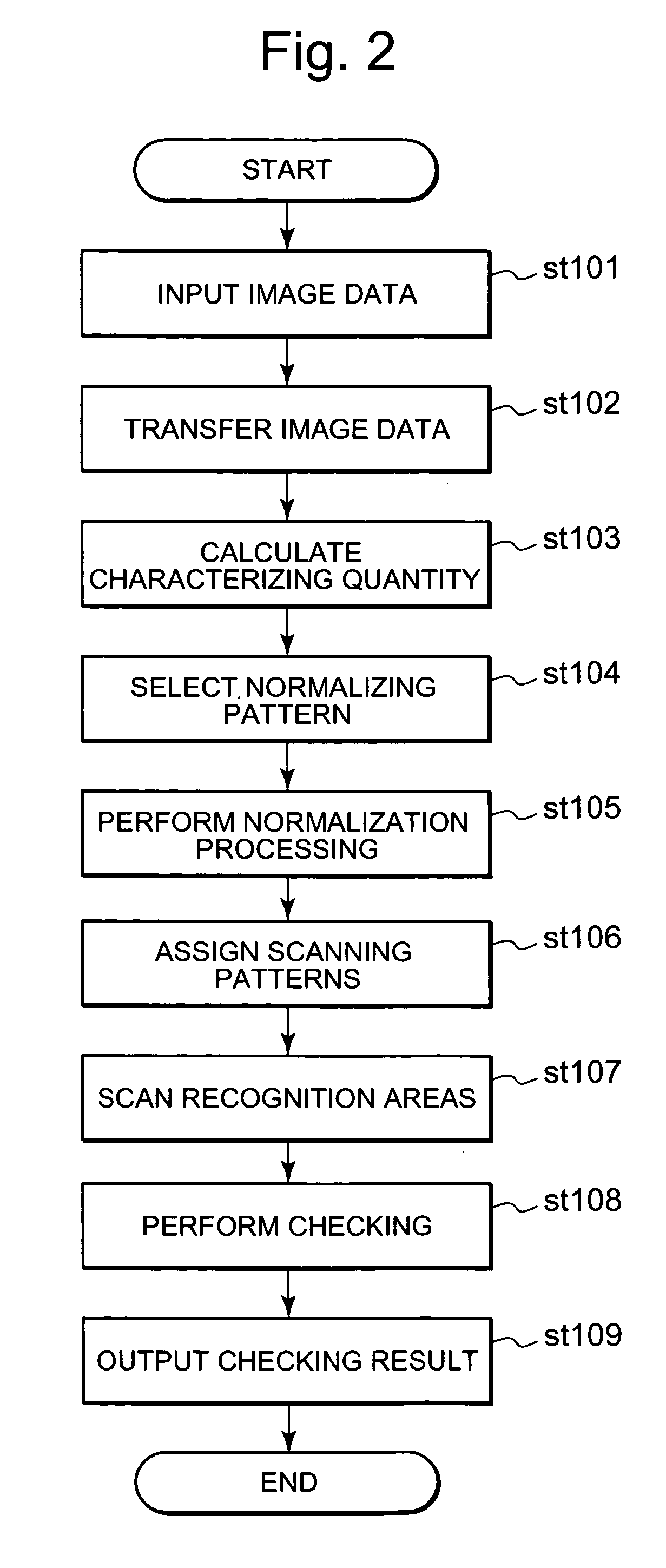
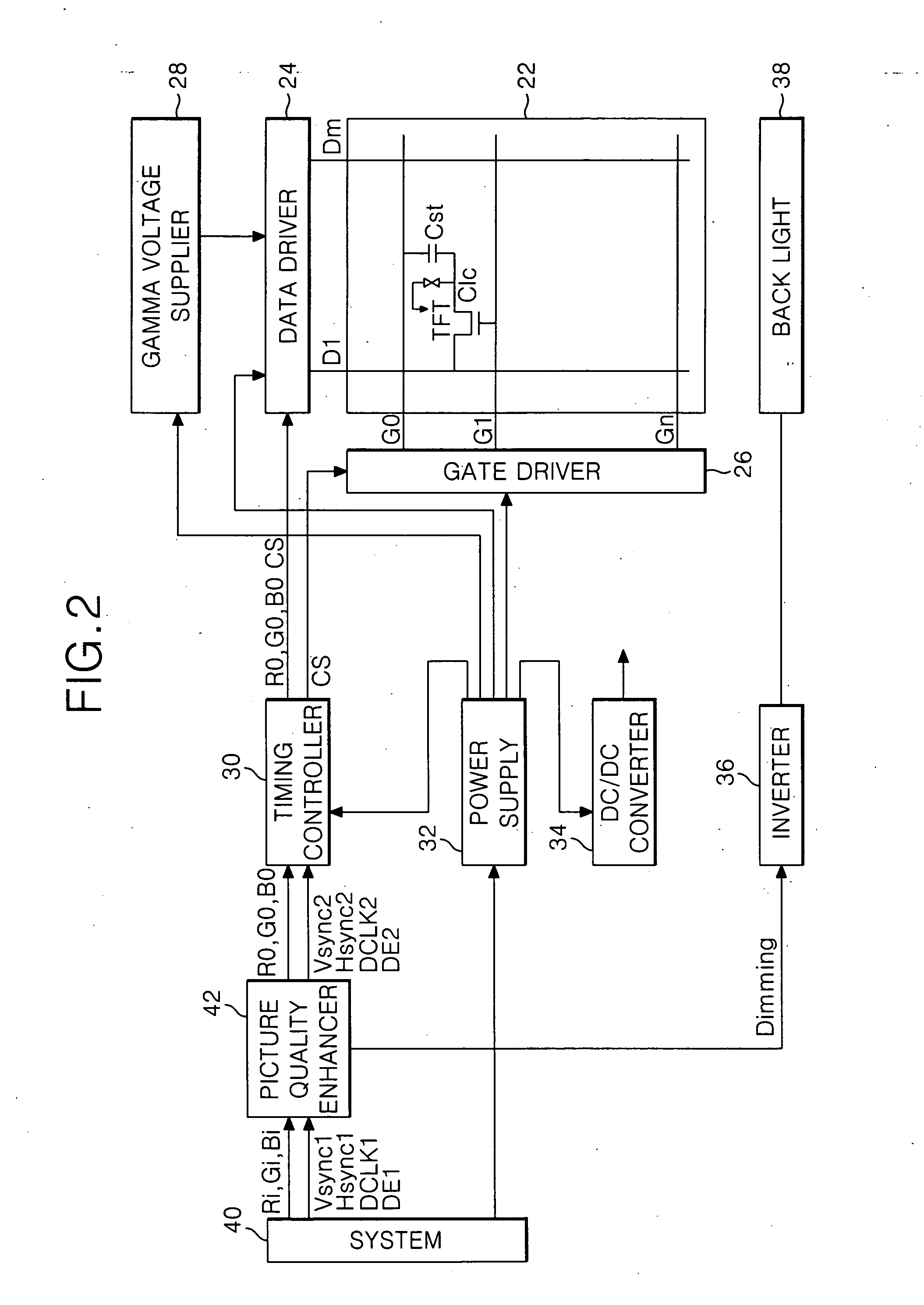
Patents
Literature
825 results about "Consecutive frame" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
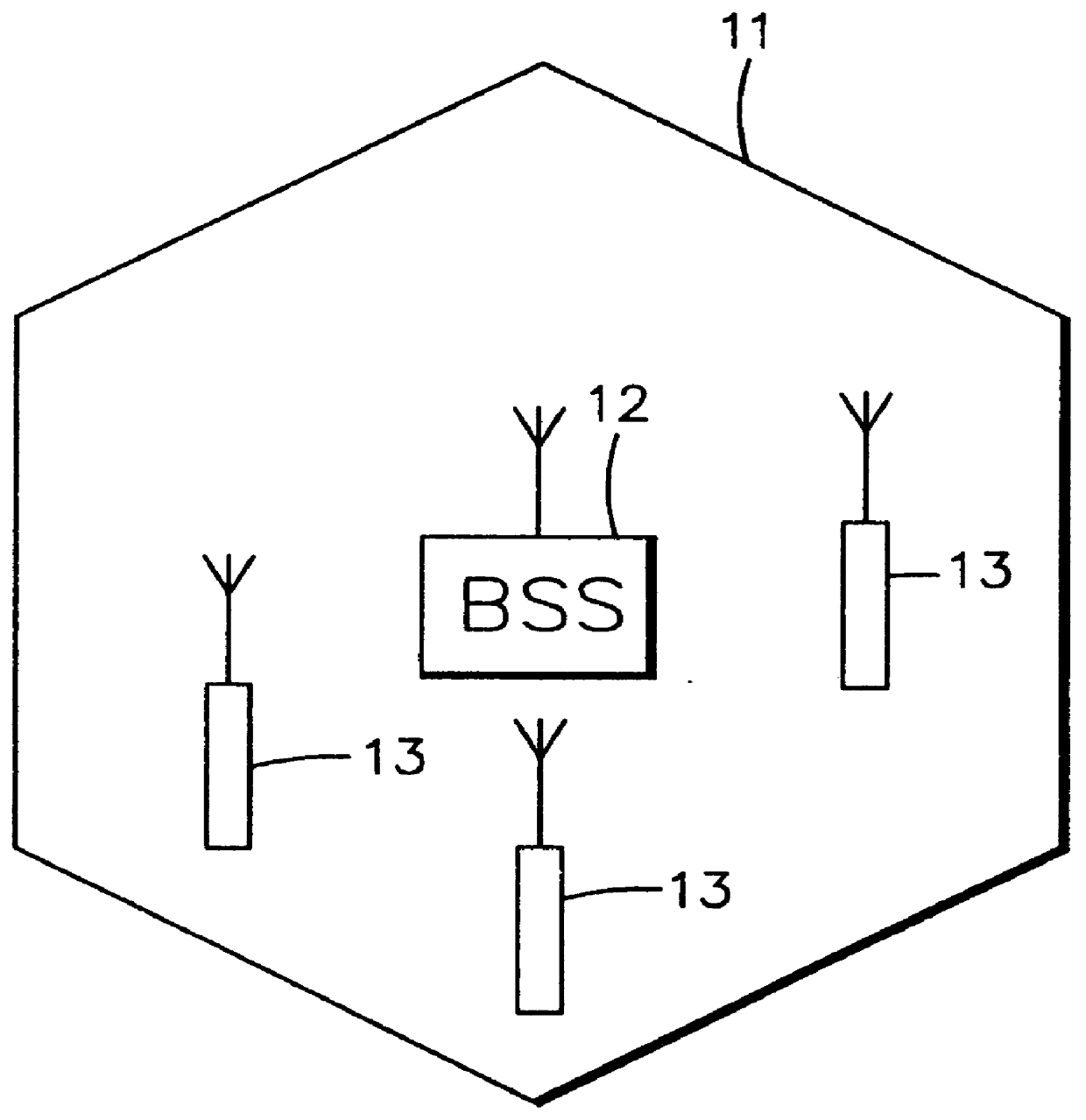
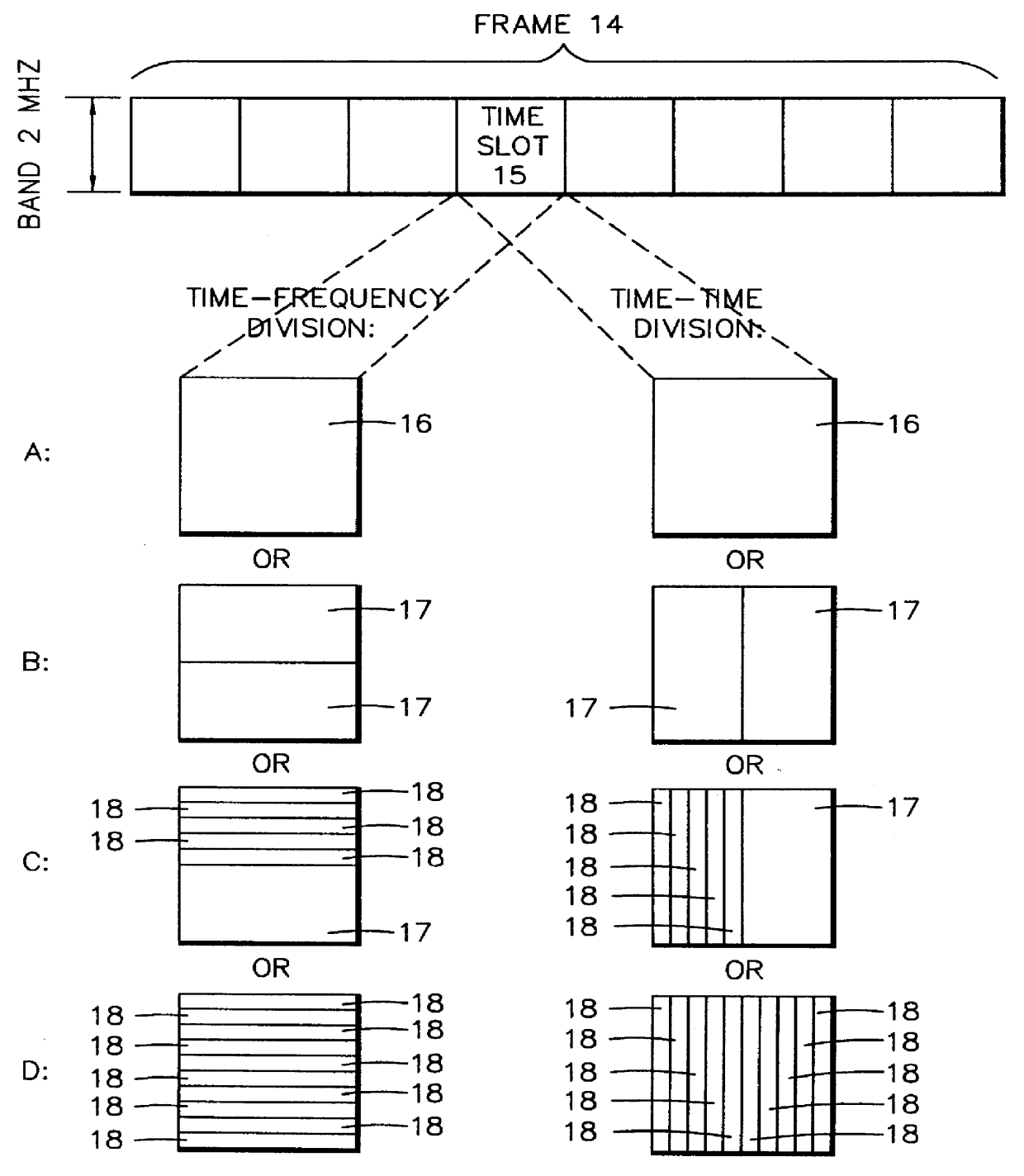
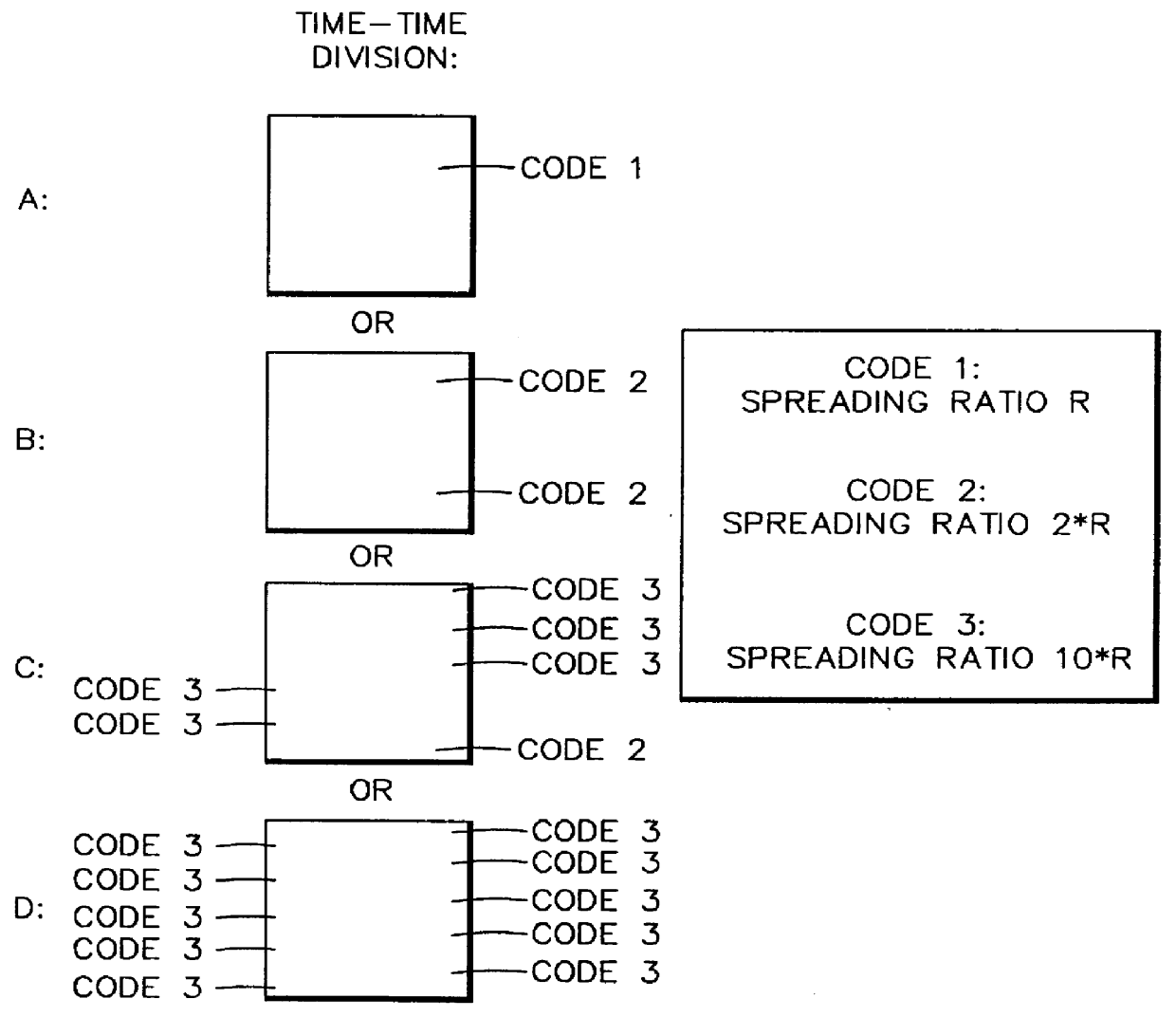
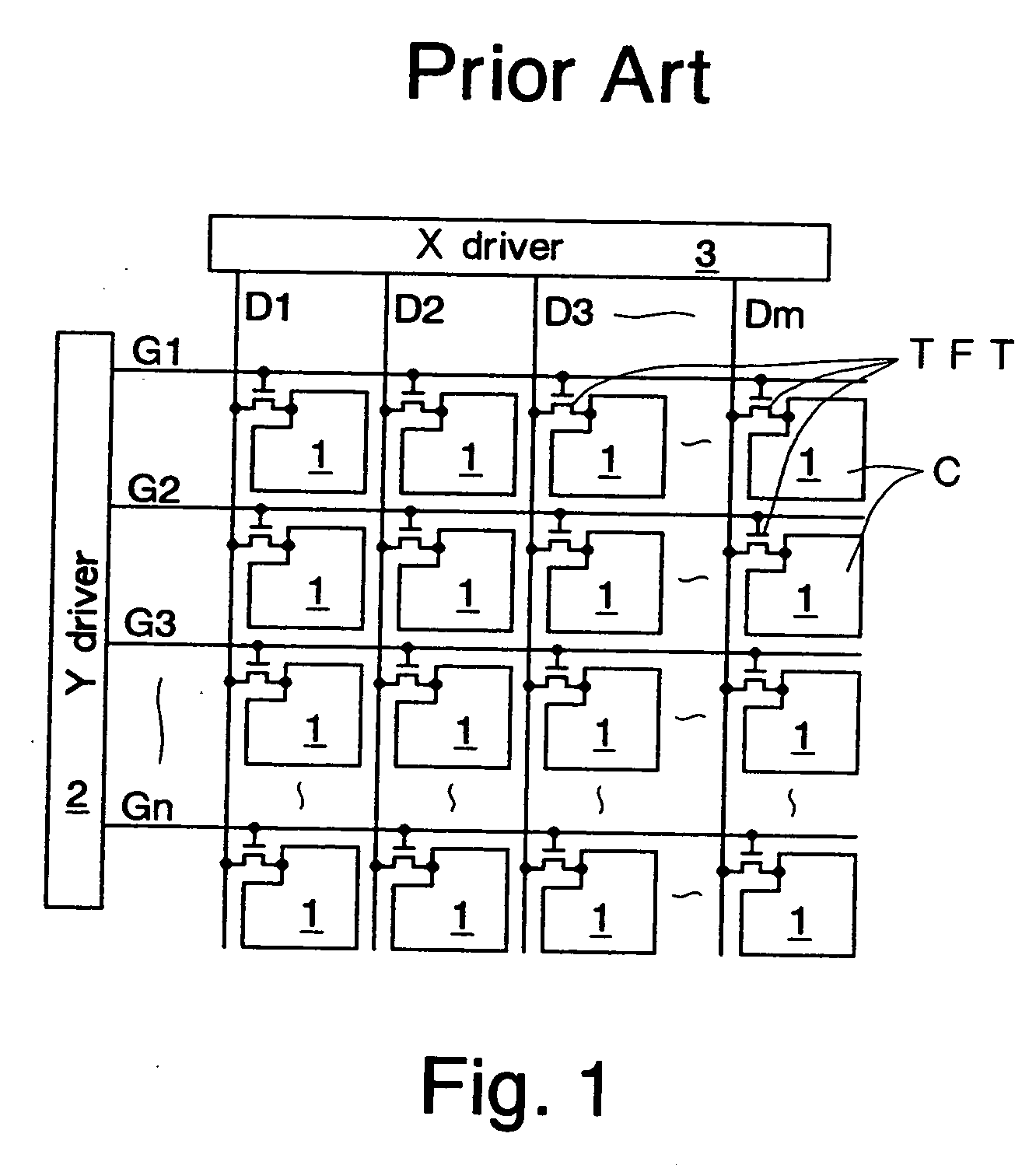
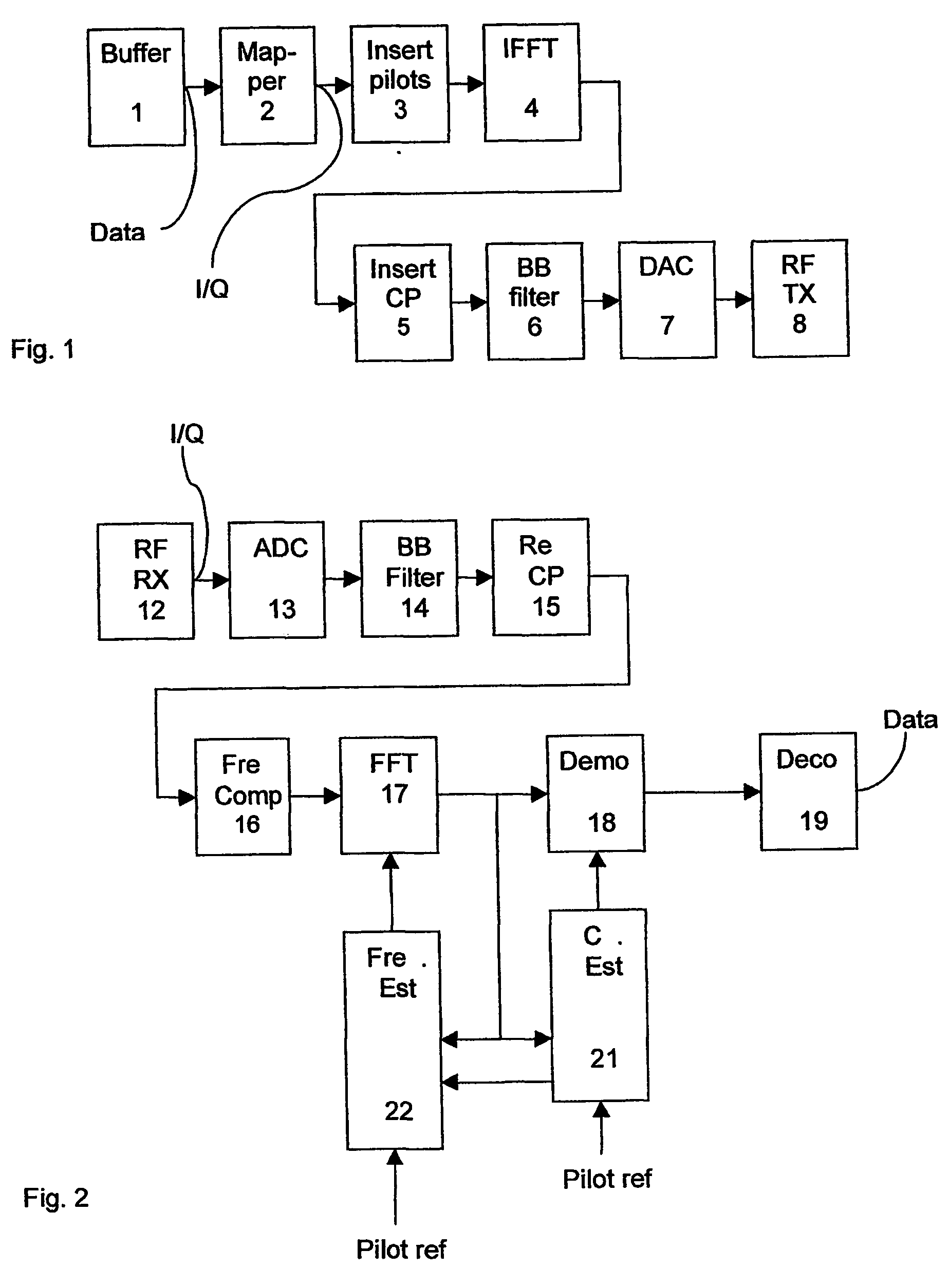
Method for radio resource control
In order to control the use of physical radio resources, the physical radio resources are divided into chronologically consecutive frames (14), so that a frame contains slots (16, 17, 18) of various sizes, which slots represent a given share of the physical radio resources contained in the frame and can be individually allocated to different radio connections. The first dimension of a frame is time and the second dimension can be time, frequency or code. In the direction of the second dimension the slots represent various sizes, and a given first integral number of slots of the first size can be modularly replaced by another integral number of slots of another size. A certain number of consecutive frames form a superframe (19), in which case frames with corresponding locations in consecutive superframes are equal in slot division and allocations, if the data transmission demands do not change. Changes in the state of occupancy of the slots are possible at each superframe. In order to form an uplink connection, the mobile station sends a capacity request, where it indicates the type of requested connection and the demand of resources. In order to form a downlink connection, the base station subsystem sends a paging call, where it indicates the location in the superframe of the slots allocated to the connection. In order to indicate the state of occupancy, the base station subsystem maintains a superframe-size parametrized reservation table.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
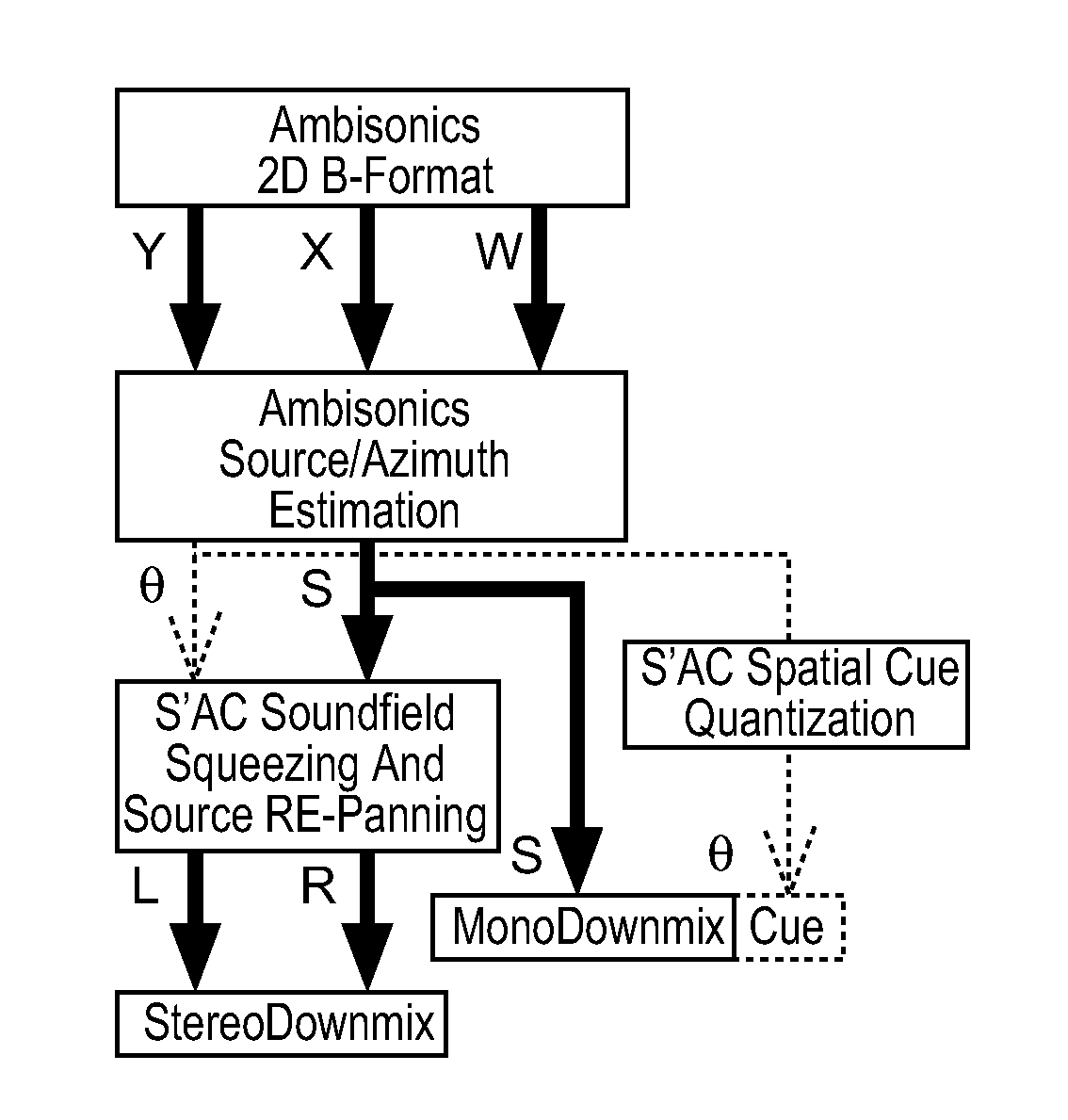
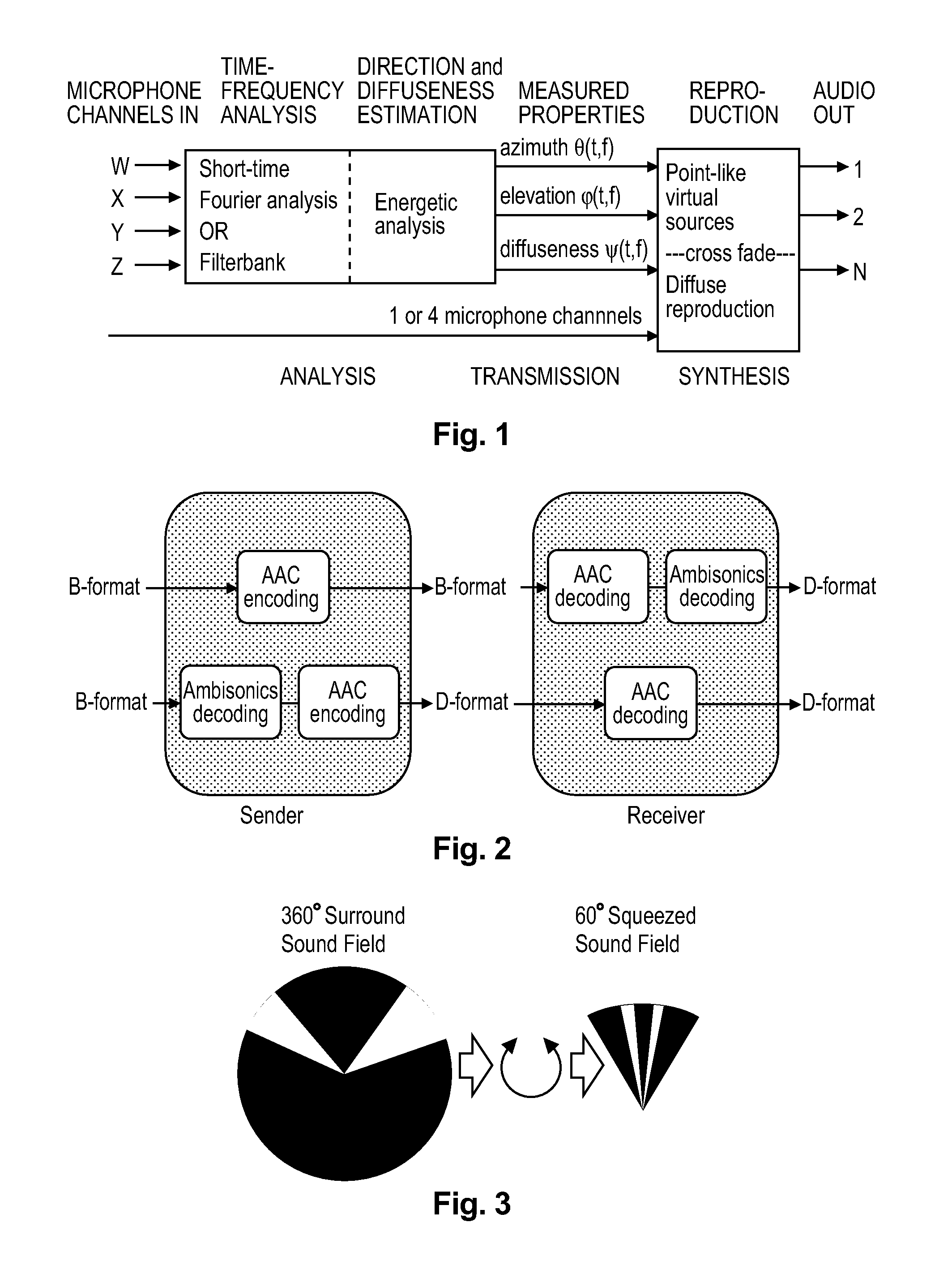
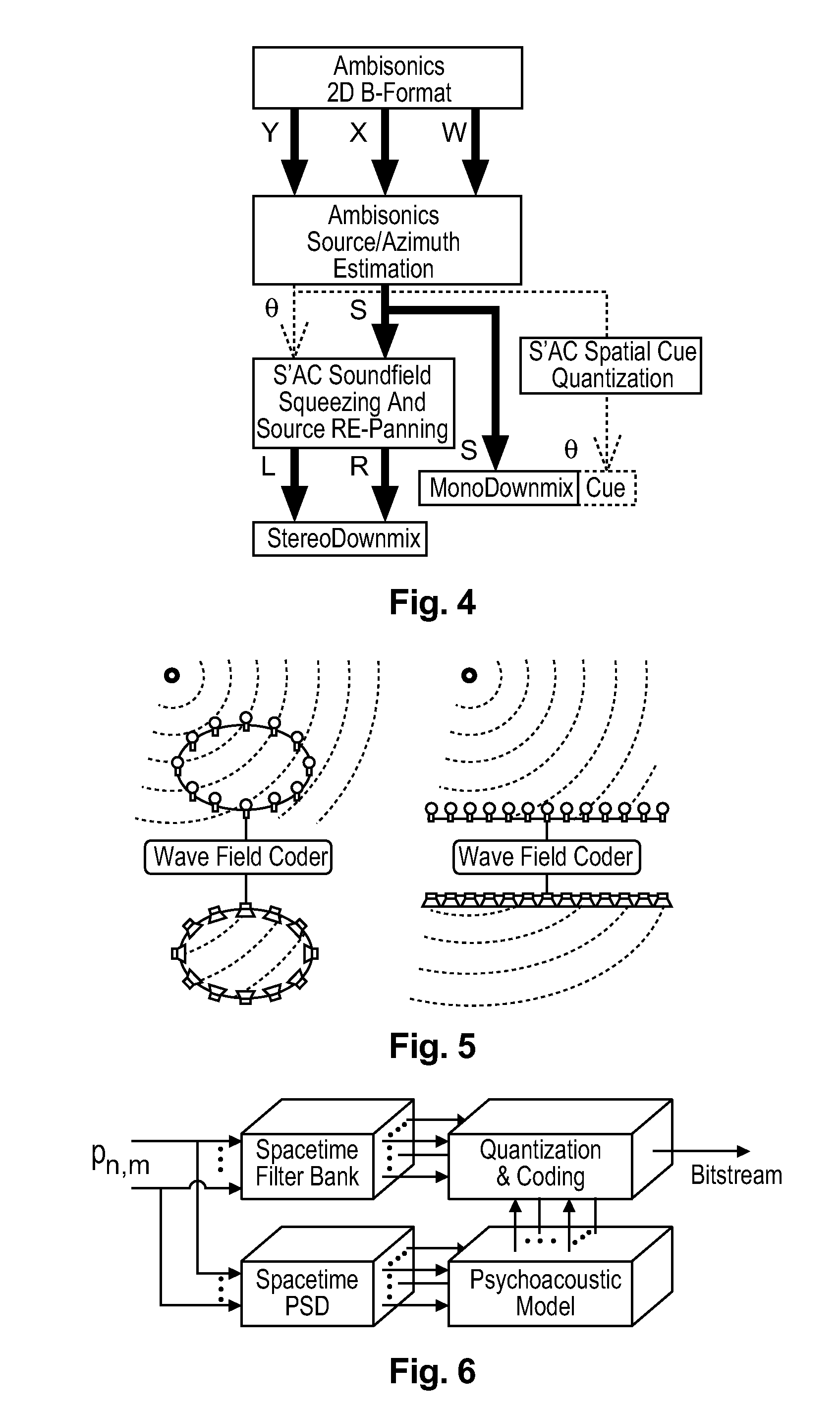
Method and apparatus for encoding and decoding successive frames of an ambisonics representation of a 2- or 3-dimensional sound field
ActiveUS20120155653A1Easy accessThe result is reasonableBroadcast information characterisationSpeech analysisTime domainData rate
Representations of spatial audio scenes using higher-order Ambisonics HOA technology typically require a large number of coefficients per time instant. This data rate is too high for most practical applications that require real-time transmission of audio signals. According to the invention, the compression is carried out in spatial domain instead of HOA domain. The (N+1)2 input HOA coefficients are transformed into (N+1)2 equivalent signals in spatial domain, and the resulting (N+1)2 time-domain signals are input to a bank of parallel perceptual codecs. At decoder side, the individual spatial-domain signals are decoded, and the spatial-domain coefficients are transformed back into HOA domain in order to recover the original HOA representation.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Linear system based, qualitative independent motion detection from compressed mpeg surveillance video
InactiveUS8164629B1Shorten the timeExtra computationImage enhancementImage analysisIndependent motionMotion vector
