Patents
Literature
1196 results about "Surface emission" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
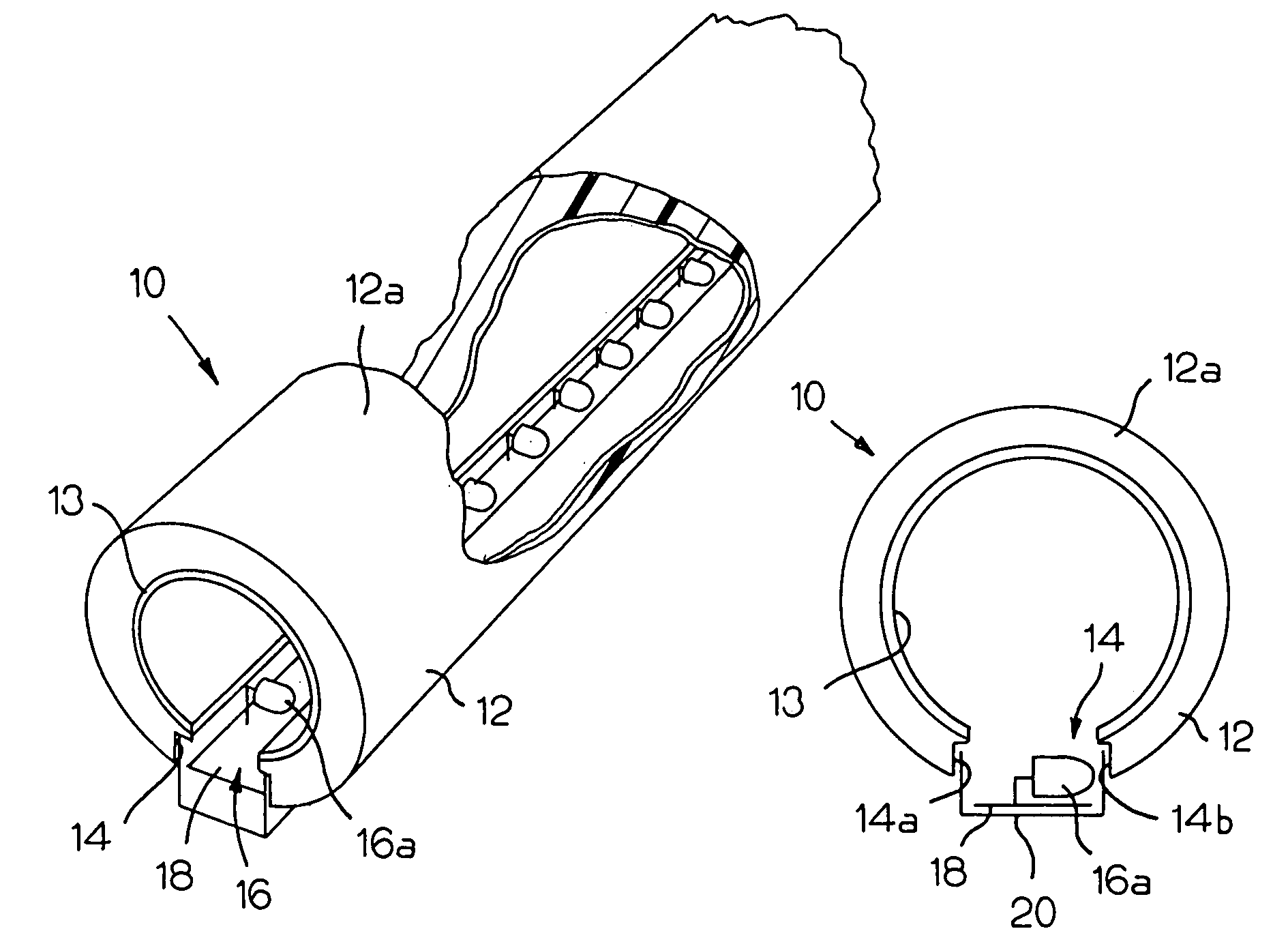
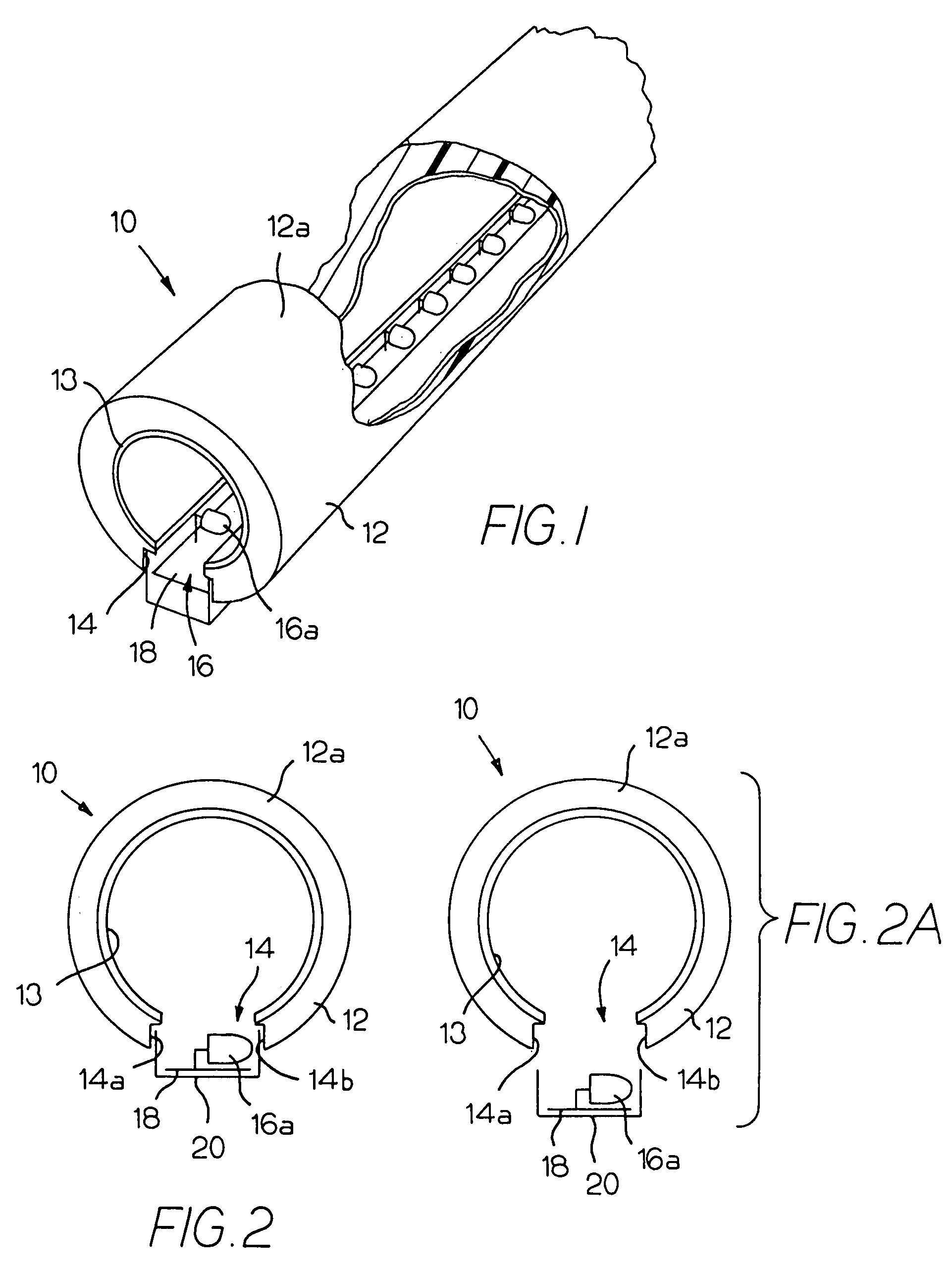
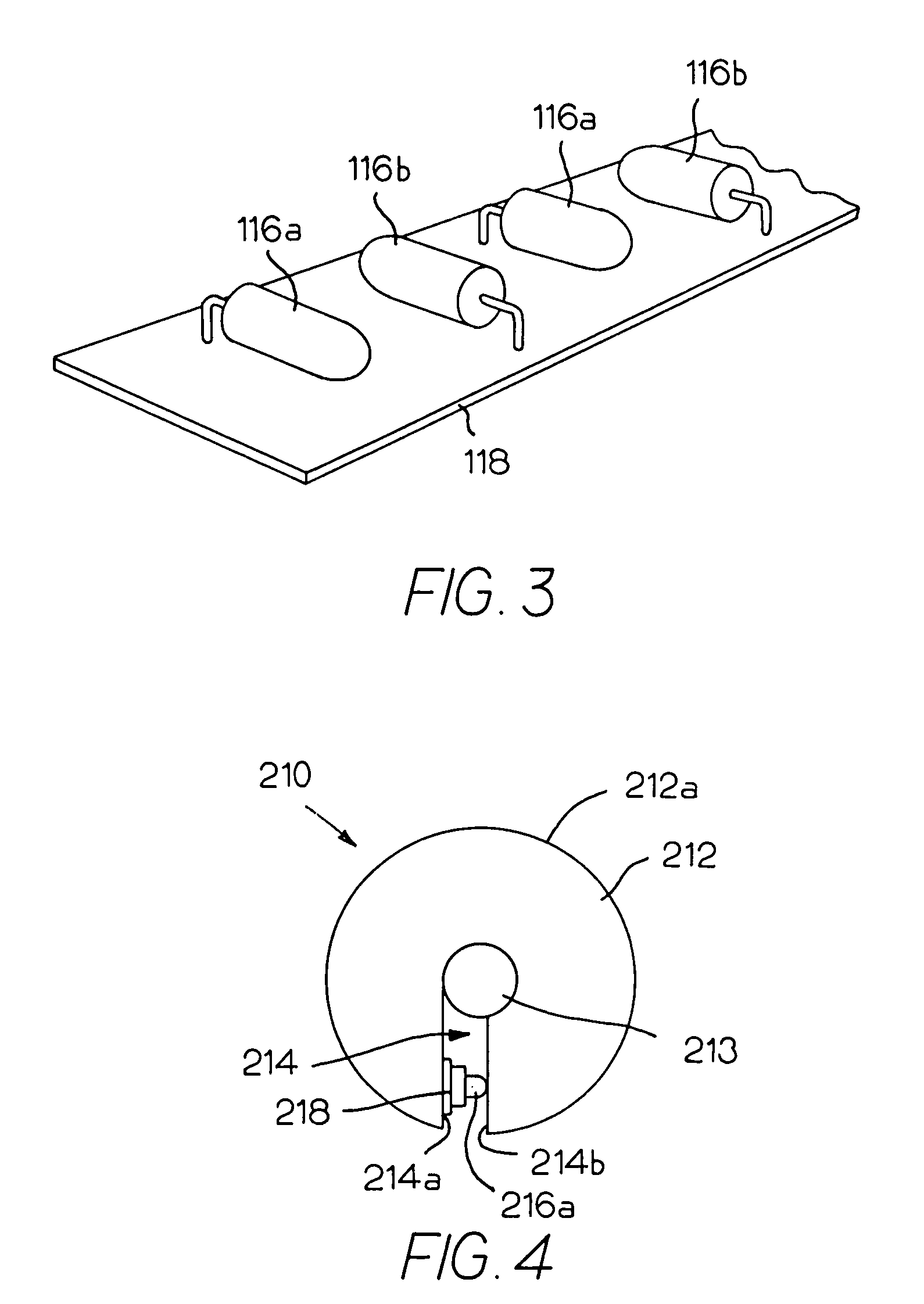
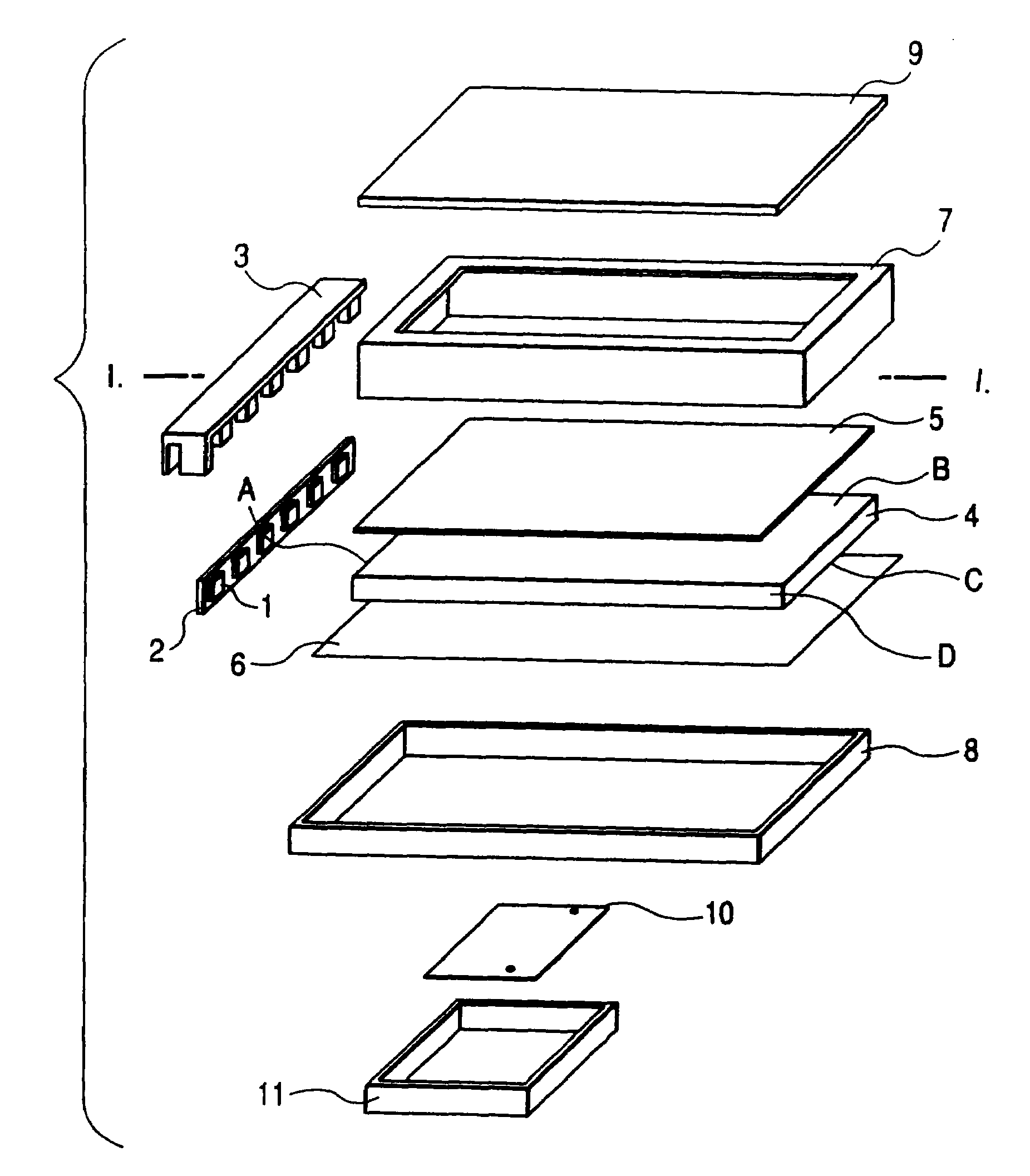
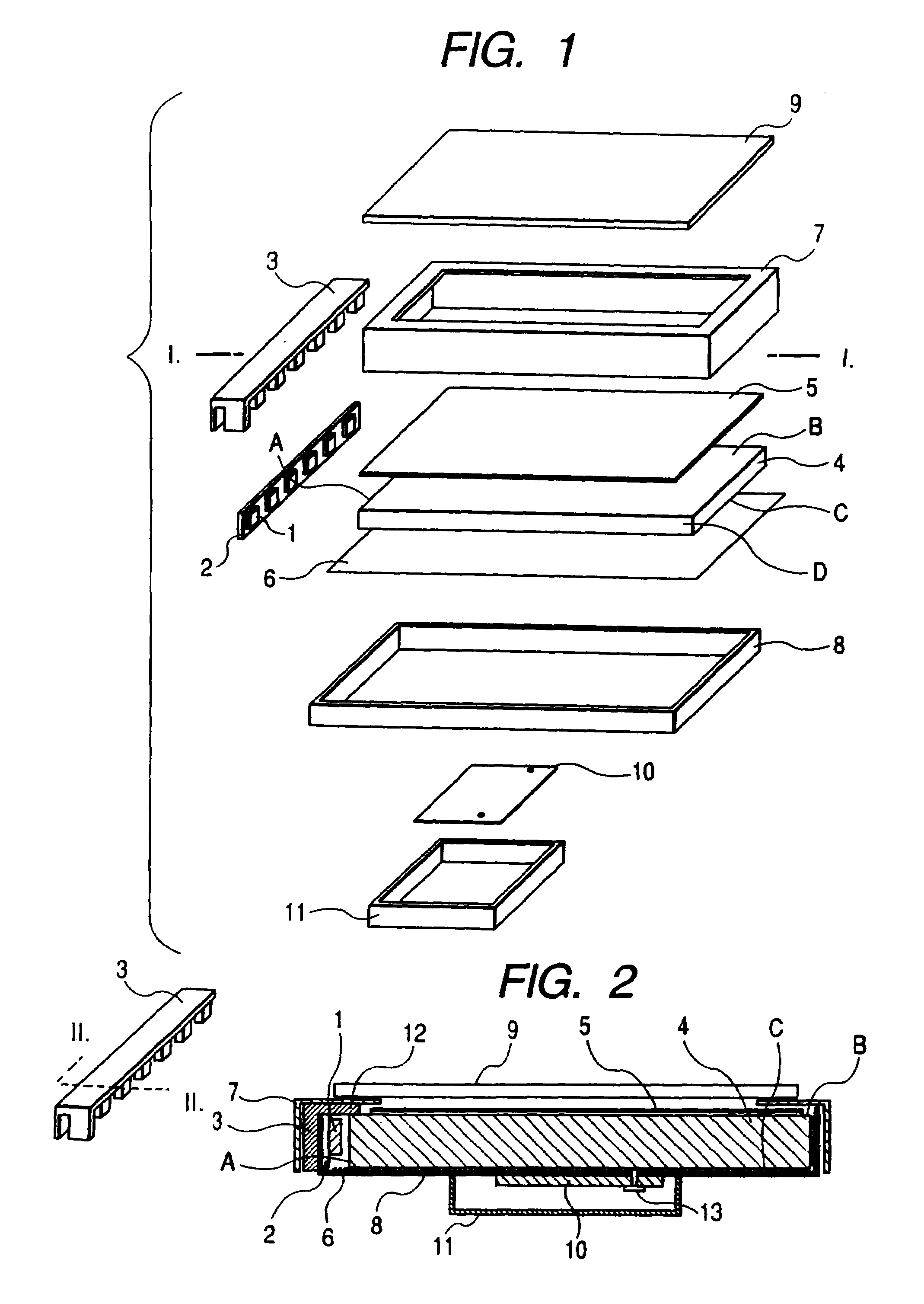
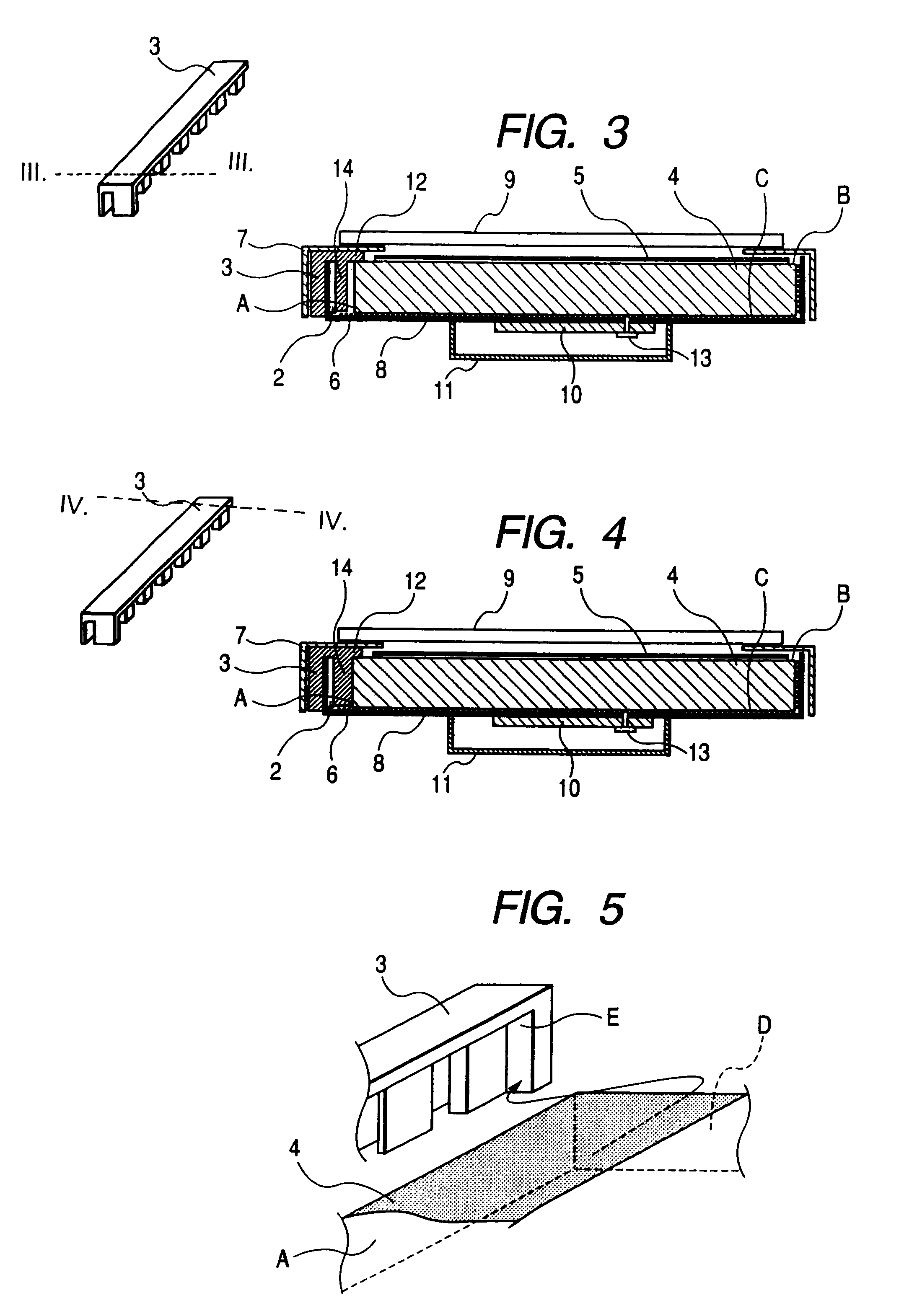
Illumination device for simulation of neon lighting
InactiveUS6874924B1Readily apparentLighting support devicesPoint-like light sourceSurface emissionLight source
An illumination device includes an elongated and substantially cylindrical waveguide, which has a light-emitting outer surface and an interior semi-reflective portion spaced at a predetermined distance from the light-emitting outer surface. A channel is defined through a portion the waveguide along the length thereof and is adapted to receive an elongated light source such that emitted light is directed into at least one of the wall surfaces defined by the channel. As the light enters and is directed about the circumference of the waveguide, a portion of the light is scattered and emitted through the light-emitting outer surface of the waveguide. Light is also reflected by the semi-reflective portion, causing additional light to be scattered and emitted through the light-emitting outer surface of the waveguide. The result of this guiding, reflecting, and emission of light is a substantially homogenous and uniform light intensity pattern over the light-emitting outer surface of the waveguide so as to simulate neon lighting.
