Patents
Literature
180 results about "Floating potential" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
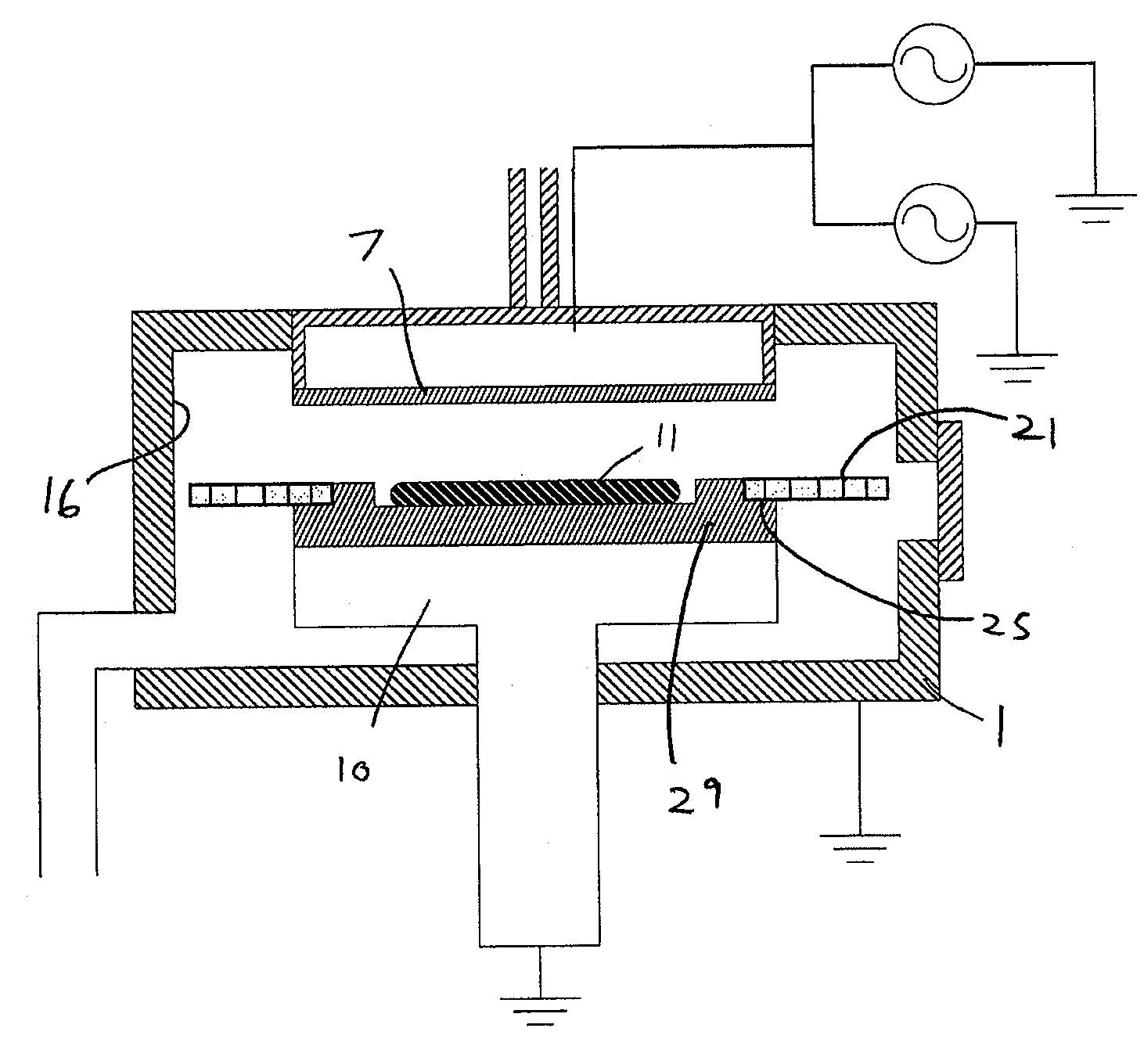
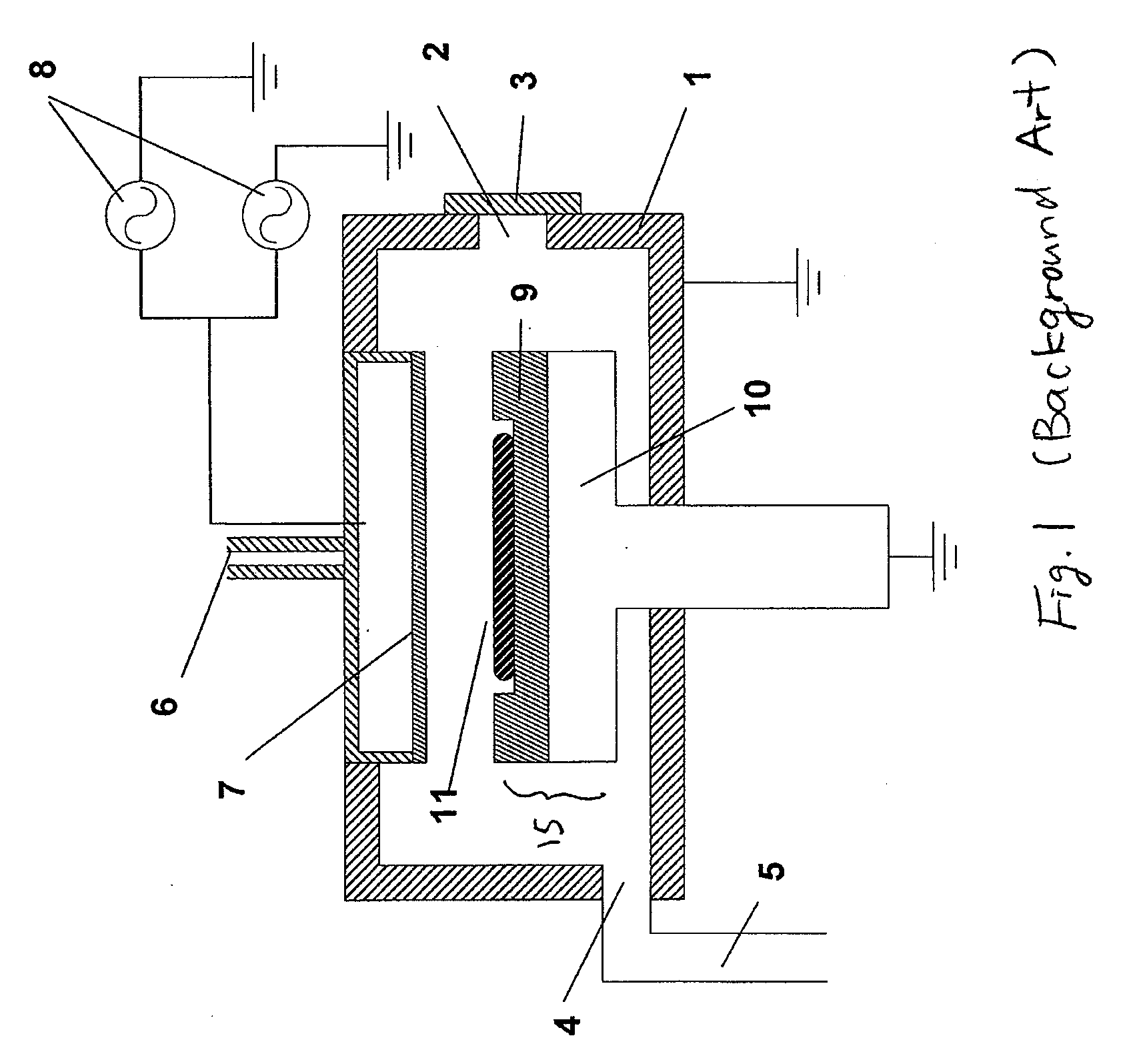
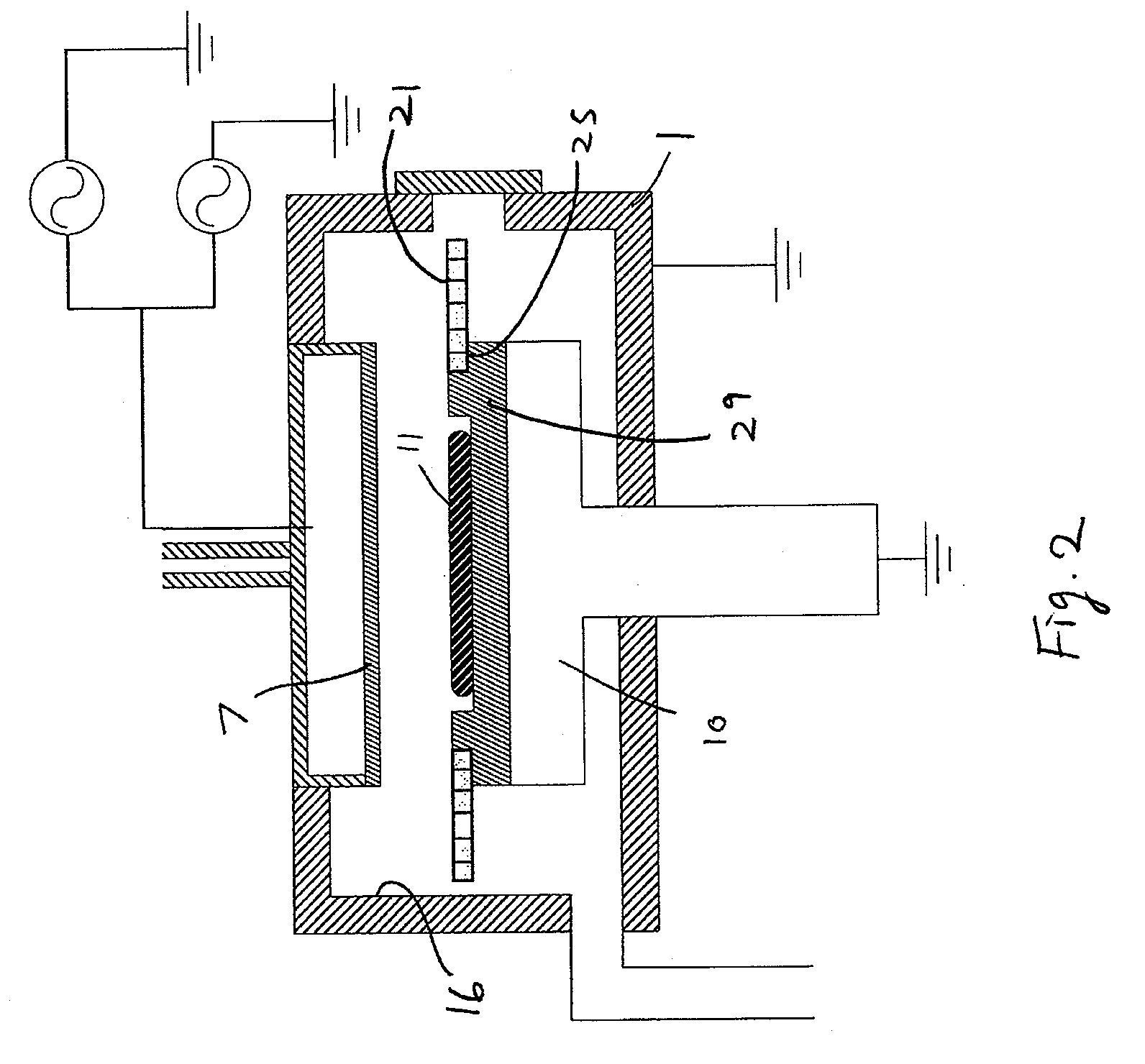
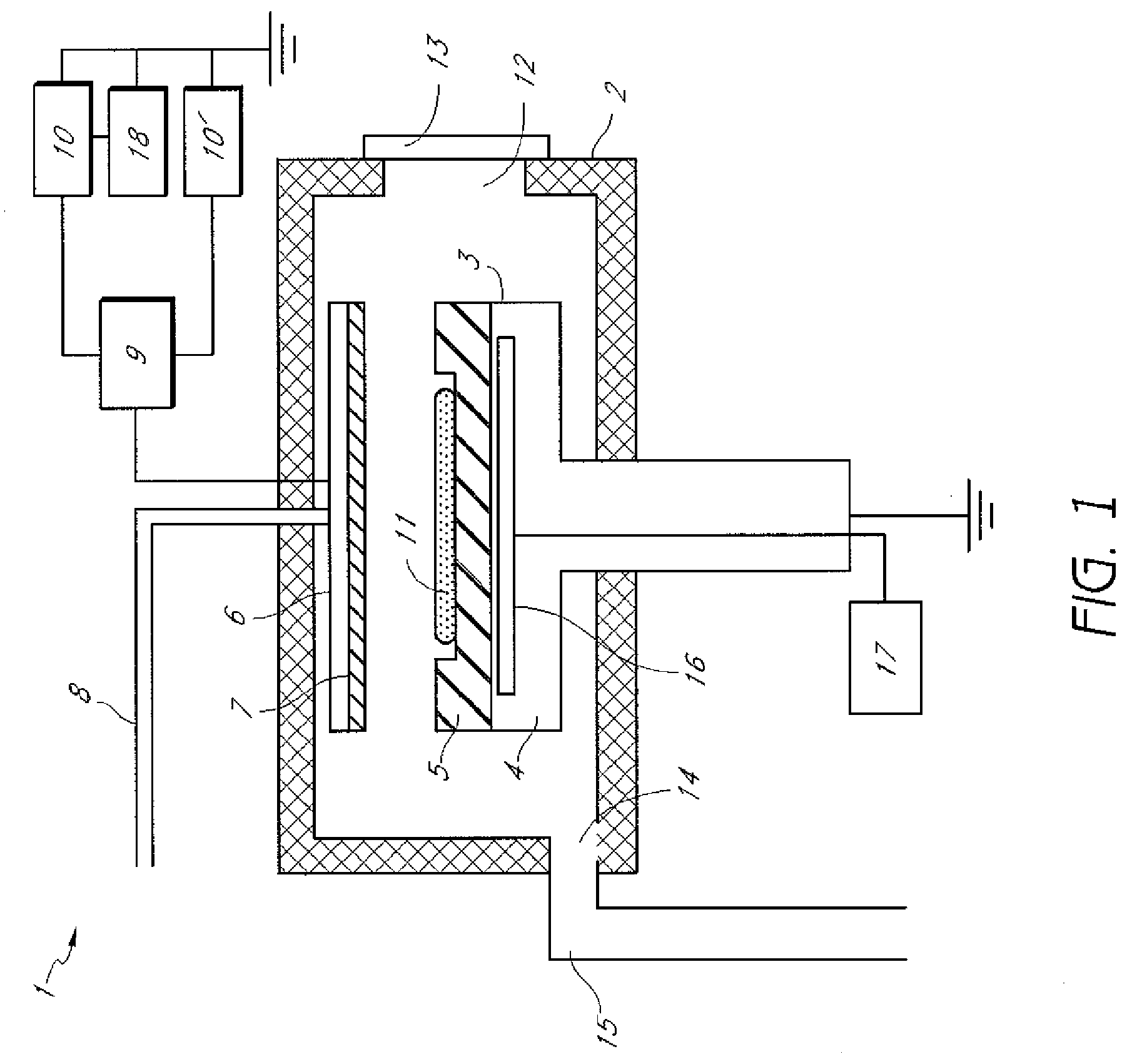
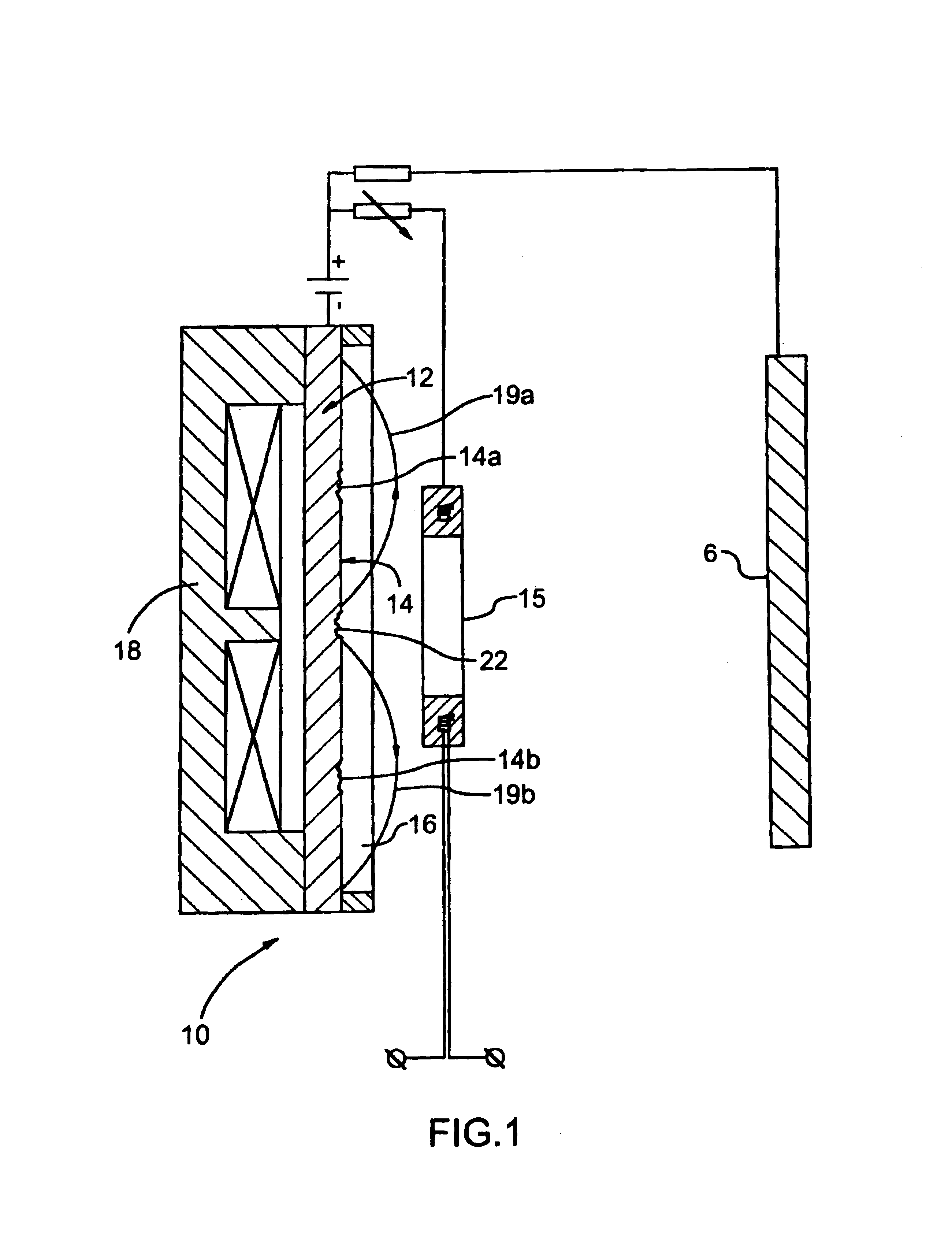
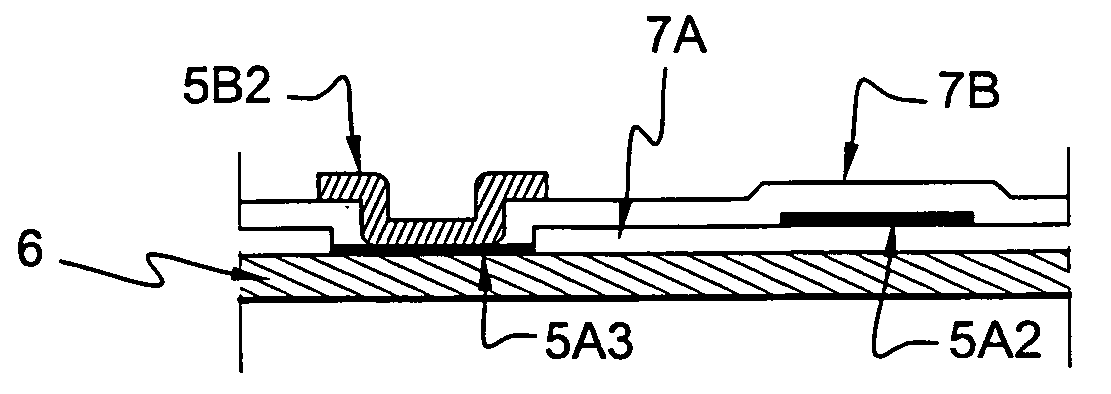
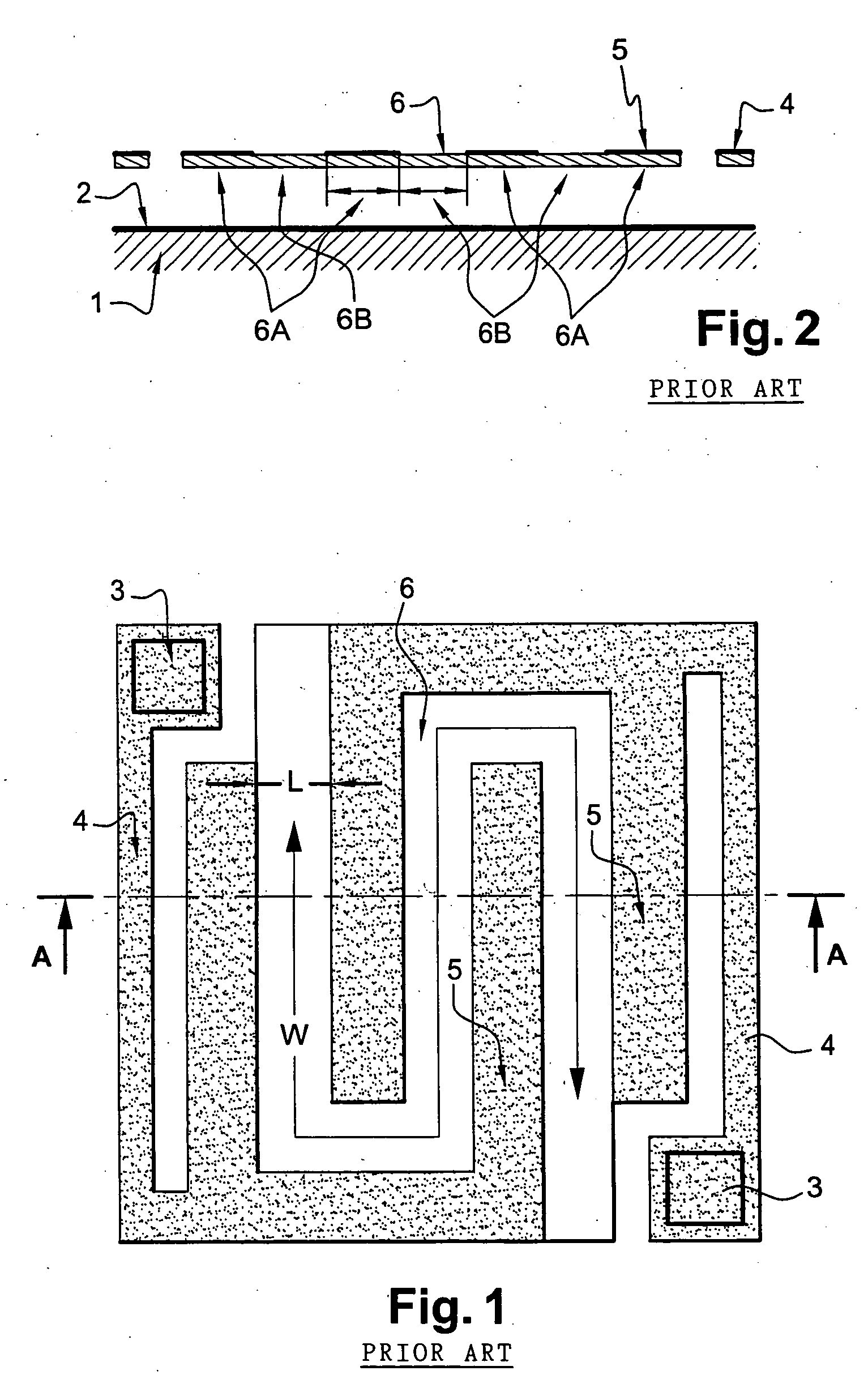
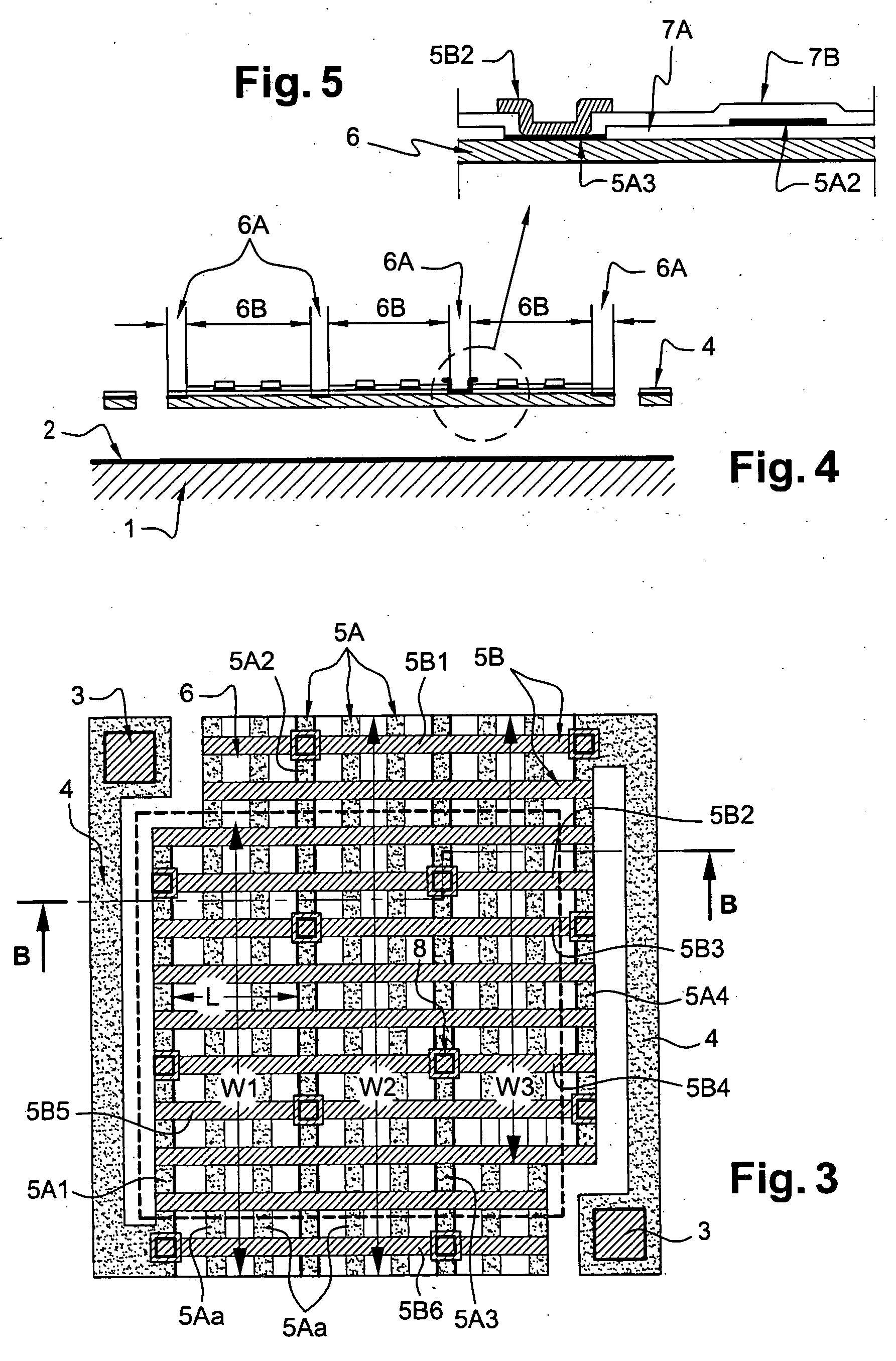
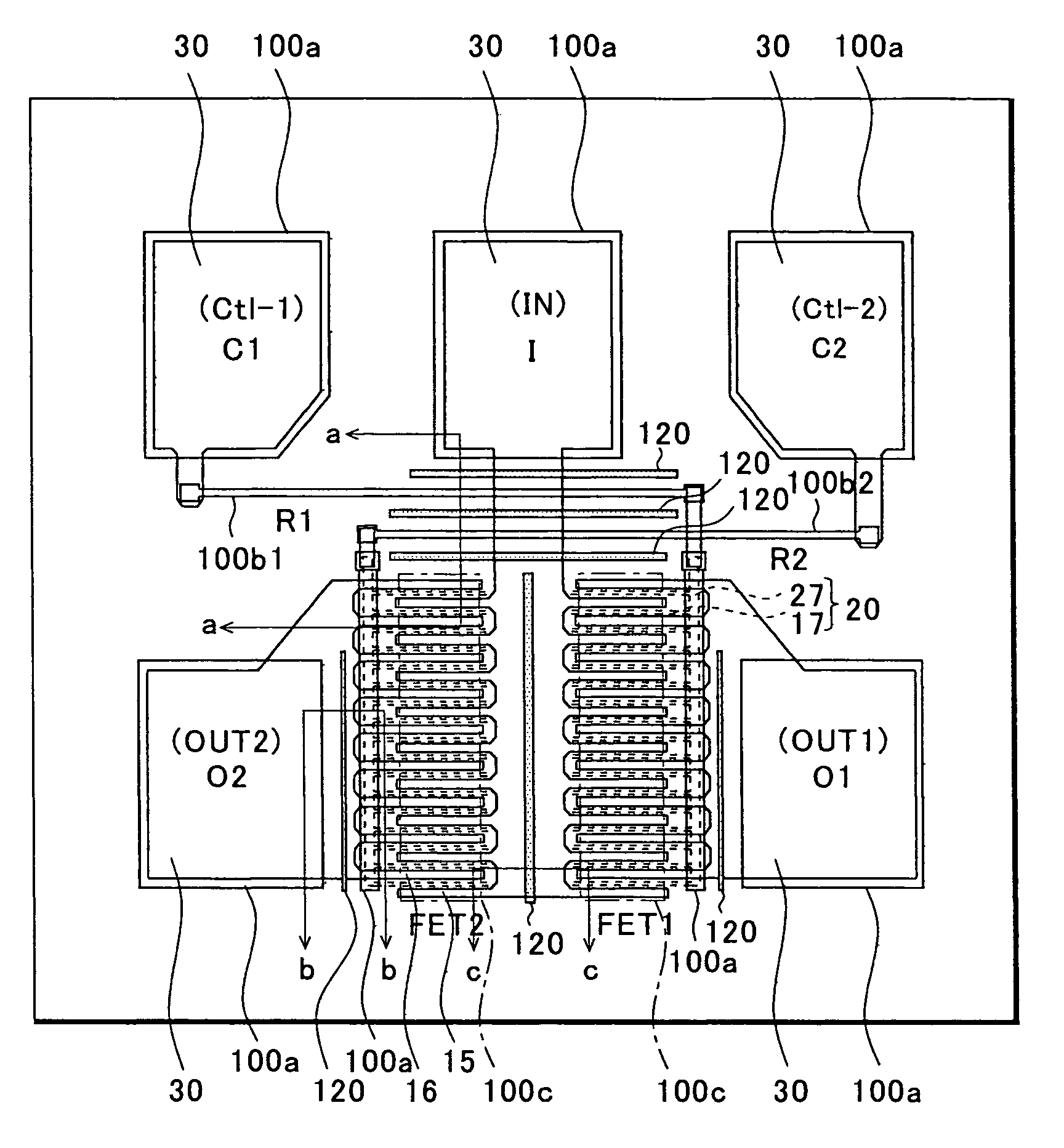
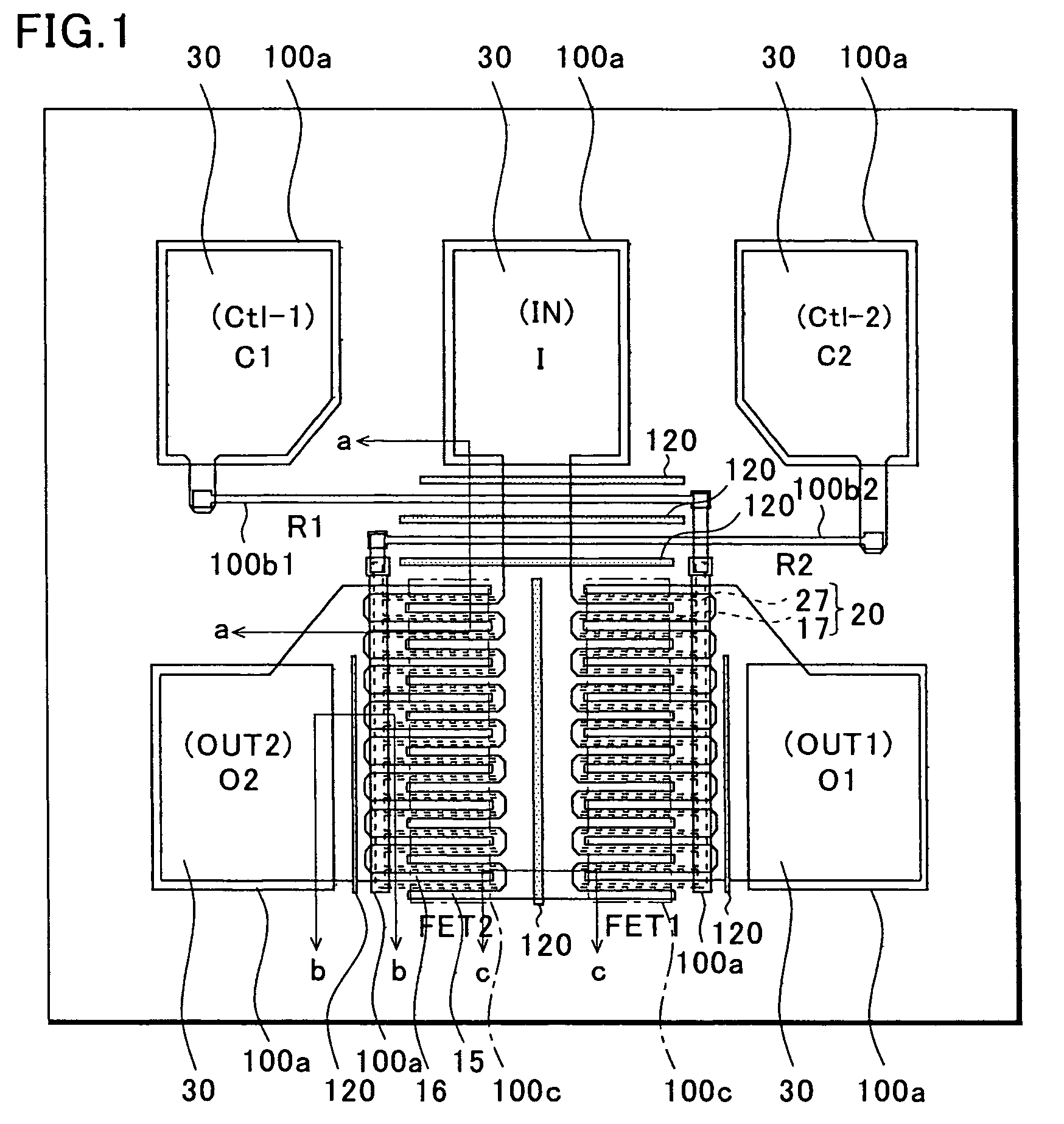
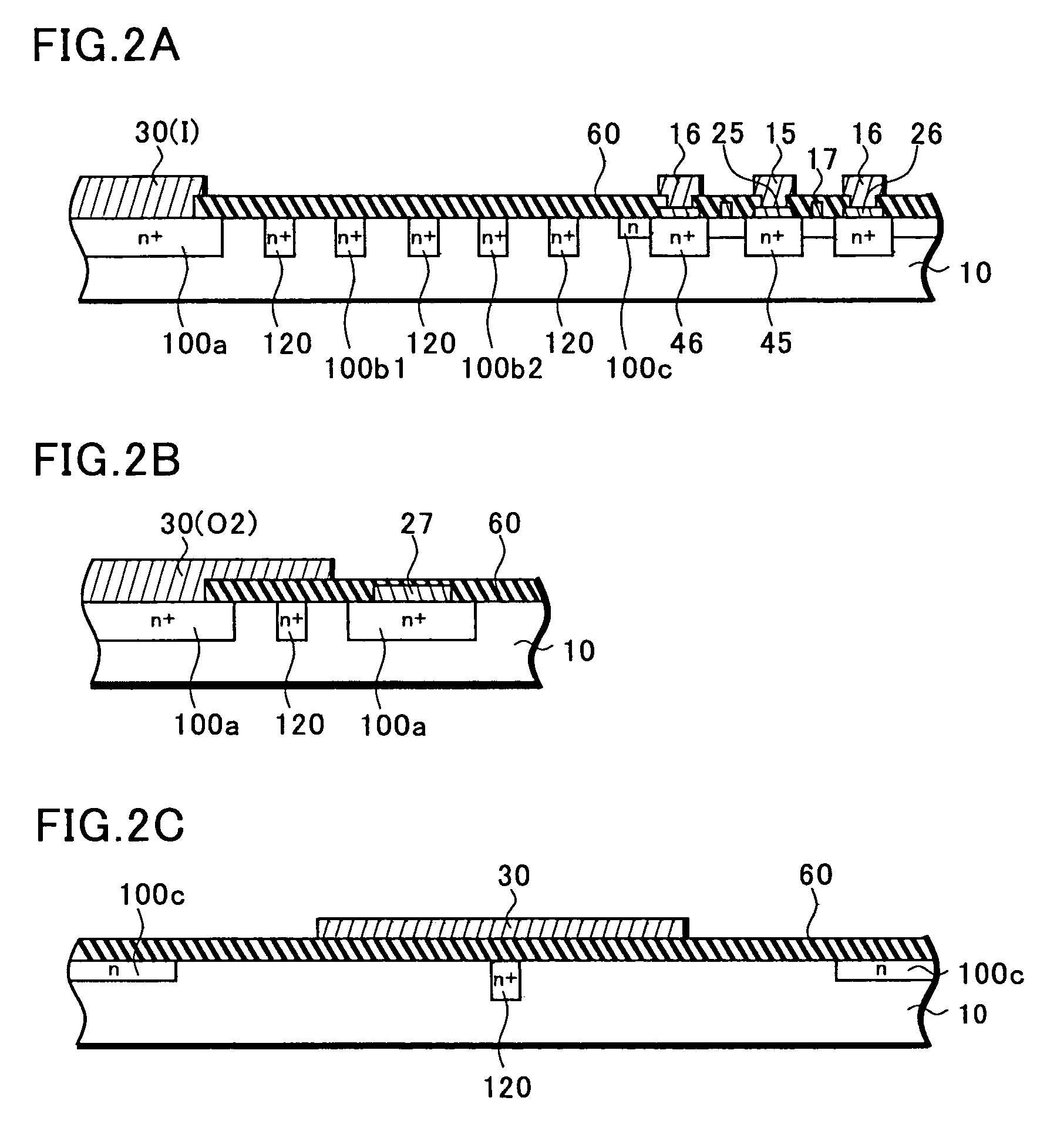
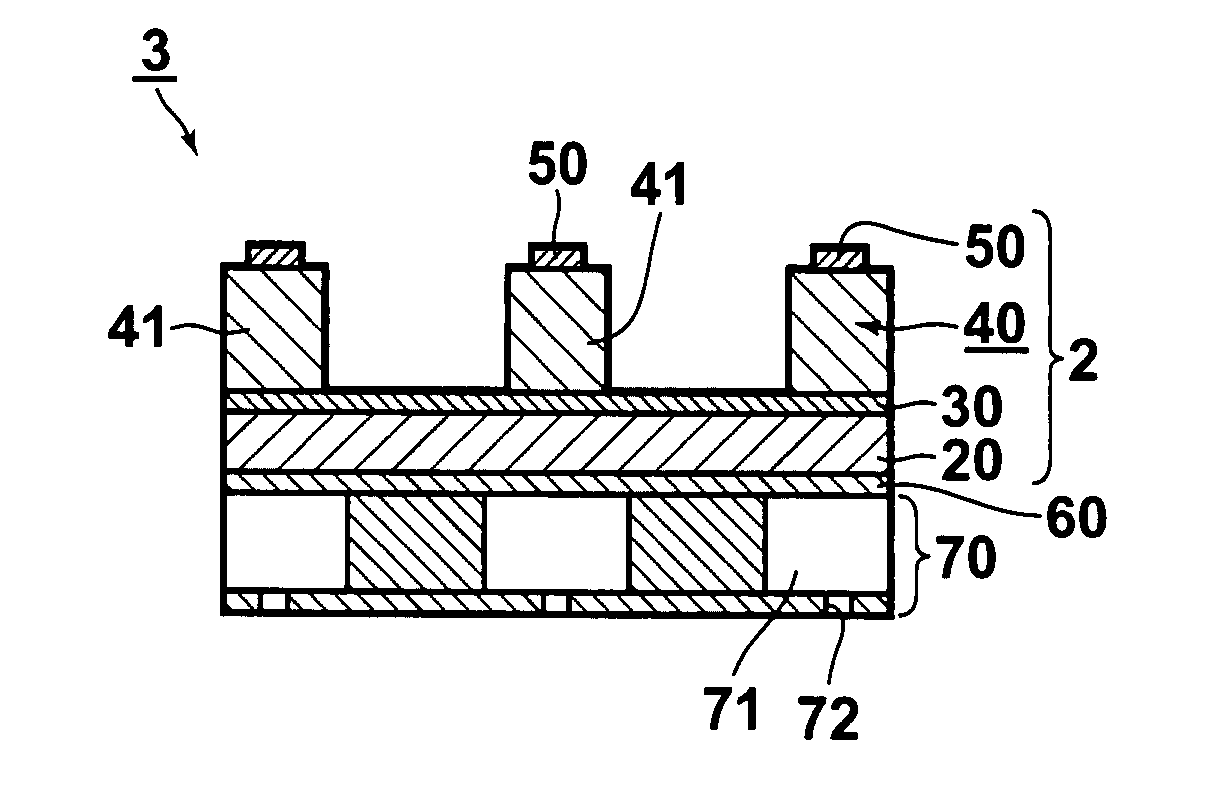
Plasma CVD apparatus equipped with plasma blocking insulation plate
InactiveUS20070266945A1Floating potentialControl areaElectric discharge tubesChemical vapor deposition coatingSusceptorEngineering
A plasma CVD apparatus for forming a thin film on a substrate includes: a vacuum chamber; an upper electrode; a susceptor as a lower electrode; and a ring-shaped insulation plate disposed in a gap between the susceptor and an inner wall of the chamber in the vicinity of or in contact with the susceptor to minimize a floating potential charged on the substrate while processing the substrate.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
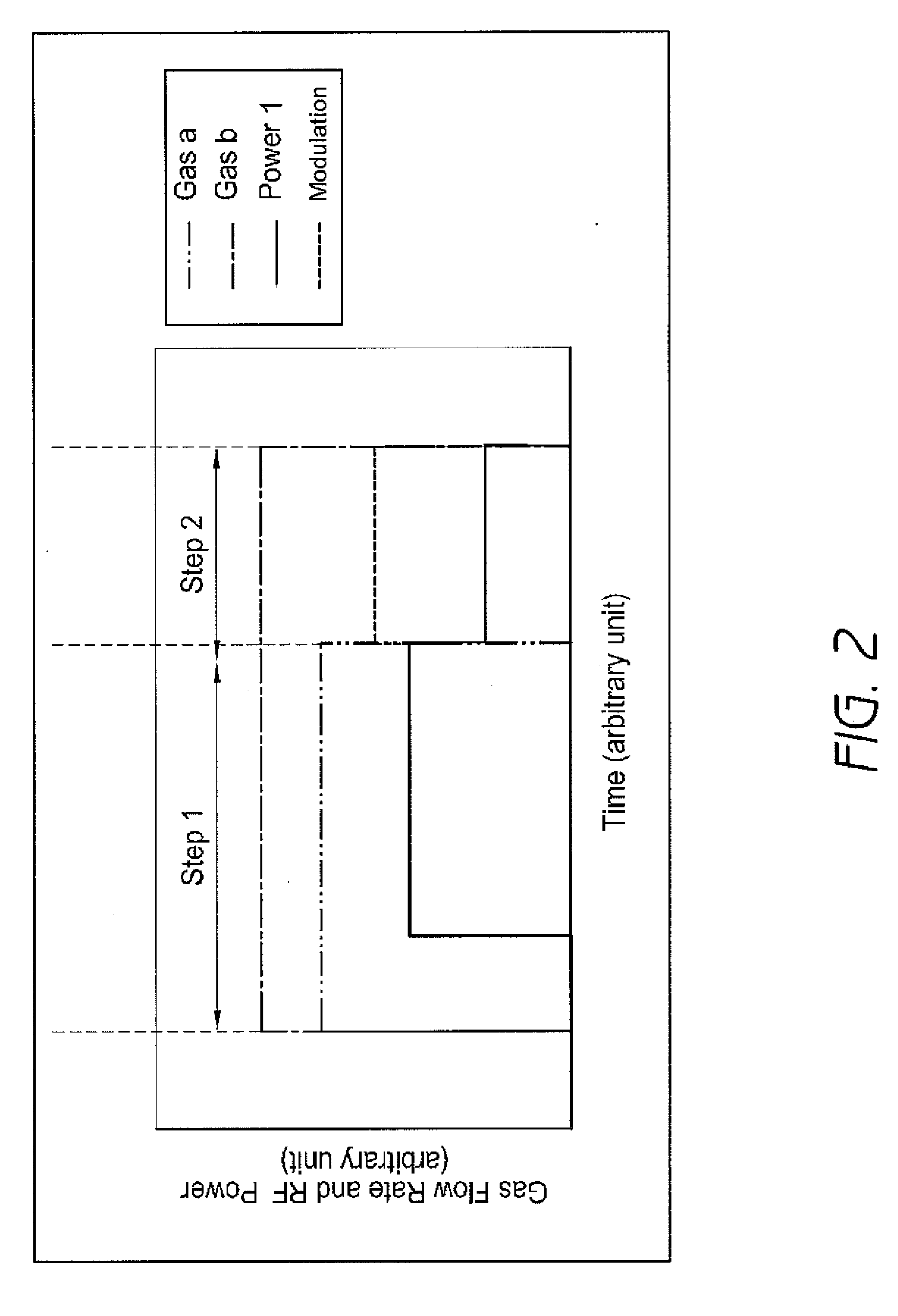
Method of plasma treatment using amplitude-modulated RF power
ActiveUS20090136683A1Reduce floating potentialSufficient voltageElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingSusceptorForming gas
A method for processing a substrate by plasma CVD includes: (i) forming a film on a substrate placed on a susceptor by applying RF power between the susceptor and a shower plate in the presence of a film-forming gas in a reactor; and (ii) upon completion of step (i), without unloading the substrate, applying amplitude-modulated RF power between the susceptor and the shower plate in the absence of a film-forming gas but in the presence of a non-film-forming gas to reduce a floating potential of the substrate.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
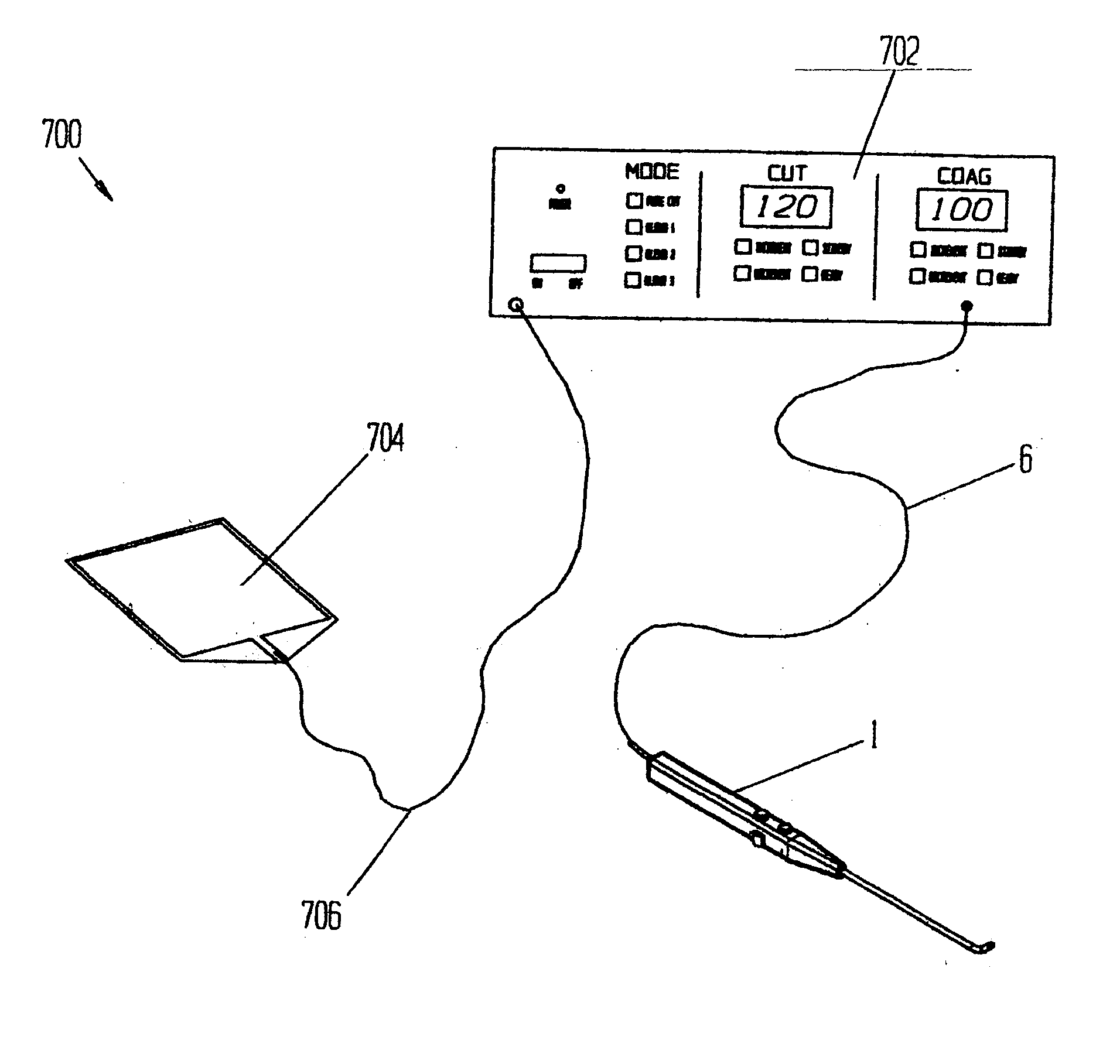
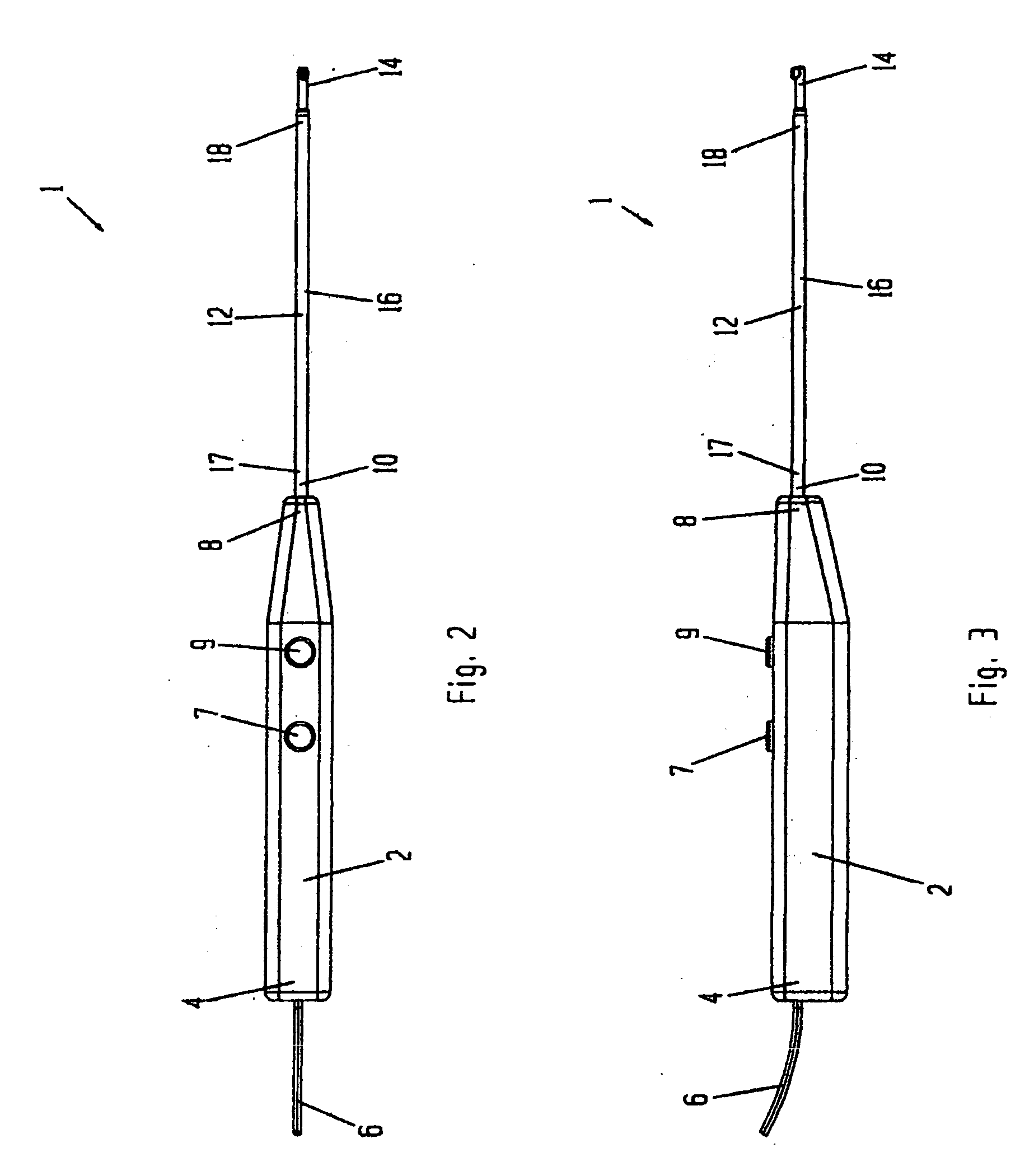
