Patents
Literature
473 results about "Zone melting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
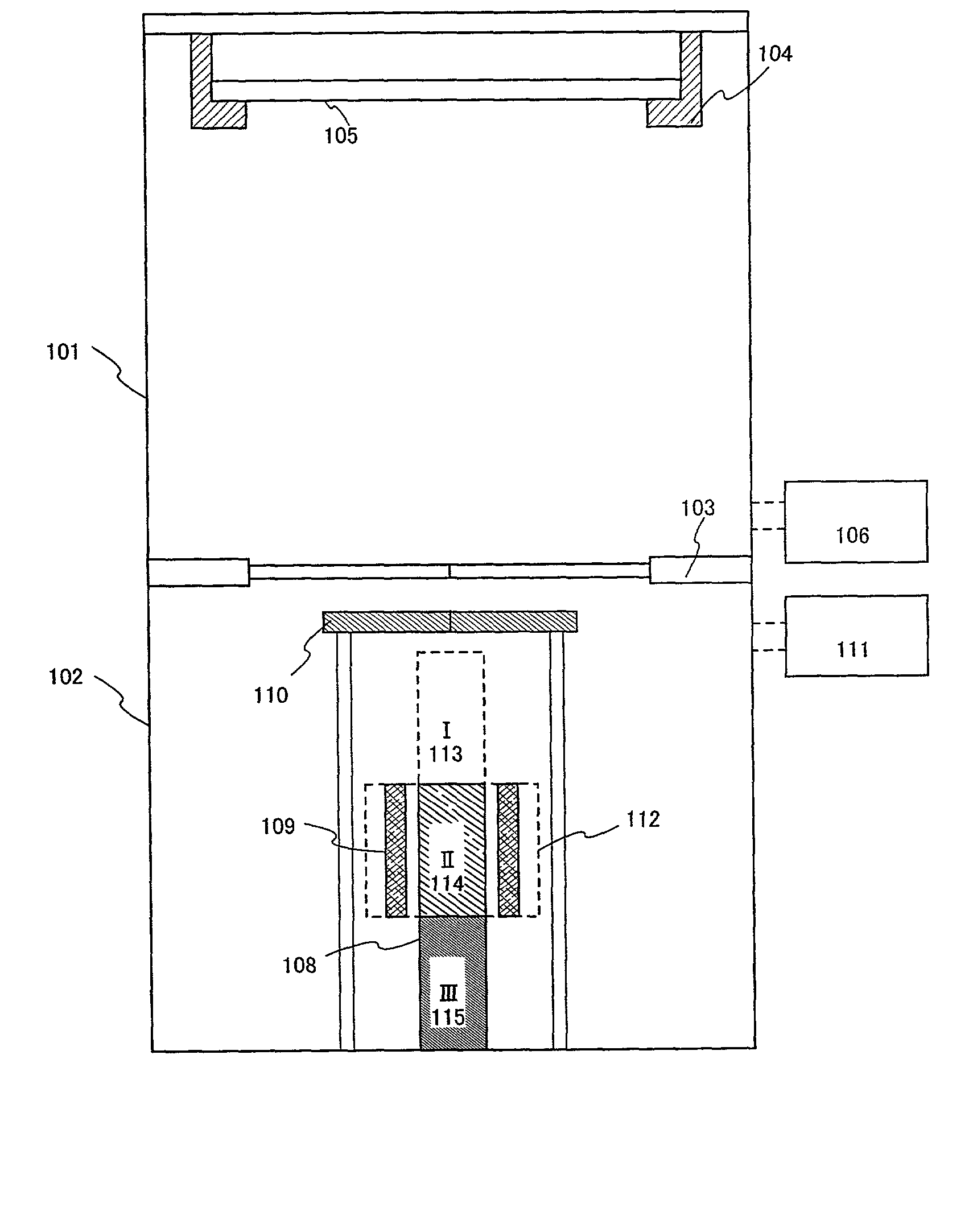
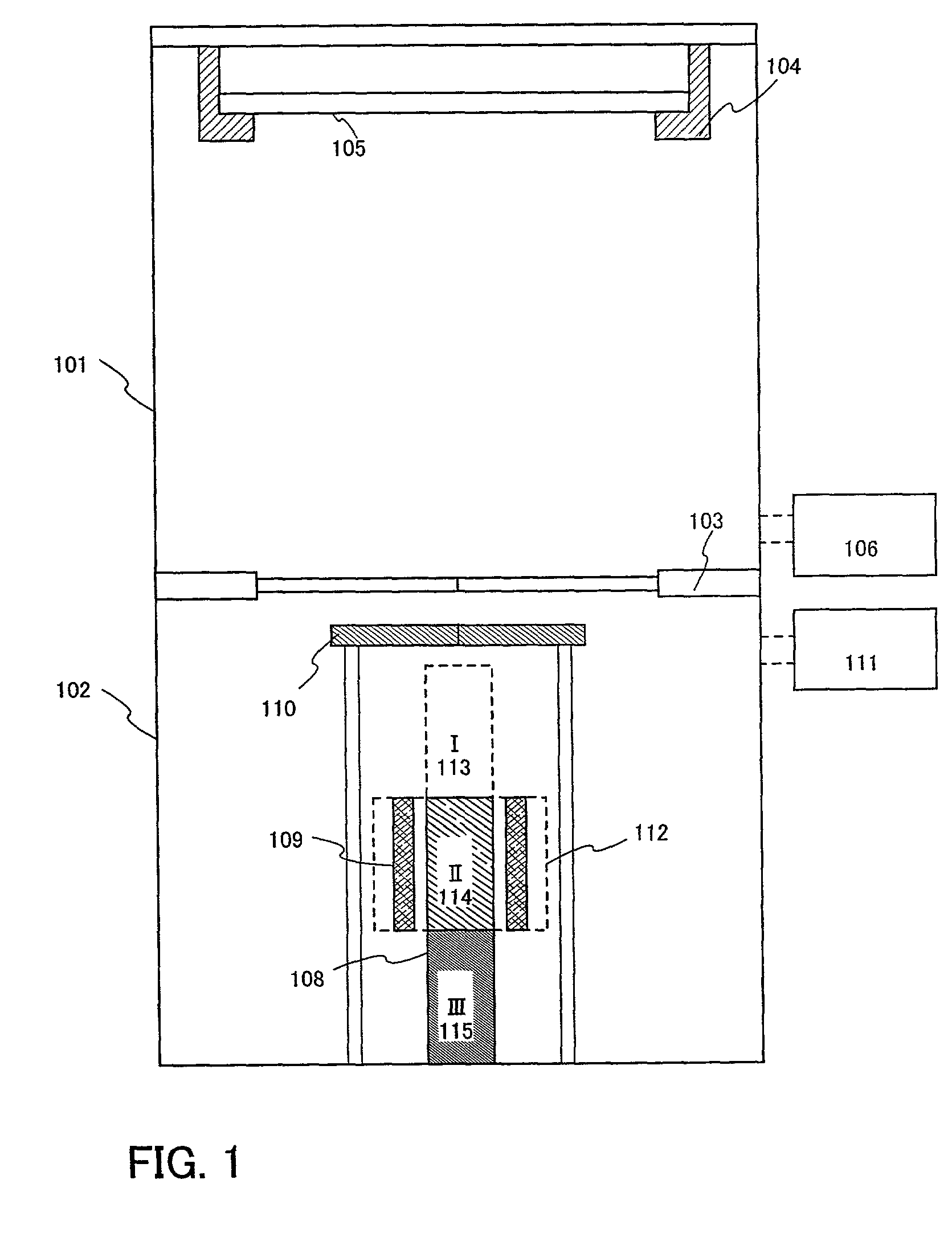
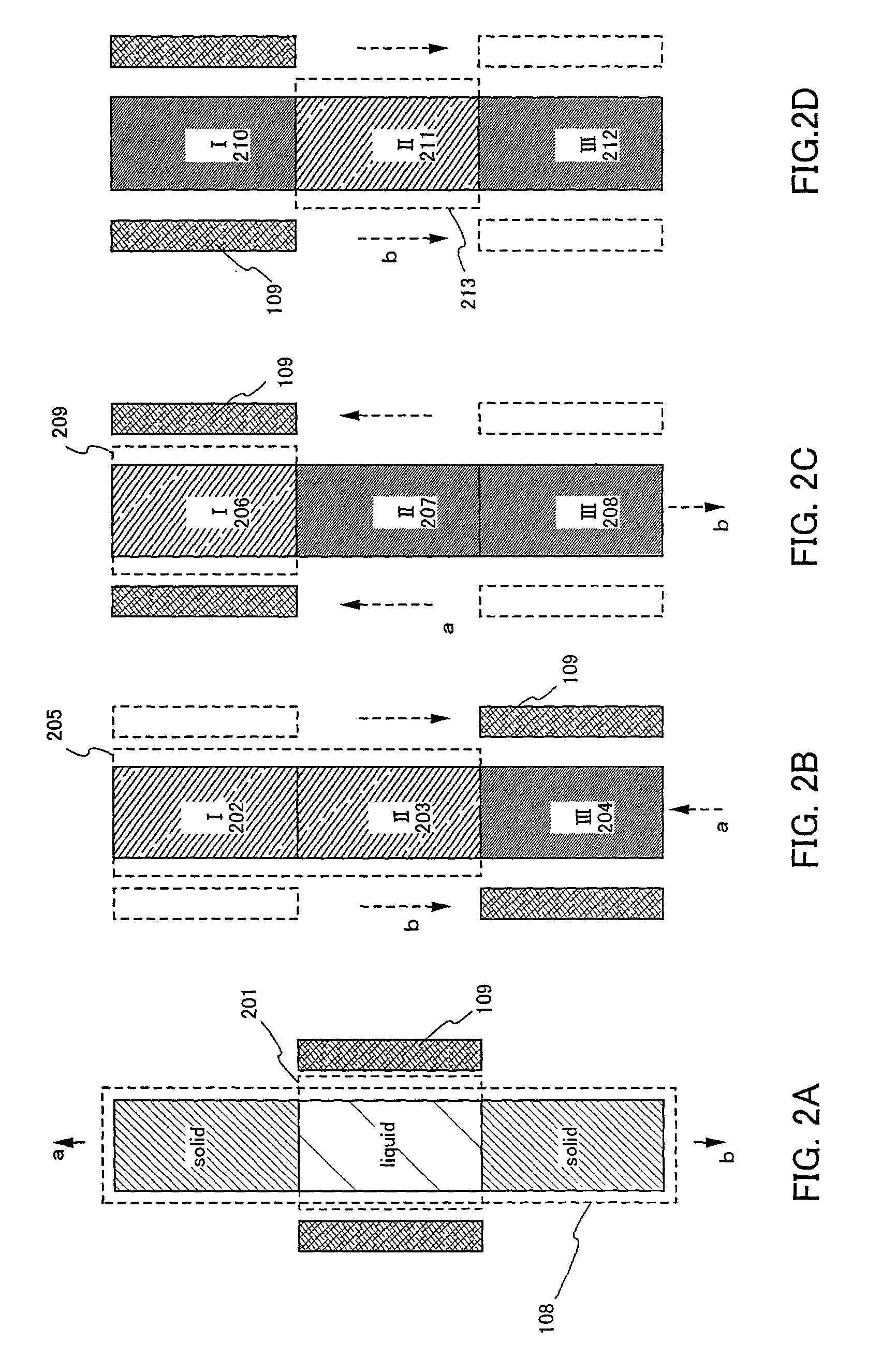
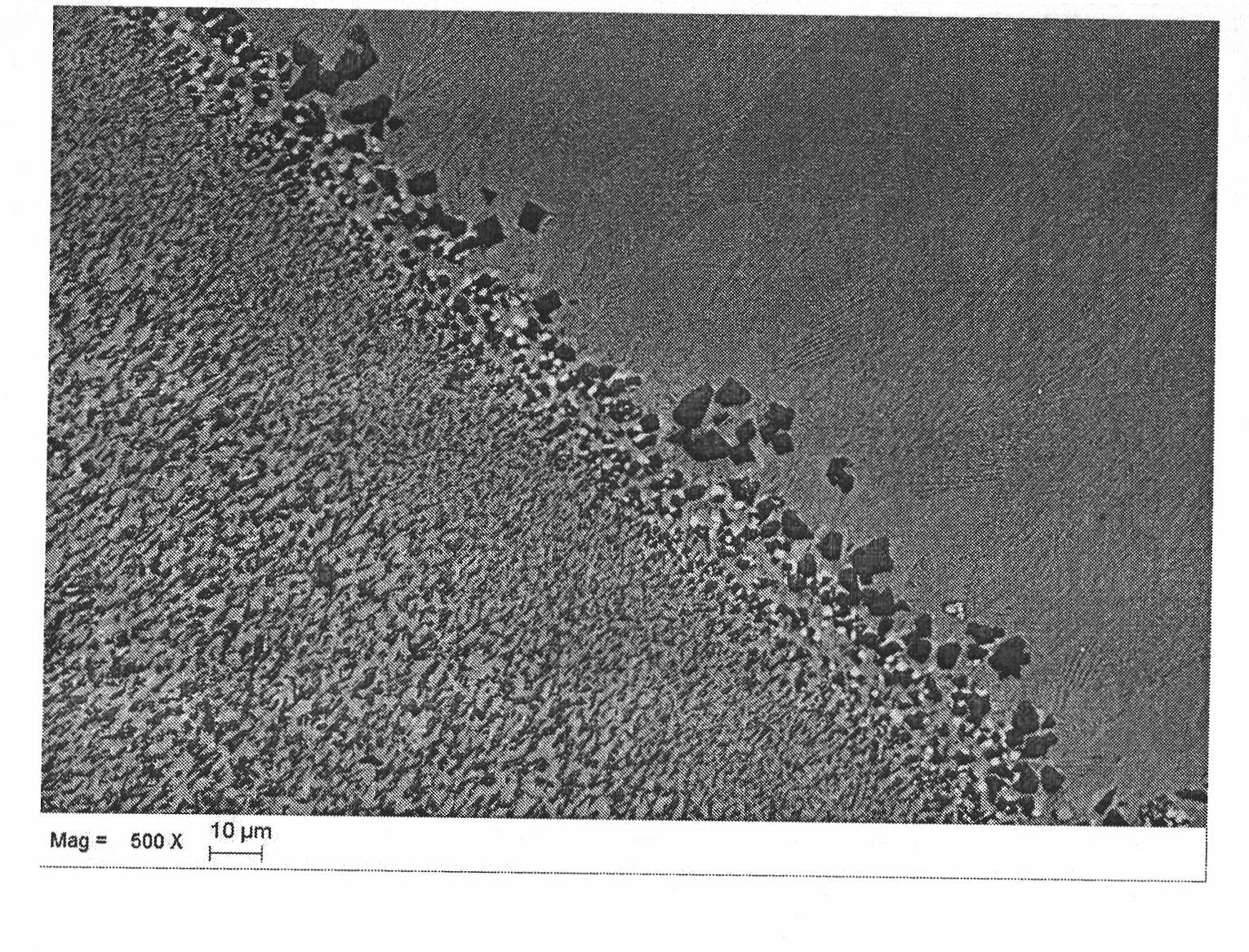
Zone melting (or zone refining or floating zone process or travelling melting zone) is a group of similar methods of purifying crystals, in which a narrow region of a crystal is melted, and this molten zone is moved along the crystal. The molten region melts impure solid at its forward edge and leaves a wake of purer material solidified behind it as it moves through the ingot. The impurities concentrate in the melt, and are moved to one end of the ingot. Zone refining was invented by John Desmond Bernal and further developed by William Gardner Pfann in Bell Labs as a method to prepare high purity materials, mainly semiconductors, for manufacturing transistors. Its first commercial use was in germanium, refined to one atom of impurity per ten billion, but the process can be extended to virtually any solute-solvent system having an appreciable concentration difference between solid and liquid phases at equilibrium. This process is also known as the float zone process, particularly in semiconductor materials processing.
