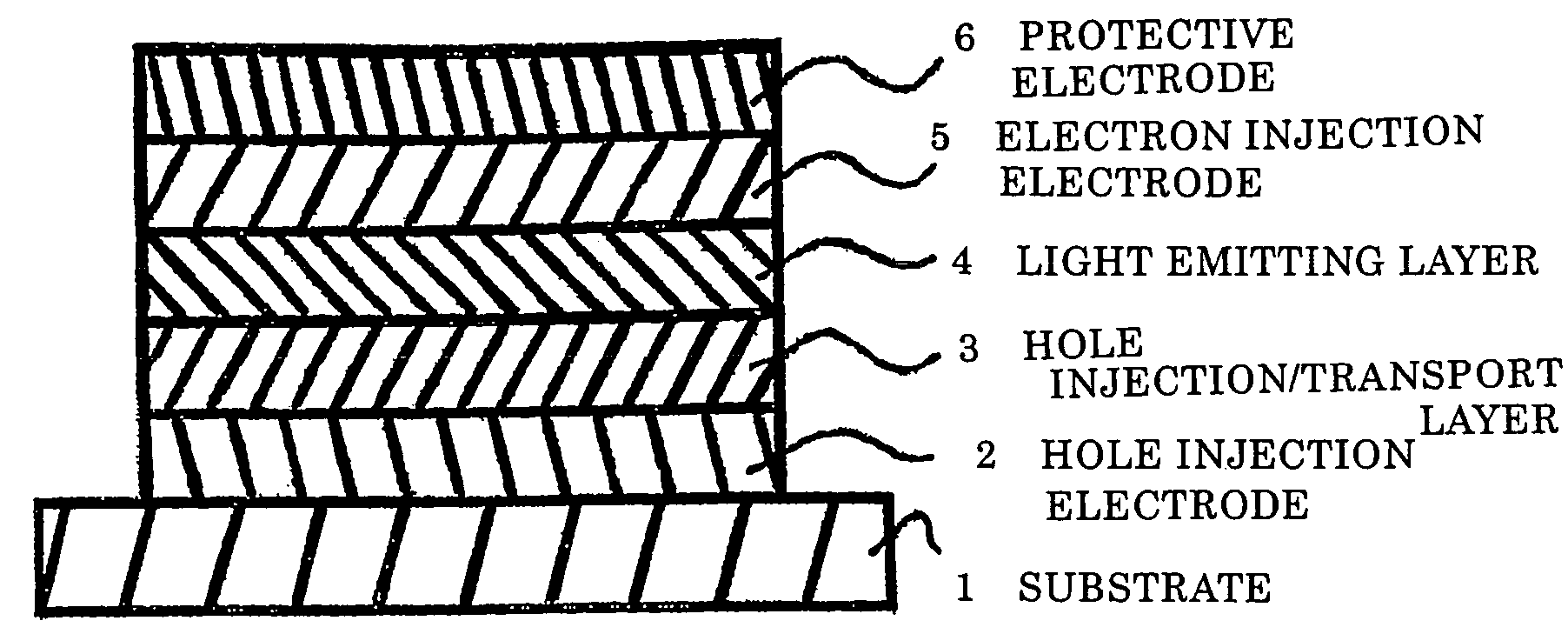
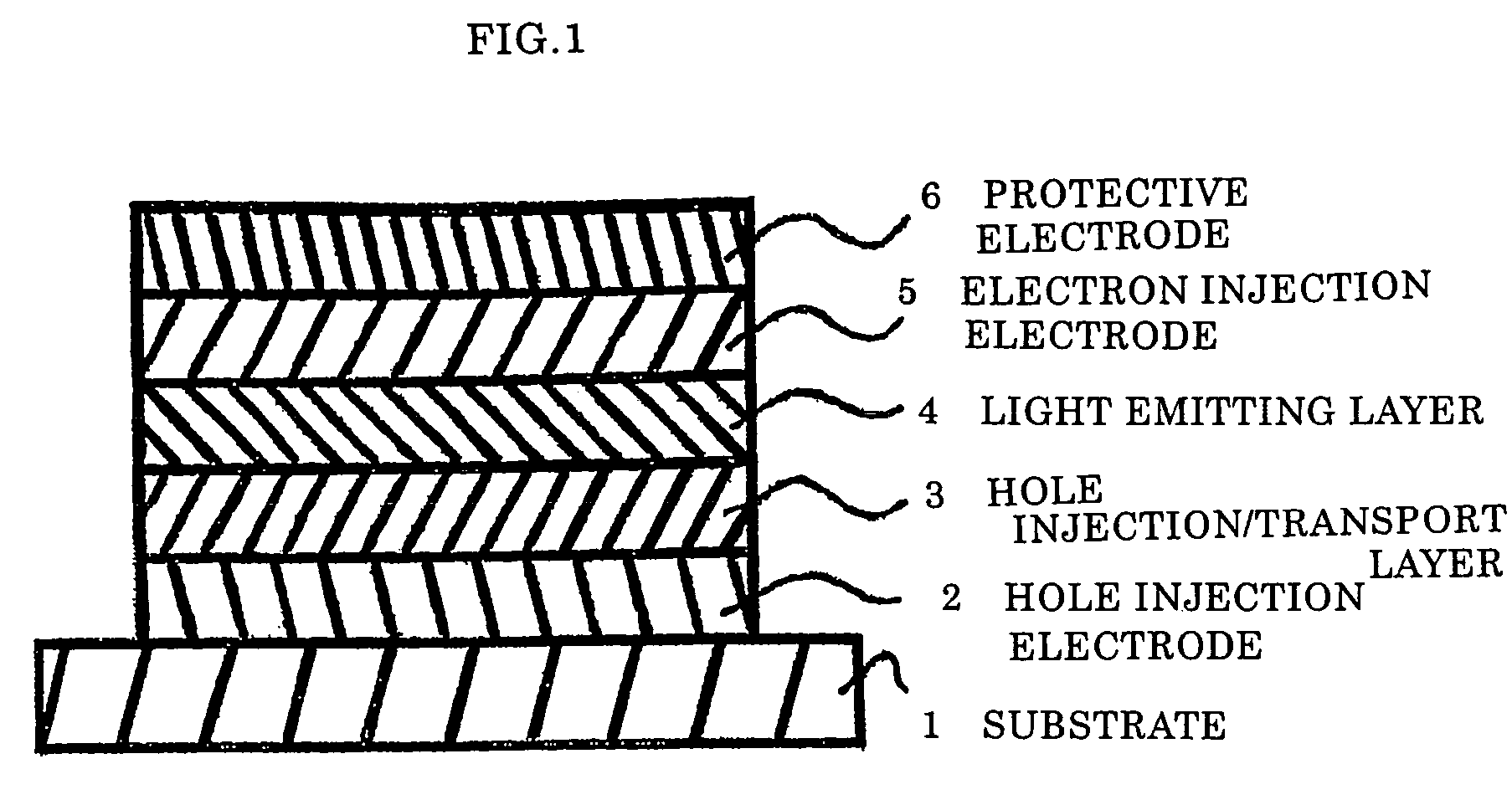
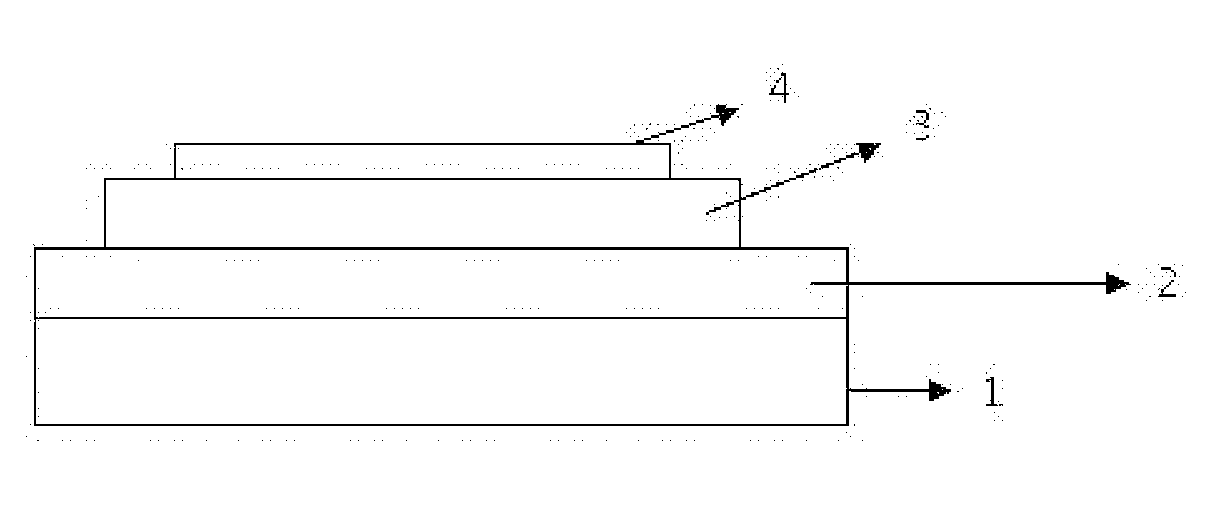
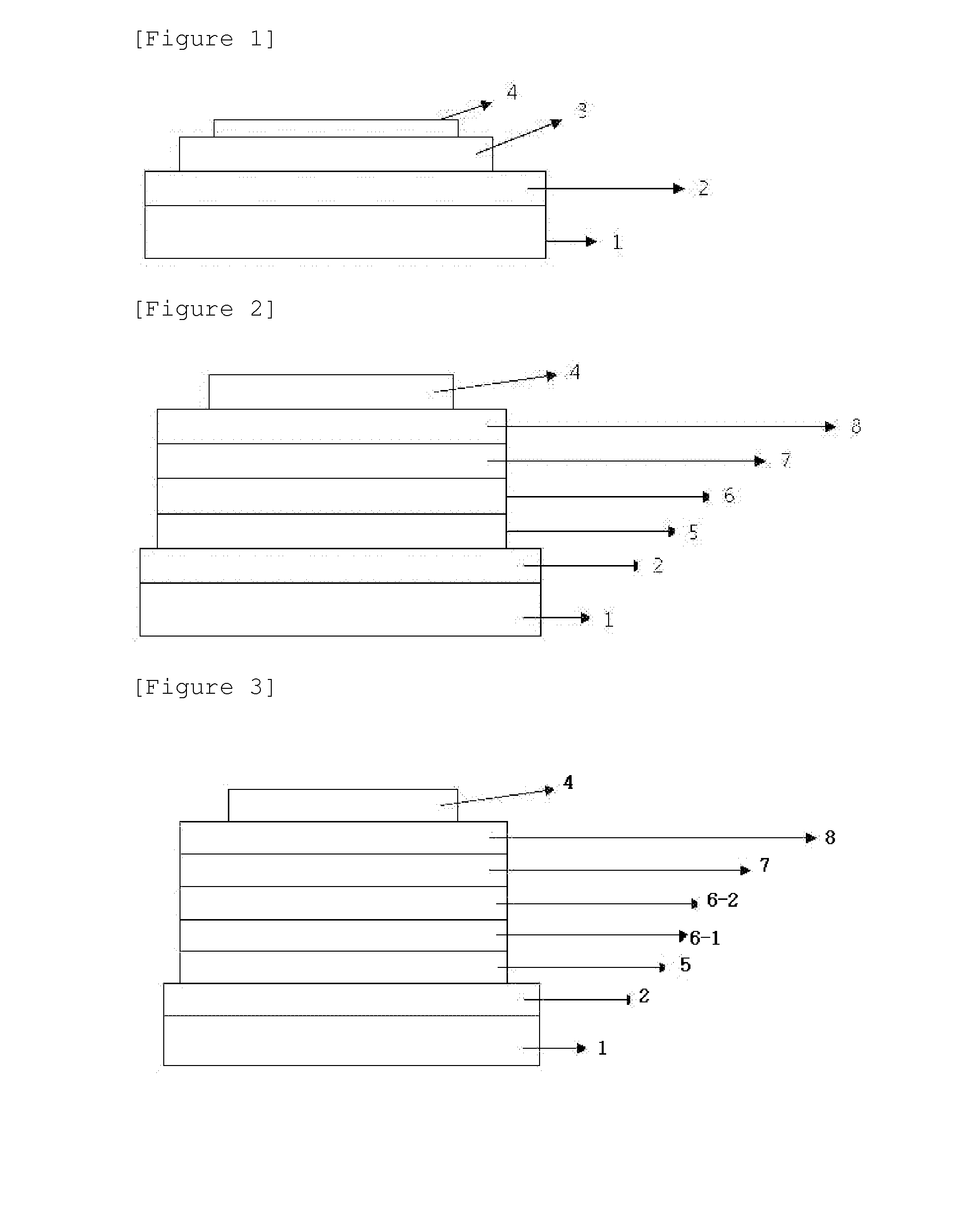
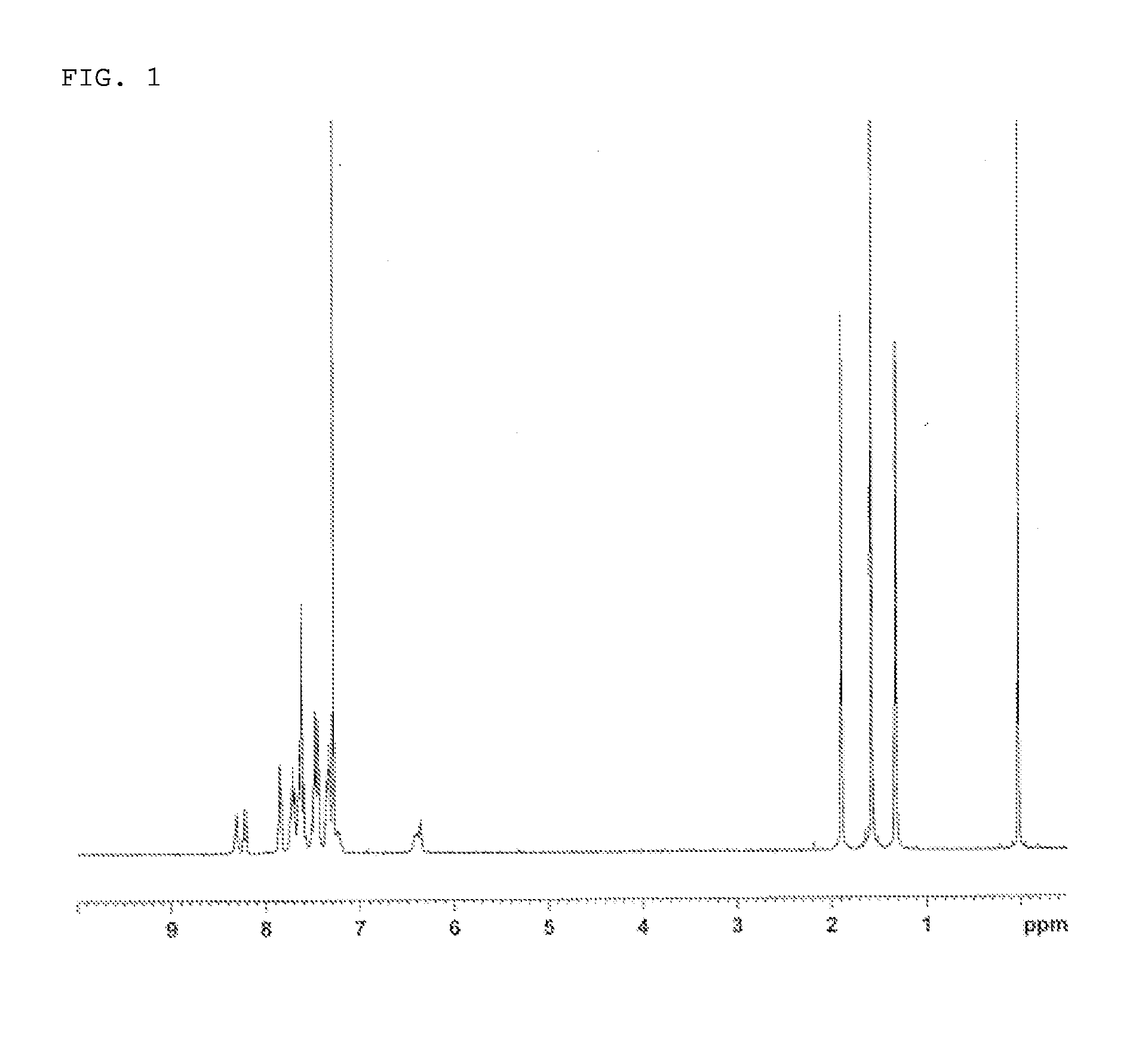
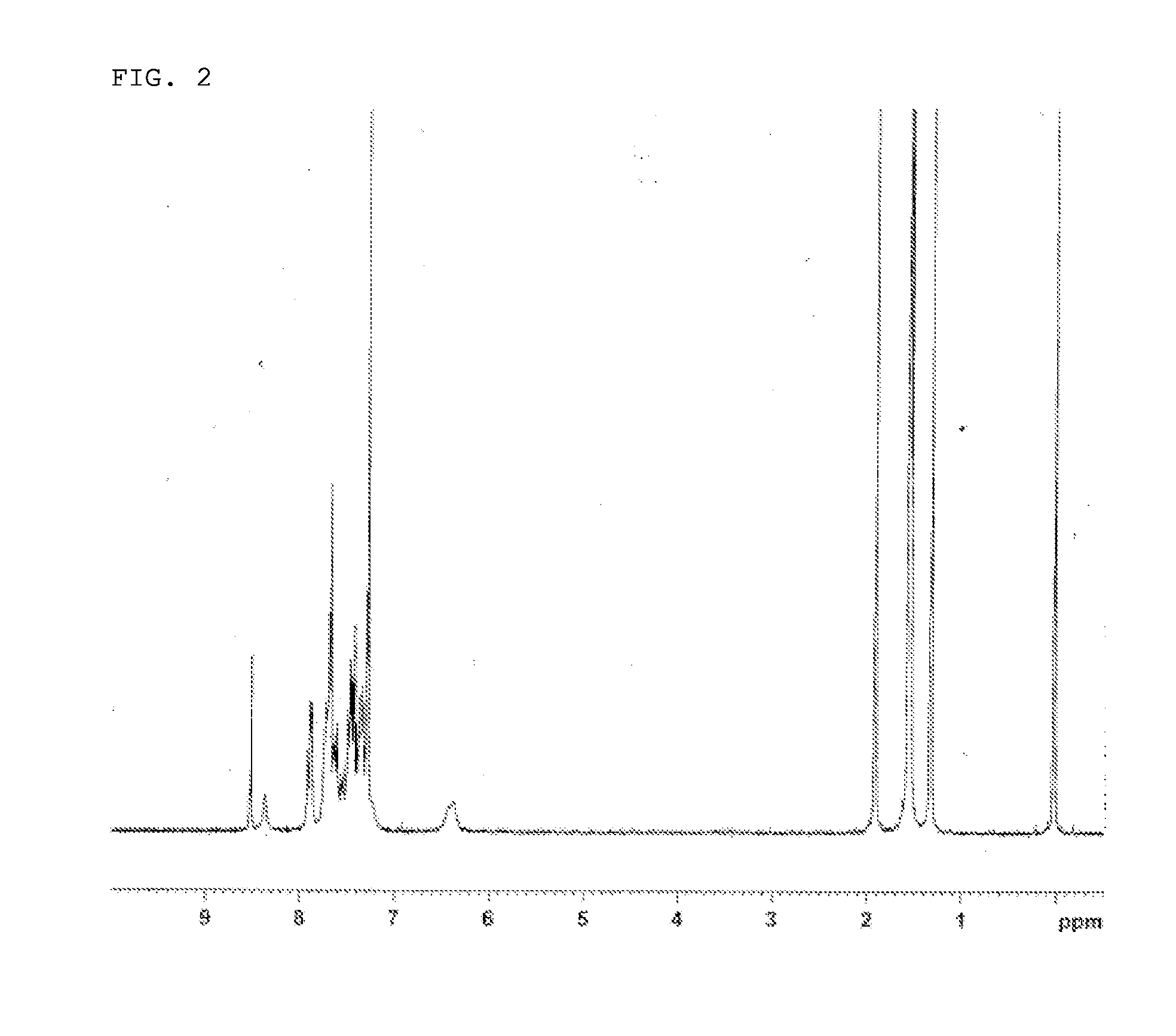
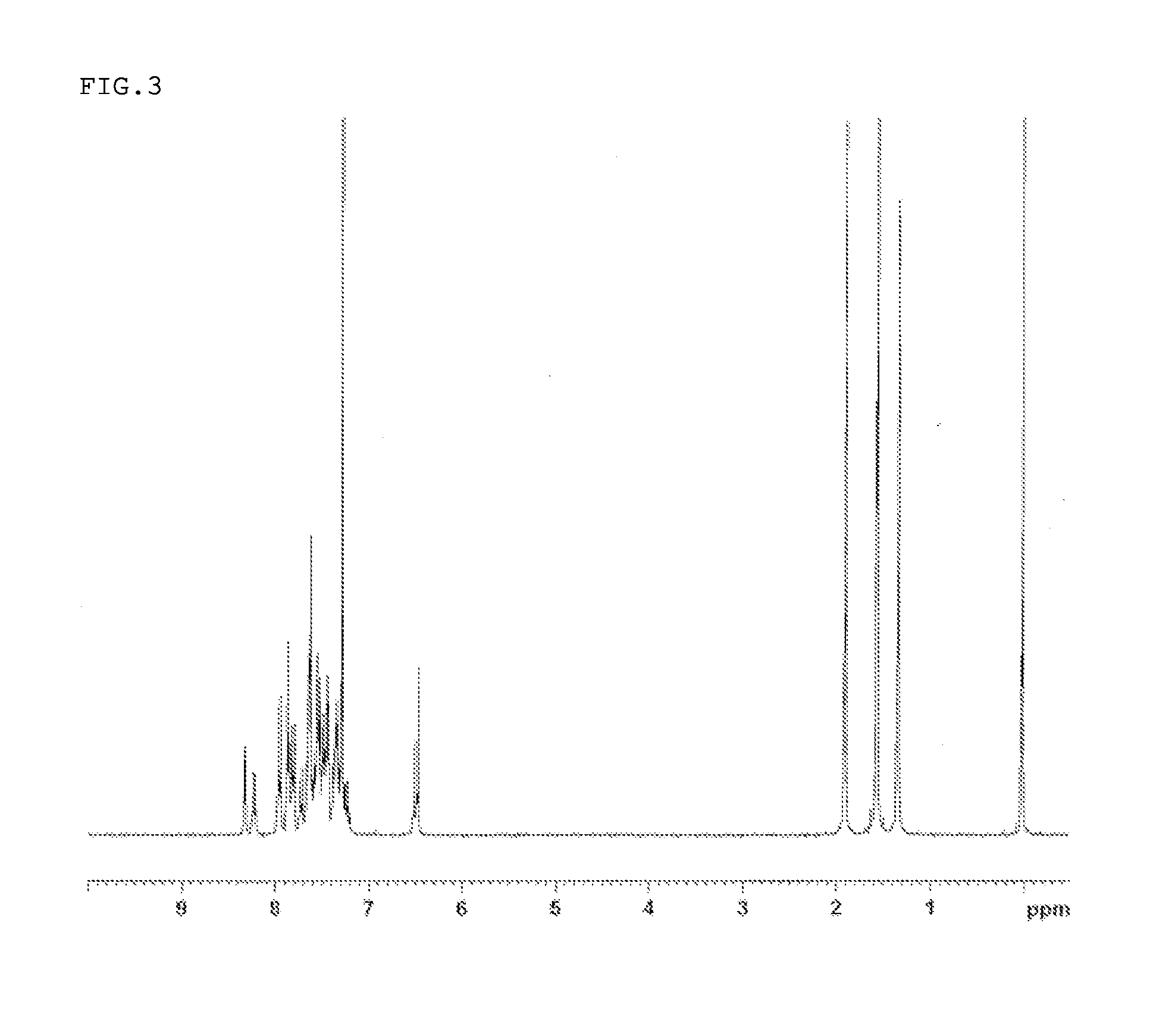
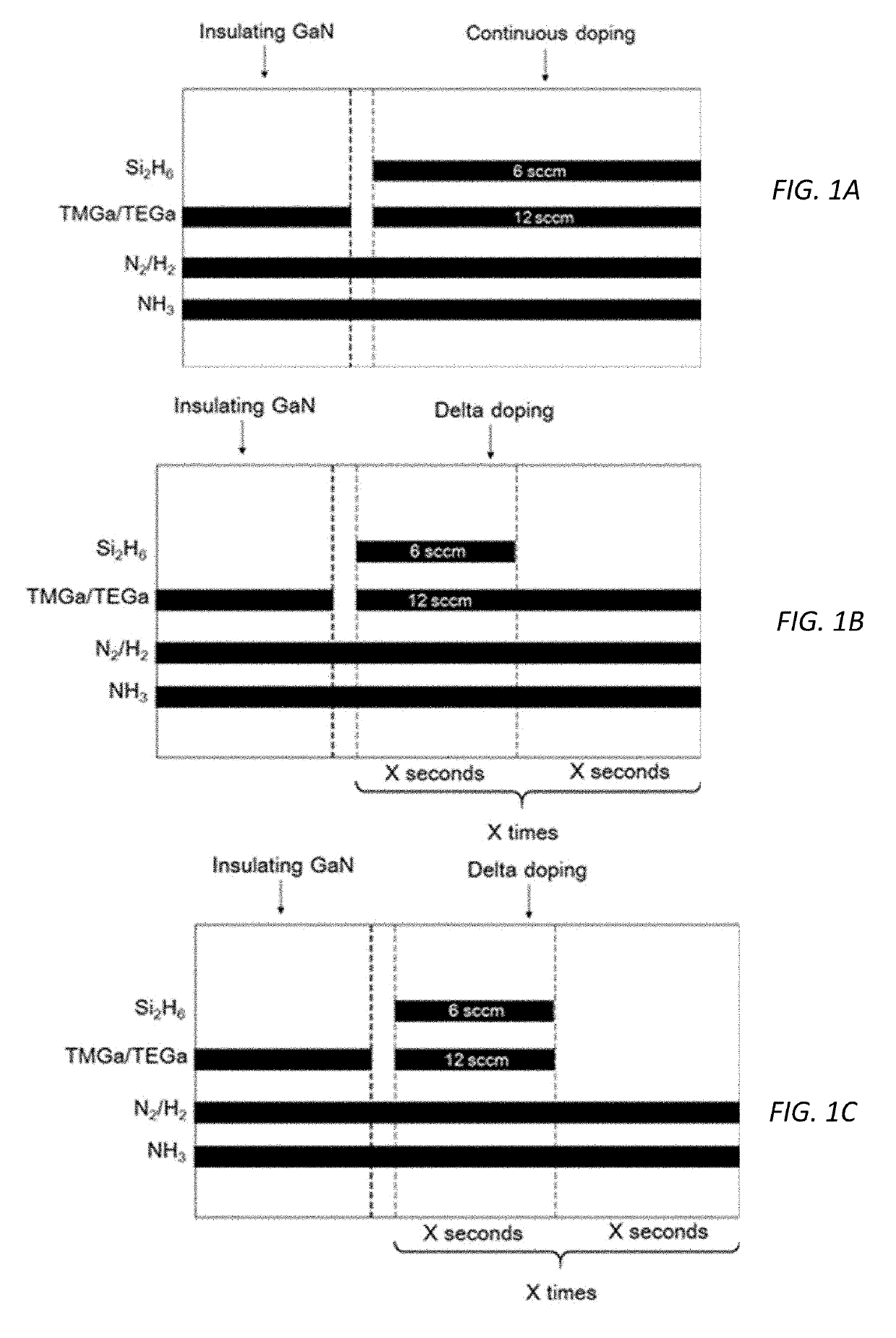
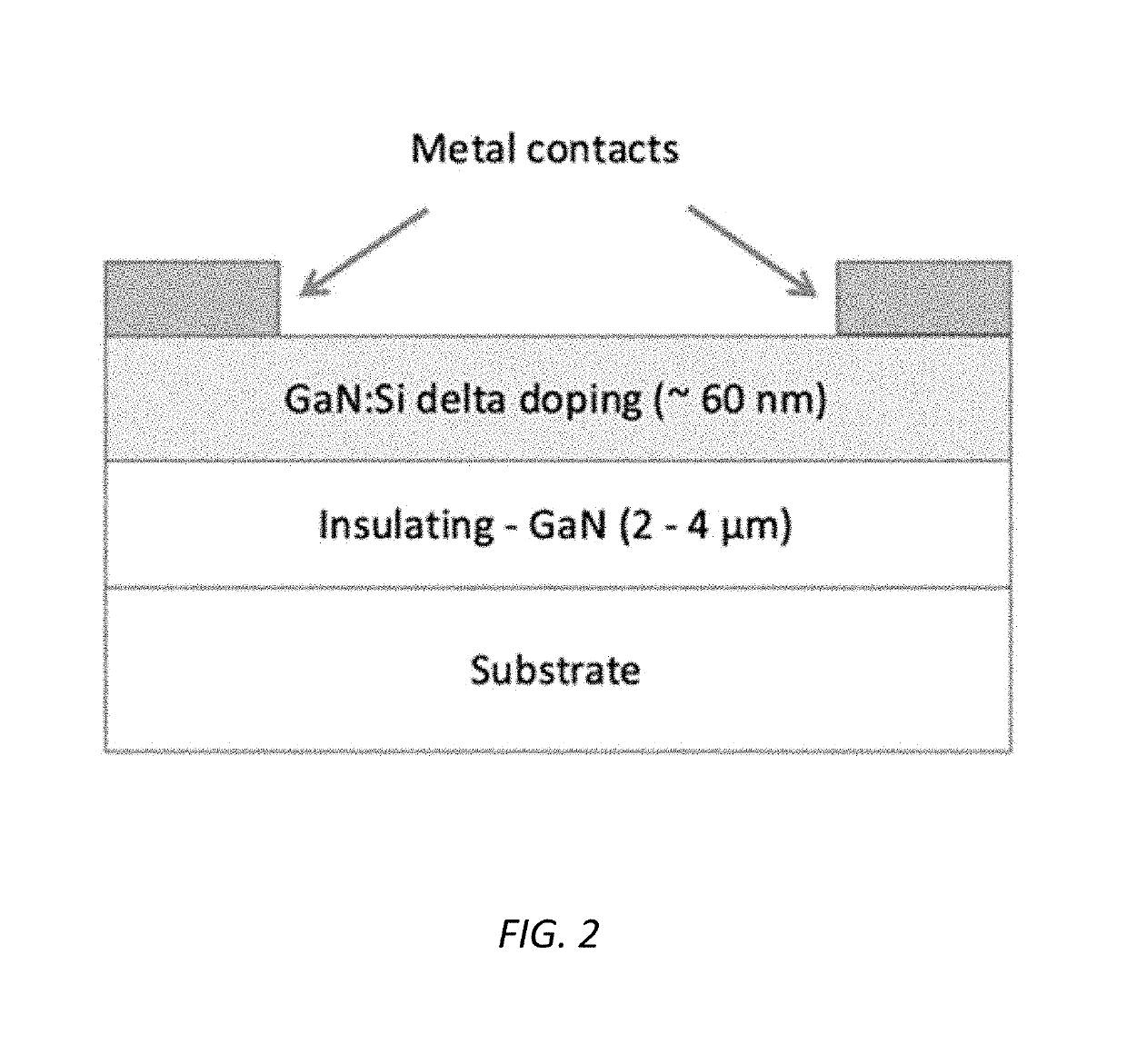
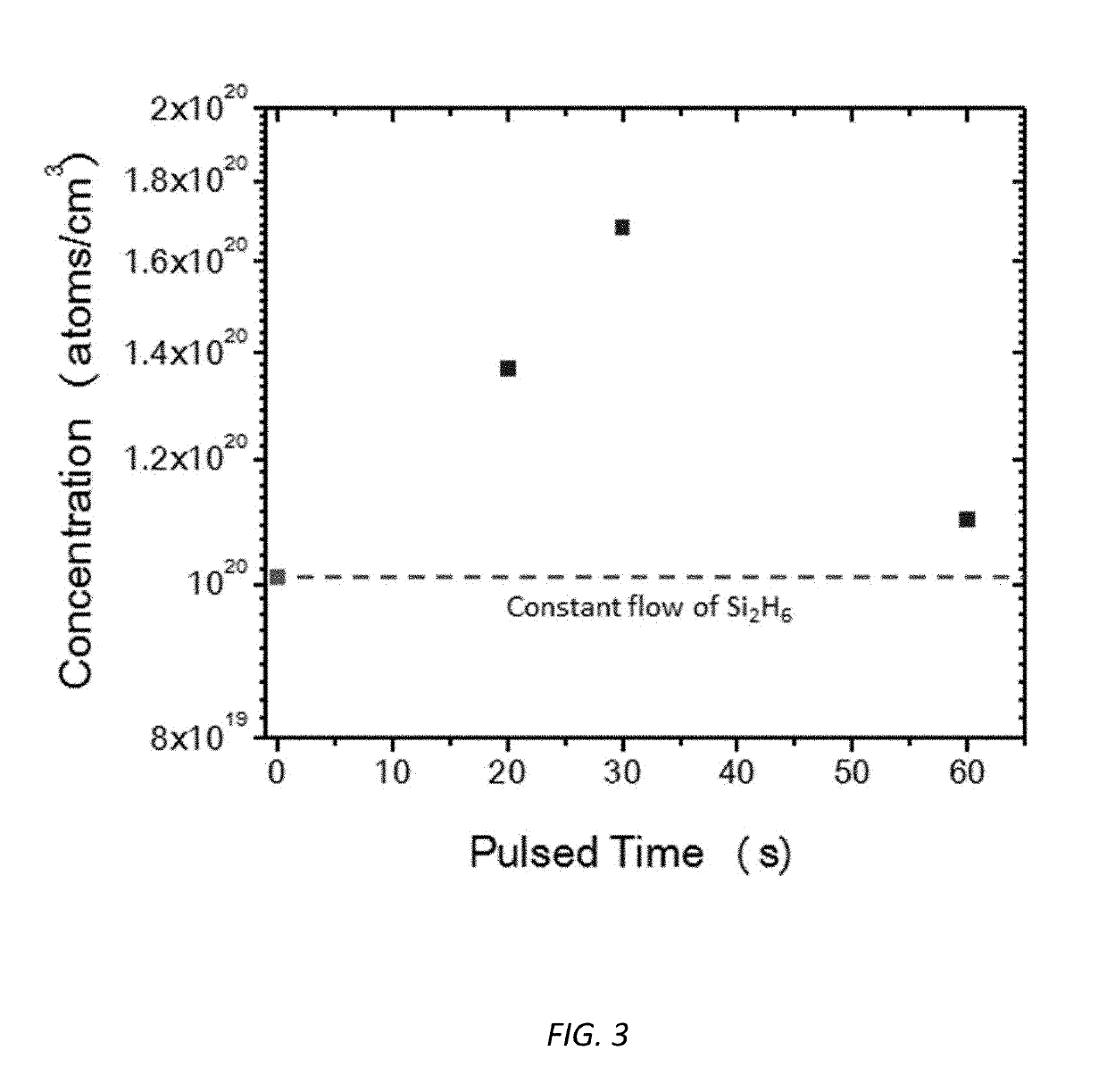
Patents
Literature
59results about How to "Reduce device voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
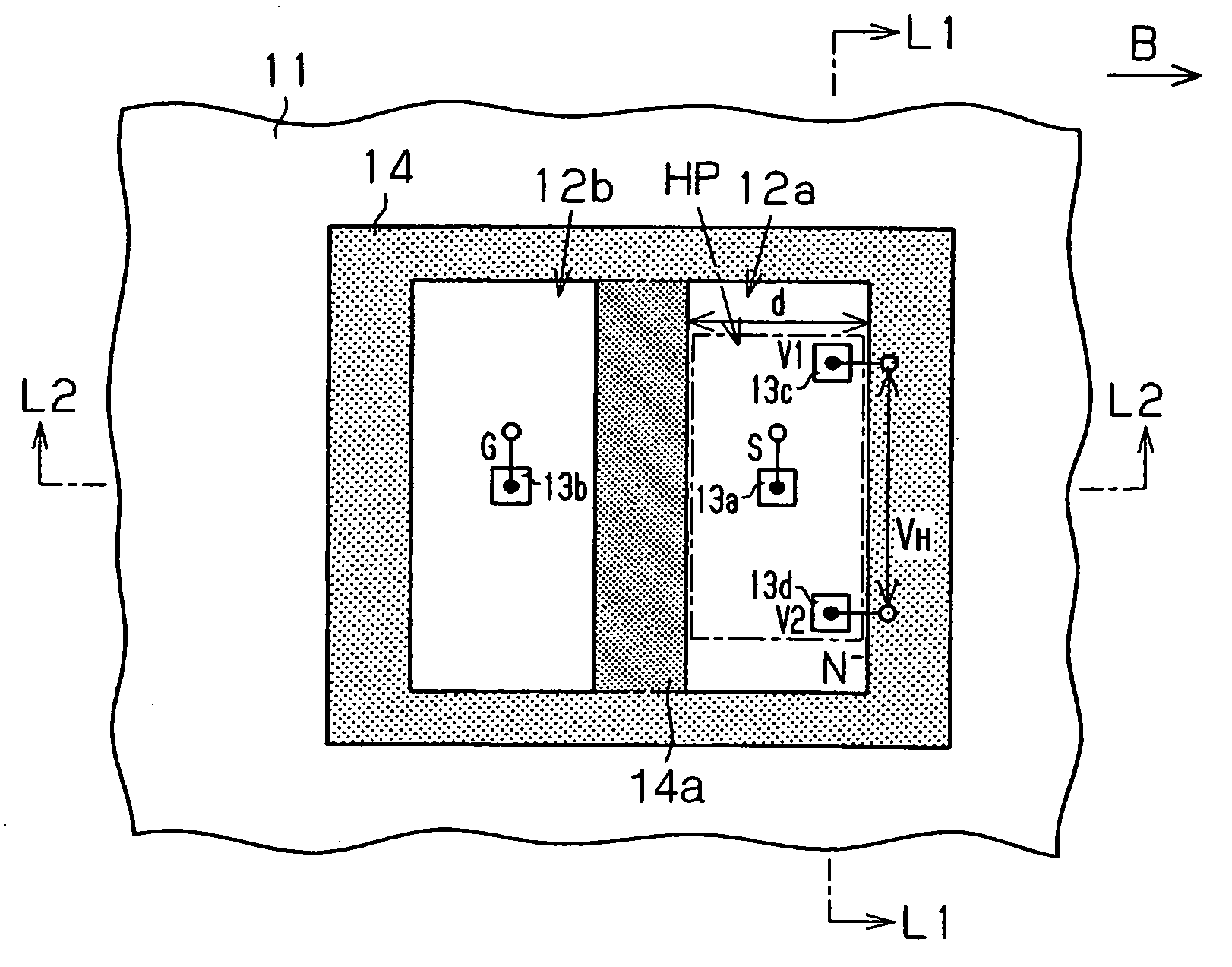
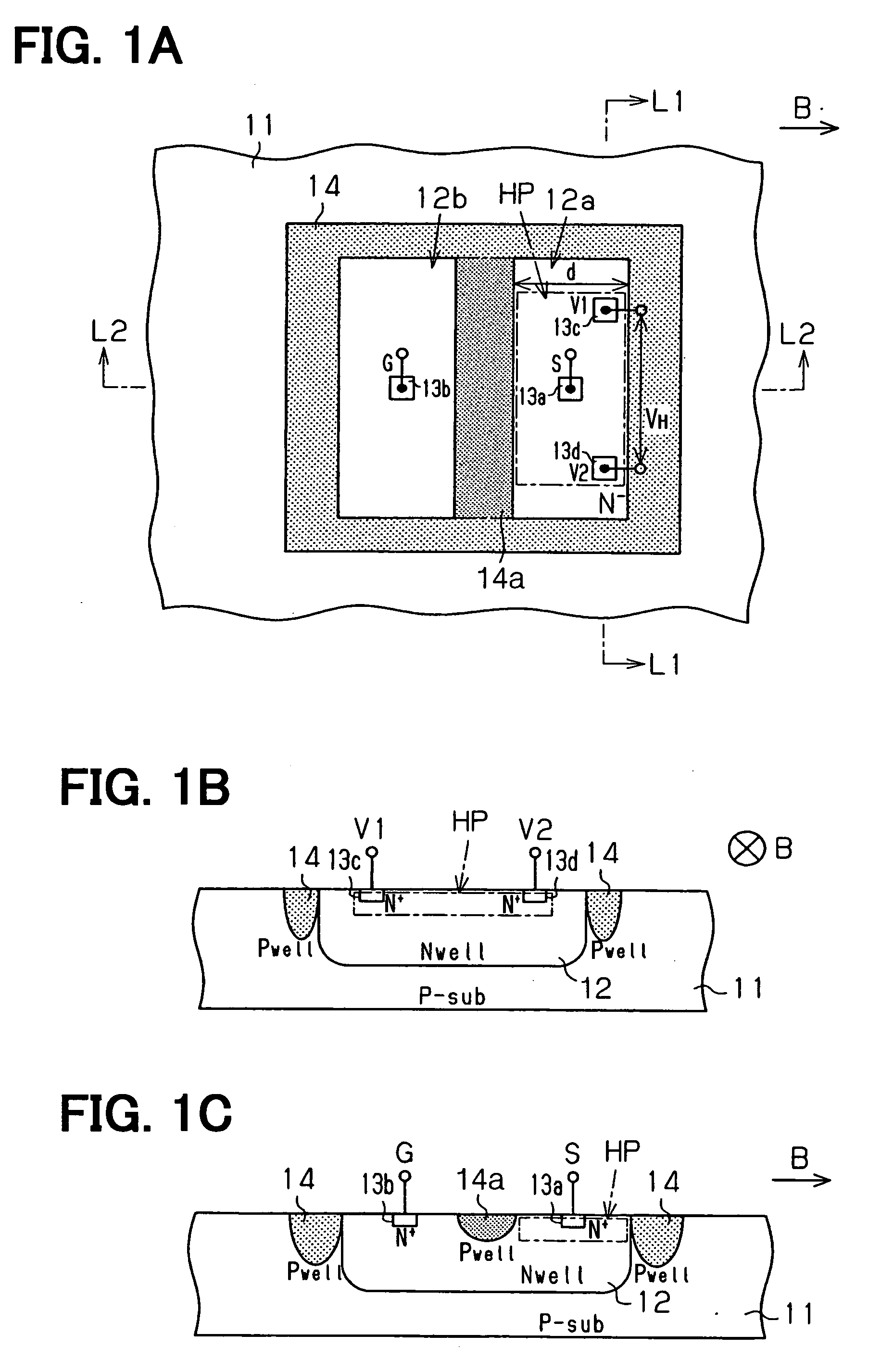
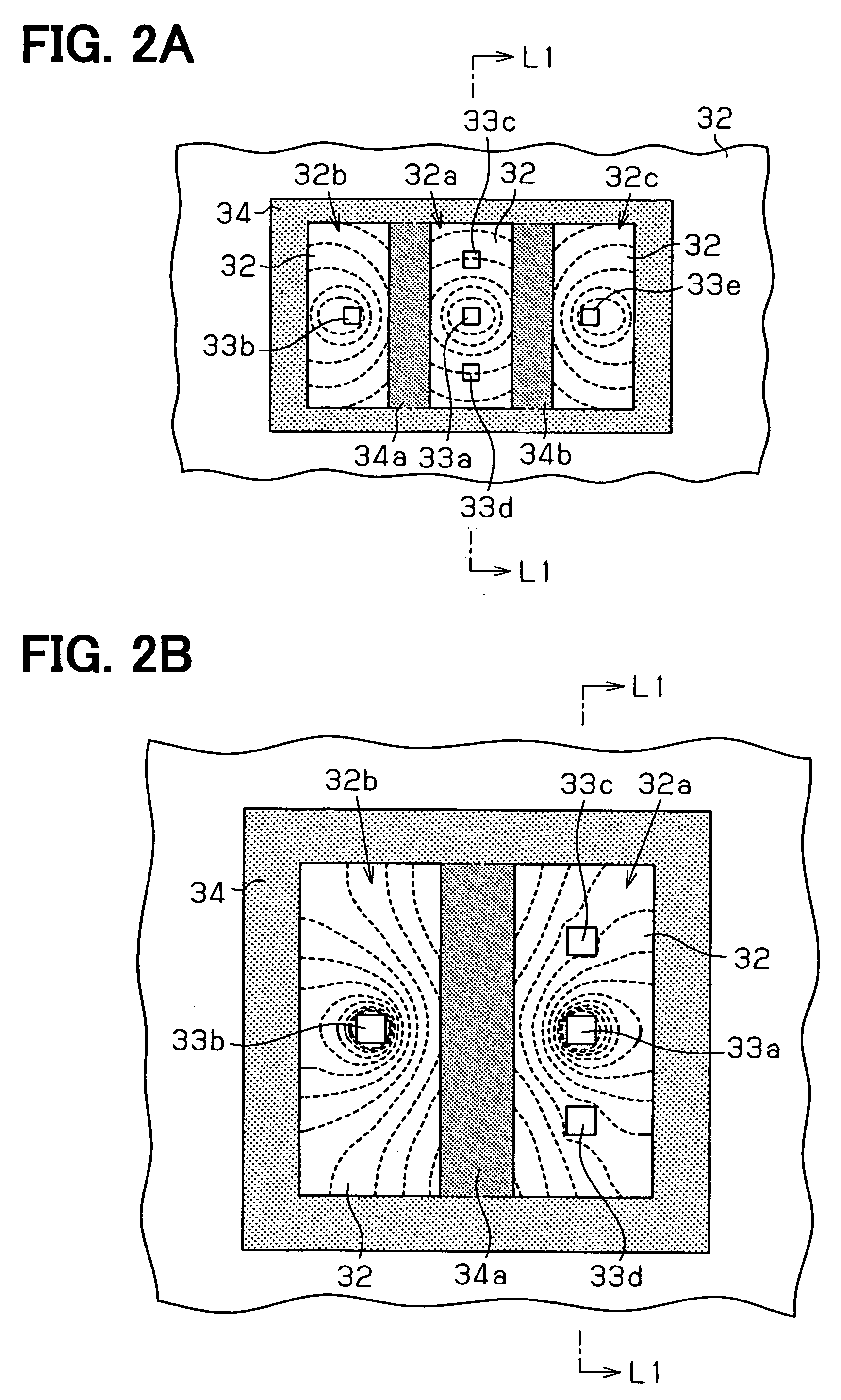
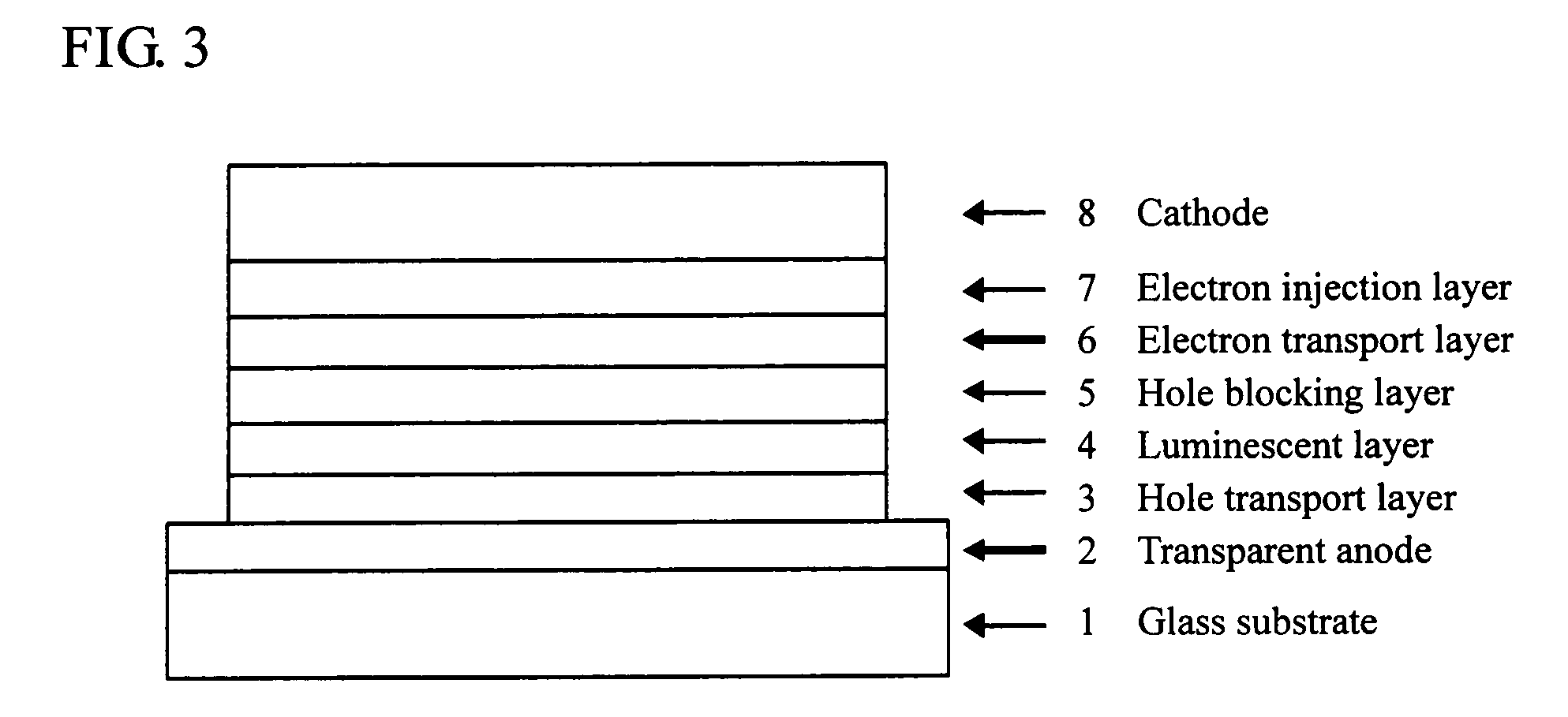
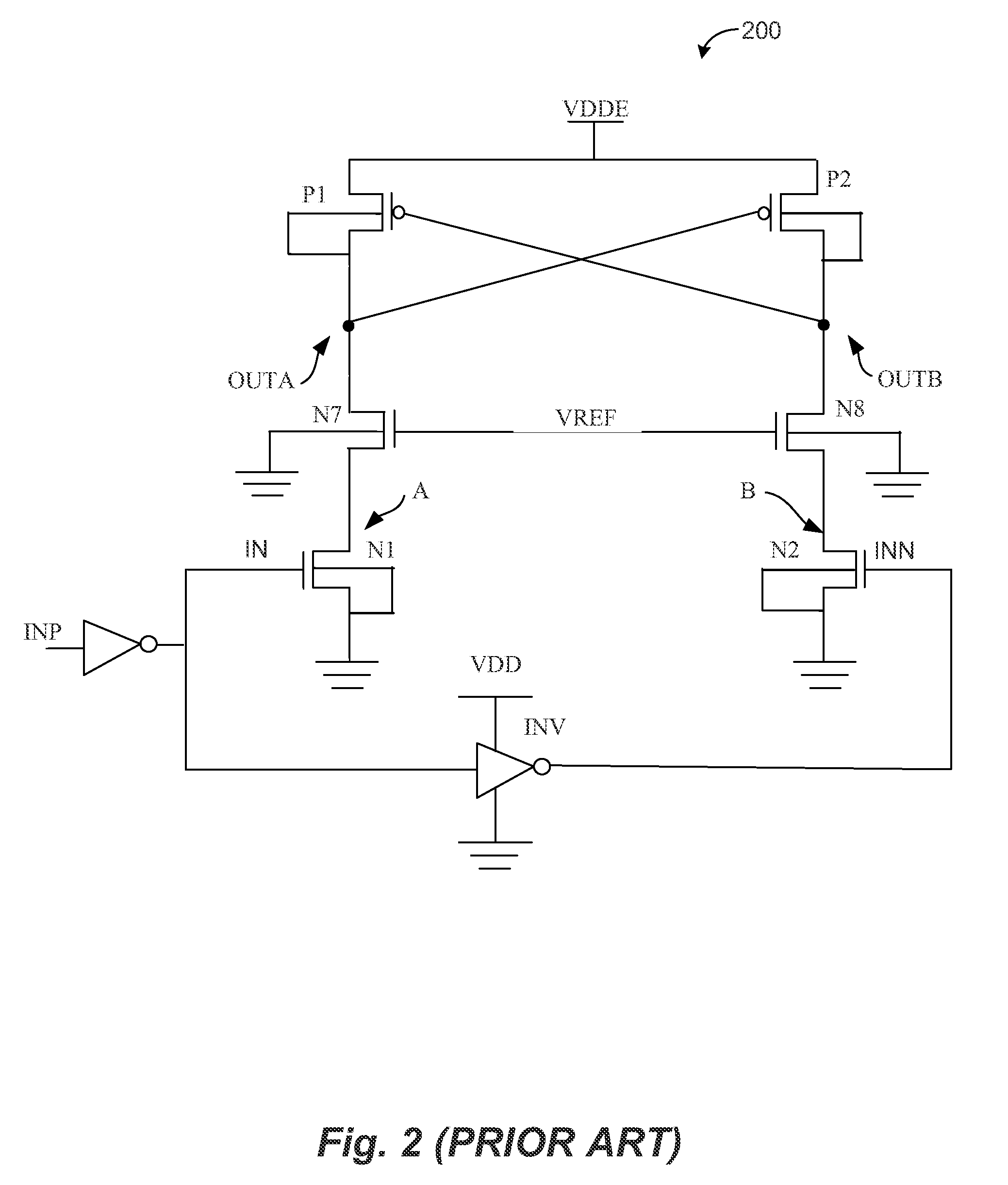
Vertical Hall device and method for adjusting offset voltage of vertical Hall device
InactiveUS20060097715A1Easily and accurately determinedReduce device voltageSolid-state devicesMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