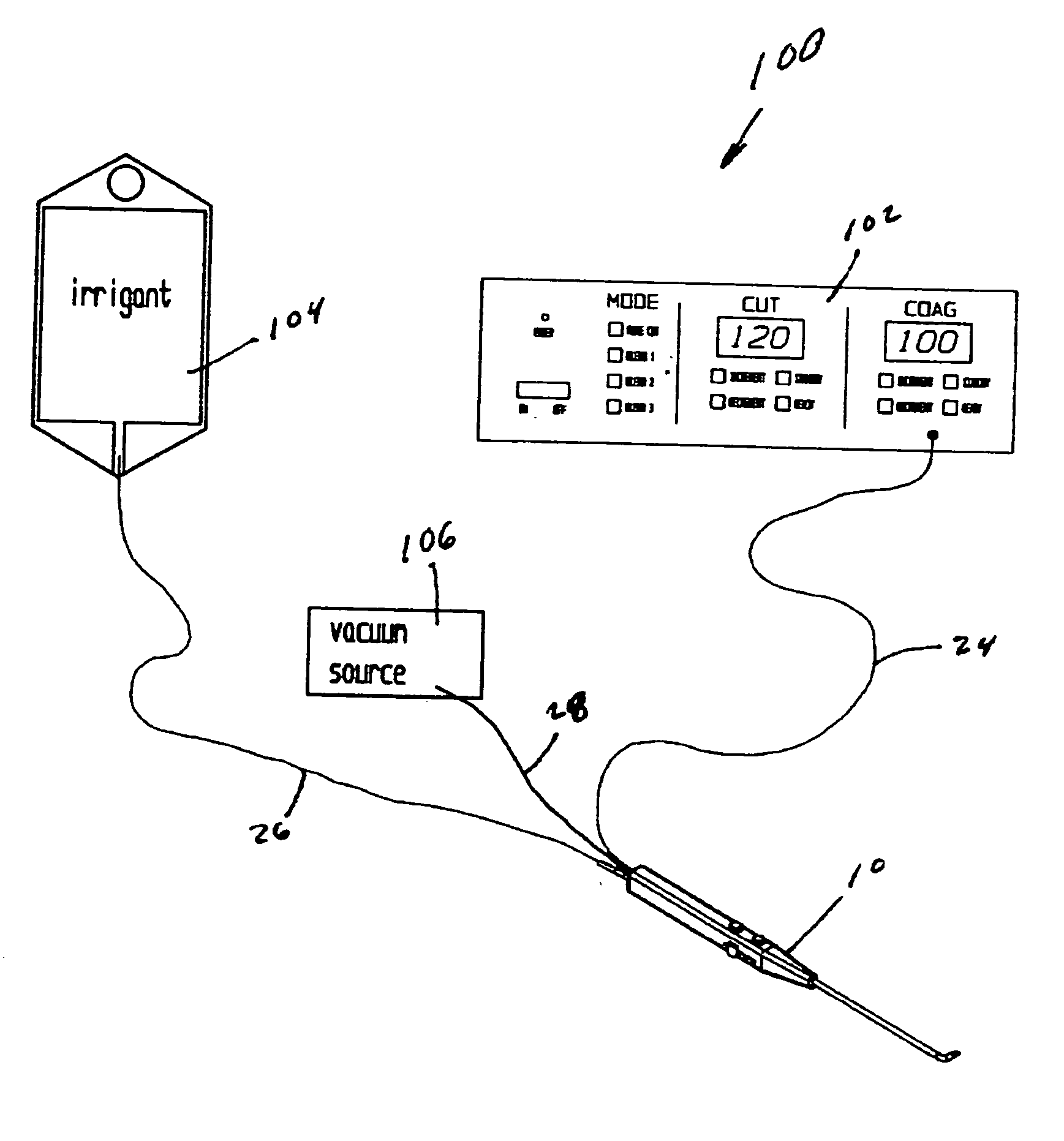
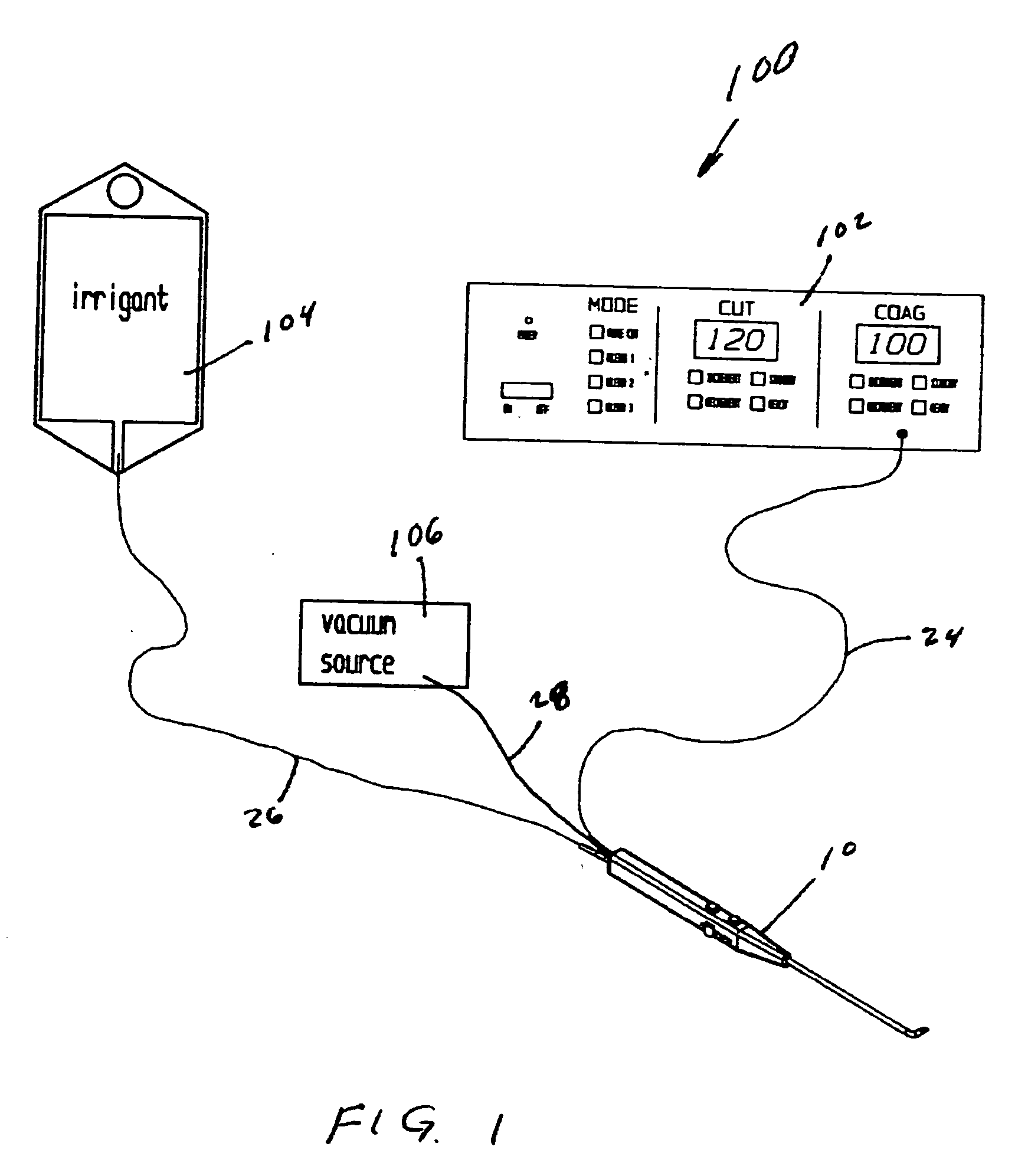
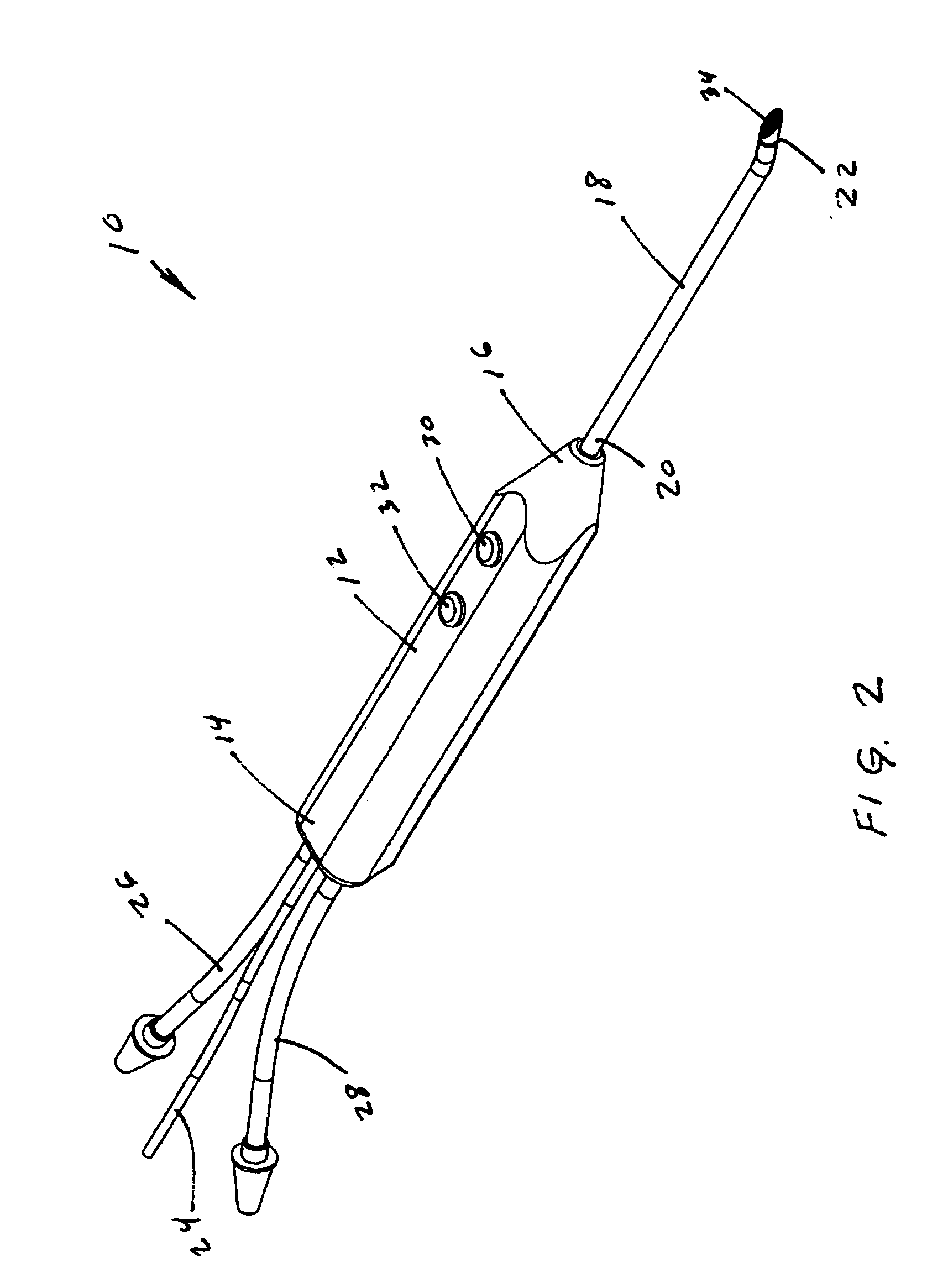
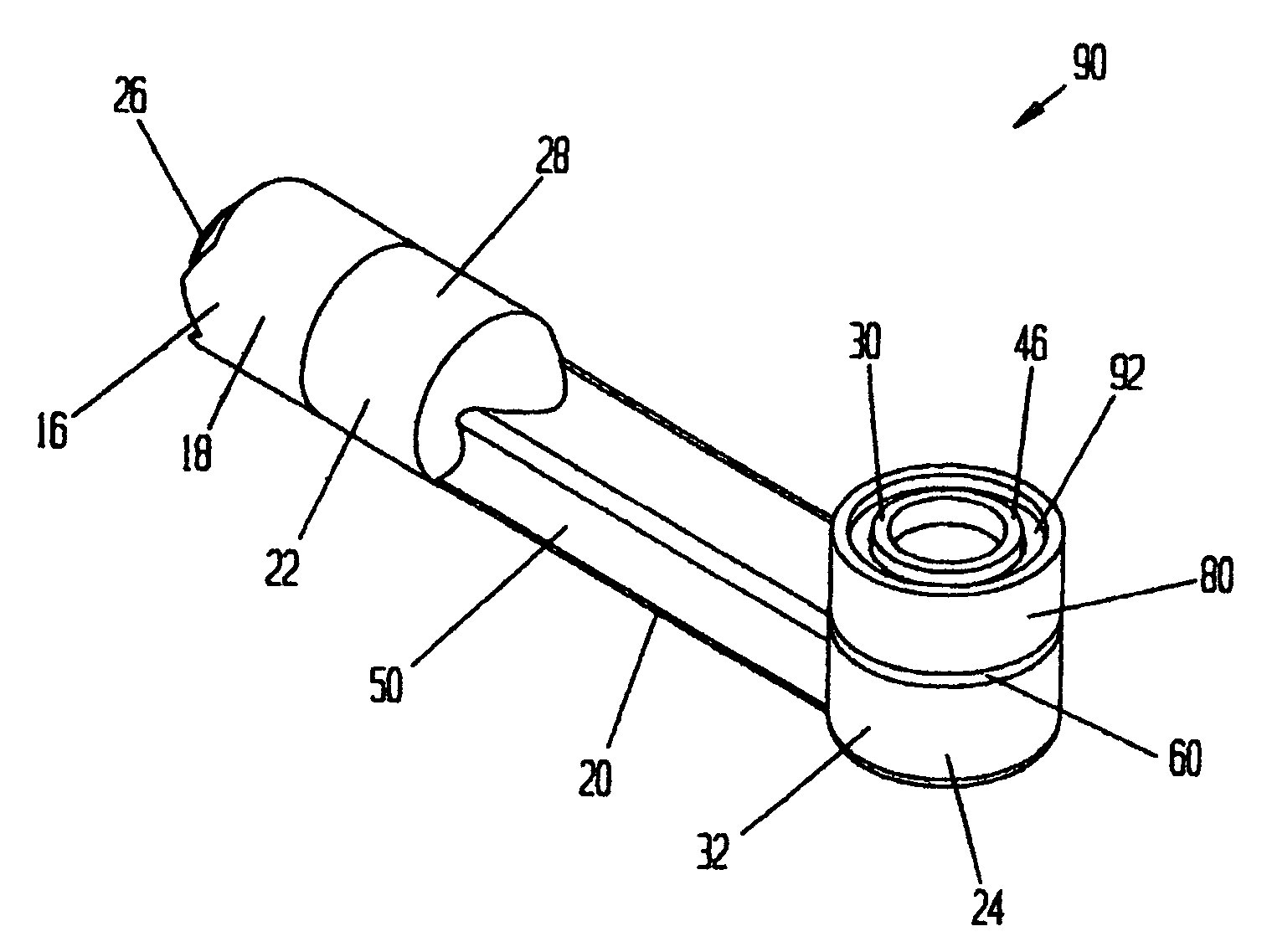
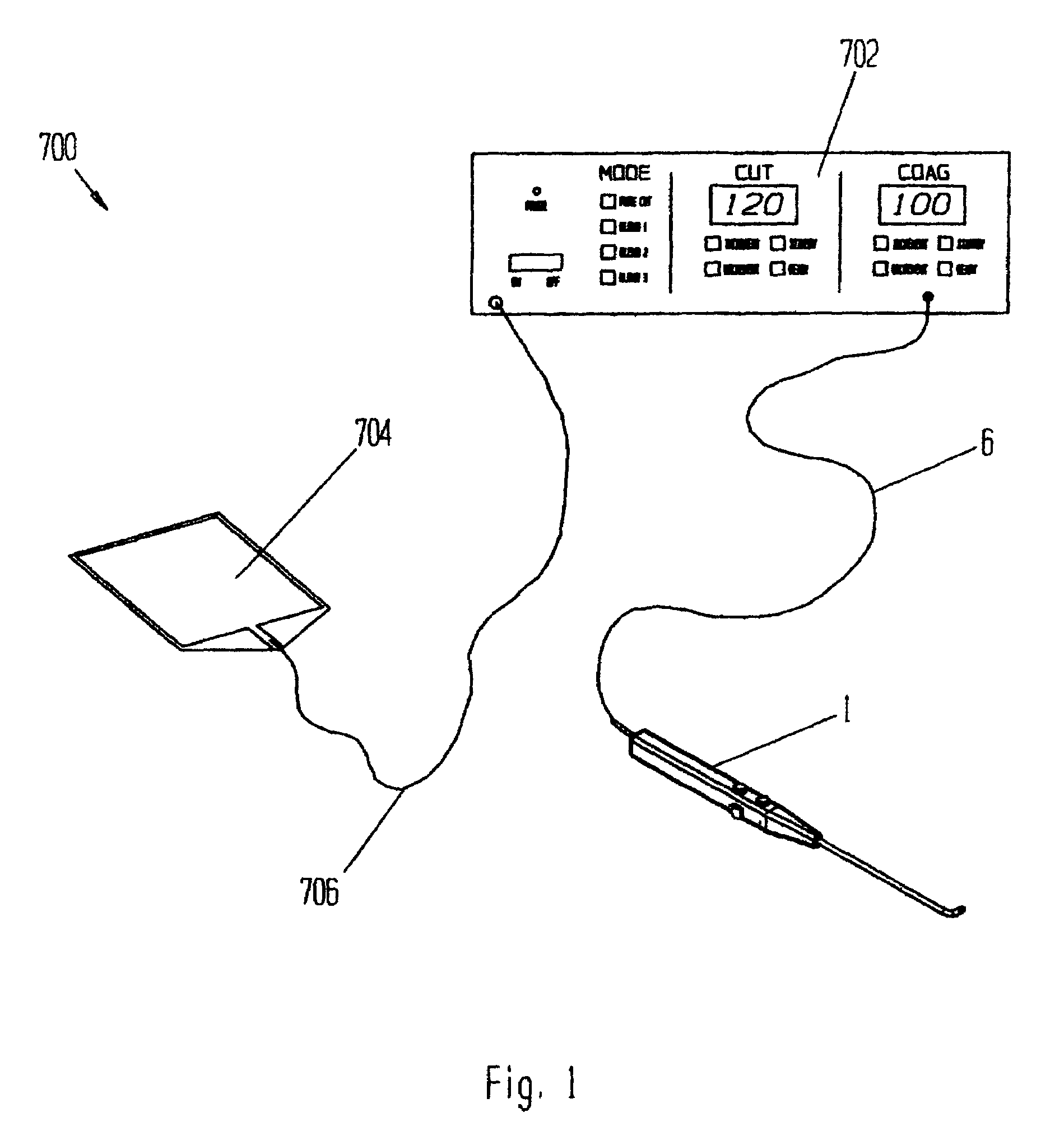
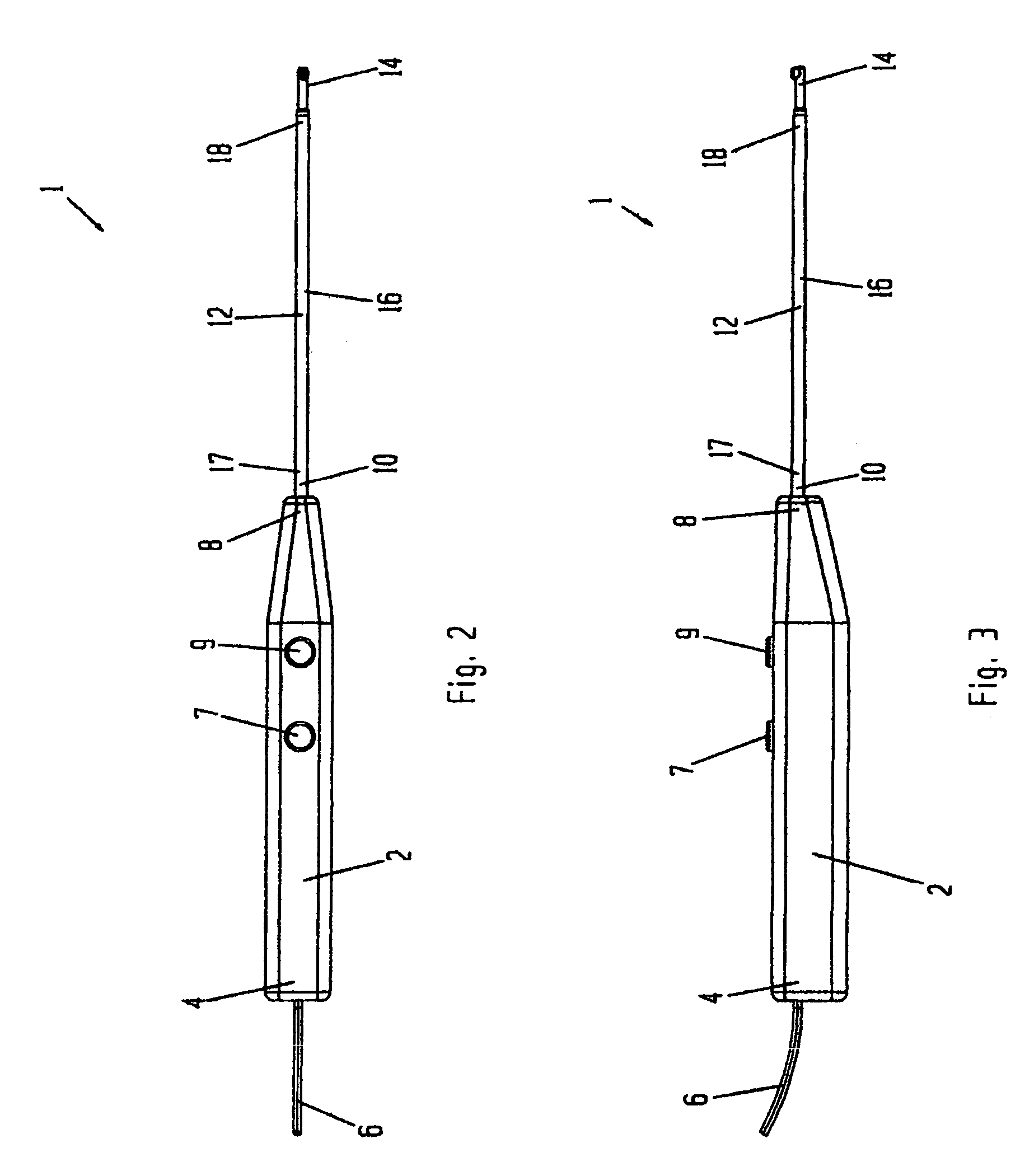
Electrosurgical device with floating-potential electrodes
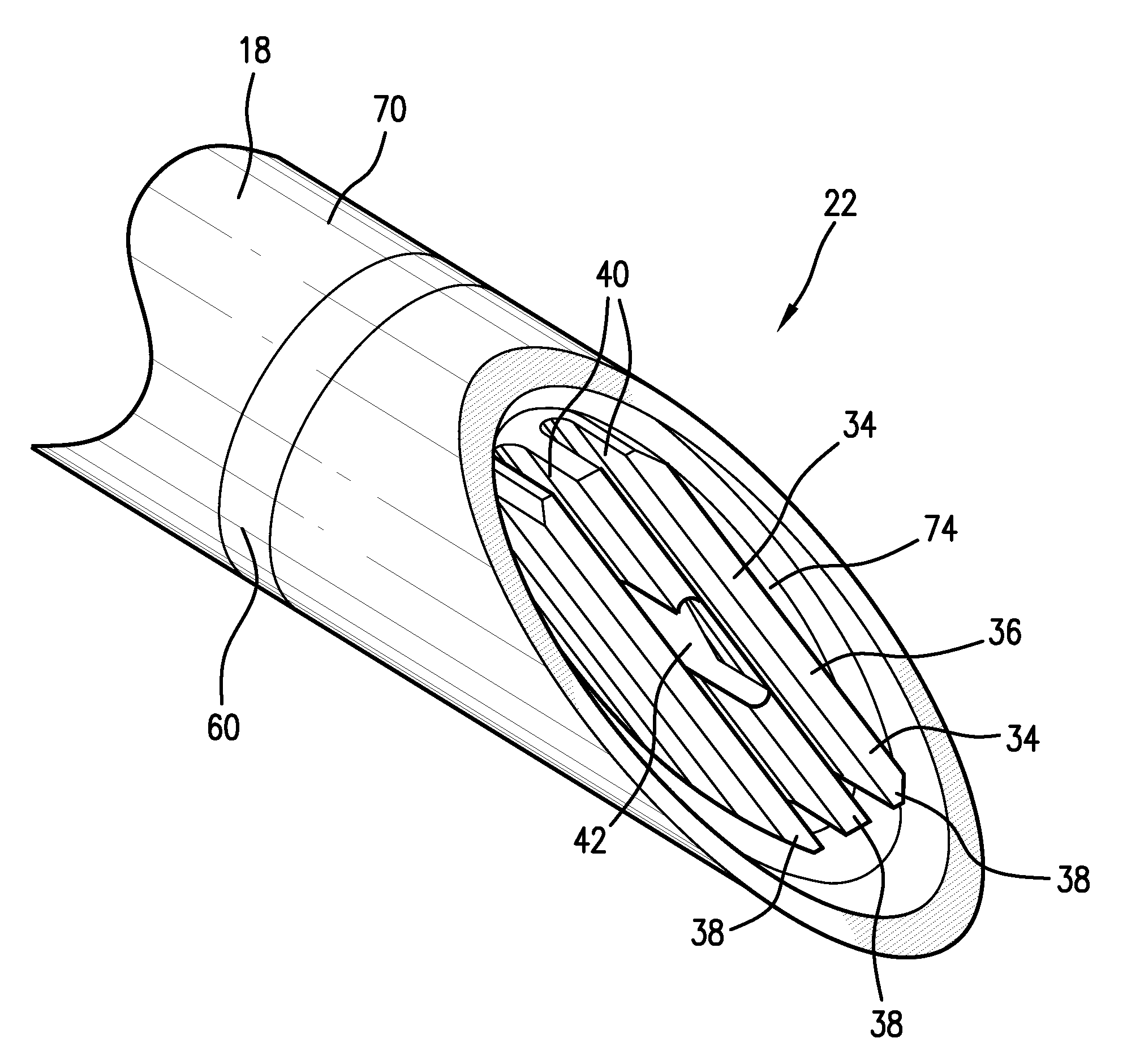
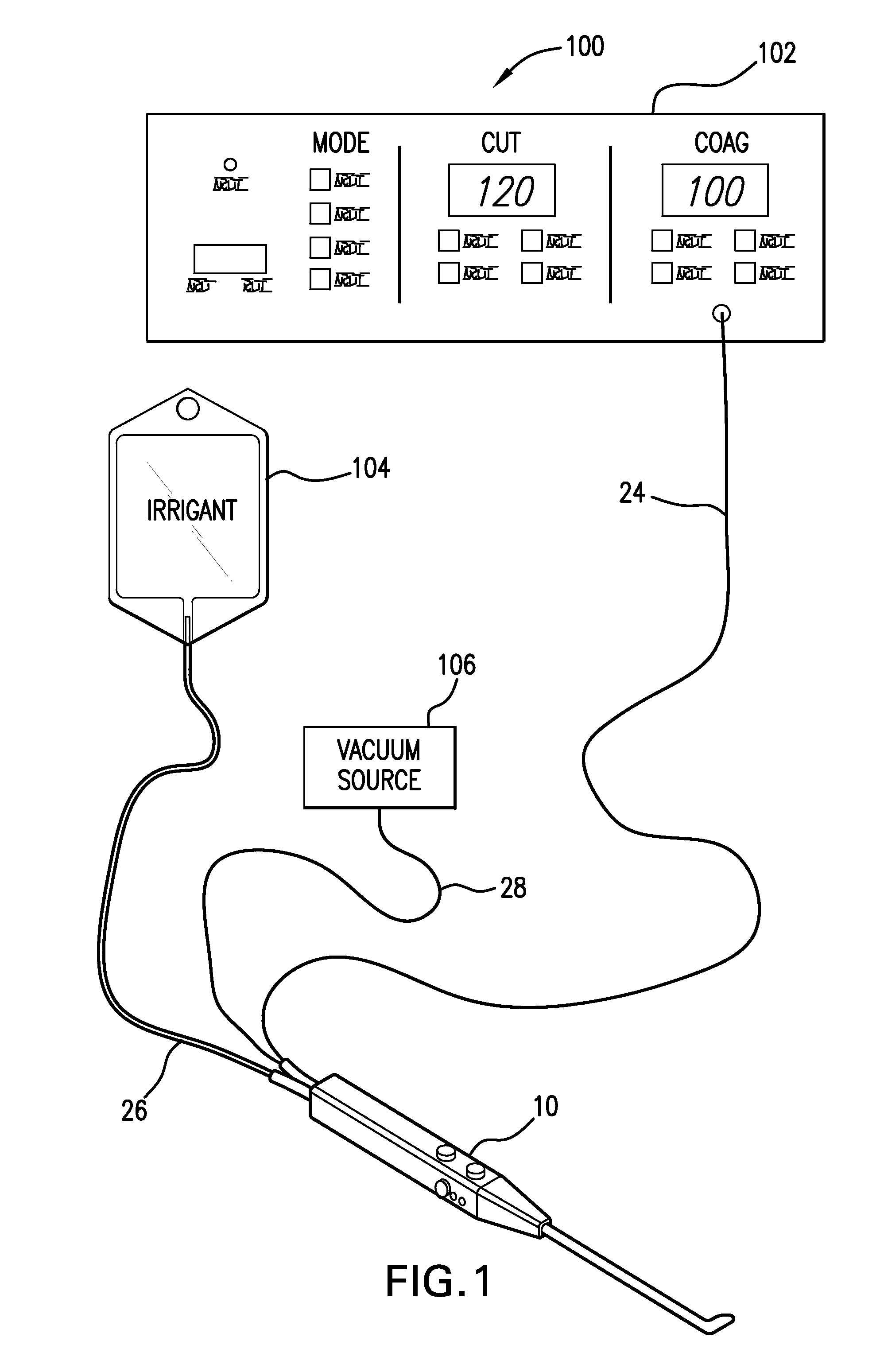
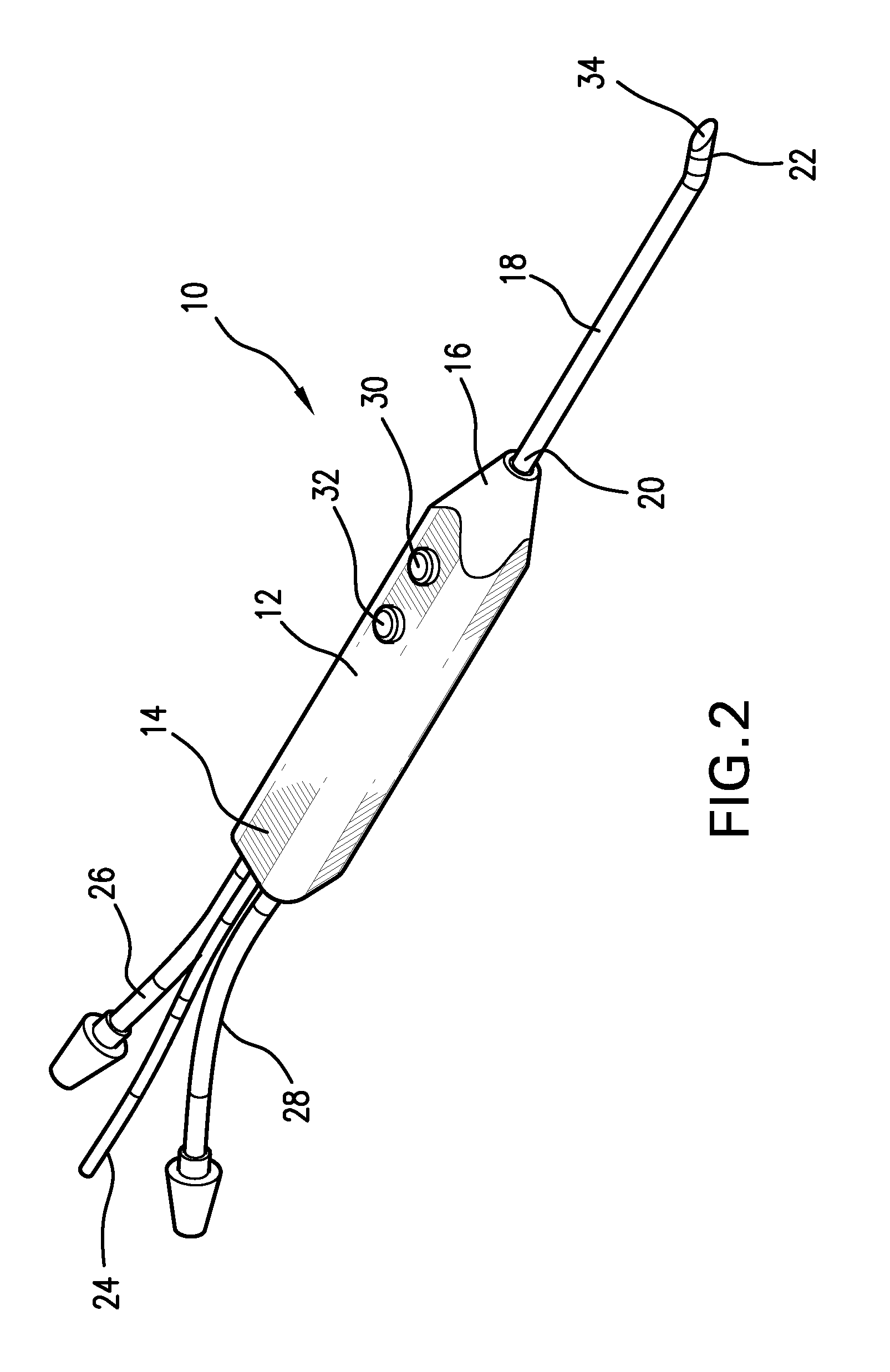
InactiveUS20050065510A1Shorten the timeLarge and more controlled and uniform lesionSurgical instruments for heatingElectricityVolumetric Mass Density
An electrosurgical instrument, system and methods are provided for the vaporization, cutting, coagulation, or treatment of tissue in the presence of an electrically conductive fluid medium. The electrosurgical probe comprises at least one active electrode, and at least one “floating” electrode having at least one end in close proximity to at least one active electrode. The floating electrode is not connected in any way to the electrosurgical power supply, but rather has a “floating” potential determined by the shape and position of the electrode. The floating electrode increases current density in the region of the probe distal end.
Owner:ELECTROMEDICAL ASSOCS
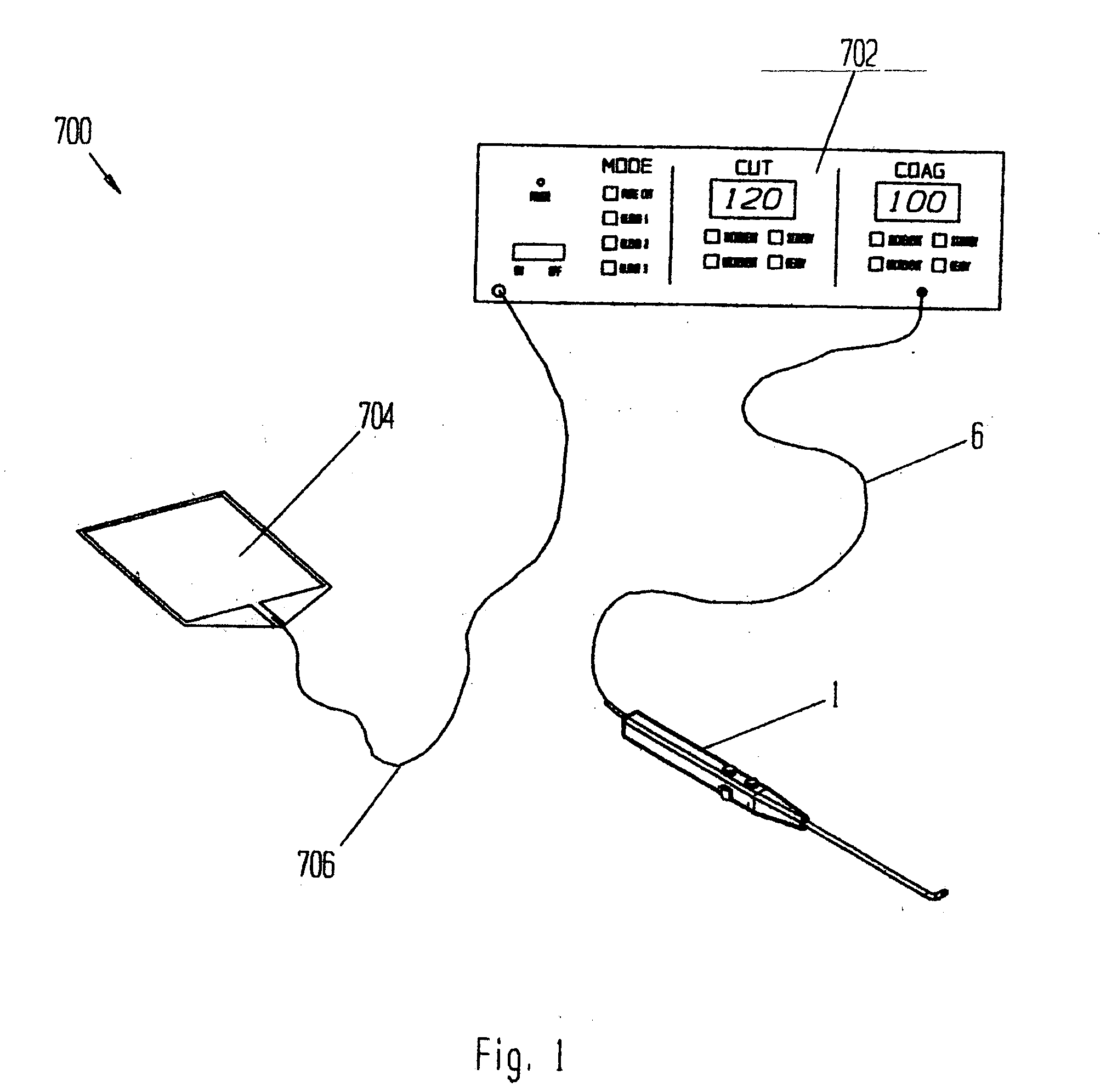
Electrosurgical device with floating-potential electrode and methods of using same
ActiveUS20050234446A1Efficient heatingImprove detection efficiencySurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesSurgical siteWater irrigation
Disclosed herein are improved, efficient electrosurgical probes suitable for tissue vaporization and cutting of tissue structures, more particularly for performing electrosurgical cutting, ablation (volumetric tissue vaporization), coagulating and / or modification within a body tissue, cavity or vessel or on the surface of a patient. The system and method of the present invention optionally include means for irrigation and / or aspiration of the surgical site and therefore may be used in relatively dry environments for, for instance, oral, otolaryngological, laparoscopic, and dermatologic procedures.
