Patents
Literature
917 results about "Laser projector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
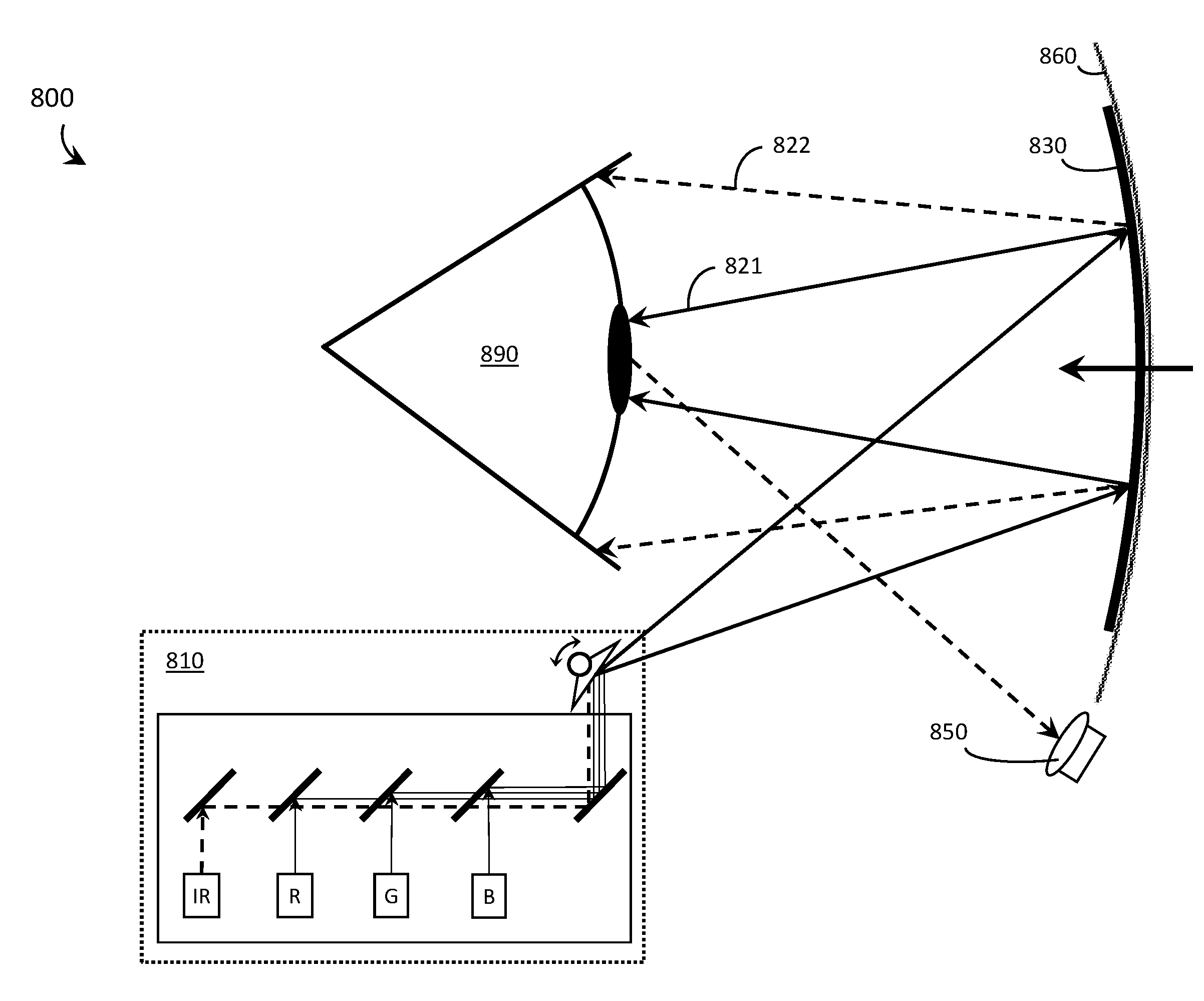
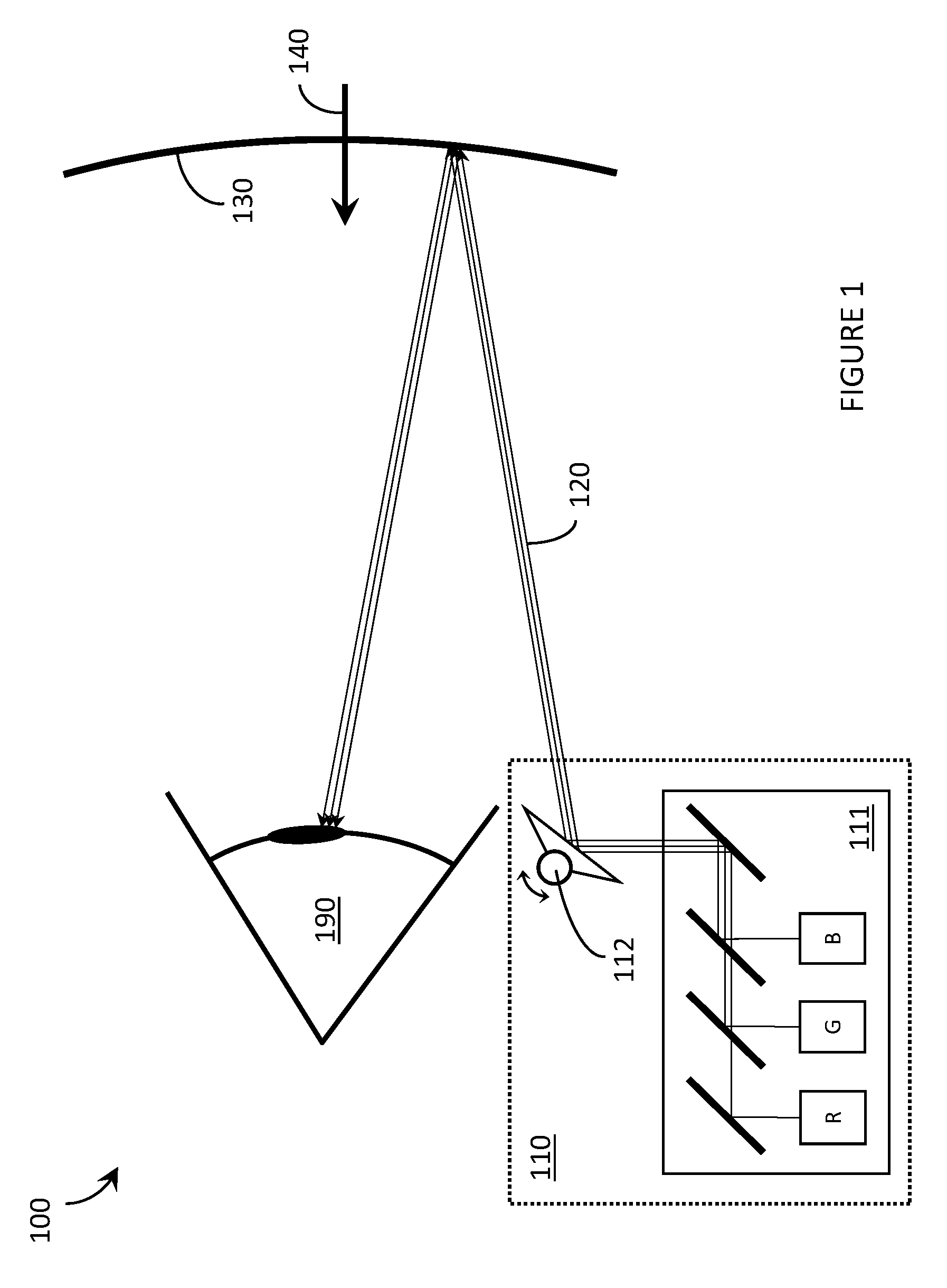
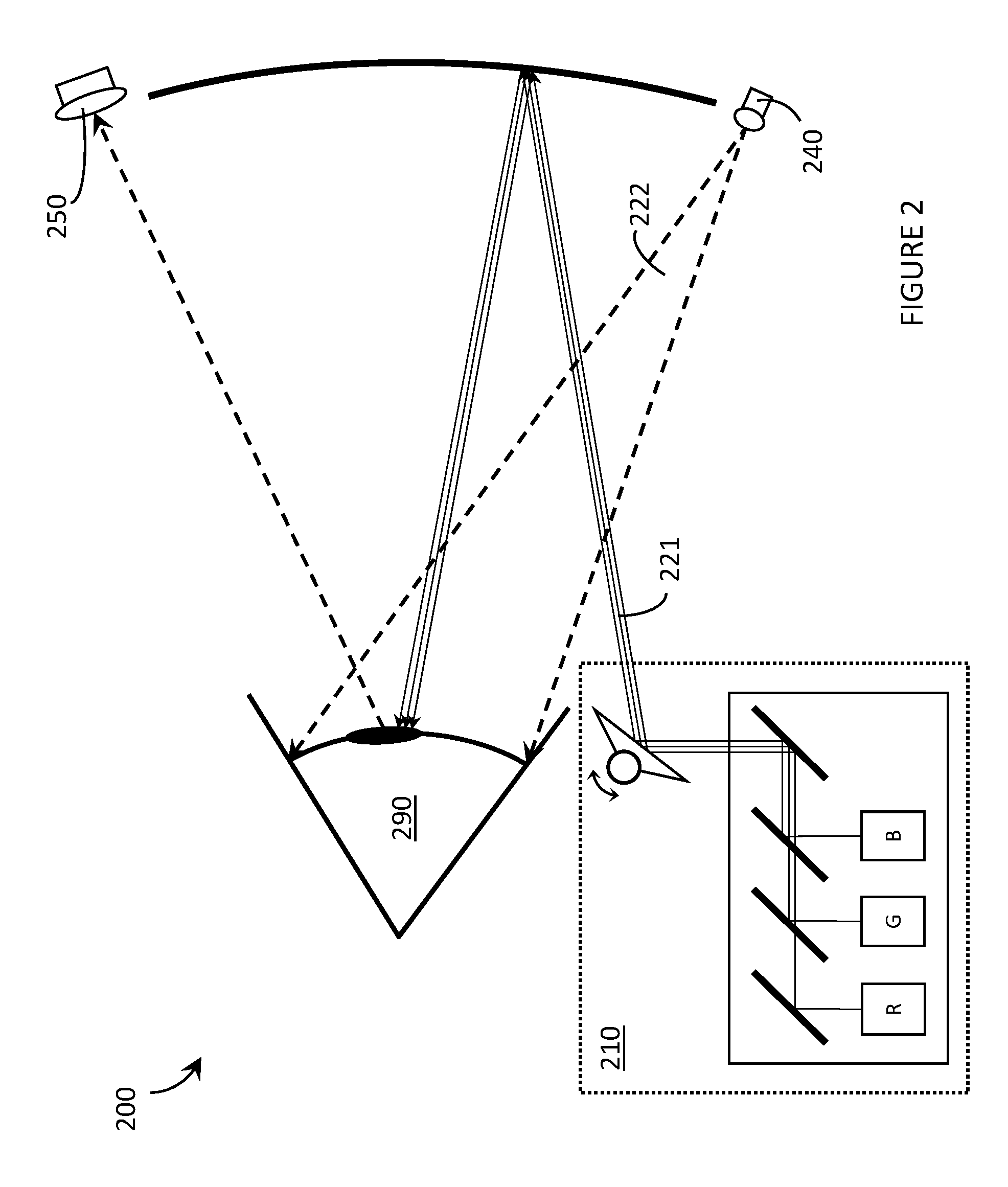
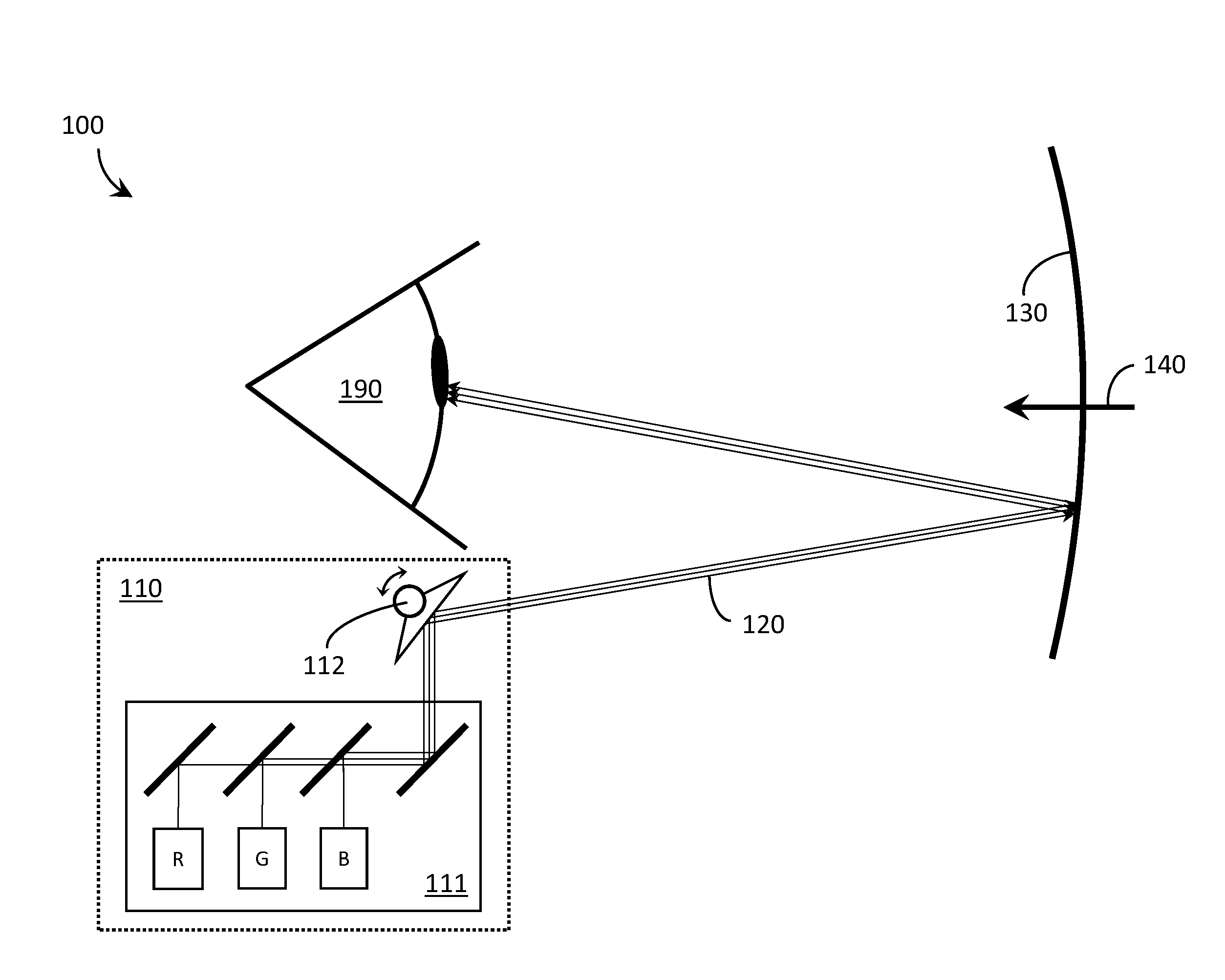
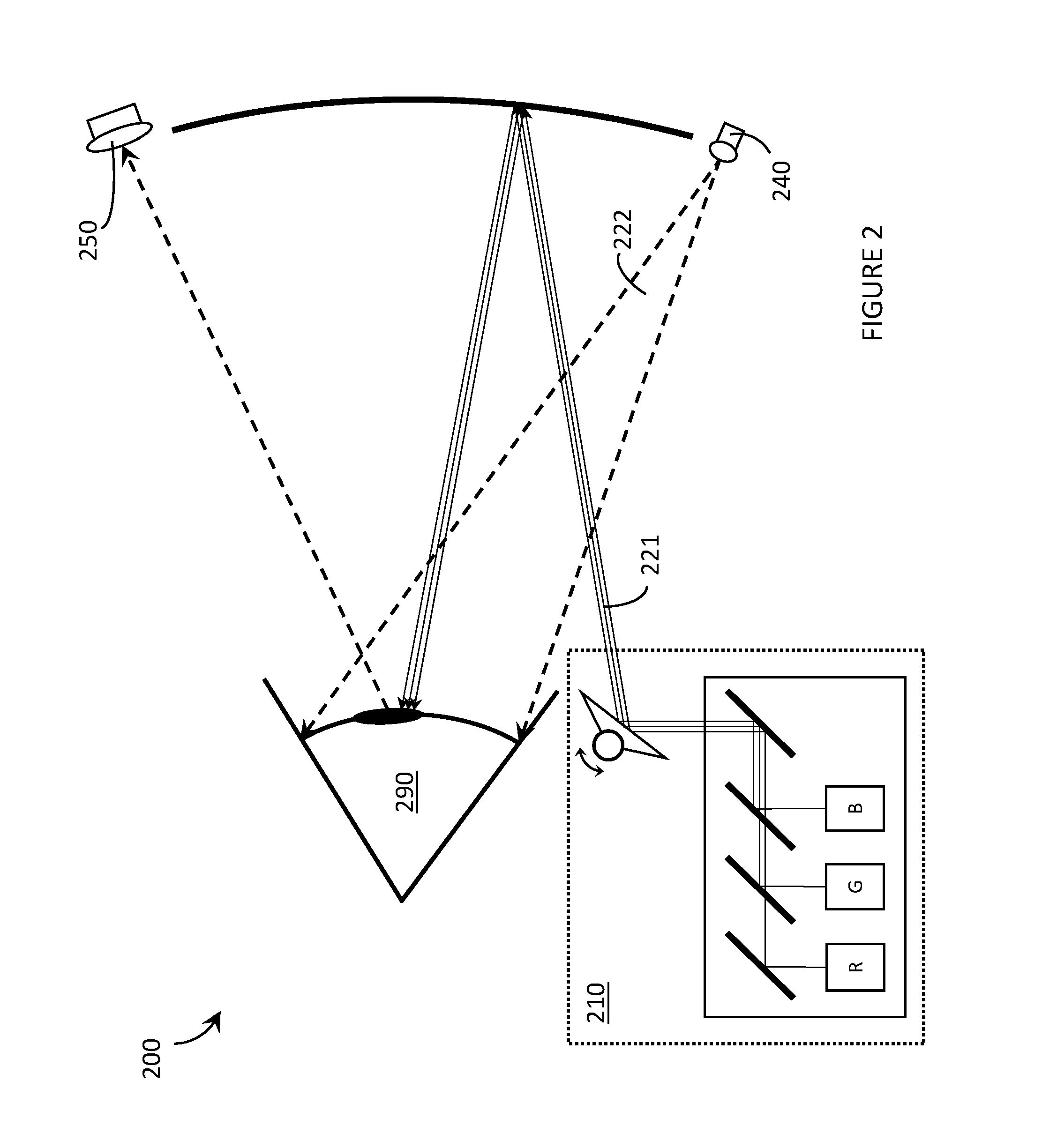
A laser projector is a device that projects changing laser beams on a screen to create a moving image for entertainment or professional use. It consists of a housing that contains lasers, mirrors, galvanometer scanners, and other optical components. A laser projector can contain one laser light source for single-color projection or three sources for RGB (red, green, and blue) full color projection.
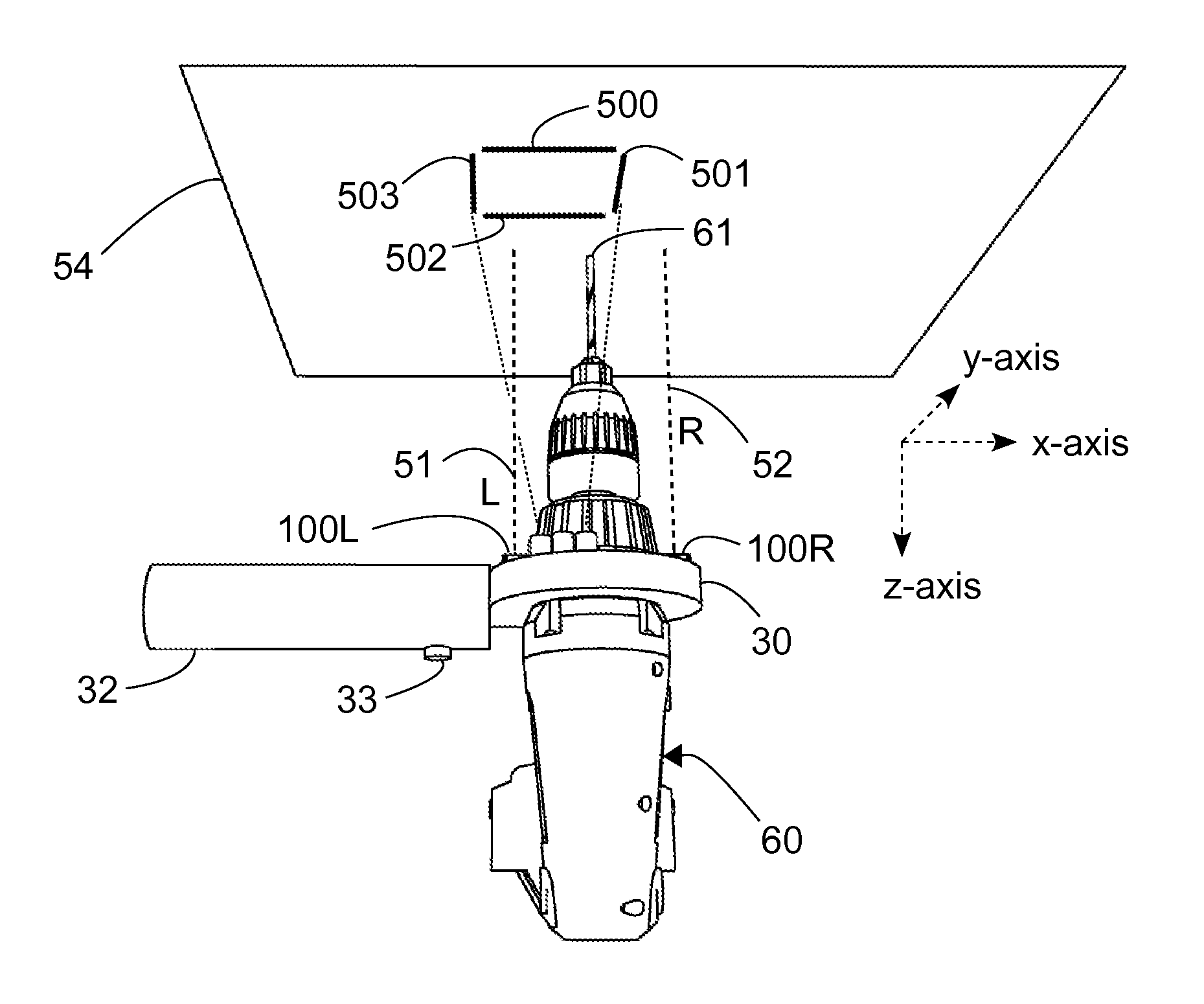
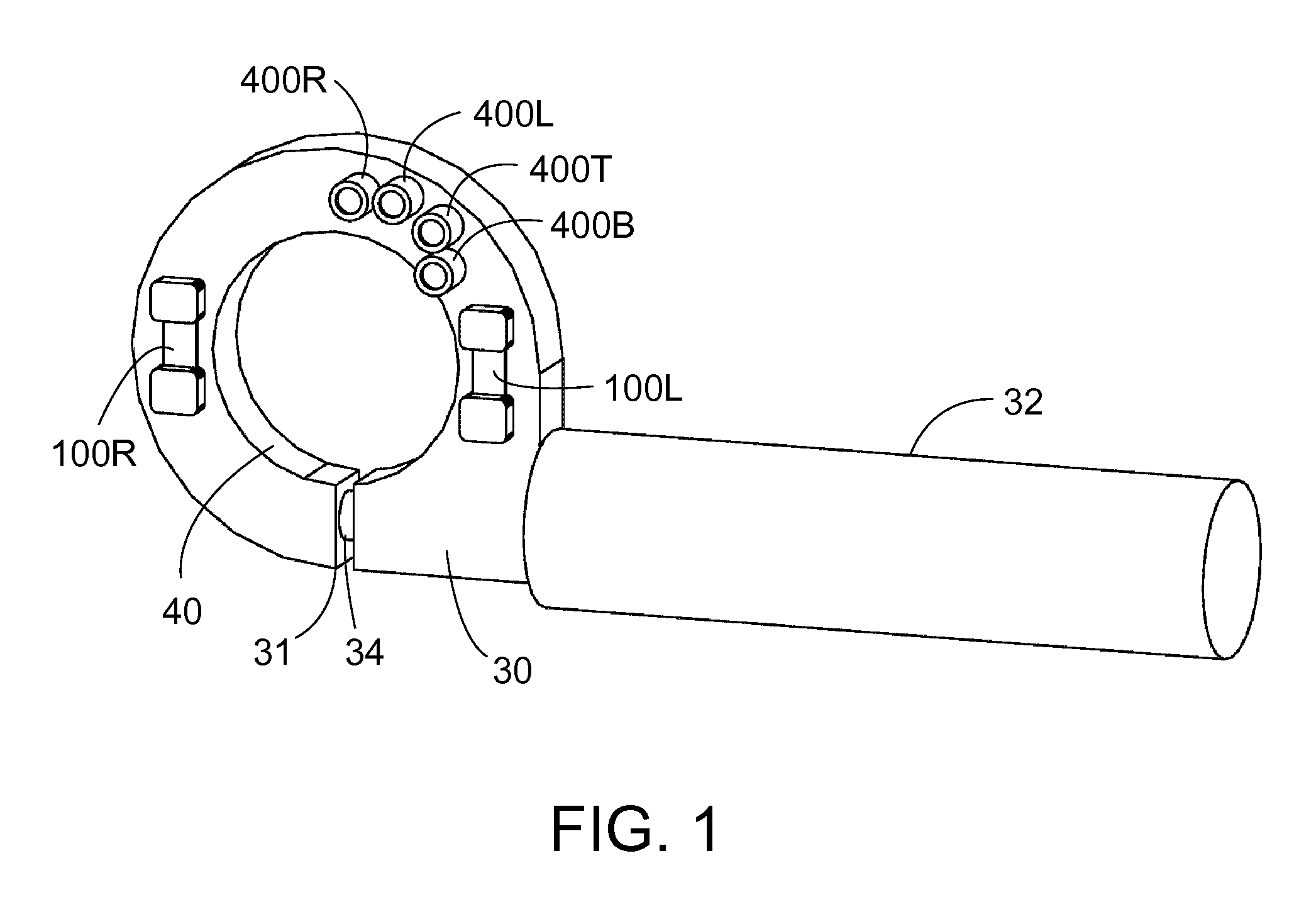
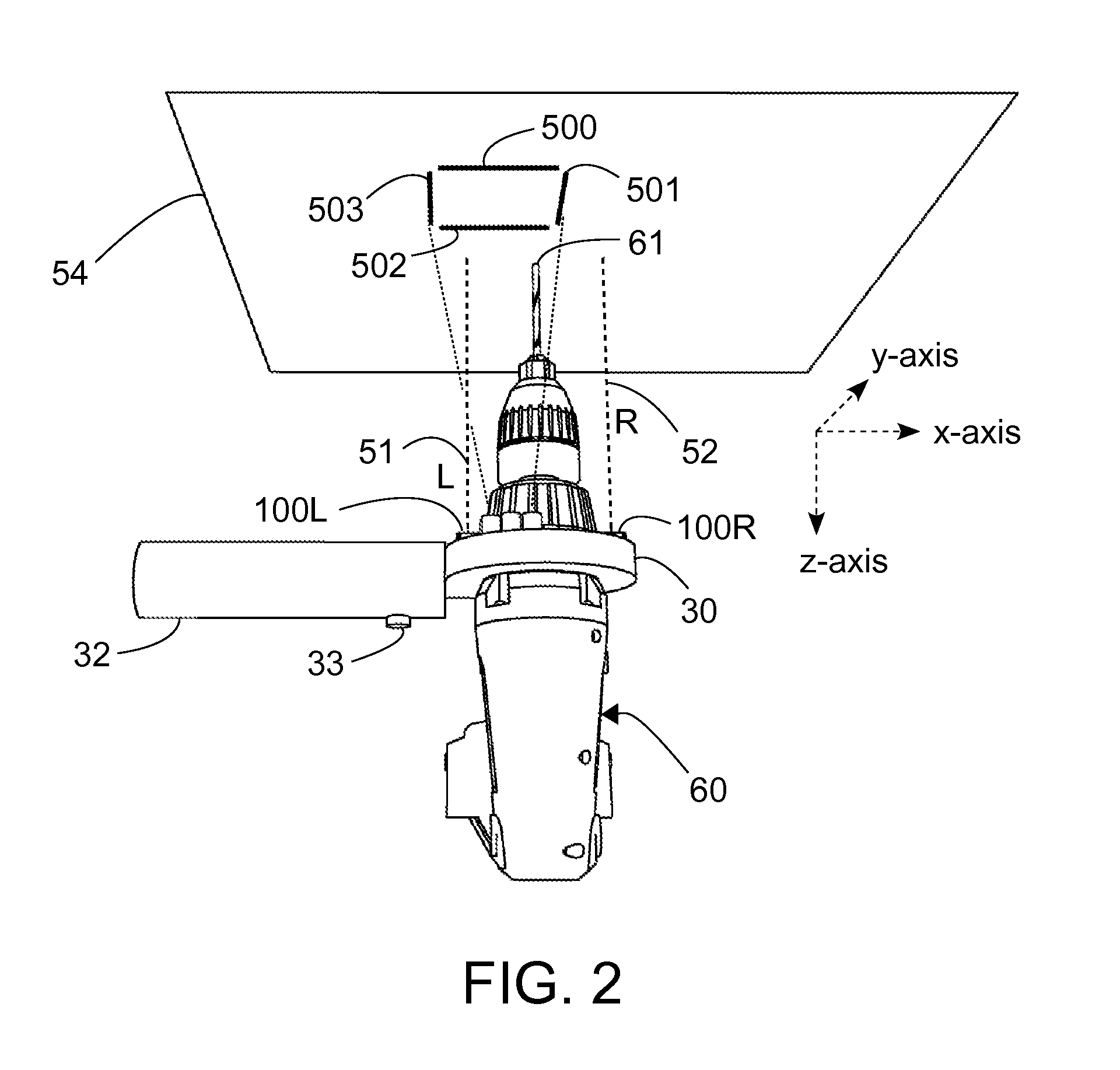
Electronic drill guide
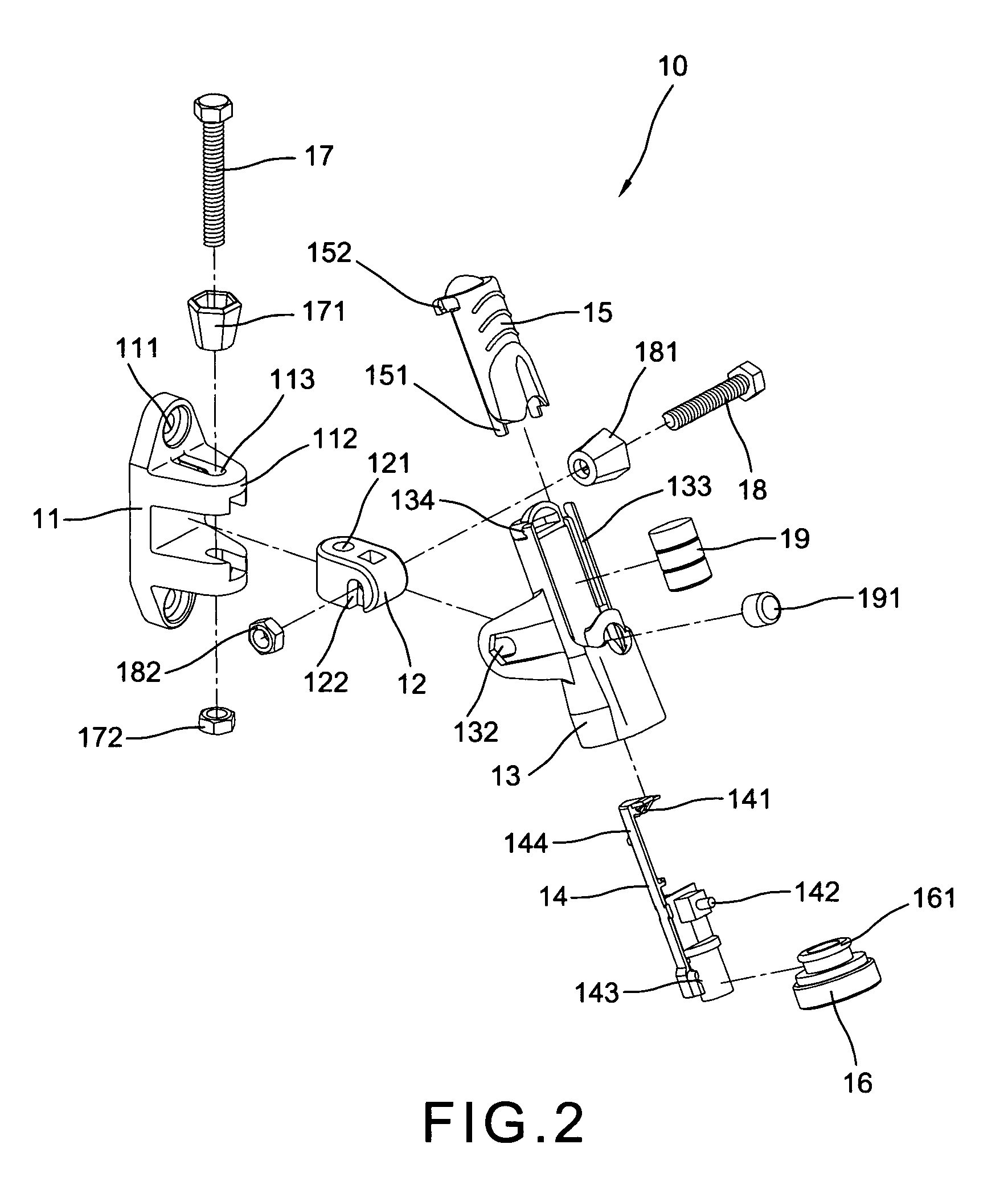
ActiveUS9114494B1Easy to viewStapling toolsDrilling/boring measurement devicesTarget surfaceThree axis accelerometer
One embodiment of an alignment apparatus for aligning an object, such as a tool or other implement, perpendicular with respect to a horizontal or a vertical target surface, comprises a three-axis accelerometer and at least two forward-facing distance sensors and a projection display comprising four addressable laser projectors. The accelerometer and distance sensor outputs are mapped to a predefined graphic symbol representing the orientation of the tool relative to the target surface, in particular when the tool is perpendicular to the target surface. The projection display projects the predefined symbol onto the target surface where it may be easily viewed by the tool operator allowing the operator to make any necessary corrections to the tool position.
