Patents
Literature
265results about How to "Lower forward voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
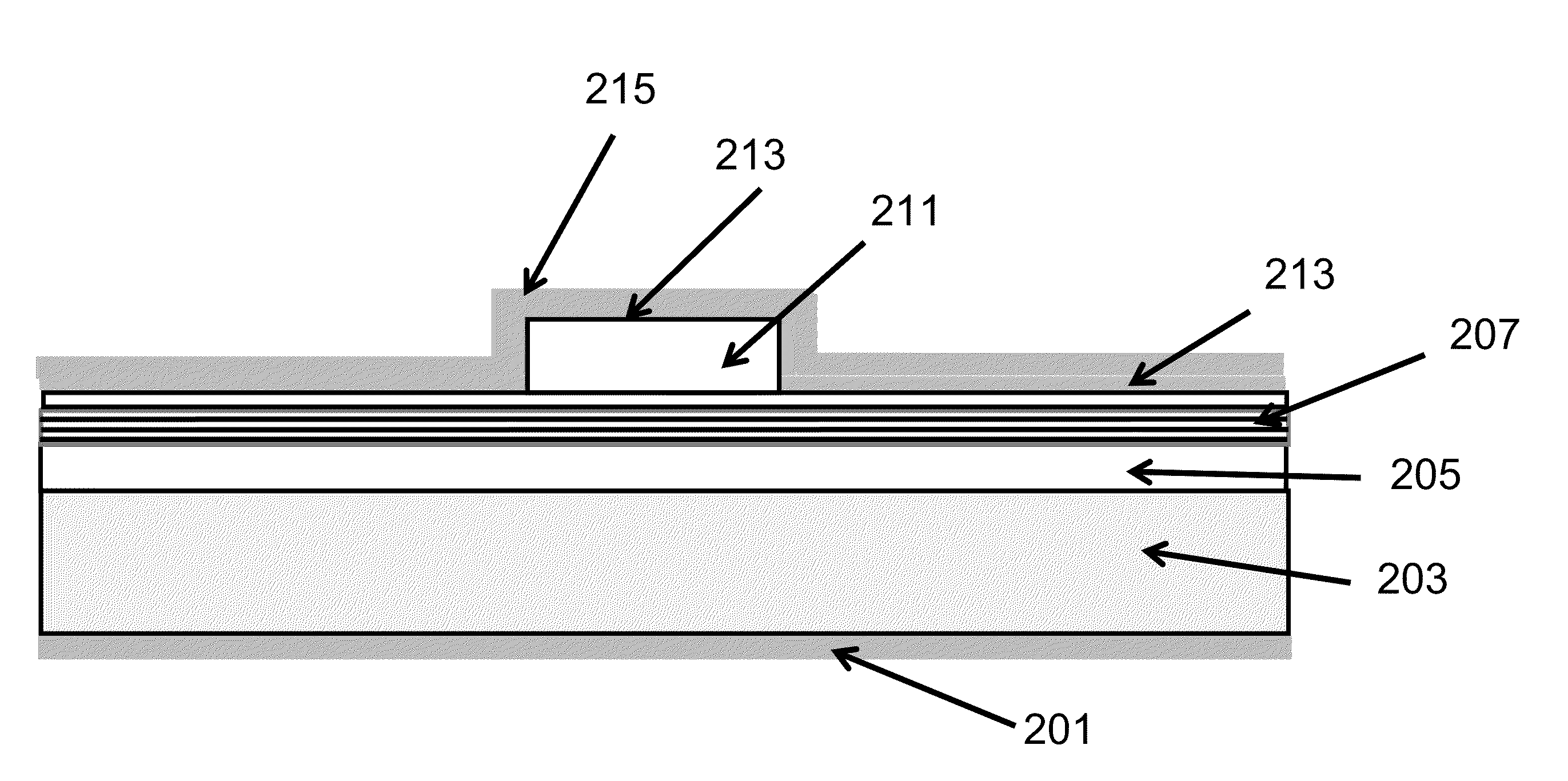
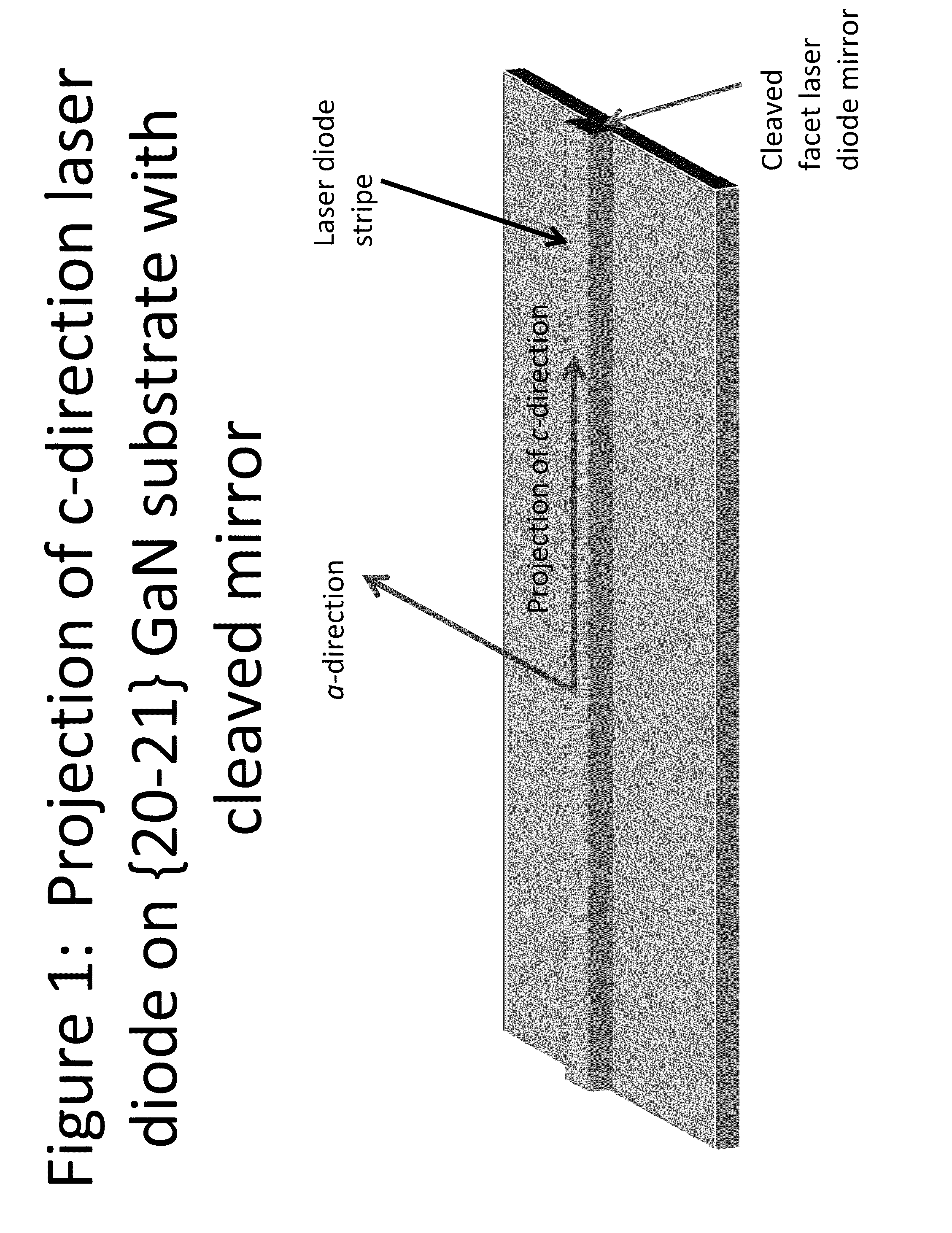
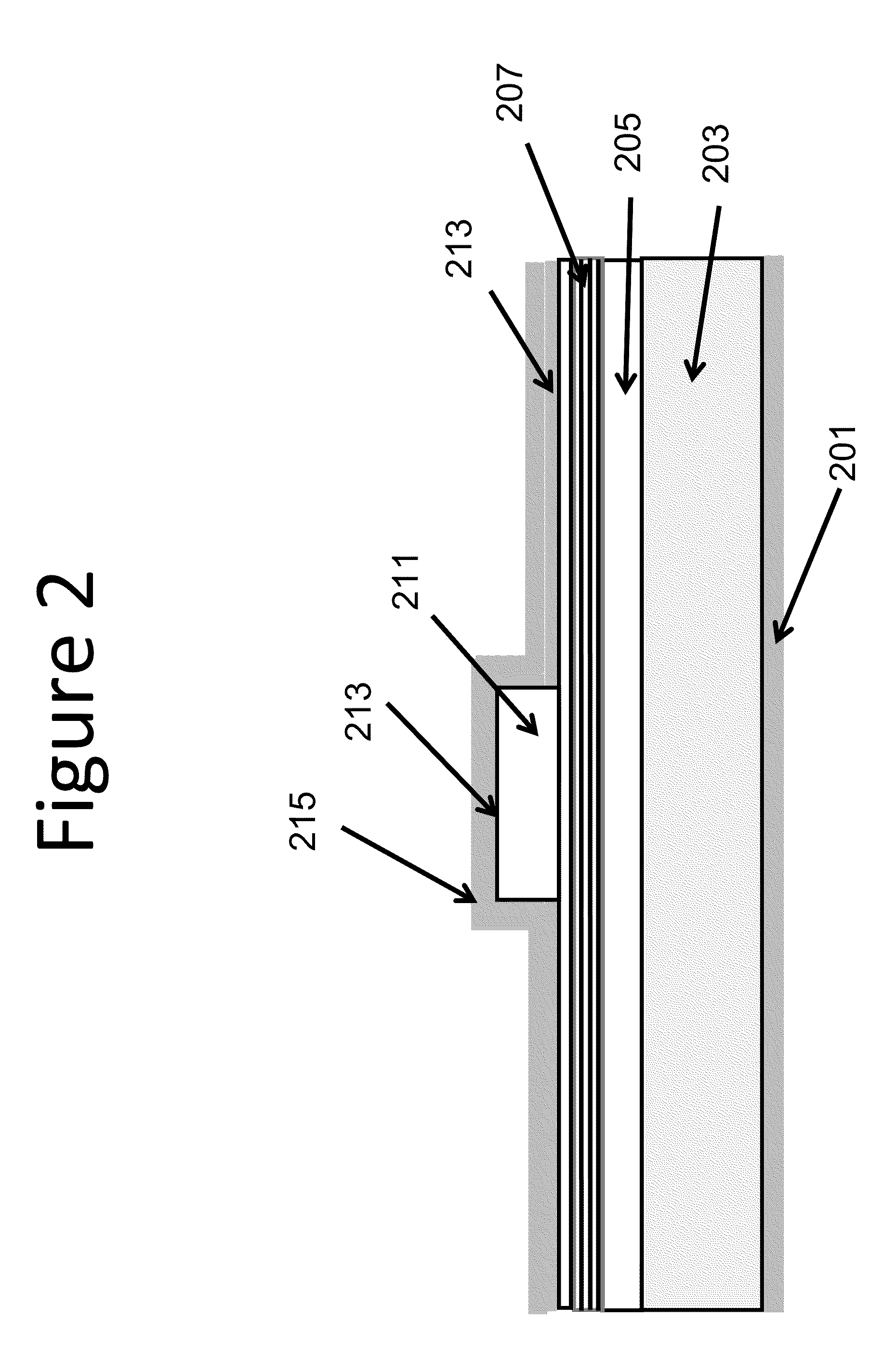
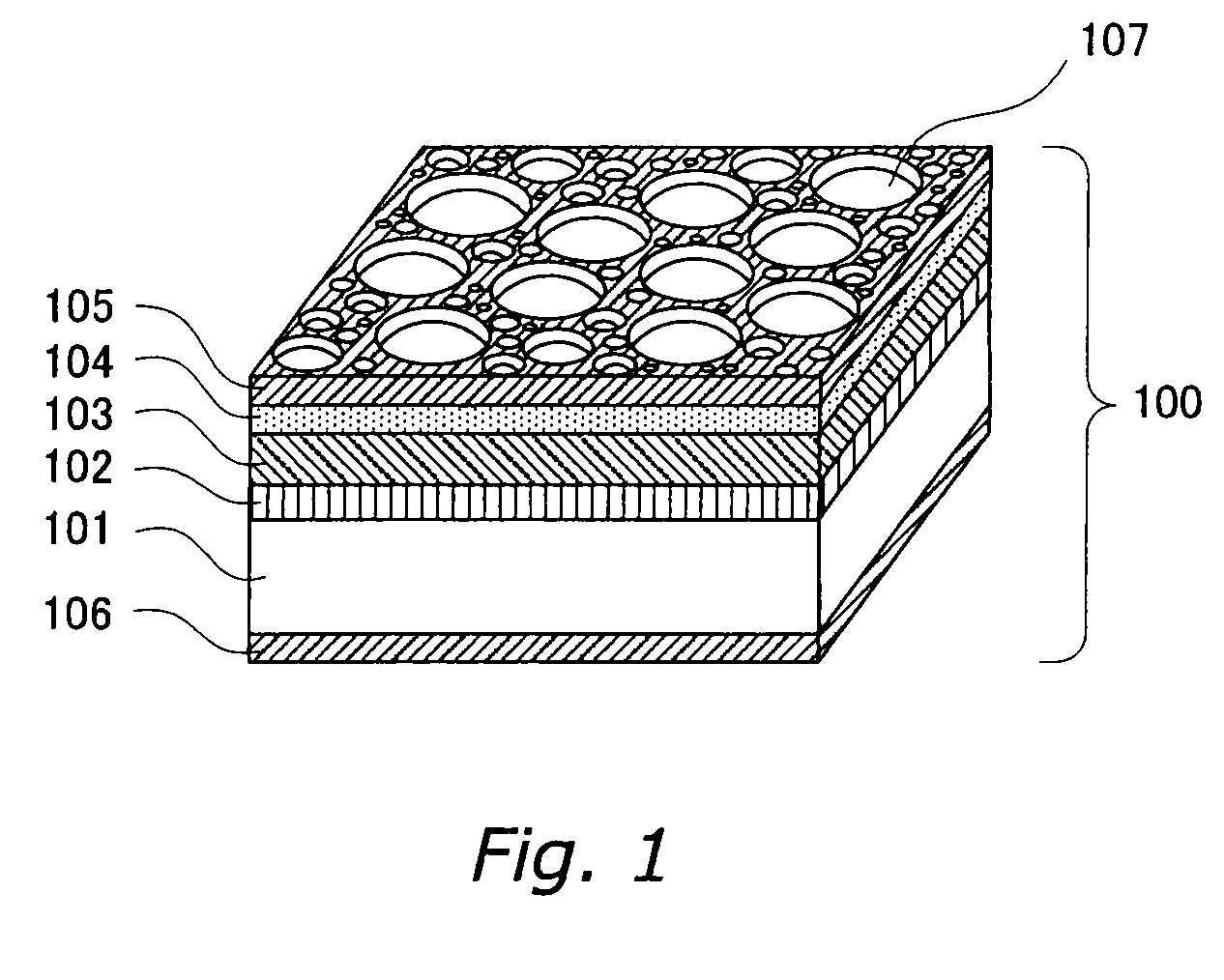
Low Voltage Laser Diodes on Gallium and Nitrogen Containing Substrates
ActiveUS20110064101A1Improved cleavesSimple and cost-effectiveOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsLow voltageNitrogen
A low voltage laser device having an active region configured for one or more selected wavelengths of light emissions.
Owner:KYOCERA SLD LASER INC
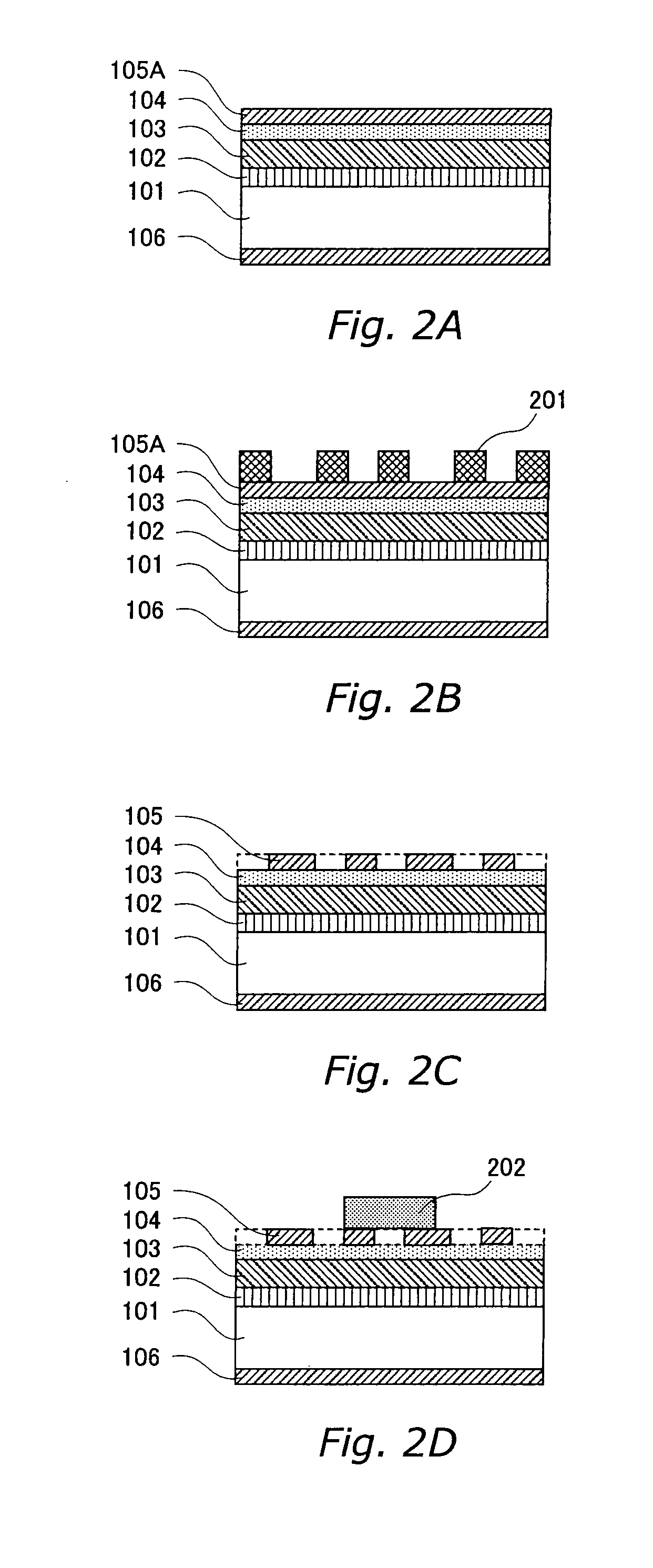
Semiconductor Device And Method For Manufacturing Same
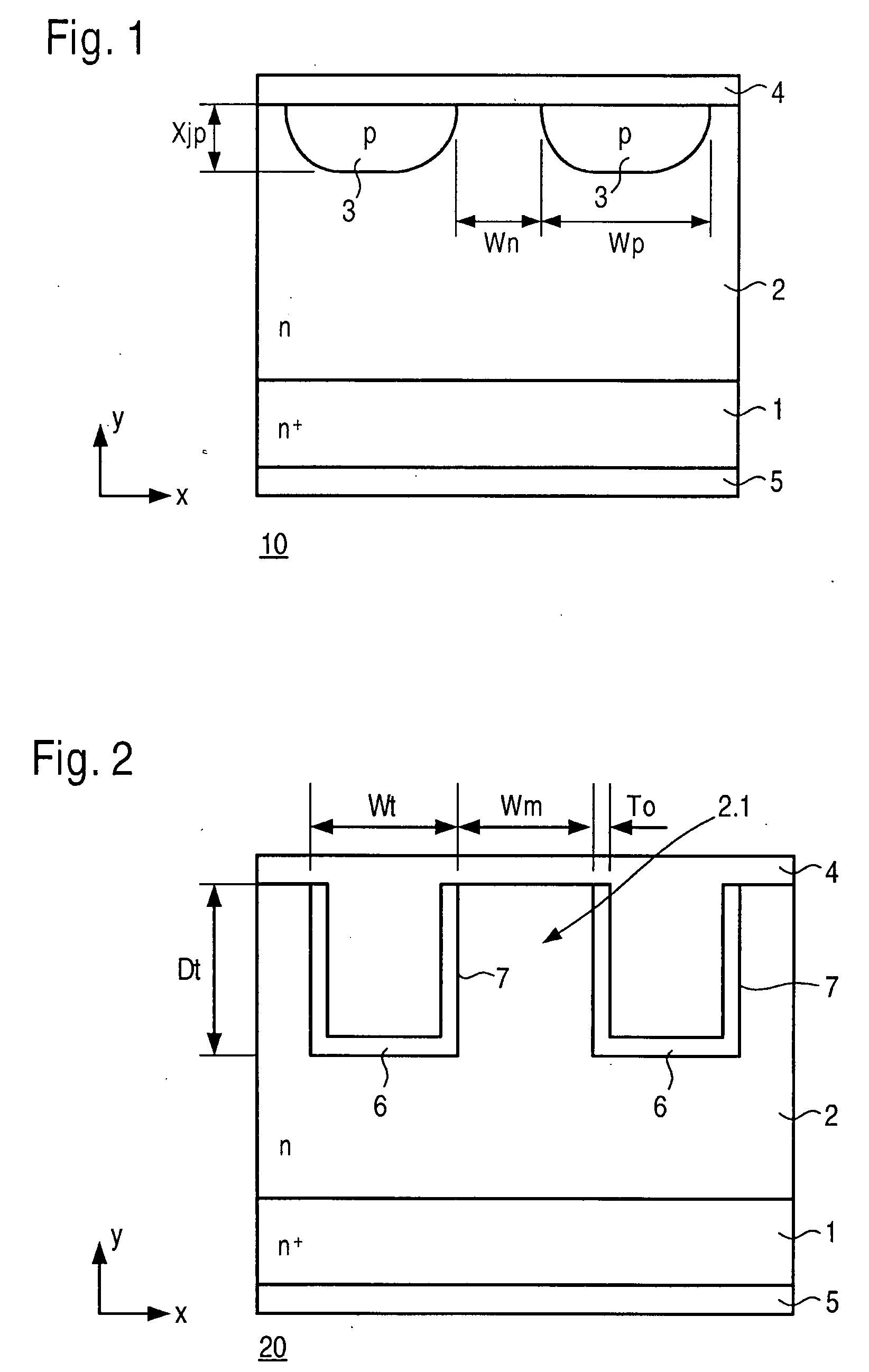
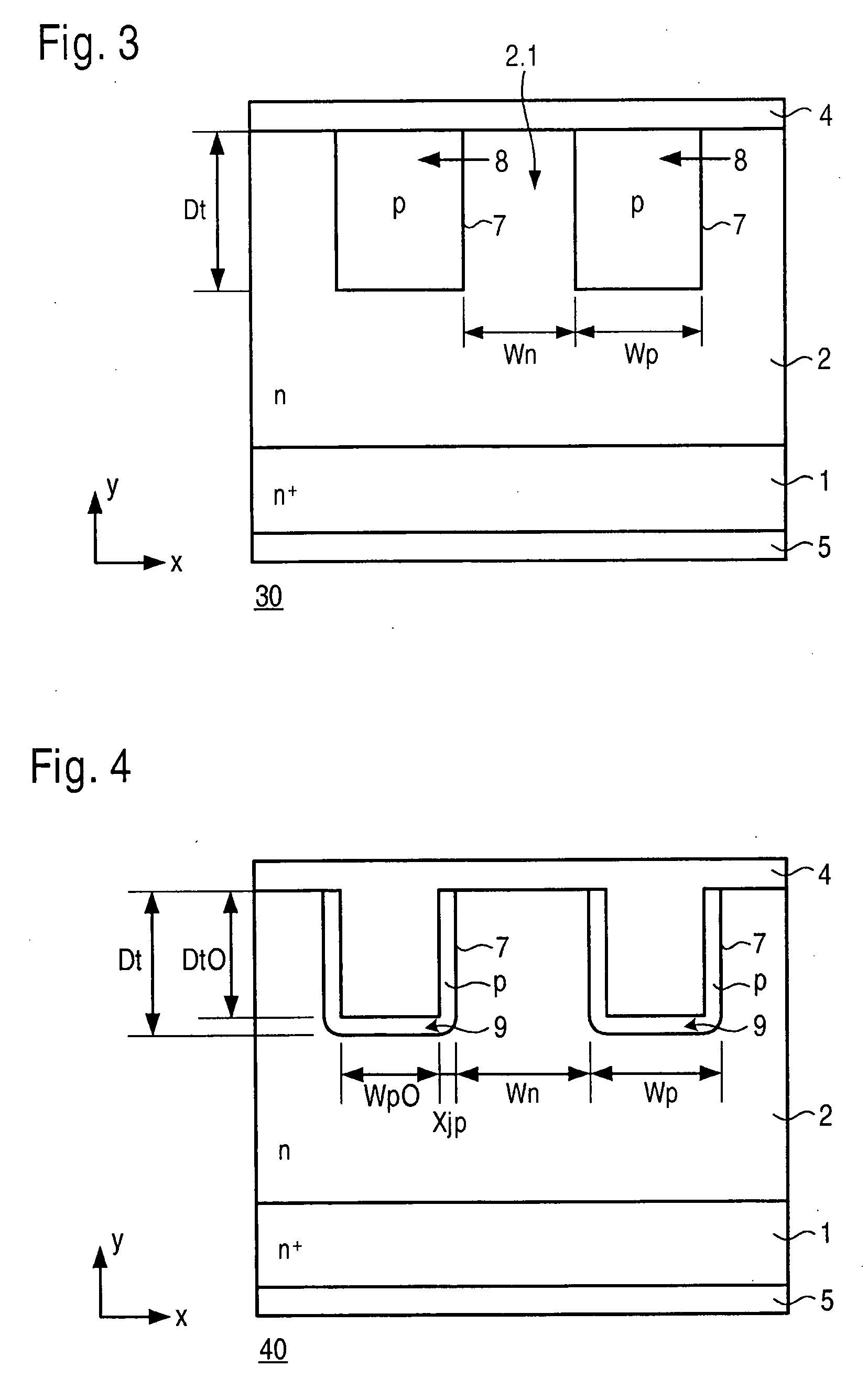
ActiveUS20080197439A1Lower forward voltageImprove sturdinessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringContact layer
A semiconductor device including a Schottky diode of the trench-junction-barrier type having an integrated PN diode, and a corresponding method for manufacturing the device, are provided. An n layer is provided on an nt substrate, and trenches are provided in the n layer. The trenches are provided with p-doped regions. The nt substrate and the n layer carry a contact layer.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Through-hole vertical semiconductor devices or chips
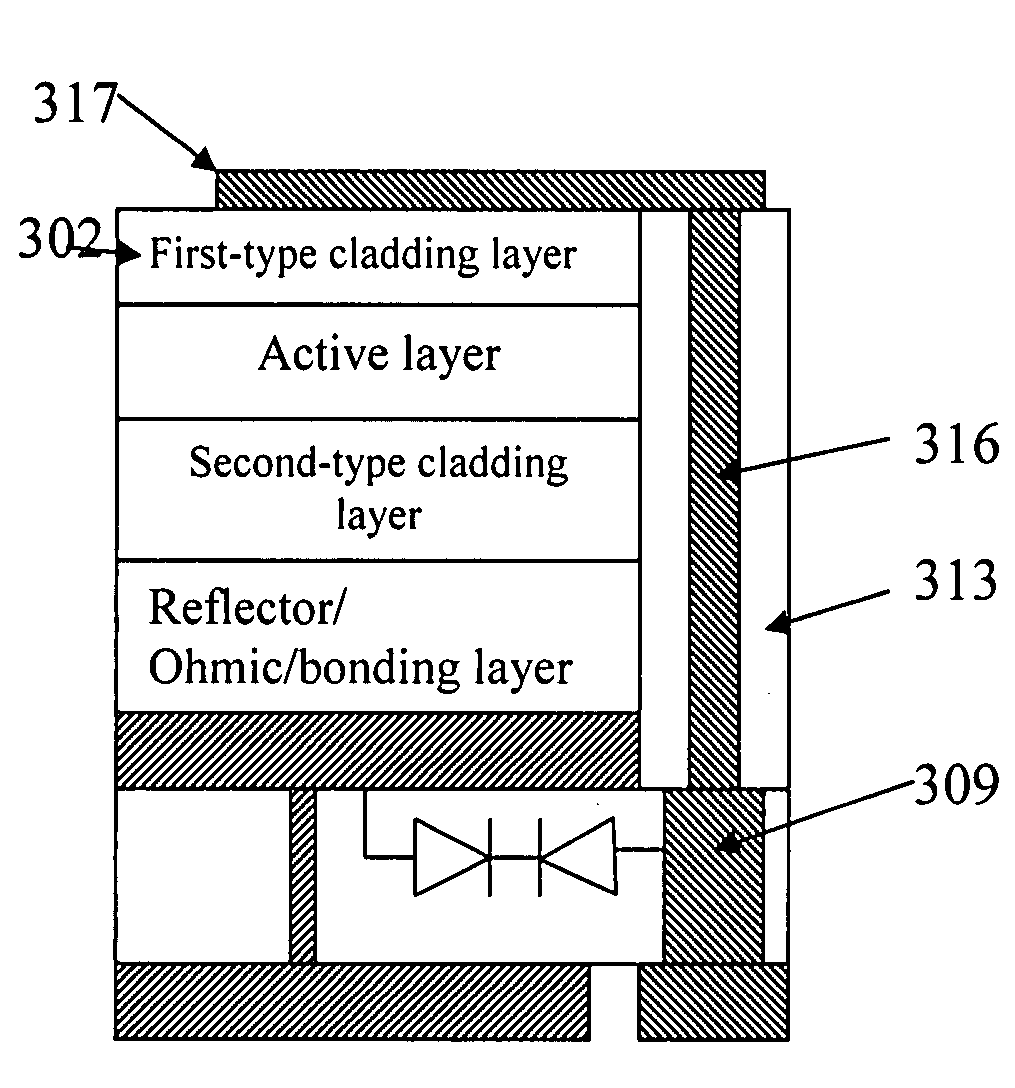
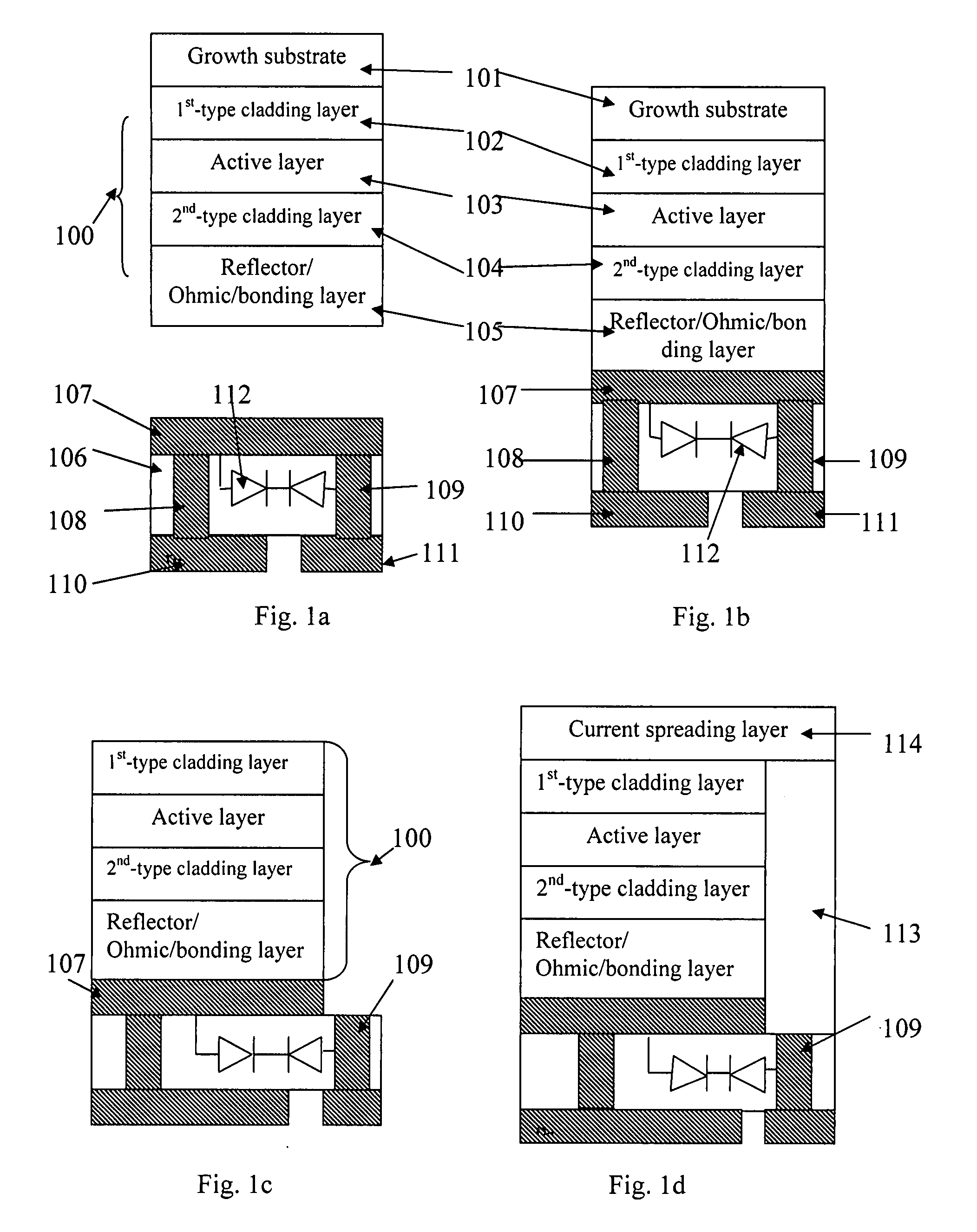
InactiveUS20080029761A1Improve cooling efficiencyReduced series resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLead bondingEngineering
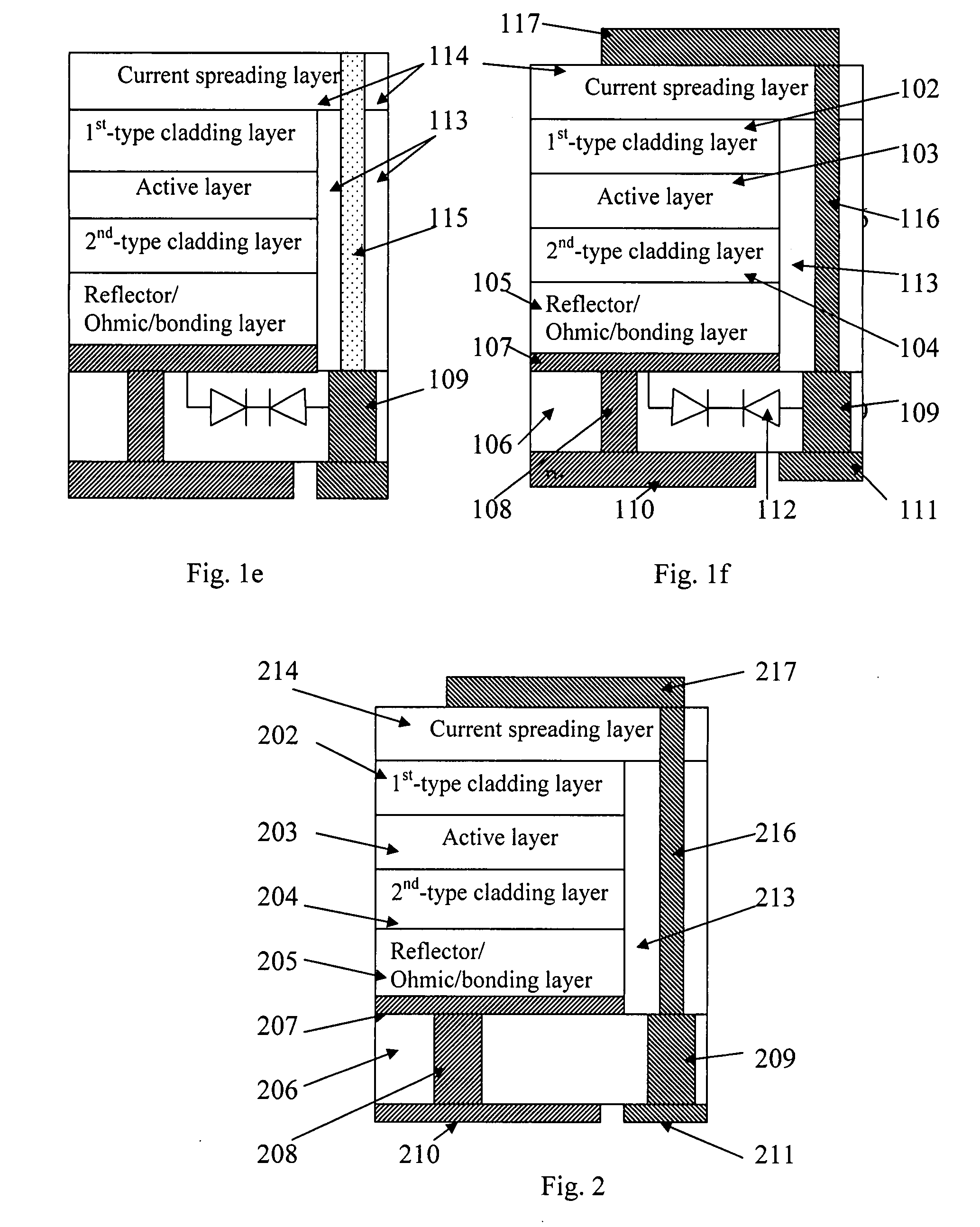
