Cylindrical type transverse magnetic-field permanent-magnet flux-switching linear motor
A permanent magnet linear motor and transverse magnetic field technology, which is applied in the direction of electrical components, electromechanical devices, electric components, etc., can solve the problems of complex manufacturing process, low space utilization rate, and large amount of permanent magnets, so as to achieve a small amount of permanent magnets, The effect of high electrical load and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
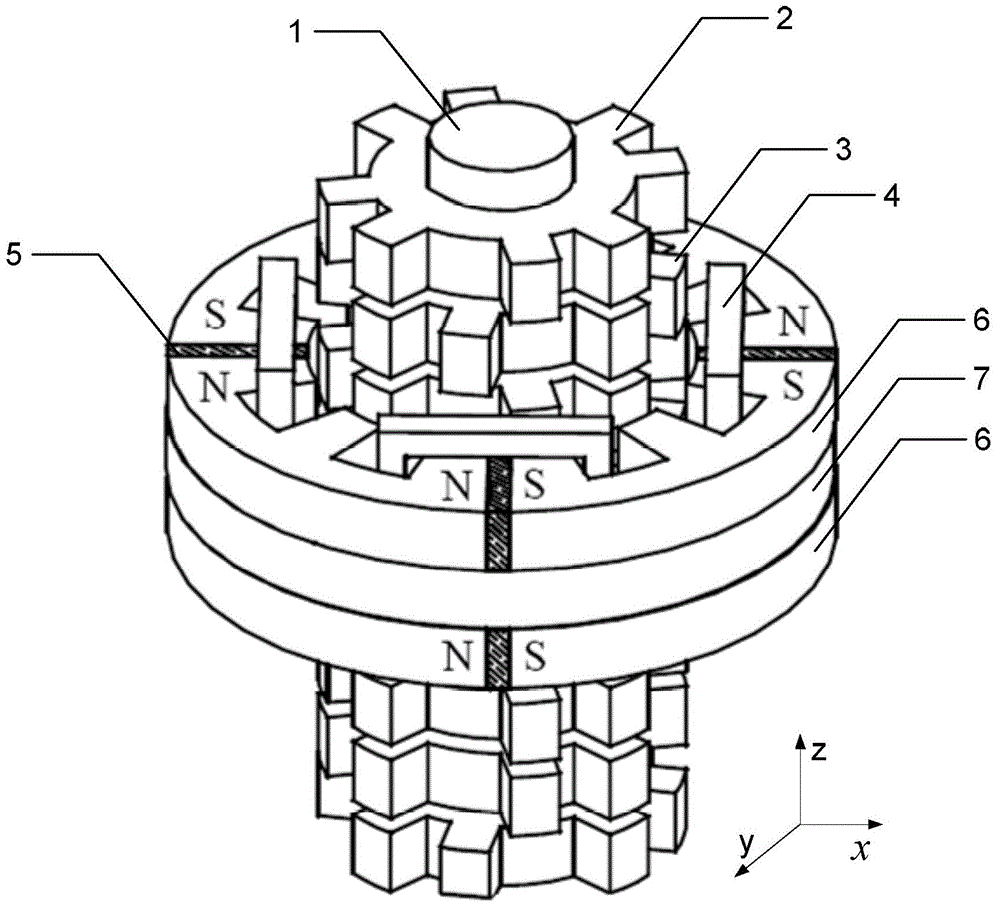
[0021] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the cylindrical transverse magnetic field switch flux linkage permanent magnet linear motor described in this embodiment includes a mover and a stator; the mover is arranged inside the stator, and the mover moves linearly inside the stator along the axial direction; And there is a radial air gap between the mover and the stator;
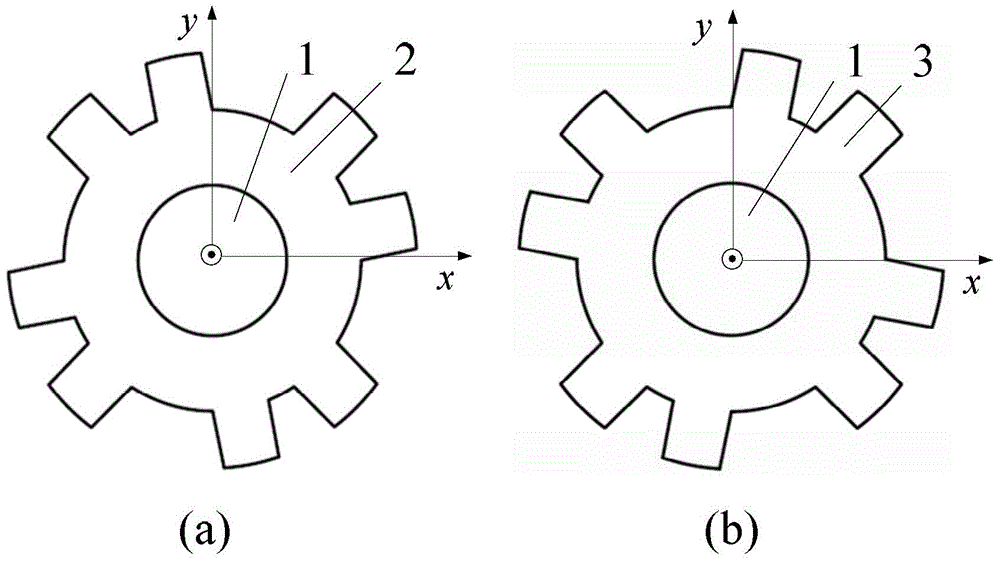
[0022] The stator includes m short stator modules, and the m short stator modules are evenly distributed along the axial direction to form an m-phase motor; each short stator module includes p stator units and a plurality of stator magnetic isolation rings 7, between two adjacent stator units The axial space between them is provided with a stator magnetic isolation ring 7; each stator unit is formed by splicing 2n E-shaped structure iron cores 6 along the circumferential direction, and the inner arc surface of the E-shaped structure iron core 6 is pr...
