Patents
Literature
622 results about "Dual gate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
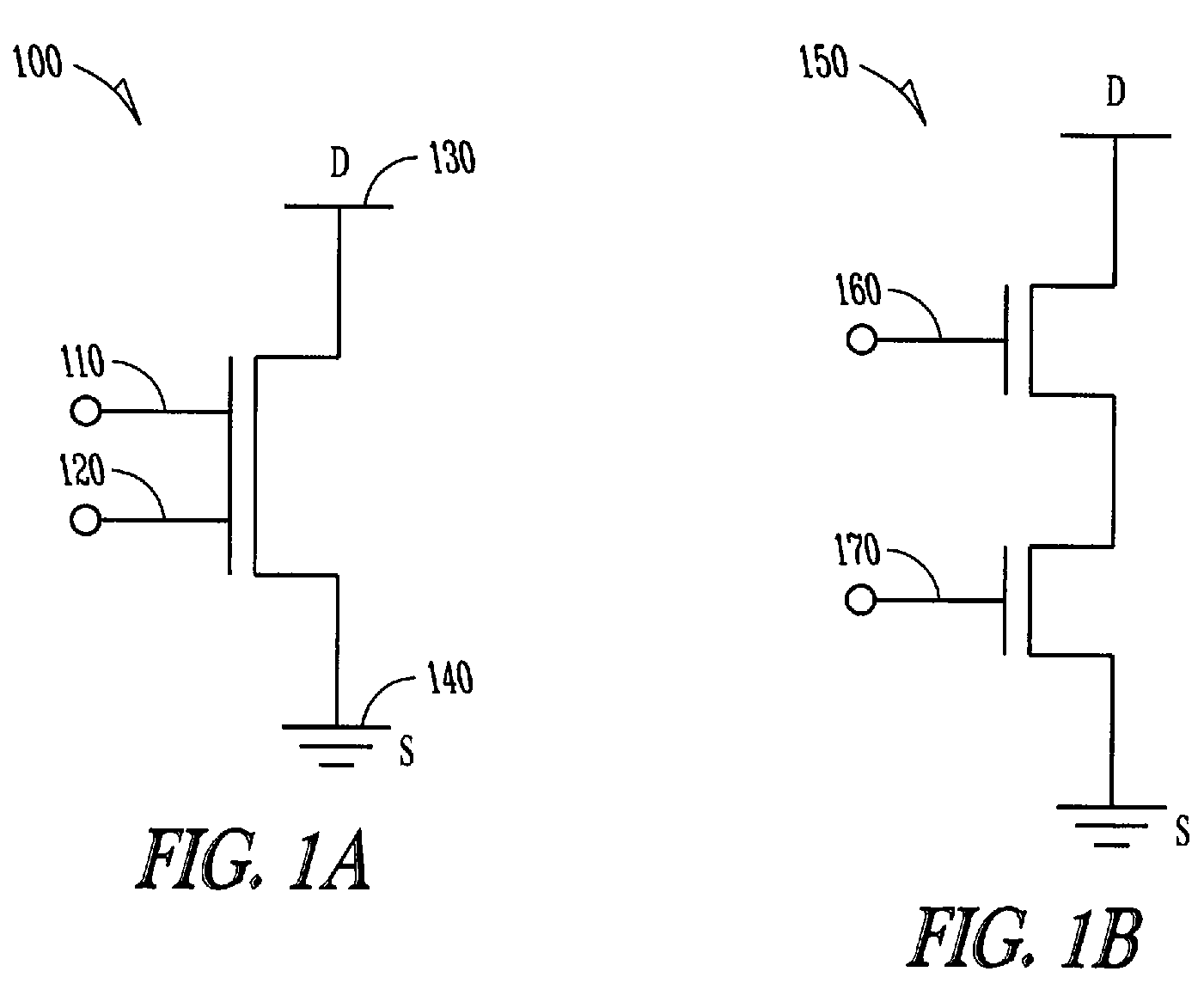
The dual-gate MOSFET (DGMOS) has a tetrode configuration, where both gates control the current in the device. It is commonly used for small-signal devices in radio frequency applications where biasing the drain-side gate at constant potential reduces the gain loss caused by Miller effect, ...
Dual gate fet structures for flexible gate array design methodologies
InactiveUS20090101940A1Easy to operateSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate arrayStandard cell
A gate array cell adapted for standard cell design methodology or programmable gate array that incorporates a dual gate FET device to offer a range of performance options within the same unit cell area. The conductivity and drive strength of the dual gate device may be selectively tuned through independent processing of manufacturing parameters to provide an asymmetric circuit response for the device or a symmetric response as dictated by the circuit application.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
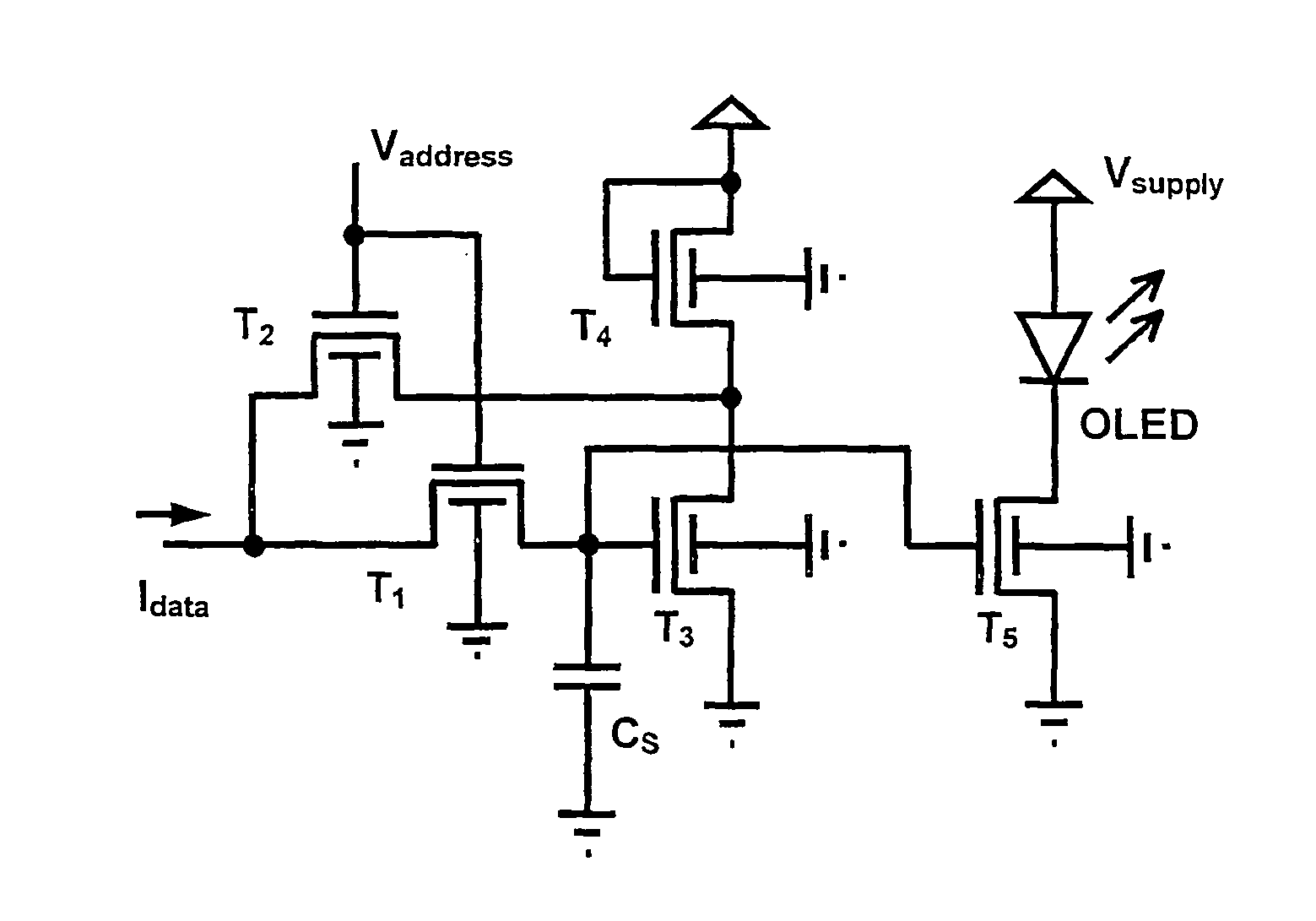
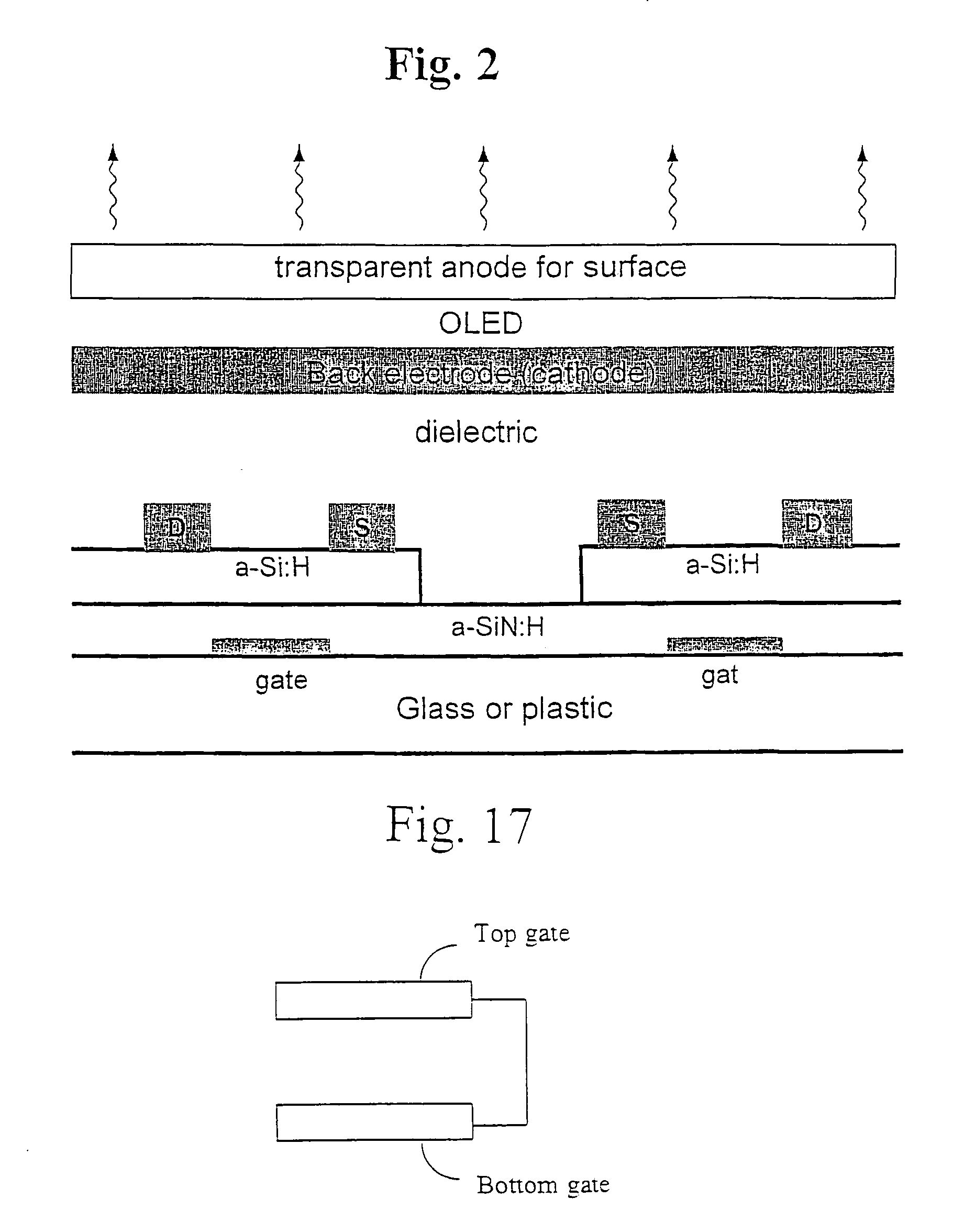
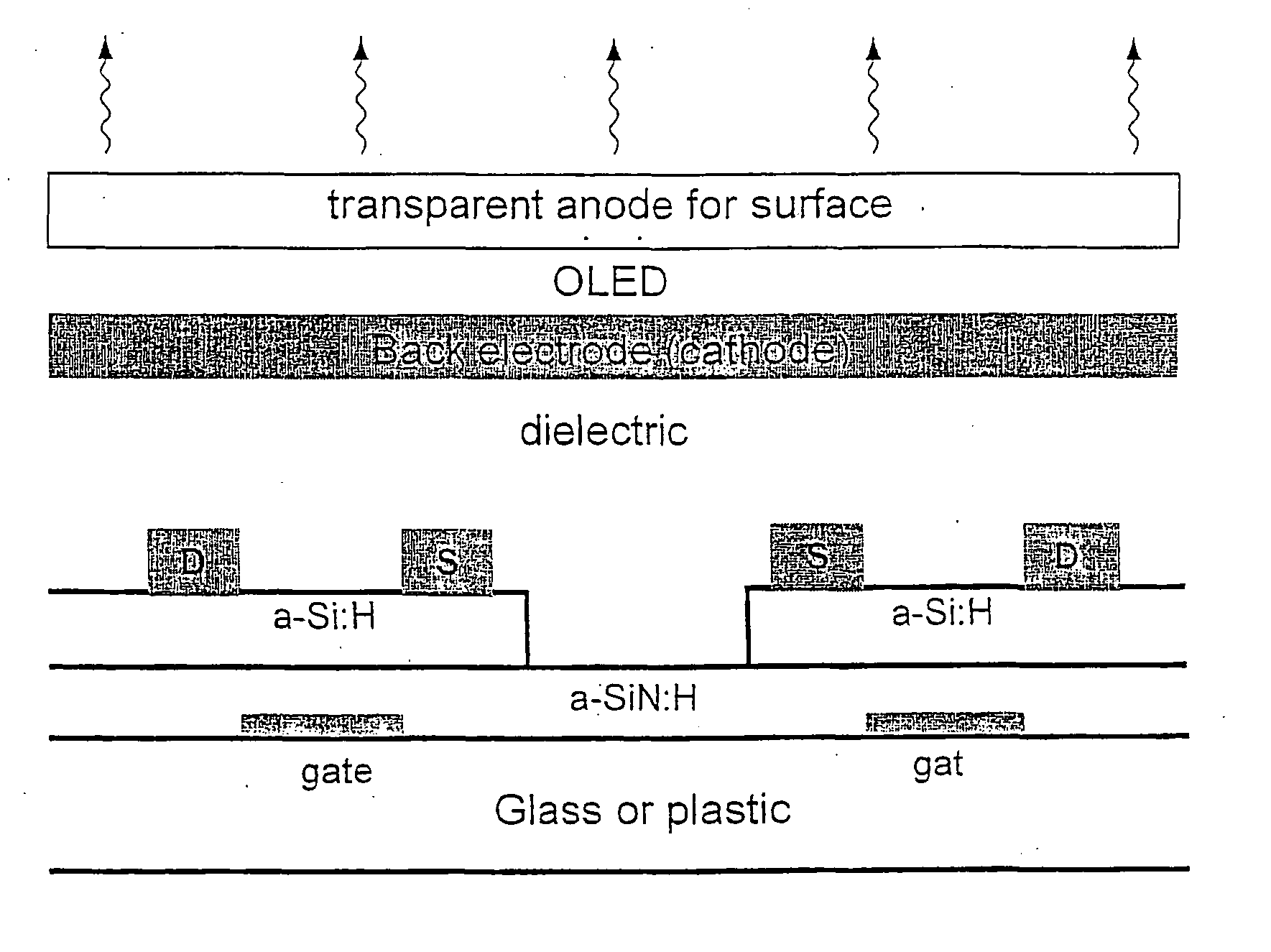
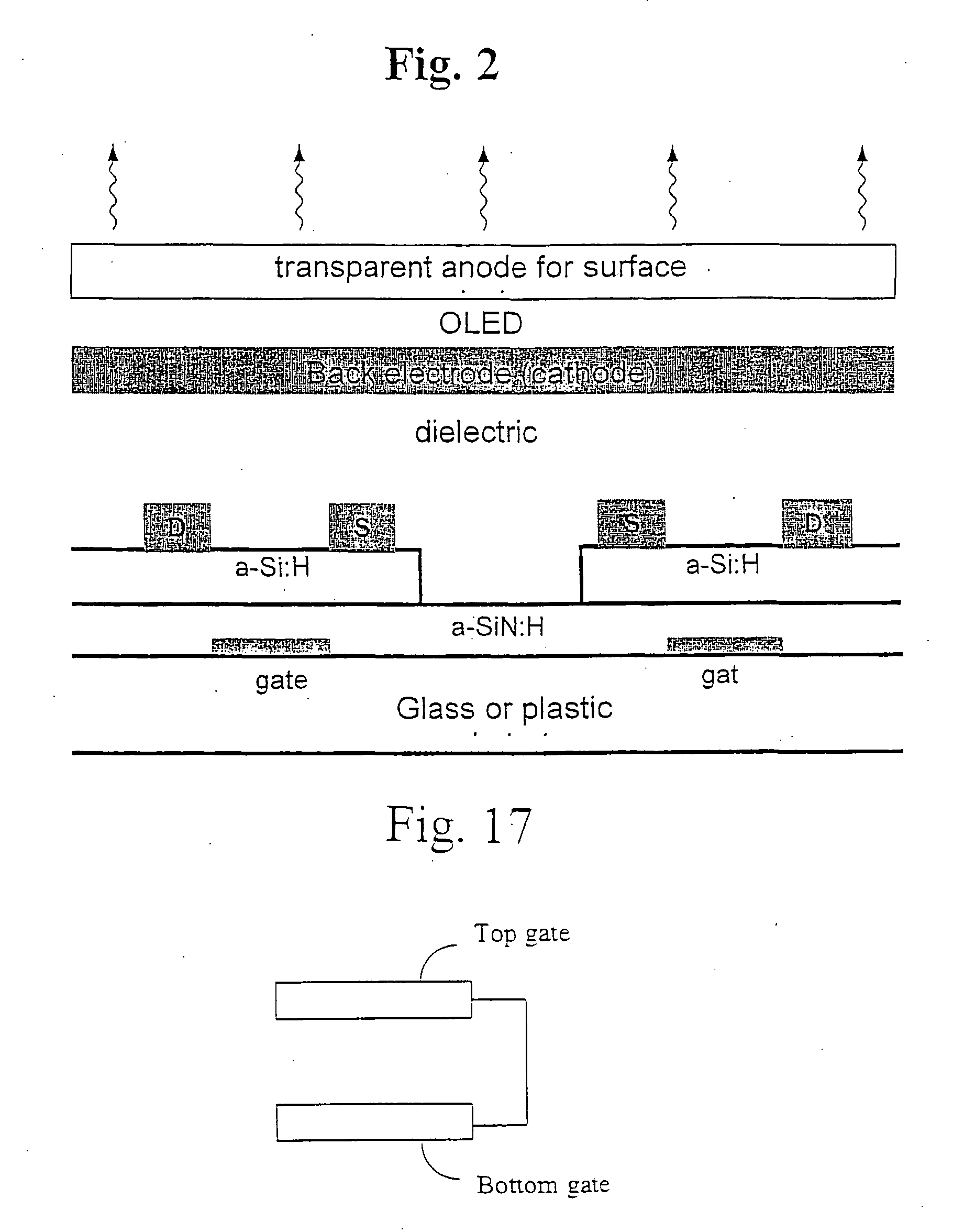
Pixel current driver for organic light emitting diode displays
InactiveUS7414600B2Minimizing parasitic couplingMinimizes parasitic capacitanceTransistorStatic indicating devicesBottom gateDisplay device
A pixel current driver comprises a plurality of thin film transistors (TFTs) each having dual gates and for driving OLED layers. A top gate of the dual gates is formed between a source and a drain of each of the thin film transistors, to thereby minimize parasitic capacitance. The top gate is grounded or electrically tied to a bottom gate. The plurality of thin film transistors may be two thin film transistors formed in voltage-programmed manner or five thin film transistors formed in a current-programmed ΔVT-compensated manner. Other versions of the current-programmed circuit with different numbers of thin film transistors are also presented that compensate for δVT. The OLED layer are continuous and vertically stacked on the plurality of thin film transistors to provide an aperture ratio close to 100%.
Owner:IGNIS INNOVATION
High density NAND non-volatile memory device
ActiveUS20070012988A1Efficient eraseReduce harmSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesCharge retentionLow voltage
Non-volatile memory devices and arrays are described that utilize dual gate (or back-side gate) non-volatile memory cells with band engineered gate-stacks that are placed above or below the channel region in front-side or back-side charge trapping gate-stack configurations in NAND memory array architectures. The band-gap engineered gate-stacks with asymmetric or direct tunnel barriers of the floating node memory cells of embodiments of the present invention allow for low voltage tunneling programming and efficient erase with electrons and holes, while maintaining high charge blocking barriers and deep carrier trapping sites for good charge retention. The memory cell architecture also allows for improved high density memory devices or arrays with the utilization of reduced feature word lines and vertical select gates.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Pixel current driver for organic light emitting diode displays
InactiveUS20060027807A1Improve circuit performanceMinimize chargeTransistorStatic indicating devicesBottom gateDisplay device
A pixel current driver comprises a plurality of thin film transistors (TFTs) each having dual gates and for driving OLED layers. A top gate of the dual gates is formed between a source and a drain of each of the thin film transistors, to thereby minimize parasitic capacitance. The top gate is grounded or electrically tied to a bottom gate. The plurality of thin film transistors may be two thin film transistors formed in voltage-programmed manner or five thin film transistors formed in a current-programmed ΔVT-compensated manner. Other versions of the current-programmed circuit with different numbers of thin film transistors are also presented that compensate for δVT. The OLED layer are continuous and vertically stacked on the plurality of thin film transistors to provide an aperture ratio close to 100%.
