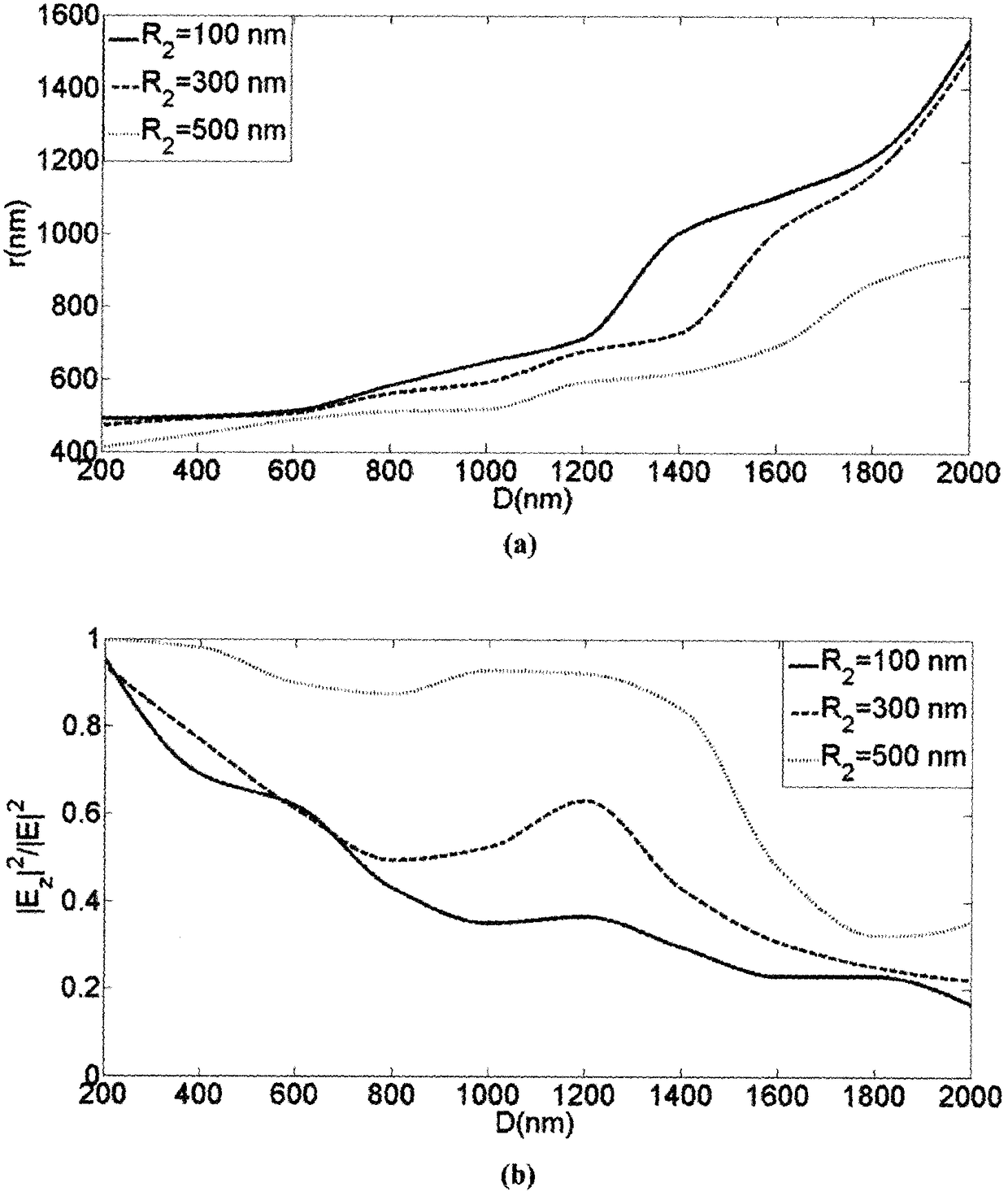
Patents
Literature
47 results about "Longitudinal field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
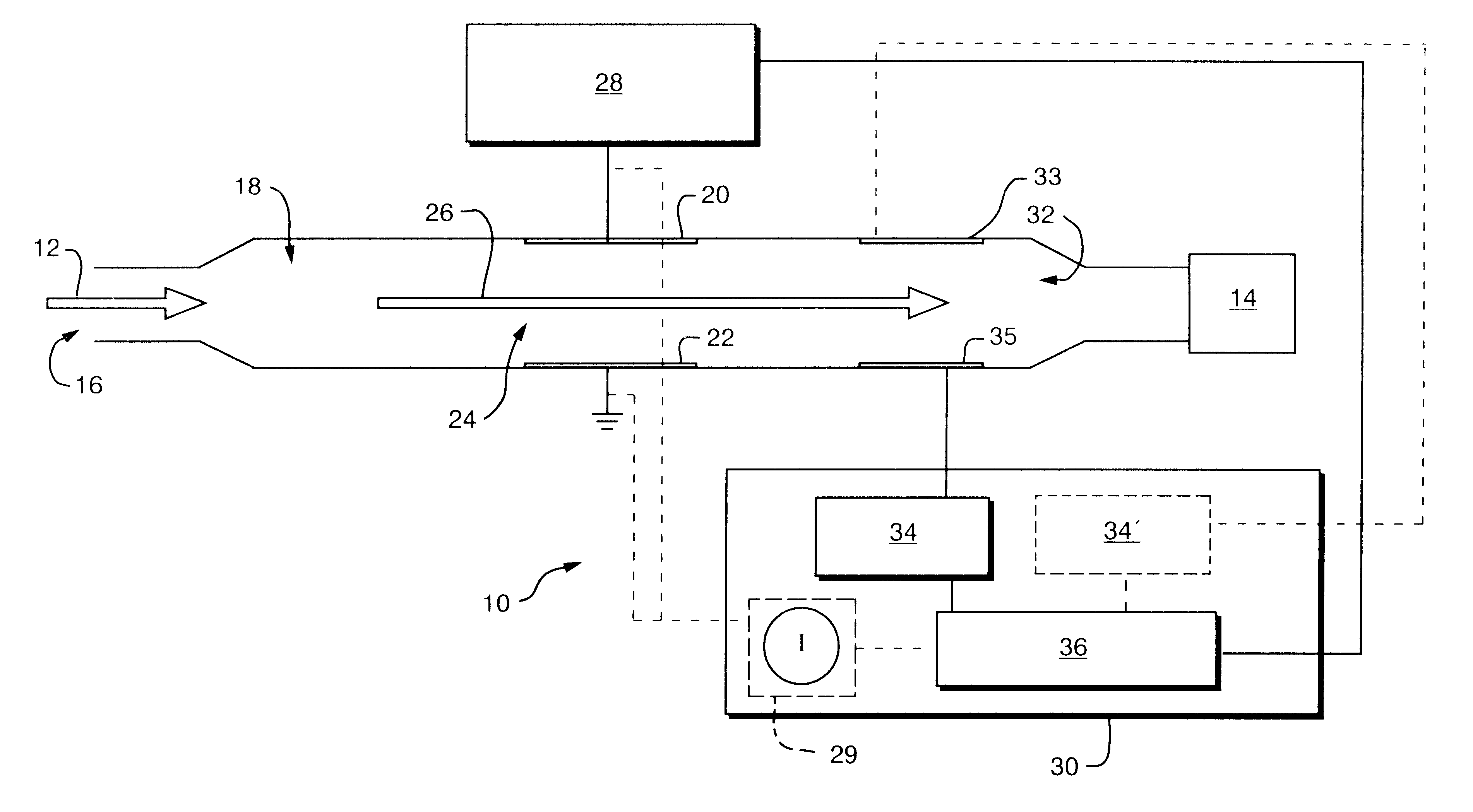
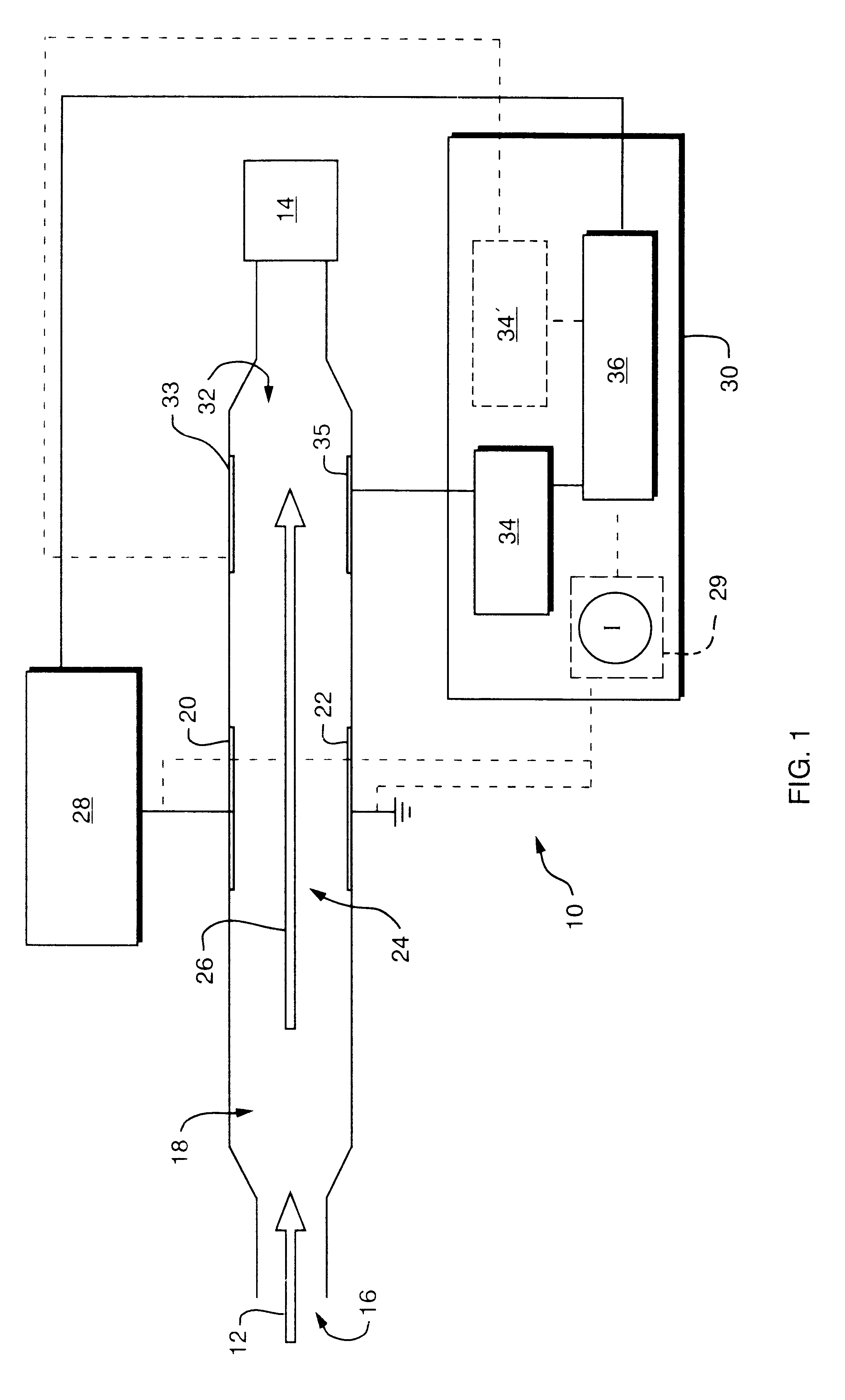
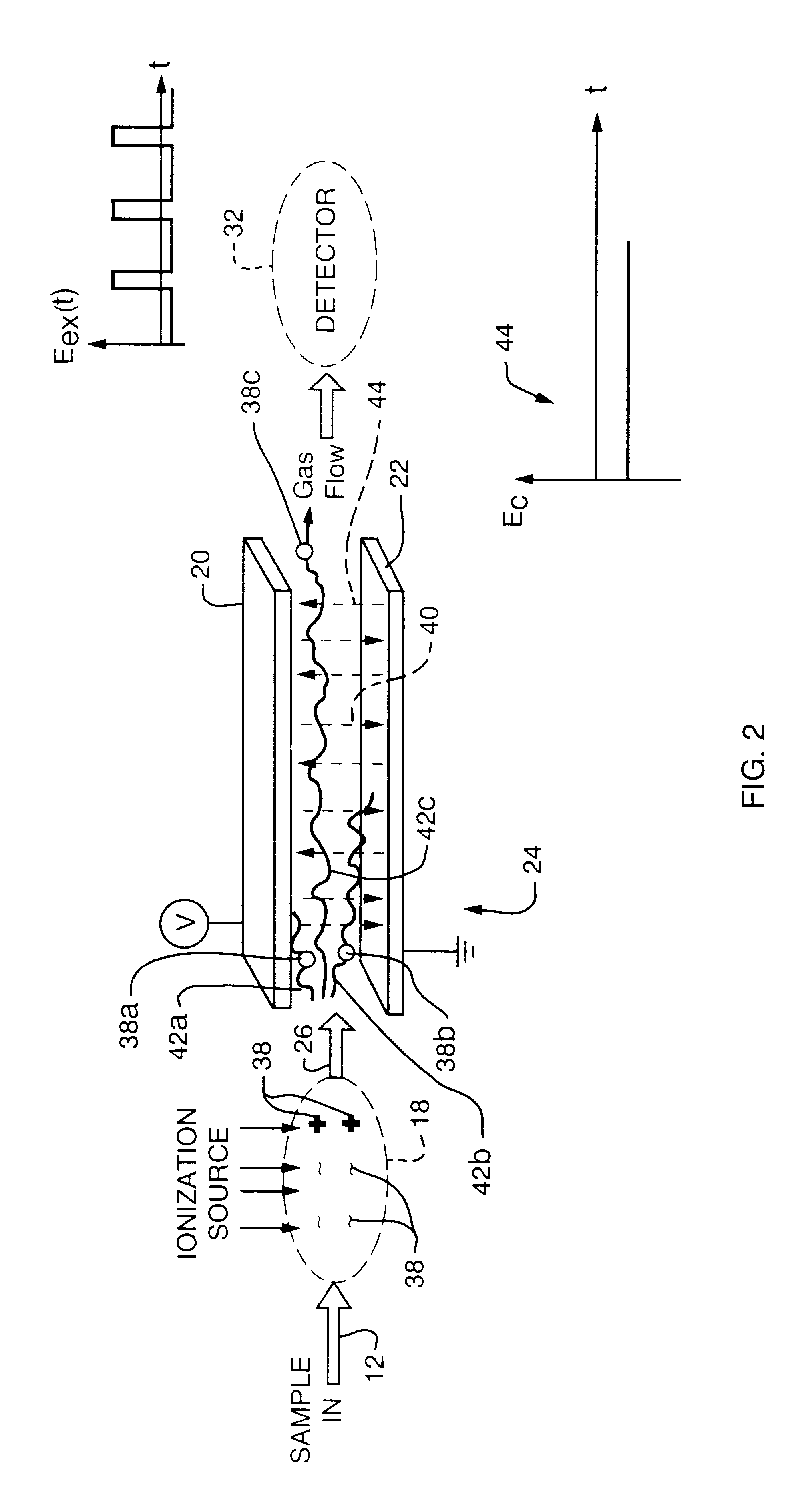
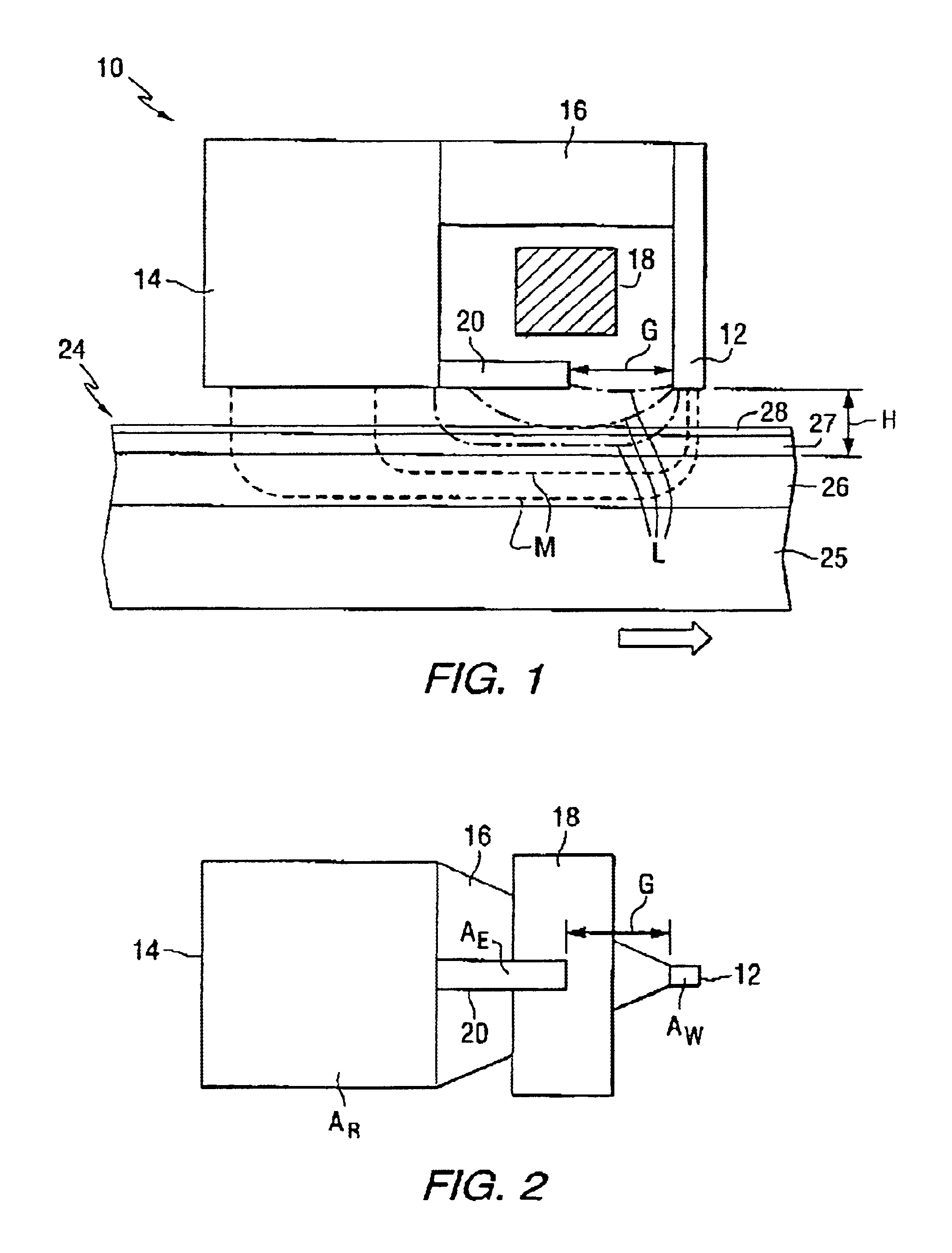
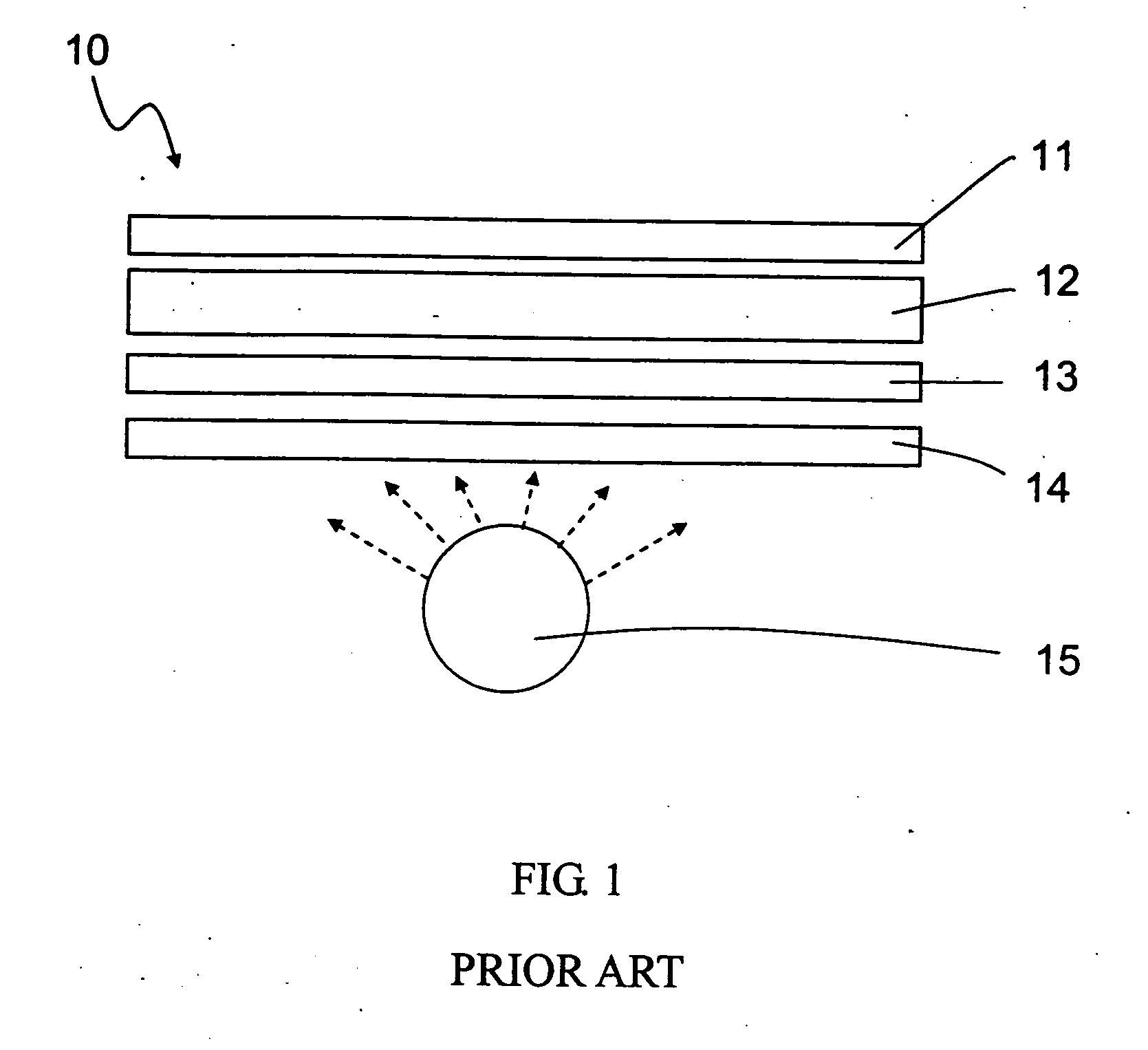
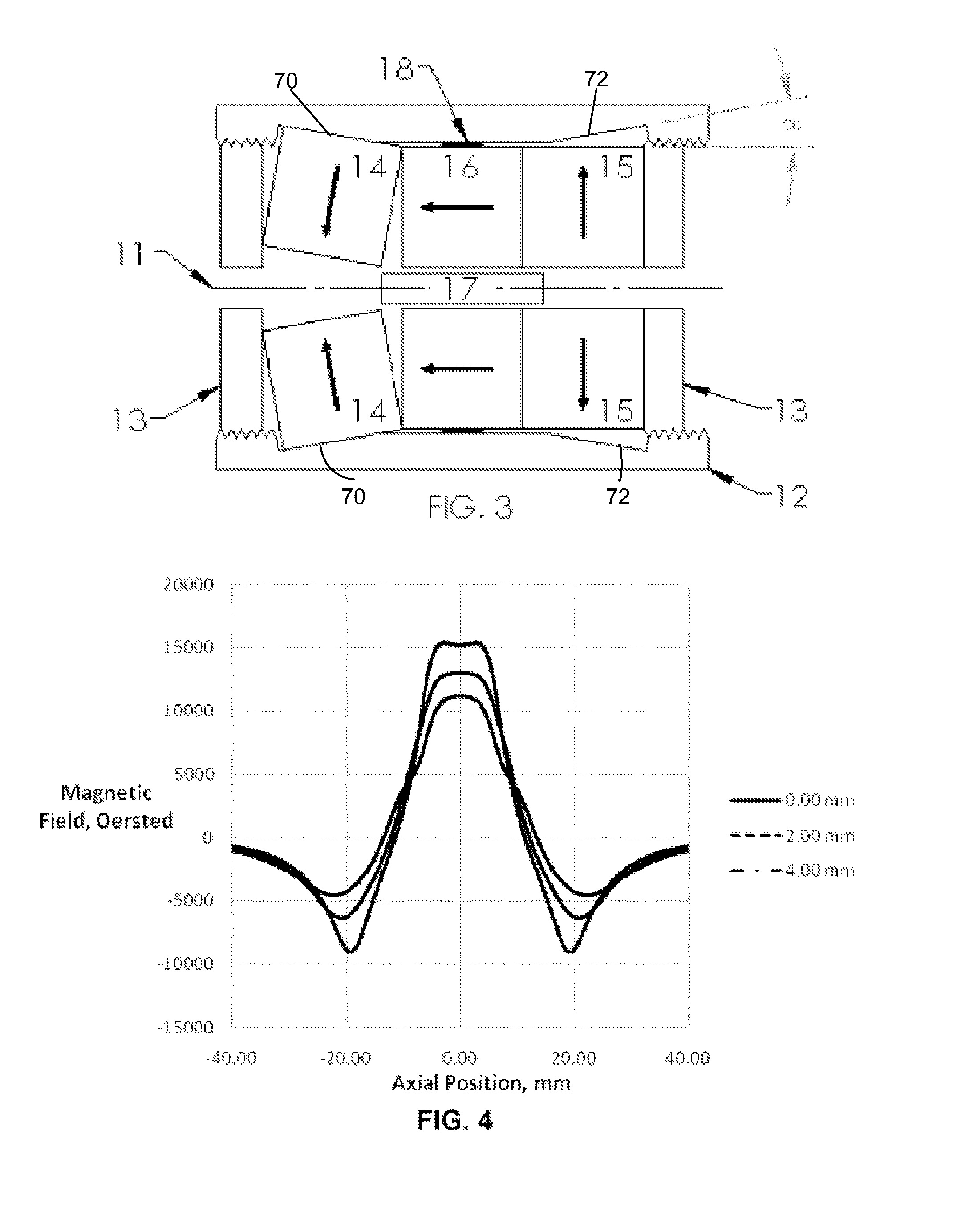
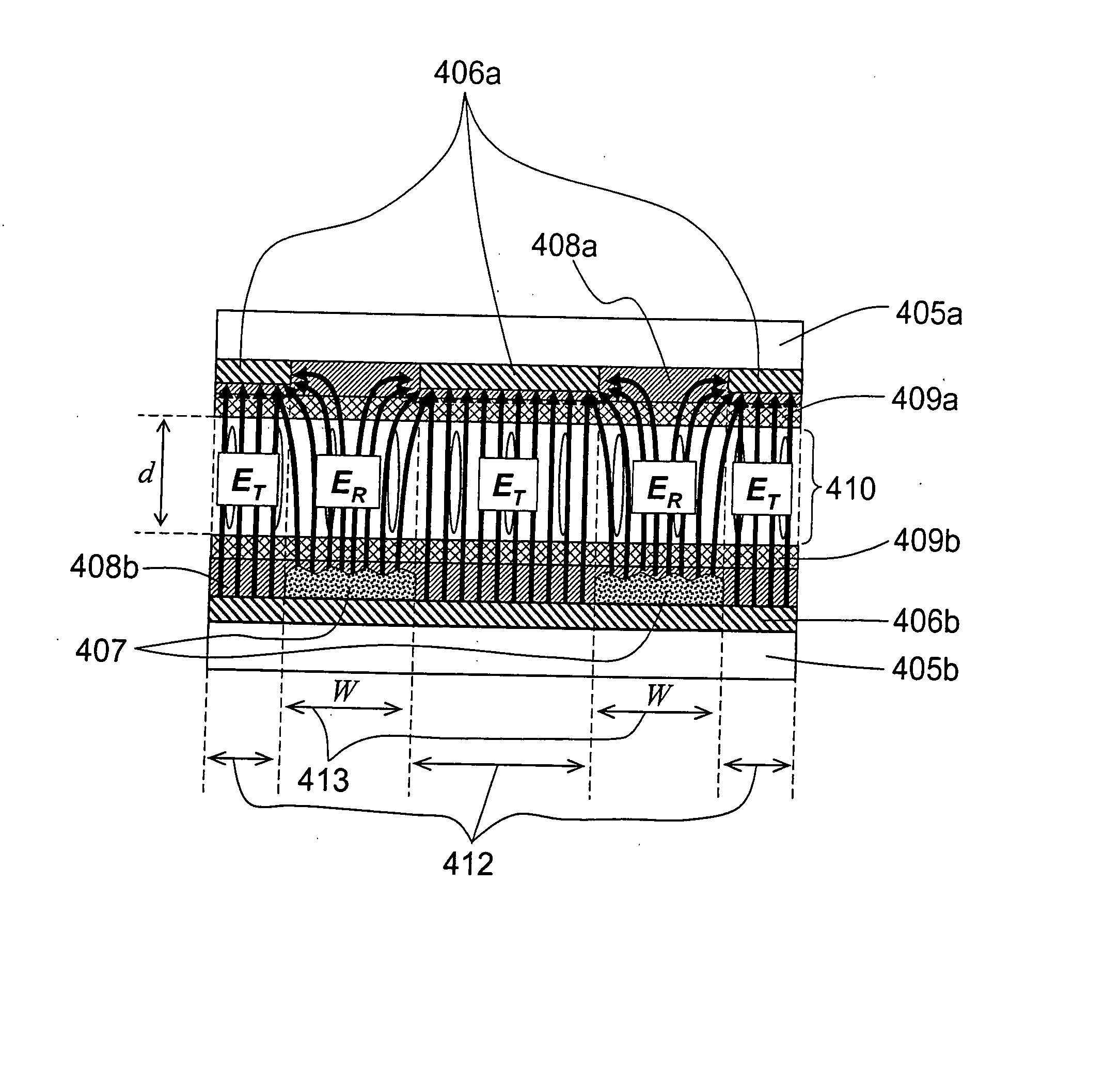
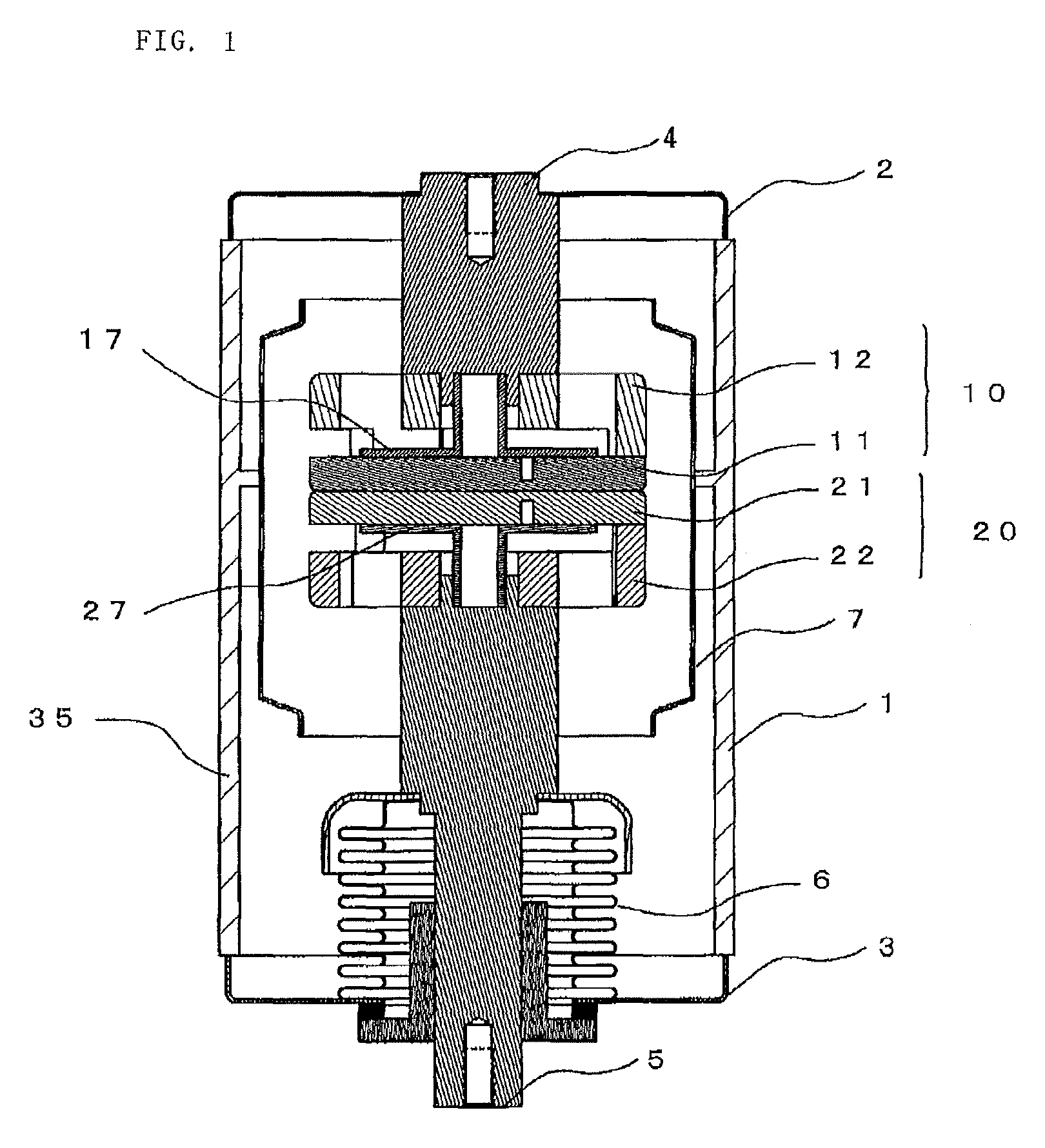
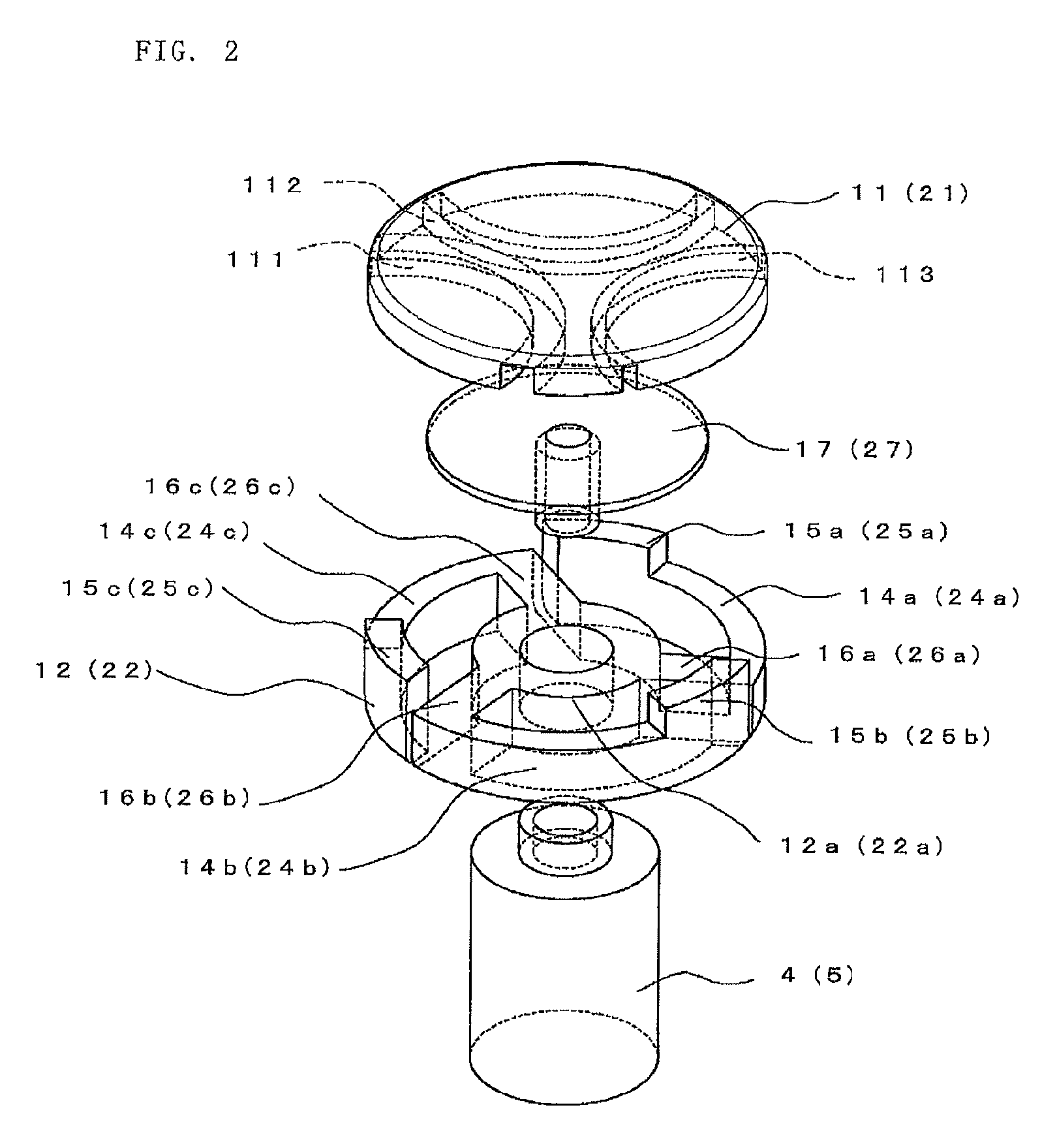
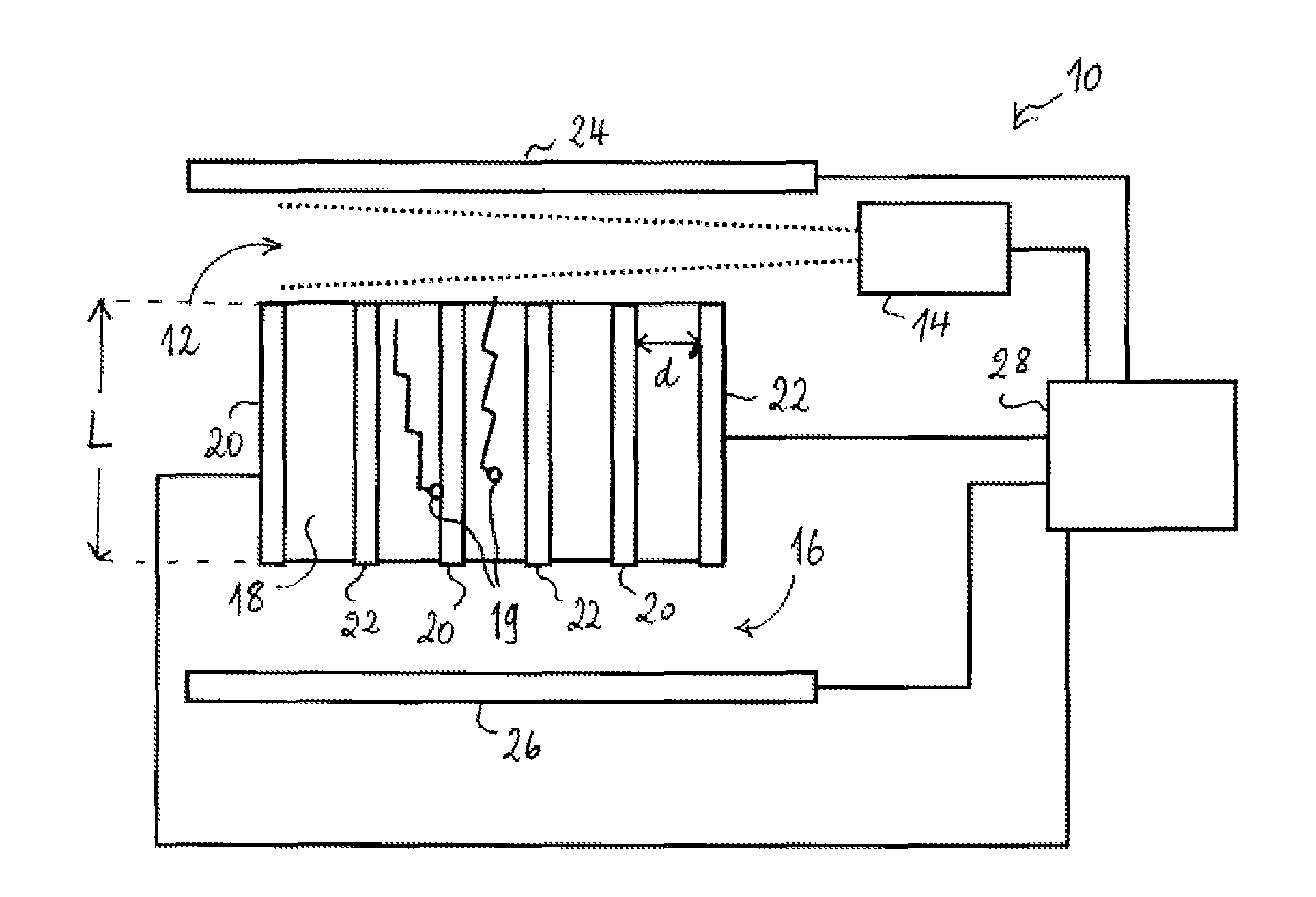
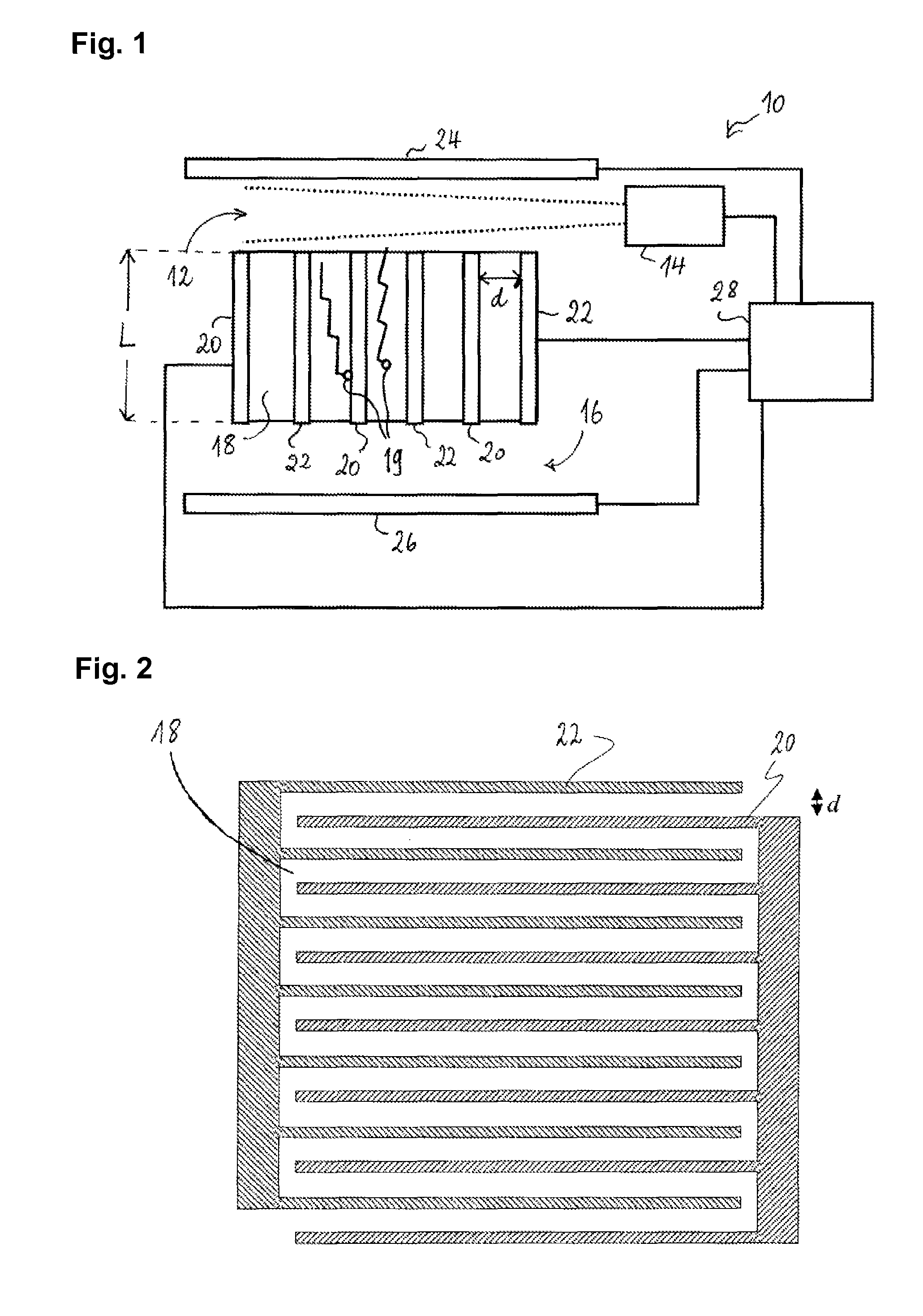
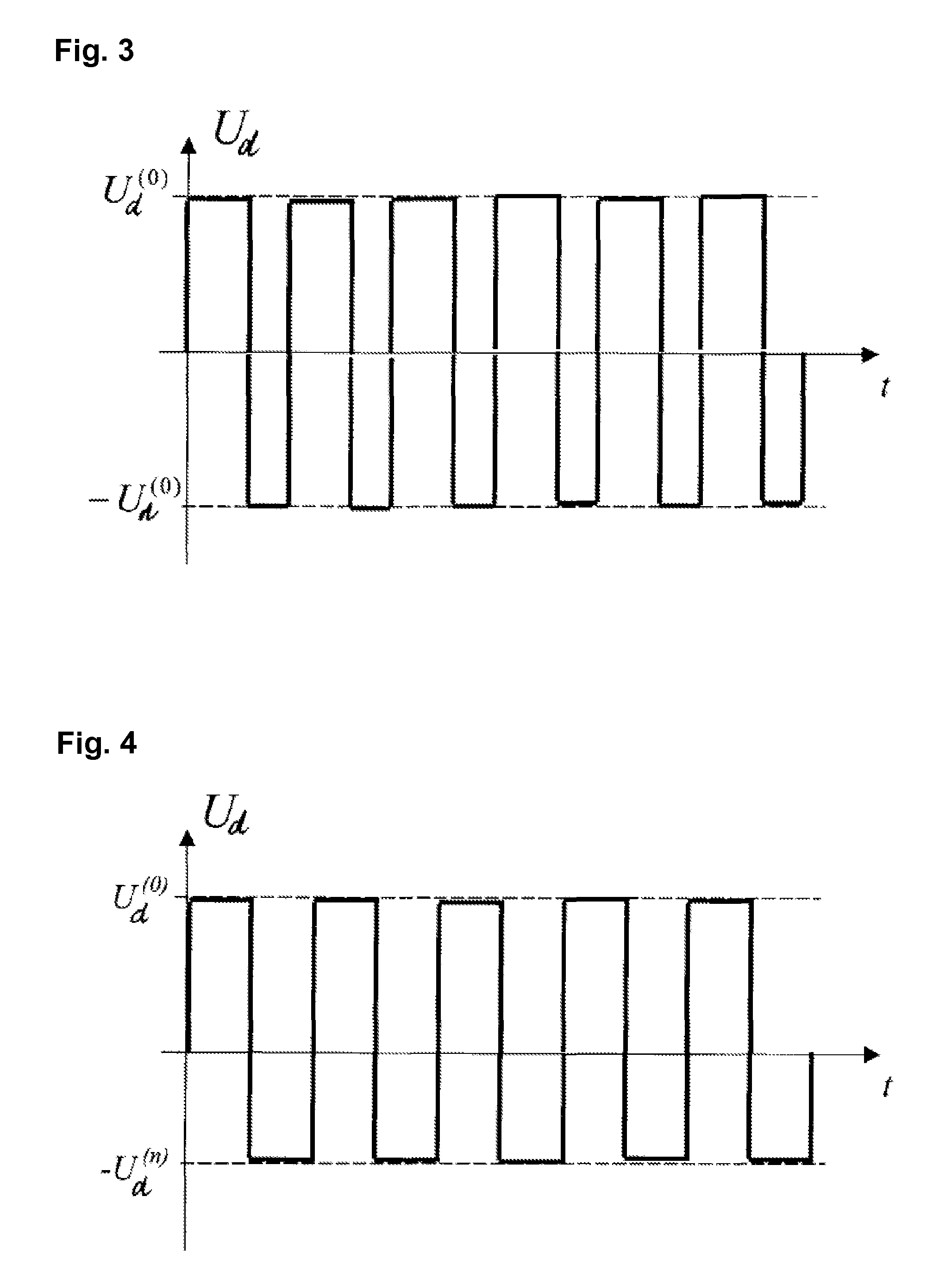
Longitudinal field driven field asymmetric ion mobility filter and detection system
InactiveUS6512224B1Improve accuracyHigh resolutionStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersNon symmetricIon-mobility spectrometry
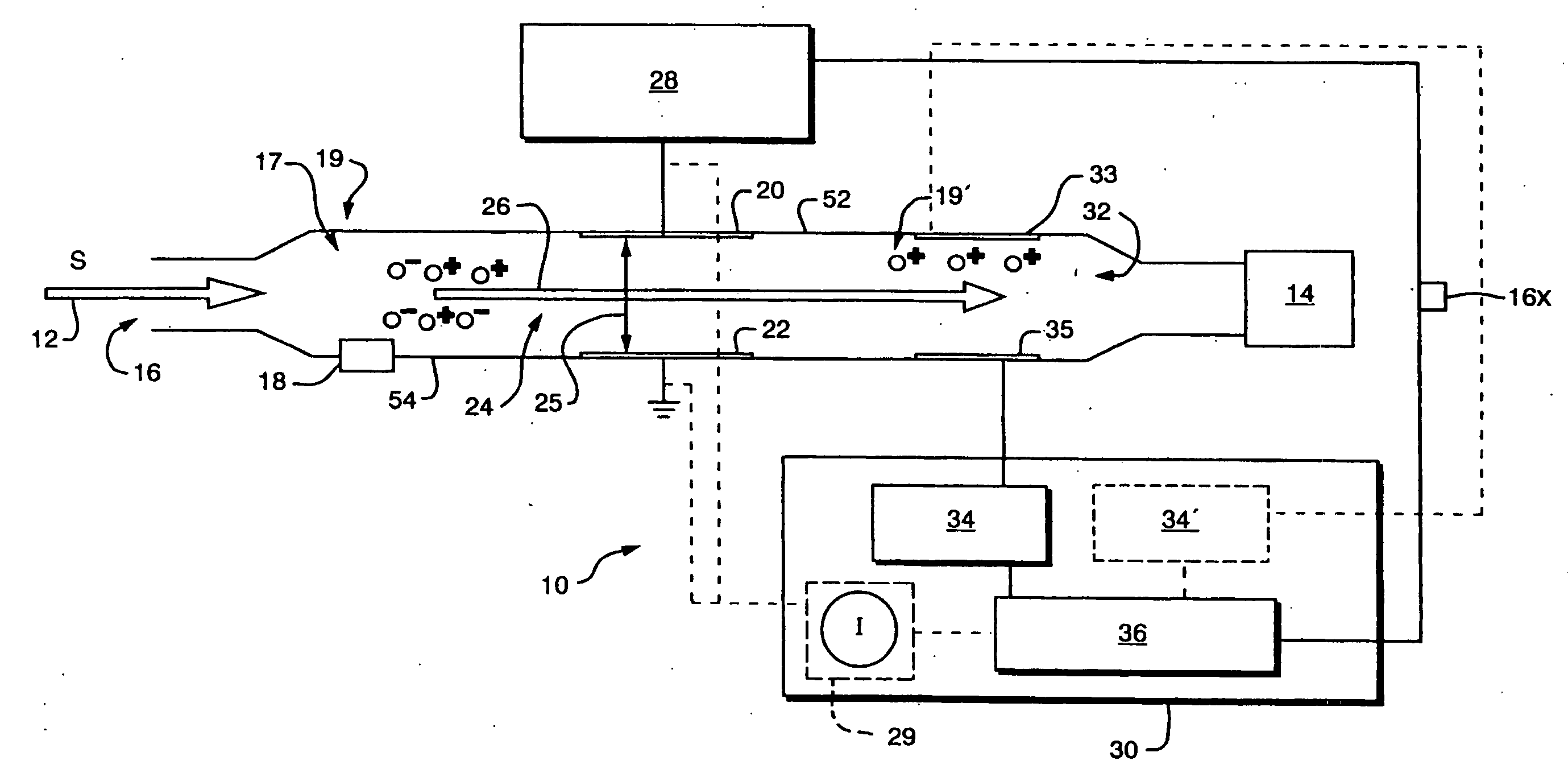
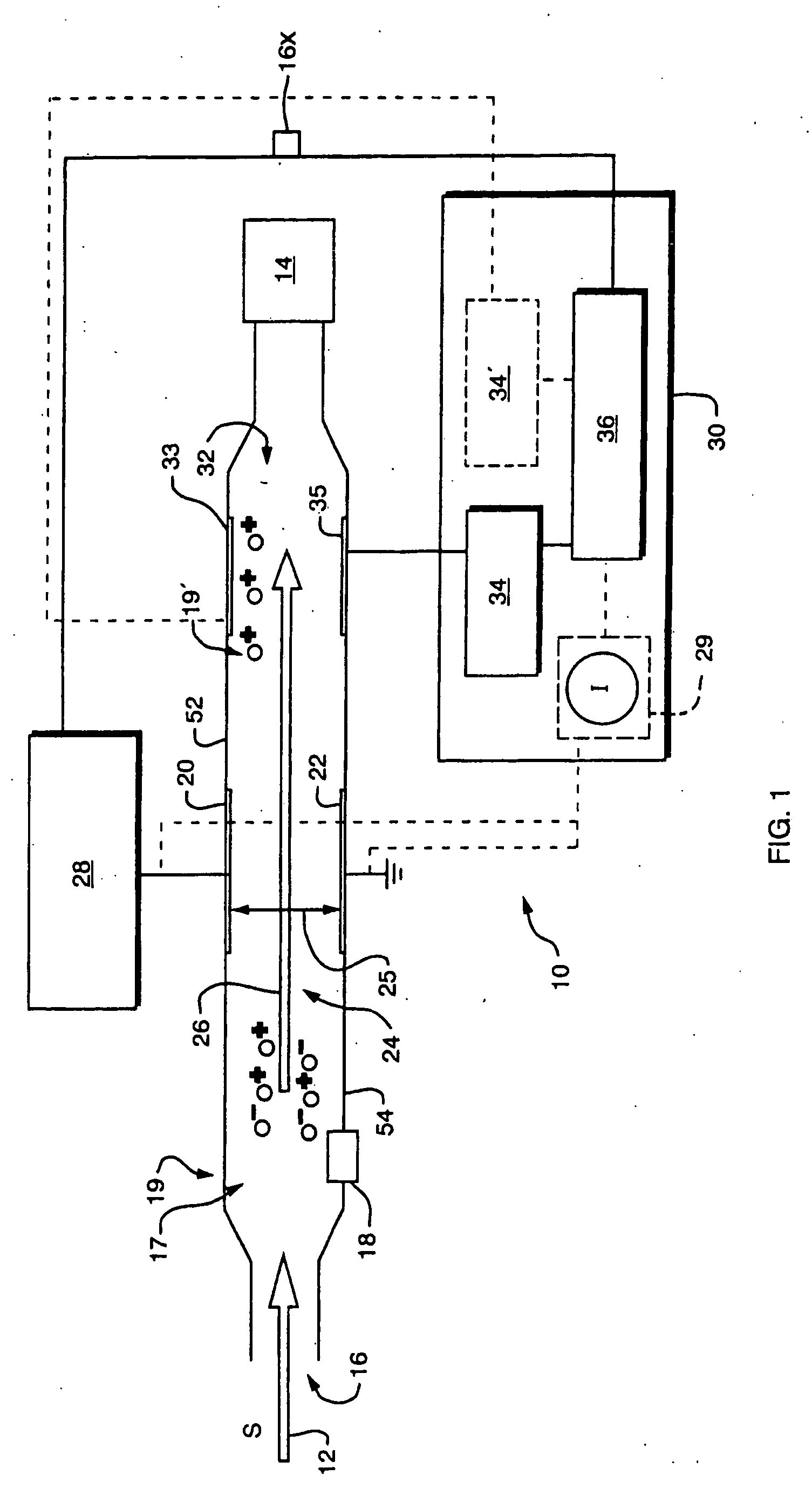
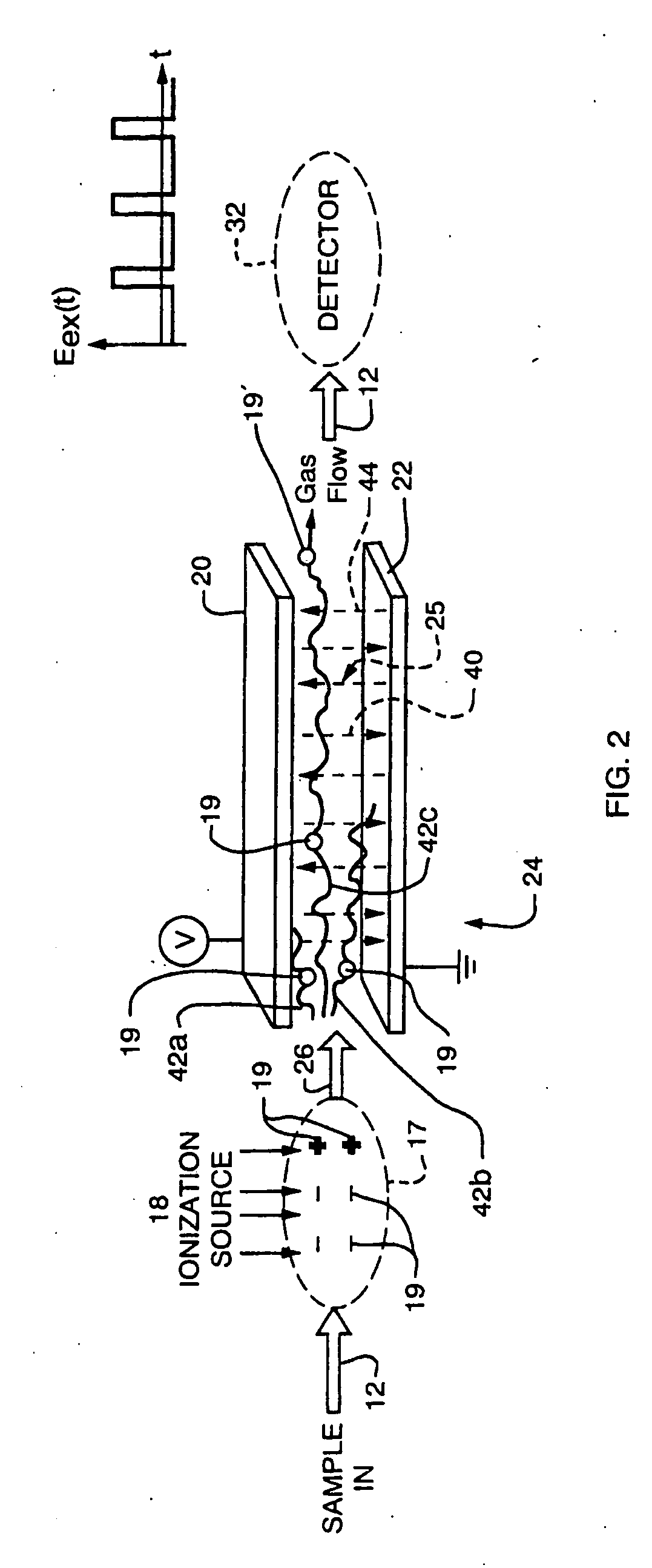
An asymmetric field ion mobility spectrometer with an ionization source for ionizing a sample media and creating ions. An ion filter is disposed in the analytical gap downstream from the ionization source for creating an asymmetric electric field to filter the ions. An ion flow generator for creating an electric field in a direction transverse to the asymmetric electric field and which propels the ions through the asymmetric electric field towards a detector.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Perpendicular magnetic recording head with longitudinal magnetic field generator to facilitate magnetization switching
InactiveUS6816339B1Increase motivationConstruction of head windingsRecord information storageMagnetizationMagnetic poles
