiationWell drillingTransverse magnetic field
A measurement-while-drilling or logging while drilling method and apparatus for determining the azimuth of providing magnetic field in a remote formation layer in the vicinity of a down hole resistivity tool. A cross-component magnetic field with substantially orthogonal transmitter and receiver coils is provided. The coil planes are either substantially orthogonal (coaxial coils) or parallel (transverse coils) with respect to, the longitudinal axis of the tool body. The coils are placed on the tool body having a external surface and a plurality of grooves are cut in the external surface of the tool body and oriented substantially horizontally with respect to the longitudinal axis of the tool body for the coils and oriented vertically with respect to the longitudinal axis of the tool body for the coaxial coils. A transverse and coaxial coil are placed in the grooves for transmission or reception of a cross-component transverse magnetic field. Ferrite materials may be inserted in the grooves in between the coil wire and the bottom of the grooves. Multiple receivers, transmitters and frequencies may be used to obtain the maximum possible signal-to-noise ratio. The in-phase or quadrature part of a magnetic field, or a combination of the two, or alternatively, the amplitude and / or phase, of the cross-component magnetic field may be measured and processed to indicate the azimuth of a remote layer boundary, provided that the layer boundary is within the depth of investigation of the tool. Measurements may also be made at continuous or multiple tool azimuths.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
Distributing clock signals using metamaterial-based waveguides
ActiveUS20070109023A1Generating/distributing signalsWaveguidesTransverse magnetic fieldElectromagnetic radiation
Various embodiments of the present invention are directed to global interconnects that employ metamaterial-based waveguides to distribute clock signals to IC internal components. In one embodiment of the present invention, a global interconnect includes an electromagnetic radiation source that radiates electromagnetic waves. The global interconnect also includes a metamaterial-based waveguide that directs a transverse magnetic field mode of the electromagnetic wave to antennae of the internal components in order to induce an oscillating current within the internal components that serves as the clock signal.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
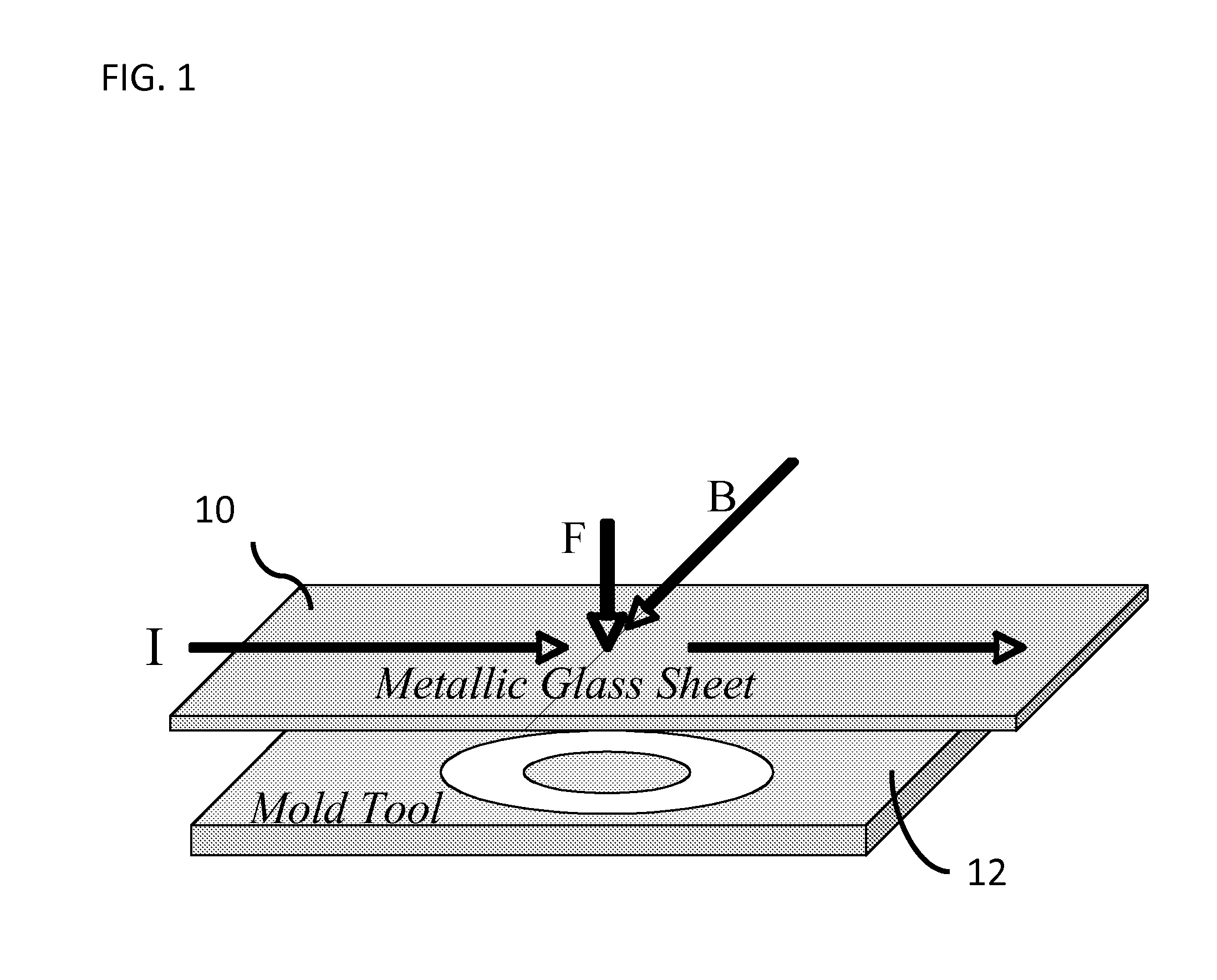
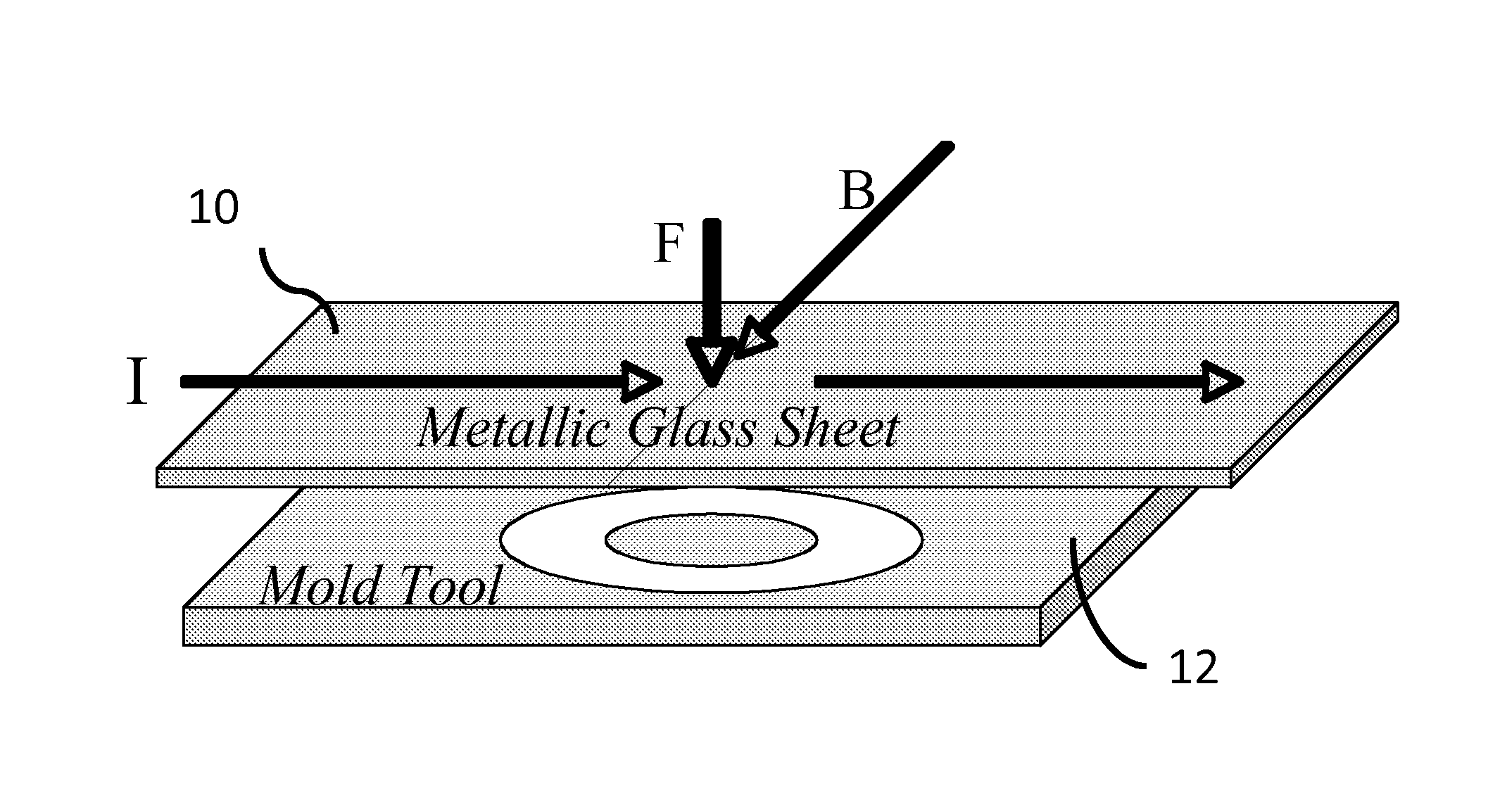
Electromagnetic forming of metallic glasses using a capacitive discharge and magnetic field
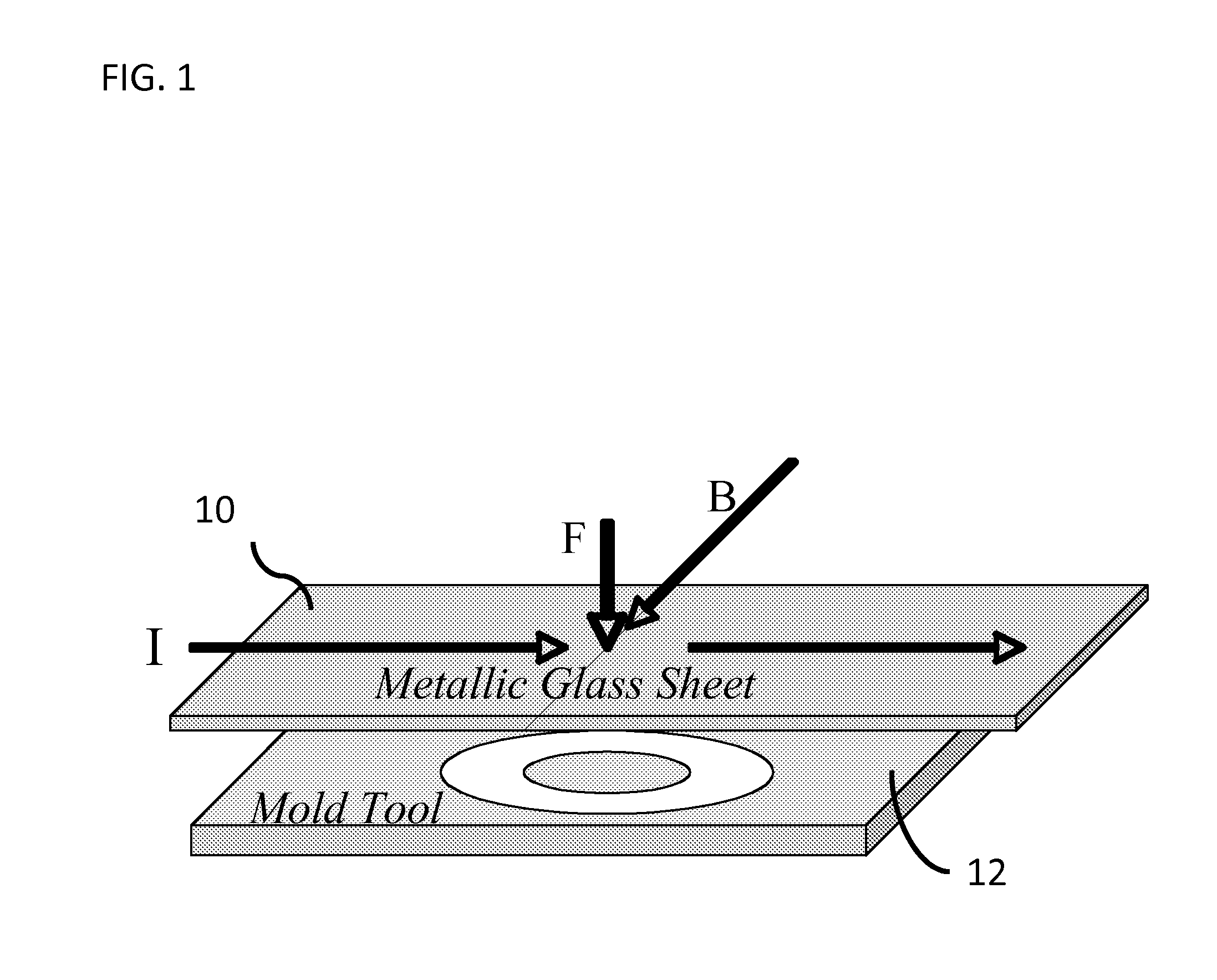
ActiveUS20120006085A1Welding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaCapacitanceTransverse magnetic field
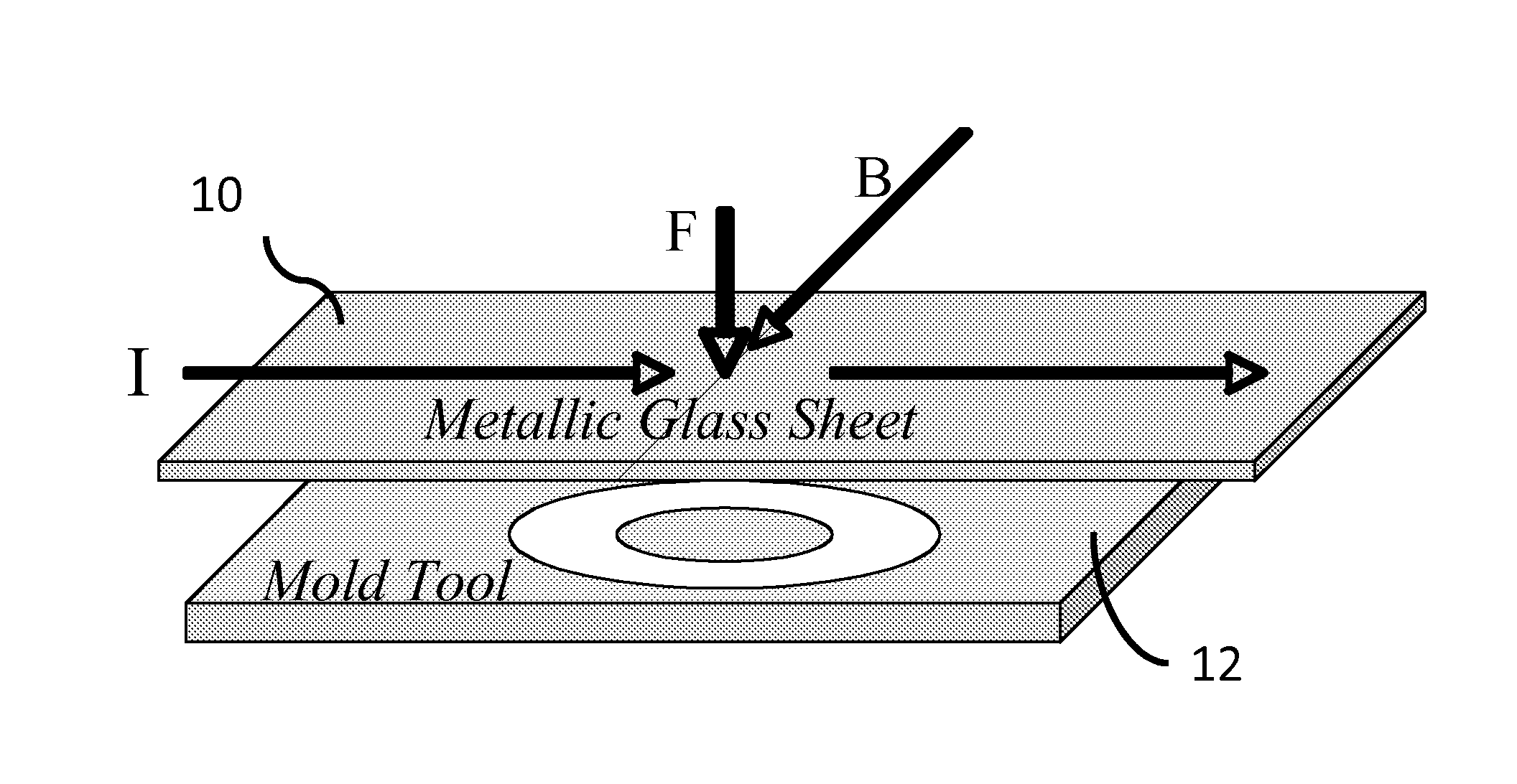
An apparatus and method of uniformly heating, rheologically softening, and thermoplastically forming metallic glasses rapidly into a net shape using a rapid capacitor discharge forming (RCDF) tool in combination with an electromagnetic force generated by the interaction of the applied current with a transverse magnetic field. The RCDF method utilizes the discharge of electrical energy stored in a capacitor to uniformly and rapidly heat a sample or charge of metallic glass alloy to a predetermined “process temperature” between the glass transition temperature of the amorphous metal and the equilibrium melting point of the alloy in a time scale of several milliseconds or less, at which point the interaction between the electric field and the magnetic field generates a force capable of shaping the heated sample into a high quality amorphous bulk article via any number of techniques including, for example, injection molding, dynamic forging, stamp forging, and blow molding in a time scale of less than one second.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Maintaining the alignment of electric and magnetic fields in an x-ray tube operated in a magnetic field
InactiveUS6976953B1Easy to controlDeflection of the electron beam by the static magnetic field is reduced or eliminatedElectric shock equipmentsMagnetic measurementsLight beamTransverse magnetic field
A new technique for maintaining the alignment of electric and magnetic fields in an x-ray tube so the tube can be operated in the presence of a static external magnetic field without being negatively affected thereby. Deflection of the electron beam of the x-ray tube by the high magnetic field is reduced or eliminated by modifying or canceling, at a location near the electron beam, the magnetic field components transverse to the beam. In a preferred embodiment, a set of electromagnet coils are positioned on or near the tube and oriented in a way that when current is applied internal magnetic fields are produced in a direction opposite to the transverse magnetic fields, thereby causing cancellation. In one implementation, one or more sensors are used to detect the transverse magnetic fields. The sensor is positioned near the electron beam, either inside or outside the x-ray tube. The sensor produces a signal dependent on a static magnetic field component transverse to the desired direction of the electron beam. This signal is used to control the amount of current applied to the coils. A controller and a feedback circuit may be included to adjust in real time the amount of current being applied.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Electric motor
InactiveUS6191516B1Reduce weightImprove efficiencyMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectric machineTransverse magnetic field