Owner:MAH KENNETH JACK
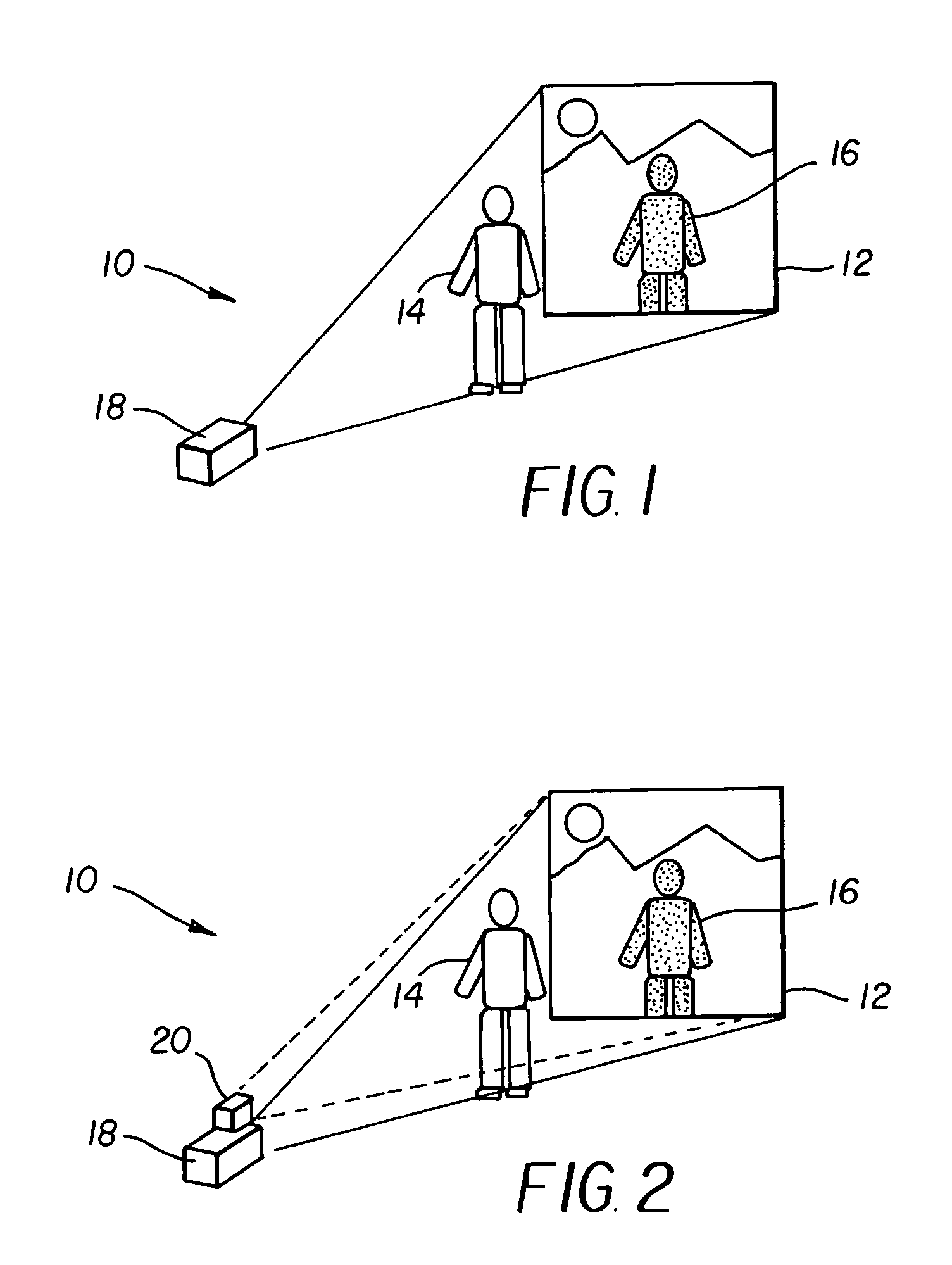
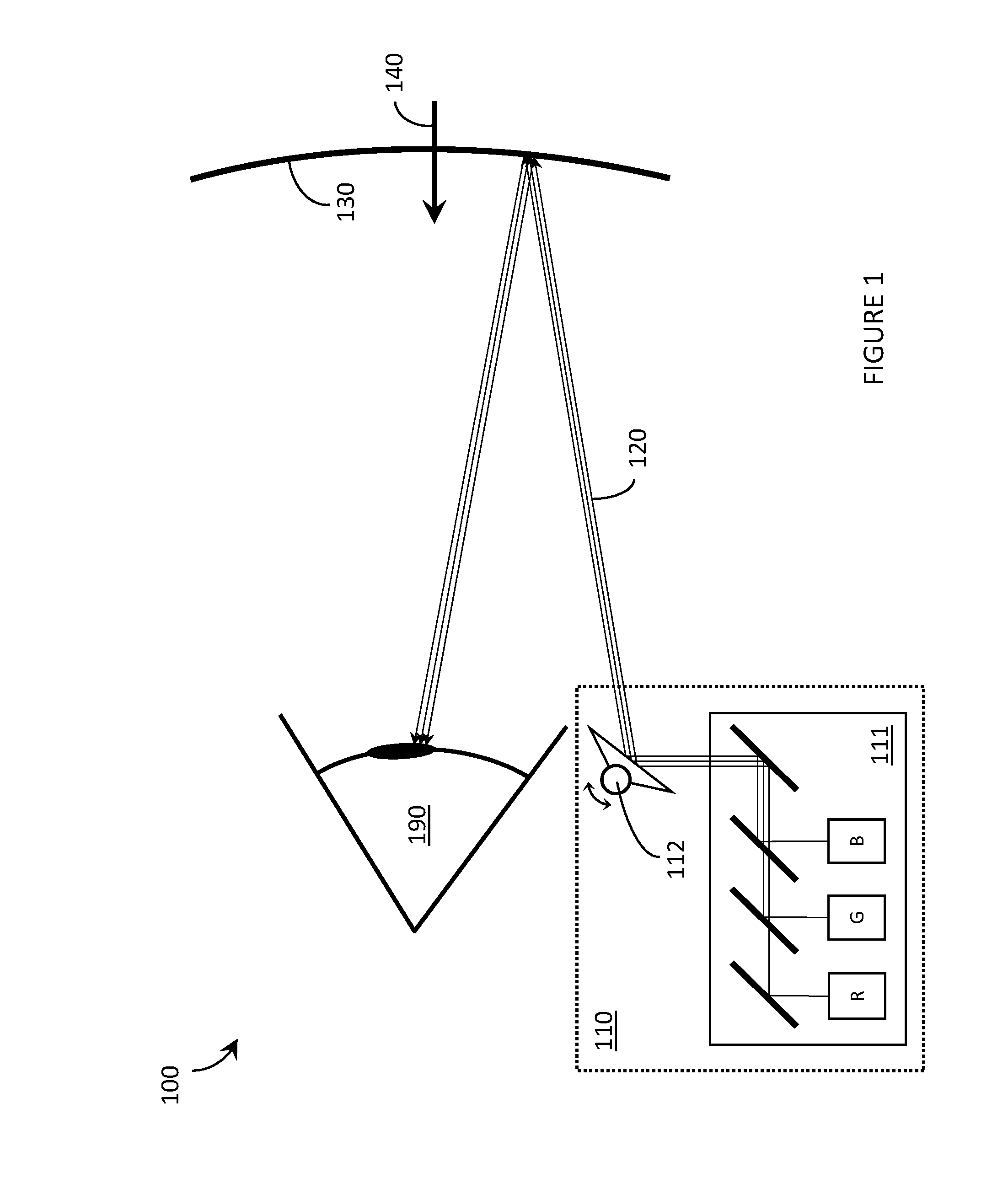
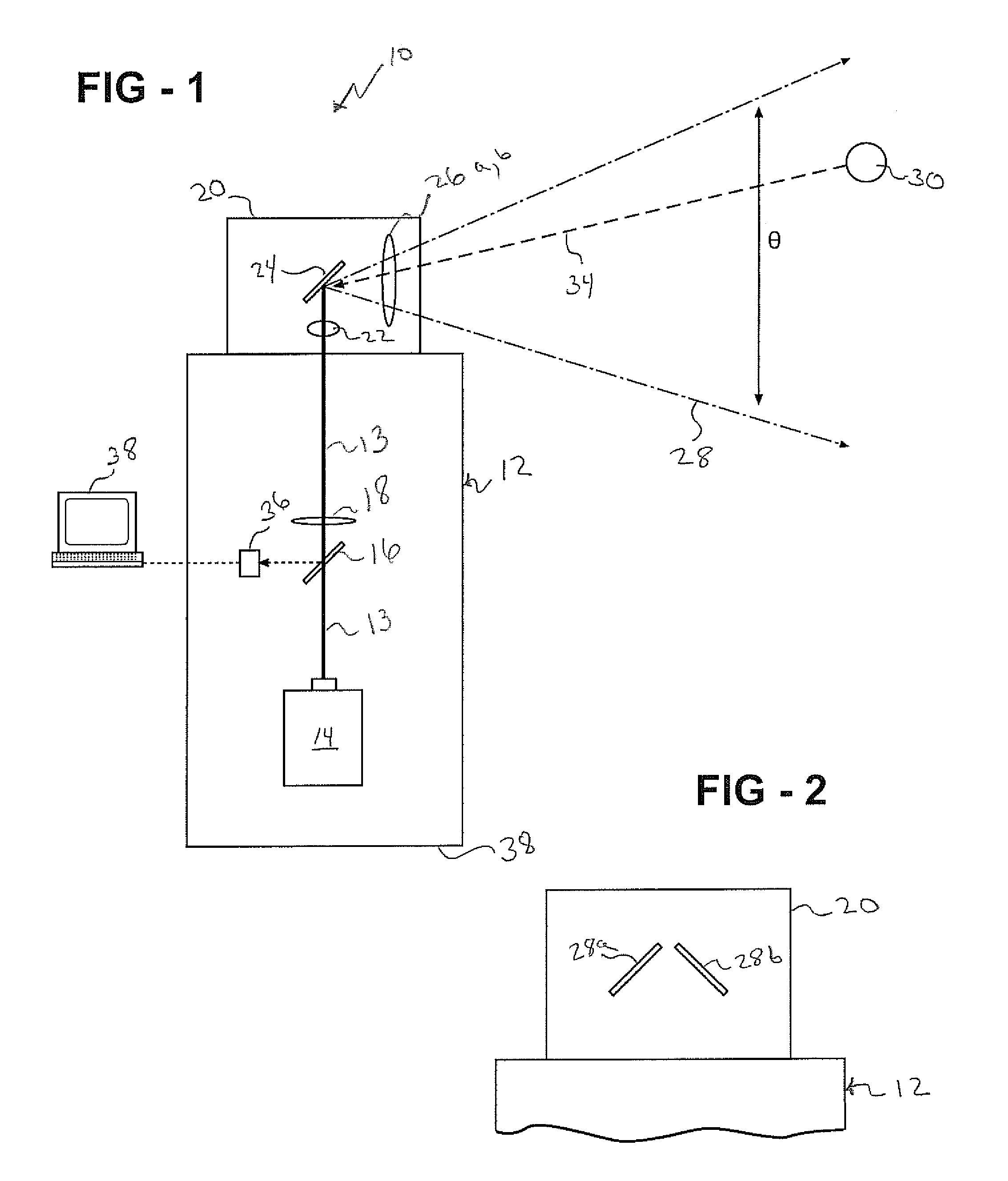
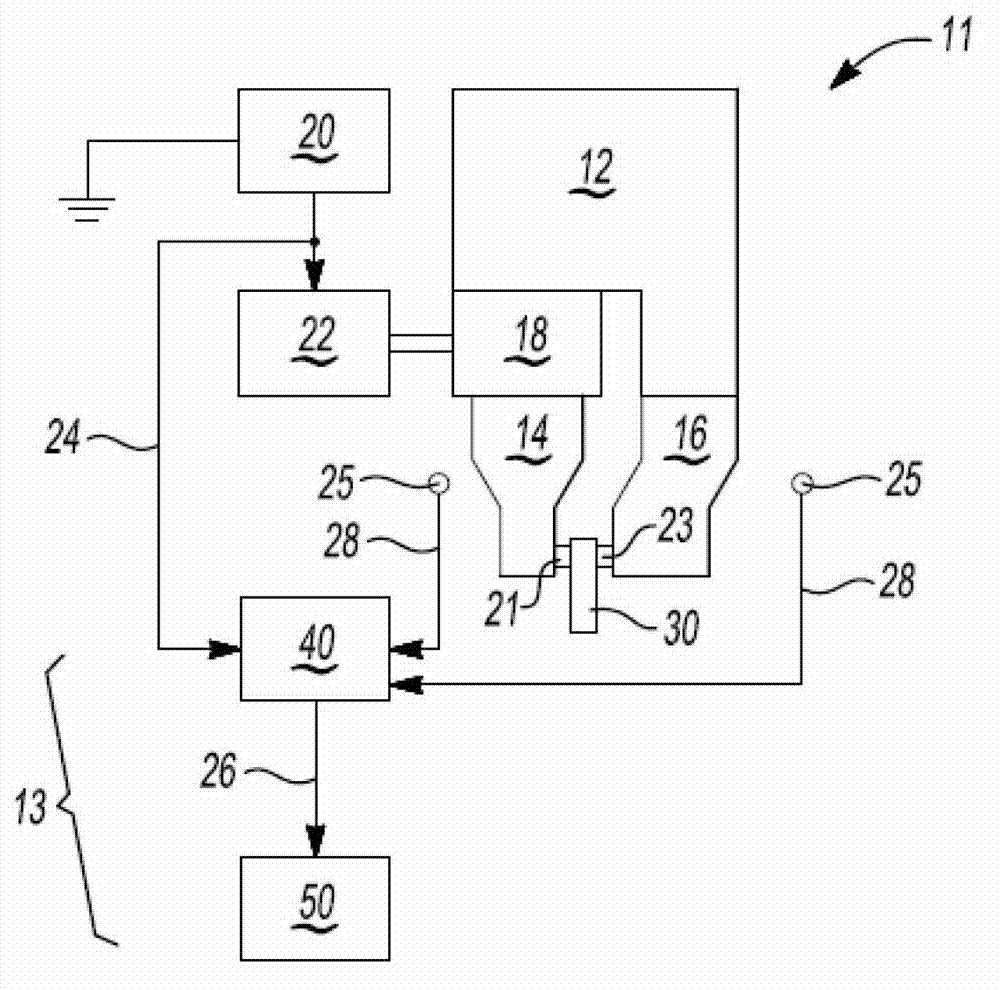
Laser projector having silhouette blanking for objects in the output light path
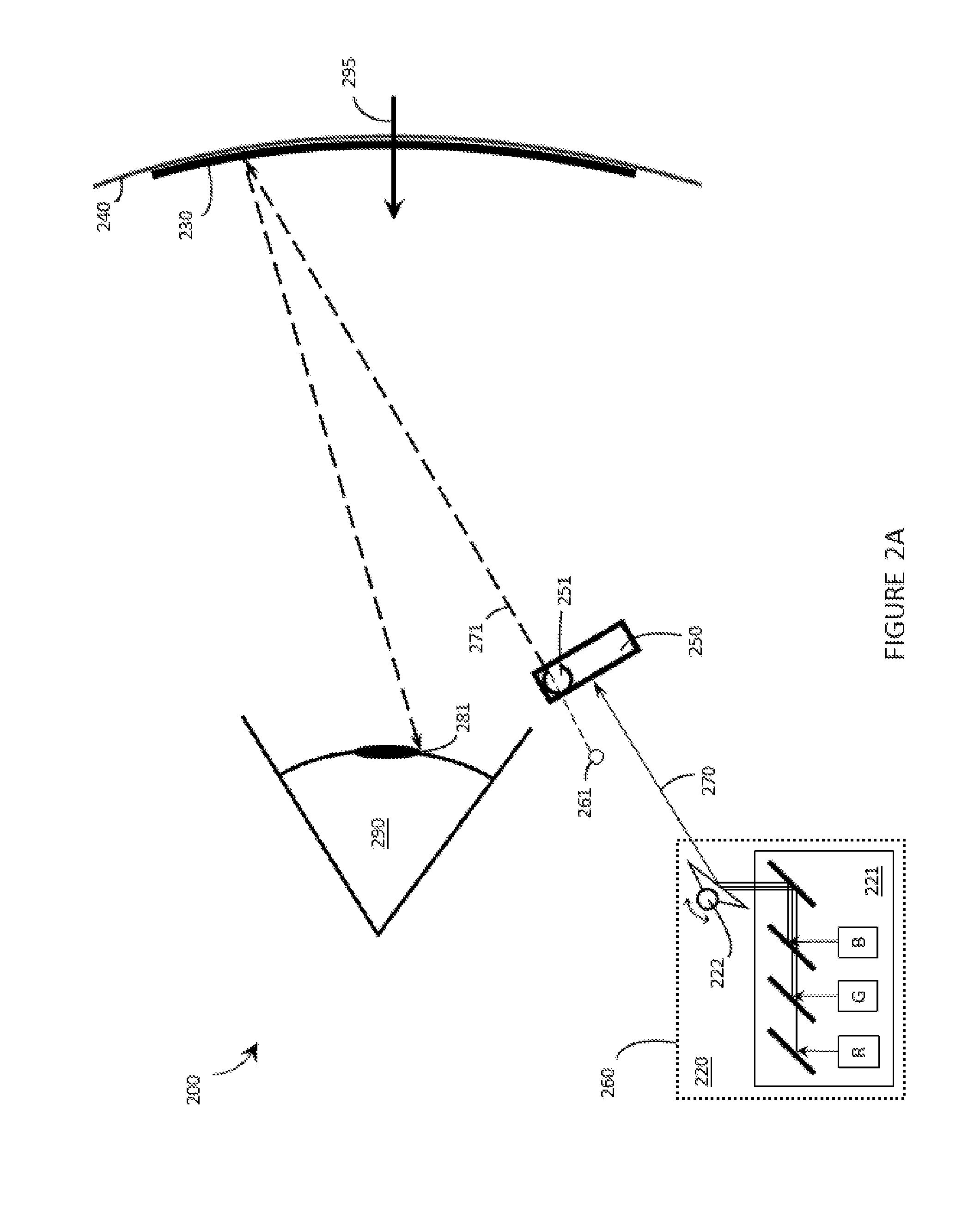
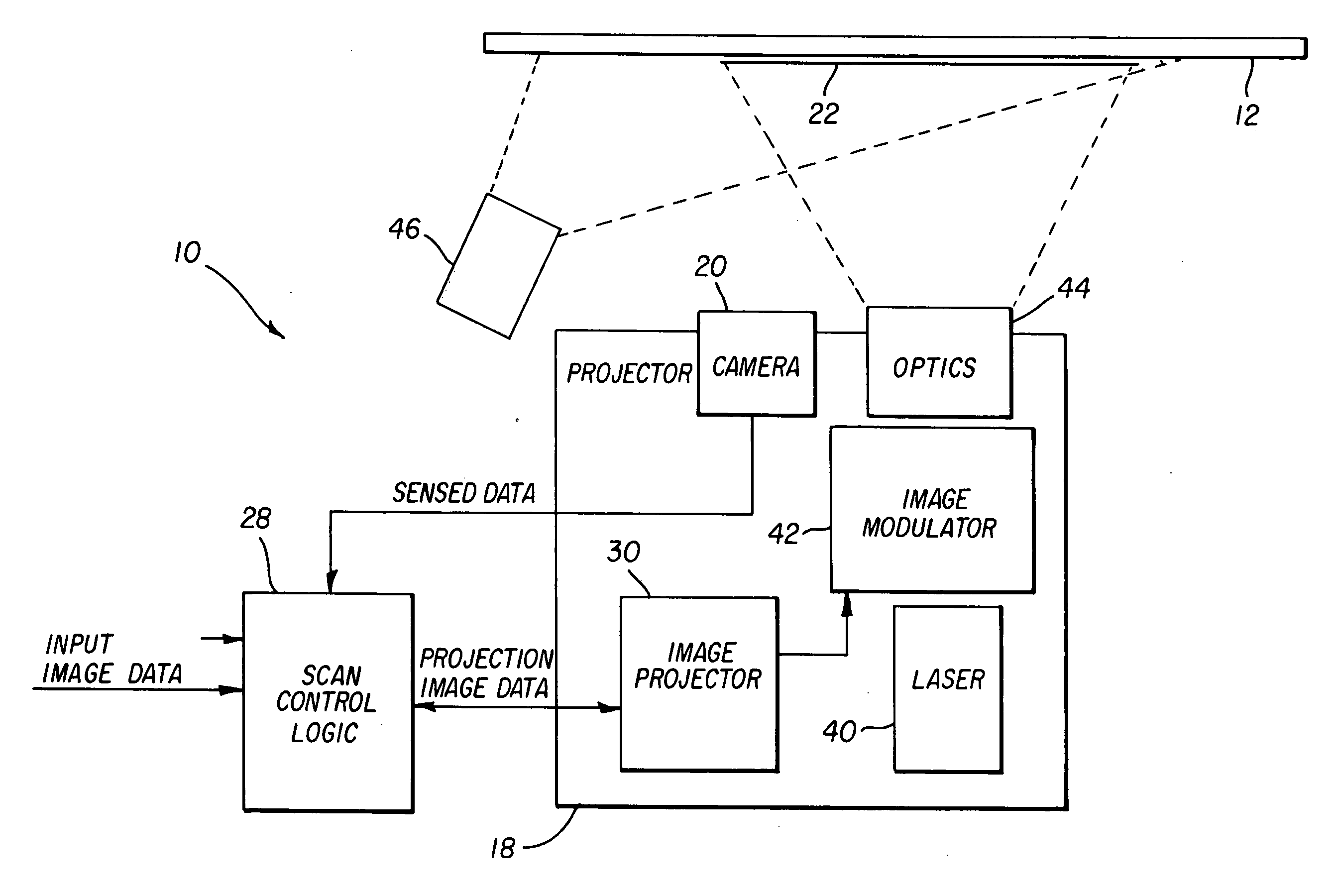
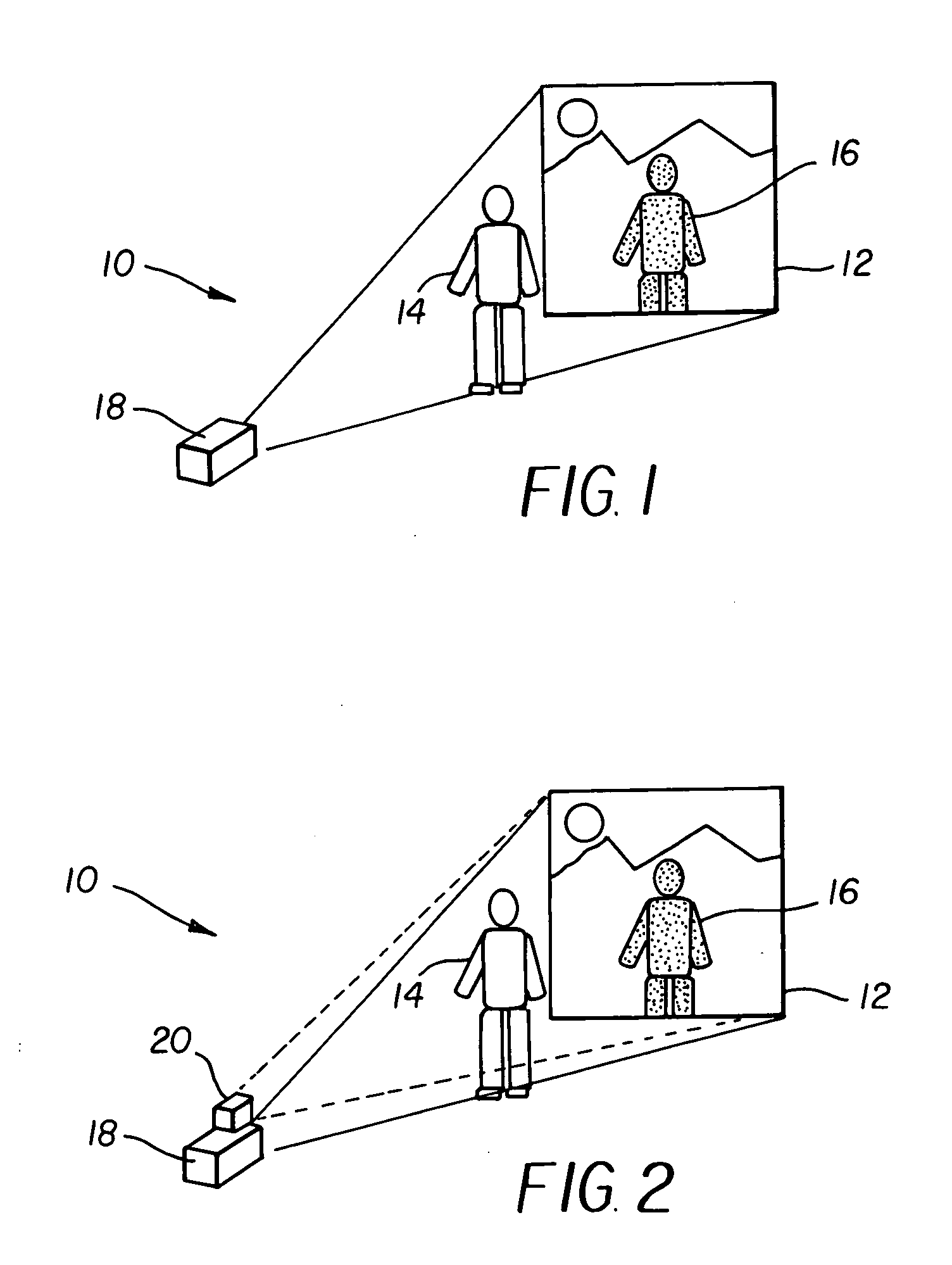
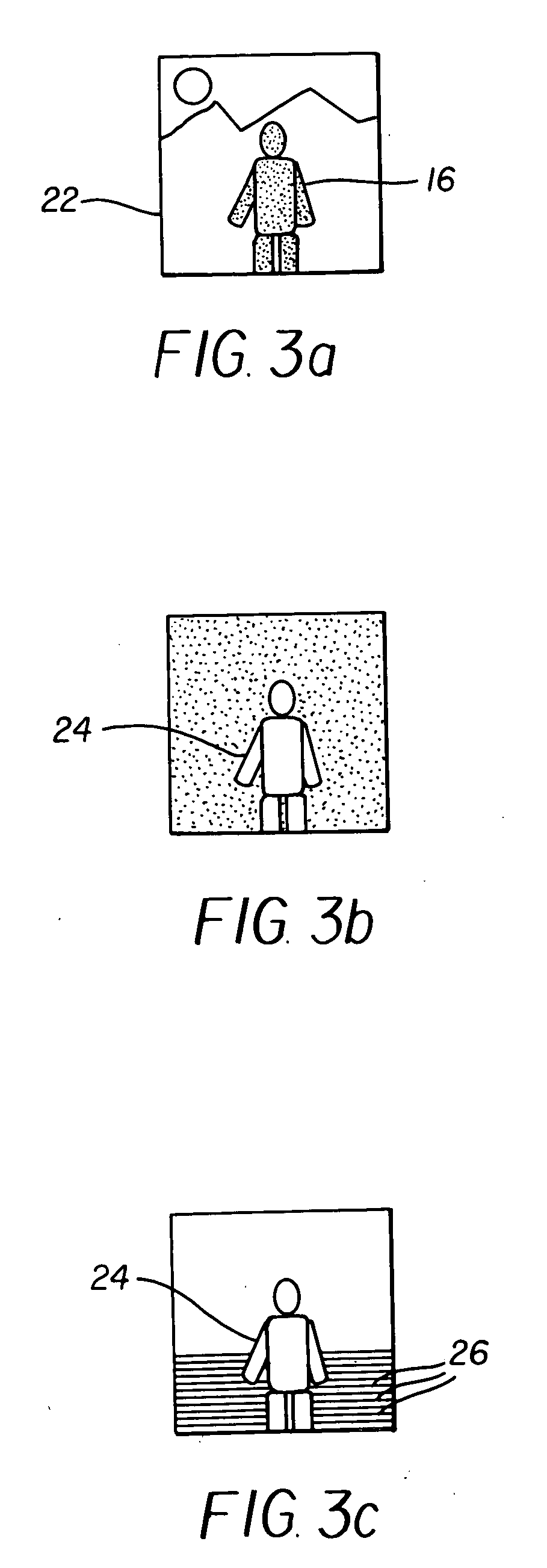
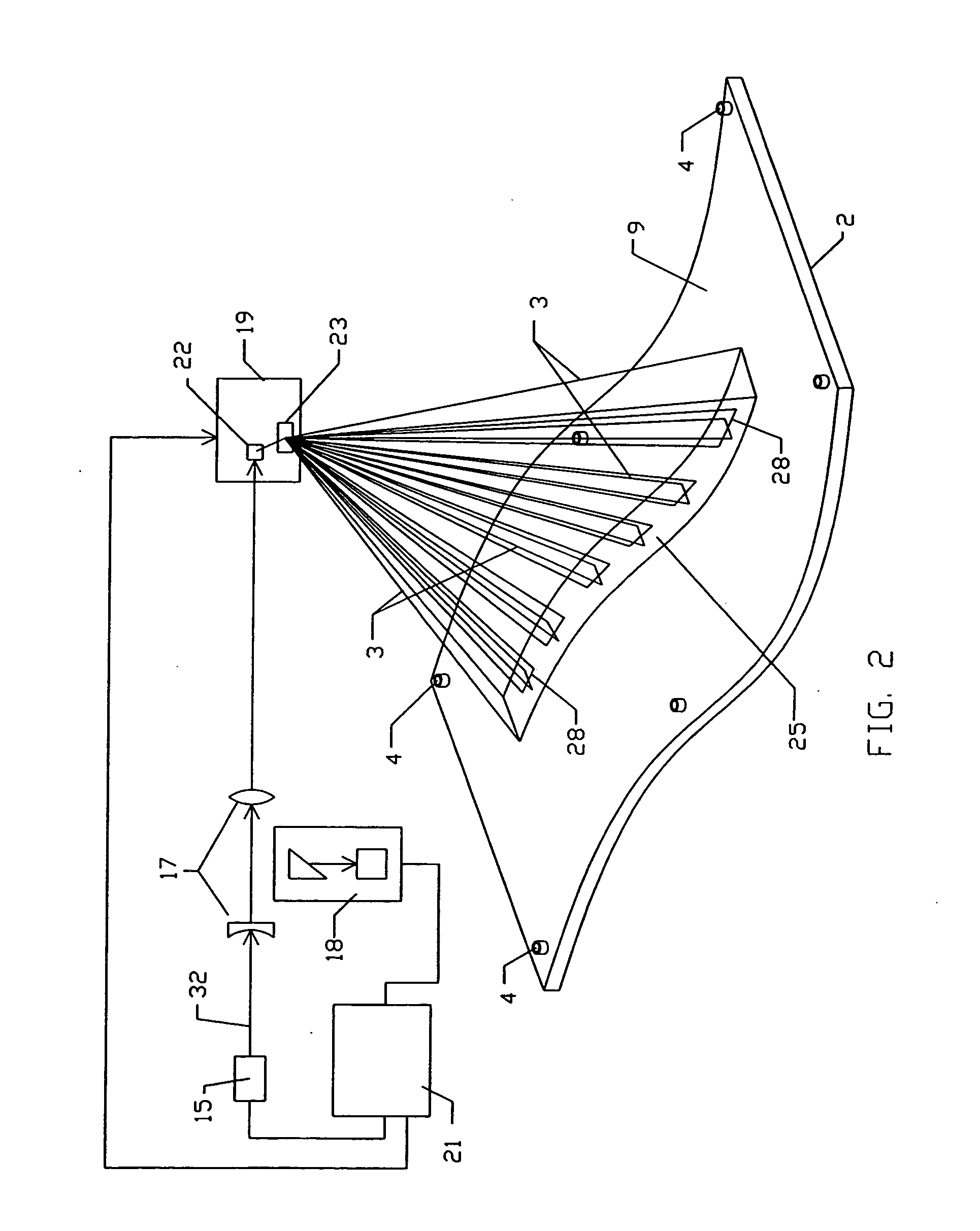
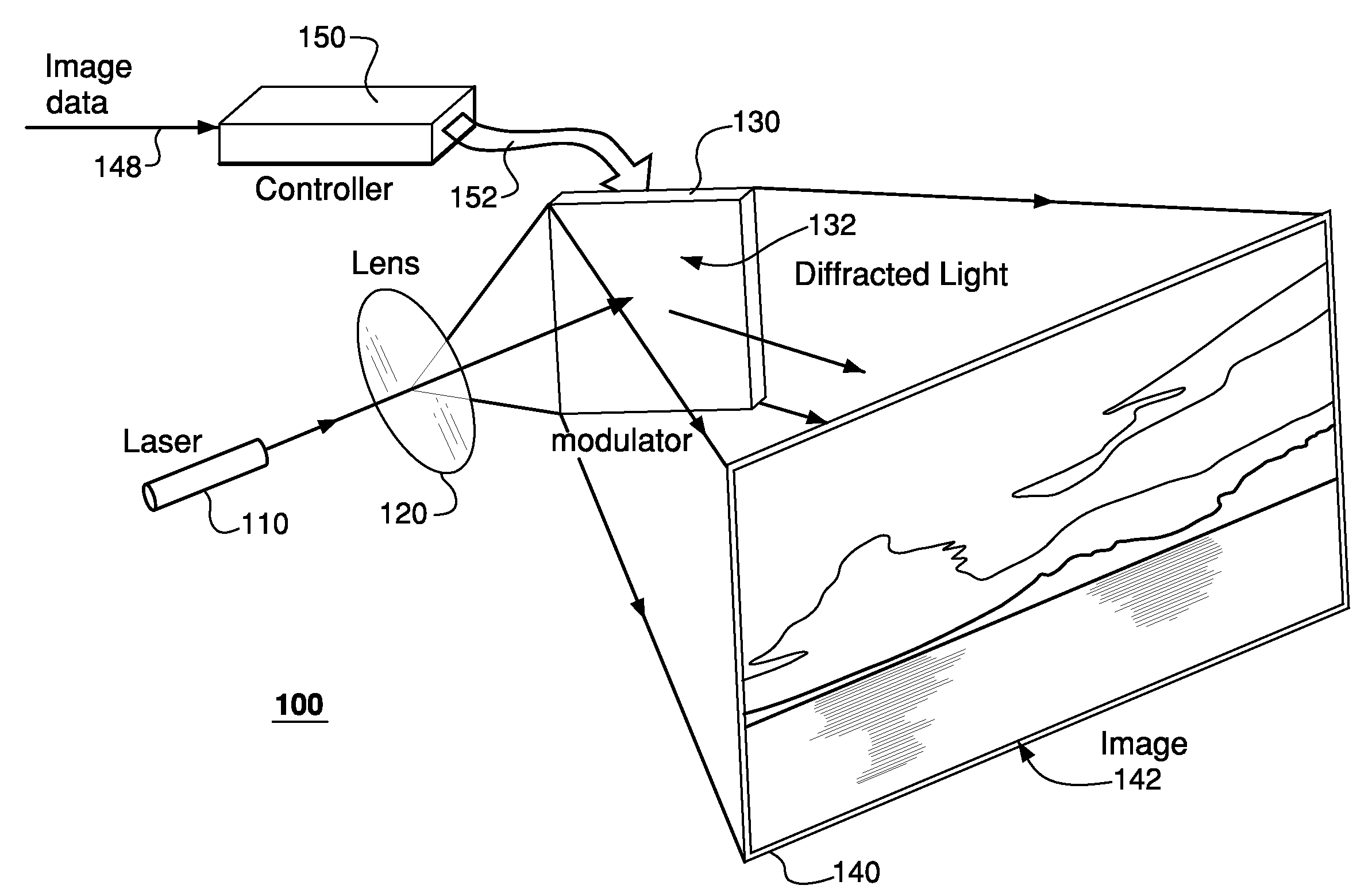
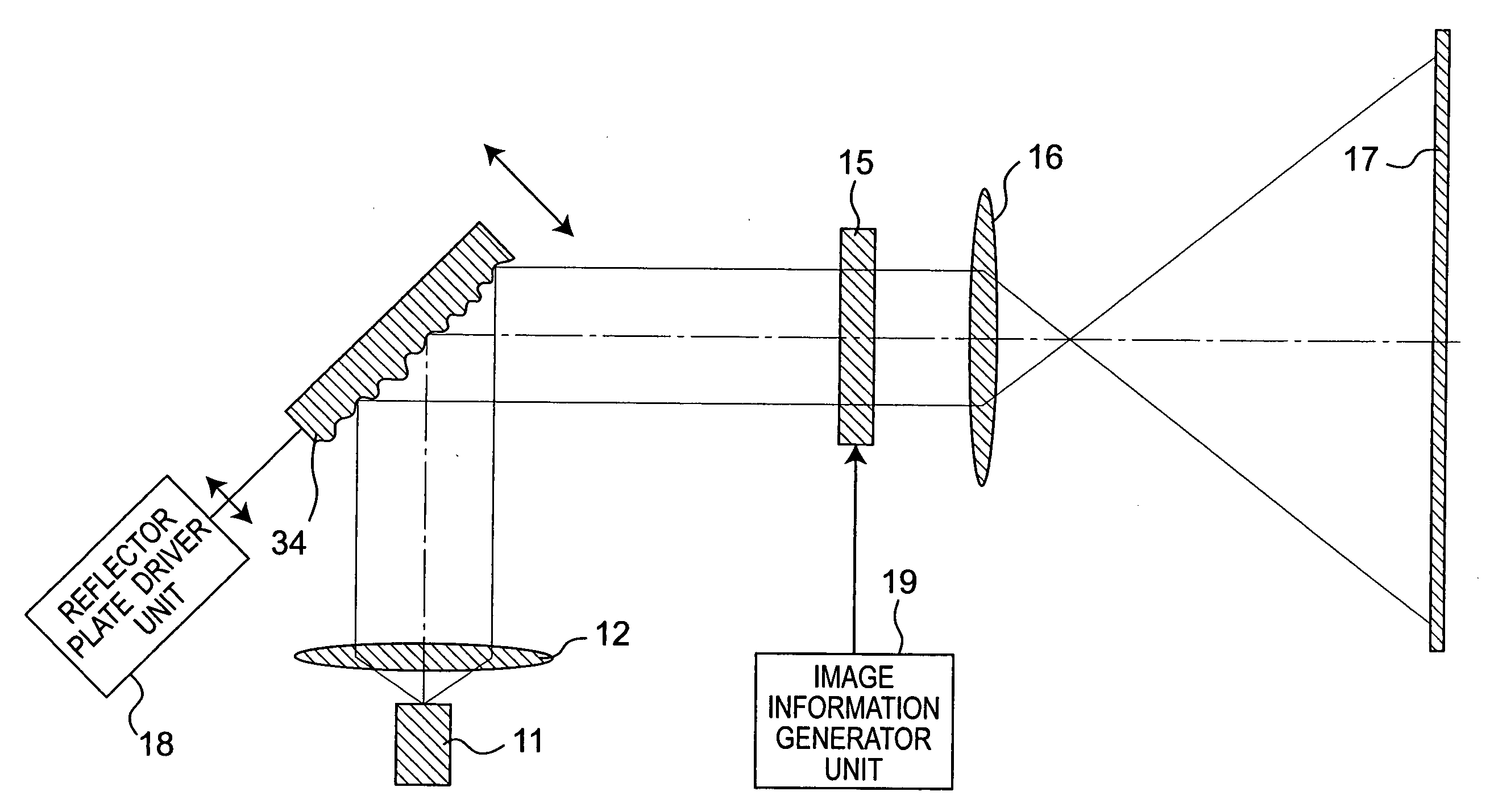
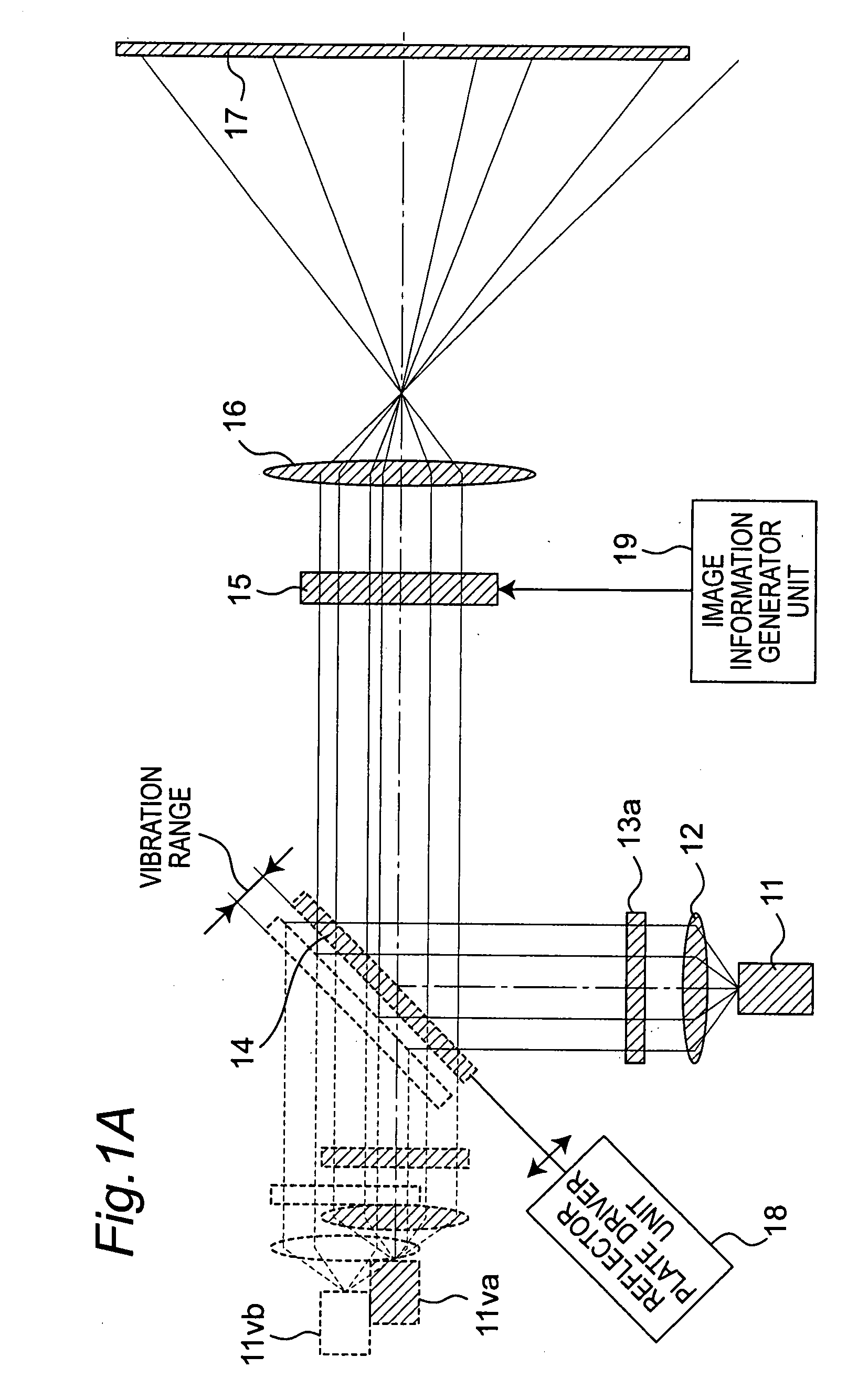
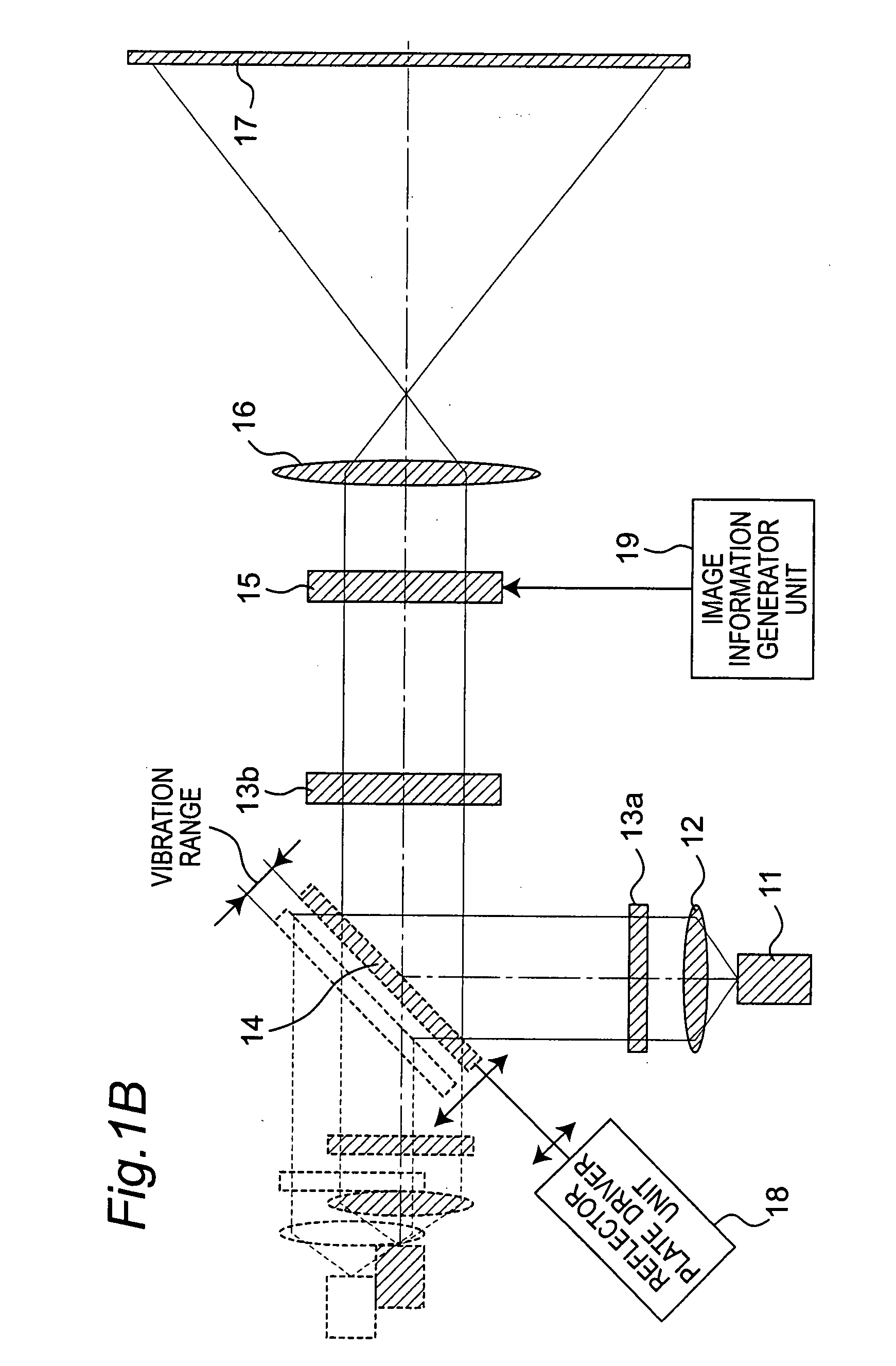
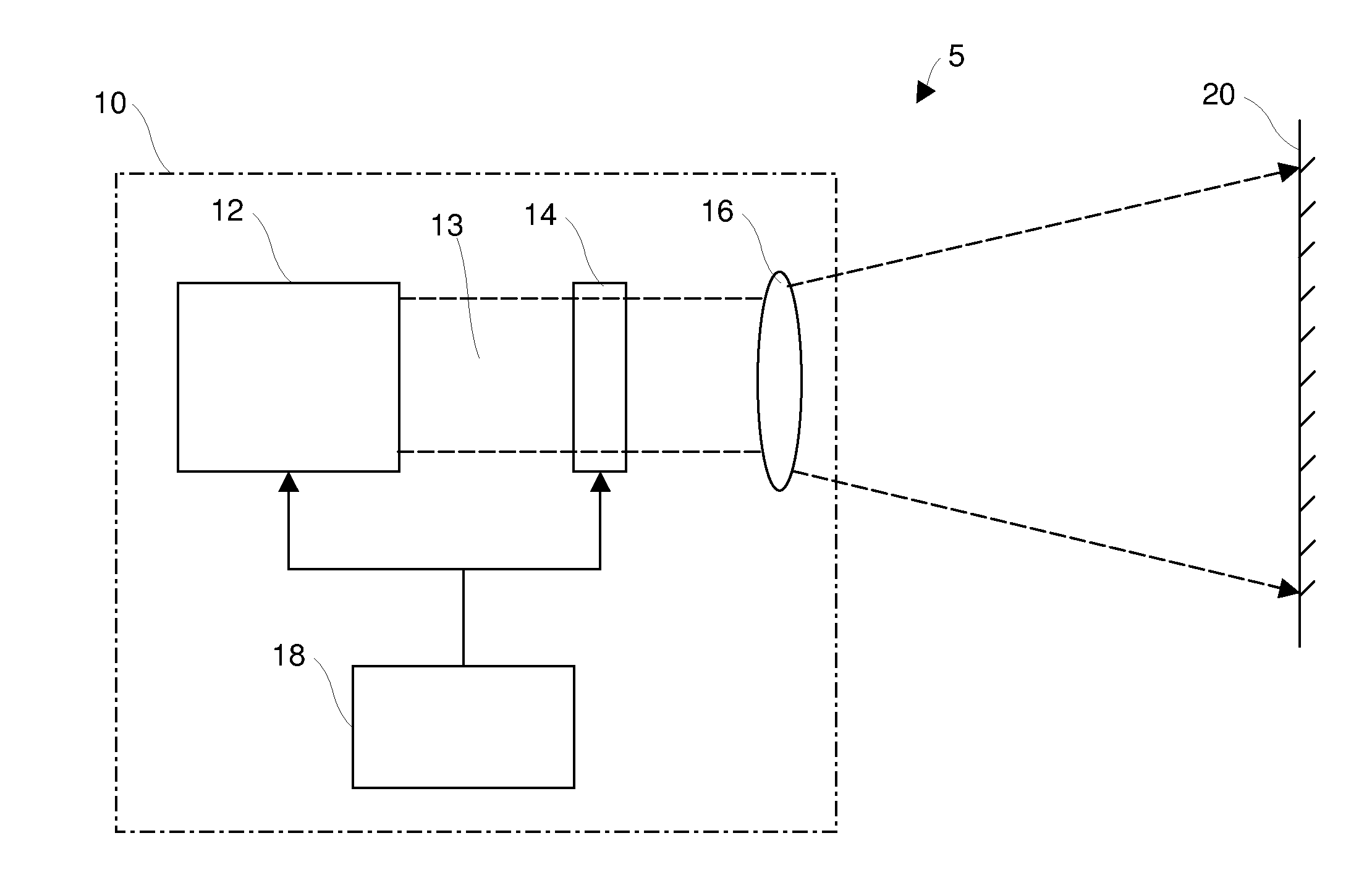
A projection apparatus (18) forms an image frame (22) on a display surface (12), where the image frame (22) is a two-dimensional array of pixels. The projection apparatus (18) has a laser (40) light source, an image modulator (42) for forming an image-bearing beam according to scanned line data, and projection optics (44) for projecting the image-bearing beam toward the display surface (12). A camera (20) obtains a sensed pixel array by sensing the two-dimensional array of pixels from the display surface (12). A control logic processor (28) compares the sensed pixel array with corresponding image data to identify any portion of the image-bearing beam that is obstructed from the display surface (12) and to disable obstructed portions of the image-bearing beam for at least one subsequent image frame (22).
Owner:IMAX THEATERS INT
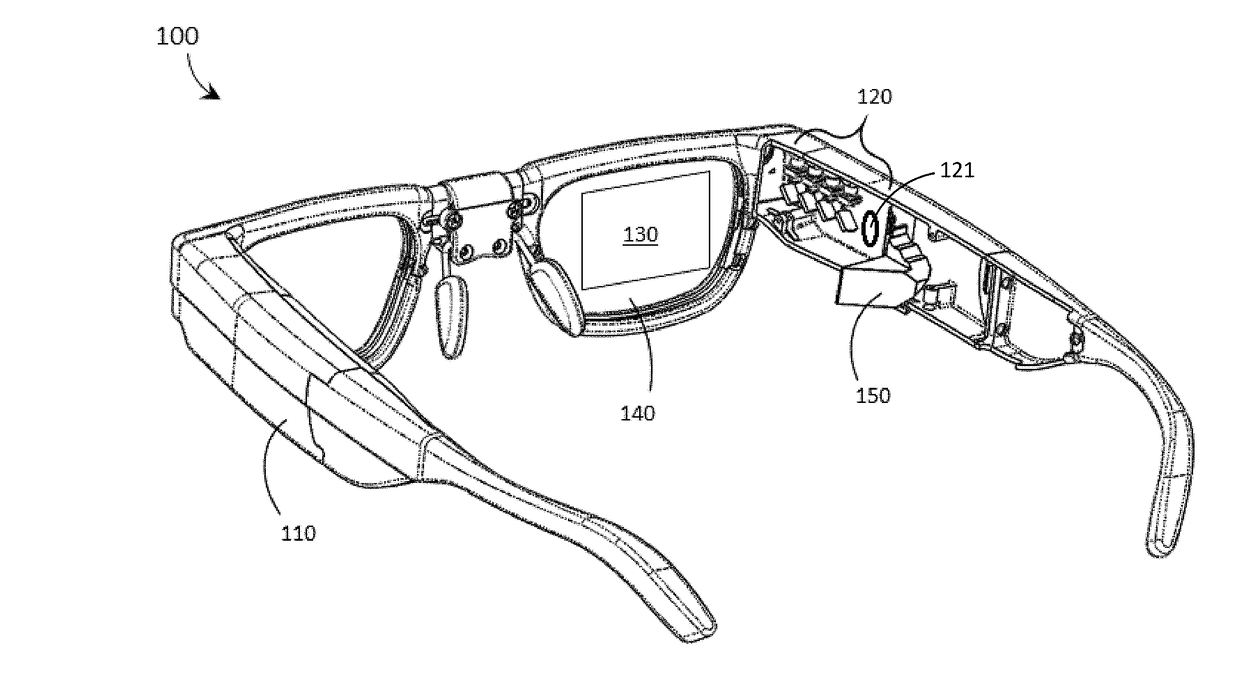
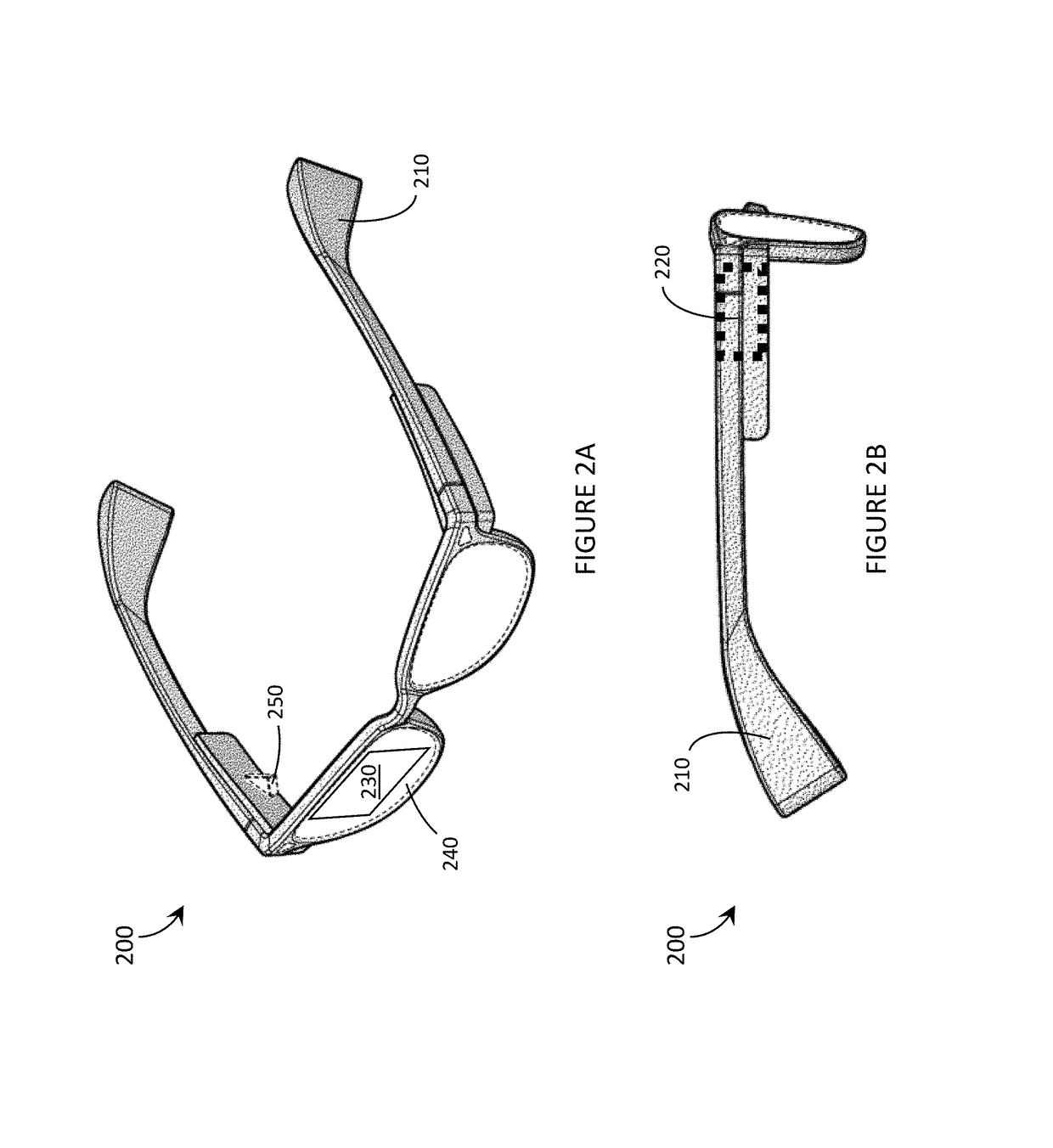
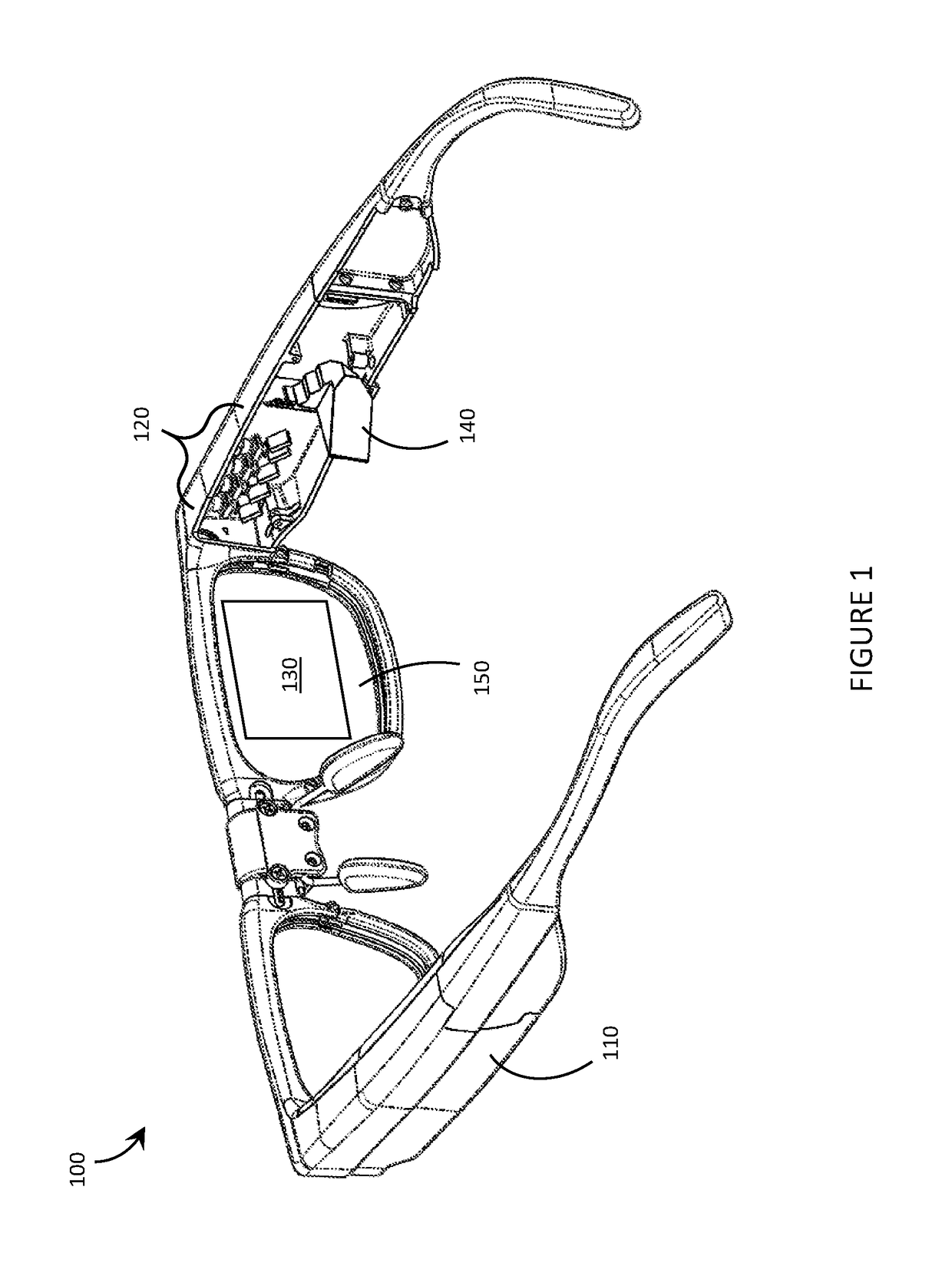
Systems, devices, and methods for eyebox expansion in wearable heads-up displays
ActiveUS20160238845A1Input/output for user-computer interactionStatic indicating devicesHead-up displayExit pupil