A perpendicular magnetic recording head includes a perpendicular writing pole and a longitudinal field generator which rotates the magnetization of the perpendicular recording media prior to writing, thereby facilitating magnetization switching. The longitudinal magnetic field may be provided by a narrowed gap between the trailing write pole and the leading return pole of the head. The gap structure is designed to provide a fringing magnetic field between the poles which generates the longitudinal magnetic field in perpendicular recording media as the media travels under the perpendicular writing pole.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
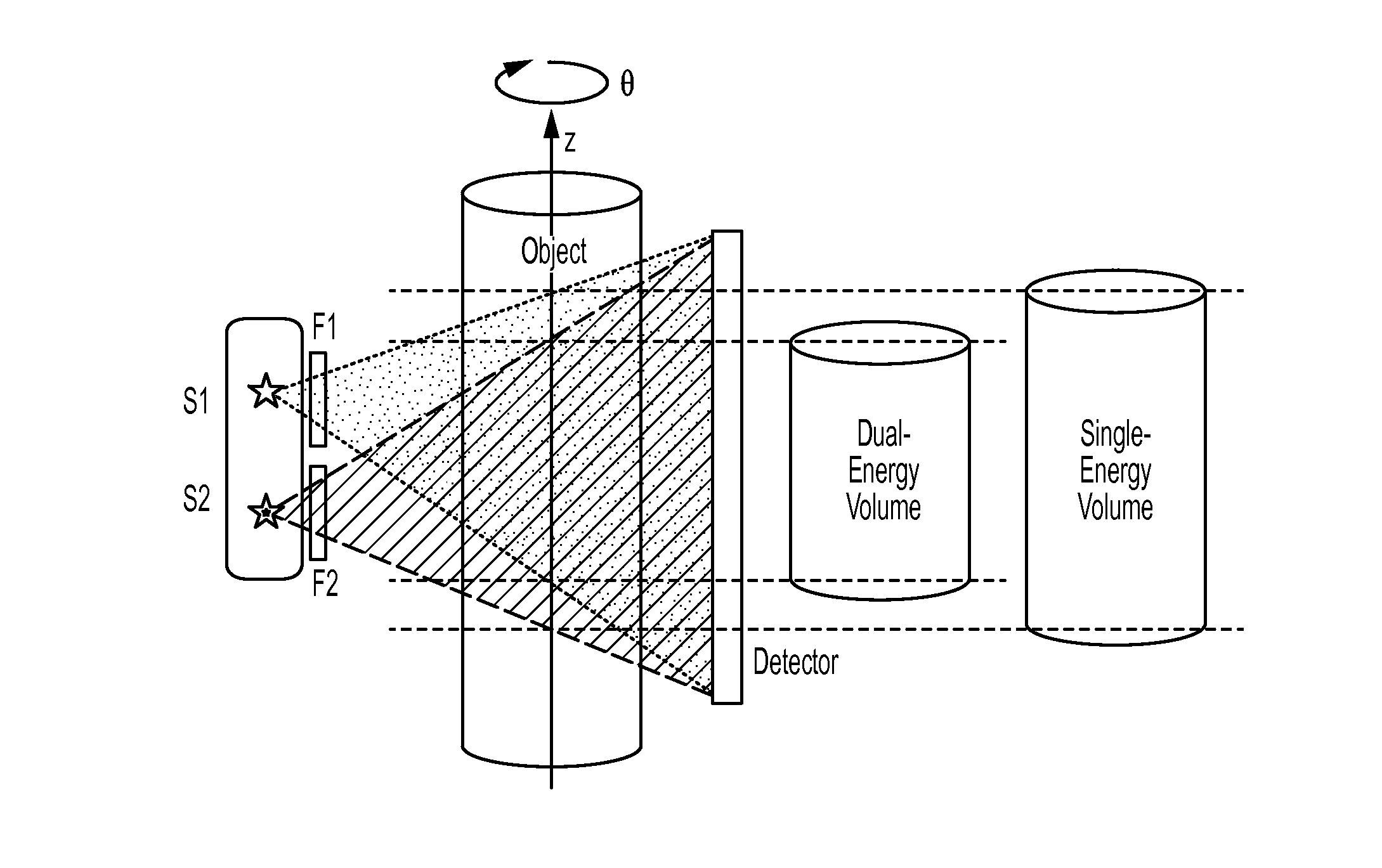
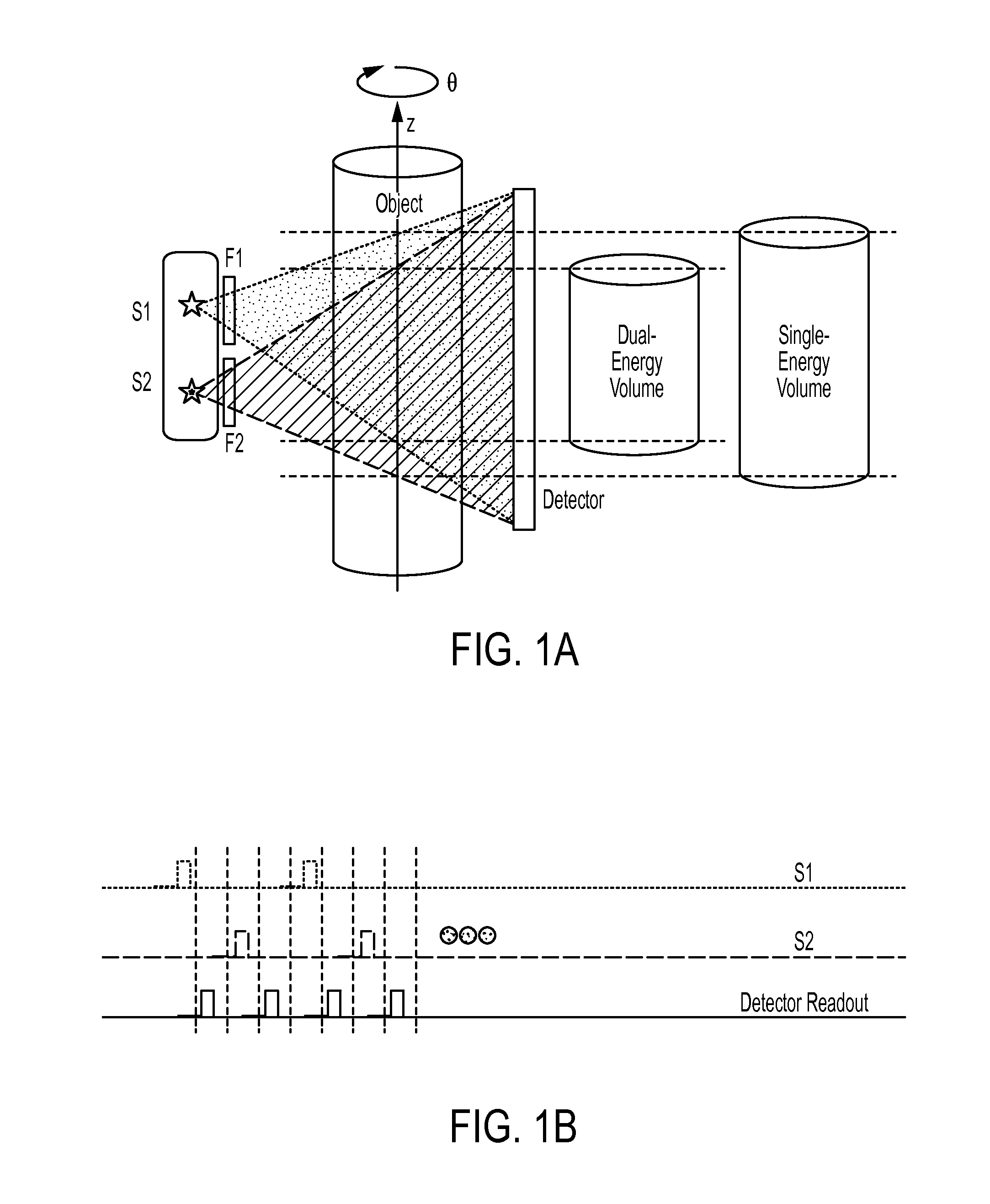
Dual-energy cone-beam computed tomography with a multiple source, single-detector configuration
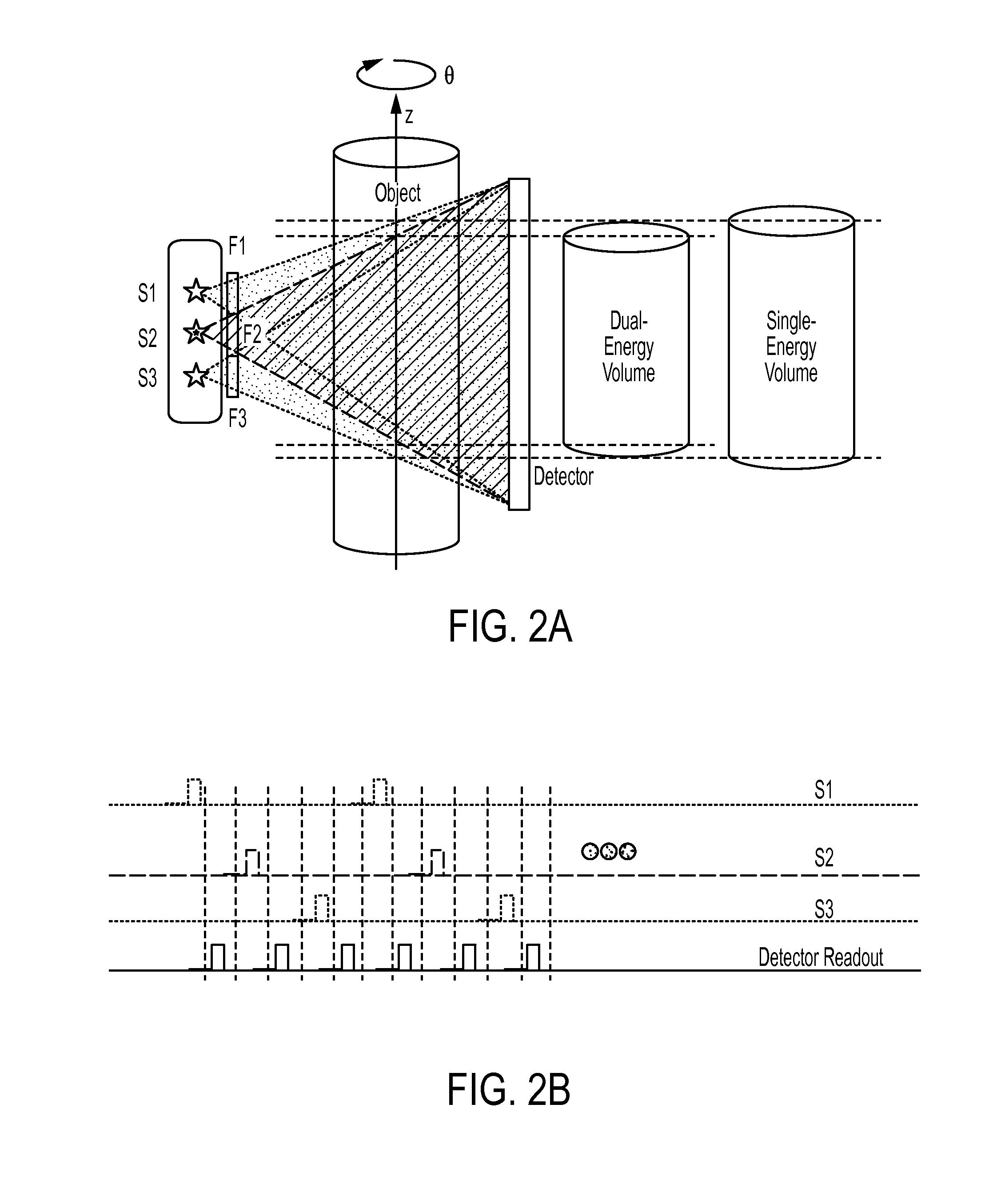
The present invention is directed to a system and method for dual-energy (DE) or multiple-energy (spectral) cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) using a configuration of multiple x-ray sources and a single detector. The x-ray sources are operated to produce x-ray spectra of different energies (peak kilovoltage (kVp) and / or filtration). Volumetric 3D image reconstruction and dual or triple energy 3D image decomposition can be executed using data from the CBCT scan. The invention allows for a variety of selections in energy and filtration associated with each source and the order of pulsing for each source (“firing pattern”). The motivation for distributing the sources along the z direction in CBCT includes extension of the longitudinal field of view and reduction of cone-beam artifacts.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC +1
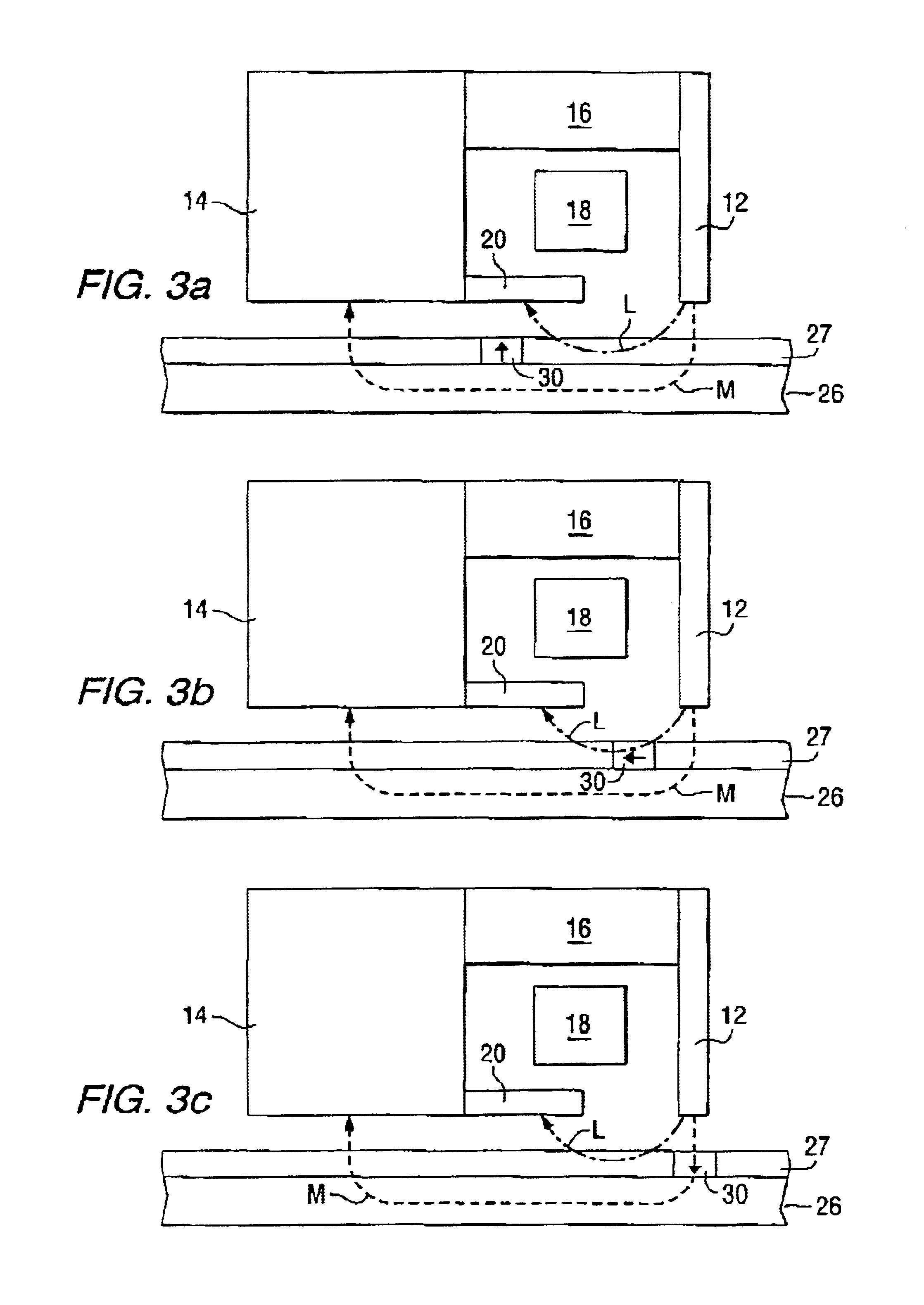
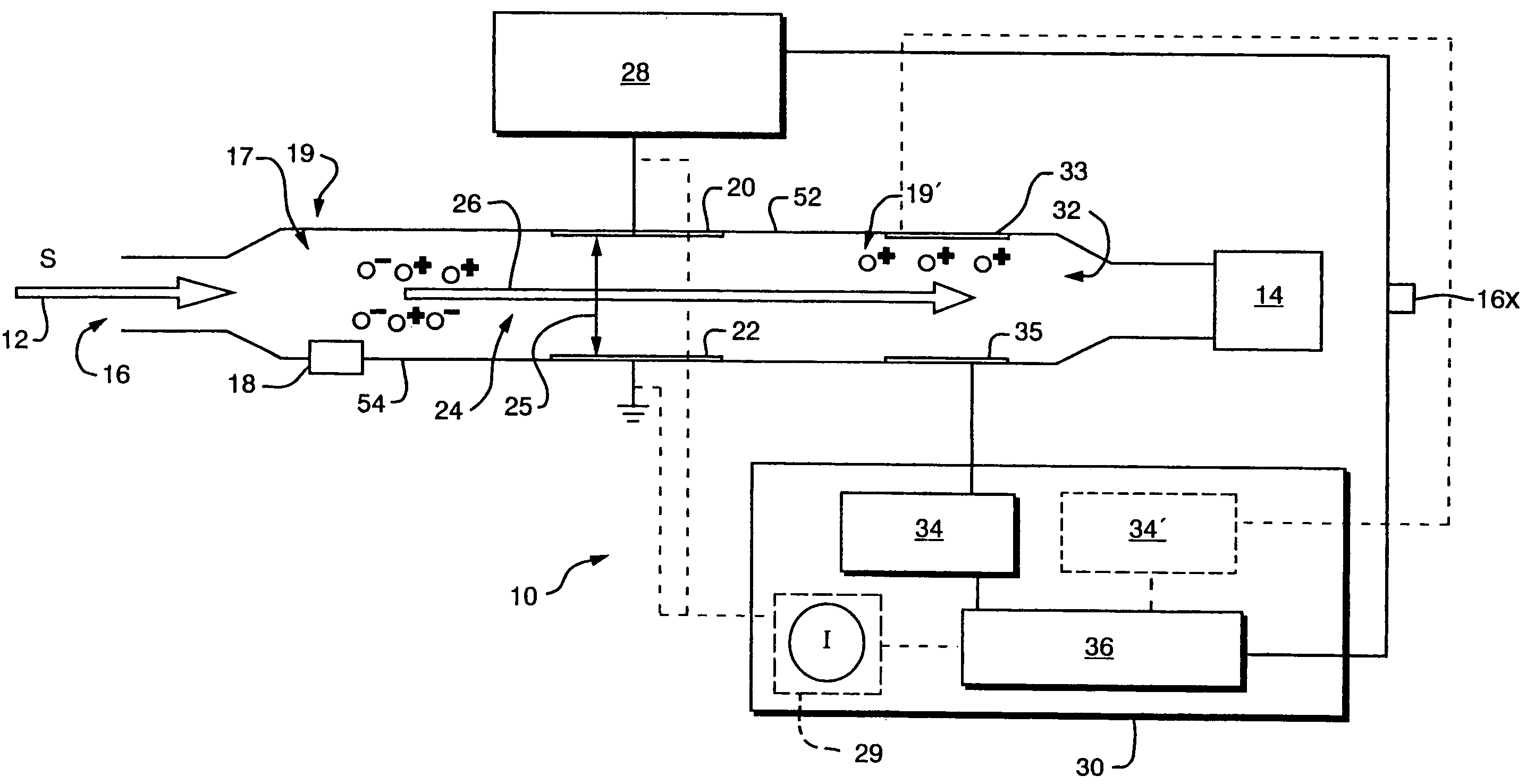
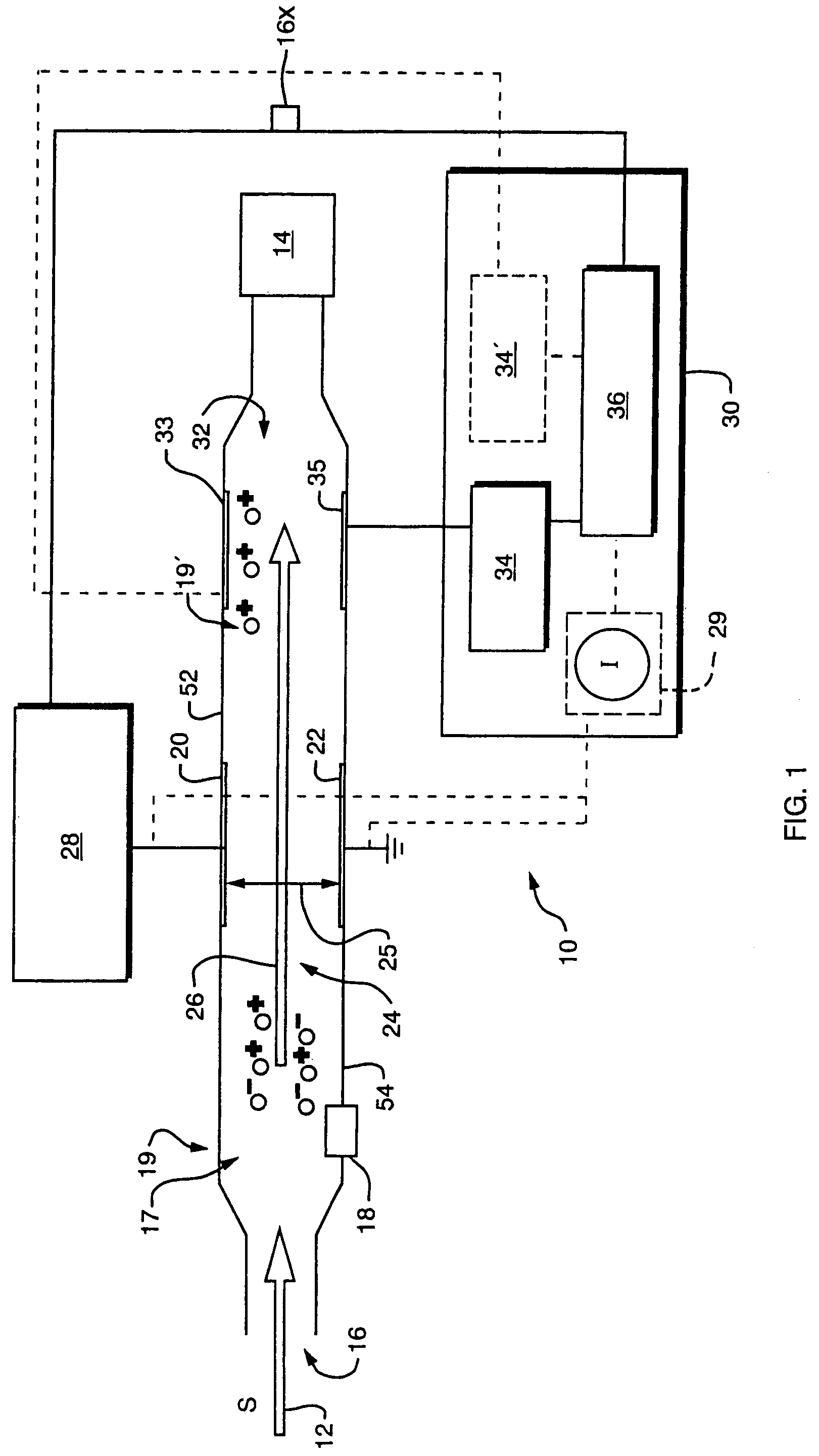
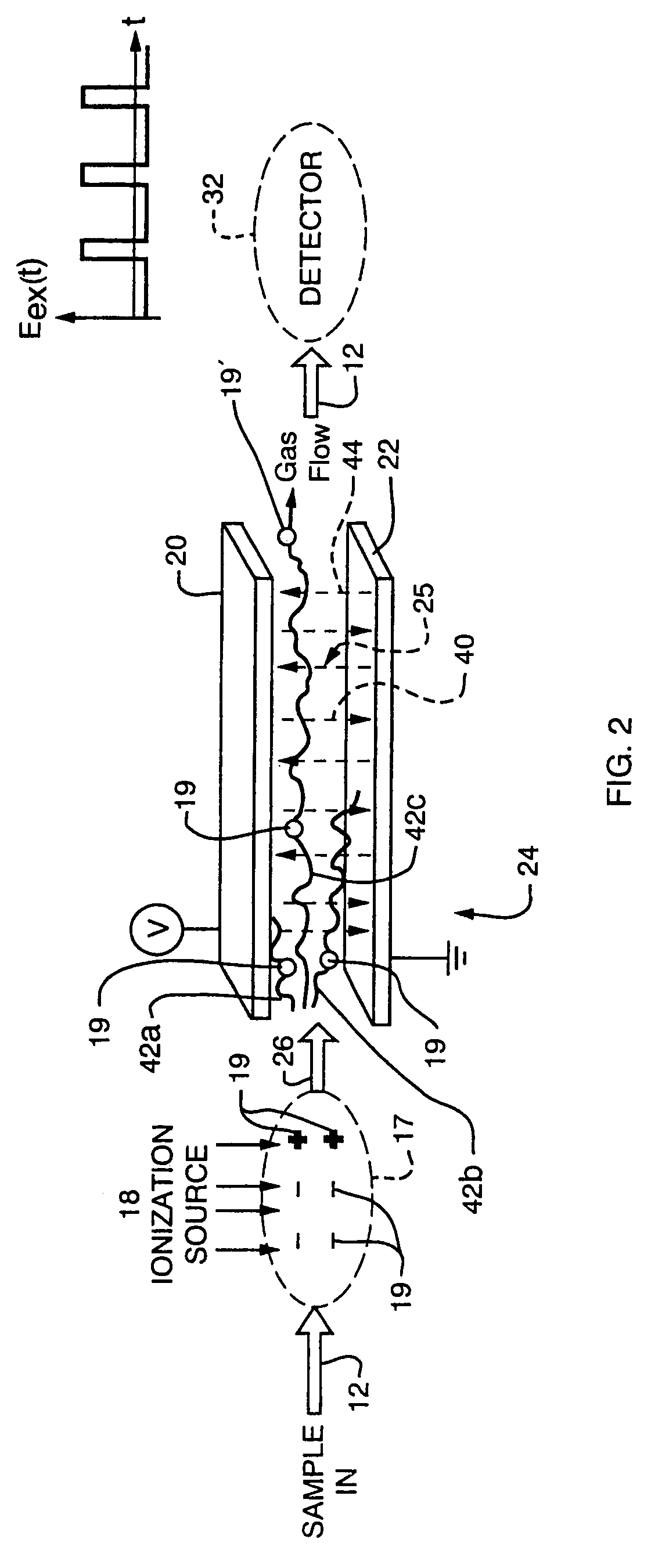
Longitudinal field driven ion mobility filter and detection system
InactiveUS20060192102A1Elimination and reduction of flow rateElimination and reduction of and power requirementStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersLongitudinal fieldSpectrometer
An asymmetric field ion mobility spectrometer for filtering ions via an asymmetric electric field, an ion flow generator propulsing ions to the filter via a propulsion field.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
