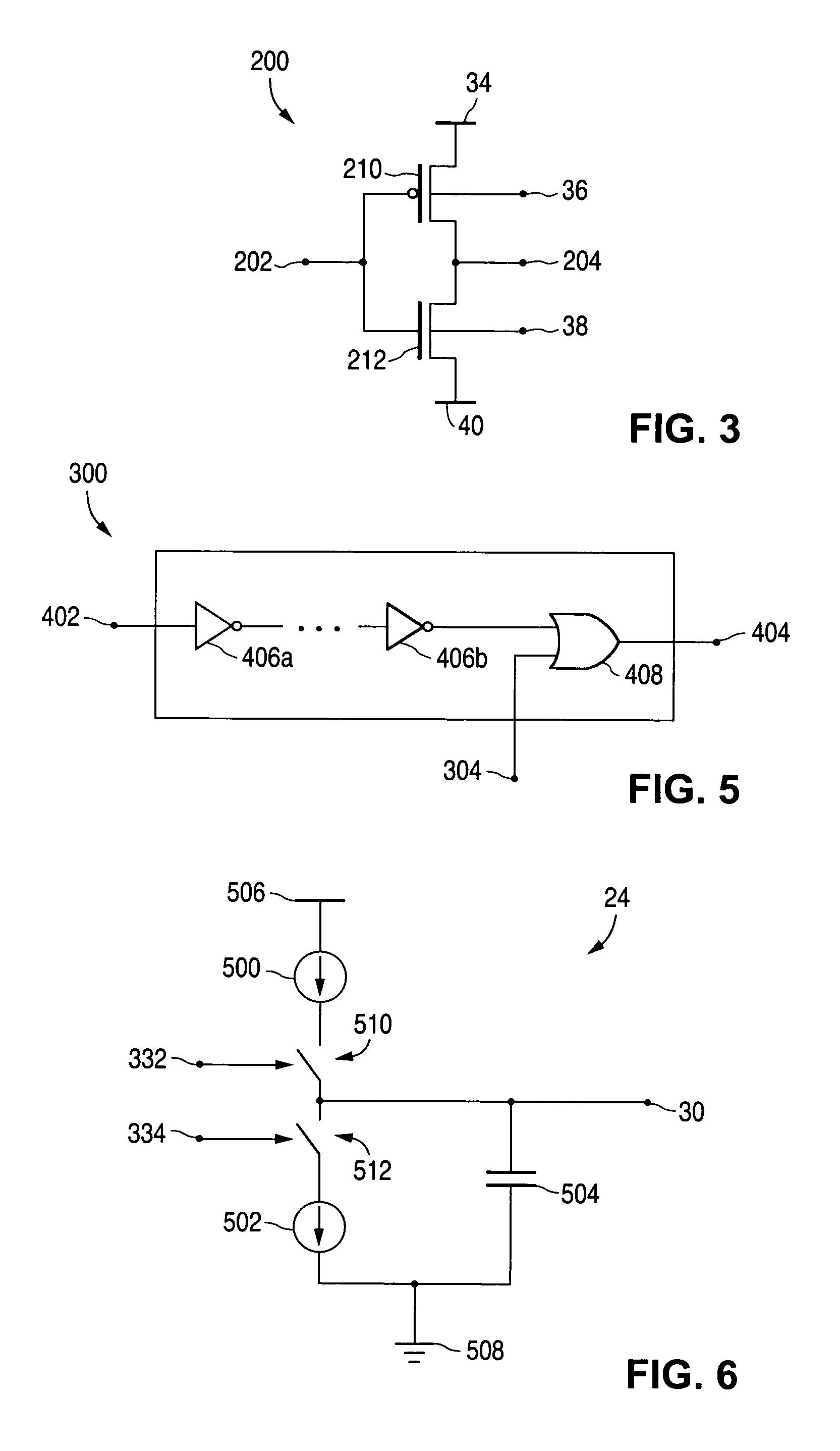
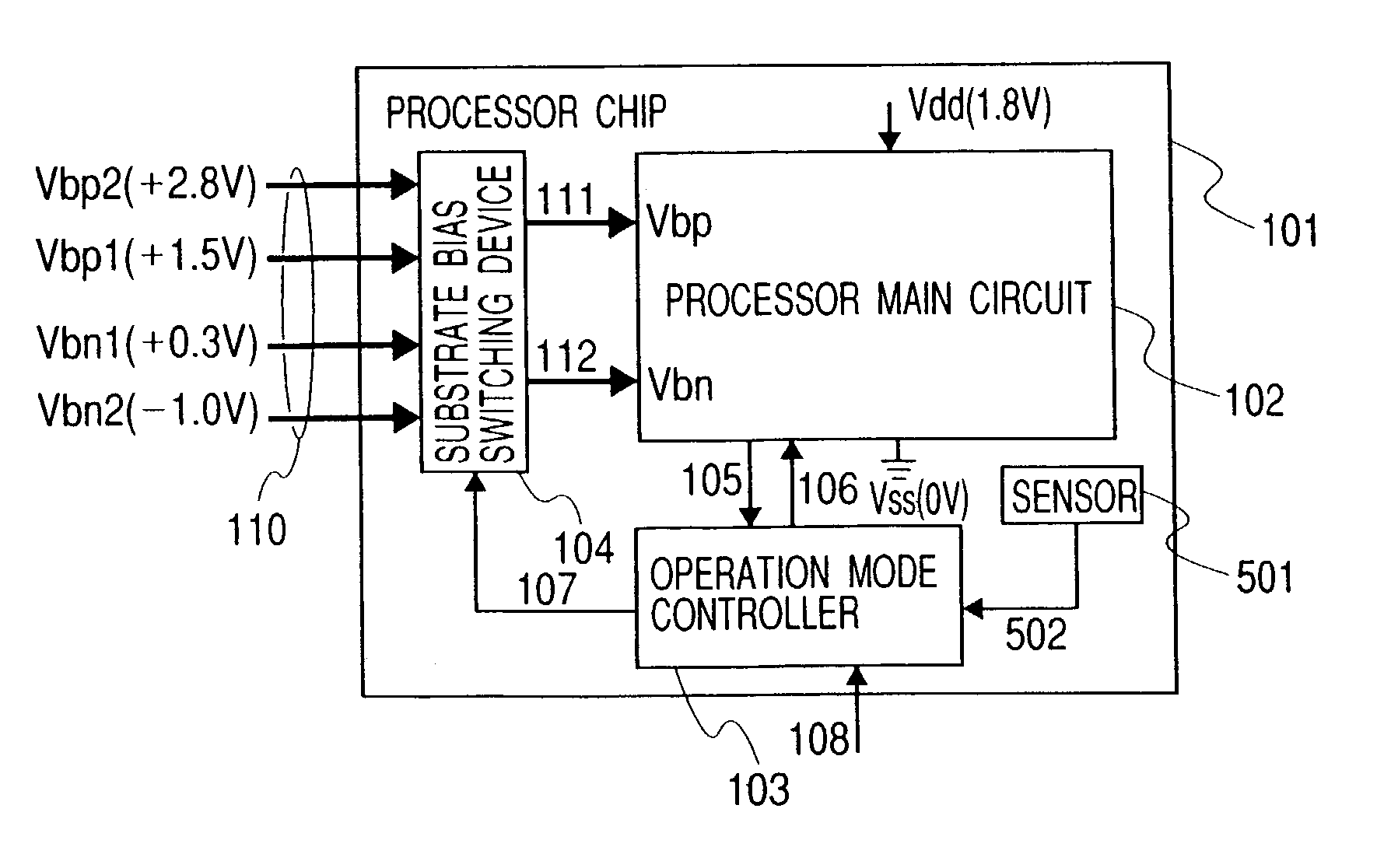
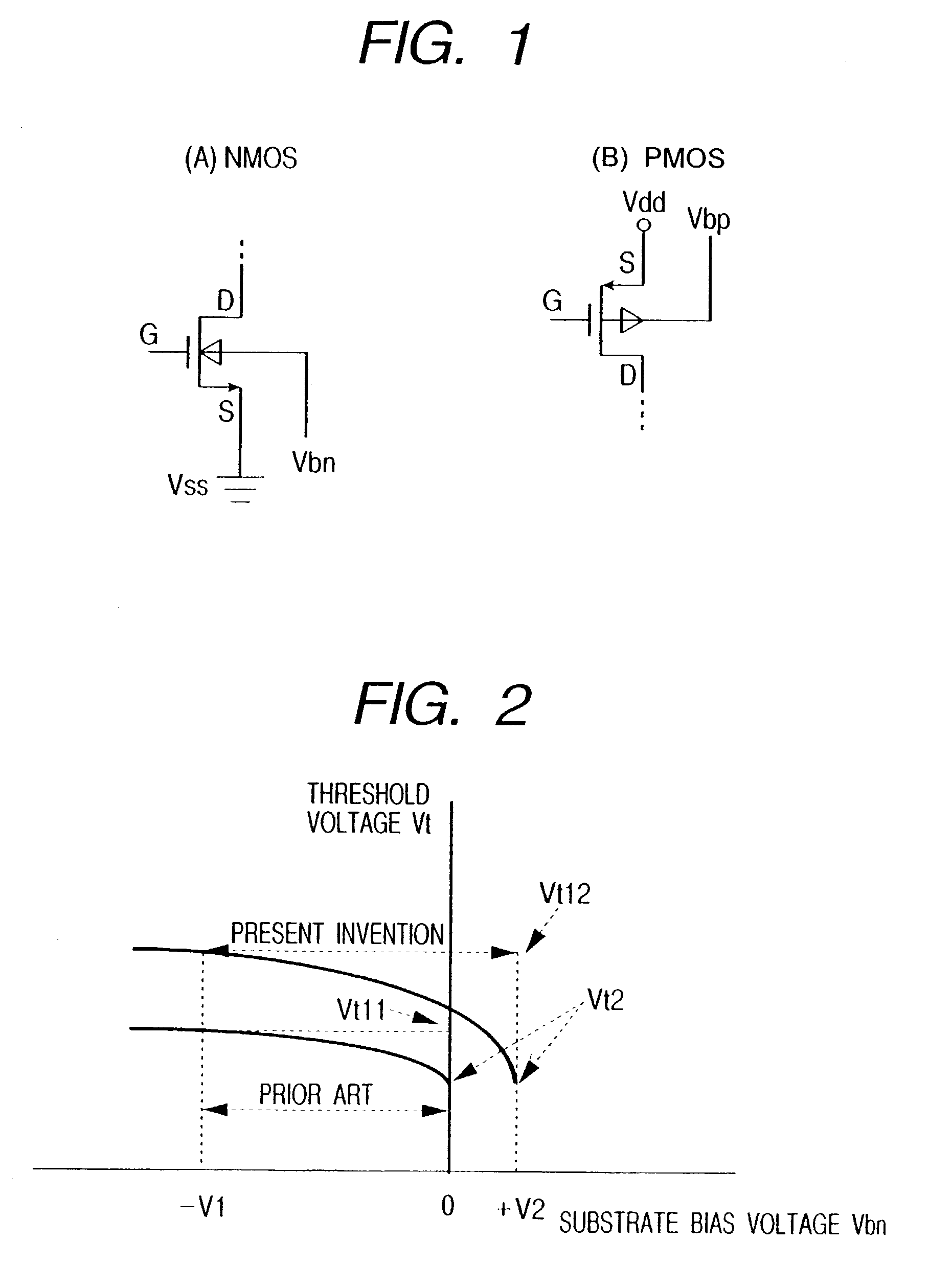
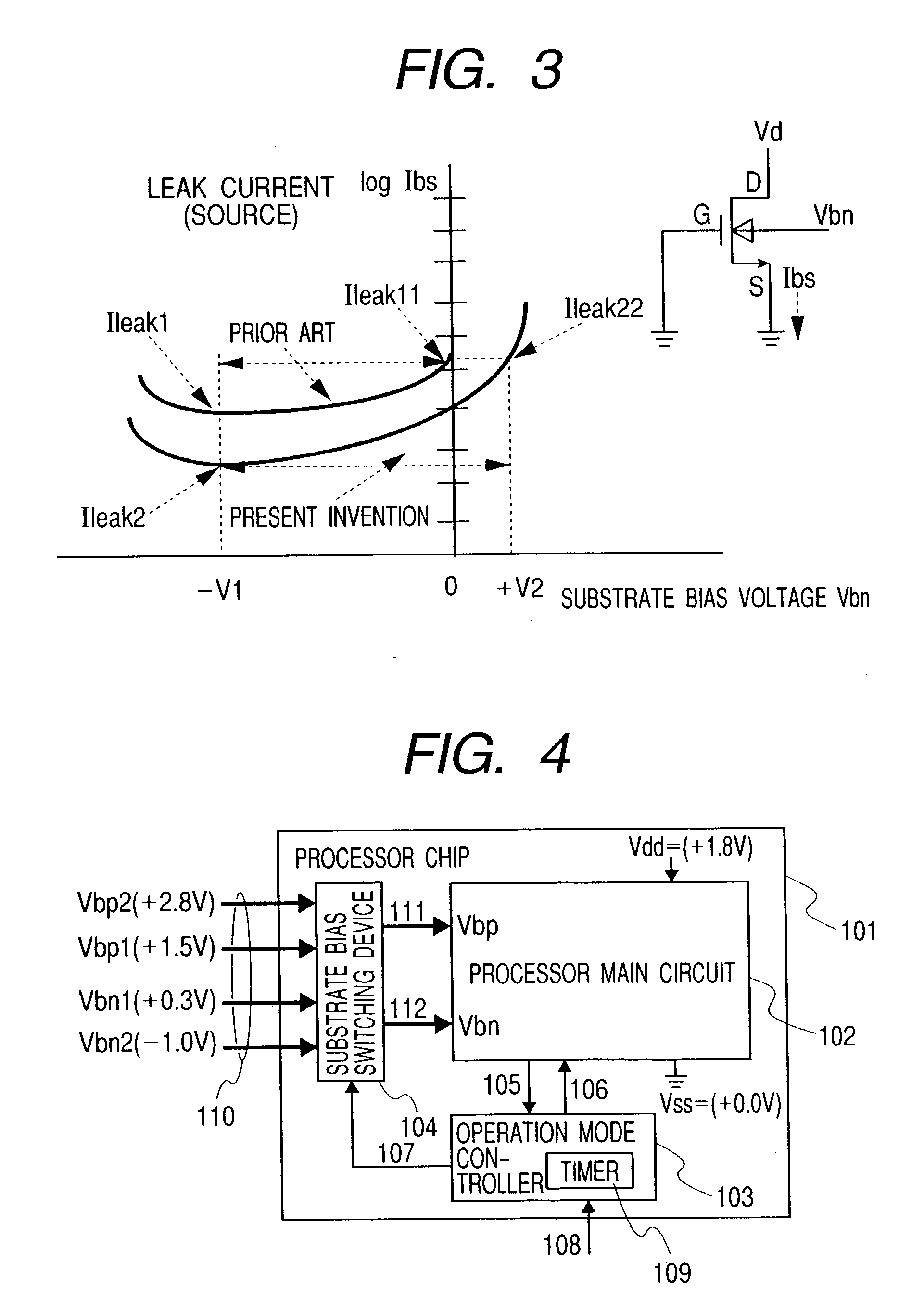
Patents
Literature
207 results about "Back bias" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Back bias. Degenerative or regenerative voltage which is fed back to circuits before its originating point; usually applied to a control anode of a tube or other device. Voltage applied to a grid of a tube (or tubes) or electrode of another device to reduce a condition which has been upset by some external cause.
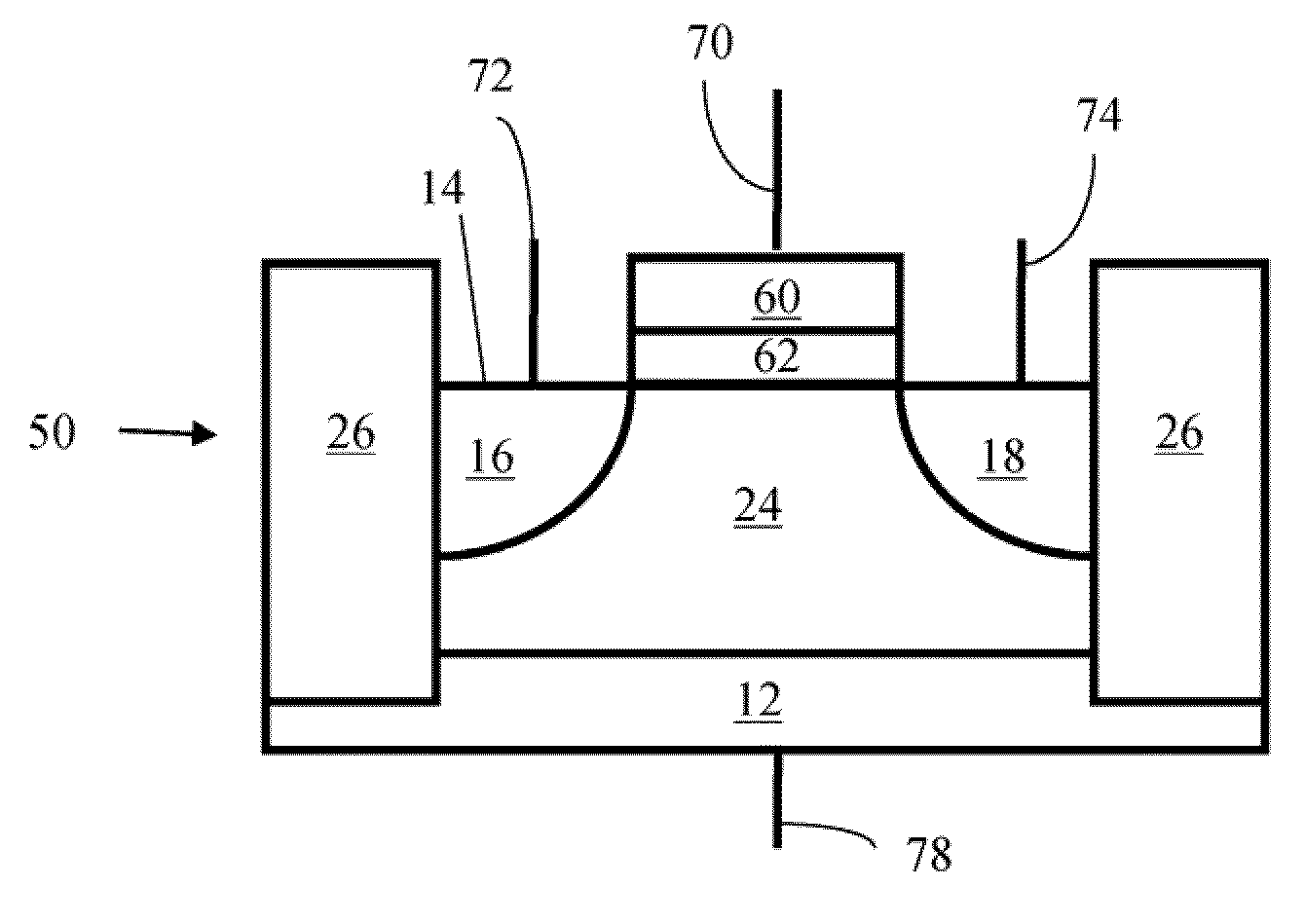
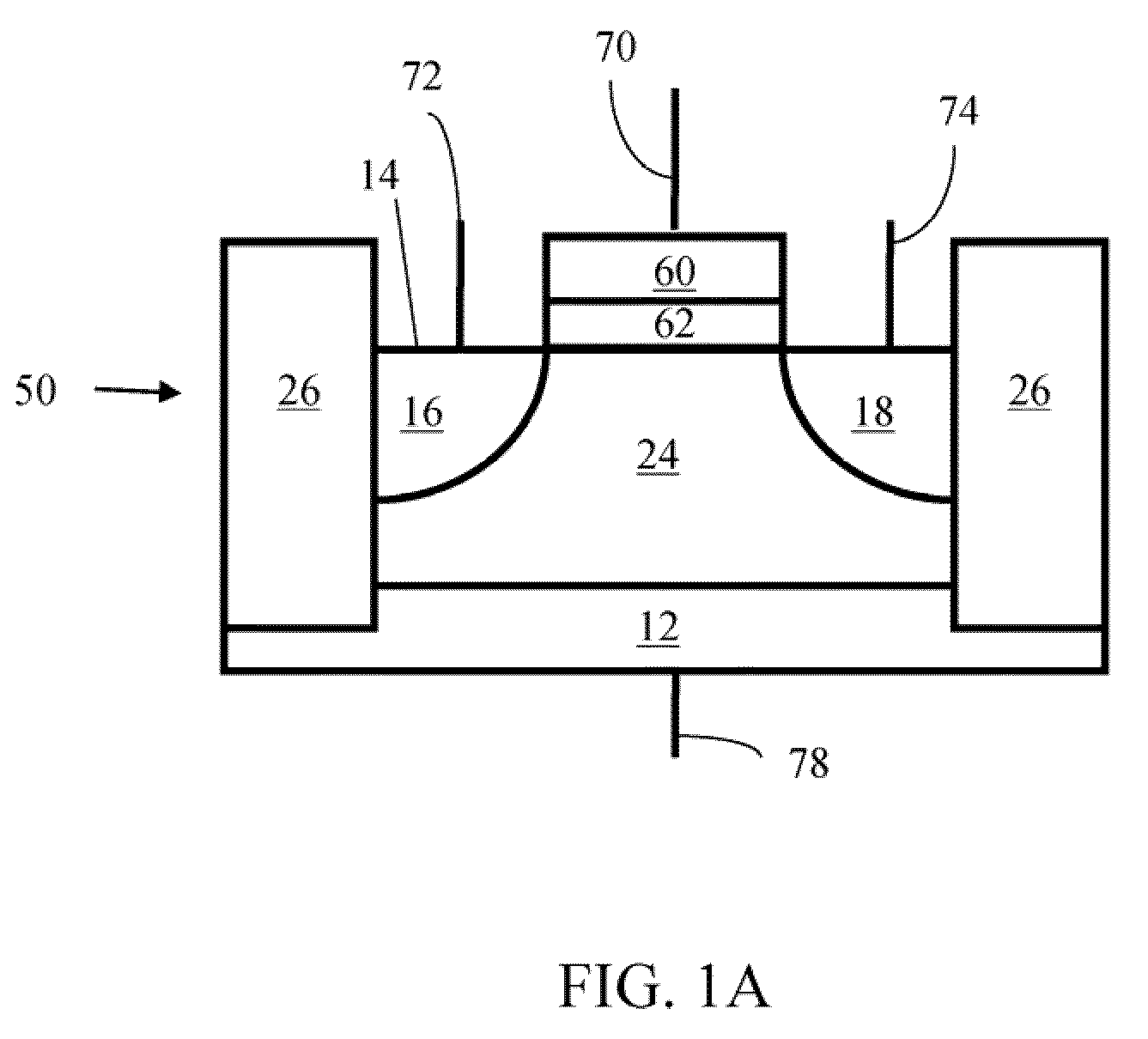
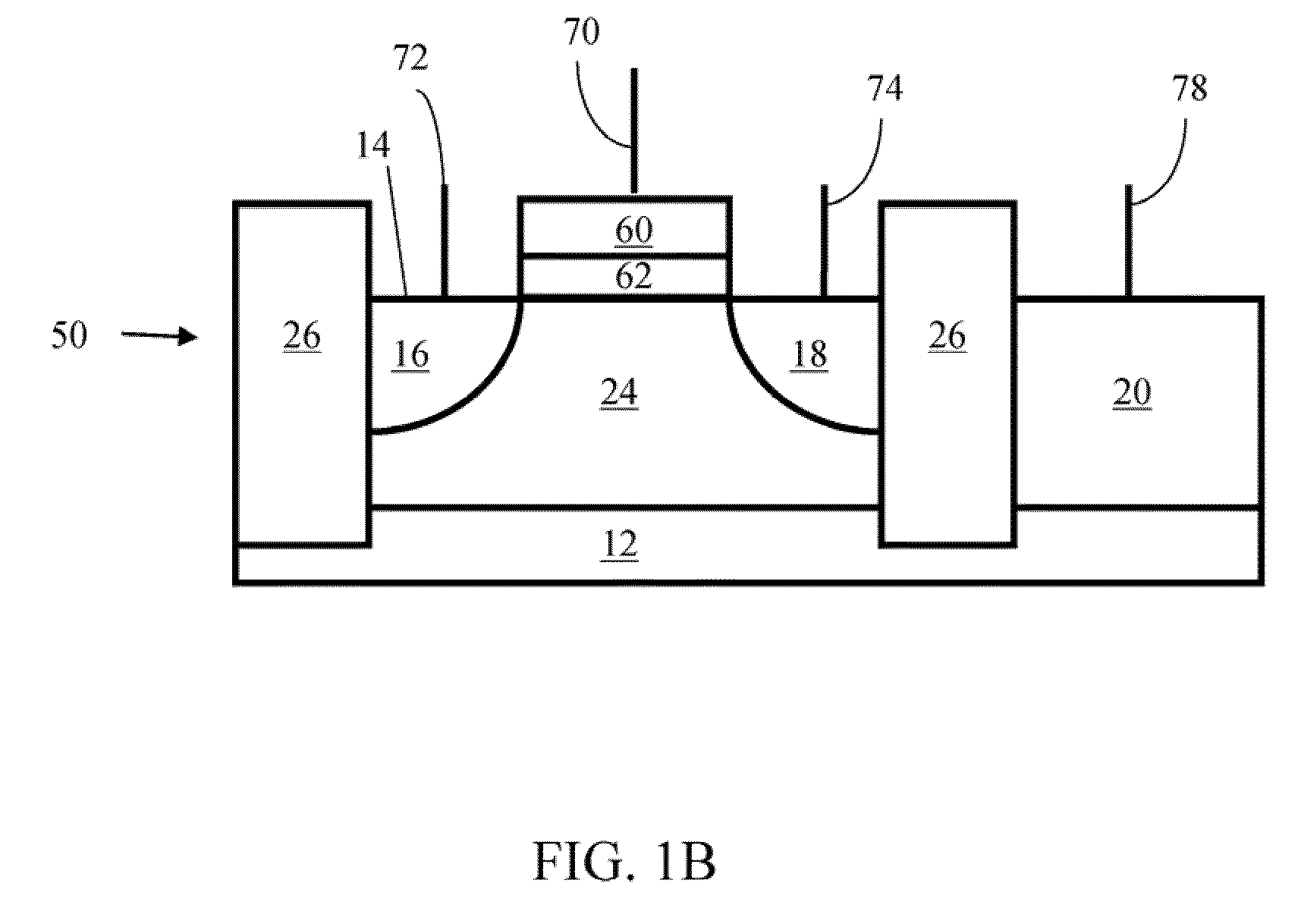
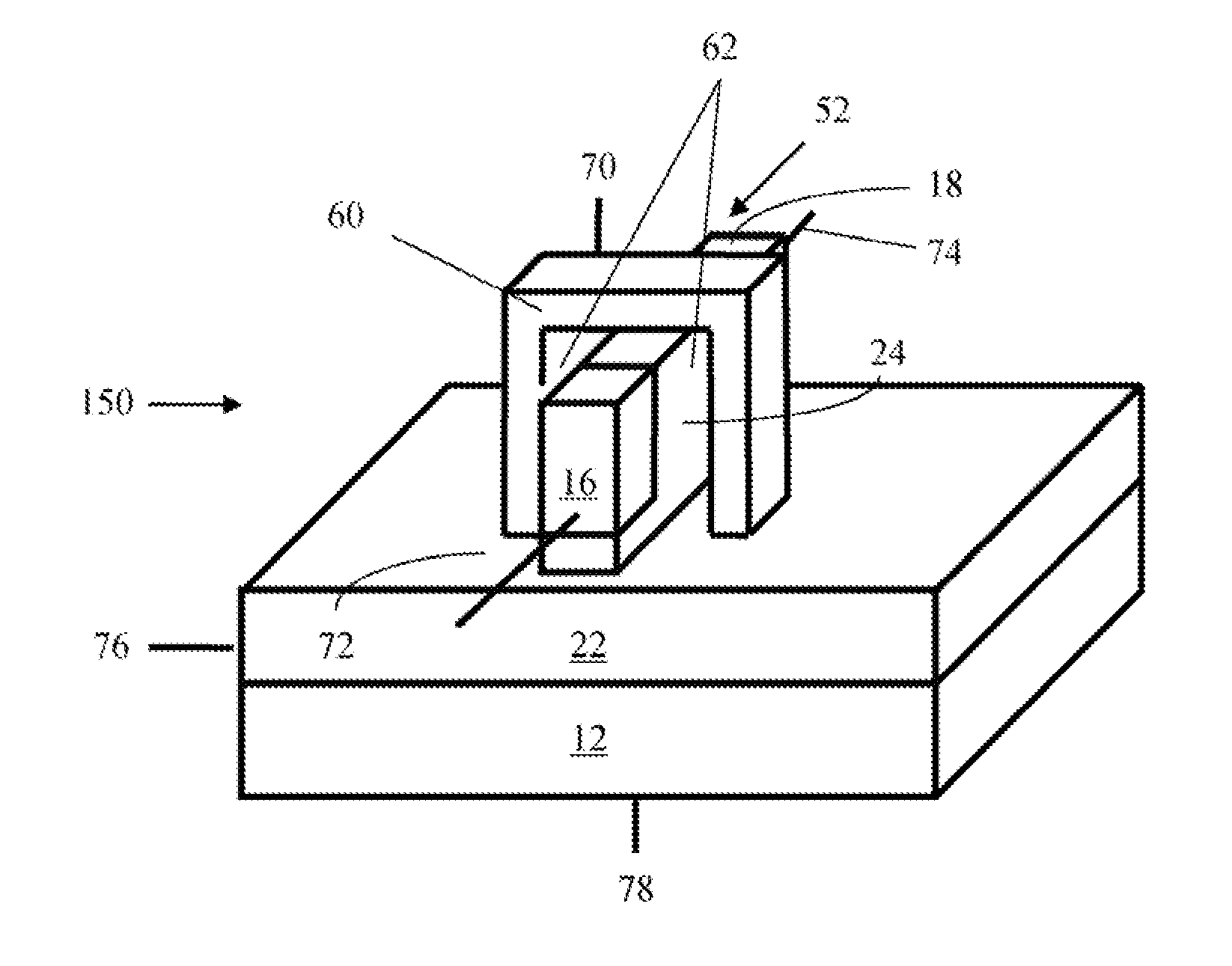
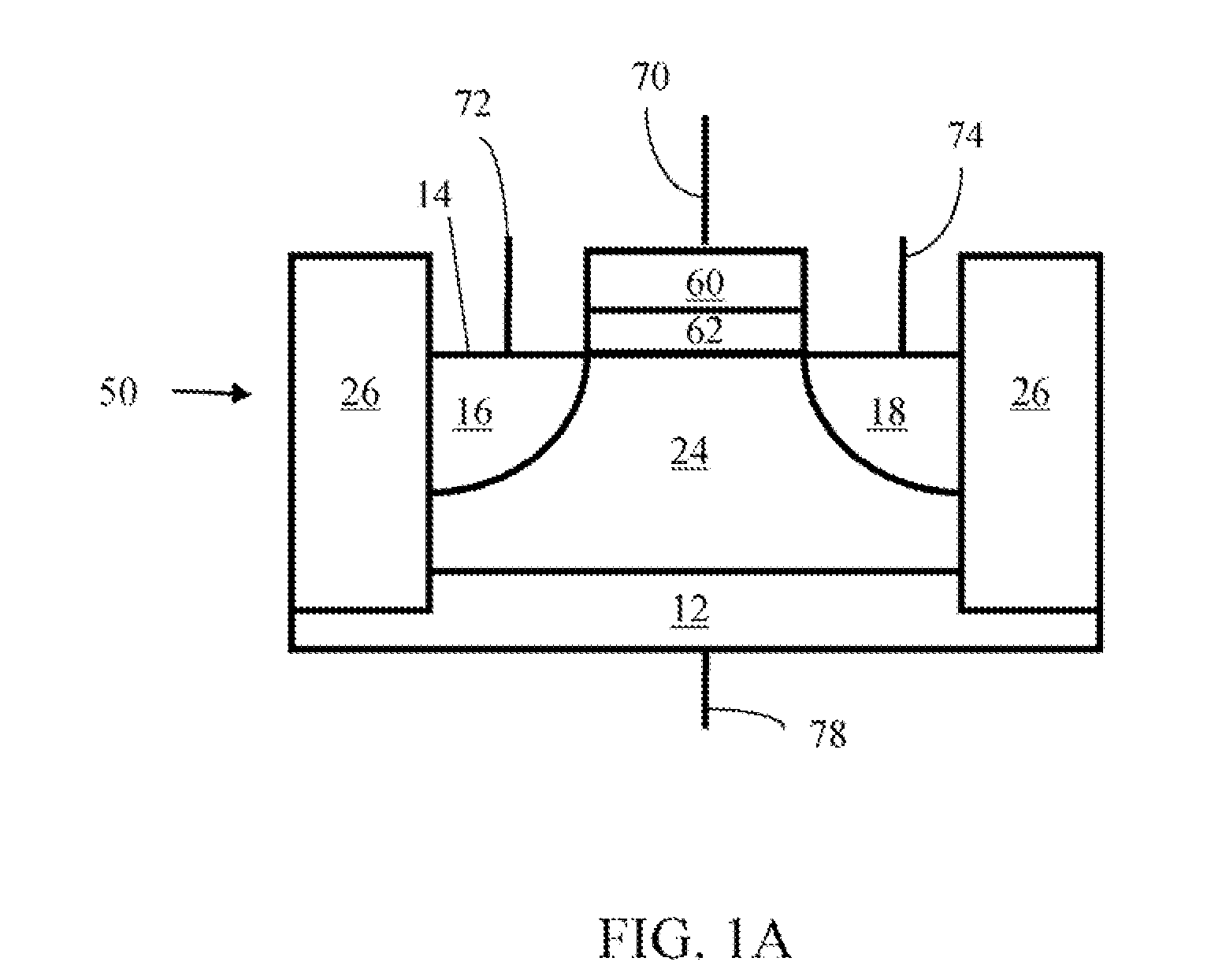
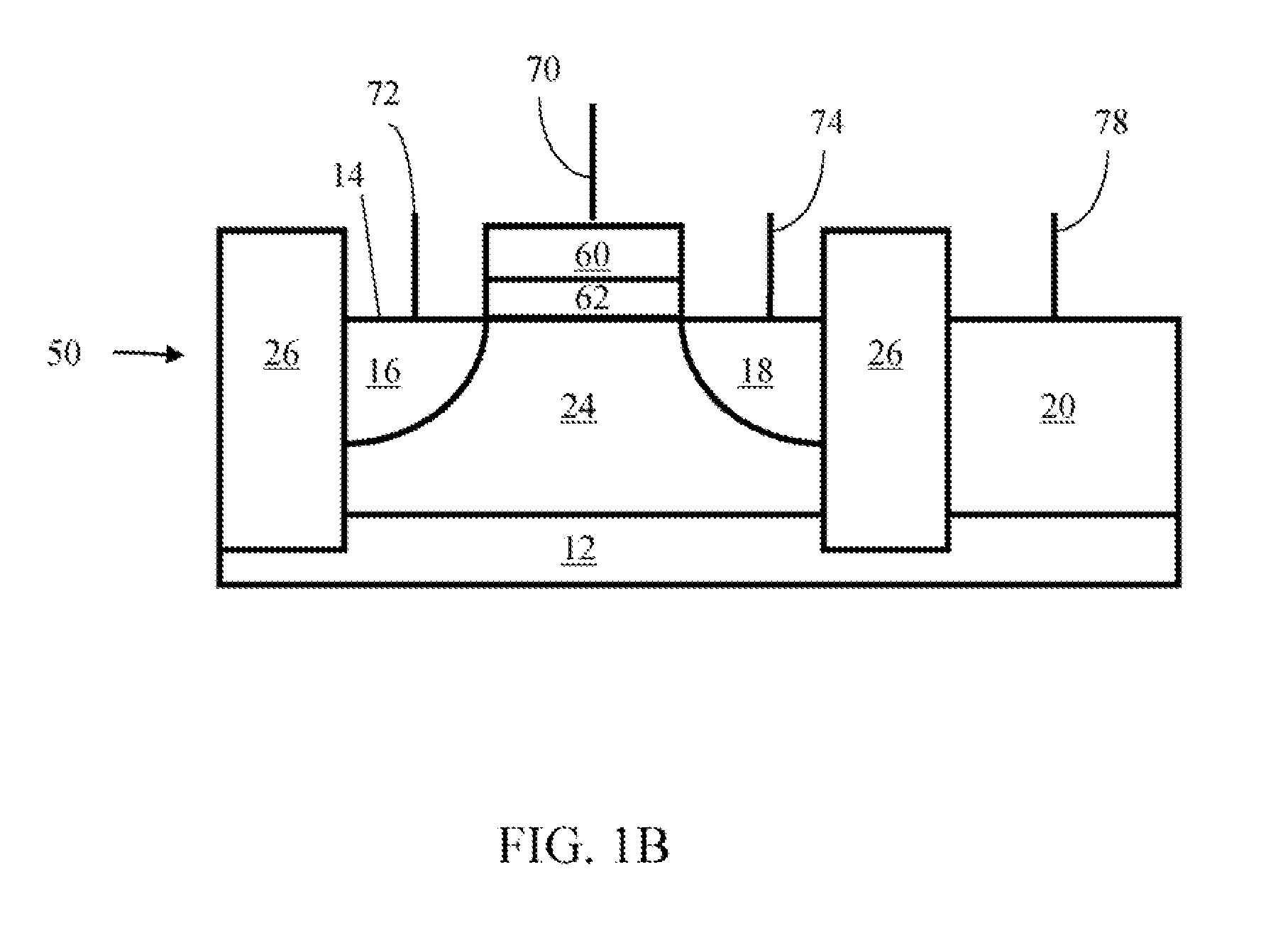
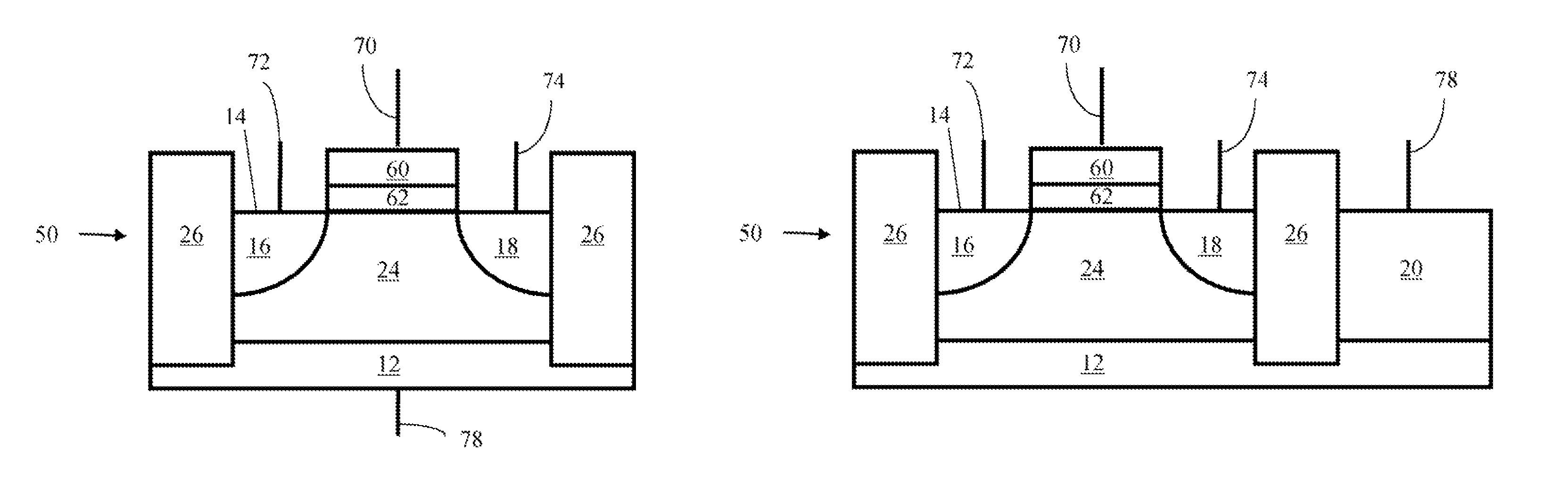
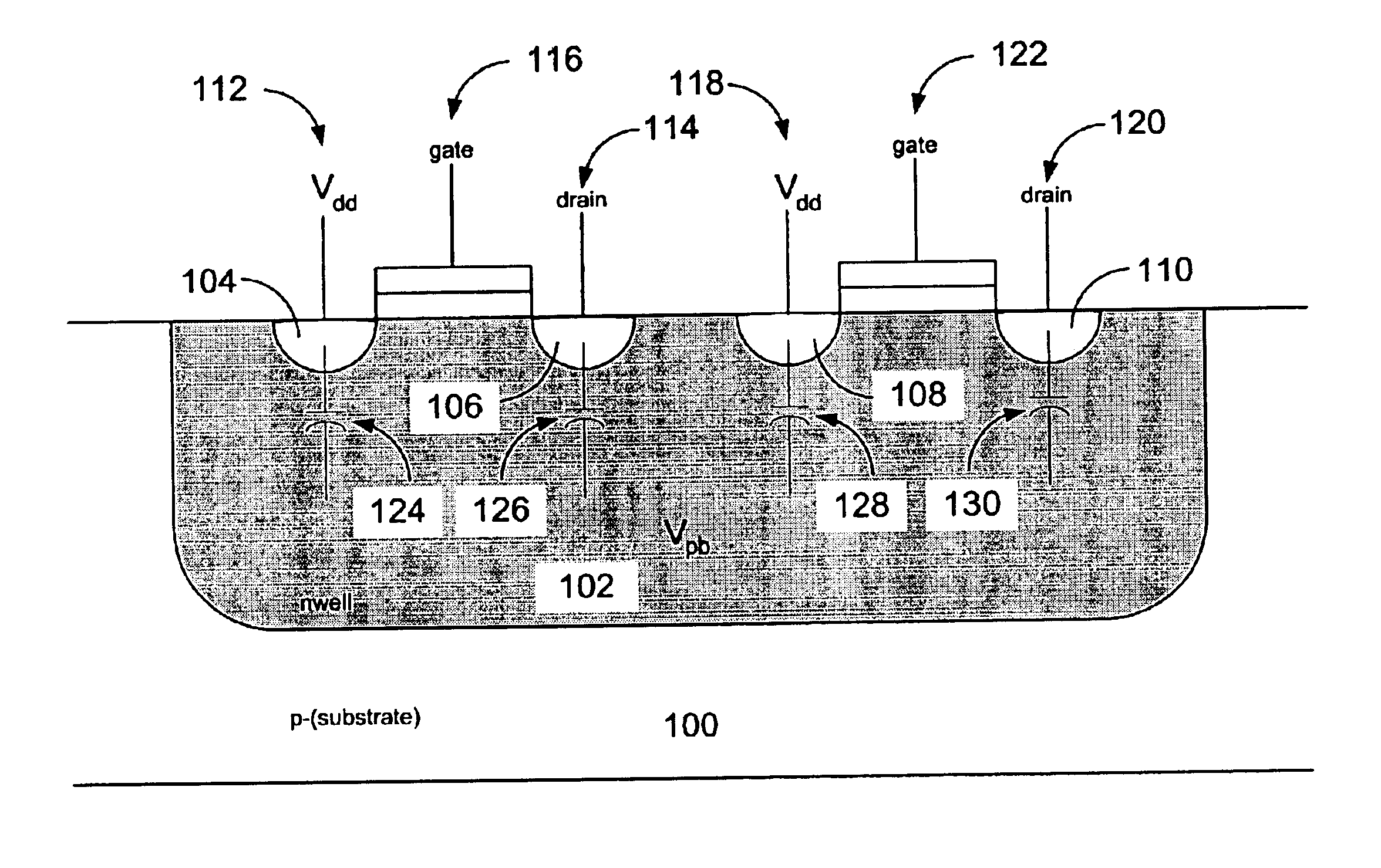
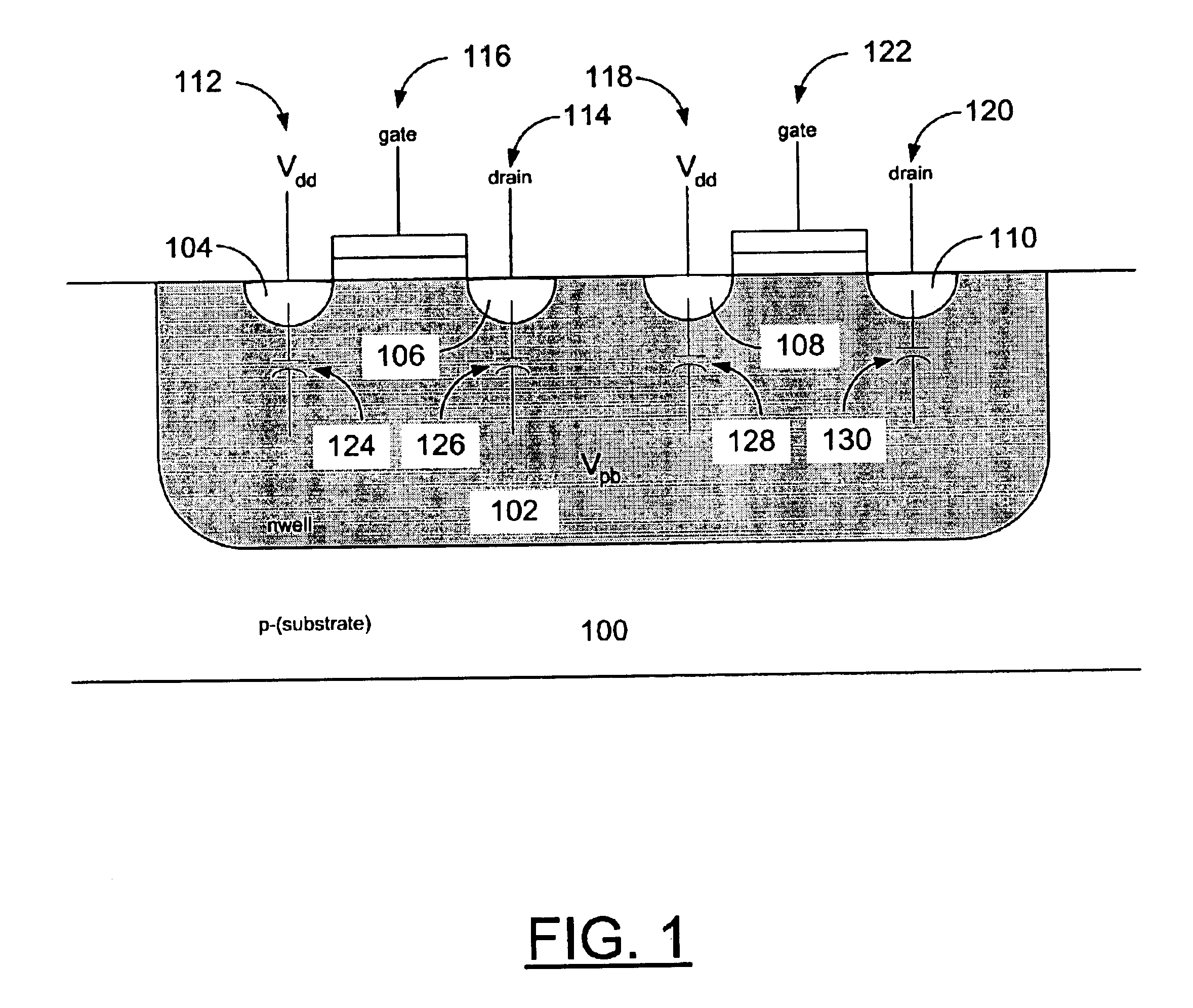
Method of maintaining the state of semiconductor memory having electrically floating body transistor
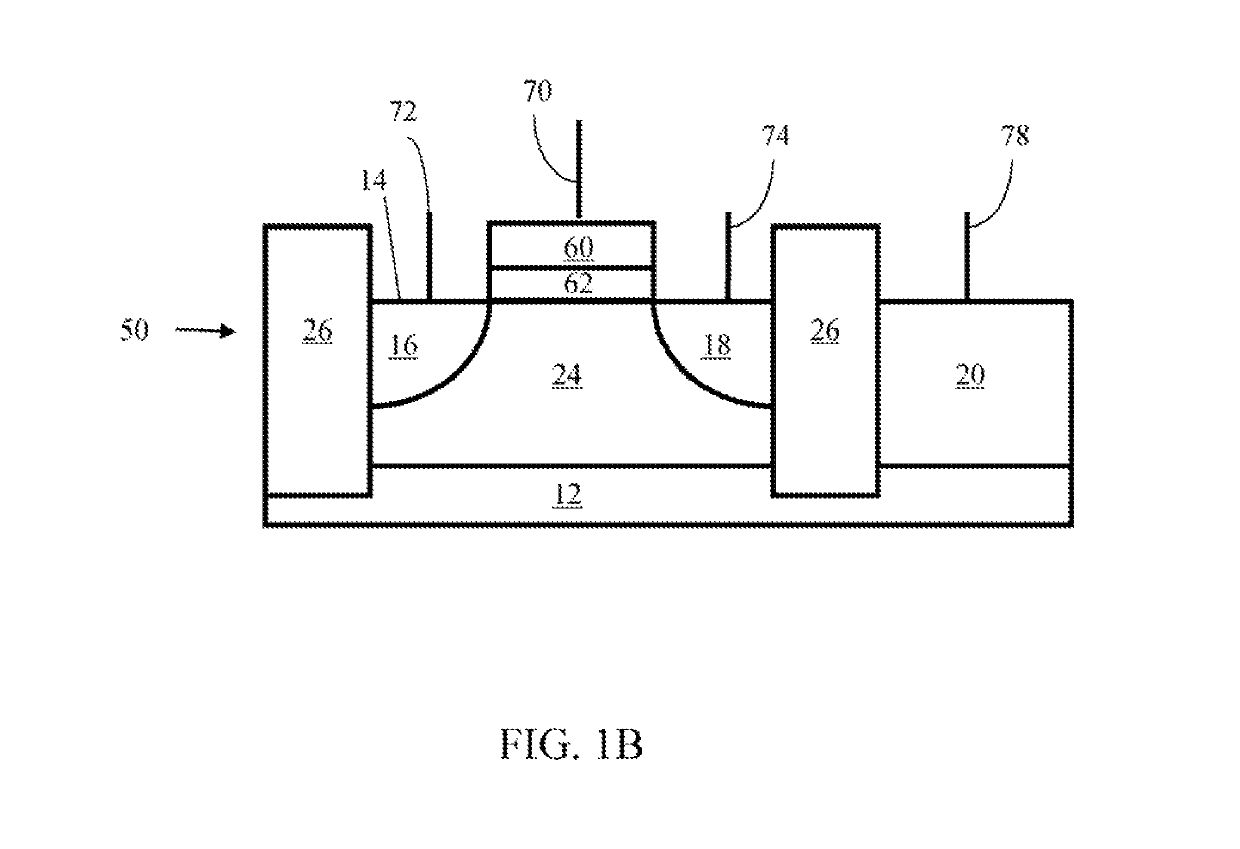
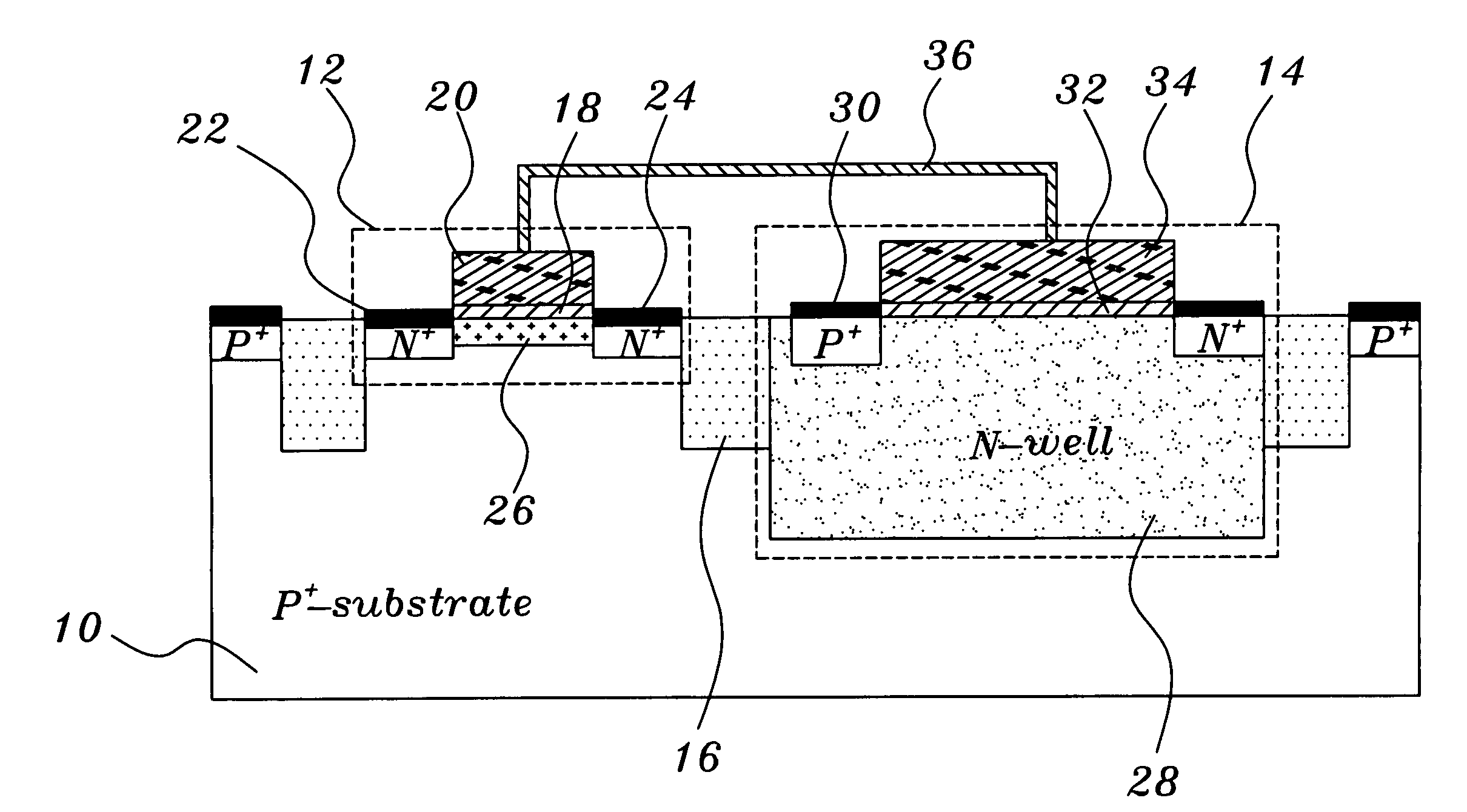
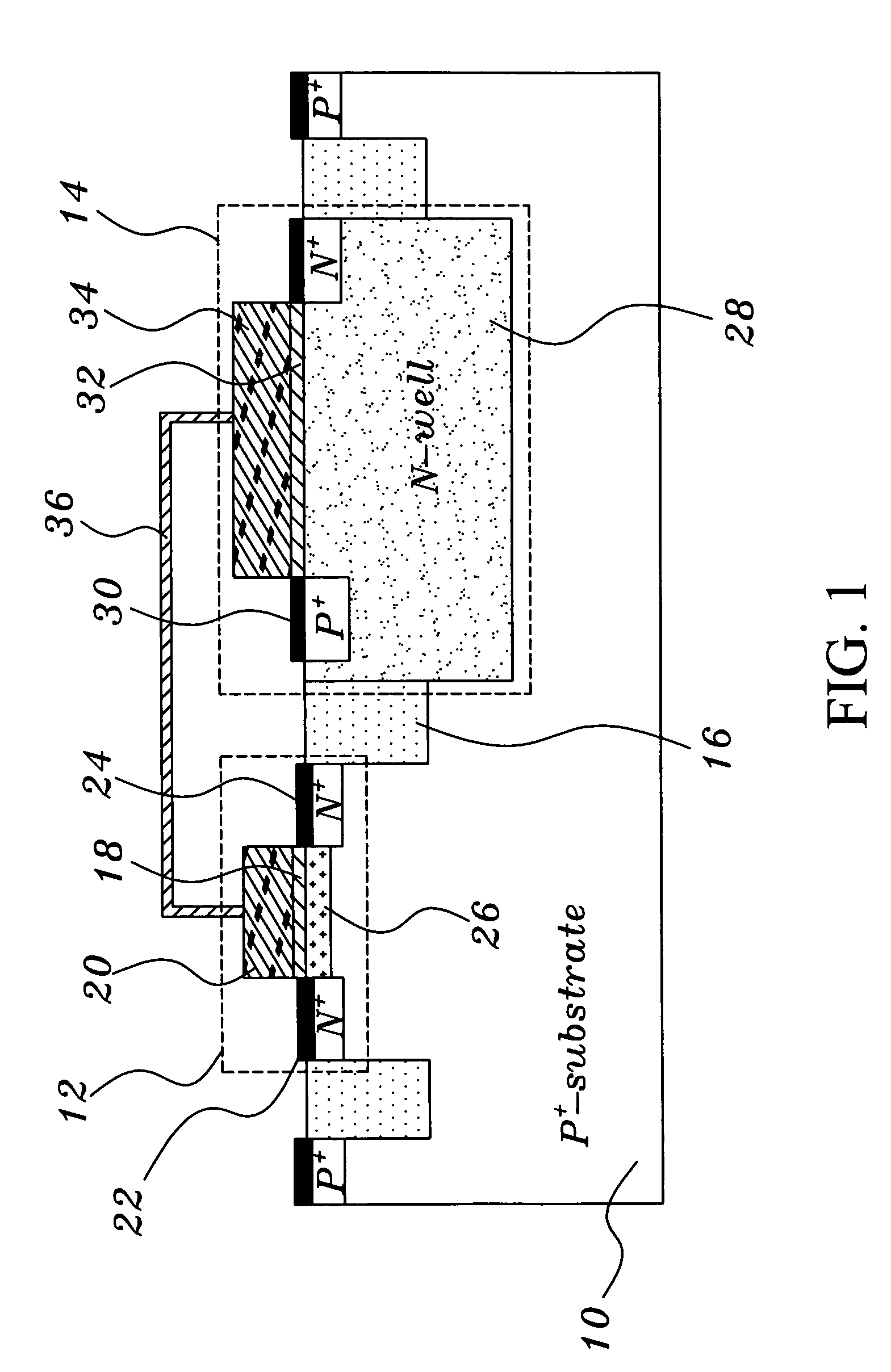
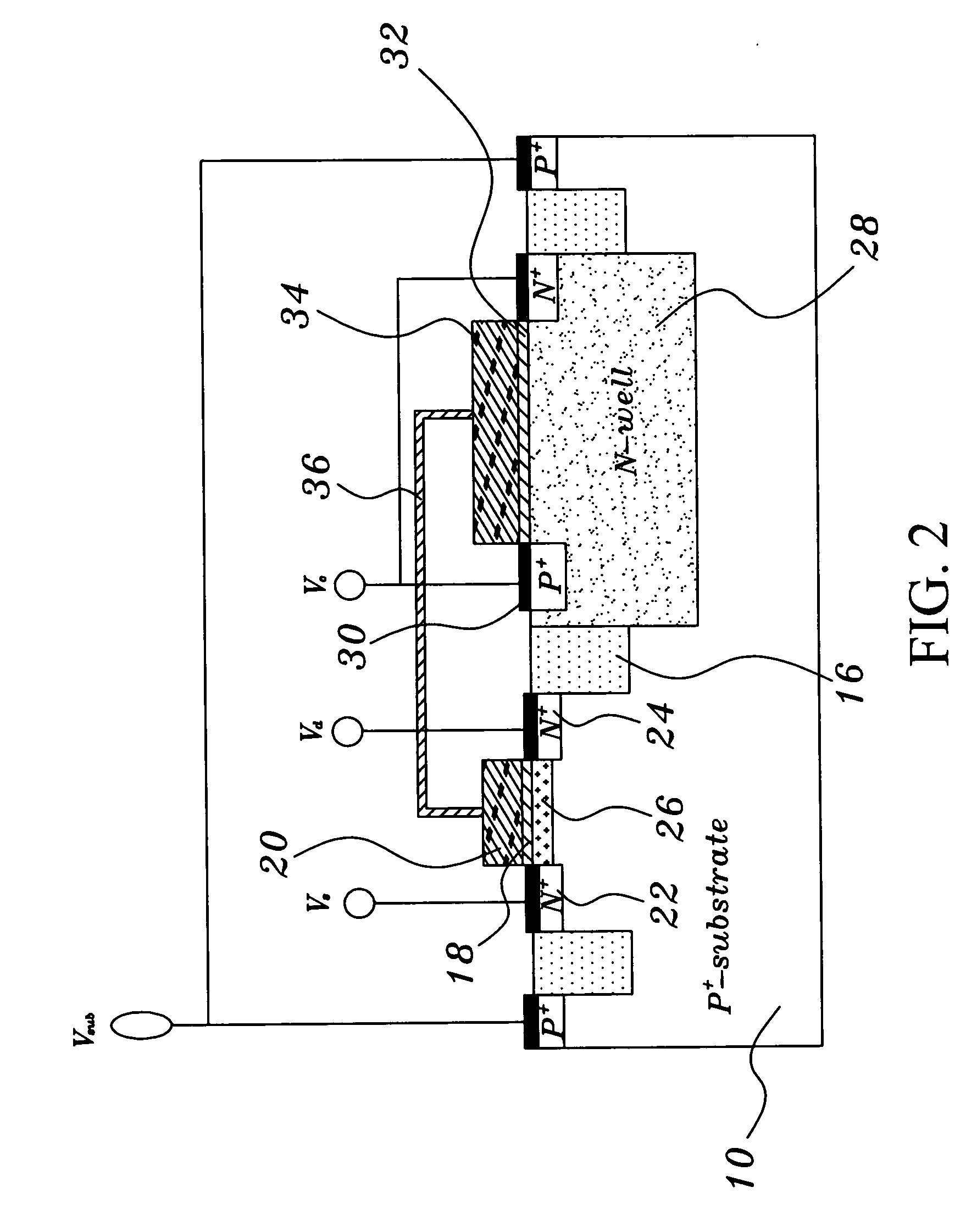
Methods of maintaining a state of a memory cell without interrupting access to the memory cell are provided, including applying a back bias to the cell to offset charge leakage out of a floating body of the cell, wherein a charge level of the floating body indicates a state of the memory cell; and accessing the cell.
Owner:ZENO SEMICON
Semiconductor memory having electrically floating body transistor
ActiveUS20120012915A1Large memory windowLarger memory windowTransistorSolid-state devicesCharge injectionBack bias
