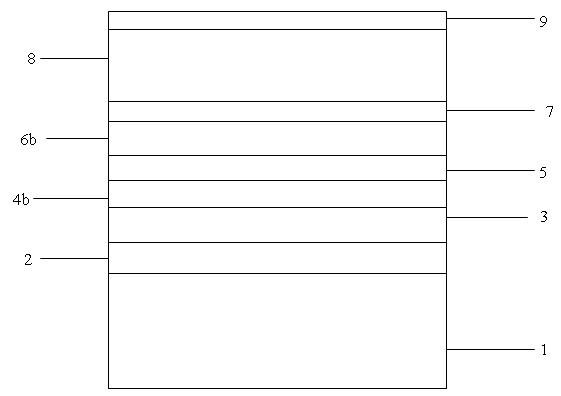
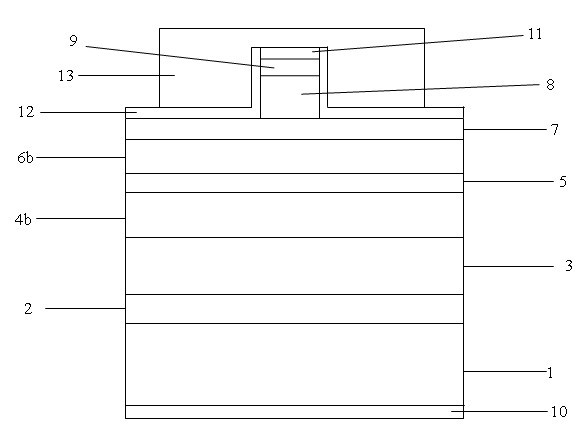
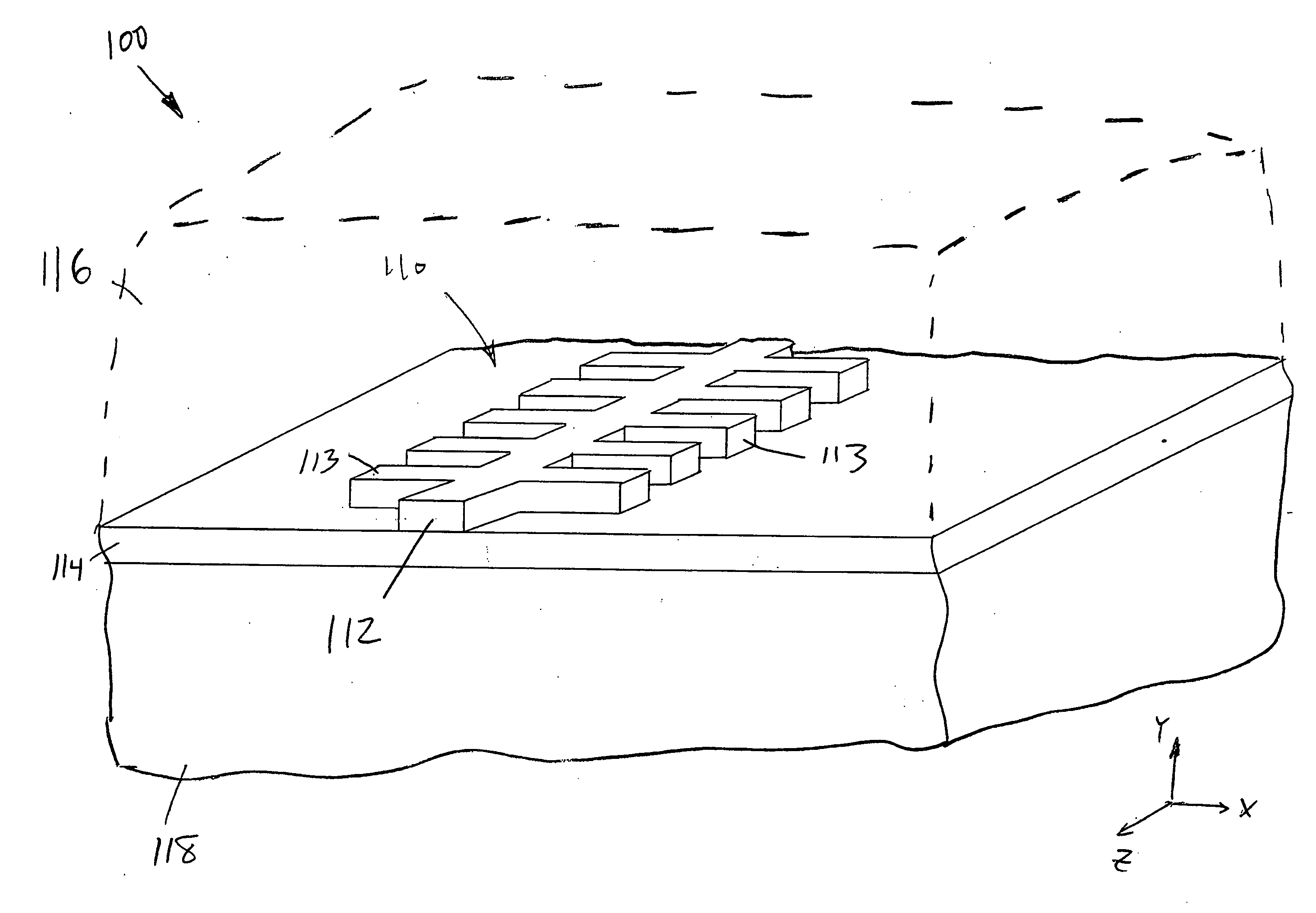
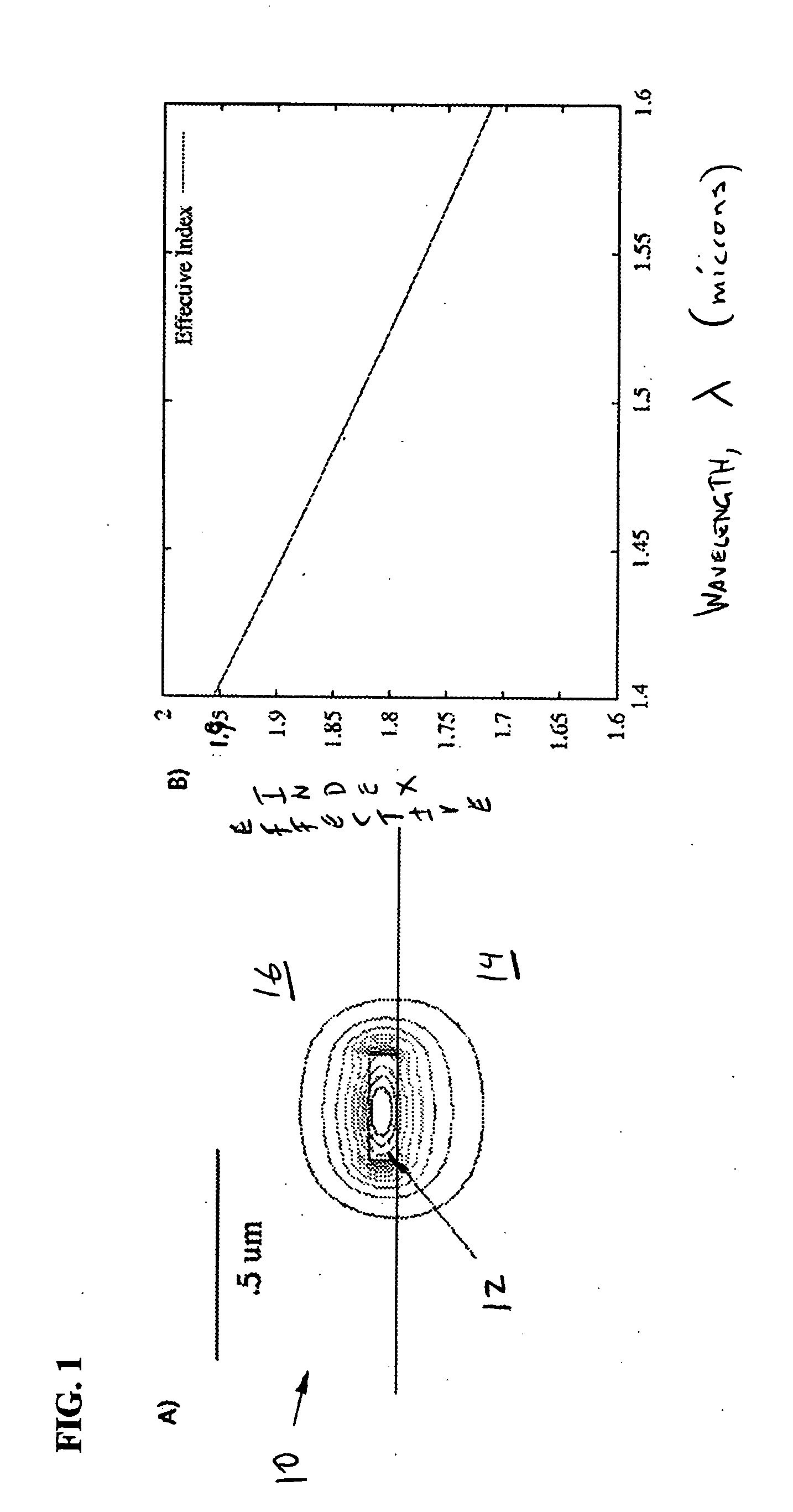
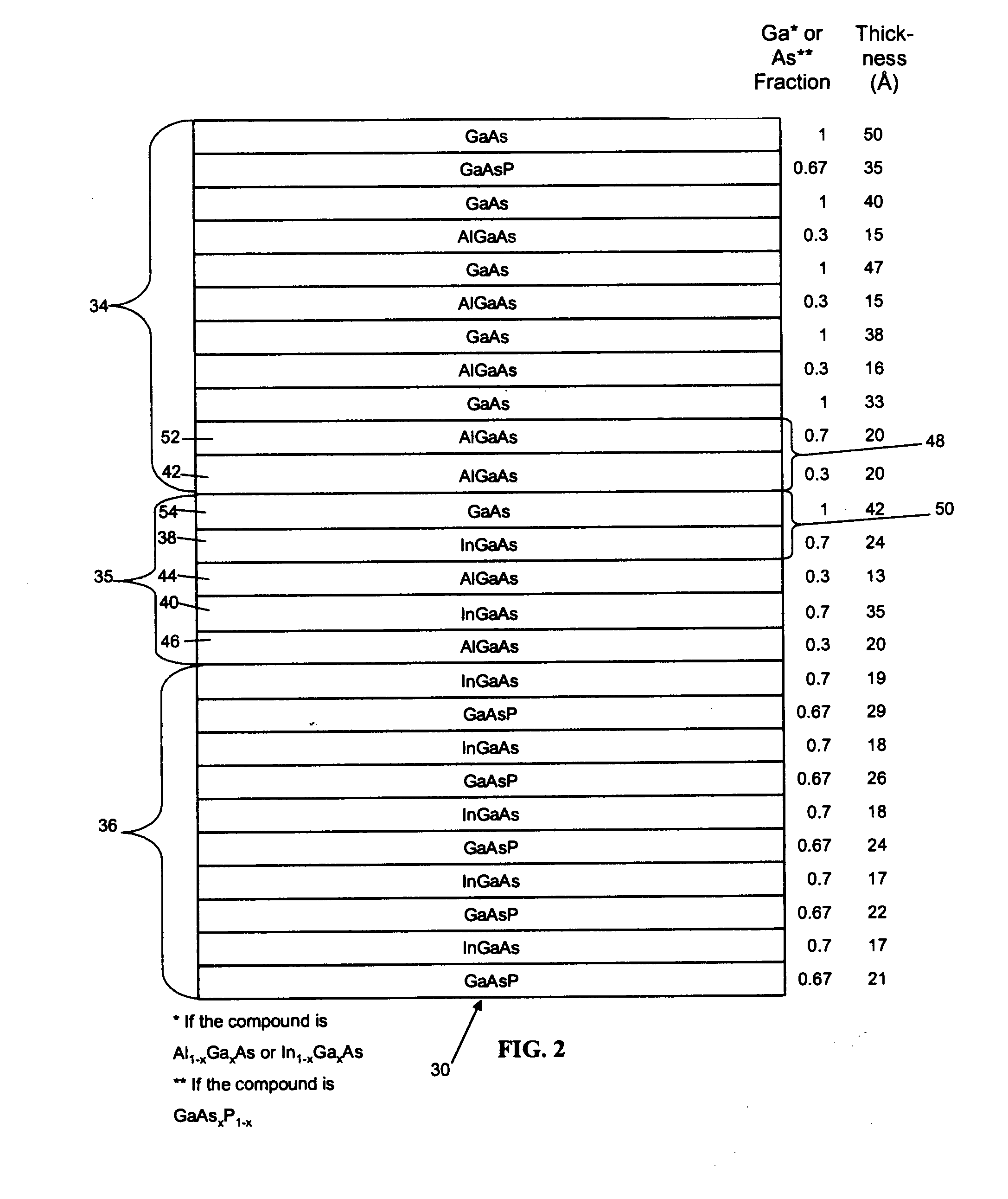
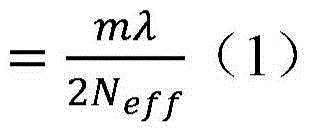Patents
Literature
220 results about "Optical limiting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
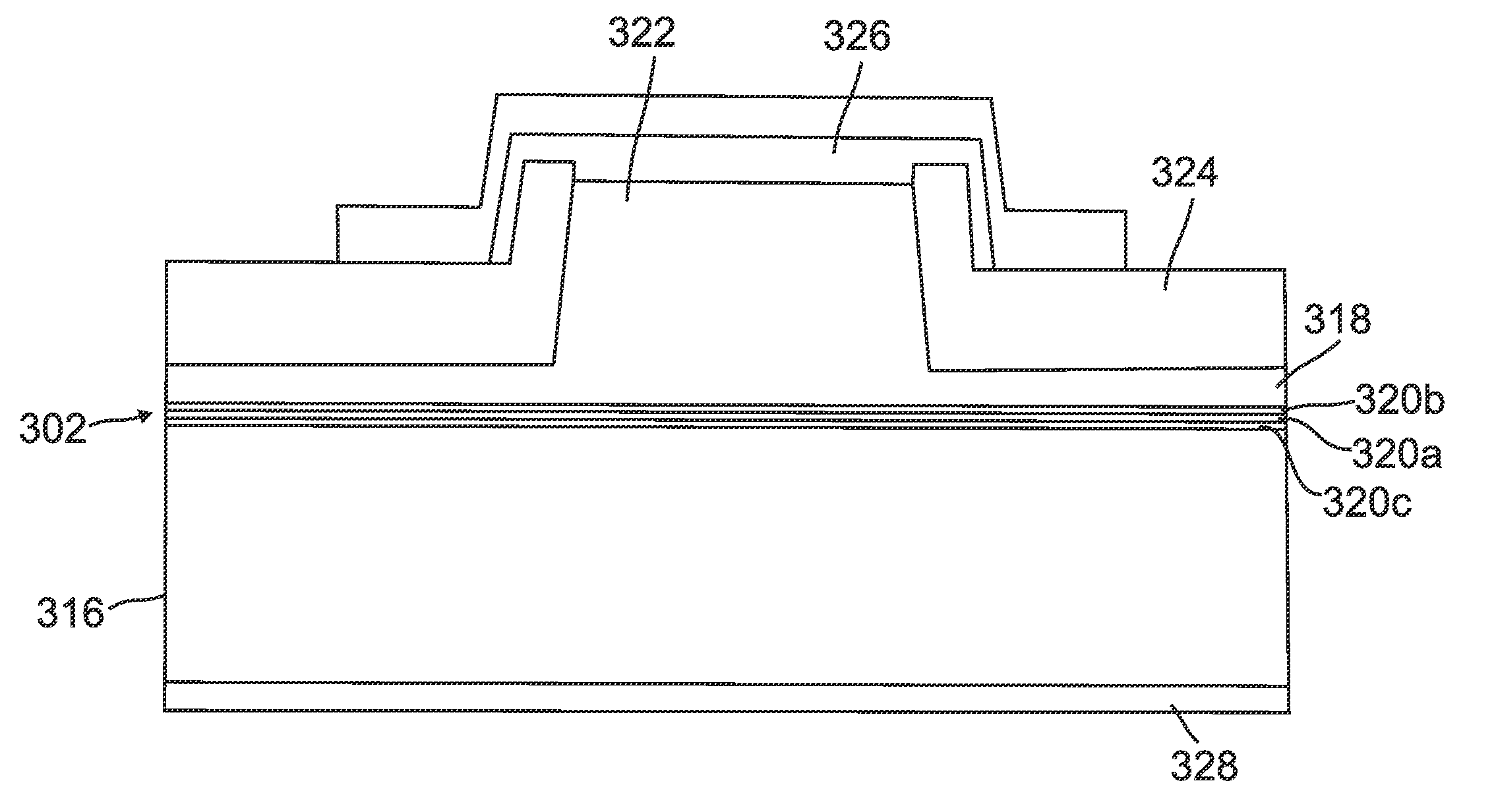
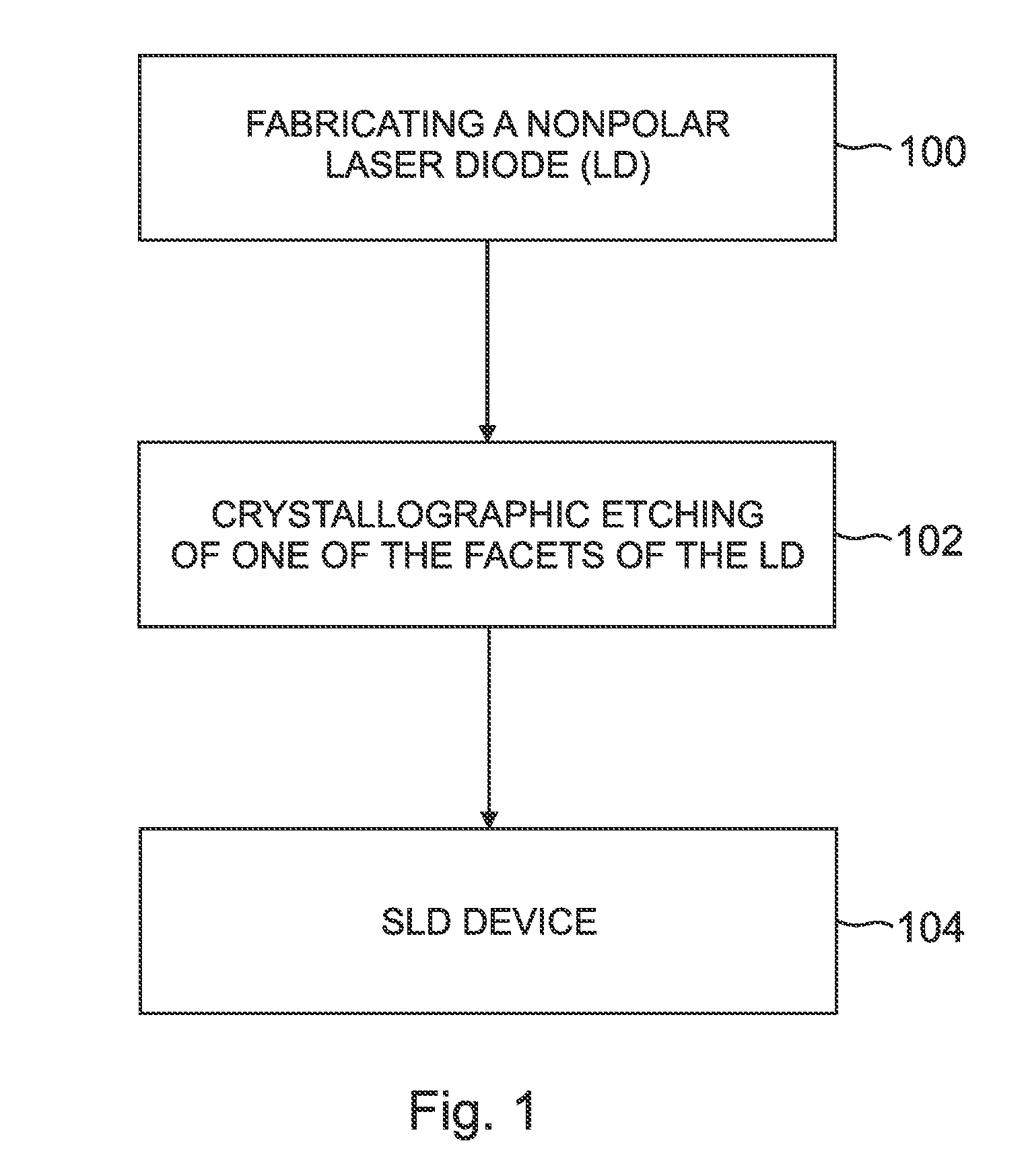
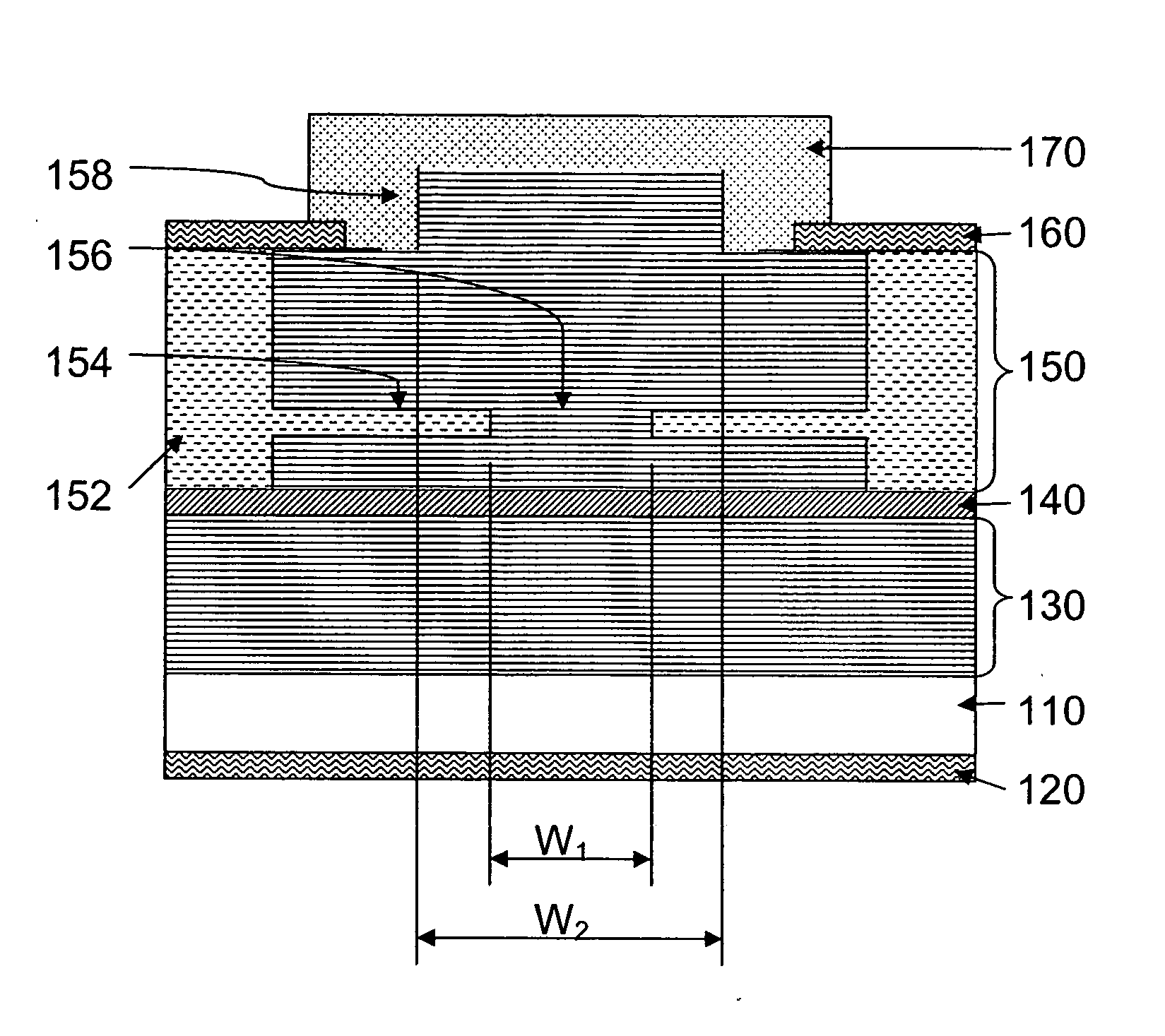
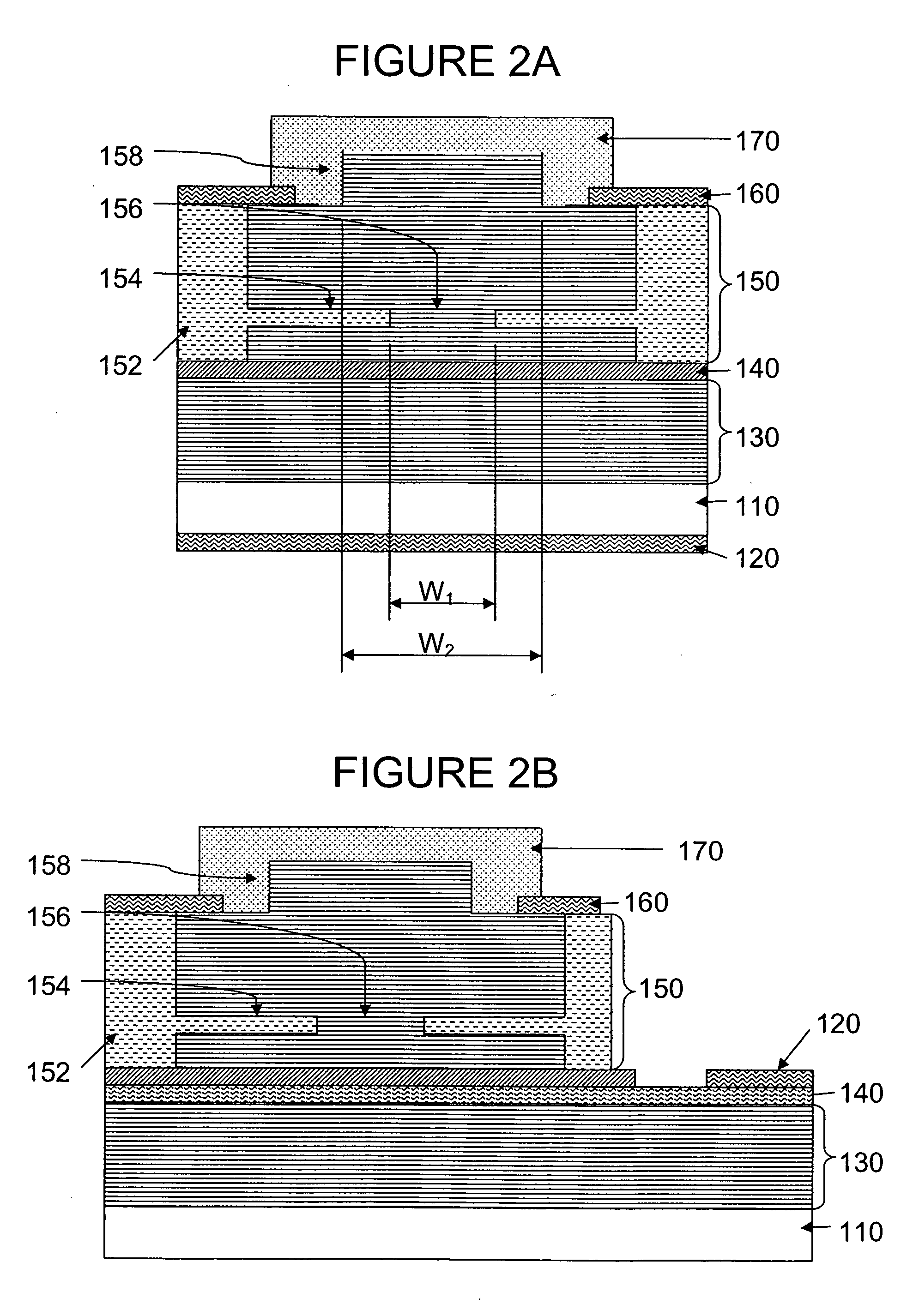
Superluminescent diodes by crystallographic etching
InactiveUS20110103418A1Reduce internal lossSignificant contributionOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsSuperluminescent diodeEtching