The present invention discloses through-hole vertical semiconductor devices and chips. The structure of an embodiment of through-hole vertical semiconductor devices and chips having static protection diodes is the following: a semiconductor epitaxial layer is bonded to the first surface of a supporting chip with static protection diode; the first-type cladding layer of the semiconductor epitaxial layer is electrically connected to a first electrode on the second surface of the supporting chip via a current spreading layer, a patterned electrode, a half-through-hole-metal-plug and a through-hole-metal-plug; the second-type cladding layer of the semiconductor epitaxial layer is electrically connected to a second electrode on the second surface of the supporting chip via a reflector / Ohmic / bonding layer and at least one through-hole-metal-plug. An external power source is electrically connected to the first and second electrodes without wire bonding.
Owner:JING PENG +2
Light emitting diode and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20120037881A1Improved electrostatic discharge characteristicReduce leakage currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesContact layerLight-emitting diode
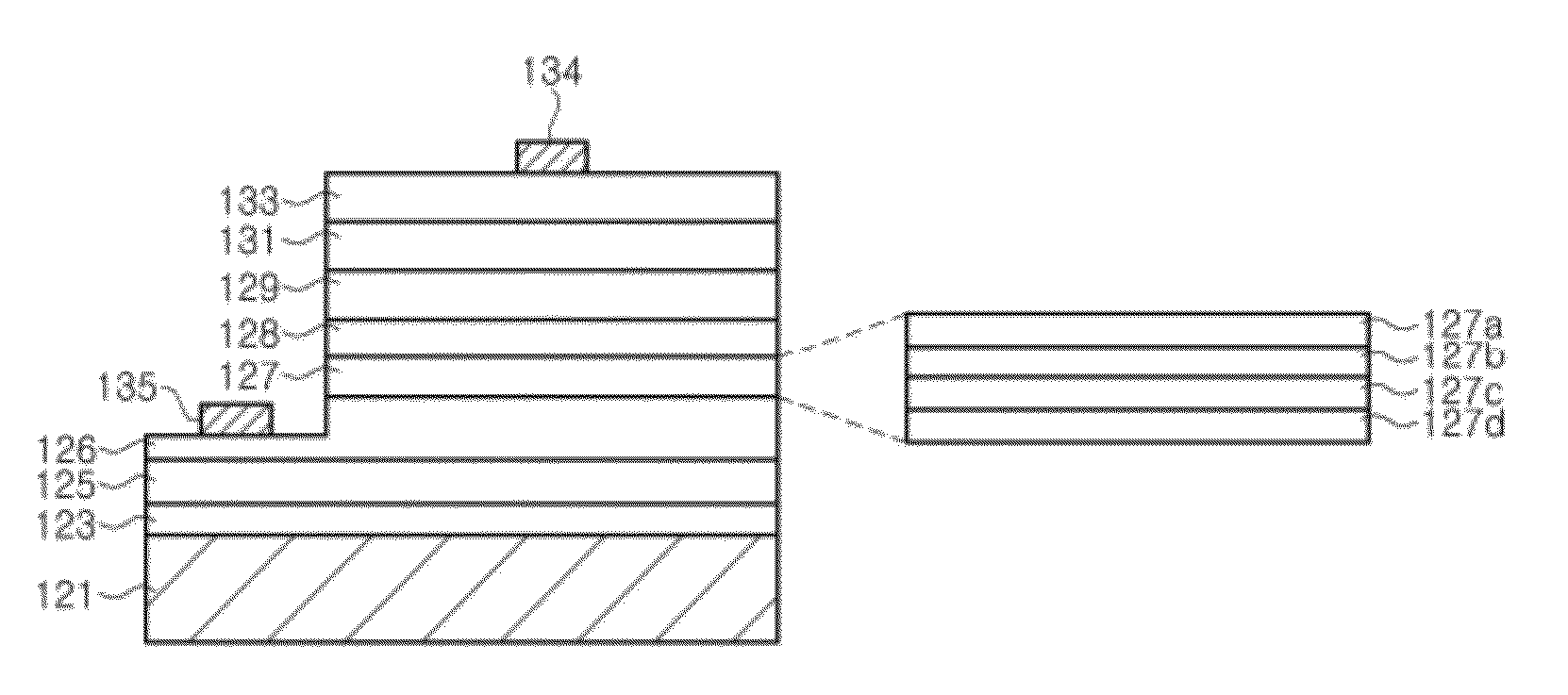
Exemplary embodiments of the present invention disclose a light emitting diode including an n-type contact layer doped with silicon, a p-type contact layer, an active region disposed between the n-type contact layer and the p-type contact layer, a superlattice layer disposed between the n-type contact layer and the active region, the superlattice layer including a plurality of layers, an undoped intermediate layer disposed between the superlattice layer and the n-type contact layer, and an electron reinforcing layer disposed between the undoped intermediate layer and the superlattice layer. Only a final layer of the superlattice layer closest to the active region is doped with silicon, and the silicon doping concentration of the final layer is higher than that of the n-type contact layer.