The present invention features a qualitative method to detect independent motion revealed in successive frames of a compressed surveillance MPEG video stream using linear system consistency analysis without decompression of the stream, identifying the segments containing independent motion in a real-time or faster manner, for the retrieval of these segments. The linear system is constructed using the macroblocks of MPEG compressed video frames. The normal flow value of the macroblock is obtained by taking the dot product between the macroblock gradient vector, computed by averaging the four block gradient vectors, and the motion vector of this macroblock. The normal flow value is filtered for inclusion in the linear system, and the statistic of the matrices of the resulting linear system is determined, filtered to screen out false negatives and outliers, and used to determine the presence or absence of independent motion.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Interactive Display System
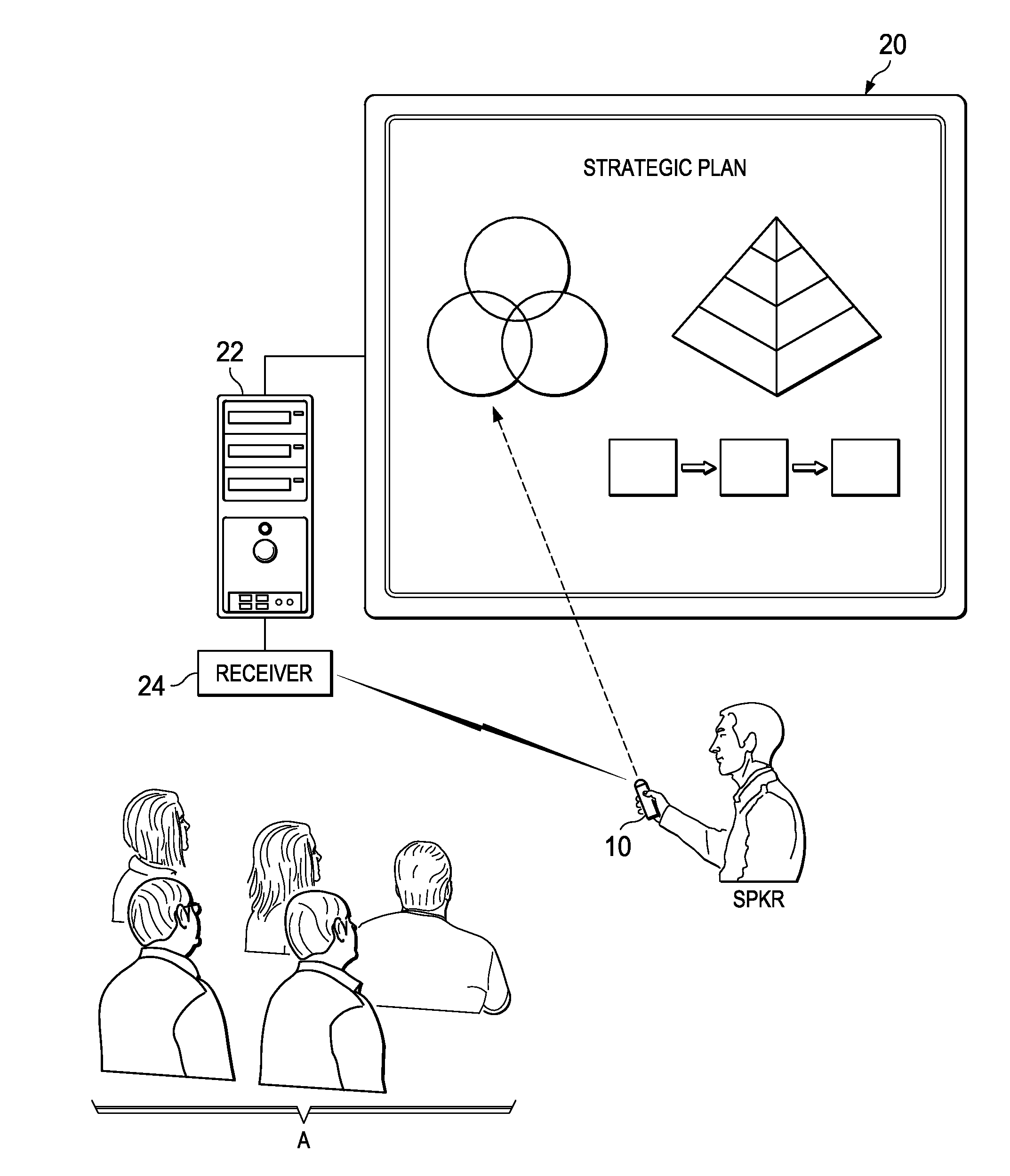
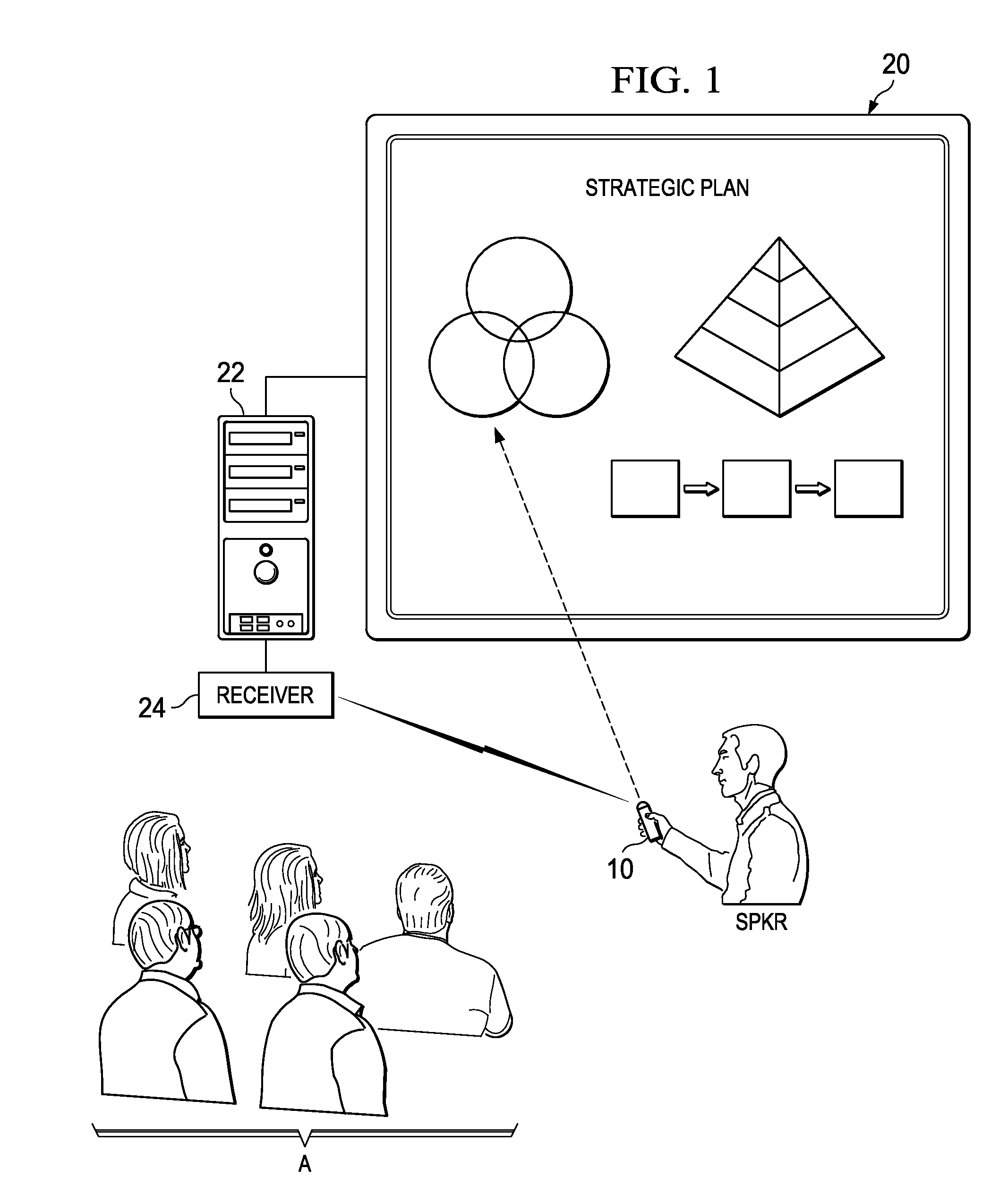
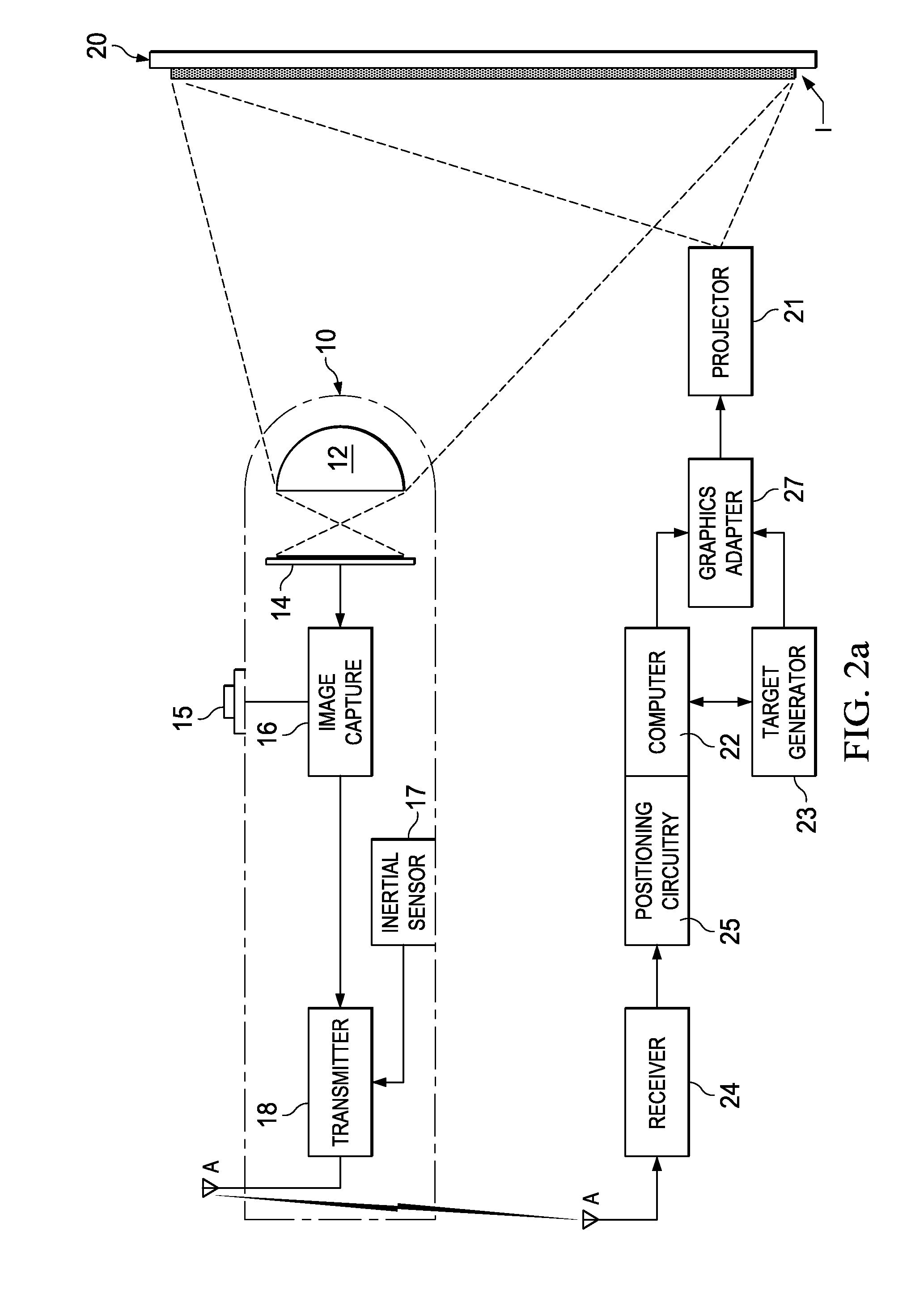
InactiveUS20110227827A1Reduce human perceptibilityPositioning can be rapidly and efficientlyInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceConsecutive frame
An interactive display system including a wireless pointing device including a camera or other video capture system. The pointing device captures images displayed by the computer, including one or more human-imperceptible positioning targets. The positioning targets are presented as patterned modulation of the intensity (e.g., variation in pixel intensity) in a display frame of the visual payload, followed by the opposite modulation in a successive frame. At least two captured image frames are subtracted from one another to recover the positioning target in the captured visual data and to remove the displayed image payload. The location, size, and orientation of the recovered positioning target identify the aiming point of the remote pointing device relative to the display. Another embodiment uses temporal sequencing of positioning targets (either human-perceptible or human-imperceptible) to position the pointing device.
Owner:INTERPHASE CORP
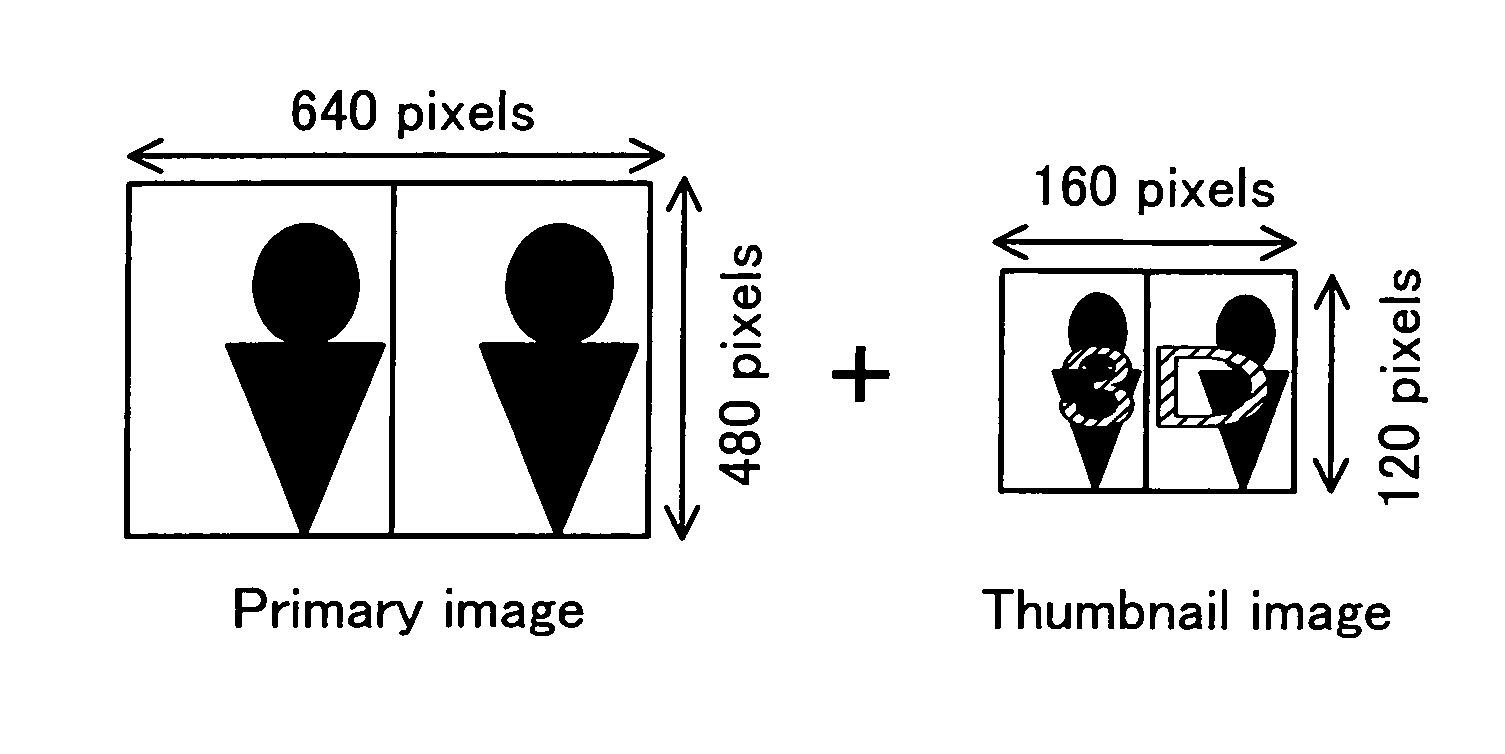
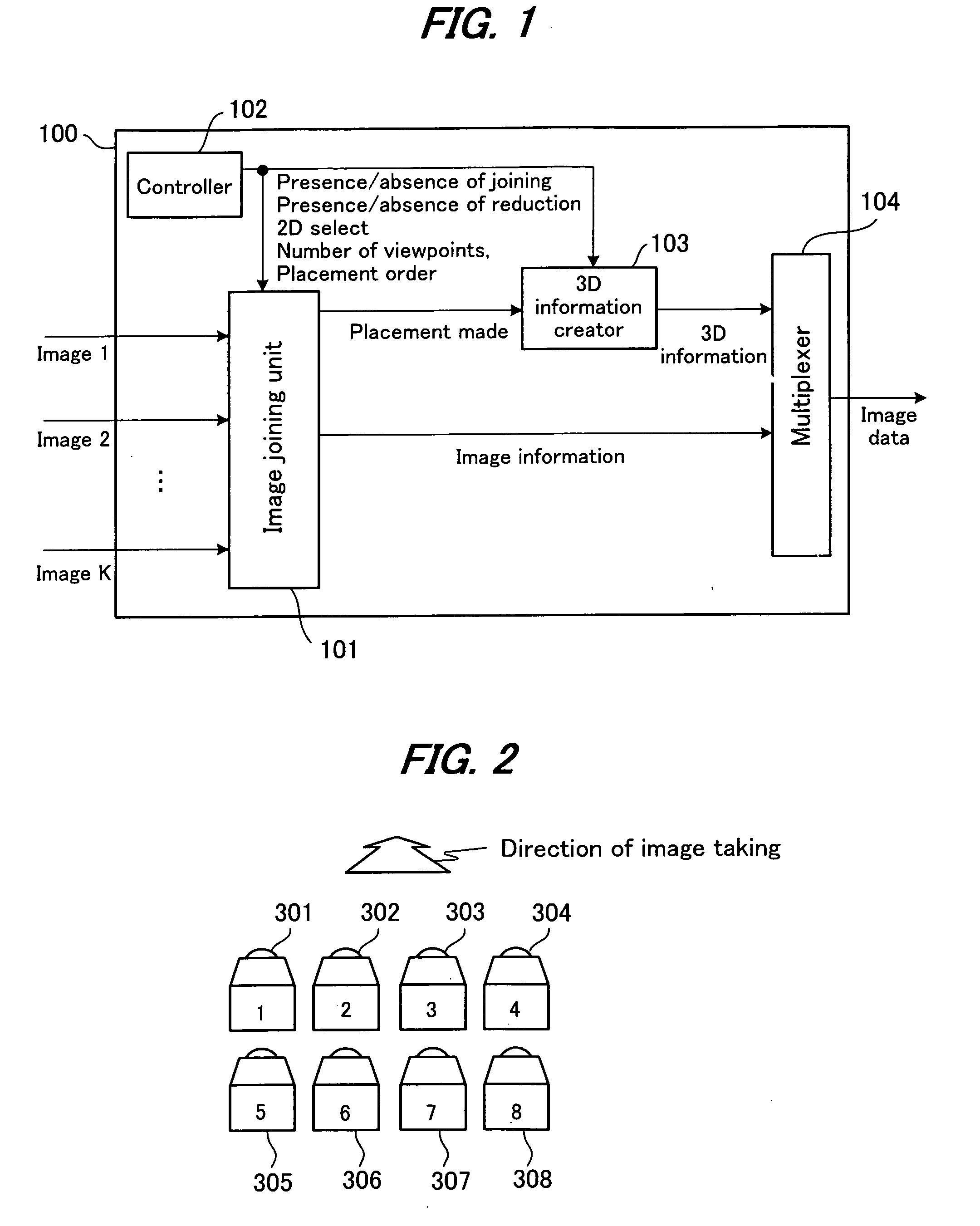
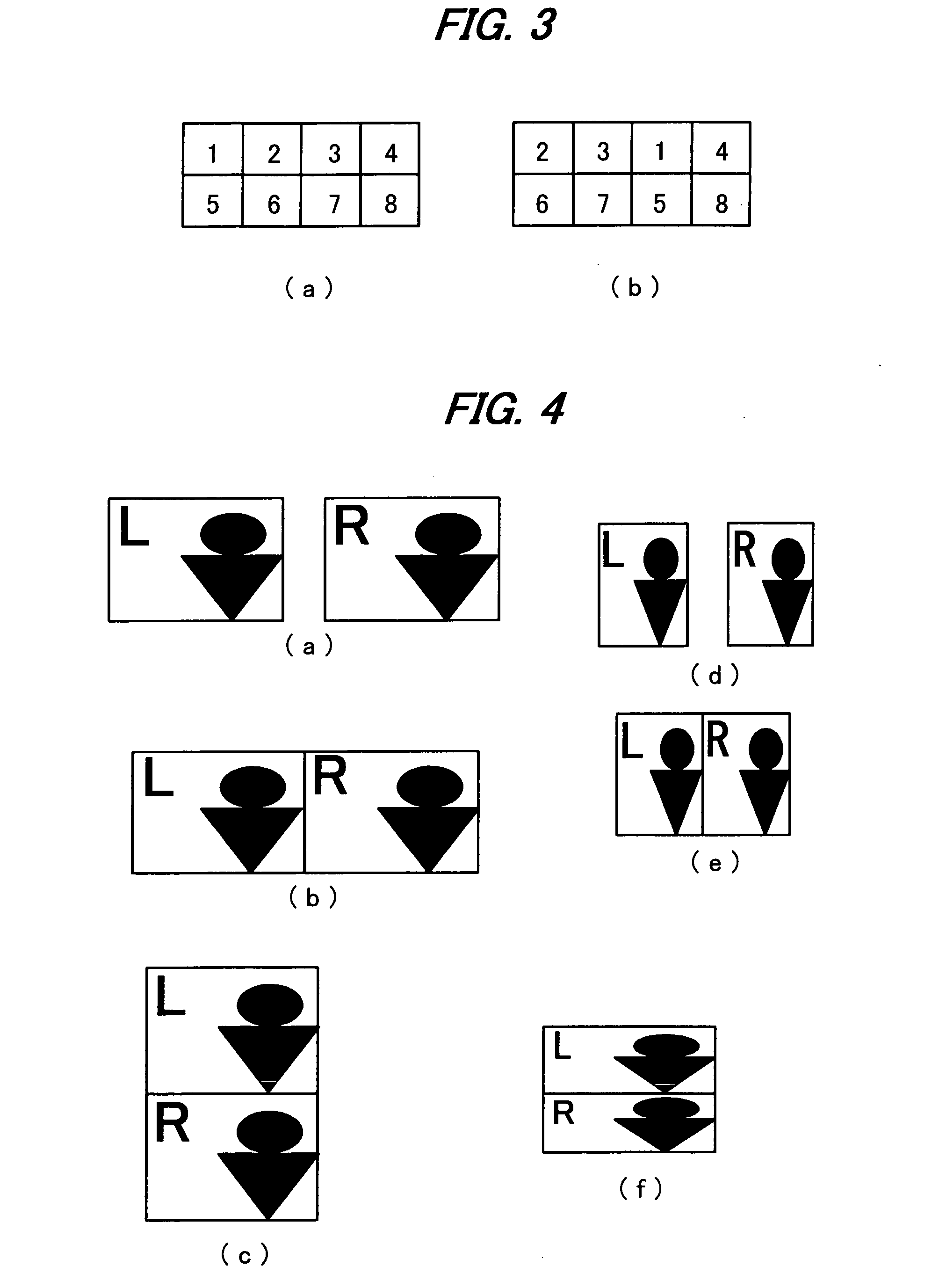
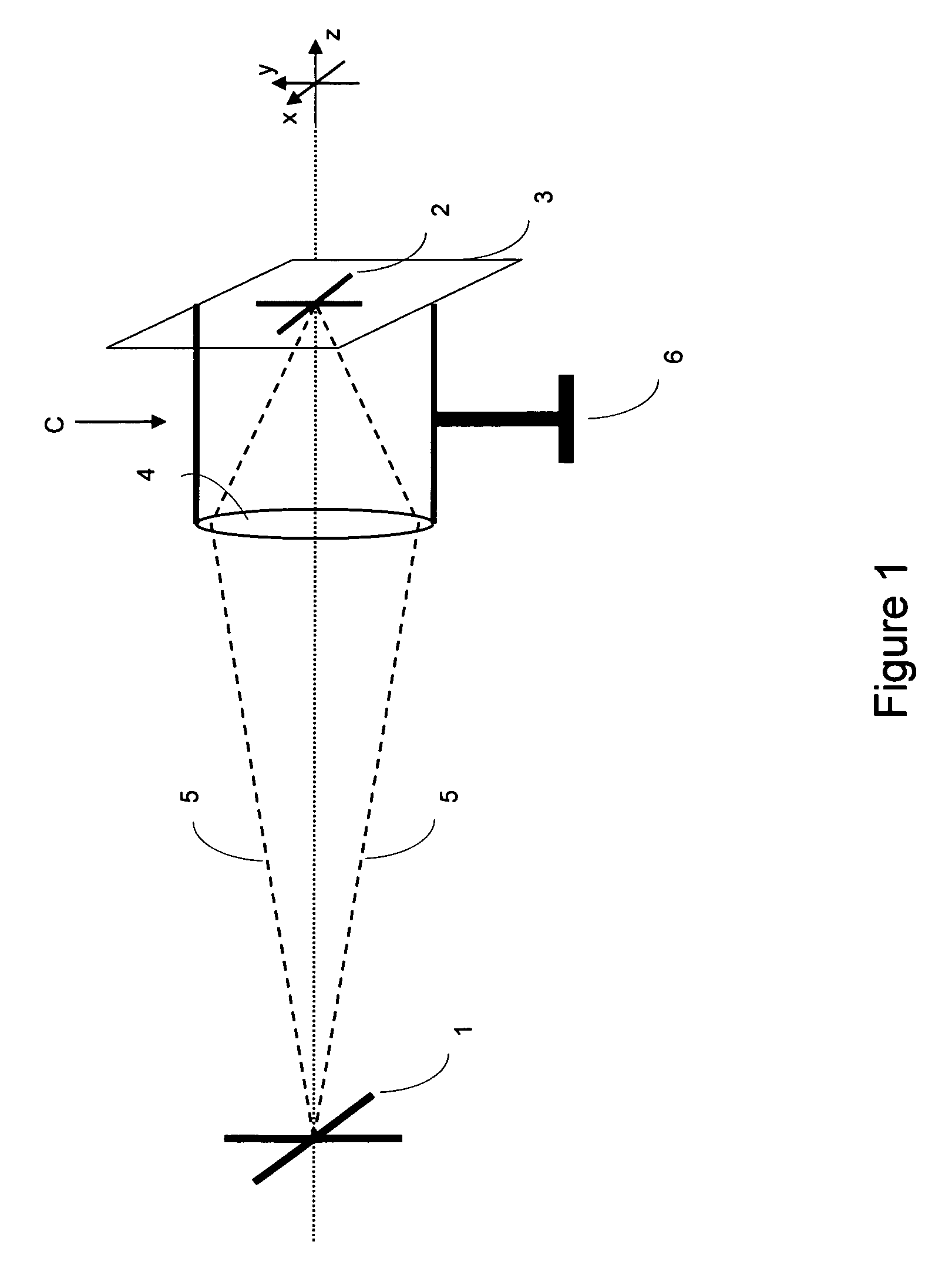
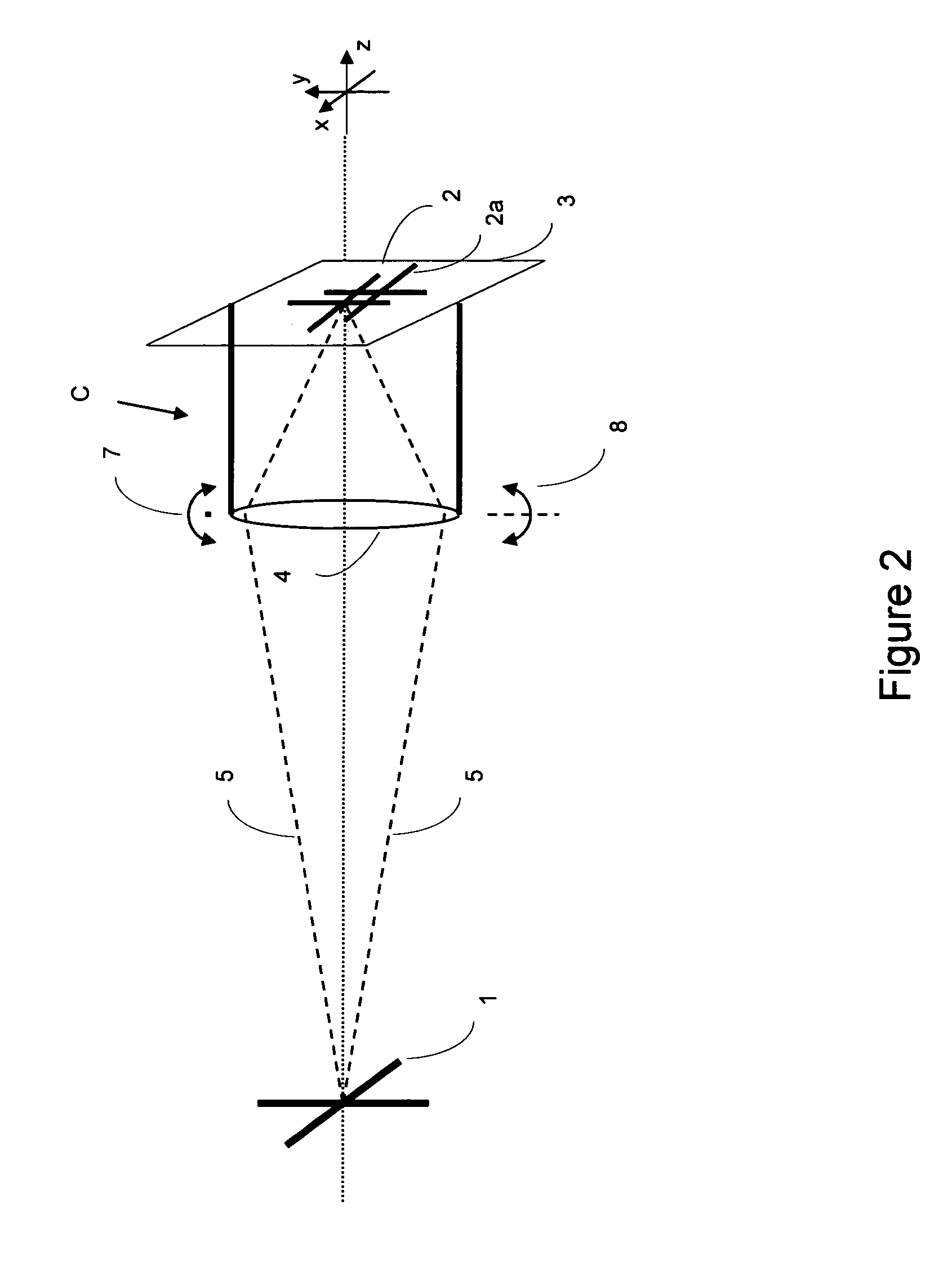
3-Dimensional image creation device, 3-dimensional image reproduction device, 3-dimensional image processing device, 3-dimensional image processing program, and recording medium containing the program
InactiveUS20060192776A1Stereoscopic view difficultValid checkCharacter and pattern recognitionSteroscopic systemsData information3d image
An image signal composed of sequential frames is input to a 3-dimensional image creating apparatus, frame by frame. A controller (102) designates the presence / absence of reduction, the presence / absence of joining and 2D select. An image converter (101) creates image data in the format designated by the presence / absence of reduction and the presence / absence of joining. A 3D information creator (103) creates 3D information necessary for displaying the image as a 3-dimensional image by formatting the presence / absence of reduction, the presence / absence of joining and 2D select. A multiplexer (104) converts image data and 3D information in a predetermined format and outputs them to the outside. In this way, it is possible to make the image data for 3-dimensional display versatile and select an arbitrary viewpoint image efficiently.