Owner:IGNIS INNOVATION
Dual gate FinFET
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Finfet-compatible metal-insulator-metal capacitor
At least one semiconductor fin for a capacitor is formed concurrently with other semiconductor fins for field effect transistors. A lower conductive layer is deposited and lithographically patterned to form a lower conductive plate located on the at least one semiconductor fin. A dielectric layer and at least one upper conductive layer are formed and lithographically patterned to form a node dielectric and an upper conductive plate over the lower conductive plate as well as a gate dielectric and a gate conductor over the other semiconductor fins. The lower conductive plate, the node dielectric, and the upper conductive plate collectively form a capacitor. The finFETs may be dual gate finFETs or trigate finFETs. A buried insulator layer may be optionally recessed to increase the capacitance. Alternately, the lower conductive plate may be formed on a planar surface of the buried insulator layer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Double gate trench transistor
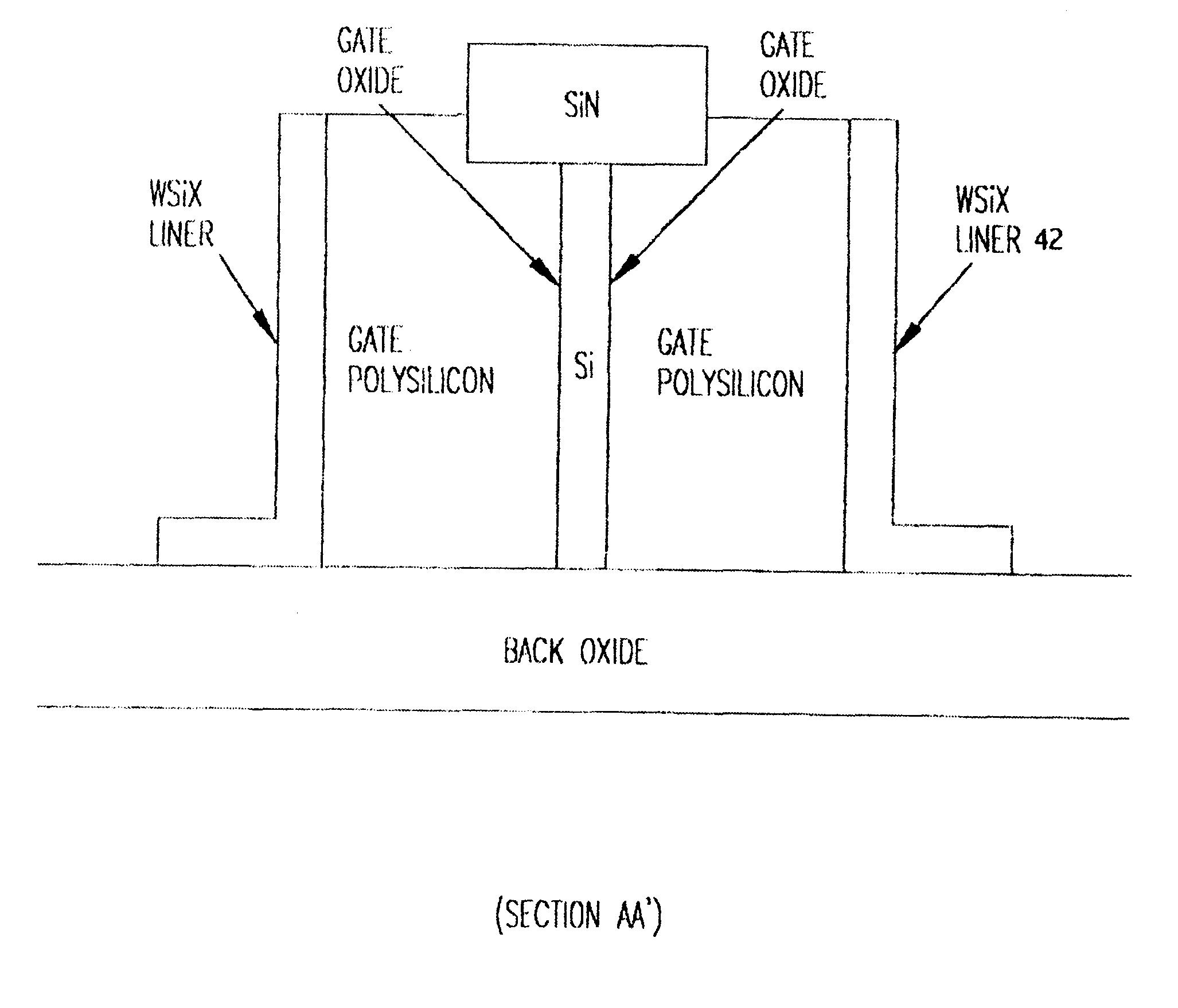
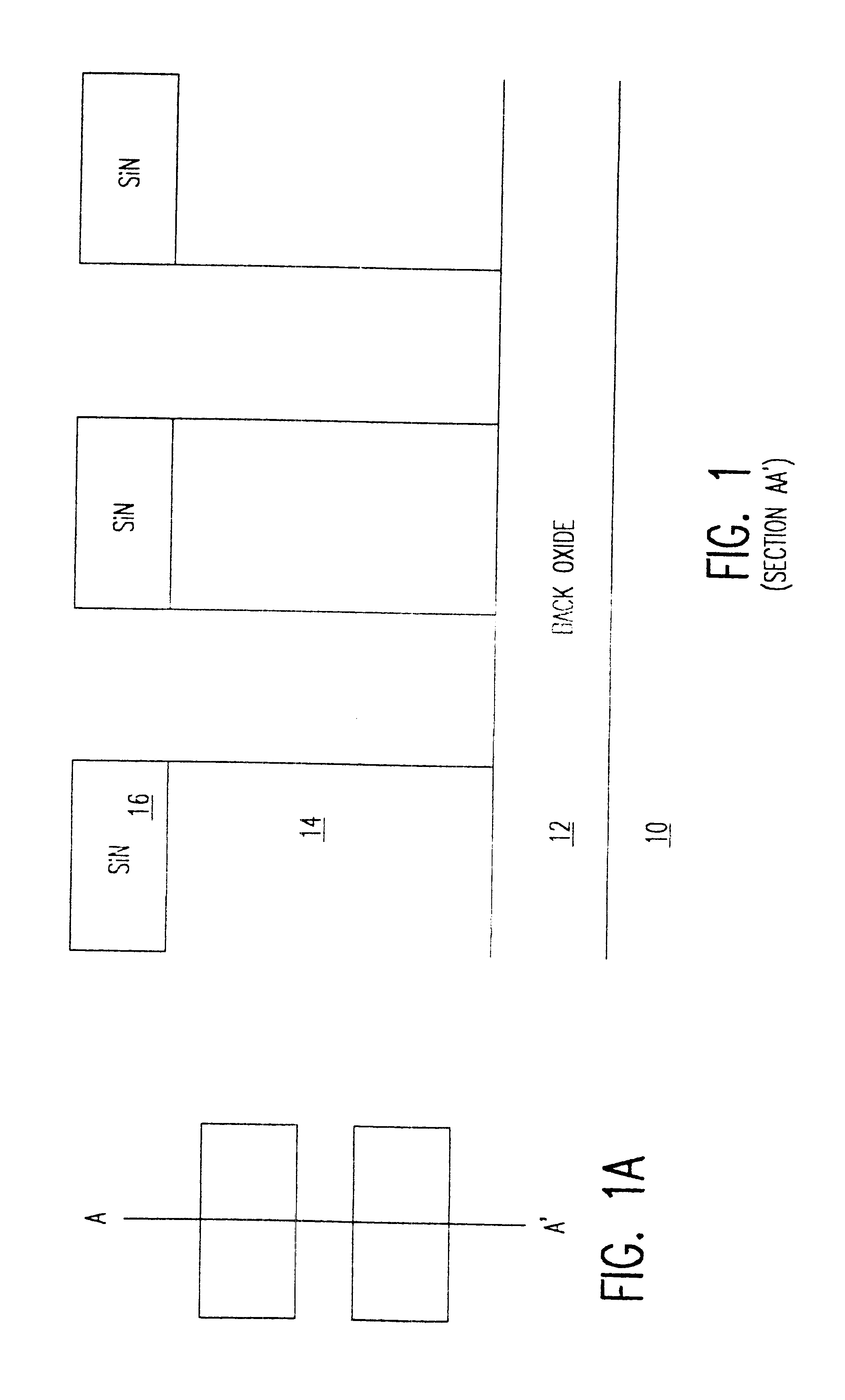
A field effect transistor is formed with a sub-lithographic conduction channel and a dual gate which is formed by a simple process by starting with a silicon-on-insulator wafer, allowing most etching processes to use the buried oxide as an etch stop. Low resistivity of the gate, source and drain is achieved by silicide sidewalls or liners while low gate to junction capacitance is achieved by recessing the silicide and polysilicon dual gate structure from the source and drain region edges.
Owner:IBM CORP
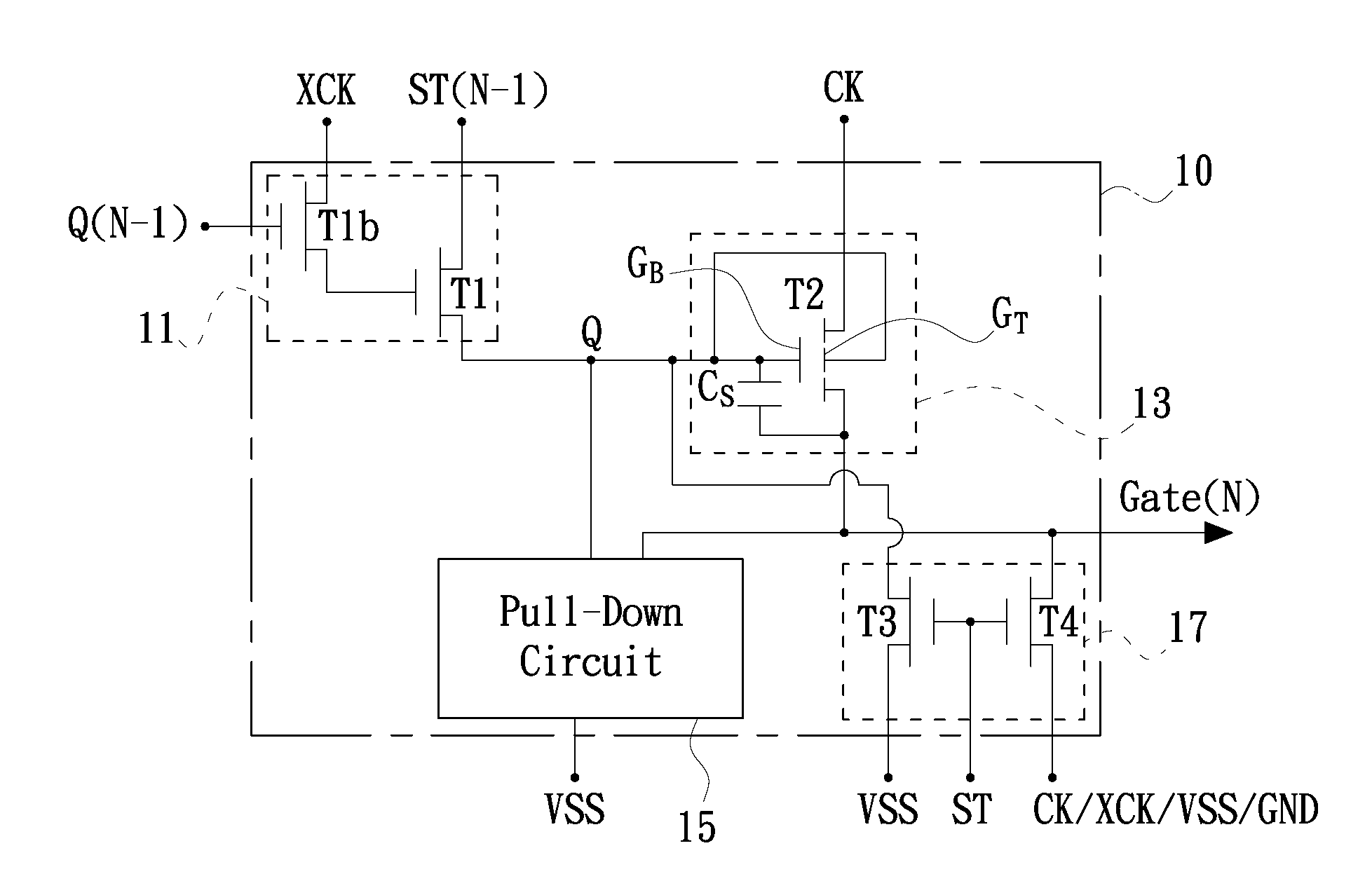
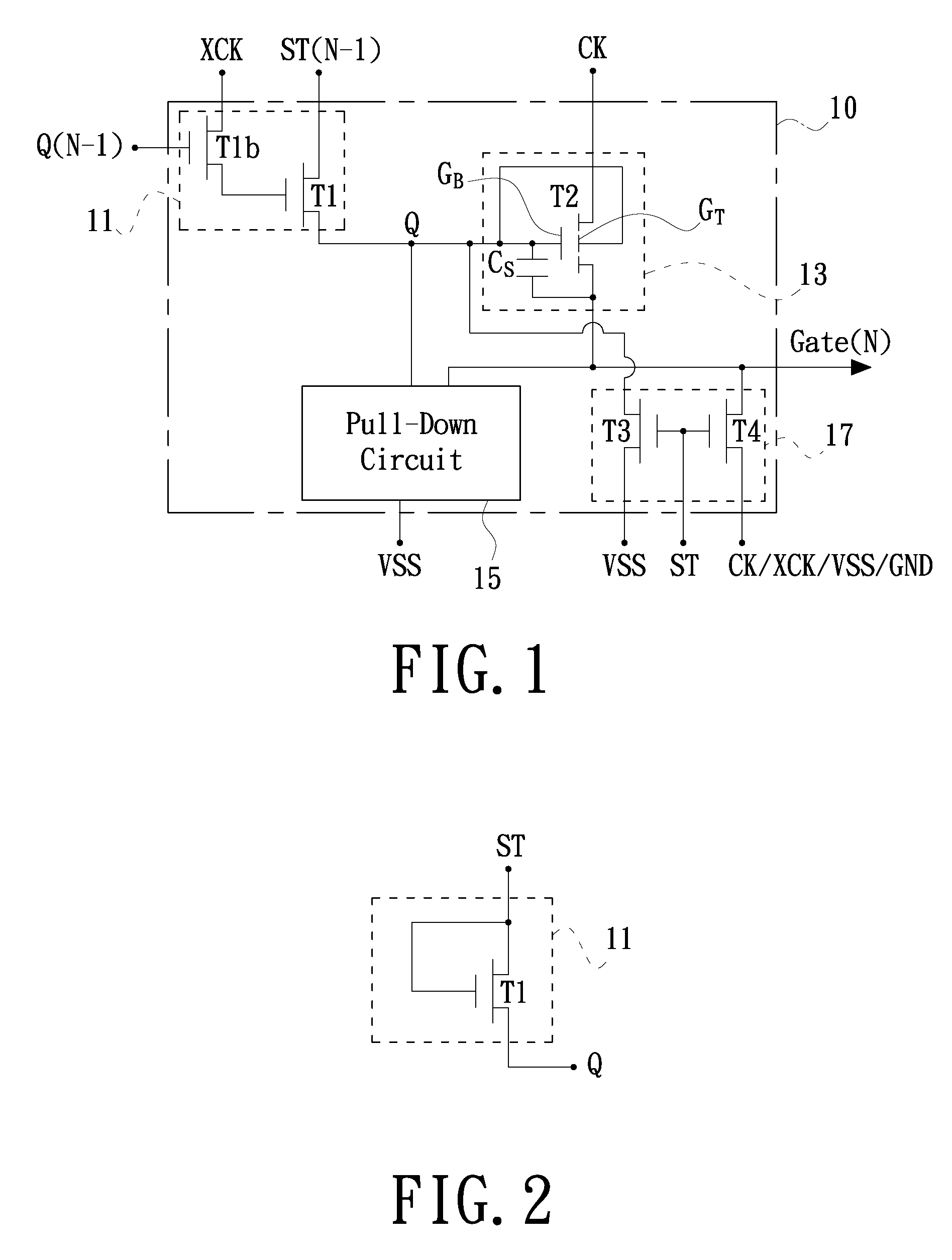
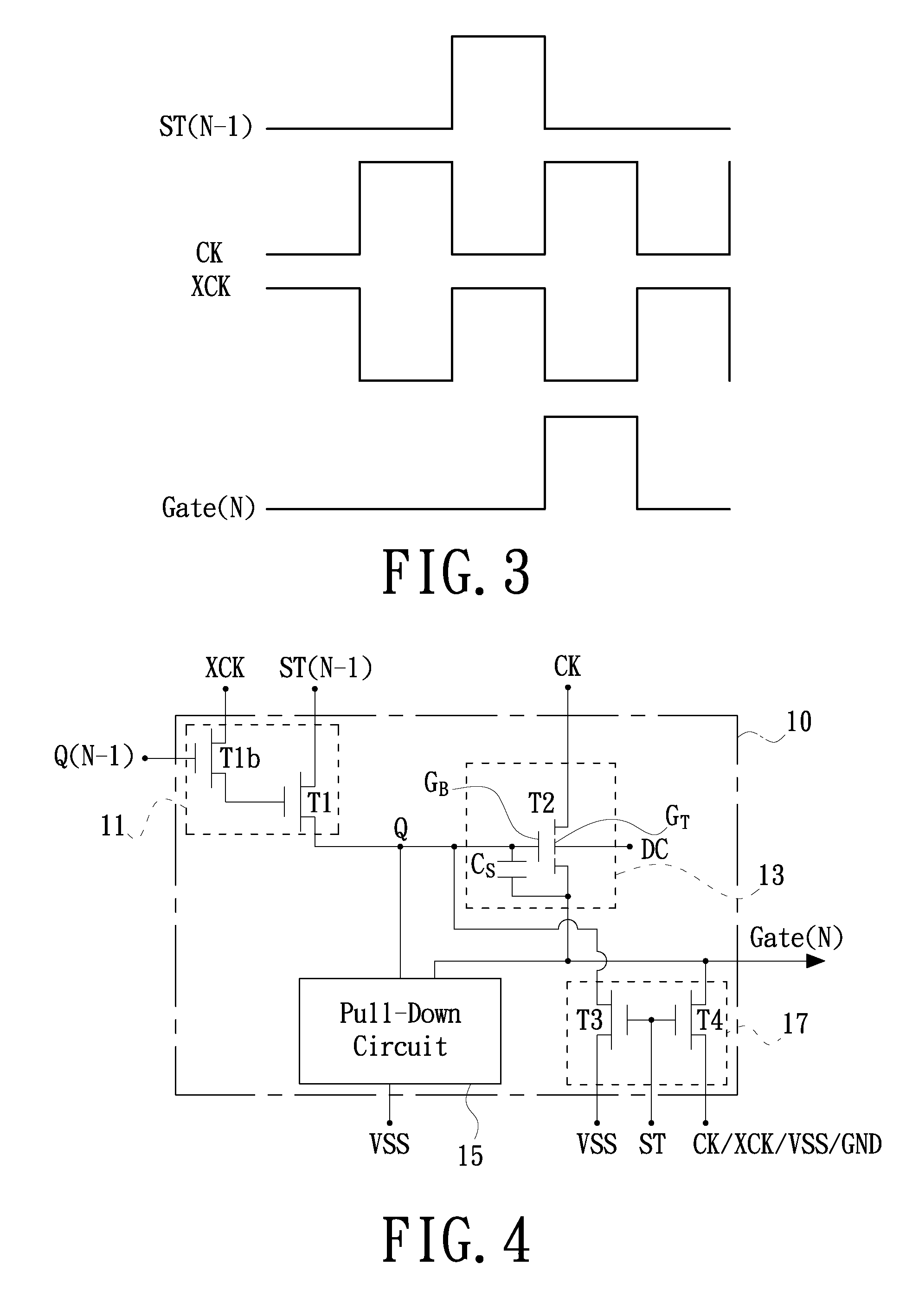
Shift register
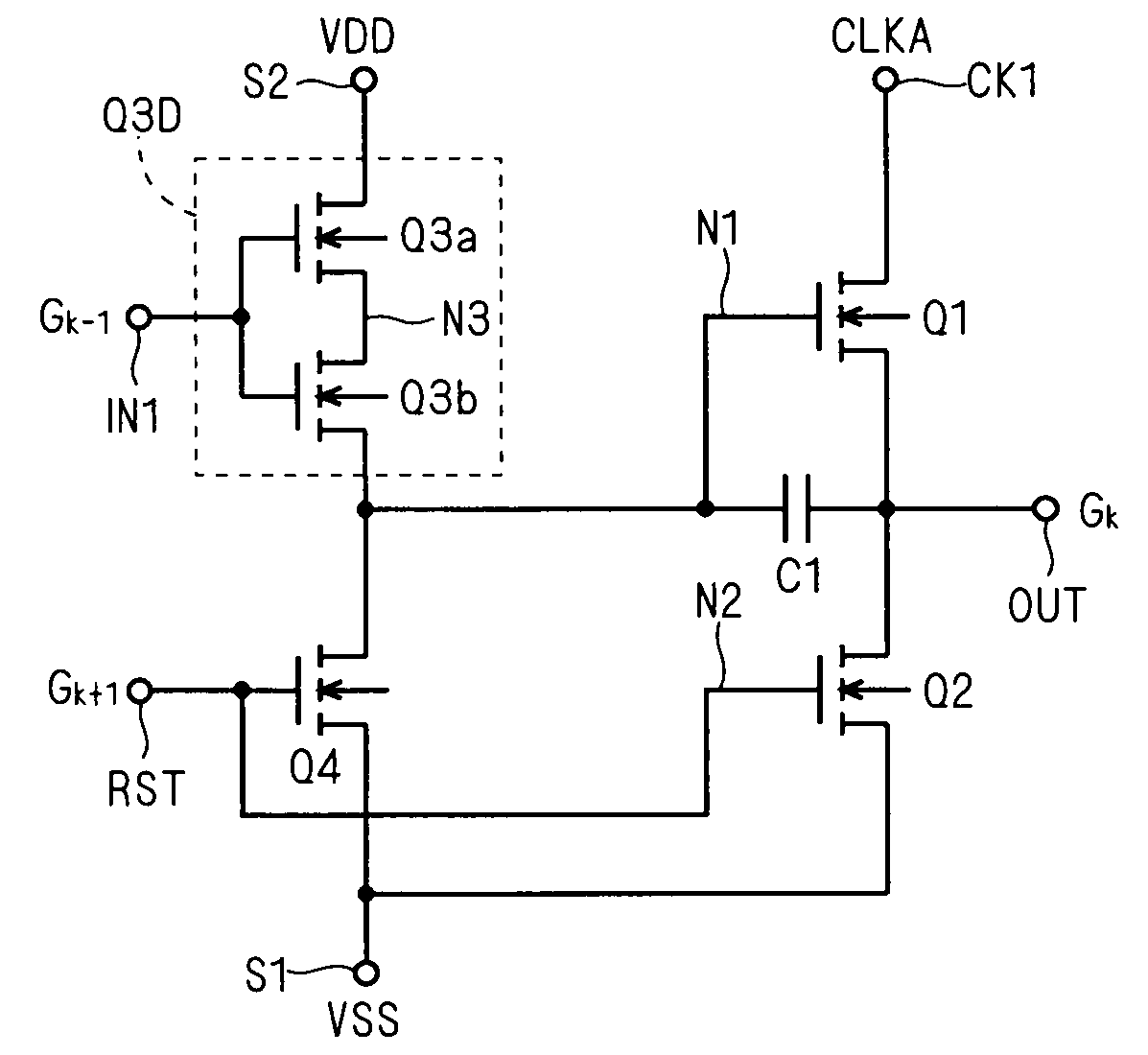
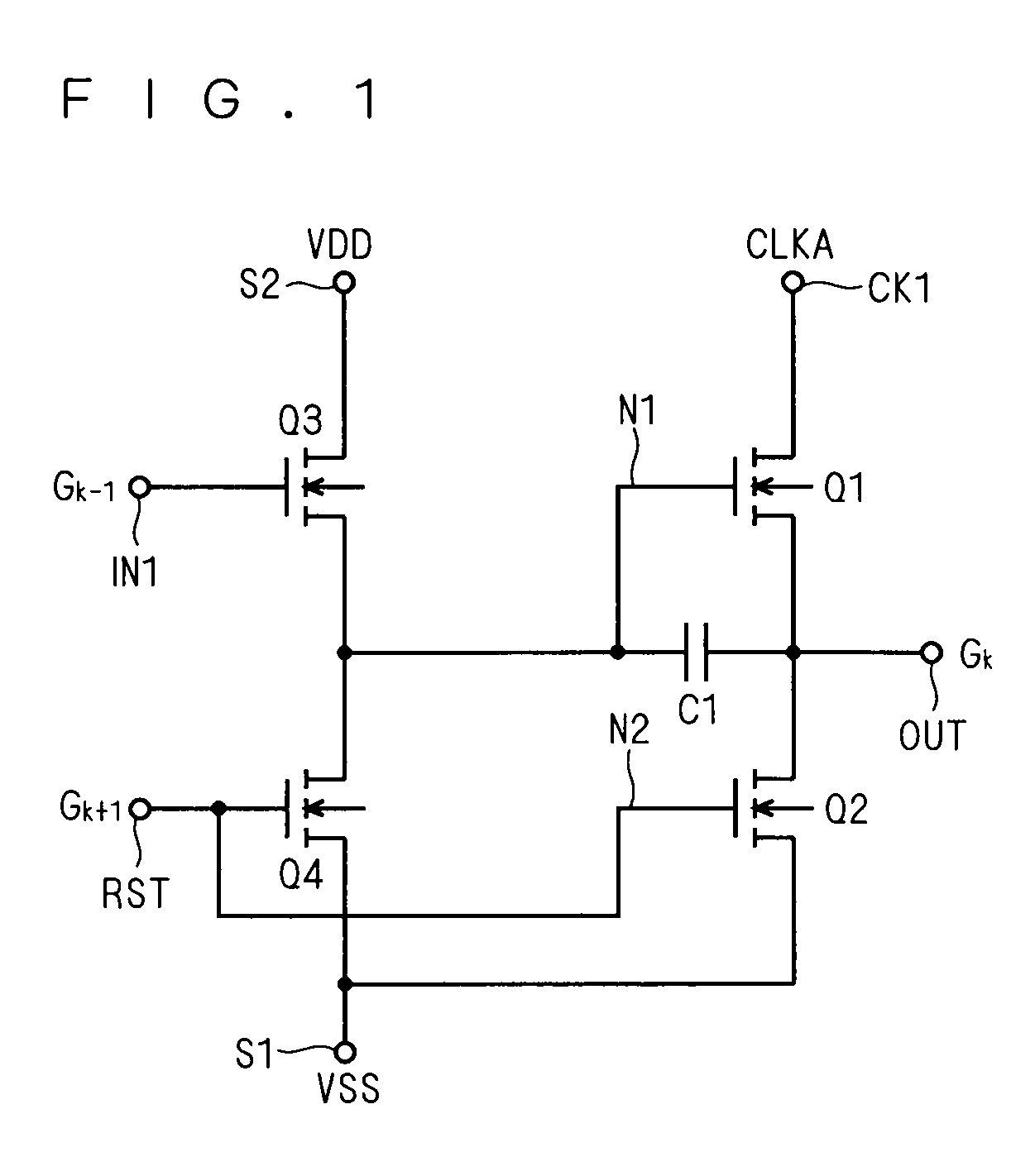
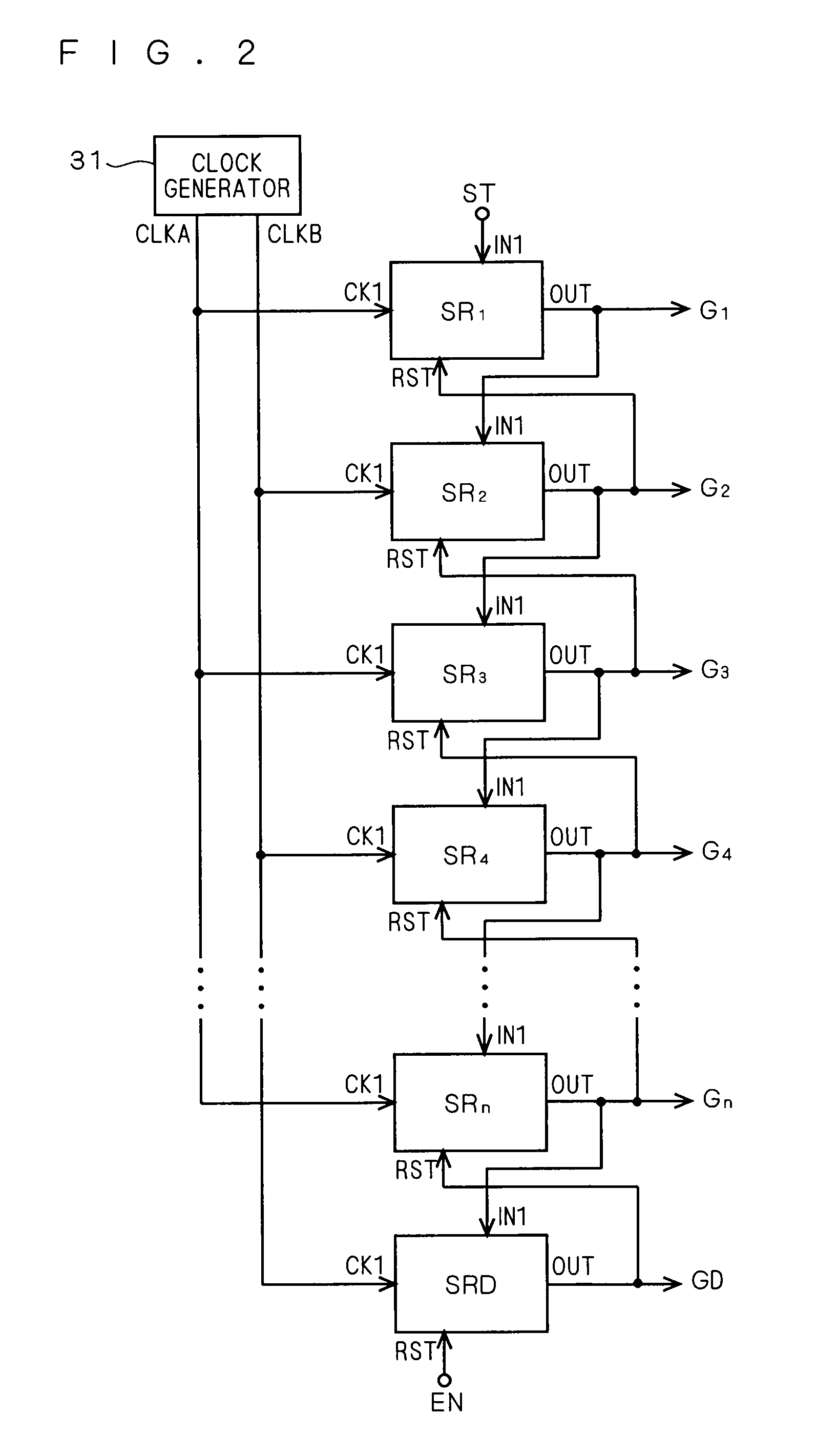
ActiveUS20110150169A1Large conduction currentReduce power consumptionStatic indicating devicesDigital storageShift registerControl signal
A shift register includes a control circuit, a pull-up circuit and a pull-down circuit. The control circuit generates a control signal according to a start pulse signal during being enabled. The pull-up circuit produces a gate pulse signal according to a clock signal during being enabled by the control signal. The pull-up circuit includes a dual-gate transistor. A first gate of the dual-gate transistor is electrically coupled to the control signal, a second gate of the dual-gate transistor is electrically coupled to a predetermined voltage, the source / drain of the dual-gate transistor serves as an output terminal for the gate pulse signal, and the drain / source of the dual-gate transistor is electrically coupled to the clock signal. The pull-down circuit pulls a potential at the first gate and another potential at the output terminal down to a power supply potential during the pull-up circuit is disabled
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
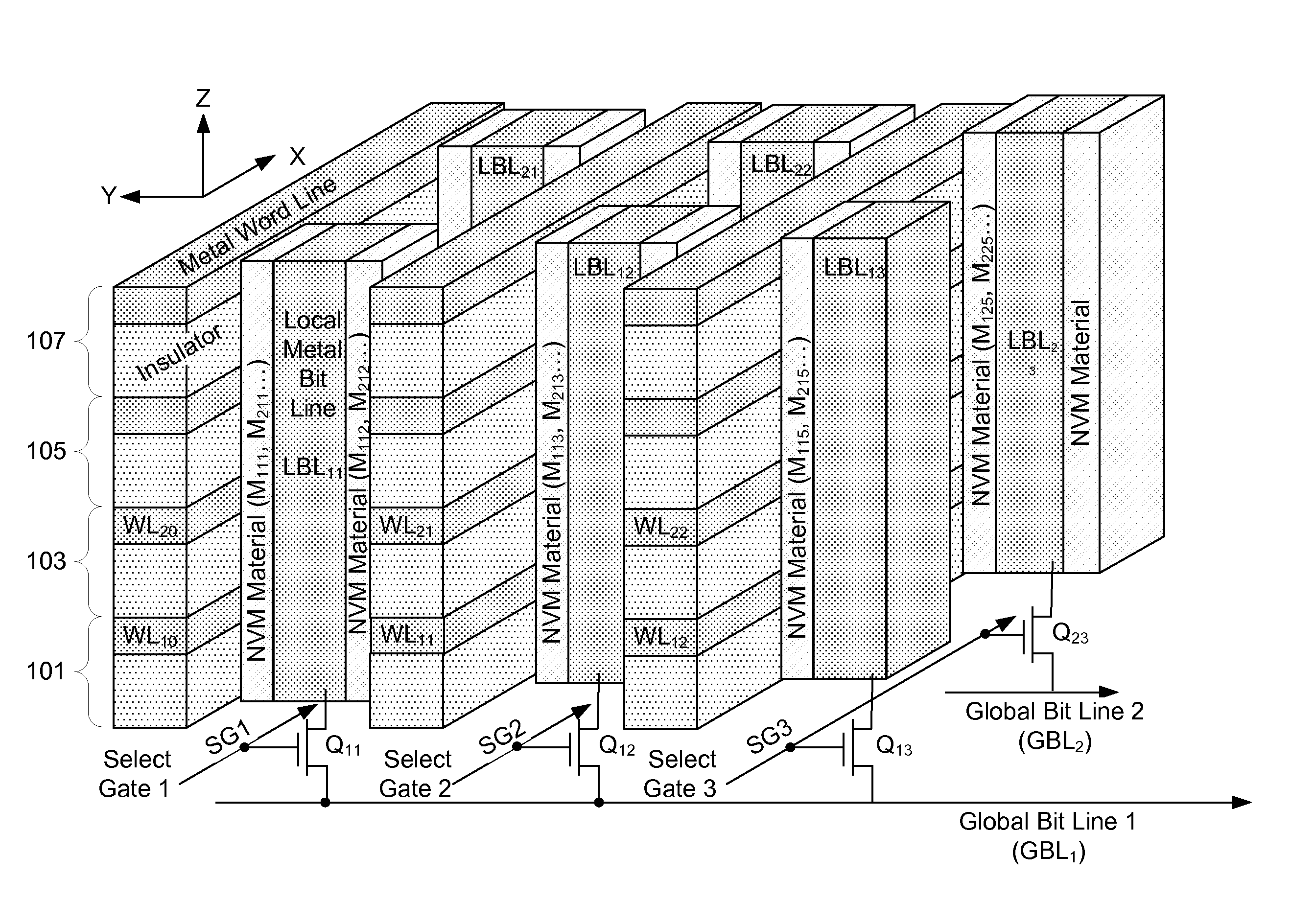
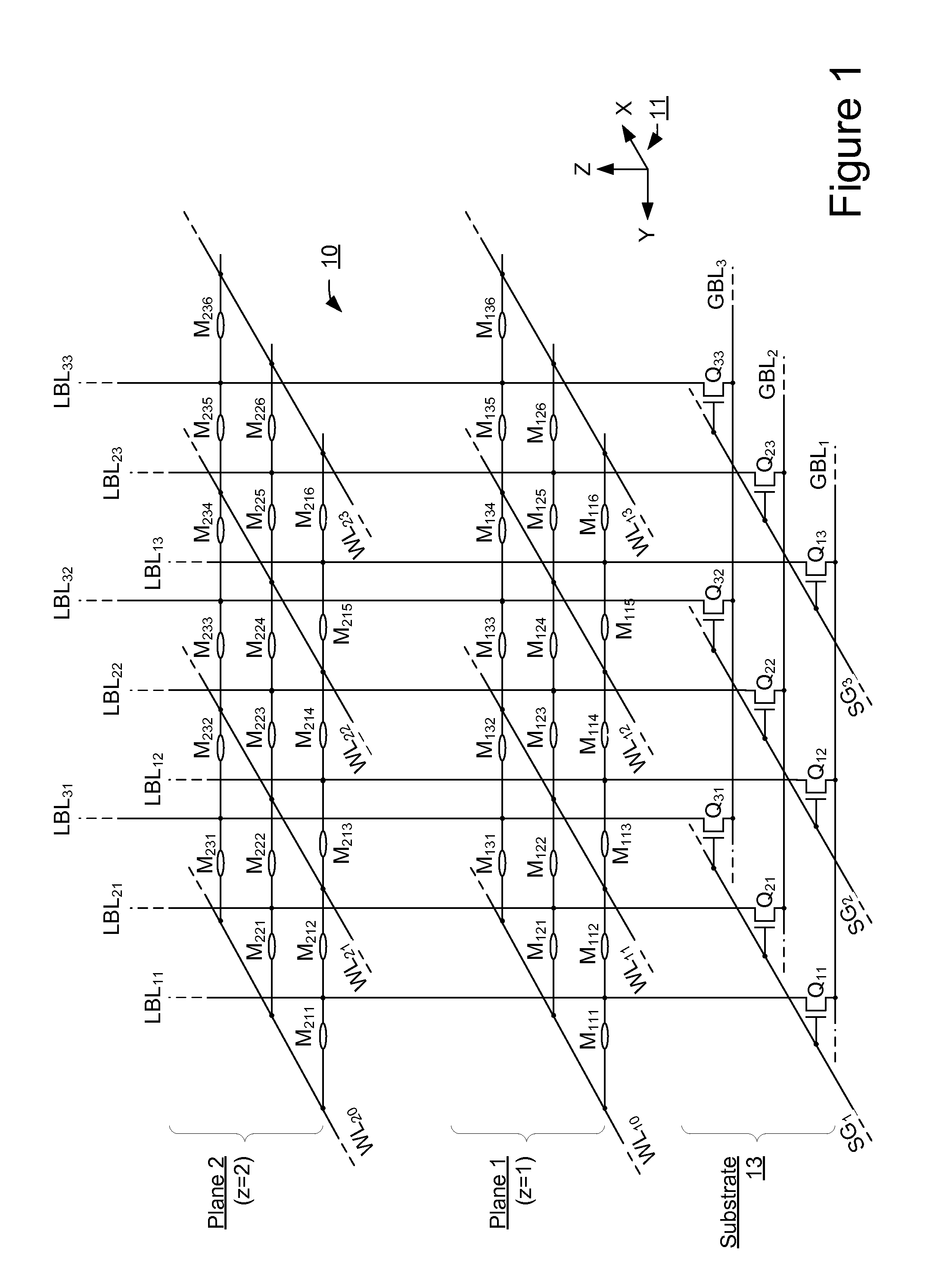
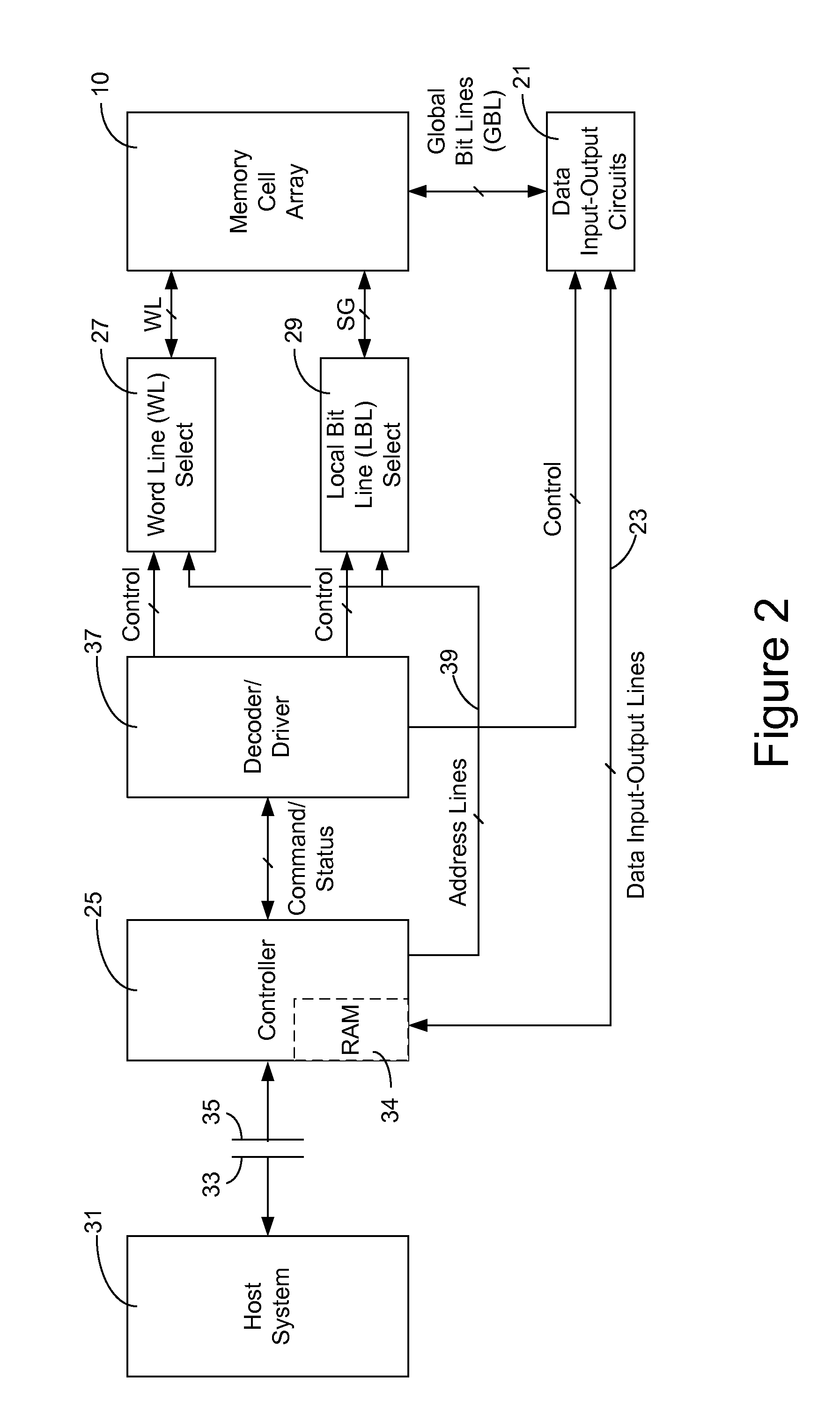