Owner:RF MEDICAL
Electrosurgical device with floating-potential electrode and methods of using the same
ActiveUS7566333B2Improve efficiencyReduce the possibilitySurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesOtolaryngology/ENTSurgical site
The present invention relates to electrosurgical probes suitable for tissue vaporization and cutting of tissue structures, more particularly for performing electrosurgical cutting, ablation (volumetric tissue vaporization), coagulating and / or modification within a body tissue, cavity or vessel or on the surface of a patient. The system and method of the present invention optionally include structure for irrigation and / or aspiration of the surgical site and therefore may be used in relatively dry environments such as in the context of oral, otolaryngological, laparoscopic, and dermatologic procedures.
Owner:RF MEDICAL
Nanotube-based transfer devices and related circuits
InactiveUS20050279988A1Electrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysNanoinformaticsElectricityTerminal equipment
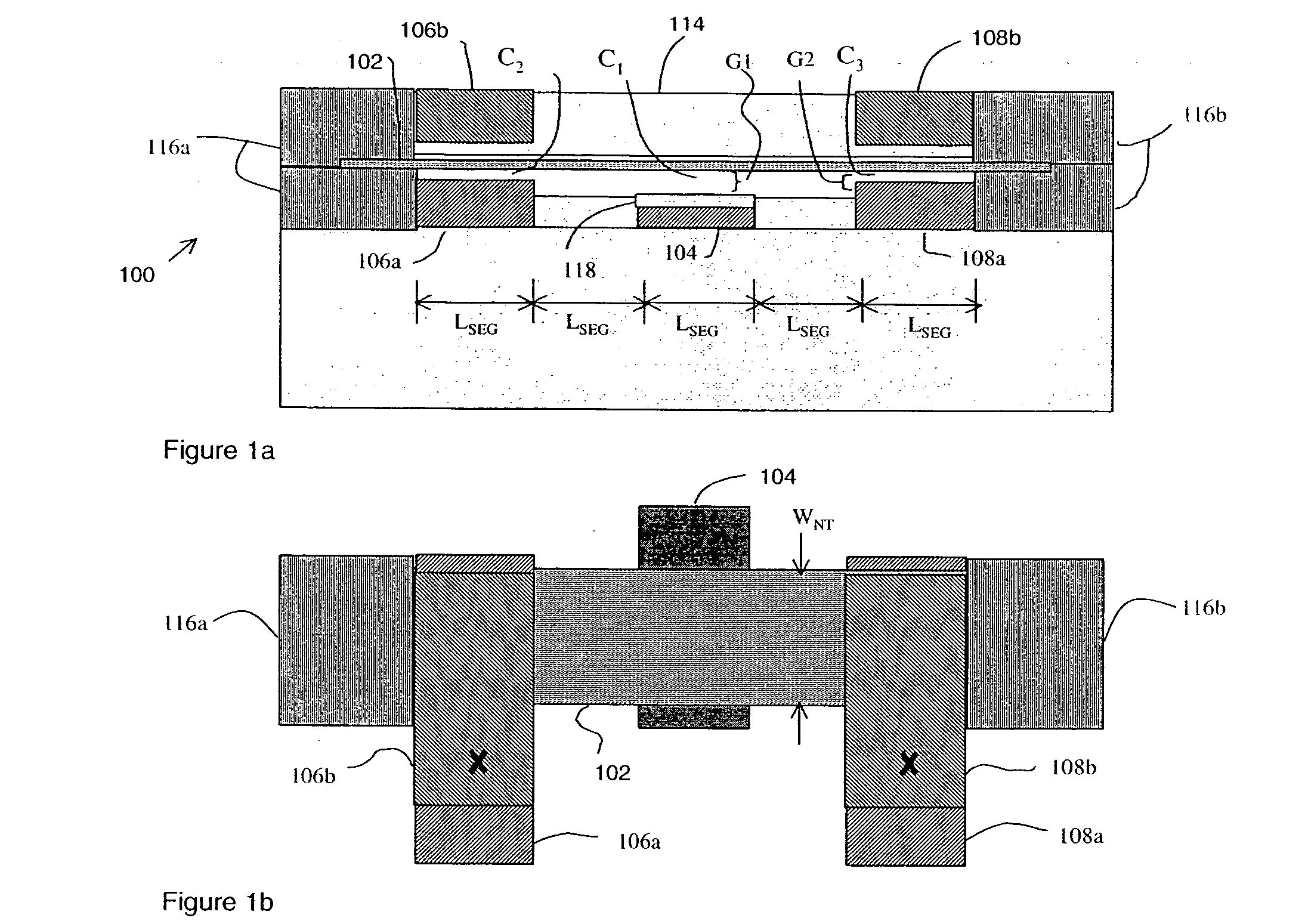
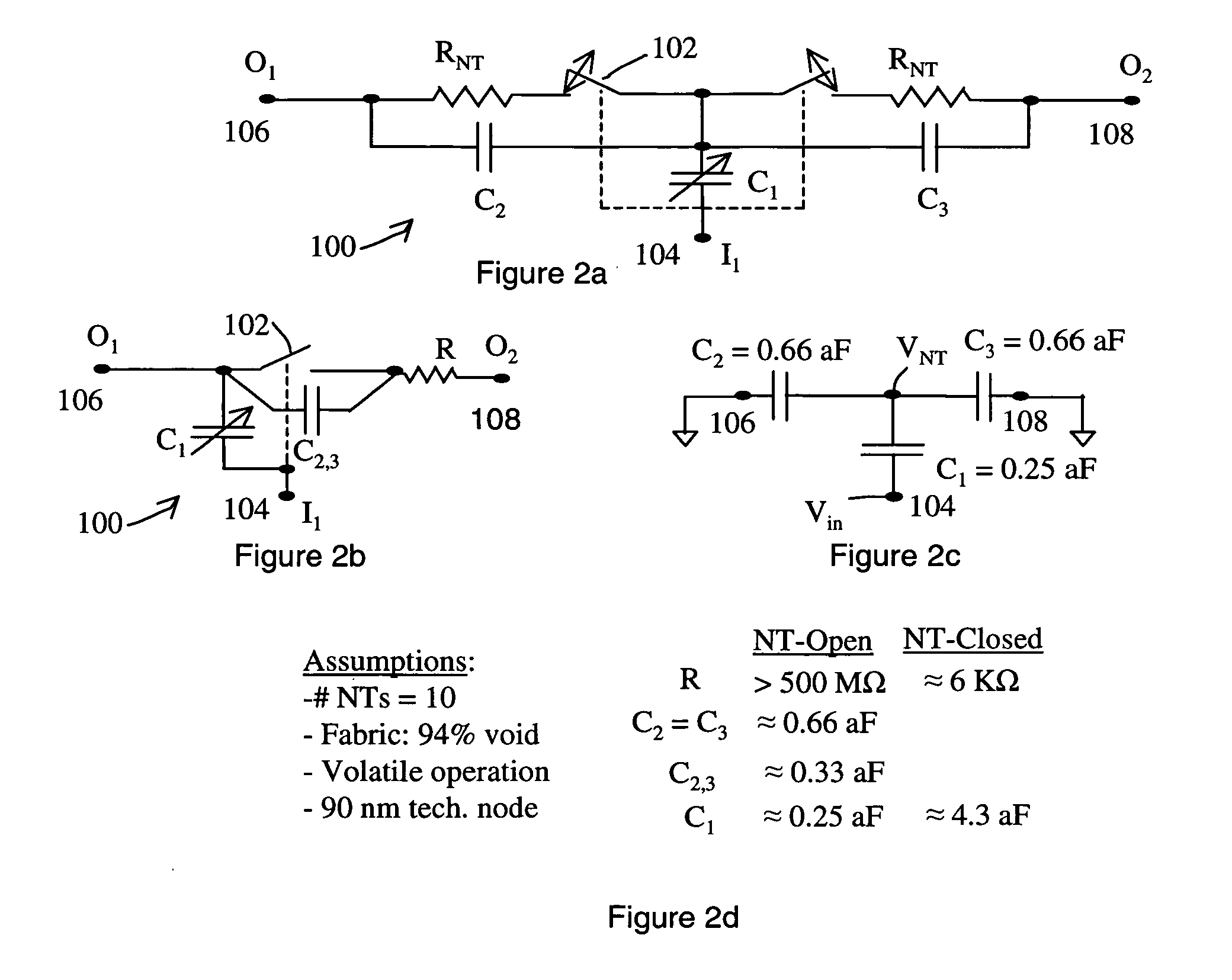
Nanotube transfer devices controllably form a nanotube-based electrically conductive channel between a first node and a second node under the control of a control structure. A control structure induces a nanotube channel element to deflect so as to form and unform the conductive channel between the nodes. The nanotube channel element is not in permanent electrical contact with either the first node or the second node. The nanotube channel element may have a floating potential in certain states of the device. Each output node may be connected to an arbitrary network of electrical components. The nanotube transfer device may be volatile or non-volatile. In preferred embodiments, the nanotube transfer device is a three-terminal device or a four-terminal device. Electrical circuits are provided that ensure proper switching of nanotube transfer devices interconnected with arbitrary circuits. The circuits may overdrive the control structure to induce the desired state of channel formation.