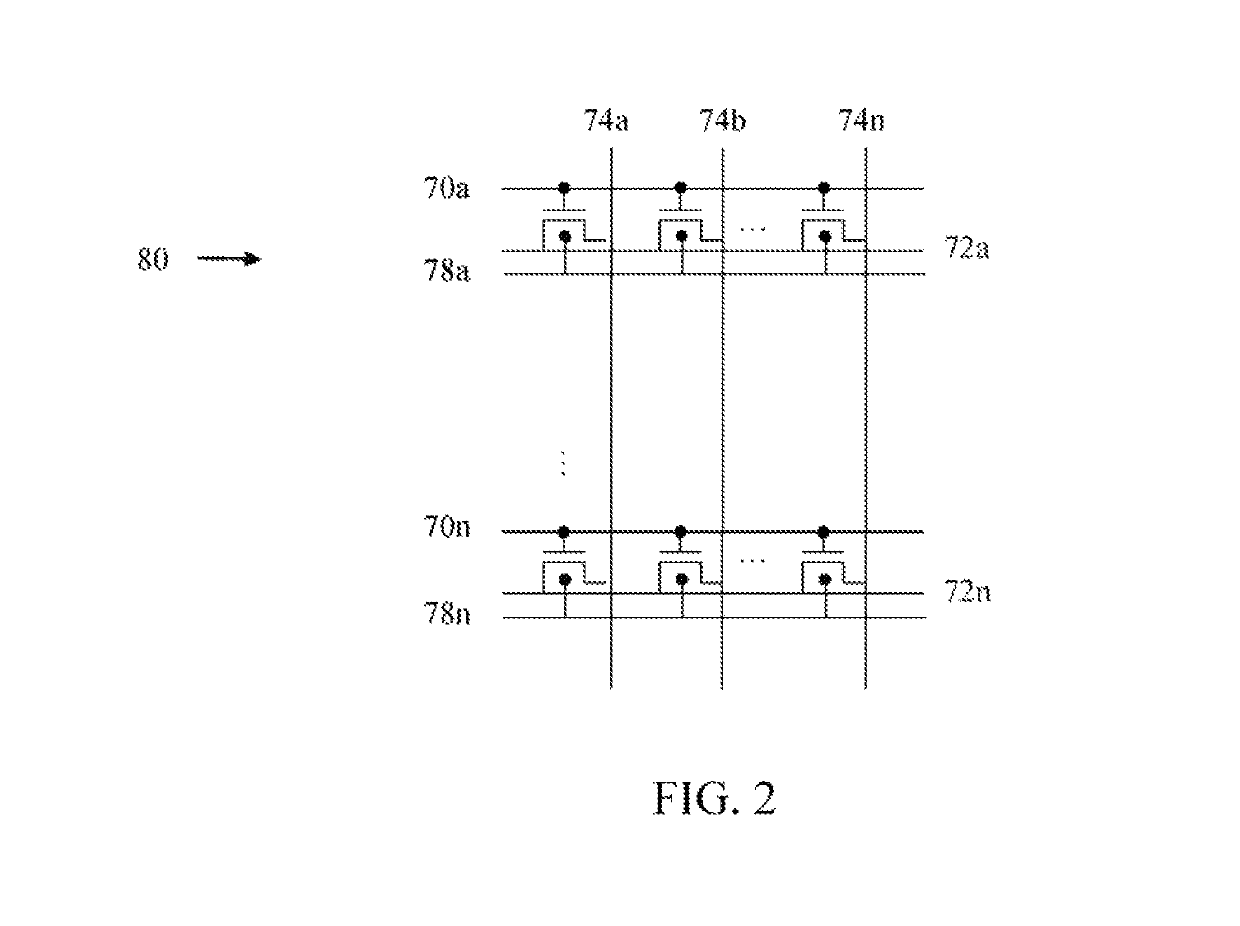
A semiconductor memory cell includes a floating body region configured to be charged to a level indicative of a state of the memory cell; a first region in electrical contact with said floating body region; a second region in electrical contact with said floating body region and spaced apart from said first region; a gate positioned between said first and second regions; and a back-bias region configured to inject charge into or extract charge out of said floating body region to maintain said state of the memory cell. Application of back bias to the back bias region offsets charge leakage out of the floating body and performs a holding operation on the cell. The cell may be a multi-level cell. Arrays of memory cells are disclosed for making a memory device.
Owner:ZENO SEMICON
Semiconductor memory having electrically floating body transistor
A semiconductor memory cell includes a floating body region configured to be charged to a level indicative of a state of the memory cell; a first region in electrical contact with said floating body region; a second region in electrical contact with said floating body region and spaced apart from said first region; a gate positioned between said first and second regions; and a back-bias region configured to inject charge into or extract charge out of said floating body region to maintain said state of the memory cell. Application of back bias to the back bias region offsets charge leakage out of the floating body and performs a holding operation on the cell. The cell may be a multi-level cell. Arrays of memory cells are disclosed for making a memory device.