An electric motor, including at least two permanent magnet segments disposed around a motor longitudinal axis, in which each permanent magnet segment has end faces extending in the direction of the motor longitudinal axis and is encompassed by two independent yoke ring segments that have a gap between them parallel to a symmetry plane extending through the motor longitudinal axis and the center of the permanent magnet segments in order to reduce the armature transverse field. In addition to the reduction of the armature transverse field, a weight reduction of the electric motor is also achieved. To this end, in a first region close to the end faces of the permanent magnet segments, the one-piece magnetically conductive yoke is provided with a larger cross section than in a second region close to the symmetry plane extending through the center of the permanent magnet segments. The construction is particularly suited for small electric motors, in particular d.c. motors that are excited by permanent magnets.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
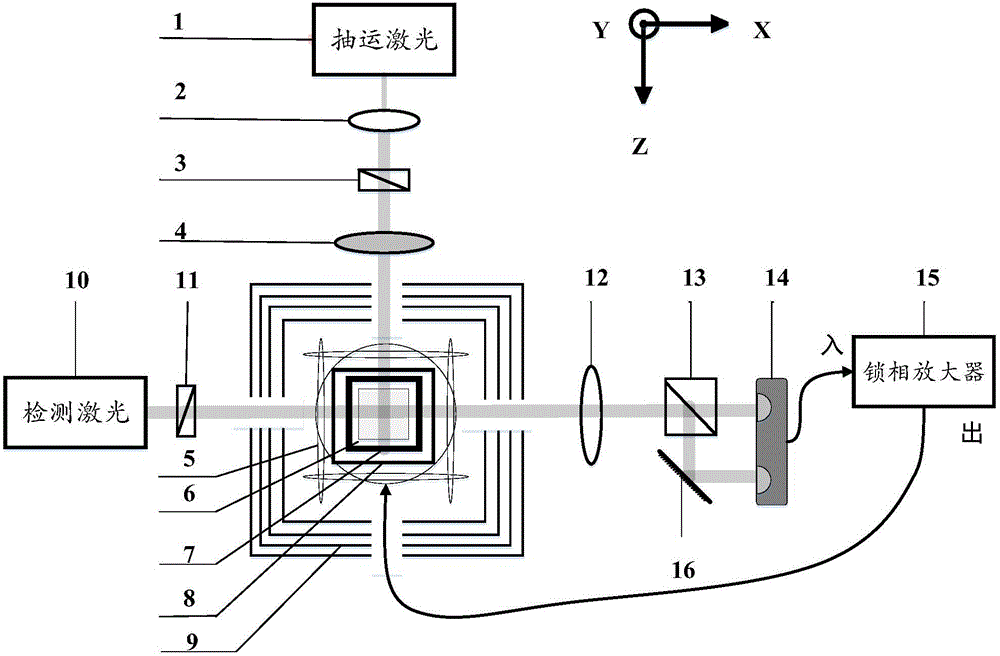
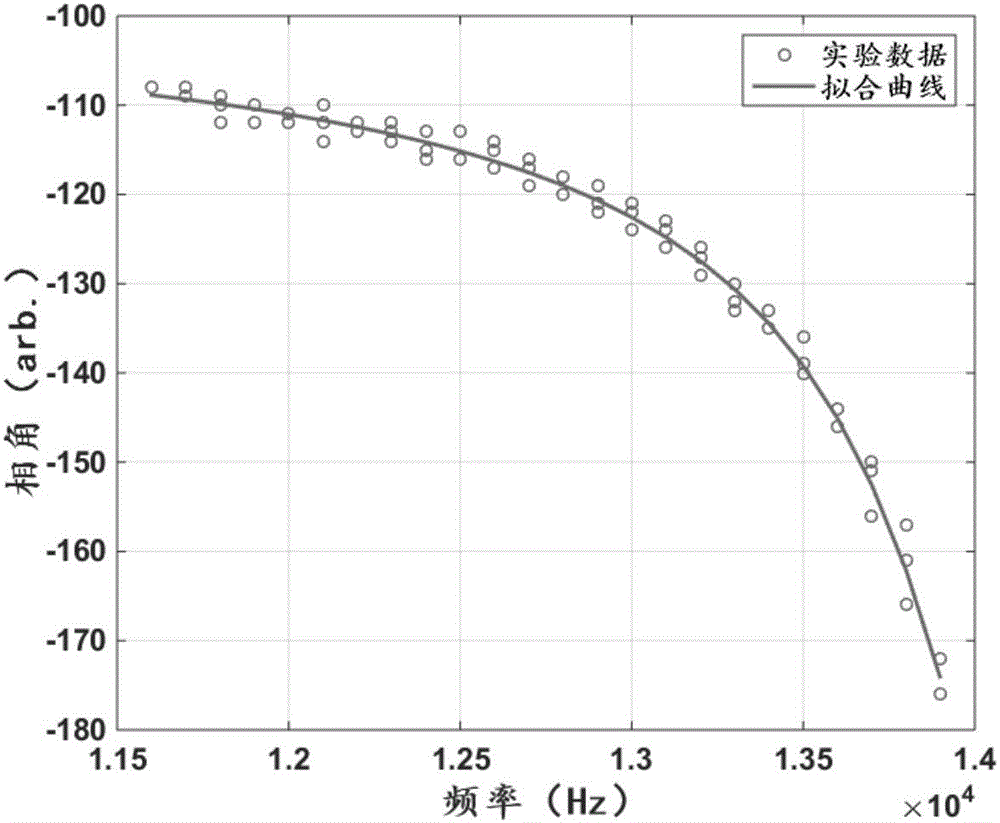
Method for measuring atomic transverse relaxation time based on electron resonance phase frequency analysis
InactiveCN106597338ASuppression of the effects of common coefficient fluctuationsExact transverse relaxation timeMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceAnalysis using electron paramagnetic resonanaceFrequency spectrumTransverse magnetic field
The invention discloses a method for measuring atomic transverse relaxation time based on an electron resonance phase frequency analysis. In a strong-background magnetic field with almost neglected residual magnetization in a magnetic shielding barrel, a swept-frequency signal that has a bandwidth covering a resonance curve and has an amplitude enabling the resonance curve to have a clear curve under low polarizability is applied in a horizontal direction; an optical swing angle signal of a magnetometer is detected and a spectral analysis is carried out on an outputted signal in a polar coordinate system to obtain a phase frequency response function of the magnetometer; the phase frequency response function is fitted to a corresponding theoretical phase frequency curve of the magnetometer to obtain atomic spinning transverse relaxation time. Because the phase angle is a result obtained by quotient processing of a spinning transverse component, the influence of common coefficient fluctuation is suppressed, so that the phase frequency signal expression is more stable by being compared with amplitude-frequency signal expression. Besides, the theoretical phase frequency curve is not affected by the magnetic induction intensity of the transverse magnetic field and the atomic spinning longitudinal relaxation time, so that complexity of data processing can be reduced. Moreover, a lorenz curve widening risk caused by the transverse magnetic field can be eliminated.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
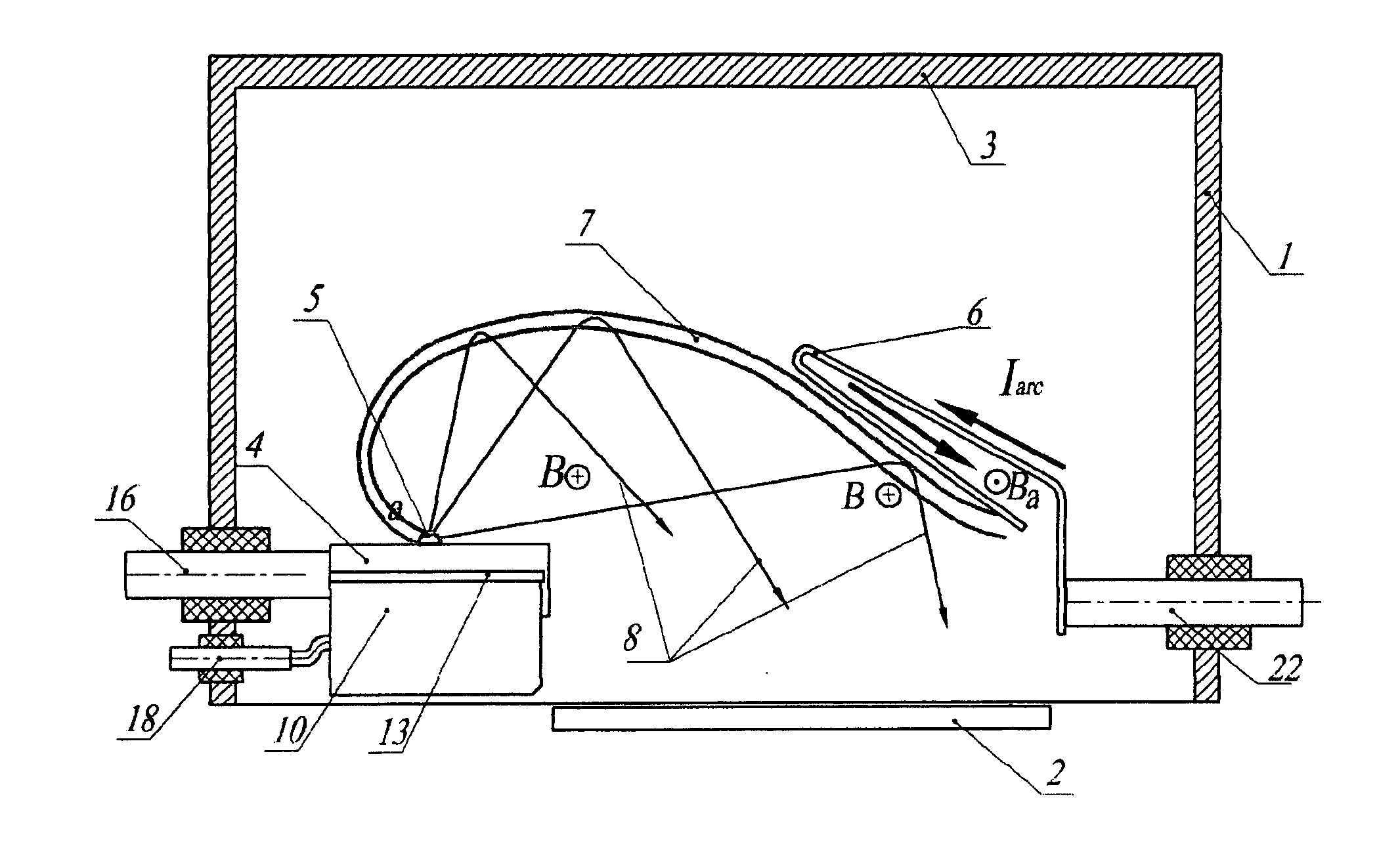
Cathode-arc source of metal/carbon plasma with filtration
InactiveUS20070034501A1Improve transportation efficiencyIncrease the number ofCellsElectric discharge tubesStationary conditionsCurrent sheet
The a cathode-arc source of metal plasma with filtration, used, in particular, for deposition of DLC, utilizes the effect of fast ions reflection from the Hall stratum in a transversal arched magnetic field to filtrate vacuum arc plasma arc from contaminating macroparticles and vapor. Various embodiments for producing maximal plasma flux at the source outlet, in particular, a pulse source with more the one cathode units for deposition of coating inside pipes / cavities, for deposition of coating in a stationary / quasi-stationary condition are offered. The cathode is made of a consumable material and is exposed to poles of magnets on both ends of cathode for creating a transversal magnetic field of an arched configuration in a discharge gap between the cathode and the anode. The anode geometry adequate to the mechanism of the arc current passage through a transversal magnetic field is offered. To avoid longitudinal and transverse short circuits of the current layer, an installation of non-conducting surfaces at ends or sectioned shields under a floating potential at the cathode sides is provided. The method of creating the Hall stratum in said transversal magnetic field of arched configuration is offered.
Owner:BENDER EFIM
CPP differential GMR sensor having antiparallel stabilized free layers for perpendicular recording
InactiveUS7242556B2DesensitizationNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsTransverse magnetic fieldEngineering
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Preparation method of electromagnetic shielding piece used for wireless charging, and electromagnetic shielding piece
PendingCN106912188AElectromagnetic performance controllablePlay electromagnetic shielding effectMagnetic/electric field screeningLaser cuttingElectromagnetic shielding
The invention provides a preparation method of an electromagnetic shielding piece used for wireless charging, and an electromagnetic shielding piece obtained through the above method. The preparation method comprises following steps: a winding step of winding amorphous and nanocrystalline ribbons in a predetermined size as required; a heat treatment step of putting the wound amorphous and nanocrystalline ribbons in a heat treatment furnace for heat treatment, and adding a transverse magnetic field, adding a longitudinal magnetic field or no adding magnetic fields during the heat treatment process; and a graphical processing step of carrying out graphical processing on uncoated surfaces of the amorphous and nanocrystalline ribbons. By employing the graphical processing technology such as laser cutting and chemical etching technologies and the like for graphical processing, electromagnetic performances (magnetic permeability, loss and the like) of the electromagnetic shielding piece are controllable, the charging efficiency is optimized, and the electromagnetic shielding effect of the electromagnetic shielding piece is maximized.