Three dimensional non-volatile storage with dual gate selection of vertical bit lines
ActiveUS20120147648A1Reduce leakage currentSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesBit lineSemiconductor
A three-dimensional array adapted for memory elements that reversibly change a level of electrical conductance in response to a voltage difference being applied across them. Memory elements are formed across a plurality of planes positioned different distances above a semiconductor substrate. Bit lines to which the memory elements of all planes are connected are oriented vertically from the substrate and through the plurality of planes.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Multi-bit non-volatile memory device having a dual-gate and method of manufacturing the same, and method of multi-bit cell operation
ActiveUS20060237777A1Eliminate the effects ofTransistorNanoinformaticsEngineeringNon-volatile memory
The present invention relates to a multi-bit non-volatile memory device having a dual gate employing local charge trap and method of manufacturing the same, and an operating method for a multi-bit cell operation.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
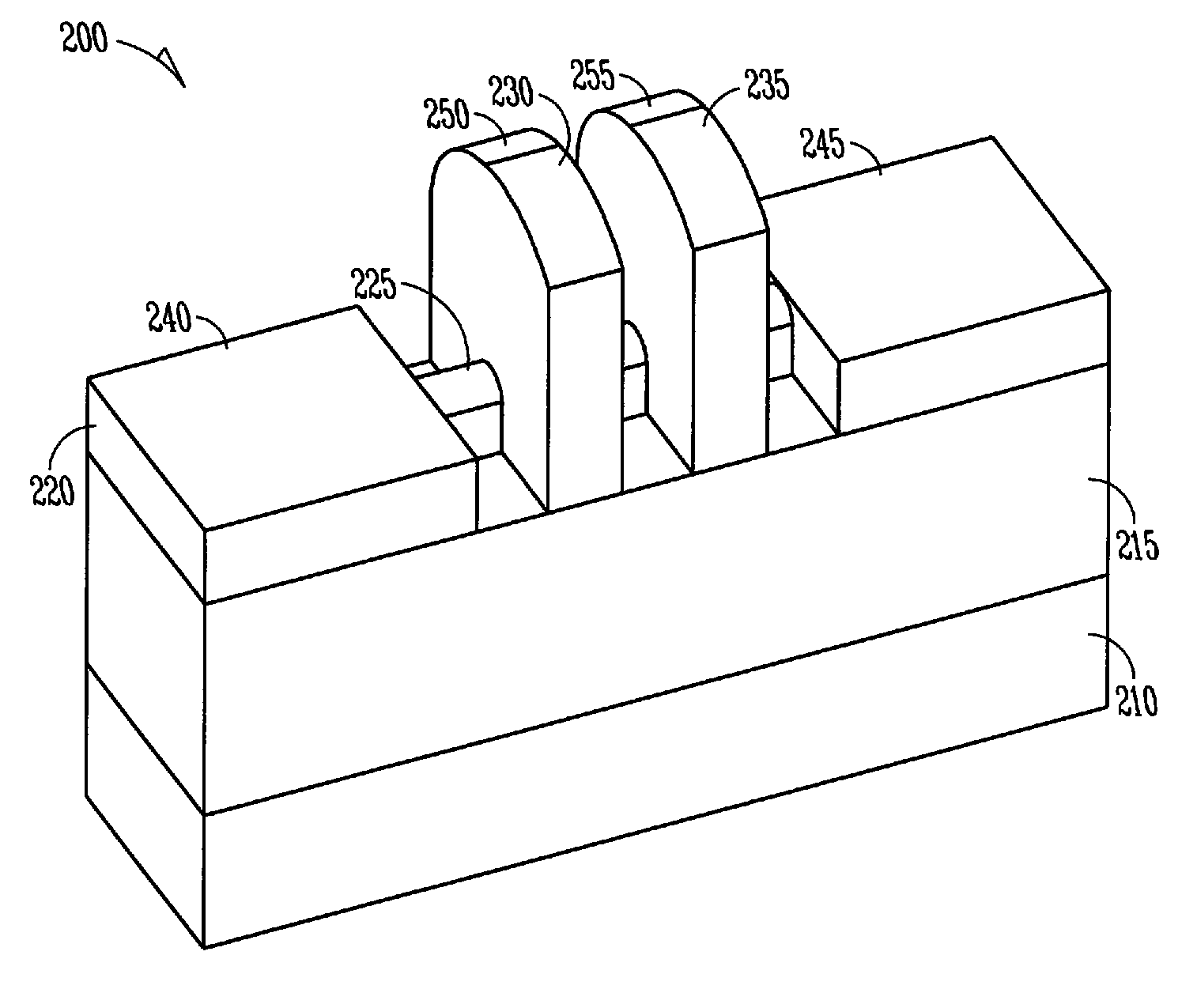
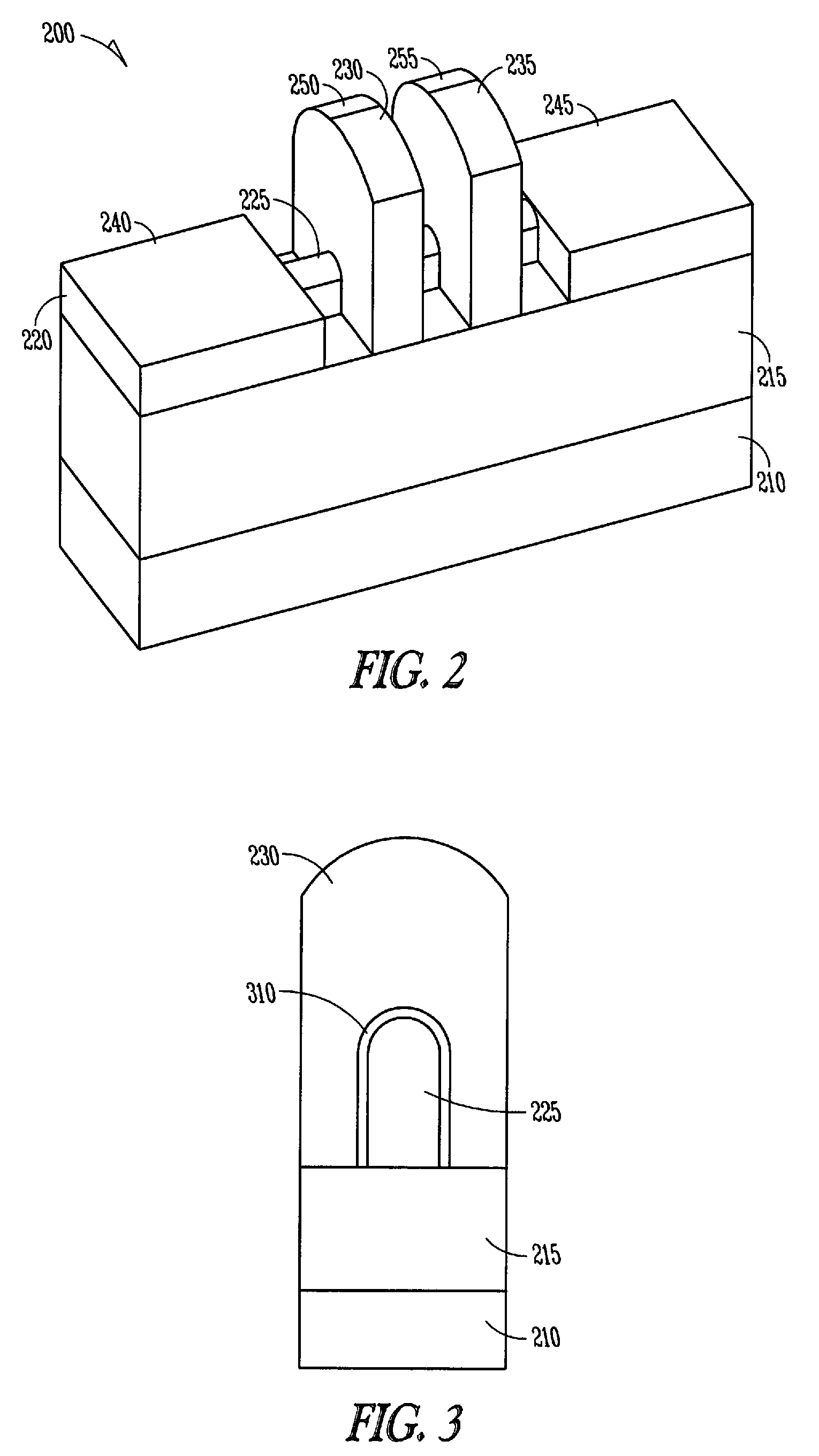
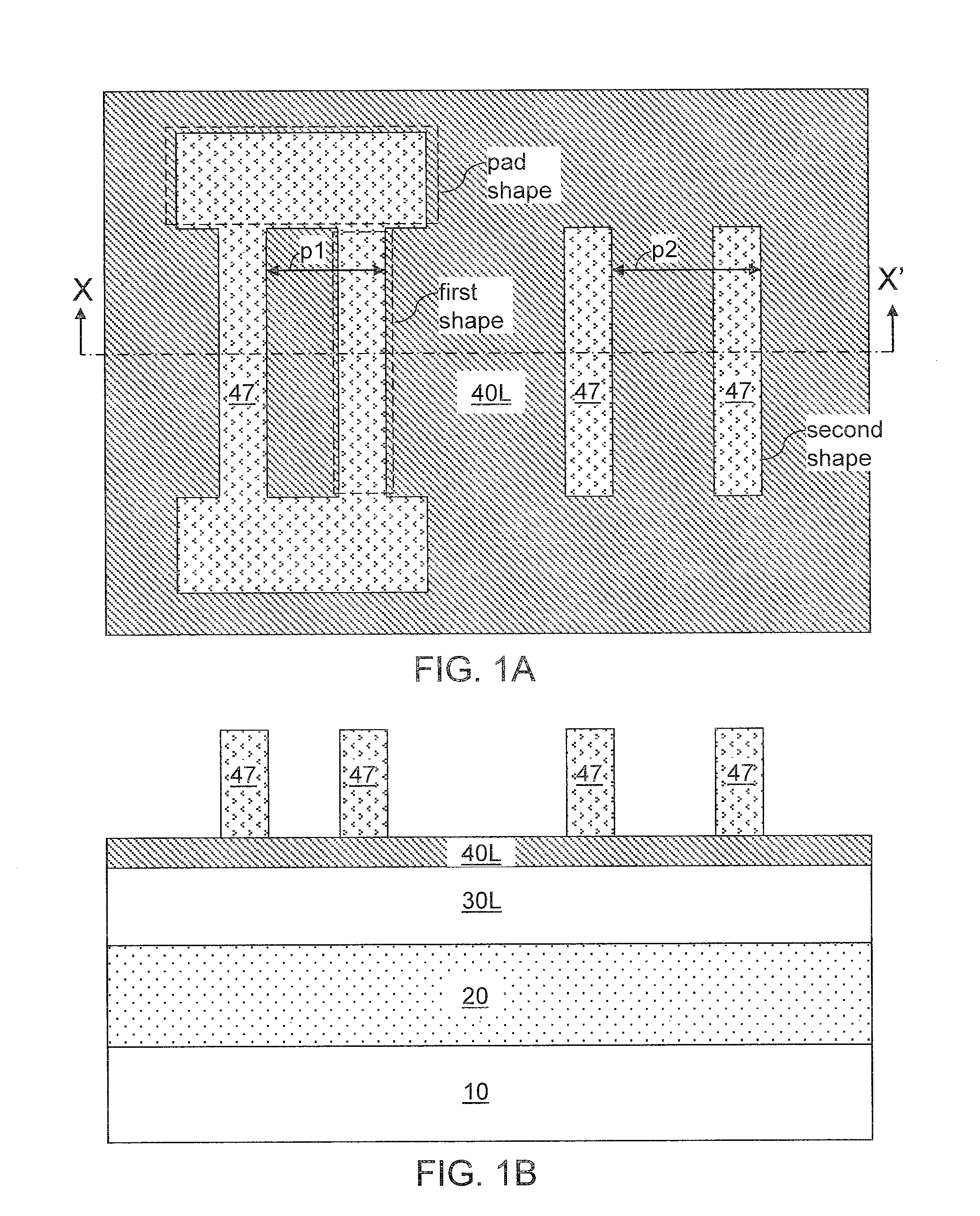
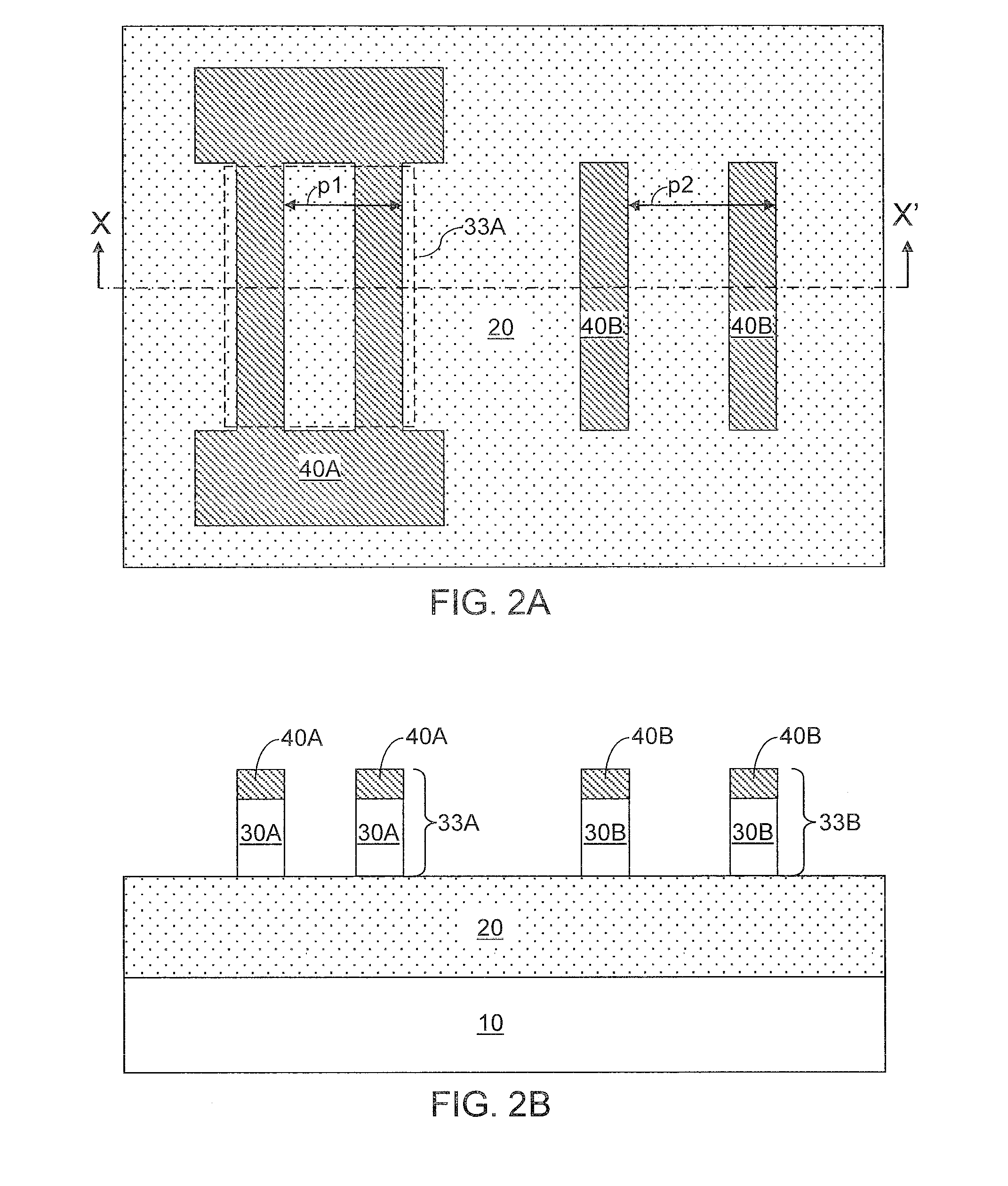
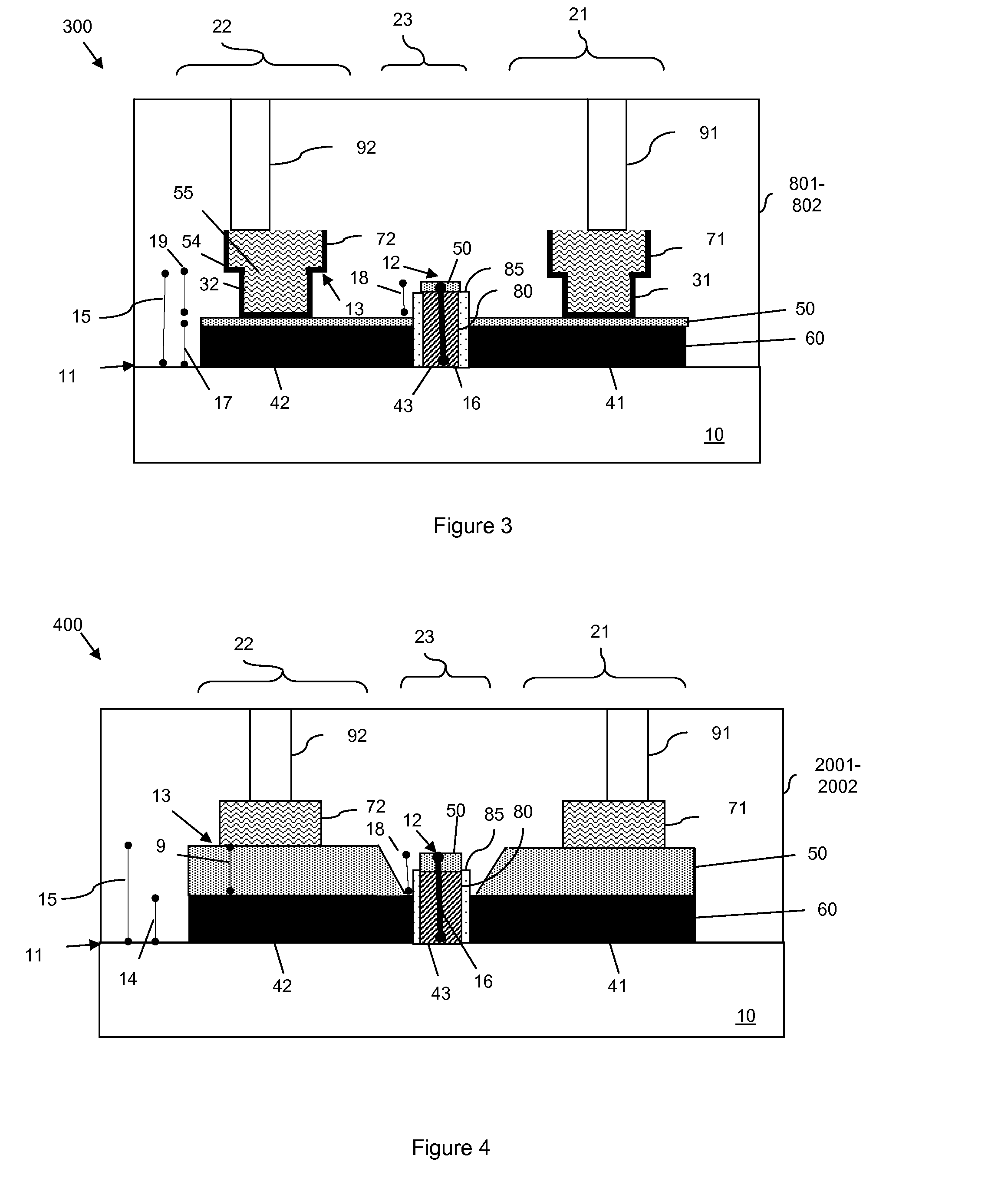
Vertical trench-formed dual-gate FET device structure and method for creation
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method of forming one or more FETs having a vertical trench-formed double-gate, with a plurality of nitride layers having oxide marker etch-stop layers provided periodically there-through, thereby adapting the FETs to have a plurality of selectable gate lengths. The present invention provides for control and formation of gate lengths scaled down to about 5 nm to about 100 nm, preferably from about 5 nm to about 50 nm. The plurality of pad nitride layers with the oxide etch-stop layers provide for the present FET to be connected to a plurality of contacts having a variety of connection depths corresponding to the gate lengths used, by etching a plurality of via in the pad nitride layers whereby such vias stop at selected ones of the etch-stop layers to provide vias adapted to connect with the selected ones of such contacts. Additional gate material may be deposited over a top surface of the selected plurality of nitride layers to allow for contacts to the gate electrodes of any given FET.
Owner:IBM CORP
Semiconductor device and shift register circuit
ActiveUS20080187089A1Avoid failurePrevent threshold voltagePulse automatic controlDigital storageCapacitanceShift register
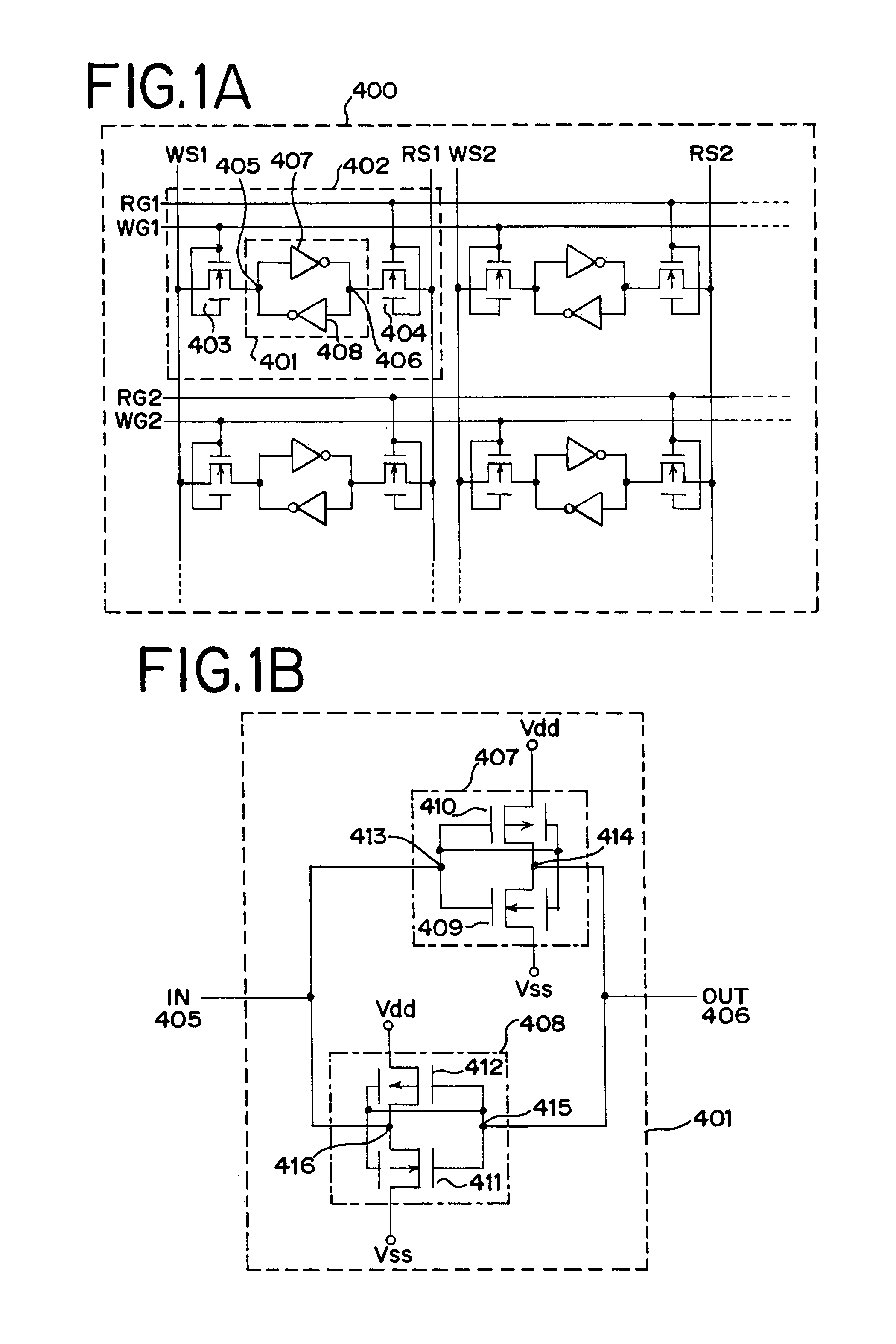
A dual-gate transistor formed of two transistors connected in series between a first power terminal and a first node is used as a charging circuit for charging a gate node (first node) of a transistor intended to pull up an output terminal of a unit shift register. The dual-gate transistor is configured such that the connection node (second node) between the two transistors constituting the dual-gate transistor is pulled down to the L level by the capacitive coupling between the gate and second node in accordance with the change of the gate from the H level to the L level.
