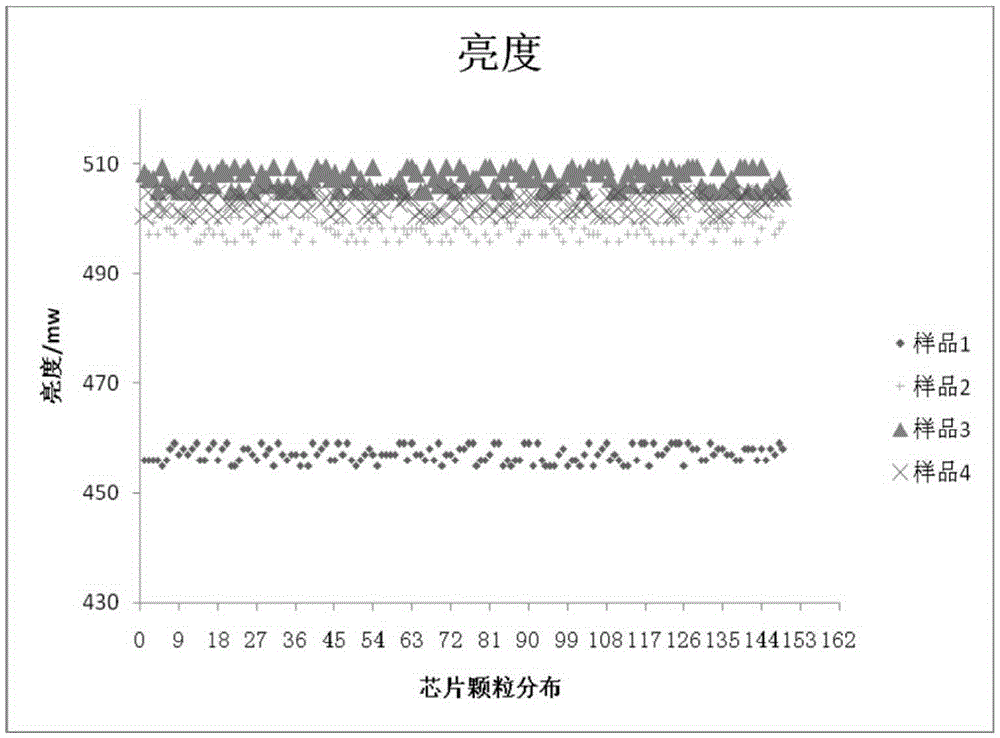
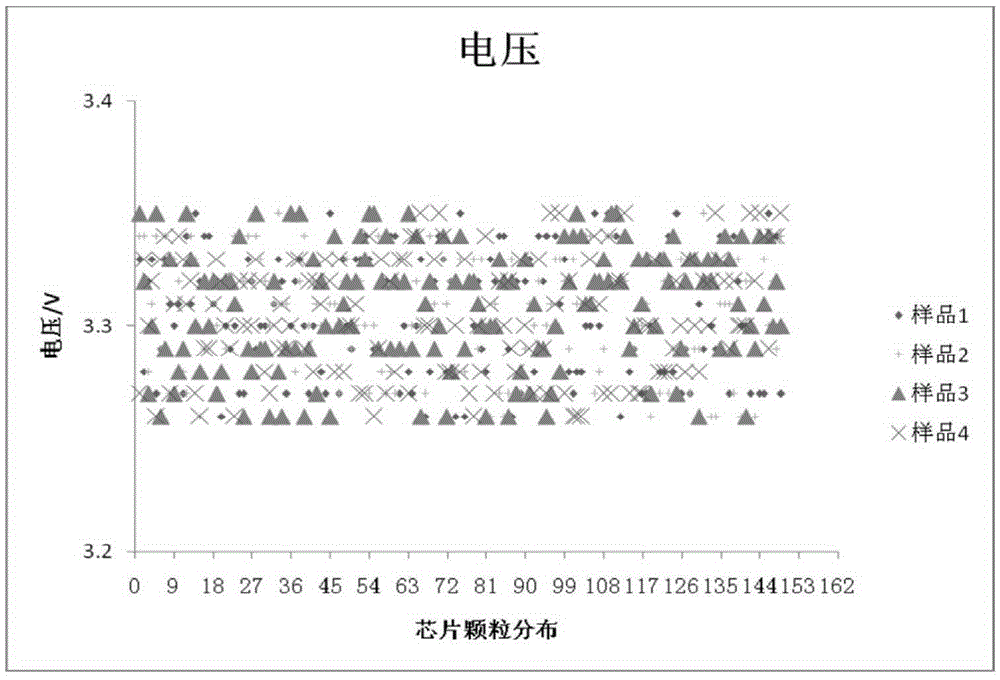
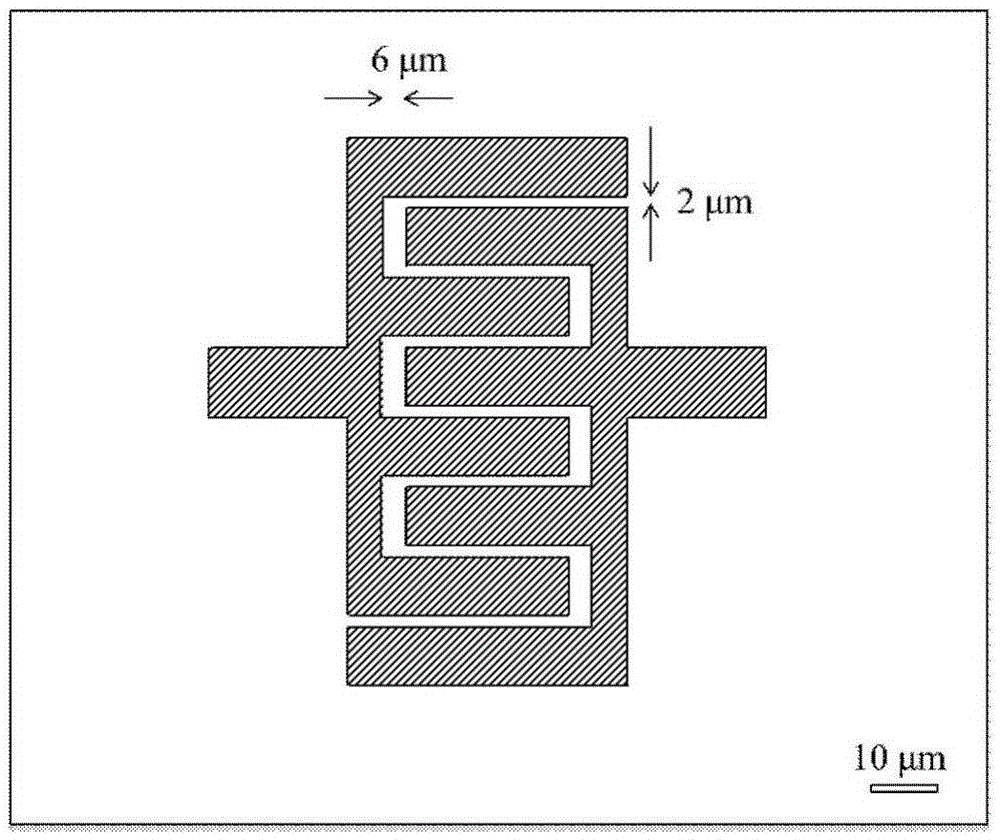
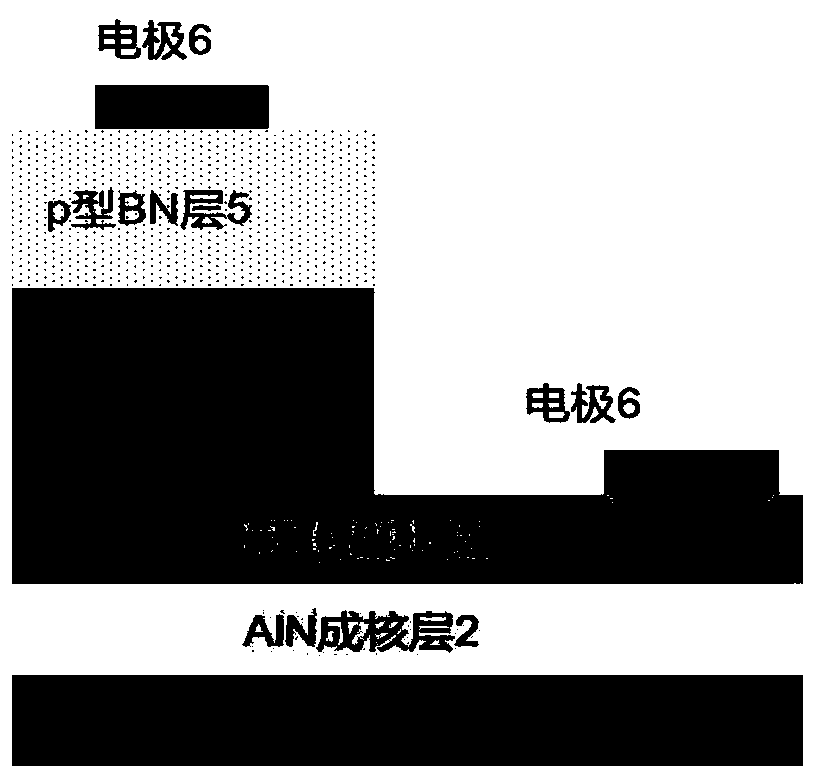
Patents
Literature
45 results about "Stark effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
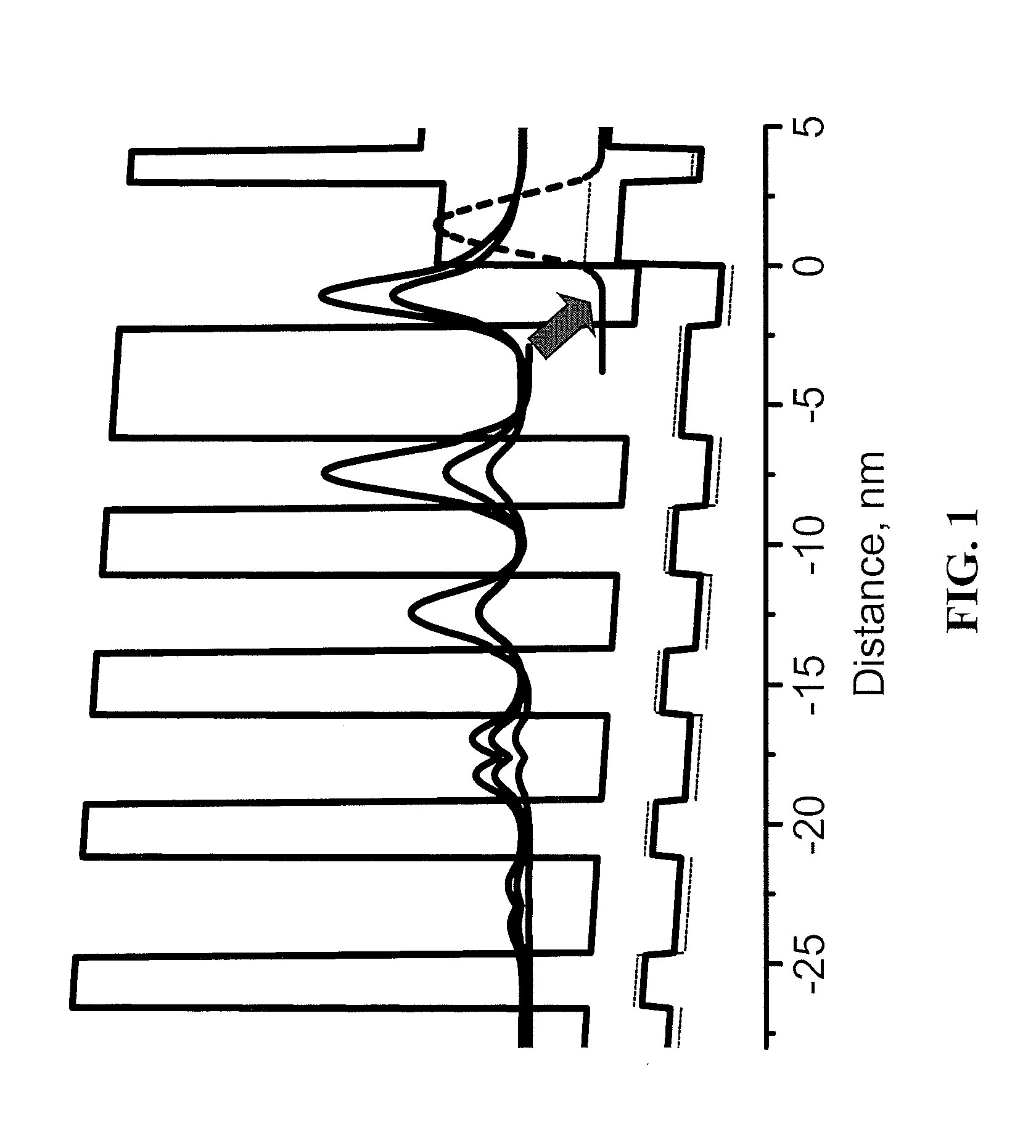
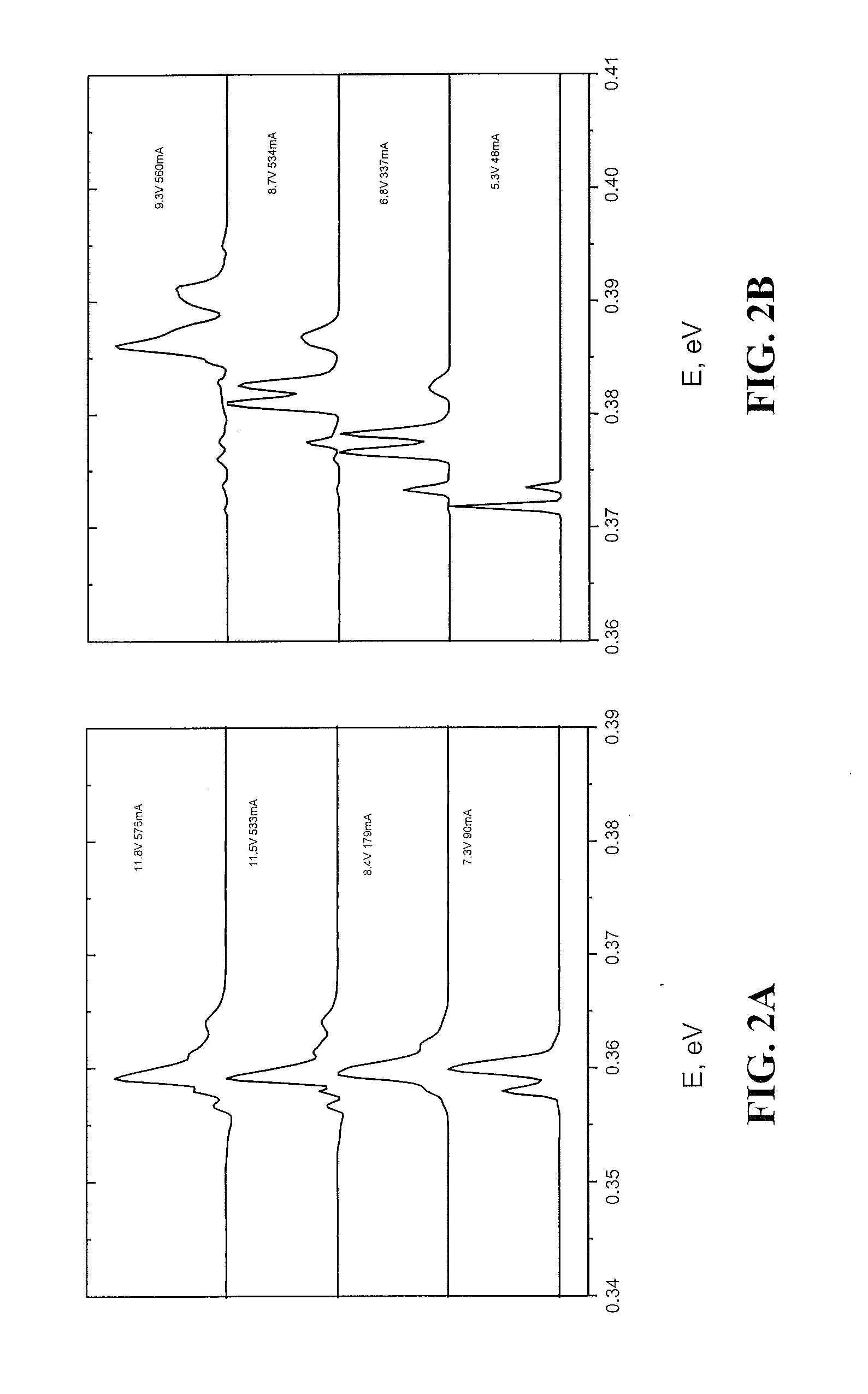
The Stark effect is the shifting and splitting of spectral lines of atoms and molecules due to the presence of an external electric field. It is the electric-field analogue of the Zeeman effect, where a spectral line is split into several components due to the presence of the magnetic field. Although initially coined for the static case, it is also used in the wider context to describe the effect of time-dependent electric fields. In particular, the Stark effect is responsible for the pressure broadening (Stark broadening) of spectral lines by charged particles in plasmas. For most spectral lines, the Stark effect is either linear (proportional to the applied electric field) or quadratic with a high accuracy.