Owner:NANTERO
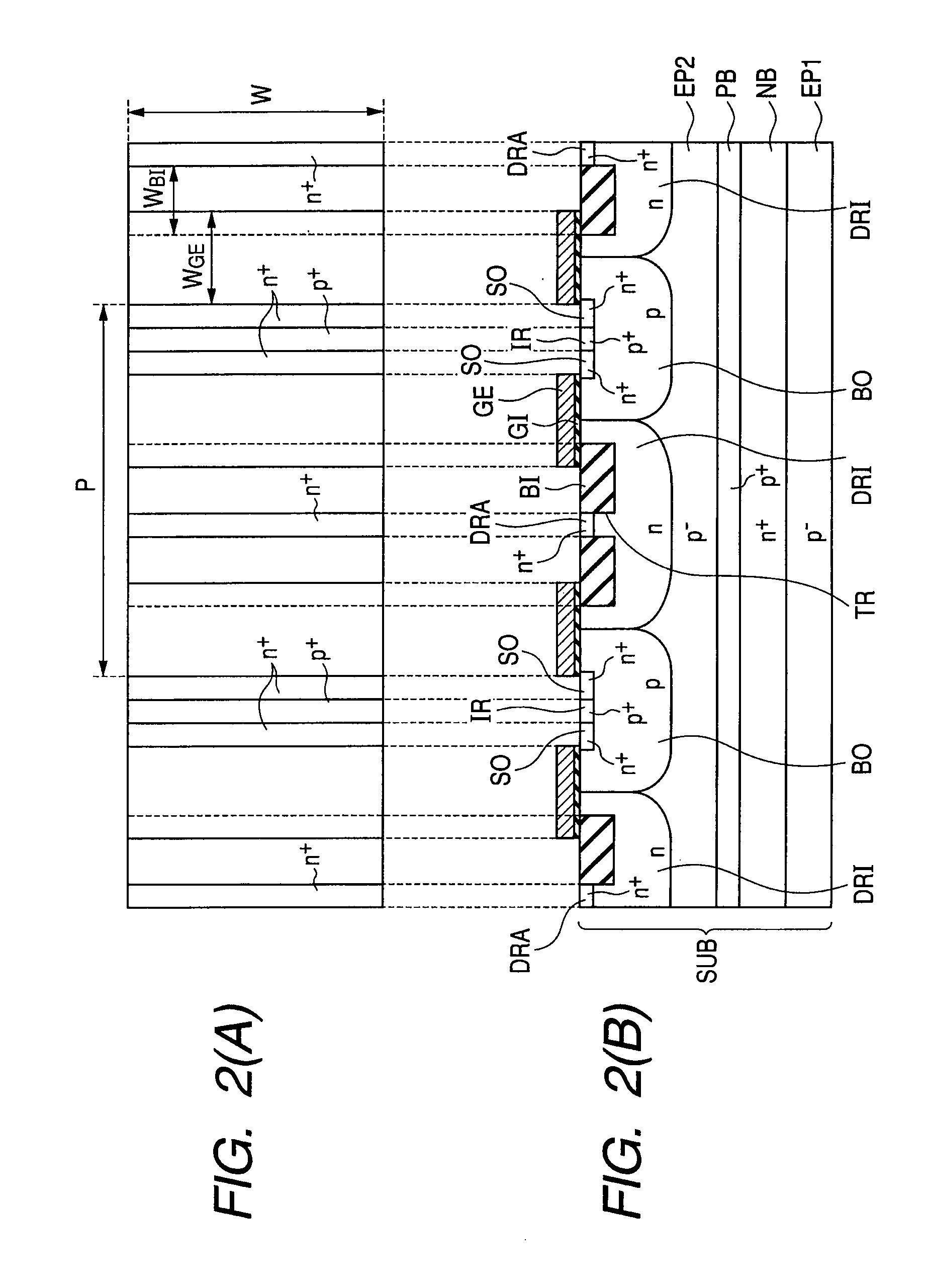
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20100314683A1High impurity concentrationAvoid it happening againTransistorSolid-state devicesFloating potentialBody region
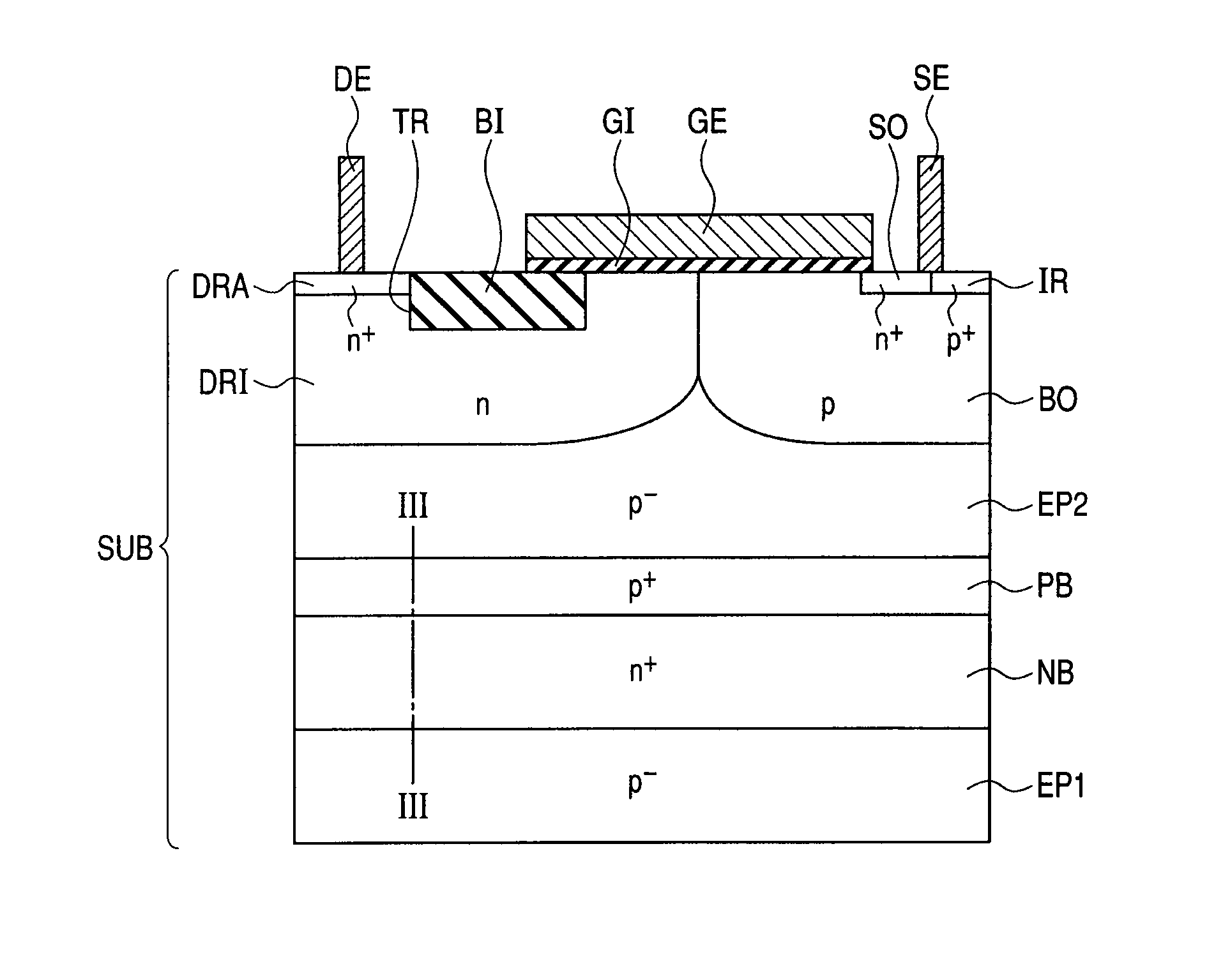
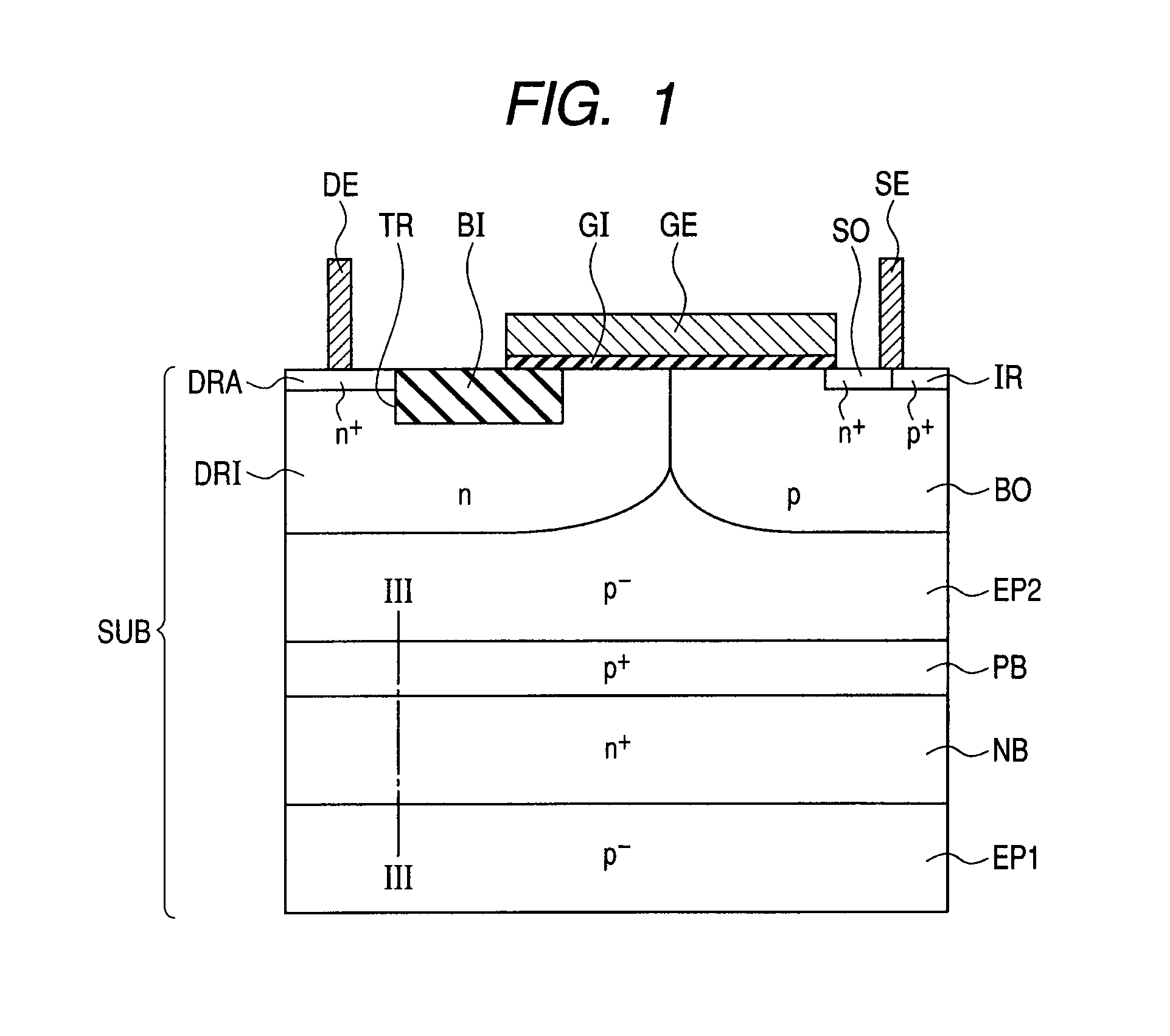
Provided is a semiconductor device which scarcely malfunctions even when the device is used as a high-side element, and can keep a high breakdown voltage. In a semiconductor substrate having a main surface, a first p− epitaxial region is formed. At the main surface side of the first p− epitaxial region, a second p− epitaxial region is formed. At the main surface side of the second p− epitaxial region, an n-type drift region and a p-type body region are formed. Between the first and second p− epitaxial regions, an n+ buried region having a floating potential is formed to isolate these regions electrically from each other. Between n+ buried region and the second p− epitaxial region, a p+ buried region is formed which has a higher p-type impurity concentration than the second p− epitaxial region.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
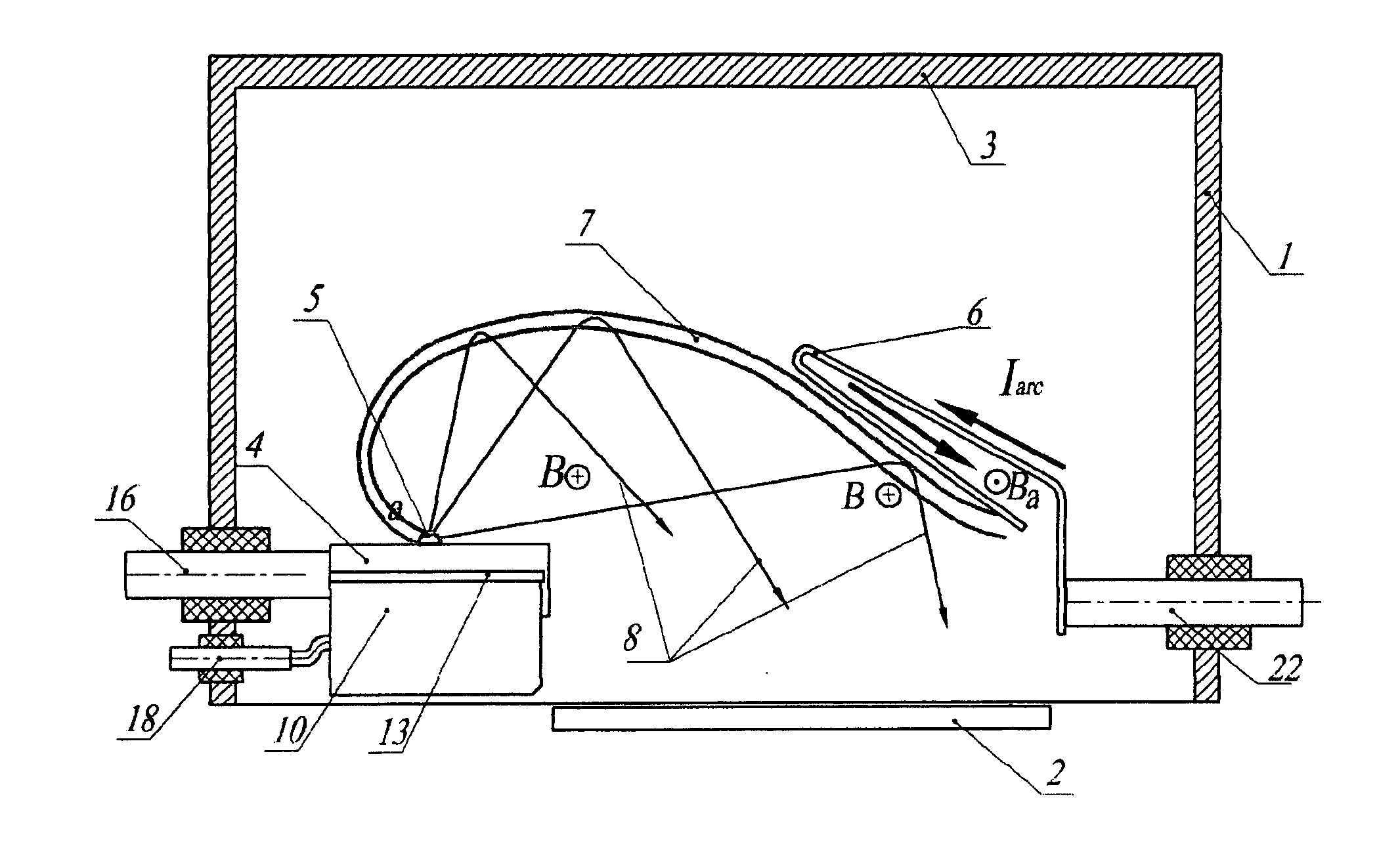
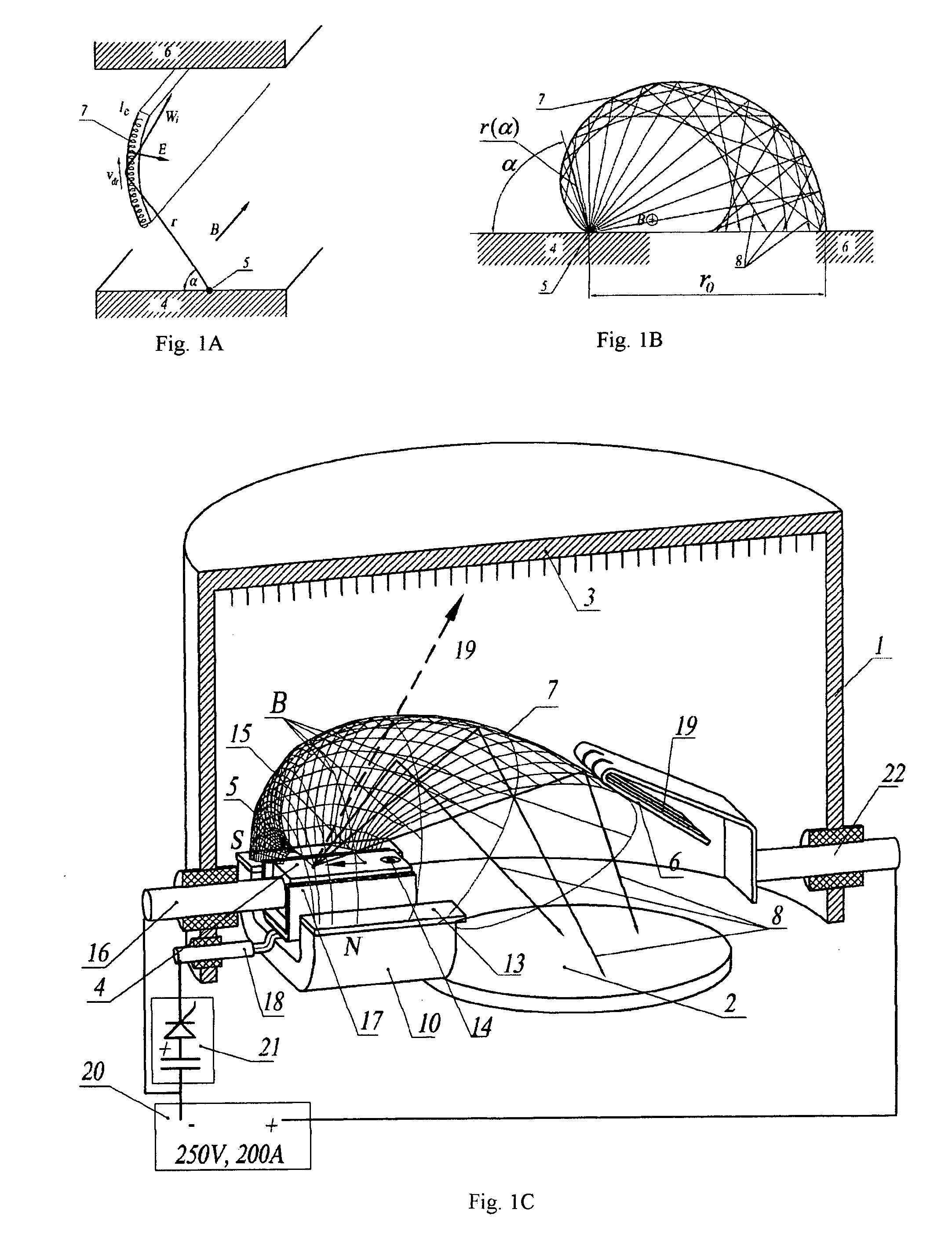
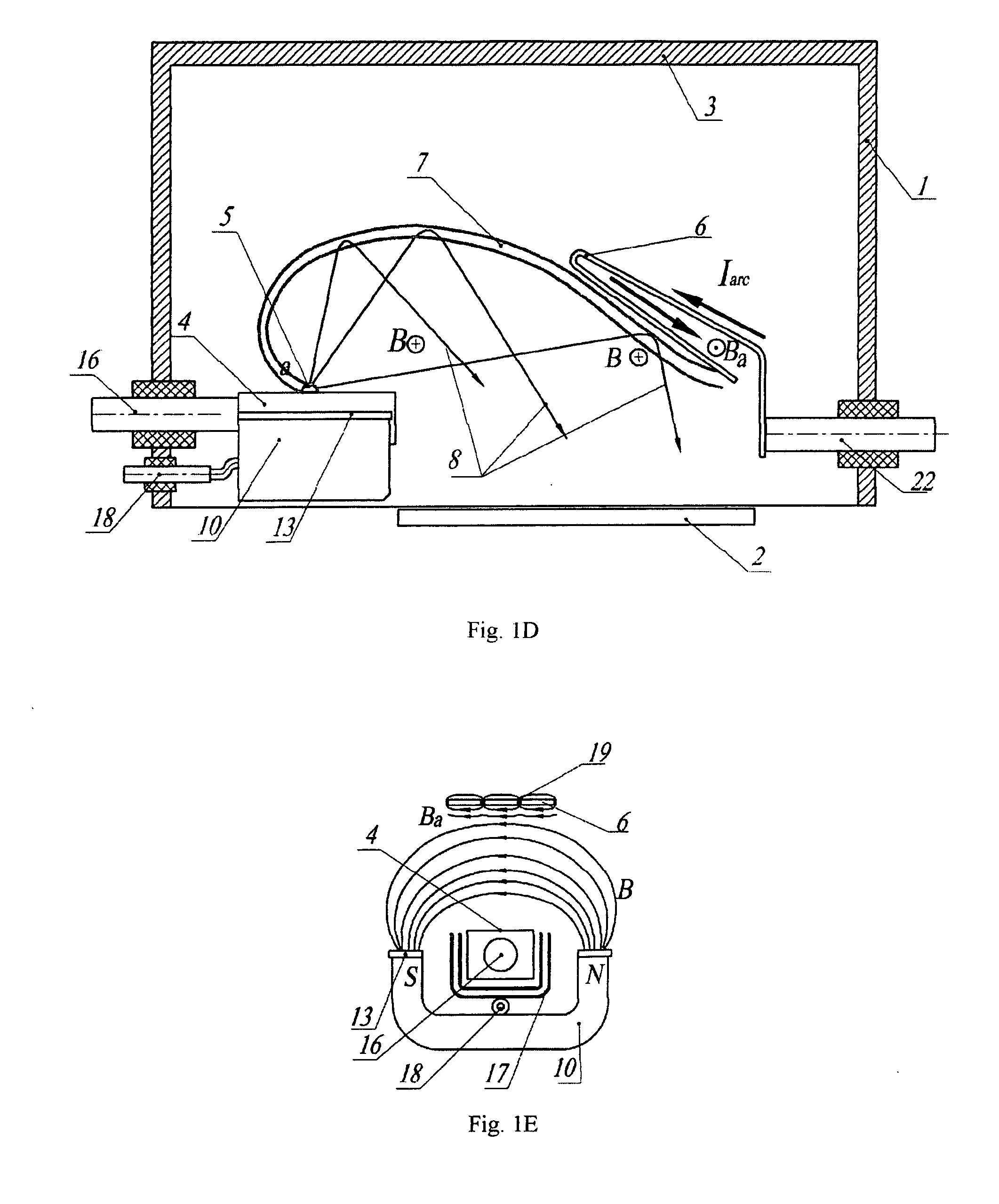
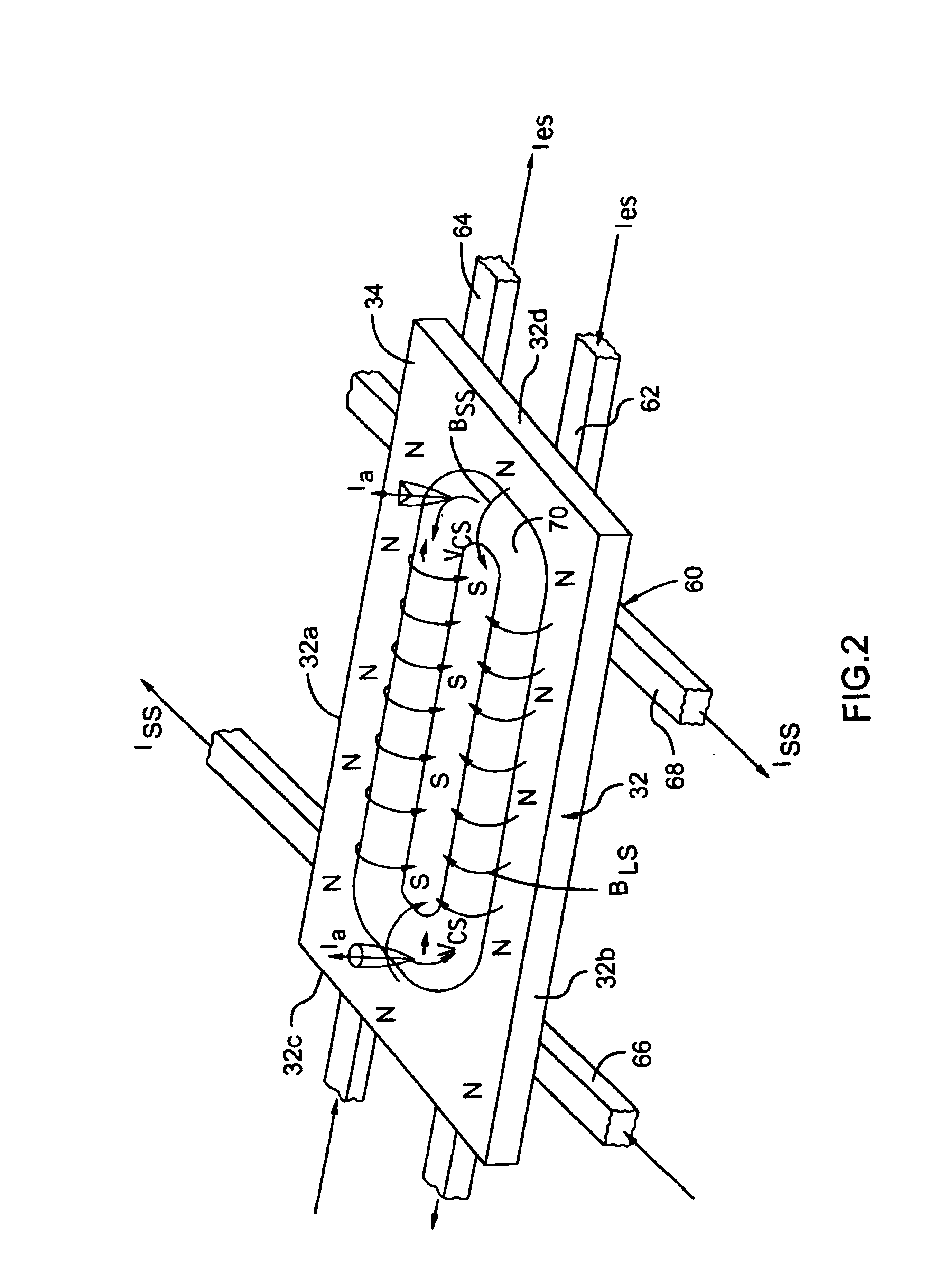
Cathode-arc source of metal/carbon plasma with filtration
InactiveUS20070034501A1Improve transportation efficiencyIncrease the number ofCellsElectric discharge tubesStationary conditionsCurrent sheet
The a cathode-arc source of metal plasma with filtration, used, in particular, for deposition of DLC, utilizes the effect of fast ions reflection from the Hall stratum in a transversal arched magnetic field to filtrate vacuum arc plasma arc from contaminating macroparticles and vapor. Various embodiments for producing maximal plasma flux at the source outlet, in particular, a pulse source with more the one cathode units for deposition of coating inside pipes / cavities, for deposition of coating in a stationary / quasi-stationary condition are offered. The cathode is made of a consumable material and is exposed to poles of magnets on both ends of cathode for creating a transversal magnetic field of an arched configuration in a discharge gap between the cathode and the anode. The anode geometry adequate to the mechanism of the arc current passage through a transversal magnetic field is offered. To avoid longitudinal and transverse short circuits of the current layer, an installation of non-conducting surfaces at ends or sectioned shields under a floating potential at the cathode sides is provided. The method of creating the Hall stratum in said transversal magnetic field of arched configuration is offered.
Owner:BENDER EFIM
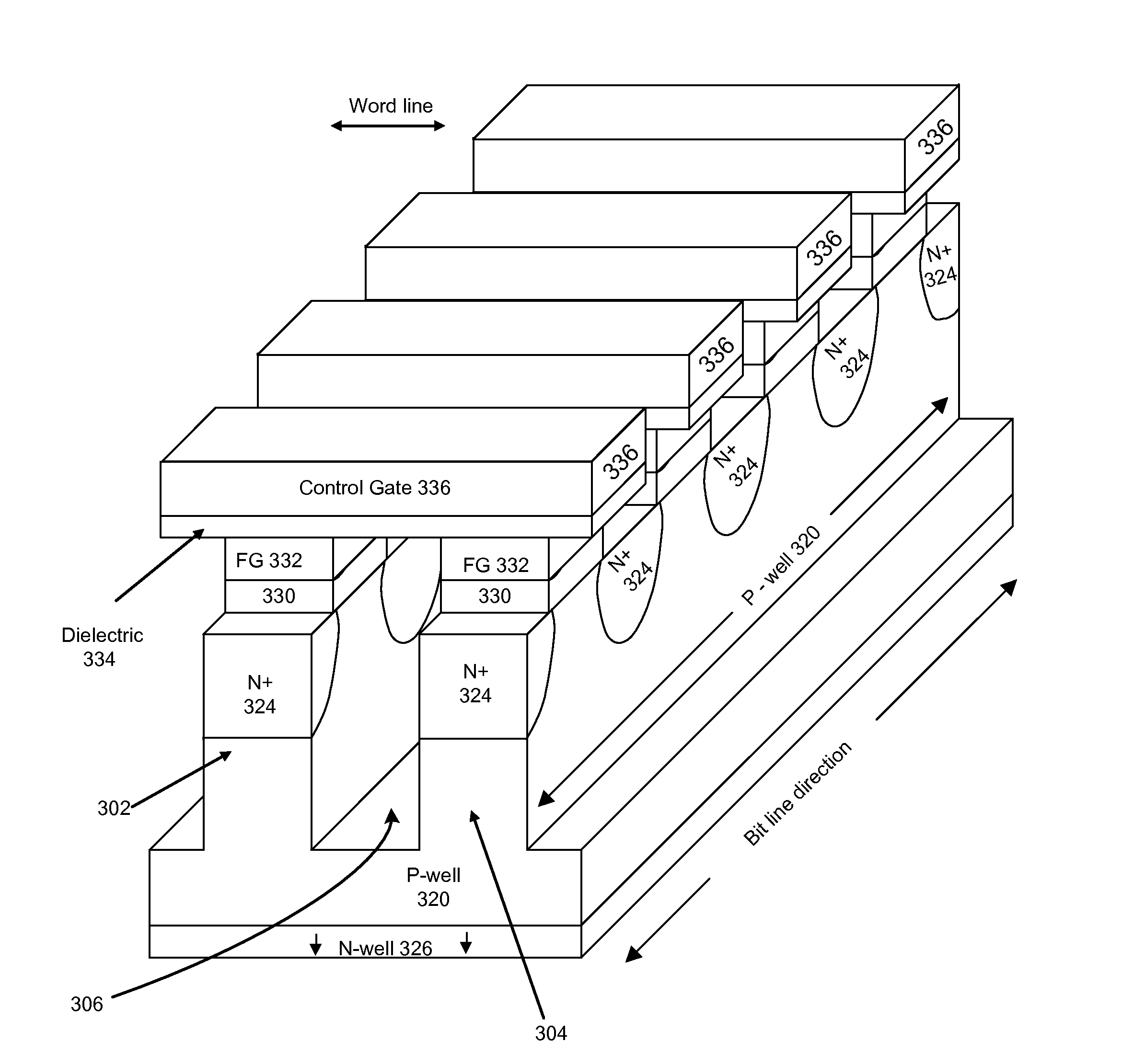
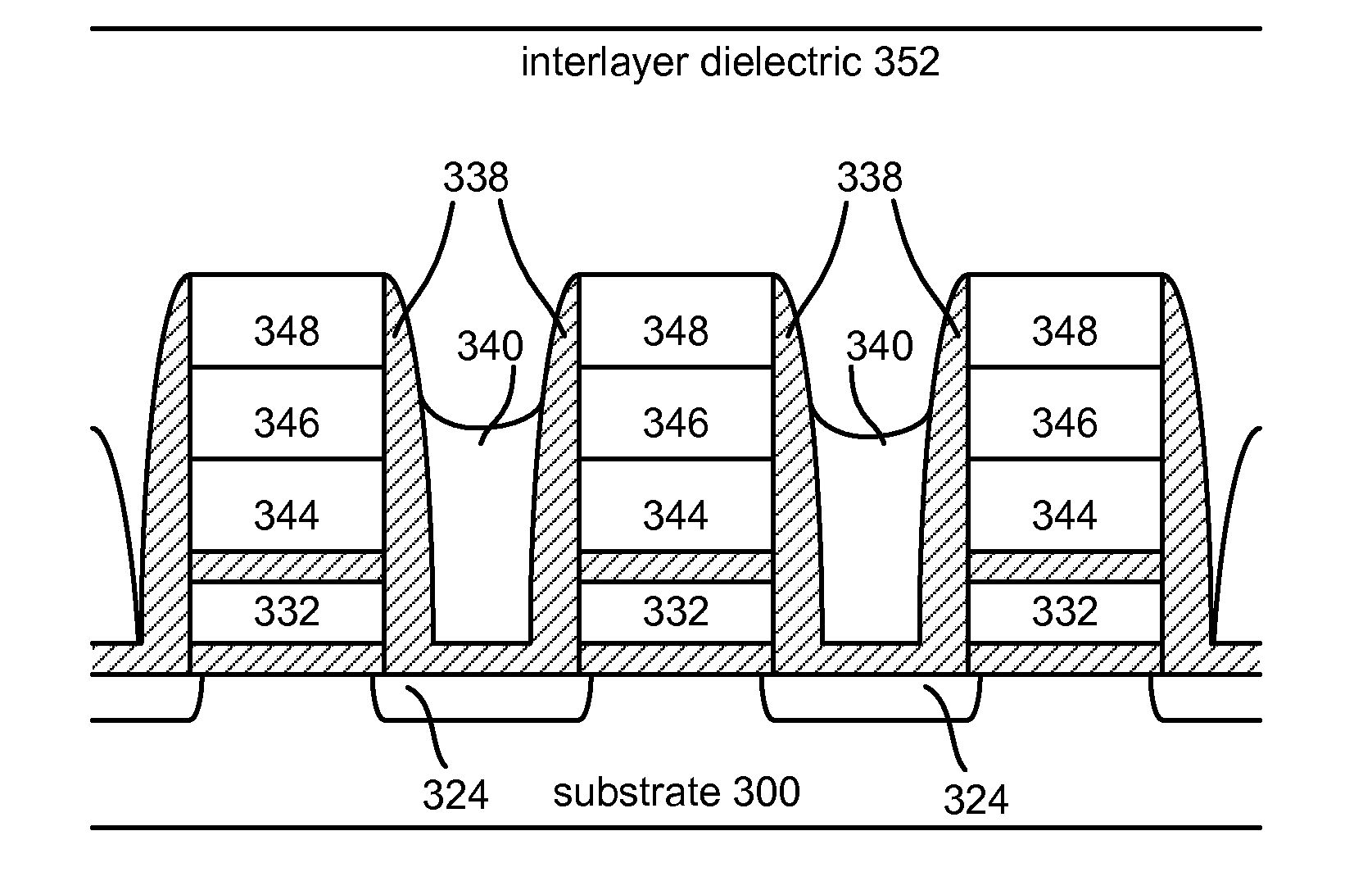
Methods of fabricating shield plates for reduced field coupling in nonvolatile memory
InactiveUS20080160680A1Reduce couplingSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesBit lineManufacturing technology
Shield plates for reduced coupling between charge storage regions in nonvolatile semiconductor memory devices, and associated techniques for forming the same, are provided. Electrical fields associated with charge stored in the floating gates or other charge storage regions of a memory device can couple to neighboring charge storage regions because of the close, and continually decreasing proximity of these regions. A shield plate can be formed adjacent to the bit line sides of floating gates that face opposing bit line sides of adjacent floating gates. Insulating layers can be formed between each shield plate and its corresponding adjacent charge storage region. The insulating layers can extend to the levels of the upper surfaces of the control gates formed above the charge storage regions. In such a configuration, sidewall fabrication techniques can be implemented to form the insulating members and shield plates. Each shield plate can be deposited and etched without complex masking to connect the control gates and shield plates. In one embodiment, the shield plates are at a floating potential.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Thin film fabrication method and thin film fabrication apparatus
InactiveUS6872289B2Sheath field strengthExpand coverageCellsElectric discharge tubesSputteringPulse height
Owner:ANELVA CORP
Differential D-dot voltage sensor
ActiveCN103235170AReduce volumeWill not affect the input sideCurrent/voltage measurementElectrical conductorSmart grid
The invention discloses a differential D-dot voltage sensor, which comprises a measuring module, an electrode plate, a signal modulation module and a collection transmission module, wherein the measuring module is provided with a first input end and a second input end, the electrode plate is provided with a first electrode and a second electrode, the measuring module is a differential amplification module, the differential amplification module is used for measuring the differential voltage between conducting layers, the sensor is not in grounding contact and is also not in direct contact with a tested conductor, and the output is floating potential difference, so the sensor can reduce the size of an insulation structure. Because the differential structure carries out non-contact measurement on the same potential, no direct energy transmission exists between the tested conductor and the sensor, and the influence cannot be generated on the input side when the sensor generates fault such as insulation breakthrough or output short circuit. The differential D-dot voltage sensor can solve the non-contact electrodeless voltage measurement problem of an intelligent electric network and can be used for 10kV to 35kV voltage measurement.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Microparticle sensor
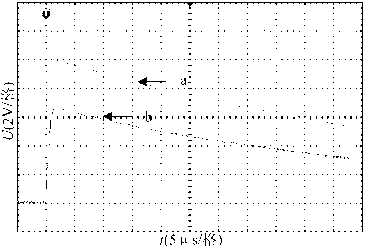
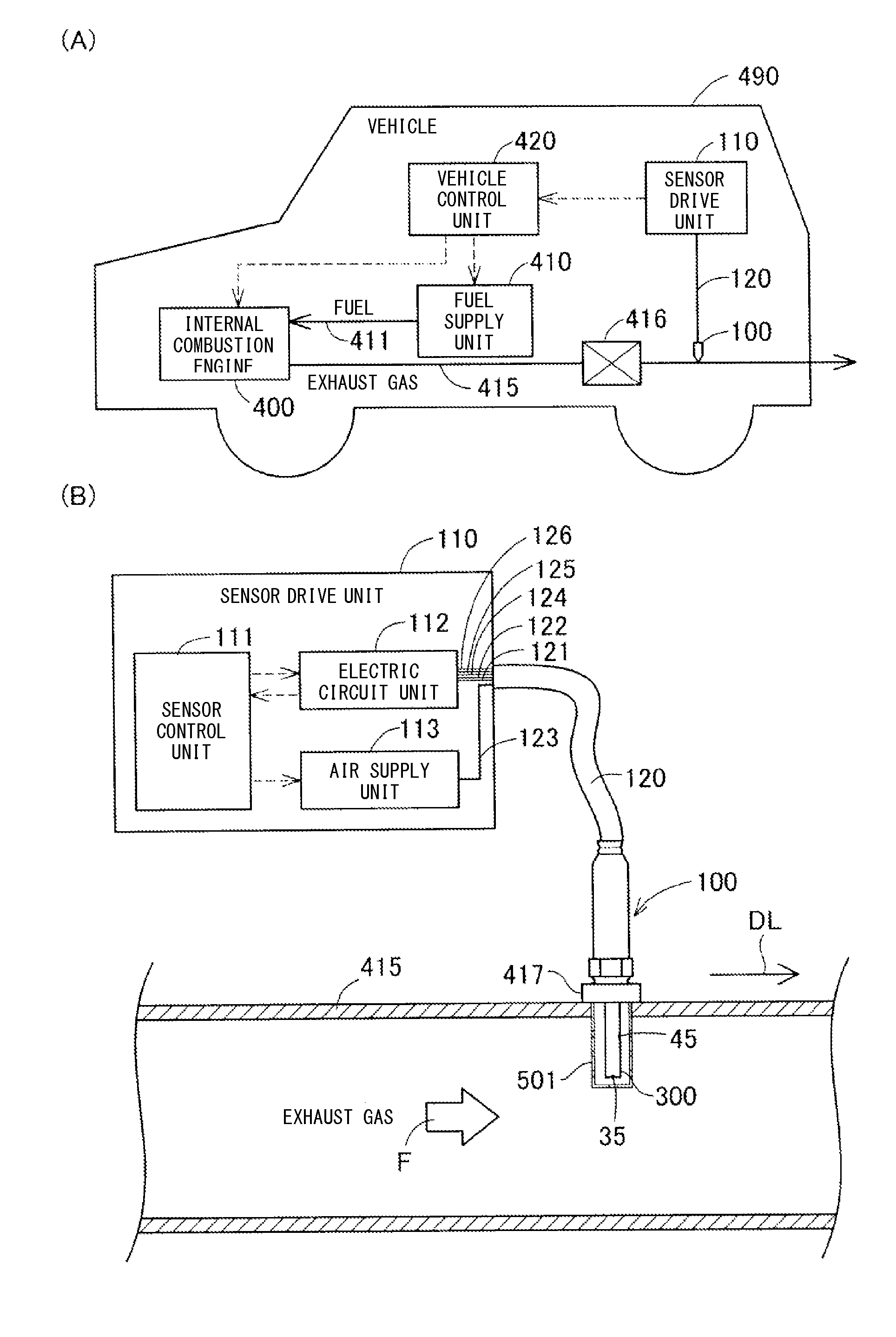
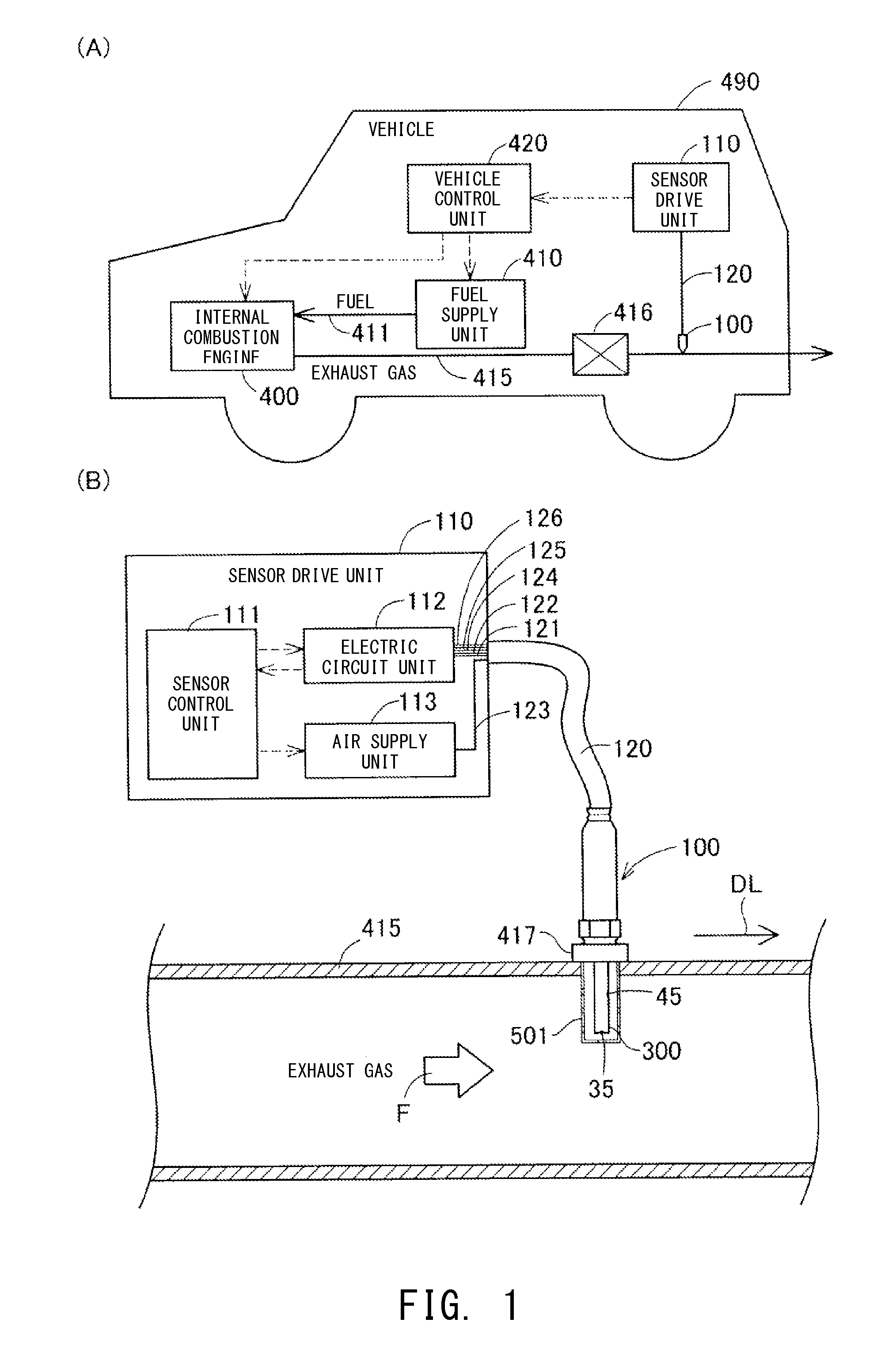
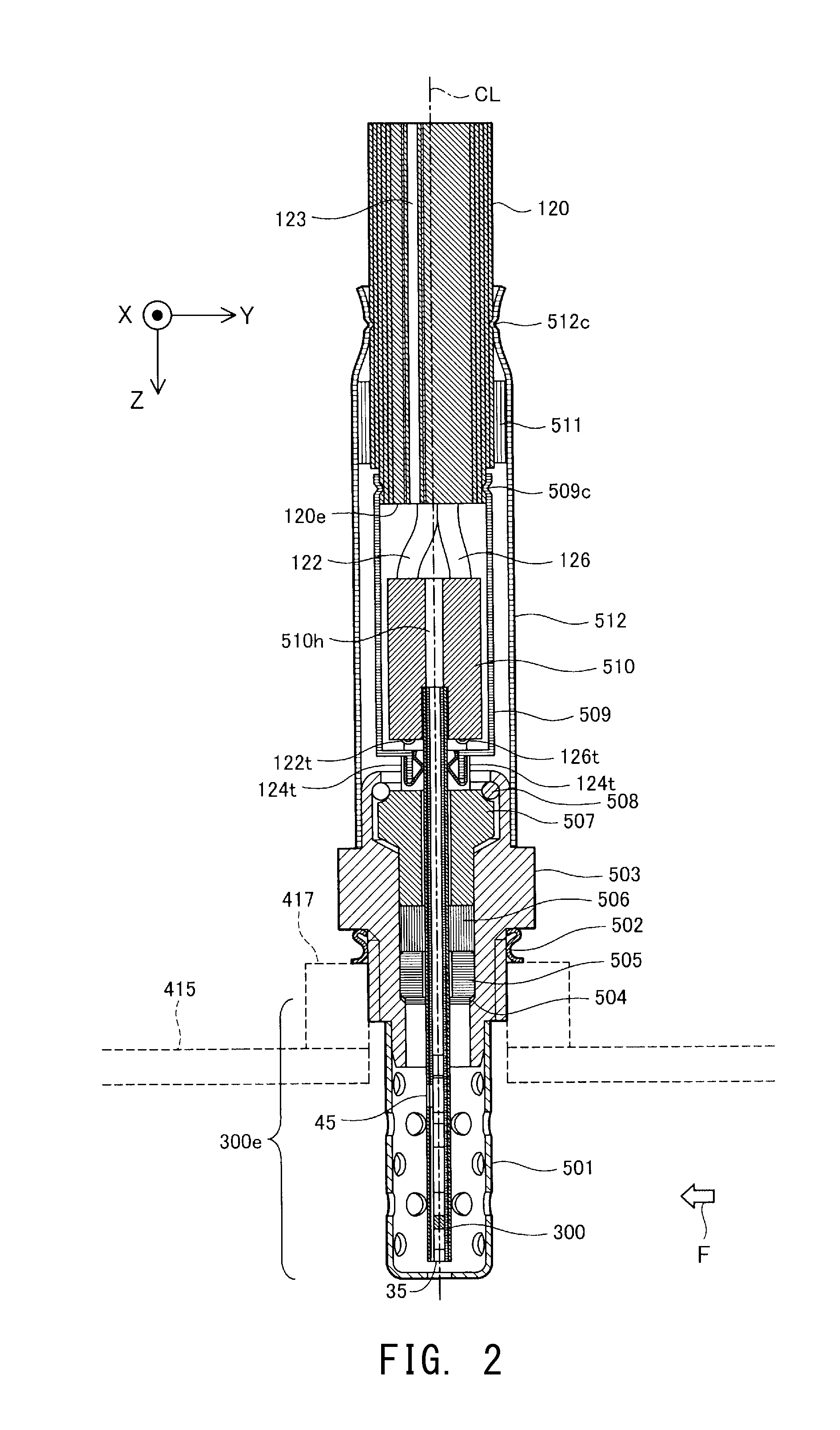
ActiveUS20150020574A1Elongated in service lifeThe right amountInternal-combustion engine testingSamplingParticulatesMicroparticle
A particulate sensor including a sensor unit (300) having an ion generation section (611, 361, 322); an electric charge section (612) for electrically charging at least portion of particulates S using ions PI; a capture section (616, 617, 316, 326, 362) for trapping at least portion of the ions PI not used for electrically charging the particulates S; and a sensor ground section (340, 310v, 330v3) connected to the capture section and having a first floating potential corresponding to the amount of the ions PI trapped by the capture section. The sensor unit can detect the amount of the particulates S in the gas on the basis of the electric potential of the sensor ground section. The sensor ground section is covered with insulating ceramic at that outer portion of the sensor unit which comes into contact with the gas.