Owner:SHARP KK
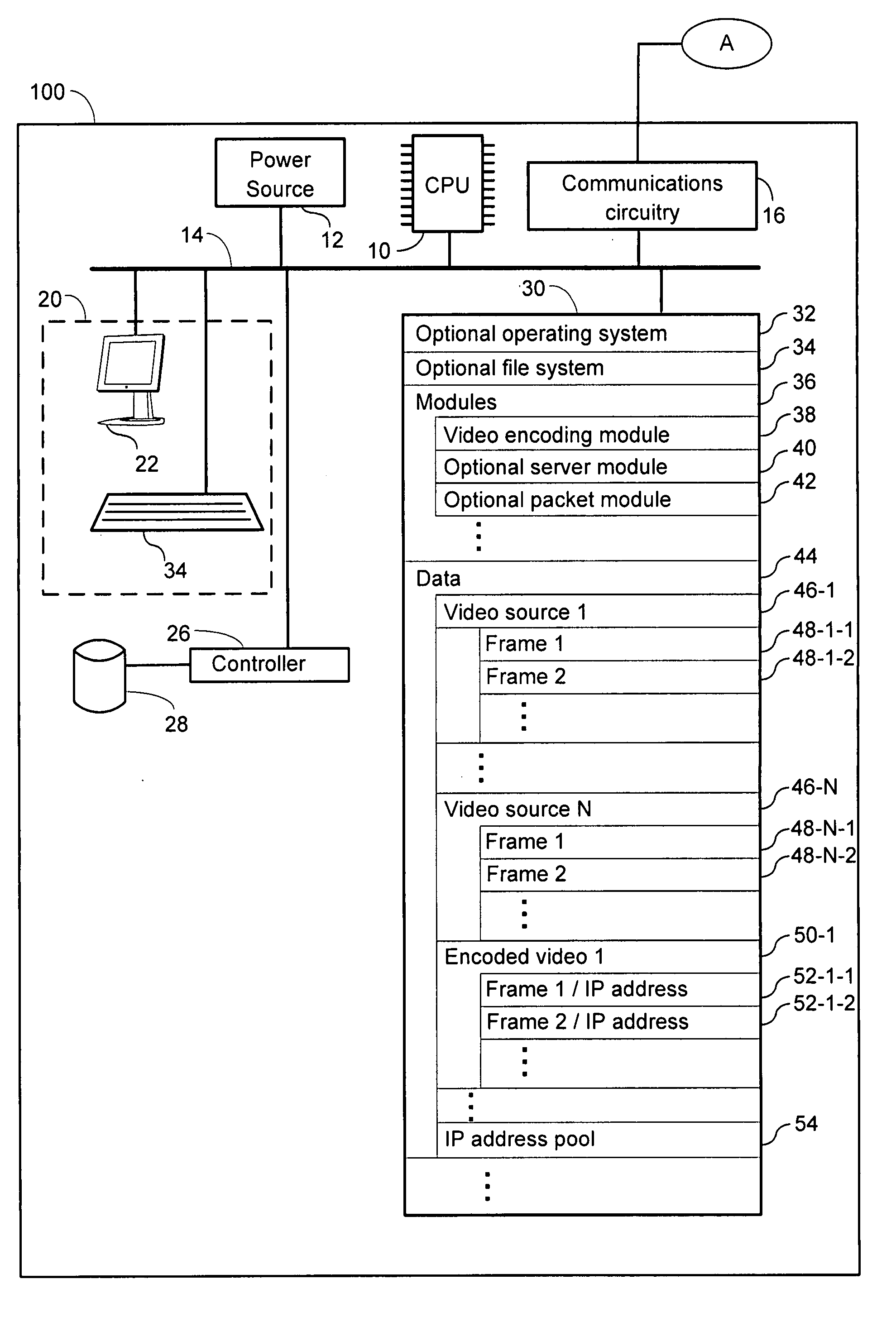
Systems and methods for securing media
InactiveUS20080192818A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo encodingThe Internet
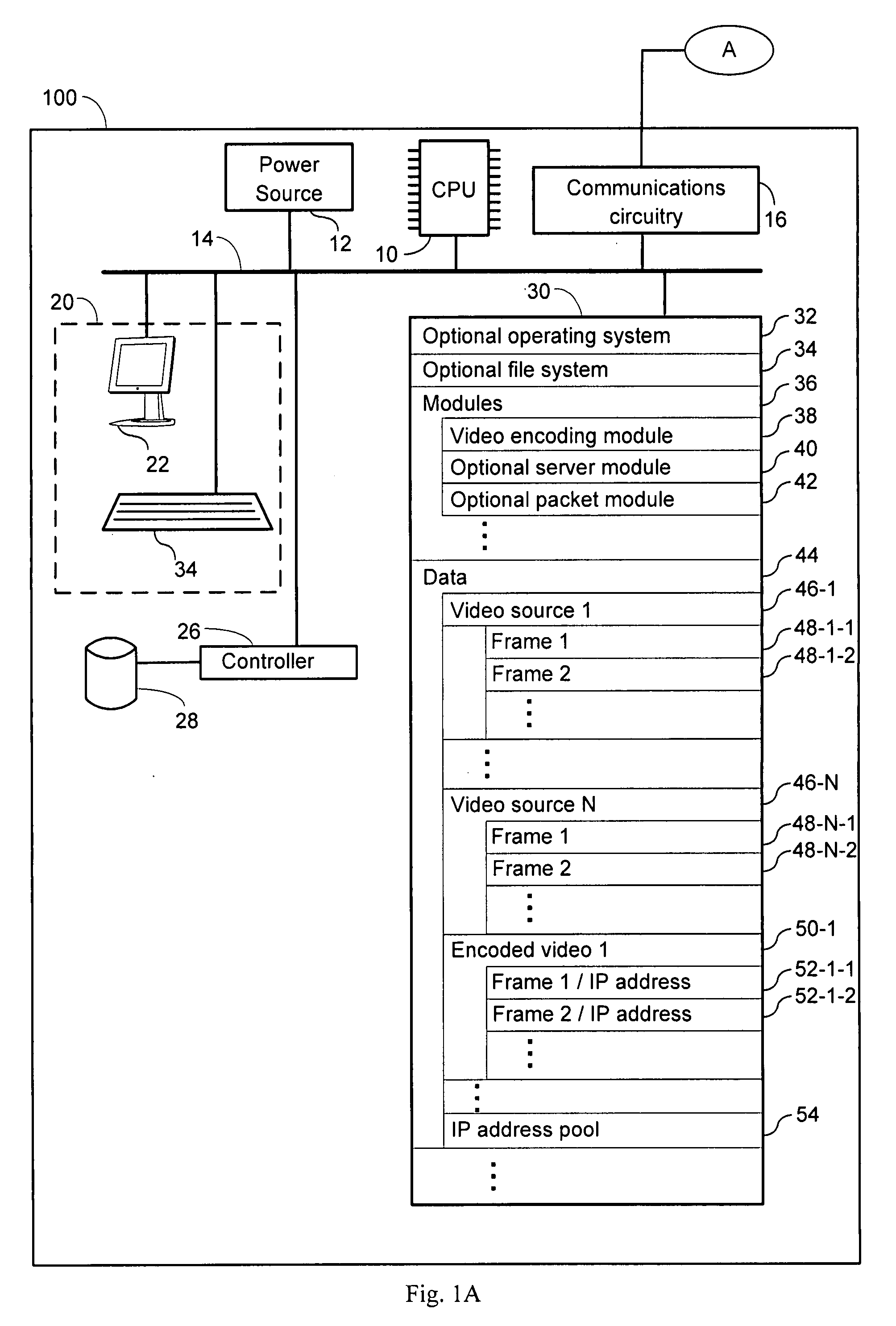
An apparatus for encoding videos having a central processing unit and a memory, coupled to the central processing unit, is provided. The memory has an Internet protocol (IP) address pool having IP addresses and a video encoding module. The video encoding module has instructions for obtaining a video source having a plurality of sequential frames. The video encoding module further has instructions for assigning select frames in the plurality of sequential frames with at least one IP address from the IP address pool, thereby forming an encoded video containing at least one embedded IP address. The video encoding module further has instructions for removing the at least one IP address from the IP address pool that is in the encoded video and instructions for storing the encoded video.
Owner:INNOFONE COM
Remote Transmission and Display of Video Data Using Standard H.264-Based Video Codecs
ActiveUS20100104021A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionQuality levelComputer graphics (images)
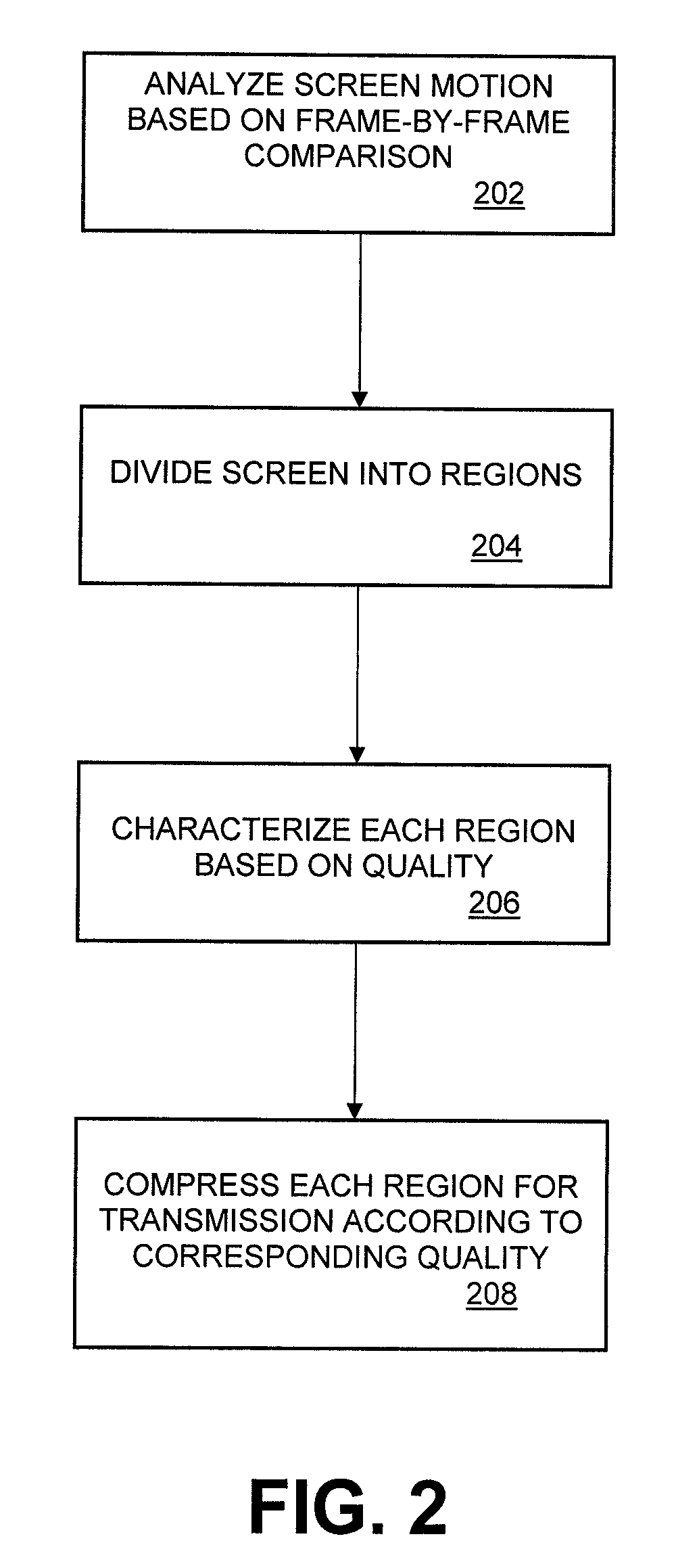
Embodiments include implementing a remote display system (either wired or wireless) using a standard, non-custom codec. In this system, the decoder side can be fully implemented using an existing standard from a decode / display point of view and using a single stream type. The encoder side includes a pre-processing component that analyzes screen images comprising the video data to determine an amount of difference between consecutive frames of the screen images, divides each screen image into a plurality of regions, including no change regions, high quality regions, and low quality regions. The pre-processor characterizes each region as requiring a minimum quality level, encodes the low quality regions for compression in accordance with the H.264 encoding standard; and encodes the high quality regions using the lossless compression scheme of the H.264 standard. A no change region is encoded using a version of the H.264 encoding standard that adaptively and dynamically selects between lossless and lossy compression in a manner that optimizes efficiency of the compression operation.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Driving system for active-matrix displays
ActiveUS20130201223A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDriving currentActive matrix
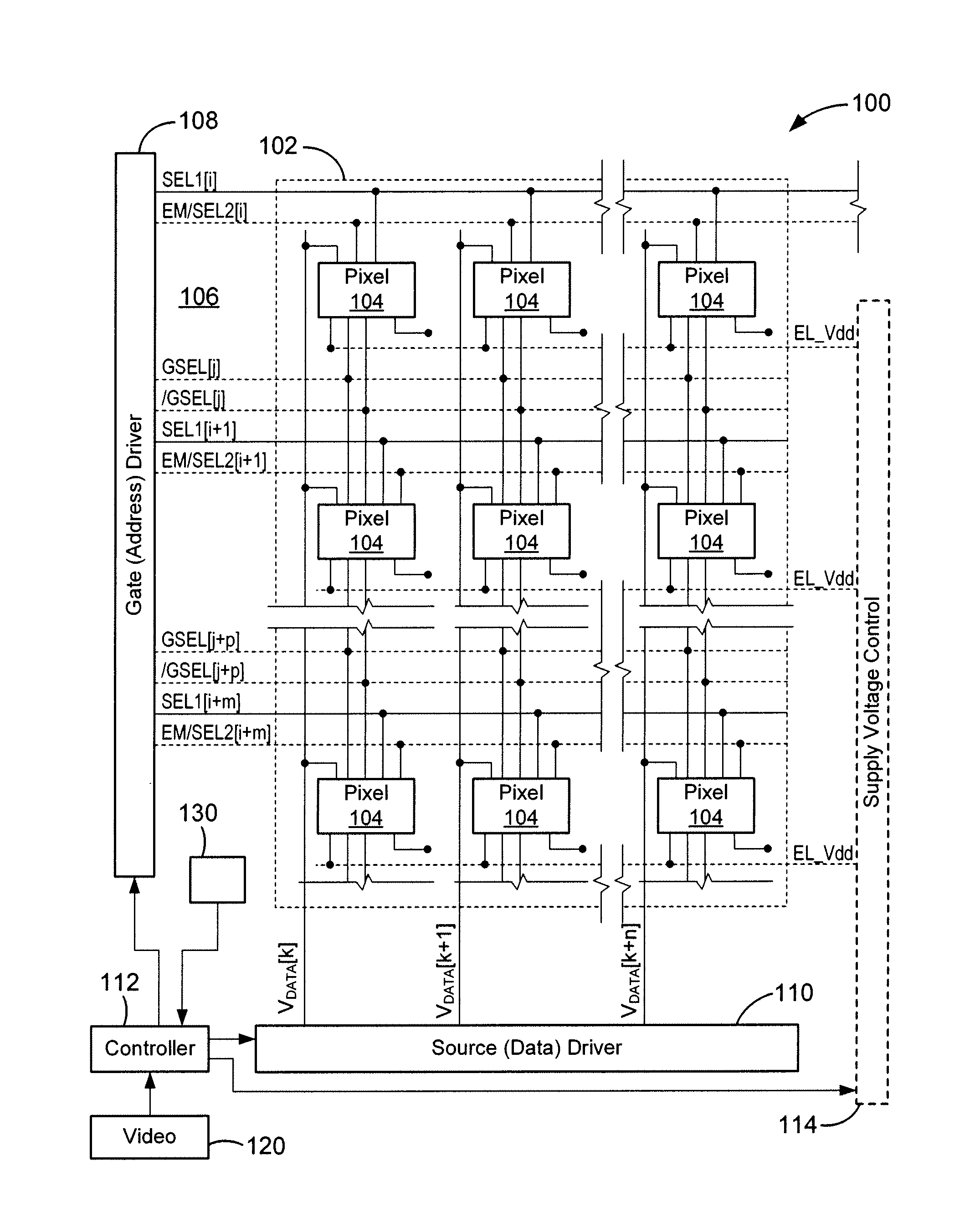
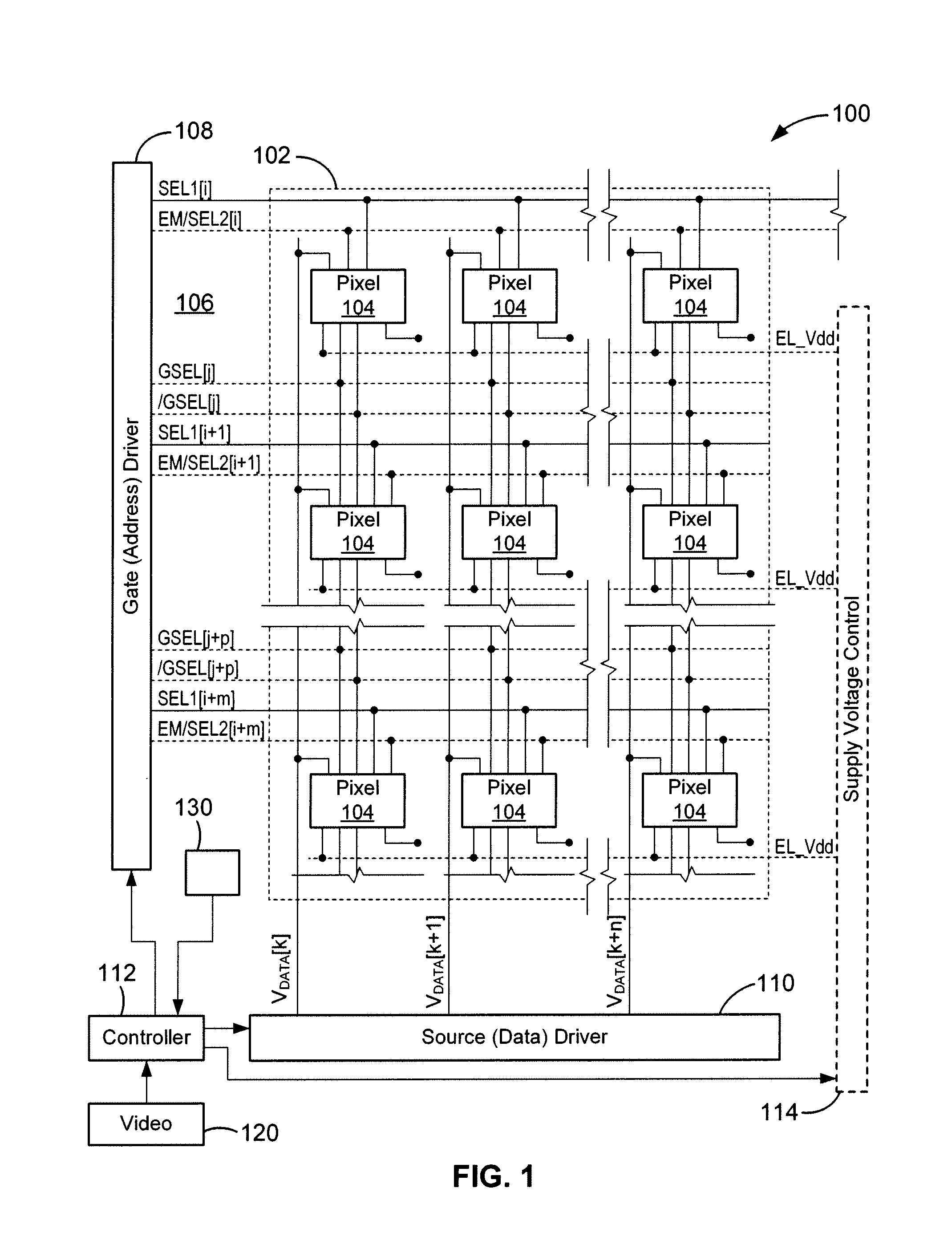
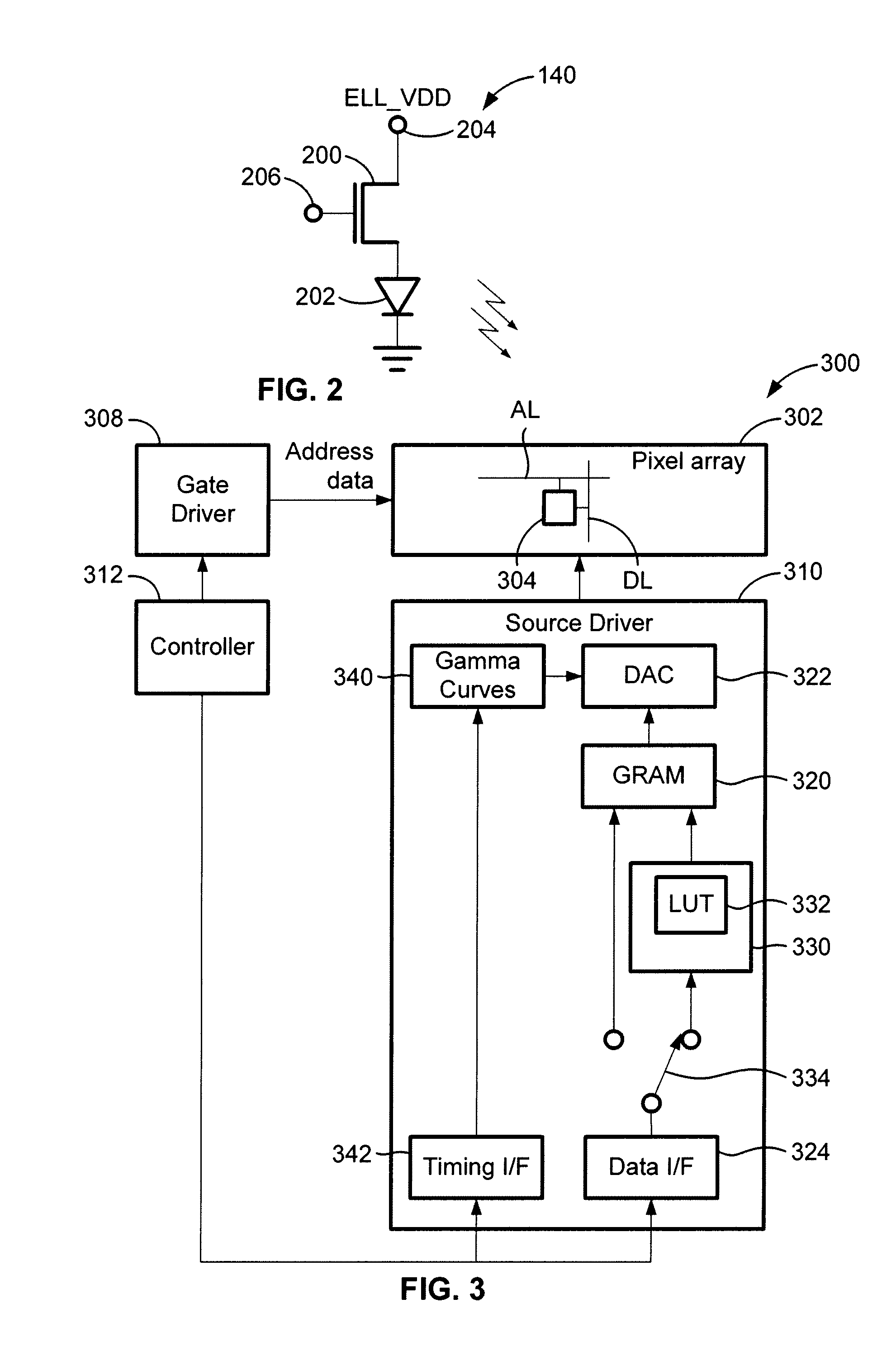
Raw grayscale image data, representing images to be displayed in successive frames, is used to drive a display having pixels that include a drive transistor and an organic light emitting device by dividing each frame into at least first and second-frames, and supplying each pixel with a drive current that is higher in the first sub-frame than in the second sub-frame for raw grayscale values in a first preselected range, and higher in the second sub-frame than in the first sub-frame for raw grayscale values in a second preselected range. The display may be an active matrix display, such as an AMOLED display.