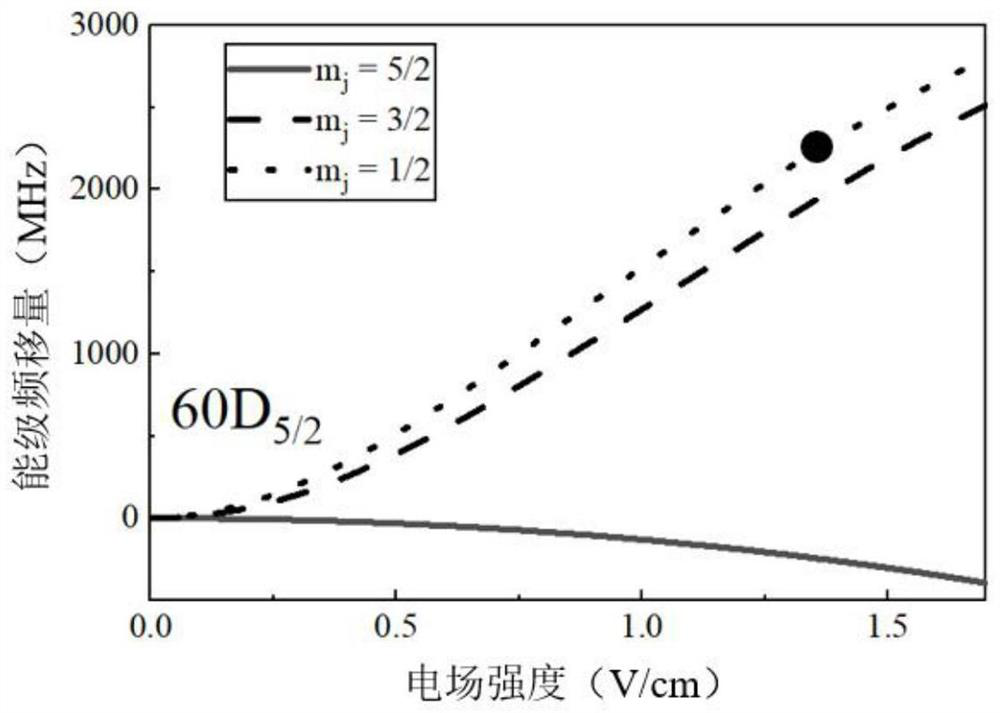
Electric field detection method and device based on stark effects of Rydberg atoms
ActiveCN103616571AUnique structureHigh measurement accuracyElectrostatic field measurementsRydberg atomElectrical field strength
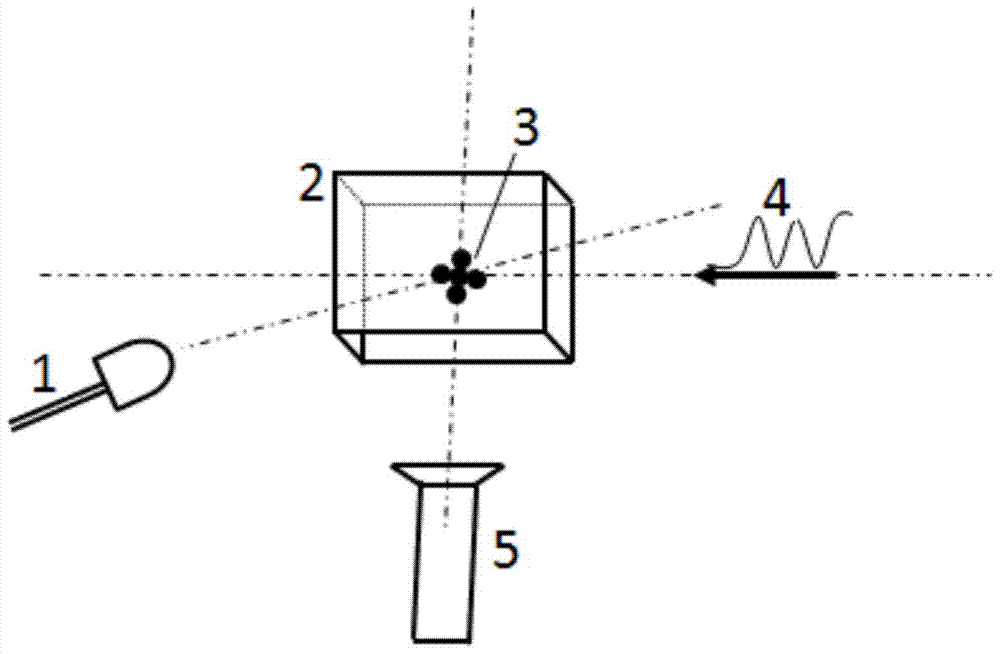
The invention relates to a weak electric field detection technology, particularly relates to an electric field detection method and device based on stark effects of Rydberg atoms, and solves the technical problems that the measurement on an electric field, particularly a weak electric field, is not accurate enough at present, and the sensitivity is not high enough. The electric field detection method based on the stark effects of the Rydberg atoms comprises the following steps: (a) oppositely arranging two beams of laser and collinearly emitting the laser into a sample tank which is internally filled with alkaline metal atom steam; (b) acquiring a signal of the second beam of the laser emitted out by the sample tank and converting the signal into a corresponding electric signal; and (c) analyzing the acquired electric signal, and if the electric field exists, observing an absorption spectrum with a stark cracking phenomenon from the signal, so as to further solve the intensity of the electric field E. According to the electric field detection method and device based on the stark effects of the Rydberg atoms, the electric field can be measured by the stark effects with an alkaline metal atom Rydberg energy level; the measurement precision is high and the electric field strength which is weakened to an mV / cm grade can be measured.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Microwave electric field intensity meter based on cold Rydberg atom interferometer and measuring method thereof
ActiveCN104880614AHigh measurement accuracyMake up for the defect that only point frequency measurement can be realizedElectrostatic field measurementsRydberg atomBeam splitting
The invention discloses a microwave electric field intensity meter based on a cold Rydberg atom interferometer and a measuring method thereof. The microwave electric field intensity meter comprises: a vacuum system, which is used for cooling and trapping atom to generate a cold atom cloud for preparing a Rydberg state and generating an interference effect so as to generate a phase difference by coherent atomic states; a laser, which is used for generating coupling light and detection light and exciting the cold atom in the vacuum system from a ground state to the Rydberg state coherently; a photoelectric detector, which is used for detecting an interference fringe generated by two beams of cold atom clouds due to coherence; and a microwave source, which is used for generating a microwave electric field. According to the invention, when the microwave electric field intensity meter is applied to the evolution process of coherent beam splitting and combination, the atom cloud in the Rydberg state interacts with a to-be-measured microwave electric field, thereby generating an alternating-current stark effect; and the to-be-measured microwave electric field intensity is associated with a phase generated by the an alternating-current stark, thereby realizing precise measurement of the microwave electric field.
Owner:清远市天之衡量子科技有限公司
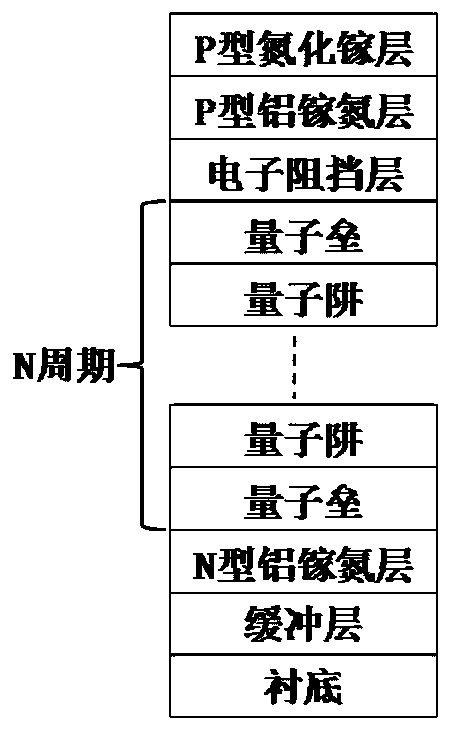
Nitride light-emitting diode (LED) epitaxial wafer and growing method thereof
InactiveCN102969416AStress reliefReduced polarizing electric fieldSemiconductor devicesPower flowHole injection layer
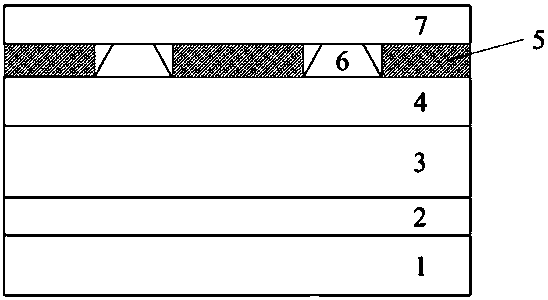
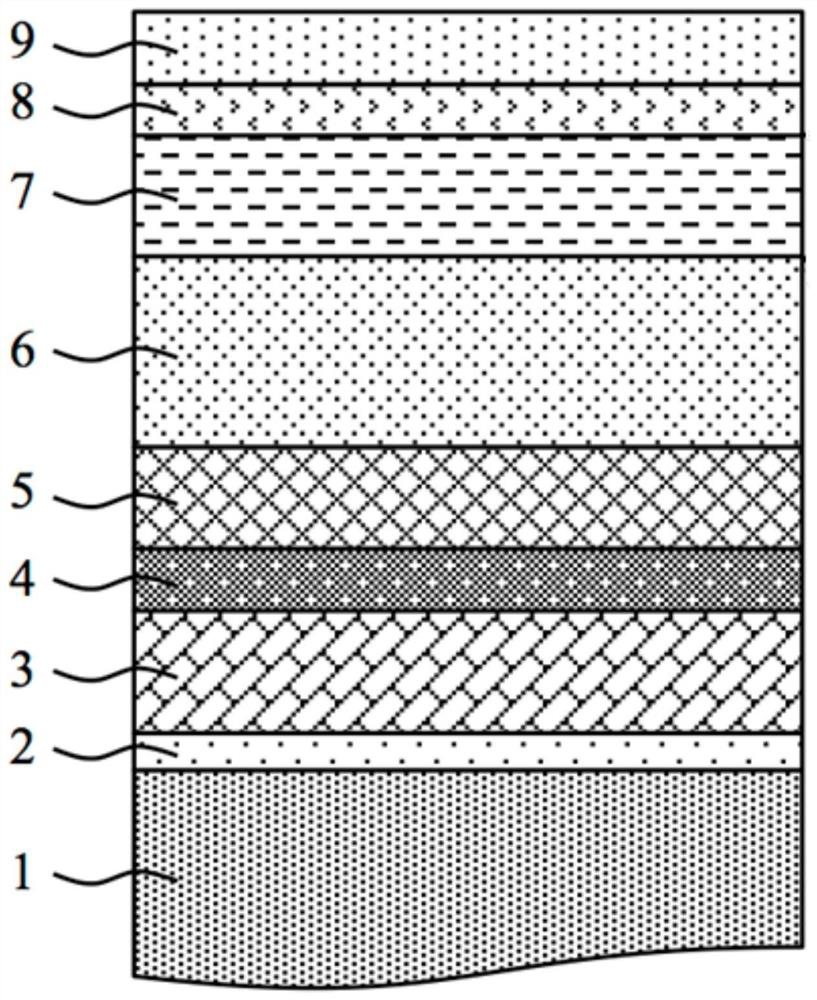
The invention provides a nitride light-emitting diode (LED) epitaxial wafer and a growing method thereof and relates to the technical field of semiconductor optoelectronics. The nitride LED epitaxial wafer structurally and sequentially comprises a substrate, a low-temperature buffer layer, an unintentionally doped GaN, an N-shaped electron-injection layer, an InGaN / GaN inserting layer, an active area, an electron blocking layer, a u-GaN / p-GaN superlattice and a p-GaN hole-injection layer from bottom to top. The InGaN / GaN inserting layer is grown between the N-shaped electron-injection layer and the active area so as to effective relieve stress of the active area, lower polarization electric fields, reduce limitation of stark effect through a quantum well, and improve luminance and anti-static properties. The u-GaN / p-GaN superlattice is inserted between the electron blocking layer and the P-shaped hole-injection layer so as to improve current expansion capacity and lower chip operating voltage.
Owner:YANGZHOU ZHONGKE SEMICON LIGHTING
Electro-absorption type semiconductor optical modulator having a quantum well structure
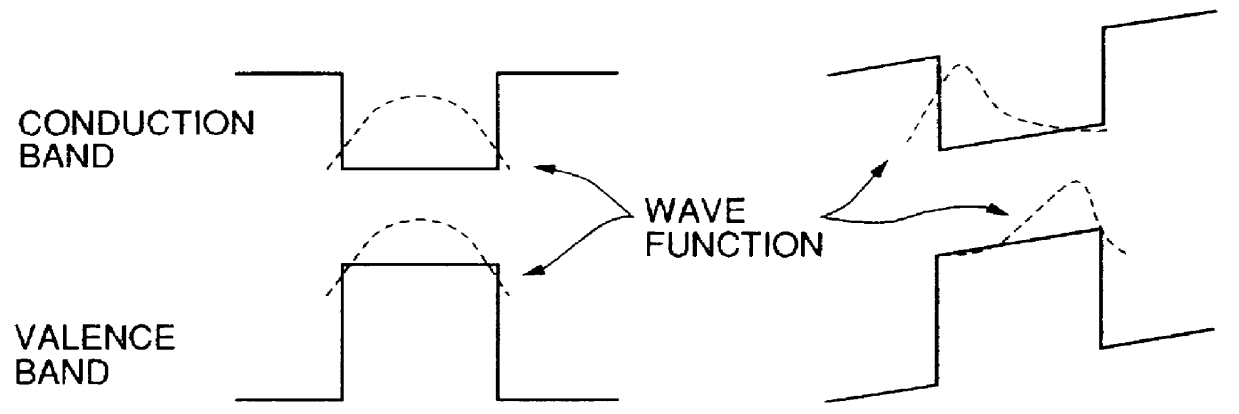
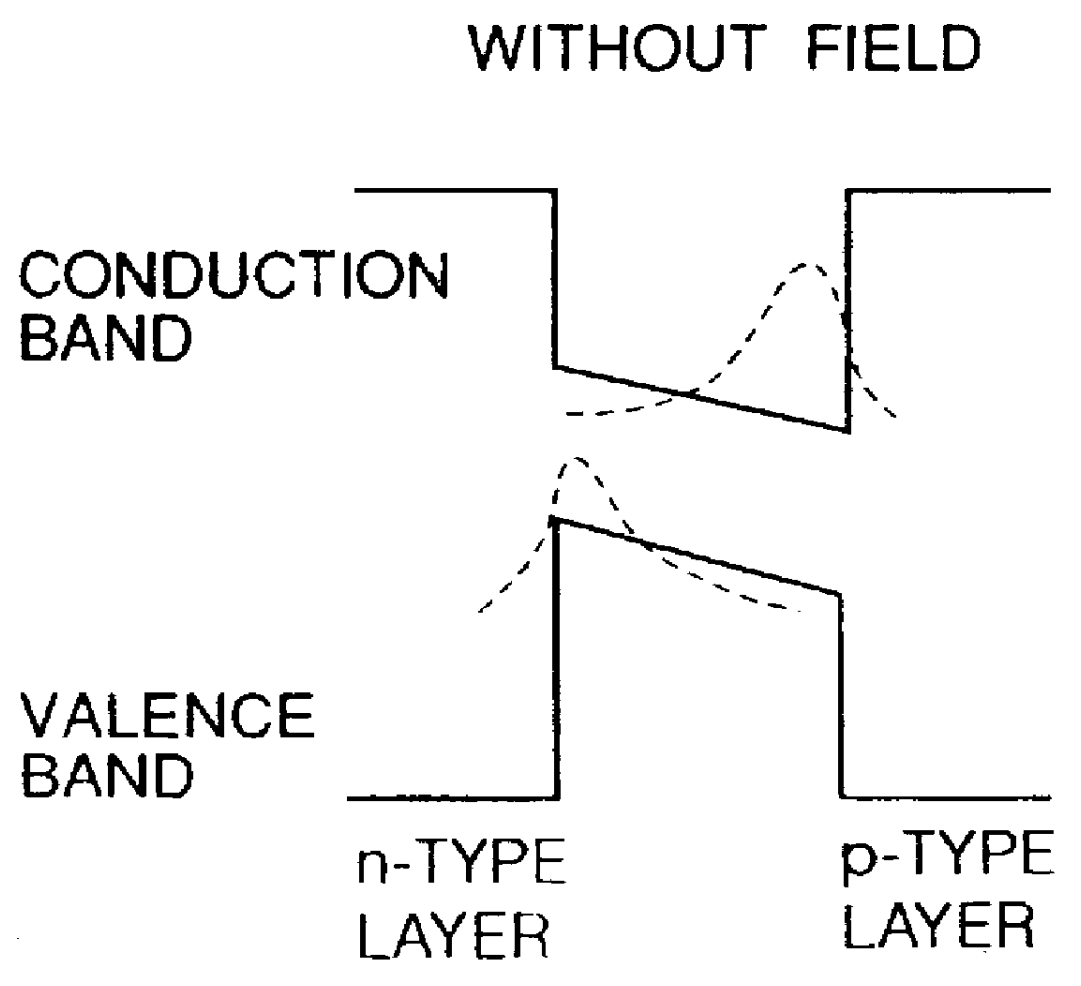
InactiveUS6100543AReduce energy differenceReduce the driving voltageNanoopticsNon-linear opticsValence bandQuantum well
Disclosed is an electro-absorption type semiconductor optical modulator utilizing the Quantum Confinement Stark Effect, in which a quantum well structure introduced in its optical absorption layer is arranged to have a potential structure such that one of the electron affinity and the energy of the top of the valence band increases in the laminating direction, while the other decreases, thereby canceling the built-in field. It is intended to lower the drive voltage and to enhance an on / off ratio (extinction ratio). Thus, the absorption peak becomes narrow at a no bias state to attain a low drive voltage and an enhanced extinction ratio.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
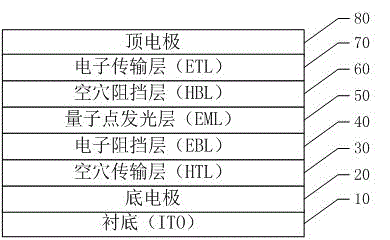
Quantum-dot Light-Emitting Diode (QLED) device based on p-i-n structure and fabrication method of QLED device
InactiveCN106549109AImprove luminous efficiencyExtended service lifeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHole transport layerQuenching
The invention discloses a quantum-dot light-emitting diode (QLED) device based on a p-i-n structure and a fabrication method of the QLED device. The QLED device comprises a substrate, a bottom electrode, a hole transmission layer, an electron blocking layer, a quantum-dot light-emitting layer, a hole blocking layer, an electron transmission layer and a top electrode. On one hand, the driving voltage of the QLED device is reduced by taking p-type material as the hole transmission layer and an n-type material as the electron transmission layer, so that the quenching of a Stark effect on quantum-dot light emitting is effectively reduced; on the other hand, cross relaxation among quantum dots is reduced by introducing an intrinsic matrix material into the quantum-dot light-emitting layer, and the radiation combination probability is improved; and meanwhile, injected electrons and holes can also be effectively captured to improve current efficiency, so that the light-emitting efficiency of the device and the stability of the device are improved, and the service lifetime of the device is prolonged.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
Wavelength-tunable vertical cavity surface emitting laser and method of making same
InactiveUS20020186726A1Reduce absorptionConstant output powerSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser arrangementsVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserRefractive index
A wavelength tunable semiconductor vertical cavity surface emitting laser which includes at least one active element including an active layer generating an optical gain by injection of a current, and at least one phase control element, and mirrors. The phase control element contains a modulator exhibiting a strong narrow optical absorption peak on a short wavelength side from the wavelength of the laser generation. The wavelength control is realized by using a position-dependent electro-optical effect. If a reverse bias is applied, the absorption maximum is shifted to longer wavelengths due to the Stark effect. If a forward bias is applied, a current is injected and results in the bleaching and reduction of the peak absorption. In both cases a strong modulation of the refractive index in the phase control element occurs. The effect tunes the wavelength of the cavity mode, and the sign and the value of the wavelength shift are defined by the position of the modulator. Two phase control cascades can be implemented into the laser, one of which shifts the wavelength of the emitted light to larger values, and the other shifts the wavelength of the emitted light to smaller values. A power equalizing element can be used in such laser allowing either to maintain the constant output power at different emission wavelengths or to realize an independent frequency and amplitude modulation. A photodetecting element can be implemented in the laser allowing calibration of the laser for all operations.