An optoelectronic device, comprising an active region and a waveguide structure to provide optical confinement of light emitted from the active region; a pair of facets on opposite ends of the device, having opposite surface polarity; and one of the facets which has been roughened by a crystallographic chemical etching process, wherein the device is a nonpolar or semipolar (Ga,In,Al,B)N based device.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
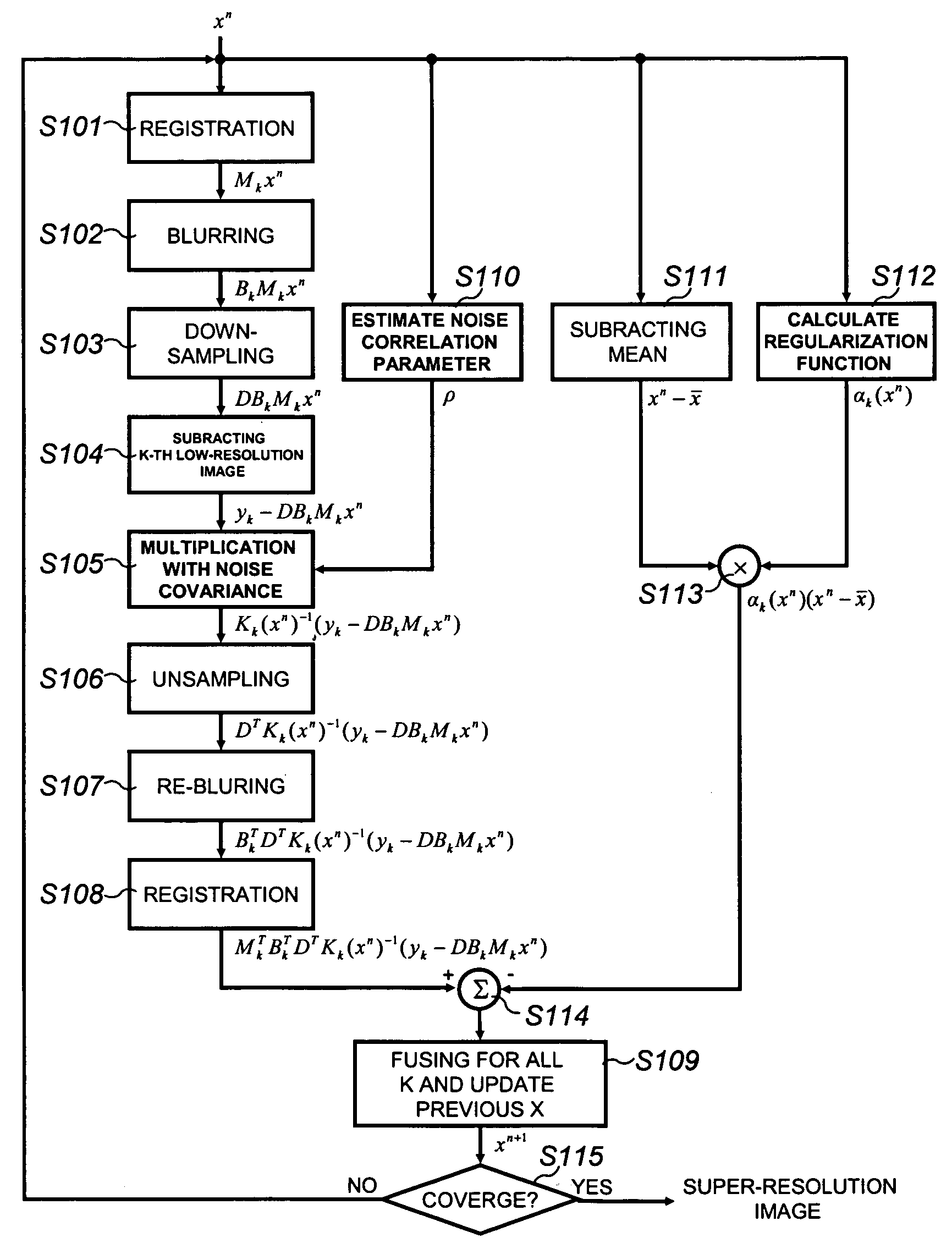
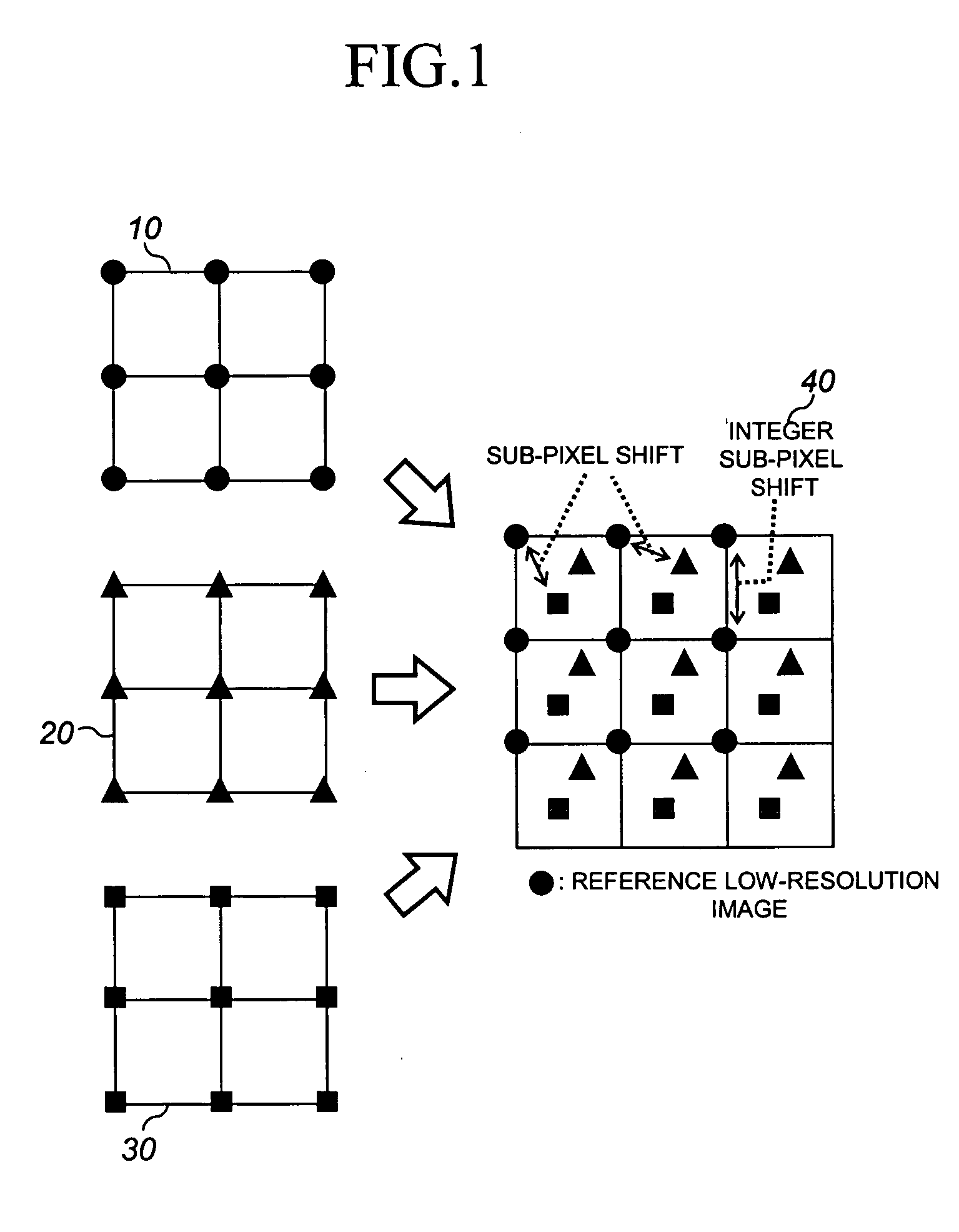
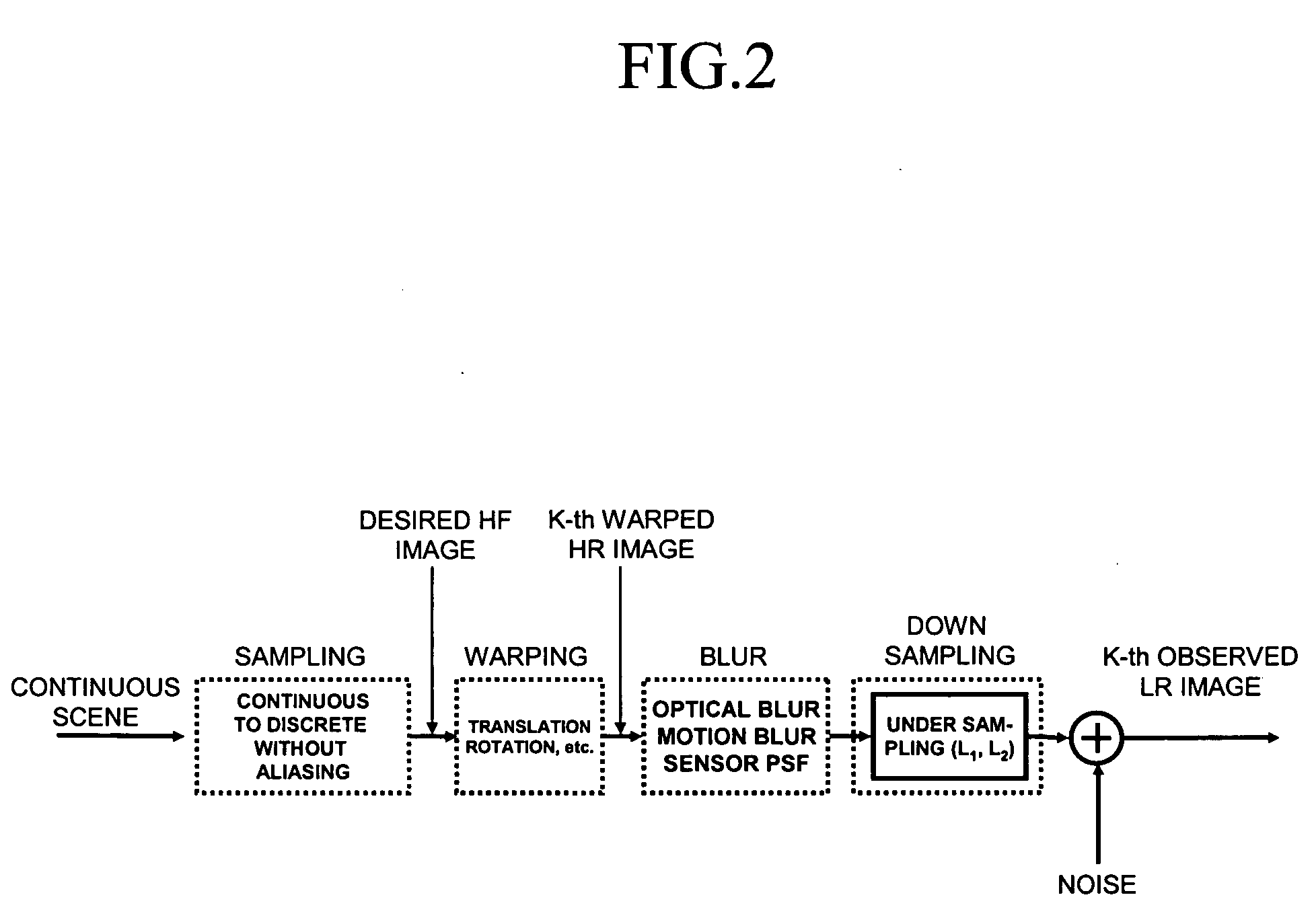
Method of restoring and reconstructing super-resolution image from low-resolution compressed image
InactiveUS20050019000A1Preserving contourRemove image blurImage enhancementTelevision system detailsDigital videoImage compression
Provided is a method of restoring and / or reconstructing a super-resolution image from low-resolution images compressed in a digital video recorder (DVR) environment. The present invention can remove a blur of a video sequence, caused by optical limitations due to a miniaturized camera of a digital video recorder monitoring system, a limitation of spatial resolution due to an insufficient number of pixels of a CCD / CMOS image sensor, and noises generated during image compression, transmission and storing processes, to restore high-frequency components of low-resolution images (for example, the face and appearance of a suspect or numbers of a number plate) to reconstruct a super-resolution image. Consequently, an interest part of a low-resolution image stored in the digital video recorder can be magnified to a high-resolution image later, and the effect of an expensive high-performance camera can be obtained from an inexpensive low-performance camera.