Owner:SEOUL VIOSYS CO LTD
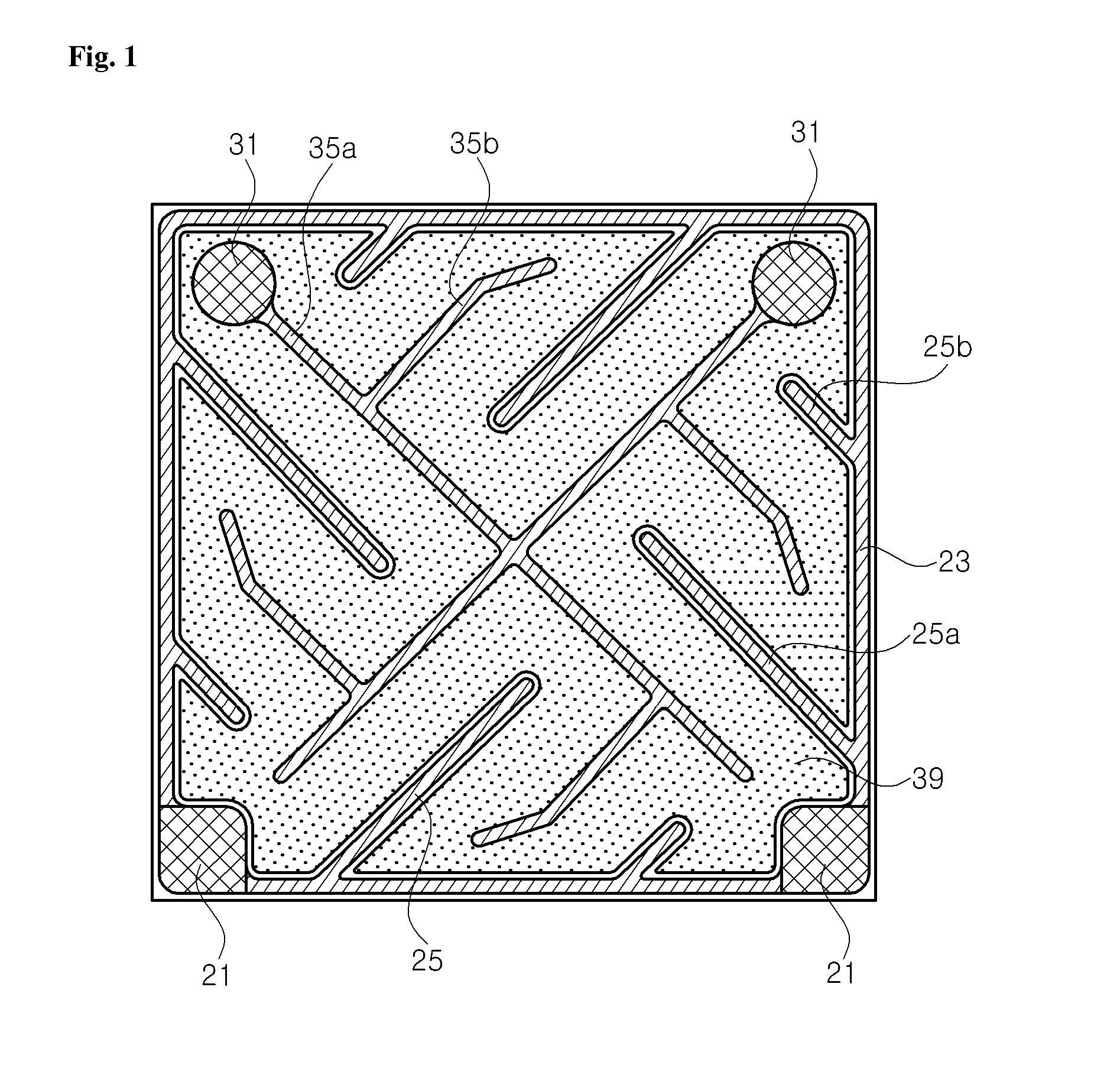
Flip chip type nitride semiconductor light-emitting diode
ActiveUS20050269588A1Lower forward voltageImprove efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesOhmic contactSingle crystal
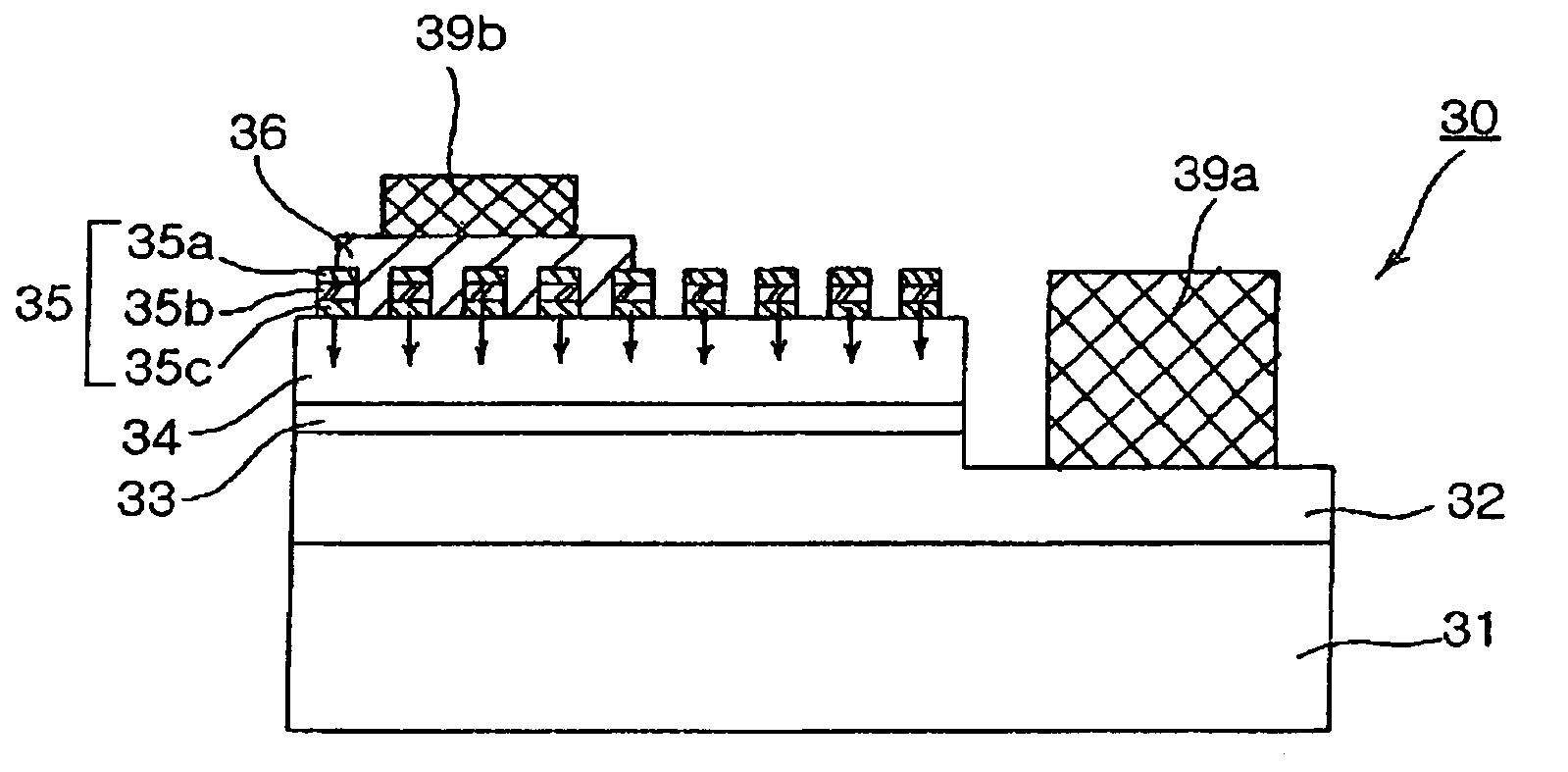
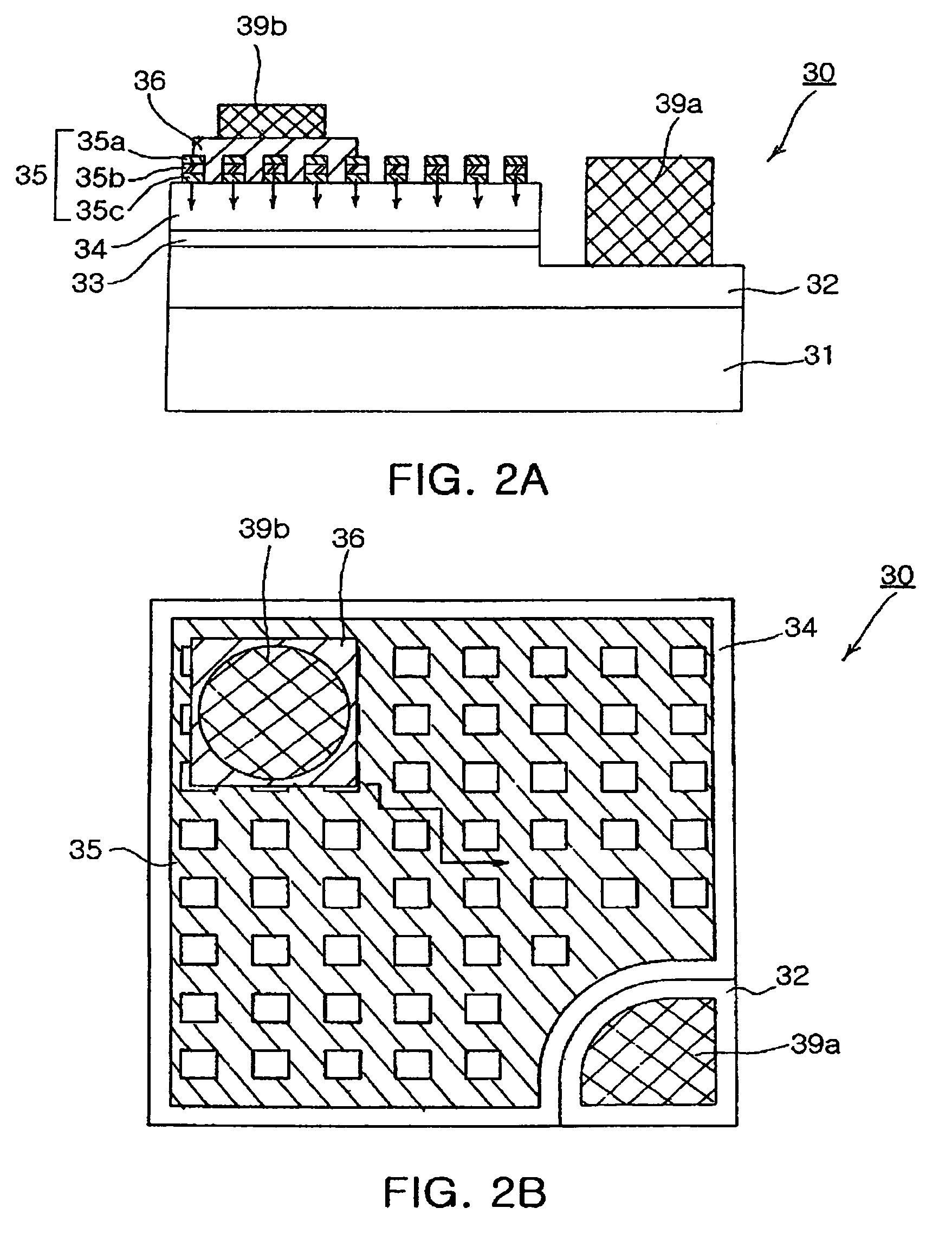
The present invention provides a flip chip type nitride semiconductor light-emitting diode comprising a light-transmissive substrate for growing nitride single crystals; an n-type nitride semiconductor layer formed on the light-transmissive substrate; an active layer formed on the n-type nitride semiconductor layer; a p-type nitride semiconductor layer formed on the active layer; a mesh-type dielectric layer formed on the p-type nitride semiconductor layer and having a mesh structure with a plurality of open regions in which the p-type nitride semiconductor layer is exposed; a highly reflective ohmic contact layer formed on the mesh-type dielectric layer and the open regions in which the p-type nitride semiconductor layer is exposed; and a p-bonding electrode and an n-electrode formed on the highly reflective ohmic contact layer and the n-type nitride semiconductor layer, respectively.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method To Reduce Stacking Fault Nucleation Sites And Reduce Forward Voltage Drift In Bipolar Devices
ActiveUS20050064723A1Reduce nucleationReduce in quantityDecorative surface effectsElectrostatic cleaningStacking faultOptoelectronics
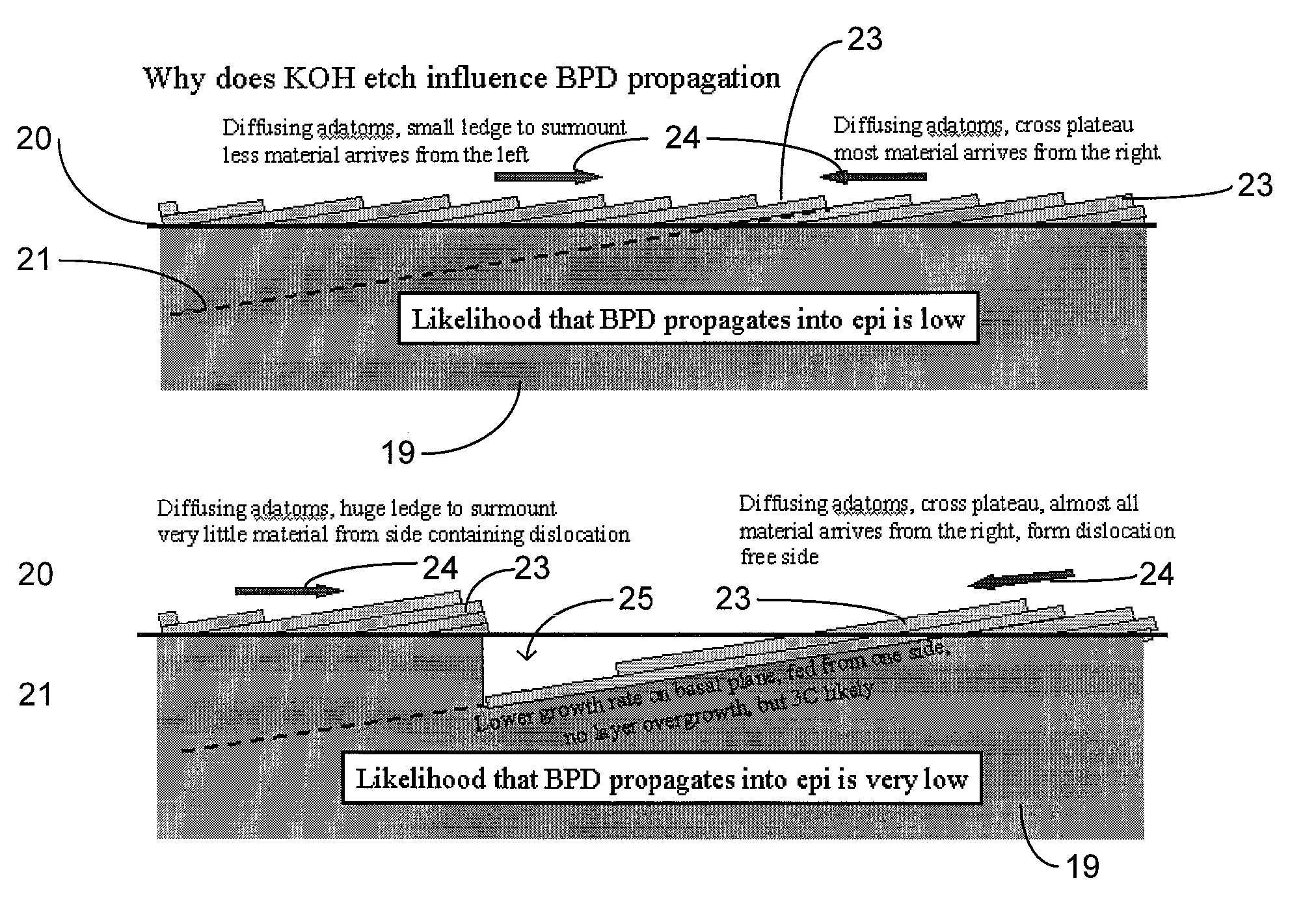
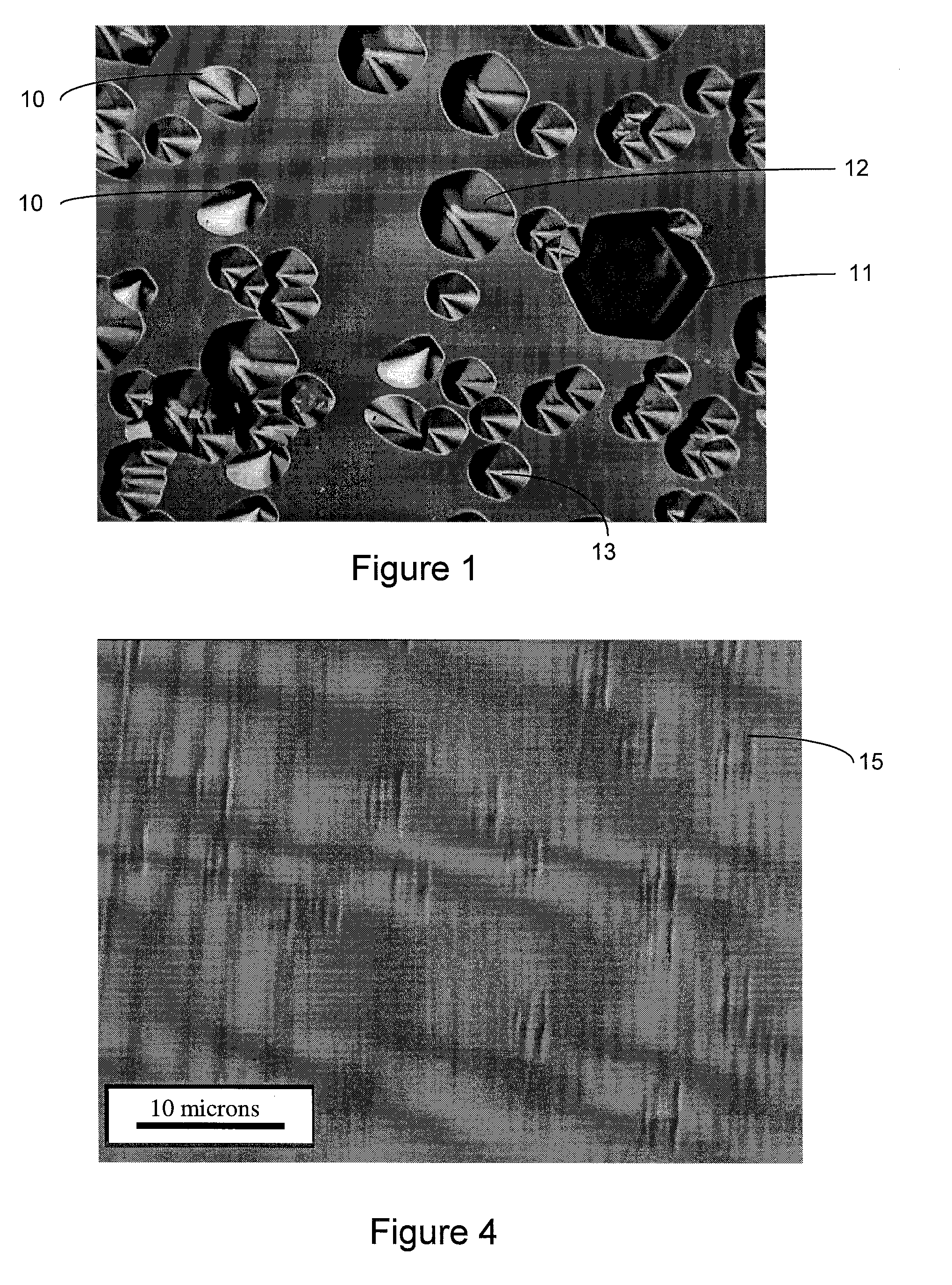
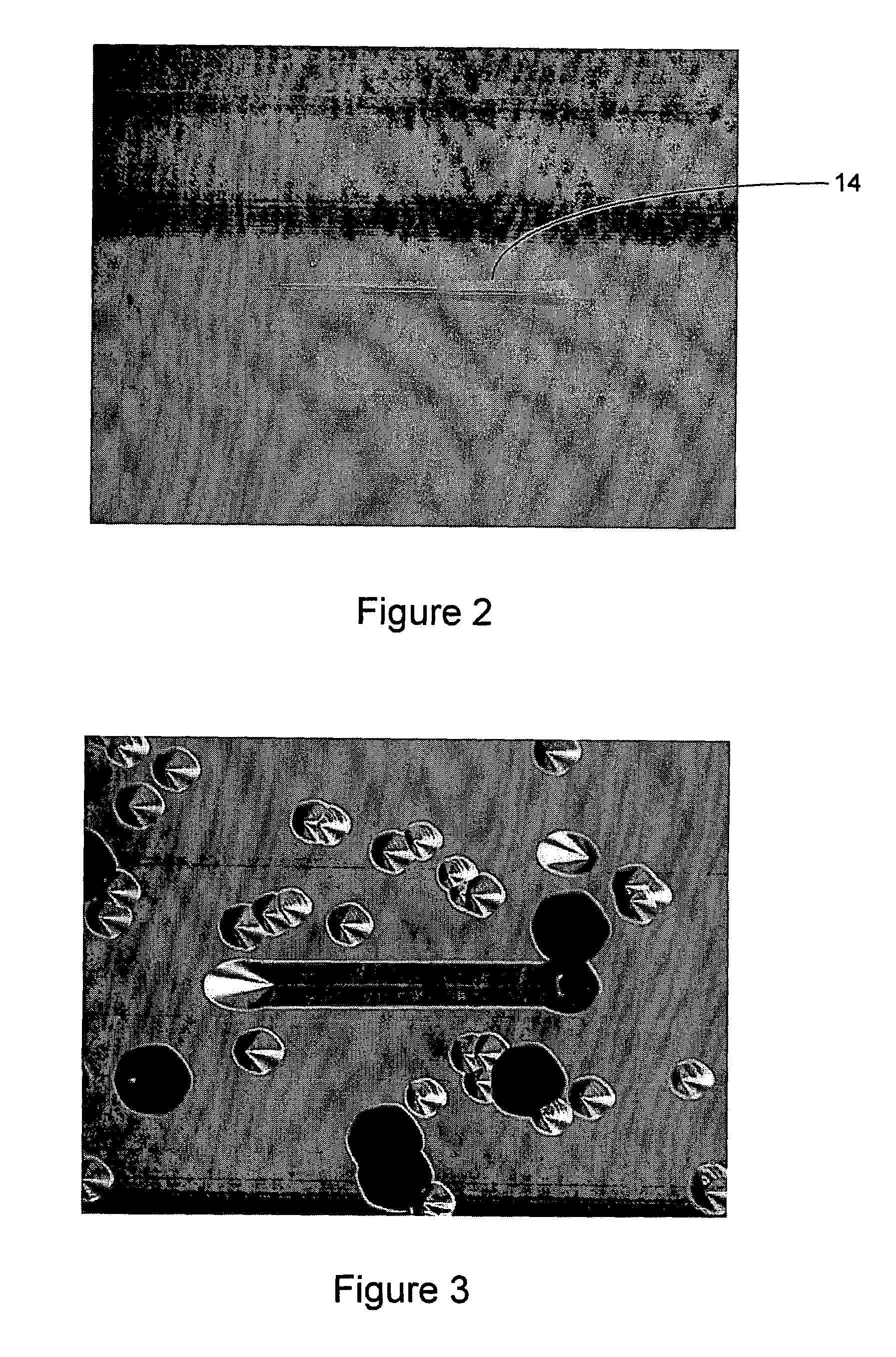
A method is disclosed for preparing a substrate and epilayer for reducing stacking fault nucleation and reducing forward voltage (Vf) drift in silicon carbide-based bipolar devices. The method includes the steps of etching the surface of a silicon carbide substrate with a nonselective etch to remove both surface and sub-surface damage, thereafter etching the same surface with a selective etch to thereby develop etch-generated structures from at least any basal plane dislocation reaching the substrate surface that will thereafter tend to either terminate or propagate as threading defects during subsequent epilayer growth on the substrate surface, and thereafter growing a first epitaxial layer of silicon carbide on the twice-etched surface.
Owner:CREE INC
Polarization field enhanced tunnel structures
InactiveUS6878975B2Moderate and light levelEnhances a dopant-induced drift fieldDiodeSemiconductor lasersTunnel diodeElectrical conductor
A novel tunnel structure is described that enables tunnel diode behavior to be exhibited even in material systems in which extremely heavy doping is impossible and only moderate or light doping levels may be achieved. In one aspect, the tunnel heterostructure includes a first semiconductor layer, a second semiconductor layer, and an intermediate semiconductor layer that is sandwiched between the first and second semiconductor layers and forms first and second heterointerfaces respectively therewith. The first and second heterointerfaces are characterized by respective polarization charge regions that produce a polarization field across the intermediate semiconductor layer that promotes charge carrier tunneling through the intermediate semiconductor layer. In another aspect, the invention features a semiconductor structure having a p-type region, and the above-described heterostructure disposed as a tunnel contact between the p-type region of the semiconductor structure and an adjacent n-type region.
