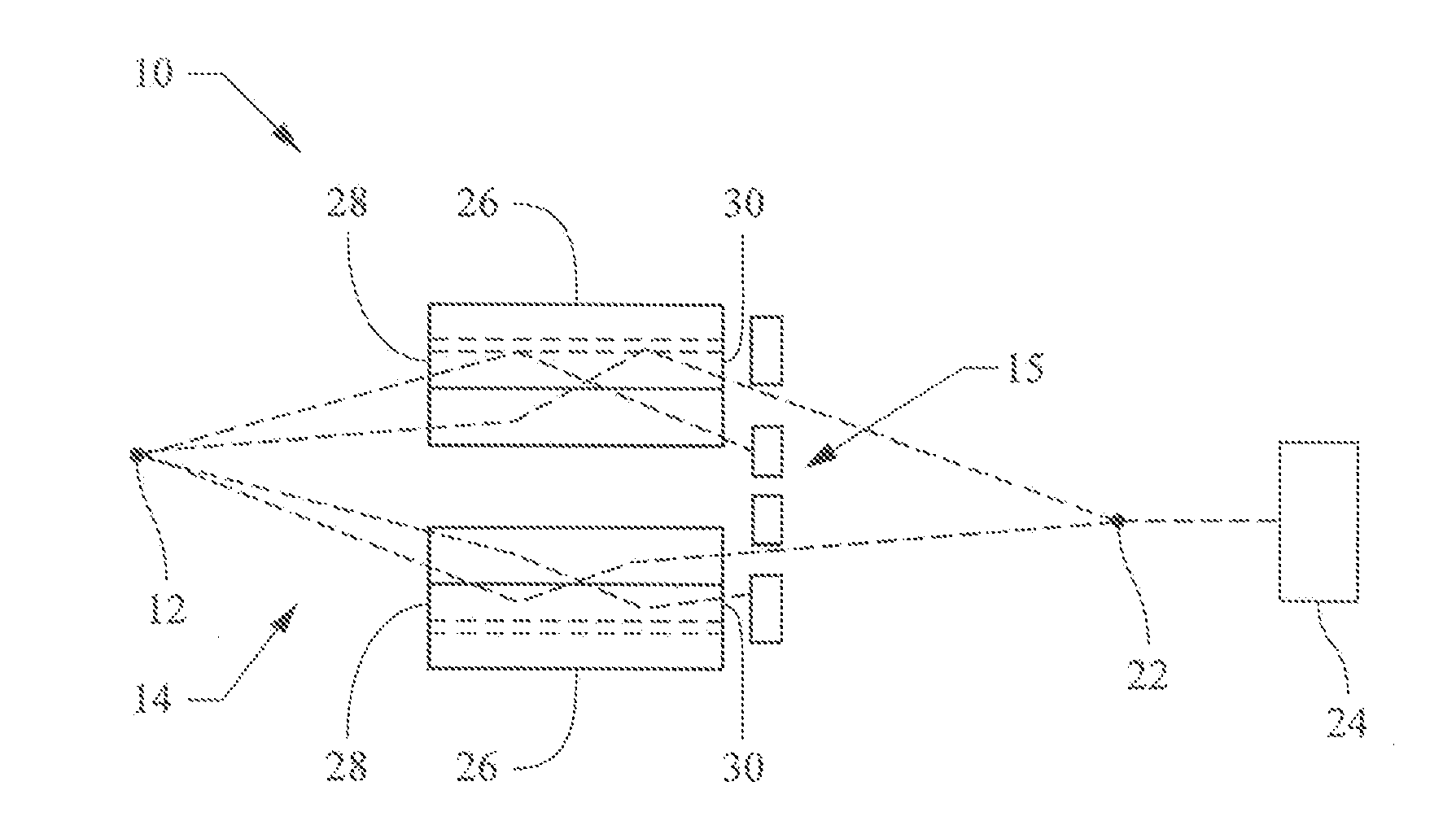
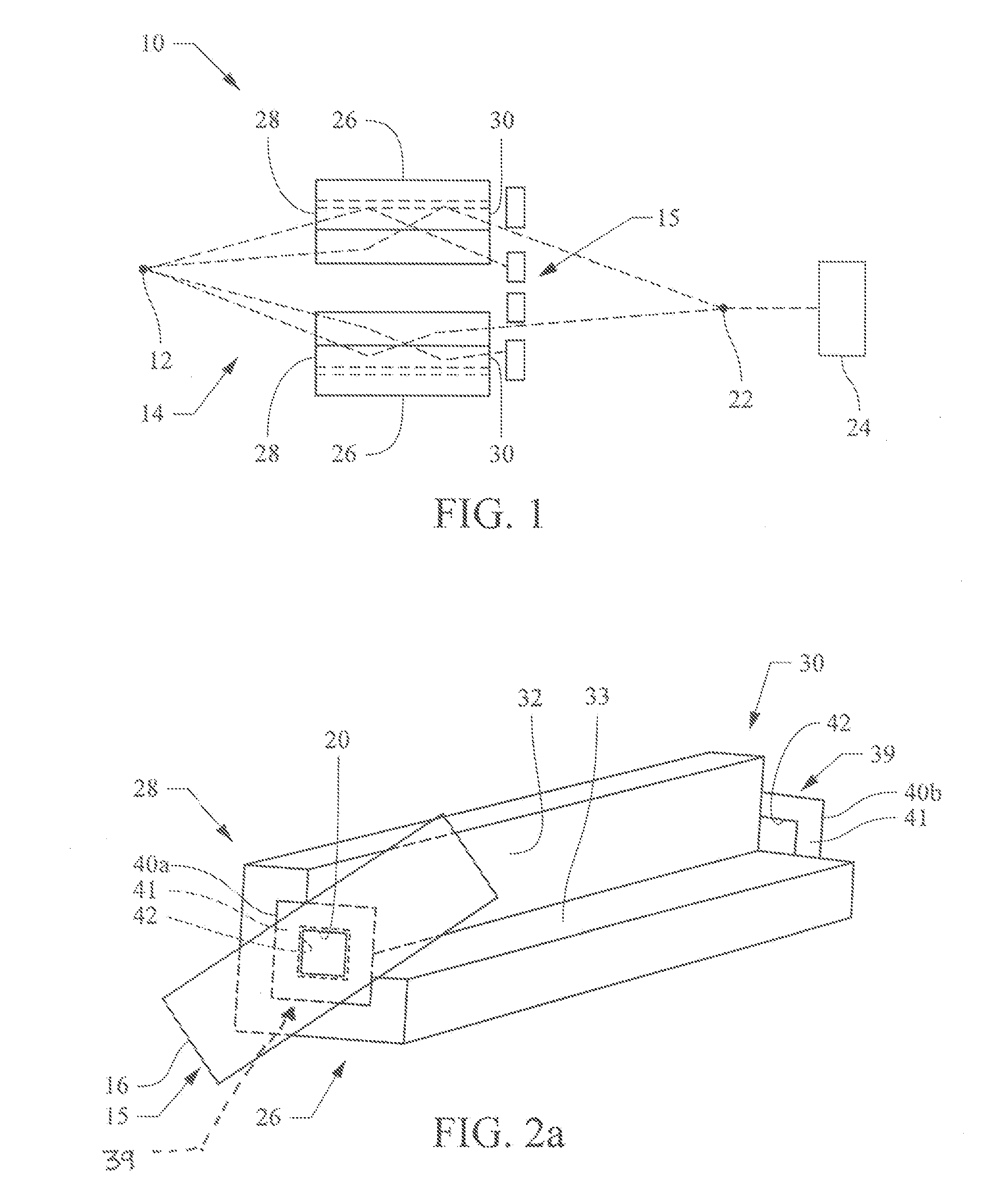
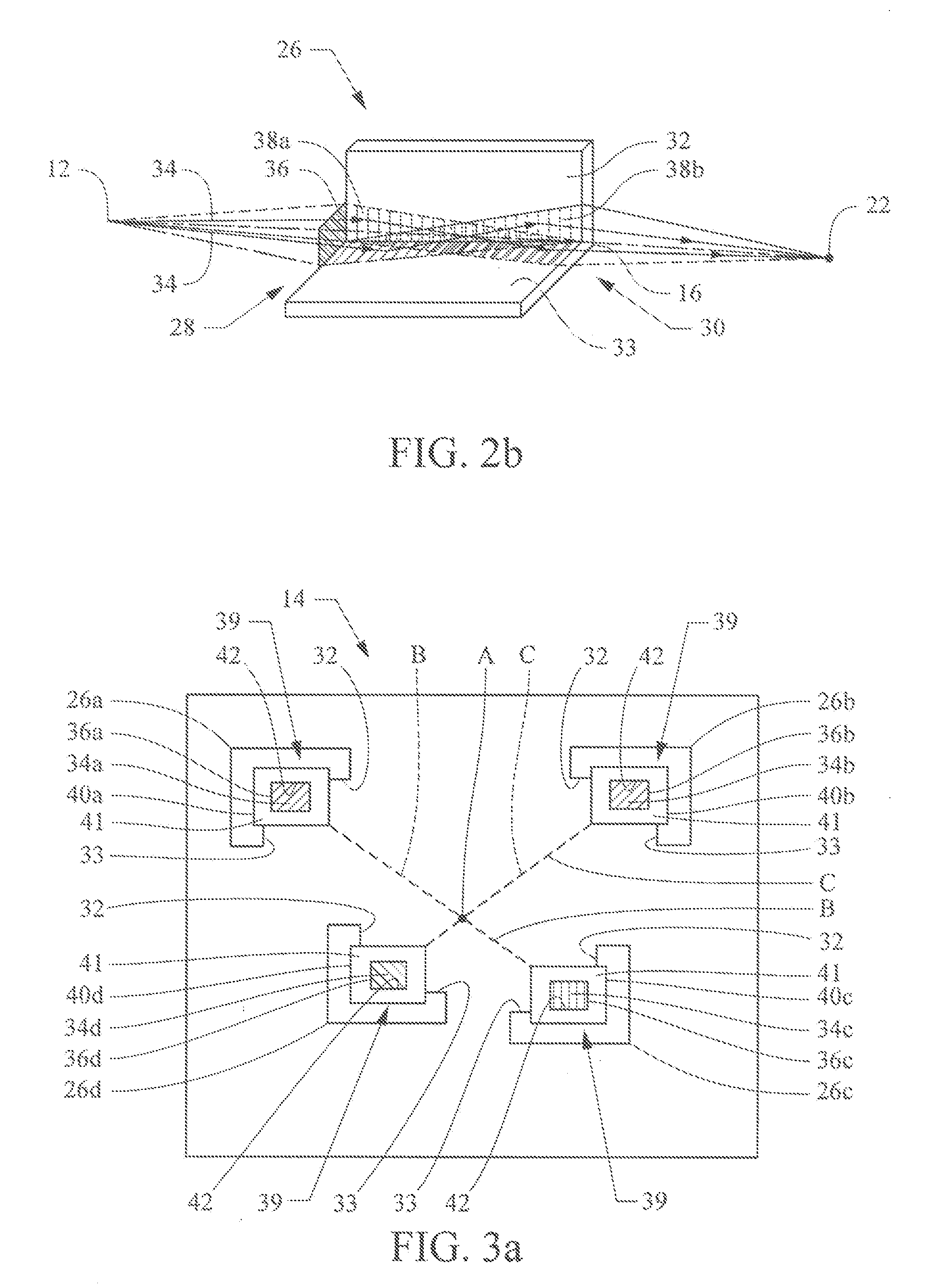
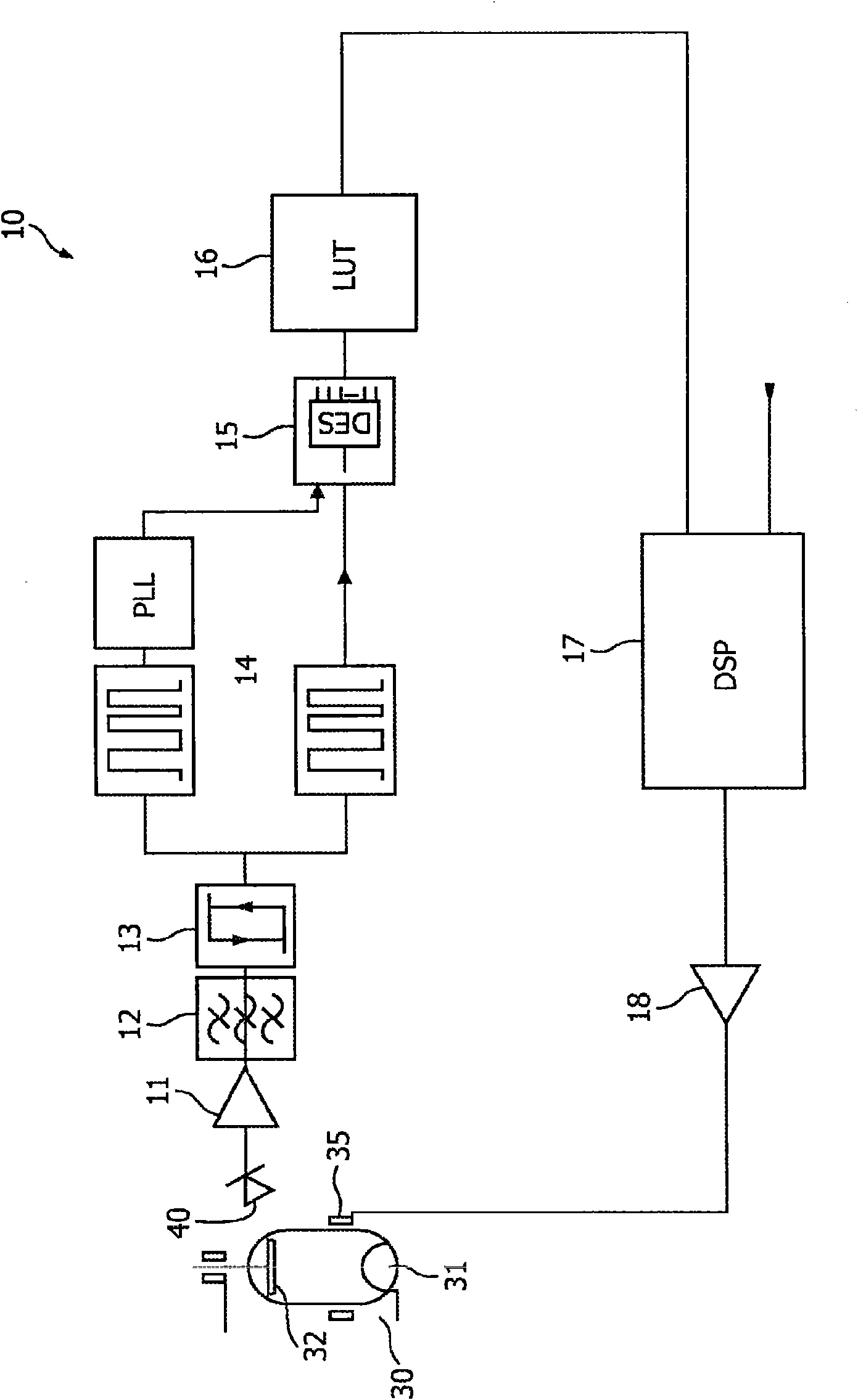
Patents
Literature
81 results about "Focal Spot Size" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
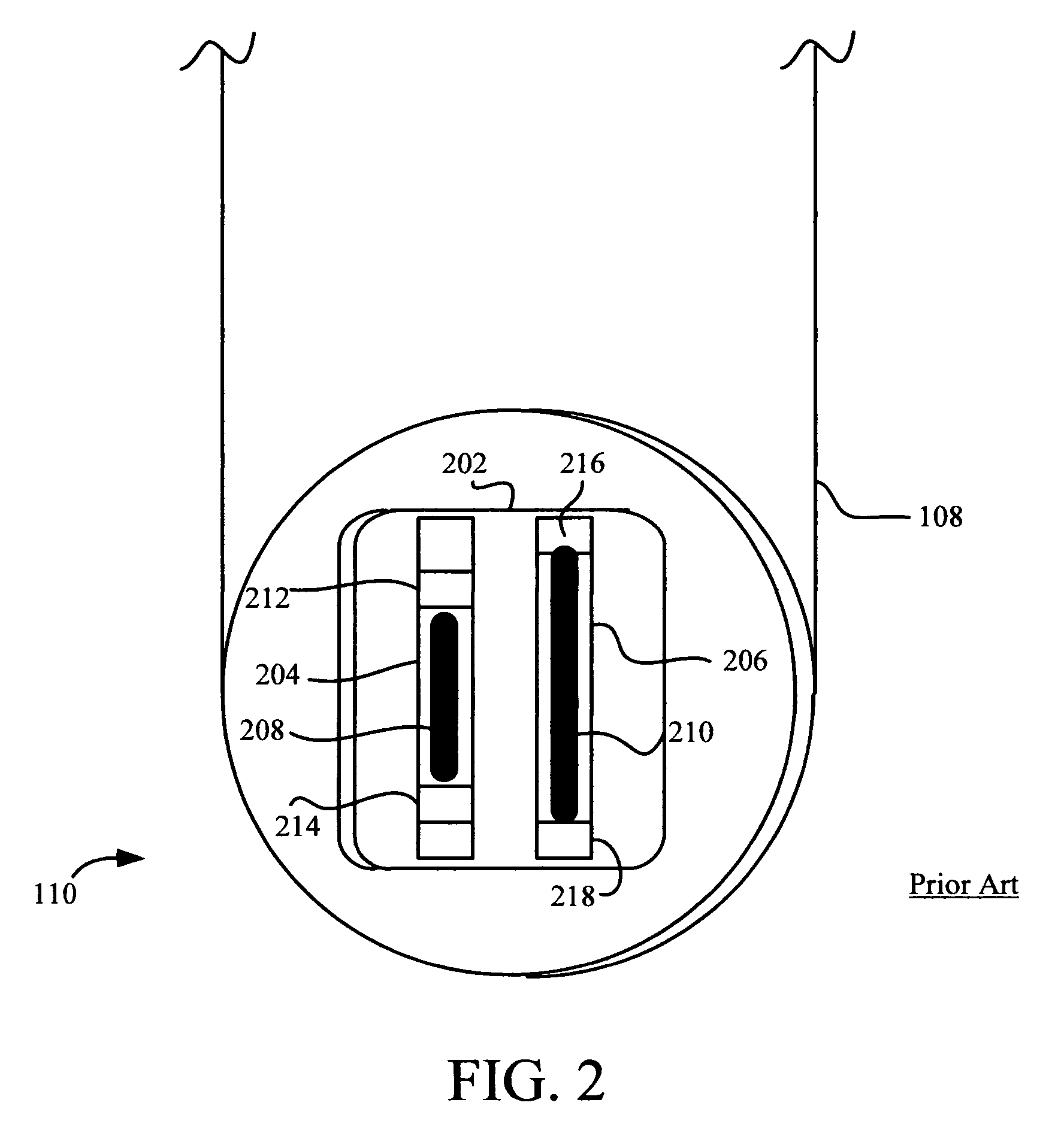
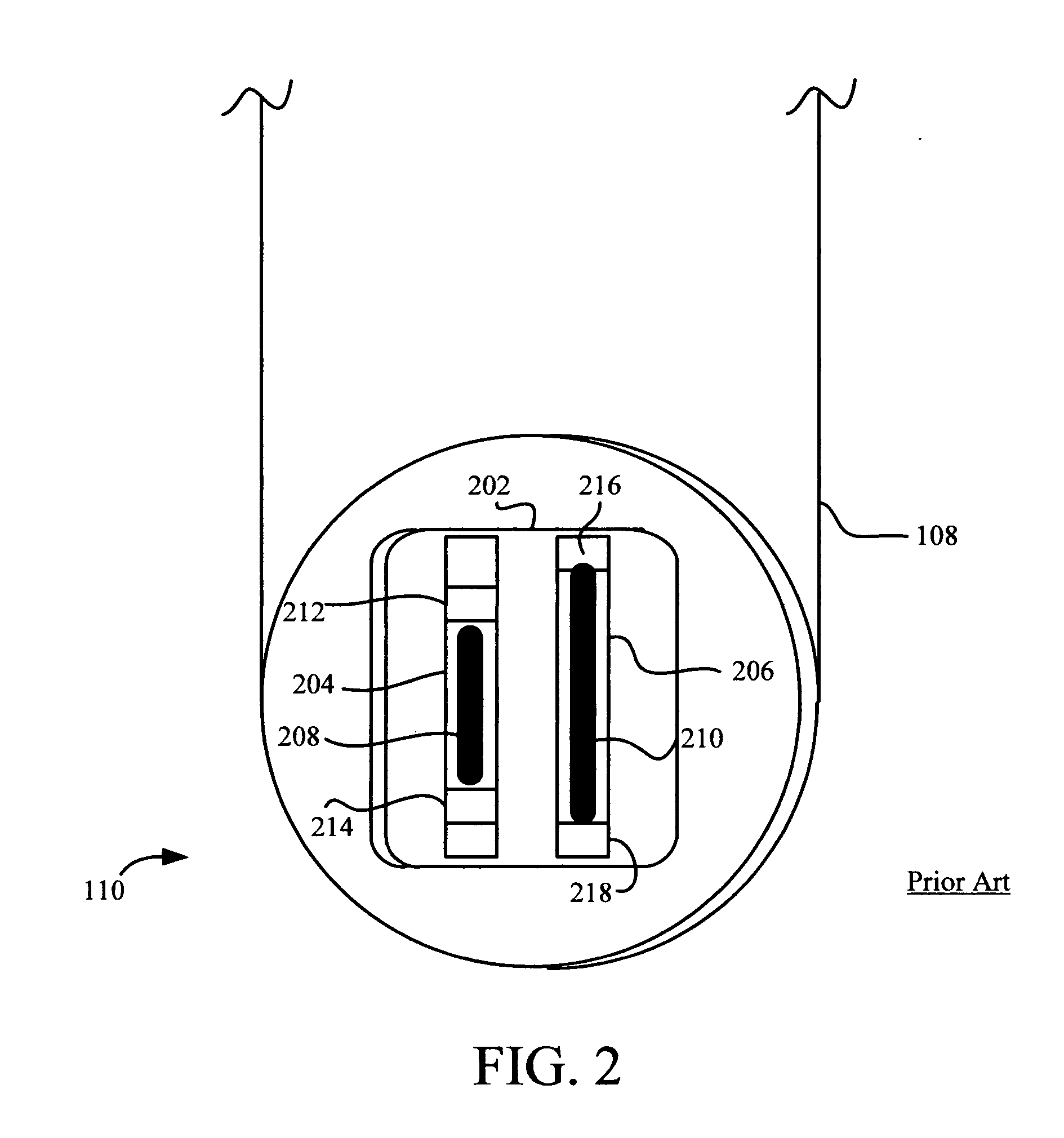
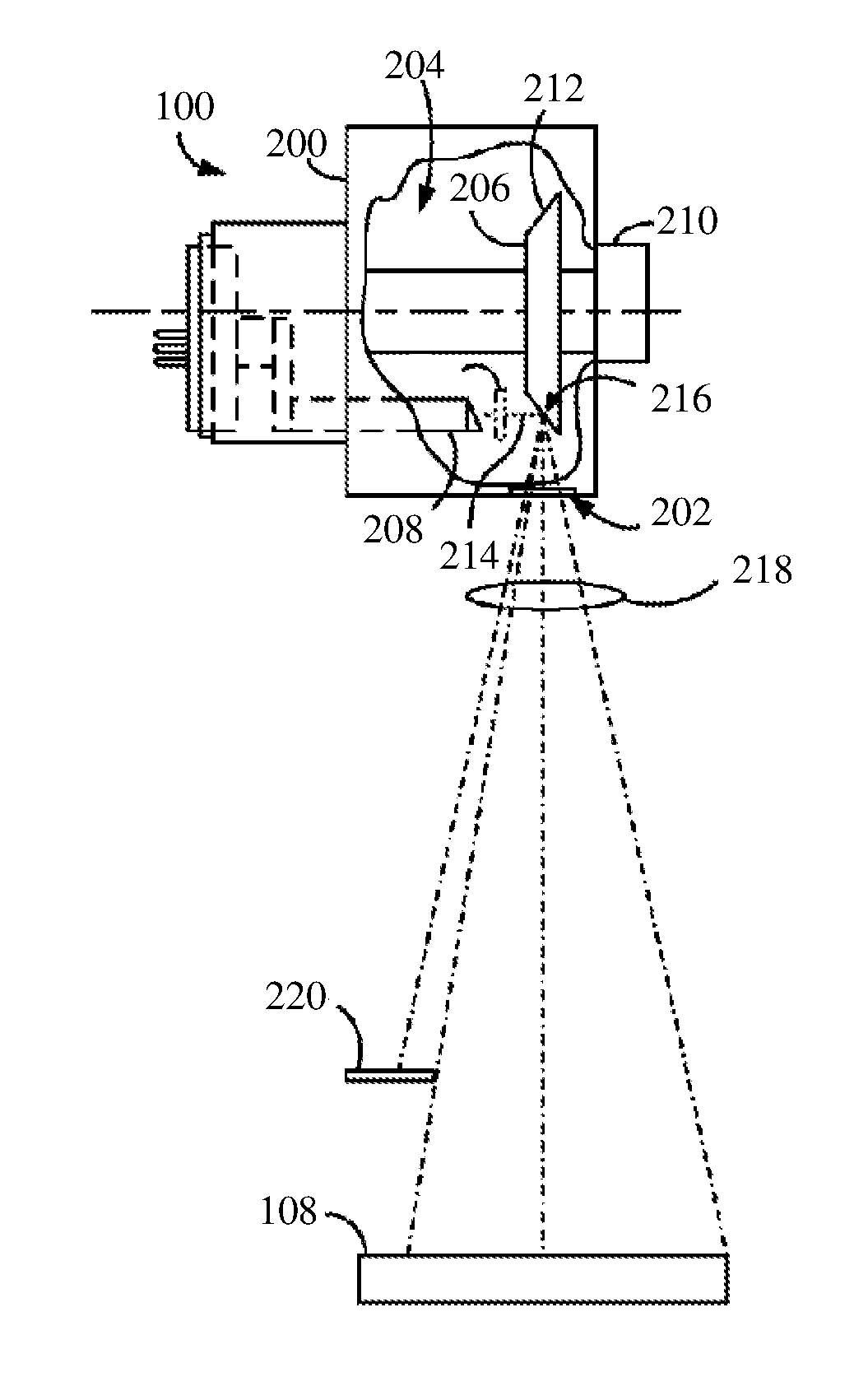
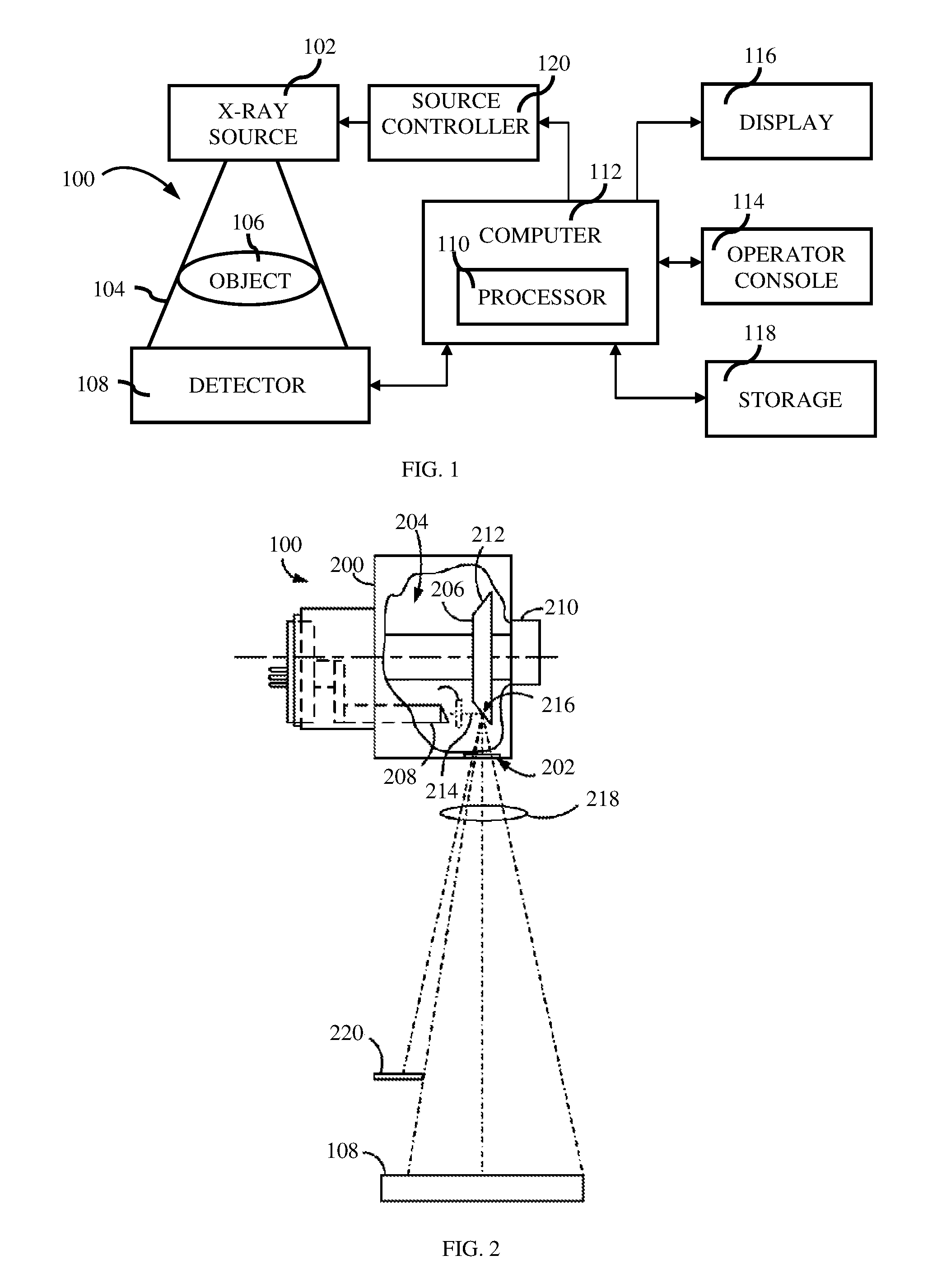
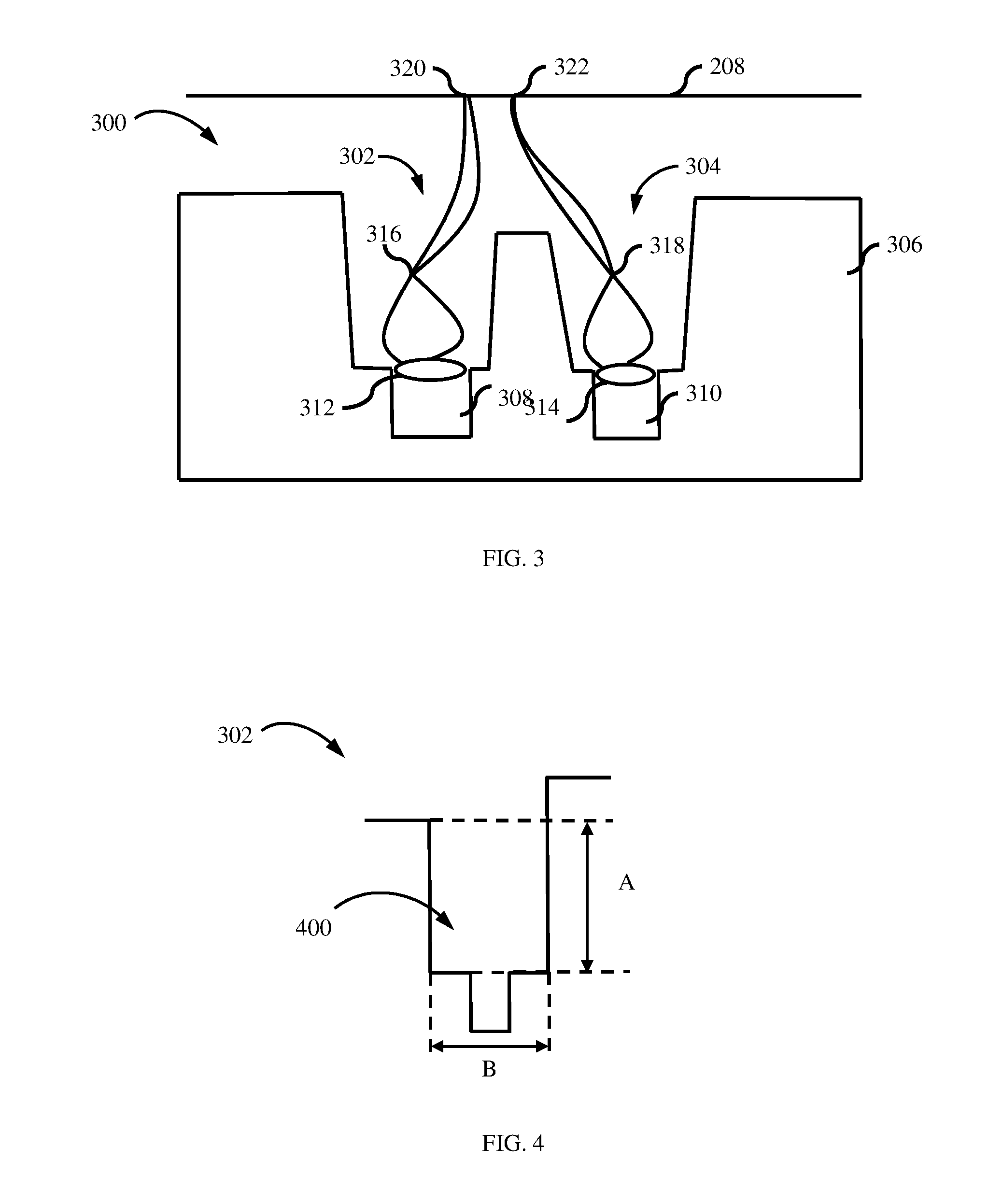
The size of the focal spot created by an X-ray tube.
Spot-size effect reduction
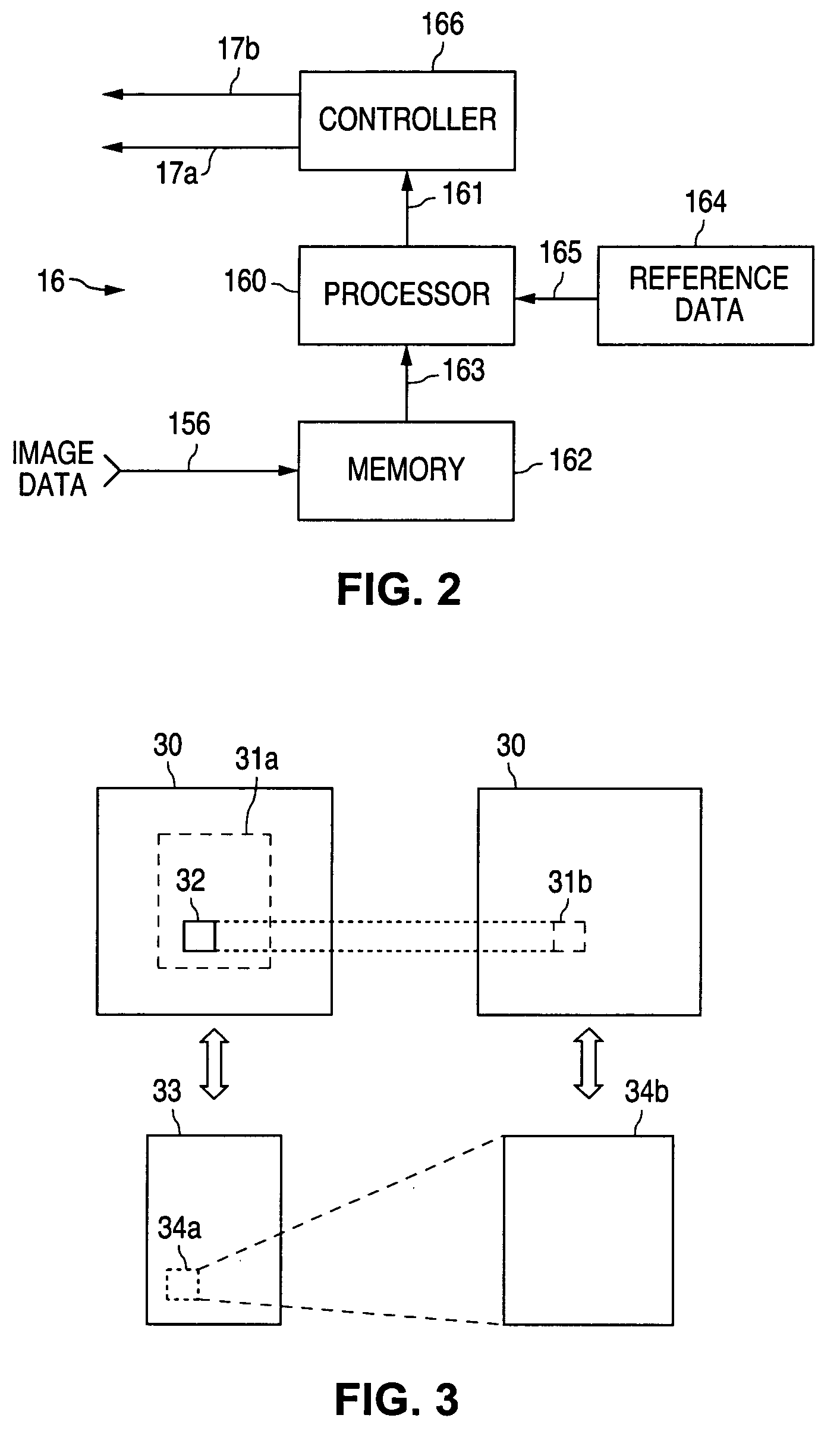
InactiveUS7418078B2Reduce adverse effectsImprove image qualityRadiation/particle handlingTomographyX-rayRadiography
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
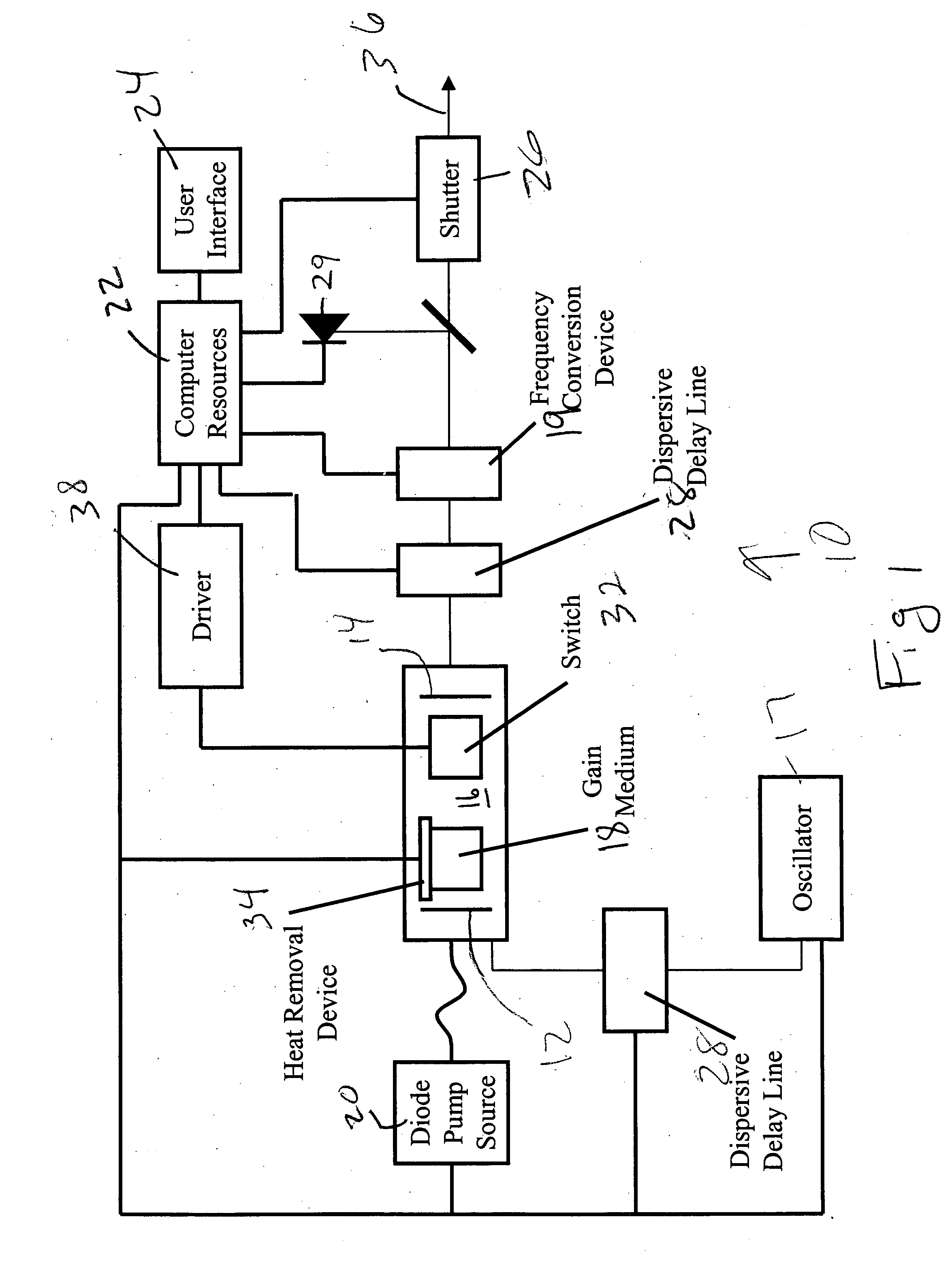
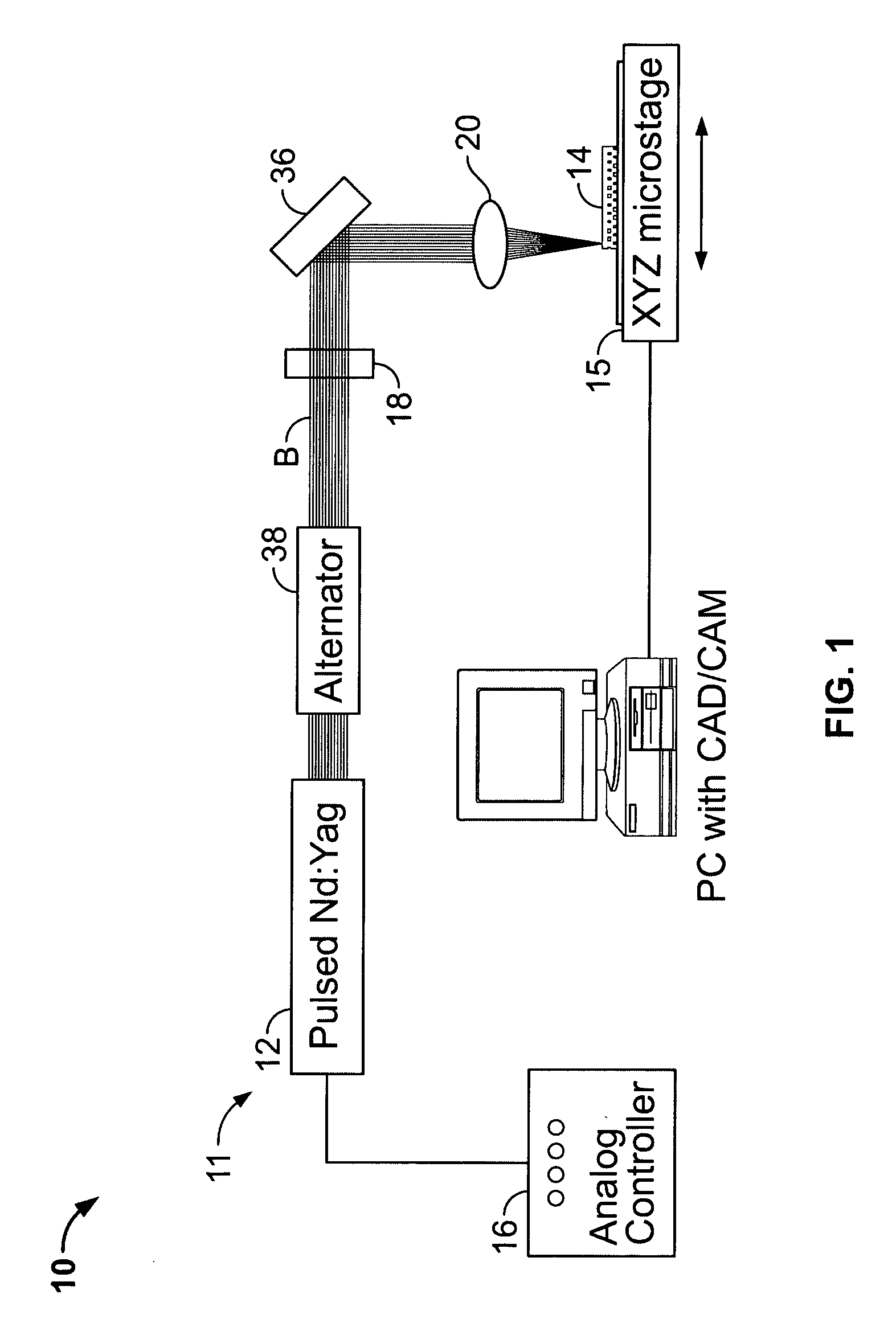
Industrial directly diode-pumped ultrafast amplifier system
InactiveUS20050157382A1Provide controlLaser arrangementsActive medium materialComputer resourcesAudio power amplifier
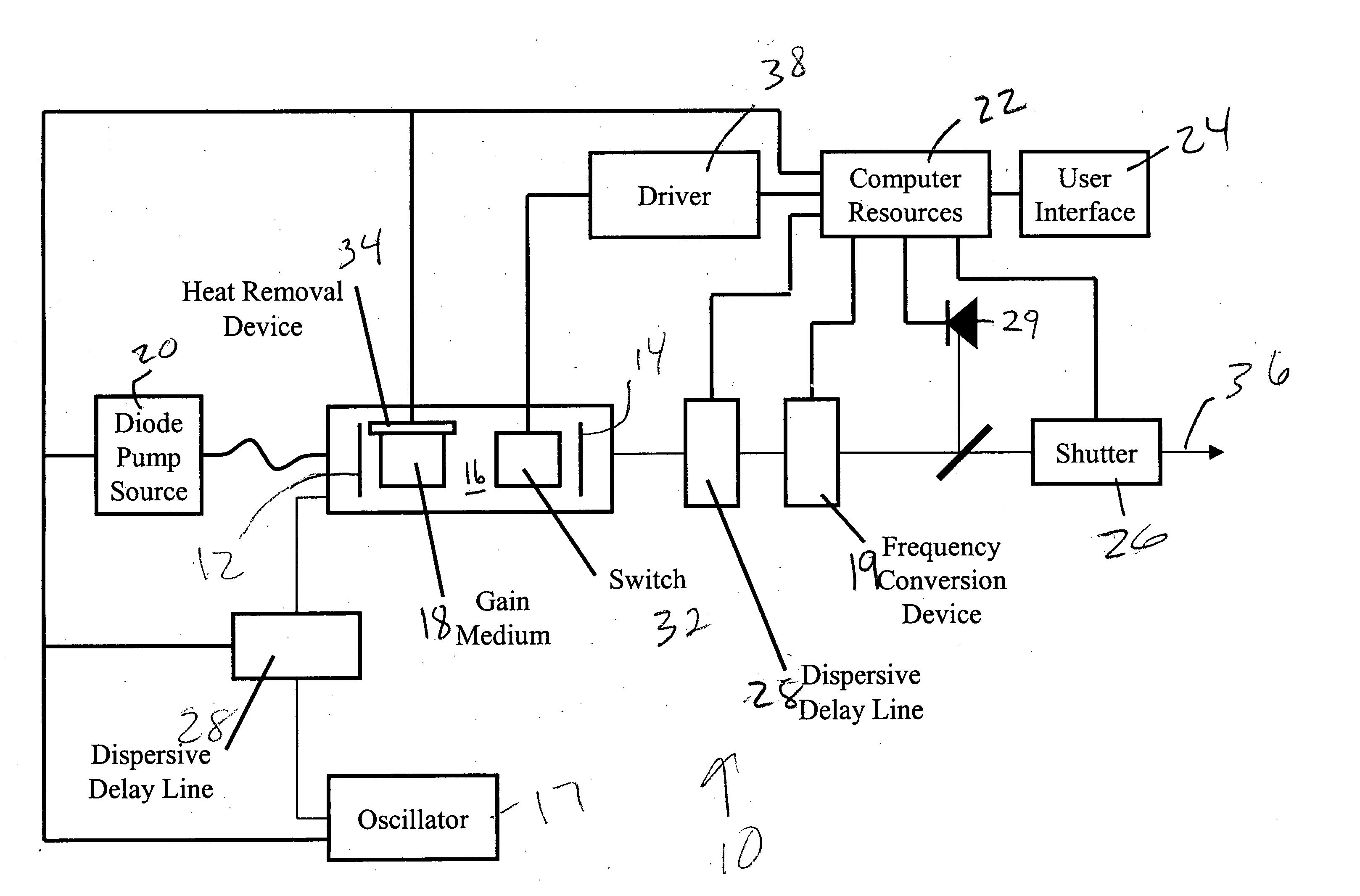
A directly diode-pumped amplifier system is disclosed which produces sub-picosecond pulses with an output power of 2 watts or more. Computer resources are coupled to the amplifier system and are configured to provide control of operating parameters of the amplifier system. An optional second harmonic generator is supplied to increase the contrast ratio and reduce the minimum focal spot size. This amplifier system can be utilized for material processing applications.
Owner:SPECTRA PHYSICS
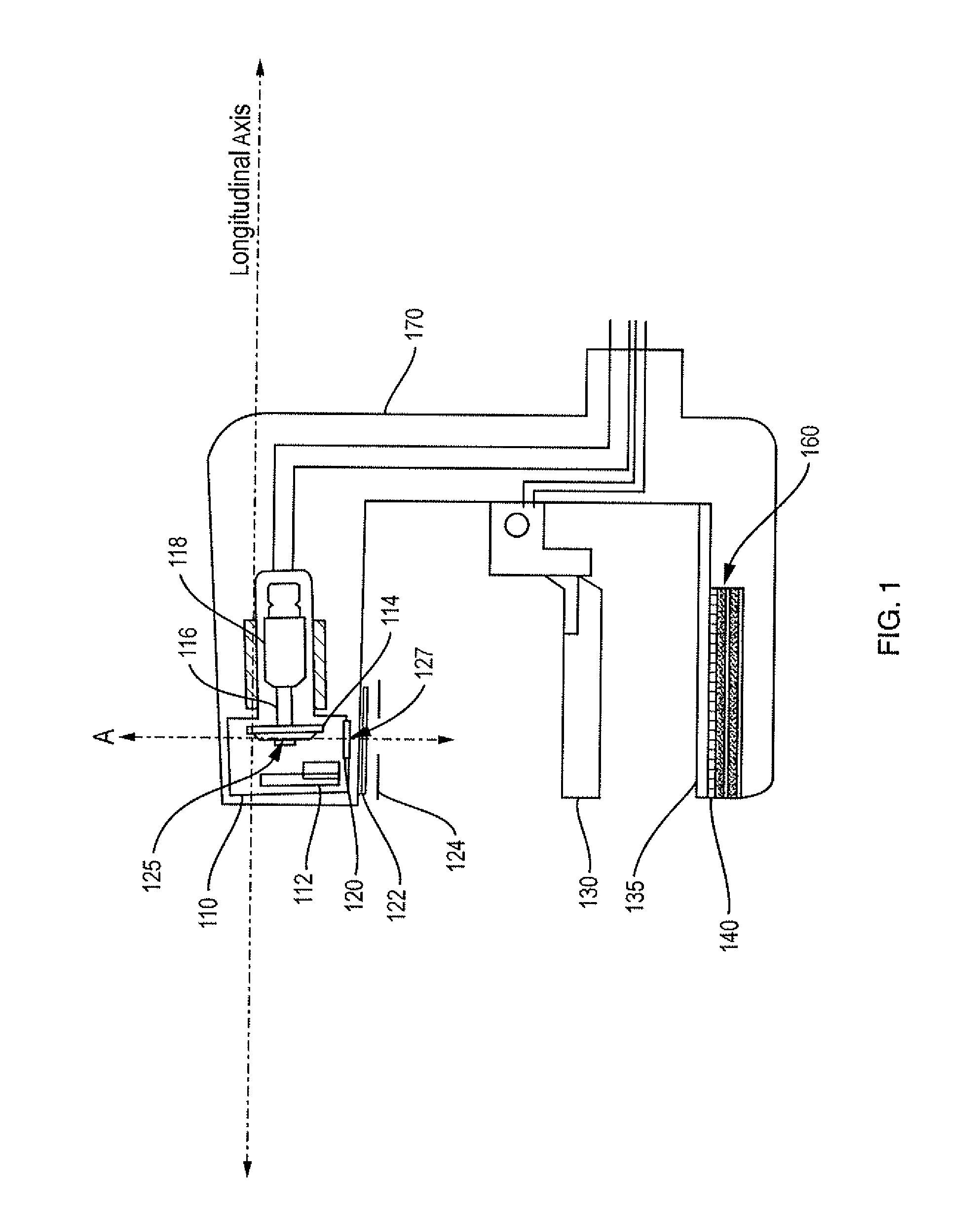
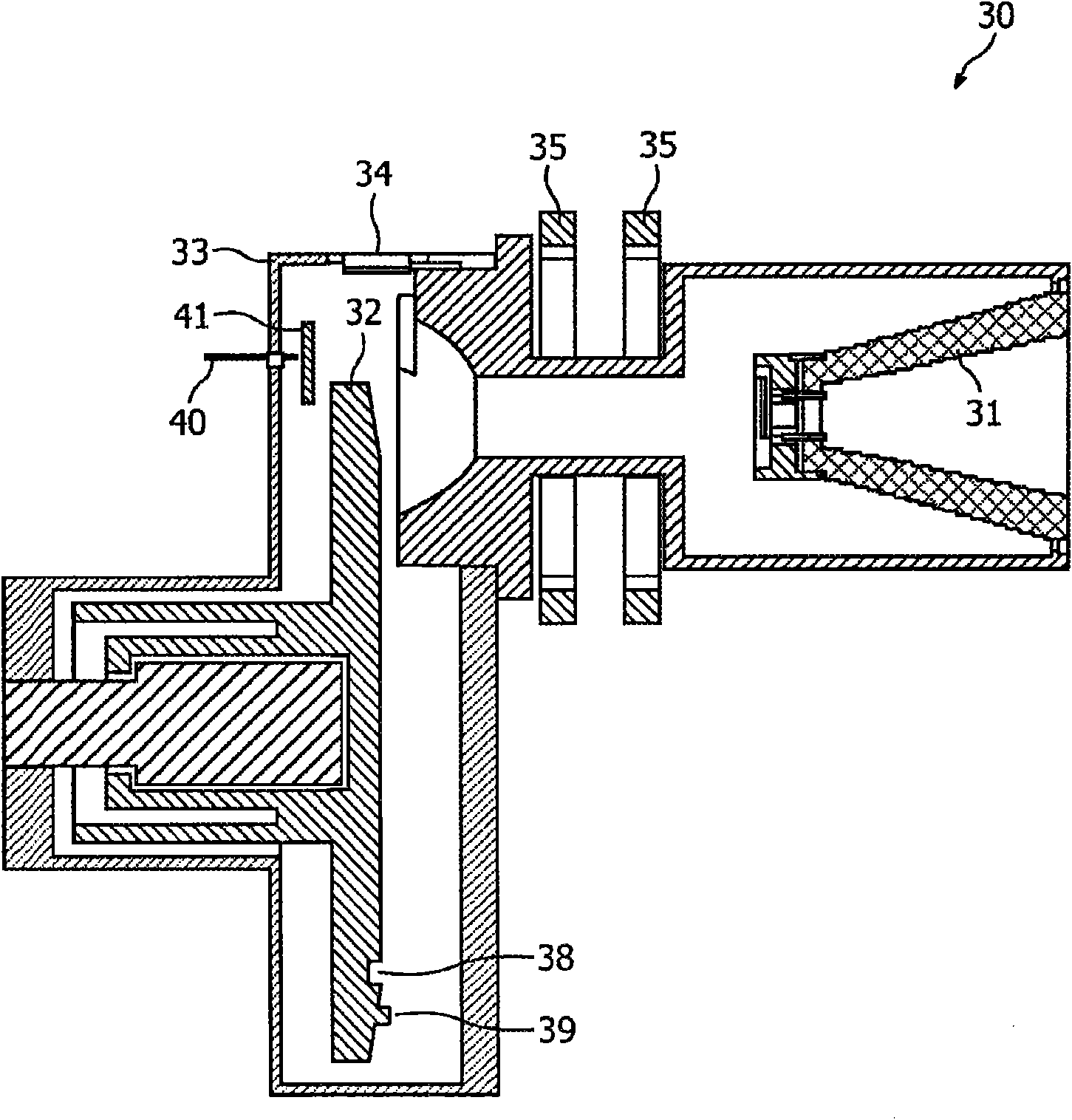
Device and method for x-ray tube focal spot size and position control
InactiveUS20100020938A1Easy to controlEasy to operateCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingX-ray apparatusControl signalParameter control