A vertical Hall device includes: a semiconductor substrate including a magnetic field detection portion, a current portion and an output portion. The output portion includes a pair of output terminals. The current portion is capable of supplying the current to the magnetic field detection portion and retrieving the current from the magnetic field detection portion. The current portion is sandwiched between a pair of the output terminals in such a manner that the current portion is disposed apart from a line connecting between a pair of the output terminals.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Gallium-containing light-emitting semiconductor device and method of fabrication
InactiveUS20050205886A1Enhanced efficiencyLower forward voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesAluminiumOhmic contact
An LED comprising a light-generating semiconductor region having an active layer sandwiched between two confining layers of opposite conductivity types. A cathode is arranged centrally on one of the opposite major surfaces of the semiconductor region from which is emitted the light. An array of discrete gold regions are formed via transition metal regions on the other major surface of the semiconductor region at which is exposed one of the confining layers which is of n-type AlGaInP semiconductor material. The gold is thermally diffused into the confining layer via the transition metal regions at a temperature less than the eutectic point of gold and gallium, thereby creating an array of ohmic contact regions of alloyed or intermingled gold and gallium, which are less absorptive of light than their conventional counterparts, to a thickness of 20 to 1000 angstroms. After removing the transition metal regions and gold regions from the surface of the light-generating semiconductor region, a reflective layer of aluminum is formed so as to cover both the ohmic contact regions and the exposed surface portions of the AlGaInP confining layer. An electroconductive base-plate of doped silicon is then bonded to the reflective layer.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
Light emitting polymer composition and polymer light emitting device