Owner:NGK SPARK PLUG CO LTD
Electrosurgical device with floating-potential electrodes
InactiveUS7563261B2Improve power densityLarger, more controlled and more uniform lesionSurgical instruments for heatingElectricityVaporization
An electrosurgical instrument, system and methods are provided for the vaporization, cutting, coagulation, or treatment of tissue in the presence of an electrically conductive fluid medium. The electrosurgical probe comprises at least one active electrode, and at least one “floating” electrode having at least one end in close proximity to at least one active electrode. The floating electrode is not connected in any way to the electrosurgical power supply, but rather has a “floating” potential determined by the shape and position of the electrode. The floating electrode increases current density in the region of the probe distal end.
Owner:ELECTROMEDICAL ASSOCS
Rectangular cathodic arc source and method of steering an arc spot
InactiveUS6929727B2Improve distributionUniform coatingCellsLiquid surface applicatorsElectrical conductorEvaporation
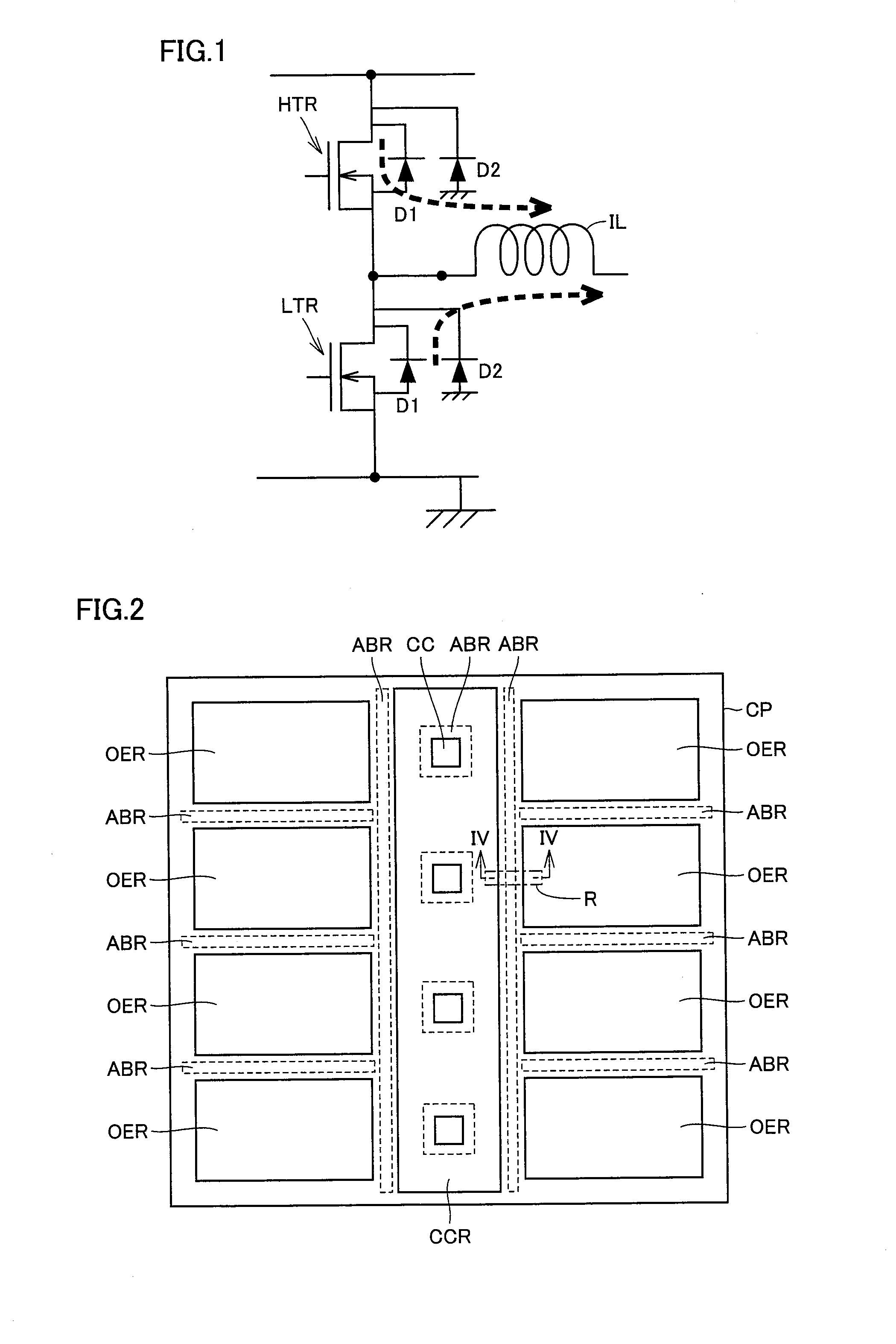
The invention provides an arc coating apparatus having a steering magnetic field source comprising steering conductors disposed along the short sides of a rectangular target behind the target, and a magnetic focusing system disposed along the long sides of the target in front of the target which confines the flow of plasma between magnetic fields generated on opposite long sides of the target. The plasma focusing system can be used to deflect the plasma flow off of the working axis of the cathode. Each steering conductor can be controlled independently. In a further embodiment, electrically independent steering conductors are disposed along opposite long sides of the cathode plate, and by selectively varying a current through one conductor, the path of the arc spot shifts to widen an erosion corridor. The invention also provides a plurality of internal anodes, and optionally a surrounding anode for deflecting the plasma flow and preserving a high ionization level of the plasma. The invention also provides a shield at floating potential, restricting the cathode spot from migrating into selected regions of the target evaporation surface outside of the desired erosion zone. The shield may be positioned immediately above the region of the target surface in the vicinity of the anode, protecting the anode from deposition of cathodic evaporate and providing better distribution of cathodic evaporate over the substrates to be coated. The invention further provides correcting magnets adjacent to the short sides of the target, to move the arc spot between the long sides.
Owner:G&H TECH LLC
Shield plates for reduced field coupling in nonvolatile memory
Shield plates for reduced coupling between charge storage regions in nonvolatile semiconductor memory devices, and associated techniques for forming the same, are provided. Electrical fields associated with charge stored in the floating gates or other charge storage regions of a memory device can couple to neighboring charge storage regions because of the close, and continually decreasing proximity of these regions. A shield plate can be formed adjacent to the bit line sides of floating gates that face opposing bit line sides of adjacent floating gates. Insulating layers can be formed between each shield plate and its corresponding adjacent charge storage region. The insulating layers can extend to the levels of the upper surfaces of the control gates formed above the charge storage regions. In such a configuration, sidewall fabrication techniques can be implemented to form the insulating members and shield plates. Each shield plate can be deposited and etched without complex masking to connect the control gates and shield plates. In one embodiment, the shield plates are at a floating potential.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Memorizer and operating method thereof
Owner:GIANTEC SEMICON LTD
Bolometric detector, device for detecting infrared radiation using such a detector and method for producing this detector
InactiveUS20060208189A1Maximise useful surface areaArea maximizationMaterial analysis by optical meansPyrometry using electric radation detectorsThermal isolationElectricity
A bolometric detector for electromagnetic radiation comprising a sensitive part or membrane comprising one or more layers of a sensitive material, the resistivity of which varies with temperature; first electric conductor elements in electrical continuity with a readout circuit associated with the bolometric detector and acting as electrodes for the detector and being in contact with the sensitive material and acting as an electromagnetic radiation absorber; second electric conductor elements at a floating potential acting only as an electromagnetic radiation absorber; at least one support area for the sensitive part fulfilling the function of positioning the sensitive part and electric conductor in relation to the readout circuit; at least one thermal isolation structure electrically and mechanically linking each support area to the sensitive part. The conductor elements are distributed as two crossed, superimposed networks of conductive tracks, the first of the two networks comprising all the first conductor elements.