Owner:LUMINII PURCHASER LLC
Light guide plate, light source device equipped therewith and display device
InactiveUS7073933B2Dispersion suppressionIncrease contrastPoint-like light sourceMeasurement apparatus componentsForming faceLight guide
A display device used for a display unit of portable electronic equipment, a light source device therefor and a light guide plate, suppressing dispersion in the brightness and featuring a high contrast and a good display quality. The constitution includes a light incidence surface on where light emitted from an LED falls, a light reflection surface formed facing the light incidence surface and reflects light from the light incidence surface, a light outgoing surface arranged between the light incidence surface and the light reflection surface, and has a circularly polarizing plate intimately adhered onto the surface thereof, and an opposing surface formed facing the light outgoing surface and in which there are alternately arranged first opposing surfaces for guiding the incident light to the light outgoing surface as well as to the light reflection surface, and second opposing surfaces for emitting the light reflected by the light reflection surface through the light outgoing surface.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method and apparatus for irradiating a surface with pulsed light
A method and apparatus irradiates a surface with at least one pulsed light beam emitted from an emission surface of an optical element. The at least one pulsed light beam comprises a plurality of pulses having a temporal pulsewidth in a range between about 0.1 millisecond and about 150 seconds. The at least one pulsed light beam has a beam cross-sectional area at the emission surface greater than about 2 cm2 and a time-averaged irradiance in a range between about 1 mW / cm2 and about 100 W / cm2.
Owner:PHOTOTHERA IP HLDG
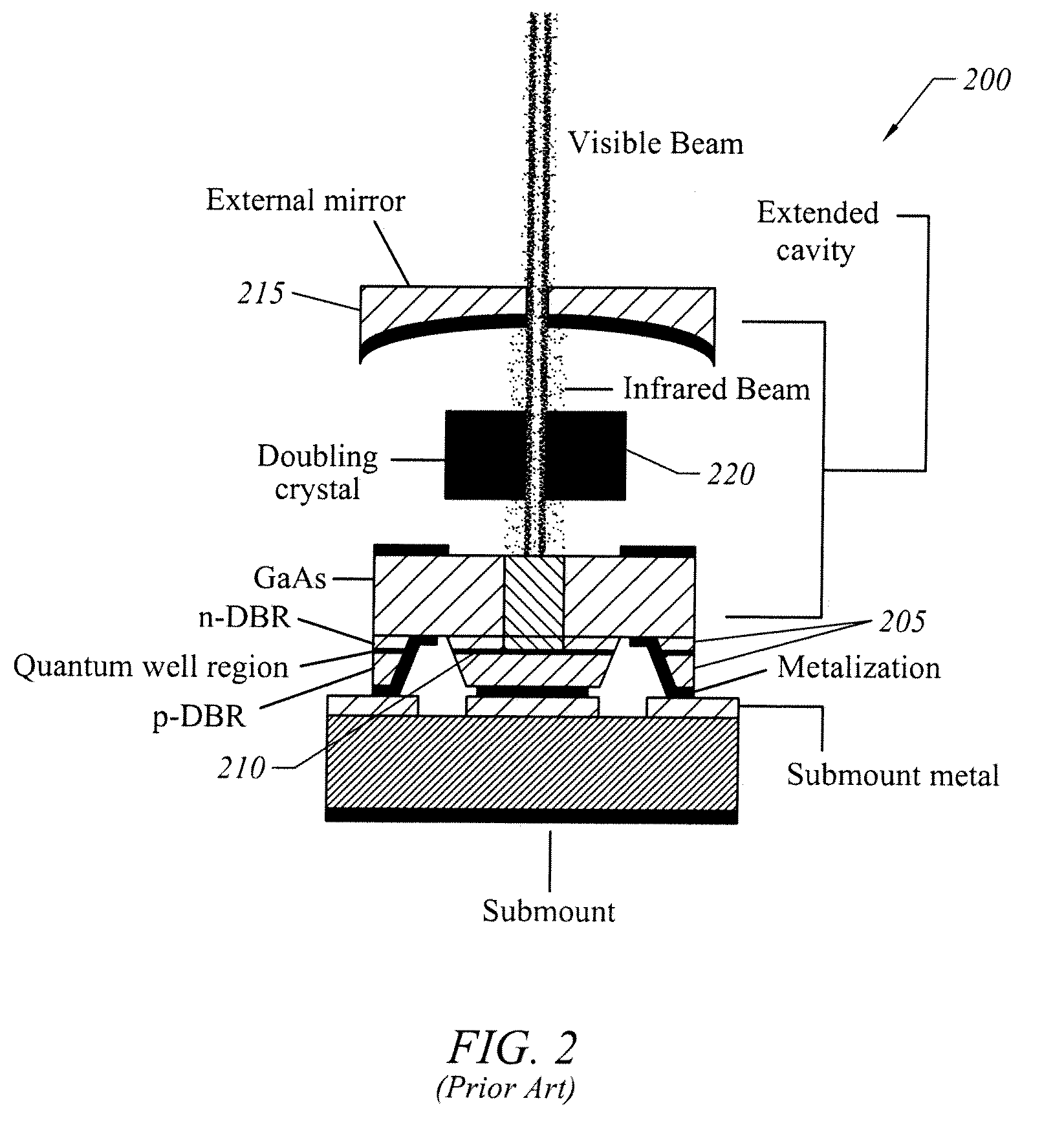
Frequency stabilized vertical extended cavity surface emitting lasers
ActiveUS20060280219A1ProjectorsOptical resonator shape and constructionFrequency stabilizationGrating
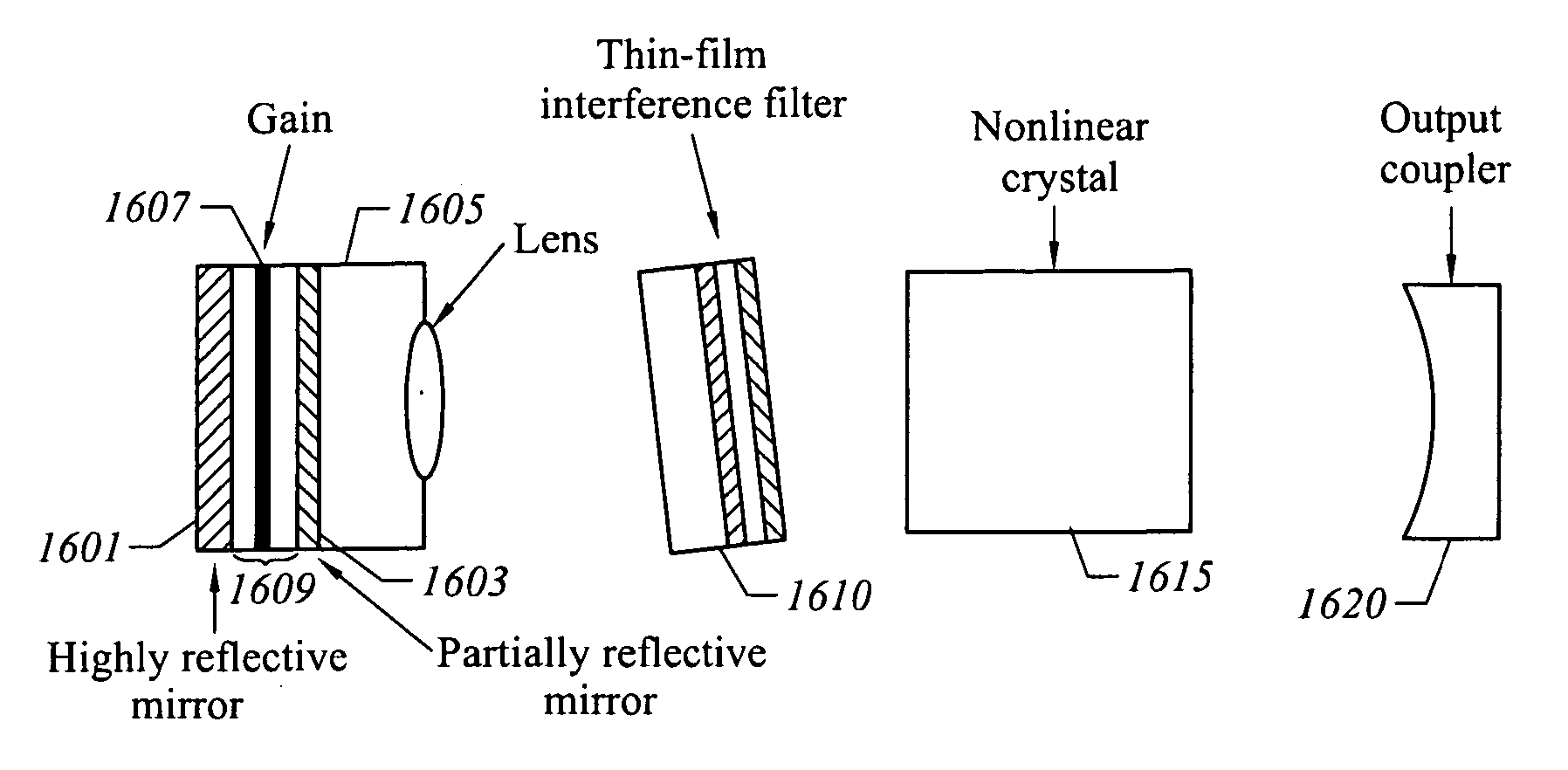
A vertical extended cavity surface emitting laser (VECSEL) includes intra-cavity frequency doubling. Conventional frequency control elements, such as etalons, are replaced with thin film interference filters or volume Bragg gratings.
Owner:NECSEL INTPROP +1
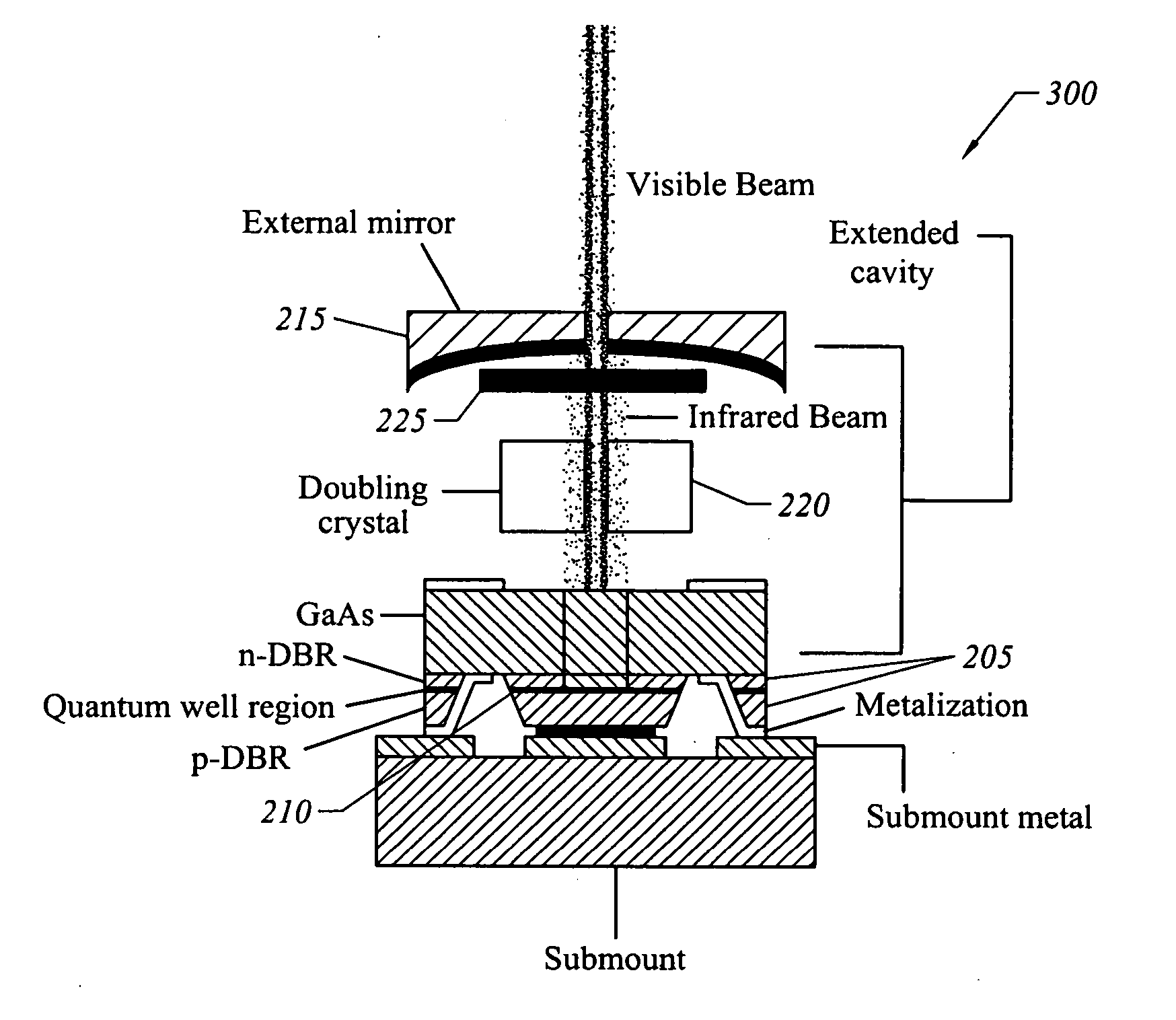
Apparatus, system, and method for wavelength conversion of mode-locked extended cavity surface emitting semiconductor lasers
InactiveUS20060023757A1Reduce polarizationReduce materialLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersFrequency conversionFundamental frequency
A mode-locked laser with intracavity frequency conversion is disclosed. In one embodiment the conversion frequency is improved by reducing the temporal, spatial, or polarization overlap between pulses at the fundamental frequency and pulses at a frequency-shifted frequency.
