Patents
Literature
1295 results about "Light scanning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
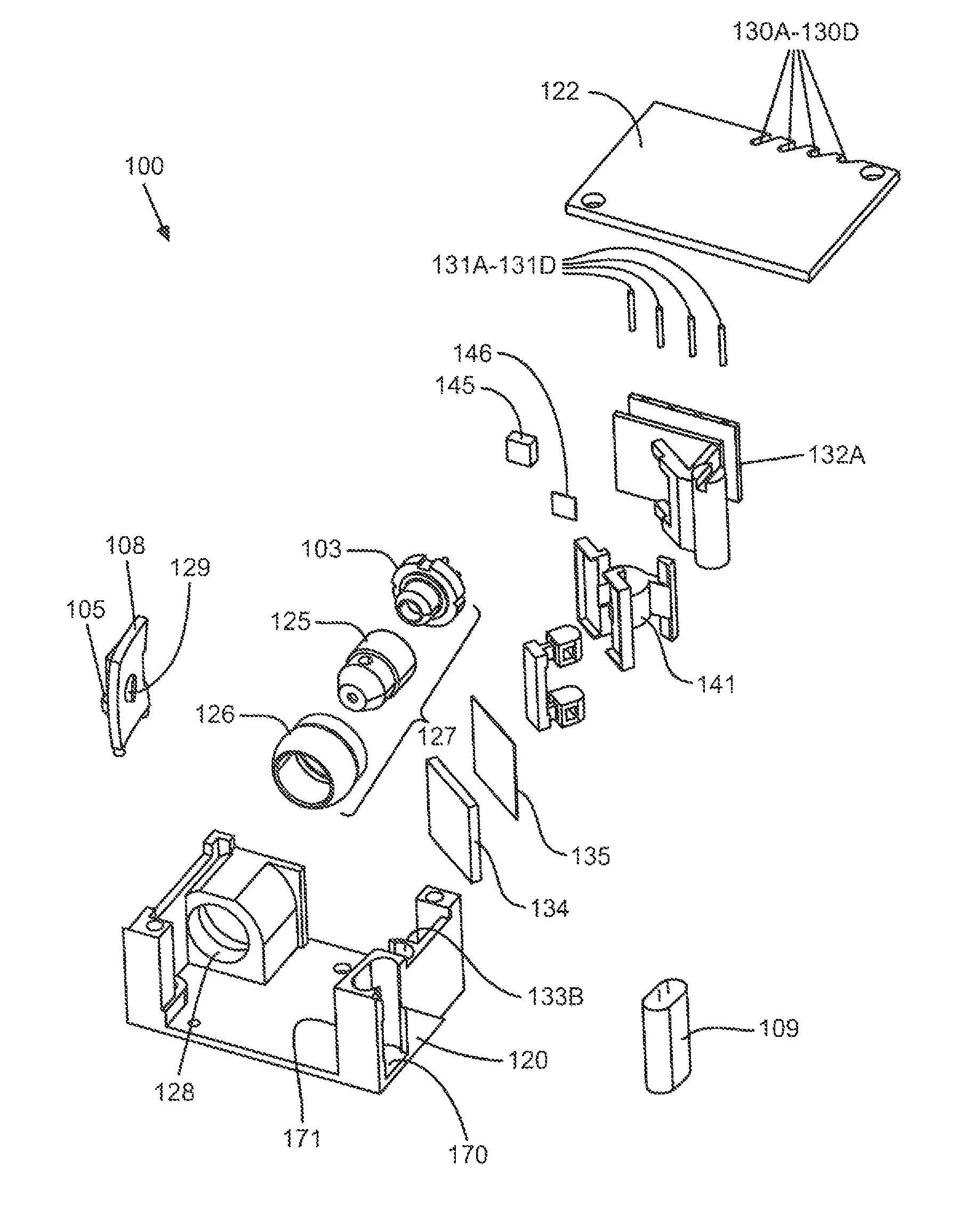
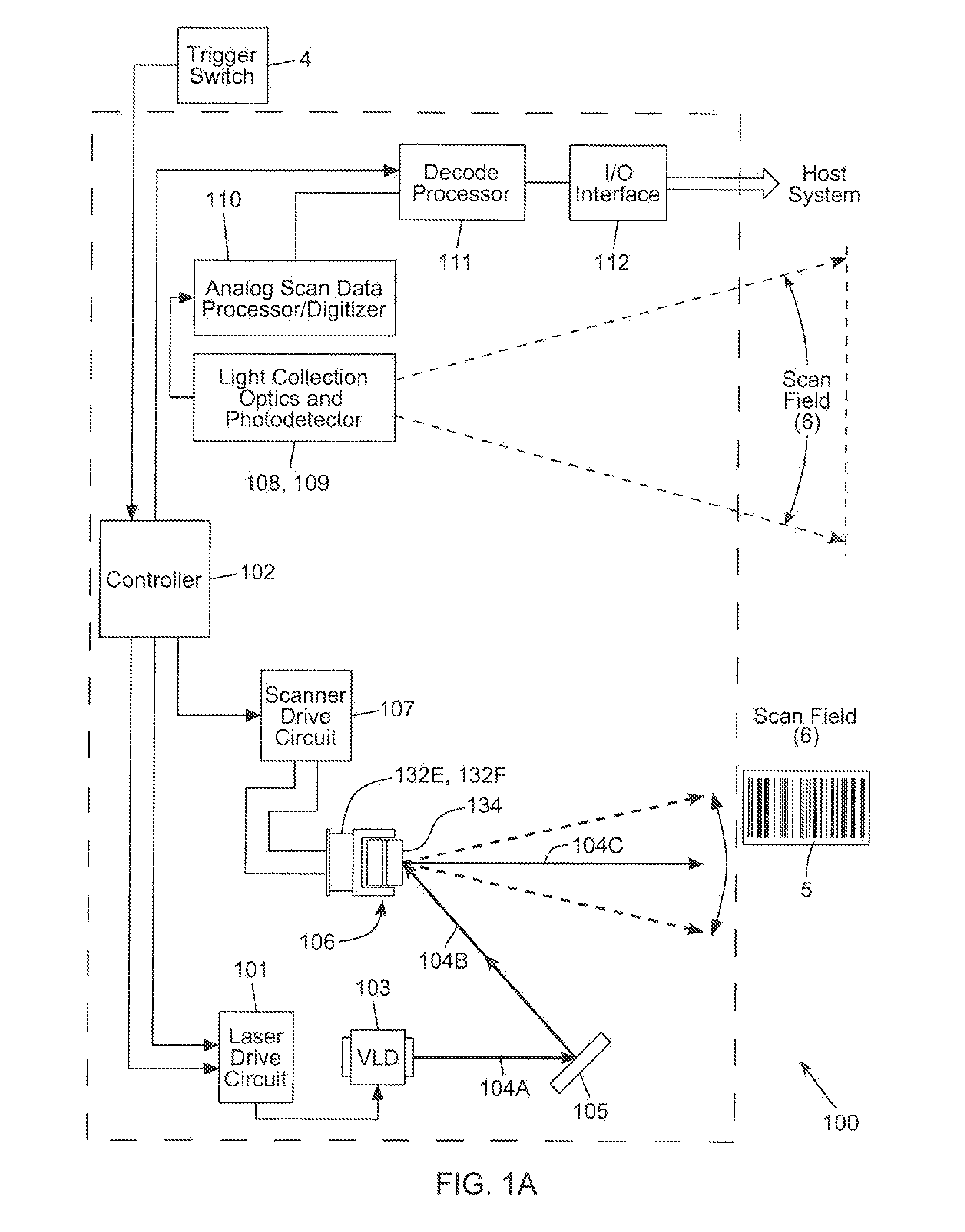
Laser scanning module with rotatably adjustable laser scanning assembly
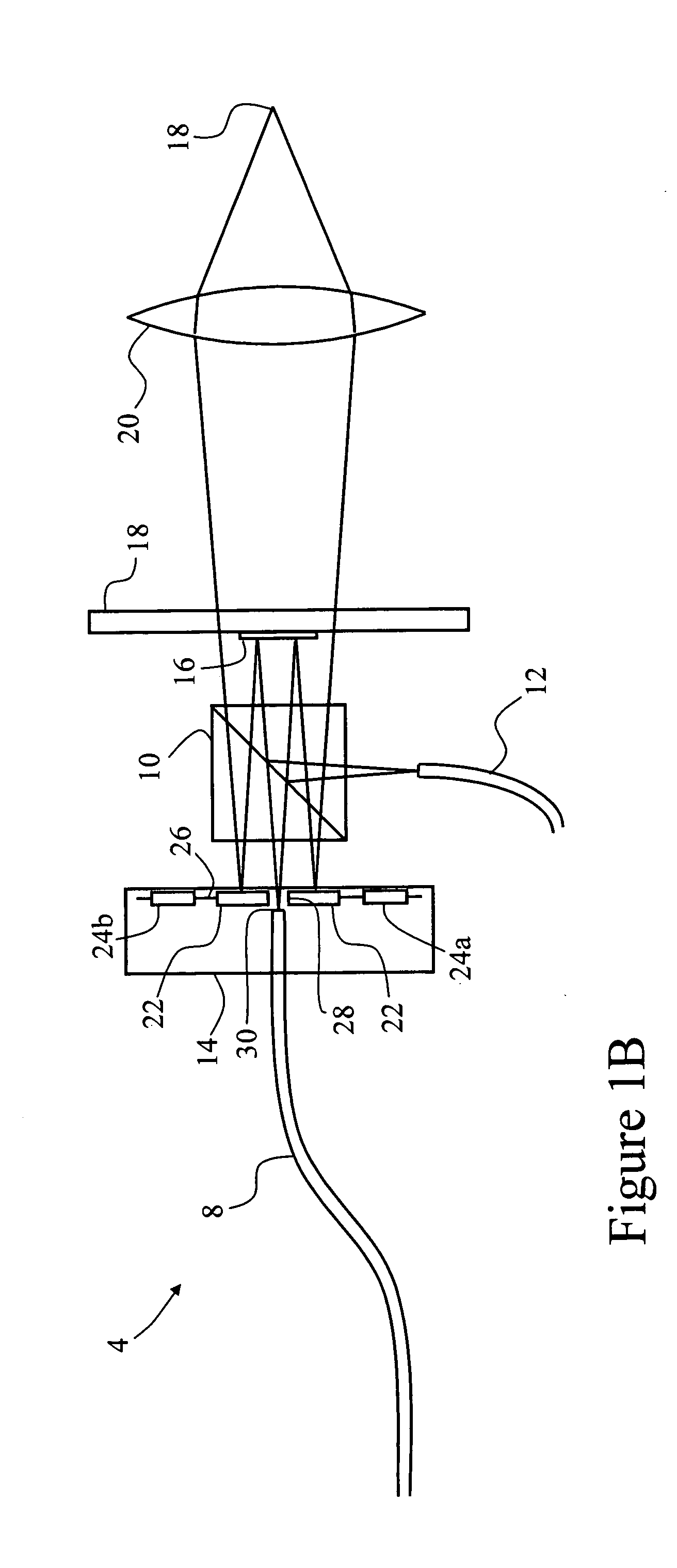
A laser scanning module employing a laser scanning assembly mounted within a module housing using a mechanism that allows the laser scanning assembly to be rotated to an angular position within the engine housing so that light collection, beam folding and light collection mirrors in the module housing are optically aligned. A PC board is mounted on a side of the housing and has a configuration of elongated apertures of open-ended and / or closed geometry, arranged in a non-parallel manner. An electromagnetic coil structure, associated with the laser scanning assembly, has a linear array of electrically-conductive pins that project through the configuration of elongated holes, at locations along the elongated holes that are determined by the angular rotation of the laser scanning assembly attained during optical alignment conditions during manufacture.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
System and method for a transparent color image display utilizing fluorescence conversion of nano particles and molecules
ActiveUS7090355B2Avoid viewingDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsColor imageWavelength filter
A system and a method of a transparent color image display utilizing fluorescence conversion (FC) of nano-particles and molecules are disclosed. In one preferred embodiment, a color image display system consists of a light source equipped with two-dimensional scanning hardware and a FC display screen board. The FC display screen board consists of a transparent fluorescence display layer, a wavelength filtering coating, and an absorption substrate. In another preferred embodiment, two mechanisms of light excitation are utilized. One of the excitation mechanisms is up-conversion where excitation light wavelength is longer than fluorescence wavelength. The second mechanism is down-conversion where excitation wavelength is shorter than fluorescence wavelength. A host of preferred fluorescence materials for the FC screen are also disclosed. These materials fall into four categories: inorganic nanometer sized phosphors; organic molecules and dyes; semiconductor based nano particles; and organometallic molecules. These molecules or nano-particles are incorporated in the screen in such a way that allows the visible transparency of the screen. Additionally, a preferred fast light scanning system is disclosed. The preferred scanning system consists of dual-axes acousto-optic light deflector, signal processing and control circuits equipped with a close-loop image feedback to maintain position accuracy and pointing stability of the excitation beam.
Owner:SUN INNOVATIONS
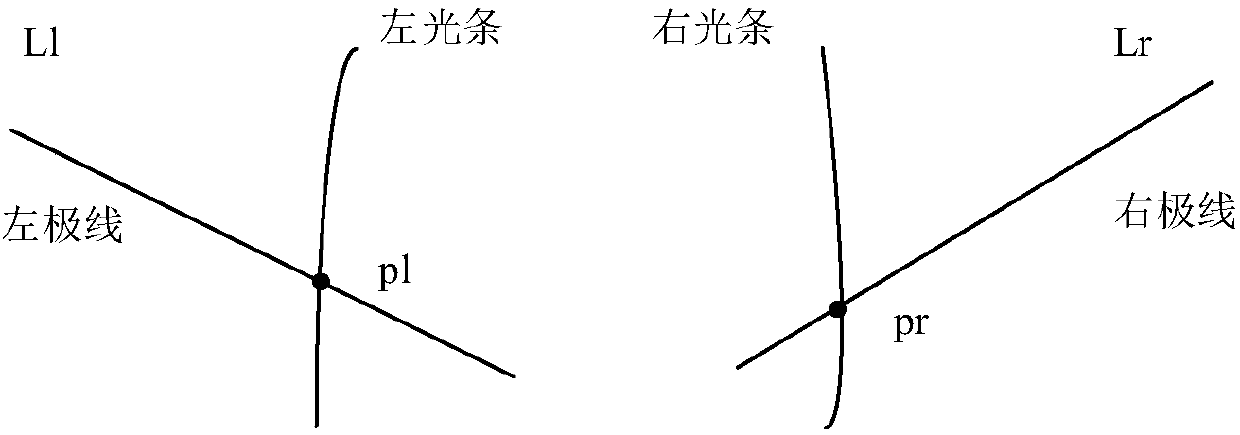
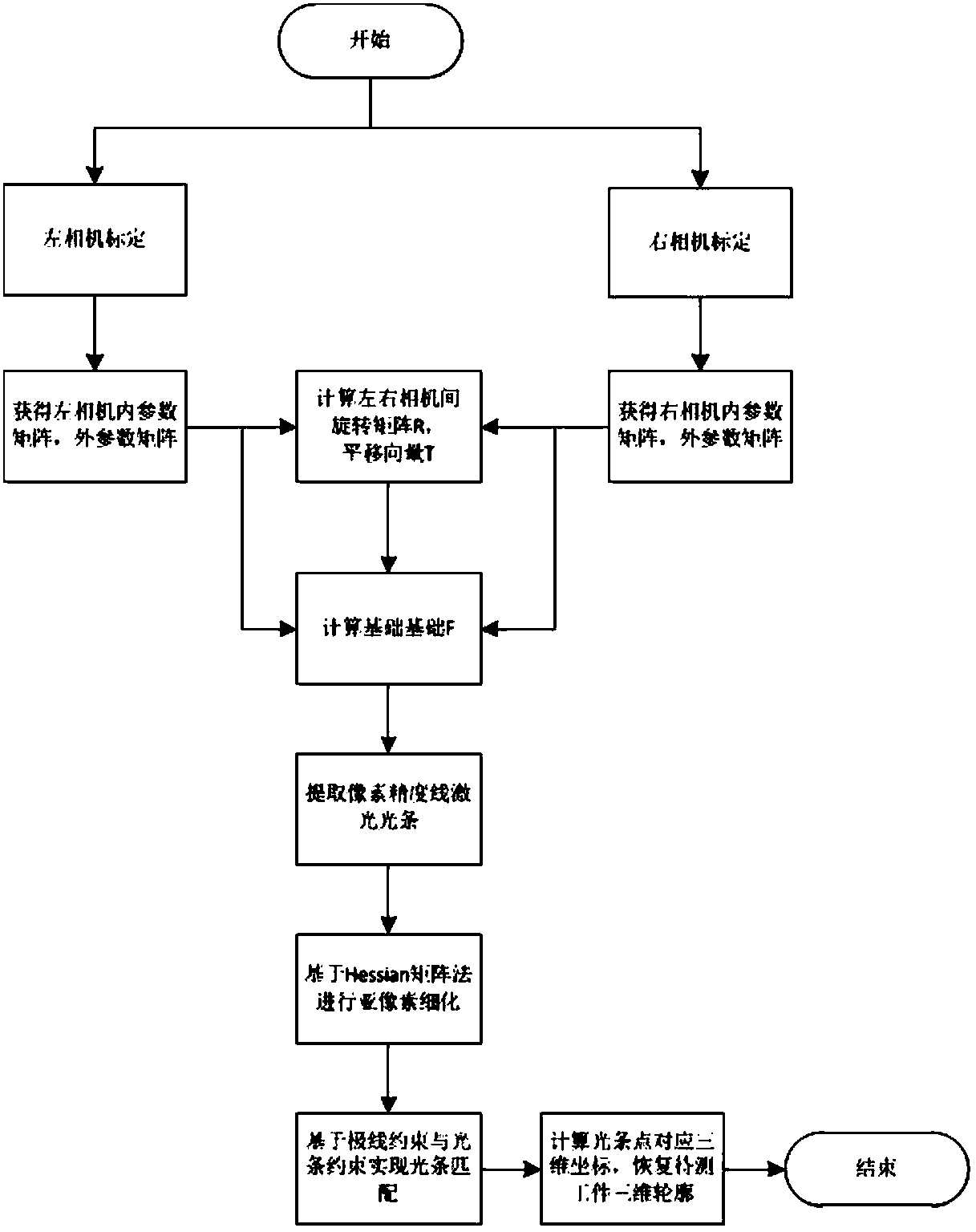
Binocular stereo vision three-dimensional measurement method based on line structured light scanning
InactiveCN107907048AReduce the difficulty of matchingImprove robustnessUsing optical meansThree dimensional measurementLaser scanning
The invention discloses a binocular stereo vision three-dimensional measurement method based on line structured light scanning, which comprises the steps of performing stereo calibration on binocularindustrial cameras, projecting laser light bars by using a line laser, respectively acquiring left and right laser light bar images, extracting light bar center coordinates with sub-pixel accuracy based on a Hessian matrix method, performing light bar matching according to an epipolar constraint principle, and calculating a laser plane equation; secondly, acquiring a line laser scanning image of aworkpiece to be measured, extracting coordinates of the image of the workpiece to be measured, calculating world coordinates of the workpiece to be measured by combining binocular camera calibrationparameters and the laser plane equation, and recovering the three-dimensional surface topography of the workpiece to be measured. Compared with a common three-dimensional measurement system combininga monocular camera and line structured light, the binocular stereo vision three-dimensional measurement method avoids complicated laser plane calibration. Compared with the traditional stereo vision method, the binocular stereo vision three-dimensional measurement method reduces the difficulty of stereo matching in binocular stereo vision while ensuring the measurement accuracy, and improves the robustness and the usability of a visual three-dimensional measurement system.
Owner:CHANGSHA XIANGJI HAIDUN TECH CO LTD
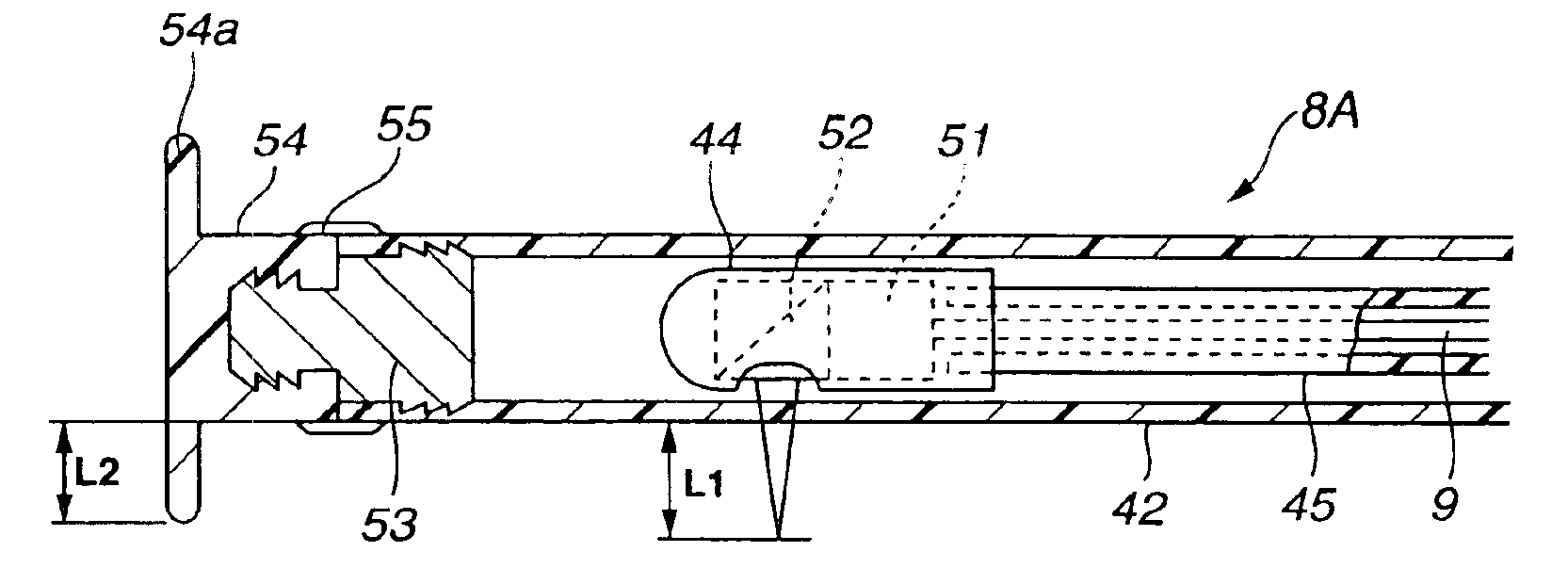
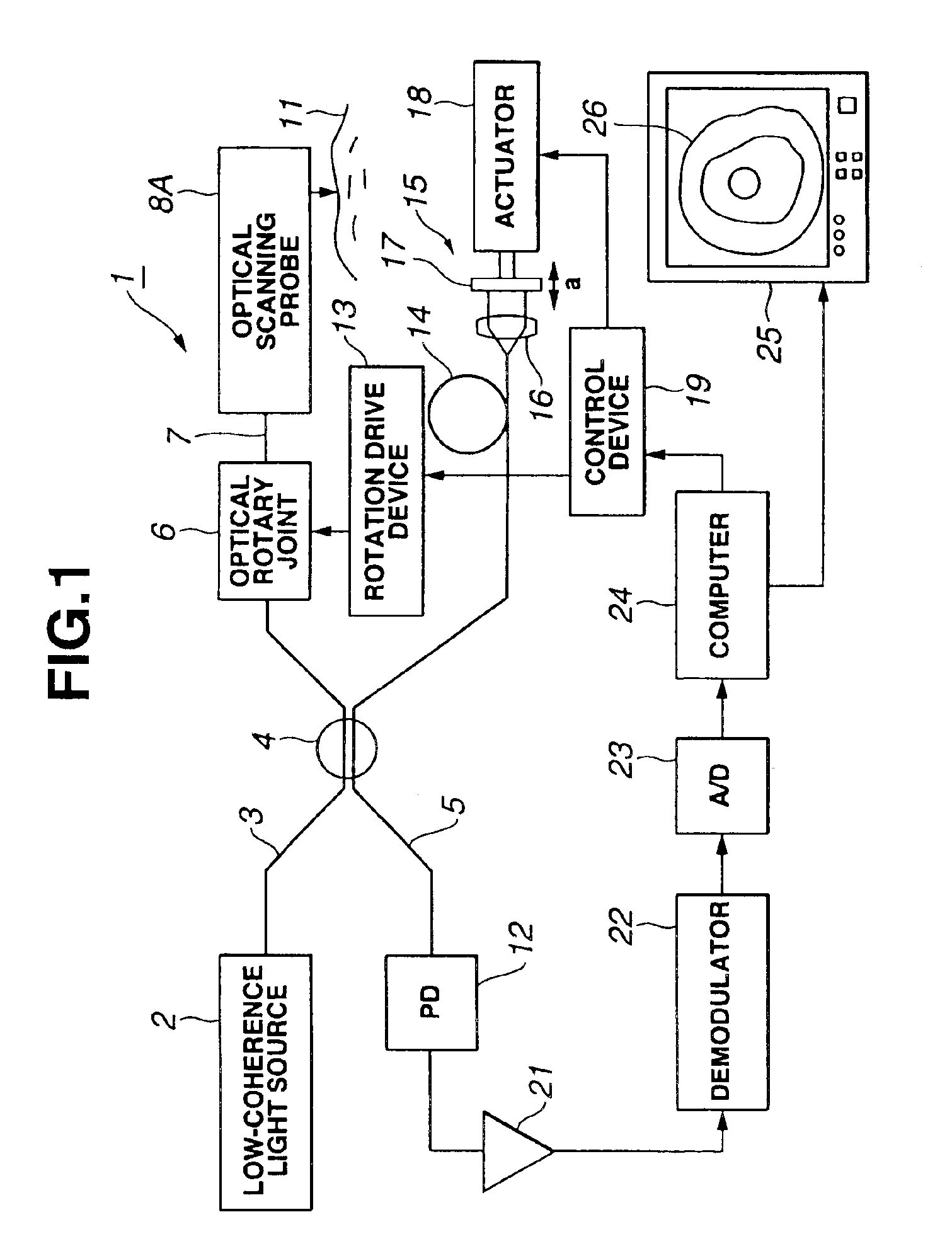
Light scanning probe apparatus using light of low coherence
InactiveUS6888119B2Easy to operateHigh light transmittanceSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsBiological bodyGrism