Owner:INNOLUME
Quantum Cascade Lasers with Electrically Tunable Emission Wavelengths
The present invention provides a QCL device with an electrically controlled refractive index through the Stark effect. By changing the electric field in the active area, the energy spacing between the lasing energy levels may be changed and, hence, the effective refractive index in the spectral region near the laser wavelength may be controlled.
Owner:MAXION TECH +2
Growing method of ultraviolet LED active area multiple quantum well
ActiveCN105977351AImprove concentration distributionContainment leakSemiconductor devicesUltravioletGallium nitride
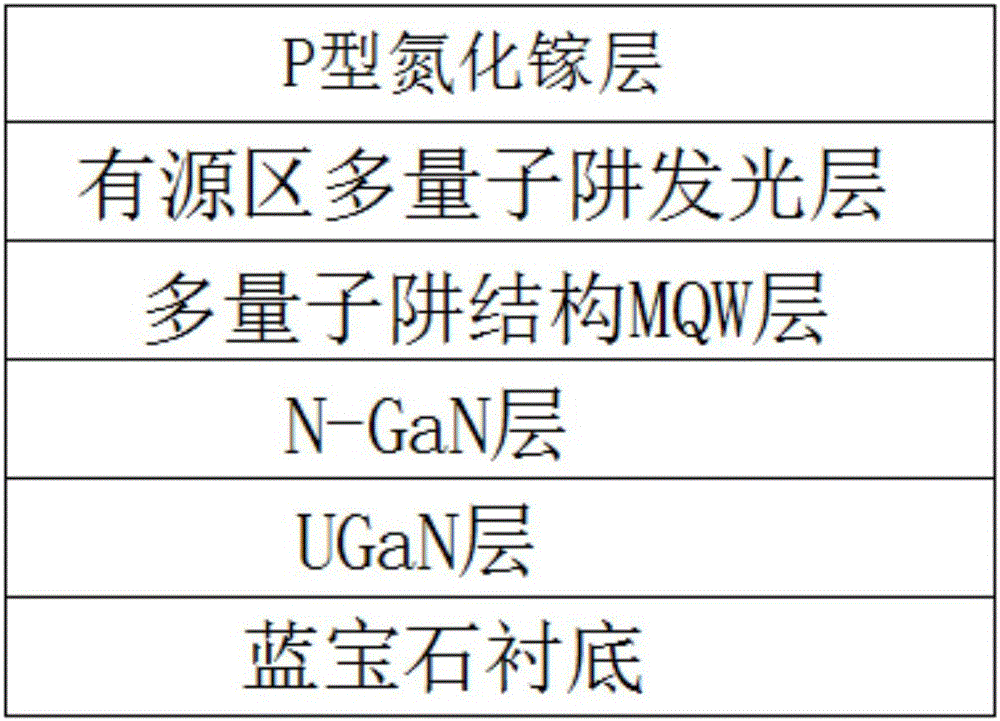
The invention provides a growing method of an ultraviolet LED active area multiple quantum well. The growing method is characterized in that step1, a UGaN layer is grown on a sapphire substrate; step2, after the growing of the UGaN layer is ended, an N-GaN layer having stable doping concentration is grown; step 3, after the growing of the N-GaN layer is ended, a multiple quantum well structure MQW layer is grown; step 4, after the growing of the multiple quantum well structure MQW layer is ended, an active area multiple quantum well light-emitting layer is grown; step 5, after the growing of the active area multiple quantum well light-emitting layer is ended, a P-type gallium nitride layer taking N2 as a carrier gas is grown; step 6, after the growing of the P-type gallium nitride layer is ended, an LED epitaxial structure is acquired by adopting annealing treatment. By adopting the production technology provided by the invention, electron concentration distribution is optimized, and electron leakage is suppressed; stress generated during a multiple quantum well growing process is reduced, and quantum confinement stark effect (QCSE) is reduced; current injection efficiency is increased, and multiple quantum well light-emitting efficiency is improved.
Owner:宁波安芯美半导体有限公司
Quantum-confinement stark effect optical modulator
A quantum confinement Stark effect (QCSE) optical modulator has a ridge stripe including a current confinement structure. The current confinement structure includes an AlInAs layer which is subjected to selective oxidation of Al content in the AlInAs layer. The current confinement structure is such that a pair of Al-oxidized regions of the AlInAs layer sandwiches therebetween a central un-oxidized region.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Quantum-confinement stark effect optical modulator
A quantum confinement Stark effect (QCSE) optical modulator has a ridge stripe including a current confinement structure. The current confinement structure includes an AlInAs layer which is subjected to selective oxidation of Al content in the AlInAs layer. The current confinement structure is such that a pair of Al-oxidized regions of the AlInAs layer sandwiches therebetween a central un-oxidized region.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Self-calibrating method and system for laser-induced-fluorescence-based speed measurement
ActiveCN106526228AImprove detection accuracyLow costTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesFluid speed measurementObservational errorIn situ calibration
The invention discloses a self-calibrating method and system for laser-induced-fluorescence-based speed measurement. The self-calibrating method comprises: exiting laser is modulated to apply two beams of laser in opposite directions in a to-be-measured flow field to a to-be-measured particle in the to-be-measured flow field; the strength of a fluorescence signal from the excited to-be-measured flow field on the laser path is measured to obtain a practical-measuring fluorescence spectrum profile; and fitting is carried out on the practical-measuring fluorescence spectrum profile to obtain a first fluorescence spectrum profile and a second fluorescence spectrum profile that correspond to the two beams of laser in opposite directions and numerical average value solving is carried out on central frequency points of the first fluorescence spectrum profile and the second fluorescence spectrum profile to obtain a laser frequency corresponding to an absolute speed zero point. Therefore, in-situ calibration is realized; and separate construction of a reference plasma source is not required. The calibration plan is simplified and the measuring cost is saved; a measuring error caused by a Stark effect under the circumstance of unequal densities between the reference plasma source and a to-be-measured plasma can be eliminated; and the measuring precision is improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
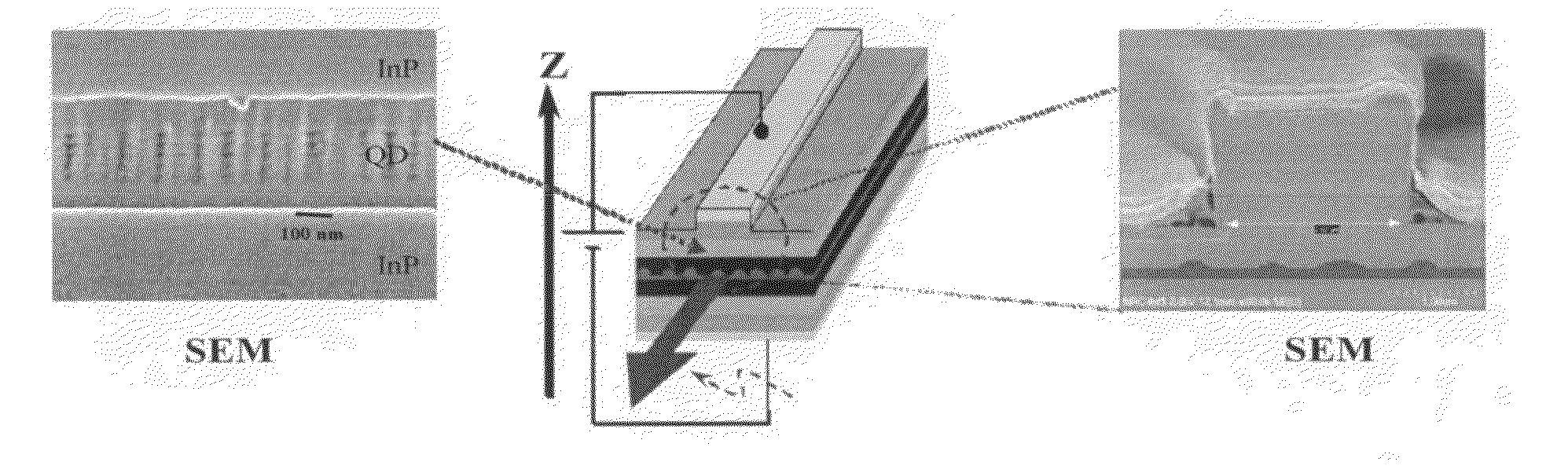
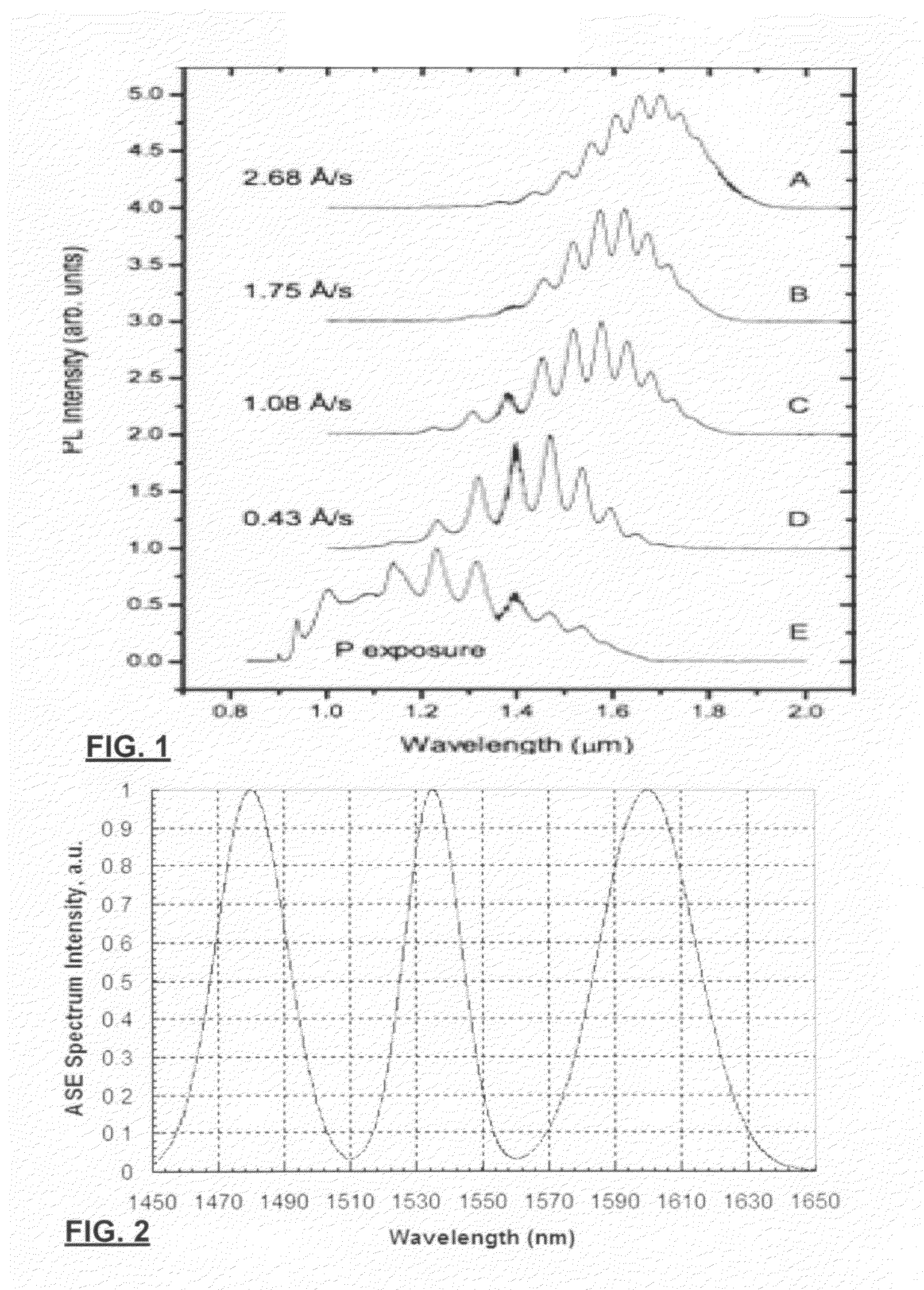
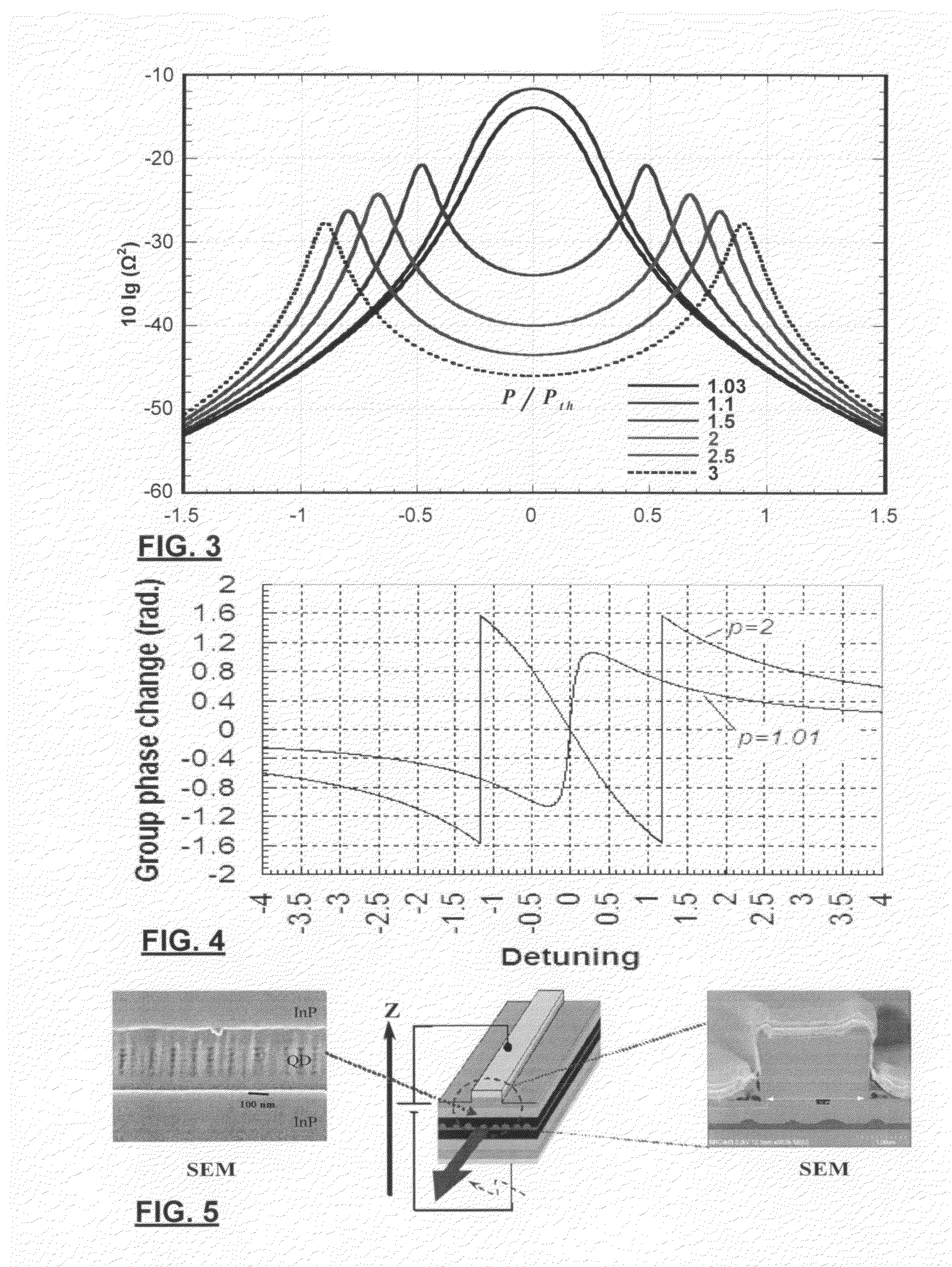
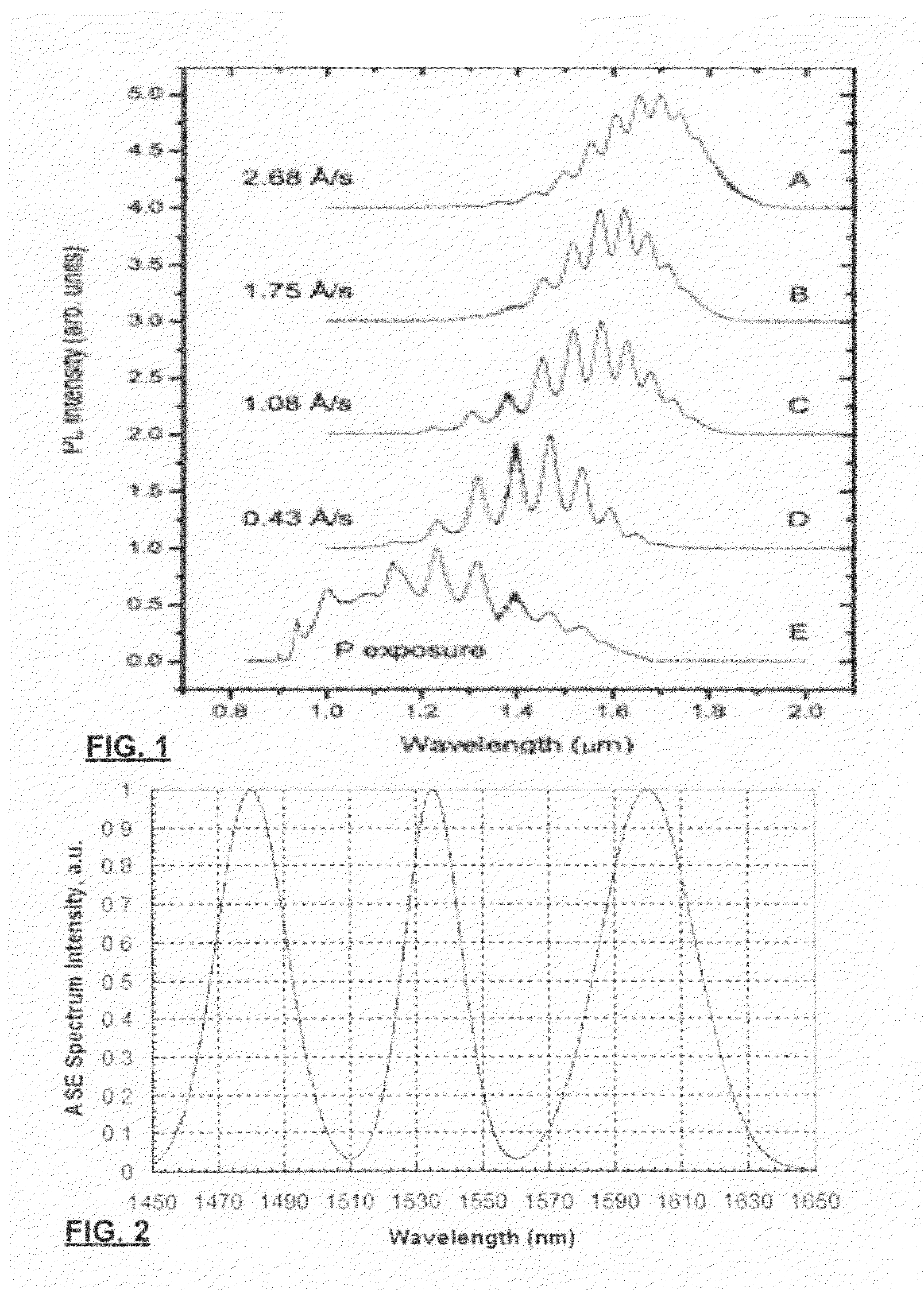
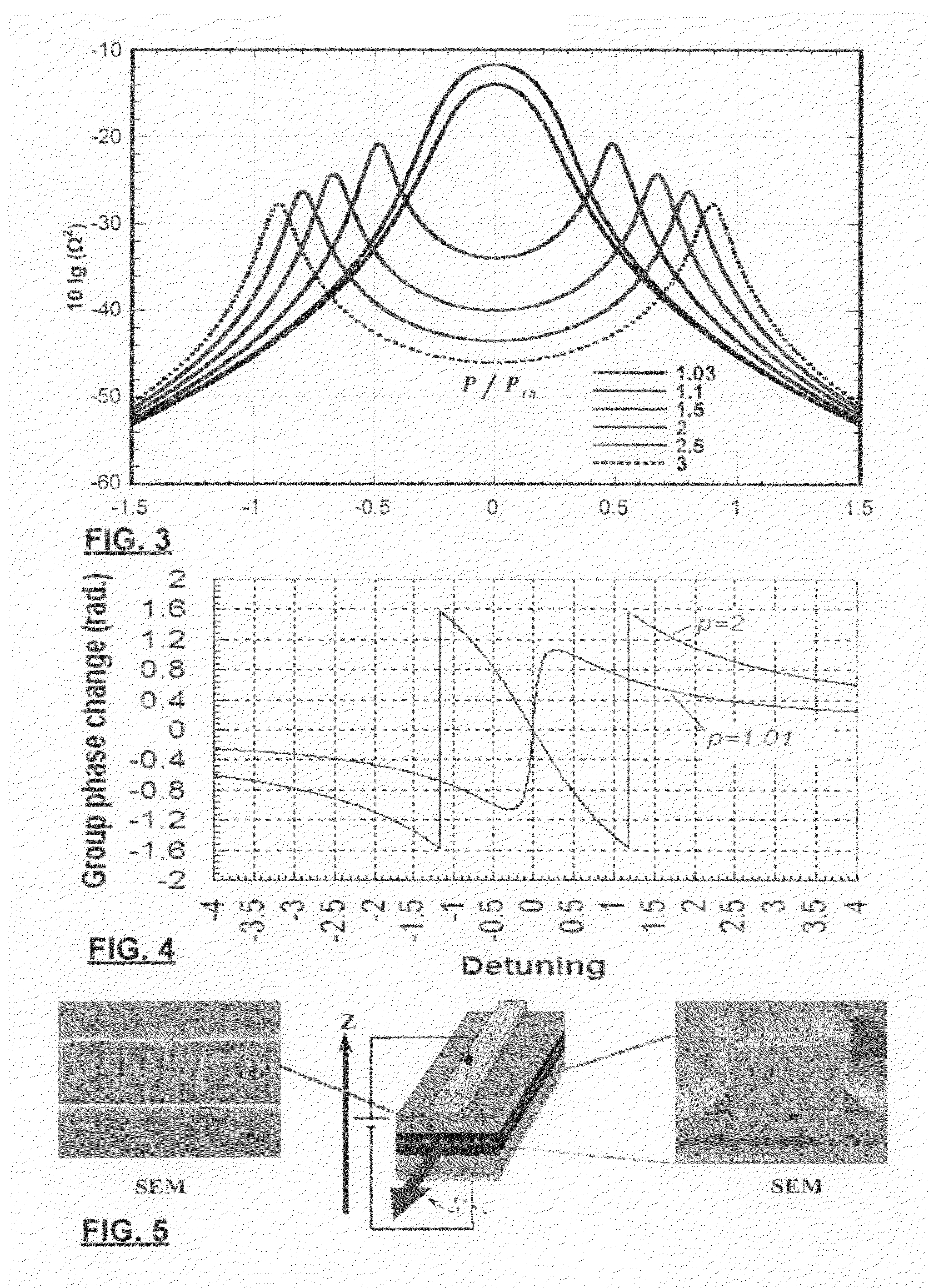
Multi-band multiwavelength quantum dot mode-locked lasers
ActiveUS20100142566A1Large wavelength separationGreat mode spacingLaser detailsLaser active region structureMulti bandChemical beam epitaxy
A multi-band (multi-colour) multiwavelength mode locked laser diode is provided by dynamic phase compensation of a quantum dot active medium. The laser diode is provided with a PIN diode structure where the active medium consists of a plurality of layers of quantum dots such as those produced by self-assembly from known chemical beam epitaxy methods. The multiplicity of bands may be produced by AC Stark splitting, frequency selective attenuation, or by the inclusion of multiple different layers having different, respective, peak ASE emissions. Dispersion compensation within laser facets, waveguides, and the optically active media permit the selection of a fixed dispersion within the cavity. A dynamic group phase change induced by the AC Stark effect permits compensation of the fixed dispersion sufficiently to produce an intraband mode-locked laser. Even interband mode locking was observed.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
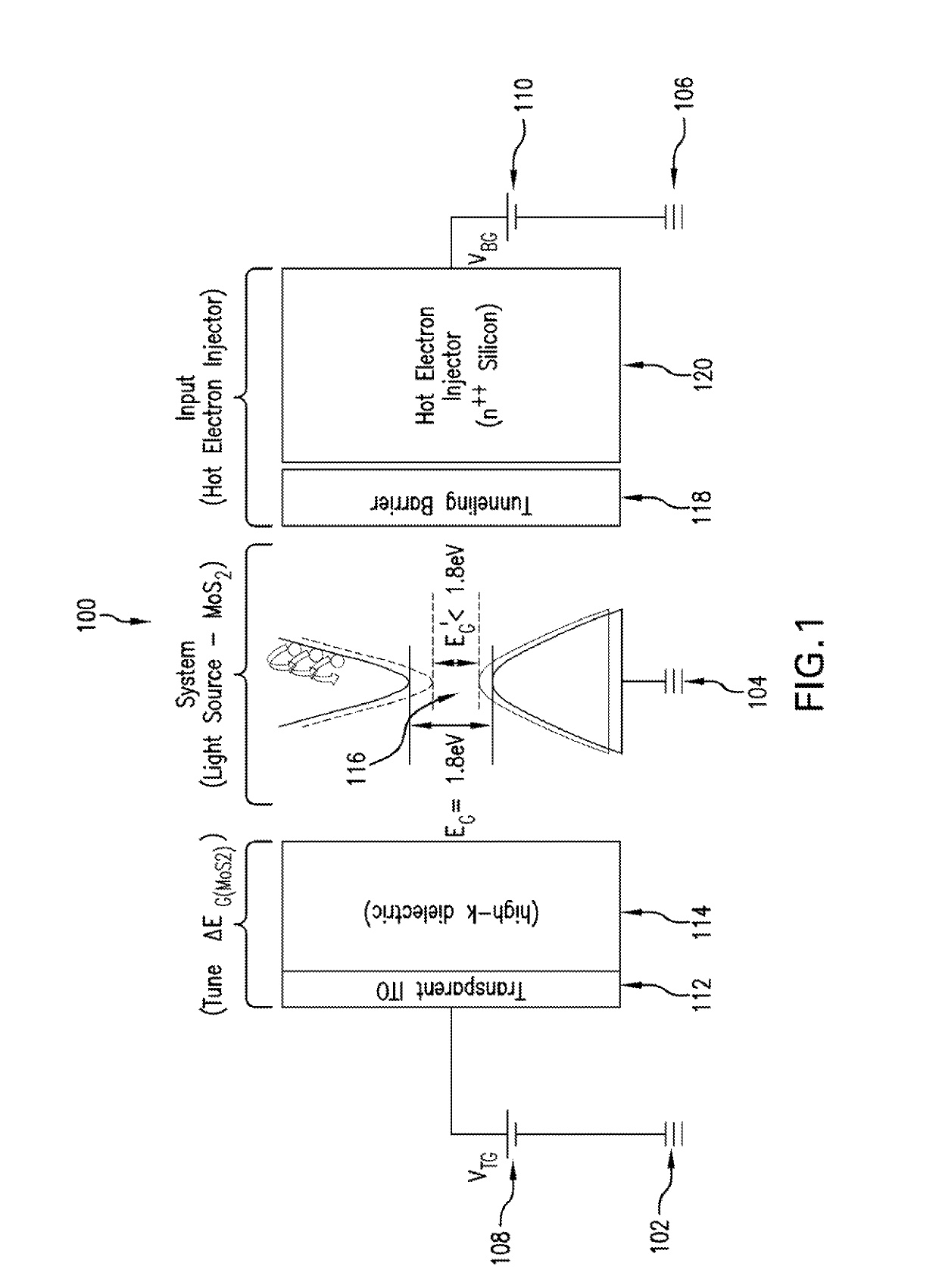