Owner:SHANGHAI LINEPRINTING MATERIALS CO LTD
Magnetic-field heat treatment method of nanocrystal magnetic core
InactiveCN105719826AImprove performanceDevelop new marketsInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureTransverse magnetic fieldEngineering
The invention discloses a magnetic-field heat treatment method of a nanocrystal magnetic core. According to the method, a transverse magnetic field is applied to heat treatment by combining a known process condition during actual production on the premise of meeting market application demand, the magnetic-field heat treatment process step is particularly considered and refined from different magnetism steps and by changing the size of magnetism current, an optimal magnetism mode of an initial heat preservation temperature of 330 DEG C to a cooling finish step and the additionally-arranged transverse magnetic field is finally obtained, and the size of the magnetism current is preferably 80-140A. The high induction value of the magnetic core sample in such heat treatment condition is maintained, the coercive force and the iron loss are obviously reduced, thus, the comprehensive performance of the magnetic core is more excellent, and the market application prospect of a nanocrystal magnetic core product is expanded.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV +1
Cylindrical type transverse magnetic-field permanent-magnet flux-switching linear motor
ActiveCN104811011AImprove fault toleranceReduce dosagePropulsion systemsElectric machineTransverse magnetic field
The invention discloses a cylindrical type transverse magnetic-field permanent-magnet flux-switching linear motor, belongs to the motor field, and aims to solve the problems of a relatively low space utilization rate, a complex manufacturing process, large permanent magnet dosage and high cost of an existing transverse magnetic-filed permanent-magnet motor. The cylindrical type transverse magnetic-field permanent-magnet flux-switching linear motor comprises a rotor and a stator, wherein the rotor is arranged inside the stator, and the rotor linearly moves inside the stator in the axial direction; a radial air gap is formed between the rotor and the stator; the stator comprises m short stator modules which are uniformly distributed in the axial direction to form an m-phase motor; each short stator module comprises p stator units and a plurality of stator magnetism isolating rings; the rotor comprises a shaft, w first rotor iron cores, w second rotor iron cores and a plurality of rotor magnetism isolating rings, and the structures of the first rotor iron cores and the second rotor iron cores are in mirror-image symmetry along the x axis or the y axis.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Magnetism transmission gear pair of novel transverse magnetic field
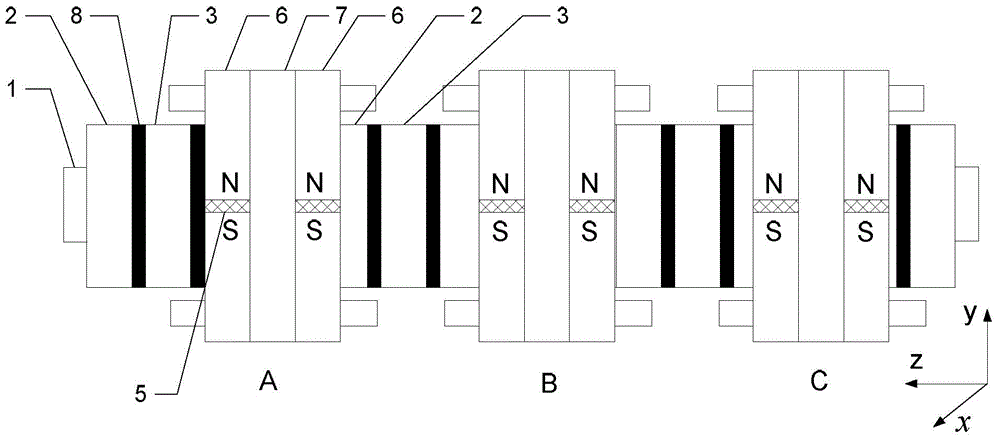
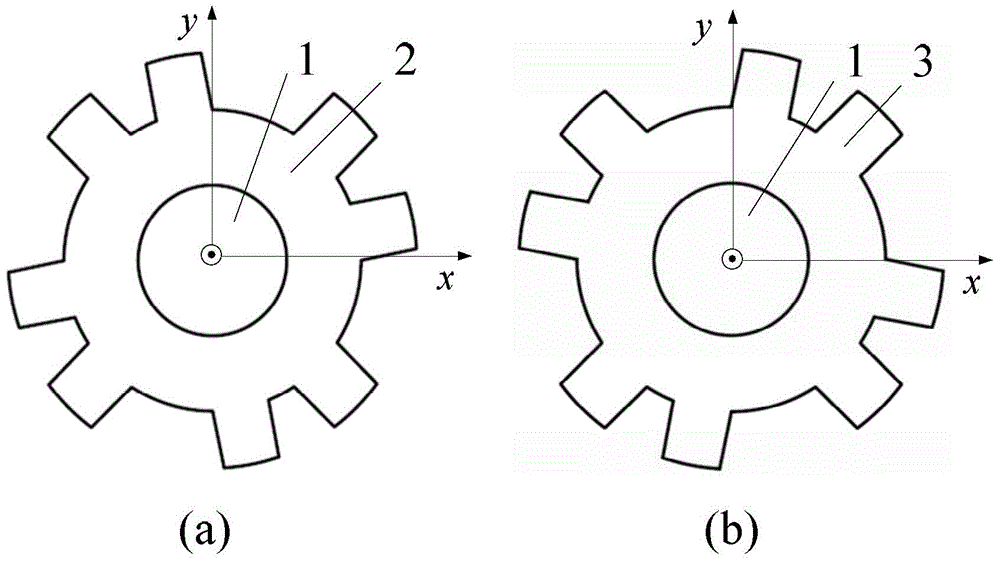
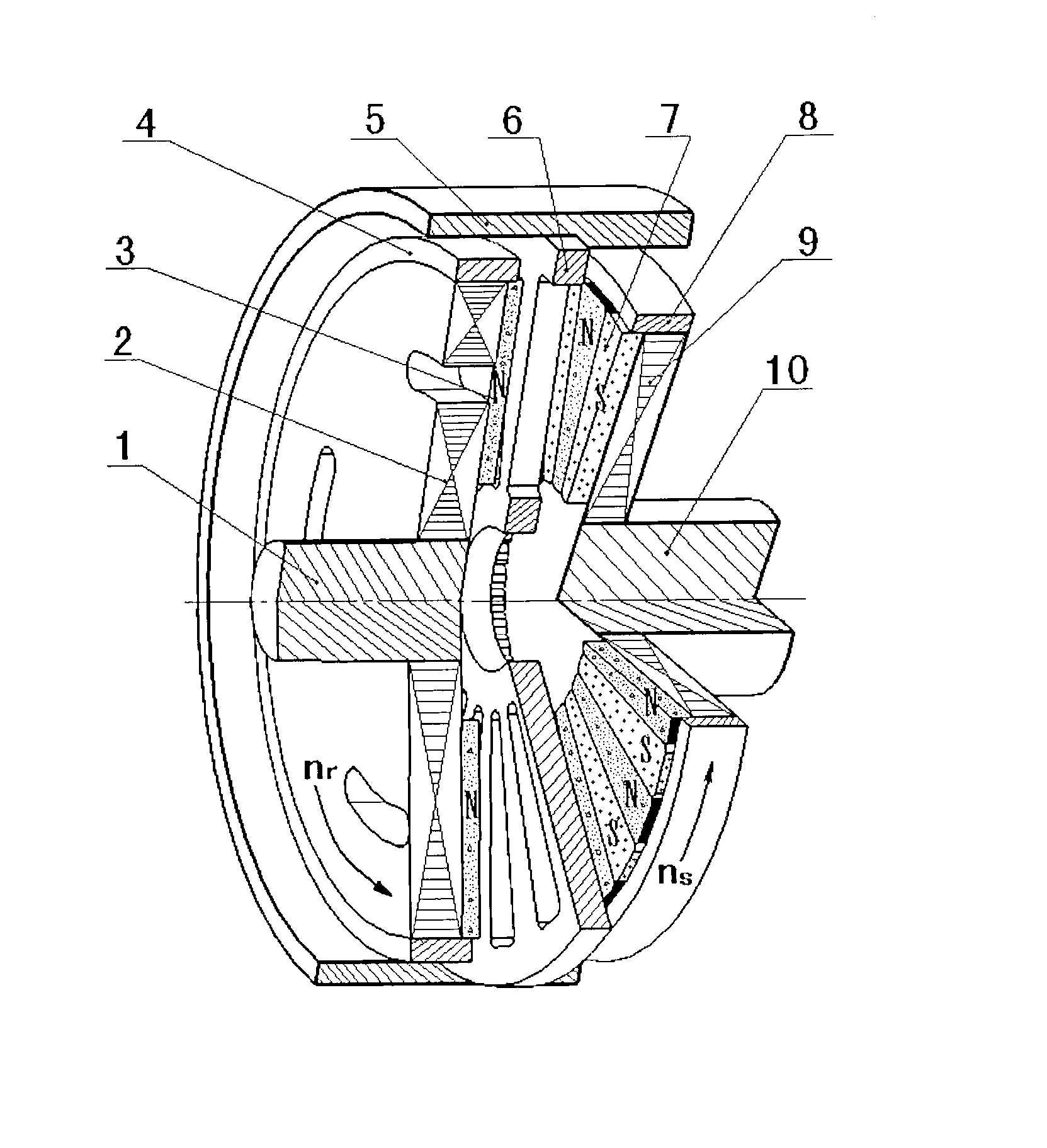
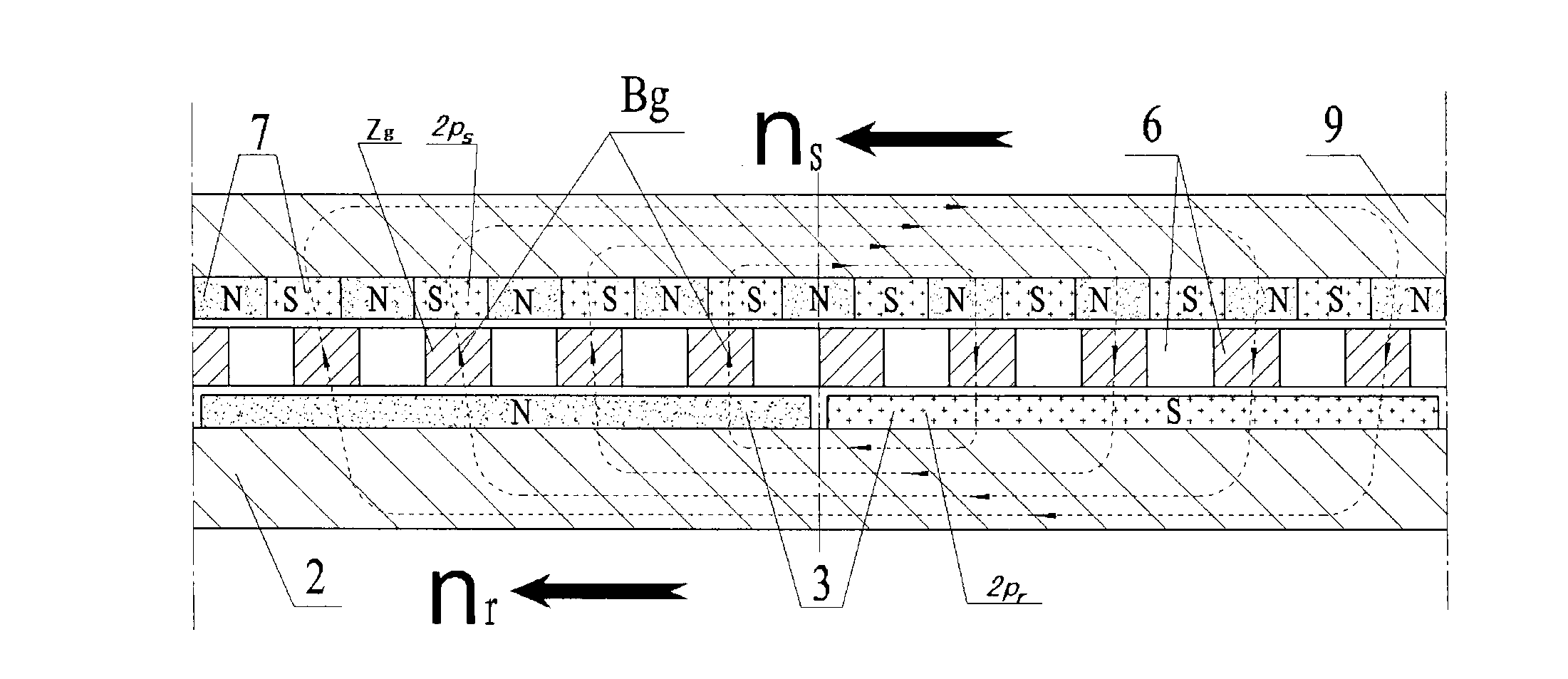
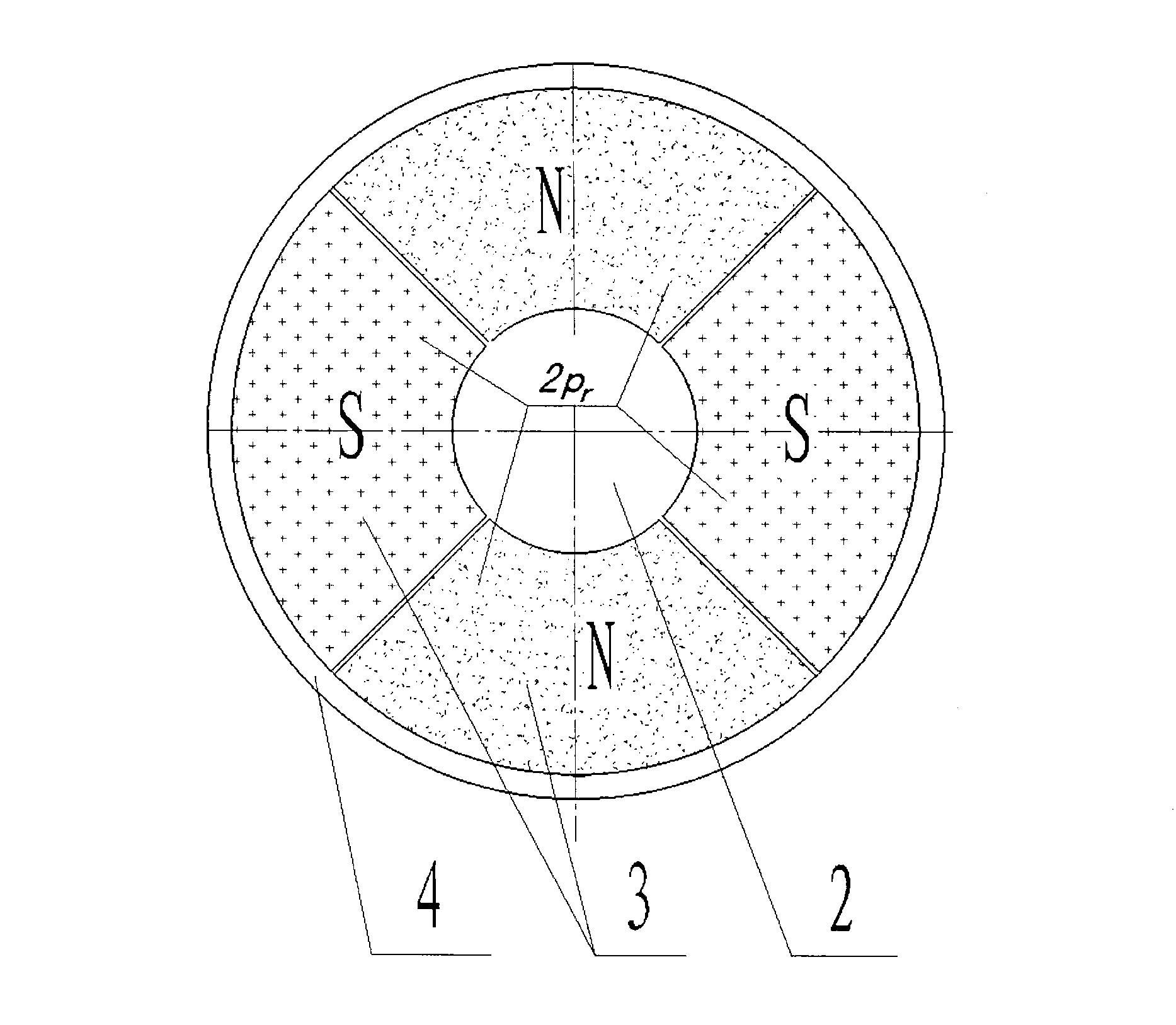
The invention relates to a magnetism transmission gear pair of a novel transverse magnetic field, which can be widely applied to wind power generation, electric cars, ship drive and other industrial transmission fields requiring direct drive. The magnetism transmission gear pair is characterized in that a driving wheel and a driven wheel of the magnetism transmission gear pair are of a flat disk shape, 2pr driving wheel permanent magnets 3 are distributed on the driving wheel, and 2ps driven wheel permanent magnets 7 are distributed on the driven wheel; a ferromagnetic magnetic modulation grid 6 playing a role of modulating an air-gap magnetic field is arranged between the driving wheel and the driven wheel, air gaps are reserved between the ferromagnetic magnetic modulation grid 6 and the end surfaces of the driving wheel and the driven wheel, and the ferromagnetic magnetic modulation grid 6, the driving wheel and the driven wheel have no mechanical contact and are distributed along the same axis; the air-gap magnetic field Bg passes through an air-gap plane along a route parallel to a rotation axis to form a transverse magnetic field of the magnetism transmission gear pair; and during working, power speed change transmission without mechanical contact and friction is realized by utilizing a principle of heteropolarity attraction of an N pole and an S pole of a permanent magnet material.
Owner:余虹锦
Multi-axis magnetic lens
ActiveUS8003953B2Small distanceElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansParticle beamTransverse magnetic field
The present invention relates to a multi-axis magnetic lens for a charged particle beam system. The apparatus eliminates the undesired non-axisymmetric transverse magnetic field components from the magnetic field generated by a common excitation coil and leaves the desired axisymmetric field for focusing each particle beam employed within the system.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Reversed-field permanent-magnet focusing system for multi-beam millimeter wave traveling-wave tubes and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101944469ADoes not affect circulationSolve the problem of large permanent magnet volume when the gain is largeTransit-time tubesNon-emitting electrodes manufactureUniform fieldTransverse magnetic field
The invention discloses a reversed-field permanent-magnet focusing system for multi-beam millimeter wave traveling-wave tubes, which consists of an electron gun end face (1), first magnetic field rectifiers (2), a first peak generation pole shoe (3), a magnetic field reversal pole shoe (4), a second peak generation pole shoe (5), second magnetic field rectifiers (6), a vacuum sealed case (7), a collector end face (8), first permanent magnets (9) and second permanent magnets (10). The reversed-field permanent-magnet focusing system for the multi-beam millimeter wave traveling-wave tubes rectifies magnetic fields on the left and right sides of a magnetic system by the first and second magnetic field rectifiers (2 and 6) so as to reduce a transverse magnetic field without influencing flux rates of electron beams, and simultaneously solves the problem of large volumes of the permanent magnets of a uniform-field permanent-magnet focusing system with large gain due to the applicability of the plurality of first and second permanent magnets (9 and 10) with small volumes to the focusing system.