InactiveUS20090039765A1Improve efficiencyReduce device voltageOrganic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensSilyleneAtomic group
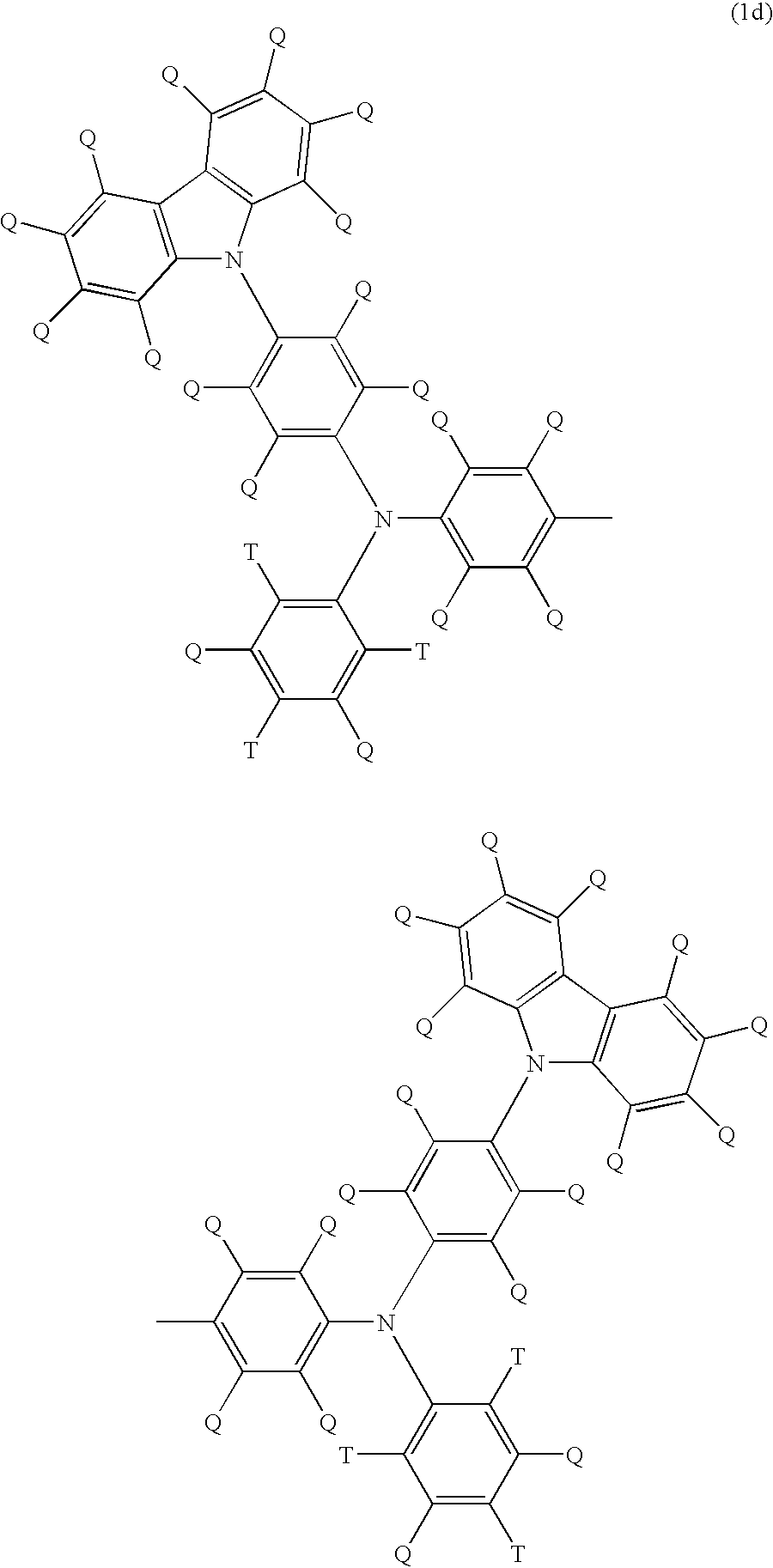
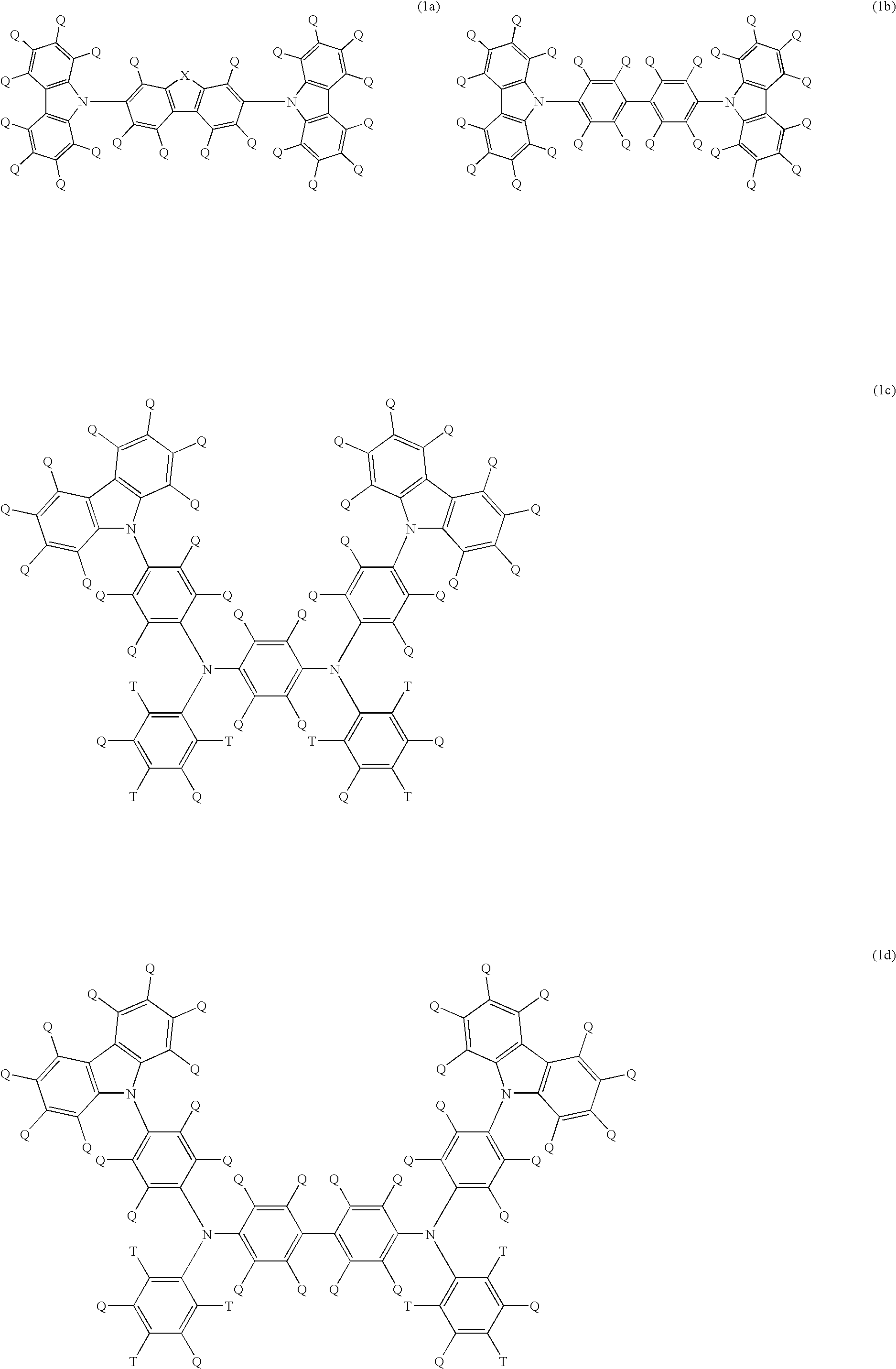
A light emitting polymer composition comprising a light emitting polymer and a compound selected from the following formulae (1a) to (1d):(wherein, X represents an atom or atomic group forming a 5-membered or 6-membered ring together with four carbon atoms on two benzene rings in the formula, Q and T represent each independently a hydrogen atom, halogen atom, alkyl group, alkyloxy group, alkylthio group, aryl group, aryloxy group, arylthio group, arylalkyl group, arylalkyloxy group, arylalkylthio group, alkenyl group, alkynyl group, arylalkenyl group, arylalkynyl group, substituted silyloxy group, substituted silylthio group, substituted silylamino group, substituted amino group, amide group, acid imide group, acyloxy group, mono-valent heterocyclic group, heteroaryloxy group, heteroarylthio group, cyano group or nitro group).