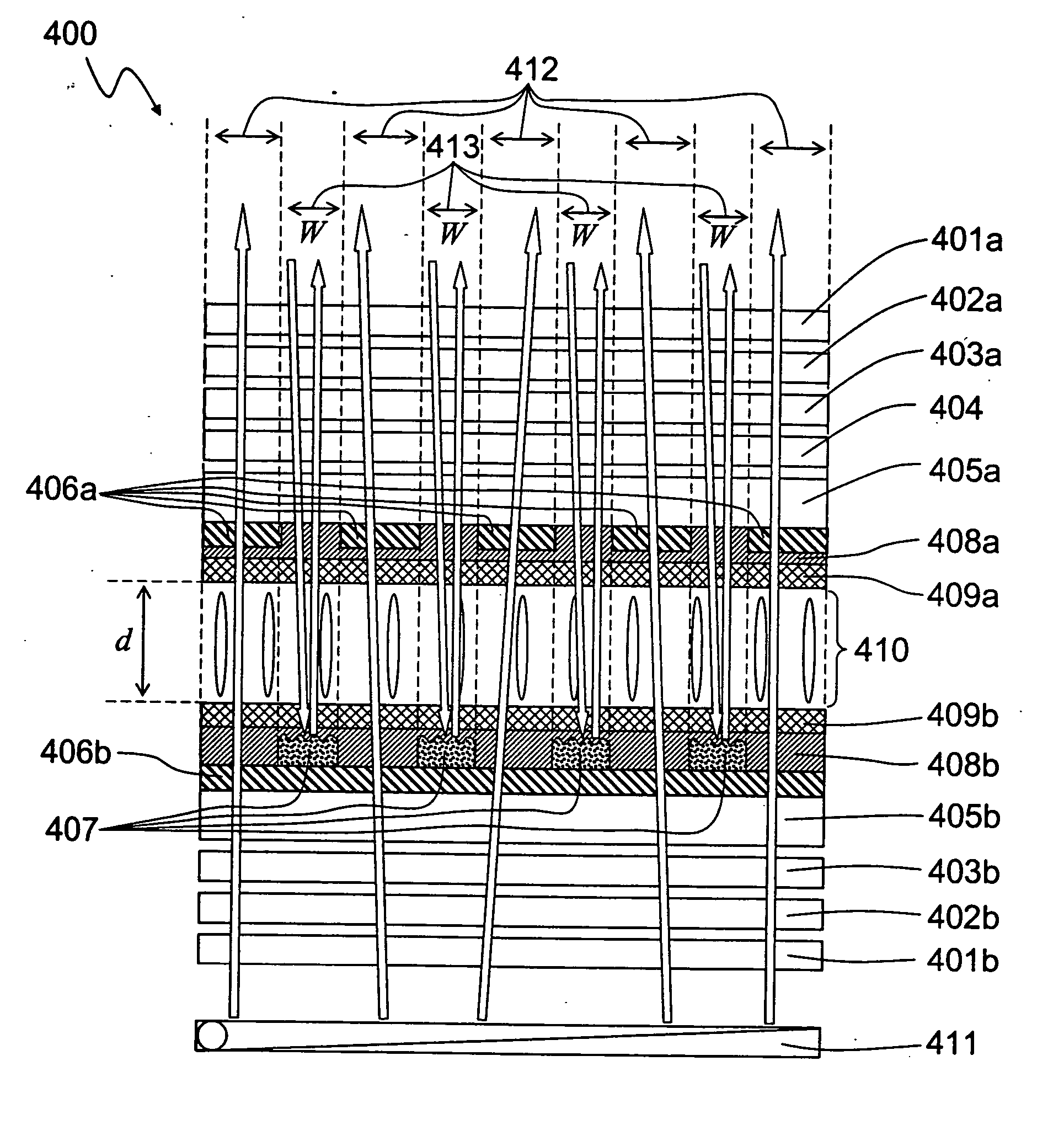
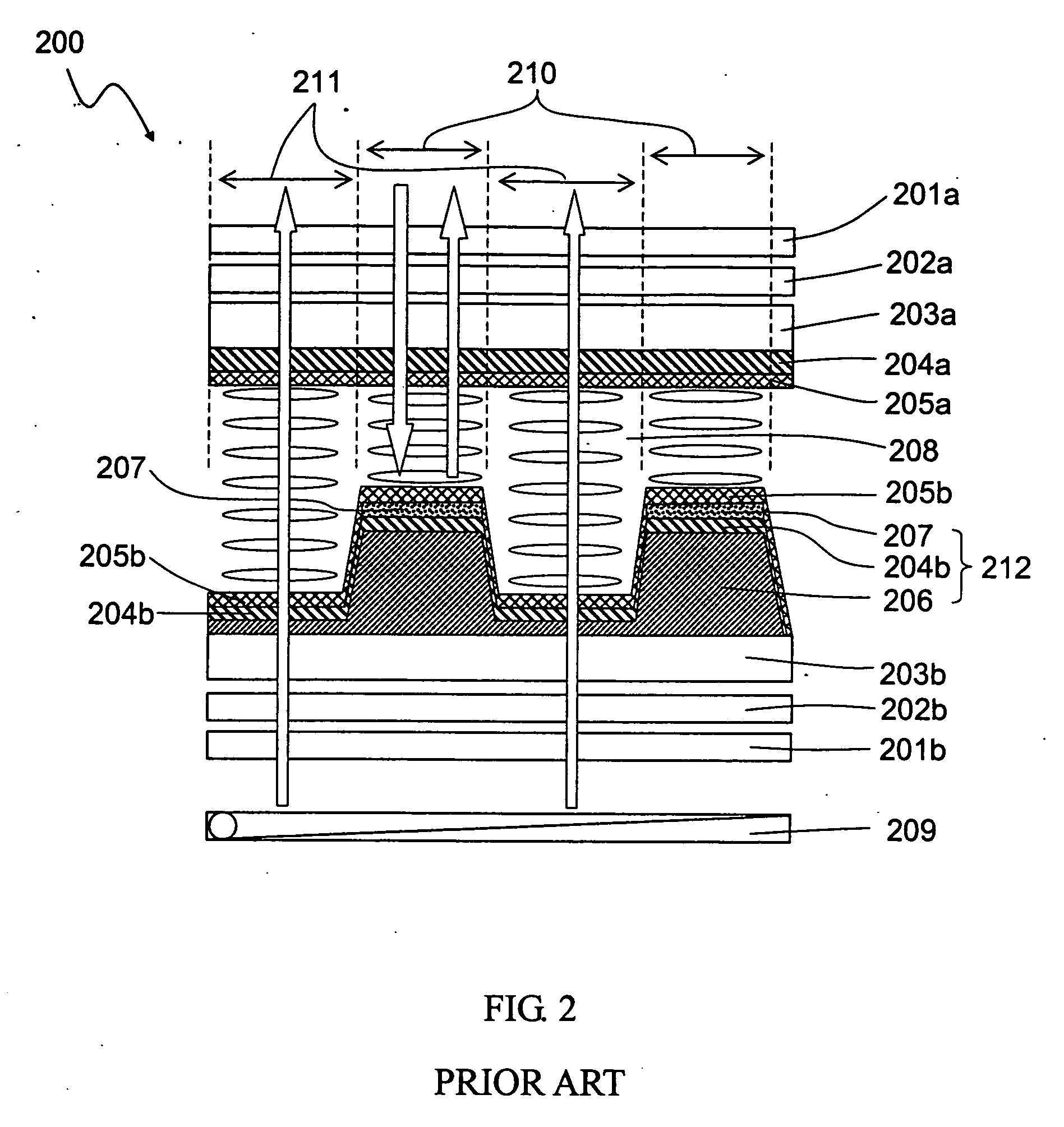
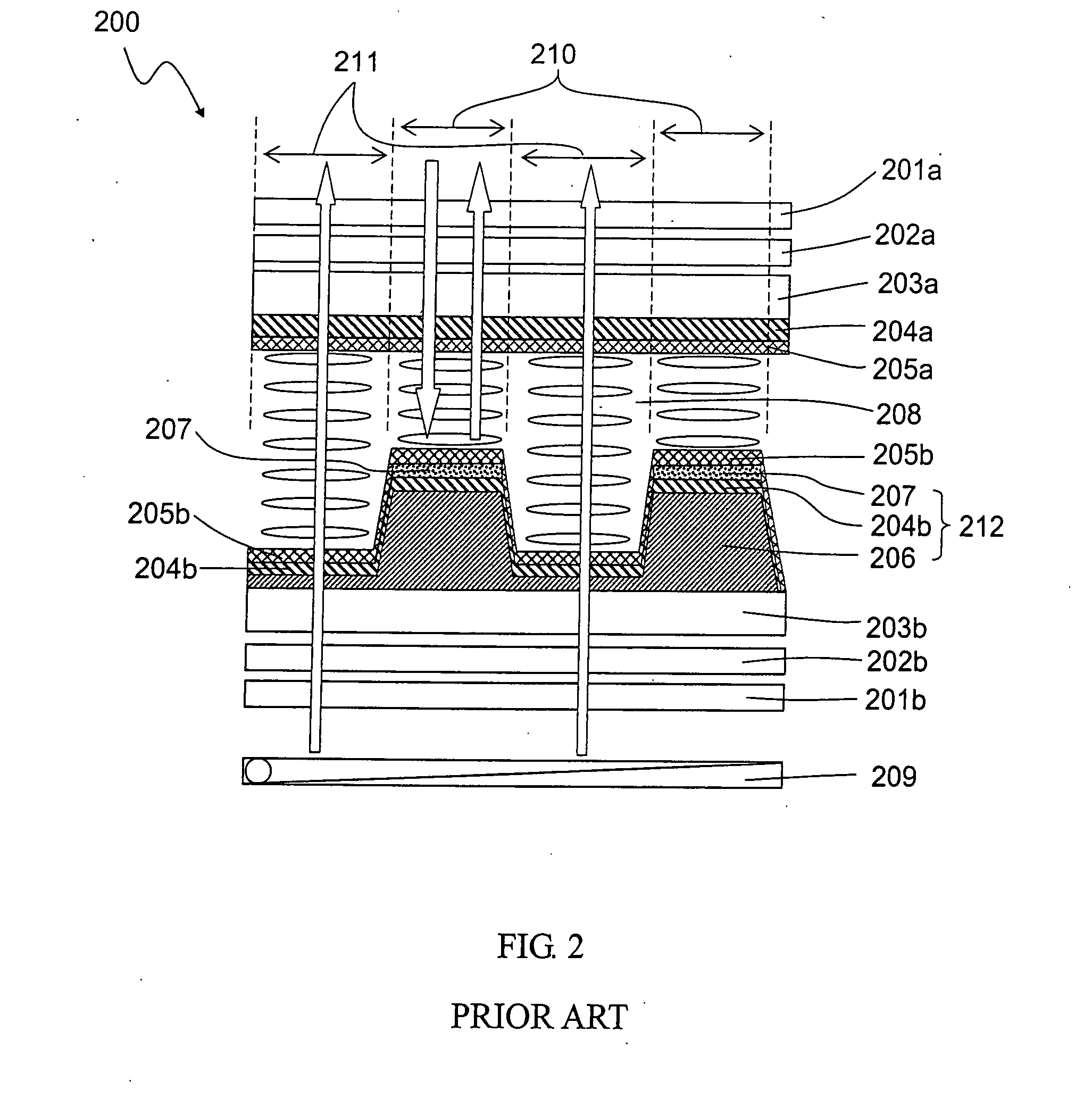
Transflective liquid crystal display with vertical alignment
InactiveUS20060238675A1Simple manufacturing processReduce manufacturing costNon-linear opticsDielectric anisotropyPhase retardation
A transflective liquid crystal display with uniform cell gap configuration throughout the transmissive and the reflective display region is invented. Mutually complementary common electrode pattern and reflector pattern or mutually complementary ITO pixel electrode pattern and reflector pattern produce an electric field in the transmissive display region that has a uniform longitudinal field and an electric field in the reflective display region that is a fringing field. An initially vertically aligned negative dielectric anisotropic nematic liquid crystal material between the electrodes forms a smaller tilt angle with respect to the substrate normal in the reflective display region while a larger tilt angle with respect to the substrate normal in the transmissive display region. Consequently, the ambient incident light experiences smaller phase retardation in the reflective display region while the light from the backlight source experiences larger phase retardation. Since the ambient light passes through the reflective display region twice while the light from the backlight source passes through the transmissive display region only once, by properly designing the electrodes and the reflector width, the light from both ambient light source and backlight source will experience almost the same phase retardation in both reflective and transmissive display regions. As a result, the electro-optical performance curves of both transmissive display mode and reflective display mode overlap.
Owner:INNOLUX CORP +1
A split-gate groove type power device with dual longitudinal field plates
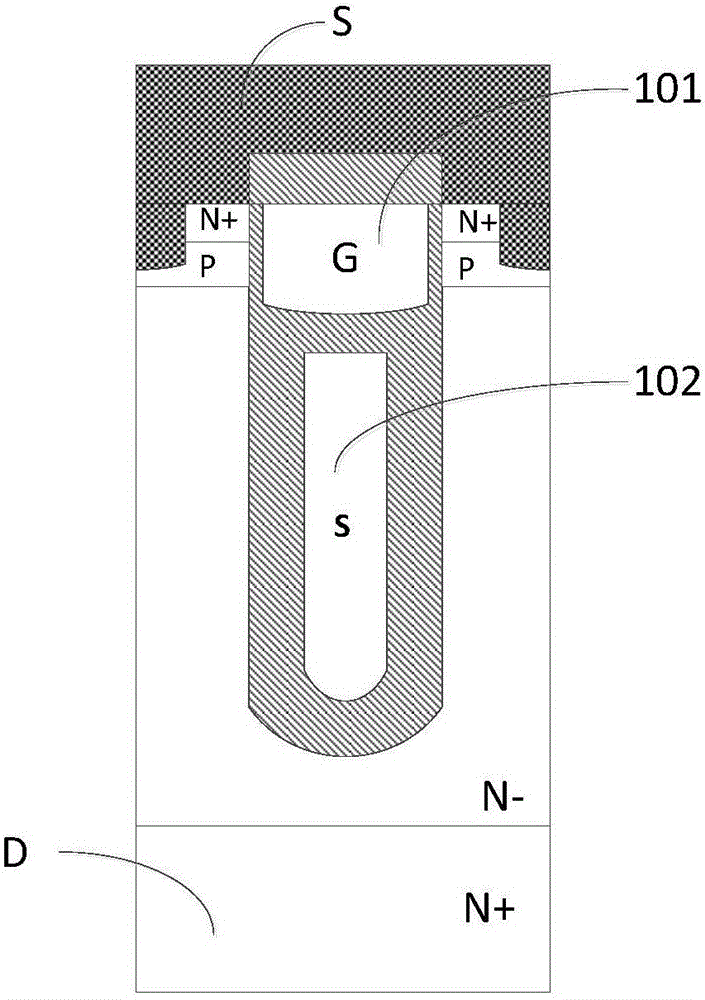