Owner:ULIS SAS
Multifunctional submerging and floating device with unmanned aerial vehicle taking-off and landing platform
PendingCN107672751AImprove battery lifePrecision landingHull interior subdivisionBatteries circuit arrangementsOcean bottomHigh pressure
The invention discloses a multifunctional submerging and floating device with an unmanned aerial vehicle taking-off and landing platform. The multifunctional submerging and floating device comprises afloating cabin, the unmanned aerial vehicle taking-off and landing platform, a high-pressure submersible pump, a balance weight cabin and a power drive device. Solar cell panels are arranged, so thatsolar energy serves as an energy source. The multifunctional submerging and floating device is provided with an energy storage device, and an unmanned aerial vehicle, all types of instruments and equipment carried on the multifunctional submerging and floating device and submarine electronic equipment can be charged. Through the maneuverability of the power drive device, the position of the multifunctional submerging and floating device can be adjusted or the multifunctional submerging and floating device can slowly move to the designated position. The multifunctional submerging and floatingdevice is simple in structure, flexible in loading and transporting and quick to arrange; and on the base of the platform, the functions of exploration, receiving, storage, launching, object transit shipment and the like can be expanded as well, and the device is extended to be the universal type multifunctional submerging and floating device which can process all types of information and integrate multiple functions.
Owner:余拓
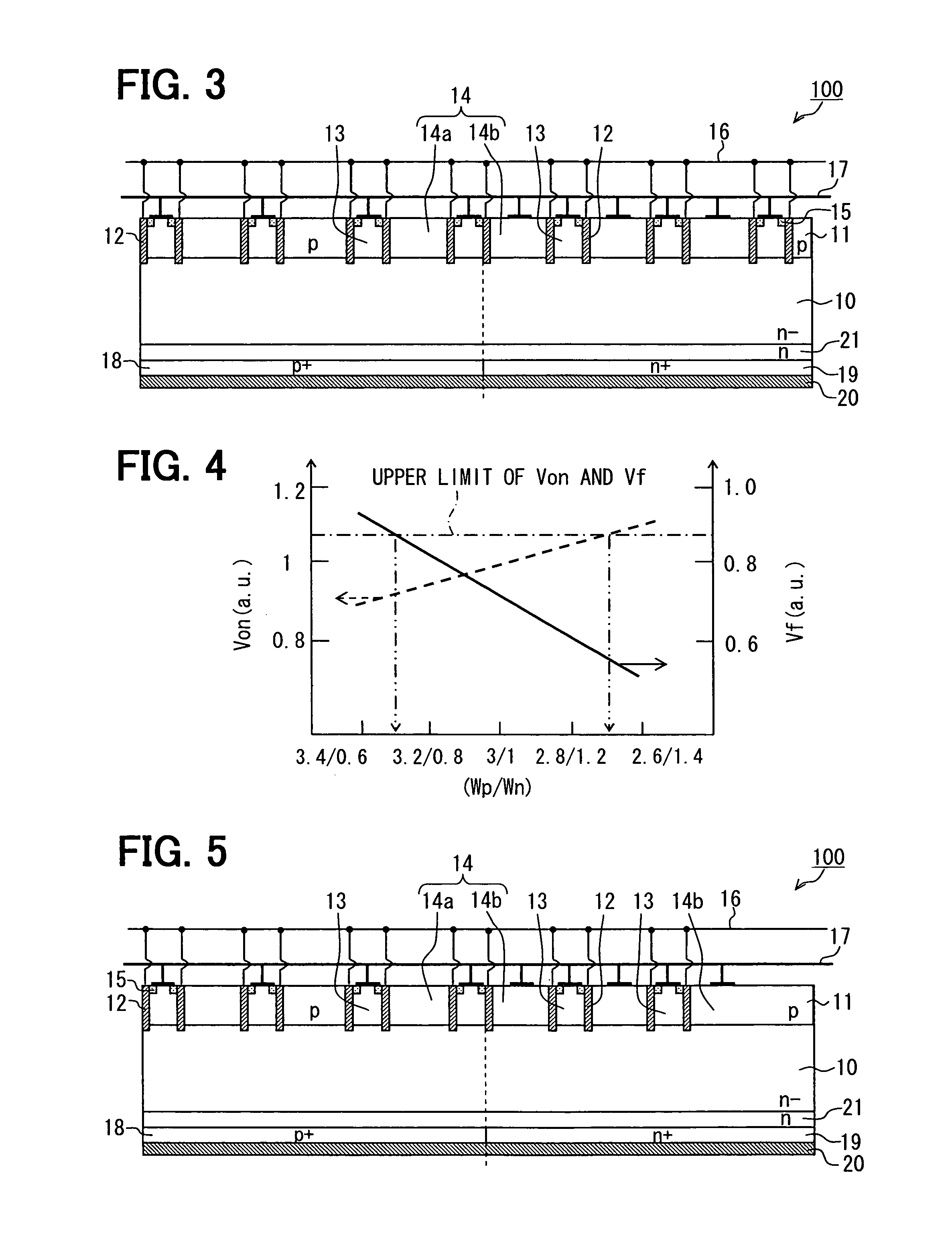
Semiconductor device having IGBT and FWD on same substrate
ActiveUS8299539B2Increase in sizeLower forward voltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceDevice material
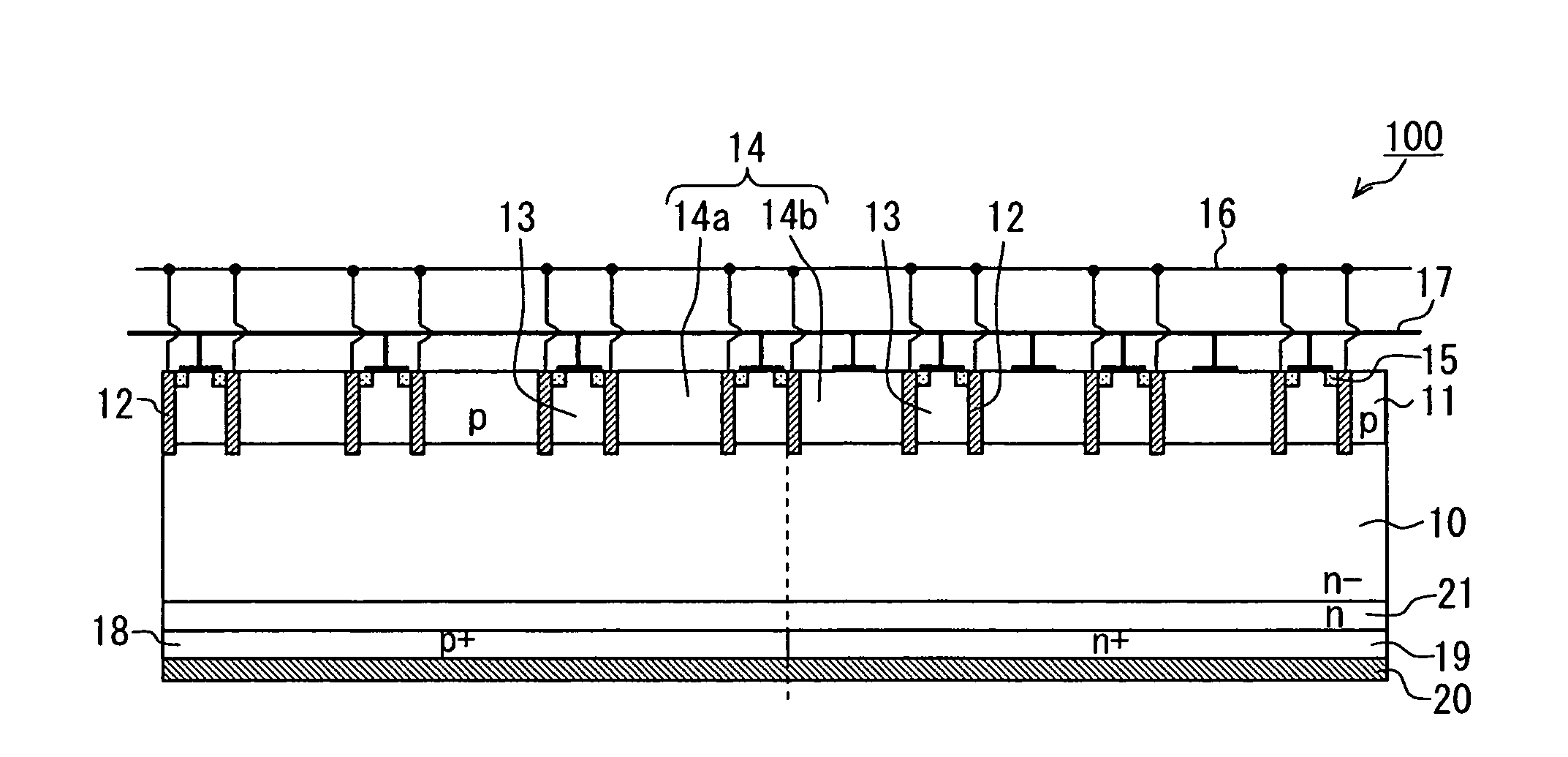
A semiconductor device includes: a semiconductor substrate; an IGBT element including a collector region; a FWD element including a cathode region adjacent to the collector region; a base layer on the substrate; multiple trench gate structures including a gate electrode. The base layer is divided by the trench gate structures into multiple first and second regions. Each first region includes an emitter region contacting the gate electrode. Each first region together with the emitter region is electrically coupled with an emitter electrode. The first regions include collector side and cathode side first regions, and the second regions include collector side and cathode side second regions. At least a part of the cathode side second region is electrically coupled with the emitter electrode, and at least a part of the collector side second region has a floating potential.
Owner:DENSO CORP
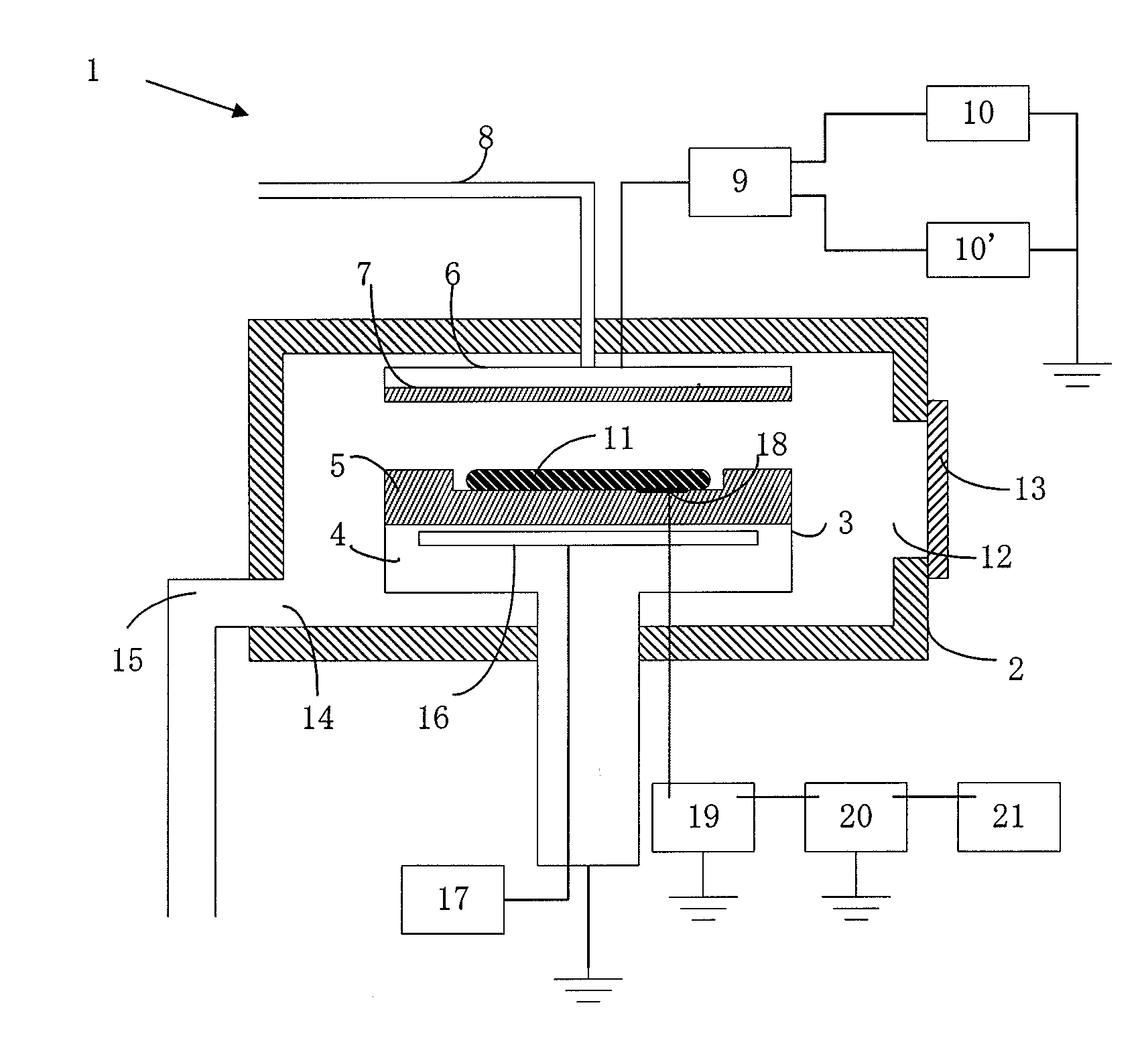
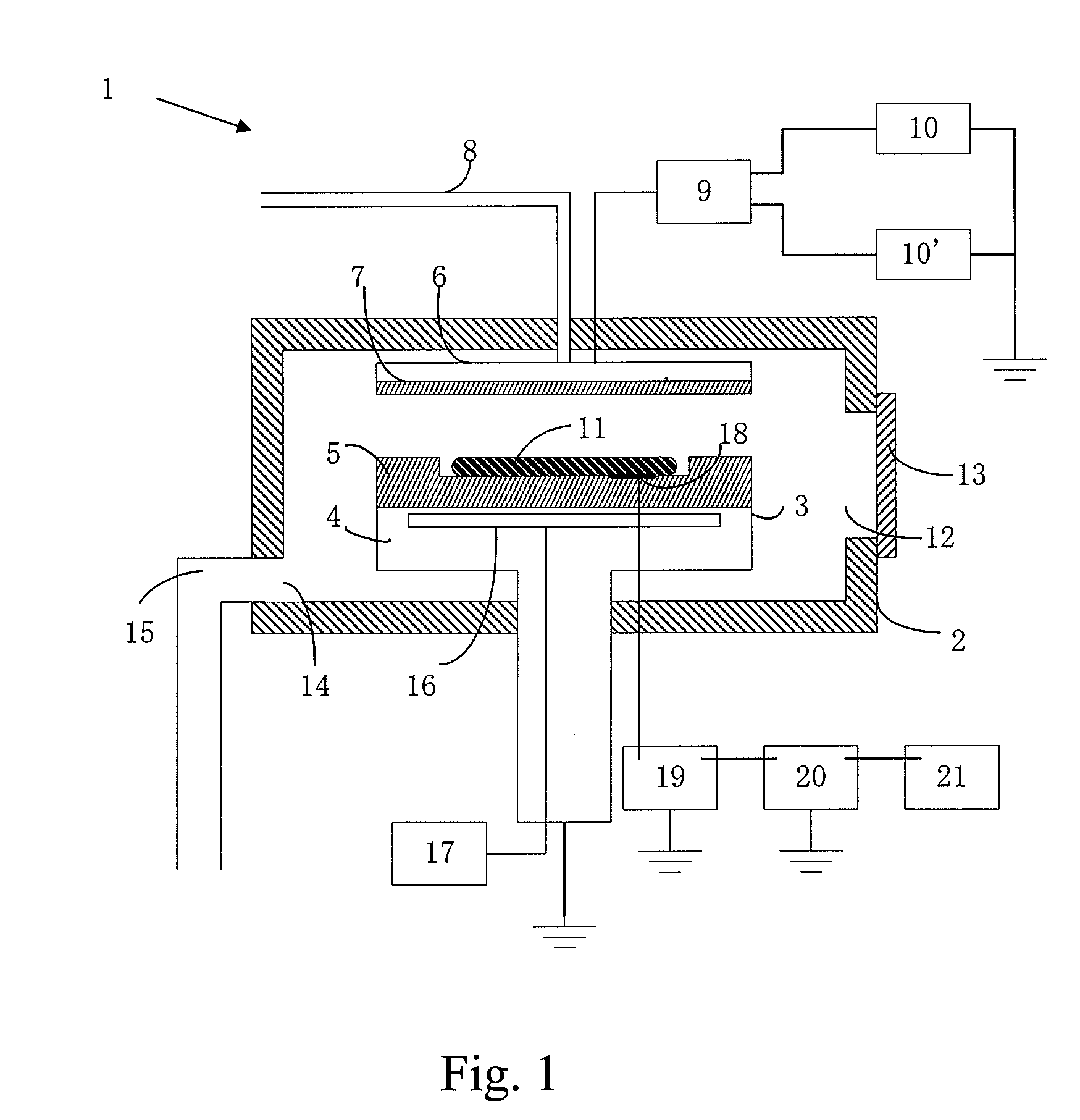
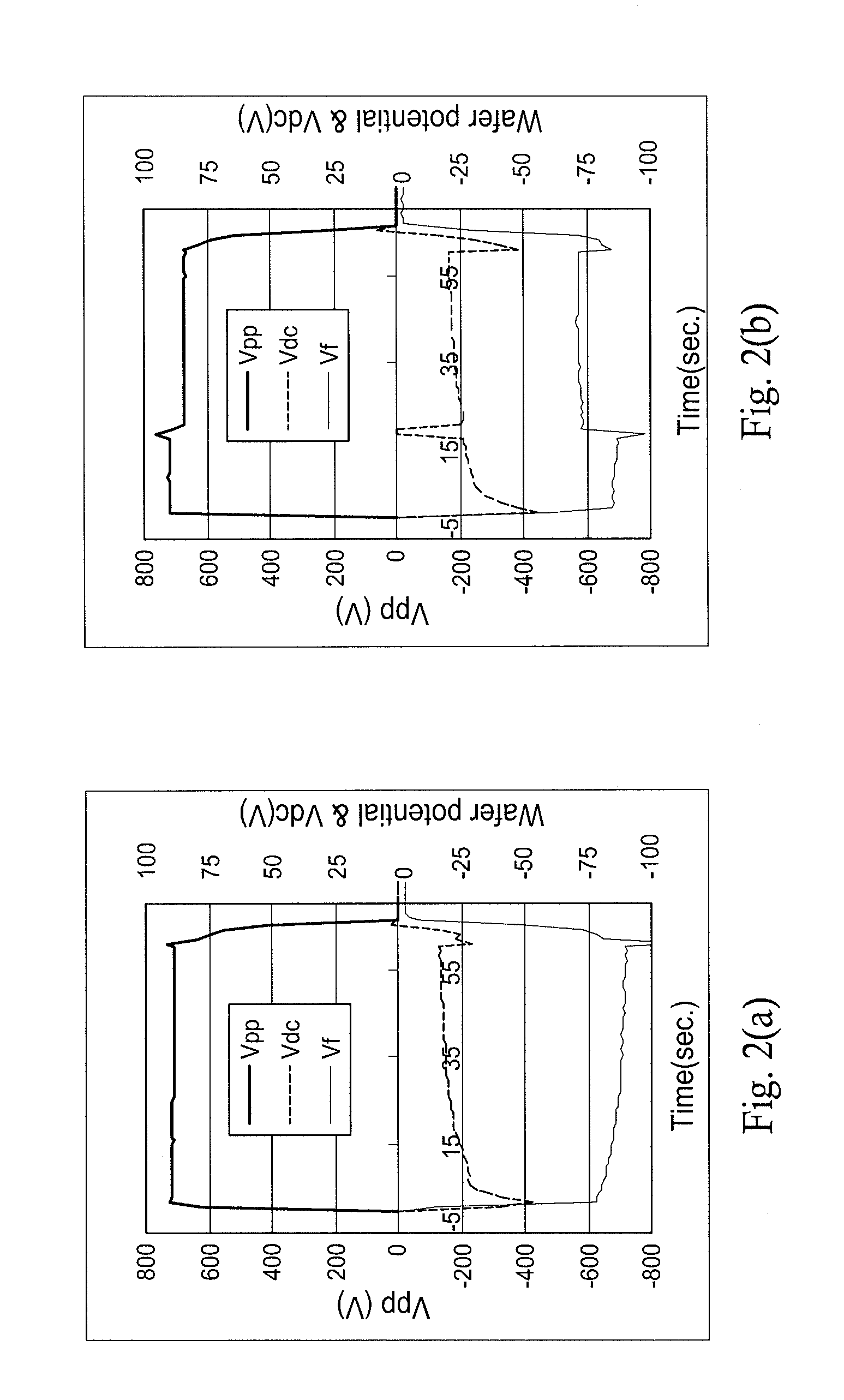
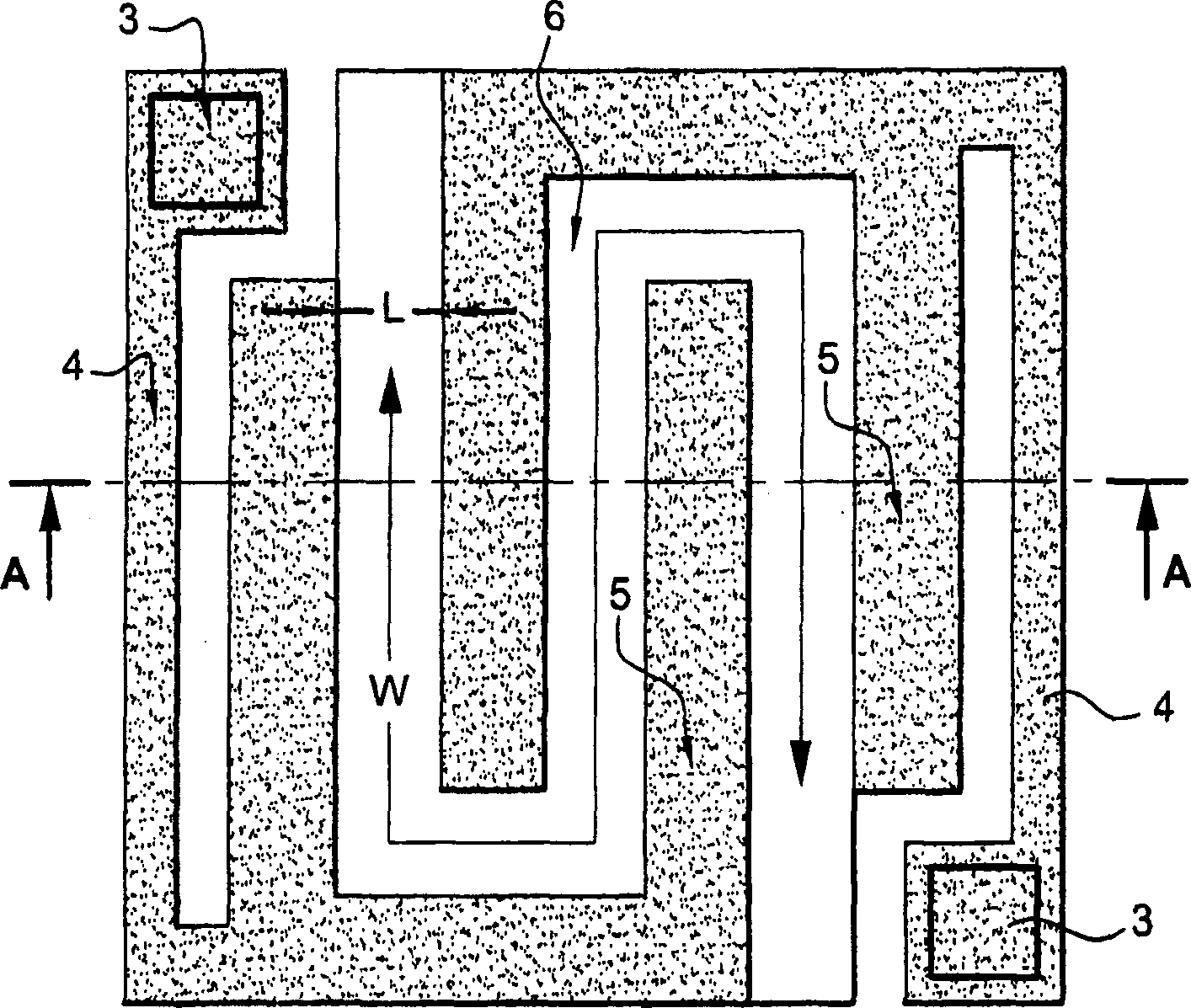
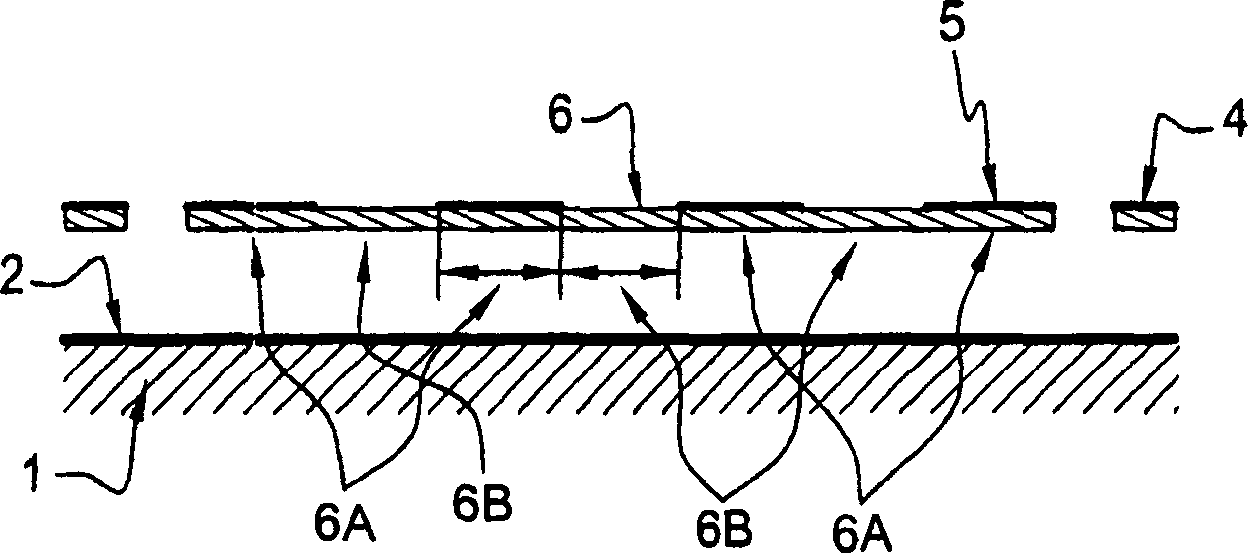
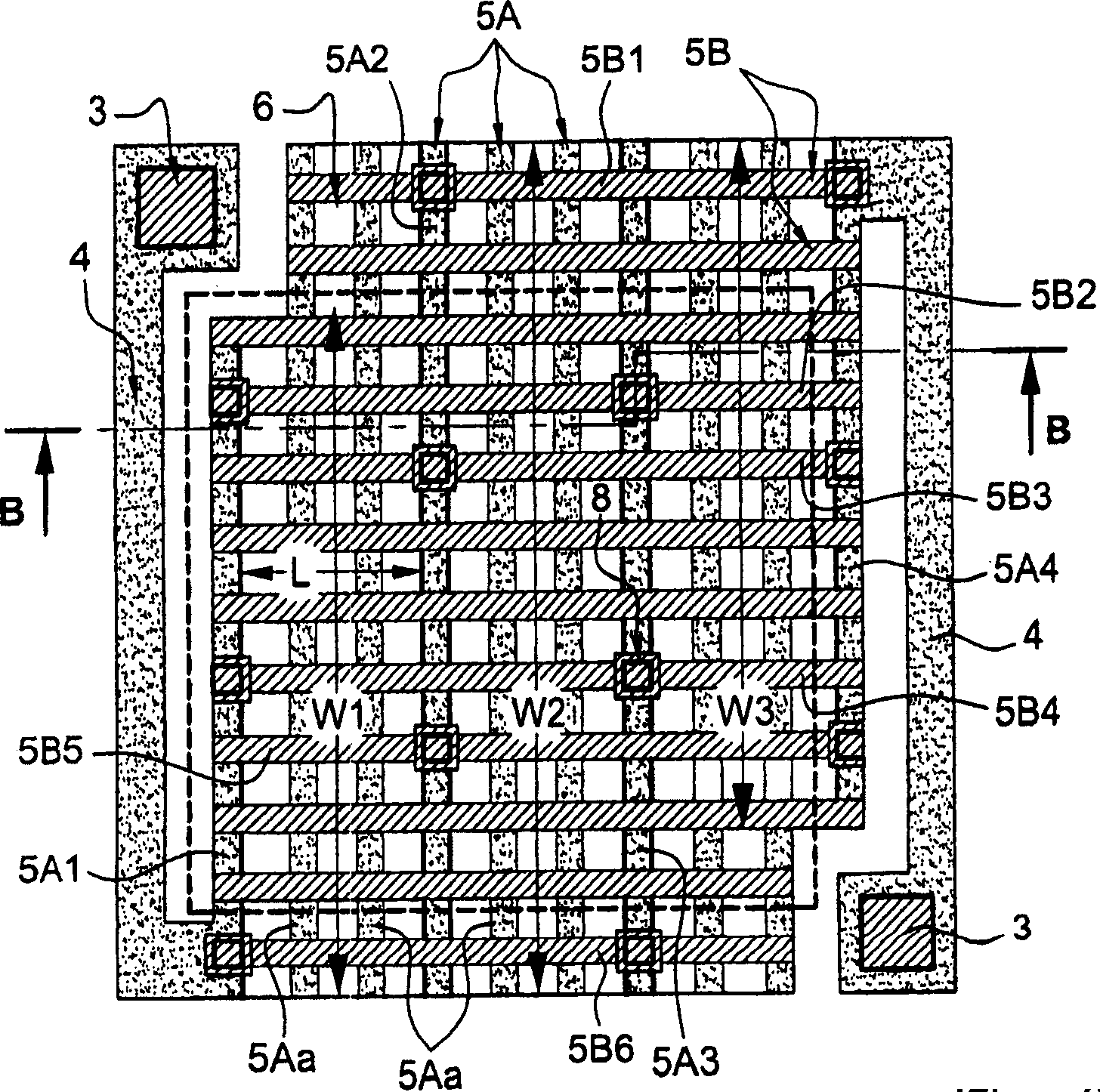
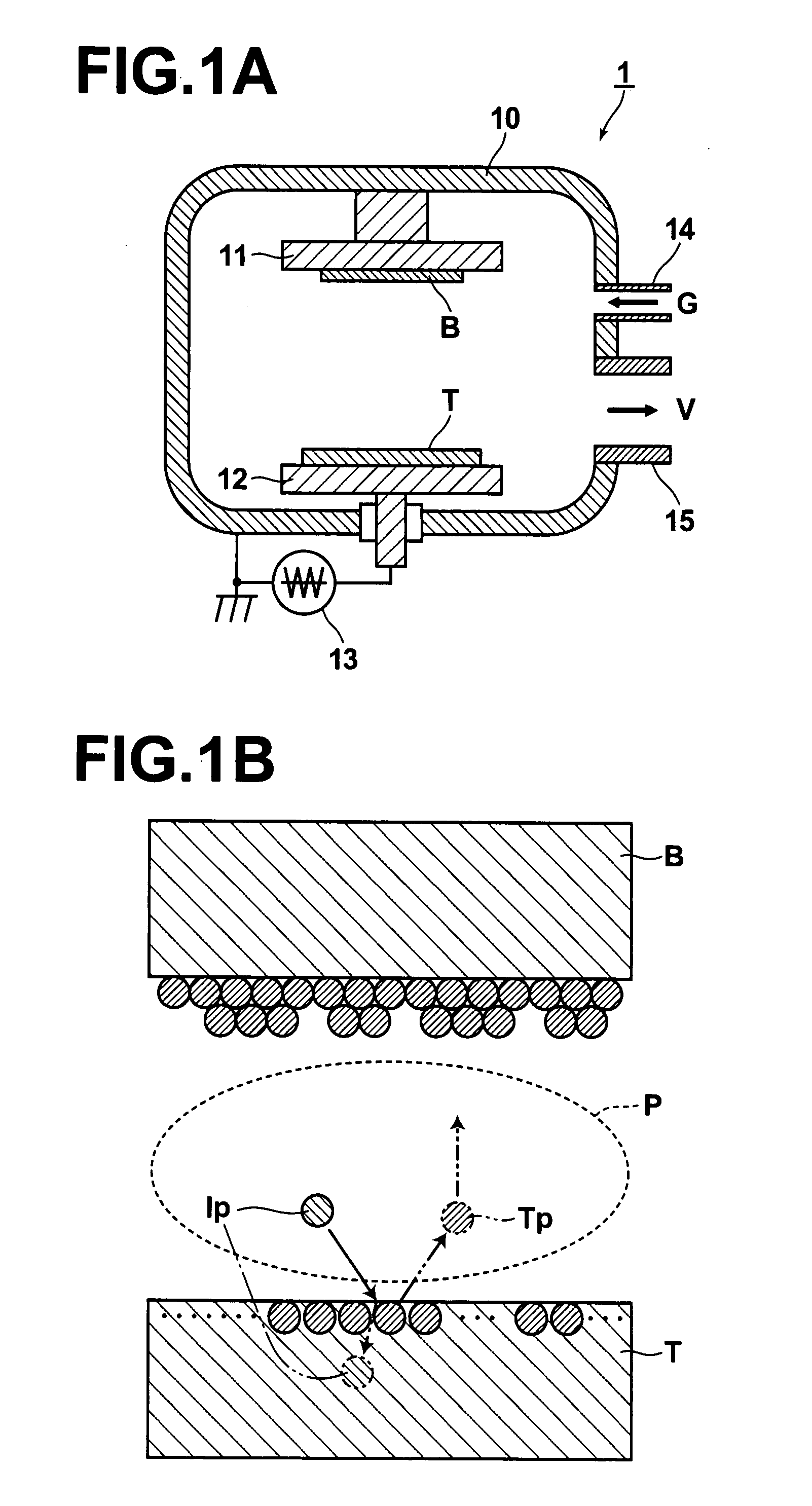
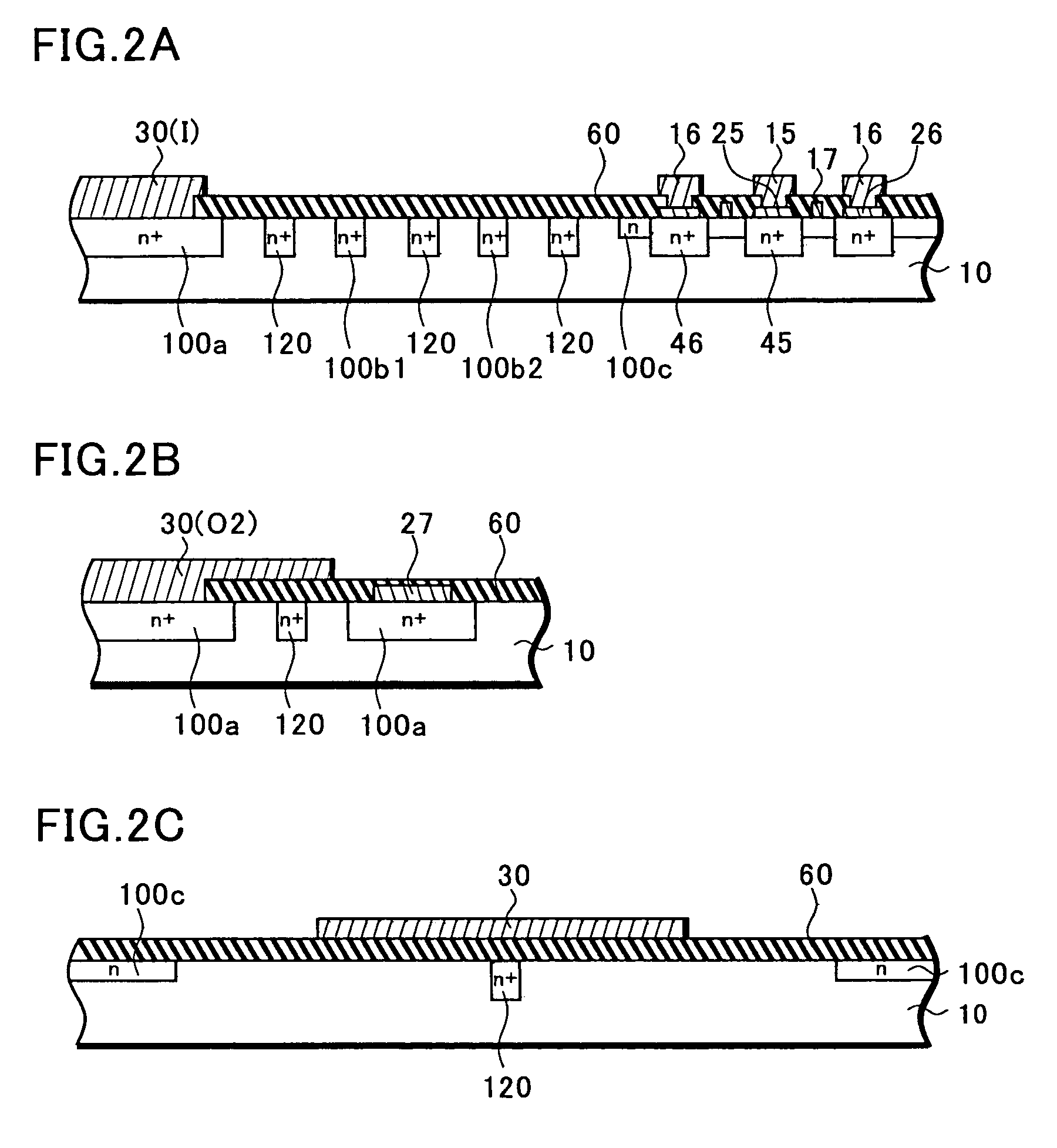
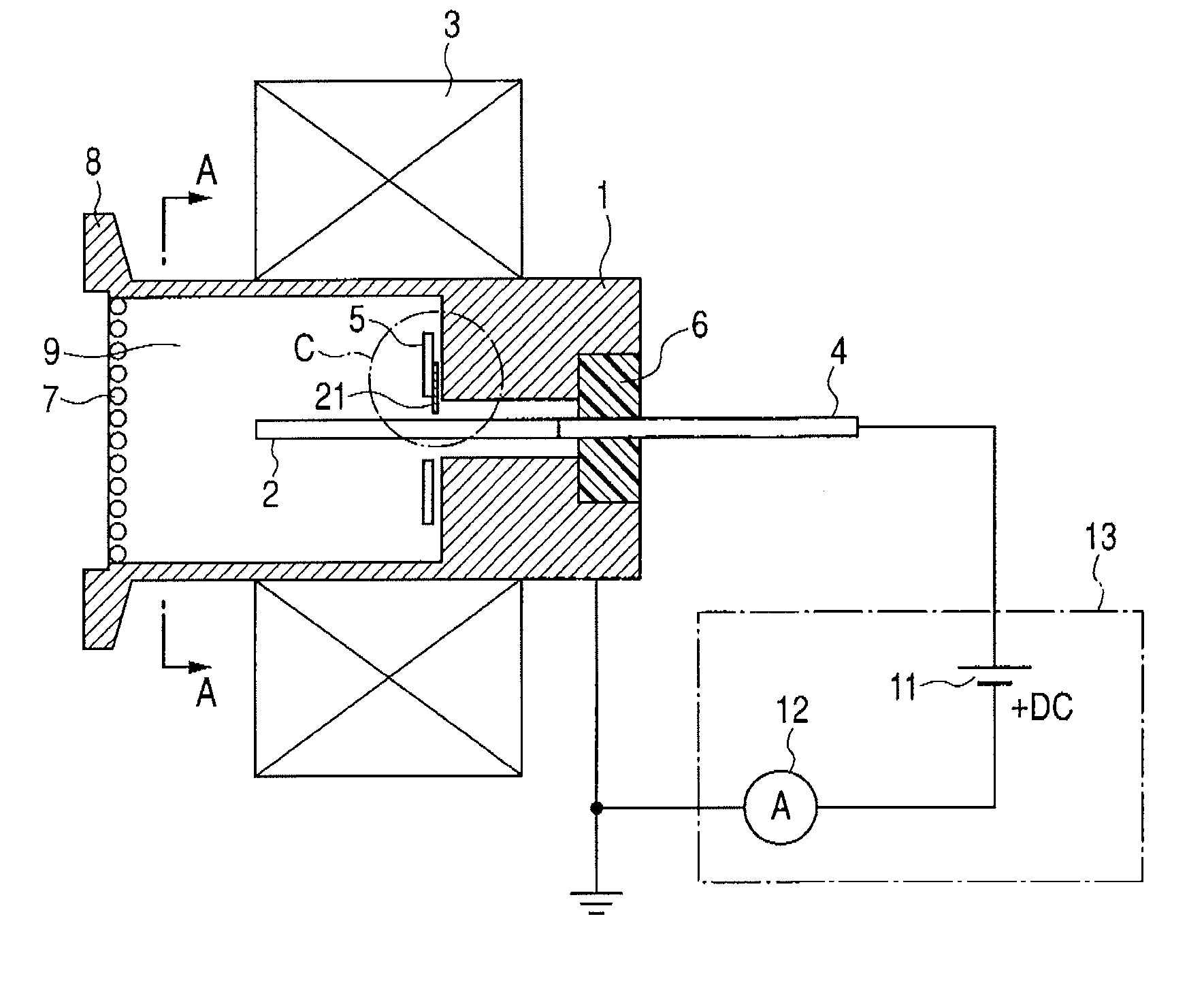
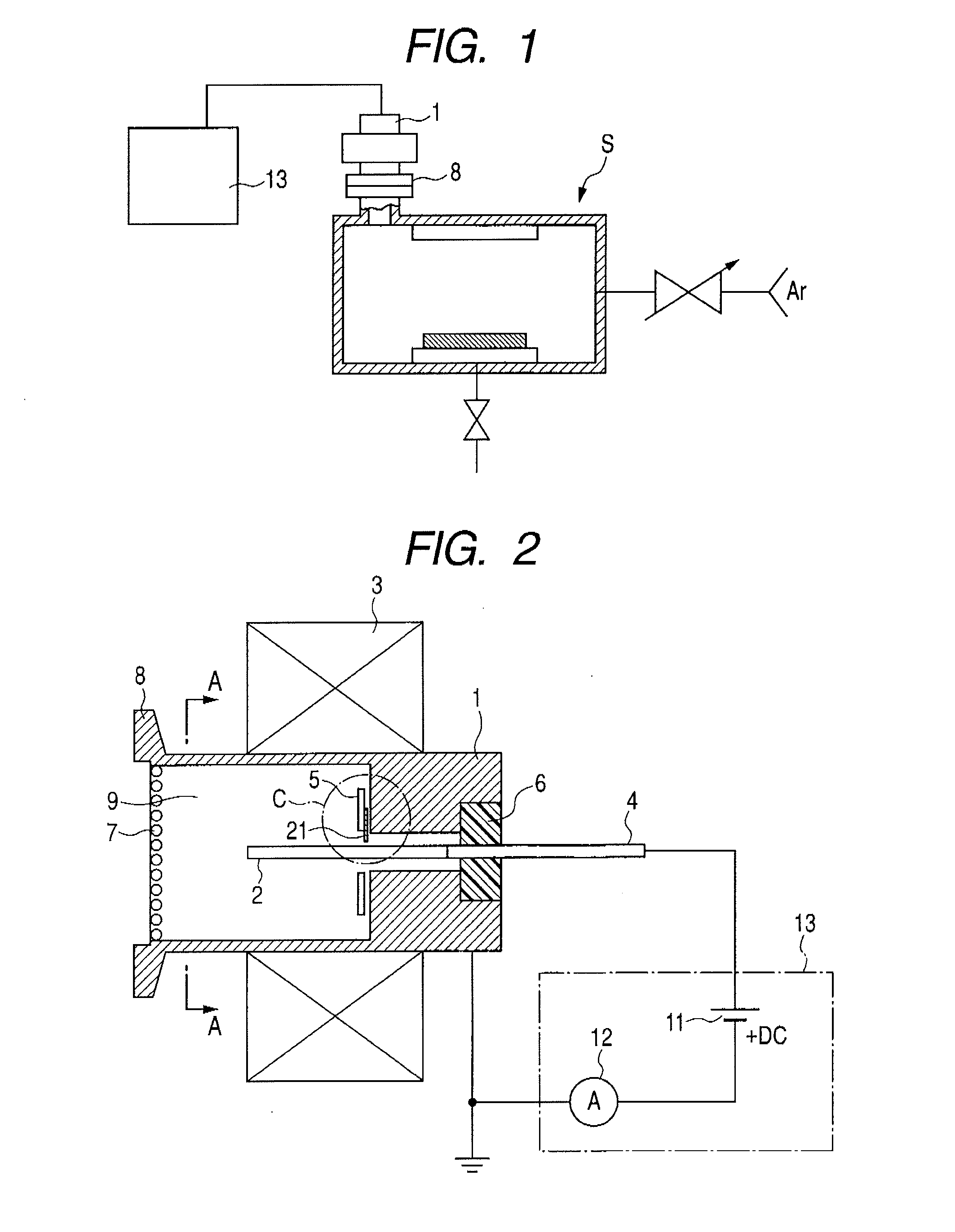
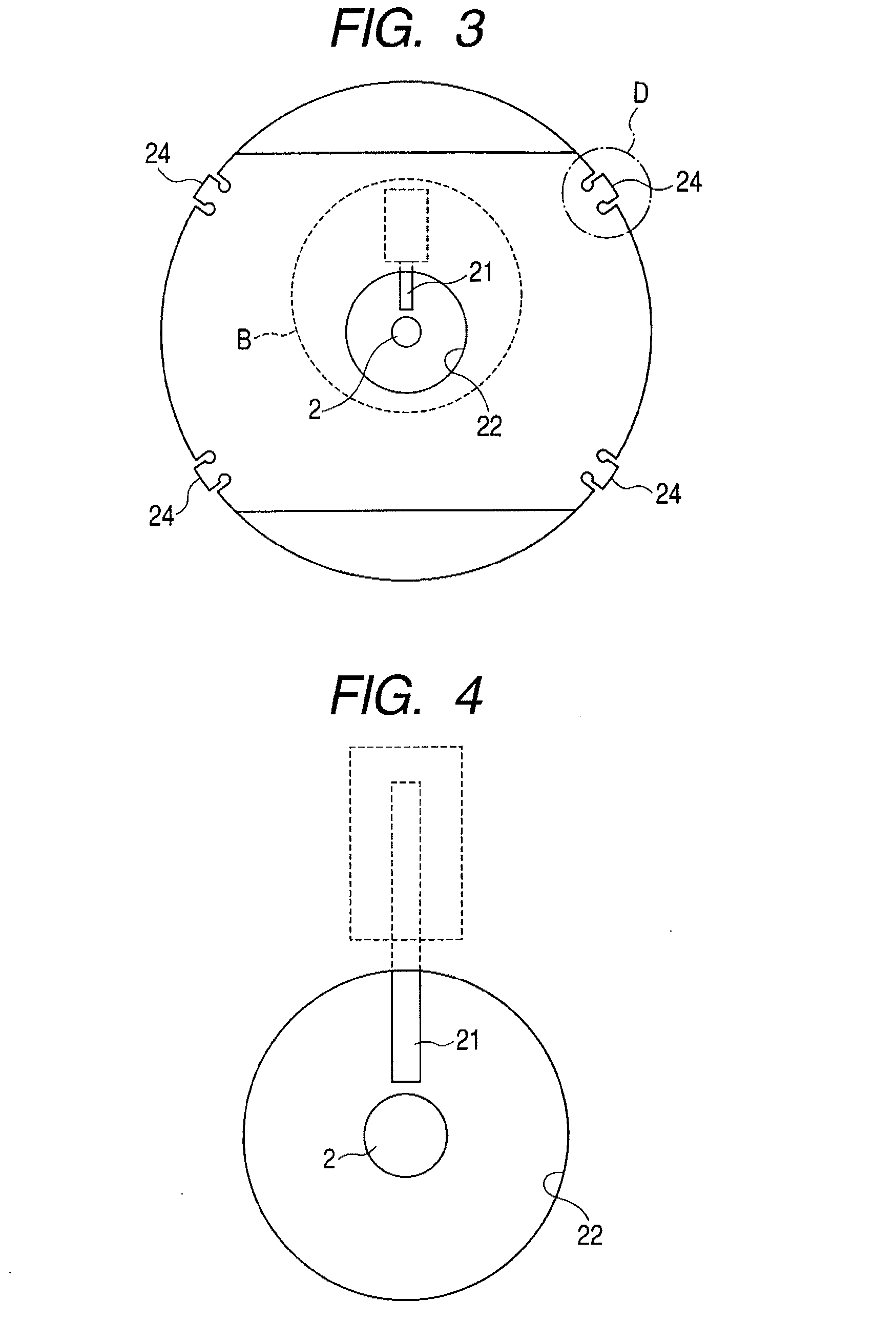
Method and apparatus for monitoring plasma-induced damage using DC floating potential of substrate
InactiveUS20090056627A1Accurate detectionCorrect damageLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementEngineeringFloating potential
A method for monitoring plasma-induced damage to a substrate while being processed in a plasma CVD apparatus includes: measuring DC floating potential of the substrate using a detection electrode in contact with the substrate while the substrate is processed in the apparatus; and detecting abnormality as plasma-induced damage based on the measured DC floating potential.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Bolometric detector, infrared detecting device using it and associated production process
InactiveCN1834599AAchieving connection redundancyImprove the correct distribution of potentialPyrometry using electric radation detectorsSemiconductor devicesThermal isolationElectricity
A bolometric detector for electromagnetic radiation comprising a sensitive part or membrane comprising one or more layers of a sensitive material, the resistivity of which varies with temperature; first electric conductor elements in electrical continuity with a readout circuit; second electric conductor elements at a floating potential acting; at least one support area for the sensitive part fulfilling the function of positioning the sensitive part and electric conductor in relation to the readout circuit; at least one thermal isolation structure electrically and mechanically linking each support area to the sensitive part. The conductor elements are distributed as two crossed, superimposed networks of conductive tracks, the first of the two networks comprising all the first conductor elements.
