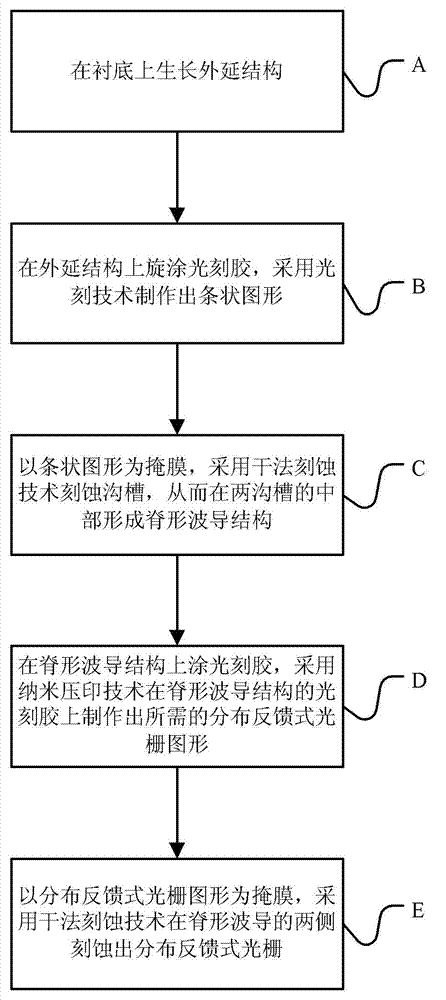
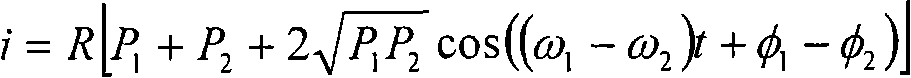Patents
Literature
276 results about "Distributed feedback laser" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A distributed