A device and method for X-ray tube focal spot parameter control, wherein stray electrons are detected in an X-ray tube. The detected electrons lead to a signal having a characteristic pattern. The characteristic pattern may be evaluated, and based on the evaluation a controlling signal may be outputted so that a fast and exact controlling of the operating parameters of an X-ray tube may be carried out based on the detected stray electrons.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
X-ray system with efficient anode heat dissipation
InactiveUS20110051895A1Increase the heating areaIncrease powerX-ray tube electrodesCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingHigh resolution imagingX-ray
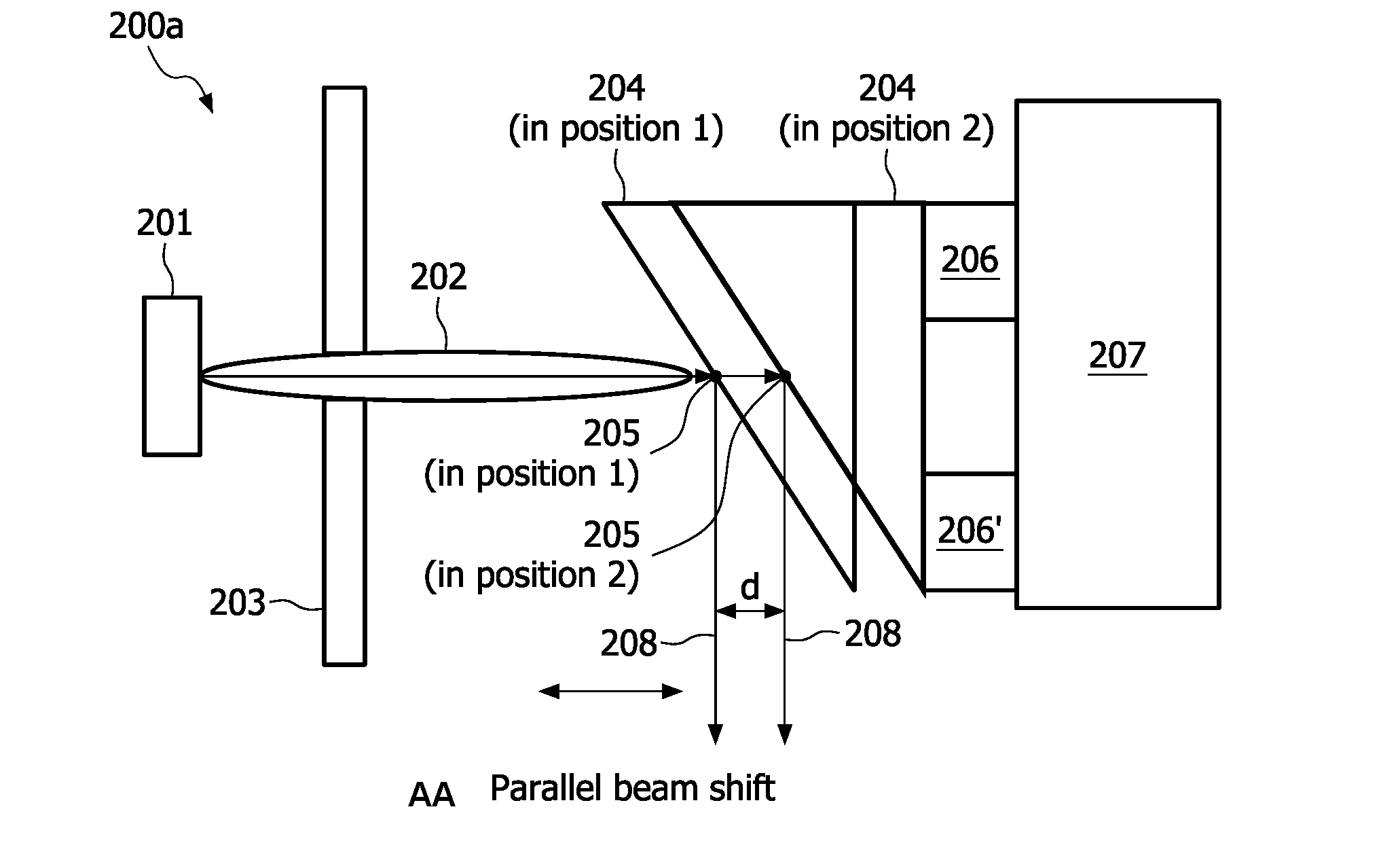
X-ray systems for use in high-resolution imaging applications with an improved power rating are provided. An X-ray source comprises at least one integrated actuator unit (206, 206′, 206a or 206b) for performing at least one translational and / or rotational displacement by moving the position of the X-ray source's anode (204, 204′, 204a′ or 204b′) relative to a stationary reference position. This helps to overcome power limitations due to an overheating of the anode at its focal ̂spot position (205). In addition to that, a focusing unit (203) for allowing an adapted focusing of the anode's focal spot (205) which compensates deviations in the focal spot size resulting from said anode displacements and / or a deflection means (211, 21 Ia or 21 Ib) for generating an electric and / or magnetic field deflecting the electron beam (202, 202a or 202b) in a direction opposite to the direction of the rotary anode's displacement movement may be provided.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and System for Controlling X-Ray Focal Spot Characteristics for Tomoysythesis and Mammography Imaging
ActiveUS20100303202A1Reduce eliminateReduce compressionRadiation/particle handlingTomosynthesisTomosynthesisSoft x ray