Owner:HUADONG PHOTOELECTRIC TECHN INST OF ANHUI PROVINCE
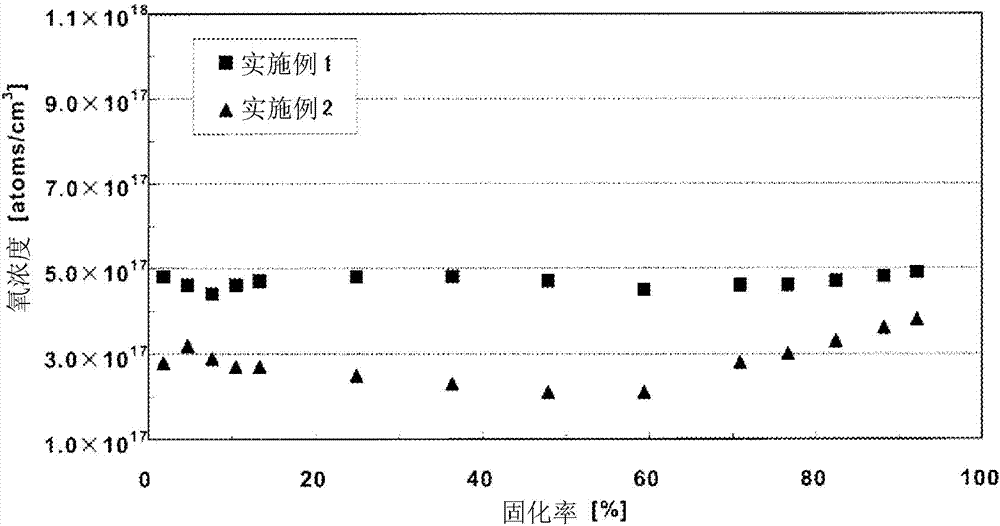
Silicon single crystal and method for manufacture thereof
ActiveCN104278321AEvaporation advantageLow costPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTransverse magnetic fieldMonocrystalline silicon
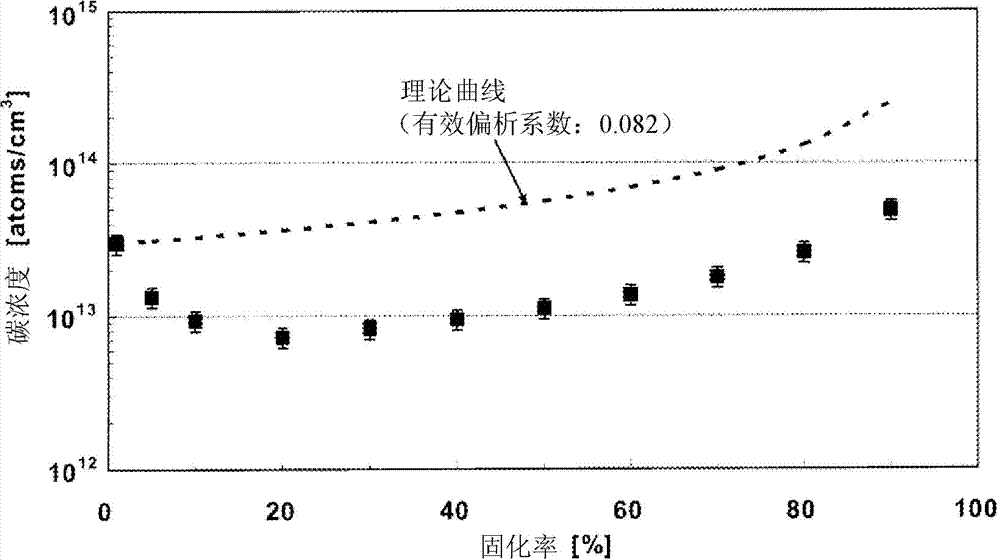
A silicon single crystal manufacturing method includes: applying a transverse magnetic field to a melt of polysilicon with a carbon concentration of at most 1.0 × 10 15 atoms / cm 3 as a raw material; rotating the crucible at 5.0 rpm or less; allowing inert gas to flow at rate A (m / sec) of formula (1) at a position 20-50% of Y above the melt surface; controlling the rate A within the range of 0.2 to 5, 000 / d (m / sec) (d: crystal diameter (mm)); and reducing the total power of side and bottom heaters by 3 to 30% and the side heater power by 5 to 45% until the solidified fraction reaches 30%. A = Q ‹ 760 1000 ‹ 60 ‹ P ‹ ± / À ‹ X ‹ Y ‹ 10 6 Q: Inert gas volumetric flow rate (L / min) P: Pressure (Torr) in furnace X: Radiation shield opening diameter Y: Distance (mm) from raw material melt surface to radiation shield lower end ± : Correction coefficient
Owner:GLOBALWAFERS JAPAN
Vacuum arc-extinguishing chamber, vacuum arc-extinguishing chamber contacts and direct current vacuum circuit breaker
ActiveCN105551881ARestoration of insulation propertiesRealization of openingHigh-tension/heavy-dress switchesAir-break switchesHigh-voltage direct currentVoltage drop
The invention relates to a vacuum arc-extinguishing chamber, vacuum arc-extinguishing chamber contacts and a direct current vacuum circuit breaker. The direct current vacuum circuit breaker comprises an operating mechanism and the vacuum arc-extinguishing chamber, wherein the vacuum arc-extinguishing chamber comprises a moving contact and a fixed contact; arc-extinguishing gate pieces are arranged on the end plane, facing to the fixed static, of the moving contact, or the end plane, facing to the moving contact, of the fixed contact; the arc-extinguishing gate pieces are extended in the radial direction of the moving contact or the fixed contact, and are uniformly distributed in the circumferential direction; and the direct current vacuum circuit breaker also comprises a magnetic field apparatus used for generating a transverse magnetic field for enabling electric arc to rotate along the axial line of the vacuum arc-extinguishing chamber. When a switch-off action is implemented, the electric arc is sent to the gaps of the arc-extinguishing gate pieces under magnetic blowing force generated by the transverse magnetic field in the electric arc movement process, and the electric arc is cut into multiple series-connected short arcs under the function of the arc-extinguishing gate pieces; the electric arc is stretched, and meanwhile, a series of proximal-polar voltage drops occur on the surfaces of the gate pieces; and in addition, the electric arc is further cooled by the gate pieces, so that the electric arc is extinguished rapidly, and disconnection for the high voltage direct current is realized.
Owner:XUJI GRP +1
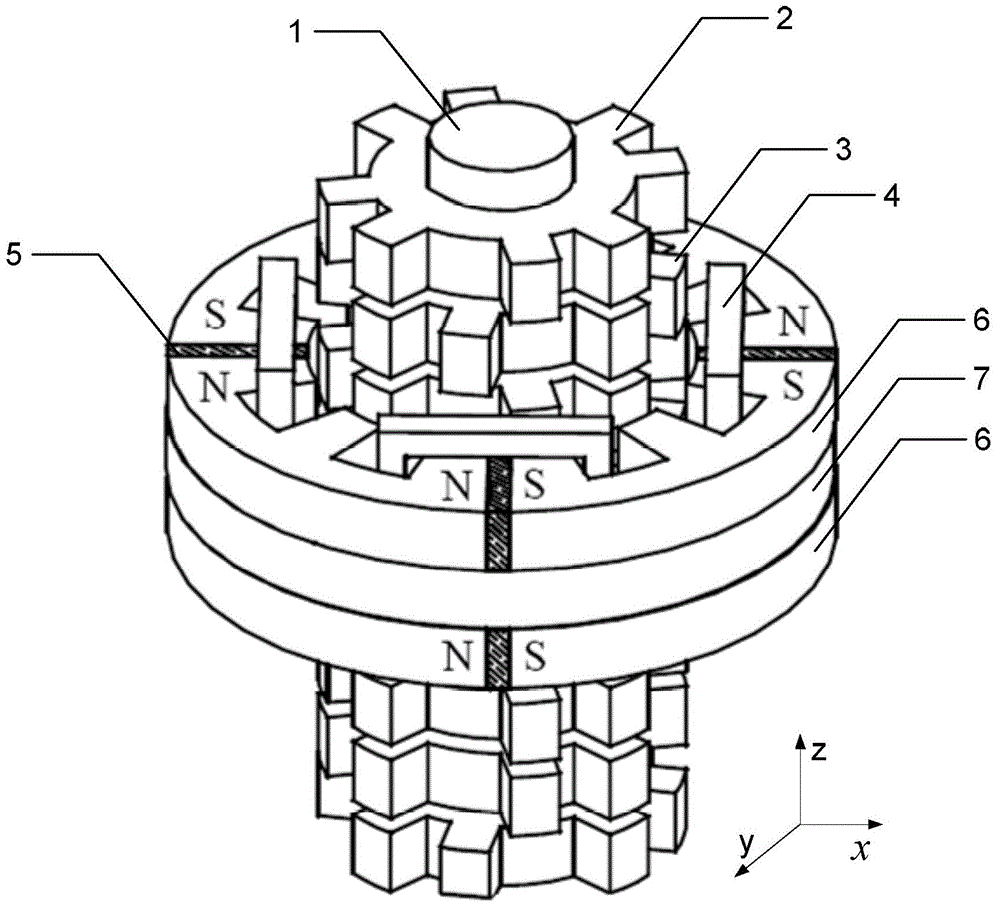
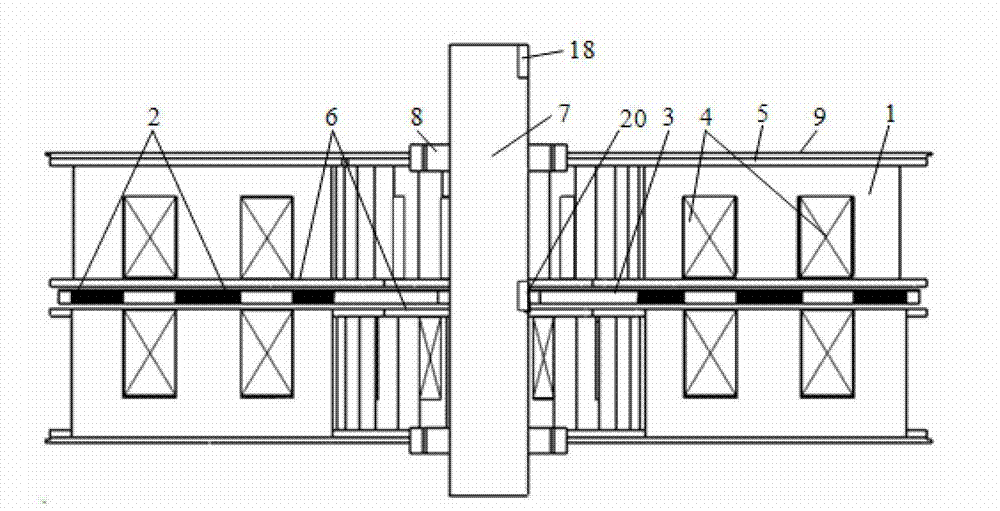
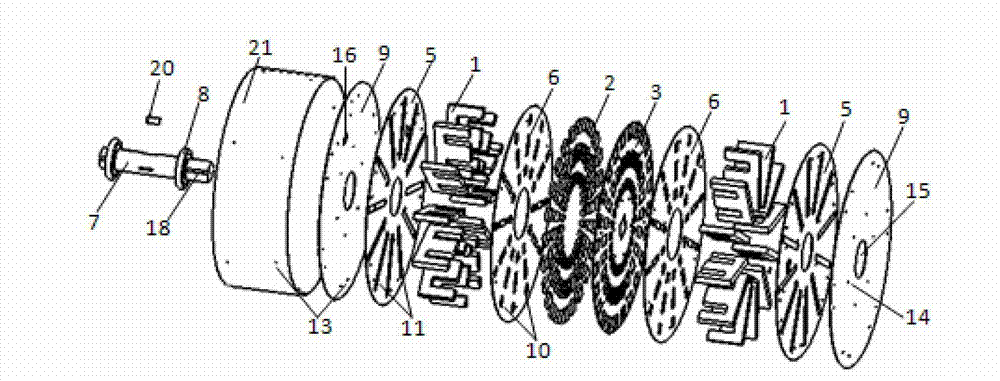
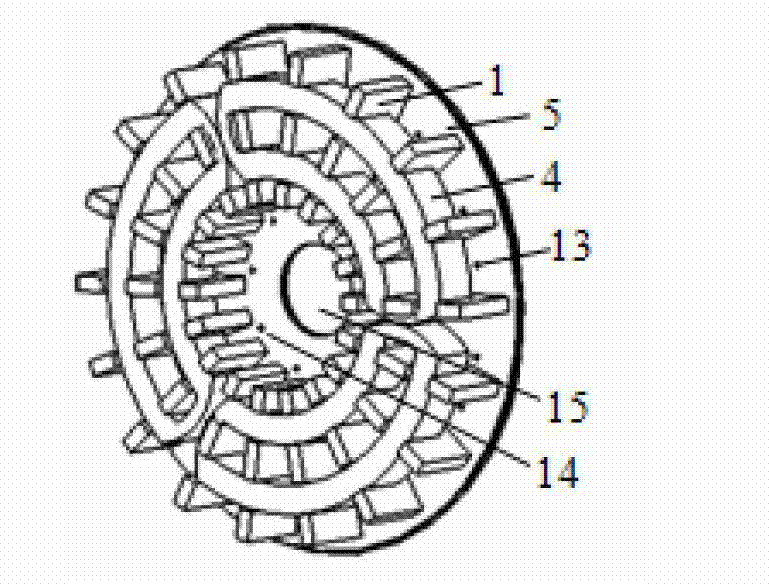
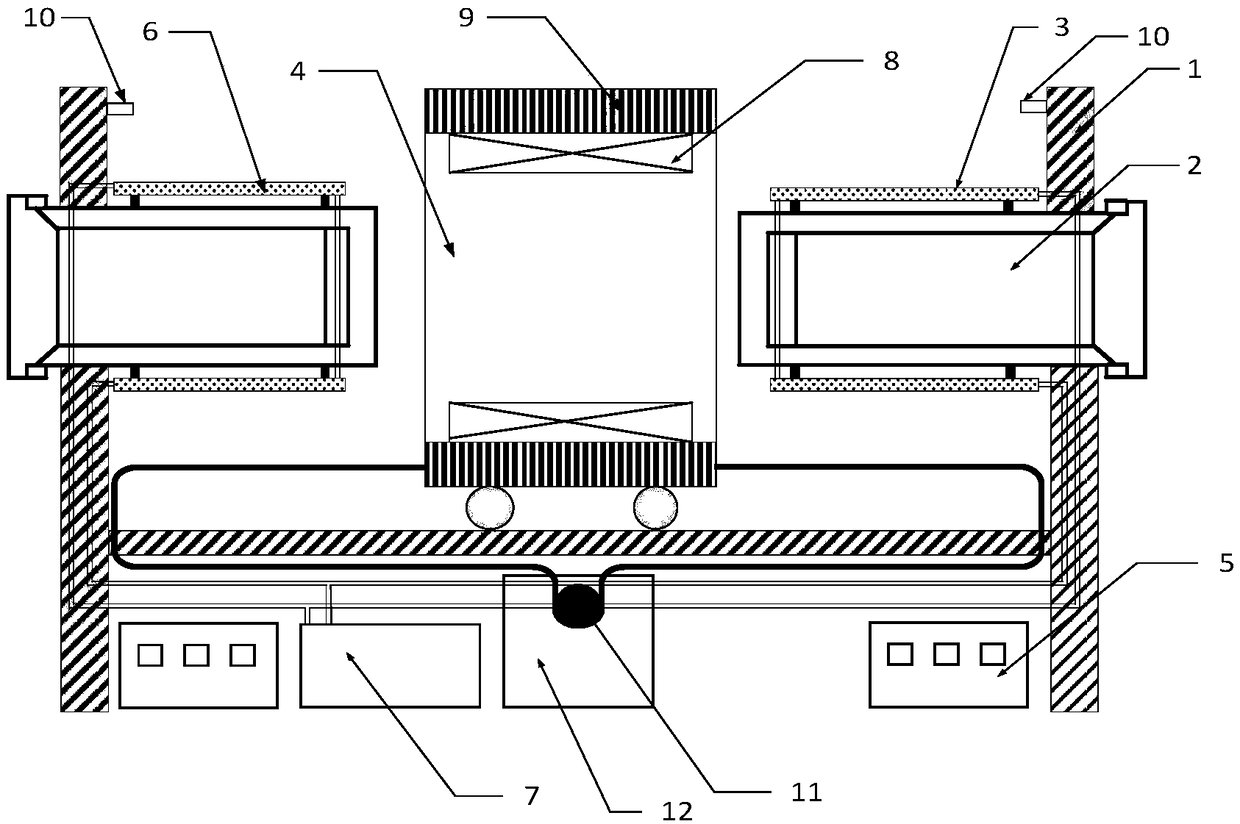
Disc type three-phase magnetic gathering type transverse magnetic field permanent magnet motor
InactiveCN102820756AReduce axial volumeIncrease profitMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsDensity of airElectric machine
The invention discloses a disc type three-phase magnetic gathering type transverse magnetic field permanent magnet motor which is used for solving the technical problem of low permanent magnet utilization rate of existing transverse magnetic field permanent magnet motors. The technical scheme includes that a combined bilateral stator structure is adopted, stators on two sides are staggered to form a mechanical angle of 360 / 2N, wherein the N refers to the number of motor poles, a stator on one side is provided with three phases which are distributed circumferentially, a stator of each phase consists of 'E'-shaped silicon steel and a winding, permanent magnets are circumferentially embedded in a disc-shaped permanent magnet panel and are distributed into three circles, polarities of two adjacent permanent magnets on the permanent magnet panel are opposite, and the permanent magnets, the permanent magnet panel and a motor shaft form a rotating portion of the permanent magnet motor. The permanent magnets and the 'E'-shaped silicon steel forms the disc type three-phase magnetic gathering type transverse magnetic field permanent magnet motor with different polarities and different power levels, so that utilization rate of the permanent magnets, magnetic flux density of air gaps and output torque are improved, and axial volume of the motor is reduced.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Electromagnetic forming of metallic glasses using a capacitive discharge and magnetic field
An apparatus and method of uniformly heating, rheologically softening, and thermoplastically forming metallic glasses rapidly into a net shape using a rapid capacitor discharge forming (RCDF) tool in combination with an electromagnetic force generated by the interaction of the applied current with a transverse magnetic field. The RCDF method utilizes the discharge of electrical energy stored in a capacitor to uniformly and rapidly heat a sample or charge of metallic glass alloy to a predetermined “process temperature” between the glass transition temperature of the amorphous metal and the equilibrium melting point of the alloy in a time scale of several milliseconds or less, at which point the interaction between the electric field and the magnetic field generates a force capable of shaping the heated sample into a high quality amorphous bulk article via any number of techniques including, for example, injection molding, dynamic forging, stamp forging, and blow molding in a time scale of less than one second.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Hall thruster with shared magnetic structure
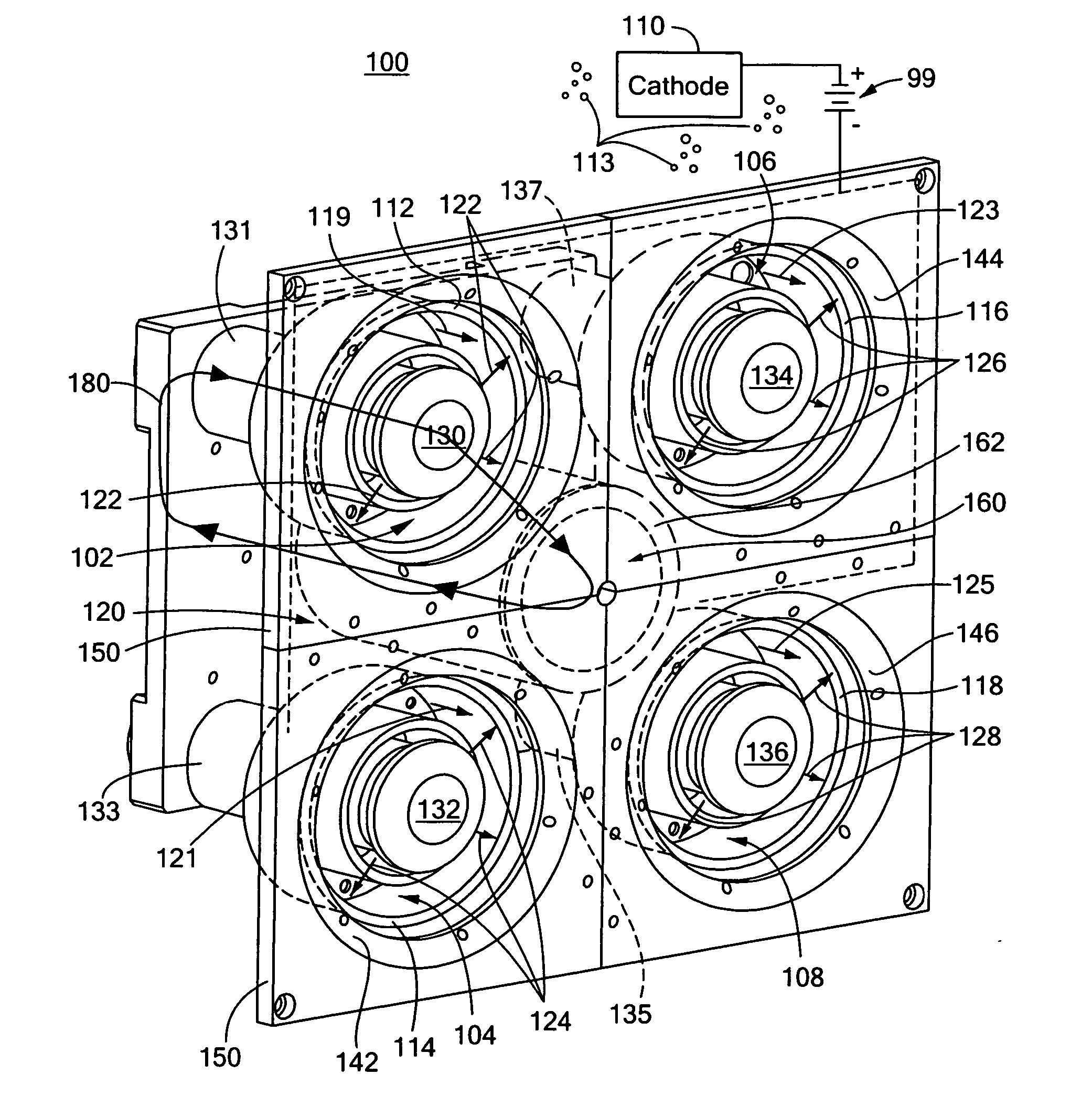
ActiveUS20060186837A1Reduce in quantityReduce weight and volume and power requirementElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsPlasma accelerationTransverse magnetic field
A Hall thruster with a shared magnetic structure including a plurality of plasma accelerators each including an anode and a discharge zone for providing plasma discharge. An electrical circuit having one or more cathodes connected to the plurality of plasma accelerators emits electrons that are attracted to the anode in each of the plasma accelerators. A shared magnetic circuit structure establishes a transverse magnetic field in each of the plurality of plasma accelerators that creates an impedance to the flow of electrons toward the anode in each of the plurality of plasma accelerators and enables ionization of a gas moving through one or more of the plurality of plasma accelerators. The impedance localizes an axial electric field in the plurality of plasma accelerators for accelerating ionized gas through the one or more of the plurality of plasma accelerators to create thrust.