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
Semiconductor device having IGBT and FWD on same substrate
ActiveUS20100090248A1Increase in sizeLower forward voltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesDevice materialEngineering
A semiconductor device includes: a semiconductor substrate; an IGBT element including a collector region; a FWD element including a cathode region adjacent to the collector region; a base layer on the substrate; multiple trench gate structures including a gate electrode. The base layer is divided by the trench gate structures into multiple first and second regions. Each first region includes an emitter region contacting the gate electrode. Each first region together with the emitter region is electrically coupled with an emitter electrode. The first regions include collector side and cathode side first regions, and the second regions include collector side and cathode side second regions. At least a part of the cathode side second region is electrically coupled with the emitter electrode, and at least a part of the collector side second region has a floating potential.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Semiconductor light emitting device
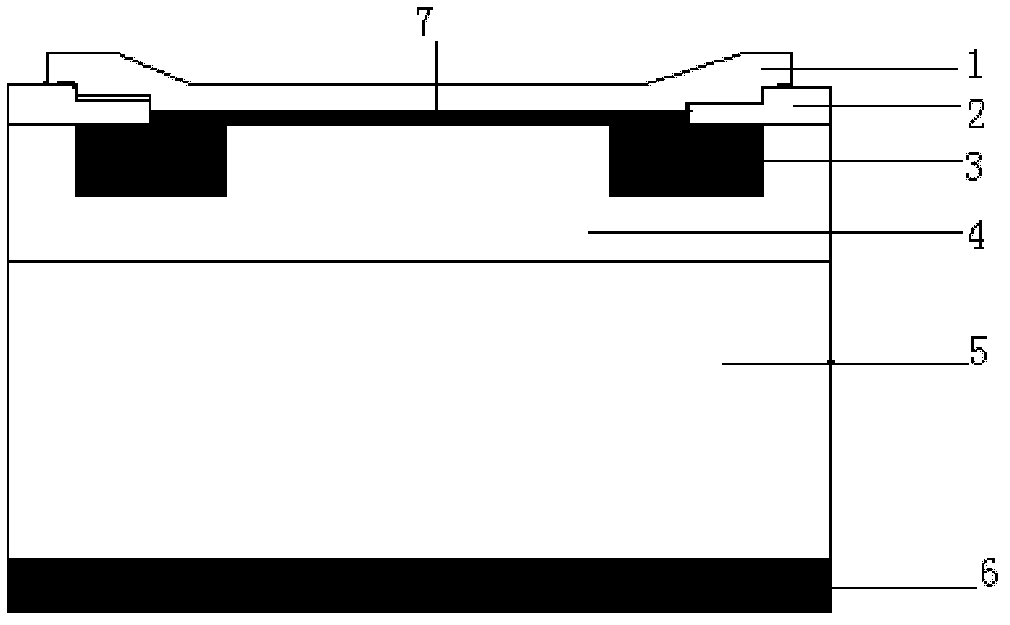
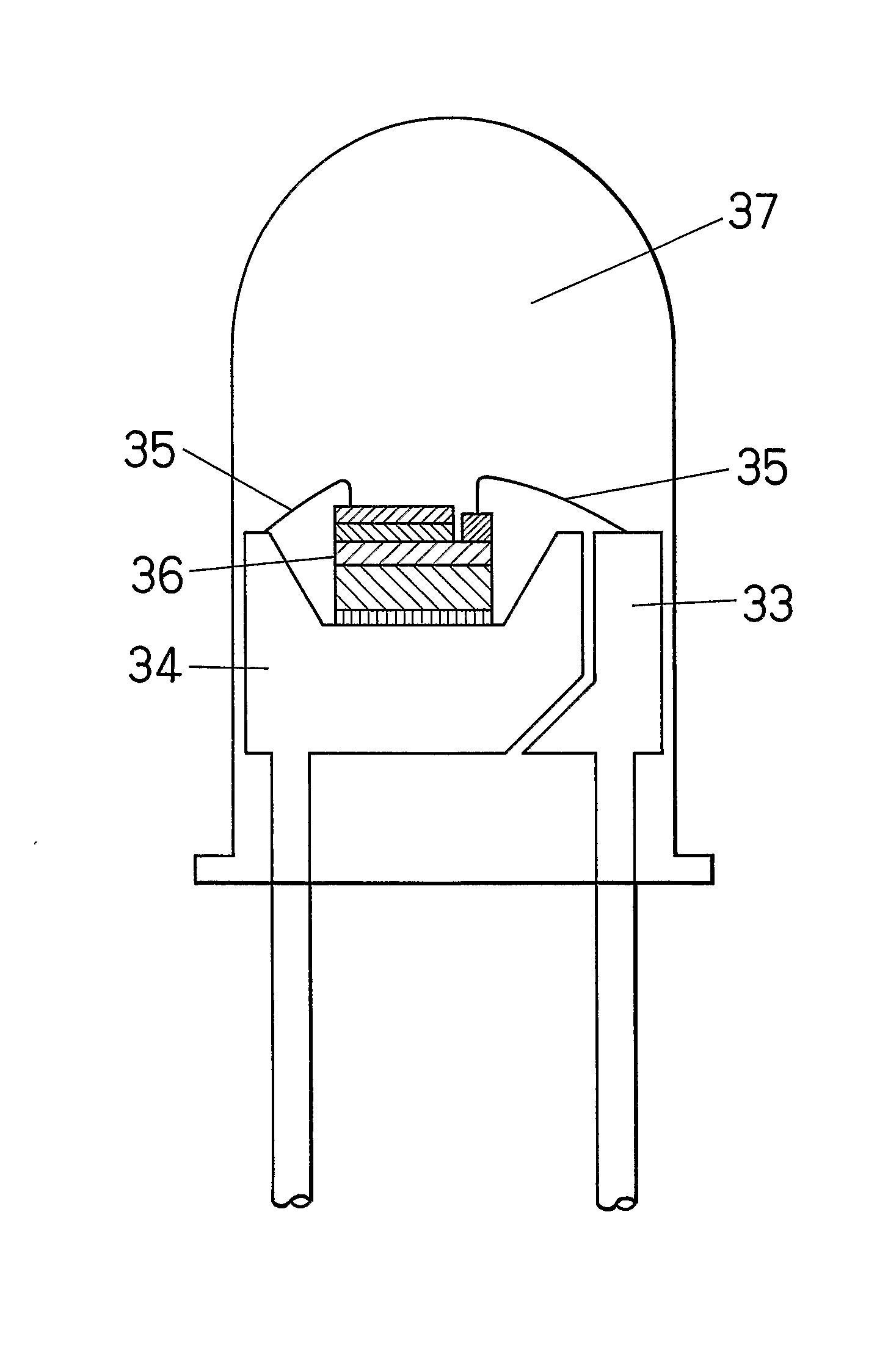
InactiveUS20080283819A1Reduce forward voltageExcellent reliabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesMetallic materialsOhmic contact
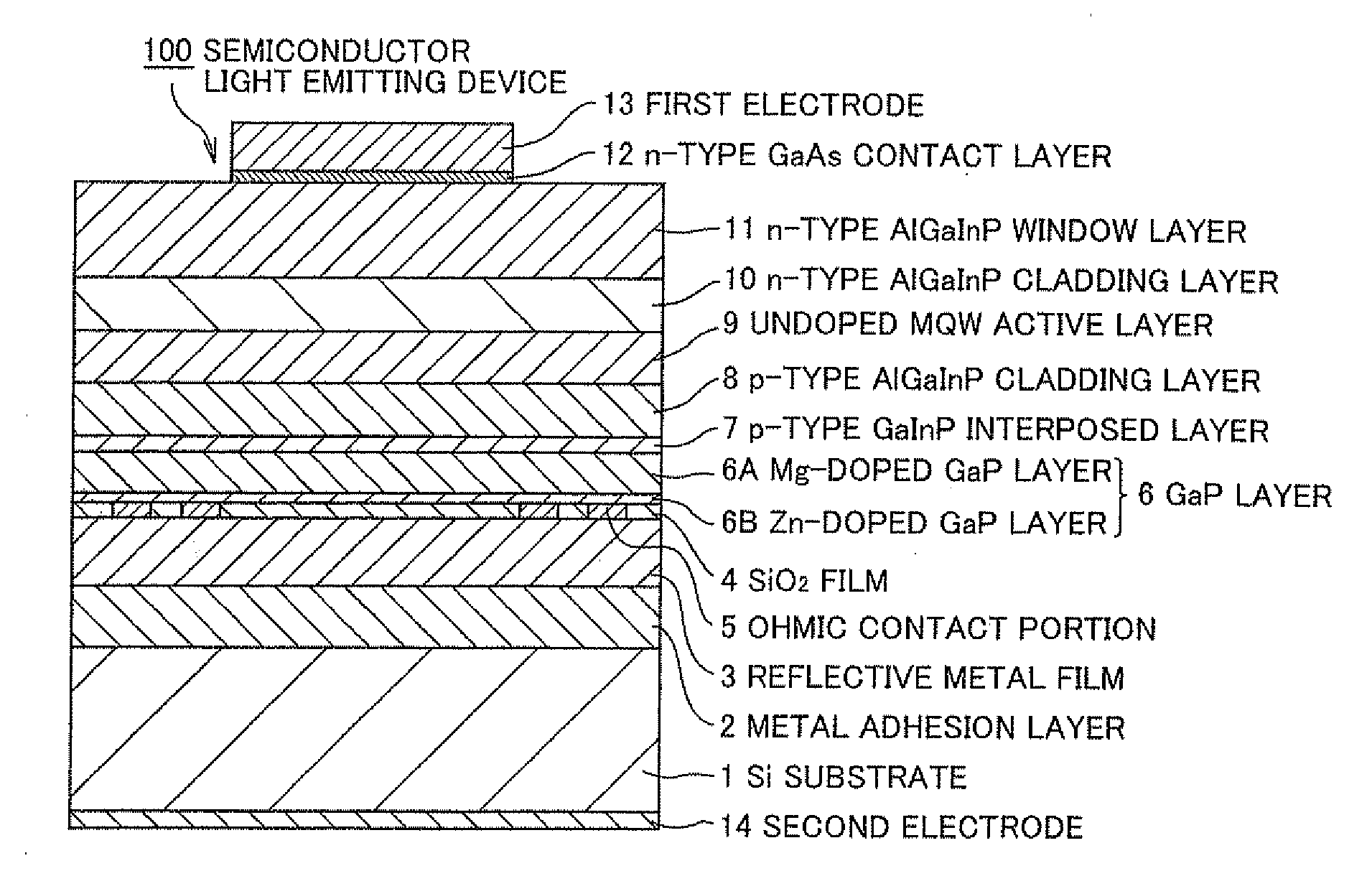
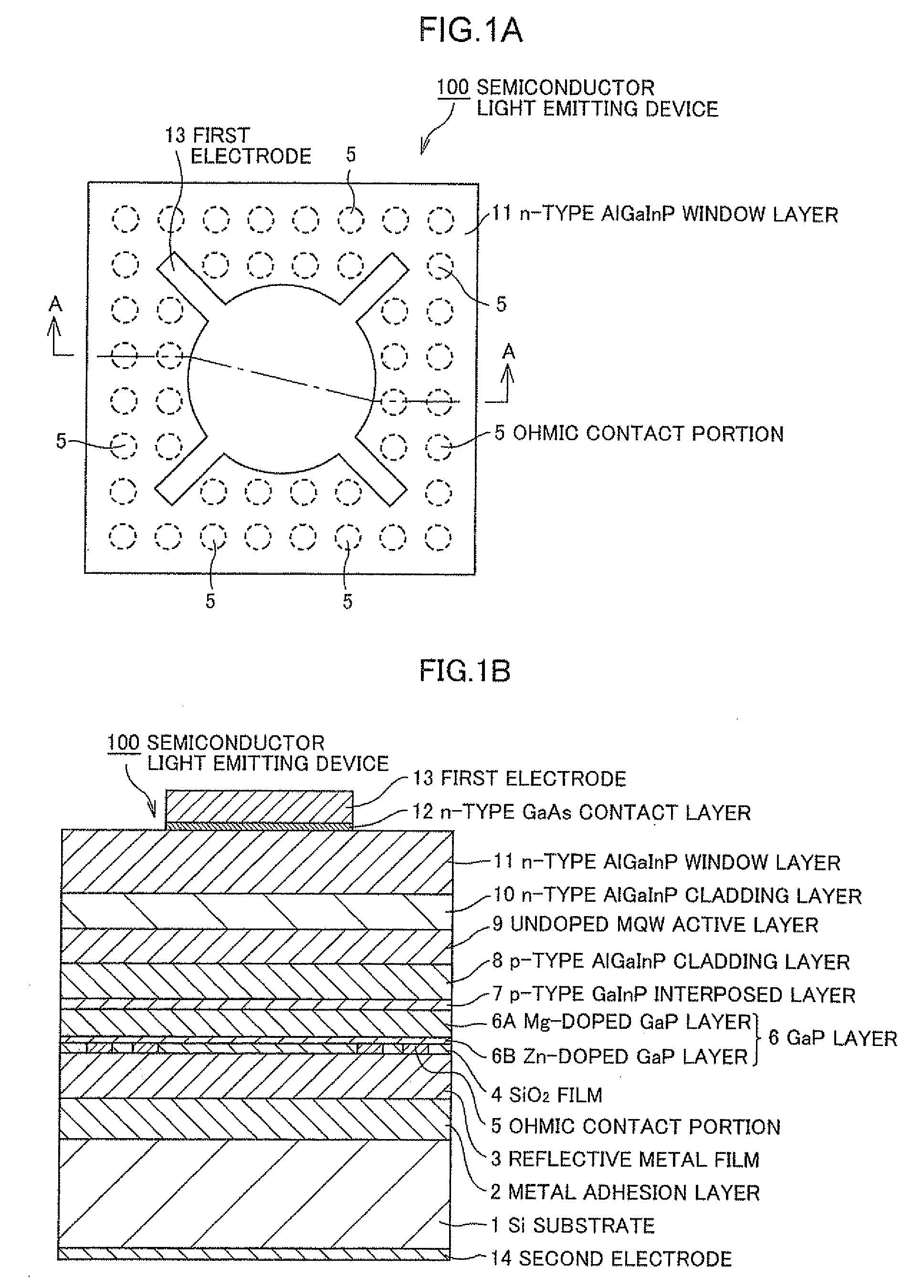
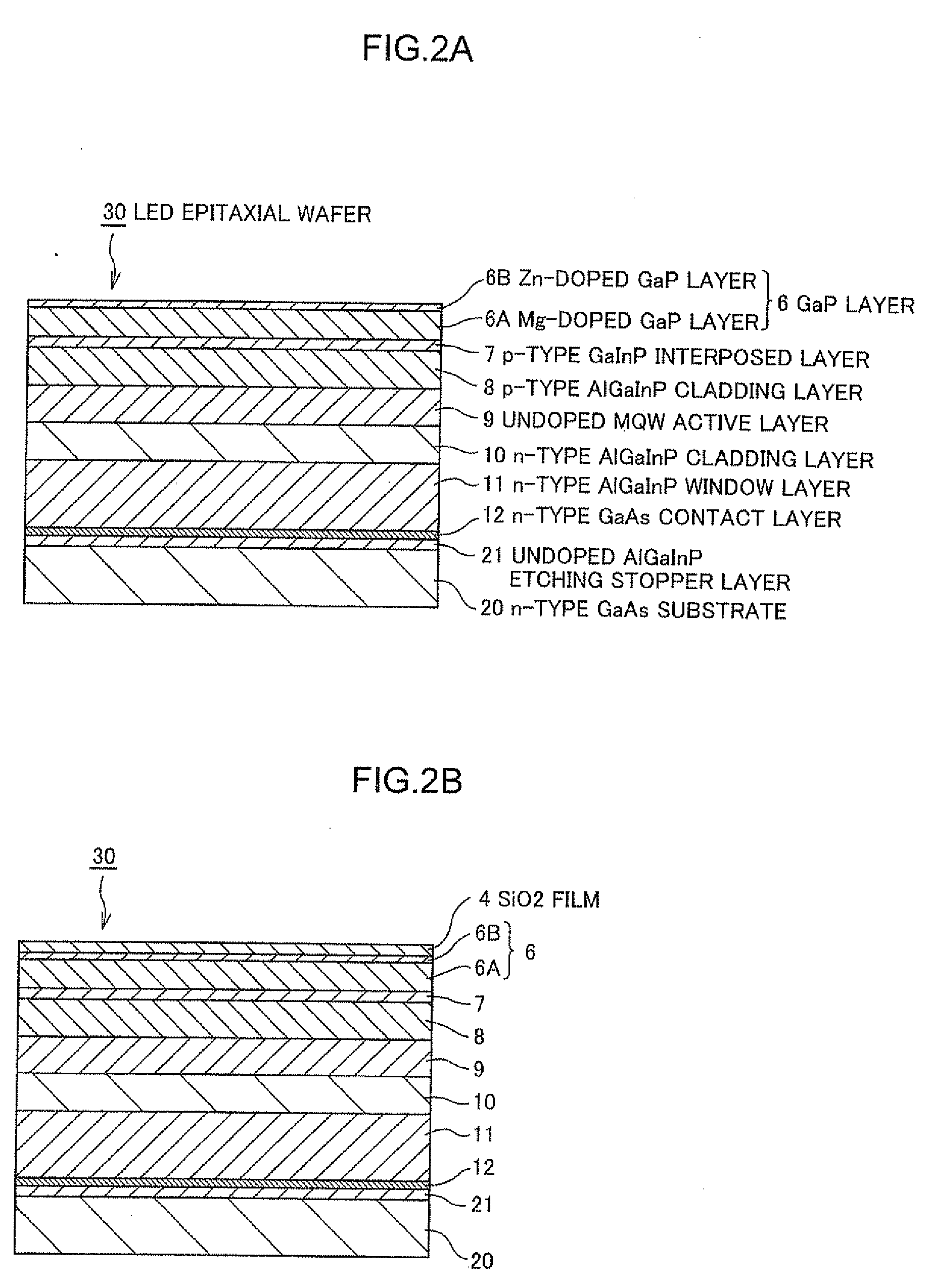
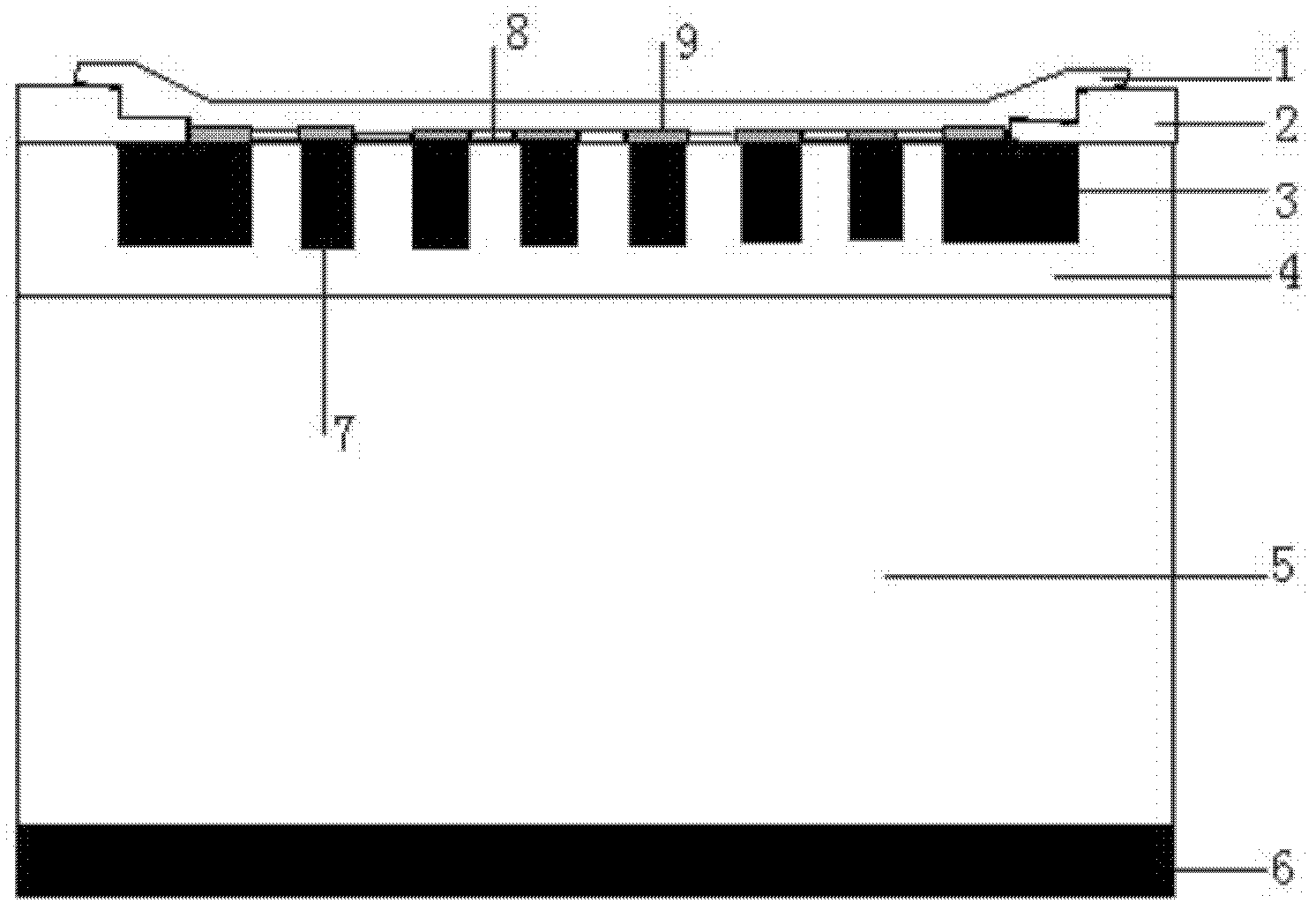
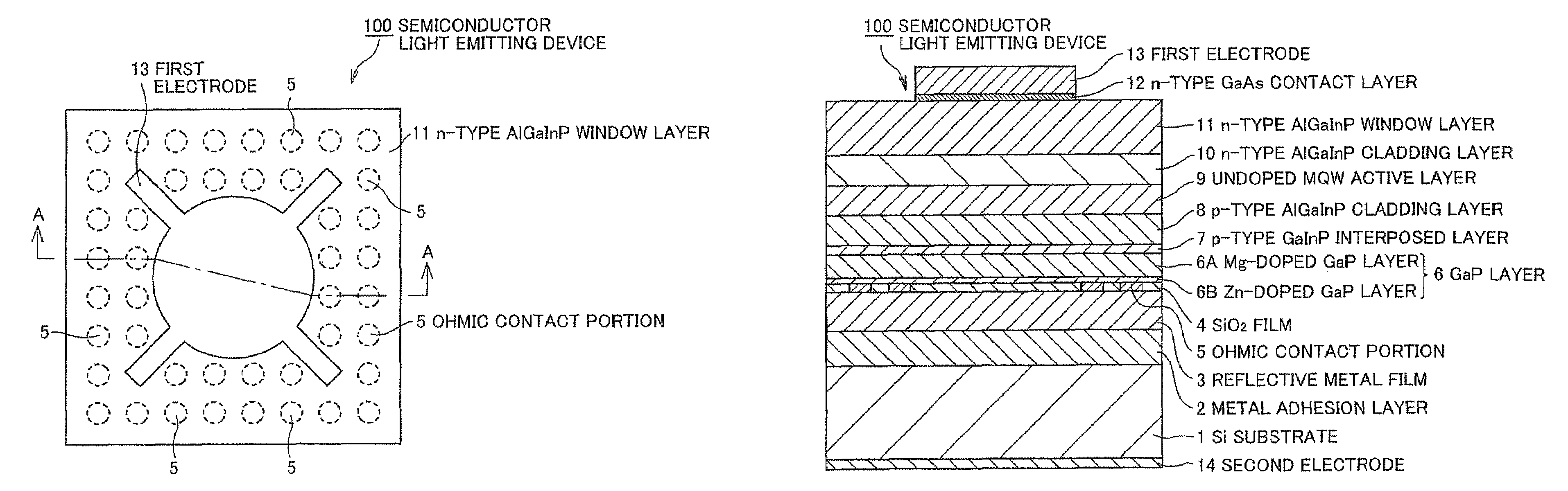
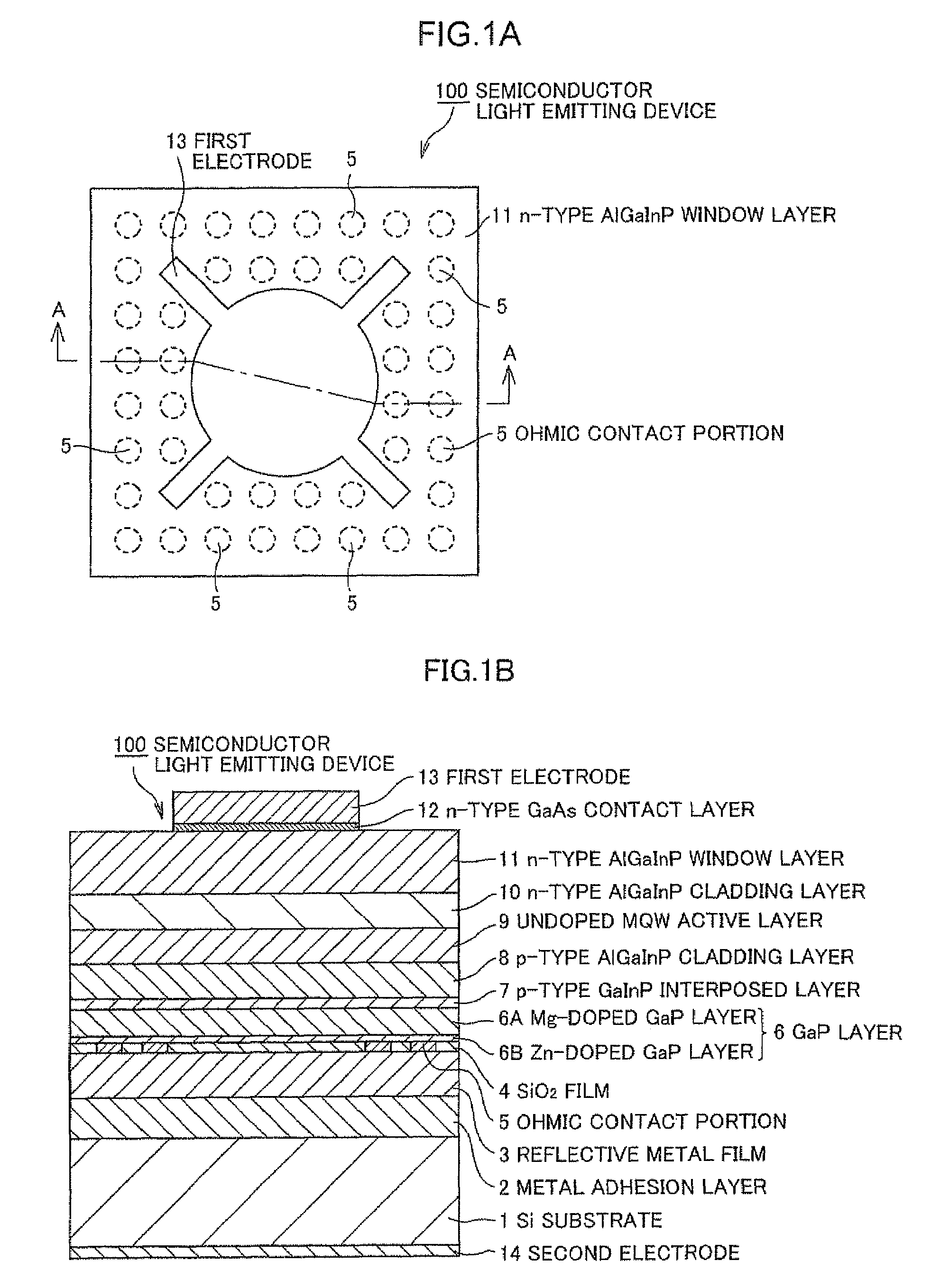
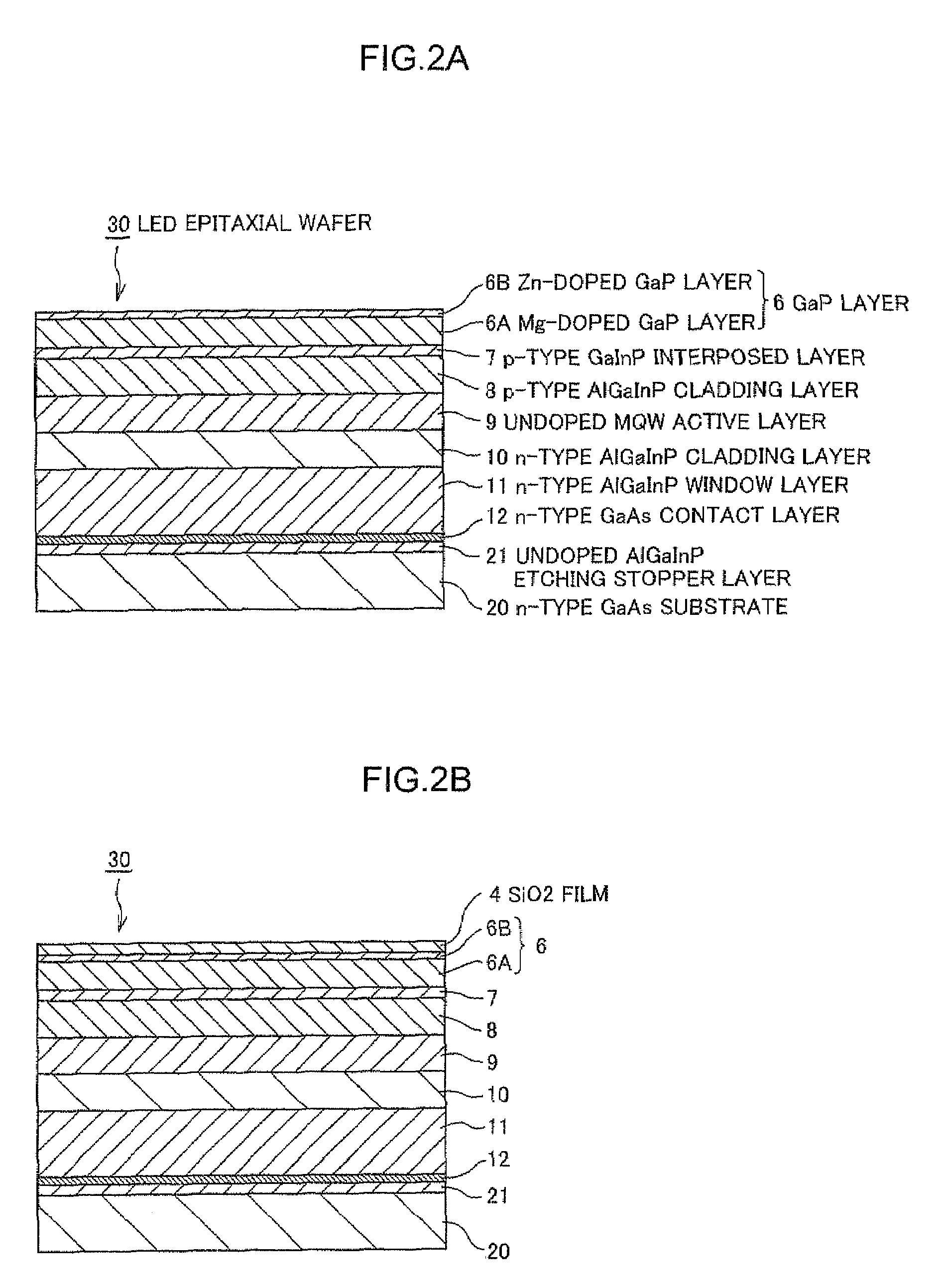
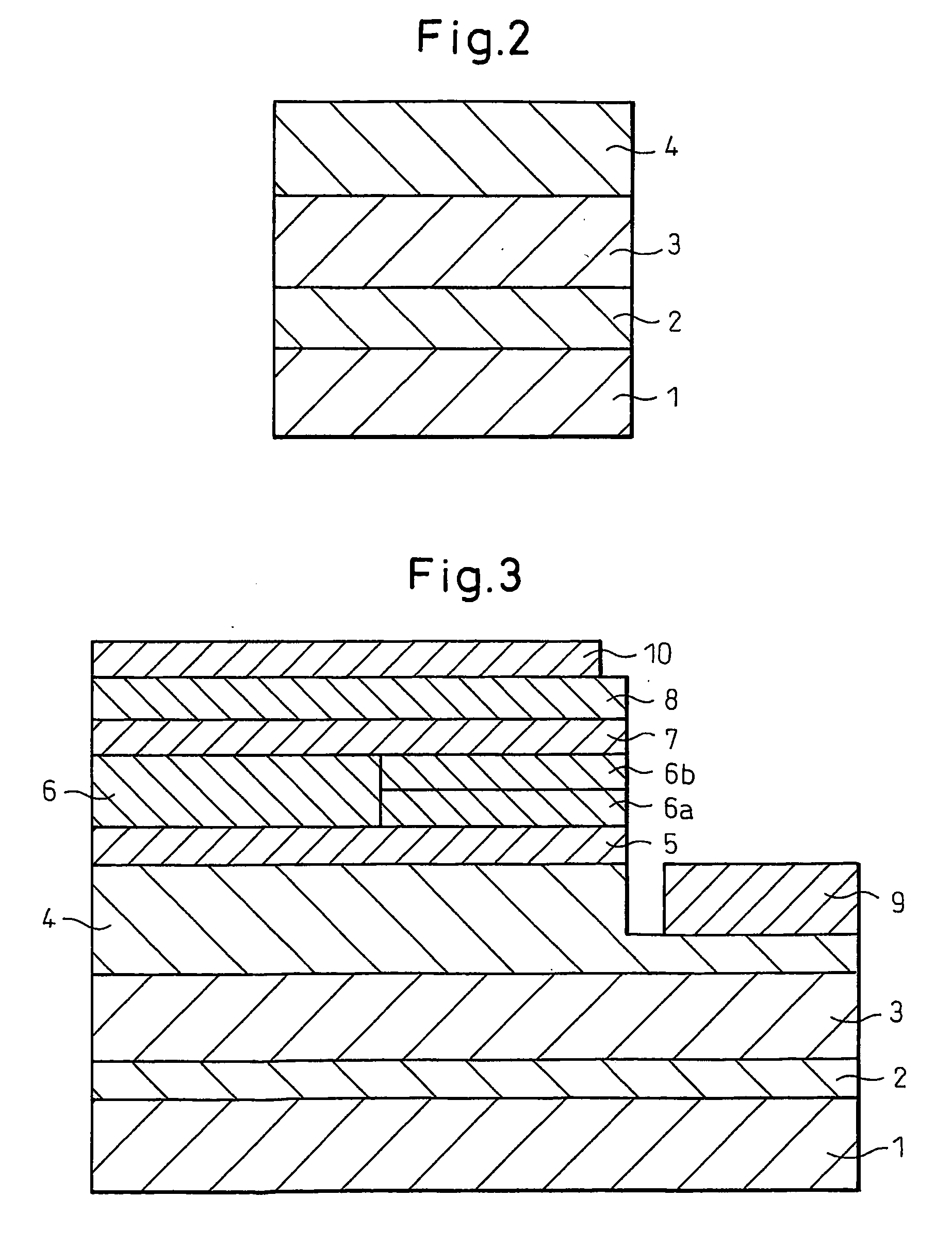
A Si substrate 1, a metal adhesion layer 2, a reflective metal film 3 comprising a multilayer of metallic material having a light reflectivity, a SiO2 film 4, an ohmic contact portion 5 provided at a predetermined position of the SiO2 film 4, a GaP layer 6 including a Mg-doped GaP layer 6A and a Zn-doped GaP layer 6B, a p-type GaInP interposed layer 7, a p-type AlGaInP cladding layer 8, an undoped MQW active layer 9, an n-type AlGaInP cladding layer 10, an n-type AlGaInP window layer 11, an n-type GaAs contact layer 12, a first electrode 13, and a second electrode 14 are formed. The ohmic contact portion 5 is distant from the light emitting part including the p-type AlGaInP cladding layer 8, the undoped MQW active layer 9 and the n-type AlGaInP cladding layer 10 by not less than 300 nm.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Body contacted hybrid surface semiconductor-on-insulator devices
ActiveUS20100155842A1Minimizing and eliminating floating body effectEliminate the effects ofTransistorSolid-state devicesPhysicsBody region
A portion of a top semiconductor layer of a semiconductor-on-insulator (SOI) substrate is patterned into a semiconductor fin having substantially vertical sidewalls. A portion of a body region of the semiconductor fin is exposed on a top surface of the semiconductor fin between two source regions having a doping of a conductivity type opposite to the body region of the semiconductor fin. A metal semiconductor alloy portion is formed directly on the two source regions and the top surface of the exposed body region between the two source regions. The doping concentration of the exposed top portion of the body region may be increased by ion implantation to provide a low-resistance contact to the body region, or a recombination region having a high-density of crystalline defects may be formed. A hybrid surface semiconductor-on-insulator (HSSOI) metal-oxide-semiconductor-field-effect-transistor (MOSFET) thus formed has a body region that is electrically tied to the source region.