An x-ray tube is described that includes components for increasing x-ray image clarity in the presence of a moving x-ray source by modifying focal spot characteristics, including focal spot size and focal spot position. In a first arrangement a static focal spot is moved in a direction contrary to the movement of the x-ray source so that an effective focal spot position is essentially fixed in space relative to one of the imaged object and / or detector during a tomosynthesis exposure. In a second arrangement, the size of the static focal spot is increased, and the resulting increase in tube current reduces the exposure time and concomitant blur effect. The methods may be used alone or in combination; for example an x-ray tube with a larger, moveable static focal spot will result in a system that fully utilizes the x-ray tube generator, provides a high quality image with reduced blur and, due to the decrease in exposure time, may scan the patient more quickly.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
In-situ heat treatment method for realizing electron beam selective melting material increase manufacturing of metal parts
ActiveCN105499566AEliminate microscopic voidsHigh surface finishAdditive manufacturingIncreasing energy efficiencyMicro structureZone melting
The invention discloses an in-situ heat treatment method for realizing electron beam selective melting material increase manufacturing of metal parts, relating to the technical field of material increase manufacturing and heat treatment. The method adds a step of secondary heating remelting to melt a forming zone after a step of forming zone melting. The secondary heating remelting parameters comprise the electron beam current scanning speed, the electron beam current, the scanning deflection amount and the focal spot size. The method carries out in-situ heat treatment in the process of part processing forming process, therefore eliminates part of micro holes in the parts, and meanwhile can improve the surface smoothness of the parts, realize micro-structure controlling and realize regulation and control for the mechanical property of forming parts in a certain range.