Owner:BUSEK
Thermal system and process for controlling 8-inch zone melting silicon monocrystals
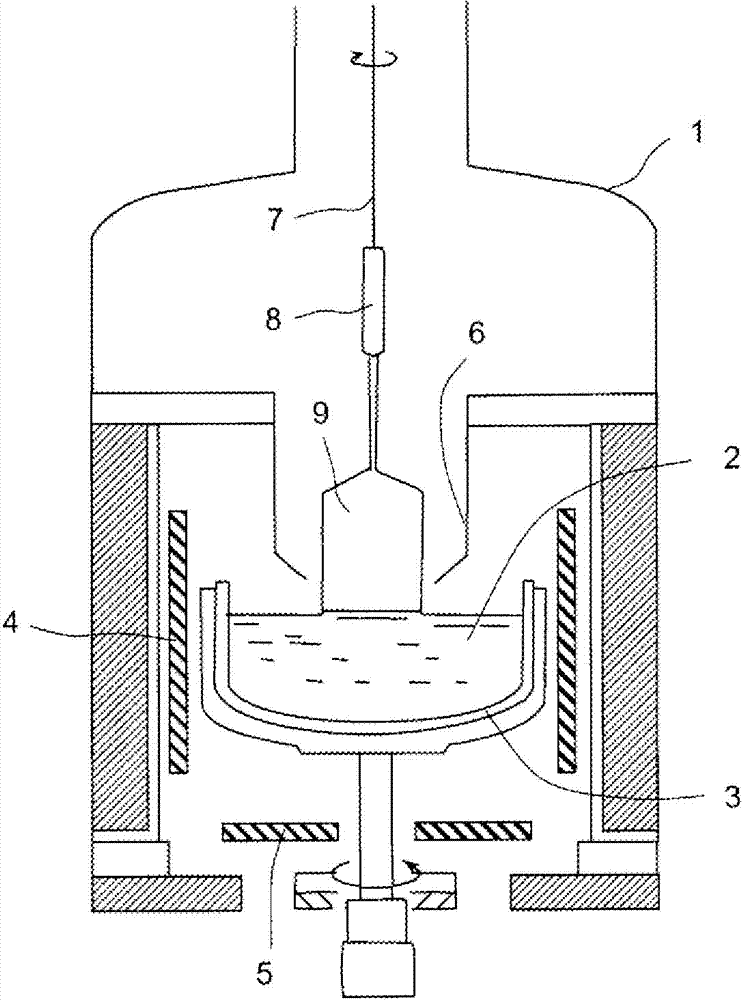
ActiveCN102321913AMeet needsSolve temperature problemsBy zone-melting liquidsBy pulling from meltZone meltingTransverse magnetic field
The invention relates to a thermal system and a process for controlling 8-inch zone melting silicon monocrystals. The thermal system comprises a coil and a heat insulating bucket; two sides outside a furnace with the same height of the coil 1 are provided with magnetic field generators for generating transverse magnetic fields; and a reflector for reflecting heat of a melting zone is arranged between the coil and the heat insulating bucket. The process comprises the following steps of: when the shoulder expanding diameter reaches 100mm, extending the reflector to form a heat insulating circle at the peripheries of the silicon monocrystals, opening the magnetic field generators, ensuring that the height of the melting area above the silicon monocrystals is 3-5mm in the shoulder expanding process; and when the diameter of the silicon monocrystals reaches 205mm, rotating an arm, wherein the furnace pressure is 4-8bar in the equal diameter keeping process. Because the newly designed zone melting silicon monocrystal thermal system is adopted and process parameters are adjusted, 8-inch zone melting silicon monocrystals are drawn successfully, the problems of temperature fluctuation and fusion flow fluctuation in large-diameter silicon monocrystal forming difficulties are solved, dislocation is avoided and reduced, and the requirement of the market on the 8-inch zone melting silicon monocrystals is met.
Owner:ZHONGHUAN ADVANCED SEMICON MATERIALS CO LTD +1
Multi-structure coupling magnetic field adaptability type rotating arc ion plating device
ActiveCN102936718ASatisfy the rotating magnetic field stateEmission reductionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingEtchingTransverse magnetic field
The invention relates to the technical field of thin film and coating preparation, in particular to a multi-structure coupling magnetic field adaptability type rotating arc ion plating device and solves the problems that in prior art, large particles exist, target material etching and coating uniformity are poor, the deposition efficiency is low, and the like. According to the rotating arc ion plating device, a special multi-function multi-structure adaptability type ion plating gun is matched with a structurally optimized water-cooling flange sleeve to serve as an entire arc source structure, an axial auxiliary magnetic field device is arranged in the rear of a target material base of the ion plating gun, a secondary rotating transverse magnetic field generator and a focusing guide magnetic field device are arranged on the outer side of the flange sleeve, a poly-type composite magnetic field with a secondary rotating transverse magnetic field as a master and other coupled magnetic fields is formed under the action of coupling of three magnetic field devices, requirements of rotating magnetic field states nearby a target surface can be met, the arc spot electro-discharge mode is improved, the power density is reduced, large particle emission is reduced, the magnetic field distribution of plasma conveying space can be guaranteed, and plasma conveying efficiency and uniformity are improved.
Owner:温州驰诚真空机械有限公司
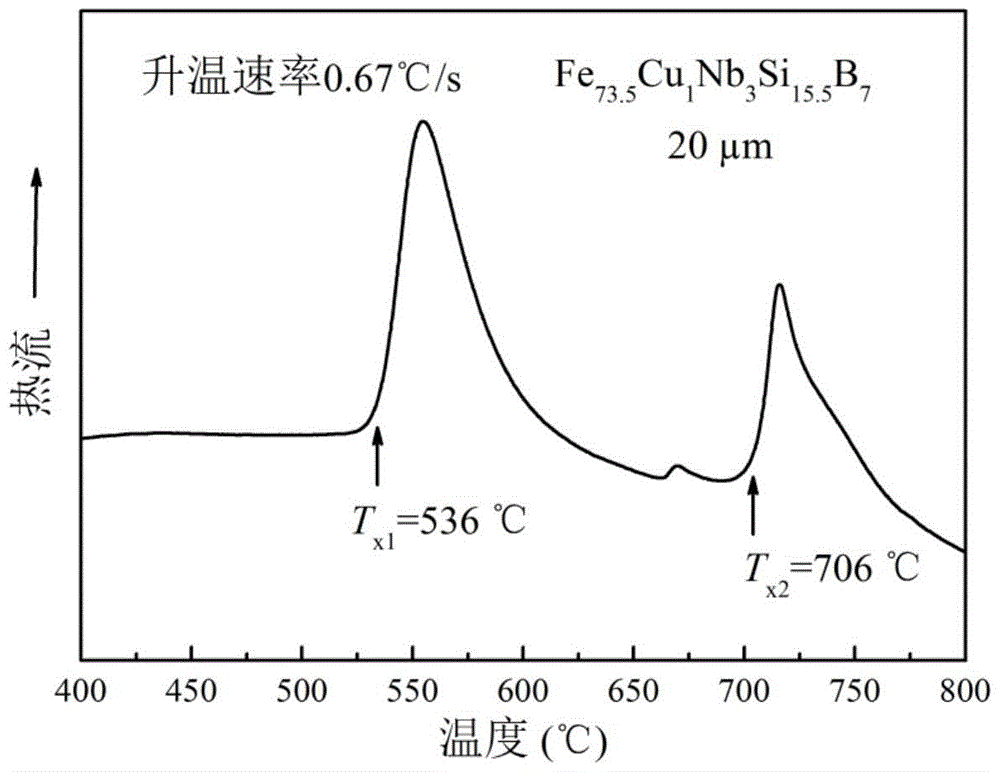
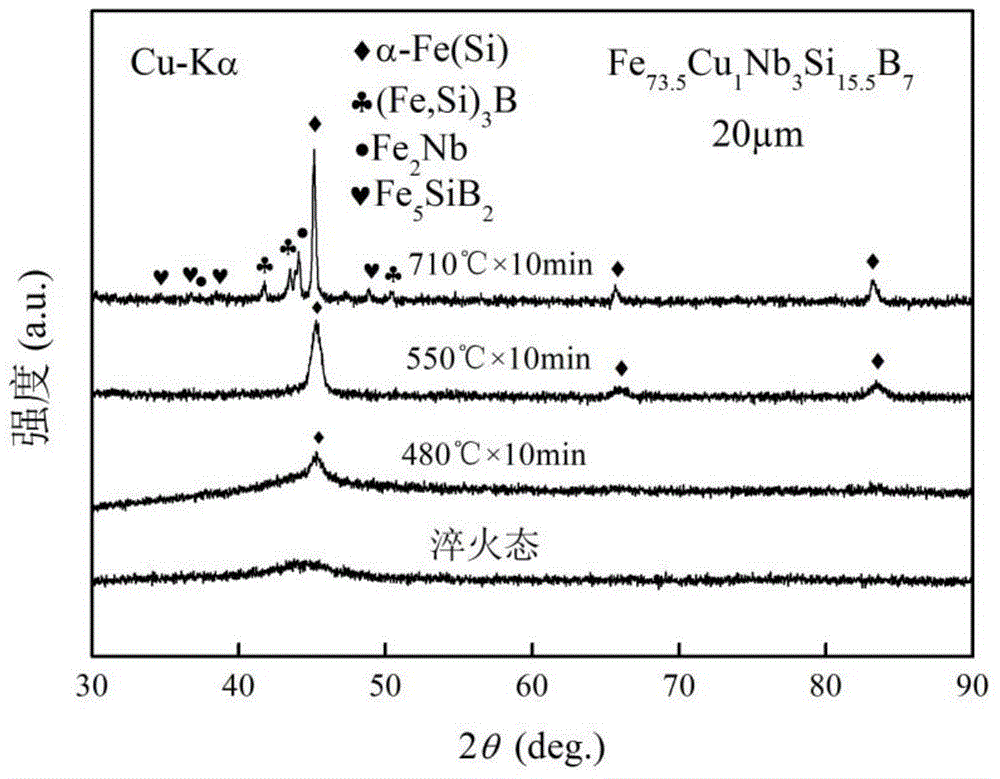
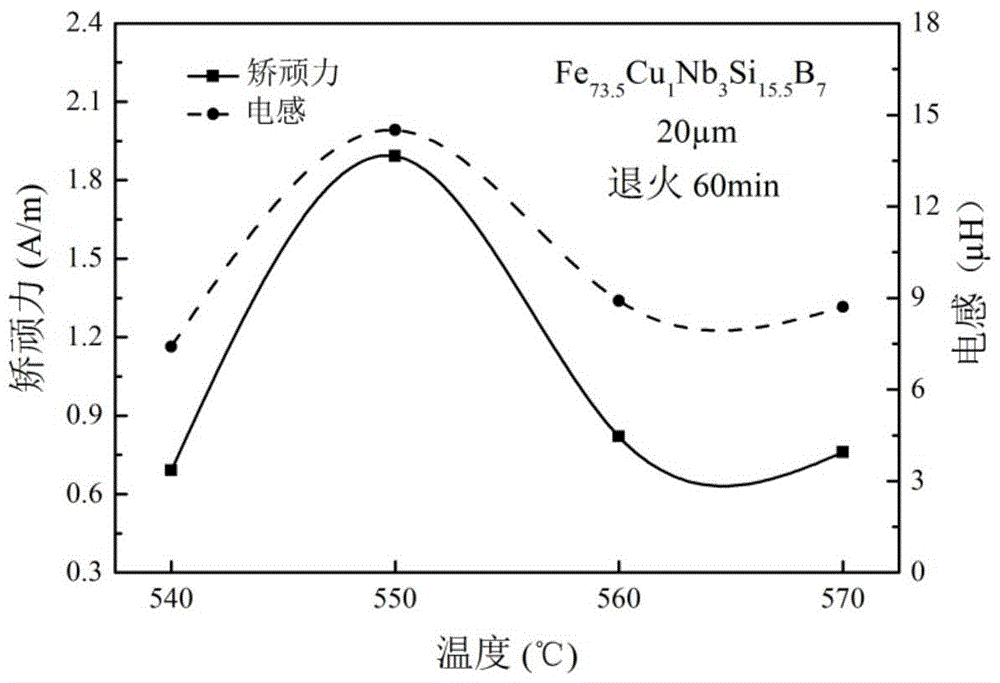
Amorphous nanocrystalline magnetic core heat treatment method
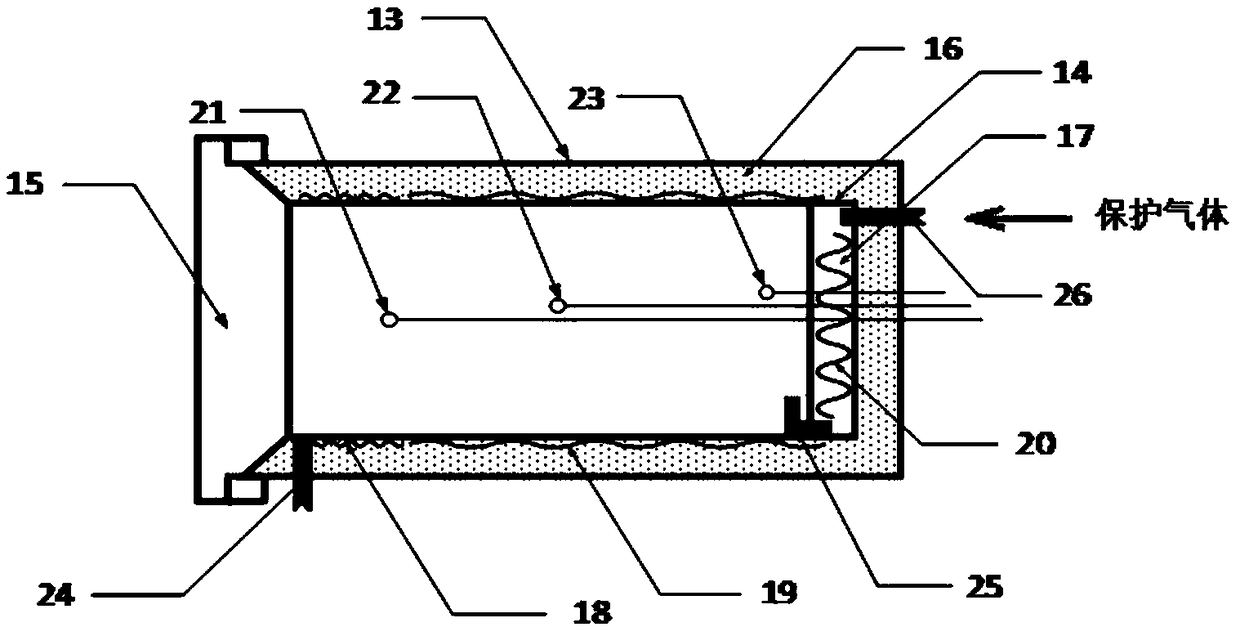
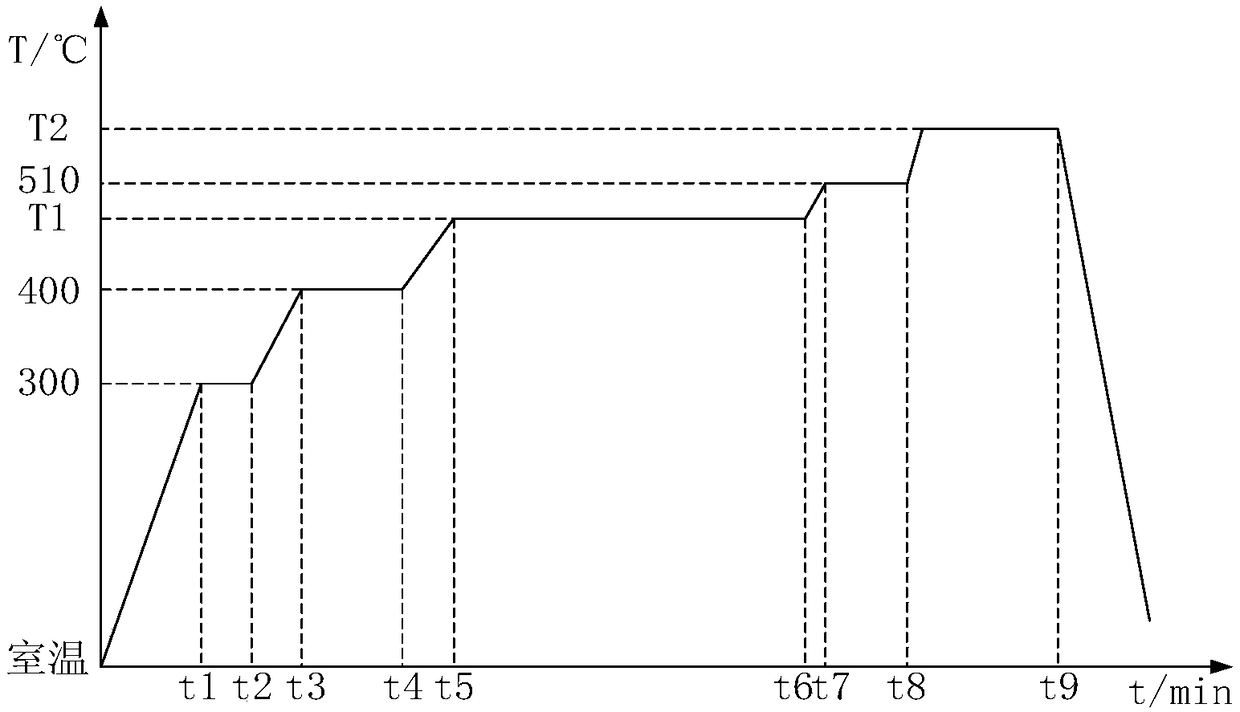
ActiveCN108998633AHigh initial permeabilityLow coercivityFurnace typesMagnetic materialsShielding gasRoom temperature
The invention discloses an amorphous nanocrystalline magnetic core heat treatment method. The amorphous nanocrystalline magnetic core heat treatment method comprises the steps that (1) a to-be-treatedmagnetic core is placed into a transverse magnetic field heat treatment furnace, and protective gas is led in; (2) heat treatment and magnetic treatment are carried out, wherein in the first stage, the temperature rises to about 300 DEG C from the room temperature, the wasted time is about 60 min, heat preservation is carried out for about 30 min, then the temperature rises to about 400 DEG C, the wasted time is about 30 min, and heat preservation is carried out for about 60 min; in the second stage, the temperature rises to T1 from about 400 DEG C, the wasted time is about 30 min, heat preservation is carried out at T1 for about 210 min, and meanwhile, a transverse magnetic field is applied in the second stage; in the third stage, the magnetic field is removed, meanwhile, the temperaturerises to about 510 DEG C from T1, the wasted time is about 20 min, heat preservation is carried out for about 40 min, then the temperature rises to T2 to be subjected to heat preservation, and the wasted time is about 90 min; and in the fourth stage, heating is stopped, cooling is carried out to the room temperature, wherein the T1 is 460 DEG C-480 DEG C, and the T2 is 560 DEG C-570 DEG C.