Owner:ZENO SEMICON
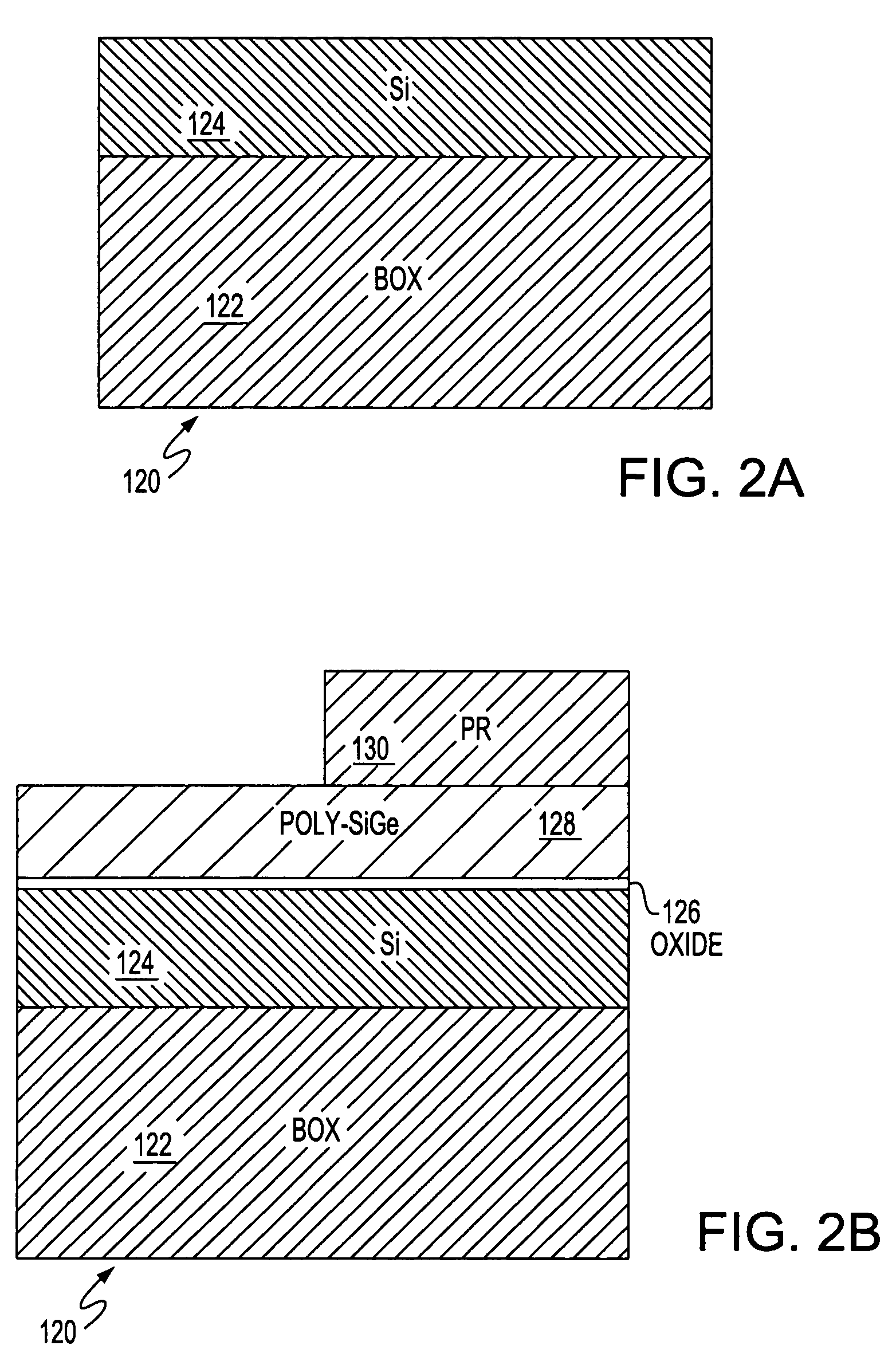
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20090057746A1High Q valueSmall parasitic capacitanceTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceGate dielectric
A semiconductor device having a passive element whose characteristic is adjustable even after manufacture by applying back bias voltage is provided. Formed on a main surface of a SOI substrate comprising a supporting substrate, a BOX layer, and an SOI layer is a MOS varactor comprising a gate dielectric formed on a surface of the SOI layer, a gate electrode formed on the gate dielectric, and a n+ type semiconductor region formed in the SOI layer located on both sides of the gate electrode. The MOS varactor, is configured so that capacitance formed by the SOI layer, gate dielectric, and gate electrode is varied by applying bias voltage to the supporting substrate (p type well) under the gate electrode.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Semiconductor integrated circuit device with low power consumption and simple manufacturing steps
InactiveUS6208171B1Reduce manufacturing stepsProduction costPower reduction by control/clock signalLogic circuits characterised by logic functionPotential clampBack bias
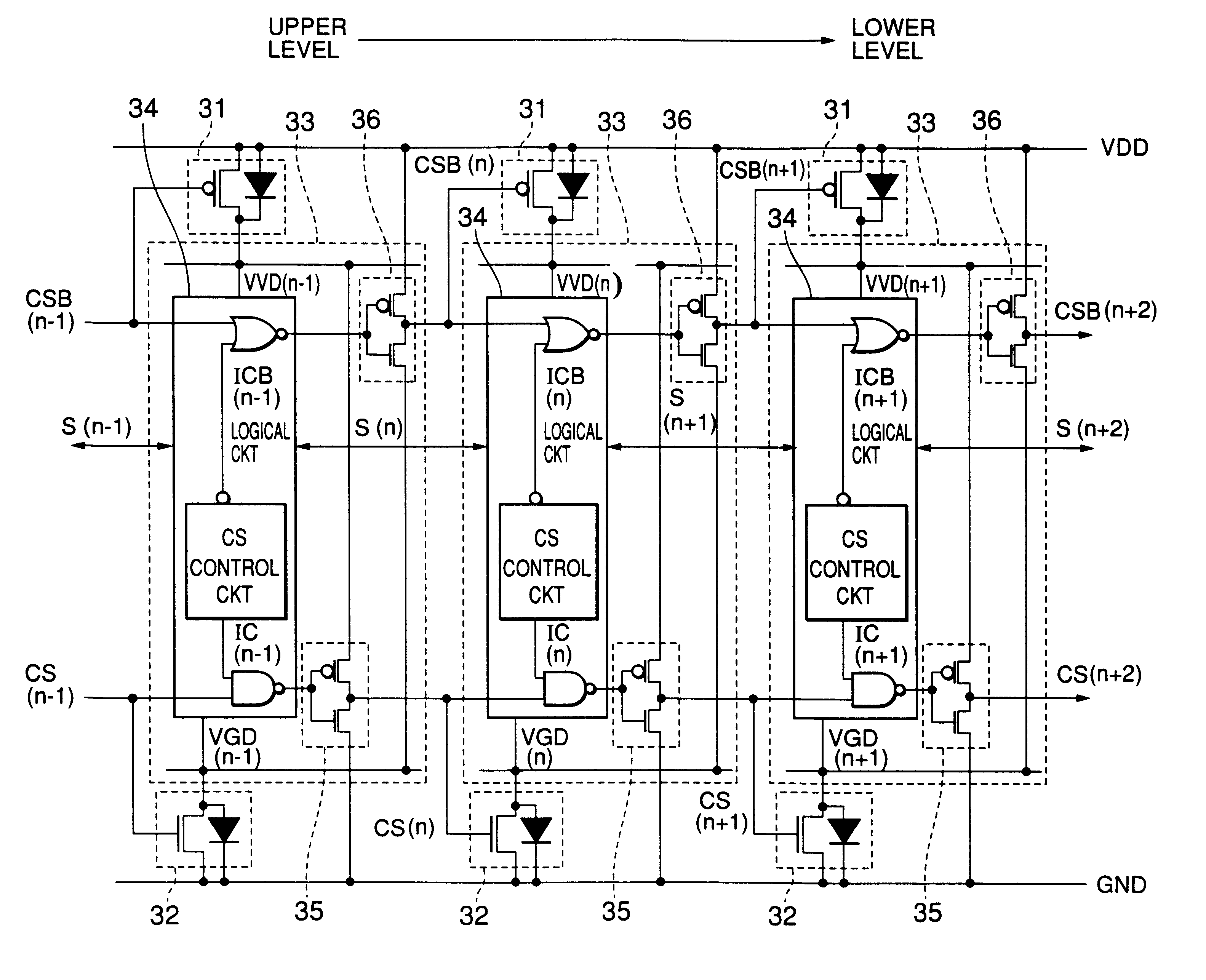
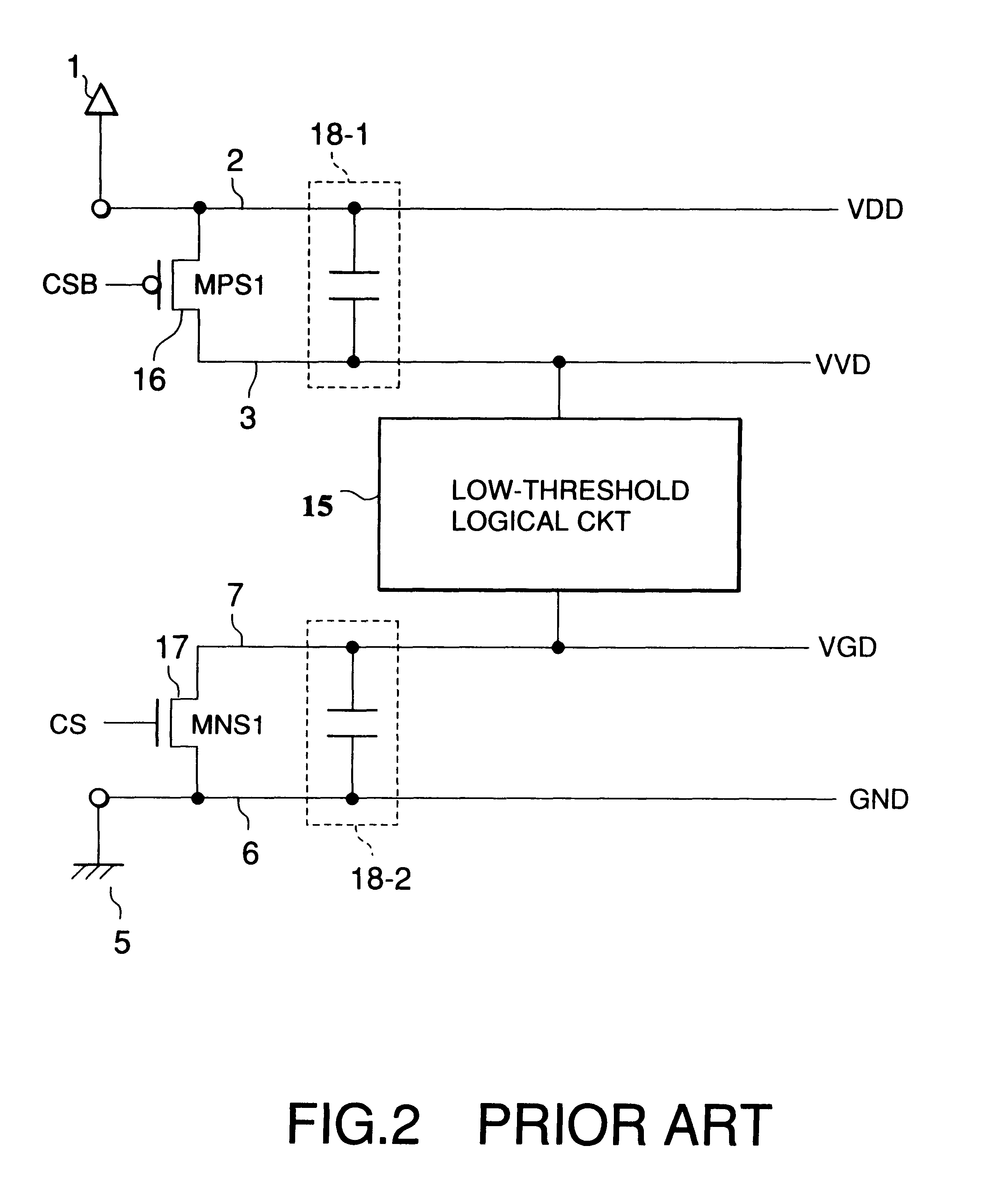
In a semiconductor integrated circuit, a control transistor 4 and a potential clamp circuit 9 are arranged between a power supply line 2 and a virtual power supply line 3. Even in a sleeve mode where the control transistor 4 is turned off, the potential clamp circuit 9-1 clamps the virtual power supply line 3 at a certain potential to hold a potential state (high level or low level) of each node of a logical circuit. At this time, each FET forming the logical circuit is applied with a back bias so that a threshold voltage Vt becomes higher than that in an active mode. Therefore, a leakage current can be decreased. In the semiconductor integrated circuit, the threshold voltage Vt of the control transistor 4 can be selected to be equal to that of one FET of the complementary FET forming the logical circuit. Therefore, the layout area and the number of manufacturing steps can be reduced.
Owner:NEC CORP
Nonvolatile flash memory and method of operating the same
ActiveUS7099192B2Improve efficiencyTotal current dropTransistorRead-only memoriesDielectricBack bias
Owner:YIELD MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Memory Device Having Electrically Floating Body Transistor
A semiconductor memory cell includes a floating body region configured to be charged to a level indicative of a state of the memory cell selected from at least first and second states. A first region of the memory cell is in electrical contact with the floating body region. A second region of the memory cell is spaced apart from the first region and is also in electrical contact with the floating body region. A gate is positioned between the first and second regions. A back-bias region is configured to generate impact ionization when the memory cell is in one of the first and second states, and the back-bias region is configured so as not to generate impact ionization when the memory cell is in the other of the first and second states.
Owner:ZENO SEMICON
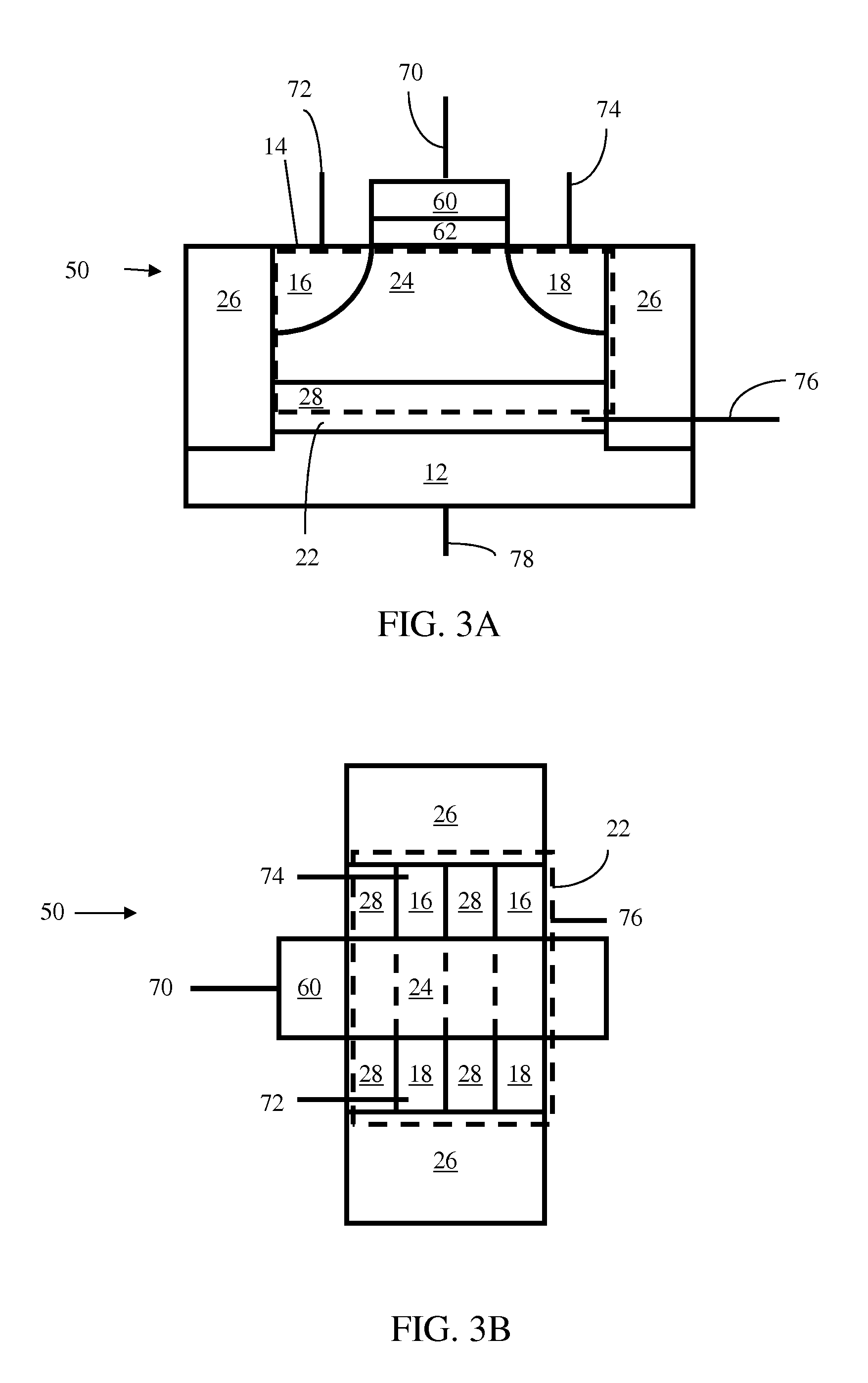
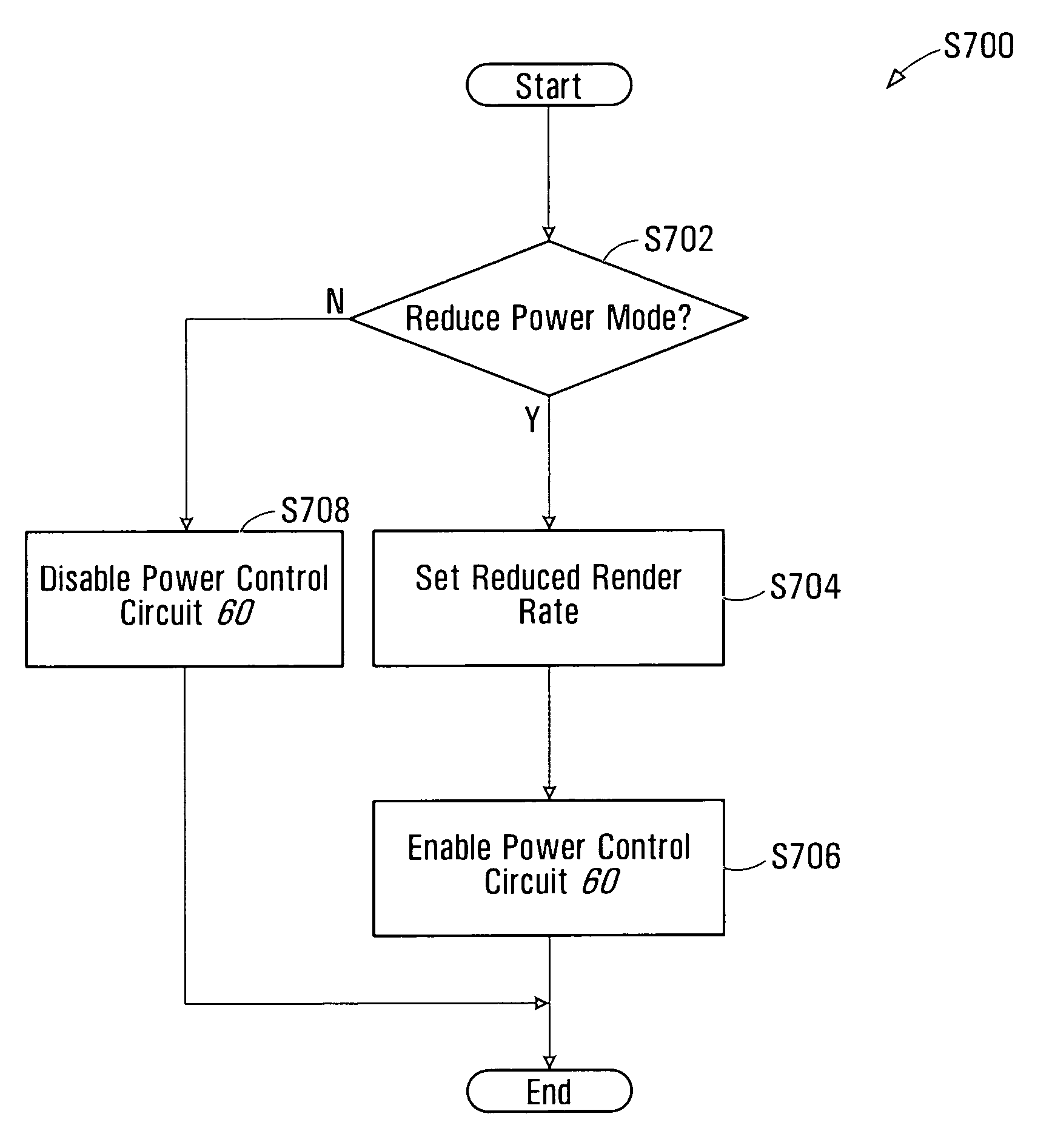
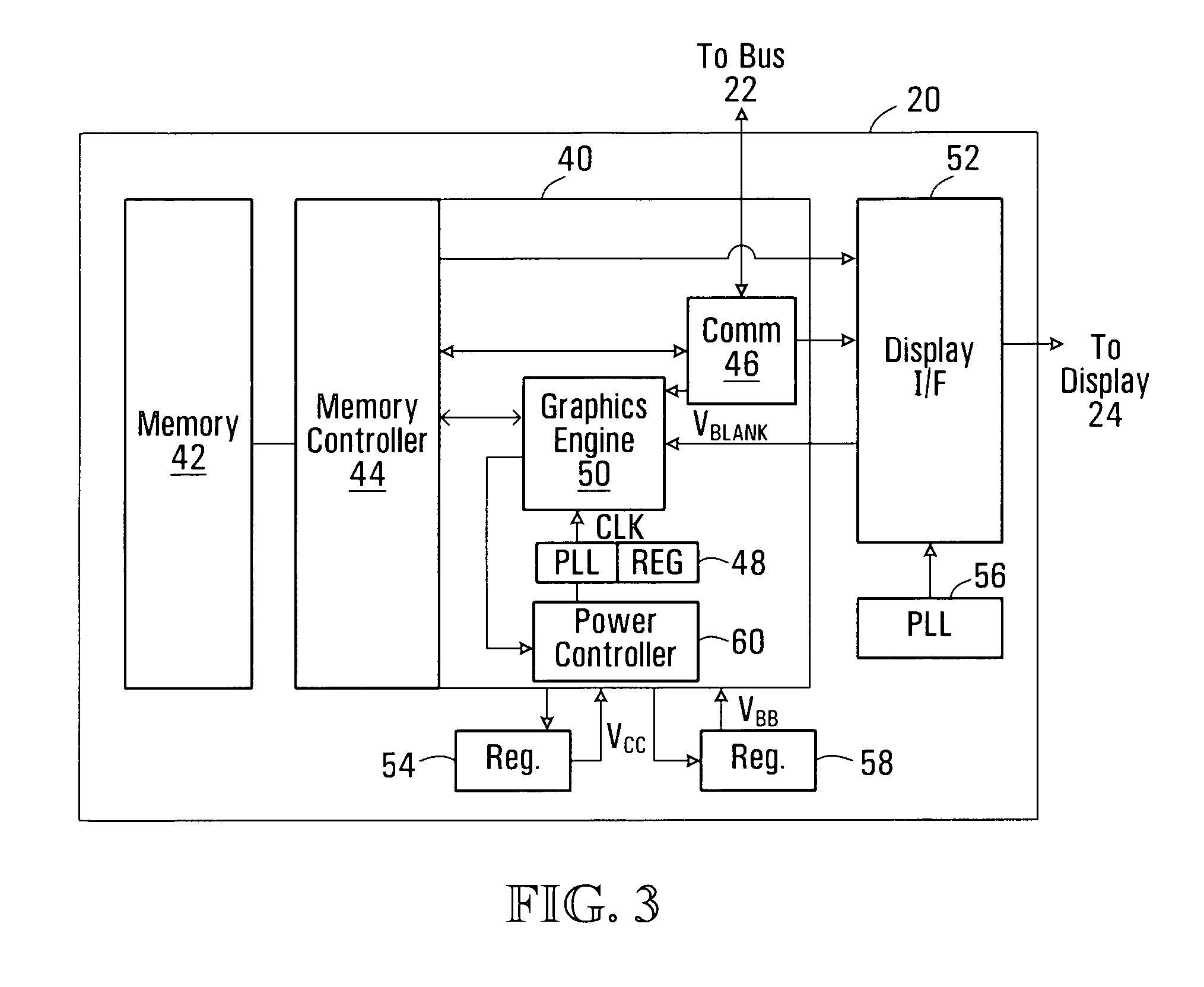
Dynamically controlled power reduction method and circuit for a graphics processor
ActiveUS20070206018A1Shorten the timeGraphics processor clock speedsEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementComputational scienceGraphics
A graphics processor may be operated in a reduced power mode to render frames at rate equal to or less than the rate at which frames are presented on an interconnected display. Graphics processor clock speeds are controlled to reduce the time during which the graphics processor is idle between rendering frames. The graphics processor clock speed may thus be slowed without impacting the quality of rendered images. At the same time the voltage applied to power the graphics processor may be reduced. Optionally, a back bias voltage may further be applied to the processor substrate to reduce power consumption. Clock speed and voltage levels may be adjusted using closed-loop control.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
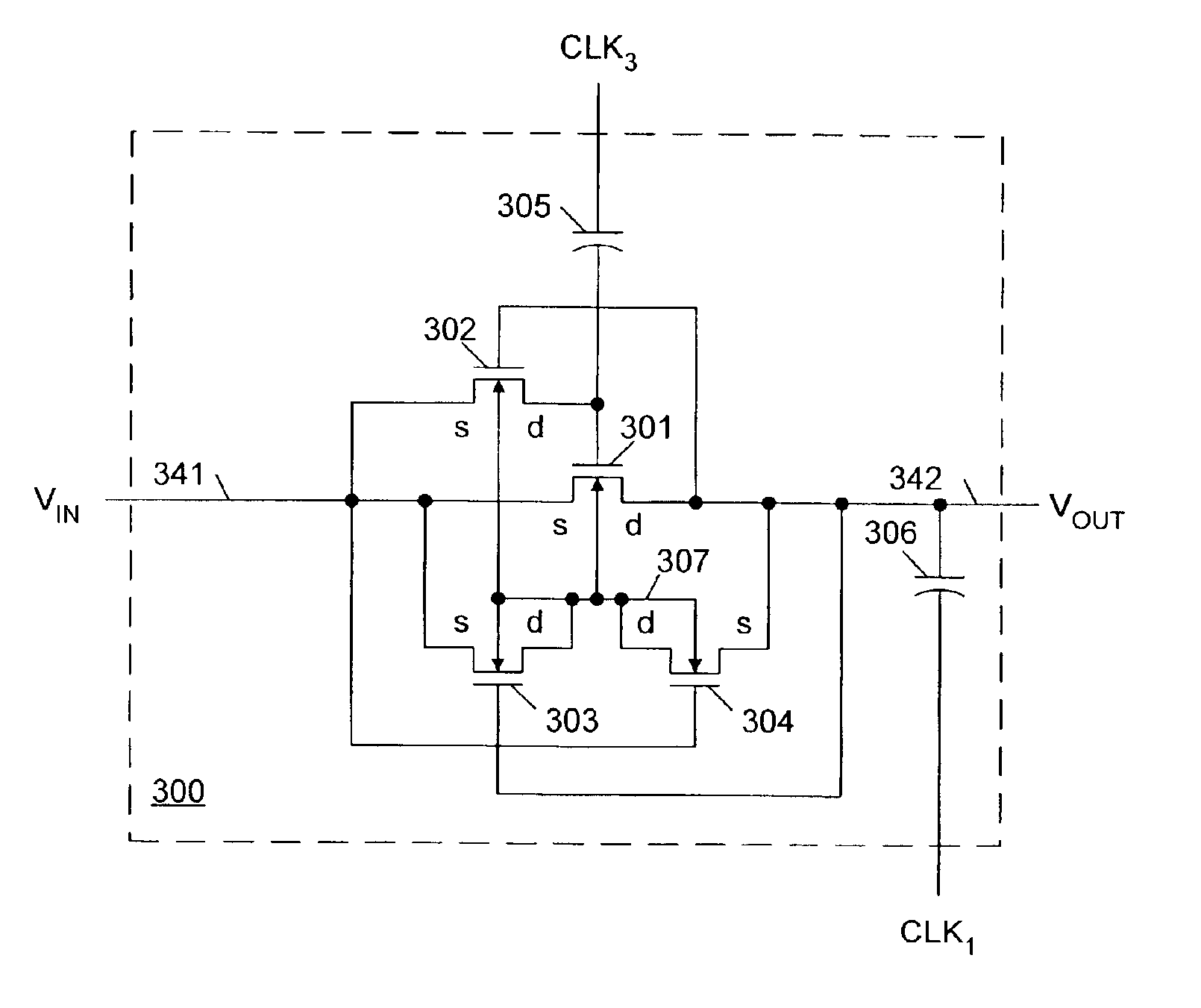
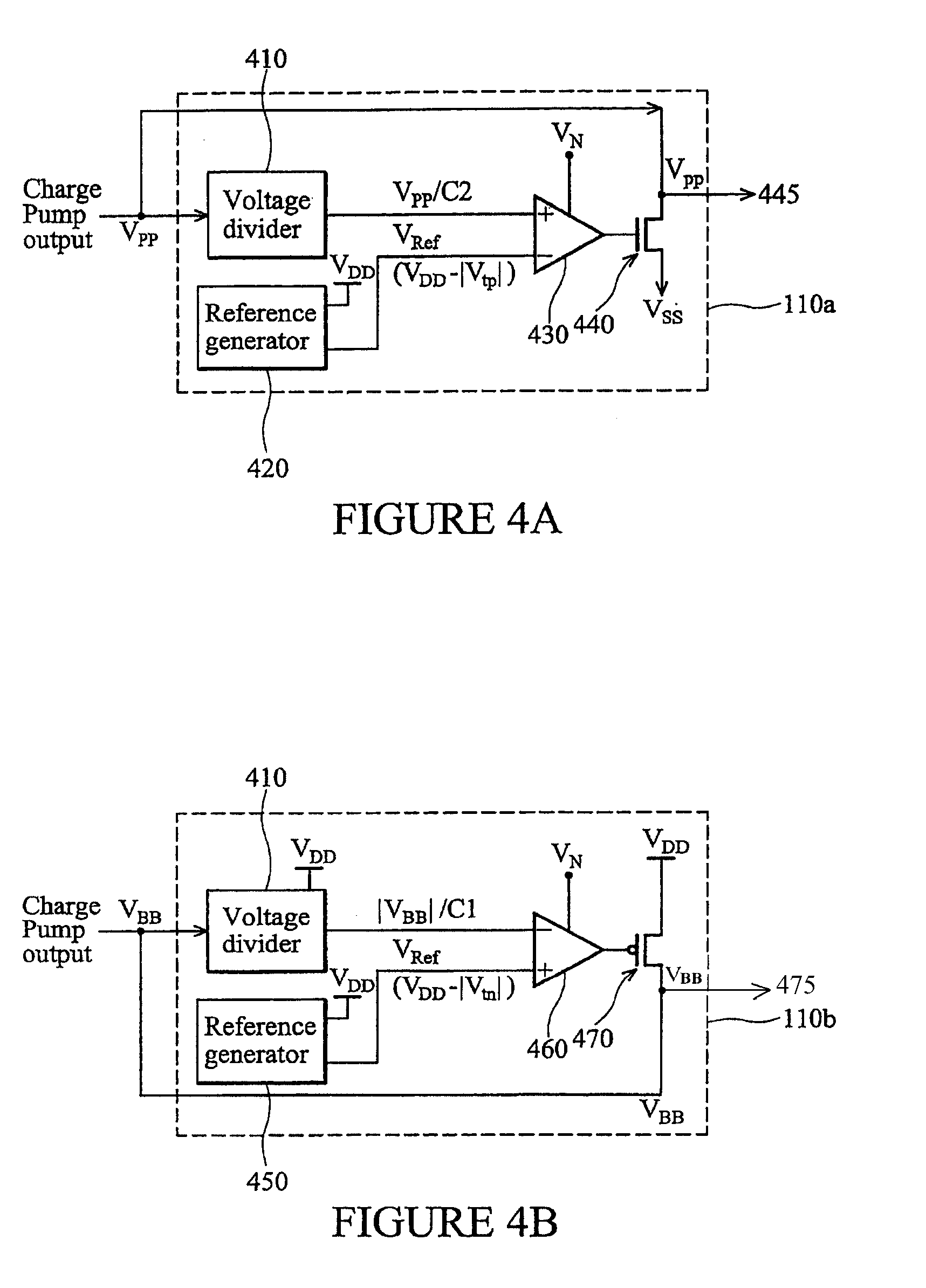
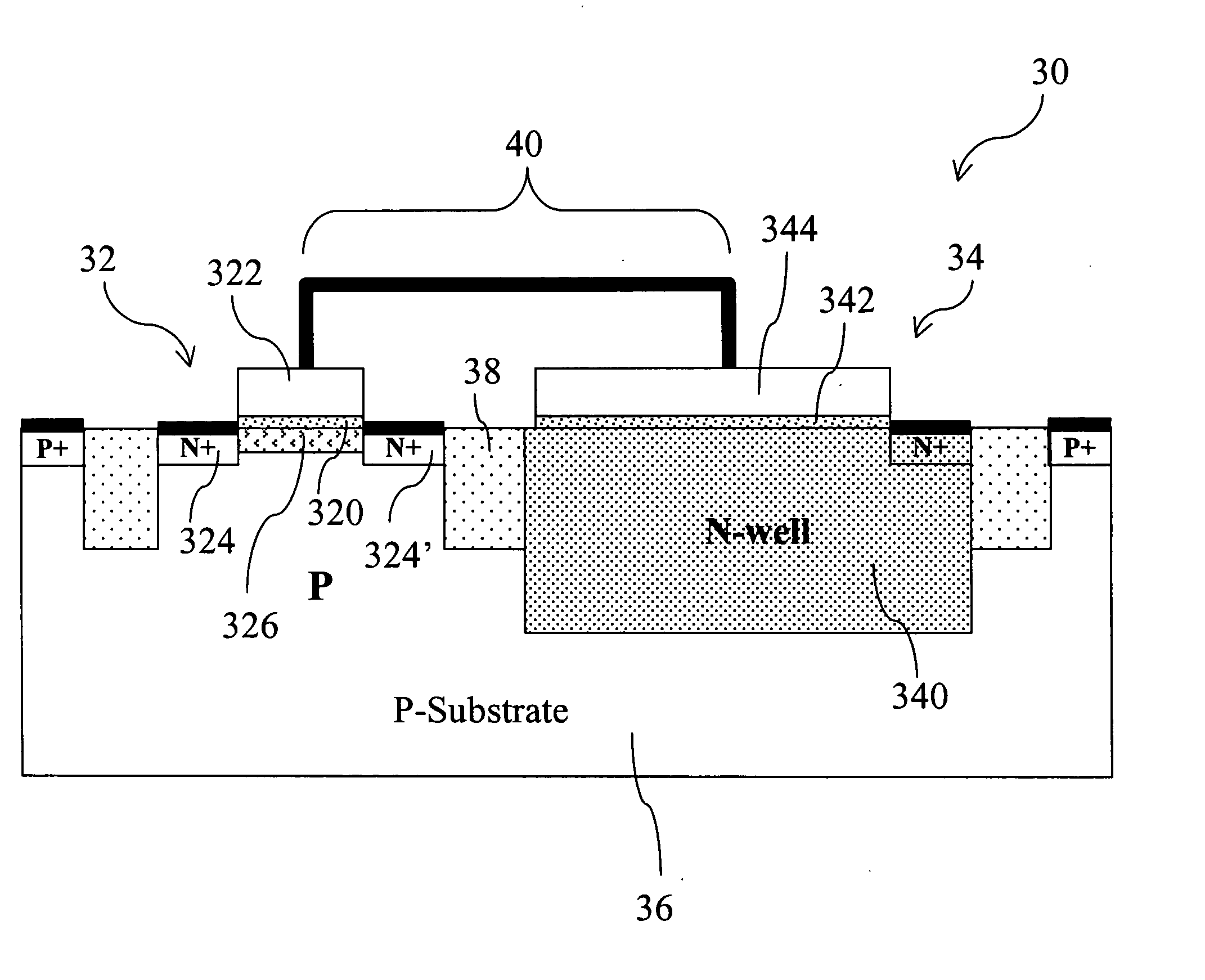
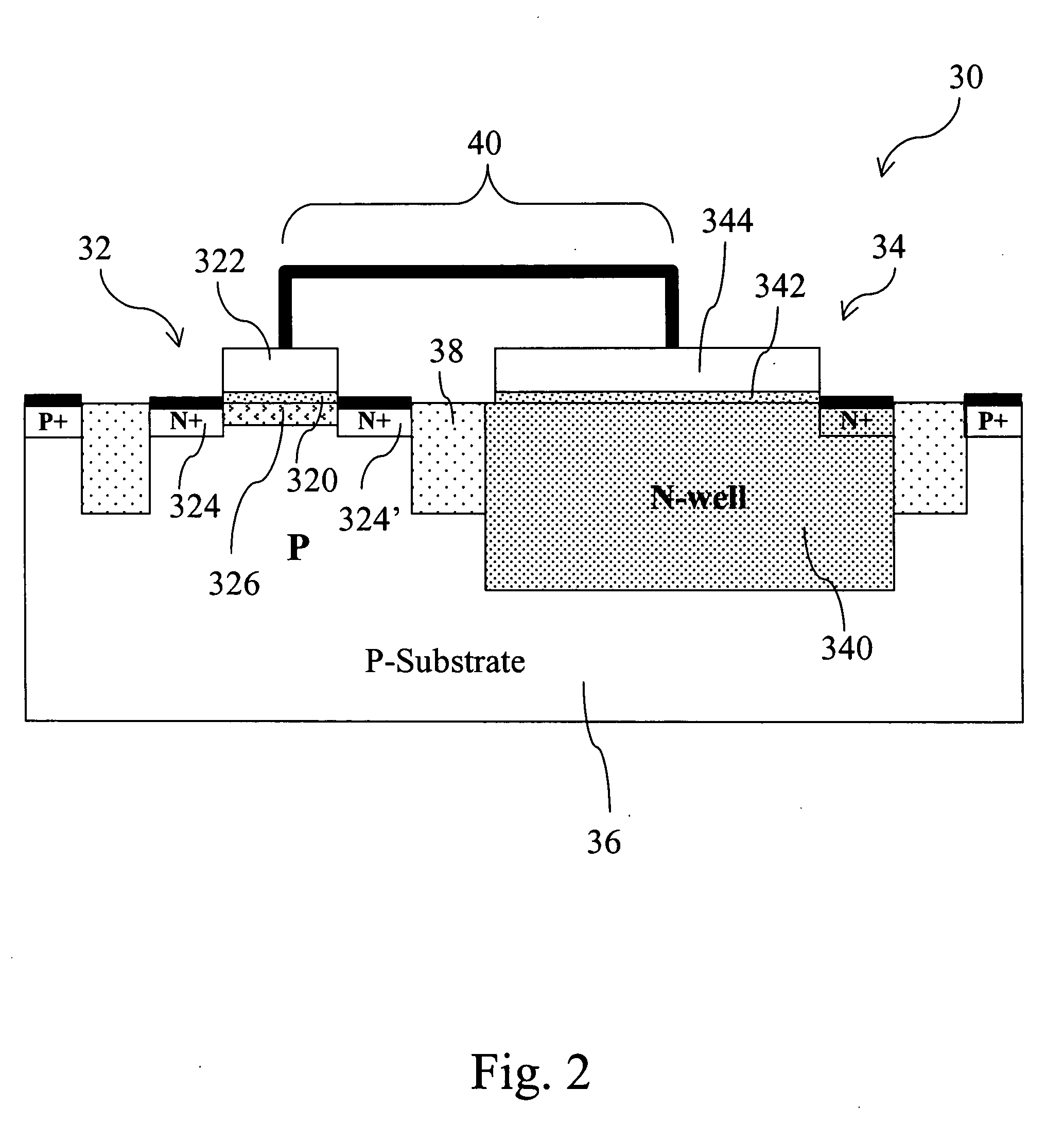
Triple-well charge pump stage with no threshold voltage back-bias effect
A charge pump stage includes a first n-channel transistor having a source coupled to an input terminal and a drain coupled to an output terminal. A second n-channel transistor has a source coupled to the input terminal, a drain coupled to a gate of the first transistor, and a gate coupled to the output terminal. A third n-channel transistor has a source coupled to the input terminal, a gate coupled to the output terminal, and a drain coupled to a p-well. A fourth n-channel transistor has a source coupled to the output terminal, a gate coupled to the input terminal, and a drain coupled to the p-well. The first, second, third and fourth transistors are fabricated in the p-well, which is surrounded by an n-well. A first capacitor is coupled to the output terminal, and a second capacitor is coupled to the gate of the first transistor.