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
New compound and organic light emitting device using the same
ActiveUS20110127495A1Reduce device voltageImprove lighting efficiencyOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesOrganic light emitting deviceThermal stability
The present invention provides a novel compound that is capable of largely improving life span, efficiency, electrochemical stability and thermal stability of the organic light emitting device, and an organic light emitting device in which said compound is included in an organic compound layer.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Compound having substituted anthracene ring structure and pyridoindole ring structure and organic electroluminescence device
InactiveUS20110175079A1Improve abilitiesHigh luminous efficiencyOrganic chemistryElectroluminescent light sourcesAnthraceneSimple Organic Compounds
The present invention provides an organic compound having excellent properties, which is excellent in electron-injection / transport performance, has hole-blocking ability and is high stability in a thin-film state, as a material for an organic electroluminescence device having a high efficiency and a high durability, and provides is an organic electroluminescence device having a high efficiency and a high durability using the compound. The present invention relates to a compound having a substituted anthracene ring structure and a pyridoindole ring structure represented by general formula (1); and an organic electroluminescence device having a pair of electrodes and at least one organic layer interposed between the electrodes in which the at least one organic layer contains the compound.
Owner:HODOGOYA CHEMICAL CO LTD
El device
InactiveUS20050003231A1Lower resistanceImprove electron injection efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesLow voltageX-ray
The present invention relates to an EL device which is driven with a lower voltage or power amount, which is superior in interface stability between layers in the device and which has a higher luminance as compared with the use of a conventional electrode, and is characterized in that in the EL device comprising a light emitting layer disposed as an essential layer between two electrodes facing each other, at least one of the electrodes includes a crystalline conductive film whose diffraction intensity ratio of (400) / (222) is 1.0 or more in X-ray diffraction by a θ / 2θ method.
Owner:NIPPON SODA CO LTD
El device
InactiveUS7309531B2Improve Interface StabilityIncrease brightnessDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesLow voltageX-ray
The present invention relates to an EL device which is driven with a lower voltage or power amount, which is superior in interface stability between layers in the device and which has a higher luminance as compared with the use of a conventional electrode, and is characterized in that in the EL device comprising a light emitting layer disposed as an essential layer between two electrodes facing each other, at least one of the electrodes includes a crystalline conductive film whose diffraction intensity ratio of (400) / (222) is 1.0 or more in X-ray diffraction by a θ / 2θ method.
Owner:NIPPON SODA CO LTD
Material for organic light-emitting device, and organic light-emitting device using same
InactiveUS20140231774A1Reduce device voltageImprove lighting efficiencyOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesOrganic light emitting deviceLight-emitting diode
The present invention provides an organic light emitting device including a compound and an organic material layer composed of one more layers including a first electrode, a second electrode and a light emitting layer disposed between the first electrode and the second electrode, in which one or more layers of the organic material layer include the compound of Formula 1 or a compound in which a heat curable or photo curable functional group is introduced into the above-described compound.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Dual gate fd-soi transistor
InactiveUS20150129967A1Improve switching performanceImprove charging capacityTransistorSolid-state devicesConvertersHemt circuits
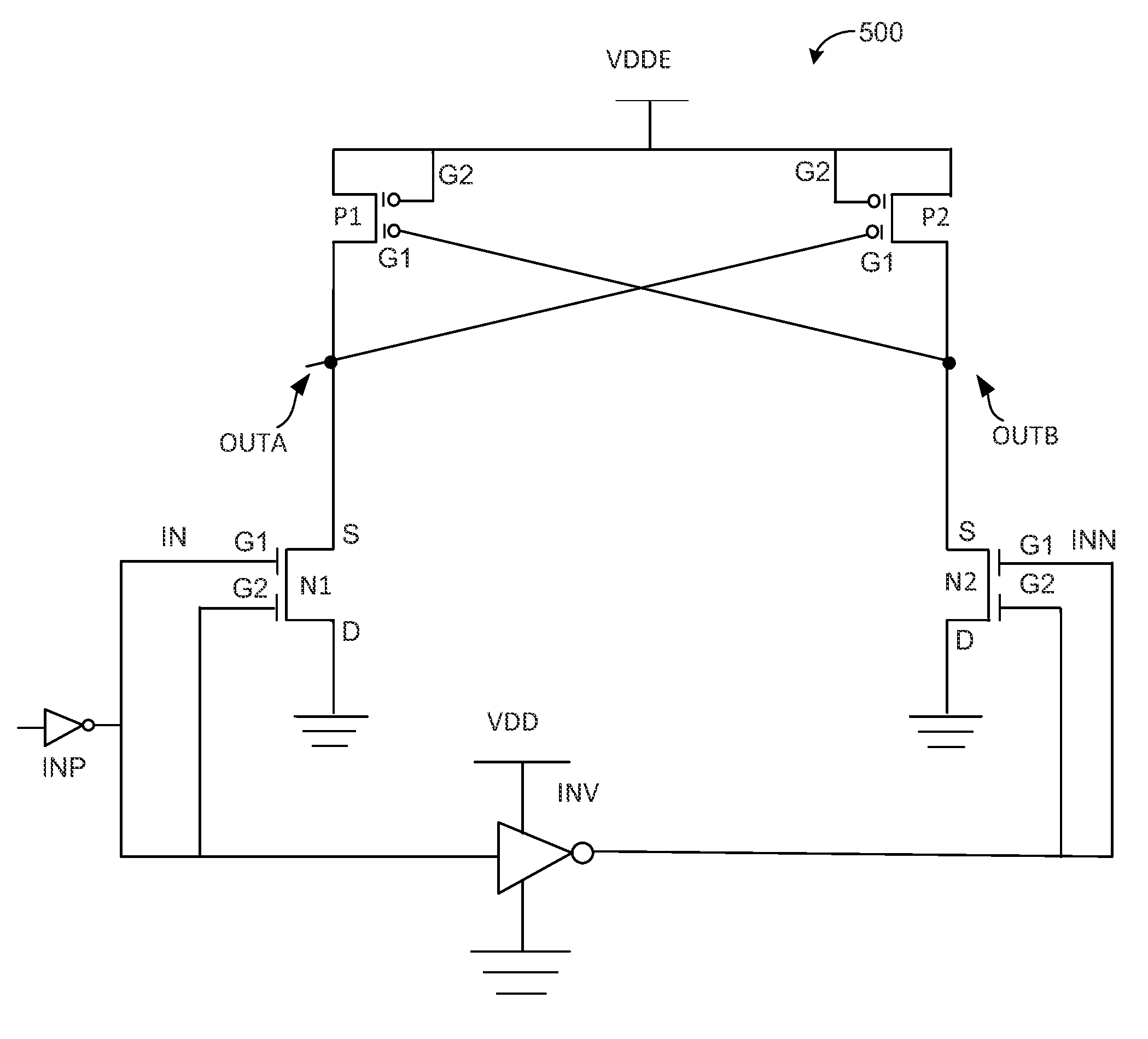
Circuit module designs that incorporate dual gate field effect transistors are implemented with fully depleted silicon-on-insulator (FD-SOI) technology. Lowering the threshold voltages of the transistors can be accomplished through dynamic secondary gate control in which a back-biasing technique is used to operate the dual gate FD-SOI transistors with enhanced switching performance. Consequently, such transistors can operate at very low core voltage supply levels, down to as low as about 0.4 V, which allows the transistors to respond quickly and to switch at higher speeds. Performance improvements are shown in circuit simulations of an inverter, an amplifier, a level shifter, and a voltage detection circuit module.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
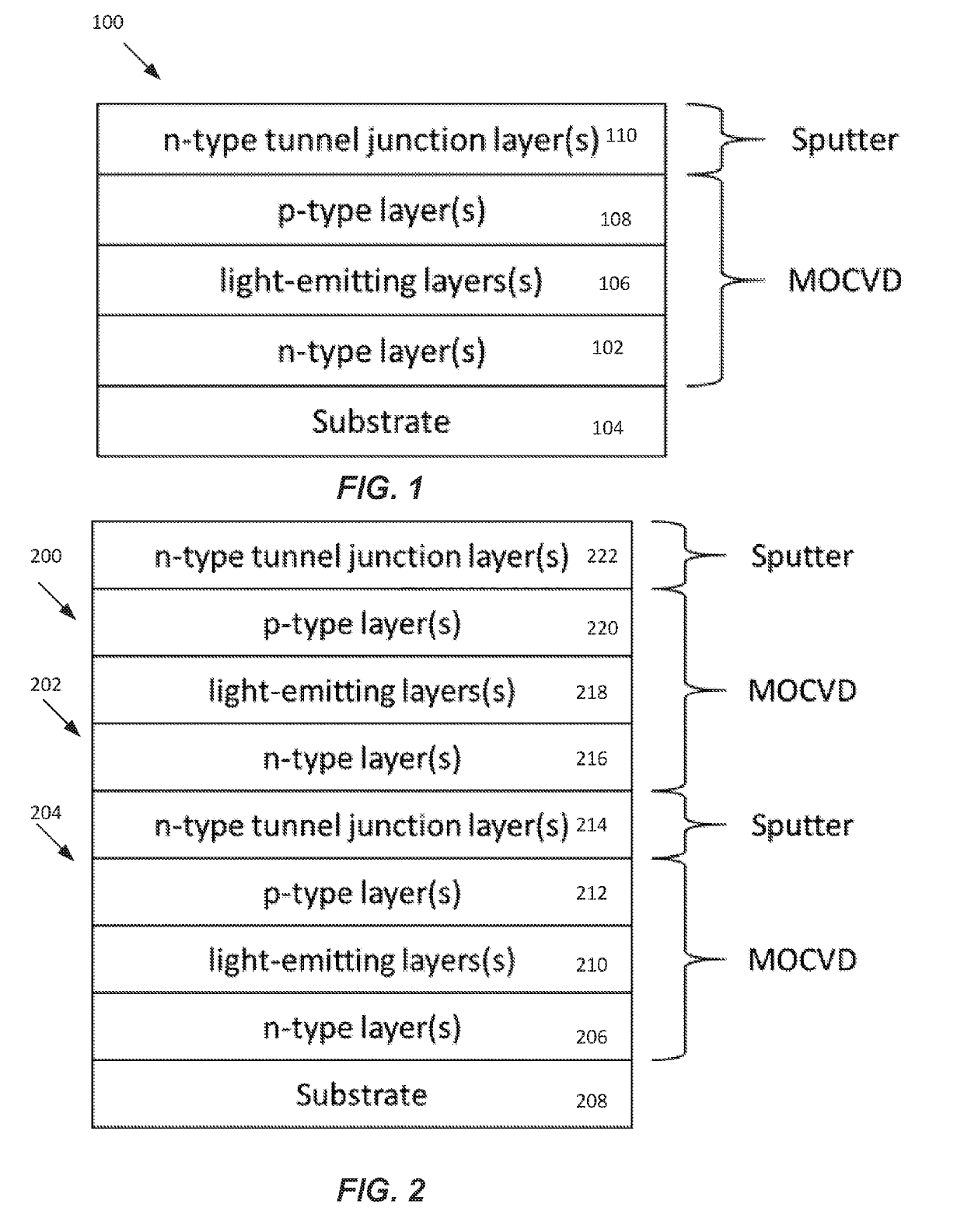
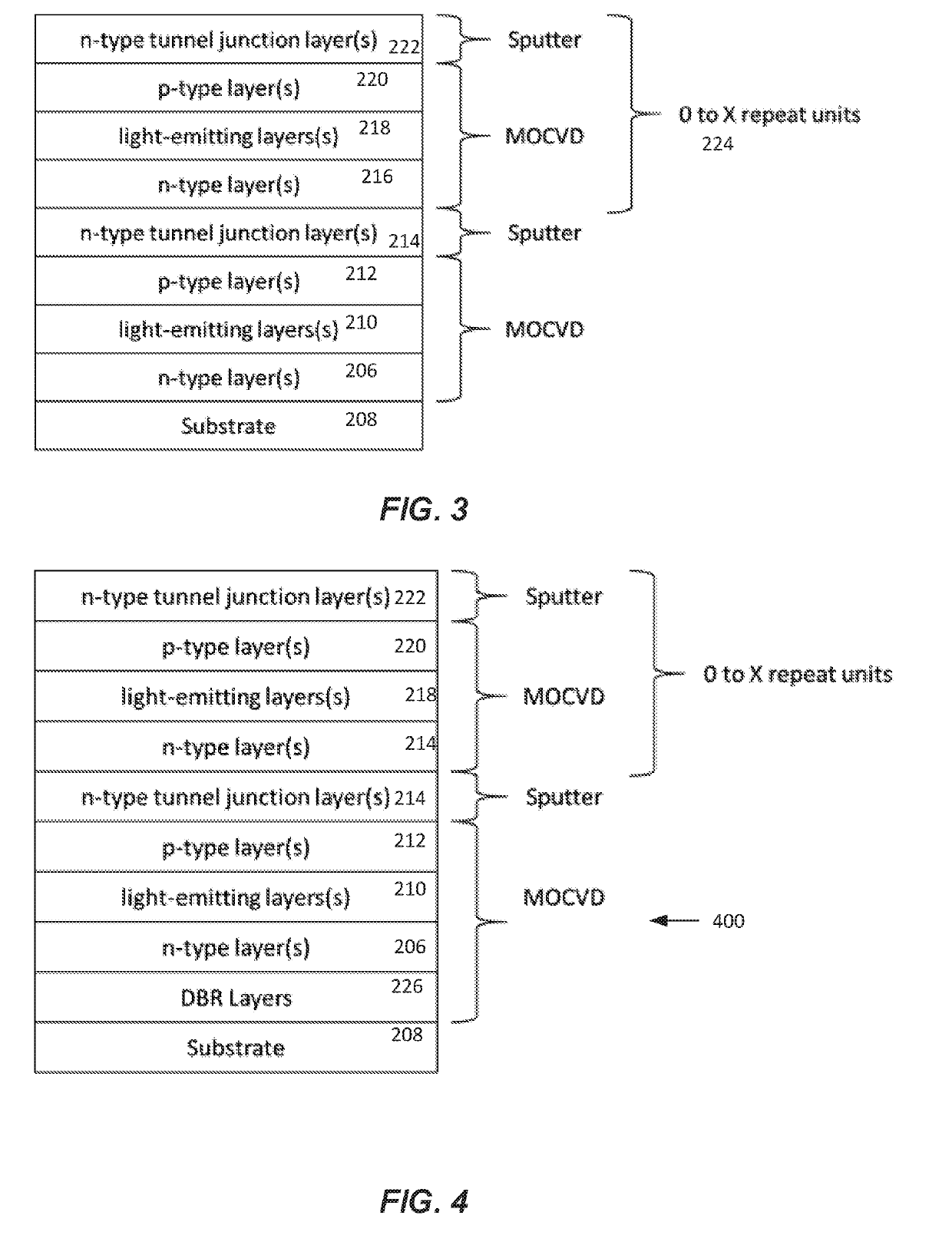
Methods for fabricating iii-nitride tunnel junction devices
ActiveUS20190207043A1Improve efficiencyReduce device voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationGas phaseDisplay device
A physical vapor deposition (e.g., sputter deposition) method for III-nitride tunnel junction devices uses metal-organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) to grow one or more light-emitting or light-absorbing structures and electron cyclotron resonance (ECR) sputtering to grow one or more tunnel junctions. In another method, the surface of the p-type layer is treated before deposition of the tunnel junction on the p-type layer. In yet another method, the whole device (including tunnel junction) is grown using MOCVD and the p-type layers of the III-nitride material are reactivated by lateral diffusion of hydrogen through mesa sidewalls in the III-nitride material, with one or more lateral dimensions of the mesa that are less than or equal to about 200 μm. A flip chip display device is also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Compound having acridan ring structure, and organic electroluminescent device
ActiveUS20130075715A1Excellent electron blocking abilitySatisfactory amorphousnessOrganic compound preparationElectroluminescent light sourcesAcridineSimple Organic Compounds
An organic compound with characteristics excelling in hole-injecting / transporting performance and having an electron blocking ability, a highly stable thin-film state, and excellent heat resistance is provided as material for an organic electroluminescent device of high efficiency and high durability, and the organic electroluminescent device of high efficiency and high durability is provided using this compound. The compound of a general formula (Chemical Formula 1) having a substituted acridan ring structure is used as a constituent material of at least one organic layer in the organic electroluminescent device that includes a pair of electrodes and one or more organic layers sandwiched between the pair of electrodes.