Owner:NECSEL INTPROP +1
Surface emitting semiconductor laser
InactiveUS6052398AImprove reflectivityLower resistanceLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersOptical cavitySemiconductor package
Two semiconductor layers of the laser form a tunnel junction enabling an electrical current for pumping the laser to pass from an N doped semiconductor Bragg mirror to a P doped injection layer belonging to the light-amplifying structure. The Bragg mirror co-operates with another mirror of the same type having the same doping to include said structure in an optical cavity of the laser. In a variant, the tunnel junction may be buried and located so as to constitute confinement means for said pumping current. The laser can be used in an optical fiber communications network.
Owner:II VI LASER ENTERPRISE
Surface-emitting laser diode having reduced device resistance and capable of performing high output operation, surface-emitting laser diode array, electrophotographic system, surface-emitting laser diode module, optical telecommunication system, optical interconnection system using the surface-emitting laser diode, and method of fabricating the surface-emitting laser diode
ActiveUS6959025B2Lower resistanceHigh-output operationOptical wave guidanceOptical resonator shape and constructionMode controlDistributed Bragg reflector
A surface-emitting laser diode device that oscillates in a direction perpendicular to the substrate is provided. This surface-emitting laser diode device includes: an active layer; a resonator structure including a first distributed Bragg reflector and a second distributed Bragg reflector that face each other and sandwich the active layer; a hole passage that extends from a first electrode to the active layer; an electron passage that extends from a second electrode to the active layer; a hole restricting structure that is located in the hole passage and defines a region for confining holes to the active layer; and an optical mode control structure that includes a non-oxide region provided in the resonator structure and an oxide region surrounding the non-oxide region, each region containing Al as a constituent element. In this surface-emitting laser diode, the area of the non-oxide region is smaller than the area of the hole restricting structure.
Owner:RICOH KK
Manufacturable vertical extended cavity surface emitting laser arrays
Arrays of vertical extended cavity surface emitting lasers (VECSELs) are disclosed. The functionality of two or more conventional optical components are combined into an optical unit to reduce the number of components that must be aligned during packaging. A dichroic beamsplitter selectively couples frequency doubled light out of the cavity. In one implementation the dichroic beamsplitter includes at least one prism.
Owner:ARASOR ACQUISITION +1
Face-lit waveguide illumination systems
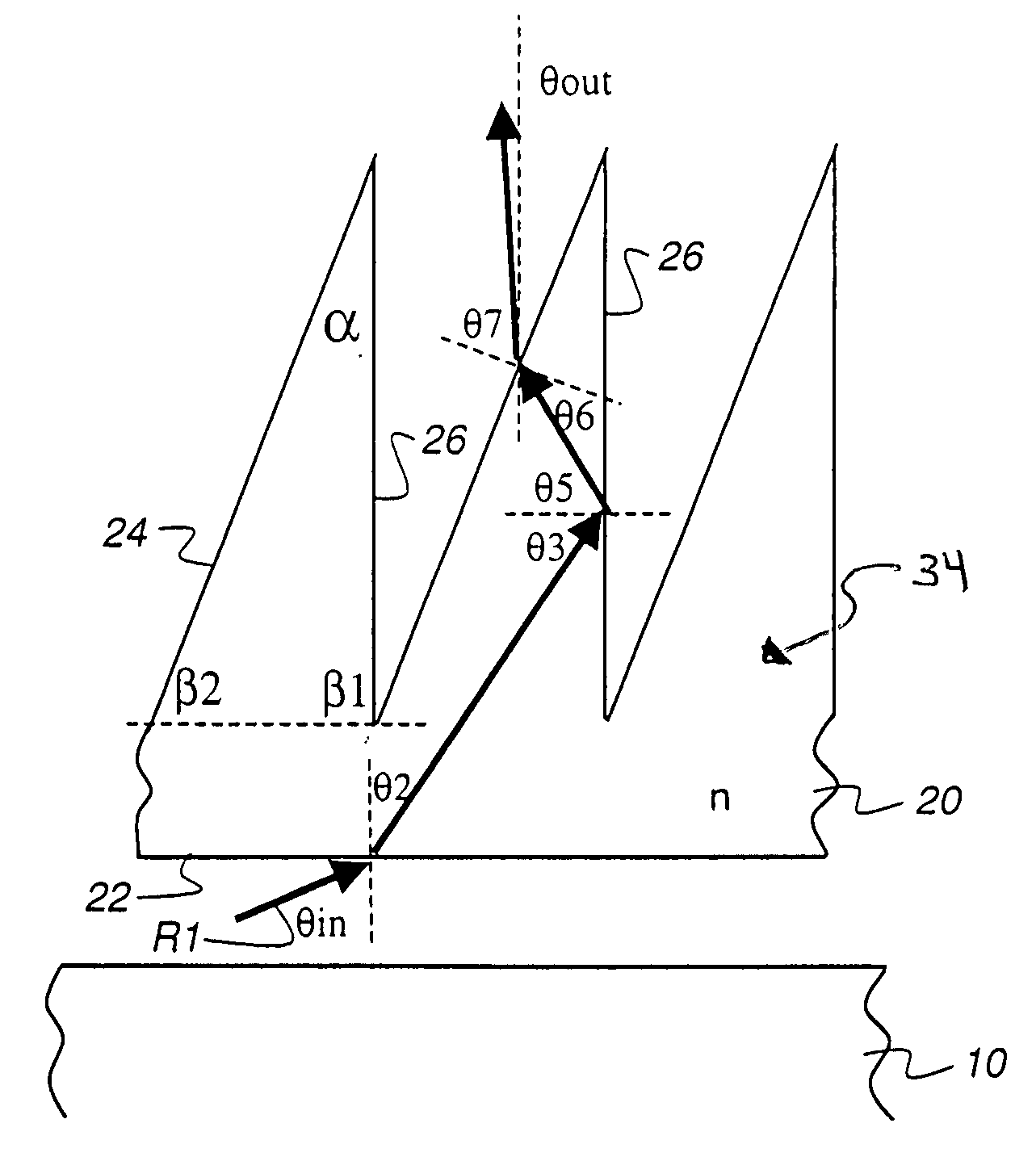
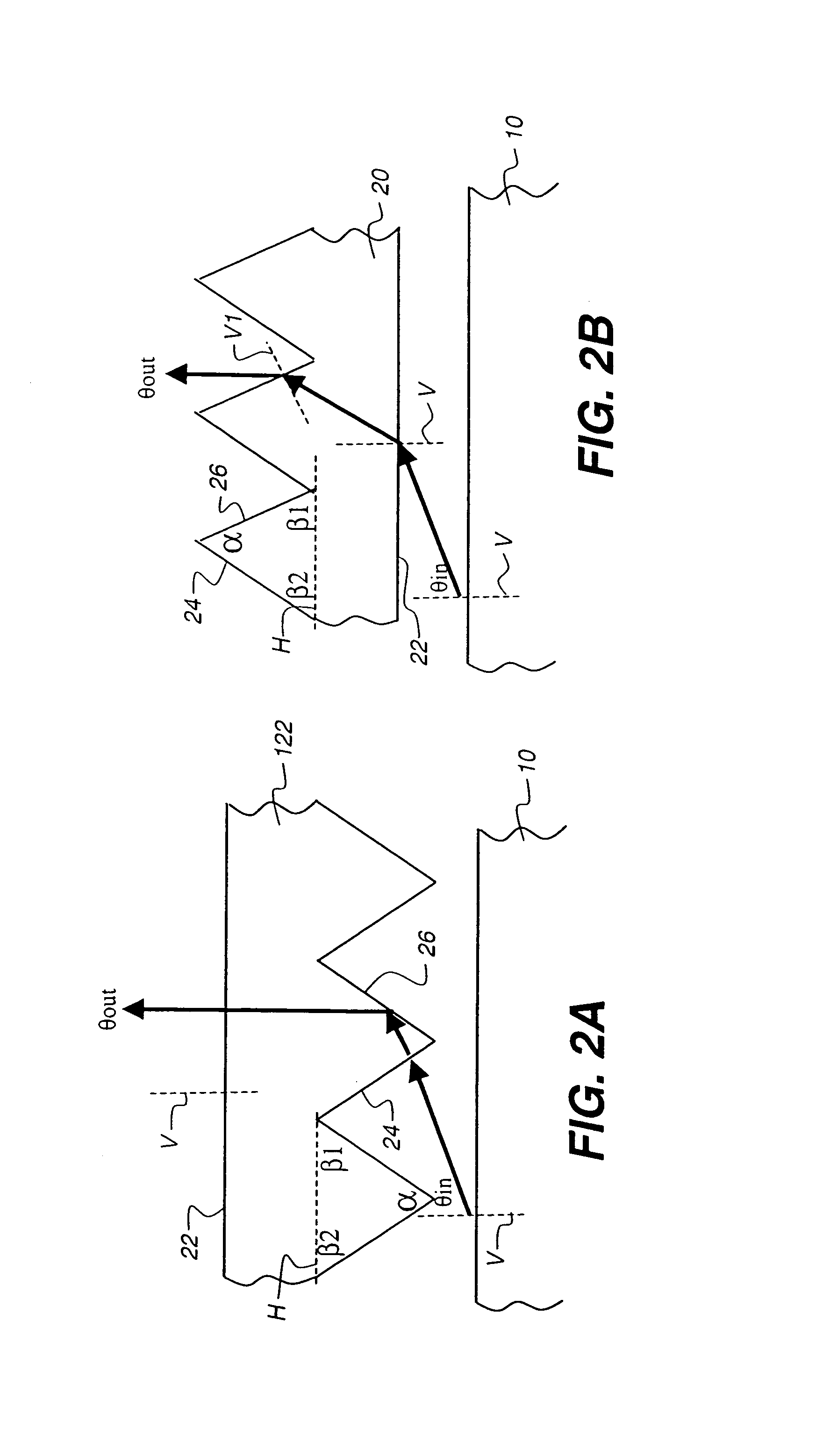
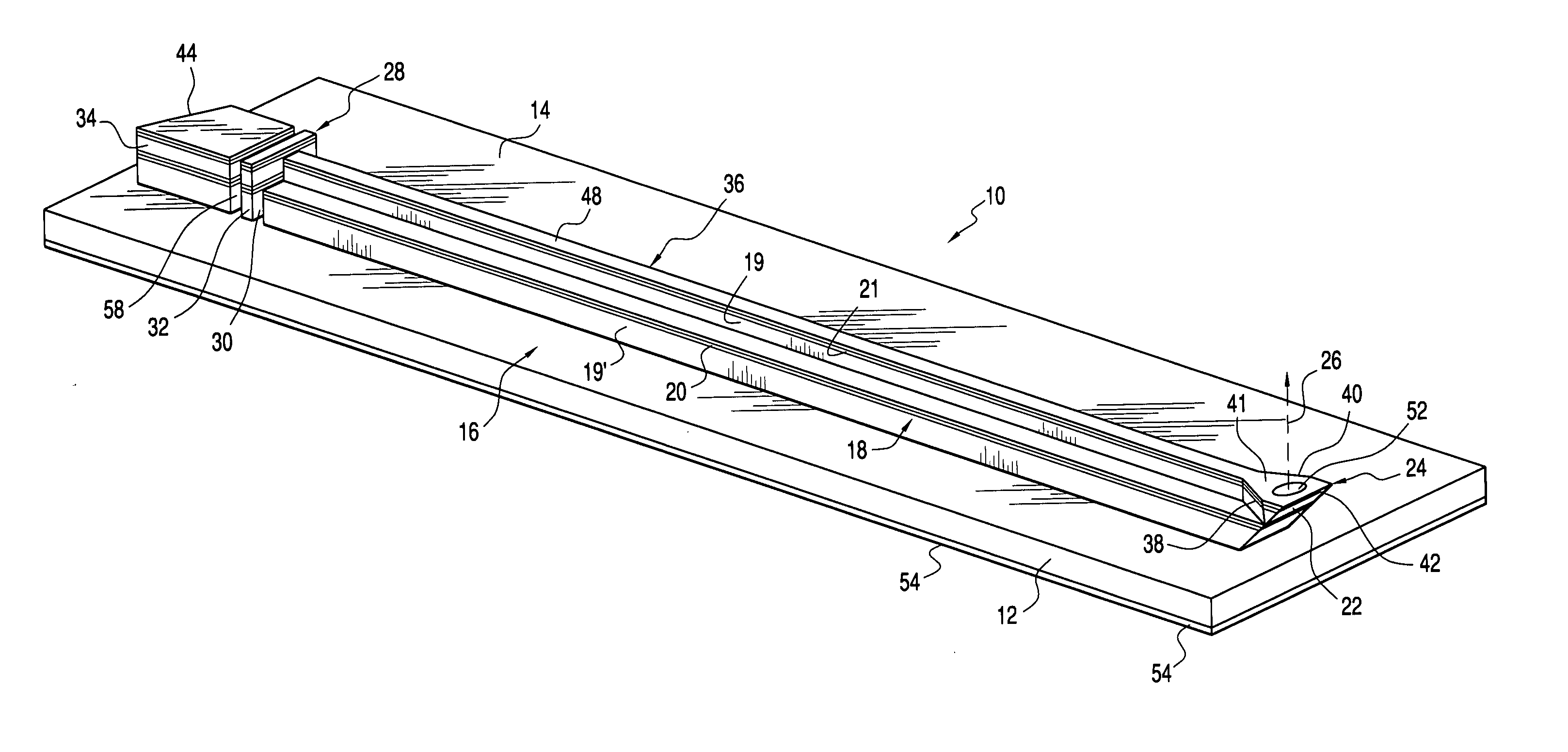
ActiveUS20140226361A1Solve problemsIncrease contactMechanical apparatusHolographic optical componentsTotal internal reflectionLighting system
A face-lit waveguide illumination system employing a planar slab or plate of an optically transmissive material. A light source is optically coupled a linear optical element which is attached to a face of the waveguide and is configured to inject light at an angle permitting for light propagation by means of a total internal reflection. Light is propagated through the waveguide towards a predetermined direction in response to optical transmission and total internal reflection. Light extraction features located along the prevailing path of light propagation extract light from the waveguide and emit such light towards a surface perpendicular. In one embodiment, the planar waveguide includes a window pane which provides light transport from one location, where light is injected through the face of the pane, to another location where light is extracted. Additional embodiments of the face-lit waveguide illumination system are also disclosed.
Owner:S V V TECH INNOVATIONS
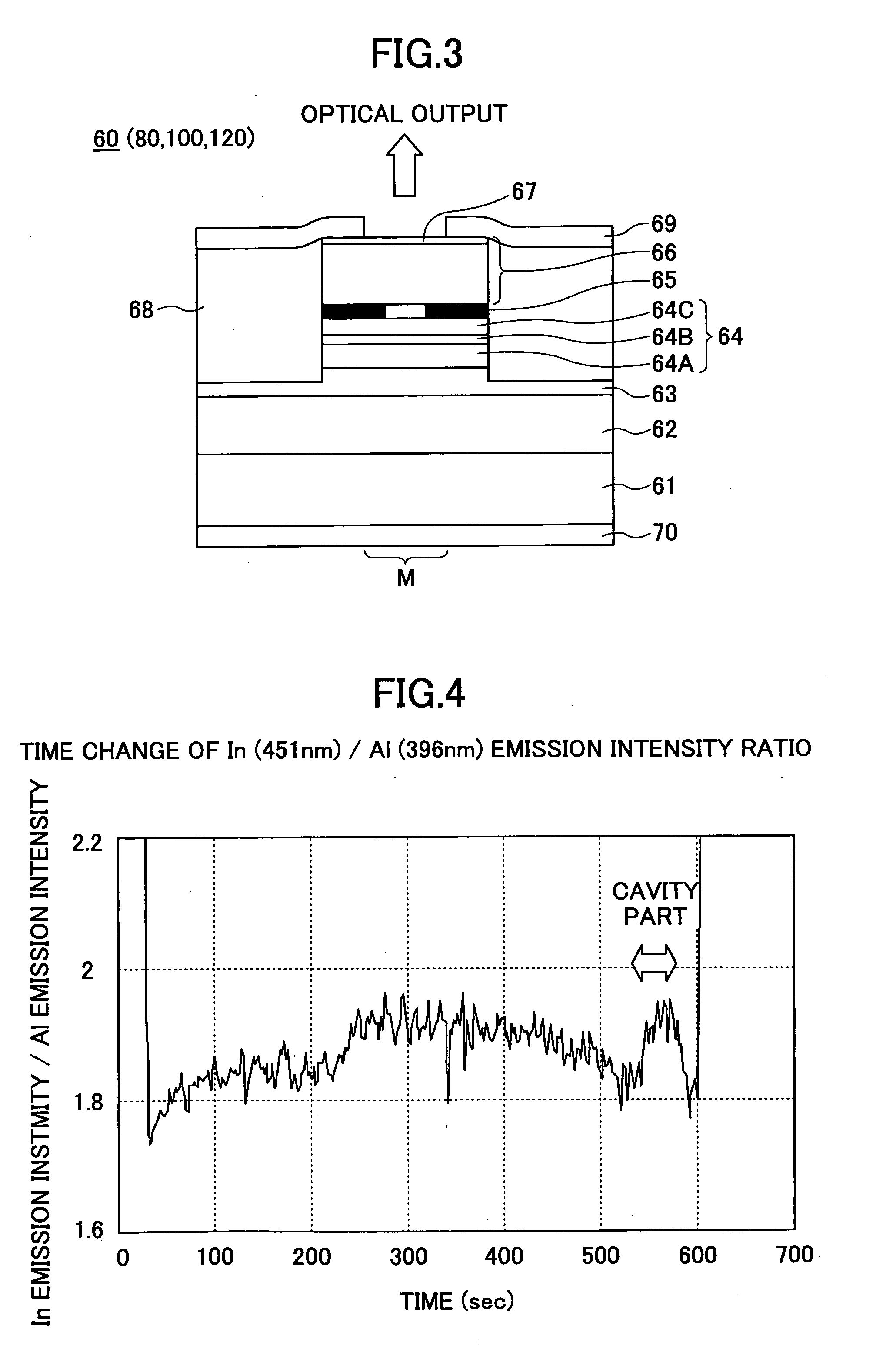
Planar waveguide surface emitting laser and photonic integrated circuit
InactiveUS20040105476A1Laser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionElectro-absorption modulatorPhotovoltaic detectors
The present invention is a planar waveguide surface emitting laser (PWSEL) and photonic integrated circuit (PIC) technology. The PWVCL can stand alone or it can be integrated with a variety of optical devices, such as tuners, electro-optic or electro-absorption modulators (EOM or EAM), optical amplifiers (OA), waveguide or traveling wave photo detectors (WPD or TWPD), narrow or broadband filters, active or passive waveguides, and waveguide splitters or couplers to form photonic integrated circuits. Most or all of the components share the same transverse waveguide. A lateral index step or other suitable technique completes the waveguide so that light is guided in the longitudinal direction. Optical taps (reduced reflectivity mirrors) allow for surface emission of the light.