Owner:AURIGA INNOVATIONS INC
High efficiency power conversion circuits
InactiveUS20060062026A1Easy to handleReduce winding voltage stress stressEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionLevel shiftingFull bridge
A composite high voltage schottky rectifier is revealed that provides a forward voltage slightly larger than a low voltage schottky rectifier combined with a high voltage breakdown capability. The composite rectifier can be formed from the combination of a low voltage schottky rectifier, a high voltage mosfet, and a few small passive components. A quarter bridge primary switching network similar in some ways to a half bridge primary switching network is revealed. The quarter bridge network consists of four switches with voltage stress equal to half the line voltage and the network applies one quarter of the line voltage to a primary magnetic circuit element network thereby reducing the number of primary winding turns required to one quarter by comparison to a common full bridge network. A synchronously switched buck post regulator is revealed for multi-output forward converters. The synchronously switched buck post regulator accomplishes precise independent load regulation for each output and reduced magnetics volume by using a coupled inductor with a common core for all outputs plus a second smaller inductor for each output except the highest voltage output. An improved capacitor coupled floating gate drive circuit is revealed that provides an effective drive mechanism for a floating or high side switch without the use of level shifting circuits or magnetic coupling. The capacitor coupled floating gate drive circuit is an improvement over prior art capacitor coupled floating gate drive circuits in that the new circuit uses a positive current feedback mechanism to reject slowly changing voltage variations that cause unintentional switch state changes in prior art capacitor coupled floating gate drive circuits.
Owner:TECHN WITTS
Gallium-containing light-emitting semiconductor device and method of fabrication
InactiveUS20050205886A1Enhanced efficiencyLower forward voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesAluminiumOhmic contact
An LED comprising a light-generating semiconductor region having an active layer sandwiched between two confining layers of opposite conductivity types. A cathode is arranged centrally on one of the opposite major surfaces of the semiconductor region from which is emitted the light. An array of discrete gold regions are formed via transition metal regions on the other major surface of the semiconductor region at which is exposed one of the confining layers which is of n-type AlGaInP semiconductor material. The gold is thermally diffused into the confining layer via the transition metal regions at a temperature less than the eutectic point of gold and gallium, thereby creating an array of ohmic contact regions of alloyed or intermingled gold and gallium, which are less absorptive of light than their conventional counterparts, to a thickness of 20 to 1000 angstroms. After removing the transition metal regions and gold regions from the surface of the light-generating semiconductor region, a reflective layer of aluminum is formed so as to cover both the ohmic contact regions and the exposed surface portions of the AlGaInP confining layer. An electroconductive base-plate of doped silicon is then bonded to the reflective layer.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