Owner:HODOGOYA CHEMICAL CO LTD
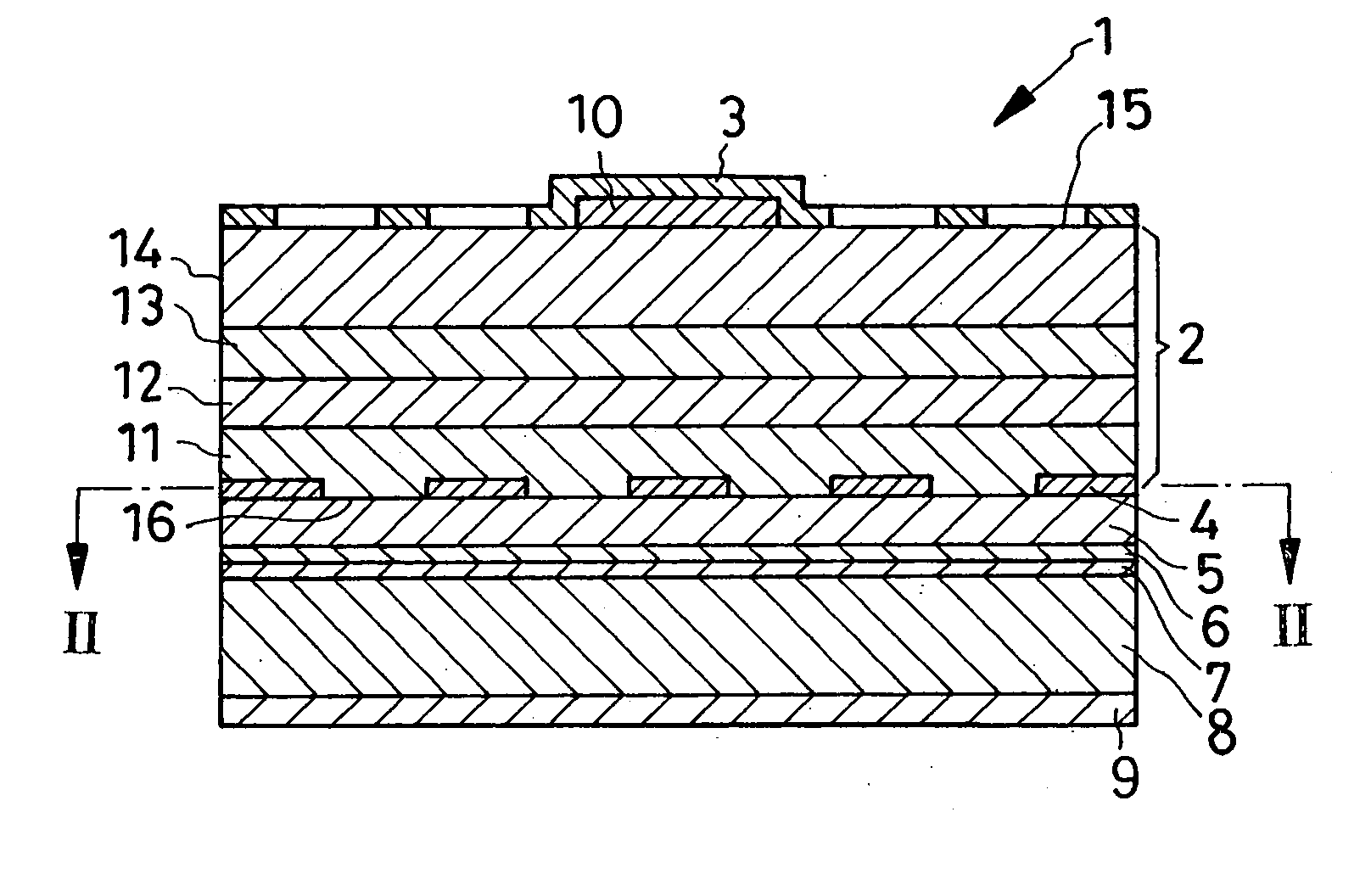
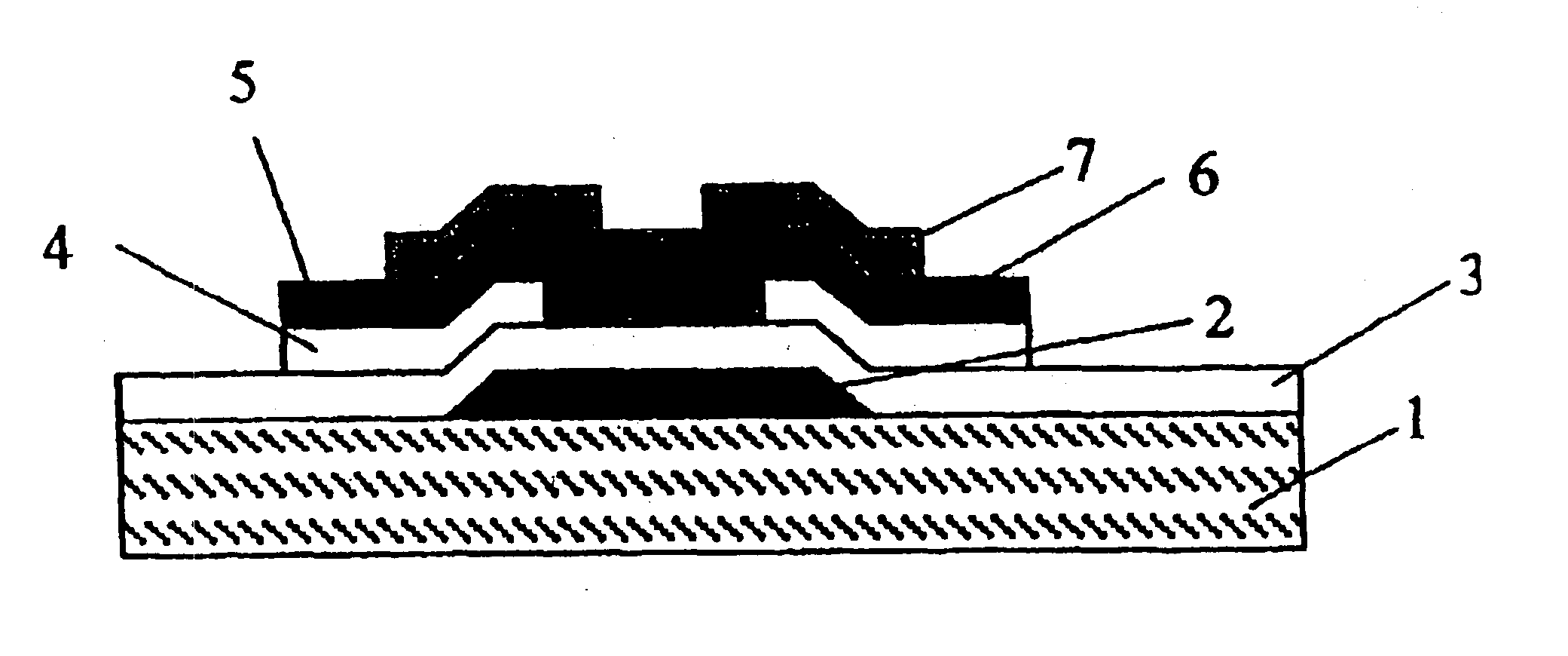
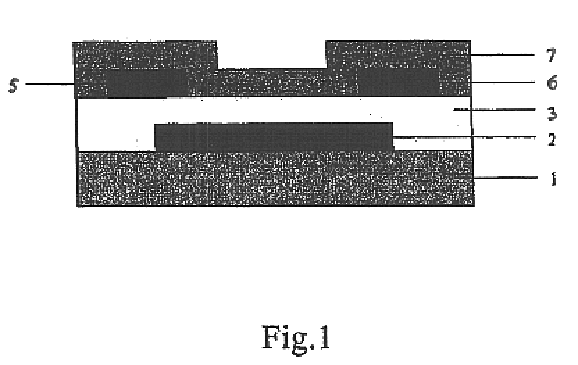
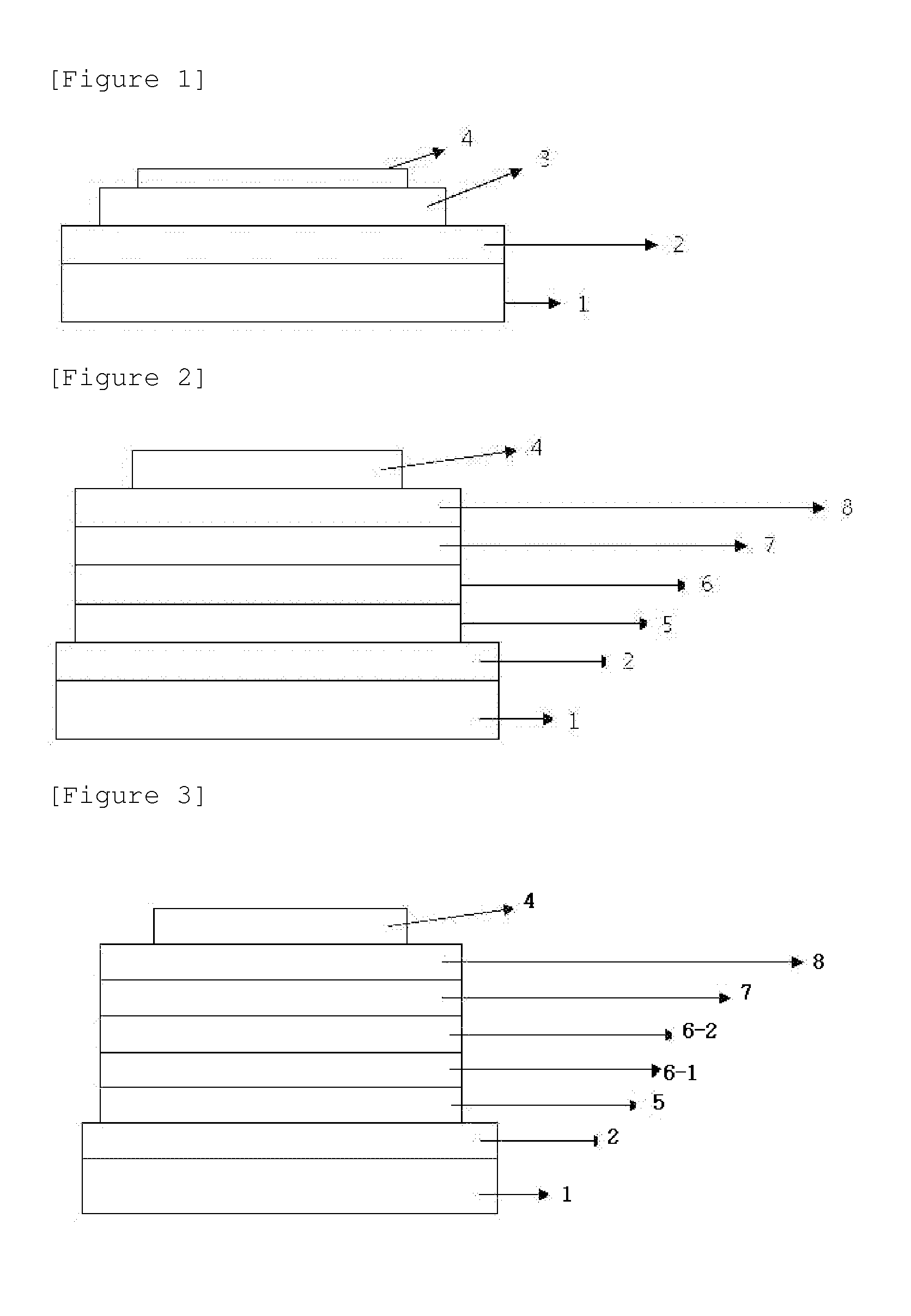
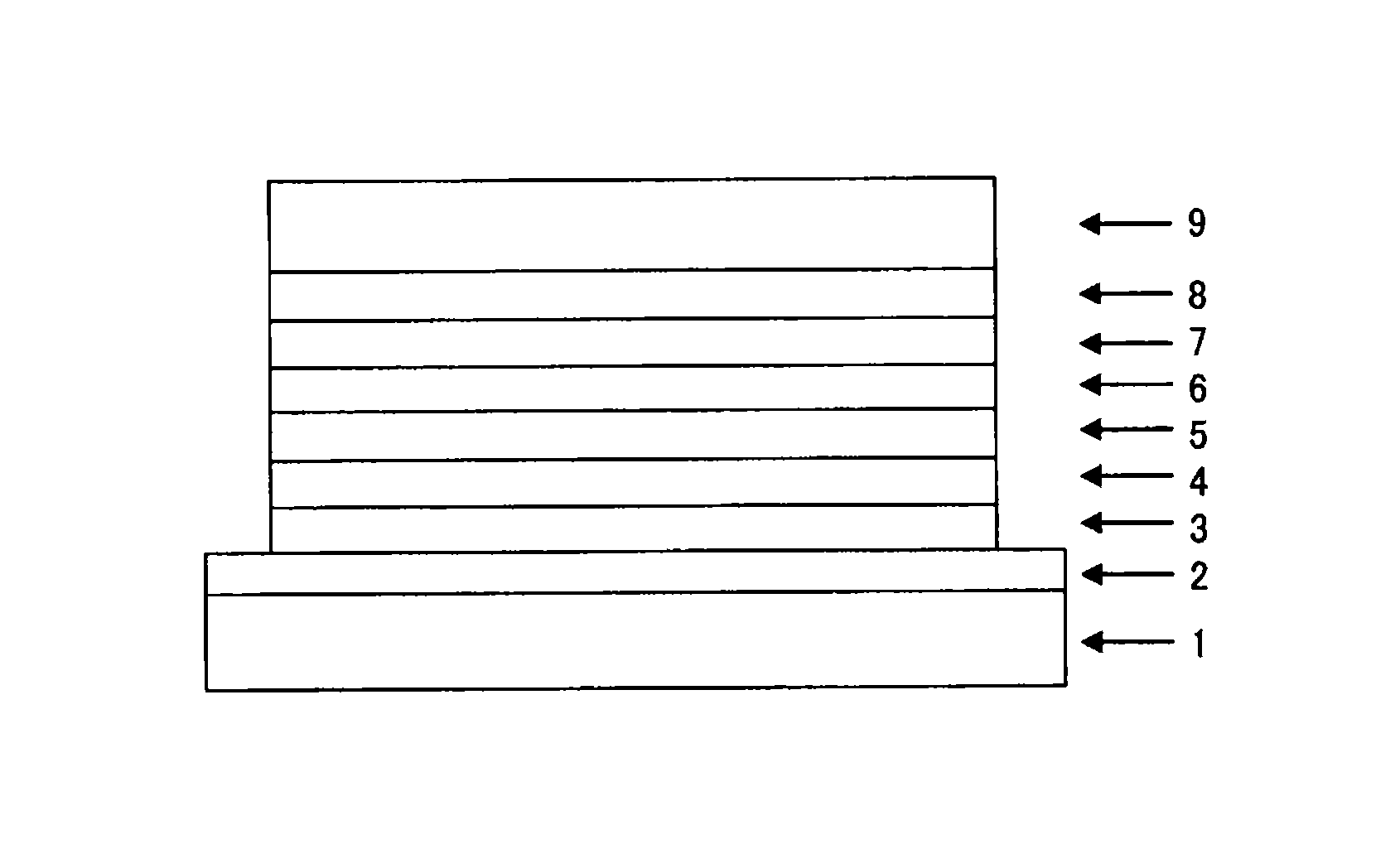
Organic thin film transistor (OTFT)
InactiveUS6847048B2Reduce leakage currentImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerGas phase
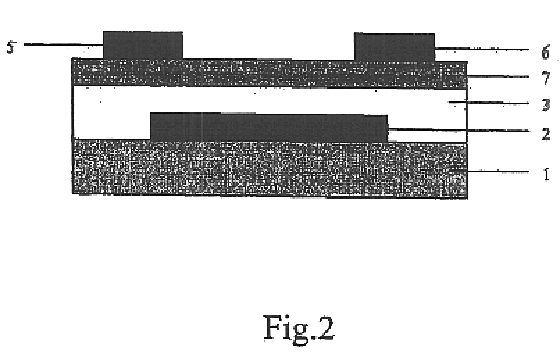
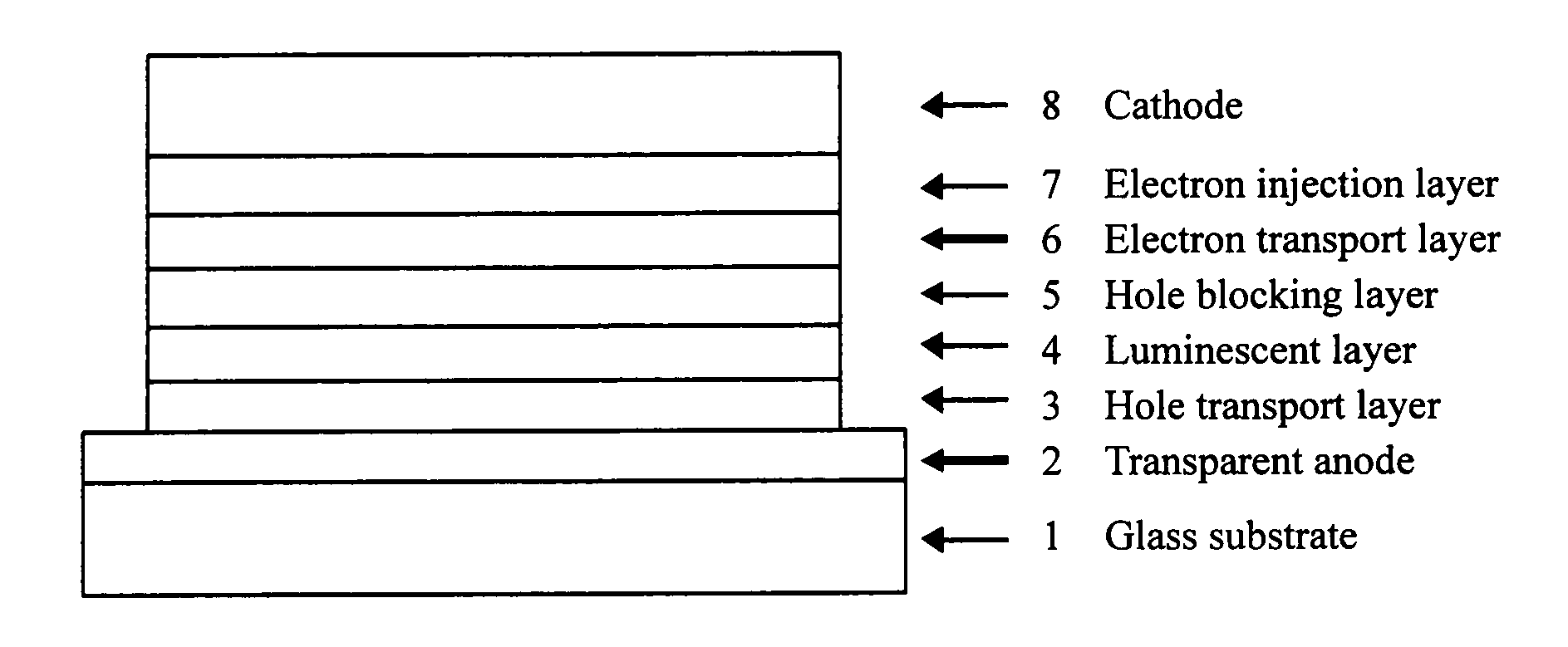
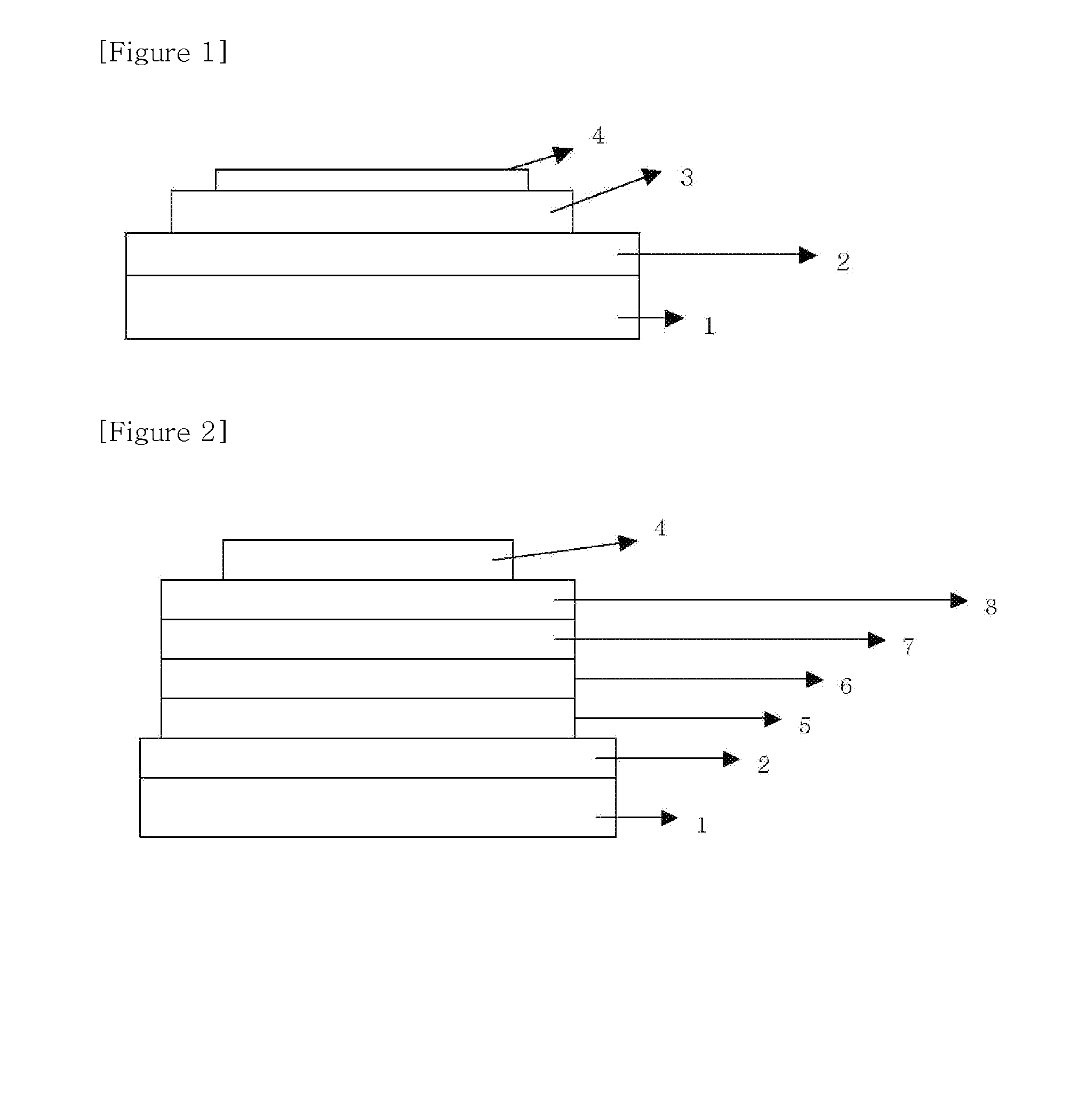
The present invention relates to an organic thin film transistor (OTFT) comprising: a substrate (1), a gate electrode (2) formed on the substrate (1), a gate insulation layer formed on the gate electrode, a source electrode (5) and a drain electrode (6) formed on the gate insulation layer including a first insulation layer (3) and a second insulation layer (4) with different dielectric constants, and an active layer (7) which overlays the source electrode (5) and the drain electrode (6). Without adding the conventional complicated processes like photolithography but adding two simple processes of spin coating or vaporously coating the second insulation film and self-aligned dry RIE, the present invention not only can improve the carrier's injection property so as to improve the OTFT device's properties, but also can block the leakage current of the gate insulation layer and reduce the device's parasitic capacitance. Therefore, the material with high dielectric constant can be used as the insulation layer to increase the channel capacitance so as to reduce threshold voltage of the device and reduce the adverse effect of the leakage between the source and gate electrodes, the gate and drain electrodes.
Owner:CHANGCHUN FULEBO DISPLAY TECH
Compound having substituted pyridyl group and pyridoindole ring structure linked through phenylene group, and organic electroluminescent device
InactiveUS20110006291A1Improve abilitiesSolve low luminous efficiencyOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesOrganic layerPhenyl group
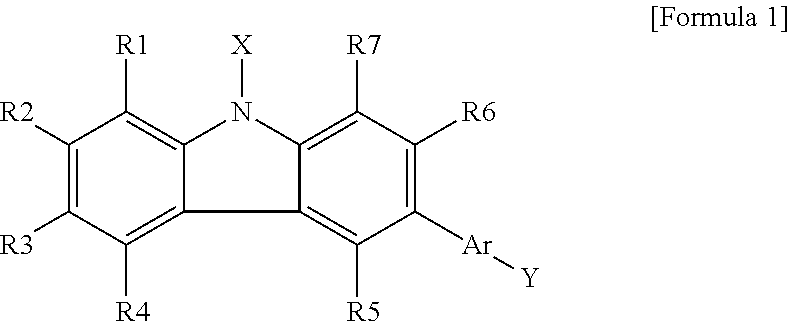
Objects of the present invention are to provide an organic compound having excellent properties, which is excellent in electron-injecting / transporting performances, has hole-blocking ability and is highly stable in a thin-film state, as a material for an organic electroluminescent device having a high efficiency and a high durability; and to provide an organic electroluminescent device having a high efficiency and a high durability using the compound. The invention relates to a compound having a substituted pyridyl group and a pyridoindole ring structure linked through a phenylene group, which is represented by the general formula (1); and an organic EL device comprising a pair of electrodes and at least one organic layer interposed between the electrodes, wherein the at least one organic layer contains the compound:wherein Ar represents a substituted or unsubstituted aromatic hydrocarbon group, a substituted or unsubstituted aromatic heterocyclic group, or a substituted or unsubstituted condensed polycyclic aromatic group; R1 to R14 may be the same or different from each other and each represents a hydrogen atom, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, a cyano group, a trifluoromethyl group, a linear or branched alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, a substituted or unsubstituted aromatic hydrocarbon group, a substituted or unsubstituted aromatic heterocyclic group, or a substituted or unsubstituted condensed polycyclic aromatic group; n represents an integer of 1 to 3; and W, X, Y, and Z respectively represent a carbon atom or a nitrogen atom, provided that only one of W, X, Y, and Z represents a nitrogen atom, and the nitrogen atom does not have the substituent of R7, R8, R9, or R10).
Owner:HODOGOYA CHEMICAL CO LTD
Compound having pyridoindole ring structure bonded with substituted pyridyl group, and organic electroluminescent device
InactiveUS20100308322A1Improve abilitiesHigh luminous efficiencyOrganic chemistryElectroluminescent light sourcesOrganic layerOrganic compound