Owner:YANGZHONG INTELLIGENT ELECTRICAL INST NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV
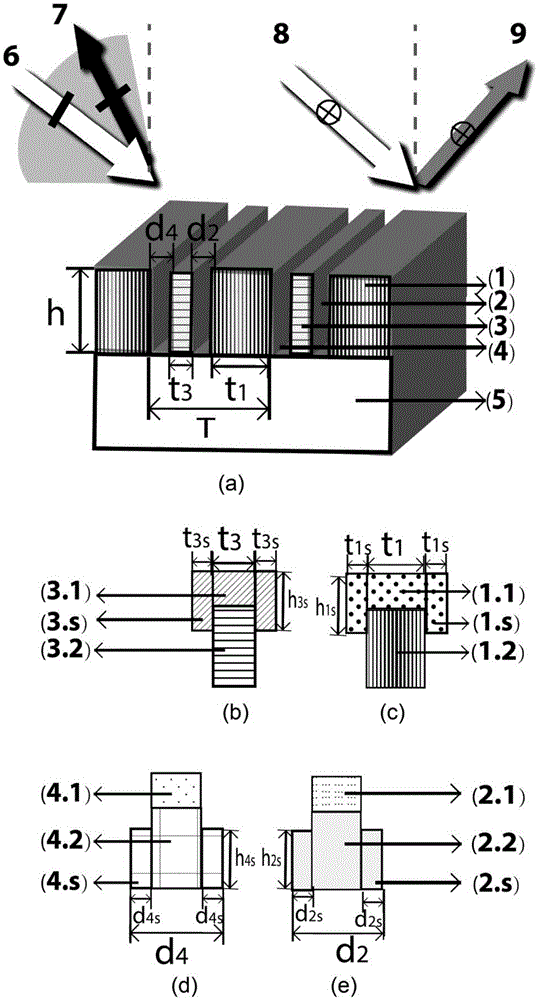
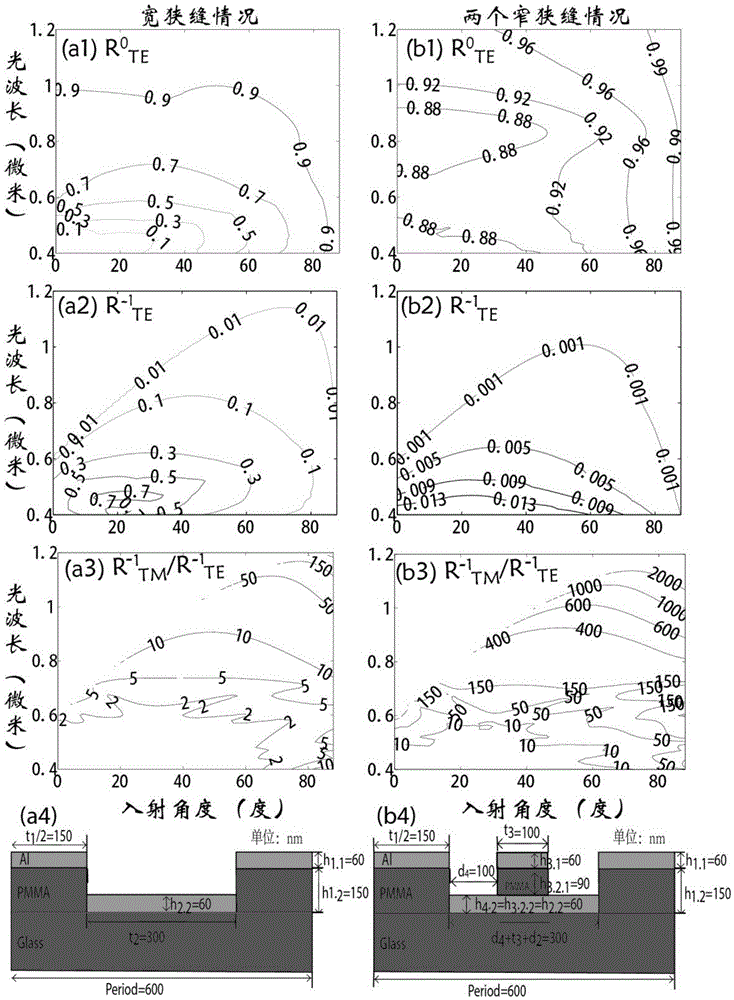
Composite-structure double-layer metal grating polarization beam splitter
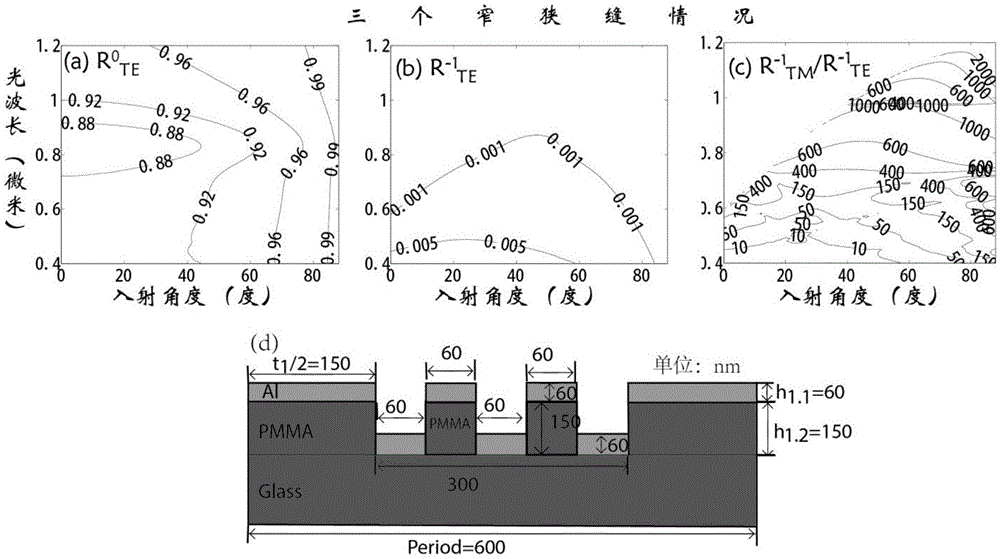
ActiveCN105629493ALong cycleGuaranteed diffractionDiffraction gratingsBeam splittingMetallic materials
Provided is a composite-structure metal grating polarization beam splitter. Each grating period has two or more medium slits separated by a metal material; and a waveguide structure formed by the plurality of medium slits meets waveguide mode cutoff of electromagnetic waves of an incident electric field parallel to grating lines in slit waveguide, and the grating period meets existence of diffraction of incident transverse magnetic field electromagnetic waves at a certain incident angle. Through the utilization of the appropriate number of medium slits, and by enabling width of waveguide formed by the plurality of slits to be smaller than mode cutoff width of working wavelength TE polarized wave, the TE polarized wave cannot be propagated in the slits, so that the TE polarized incident waves only have reflected waves, but does not have other diffracted waves; meanwhile, by controlling the grating period, the polarization beam splitter grating is allowed to have 0-level and+ / -1-level and above reflection diffraction or transmission diffraction for the TE polarized light; and broadband, large-angle range, reflection / diffraction / transmission polarization beam splitting under a larger metal grating period can be realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Production technology of semiconductor grade silicon single crystal
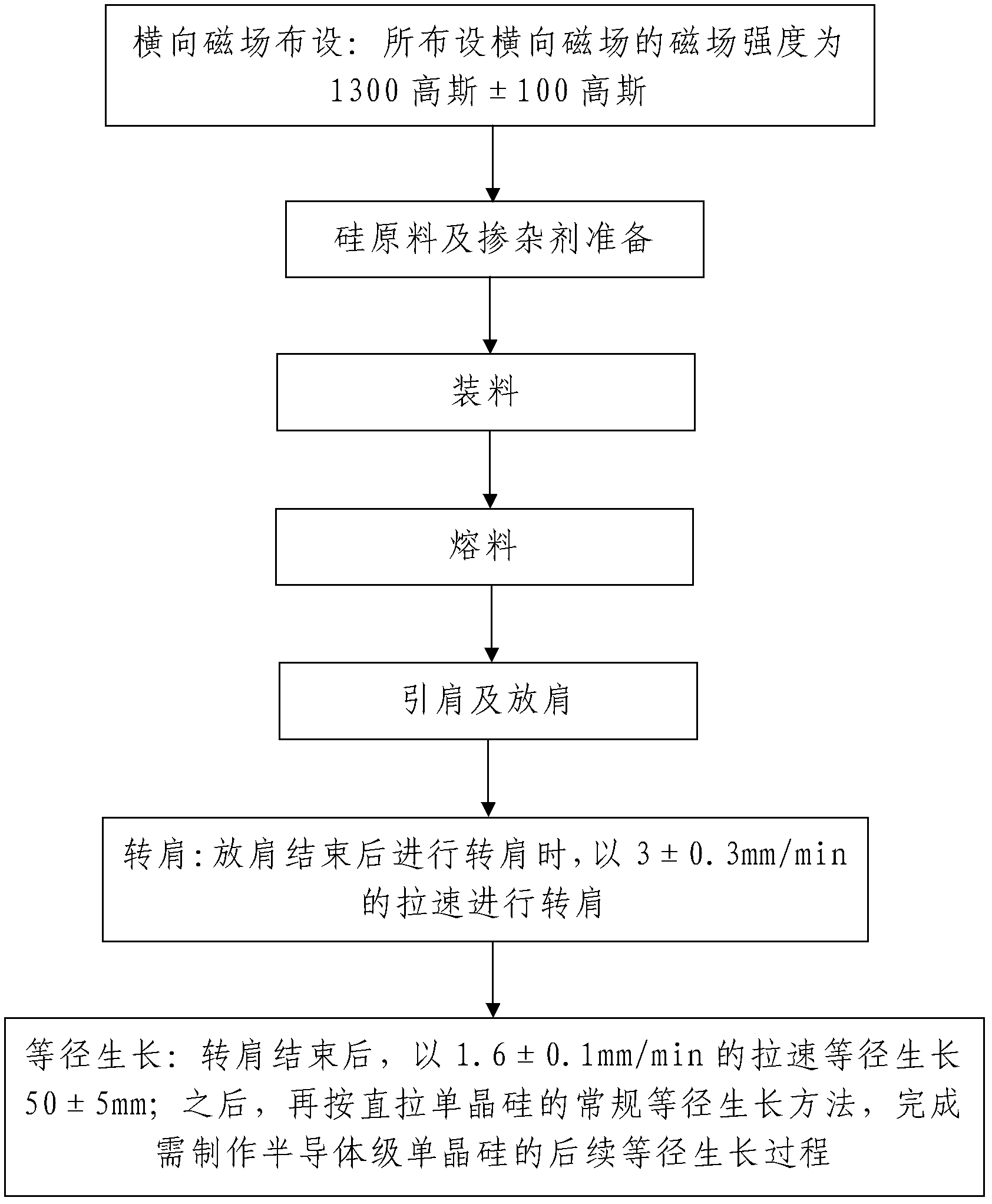
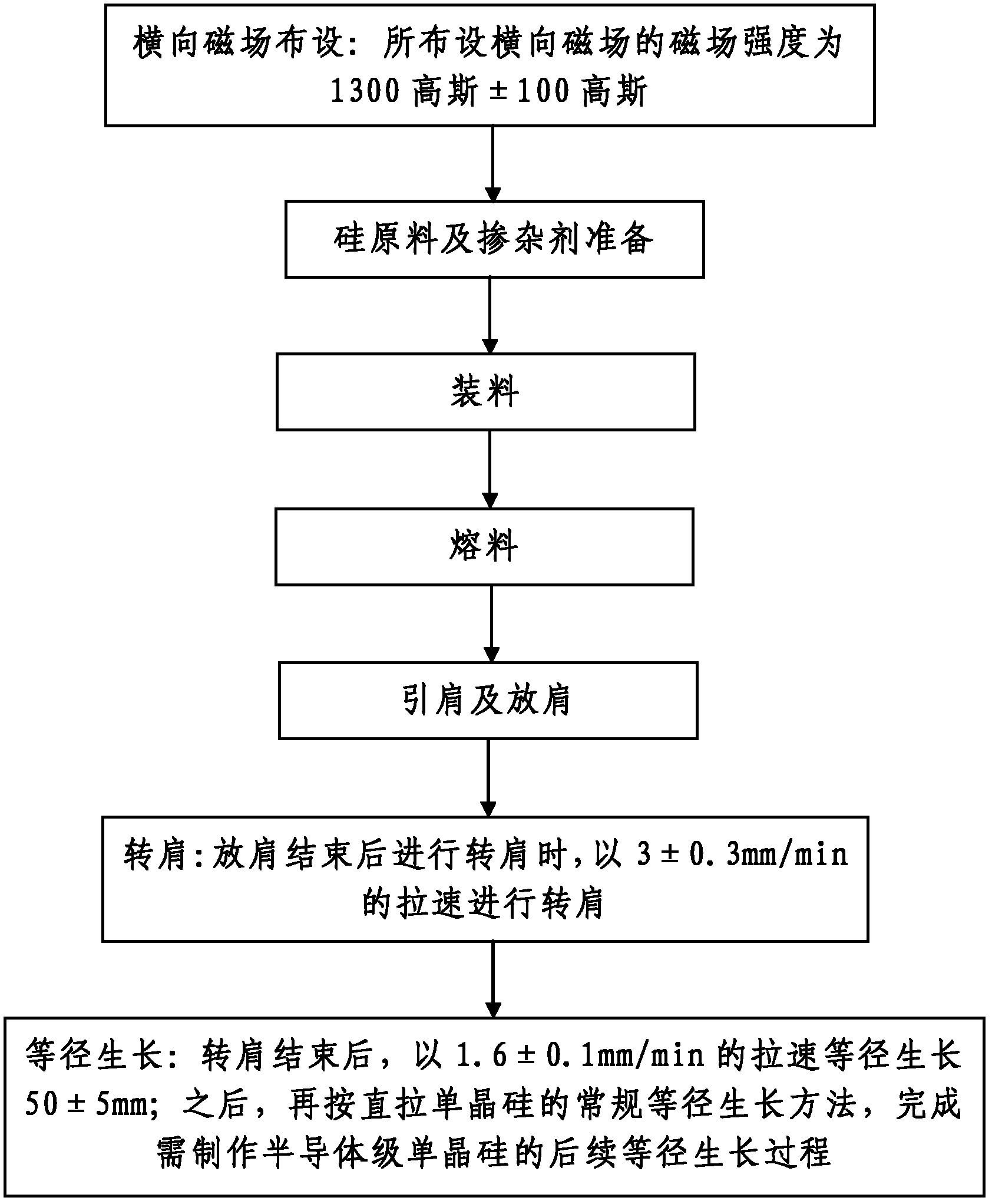
InactiveCN102220633AReasonable designThe process steps are simplePolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltTransverse magnetic fieldSingle crystal
The invention discloses a production technology of semiconductor grade silicon single crystal, comprising the following steps: 1, arranging a transverse magnetic field: the magnetic field intensity of the transverse magnetic field is 1300 + / - 100 gausses; 2, preparing silicon material and doping agent; 3, charging; 4, melting material; 5, introducing shoulder and expanding shoulder; 6, rotating shoulder: after the step of expanding shoulder, the step of rotating shoulder is carried out with a casting speed of 3 + / - 0.3 mm / min; and 7, growing at the same diameter: after the step of rotating shoulder, the material grows up to 50 + / - 5 mm with a casting speed of 1.6 + / - 0.1 mm / min; then, a conventional method of growing at the same diameter for direct pulling silicon single crystal is used to complete the subsequent process of growing at the same diameter of the semiconductor grade silicon single crystal. The method has the advantages of reasonable design, simple steps, easiness in realization, easiness in mastering and good using effect, and is capable of effectively guaranteeing the quality of the produced semiconductor grade silicon single crystal. The produced semiconductor grade silicon single crystal has high uniformity of cross-section electric resistivity and no micro-defects such as swirl.