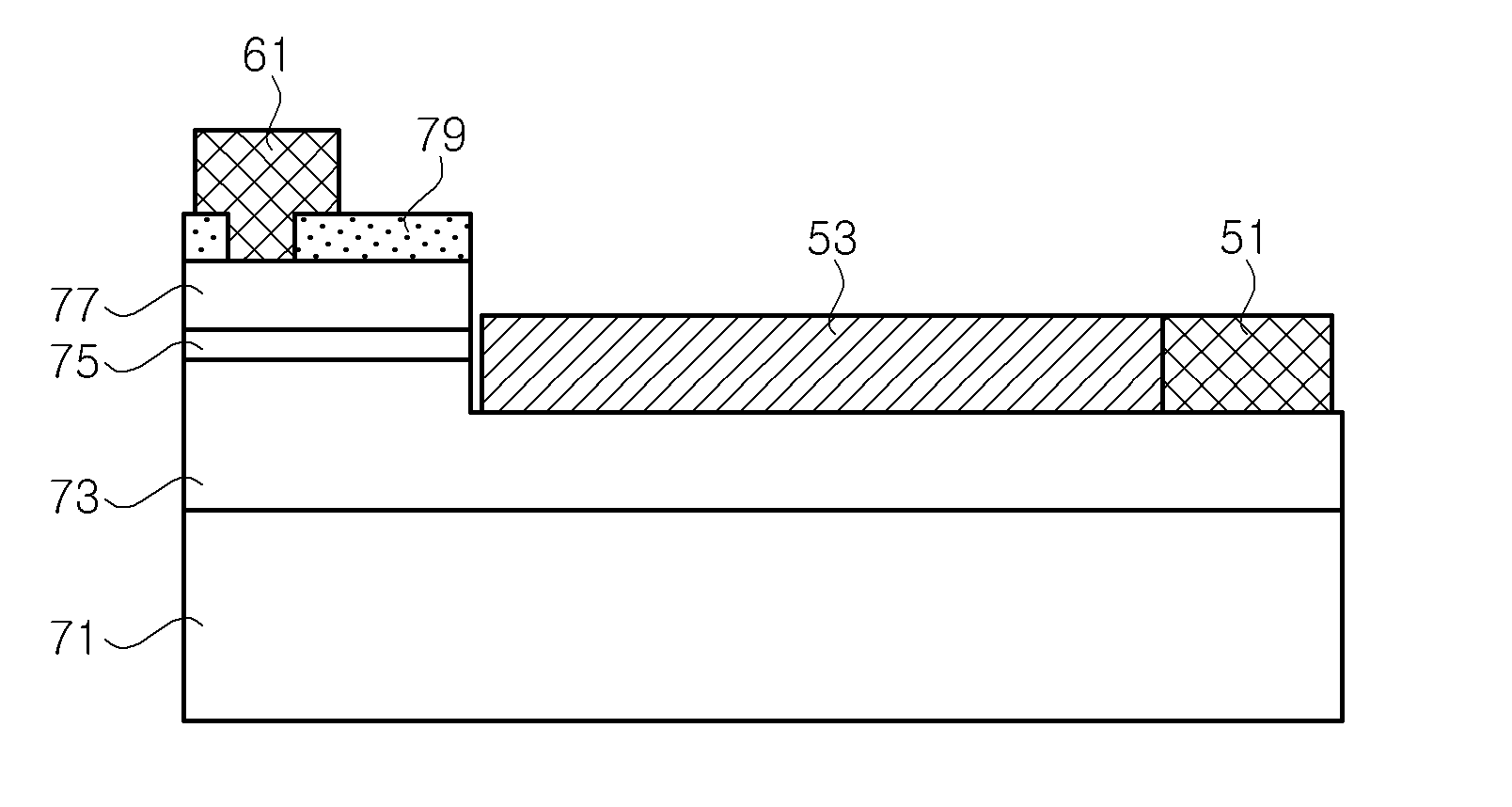
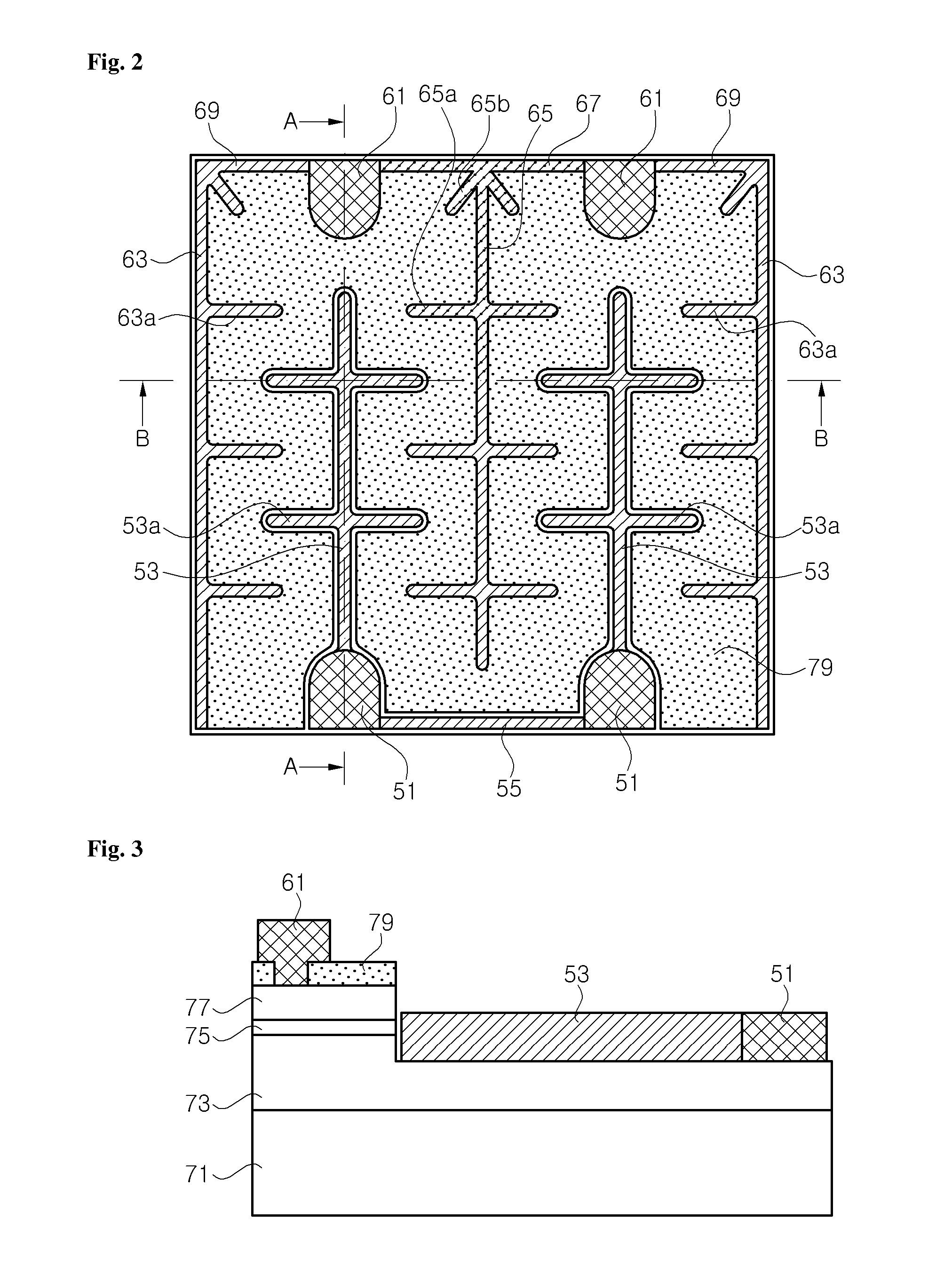
Flip chip nitride semiconductor light emitting diode
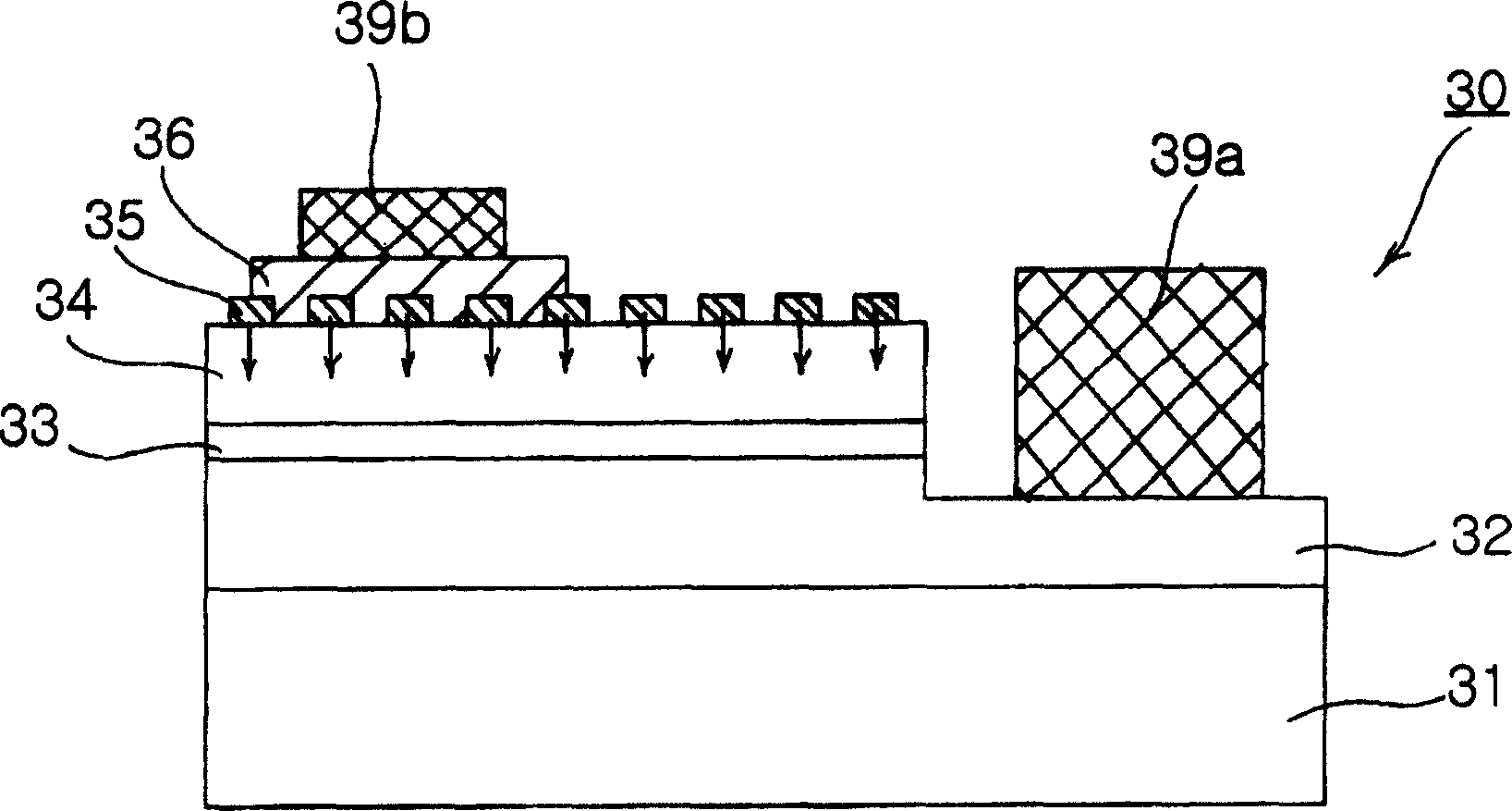
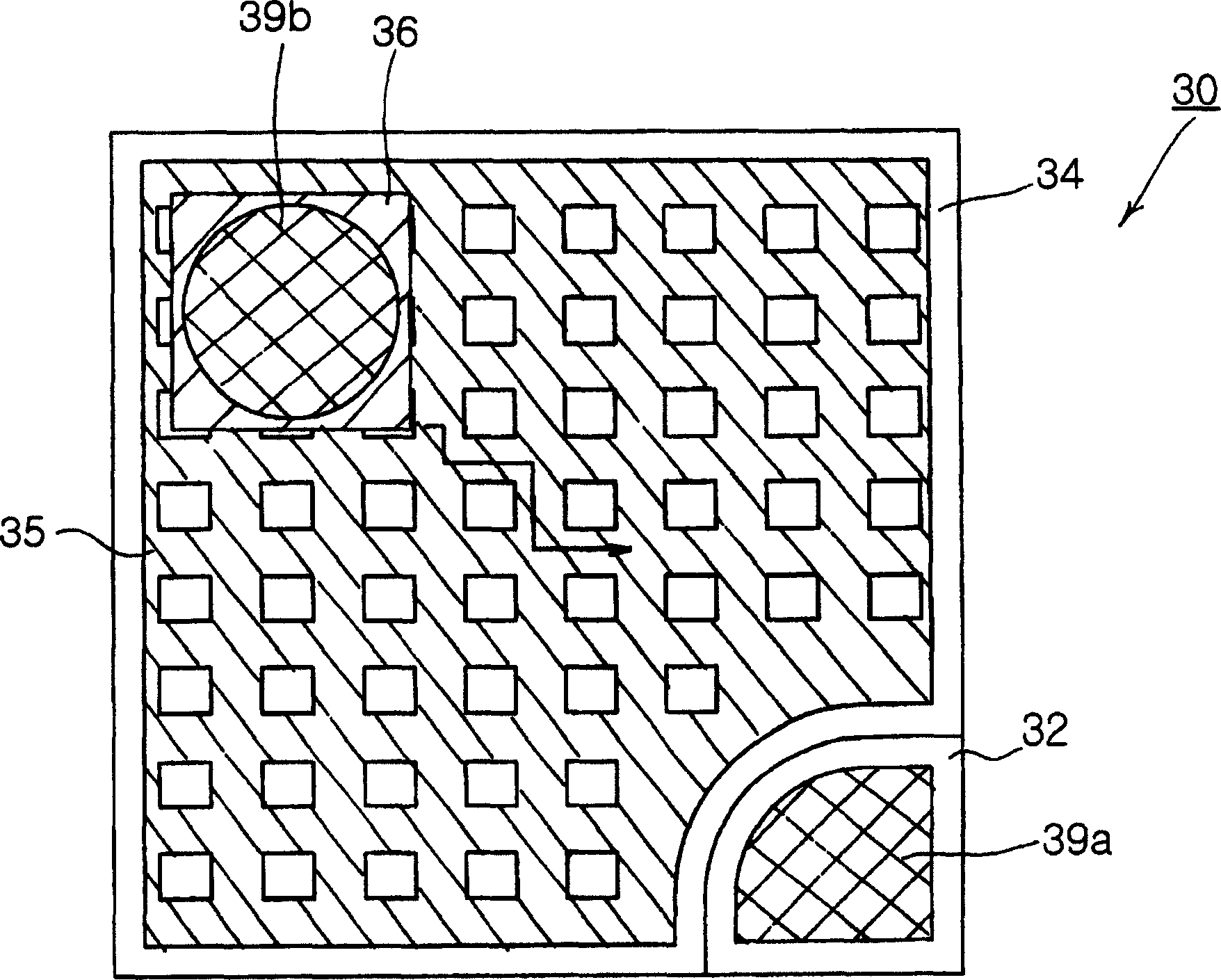
ActiveUS7057212B2Less crowdedSimple structureJoints with sealing surfacesSolid-state devicesOhmic contactHigh reflectivity
In a nitride semiconductor LED, an n-doped nitride semiconductor layer is formed on a transparent substrate. An active layer is formed on the n-doped nitride semiconductor layer. A p-doped nitride semiconductor layer is formed on the active layer. A high reflectivity Ohmic contact layer of a mesh structure is formed on the p-doped nitride semiconductor layer and has a number of open areas for exposing the p-doped nitride semiconductor layer. A metal barrier layer is formed on at least a top region of the high reflectivity Ohmic contact layer. A p-bonding electrode is formed on the metal barrier layer. An n-electrode is formed on the n-doped nitride semiconductor layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
N-type group III nitride semiconductor stacked layer structure
ActiveUS7612363B2Lower resistanceImprove flatnessSolid-state devicesNanoopticsHigh concentrationOptoelectronics
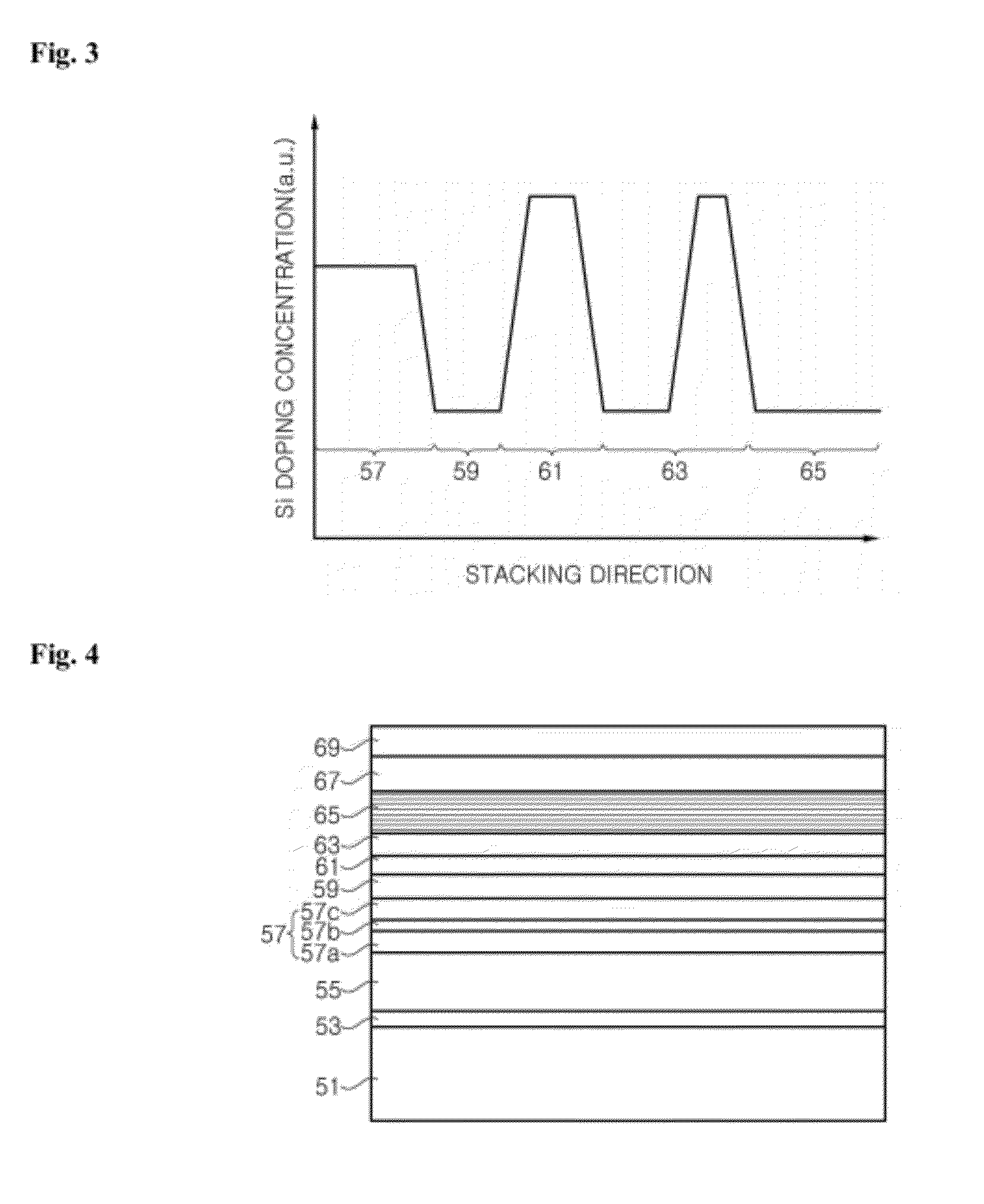
An n-type Group III nitride semiconductor stacked layer structure including a first n-type layer which includes a layer containing n-type impurity atoms at a high concentration and a layer containing n-type impurity atoms at a low concentration, a second n-type layer containing n-type impurity atoms at an average concentration smaller than that of the first n-type layer, the second n-type layer neighboring the layer containing n-type impurity atoms at a low concentration in the first n-type layer.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Semiconductor light-emitting device, method of manufacturing the same, and lamp including the same
ActiveUS20090173962A1Good light transmissionIncrease brightnessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLight emissionLight emitting device
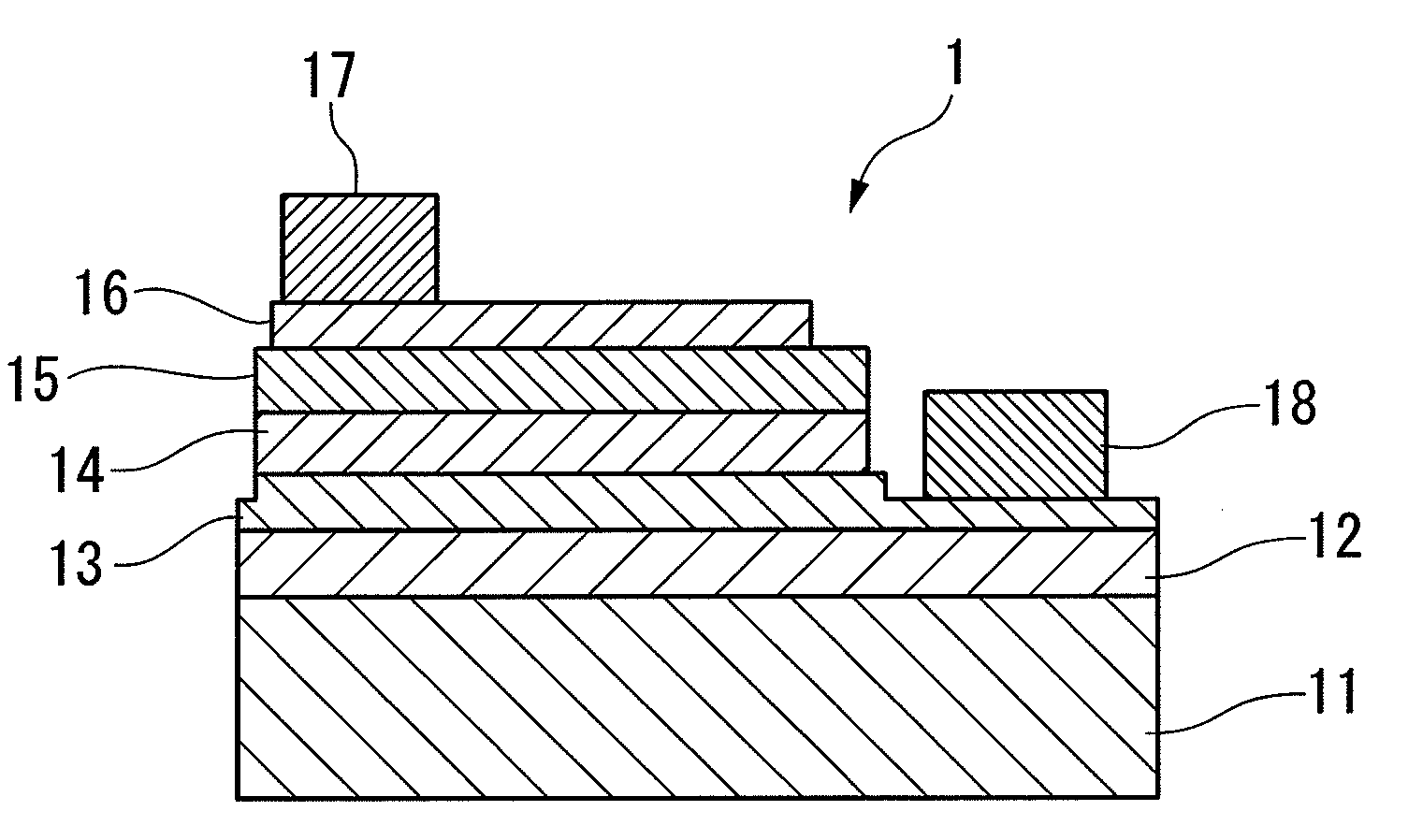
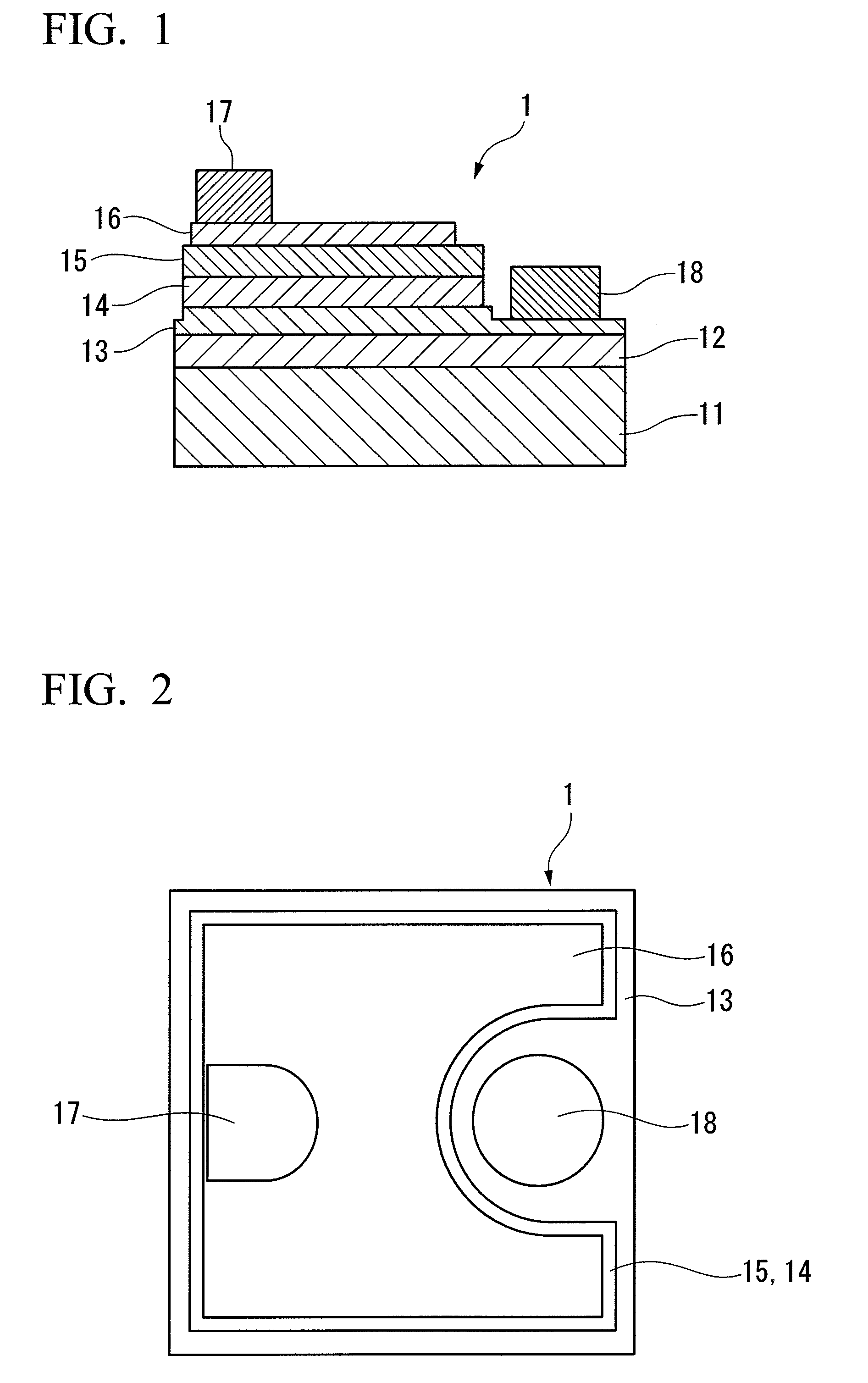
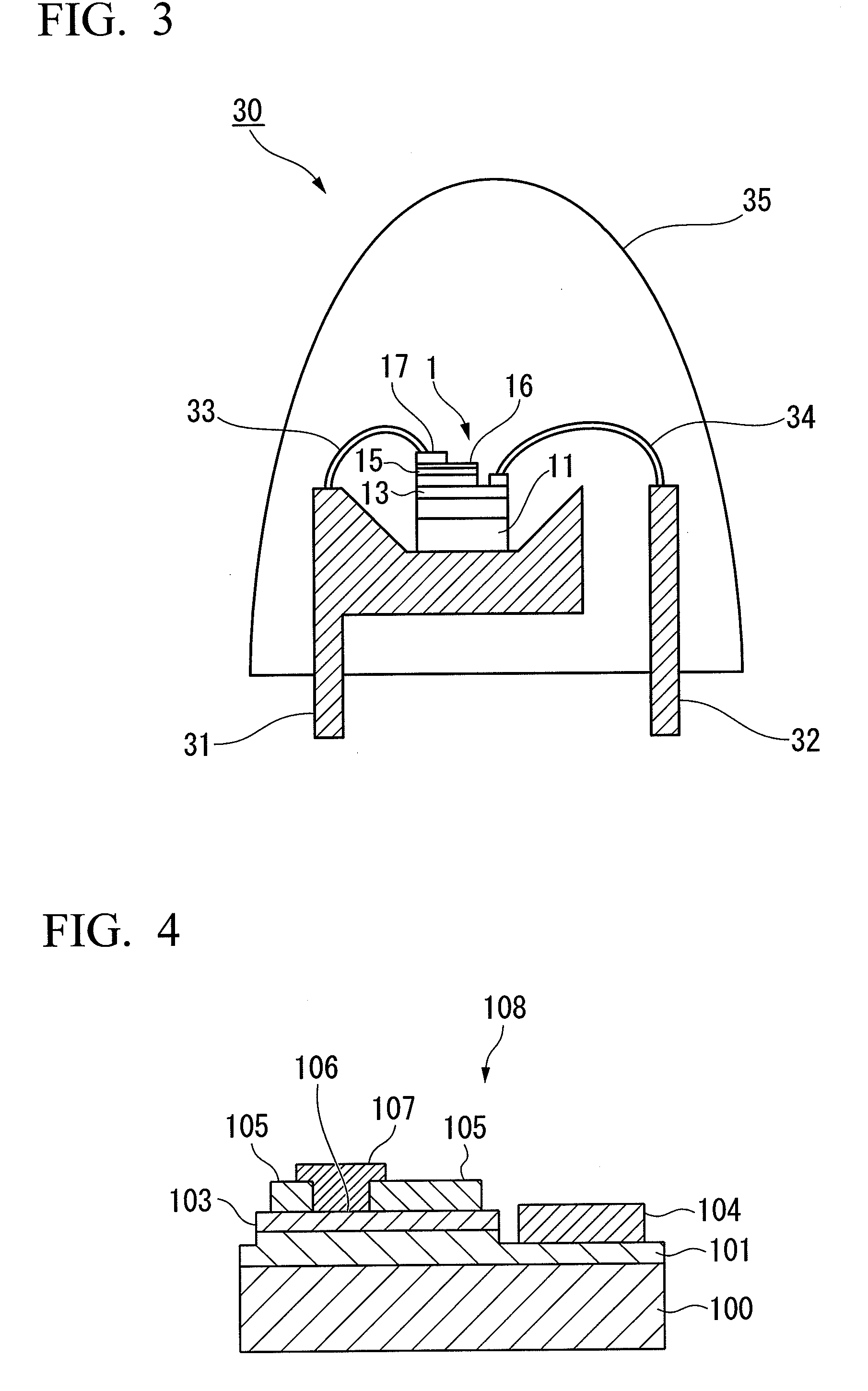
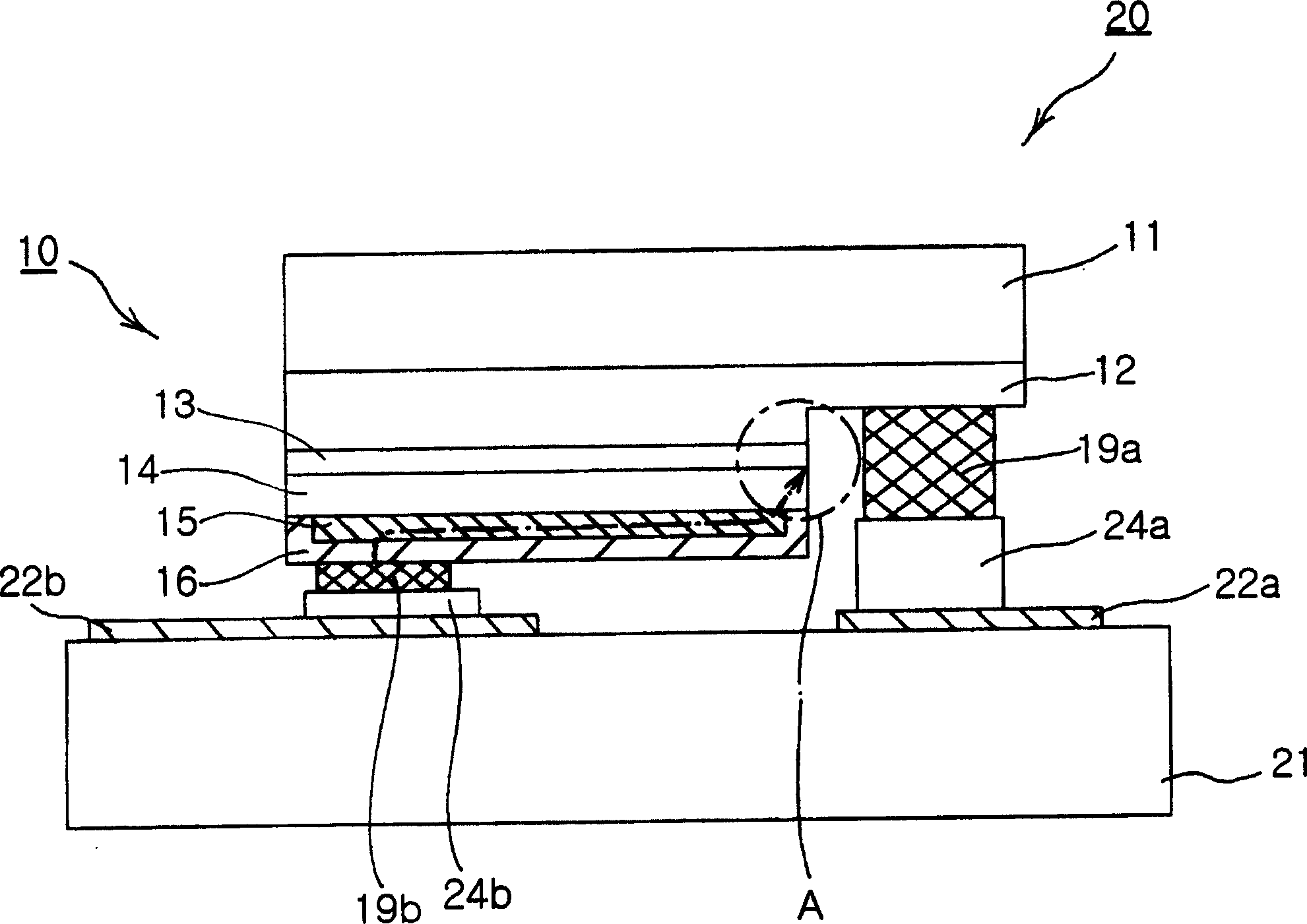
A semiconductor light-emitting device having a high light emission property and preventing an electrode from being peeled off during wire bonding. Also disclosed is a method of manufacturing a semiconductor light-emitting device 1 in which an n-type semiconductor layer (13), a light-emitting layer (14), and a p-type semiconductor layer (15) are formed on a substrate (11), a transparent positive electrode (16) is formed on the p-type semiconductor layer (15), a positive electrode bonding pad (17) is formed on the transparent positive electrode (16), and a negative electrode bonding pad (18) is formed on the n-type semiconductor layer (13).