Owner:YONSEI UNIVERSITY +1
Single or multi-color high efficiency light emitting diode (LED) by growth over a patterned substrate
InactiveUS20060202226A1Improve extraction efficiencyEmission controlSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesMetallic materialsRefractive index
A single or multi-color light emitting diode (LED) with high extraction efficiency is comprised of a substrate, a buffer layer formed on the substrate, one or more patterned layers deposited on top of the buffer layer, and one or more active layers formed on or between the patterned layers, for example by Lateral Epitaxial Overgrowth (LEO), and including one or more light emitting species, such as quantum wells. The patterned layers include a patterned, perforated or pierced mask made of insulating, semiconducting or metallic material, and materials filling holes in the mask. The patterned layer acts as an optical confining layer due to a contrast of a refractive index with the active layer and / or as a buried diffraction grating due to variation of a refractive index between the mask and the material filling the holes in the mask.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
High efficiency light emitting diode (LED) with optimized photonic crystal extractor
InactiveUS20060192217A1Improve efficiencyGood orientationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesPhotonic crystalOptical limiting
A high efficiency, and possibly highly directional, light emitting diode (LED) with an optimized photonic crystal extractor. The LED is comprised of a substrate, a buffer layer grown on the substrate (if needed), an active layer including emitting species, one or more optical confinement layers that tailor the structure of the guided modes in the LED, and one or more diffraction gratings, wherein the diffraction gratings are two-dimensional photonic crystal extractors. The substrate may be removed and metal layers may be deposited on the buffer layer, photonic crystal and active layer, wherein the metal layers may function as a mirror, an electrical contact, and / or an efficient diffraction grating.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Micromirror arrays having self aligned features
ActiveUS20110222179A1Easy alignmentEliminate needMirrorsDecorative surface effectsOptical limitingNanostructure
Methods, arrays, and systems for the optical analysis of multiple chemical, biological, or biochemical reactions are provided. The invention includes methods for producing arrays of micromirrors on transparent substrates, each micromirror comprising a nanostructure or optical confinement on its top. The arrays are produced by a process in which lateral dimensions of both the nanostructures and micromirrors are defined in a single step, allowing for control of the relative placement of the features on the substrate, minimizing the process-related defects, allowing for improved optical performance and consistency. In some aspects, the invention provides methods of selectively etching large features on a substrate while not concurrently etching small features. In some aspects, the invention provides methods of etching large features on a substrate using hard mask materials.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Horizontal emitting, vertical emitting, beam shaped, distributed feedback (DFB) lasers fabricated by growth over a patterned substrate with multiple overgrowth
InactiveUS20070125995A1Improve propertiesEffective limitOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionDistributed feedback laserGrating
A structure using integrated optical elements is comprised of a substrate, a buffer layer grown on the substrate, one or more first patterned layers deposited on top of the buffer layer, wherein each of the first patterned layers is comprised of a bottom lateral epitaxial overgrowth (LEO) mask layer and a LEO nitride layer filling holes in the bottom LEO mask layer, one or more active layers formed on the first patterned layers, and one or more second patterned layers deposited on top of the active layer, wherein each of the second patterned layers is comprised of a top LEO mask layer and a LEO nitride layer filling holes in the top LEO mask layer, wherein the top and / or bottom LEO mask layers act as a mirror, optical confinement layer, grating, wavelength selective element, beam shaping element or beam directing element for the active layers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
High efficiency light emitting diode (LED) with optimized photonic crystal extractor
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Horizontal emitting, vertical emitting, beam shaped, distributed feedback (DFB) lasers by growth over a patterned substrate
InactiveUS20060194359A1Laser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetallic materialsRefractive index
A structure using integrated optical elements is comprised of a substrate, a buffer layer grown on the substrate, one or more patterned layers formed on the buffer layer and one or more active layers formed on or between the patterned layers, for instance by Lateral Epitaxial Overgrowth (LEO), and including one or more light emitting species. The patterned layer comprises a mask (made of insulating, semiconducting or metallic material) and material filling holes in the mask. The patterned layer, due to a large index difference with the active layer and / or variations of a refractive index between the mask and materials filling holes in the mask, acts as an optical confinement layer, a mirror, a diffraction grating, a wavelength selective element, a beam shaping element or a beam directing element.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Long wavelength vertical cavity surface emitting lasers
InactiveUS20060002444A1Optical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserDriving current
A vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) includes independently definable current and optical confinement structures that provide unique forms of drive current and transverse mode confinement, respectively. The optical guide may be formed from an upper distributed Bragg reflector (DBR), as an etched mesa structure and / or as an intracavity optical guide. The current guide may include an ion-implanted region within the upper DBR. A dielectric structure is formed over the upper DBR and surrounds the optical guide.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Substrate For Thin Film Photoelectric Conversion Device and Thin Film Photoelectric Conversion Device Including the Same