Voltage-tunable wavelength-agile 2D material-based light-emitting transistors
ActiveUS10381506B1Low costElectroluminescent light sourcesSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor materialsLuminescence
An optoelectronic device is provided that includes a doped substrate, a tunneling barrier, a direct bandgap two dimensional semiconductor material, a hot electron emitter, a gate electrode, and a voltage bias. The hot electron emitter injects hot electrons from the underlying substrate into the conduction band of the direct bandgap two dimensional semiconductor material via quantum tunneling. The gate electrode is operable to provide the voltage bias in a direction normal to the X-Y plane of the direct bandgap two dimensional semiconductor material so as to generate an electric field perpendicular to the direct bandgap two dimensional semiconductor material. The voltage bias provided by the gate is operable to change an optical bandgap of the direct bandgap two dimensional semiconductor material continuously from the visible to the mid-infrared spectral regime via an electric dipole layer enhanced Giant Stark Effect for electrically-tunable hot electron luminescence applications.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Continuous frequency electric field measuring device and method based on Rydberg atom AC Stark effect
PendingCN114487621AOvercome errorOvercoming technical issues requiring pre-calibrationElectrostatic field measurementsRydberg atomElectrical field strength
The invention discloses a device and a method for measuring the intensity of a continuous frequency microwave electric field based on a Rydberg atom AC Stark effect, a cesium atom steam pool is used as an atom sample pool, cesium atoms are excited to a Rydberg state under the action of detection light and coupling light emitted by two laser light sources, an electromagnetic induction transparent spectrum is generated, and the intensity of the continuous frequency microwave electric field is measured. Meanwhile, a strong electric field is used as a local field EL, the Rydberg energy level is subjected to AC Stark frequency shift and splitting, the energy level frequency shift of the Rydberg atoms is shifted to the position with the large polarizability through the AC Stark frequency shift, the induction sensitivity of the atoms to the electric field can be greatly improved, then a to-be-measured signal electric field ES is applied, the difference delta f between the frequency of the signal electric field and the frequency of the local field is smaller than 10 MHz, and the frequency of the to-be-measured signal electric field ES is smaller than 10 MHz. At the moment, the Rydberg atom serves as a frequency converter, a difference frequency signal delta f of a local field and a signal field is directly read out, the size of the difference frequency signal is in direct proportion to the ELS, the size of the signal field ES can be directly read out according to the size of the difference frequency signal, and the problem that a traditional microwave electric field measuring method is large in error is solved.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
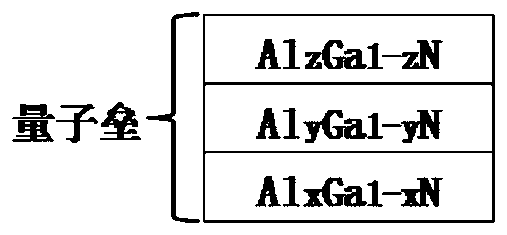
Ultraviolet LED epitaxial structure with novel quantum barrier structure and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110098294AImprove internal quantum efficiencyReduce leakageSemiconductor devicesQuantum efficiencyQuantum well
The invention discloses an ultraviolet LED epitaxial structure with a novel quantum barrier structure and a preparation method thereof. The ultraviolet LED epitaxial sheet comprises a substrate, a buffer layer, an N-type AlGaN layer, a luminous layer, an electron barrier layer, a P-type AlGaN layer and a P-type GaN layer in turn from bottom to top. Each quantum barrier of the luminous layer comprises an Al<x>Ga<1-x>N layer, an Al<y>Ga<1-y>N layer and an Al<z>Ga<1-z>N layer in turn from bottom to top. For all the quantum barriers from bottom to top in the luminous layer except the first and last quantum barriers, the aluminum molecule content y in the Al<y>Ga<1-y>N layers is a fixed value, the aluminum molecule content x in the Al<x>Ga<1-x>N layers increases gradually from an initial valueb to y, and the aluminum molecule content z in the Al<z>Ga<1-z>N layer decreases gradually from an initial value y to b. The epitaxial structure provided by the invention can alleviate the quantum confinement Stark effect in multi-quantum wells and the polarization effect between the luminous layer and the electron barrier layer, so as to improve the radiation recombination efficiency of electronsand holes, reduce the leakage of electrons, and finally, improve the internal quantum efficiency of ultraviolet LEDs.
Owner:UNILUMIN GRP
LED (Light Emitting Diode) epitaxial wafer and preparation method therefor
ActiveCN105428478AImprove internal quantum efficiencyReduce the degree of separationSemiconductor devicesQuantum efficiencyCavitation
The present invention discloses an LED (Light Emitting Diode) epitaxial wafer and a preparation method therefor. The LED epitaxial wafer comprises a substrate, a low-temperature buffer GGaN layer, an undoped GaN layer, an N-type GaN layer, a multi-cycle quantum well layer, a P-type AlGaN layer and a P-type GaN layer, which are arranged sequentially from bottom to top. The multi-cycle quantum well layer comprises an InxGa1-xN layer / GaN layer from 6-14 cycles, and in any one cycle, the GaN layer is arranged on the In<x>Ga<1-x>N layer, and an InN thin layer is arranged below the In<x>Ga<1-x>N layer, and the thickness of the InN thin layer is 0.2-1nm, and x is 0.20-0.22. The InN thin layer enables In atoms to achieve a dynamic saturation balance before reaching the In<x>Ga<1-x>N layer, so that a segregation phenomenon of In in the In<x>Ga<1-x>N layer is reduced, thereby reducing a separation degree of electrons and a cavitation wave function caused by a quanta stark effect, so as to improve internal quanta efficiency of an LED.
