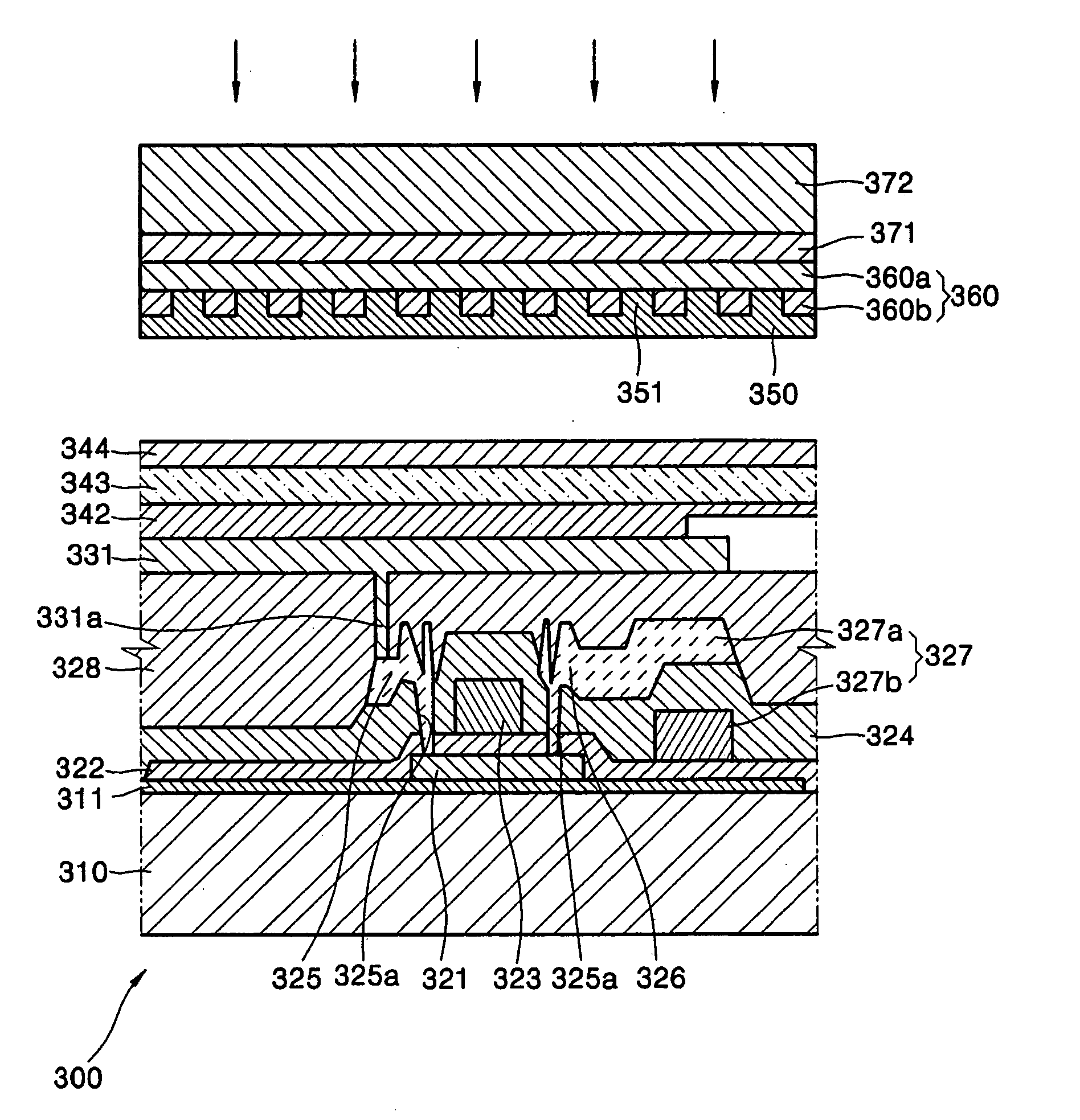
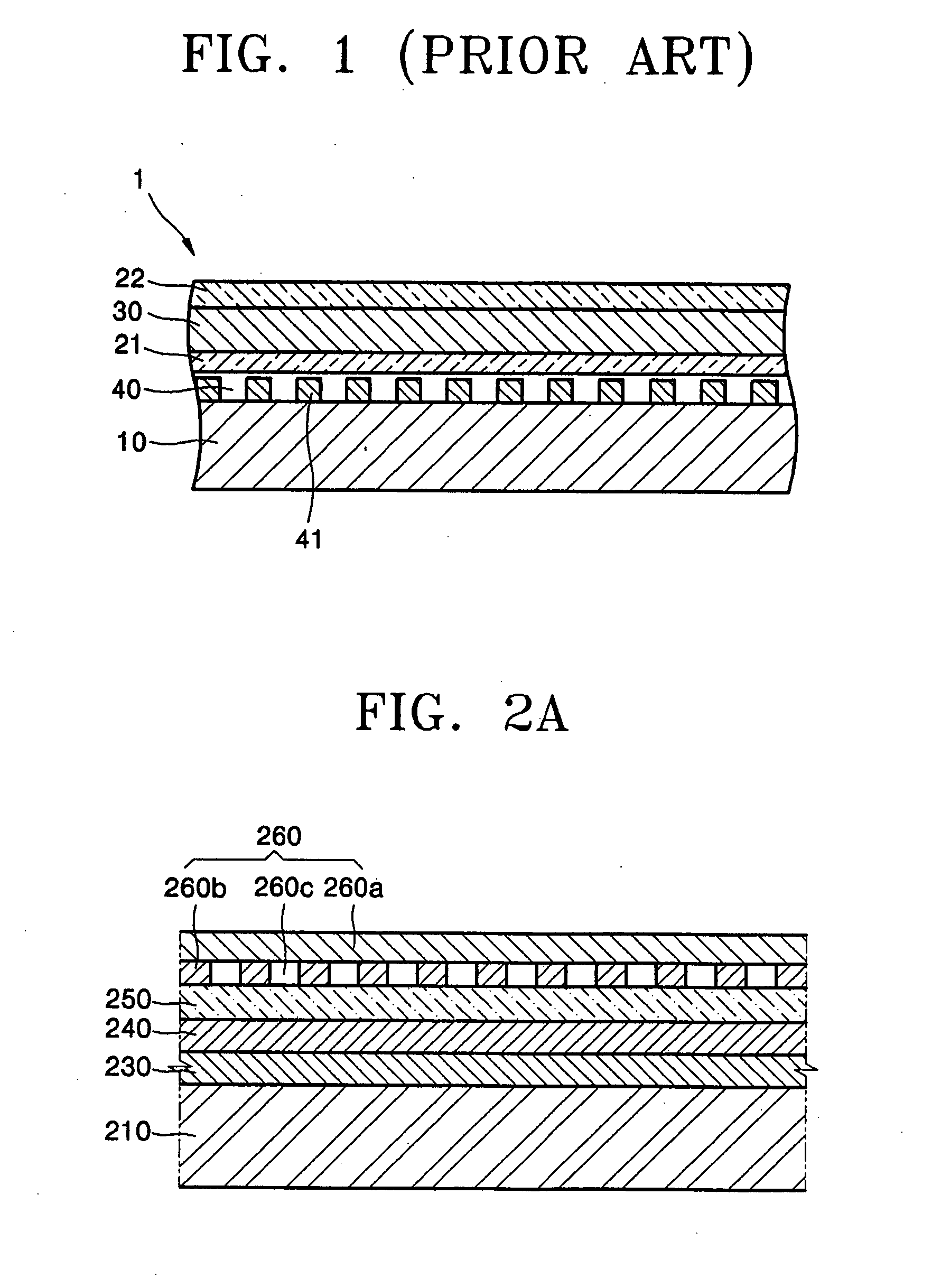
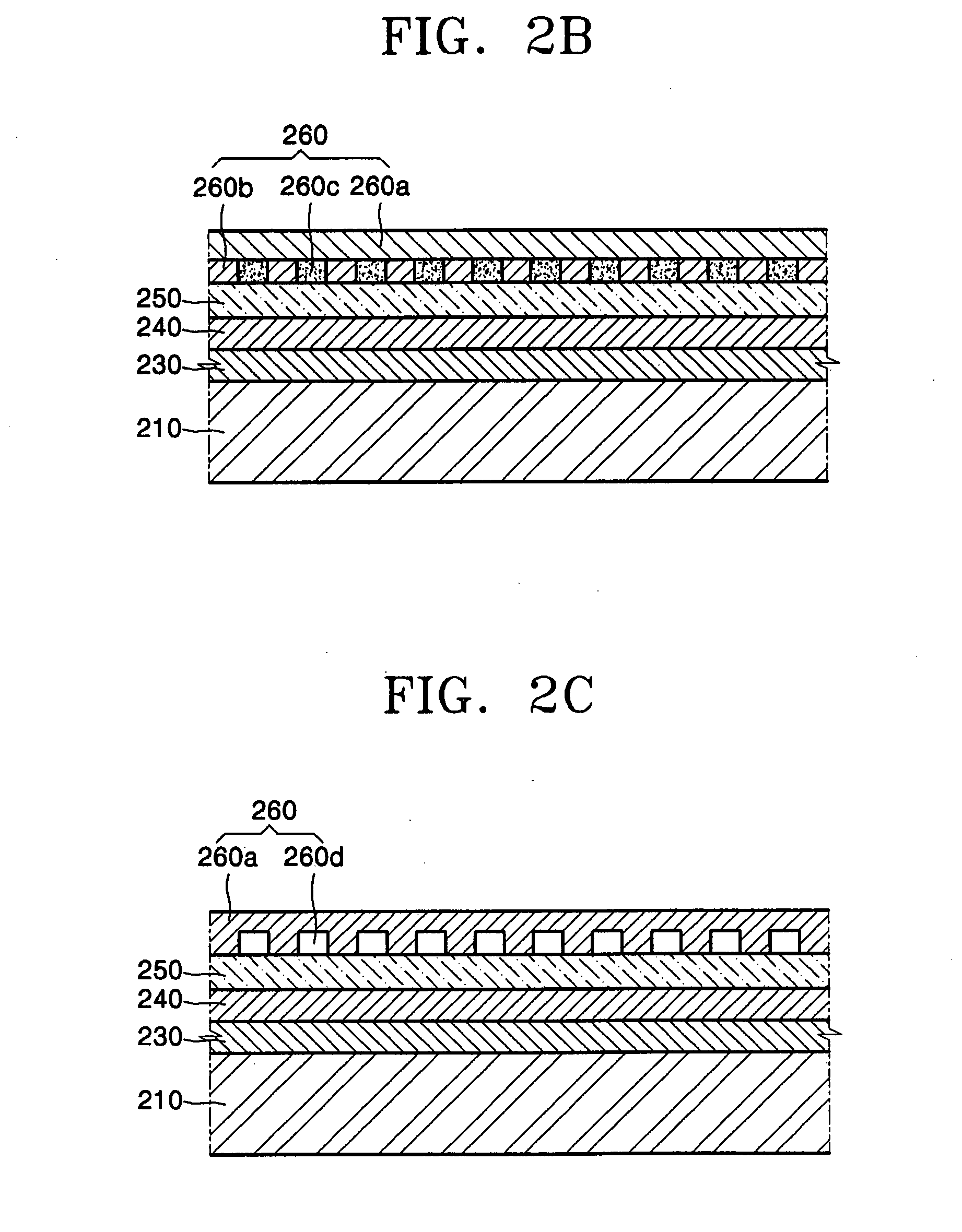
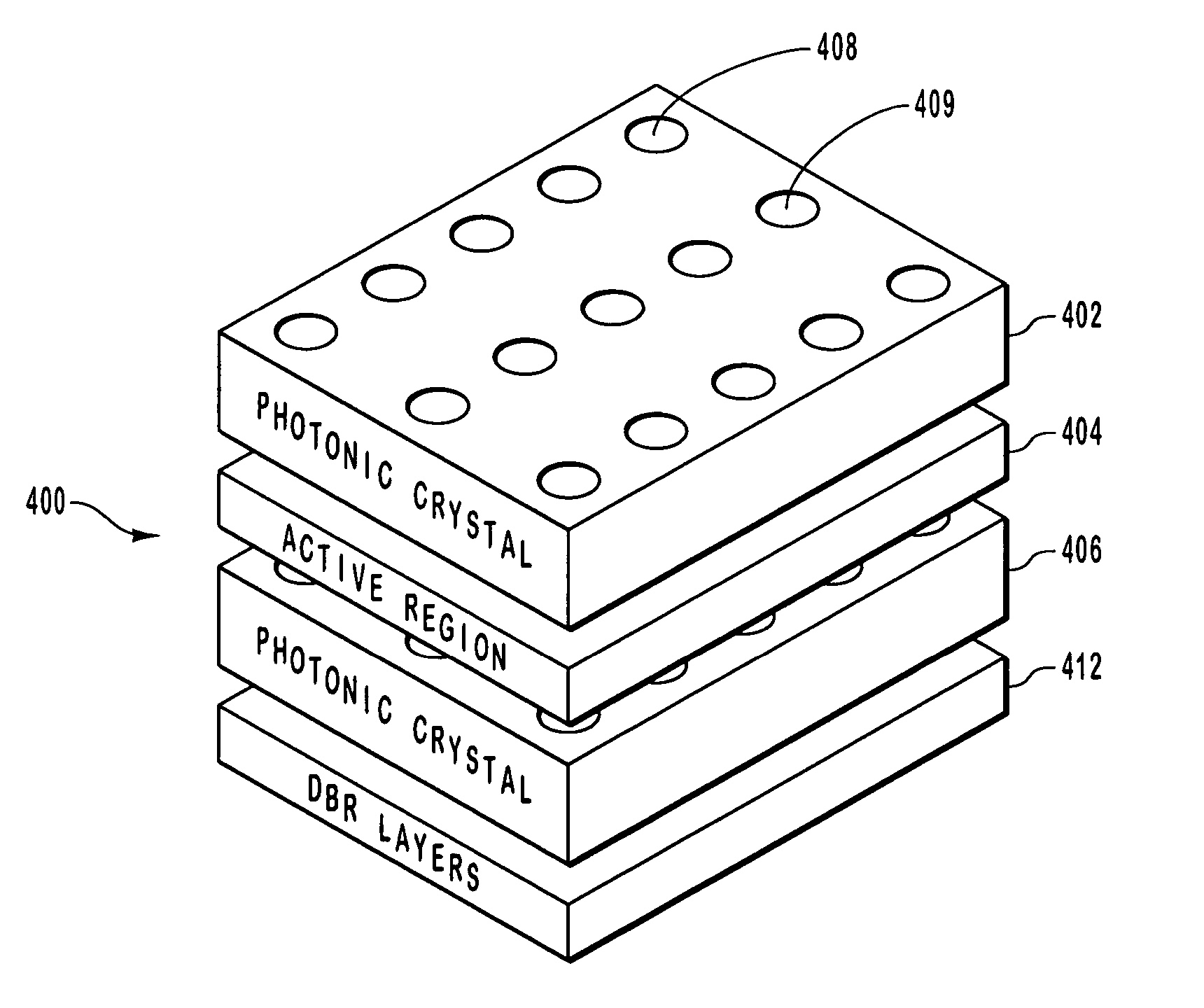
Patents
Literature
1636 results about "Photonic-crystal fiber" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
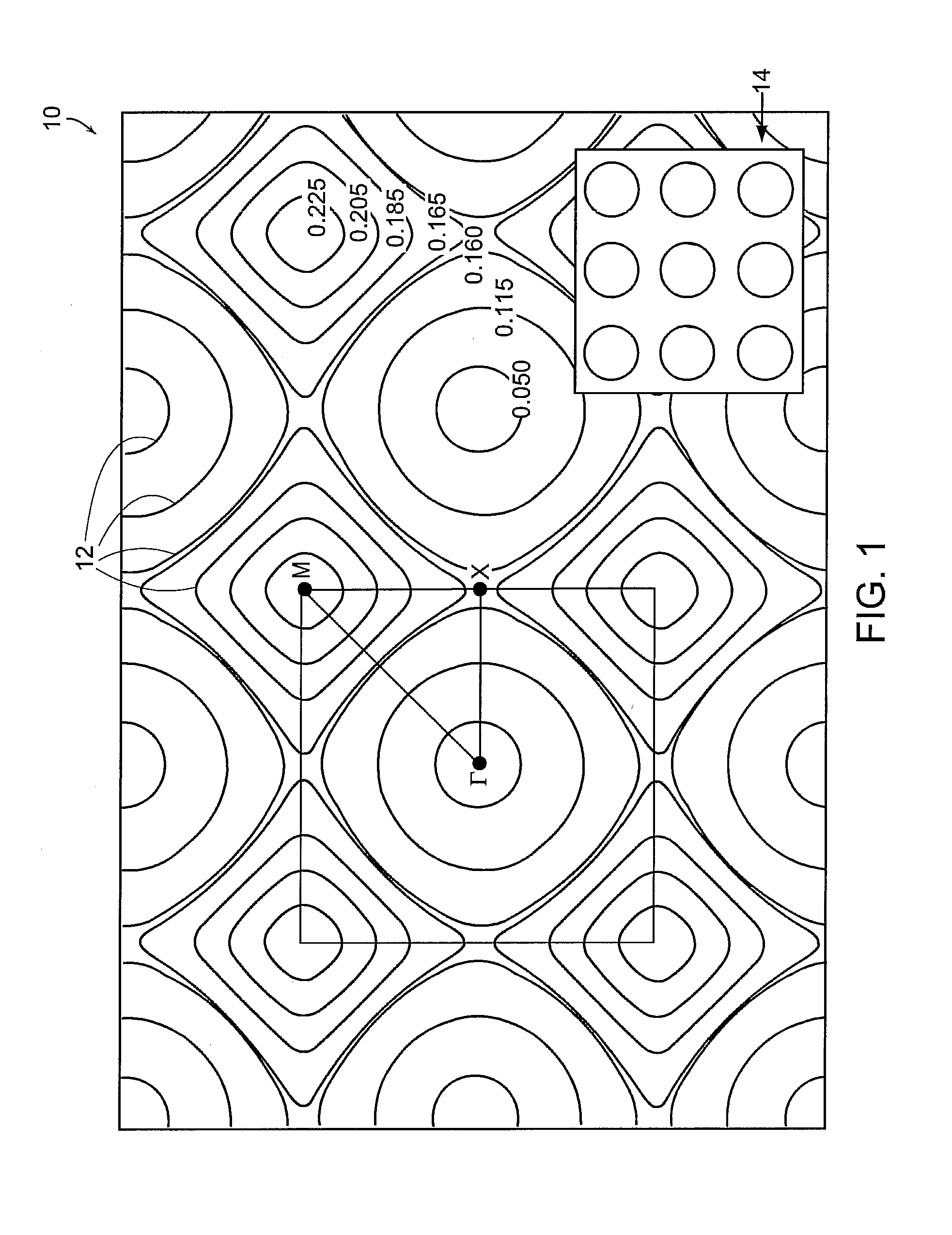
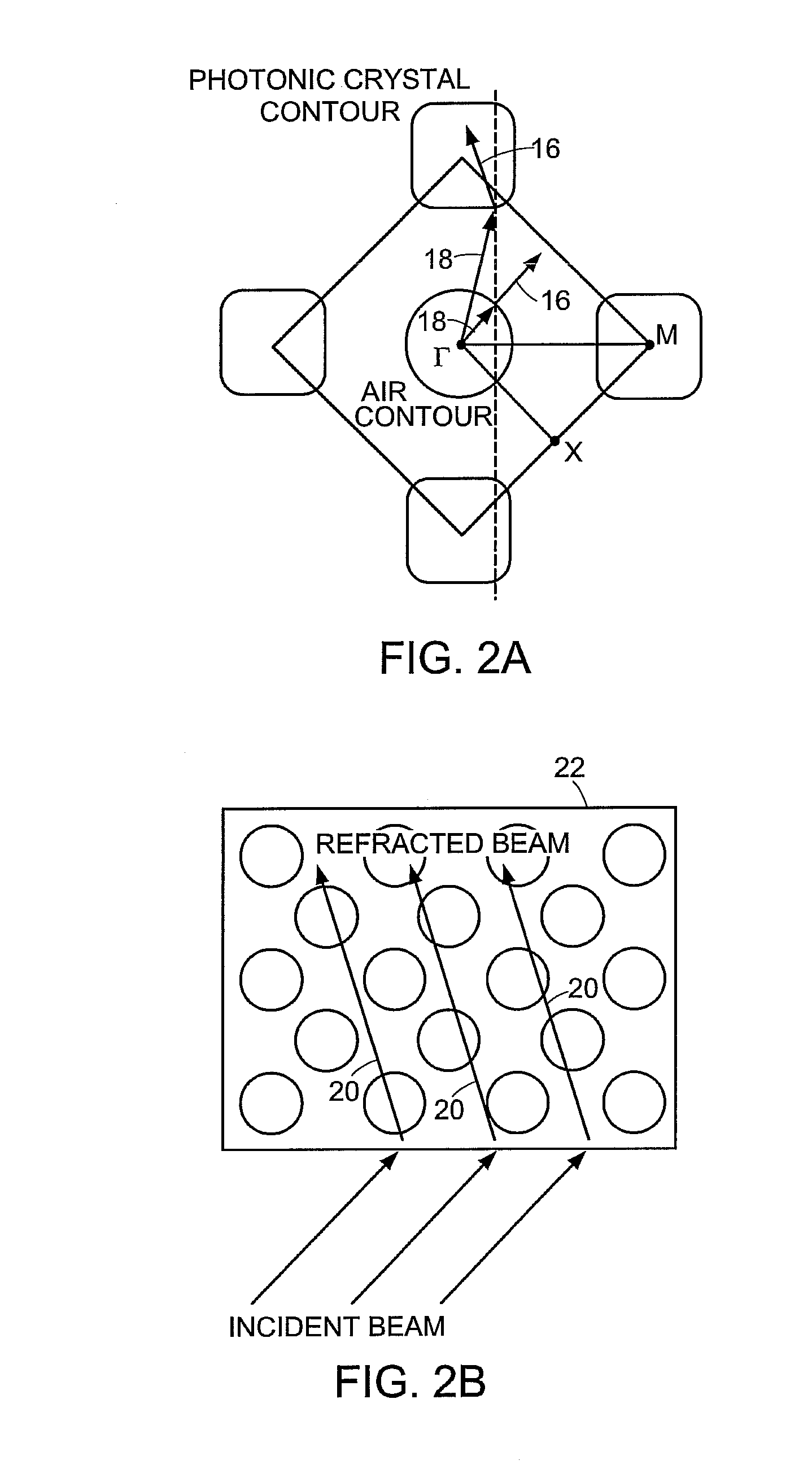
Photonic-crystal fiber (PCF) is a class of optical fiber based on the properties of photonic crystals. It was first explored in 1996 at University of Bath, UK. Because of its ability to confine light in hollow cores or with confinement characteristics not possible in conventional optical fiber, PCF is now finding applications in fiber-optic communications, fiber lasers, nonlinear devices, high-power transmission, highly sensitive gas sensors, and other areas. More specific categories of PCF include photonic-bandgap fiber (PCFs that confine light by band gap effects), holey fiber (PCFs using air holes in their cross-sections), hole-assisted fiber (PCFs guiding light by a conventional higher-index core modified by the presence of air holes), and Bragg fiber (photonic-bandgap fiber formed by concentric rings of multilayer film). Photonic crystal fibers may be considered a subgroup of a more general class of microstructured optical fibers, where light is guided by structural modifications, and not only by refractive index differences.
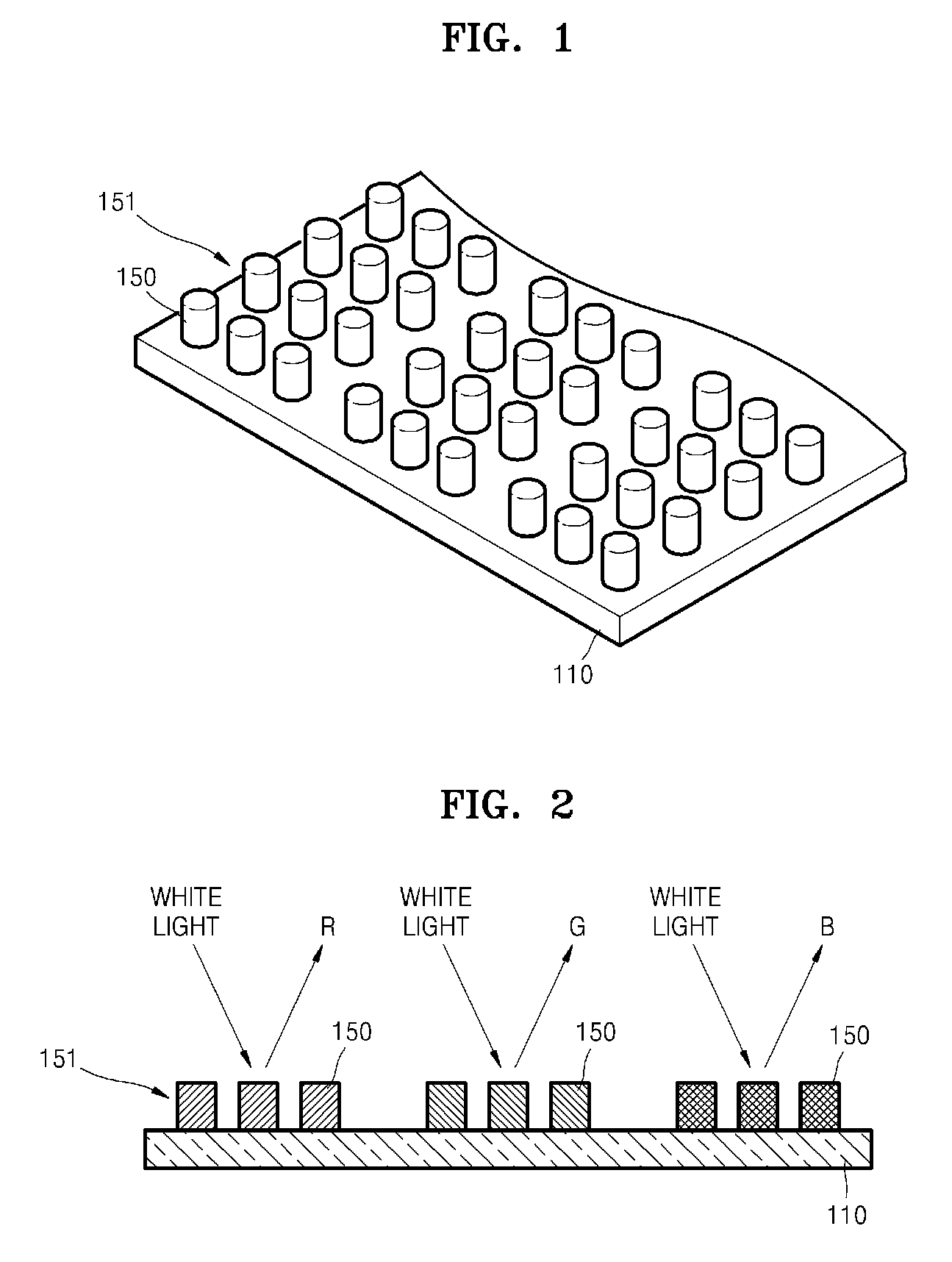
Light emitting device having a layer of photonic crystals and a region of diffusing material and method for fabricating the device
A light emitting device and method for fabricating the device utilizes a layer of photonic crystals and a region of diffusing material to enhance the light output of the device. The layer of photonic crystals is positioned over a light source, such as a light emitting diode die, and the region of diffusing material is positioned over the layer of photonic layer.