Owner:TRIVALE TECH
Fin-type field effect transistor structure with merged source/drain silicide and method of forming the structure
ActiveUS7851865B2Increase capacitanceSeries resistance is minimizedSemiconductor devicesMetal silicideParasitic capacitance
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Monolithic 3-d dynamic memory and method
InactiveUS20170278858A1Accelerated programReduced P/E voltageSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesEngineeringDram
A monolithic 3-D dynamic memory structure includes independently addressable strings of dual-gate devices. In each dual-gate device charge is deliberately stored on one side of the dual-gate. Although the stored charge may leak away, the stored charge in a dual-gate device of the present invention need only be refreshed at much longer intervals than conventional DRAM cells.
Owner:SCHILTRON
Field effect transistor with raised source/drain fin straps
ActiveUS20080067613A1Lower resistanceReduce capacitanceTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceEngineering
Therefore, disclosed above are embodiments of a multi-fin field effect transistor structure (e.g., a multi-fin dual-gate FET or tri-gate FET) that provides low resistance strapping of the source / drain regions of the fins, while also maintaining low capacitance to the gate by raising the level of the straps above the level of the gate. Embodiments of the structure of the invention incorporate either conductive vias or taller source / drain regions in order to electrically connect the source / drain straps to the source / drain regions of each fin. Also, disclosed are embodiments of associated methods of forming these structures.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
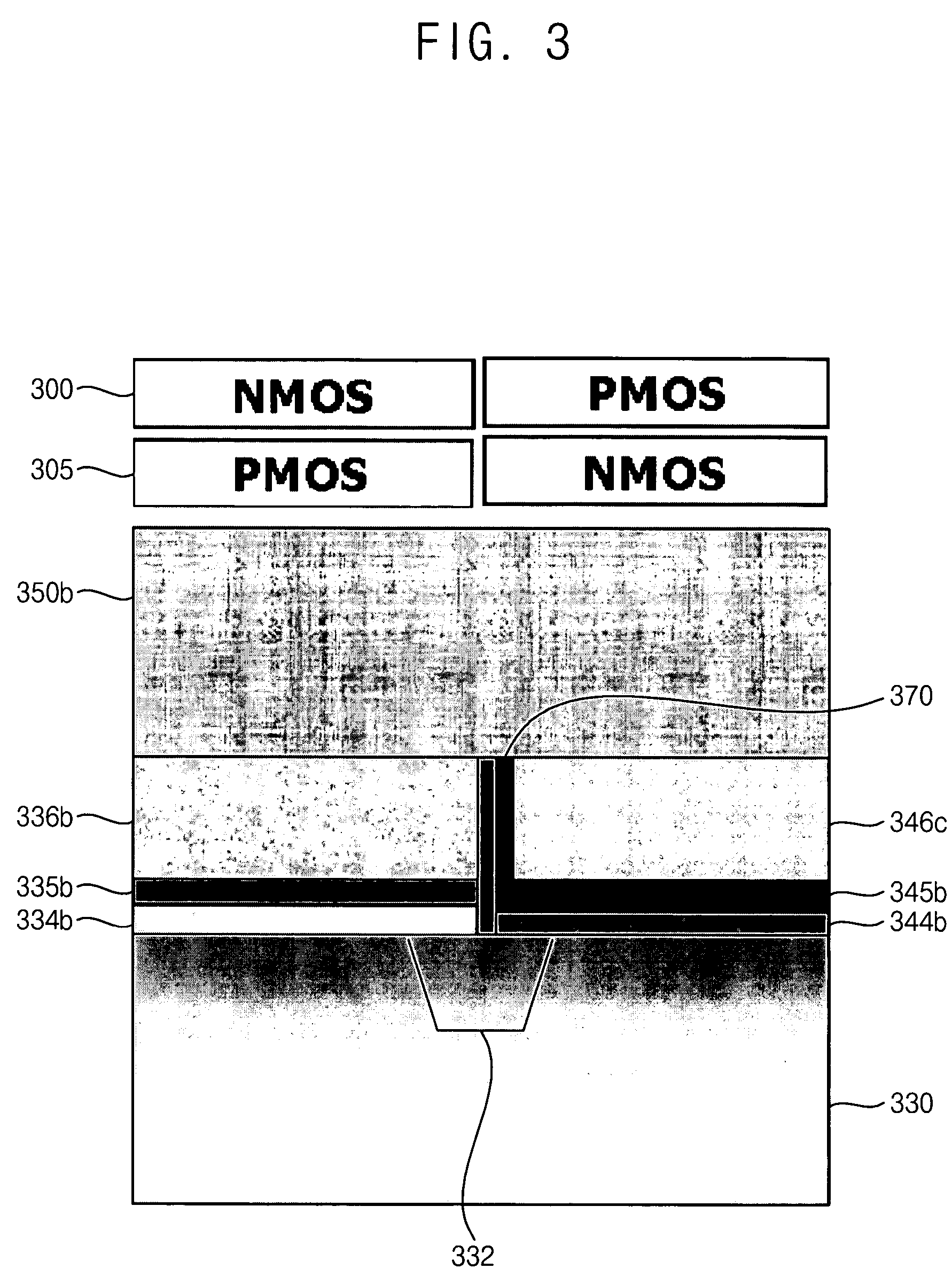
Method for dual gate oxide dual workfunction CMOS
InactiveUS6087225AIncrease flexibilityIncrease junction formation flexibilityTransistorSolid-state devicesThin oxideCMOS
A method of forming integrated circuit chips including two dissimilar type NFETs and / or two dissimilar type PFETs on the same chip, such as both thick and thin gate oxide FETs. A DRAM array may be constructed of the thick oxide FETs and logic circuits may be constructed of the thin oxide FETs on the same chip. First, a gate stack including a first, thick gate SiO2 layer is formed on a wafer. The stack includes a doped polysilicon layer on the gate oxide layer, a silicide layer on the polysilicon layer and a nitride layer on the silicide layer. Part of the stack is selectively removed to re-expose the wafer where logic circuits are to be formed. A thinner gate oxide layer is formed on the re-exposed wafer. Next, gates are formed on the thinner gate oxide layer and thin oxide NFETs and PFETs are formed at the gates. After selectively siliciding thin oxide device regions, gates are etched from the stack in the thick oxide device regions. Finally, source and drain regions are implanted and diffused for the thick gate oxide devices.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Fin-type field effect transistor structure with merged source/drain silicide and method of forming the structure