feedback laser (DFB) is a type of laser diode, quantum cascade laser or optical fiber laser where the active region of the device contains a periodically structured element or diffraction grating. The structure builds a one-dimensional interference grating (Bragg scattering) and the grating provides optical feedback for the laser. This longitudinal diffraction grating has periodic changes in refractive index that cause reflection back into the cavity. The periodic change can be either in the real part of the refractive index, or in the imaginary part (gain or absorption). The strongest grating operates in the first order - where the periodicity is one-half wave, and the light is reflected backwards. DFB lasers tend to be much more stable than Fabry-Perot or DBR lasers and are used frequently when clean single mode operation is needed, especially in high speed fiber optic telecommunications. Semiconductor DFB lasers in the lowest loss window of optical fibers at about 1.55um wavelength, amplified by Erbium-doped fiber amplifiers (EDFAs), dominate the long distance communication market, while DFB lasers in the lowest dispersion window at 1.3um are used at shorter distances.
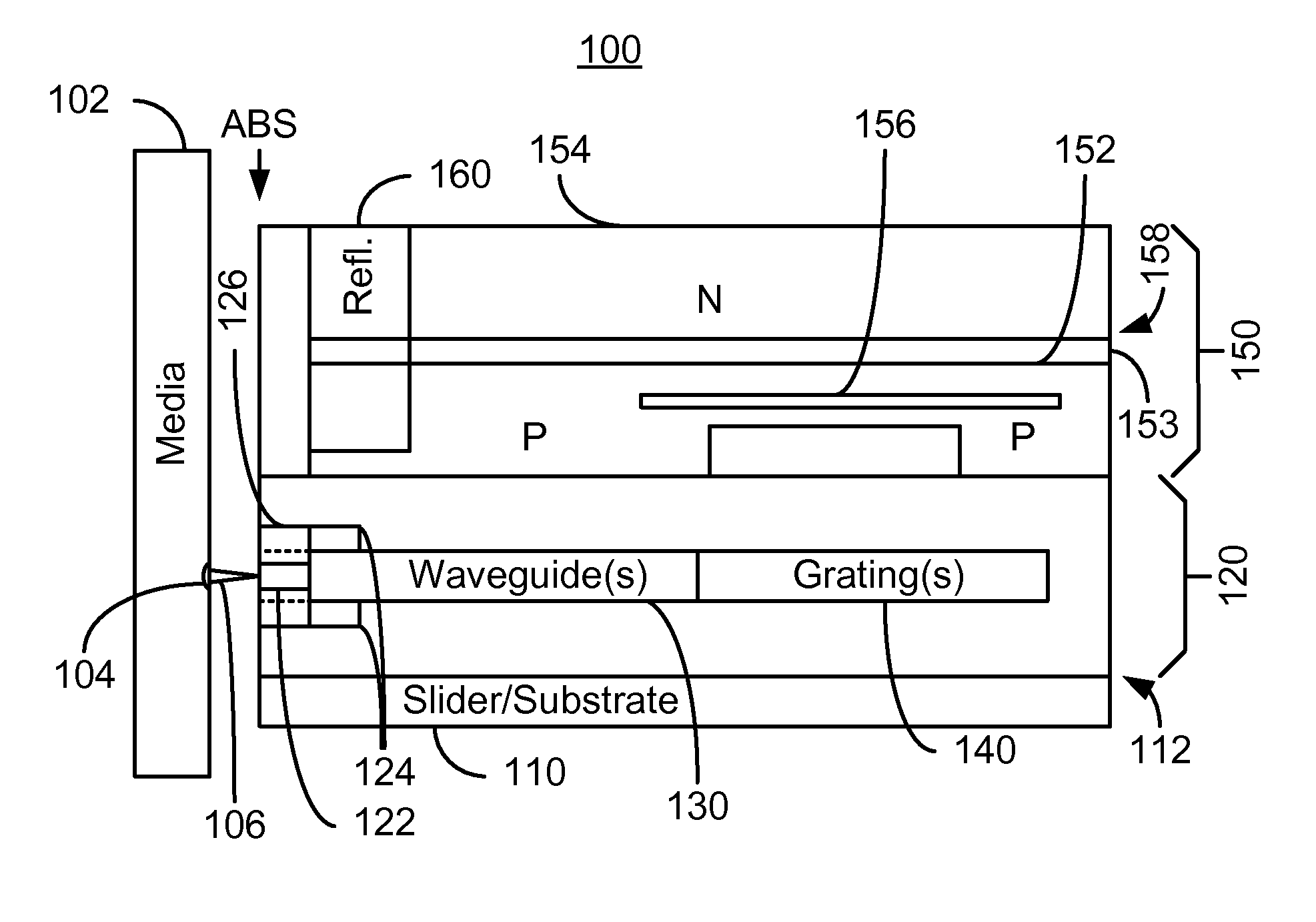
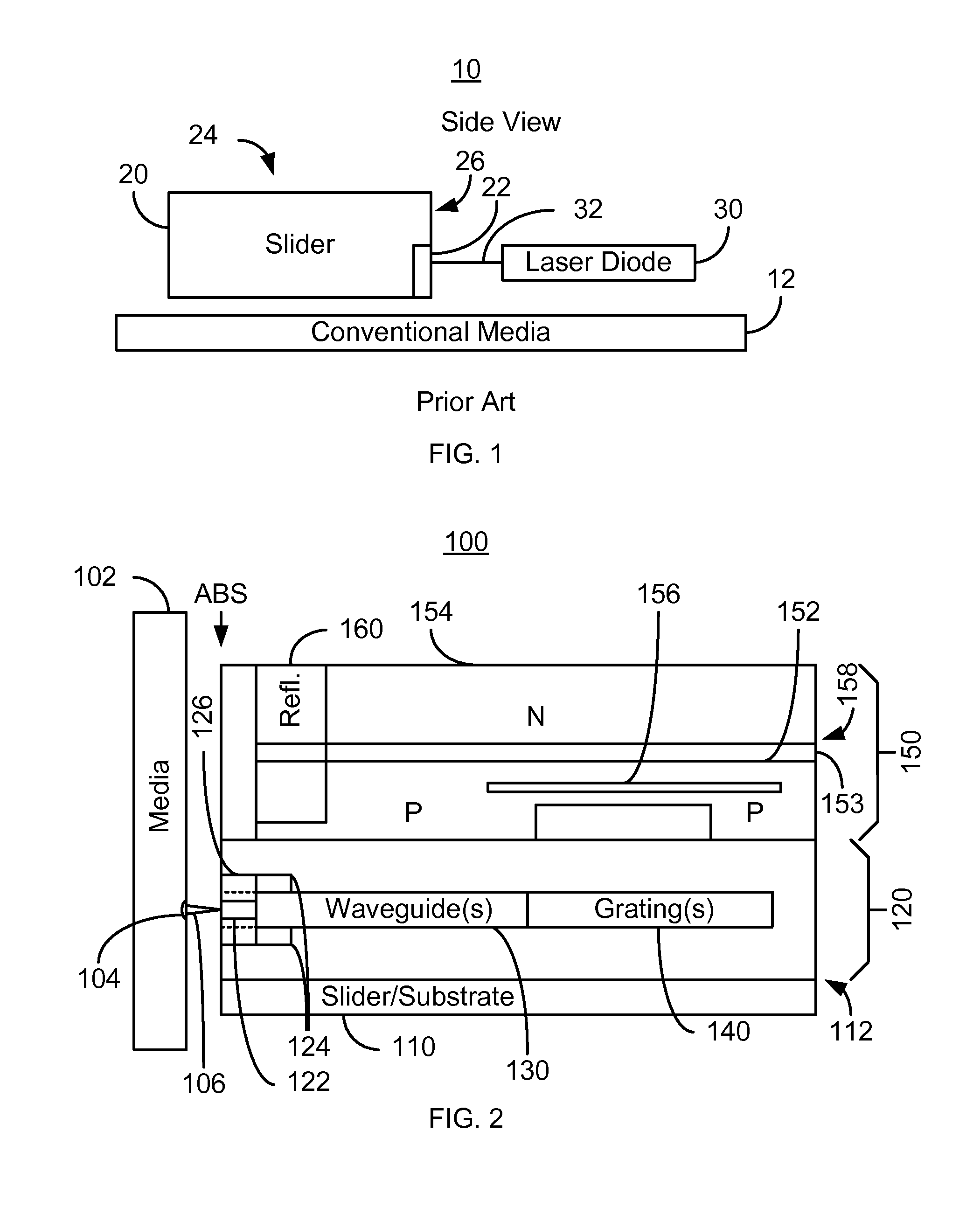
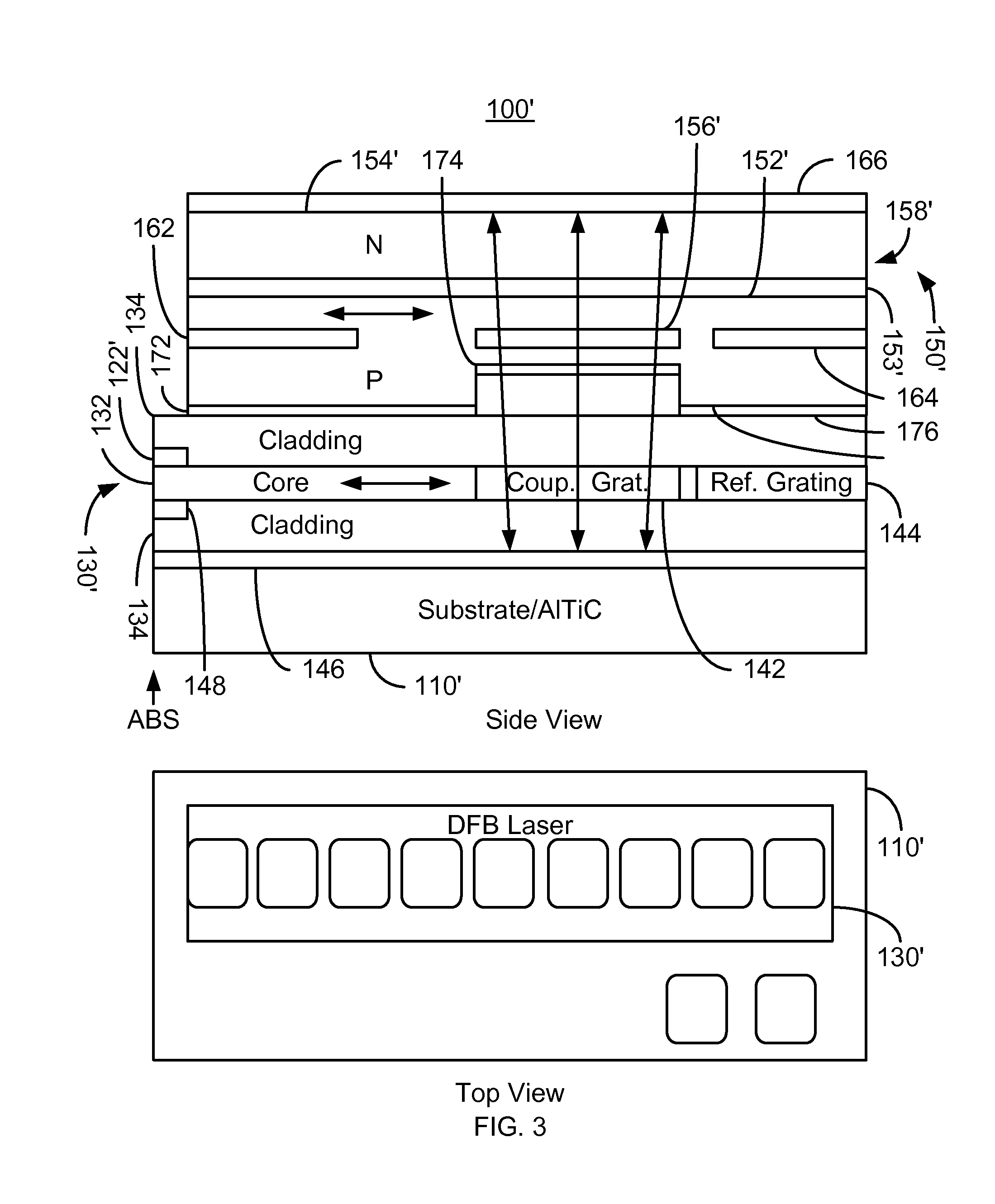