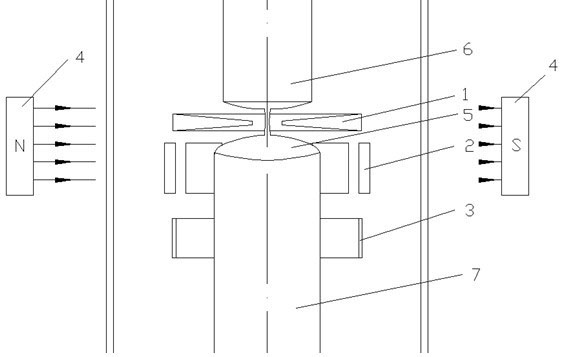
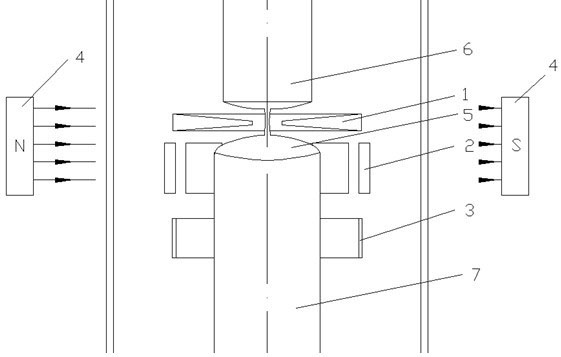
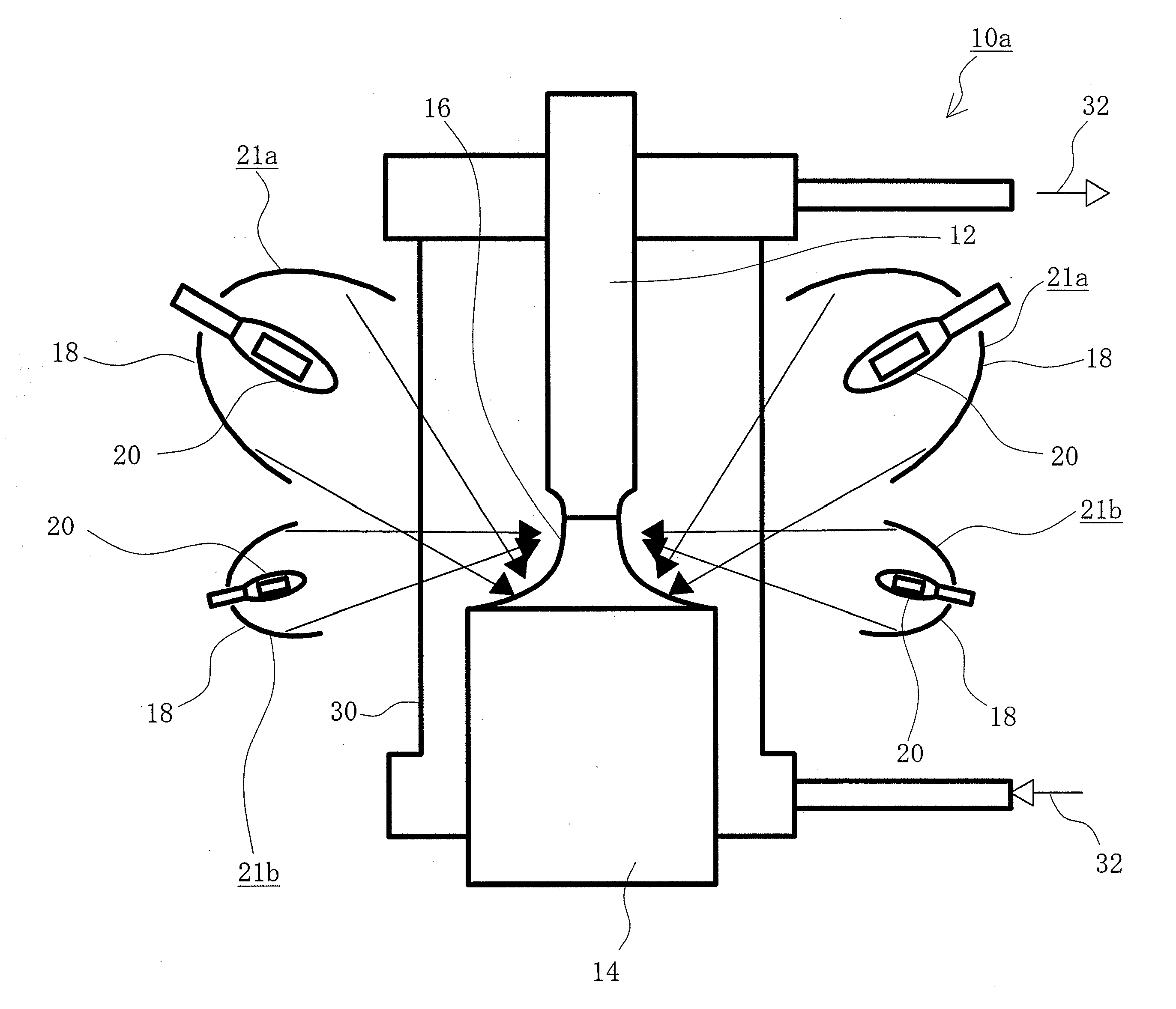
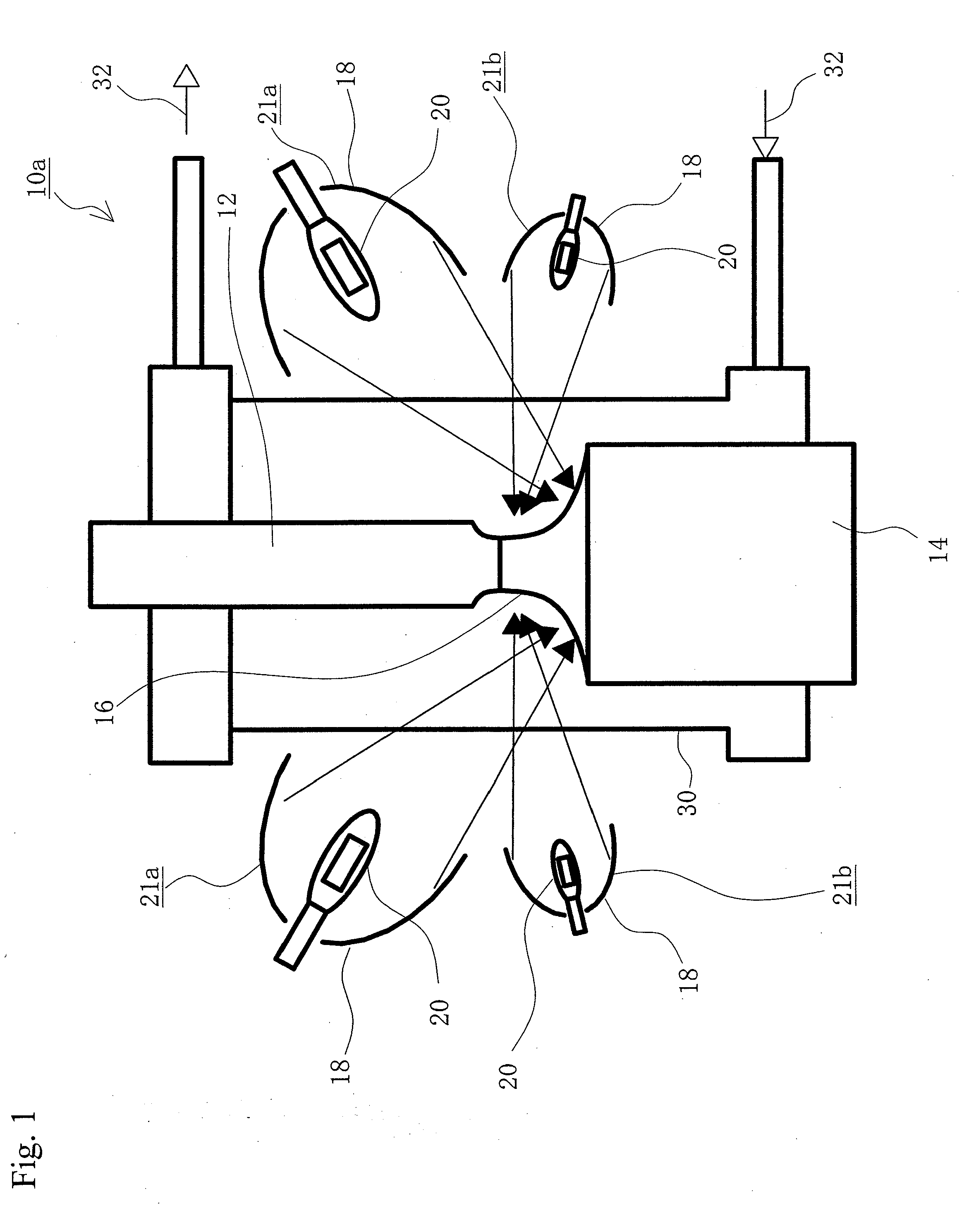
Method for producing silicon for use in solar cells
InactiveUS6090361AAvoid energy wasteAvoid material lossPolycrystalline material growthSiliconElectrical batteryZone melting
Method for producing highly purified silicon for use in solar cells by a single solidification purification, pouring silicon into a mold and gradually fractionally solidifying it while solidifying the liquid surface, followed by purifying the solidified silicon by zone melting or continuous casting using an electromagnetic mold, or by zone melting in combination with continuous casting, and optionally causing directional solidification to concentrate impurities, leaching and recycling.
Owner:KAWASAKI STEEL CORP
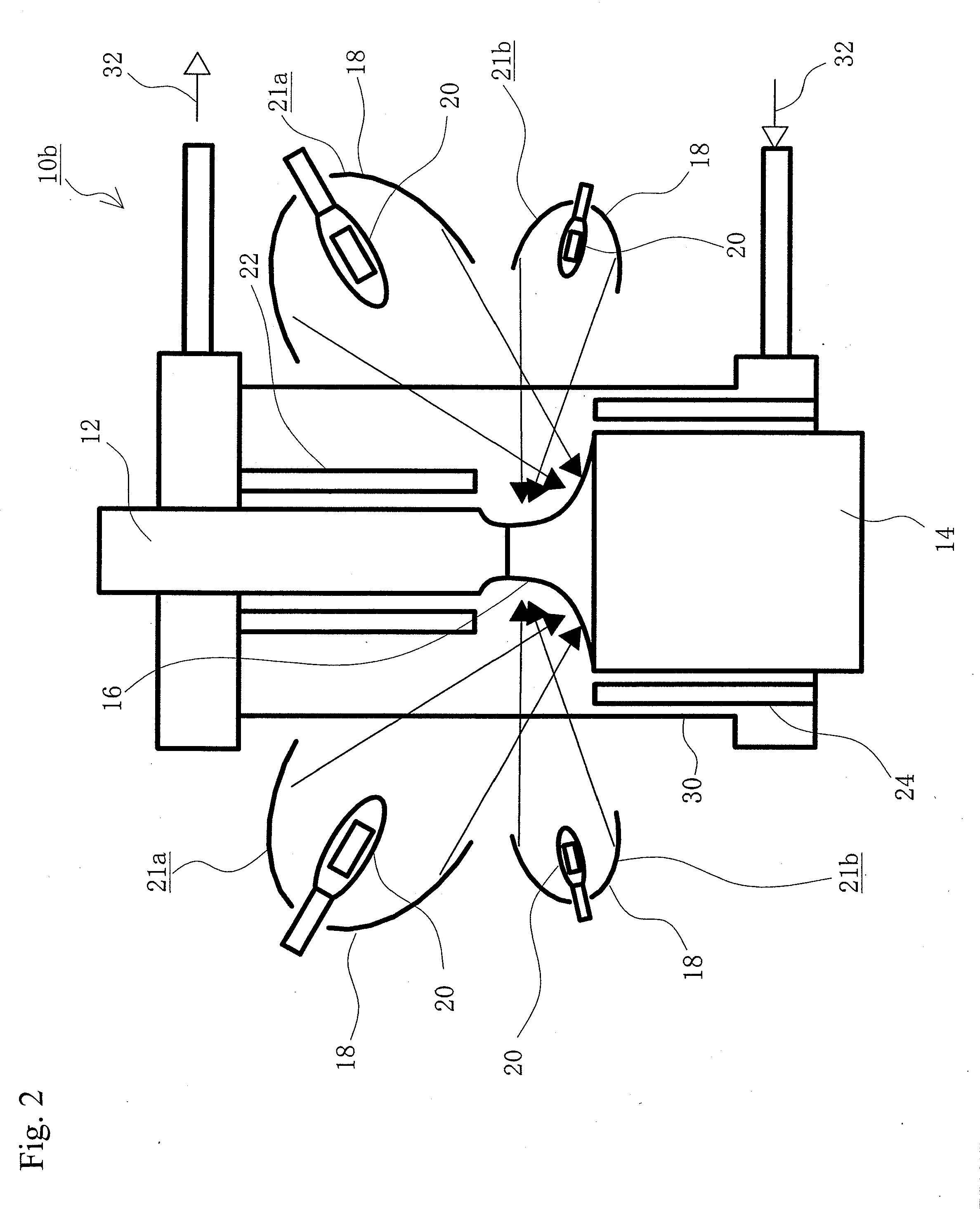
Film forming apparatus and film forming method
To provide a film forming apparatus in which an impurity contained in an organic compound is separated to be removed and a film is formed without decreasing the purity of the purified organic compound, whereby a high-purity organic compound is formed. A film forming apparatus of the present invention includes a purifying chamber for purifying an organic compound and a film forming chamber for vapor-depositing the purified organic compound onto a substrate. The organic compound purified by a zone melting method in the purifying chamber can be vapor-deposited onto the substrate provided in the film forming chamber without decreasing the purity thereof, so that a high-purity organic compound layer can be formed.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
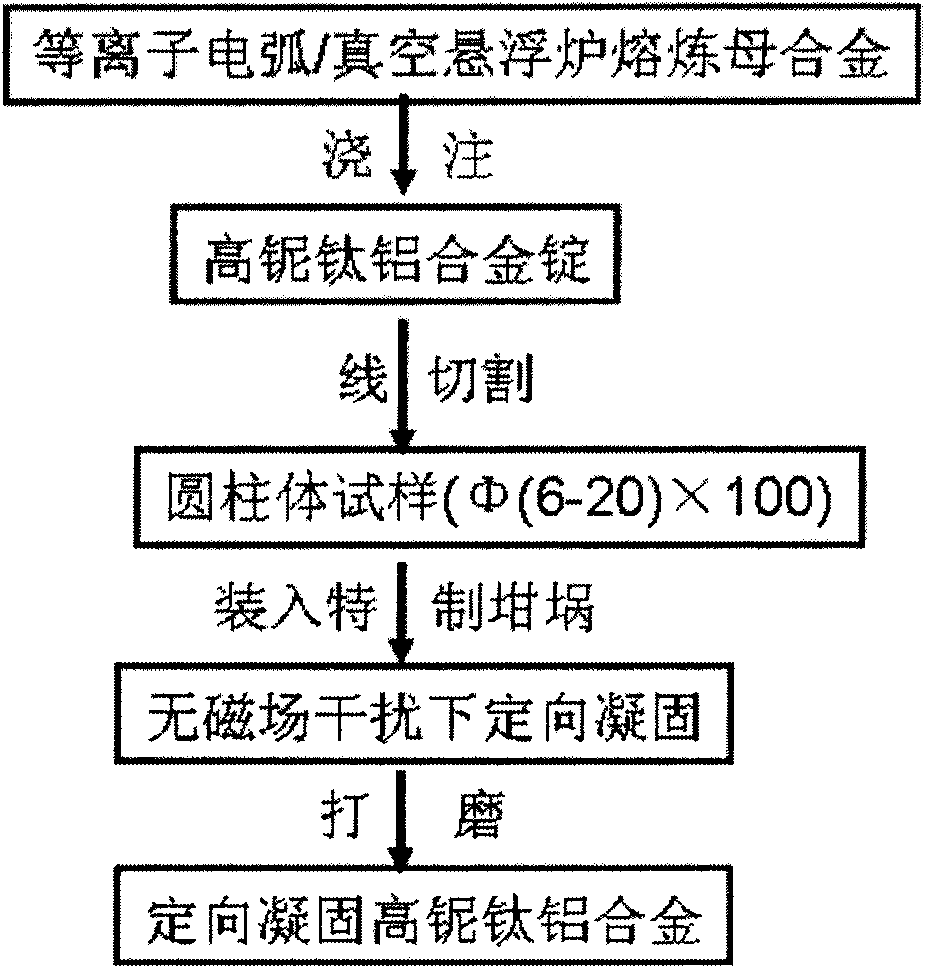
Preparation method of directional solidification high-niobium TiAl-base alloy
ActiveCN101875106AHigh melting pointImprove room temperature performanceMetallic materialsZone melting
The invention discloses a preparation method of a directional solidification high-niobium TiAl-base alloy, which belongs to the field of metal material preparation. The high-niobium TiAl-base alloy contains Ti, Al, Nb, W, Mn, C, B and Y, and the atomic percentage is: (43-49) Ti-(45-46) Al-(6-9) Nb-(0-0.5) (W and Mn)-(0-0.5) (C and B)-(0-0.5) Y, an as-cast master alloy rod which is smelted by plasma arc or vacuum suspension is taken as a raw material, a high-purity alumina ceramic tube with a coating layer of which the main component is yttrium oxide is used as a crucible, Ga-In-Sn alloy liquid is cooling liquid, and the directional solidification high-niobium TiAl-base alloy is successfully prepared by using an improved zone-melting and directional solidification system. The processing technology is simple and reliable, the directional solidification effect is obvious, and the method has universal applicability. The directional solidification high-niobium TiAl-base alloy which is prepared by the directional solidification method has comprehensive and good high temperature performance and room temperature ductility and has wide application prospect in terms of high temperature structural materials.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
High pressure liquid-liquid extraction method
InactiveCN102179063AReduce labor intensitySimple and fast operationLiquid solutions solvent extractionOrganic solventZone melting
The invention discloses a high pressure liquid-liquid extraction method, which comprises the step of sealing and refrigerating solution requiring extraction and organic extraction solvent in a pressure resistant container, the volume of water increases below 4 DEG C and in the solidification process of water to ice, so the pressure in the pressure resistant container increases to improve the dissolubility of organic impurities in organic solvent during extraction, and simultaneously, based on the principal of zone melting, the organic impurities are squeezed out of ice in the solidification process of water to ice, thereby further enhancing the extraction efficiency. The liquid-liquid extraction method has the advantages of being low in labor intensity, simple and convenient in operation and short in extraction time, and can improve the extraction effect remarkably.