ActiveUS7692254B2Increase capacitanceSeries resistance is minimizedTransistorSolid-state devicesParasitic capacitanceMetal silicide
Disclosed herein are embodiments of a multiple fin fin-type field effect transistor (i.e., a multiple fin dual-gate or tri-gate field effect transistor) in which the multiple fins are partially or completely merged by a highly conductive material (e.g., a metal silicide). Merging the fins in this manner allow series resistance to be minimized with little, if any, increase in the parasitic capacitance between the gate and source / drain regions. Merging the semiconductor fins in this manner also allows each of the source / drain regions to be contacted by a single contact via as well as more flexible placement of that contact via.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
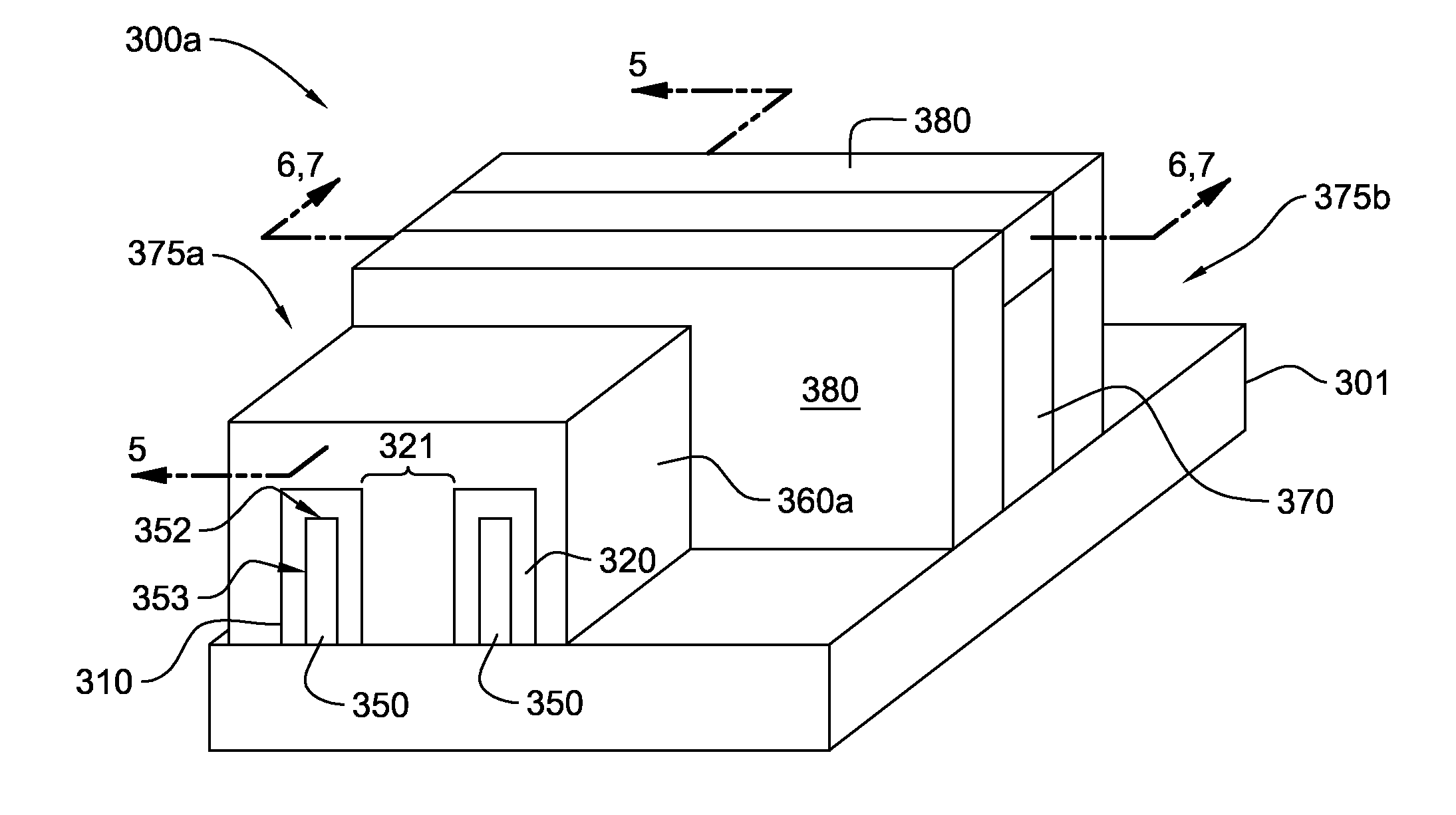
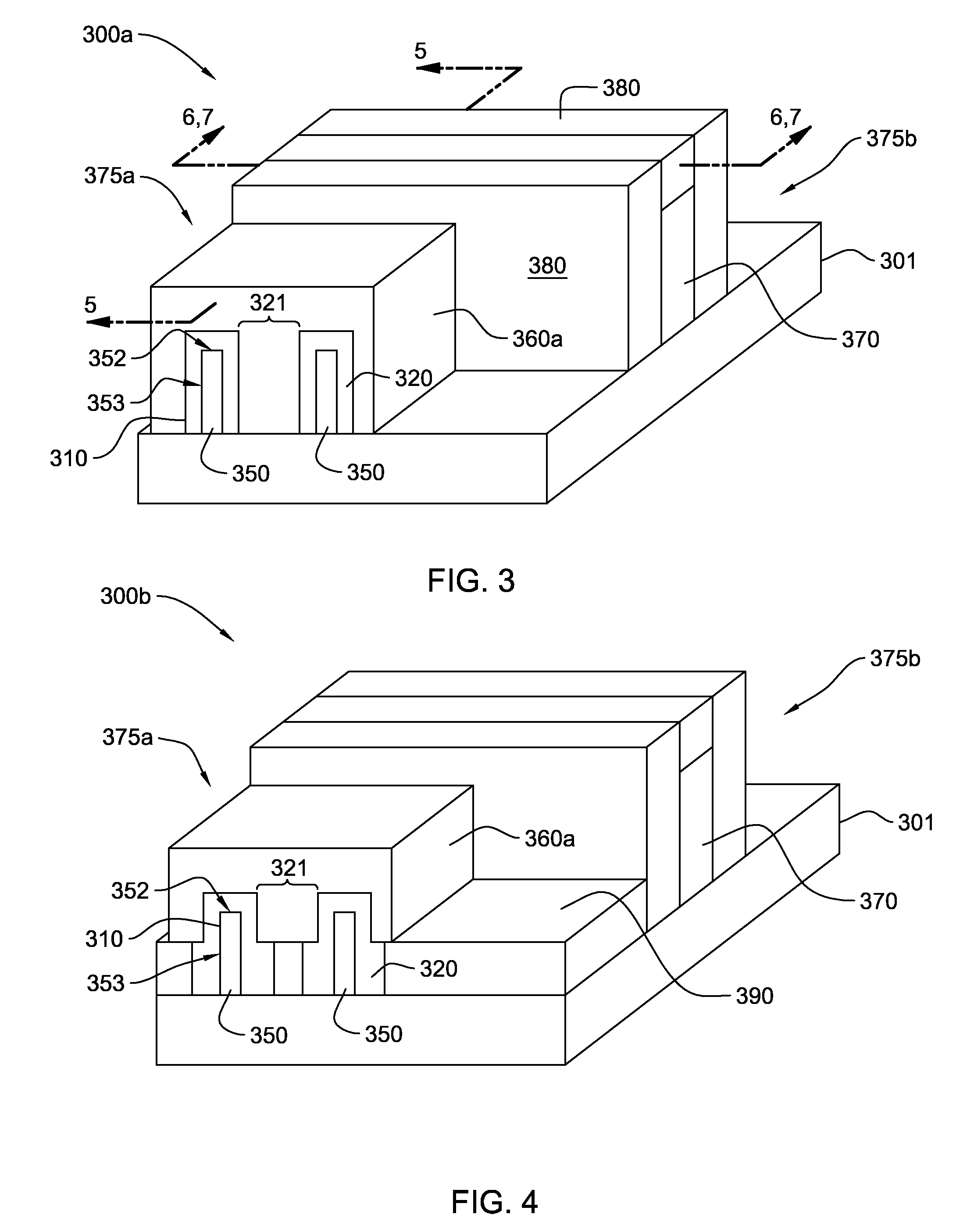
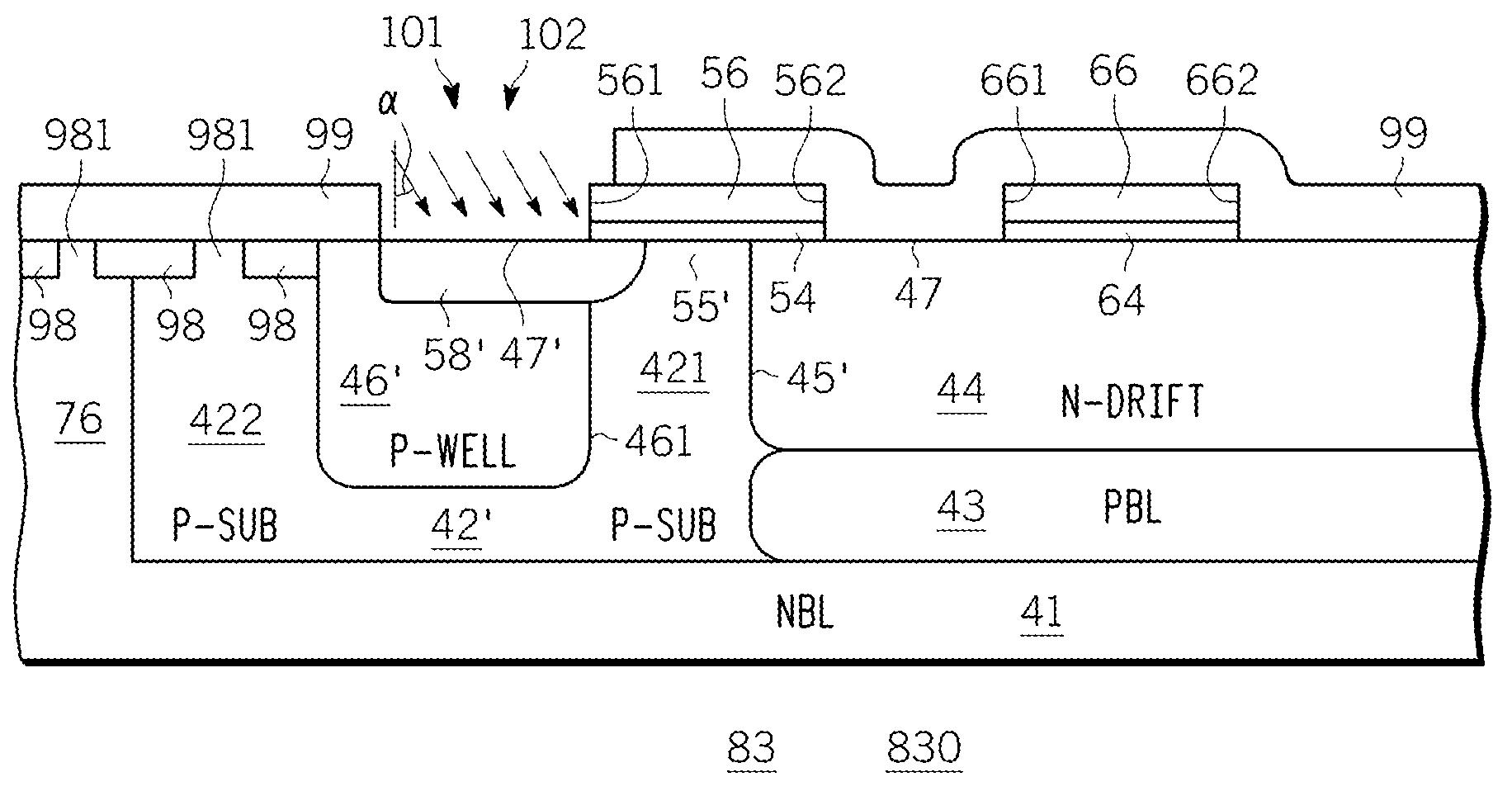
Dual gate ldmos device and method
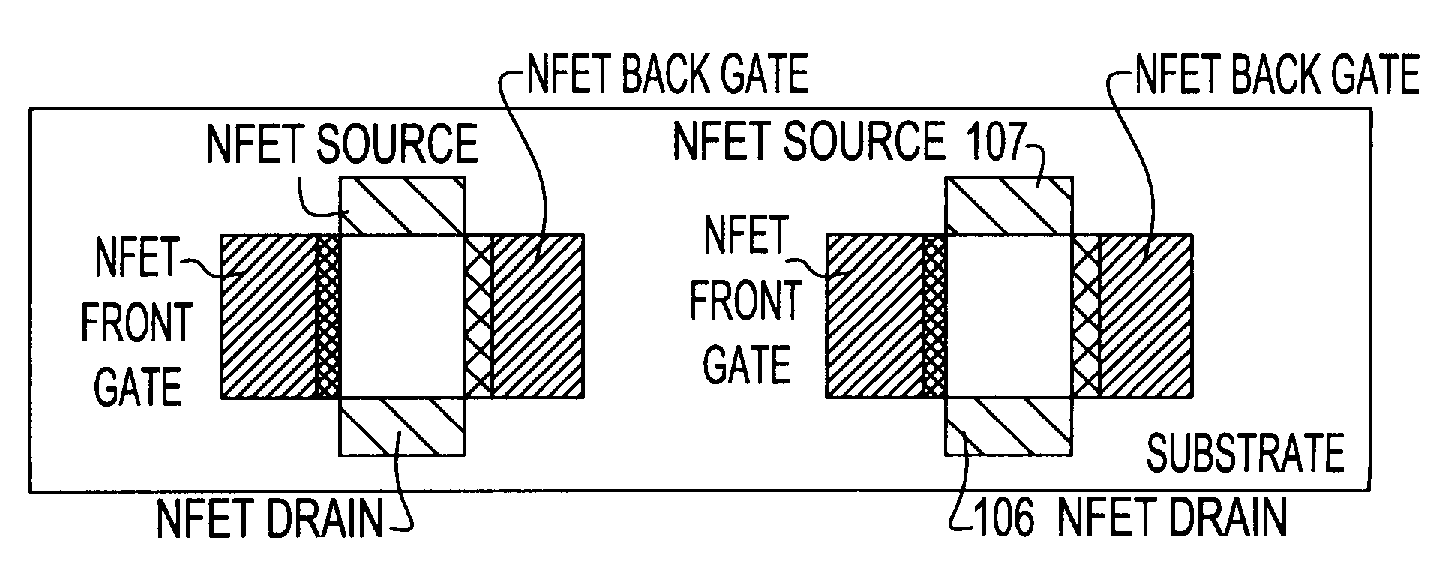
InactiveUS20080182394A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLDMOSBody contact
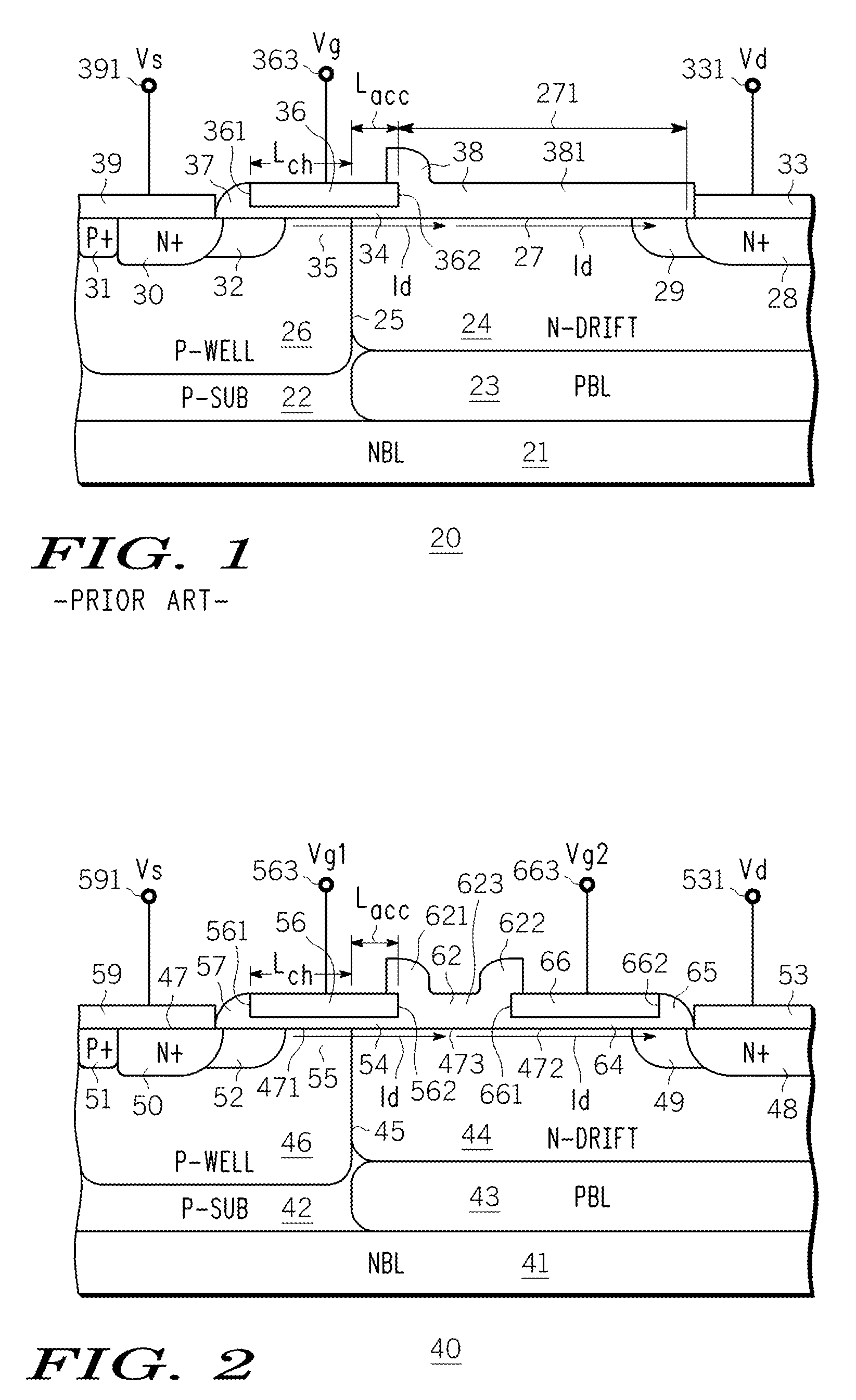
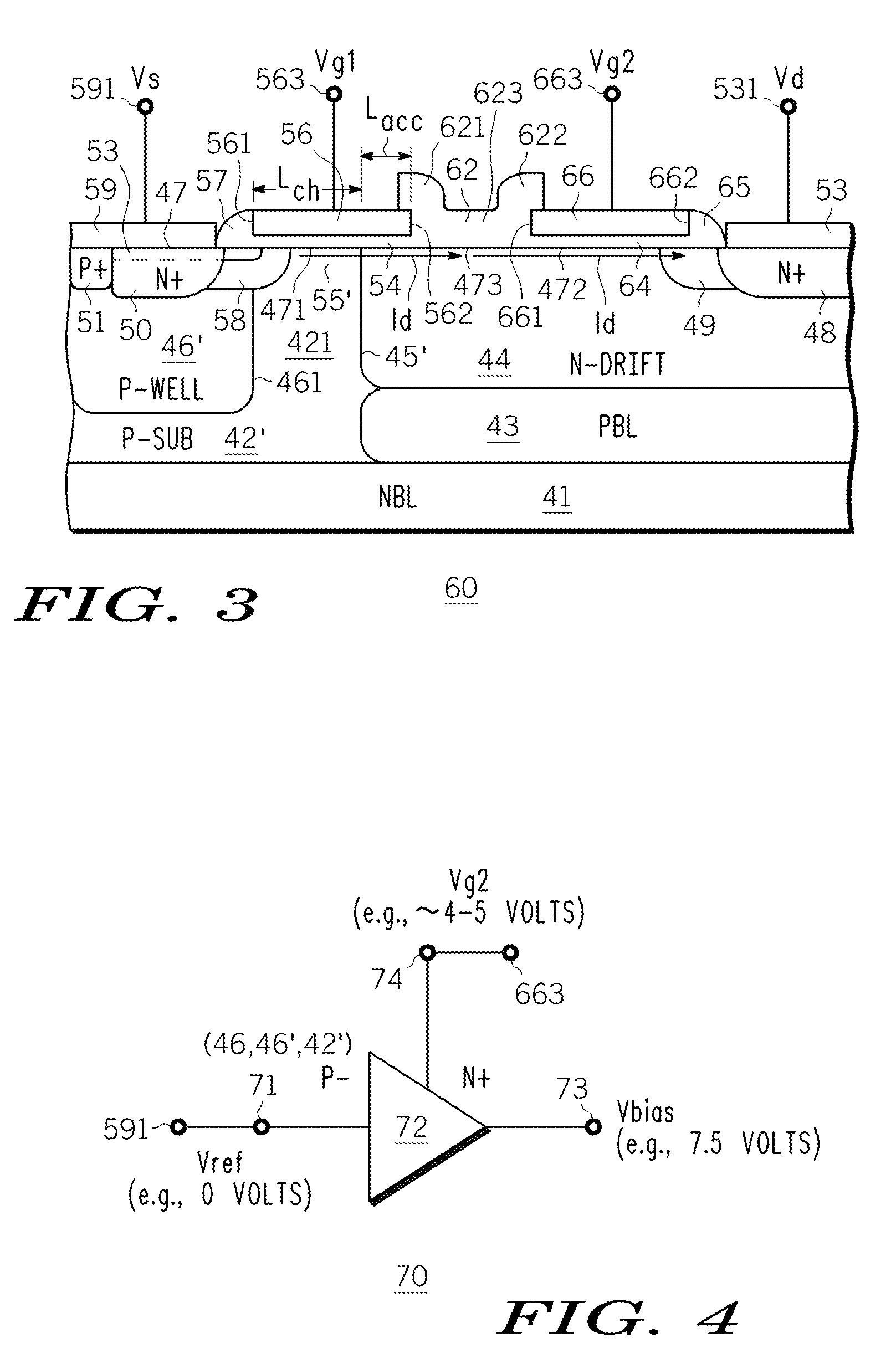
An N-channel device (40, 60) is described having a lightly doped substrate (42, 42′) in which adjacent or spaced-apart P (46, 46′) and N (44) wells are provided. A lateral isolation wall (76) surrounds at least a portion of the substrate (42, 42′) and is spaced apart from the wells (46, 46′, 44). A first gate (G1) (56) overlies the P (46) well or the substrate (42′) between the wells (46′, 44) or partly both. A second gate (G2) (66), spaced apart from G1 (56), overlies the N-well (44). A body contact (74) to the substrate (42, 42′) is spaced apart from the isolation wall (76) by a first distance (745) within the space charge region of the substrate (42, 42′) to isolation wall (76) PN junction. When the body contact (74) is connected to G2 (66), a predetermined static bias Vg2 is provided to G2 (66) depending upon the isolation wall bias (Vbias) and the first distance (745). The resulting device (40, 60) operates at higher voltage with lower Rdson and less HCI.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Dual-gate transistor display
ActiveUS20060066512A1Minimize leakage currentImprove featuresStatic indicating devicesSemiconductor devicesHemt circuitsDisplay device
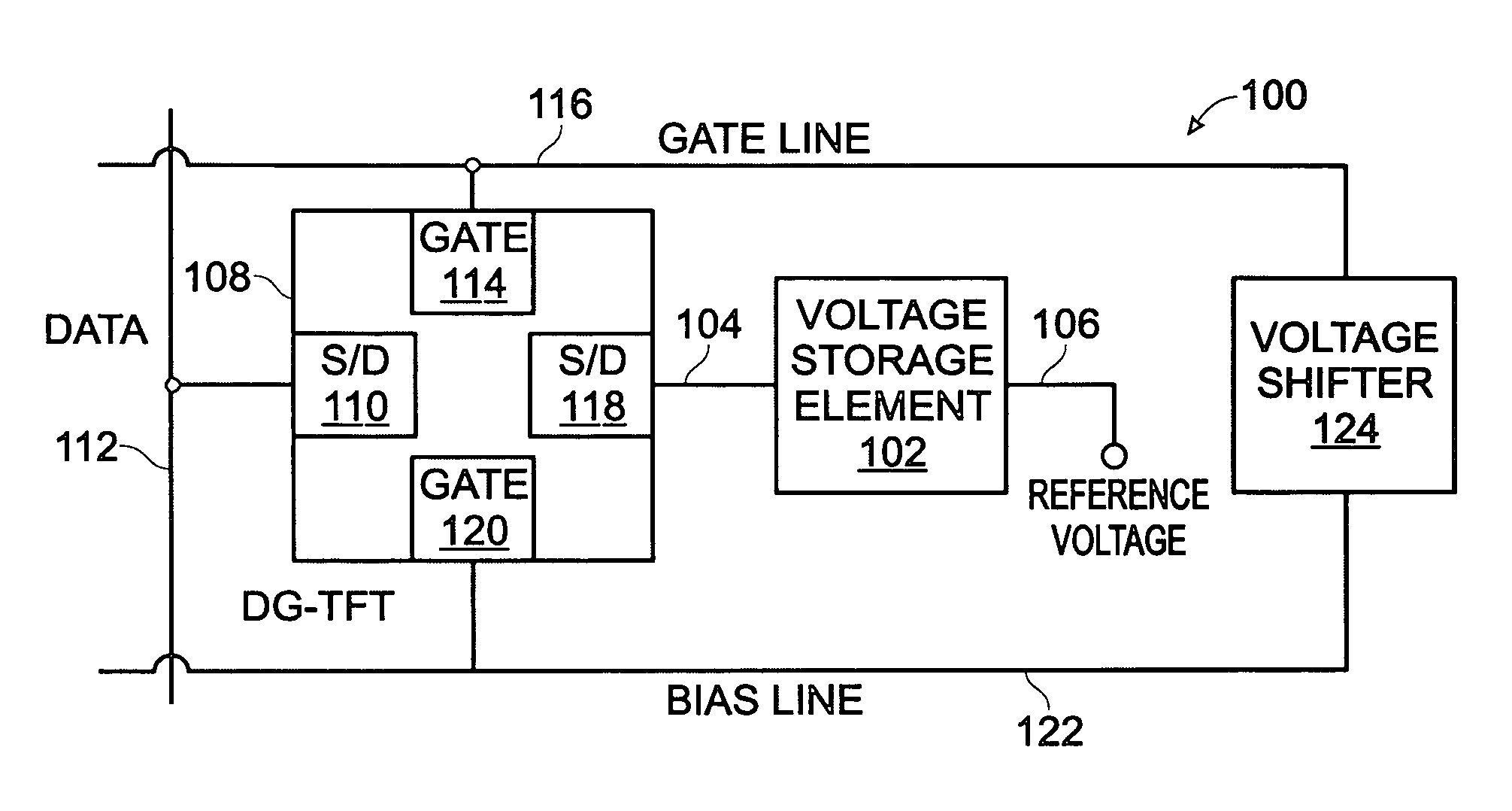
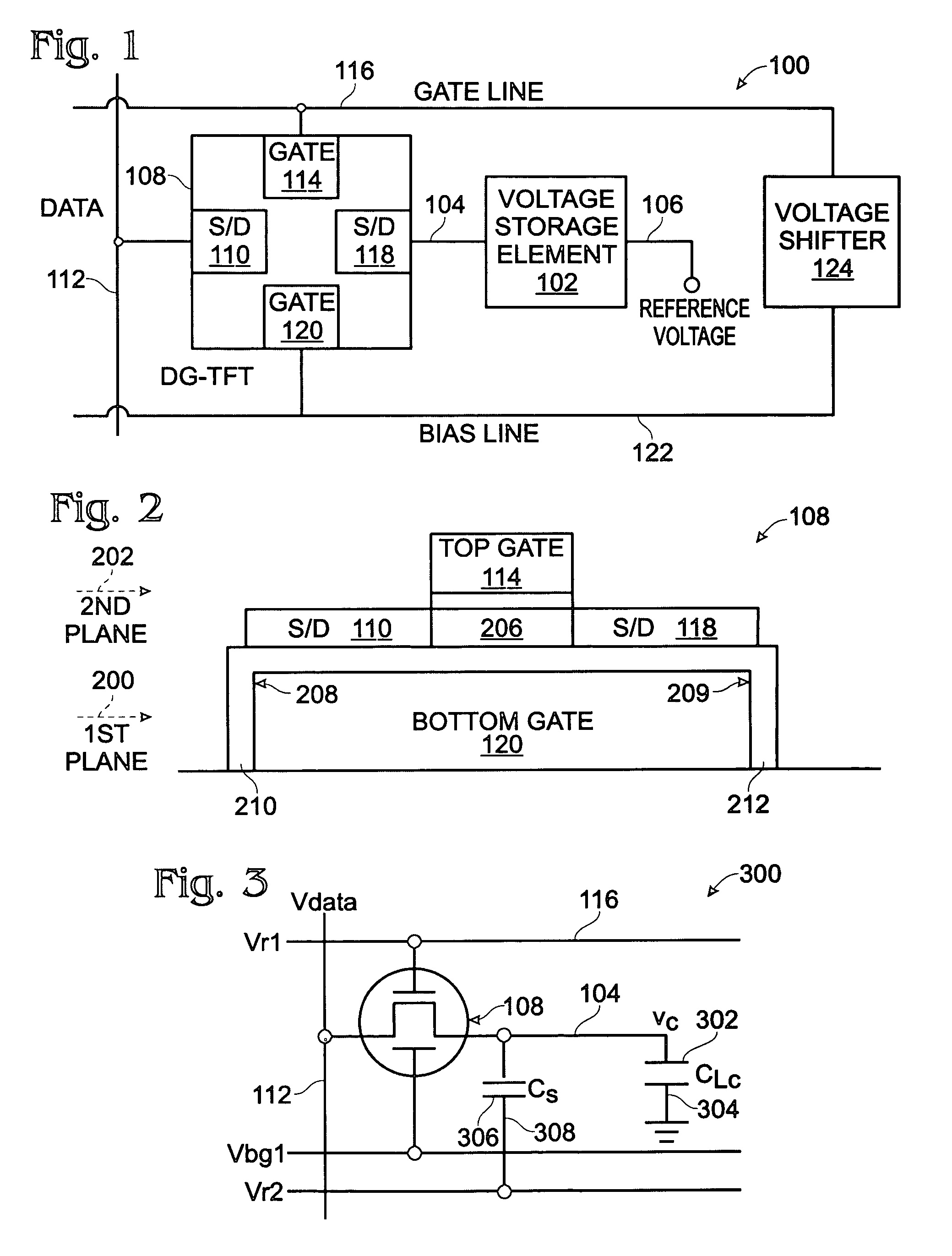
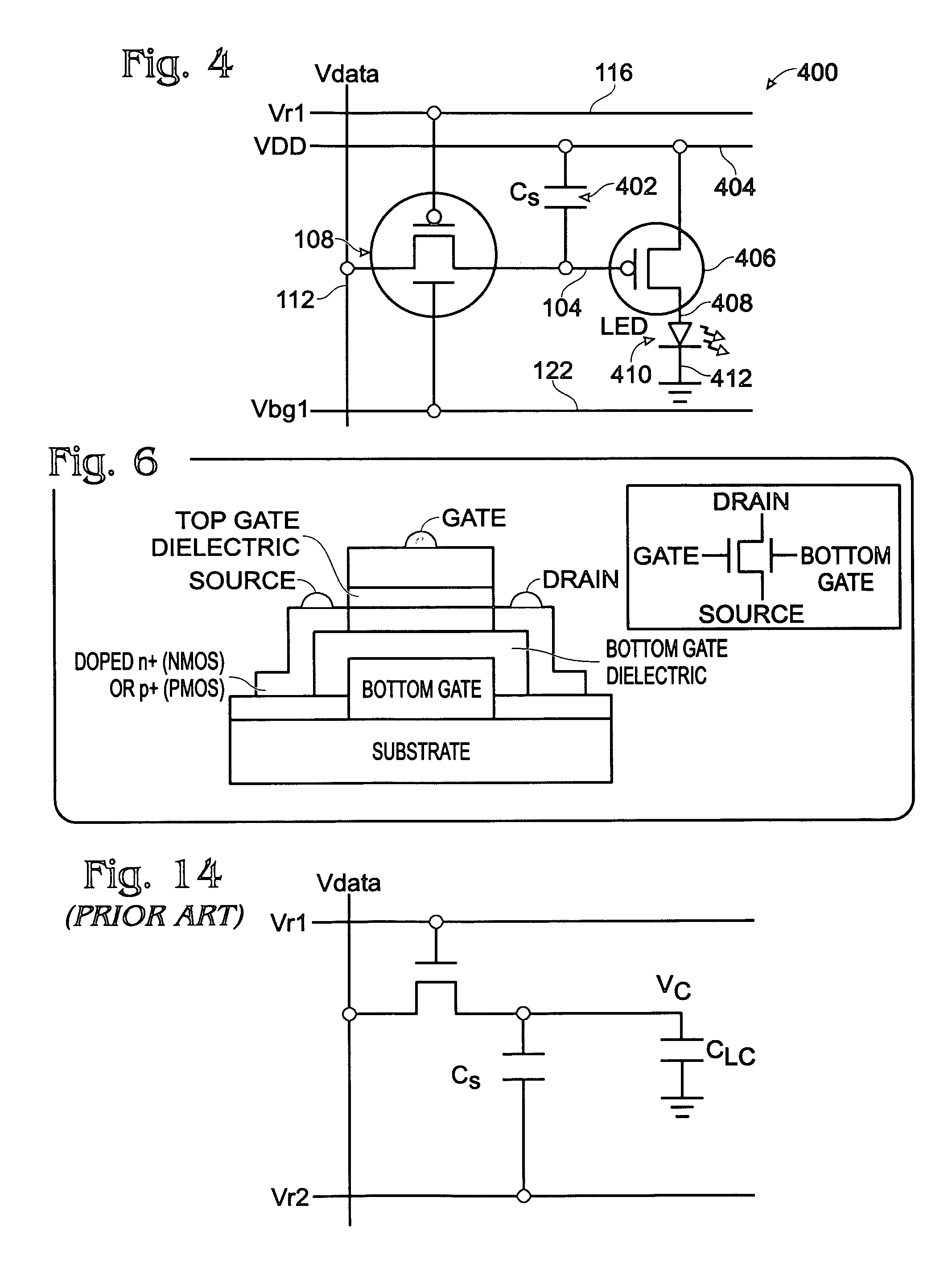
A dual-gate thin-film transistor (DG-TFT) voltage storage circuit is provided. The circuit includes a voltage storage element, a DG-TFT having a first source / drain (S / D) connected to a data line, a top gate connected to a first gate line, a second S / D region connected to the voltage storage element, and a bottom gate connected to a bias line. In one aspect, the circuit further includes a voltage shifter having an input connected to the first gate line and an output to supply a bias voltage on the bias line. Examples of a voltage storage element include a capacitor, a liquid crystal (LC) pixel, and a light emitting diode (LED) pixel.