Owner:IGNIS INNOVATION
Method and apparatus for graphically representing information stored in electronic media
InactiveUS6211873B1Suppress mutationEasy to displayOther databases browsing/visualisationSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsDisplay device
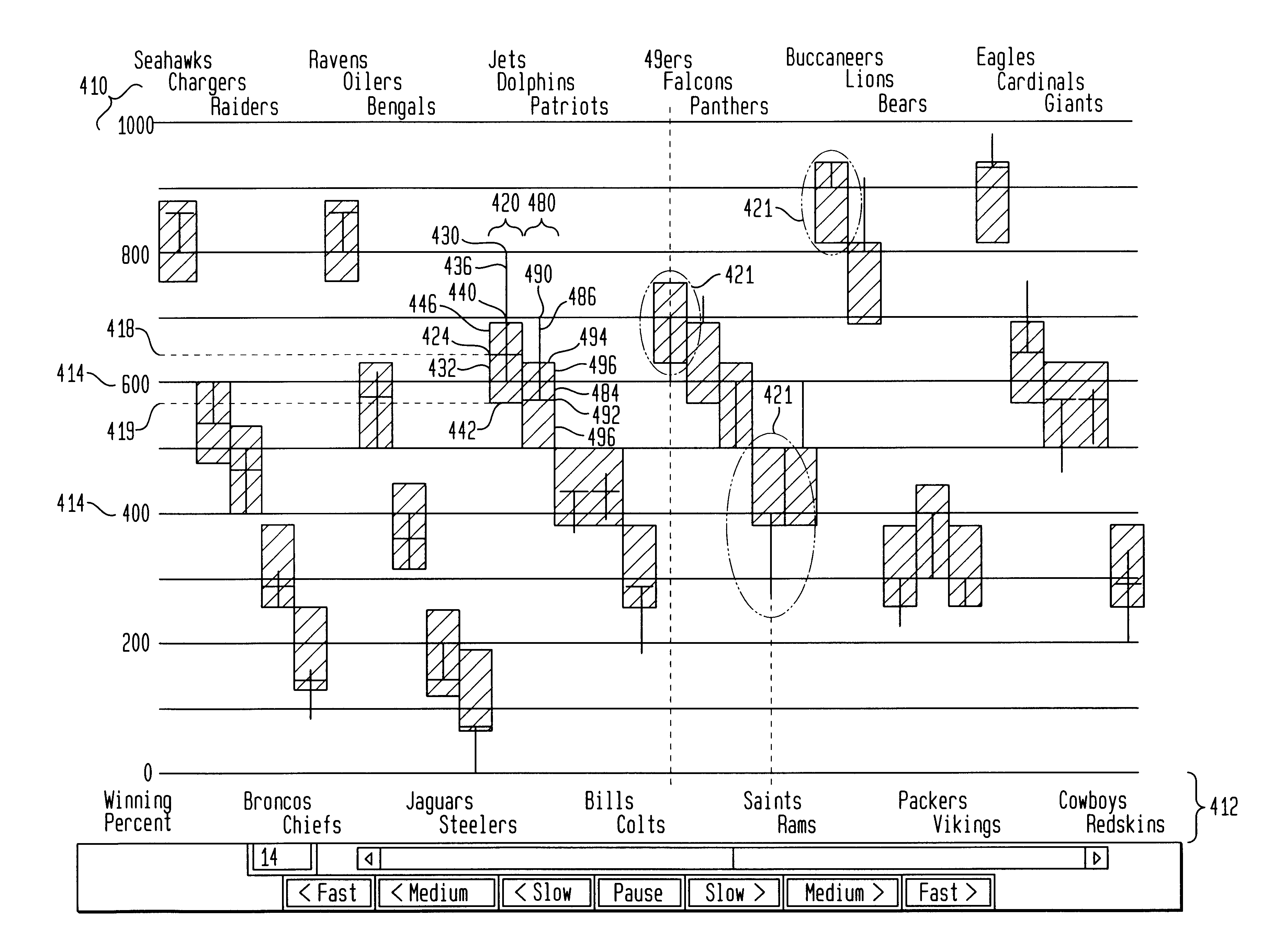
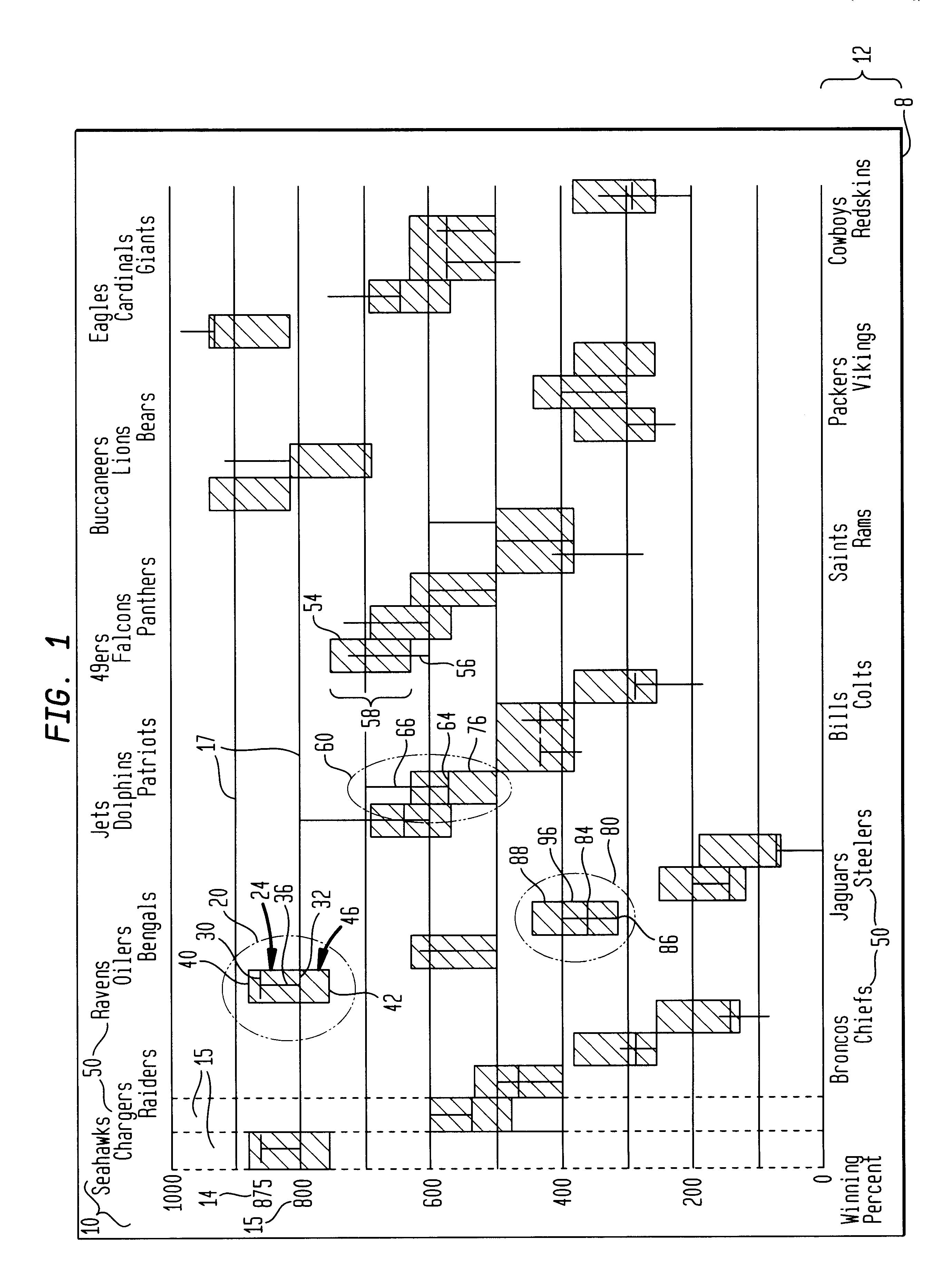
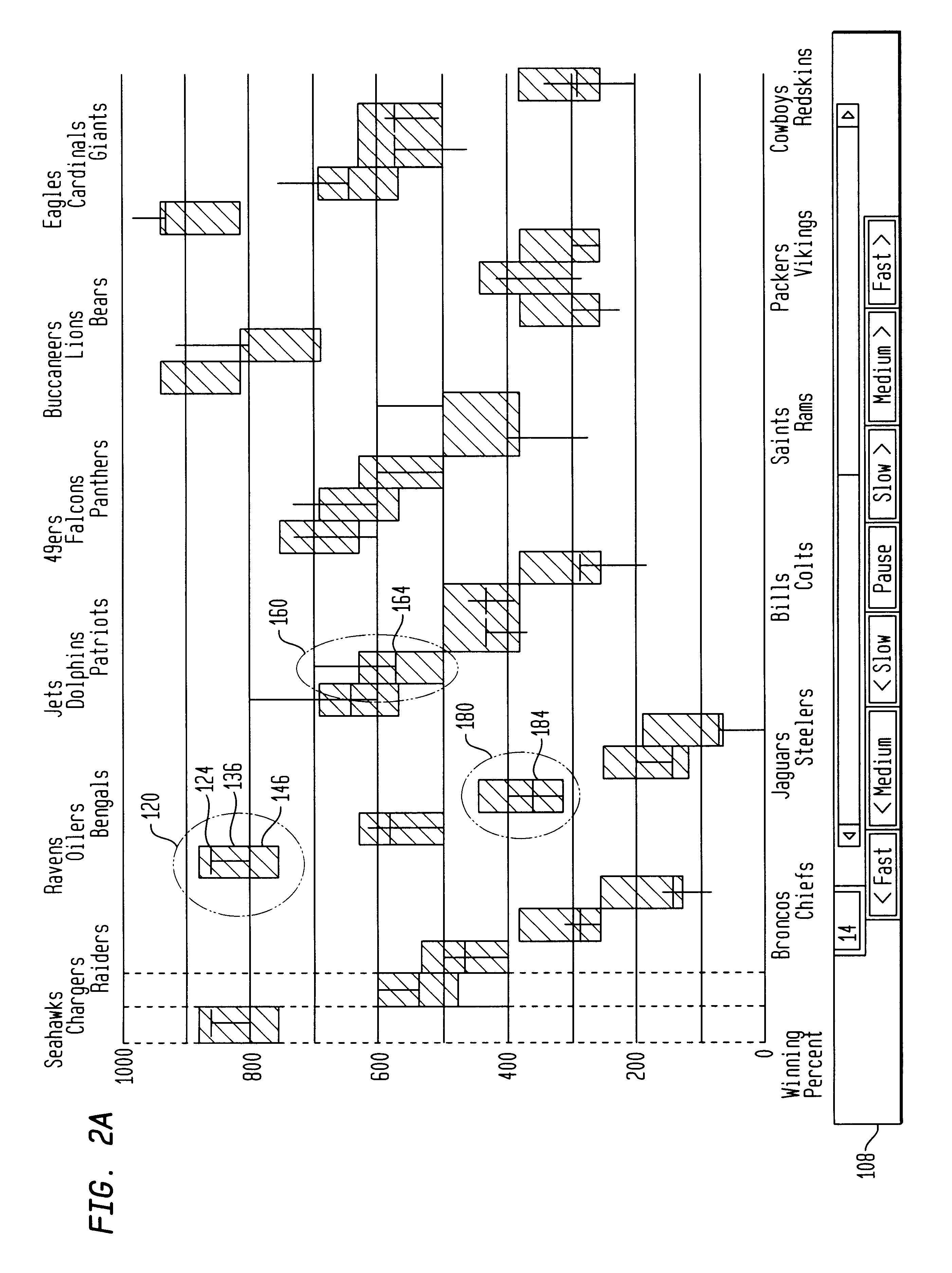
Apparatus and methods for displaying dynamic electronic data are provided for a computer-based display system. The apparatus includes a display, a frame within the display for displaying the data and a measure along a first frame axis for indicating a value of the displayed data. Entity display areas, each containing one entity defined by five data points, are displayed within the frame in non-overlapping, fixed positions along a second frame axis. The five data points include: a current data point, represented by a marker and indicting a current value of the entity in the display, first and second end data points of a first data range relating to the entity, represented by a first range marker, and first and second end data points of a second data range relating to the entity, represented by a second range marker. A label associated with the entities is also displayed in a fixed position with respect to the entity display areas. In one method of the invention, the dynamic data is displayed in sequential frames wherein the current marker and first and second range markers move dynamically within the entity display area to reflect the changing data related to each entity.
Owner:MOYER TODD
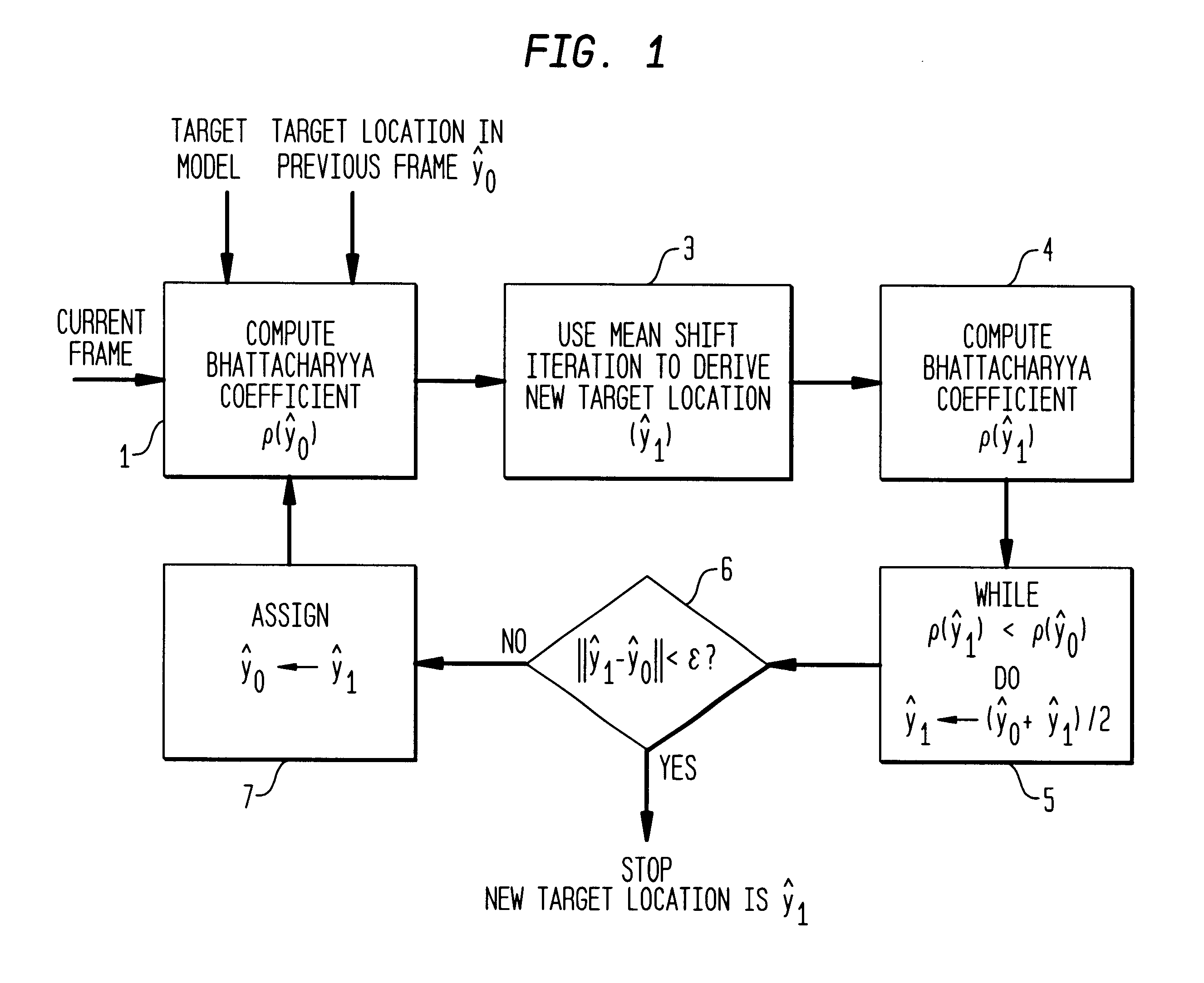
Real-time tracking of non-rigid objects using mean shift
InactiveUS6590999B1Color television with pulse code modulationImage analysisMean-shiftConsecutive frame
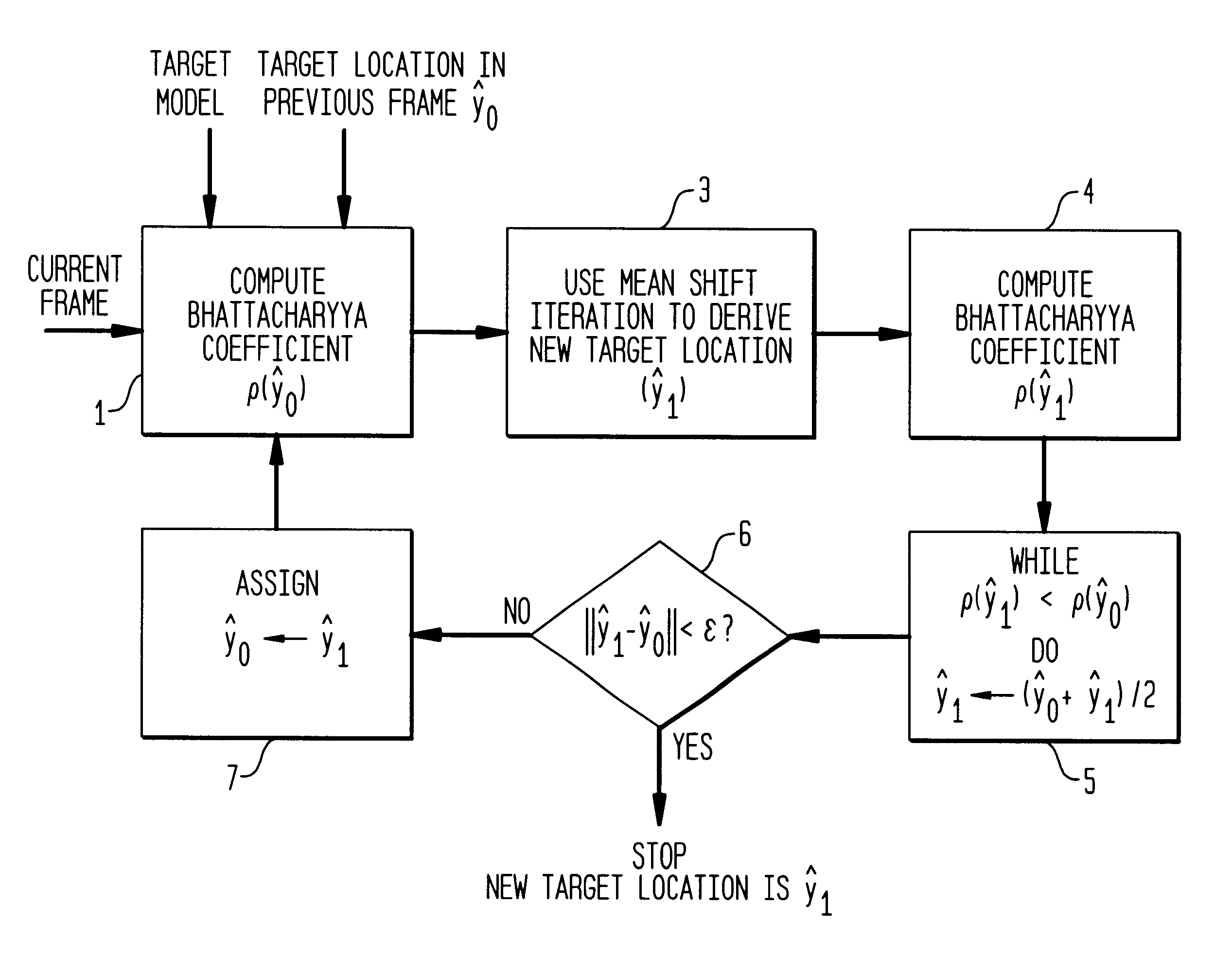
A method and apparatus for real-time tracking of a non-rigid target. The tracking is based on visual features, such as color and / or texture, where statistical distributions of those features characterize the target. A degree of similarity (rho(y0)) is computed between a given target (at y0) in a first frame and a candidate target (at y1) in a successive frame, the degree being expressed by a metric derived from the Bhattacharyya coefficient. A gradient vector corresponding to a maximization of the Bhattacharyya coefficient is used to derive the most probable location of the candidate target in the successive frame.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Content-based matching of videos using local spatio-temporal fingerprints
ActiveUS20100049711A1Poor discriminationImprove discriminationDigital data processing detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesData matchingPattern recognition
A computer implemented method computer implemented method for deriving a fingerprint from video data is disclosed, comprising the steps of receiving a plurality of frames from the video data; selecting at least one key frame from the plurality of frames, the at least one key frame being selected from two consecutive frames of the plurality of frames that exhibiting a maximal cumulative difference in at least one spatial feature of the two consecutive frames; detecting at least one 3D spatio-temporal feature within the at least one key frame; and encoding a spatio-temporal fingerprint based on mean luminance of the at least one 3D spatio-temporal feature. The least one spatial feature can be intensity. The at least one 3D spatio-temporal feature can be at least one Maximally Stable Volume (MSV). Also disclosed is a method for matching video data to a database containing a plurality of video fingerprints of the type described above, comprising the steps of calculating at least one fingerprint representing at least one query frame from the video data; indexing into the database using the at least one calculated fingerprint to find a set of candidate fingerprints; applying a score to each of the candidate fingerprints; selecting a subset of candidate fingerprints as proposed frames by rank ordering the candidate fingerprints; and attempting to match at least one fingerprint of at least one proposed frame based on a comparison of gradient-based descriptors associated with the at least one query frame and the at least one proposed frame.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
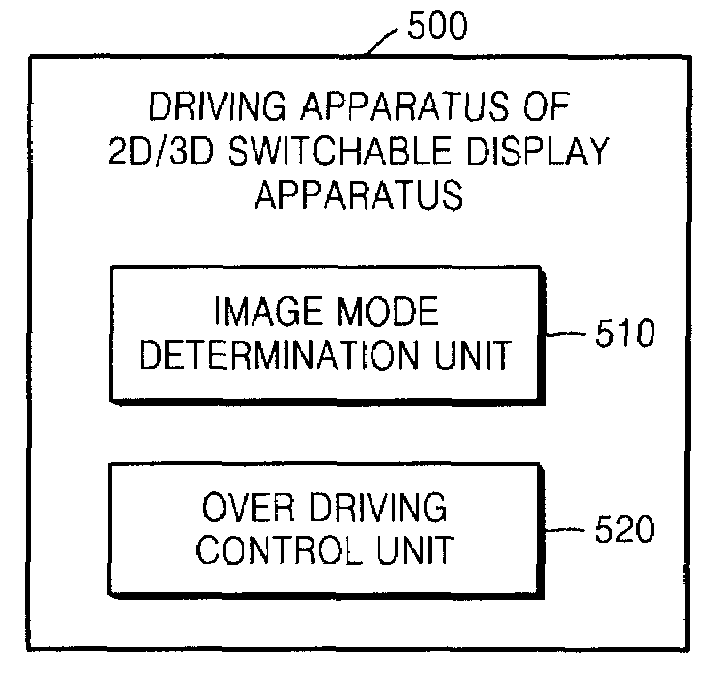
Apparatus and method for driving 2d/3d switchable display
InactiveUS20090009508A1Degradation of picture qualityShort response timeCathode-ray tube indicatorsSteroscopic systemsConsecutive frameImage mode
Provided are an apparatus and method for driving a 2-dimensional (2D) / 3-dimensional (3D) switchable display for improving the quality of image. The apparatus for driving a 2D / 3D switchable display includes: an image mode determination unit determining whether input image signals of continuous frames are in a 2D mode or 3D mode; and an over-driving control unit over-driving the input image signal of a current differently according to the determined image mode. According to the apparatus and method, the response time in each of the 2D mode and the 3D mode can be increased, while motion blur and cross-talk effects can be decreased, thereby improving the quality of image.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
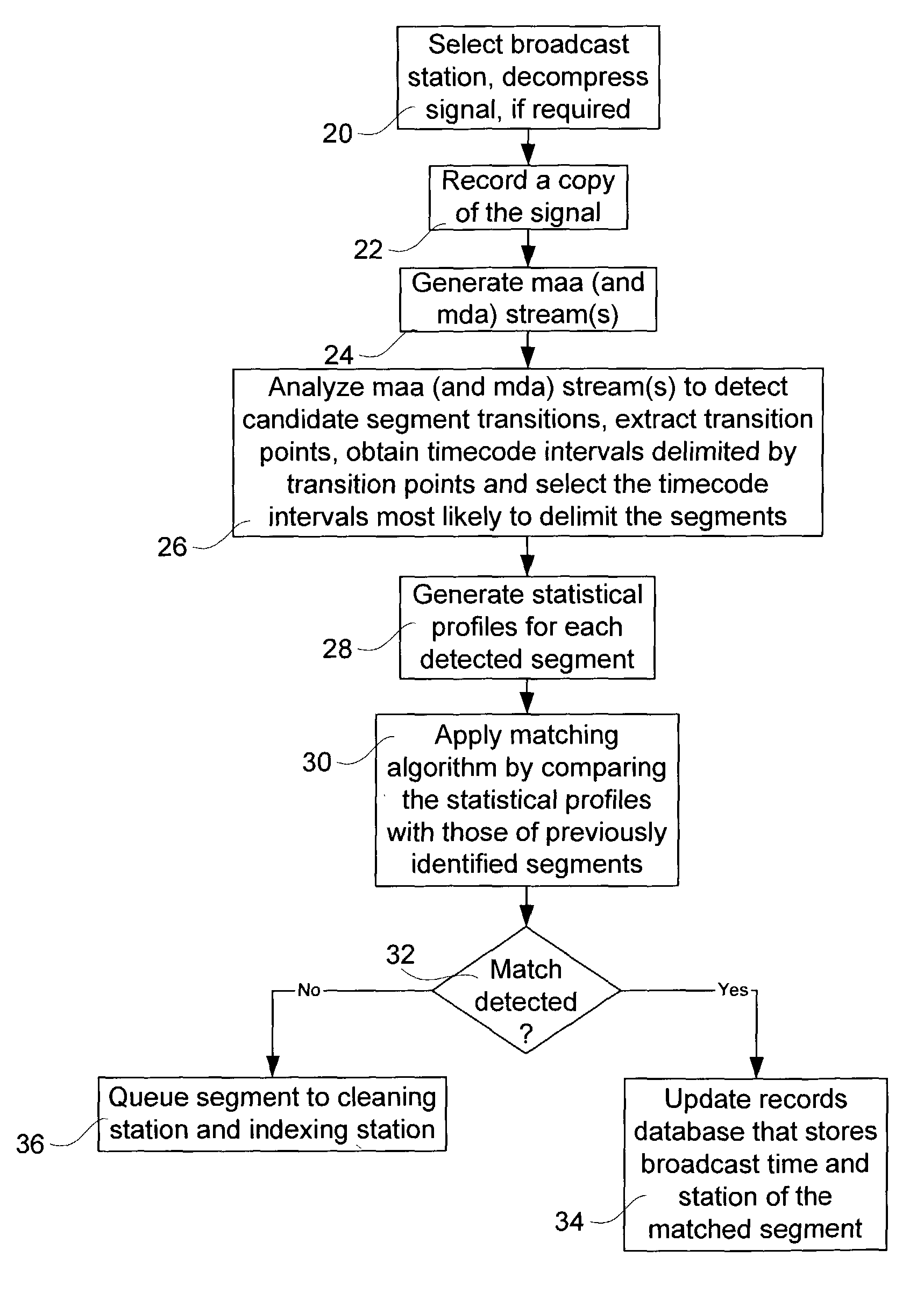
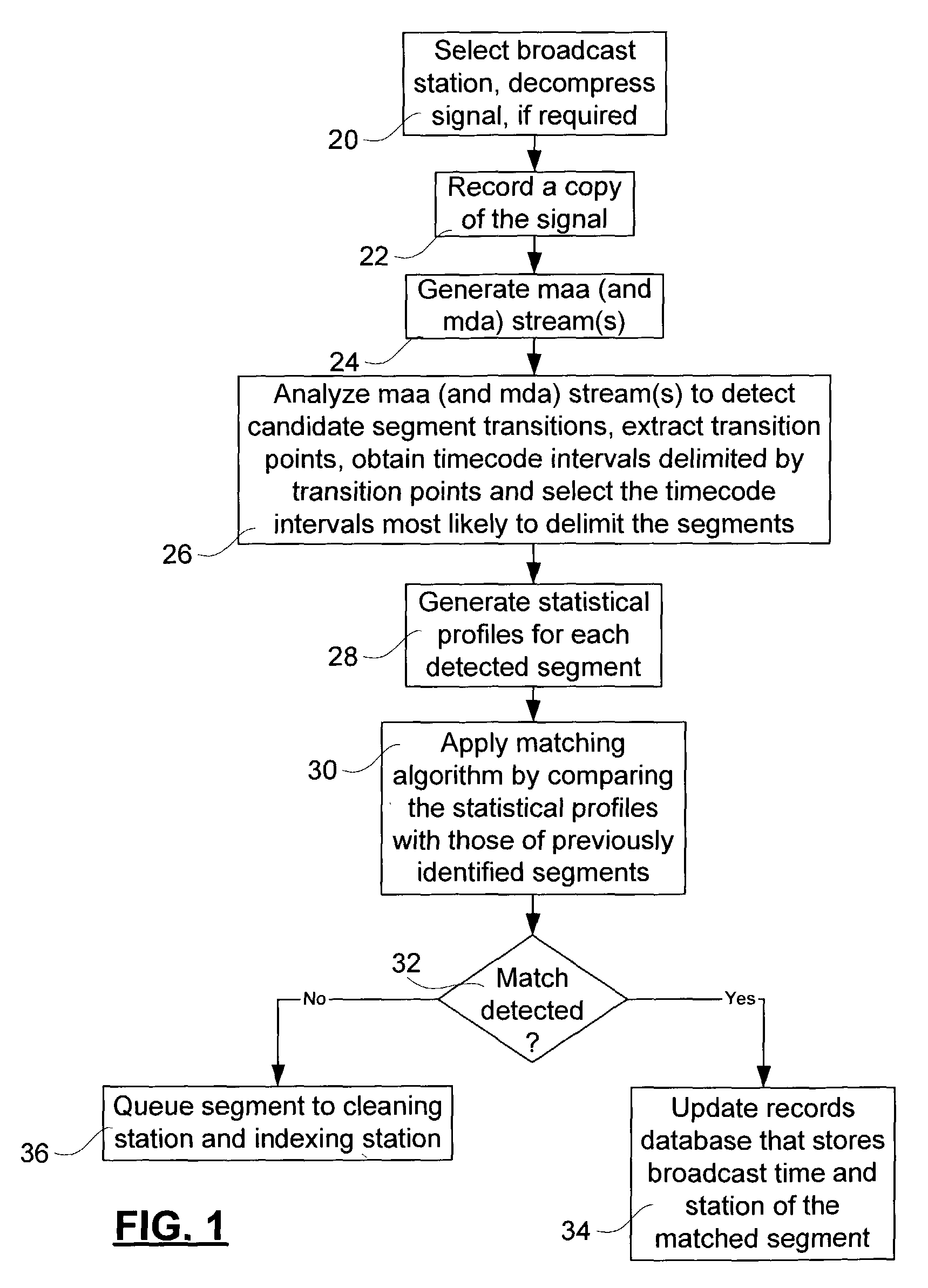
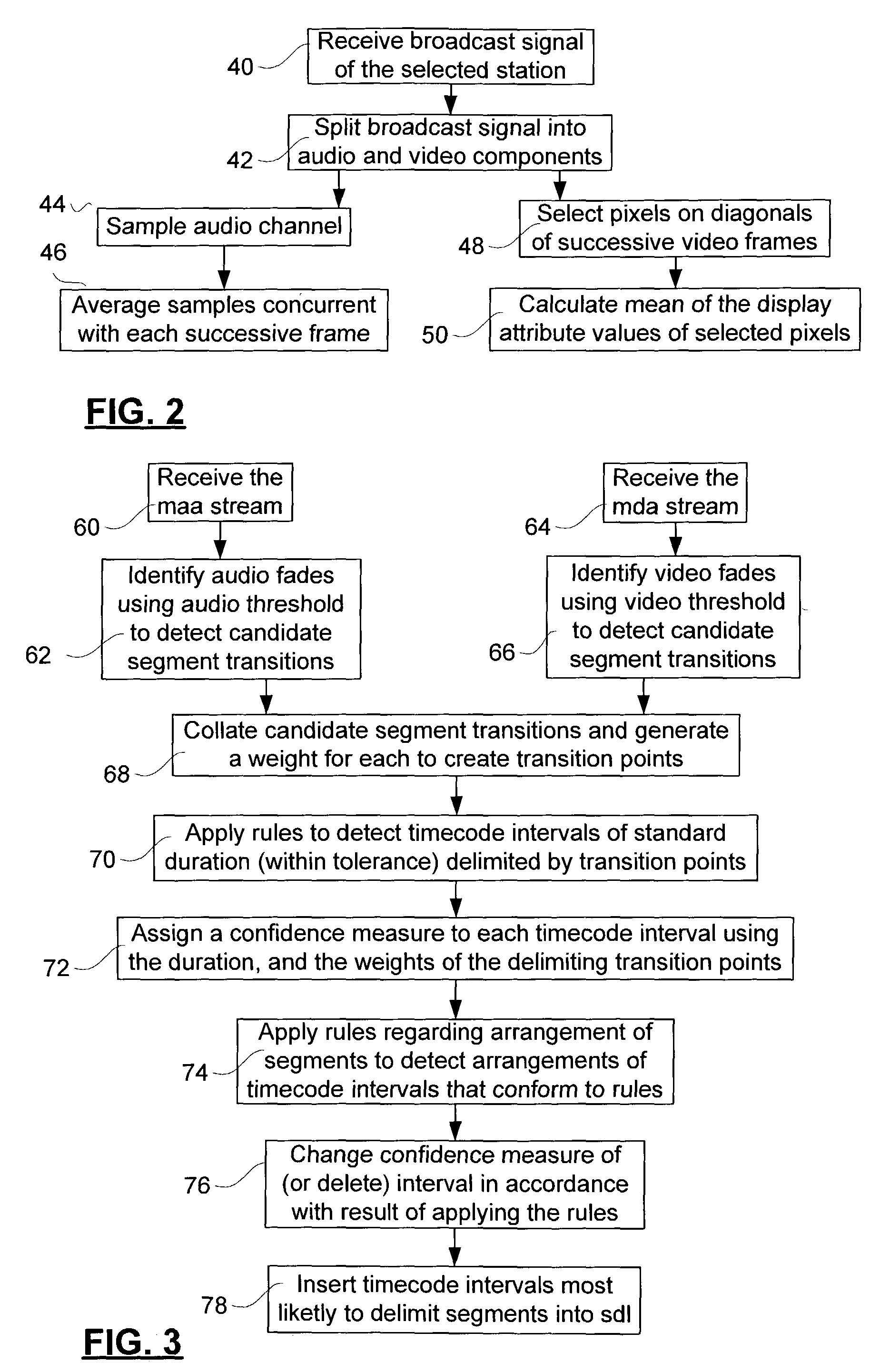
Method and system for re-identifying broadcast segments using statistical profiles
InactiveUS7064796B2Easy to identifyMinimize impactTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesRe identificationConsecutive frame
A method and system for extracting segments from a broadcast television signal uses a mean display attribute value of pixels of each successive frame of a video component of the signal to identify segment transitions. Elapsed times between the identified segment transitions are compared with expected durations of segments, in order to detect intervals that are likely to constitute segments. Groups of the detected intervals are subjected to tests to see if they are temporally arranged in an expected distribution typical of segments in broadcast signals. The mean display attribute values concurrent with each detected segment are then used to form a statistical profile for the segment. These statistical profiles may be used to identify re-broadcast segments. Further a stream of mean audio amplitudes is preferably used to supply further segment transitions, to improve segment detection, and to provide more statistical values.