Objects of the invention are to provide an organic compound having excellent properties, which is excellent in electron-injecting / transporting performance, has hole-blocking ability, and is highly stable in a thin-film state, as a material for an organic electroluminescent devices having a high-efficiency and a high durability; and to provide an organic electroluminescent device having a high-efficiency and a high durability using the compound. The invention relates to: a compound having a pyridoindole ring structure bonded with a substituted pyridyl group, which is represented by the following general formula (1); and an organic electroluminescent device comprising a pair of electrodes and at least one organic layer interposed between the electrodes, wherein the at least one organic layer contains the compound.in which Ar represents a substituted or unsubstituted aromatic hydrocarbon group, a substituted or unsubstituted aromatic heterocyclic group, or a substituted or unsubstituted condensed polycyclic aromatic group; R1 to R3 may be the same or different and represent a hydrogen atom, a substituted or unsubstituted aromatic heterocyclic group, or a substituted or unsubstituted condensed polycyclic aromatic group; R4 to R11 may be the same or different and represent a hydrogen atom, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, a cyano group, a trifluoromethyl group, a linear or branched alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, a substituted or unsubstituted aromatic hydrocarbon group, a substituted or unsubstituted aromatic heterocyclic group, or a substituted or unsubstituted condensed polycyclic aromatic group; m and n represent an integer of 1 to 3; and W, X, Y, and Z represent a carbon atom or a nitrogen atom, provided that the case where R1 to R3 in the molecule are simultaneously all hydrogen atoms is excluded, and that only one of W, X, Y, and Z is a nitrogen atom and the nitrogen atom does not have the substituent of R8, R9, R10, or R11.
Owner:HODOGOYA CHEMICAL CO LTD
Compound having benzotriazole ring structure and organic electroluminescent element
ActiveUS20120012831A1Improve abilitiesSolve low luminous efficiencyOrganic chemistryElectroluminescent light sourcesBenzotriazoleOrganic electroluminescence
A compound having a benzotriazole ring structure and a formula (1):wherein Ar is a substituted or unsubstituted aromatic hydrocarbon group, aromatic heterocyclic group, or condensed polycyclic aromatic group; A and B are the same as or different from each other and each represent a hydrogen atom or a monovalent group of formula (2), provided that A and B are not simultaneously hydrogen atoms:wherein R1 to R8 are the same as or different and each represent a hydrogen atom, a deuterium atom, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, a cyano group, a trifluoromethyl group, a linear or branched alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, aromatic hydrocarbon group, a substituted or unsubstituted aromatic heterocyclic group, or condensed polycyclic aromatic group; m is an integer of 0, 1 or 2; X represents a carbon atom or a nitrogen atom; when X is a nitrogen atom, the nitrogen atom does not have substituents or bonding groups of R1, R2, R3 and R4; and when m is 2, a plurality of R1, R2, R3, R4 and X each are the same or different.
Owner:HODOGOYA CHEMICAL CO LTD +1
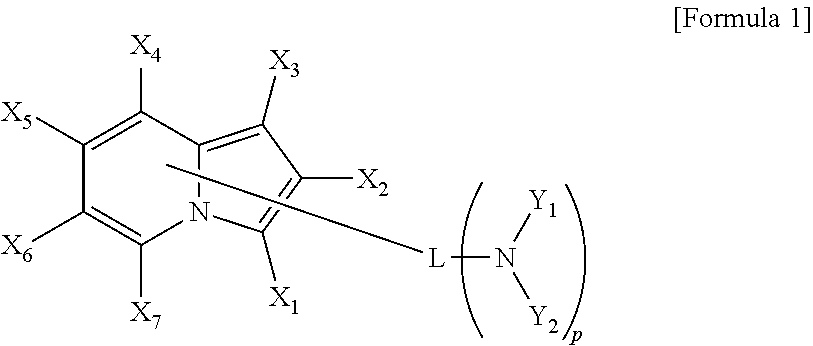
New heterocyclic derivative and organic light emitting device using same
ActiveUS20120161612A1Reduce device voltageImprove lighting efficiencyOrganic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensChemical compoundOrganic light emitting device
The present invention relates to a novel heterocyclic derivative and an organic light emitting device using the compound, and the heterocyclic derivative may largely improve a life span, efficiency, electrochemical stability and thermal stability of the organic light emitting device.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Compound having indenoacridan ring structure, and organic electroluminescent device
InactiveUS20150249218A1Excellent electron block abilitySatisfactory amorphousnessOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesOrganic electroluminescenceChemical compound
An organic compound with excellent characteristics excelling in hole injecting and transporting performance and having an electron-blocking ability, high stability in a thin film state and excellent heat resistance is provided as a material for an organic electroluminescent device of high efficiency and high durability, and the organic electroluminescent device of high luminous efficiency and high durability is provided using this compound. The compound of a general formula (1) having an indenoacridan ring structure is used as a constituent material of at least one organic layer in the organic electroluminescent device that includes a pair of electrodes and one or more organic layers sandwiched between the pair of electrodes.