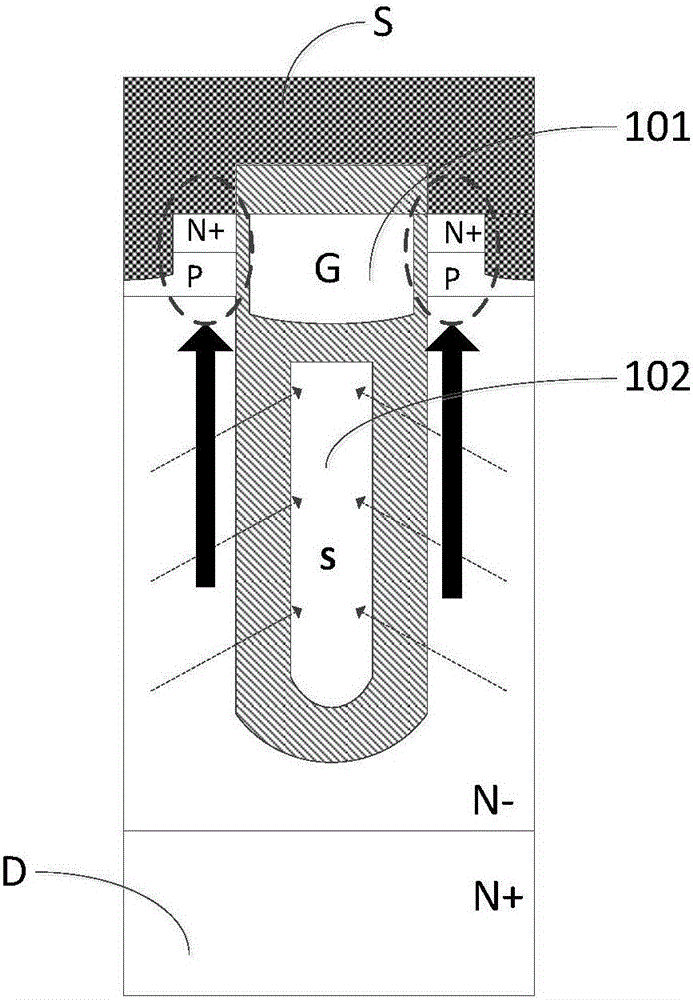
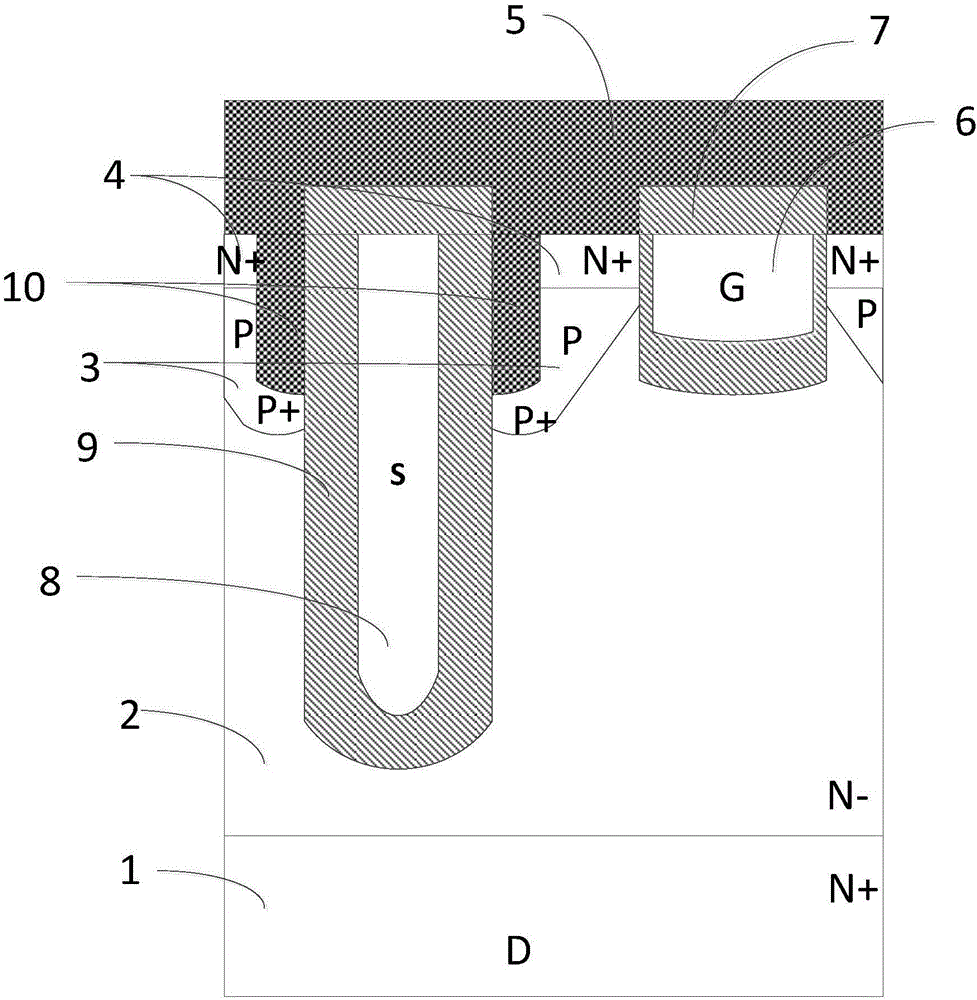
InactiveCN109192778AImprove breakdown voltageReduce switching lossesSemiconductor devicesGate oxideLongitudinal field
The invention belongs to the technical field of power semiconductors, in particular to a separated gate groove type power device with dual longitudinal field plates. A main characteristic of that invention is that a separation gate is introduce into the drift region, the thickness of the gate oxide layer between the gate electrode and the drain electrode is increase to reduce the gate drain chargeQGD, the volume electric field distribution is optimized, and the breakdown voltage of the device is increased; By introducing two longitudinal field plates into the dielectric groove, the contact area between the gate and drain is reduced, the gate-drain charge QGD is further reduced, and the on-resistance of the device is reduced by assisting the depletion drift region, and the internal electric field distribution of the device is further modulated to increase the breakdown voltage of the device. Longitudinal RESURF technique is used to introduce longitudinal P-pillar into the right side ofthe dielectric slot to further modulate the internal electric field of the device and increase the breakdown voltage of the device. Finally, the gate-drain charge is reduced, the device withstand voltage is improved, and the specific on-resistance is reduced.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Tunable magnet structure
ActiveUS8547636B1Strength longitudinal fieldImprove efficiencyPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsOptical isolatorOptoelectronics
An axially symmetric permanent magnet structure with tunable longitudinal fields is described wherein selected radial magnet sectors in a truncated Halbach array configuration are tiltable. The tunable magnet structure is particularly useful in Faraday devices, such as Faraday rotators, Faraday mirrors, optical circulators and optical isolators.