Owner:ELODA
Image recognition device
InactiveUS20070076951A1Reduce the amount of calculationImprove recognition accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionIdentification device
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
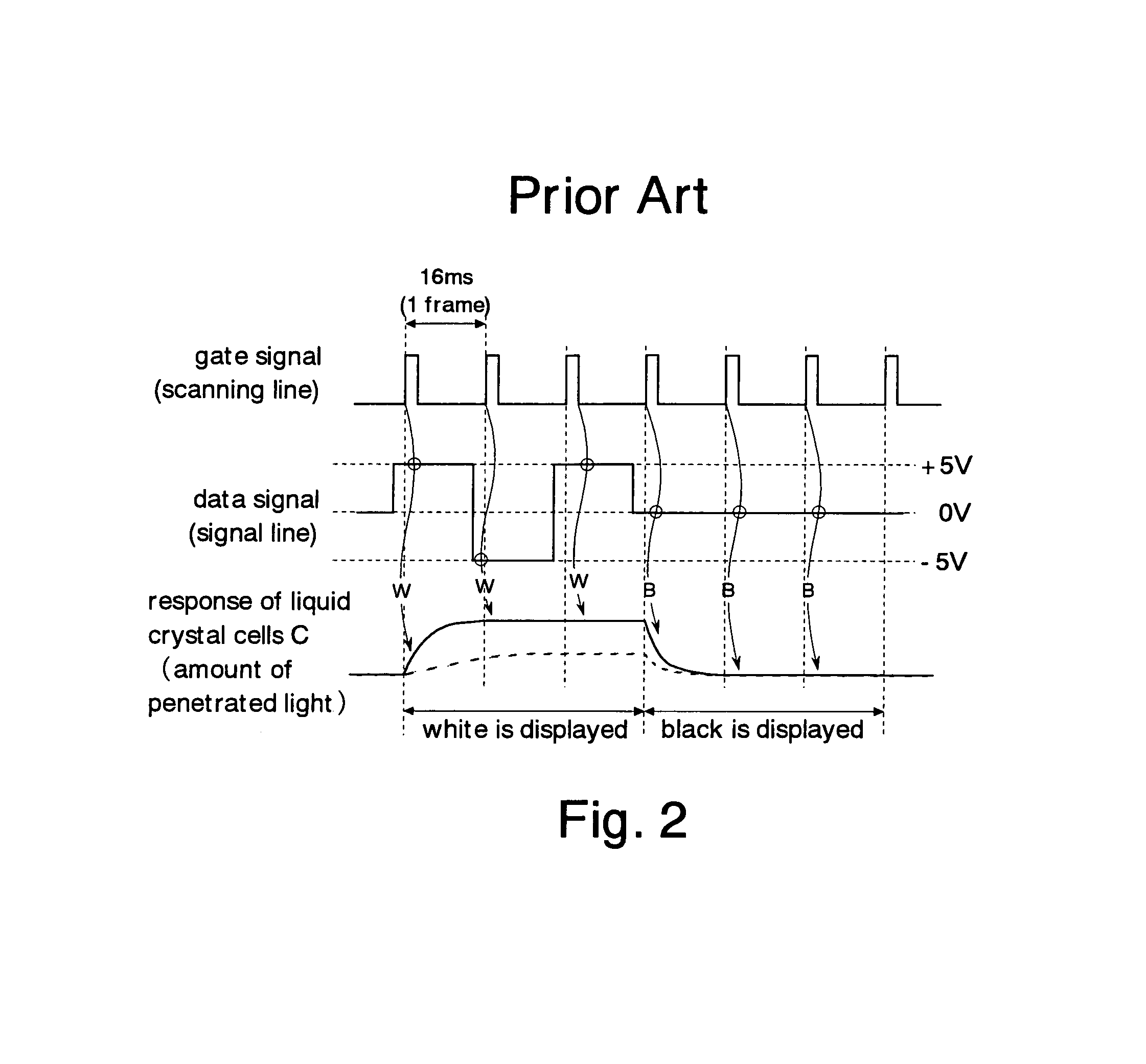
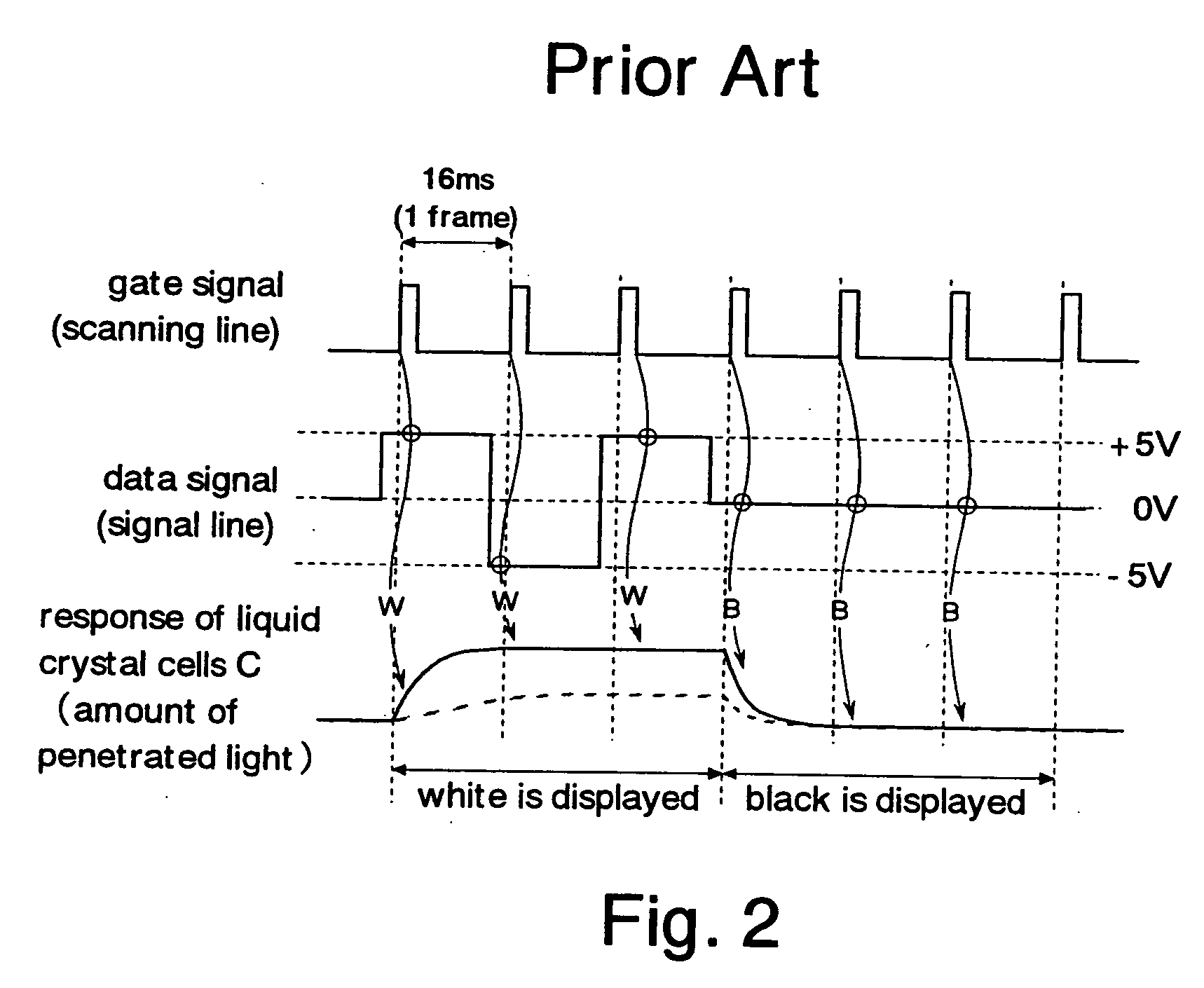
Method and apparatus for driving liquid crystal display
ActiveUS20050104840A1Static indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayConsecutive frame
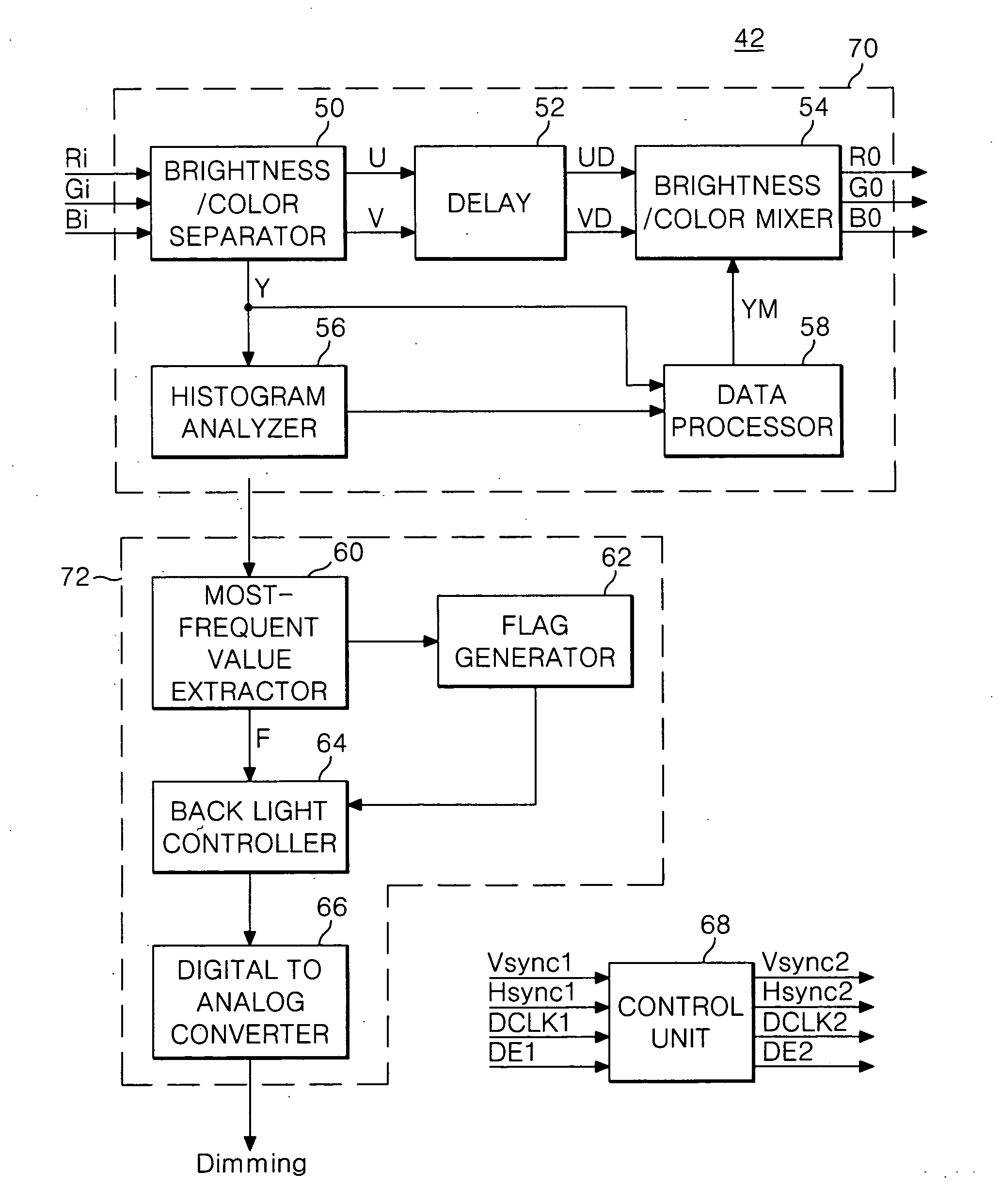
A driving method and apparatus for a liquid crystal display stabilizing variations in the brightness of a back light dependent upon brightness components extracted from data to be displayed are disclosed. In the method, the brightness components of each frame are arranged into a histogram, which is divided into a plurality of brightness areas. The most-frequent value of the brightness components or the average value of the brightness components is extracted. The brightness of a back light is controlled to correspond to the brightness areas to which the extracted most-frequent value or the average value belongs. One or more particular areas within the brightness areas are selected such that if the extracted most-frequent value or the average value belongs to the particular areas, the brightness of the back light may not be changed in successive frames.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Method and apparatus for encoding high dynamic range video
InactiveUS20060002611A1Good colorIncrease rangeColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionData stream
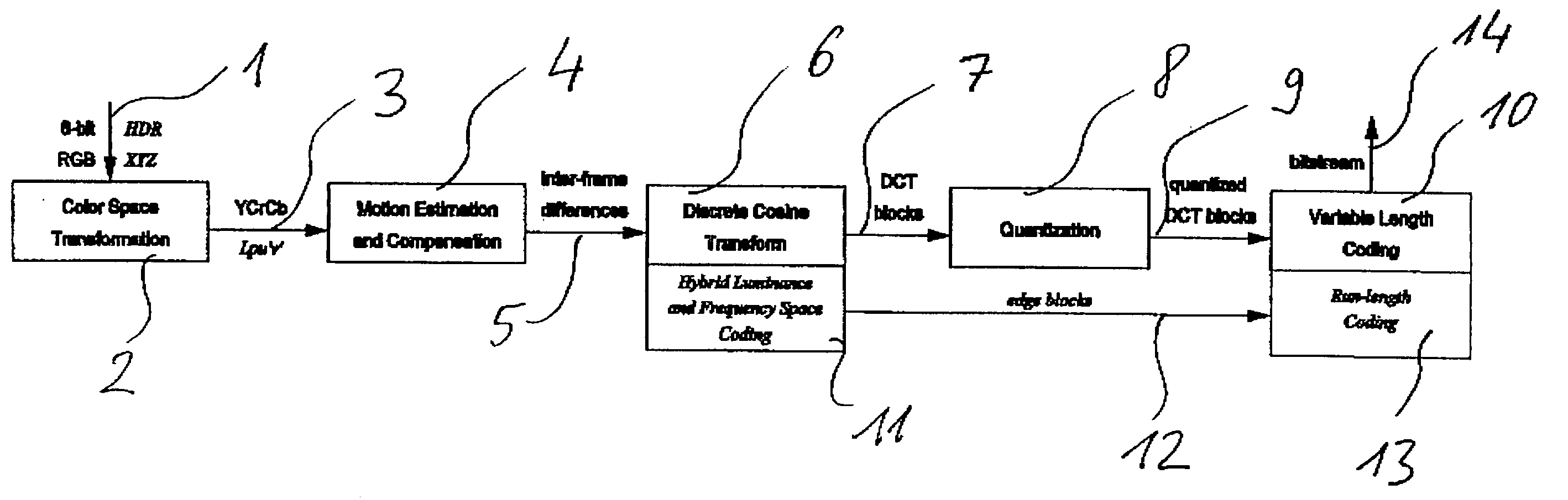
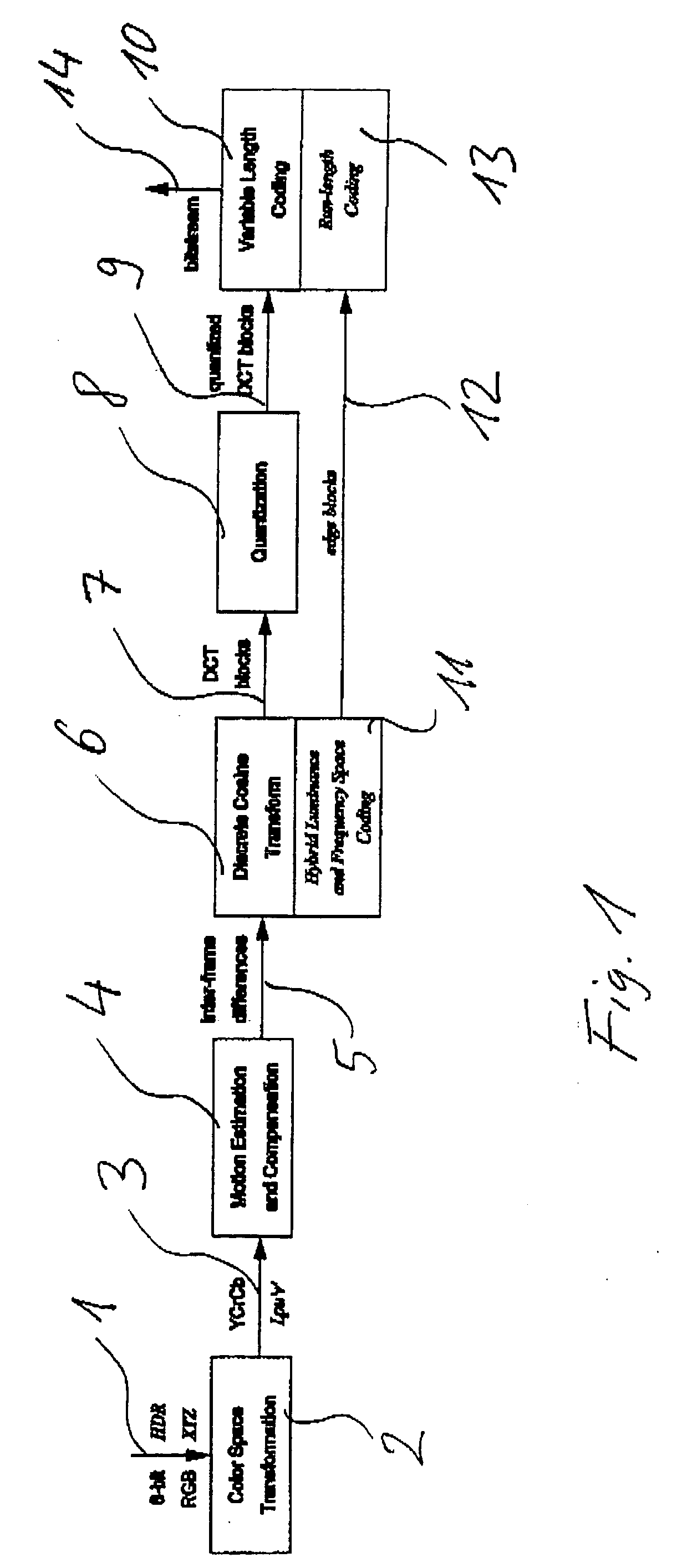
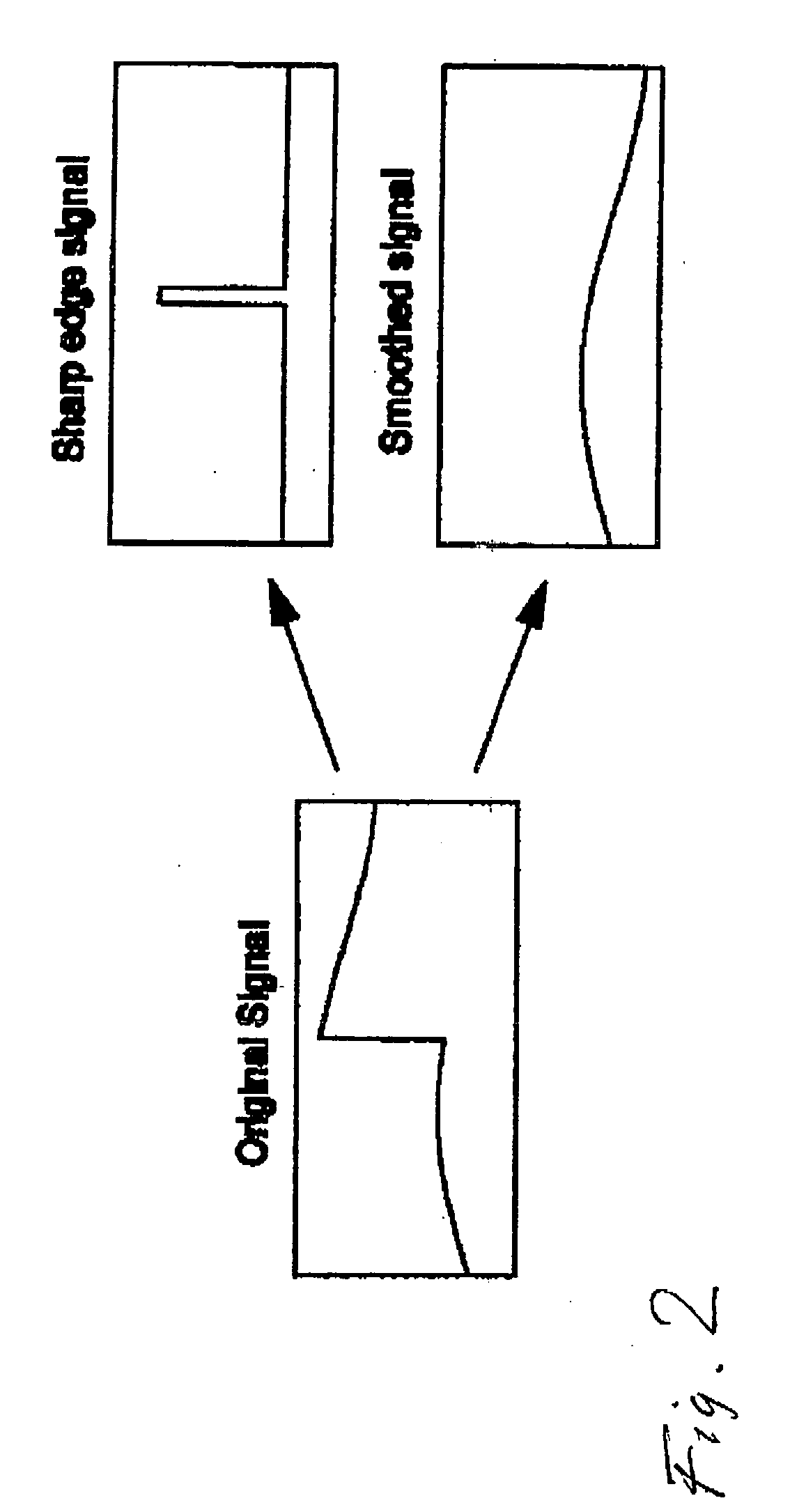
A method and apparatus for encoding high dynamic range video by means of video compression is shown. The method comprises the steps of providing high dynamic range (HDR) tristimulus color data (XYZ) for each frame of the video and threshold versus intensity data for a human observer; constructing a perceptually conservative luminance transformation from continuous luminance data (Y) to discrete values (Lp) using said threshold versus intensity data for the human observer; transforming the HDR tristimulus color data into perceptually linear color data of three color channels (Lp, u′, v′) for obtaining visually lossless compressed frames; estimating motion vector of said consecutive frames of the video and compensating the difference of the tristimulus color data for performing an inter-frame encoding and an inter-frame compression; transforming the compensated differences of the tristimulus color data to frequency space data; quantizing said frequency space data; variable-length encoding of the quantized frequency space data and storing or transmitting a stream of visual data resulting from the encoded quantized frequency space data;
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Apparatus and method for improving dynamic range and linearity of CMOS image sensor
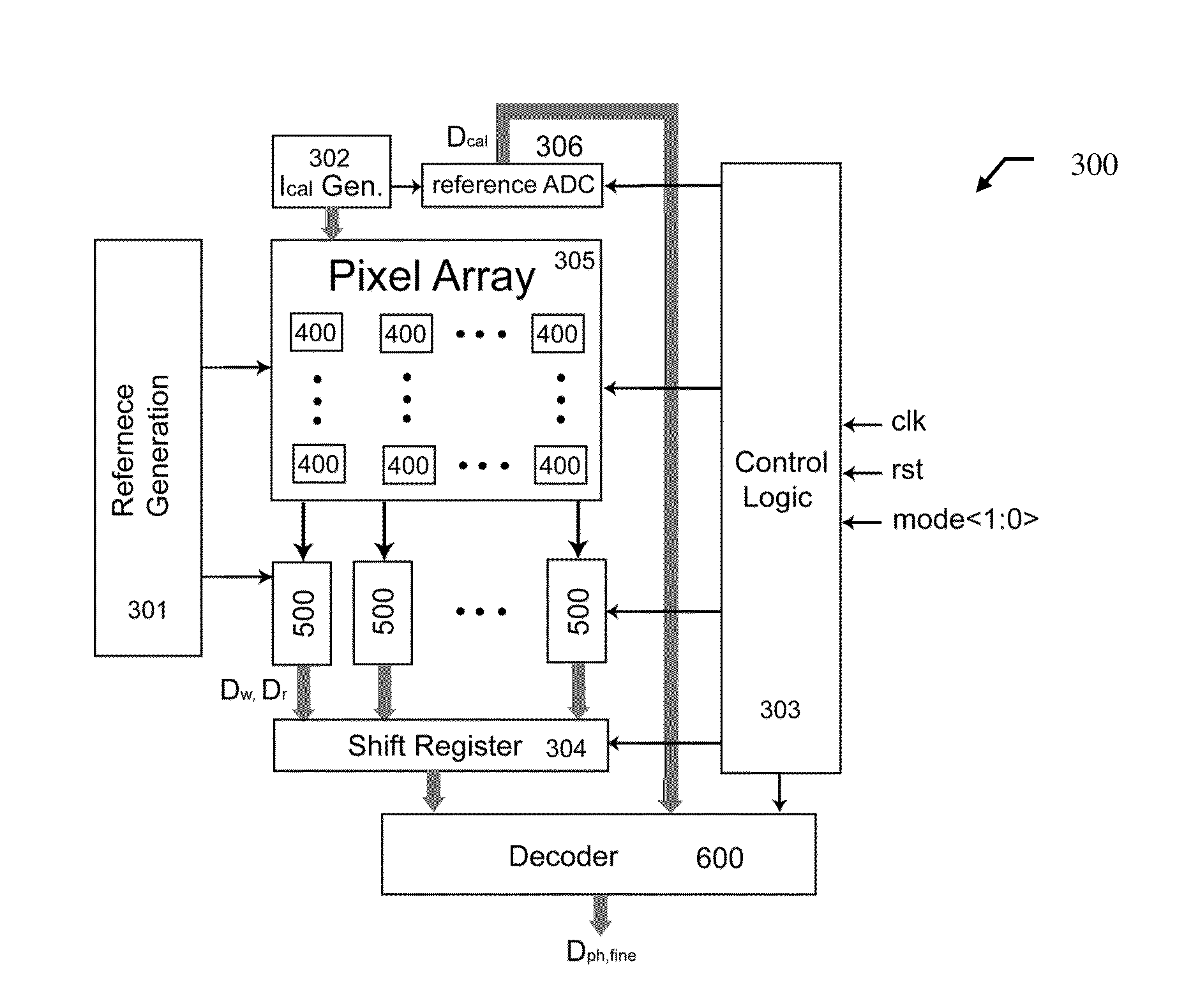
ActiveUS20100194956A1Improve linearityImprove signal-to-noise ratioTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOSControl signal
Described herein is a circuit and related method for improving the dynamic range and the linearity characteristic of a CMOS image sensor. In various embodiments of the CMOS image sensor, a current sampler, a comparator, and a 1-bit memory are incorporated in each pixel circuit. In the image sensor, pixels are arranged in columns and a column slice is used to read the digital and analog singles from each column. In addition, a calibration circuit is incorporated in the sensor circuit for providing calibration current, which is used to generate calibration parameter. The image sensor operates in three non-overlapping modes: the difference mode, the WDR mode, and the calibration mode. The image sensor is switched among the three modes by control signals, which are provided to the image sensor by various control circuits. The image sensor normally operates in the difference mode and switches to the WDR mode when the difference between consecutive frames is over a threshold. The calibration mode allows the image sensor generate calibration parameters which are used to improve the linearity of the sensor through a interpolation method.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
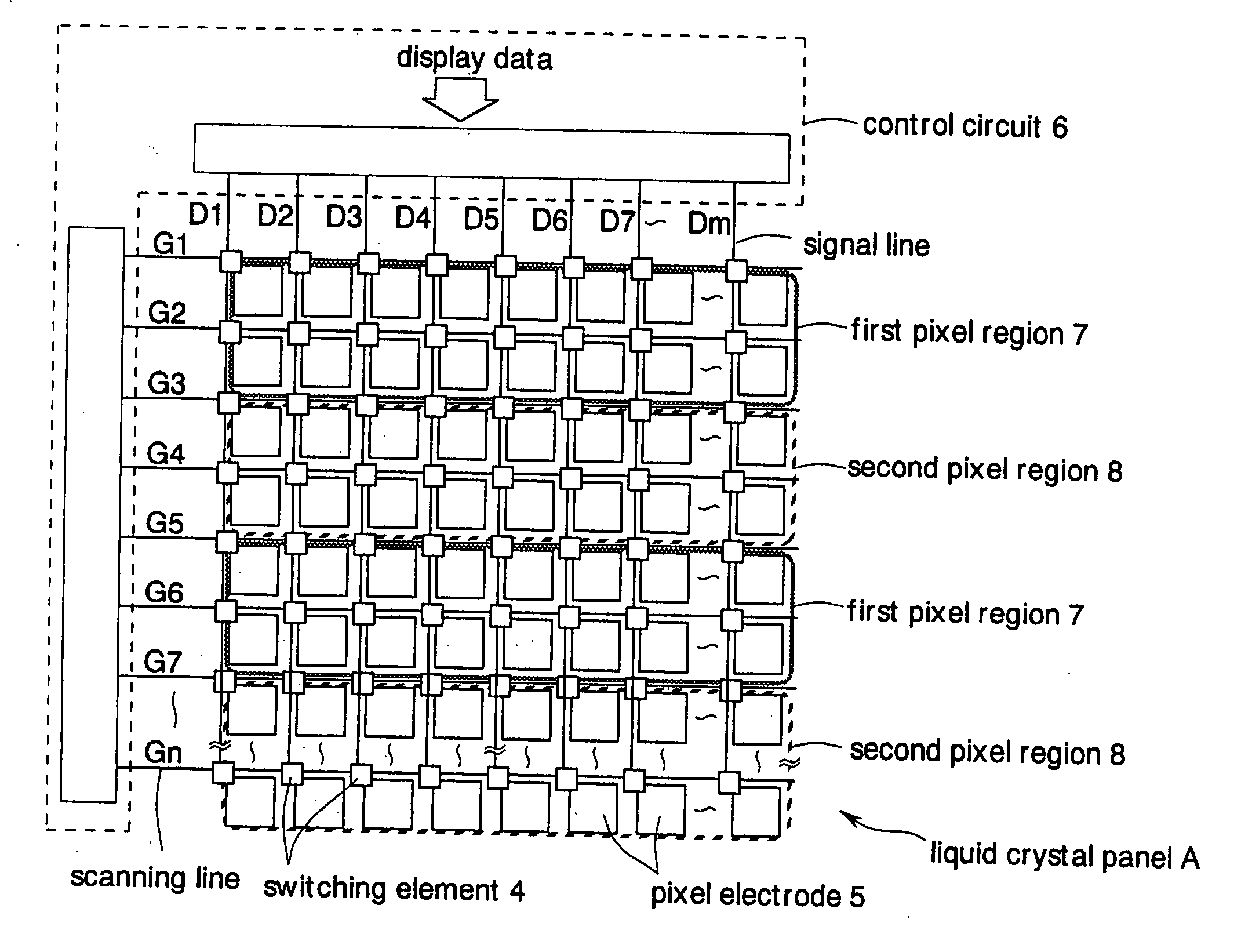
Apparatus and method to improve quality of moving image displayed on liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS7133015B1Quality improvementReduce blurStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayControl signal
A liquid crystal display device comprises a panel having pixel electrodes arranged at intersections of a plurality of signal lines via switching elements for transmitting display data and a plurality of scanning lines for transmitting control signals, and a control circuit for controlling the panel. The liquid crystal panel is divided into first pixel regions and second pixel regions adjacent to the first pixel regions. The control circuit carries out impulse driving in which the control signals transmitted to each of the scanning lines are activated two times in one frame period for displaying an image. The control circuit writes the display data in either one of the pixel regions and writes reset data in the other pixel regions when the control signals are activated once of the two times. By writing the reset data in the pixel regions, the display data written in an immediately preceding frame are reset. In consecutive frames, the display data written in the pixel regions are always reset in one frame period. Therefore, blurring in a moving image can be alleviated. Since writing the display data and the reset data is carried out separately in the first pixel regions and in the second pixel regions, flicker is prevented from occurring in a display screen.