Owner:RPX CORP
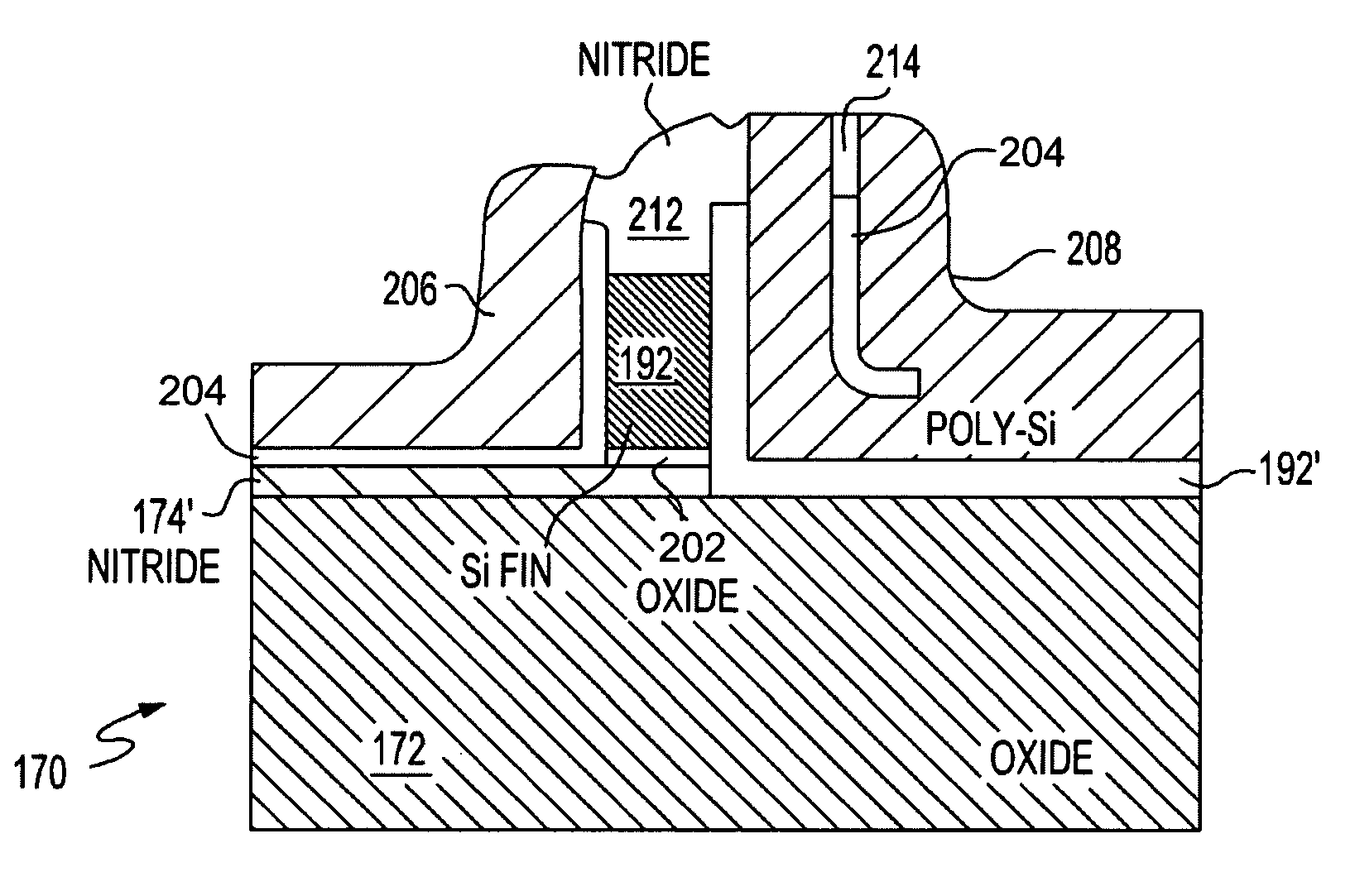
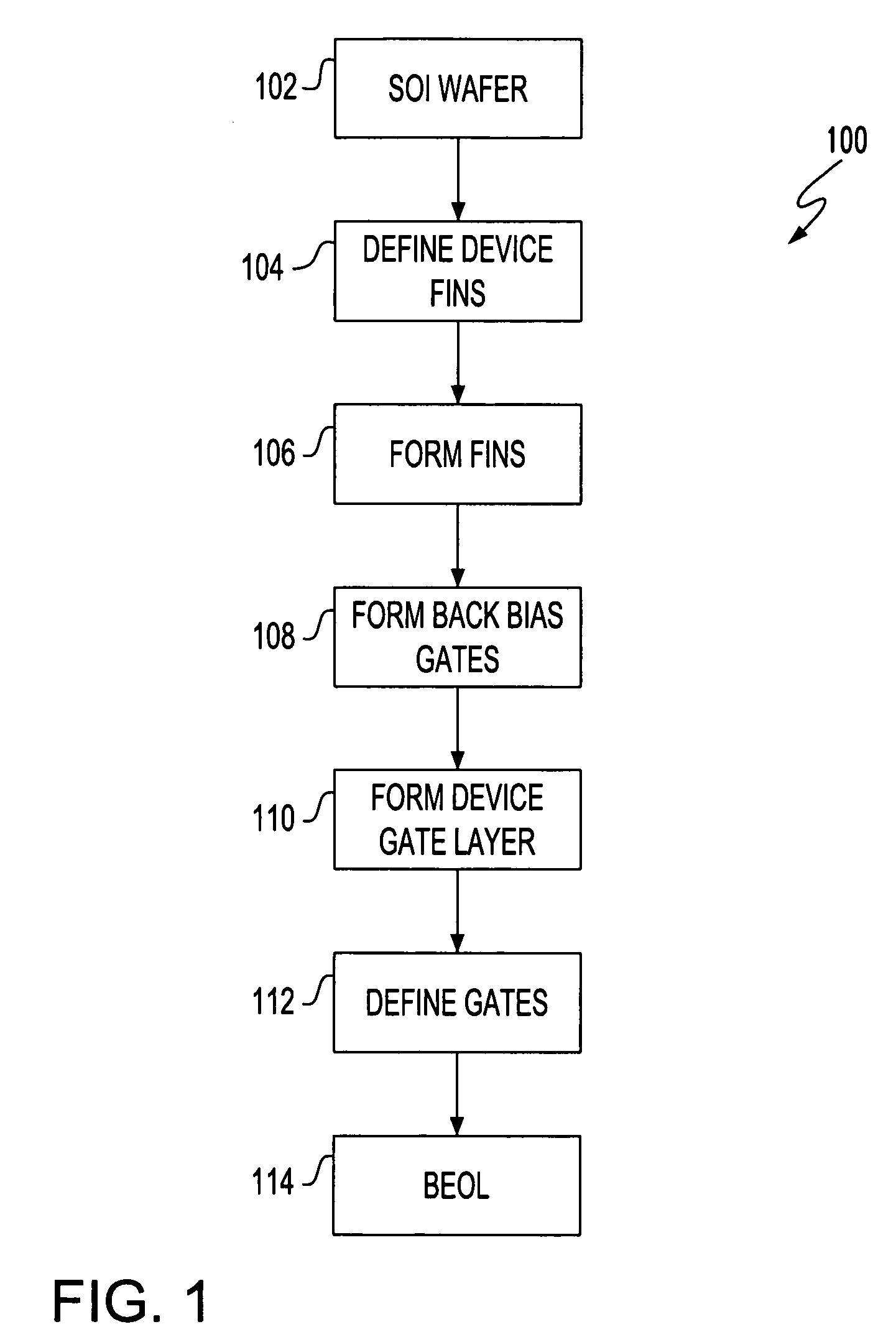
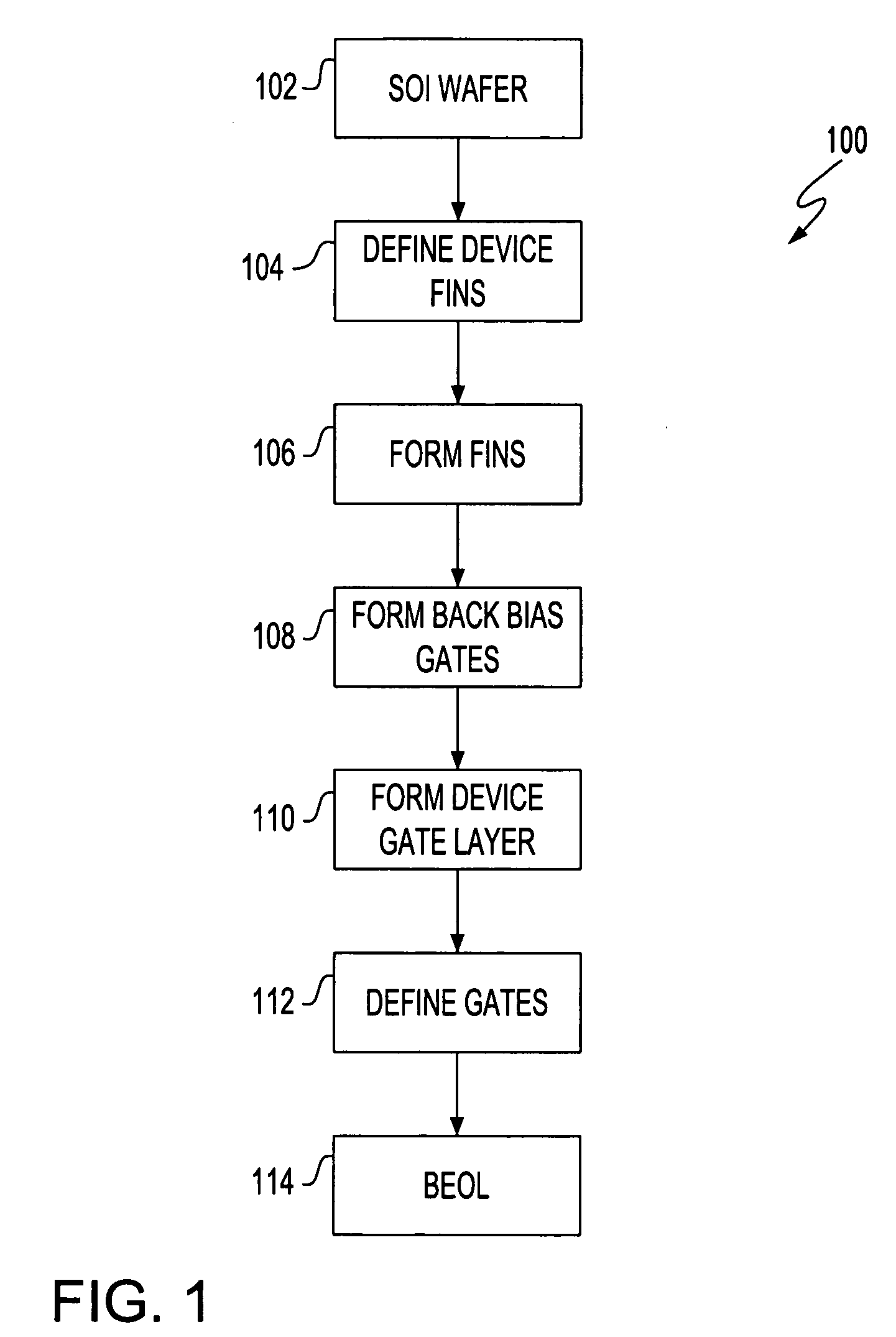
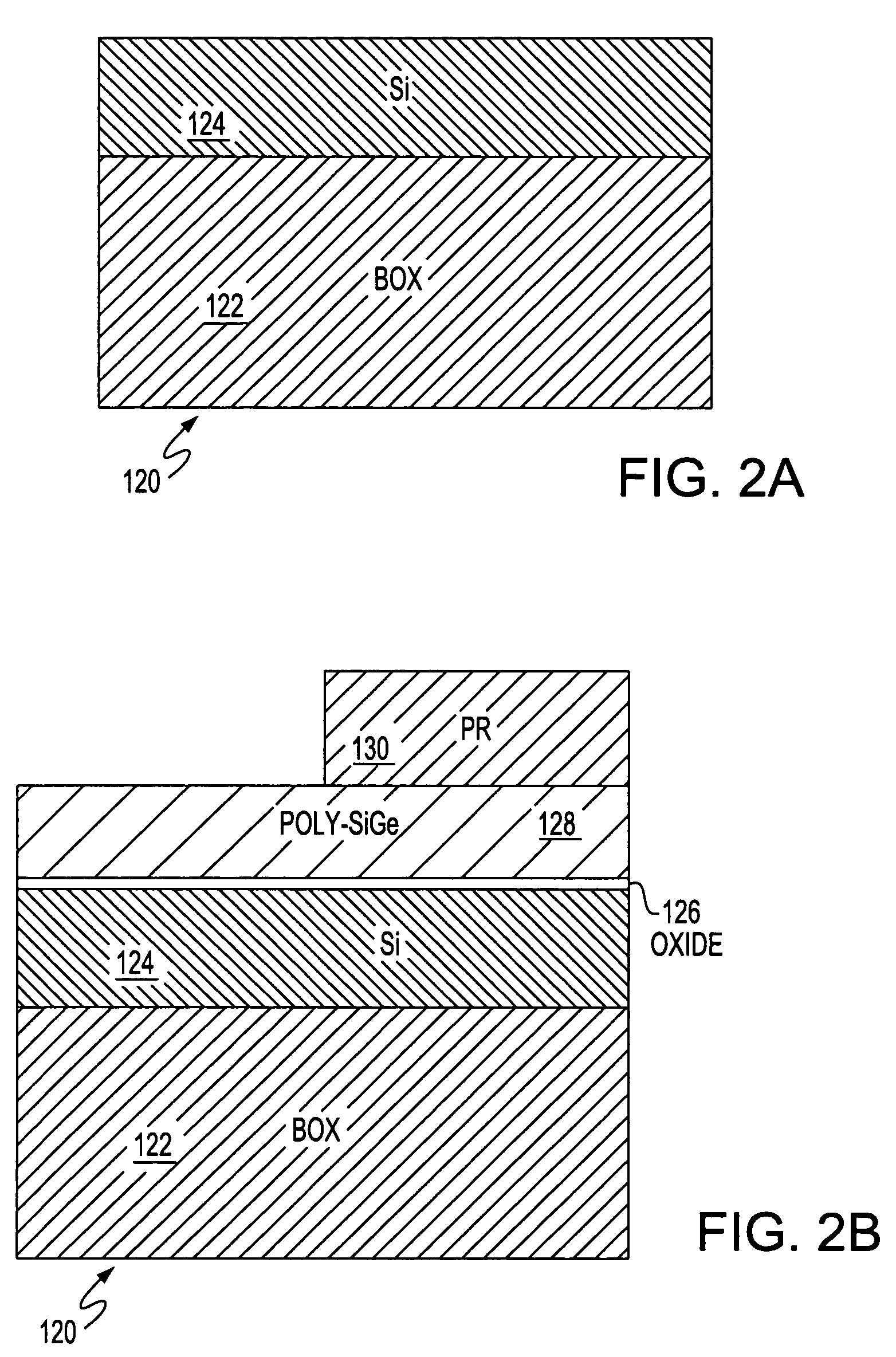
Dual gate FinFet
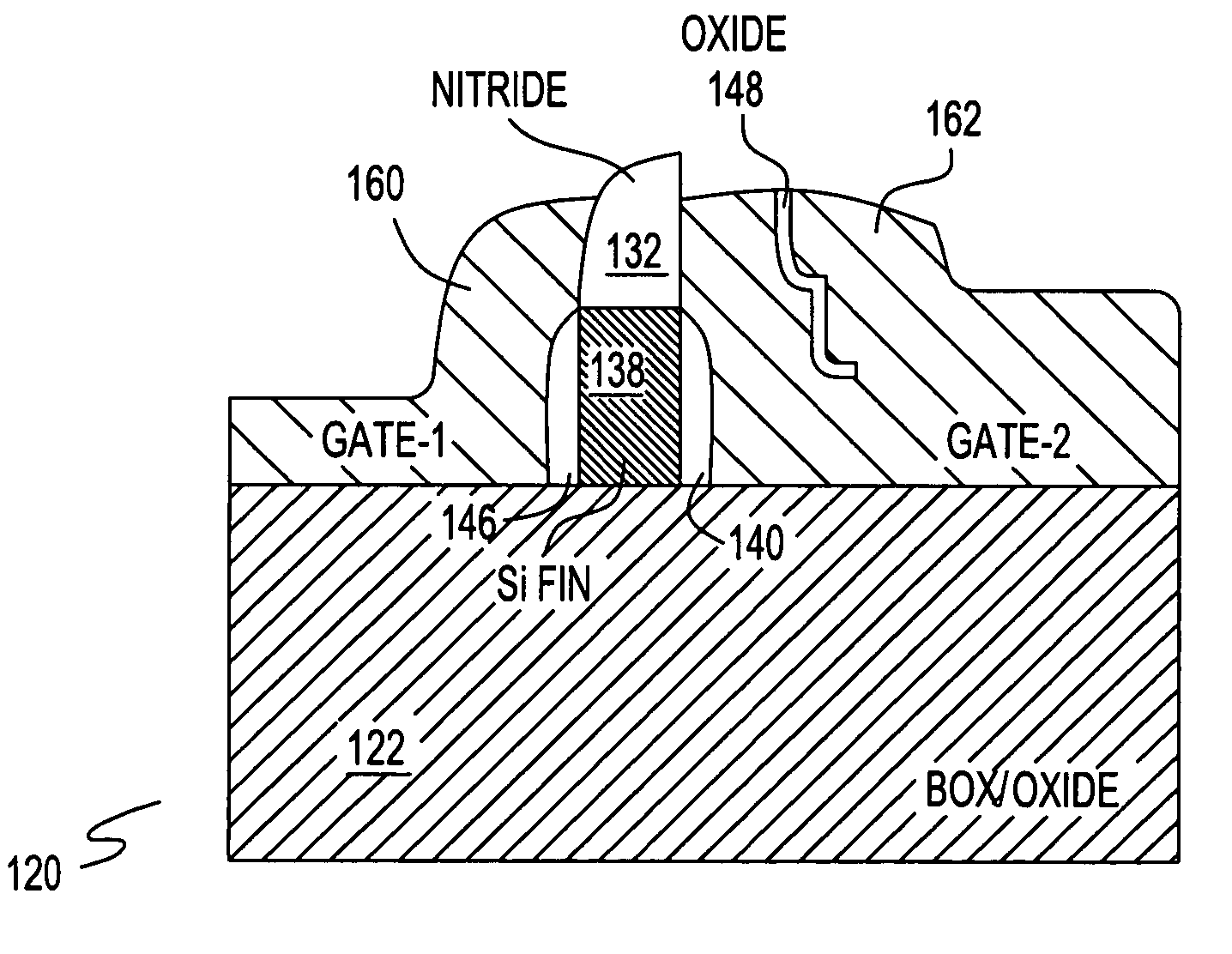
A field effect transistor (FET), integrated circuit (IC) chip including the FETs and a method of forming the FETS. Each FET includes a device gate along one side of a semiconductor (e.g., silicon) fin and a back bias gate along an opposite of the fin. Back bias gate dielectric differs from the device gate dielectric either in its material and / or thickness. Device thresholds can be adjusted by adjusting back bias gate voltage.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
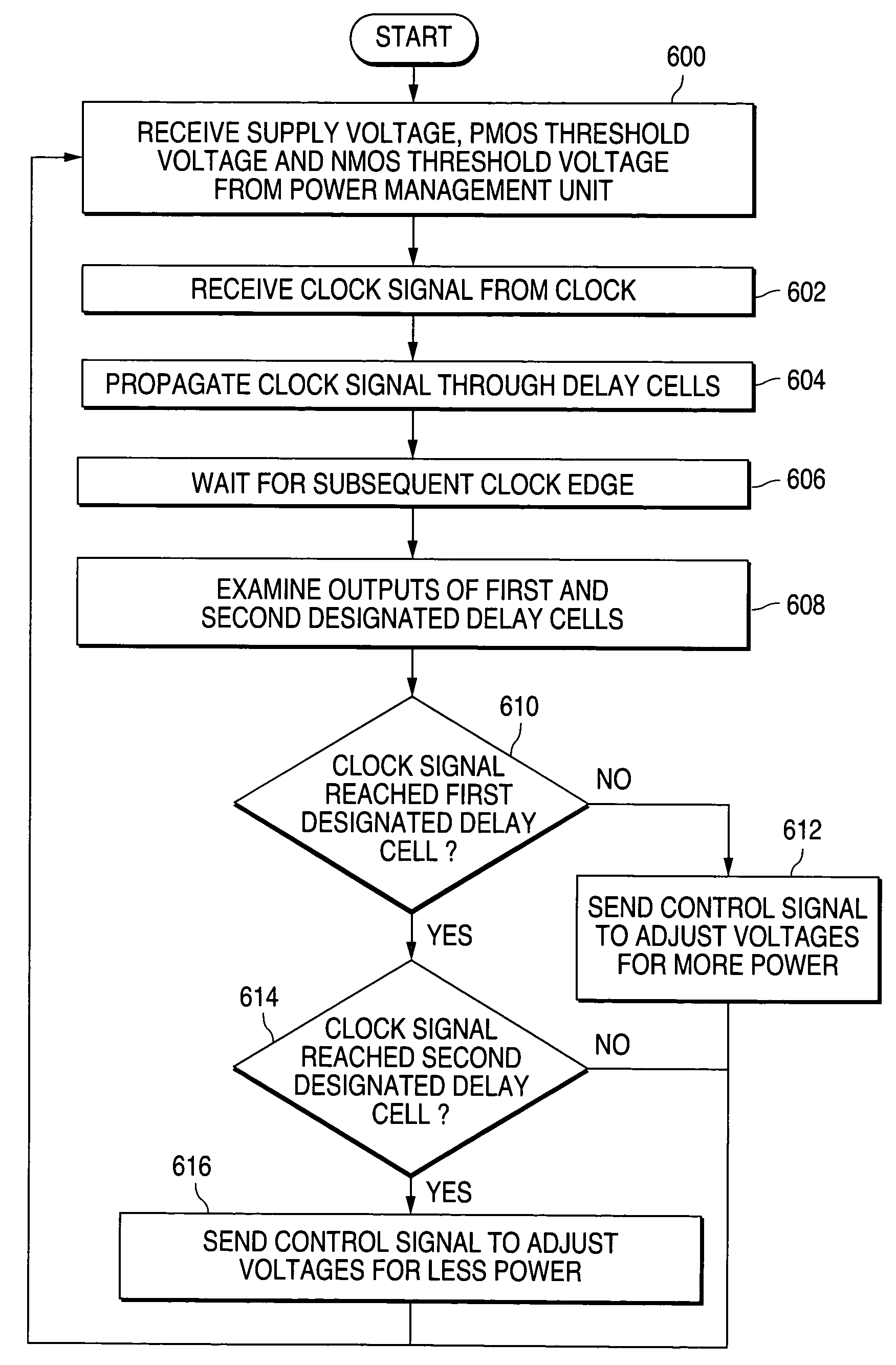
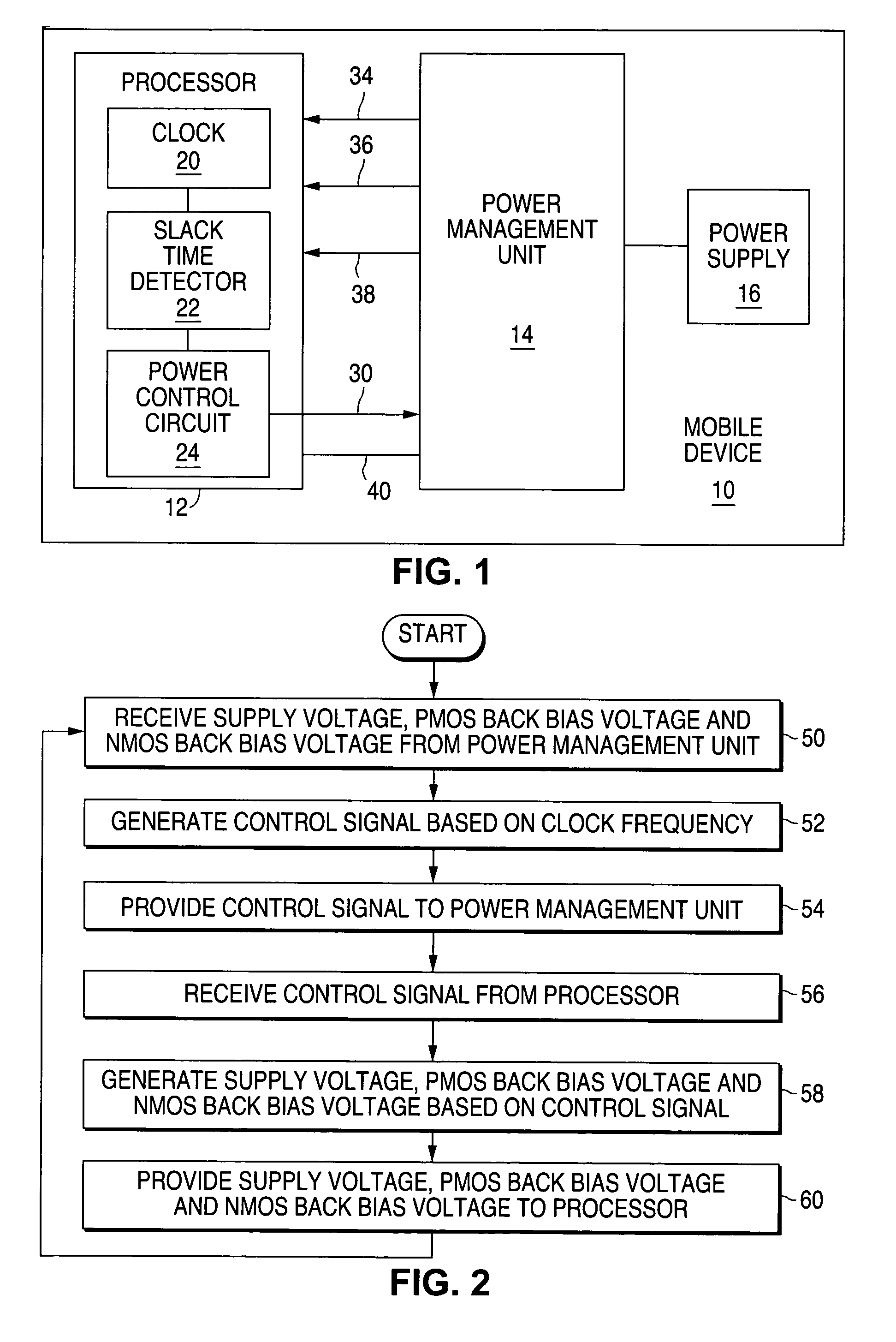
Method and system for minimizing power consumption in mobile devices using cooperative adaptive voltage and threshold scaling
ActiveUS7493149B1Eliminate and reduce disadvantageEliminate and reduce and problemReliability increasing modificationsEnergy efficient ICTBack biasEngineering
A method for minimizing power consumption in a mobile device using cooperative adaptive voltage and threshold scaling is provided that includes receiving a supply voltage, a PMOS back bias voltage, and an NMOS back bias voltage. A clock signal is received. The clock signal is propagated through a timing comparison circuit. An output of the timing comparison circuit is examined. A determination is made regarding whether to request more power based on the output of the timing comparison circuit. A voltage control signal is sent to request more power when a determination is made to request more power based on the output of the timing comparison circuit.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
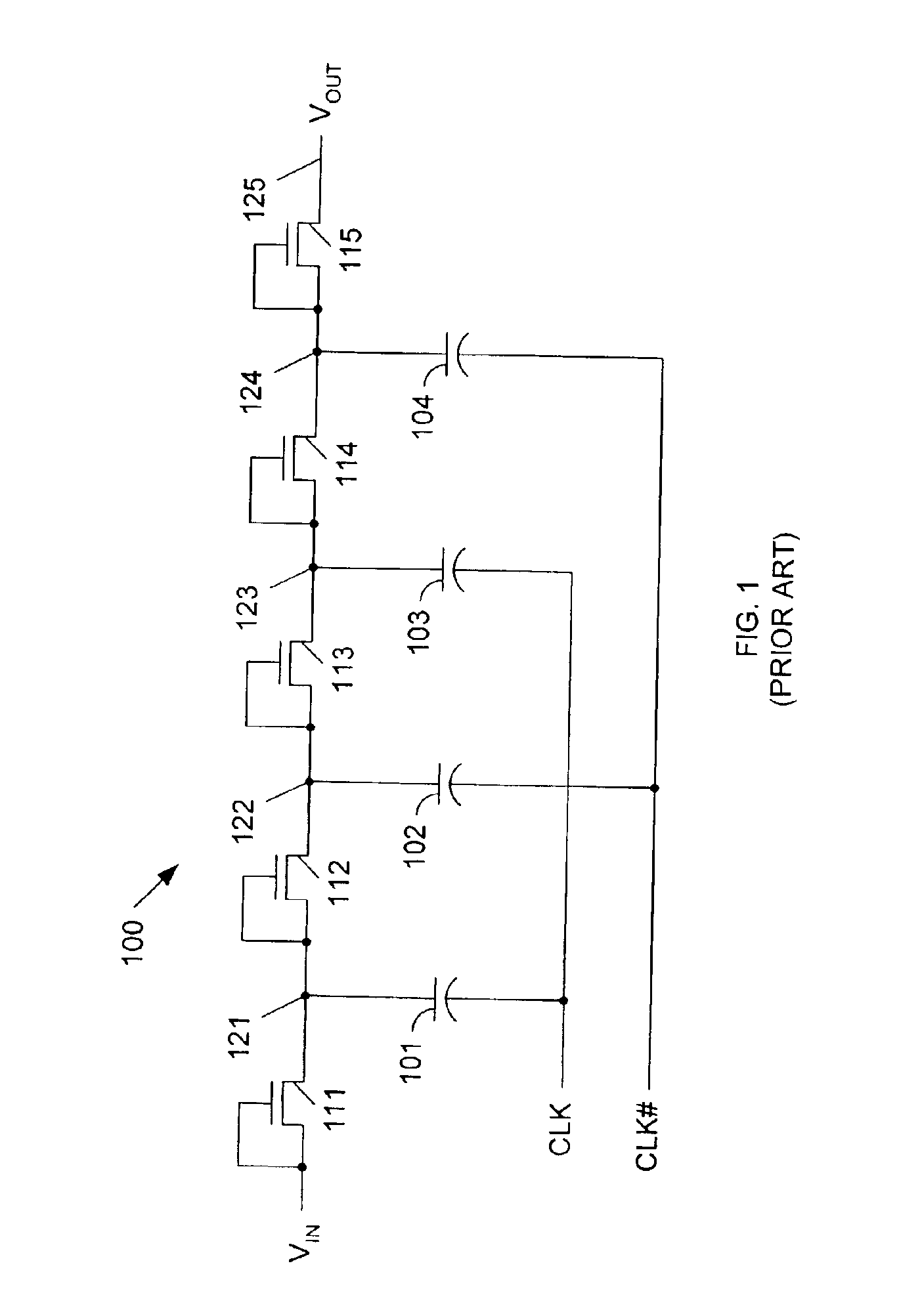
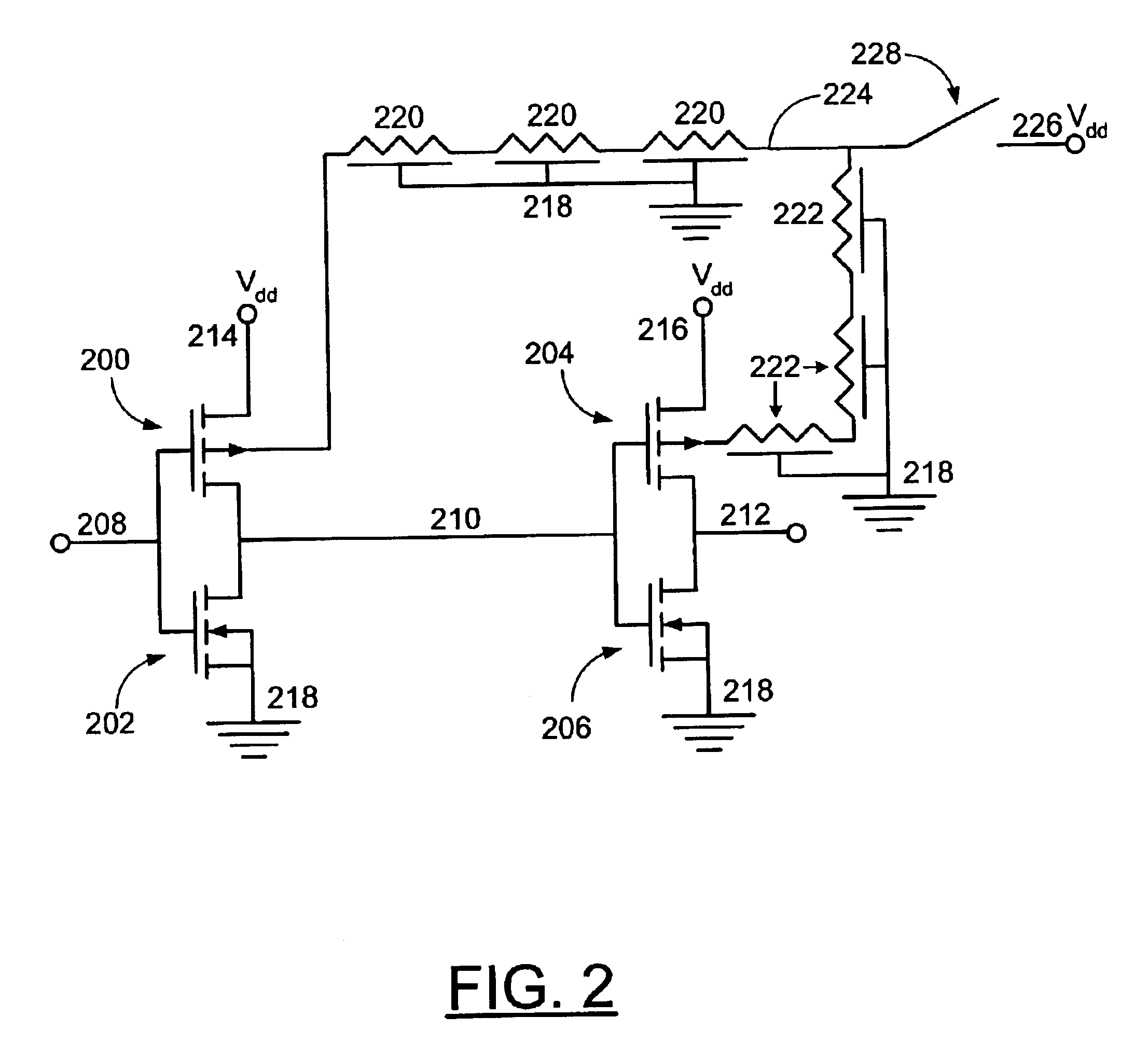
Method of setting back bias of MOS circuit, and MOS integrated circuit
In a MOS circuit comprising a plurality of MOSFETs constituting a digital circuit, an input signal is supplied to the digital circuit, and a first back bias voltage is supplied to a semiconductor substrate or a semiconductor well region in which the MOSFETs are formed, so that a pn junction between the semiconductor substrate or the semiconductor well region and a source region is brought to a forward voltage. In a non-operating state in which a circuit operation is suspended by the input signal supplied to the digital circuit as a fixed level, a second back bias voltage is applied to the semiconductor substrate or the semiconductor well region so that the pn junction between the semiconductor substrate or the semiconductor well region and the source region is brought to a reverse voltage.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
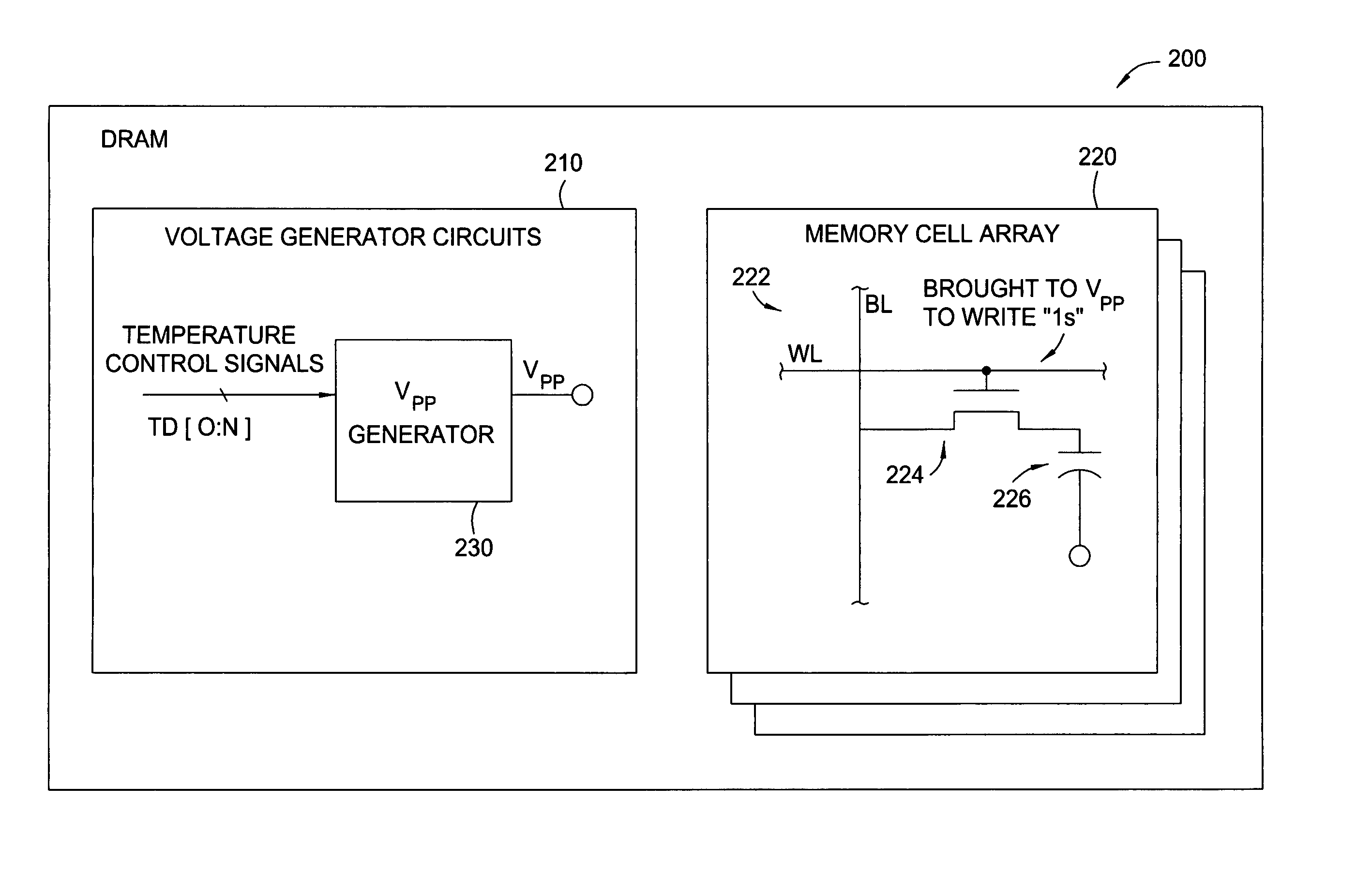
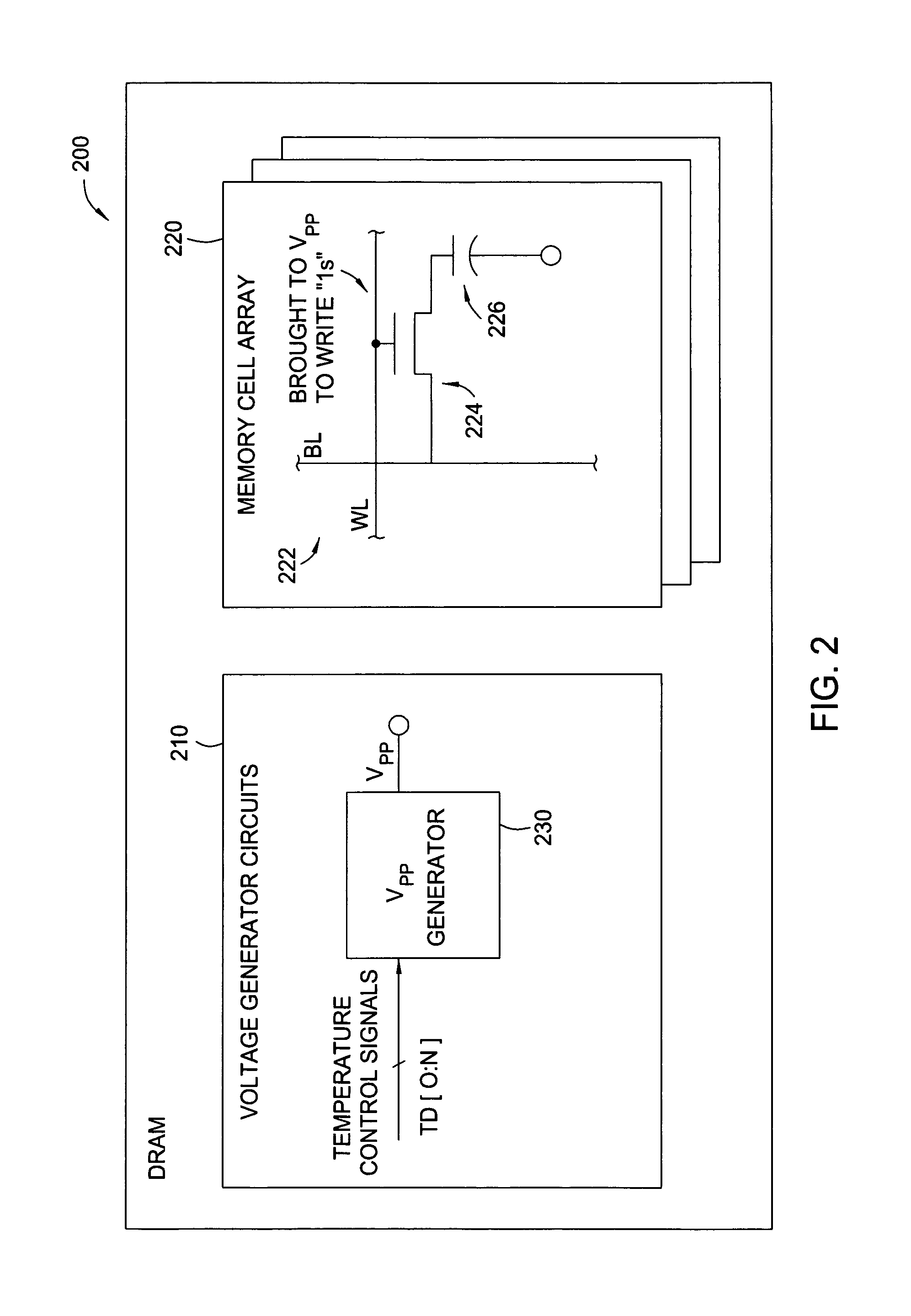
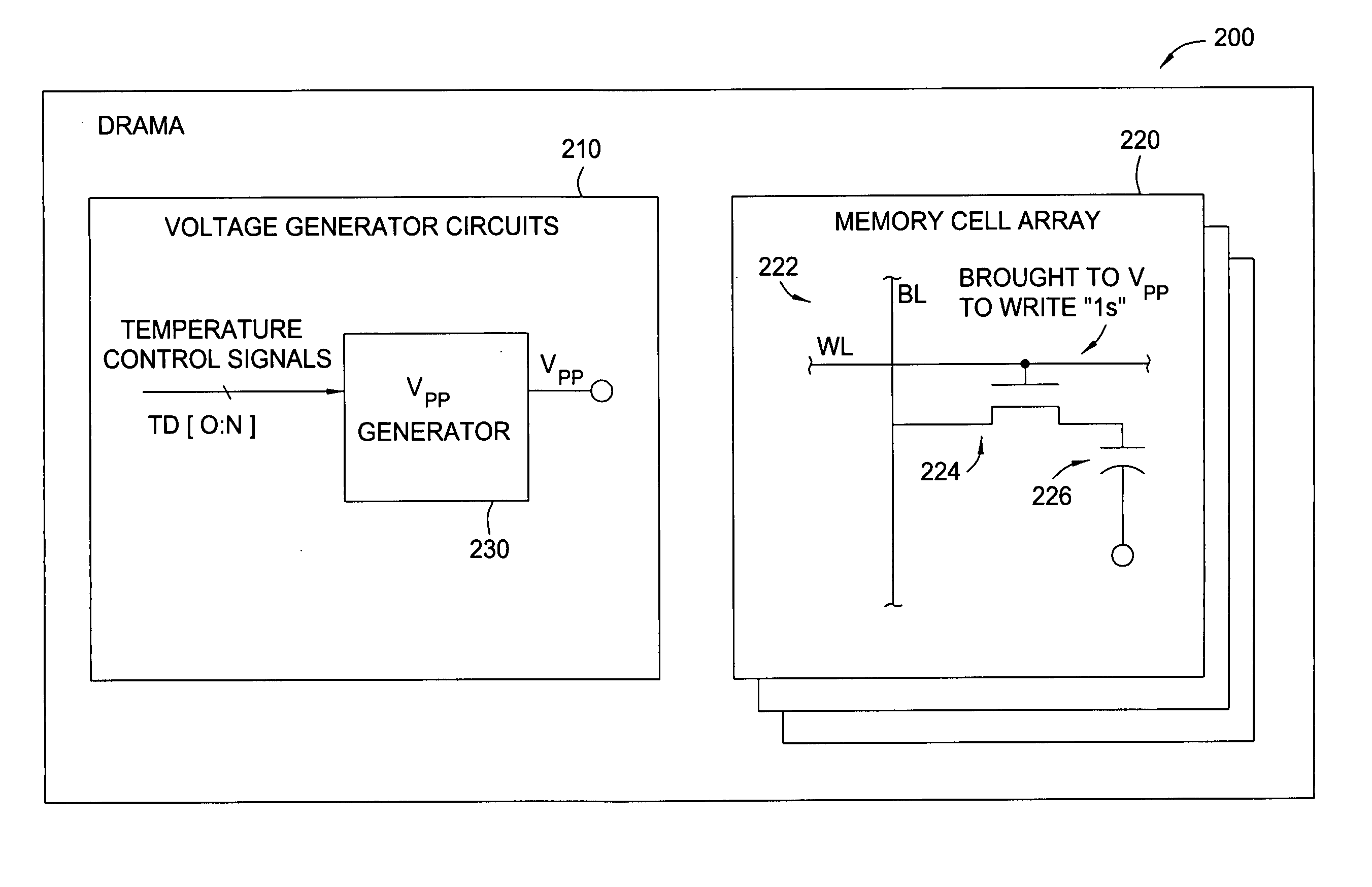
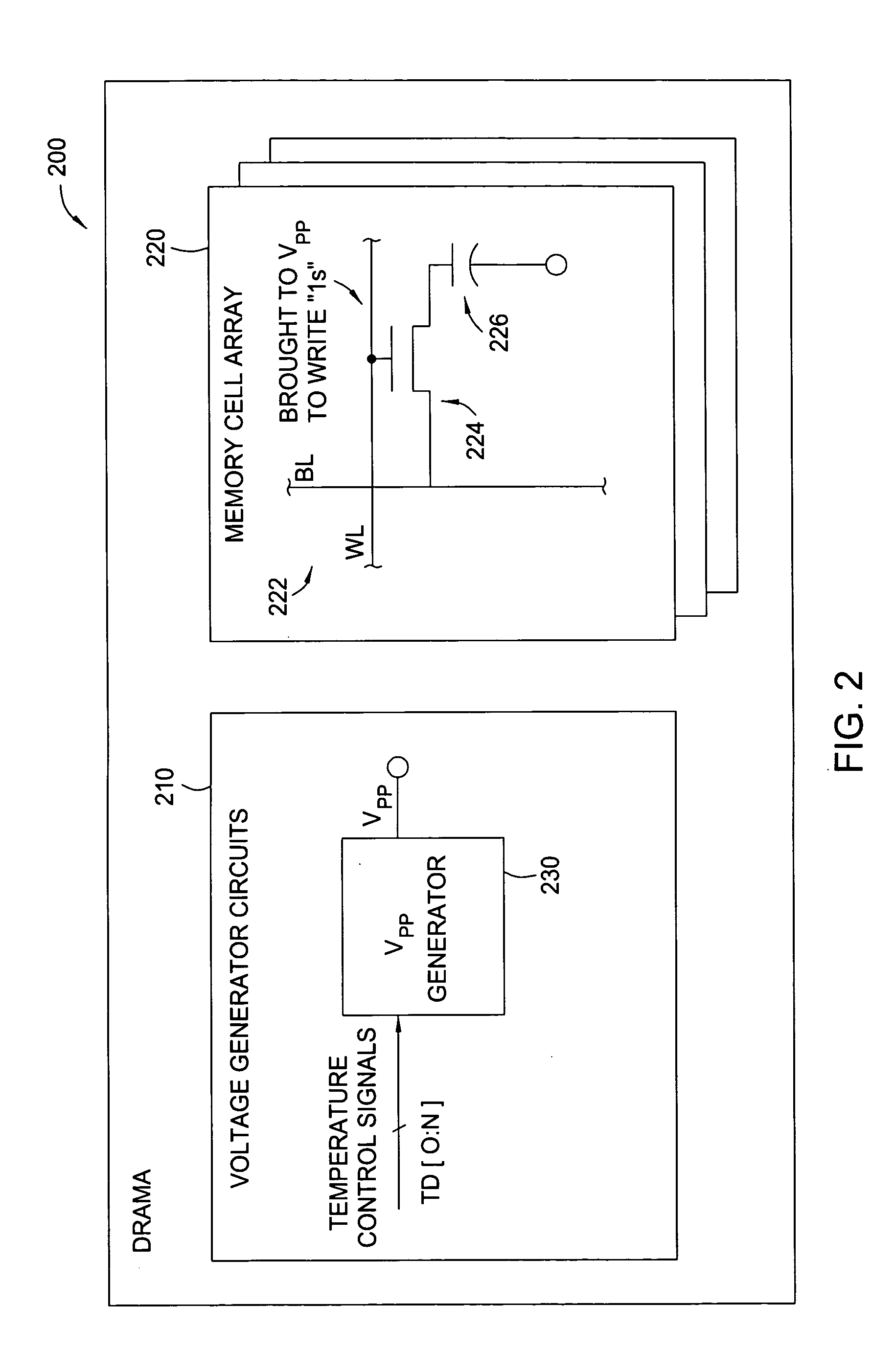
Back-bias voltage generator with temperature control