Owner:ELECTRO OPTICS TECH
Longitudinal field driven ion mobility filter and detection system
InactiveUS7456390B2Elimination and reduction of flow rate and power requirementStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersNon symmetricIon-mobility spectrometry
An asymmetric field ion mobility spectrometer for filtering ions via an asyretric electric field, an ion flow generator propulsing ions to the filter via a propulsion field.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Transflective liquid crystal display with vertical alignment
InactiveUS20080043188A1Simple manufacturing processReduce manufacturing costTube/lamp screens manufactureVessels or leading-in conductors manufacturePhase retardationDielectric anisotropy
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC +1
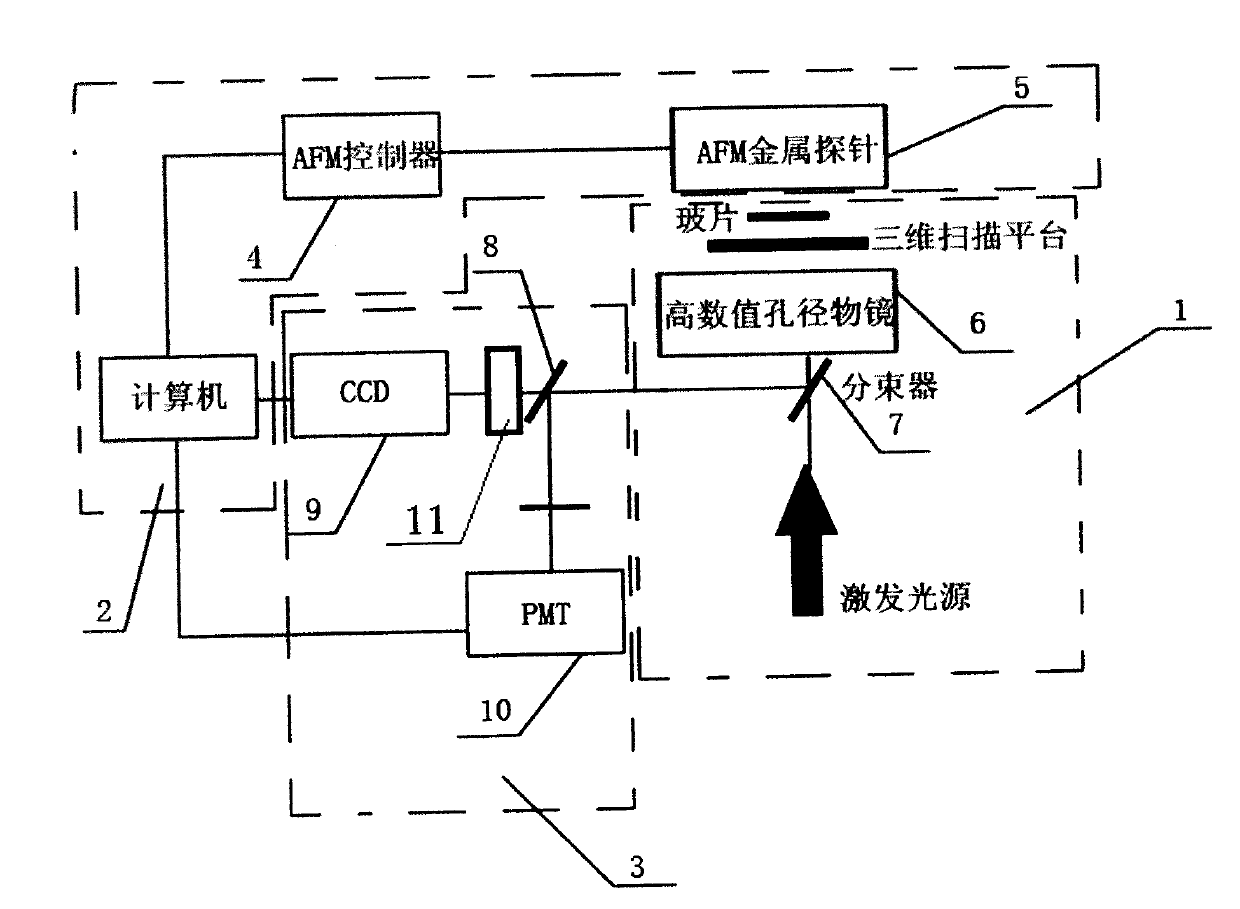
Surface plasma longitudinal field scanning near-field optic microscope device and detection method
InactiveCN103105511AReduce distractionsImprove reliabilityScanning probe microscopyHigh numerical apertureNear-field optics
The invention provides a surface plasma longitudinal field scanning near-field optic microscope device and a detection method. The device is provided with a surface plasma excitation unit (1). After being focused through a high numerical aperture objective lens (6), incident light excites an SPP field on an interface of a metal membrane and air, raman signals and the SPP field interfere each other to form a stationary field of the SPP field around a focus, a scanning control unit (2) can achieve three-dimensional scanning and positioning for an atomic force microscope (AFM) metal probe (5) by means of an AFM controller (4), and a detection unit (3) achieves three-dimensional measurement and analysis for a longitudinal field component of a surface plasma field.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
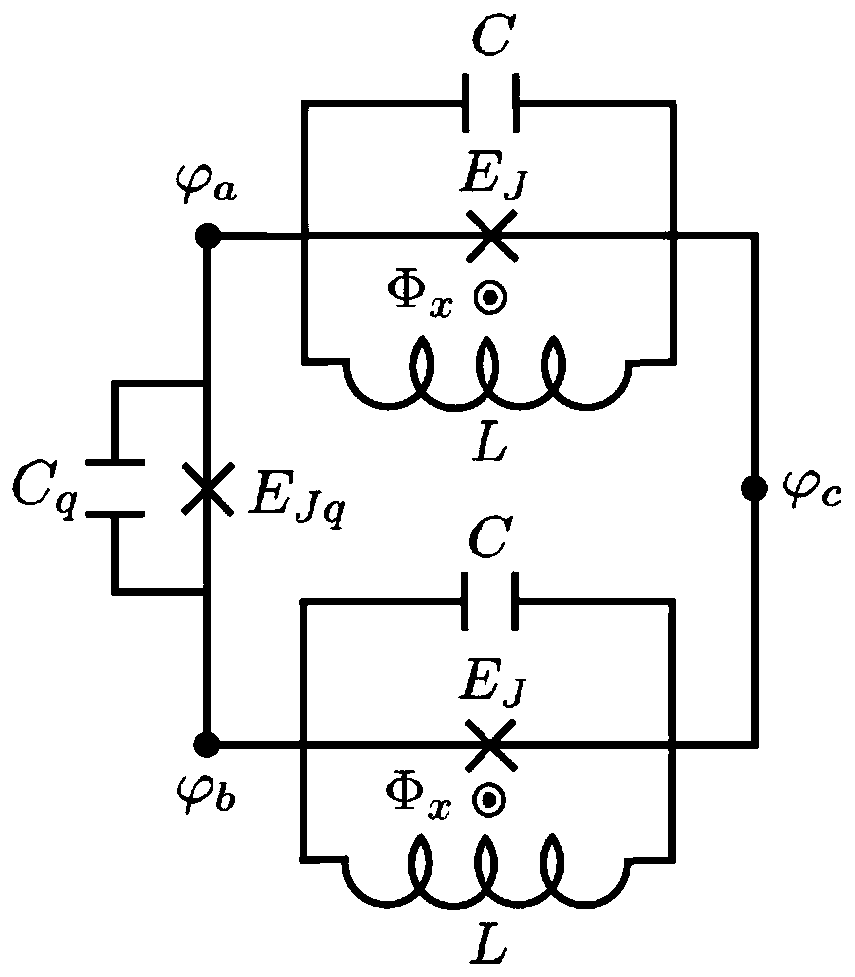
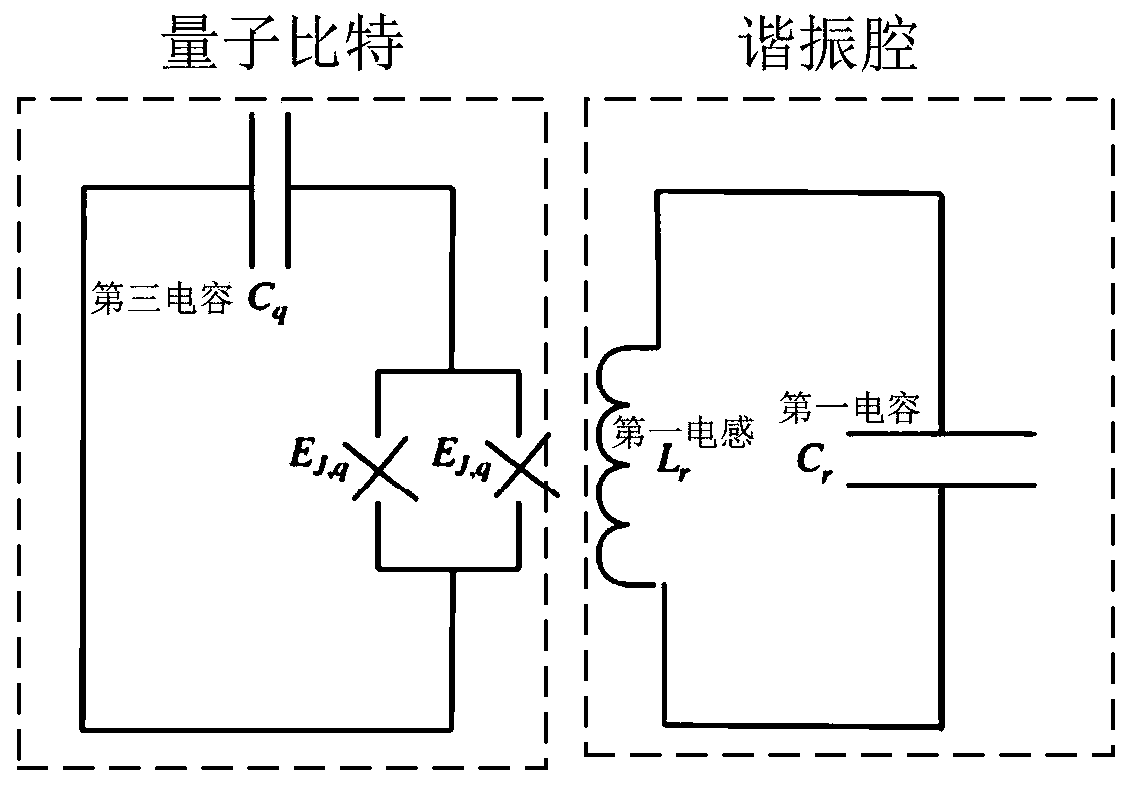
Superconducting circuit structure, superconducting quantum chip and superconducting quantum computer
The embodiment of the invention provides a superconducting circuit structure, a superconducting quantum chip and a superconducting quantum computer, and the superconducting circuit structure comprisesat least two basic units and a coupling structure, wherein the basic unit at least comprises a quantum bit and a resonant cavity coupled with the longitudinal field of the quantum bit, the resonant cavity comprises a first inductor and a first capacitor connected with the first inductor in parallel, and the resonant cavity and the quantum bit are subjected to longitudinal field coupling by utilizing the first inductor; and the coupling structure is used for coupling the resonant cavities in the two basic units so as to realize linear coupling between the two basic units. Thus, the problem ofcrosstalk among the quantum bits is solved, and the purposes of simple structure, easiness in regulation and control and expandability of the superconducting circuit are achieved on the basis of no crosstalk among the quantum bits.
Owner:BEIJING BAIDU NETCOM SCI & TECH CO LTD
Transflective liquid crystal display with fringing and longitudinal electric field
InactiveUS7339641B2Simple manufacturing processReduce manufacturing costNon-linear opticsDielectric anisotropyPhase retardation
A transflective liquid crystal display with uniform cell gap configuration throughout the transmissive and the reflective display region is invented. Mutually complementary common electrode pattern and reflector pattern or mutually complementary ITO pixel electrode pattern and reflector pattern produce an electric field in the transmissive display region that has a uniform longitudinal field and an electric field in the reflective display region that is a fringing field. An initially vertically aligned negative dielectric anisotropic nematic liquid crystal material between the electrodes forms a smaller tilt angle with respect to the substrate normal in the reflective display region while a larger tilt angle with respect to the substrate normal in the transmissive display region. Consequently, the ambient incident light experiences smaller phase retardation in the reflective display region while the light from the backlight source experiences larger phase retardation. Since the ambient light passes through the reflective display region twice while the light from the backlight source passes through the transmissive display region only once, by properly designing the electrodes and the reflector width, the light from both ambient light source and backlight source will experience almost the same phase retardation in both reflective and transmissive display regions. As a result, the electro-optical performance curves of both transmissive display mode and reflective display mode overlap.
Owner:INNOLUX CORP +1
Radial leak coaxial cable
InactiveCN101587978AFix stability issuesSolve for uniformityWaveguidesLeaky-waveguide antennasElectrical conductorCoaxial cable
A radial leak coaxial cable includes a center conductor (1) extending along center axis of the cable toward the longitudinal direction, a spume insulation layer (2), a radiation external conductor (3) and a protective cover (4) from inside to outside in sequence, the spume insulation layer (2) separates the center conductor (1) with the radiation external conductor (3), the radiation external conductor (3) has radiation slots that are circular arc slots (5) arranged alternately in positive and negative, and adjacent circular arc slots (5) have openings with opposite directions. The invention provided adjacent 'coupling mouth' reverse configuration can reduce vertical polarized longitudinal field of to minimum and can eliminate reversion of vertical polarized transverse field caused by inter-reflection of the vertical polarized longitudinal field, which resolves affects to transmission signal stability and homogeneity caused by mutual interference of primary vertical polarized transverse fields.
Owner:JIANGSU TRIGIANT TECH
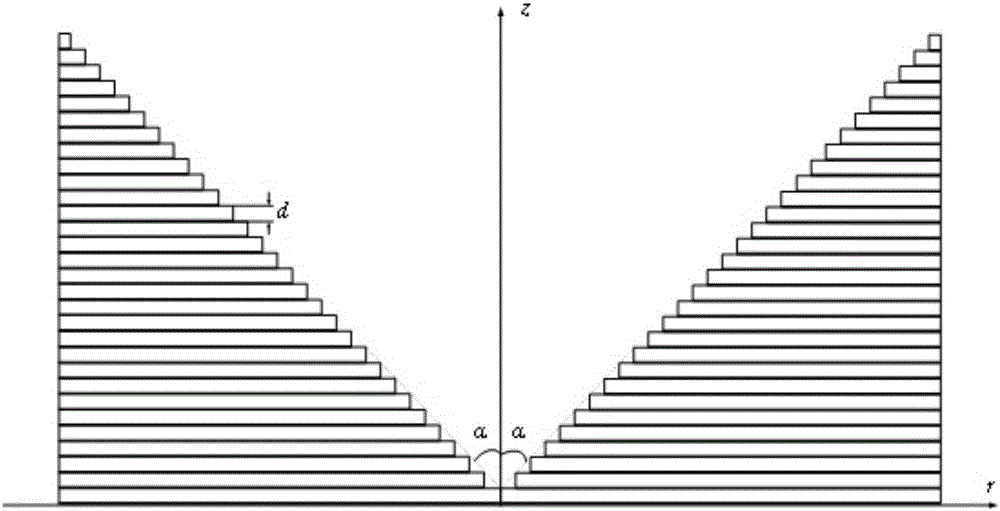
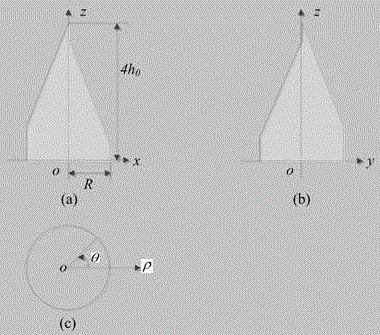
Long-focal-depth and deep-sub-wavelength-focused one-dimensional photonic crystal flat cone mirror for column vector beams
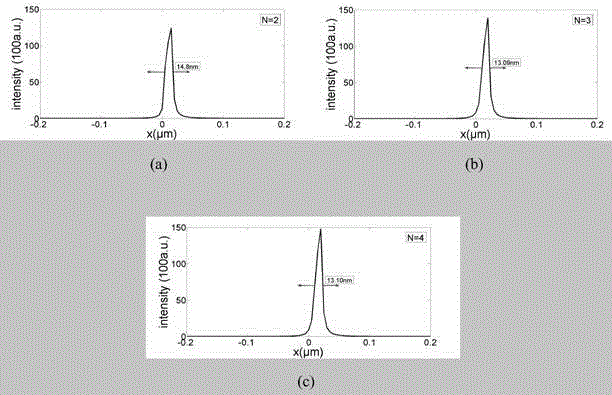
The invention discloses a long-focal-depth and deep-sub-wavelength-focused one-dimensional photonic crystal flat cone mirror for column vector beams. The one-dimensional photonic crystal flat cone mirror is composed of one-dimensional photonic crystals formed through the alternate arrangement of a material A and a material B. The emitting surface of the flat cone mirror is in the form of an inverted cone-shaped surface. The inverted cone-shaped surface is not a continuous cone-shaped surface, wherein circular rings of fixed thickness are stacked up to form the inverted cone-shaped surface, with one cycle (d) of the photonic crystals as one unit and the internal diameters of the circular rings being gradually and equivalently increased from bottom to top. The inner sides of the circular rings are in the form of a vertical wall, and the connecting line of the vertex angles of the circular rings is at an included angle relative to the horizontal plane. By means of the flat cone mirror, radially polarized beams and rotatably polarized beams are focused at the same time, so that light needle-shaped focuses and light pipe-shaped focuses that are uniformly distributed in the longitudinal field can be respectively obtained. Through changing the structural parameters of photonic crystals, the wide-band focusing is realized. Meanwhile, through stretching out or drawing back the flat cone mirror, the length of the focal depth can be controlled. The flat cone mirror is simple in structure, and simple and convenient in design process. The structure of the flat cone mirror can be easily prepared. Therefore, the flat cone mirror is good in application prospect in the fields of near-field optics, laser processing, medical science and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for removing hydrogen detained on first wall in magnetic constraint device by ion involution oxygen plasma
InactiveCN101533679AAchieve clearingEfficient removalNuclear energy generationPlasma techniqueChemical reactionPlasma technology
The invention discloses a method for removing hydrogen detained on a first wall in a magnetic constraint device by ion involution oxygen plasma. According to carbon and hydrogen codeposition characteristic in the magnetic constraint device, a plasma auxiliary chemical removing method is used, on a HT-7 superconducting tokmak and a EAST device having similar bit-type with ITER, under condition of keeping longitudinal magnetic fields of 1.5-2.0T and wall temperature of 400-470K, a ion involution plasma technology is employed, oxygen which is easy to react with carbon and hydrogen is employed to form ion involution oxygen plasma for removing carbon hydrogen re-deposition layer on the first wall, thereby effectively removing hydrogen detained on the first wall of a device. The technology is a unique and effective technology, creates excellent wall condition for re-deposition layer removal on the first wall, reduction of hydrogen detained in the device, particle recirculation lowering and nuclear fusion device high efficiency operation, and reduces safely and environment problems of future nuclear fusion device due to radioactive tritium detained on the first wall. Simultaneously, the treatment for the first wall can be carried out under condition that longitudinal field coil is not demagnetized, and is more suitable for future international thermonuclear fusion experiment reactor ITER and future fusion reactor.