Owner:WASSERBAUER JOHN G
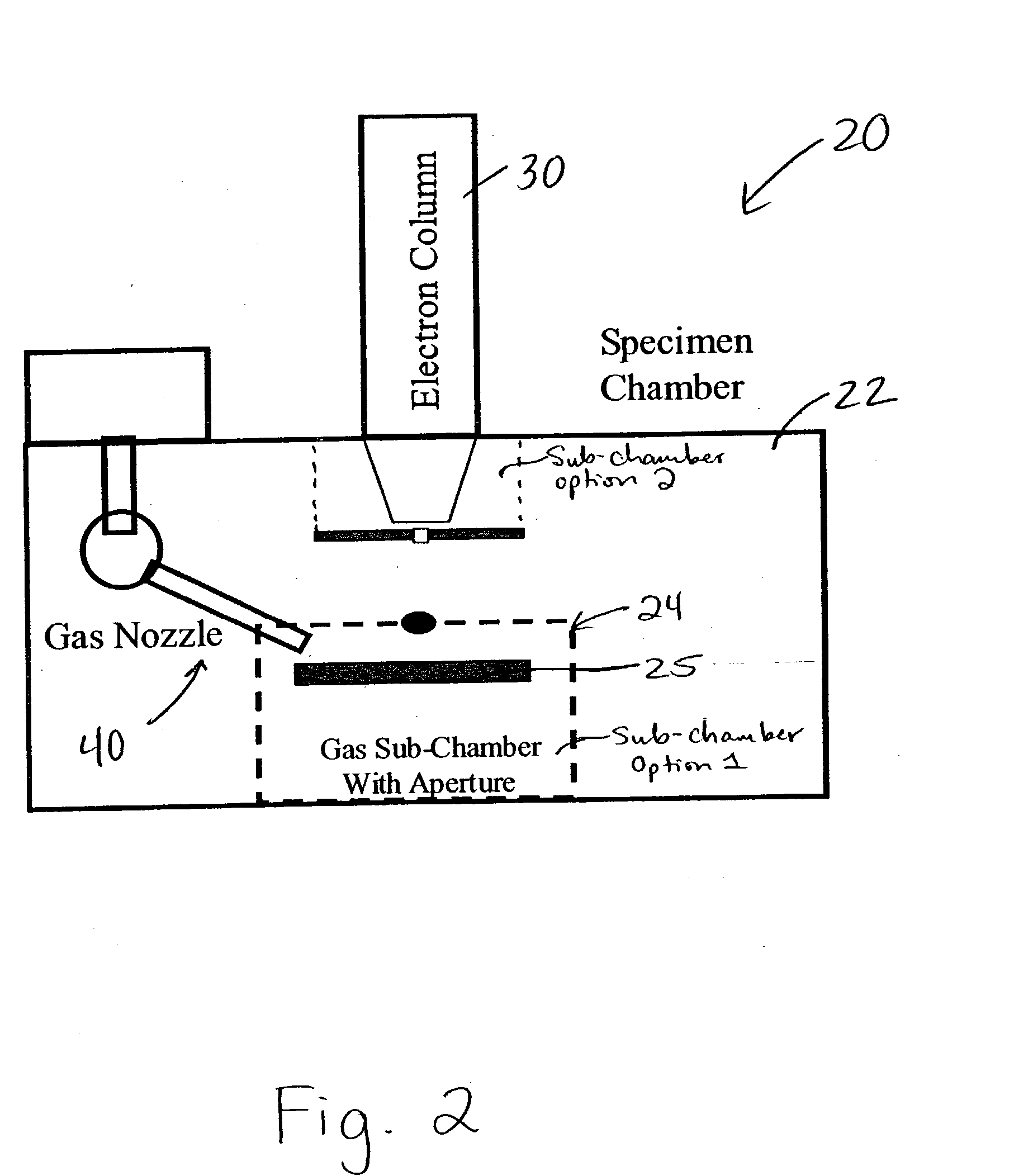
Electron beam apparatus and device manufacturing method using same
InactiveUS6909092B2Reduce image distortionLess aberrationThermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsElectron sourceImaging processing
A defect inspecting apparatus is provided for generating a less distorted test image to reliably observe a surface of a sample for detecting defects thereon. The defect detecting apparatus comprises a primary electron beam source for irradiating a sample, electrostatic lenses for focusing secondary electrons emitted from the surface of the sample irradiated with the primary electron beam, a detector for detecting the secondary electrons, and an image processing unit for processing a signal from the detector. Further, a second electron source may be provided for emitting an electron beam irradiated to the sample, wherein the sample may be irradiated with the electron beam from the second electron source before it is irradiated with the primary electron beam from the first electron source for observing the sample. A device manufacturing method is also provided for inspecting devices under processing with high throughput using the defect detecting apparatus.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Surface emitting device
InactiveUS20070159846A1Reduce the amount of lightSmall sizeMeasurement apparatus componentsPlanar/plate-like light guidesLight guideHollow form
A surface emitting device is provided. The surface emitting device includes a light guide and a light source. The light guide includes a circular portion that curves light, and a light entrance portion that protrudes from the outer peripheral surface of the circular portion. The light source emits light toward the light entrance portion. The light source is disposed in a hollow formed in the center of the light entrance portion. The outer wall surface of the light entrance portion has a reflecting portion. The reflecting portion includes first and second reflecting surfaces that adjoin at an obtuse angle. Light of the light source heading from the inner wall surface to the outer wall surface of the light entrance portion is reflected by the reflecting portion so as to head into the circular portion.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
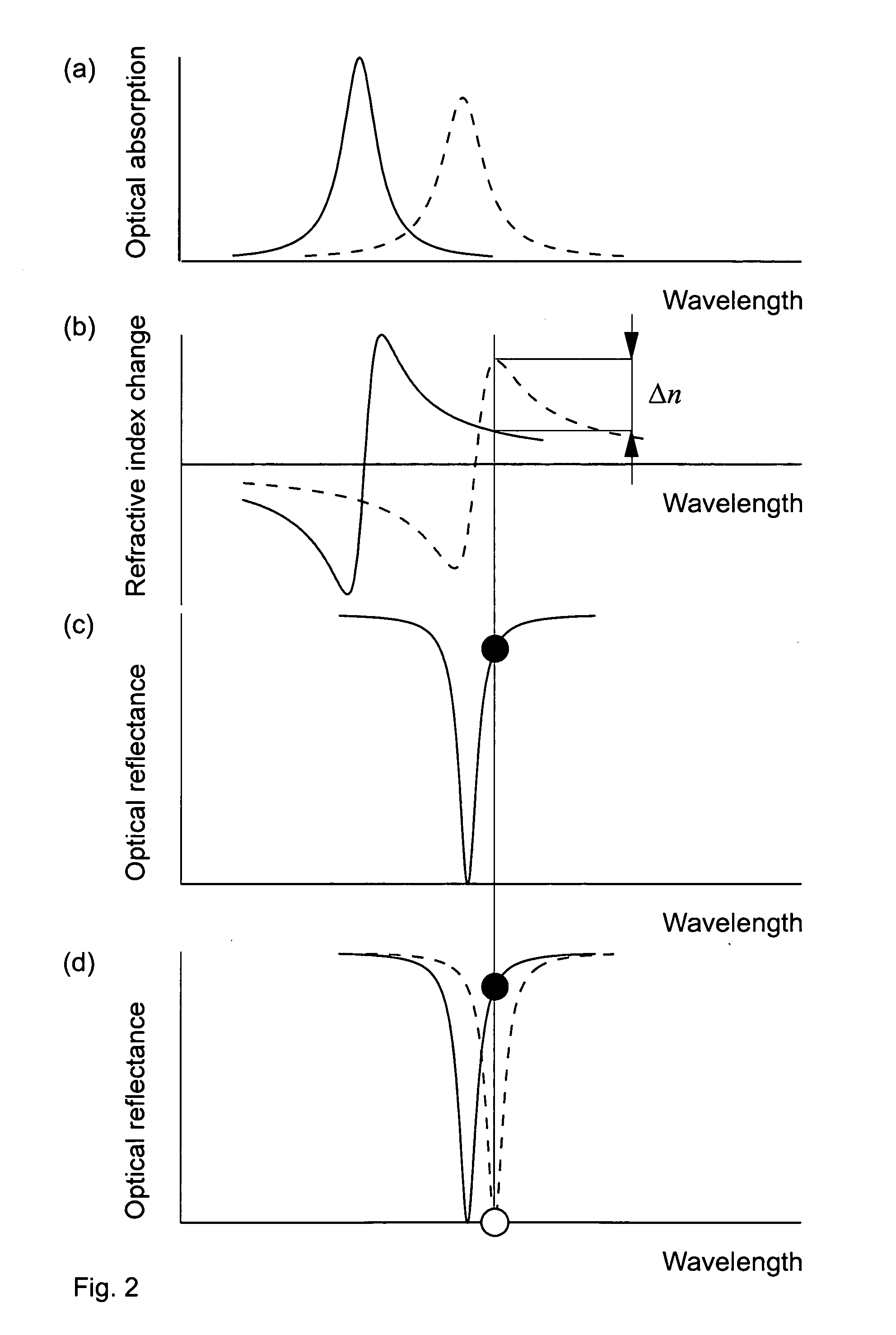
Electrooptically Bragg-reflector stopband-tunable optoelectronic device for high-speed data transfer
ActiveUS20070291808A1Modulated transmittance of the multilayer interference reflectorLaser detailsSolid-state devicesPhotodetectorIntensity modulation
A device contains at least one wavelength-tunable multilayer interference reflector controlled by an applied voltage and at least one cavity. The stopband edge wavelength of the wavelength-tunable multilayer interference reflector is preferably electrooptically tuned using the quantum confined Stark effect in the vicinity of the cavity mode (or a composite cavity mode), resulting in a modulated transmittance of the multilayer interference reflector. A light-emitting medium is preferably introduced in the cavity or in one of the cavities permitting the optoelectronic device to work as an intensity-modulated light-emitting diode or diode laser by applying an injection current. The device preferably contains at least three electric contacts to apply forward or reverse bias and may operate as a vertical cavity surface emitting light-emitter or modulator or as an edge-emitting light emitter or modulator. Using a multilayer interference reflector containing tunable section allows also obtaining a wavelength-tunable laser or a wavelength-tunable resonant cavity photodetector in the case where the optical field profile in the active cavity or cavities is affected by the stopband wavelength shift. Adding additional modulator sections enables applications in semiconductor optical amplifiers, frequency converters or lock-in optical amplifiers.