Owner:SHARP KK
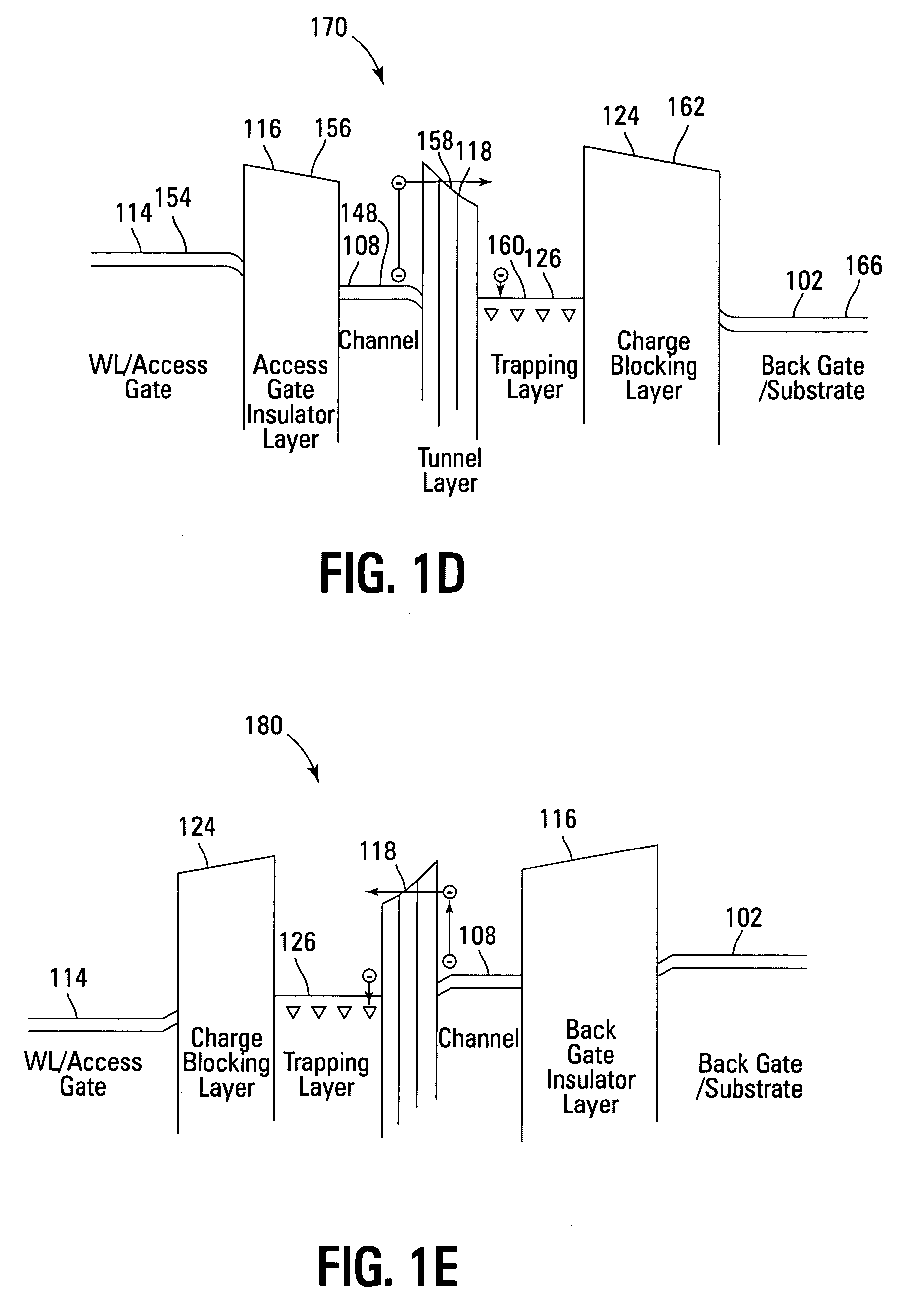
Method of Forming Different Voltage Devices with High-K Metal Gate
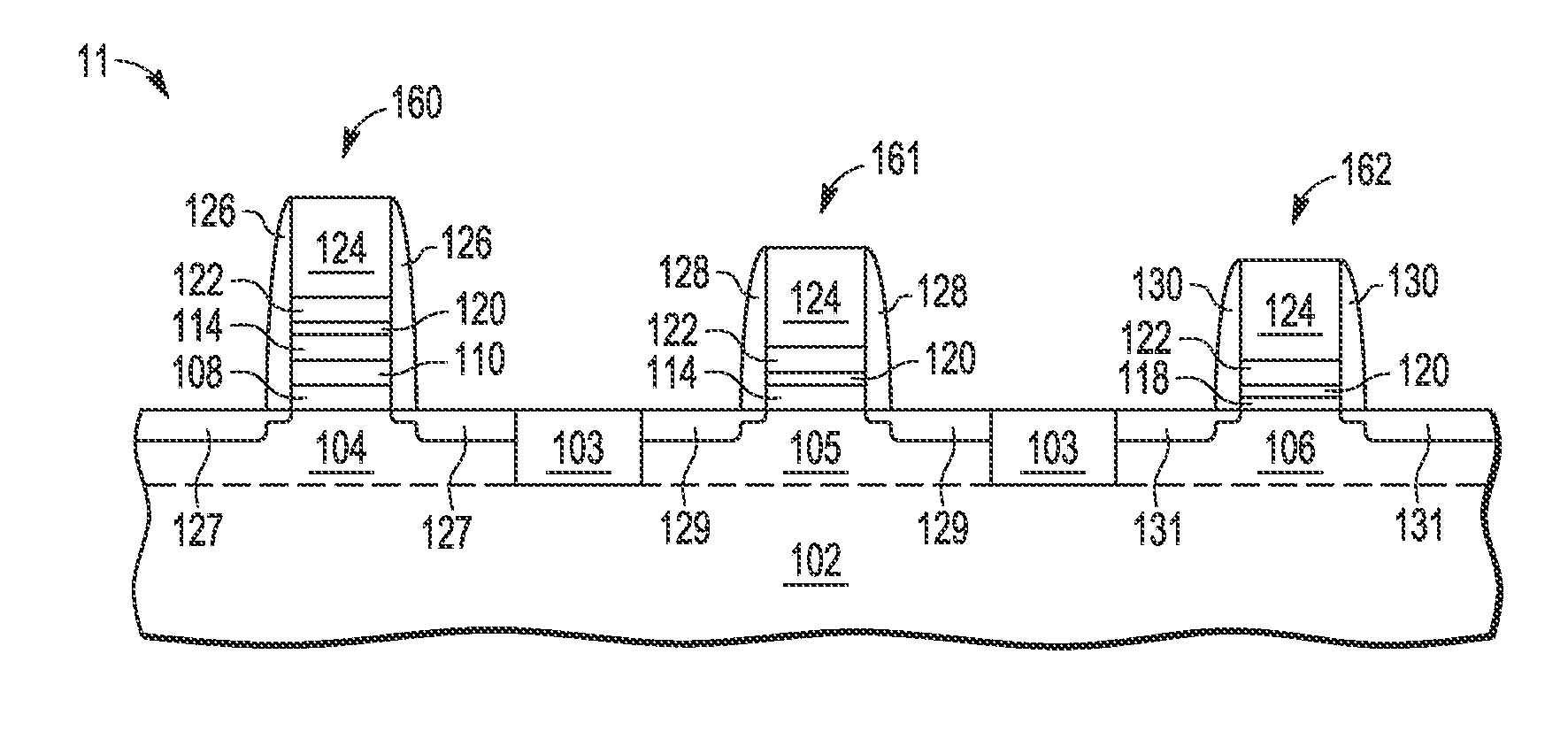
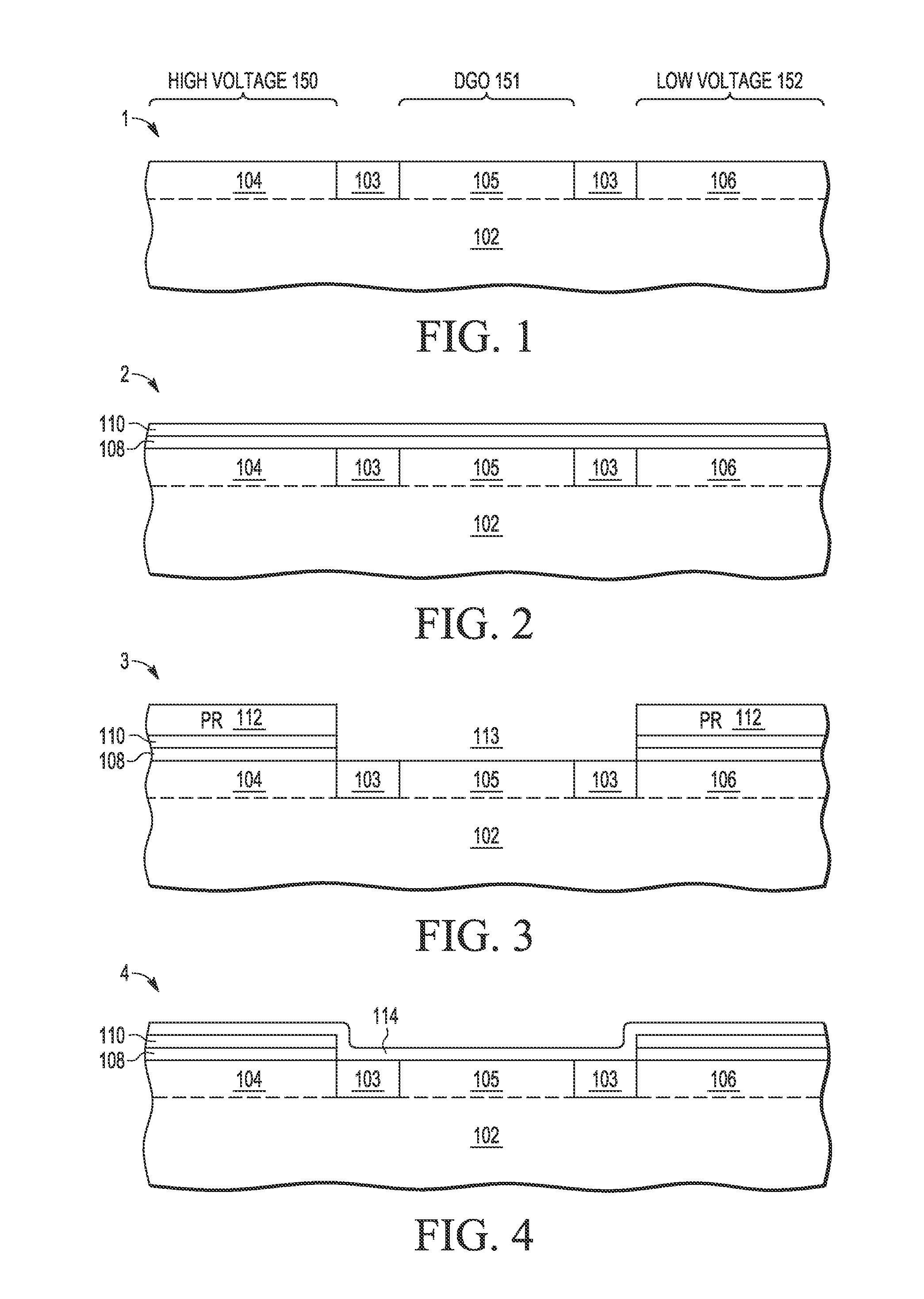
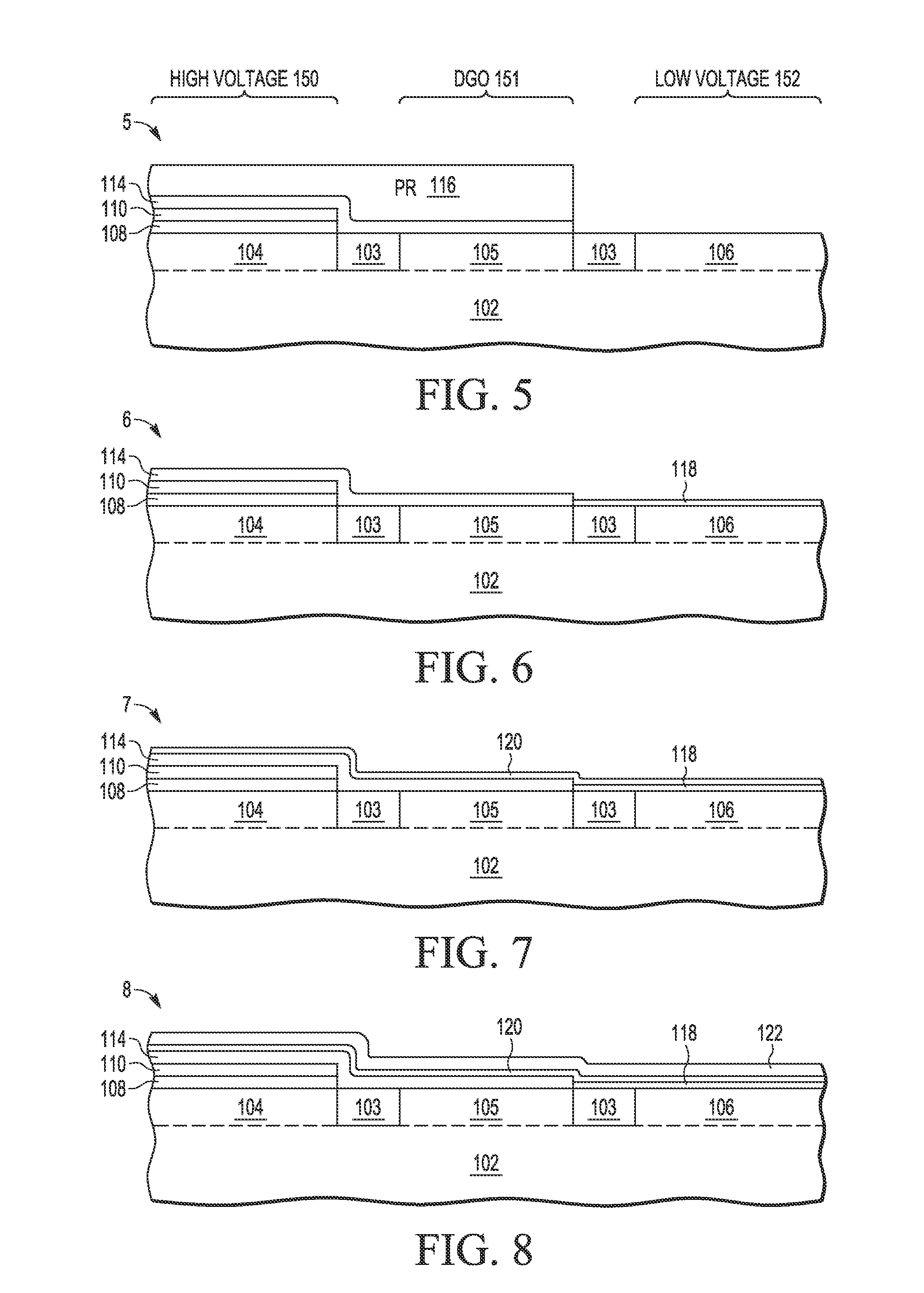
A method and apparatus are described for integrating high voltage (HV) transistor devices and medium voltage or dual gate oxide (DGO) transistor devices with low voltage (LV) core transistor devices on a single substrate, where each high voltage transistor device (160) includes a metal gate (124), an upper high-k gate dielectric layer (120), a middle gate dielectric layer (114) formed with a relatively lower high-k dual gate oxide layer, and a lower high voltage gate dielectric stack (108, 110) formed with one or more low-k gate oxide layers (22), where each DGO transistor device (161) includes a metal gate (124), an upper high-k gate dielectric layer (120), and a middle gate dielectric layer (114) formed with a relatively lower high-k dual gate oxide layer, and where each core transistor device (162) includes a metal gate (124), an upper high-k gate dielectric layer (120), and a base oxide layer (118) formed with one or more low-k gate oxide layers.