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Wafer level light-emitting diode array
ActiveUS20150280086A1Improve reliabilityAvoid crackingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesElectrical conductorLed array
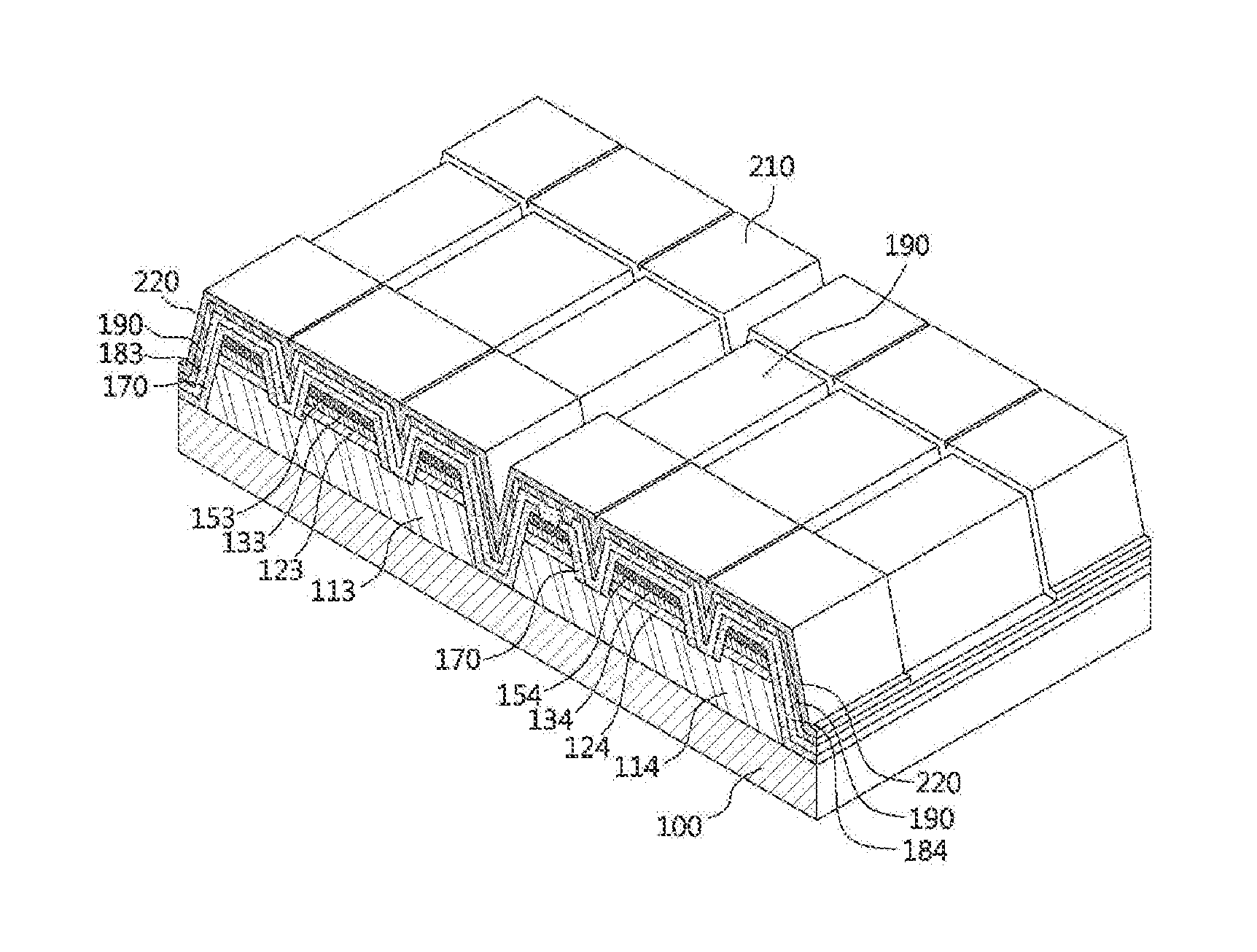
A wafer level light-emitting diode (LED) array includes: a growth substrate; a plurality of LEDs arranged over the substrate, each including a first semiconductor layer, an activation layer, and a second semiconductor layer; a plurality of upper electrodes formed from a common material and electrically connected to the first semiconductor layers of the corresponding LEDs; and first and second pads arranged over the upper electrodes. The LEDs are connected in series by the upper electrodes, the first pad is electrically connected to an input LED from among the LEDs connected in series, and the second pad is electrically connected to an output LED from among the LEDs connected in series. Accordingly, a flip chip-type LED array can be provided which can be driven with a high voltage.
Owner:SEOUL VIOSYS CO LTD
Method to reduce stacking fault nucleation sites and reduce forward voltage drift in bipolar devices
InactiveUS7018554B2Reduce in quantityReduce nucleationDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStacking faultOptoelectronics
A method is disclosed for preparing a substrate and epilayer for reducing stacking fault nucleation and reducing forward voltage (Vf) drift in silicon carbide-based bipolar devices. The method includes the steps of etching the surface of a silicon carbide substrate with a nonselective etch to remove both surface and sub-surface damage, thereafter etching the same surface with a selective etch to thereby develop etch-generated structures from at least any basal plane dislocation reaching the substrate surface that will thereafter tend to either terminate or propagate as threading defects during subsequent epilayer growth on the substrate surface, and thereafter growing a first epitaxial layer of silicon carbide on the twice-etched surface.
Owner:CREE INC
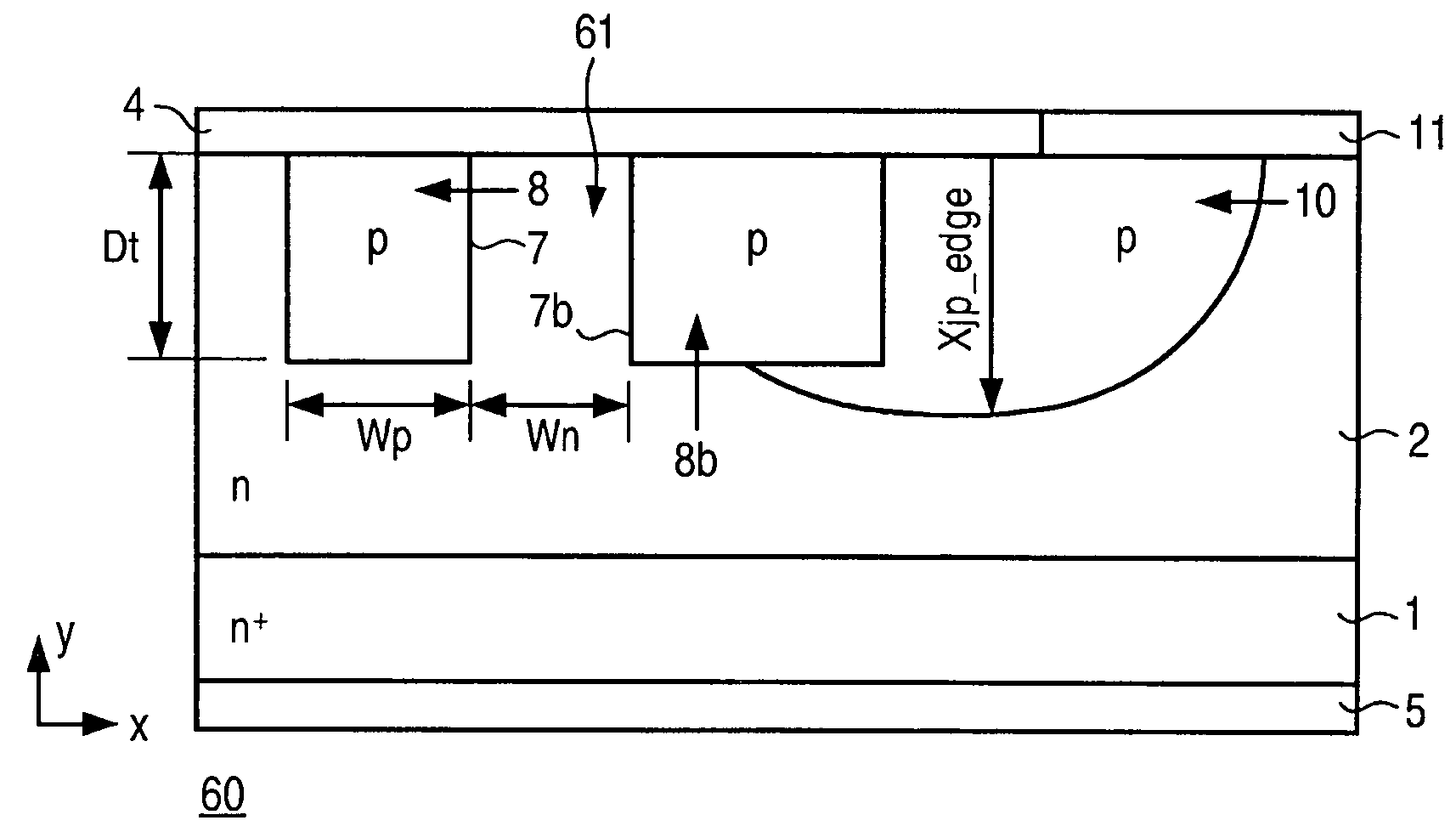
Schottky diode with high reverse-blocking performance and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102354704AAvoid lowering effectAvoid reducing reverse leakage currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEffective potentialDot matrix
The invention provides a schottky diode with high reverse-blocking performance and a manufacturing method thereof. The schottky diode core is structurally characterized in that: a lightly doped epitaxial layer of a drift region is provided with a P-type structure region which is composed of a P-type ring and P-type dot matrixes uniformly spaced on the epitaxial layer in the P-type ring; the surface of the epitaxial layer in the P-type ring is provided with a schottky potential barrier contact metal layer; and the surface of the P-type structure region is in Ohm metal contact. When the schottky diode is in reverse application, a PN junction depletion region gradually spreads to a channel region along with the increase of the reverse voltage until the depletion region is communicated, and extends towards the substrate along with further increase of the reverse voltage to form an effective potential barrier in the channel region and effectively shield the schottky potential barrier region, thereby improving the reverse blocking ability that the reverse blocking voltage can reach 200 V or above; and moreover, the schottky diode also has good technical indexes such as reverse recovery time, reverse leakage current and the like, realizes low working loss of switches and prevents noise.
Owner:丹东安顺微电子有限公司
Highly efficient LED having current spread layer construction improved and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101388430AImprove efficiencyLower forward voltageSemiconductor devicesEngineeringLight-emitting diode
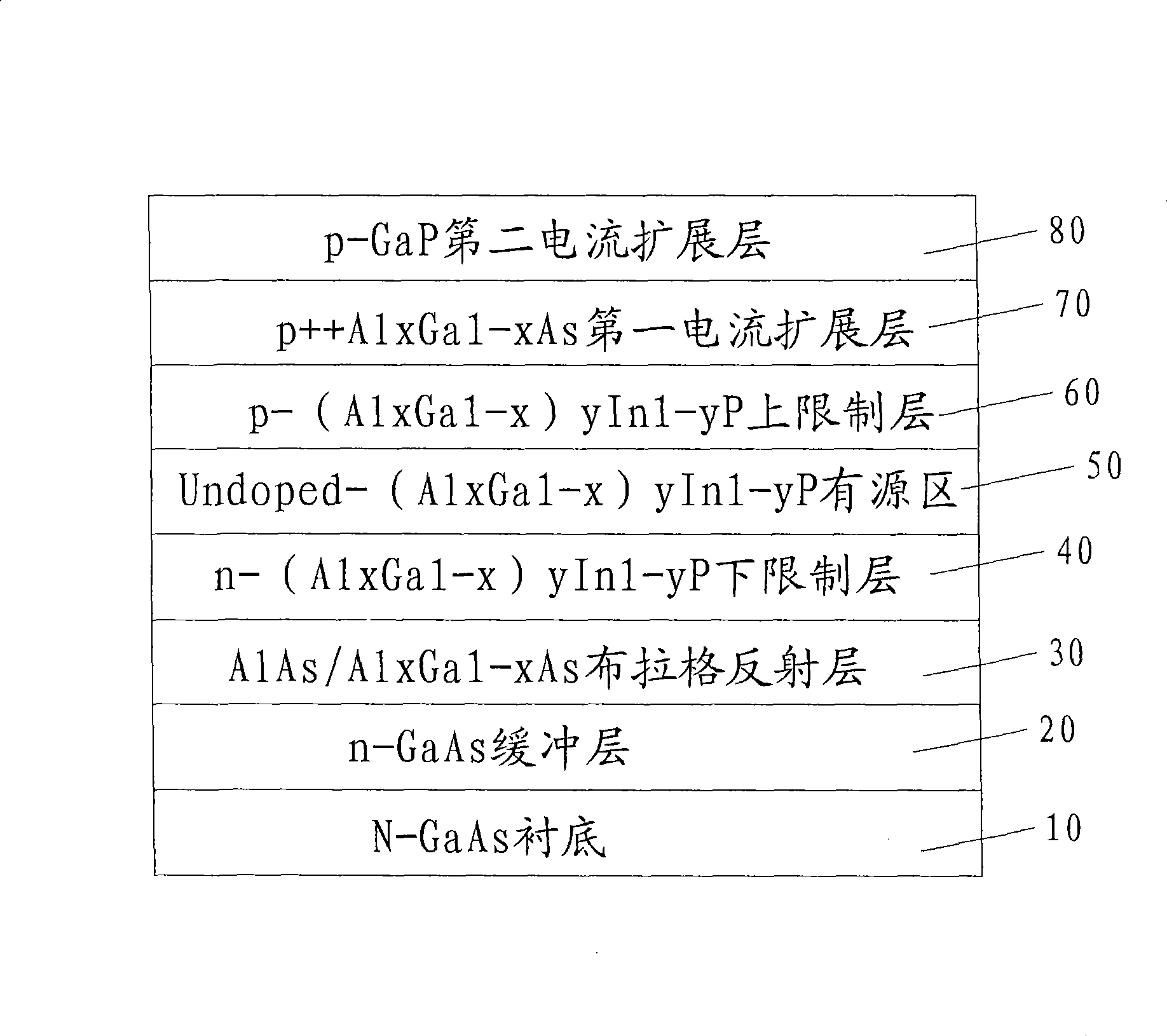
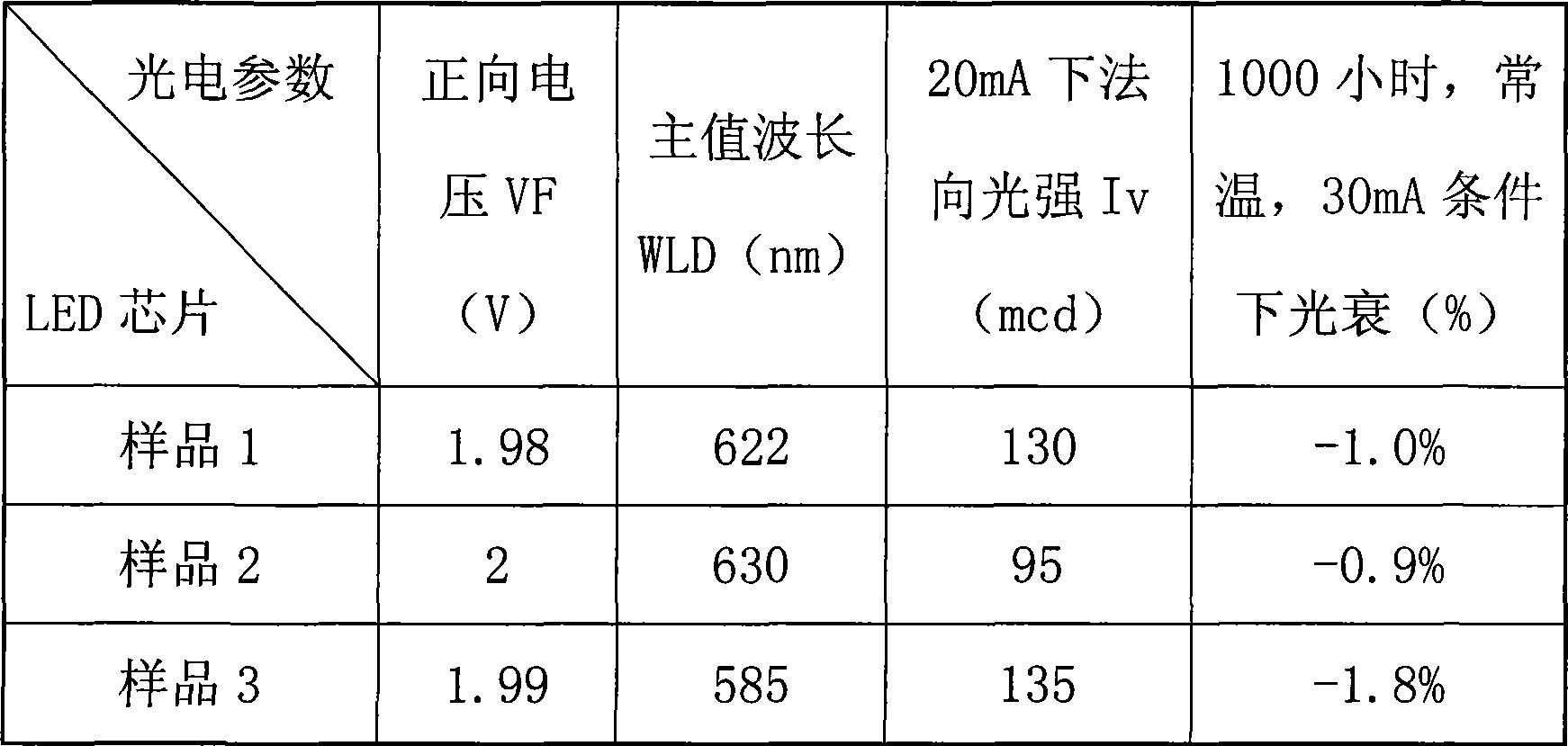
The invention discloses a highly-effective light-emitting diode with an improved current spreading layer structure and a production method thereof. Material which is extended on an N-GaAs under-layer comprises an n-GaAs buffer layer, or an AlAs / AlxGal-xAs or AlInP / (A1x Ga1-x)yIn1-yP Bragg reflection layer, an n-(AlxGa1-x)yIn1-yP lower limiting layer, an Undoped-(AlxGa1-x)yIn1-yP active region, a p-(A1xGa1-x)yIn1-yP upper limiting layer, and a p++AlxGal-xAs and p-GaP combined current spreading layer, wherein the p++AlxGal-xAs is arranged on the lower surface as a first current spreading layer, and the p-GaP is arranged on the upper surface as a second current spreading layer. The structure integrates the advantages of GaP and A1xGal-xAs materials, avoids the oxidization of materials, and guarantees the reliability and the stability of the current spreading and apparatuses.