Owner:HODOGAYA KAGAKU IND
Material for organic light-emitting device, and organic light-emitting device using same
ActiveUS20140197402A1Reduce device voltageImprove lighting efficiencyOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesOrganic light emitting deviceLight emitting device
The present invention provides an organic light emitting device including a dibenzothiophene-based compound and an organic material layer composed of one more layers including a first electrode, a second electrode and a light emitting layer disposed between the first electrode and the second electrode, in which one or more layers of the organic material layer include the dibenzothiophene-based compound of Formula 1 or a compound in which a heat curable or photo curable functional group is introduced into the dibenzothiophene-based compound.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Dual gate fd-soi transistor
ActiveUS20160111534A1Improve switching performanceImprove charging capacitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConvertersHemt circuits
Circuit module designs that incorporate dual gate field effect transistors are implemented with fully depleted silicon-on-insulator (FD-SOI) technology. Lowering the threshold voltages of the transistors can be accomplished through dynamic secondary gate control in which a back-biasing technique is used to operate the dual gate FD-SOI transistors with enhanced switching performance. Consequently, such transistors can operate at very low core voltage supply levels, down to as low as about 0.4 V, which allows the transistors to respond quickly and to switch at higher speeds. Performance improvements are shown in circuit simulations of an inverter, an amplifier, a level shifter, and a voltage detection circuit module.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
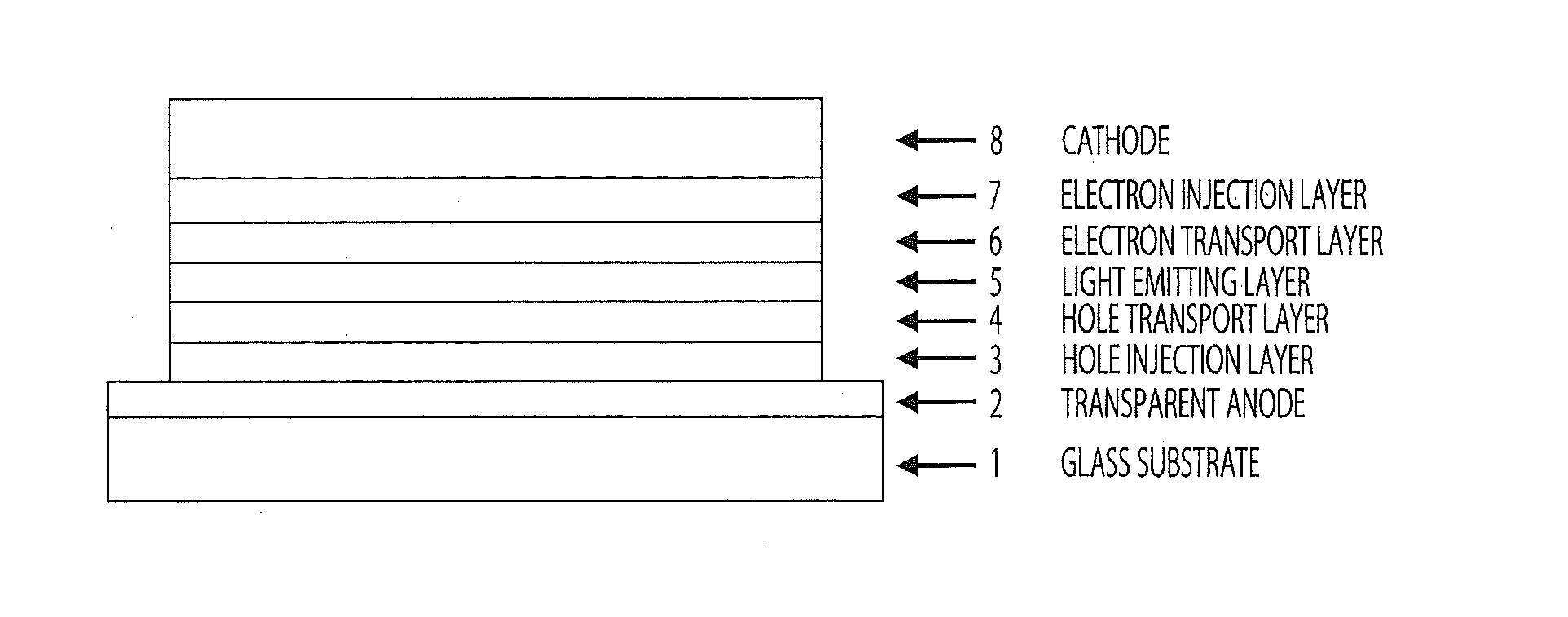
White organic electroluminescent device and preparation method thereof
ActiveUS20180248138A1Improve energy transferImprove efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRare earthEnergy transport
Provided is a white organic electroluminescent device, composed of a substrate, an anode layer, an anode modification layer, a hole transporting-electron blocking layer, a hole-dominated light-emitting layer, an electron-dominated light-emitting layer, a hole blocking-electron transporting layer, a cathode modification layer, and a cathode layer arranged in turn, wherein the electron-dominated light-emitting layer is composed of an organic sensitive material, a blue organic light-emitting material, and an electron-type organic host material. A rare earth complex having a matched energy level, such as Tm(acac)3Phen or Dy(acac)3phen is selected as the organic sensitive material, and a trace amount of the same is doped into the electron-dominated light-emitting layer, which has the function of an energy transporting ladder and a deep binding center for charge carriers, so as to improve the light-emitting effectiveness, spectral stability, and service life of the device, reduce the operating voltage of the device, and delay the attenuation of the effectiveness of the device.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Compound and organic device using same
ActiveUS8921832B2Reduce device voltageImprove lighting efficiencySilicon organic compoundsSolid-state devicesOrganic light emitting deviceThermal stability
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Silicon Controlled Rectifier
ActiveUS20170012037A1Efficient triggerIncrease holding voltageTransistorSolid-state devicesSilicon-controlled rectifierSemiconductor
A silicon controlled rectifier, an electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection circuit including the silicon controlled rectifier and an integrated circuit including the silicon controlled rectifier or ESD protection circuit. The silicon controlled rectifier includes a first region having a first conductivity type and a second region having a second conductivity type located adjacent the first region in a semiconductor substrate. A junction is formed at a boundary between the first region and the second region. Contact regions of the first conductivity type and the second conductivity type located in each of the first region and the second region. A further contact region of the second conductivity type is located in the second region, in between the contact region of the first conductivity type and the junction. The further contact region and the contact region of the second conductivity type in the second region are connected together for biasing the second region.
Owner:NXP BV
Silicon controlled rectifier
ActiveUS9704851B2Increase holding voltageHigh voltageTransistorThyristorSilicon-controlled rectifierSemiconductor
Owner:NXP BV
Material for organic electronic device, and organic electronic device using same
ActiveUS20140231783A1Reduce device voltageImprove lighting efficiencyOrganic chemistryFinal product manufactureThermal stabilityLife time
The present invention provides a novel compound that is capable of largely improving a life time, efficiency, electrochemical stability, and thermal stability of an organic electronic device, and an organic electronic device that comprises an organic material layer comprising the compound.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
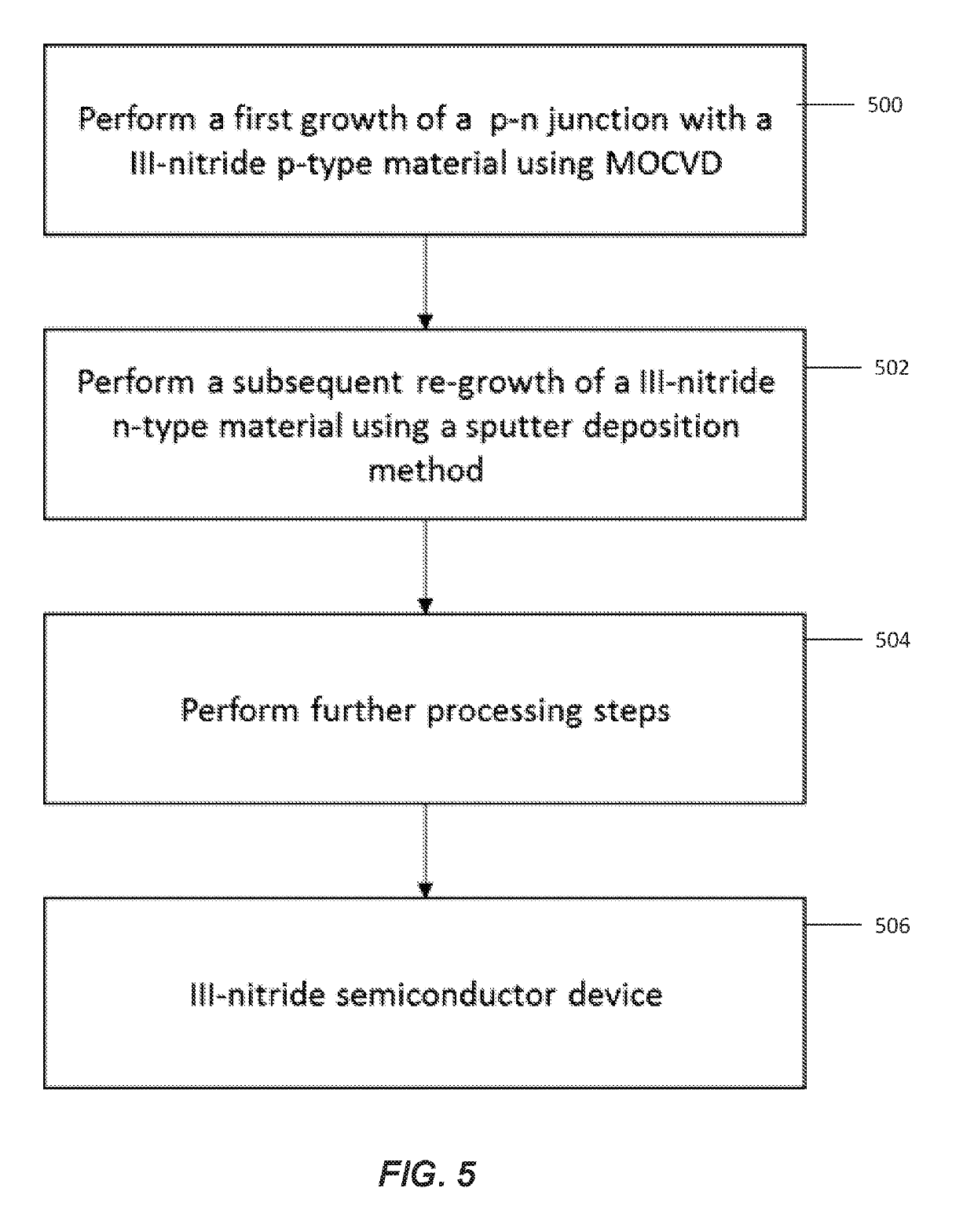
Metal organic chemical vapor depostion (MOCVD) tunnel junction growth in iii-nitride devices
ActiveUS20190245112A1Improve performance and reliabilityImprove performancePolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesSmooth surfaceOrganic chemicals
A method for fabricating an (Al,Ga,In,B)N or III-nitride semiconductor device, including performing a growth of III-nitride or (Al,Ga,In,B)N material including a p-n junction with an active region and using metal-organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) or chemical vapor deposition; and performing a subsequent regrowth of n-type (Al,Ga,In,B)N or III-nitride material using MOCVD or chemical vapor deposition while utilizing a pulsed delta n-type doping scheme to realize an abrupt, smoother surface of the n-type material and a higher carrier concentration in the n-type material. In another example, the method comprises forming a mesa having a top surface; and activating magnesium in the p-type GaN of the (Al,Ga,In,B)N material through openings in the top surface that expose the p-type GaN's surface. The openings are formed before or after the subsequent regrowth of the tunnel junction.
Owner:KING ABDULAZIZ CITY FOR SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY +1
Compound having indenocarbazole ring structure, and organic electroluminescent device
ActiveUS9196837B2Excels in electron blocking abilityImprove power efficiencyOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesOrganic layerOrganic electroluminescence
An organic compound with excellent characteristics excelling in hole-injecting / transporting performance and having electron blocking ability, high stability in a thin-film state and high luminous efficiency is provided as material for an organic electroluminescent device.The compound of a general formula (1) having an indenocarbazole ring structure is used as a constituent material of at least one organic layer in the organic electroluminescent device that includes a pair of electrodes and one or more organic layers sandwiched between the pair of electrodes.
Owner:HODOGOYA CHEMICAL CO LTD
Wide range core supply compatible level shifter circuit
ActiveUS9178517B2Lower threshold voltageImprove charging capacityPower reduction in field effect transistorsPulse automatic controlLevel shiftingCurrent consumption
A level shifter circuit is implemented with dual gate fully depleted silicon-on-insulator (FDSOI) technology. By enhancing the performance of the NMOS and devices within the level shifting circuit, the Vt of the dual gate FDSOI NMOS transistors is lowered without a need for additional control circuitry. Lowering the Vt can be accomplished through dynamic secondary gate control, by coupling together primary and secondary gates of the NMOS devices, while secondary gates of the PMOS devices can be coupled to a high voltage supply level. Such high performance NMOS devices can then operate at higher frequencies and run on a much wider range of core power supplies. Meanwhile, conventional DC conditions are maintained during steady state operation. Because no components are added to the level shifter circuit, the higher performance is achieved without an increase in size and current consumption.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
Compound having substituted anthracene ring structure and pyridoindole ring structure and organic electroluminescence device
InactiveUS20130341604A1Improve abilitiesHigh luminous efficiencyOrganic chemistryElectroluminescent light sourcesAnthraceneElectron injection
The present invention provides an organic compound having excellent properties, which is excellent in electron-injection / transport performance, has hole-blocking ability and is high stability in a thin-film state, as a material for an organic electroluminescence device having a high efficiency and a high durability, and provides is an organic electroluminescence device having a high efficiency and a high durability using the compound. The present invention relates to a compound having a substituted anthracene ring structure and a pyridoindole ring structure represented by general formula (1); and an organic electroluminescence device having a pair of electrodes and at least one organic layer interposed between the electrodes in which the at least one organic layer contains the compound.
Owner:YOKOYAMA NORIMASA +4
Novel compound and organic light-emitting device using same
ActiveUS20140091298A1Improve light efficiencyLife span property be improveOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesElectrochemistryOrganic compound
The present invention provides a novel compound that is capable of largely improving a life span, efficiency, electrochemical stability and thermal stability of an organic light emitting device, and an organic light emitting device in which the compound is included in an organic compound layer.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Compound having a substituted anthracene ring structure and pyridoindole ring structure, and organic electroluminescent device
ActiveUS8748014B2Improve abilitiesHigh luminous efficiency and power efficiencyOrganic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensAnthraceneOrganic layer
The present invention relates to a compound having a substituted anthracene ring structure and a pyridoindole ring structure, which is represented by the following general formula (1) or the following general formula (2); and an organic electroluminescent device having a pair of electrodes and at least one organic layer interposed therebetween, in which the compound having a substituted anthracene ring structure and a pyridoindole ring structure, which is represented by the following general formula (1) or the following general formula (2), is used as a constituent material of the aforementioned at least one organic layer.
Owner:HODOGOYA CHEMICAL CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com