Owner:XIANGNENG HUALEI OPTOELECTRONICS
Electro-optical modulating device preparing method based on quantum restriction Stark effect
ActiveCN105487264AThe synthesis method is simpleNovel electrode structureNon-linear opticsQuartz substrateHigh heat
The invention provides a preparing method based on CdSe / CdS quantum dots and a quantum restriction Stark device thereof. The quantum dots are prepared to be mixed and injected into a precursor through a constant flow pump. The method is novel, simple and capable of obtaining pure-wurtzite-phase non-blinking CdSe / CdS quantum dots; the device is manufactured on a quartz substrate, the periodic cross electrode structure is obtained by means of the process of gluing, exposing, developing, evaporating, cleaning and the like, electrodes are evaporated through Au, the distance between every two electrodes is 2 micrometers, and under an inverted microscope, a white light source is utilized for measuring transmission spectrum changes of the quantum dots on the structure before and after voltage is connected.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
High-efficiency light-emitting diode structure and manufacturing method thereof
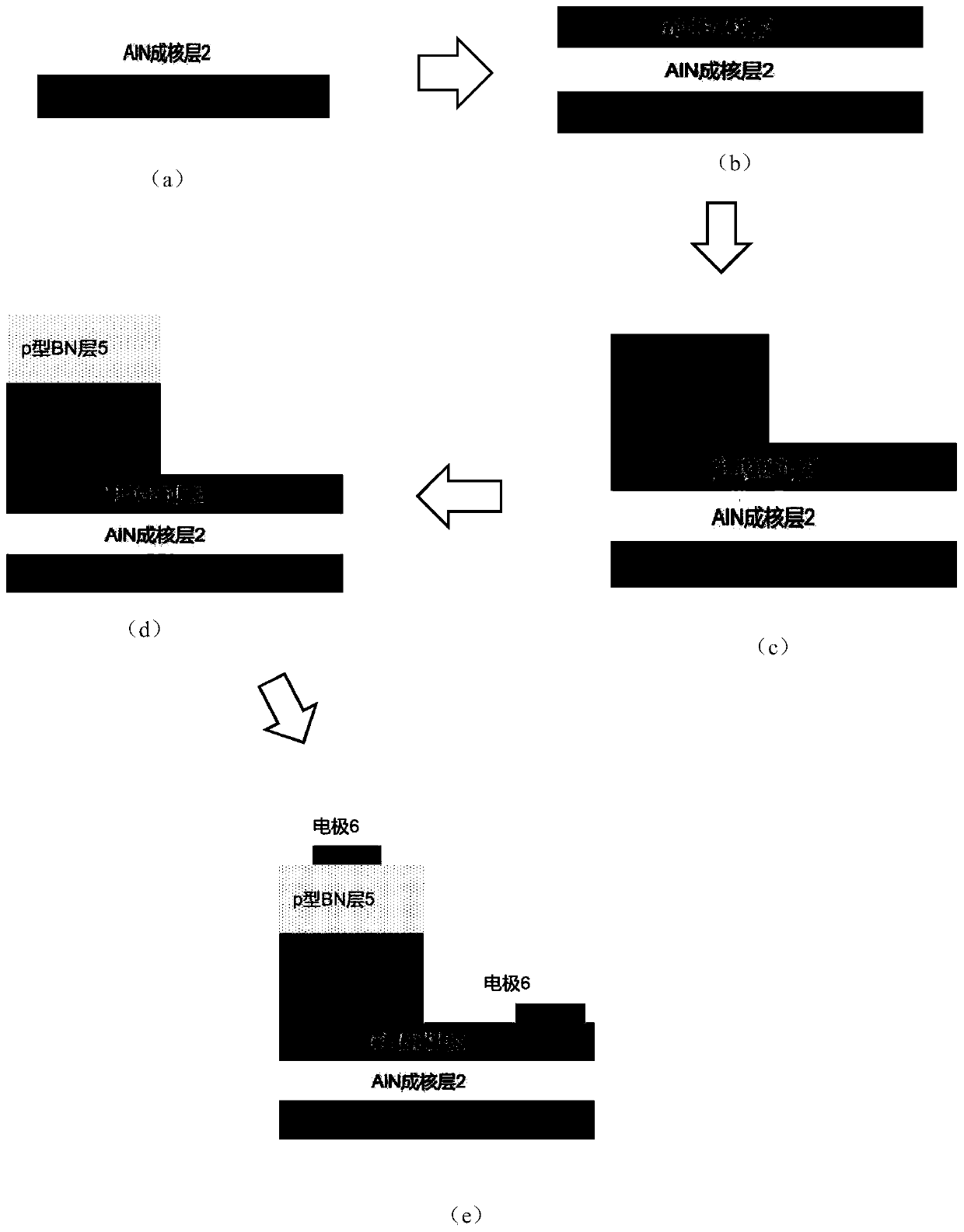
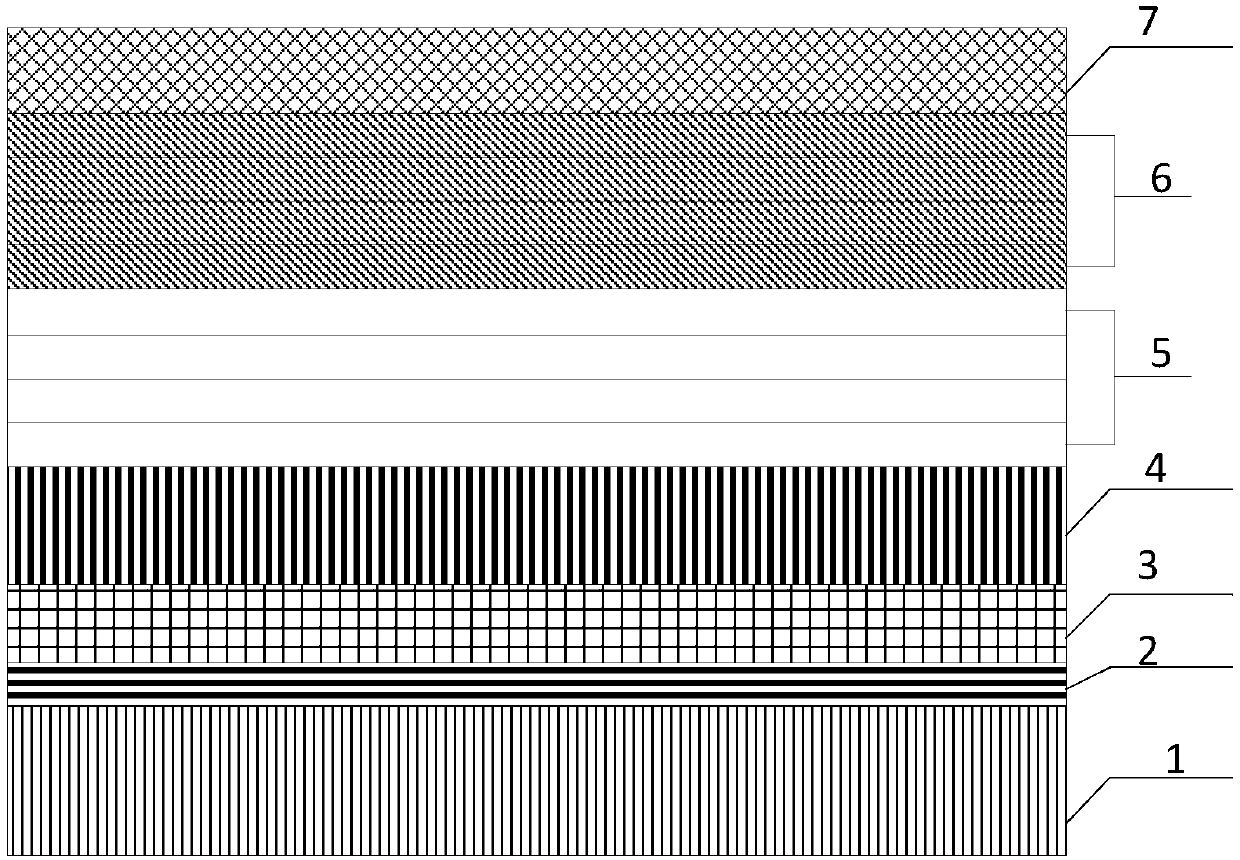
InactiveCN110518099ARaise the barrier heightIncrease concentrationSemiconductor devicesUltraviolet lightsIonization
The invention discloses a high-efficiency light-emitting diode structure and a manufacturing method thereof, and mainly solves the problems of low ionization rate and hole mobility of Mg in a p-type region and poor carrier confinement in a quantum well in the prior art. The high-efficiency light-emitting diode structure comprises from bottom to top: a substrate (1), a high-temperature AlN nucleating layer (2) and an n-type Ga2O3 layer (3), wherein an electrode (6) and a working region layer (4) are arranged on the n-type Ga2O3 layer, the working region layer comprises multiple quantum well barrier layers with six periods, each period comprises an AlxGa1-xN quantum well layer and a quantum barrier layer, and a p-type layer (5) and an electrode (6) are arranged on the working region layer. The quantum barrier layer and the p-type layer are prepared from a BN material, so that the quantum confinement stark effect between multiple quantum well barrier layers is eliminated, the ionization rate and the hole mobility of Mg in the p-type layer are improved, the confinement of holes and electrons in quantum wells is enhanced, and the high-efficiency light-emitting diode structure can be used for manufacturing high-efficiency ultraviolet and deep ultraviolet light-emitting equipment.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Ultraviolet LED epitaxial structure and growth method thereof
InactiveCN109585622AReduce tunnelingSuppressing the Quantum Confinement Stark EffectSemiconductor devicesQuantum efficiencyUltraviolet
The present application discloses an ultraviolet LED epitaxial structure. The structure comprises a substrate; a buffer layer on a first side of the substrate; an undoped GaN layer on a side, far awayfrom the substrate, of the buffer layer; an N-type GaN layer at one side, far away from the buffer layer, of the undoped GaN layer; a multi-quantum well structure layer at one side, far away from theundoped GaN layer, of the N-type GaN layer; an electron blocking layer with a changed Al composition located at one side, far away from the N-type GaN layer, of the multi-quantum well structure layer; and a P-type GaN layer located at one side, far away from the multi-quantum well structure layer, of the electron blocking layer with the changed Al composition. The barrier layer is the electron blocking layer with the changed Al composition to inhibit the quantum confinement Stark effect caused by the polarization electric field and reduce the electrons tunneling from the multiple quantum wellstructure layer to the P-type GaN layer so as to improve the internal quantum efficiency. The present invention further provides a growth method of an ultraviolet LED epitaxial structure having the advantages mentioned above.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Multi-band multiwavelength quantum dot mode-locked lasers
ActiveUS7991023B2Large wavelength separationOutput spectrum broadensNanoopticsSemiconductor lasersMulti bandChemical beam epitaxy
A multi-band (multi-color) multiwavelength mode locked laser diode is provided by dynamic phase compensation of a quantum dot active medium. The laser diode is provided with a PIN diode structure where the active medium consists of a plurality of layers of quantum dots such as those produced by self-assembly from known chemical beam epitaxy methods. The multiplicity of bands may be produced by AC Stark splitting, frequency selective attenuation, or by the inclusion of multiple different layers having different, respective, peak ASE emissions. Dispersion compensation within laser facets, waveguides, and the optically active media permit the selection of a fixed dispersion within the cavity. A dynamic group phase change induced by the AC Stark effect permits compensation of the fixed dispersion sufficiently to produce an intraband mode-locked laser. Even interband mode locking was observed.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
High-precision magnetic field inclination angle measuring system applied to magnetic confinement fusion device
InactiveCN105277906AImprove reliabilityHigh measurement accuracyLight polarisation measurementMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsGratingData acquisition