Owner:成都航大新材料有限公司
Laser welding apparatus and method
InactiveUS20070193984A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationRecord carriers used with machinesLight beamOptoelectronics
A laser welding apparatus includes a laser welding unit including a first lens adapted to focus a laser beam; a second lens adapted to diffuse the laser beam to the first lens; and a third lens adapted to guide the laser beam to the second lens. The relative positions of the first lens, the second lens, and the third lens, are adjusted to adjust a diffusion angle and a beam width of the laser beam entering the first lens. The laser welding apparatus performs: actuating the laser welding unit to travel at a predetermined speed along a predetermined trajectory; directing the laser beam at a first welding spot; adjusting the focal length to focus the laser beam at the first welding spot; holding the laser focal spot size substantially constant; and directing the laser beam at a second welding spot after completion of welding for the first welding spot.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD +1
Method and system for controlling X-ray focal spot characteristics for tomosynthesis and mammography imaging
ActiveUS8457282B2Reduce eliminateReduce compressionRadiation/particle handlingCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingSoft x rayTomosynthesis
An x-ray tube is described that includes components for increasing x-ray image clarity in the presence of a moving x-ray source by modifying focal spot characteristics, including focal spot size and focal spot position. In a first arrangement a static focal spot is moved in a direction contrary to the movement of the x-ray source so that an effective focal spot position is essentially fixed in space relative to one of the imaged object and / or detector during a tomosynthesis exposure. In a second arrangement, the size of the static focal spot is increased, and the resulting increase in tube current reduces the exposure time and concomitant blur effect. The methods may be used alone or in combination; for example an x-ray tube with a larger, moveable static focal spot will result in a system that fully utilizes the x-ray tube generator, provides a high quality image with reduced blur and, due to the decrease in exposure time, may scan the patient more quickly.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
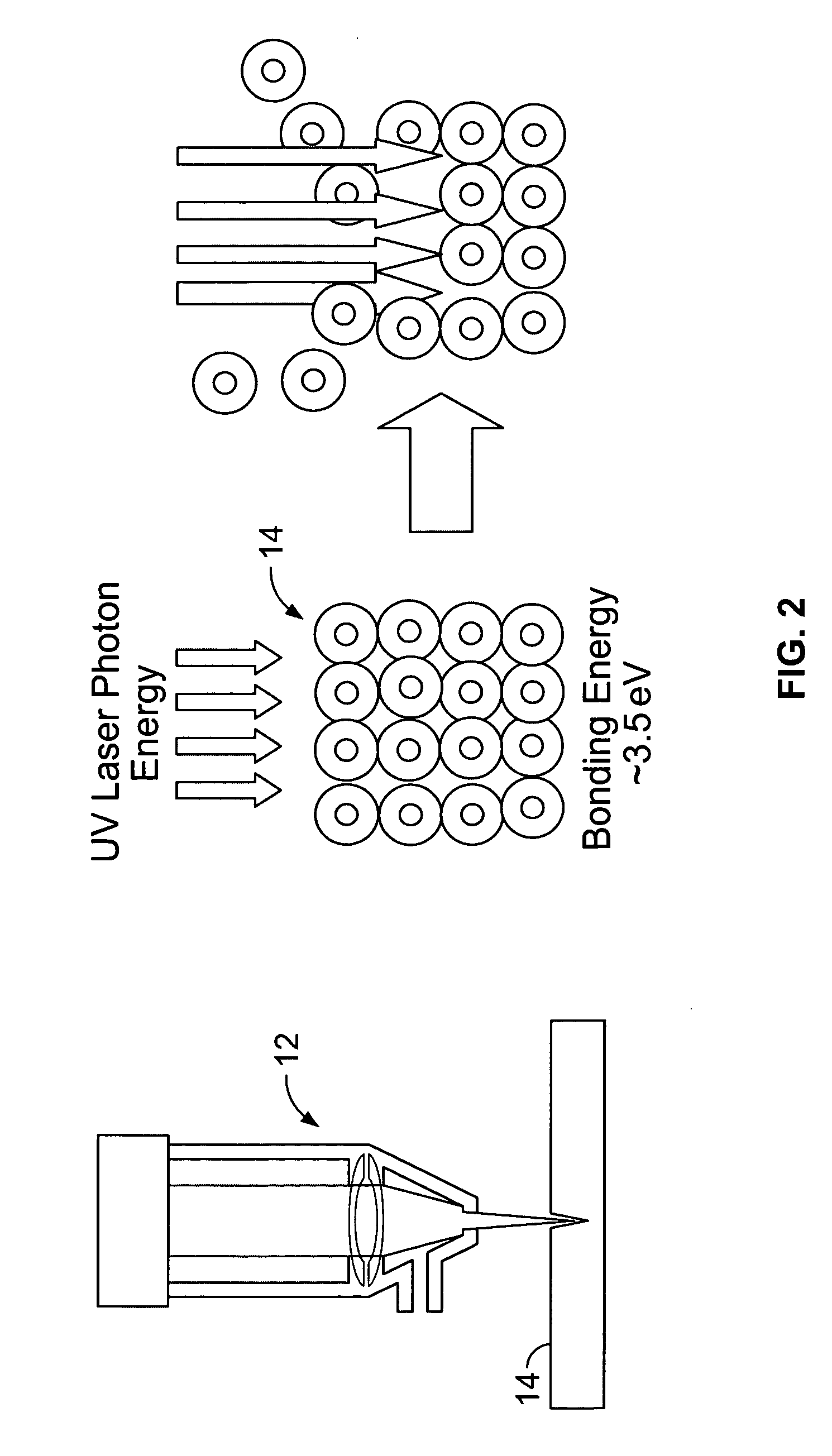
UV pulsed laser machining apparatus and method
InactiveUS20060097430A1Improve cut qualityQuantity minimizationWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser beam welding apparatusLaser processingUltraviolet
A method of cutting polycarbonate thin sheets generally less than 2 millimeters includes providing a source of pulse ultraviolet (UV) radiation. In operation, the method includes directing the UV radiation at the polycarbonate sheet to photo-ablate the polycarbonate sheet. A combination of parameters associated with the radiation may be selected, including at least one of a group of fluence, speed, coating of polycarbonate, number of passes, increasing or decreasing focal length, changing focus position and focus spot size.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