Systems, devices, and methods for eyebox expansion by exit pupil replication in wearable heads-up displays (“WHUDs”) are described. A WHUD includes a scanning laser projector (“SLP”), a holographic combiner, and an exit pupil selector positioned in the optical path therebetween. The exit pupil selector is controllably switchable into and between N different configurations. In each of the N configurations, the exit pupil selector receives a light signal from the SLP and redirects the light signal towards the holographic combiner effectively from a respective one of N virtual positions for the SLP. The holographic combiner converges the light signal to a particular one of N exit pupils at the eye of the user based on the particular virtual position from which the light signal is made to effectively originate. In this way, multiple instances of the exit pupil are distributed over the eye and the eyebox of the WHUD is expanded.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
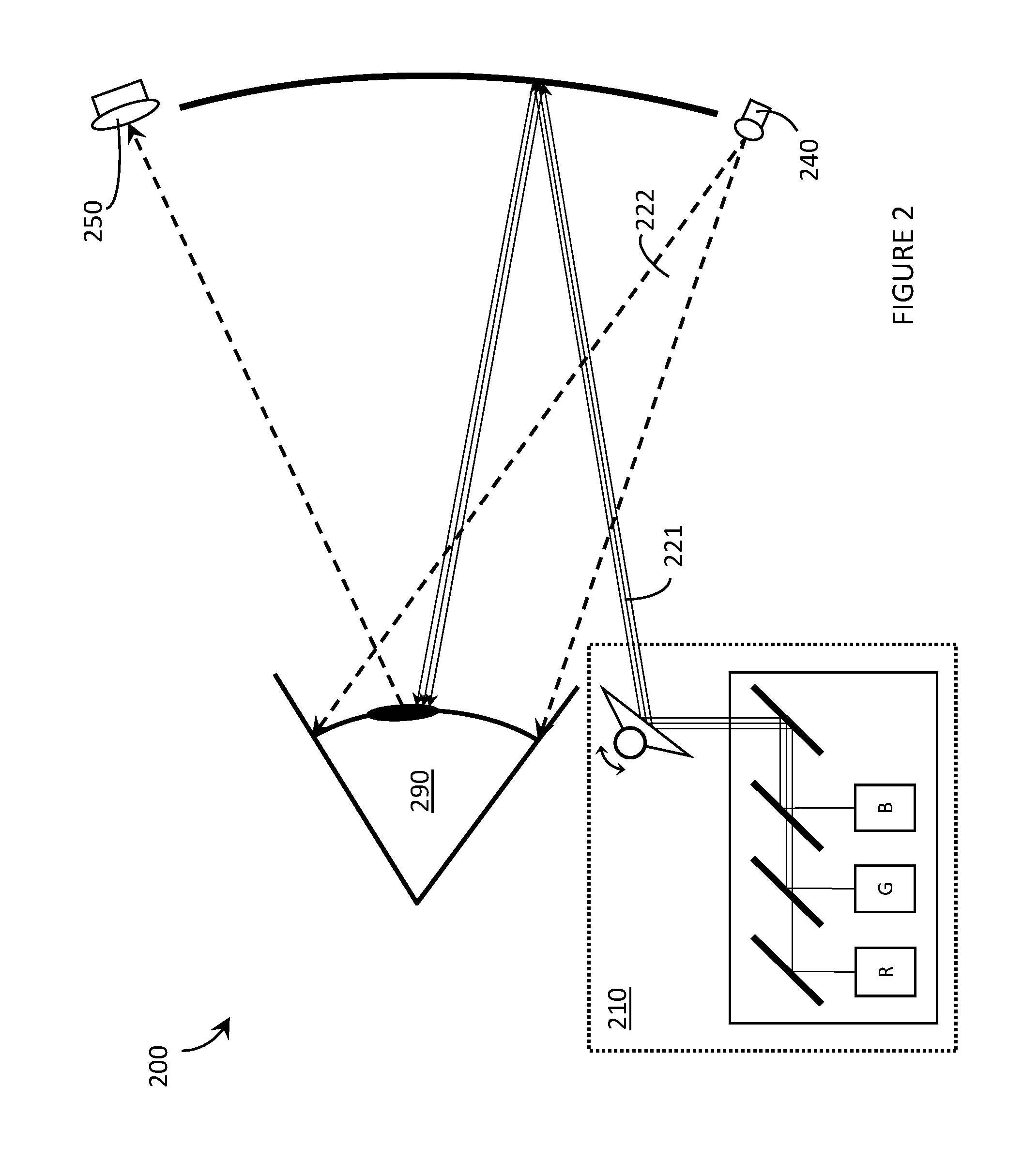
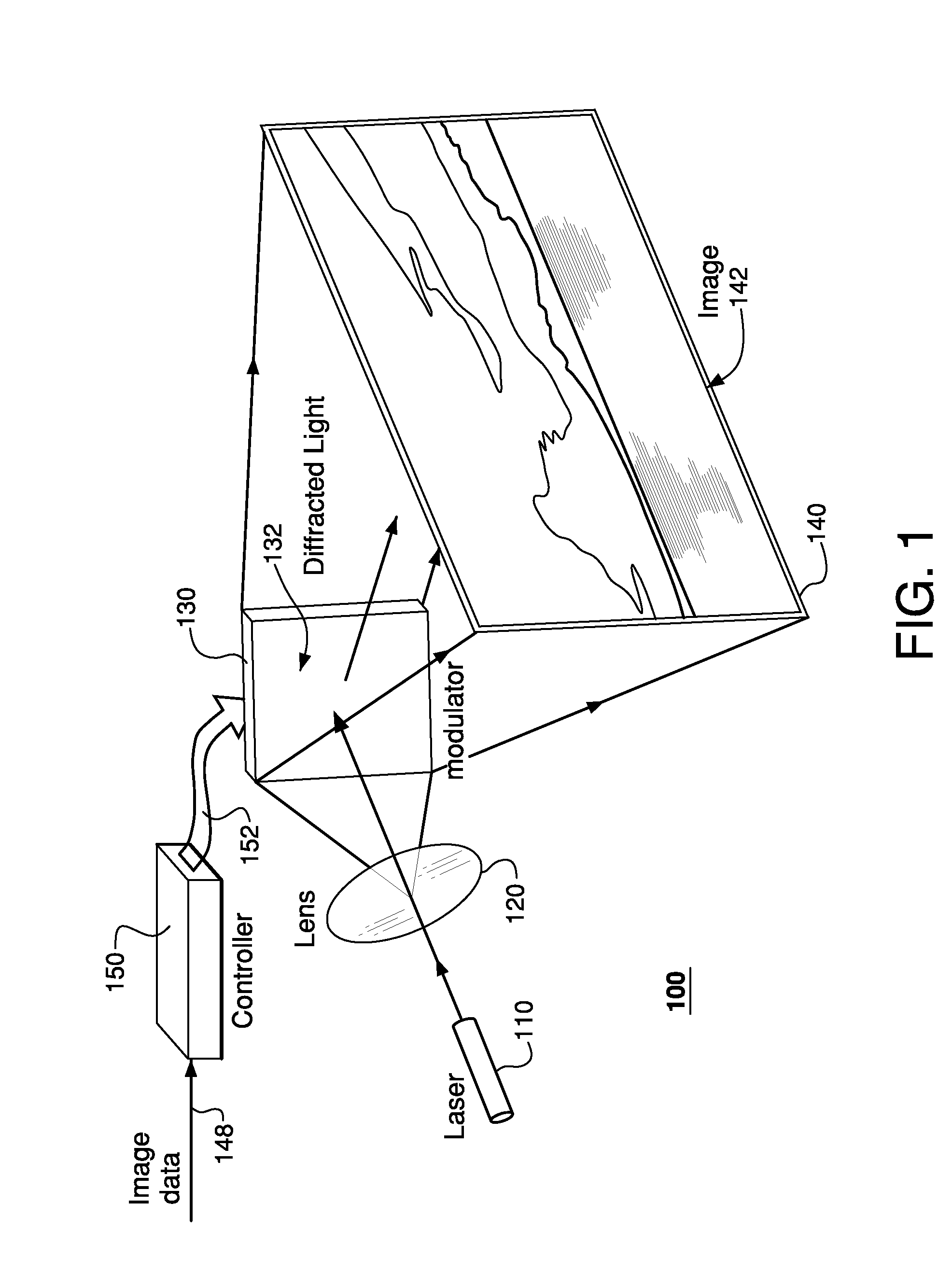
Laser projector having silhouette blanking for objects in the output light path
A projection apparatus (18) forms an image frame (22) on a display surface (12), where the image frame (22) is a two-dimensional array of pixels. The projection apparatus (18) has a laser (40) light source, an image modulator (42) for forming an image-bearing beam according to scanned line data, and projection optics (44) for projecting the image-bearing beam toward the display surface (12). A camera (20) obtains a sensed pixel array by sensing the two-dimensional array of pixels from the display surface (12). A control logic processor (28) compares the sensed pixel array with corresponding image data to identify any portion of the image-bearing beam that is obstructed from the display surface (12) and to disable obstructed portions of the image-bearing beam for at least one subsequent image frame (22).