A flexible shaft driven to rotate is inserted through a transparent sheath having pliability. By a fiber inserted through the inside thereof, low-coherence light is guided and is made to exit to a living-body tissue side which is an observation target through a lens and a prism forming an exit and entrance portion at the tip portion. Subsequently, the light reflected on the living-body tissue side is guided in order to produce an image. In that case, a positioning member for keeping the exit and entrance portion and the living-body tissue at a proper distance is formed at the tip portion of the sheath or the tip portion of an endoscope through which an optical probe is inserted and, therefore, a stable tomogram image can be produced.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
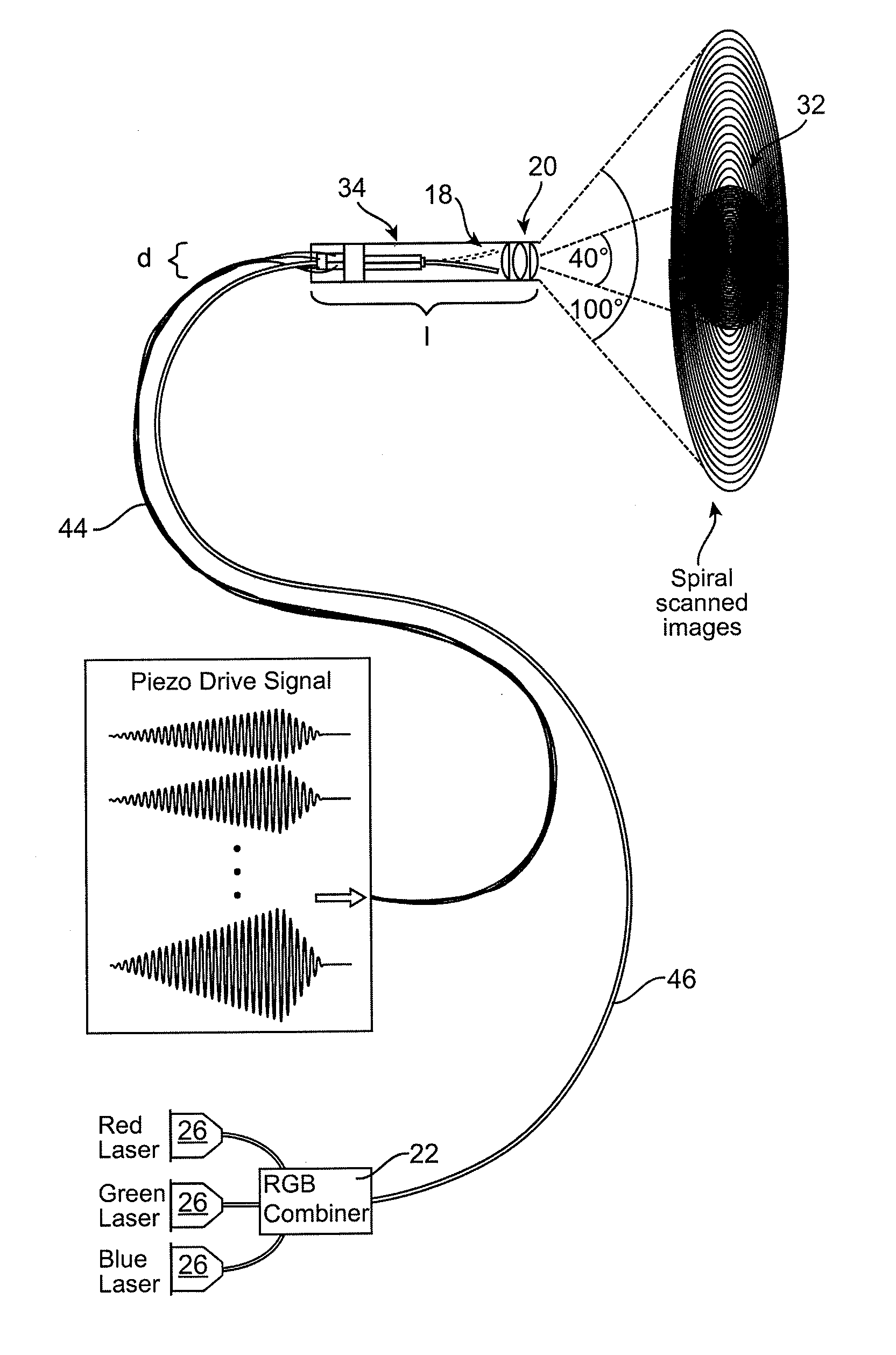
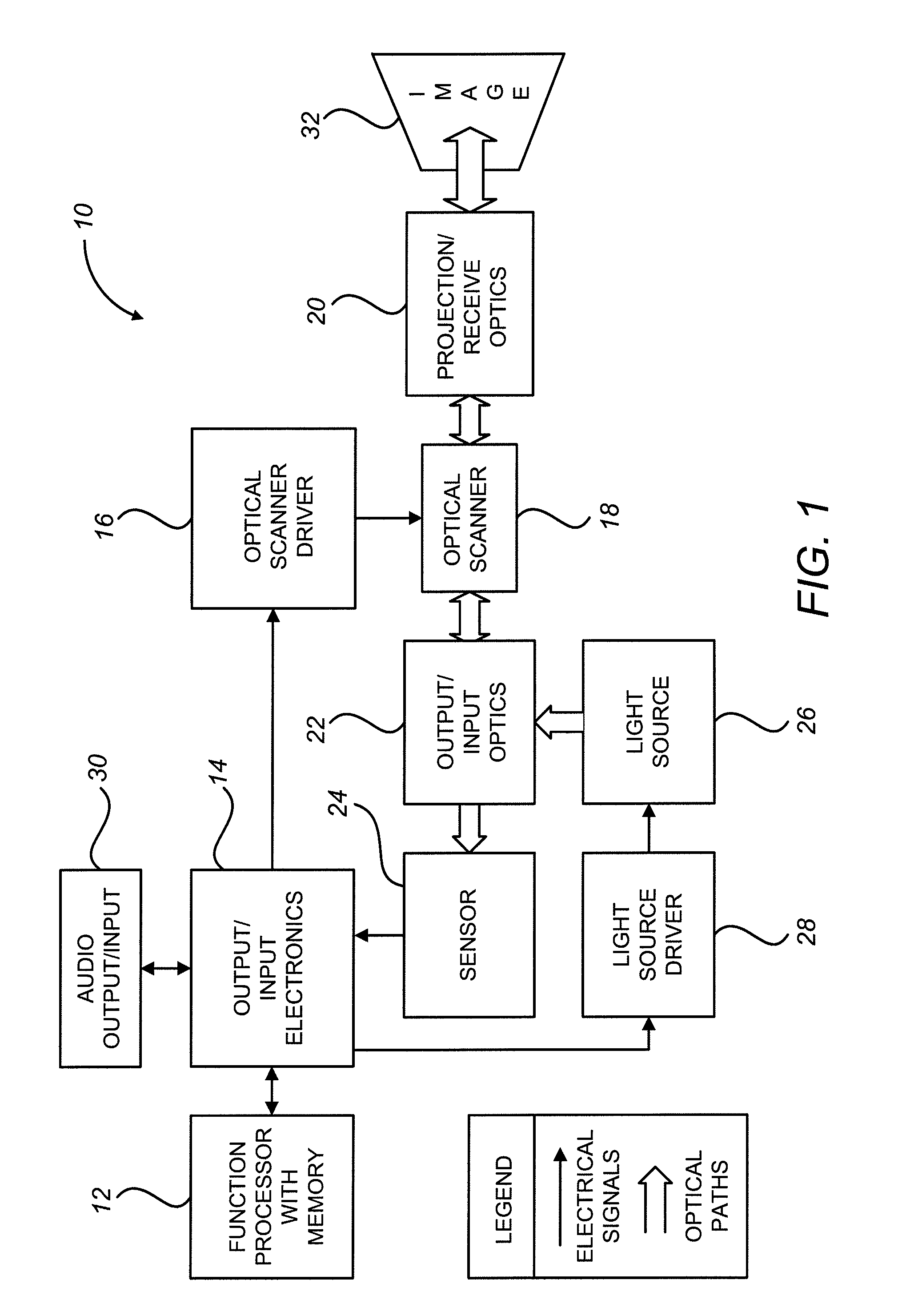
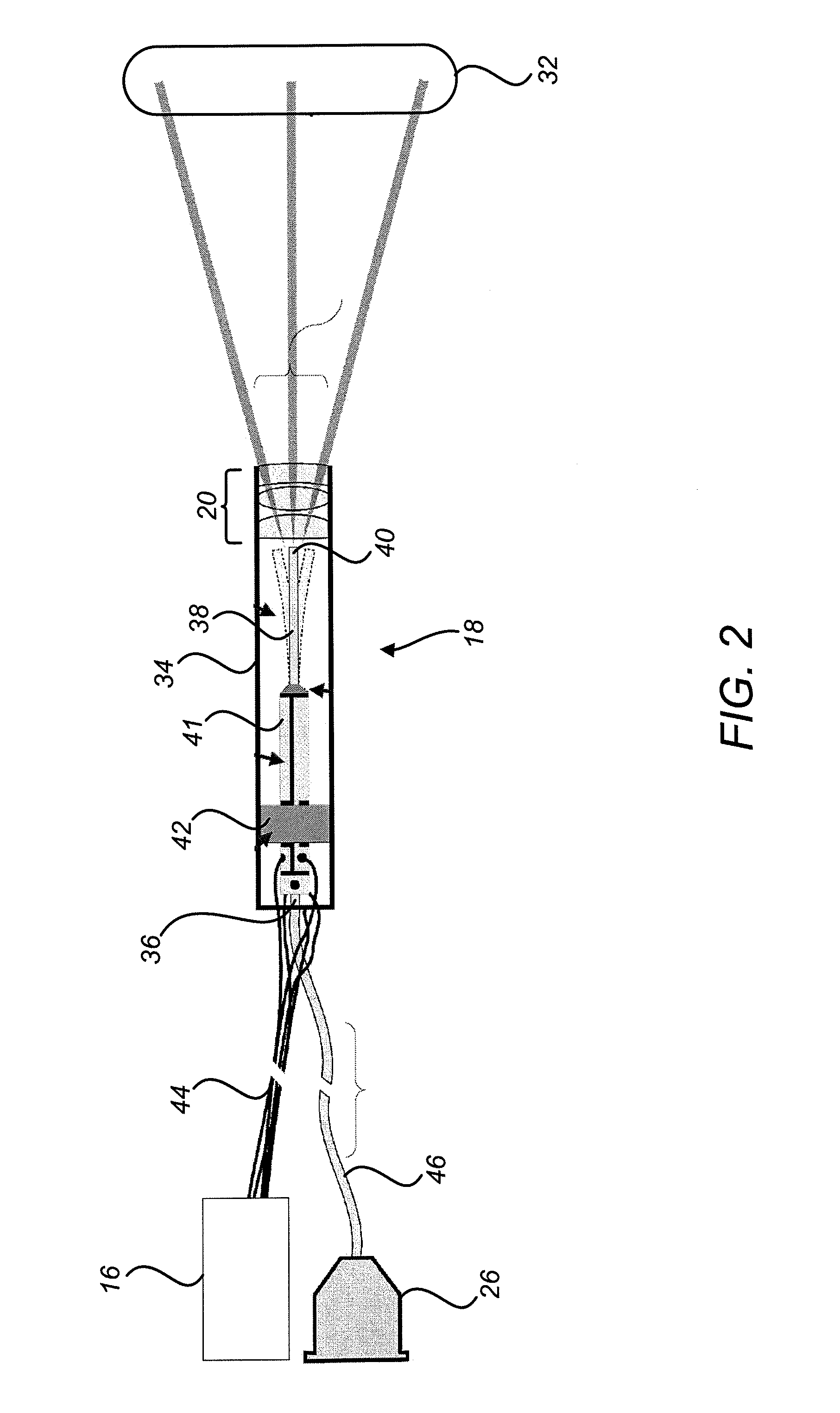
Scanning laser projection display devices and methods for projecting one or more images onto a surface with a light-scanning optical fiber
Image projection devices, high-speed fiber scanned displays and related methods for projecting an image onto a surface and interfacing with the projected image are provided. A method for projecting one or more images and obtaining feedback with an optical input-output assembly is provided. The input-output assembly comprising a light-scanning optical fiber and a sensor. The method includes generating a sequence of light in response to one or more image representations and a scan pattern of the optical fiber, articulating the optical fiber in the scan pattern, projecting the sequence of light from the articulated optical fiber, and generating a feedback signal with the sensor in response to reflections of the sequence of light.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
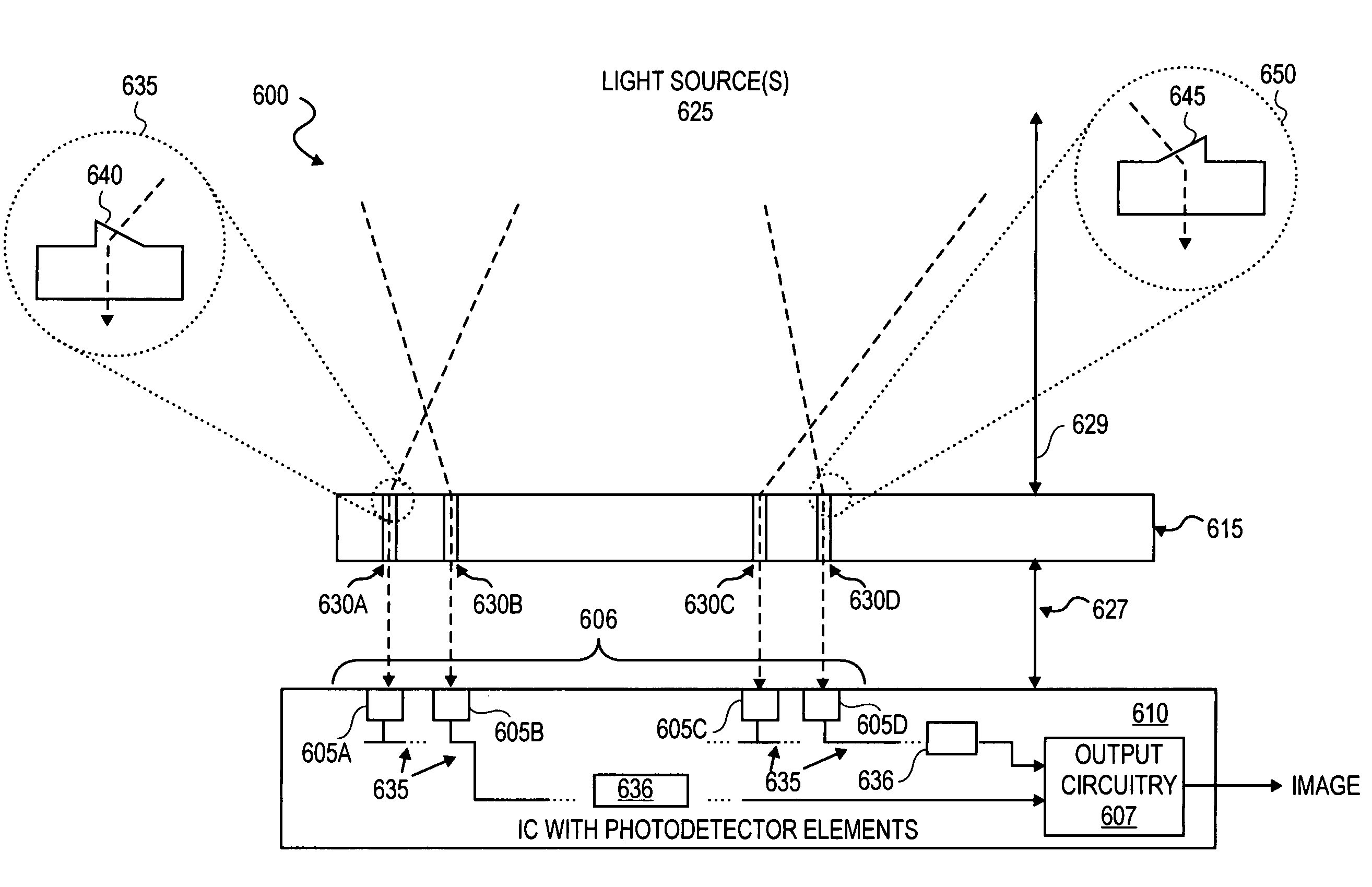
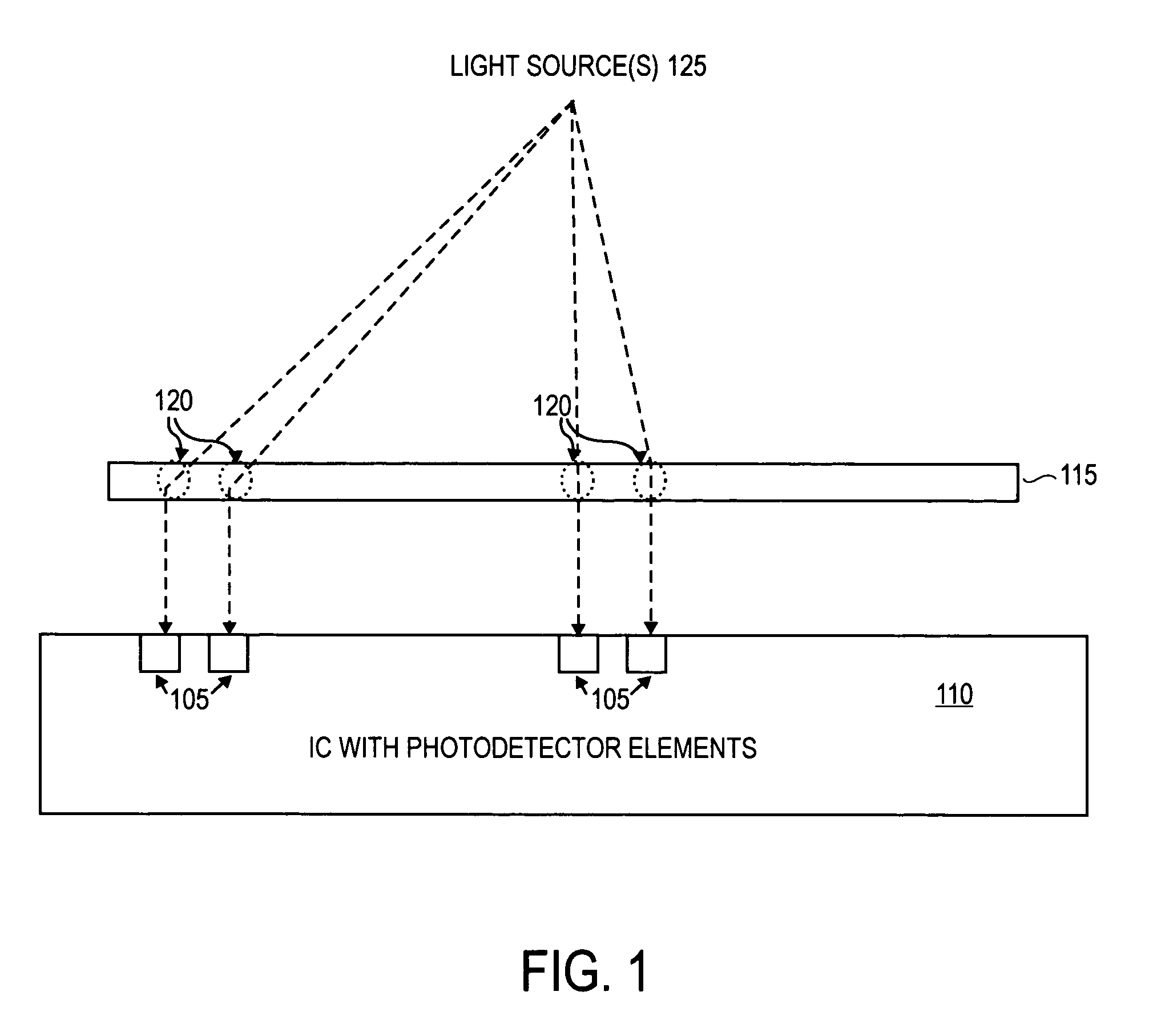
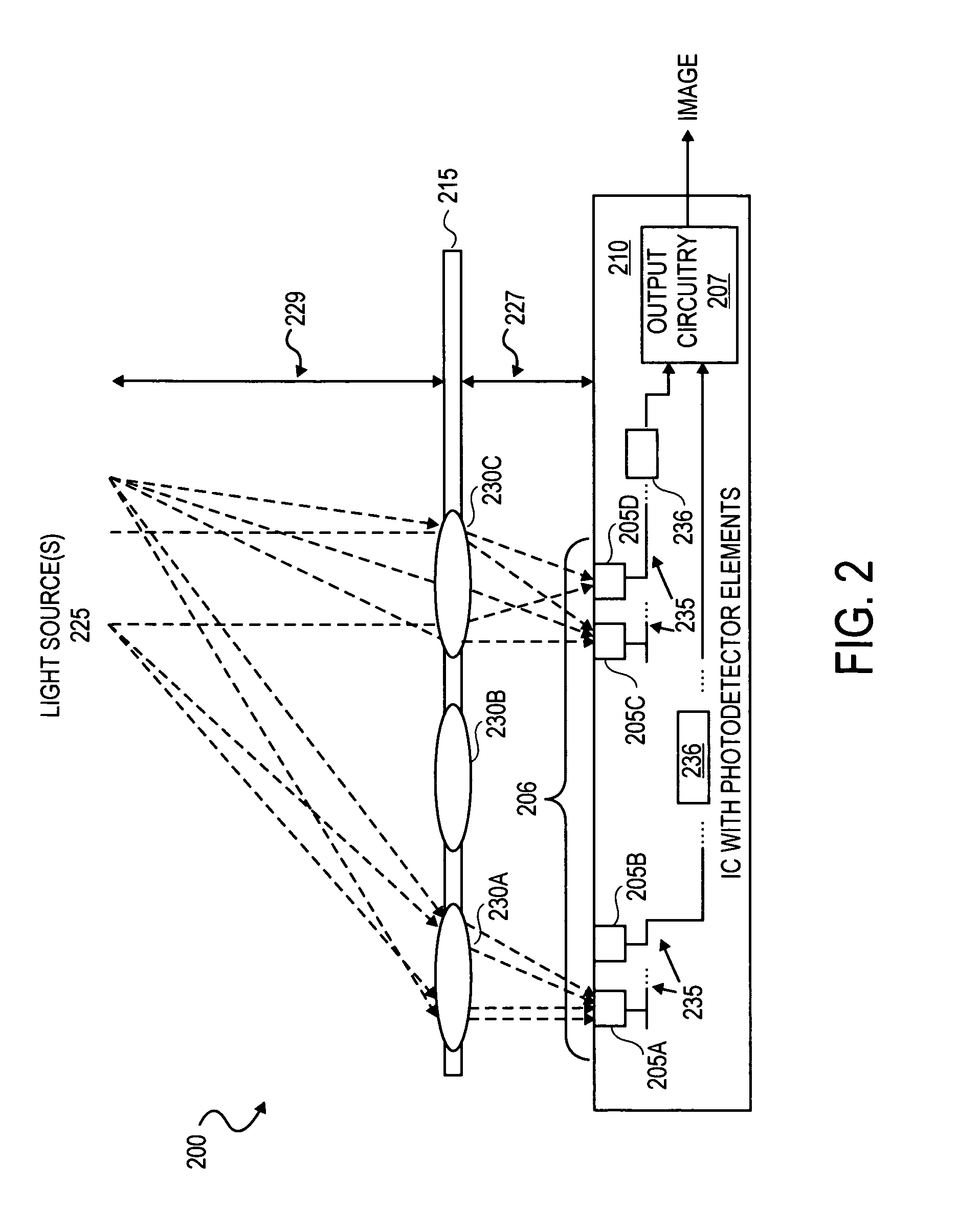
Integrated circuit-based compound eye image sensor using a light pipe bundle
An integrated circuit-based compound eye includes a plurality of photodetector elements disposed on a semiconductor substrate. A compound light directing member includes a light pipe bundle wherein at least some of the light pipes are to individually direct light energy from one or more sources onto one or more of the photodetector elements. The compound light directing member is the primary mechanism to direct light energy onto the one or more of the photodetector elements. Outputs of the photodetector elements are electrically coupled in such a way that an image associated with the source may be synthesized at output circuitry.For another aspect, a compound exposure determining member includes a plurality of light scanning elements, each of the light scanning elements including an integrated photodetector. Each of the light scanning elements is controllable to vary an angle of the photodetector with respect to a substrate to determine from which point sources and angles light energy is received at the photodetector.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Laser scanning module with rotatably adjustable laser scanning assembly
A laser scanning module employing a laser scanning assembly mounted within a module housing using a mechanism that allows the laser scanning assembly to be rotated to an angular position within the engine housing so that light collection, beam folding and light collection mirrors in the module housing are optically aligned. A PC board is mounted on a side of the housing and has a configuration of elongated apertures of open-ended and / or closed geometry, arranged in a non-parallel manner. An electromagnetic coil structure, associated with the laser scanning assembly, has a linear array of electrically-conductive pins that project through the configuration of elongated holes, at locations along the elongated holes that are determined by the angular rotation of the laser scanning assembly attained during optical alignment conditions during manufacture.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
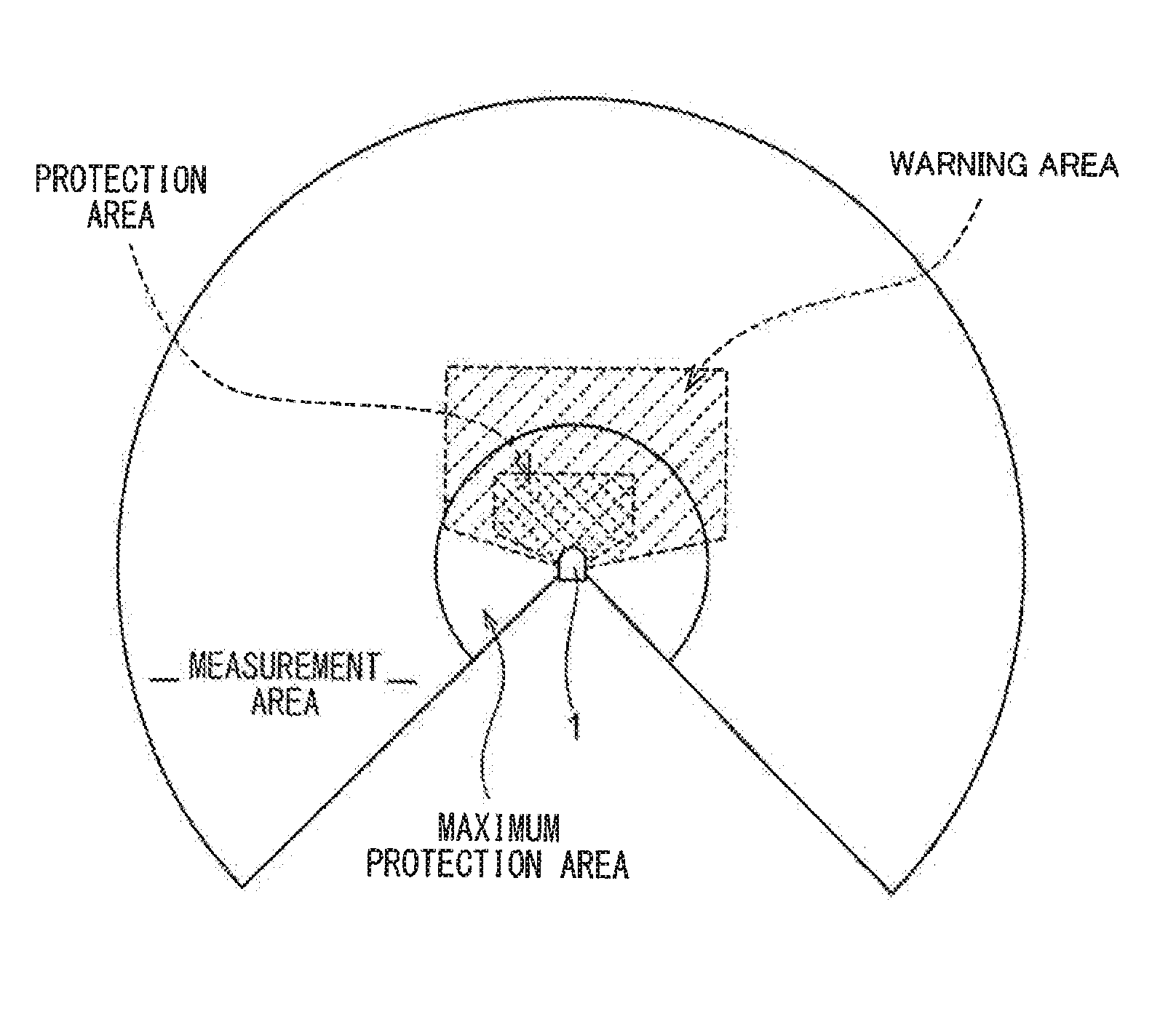
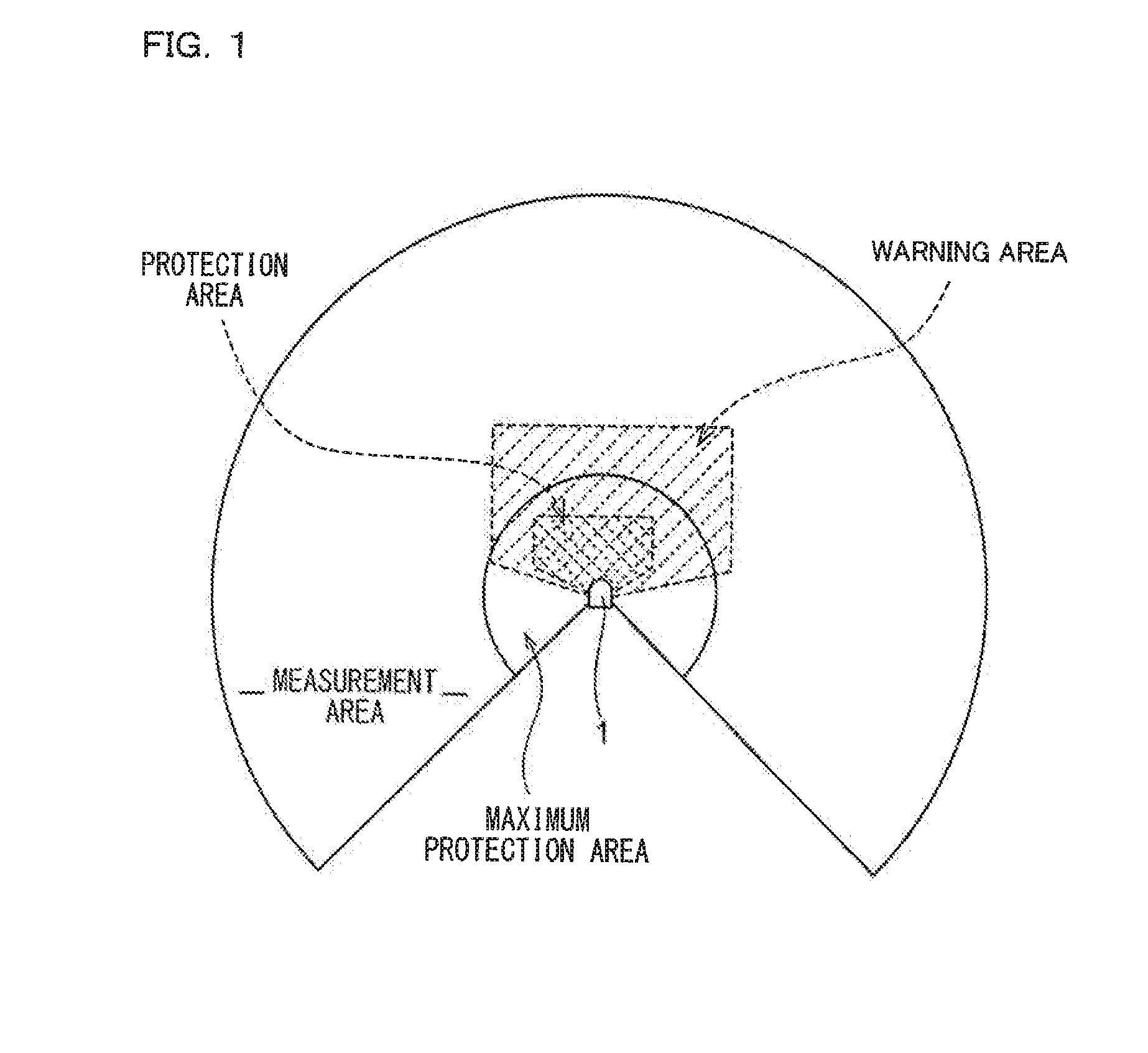
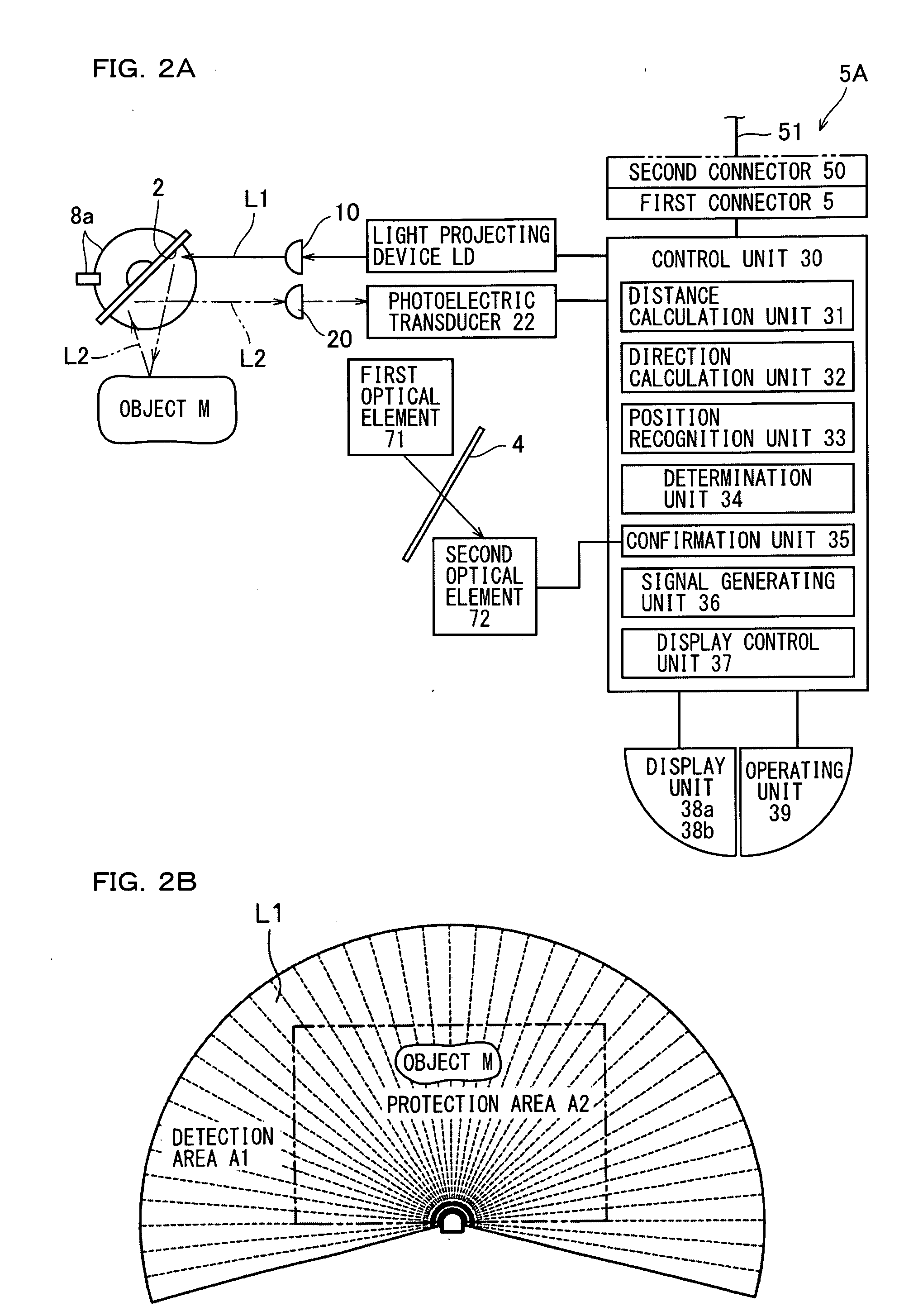
Safety Photoelectric Switch
ActiveUS20100194583A1Solve the real problemAvoid interferenceElectric signal transmission systemsOptical detectionPhotoswitchOptical axis
There is provided an optical scanning type photoelectric switch capable of preventing interference with another photoelectric switch by use of its own capability, wherein, as for light projection pulse periods of the first and second optical scanning type photoelectric switches, the period is set to 30 μs in the first optical scanning type photoelectric switch while the period is set to 33 μs in the second optical scanning type photoelectric switch 1B, the light projection pulses have the same pulse width, and by setting the light projection periods different between the first and second optical scanning type photoelectric switches, even if mutual interference occurs between any optical axes, a phase difference of 36 degrees in rotation period is generated therebetween in a next scan, thereby preventing occurrence of the interference in succession in a plurality of times of scanning.
