Gallium-containing light-emitting semiconductor device and method of fabrication
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment
of FIG. 10
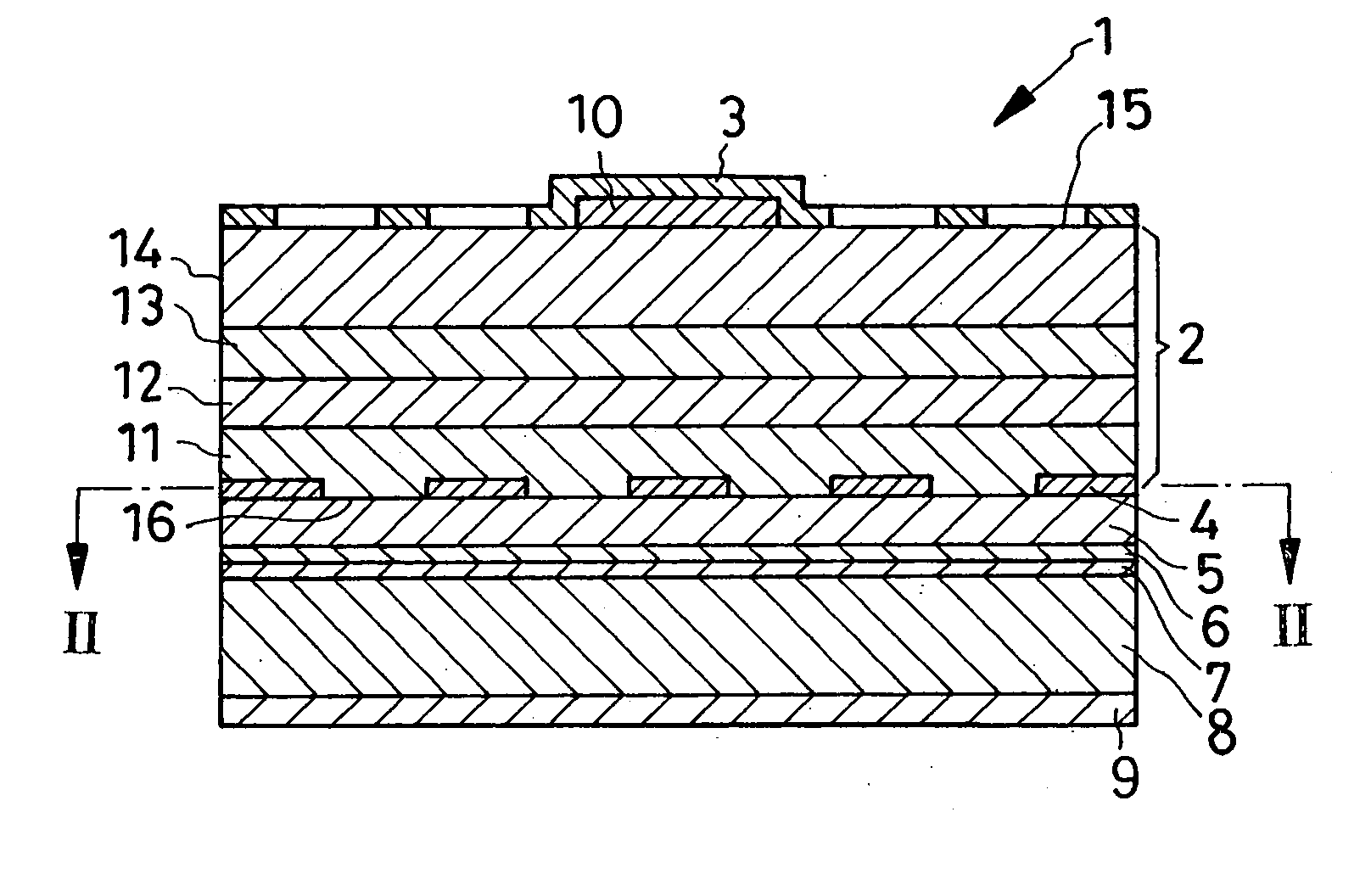
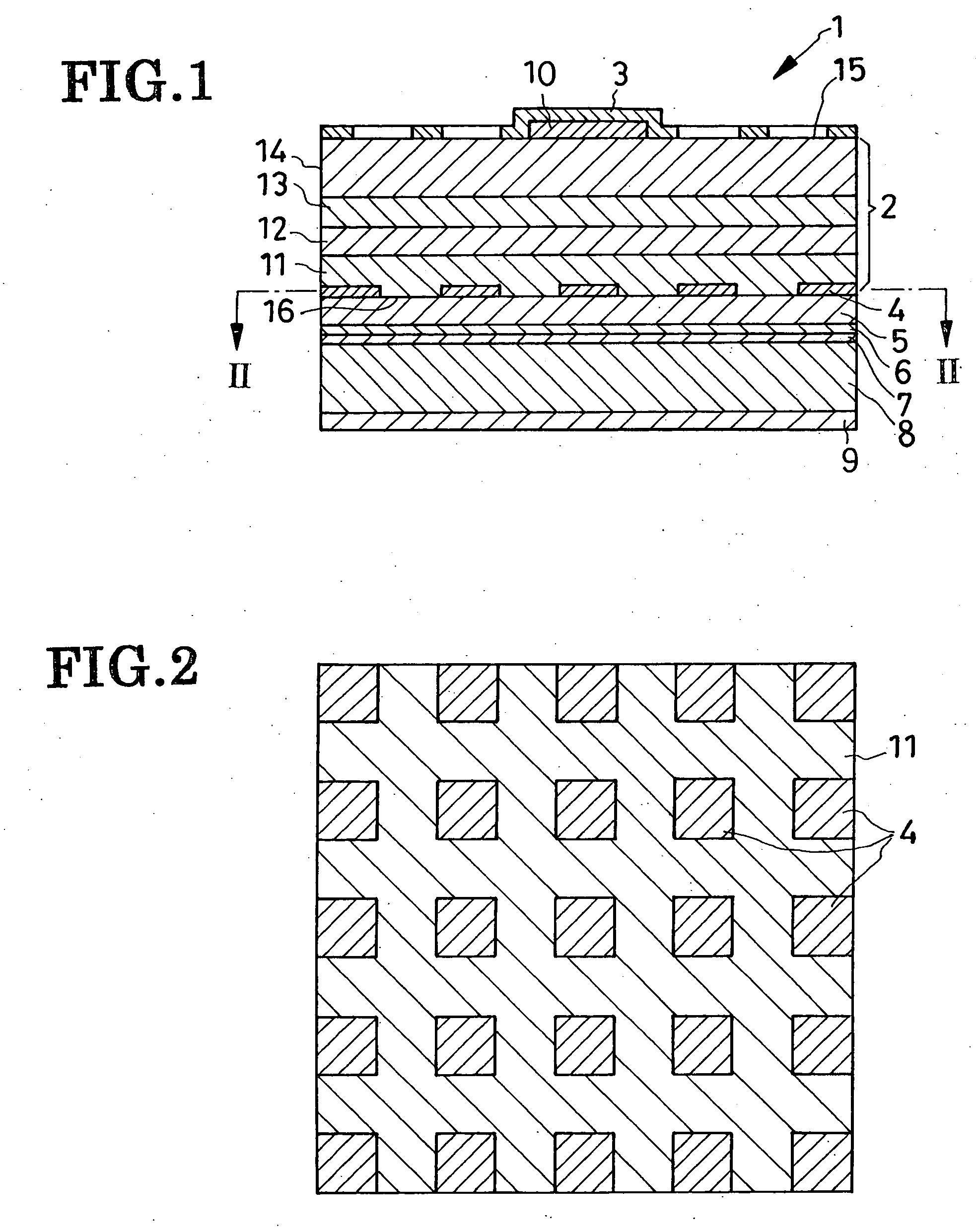
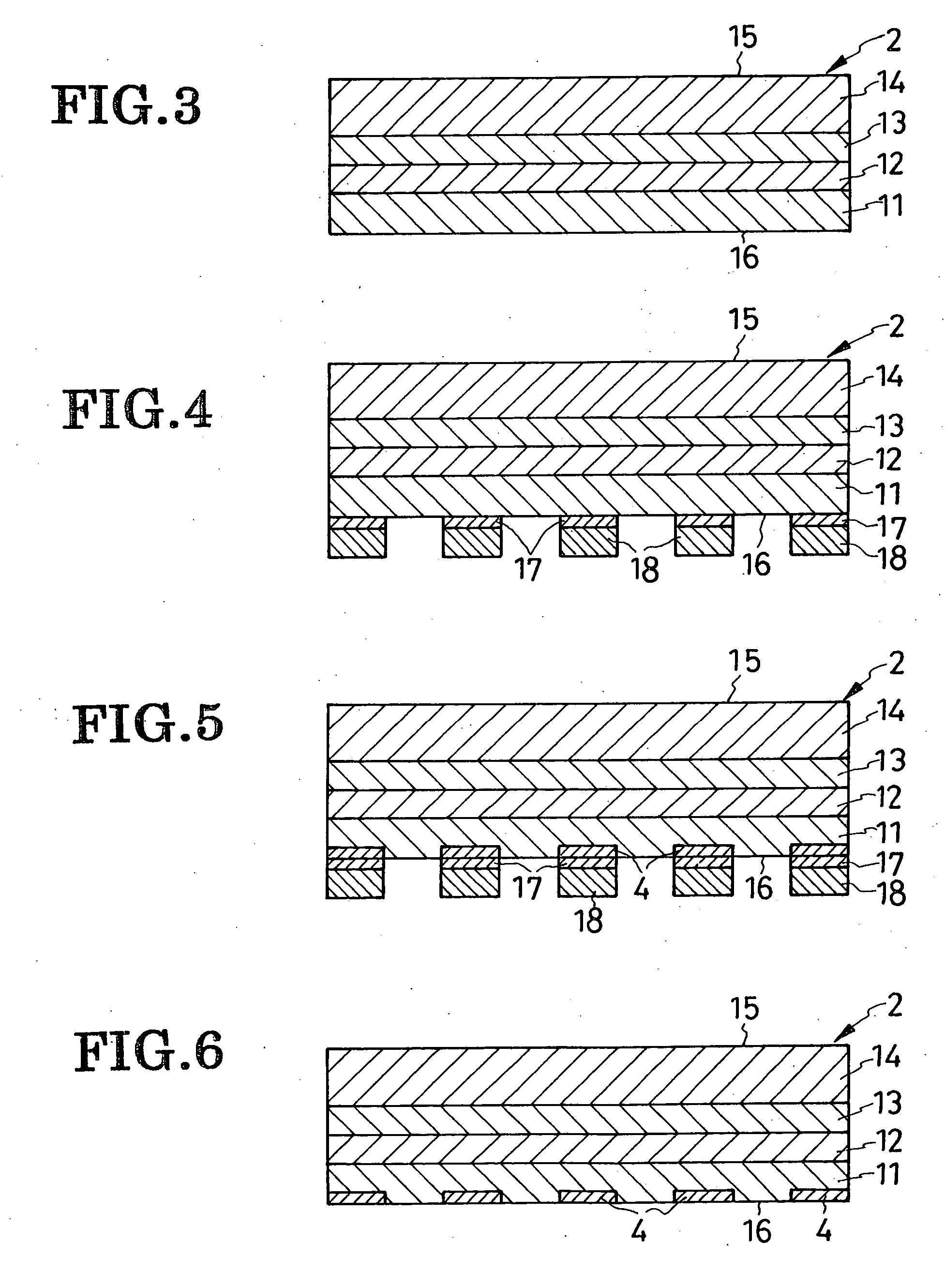
[0082] Another preferred form of LED 1a shown in FIG. 1 has an integral ohmic contact region 4a covering the entire bottom surface 16 of the lower cladding 11. A relatively high efficiency is nevertheless obtainable because the total reflectivity of the ohmic contact region 4a and reflective layer 5 is as high as 60 percent. As the ohmic contact region 4a is larger than all the isolated ohmic contact regions 4 of FIGS. 1 and 2 combined, so much is reduced the resistance to forward current flow, with a corresponding diminution of power loss.
[0083] Another feature of the alternative LED 1a resides in a metal-made baseplate 8a which is affixed to the reflective layer 5 under heat and pressure in place of the silicon baseplate 8 of the previous embodiment. No dedicated cathode is provided as the baseplate 8a serves as both mechanical support and cathode.
[0084] The alternative LED 1a is akin to the first disclosed LED 1 in all the other details of construction. The integrated...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com