Owner:VLSI TECH LLC
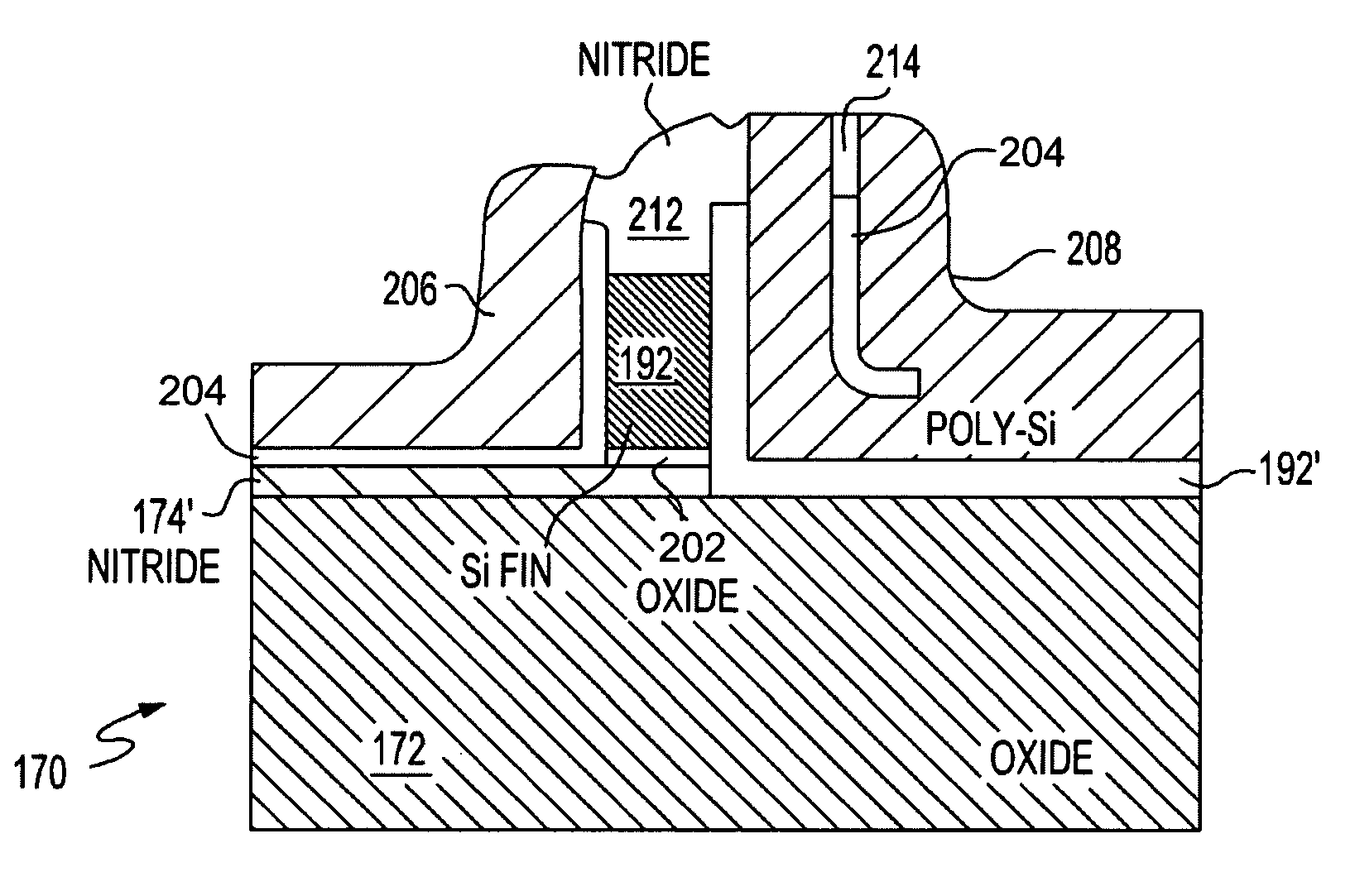
Dual gate FinFet
A field effect transistor (FET), integrated circuit (IC) chip including the FETs and a method of forming the FETS. Each FET includes a device gate along one side of a semiconductor (e.g., silicon) fin and a back bias gate along an opposite of the fin. Back bias gate dielectric differs from the device gate dielectric either in its material and / or thickness. Device thresholds can be adjusted by adjusting back bias gate voltage.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20140340608A1Excellent electrical propertiesIncrease productionSolid-state devicesNon-linear opticsDevice materialChannel width
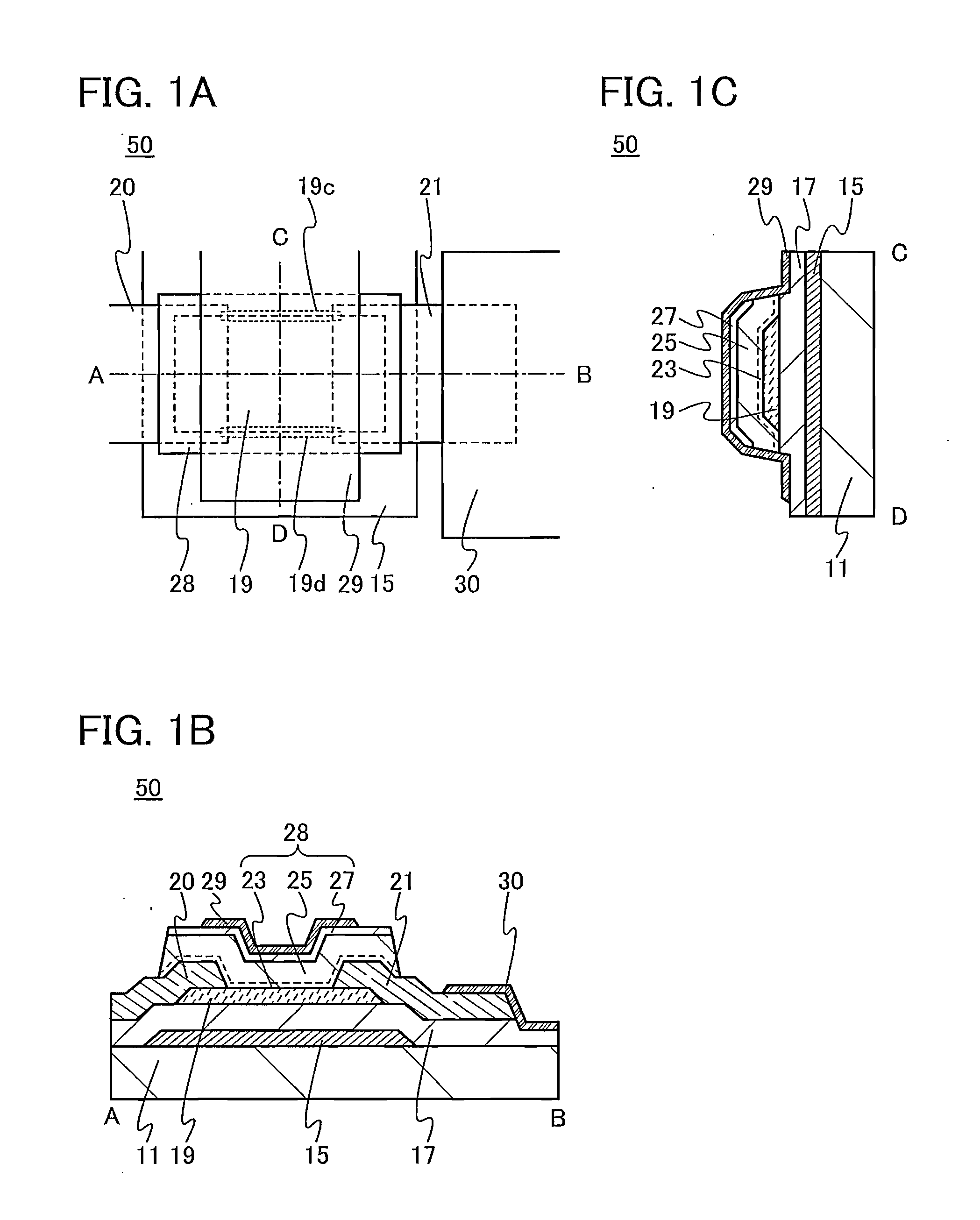
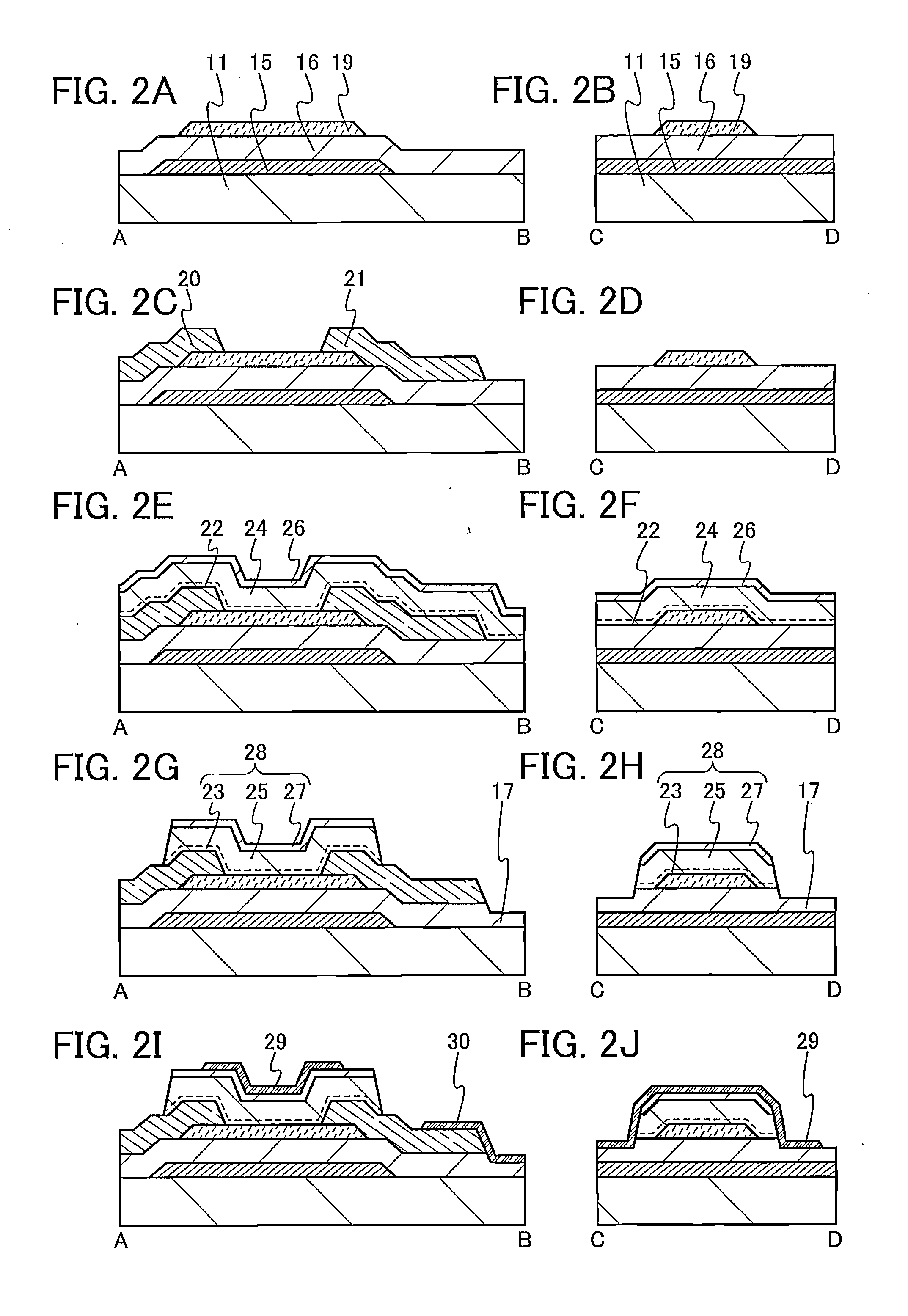
A semiconductor device which includes an oxide semiconductor and in which formation of a parasitic channel due to a gate BT stress is suppressed is provided. Further, a semiconductor device including a transistor having excellent electrical characteristics is provided. The semiconductor device includes a transistor having a dual-gate structure in which an oxide semiconductor film is provided between a first gate electrode and a second gate electrode; gate insulating films are provided between the oxide semiconductor film and the first gate electrode and between the oxide semiconductor film and the second gate electrode; and in the channel width direction of the transistor, the first or second gate electrode faces a side surface of the oxide semiconductor film with the gate insulating film between the oxide semiconductor film and the first or second gate electrode.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Display system
InactiveUS7230601B2Reduce power consumptionWiring capacitanceTransistorElectroluminescent light sourcesDriver circuitCapacitance
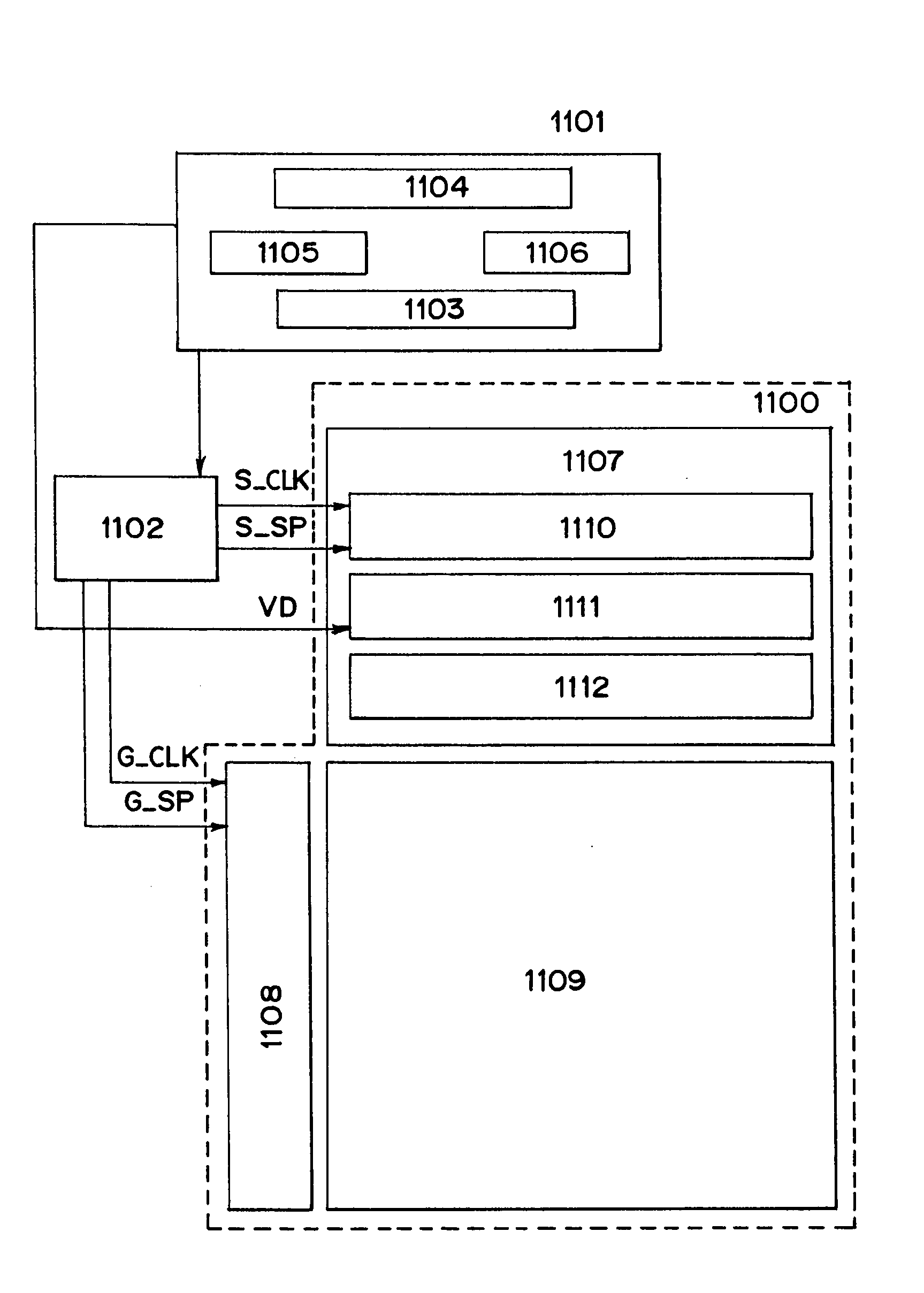
To solve a problem of increased power consumption power due to wiring capacitances, which occurs when connecting onto a display substrate a substrate on which a memory, a memory controller, and the like are formed. The memory, the memory controller, and the like are integrally formed on the display substrate. At this time, these circuits are formed using a dual gate TFT. Thus, a display device in which wiring capacitances of connection portions between driver circuits composing a display and the memory controller and the like are reduced and which has thus low power consumption can be provided.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Dual-gate dynamic random access memory device having vertical channel transistors and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20070051994A1Improve layout efficiencyImprove efficiencyTransistorSolid-state devicesBit lineEngineering
A dynamic random access memory (DRAM) device has dual-gate vertical channel transistors. The device is comprised of pillar-shaped active patterns including source regions contacting with a semiconductor substrate, drain regions formed over the drain regions, and channel regions formed between the source and drain regions. The active patterns are disposed in a cell array field. On the active patterns, bit lines are arranged to connect the drain regions along a direction. Between the active patterns, word lines are arranged intersecting the bit lines. Gat insulation films are interposed between the word lines and active patterns.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
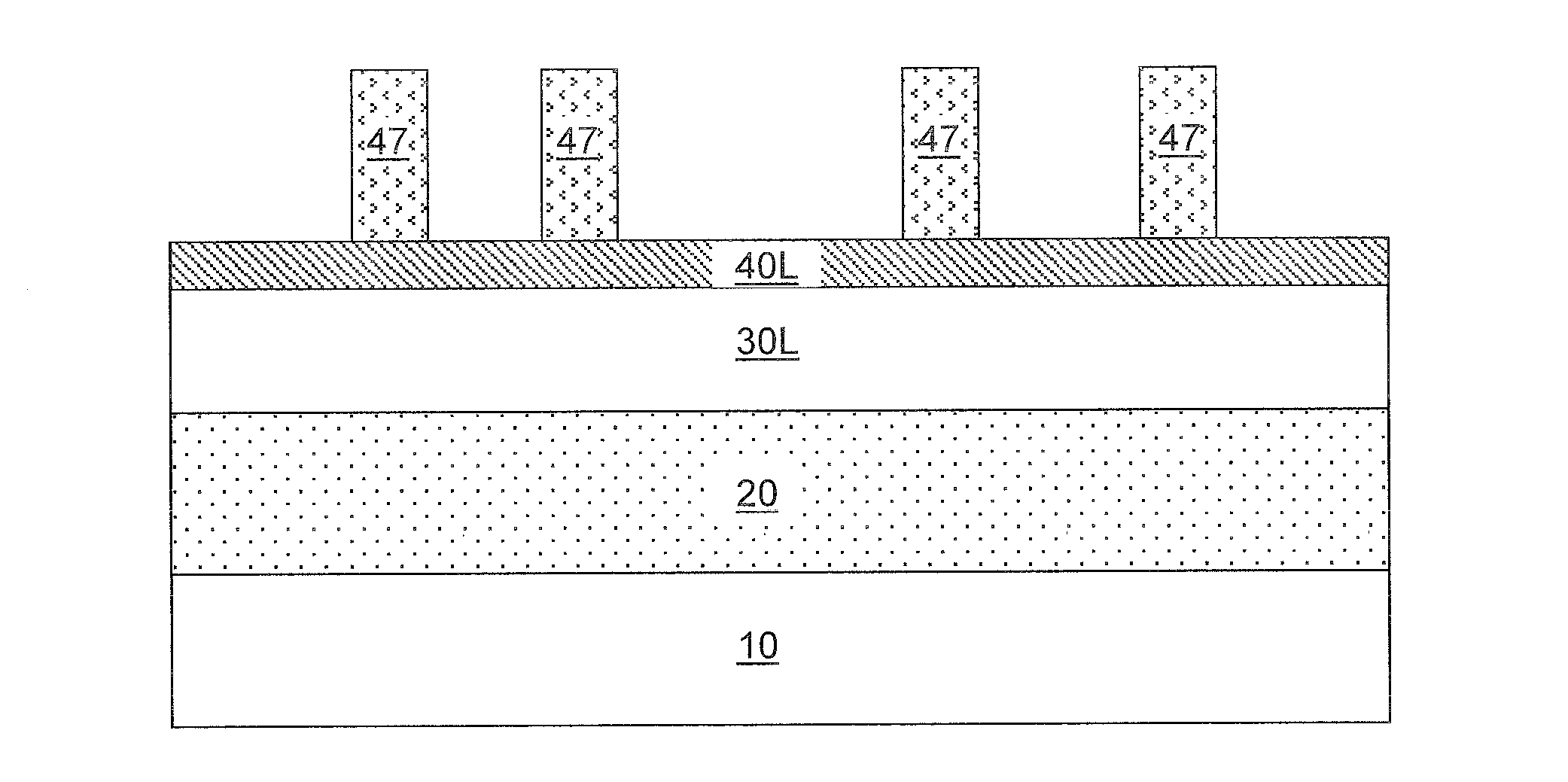
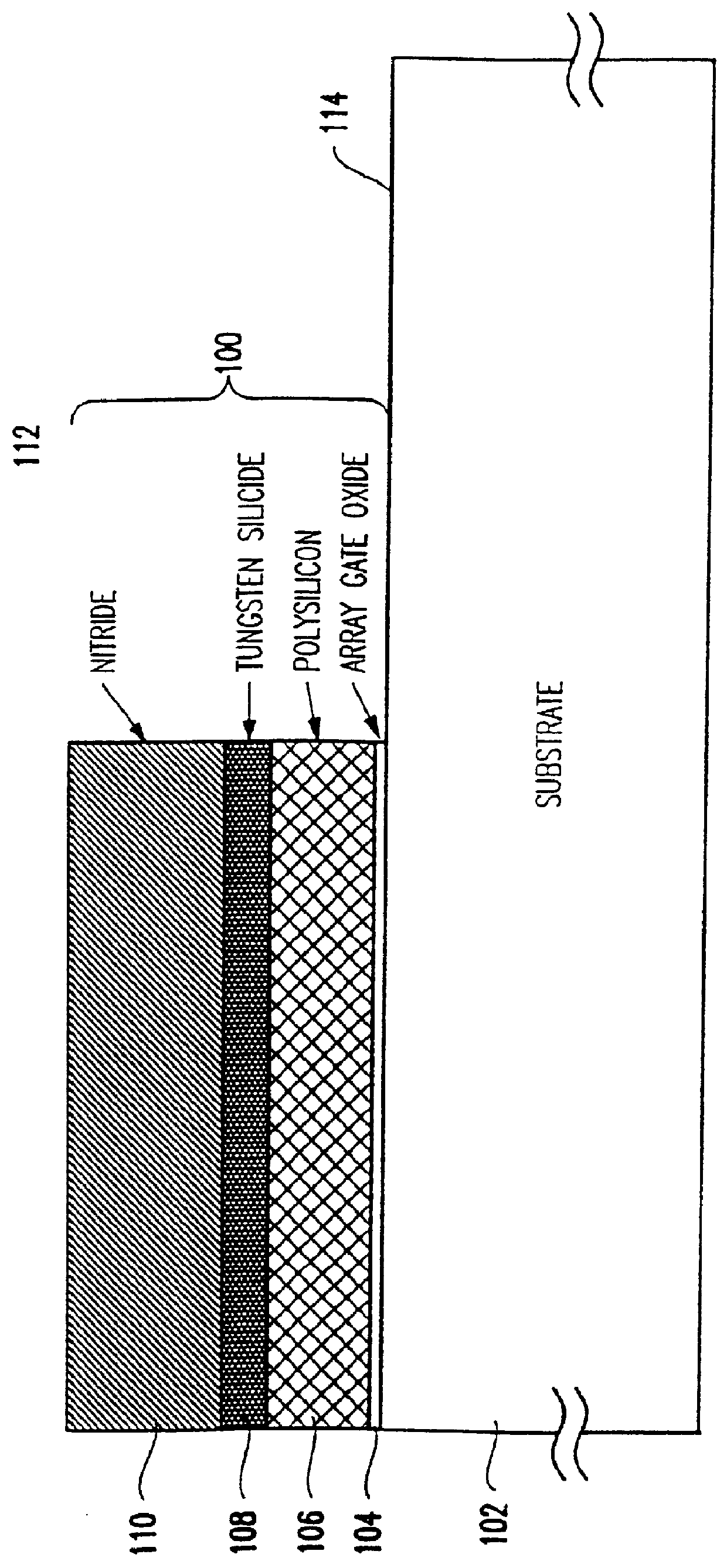
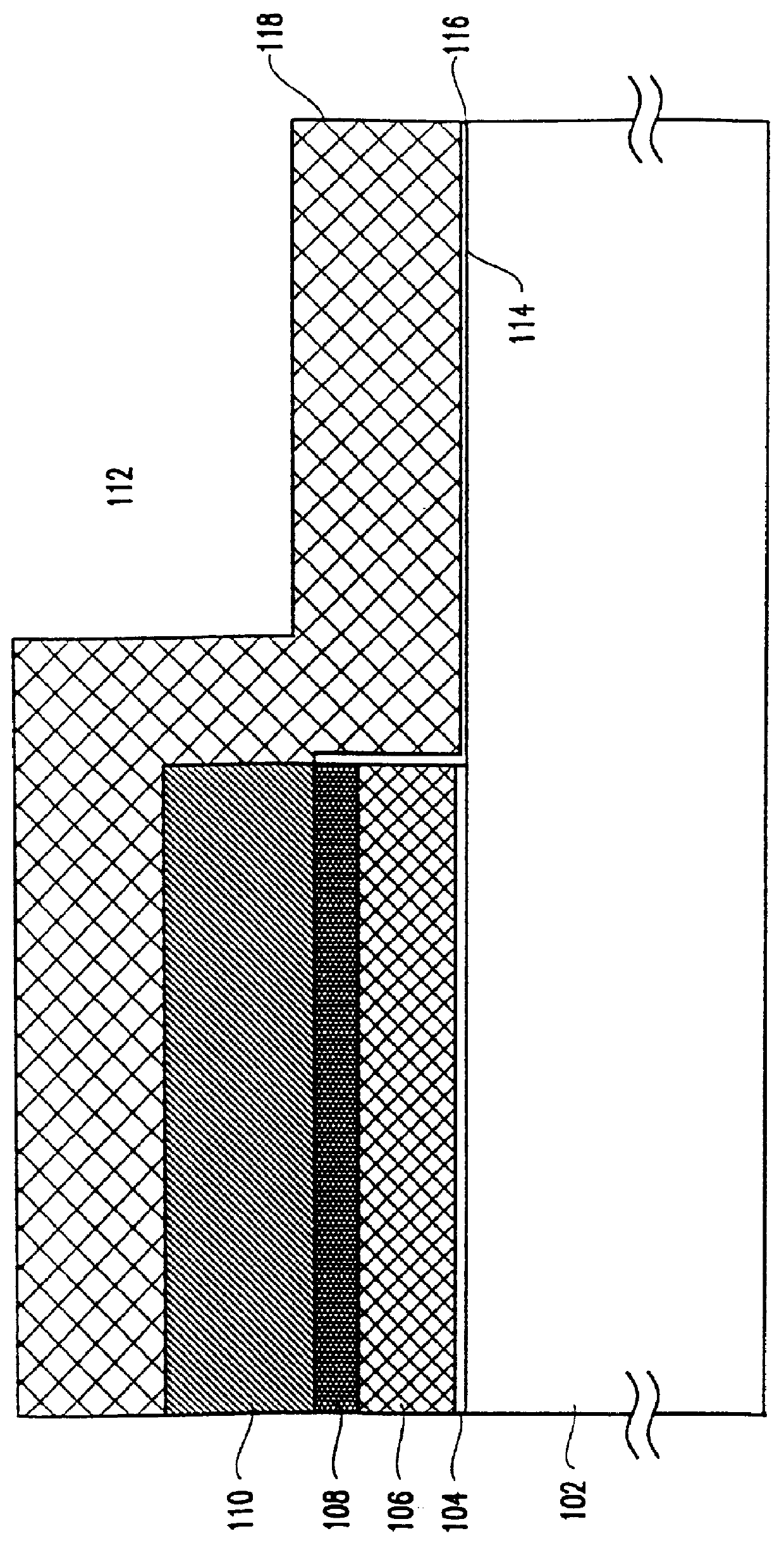
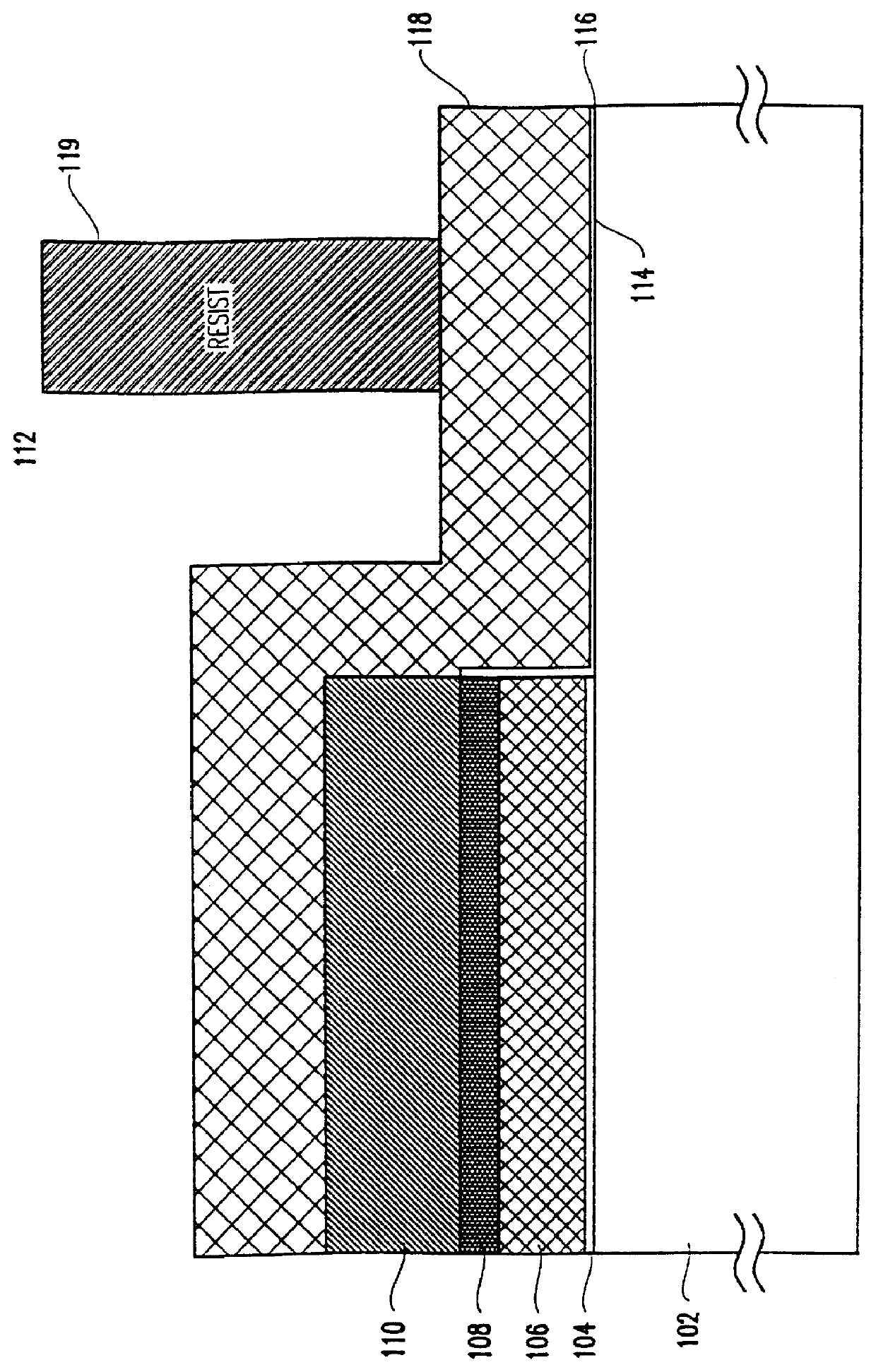
A Method Of Fabricating A DRAM Transistor With A Dual Gate Oxide Technique
InactiveUS20010008808A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsPhotoresist
The process comprises the steps of growing a first oxide layer on the upper surface of a substrate; depositing a silicon nitride layer on top of the first oxide layer; patterning the silicon nitride layer with a photoresist mask to define field oxide areas; stripping the oxide layer and regrowing a pad oxide layer on the upper surfaces of the substrate not covered by the remnants of the silicon nitride layer; removing the remnants of the silicon nitride layer; stripping the pad oxide layer and growing a sacrificial oxide layer; masking the sacrificial oxide layer with a photoresist to protect the area where the memory array will be formed; stripping the sacrificial oxide not protected by the photoresist; stripping the photoresist; and growing a gate oxide layer which is thinner than the sacrificial oxide layer. Thereafter, fabrication of the memory device may be completed using any known prior art techniques.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Dual gate dielectric scheme: SiON for high performance devices and high k for low power devices