Owner:KEYENCE
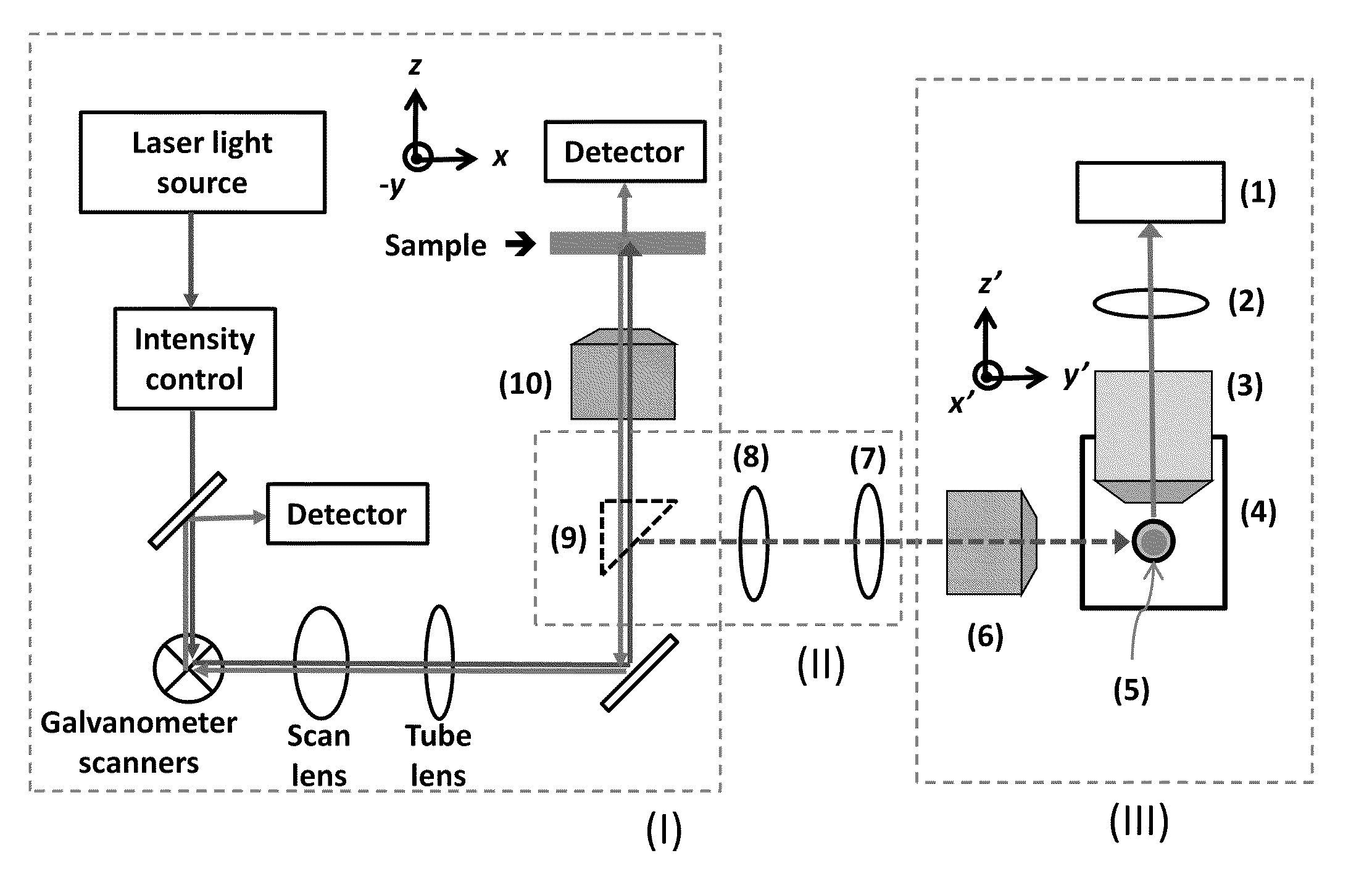
Dual-mode raster point scanning/light sheet illumination microscope
An apparatus for and method of performing light sheet microscopy (LISH) and light scanning microscopy (RAPS) in a single device are provided. The dual-mode imaging microscope allows for the use of both LISH and RAPS in a single instrument. This dual-mode device will allow researchers to have access to both types of microscopy, allowing access to the widest possible selection of samples. In addition, the device will reduce the high costs and space requirements associated with owning two different microscopes (LISH and RAPS).
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
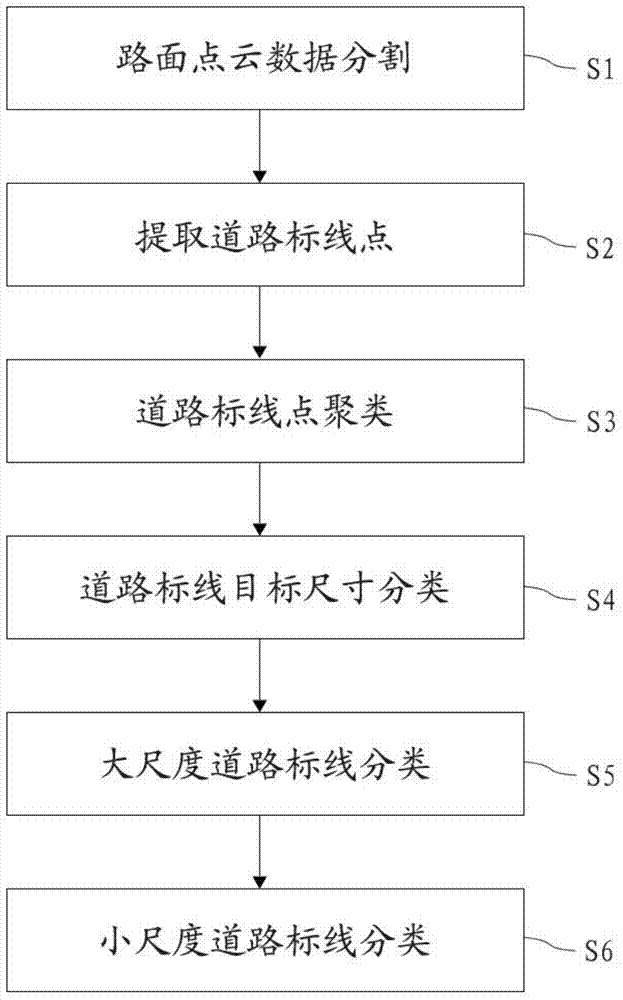
Urban road marker automatic sorting method based on vehicle-mounted laser scanning point cloud
ActiveCN104197897AQuick extractionQuick classificationPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryCharacter and pattern recognitionPoint cloudPrincipal component analysis
The invention discloses an urban road marker automatic sorting method based on vehicle-mounted laser scanning point cloud. The method includes: S1) a step of subjecting original point cloud data to road surface segmentation based on wheel path data to obtain road surface point cloud data; S2) a step of subjecting the obtained road surface point cloud data to binarization processing and extracting road marker points; S3) a step of clustering the road marker points and separating independent road marker targets; S4) a step of sorting large road markers and small road markers according to the dimensions of the obtained road marker targets; S5) a step of subjecting the large road markers to sorting processing based on wheel paths and road edge lines; and S6) a step of subjecting the small road markers to sorting processing based on deep learning and principal component analysis. The method rapidly and accurately extracts and sorts urban road markers, largely reduces the time and labor cost for data processing, and effectively guarantees traffic safety and intelligent drive reliability.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
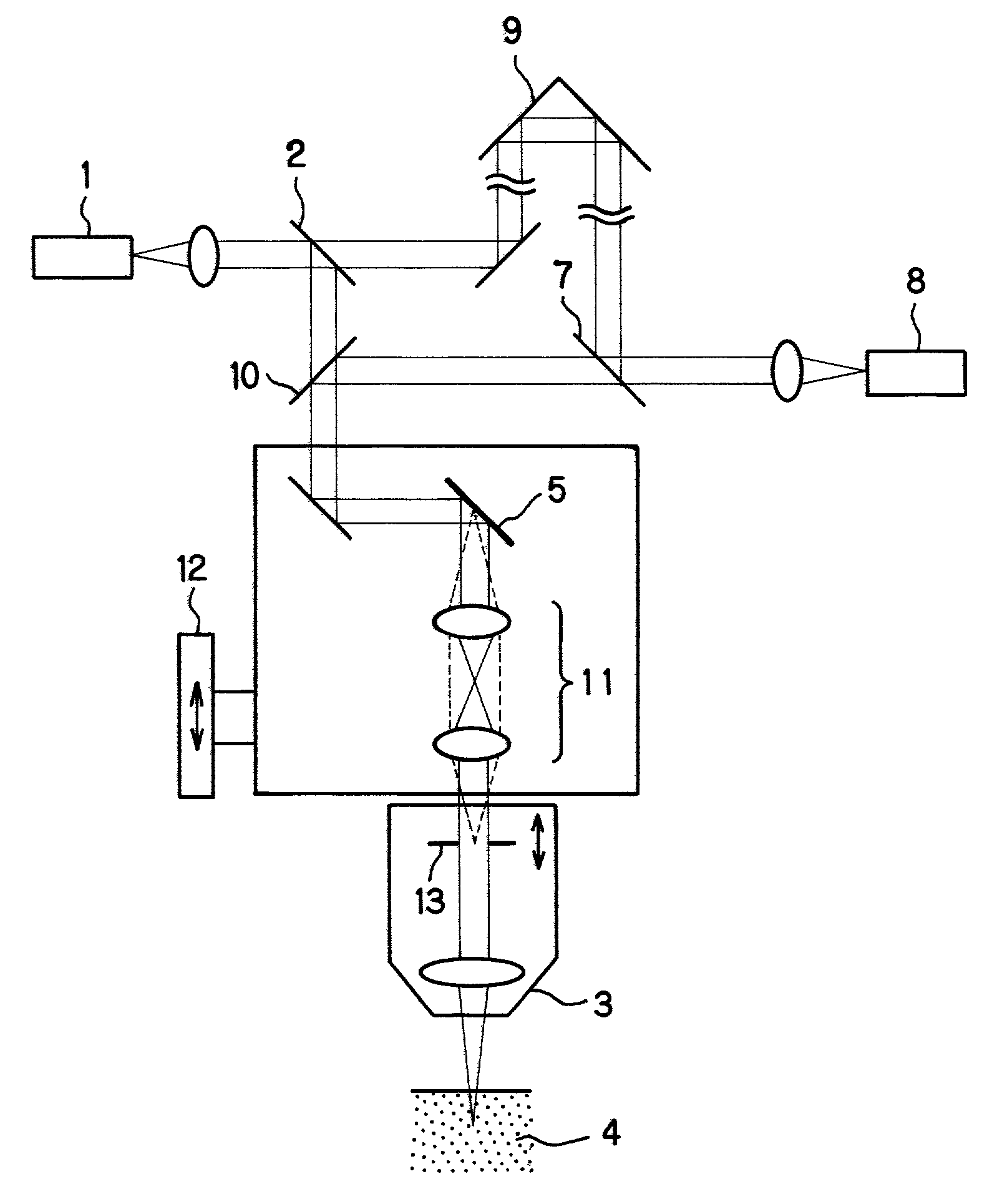
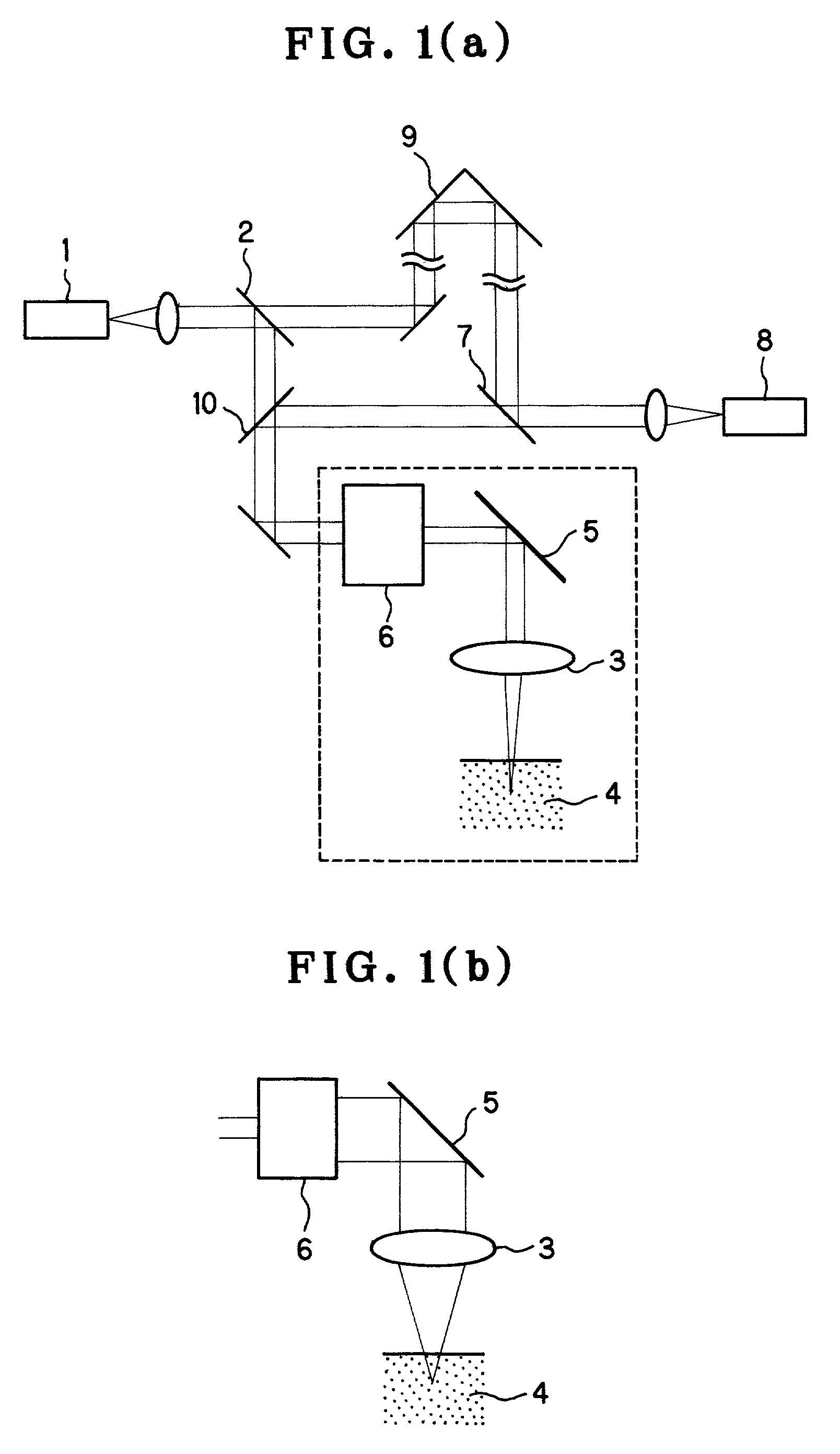
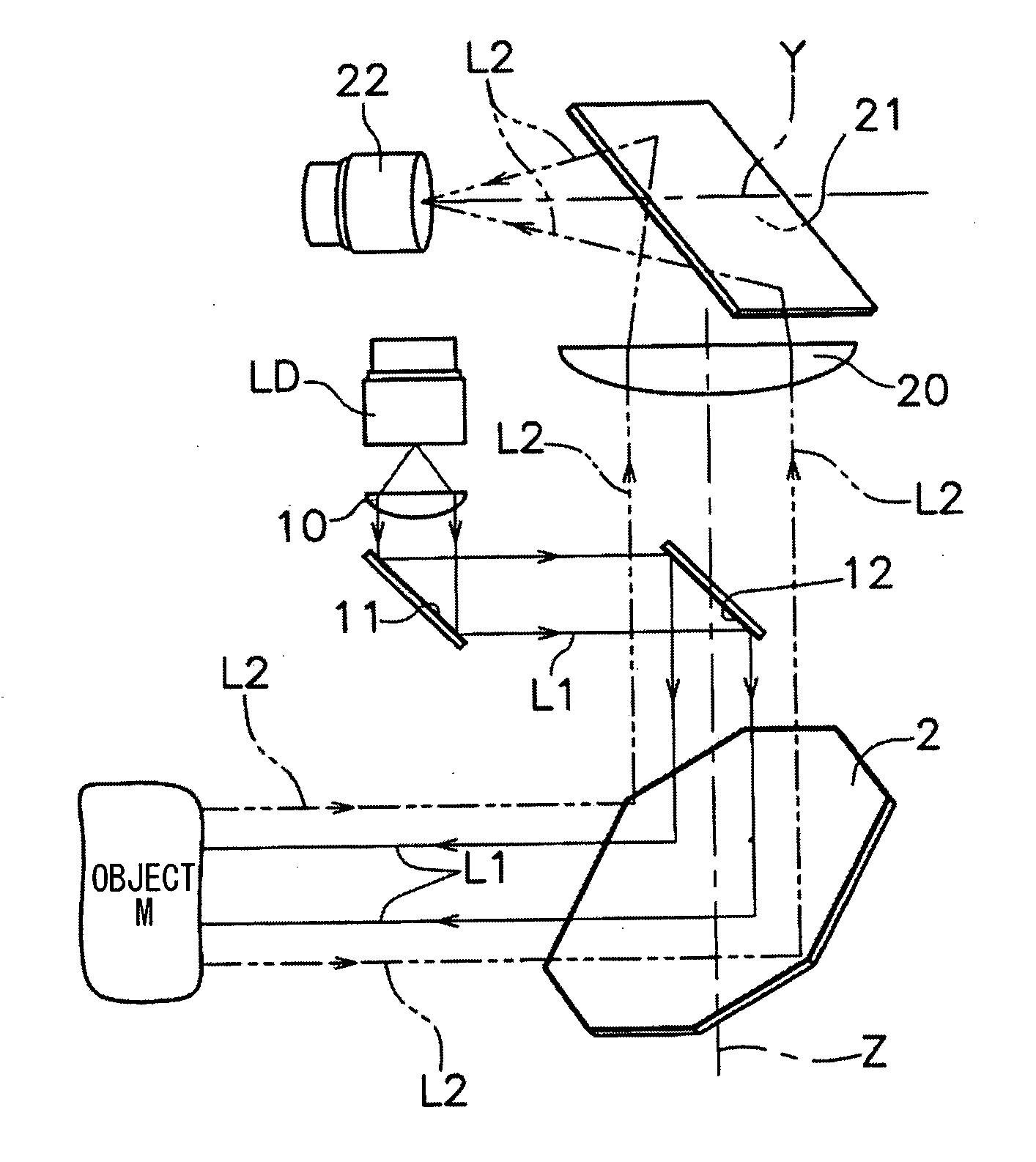
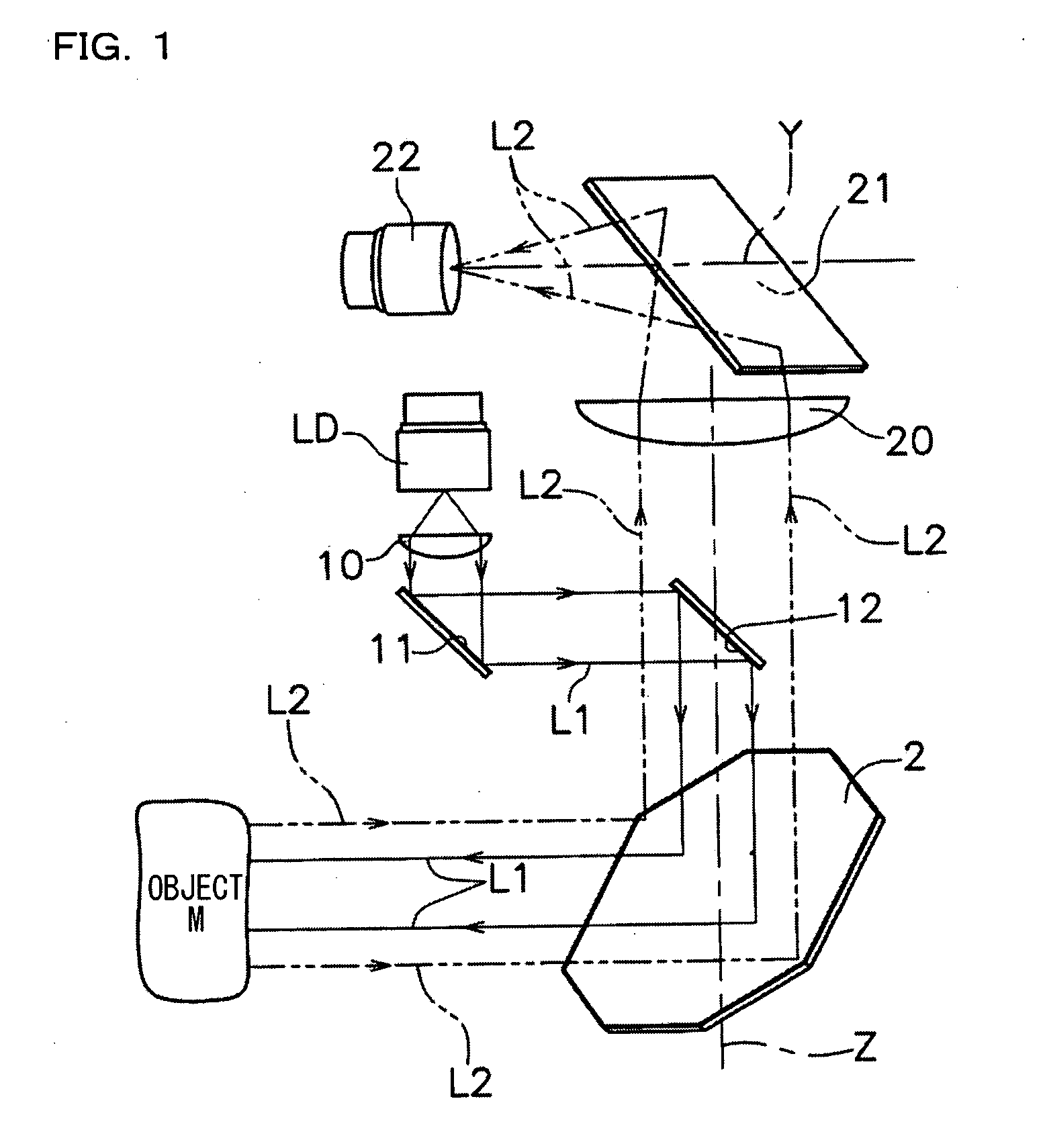
Optical system and optical apparatus capable of switching between optical coherence tomography observation and optical coherence microscopy observation
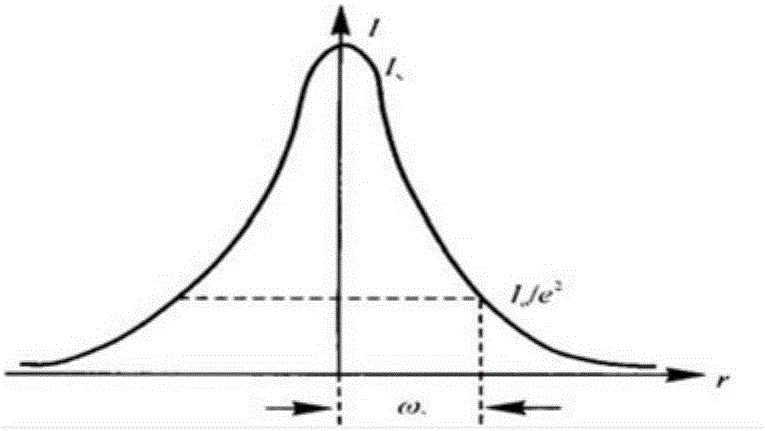
InactiveUS7236251B2Easy to findHigh resolutionScattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansBeam diameterLight beam