Owner:IMAX THEATERS INT
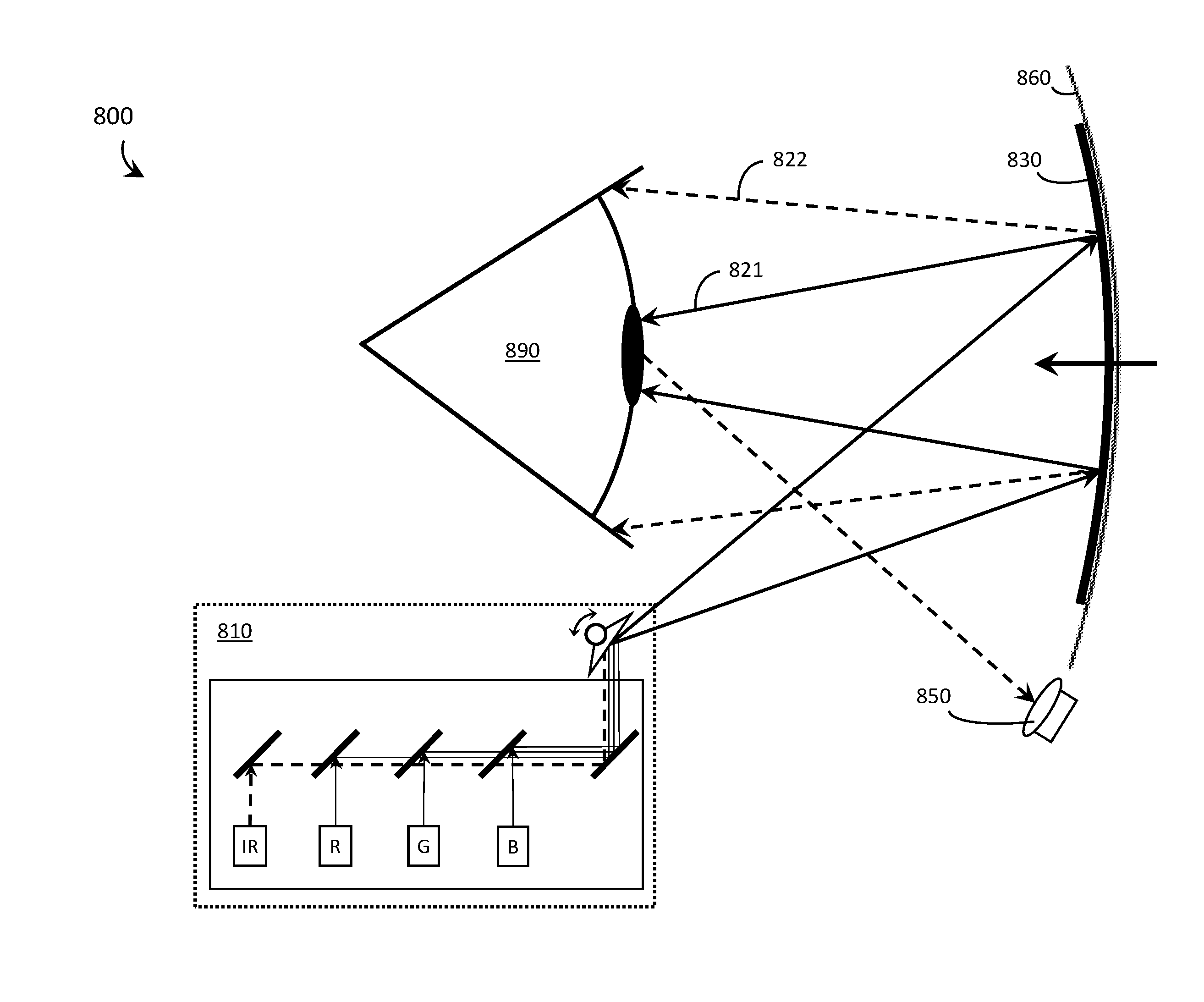
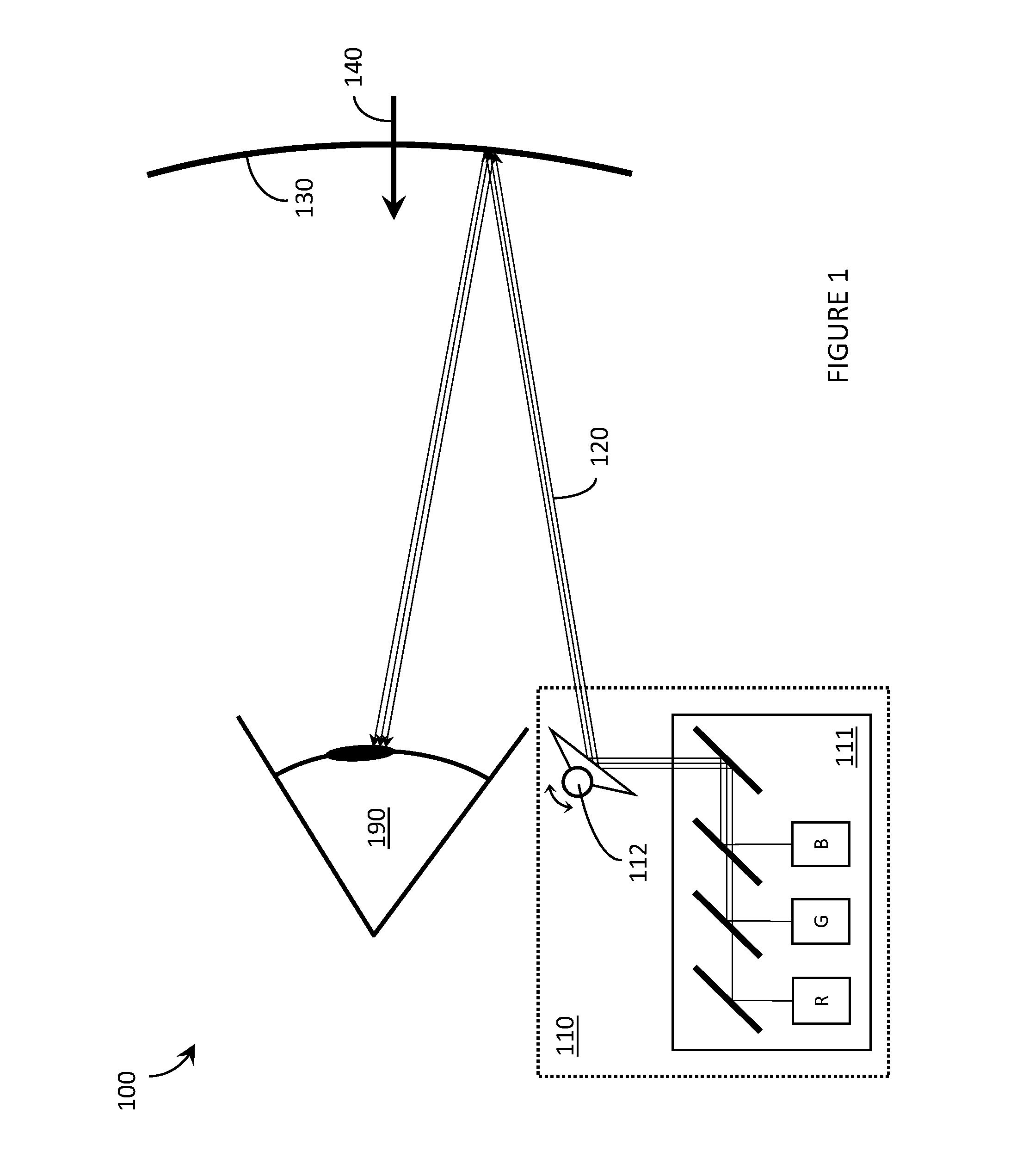
Systems, devices, and methods that integrate eye tracking and scanning laser projection in wearable heads-up displays
ActiveUS20160349514A1Picture reproducers using projection devicesInput/output processes for data processingHead-up displayPhotodetector
Systems, devices, and methods that integrate eye tracking capability into scanning laser projector (“SLP”)-based wearable heads-up displays are described. An infrared laser diode is added to an RGB SLP and an infrared photodetector is aligned to detect reflections of the infrared light from features of the eye. A holographic optical element (“HOE”) may be used to combine visible light, infrared light, and environmental light into the user's “field of view.” The HOE may be heterogeneous and multiplexed to apply positive optical power to the visible light and zero or negative optical power to the infrared light.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Systems, devices, and methods that integrate eye tracking and scanning laser projection in wearable heads-up displays
ActiveUS20160349516A1Color television detailsInput/output processes for data processingHead-up displayMultiplexing
Systems, devices, and methods that integrate eye tracking capability into scanning laser projector (“SLP”)-based wearable heads-up displays are described. An infrared laser diode is added to an RGB SLP and an infrared photodetector is aligned to detect reflections of the infrared light from features of the eye. A holographic optical element (“HOE”) may be used to combine visible light, infrared light, and environmental light into the user's “field of view.” The HOE may be heterogeneous and multiplexed to apply positive optical power to the visible light and zero or negative optical power to the infrared light.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
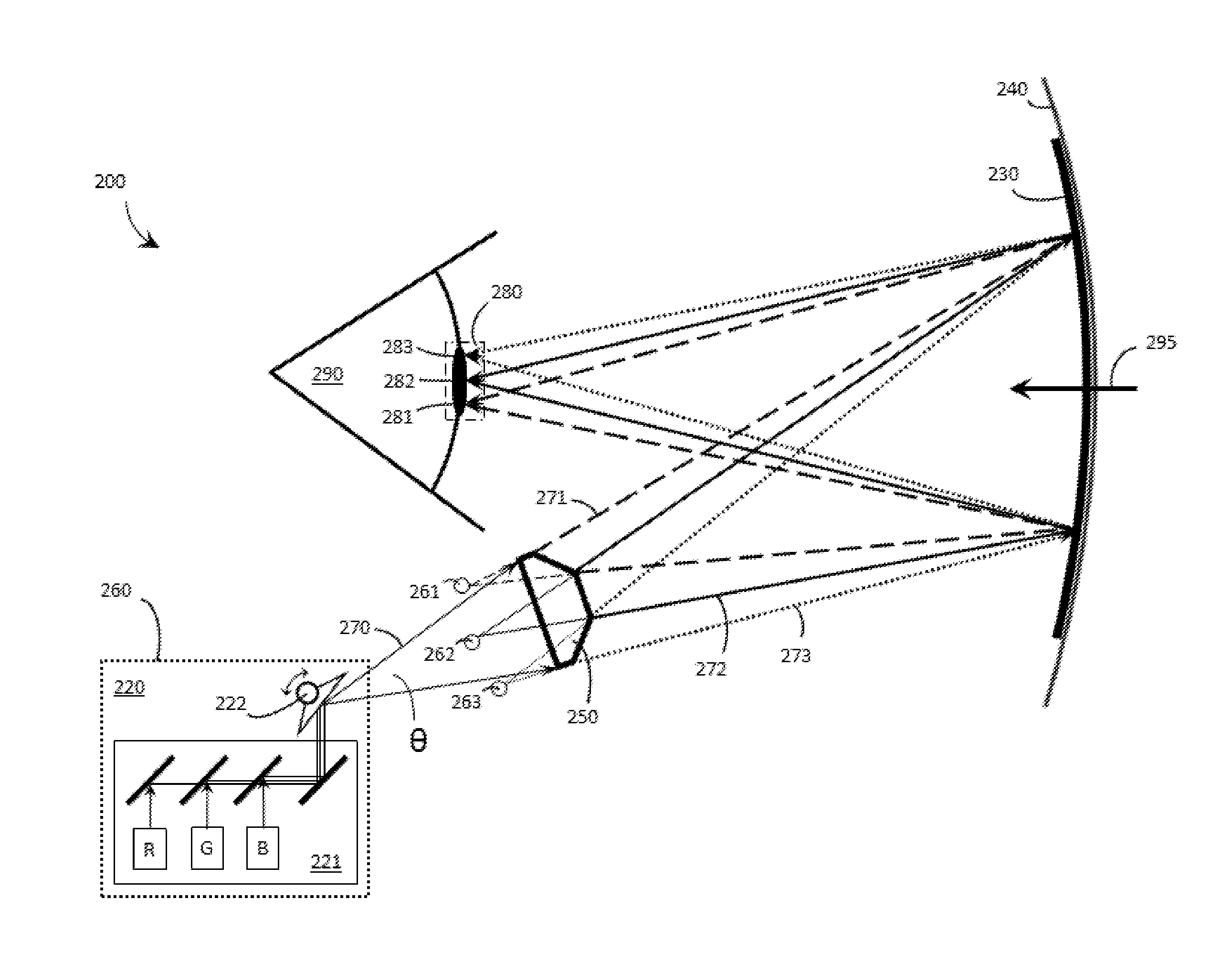
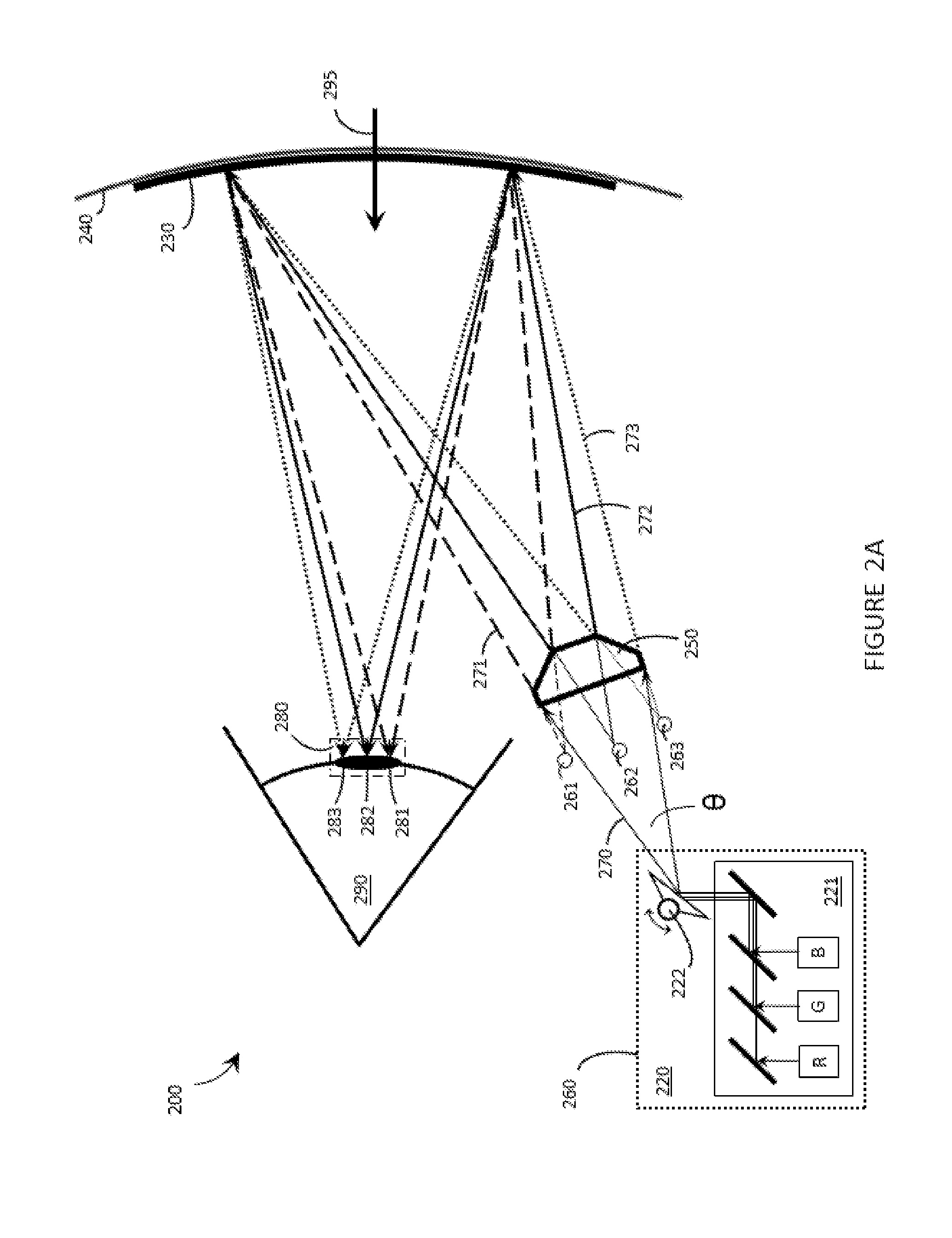
Systems, devices, and methods for focusing laser projectors
ActiveUS20170299956A1Reduce disagreementSemiconductor laser arrangementsNon-optical adjunctsHead-up displayLaser light
Systems, devices, and methods for focusing laser projectors are described. A laser projector includes N≧1 laser diodes, each of which emits laser light having a divergence. Each laser diode is paired with a respective primary or collimation lens to at least reduce a divergence of the laser light that the laser diode produces. Downstream from the primary lens(es) in the optical path(s) of the laser light, a single dedicated secondary or convergence lens converges the laser light to a focus. By initiating the convergence of the laser light at the secondary or convergence lens as opposed to at the primary or collimation lens(es), numerous benefits that are particularly advantageous in laser projection-based wearable heads-up displays are realized.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
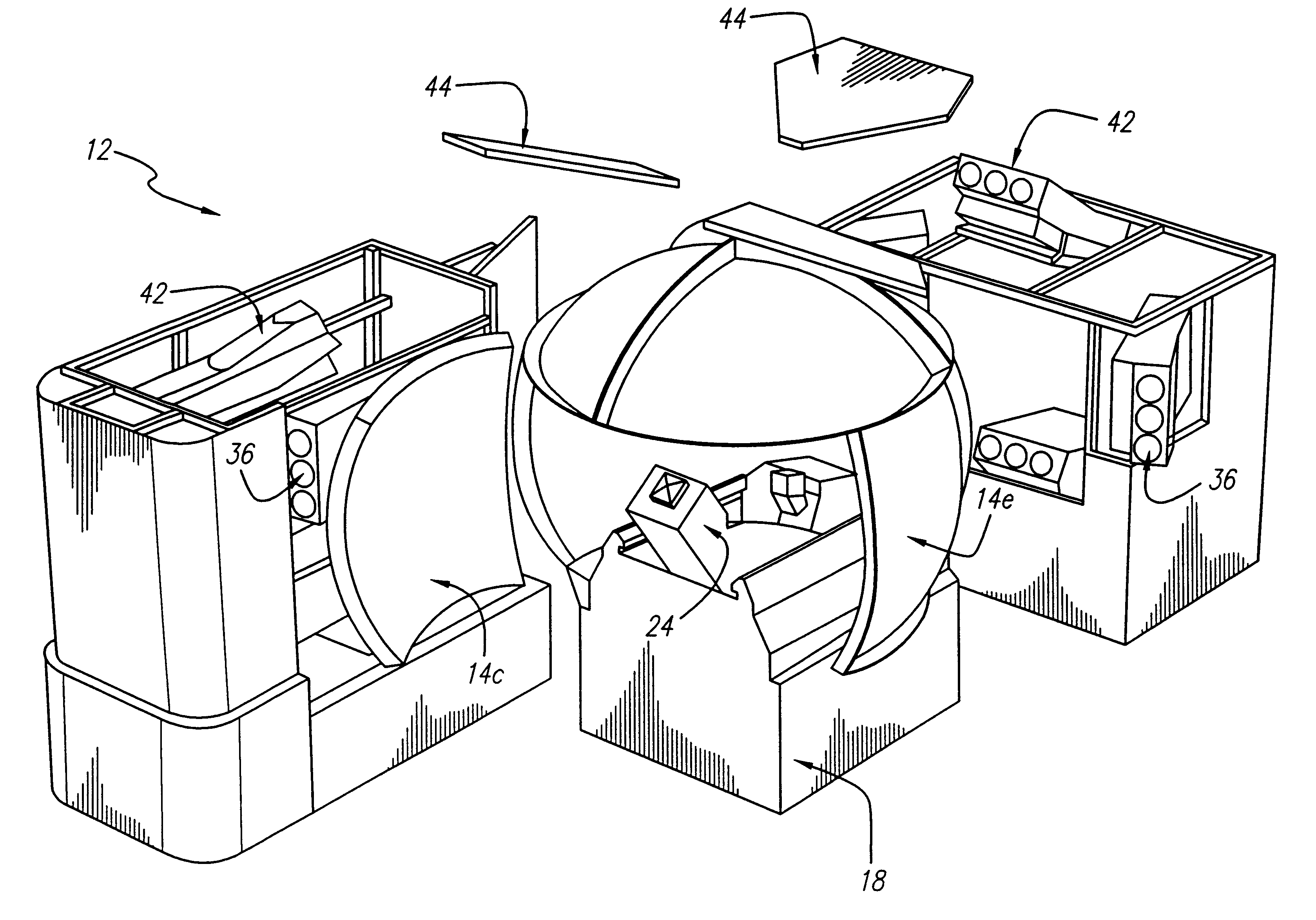
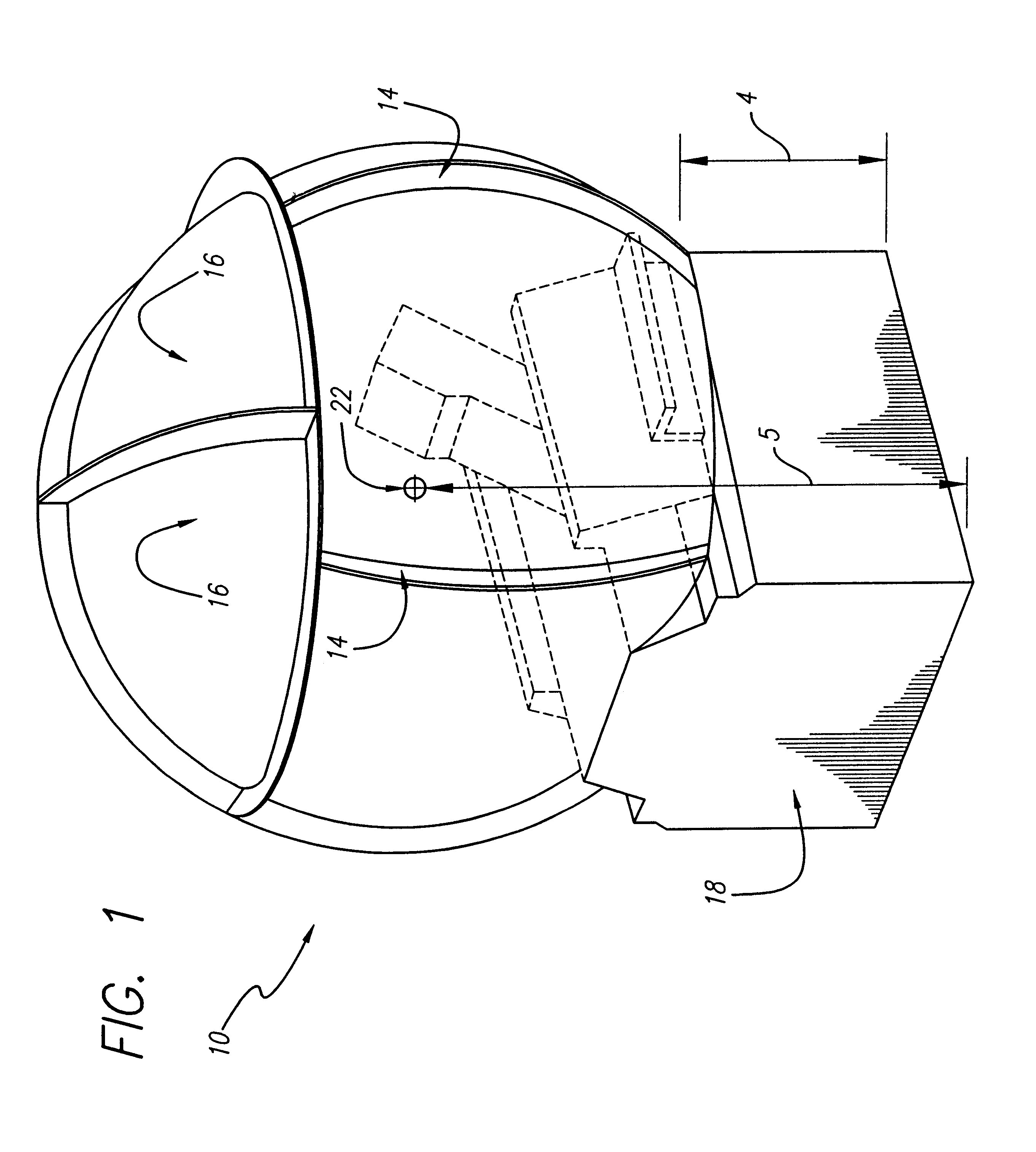
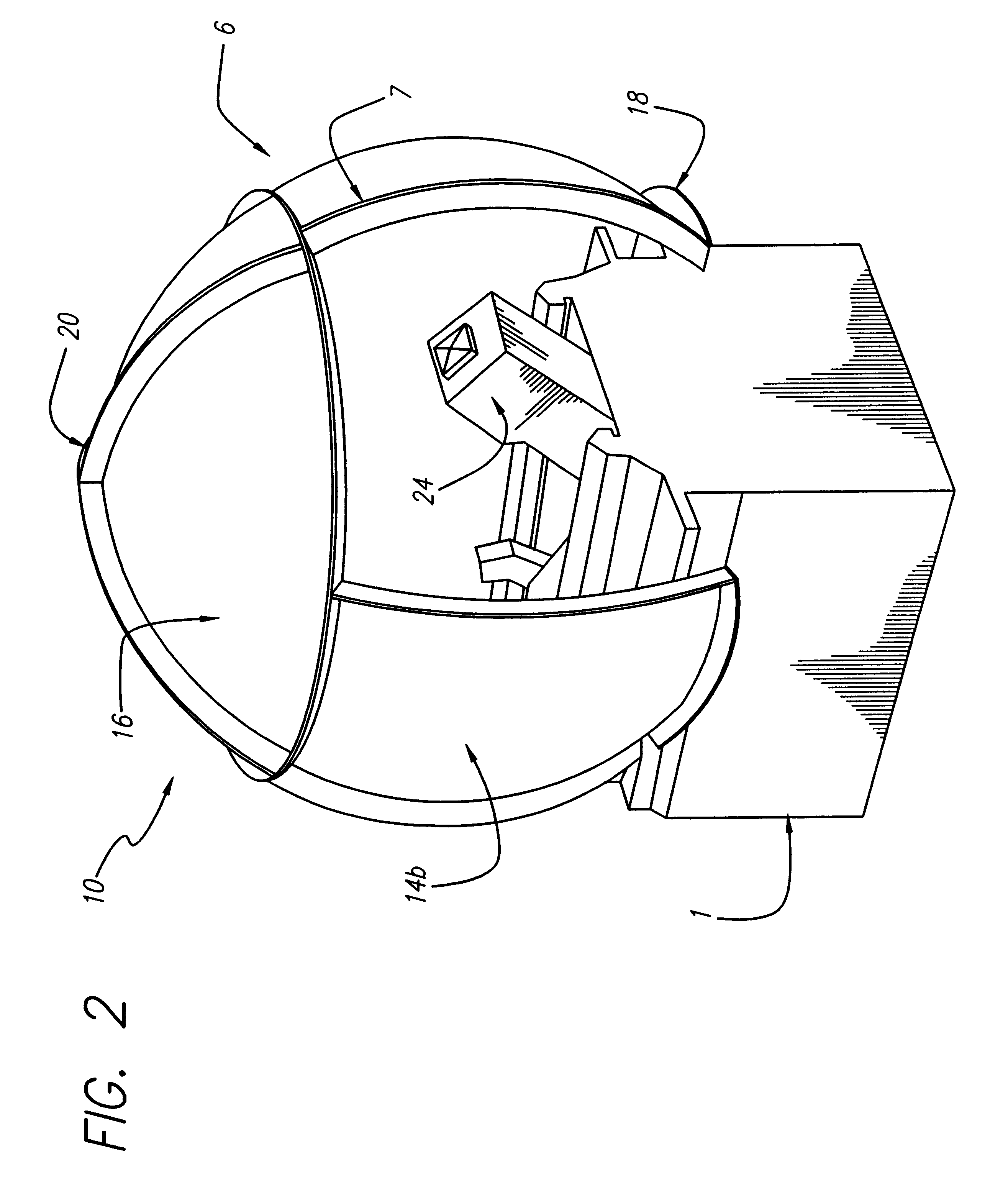
Curved surface, real image dome display system, using laser-based rear projection
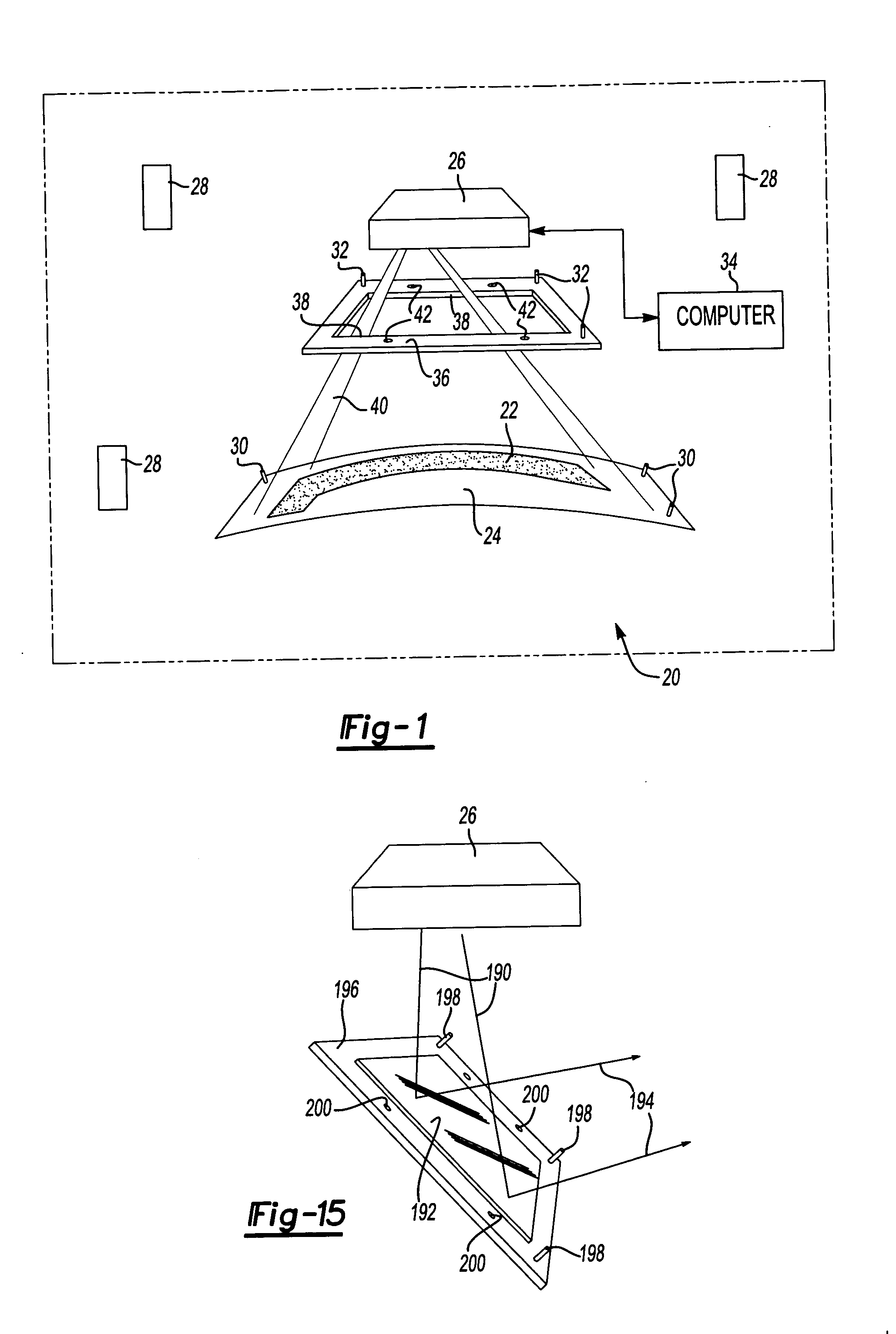
The present invention is related to a curved surface, real image, laser-based rear projection display system. A plurality of translucent panel members are assembled into a spherical dome assembly. The panels have concave inner surfaces treated with an optical medium to create a diffusion surface onto which the projected visual image is displayed to a design eye point located within the dome. The laser-based projectors have a greatly expanded focal range as compared to conventional sources of illumination. This allows the curved panel members to remain in focus when the dome is moved as much as two (2) relative to the location of the laser projector.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
3D projection with image recording
ActiveUS6935748B2Increase refresh rateSolve the lack of densityProjectorsCharacter and pattern recognitionLight energyLaser light
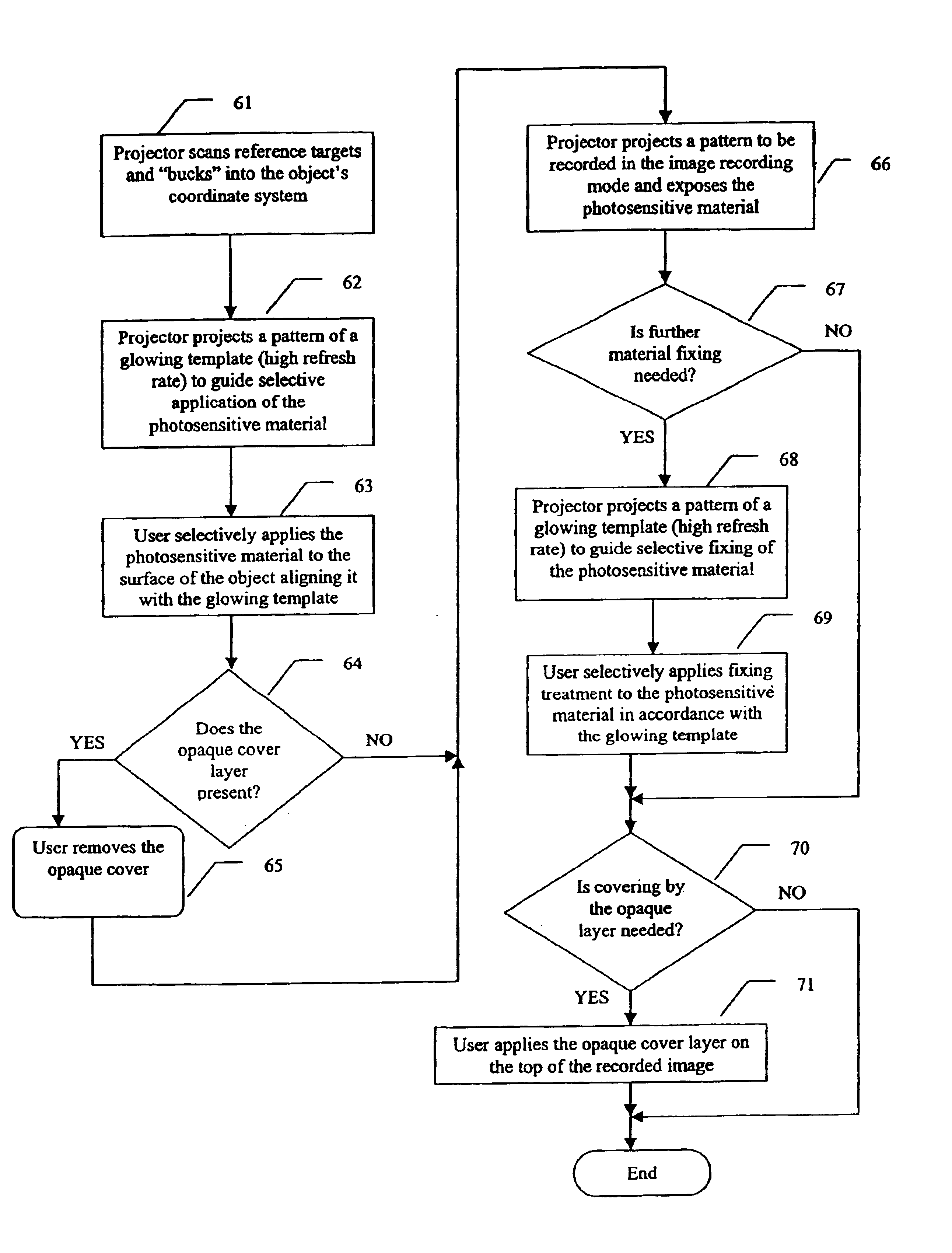
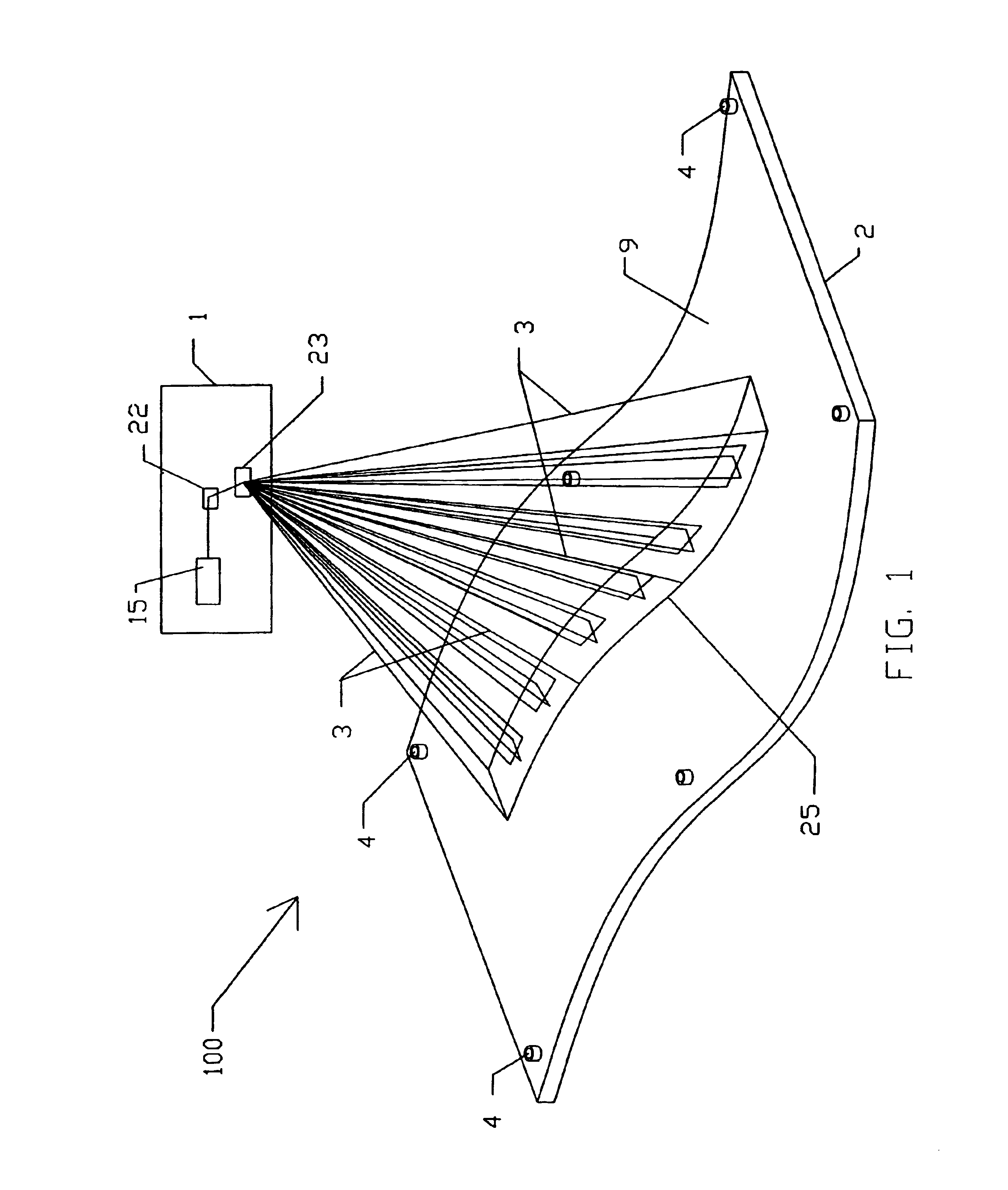
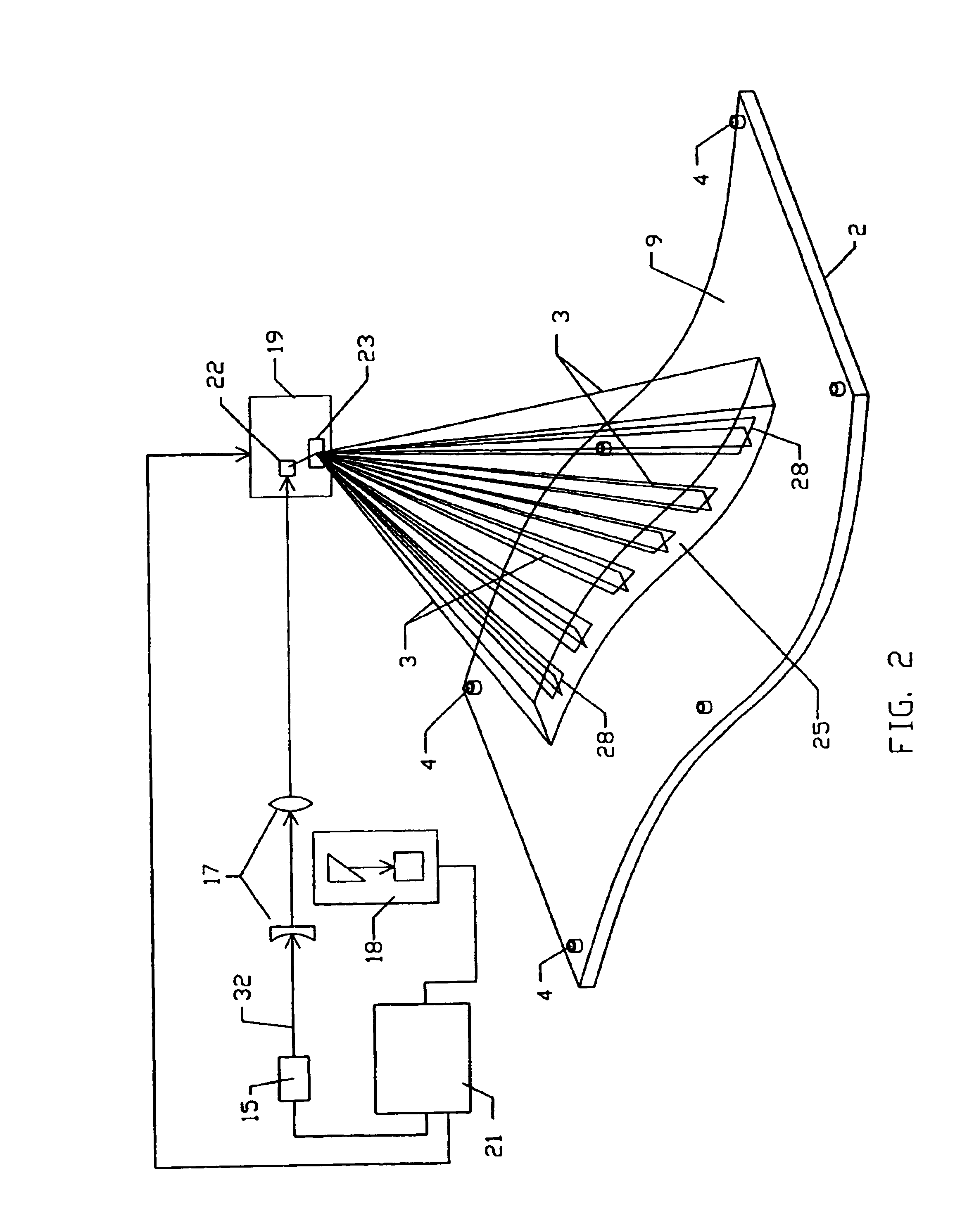
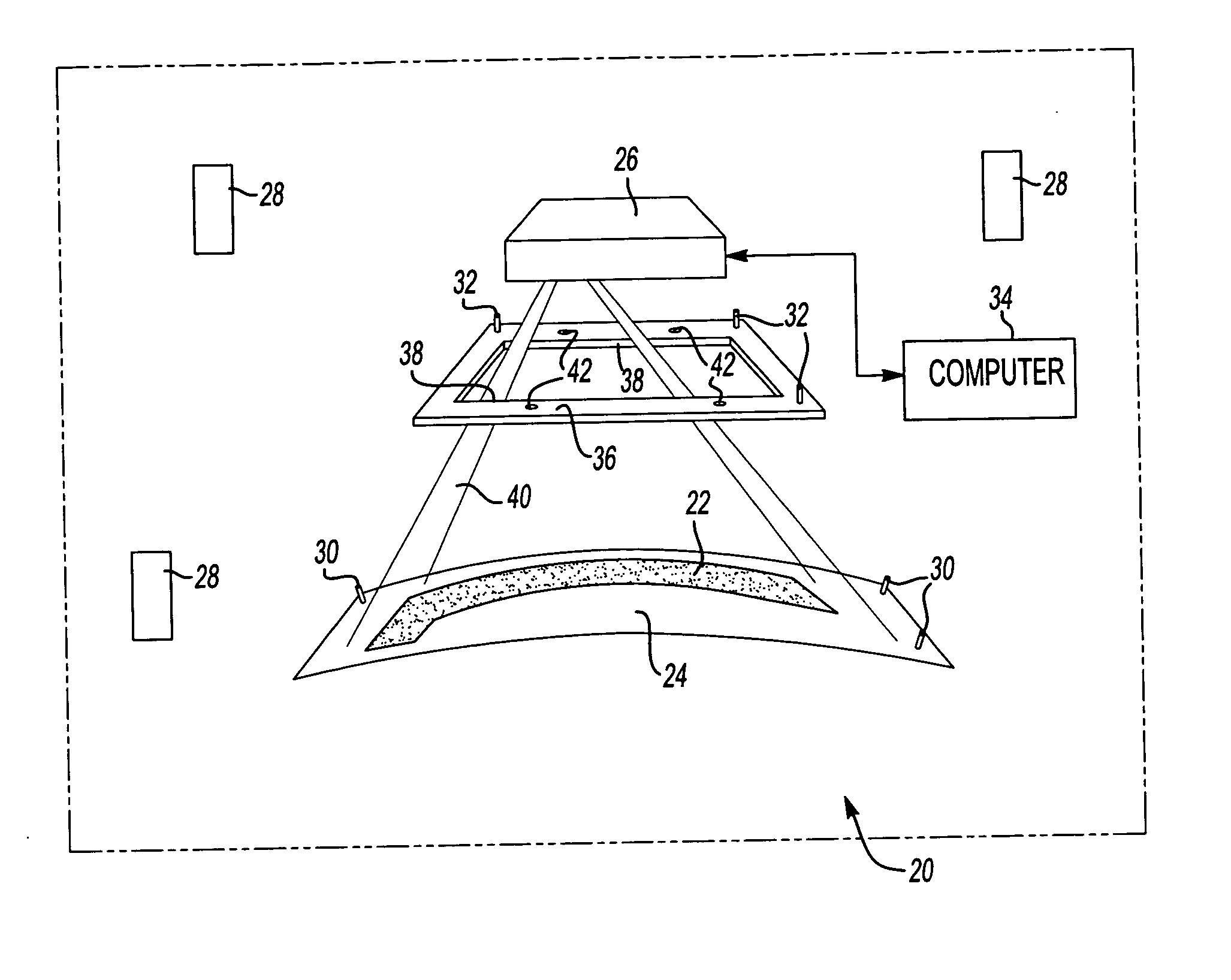
An apparatus and method for recording an image on the surface of a 3D object uses a laser projector that scans a light beam over the surface in an image pattern. The projector operates in a template imaging mode and an image recording mode where the beam scans at a speed that in a single pass / scan mode is typically four to five orders of magnitude slower than in the template imaging mode. A layer of a photosensitive material is applied to the surface of the object either partially or fully. Projection in the template imaging mode can guide the applying. The layer is substantially insensitive to ambient light for at least a period of time necessary to perform a desired processing step on the object. The layer has a maximum spectral sensitivity in the vicinity of the wavelength of the laser light beam. In one or multiple passes of the beam over the image pattern operating in the image record mode, the accumulated light energy dose density is sufficient to react the material and record the image.