Owner:XIAMEN CHANGELIGHT CO LTD
N-Type Group III Nitride Semiconductor Layer Stacked Structure
ActiveUS20080093621A1Good flatnessLow resistanceSolid-state devicesNanoopticsHigh concentrationNitride semiconductors
An object of the present invention provides an n-type Group III nitride semiconductor stacked layer structure of a low resistance having excellent flatness generating few cracks and pits in the uppermost surface. The inventive n-type Group III nitride semiconductor stacked layer structure comprises a first n-type layer which includes a layer containing n-type impurity atoms at a high concentration and a layer containing n-type impurity atoms at a low concentration, a second n-type layer containing n-type impurity atoms at an average concentration smaller than that of the first n-type layer, the second n-type layer neighboring the layer containing n-type impurity atoms at a low concentration in the first n-type layer.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Semiconductor light-emitting device and process for production thereof
ActiveUS20110049556A1Less generate heatLuminance intensity be not lowSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesNanometreHigh luminance
The present invention provides a semiconductor light-emitting device capable of keeping high luminance intensity even if electric power increases, and hence the device is suitable for lighting instruments such as lights and lamps. This semiconductor device comprises a metal electrode layer provided with openings, and is so large in size that the electrode layer has, for example, an area of 1 mm2 or more. The openings have a mean diameter of 10 nm to 2 μm, and they penetrate through the metal electrode layer. That metal electrode layer can be produced by use of self-assembling of block copolymer or by nano-imprinting techniques.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method for epitaxial growth of ultraviolet LED with high luminous efficacy
The invention provides a new method for epitaxial growth of an ultraviolet LED. By the adoption of the method for epitaxial growth of the ultraviolet LED, the growth difficulty can be greatly lowered, and the radiant power of the ultraviolet LED is greatly increased. An AlGaN / AlxInyGa1-x-y layer is grown for a plurality of periods, wherein x, y, z and w meet the following requirements for x
Owner:西安利科光电科技有限公司
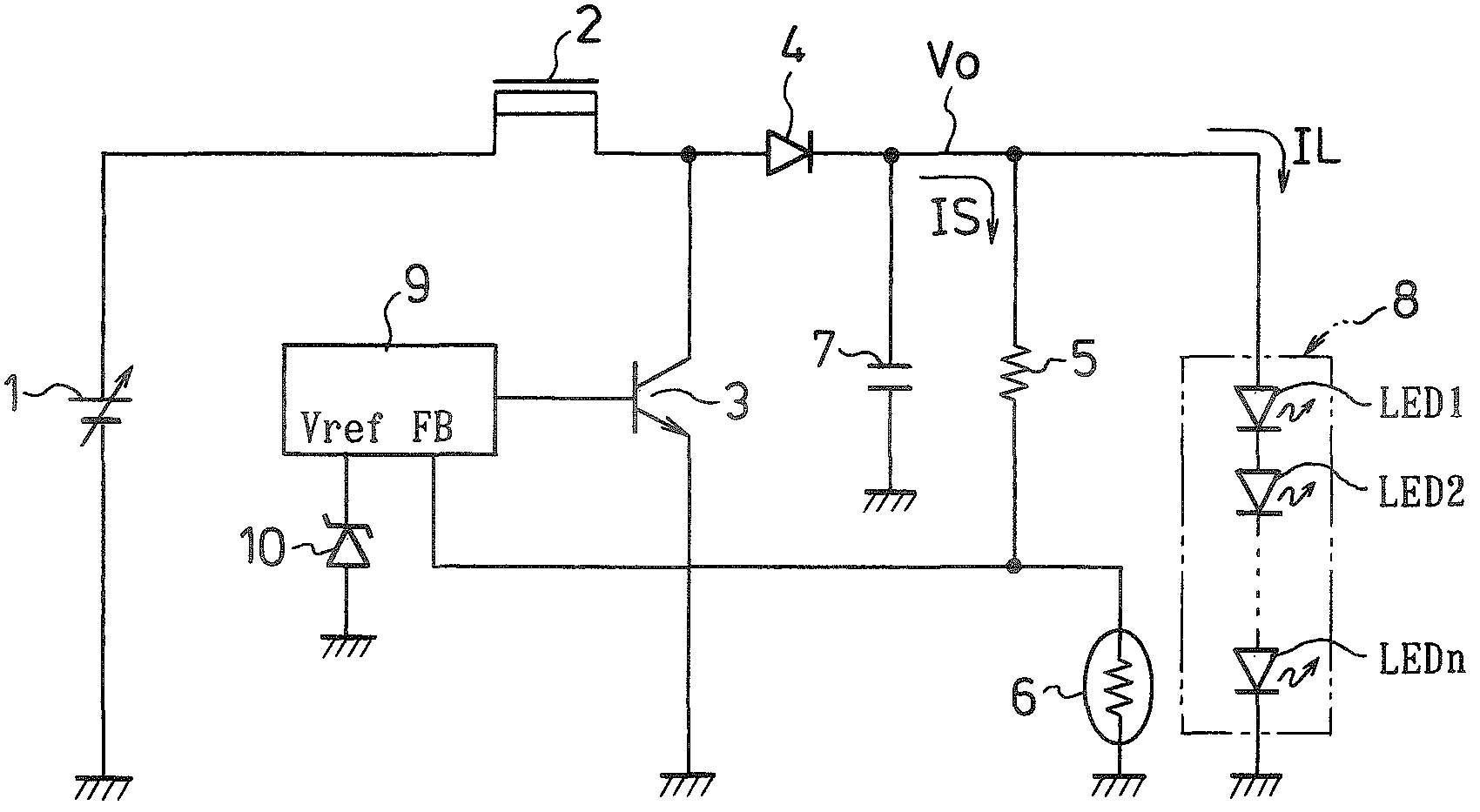
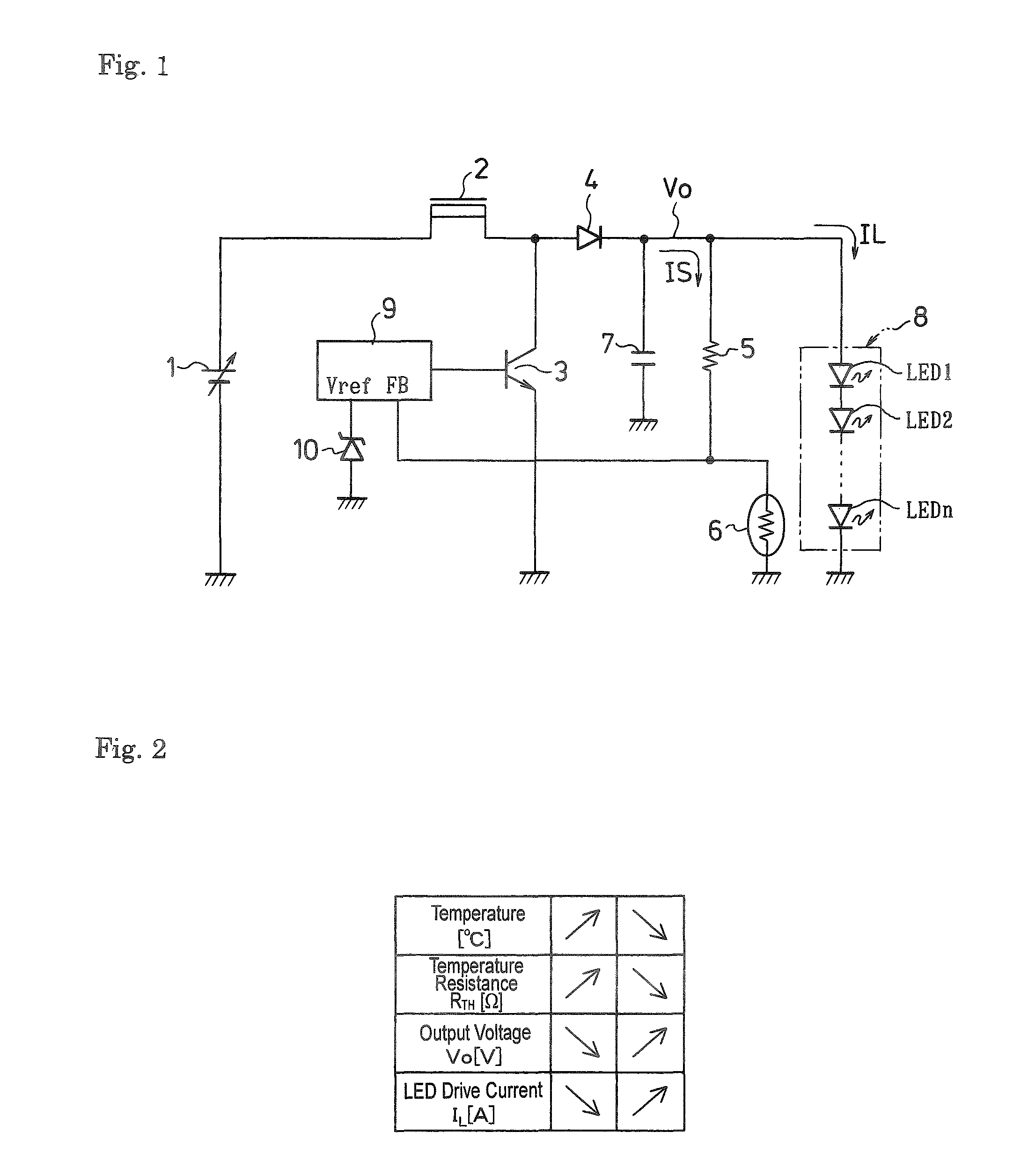
LED drive circuit
InactiveUS7800567B2Reduce voltageReduce current flowingStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesSubject matterVoltage reference
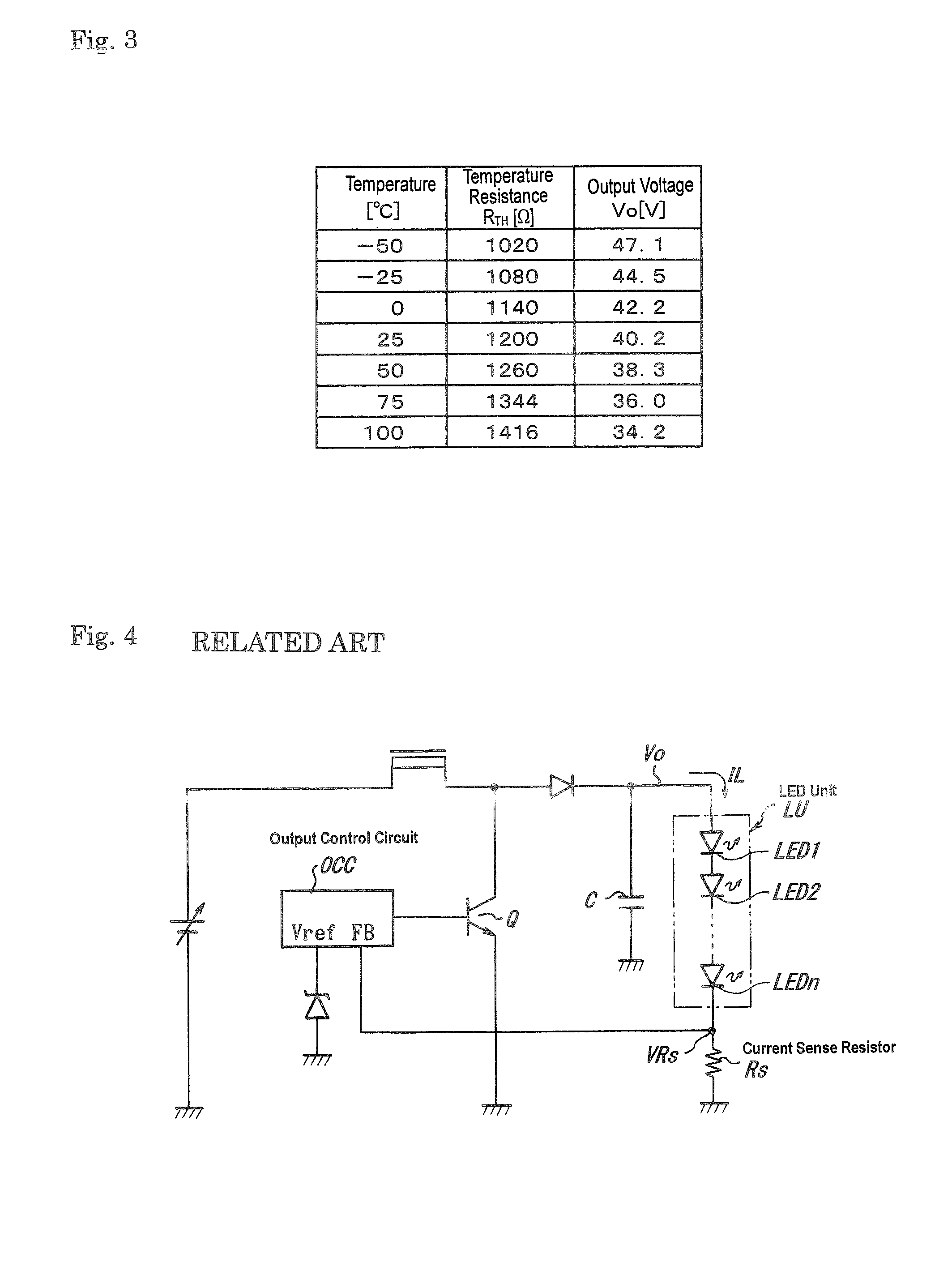
An LED drive circuit of the disclosed subject matter can include an LED unit and a serial circuit connected in parallel therewith. The serial circuit includes a resistor and a positive temperature coefficient resistor having a positive linear temperature coefficient. A voltage across the positive temperature coefficient resistor is fed back to an output control circuit. An output voltage that is PWM-controlled on the basis of a reference voltage set at the output control circuit is used to drive the LED unit.
Owner:STANLEY ELECTRIC CO LTD
Semiconductor device having transistor and rectifier
InactiveUS20110254056A1Optimized areaLower forward voltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesDevice materialAuxiliary electrode
A semiconductor device having a transistor and a rectifier includes: a current path; a first main electrode having a rectifying function and arranged on one end of the current path; a second main electrode arranged on the other end of the current path; an auxiliary electrode arranged in a region of the current path between the first main electrode and the second main electrode; a third main electrode arranged on the one end of the current path apart from the first main electrode along a direction intersecting the current path; and a control electrode arranged in a region of the current path between the second main electrode and the third main electrode. The transistor includes the current path, the second main electrode, the third main electrode, and the control electrode. The rectifier includes the current path, the first main electrode, the second main electrode, and the auxiliary electrode.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
Light emitting diode having electrode extensions for current spreading
ActiveUS20110114990A1Reduce pruningCurrent spreadSemiconductor devicesElectrical conductorSemiconductor
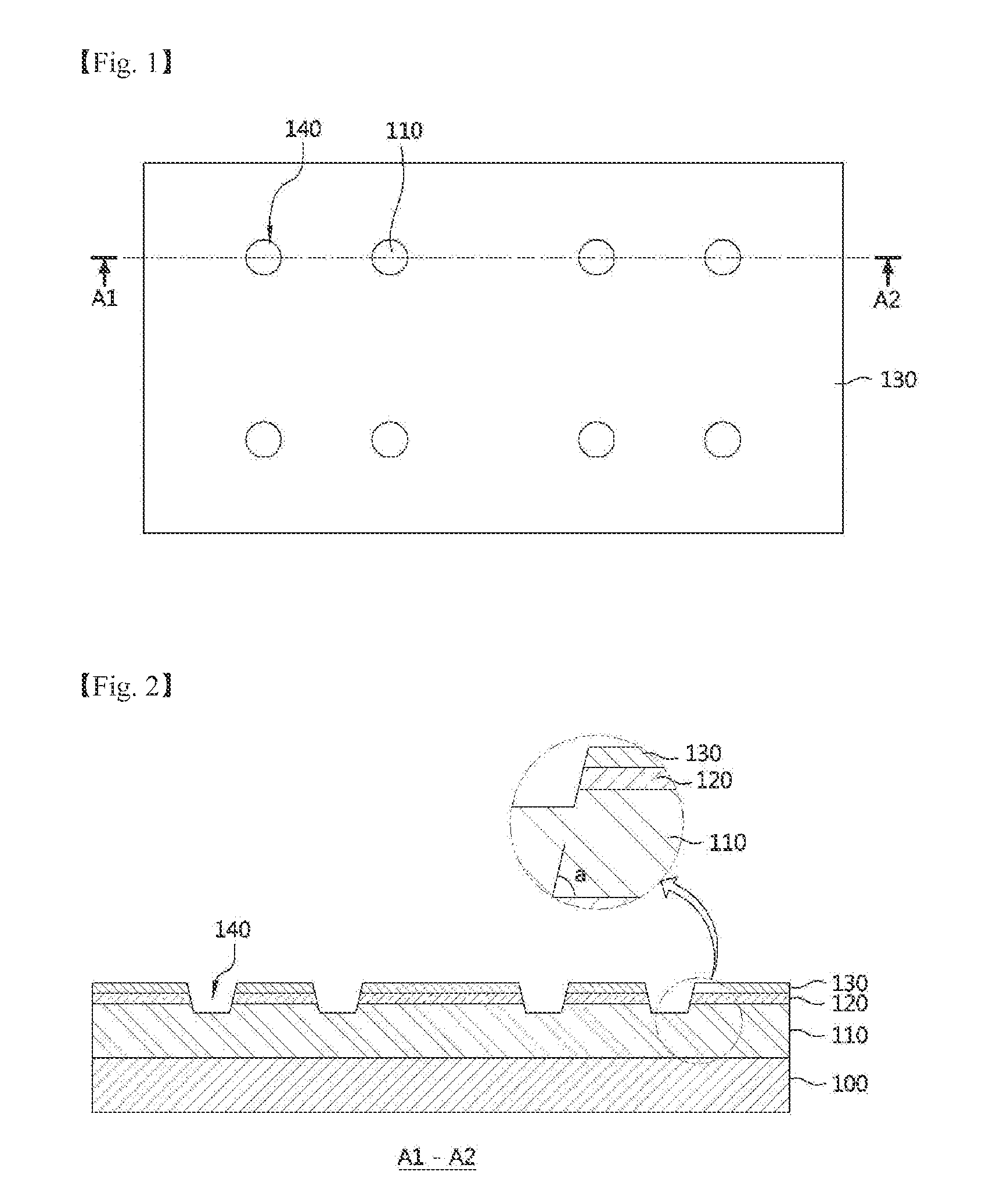
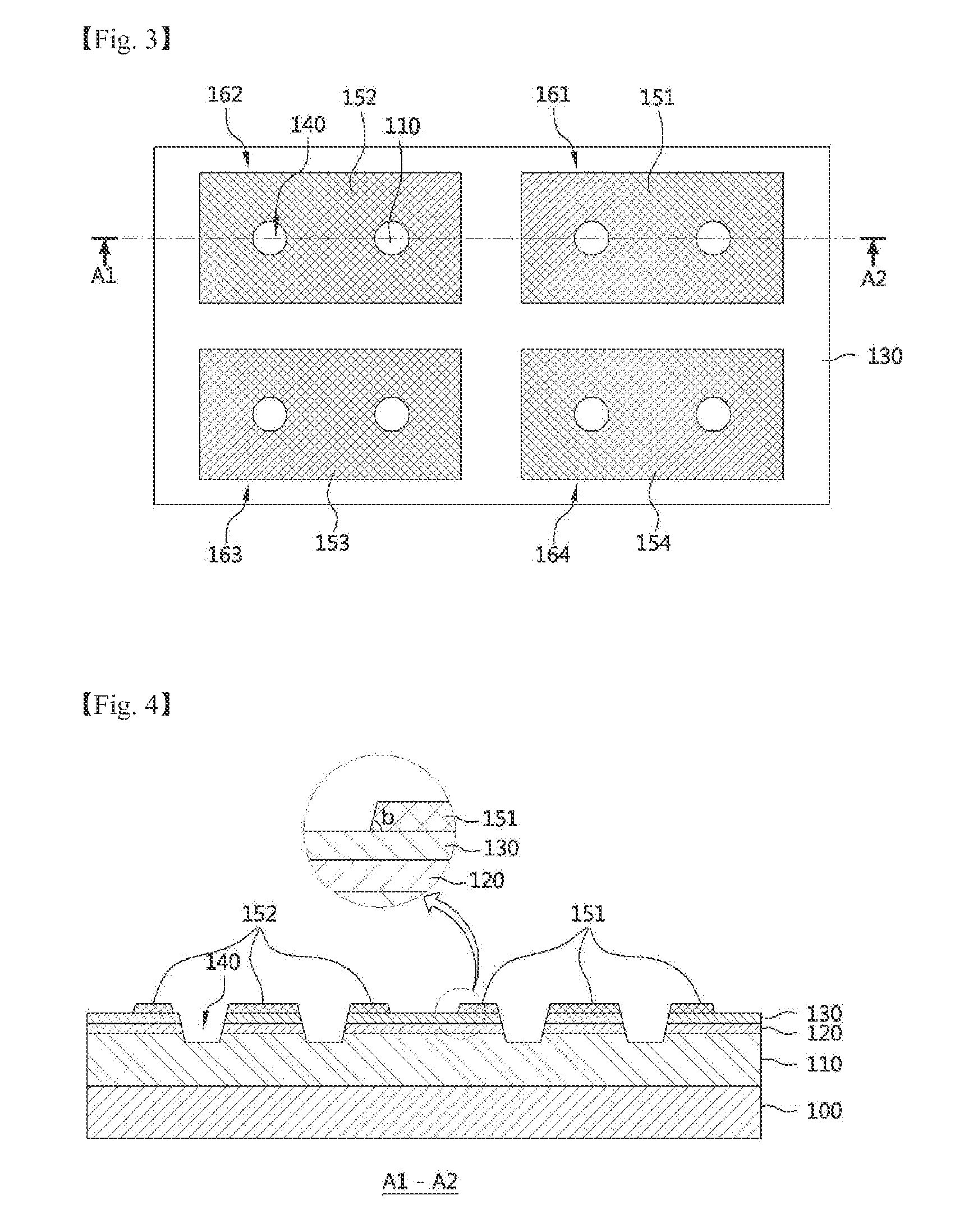
An exemplary embodiment of the present invention discloses a light emitting diode including a substrate having a first edge and a second edge opposite to each other, a light emitting structure disposed on the substrate, the light emitting structure including a first semiconductor layer and a second semiconductor layer, a plurality of first electrode pads arranged on an upper surface of the first semiconductor layer, the first electrode pads arranged in a vicinity of the first edge, a plurality of second electrode pads arranged on the second semiconductor layer, the second electrode pads arranged in a vicinity of the second edge, a plurality of first extensions, each first extension extending from a first electrode pad, and a plurality of second extensions, each second extension extending from a second electrode pad. The first extensions include intrusion parts extending in a direction from the first edge to the second edge, wherein the intrusion parts are spaced apart from each other and not connecting with the second electrode pads. Further, the second extensions include intrusion parts extending in a direction from the second edge to the first edge, wherein the first extension intrusion parts each extend into a region between two of the second extension intrusion parts.
Owner:SEOUL VIOSYS CO LTD
Mains complementation controller for solar street lamp and control method of controller
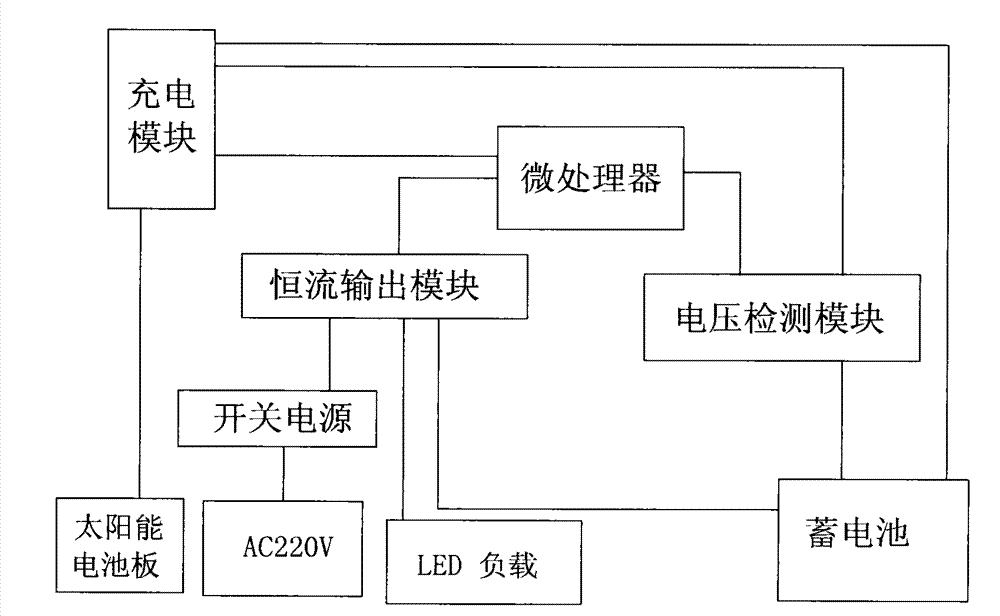
ActiveCN103209522AIngenious structural designReasonable structural designElectric light circuit arrangementEnergy saving control techniquesAutomatic controlSolar street light
The invention discloses a mains complementation controller for a solar street lamp. The controller comprises a solar cell panel, a charging module, a microprocessor, a constant-current output module, a switching power supply, a voltage detection module and a battery. The invention also discloses a control method of the controller. The controller is skillful and reasonable in structural design, when the electric quantity stored in the battery by the solar energy is insufficient, the controller is switched to a mains supply automatically in a seamless mode, the effect that the solar energy is used preferentially and the mains supply serves as a supplement can be effectively achieved, and charging and discharging can be controlled automatically according to different working parameters and states, so that the charging and the discharging are kept at the optimal states, the utilization efficiency of the solar energy is improved, the energy resources are effectively saved, the whole process is automatic, and the intelligent degree is high. The control method is simple in step, easy to implement, capable of supplying electricity by the battery and achieving seamless switching to the mains supply, effectively guaranteeing the sufficient utilization of solar energy resources, greatly prolonging the service life of the battery and reducing the maintenance cost and beneficial to popularization and application.
Owner:SICHUAN TAIYI NEW ENERGY DEV
Flip chip nitride semiconductor light emitting diode
ActiveCN1645634AReduce congestionLower forward voltageJoints with sealing surfacesSolid-state devicesOhmic contactHigh reflectivity
In a nitride semiconductor LED, an n-doped nitride semiconductor layer is formed on a transparent substrate. An active layer is formed on the n-doped nitride semiconductor layer. A p-doped nitride semiconductor layer is formed on the active layer. A high reflectivity Ohmic contact layer of a mesh structure is formed on the p-doped nitride semiconductor layer and has a number of open areas for exposing the p-doped nitride semiconductor layer. A metal barrier layer is formed on at least a top region of the high reflectivity Ohmic contact layer. A p-bonding electrode is formed on the metal barrier layer. An n-electrode is formed on the n-doped nitride semiconductor layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Semiconductor light emitting device
InactiveUS7564071B2Improve reliabilityLower forward voltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesOhmic contactMetallic materials
A Si substrate 1, a metal adhesion layer 2, a reflective metal film 3 comprising a multilayer of metallic material having a light reflectivity, a SiO2 film 4, an ohmic contact portion 5 provided at a predetermined position of the SiO2 film 4, a GaP layer 6 including a Mg-doped GaP layer 6A and a Zn-doped GaP layer 6B, a p-type GaInP interposed layer 7, a p-type AlGaInP cladding layer 8, an undoped MQW active layer 9, an n-type AlGaInP cladding layer 10, an n-type AlGaInP window layer 11, an n-type GaAs contact layer 12, a first electrode 13, and a second electrode 14 are formed. The ohmic contact portion 5 is distant from the light emitting part including the p-type AlGaInP cladding layer 8, the undoped MQW active layer 9 and the n-type AlGaInP cladding layer 10 by not less than 300 nm.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Flip chip type nitride semiconductor light-emitting diode
ActiveUS7294864B2Lower forward voltageImprove efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOhmic contactSingle crystal
A flip chip type nitride semiconductor light-emitting diode includes a light-transmissive substrate for growing nitride single crystals; an n-type nitride semiconductor layer formed on the light-transmissive substrate; an active layer formed on the n-type nitride semiconductor layer; a p-type nitride semiconductor layer formed on the active layer; a mesh-type dielectric layer formed on the p-type nitride semiconductor layer and having a mesh structure with a plurality of open regions in which the p-type nitride semiconductor layer is exposed; a highly reflective ohmic contact layer formed on the mesh-type dielectric layer and the open regions in which the p-type nitride semiconductor layer is exposed; and a p-bonding electrode and an n-electrode formed on the highly reflective ohmic contact layer and the n-type nitride semiconductor layer, respectively.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
N-Type Group III Nitride Semiconductor Layered Structure
InactiveUS20080230800A1Improve flatnessLess pittingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh concentrationImpurity
An object of the present invention is to provide a low-resistance n-type Group III nitride semiconductor layered structure having excellent flatness and few pits. The inventive n-type group III nitride semiconductor layered structure comprises a substrate and, stacked on the substrate, an n-type impurity concentration periodic variation layer comprising an n-type impurity atom higher concentration layer and an n-type impurity atom lower concentration layer, said lower concentration layer being stacked on said higher concentration layer.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com