Owner:DOCUMENT SECURITY SYST
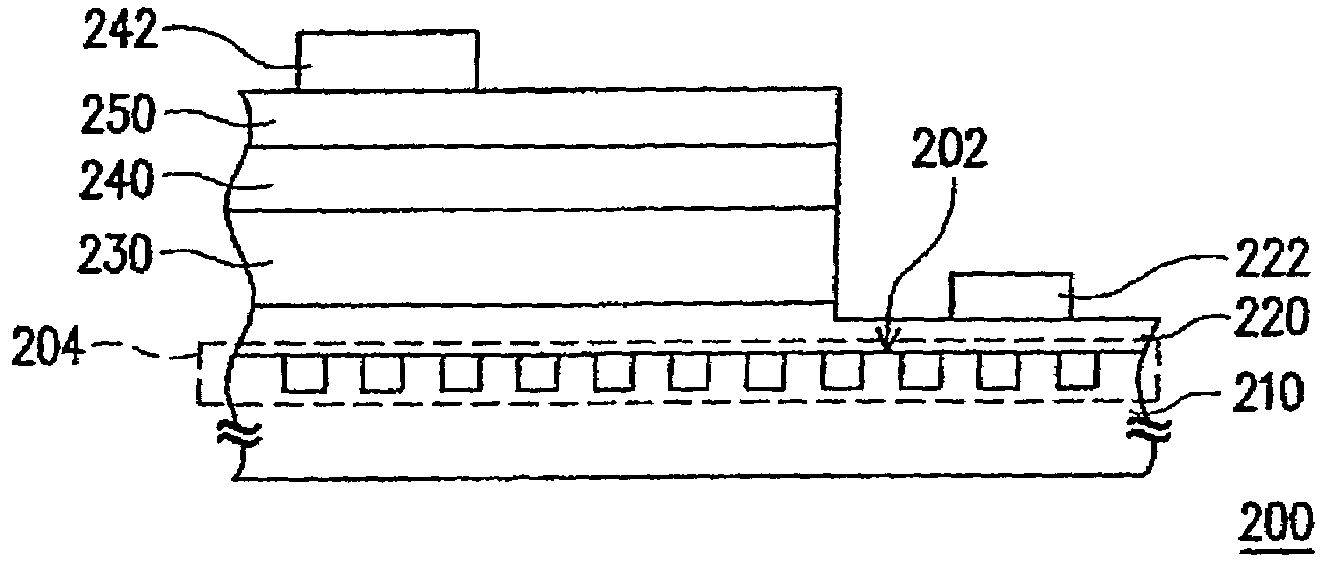
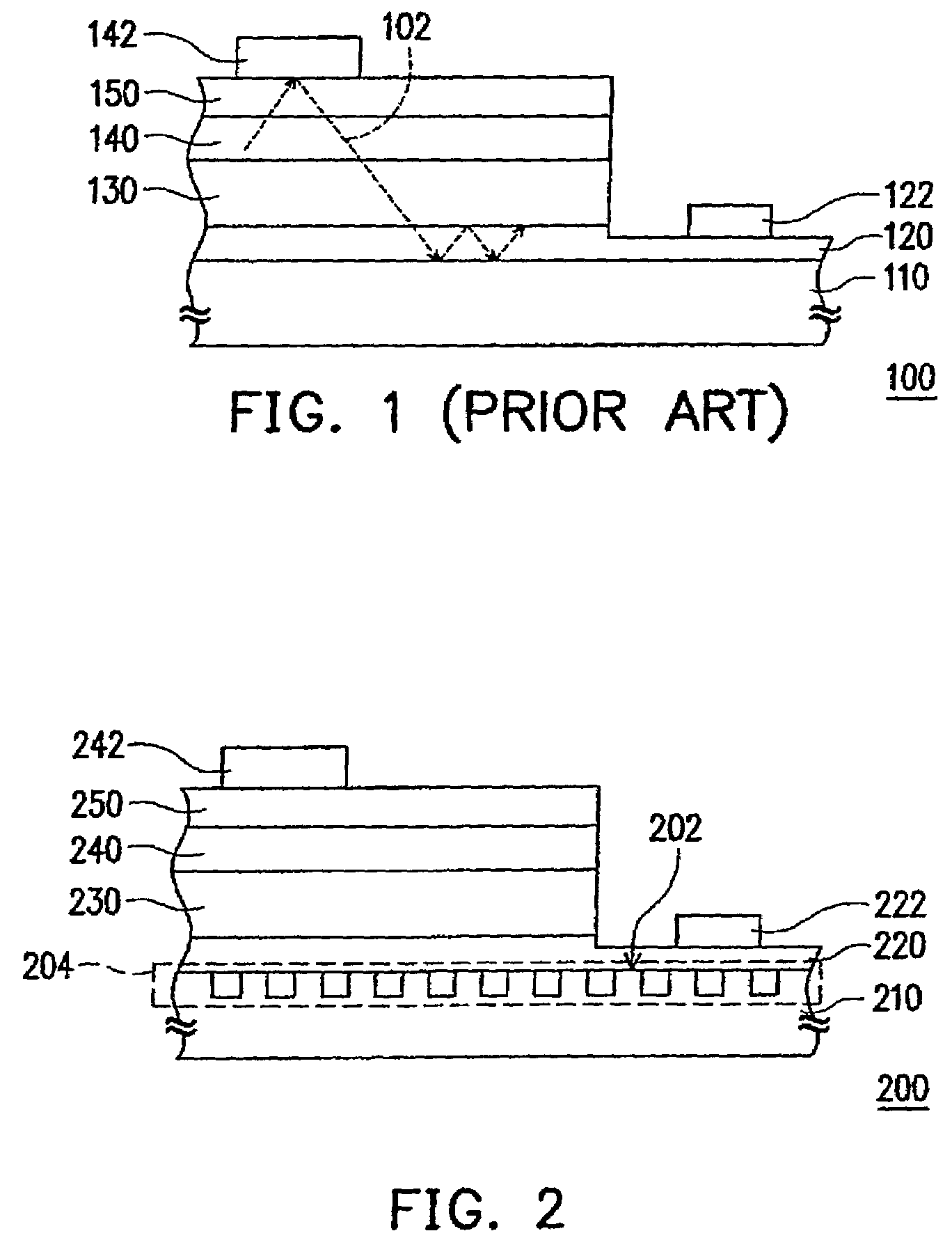
Single mode optical fiber
InactiveUS6334019B1High refractive indexGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRefractive indexFiber disk laser
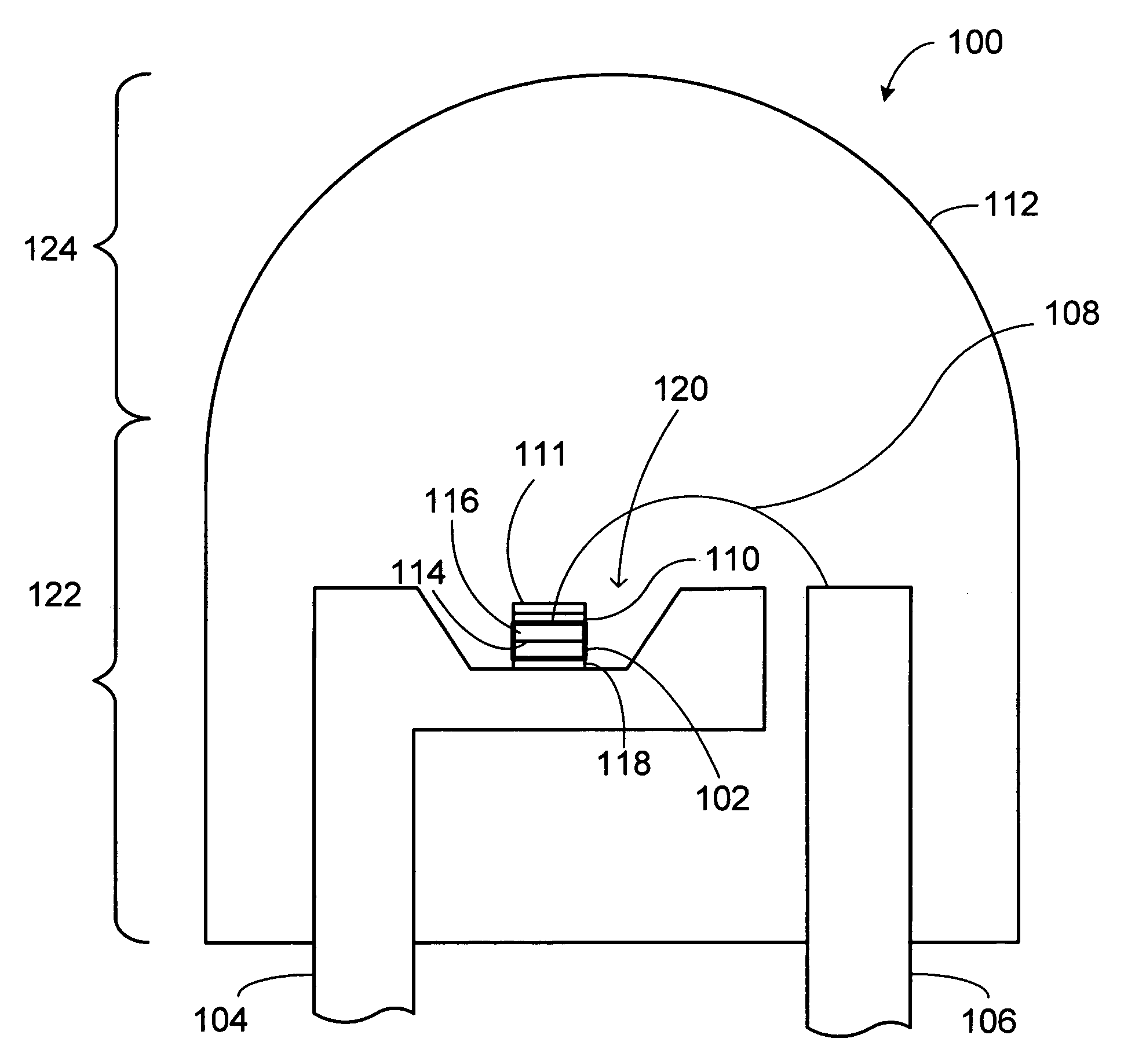
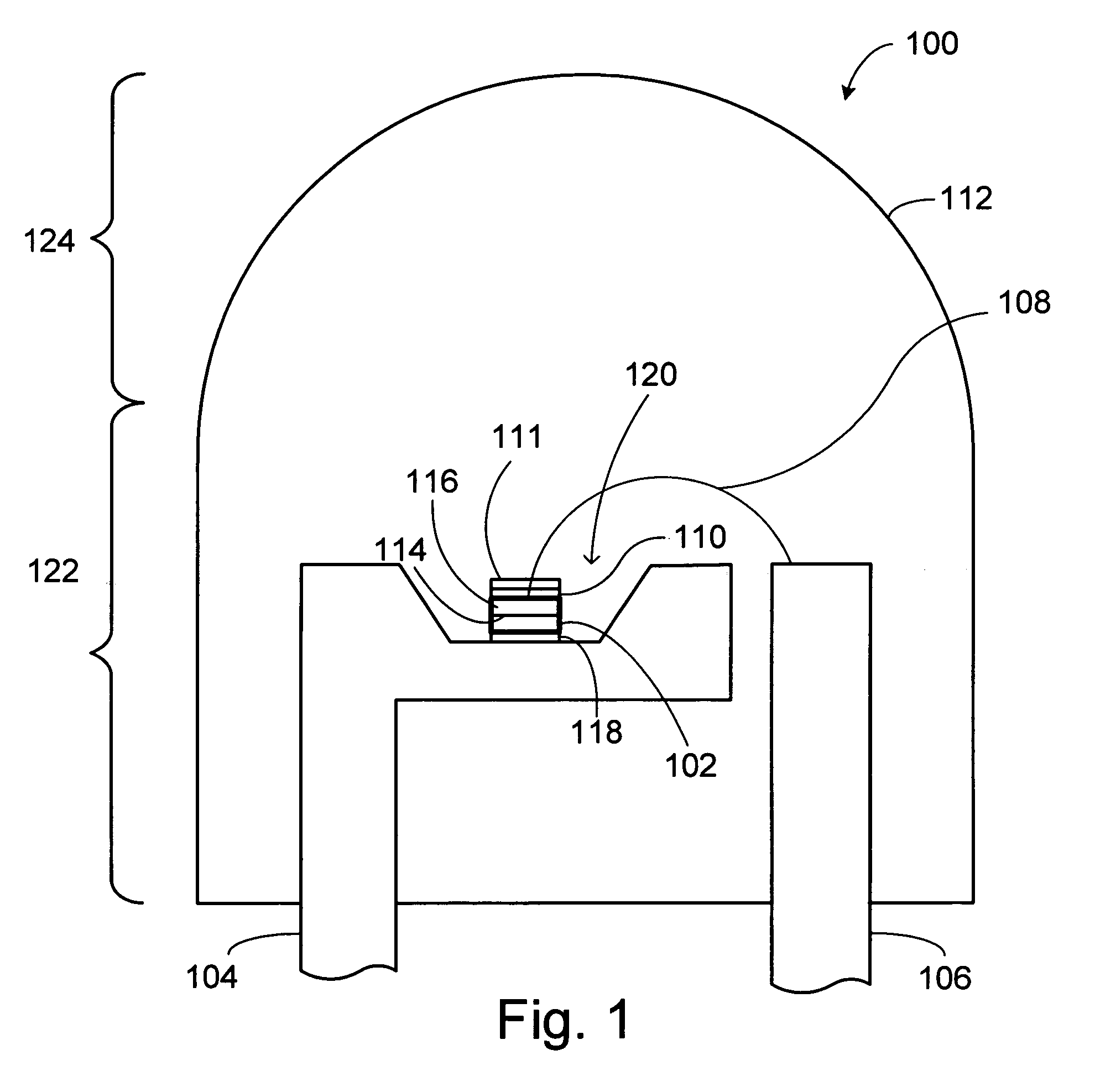
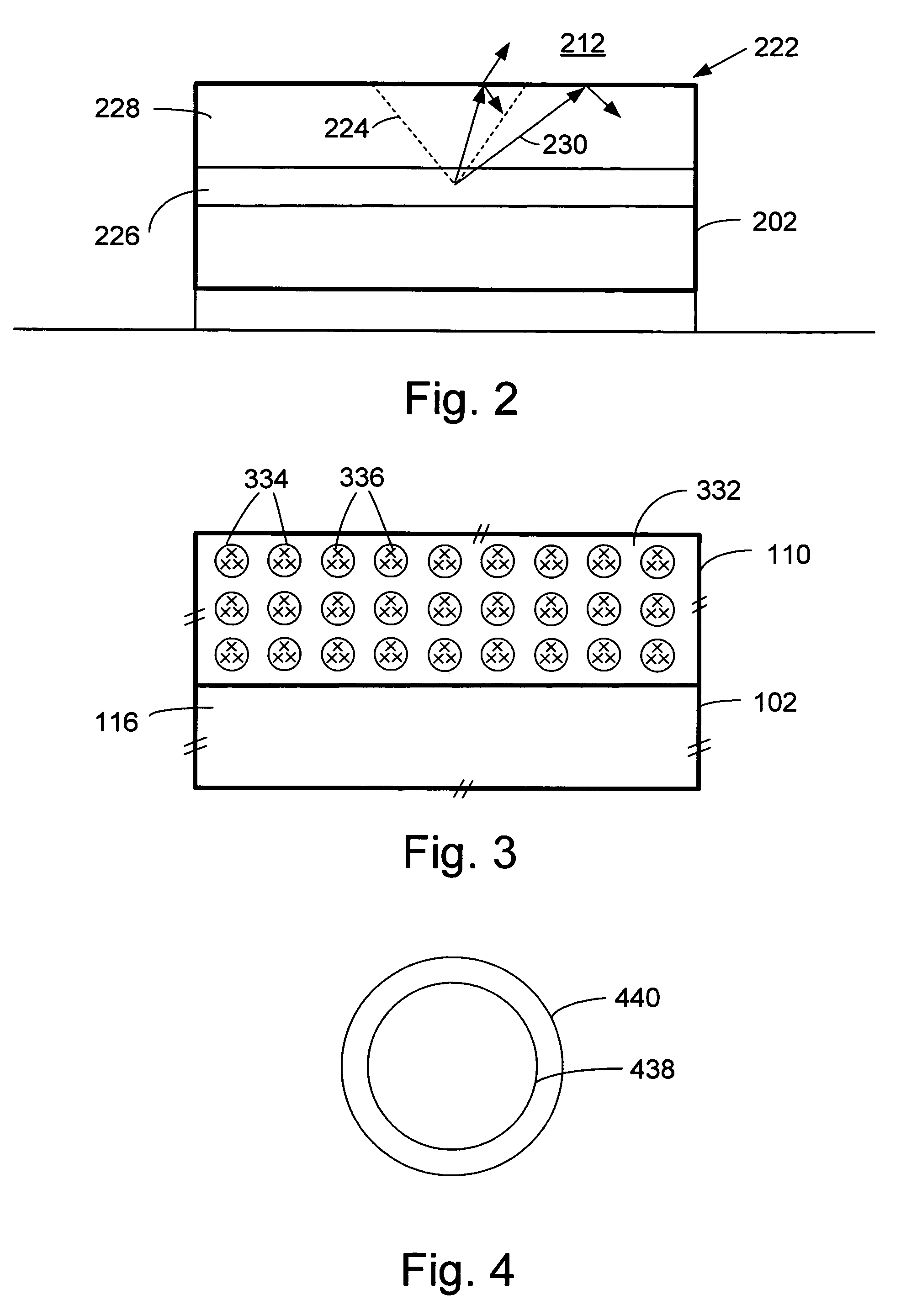
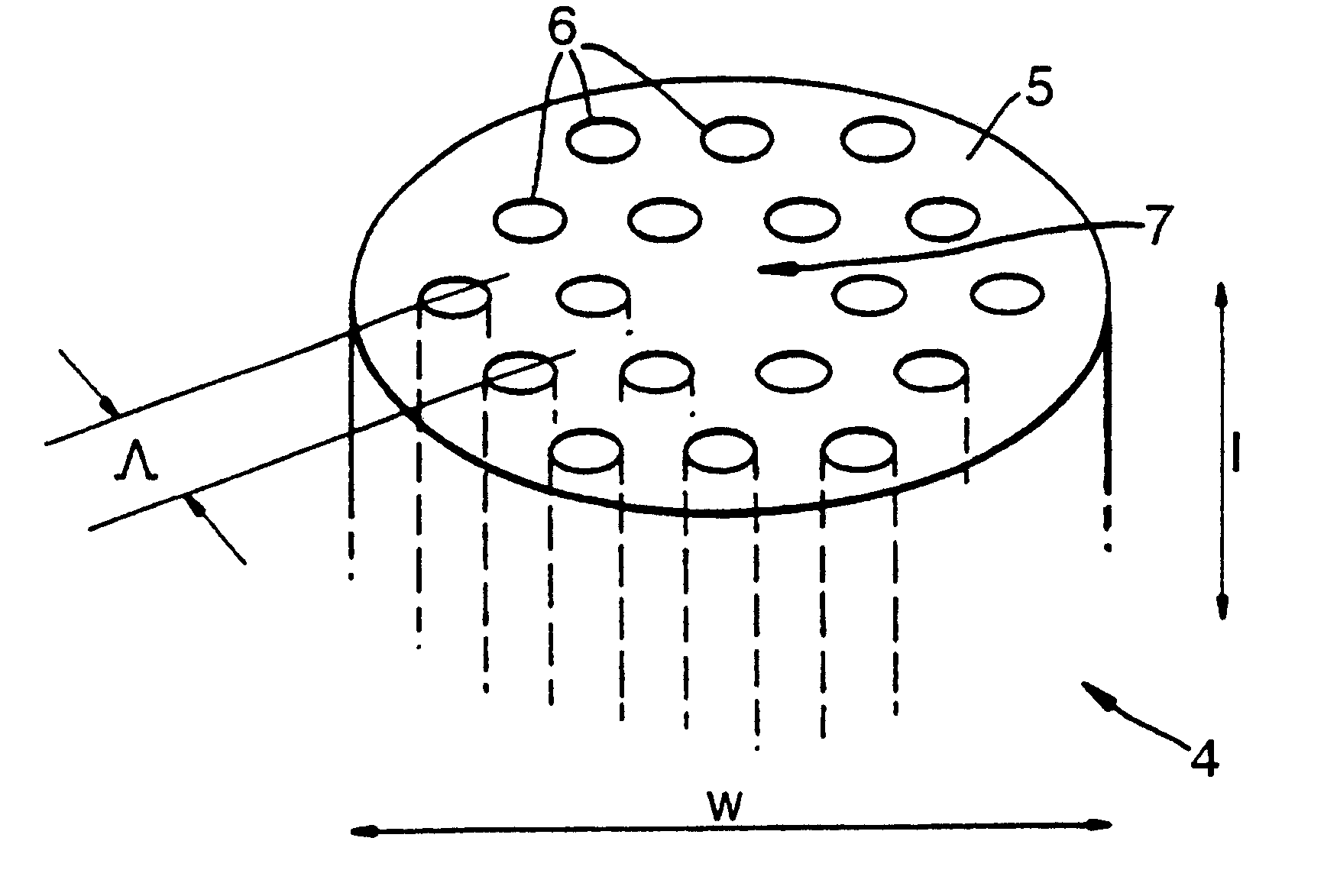
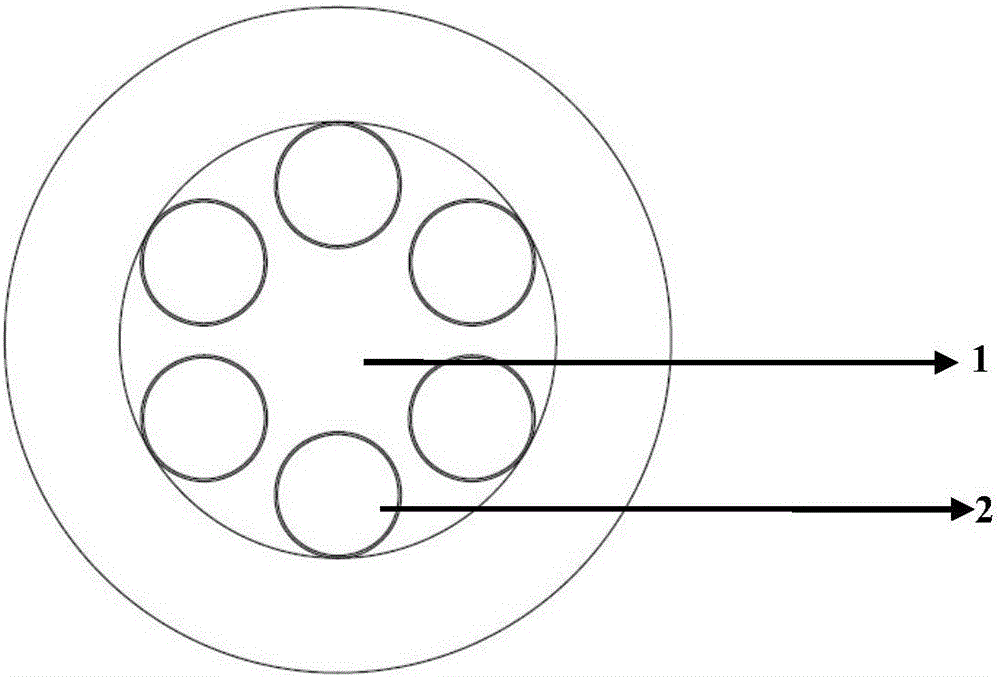
A large core photonic crystal fiber for transmitting radiation having a core comprising a substantially transparent core material and having a core diameter of at least 5 mu. The fiber also comprises a cladding region surrounding the length of core material, wherein the cladding region comprises a first substantially transparent cladding material, having a first refractive index, and wherein the first substantially transparent cladding material has embedded along its length a substantially periodic array of holes, wherein the holes are filled with a second cladding material having a second refractive index less than the first refractive index, such that radiation input to the optical fiber is transmitted along the length of the core material in a single mode of propagation. In a preferred embodiment, the core diameter may be at least 20 mu, and may be as large as 50 mu. The fiber is capable of transmitting higher power radiation than conventional fibres, whilst maintaining propagation in a single mode. The core material may be doped with a material capable of providing amplification under the action of pump radiation input to the fiber. The invention also relates to a fiber amplifier and a fiber laser comprising a doped large core photonic crystal fiber. The fiber may also be used in a system for transmitting radiation comprising a plurality of lengths of large core photonic crystal fiber, separated by large core photonic crystal fiber amplifiers, such that the power of radiation transmitted through the system is maintained above a predetermined threshold power.