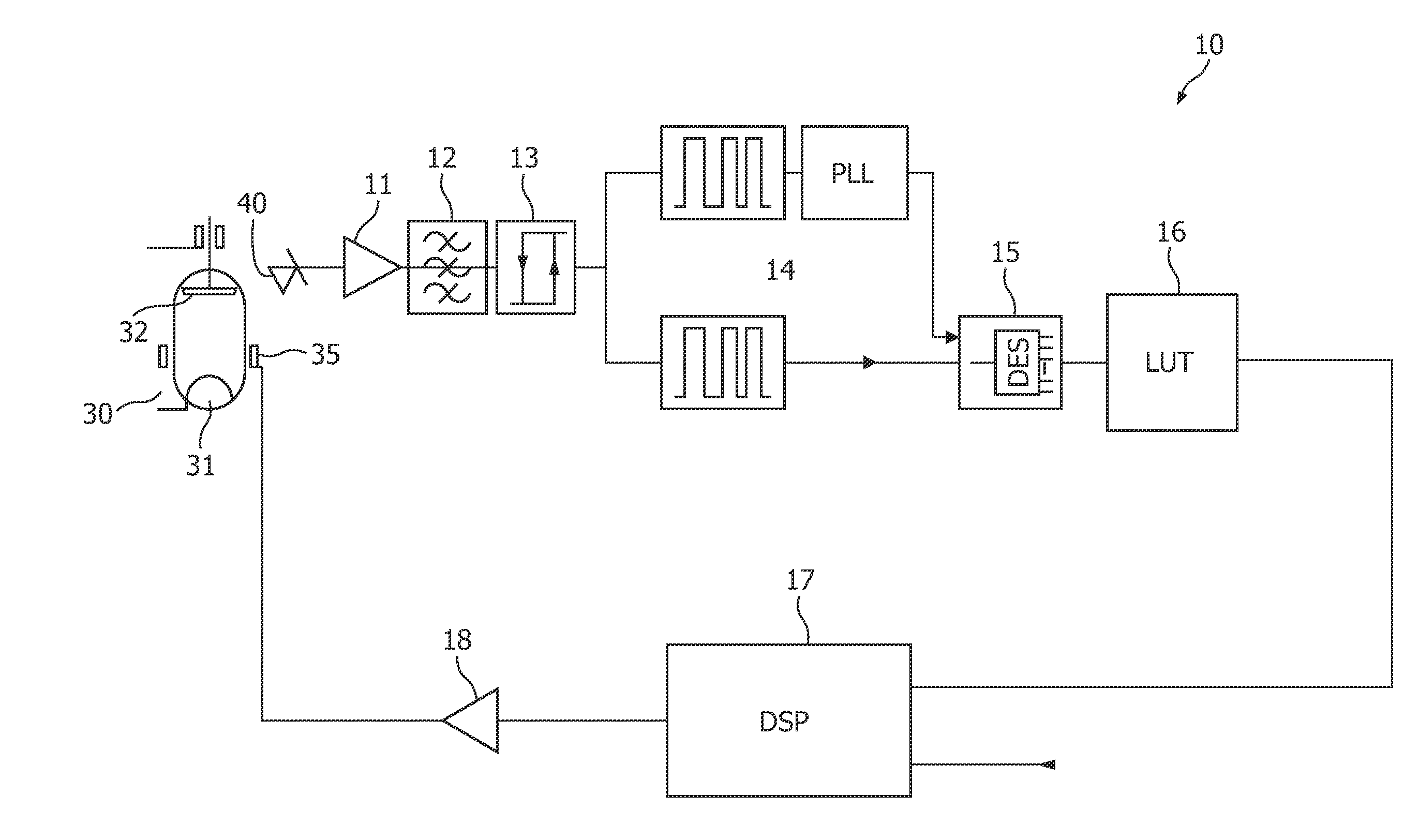
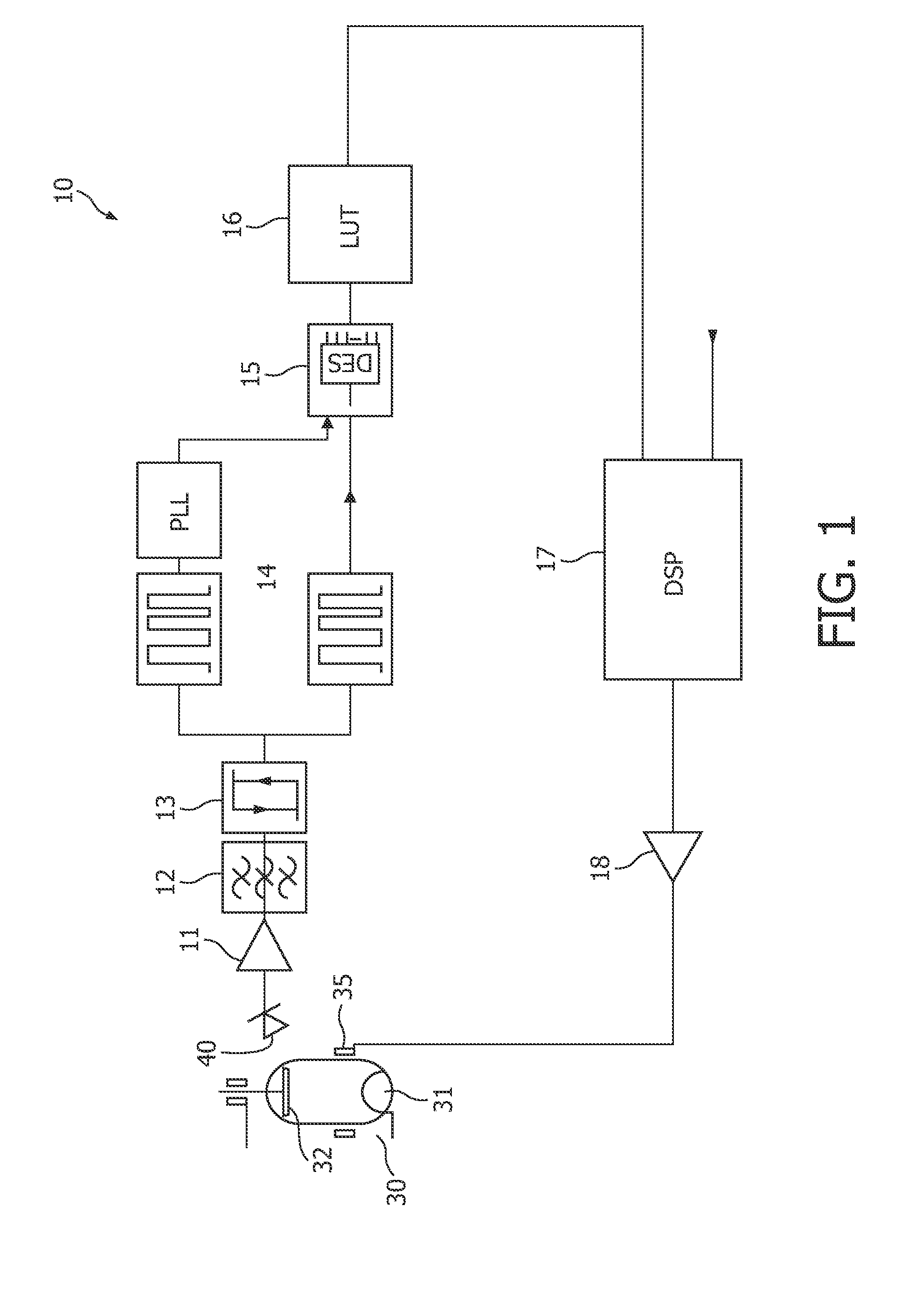
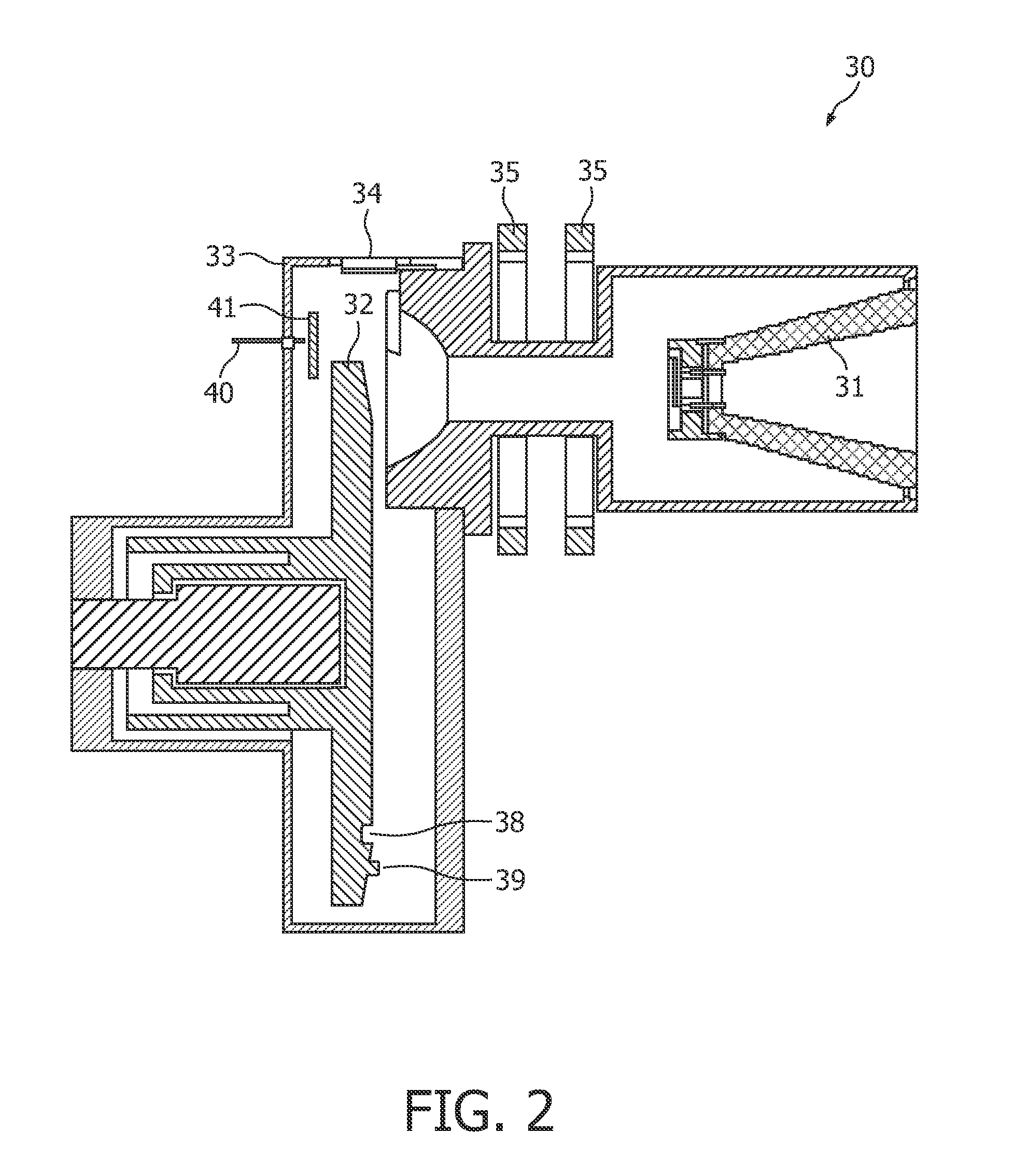
Method and apparatus to control radiation tube focal spot size
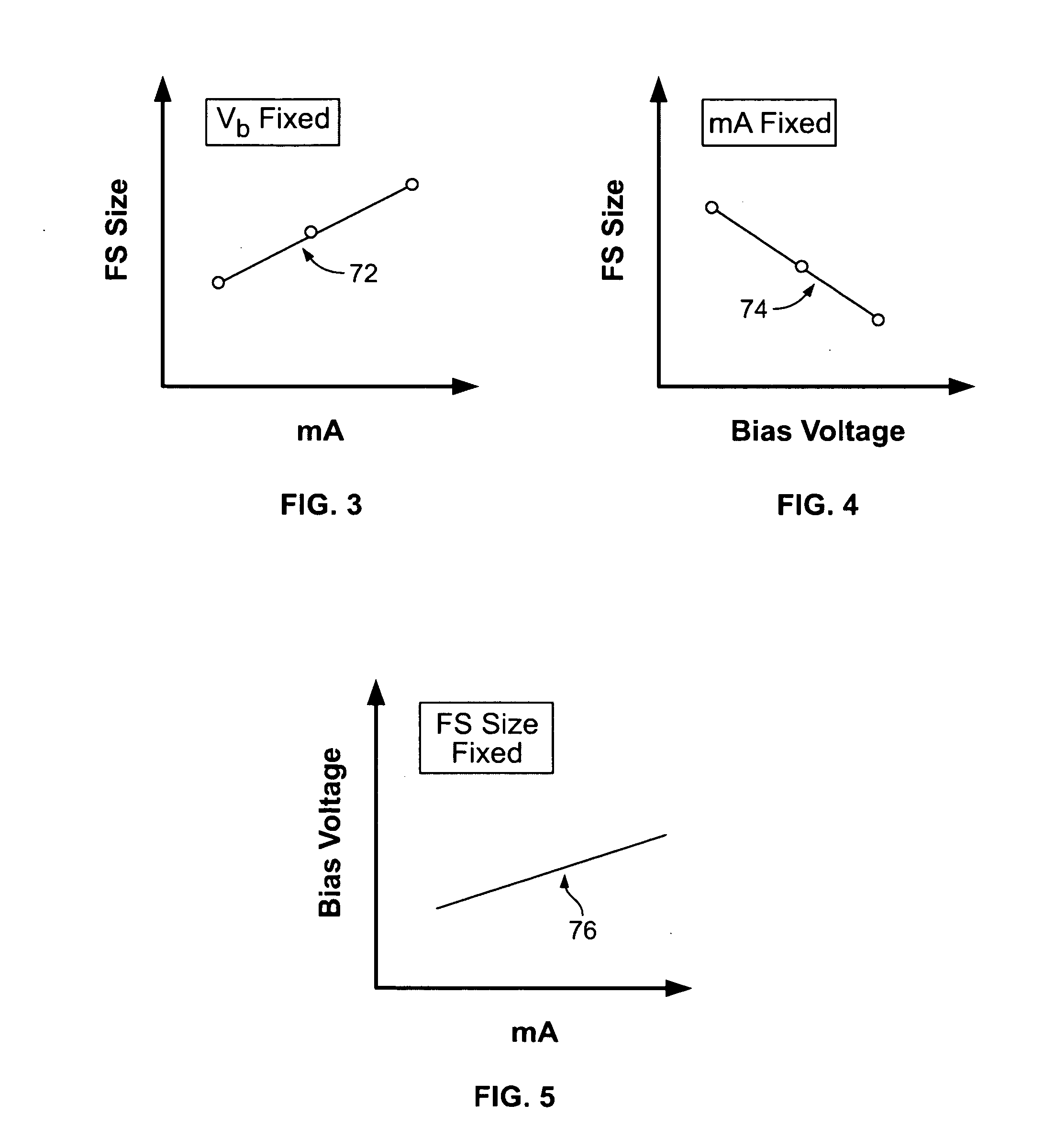
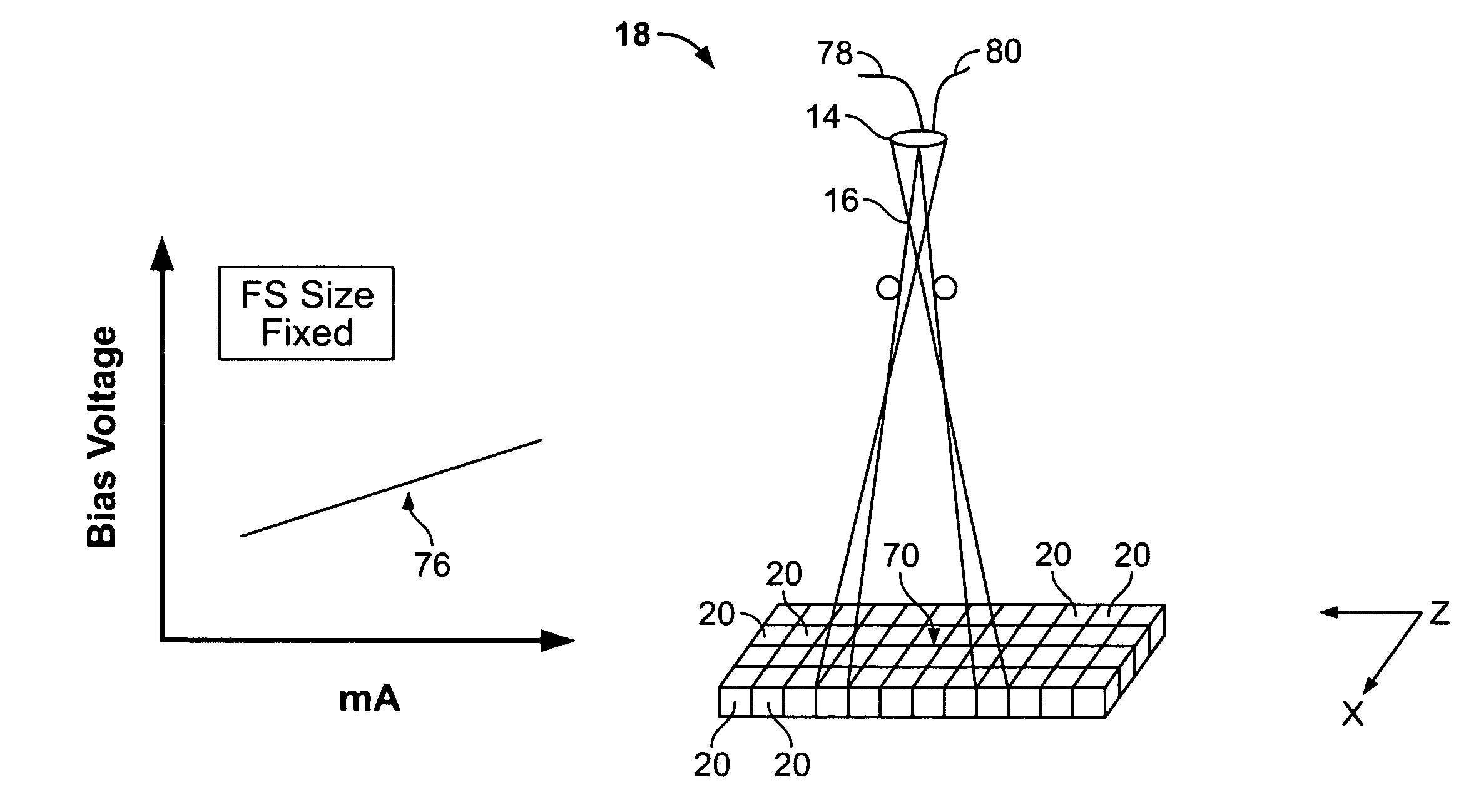
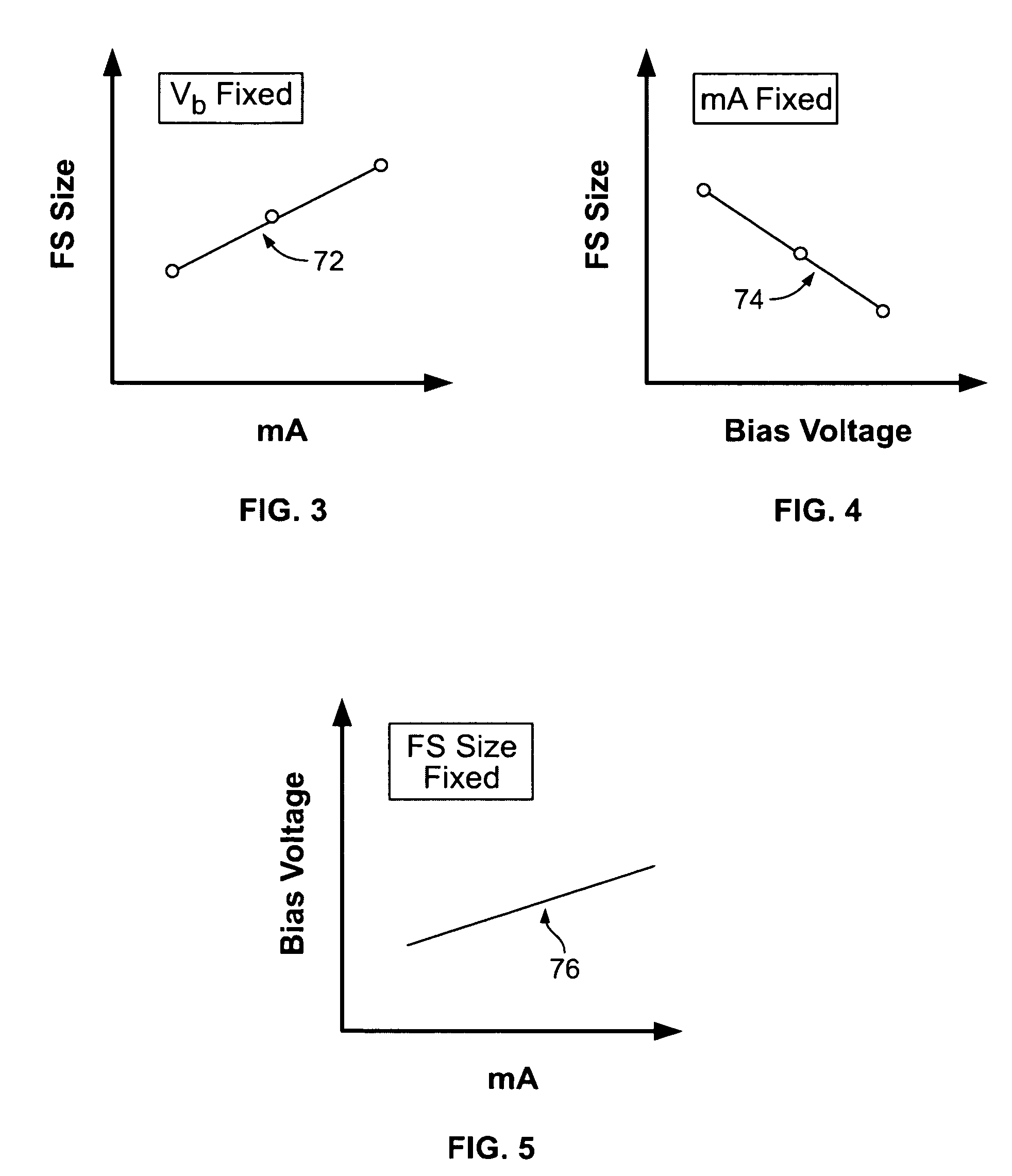
ActiveUS20070274457A1High peak powerCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingTomographyX-rayFocal Spot Size
A method for controlling focal spot size changes of an x-ray source in an imaging system includes measuring focal spot sizes as a function of a plurality of x-ray source operating parameters, determining a calibration table or transfer function utilizing the measured focal spot sizes as a function of the plurality of x-ray tube operating parameters, and utilizing the calibration table or transfer function to control focal spot size variations during operation of the imaging system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus to control radiation tube focal spot size
ActiveUS7409043B2High peak powerCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingTomographyX-rayFocal Spot Size
A method for controlling focal spot size changes of an x-ray source in an imaging system includes measuring focal spot sizes as a function of a plurality of x-ray source operating parameters, determining a calibration table or transfer function utilizing the measured focal spot sizes as a function of the plurality of x-ray tube operating parameters, and utilizing the calibration table or transfer function to control focal spot size variations during operation of the imaging system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
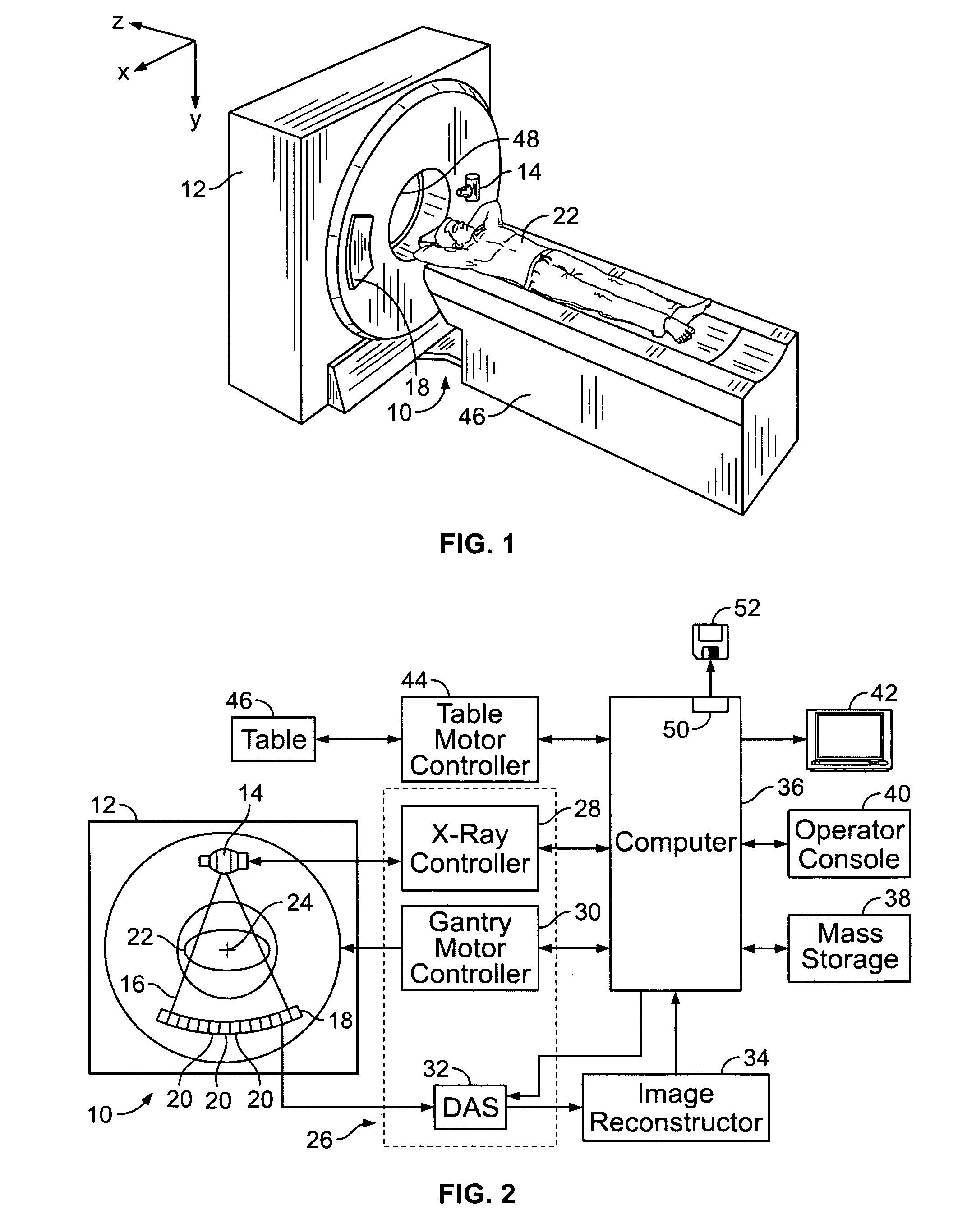
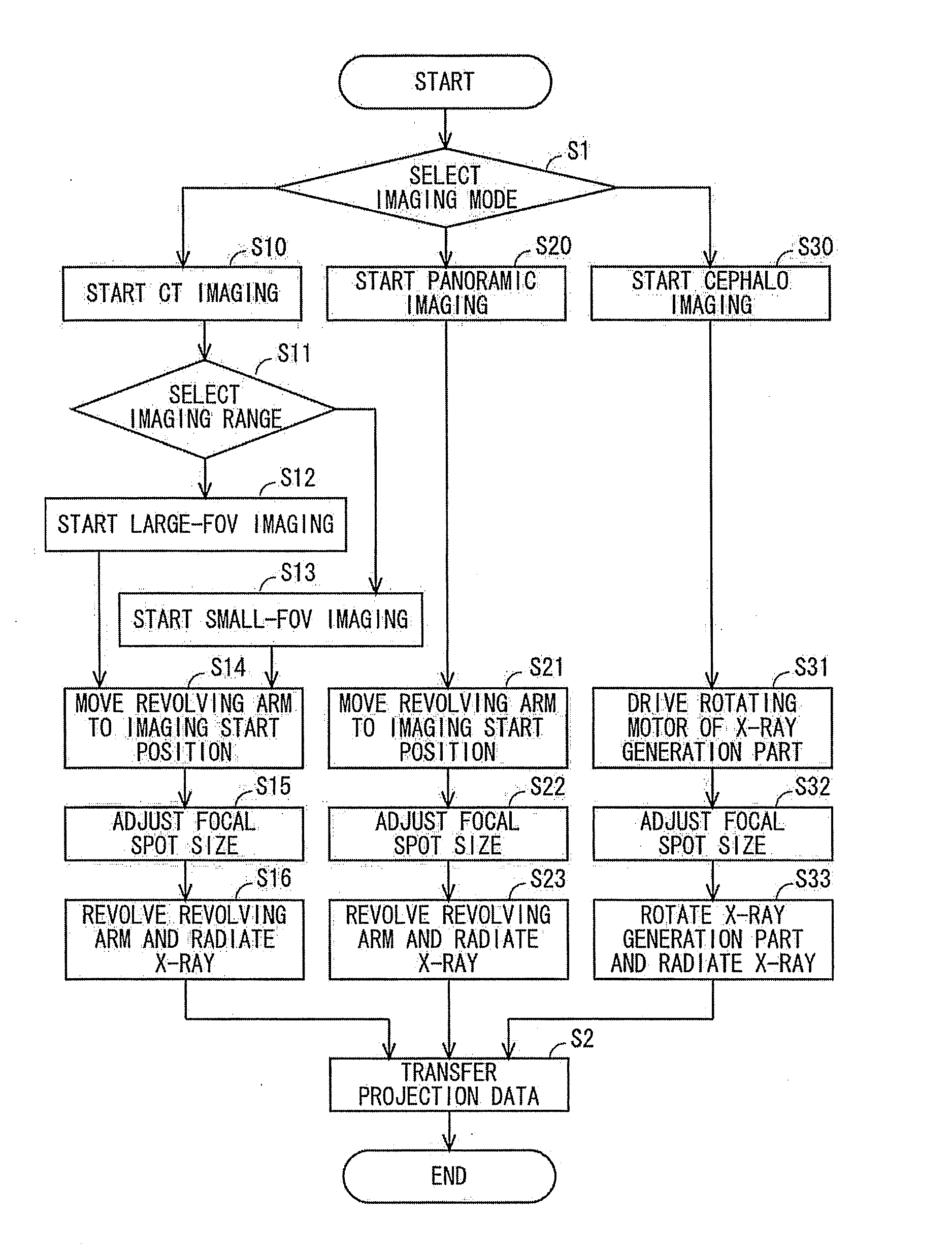
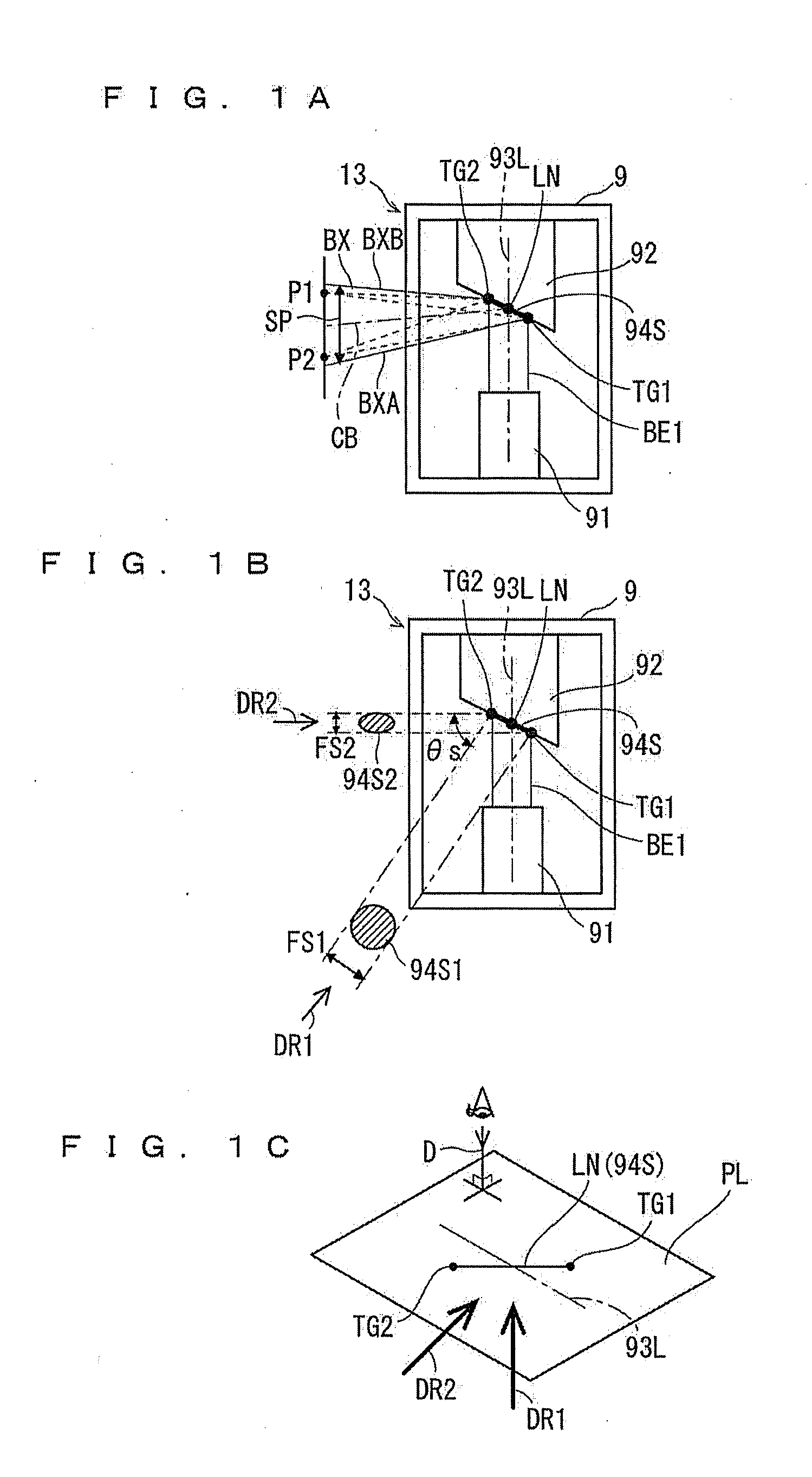
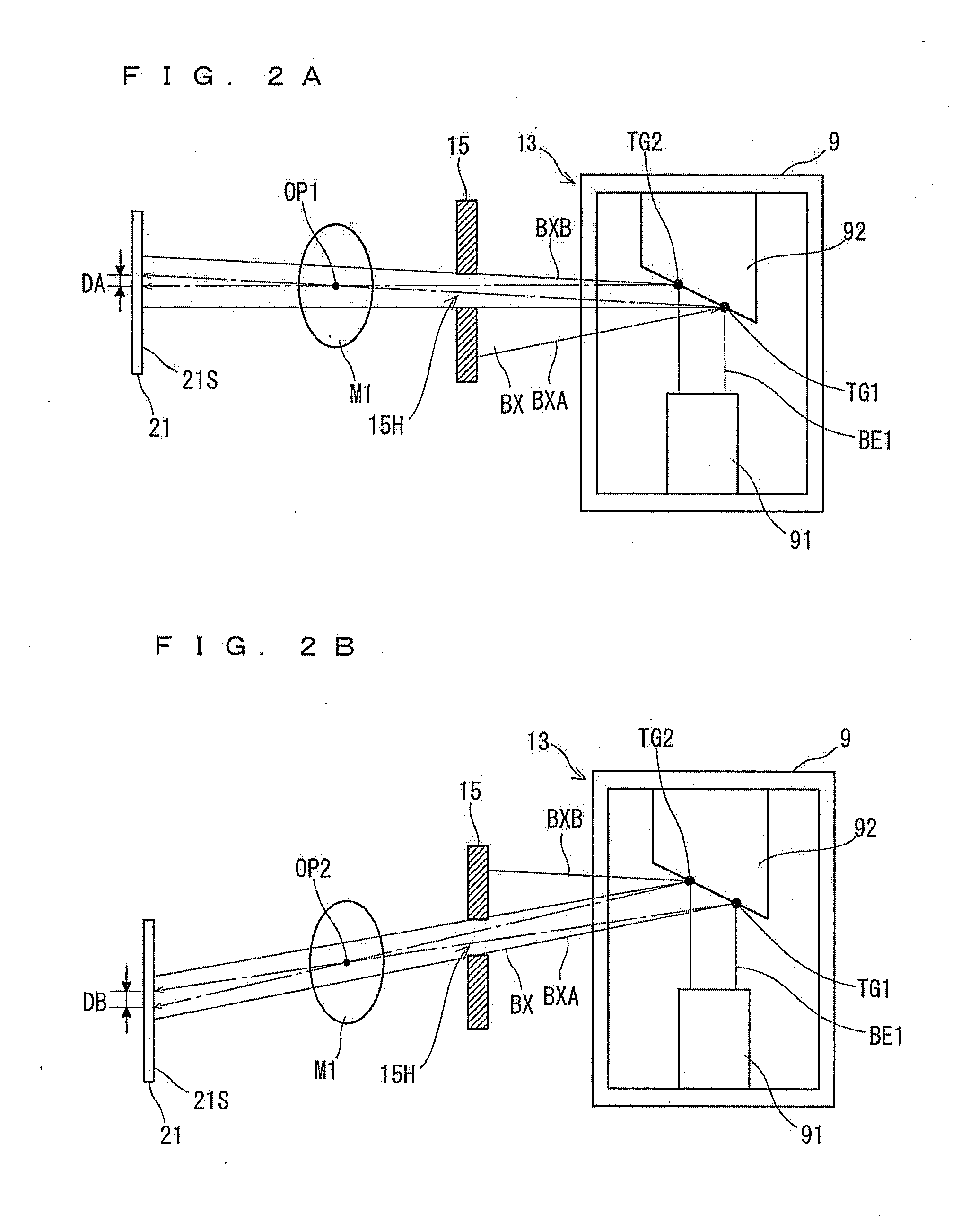
X-Ray Imaging Apparatus
ActiveUS20110222646A1Improve accuracyReduce opening widthRadiation/particle handlingX-ray tube electrodesSoft x rayX ray image
An X-ray imaging apparatus includes an X-ray generation part, an X-ray detection part, and a revolution drive mechanism. The X-ray generation part has an X-ray generator including a cathode and an anode, and emits an X-ray beam from the X-ray generator. The X-ray detection part detects the X-ray beam. The revolution drive mechanism performs X-ray imaging by revolving the X-ray generation part and the X-ray detection part around the object while the X-ray generation part and the X-ray detection part are opposed to each other with said object interposed therebetween. The X-ray imaging apparatus controls a restriction part to thereby restrict an X-ray transmission in such a manner that the focal spot size of an X-ray beam used in X-ray CT imaging of a relatively narrow imaging region is smaller than the focal spot size of an X-ray beam used in X-ray CT imaging of a relatively large imaging region.