Owner:CONNECTOR OPTICS
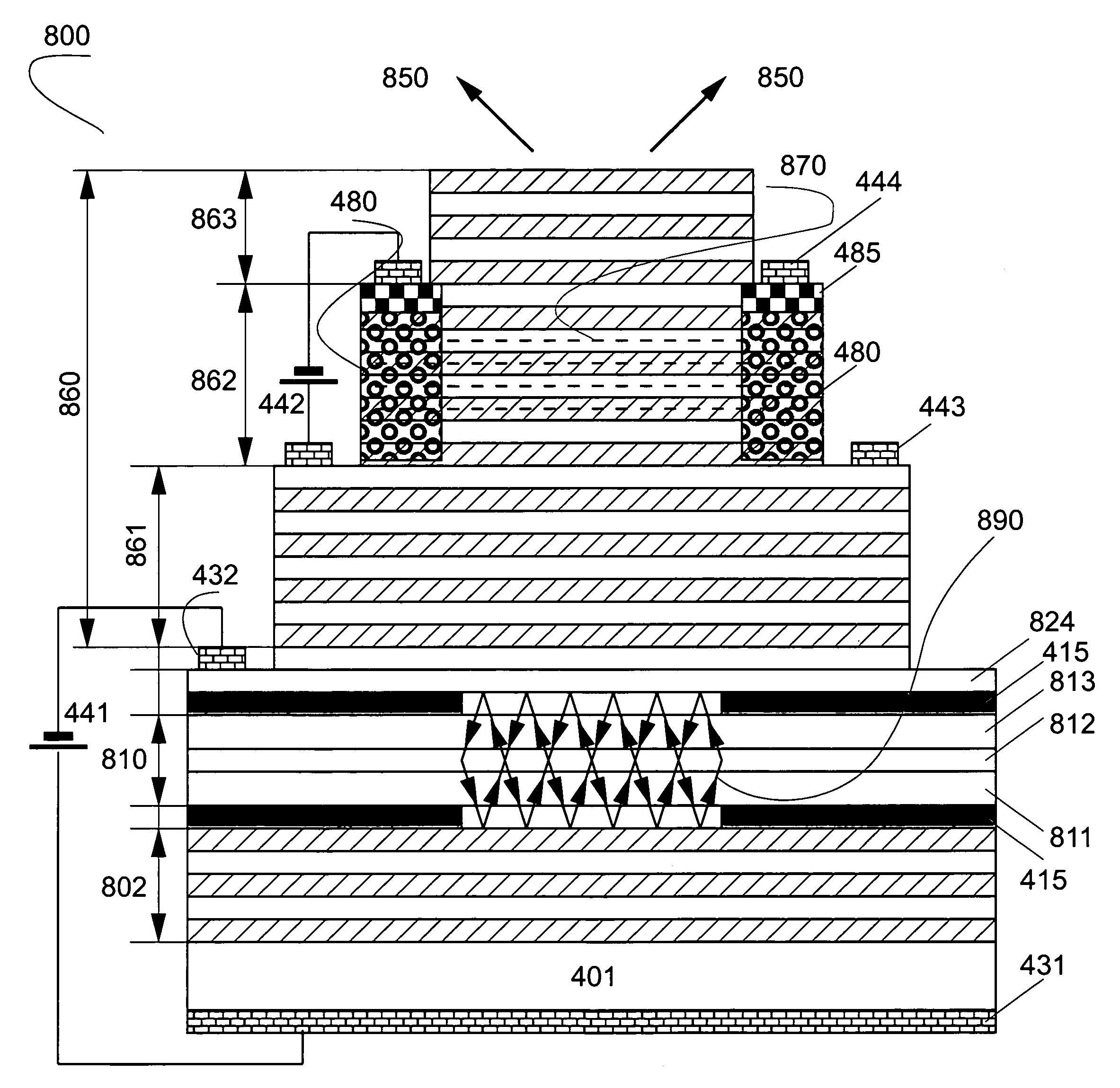
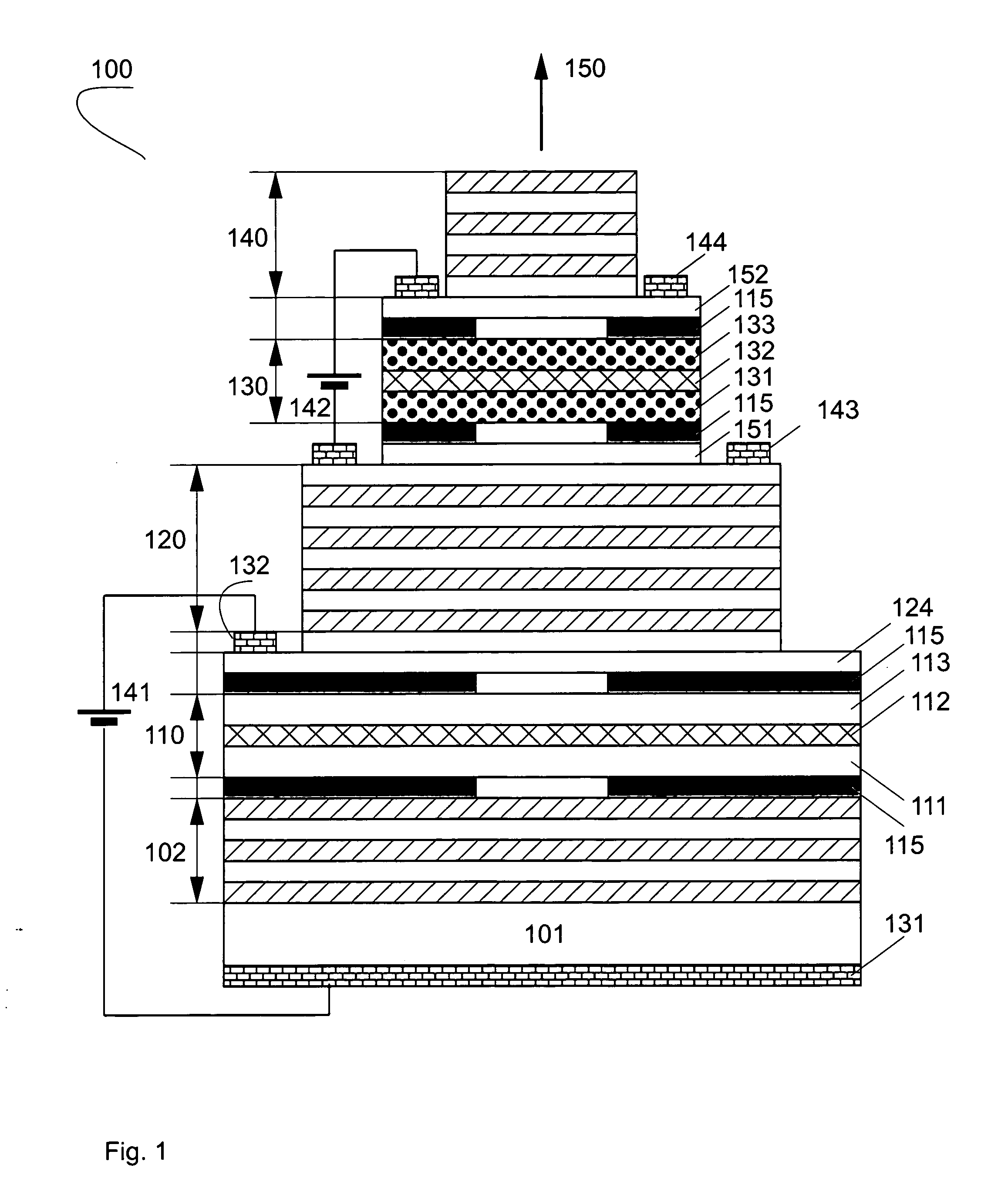
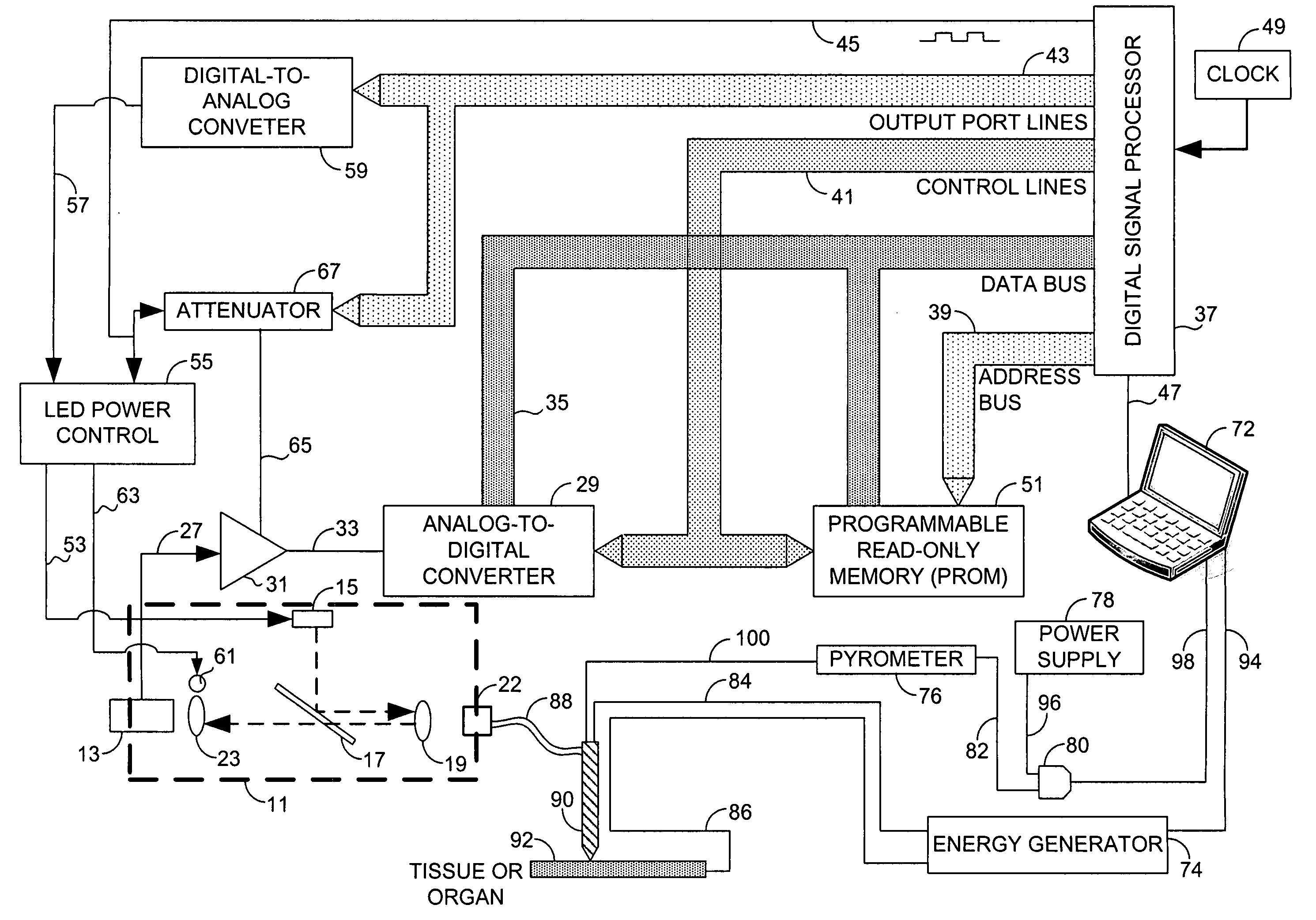
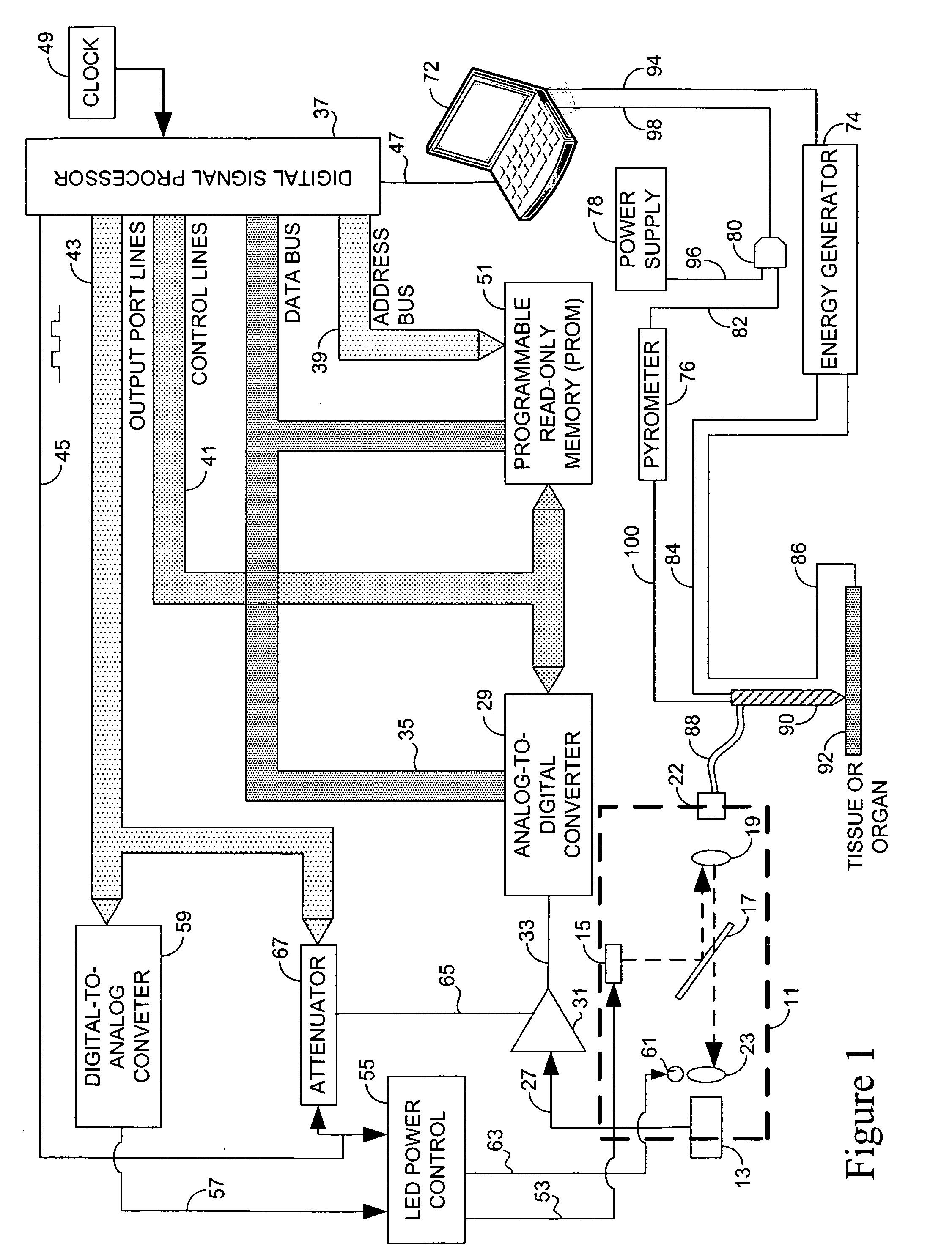
Systems and methods for monitoring temperature during electrosurgery or laser therapy
InactiveUS20080033300A1Diagnostic recording/measuringSurgical instruments for heatingLaser probeHigh heat
Systems that measure temperatures of tissue during electrosurgery or laser therapy of the tissue or organs is provided. One system provides a pyrometer that measures infrared electromagnetic energy emitted by a surface of a tissue or organ thereby determining a sub-surface temperature of the tissue or organ. The system further has an energy generator and an ablation electrode or laser probe that delivers energy from the energy generator to a tissue or organ, responsive to a sub-surface temperature determined by the pyrometer. The pyrometer can be calibrated using a luminescent material having known optical properties as a function of temperature. The luminescent material can be positioned on the surface of the tissue or organ or inserted directly into the tissue or organ using a catheter. Methods in which the surface or sub-surface temperature of the tissue is measured during therapy are also provided.
Owner:LUMASENSE TECH HLDG
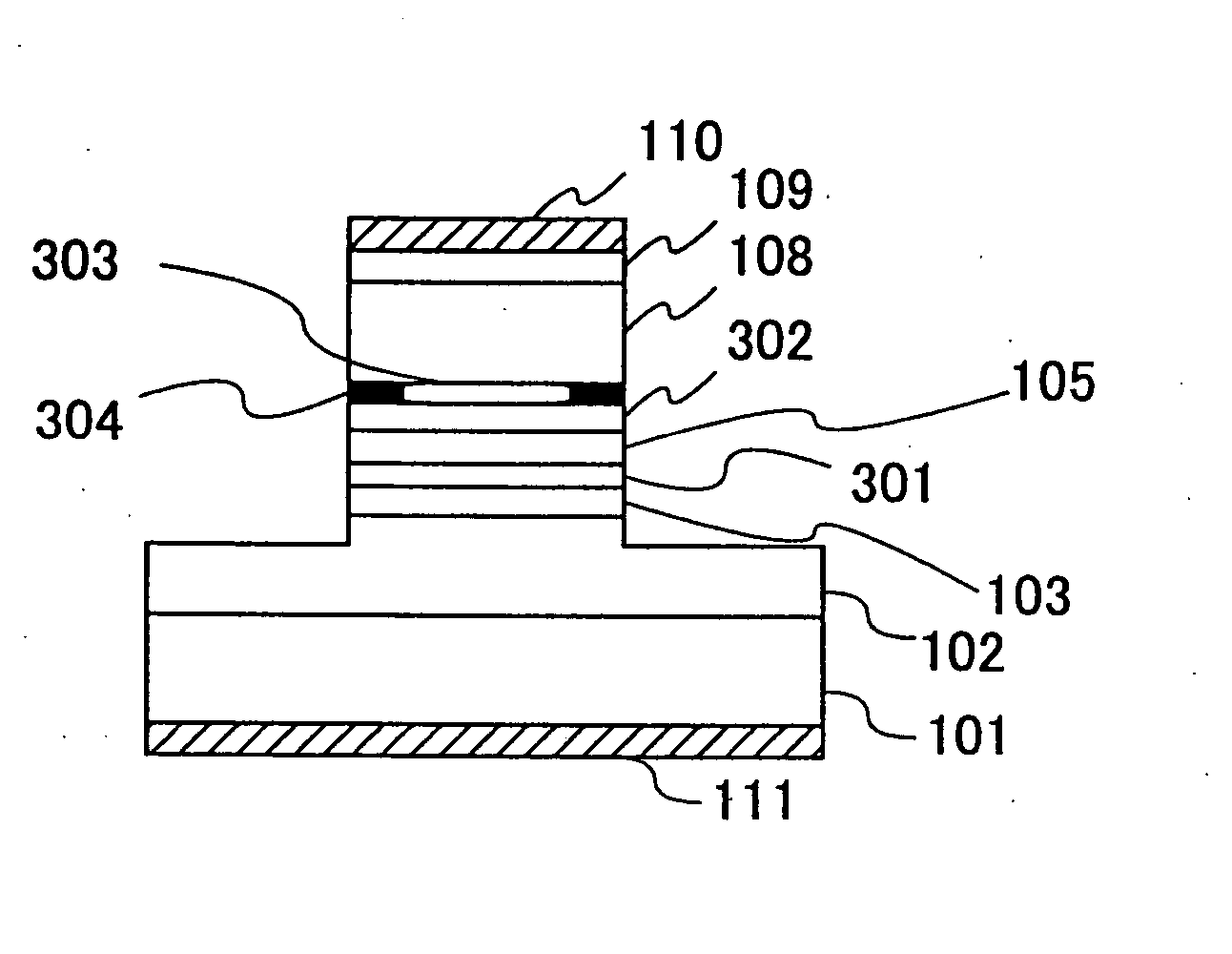
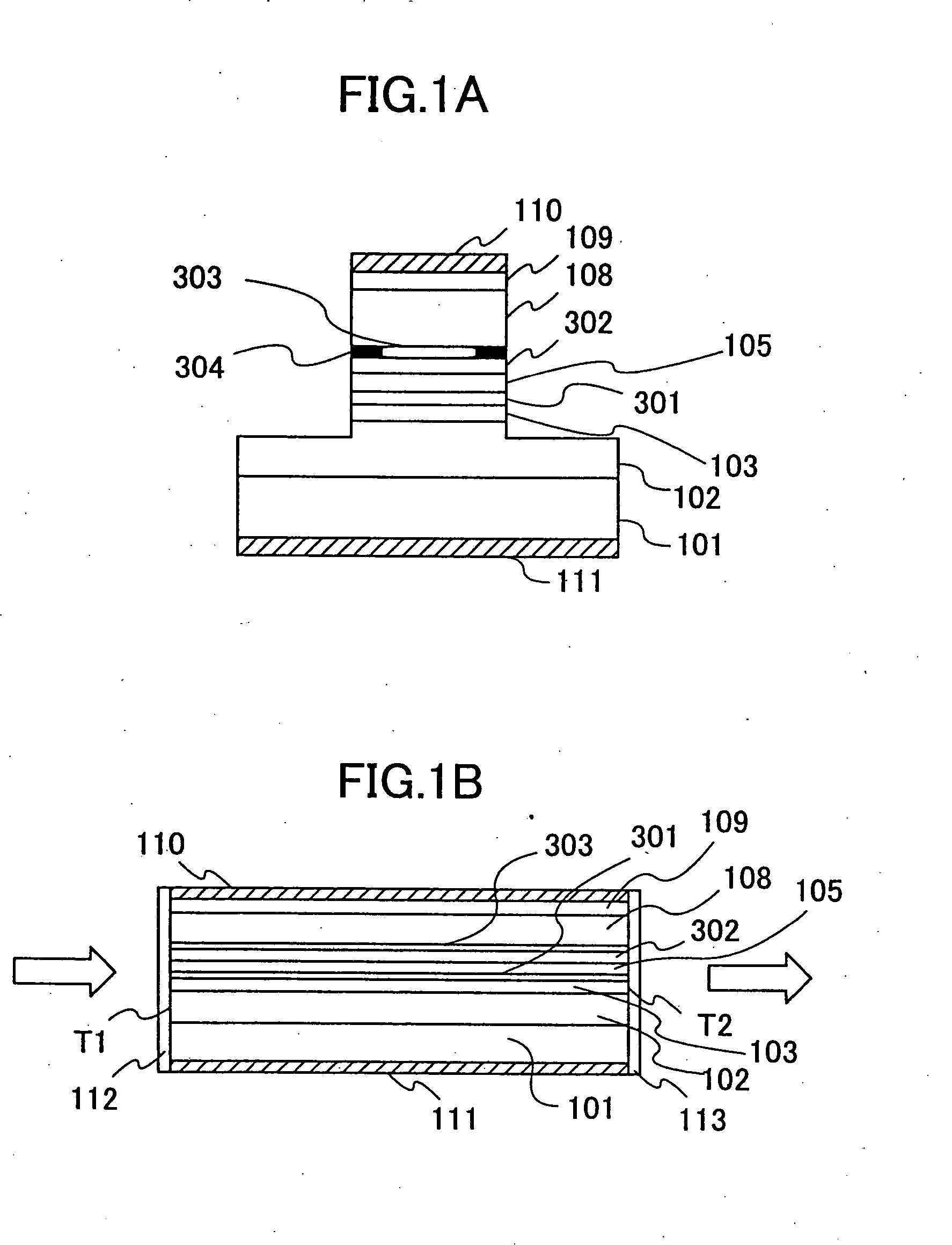
Semiconductor optical modulator, an optical amplifier and an integrated semiconductor light-emitting device
InactiveUS20060054899A1Eliminate the problemLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsLight emitting deviceSurface emission
An integrated semiconductor optical-emitting device includes a surface-emission laser diode and an EA-type semiconductor optical modulator integrated commonly on a GaAs substrate in a direction perpendicular to the GaAs substrate.
Owner:TAKAHASHI TAKASHI +1
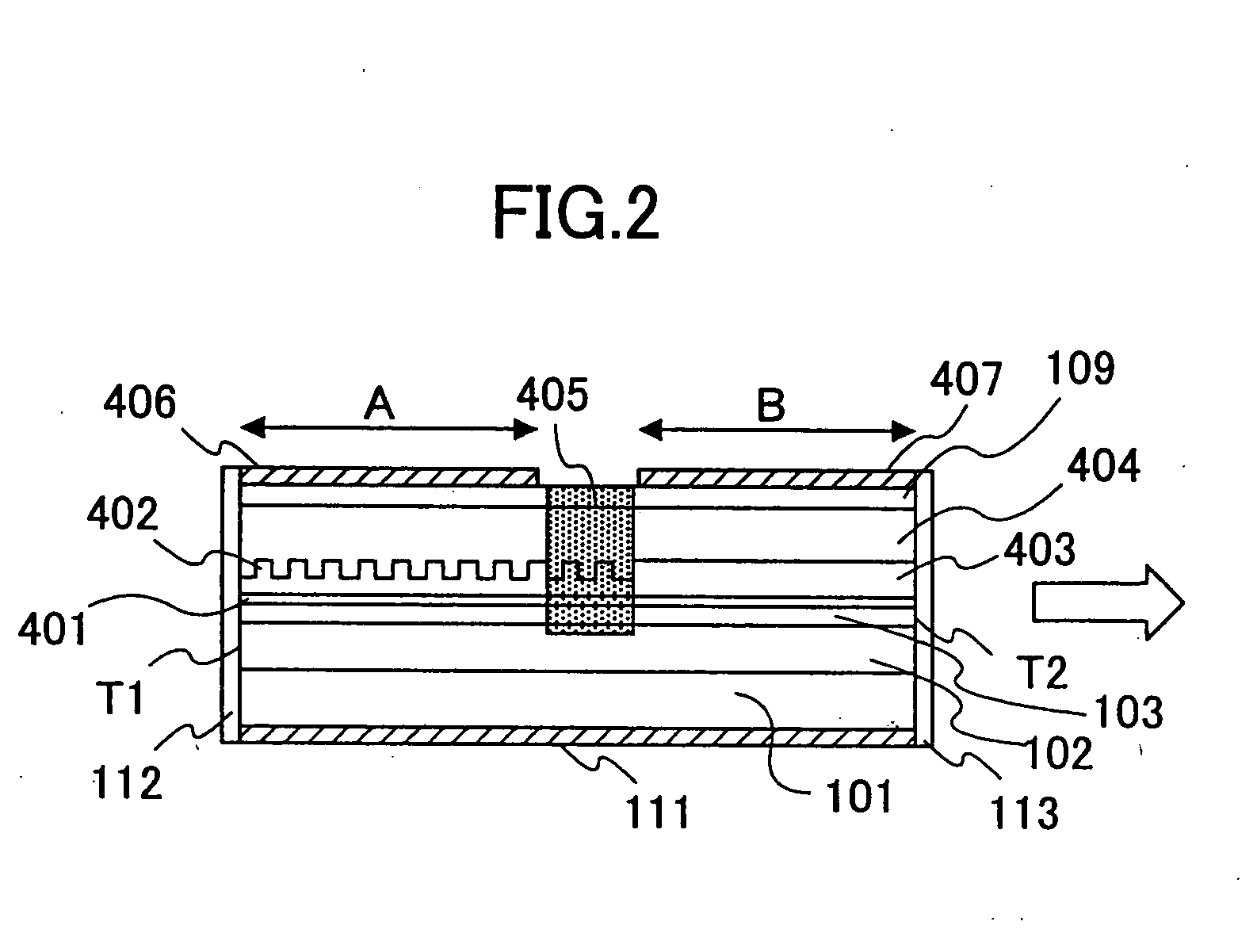
Surface-emitting laser array, optical scanning device, and image forming device
InactiveUS20090295902A1Avoid contactPrevent oxidationRecording apparatusLaser detailsLaser arrayRefractive index
A surface-emitting laser array includes a plurality of surface-emitting laser elements. Each surface-emitting laser element includes a first reflection layer formed on a substrate, a resonator formed in contact with the first reflection layer and containing an active layer, and a second reflection layer formed over the first reflection layer and in contact with the resonator. The second reflection layer contains a selective oxidation layer. The first reflection layer contains on the active layer side at least a low refractive index layer having an oxidation rate equivalent to or larger than an oxidation rate of a selective oxidation layer contained in the second reflection layer. The resonator is made of an AlGaInPAs base material containing at least In. A bottom of a mesa structure is located under the selective oxidation layer and over the first reflection layer.