Owner:FARO TECH INC
Laser projection systems and methods
ActiveUS20050082262A1Easy to disassemblePrecise positioningProjectorsPosition fixationMetrologyKinematics
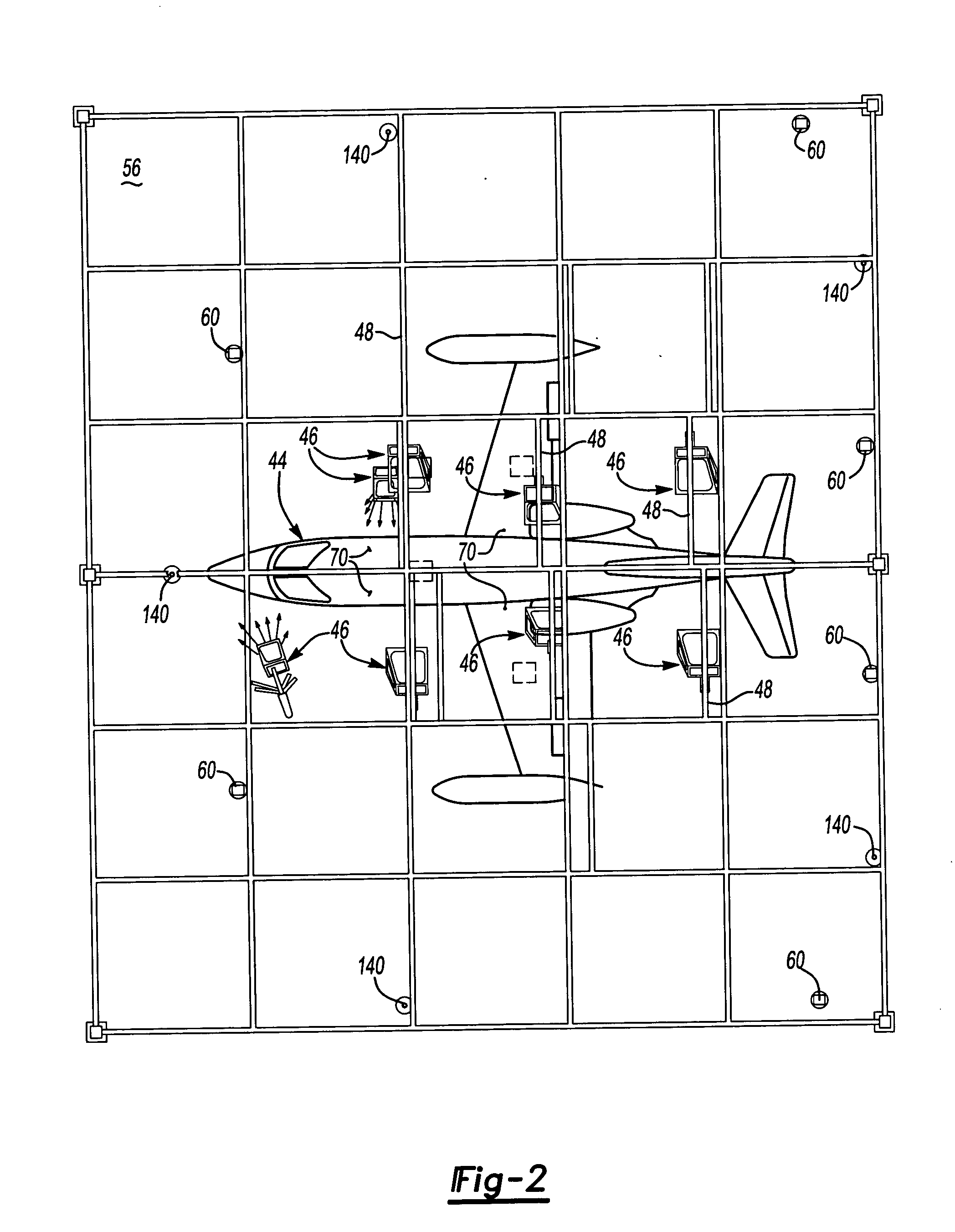
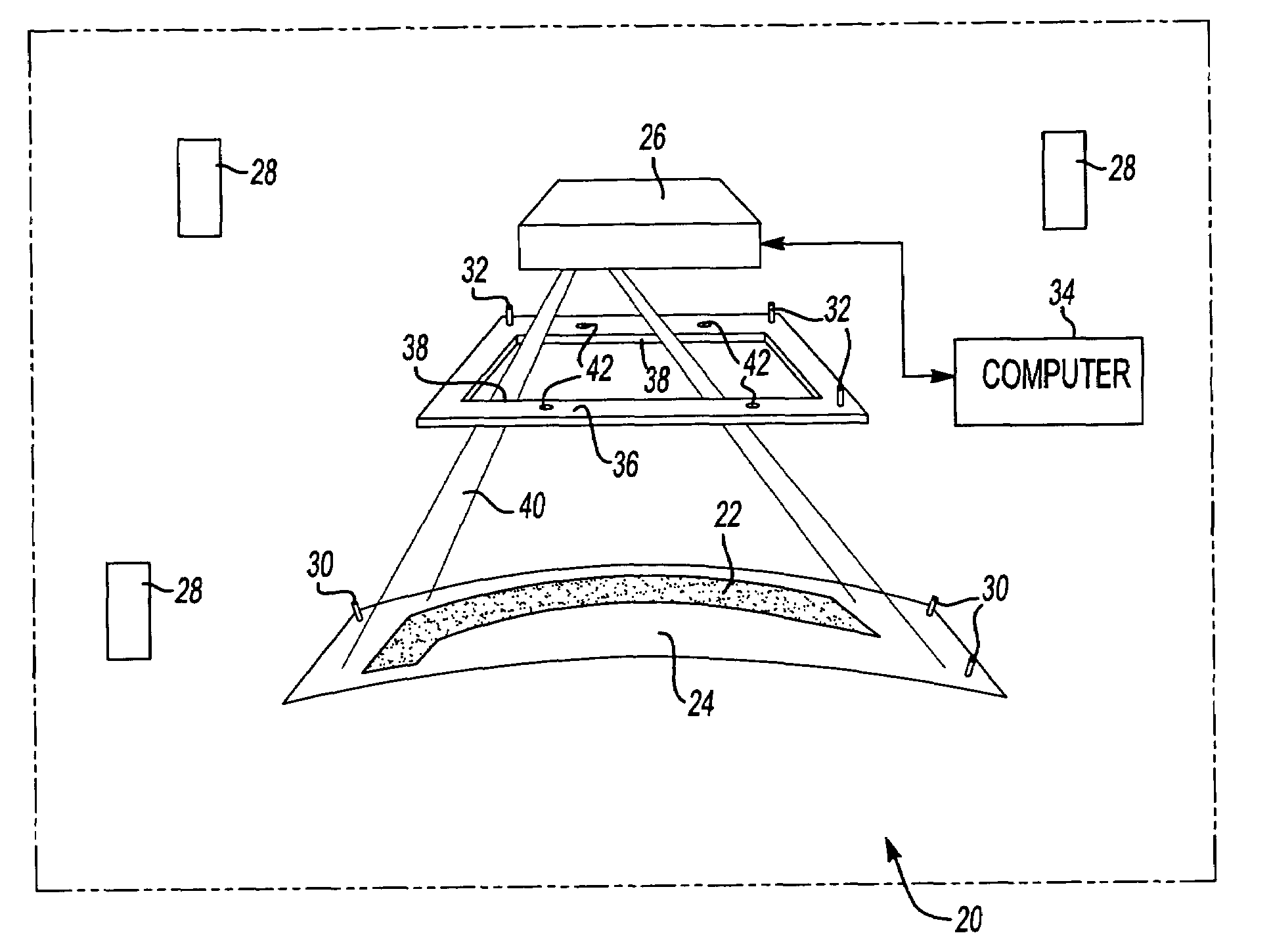
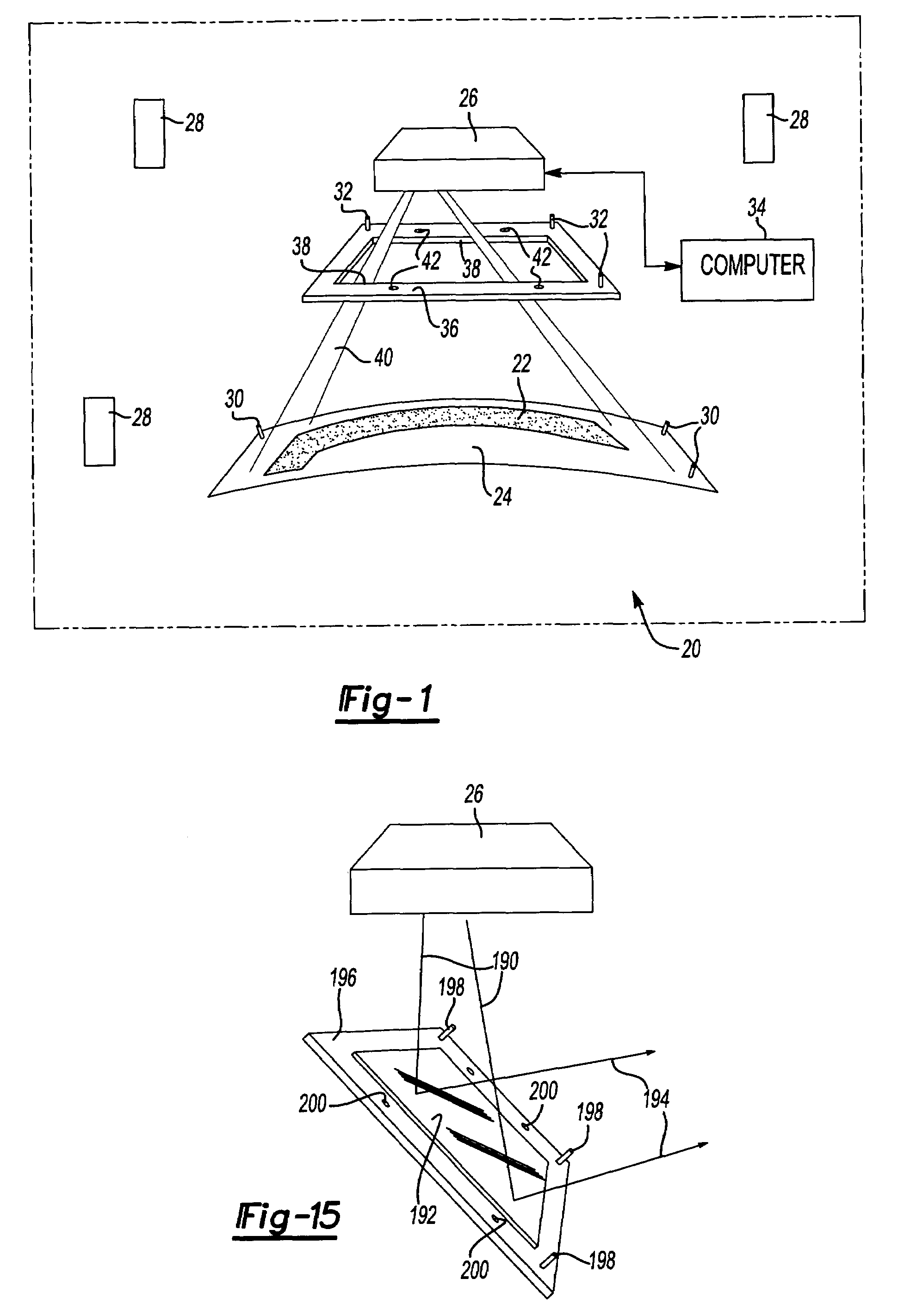
A laser imaging system and method of projecting a laser template on a surface, including independently determining a position and orientation of the surface using an external metrology device, independently determining a position and orientation of a laser projector using the metrology device, generating a signal from the metrology device to a computer and orienting the laser projector relative to the surface to project a laser template. The apparatus includes a plurality of metrology transmitters at fixed locations, a plurality of metrology receivers at fixed locations relative to the surface and a plurality of metrology receivers at fixed locations relative to either the laser projector or laser targets within a field of view of the laser projector. A laser projector and frame assembly is also disclosed, wherein the metrology receivers are located on the frame and the frame includes laser targets for correcting laser drift. Kinematic supports for the metrology receivers are disclosed as well as an independent laser tracker.
Owner:NIKON METROLOGY
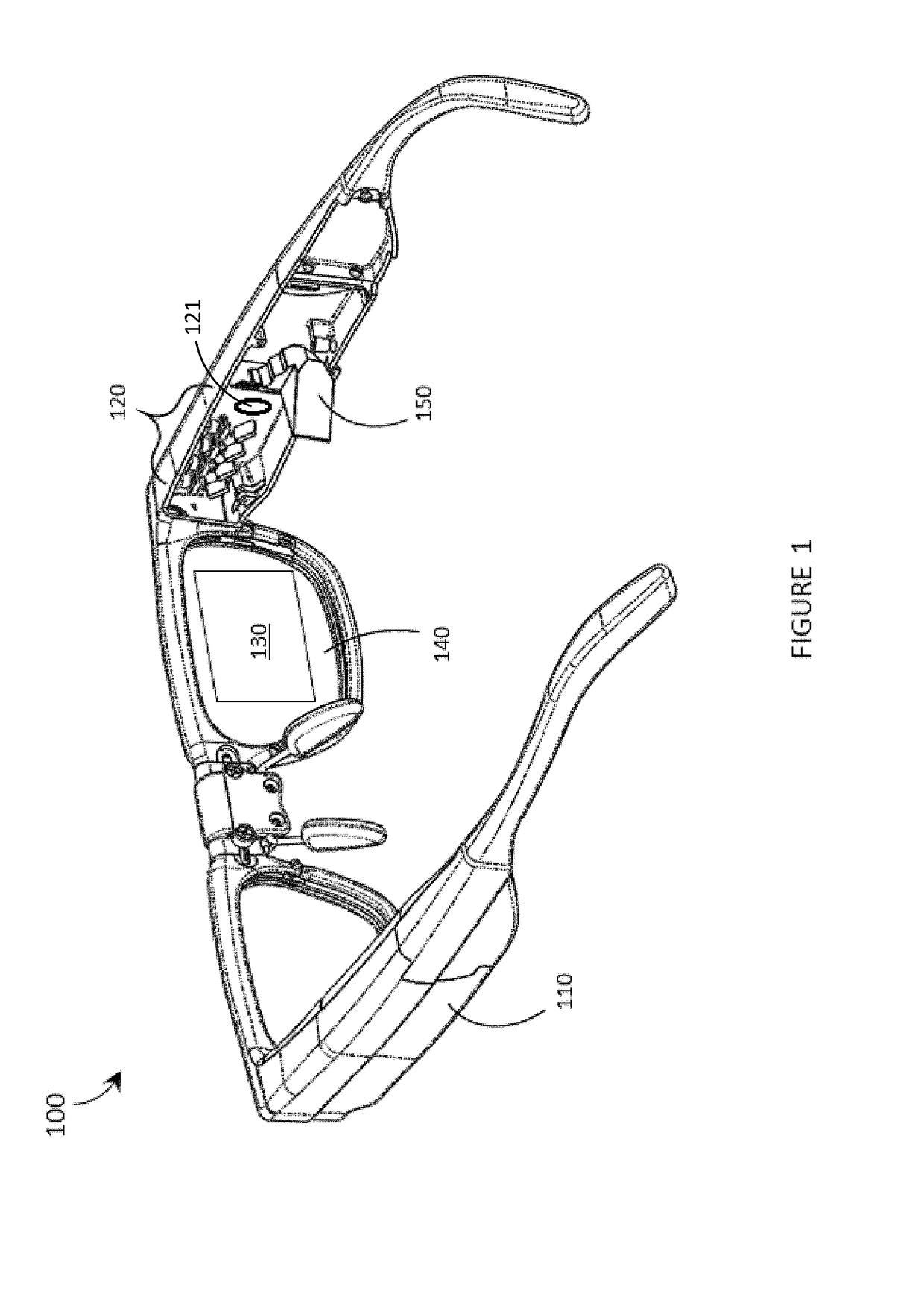
Systems, devices, and methods for eyebox expansion in wearable heads-up displays
ActiveUS20160377865A1Input/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsHead-up displayExit pupil
Systems, devices, and methods for eyebox expansion by exit pupil replication in scanning laser-based wearable heads-up displays (“WHUDs”) are described. The WHUDs described herein each include a scanning laser projector (“SLP”), a holographic combiner, and an optical replicator positioned in the optical path therebetween. For each light signal generated by the SLP, the optical replicator receives the light signal and redirects each one of N>1 instances of the light signal towards the holographic combiner effectively from a respective one of N spatially-separated virtual positions for the SLP. The holographic combiner converges each one of the N instances of the light signal to a respective one of N spatially-separated exit pupils at the eye of the user. In this way, multiple instances of the exit pupil are distributed over the area of the eye and the eyebox of the WHUD is expanded.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
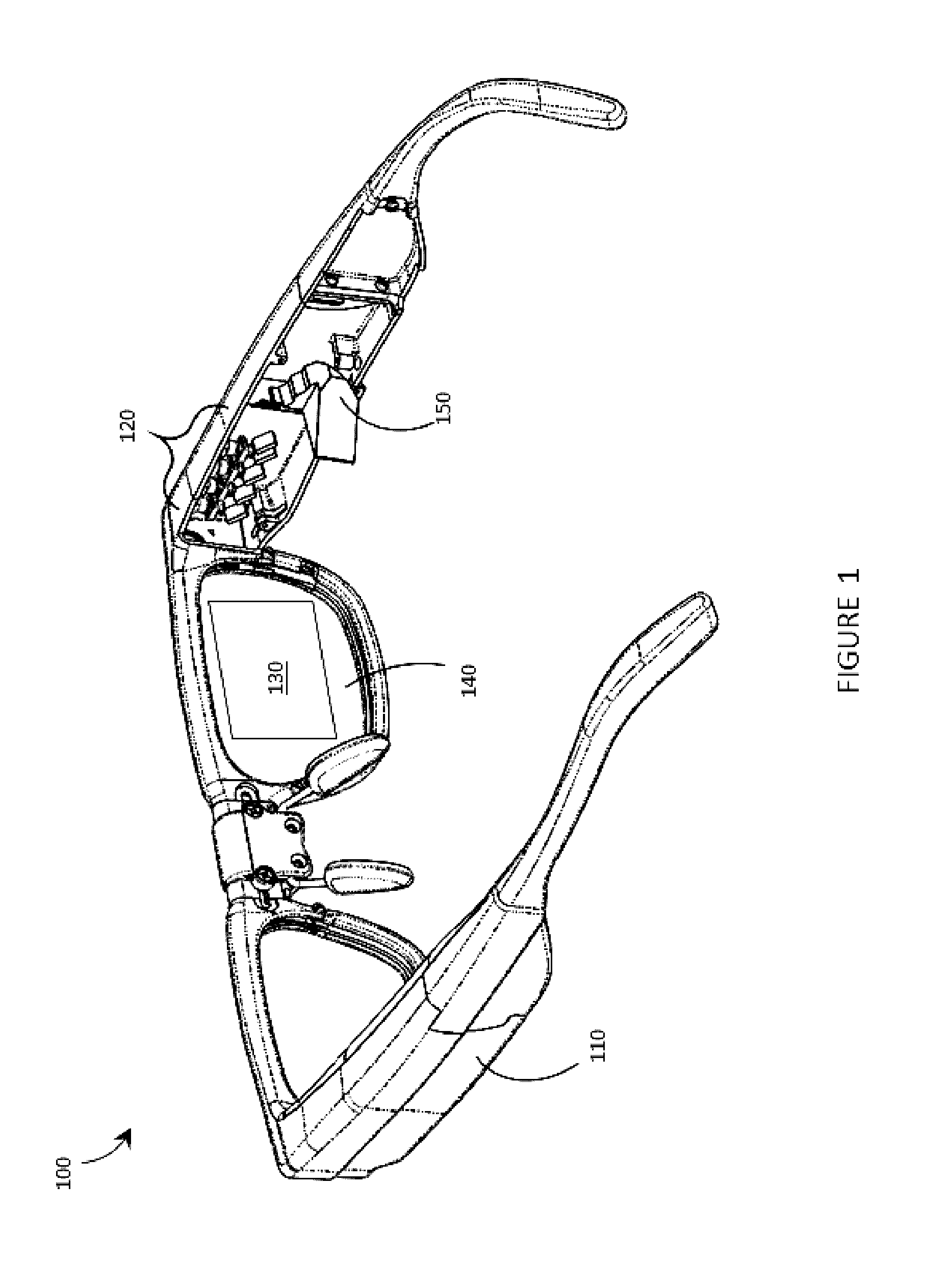
Systems, articles, and methods for integrating holographic optical elements with eyeglass lenses
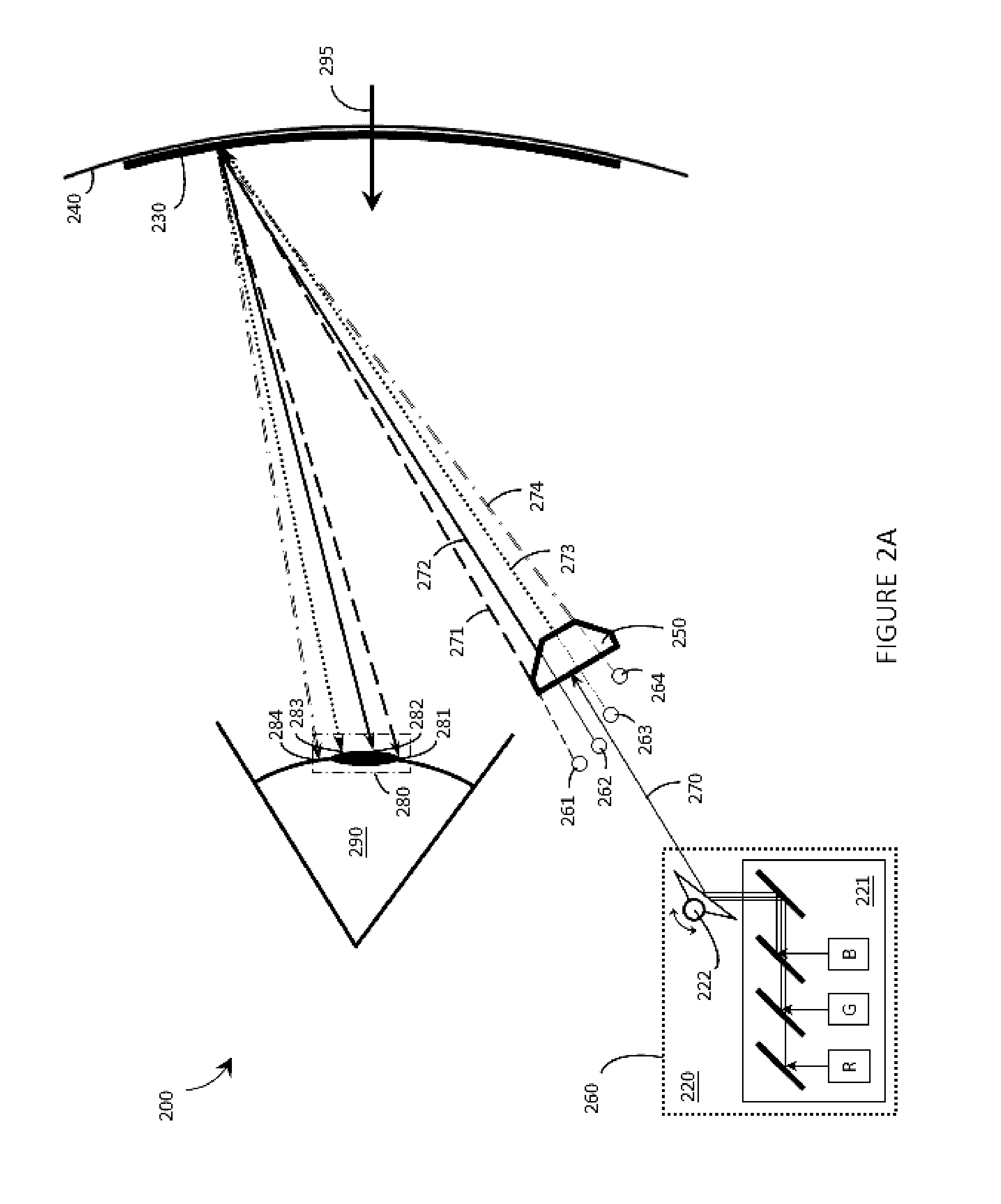
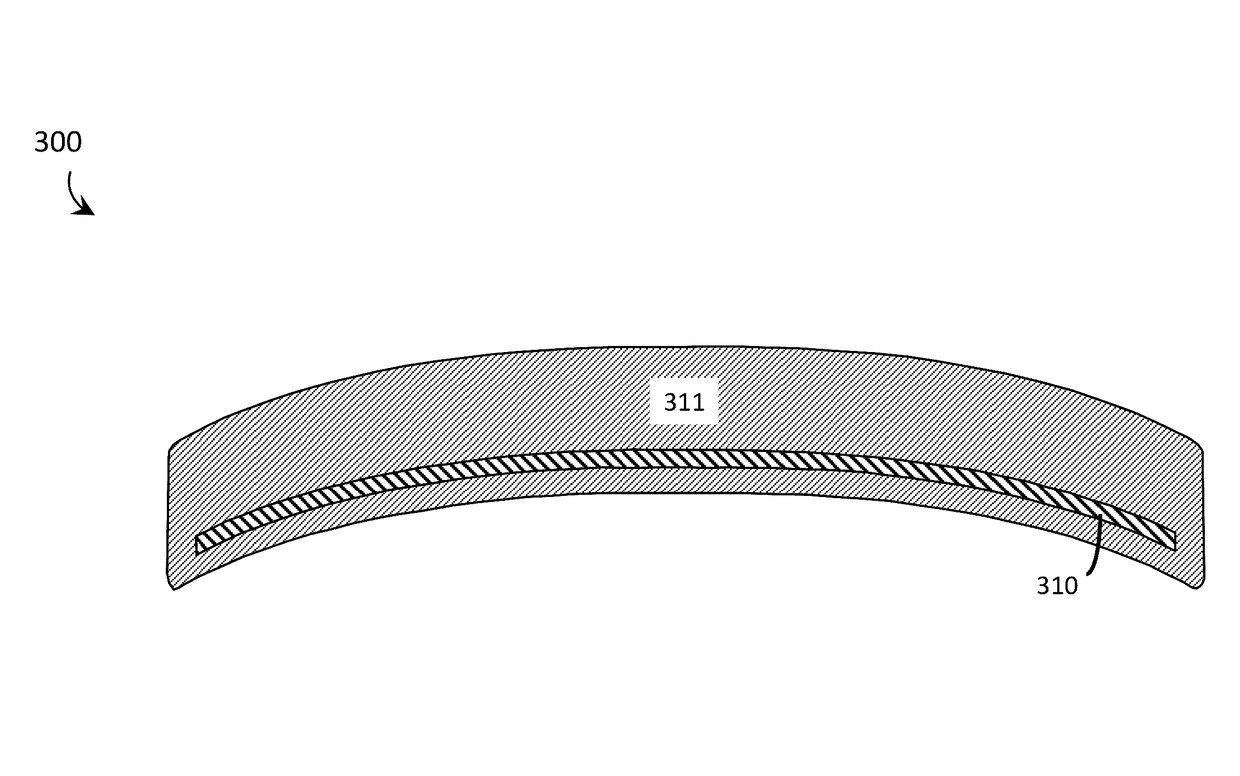
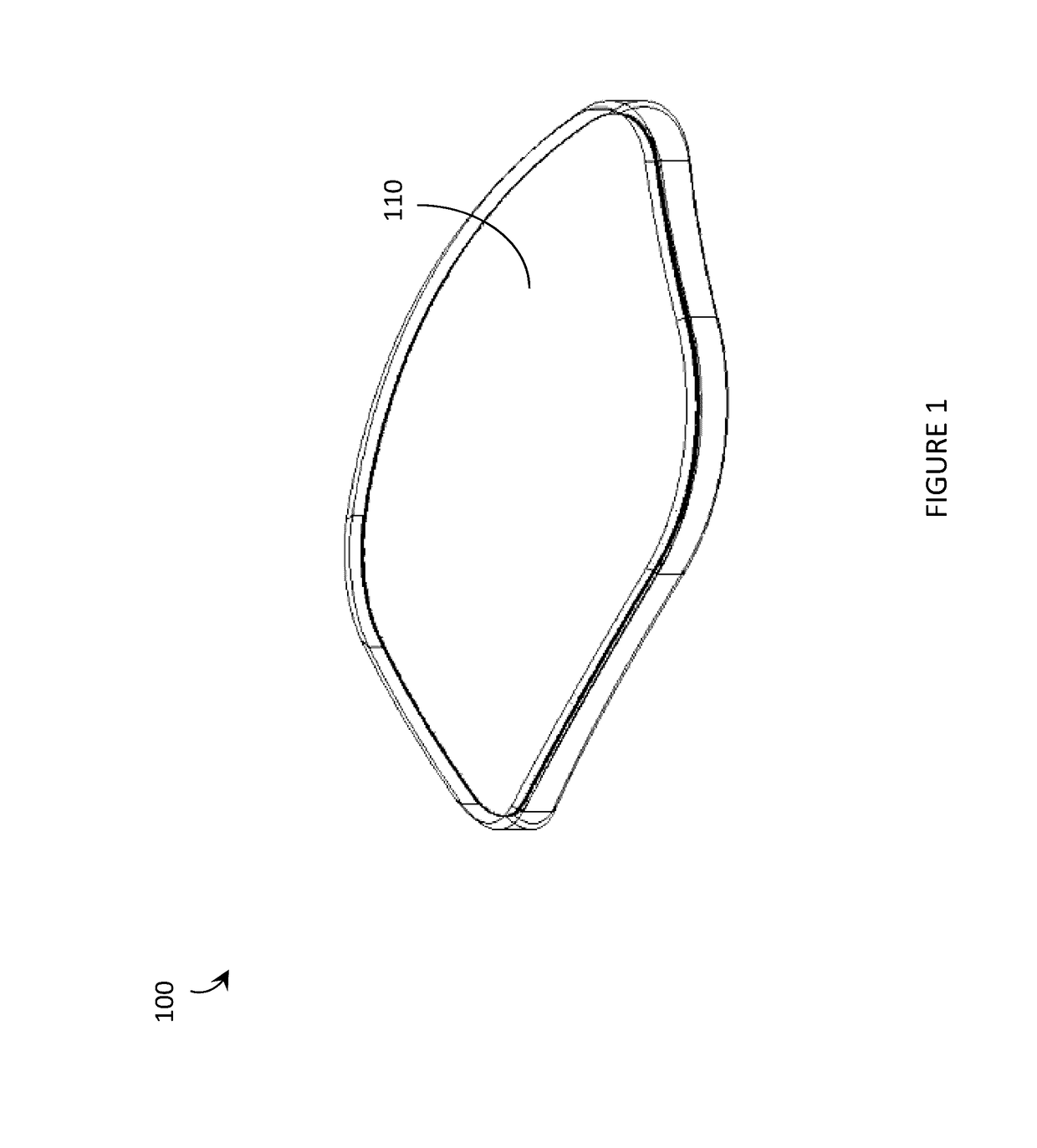
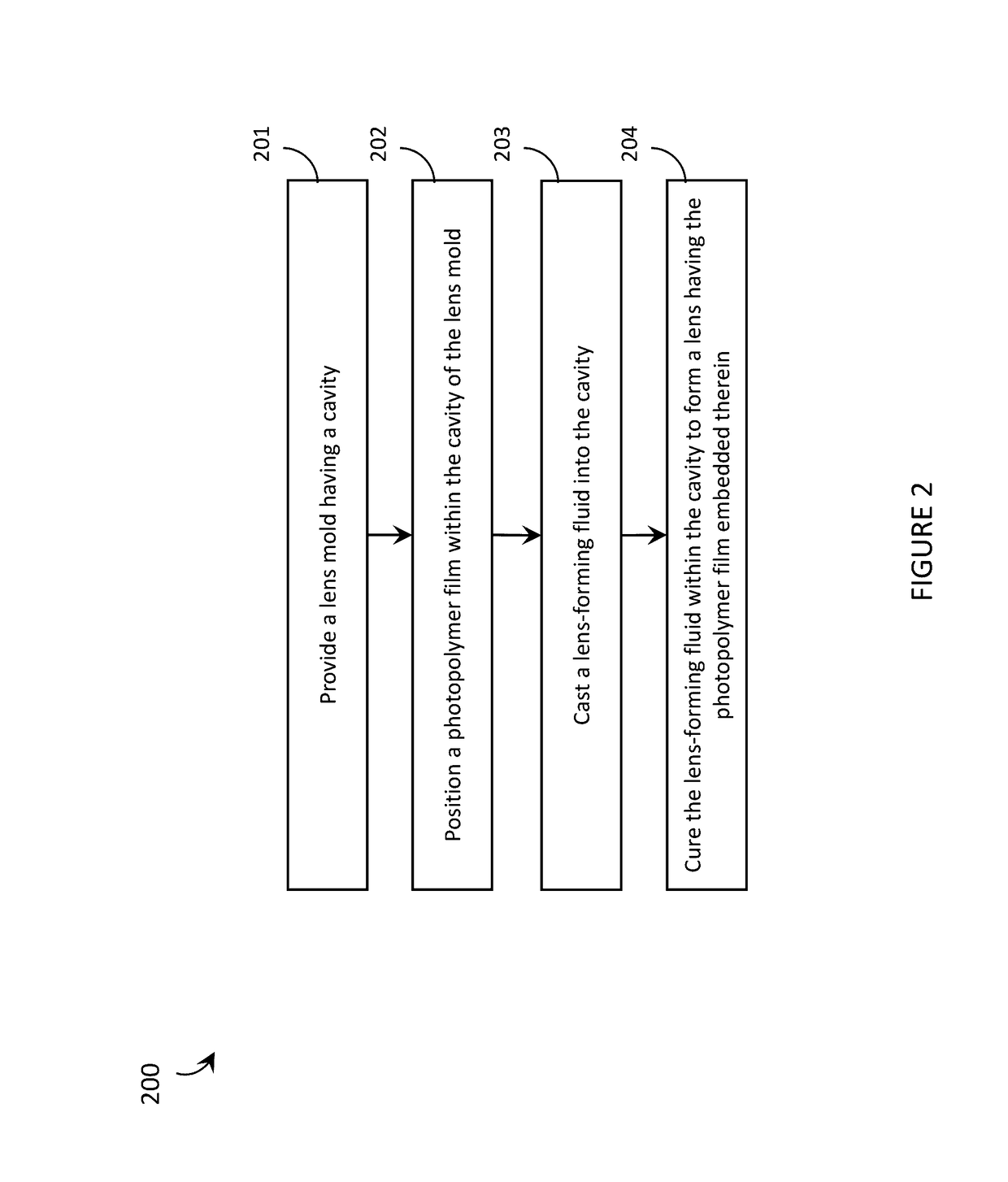
Systems, articles, and methods that integrate photopolymer film with eyeglass lenses are described. One or more hologram(s) may be recorded into / onto the photopolymer film to enable the lens to be used as a transparent holographic combiner in a wearable heads-up display employing an image source, such as a microdisplay or a scanning laser projector. The methods of integrating photopolymer film with eyeglass lenses include: positioning photopolymer film in a lens mold and casting the lens around the photopolymer film; sandwiching photopolymer film in between two portions of a lens; applying photopolymer film to a concave surface of a lens; and / or affixing a planar carrier (with photopolymer film thereon) to two points across a length of a concave surface of a lens. Respective lenses manufactured / adapted by each of these processes are also described.