Owner:NKT RES & INNOVATION
Photonic crystal light emitting device
ActiveUS7012279B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCrystal structurePhotonic crystal structure
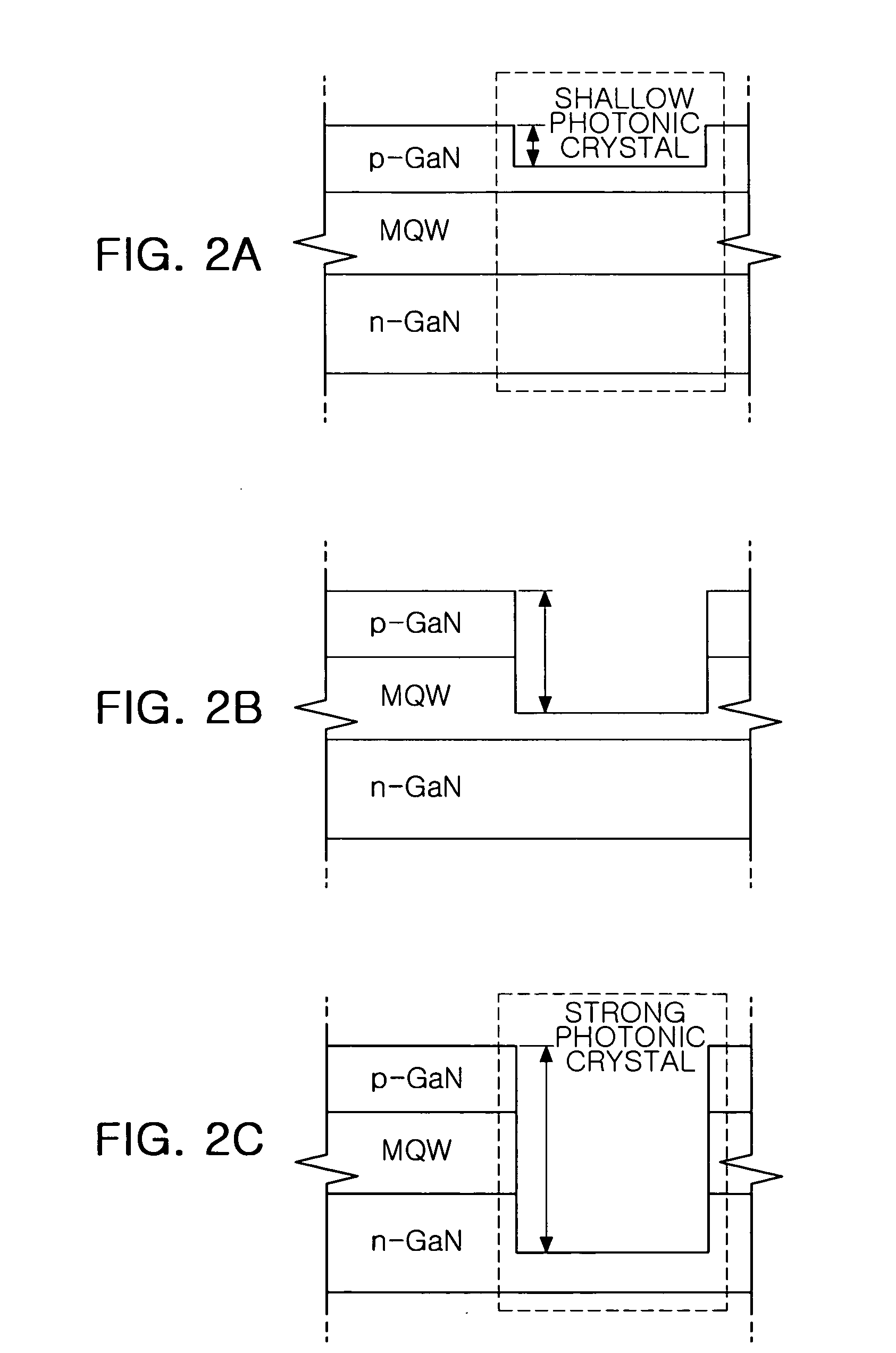
A photonic crystal structure is formed in an n-type layer of a III-nitride light emitting device. In some embodiments, the photonic crystal n-type layer is formed on a tunnel junction. The device includes a first layer of first conductivity type, a first layer of second conductivity type, and an active region separating the first layer of first conductivity type from the first layer of second conductivity type. The tunnel junction includes a second layer of first conductivity type and a second layer of second conductivity type and separates the first layer of first conductivity type from a third layer of first conductivity type. A photonic crystal structure is formed in the third layer of first conductivity type.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD +1
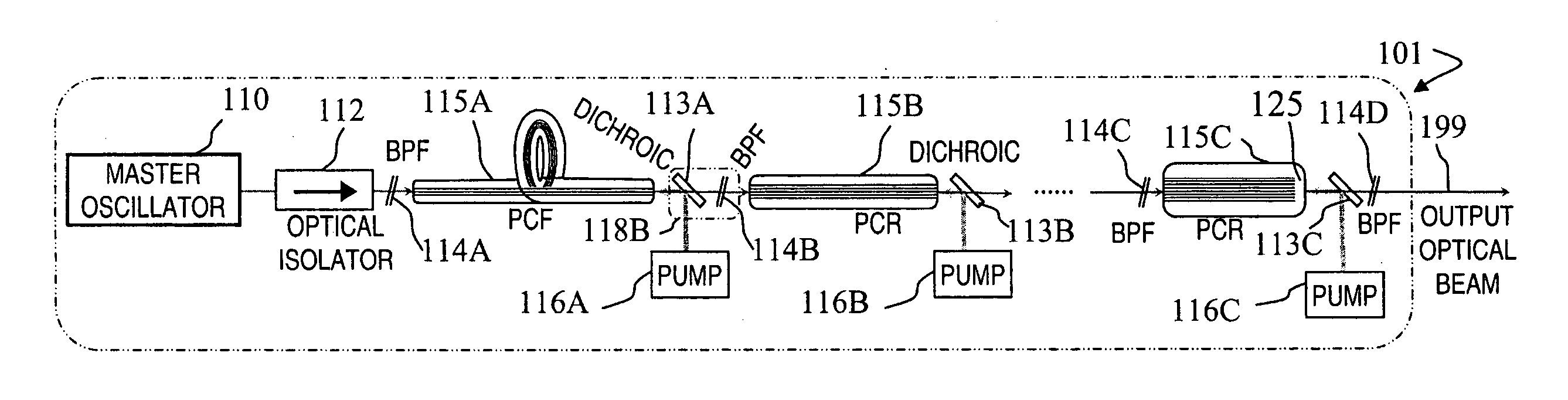
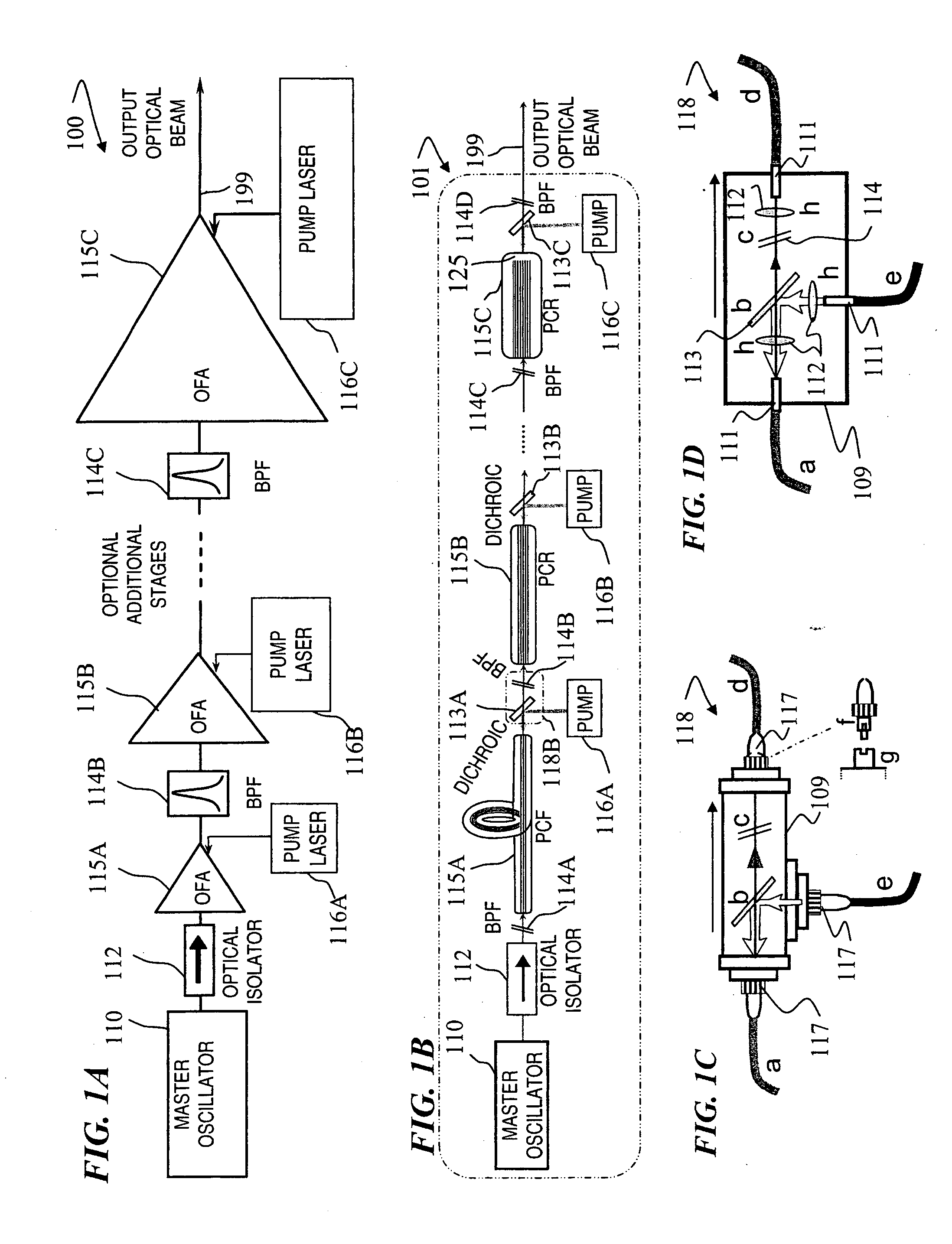
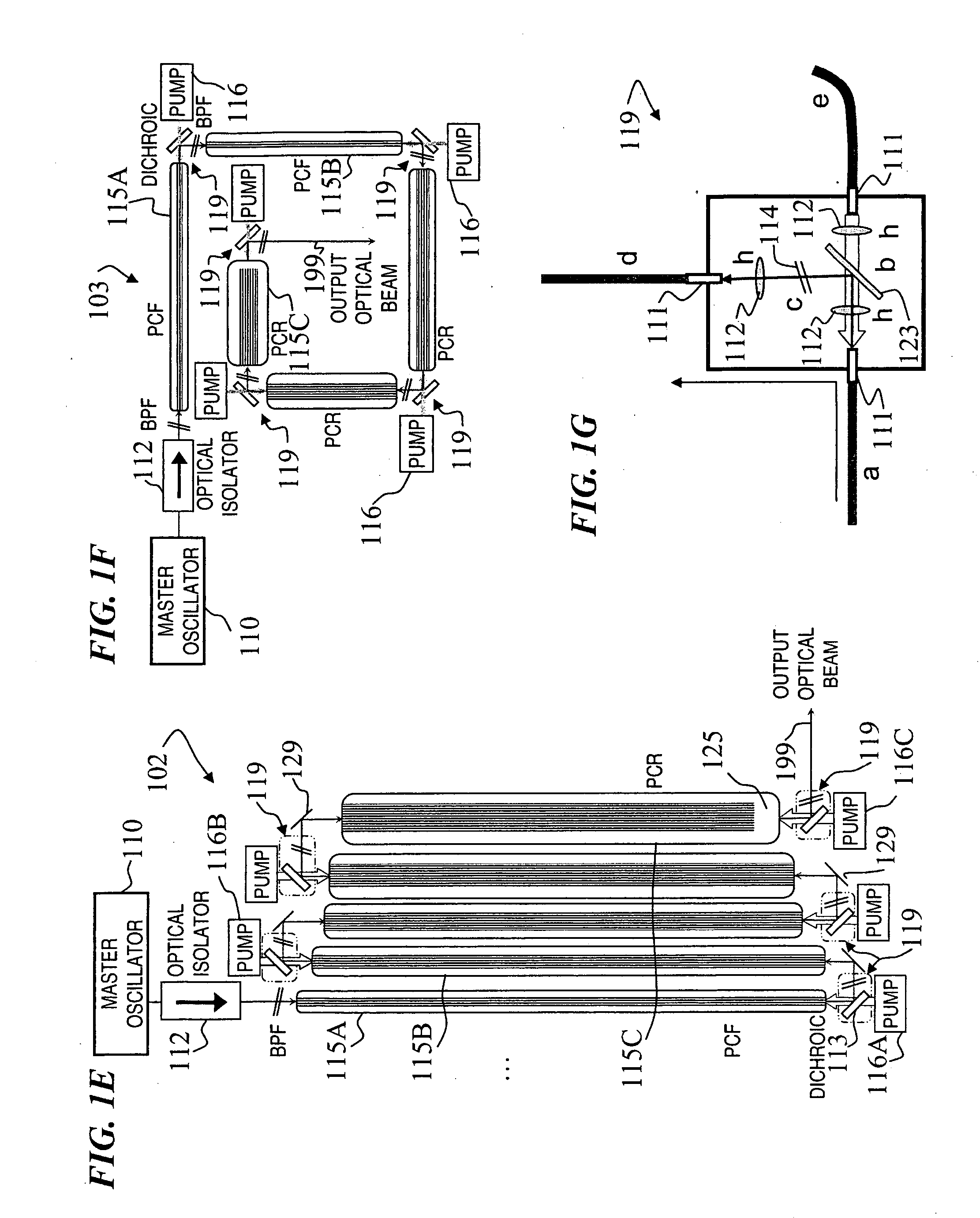
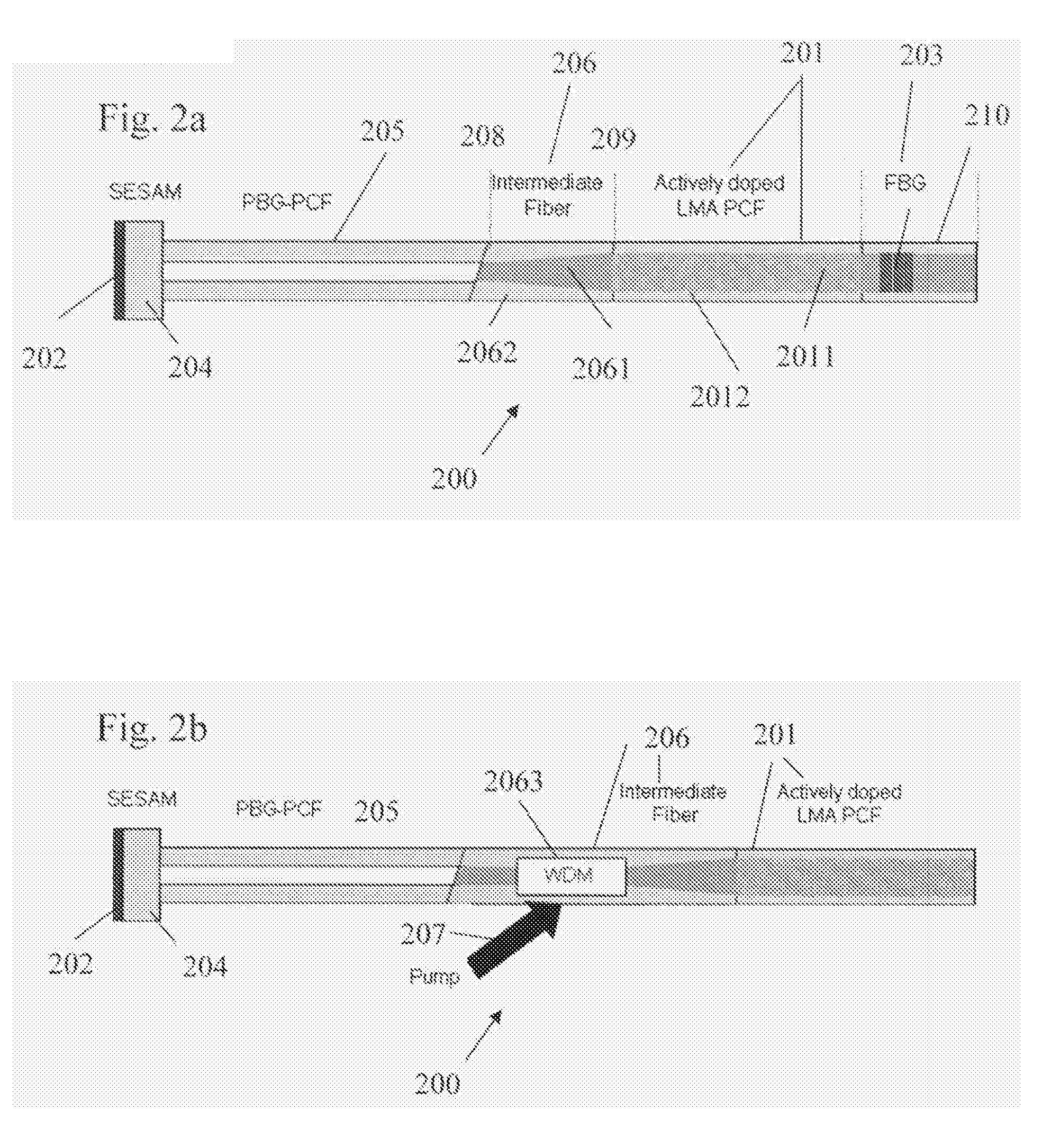
Fiber- or rod-based optical source featuring a large-core, rare-earth-doped photonic-crystal device for generation of high-power pulsed radiation and method
ActiveUS20070041083A1High peak powerHigh pulse energyGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRare earthEngineering
A method and apparatus use a photonic-crystal fiber having a very large core while maintaining a single transverse mode. In some fiber lasers and amplifiers having large cores problems exist related to energy being generated at multiple-modes (i.e., polygamy), and of mode hopping (i.e., promiscuity) due to limited control of energy levels and fluctuations. The problems of multiple-modes and mode hopping result from the use of large-diameter waveguides, and are addressed by the invention. This is especially true in lasers using large amounts of energy (i.e., lasers in the one-megawatt or more range). By using multiple small waveguides in parallel, large amounts of energy can be passed through a laser, but with better control such that the aforementioned problems can be reduced. An additional advantage is that the polarization of the light can be maintained better than by using a single fiber core.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
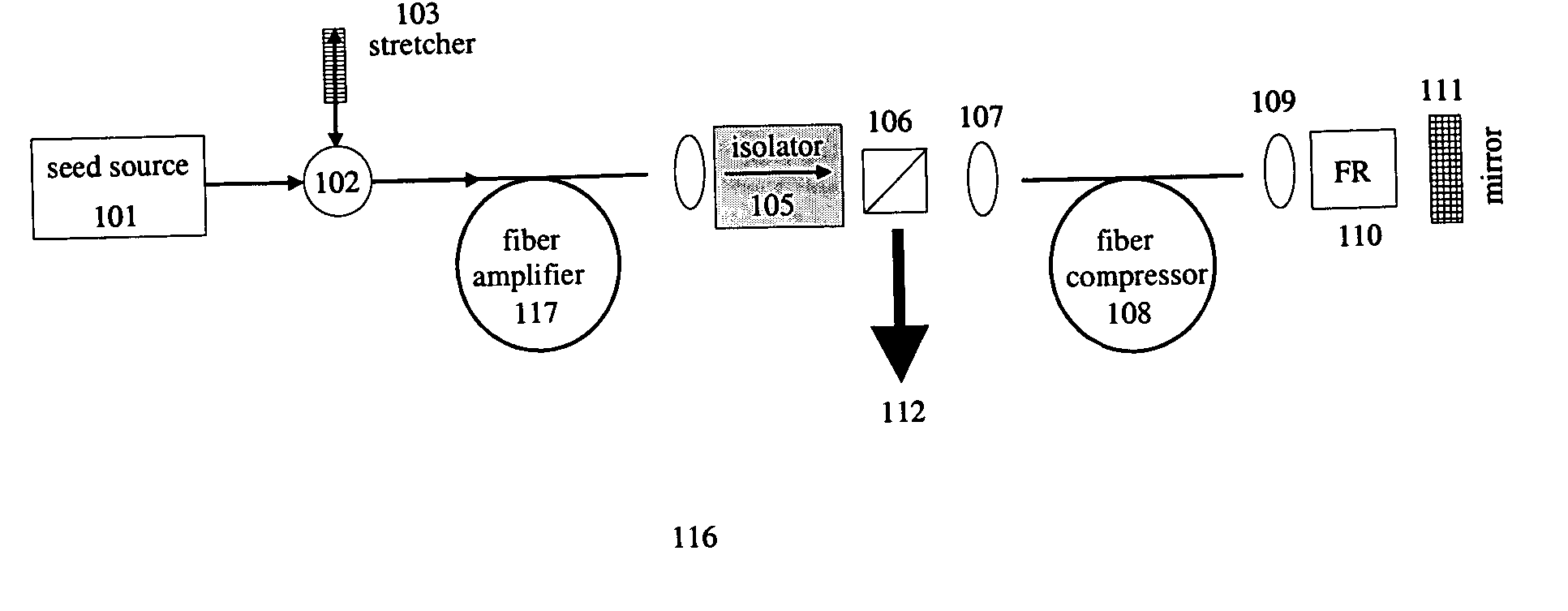
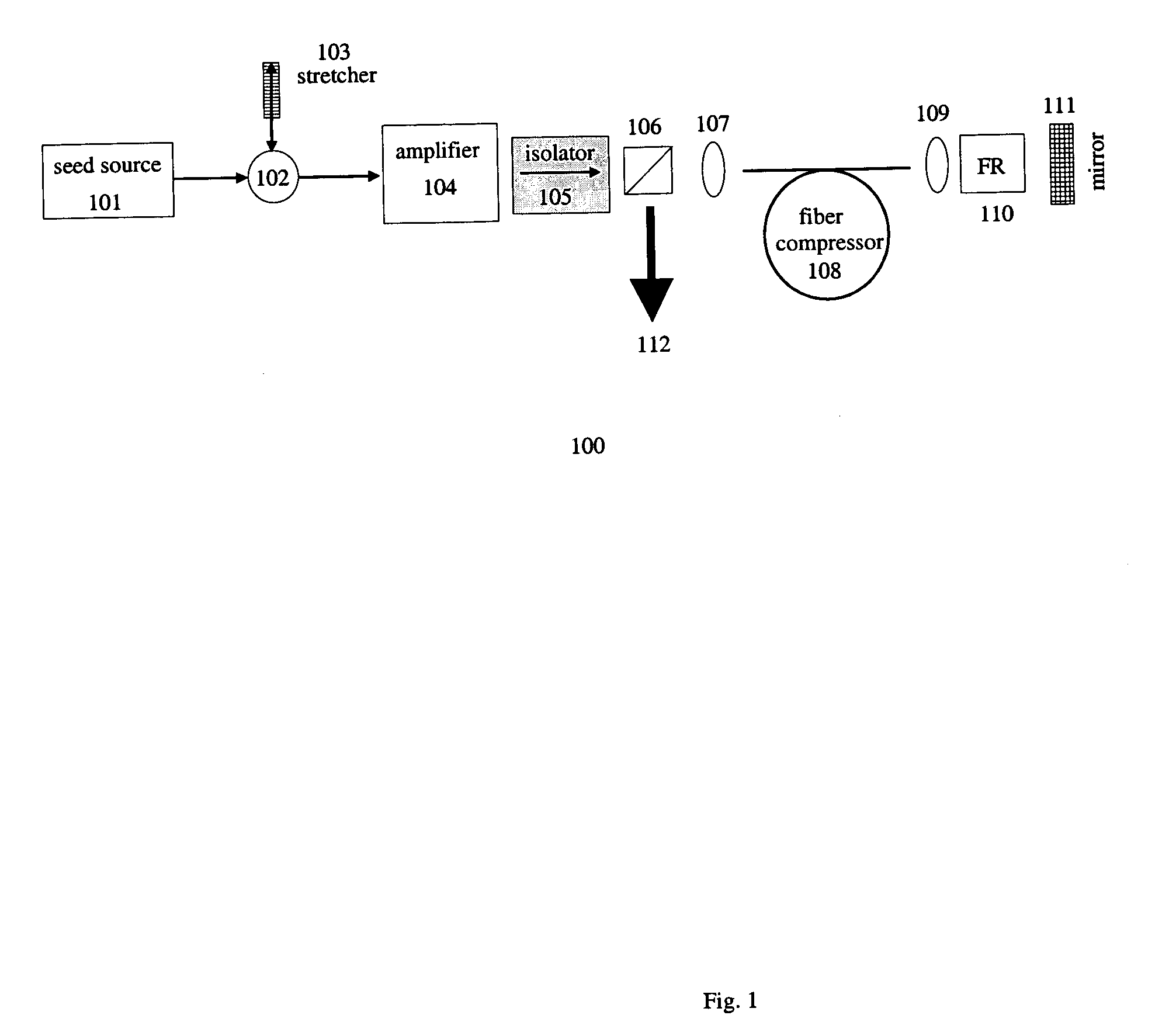
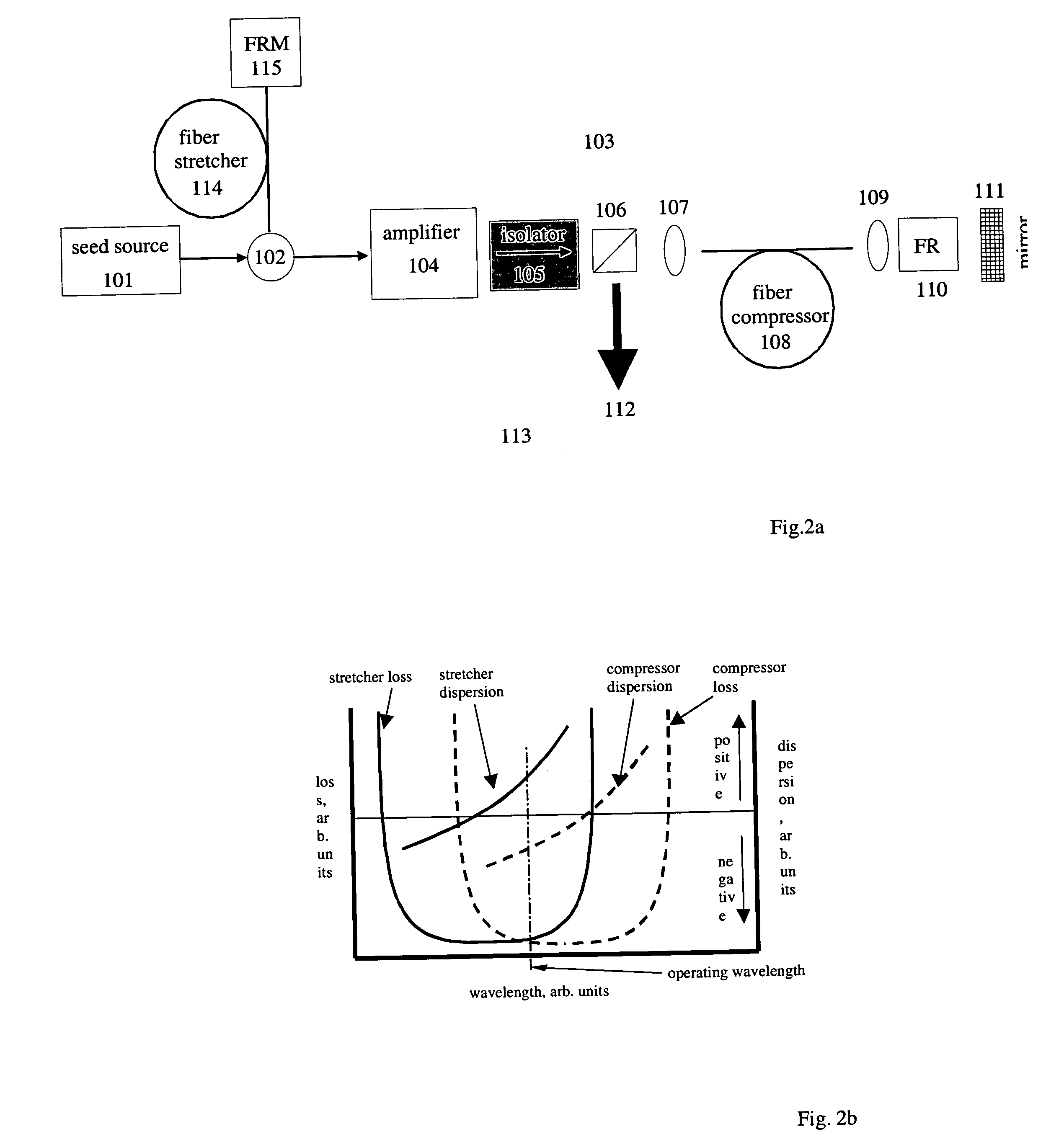
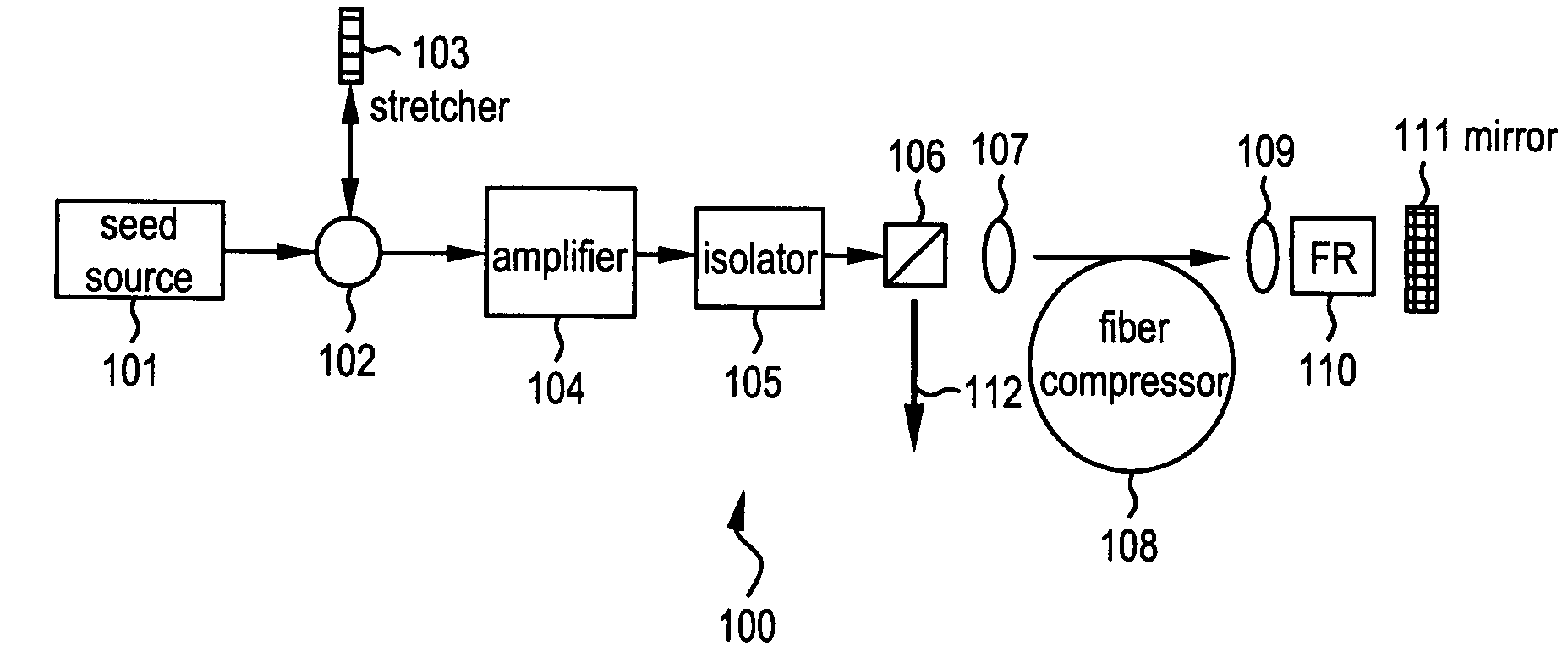
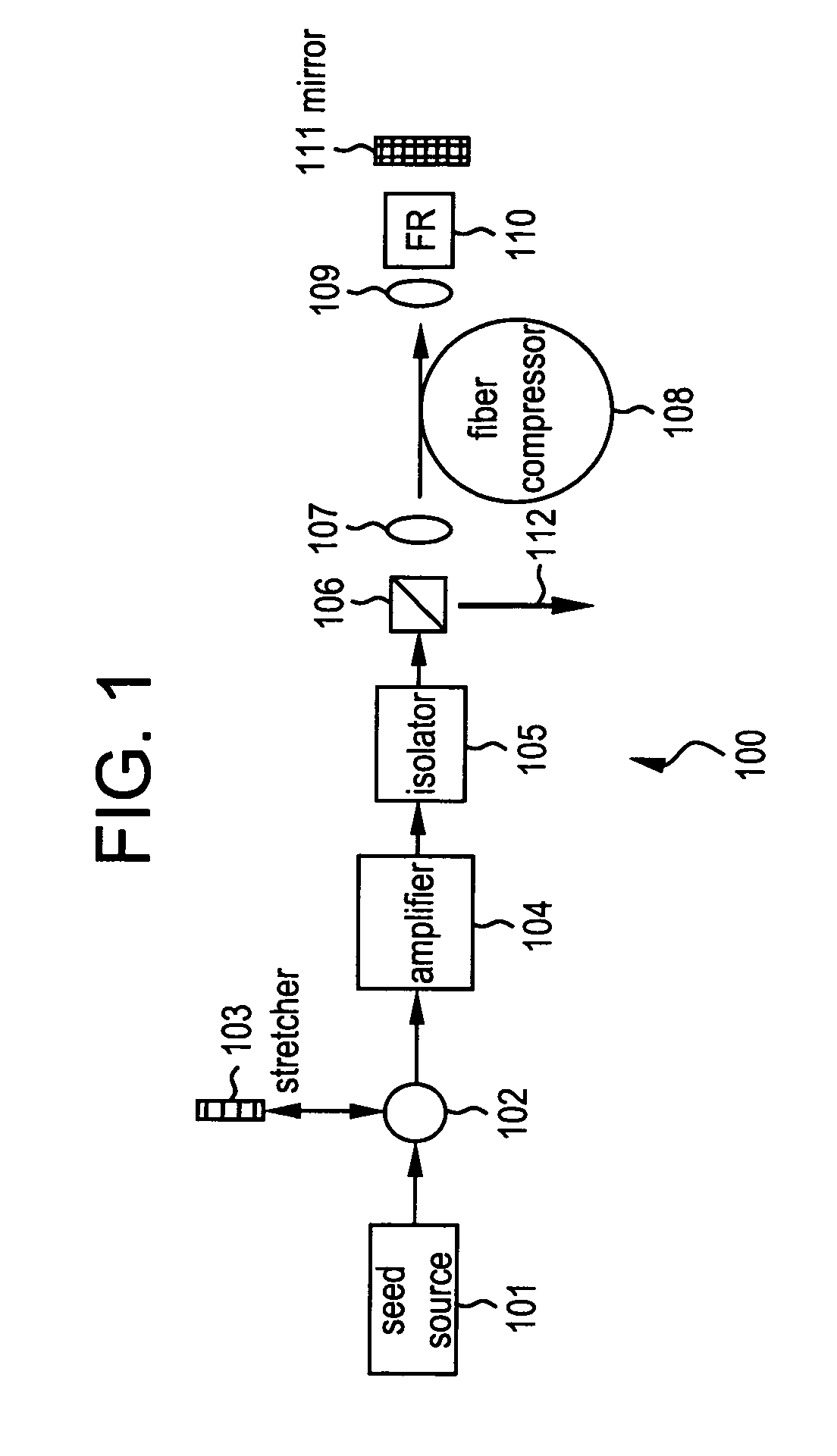
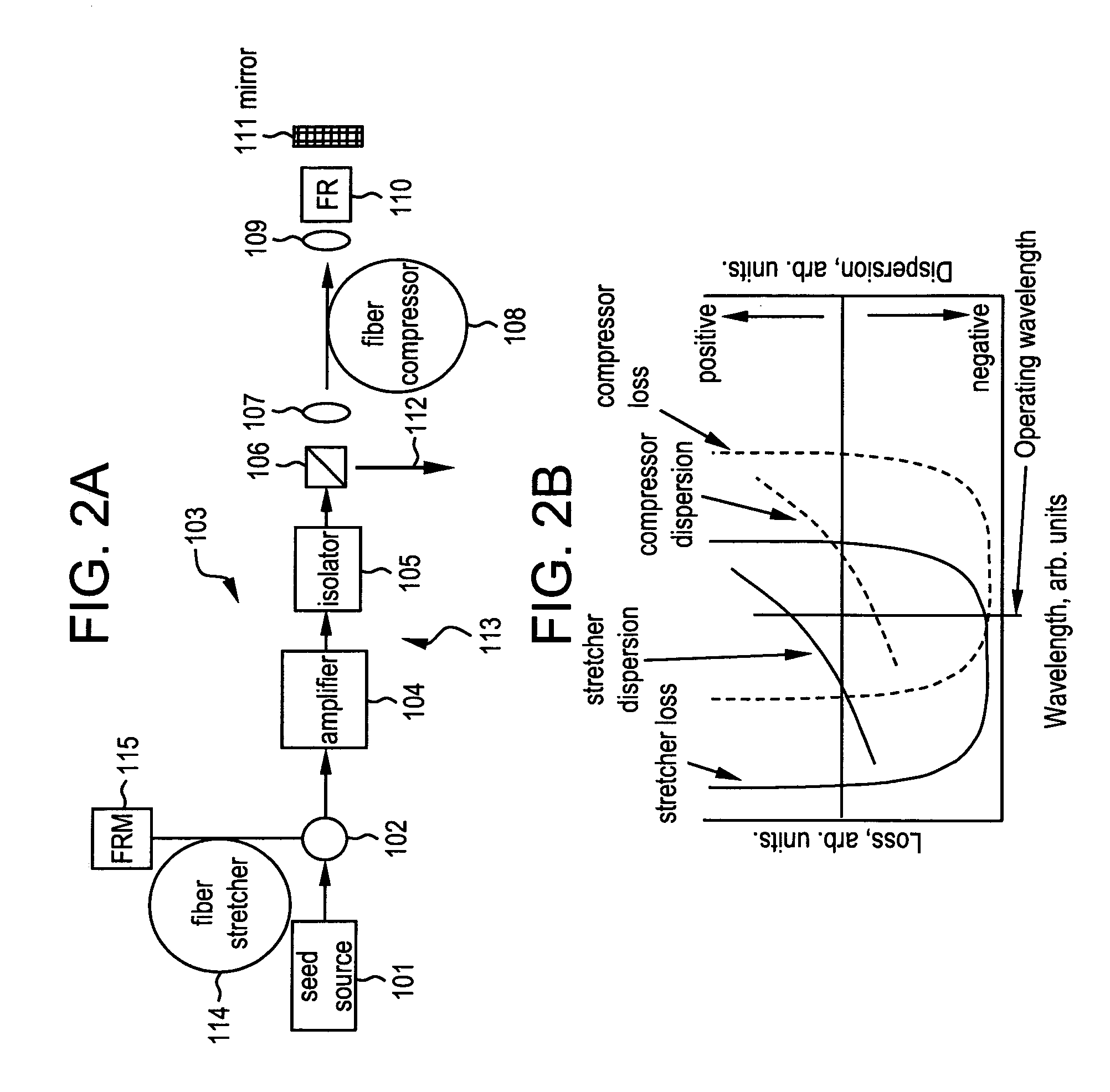
All-fiber chirped pulse amplification systems
InactiveUS20050105865A1Improve overall utilizationImprove performanceFibre transmissionCoupling light guidesLow noiseGrating
By compensating polarization mode-dispersion as well chromatic dispersion in photonic crystal fiber pulse compressors, high pulse energies can be obtained from all-fiber chirped pulse amplification systems. By inducing third-order dispersion in fiber amplifiers via self-phase modulation, the third-order chromatic dispersion from bulk grating pulse compressors can be compensated and the pulse quality of hybrid fiber / bulk chirped pulse amplification systems can be improved. Finally, by amplifying positively chirped pulses in negative dispersion fiber amplifiers, low noise wavelength tunable seed source via anti-Stokes frequency shifting can be obtained.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
All-fiber chirped pulse amplification systems
InactiveUS7414780B2Improve overall utilizationImprove performanceCoupling light guidesFibre transmissionLow noiseGrating
By compensating polarization mode-dispersion as well chromatic dispersion in photonic crystal fiber pulse compressors, high pulse energies can be obtained from all-fiber chirped pulse amplification systems. By inducing third-order dispersion in fiber amplifiers via self-phase modulation, the third-order chromatic dispersion from bulk grating pulse compressors can be compensated and the pulse quality of hybrid fiber / bulk chirped pulse amplification systems can be improved. Finally, by amplifying positively chirped pulses in negative dispersion fiber amplifiers, low noise wavelength tunable seed source via anti-Stokes frequency shifting can be obtained.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Splicing and connectorization of photonic crystal fibres
InactiveUS20060067632A1Reduce lossReduce couplingCladded optical fibreCoupling light guidesPhotonic crystalCoupling
A method of coupling a spliceable optical fibre for transmission of light in its longitudinal direction to an optical component, the method comprising (A) providing the spliceable optical fibre, said spliceable optical fibre comprising: (a) a core region (10, 20, 25, 30, 110); and (b) a microstructured cladding region, said cladding region surrounding said core region and comprising: (b1) an inner cladding region with inner cladding features (13, 22, 112) arranged in an inner cladding background material (11, 21, 111) with a refractive index n1, said inner cladding features comprising thermally collapsible holes or voids, and (b2) an outer cladding region with an outer cladding background material (12, 24, 114) with a refractive index n2; said spliceable optical fibre having at least one end; (B) collapsing said thermally collapsible holes or voids by heating said least one end of said spliceable optical fibre; and (C) coupling said collapsed spliceable optical fibre end to the optical component. A spliceable optical fibre; a preform for producing a spliceable optical fibre; a method of producing a spliceable optical fibre comprising drawing of the preform; a heat-treated spliceable optical fibre; an article comprising a spliceable optical fibre is further disclosed.