A method of forming dual gate dielectric layers that is extendable to satisfying requirements for 50 nm and 70 nm technology nodes is described. A substrate is provided with STI regions that separate device areas. An interfacial layer and a high k dielectric layer are sequentially deposited on the substrate. The two layers are removed over one device area and an ultra thin silicon oxynitride layer with an EOT<10 nm is grown on the exposed device area. The high k dielectric layer is annealed during growth of the SiON dielectric layer. The high k dielectric layer is formed from a metal oxide or its silicate or aluminate and enables a low power device to be fabricated with an EOT<1.8 nm with a suppressed leakage current. The method is compatible with a dual or triple oxide thickness process when forming multiple gates.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Integrated circuit devices including a dual gate stack structure and methods of forming the same
InactiveUS20060003507A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerSemiconductor
Integrated circuit devices include a semiconductor substrate having a first doped region and a second doped region having a different doping type than the first doped region. A gate electrode structure on the semiconductor substrate extends between the first and second doped regions and has a gate insulation layer of a first high dielectric constant material in the first doped region and of a second high dielectric constant material, different from the first high dielectric constant material, in the second doped region. A gate electrode is on the gate insulation layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
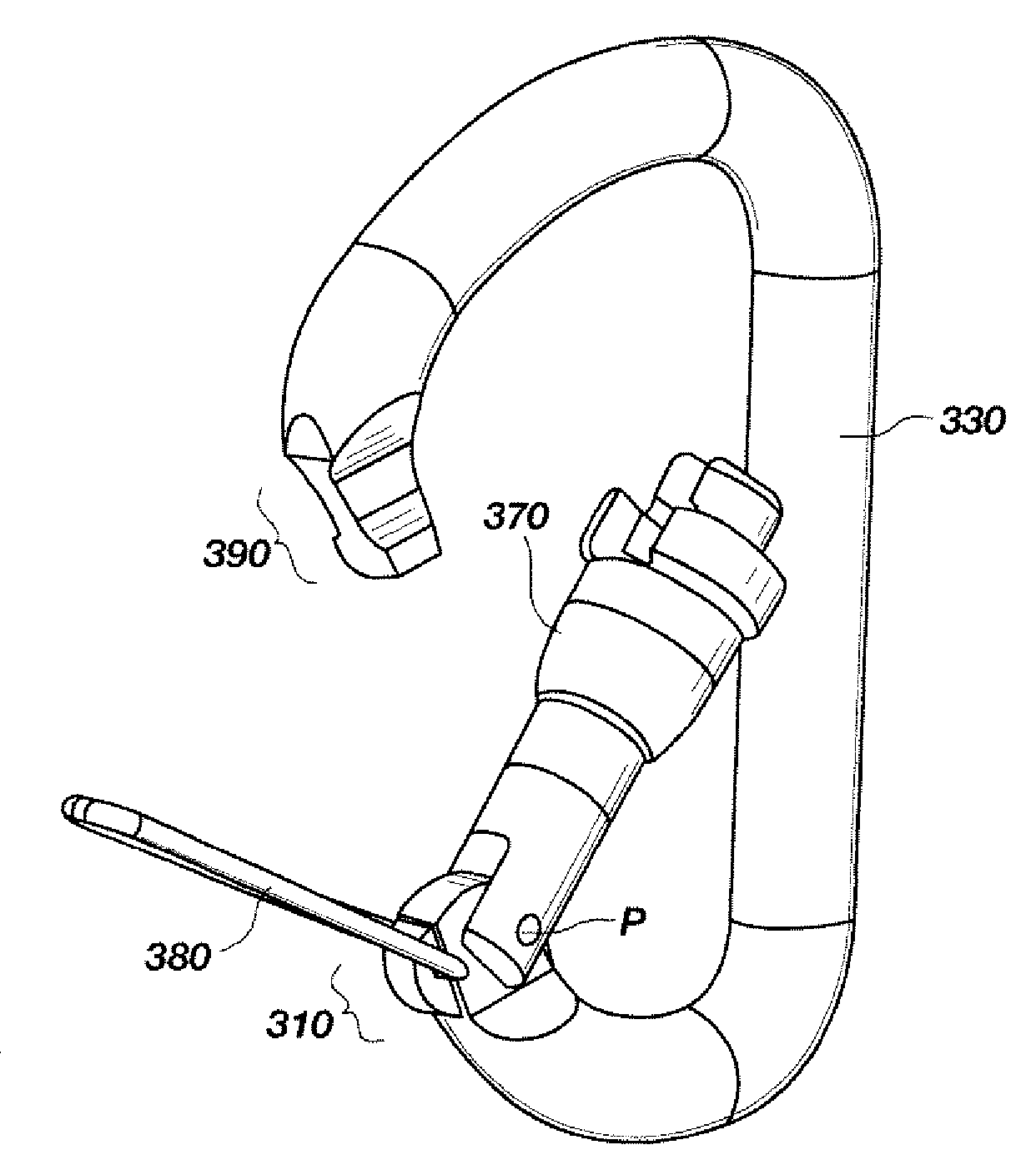
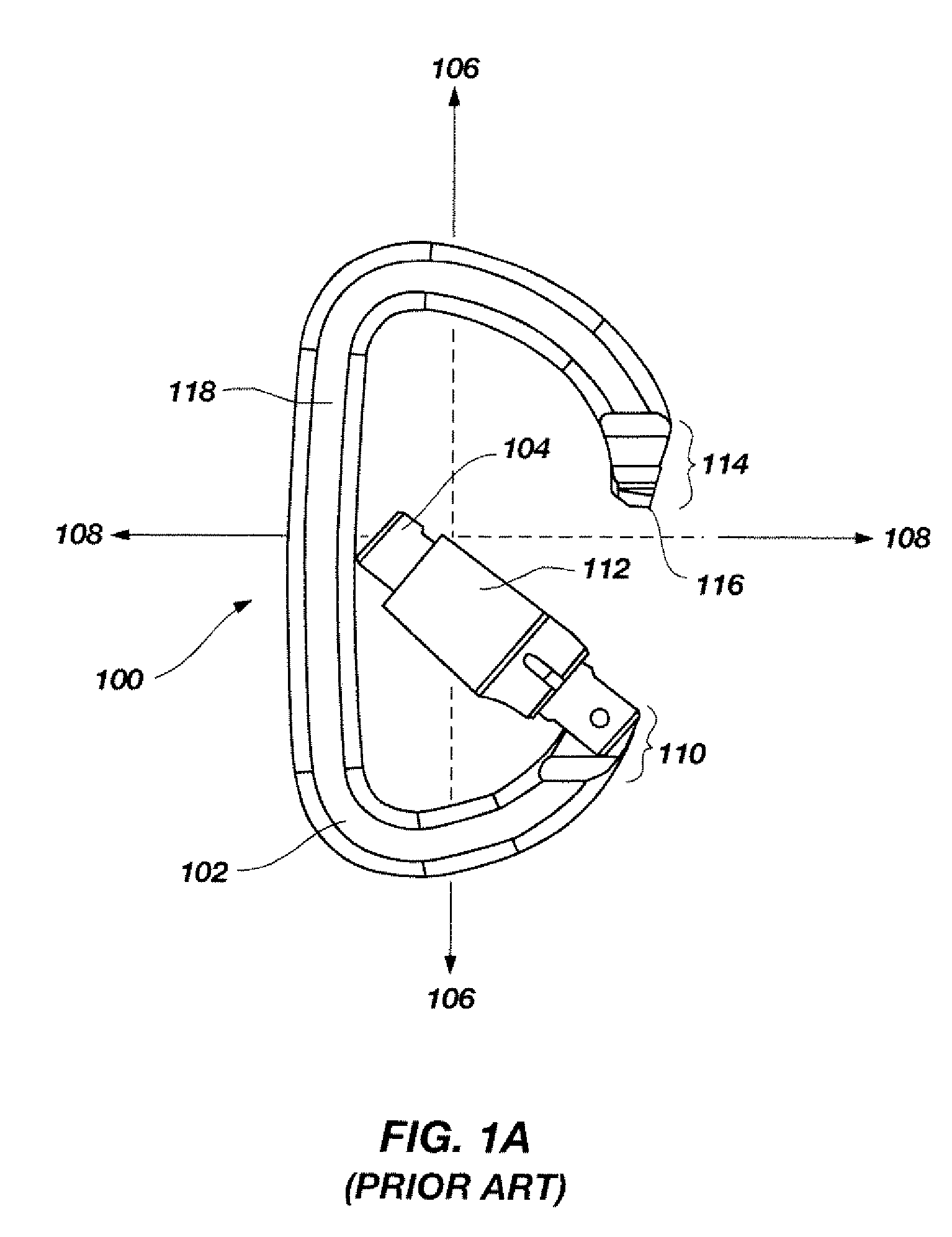
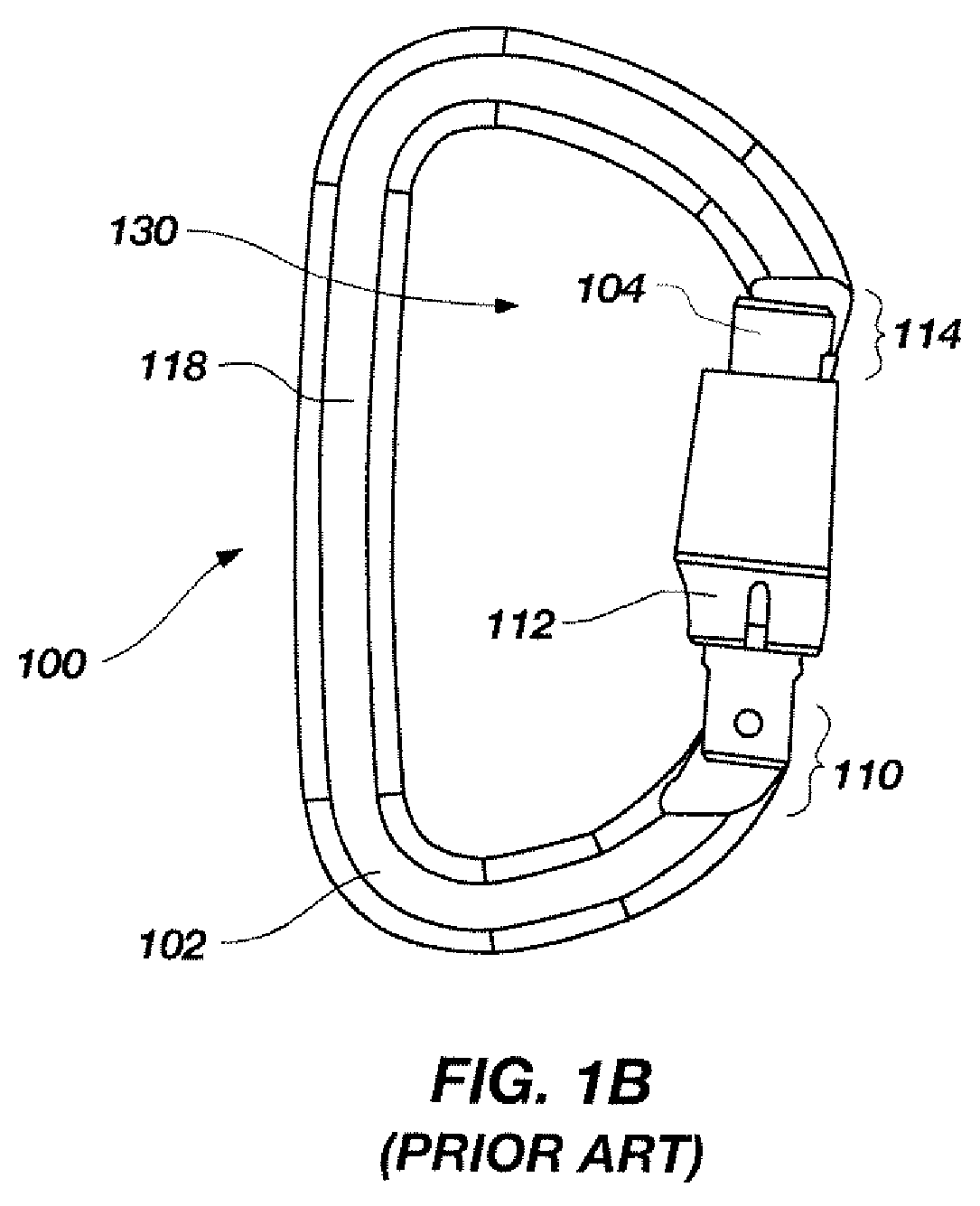
Carabiner having dual gates and associated methods
Various embodiments for carabiners having two gates are disclosed. The carabiners of the present invention include a C-shaped body having a nose region and an end region. An inner gate is configured to pivot about the end region from a closed position in contact with the nose region, and an open position, wherein the inner gate pivots toward the spine of the C-shaped body. An outer gate is configured to pivot about the end region from a closed position in contact with the nose region, and an open position, extending away from the C-shaped body. The inner and the outer gate may each comprise wire gates, alternatively one gate may comprise a generally cylindrical gate and the other gate may comprise a wire gate. Methods of preventing a carabiner from opening are also disclosed.
Owner:ROCK EXOTICA
Molecularly controlled dual gated field effect transistor for sensing applications
A sensing device and method of making and using the sensing device. The device comprises a sensing gate layer of multifunctional organic sensing molecules having at least one functional group that binds to the semiconductor layer and at least another functional group that serves as a sensor. The device further comprises a semiconductor channel layer, a drain electrode, a source electrode, and a biasing gate. The source and drain electrodes and biasing gate are situated on the same side of the device and simultaneously on the opposite side of the sensing gate layer. The sensing gate layer may be directly in contact with the intermediate layer or the semiconductor channel layer.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
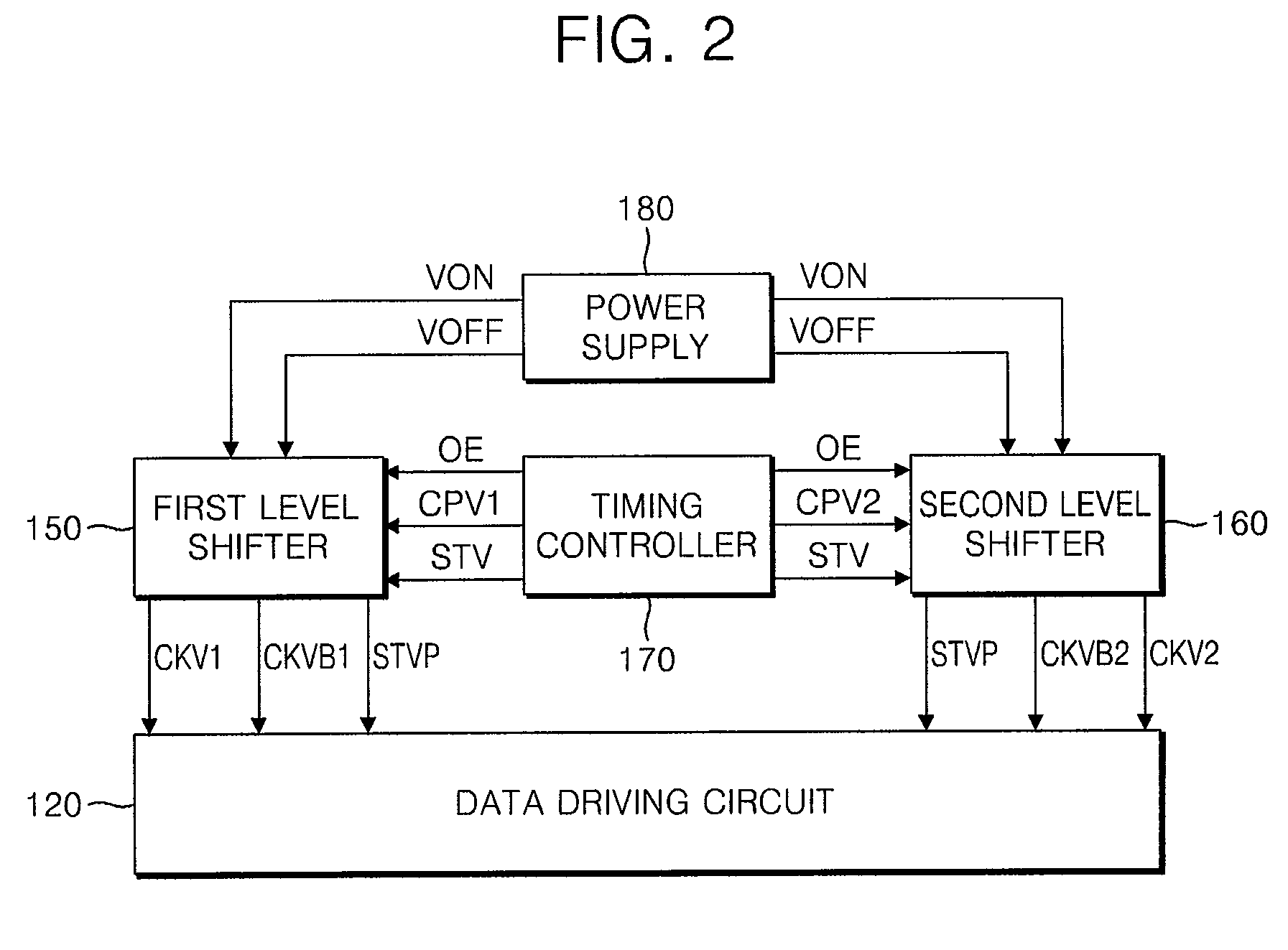
Liquid Crystal Display and Gate Driving Circuit Thereof
InactiveUS20080211760A1Lower requirementStatic indicating devicesDigital storageLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
A liquid crystal display and a dual gate driving circuit therefor wherein the number of signal lines are reduced by sharing a start pulse and an output signal of a dummy stage. The liquid crystal display includes a timing controller generating an output enable signal, a gate clock, and a signal start signal in response to an external input signal, a level shifter generating a gate clock pulse and a gate clock bar pulse in response to the output enable signal and the gate clock and generating a single start pulse in response to the start signal and the gate clock, and first and second gate driving circuits outputting the gate clock pulse or the gate clock bar pulse as a gate driving signal to the plurality of gate lines in response to the single start pulse.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com