Owner:THALMIC LABS +1
Laser projection systems and methods
ActiveUS7545517B2Precise positioningEasy to disassembleProjectorsPosition fixationKinematicsLaser target
A laser imaging system and method of projecting a laser template on a surface, including independently determining a position and orientation of the surface using an external metrology device, independently determining a position and orientation of a laser projector using the metrology device, generating a signal from the metrology device to a computer and orienting the laser projector relative to the surface to project a laser template. The apparatus includes a plurality of metrology transmitters at fixed locations, a plurality of metrology receivers at fixed locations relative to the surface and a plurality of metrology receivers at fixed locations relative to either the laser projector or laser targets within a field of view of the laser projector. A laser projector and frame assembly is also disclosed, wherein the metrology receivers are located on the frame and the frame includes laser targets for correcting laser drift. Kinematic supports for the metrology receivers are disclosed as well as an independent laser tracker.
Owner:NIKON METROLOGY
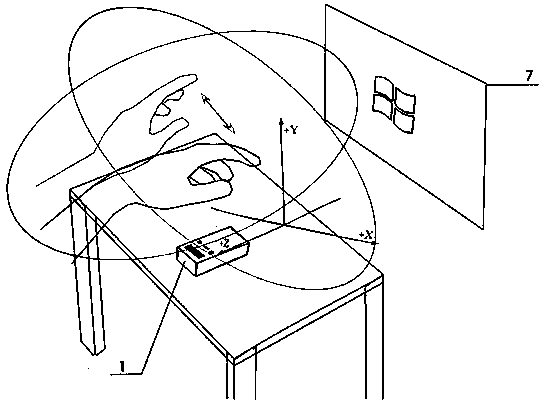
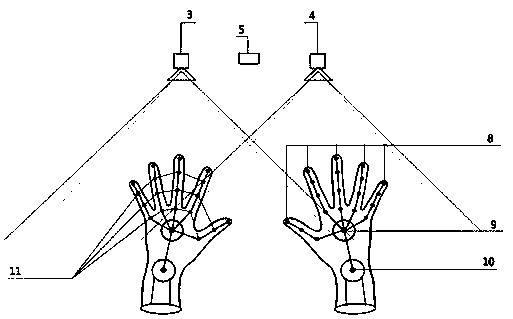
Recognition method and system for multi-point touch and gesture movement capturing in three-dimensional space
InactiveCN103914152AHigh precisionIncreased image capture capabilitiesInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingLaser transmitterThree-dimensional space
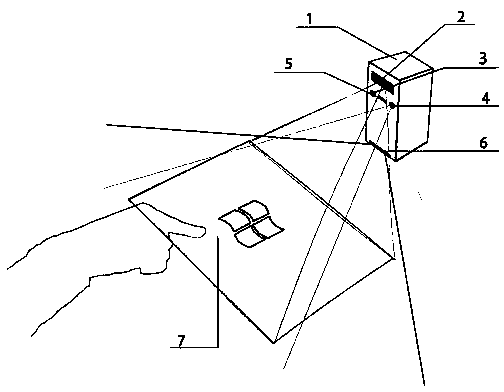
The invention discloses a recognition system for multi-point touch and gesture movement capturing in three-dimensional space, and belongs to the technical field of intelligent recognition. The recognition system for multi-point touch and gesture movement capturing in the three-dimensional space comprises a miniature computer host, a laser projector, a first infrared camera, a second infrared camera, an LED (light emitting diode) lamp, a linear laser transmitter and a projection plane, wherein the laser projector projects contents processed by the miniature computer host, so that the projection plane is generated; the illumination plane of the linear laser transmitter is parallel to the projection plane; and the view field of the first infrared camera and the view field of the second infrared camera cover the projection plane and an aerial gesture recognition area. By using the recognition system for multi-point touch and gesture movement capturing in the three-dimensional space, the shortcoming that the present gesture recognition is based on a computer display is overcome. The recognition system for aerial gestures can be conveniently applied to the fields such as speech presentation by projectors, and is high in recognition precision.
Owner:异象科技(北京)有限公司
3D projection with image recording
ActiveUS20050058332A1Easy to disassembleLow costProjectorsCharacter and pattern recognitionLight energyLaser light
An apparatus and method for recording an image on the surface of a 3D object uses a laser projector that scans a light beam over the surface in an image pattern. The projector operates in a template imaging mode and an image recording mode where the beam scans at a speed that in a single pass / scan mode is typically four to five orders of magnitude slower than in the template imaging mode. A layer of a photosensitive material is applied to the surface of the object either partially or fully. Projection in the template imaging mode can guide the applying. The layer is substantially insensitive to ambient light for at least a period of time necessary to perform a desired processing step on the object. The layer has a maximum spectral sensitivity in the vicinity of the wavelength of the laser light beam. In one or multiple passes of the beam over the image pattern operating in the image record mode, the accumulated light energy dose density is sufficient to react the material and record the image.
Owner:FARO TECH INC
Systems, devices, and methods for eyebox expansion in wearable heads-up displays
ActiveUS20160377866A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsDetails for portable computersHead-up displayExit pupil
Systems, devices, and methods for eyebox expansion by exit pupil replication in wearable heads-up displays (“WHUDs”) are described. A WHUD includes a scanning laser projector (“SLP”), a holographic combiner, and an optical splitter positioned in the optical path therebetween. The optical splitter receives light signals generated by the SLP and separates the light signals into N sub-ranges based on the point of incidence of each light signal at the optical splitter. The optical splitter redirects the light signals corresponding to respective ones of the N sub-ranges towards the holographic combiner effectively from respective ones of N spatially-separated virtual positions for the SLP. The holographic combiner converges the light signals to respective ones of N spatially-separated exit pupils at the eye of the user. In this way, multiple instances of the exit pupil are distributed over the area of the eye and the eyebox of the WHUD is expanded.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Speckle reduction in laser-projector images
InactiveUS20080212034A1Reduce appearance problemsSpeckle reductionProjectorsMountingsSpatial light modulatorSpecular reflection
A laser projector having a configurable spatial light modulator (SLM) adapted to display various spatial modulation patterns and redirect illumination from a laser to form an image on the viewing screen. The laser projector drives the SLM to change spatial modulation patterns at a rate that causes the corresponding sequence of projected images to fuse to mitigate appearance of speckle in the resulting fused image. The SLM can be designed to redirect the illumination using either diffraction or specular reflection of light from the displayed spatial modulation pattern. In one embodiment, the SLM is a MEMS device having an array of individually addressable mirrors supported over a substrate and adapted to move (e.g., translate and / or rotate) with respect to the substrate.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
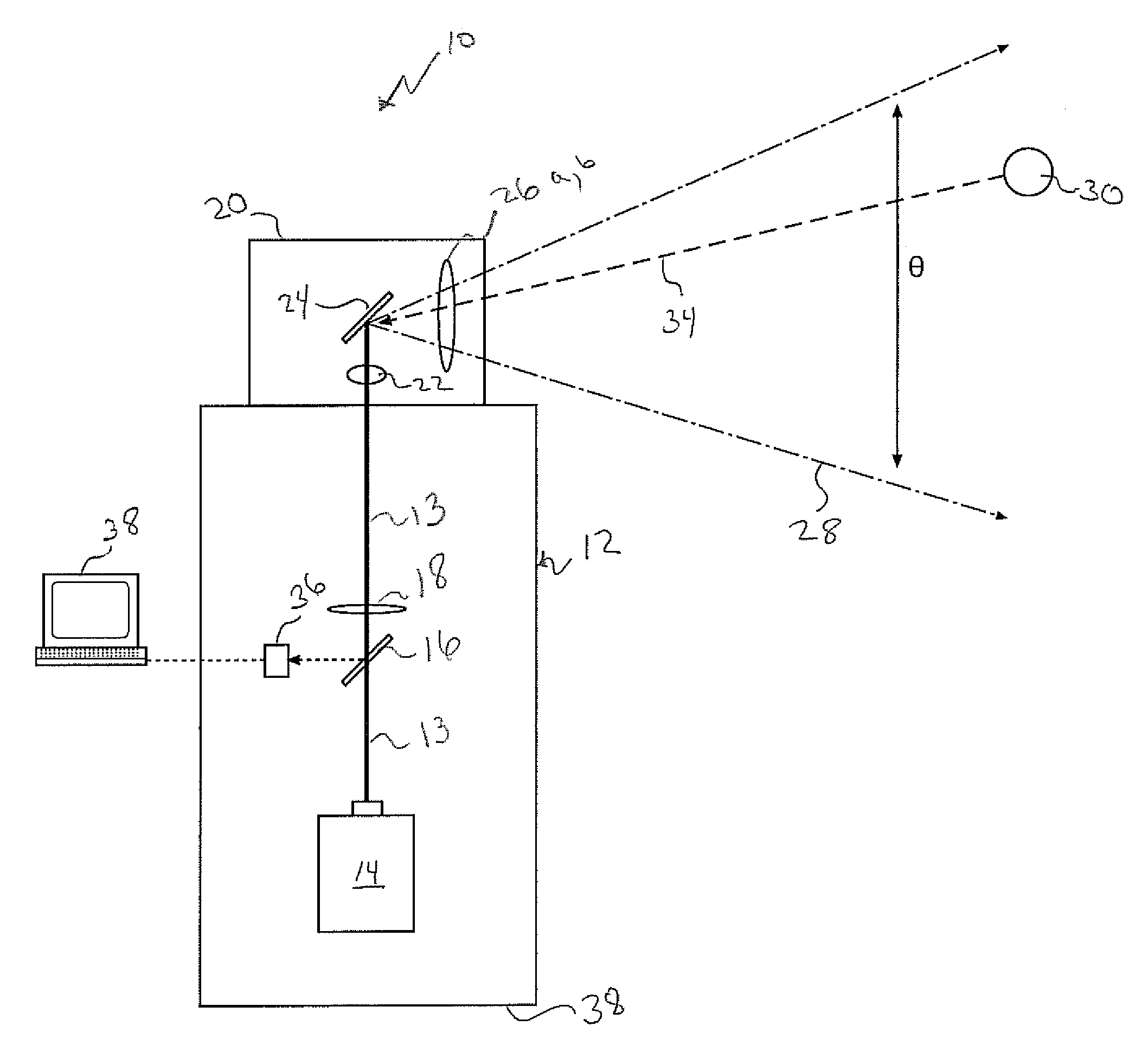
Laser metrology system and method
ActiveUS20080309949A1Reduce complexityLow costActive open surveying meansUsing optical meansMetrologyLight beam
A laser metrology system for determining a location of a target utilizes a laser projector having a laser source for projecting a laser beam. A rotating head directs the laser beam in a lateral direction. A sensor associated with the laser projector is capable of sensing the laser beam. A reflective target is configured to reflect the laser beam projector from the laser source toward the sensor in a manner indicative of the angle of the rotating head and the pulse of the laser beam to determine location of the target.
Owner:NIKON METROLOGY
Systems, devices, and methods that integrate eye tracking and scanning laser projection in wearable heads-up displays