Owner:CRYSTAL FIBRE AS
Tunable Photonic Crystal Device
This application describes a tunable photonic crystal device based on the electrical actuation of photonic crystal films. This device displays non-bleachable structural color, reflecting narrow bands of wavelengths tuned throughout the entire visible spectrum by expansion and contraction of the photonic crystal lattice
Owner:THE GOVERNINIG COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORANTO
Multi-segment photonic-crystal-rod waveguides for amplification of high-power pulsed optical radiation and associated method
InactiveUS20070104431A1High peak powerHigh pulse energyLaser detailsCladded optical fibreOptical radiationPromiscuous behaviour
A method and apparatus use a photonic-crystal fiber having a very large core while maintaining a single transverse mode. In some fiber lasers and amplifiers having large cores problems exist related to energy being generated at multiple-modes (i.e., polygamy), and of mode hopping (i.e., promiscuity) due to limited control of energy levels and fluctuations. The problems of multiple-modes and mode hopping result from the use of large-diameter waveguides, and are addressed by the invention. This is especially true in lasers using large amounts of energy (i.e., lasers in the one-megawatt or more range). By using multiple small waveguides in parallel, large amounts of energy can be passed through a laser, but with better control such that the aforementioned problems can be reduced. An additional advantage is that the polarization of the light can be maintained better than by using a single fiber core.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Hollow anti-resonance optical fiber
InactiveCN105807363AImprove efficiencyHigh sensitivityCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideTransmission lossElectron
The invention discloses a hollow anti-resonance optical fiber, and belongs to the technical field of optics and laser photoelectrons.The basic structure of the hollow anti-resonance optical fiber comprises a fiber core area with low refraction rate and a wrapping layer area with high refraction rate.The wrapping layer area with high refraction rate is divided into an inner wrapping layer region and an outer wrapping layer region.The inner wrapping layer region is composed of one or two layers of micro capillary pipes.The fiber core area with low refraction rate is wrapped by the inner wrapping layer region.Compared with a traditional band gap type hollow-core photonic crystal fiber, the hollow anti-resonance optical fiber has the advantages of being large in spectral bandwidth, small in bending loss, low in transmission loss, high in damage threshold and capable of keeping single-modulus transmission.A high-efficiency and high-sensitivity ideal platform is created for nonlinear frequency conversion, trace gas / liquid detection, high-power pulse compression and other foremost application.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
An Optical System For Providing Short Laser-Pulses
InactiveUS20060209908A1High core diameterIncrease valueCladded optical fibreLaser using scattering effectsCost effectivenessPhotonic bandgap
The present invention deals with optical systems for providing short laser pulses. An object of the invention is to provide an optical system providing compact and cost-effective short laser-pulses using fibers with anomalous dispersion and high non-linear thresholds. The object is achieved by a short pulse optical system for generating or processing short laser-pulses, said optical system comprises an optical fiber in the form of a photonic crystal fiber arranged to provide guidance of light in the core region due to the photonic bandgap effect (PBG), where light propagates in a hollow or solid core surrounded by a Silica cladding comprising a substantially periodic distribution of micro-structural elements, and where the refractive index of the core is lower than the effective refractive index of the cladding. The invention may be useful in applications such as laser-based micromachining, thin-film formation, laser cleaning, in medicine and biology.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS
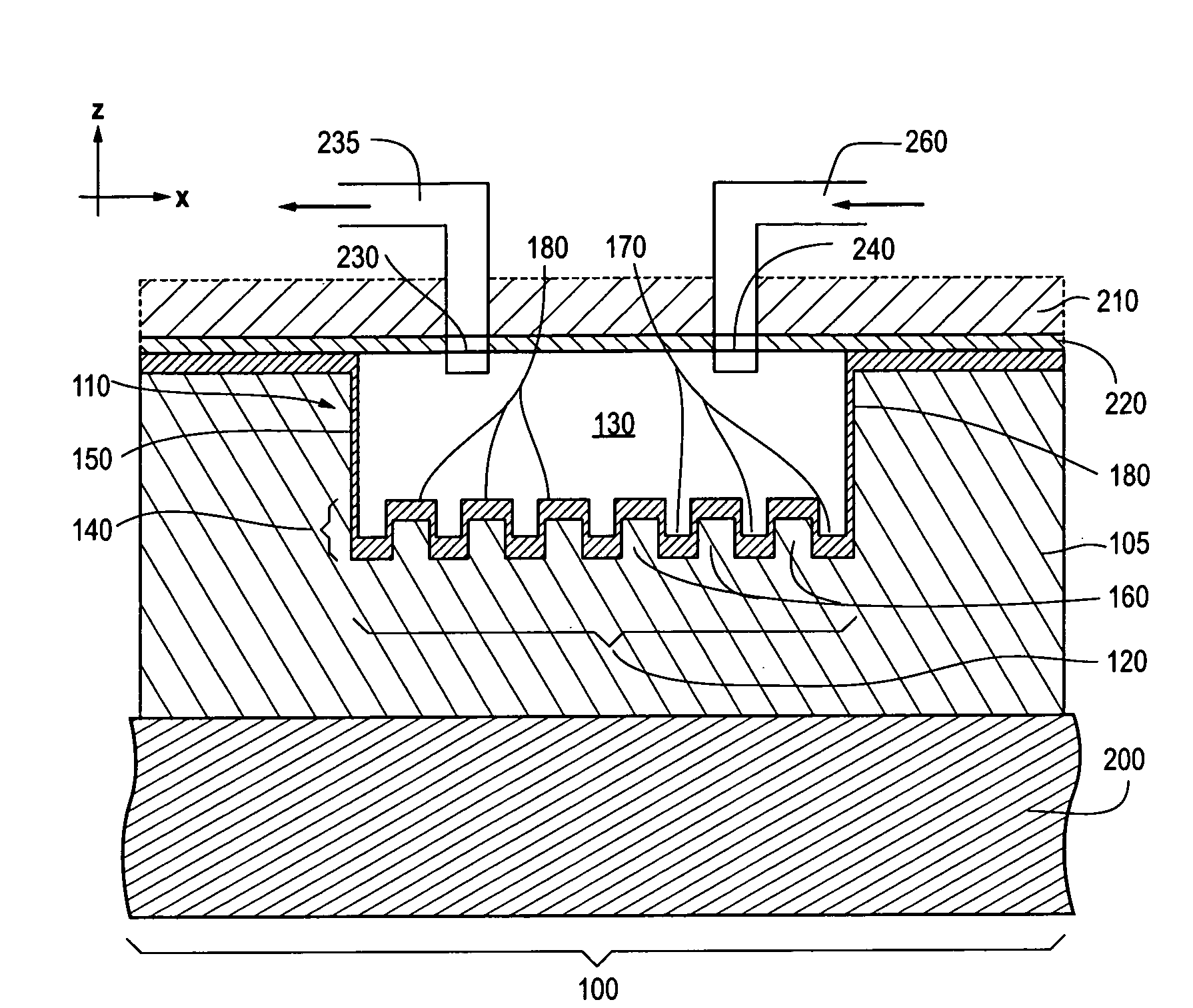
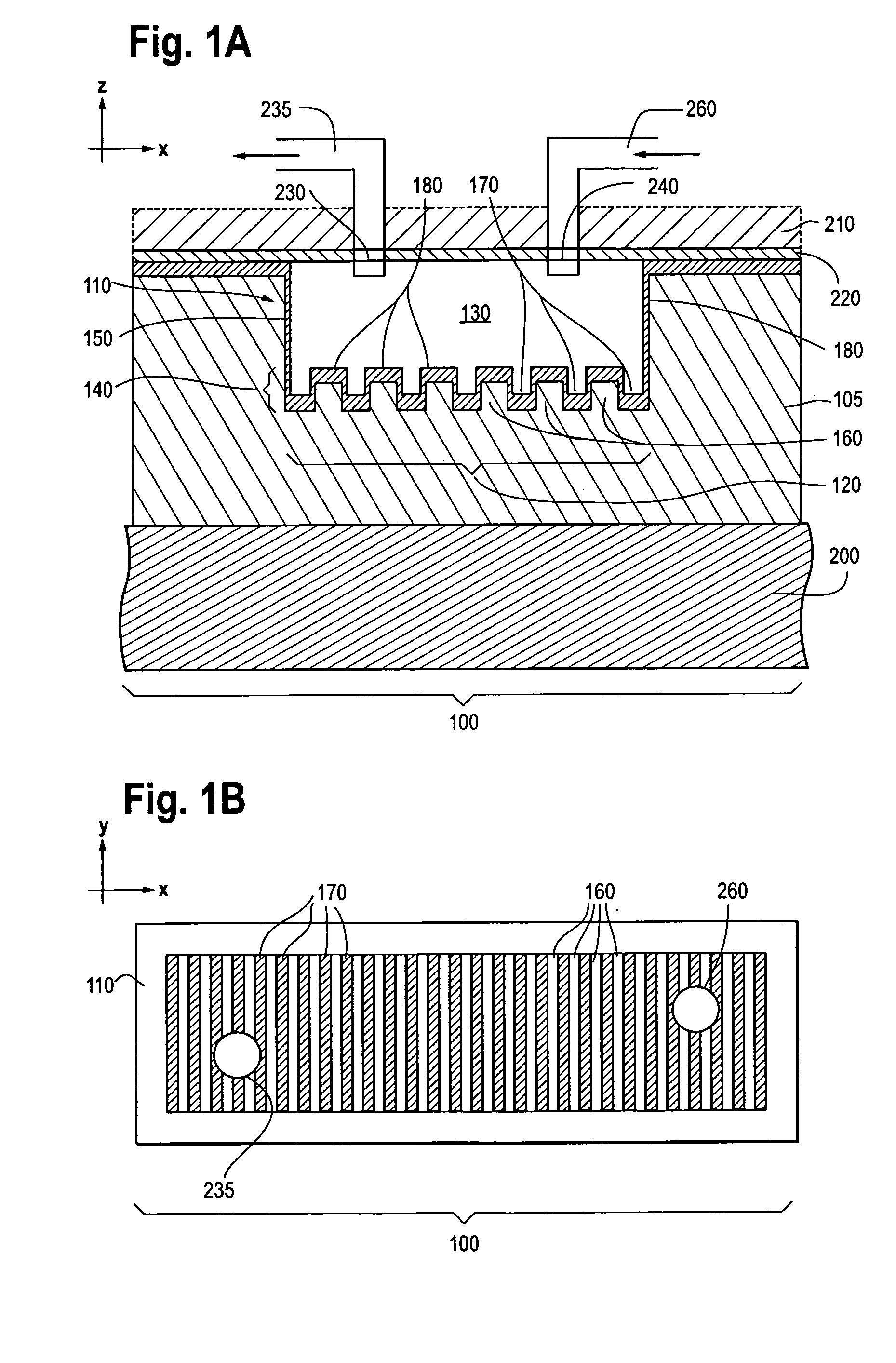
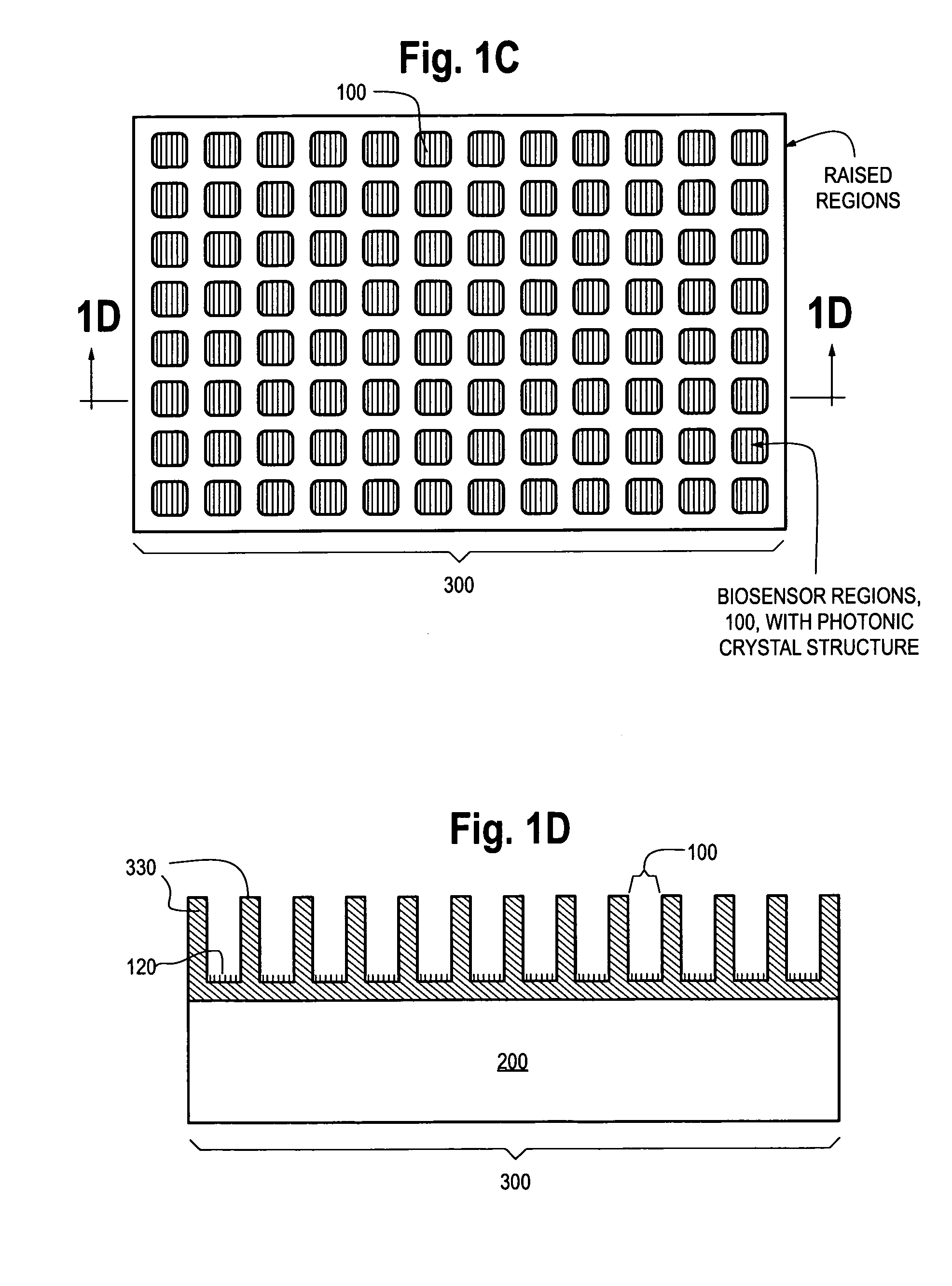
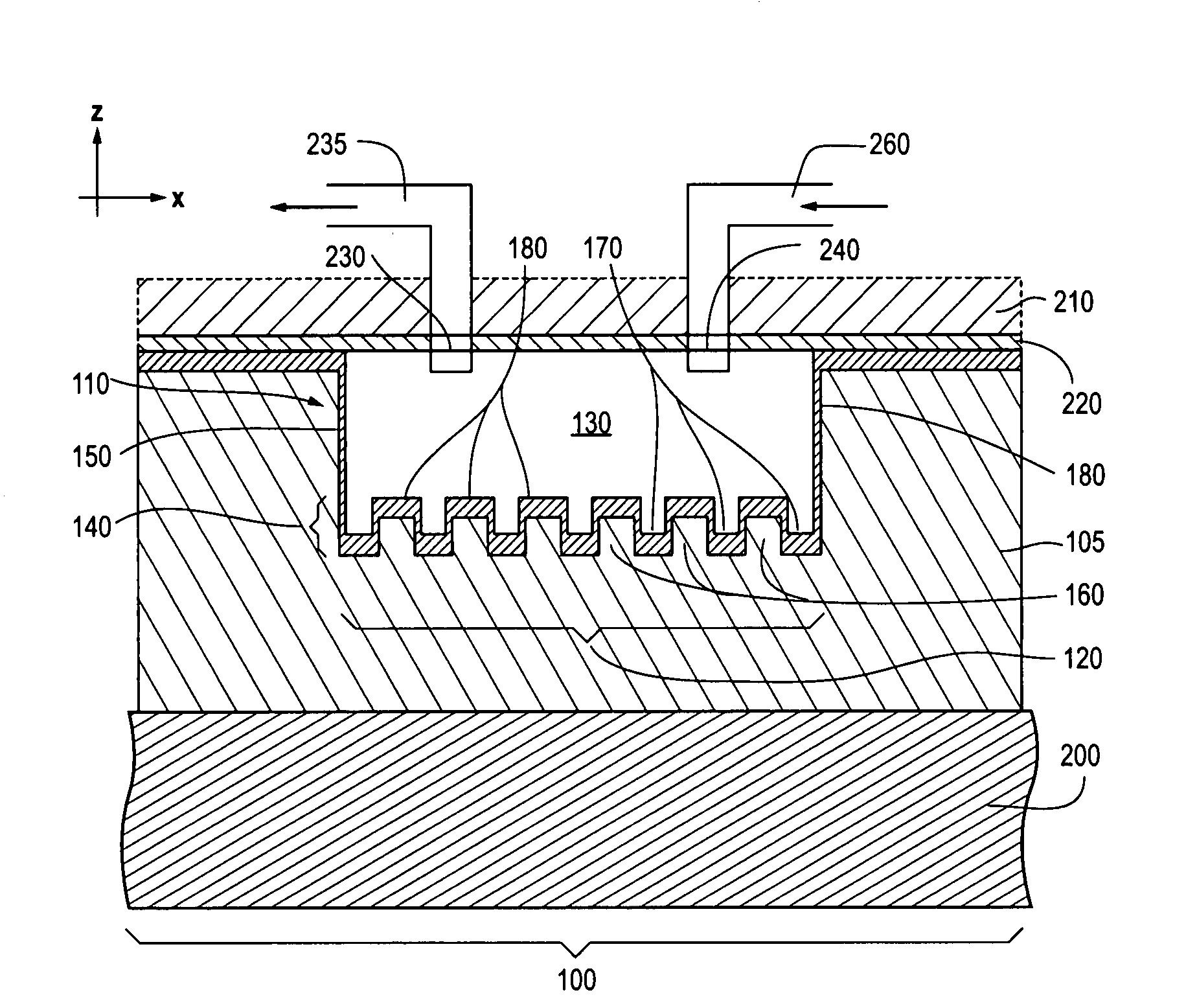
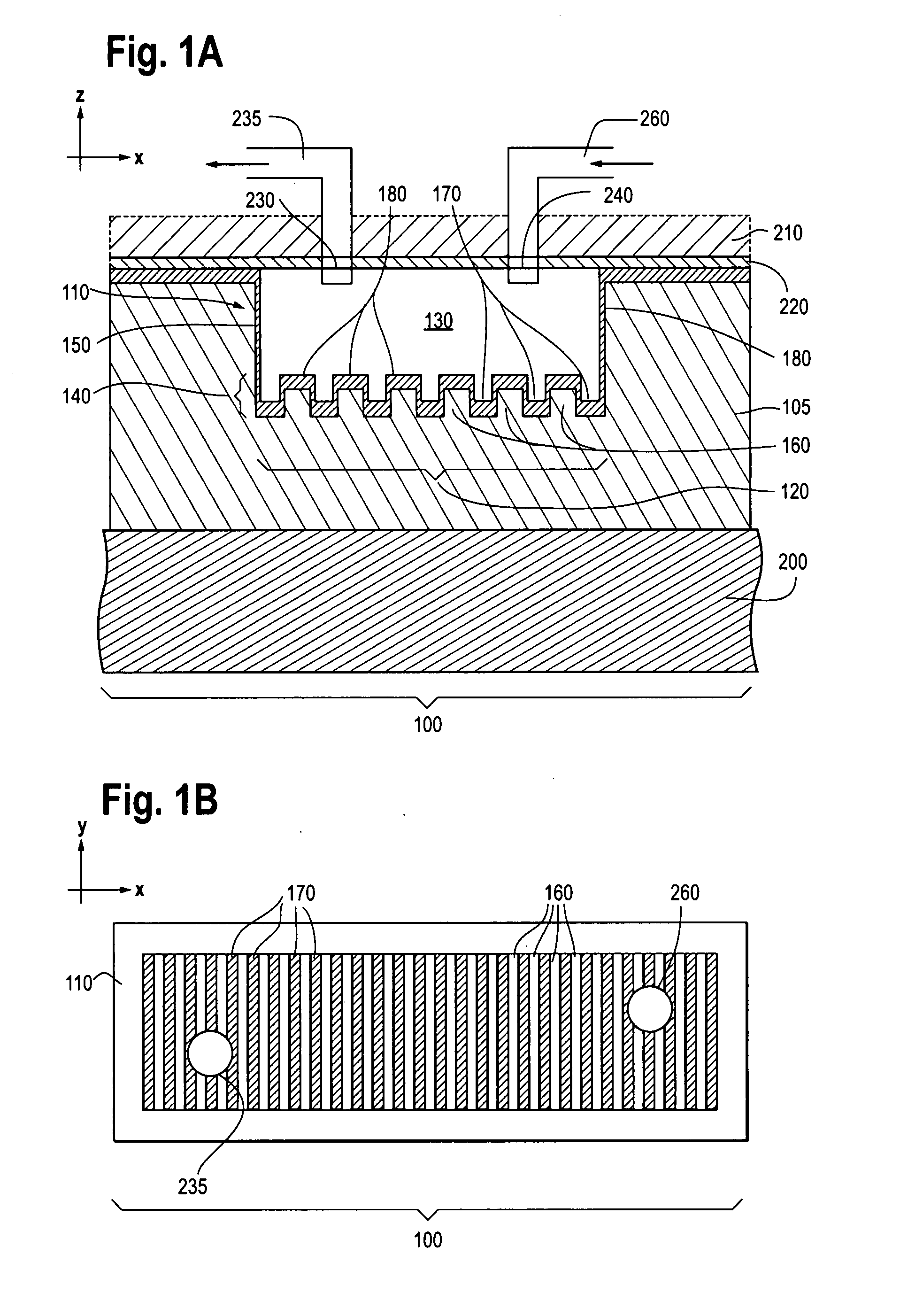
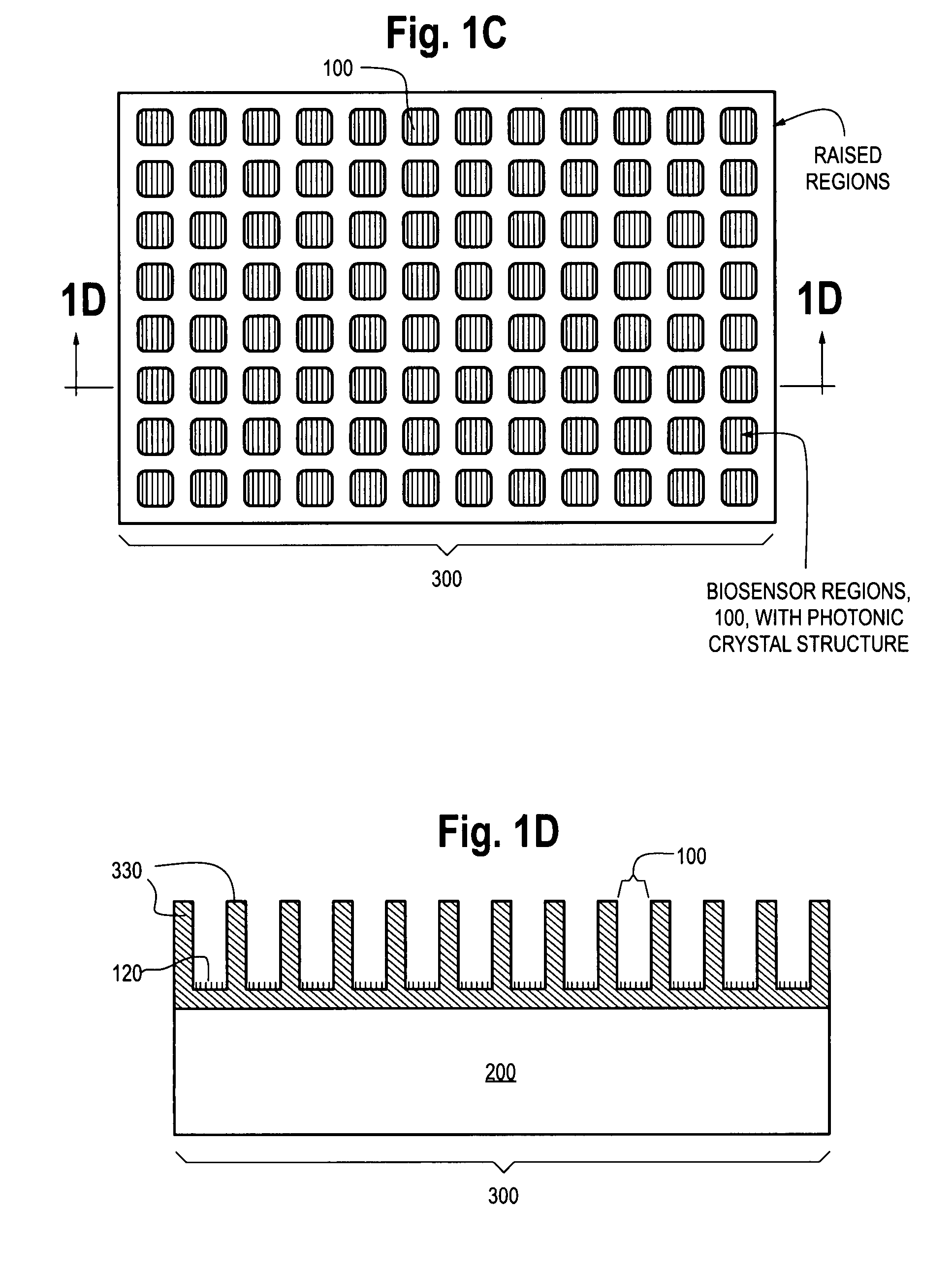
Photonic crystal sensors with integrated fluid containment structure, sample handling devices incorporating same, and uses thereof for biomolecular interaction analysis
ActiveUS20090079976A1Prevent leakageEasy to carryWithdrawing sample devicesInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsSensor arrayPhotonic crystal structure
Photonic crystal (PC) sensors, and sensor arrays and sensing systems incorporating PC sensors are described which have integrated fluid containment and / or fluid handling structures. The PC sensors are further integrated into a sample handling device such as a microwell plate. Sensors and sensing systems of the present disclosure are capable of high throughput sensing of analytes in fluid samples, bulk refractive index detection, and label-free detection of a range of molecules, including biomolecules and therapeutic candidates. The present disclosure also provides a commercially attractive fabrication platform for making photonic crystal sensors and systems wherein an integrated fluid containment structure and a photonic crystal structure are fabricated in a single molding or imprinting processing step amendable to high throughput processing.