Owner:SOOCHOW HIGH TECH CHROMATOGRAPHY
In-situ heat treatment method for realizing electron beam selective melting material increase manufacturing of metal parts
ActiveCN105499566AEliminate microscopic voidsHigh surface finishAdditive manufacturingIncreasing energy efficiencyMicro structureZone melting
The invention discloses an in-situ heat treatment method for realizing electron beam selective melting material increase manufacturing of metal parts, relating to the technical field of material increase manufacturing and heat treatment. The method adds a step of secondary heating remelting to melt a forming zone after a step of forming zone melting. The secondary heating remelting parameters comprise the electron beam current scanning speed, the electron beam current, the scanning deflection amount and the focal spot size. The method carries out in-situ heat treatment in the process of part processing forming process, therefore eliminates part of micro holes in the parts, and meanwhile can improve the surface smoothness of the parts, realize micro-structure controlling and realize regulation and control for the mechanical property of forming parts in a certain range.
Owner:成都航大新材料有限公司
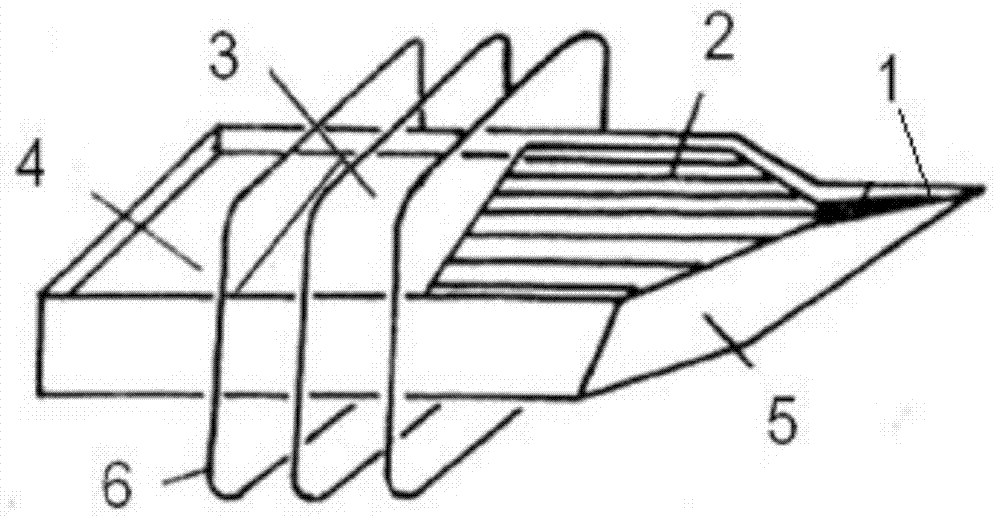
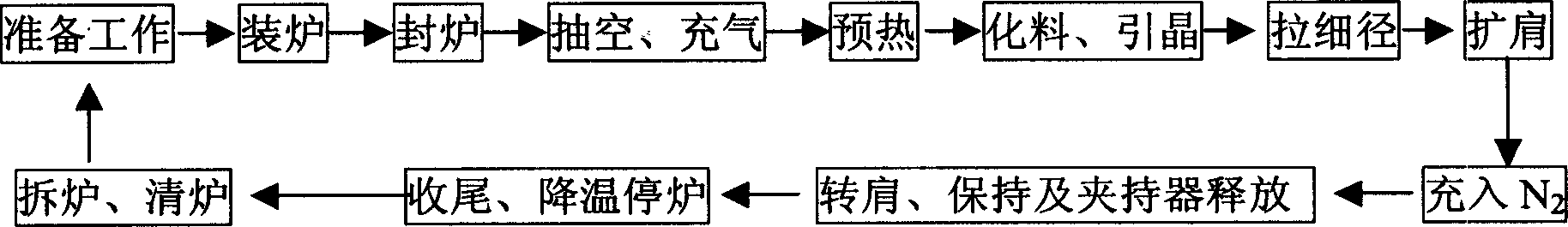
Large-diameter zone-melting silicon single crystal growth method
ActiveCN1865528AMeet the needs of large diameter zone molten silicon single crystalPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsNitrogenZone melting
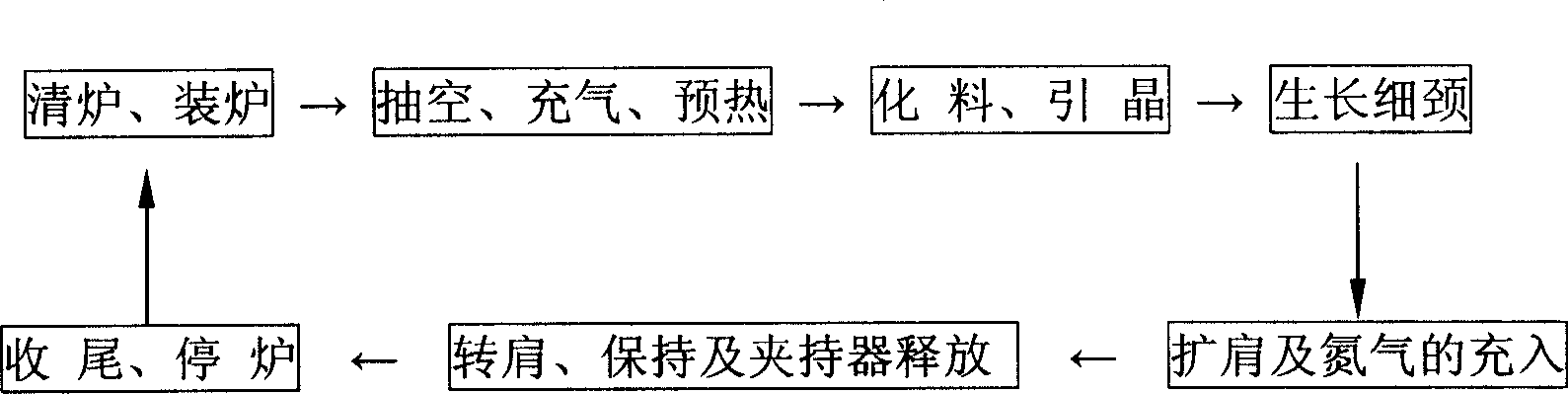
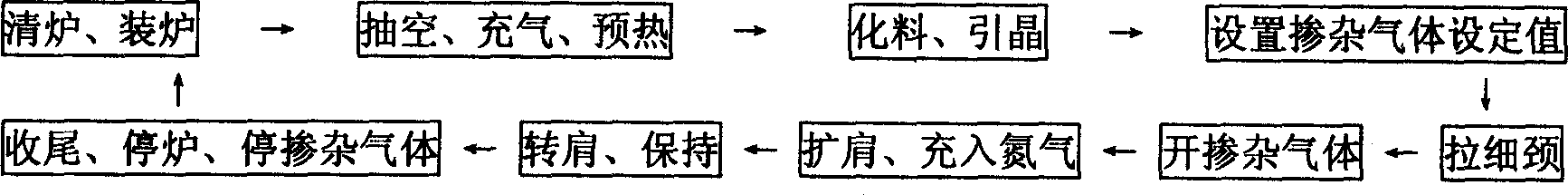
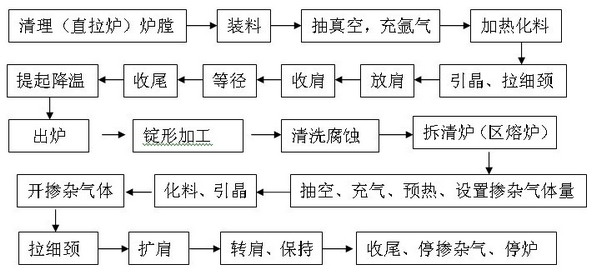
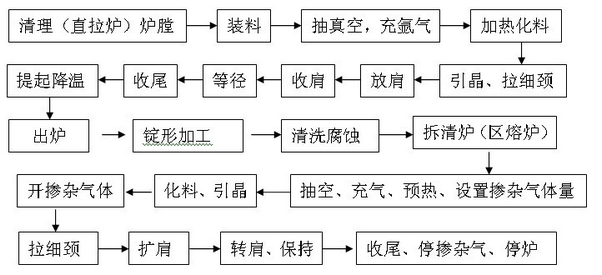
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of silicon monocrystal, which comprises the following steps: 1. clearing furnace; loading furnace; 2. extracting; aerating; preheating; 3. digesting material; introducing seed; 4. growing thin neck; 5. expanding shoulder; aerating nitrogen; 6. transmitting; keeping; releasing clamper; 7. ending; stopping furnace. The invention realizes the large diameter zone melting silicon monocrystal, which reaches SEMI standard.
Owner:ZHONGHUAN ADVANCED SEMICON MATERIALS CO LTD +1
Method for preparing vacuum zone melting high resistant silicon single crystal
ActiveCN101525764AHigh resistivityEnhanced ultra-high purityPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsZone meltingSingle crystal
The invention discloses a method for preparing vacuum zone melting high resistant silicon single crystal, comprising the two sequential major processes: polysilicon purification and crystal forming of silicon single crystal, wherein, the process of polysilicon purification comprises the steps of cleaning fire, charging, evacuating, preheating, melting materials heat sealing, growing narrow necks, shouldering, shoulder circuiting, equating diameter, ending and repeating; the process of crystal forming of silicon single crystal comprises the steps of cleaning fire, charging, evacuating, preheating, processing of chemicals, crystal seeding, shouldering, shoulder circuiting, equating diameter, ending and blowing out. With the method of the invention adopted to prepare silicon single crystal, electric resistivity, ultra-high purity, resistivity profile, uniformity of cross-section electric resistivity and minority carrier lifetime are greatly improved; purity of the silicon single crystal is above 11N, electric resistivity reaches 8000 omega / cm-30000omega / cm, uniformity of cross-section electric resistivity is less than 15%, and minority carrier lifetime is more than 600-1000Mus, thus greatly improving performance, stability and safety of the devices while realizing mass production of vacuum zone melting high resistant silicon single crystal.
Owner:峨嵋半导体材料研究所
Method for recovering solar-grade polysilicon from single crystal silicon/polysilicon cutting slurry
The invention relates to a method for recovering solar-grade polysilicon from single crystal silicon / polysilicon cutting slurry, belonging to the technical field of silicon material. The method comprises: first, drying the slurry and preparing polyethylene glycol water solution; then, carrying out physical settlement to obtain crude powder material; pickling, filtering and drying the obtained crude powder material, and obtaining refined powder material; carrying out fusion casting on the obtained refined powder material at 1500-1600 DEG C, and obtaining metallic silicon ingots and silicon carbide powder; and finally, purifying the metallic silicon ingots by directional solidification and zone fusion casting technology, and obtaining the solar-grade polysilicon. The method does not introduce impurity elements which are harmful to the performance of high-purity silicon when the high-purity silicon is purified, has simple and easy technique and experienced equipment, is easy for realizingindustrialization, and becomes one of the effectively way for solving the shortage of the silicon material.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
SnSe-based thermoelectric material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105047809AEasy to prepareShorten the growth cyclePolycrystalline material growthThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentZone meltingIngot
The invention discloses an SnSe-based thermoelectric material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method includes steps: S100 weighing reaction raw material according to the stoichiometric ratio of the SnSe-based thermoelectric material; S200 refining the reaction raw material through a melt-refining process to obtain SnSe-based thermoelectric material ingots; and S300 placing SnSe-based thermoelectric material ingots obtained from the S200 in a zone smelting furnace and growing polycrystalline SnSe-based thermoelectric material through a zone melting method. The SnSe-based thermoelectric material obtained through the method is preferential and has better thermoelectric performance. Compared with a method for preparing monocrystalline SnSe-based thermoelectric material, the method is simple and is short in growth period, low in cost, and suitable for mass industrial production.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method and system for controlling automatic growth of zone-melt crystal by adopting diameter process
ActiveCN102220629AImprove consistent qualityIncrease production capacityBy zone-melting liquidsZone meltingSingle crystal
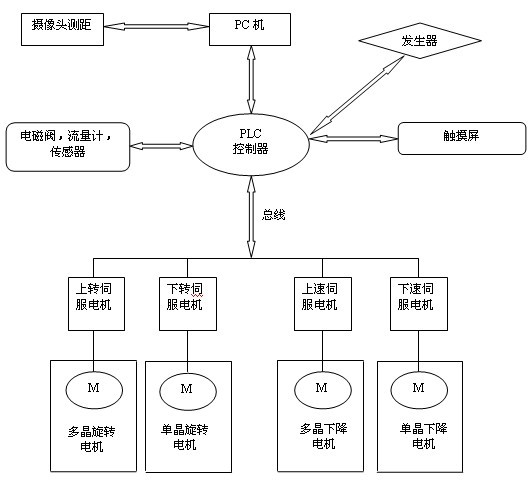
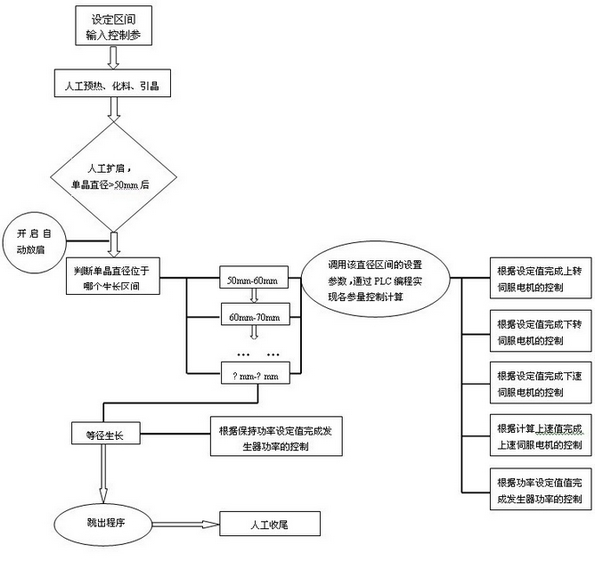
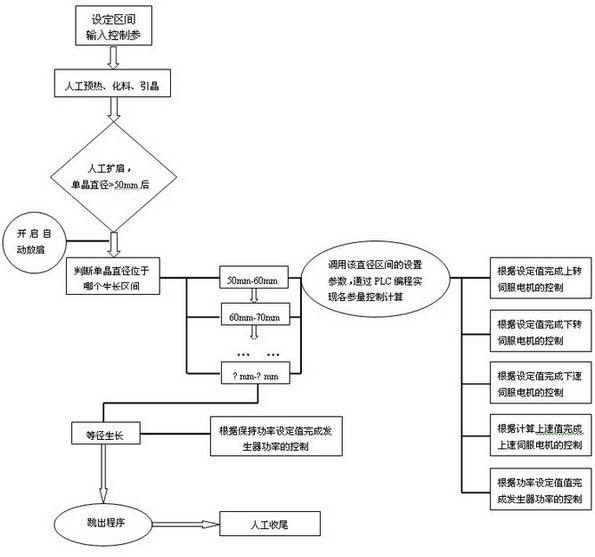
The invention relates to a method and system for controlling automatic growth of zone-melt crystal by adopting a diameter process. The method comprises the steps of: setting a growing interval and inputting control parameters; opening a control program when the diameter is more than 50 mm; judging the growing interval by the program according to the detected single crystal diameter and dispatching and calculating the interval parameters; controlling according to the parameters and the calculated value; running the program in the next interval after finishing growing until entering the isometrical growing step; and controlling according to a preset value of a keeping power. The system for controlling automatic growth of zone-melt crystal by adopting the diameter process comprises a PLC controller, a PC, a camera, a generator, a touch screen, an upper-rotating servo motor, a lower-rotating servo motor, a speed-increasing servo motor and a speed-reducing servo motor, a polycrystal rotating motor and a monocrystal rotating motor, a polycrystal descending motor and a monocrystal descending motor, an electromagnetic valve, a flowmeter and a sensor. According to the method and the systemin the invention, the capacity of a zone-melting process for producing large-diameter monocrystals is improved greatly; the artificial error and loss in the zone-melting process are reduced; the working intensity of growing the monocrystals in the zone-melting process is reduced; and the consistency of the monocrystals can be improved effectively.