An optical system and optical apparatus prevent degradation of the S / N ratio due to switching between OCT and OCM observation modes and attain a high S / N ratio in both the observation modes. The optical system includes a light source 1 and a light-branching member 2 for branching light from the light source 1 into a reference light path and a signal light path. An objective 3 is placed in the signal light path. A light-scanning system 5 scans light in the signal light path with respect to a sample 4 placed in the signal light path. A beam diameter changing optical system 6 changes the beam diameter of light entering or exiting the light-scanning system 5. A light-combining member 7 combines together the reference light path and the signal light path. A light-detecting element 8 detects light combined by the light-combining member 7.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Scanning laser projection display devices and methods for projecting one or more images onto a surface with light-scanning optical fiber
ActiveUS20150281630A1More compactFunction increaseTelevision system detailsImage analysisFiberDisplay device
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Scanning confocal microscope
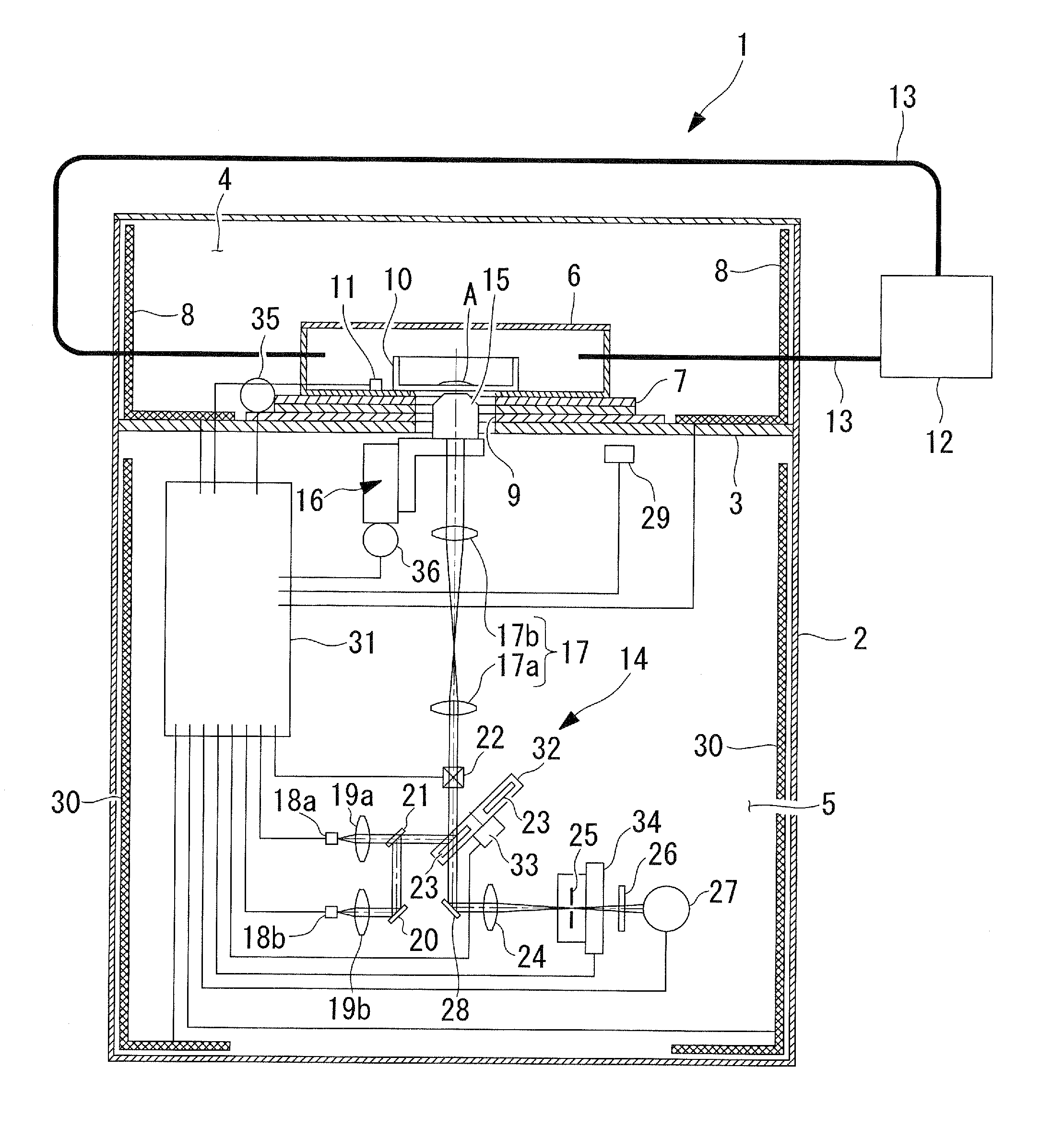
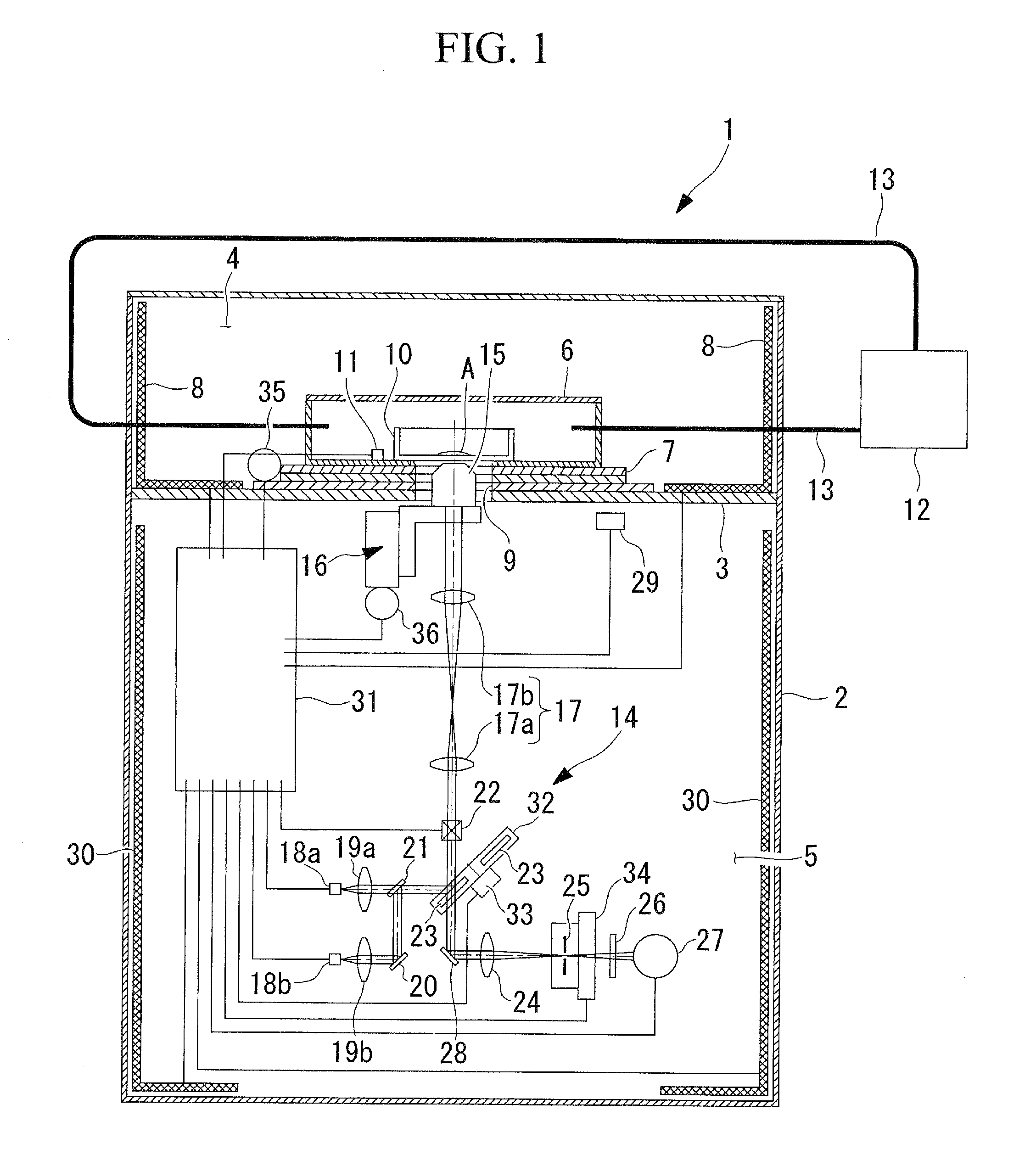
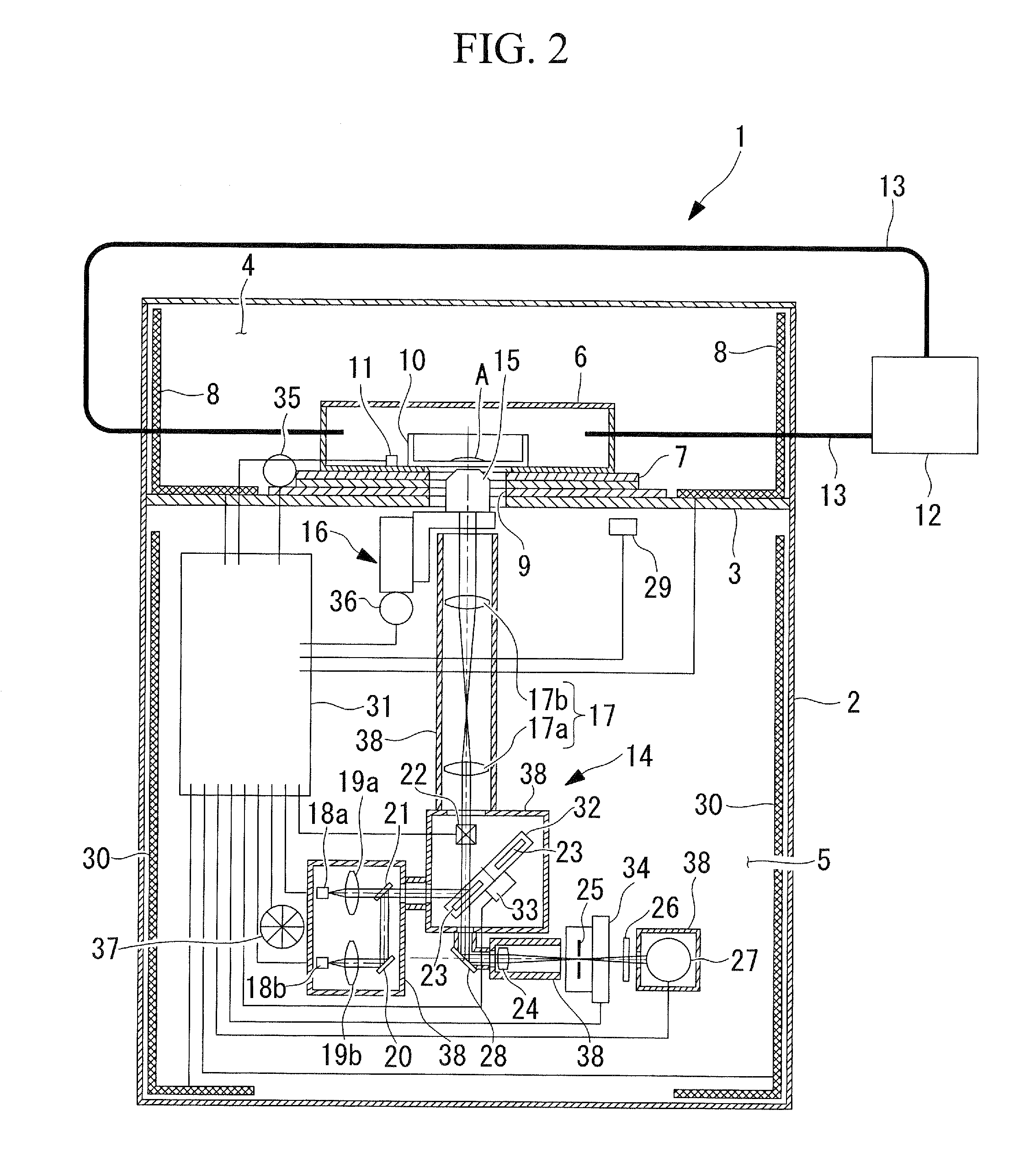
A scanning confocal microscope can provide an image while preventing a decrease in brightness and blurring due to strain caused in optical and mechanical systems by thermal effects in a high-temperature, high-humidity incubation container. This scanning confocal microscope includes an incubation container that has a space in which a specimen is disposed and that can maintain an internal environment thereof at a predetermined temperature and high humidity and an optical system space adjacent to the incubation container and separated therefrom based on humidity. The optical system space accommodates a light-scanning unit and a scanner optical system, an objective lens, a confocal pinhole, and a focus adjustment mechanism. The optical system space further accommodates a temperature-maintaining unit for the optical system space to maintain the optical system space at a temperature substantially equal to the temperature in the incubation container.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Light scanning apparatus and scanning display apparatus
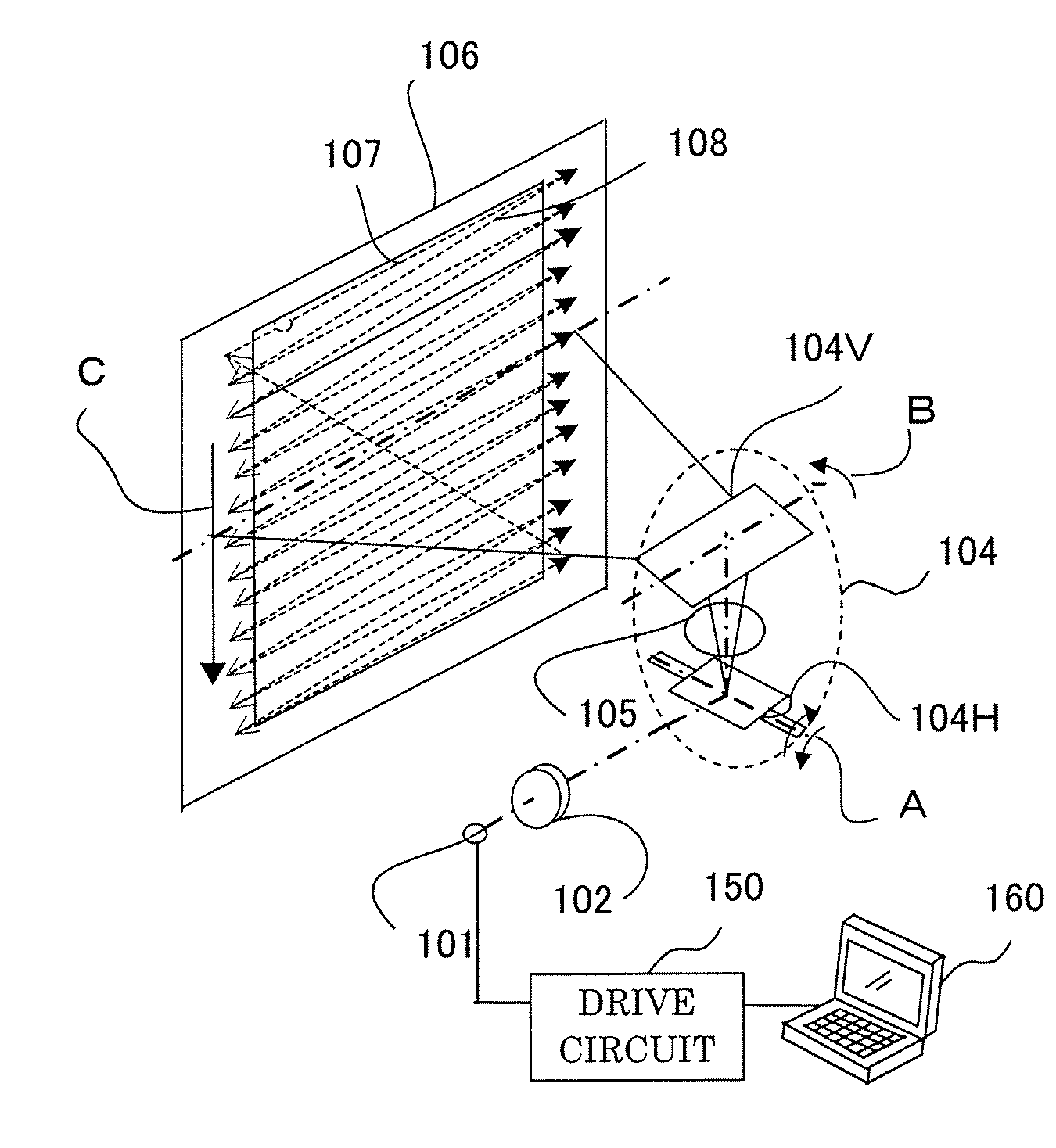
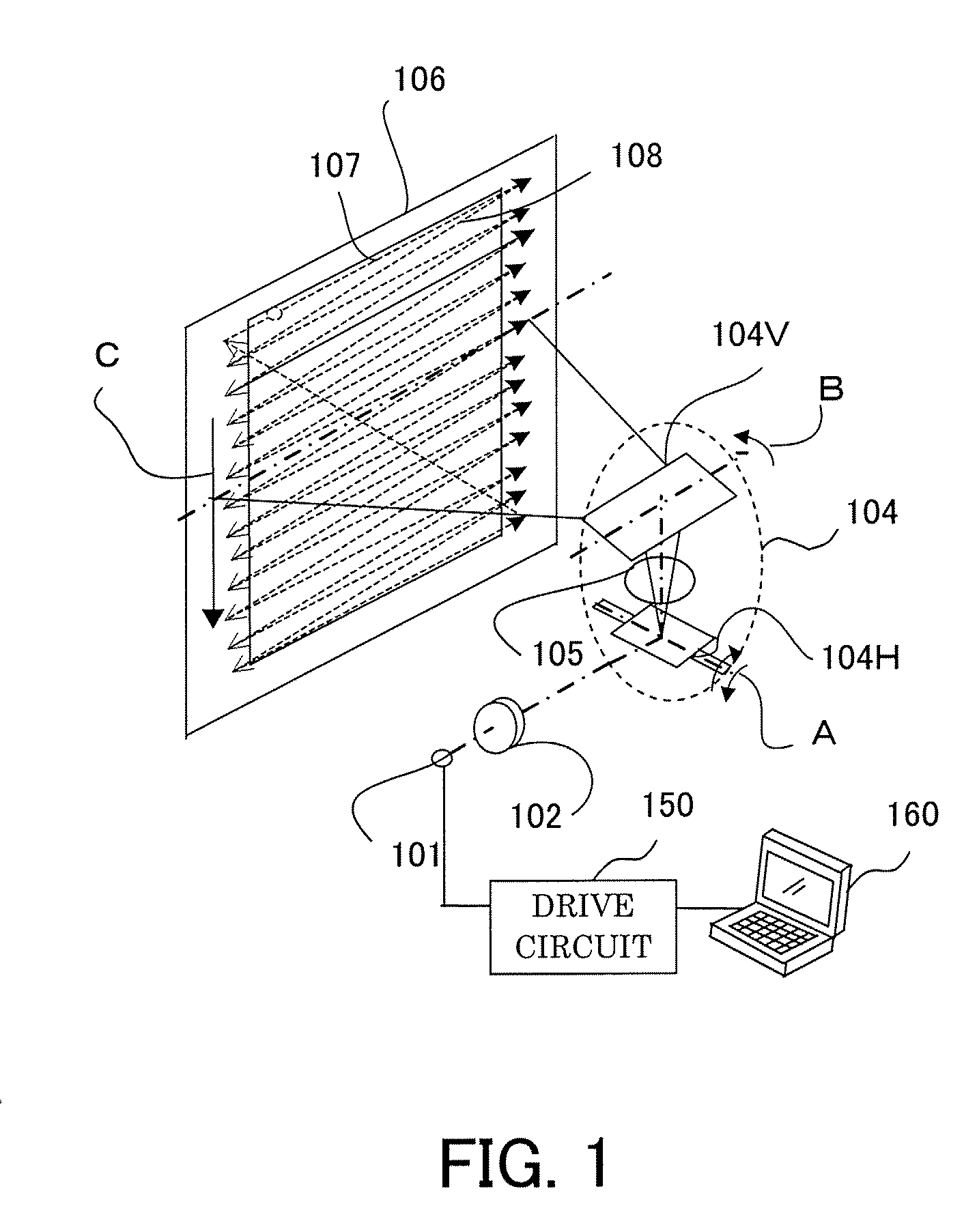
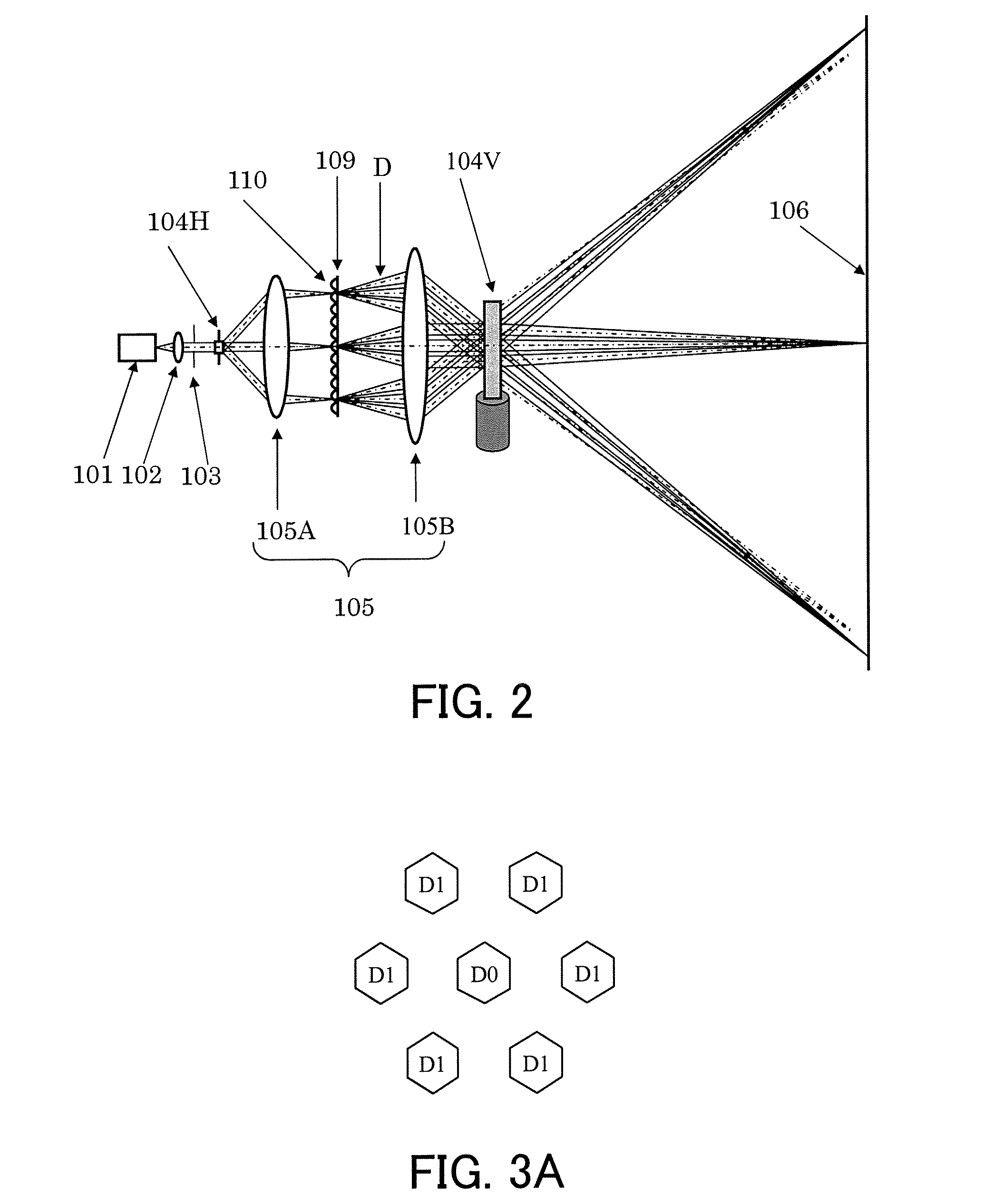
InactiveUS20090021801A1Improve noiseSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansLight beamLight scanning
A light scanning apparatus includes a scanner 104 which scans a coherent light beam from a light source 101, a light beam component generator 110 which divides the coherent light beam outgoing from the scanner 104 into a plurality of light beam components, and an optical system 105 which collects the plurality of light beam components so that they are incident on a scan surface 106 at an incident angle different from each other, and superposes the light beam components at an identical position on the scan surface.