The invention belongs to a magnetic confinement plasma diagnostic device, and particularly relates to a high-precision magnetic field inclination angle measuring system applied to a magnetic confinement fusion device. The high-precision magnetic field inclination angle measuring system comprises a neutral beam injection system which is installed in a fusion plasma. The external part of the fusion plasma is provided with a front-end optical lens which is connected with an optical modulation system. The optical modulation system is connected with gratings via optical fibers. The gratings are opposite to optical fiber arrays and a photoelectric conversion system. The optical fiber arrays and the photoelectric conversion system are connected with a phase-locked amplifier. Meanwhile, the optical modulation system is connected with the phase-locked amplifier so as to provide reference signals to the phase-locked amplifier. The phase-locked amplifier is connected with a data acquisition and control computer. The advantages of the high-precision magnetic field inclination angle measuring system are that reliability is great and measuring precision is quite high so that the high-precision magnetic field inclination angle measuring system can be applied to measurement of a plasma magnetic field deflection angle under the weak stark effect and can also be applied to high-precision and high-speed measurement of other linearly polarized light polarization direction.
Owner:SOUTHWESTERN INST OF PHYSICS
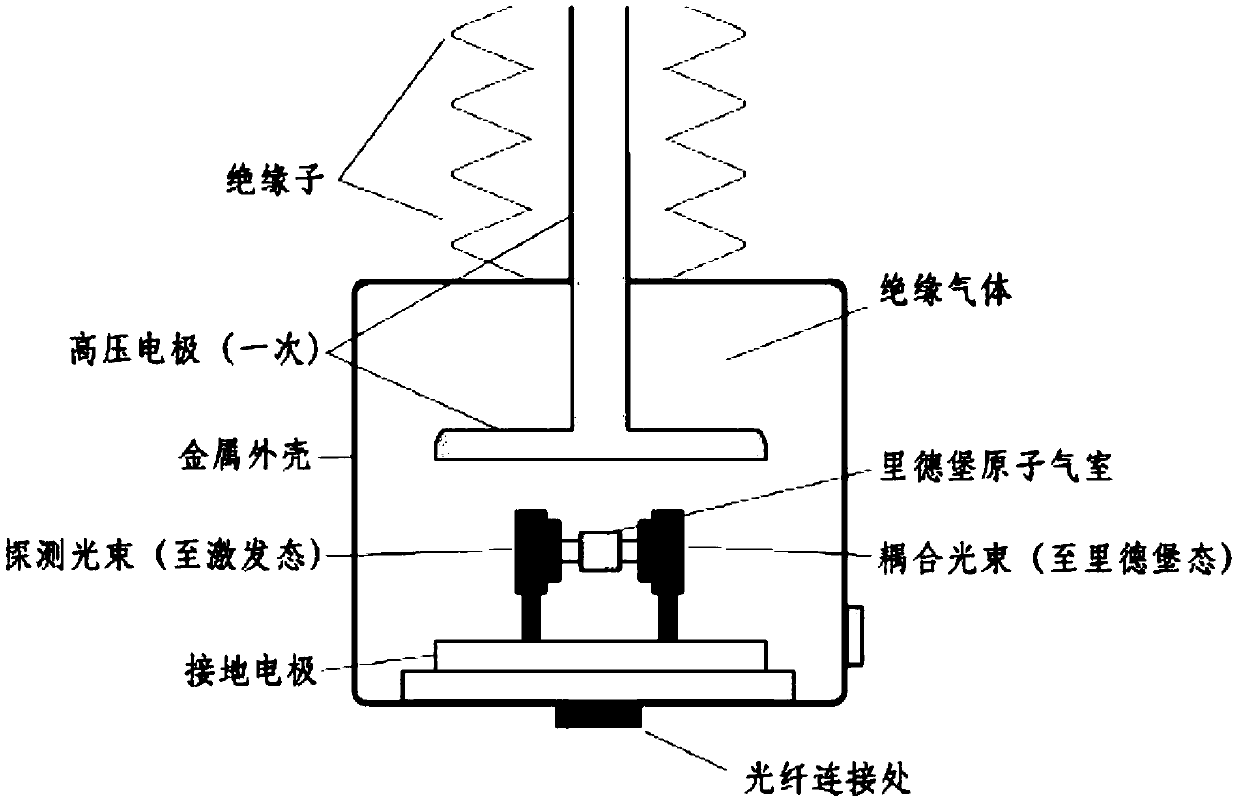
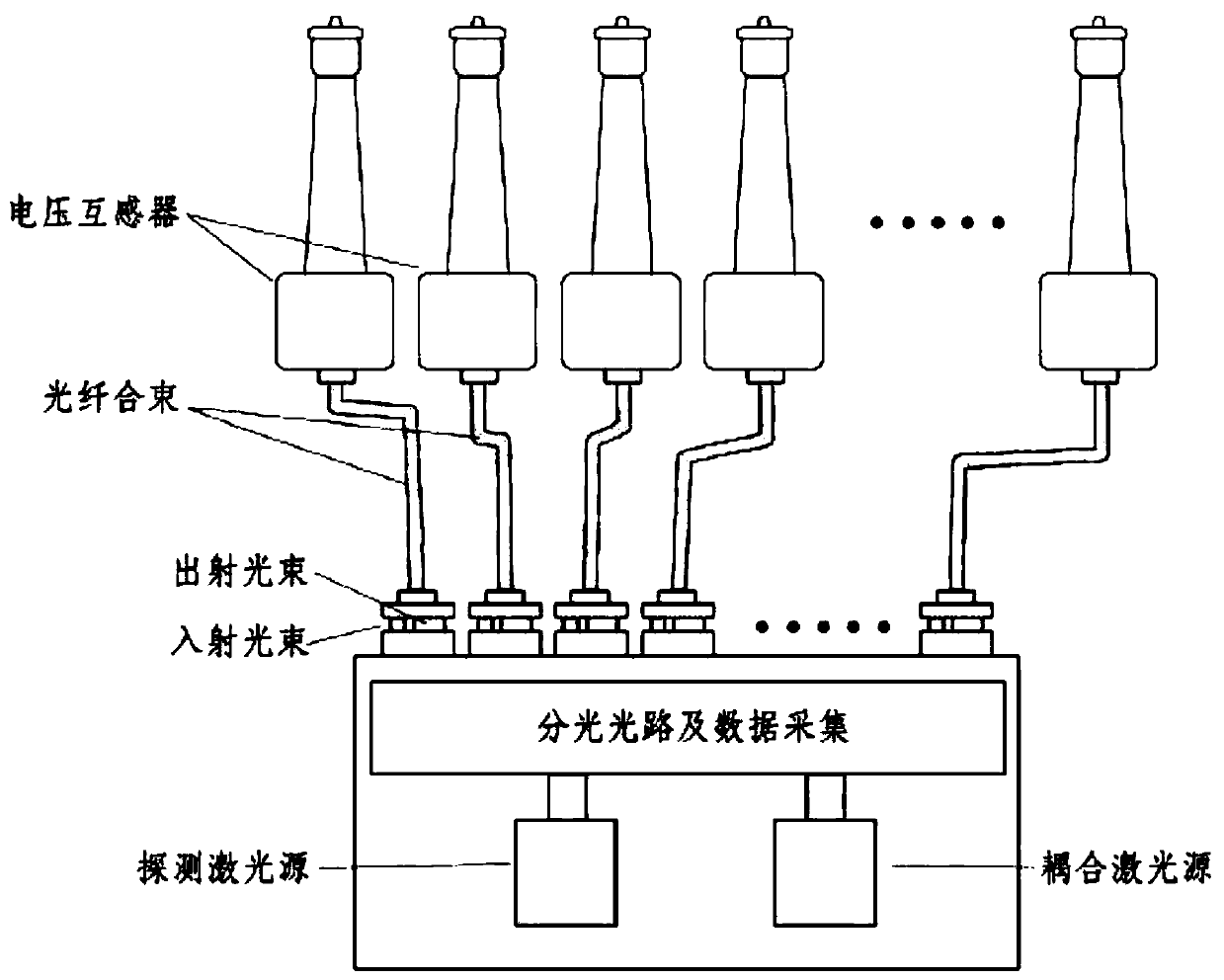
High-voltage power frequency voltage measurement method and device based on Stark effect
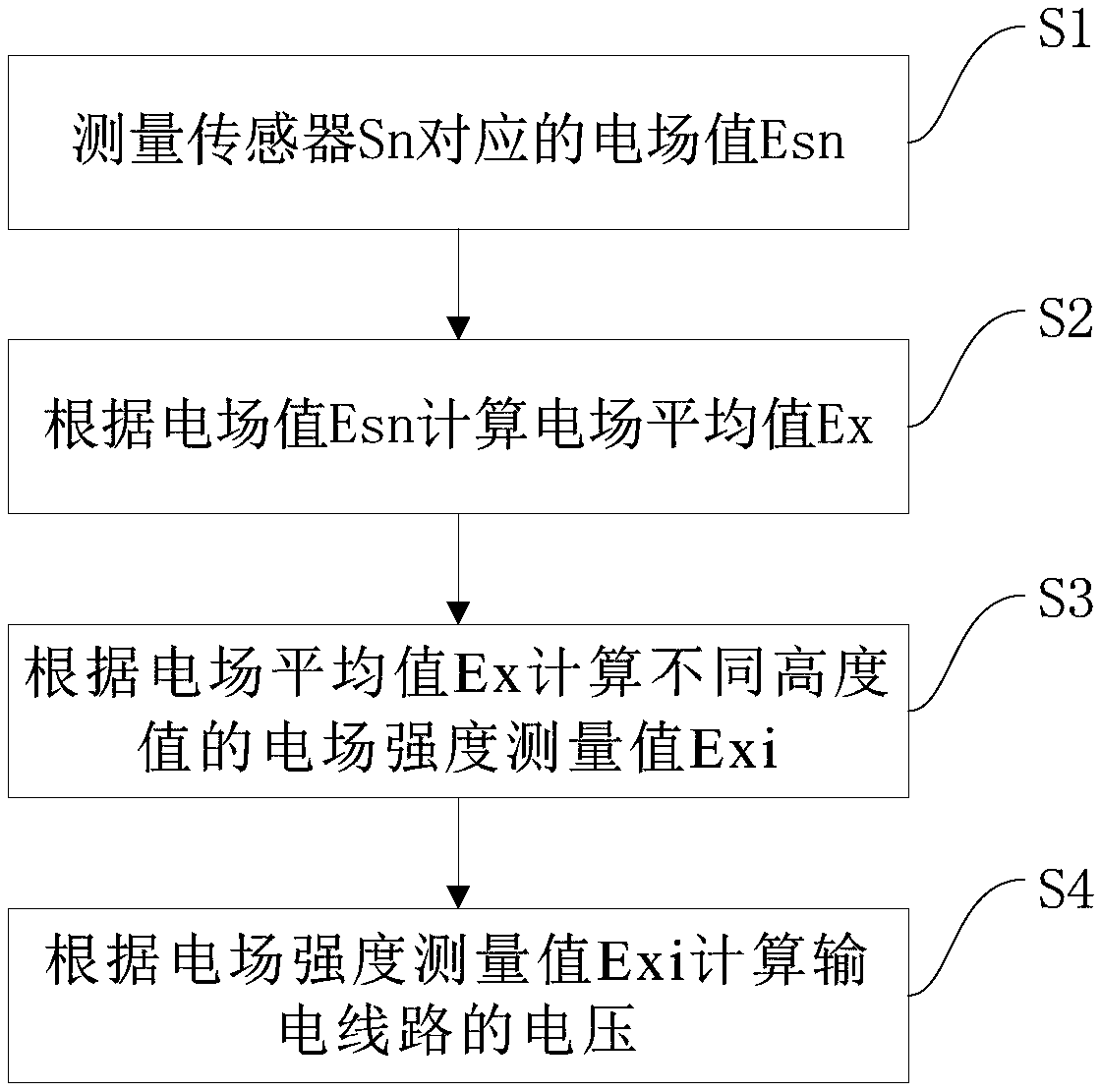
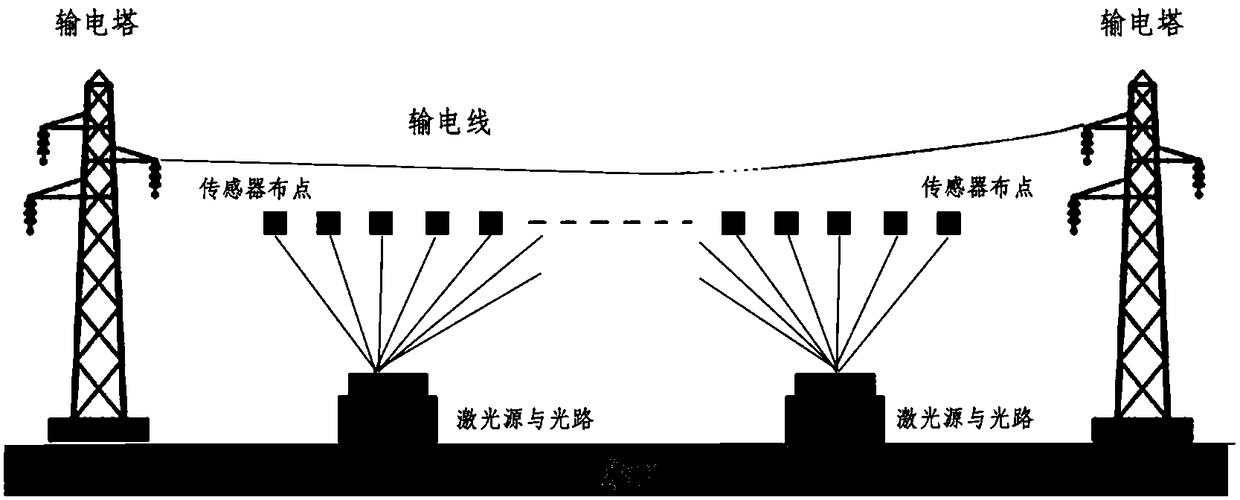
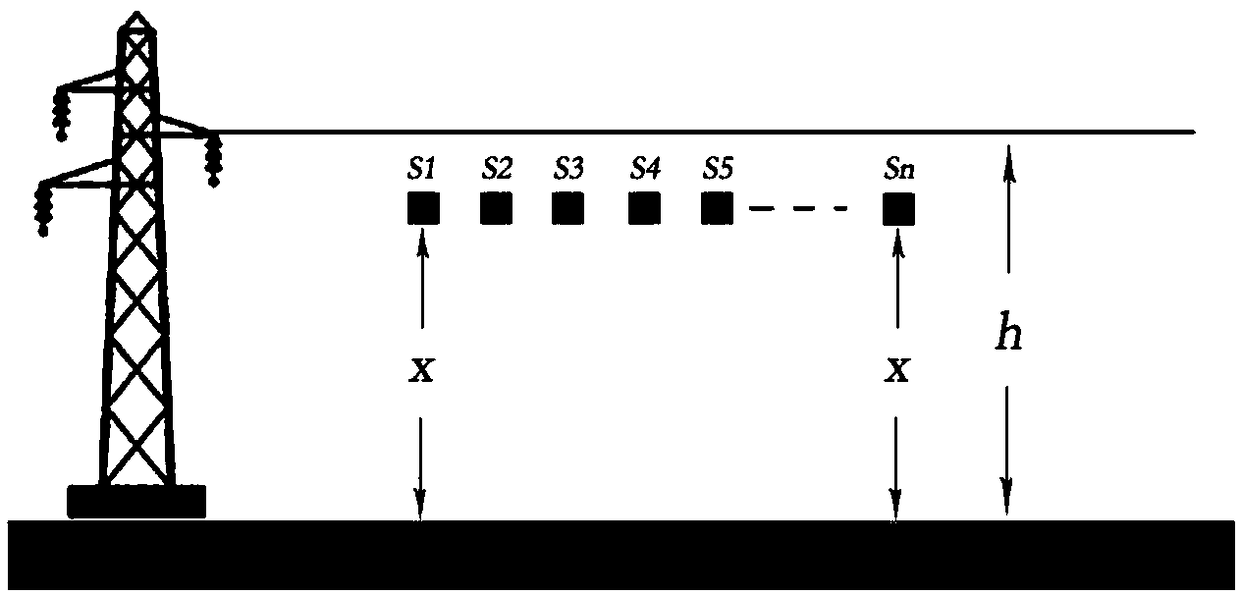
InactiveCN109342838AFibre light guidesVoltage/current isolationElectrical field strengthRydberg atom
The invention discloses a high-voltage power frequency voltage measurement method and device based on the Stark effect. The method includes the following steps: S1, setting m sensors for measuring theelectric field intensity of corresponding height according to the Stark effect in a line space with a height of x from the ground, and measuring the electric field values Esn corresponding to the sensors Sn; S2, calculating the average electric field value Ex according to the electric field values Esn; S3, selecting a number of height values Xi in the vertical direction of a transmission line, and calculating the measured electric field intensity values Exi corresponding to different height values according to the average electric field value Ex; and S4, calculating the voltage of the transmission line according to the measured electric field intensity values Exi. According to the invention, the spatial electric field intensity is measured by using cesium atoms excited to a high Rydberg state and utilizing the Stark effect of Rydberg atoms producing energy level splitting under the action of an external electric field according to the relationship between the degree of atomic energy level splitting and the intensity of the external electric field. High-voltage power frequency measurement of a transmission line and substation environment is realized. Non-contact voltage measurementis realized based on the method.
Owner:STATE GRID CHONGQING ELECTRIC POWER CO ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
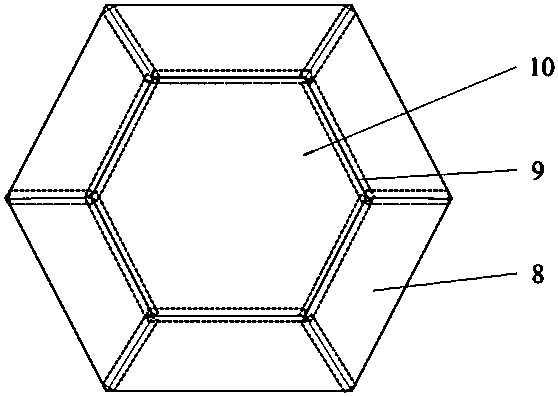
Full-color emitting LED epitaxial structure based on GaN hexagonal prism array and preparation method of epitaxial structure
InactiveCN110212068ALarge luminous areaReduce reflection lossNanotechnologySemiconductor devicesStructure basedCrystal
The invention relates to a full-color emitting LED epitaxial structure based on a GaN hexagonal prism array and a preparation method of the epitaxial structure, belongs to the technical field of semiconductors, and can solve the problem that in the prior art, the fluorescent powder conversion efficiency is low, and it is difficult to accurately control an in-situ deposition mask and the GaN micron / nano array dimension and distribution; the epitaxial structure comprises a sapphire substrate, a nucleation layer, a non-doped GaN layer, an n-type GaN layer, a patterned SiO2 mask layer, an n-type GaN hexagonal prism array at the gap of the patterned SiO2 mask layer, quantum dots located at the top surface of the hexagonal prism, quantum wires on the edges, and a multi-quantum-well layer on a top surface (0001) crystal surface and six half-polarity (10-11) crystal surfaces, and a final p type GaN layer. By virtue of the structure, the GaN micron / nano array dimension and distribution can be accurately controlled, the problems that a stark effect is limited by the quantum well, the efficiency is lowered suddenly, the light-emitting wavelength is single and the like in the two-dimensional GaN-based thin film LED can be solved, and full-color emission is realized.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Novel voltage transformer based on Rydberg atom Stark effect
ActiveCN109686552AHigh measurement accuracyReduce measurement errorTransformersTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsElectrical field strengthRydberg atom
The invention discloses a novel voltage transformer based on a Rydberg atom Stark effect. The novel voltage transformer comprises a primary wiring terminal and a sensing probe; the sensing probe comprises a primary high-voltage electrode plate, a ground electrode plate and a Rydberg atom air chamber; the primary wiring terminal and the primary high-voltage electrode plate are connected to introduce the high-voltage line voltage; and through the introduced high-voltage line voltage, the electric field intensity between the primary high-voltage electrode plate and the ground electrode plate is measured in the Rydberg atom air chamber based on the Stark effect, and the voltage value is measured. A voltage measuring method based on the principle of the Rydberg atom Stark effect can be traced back to fundamental physical quantities such as atomic energy level, the measuring precision of the novel voltage transformer is improved greatly, and the measuring error is obviously lowered comparedwith that of a traditional transformer; and compared with the traditional electromagnetic voltage transformer, an iron core and a secondary winding are not included, the characteristics of small sizeand low weight are achieved, miniaturization is easy, and meanwhile limitation of magnetic saturation is also avoided.