Owner:ZHONGHUAN ADVANCED SEMICON MATERIALS CO LTD +1
10<5> K/cm temperature gradient directional solidification device and directional solidification method
ActiveCN102051668AUniform tissueGood orientationPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsIndiumZone melting
The invention relates to a 10<5> K / cm temperature gradient directional solidification device and a directional solidification method. The 100000 K / cm temperature gradient directional solidification device is characterized in that laser light generated by a laser horizontally passes through a plate lens to enter a vacuum chamber, intersects vertically the axis of a drawing system, and is used for heating a preform; and liquid gallium-indium-tin alloy serves as cooling medium. The distance between the lower surface of a melting zone and the liquid level of the liquid gallium-indium-tin alloy is 1mm to 5 mm. When directional solidification is performed to the preform, the power of the laser is increased to 200 w to 1400 w. After the preform is zone-melted, a drawing mechanism is started to enable the preform to move at the speed of 1 to 300 microns per second and to be cooled, so that directional solidification of the preform is accomplished. In the invention, laser floating zone melting is combined with liquid metal cooling, so that the obtained oxide eutectic in-situ composite is uniform in structure, fine and compact, has good directing property, and is remarkably improved in mechanical property and other functions, the sizes and the shapes of produced function materials can satisfy the application of various photoelectric components.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Process of preparing bismuth telluride-base thermoelectric material
InactiveCN1974079AIncrease profitImprove machinabilityThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentIncreasing energy efficiencyBismuth tellurideZone melting
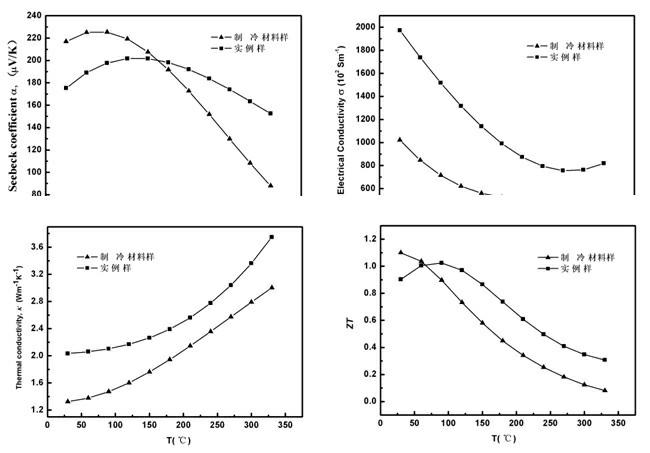
The present invention discloses process of preparing bismuth telluride-base thermoelectric material. By means of controlling the technological parameters in mechanical alloying and SPS process to maintain the powder material size within certain range, and the fast densification of SPS technology to avoid the growth of crystal grain in the sintered block material, the present invention lowers the heat conductivity of the material while maintaining the electric performance unchanged basically, so as to improve the thermoelectric performance and mechanical performance, raise the utilization rate of the prepared material and improve the stability and reliability of the corresponding thermoelectric device. The bismuth telluride-base thermoelectric material preparing process combining mechanical alloying and SPS technology of the present invention is superior to available zone melting growth process, which is slow and needs precise control.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Process for preparing vapor doping zone-melted silicon single crystal
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of gas-phase pre-blending zone melting process monocrystalline silicon, which comprises the following steps: shoving; exhausting; filling argon gas; doping; mitering; utilizing zone melting process monocrystalline silicon furnace electric control system to do the following operation in the metering growing procedure: setting positive, inversed movement for touching screen and coil heating moving order; moving positively for 1-90 s and moving inversely; repeating the movement to coincidence with the coil center and lower shaft or eccentric 1-50 mm. The invention reduces the radial and axial resistance heterogeneous problem of silicon single-crystal to improve the stability and reliability, which satisfies different needs of zone melting process monocrystalline silicon.
Owner:ZHONGHUAN ADVANCED SEMICON MATERIALS CO LTD +1
Process for preparing zone-melted vapor doping solar cell silicon single crystal
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of gas-phase pre-blending zone melting process monocrystalline silicon to produce solar battery, which comprises the following steps: shoving; exhausting; filling argon gas; doping; mitering; utilizing zone melting process monocrystalline silicon furnace electric control system to do the following operation in the metering growing procedure: setting positive, inversed movement for touching screen and coil heating moving order; moving positively for 1-90 s and moving inversely; repeating the movement to coincidence with the coil center and lower shaft or eccentric 1-50 mm; setting value for blending gas; dragging thin neck; opening to blend gas; expanding shoulder; charging nitrogen gas; transmitting shoulder; keeping; ending; stopping furnace; stopping blending gas. The invention solves high-pressure ionizing problem, which improves the stability and reliability for monocrystalline silicon to prepare high-effective solar battery.
Owner:ZHONGHUAN ADVANCED SEMICON MATERIALS CO LTD +1
Metal porous body manufacturing method
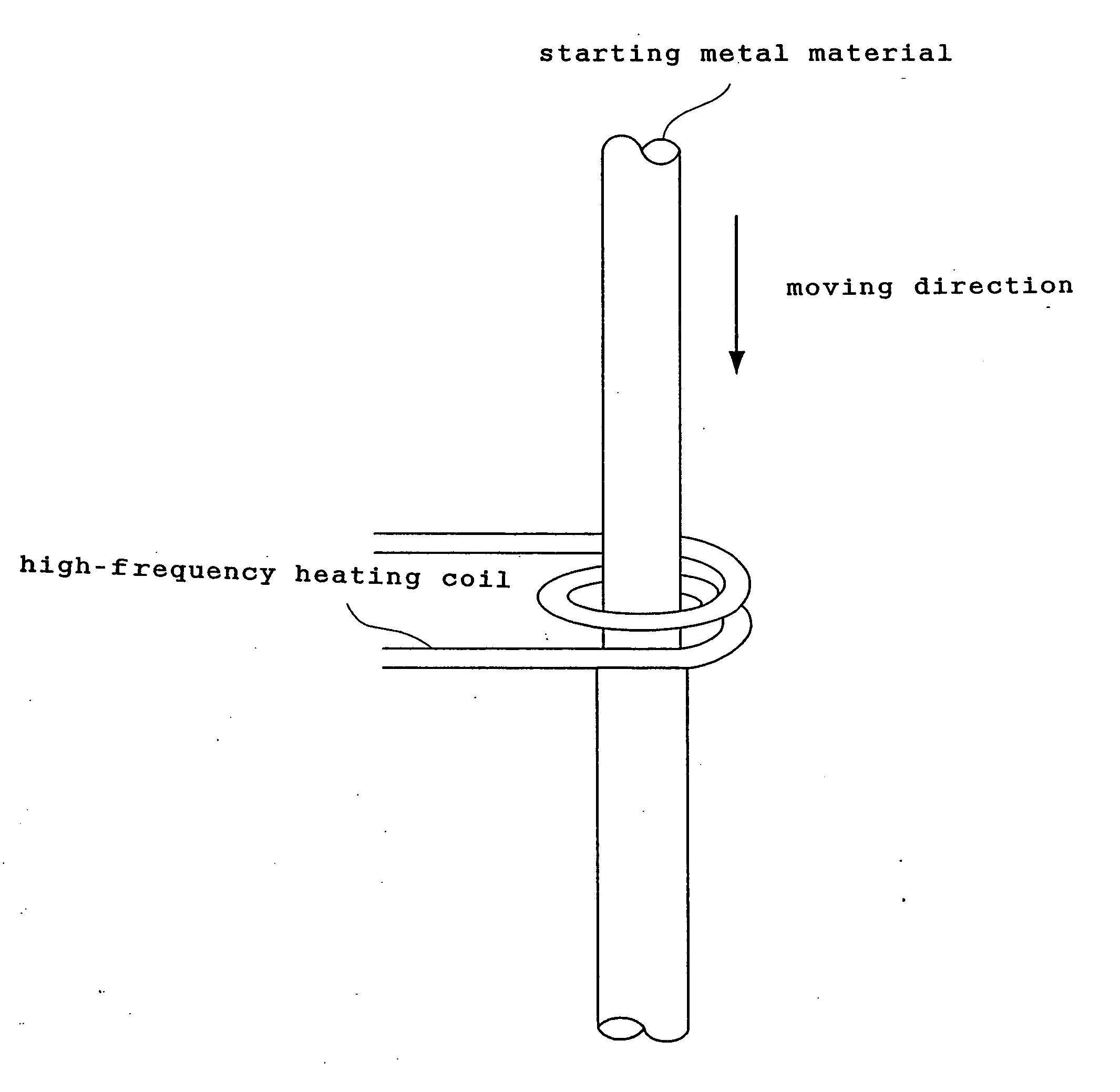
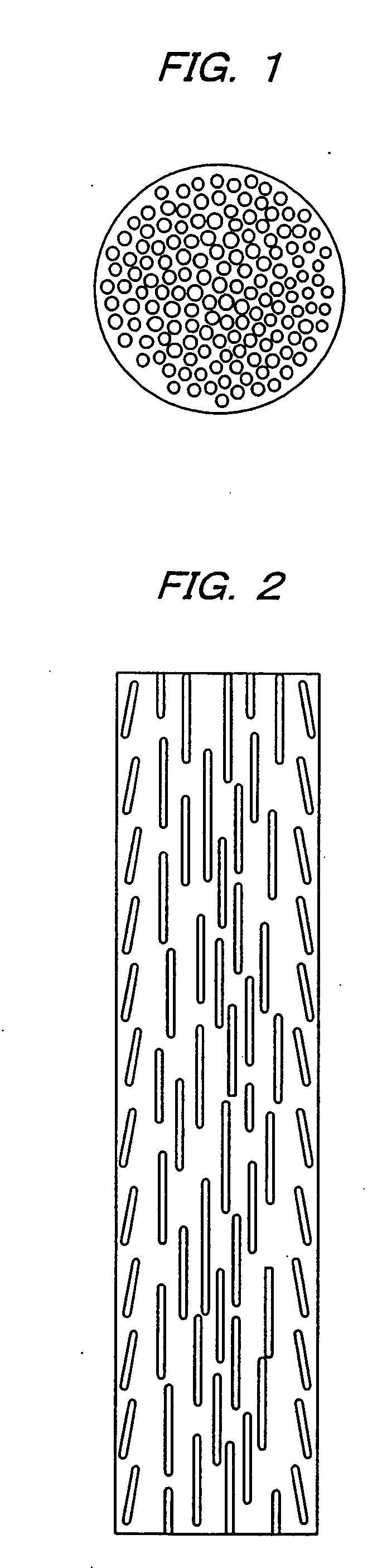
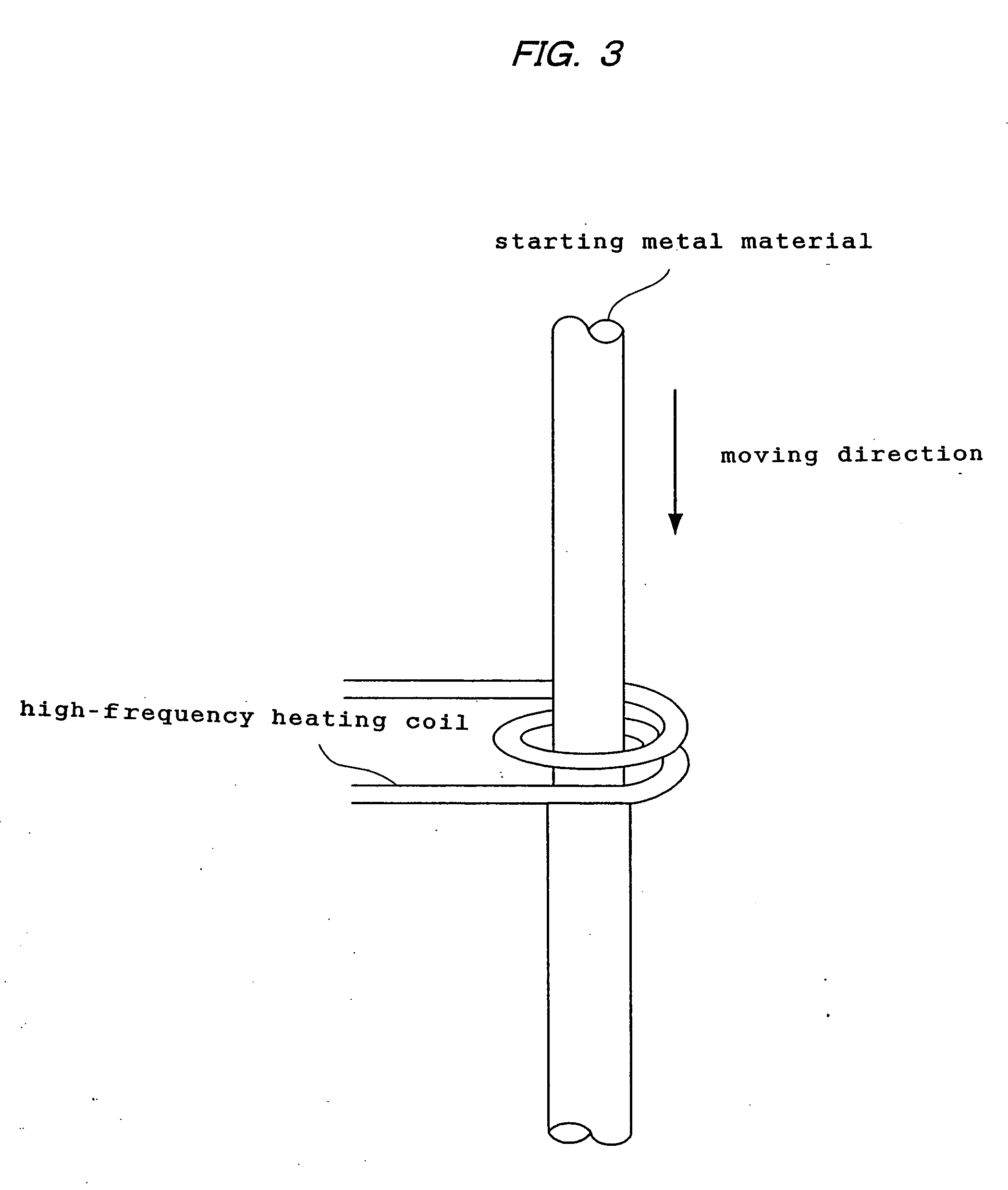
The present invention provides a process for producing a porous metal body, the process comprising: melting part of a starting metal material in succession while moving the material by a floating zone melting method under a gas atmosphere to dissolve a gas into a resultant molten metal; and solidifying the molten metal zone in succession by cooling. According to the process of the present invention, even when the starting metal material is of low thermal conductivity, a porous metal body with uniform and micro pores grown only in the longitudinal direction is produced.