Owner:MORITA MFG CO LTD
Air coupled ultrasonic phased array detection device
InactiveCN107688050AImprove signal-to-noise ratioEasy to quantifyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSignal-to-quantization-noise ratioPhased array
An air-coupled ultrasonic phased array detection device, the transmission signal is sent to the air-coupled ultrasonic probe by the ultrasonic transmitter receiver, and the ultrasonic wave excited by the probe is incident into the inside of the test piece at a certain angle; The wave signal is received by the ultrasonic probe and transmitted to the signal receiver. The signal is amplified by the preamplifier and enters the data processing unit. After delay superposition and imaging processing, the imaging of the scanning result at a certain angle is completed. Scanning in multiple angles and depth directions can be completed through different emission pulse settings without moving the probe, and a wide range of detection results can be obtained from the content of the tested specimen. Because the air-coupled ultrasonic probe is used, there is no need to touch the detection surface during work, which prolongs the service life of the probe; through the parameter setting of the transmission waveform in the early stage, the length of the focal column, the size of the focus and the direction of the sound beam can be optimally controlled. It has certain advantages in terms of ratio and defect detection rate.
Owner:日探科技(苏州)有限公司
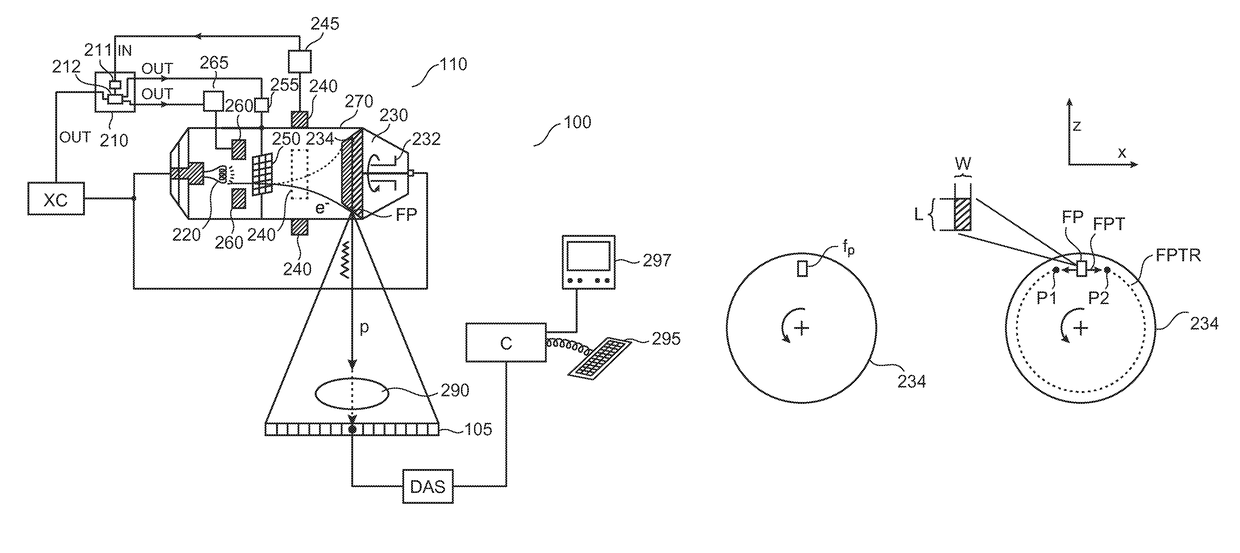
Blanking of electron beam during dynamic focal spot jumping in circumferential direction of a rotating anode disk of an x-ray tube
ActiveUS20150098548A1Secure advantageReduce in quantityRadiation diagnostic device controlCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingLight beamElectron
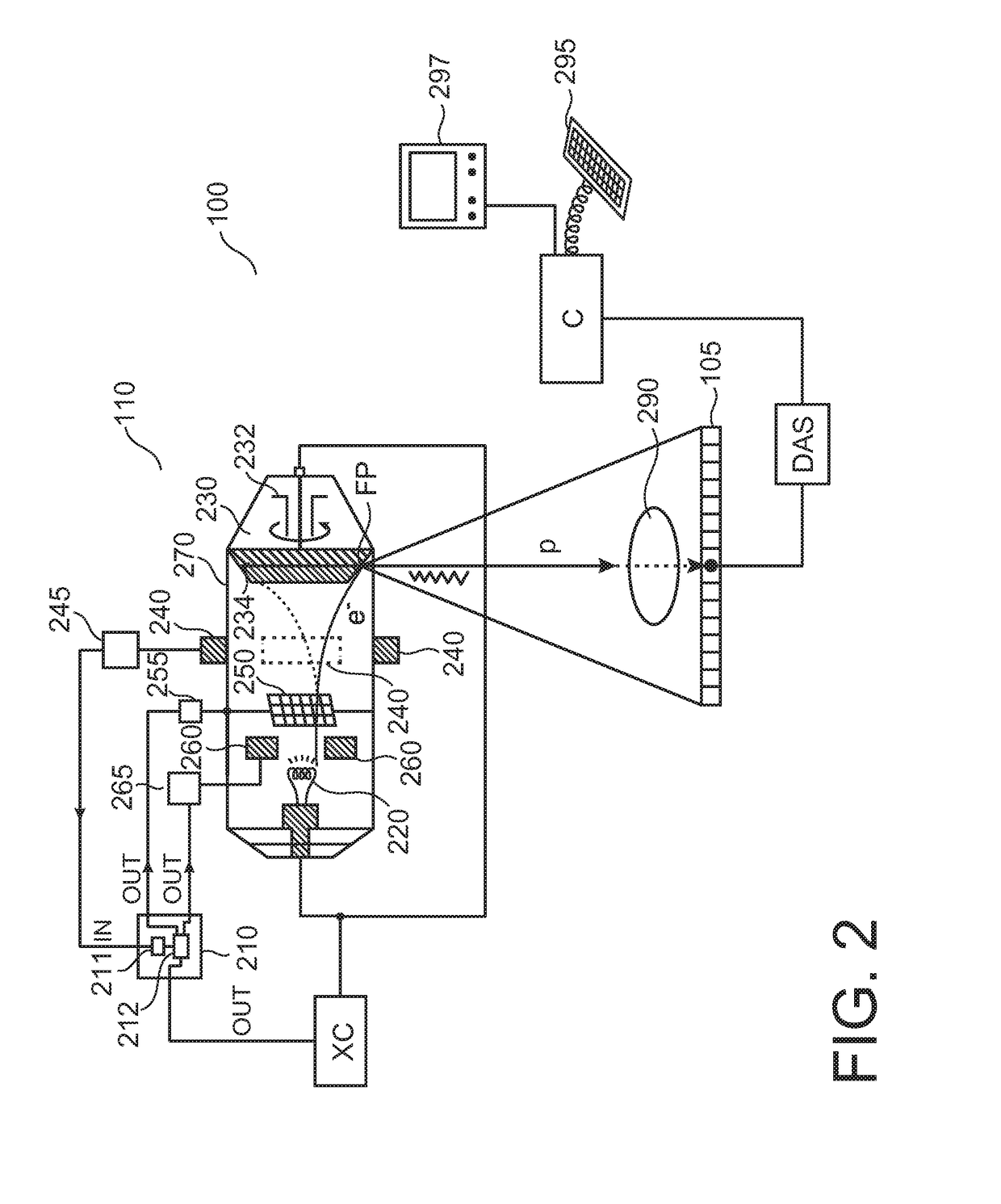
An apparatus (210) and method for total or partial blanking of an electron beam (e) during a jump between the 2 or more positions of a dynamic focal spot (FP) movement in circumferential direction of the electron beam impinging on the focal track (FPTR) of a rotating target disk (230) of a X-ray tube (110). Alternatively the focal spot size can be increased during this short time interval. Overheating of the anode at the focal spot can be prevented.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
X-ray system with efficient anode heat dissipation
InactiveCN102088909ACathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingComputerised tomographsHigh resolution imagingX-ray
X-ray systems for use in high-resolution imaging applications with an improved power rating are provided. An X-ray source comprises at least one integrated actuator unit (206, 206', 206a or 206b) for performing at least one translational and / or rotational displacement by moving the position of the X-ray source's anode (204, 204', 204a' or 204b') relative to a stationary reference position. This helps to overcome power limitations due to an overheating of the anode at its focal spot position (205). In addition to that, a focusing unit (203) for allowing an adapted focusing of the anode's focal spot (205) which compensates deviations in the focal spot size resulting from said anode displacements and / or a deflection means (211, 21 Ia or 21 Ib) for generating an electric and / or magnetic field deflecting the electron beam (202, 202a or 202b) in a direction opposite to the direction of the rotary anode's displacement movement may be provided.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Laser welding apparatus and method
A laser welding apparatus includes a laser welding unit including a first lens adapted to focus a laser beam; a second lens adapted to diffuse the laser beam to the first lens; and a third lens adapted to guide the laser beam to the second lens. The relative positions of the first lens, the second lens, and the third lens, are adjusted to adjust a diffusion angle and a beam width of the laser beam entering the first lens. The laser welding apparatus performs: actuating the laser welding unit to travel at a predetermined speed along a predetermined trajectory; directing the laser beam at a first welding spot; adjusting the focal length to focus the laser beam at the first welding spot; holding the laser focal spot size substantially constant; and directing the laser beam at a second welding spot after completion of welding for the first welding spot.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD +1
X-ray imaging system with automatic image resolution enhancement
InactiveUS20050238140A1Improve imaging resolutionExpand field of viewRadiation/particle handlingMammographyImage resolutionX-ray
An automated X-ray imaging system and method for producing a plurality of X-ray imaging signals having selectively enhanced image resolutions, e.g., for magnifying the field of view and providing a display image having features not otherwise visible to an unaided human eye. Successive doses of X-ray radiation are applied to a portion of the subject to produce corresponding image signals. Such doses of X-ray radiation are controlled by controlling X-ray radiation characteristics, such as intensity, focal spot size, focal spot location, focal spot shape, or collimation, to cause a subsequent image signal to differ from a prior image signal in one or more image characteristics, such as image resolution.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST TECH
Reflecting-type super diffraction line focusing device based on metal strip-shaped antenna array
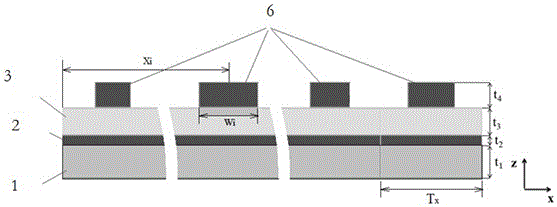