Owner:ULIS SAS
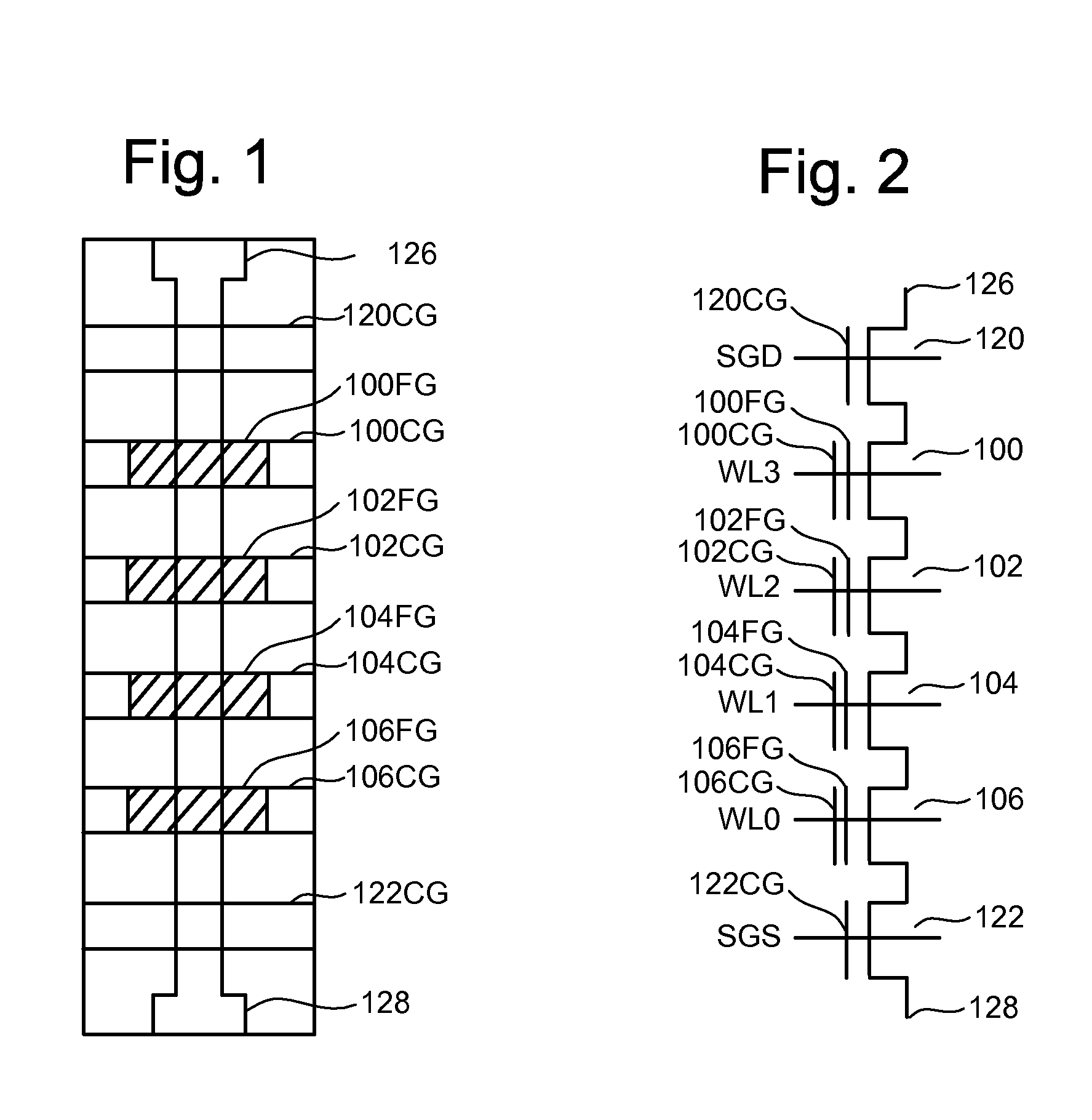
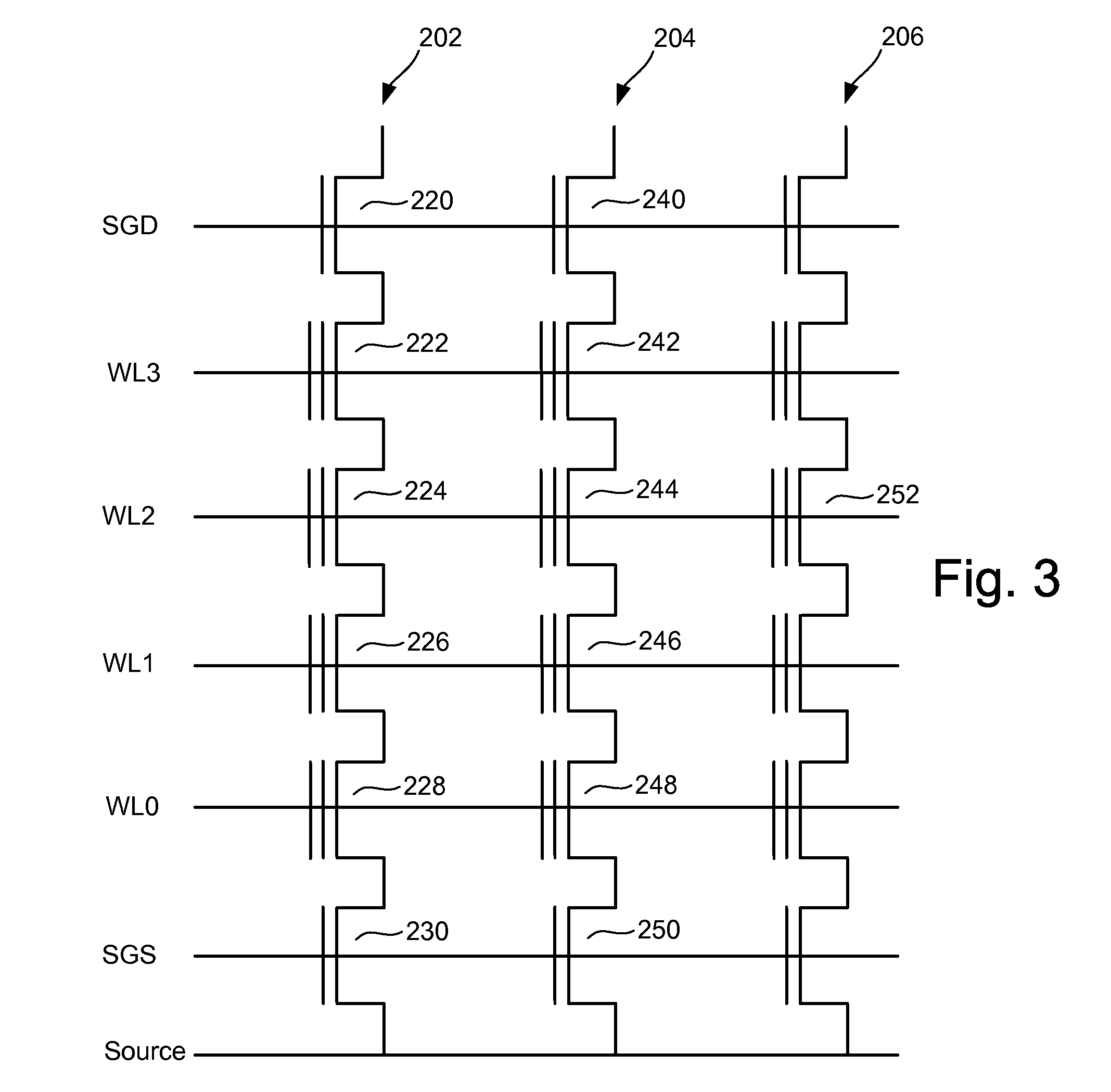
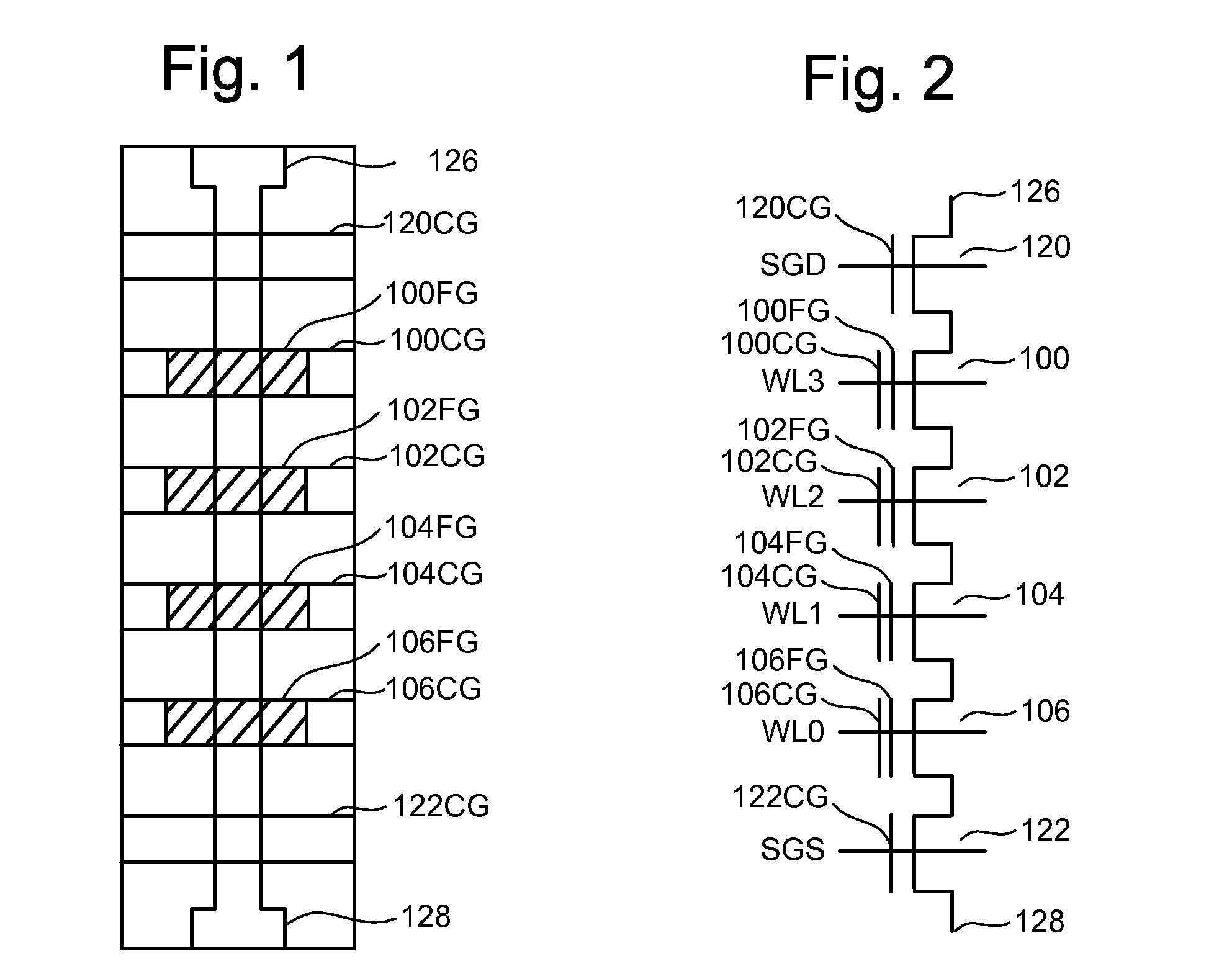
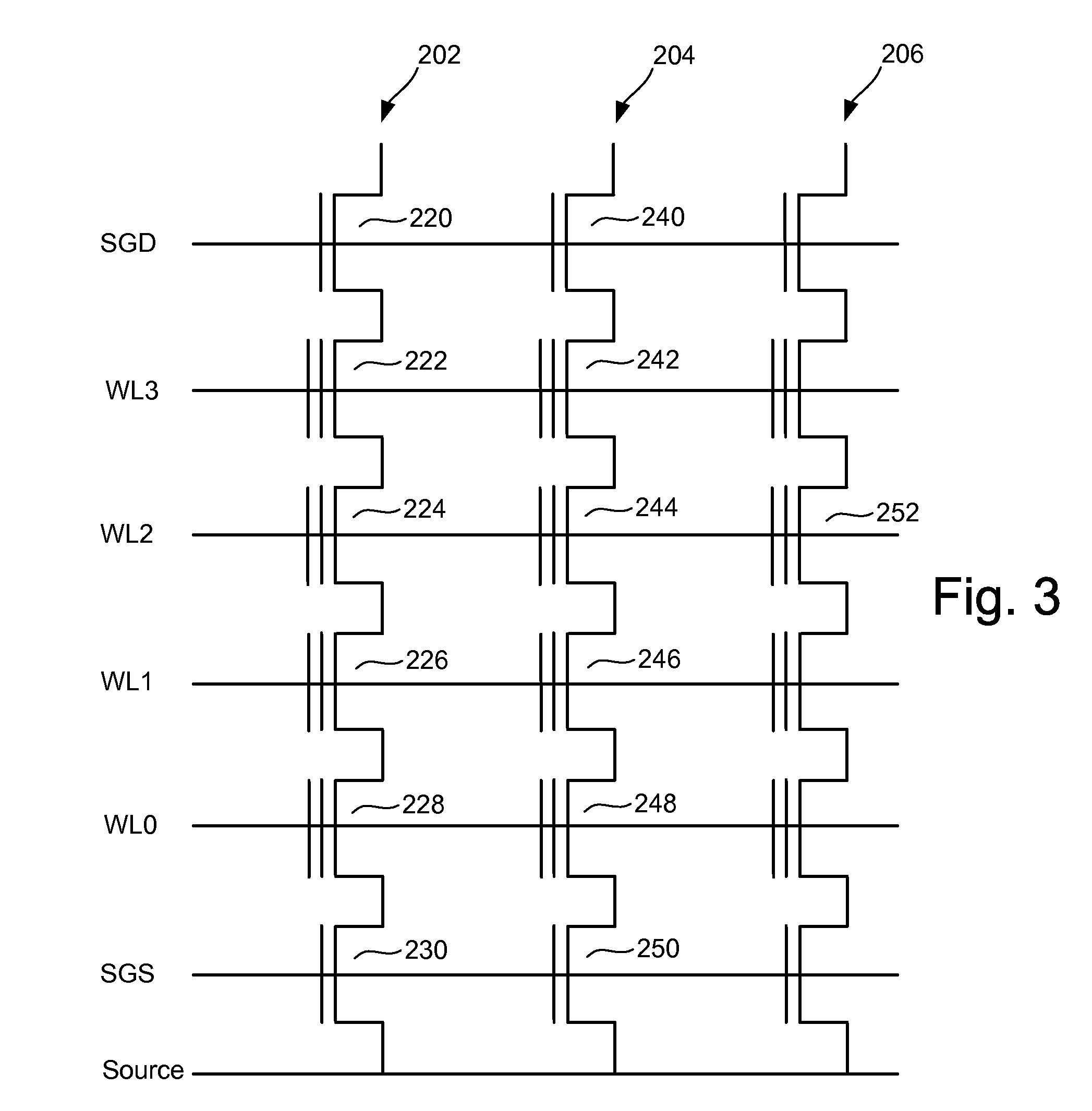
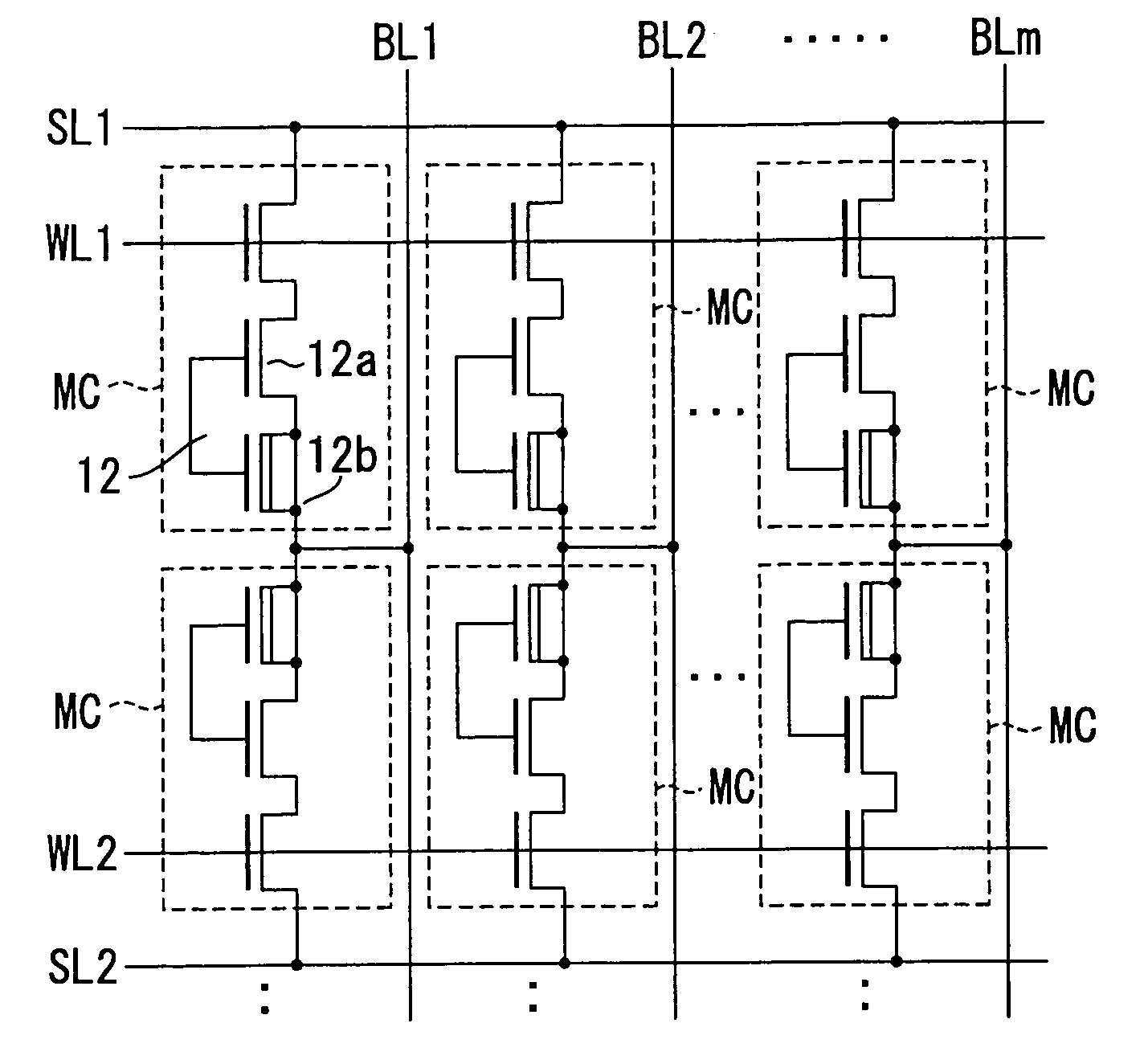
Non-volatile semiconductor memory device
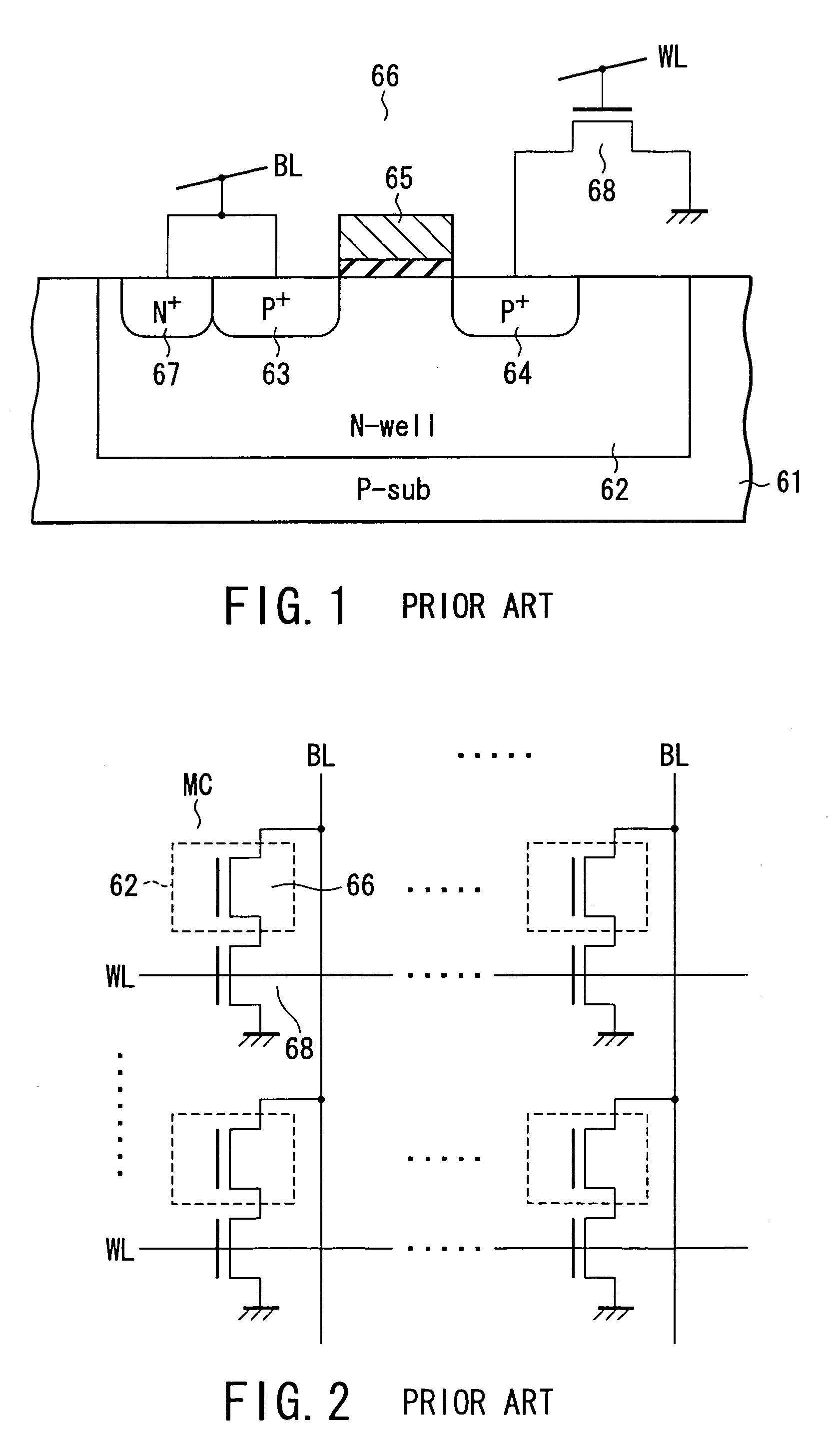
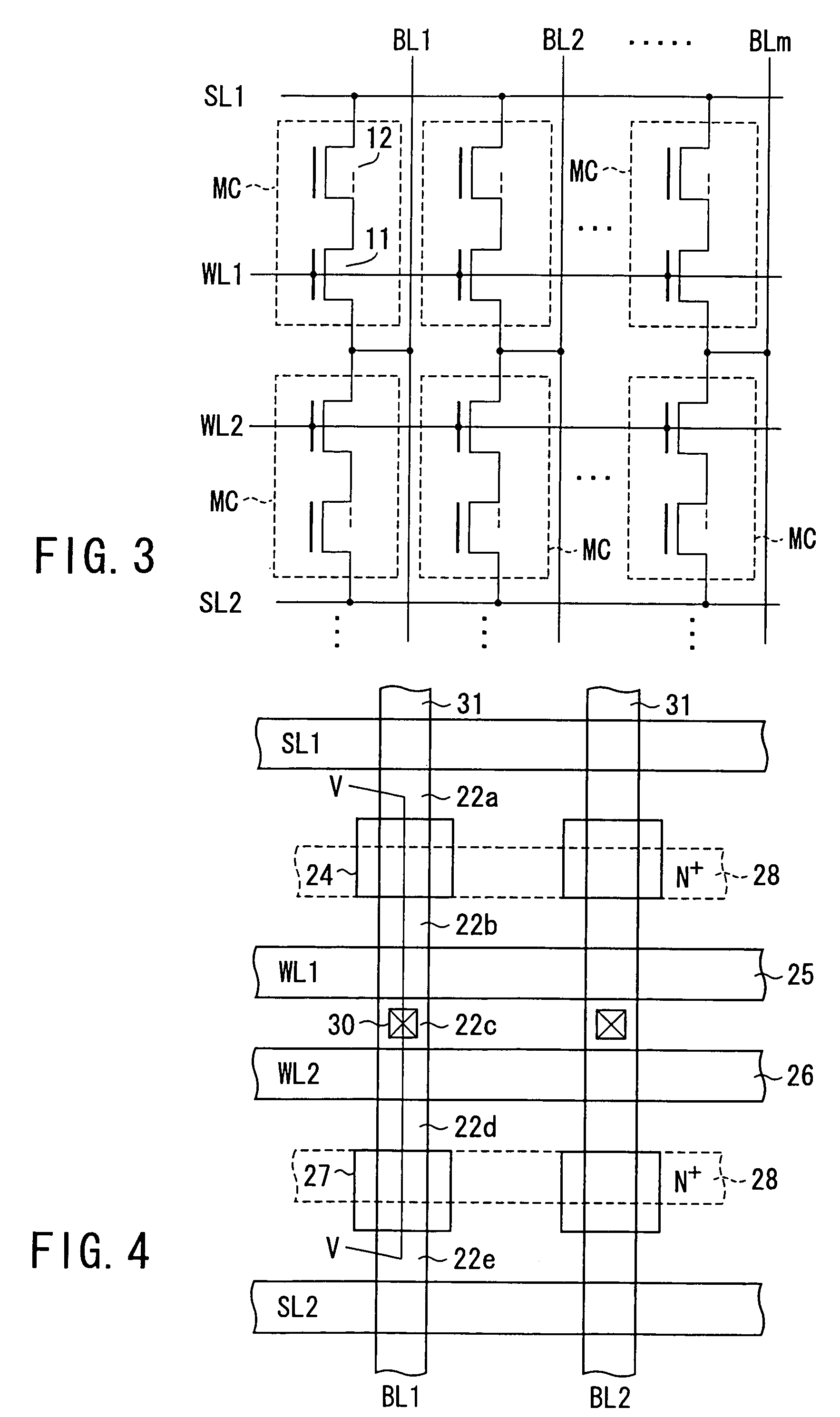
A memory cell has a selection transistor constituted of an MOS transistor having a gate electrode and a cell transistor constituted of an MOS transistor having the same polarity as the selection transistor, in such a configuration that these two transistors are connected in series. A bit line is connected to a drain region of the selection transistor and a word line is connected to the gate electrode thereof. A gate electrode of the cell transistor is not electrically connected anywhere so as to be in a floating potential state, while a drain region thereof is connected to a source region of the selection transistor. A source line is connected to a source region of the cell transistor.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20090189247A1Effective movementSmall sizeTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChip sizeEngineering
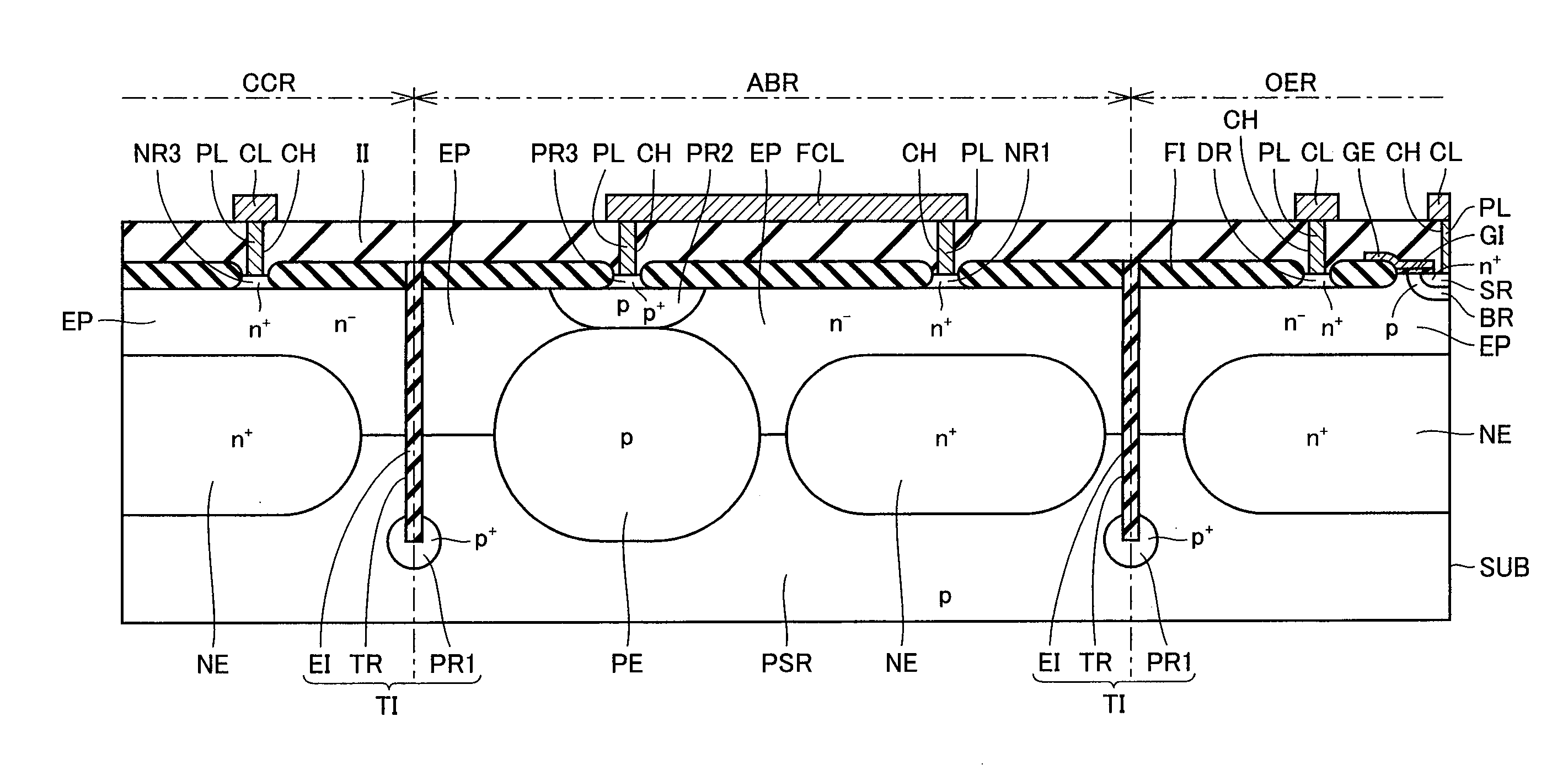
An active barrier structure has a p-type region and an n-type region, each of which is in contact with a p-type impurity region and which are ohmic-connected to each other to attain a floating potential. A trench isolation structure is formed between an active barrier region and the other region (an output transistor formation region and a control circuit formation region). The trench isolation structure has a trench extending from the main surface of the semiconductor substrate through the n− epitaxial layer to reach the p-type impurity region. Therefore, a semiconductor device is obtained which allows the chip size to be reduced easily and is highly effective in preventing movement of electrons from the output transistor formation region to the other element formation region.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Touch panel and touch display panel
InactiveCN103576984AAvoid breakingReduce voltageInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringFloating potential
The invention provides touch panel comprises a substrate, a first conductive layer, a second conductive layer, and an insulation layer. The first conductive layer is disposed on the substrate, and the first conductive layer comprises a bridging line and a patterning static protective layer, which are separated from each other. The patterning static protective layer is provided with a floating potential or a grounding potential. The second conductive layer is disposed on the first conductive layer, and comprises a first sensing string and at least two sensing pads disposed on two opposite sides of the first sensing string. The insulation layer is disposed between the first conductive layer and the second conductive layer in a clamped manner. The insulation layer is provided with two contact holes. The bridging line is respectively connected with the adjacent two sensing pads to form a second sensing string. The invention also provides a touch control panel comprising the above mentioned touch panel and the display module.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor device with floating conducting region placed between device elements
ActiveUS7193255B2Prevent leakageClosely placedTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringFloating potential
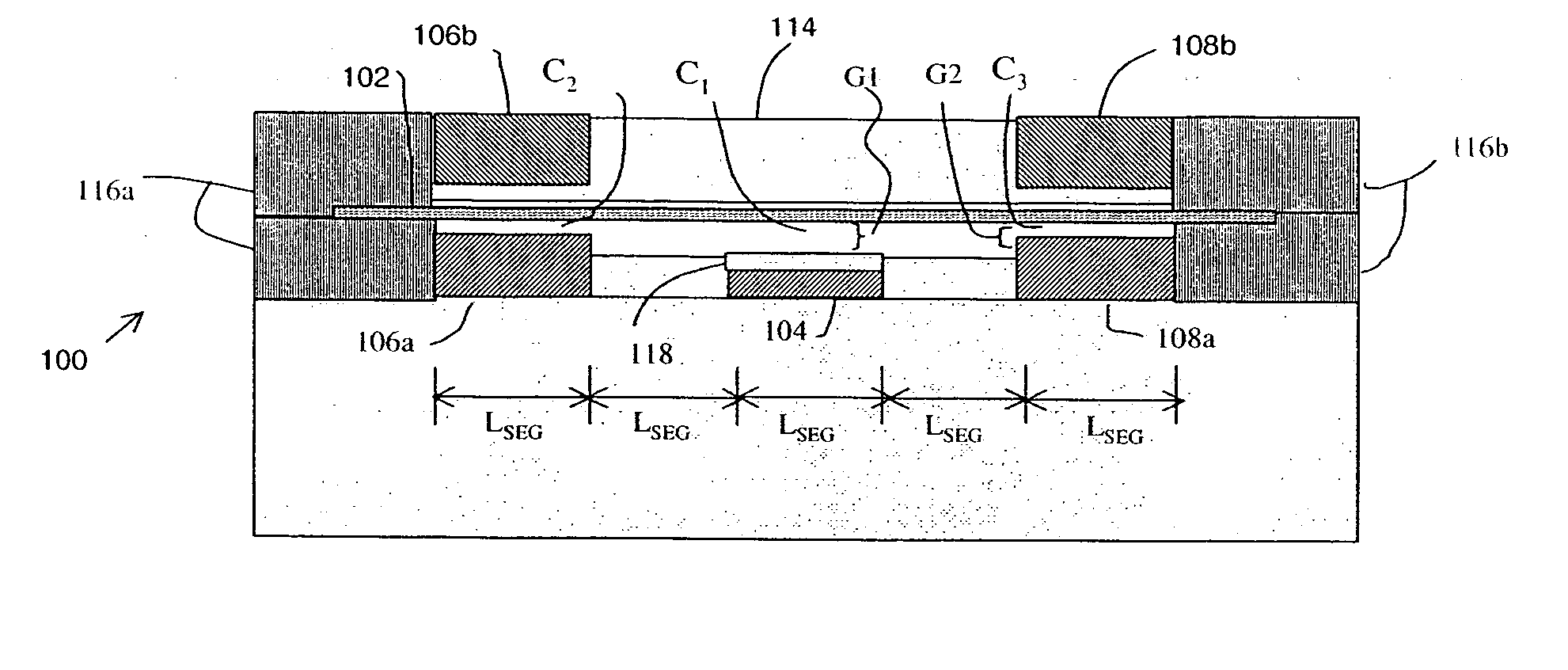
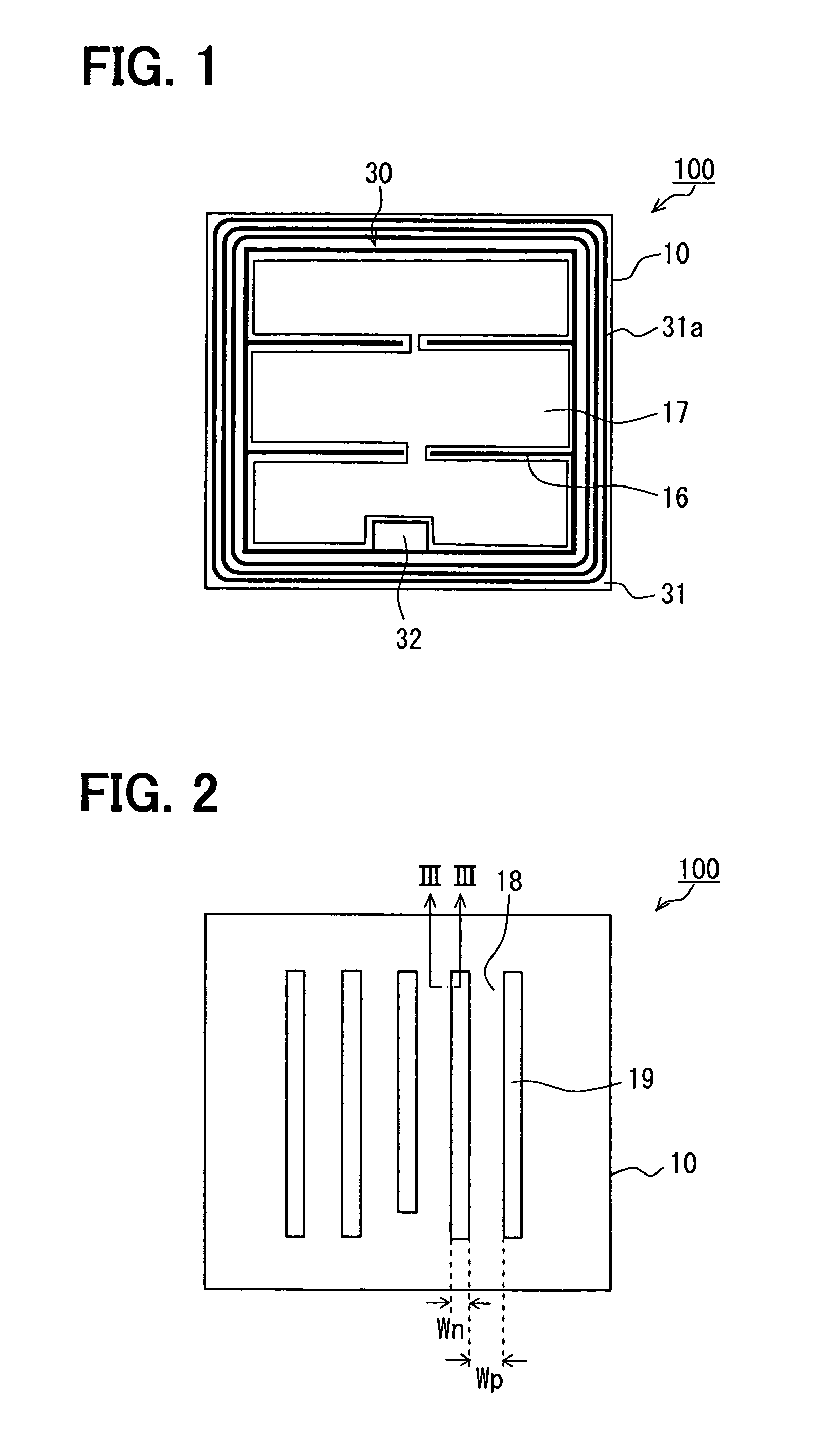
Floating conducting regions at floating potentials are placed on a substrate surface between adjacent conducting regions to which predetermined potentials are applied. This makes it possible to block the spread of a depletion layer to the substrate between the conducting impurity regions. Thus, the leakage of high-frequency signals can be suppressed. In particular, in a case where a floating conducting region is placed between a peripheral impurity region of a common input terminal pad and a resistor in a switch circuit device, it is possible to suppress the leakage of high-frequency signals from an input terminal to control terminals which become high frequency GND and to suppress an increase in insertion loss.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Process for forming a film, piezoelectric film, piezoelectric device, and liquid discharge apparatus
ActiveUS20080081216A1Quality improvementVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingEngineeringFloating potential