Owner:NAKAJIMA HIDEO
Preparation method of tungsten carbide particle enhanced steel-base surface layer composite bar
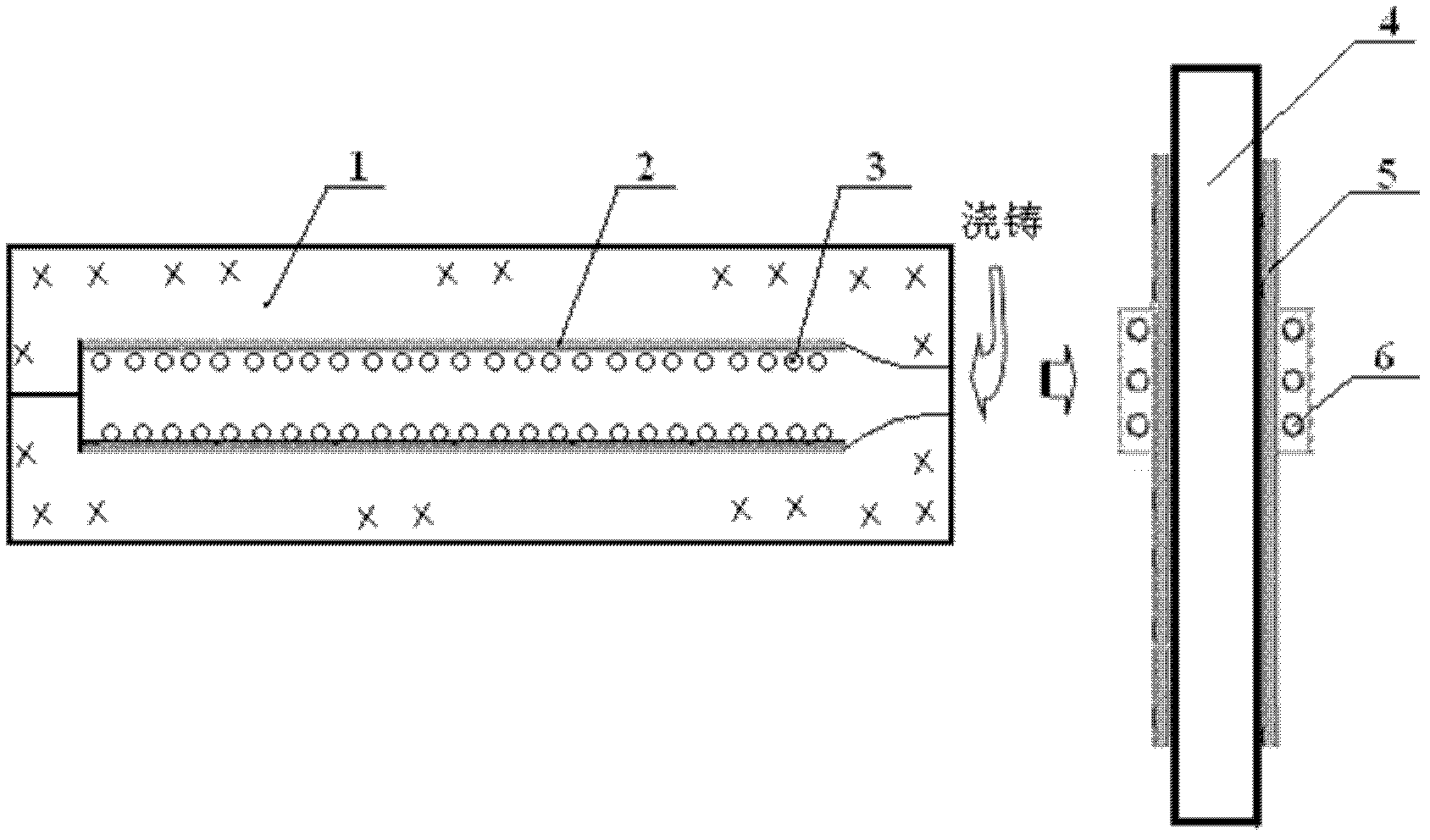
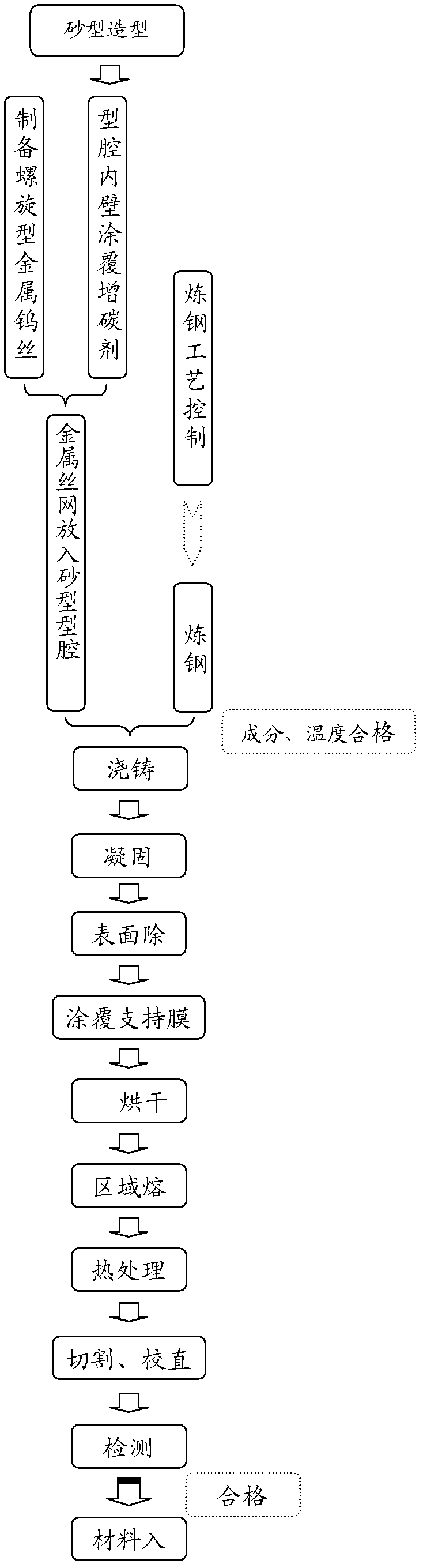
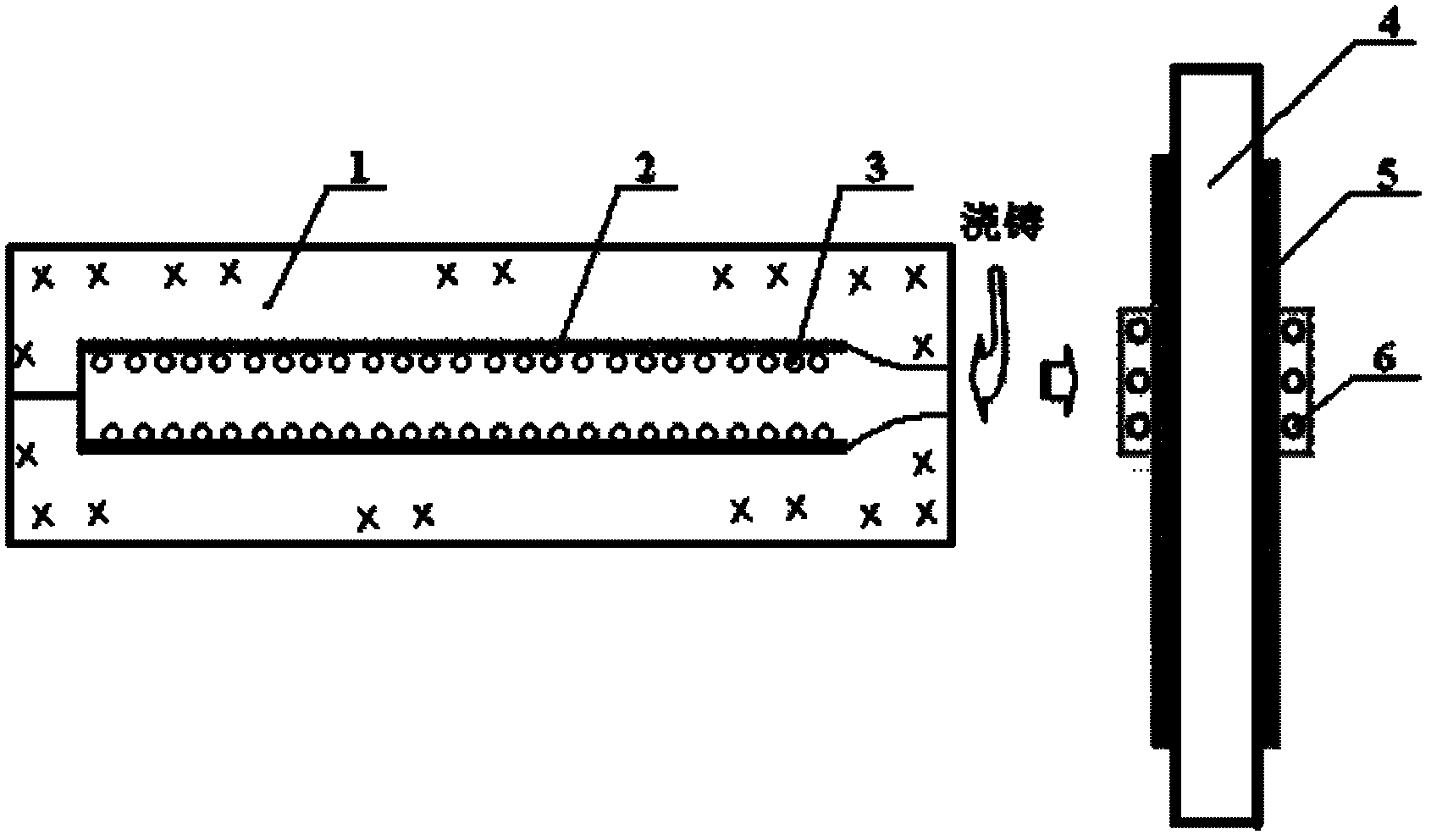
The invention discloses a preparation method of a tungsten carbide particle enhanced steel-base surface layer composite bar. The method comprises the following steps of: coating recarbonizer on the cavity surface of a sand mould; acid-washing the tungsten filament to be used as a strengthening phase and making into a spiral shape; placing the spiral-shaped tungsten filament in the cavity, and pouring, wherein after the metal liquid is solidified to room temperature, a metal steel bar is obtained; removing rust of the surface of the metal bar; then coating a support film on the outer surface of the metal bar; after the support film is dried, performing surface rapid zone melting through a zone melting sensor, and performing rapid solidification, wherein the heating temperature for the surface rapid zone melting is controlled to be 20-30 DEG C higher than the melting point of the base material; after the zone melting, performing thermal treatment on the metal bar; and then performing cutting, mechanical straightening and the like to achieve the required size to finally obtain the tungsten carbide particle enhanced steel-base surface layer composite bar. The tungsten carbide particleenhanced steel-base surface layer composite bar not only maintains the characteristics of good toughness and plasticity of metal materials, but also has strong wear resistance. The thickness of a WC composite layer can reach 10-15 mm, and the hardness HRC can reach 50-56. The invention is easy to realize large-scale industrial production.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
Film forming apparatus and film forming method
InactiveUS6946406B2Without decreasing purityHigh purityElectroluminescent light sourcesVacuum evaporation coatingGas phaseZone melting
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method for producing ultra-pure yellow phosphorus
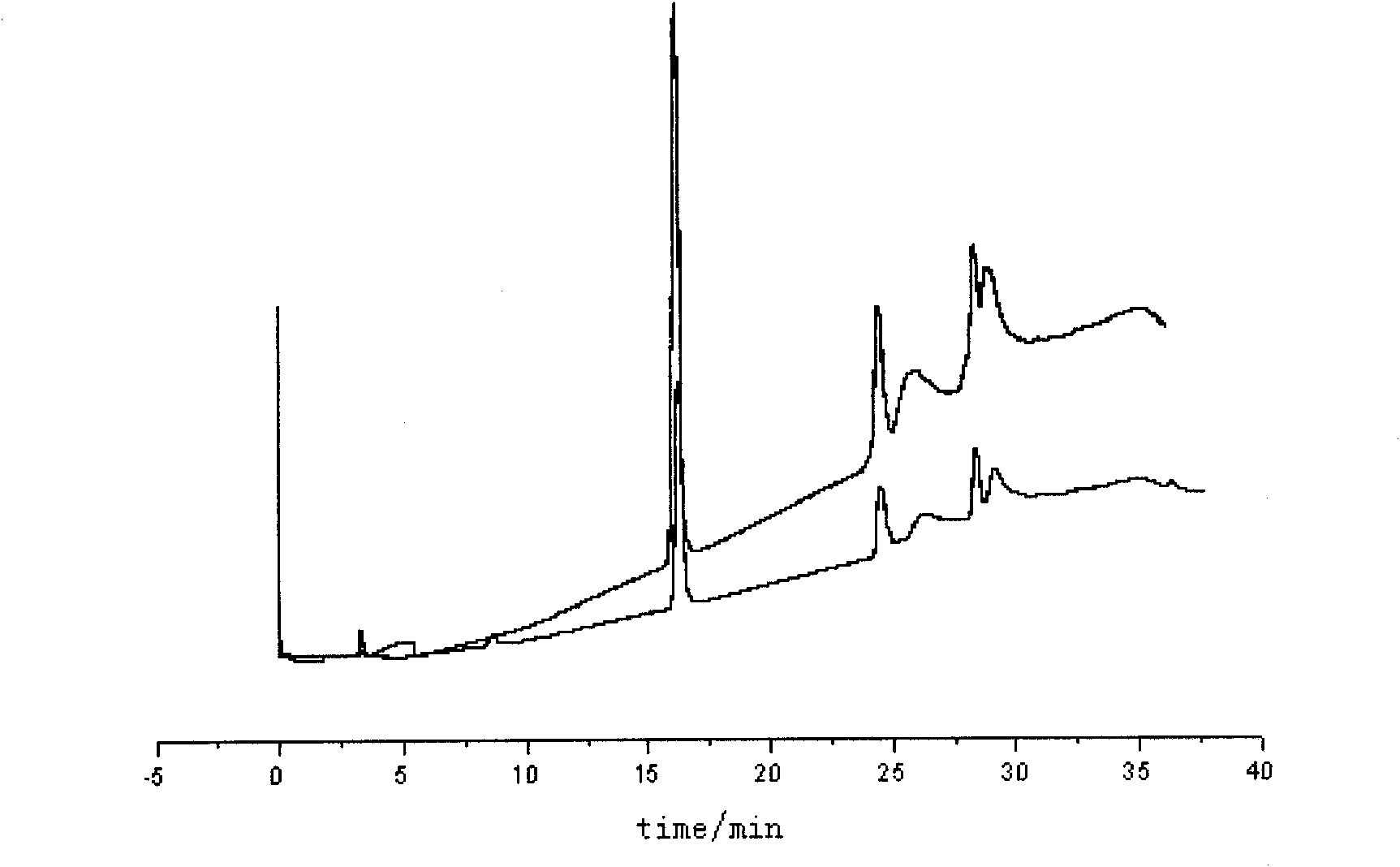
ActiveCN101214938AOperational securityNo pollution in the processPhosphorus compoundsFiltrationKerosene
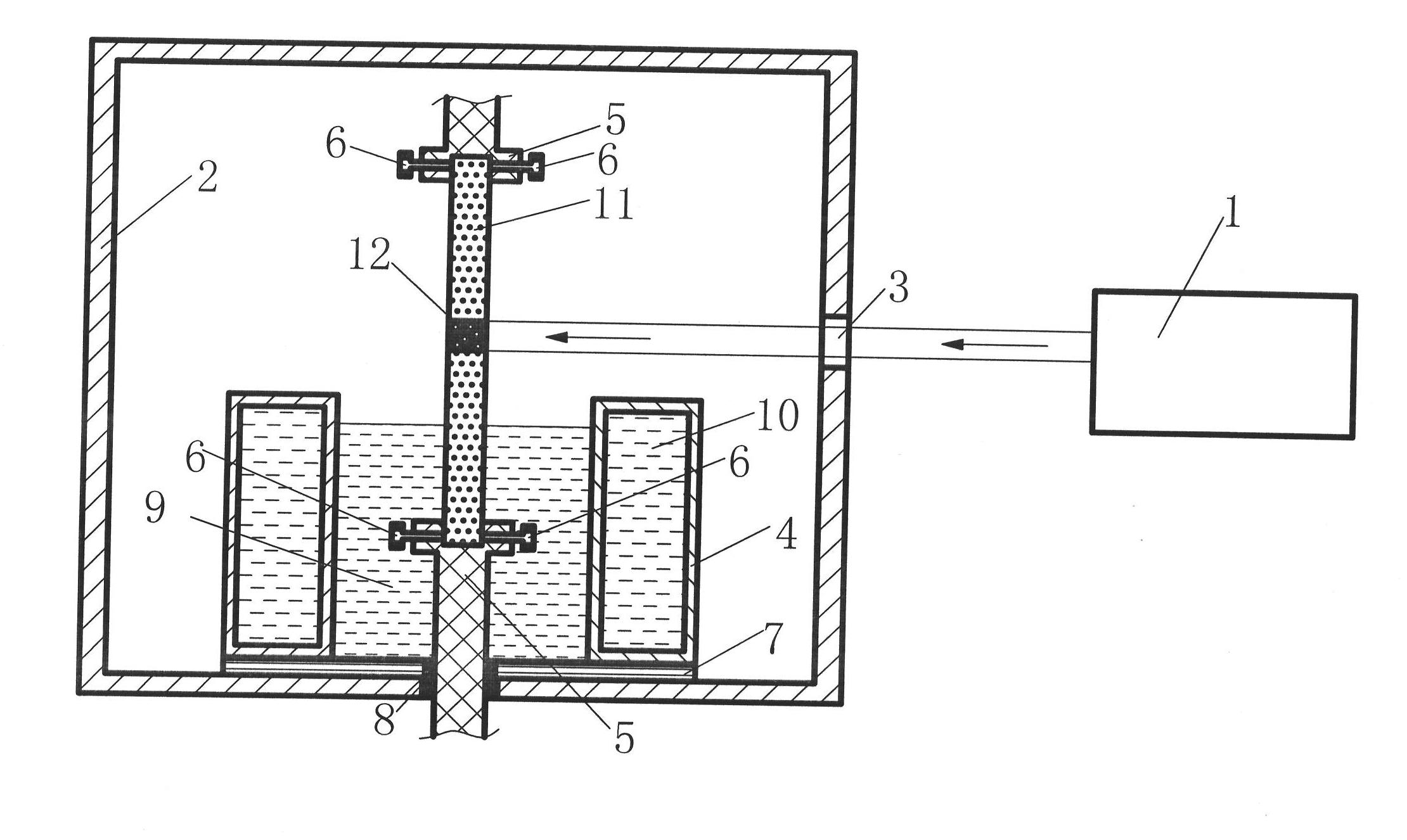
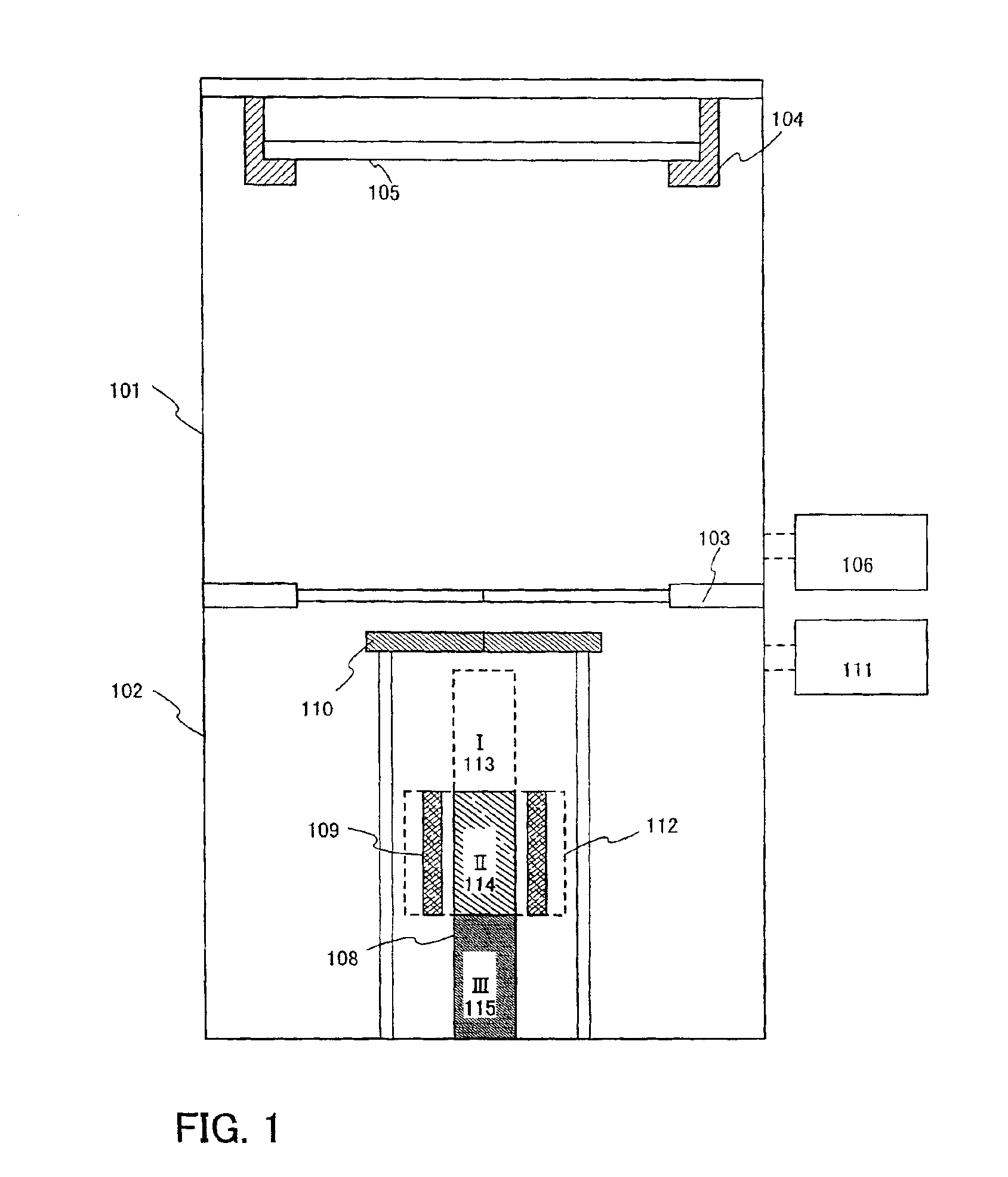
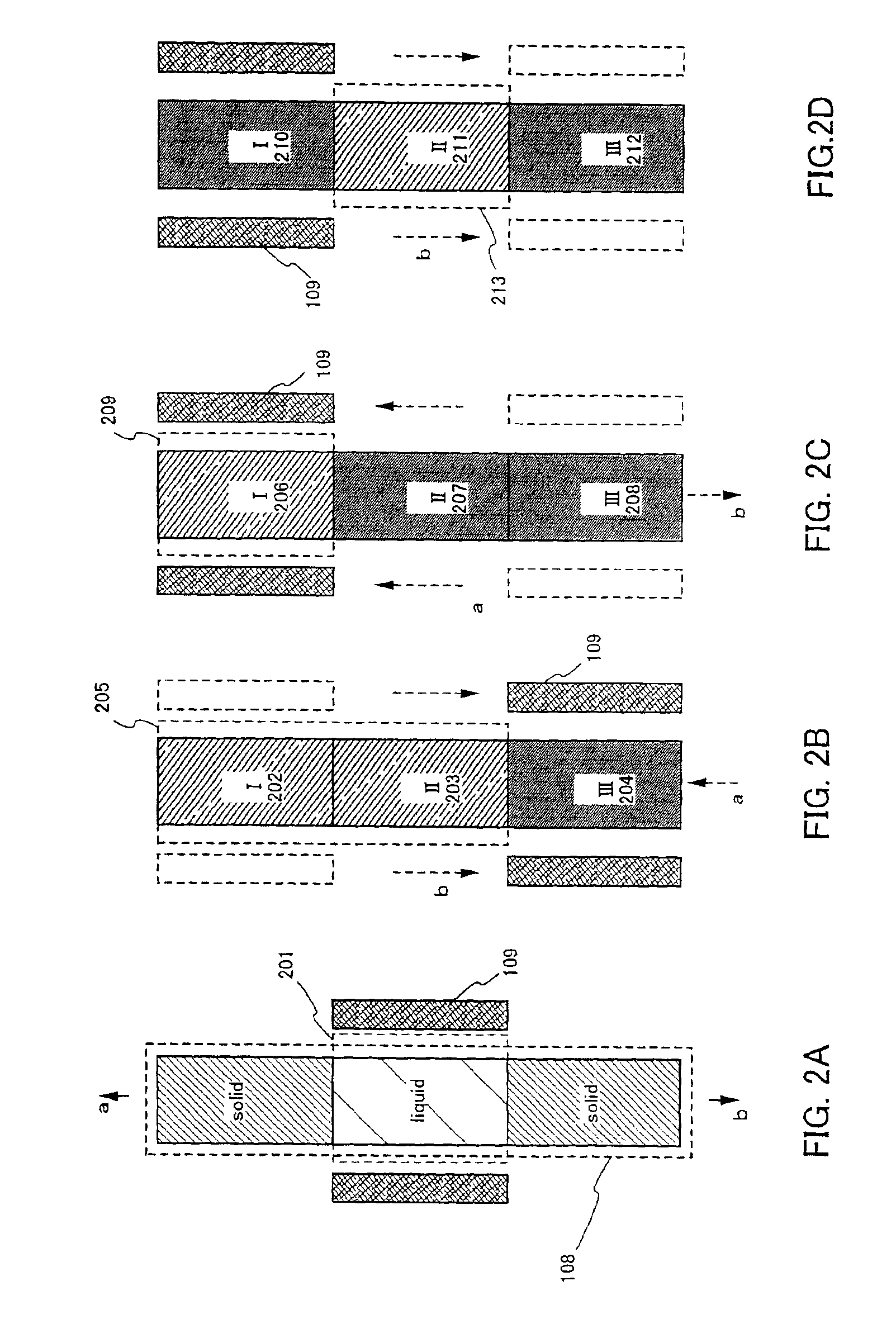
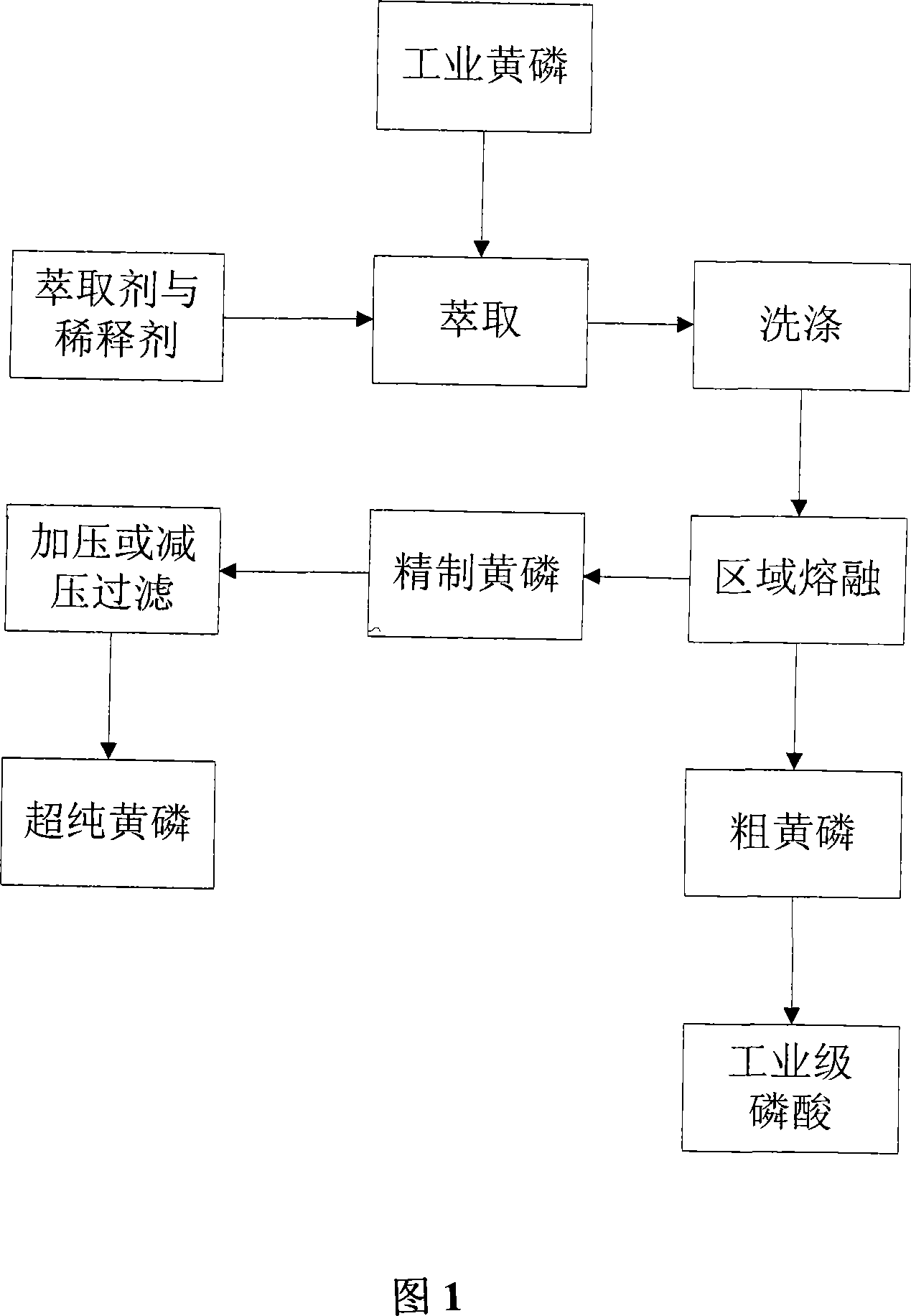
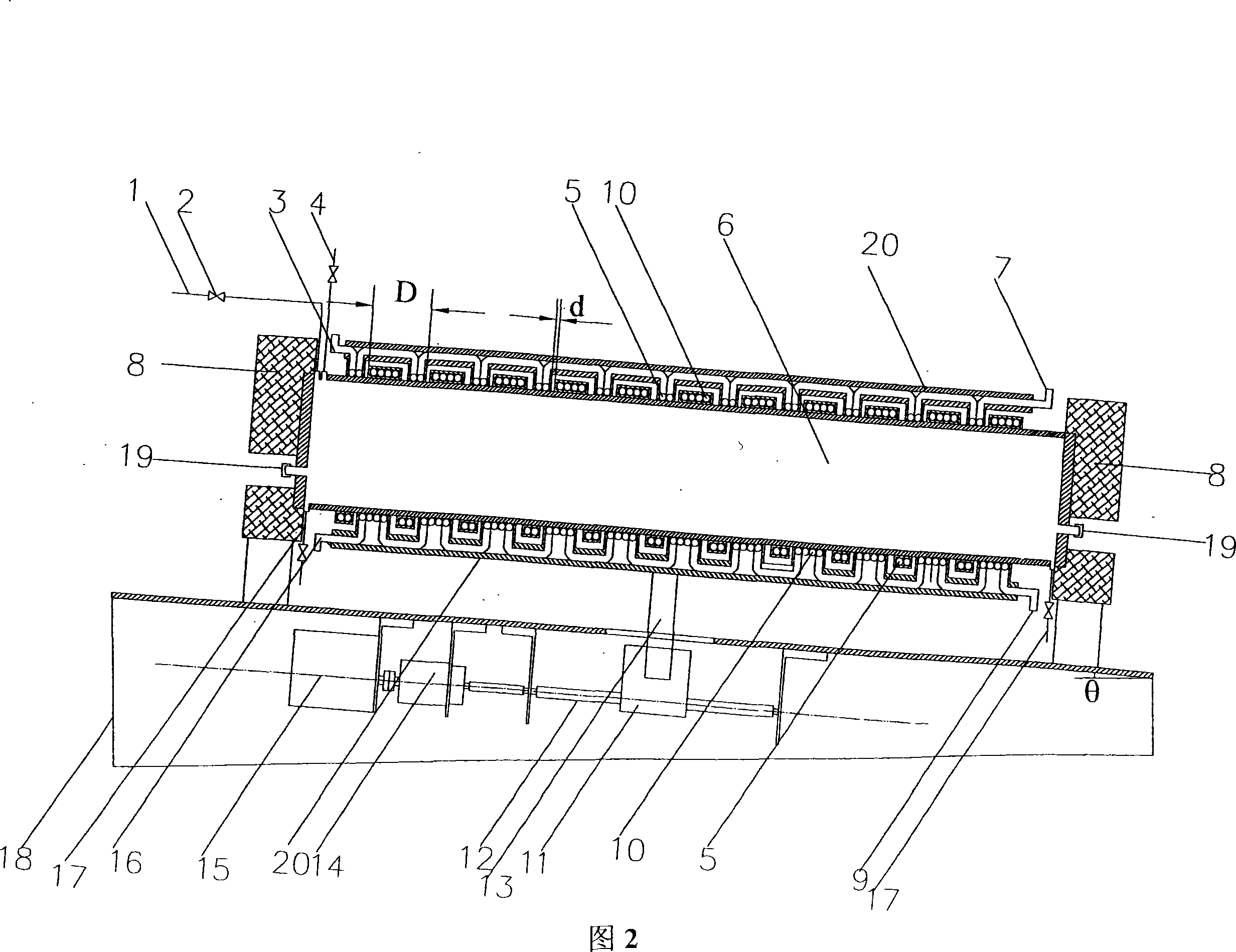
Disclosed is a production method of ultra-pure yellow phosphorus, which uses the material of industrial yellow phosphorus, and the industrial yellow phosphorus is prepared to be the ultra-pure yellow phosphorus via extracting, zone melting, pressurizing or depressurizing micro-filtration sequentially. Extracting agent is at least one of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phosphoric acid, tributyl phosphate or calixarene, diluting agent is kerosene or paraffin oil or chloroform or carbon tetrachloride, and extraction technological parameter is that the volume ratio of organic phase and the industrial yellow phosphorus is 1:2-1:3. Apparatus for zone melting comprises a zone molten pool, a ring heater, an annular chiller and a driving device, wherein the ring heater and the annular chiller are assembled around the zone molten pool, and are arranged at intervals along the axial direction of the zone molten pool, the pressurizing or depressurizing micro-filtration utilizes a pressurizing or depressurizing filter with grade of 0.1 um-0.5 um. Utilizing the invention of the method to purify the industrial yellow phosphorus, the purity of yellow phosphorus products can reach 99.99%-99.9999%, and the yield coefficient can reach 73.2%-88.4%.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
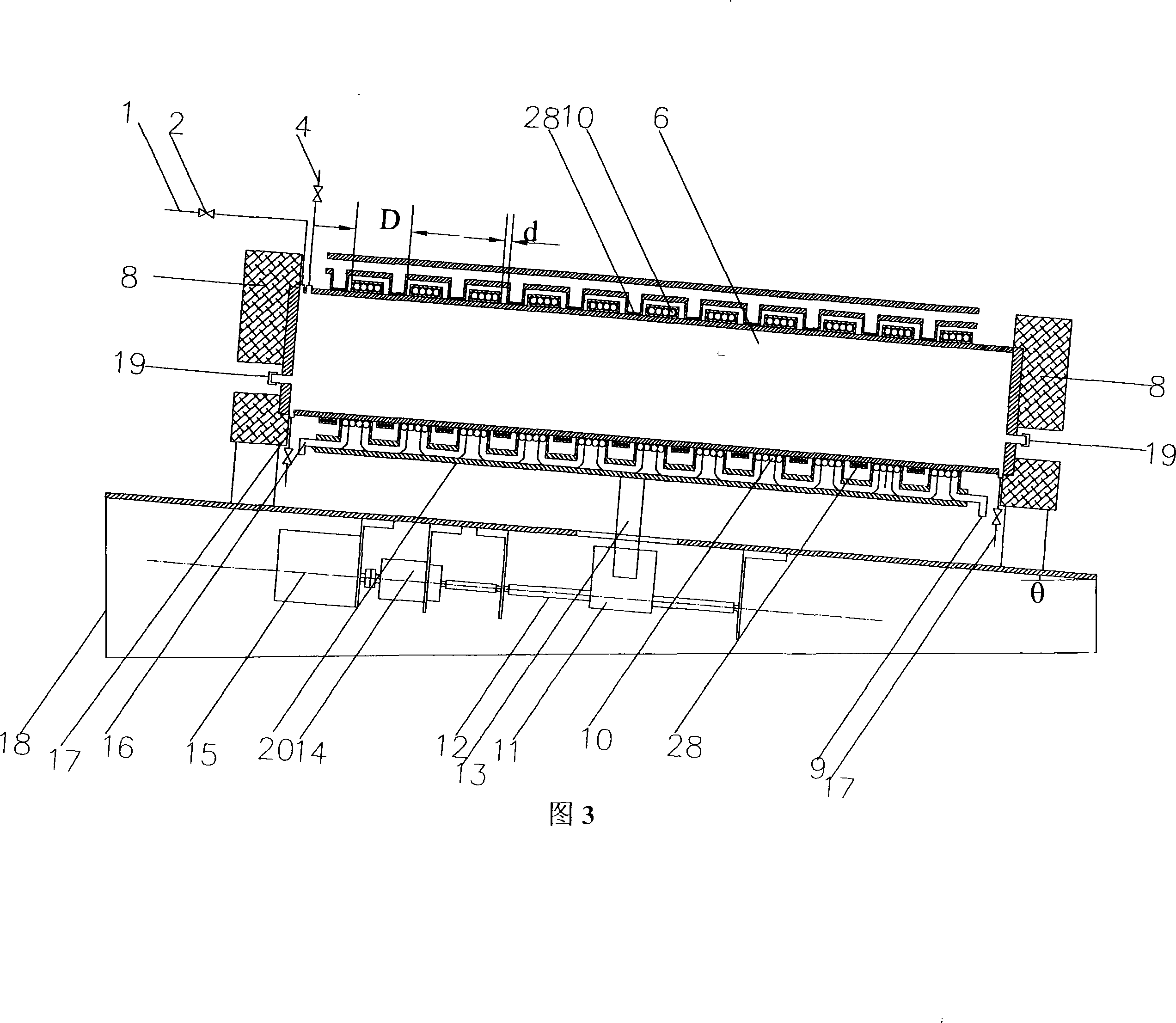
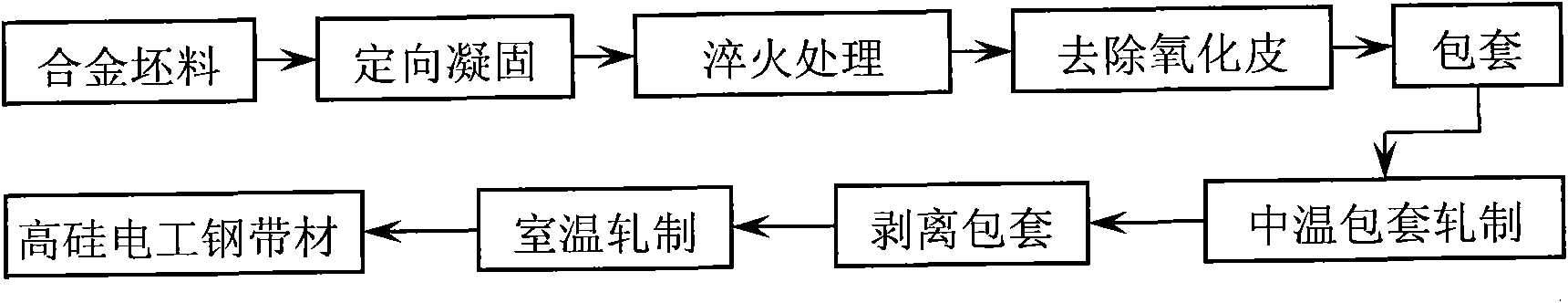
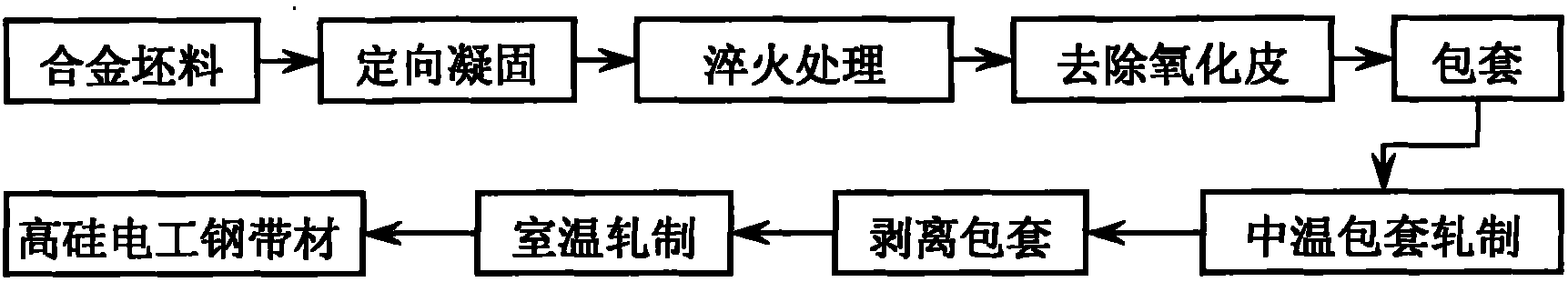
Short-flow high-efficiency preparation method of thin high-silicon electrical steel strip
ActiveCN101886215AImprove organizational structureImprove the shape of the precipitated phaseMetal rolling arrangementsSurface oxidationWhole body
The invention discloses a short-flow high-efficiency preparation method of a thin high-silicon electrical steel strip, which belongs to the field of metal material preparation and processing. The short-flow high-efficiency preparation method of the thin high-silicon electrical steel strip is characterized by comprising the following steps of: preparing a column-shaped crystal rod blank or plate blank, which contains more than 80 percent (100) of silk texture, from a Fe-(6.5 wt percent) Si alloy blank and by using zone melting directional solidification technology; keeping the rod blank or the plate blank at the temperature of between 700 and 1,000 DEG C in an argon protective atmosphere for 1 to 5 hours and then performing quenching treatment, and removing the oxide skin on the surface of the quenched rod blank or the quenched plate blank by a mechanical method or manual grinding; wrapping the rod blank or the plate blank by using stainless steel, common carbon steel or pure iron as a wrapping material, heating the whole body after the wrapping and performing middle-temperature rolling; and peeling the wrapped sheath, washing the high-silicon electrical steel with acid and then performing room-temperature rolling to obtain the thin high-silicon electrical strip with a splendid surface. The short-flow high-efficiency preparation method of the thin high-silicon electrical steel string has the advantages that: the yield of the thin strip prepared by the process approaches 100 percent; the prepared thin high-silicon electrical steel strip has a splendid surface and a uniform texture, the minimal bending radius is less than 2.5 millimeters, and the thin high-silicon electrical steel strip can be directly coiled to form an annular core of a transformer or an inductor and also can be prepared into high-silicon electrical steel through subsequent treatment.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Method for preparing 6-inch P-type solar silicon single crystals through Czochralski method and zone melting method