Owner:X BODY
Light emitting diode structure having photonic crystals
ActiveUS7173289B1Improve epitaxy qualitySurface lightSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesPhotonic crystalPhotonics
A light emitting diode (LED) structure includes a substrate with a surface and cylindrical photonic crystals, a first type doping semiconductor layer, a first electrode, a light emitting layer, a second type doping semiconductor layer and a second electrode. The first type doping semiconductor layer is formed on the substrate to cover the photonic crystals. The light emitting layer, the second type doping semiconductor layer and the second electrode are sequentially formed on a portion of the first type doping semiconductor layer. The first electrode is formed on the other portion of the first type doping semiconductor layer without being covered by the light emitting layer. Because the substrate with photonic crystals can improve the epitaxial quality of the first type doping semiconductor layer and increase the energy of the light forwardly emitting out of the LED, the light emitting efficiency of the LED is effectively enhanced.
Owner:FORMOSA EPITAXY INCORPORATION +1
Large flattened mode tuned cladding photonic crystal fiber laser and amplifier
A modified photonic crystal fiber yielding a higher peak power for a given maximum intensity. The multi-mode signal core has a depressed index of refraction that pushes the mode distribution to the core edges while a pattern of larger air holes is used to flatten the mode distribution. The core is further surrounded by tuned cladding elements defined by a pattern of smaller air holes that cause loss in all of the core modes except the fundamental while maintaining robust guiding of the fundamental mode.
Owner:AIR FORCE THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE
Photonic crystal light emitting device using photon-recycling
ActiveUS20080217639A1Take advantage ofImprove efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesPhoton recyclingPhotonic crystal structure
A photonic crystal light emitting device including: a light emitting diode (LED) light emitting structure including a first conductive semiconductor layer, a second conductive semiconductor layer, and an active layer interposed between the first and second conductive semiconductor layers; and a first photon-recycling light emitting layer formed on one surface of the first conductive semiconductor layer, opposite to the active layer, wherein the first photon-recycling light emitting layer absorbs a primary light emitted from the LED light emitting structure and emits a light having a different wavelength from that of the primary light, and a photonic crystal structure is formed on an entire thickness of the first photon-recycling light emitting layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Photonic crystal magneto-optical circulator and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102043261AWell formedCompact structureOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsPhotonic crystalCross connection
The invention relates to a photonic crystal magneto-optical circulator comprising a first medium material columns in an air background, the first medium material columns are arranged in the shape of two-dimensional tetragonal lattice; the photonic crystal magneto-optical circulator also comprises a photonic crystal waveguide which includes a transverse photonic crystal waveguide and a longitudinal photonic crystal waveguide which are mutually intercrossed, a second medium material column used for guiding light and positioned at the cross connection of the transverse photonic crystal waveguideand the longitudinal photonic crystal waveguide, four identical magneto-optical material columns uniformly positioned around the second medium material columns, and at least three identical third medium material columns respectively positioned outside the three magneto-optical material columns. The photonic crystal magneto-optical circulator provided by the invention can respectively realize single direction optical circulating transmission among three ports arranged in the shape of T and among four ports arranged in the shape of a cross. The photonic crystal magneto-optical circulator provided by the invention is advantageous in that it has a concise form and a compact structure, and is suitable for serving as an anti-interference component in a photonic crystal integrated optical circuit.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Magnetofluid filling photonic crystal optical fiber F-P magnetic field sensor
InactiveCN102221679ASimple structureInnovative designCladded optical fibreMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesSpectrum analyzerOptical fiber coupler
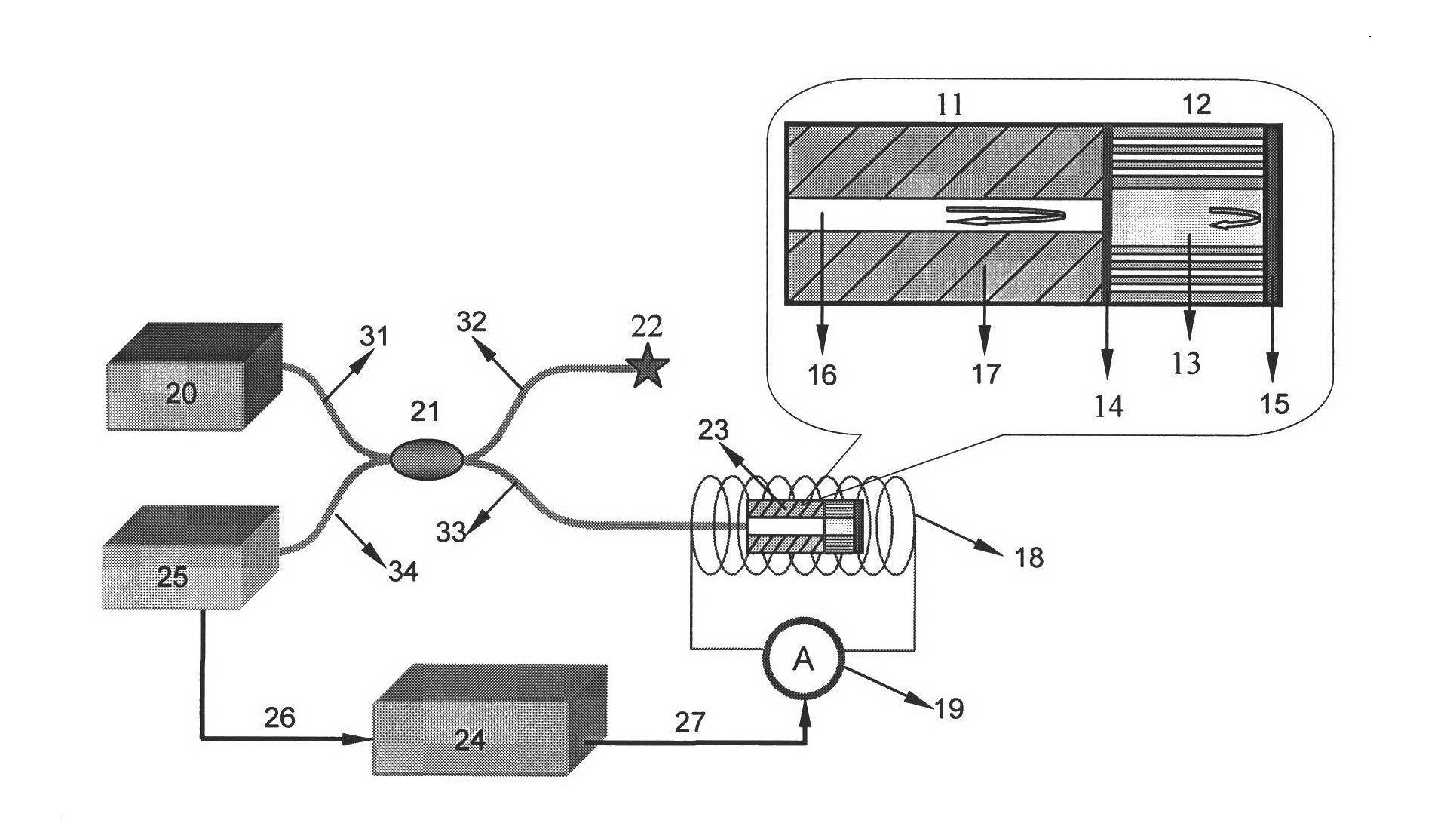
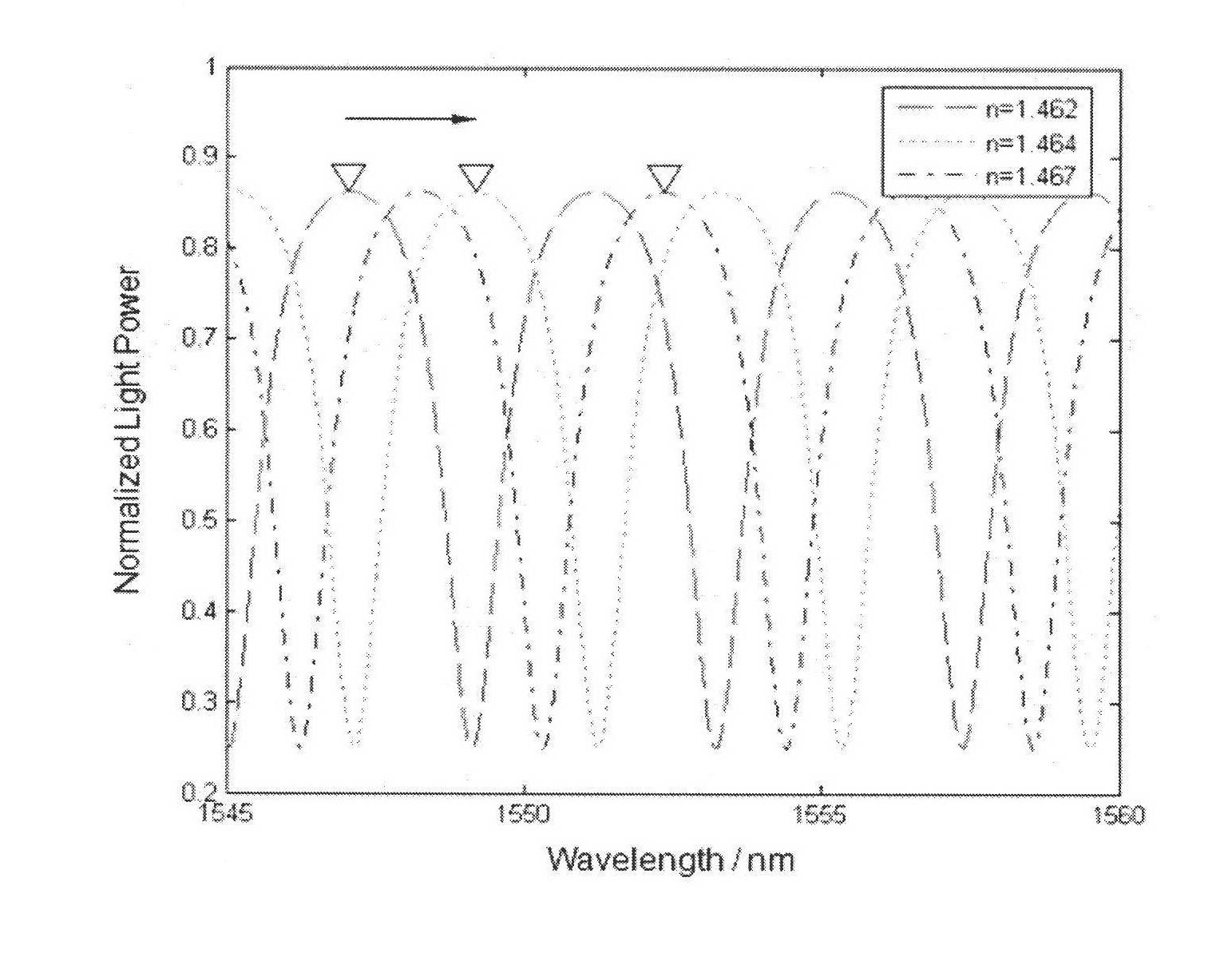
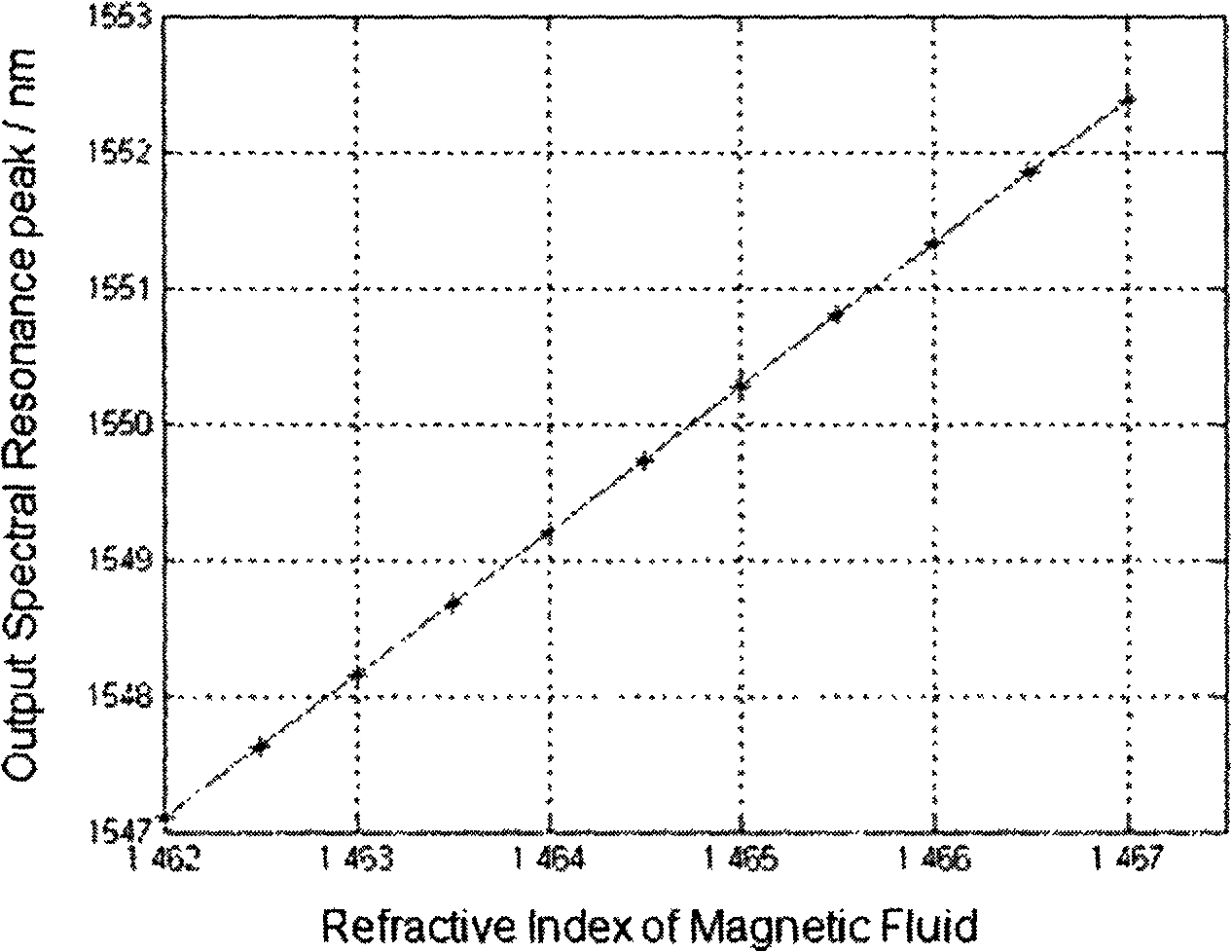
The invention discloses a magnetofluid filling photonic crystal optical fiber F-P magnetic field sensor, which belongs to the technical field of optical fiber sensing, and consists of a broadband light source 20, an optical fiber coupler 21 and optical fiber links (31, 32, 33 and 34) of the optical fiber coupler 21, a refractive index matching fluid 22, a sensor probe 23, an electromagnetic coil 18 and a current driving system 19 of the electromagnetic coil, a spectrum analyzer, a computer 24 as well as a connecting cable 26 and a connecting cable 27. The magnetofluid filling photonic crystal optical fiber F-P magnetic field sensor is characterized in that the sensor probe is formed by fusing a section of hollow photonic crystal optical fiber 12 filled with a magnetofluid 13 and a simple module optical fiber 11; the two ends of the hollow photonic crystal optical fiber are respectively stuck by a partial reflection film 14 and a total reflection mirror 15 to form an optical fiber F-P interferometric cavity structure; and the reflection rate of the magnetofluid serving as a medium in the F-P interferometric cavity is changed due to a magnetic field generated by the electromagnetic coil after conducted with a current, thereby causing the change of output spectrums so as to realize magnetic field measurement. The magnetofluid filling photonic crystal optical fiber F-P magnetic field sensor has the advantages of being low in temperature influences, simple in structure, small in size and easy to realize multi-point distribution type sense.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Photonic crystal exhibiting negative refraction without requiring a negative effective index
InactiveUS7339539B2Small sizeNanoopticsOptical waveguide light guideNegative refractionPhotonic crystal
A periodic electromagnetic medium is disclosed that includes a surface that provides an interface with an ambient medium and a periodic structure that provides negative refraction within the medium of an incident electromagnetic field incident on the surface. In various embodiments the incident electromagnetic field is within a range of frequencies, the medium may include dielectric or metallic material, and has either a positive or negative effective index.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Photonic crystal type color filter and reflective liquid crystal display device having the same
InactiveUS20090284696A1Wavelength selectivity is not optimumLow light transmittanceOptical filtersNanoopticsPhotonic crystalGrating
Provided are a photonic crystal type color filter and a reflective liquid crystal display (“LCD”) device having the same. The photonic crystal type color filter includes a substrate, and a photonic crystal disposed on the substrate and having a two-dimensional (2D) grating structure.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Fiber mopa system without stimulated brillouin scattering
ActiveUS20090010288A1Shorten fiber lengthIncreasing mode areaLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionNanosecondSeeds source
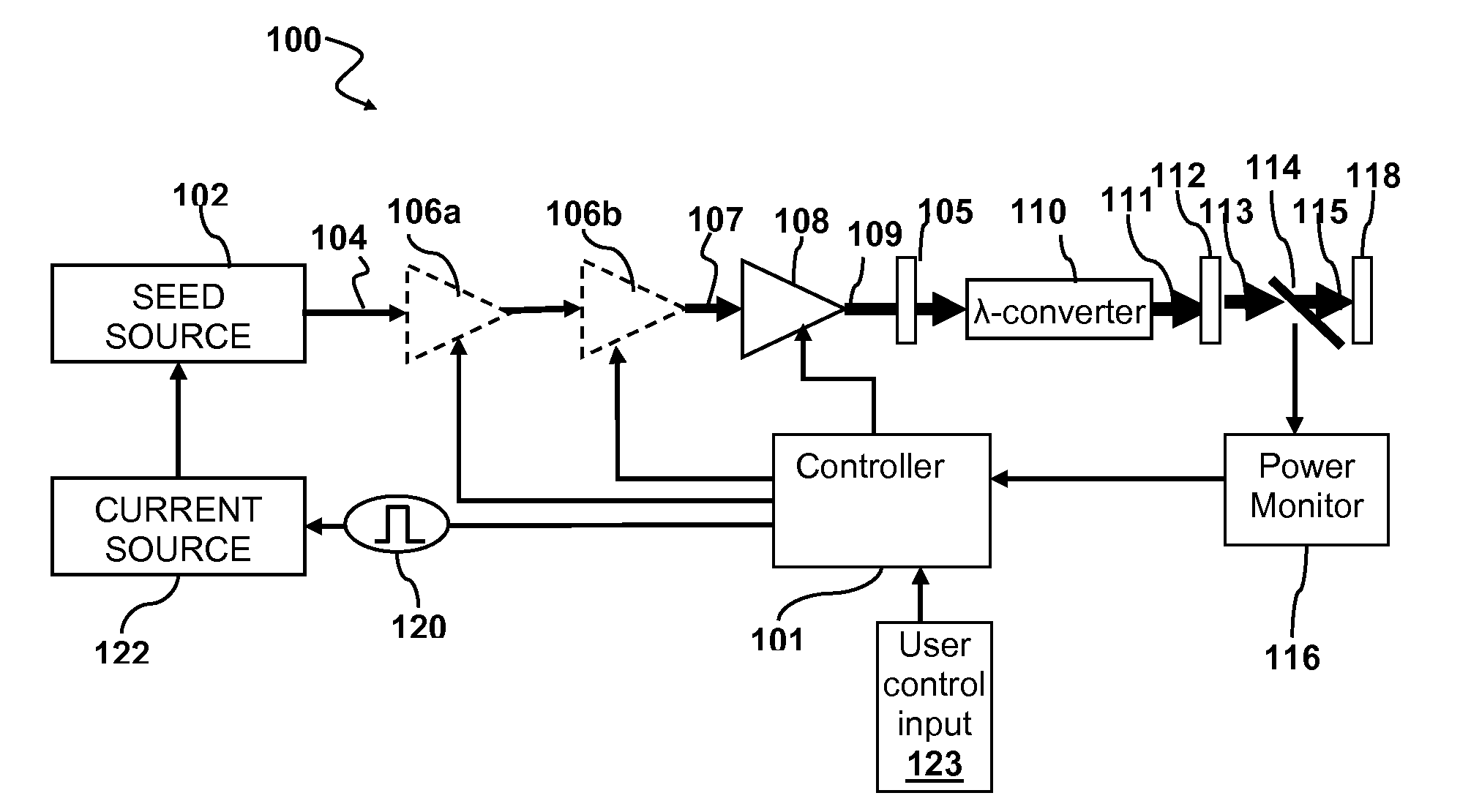
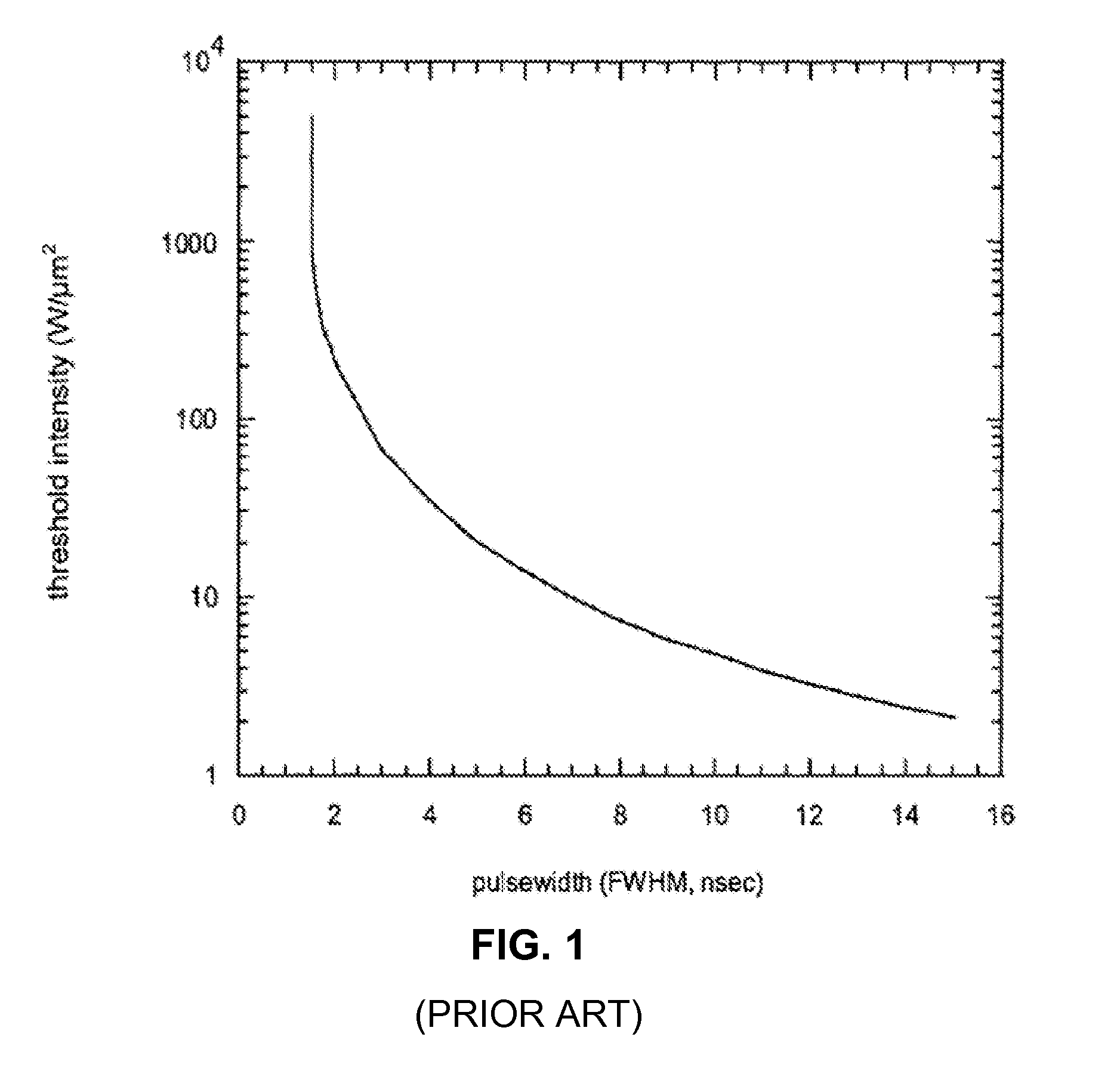
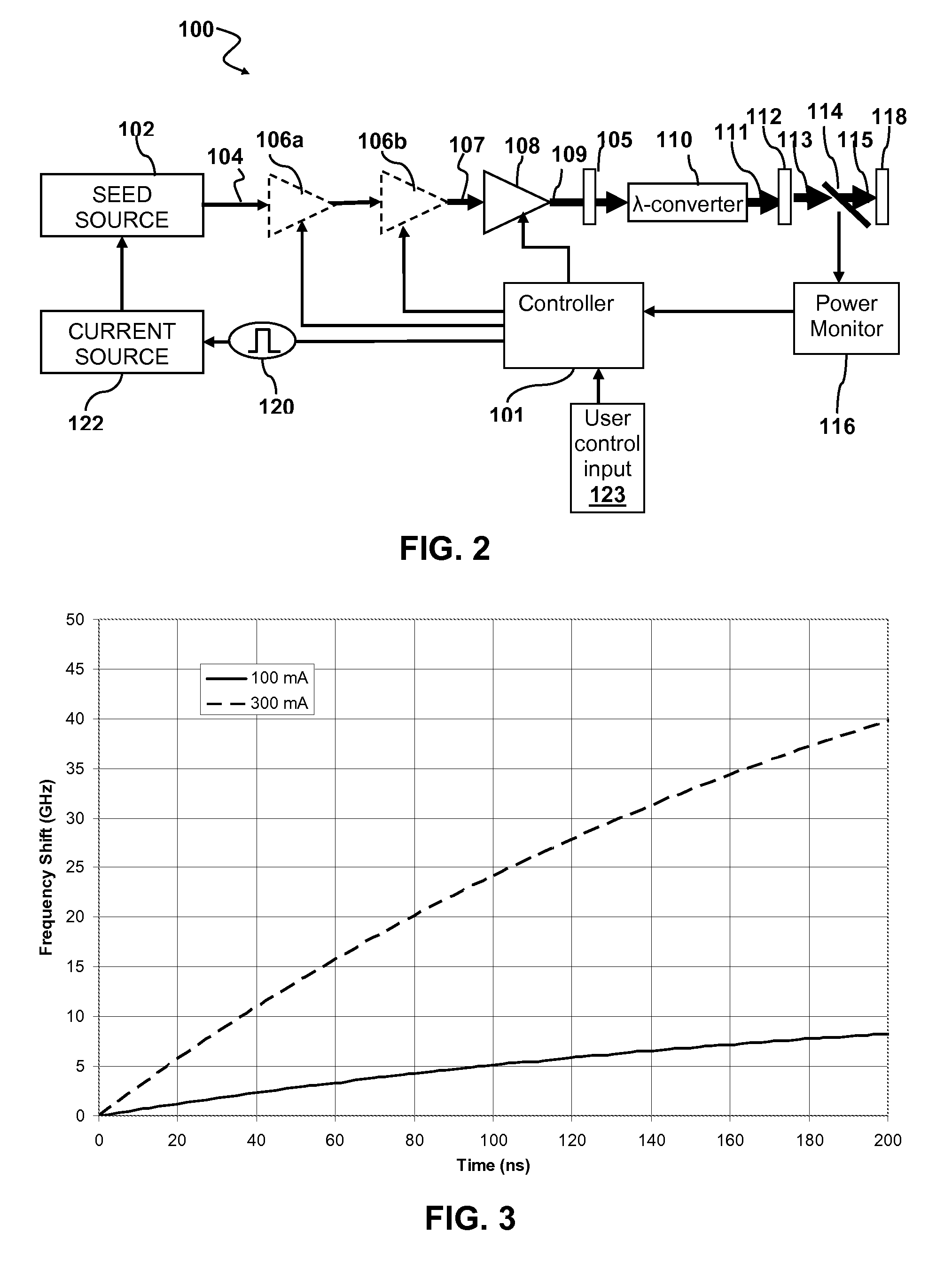
Methods and systems for increasing the threshold for stimulated Brillouin scattering are described. A seed source may generate one or more chirped seed pulses characterized by a pulse duration τ, and a frequency chirp. The pulse duration τ may be greater than about 2 nanoseconds. A photonic crystal amplifier amplifies the seed pulses to produce one or more amplified pulses characterized by a peak power P greater than about 1 kilowatt. The pulse duration τ, frequency chirp, and the photonic crystal fiber may be selected such that a threshold for stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) in the photonic crystal fiber is greater than the peak power P.