Methods and apparatus for varying one or more internally generated voltages of a memory device based on the temperature of the memory device are provided. The device temperature may be measured directly, for example, via an on-chip temperature sensor, or may be supplied as bits in a mode register containing temperature information.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
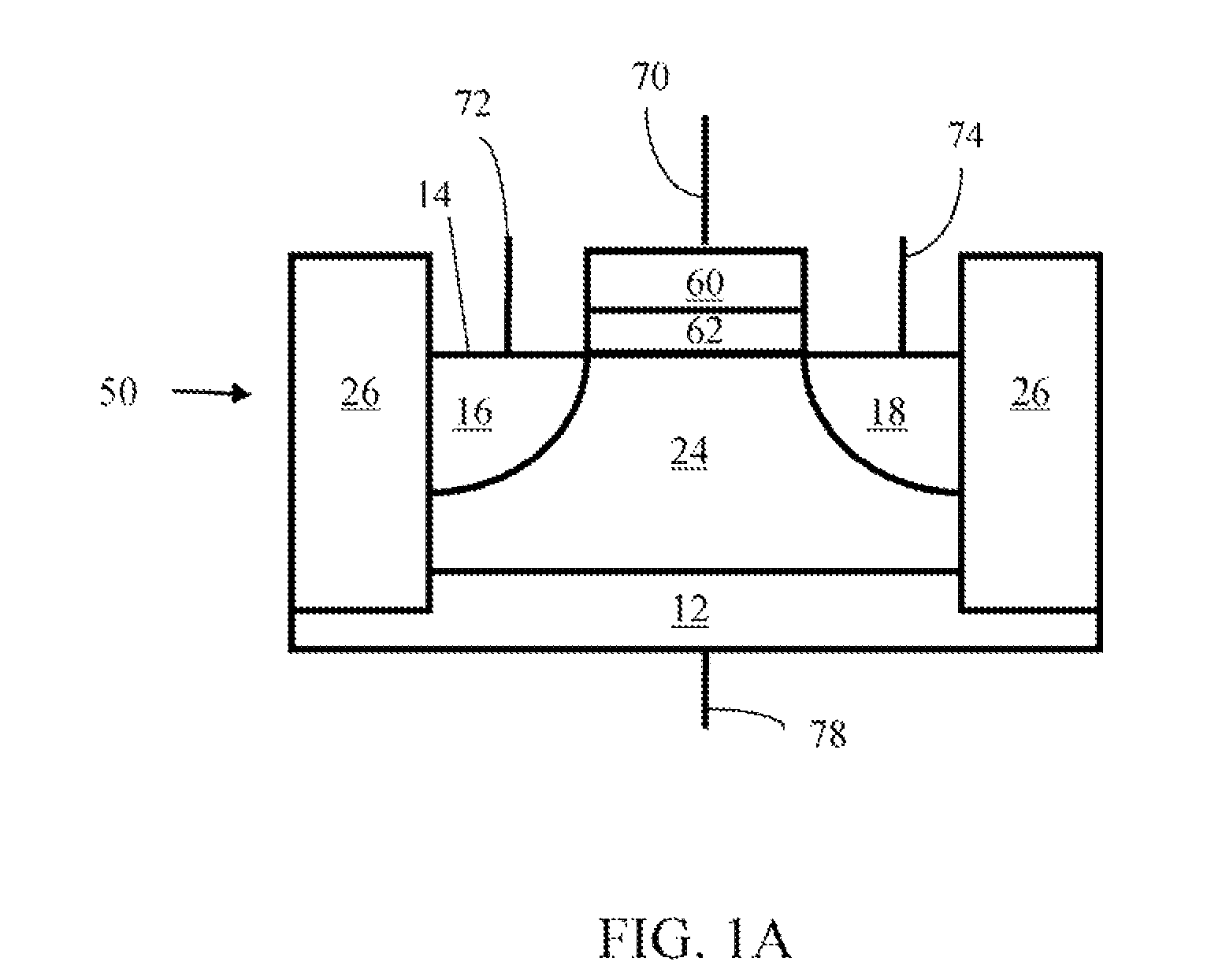
Method of maintaining the state of semiconductor memory having electrically floating body transistor
ActiveUS10340276B2Larger memory windowTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsBack biasEngineering
Methods of maintaining a state of a memory cell without interrupting access to the memory cell are provided, including applying a back bias to the cell to offset charge leakage out of a floating body of the cell, wherein a charge level of the floating body indicates a state of the memory cell; and accessing the cell.
Owner:ZENO SEMICON
Back-bias voltage regulator having temperature and process variation compensation and related method of regulating a back-bias voltage
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
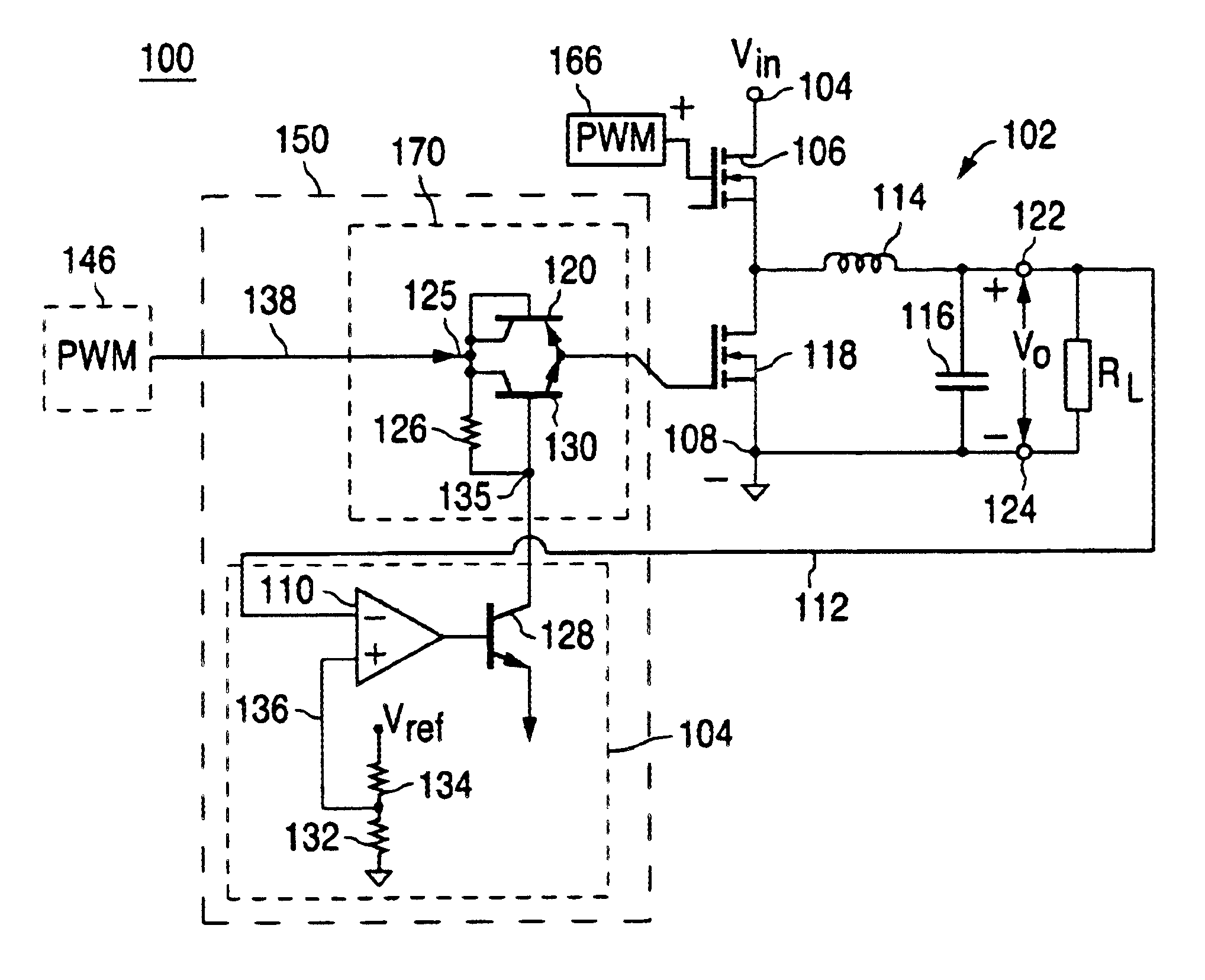
Soft-start with back bias conditions for PWM buck converter with synchronous rectifier
InactiveUS6841977B2Effective preventionPreventing current reversing (sinking)Efficient power electronics conversionPower supply linesStart timeTransverter
A circuit that efficiently prevents the turning on of the synchronous rectifier in a buck converter during a predetermined condition, so as to prevent current reversing through the synchronous rectifier during that time. In one embodiment, the circuit provides control of the synchronous rectifier during the soft-start time for a non-isolated DC-DC buck converter, thereby preventing current reversing (sinking), referred to as the back bias condition, during its soft start process. In another embodiment, a circuit uses a signal indicative of a soft-start condition for a converter to prevent the turning on of the synchronous rectifier during the soft-start time. A corresponding system solves the aforementioned synchronous rectifier back bias problem for converters used in a paralleled converter configuration.
Owner:ASTEC INT LTD
Non-volatile flash memory structure and method for operating the same
InactiveUS20070241392A1Increase capacitanceReduce areaTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceBack bias
A non-volatile memory structure and a method for operating the same are proposed. The non-volatile memory structure makes use of a single floating gate structure and a capacitor structure including a pair of regions doped with different type impurities to increase the capacitance and shrink the area. When performing programming operations to this memory structure, a voltage is applied to the source or a back bias is applied to the substrate of the transistor to greatly reduce the current requirement of a single-gate EEPROM device. When performing erase operations, the drain voltage is raised, and a small voltage is added to the gate to increase the F-N tunneling current, thereby accomplishing the effect of fast erase.