InactiveCN102304757AMeet the requirements for the production of 6-inch P-type solar silicon single crystalBy zone-melting liquidsBy pulling from meltCzochralski methodZone melting
The invention relates to a method for preparing 6-inch P-type solar silicon single crystals through a Czochralski method and a zone melting method. The method comprises the following steps: adopting the Czochralski method to clean a Czochralski hearth, charge, vacuumize, inject argon, heat and melt materials, perform seeding, pull narrow necks, grow shoulders, obtain the shoulders, obtain crystals with equal diameter, end, lift and cool and discharge; and then processing the ingot shape, cleaning and corroding to meet the standard of the zone melting material, and then adopting the zone melting method to continue to pull gas-doped single crystals. The gas-doped single crystal zone melting method is combined with the single crystal Czochralski production method; and by controlling vacuumizing and aerating, the concentration of the doping gas and the Czochralski method technological parameter range, the process method can meet the requirement for producing the 6-inch P-type solar silicon single crystals.
Owner:TIANJIN HUANOU SEMICON MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Method for preparing high-performance p-type bismuth telluride-based thermoelectric materials
ActiveCN102108554ACheap performanceRaw materials are cheap and easy to getPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsHigh volume manufacturingBismuth telluride
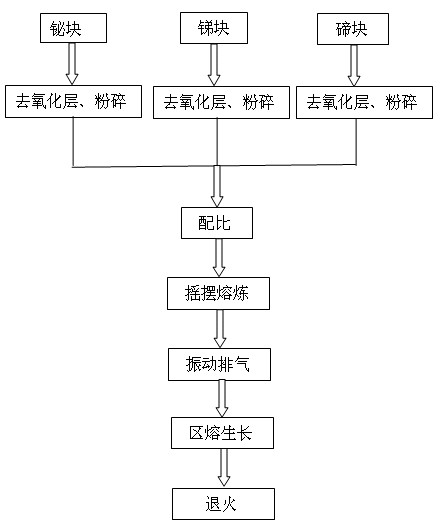
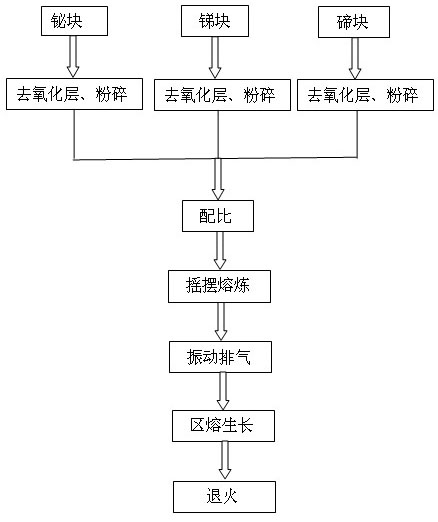
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-performance p-type bismuth telluride-based thermoelectric materials. High-purity tellurium blocks, bismuth blocks and stibium blocks which are industrially produced are used as raw materials, and the method comprises the following steps of: removing oxide layers, crushing, weighing in a certain ratio, and putting into a treated glass tube; and performing packaging, melting, zone-melting growth and annealing to obtain p-type bismuth telluride-based thermoelectric semiconductor crystal bars. At the temperature of between 30 and 300DEG C, the average ZT value is more than 0.75. The raw materials are cheap, readily available, nontoxic, and environment-friendly; and the equipment and process are simple, the energy consumption is low, the yield is high, and the method is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:江西纳米克热电电子股份有限公司
Thermal system and process for controlling 8-inch zone melting silicon monocrystals
ActiveCN102321913AMeet needsSolve temperature problemsBy zone-melting liquidsBy pulling from meltZone meltingTransverse magnetic field
The invention relates to a thermal system and a process for controlling 8-inch zone melting silicon monocrystals. The thermal system comprises a coil and a heat insulating bucket; two sides outside a furnace with the same height of the coil 1 are provided with magnetic field generators for generating transverse magnetic fields; and a reflector for reflecting heat of a melting zone is arranged between the coil and the heat insulating bucket. The process comprises the following steps of: when the shoulder expanding diameter reaches 100mm, extending the reflector to form a heat insulating circle at the peripheries of the silicon monocrystals, opening the magnetic field generators, ensuring that the height of the melting area above the silicon monocrystals is 3-5mm in the shoulder expanding process; and when the diameter of the silicon monocrystals reaches 205mm, rotating an arm, wherein the furnace pressure is 4-8bar in the equal diameter keeping process. Because the newly designed zone melting silicon monocrystal thermal system is adopted and process parameters are adjusted, 8-inch zone melting silicon monocrystals are drawn successfully, the problems of temperature fluctuation and fusion flow fluctuation in large-diameter silicon monocrystal forming difficulties are solved, dislocation is avoided and reduced, and the requirement of the market on the 8-inch zone melting silicon monocrystals is met.
Owner:ZHONGHUAN ADVANCED SEMICON MATERIALS CO LTD +1
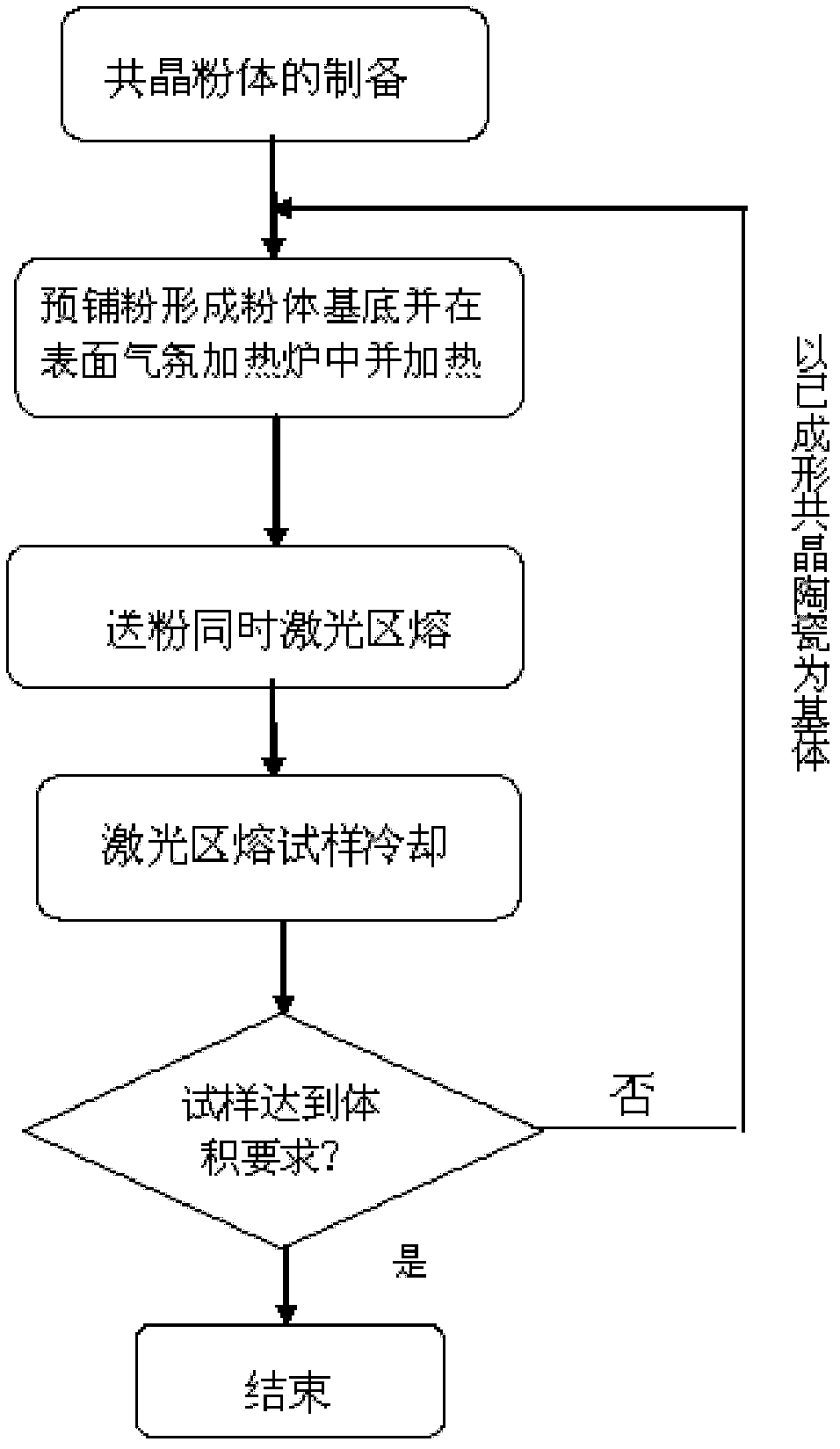
Method for preparing aluminum oxide-based eutectic ceramic through laser powder feeding method
ActiveCN102557596ASolve the bottleneck problem of engineering applicationReduce thermal stressZone meltingCrystal growth