Owner:RICOH KK
Light emitting device, projection device and lighting device
ActiveCN102563410AEfficiency impactEfficient collectionPoint-like light sourceProjectorsLight guideEffect light
The invention provides a light emitting device, a projection device and a lighting device. The light emitting device comprises a wavelength conversion material layer and a light guiding device, wherein the wavelength conversion material layer with a first surface and a second surface comprises a wavelength conversion material and a scattering material, and the light guiding device is positioned on one side of the first surface of the wavelength conversion material layer and used for guiding exciting light into the first surface of the wavelength conversion material layer, and guiding stimulated light and residual exciting light to enter a light emitting channel, wherein the stimulated light is emitted by the first surface of the wavelength conversion material layer, and the residual exciting light is absorbed by the wavelength conversion material layer. By the aid of the light emitting device, the light guiding device positioned on one side of the first surface of the wavelength conversion material layer is effectively positioned can be used for effectively collecting the exciting light reflected by the wavelength conversion material layer, so that the efficiency of the light emitting device cannot be affected by the scattering material added by the scattering material, and the contradiction between color uniformity and light emitting efficiency is solved.
Owner:APPOTRONICS CORP LTD
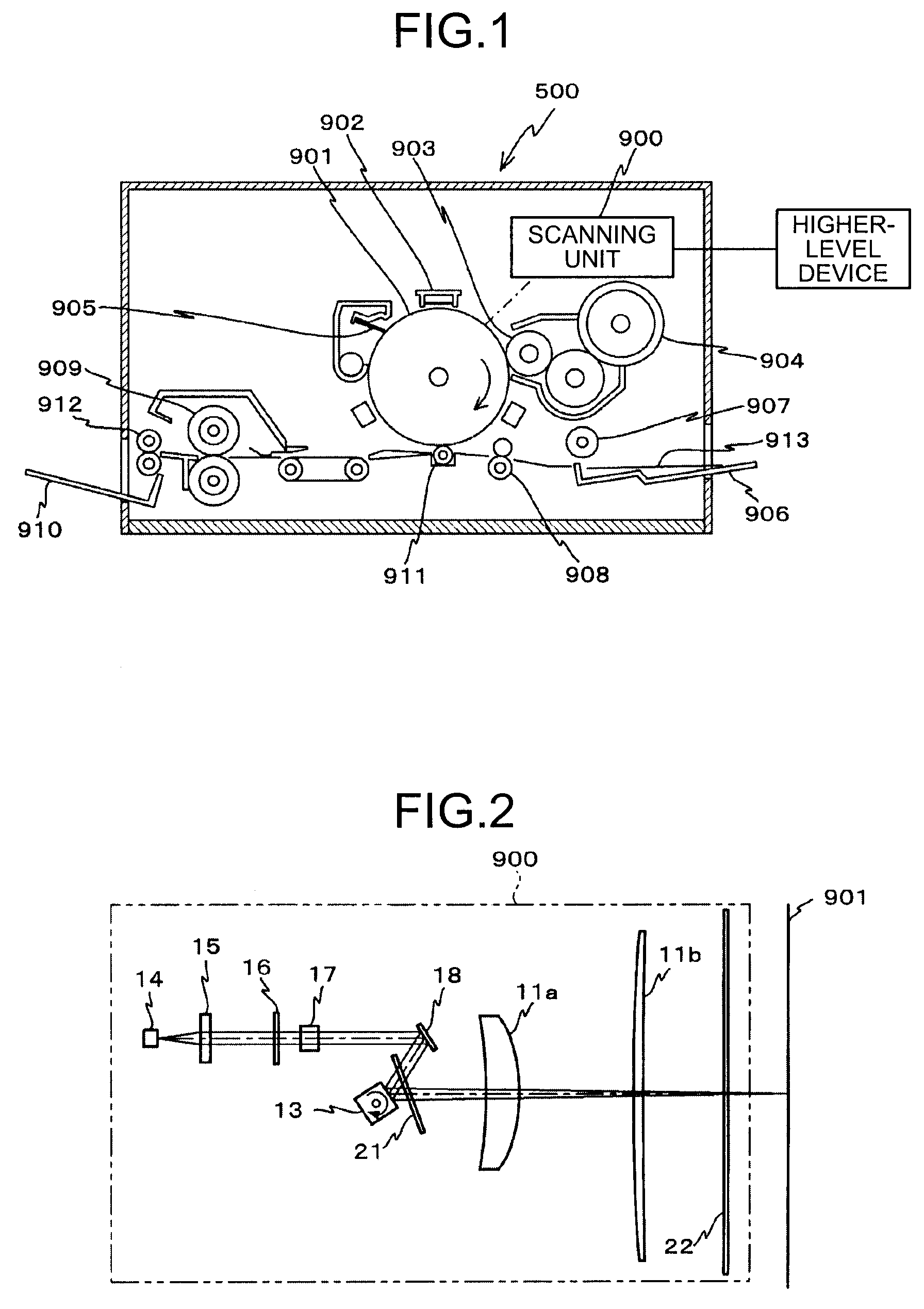
Scanning unit and image forming apparatus
A scanning unit in an image forming apparatus includes a light source, a coupling lens, an aperture, an image forming lens, and a polygon mirror. The light source includes a plurality of surface-emitting lasers. The coupling lens, the aperture, and the image forming lens are arranged on the optical path of light beams emitted by the light source. The polygon mirror deflects light beams of an image formed by the coupling lens towards a photosensitive drum for scanning. The focal length of the image forming lens in a sub-scanning direction is set to be equal to or smaller than an optical path length between the image forming lens and the aperture.
Owner:RICOH KK
Surface-emission laser diode operable in the wavelength band of 1.1-1.7 um and optical telecommunication system using such a laser diode
InactiveUS20060093010A1Resistance minimizationImprove reflectivitySolid-state devicesOptical resonator shape and constructionDistributed Bragg reflectorRefractive index
A surface-emission laser diode includes a distributed Bragg reflector tuned to a wavelength of 1.1 μm or longer, wherein the distributed Bragg reflector includes an alternate repetition of a low-refractive index layer and a high-refractive index layer, with a heterospike buffer layer having an intermediate refractive index interposed therebetween with a thickness in the range of 5-50 nm
Owner:SEKIYA TAKURO +14
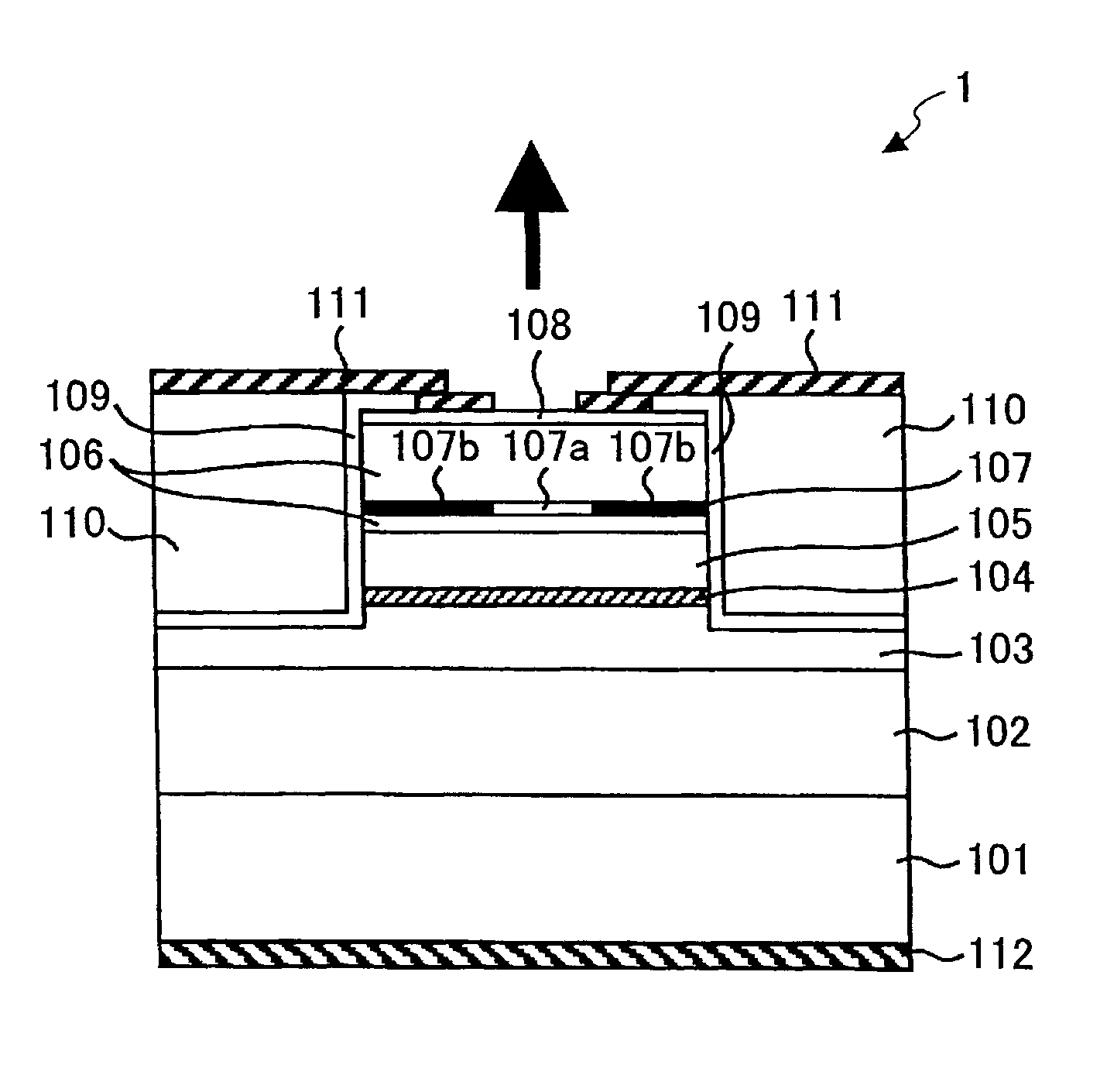
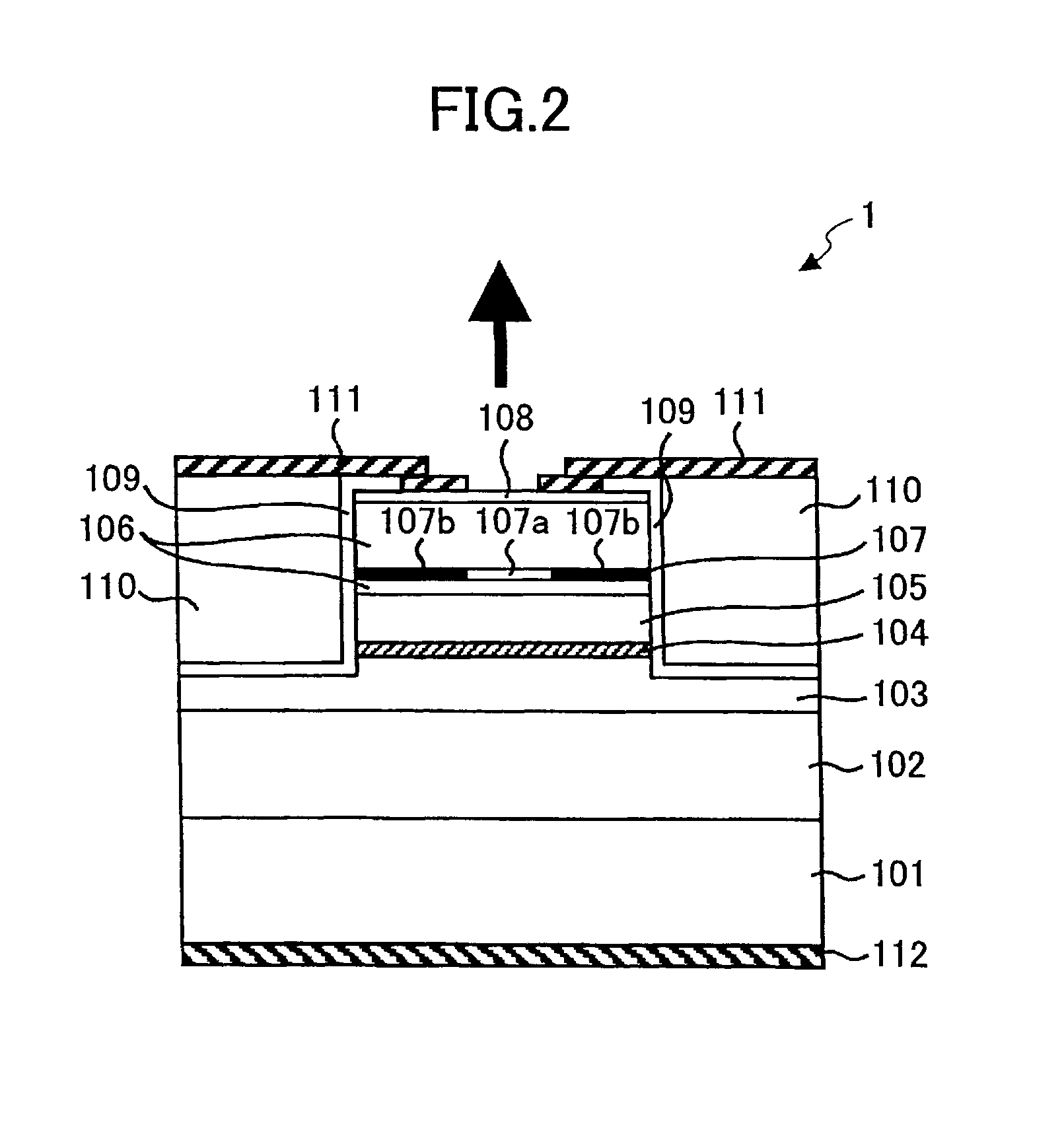
Surface emitting and receiving photonic device with lens
ActiveUS20050123016A1Easy to monitorImprove equipment efficiencyOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionPhotonicsSurface emission
A surface-emitting laser, in which light is emitted vertically at one end from a near 45°-angled facet, includes a second end having a perpendicular facet from which light is emitted horizontally, for monitoring. The surface-emitting laser comprises a divergence-compensating lens on the surface above the near 45°-angled facet.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
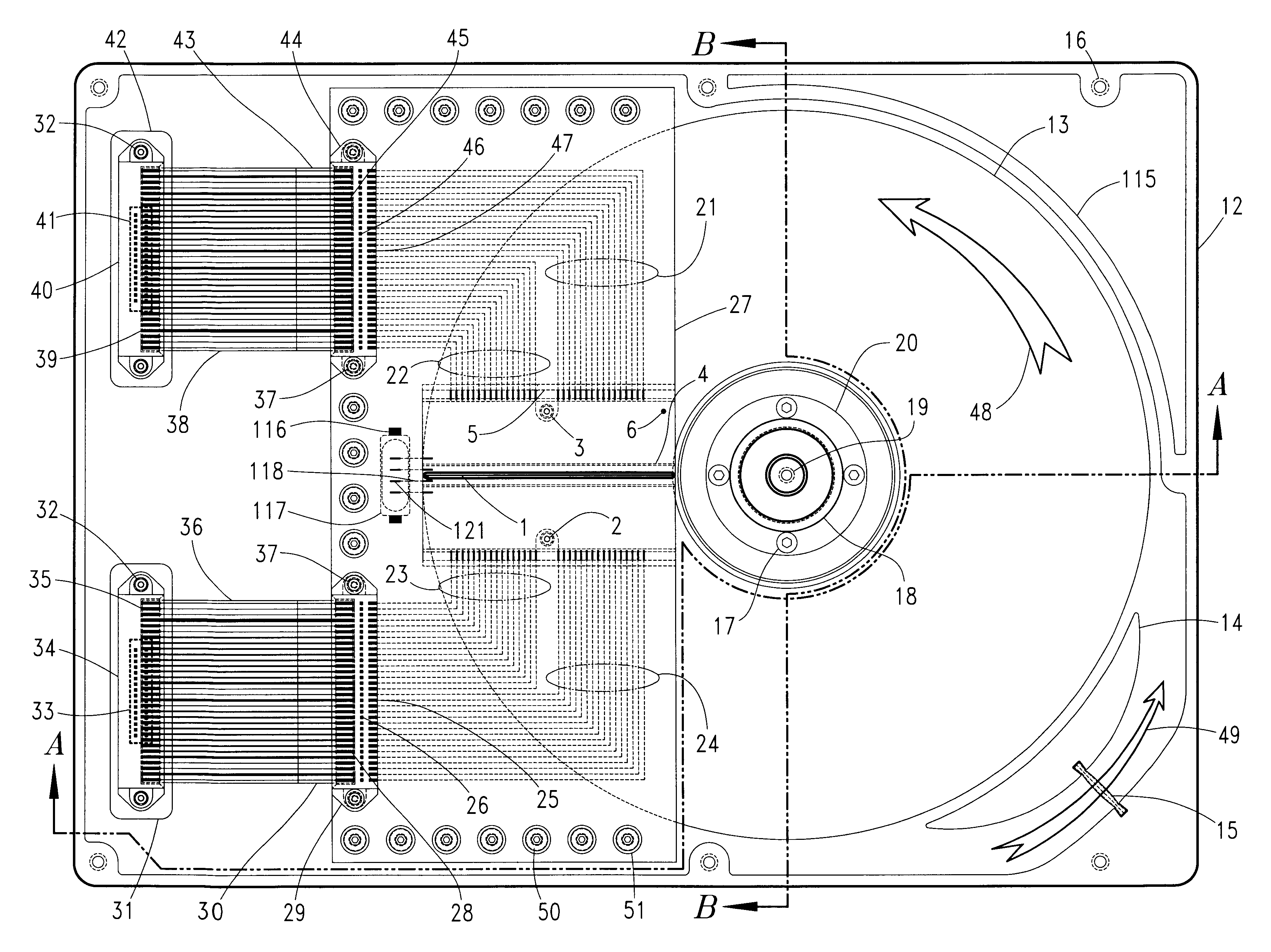
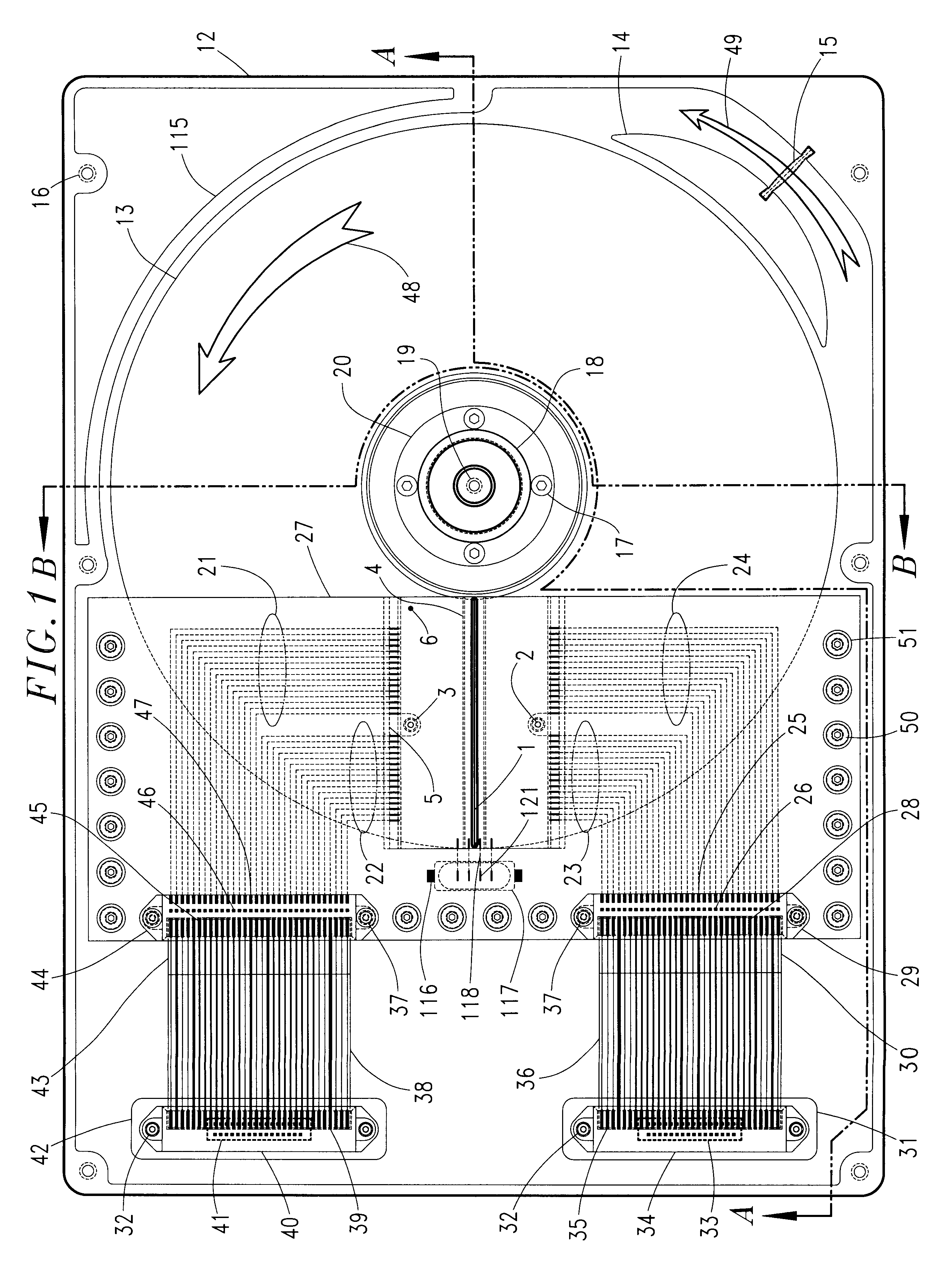
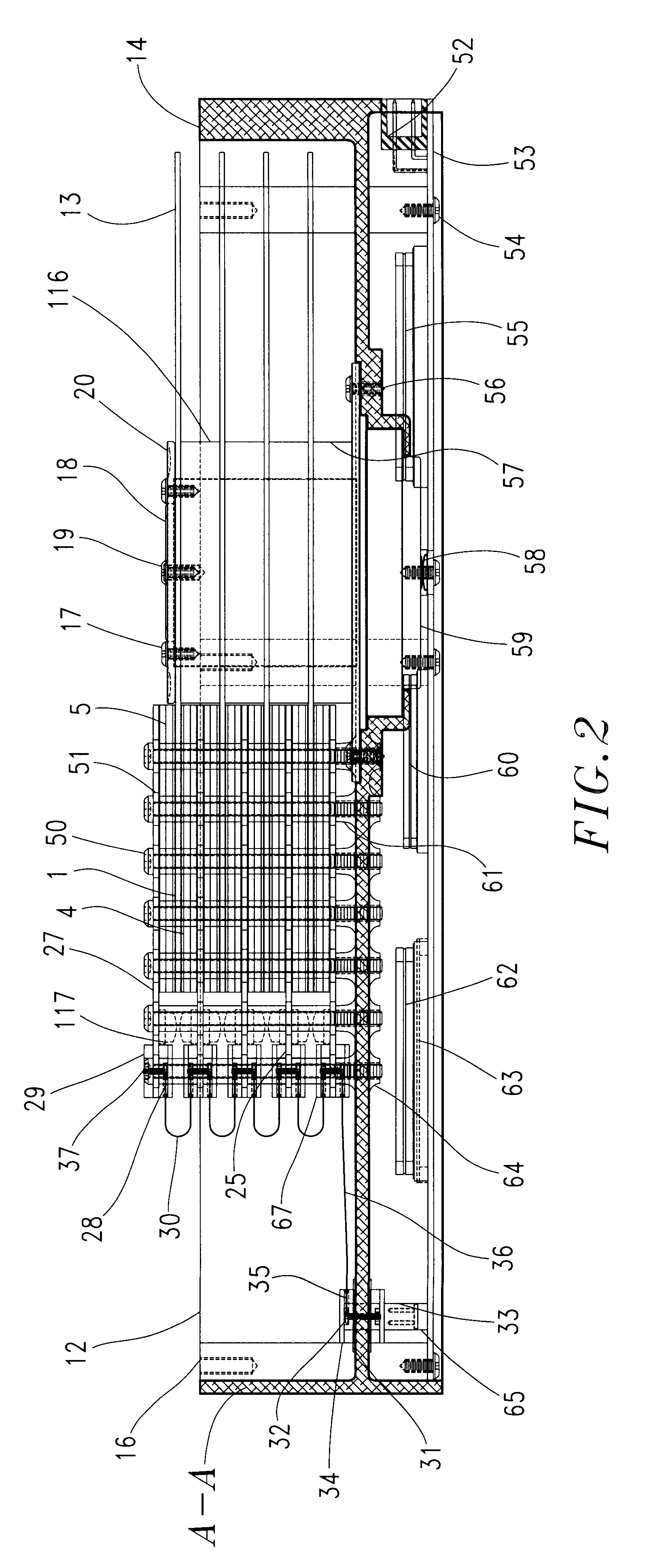
Optical data storage fixed hard disk drive using stationary magneto-optical microhead array chips in place of flying-heads and rotary voice-coil actuators
InactiveUS6266712B1Input/output to record carriersHard disc driveVertical-cavity surface-emitting laser