Owner:YIELD MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Dual gate finfet
ActiveUS20050110085A1Improve device leakage controlEasy to controlTransistorSolid-state devicesGate dielectricBack bias
A field effect transistor (FET), integrated circuit (IC) chip including the FETs and a method of forming the FETS. Each FET includes a device gate along one side of a semiconductor (e.g., silicon) fin and a back bias gate along an opposite of the fin. Back bias gate dielectric differs from the device gate dielectric either in its material and / or thickness. Device thresholds can be adjusted by adjusting back bias gate voltage.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Back-bias voltage generator with temperature control
InactiveUS20050104566A1Change levelDigital storageElectric variable regulationVoltage generatorTemperature control
Methods and apparatus for varying one or more internally generated voltages of a memory device based on the temperature of the memory device are provided. The device temperature may be measured directly, for example, via an on-chip temperature sensor, or may be supplied as bits in a mode register containing temperature information.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
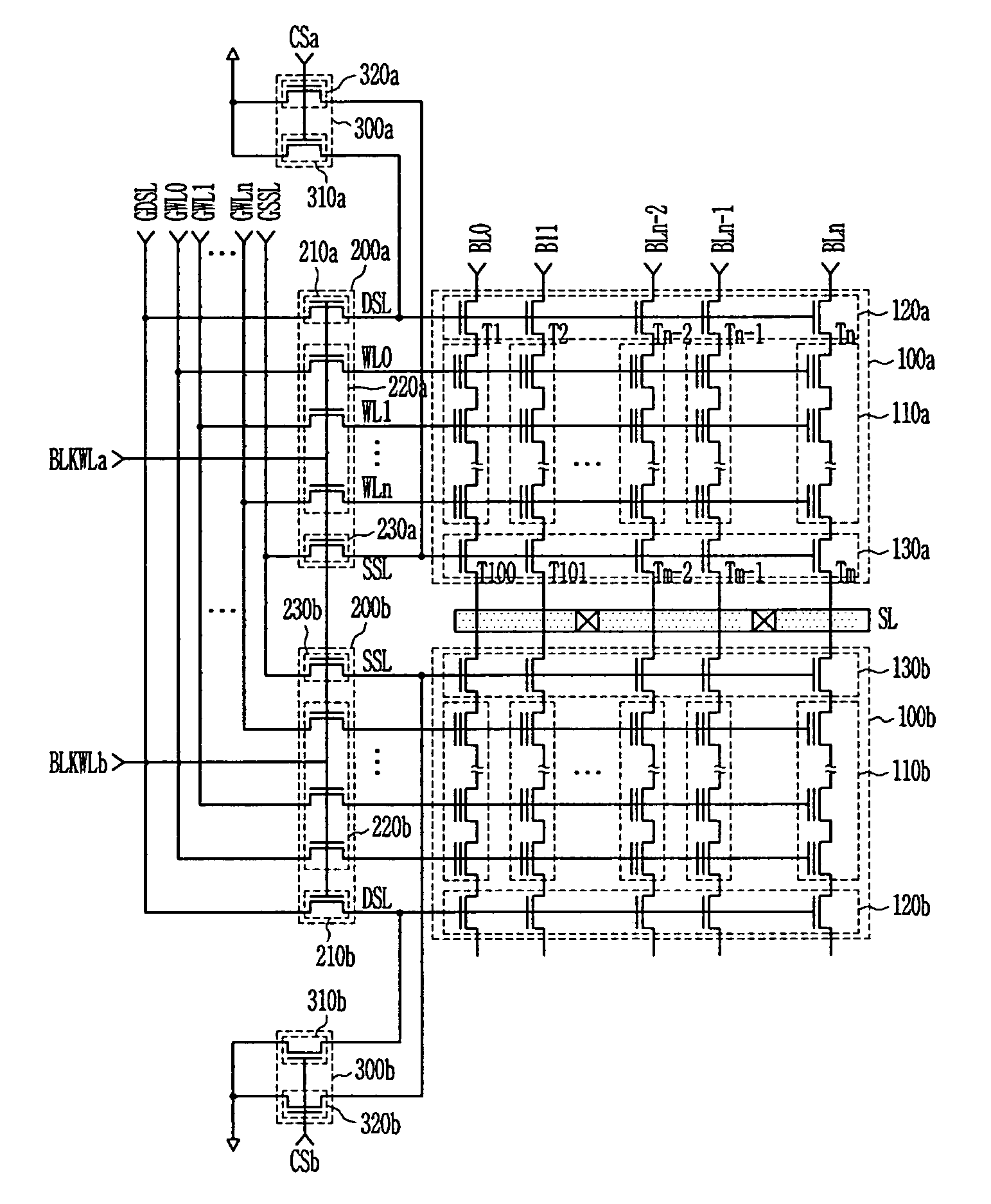
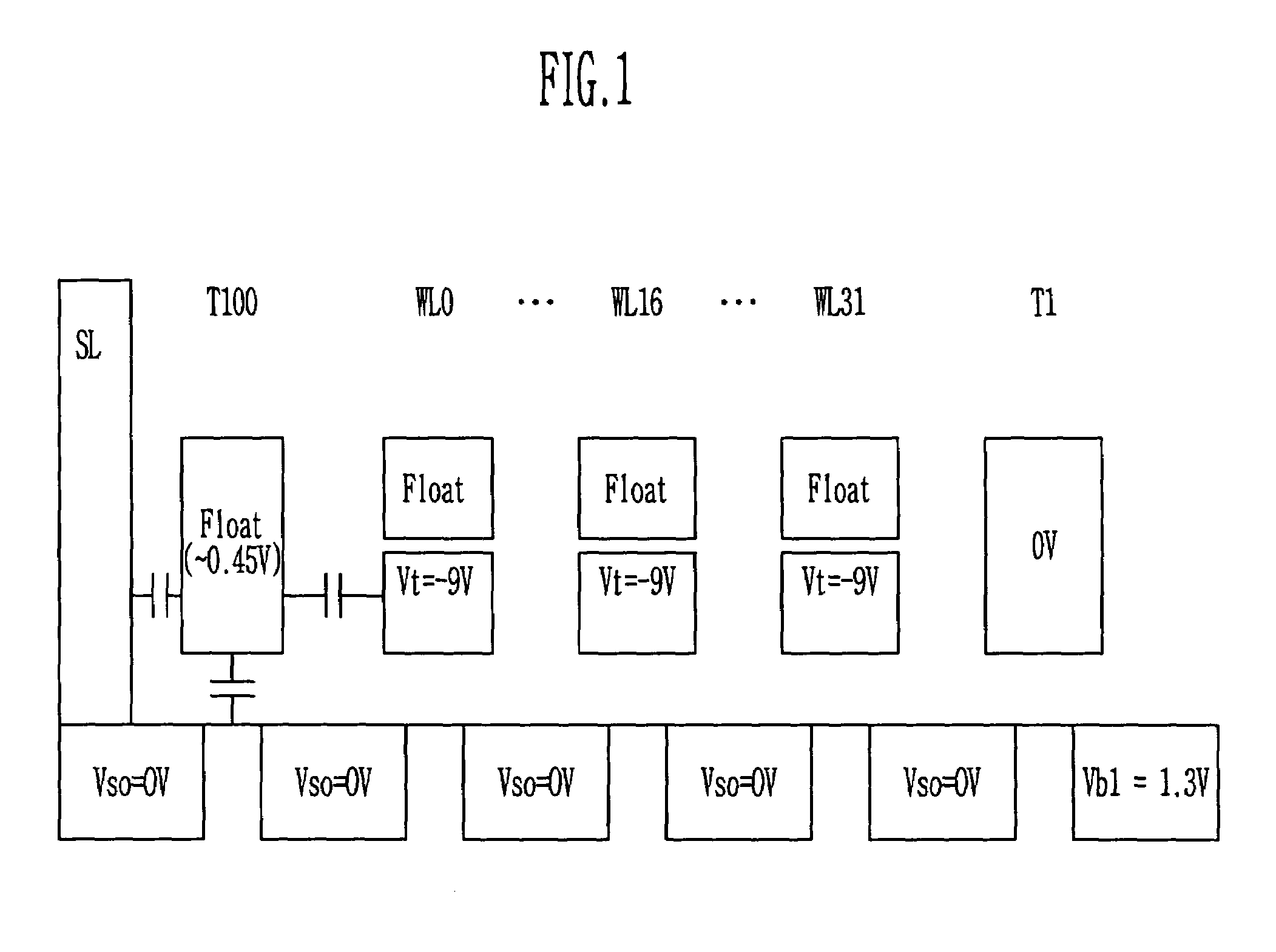
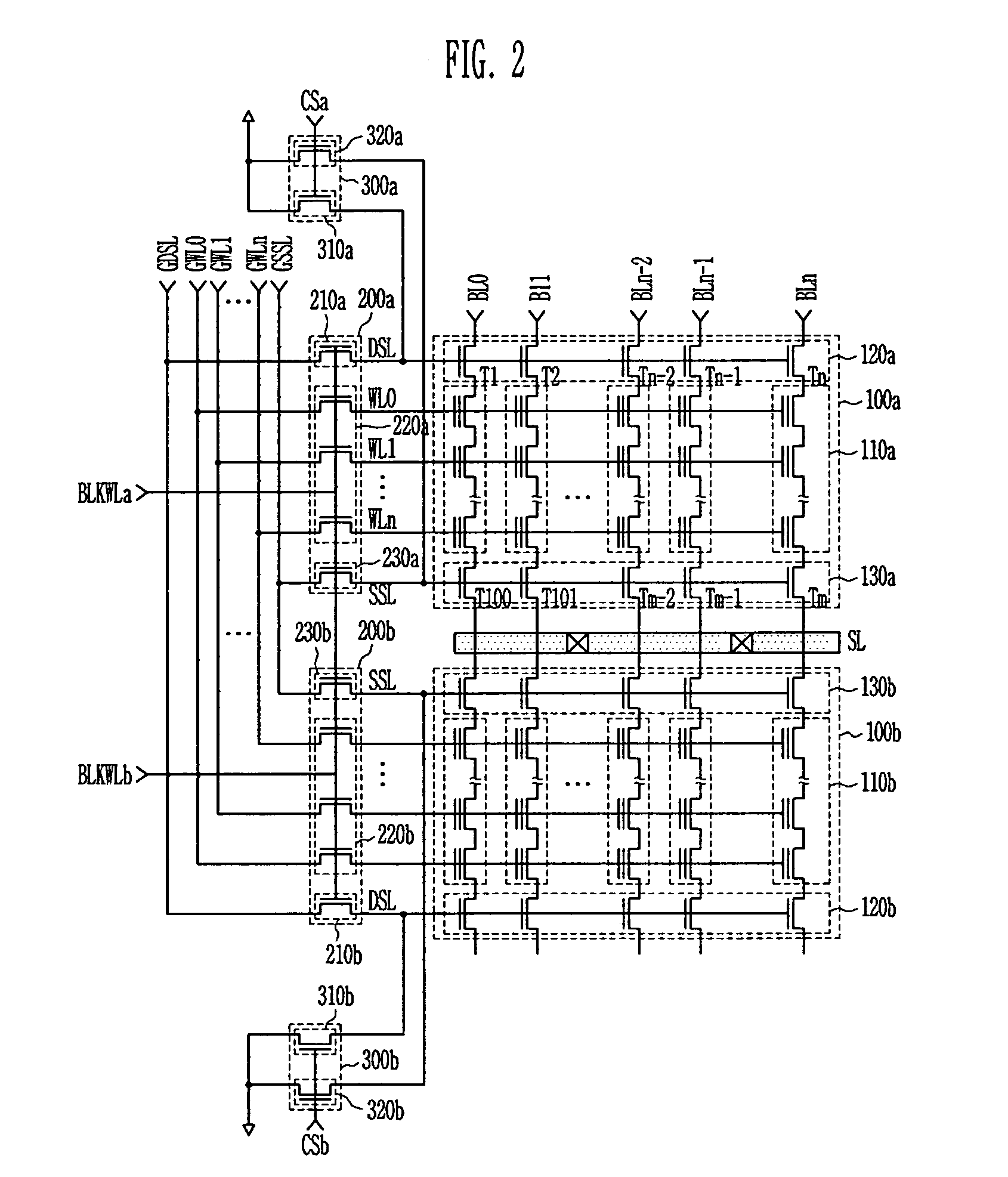
NAND flash memory device and method of reading the same
ActiveUS7035143B2Reduce leakage currentIncreasing source-side resistance of selection transistorsTransistorSolid-state devicesBack biasEngineering
Provided is related to a NAND flash memory device and method of reading the same, in which during a read operation, a ground voltage is applied to string and ground selection transistors of deselected cell blocks so as to increase resistance of a string line to prevent leakage currents due to a back-bias effect. A reduced bitline leakage current increases an ON / OFF current ratio between programmed and erased cells to reduce a sensing time therein, which makes a read trip range so as to prevent variation of threshold voltages due to data retention and reading disturbance. Voltages can be independently applied to source selection lines by electrically isolating source selection transistors between the cell blocks. It is available to reduce the number of source discharge transistors by electrically connecting the source selection transistors between adjacent cell blocks.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL +1
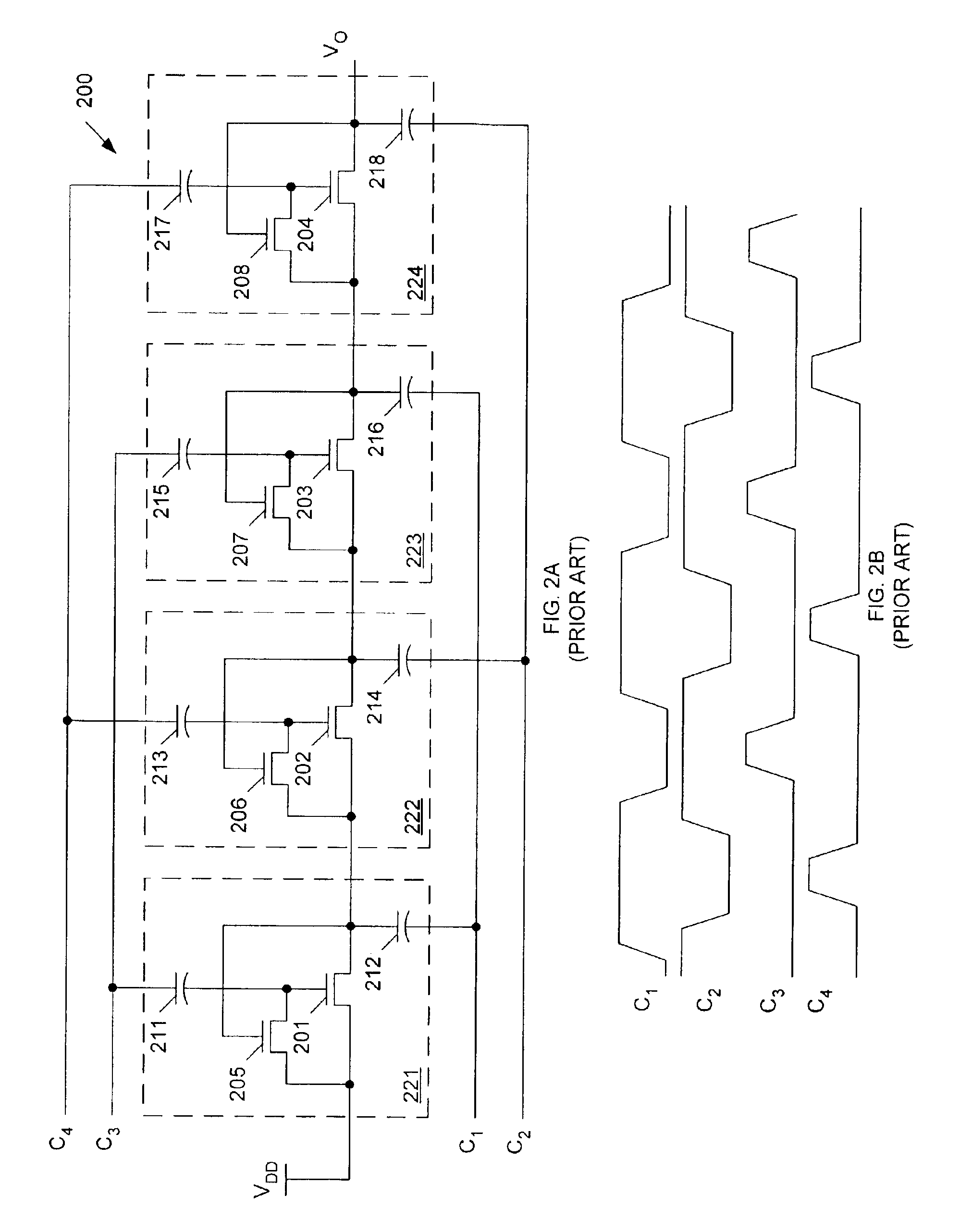
Internal voltage generator
InactiveUS7046074B2Reduce power consumptionDc network circuit arrangementsDiffusing elementsVoltage generatorBack bias
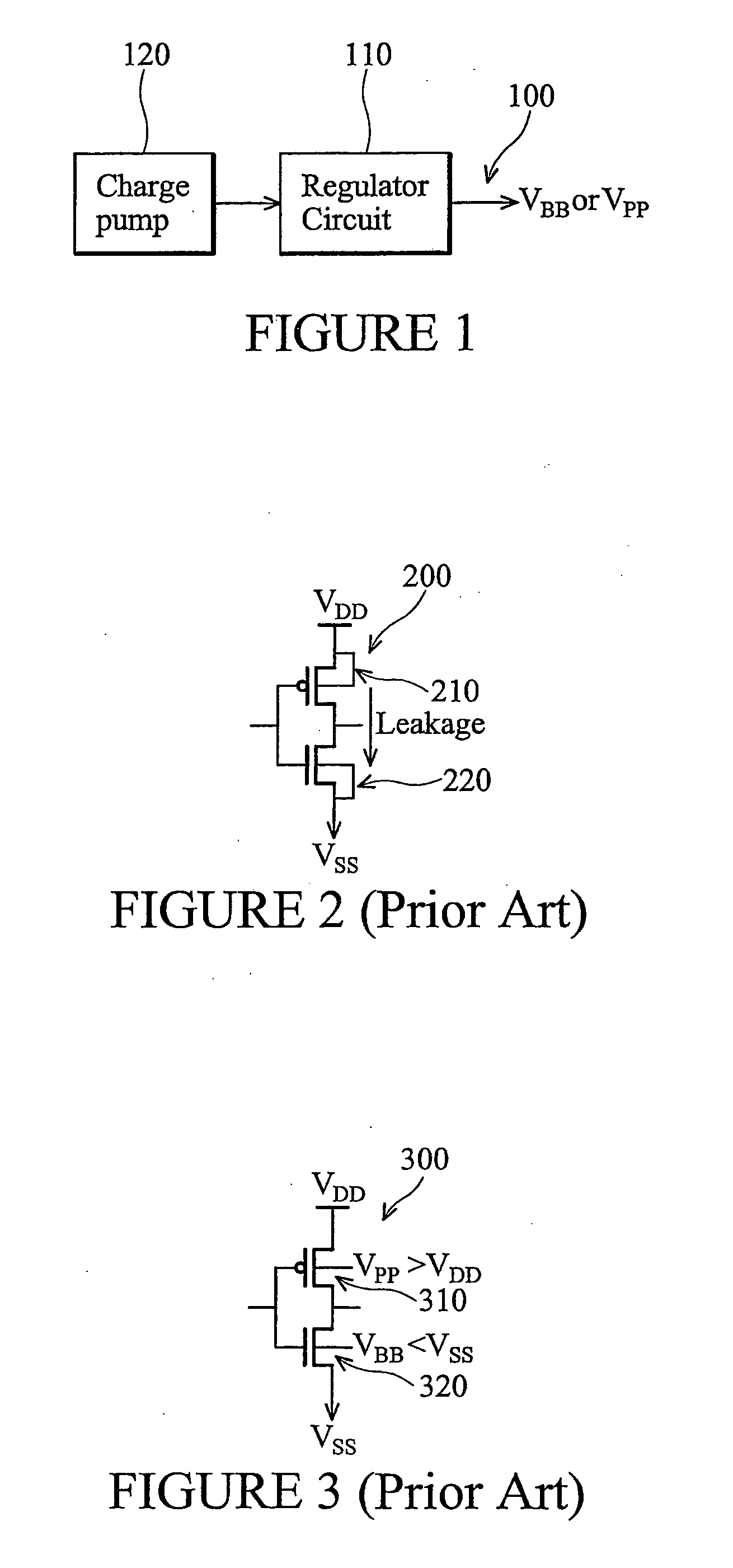
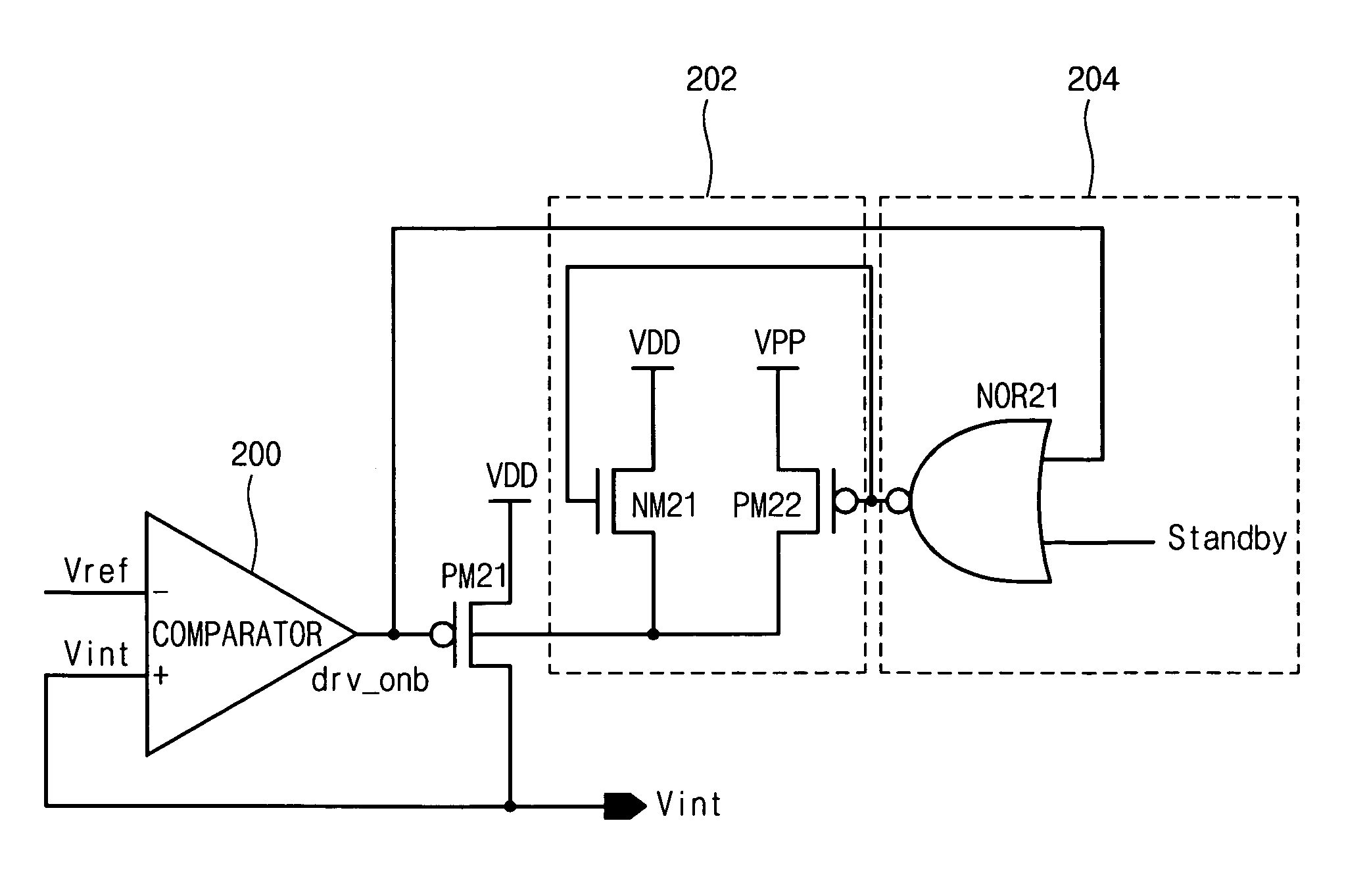
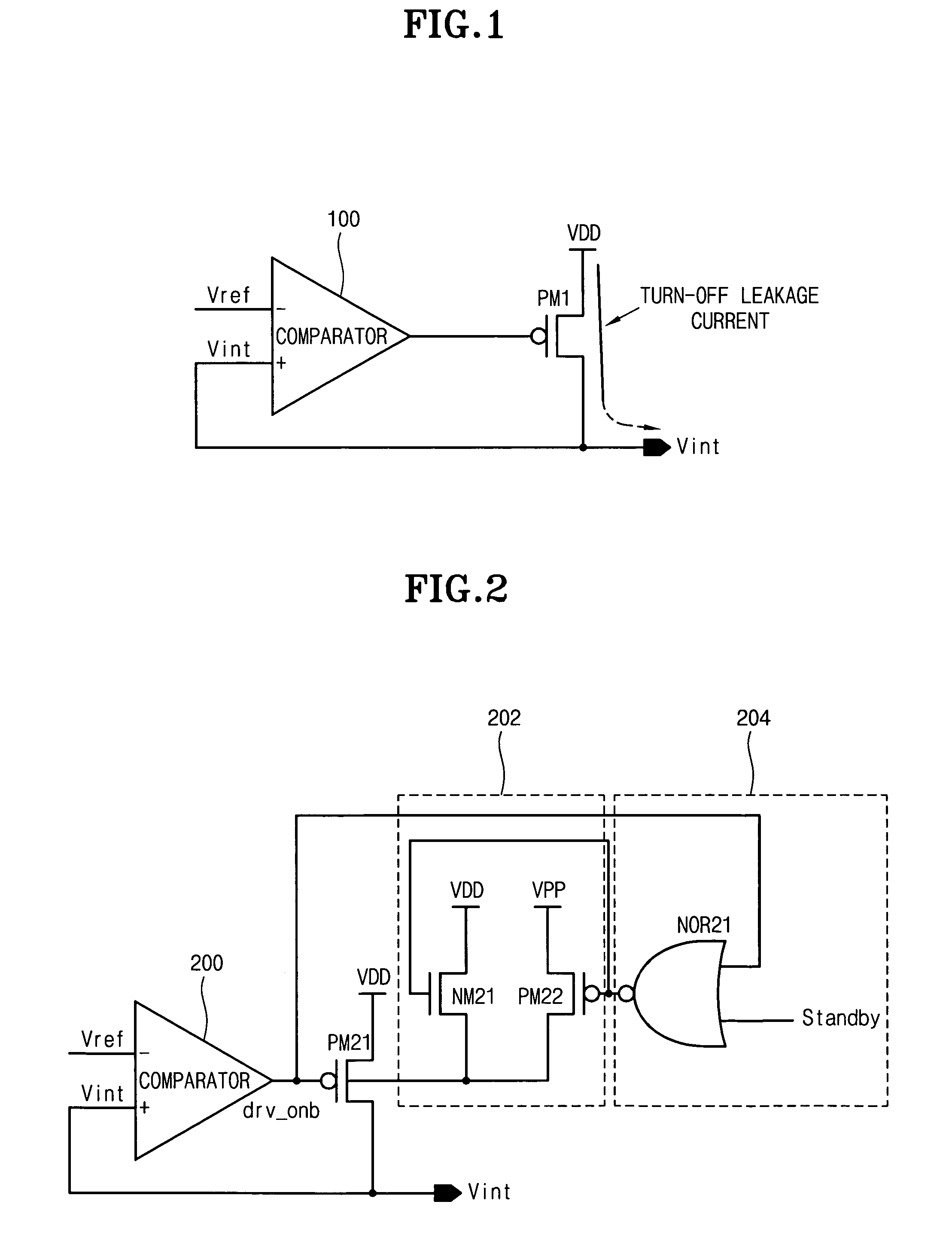
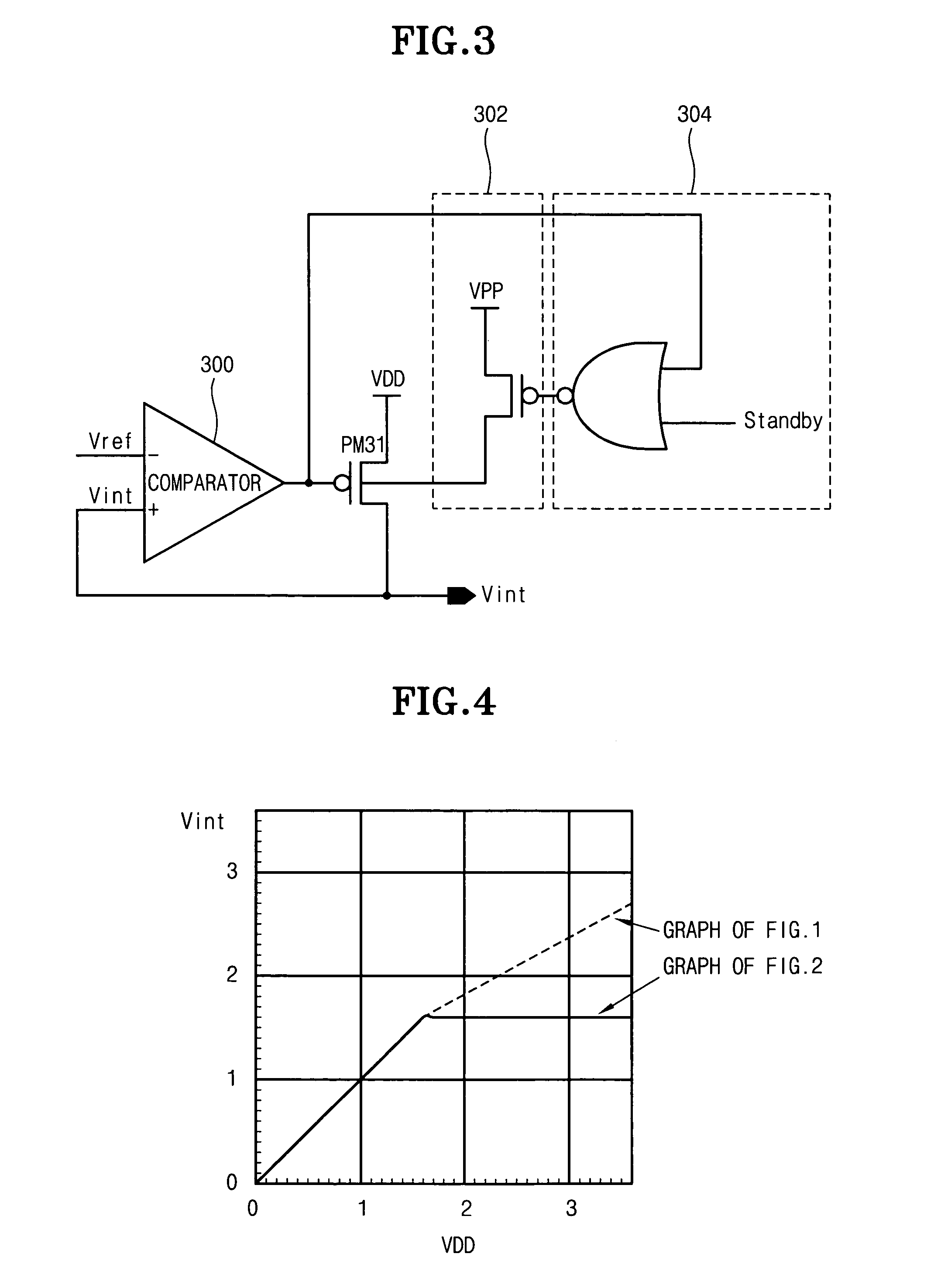
The present invention discloses an internal voltage generator which can restrict abnormal variations of an internal voltage resulting from a leakage current generated in a driving transistor. The internal voltage generator includes a comparator for receiving a reference voltage through its first input terminal, receiving the internal voltage through its second input terminal, and comparing the reference voltage with the internal voltage, a driving transistor for receiving the output signal from the comparator through its gate terminal, a first terminal of which being coupled to a driving voltage, a second terminal of which being an output terminal for outputting the internal voltage, a back bias circuit for supplying a predetermined potential of back bias voltage to a well region of the driving transistor, and a controller for receiving the output signal from the comparator, and controlling the operation of the back bias circuit. The second terminal of the driving transistor is feedback-coupled to the second input terminal of the comparator. When the driving transistor is turned off according to the output signal from the comparator, the controller for receiving the output signal from the comparator supplies the predetermined potential of back bias voltage to the well region of the driving transistor by driving the back bias circuit.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Current source architecture for memory device standby current reduction
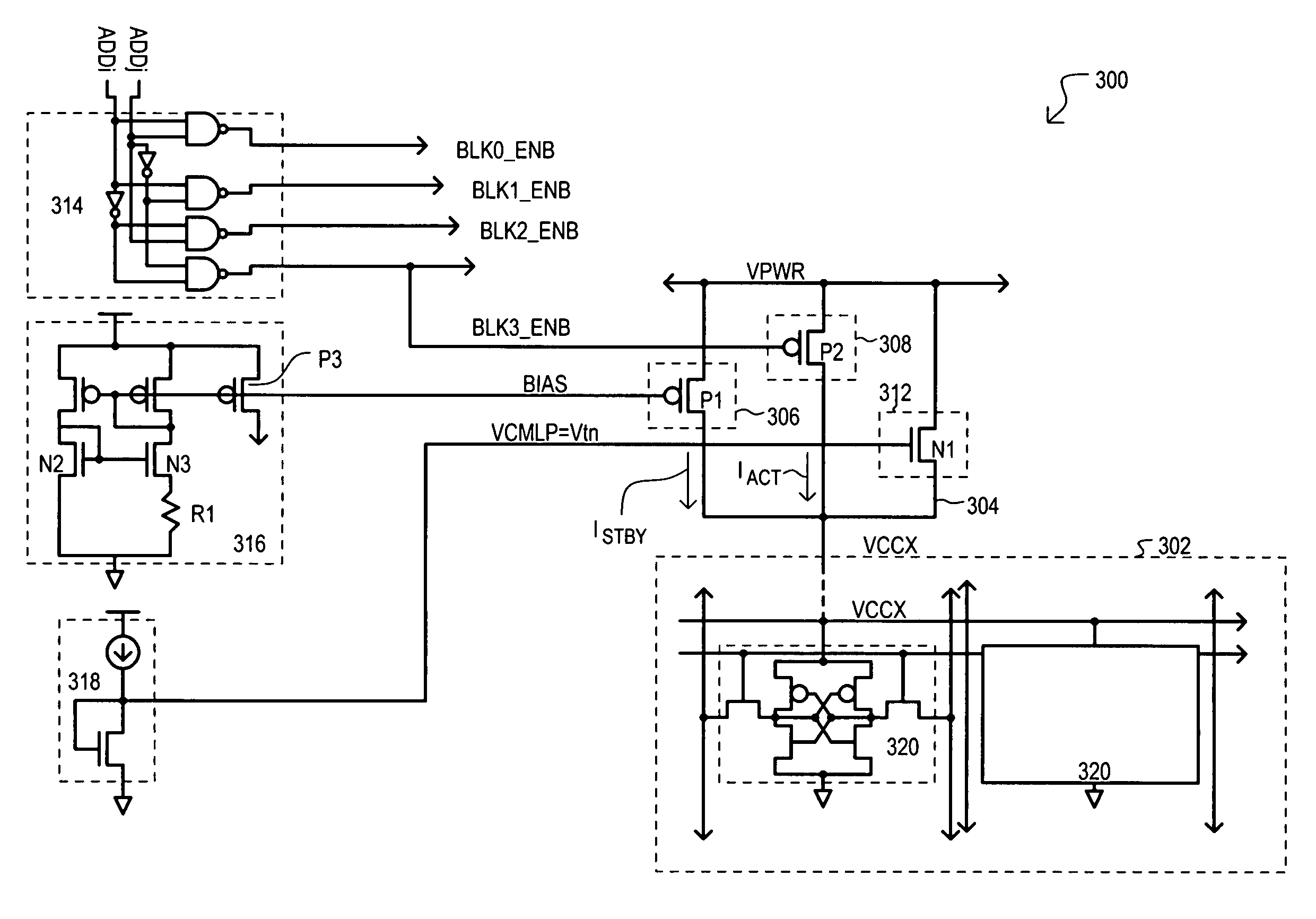
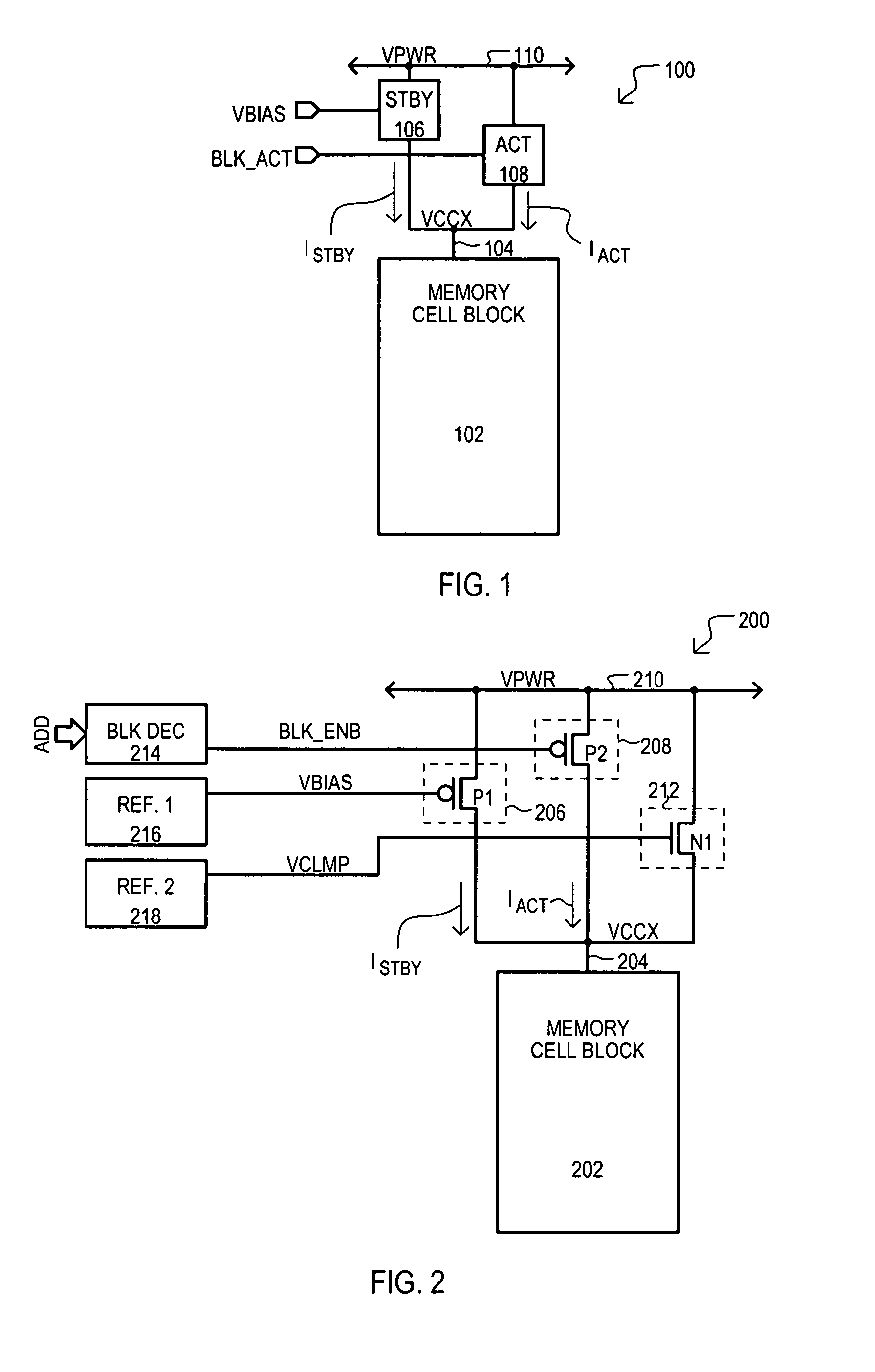
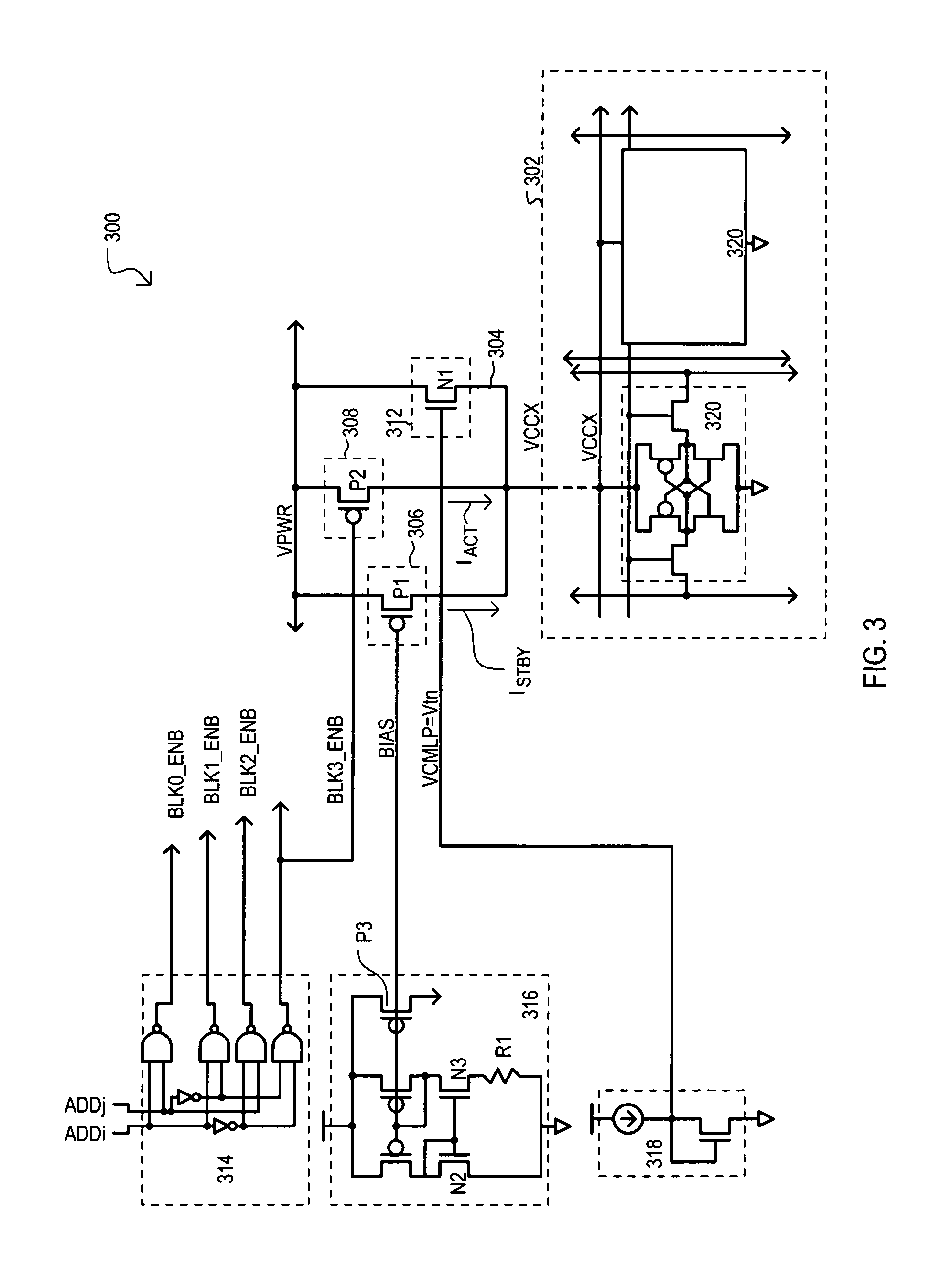
A memory device (200) can include a memory cell block (202), a standby current source (206), an active current source (208), and a clamping device (212). In a standby mode, a standby current source (206) can provide constant standby current ISTBY to memory cell block (202) via block supply node (204). In an active mode, active current source (208) can provide current to accommodate current necessary for active operations (e.g., accessing the memory cell block). A clamping circuit (212) can provide additional current in the event a block supply node (204) potential VCCX collapses due to the presence of micro-defects. In addition, compensation for process variation can be achieved by a self regulating well (454) to source (404) back bias that can modulate the threshold voltage of p-channel transistors of memory cells within the well (454), reducing overall leakage.