Film formation conditions are determined in accordance with relationships among a film formation temperature Ts (° C.), a difference Vs−Vf (V), which is the difference between a plasma potential Vs (V) in the plasma at the time of the film formation and a floating potential Vf (V), and characteristics of the formed film. For a piezoelectric film containing at least one kind of Pb-containing perovskite type oxide, the film formation conditions should preferably be determined within a range such that Formulas (1) and (2) shown below are satisfied:Ts(° C.)≧400 (1)−0.2Ts+100<Vs−Vf(V)<−0.2Ts+130 (2)
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20050263796A1Prevent leakageClosely placedTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringFloating potential
Floating conducting regions at floating potentials are placed on a substrate surface between adjacent conducting regions to which predetermined potentials are applied. This makes it possible to block the spread of a depletion layer to the substrate between the conducting impurity regions. Thus, the leakage of high-frequency signals can be suppressed. In particular, in a case where a floating conducting region is placed between a peripheral impurity region of a common input terminal pad and a resistor in a switch circuit device, it is possible to suppress the leakage of high-frequency signals from an input terminal to control terminals which become high frequency GND and to suppress an increase in insertion loss.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
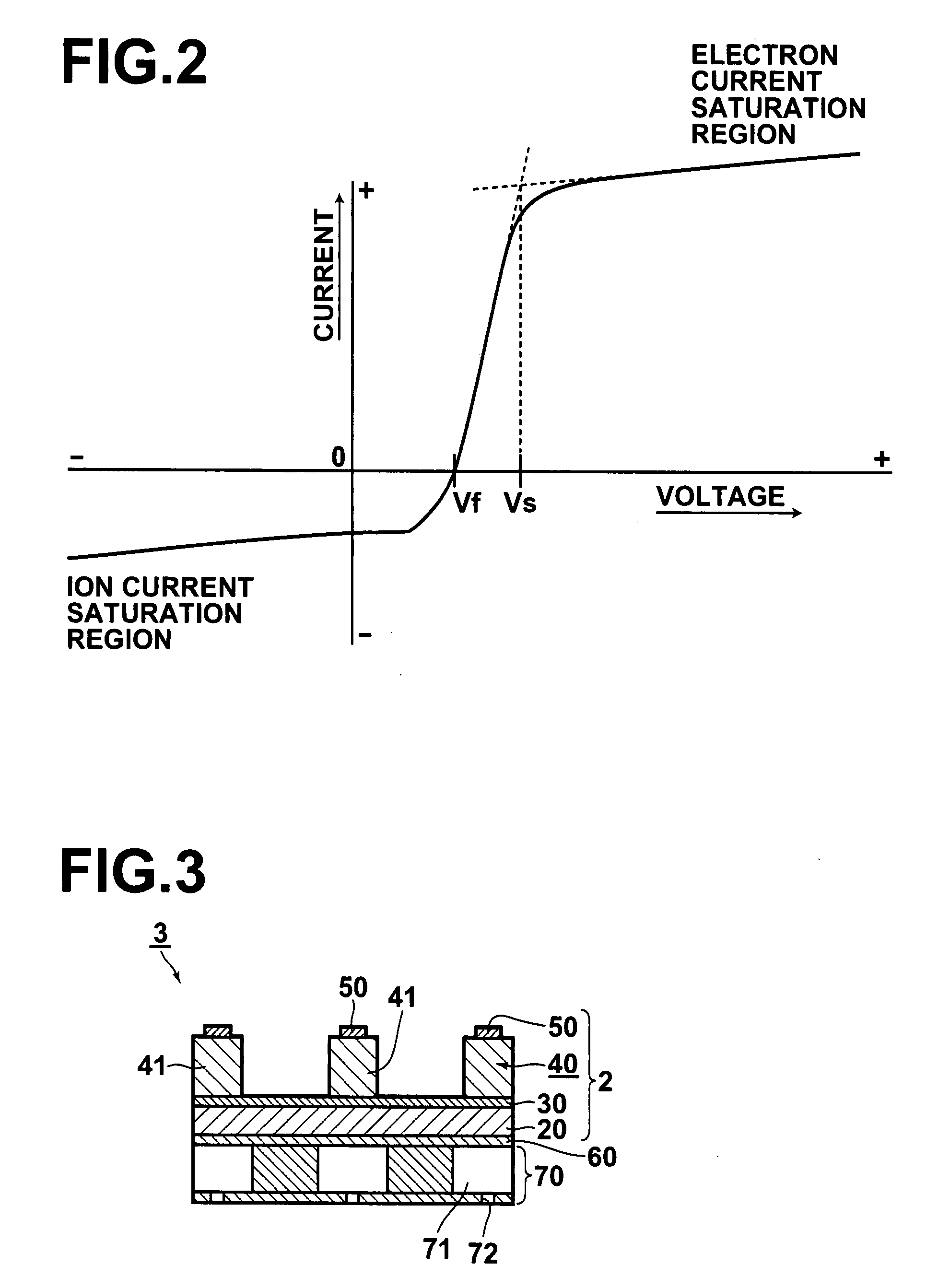
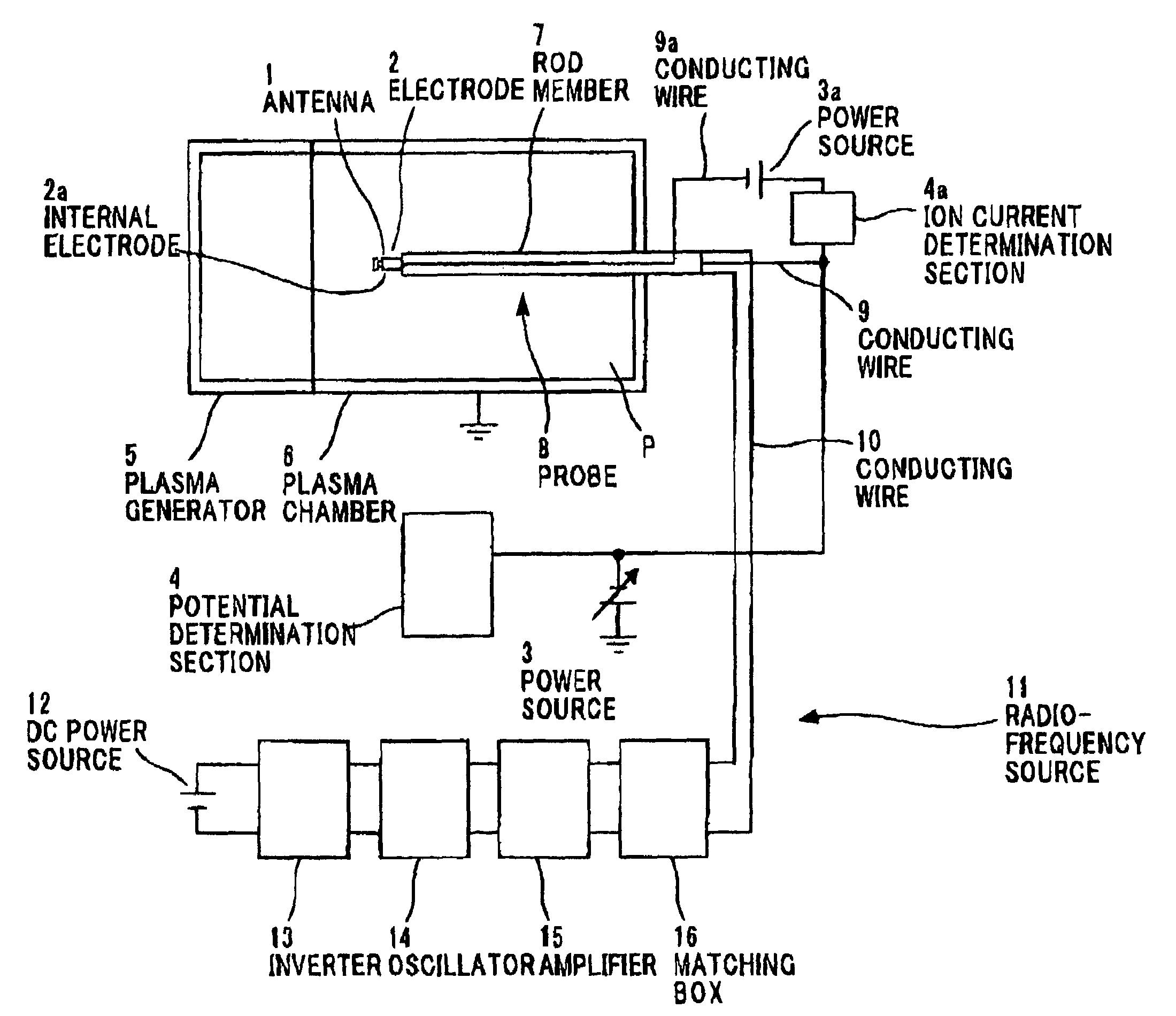
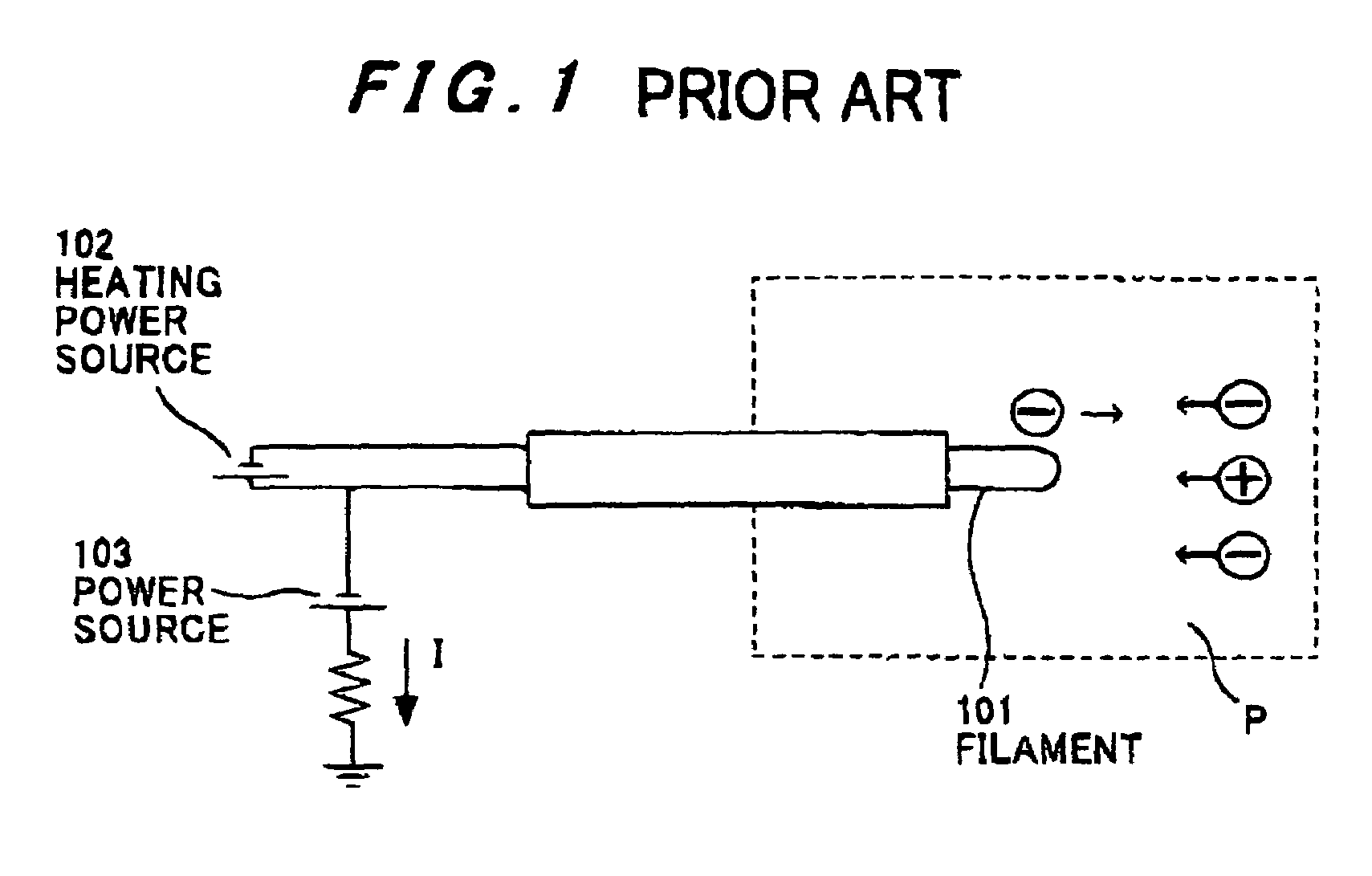
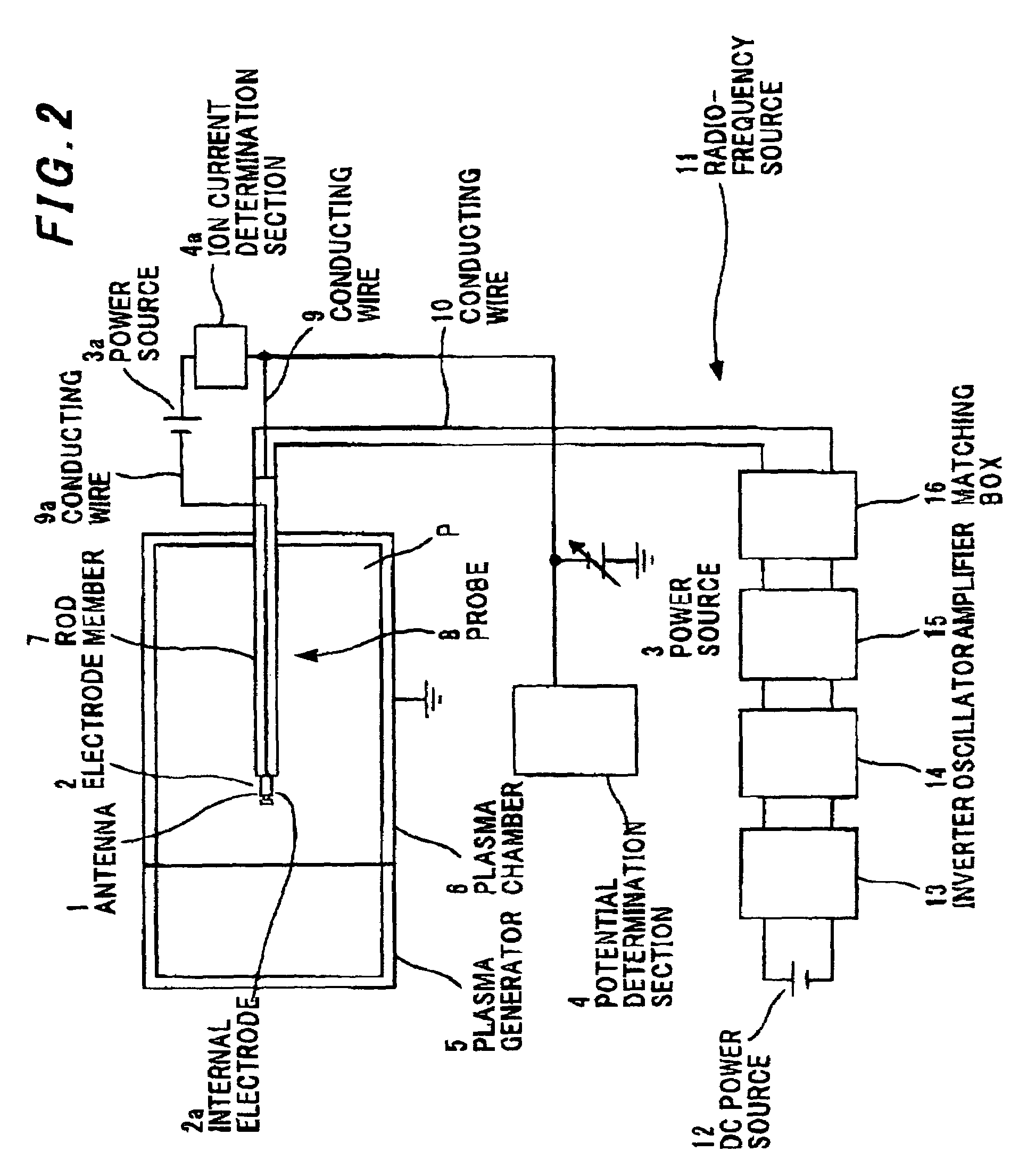
Plasma potential measuring method and apparatus, and plasma potential measuring probe
InactiveUS7288942B2Good repeatabilityReduce errorsCurrent/voltage measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPotential measurementIon current
Owner:HITACHI CABLE +1
Cold cathode ionization vacuum gauge, auxiliary discharge starting electrode, and vacuum processing apparatus
ActiveUS20100301869A1Short timeImprove performanceVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsCold cathodeEngineering
The present invention provides a cold cathode ionization vacuum gauge, an auxiliary discharge starting electrode plate, and a vacuum processing apparatus which have simple configurations and, even after long-term-use, which allow discharge to be initiated in a short-period of time and also to be performed stably after the start of the discharge. A cold cathode ionization vacuum gauge according to one embodiment of the present invention includes: an anode; a gauge head chamber (cathode) placed in such a manner as to form a discharge space together with the anode; and a protruding configured so that, in voltage-application to the anode and the cathode, an electric field should be concentrated at the protruding portion to a larger extent than an electric field at the gauge head chamber is. The protruding portion is provided inside the discharge space in such a manner that the protruding portion has a floating potential.
Owner:CANON ANELVA CORP
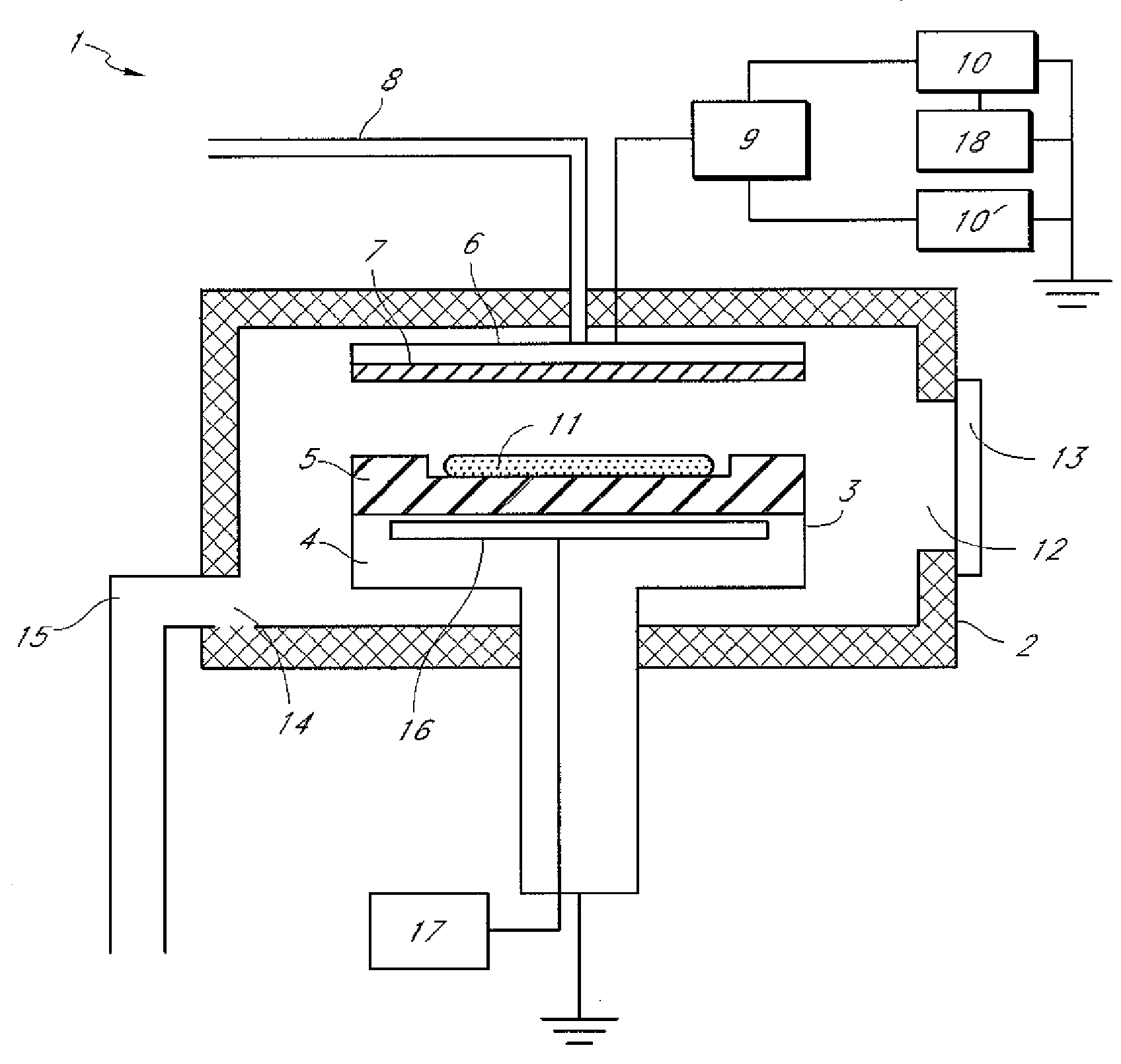
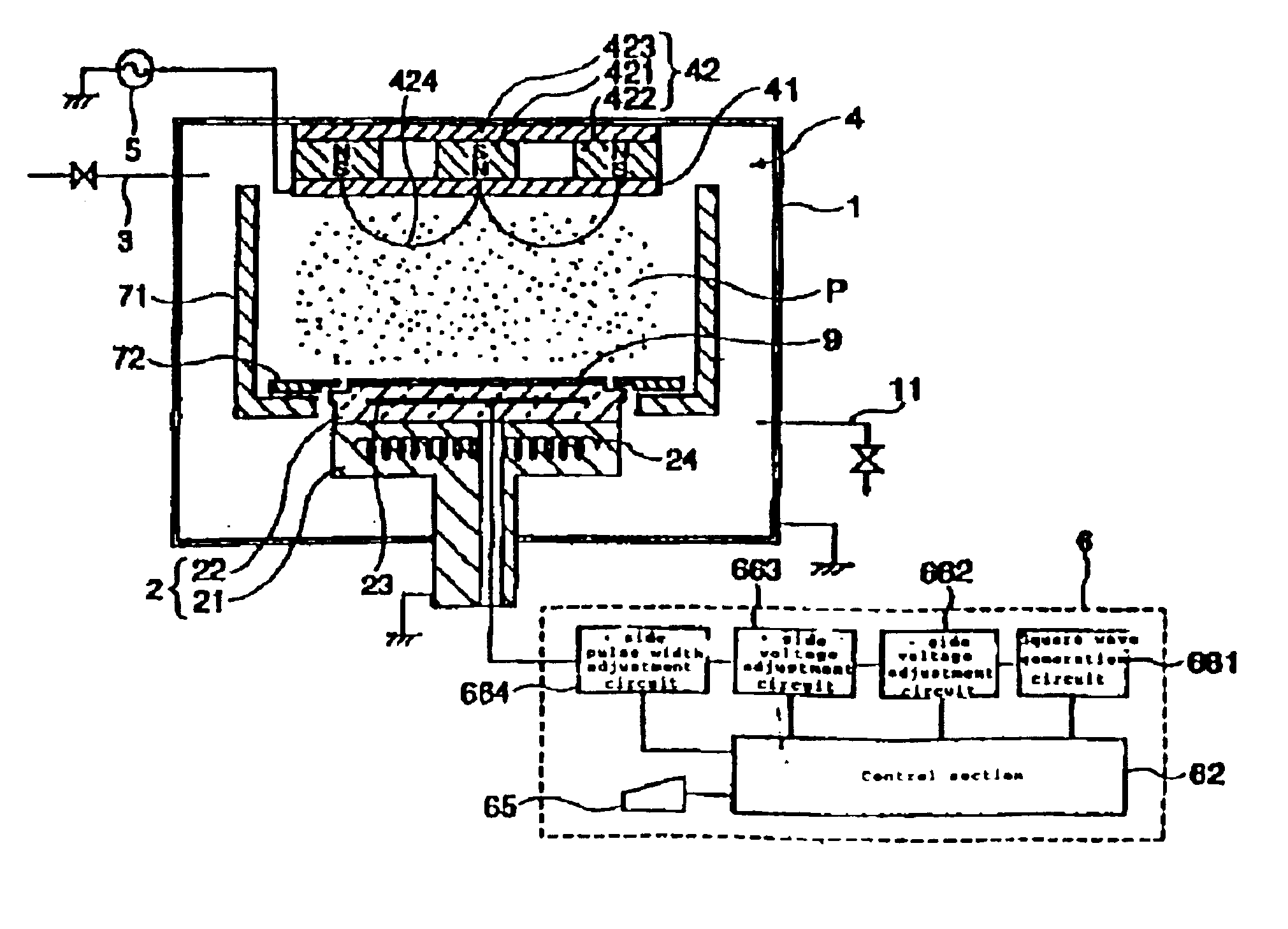
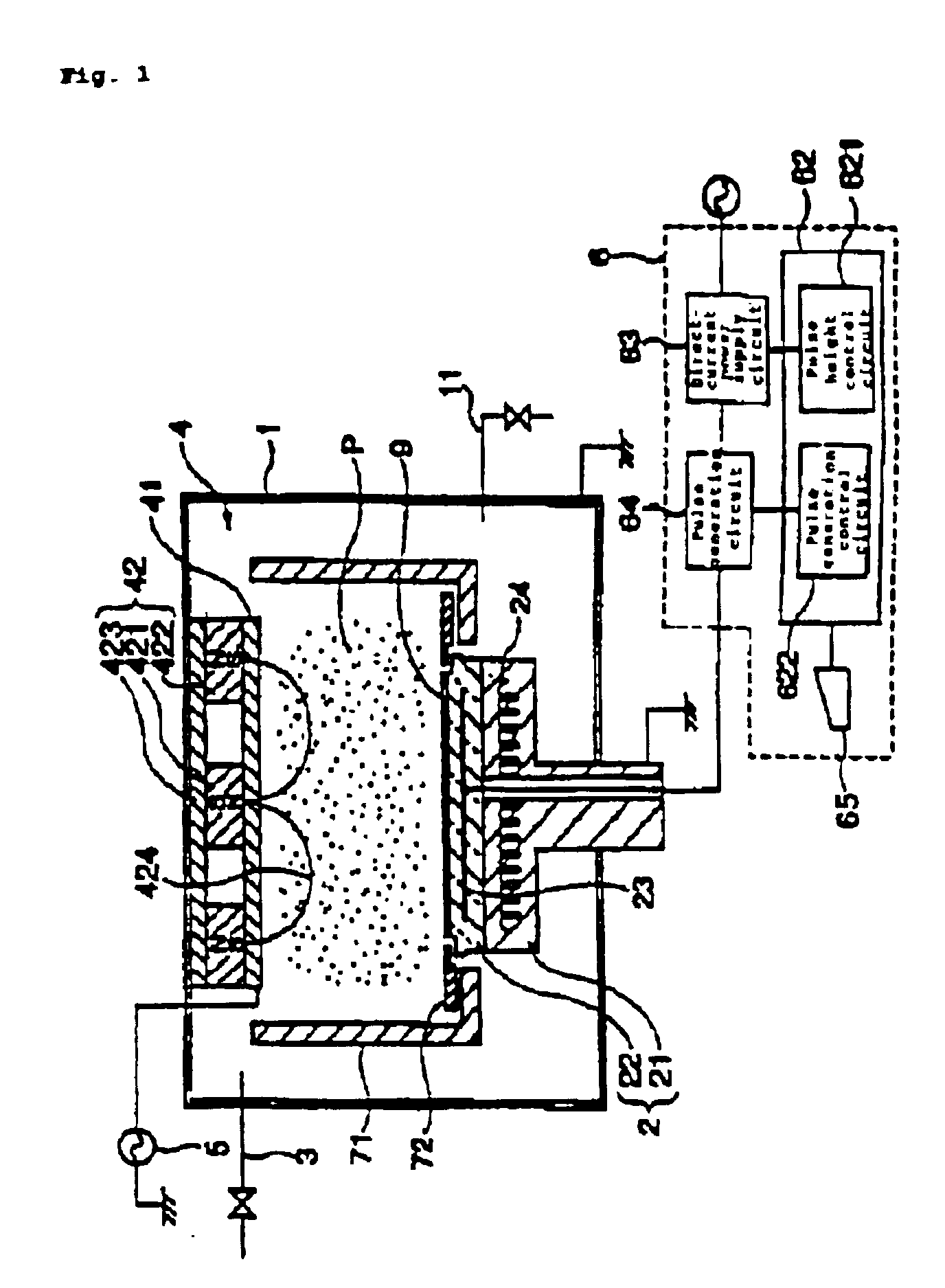
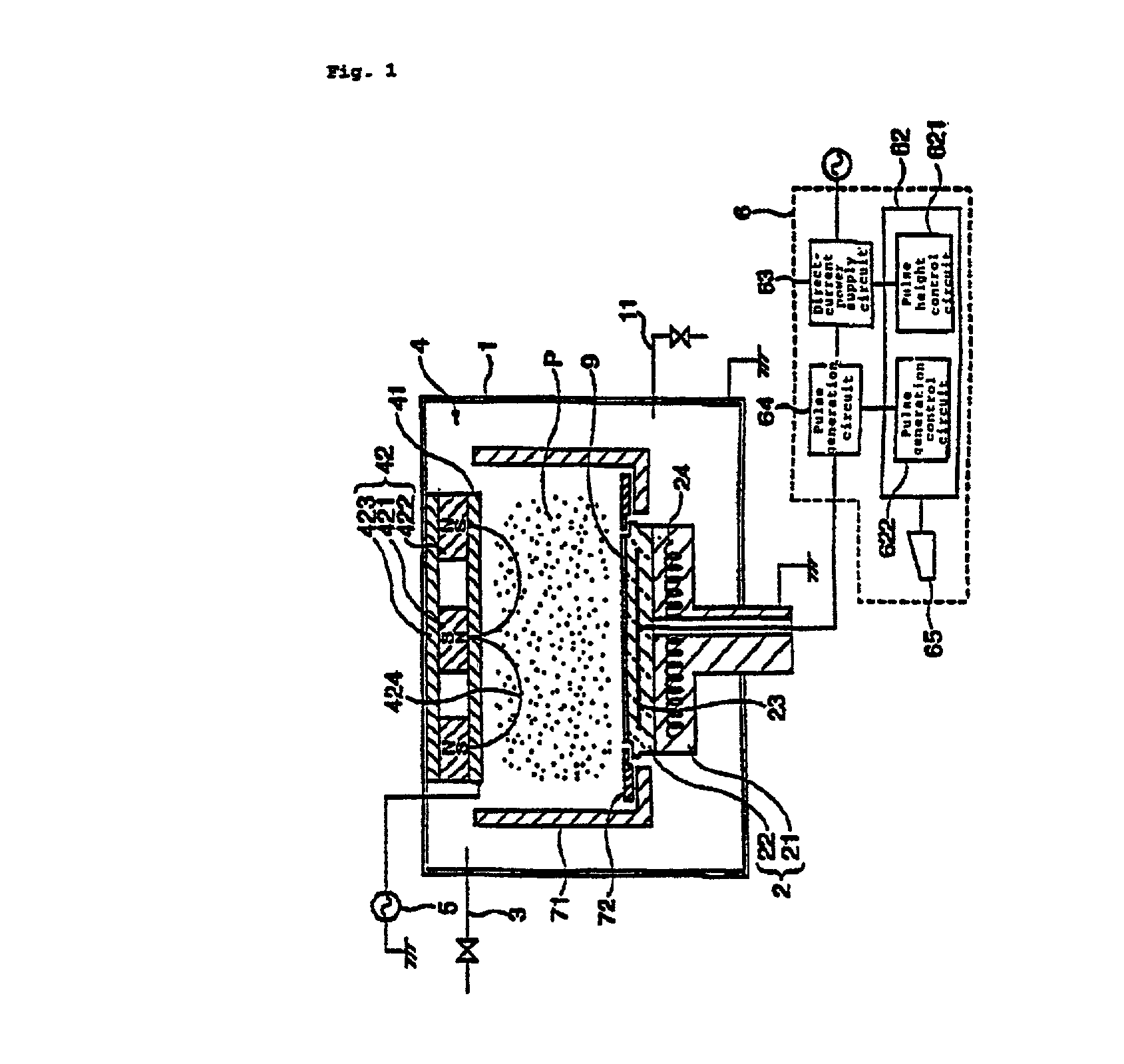
Thin film fabrication method and thin film fabrication apparatus
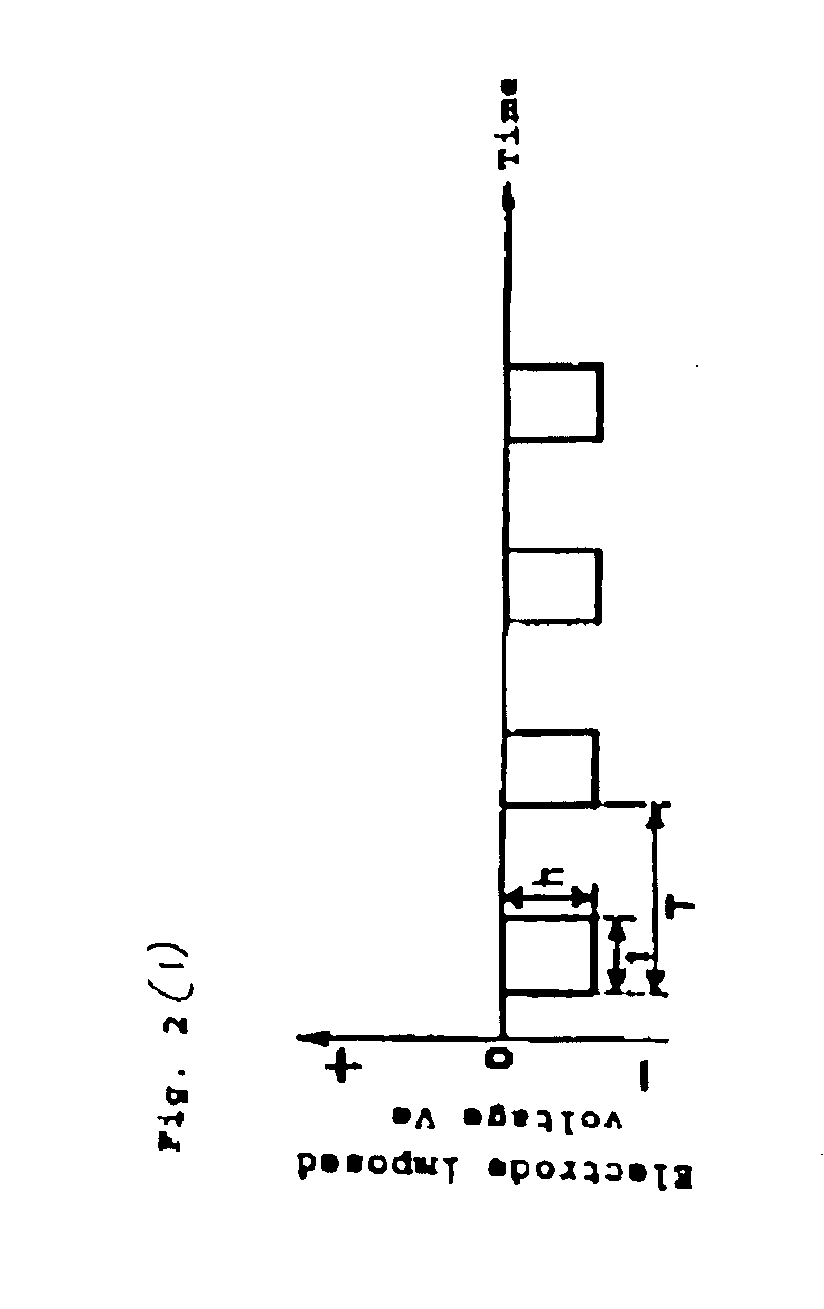
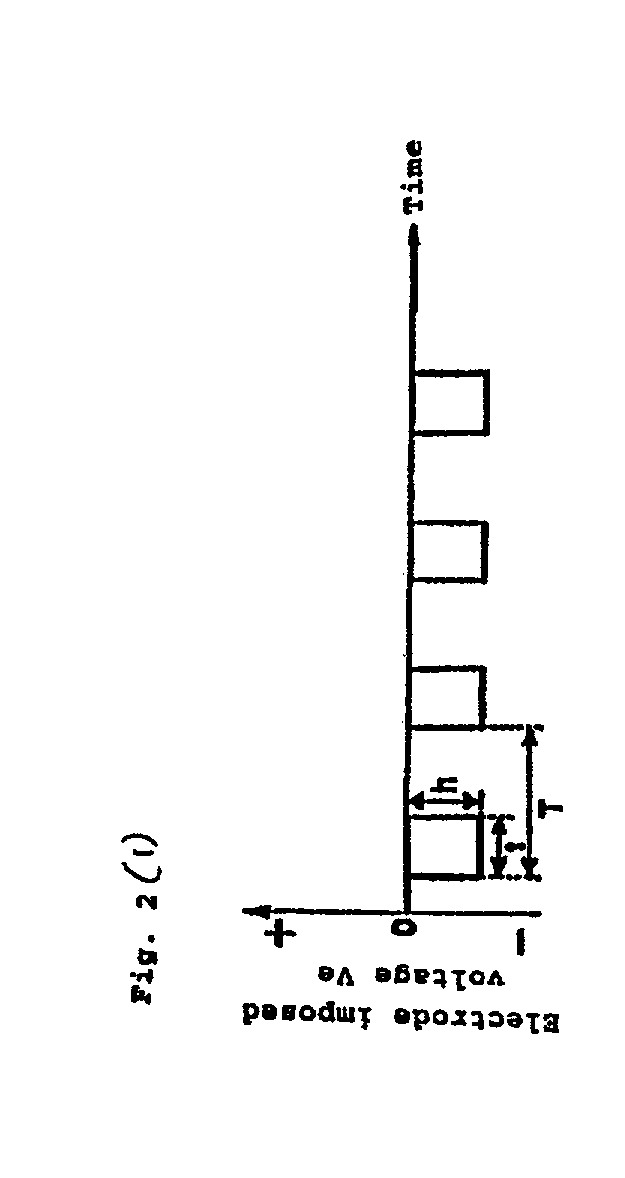
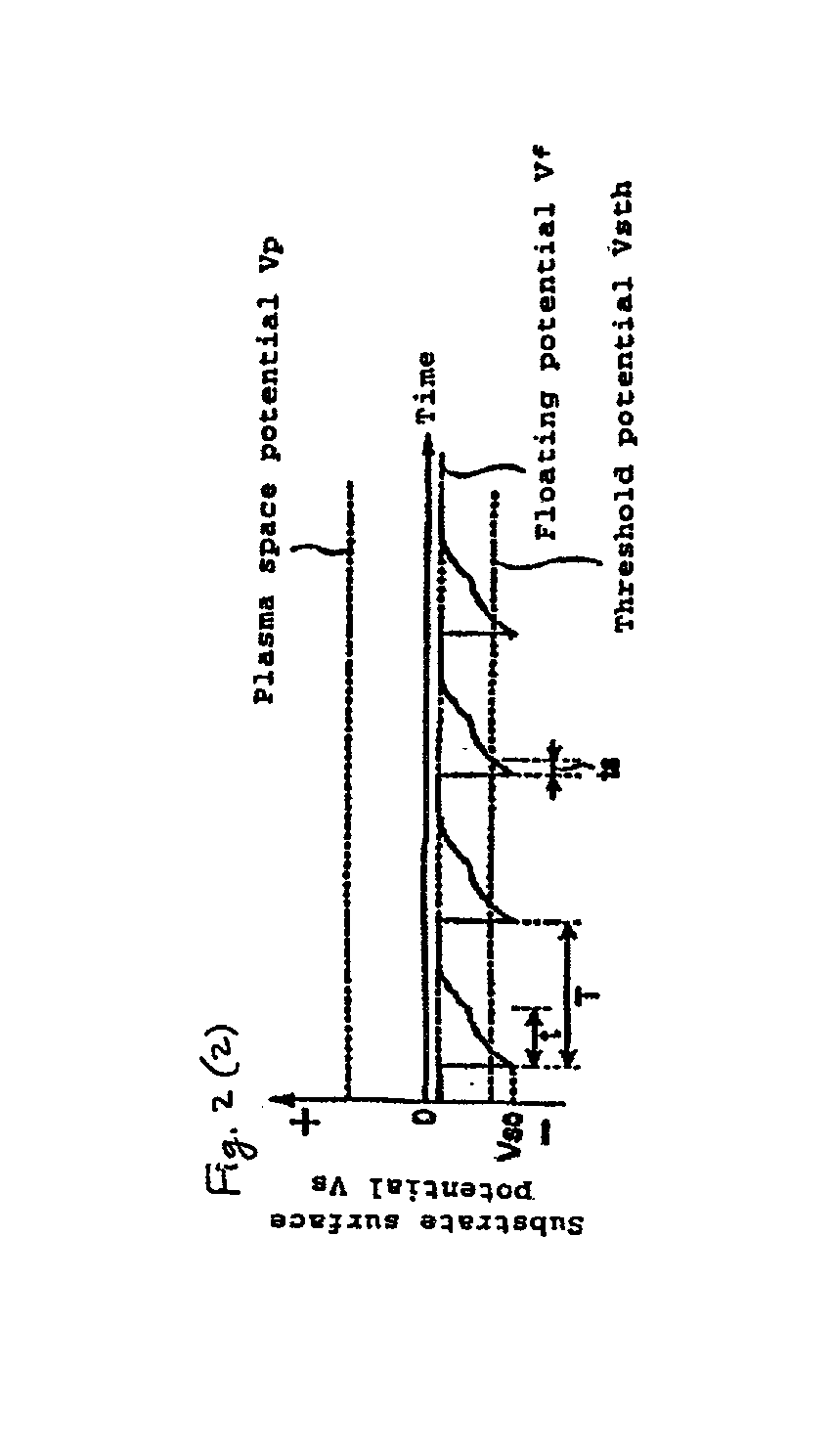
A thin film is fabricated while causing ions in a plasma P to be incident by effecting biasing relative to the space potential of the plasma P by imparting a set potential to the surface of a substrate 9. A bias system 6 causes the substrate surface potential Vs to vary in pulse form by imposing an electrode imposed voltage Ve in pulse form on a bias electrode 23 which is in a dielectric block 22. The pulse frequency is lower than the oscillation frequency of ions in the plasma P, and the pulse period T, pulse width t and pulse height h are controlled by a control section 62 in a manner such that the incidence of ions is optimized. The imposed pulses are controlled in a manner such that the substrate surface potential Vs recovers to a floating potential Vf at the end of a pulse period T, and that the ion incidence energy temporarily crosses a thin film sputtering threshold value in a pulse period T.
Owner:ANELVA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com