InactiveUS20080185036A1Improve surface roughnessSuppressing deterioration in propertyPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesOptical limitingSurface level
An object of the present invention is to provide a substrate for a thin film photoelectric conversion device, in which its properties are not deteriorated when its surface unevenness is effectively increased, and then provide the thin film photoelectric conversion device having its performance improved by using the substrate.According to the present invention, by setting the surface area ratio of a transparent electrode layer in the substrate for the thin film photoelectric conversion device to at least 55% and at most 95%, the surface unevenness are effectively increased to increase the optical confinement effect, while deterioration in properties due to sharpening of the surface level variation is suppressed, whereby making it possible to provide a substrate for a thin film photoelectric conversion device, which can enhance output properties of the thin film photoelectric conversion device.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
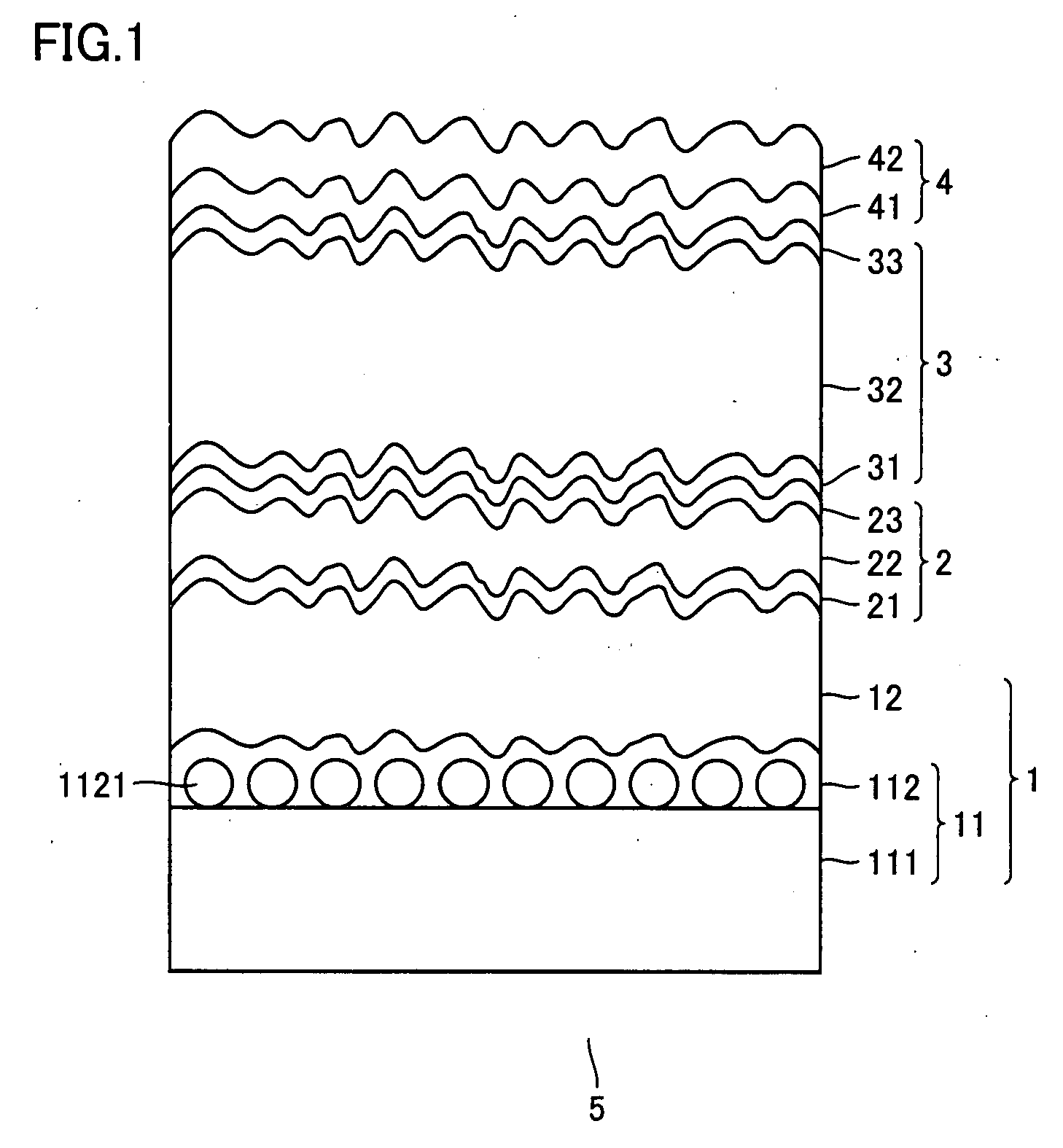
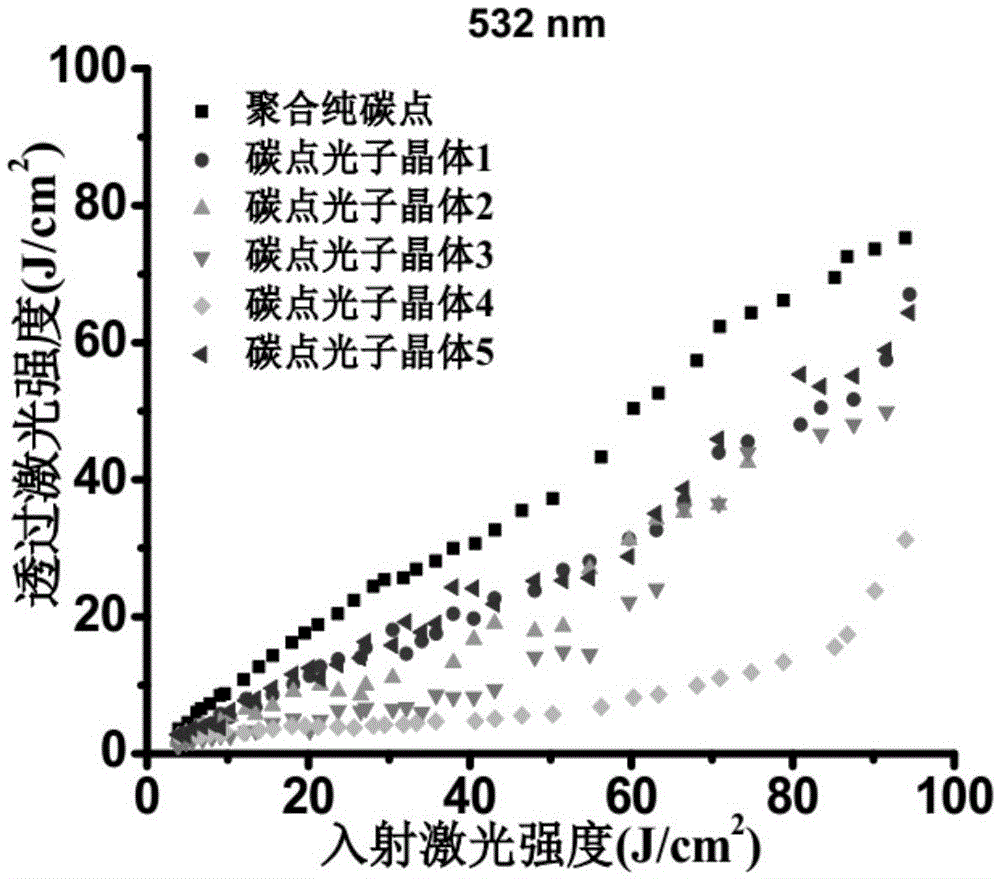
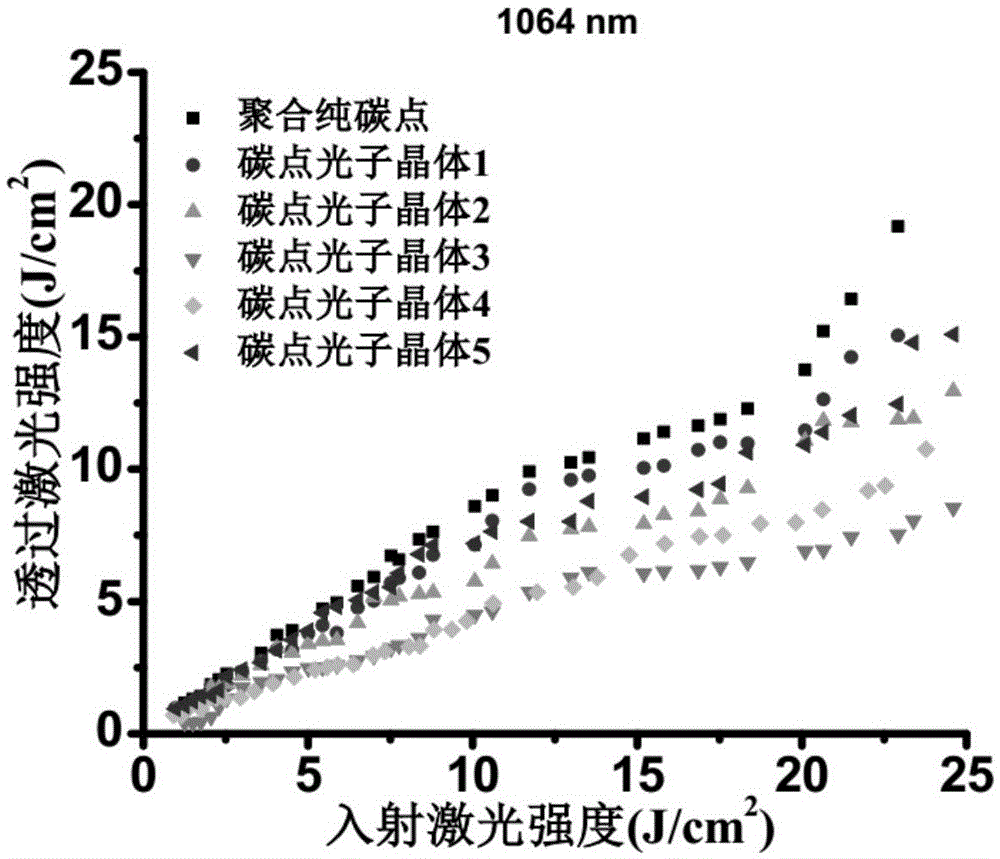
Preparation method and application of carbon dot photonic crystal having opal structure or inverse opal structure
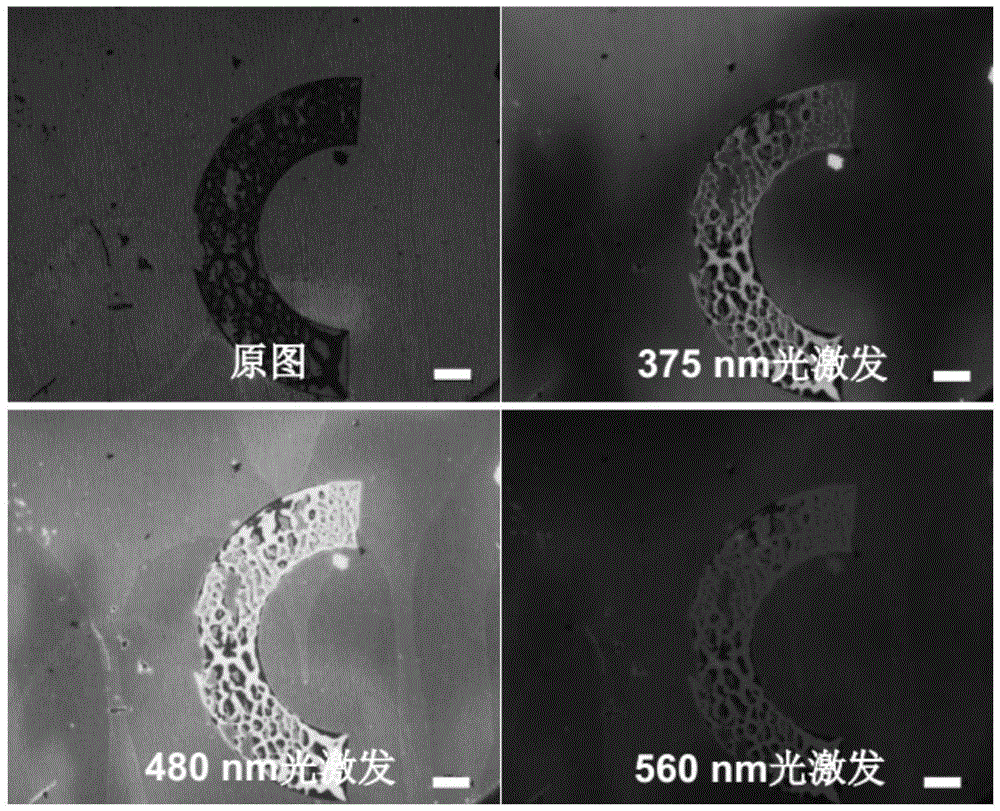
ActiveCN105525343AEasy to operateLow costPolycrystalline material growthLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthPhotonic bandgapMicrosphere
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a carbon dot photonic crystal having an opal structure or an inverse opal structure and having photonic band gap modulation of optical limiting and anti-fake performance. According to the method, with polystyrene microspheres as a raw material, a photonic crystal template is assembled by a vertical deposition method, then the carbon dot photonic crystal having the inverse opal structure is prepared by a sacrificial template method; or a carbon dot solution is added in the process of synthesis of silica microspheres, silica microspheres containing carbon dots and having different particle sizes are prepared, and then the carbon dot photonic crystal having the opal structure is assembled by a vertical deposition method. The obtained carbon dot photonic crystal has good optical limiting modulation behavior on laser according to difference of band gaps. At the same time, the prepared carbon dot photonic crystal is patterned by using a photoetching template, and can be used in anti-fake patterns with combination of the characteristic that the carbon dot photonic crystal emits fluorescence with different colors under different excitation light. The method has the advantages of simple operation and low cost, and is suitable for large-scale preparation of the carbon dot photonic crystal having special functions.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nitride light-emitting device for improving light-emitting efficiency by electron barrier layer
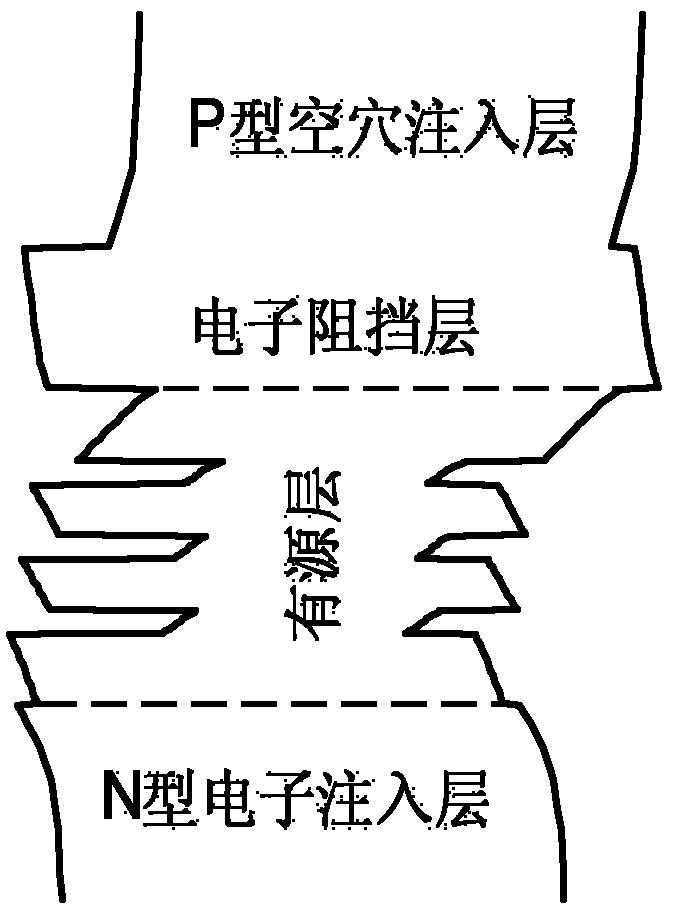
ActiveCN102544285AImprove injection efficiencyReduced tunneling barrierSemiconductor devicesLuminous intensityQuantum well
The invention discloses a nitride light-emitting device for improving the light-emitting efficiency by an electron barrier layer. The light-emitting device disclosed by the invention is provided with the electron barrier layer which is doped with aluminum in a non-uniform and non-periodic manner, and has changed Al components. According to the invention, two key problems of improving the light-emitting efficiency are effectively and simultaneously solved, namely a potential barrier of hole tunneling is reduced and the injection efficiency of a hole is improved; and furthermore, parasitic electron inversion layers are prevented from being formed on interfaces of a quantum barrier and the electron barrier layer by a traditional structure. However, the effect on stopping electrons by a multilayer structure is more obvious and two current carriers of the electrons and the hole are distributed in each quantum well of an active layer in a more balanced and uniform way, so as to obtain the more uniform light gain. Therefore, the light-emitting device provided by the invention can effectively overcome a parasitic quantum well phenomenon and has a smaller threshold current. Furthermore, a waveguide structure is provided with a higher optical limiting factor so that a stronger light-emitting strength is obtained; and therefore, the electric performance and the optical performance of a laser device can be simultaneously improved.
Owner:北京飓芯科技有限公司
Nitride semiconductor laser
InactiveCN102570308AEnhanced Optical Confinement FactorImprove performanceOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsOptical limitingContact layer
The invention discloses a nitride semiconductor laser, which comprises sequentially a GaN substrate, a n-GaN layer, a n-AlGaN / GaN superlattice limiting layer, a lower InxGa1-xN gradual change waveguide layer, an InGaN / GaN multiple quantum well active area, an upper InyGa1-yN gradual change waveguide layer, a p-AlGaN electron barrier layer, a p-AlGaN / GaN superlattice limiting layer and a p-GaN contacting layer from bottom to top. In component content increases gradually from bottom to top in the lower InxGa1-xN gradual change waveguide layer and In component content decreases gradually from bottom to top in the upper InyGa1-yN gradual change waveguide layer. The nitride semiconductor laser can decrease the stress between an upper InGaN waveguide layer and the p-AlGaN electron barrier layer effectively, so that ragged steps can be avoided during cleavage. Simultaneously, the nitride semiconductor laser can strengthen optical limiting factors of the laser so as to improve performance of the laser effectively and acquire significant effect.