The invention relates to a method for preparing aluminum oxide-based eutectic ceramic through a laser powder feeding method. By the method, the thermal stress in the zone-melting process is reduced by heating the eutectic ceramic, so that crack generated in the powder melting process is reduced. The powder is conveyed to be in front of a layer molten pool, laser zone-melting orienting solidification is finished when the powder falls off a substrate, power is conveyed continuously by using a powder feeding device on the eutectic ceramic surface, the powder on a second layer is molten through laser zone-melting, and the power and the laser zone-melting eutectic ceramic are molten and combined into a whole. Repeatedly, the large-volume eutectic ceramic material is prepared by a laser quick forming method. In the heating and forming process, the powder feeding quantity laser power, the scanning speed and the facula are controlled and high-purity inert gas is introduced, so that air in thefurnace body can be escaped completely, air holes in the forming material are eliminated and stable growth of the crystal is realized. Powder is repeatedly molten into a matrix the method of repeatedaccumulation and multi-time cladding, so that the large-volume eutectic ceramic can be prepared.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Bismuth telluride based N type thermoelectric material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106571422ALow purity requirementHigh densityThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric device junction materialsSingle substanceSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a preparation method of a bismuth telluride based N type thermoelectric material Bi2(Te<1-x>Se<x>)3. A melt mixing step and a zone melting step are used for synthesis. The synthesis method comprises that single-substance raw materials can be selected and weighed according to a chemical formula Bi2(Te<1-x>Se<x>)3 in which x is greater than or equivalent to 0.02 and lower than or equivalent to 0.1, metal antimony (Sb) in the weight percentage of 0.01% to 0.03% and nonmetal iodine (I) in the weight percentage of 0.03% to 0.06% are added on the basis of the weight obtained by weighing, and the purities of all the single-substance raw materials are greater than 4N; the materials are filled into a quartz tube whose bottom is relatively flat by sintering to implement vacuum-pumped tube sealing, and then filled into a rocking furnace of resistance heating, and the quartz tube is placed in a vertical position and then sintered by melt mixing synthesis. The quartz tube is cooled naturally to the room temperature after sintering, and then removed and placed in a melting furnace in a vertical zone for pulse zone melting. The bismuth telluride based N type thermoelectric material and the preparation method thereof have the advantages that the preparation method is simple, a high-density body material of a monocrystalline similar structure and including a few of inlaid nanometer crystal grains can be obtained, via measurement, the ZT value of the thermoelectric material Bi2(Te<1-x>Se<x>)3 can reach 1.33 during 340K, and the material can be applied to fields including waste heat recovery and space exploration.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
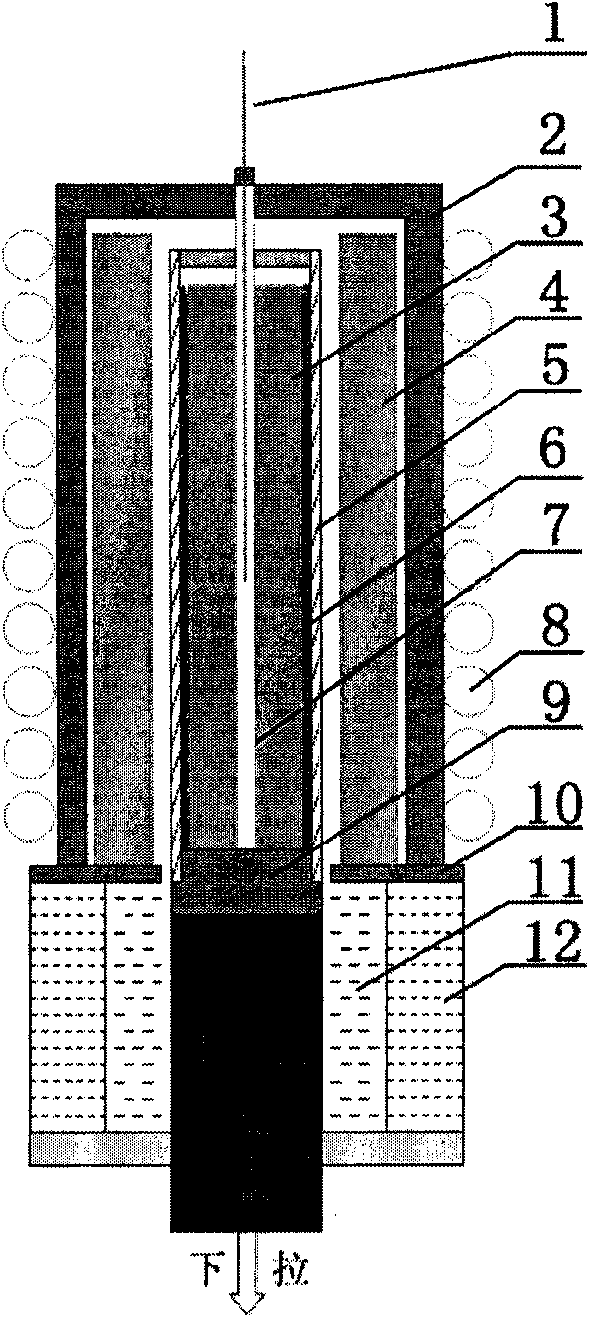
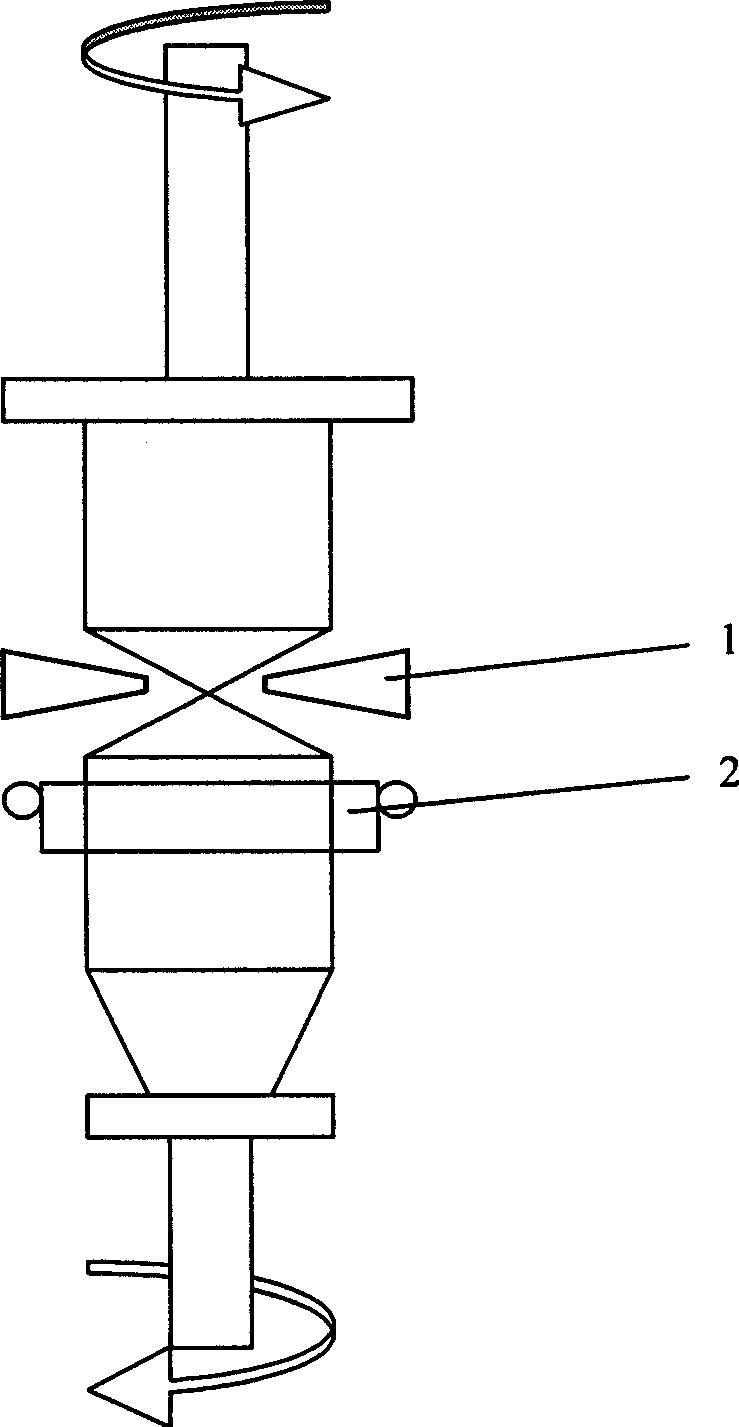
Zone melting furnace for purifying crystalline silicon and method for purifying crystalline silicon
ActiveCN102041548AIncrease surface areaHigh purityBy zone-melting liquidsZone meltingLiquid surfaces
The invention provides a method for purifying crystalline silicon, comprising a furnace body and an induction heating device which is arranged in the furnace body. The induction heating device comprises a multi-loop induction coil and an induction short circuit ring; the induction short circuit ring comprises an induction short circuit upper ring which is arranged above the multi-loop induction coil and an induction short circuit lower ring which is arranged below the multi-loop induction coil. The multi-loop induction coil can provide larger power so as to increase a melting area of a crystalline silicon rod and obtain the crystalline silicon with high purity. In order to prevent the melting area from dropping off after the melting area is increased, the upper part and lower part of the multi-loop induction coil are provided with two induction short circuit rings so that a part of a leakage magnetic field generated by the multi-loop induction coil generates high-frequency current on the two induction short circuit rings; the high-frequency current respectively generates an induction magnetic field; the tension of the liquid surface of the melting area is increased by action force generated by the induction magnetic field on the induction short circuit ring and a melting area magnetic field of the crystalline silicon rod, thereby preventing the melting area from dropping off.
Owner:YINGLI GRP
Method for smelting and purifying metal in electro-magnetism composite field and device thereof
The present invention relates to process and apparatus for zone metal melting purification under composite electromagnetic field, and belongs to the field of technology of separating and purifying metal under electromagnetic field. The present invention features that metal or alloy containing mixed metal element is set inside one electromagnetic field comprising parallel magnetic field and electric field in electrically migrating zone melting apparatus, and under the cooperation of the magnetic field and the electric field, the mixed metal element migrates in phase grain form toward the negative pole and the metal or alloy in the lower end is purified. The present invention adopts magnetic field intensity of 0.1-20 T, and DC current density of 10-100 A / aq cm.