Owner:SHARP KK
Apparatus and method to improve quality of moving image displayed on liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20060139289A1Brightness can be prevented from becoming unevenUniform brightnessStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayControl signal
A liquid crystal display device includes a panel having pixel electrodes arranged at intersections of a plurality of signal lines via switching elements for transmitting display data and a plurality of scanning lines for transmitting control signals, and a control circuit for controlling the panel. The liquid crystal panel is divided into first pixel regions and second pixel regions adjacent to the first pixel regions. The control circuit carries out impulse driving in which the control signals transmitted to each of the scanning lines are activated two times in one frame period for displaying an image. The control circuit writes the display data in either one of the pixel regions and writes reset data in the other pixel regions when the control signals are activated once of the two times. By writing the reset data in the pixel regions, the display data written in an immediately preceding frame are reset. In consecutive frames, the display data written in the pixel regions are always reset in one frame period. Therefore, blurring in a moving image can be alleviated. Since writing the display data and the reset data is carried out separately in the first pixel regions and in the second pixel regions, flicker is prevented from occurring in a display screen.
Owner:SHARP KK
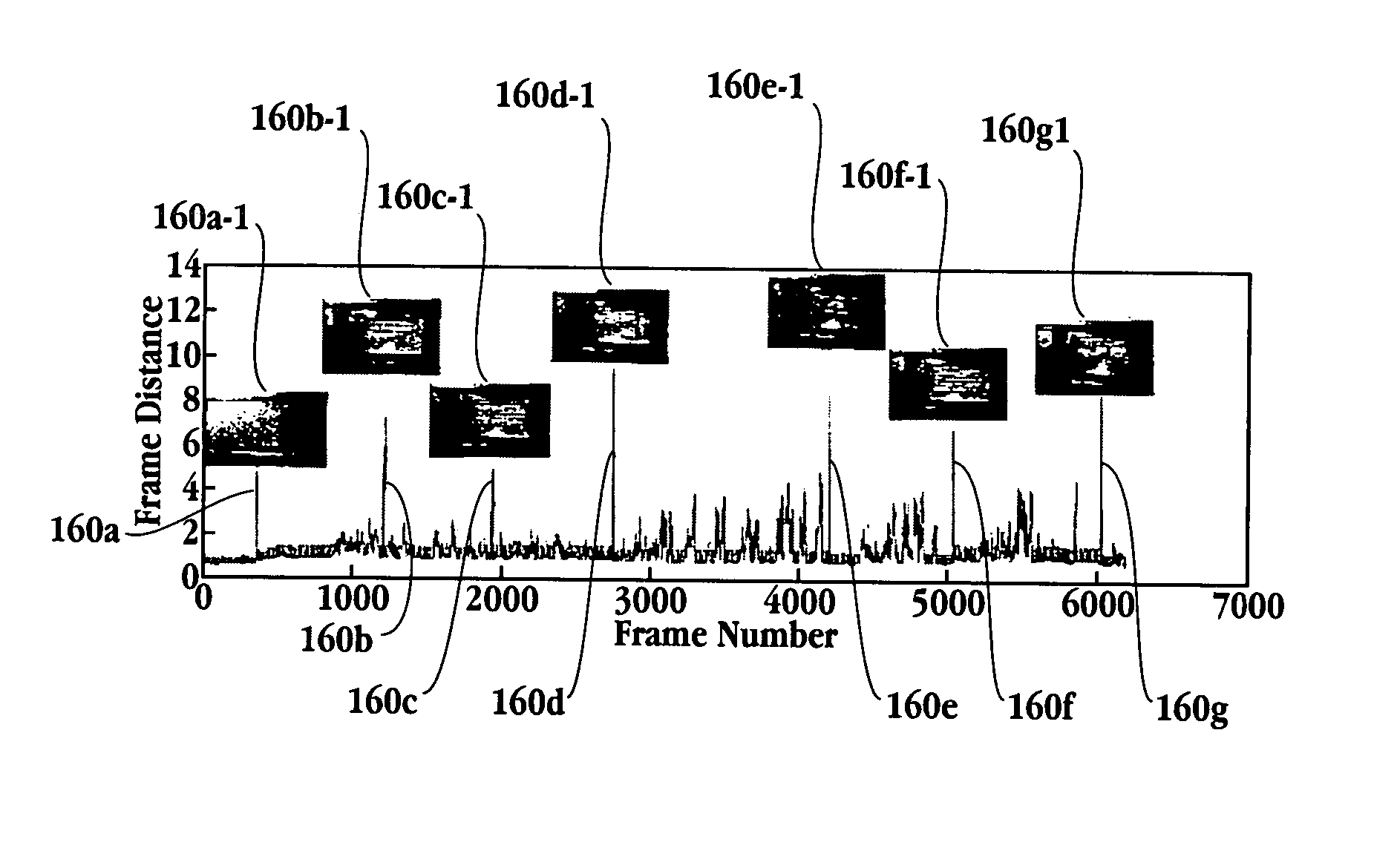
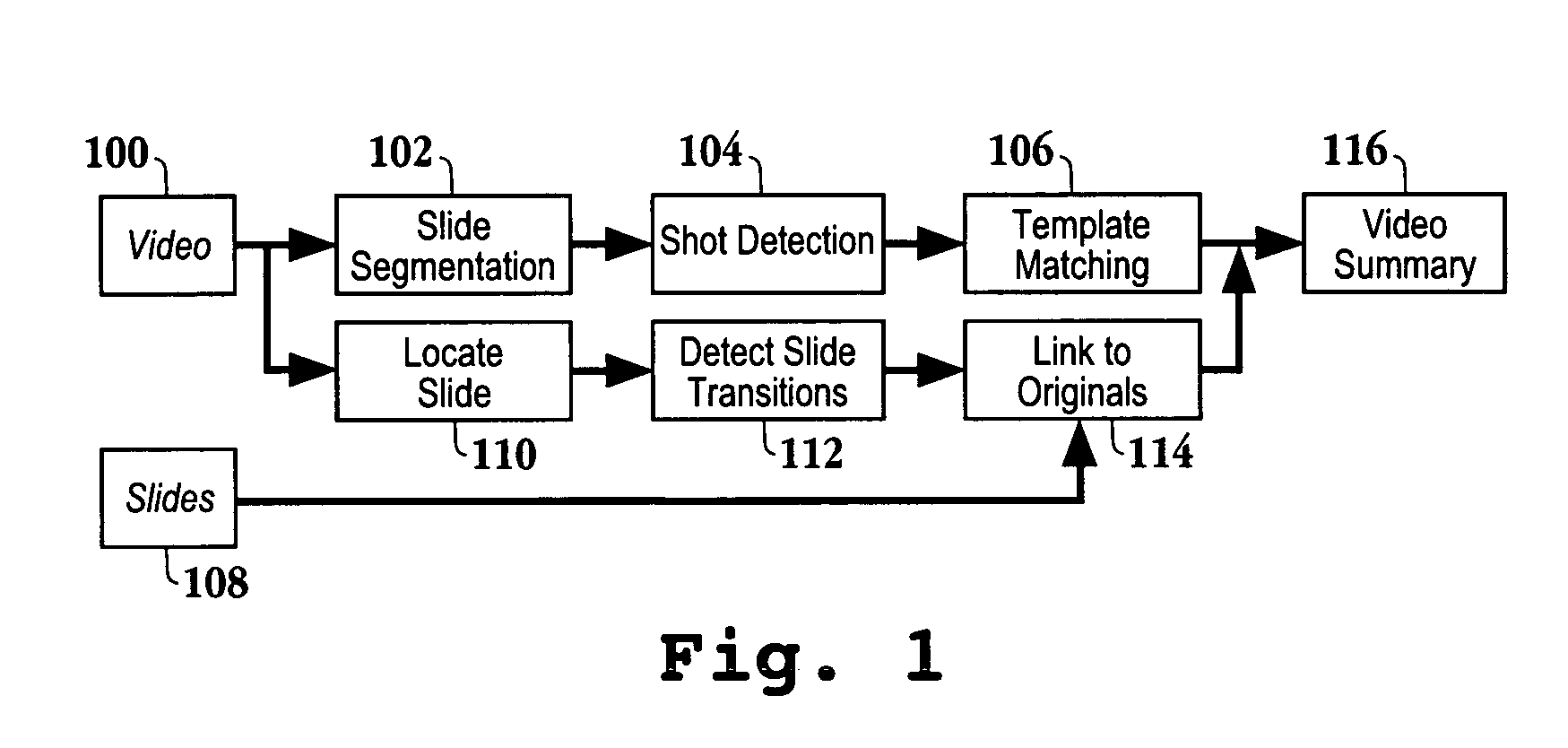
Method and apparatus for summarizing and indexing the contents of an audio-visual presentation
InactiveUS20050078868A1Television system detailsImage enhancementVisual presentationConsecutive frame
A method for creating a summary of an audiovisual presentation initiates with segmenting a frame of the audiovisual presentation. Then, a slide region of the segmented frame is identified. Next, a histogram representing lines in the slide region is generated. Next, moving regions associated with successive frames from the histogram are suppressed. A computer readable medium, a system for providing a real time summarization of a meeting and an integrated circuit are also provided.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method and apparatus for electronically stabilizing digital images
ActiveUS7557832B2Fast readoutEffective timeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCorrelation functionConsecutive frame
An electronic image stabilizer in a digital camera compensates for camera motion-induced blurriness by segmenting exposure times into multiple shorter exposure times and summing the individual pixels from successive frames after applying an appropriate motion correction. Motion is detected by computing the correlation function between successive images, and compensation is applied by maximizing the correlation function. This avoids the need for mechanical stabilization devices in order to detect or correct the motion as is done in prior art. This method further enables the detection of moving objects in a still background, and correction of blurriness images due to such motion.
Owner:LINDENSTRUTH VOLKER +2
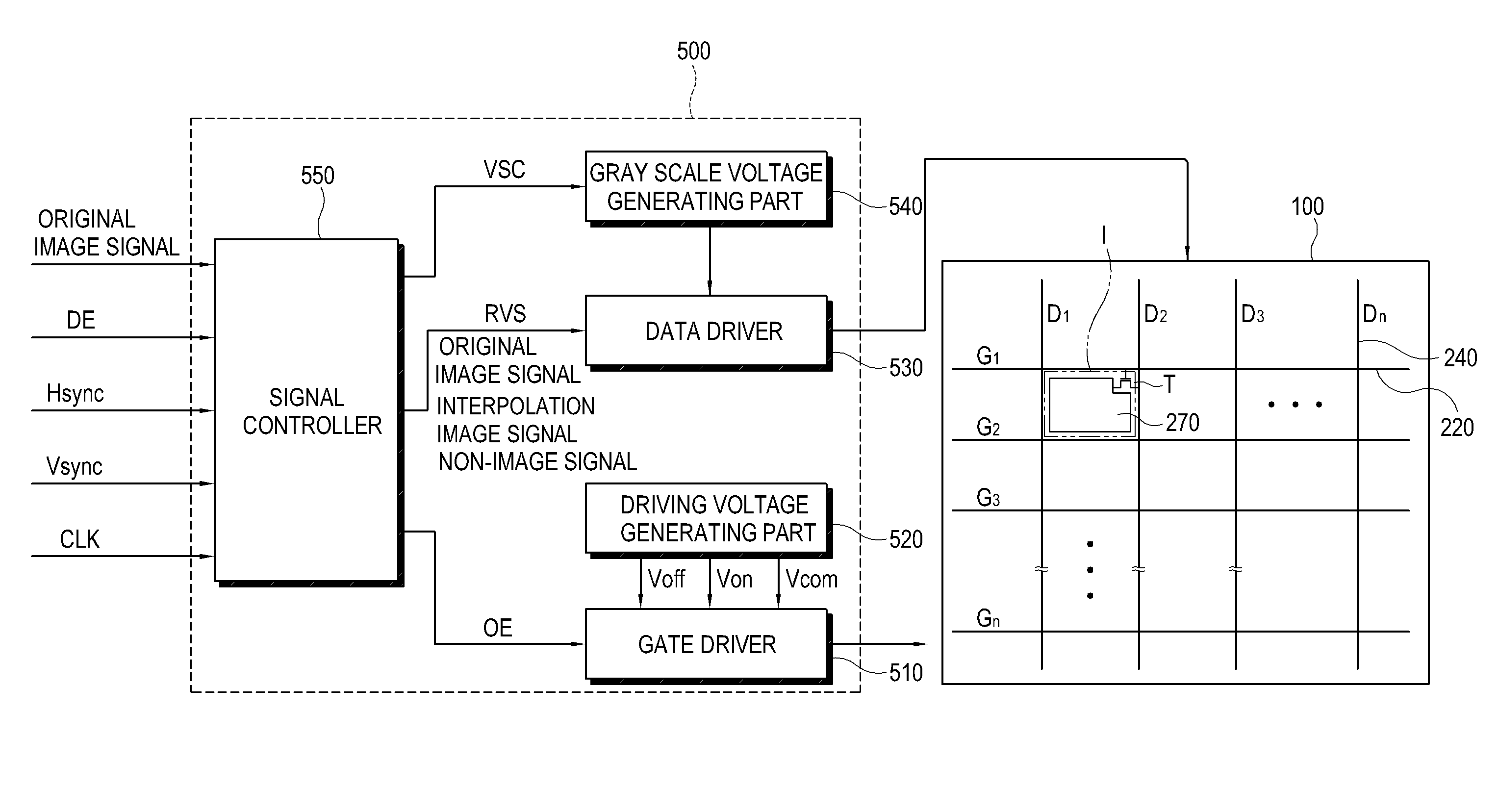
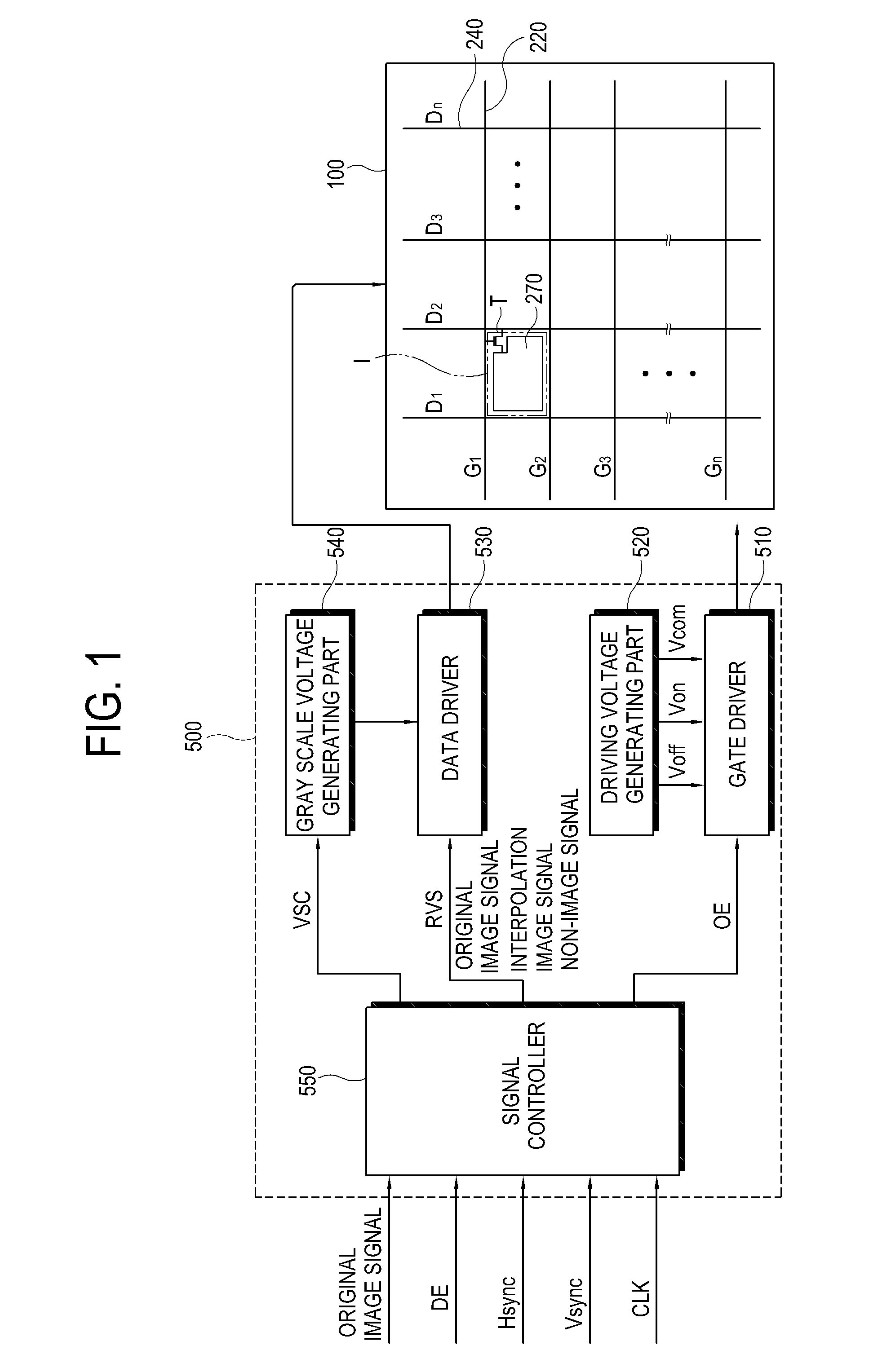
Display apparatus and control method thereof
InactiveUS20080246713A1Increase awarenessStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsConsecutive frameImage signal
A display apparatus includes a display panel that includes a plurality of pixels and a panel driver. The panel driver receives original image signals corresponding to successive frames which are displayed in a predetermined number within a predetermined period of time, forms an interpolation image signal on the basis of original image signals corresponding to two successive frames, and forms a non-image signal, and applies the original image signal, the interpolation image signal, and the non-image signal to the respective pixels during a display period.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
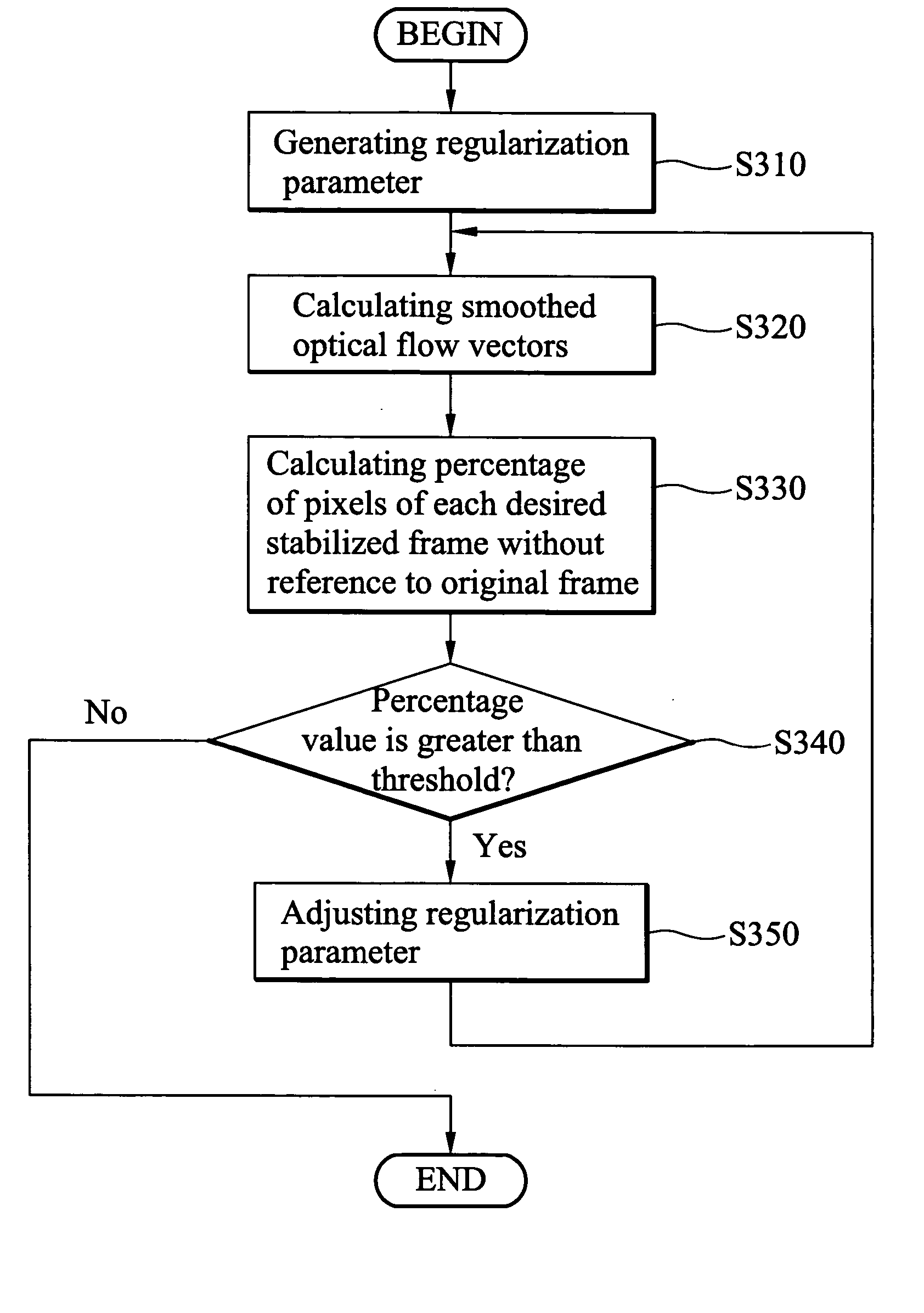
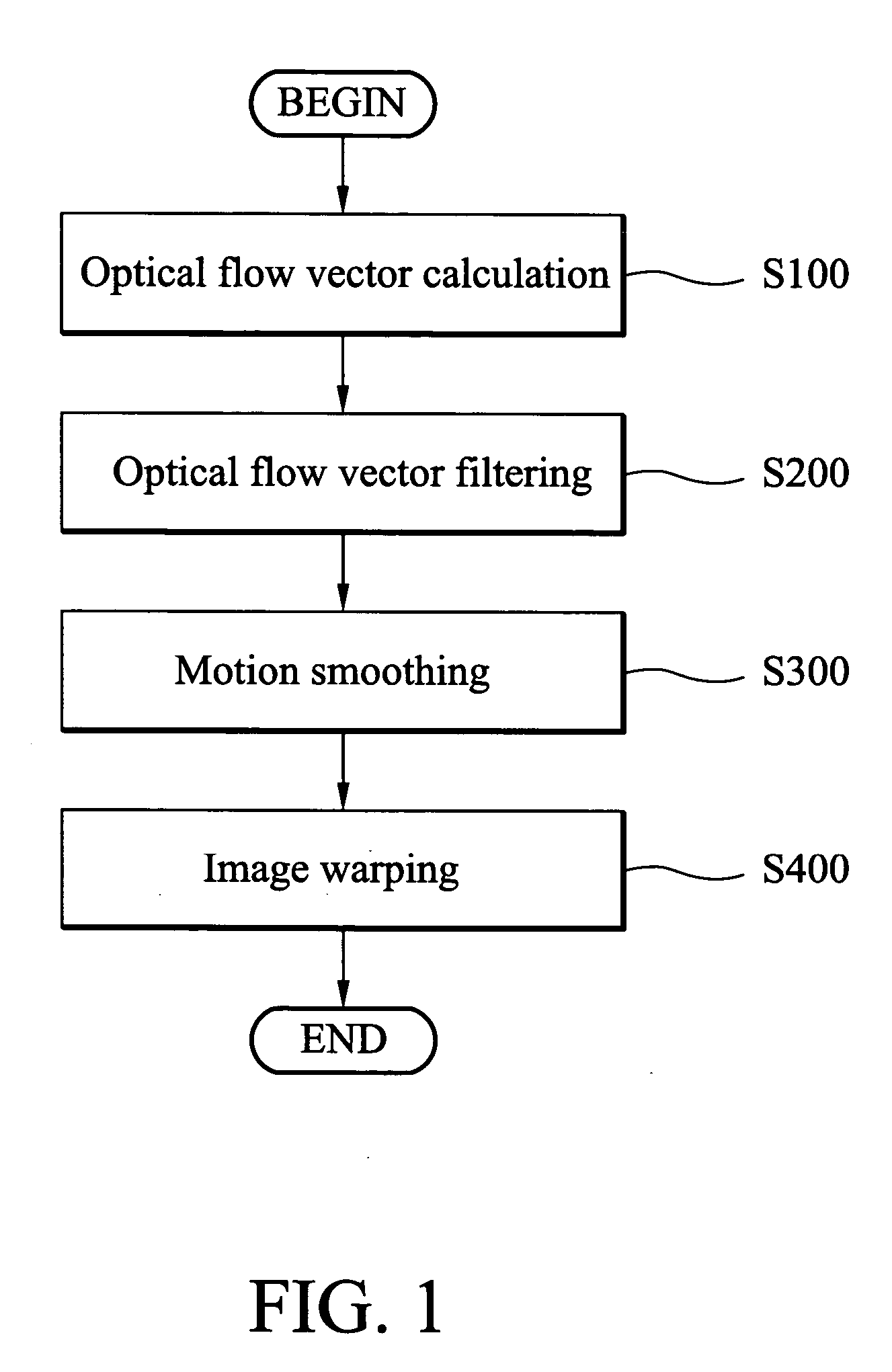
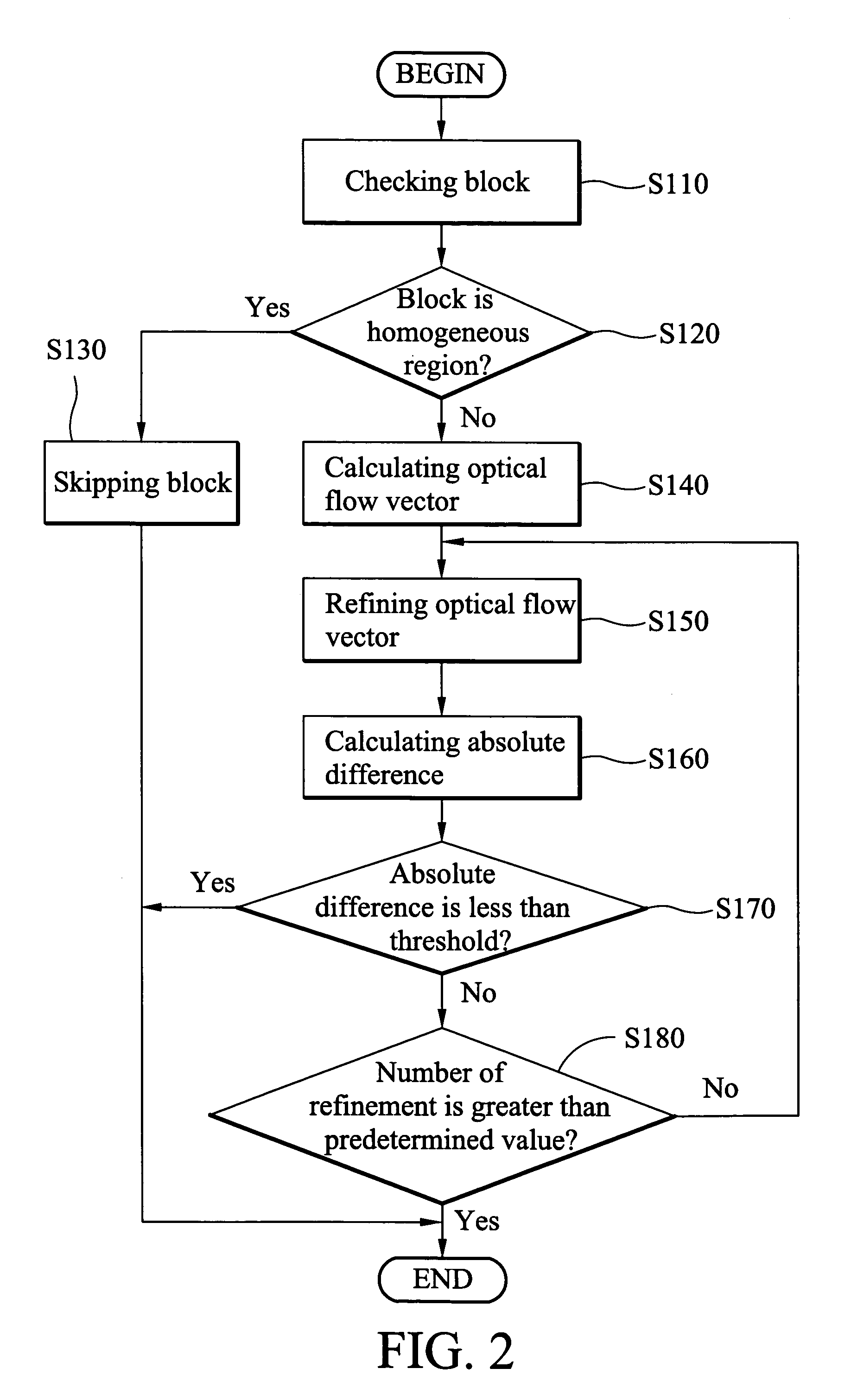
Video stabilization method
A video stabilization method. First, optical flows between successive frames are calculated. The camera motion is then estimated by fitting the computed optical flow field to a simplified affine motion model with a trimmed least square method. Then, the computed camera motions are smoothed to reduce the motion vibrations by using a regularization method. Finally, all frames of the video are transformed based on the original and smoothed motions to obtain a stabilized video.