Owner:INST OF PLASMA PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
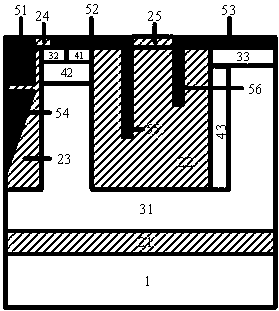
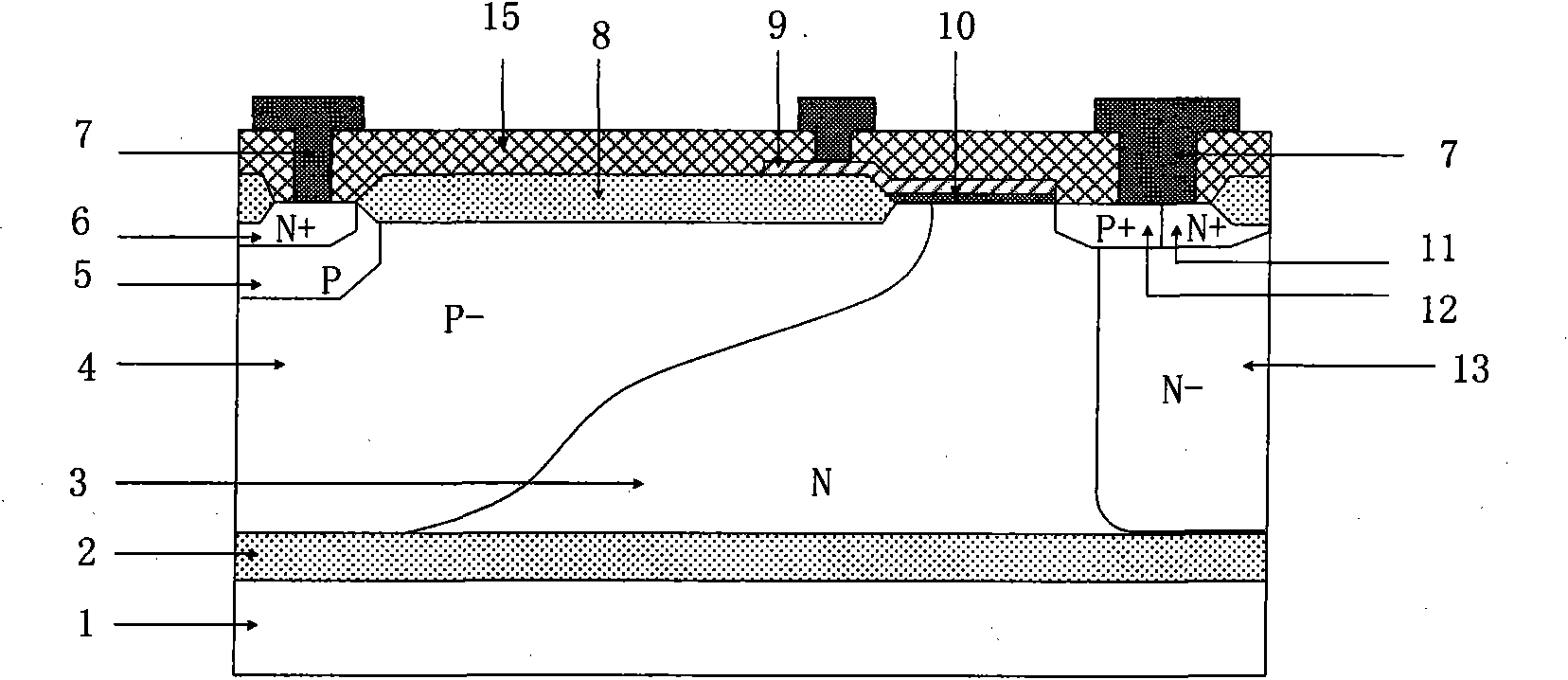
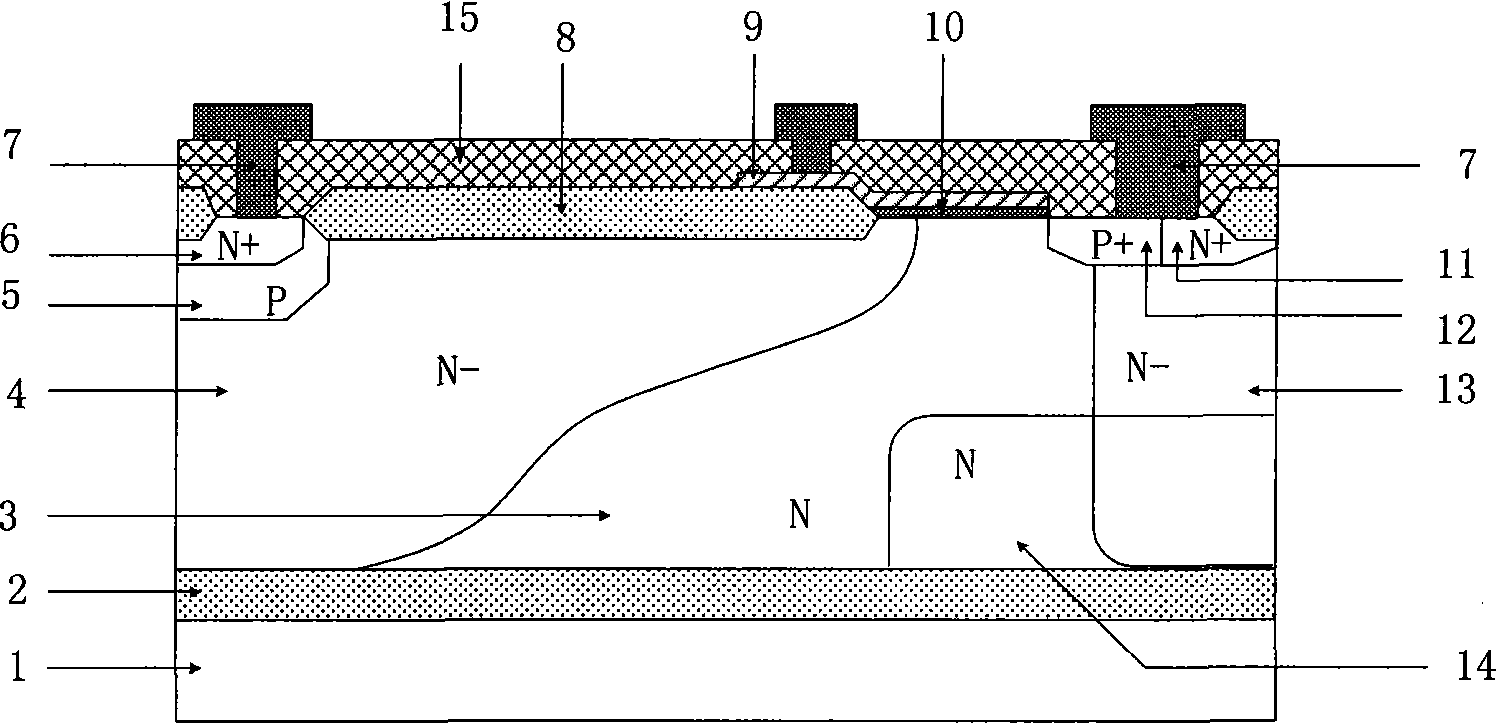
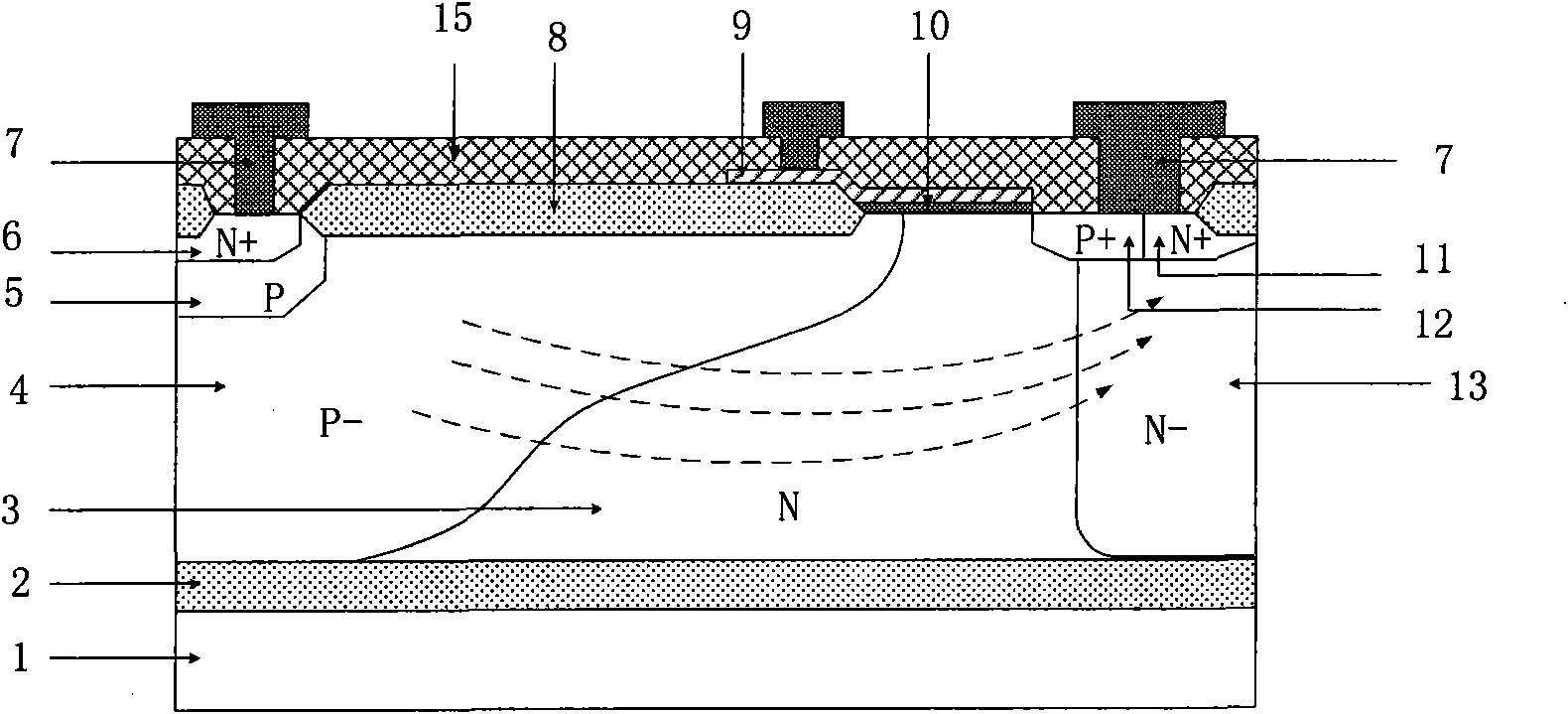
P type lateral insulated gate bipolar device for reducing hot carrier effect
InactiveCN101819993ASmall doseReduce incidenceSemiconductor devicesGeneration rateLongitudinal field
The invention relates to a P type lateral insulated gate bipolar device for reducing the hot carrier effect, comprising an N type substrate. Buried oxide is arranged on the N type substrate, an N type epitaxial layer is arranged on the buried oxide, a P type well and an N well region are arranged on the N type epitaxial layer, a P type buffer well is arranged on the P type well, an N type positive region is arranged on the P type buffer well, a P type negative region and an N type physical contact region are arranged on the N well region, and a field oxide, a metal layer, a gate oxide, a polysilicon gate and an oxide layer arranged on the surface of the device. The P type lateral insulated gate bipolar device for reducing the hot carrier effect is characterized in that N type buried layers are arranged at the lower part of the N well region and on the buried oxide, and the N type buried layers are partially inserted into the N type epitaxial layer to integrally form a reverse L type N region with the N well region. The structure can introduce the electronic current of the device to the bottom, reduce ion generation rate and longitudinal field of a channel region of the device, and lower the thermionic temperature, thereby effectively restraining the hot carrier effect of the device.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Non-linear nanocrystalline metal spiral cone probe
InactiveCN105807096AIncrease profitHigh sensitivityMaterial nanotechnologyScanning probe techniquesNanolithographyScanning probe microscopy
The invention relates to an improved non-linear nanocrystalline metal spiral cone probe with high sensitivity and high spatial resolution and for generating a strong vertical polarization electric field and a rotating electric field. The probe is formed by a combination of a metal nanocone structure and a metal non-linear spiral structure, on the basis of a condition that the cone and spiral structure is 3:1 combined in the nanocrystalline metal spiral cone probe with the prior best regulation effect, a spiral structure non-linear factor N (1<N<6) is introduced, the regulation of strength and polarization of a nano-focussing field of the non-linear factor can be realized through changing the non-linear factor, the strength can reach 4 orders of magnitude, and a longitudinal field is more than 54.4% of a total field. According to the invention, the probe can serve as the probe of scanning probe microscope such as an atomic force microscope, a scanning near-field microscope and the like and a tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy probe, and the probe has important application value in fields including nano-sensing, nano-photoetching, nano-manipulating and the like.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
GaN heterojunction longitudinal field effect transistor
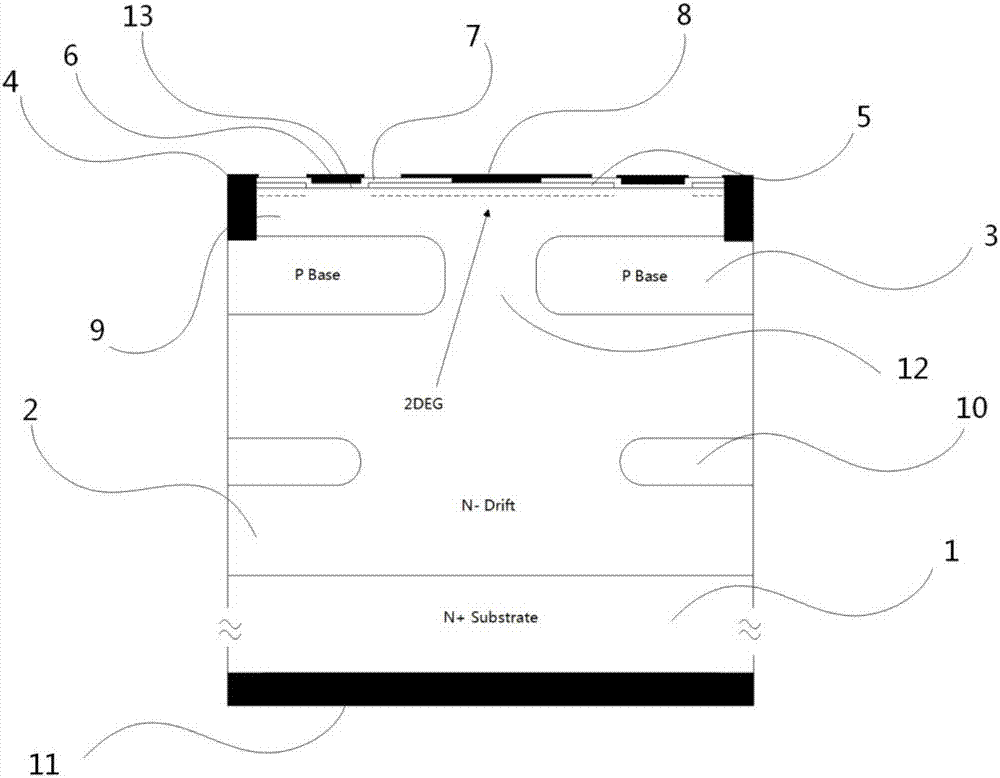
ActiveCN107393954ALower on-resistanceIncrease saturation currentSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionGrating
The invention relates to the technical field of a semiconductor device, and relates to a GaN heterojunction longitudinal field effect transistor. The GaN heterojunction longitudinal field effect transistor is characterized in that a longitudinal discrete grating structure is utilized, and a schottky source electrode is deposited between grids to form an anode of a reverse conducting diode; by introducing back barriers and grooved gates formed in P type base regions, the two dimensional electron gas (2DEG) at the channel below the gate is used up through the combined action of the back barriers and the grooved gates, and the threshold-voltage can be accurately regulated and controlled by adjusting the etching thickness of an AlMN barrier layer. In the working state of a forward direction switch, the GaN heterojunction longitudinal field effect transistor has the advantages of being adjustable in the threshold-voltage, being low in the conduction resistance, being large in the saturation current, being high in the off state withstand voltage, being high in the working frequency and being low in power consumption. In the reverse conducting state, the GaN heterojunction longitudinal field effect transistor has the advantages of being low in the starting voltage, being low in the conduction resistance, being high in the reverse withstand voltage, being short in the reverse recovery time and being low in power consumption. And at the same time, the manufacturing technique of the GaN heterojunction longitudinal field effect transistor is compatible with a traditional GaN heterojunction HEMT device. The GaN heterojunction longitudinal field effect transistor is especially suitable for a GaN heterojunction longitudinal power field effect transistor.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Grooved gate VDMOS
The invention discloses a grooved gate VDMOS, which comprises a substrate, an epitaxial layer, a first well region, a second well region, a first source located on the surface of the second well region, a grooved gate, a gate oxide layer surrounding the grooved gate, a second source longitudinal field plate and a silicon dioxide layer surrounding the second source longitudinal field plate, wherein the substrate, the epitaxial layer and the second well region all have first doping types; the first well region has a second doping type; and the gate oxide layer and the silicon dioxide layer are isolated by the first well region and the second well region. The grooved gate VDMOS provided by the invention aims at solving the technical problems that in the case of space radiation existing in the grooved gate VDMOS by applying a charge coupling technology in the prior art, SEB (Singer Even Burnout) and SEGR (Single Event Gate Rupture) are likely to happen. Technical effects of reducing SEB and SEGR risks and improving the reliability are realized.
Owner:北京中科微投资管理有限责任公司
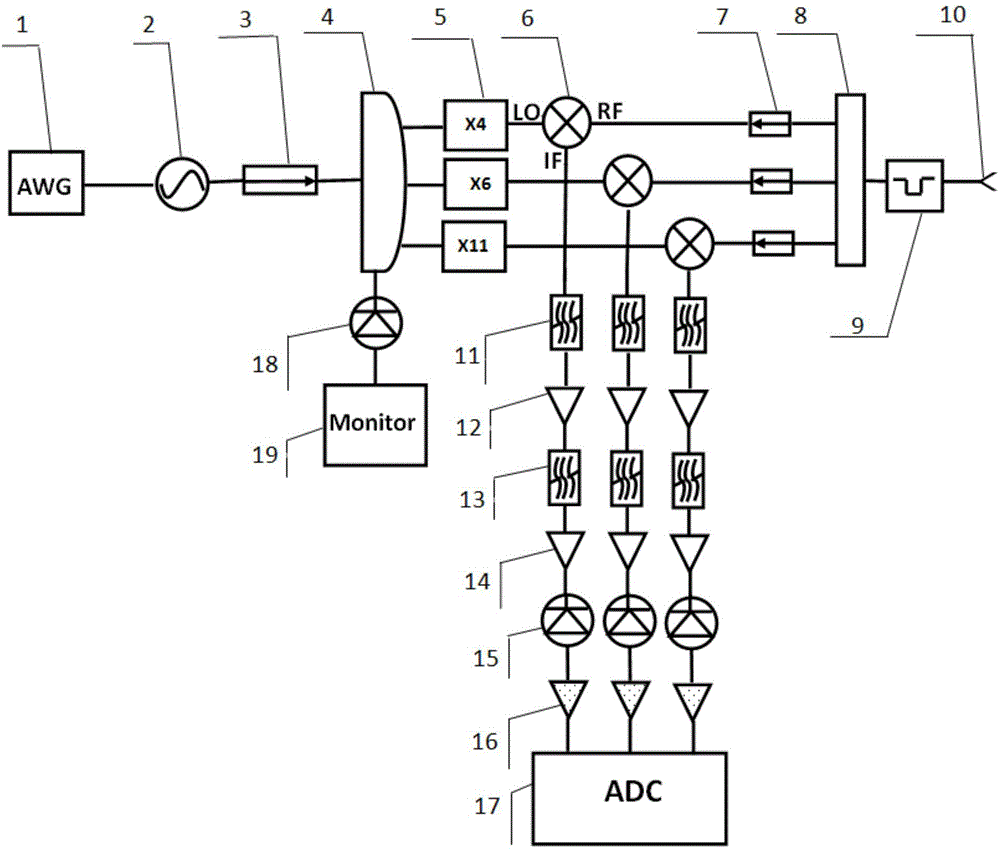
Ultra wide band swept-frequency microwave radiometer based on frequency doubling technology
ActiveCN104569584AImprove protectionAvoid interferenceSpectral/fourier analysisBandpass filteringElectronic temperature
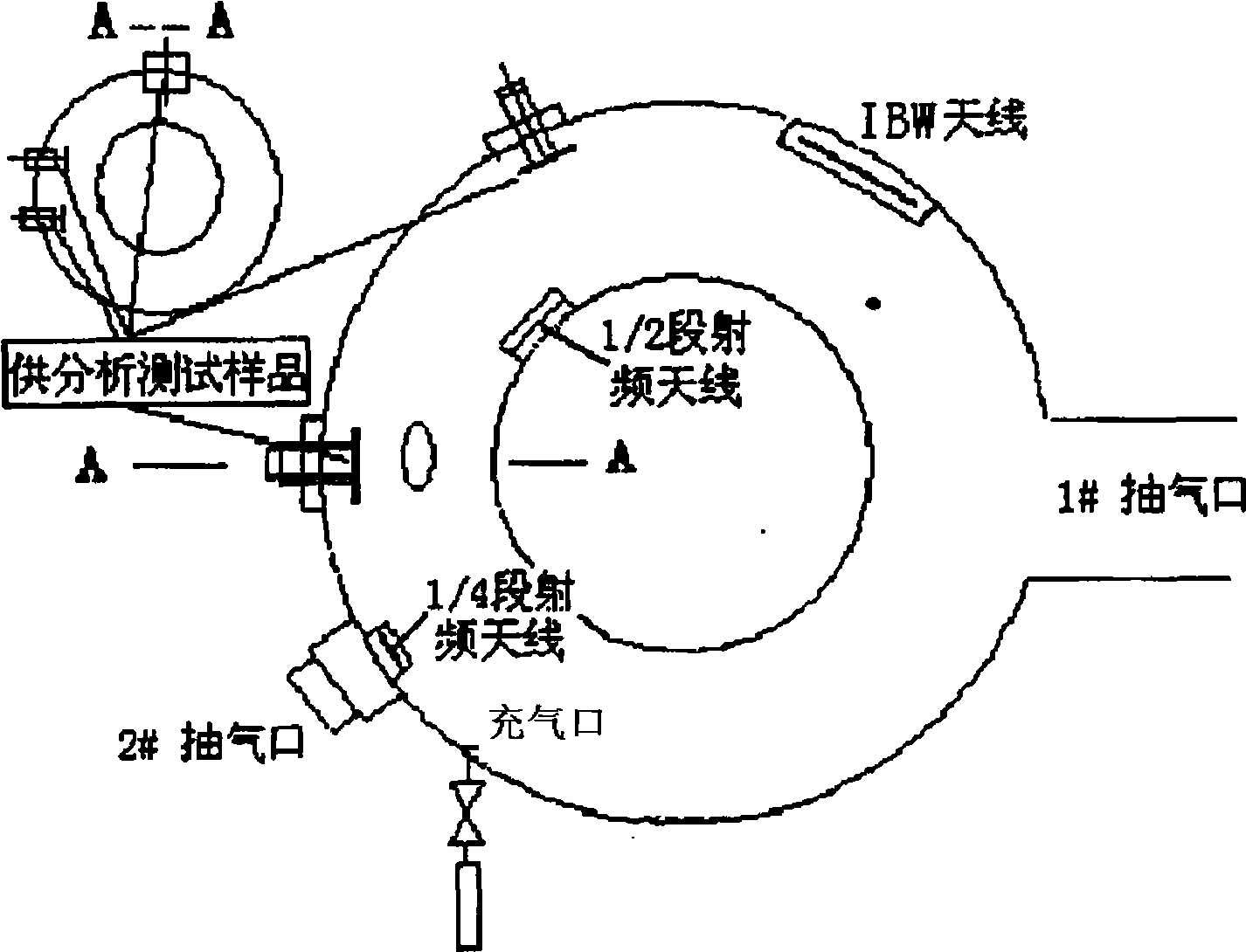
The invention belongs to an ultra wide band swept-frequency microwave radiometer based on a frequency doubling technology. The ultra wide band swept-frequency microwave radiometer comprises an arbitrary waveform generator and a wide band VCO (voltage controlled oscillator) source, wherein the arbitrary waveform generator is connected with the input ends of the wide band VCO source, an isolator and a power distributor in sequence; the previous three output ends of the power distributor are connected with the LO input ends of a frequency doubler group and a frequency mixer group; the fourth output end of the power distributor is connected with a detector and an oscilloscope; the input end of a receiving antenna receives a signal radiated from a plasma; the output end of the receiving antenna is connected with RF input ends of a band-stop filter, a waveguide power distribution array and the frequency mixer group in sequence; the IF output end of the frequency mixer group is connected with a bandpass filter, a power amplifier and an analog / digital converter in sequence. The ultra wide band swept-frequency microwave radiometer has the advantages that the measurement of the electronic temperature distribution on the whole section of a longitudinal field under the plasma discharge condition of 1.0-2.5T can be realized, and the measurement frequency range can be 40-220GHz.