Owner:苏州纳睿光电有限公司
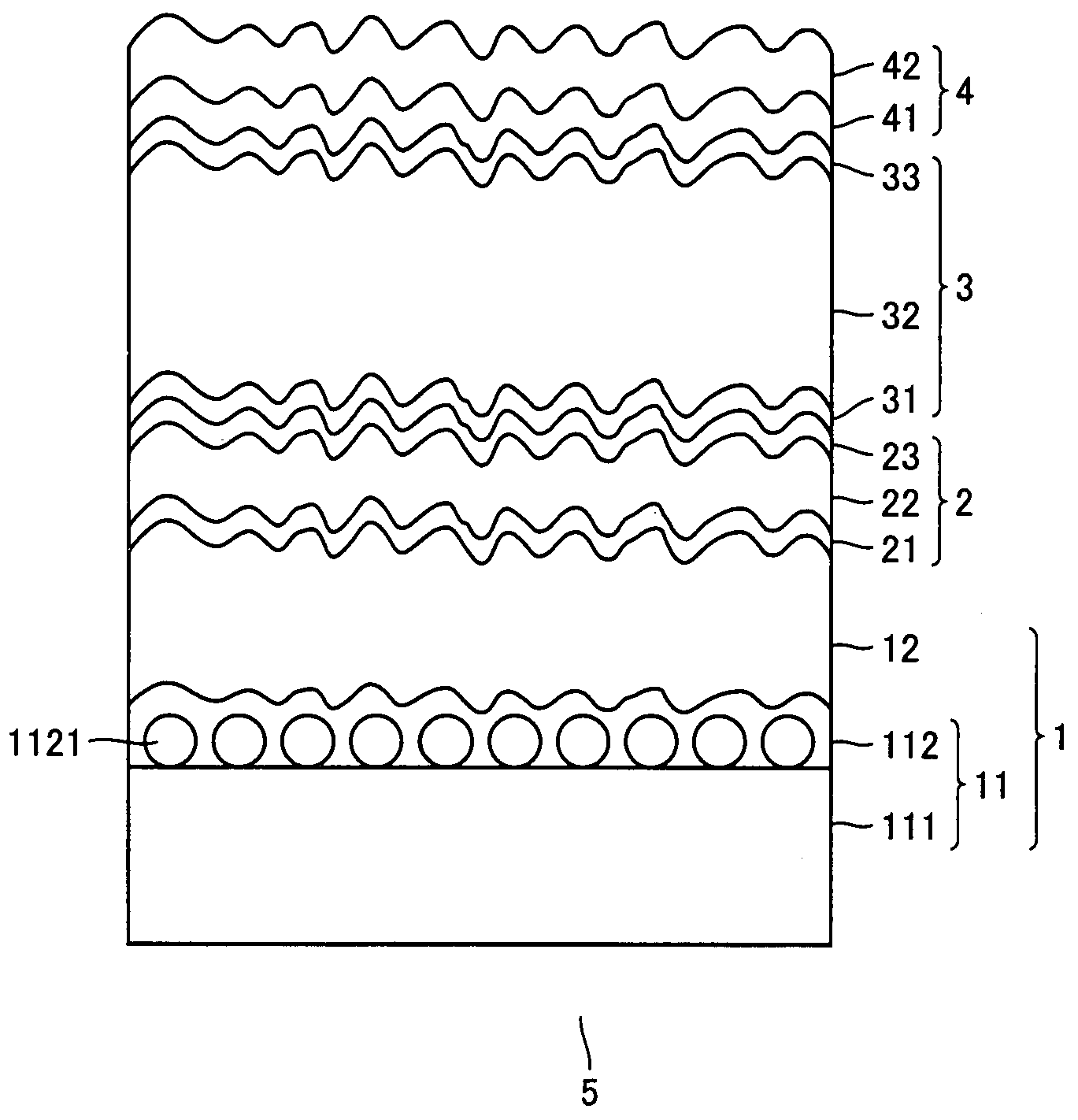
Segmented waveguide structures
InactiveUS20060233504A1Reduce reflectionHigh index contrastNanoinformaticsAnalysis by electrical excitationRefractive indexOptical limiting
Various embodiment comprise silicon-on-insulator waveguide designs that simultaneously achieve both high optical confinement, low-loss, and provide for electrical connections. In certain embodiments, high index contrast waveguides comprise a central elongate waveguide portion and a segmented portion comprising a single thin layer of Silicon-On-Insulator that achieves both high optical confinement and minimal insertion loss. Other devices, such as chemical and biological sensors, and optical elements may also be fabricated.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Single or multi-color high efficiency light emitting diode (LED) by growth over a patterned substrate
InactiveUS7291864B2Improve extraction efficiencyEmission controlSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesMetallic materialsRefractive index
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Advantageous recording media for holographic applications
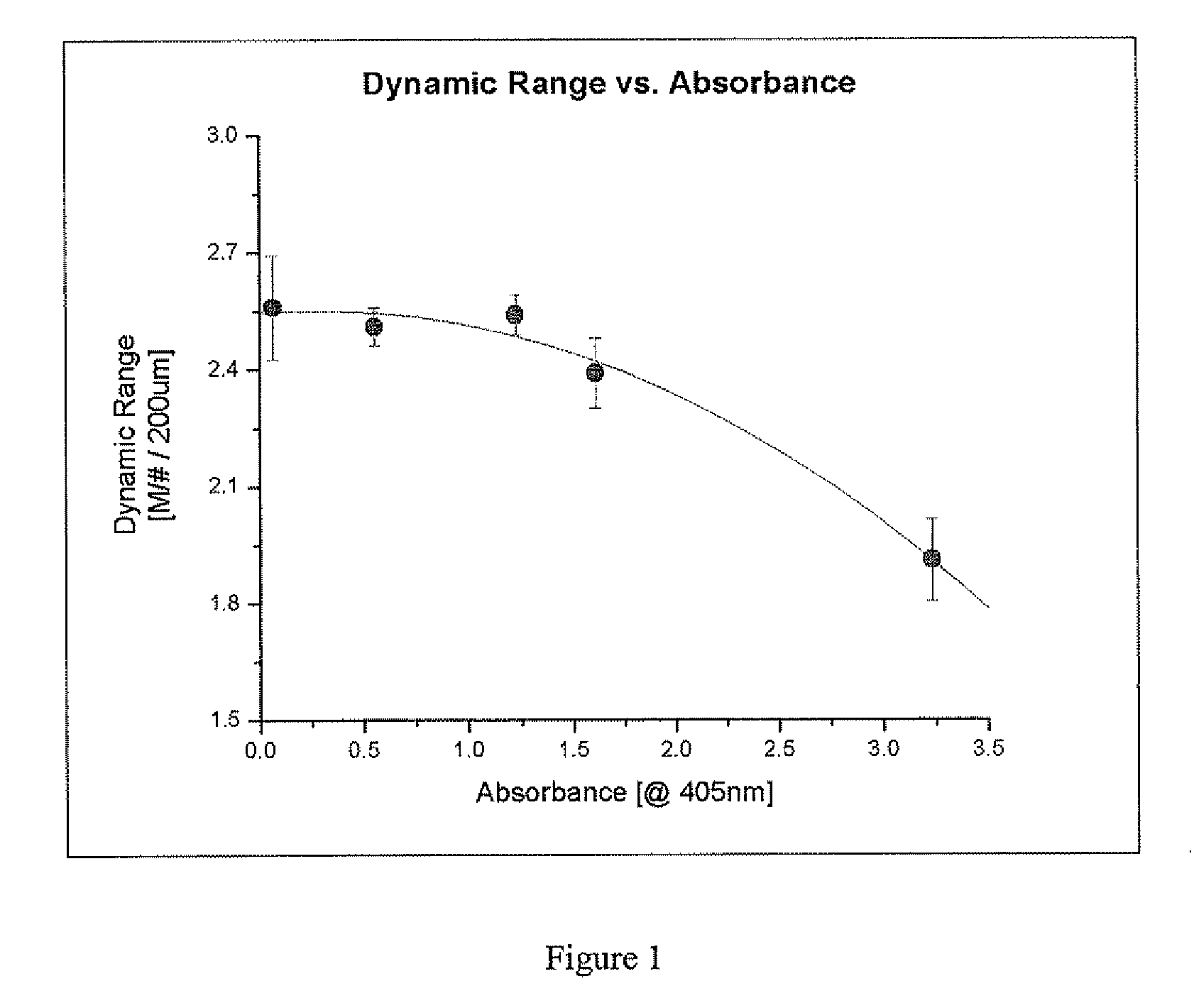
ActiveUS20090185470A1Improve performanceHigh diffraction efficiencyPhotosensitive materialsPhotomechanical apparatusOptical limitingWaveguide
High performance media suitable for recording with a blue laser is disclosed. The blue-sensitized holographic media provides greater dynamic range and higher sensitivity than previously disclosed blue-sensitized holographic media. These media can be used for diverse applications such as data storage where the articles provide denser data storage and more rapid hologram writing times or for optical waveguides where the articles provide greater optical confinement and more rapid manufacturing times.
Owner:AKONIA HOLOGRAPHIES +1
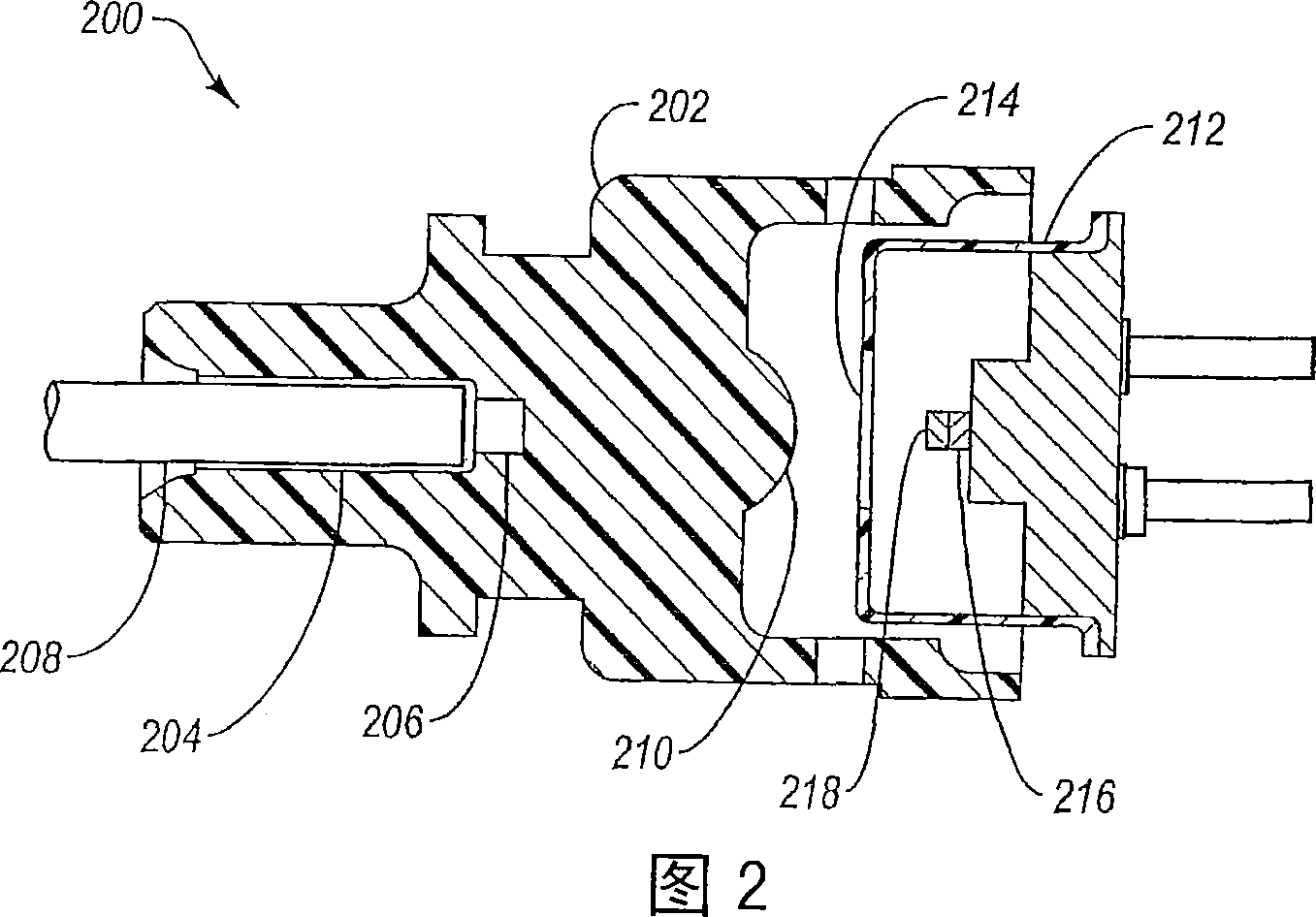
Transmitter and receiver optical sub-assemblies with optical limiting elements
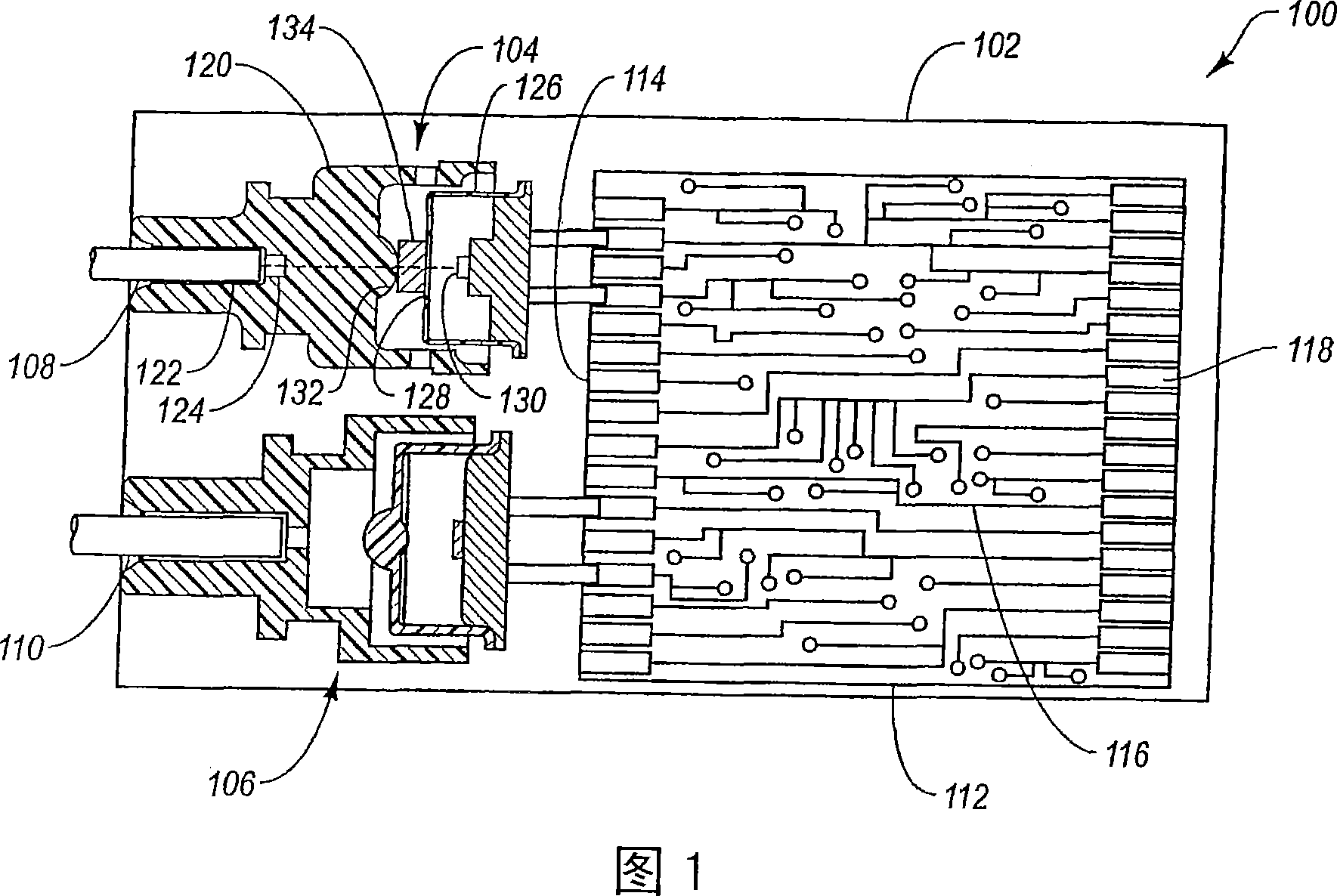
InactiveCN1926727ASemiconductor laser optical deviceOptical resonator shape and constructionFiberOptical limiting
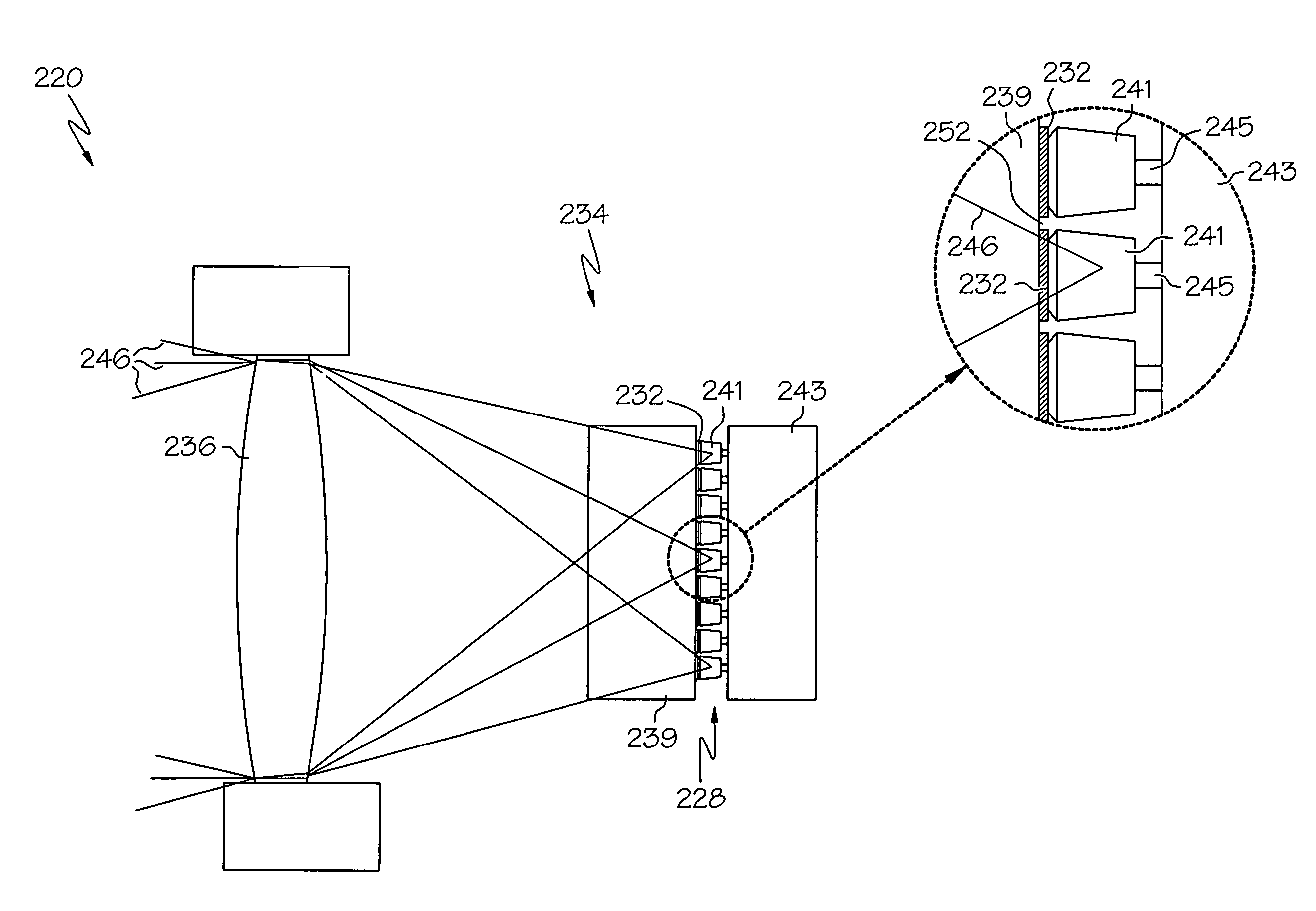
A transmitter optical subassembly (104) includes an optical emitter (130) and a fiber receptacle (122) within which an optical fiber (108) is received. An optical limiting element (134) is positioned between the optical emitter (103) and the fiber receptacle (122). When an optical signal is emitted from the optical emitter, the optical signal passes through the optical limiting (134) element before the optical signal reaches the fiber receptacle (122) and is received the optical fiber. The optical limiting element (134) has a property such that if the power of the optical signal entering the optical limiting element (134) exceeds a predetermined limit, the power of the optical signal is optically attenuated so that the power of the optical signal exiting the optical limiting element remains below a predetermined limit.
Owner:FINISAR
Optoelectronic systems providing high-power high-brightness laser light based on field coupled arrays, bars and stacks of semicondutor diode lasers
ActiveUS20090116525A1Improve discriminationEfficient couplingLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser arrayLow leakage
A semiconductor diode laser having a broad vertical waveguide and a broad lateral waveguide is disclosed emitting laser-light in a single vertical mode and a single lateral mode narrow beam. The vertical waveguide comprises a coupled cavity structure, wherein light, generated in the active medium placed in the first cavity leaks into the second cavity and returns back. Phase matching conditions govern the selection of a single vertical mode. A multi-stripe lateral waveguide comprises preferably a lateral photonic band crystal with a lateral optical defect created by selected pumping of multistripes. This approach allows the selection of a single lateral mode having a higher optical confinement factor and / or a lower absorption loss and / or a lower leakage loss compared to the rest lateral optical modes. This enables a single lateral mode lasing from a broad area field coupled laser array. A laser system comprised of multiple field coupled laser arrays on a single wafer and a set of external mirrors enables an ultra-broad field coupled laser bar emitting a coherent laser light in a single vertical optical mode and a single lateral optical mode. A laser system comprised of multiple ultra-broad field coupled laser bars on different wafers and a set of external mirrors enables an ultra-broad field coupled laser stack emitting coherent laser light in a single vertical optical mode and a single lateral optical mode. This allows realization of ultrahigh power ultrahigh brightness laser systems based on semiconductor diode lasers.