Owner:新兴发展集团有限公司
Method for obtaining aluminum oxide-based ternary melt grown ceramic tissue morphology
ActiveCN102153334AIncrease superheatIncreasing the temperature gradient of the solid phaseZone meltingLiquid metal
The invention discloses a method for obtaining aluminum oxide-based ternary melt grown ceramic tissue morphology, which comprises the following steps of: combining zone melting and liquid metal cooling, and performing directional solidification on a plurality of precast bodies formed by using aluminum oxide, yttrium oxide and zirconium oxide respectively; and taking the longitudinal sections and the transverse sections of the directional solidified precast bodies, performing conventional metallographic treatment, and performing surface metal spraying to obtain tissue morphology and interface morphology of the aluminum oxide-based ternary eutectic oxide melt grown ceramic at different growth rates. In the directional solidification, the withdrawing rate is 1 to 10,000mum / s, and the laser power is 200 to 1,500W. The obtained directional solidification tissues are greatly different from the tissues in a melting zone and have no obvious tissue transition zone, and the interface morphologyis preserved perfectly.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Floating zone melting apparatus
InactiveUS20100307406A1Reduce loadBy zone-melting liquidsFrom frozen solutionsZone meltingInfra-red color
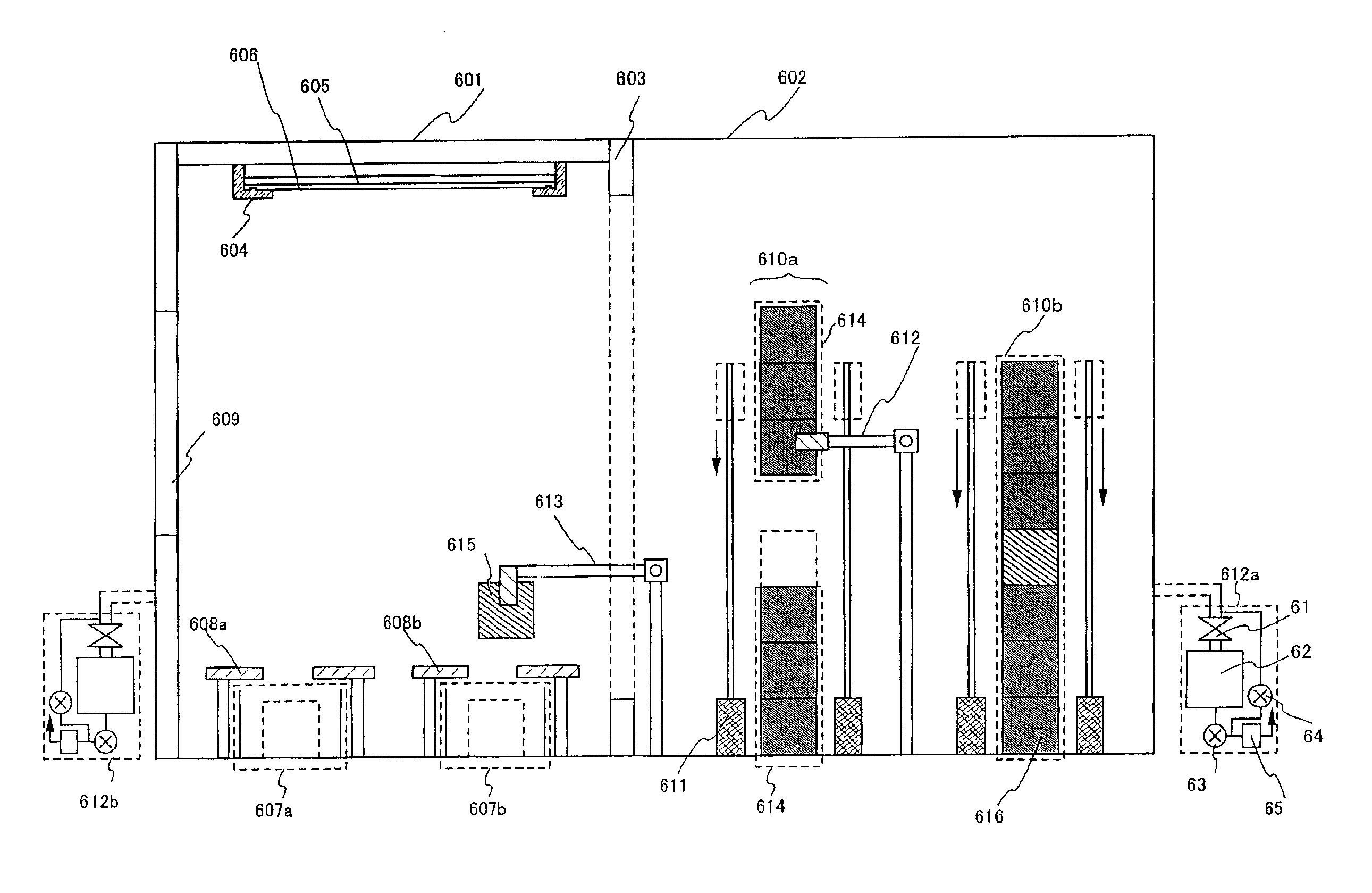
This invention provides a floating zone melting apparatus in which a sample rod especially having a large diameter can be stably melted with a certainty and the crystal being grown can retain a flat shape at the interface of the solid phase and the liquid phase, whereby a single crystal having a large diameter can be grown.[Problem] It is an object to provide a floating zone melting apparatus of the infrared concentration heating type in which a sample is set in a sample chamber made of a transparent quartz tube, an atmospheric gas is introduced into the sample chamber, infrared rays emitted from a plurality of infrared ray irradiation means are converged to the sample to heat and melt the sample in this state, thereby obtaining a melt, and the melt is solidified on a seed crystal to grow a single crystal. The plurality of infrared ray irradiation means comprise a plurality of infrared ray irradiation means of the downward irradiation type that emit an infrared ray downward from an oblique upper direction and a plurality of infrared ray irradiation means of the upward irradiation type that emit an infrared ray upward from an oblique lower direction.
Owner:CRYSTAL SYST
Method for preparing large-size aluminum oxide-yttrium aluminum garnet eutectic ceramic through horizontal orientation zone melting crystallization
InactiveCN104762658AIncrease the area of actionHigh hardnessPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltHeat stabilityZone melting
The invention provides a method for preparing large-size aluminum oxide-yttrium aluminum garnet eutectic ceramic through horizontal orientation zone melting crystallization, and relates to the method for preparing the large-size aluminum oxide-yttrium aluminum garnet eutectic ceramic. The method solves the problems that the number of growth defects is large, and the eutectic quality is poor in the excising preparing process of the large-size eutectic ceramic. The method includes the steps of ceramic mixing, material melting, seeding, cooling and annealing. The method integrates the advantages of a directional crystallizing method and a vertical zone melting method for growth of crystal, the prepared aluminum oxide-yttrium aluminum garnet eutectic ceramic is made to have the advantages of being large in size, less in defect, high in hardness, remarkable in normal-temperature and high-temperature mechanical property, high in heat stability, easy to machine and the like. The method is used for preparing the large-size aluminum oxide-yttrium aluminum garnet eutectic ceramic.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Preparation method of large diameter zone melting silicon single crystal
ActiveCN1724723AMeet the needs of large diameter zone molten silicon single crystalPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltElectricityAnode voltage
The invention relates to a silicon single-crystal manufacture method, especially a method to produce major diameter zone melting silicon single-crystal for high-power high voltage, big current semiconductor device. When the diameter of zone melting silicon single-crystal expands to 110mm-130mm, interface turning would happen, adjusting the anode voltage set by zone melting silicon single-crystal furnace generator after an interval of 5-10 seconds and increasing voltage 0.1-0.3%. When the diameter expanding to 110mm, the sporting speed downward the axial is set at the range of 2.0-2.4mm / minute and the rotating speed is set at the range of 4-6 round per minute. In the air pumping and filling process, the hearth pressure should reach 3.0bar-3.2bar, when the diameter expanding to 110mm, the N2 would be filled in and the ratio is 0.5-0.6% compared to Ar. The invention also improves the heat field system of the zone melting silicon single-crystal. Every index of the zone melting silicon single crystal reaches the SEMI standard.
Owner:ZHONGHUAN ADVANCED SEMICON MATERIALS CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com