Owner:SOUTHWESTERN INST OF PHYSICS
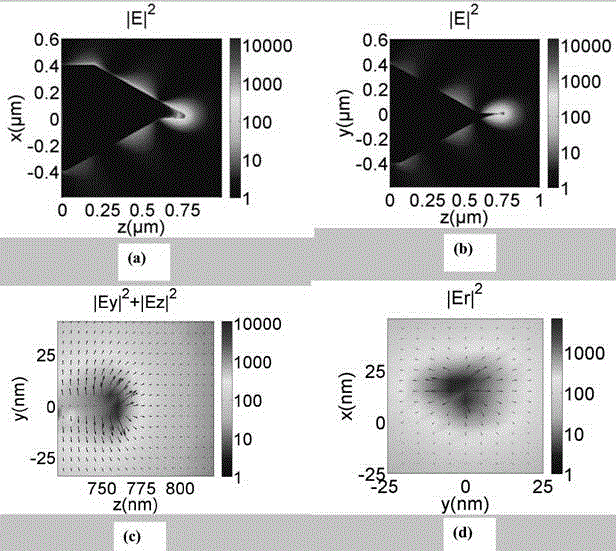
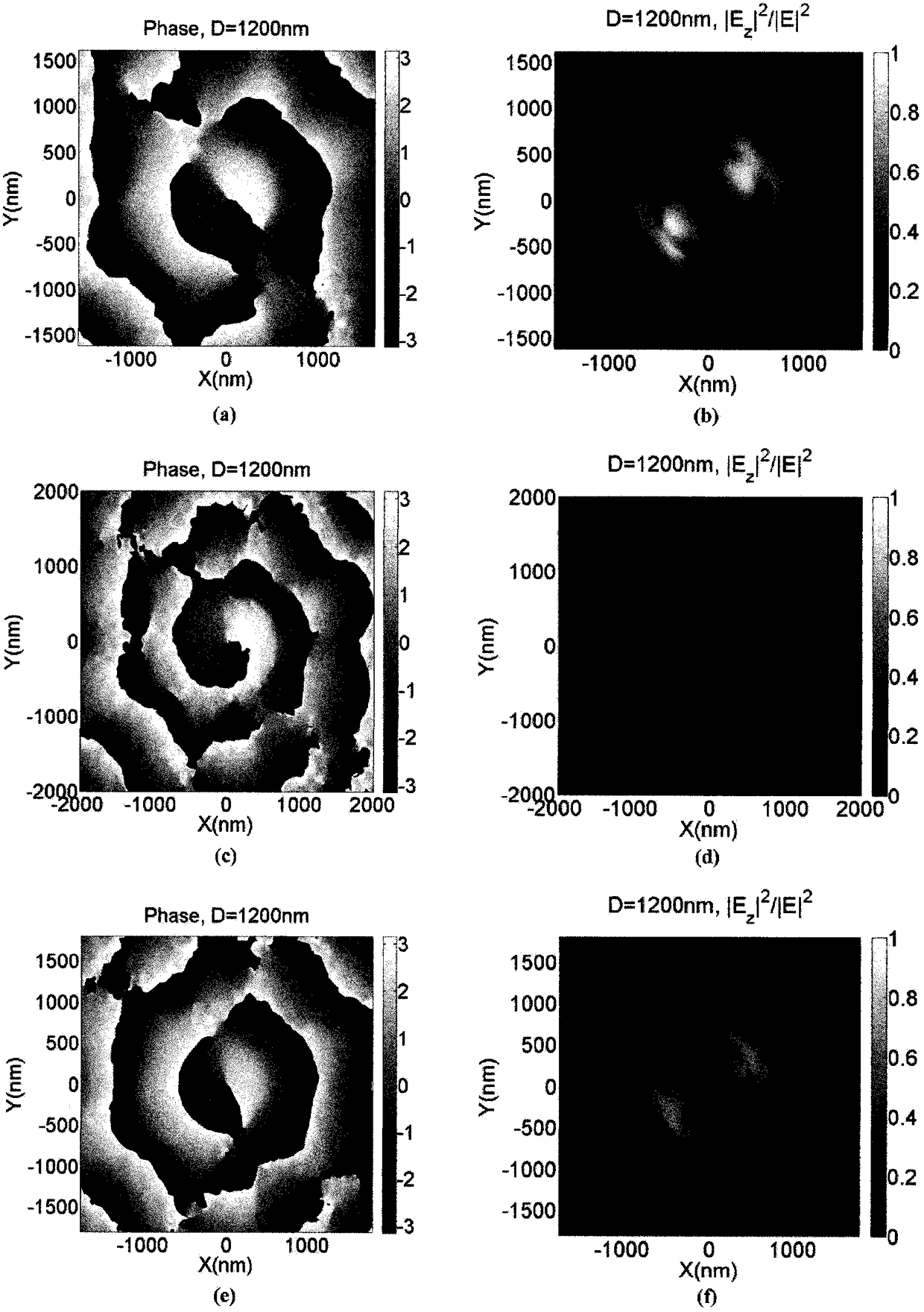
Assembly for Detecting the Intensity Distribution of Components of the Electromagnetic Field in Beams of Radiation
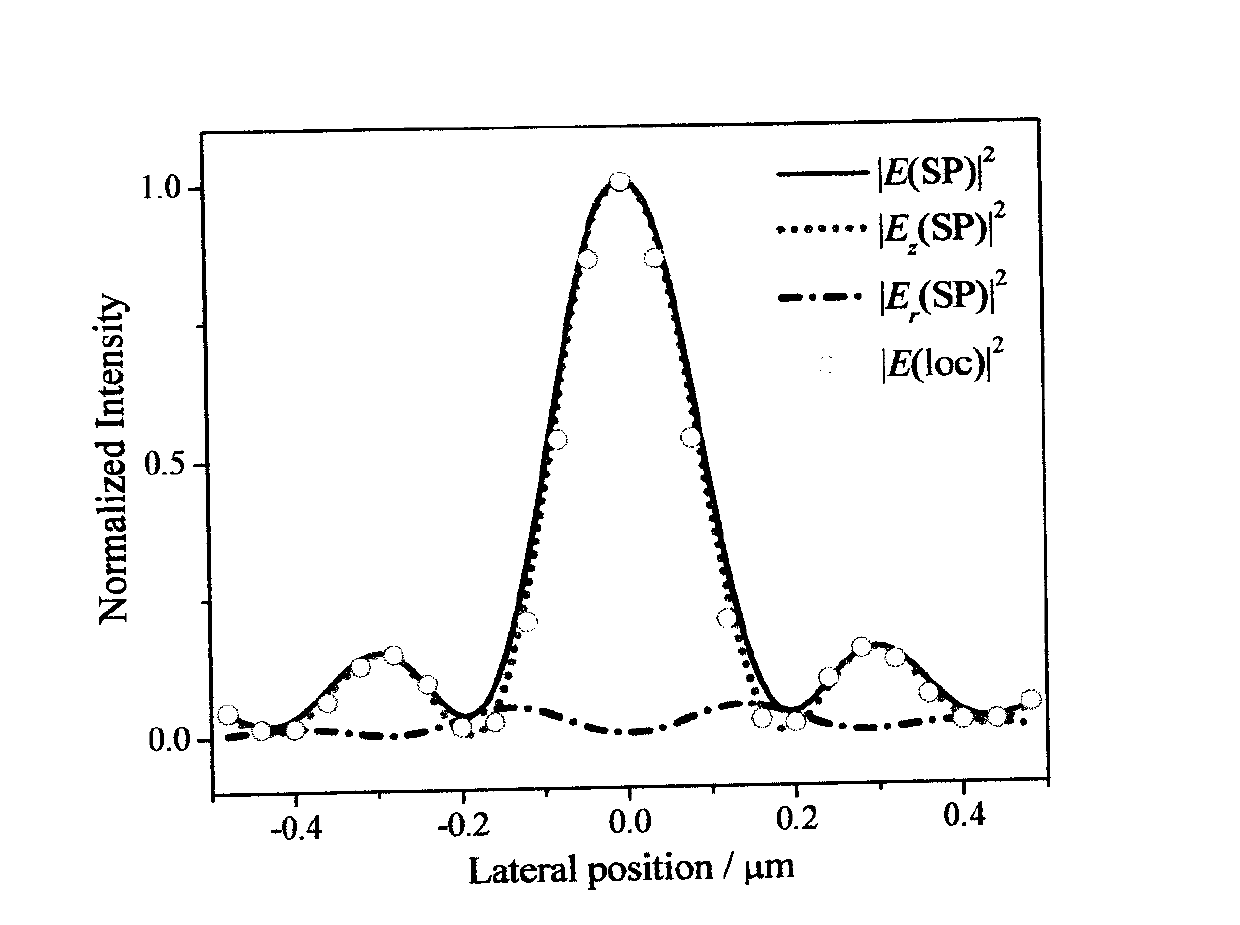
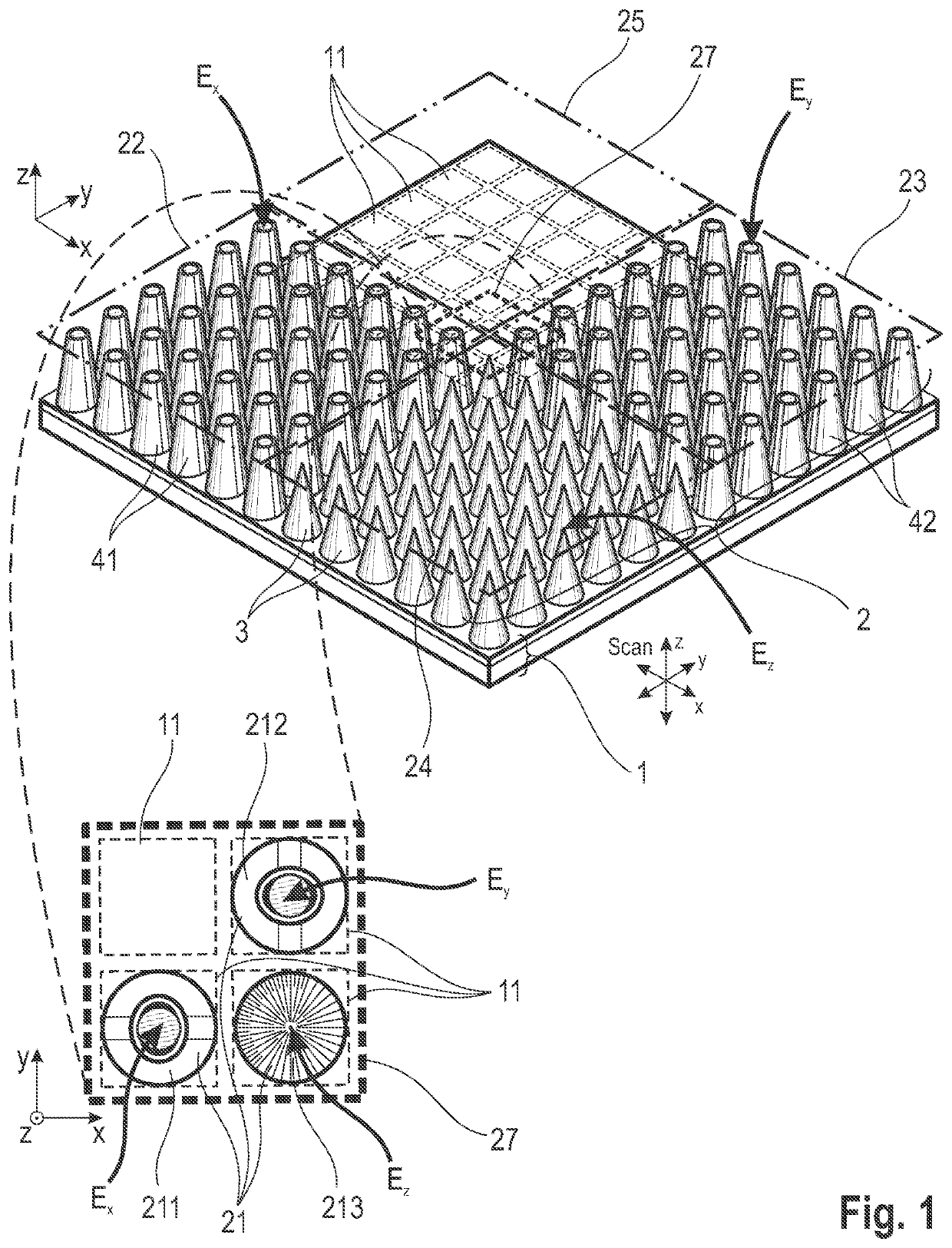
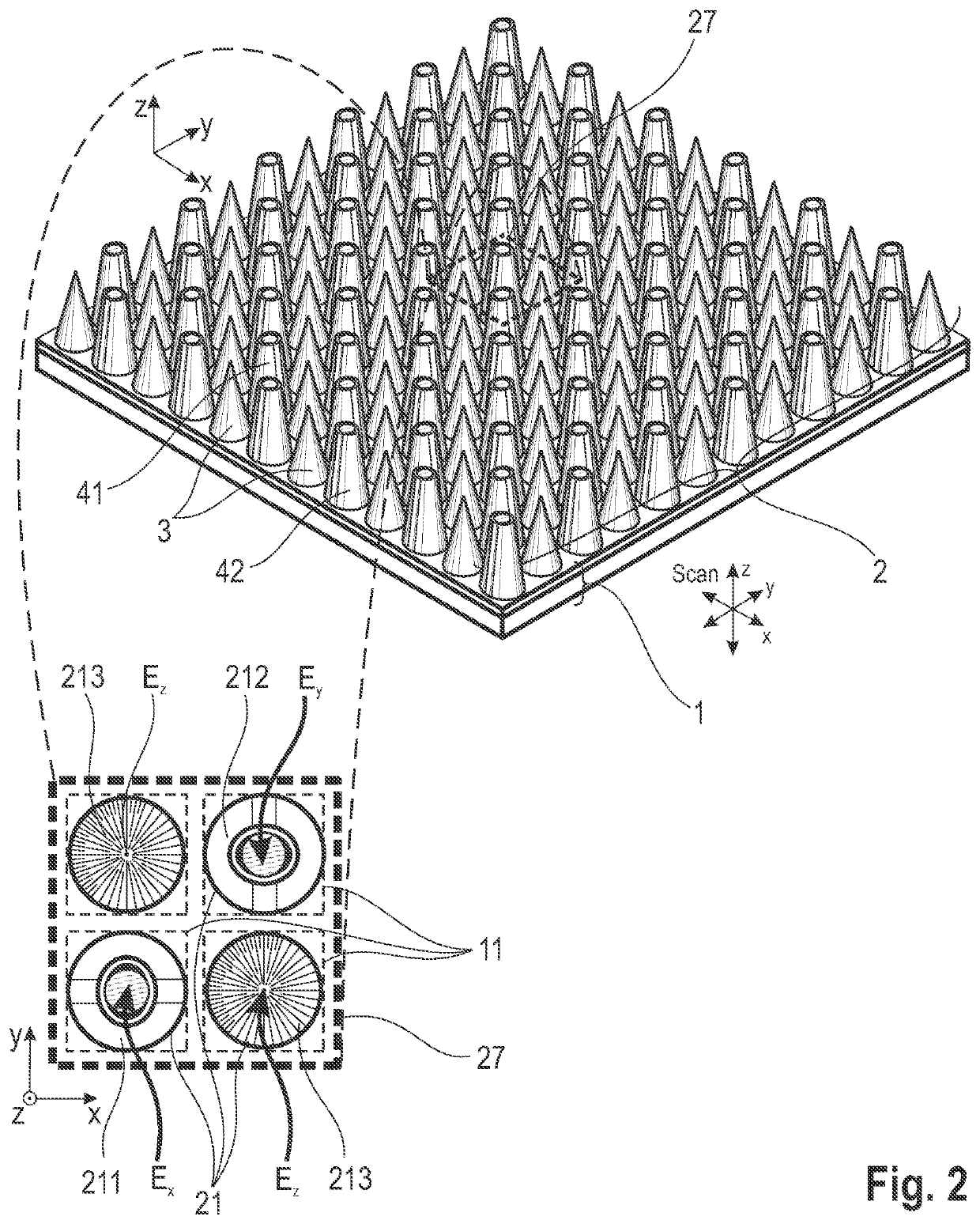
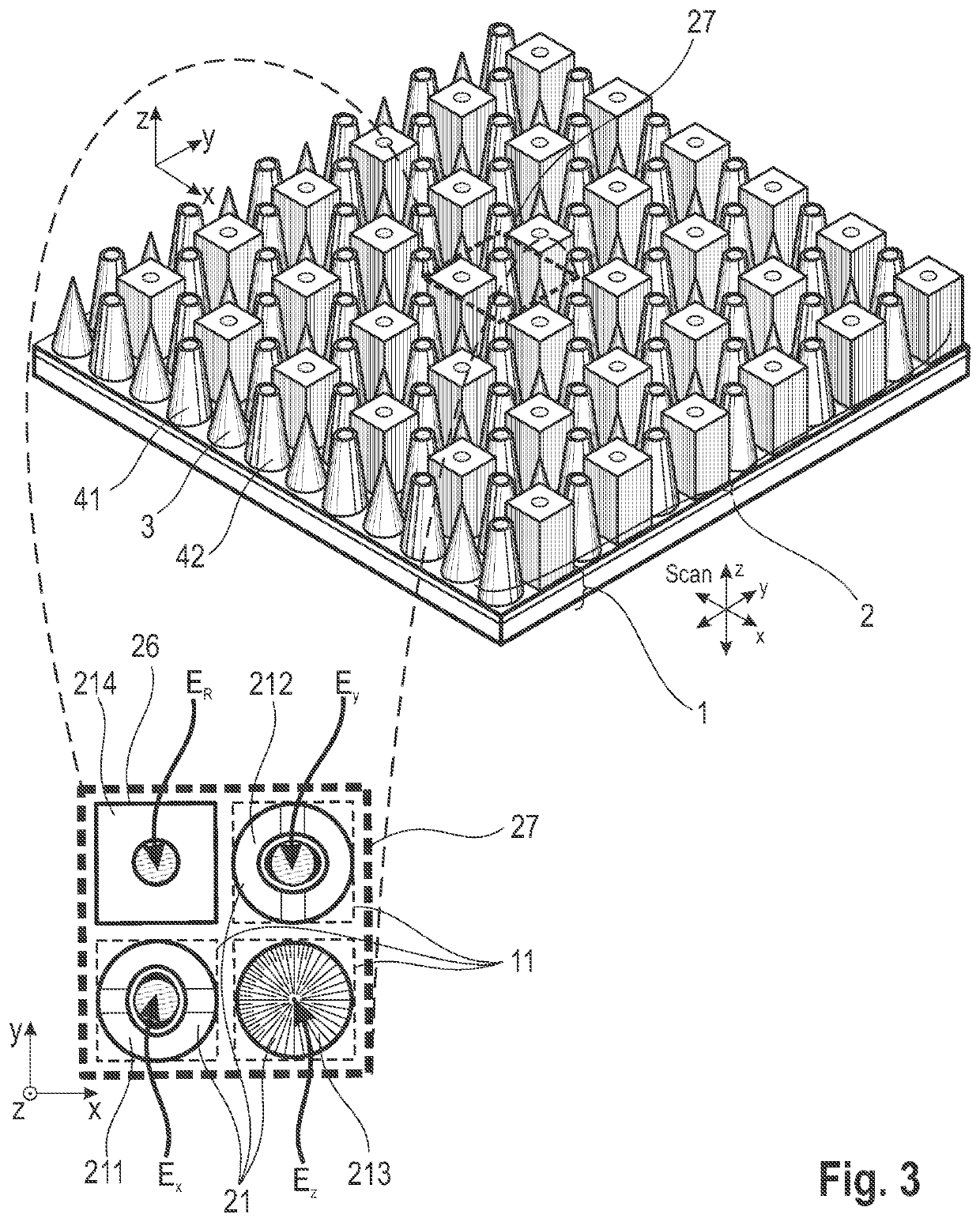
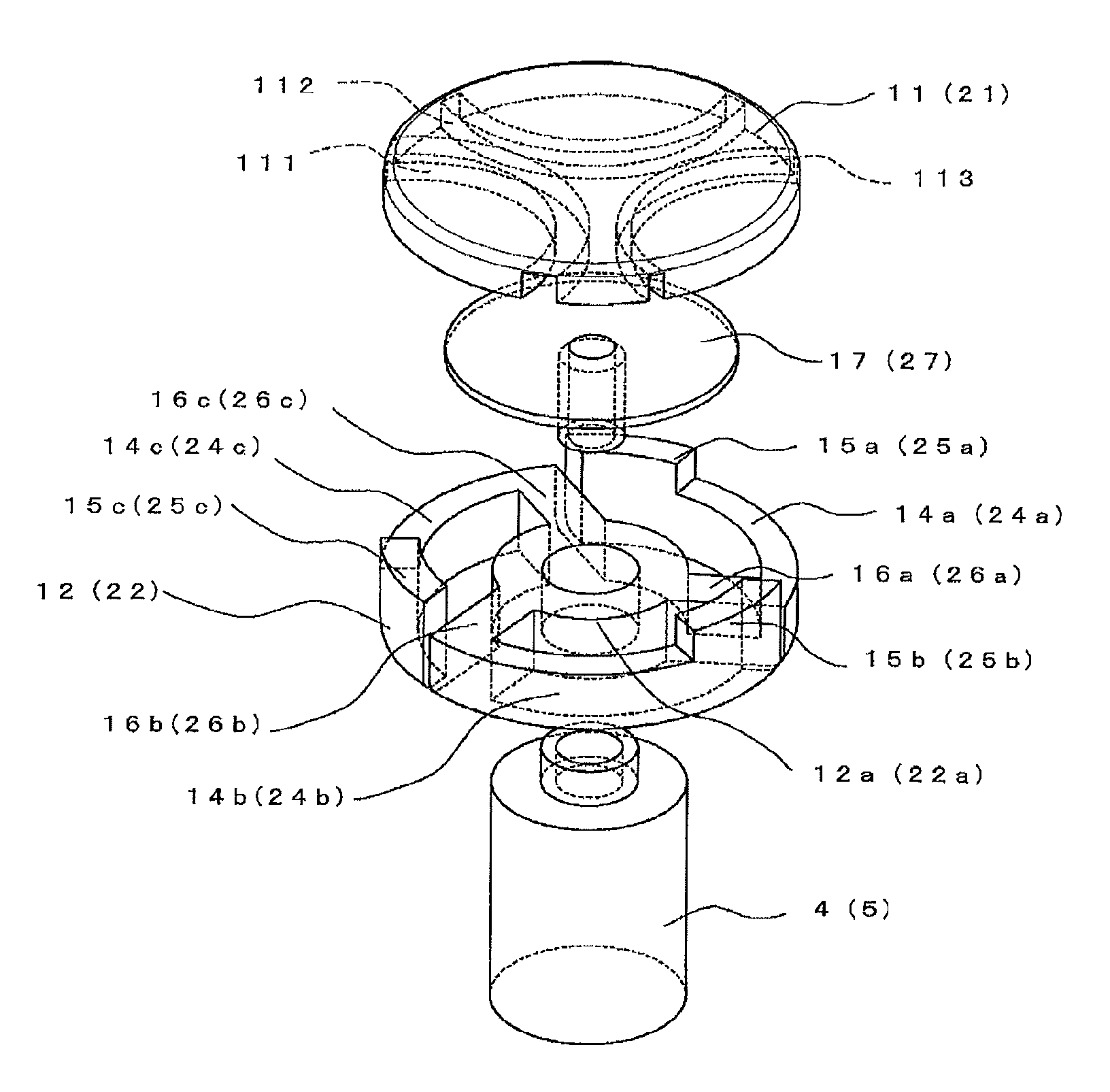
ActiveUS20210263070A1High resolutionImprove detection angleOptical measurementsRadiation pyrometrySensor arraySurface plasmon
The invention is directed to an arrangement for detecting the intensity distribution of components of the electromagnetic field in beams of radiation. The object of the invention is met, according to the invention, in that a high-resolution two-dimensional intensity sensor array and a field vector detector array comprising different regions with individual detector structures for two transverse and longitudinal field vector components Ex, Ey, Ez are combined, wherein the detector structures are formed as nanostructures, metallic jacket-shaped tips with different apices, for utilization of localized plasmon resonance (LPR) of the individual detector structures and localized surface plasmons (LSP) excited through LPR for a polarization selection of the field distribution according to field vector components Ex, Ey, Ez and transmission thereof to associated sensor elements by means of surface plasmon polaritons (SPP) and wave guiding (WGM).