ActiveUS20160349515A1Picture reproducers using projection devicesInput/output processes for data processingHead-up displayPhotodetector
Systems, devices, and methods that integrate eye tracking capability into scanning laser projector (“SLP”)-based wearable heads-up displays are described. At least one narrow waveband laser diode is used in an SLP to define one or more portion(s) of a visible image. At least one corresponding narrow waveband photodetector is aligned to detect reflections of the portion(s) of the image from features of the eye. A holographic optical element (“HOE”) may be used to combine the image and environmental light into the user's “field of view.” Three narrow waveband photodetectors each responsive to a respective one of three narrow wavebands output by the RGB laser diodes of an RGB SLP are aligned to detect reflections of a projected RGB image from features of the eye.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
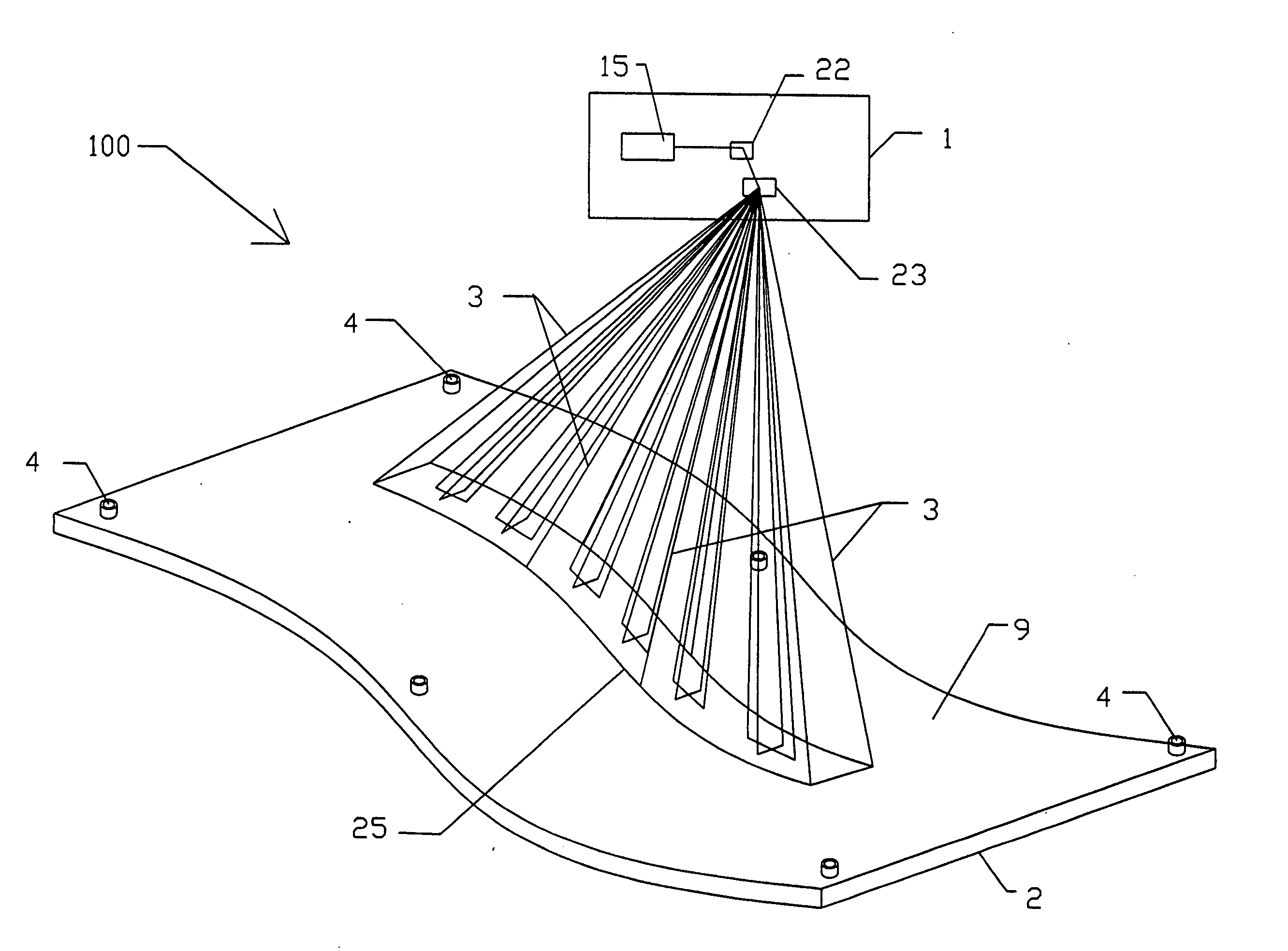
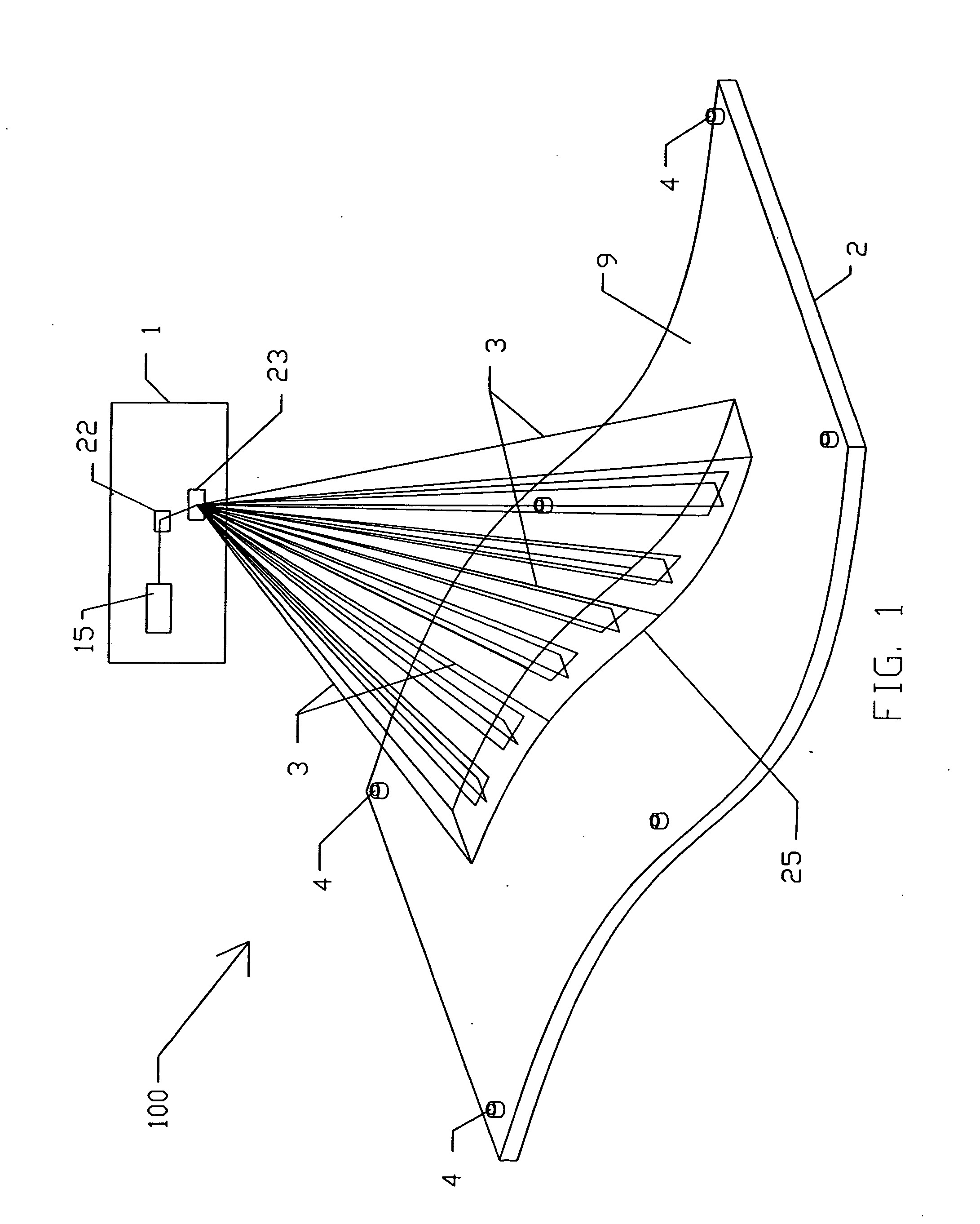
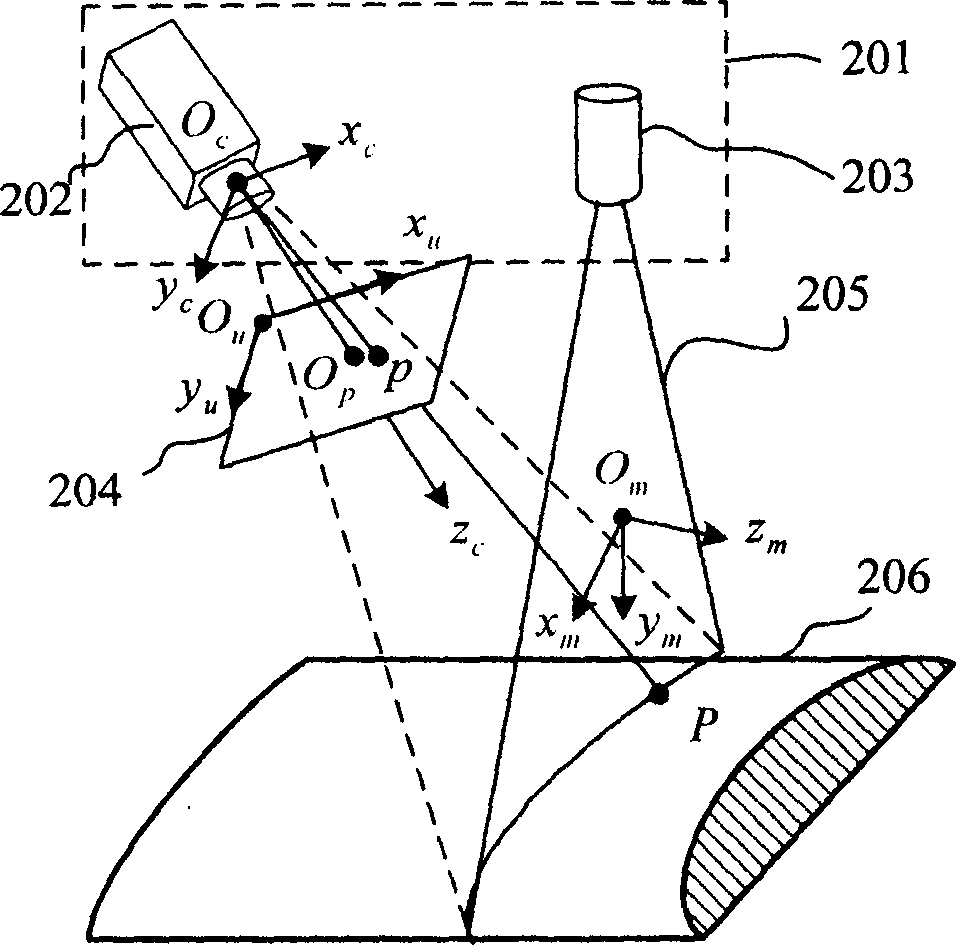
Method for measuring diameter and straightness accuracy parameters of seamless round steel pipe
InactiveCN101571379ARealize onlineRealize non-contact measurementUsing optical meansEllipseEngineering
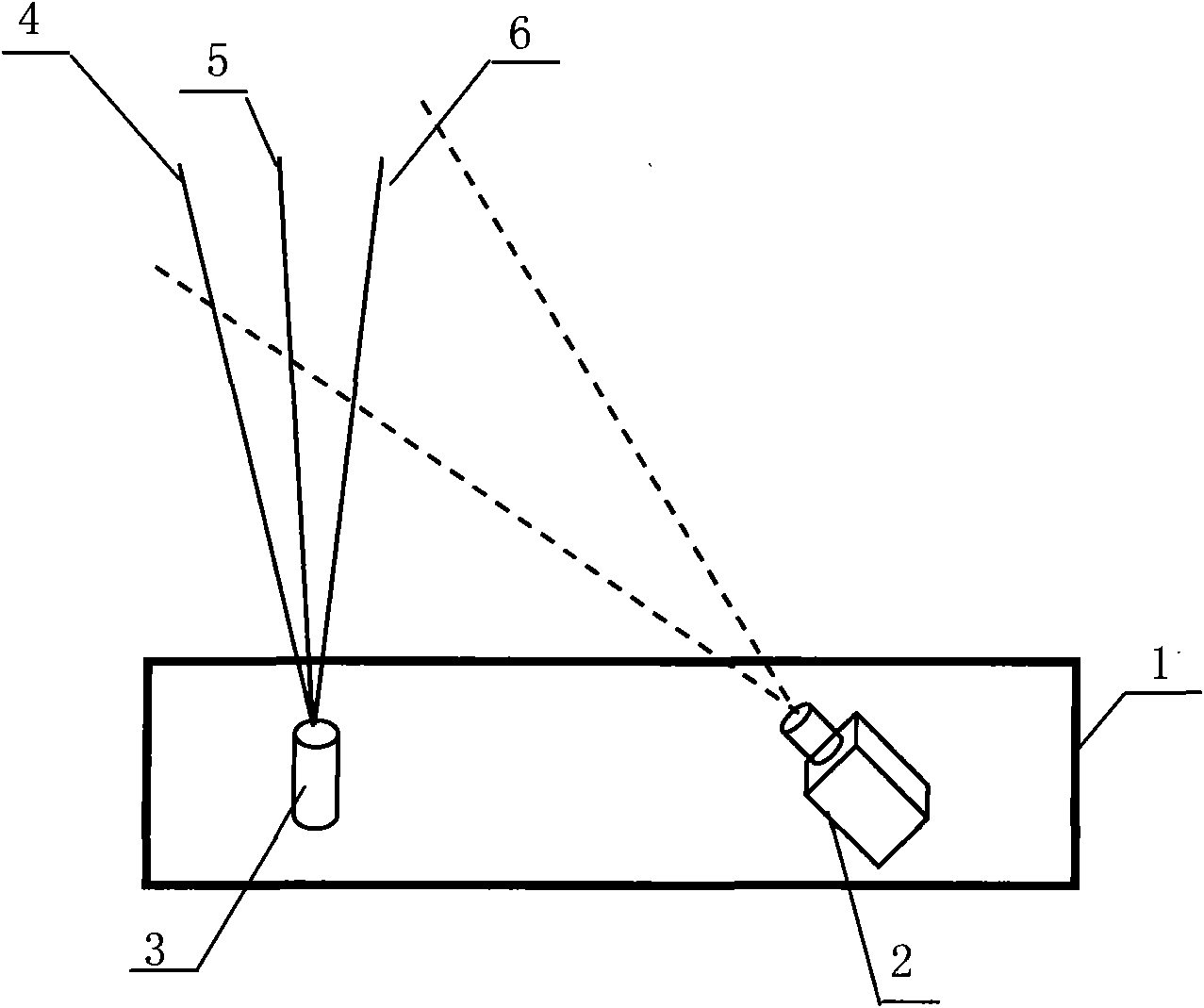
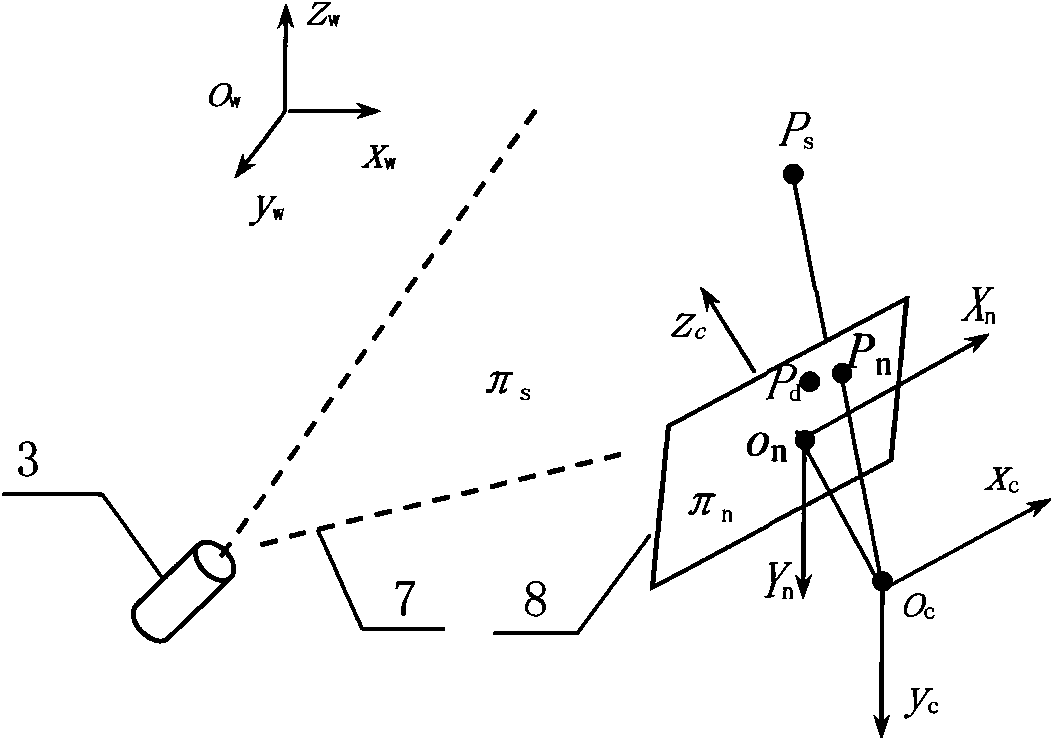
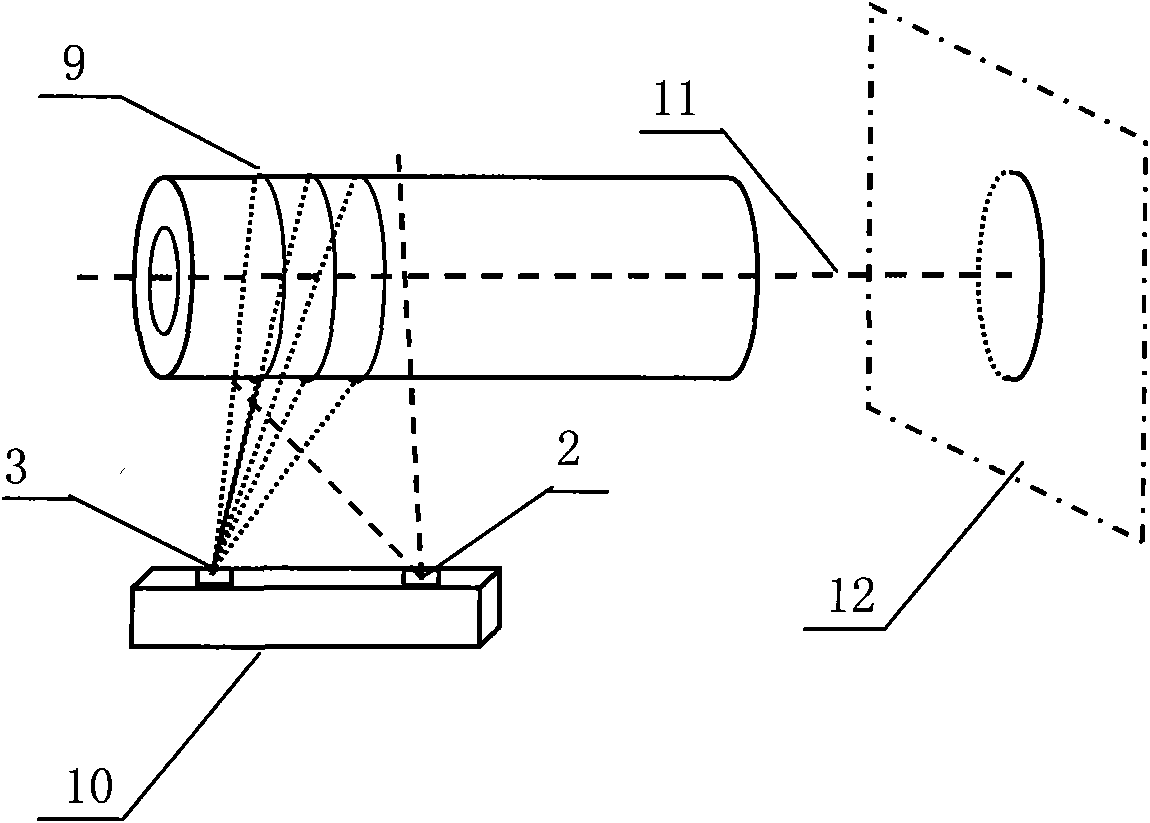
The invention relates to a method for measuring the diameter and the straightness accuracy parameters of a seamless round steel pipe. The method includes the steps as follows: accomplishing the calibration of parameters of a multi-linear structured light vision sensor formed by one video camera and multi-line laser projectors; distributing the multi-linear structured light vision sensors on the periphery of the seamless round steel pipe to be tested; respectively controlling the laser projectors to project structured light plane onto the measured section of the seamless round steel pipe by a computer, collecting the images of laser stripes on the surface of the seamless round steel pipe and processing the images of the laser strip by a video camera, and calculating the three-dimensional coordinates of different sections according to a measurement model; determining the elliptical center of each section of the space, realizing the measurement of the straightness accuracy of the seamless round steel pipe and establishing the dynamic and virtual central axis of the seamless round steel pipe; establishing the reference plane of the dynamic and virtual projection of ellipse of the section of the space; and front projecting the ellipse of the section of the space onto the reference plane of the dynamic and virtual projection, and carrying out the operation of circle fitting on the reference plane, thereby obtaining the section circle of the steel pipe. The method can realize the on-line, real-time, automatic and noncontact measurement of the diameter and the straightness accuracy parameters of the seamless round steel pipe.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Image Projector
An image projector realizing image projection with high image quality by reducing speckle noise. An image projector comprising a coherent light source, a collimation lens for transforming coherent light emitted from the coherent light source into coherent parallel light, and a projection optical system for projecting coherent parallel light is further provided with a reflection element for reflecting the coherent parallel light and capable of oscillating in parallel with the direction normal to the reflection plane, and a reflection element drive means for causing oscillatory motion of the reflection element.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
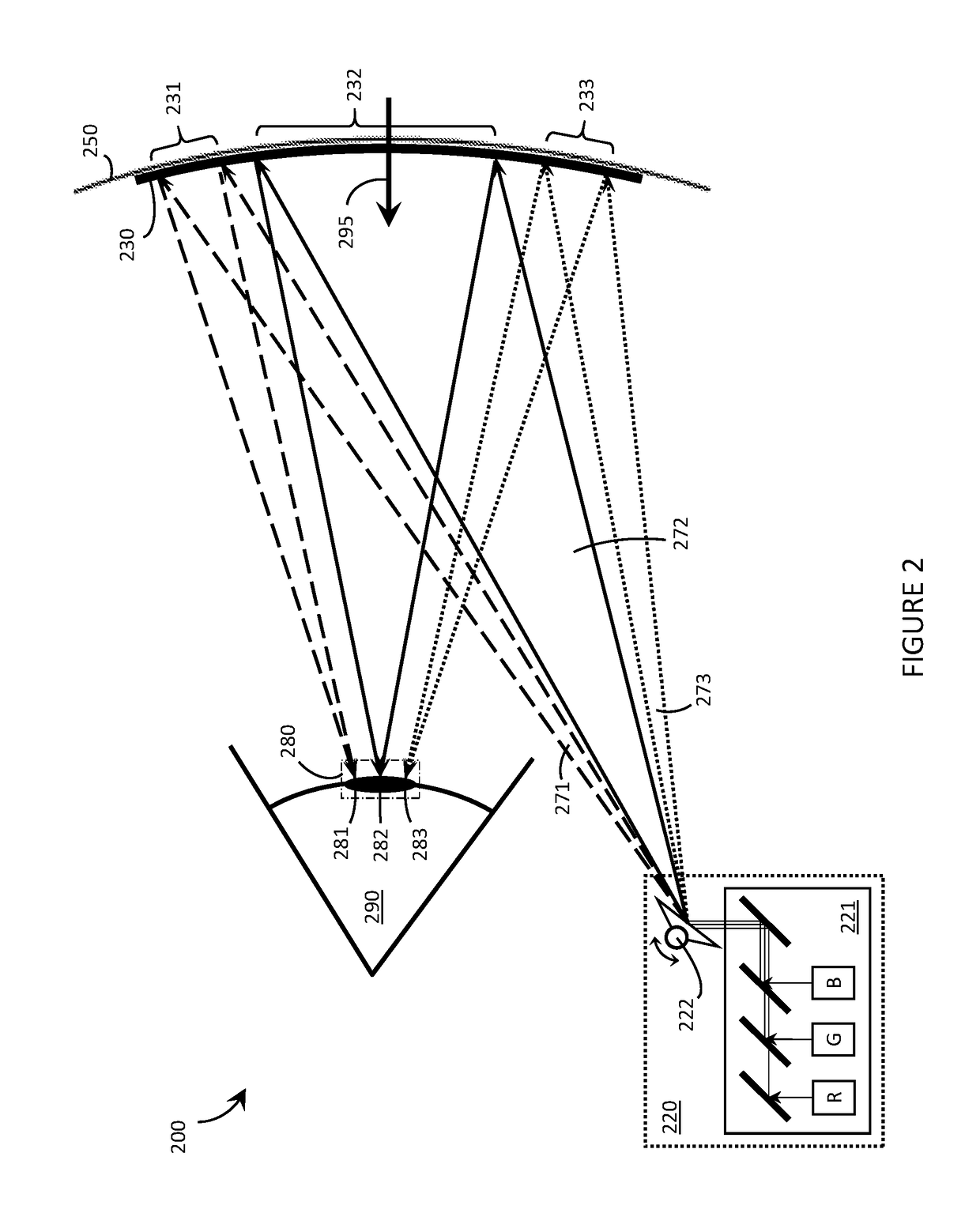
Systems, devices, and methods for spatially-multiplexed holographic optical elements
Systems, devices, and methods for spatial multiplexing in holographic optical elements (“HOEs”) are described. A spatially-multiplexed HOE includes multiple spatially-separated holographic regions and each spatially-separated region applies a respective optical function to light that is incident thereon. An exemplary application as a spatially-multiplexed holographic combiner (“SMHC”) in a scanning laser-based wearable heads-up display (“WHUD”) is described. In this exemplary application, a scanning laser projector directs multiple light signals over the area of the SMHC and the SMHC converges the light signals towards multiple spatially-separated exit pupils at or proximate the eye of the user. The particular exit pupil at the eye of the user towards which any particular light signal is converged by the SMHC depends on the particular region of the SMHC upon which the light signal is incident. Such may be useful in engineering particular eyebox and / or user interface display configurations in the operation of the WHUD.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
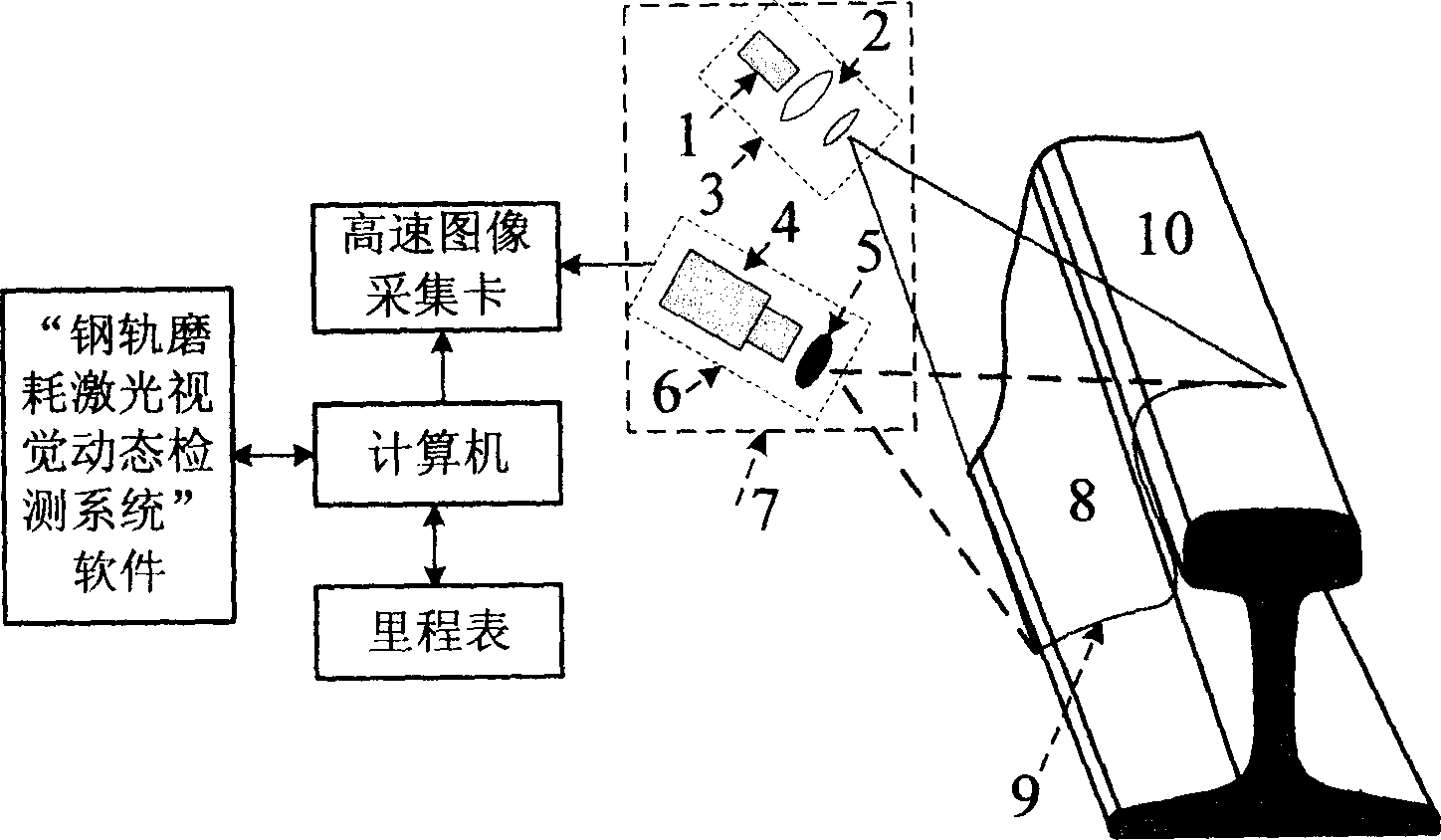
Steel rail near laser visual dynamic measuring device and method
InactiveCN1776364ALow costRealize on-site measurementUsing optical meansRailway auxillary equipmentMeasurement deviceLaser projector
The disclosed measuring device is composed of laser vision sensor, computer, image acquisition card in high speed, calibrating target drone and measuring software. The method includes steps: after imaging system for rail section images light plane projected from laser projector, the image acquisition card captures rail section images and sands them to computer. Processing the collected images, the computer picks up image coordinates of sectional feature contour, as well as calculates out vertical abrasion, side abrasion and total abrasion based on measured model. The invention is capable of measuring sectional contour of rail in single side, vertical abrasion, side abrasion and parameter of total abrasion through single laser vision sensor.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
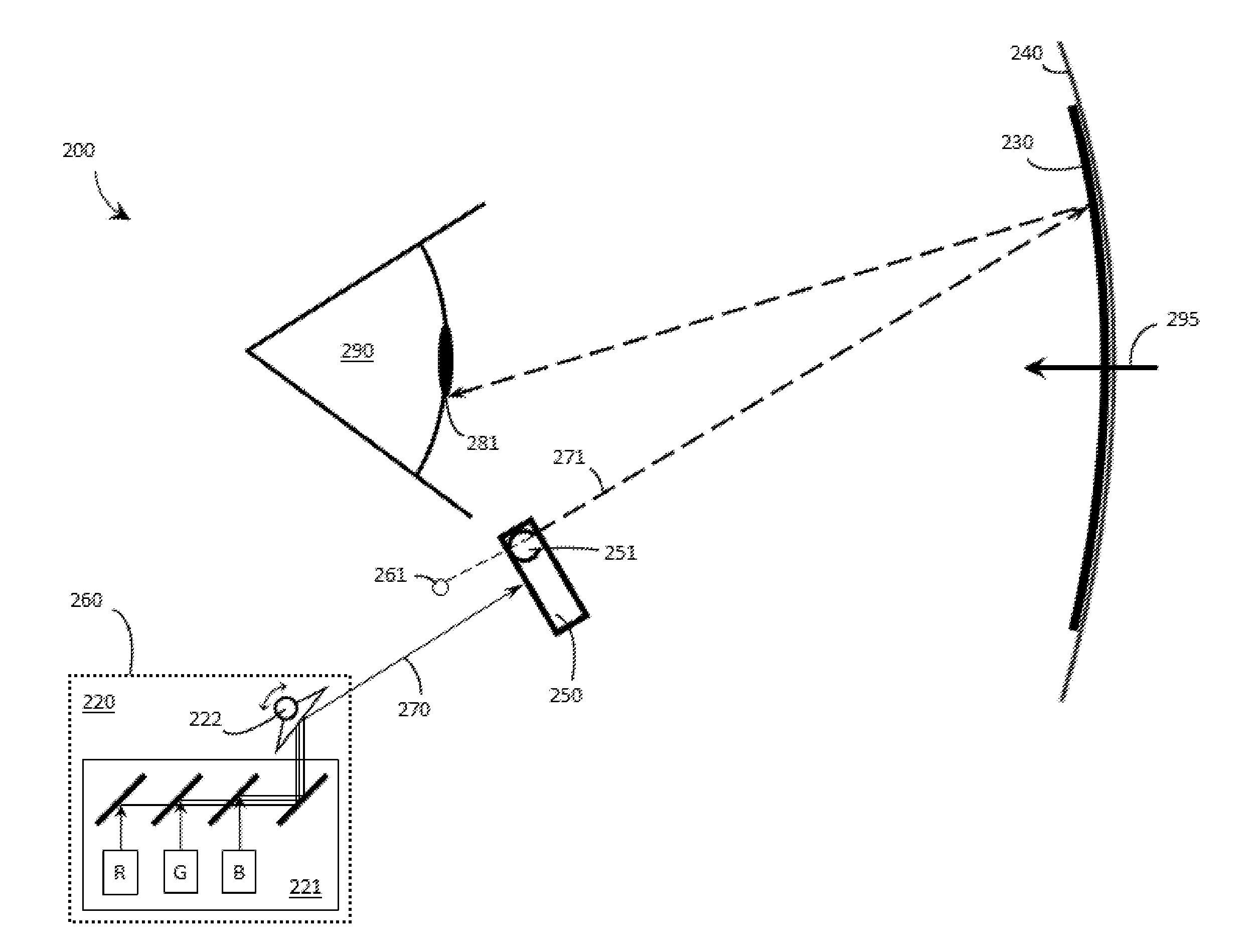
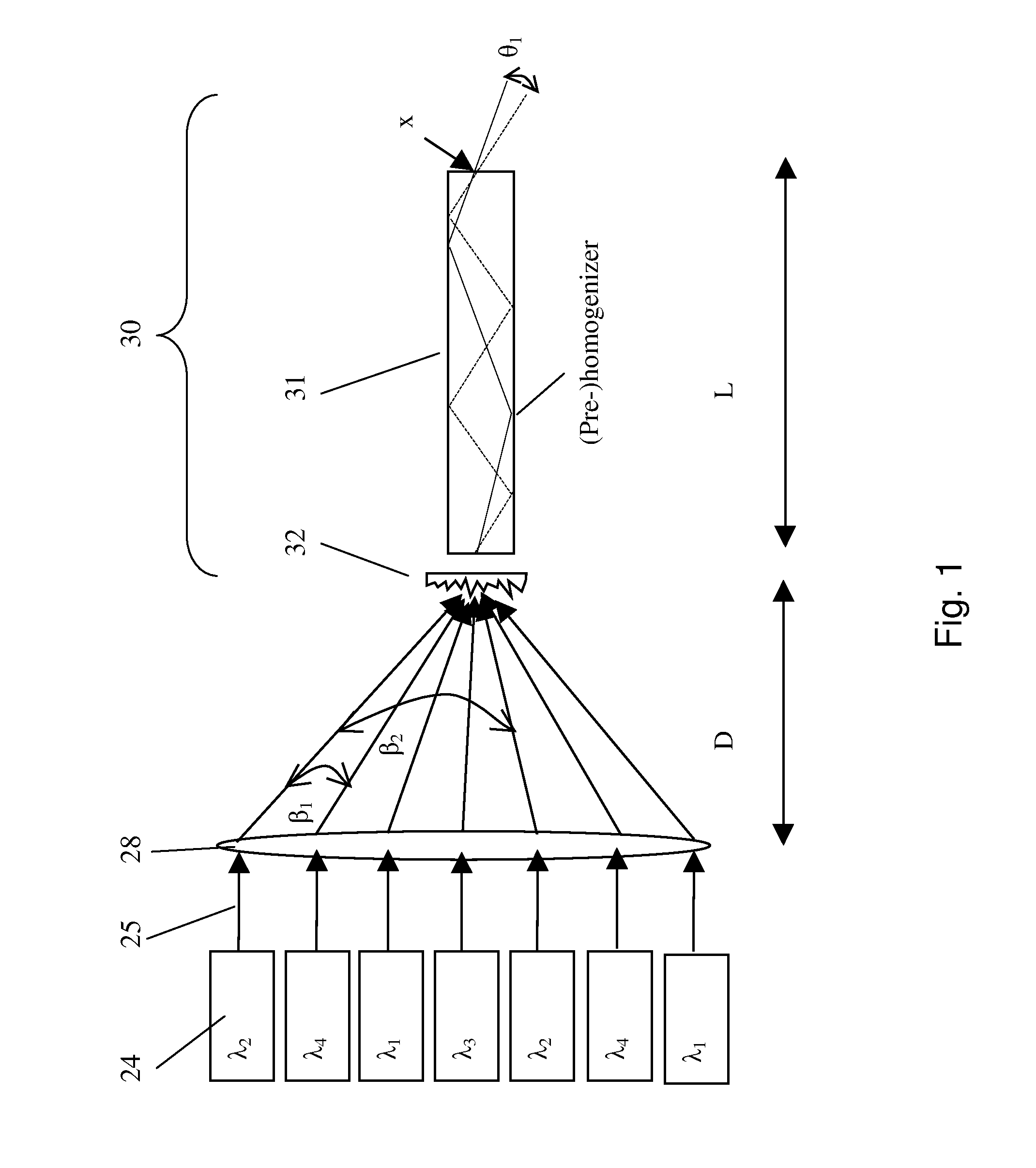
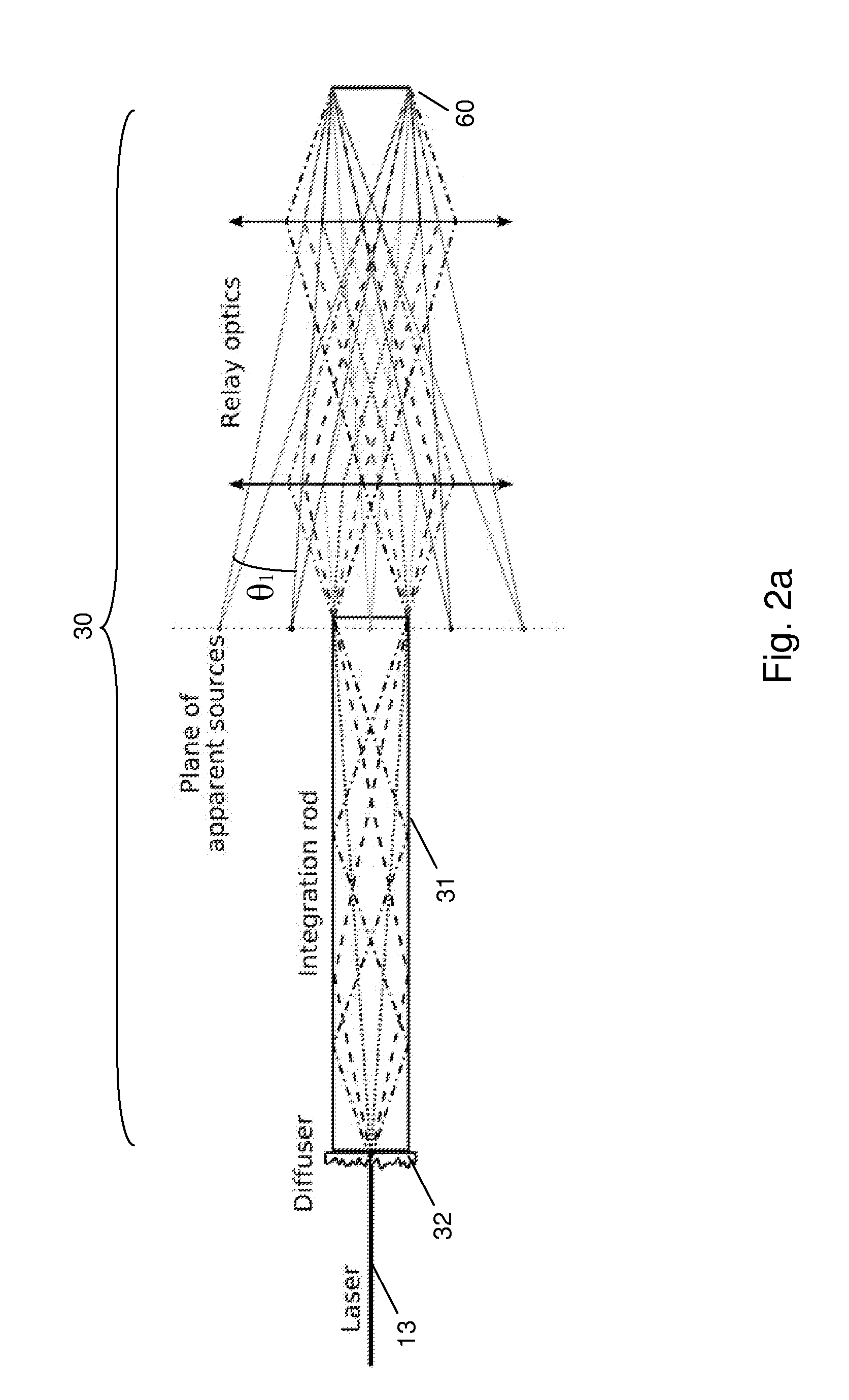
Laser projector with reduced speckle
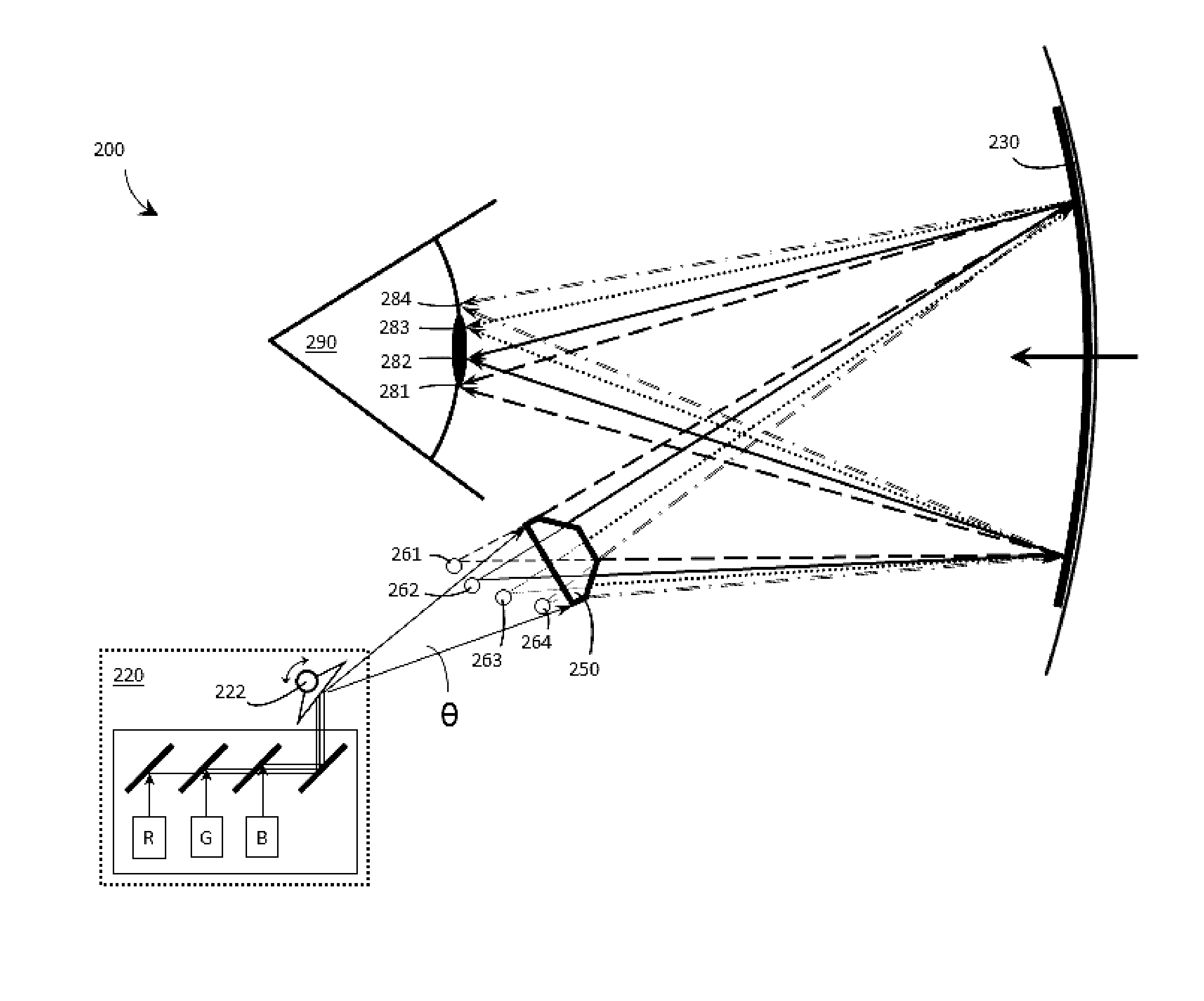
The present invention provides a light source for a projector system, and method of operating the light source as well as a projector system that provides:i. a substantially uniform brightness across the surface of an image modulator, andii. at each point of the surface of the image modulator a more uniform filling of the available angular space.Embodiments of the present invention use a laser light source for use with an image modulator, the light source emitting light with multiple wavelengths for at least one primary color and a light integrator system that for each of the wavelengths is adapted to provide:i. a substantially uniform brightness across the surface of the image modulator, andii. at each point of the surface of the image modulator a more uniform filling of the available angular space.