Owner:INTEL CORP
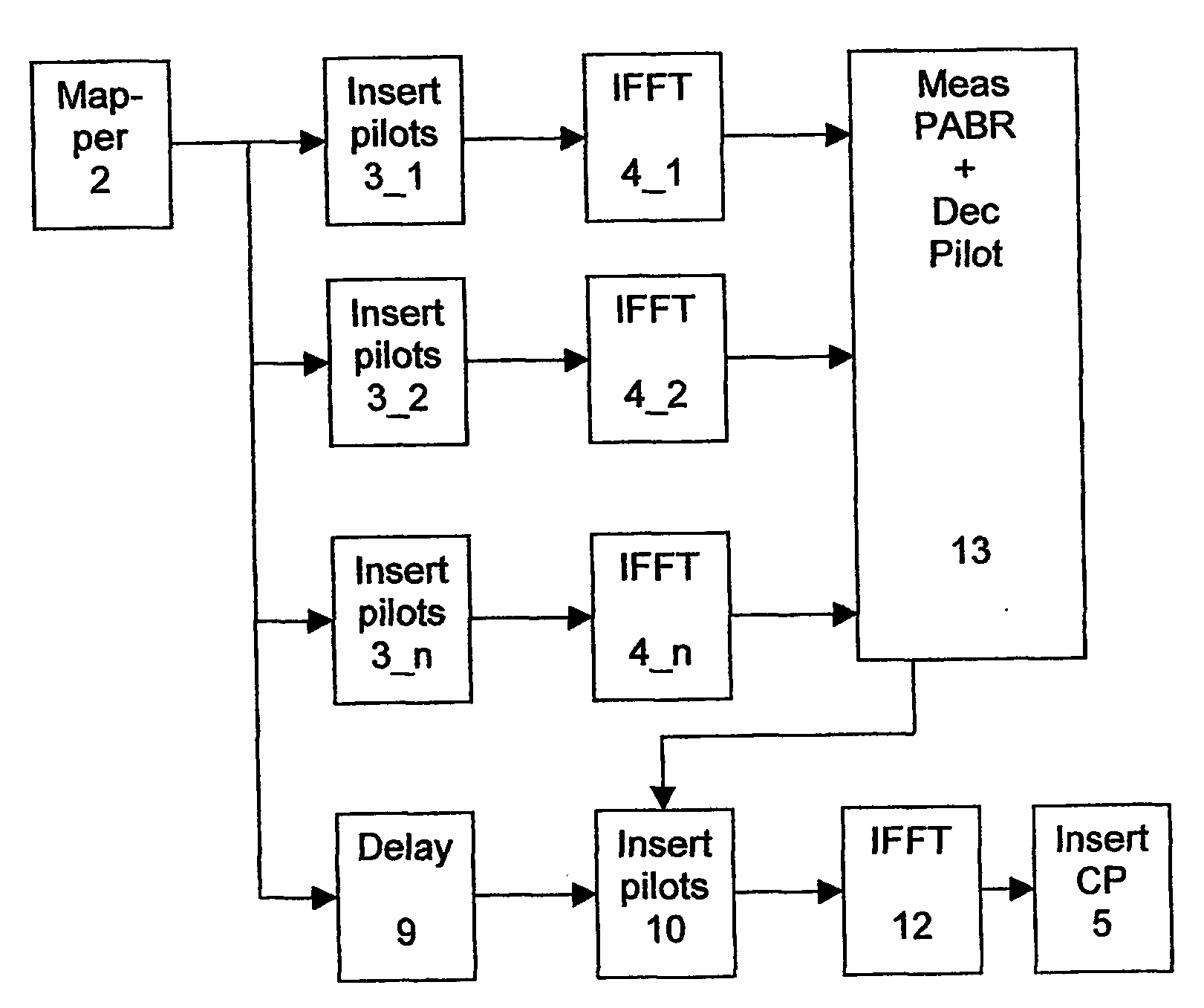
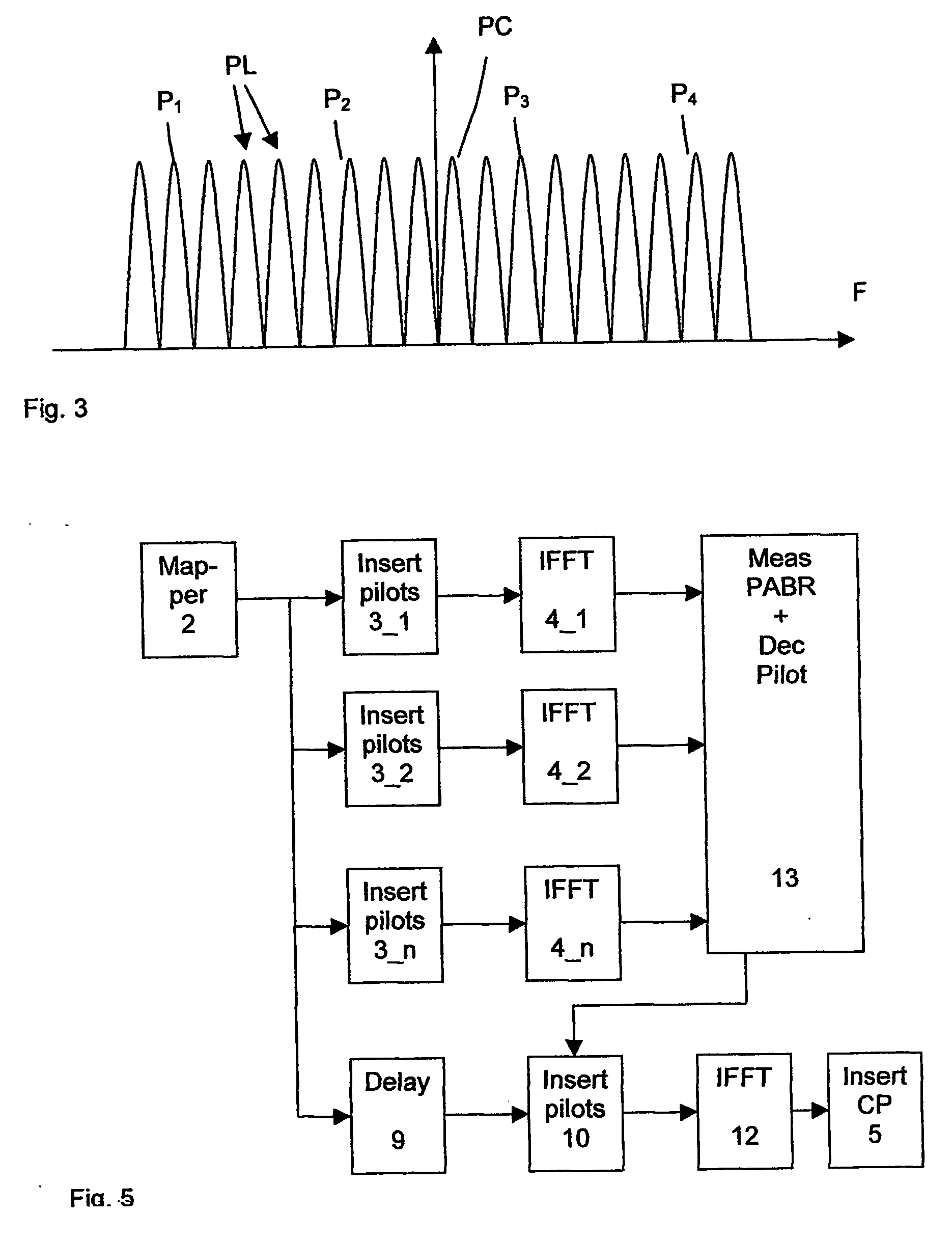
Papr reduction
InactiveUS20060034378A1Guaranteed normal transmissionDecreasing level of fluctuation of levelSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsDigital dataConsecutive frame
Method of communicating frames of digital data by OFDM modulated signals comprising a first plurality of payload carrying sub-channels and a second plurality of pilot carrying sub-channels, whereby consecutive frames of payload data is are associated with a given pilot configuration and transmitted. Prior to the transmission of a frame of payload data, each of the plurality of pilot configurations are evaluated with regard to PAPR, whereby the pilot configuration being associated with the lowest PAPR value is being chosen for transmission.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
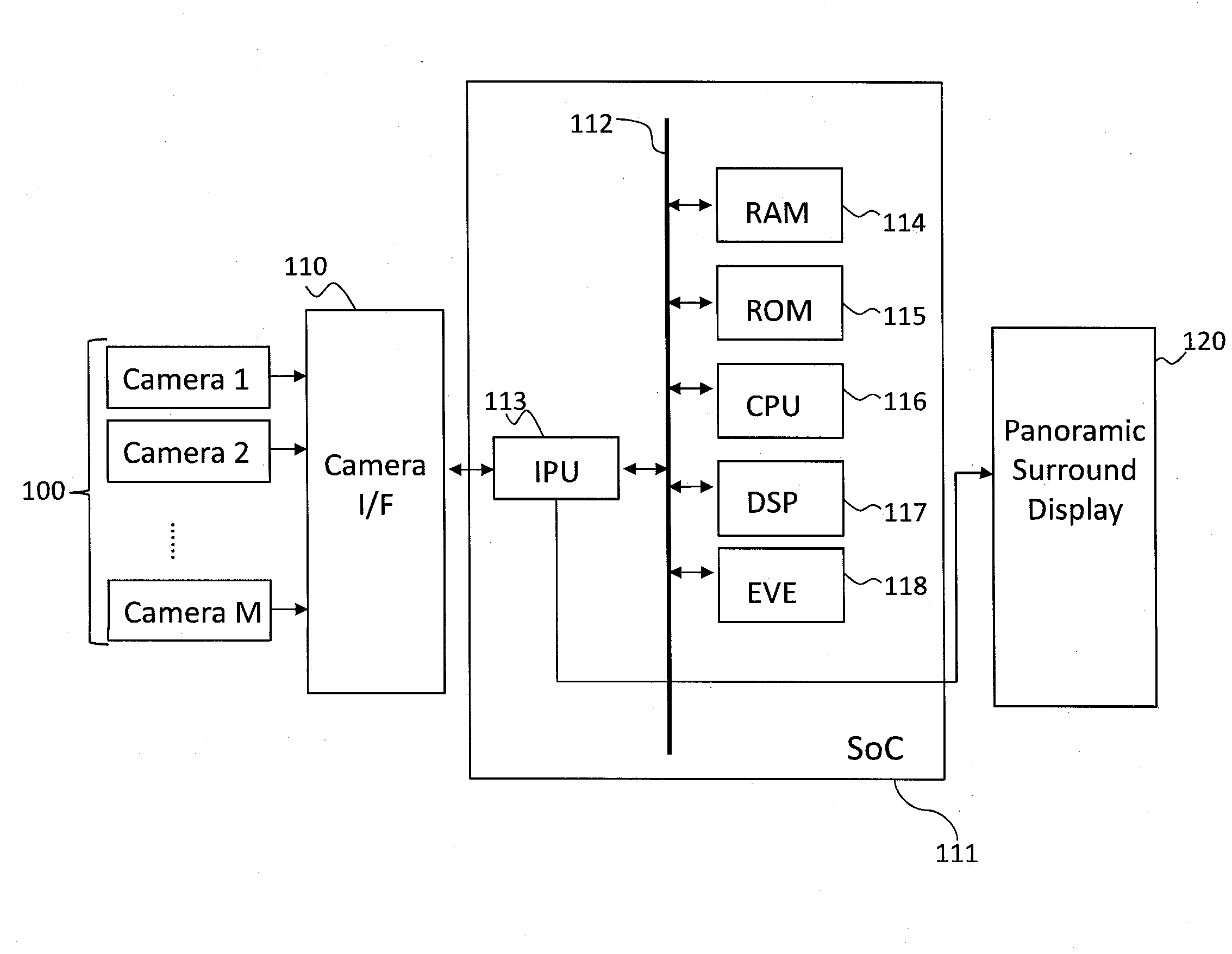
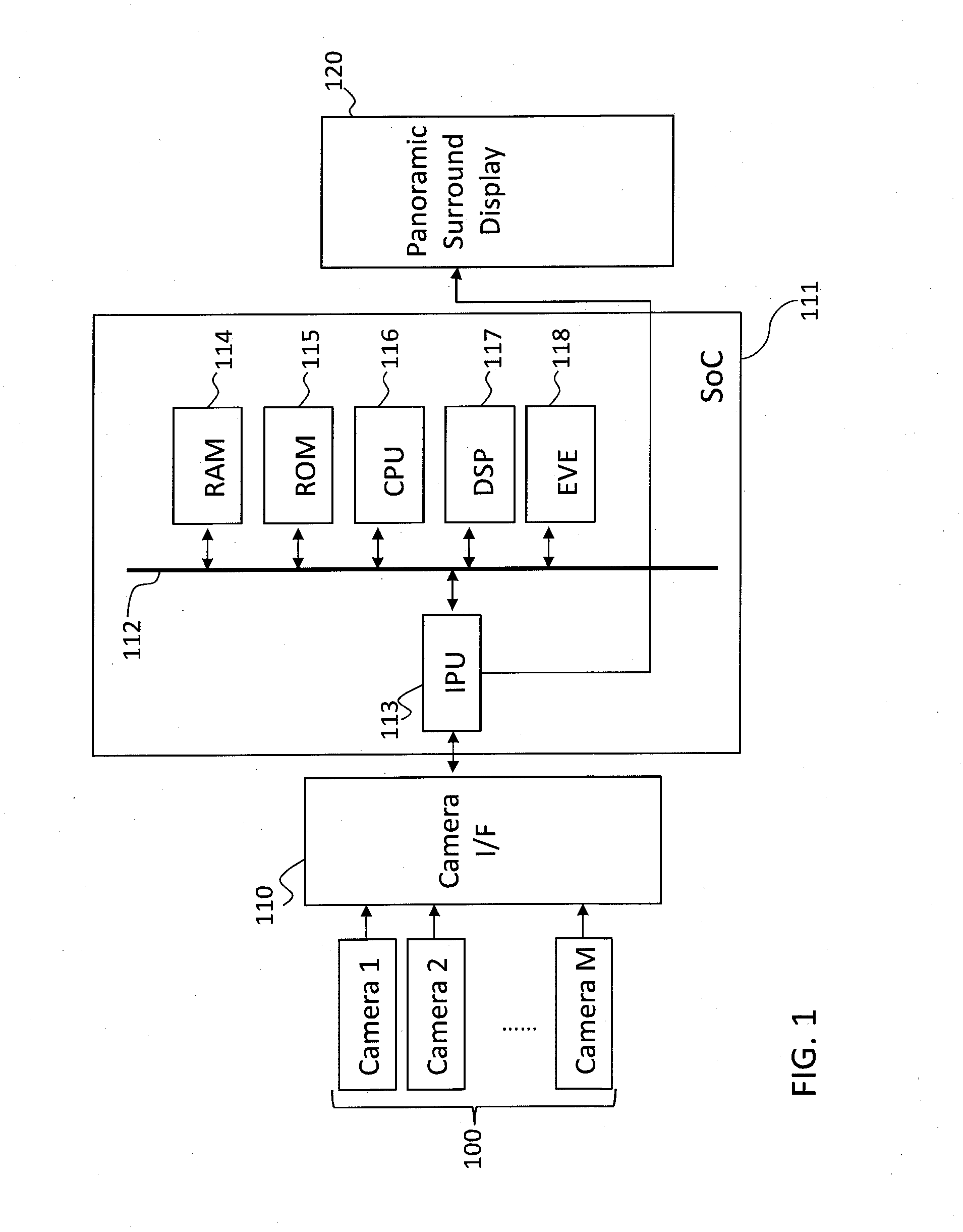
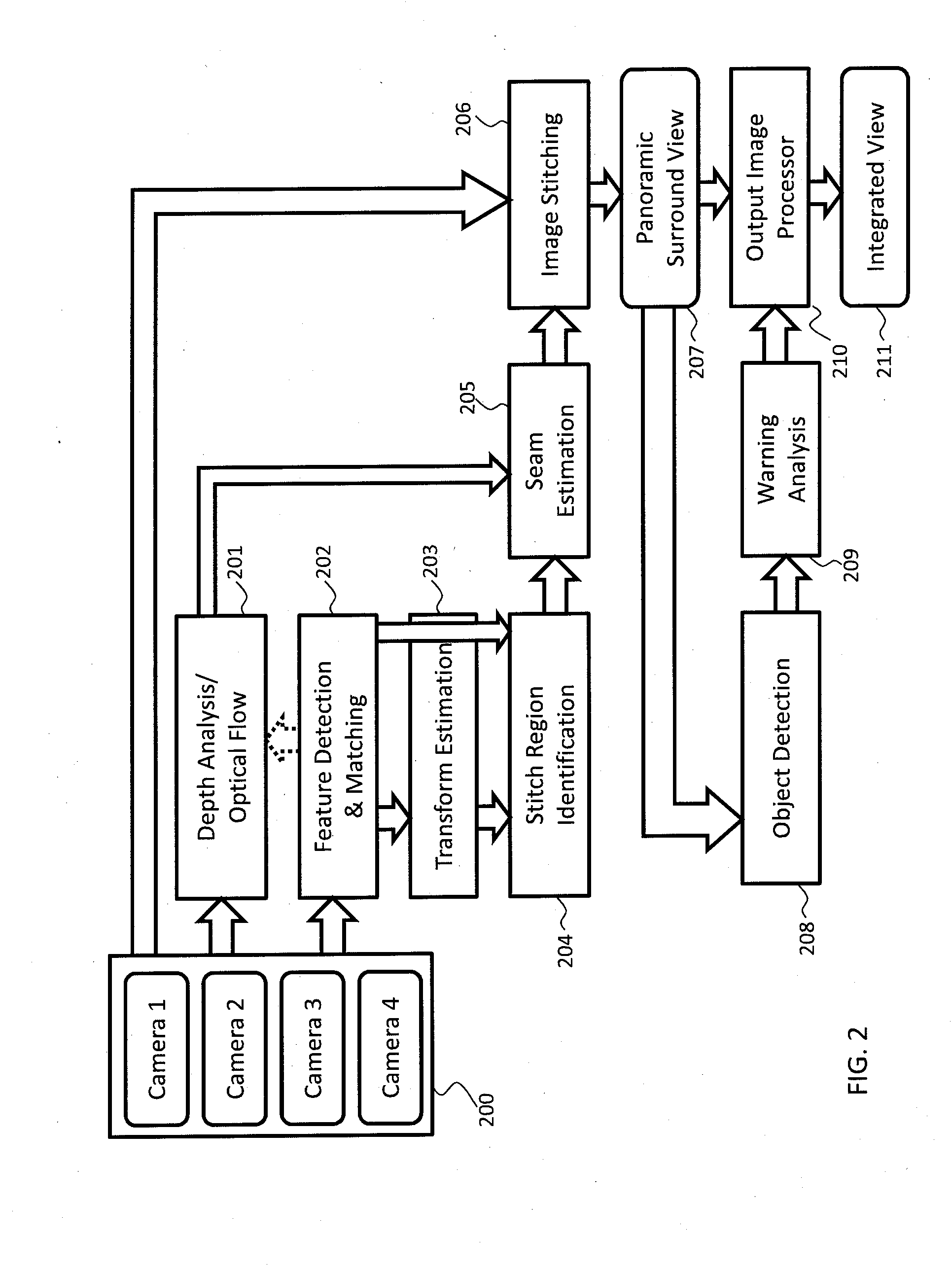
Method and system for presenting panoramic surround view in vehicle
A method and system of presenting a panoramic surround view in a vehicle is disclosed. Once frames are captured by a plurality of cameras for a period of time, features in consecutive frames of the plurality of cameras are detected and matched to obtain feature associations and transform is estimated based on the matched features. Based on the detected features, the feature associations and the estimated transform, a stitching region is identified. Particularly, an optical flow from the consecutive frames is estimated for the period of time and translated into a depth of an image region in the consecutive frames. Based on the depth information, a seam in the identified stitching region is estimated and the frames are stitched using the estimated seam, and presented as the panoramic surround view with priority information indicating an object of interest. In this manner, the occupant obtains an intuitive view without blind spots.
Owner:ALPINE ELECTRONICS INC
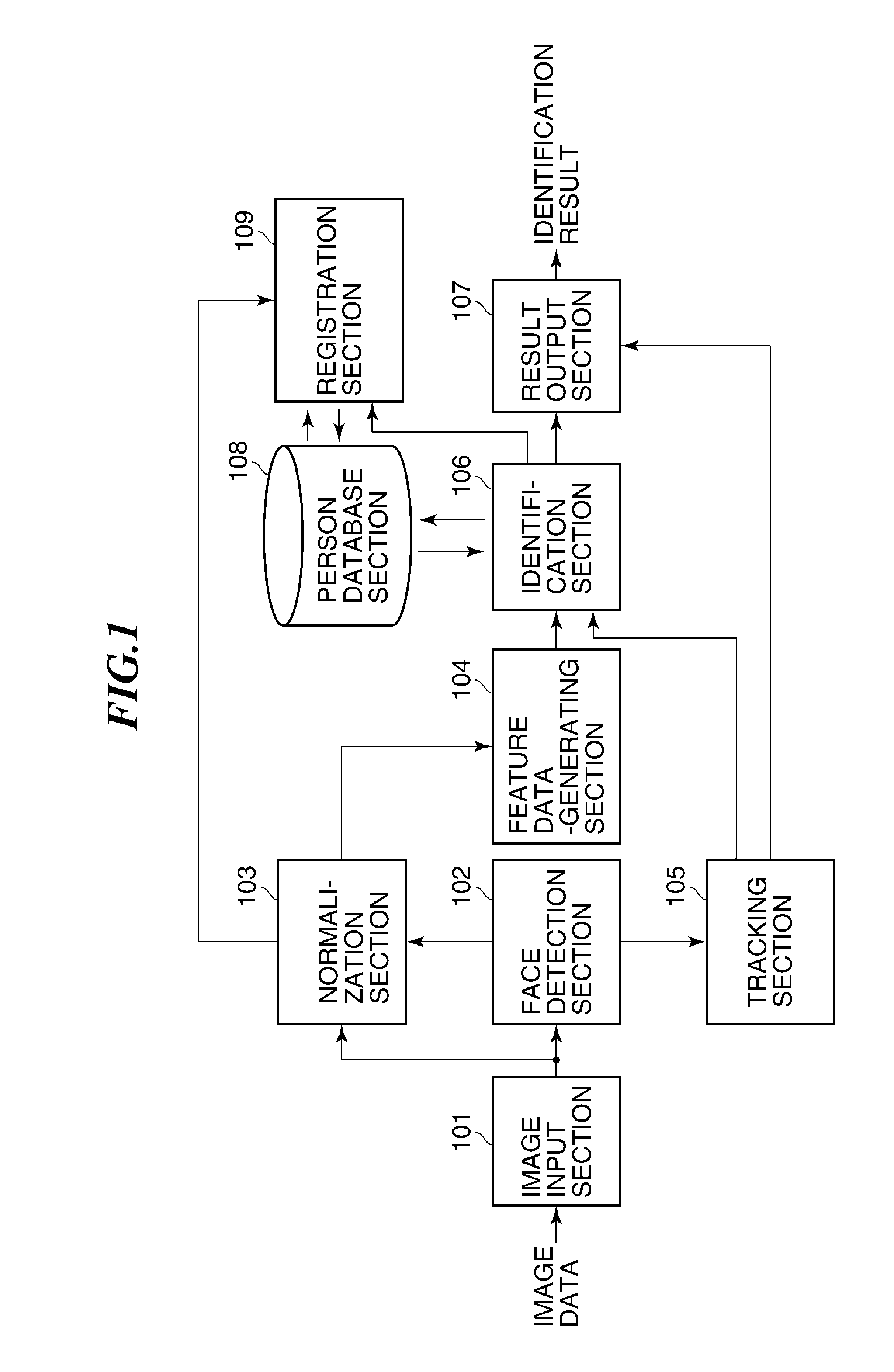
Identification device, identification method, and storage medium
ActiveUS20110311112A1Improve recognition accuracySmall processing loadCharacter and pattern recognitionConsecutive frameFeature data
An identification device capable of improving identification accuracy. The identification device performs identification according to a face area contained in image data. Feature data is extracted from a face area in each of frames of image data. The extracted feature data is registered in a person database section. Identification is performed through comparison between the feature data registered in the person database section and the extracted feature data. A tracking section identifies an identical face area in consecutive frames. If a face area is identified in a first frame, but a face area in a second frame following the first frame, which is identified by the tracking section as identical to the identified face area in the first frame, is not identified, the extracted feature data associated with the face area in the second frame is registered as additional feature data in the person database section.