Owner:JANUNTS NORIK
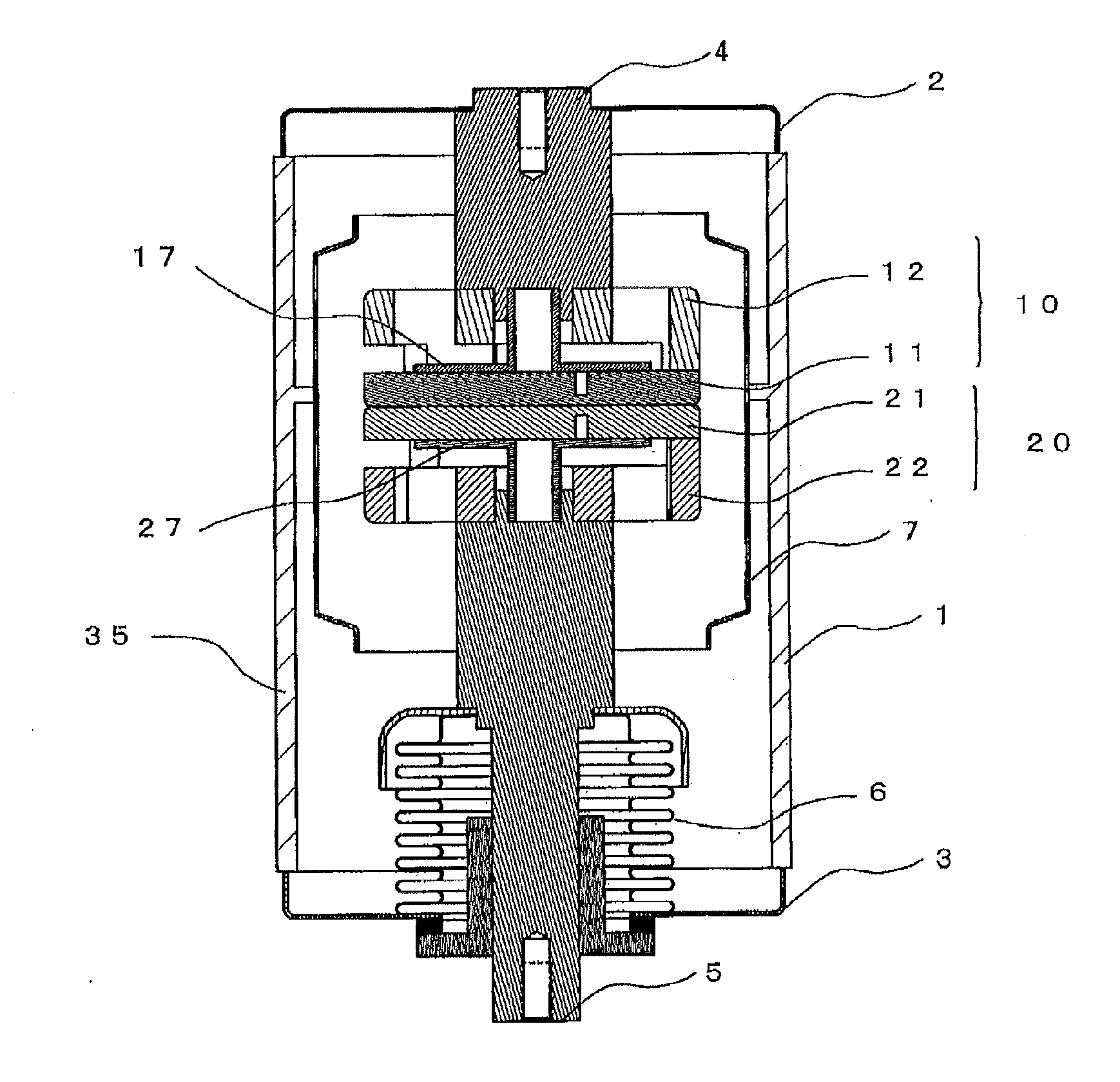
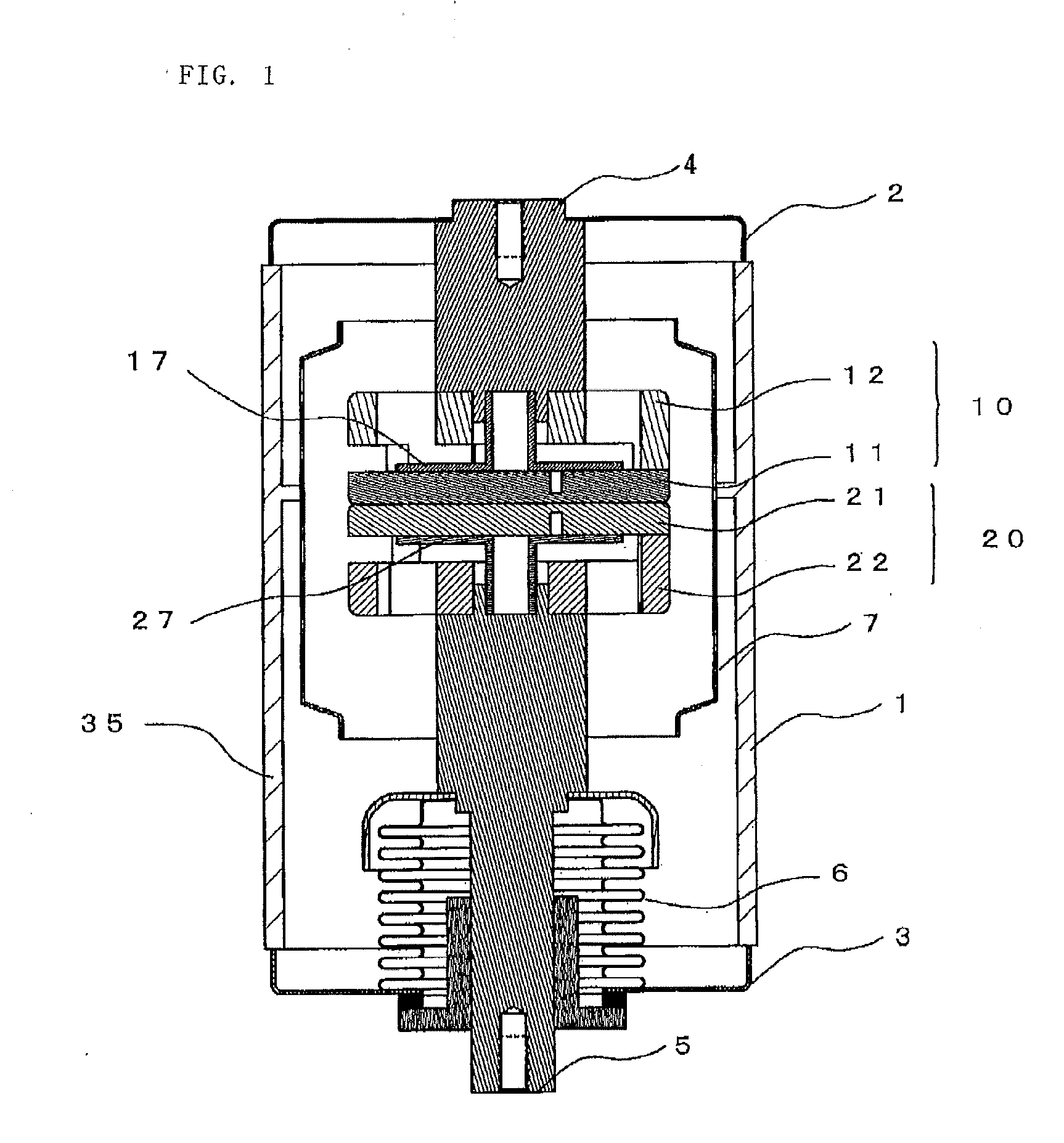
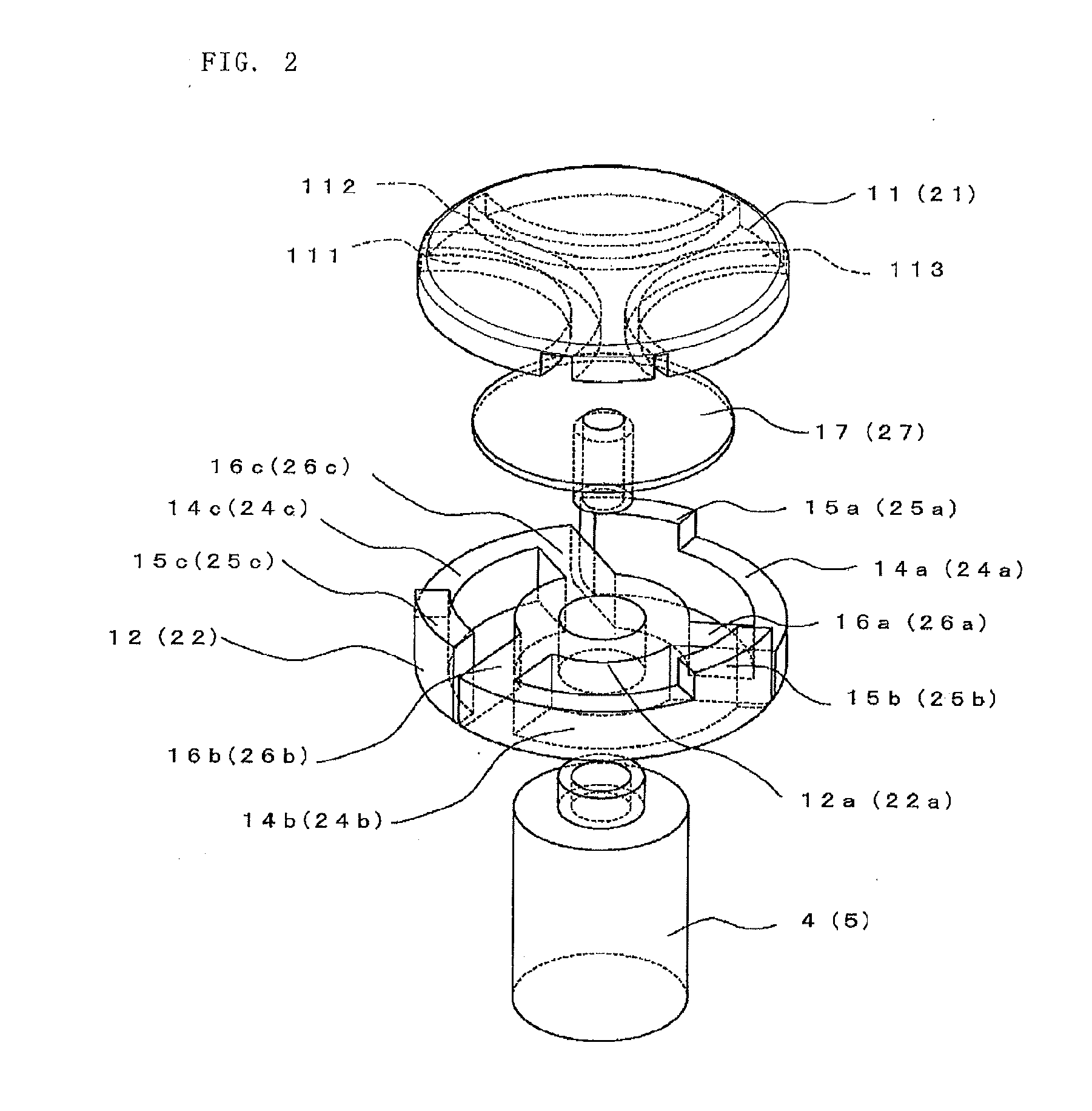
Vacuum valve
ActiveUS8754346B2Low costEasy to shapeContact mechanismsHigh-tension/heavy-dress switchesPower flowLongitudinal field
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Multi-structure combined artificial electromagnetic surface
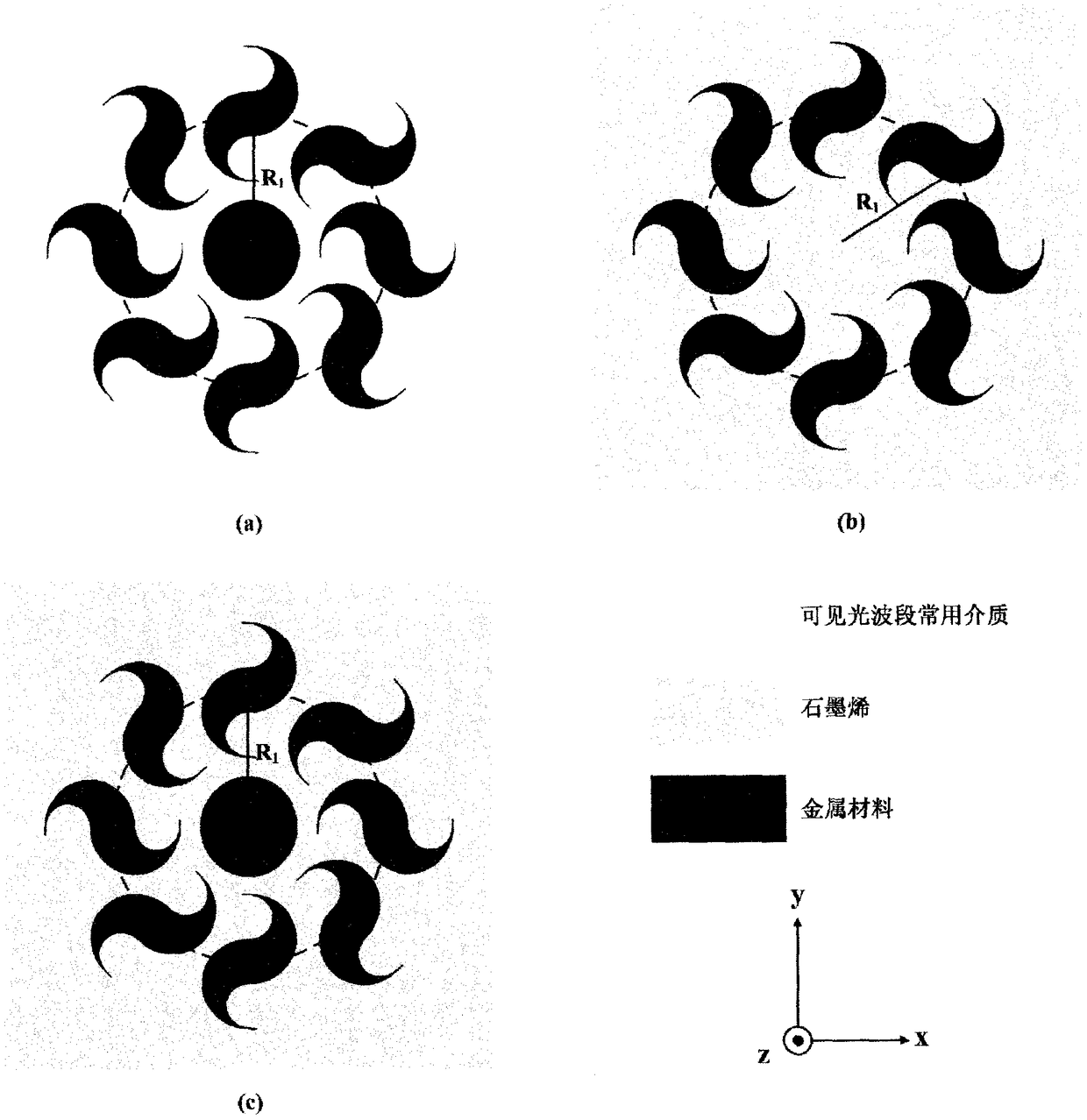
InactiveCN108363129ARealize precise controlHigh sensitivityOptical elementsGaussian beamStructure of the Earth
The invention discloses a multi-structure combined artificial electromagnetic surface that produces a local composite polarized light field with high locality and high longitudinal field component ratio characteristics. The artificial electromagnetic surface has three combinations of a metal dolphin-shaped cell circular array metal cylinder, a dolphin-shaped cell circular array graphene layer, anda metal dolphin-shaped cell circular array metal cylindrical graphene layer. The substrate is a commonly used dielectric material in the visible light band, and a linearly polarized Gaussian beam inthe visible light band is used as an incident source. The radius of the circular array is R1, the radius of the metal cylinder is R2, the thickness of the metal material layer is D1, and the thicknessof the graphene layer is D2. Metal dolphin-shaped cell circular array metal cylinder composite structure can excite high locality and high longitudinal field component ratio of vector vortex light field and metal cylinder. The larger the radius, the stronger the locality of the light field and the larger the proportion of the longitudinal field component. The metal dolphin-shaped cell circular array graphene layer combination structure can generate a high locality vector vortex light field. The vector vortex light field excited by the metal dolphin-shaped cell circular array metal cylindricalgraphene layer combined structure takes into account the high locality and high longitudinal field component ratio. The electromagnetic surface has important application value in the fields of quantum communication, molecular screening and nano manipulation.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for correcting error of quasi-optical cavity dielectric constant test along with frequency change
PendingCN111856150AHigh precisionSolve the calculation result errorDielectric property measurementsGaussian beamOptical cavity
The invention discloses a method for correcting an error of a quasi-optical cavity dielectric constant test along with frequency change, belongs to the field of detection, and can solve the problem ofthe error of the quasi-optical cavity dielectric constant test along with the frequency change. The method comprises the following steps of: analyzing Gaussian beam phase distribution in a quasi-optical cavity; obtaining actual phase distribution and an electric field and magnetic field expression of the upper surface of a sample according to the boundary condition relationship of the upper surface of the to-be-detected sample, namely an electromagnetic field at an interface of air and a medium region; considering the longitudinal field component of the electric field in the quasi-optical cavity, and listing the transverse field component and the longitudinal field component of the electric field in the quasi-optical cavity into a calculation step; and substituting the transverse field component and the longitudinal field component into a formula for calculation.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIS TECH INSTR CO LTD
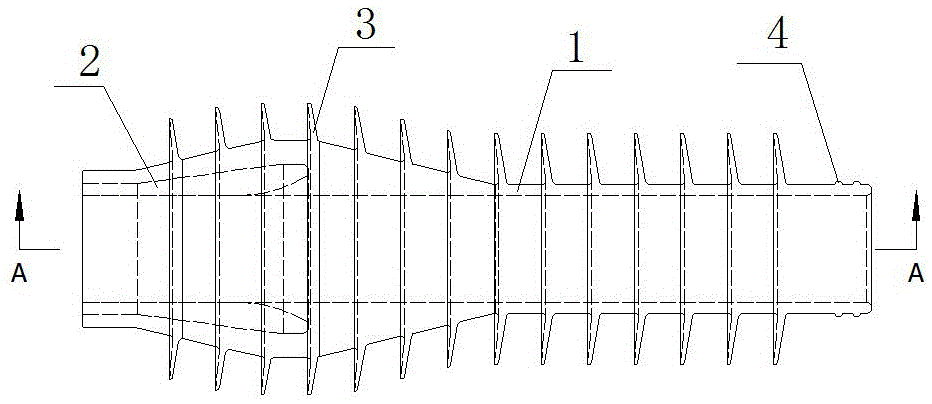
Detachable connector of high current flat plate copper conductor
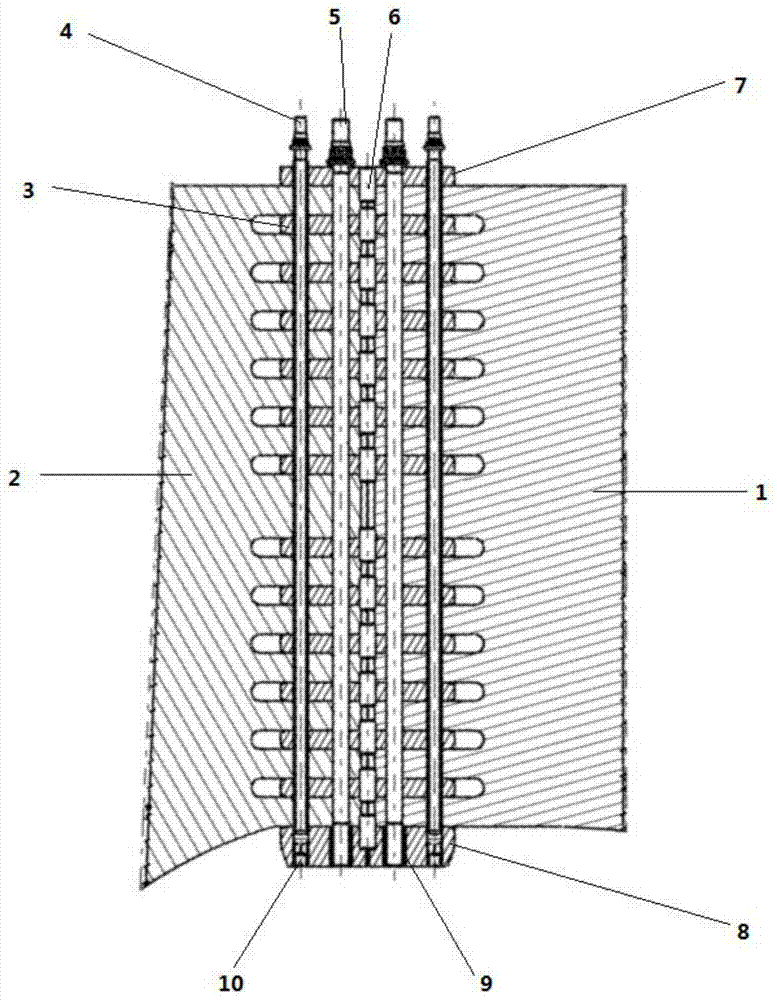
ActiveCN104733058AHigh mechanical strengthIncreased shear strengthNuclear energy generationThermonuclear fusion reactorCopper conductorPower flow
The invention belongs to a detachable connector of a flat plate copper conductor longitudinal field coil in a fusion reaction experimental device. The detachable connector comprises copper plates at the two ends, the copper plates at the two ends are provided with slots which are all shaped like a finger, an insertion bar is inserted in each slot, a circular hole is formed in the middle of each insertion bar, and a locating pin is driven in the circular hole; two long holes are formed in each copper plate of the two ends, and four same holes are correspondingly formed in each insertion bar, wherein the holes near a seam are used for mounting draw-in bolt components, and the outer side holes are used for mounting expansion bolt components. The detachable connector of the high current flat plate copper conductor has the advantages that in the structure of the detachable connector of the high current flat plate copper conductor, the insertion bars play a role of conducting currents of the copper plates at the two ends, the material selection of the insertion bars is improved simultaneously, and the strength of the copper plate bodies is reduced due to the slots; the draw-in bolt components are pre-tightened to guarantee that the insertion bars are closely attached to the slot faces of the copper plates, and the good conductive performance is guaranteed; meanwhile, the mechanical strength of the whole connector is improved simultaneously.
Owner:SOUTHWESTERN INST OF PHYSICS
Vacuum valve
ActiveUS20120228265A1Improve interrupt performanceEasy to shapeHigh-tension/heavy-dress switchesAir-break switchesLongitudinal fieldElectrical and Electronics engineering
A fixed electrode 10 and a movable electrode have coil electrodes formed of plural coil portions installed at both contacts and on a rear surface side in a divided manner in a circumferential direction along peripheries of the contacts such that a longitudinal field is generated in a direction in which the fixed contact and the movable contact come close to and move apart from each other. Protruding portions joined to the contacts are provided to tip ends of the respective coil portions to form joint portions to the respective contacts. A current to be flowed is controlled by changing resistance values between the contacts and the coil electrodes for each joint portion.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Differential mobility spectrometer with asymmetrically oscillating driving electrical field
ActiveUS8884219B2Stability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalyteIonization chamber
Owner:IEE INT ELECTRONICS & ENG SA
Bus terminal accessory of ethylene-propylene insulation copper pipe
InactiveCN106451315AReduce subsequent processesUniform radial field strengthBus-bar installationCable terminationsInsulation layerInsulation Problem
The invention relates to a bus terminal accessory of an ethylene-propylene insulation copper pipe, and belongs to the technical field of power equipment. The accessory comprises a hollow insulation pipe and semiconduction stress cones, wherein the semiconduction stress cones are arranged at one end of the insulation pipe and are in hollow truncated cone shapes, one end with a large radius of each semiconduction stress cone faces the insulation pipe, the semiconduction stress cones are wrapped by the insulation pipe, and a plurality of umbrella skirts are arranged on an outer surface of the insulation pipe. In the bus terminal accessory of the ethylene-propylene insulation copper pipe, provided by the invention, a liquid silicone rubber material is adopted, the accessory is formed by die pressing high-temperature curing, the semiconduction stress cones are overlapped with the insulation pipe to achieve an effect of uniform insulation shielding, and the radial field intensity and longitudinal field intensity of an insulation shielding opening can be perfectly uniform; the insulation layer is provided with umbrella skirts, the insulation problem of a voltage of a semiconduction outer side can be ensured very well by the insulation layer, and meanwhile, the voltage problem of the whole bus terminal is ensured; and the umbrella skirts are used for extending the creepage distance of a high potential and a low potential very well, and the subsequent process of a bus due to the creepage distance problem is saved.
Owner:JIANGSU HUAQIANG ELECTRIC EQUIP
Device and method for generating extreme ultraviolet source based on radial polarization laser driving
InactiveCN103149804AIncrease powerEnhanced radiationPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusLight spotOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a device and a method for generating an extreme ultraviolet source based on radial polarization laser driving. The device comprises a radial polarization pulse laser device, a laser amplifier, a collecting mirror and a drop generator. The radial polarization pulse laser device outputs radial polarization pulse laser, the laser amplifier amplifies the radial polarization pulse laser with low power and high repetition rate and outputs the radial polarization pulse laser with high repetition rate and high power, the radial polarization pulse laser with the high repetition rate and the high power is focused and illuminated on the drop, and generates extreme ultraviolet. According to the device and the method for generating the extreme ultraviolet source based on radial polarization laser driving, the beam is focused by utilizing the radial polarization pulse laser, the focus position has a longitudinal field component, energy carried by the longitudinal field component cannot be propagated, the energy is absorbed by Sn to be stimulated into ions in valence states, and extreme ultraviolet (EUV) of 13.5nm is effectively radiated. Meanwhile, the radial polarization pulse laser can obtain smaller focusing light spots during focusing, the smaller the light spots are, the higher the energy intensity of the laser is, and EUV radiation with stronger energy is generated.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
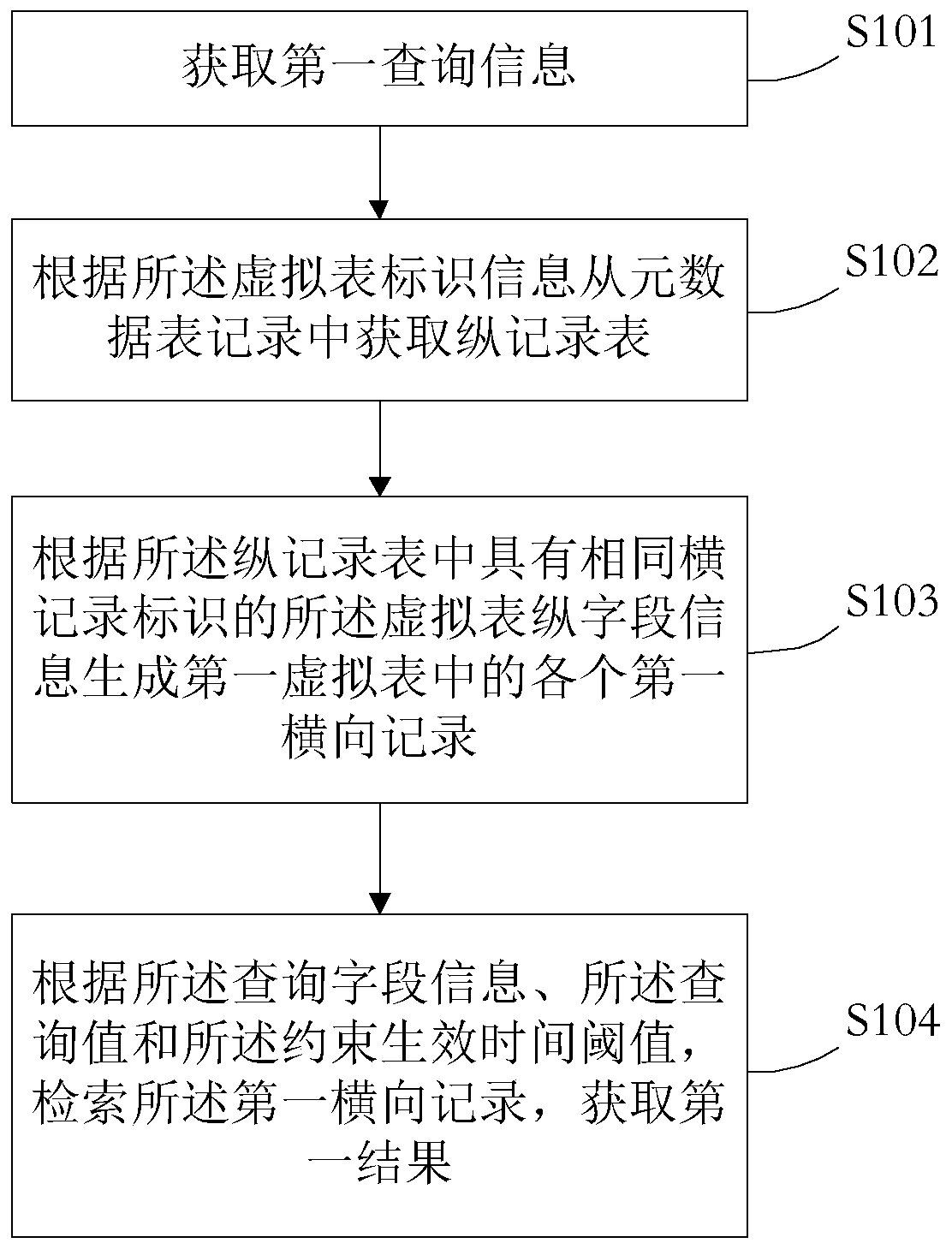
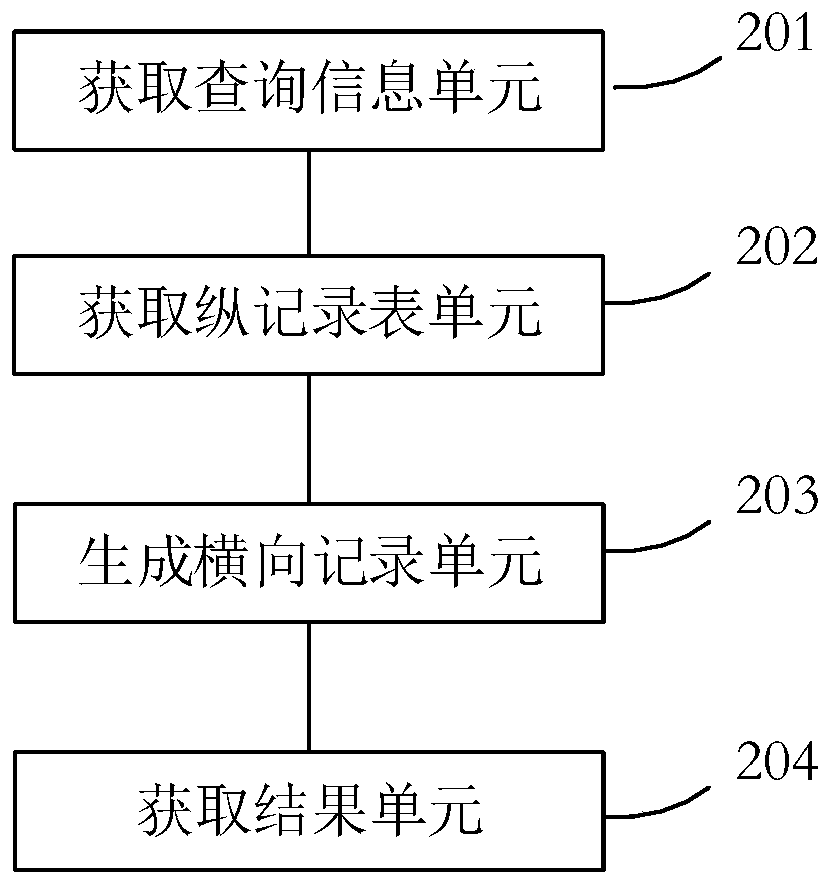
Data processing method and device, medium and electronic equipment
ActiveCN110489412AIncrease flexibilityEasy querySpecial data processing applicationsDatabase indexingTime informationData recording
The invention provides a data processing method and device, a medium and electronic equipment. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining first query information, with the first query information comprising virtual table identification information, query field information, a query value and a constraint effective time threshold; obtaining a longitudinal record table from metadata tablerecords according to the virtual table identification information; generating each first transverse record in a first virtual table according to the virtual table longitudinal field information with the same transverse record identifier in the longitudinal record table; and retrieving the first transverse record according to the query field information, the query value and the constraint effectivetime threshold to obtain a first result. The information with asynchronous time is stored in the same metadata table, and the data record is stored in a longitudinal storage mode. The field information in the metadata table can be changed at any time. The flexibility of data application is improved. Meanwhile, a plurality of asynchronous time can exist at the same time, so that the asynchronous time information can be inquired simply and conveniently.
Owner:BEIJING BYTEDANCE NETWORK TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com