Owner:CANON KK
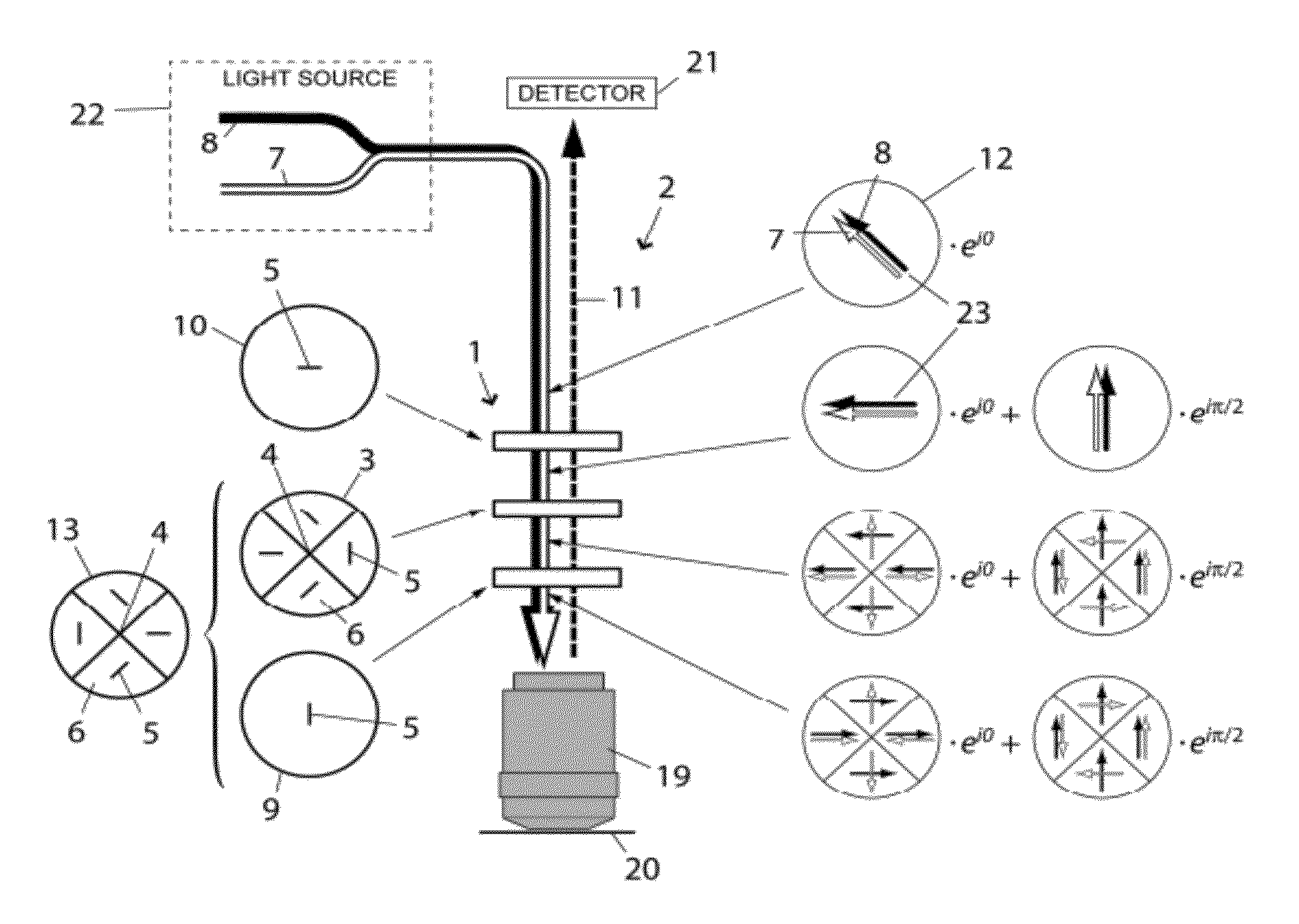
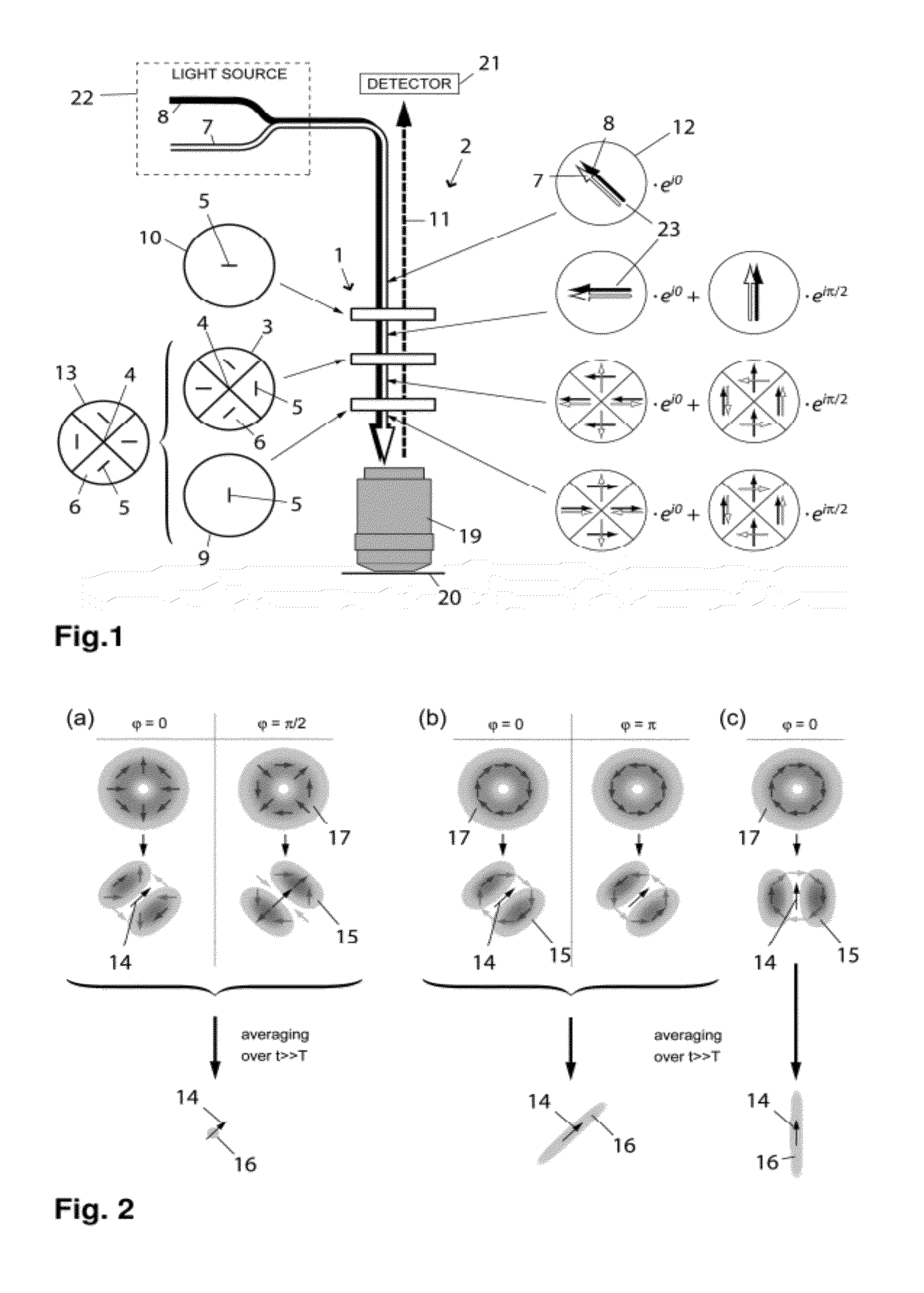
Fluorescence Light Scanning Microscope Having a Birefringent Chromatic Beam Shaping Device
A fluorescence light scanning microscope (2) comprises a light source providing excitation light (8) for exciting a fluorophore in a sample to be imaged for spontaneous emission of fluorescence light, and suppression light (7) for suppressing spontaneous emission of fluorescence light by the fluorophore on a common optical axis (4), the suppression wavelength differing from the excitation wavelength; an objective (19) focusing both the excitation (8) and the suppression (7) light to a focus point; a detector (21) detecting fluorescence light (11) spontaneously emitted by the fluorophore; and a chromatic beam shaping device (1) arranged on the common optical axis (4), and including a birefringent chromatic optical element (3) adapted to shape a polarization distribution of the suppression light (7) such as to produce an intensity zero at the focus point, and to leave the excitation light such as to produce a maximum at the focus point.
Owner:DEUTES KREBSFORSCHUNGSZENT STIFTUNG DES OFFENTLICHEN RECHTS
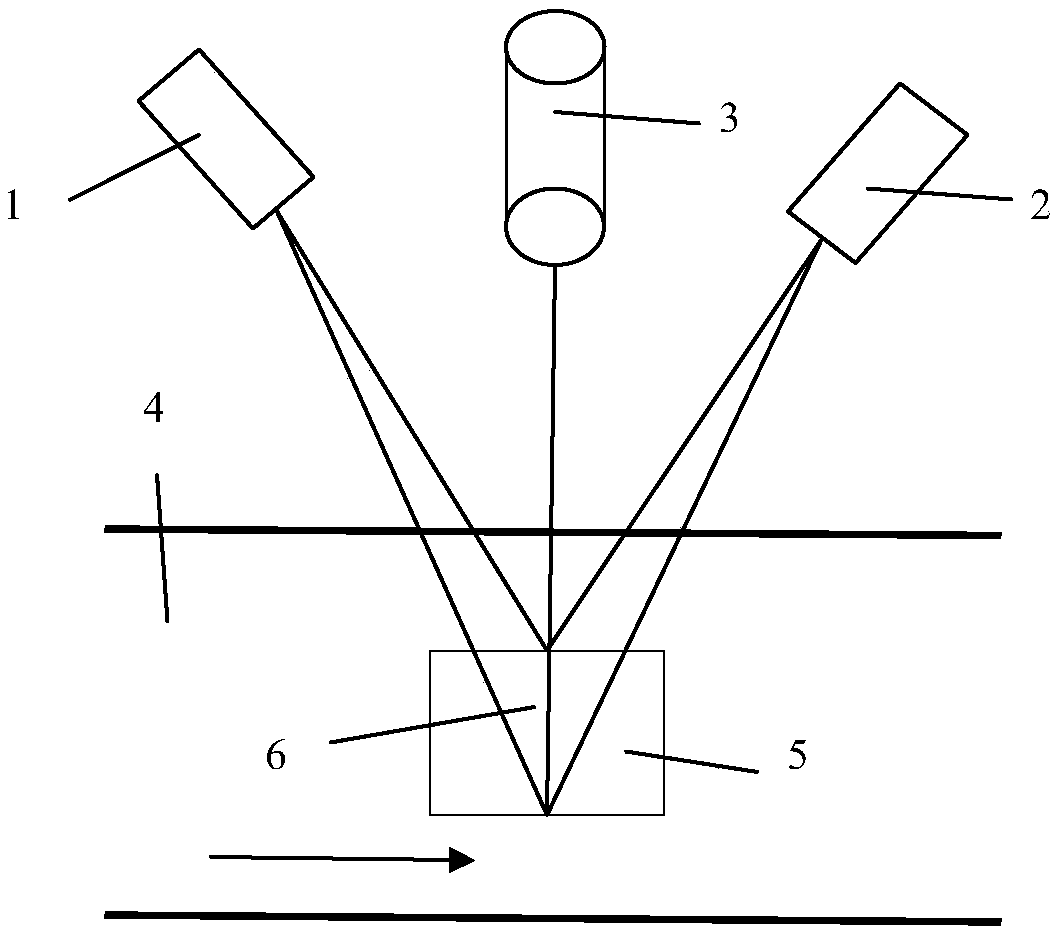
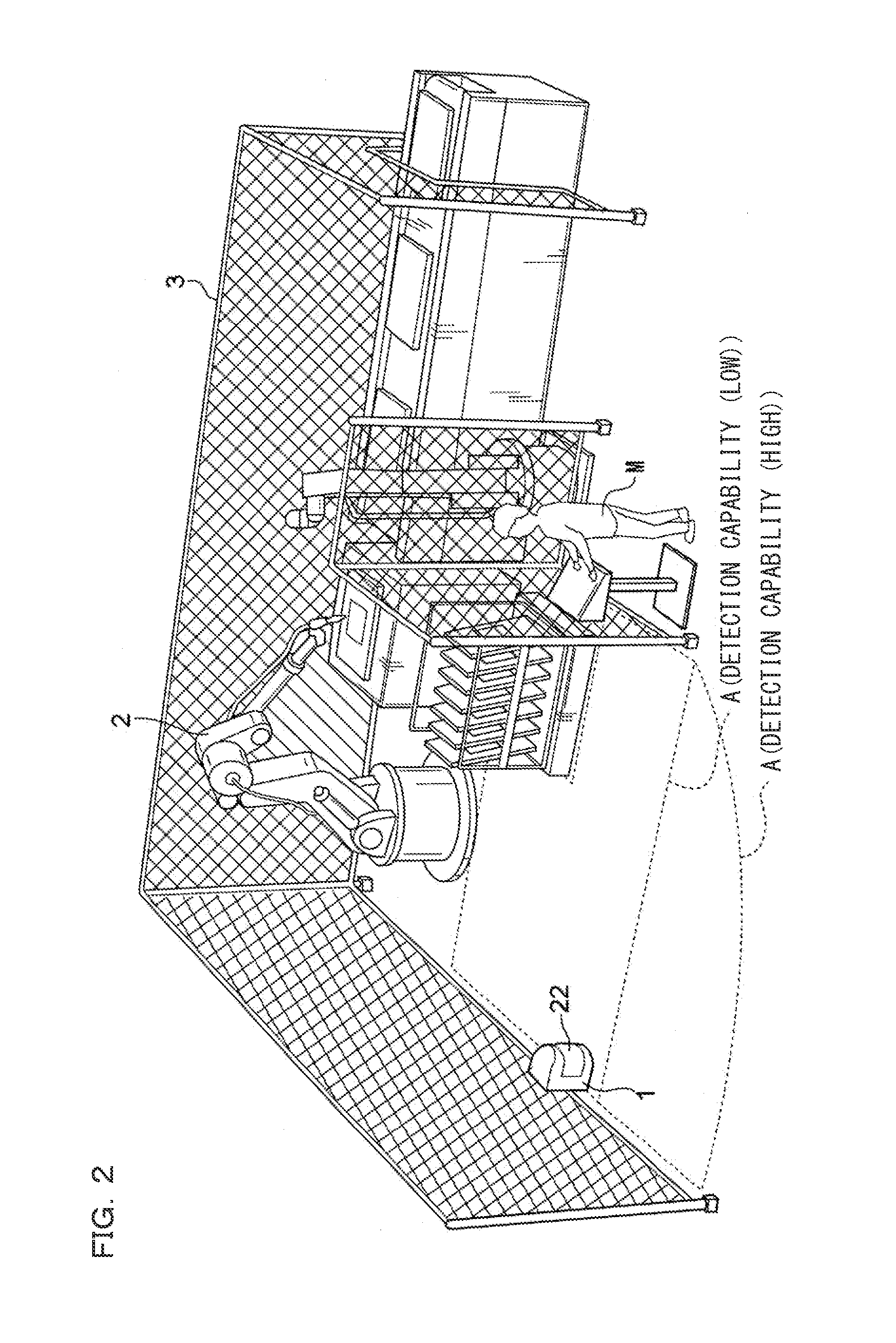
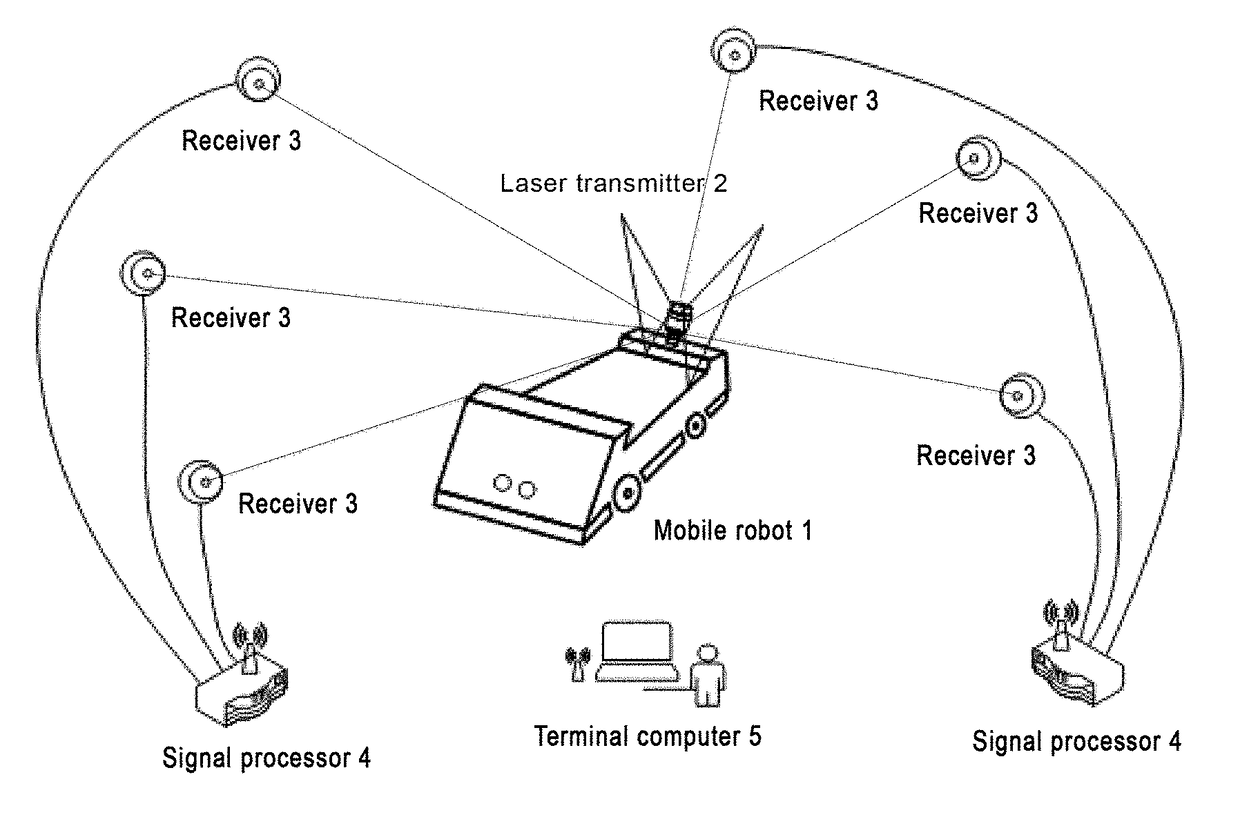
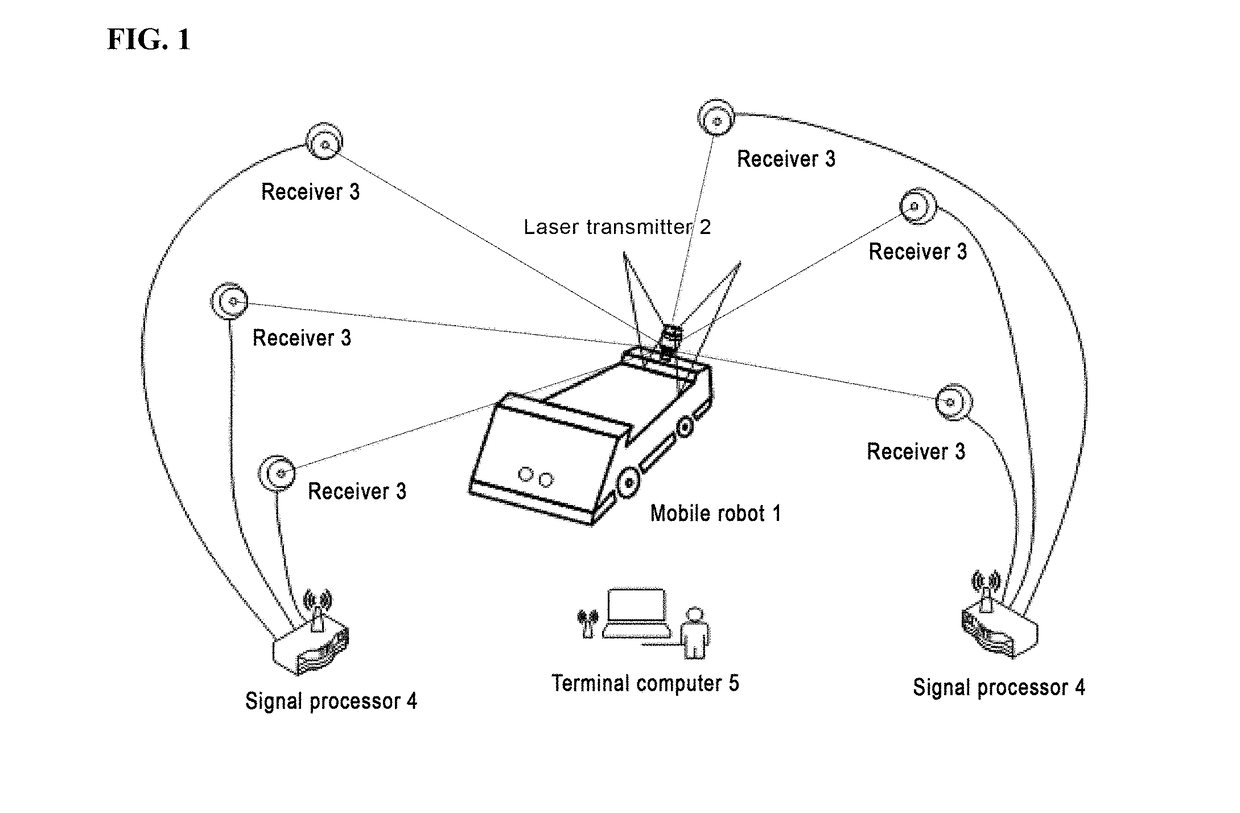
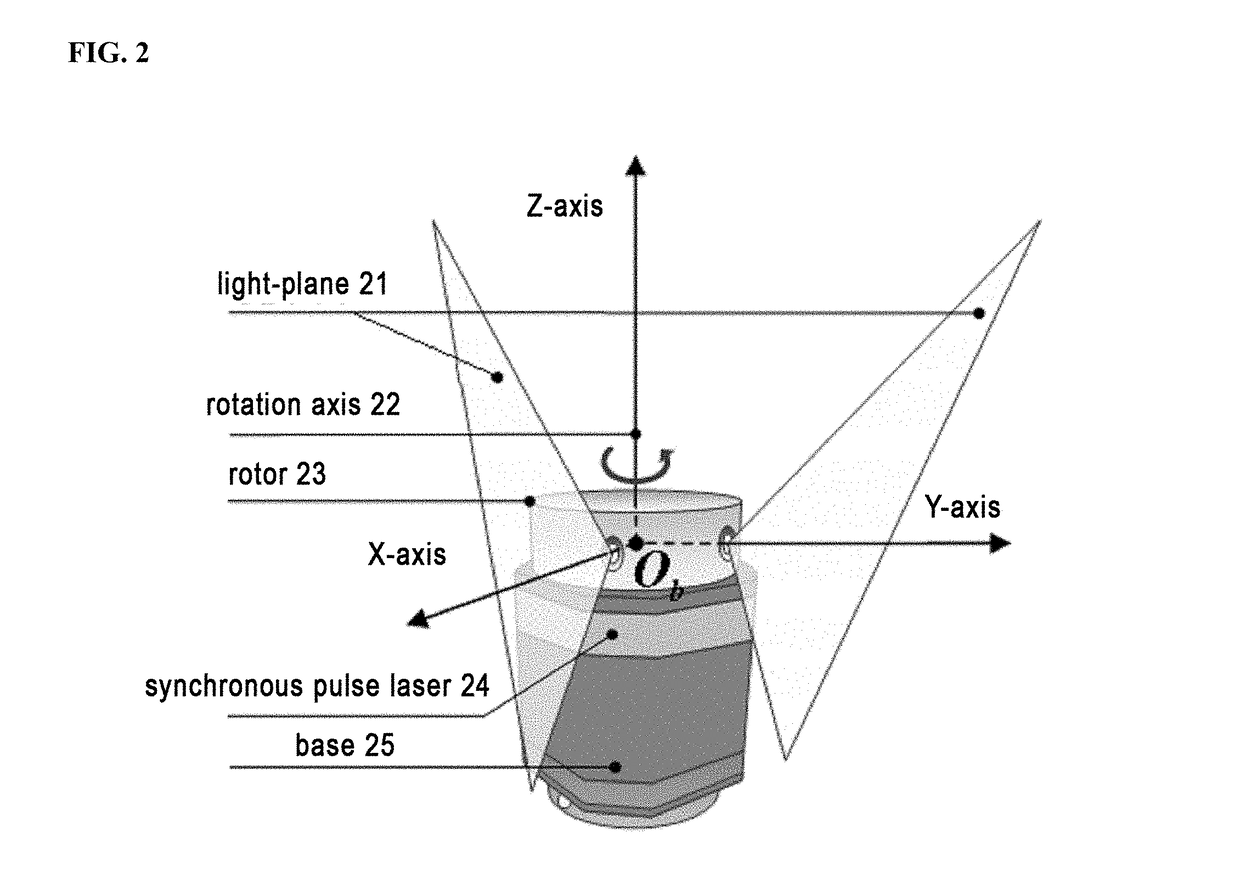
Indoor mobile robot position and posture measurement system based on photoelectric scanning and measurement method
ActiveUS20180216941A1Improve accuracyImprove convenienceAngle measurementOptical rangefindersLaser transmitterLaser scanning
An indoor mobile robot position and posture measurement system based on photoelectric scanning and the measurement method thereof, the measurement system includes: a mobile robot (1) which is arranged with a laser transmitter (2), the peripheral of the laser transmitter (2) is provided with no less than three receivers (3) for receiving the light signals emitted by the laser transmitter (2), and at least one signal processor (4) connected to the receivers (3) for processing signals received by the receivers (3) to determine precise coordinates of the receivers in laser transmitter coordinate system, and a terminal computer (5) wirelessly connected with the signal processor (4) to determine the posture angle and the position of the mobile robot through the distances between the laser transmitter (2) and each receiver (3). Without arranging multiple transmitters when measuring and performing tedious global orientation, the operators by using the measurement system and the measurement method of the present invention may measure the 3D position and posture of the indoor mobile robot in real time by multiple guidance signals consisting of photoelectric receiver and a high-speed laser scanning turntable fixed on the mobile robot.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
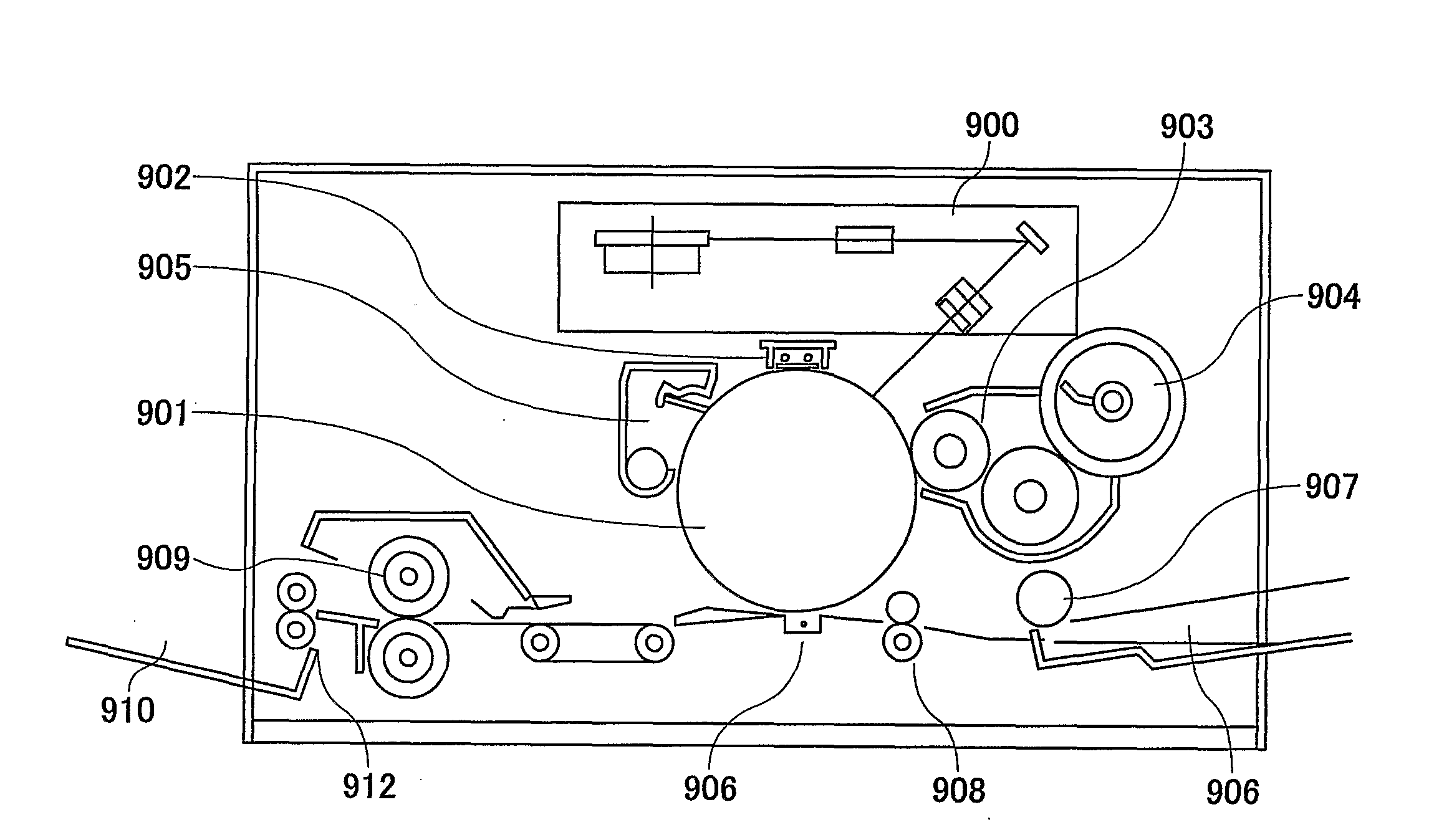
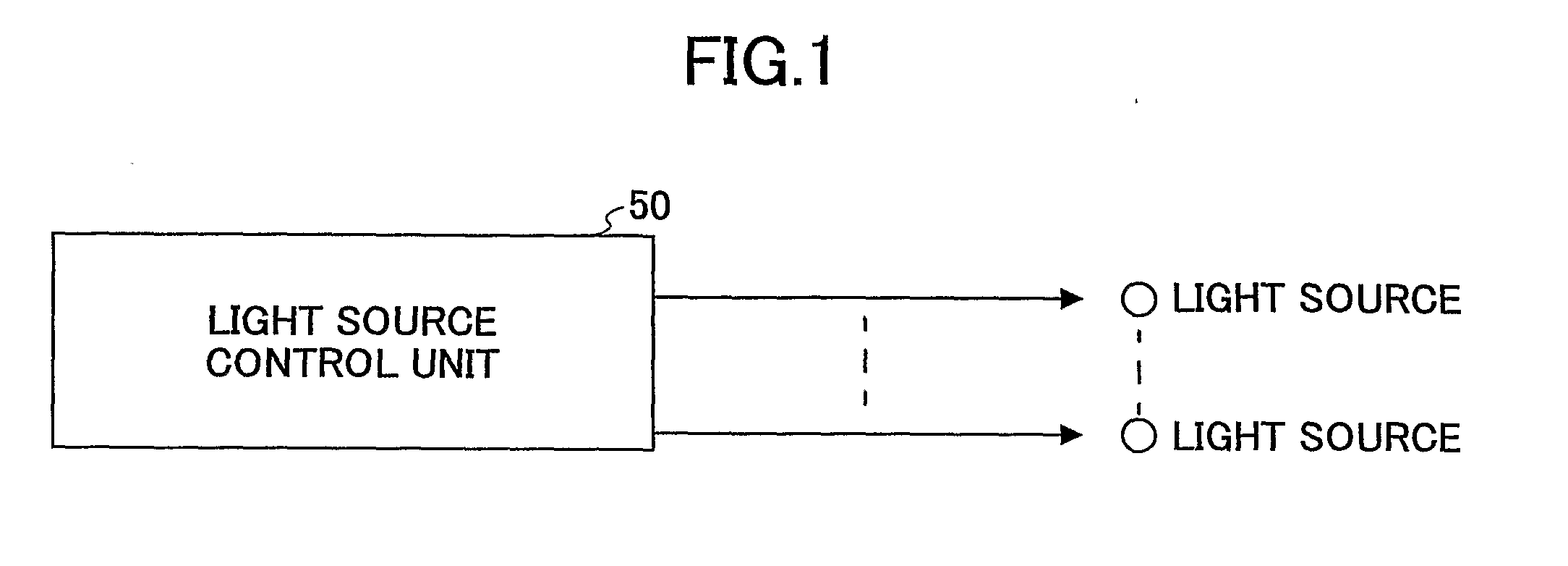
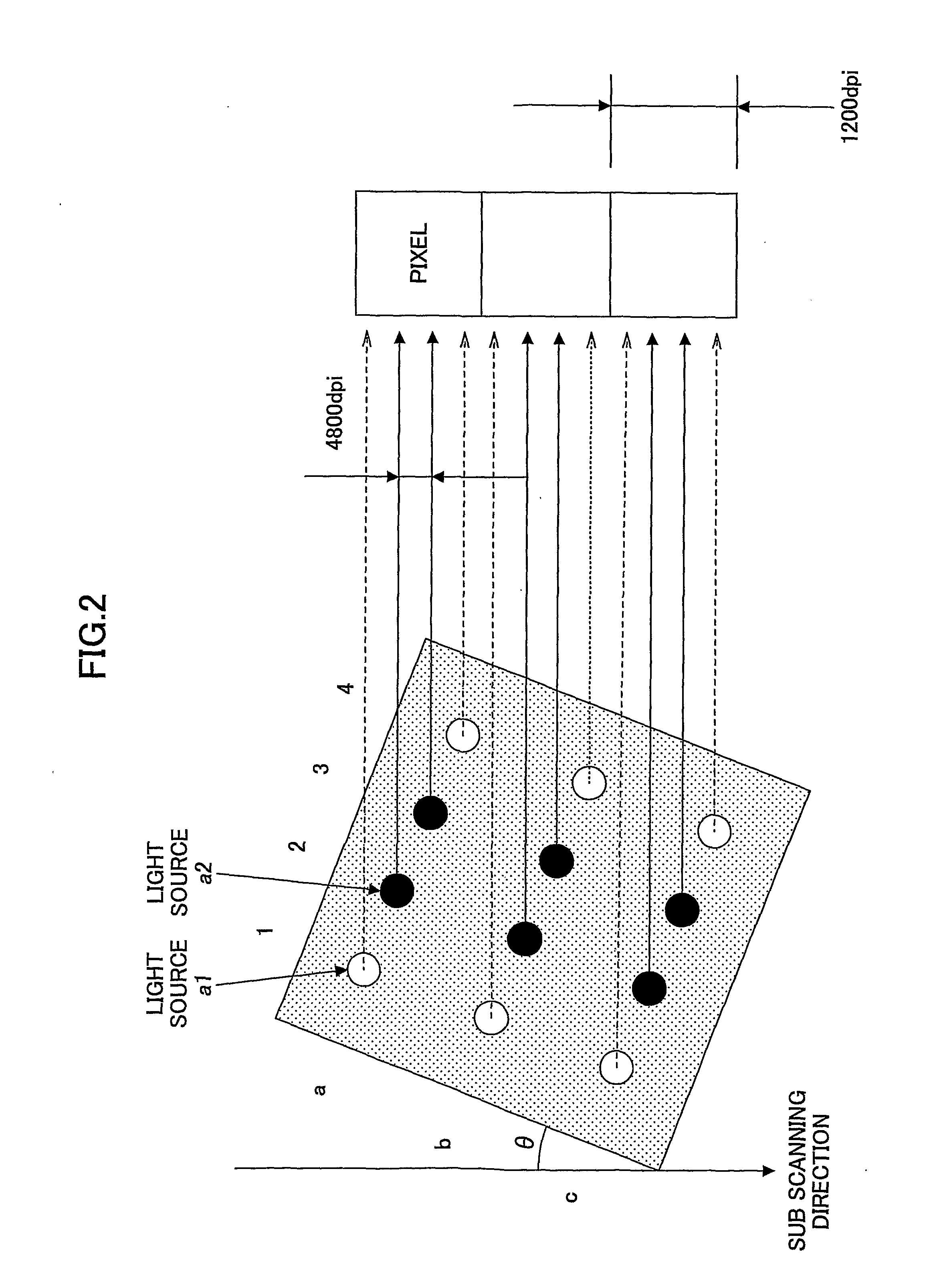