The invention provides a reflecting-type super diffraction line focusing device based on a metal strip-shaped antenna array. The device sequentially comprises the metal strip-shaped antenna array, a dielectric layer, a metal membrane layer and a substrate layer. Each metal strip-shaped antenna array unit is of a Y-direction array structure formed by arranging metal strip-shaped antennas in the Y direction by taking Ty as a cycle, and the metal strip-shaped antenna array units are arranged in the X direction by taking Tx as a cycle to form the metal strip-shaped antenna array. For the given incident light wavelength gamma, regulation and control over the amplitude and the phase of reflected light in the space plane are achieved by selecting a metal material, a material of the dielectric layer and the thickness of the metal strip-shaped antennas and changing the length L and the width W of metal strips, the length Li and the width Wi of the i metal-shaped antenna of which the center is located at xi are obtained according to amplitude space distribution A(xi) and phase space distribution P(xi), and then a far-field super diffraction line focusing function on the reflected light is achieved. According to device, the diffraction limit can be broken through, the focal spot size smaller than the diffraction limit is achieved, the sidelobe peak ratio is low, and the peak strength is high.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
X-ray optical systems with adjustable convergence and focal spot size
ActiveUS20110317814A1NanoinformaticsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionX-ray opticsLength wave
An x-ray optical system includes a multiple corner optic assembly including an adjustable aperture assembly located in close proximity to the optic assembly. The adjustable aperture assembly enables a user to easily and effectively adjust the convergence of an incident beam of x-rays or the optic focal spot size. The adjustable aperture assembly may further enable a user to condition x-rays of one wavelength and block x-rays of another wavelength and thereby reduce the amount of background radiation exhibited from x-rays of more than one wavelength.
Owner:RIGAKU INNOVATIVE TECH
Device and method for x-ray tube focal spot size and position control
InactiveCN101558468ACathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingX-ray apparatusControl signalParameter control
A device and method for X-ray tube focal spot parameter control, wherein stray electrons are detected in an X-ray tube. The detected electrons lead to a signal having a characteristic pattern. The characteristic pattern may be evaluated, and based on the evaluation a controlling signal may be outputted so that a fast and exact controlling of the operating parameters of an X-ray tube may be carried out based on the detected stray electrons.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
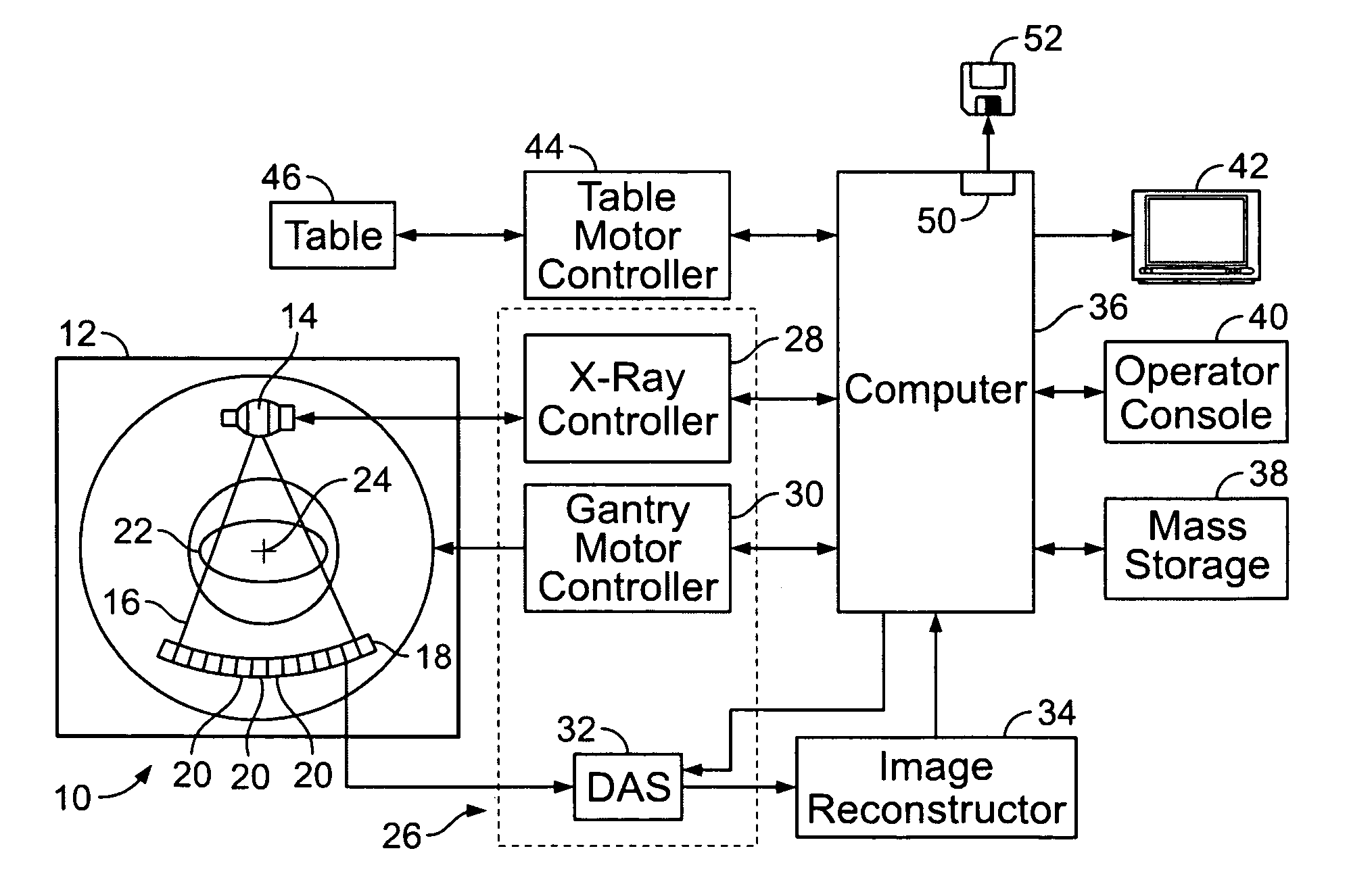
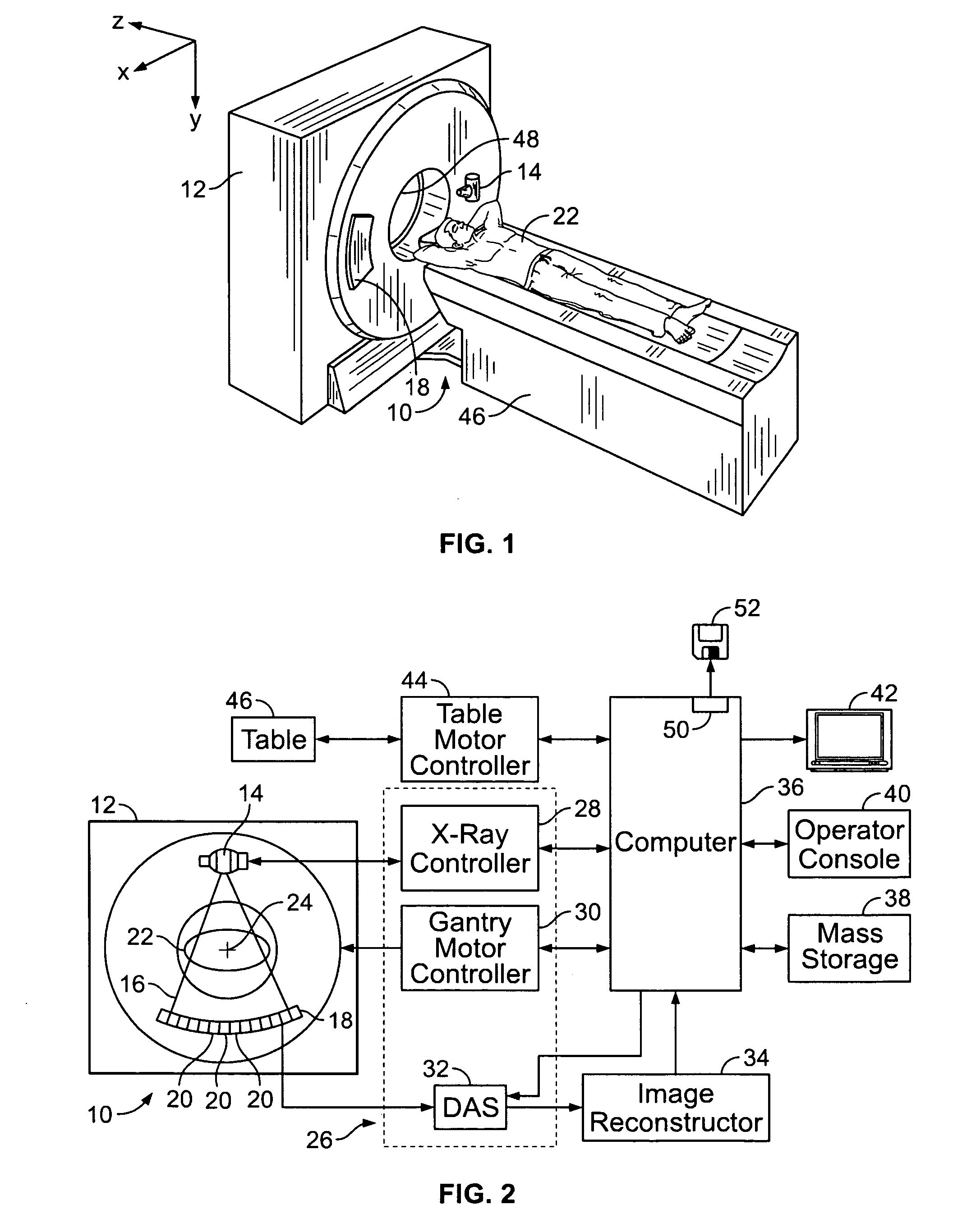
Systems, apparatus and methods for X-ray imaging
A cathode cup is provided. The cathode cup includes one or more pockets; and one or more filaments associated with the one or more pockets. A same number of pockets as filaments are present. Each pocket is associated with exactly one filament and is configured to have a length that is tailored to a length of the filament. The cathode cup can be used in an X-ray system having an anode and a cathode. A method of electron beam shaping is provided. The method includes the following steps. A computer-simulated model of a cathode cup is created. The model is used to predict focal spot dimensions. The predicted focal spot dimensions are compared to desired focal spot dimensions. The steps of creating, using and comparing are repeated until the predicted focal spot dimensions match the desired focal spot dimensions. A cathode cup is created based on the computer-simulated model.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
High-resolution computed tomography or c-arm imaging
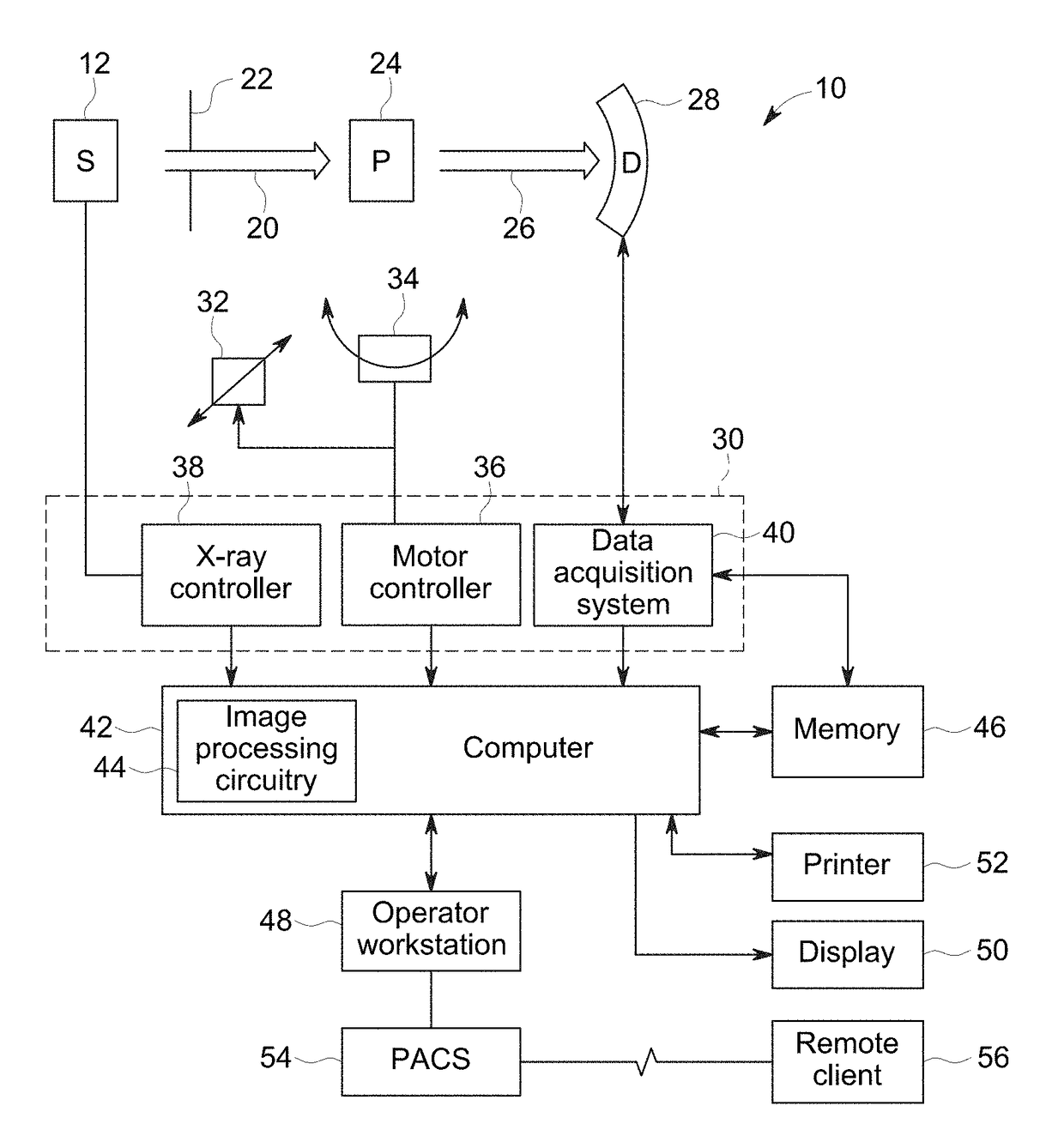
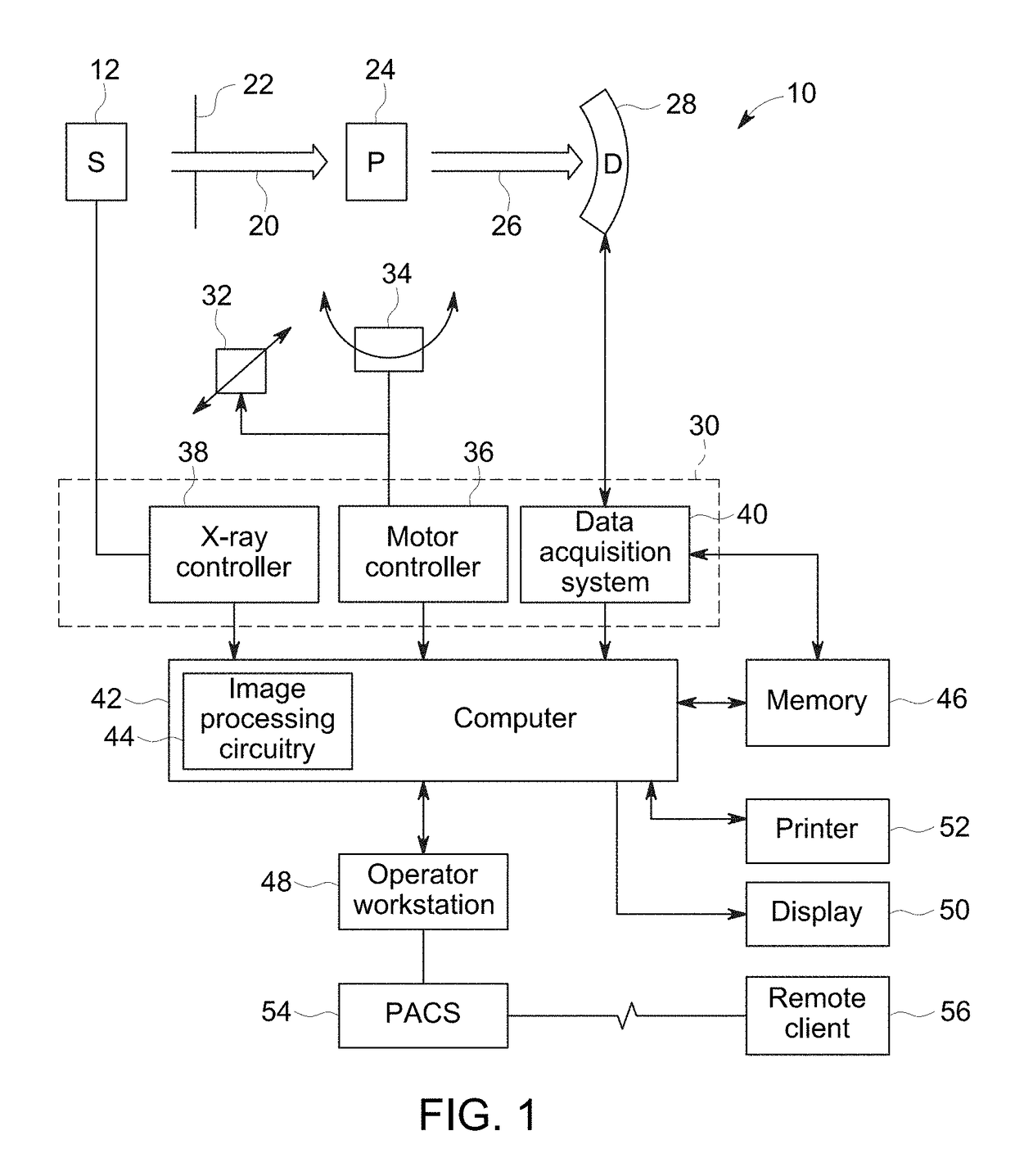
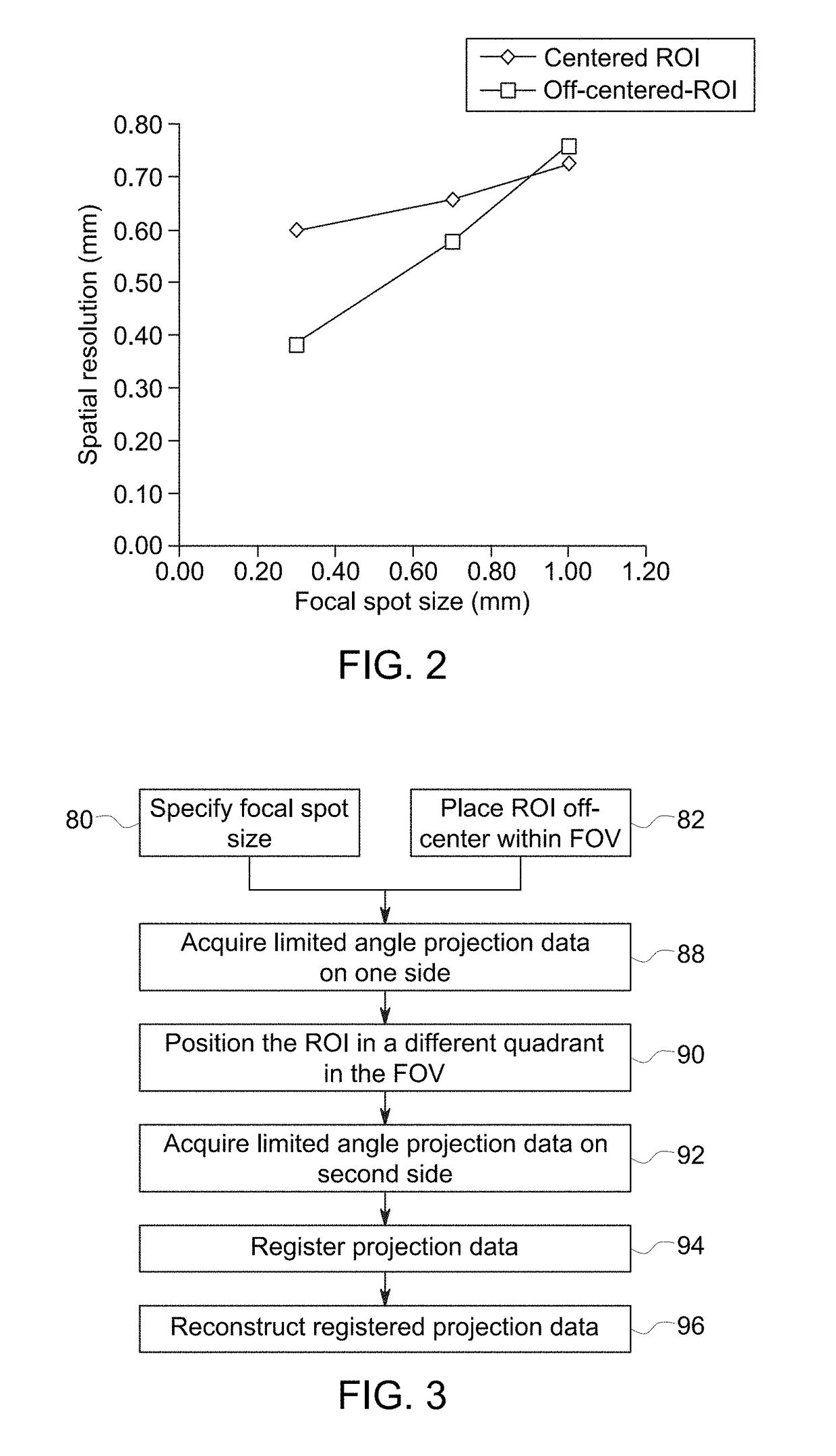
InactiveUS20170215818A1High resolutionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingHigh-resolution computed tomographyHigh resolution imaging
A high-resolution imaging approach is described. The described approach includes use of a small focal spot size and positioning of the patient offset from the center of the imaging volume. The off-center displacement is combined with a small focal spot size and with modified image reconstruction methods to provide high intrinsic spatial resolution without hardware changes to the imaging system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
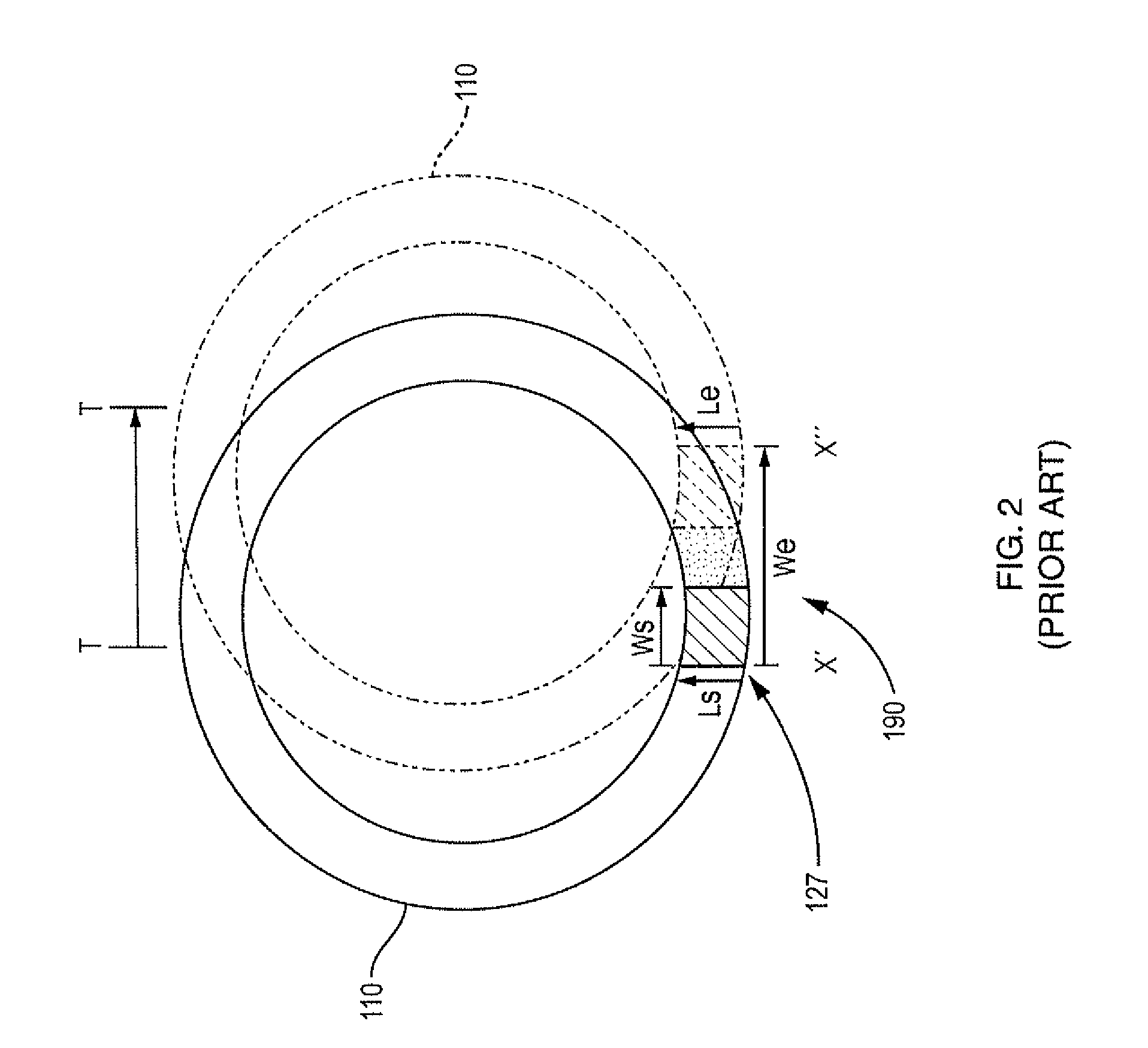
Focal spot size measurement with a movable edge located in a beam-shaping device
InactiveCN101500487AHigh edge response magnificationReduce noiseHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-ray apparatusX-rayMagnification
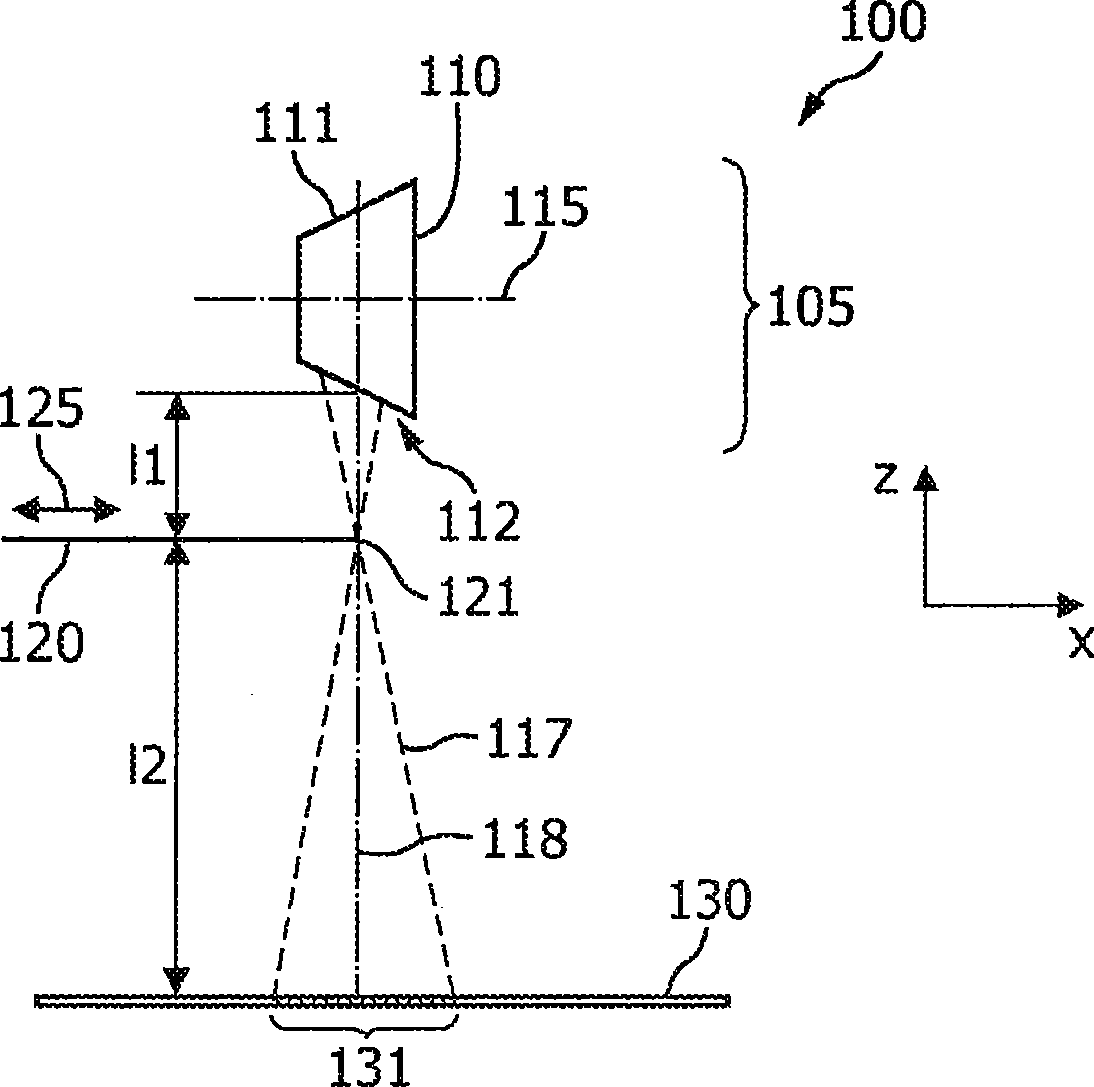
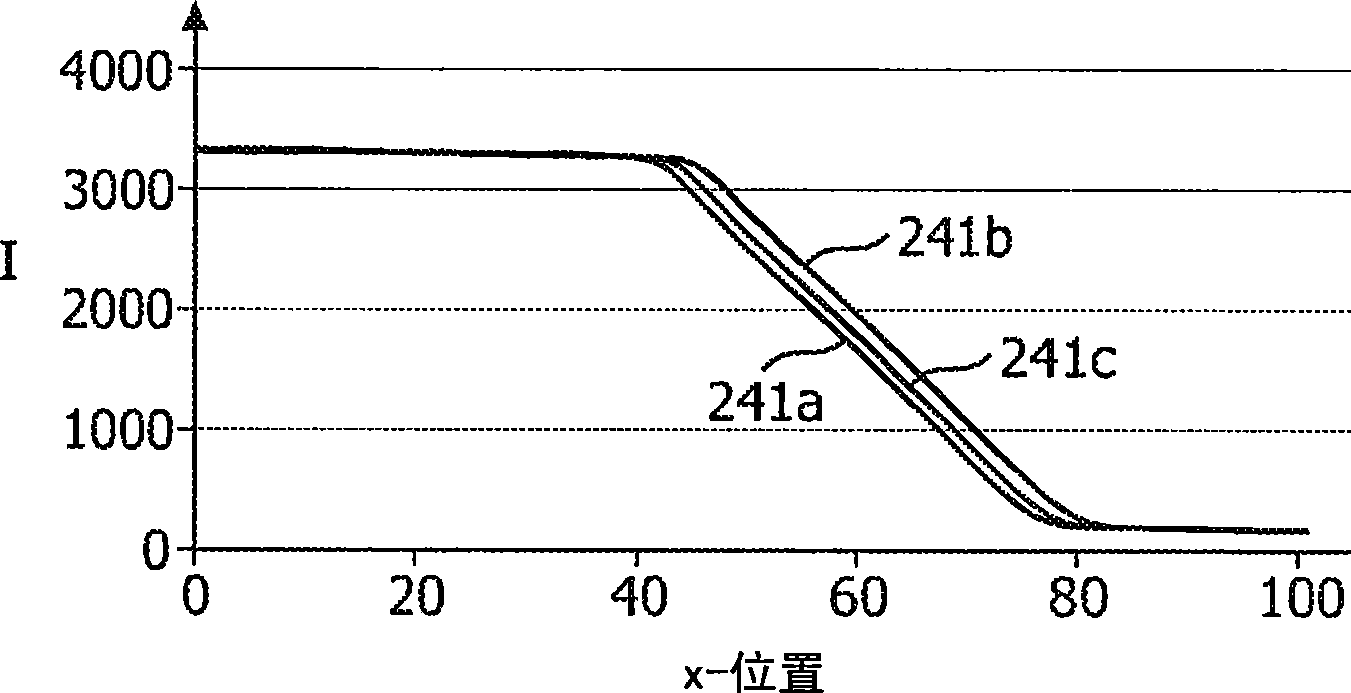
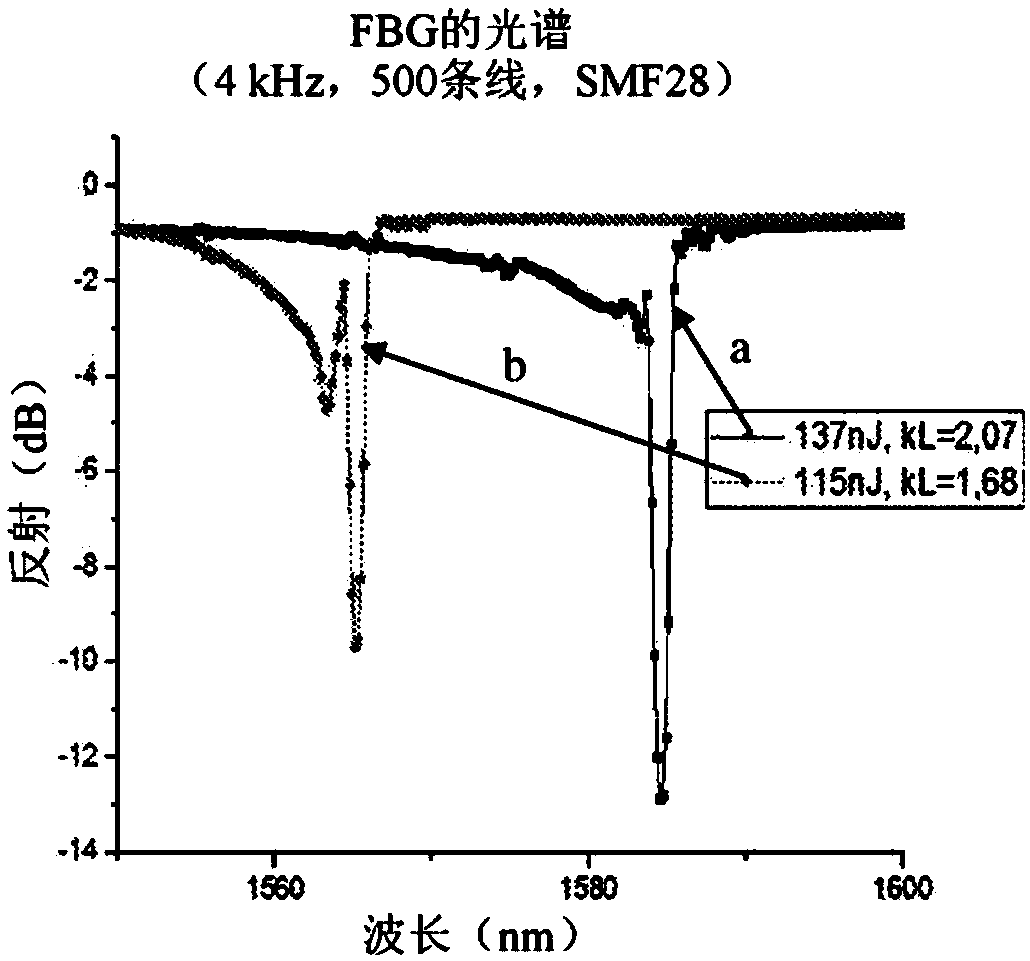
It is described a method for measuring the sharpness in an X-ray system (100). The measurement is based on a common edge response. An edge device (120) representing the projection device is placed within a beam-shaping device (470). Due to a high geometrical magnification factor the edge response function (241a) and also both an impulse response function (246a) and a modulation transfer function (251a) will predominately depend on the size of the focal spot (112) rather than on a pre- sampling spread function of a detector (130) being used for receiving the X-radiation (117), which has laterally passed the edge device (120).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
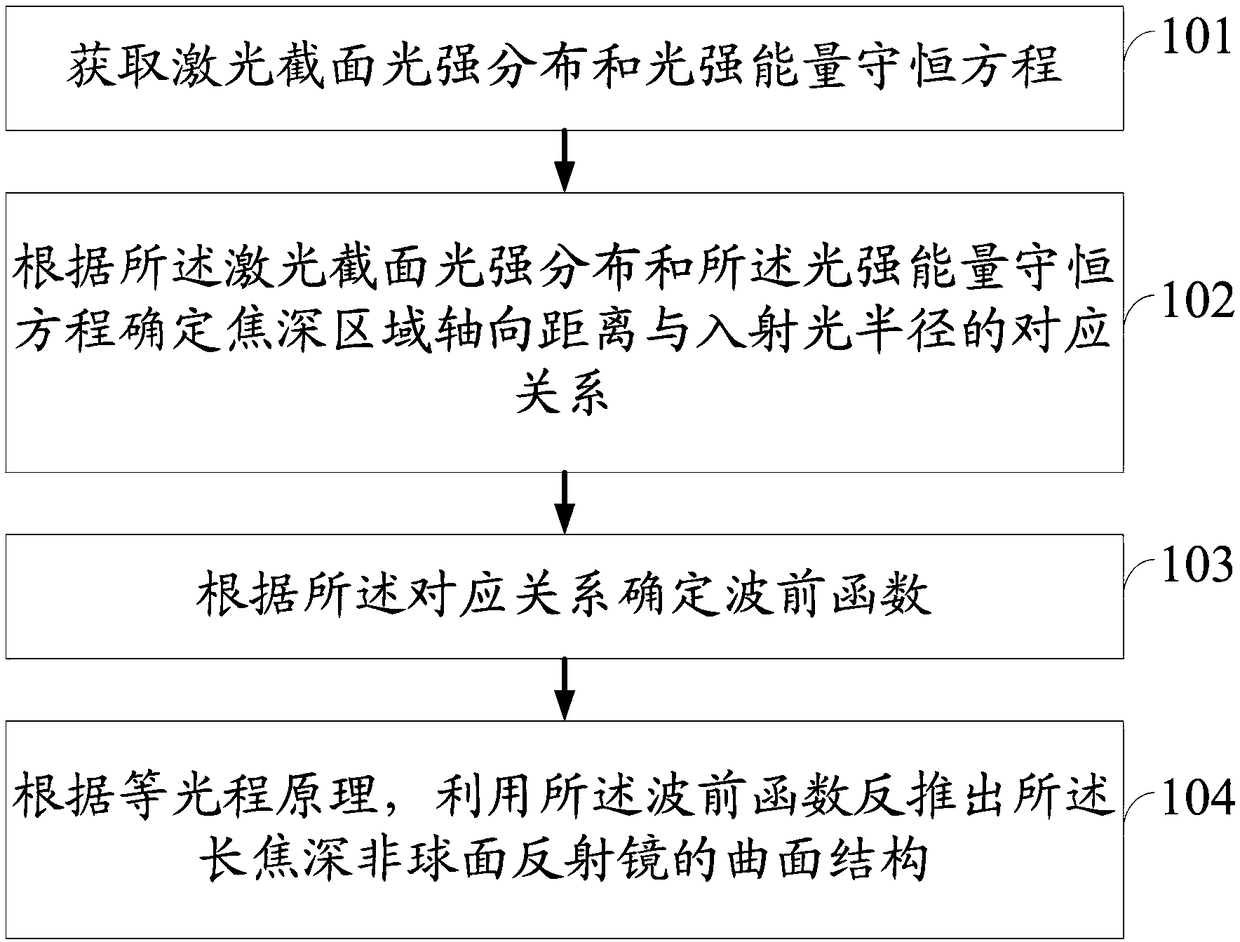
Method and system for determining curved surface structure of long-focal-length non-spherical reflector
ActiveCN108873322AUniform long focal depth characteristicsAchieve small focal spotOptical elementsHigh power lasersSurface structure