Owner:INFINEON TECH LLC
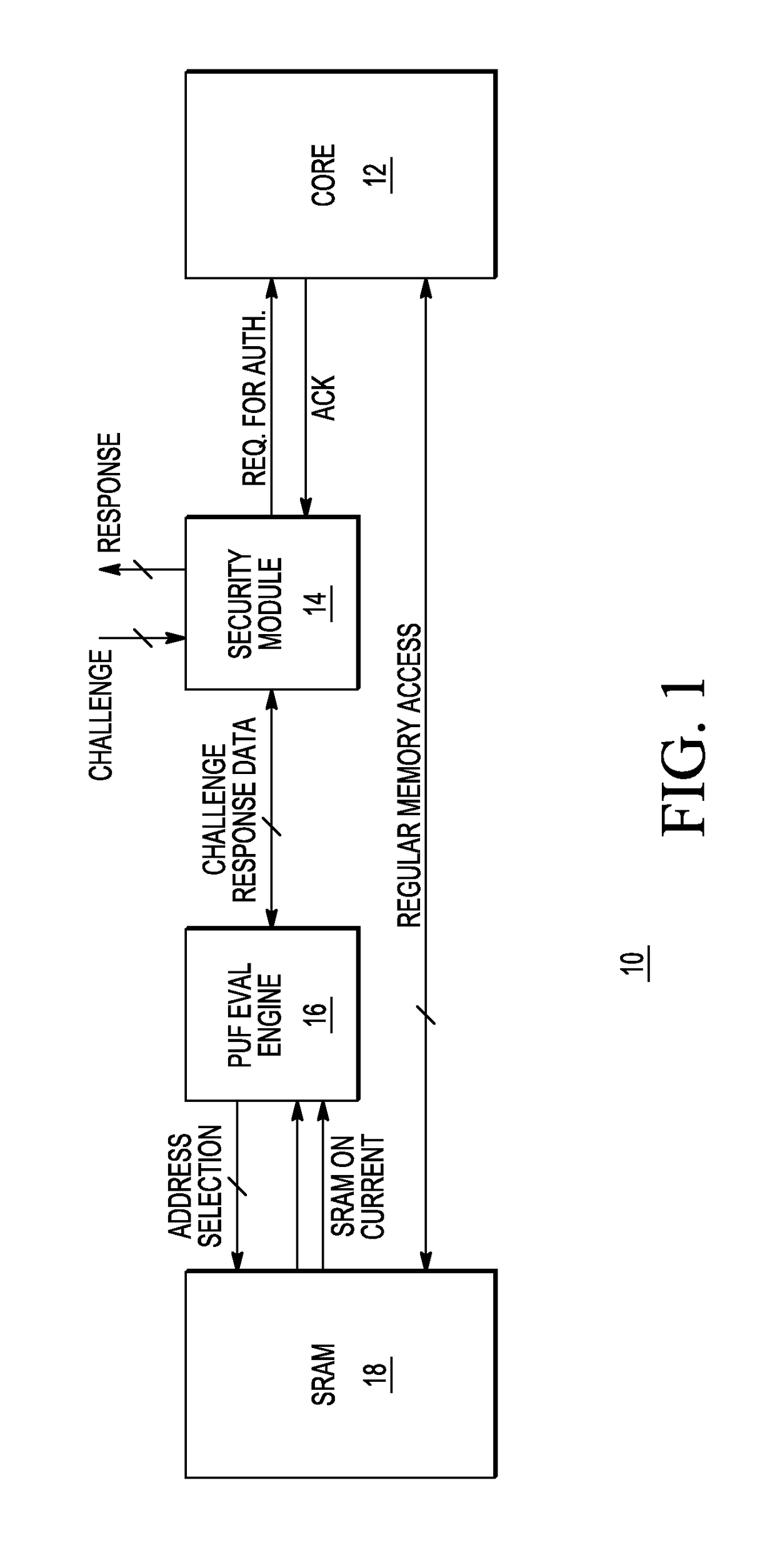
SRAM based physically unclonable function and method for generating a PUF response
ActiveUS9947391B1Digital storageInternal/peripheral component protectionShift registerData processing system
A physically unclonable function (PUF) is implemented in a plurality of SRAM cells. In a method for generating a PUF response, a logic zero is first written to all the SRAM cells of the PUF. A bit line coupled to the storage node that stores the logic zero of each SRAM cell is biased to a predetermined voltage. The bit lines are then selected for an evaluation read operation. During the evaluation read, a read current of one of the bit lines from one column is converted to a first voltage and a read current of another bit line of another column is converted to a second voltage. The first voltage is then compared to the second voltage. A logic state of a bit of the PUF response is determined as a result of the comparison. The logic bit may be provided to the input of a parallel-in serial-out shift register. There may be a comparator for each logic bit, or a few comparators may be shared between the logic bits. The PUF response may be used to provide a signature for the data processing system. The back-bias of each cell may be selectively adjusted.
Owner:NXP USA INC
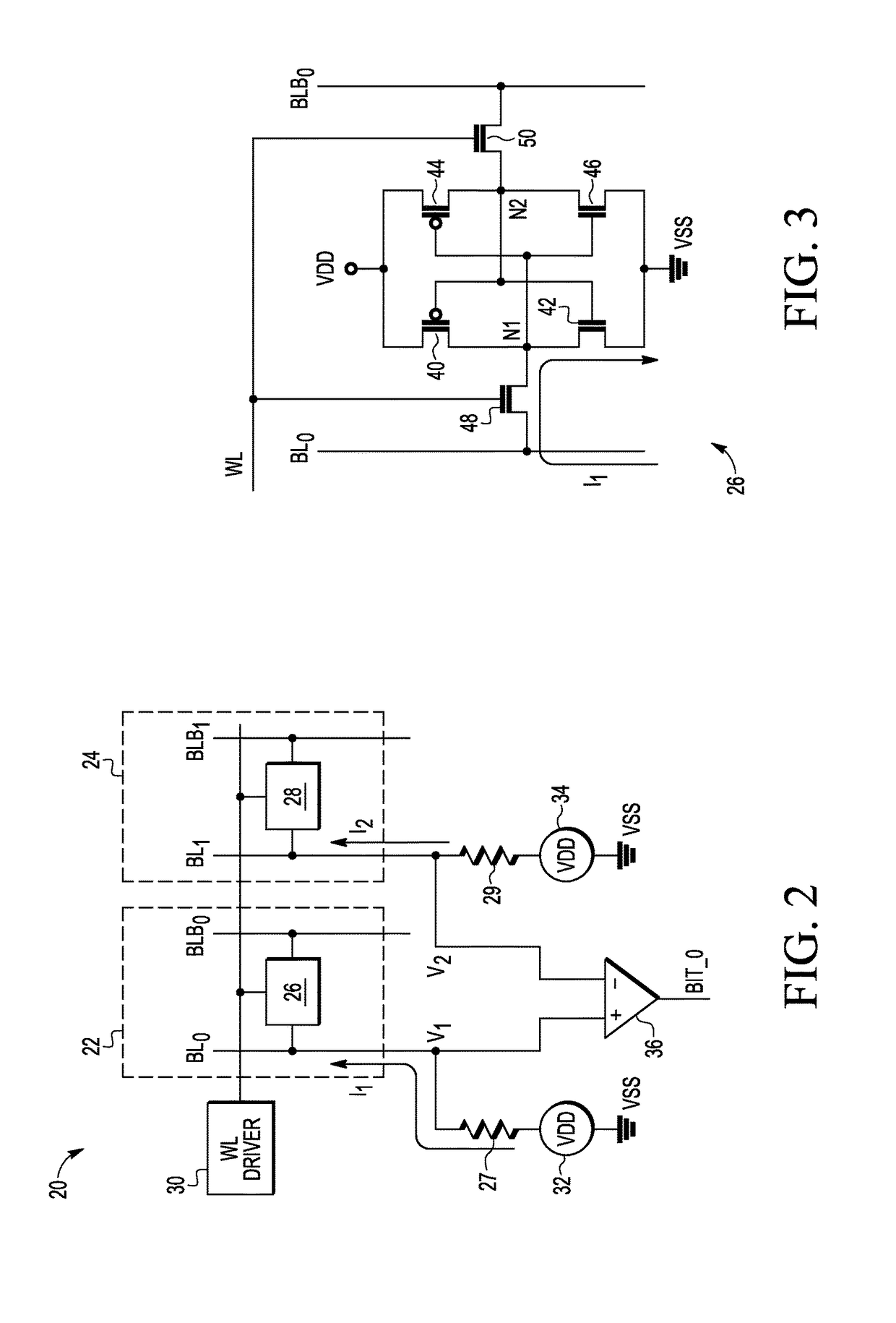
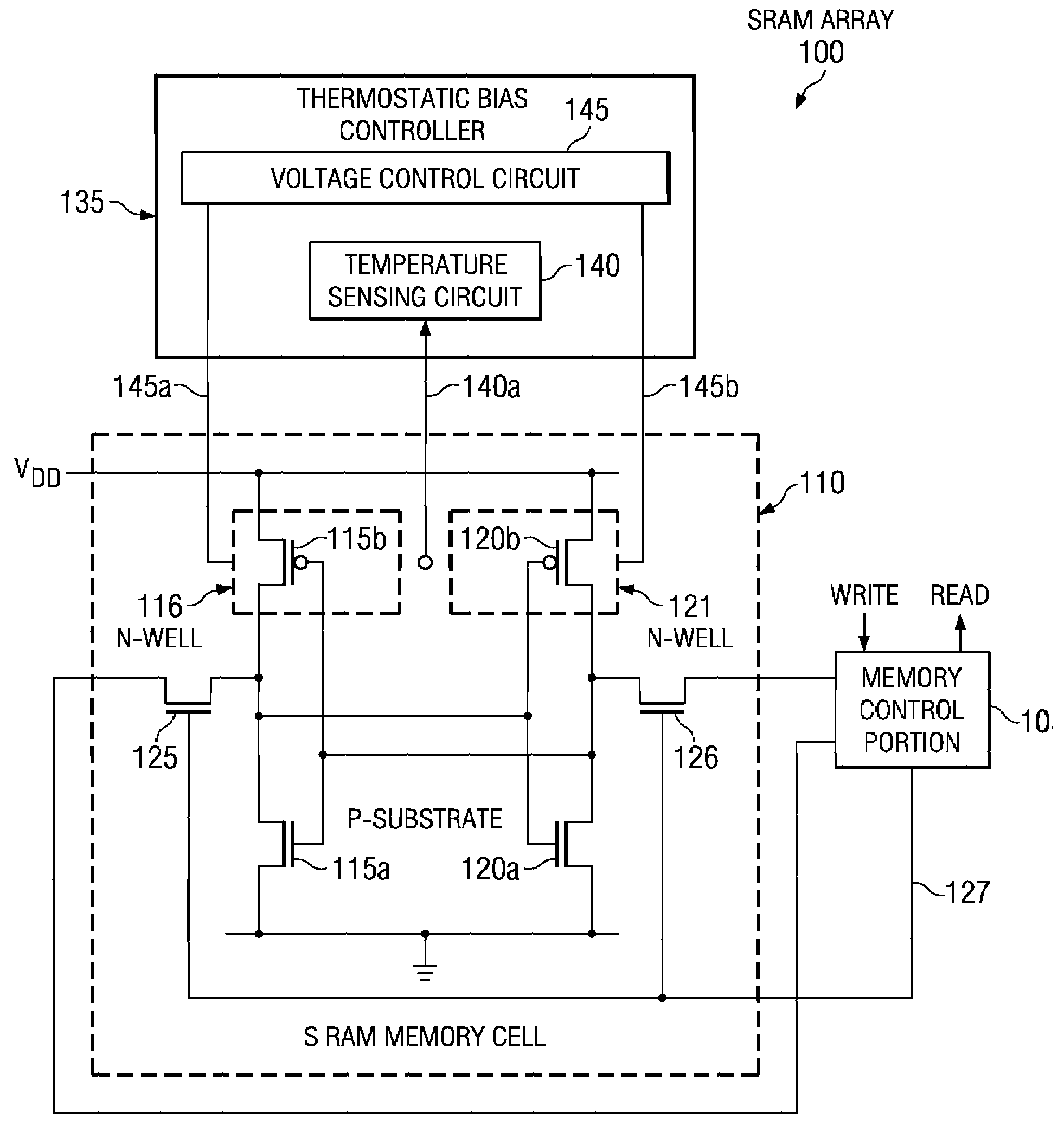
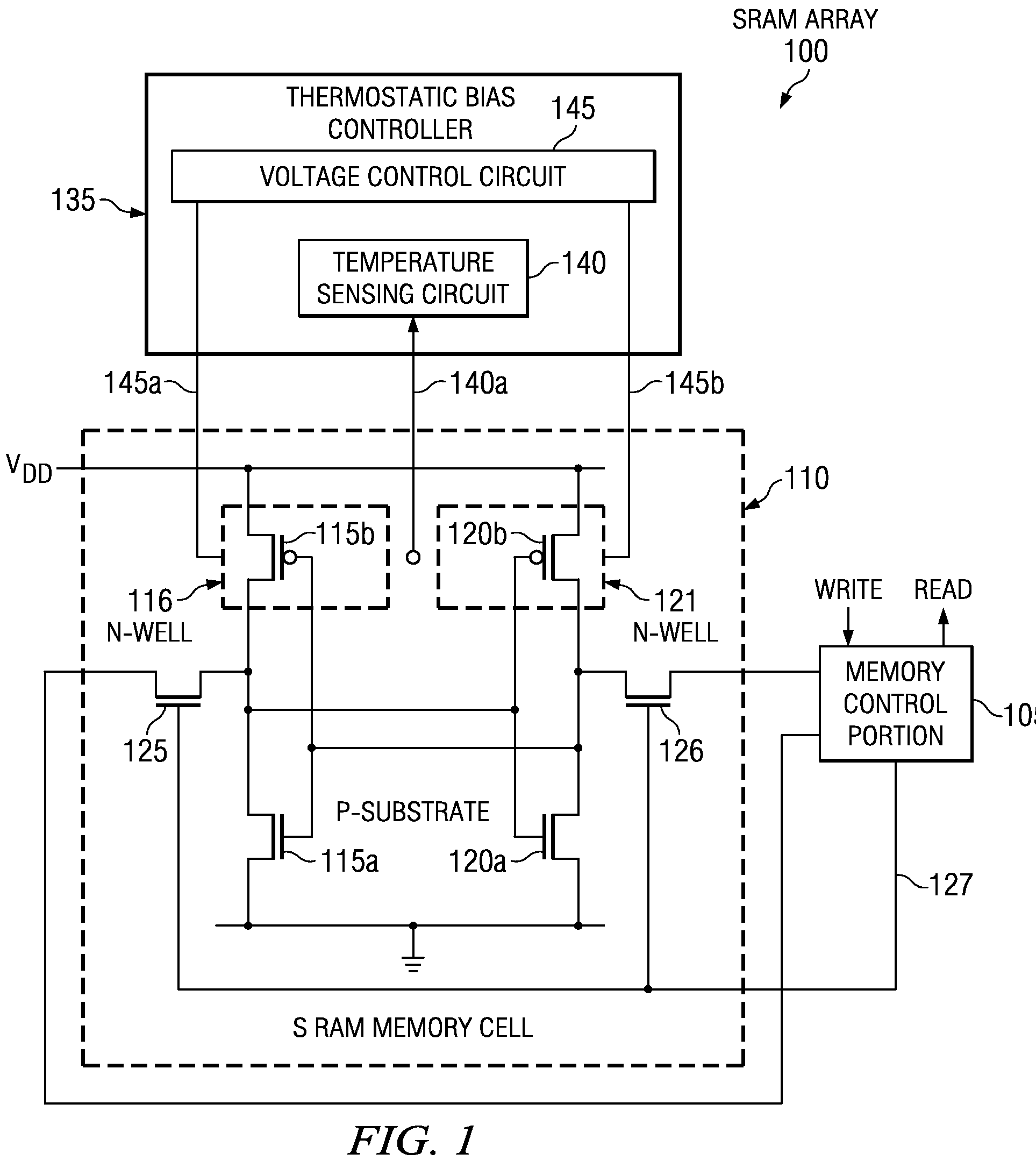
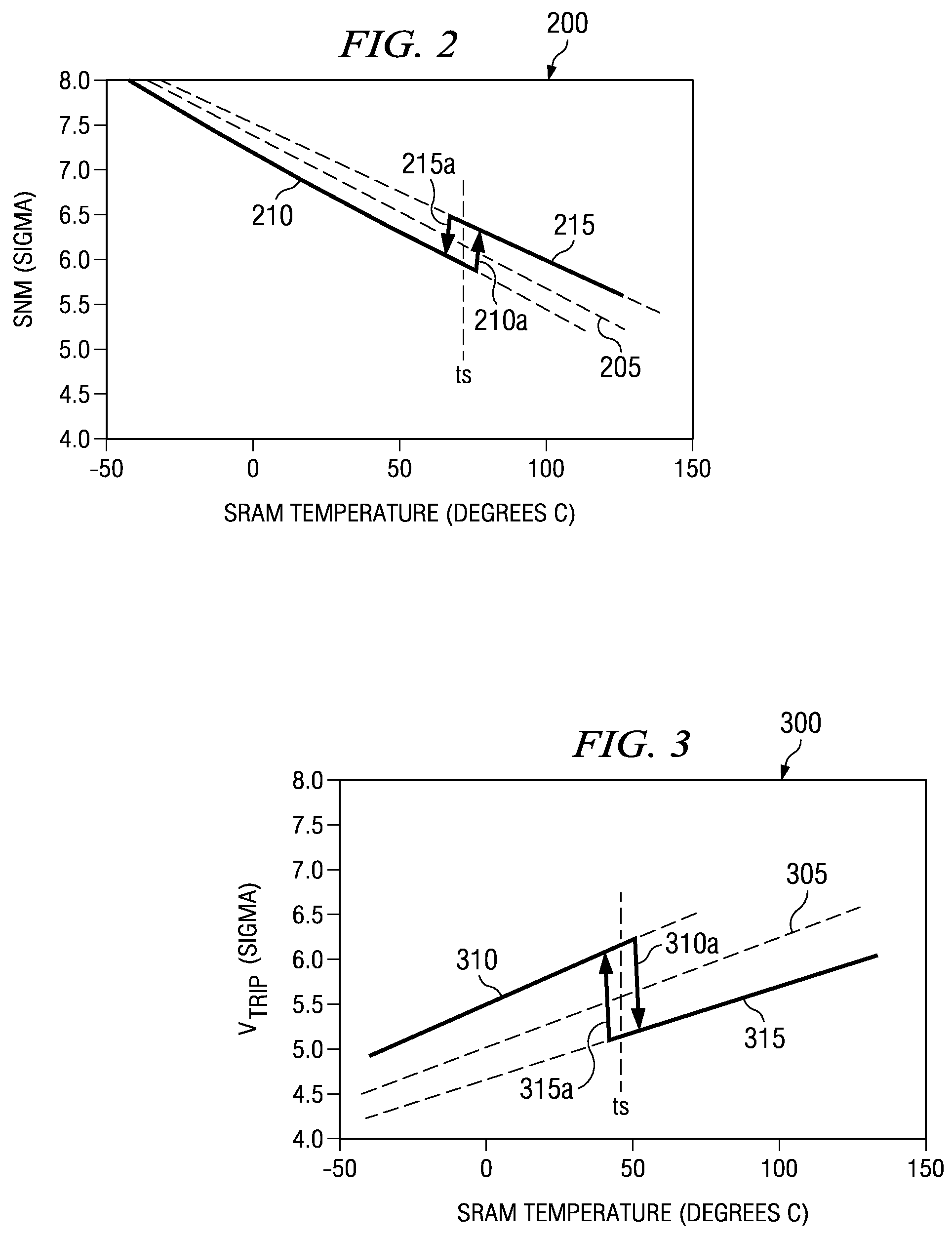
Temperature dependent back-bias for a memory array
The present invention provides a thermostatic bias controller for use with a memory array. The thermostatic bias controller includes a temperature sensing circuit configured to sense a temperature associated with the memory array. The thermostatic bias controller also includes a voltage control circuit coupled to the temperature sensing circuit and configured to provide a bias voltage to at least one back-gate of the memory array based on the temperature.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
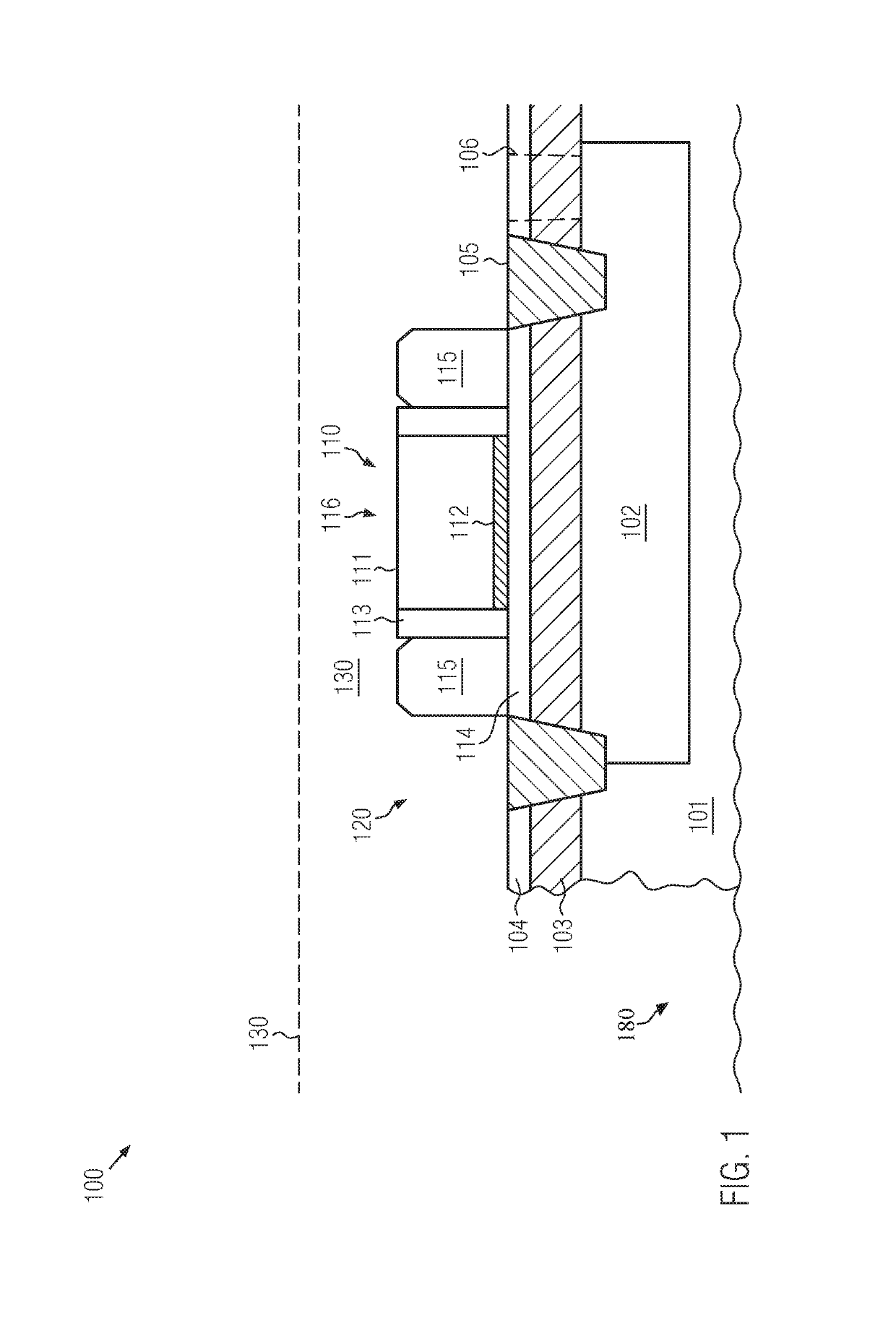
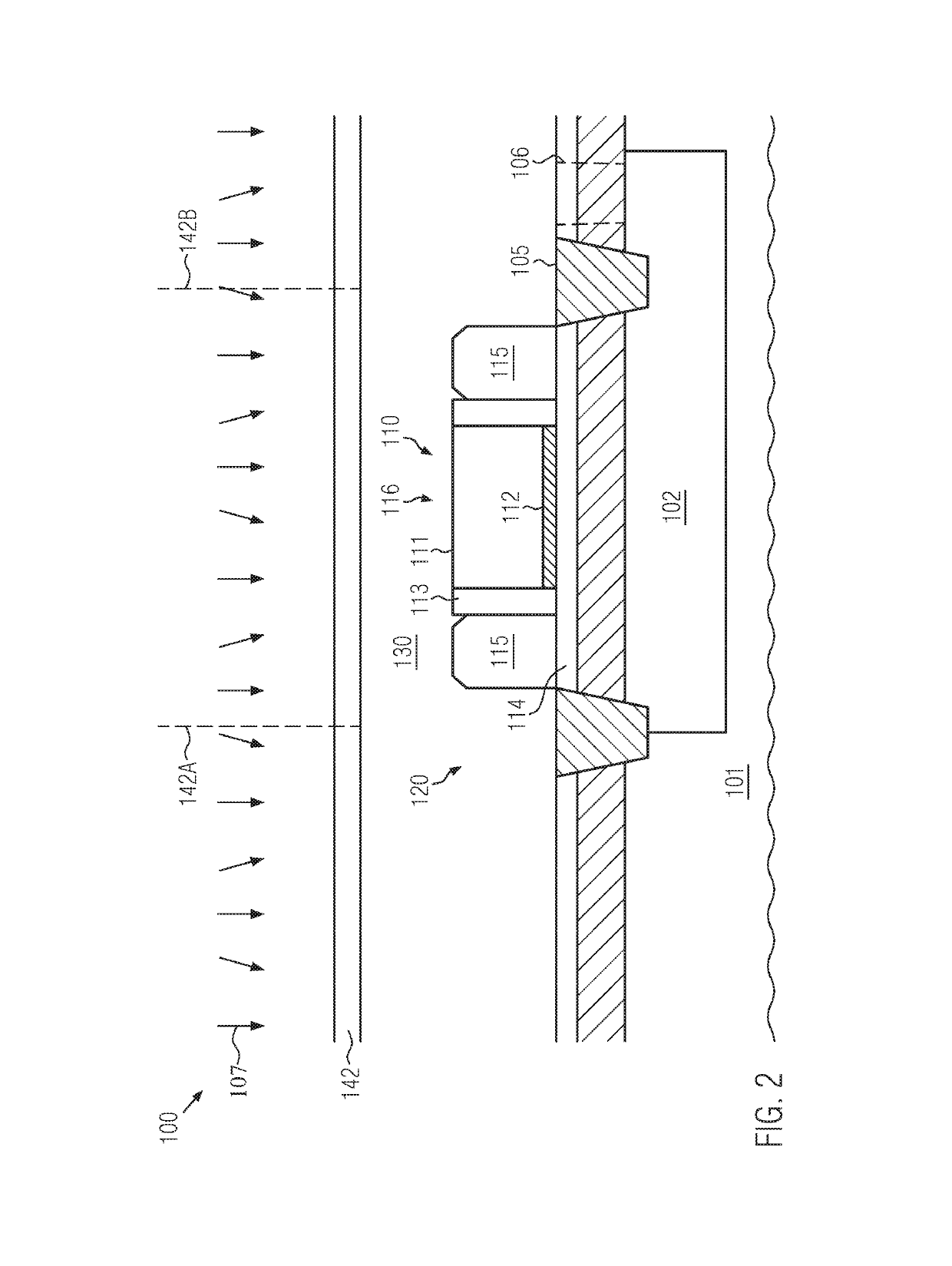
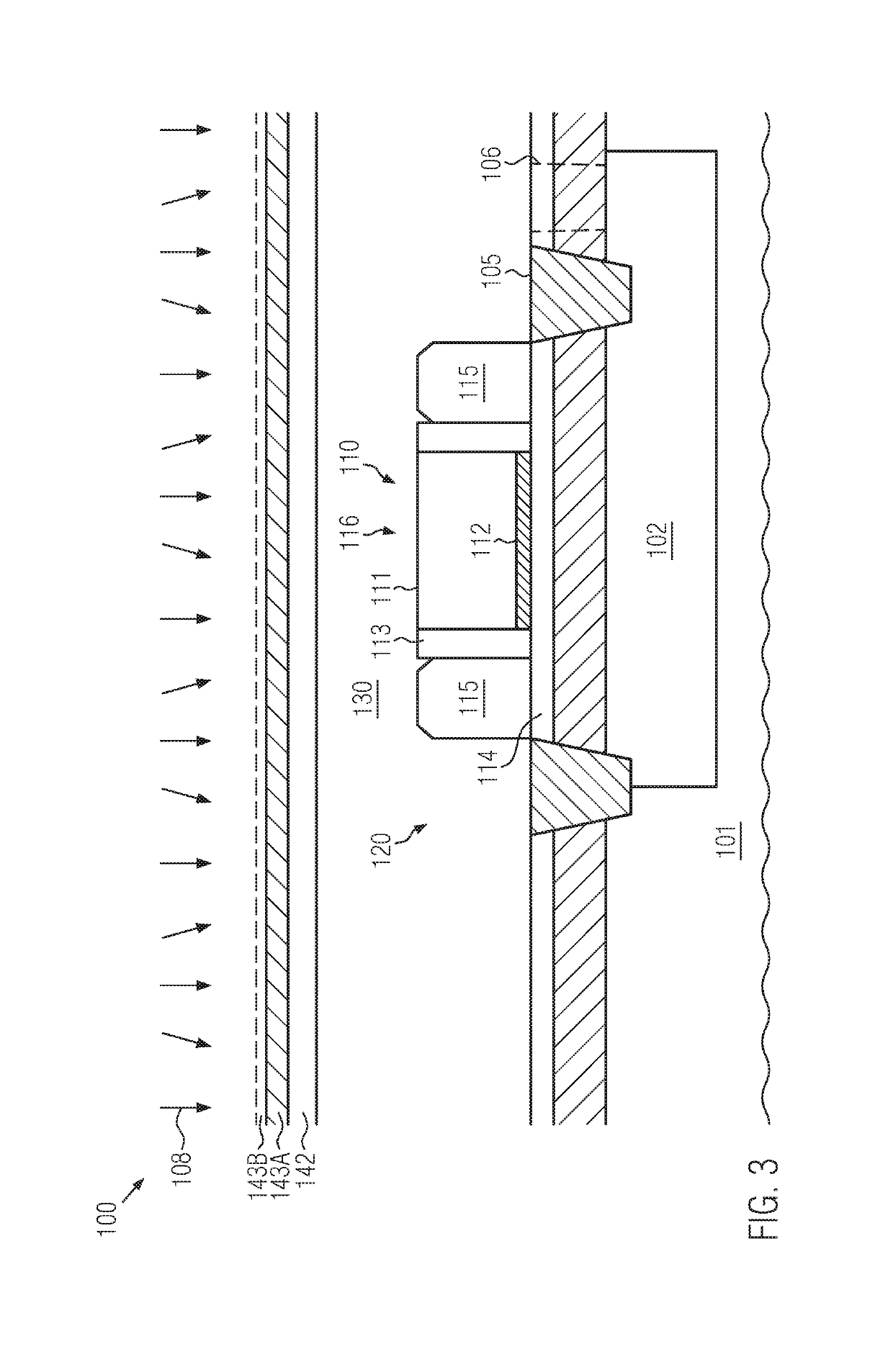
Stacked SOI semiconductor devices with back bias mechanism
ActiveUS10340290B2Improve performanceHigh bulk densityTransistorSolid-state devicesBack biasEngineering
A semiconductor device includes at least two stacked SOI levels or configurations, each of which may include transistor elements formed on the basis of a given technology node. At least the uppermost device level may include a back bias mechanism for providing superior controllability of the respective transistor elements. In some illustrative embodiments, at least two of the stacked SOI configurations may have implemented therein a back bias mechanism, wherein an appropriate contact regime is provided so as to connect to the respective conductive regions or layers below the corresponding buried insulating layers for each stacked device level. Consequently, increased lateral packing density may be accomplished on the basis of a given technology node.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
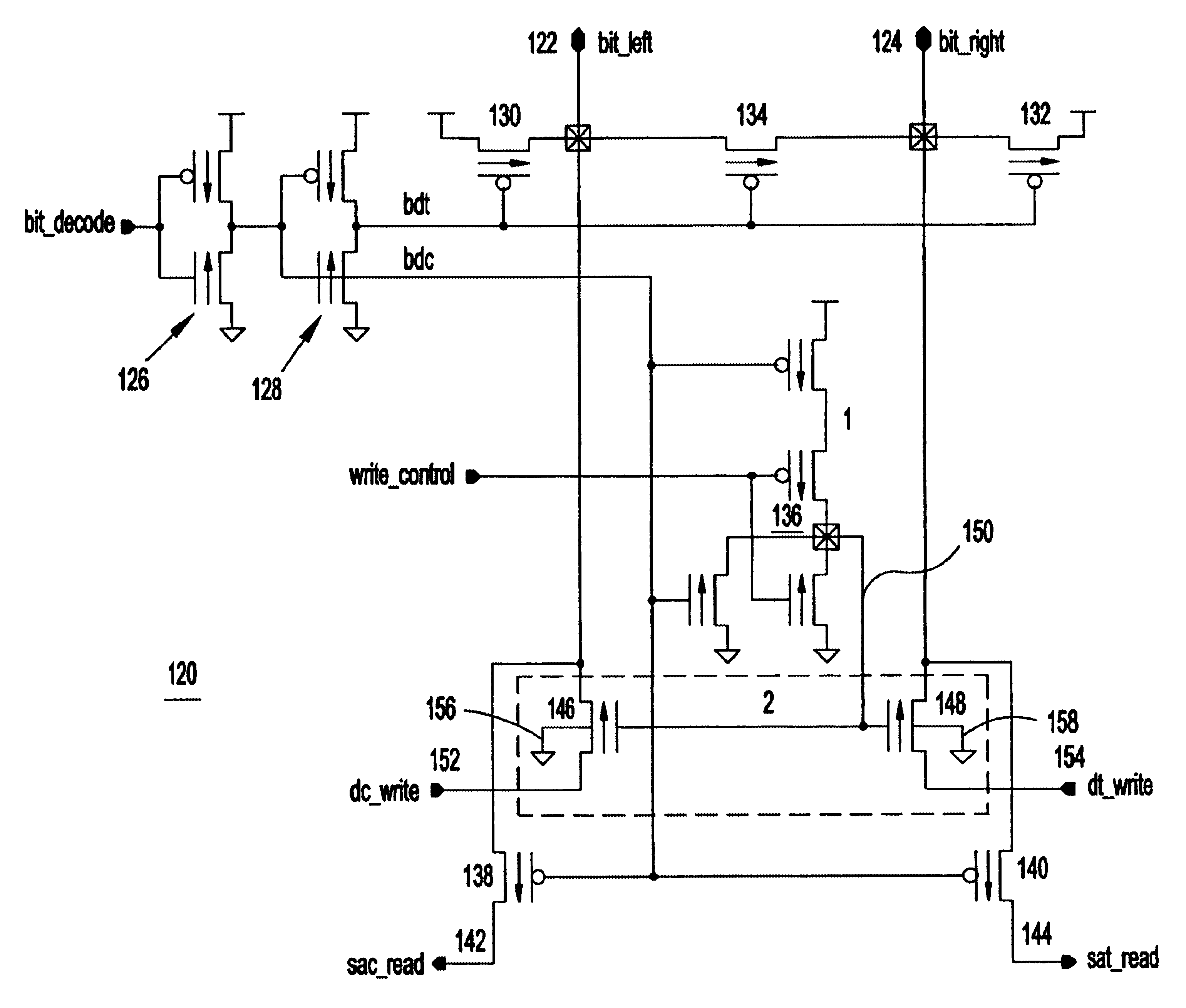
Coupled body contacts for SOI differential circuits
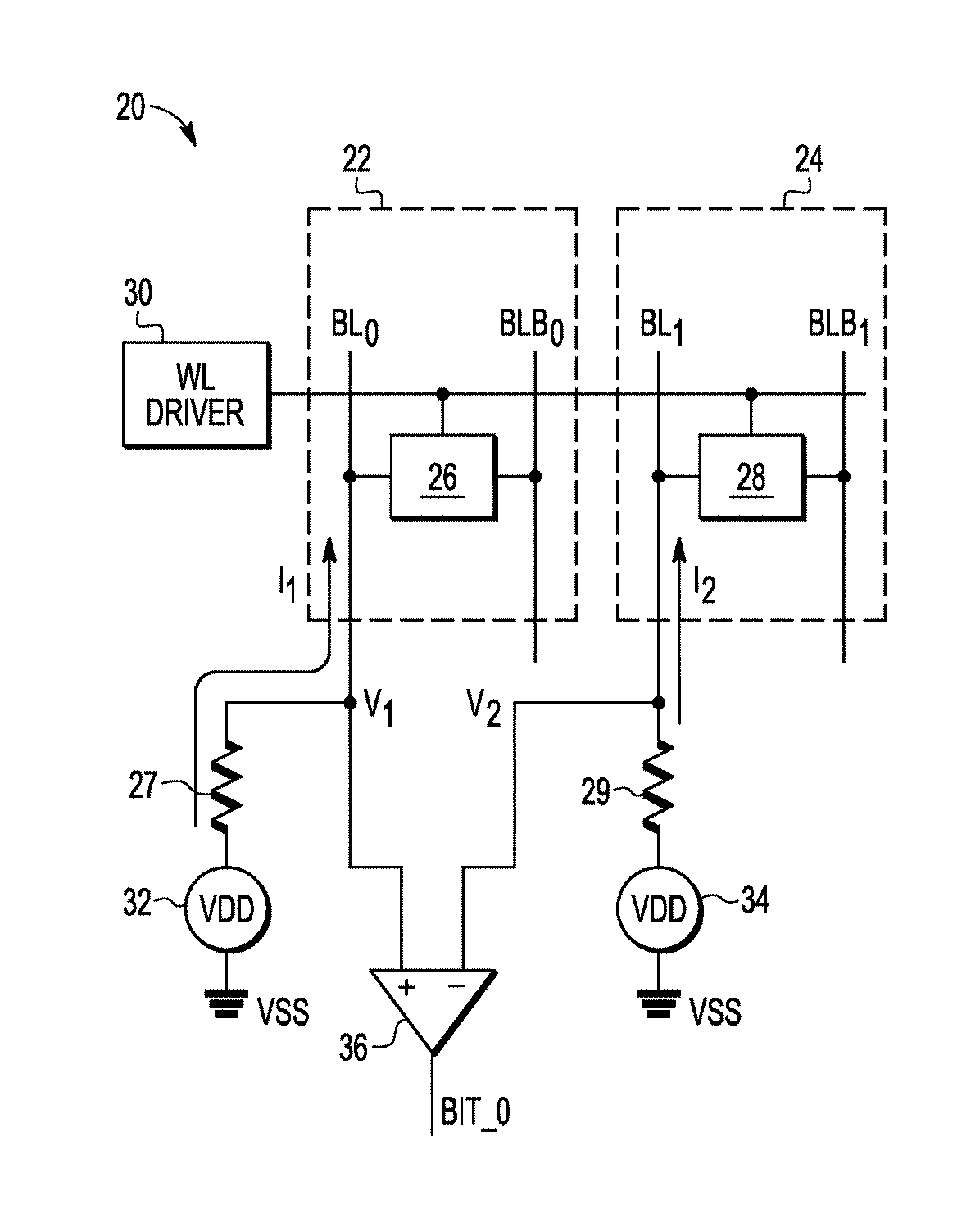
A silicon on insulator (SOI) CMOS circuit, macro and integrated circuit (IC) chip. The chip or macro may include be an SRAM in partially depleted (PD) SOI CMOS. Most field effect transistors (FETs) do not have body contacts. FETs otherwise exhibiting a sensitivity to history effects have body contacts. The body contact for each such FET is connected to at least one other body contact. A back bias voltage may be provided to selected FETs.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
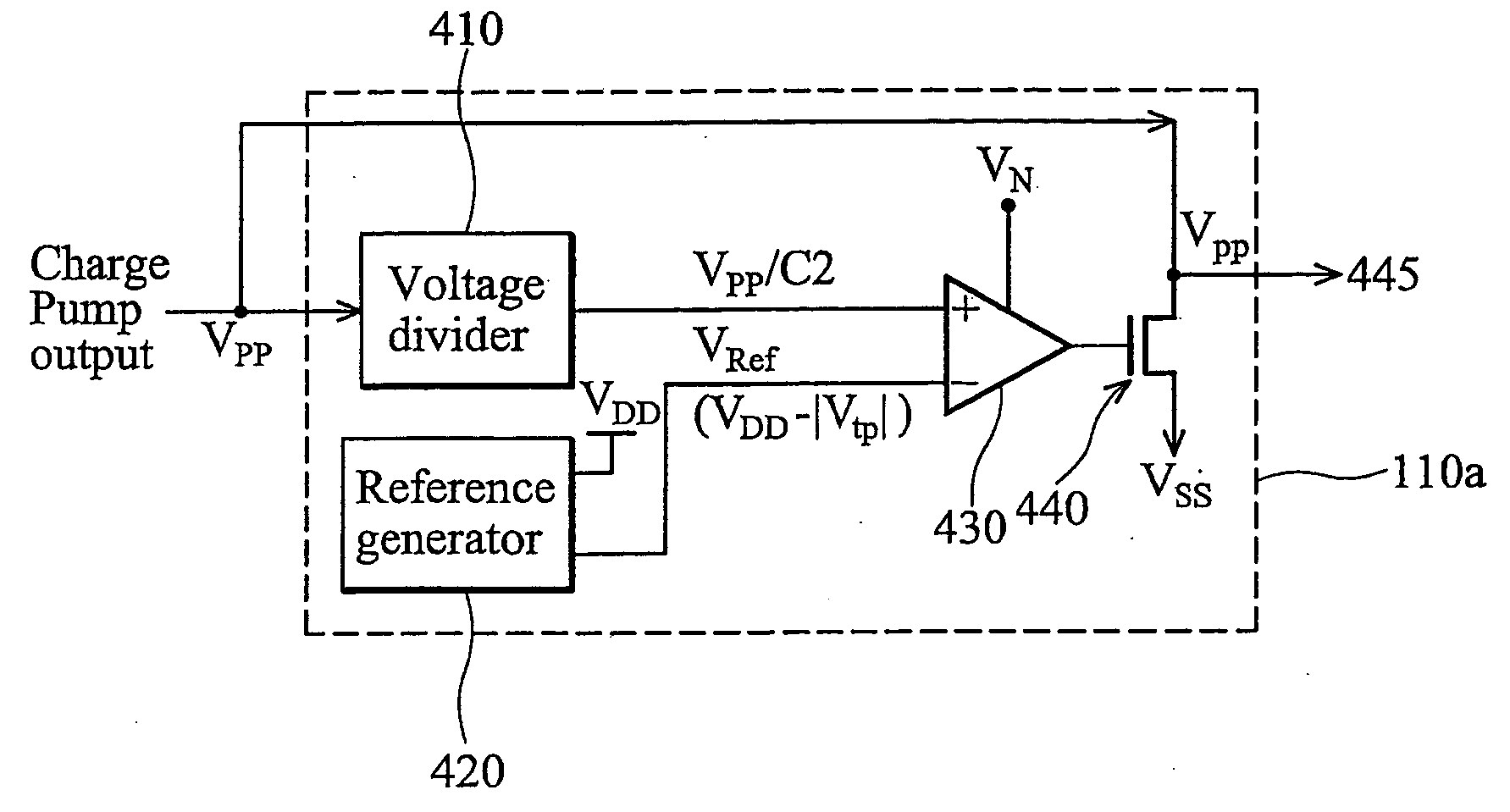
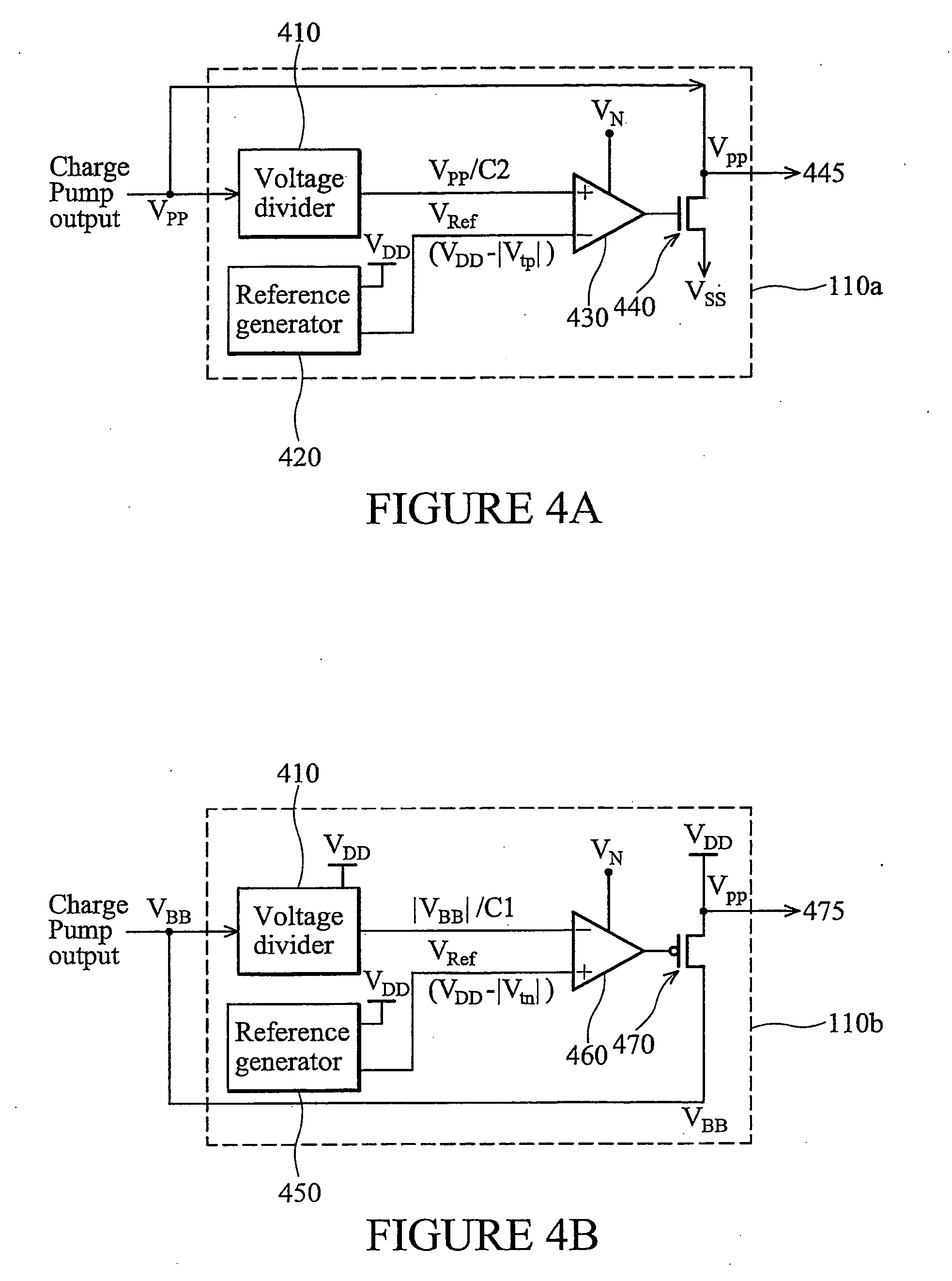
Back-bias voltage regulator having temperature and process variation compensation and related method of regulating a back-bias voltage
InactiveUS20050280463A1Electric pulse generator detailsElectric variable regulationElectrical resistance and conductanceBack bias