Owner:CANON KK
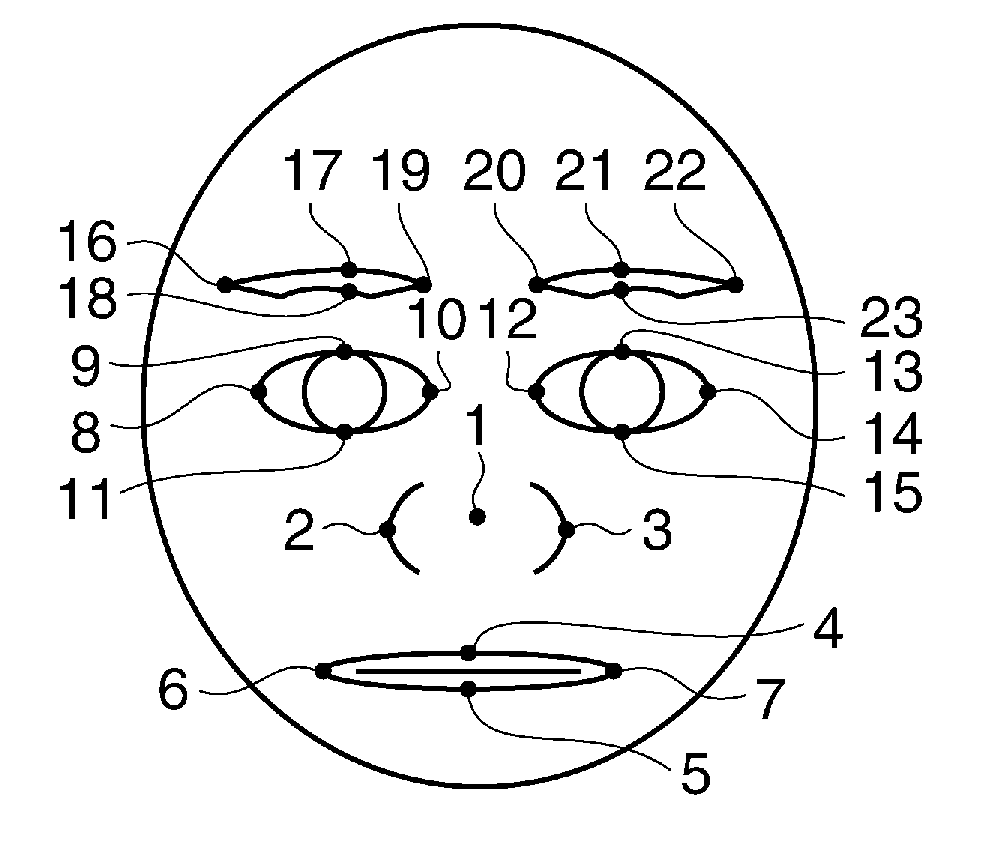
Bio-assay detection method and device
ActiveCN104751110AImprove accuracyImprove reliabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionAssayConsecutive frame
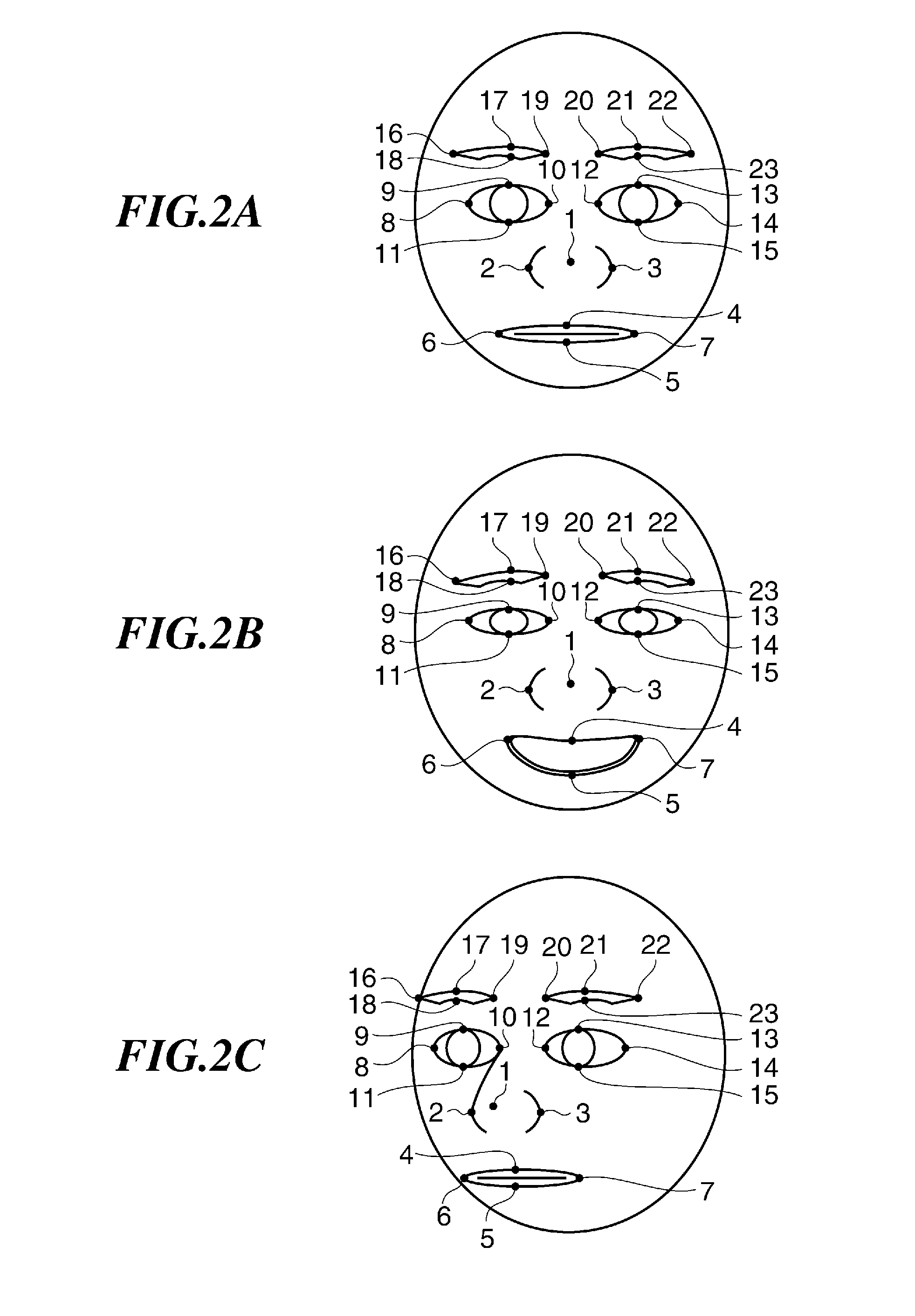
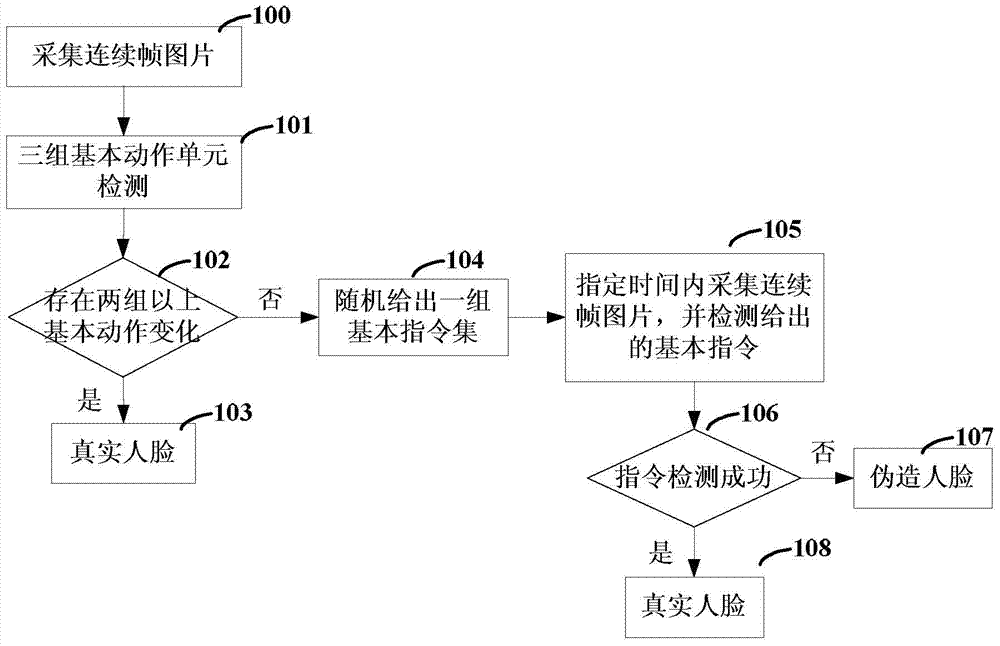
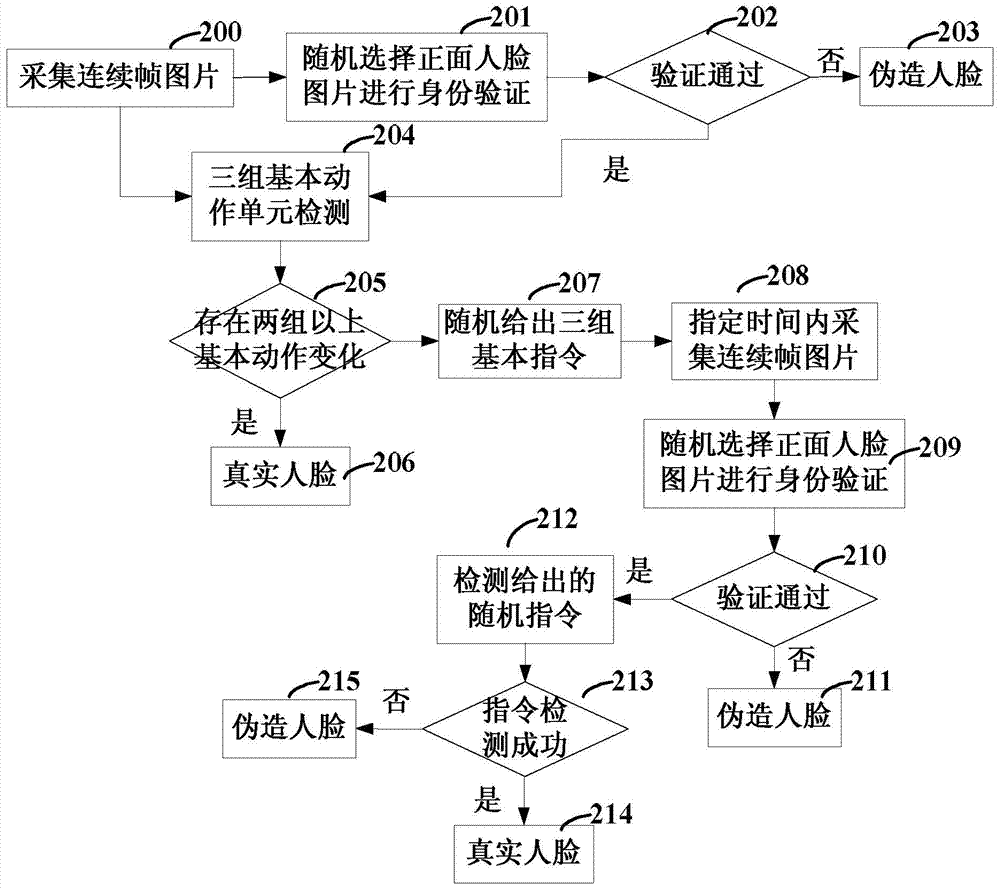
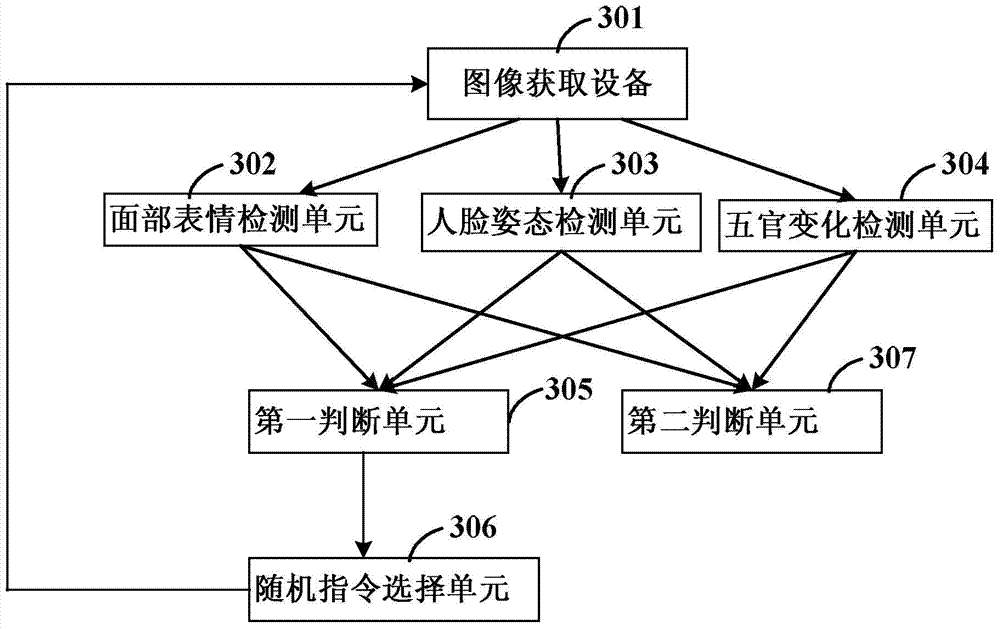
The invention discloses a bio-assay detection method. The method comprises the steps of 1, continuously acquiring frame pictures of a face through an image acquiring device; 2, detecting the acquired continuous frame pictures through a trained facial expression detecting unit, a face posture detecting unit and an expression change detecting unit; 3, determining that the face is a true human face if more than two groups of basic actions change according to the detection result in step 2, and otherwise, entering step 4; 4, randomly selecting a group of basic instructions from state element sets of the three detecting units, and prompting a user of finishing the group of basic instructions within the specified time; if that the user finishes the basic instructions is determined according to the detecting results of the three units, determining that the face is the true human face, and otherwise, determining that the face is a false face. With the adoption of the method, the effective deformation of the human face can be accurately caught and accurately detected, so that the true human face and the false face can be distinguished, and the invasion of a human face recognition system can be reduced.
Owner:HANVON CORP
Display device and driving method thereof
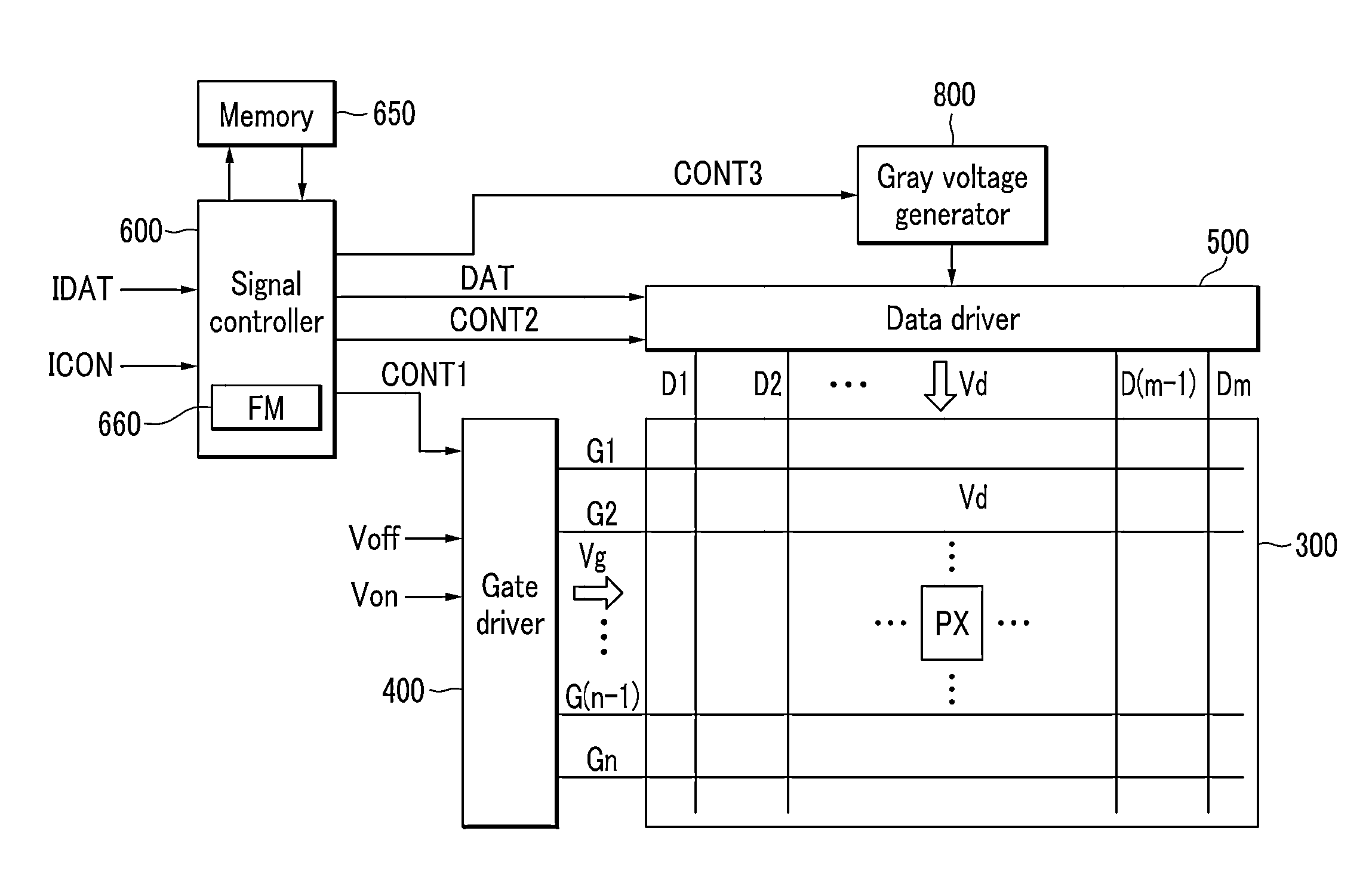
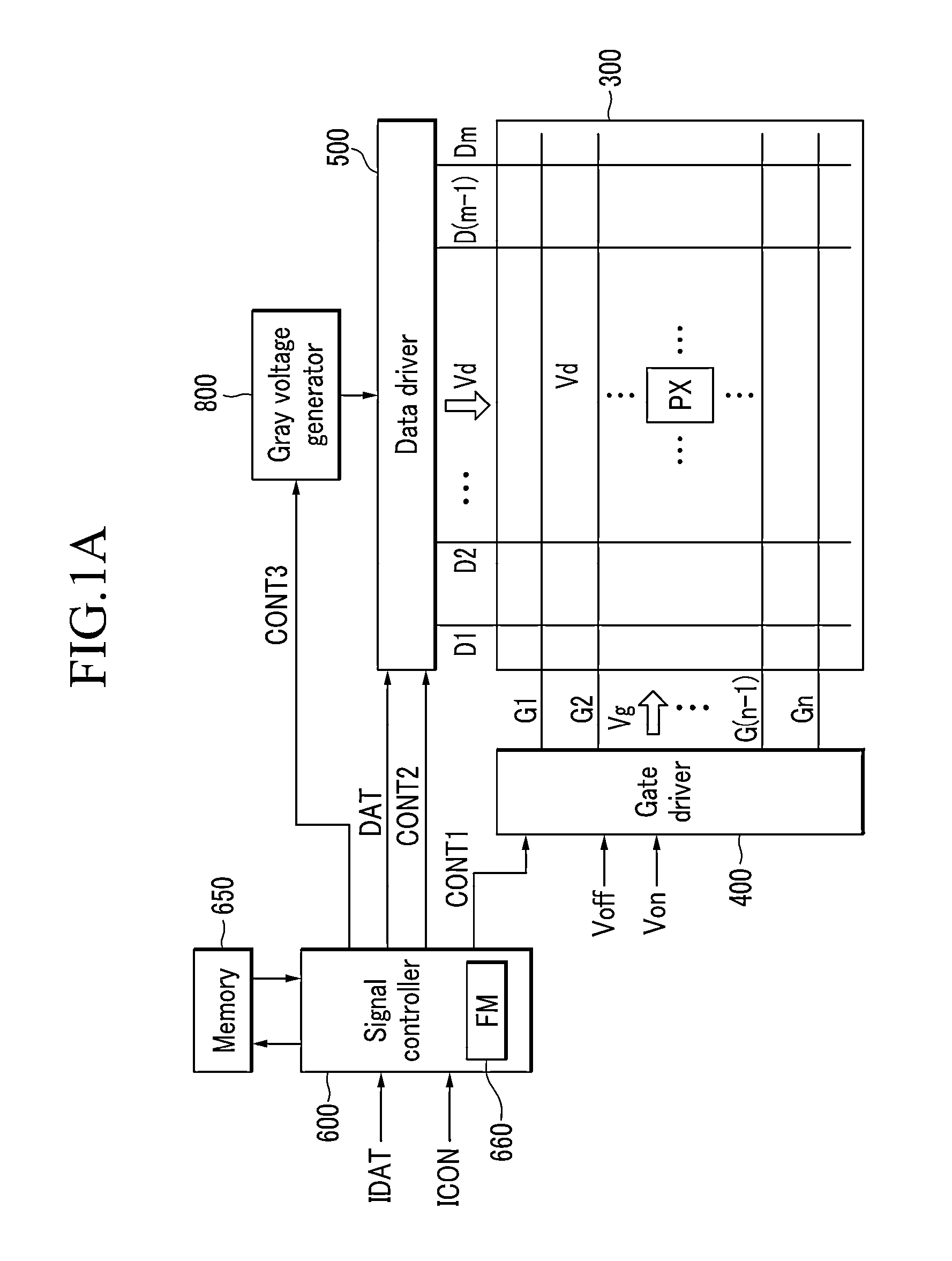
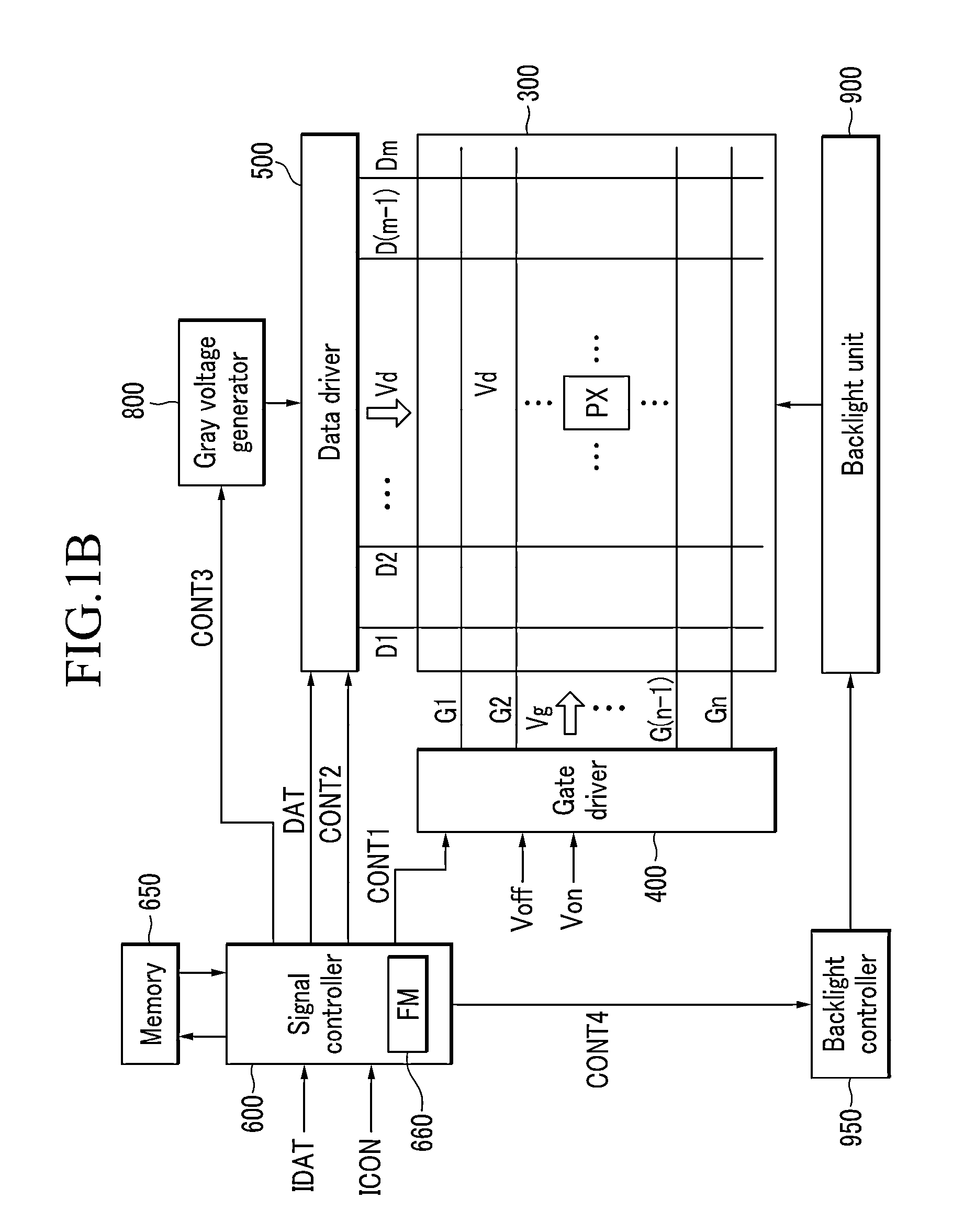
ActiveUS20130321483A1Improve display qualityLateral visibility improvedCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsVoltage generatorDisplay device
A display device includes a memory which stores gamma data for gamma curves including a first gamma curve and a second gamma curve; a gray voltage generator which generates gray voltages based on the gamma data; a data driver which receives an input image signal from a signal controller and converts the input image signal into a data voltage using the gray voltages; and a display panel including pixels which receives the data voltage and may display an image, where the pixel displays images corresponding to the input image signal during one frame set, one frame set includes consecutive frames, the images displayed by a pixel includes first and second images displayed based on the first and second gamma curves, respectively, a luminance of the first image is not less than a luminance of the second image, and the second image is displayed in two consecutive frames.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Method and system for spatio-temporal video warping
ActiveUS20060262184A1Realistic impression of the dynamic environmentTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationConsecutive frameSpacetime
A computer-implemented method and system for transforming a first sequence of video frames of a first dynamic scene captured at regular time intervals to a second sequence of video frames depicting a second dynamic scene wherein for at least two successive frames of the second sequence, there are selected from at least three different frames of the first sequence portions that are spatially contiguous in the first dynamic scene and copied to a corresponding frame of the second sequence so as to maintain their spatial continuity in the first sequence. In a second aspect, for at least one feature in the first dynamic scene respective portions of the first sequence of video frames are sampled at a different rate than surrounding portions of the first sequence of video frames; and the sampled portions are copied to a corresponding frame of the second sequence.
Owner:BRIEFCAM LTD
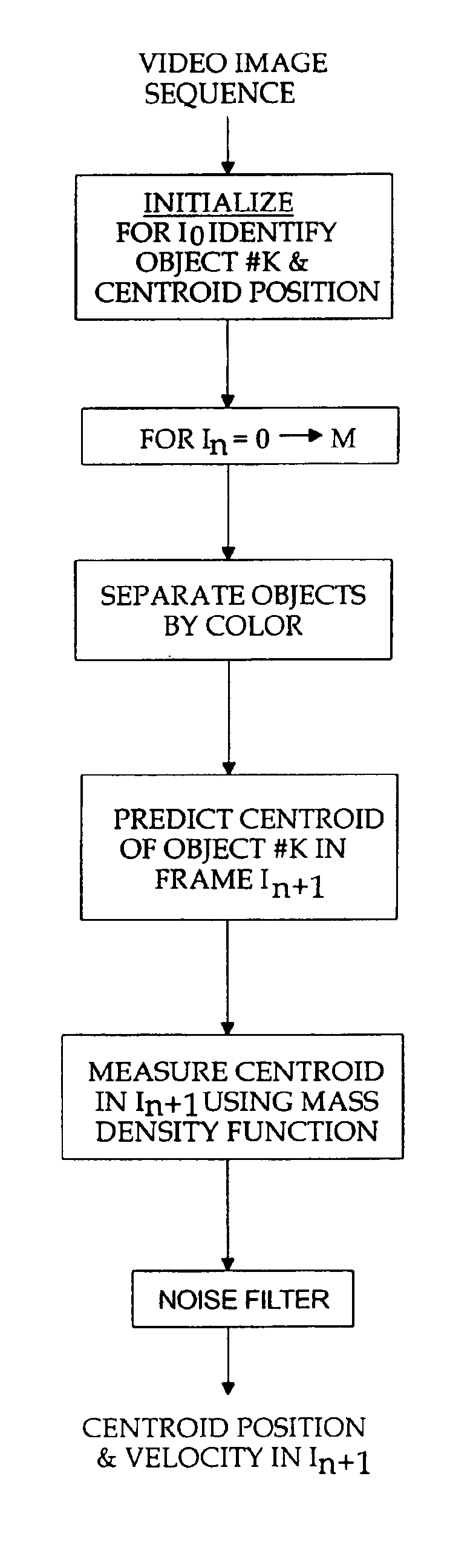
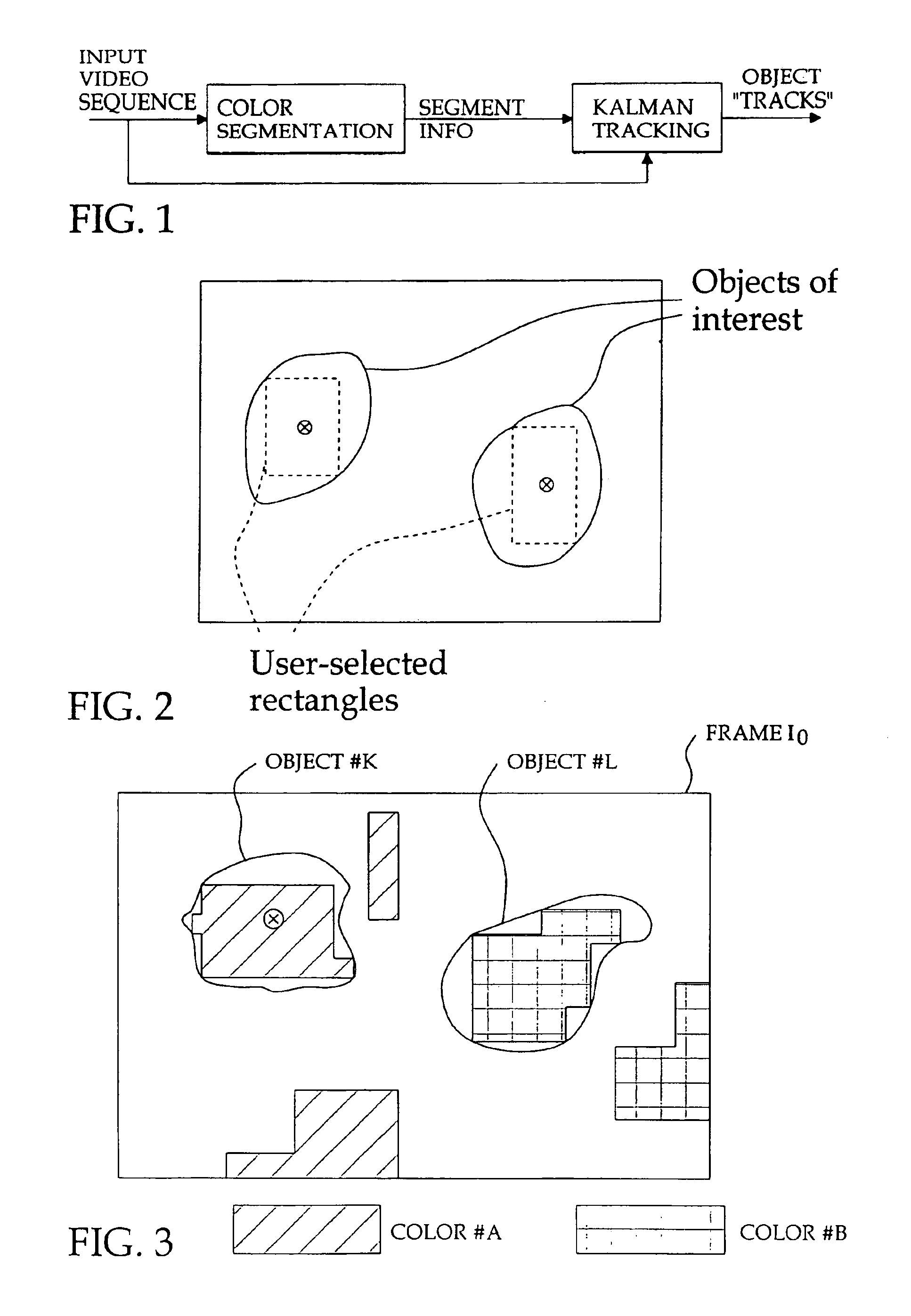
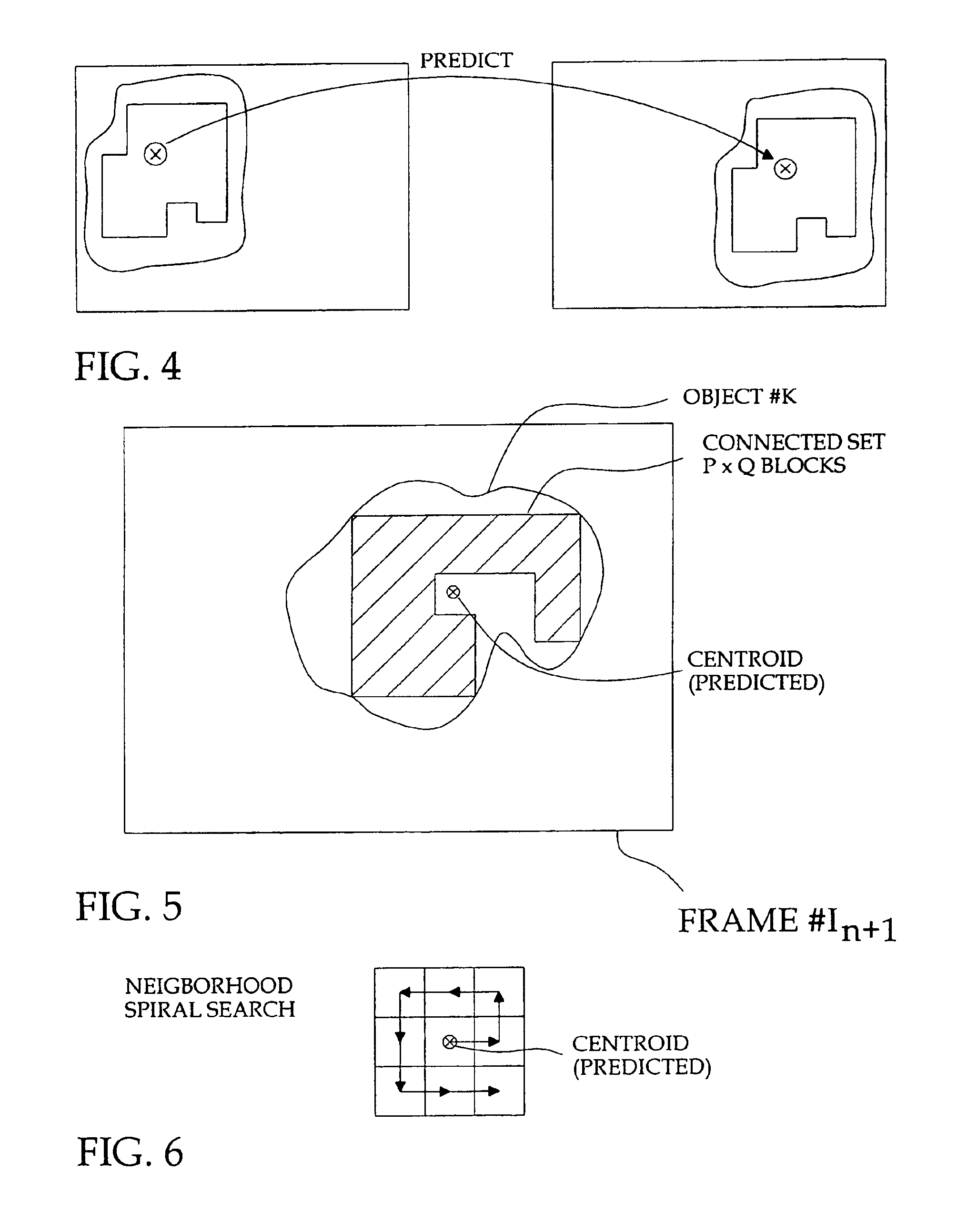
Kalman tracking of color objects
A semi-automatic method of tracking color objects in a video image sequence starts by separating the objects on the basis of color and identifying an object of interest to track. A Kalman predictive algotithm in used to predict the position of the centroid of the object of interest through successive frames. From the predicted position the actual centroid is measured and the position and velocity are smoothed using a Kalman filter. Error recovery is provided in the event the centroid falls outside the field of view or falls into an area of a different color, or in the event the tracking algorithm breaks down.
Owner:GVBB HLDG R L
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com