Owner:STATE GRID CHONGQING ELECTRIC POWER CO ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
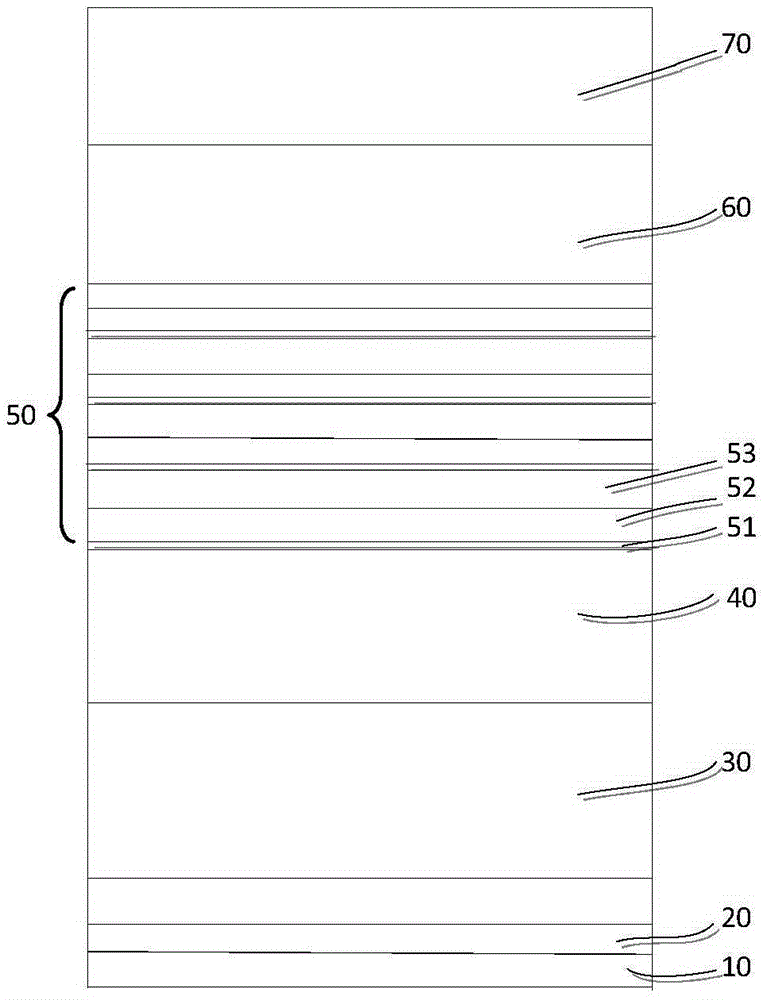
Nitride light emitting diode structure
PendingCN108336199ALight in massImprove internal quantum efficiencySemiconductor devicesQuantum efficiencyElectron blocking layer
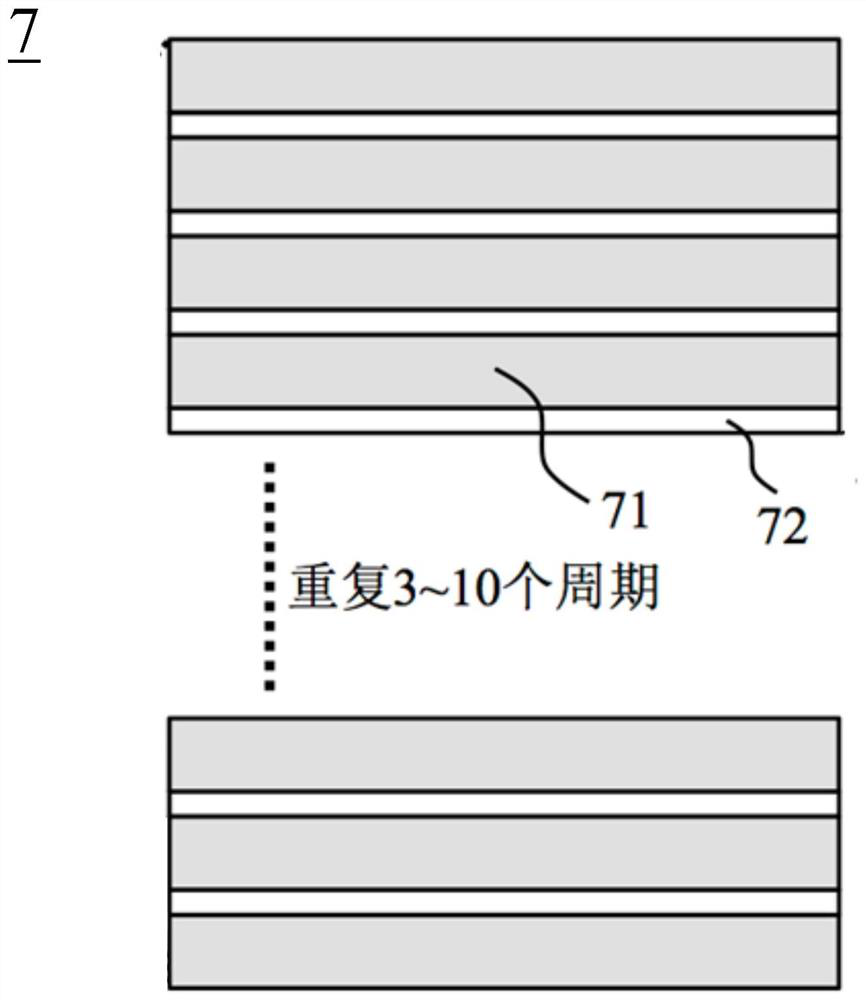
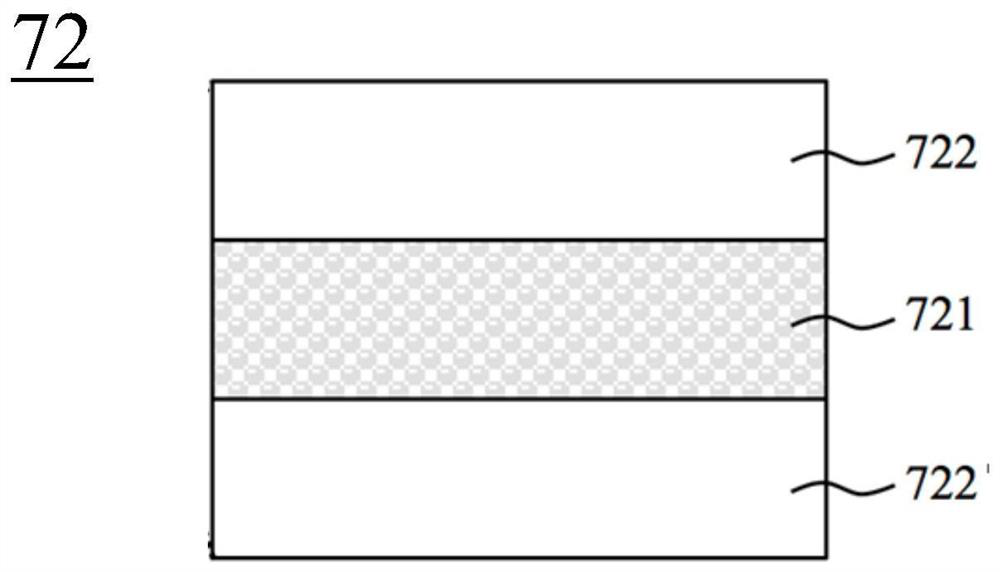
The invention provides a nitride light emitting diode structure. The structure comprises a substrate, the substrate is provided with a buffer layer, the buffer layer is provided with a N-type layer, apreparation layer, a first multiple quantum well layer, a second multiple quantum well layer, a P-type electron clocking layer and a P-type layer in sequence, and the first multiple quantum well layer comprises quantum wells of the first multiple quantum well layer and quantum barriers of the first multiple quantum well layer; the second multiple quantum well layer comprises quantum wells of thesecond multiple quantum well layer and quantum barriers of the second multiple quantum well layer; and the thickness of the quantum barriers of the first multiple quantum well layer is greater than that of the second multiple quantum well layer. According to the nitride light emitting diode structure, the thickness of the quantum barriers close to one side of the P-type layer is thinned, thereby effectively slowing down a 'quantum restriction stark effect' of light emitting wells close to one side of the P-type layer and improving the inner quantum efficiency of a light emitting diode.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV +1
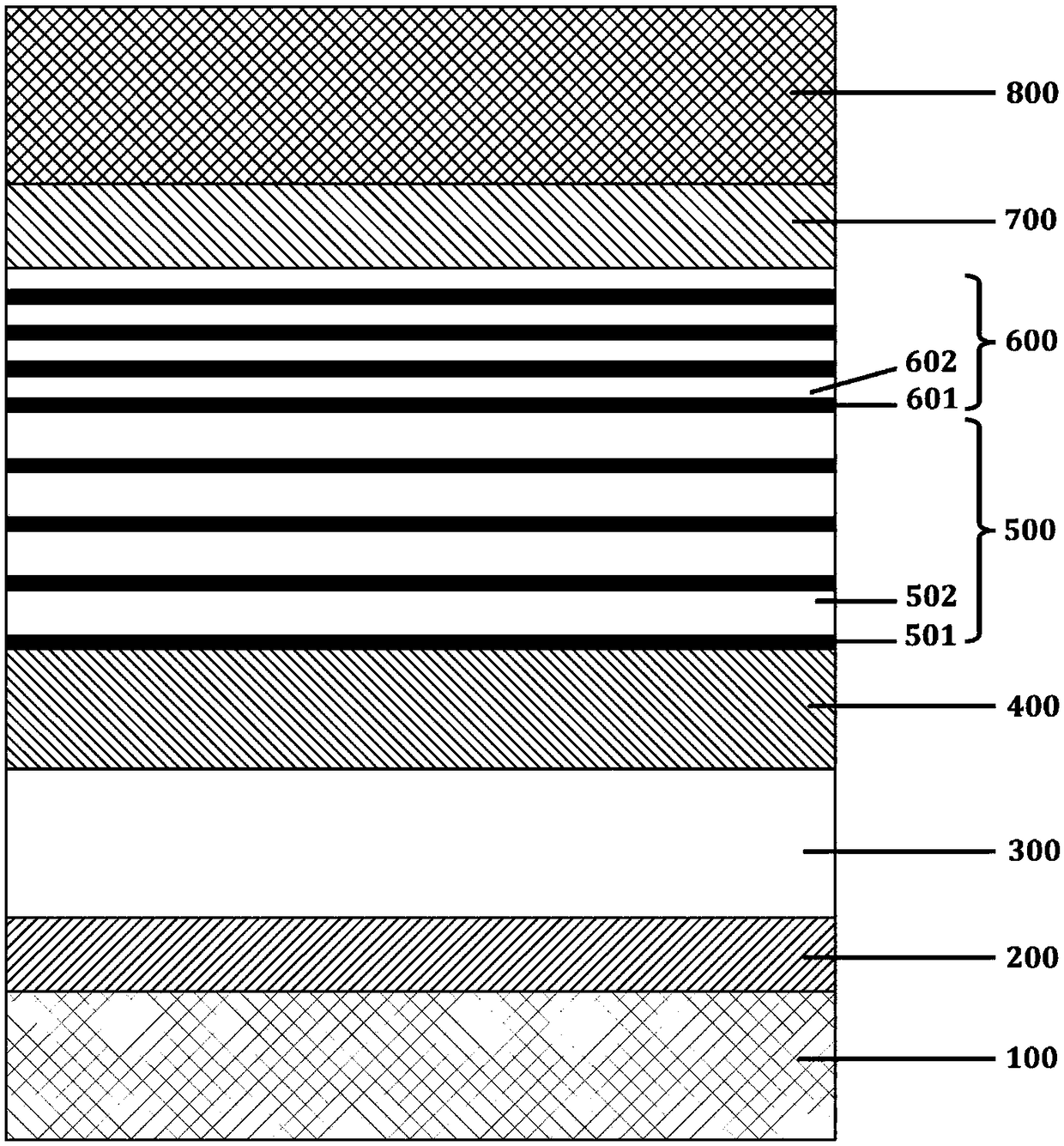
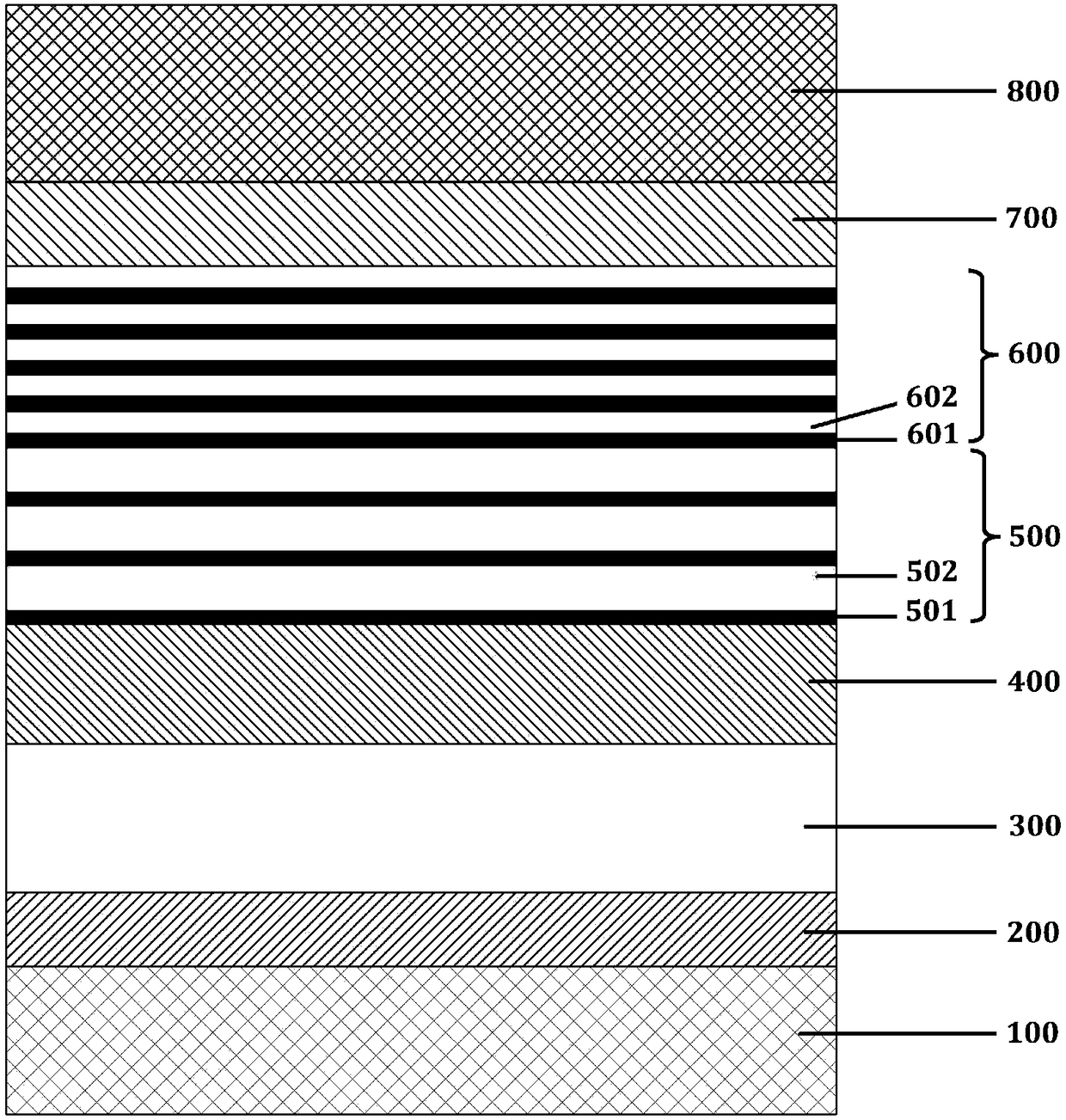
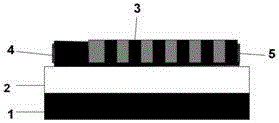
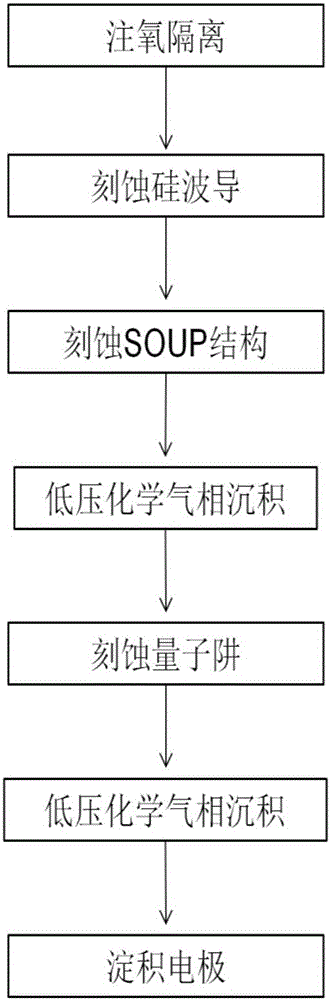
SOUP structured electrooptic modulator based on stark effect and manufacturing method
ActiveCN105759468AOvercomes the disadvantage of easy leakage into high refractive index silicon substratesReduce light lossMaterial nanotechnologyNon-linear opticsLattice mismatchGas phase
The invention discloses an SOUP structured electrooptic modulator based on a stark effect and a manufacturing method, and mainly aims to solve the problems that infrared light of a conventional electrooptic modulator is easy to leak, lattice mismatch exists and manufacturing methods are complex. The SOUP structured electrooptic modulator comprises a substrate (1), a silicon SOUP structure waveguide (2) on an oxidized lower envelope base, an absorbing area (3), a left electrode (4) and a right electrode (5). The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: performing implanted oxygen separation, performing etching silicon waveguide, etching an SOUP structure, etching a quantum well, performing low-pressure chemical vapor deposition and depositing electrodes. Due to the silicon SOUP structure on the oxidized lower envelope base and the quantum well and a barrier layer adaptive to lattices, light loss can be reduced, and the wavelength range of an absorption spectrum is widened; meanwhile, a film can be deposited by using a low-pressure chemical vapor deposition method, so that a manufacture process is simple, and the mid-infrared electrooptic modulator can be manufactured.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
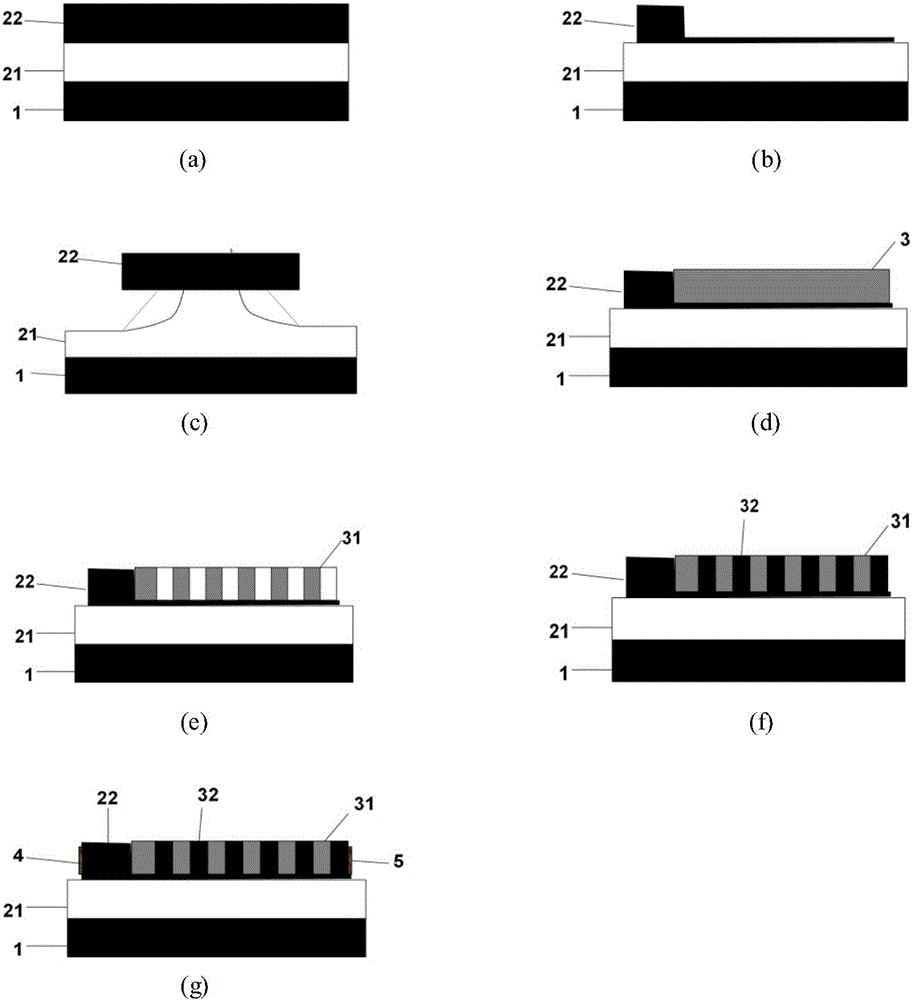
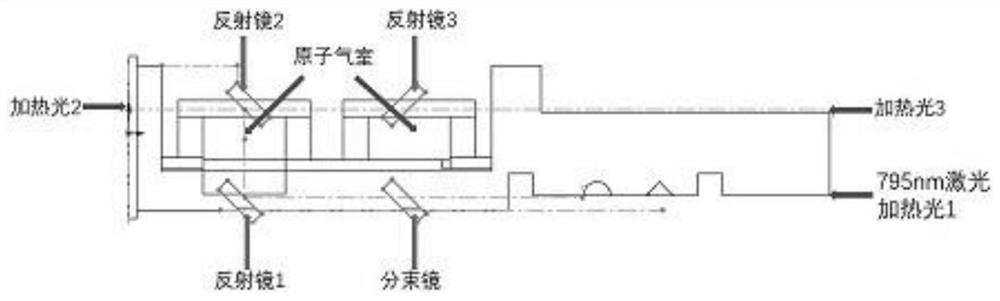
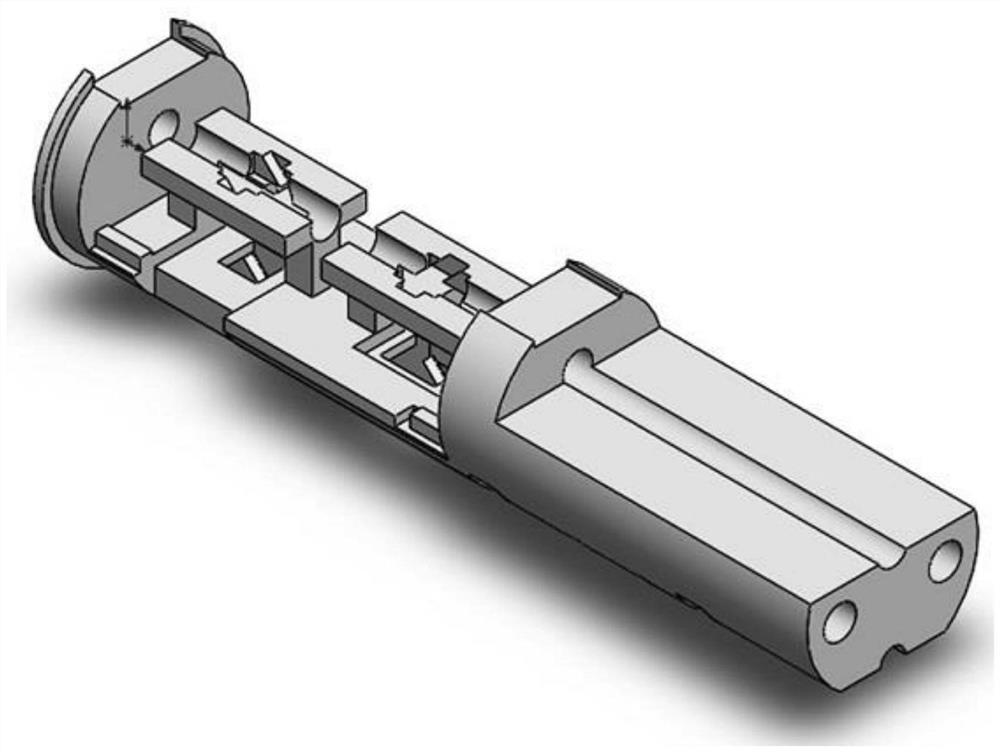
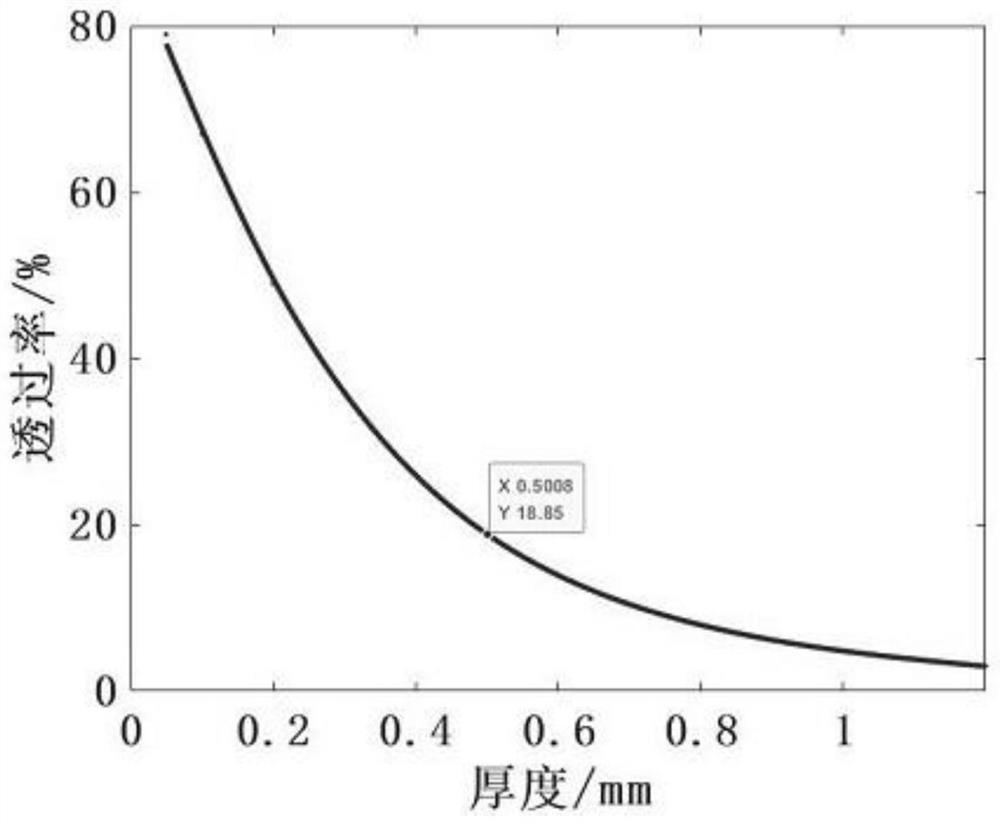
Heating structure and method for eliminating alternating current stark effect in atomic magnetometer
InactiveCN113126006APrecise control of remanence levelsHigh sensitivityMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesOhmic-resistance heating devicesLight spotParticle physics
The invention relates to the technical field of weak magnetic detection, and discloses a method for eliminating an alternating current stark effect in an atomic magnetometer. Two beams of 1550 nm laser with the same power, polarization state and light spot size are adopted as a heating light source of a rubidium atom gas chamber in a magnetometer. The two beams of heating light are emitted into an atomic gas chamber from opposite directions, and light paths in the rubidium atomic gas chamber are overlapped. The structure of the two beams of heating light described by the invention can effectively reduce the alternating-current stark effect generated by the heating light on the atomic gas chamber, and the alternating-current stark effect can be equivalent to a virtual magnetic field to influence the performance of the magnetometer. The two beams of light generate same and reverse virtual magnetic fields respectively, and the virtual magnetic fields are offset according to the magnetic field superposition principle. The method is suitable for a light heating type atom magnetometer system, a light heating type magnetometer is rapid in development and bright in foreground, and the touch magnetic sensitivity limit of the atom magnetometer is facilitated.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Algan-based deep ultraviolet LED epitaxial structure and preparation method of mg-doped quantum well