Owner:VI SYST GMBH
Horizontal emitting, vertical emitting, beam shaped, distributed feedback (DFB) lasers by growth over a patterned substrate
InactiveUS7345298B2Laser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetallic materialsRefractive index
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
High efficiency intersubband semiconductor lasers
ActiveUS20070248131A1Improve efficiencyEfficient emissionsNanoopticsSemiconductor lasersElectron injectionHigh energy
An intersubband quantum cascade laser structure includes multiple coupled laser stages, wherein each stage has a multilayer structure including an electron injector, an active region with at least one quantum well, and an electron reflector. Electrons injected from the injector into the active region at a high energy level relax to a lower energy level with the emission of a photon at, for example, mid-infrared wavelengths. The reflector reflects electrons at the higher energy level at which they were injected and transmits electrons from the lower energy level after emission of a photon. Multiple layers of semiconductor are formed on each side of the multistage structure to provide conduction across the device and to provide optical confinement of the photons emitted.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Methods for forming index guided vertical cavity surface emitting lasers
InactiveUS6852558B2Improved implantMinimizes thermal lensing effectOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserCurrent limiting
Planar index guided vertical cavity surface emitting laser (PIG VCSEL) utilizes index guiding to provide improved optical confinement and proton implantation to improve current confinement. Index guiding is achieved by etching index guide openings (holes or partial ridges) around the optical confinement region and may be adjusted by varying the etched volume of the index guide openings (holes and partial ridges). The top contact surface area is increased in the PIG VCSEL thereby lowering contact and device resistance to improve VCSEL performance further. The PIG VCSEL is a substantially planarized device for ease of manufacture.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Laser diode with improved heat dissipation
ActiveUS20090219966A1Good optical confinementImprove cooling effectOptical wave guidanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical limitingRidge
Owner:SHARP FUKUYAMA LASER CO LTD
GaN-based semiconductor laser epitaxial structure and fabrication method thereof
ActiveCN102299482AImprove radiation compliance efficiencyImprove the blocking effectOptical wave guidanceAcceptorPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a novel gallium nitride based semiconductor laser epitaxial structure and a preparation method thereof. According to the invention, p-AlGaN with gradually variable Al components is adopted to act as an optical confinement layer, and through the principle of polarization doping, three-dimensional hole gas is realized. According to the invention, the activation efficiency ofan acceptor Mg impurity can be improved, the device voltage can be reduced, and simultaneously the internal loss of a laser can be reduced effectively.
Owner:HANGZHOU HONGSHI TECH
Methods and apparatuses for selectively limiting undesired radiation
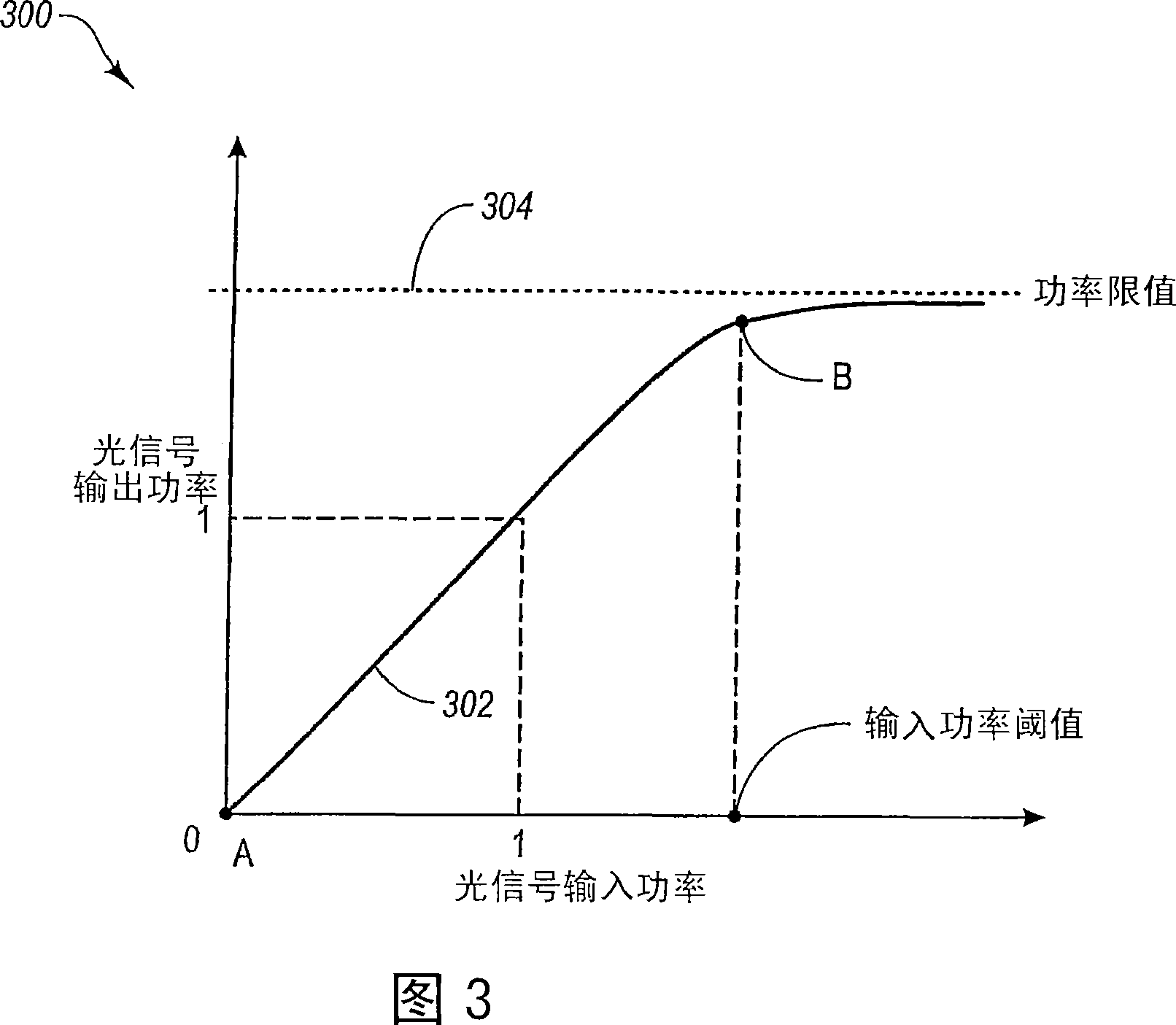
ActiveUS7095026B2Prevent overflowRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansLight energyOptical limiting
An apparatus for selectively limiting undesired radiation from a scene which, in one embodiment, includes an optic that is operative to attenuate radiation by selectively losing transparency in response to radiation within a first wavelength band from a source. The loss of transparency affects the passage through the optic of radiation within a second wavelength band from that source. The optic can be positioned between a sensor and the scene such that the sensor is configured to receive radiation from the scene through the optic. In one embodiment, an optical limiter includes a plurality of such optics, wherein the optical limiter is configured to facilitate transmission of light corresponding to a scene, and wherein each optic is configured to receive a respective portion of the light corresponding to a respective portion of the scene. A light detector assembly and a method of limiting light energy are also included.