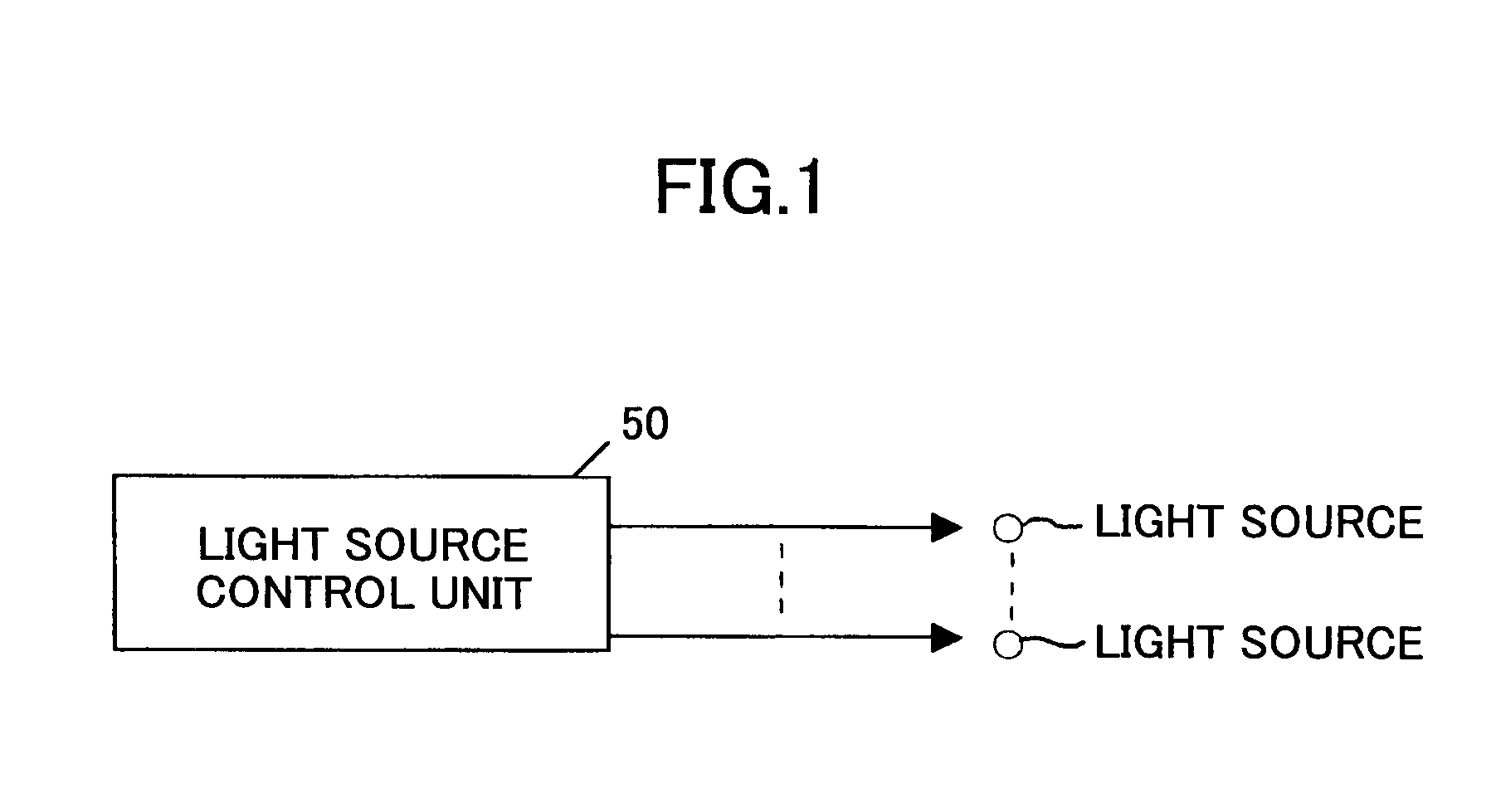
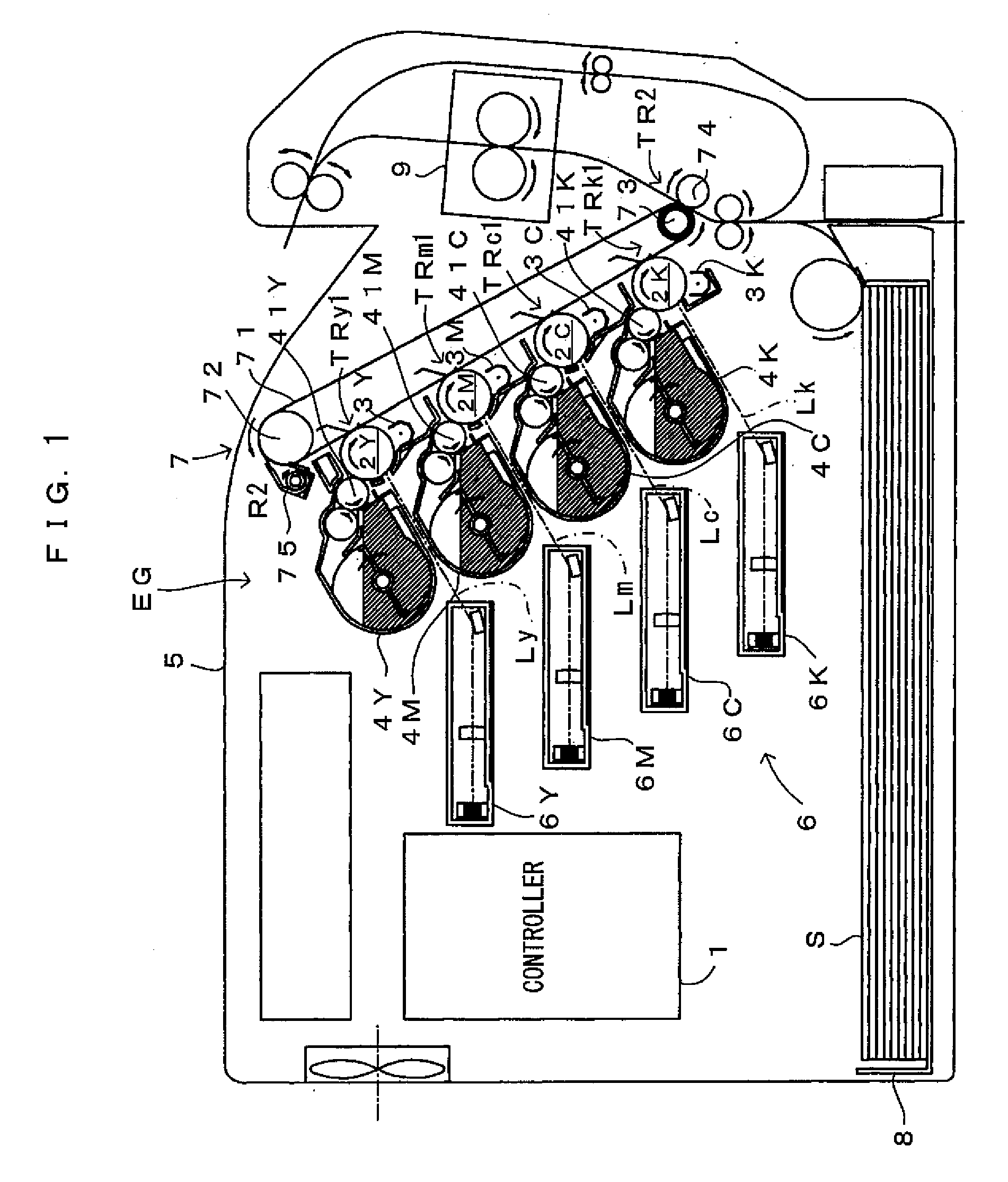
Light scanning apparatus, light scanning method, image forming apparatus, color image forming apparatus, and recording medium having program
A light scanning apparatus having plural light sources includes a light source control unit configured to control the light sources to form L (L≧2) light beam arrays aligned in a sub scanning direction each of which L light beam arrays are formed by causing M ((N−1)≧M≧1) light sources out of N (N≧2) light sources assigned to each of the L light beam arrays to emit light as M light emitting sources, wherein each of the L light beam arrays forms a pixel and a total of L pixels aligned in the sub scanning direction are formed.
Owner:RICOH KK
Multi-scale segmentation and partial matching 3D models
ActiveUS20080215510A1Improve performance consistencyConsistency in its performanceDigital data information retrievalDigital computer detailsViewpointsDecomposition
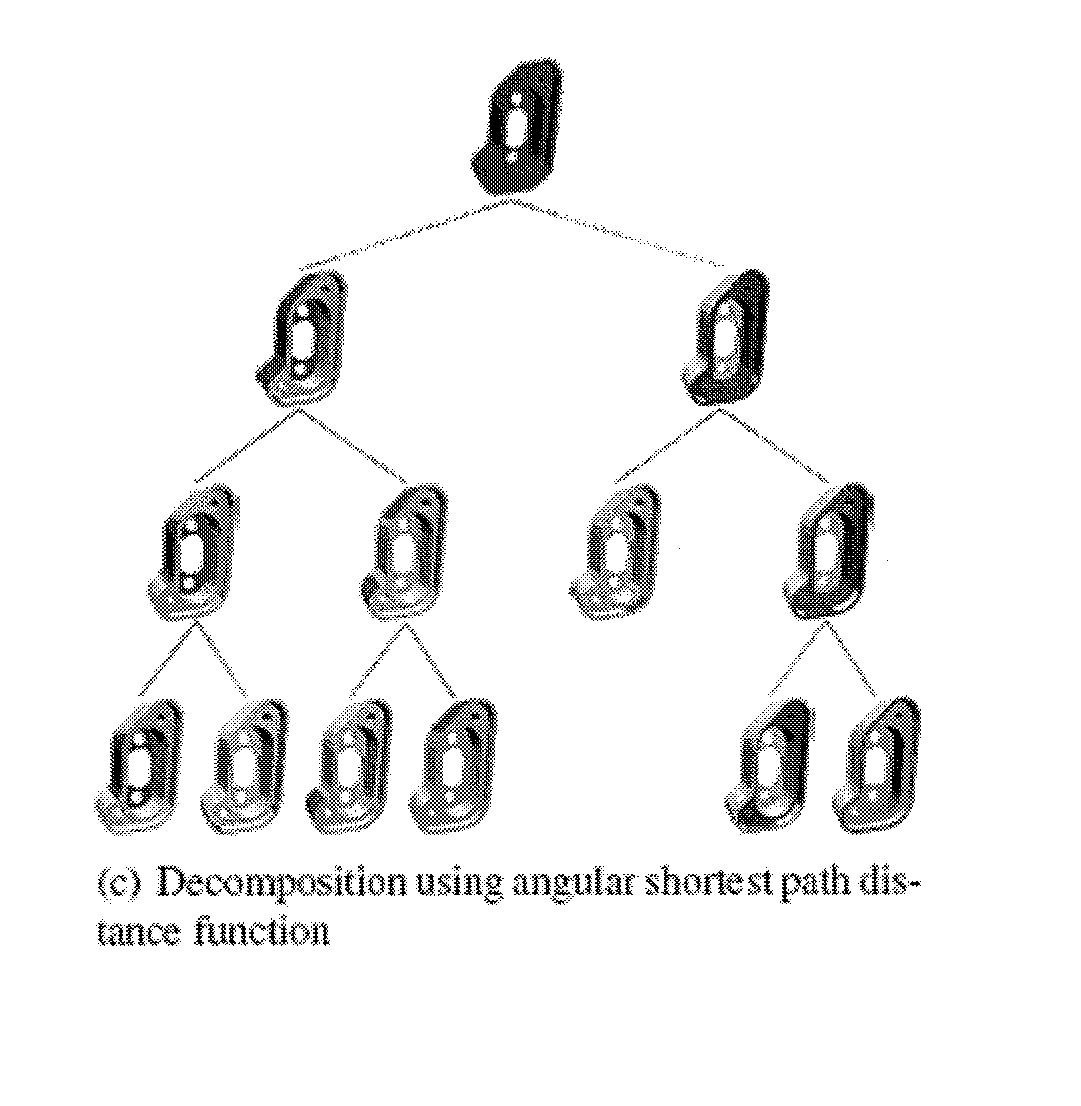
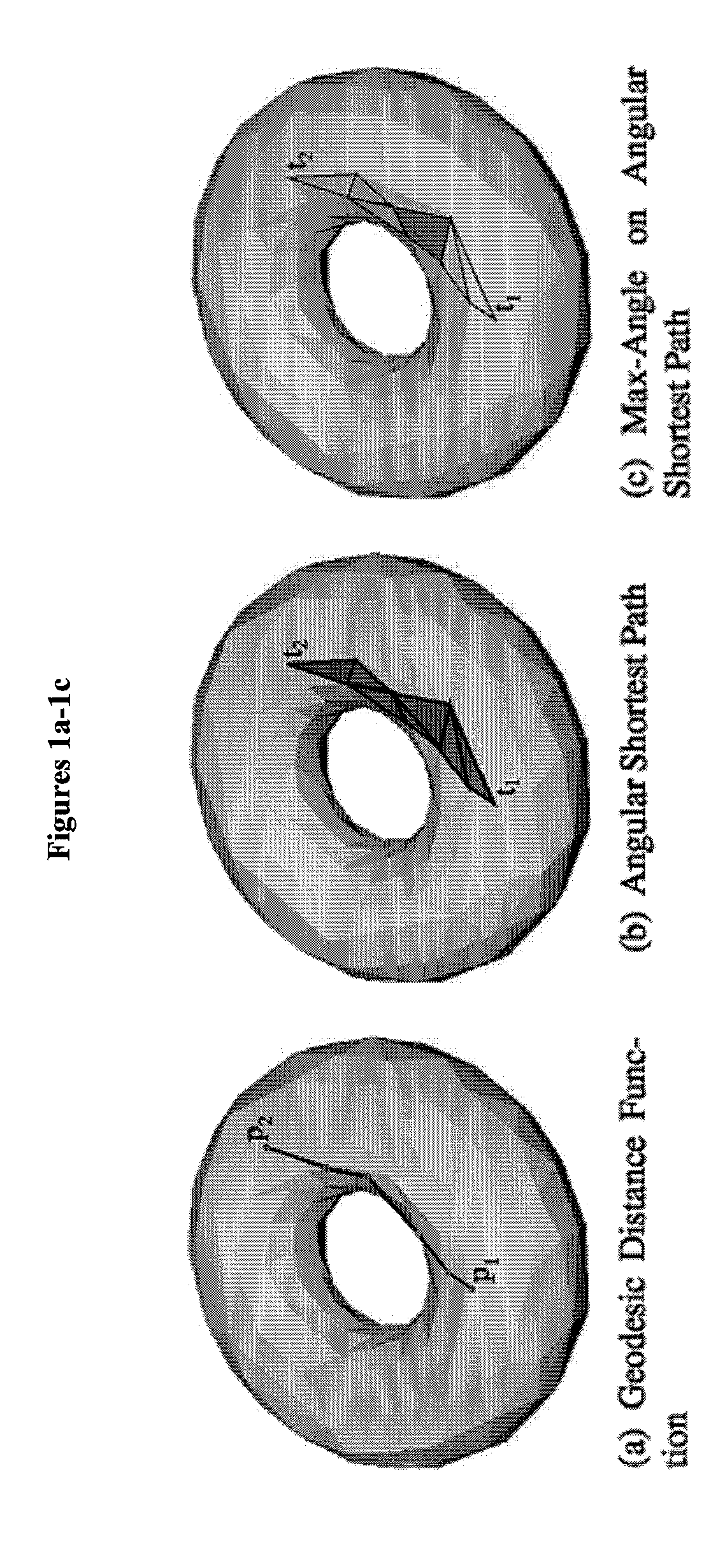
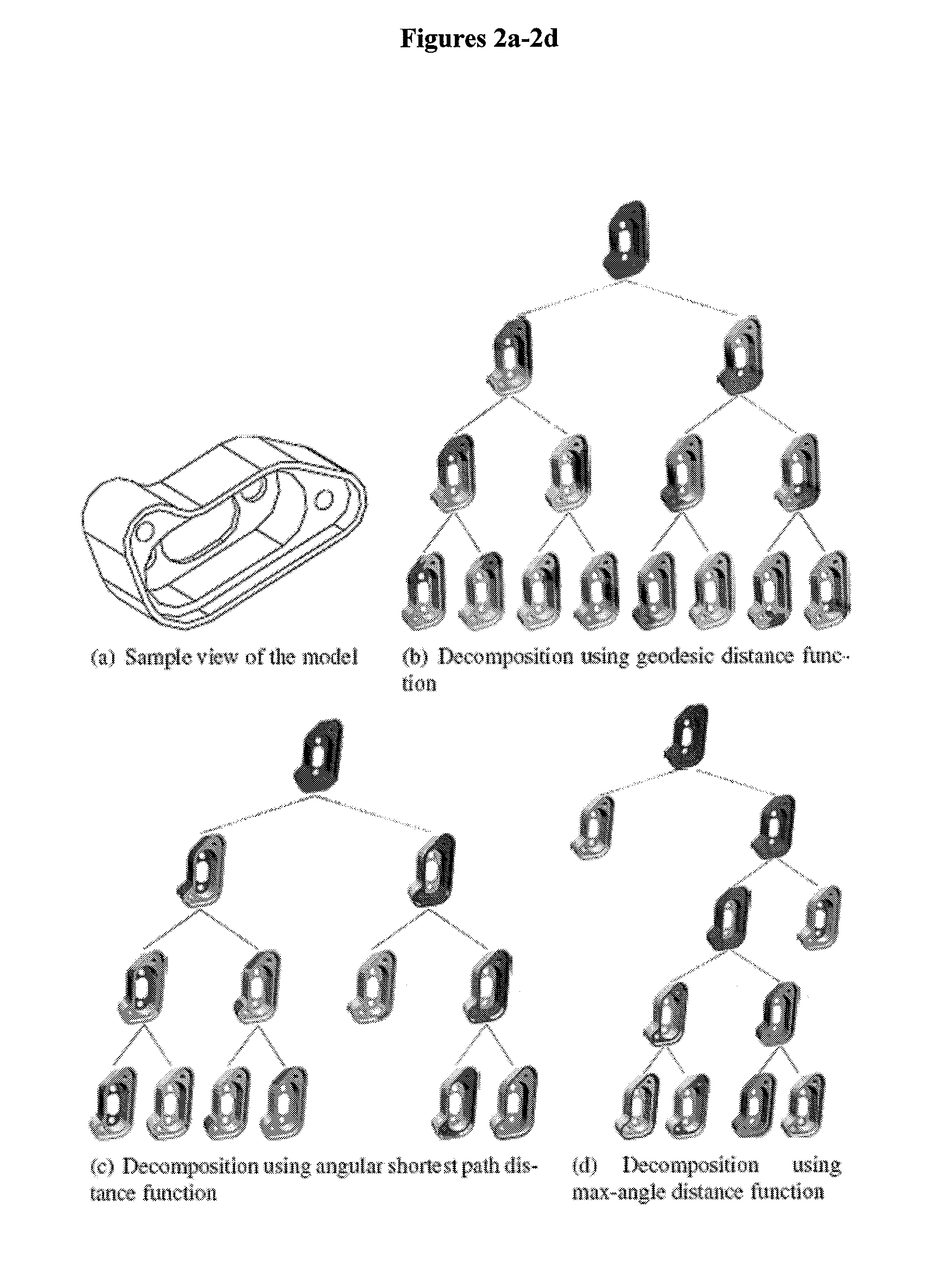
A scale-Space feature extraction technique is based on recursive decomposition of polyhedral surfaces into surface patches. The experimental results show that this technique can be used to perform matching based on local model structure. Scale-space techniques can be parameterized to generate decompositions that correspond to manufacturing, assembly or surface features relevant to mechanical design. One application of these techniques is to support matching and content-based retrieval of solid models. Scale-space technique can extract features that are invariant with respect to the global structure of the model as well as small perturbations that 3D laser scanning may introduce. A new distance function defined on triangles instead of points is introduced. This technique offers a new way to control the feature decomposition process, which results in extraction of features that are more meaningful from an engineering viewpoint. The technique is computationally practical for use in indexing large models.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
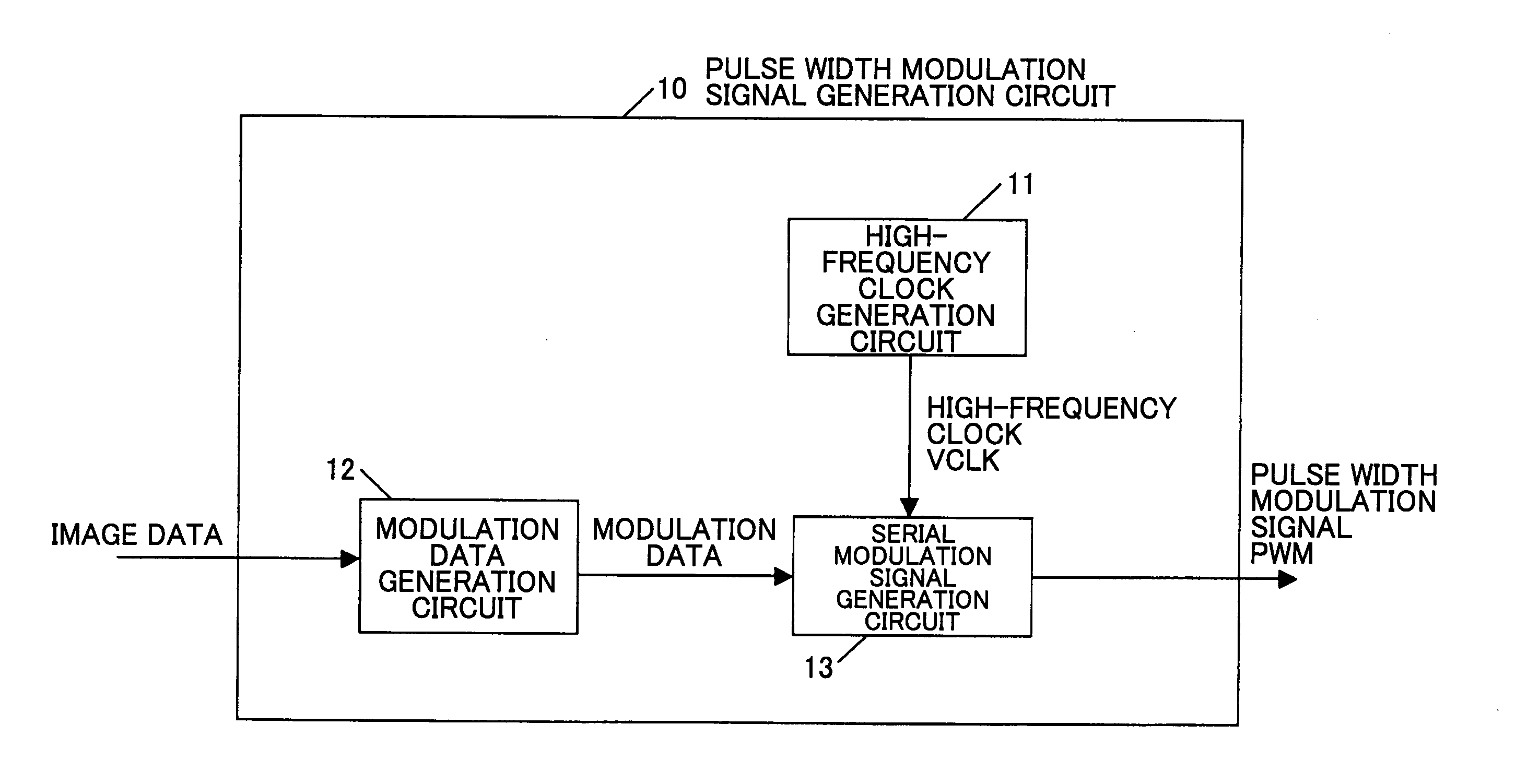
Beam light scanning device and image forming apparatus using same
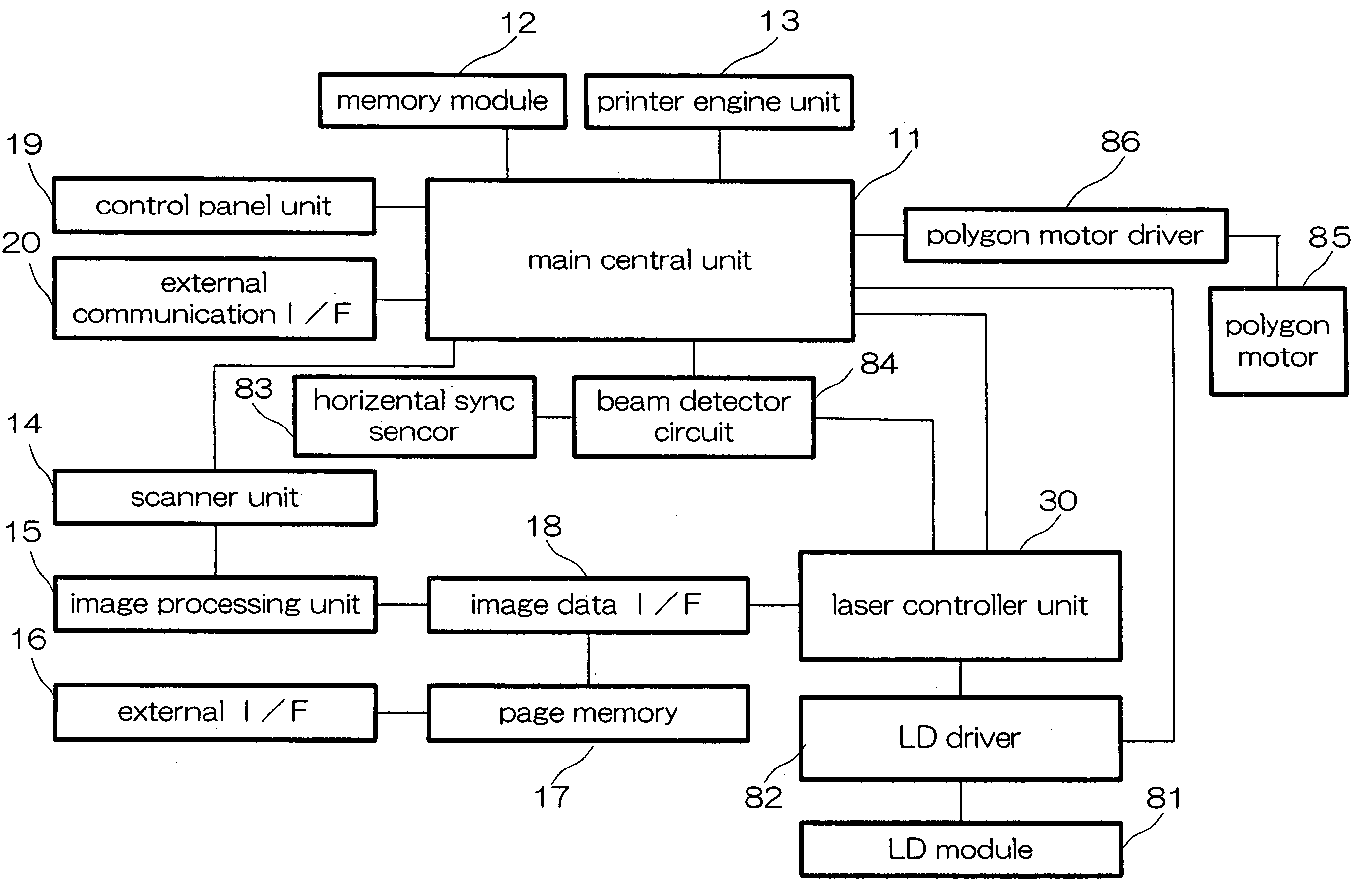
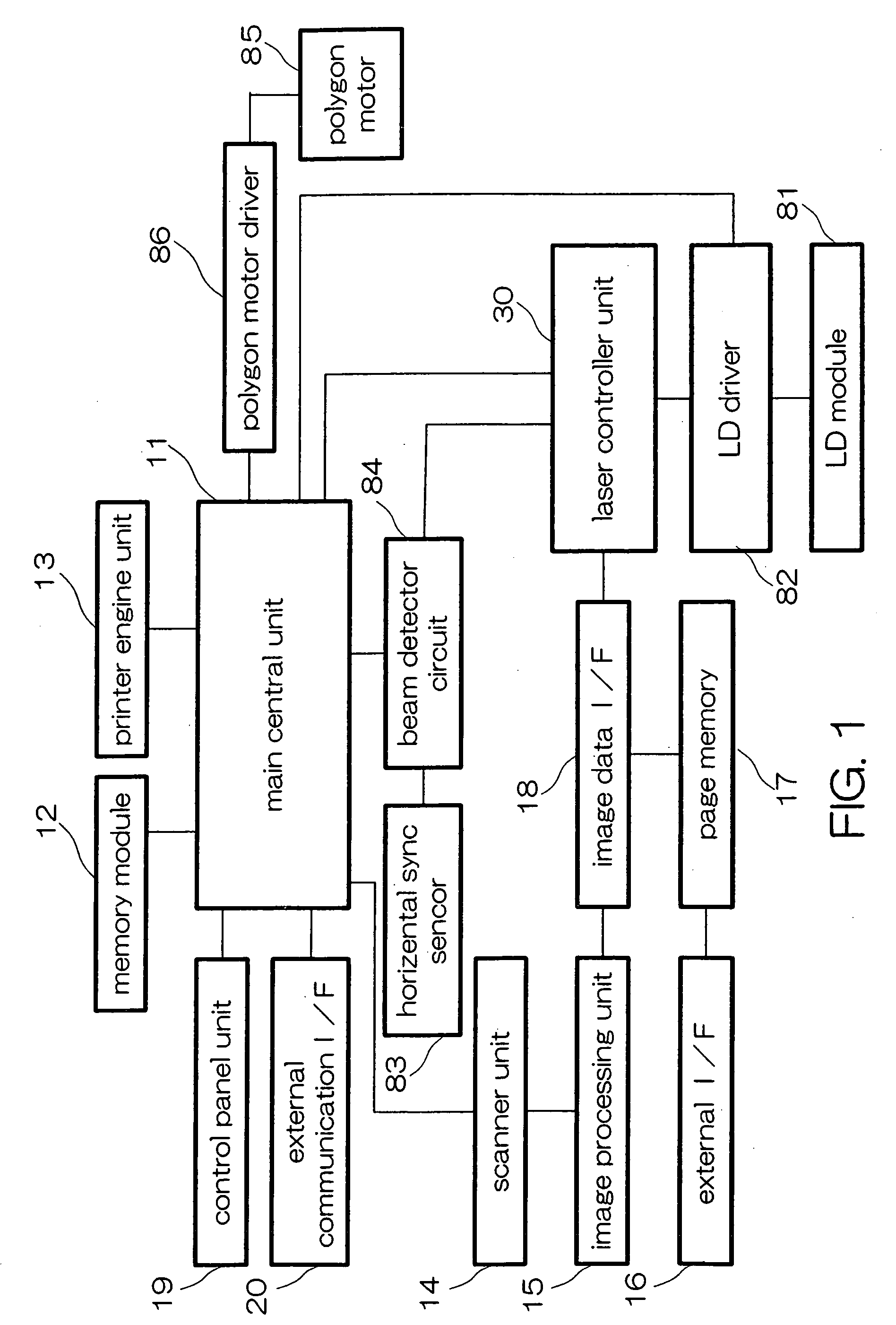
InactiveUS20050157159A1Low production costReduce in quantityVisual representatino by photographic printingElectrographic process apparatusLight beamImage formation
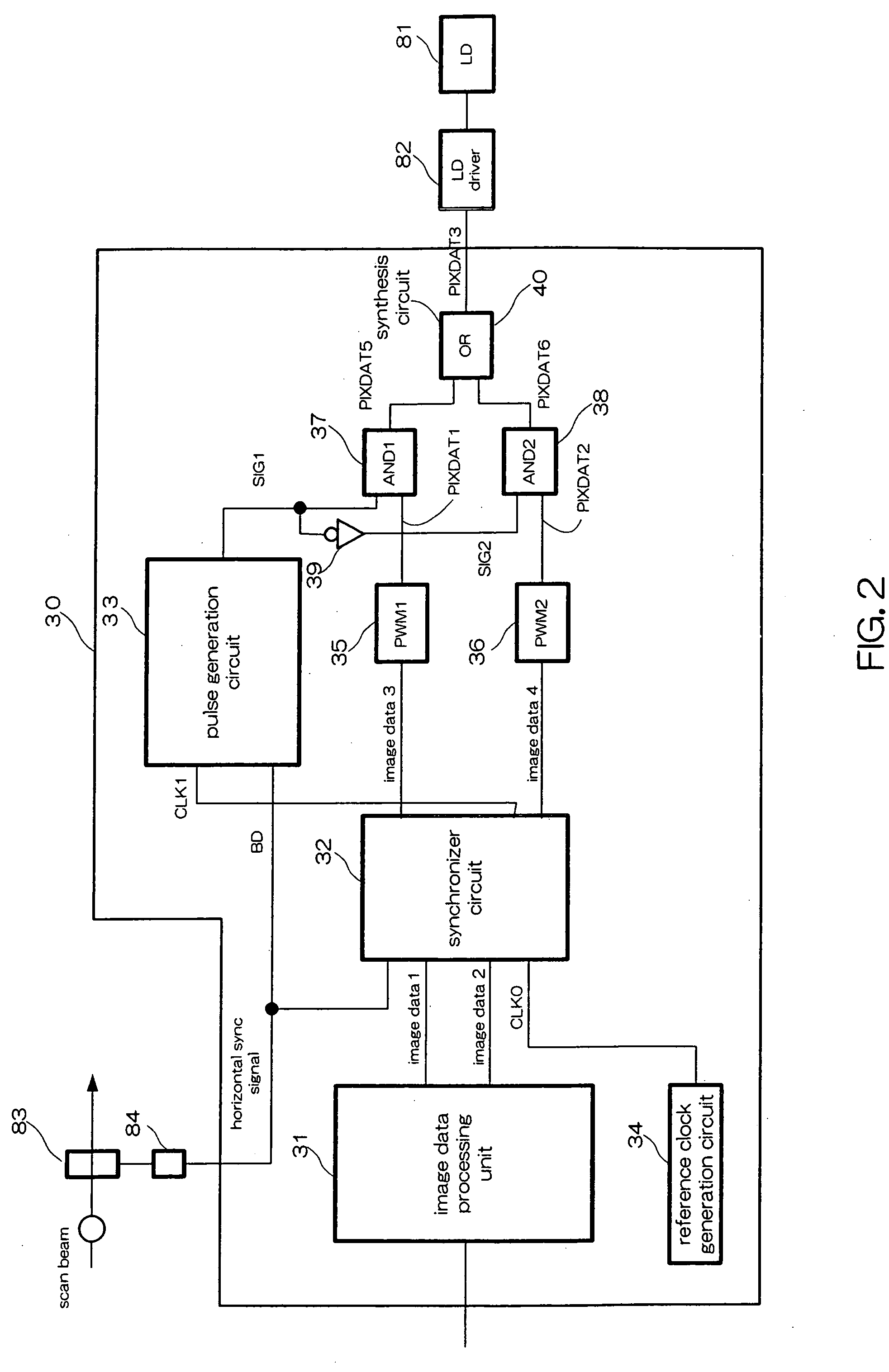
A beam light scanning device includes an image data processing unit operable to output image-processed data of neighboring pixels in such a way that the data is divided for distribution into first pixel data and second pixel data. The scanner also includes a synchronizer circuit that receives the first and second pixel data as output from the image data processor and outputs these pixel data while letting them be synchronized with clocks as synchronized based on a horizontal synchronous signal. The scanner further includes a couple of pulse width modulators or “PWMs”, a synthetic circuit, and a laser diode module. The PWMs are for adjustment of the pulse widths of the first and second pixel data as output from the synchronizer circuit respectively. The synthetic circuit combines together the pulse width-adjusted first and second pixel data. The LD emits a light beam indicative of the resultant combined pixel data.