Owner:BARCO NV
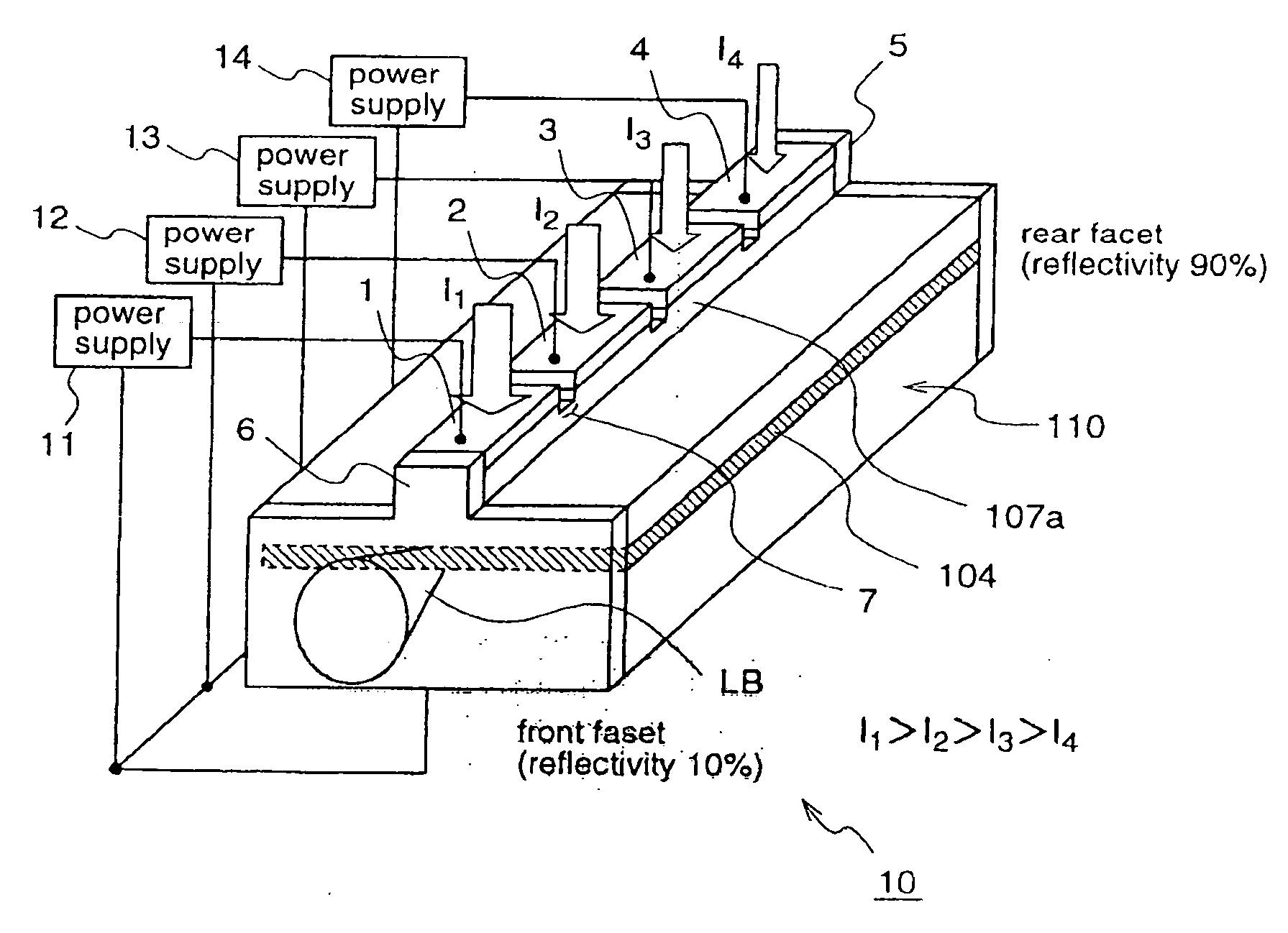
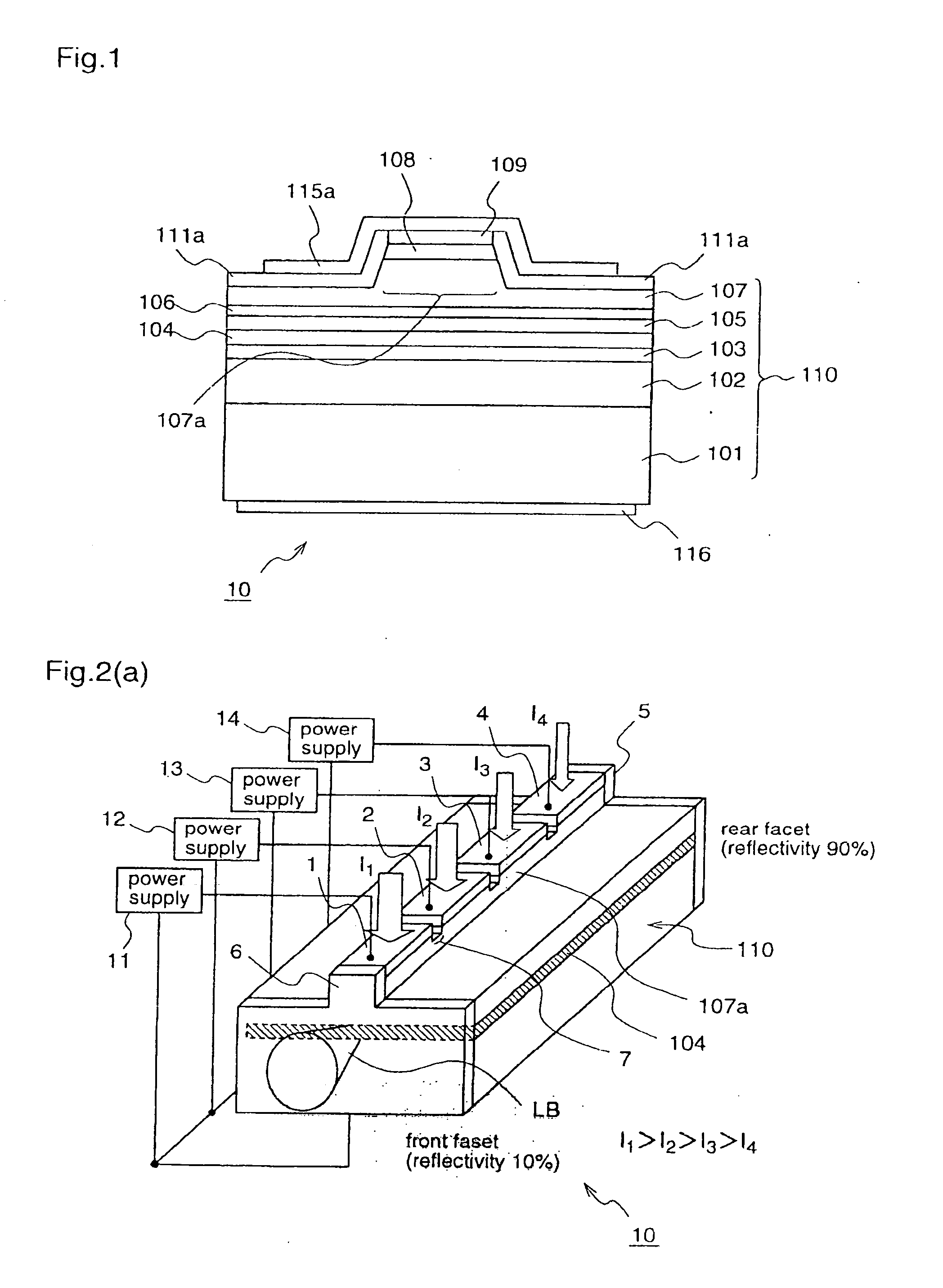
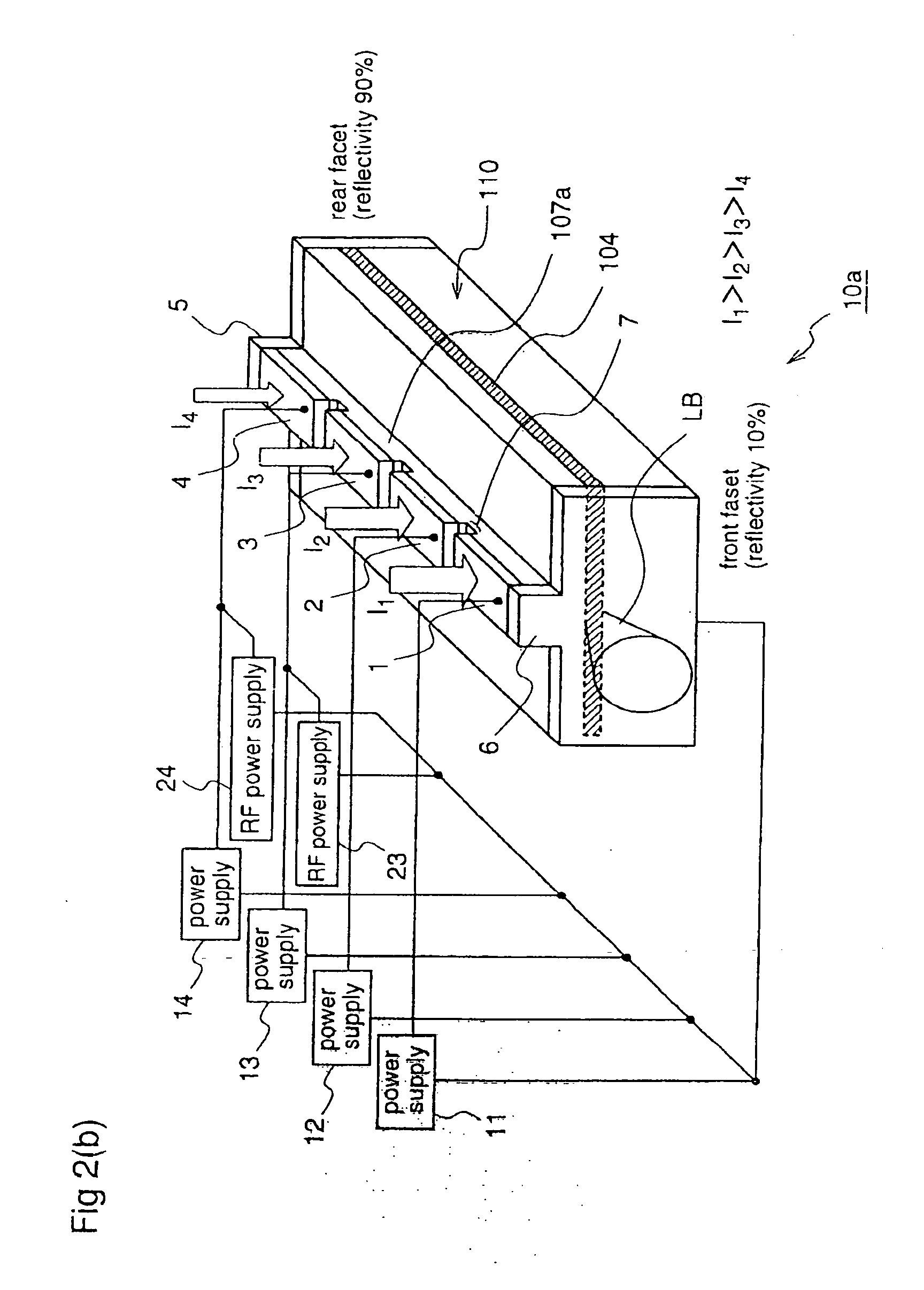
Semiconductor laser device and laser projector
ActiveUS20070165685A1High densityHigh differential gainOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsCharge-carrier densityDensity distribution
According to the present invention, in a semiconductor laser device (10) having different facet reflectivities, an electrode disposed on a stripe ridge (107a) is divided into four electrode parts (1), (2), (3), and (4), and a larger injection current is injected to an electrode part that is closer to a light emission facet side. According to this semiconductor laser device, a carrier density distribution in an active layer that is opposed to the stripe ridge can be matched to a light intensity distribution in the active layer, thereby preventing degradation in high output characteristic due to destabilization of transverse mode and reduction in gain which are caused by spatial hole burning.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
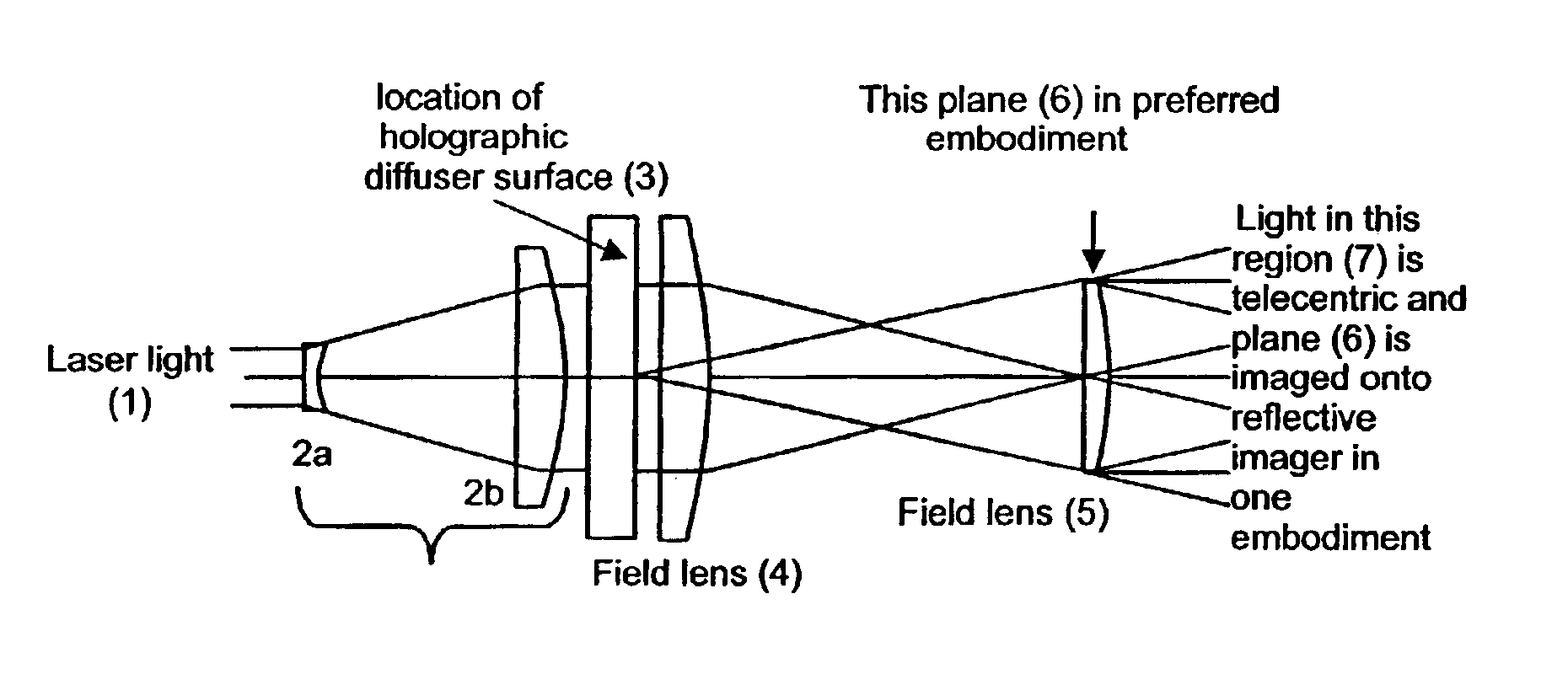
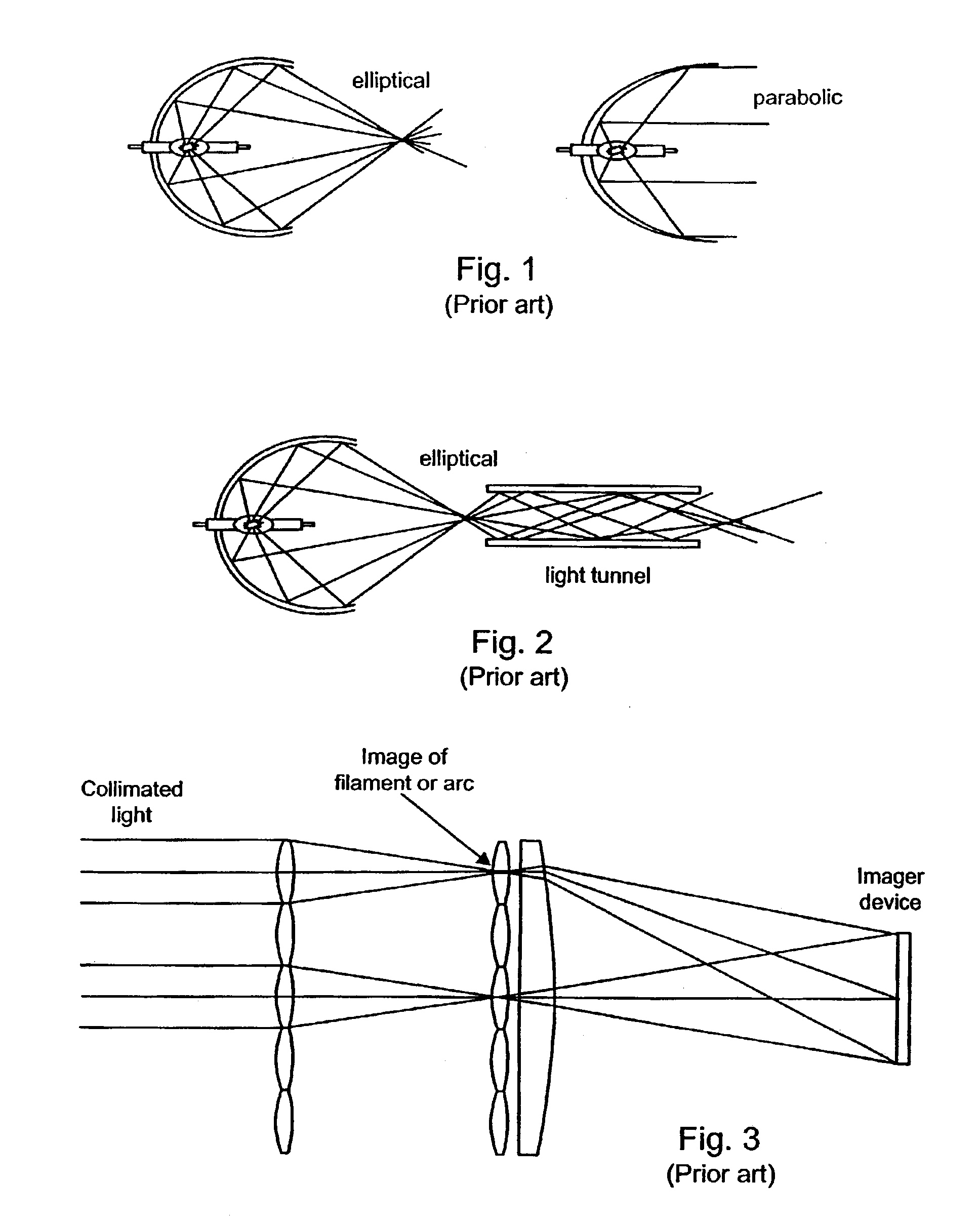
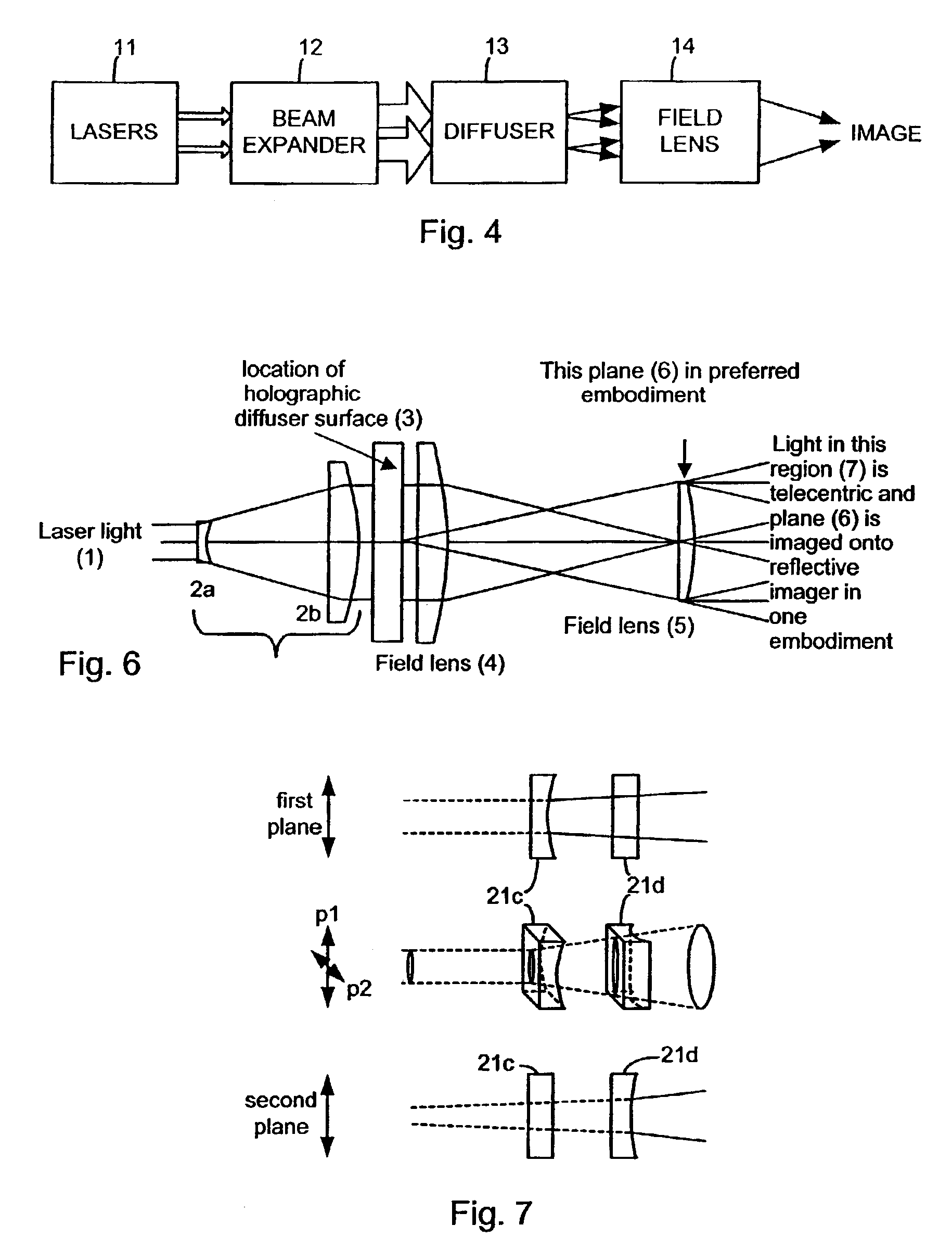
Illumination device and method for laser projector
InactiveUS6870650B2Few and low componentImprove design flexibilityTelevision system detailsDiffusing elementsLight beamDisplay device
Systems and methods for providing illumination suitable for imaging devices such as laser projection systems. In one embodiment, a highly collimated (e.g., laser light) beam is passed through a holographic diffuser to create a well defined cone angle for the light emanating from each point on the diffuser. This light is focused into an illumination image that is controlled by the prescription of the diffuser. In one embodiment, the image is a uniformly intense rectangle having a 4:3 aspect ratio to match an imager for a projection display. The diffuser prescription and resulting illumination image can be selected to match any desired imager. The present systems and methods may provide the advantages of high level of light efficiency, reduction or elimination of speckle and “worminess” and reduction or elimination of cosine4 and gaussian intensity falloff, all of which are common in prior art designs.
Owner:FLIR SYSTEMS TRADING BELGIUM BVBA
Laser light beam guiding device on a stone cutter
InactiveUS7066627B1Precise and rapid cutting activityPrecise and rapid activityMetal sawing accessoriesLighting elementsSTONE CUTTERLight beam
A laser light beam guiding device on a stone cutter includes a tubular main body pivoted to a lug of a seat which is secured to a front top of a blade guard of the stone cutter, a battery chamber in the main body controlled by a switch button on the top, a tubular sleeve on the rear portion of the main body and a laser projector rotatably engaged with the front end of the main body to emit the light beam on a working piece to decide a cutting line for the saw blade to follow up.
Owner:CHEN YUEH TING
Real-time detection and weld quality prediction in vibration welding process
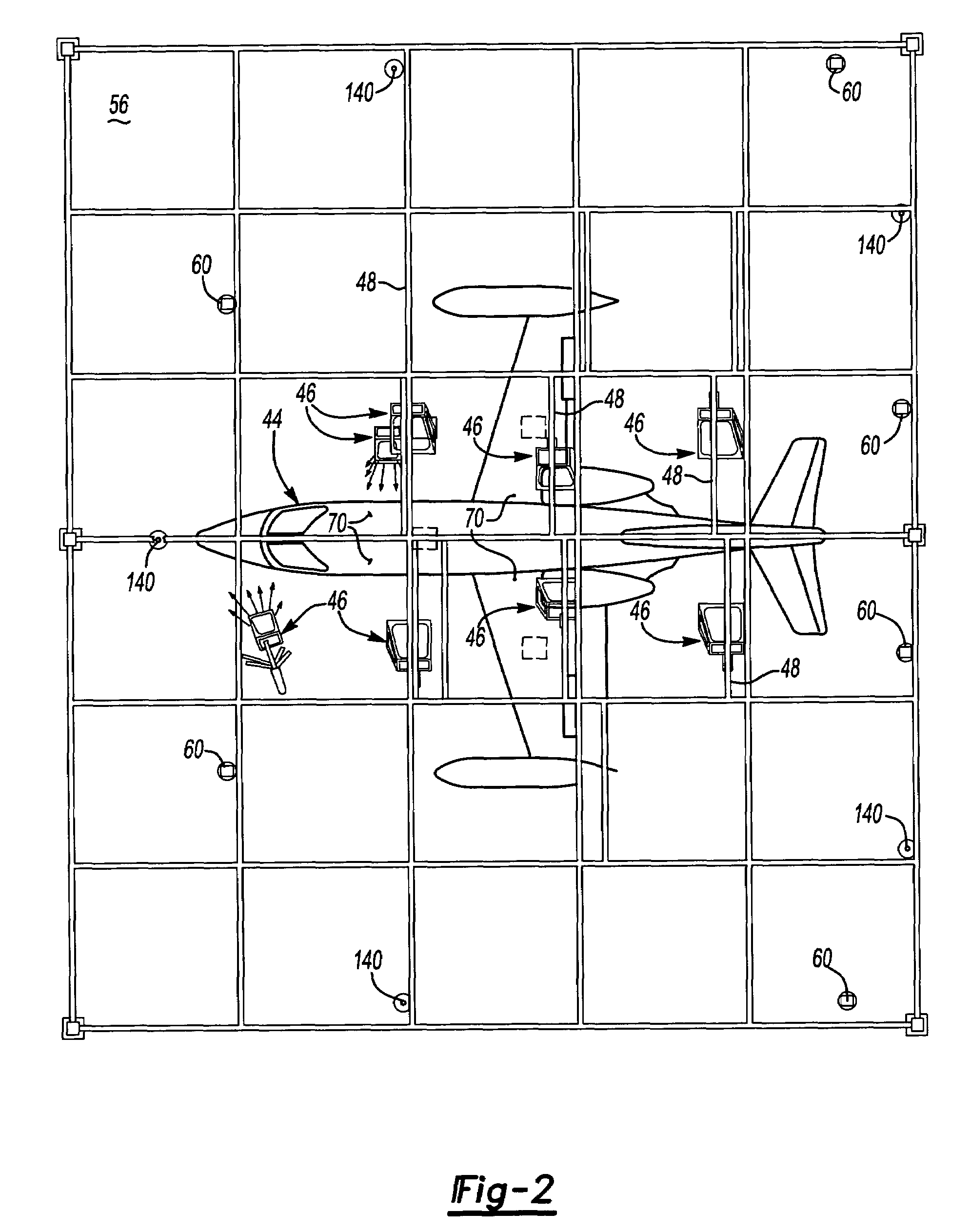
A system includes a host machine and a status projector. The host machine is in electrical communication with a collection of sensors and with a welding controller that generates control signals for controlling the welding horn. The host machine is configured to execute a method to thereby process the sensory and control signals, as well as predict a quality status of a weld that is formed using the welding horn, including identifying any suspect welds. The host machine then activates the status projector to illuminate the suspect welds. This may occur directly on the welds using a laser projector, or on a surface of the work piece in proximity to the welds. The system and method may be used in the ultrasonic welding of battery tabs of a multi-cell battery pack in a particular embodiment. The welding horn and welding controller may also be part of the system.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Laser projection method and laser projector
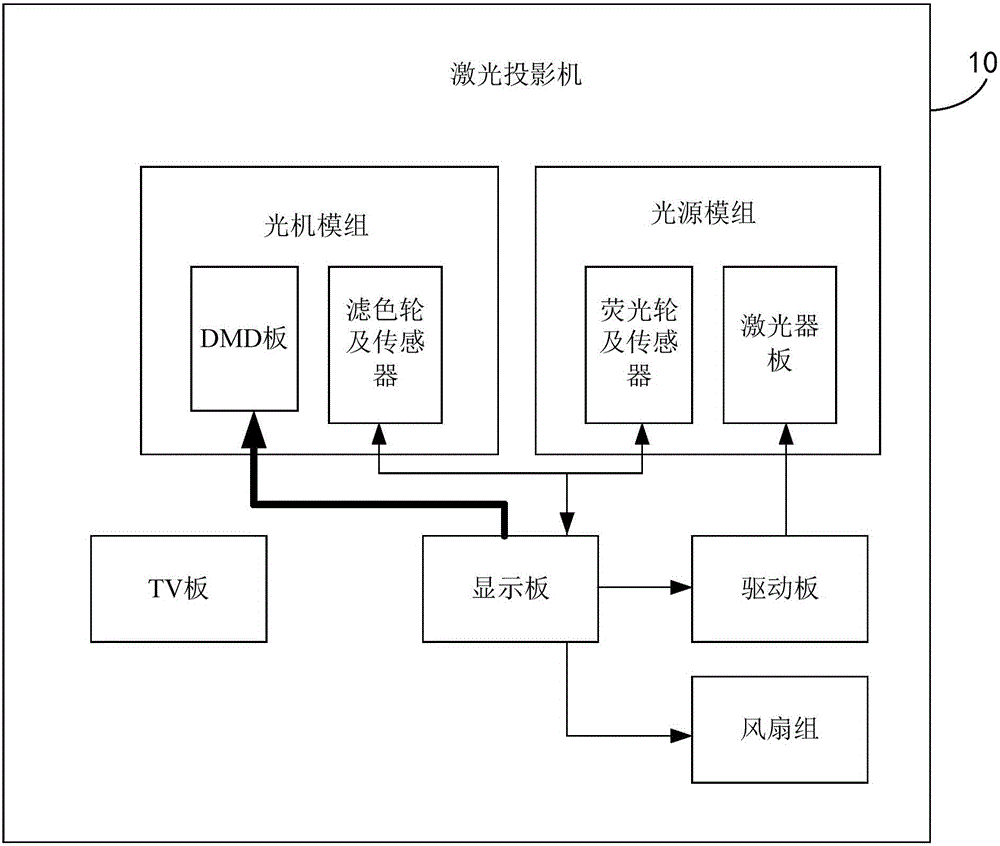
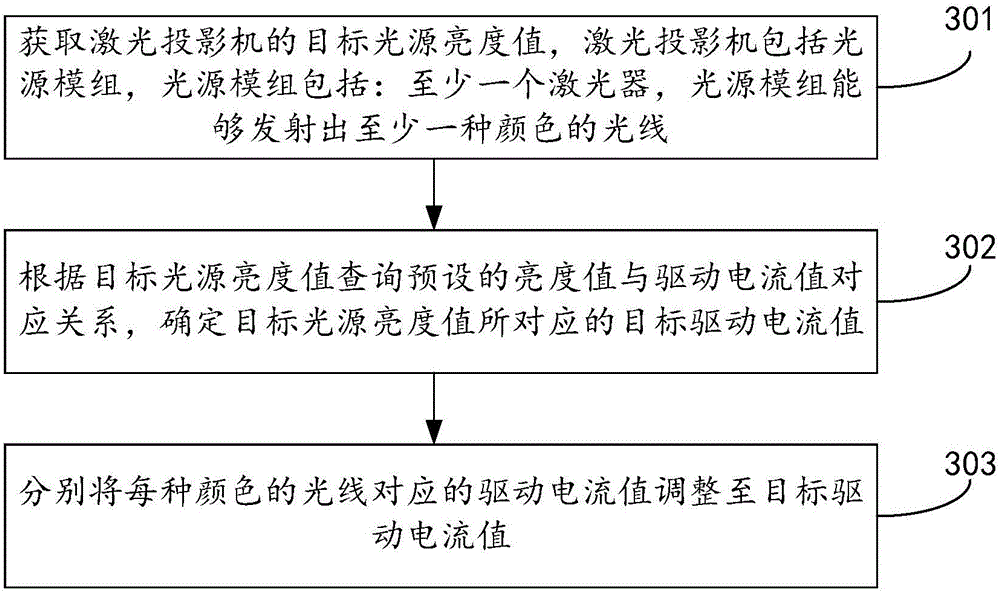
ActiveCN105911807AImprove color temperature consistencyQuality improvementProjectorsDriving currentLaser projector
The invention discloses a laser projection method and a laser projector and belongs to the projection field. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring a target light source brightness value of the laser projector, wherein the laser projector includes a light source module; the light source module includes at least one laser; and the light source module can emit at least one color of light; according to the target light source brightness value, inquiring a corresponding relation of a preset brightness value and a driving current value and determining a target driving current value corresponding to the target light source brightness value, wherein the corresponding relation is used for recording that the light source brightness values of the laser projector are n brightness values respectively and recording the driving current value of the corresponding laser in a period of generating each color of light when a color temperature value of synthesis light synthesized by the at least one color of light is a target color temperature value; and adjusting the driving current value corresponding to the each color of light to the target driving current value. In the prior art, color temperature consistency is low. By using the method and the projector of the invention, the above problem is solved. And the method and the projector of the invention are used for laser projection.
Owner:HISENSE VISUAL TECH CO LTD
Working position measuring system
ActiveUS7110102B2Improve working efficiencySimple and inexpensive mannerActive open surveying meansPosition fixationElevation angleLight beam
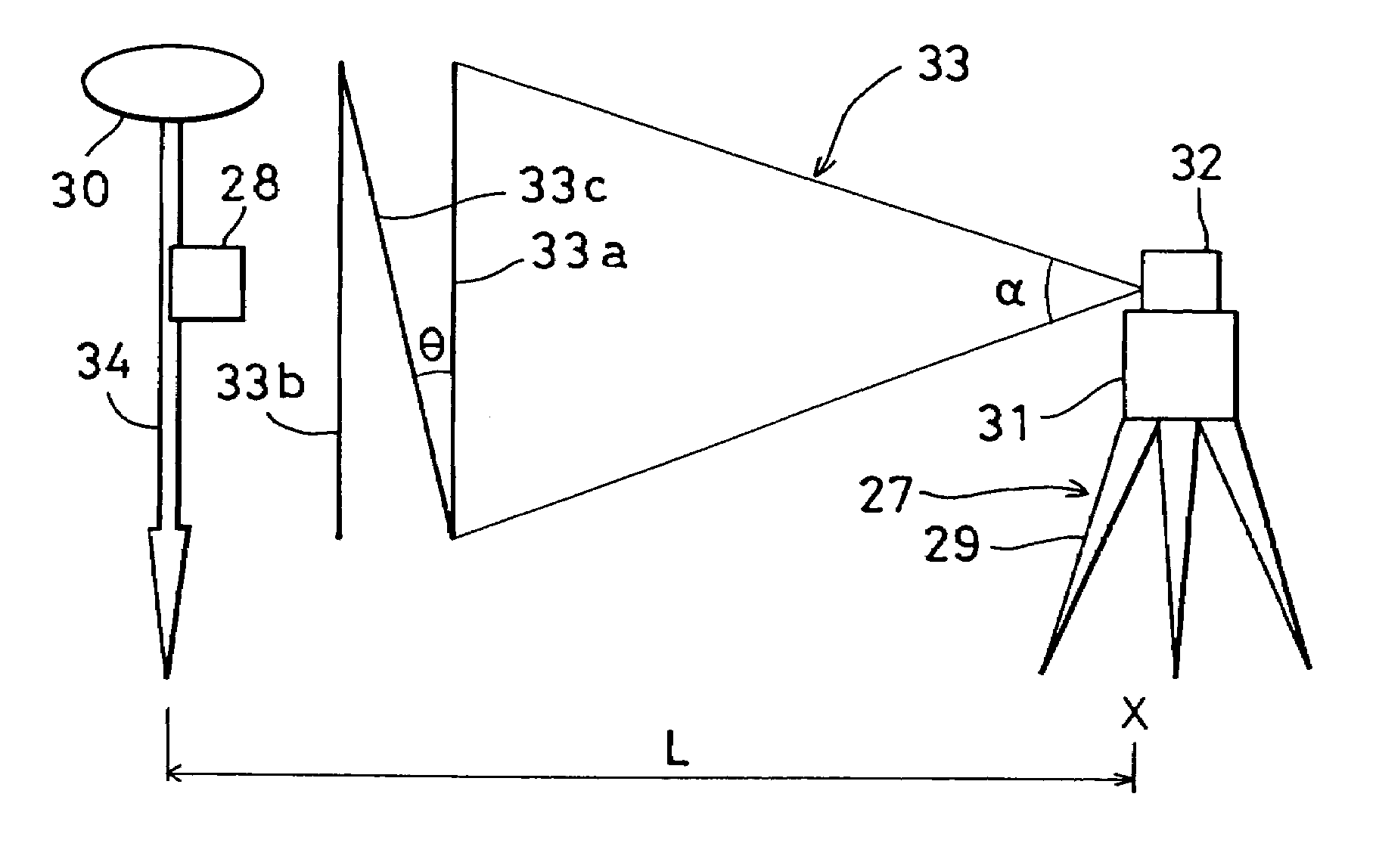
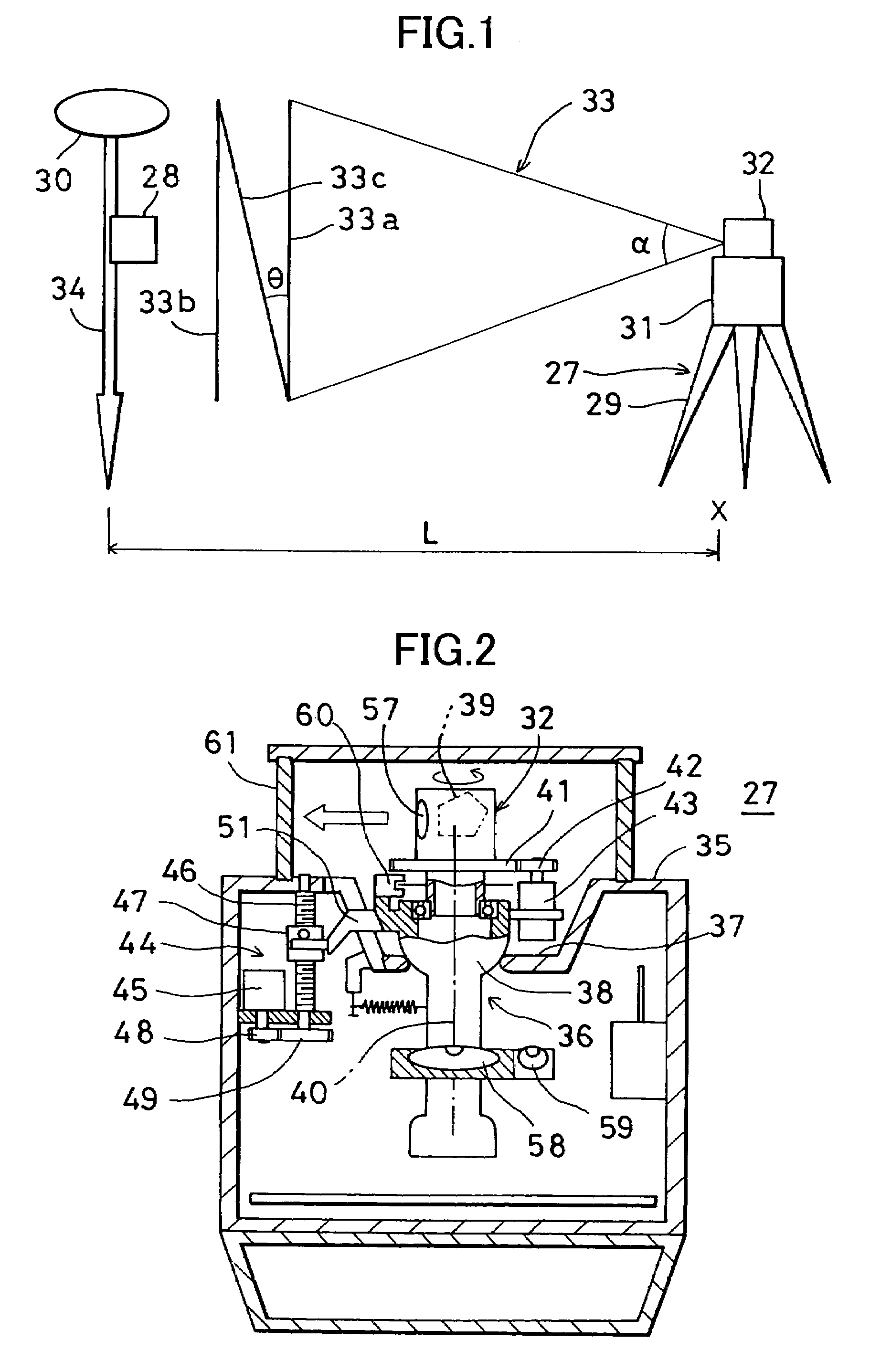
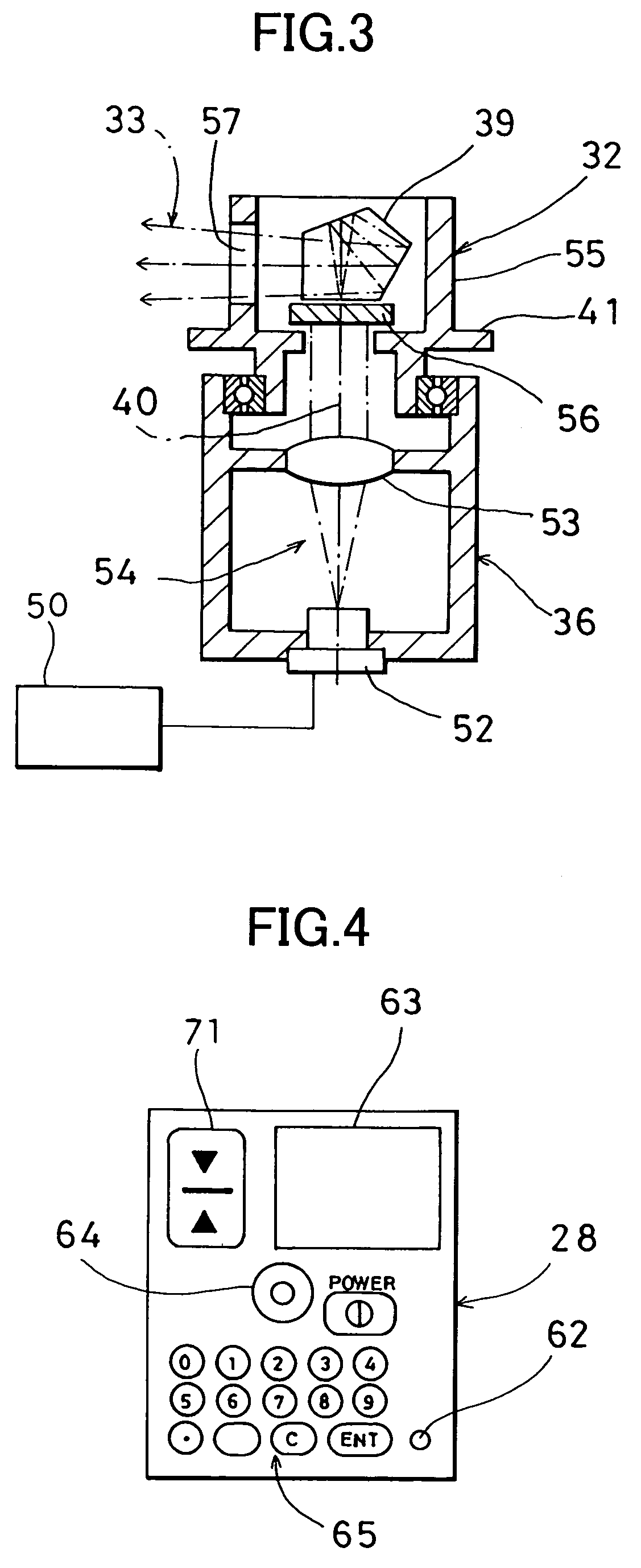
A working position measuring system, comprising a rotary laser device for irradiating and rotating a laser beam and a photodetection sensor device for receiving the laser beam and for detecting a working position, wherein the rotary laser device comprises a laser projector for projecting at least two fan-shaped beams with at least one beam tilted, and the photodetection sensor device comprises at least one photodetection unit for receiving the fan-shaped beams and an arithmetic unit for calculating an elevation angle relative to the rotary laser device based on photodetection signals produced when the photodetection unit receives the light beam.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com