An optical data-storage hard disk drive, which uses stationary Magneto-Optical Microhead Array Chips in place of conventional Flying-Heads, Rotary Voice-Coil Actuators and other similar types of Servo-Tracking mechanisms to transcribe or retrieve digital information to or from at least one non-volatile memory medium's data-surface, using an optical magnetic process of recording and reading data. The Magneto-Optical Microhead Array Chip Hard Disk Drives will have at least one storage disk-platter with two disk-platter data-surfaces containing a multiplicity of concentric data-tracks that rotates at a substantially constant angular velocity. Every Magneto-Optical Microhead Array Chip will comprise a (VCSEL) "Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Laser" microhead array having a minimum of one thousand or a maximum of four billion individually addressable VCSELs. Each Magneto-Optical Microhead Array Chip is placed into a stationary position above each disk platter data-surface using a chip-positioning circuit board. While the number of cylinder / tracks available to each Magneto-Optical Microhead Array Chip is determined by the number of VCSEL microheads contained within a Magneto-Optical Microhead Array Chip's microhead array (e.g., "325,000" vertical cavity surface emitting laser microheads would therefore equal "325,000" corresponding cylinder / tracks).
Owner:OPTICAL STORAGE DEVICES
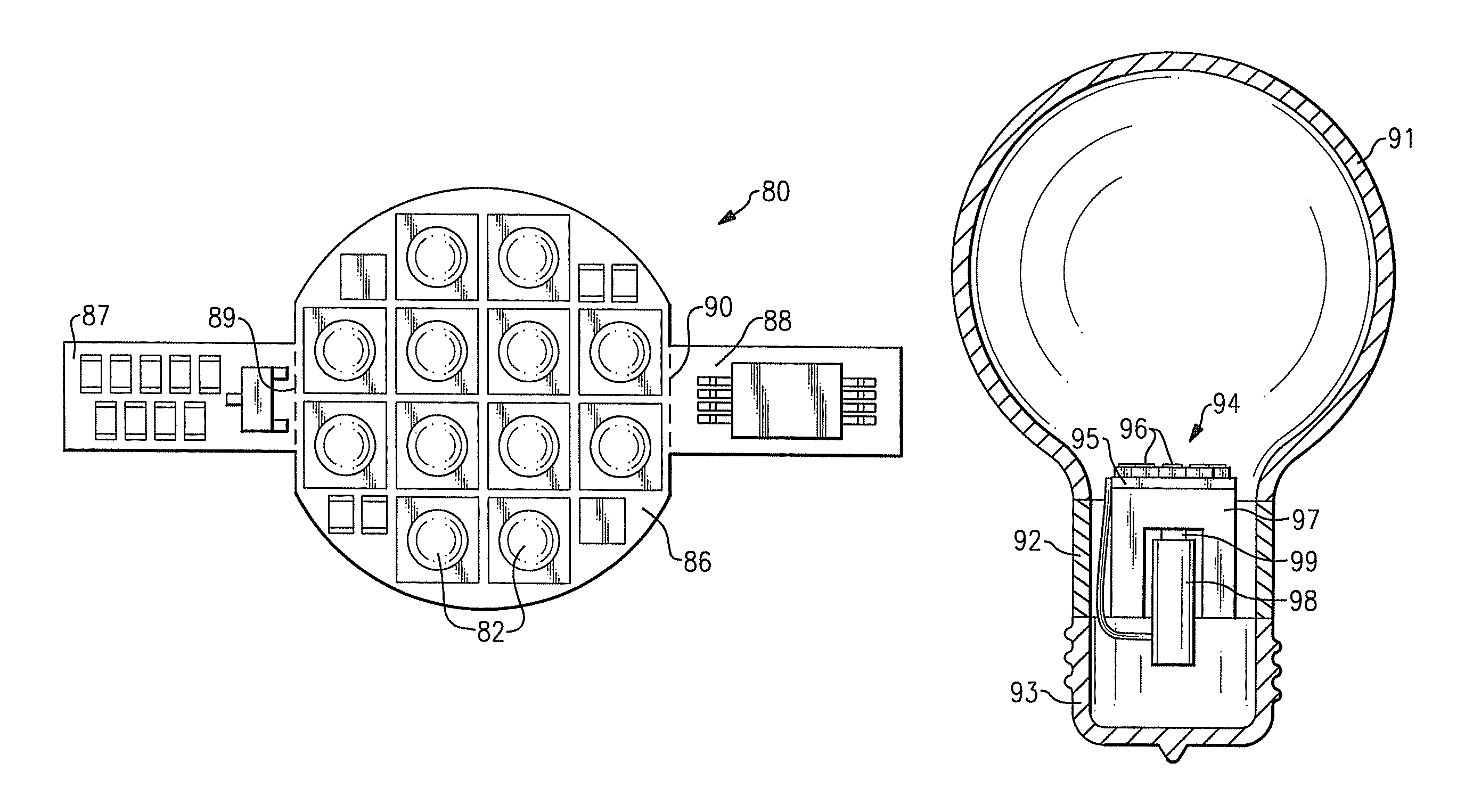
Lighting devices that comprise one or more solid state light emitters
ActiveUS8773007B2Reduce operating costsCost timeLighting support devicesPoint-like light sourceEffect lightComputer module
Light engine modules comprise a support member and a solid state light emitter, in which (1) the emitter is mounted on the support member, (2) a region of the support member has a surface with a curved cross-section, (3) the emitter and a compensation circuit are mounted on the support member, (4) an electrical contact element extends to at least two surfaces of the support member, and / or (5) a substantial entirety of the module is located on one side of a plane and the emitter emits light into another side of the plane. Also, a module comprising means for supporting a light emitter and a light emitter. Also, a lighting device comprising a housing member and a light emitter mounted on a removable support member. Also, a lighting device comprising a module mounted in a lighting device element. Also, a method comprising mounting a module to a lighting device element.
Owner:CREELED INC
Apparatus and techniques for scanning electron beam based chip repair
A method and apparatus for editing an integrated circuit by bombarding a feature in need of editing with either a low-energy or high-energy electron beam in the presence of a gas whereby low energy electrons activate reactants adsorbed on the surface of the feature in need of editing to form active species on the feature surface. The reaction products from the process can be easily removed whereby IC damage, leakage between metal features, wafer contamination and physical sputtering of undesired material can be significantly minimized while still possessing nanometer-scale spatial resolution. The low energy electrons for activating the reactants adsorbed on the surface of the feature to be edited may be emitted from the electron beam itself or they may be secondary low energy electrons emitted from the surface of the feature being edited.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
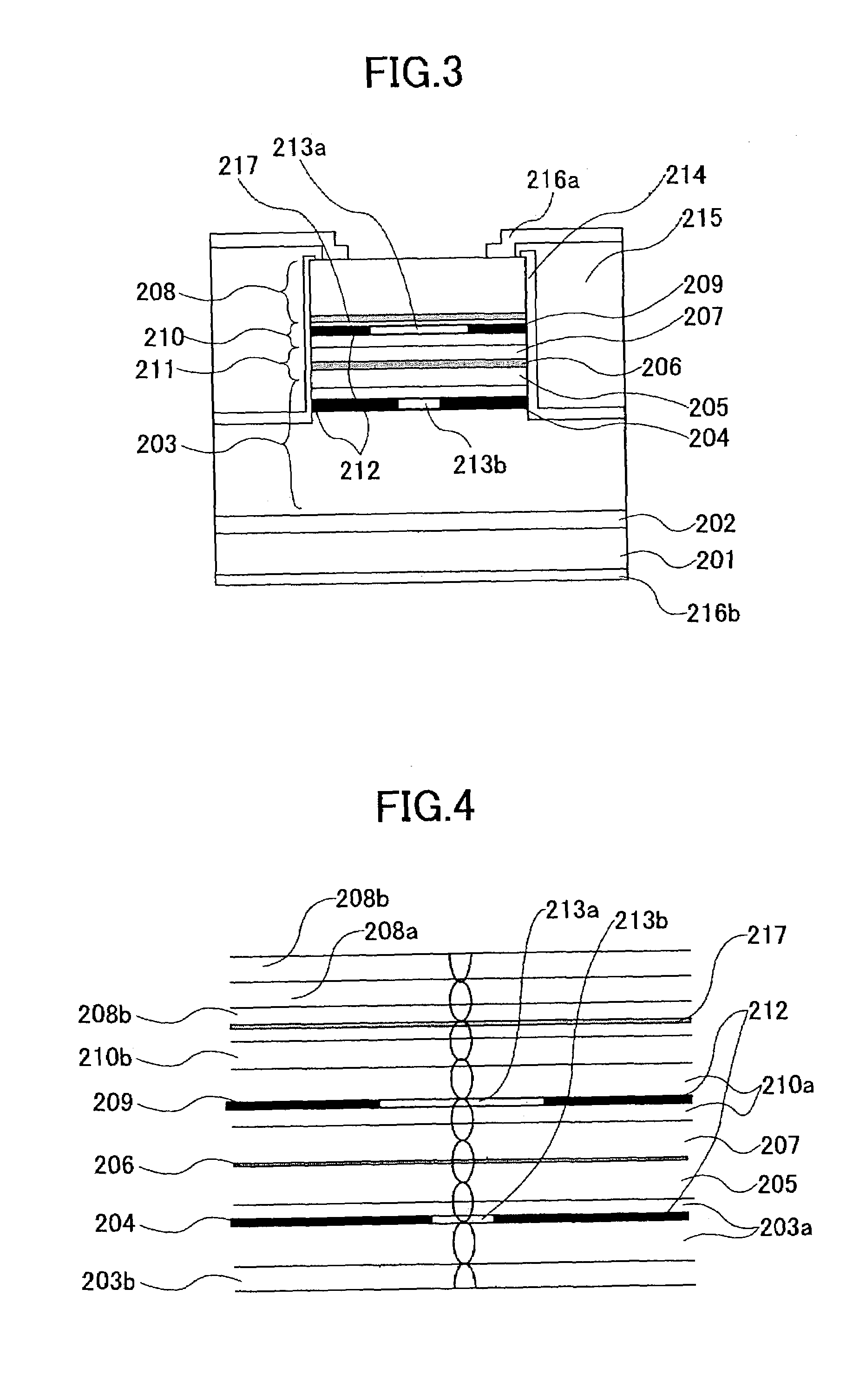
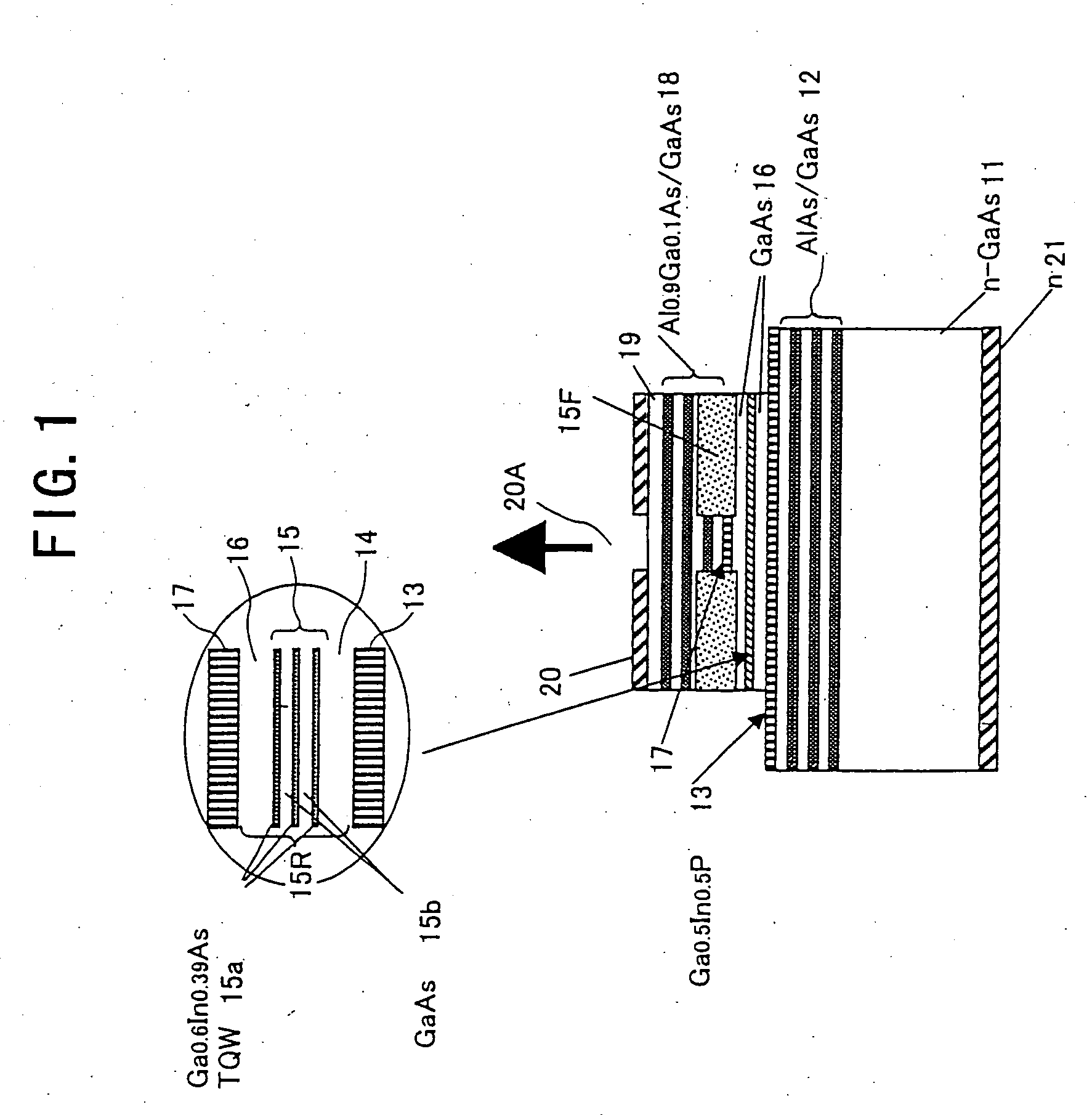
Surface-Emission Laser Diode and Fabrication Process Thereof
ActiveUS20080212636A1Large gainExcellent high-temperature characteristicOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsQuantum wellDistributed Bragg reflector
A surface-emission laser diode comprises a cavity region over a semiconductor substrate and includes an active layer containing at least one quantum well active layer producing a laser light and a barrier layer, a spacer layer is provided in the vicinity of the active layer and formed of at least one material, an upper and lower reflectors are provided at a top part and a bottom part of the cavity region, the cavity region and the upper and lower reflectors form a mesa structure over the semiconductor substrate, the upper and lower reflectors being formed of a semiconductor distributed Bragg reflector having a periodic change of refractive index and reflecting incident light by interference of optical waves, at least a part of the semiconductor distributed Bragg reflector is formed of a layer of small refractive index of AlxGa1-xAs (0<x≦1) and a layer of large refractive index of AlyGa1-yAs (0≦y<x≦1), the lower reflector is formed of a first lower reflector having a low-refractive index layer of AlAs and a second lower reflector formed on the first lower reflector, the second lower reflector has a low-refractive index layer of AlGaAs, any one layer constituting the cavity region contains In.