The invention discloses a method and system for determining a curved surface structure of a long-focal-length non-spherical reflector. The method and system can determine the curved surface structureof the long-focal-length non-spherical reflector, so as to prepare the non-spherical reflector with the uniform long focal length characteristic according to the curved structure. Compared with a conventional parabolic reflector, the non-spherical reflector prepared according to the curved structure is equivalent in technical implementation difficulty, can achieve the same lateral focal spot size,also can enable the long focal length to be prolonged by 10-100 times, and achieves a small focal spot and the long focal length, so the non-spherical reflector is good in application prospect for astrong field of high-power laser and material interaction.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Blanking of electron beam during dynamic focal spot jumping in circumferential direction of a rotating anode disk of an X-ray tube
ActiveUS9659739B2Small sizeReduced Power SpecificationsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation diagnostic device controlLight beamElectron
An apparatus (210) and method for total or partial blanking of an electron beam (e) during a jump between the 2 or more positions of a dynamic focal spot (FP) movement in circumferential direction of the electron beam impinging on the focal track (FPTR) of a rotating target disk (230) of a X-ray tube (110). Alternatively the focal spot size can be increased during this short time interval. Overheating of the anode at the focal spot can be prevented.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Femtosecond laser inscription
InactiveCN109641318AWelding/soldering/cutting articlesOptical waveguide light guidePulse beamFemto second laser
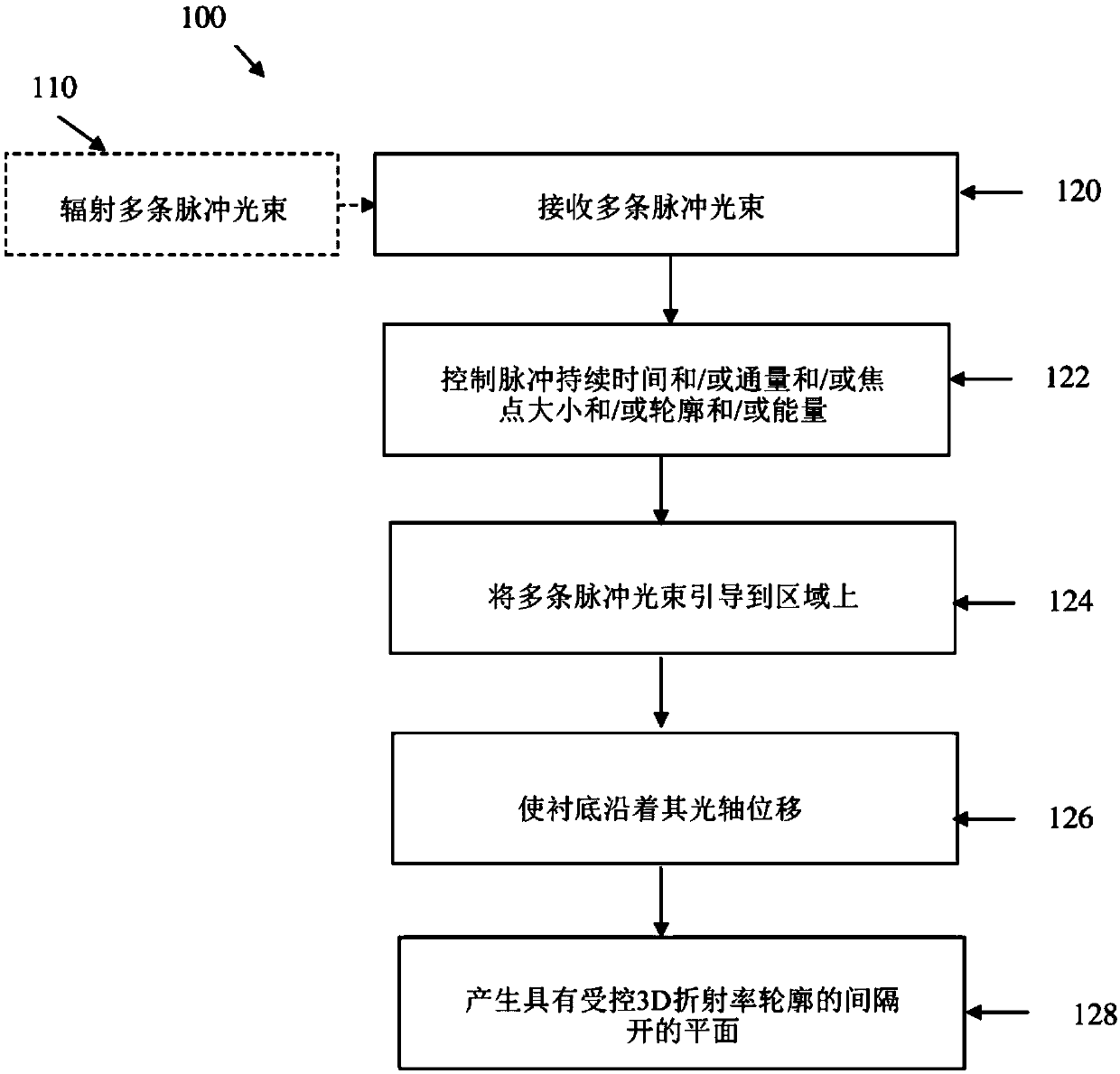
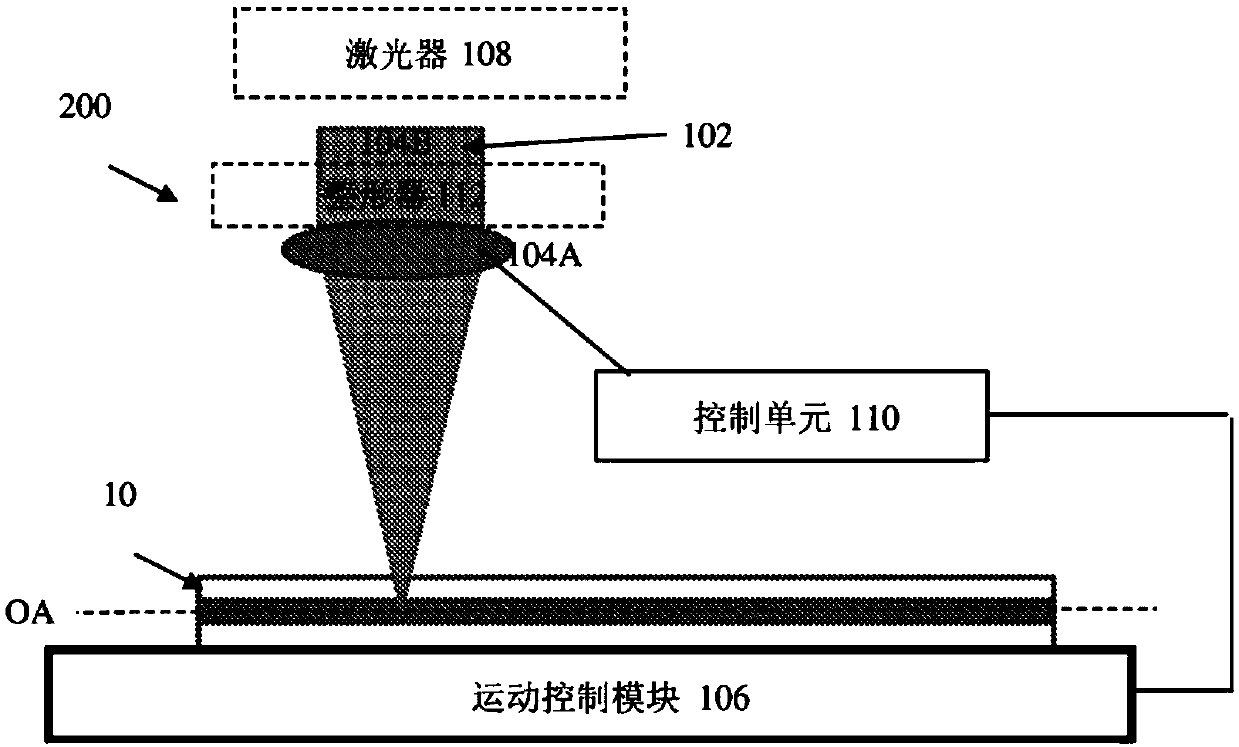
The present invention relates to a novel method and system for inscription of periodic patterns inside or on a surface of a substrate using femtosecond pulse lasers. The method comprises the followingsteps: (a) receiving a plurality of femtosecond laser pulsed beams, each beam having a certain pulse duration, flux, focal spot size, profile and energy at a certain wavelength of operation; (b) controlling at least one of the pulse duration, flux, focal spot size, focal spot shape, profile and energy of the plurality of laser pulsed beams; (c) directing the plurality of laser pulsed beams onto acertain region of a substrate having an optical axis, to thereby selectively induce at least one of local index change, microvoids and stress-modulated region at a point of interaction between each beam and the certain region; (d) controllably displacing the substrate along its optical axis to create the periodic patterns on a first plane of inscription along the optical axis; and (e) creating spaced-apart planes across the substrate having a controlled index profile at least in two dimensions.
Owner:CYPRUS UNIV OF TECH
Cathode assembly for use in x-ray generation
ActiveUS20170372863A1X-ray tube electrodesCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingX-rayOptoelectronics
A cathode assembly design is provided that includes two flat emitters, a longer emitter filament and a shorter emitter filament. In one implementation the focal spot sizes produced by the long and short emitters overlap over a range. Thus, one emitter filament may be suitable for generating small and concentrated focal spot sizes while the other emitter filament is suitable for generating small and large focal spots sizes.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Single beam dynamic focusing method
The invention relates to a single beam dynamic focusing method and belongs to the technical field of a laser device. A laser source emits a laser pulse which is focused on a pellet through a holographic grating. The wavelength of the laser pulse shows an increasing trend, and the variation range of the wavelength matches the focal spot size during a pellet compression variation process. The focusing, color separation and dynamic focusing functions on the laser pulse are realized simultaneously through the holographic grating. The single beam dynamic focusing method needs few optical elements and implements many functions. Compared with a traditional beam combination dynamic focusing method, the single beam dynamic focusing method generates more focal spots with different sizes. The variation process of the focal spots further matches the pellet compression variation process. The single beam dynamic focusing method has the characteristics of easy operation and high achievable degree, and does not have the problem that the amplification and saturation of short pulses reduce the output capacity of a laser system.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Systems, apparatus and methods for x-ray imaging
A cathode cup is provided. The cathode cup includes one or more pockets; and one or more filaments associated with the one or more pockets. A same number of pockets as filaments are present. Each pocket is associated with exactly one filament and is configured to have a length that is tailored to a length of the filament. The cathode cup can be used in an X-ray system having an anode and a cathode. A method of electron beam shaping is provided. The method includes the following steps. A computer-simulated model of a cathode cup is created. The model is used to predict focal spot dimensions. The predicted focal spot dimensions are compared to desired focal spot dimensions. The steps of creating, using and comparing are repeated until the predicted focal spot dimensions match the desired focal spot dimensions. A cathode cup is created based on the computer-simulated model.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Deep channel cathode assembly
ActiveUS20160358739A1Little generationX-ray tube electrodesX-ray tube multi-cathode assemblyEngineeringElectron
An improved cathode assembly is disclosed. The improved cathode assembly provides a deep channel for holding filament that enables generation of small focal spots, but is not limited in achieving larger focal spot sizes. The cathode assembly includes at least one deep channel and a filament arranged in a deep channel. The deep channel is configured in a cathode cup surface of the cathode assembly. The filament is arranged in the deep channel for enabling emission of electron beams from the cathode assembly.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com