specific Embodiment approach 2
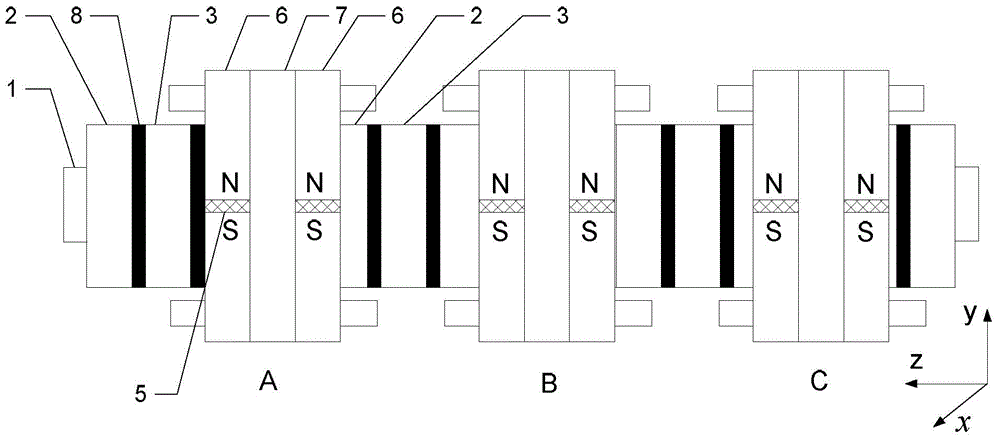
[0030] Specific implementation mode two: the following combination figure 2 Describe this embodiment. This embodiment will further explain Embodiment 1. The short stator modules of each phase are independent, and the distance d between two adjacent short stator modules is:
[0031] d=(2k+2 / m)τ p ;
[0032] Among them, τ p is the pole distance of the mover, and k is the reserved end winding space coefficient.
[0033] The axial direction is set as the z direction, and the plane where the first mover core 2 is located is the xoy plane. Arrange m sets of short stator modules in parallel along the axial direction, with a distance of (2k+2 / m)τ p , so that the electrical angle difference between two adjacent groups of short stator modules is 360 / m degrees to form an m-phase motor. figure 2 Given a motor p=2, m=3, two stator units are arranged in each group of short stator modules, a three-phase motor. Each phase is modularized and the magnetic circuit is independent, which fac...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0034] Specific implementation mode three: the following combination figure 2 Describe this embodiment, this embodiment will further explain Embodiment 1, the axial thickness L of the first mover core 2 and the second mover core 3 r and the axial thickness L of the stator unit s equal.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com