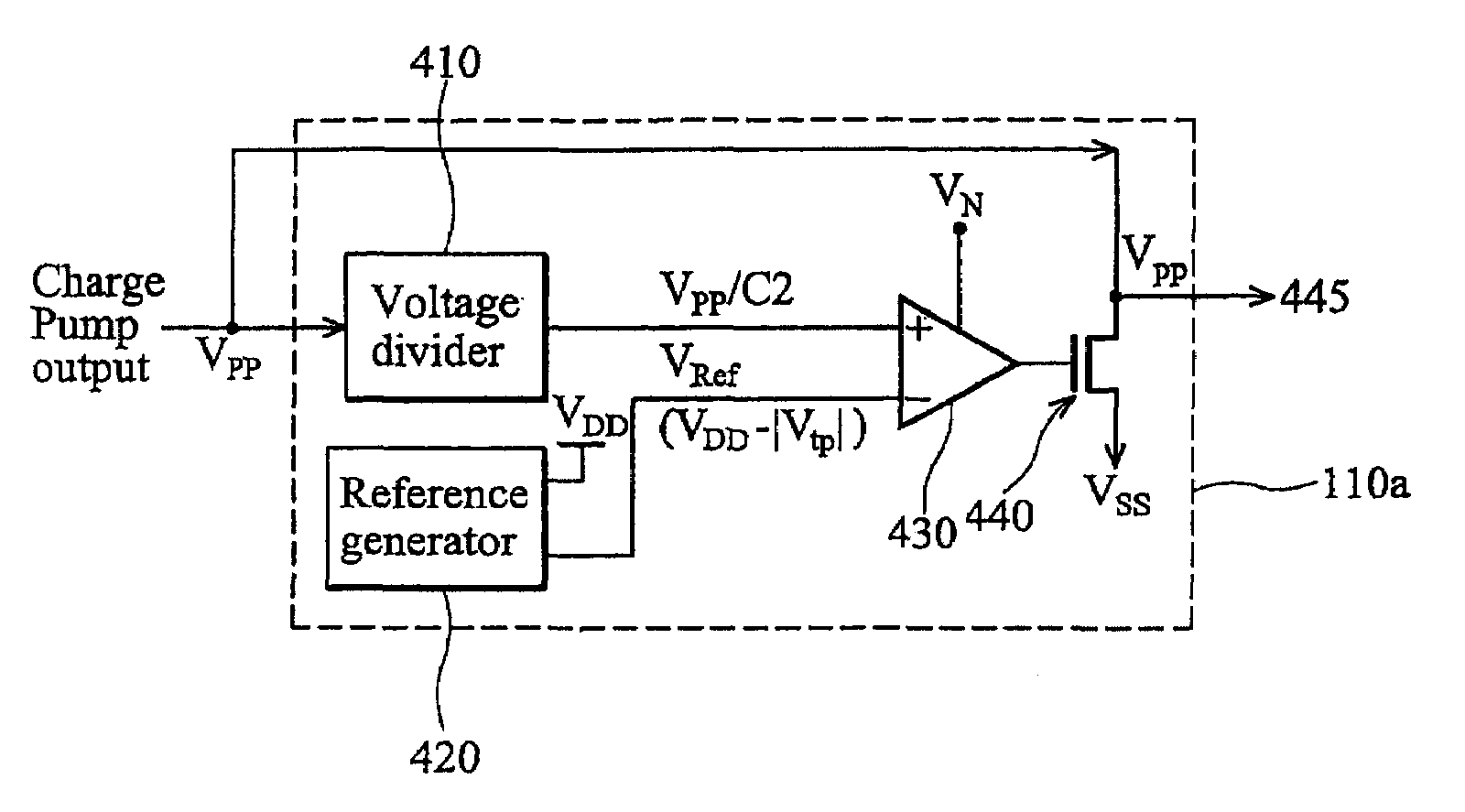
Disclosed herein is a back-bias voltage regulator circuit for regulating a back-bias voltage used to control leakage current in at least one transistor within a primary circuit. In one embodiment, the back-bias voltage regulator circuit includes a voltage divider circuit configured to receive a back-bias voltage from a charge pump, and to generate a divided voltage signal by dividing the back-bias voltage based on a ratio of resistances of resistive elements within the voltage divider. In addition, the regulator circuit includes an output circuit configured to receive the back-bias voltage from the charge pump and having an output node for outputting the back-bias voltage, as well as a reference voltage circuit configured to generate a reference voltage signal based on a threshold voltage of the at least one transistor in the primary circuit. Also in such an embodiment, the regulator circuit includes a comparison circuit configured to compare the divided voltage signal to the reference voltage signal and to operate the output circuit to regulate the back-bias voltage level based on the comparison. Also disclosed is a related method of regulating a back-bias voltage to control leakage current in at least one transistor within a primary circuit.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Nonvolatile flash memory and method of operating the same
ActiveUS20050270850A1Improve efficiencyTotal current dropTransistorRead-only memoriesDielectricBack bias
A nonvolatile memory and a method of operating the same are proposed. The nonvolatile memory has single-gate memory cells, wherein a structure of a transistor and a capacitor is embedded in a semiconductor substrate. The transistor comprises a first conducting gate stacked on the surface of a dielectric with doped regions formed at two sides thereof as a source and a drain. The capacitor comprises a doped region, a dielectric stacked thereon, and a second conducting gate. The conducting gates of the capacitor and the transistor are electrically connected together to form a single floating gate of the memory cell. The semiconductor substrate is p-type or n-type. Besides, a back-bias program write-in and related erase and readout operation ways are proposed for the single-gate memory cells.
Owner:YIELD MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Individually adjustable back-bias technique
An individual-well adaptive method of body bias control that mitigates the effects of D2D and WD process variations is shown. It is assumed that p-type transistors are grouped in sections. The bodies of all the p-type transistors within a section are connected to a single n-well. This section size can be small enough to provide fine-granular adjustments to the circuit without having any impact on area overhead. With a small amount of additional circuitry and routing, individual well biases can be intelligently adjusted resulting in closely controlled chip power and performance. Experimental results show that binning yields as low as 17% can be improved to greater than 90% using the proposed method.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
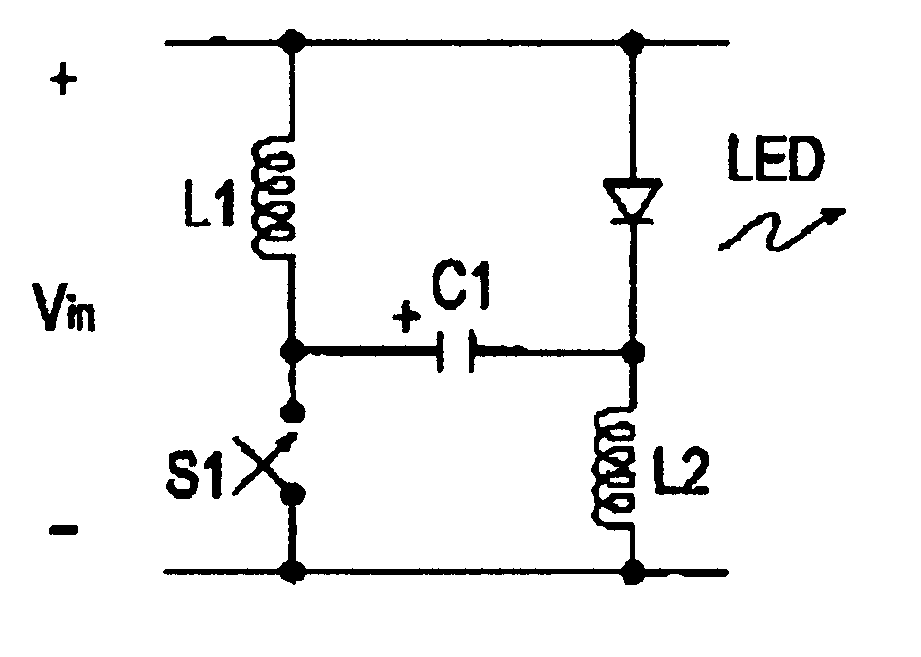
Voltage-adder LED driver
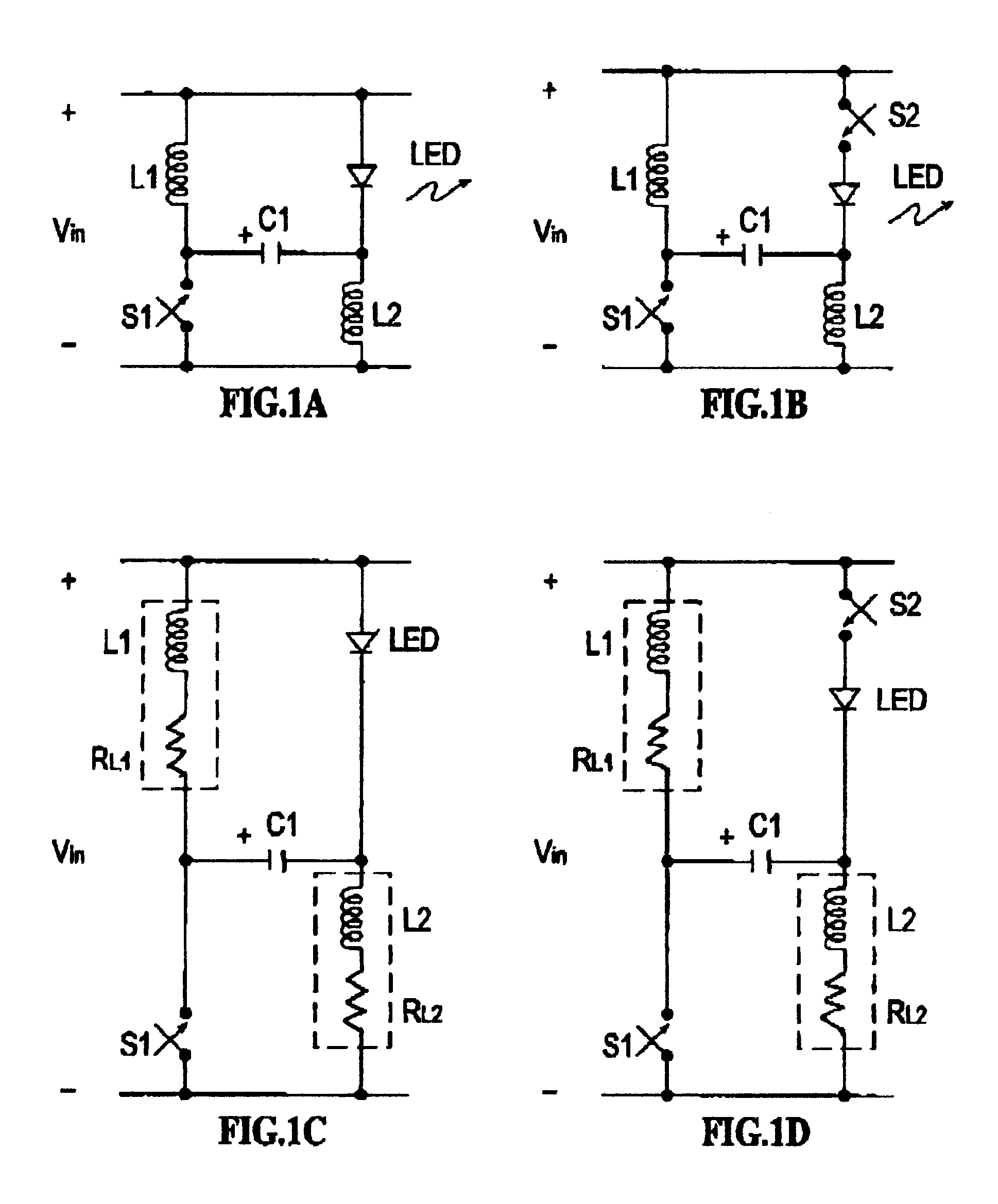
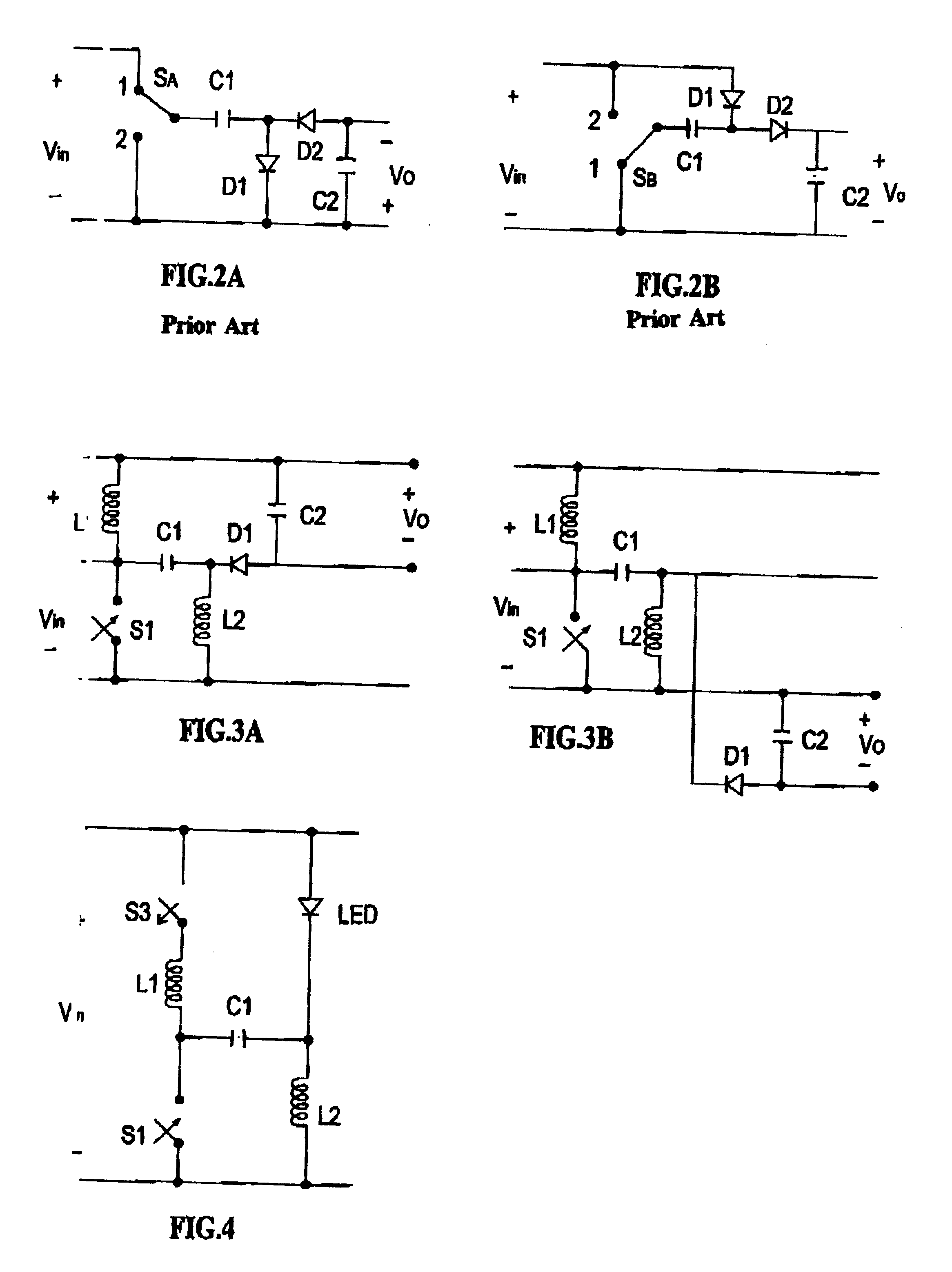
A voltage-adder circuit, which adds the charge stored on a capacitor during a switch off-time, to the voltage of the input battery / power-supply, to provide an output voltage greater than the input voltage. The circuit is especially well-suited for use as an LED driver, and may be also used as a voltage booster for low-voltage electronic circuitry, such as electronic watches; as a back-bias generator for use inside integrated circuits; and, as a gate-bias-voltage generator, for use with depletion-mode GaAsFETs, such as are used in the transmitters of cellular telephones. The circuit obtains high efficiency operation by the use of inductors to charge a storage capacitor. Switches may be added. The invention includes a novel self-operating switch.
Owner:LEDI LITE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com