Owner:XIAN HUAJING ELECTRONICS TECH
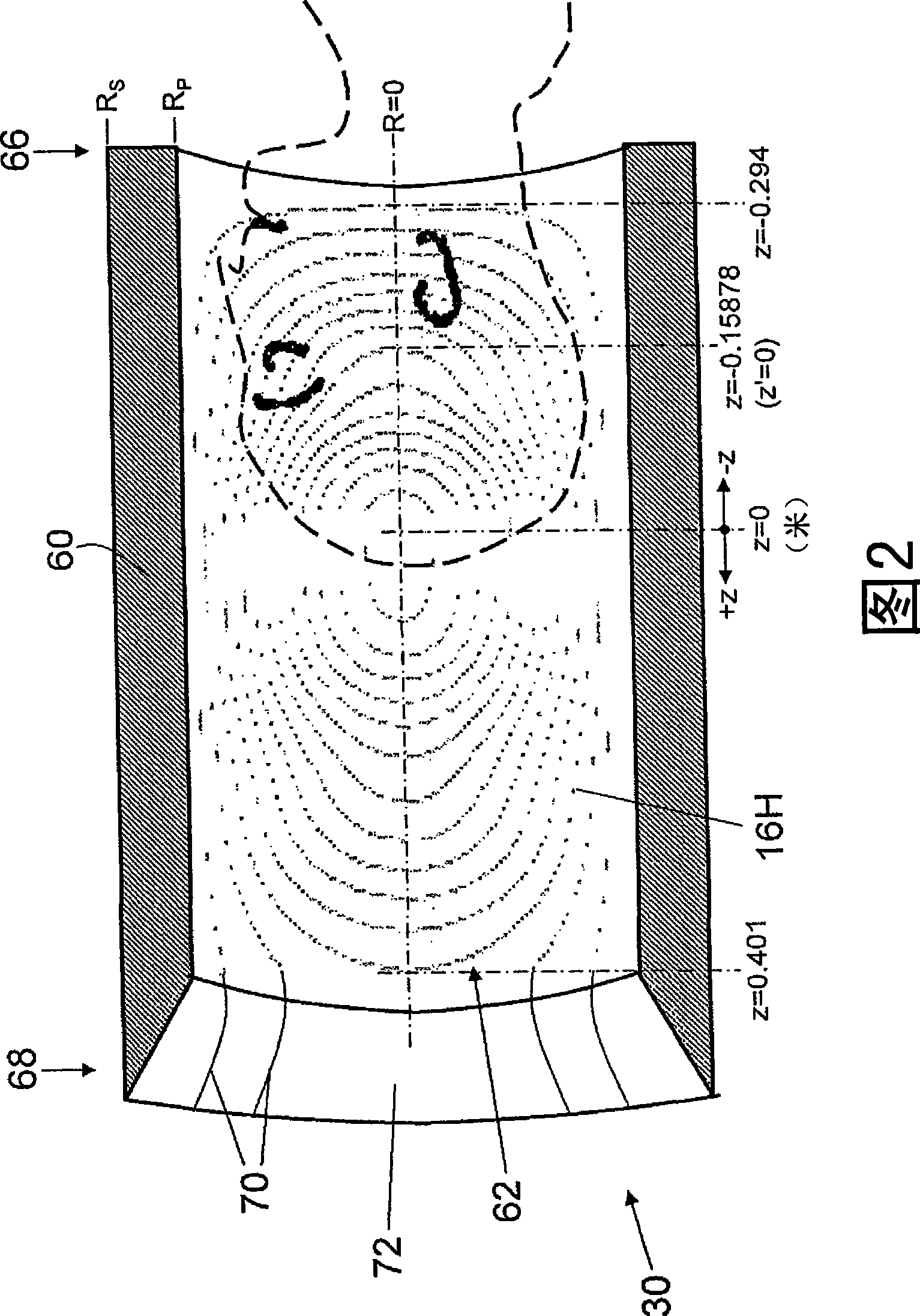
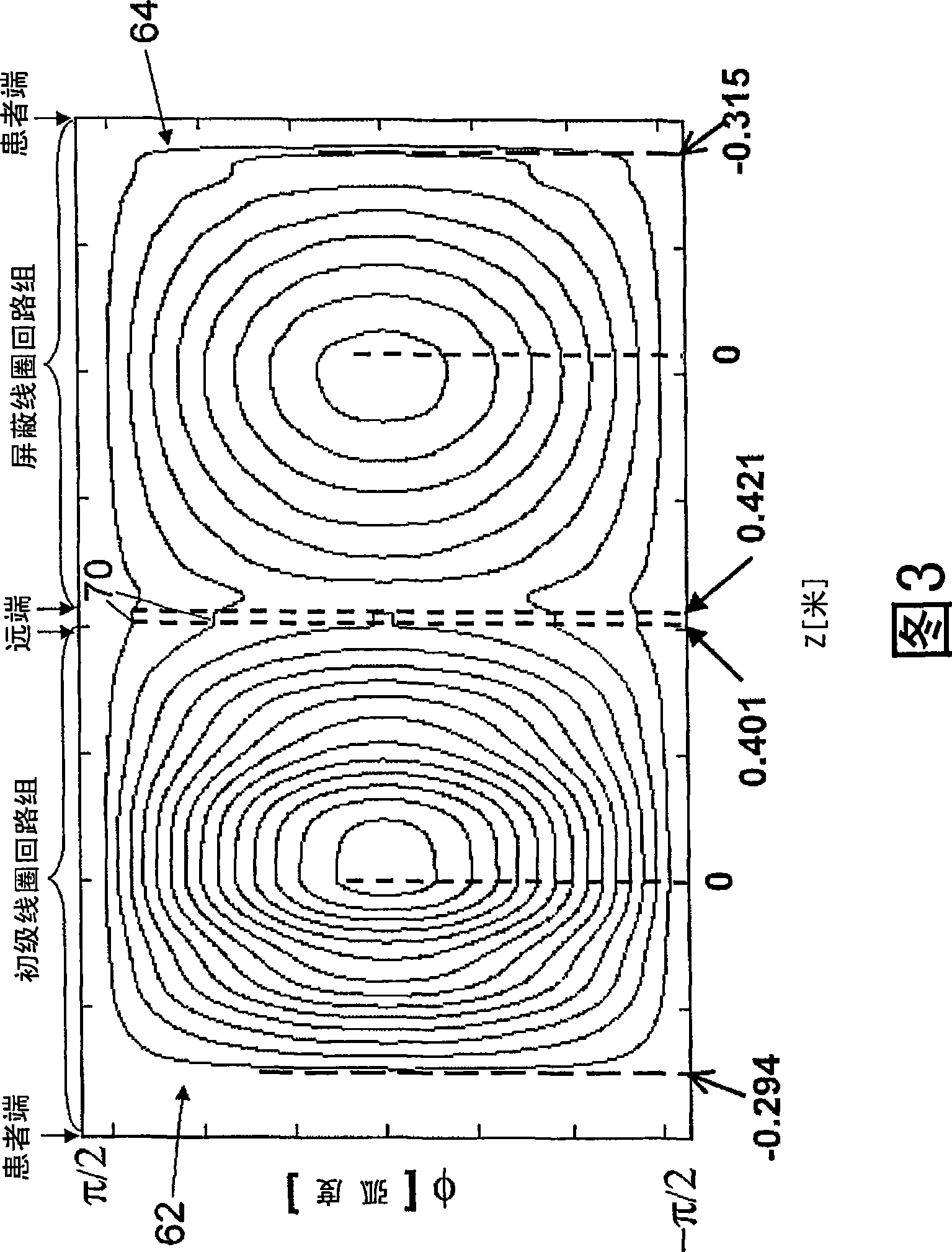
Three-dimensional asymmetric transverse gradient coils
InactiveCN101454686AImprove gradient uniformityLarge magnetic field gradient strengthMagnetic measurementsMagnetic field gradientTransverse magnetic field
A transverse magnetic field gradient coil includes a set of primary coil loops (62) defining an operative coil end (66) and a distal coil end (68). The set of primary coil loops are configured to generate a magnetic field gradient in a selected region asymmetrically disposed relatively closer to the operative coil end and relatively further from the distal coil end. A set of shield coil loops (64) are disposed outside the set of primary coil loops and are configured to substantially shield the set of primary coil loops. Two or more current jumps (70) are disposed at the distal end. Each current jump electrically connects an incomplete loop of the set of primary coil loops with an incomplete loop of the set of shield coil loops.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
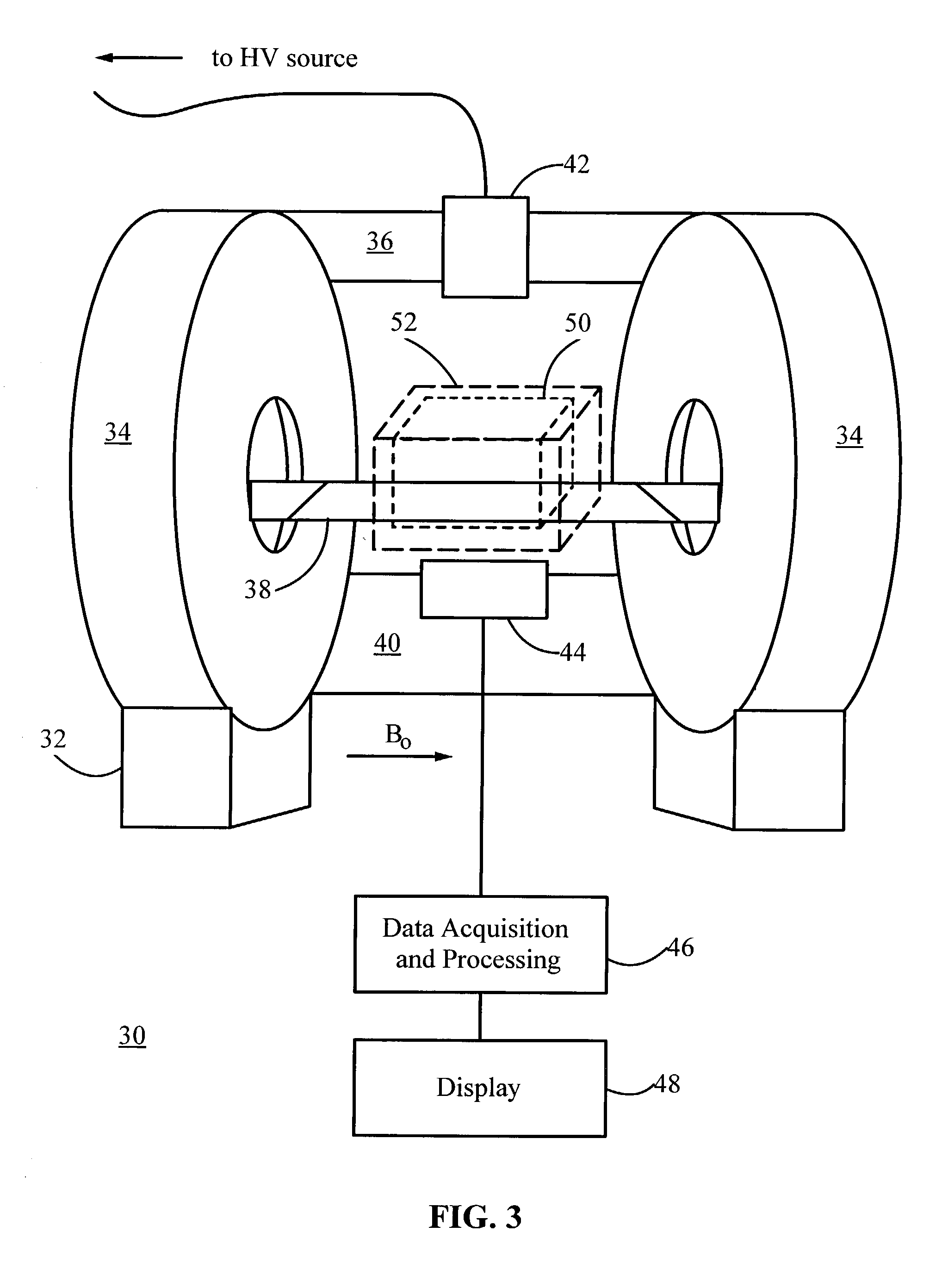
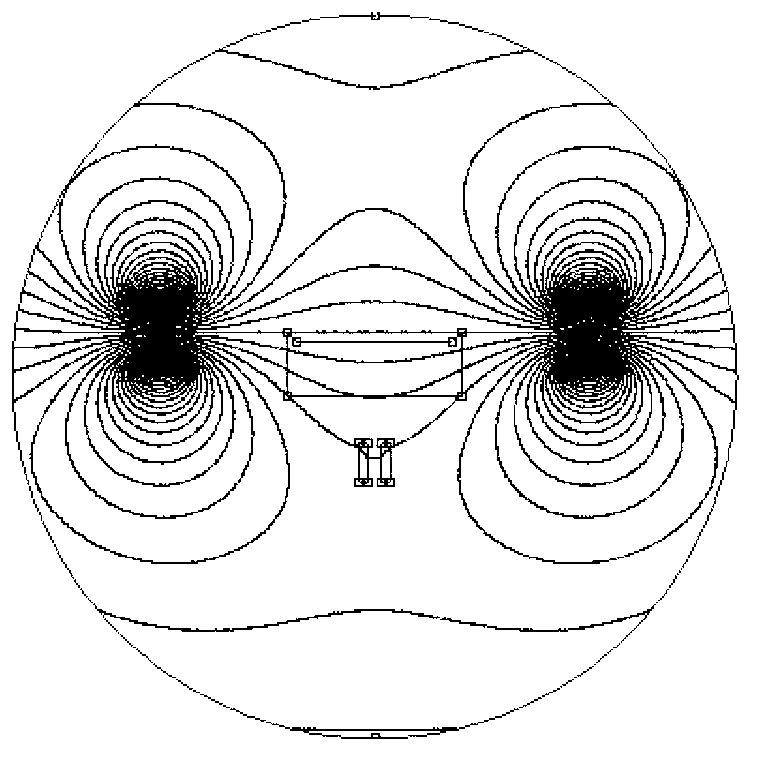
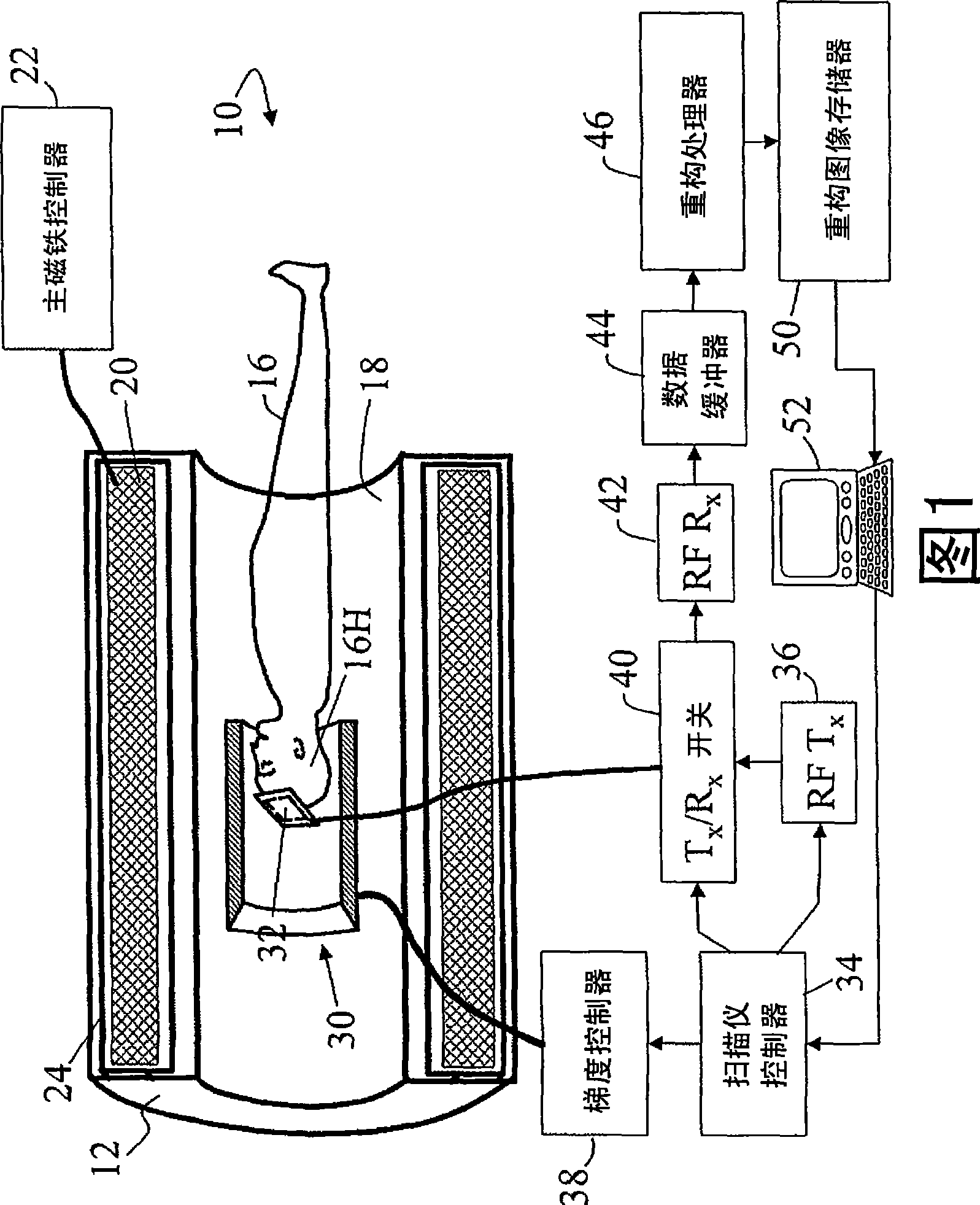
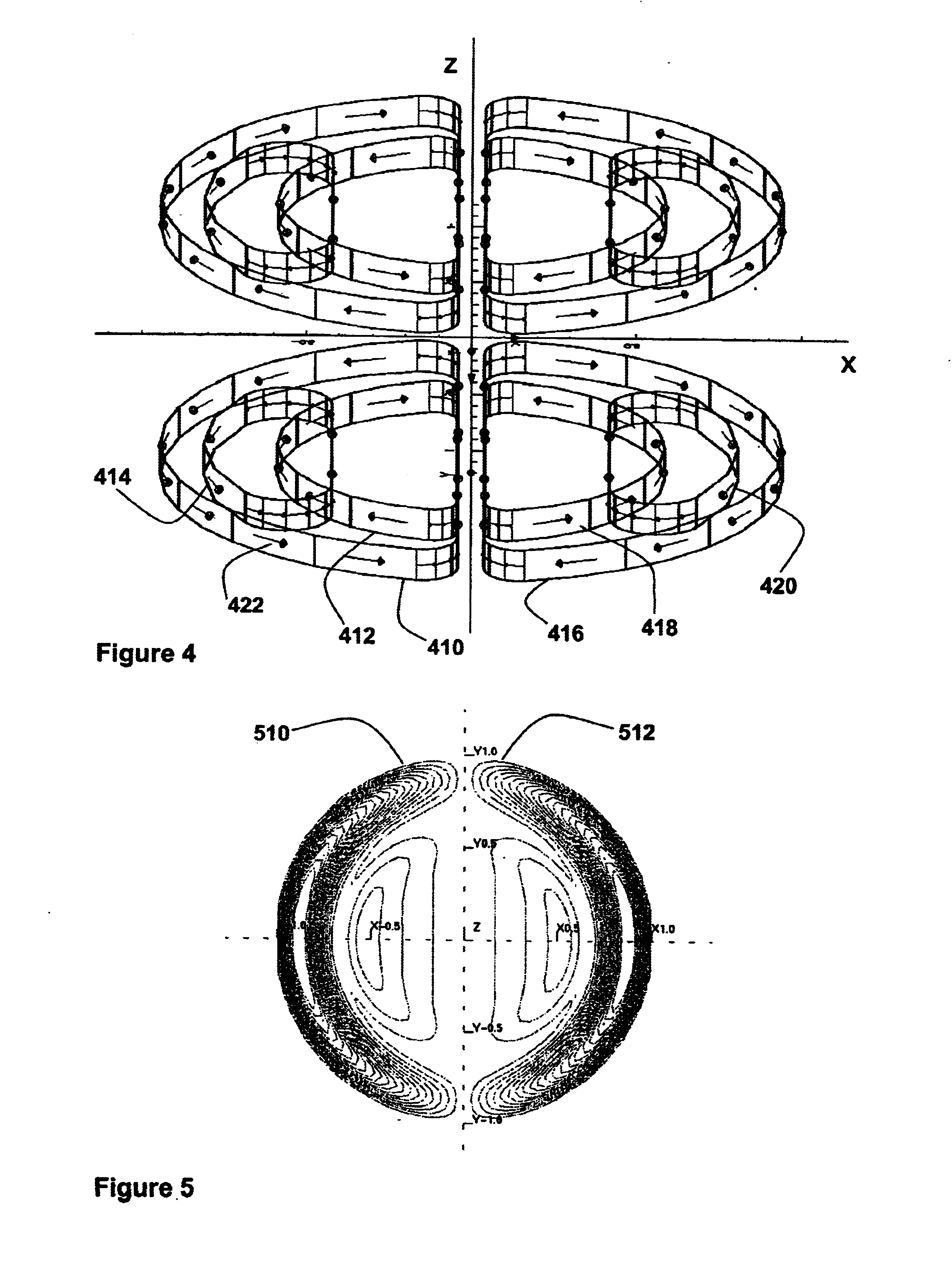
Superconducting open MRI magnet with transverse magnetic field
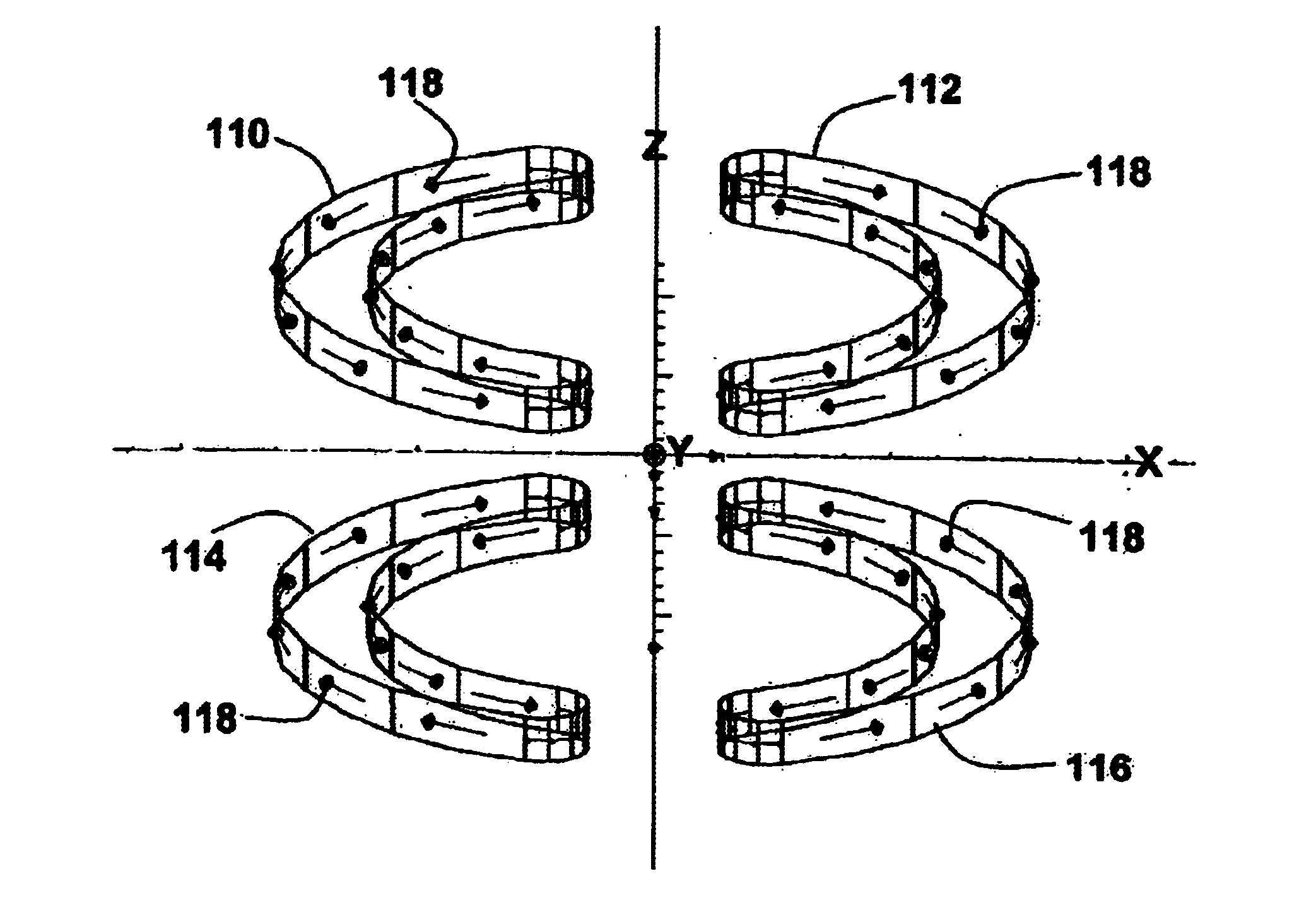
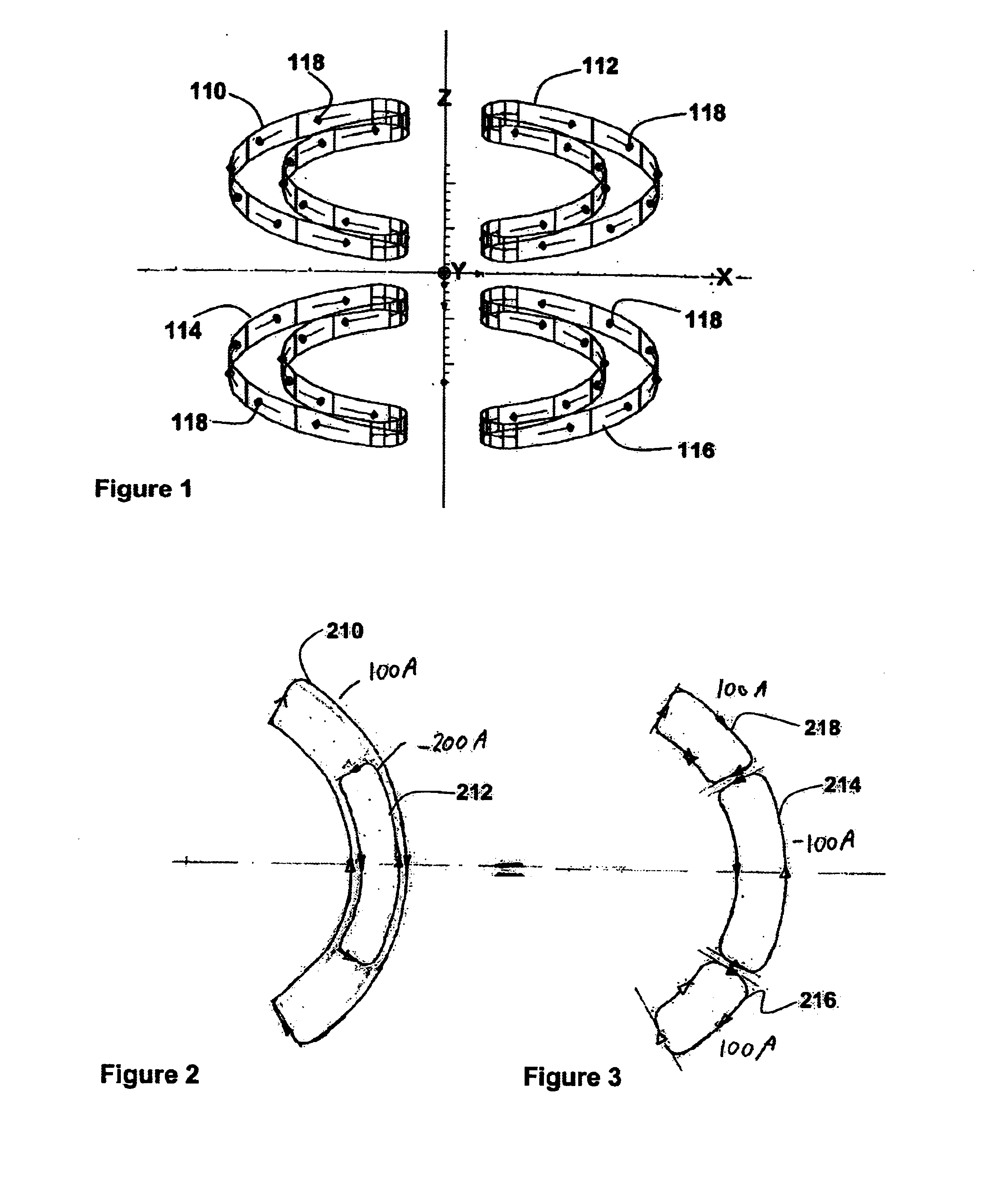
InactiveUS6950001B2Easy to manufactureImprove homogeneityMagnetsDiagnostic recording/measuringVertical planeTransverse magnetic field