Owner:L3HARRIS CINCINNATI ELECTRONICS CORP
Platinum (II) alkyne complex and application thereof
The invention provides a platinum (II) alkyne complex and application thereof. The platinum (II) alkyne complex is structurally a platinum (II) alkyne naphthalene imide compound by using bipyridine derivative as a ligand. A preparation method of the platinum (II) alkyne complex comprises the following steps: firstly, enabling potassium tetrachloroplatinate to react with dimethyl sulfoxide to obtain a potassium tetrachloroplatinate-dimethyl sulfoxide complex; secondly, enabling the potassium tetrachloroplatinate-dimethyl sulfoxide complex to react with the bipyridine ligand to a obtain bipyridine platinum (II) chloride complex; finally, performing Sonogashira reaction on the bipyridine platinum (II) chloride complex and alkyne ligand to obtain a series of the bipyridine platinum (II) alkyne naphthalene imide compounds. Test results show that the platinum complexes synthesized by the preparation method have a good optical limiting property and can be applied to nonlinear absorbent materials.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
High efficiency intersubband semiconductor lasers
ActiveUS20090022196A1Efficient emissionsEasy to separateLaser detailsLaser active region structureElectron injectionHigh energy
An intersubband quantum cascade laser structure includes multiple coupled laser stages, wherein each stage has a multilayer structure including an electron injector, an active region with at least one quantum well, and an electron reflector. Electrons injected from the injector into the active region at a high energy level relax to a lower energy level with the emission of a photon at, for example, mid-infrared wavelengths. The reflector reflects electrons at the higher energy level at which they were injected and transmits electrons from the lower energy level after emission of a photon. Multiple layers of semiconductor are formed on each side of the multistage structure to provide conduction across the device and to provide optical confinement of the photons emitted.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Semiconductor laser and manufacturing method thereof
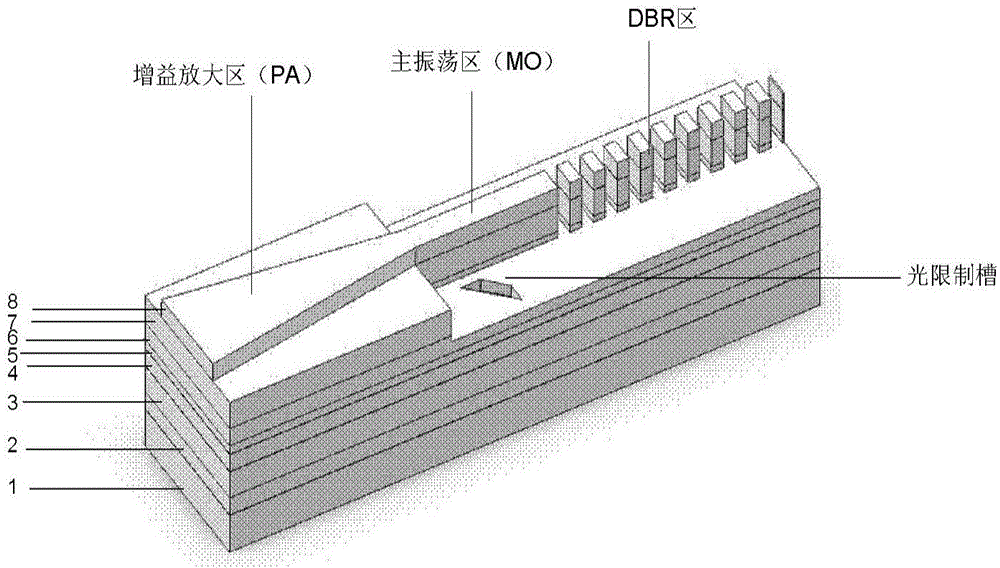
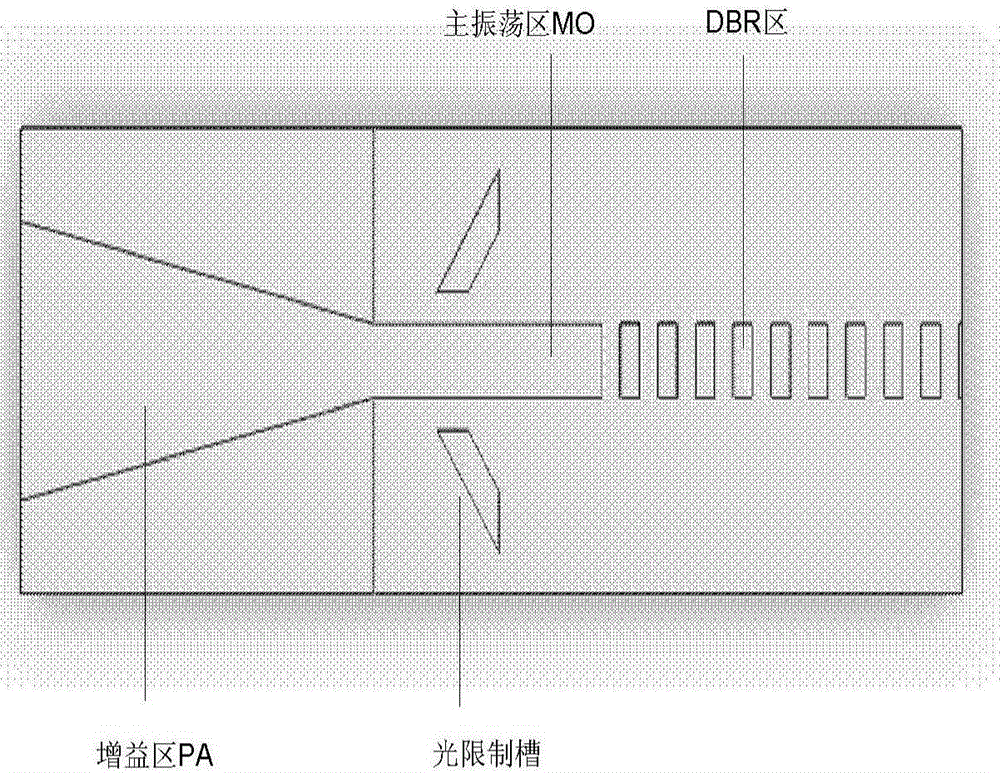
InactiveCN105161976AGuaranteed to workHigh beam quality of the output light is guaranteed while workingLaser detailsLaser active region structureGratingOptical limiting
The invention discloses a single-mode high-power high-brightness GaSb-based bragg reflection master oscillator power amplifier (MOPA) integrated semiconductor laser and a manufacturing method thereof. The bragg reflection MOPA integrated semiconductor device comprises a substrate, an epitaxy structure, a gain amplification region, a master oscillator region, a bragg reflection region and optical limiting grooves, wherein the epitaxy structure grows on the substrate and comprises an N-type lower contact layer, an N-type lower limiting layer, a lower waveguide layer, an active region, an upper waveguide region, a P-type upper limiting layer and a P-type upper contact layer from bottom to top; the gain amplification region is located on the front part, namely a light outlet part, of the semiconductor laser, and is in a conical structure which is formed by etching the P-type upper contact layer downwards; the master oscillator region is located at the rear part of the gain amplification region and is in a ridge waveguide structure which is formed by etching the P-type upper limiting layer downwards; the bragg reflection region is located at the rear part of the master oscillator region and is in a periodical bragg grating structure which is formed by etching the P-type upper limiting layer downwards; and the optical limiting grooves are symmetrically distributed in two sides of the ridge waveguide and are obliquely arranged together with the ridge waveguide.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
808nm large-power quantum well laser in non-aluminum active region of asymmetric structure
ActiveCN101340060AIncreased light confinement factorReduce leakageOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsIndium arsenideWaveguide
The invention provides an aluminum-free active region 808nm high-power quantum-well laser with asymmetric structure. From the bottom to the top, the structure of the laser sequentially comprises a substrate, a buffer layer, an N-type lower limiting layer, a lower waveguide layer, a quantum-well layer, an upper waveguide layer, a potential barrier limiting layer, a P-type upper limiting layer, a transition layer and an ohmic contact layer, wherein, the upper waveguide layer and the lower waveguide layer are made of aluminum-free material Indium gallium phosphide, the quantum-well layer made of gallium indium arsenide phosphide material, the waveguide layer and the quantum-well layer form the aluminum-free active region, and one layer potential barrier limiting layer which is made of P-type aluminum gallium indium phosphide material and 50nm-150nm thick and has a band gap wider than that of the upper limiting layer is arranged between the upper limiting layer and the upper waveguide layer. The laser of the invention can increase the optical limiting factor of the P-type material region, reduce the optical leakage towards the P-type material region, reduce optical absorption loss of a current carrier at the highly doped area, and improve the work efficiency of the laser; the structure of the invention also improves the limiting effect of the active region on the carrier, reduce the leakage of the carrier and is favorable to the decrease of the threshold current.
Owner:Shandong Huaguang Optoelectronics Co. Ltd.
Marker structure for alignment or overlay, mask pattern defined it and lithographic projector using the same
InactiveCN1577080AReduce the influence of lens aberrationReduce the impact of optical projection boundsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusImage resolutionProjection image
A mask pattern for imaging a marking structure on a substrate in lithographic projection, the marking structure being arranged in use for determining optical alignment or overlay, the mask pattern comprising constituent parts to define the marking structure, the composition The part is divided into a plurality of segmented elements (EL; ML), each segmented element has substantially the size of a device feature, the mask pattern includes a segmented shape for each segmented element (EL; ML), which It is characterized in that the mask pattern for the marking structure comprises at least one auxiliary feature (EL_sub) located at a critical part of the segment shape for balancing optical aberrations or optical confinement generated at the critical part in the lithographic projection, which At least one assist feature (EL_sub) has a size substantially smaller than the resolution of the lithographic projection.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Polyimide-based composite film with optical limiting performance
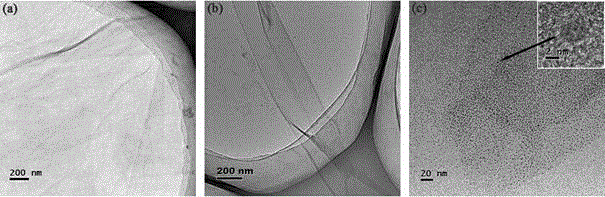
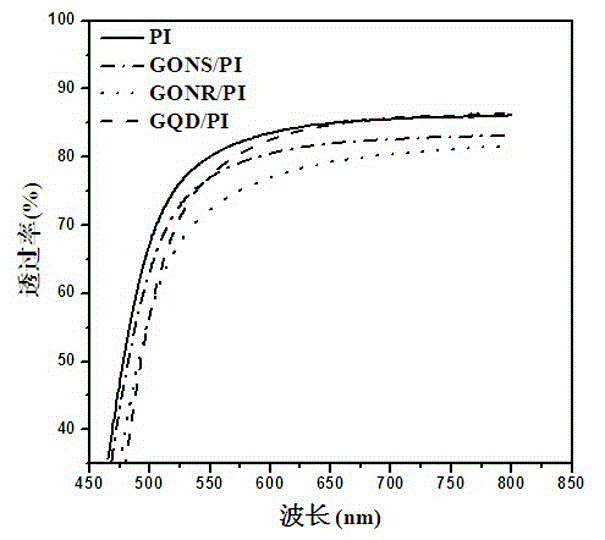
The invention discloses a polyimide-based composite film with optical limiting performance and a preparation method and application of the polyimide-based composite film with optical limiting performance. According to the method, condensation polymerization is conducted on diamidogen and dianhydride to synthesize polyamic acid, then optical limiting material is introduced, and the polyimide-based composite film is obtained through heat amidation processing; the optical limiting material comprises organic dyestuff, carbon black, a carbon nano tube, two-dimensional graphene oxide nano-sheet, two-dimensional reduction graphene nano-sheet, a one-dimensional graphene oxide nanobelt, a one-dimensional reduction graphene nanobelt and a zero-dimensional graphene quantum dot. The prepared composite film has good transmission of light, mechanical property and heat stability, meanwhile has the optical limiting performance prior to that of single optical limiting material, and is hopeful to be applied in the field of laser protection.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com