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
Scanning exposure apparatus that compensates for positional deviation caused by substrate inclination
InactiveUS6084244AMinimize relative positional deviationInvestigating moving sheetsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingImage planeProjection optics
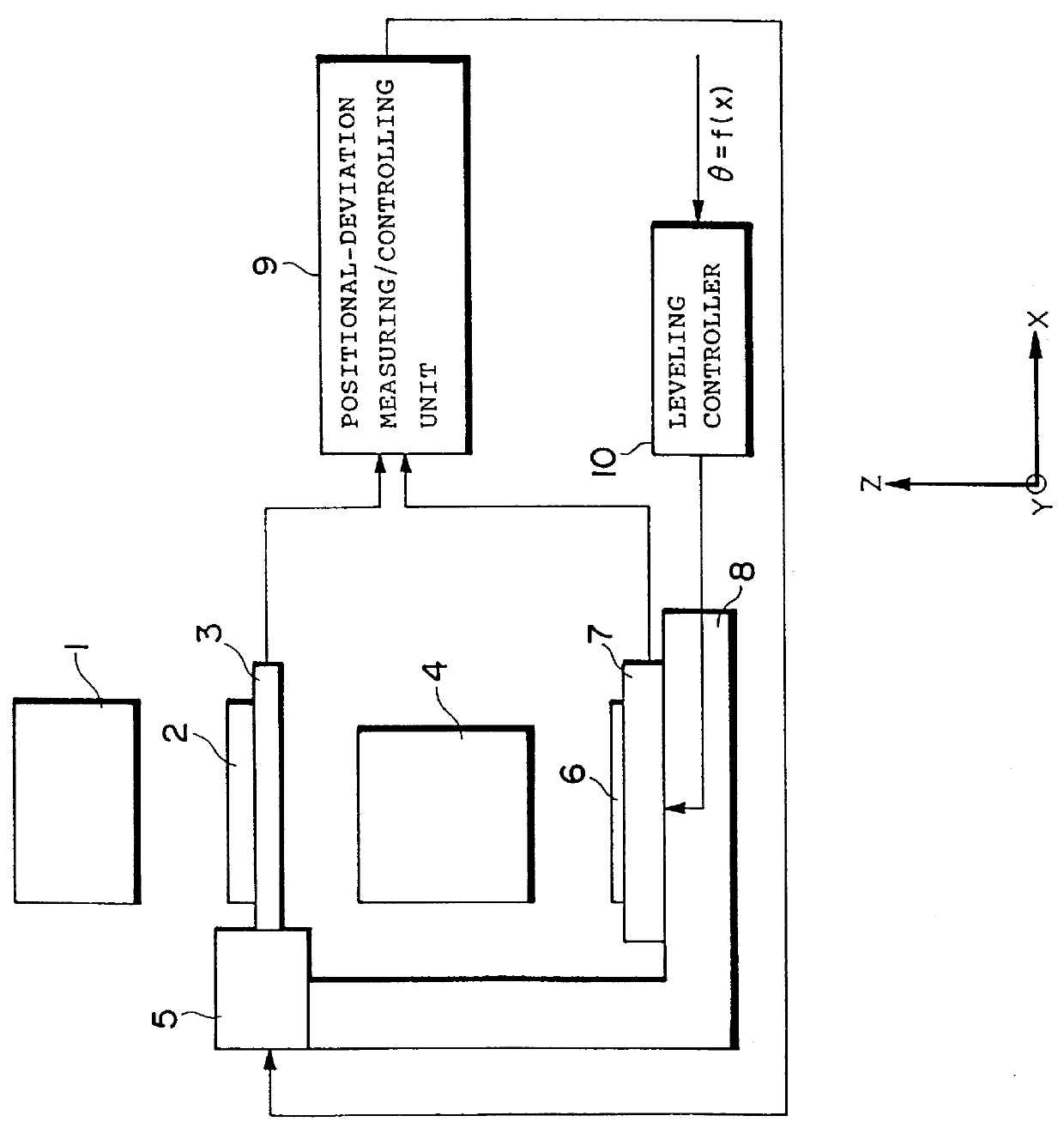
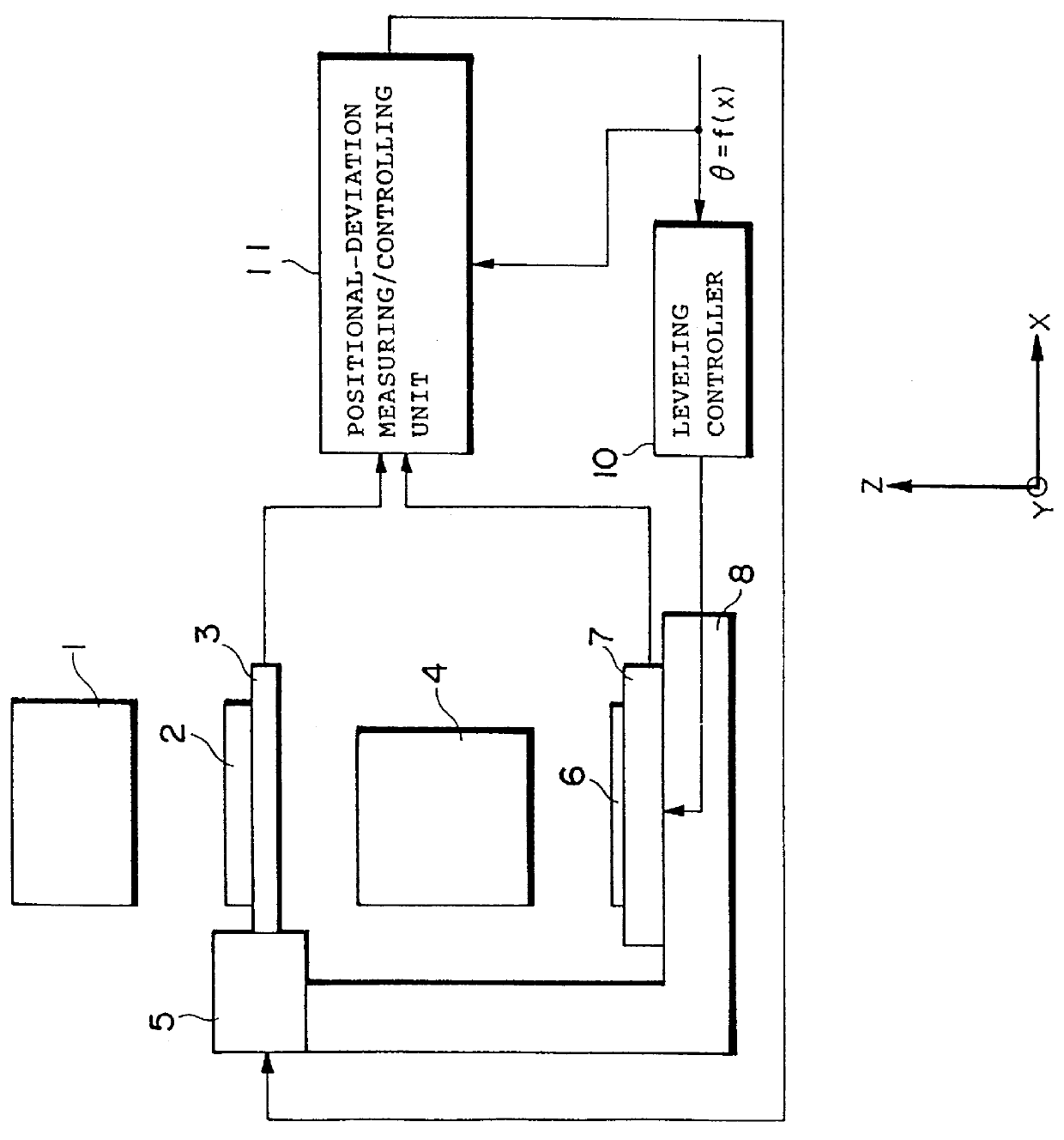
A scanning exposure apparatus of the present invention is constructed in such an arrangement that while a mask and a substrate are moved relatively to a projection optical system, a pattern formed on the mask is projected for exposure through the projection optical system onto the substrate. The scanning exposure apparatus is provided with a leveling control portion for successively controlling an amount of relative inclination between the substrate and the mask with movement thereof, based on a predetermined leveling angle command .theta., so that an exposure area of the substrate becomes approximately coincident with an image plane of the pattern of the mask, a positional deviation measuring and control portion for measuring and controlling an amount of relative positional deviation between the mask and the substrate, and a positional deviation calculating and correcting portion for calculating an amount of relative positional deviation between the mask and the substrate, which will be caused by the control of the leveling control portion, based on the leveling angle command, and effecting correction of the relative positional deviation on the positional deviation measuring and control portion.
Owner:NIKON CORP
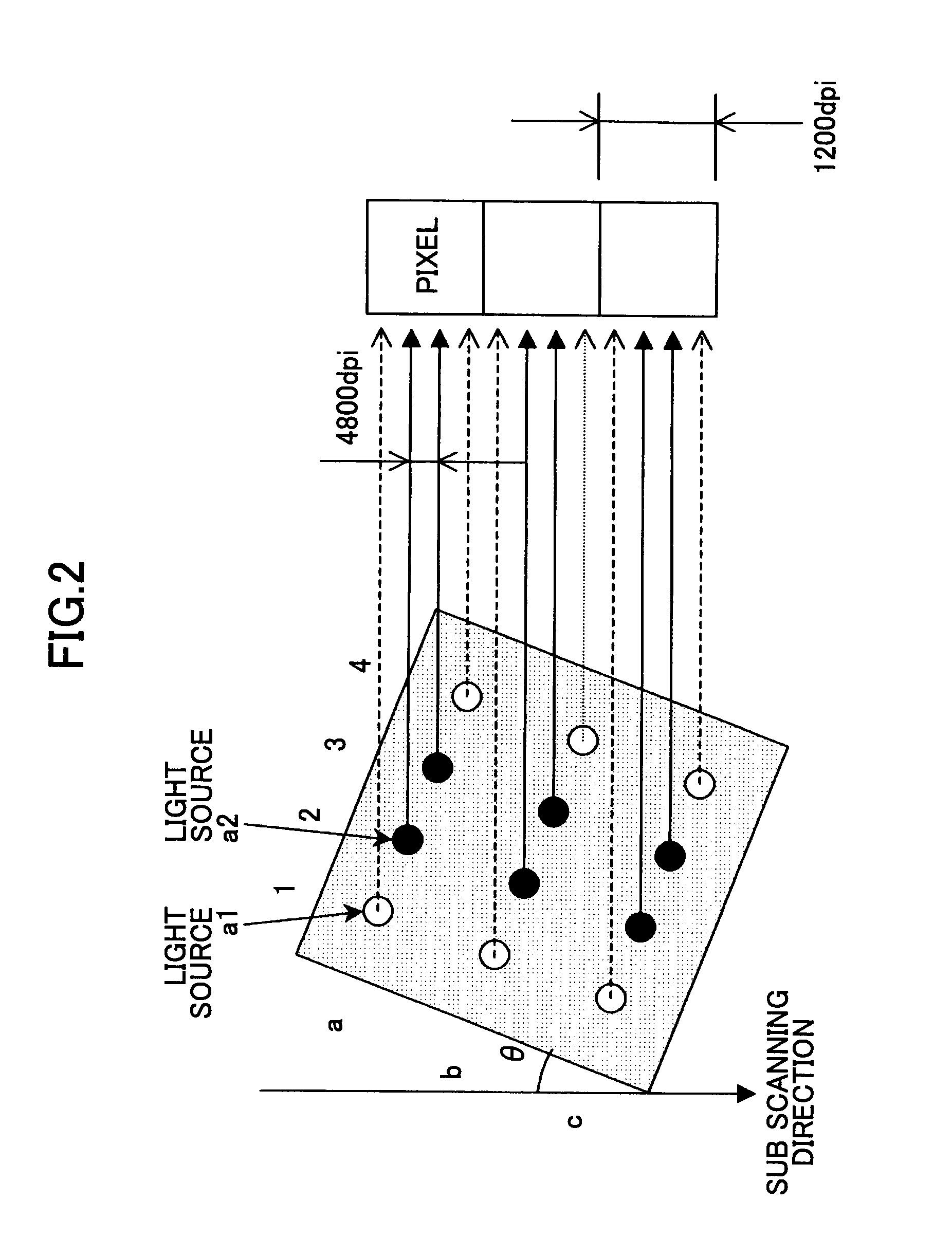
Light scanning apparatus, light scanning method, image forming apparatus, and color image forming apparatus
A light scanning apparatus is provided that has plural light sources which scan plural light beams in a main scanning direction. The light scanning apparatus comprises a light source control unit that controls the plural light sources. Where an array of N (N≧2) light sources aligned in a sub scanning direction and capable of scanning different positions in the sub scanning direction is called a virtual light source array, and where L (L≧2) virtual light source arrays aligned in the sub scanning direction are formed, the light source control unit causes M ((N−1)≧M≧1) light sources out of the N light sources of each of the L virtual light source arrays to emit light to form a pixel and thereby to form a total of L pixels aligned in the sub scanning direction by giving the same data to the M light sources of each of the L virtual light source arrays.