Owner:DISCO CORP
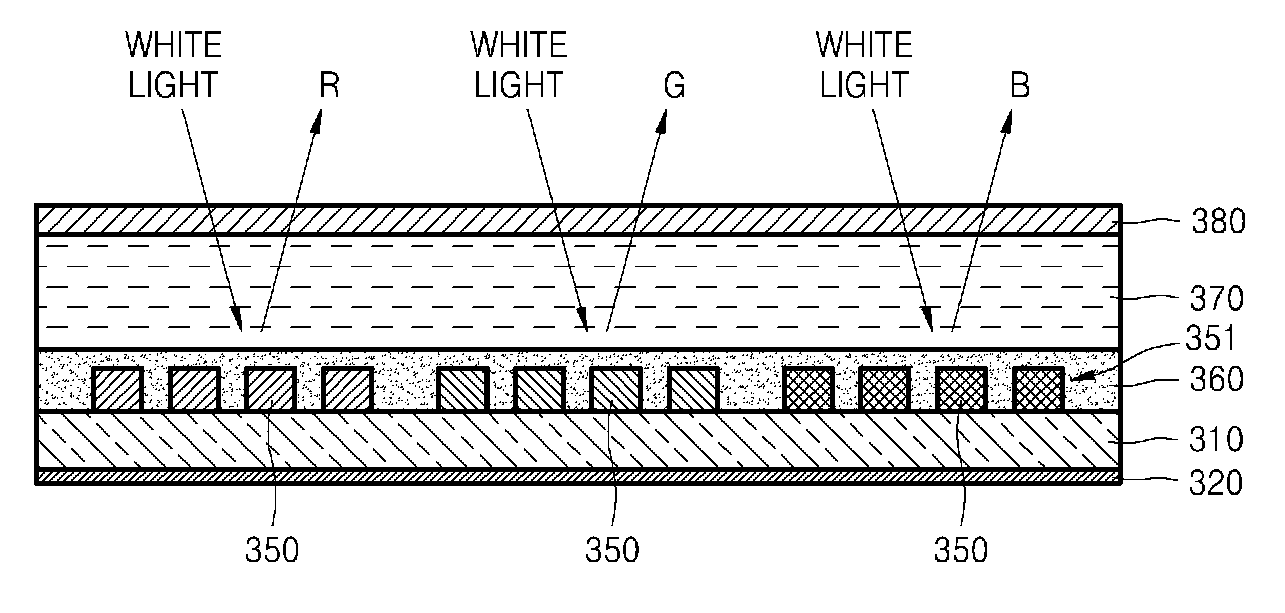
Electroluminescent display device and thermal transfer donor film for the electroluminescent display device
ActiveUS20050116625A1Light extraction efficiencyImprove light extractionDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesPhotonic crystalLength wave
The invention is directed to an organic electroluminescent (EL) display device having an improved light extracting efficiency due to a photonic crystal layer formed proximate one side of a stack. Among other elements, the stack may include a first electrode formed on a substrate, an organic light emitting layer formed above the first electrode, and a second electrode formed above the organic light emitting layer. Additionally, the photonic crystal layer may be configured to correspond to a wavelength of colored light. An organic EL display device having an improved light extracting efficiency may be manufactured using a thermal transfer donor film to adhere the photonic crystal layer to the stack.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
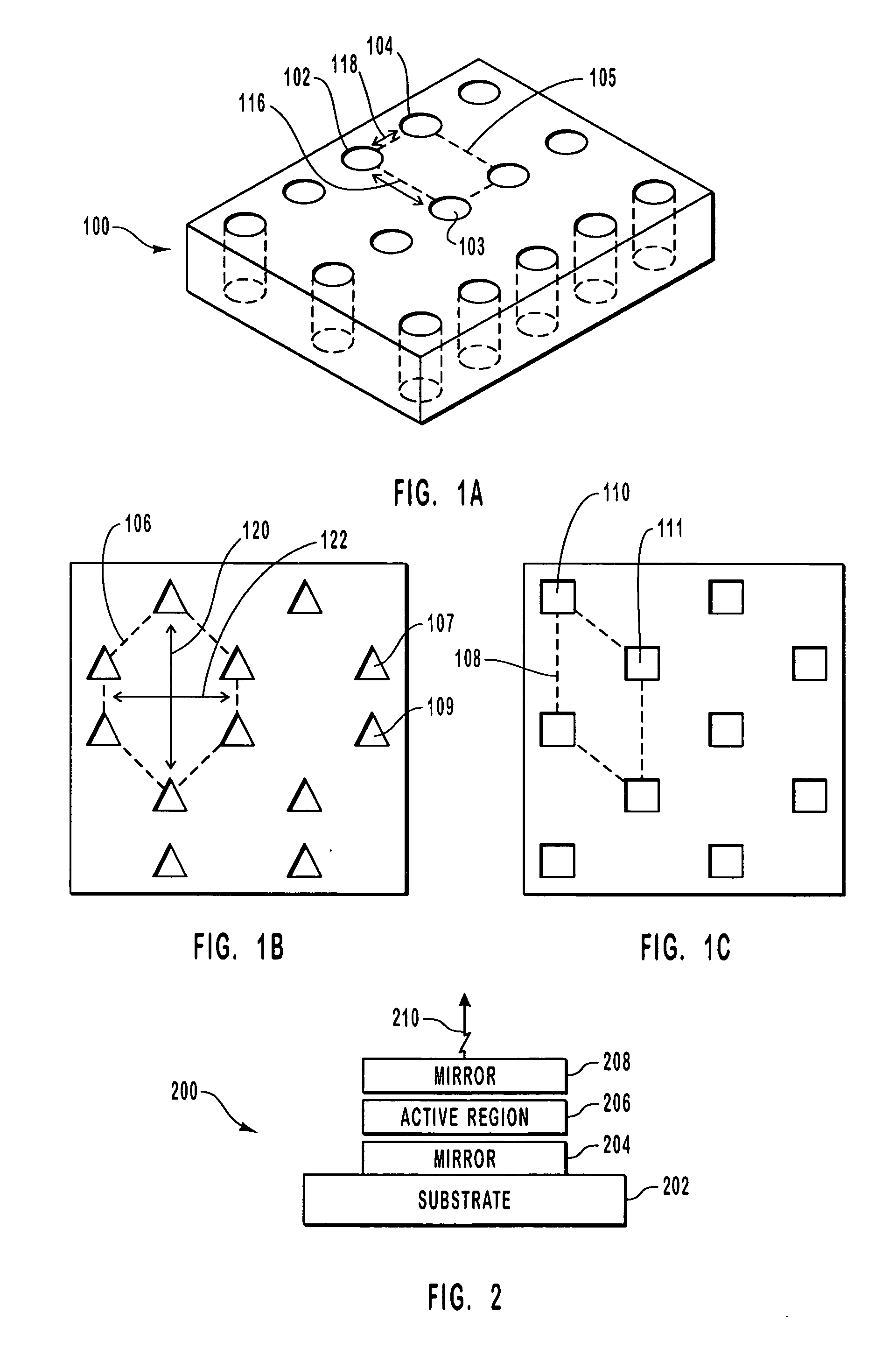
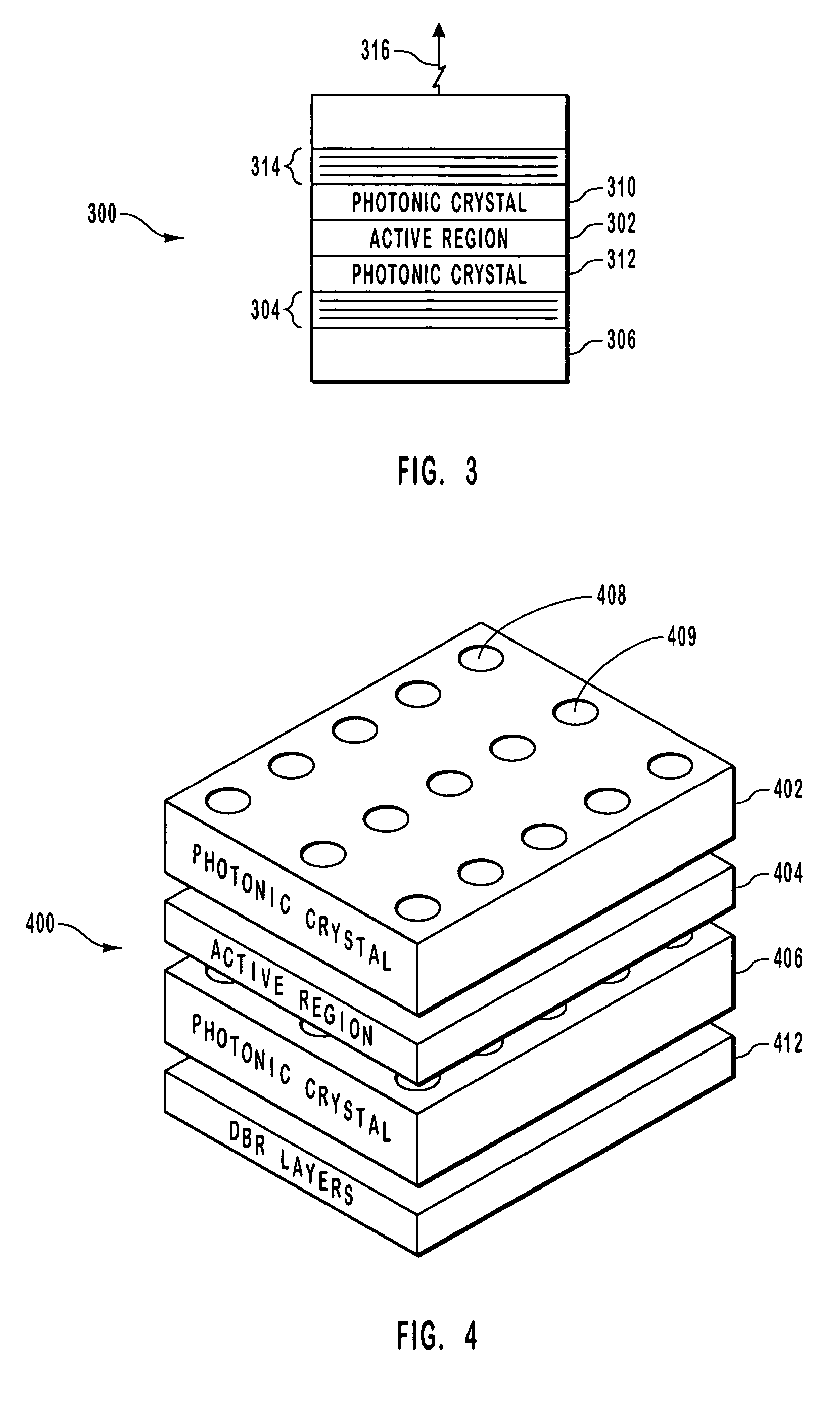
Polarization control in VCSELs using photonics crystals
InactiveUS20070030873A1Lower threshold voltageOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserPhotonic crystal
An optical device including a polarization control photonic crystal. The optical device includes a vertical cavity surface emitting laser. The optical device further includes a lower mirror formed on a substrate. The optical device also includes an upper mirror. An active region is between the lower mirror and the upper mirror. Photons generated in the active region are reflected between the upper mirror and the lower mirror through the active region. An asymmetrical photonic crystal including cavities is optically coupled in the optical device such that one polarization of light is better reflected by the asymmetrical photonic crystal than a competing polarization of light.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
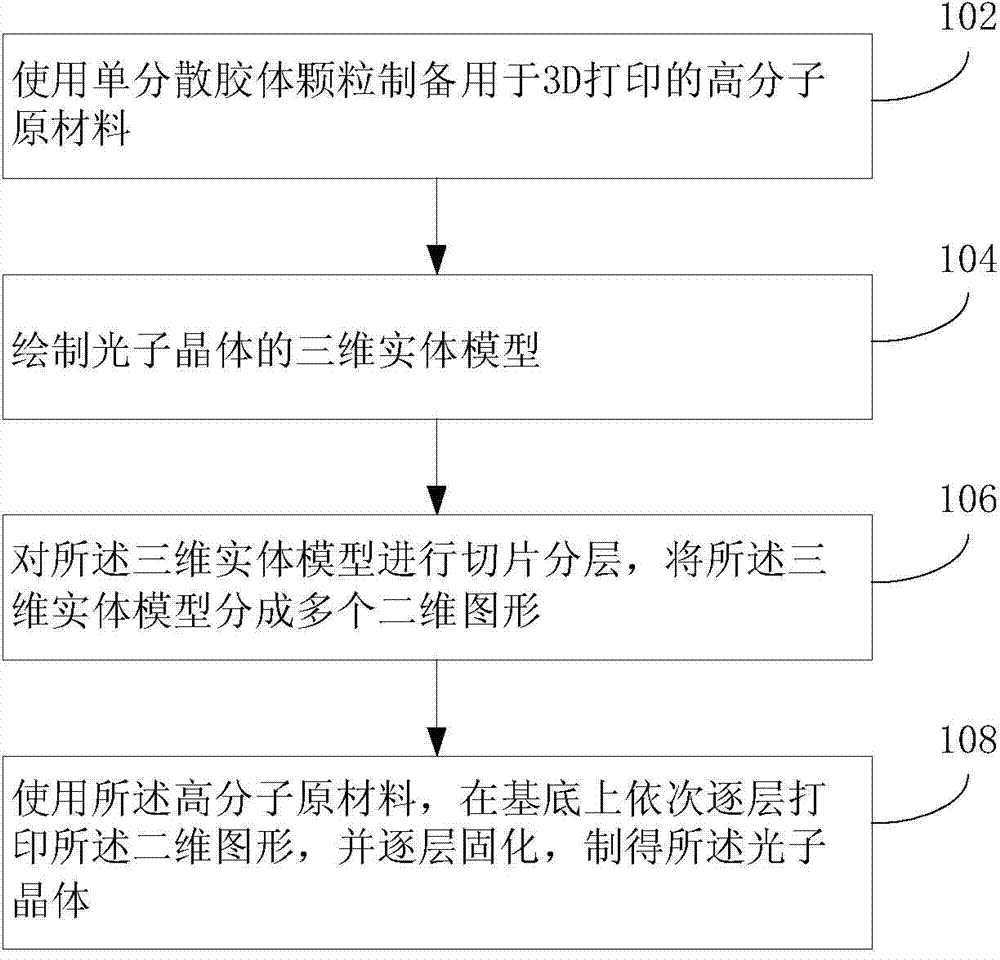
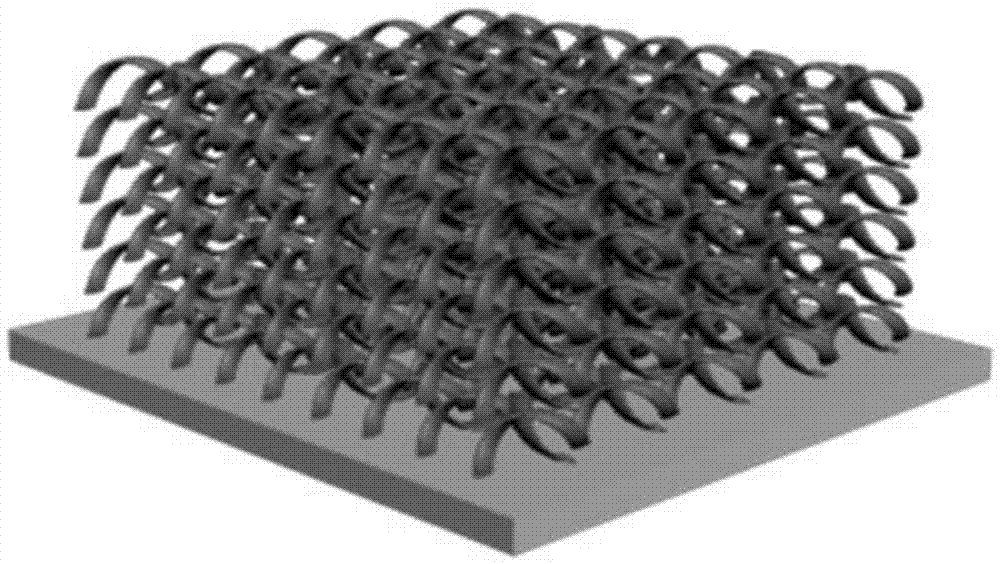
Method for preparing photonic crystals through 3D (Three-Dimensional) printing
ActiveCN103802315ADiversified structure and morphologyGeneralization of structural morphologyPhotonicsEngineering
The invention discloses a method for preparing photonic crystals through 3D (Three-Dimensional) printing. The method comprises the following steps of preparing macromolecule raw materials for 3D printing by using monodisperse colloidal particles, layering a three-dimensional solid model of photonic crystals into a plurality of two-dimensional patterns, printing the two-dimensional patterns layer by layer in sequence on a substrate and curing layer by layer to prepare three-dimensional photonic crystals which having high dielectric ratios or are suitable for network topology structures. Compared with a current preparation method of the photonic crystals, the method is quick and convenient, lo in investment costs of devices, simple in process, energy-saving and environmentally friendly and short in consumed time, and three-dimensional structure shapes of the prepared photonic crystals are diversified and extensive. The method is an ideal manner of preparing special-purpose photonic crystals in the future. The method is capable of realizing batch production; the prepared photonic crystals can be widely applicable to the scientific research and life of optical devices, tissue culture frames, super lyophobic liquid surface, anti-counterfeiting marks and ornaments, so that the photonic crystals are wide in market prospects.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
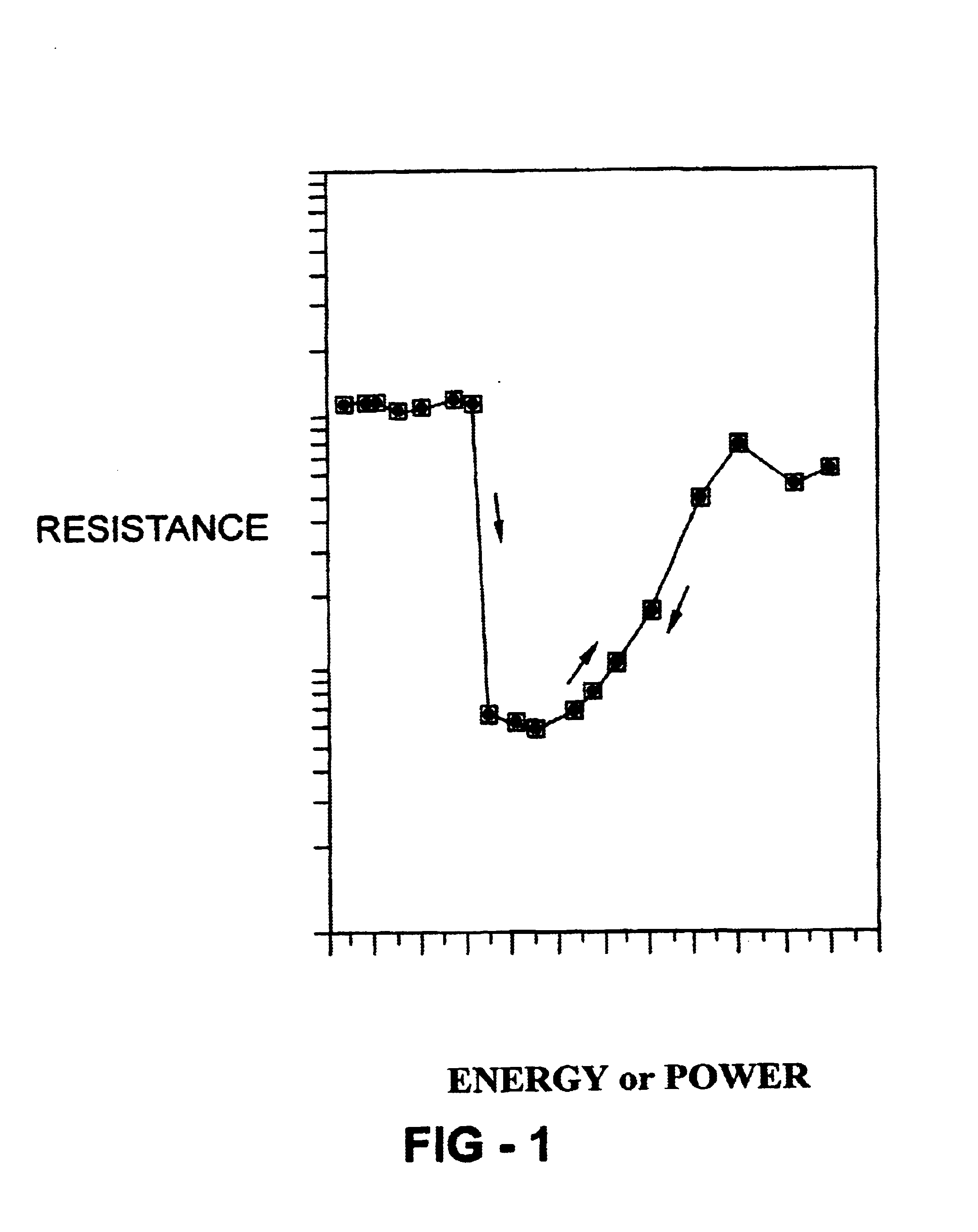
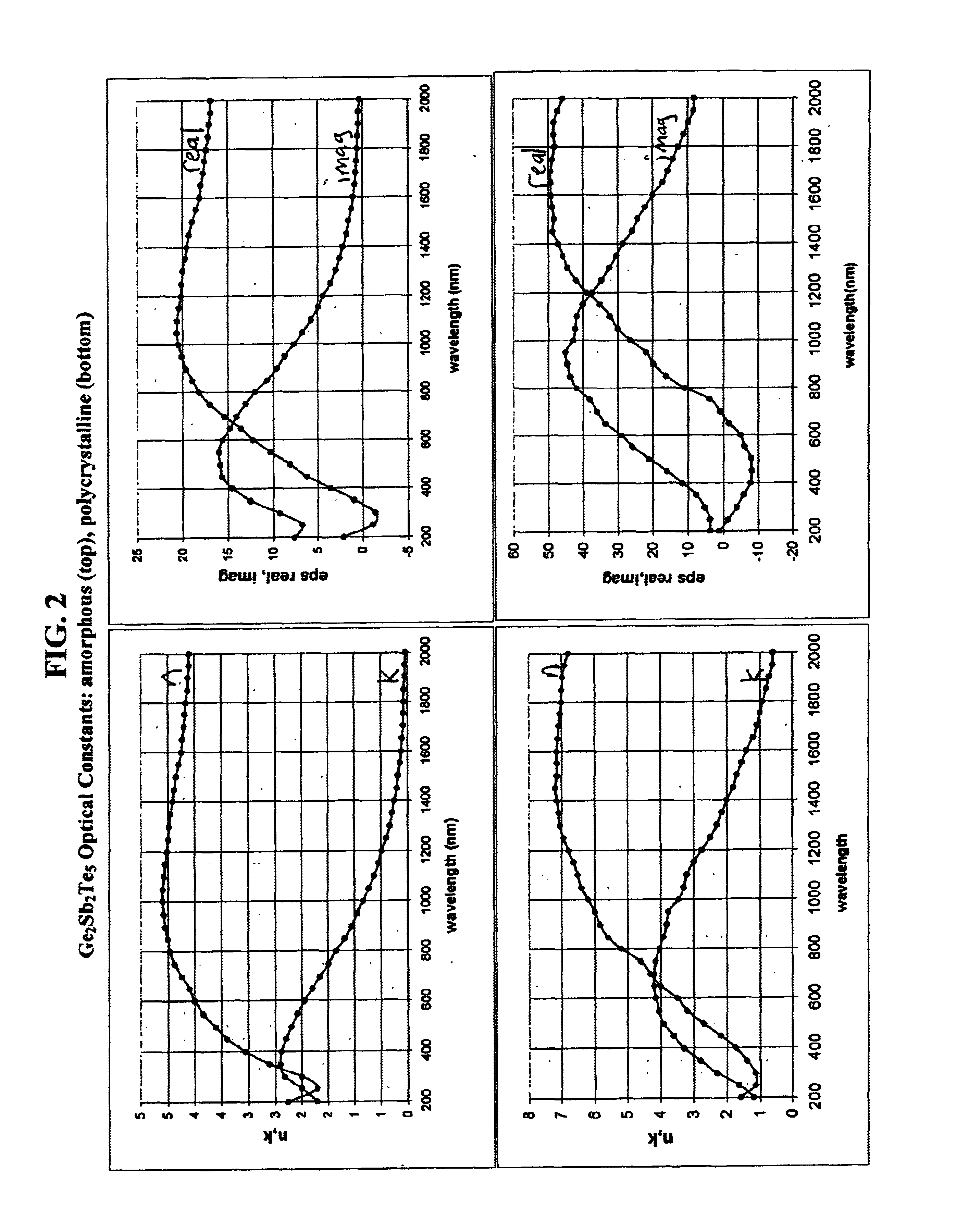
Photonic crystals and devices having tunability and switchability
A photonic crystal having reversibly tunable photonic properties. The photonic crystal includes a phase change material having a plurality of structural states that vary with respect to fractional crystallinity. Optical constants including refractive index, extinction coefficient and permittivity vary as the fractional crystallinity of the phase change material is varied thereby providing tunability of photonic crystal properties. Variations among the structural states of the phase change material are reversibly effected through the addition of energy in forms including optical or electrical energy. The photonic crystals may include defects that provide photonic states within the photonic band gap. The position of these states is tunable through the control of the fractional crystallinity of the phase change material included in the photonic crystal. Electromagnetic radiation resonators including photonic crystals having photonic states in the photonic band gap are further provided. These resonators may be used for frequency selective filtering or routing of electromagnetic radiation and permit tunable variation in the frequency and decay rates of resonant modes through control of the structural state of the phase change material. These resonators are further coupled to waveguides to provide tunable channel drop filters and narrowband reflectors.