The present invention relates to magnets and to magnetic resonance imaging systems. The magnet is open with magnetic coils arranged in quadrant, separated about two perpendicular planes, a midplane and a plane of reflection, and wherein the windings are configured such that, in operation, current flow is symmetrical about the plane of reflection and anti-symmetrical about the midplane, to produce a nett magnetic field at the center in a direction perpendicular to the plane of reflection.
Owner:OXFORD MAGNET TECH LTD
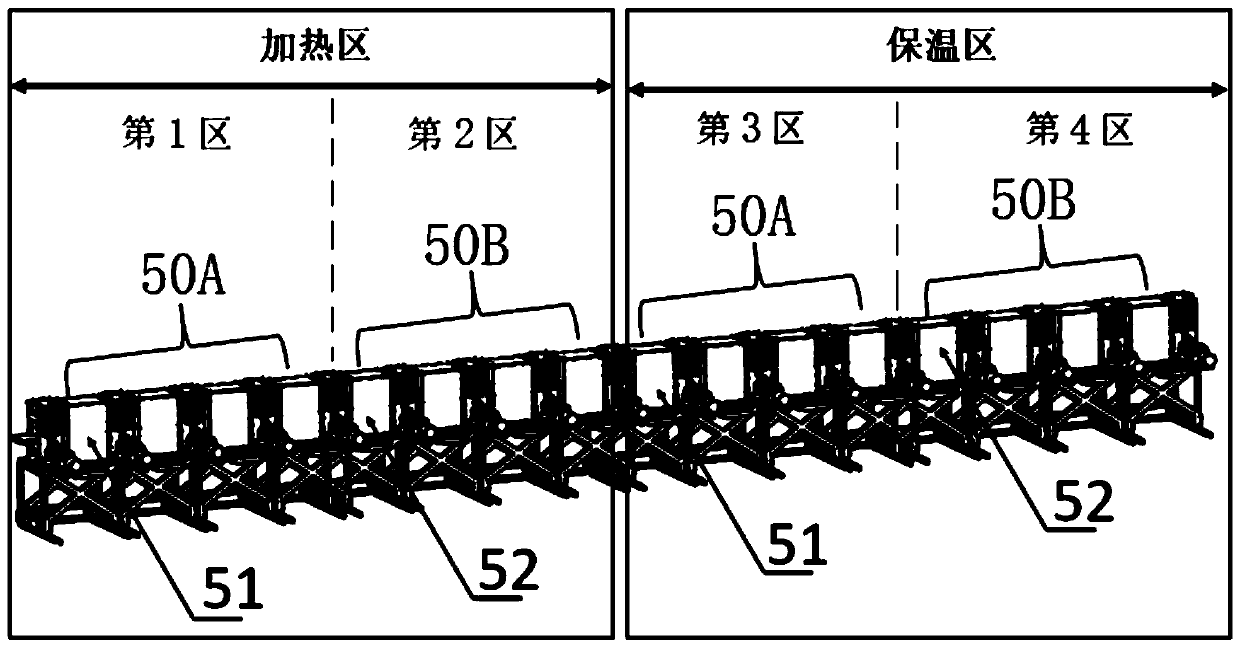
Transverse and longitudinal magnetic alternating induction heating system and heating method
PendingCN111278182AImprove uniformityUniform temperatureWork treatment devicesIncreasing energy efficiencyTransverse magnetic fieldInductor
The invention provides a transverse and longitudinal magnetic alternating induction heating system and heating method. A channel for a plate blank to pass through is defined as a plate blank channel,and the induction heating system comprises a first induction heating unit and a second induction heating unit which are alternately arranged in the running direction of the plate blank at intervals. The first induction heating unit comprises K1 first inductors used for generating a transverse magnetic field with the magnetic field direction perpendicular to the surface of the plate blank, and therefore the plate blank located on the plate blank channel is heated. The second induction heating unit comprises K2 second inductors used for generating a longitudinal magnetic field with the magneticfield direction parallel to the surface of the plate blank, and therefore the plate blank located on the plate blank channel is heated. By the adoption of the heating system with the transverse magnets and the longitudinal magnets arranged alternately, the temperature deviation between the corners and the surface of the plate blank can be effectively reduced.
Owner:HUNAN ZHONGKE ELECTRIC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com