ActiveCN111063753BImprove internal quantum efficiencyImprove light extraction efficiencyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesImpurity dopingUltraviolet
The invention discloses an AlGaN-based deep-ultraviolet LED epitaxial structure and a preparation method thereof, which utilize Mg-doped quantum wells to enhance luminous efficiency. The deep ultraviolet LED structure includes a substrate, a buffer layer, an AlN layer, a superlattice stress regulation / dislocation filter layer, a non-doped AlGaN layer, an n-type AlGaN layer, a Mg-doped active light-emitting region multi-quantum well layer, A p-type AlGaN layer and a p-type GaN contact layer. In the invention, Mg impurity is doped in the middle third of the well layer of the multi-quantum well active luminescent layer of the LED, so as to improve the internal quantum efficiency and light extraction efficiency of the LED. Compared with the non-doped multiple quantum well structure, the Mg-doped multiple quantum well structure can suppress the quantum confinement Stark effect, improve the spatial overlap of electron and hole wave functions and radiative recombination efficiency, and provide more holes Participate in radiative recombination and improve internal quantum efficiency. Moreover, Mg doping can also introduce a local strain field, increase the compressive strain in the quantum well, increase the ratio of TE polarized light, and finally improve the light extraction efficiency of AlGaN-based deep ultraviolet LEDs.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Microwave Electric Field Intensity Meter and Its Measurement Method Based on Cold Rydberg Atom Interferometer
ActiveCN104880614BHigh measurement accuracyMake up for the defect that only point frequency measurement can be realizedElectrostatic field measurementsRydberg atomPhase difference
The invention discloses a microwave electric field strength meter based on a cold Rydberg atom interferometer and a measurement method thereof. The microwave electric field strength meter includes: a vacuum system for cooling trapped atoms to generate cold atomic groups, and the cold atomic groups are used for Preparation of Rydberg state and interference effect, so that coherent atomic state produces phase difference; laser, used to generate coupling light and detection light, to coherently excite cold atoms in the vacuum system from ground state to Rydberg state; photodetector, It is used to detect the interference fringes produced by the coherence of two beams of cold atomic groups; the microwave source is used to generate a microwave electric field. In the evolution process between coherent beam splitting and beam combining, the microwave electric field intensity meter of the present invention allows the atomic groups in the Rydberg state to interact with the microwave electric field to be measured to produce an AC Stark effect, and the microwave electric field strength to be measured Correlated with the phase generated by the AC Stark, the precise measurement of the microwave electric field is achieved.
Owner:清远市天之衡量子科技有限公司
Isotropic and all-optical scalar magnetometer for measuring an ambient magnetic field
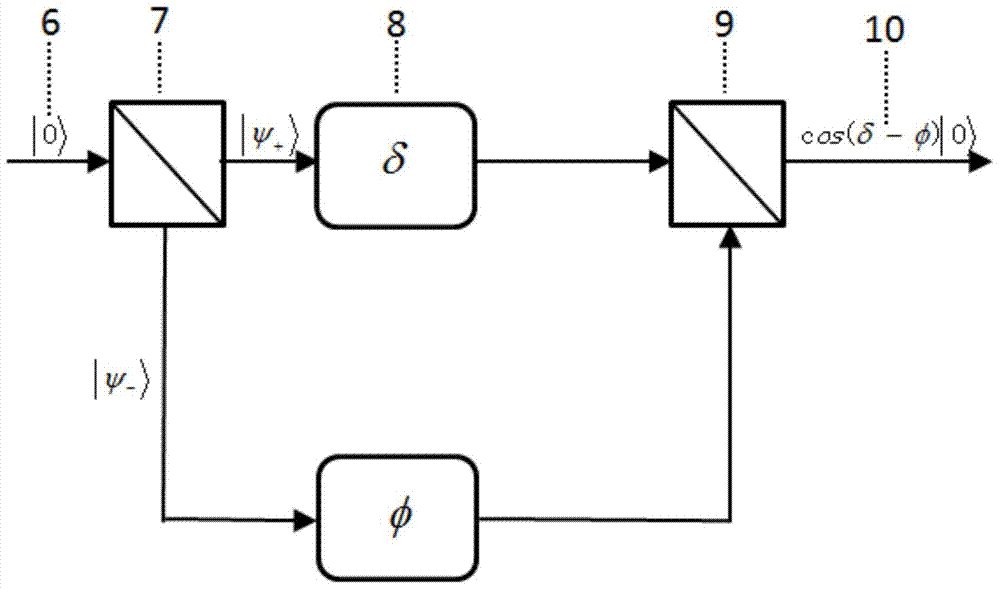
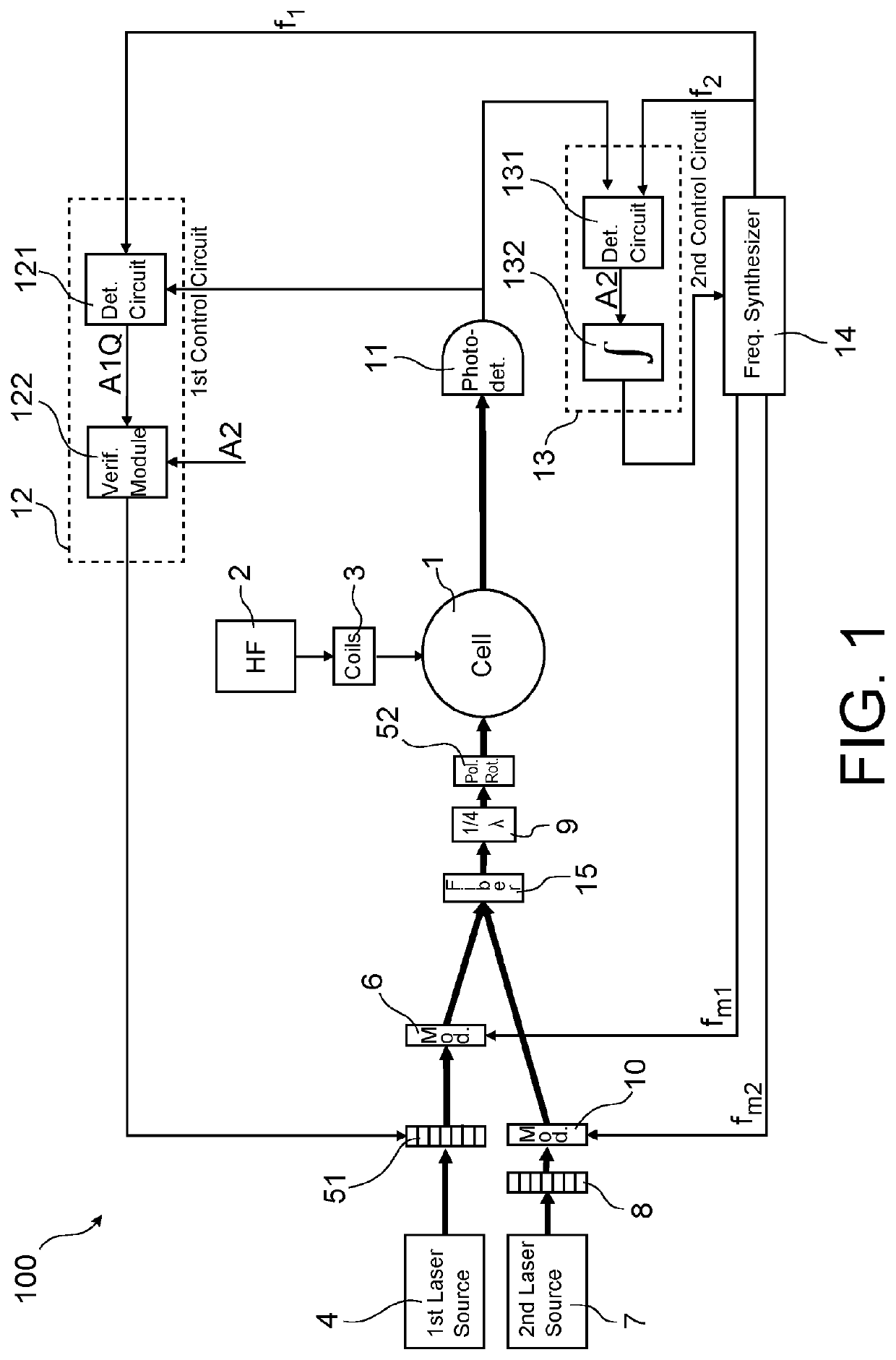
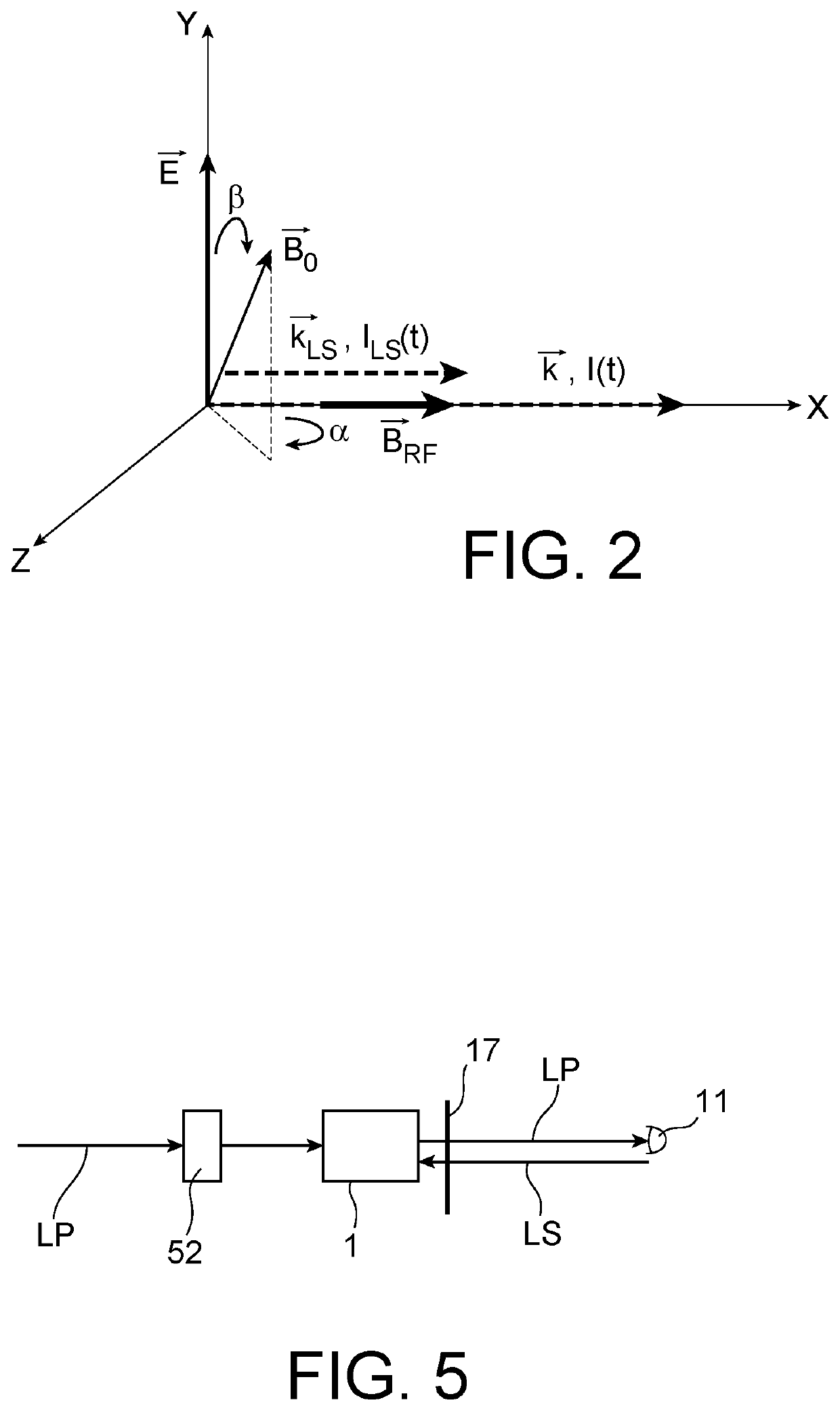
An optical-pumping magnetometer intended to measure an ambient magnetic field. It comprises: an arrangement for illuminating a cell filled with an atomic gas with a pump beam and an AC Stark effect beam propagating collinearly or almost collinearly in the cell, the pump beam being tuned to an atomic transition line, modulated by a first modulator by way of a first modulation frequency (fm1) and polarised linearly in a polarisation direction that can be turned by a polarisation rotator, the AC Stark effect beam being offset from the atomic transition line, modulated by a second modulator by way of a second modulation frequency (fm2) and polarised circularly, a first control circuit acting on the polarisation rotator in order to keep a constant angle (β) between the polarisation direction of the pump beam and the ambient magnetic field, a second control circuit acting on the first and second modulator in order to keep the first and second modulation frequency at the Larmor frequency of the atomic gas or at one of the harmonics thereof.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com