Owner:ENERGY CONVERSION DEVICES INC
Tunable photonic crystal device
This application describes a tunable photonic crystal device based on the electrical actuation of photonic crystal films. This device displays non-bleachable structural color, reflecting narrow bands of wavelengths tuned throughout the entire visible spectrum by expansion and contraction of the photonic crystal lattice
Owner:THE GOVERNING COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORONTO
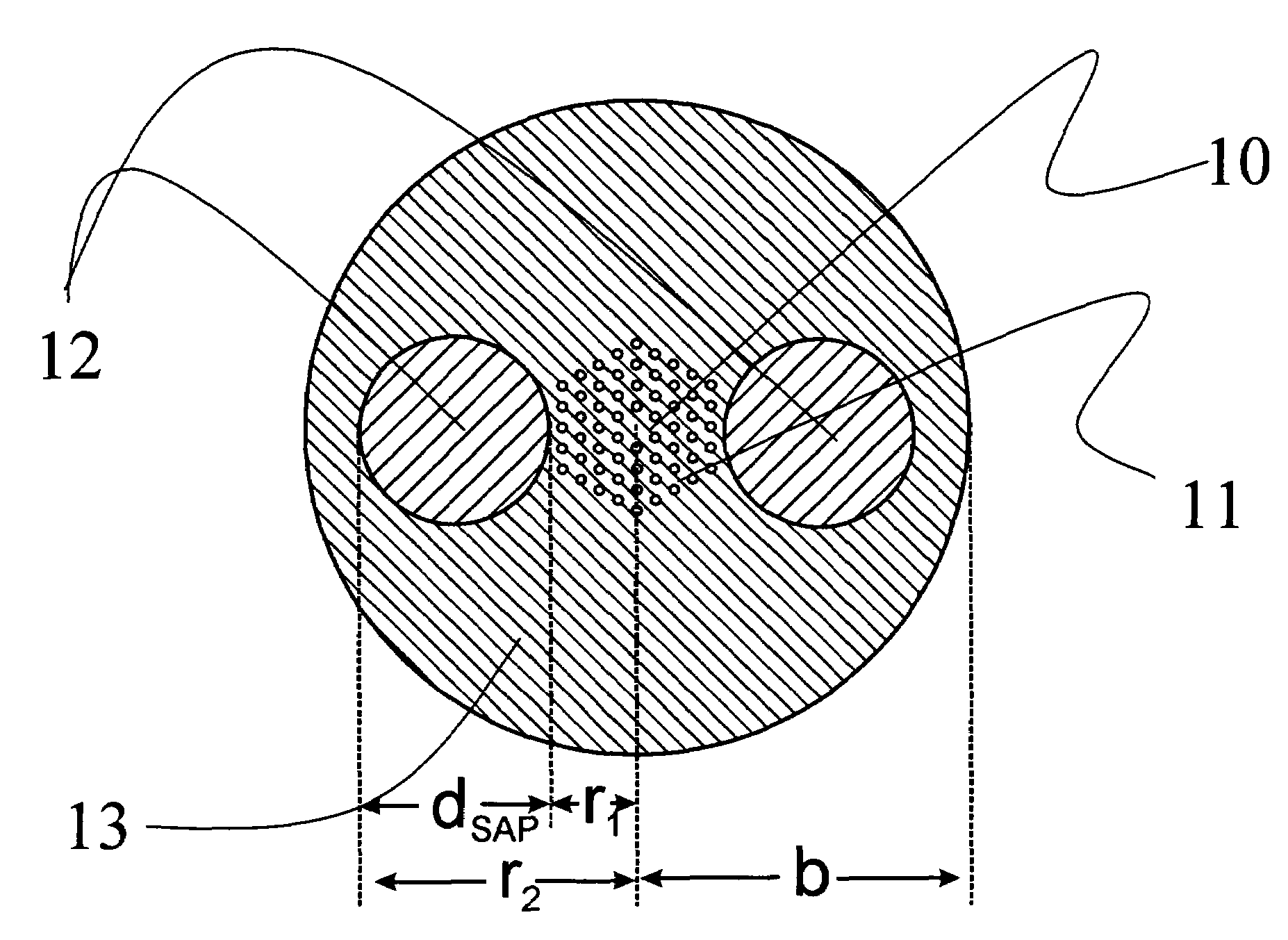
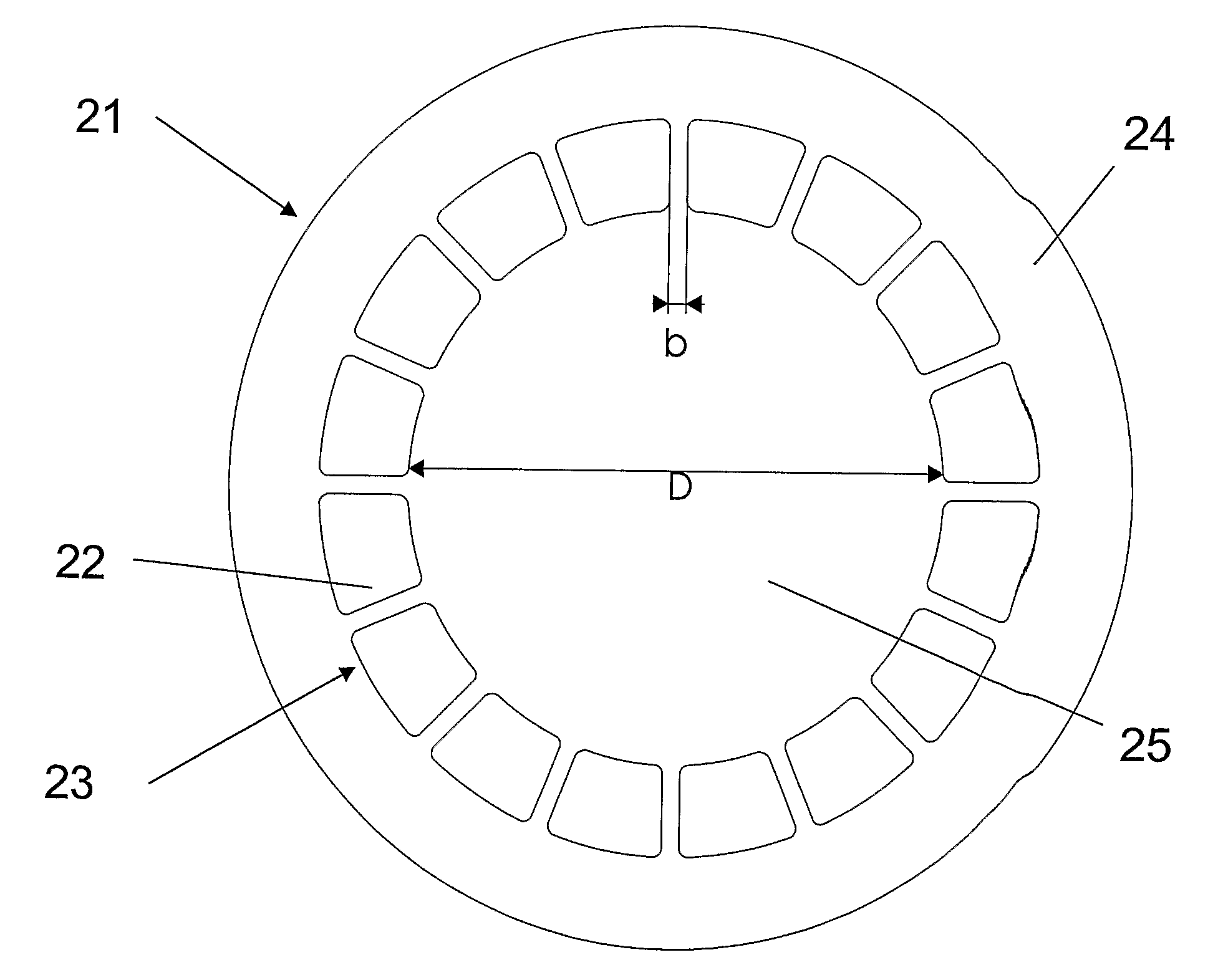
Photonic crystal fibres comprising stress elements
ActiveUS7289709B2Constant birefringenceSimple and economic wayGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with polarisationStress inducedPhotonic crystal
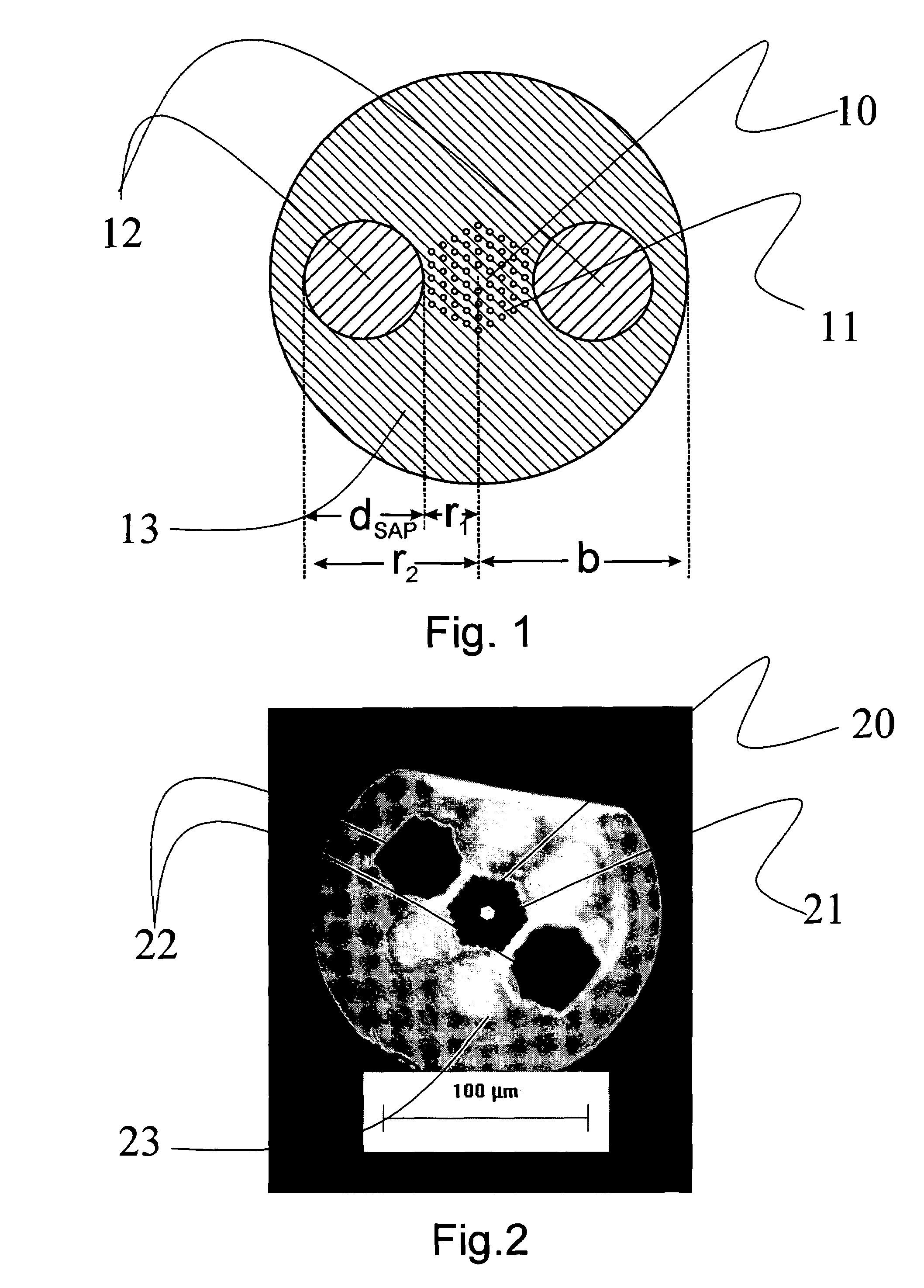
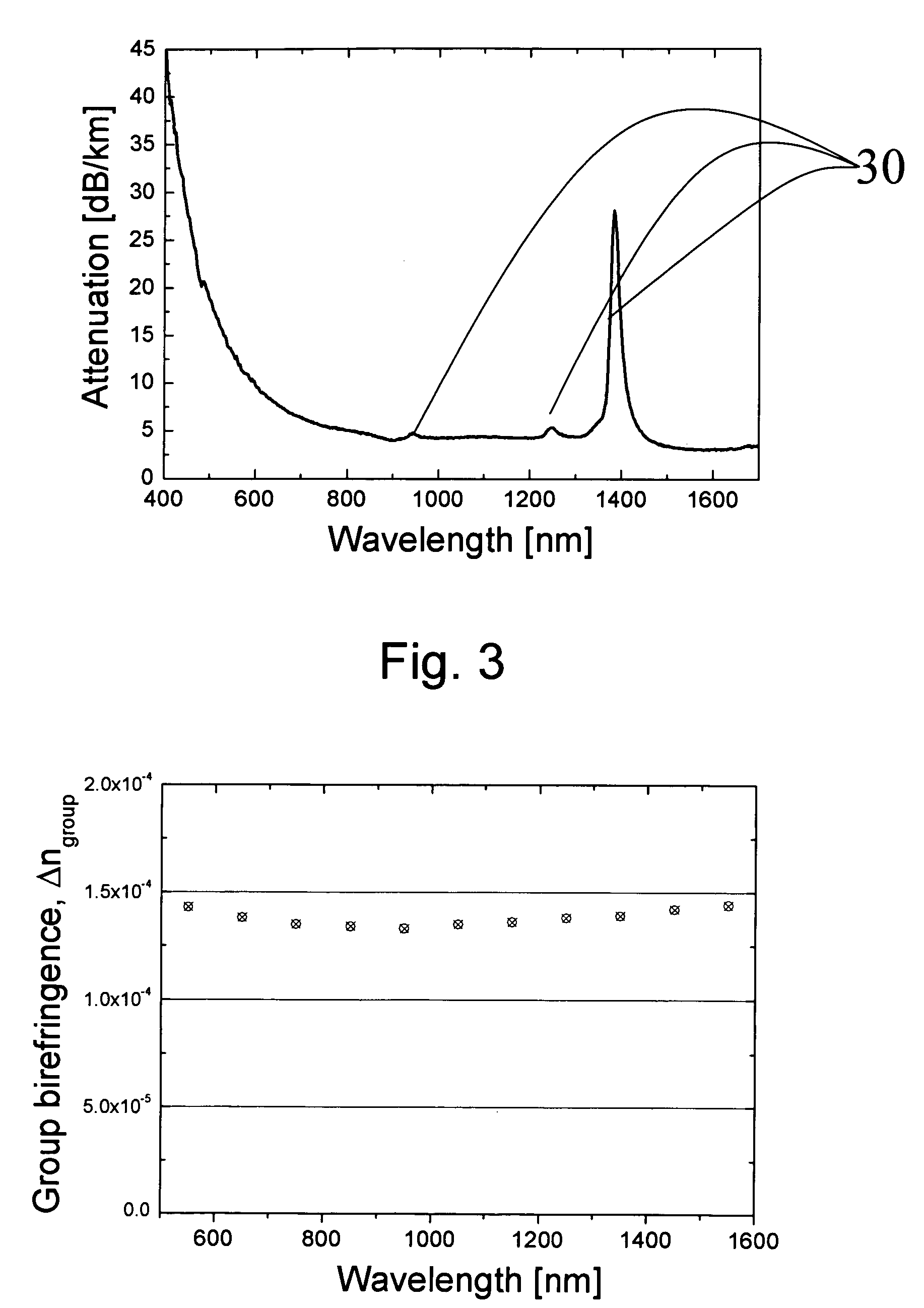
A photonic crystal fiber includes a core region for propagating light in a longitudinal direction of the fiber, a cladding region surrounding the core region, the cladding region including micro-structural elements extending in the longitudinal direction. The cladding region further includes at least one stress element having a coefficient of thermal expansion αT,SAP and extending in the longitudinal direction of the photonic crystal fiber, the stress element(s) being located in a cladding background material having a coefficient of thermal expansion αT,cladback different from αT,SAP. The location of the at least one stress element relative to the core region and the micro-structural elements and the coefficients of thermal expansion αT,SAP and αT,cladback are adapted to provide a stress induced birefringence in the core region of the photonic crystal fiber. An article includes a photonic crystal fiber, a method of manufacturing and the use of a photonic crystal fiber are furthermore provided.
Owner:CRYSTAL FIBRE AS
Thermally powered terahertz radiation source using photonic crystals
ActiveUS7078697B2Efficient collectionRadiation pyrometryTransit-time tubesTerahertz radiationPhotonics
Although THz radiation is naturally emitted by hot objects, the intensity levels are too weak to be considered as a practical THz source for most applications. Photonic crystal structures are used to modify the thermal emission peak associated with the standard Planck blackbody spectral distribution so that the THz region is dramatically enhanced. The photonic crystal core is preferably combined with variable Q defect cavities and a wave guiding and power combining structure so that the radiated THz energy is efficiently collected and directed to an output antenna. Higher THz emissions are realized by embedding a finer (higher frequency) photonic crystal structure within a coarser (lower frequency) structure.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
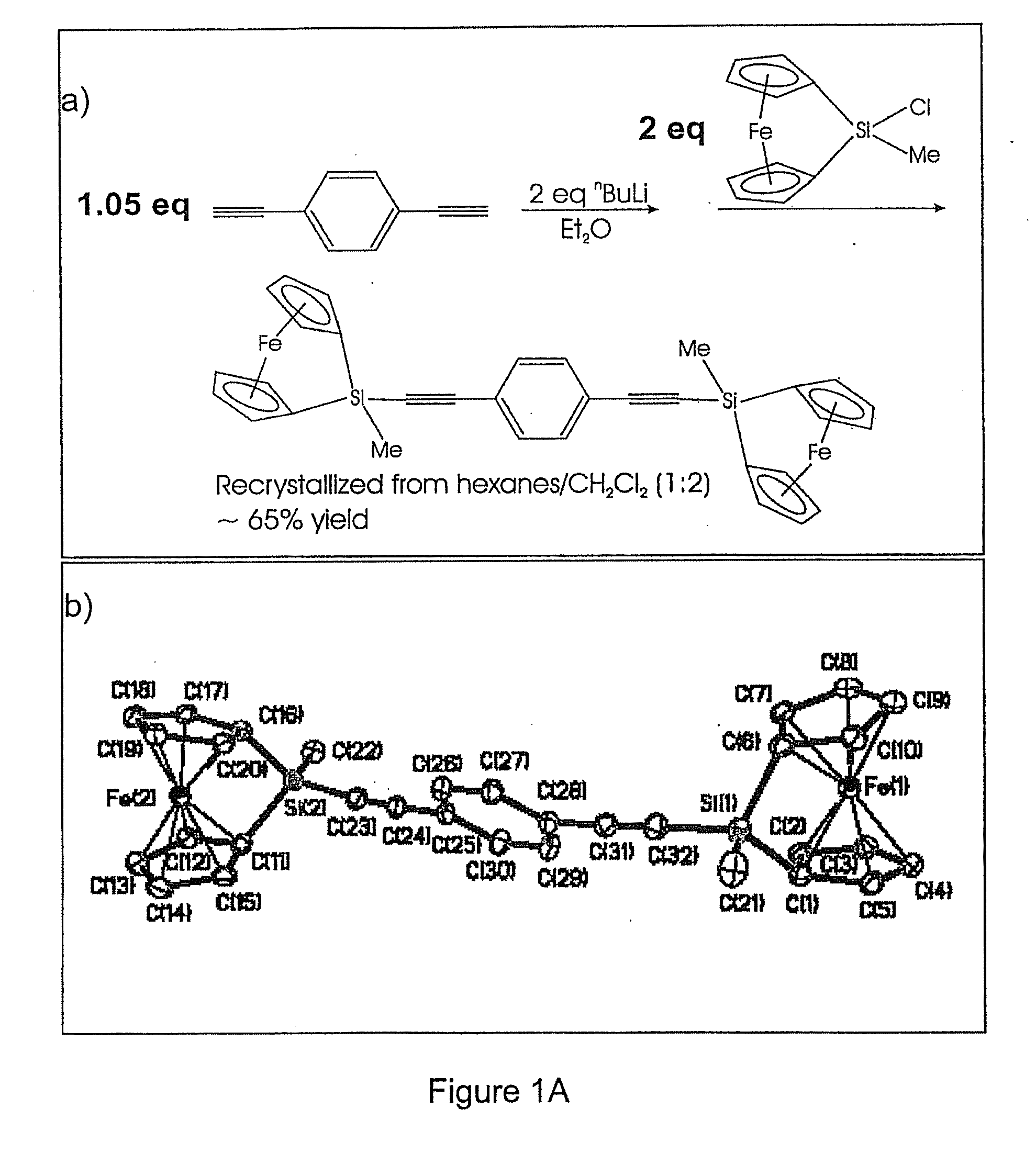
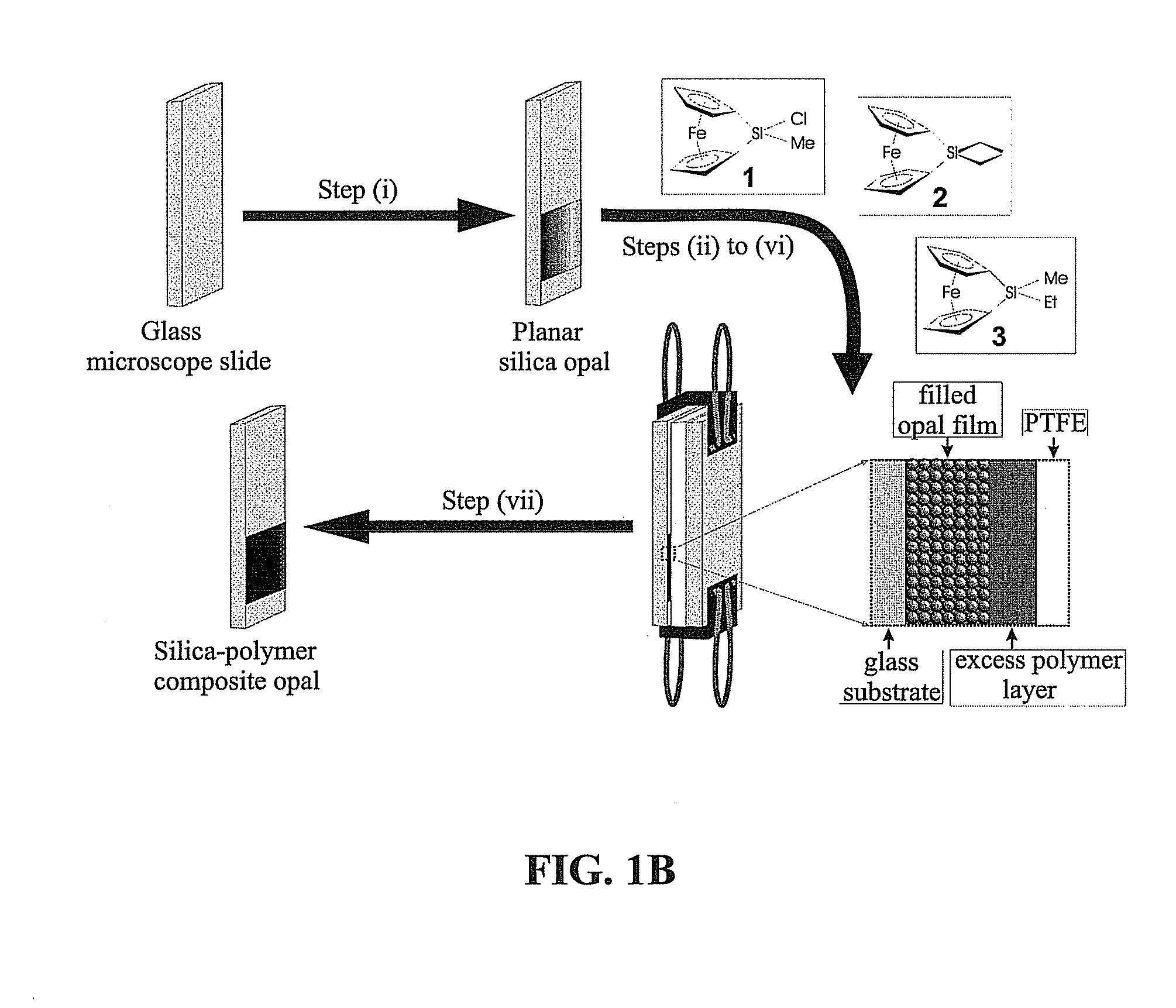
Self-assembled photonic crystals and methods for manufacturing same
InactiveUS6858079B2Well formedImprove assembly strengthFrom gel stateMaterial nanotechnologyPhotonic crystalGlobular shaped
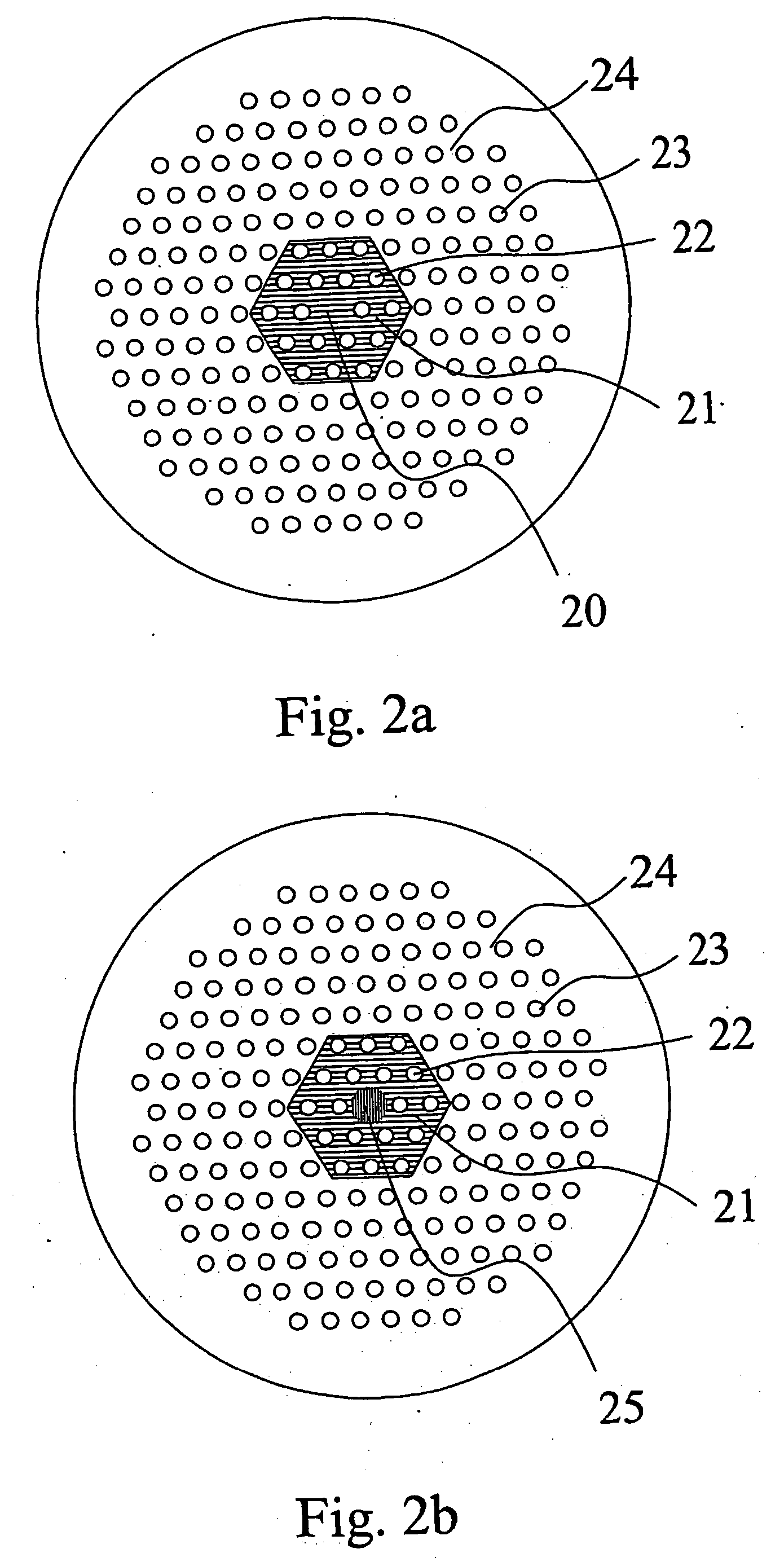
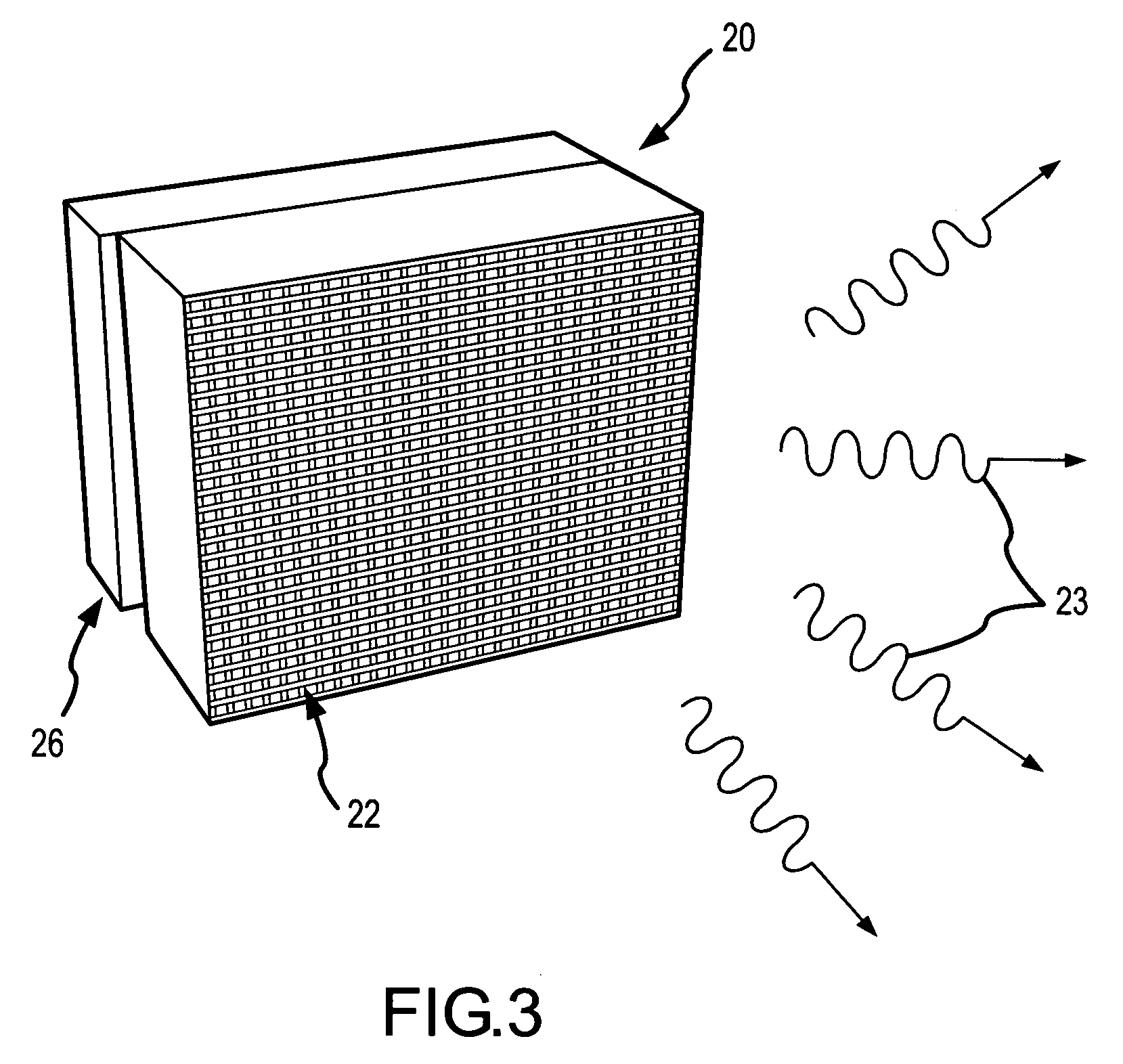
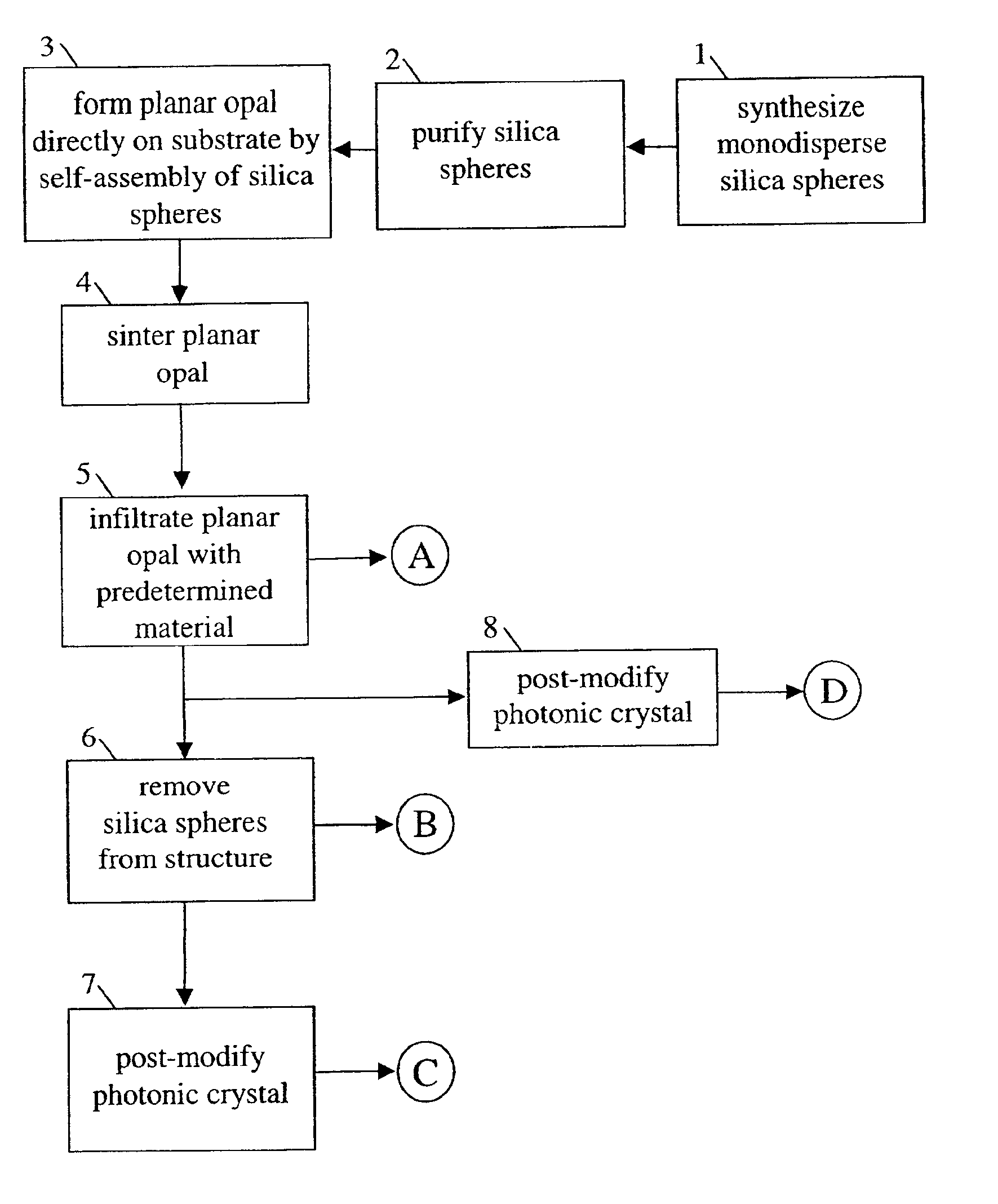
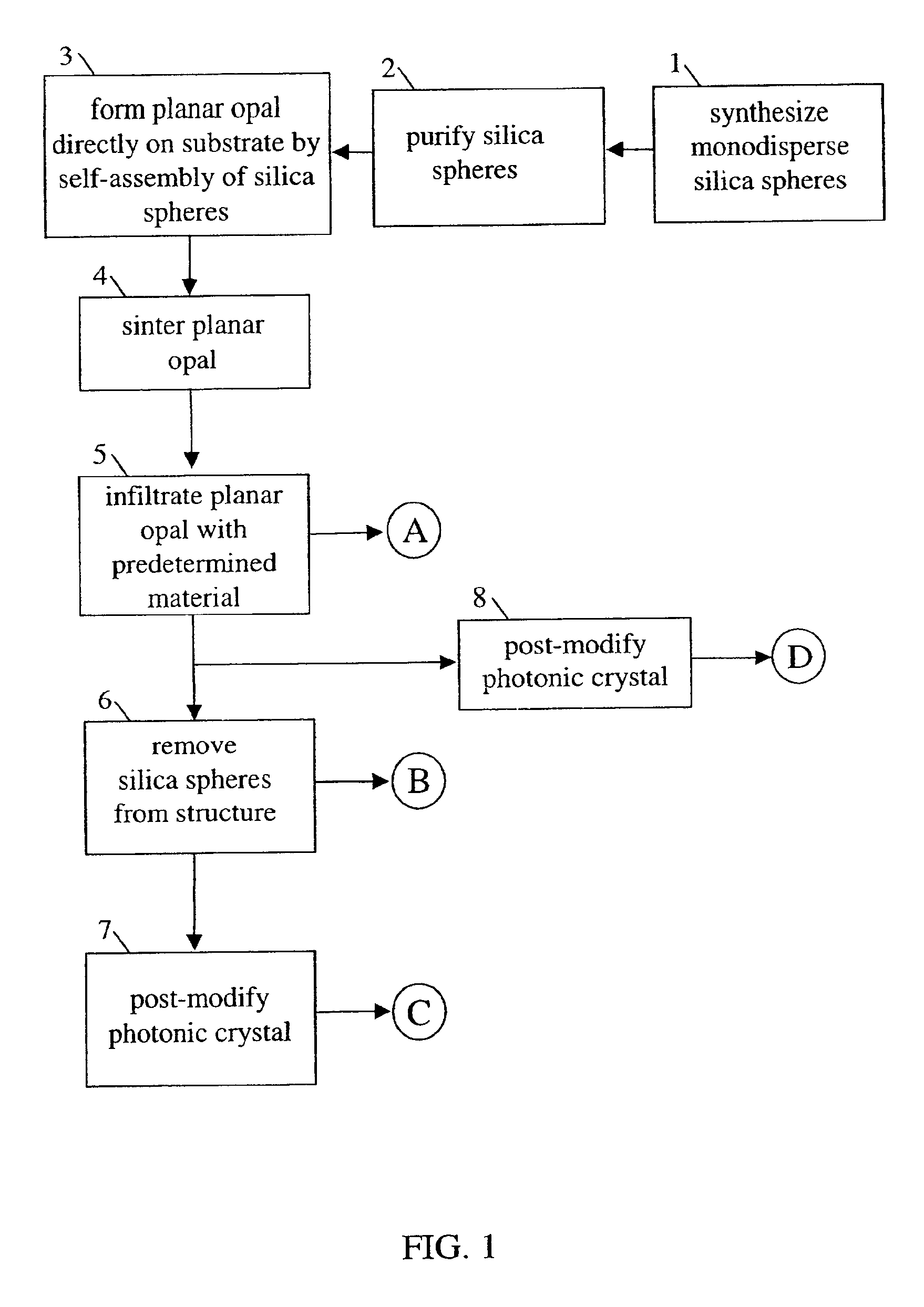
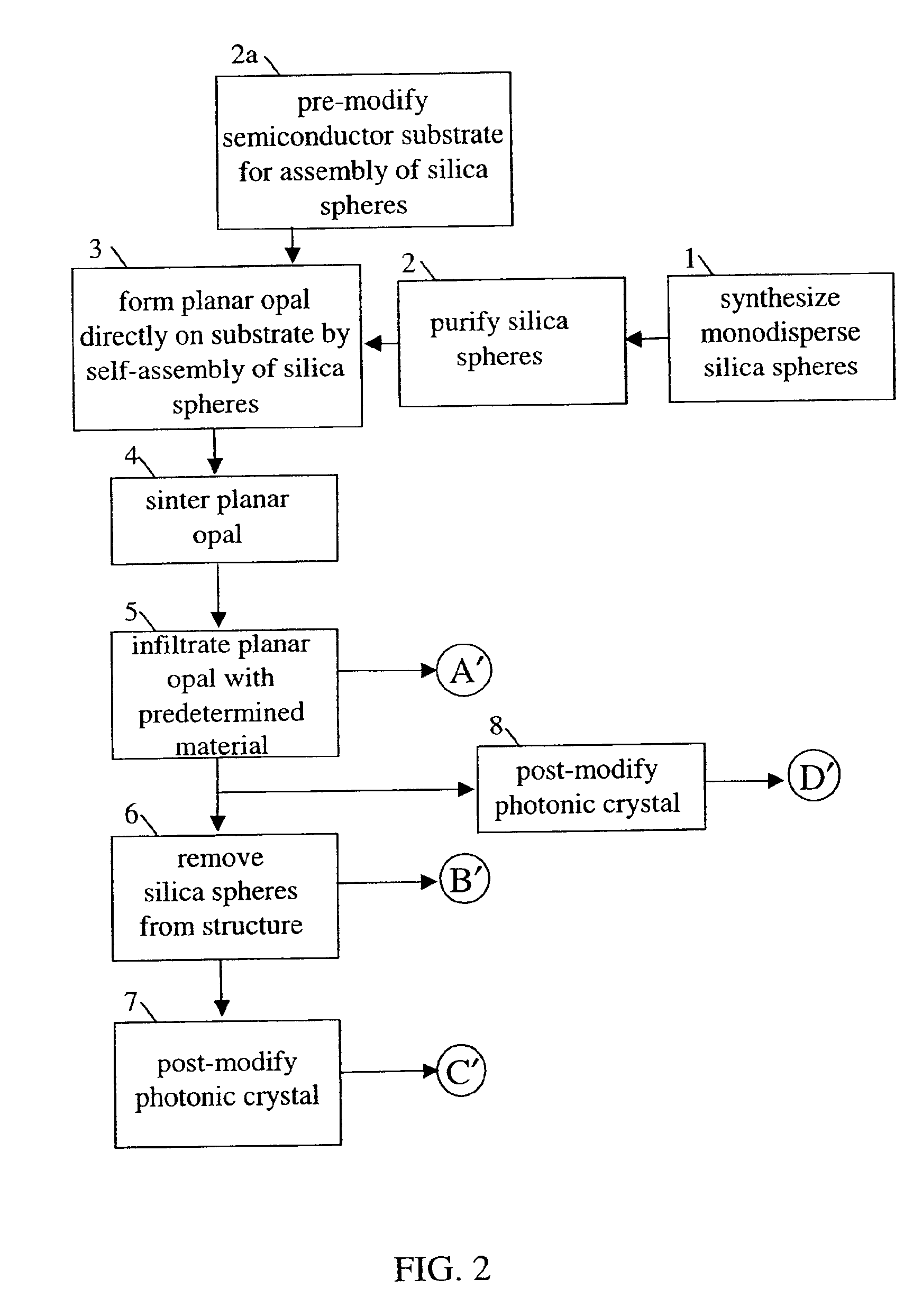