Owner:RICOH KK
Polarizing turning film using total internal reflection
A light redirecting article redirects light toward a target angle. The light redirecting article has an input surface for accepting incident illumination over a range of incident angles and an output surface with a plurality of light redirecting structures, each light redirecting structure having an internal reflection surface oriented at a first angle with respect to the plane of the input surface and an exit surface for emitting an output light at an emitted light angle, wherein the exit surface is oriented at a second angle relative the plane of the input surface. For incident illumination at a principal angle greater than 60 degrees from normal, light is reflected from the internal reflection surface and emitted from the exit surface at an emitted light angle that is within 5 degrees of the target angle.
Owner:SK MICROWORKS SOLUTIONS CO LTD
Surface emitting and receiving photonic device
InactiveUS20050083982A1Easy to monitorImprove equipment efficiencyOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionPhotonicsSurface emission
Owner:BINOPTICS CORP
Apparatus and techniques for scanning electron beam based chip repair
A method and apparatus for editing an integrated circuit by bombarding a feature in need of editing with either a low-energy or high-energy electron beam in the presence of a gas whereby low energy electrons activate reactants adsorbed on the surface of the feature in need of editing to form active species on the feature surface. The reaction products from the process can be easily removed whereby IC damage, leakage between metal features, wafer contamination and physical sputtering of undesired material can be significantly minimized while still possessing nanometer-scale spatial resolution. The low energy electrons for activating the reactants adsorbed on the surface of the feature to be edited may be emitted from the electron beam itself or they may be secondary low energy is electrons emitted from the surface of the feature being edited.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Grating-outcoupled cavity resonator having uni-directional emission
InactiveUS20050135453A1High output levelEasy to makeLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser structural detailsGratingWhispering gallery
A grating-outcoupled microcavity disk resonator has whispering gallery modes existing in a nearly circular resonator. Light is outcoupled by providing a grating region in the plane of the grating-outcoupled microcavity disk resonator. The grating region provides an outcoupling or lass mechanism that symmetrically interacts with the clockwise and counterclockwise whispering gallery modes, thereby making the resonator capable of surface emission.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
Planar light source device
ActiveUS7441938B2Reliable excellent heat dissipating structureReduce brightness unevennessMechanical apparatusMeasurement apparatus componentsPoint lightLight guide
A planar light source device includes: a plurality of point light sources, each of which emits a light; a light guide plate that includes a first surface, and a second surface perpendicular to the first surface, and that is configured to guide the emitted lights incident from the first surface to be emitted from the second surface; a bottom case including a side portion substantially parallel to the first surface; a light source substrate that includes the plurality of point light sources arranged thereon at a predetermined interval, and that is arranged at a side of the first surface; a frame that sandwiches the light source substrate and the side portion of the bottom case and holds the second surface and that includes a plurality of gaps at positions facing the point light source.
Owner:TRIVALE TECH
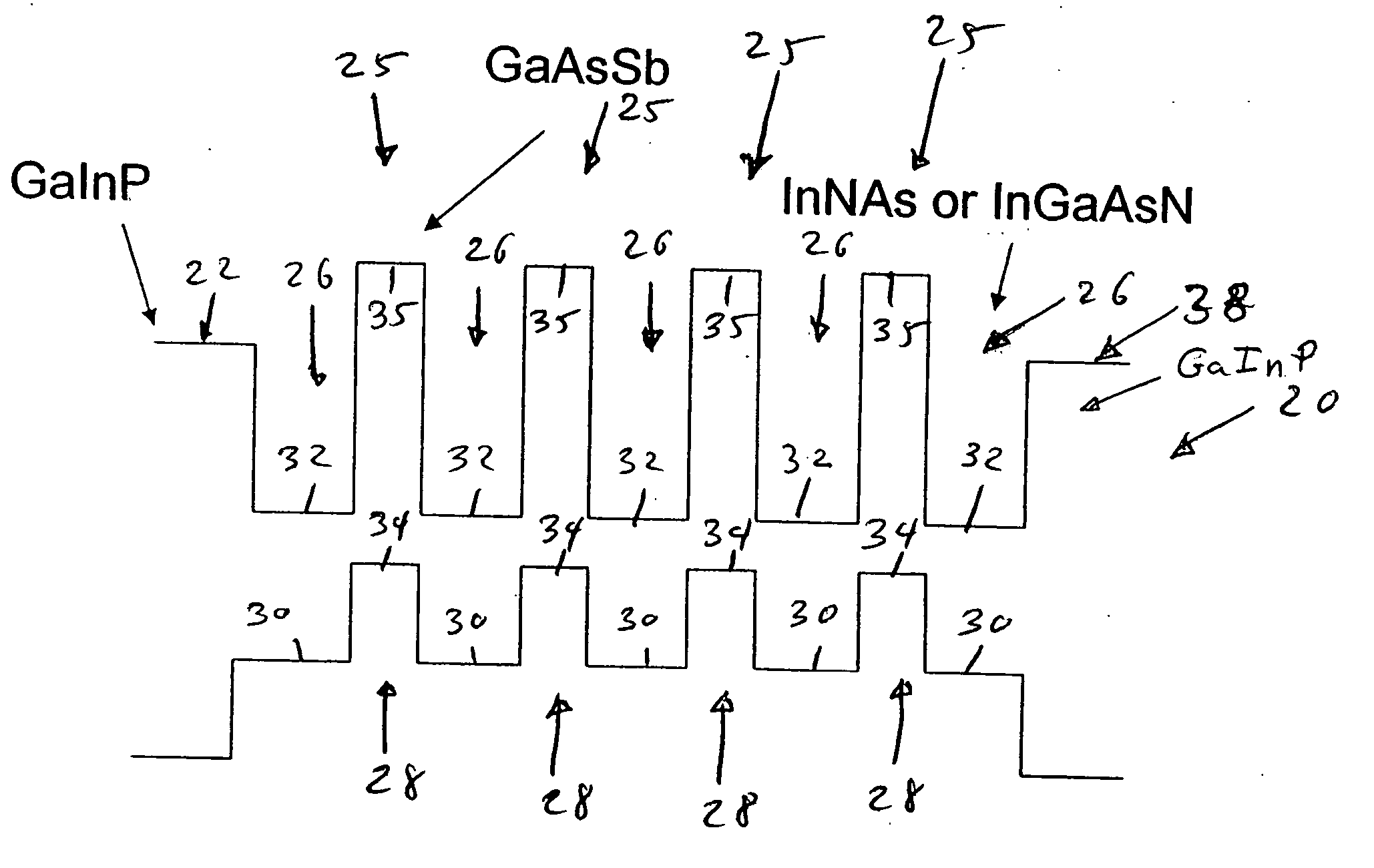
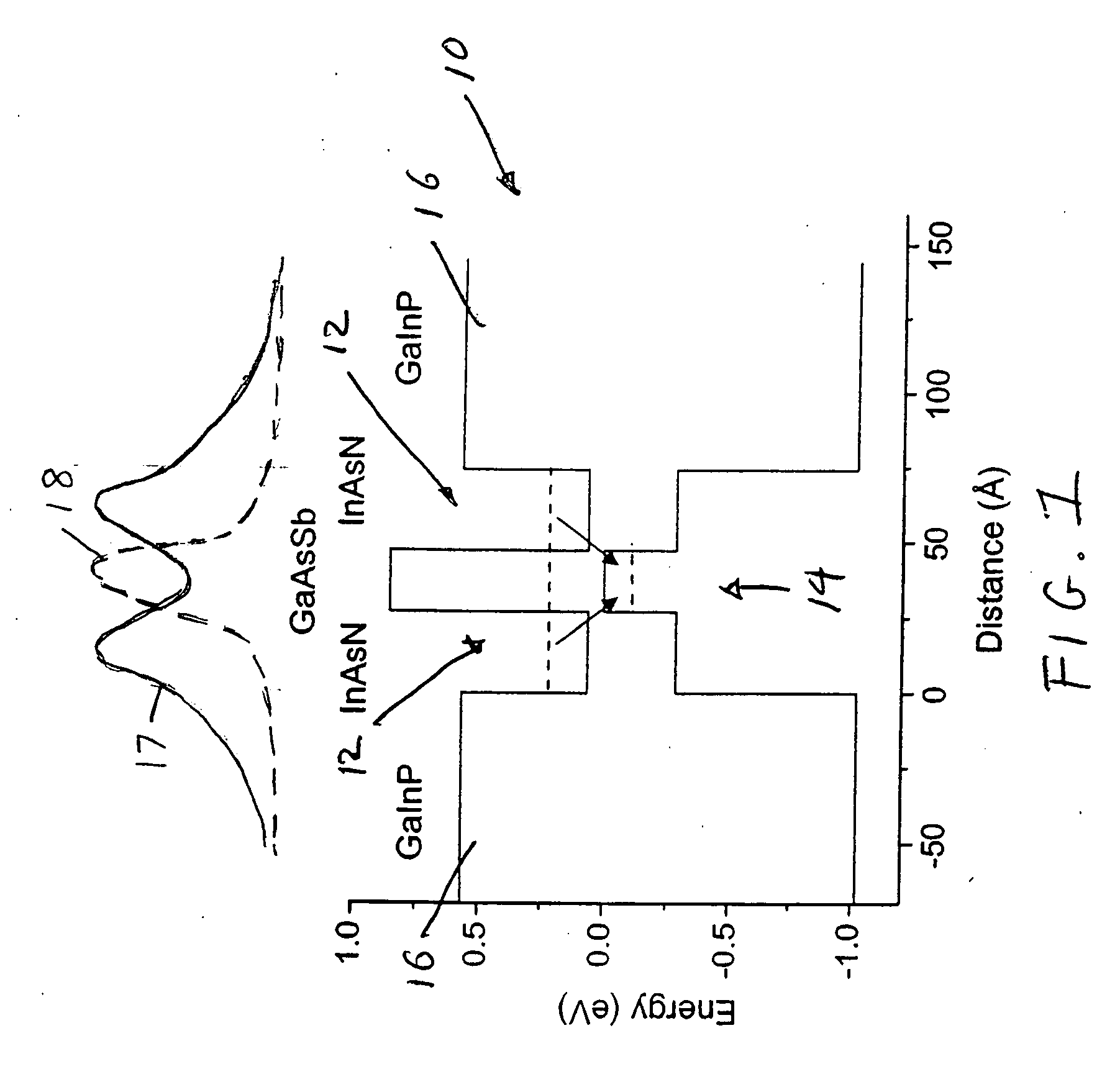
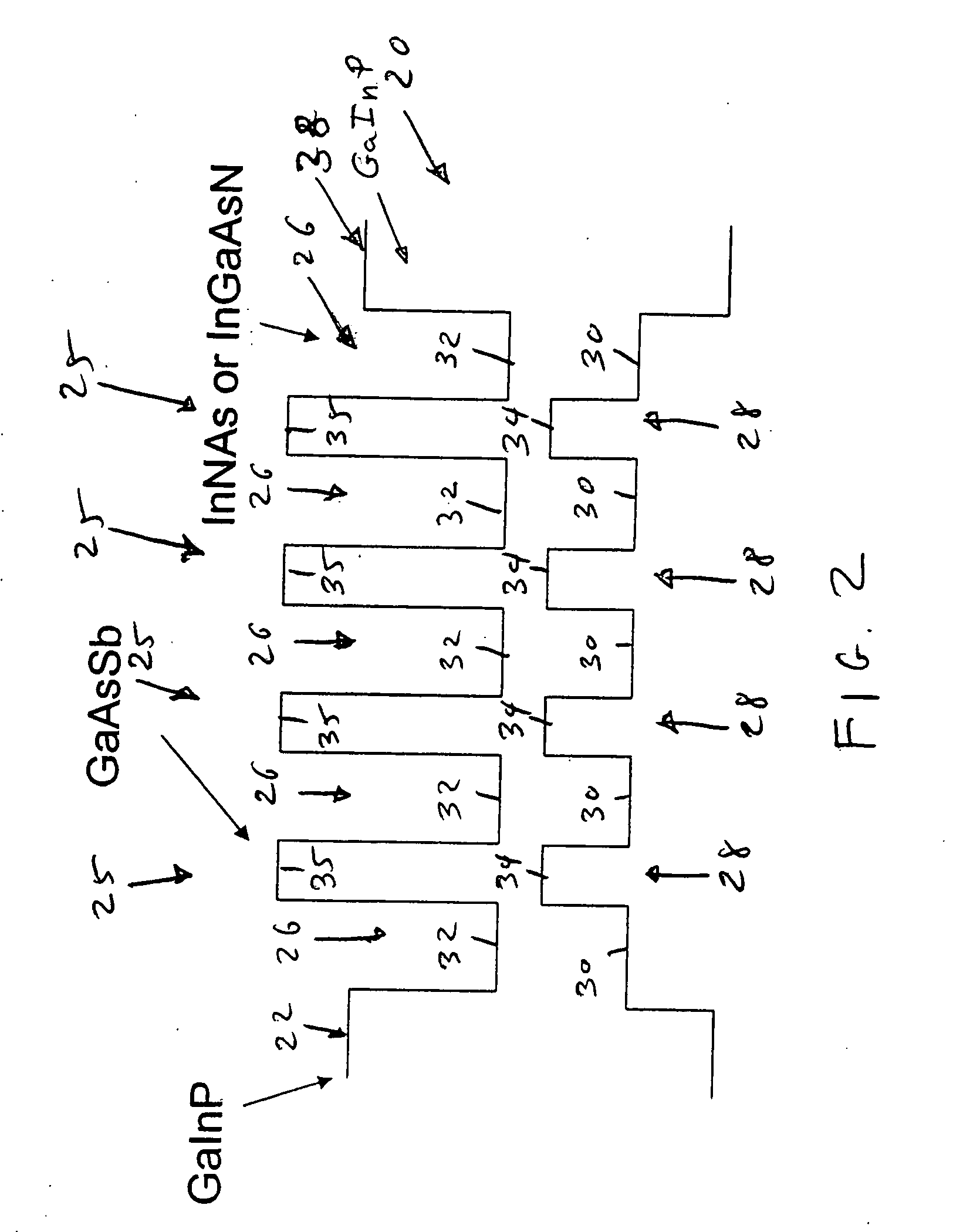
Type II quantum well mid-infrared optoelectronic devices
Semiconductor optoelectronic devices such as diode lasers are formed on InP substrates with an active region with an InAsN or InGaAsN electron quantum well layer and a GaAsSb or InGaAsSb hole quantum well layer which form a type II quantum well. The active region may be incorporated in various devices to provide light emission at relatively long wavelengths, including light emitting diodes, amplifiers, surface emitting lasers and edge-emitting lasers.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com