Owner:RICOH KK
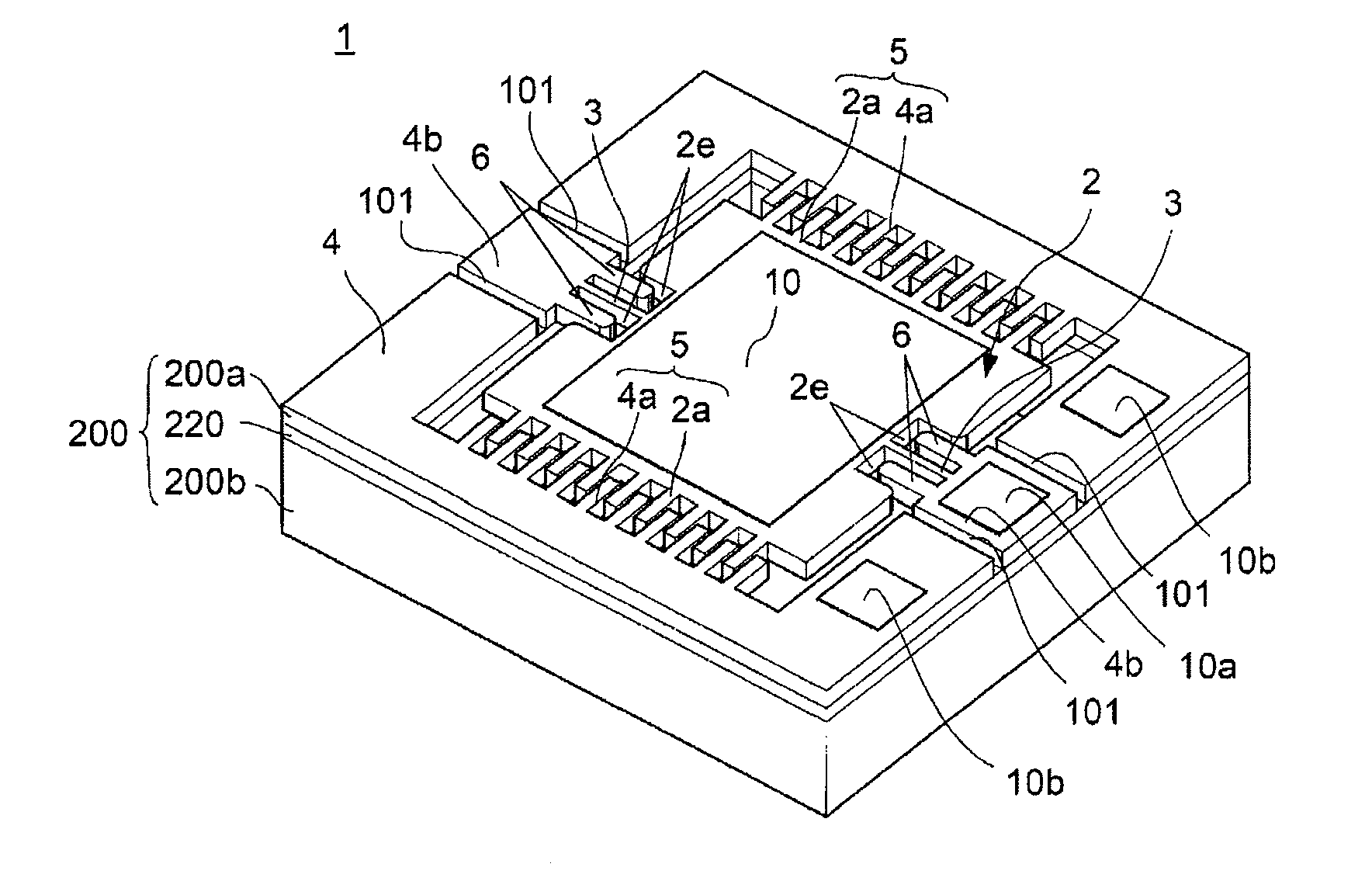
Moving structure and light scanning mirror using the same
InactiveUS20110188104A1Improve crashworthinessAvoid displacementYielding couplingCouplings for rigid shaftsFixed frameEngineering
In a semiconductor mechanical structure, hinges may not be broken even when a mechanical shock is applied from outside, and thus, crashworthy is enhanced. A light scanning mirror includes a moving plate, a twin hinges constituting an axis of swing motion of the moving plate wherein an end of each hinge is connected to both ends of the moving plate, a stationary frame which is disposed to surround peripheries of the moving plate and supports another end of each of the twin hinges, and stoppers formed on the stationary frame. When the moving plate displaces in a lateral direction, the stopper contacts a side end portion of a recess of the moving plate, so that the displacement of the moving plate in the lateral direction is restrained. Thereby, the breakage of the hinges is prevented even when the mechanical shock is applied from outside.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
System and method for a transparent color image display utilizing fluorescence conversion of nanoparticles and molecules
InactiveUS20060290898A1ProjectorsPicture reproducers using projection devicesColor imageWavelength filter
Owner:SUPERIMAGING
Light Scanning Photoelectric Switch
InactiveUS20090283666A1Tighten evenlyFixed and accurateBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansTransducerLight scanning
Provided is a light scanning photoelectric switch that can be attached to a cover correctly even by an inexperienced person. The light scanning photoelectric switch includes: a casing that contains a light scanning unit and a photoelectric transducer and has an opening substantially in U-shape in cross section perpendicular to an axis; a cover that is detachably provided for the casing and is for covering the opening of the casing; an elastically deformable sealing member provided between the casing and the cover; an engagement unit provided for the cover and the casing so that the cover engages with the casing in a state in which the sealing member is compressed in an attachment direction along which the cover is attached to the casing; and a fixation portion capable of receiving a fixing member that compresses the sealing member in a direction different from the attachment direction in a state in which the cover engages with the casing.
Owner:KEYENCE
Method and system for three-dimensionally reconstructing object surface based on cross-structured light
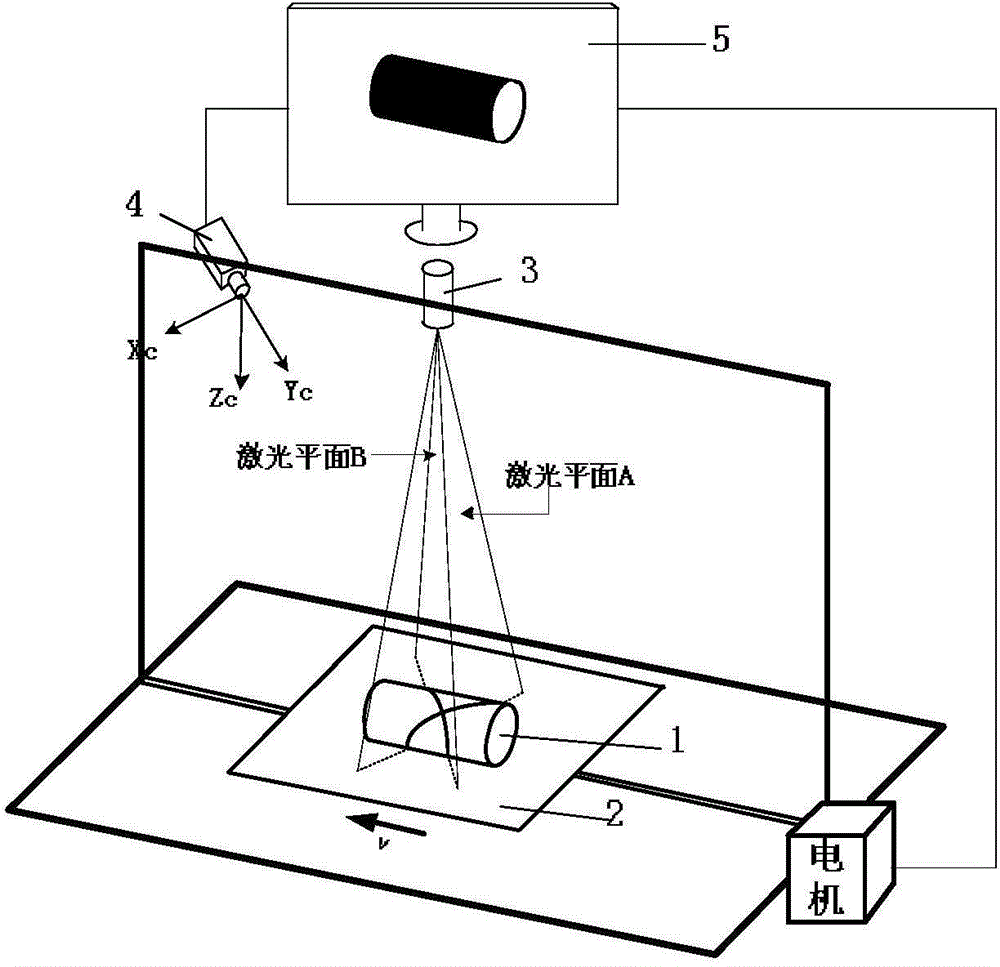
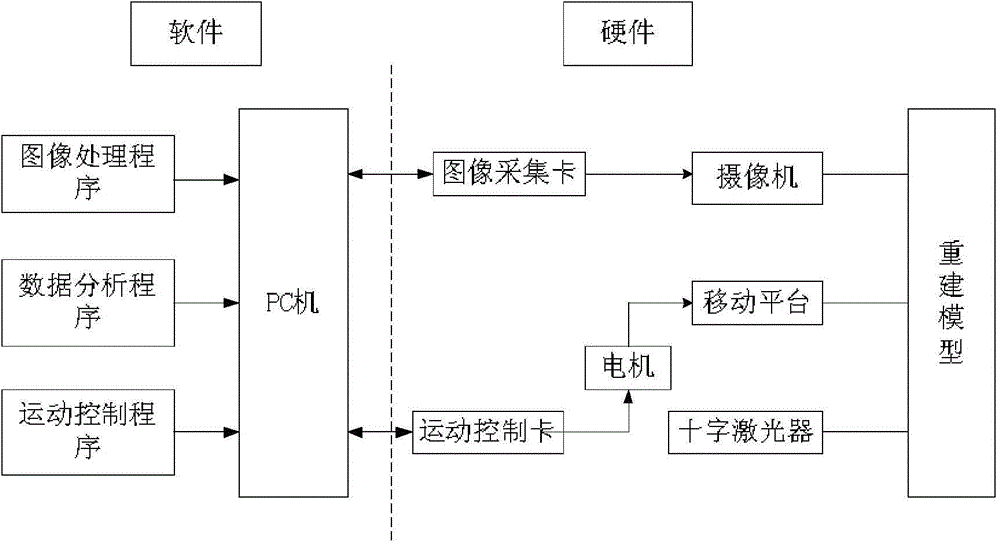
ActiveCN104677305ASuitable for on-site calibrationEasy to operateImage analysisUsing optical meansReconstruction methodLaser projector
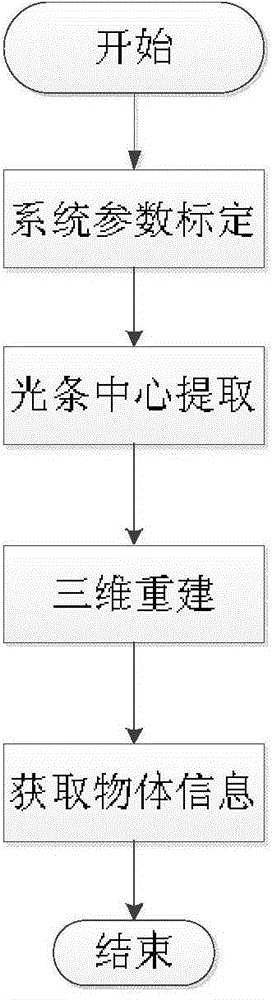
The invention relates to a method and a system for three-dimensionally reconstructing object surface based on cross-structured light. The three-dimensional reconstruction method and the three-dimensional reconstruction system are characterized in that geometric parameter information of a matter is obtained or object surface is reconstructed in a manner of scanning the matter through the cross-structured light, so that marginal information of horizontal-linear-structured light is prevented from losing, and timeliness is good. The method for three-dimensionally reconstructing the object surface based on the cross-structured light comprises the following steps: step 1: calibrating the system parameters; step 2: extracting laser strip center; step 3: realizing three-dimensional reconstruction; step 4: obtaining the matter information. The system for three-dimensionally reconstructing the object surface based on the cross-structured light comprises a machine frame, a mobile platform, a screw rod, a motor, a cross laser projector and a camera. The motor is connected with a computer, and the camera is connected with the computer through an image collection card.
Owner:东开数科(山东)产业园有限公司
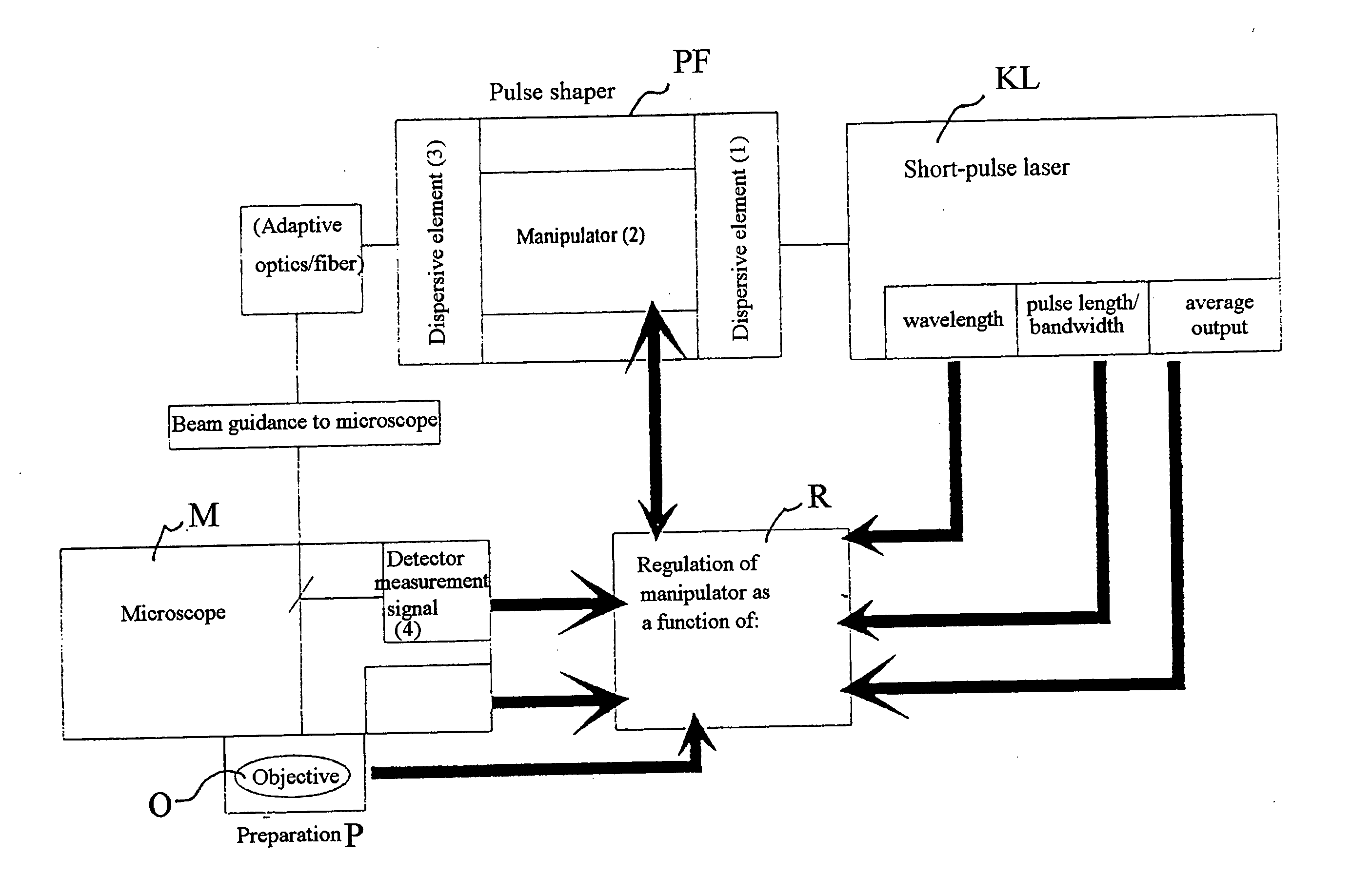
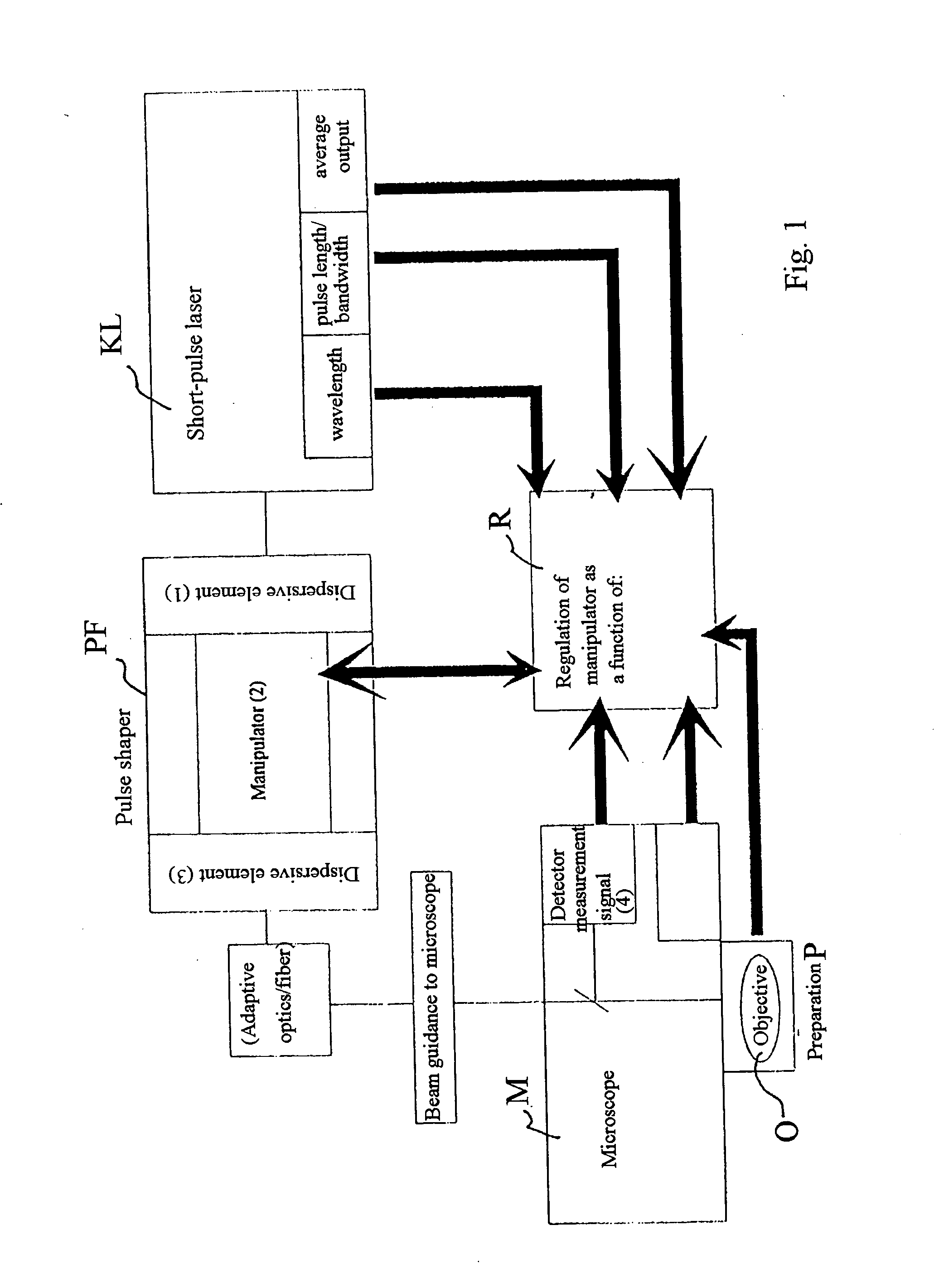
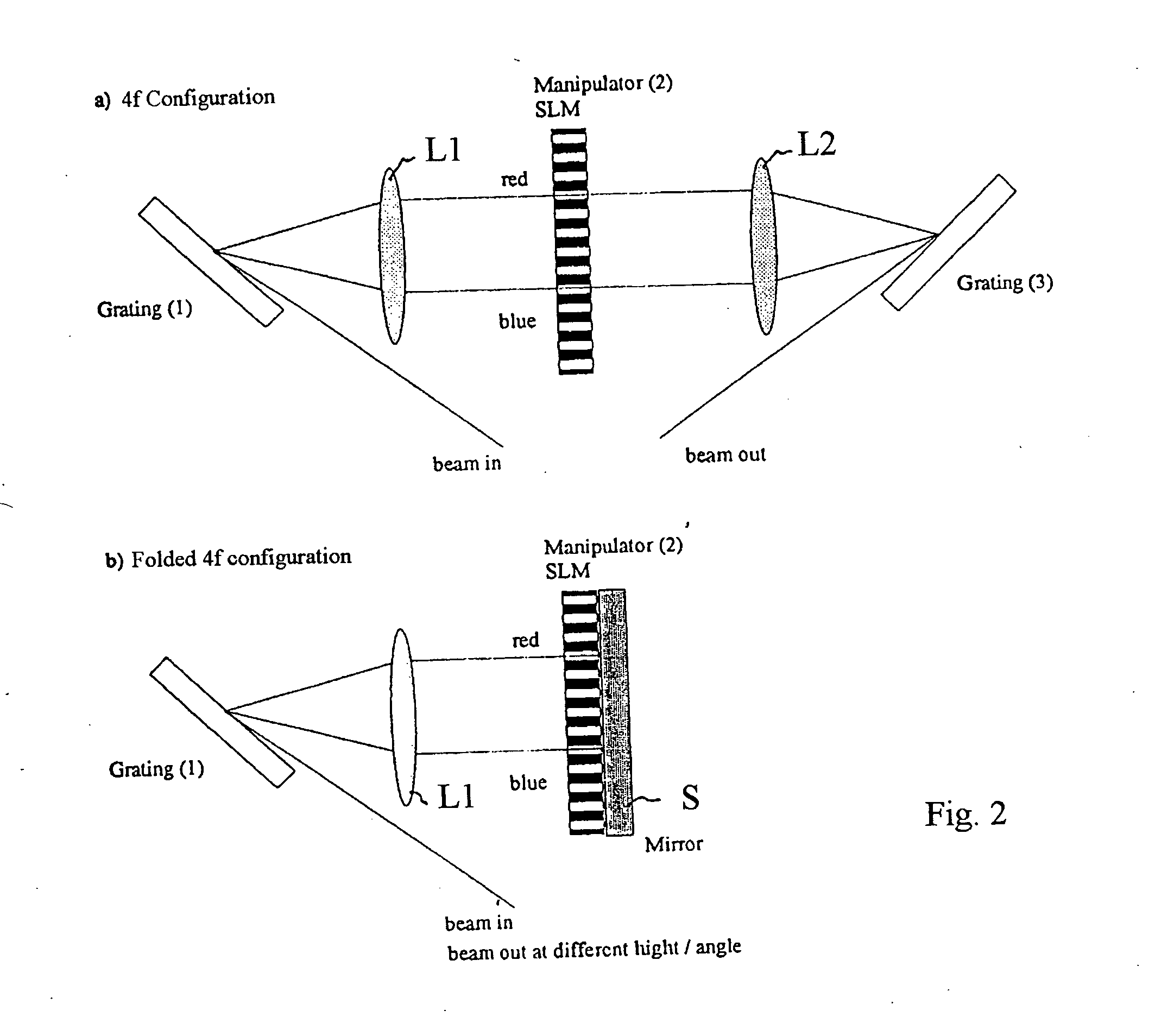
Arrangement for optimizing the pulse shape in a laser scanning microscope
InactiveUS20050017160A1Laser detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsLaser scanning microscopeLight beam
A Device for coupling a short pulse laser into a microscope beam path, wherein the spectral components of the laser radiation are spatially separated by means of a dispersive element, the individual spectral components are manipulated and are then spatially superimposed again by means of another dispersive element.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Light scanning device
InactiveUS20050162722A1Reduce vibrationReduce transmissionMicroscopesTelescopesOptoelectronicsLight scanning
The invention provides a light scanning device for scanning light from a light source, the light scanning device having: a pivotably mounted mirror for receiving light from the light source; a counterbalance; and a drive for oscillatorily pivoting the mirror and the counterbalance simultaneously in opposite directions to reduce uncoupled forces.
Owner:OPTISCAN +1
Light scanning microscope and use
ActiveUS7561326B2Raise the ratioIncrease speedRadiation pyrometryMicroscopesConfocal laser scanning microscopeLaser scanning microscope
In a confocal laser scanning microscope with an illuminating configuration (2), which provides an illuminating beam for illuminating a specimen region (23), with a scanning configuration (3, 4), which guides the illuminating beam over the specimen while scanning, and with a detector configuration (5), which via the scanning configuration (3, 4) images the illuminated specimen region (23) by means of a confocal aperture (26) on to at least one detector unit (28), it is provided that the illuminating configuration (2) of the scanning configuration (3, 4) provides a line-shaped illuminating beam, that the scanning configuration (3, 4) guides the line-shaped illuminating beam over the specimen f while scanning and that the confocal aperture is designed as a slit aperture (26) or as a slit-shaped region (28, 48) of the detector unit (28) acting as a confocal aperture.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Three-dimension laser fine machining system and method for crisp and hard materials
InactiveCN107175409AGuaranteed uniformityUniform focal spotLaser beam welding apparatusLaser scanningMachining process
The invention provides a three-dimension laser fine machining system and method for crisp and hard materials. The method comprises the steps that a laser scanning machining scheme according to the model of a to-be-machined part, the model of a machining pattern and the machining requirements, specifically, the scheme comprises the process of determining the laser machining parameters and the process of determining the number of machining layers; scanning filling schemes corresponding to the machining layers are made in the pattern filling area; the laser focus is adjusted dynamically in the machining process, light spots are made to keep focusing in each machining position, and focus spots are uniform and coincident; the laser scanning filling schemes are changed every time one or more layers of materials are scanned and removed; and after one or more layers are scanned in the pattern filling area, laser contour scanning is conducted in the pattern contour area one or more times. The three-dimension laser fine machining system and method for the crisp and hard materials can achieve high-precision and efficient machining of the crisp and hard materials by making full use of the various advantages of fine light spot laser scanning machining.
Owner:苏州菲镭泰克激光技术有限公司
Light scanning apparatus, method of controlling the same and image forming apparatus equipped with the same
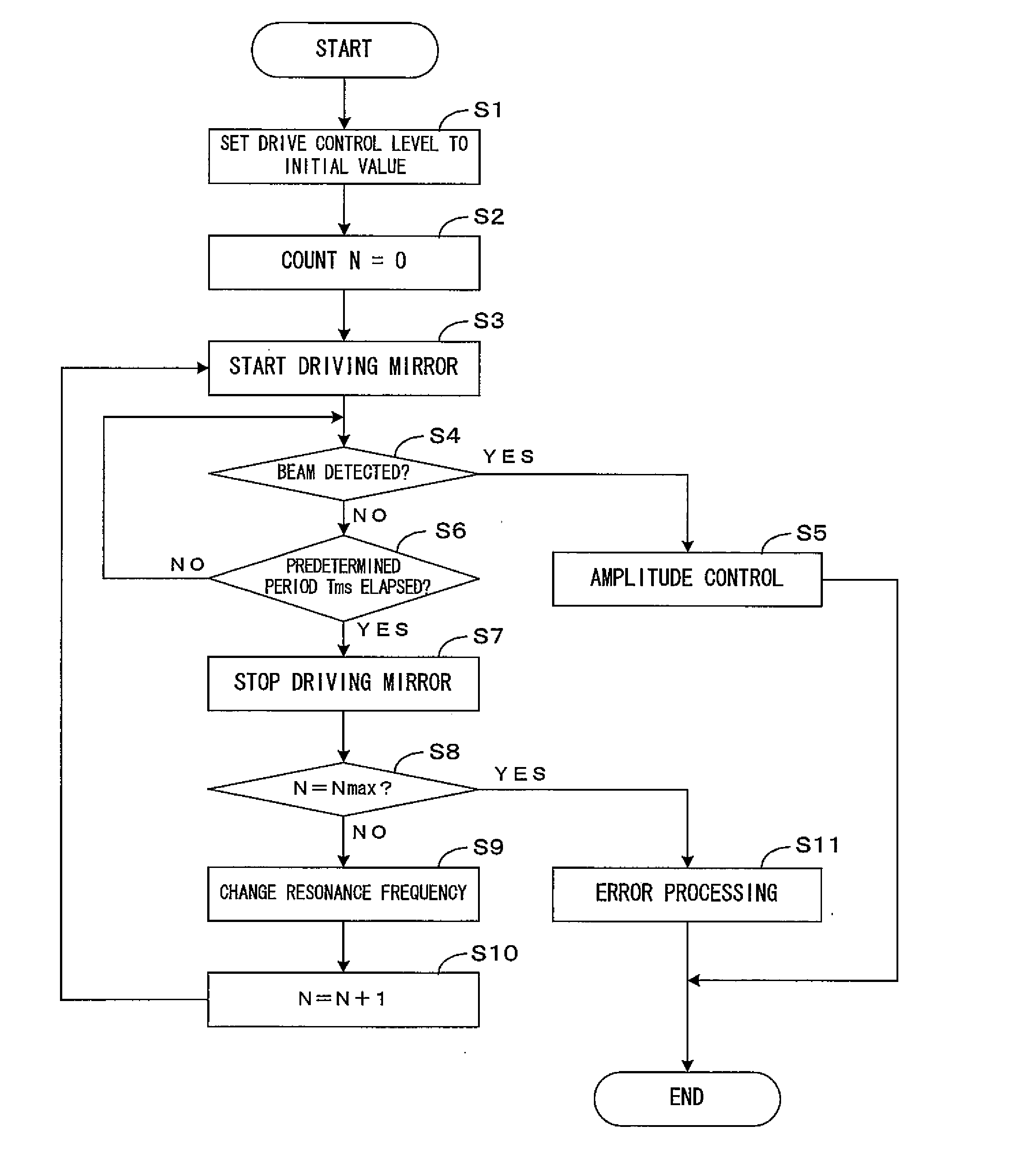
InactiveUS20070035799A1Avoid vibrationAvoid destructionBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansLight beamImage formation
A light scanning apparatus makes a light beam scan along a main scanning direction on an effective scanning region which has a predetermined width. The apparatus comprises: a light source which emits the light beam; a deflector which includes an oscillation mirror which oscillates about an oscillatory axis which is orthogonal or approximately orthogonal to the main scanning direction, deflects the light beam emitted from the light source using the oscillation mirror, and makes the light beam scan a second scanning range which contains but extends beyond a first scanning range which corresponds to the effective scanning region; a detector which detects the scanning light beam which moves through a position which is outside the first scanning range but is within the second scanning range, and outputs a signal; and a controller which controls a mirror drive signal fed to the oscillation mirror based on the output signal from the detector and accordingly adjusts the amplitude of the oscillation mirror. In the apparatus above, the controller stops driving the oscillation mirror when confirming based on the output signal that the oscillation mirror is under abnormal control.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com