Self-assembled photonic crystals, including large sphere planar opals, infiltrated planar opals and inverted planar opals, as well as methods for manufacturing same are provided. Large sphere planar opals are manufactured according to a method comprising the steps of: synthesizing monodisperse silica spheres, wherein each of the silica spheres has a diameter greater than or equal to about 400 nanometers; purifying the silica spheres; and self-assembling the silica spheres into a plurality of ordered, planar layers on a substrate. Infiltrated planar opals may also be manufactured by further processing the large sphere planar opal by sintering the planar opal and infiltrating the planar opal with a predetermined material. Inverted planar opals may further be manufactured by removing the silica spheres from the infiltrated planar opal. Various modifications to the substrate and planar opal are also provided to enhance the properties of these photonic crystals.
Owner:NEC CORP
Photonic crystal sensors with intergrated fluid containment structure
ActiveUS20080219615A1Efficiently conveyedPrevent leakageMaterial analysis by optical meansNanoopticsSensor arrayRefractive index
Photonic crystal (PC) sensors, and sensor arrays and sensing systems incorporating PC sensors are described which have integrated fluid containment and / or fluid handling structures. Sensors and sensing systems of the present disclosure are capable of high throughput sensing of analytes in fluid samples, bulk refractive index detection, and label-free detection of a range of molecules, including biomolecules and therapeutic candidates. The present disclosure also provides a commercially attractive fabrication platform for making photonic crystal sensors and systems wherein an integrated fluid containment structure and a photonic crystal structure are fabricated in a single molding or imprinting processing step amendable to high throughput processing.
Owner:X BODY +1
Optical coupler devices, methods of their production and use
InactiveUS7526165B2Laser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingDouble-clad fiberWaveguide
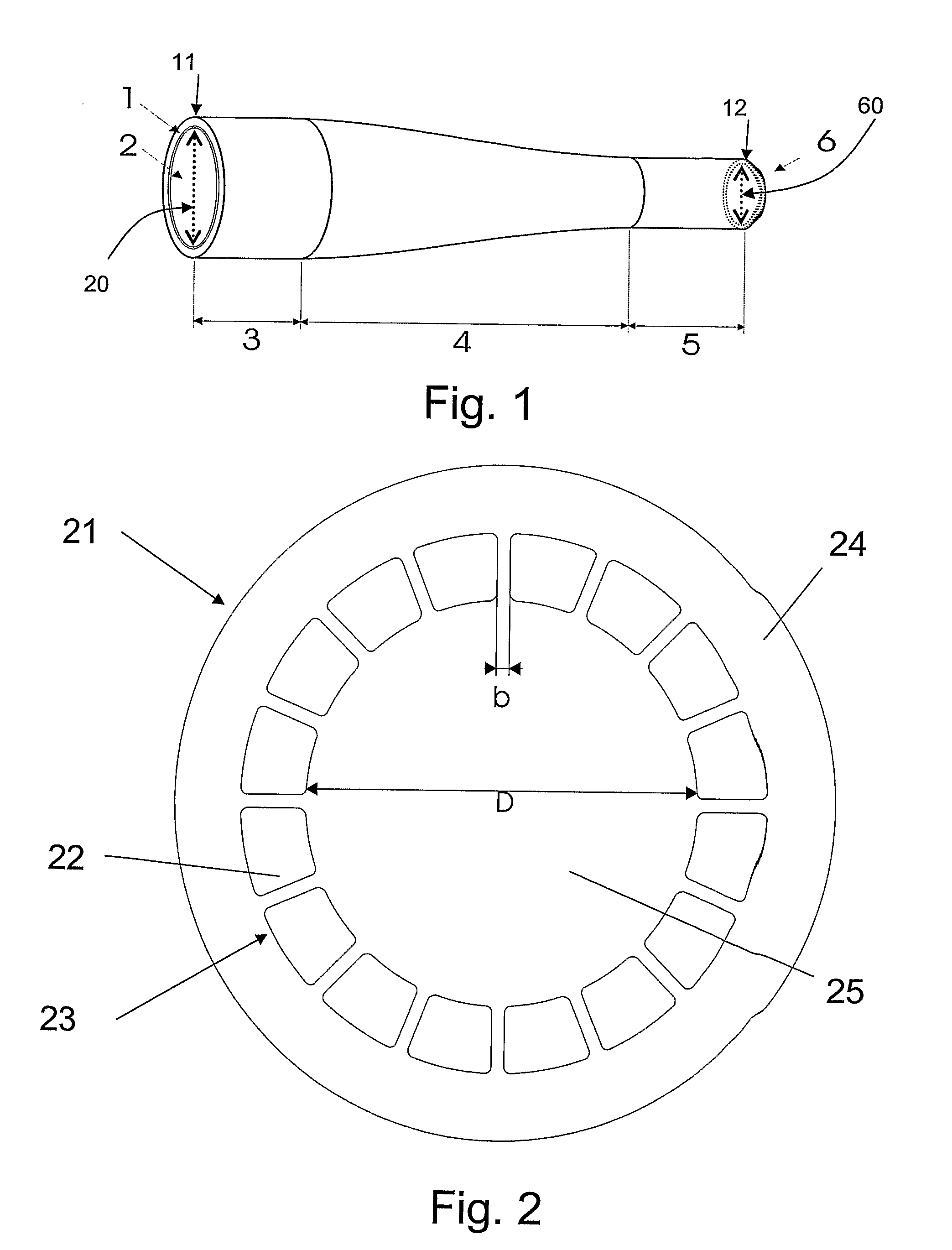
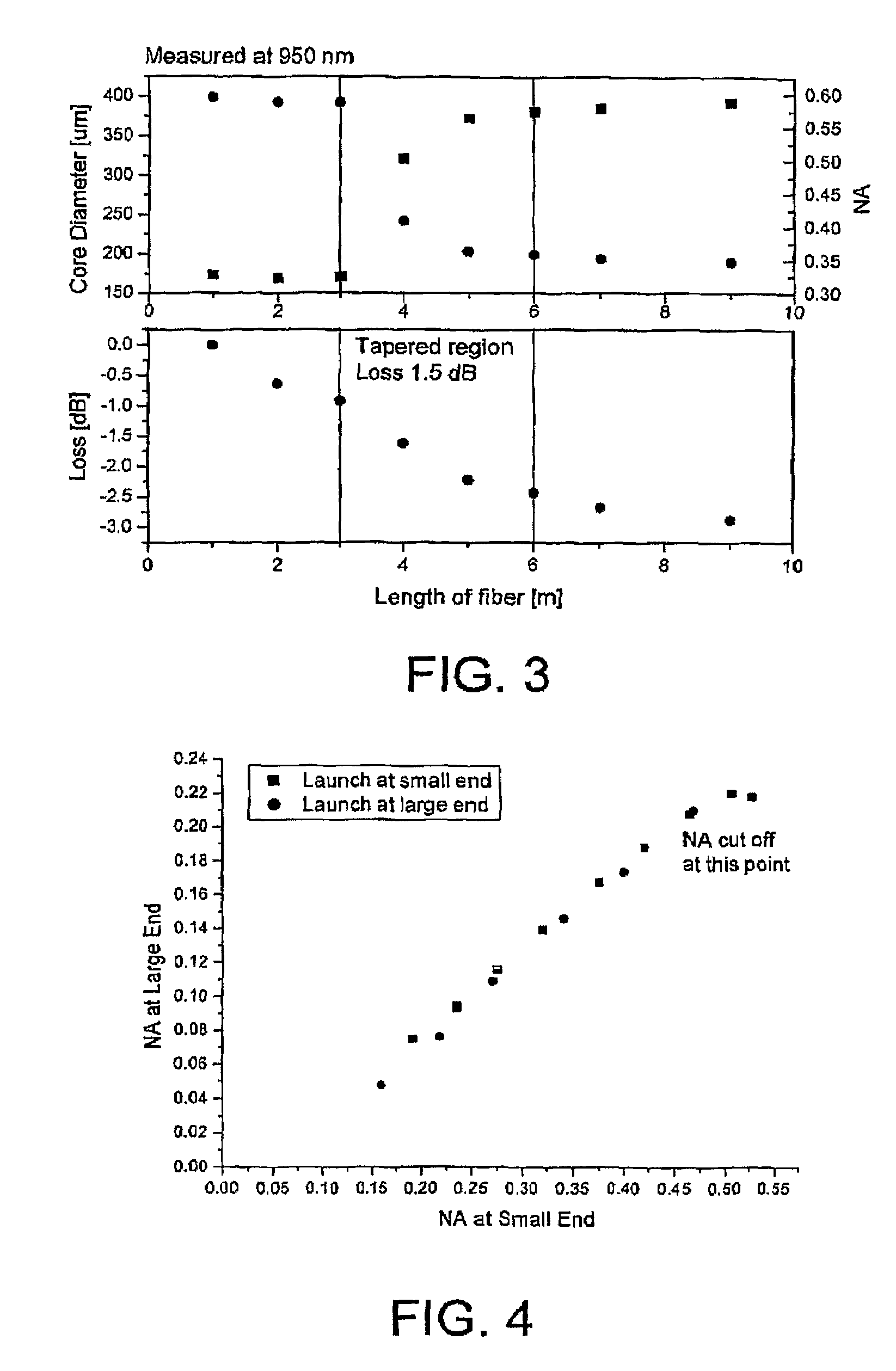
The present invention relates in general to coupling of light from one or more input waveguides to an output waveguide or output section of a waveguide having other physical dimensions and / or optical properties than the input waveguide or waveguides. The invention relates to an optical component in the form of a photonic crystal fiber for coupling light from one component / system with a given numerical aperture to another component / system with another numerical aperture. The invention further relates to methods of producing the optical component, and articles comprising the optical component, and to the use of the optical component. The invention further relates to an optical component comprising a bundle of input fibers that are tapered and fused together to form an input coupler e.g. for coupling light from several light sources into a single waveguide. The invention still further relates to the control of the spatial extension of a guided mode (e.g. a mode-field diameter) of an optical beam in an optical fiber. The invention relates to a tapered longitudinally extending optical waveguide having a relatively larger cross section that over a certain longitudinal distance is tapered down to a relatively smaller cross section wherein the spatial extent of the guided mode is substantially constant or expanding from the relatively larger to the relatively smaller waveguide cross section. The invention may e.g. be useful in applications such as fiber lasers or amplifiers, where light must be coupled efficiently from pump sources to a double clad fiber.
Owner:CRYSTAL FIBRE AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com