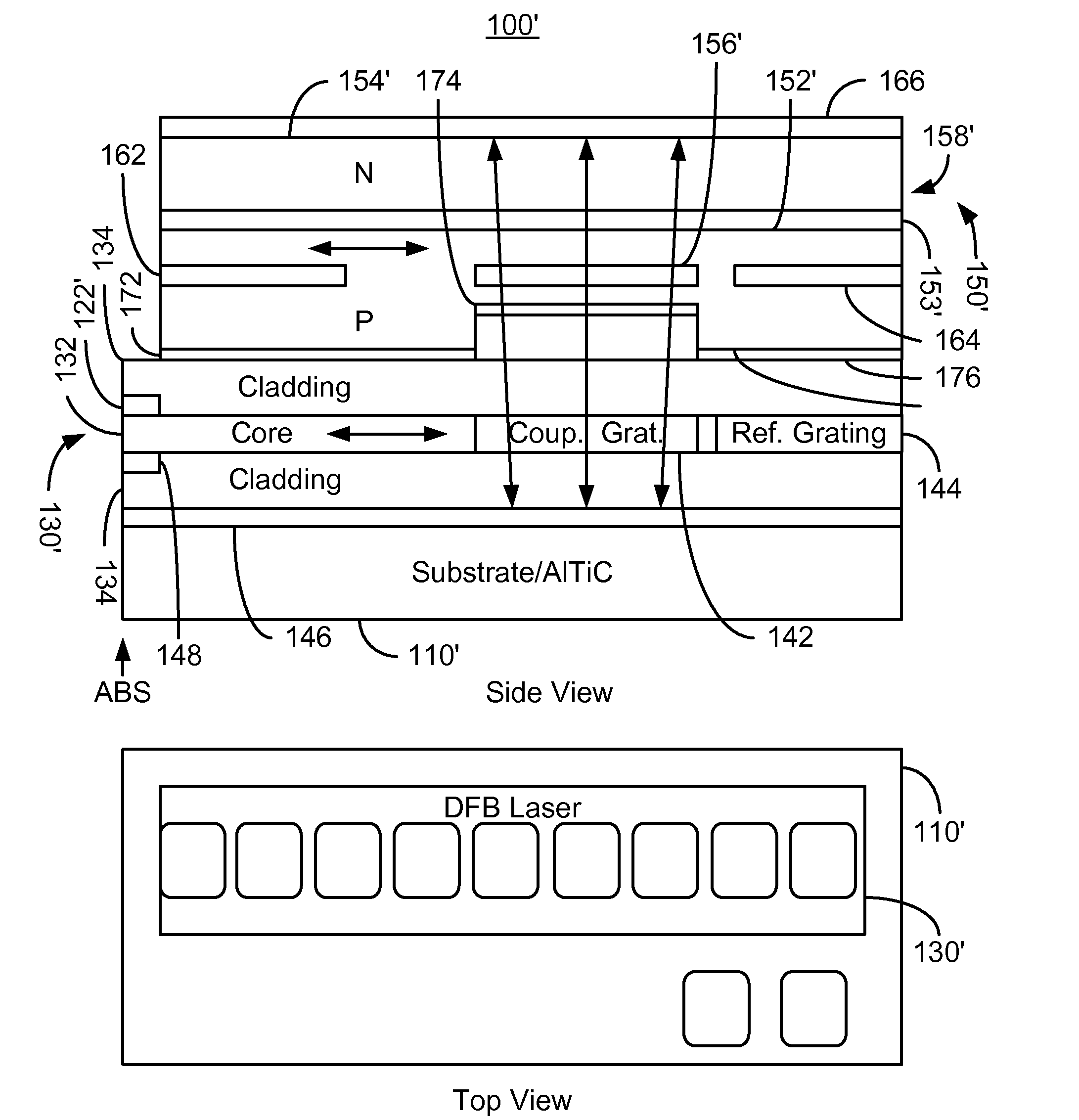
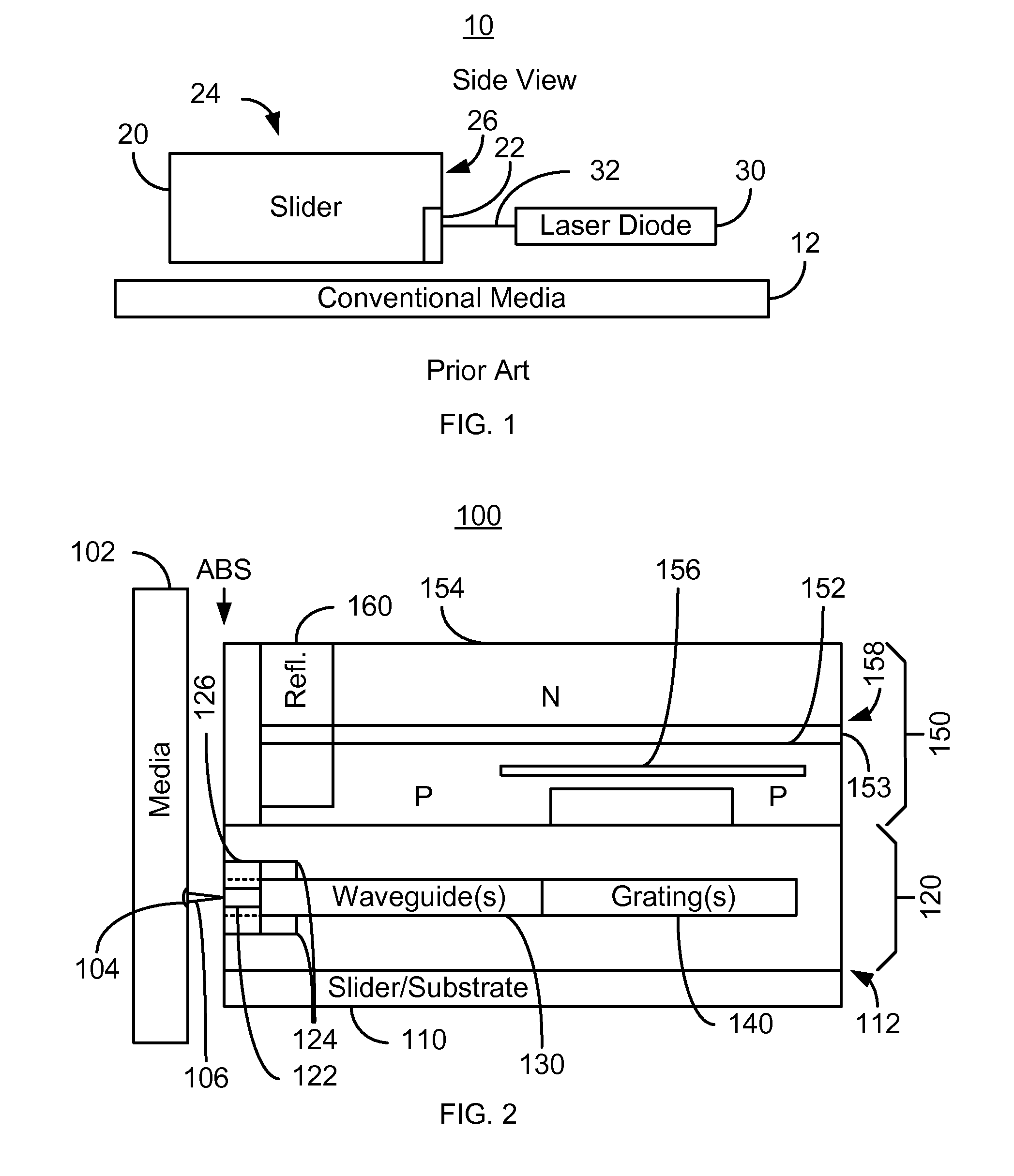
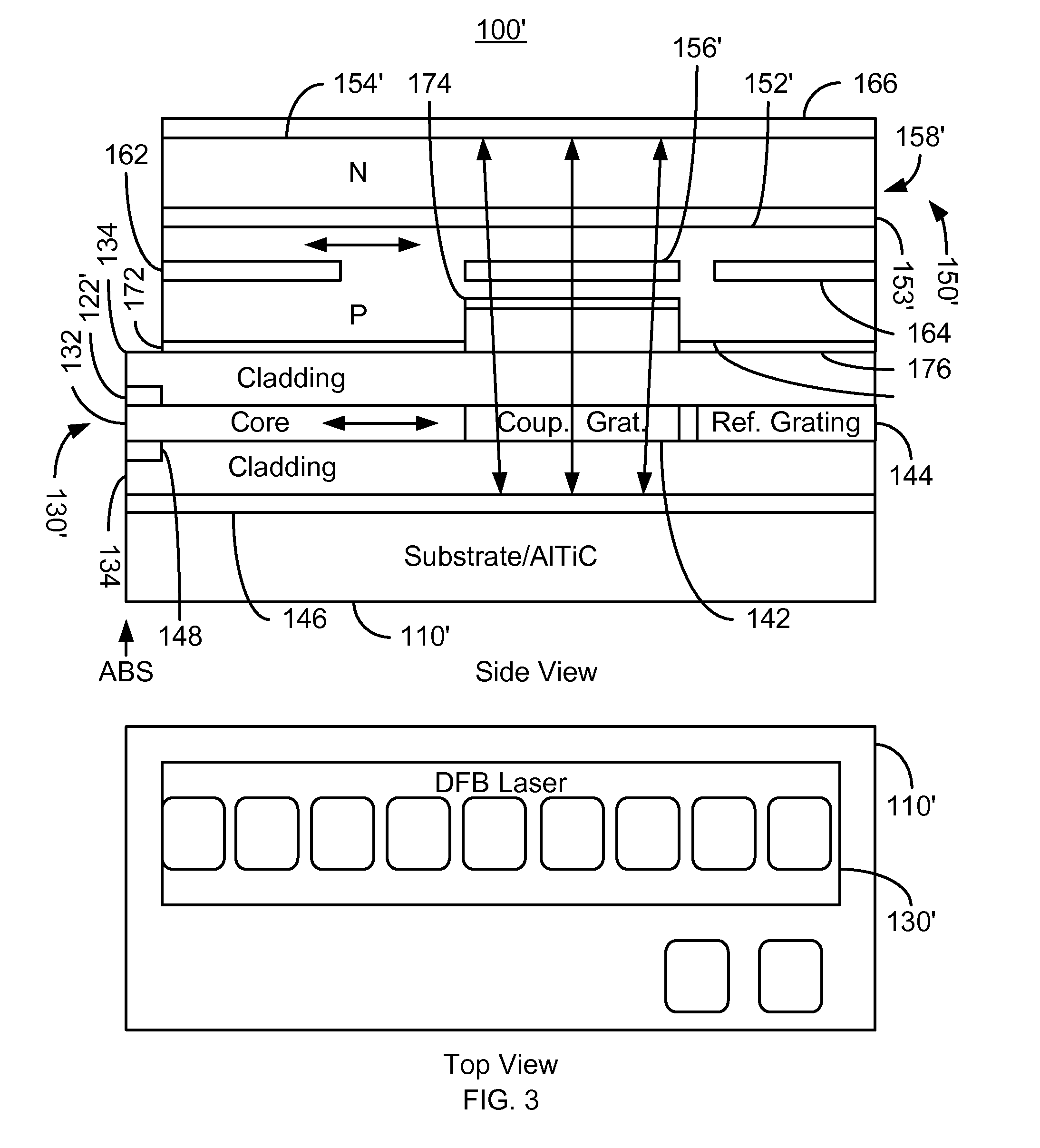
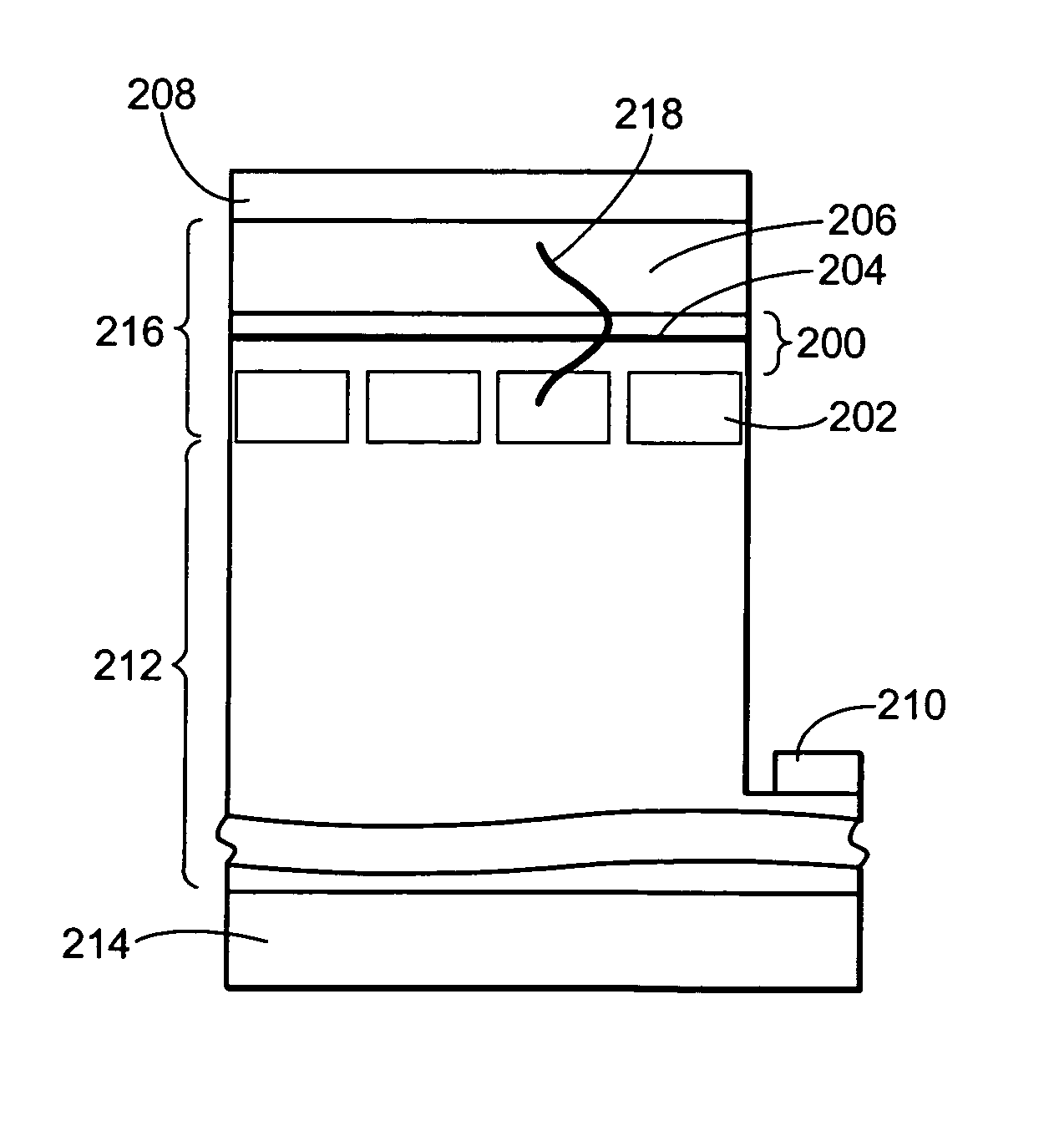
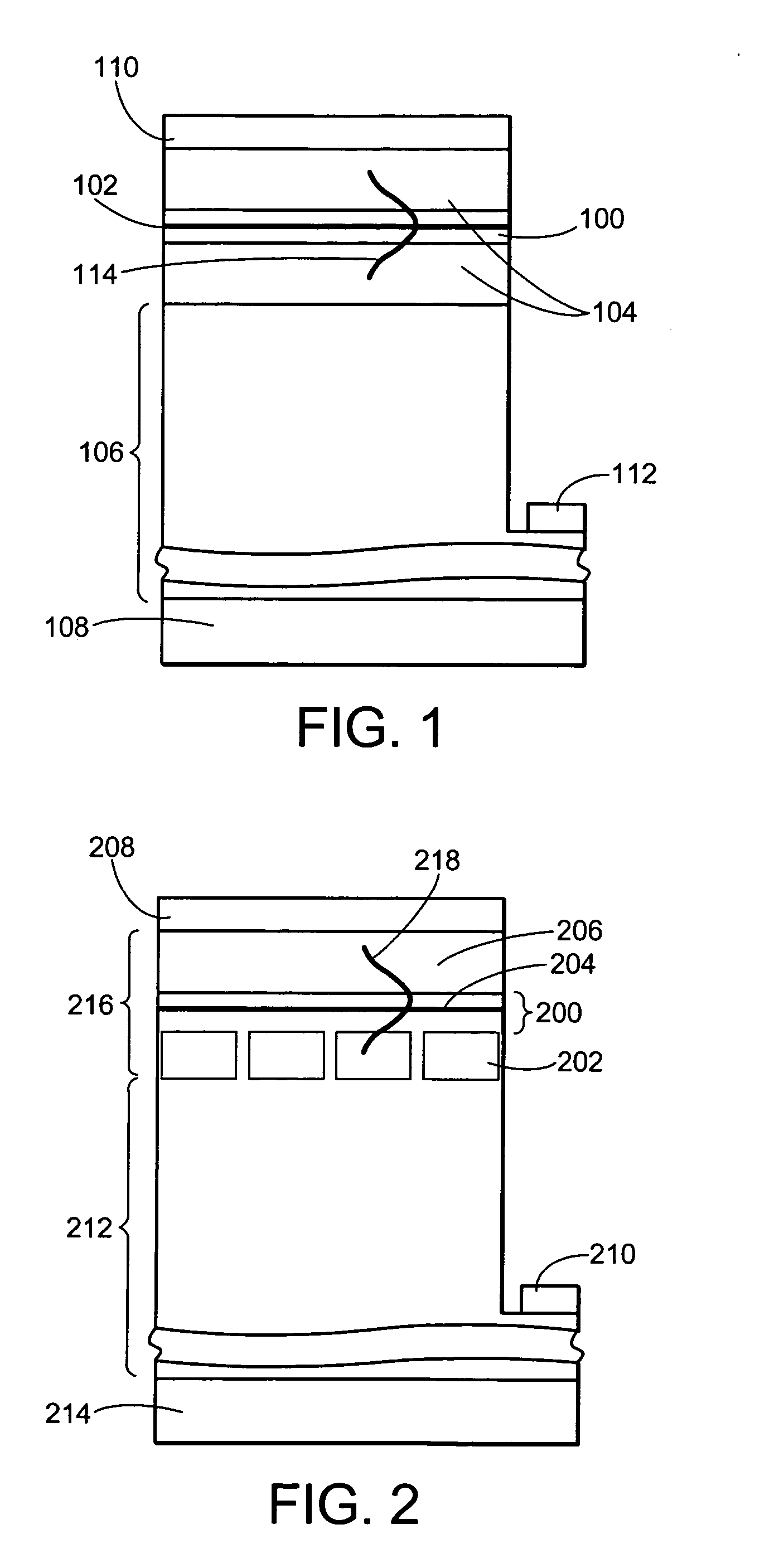
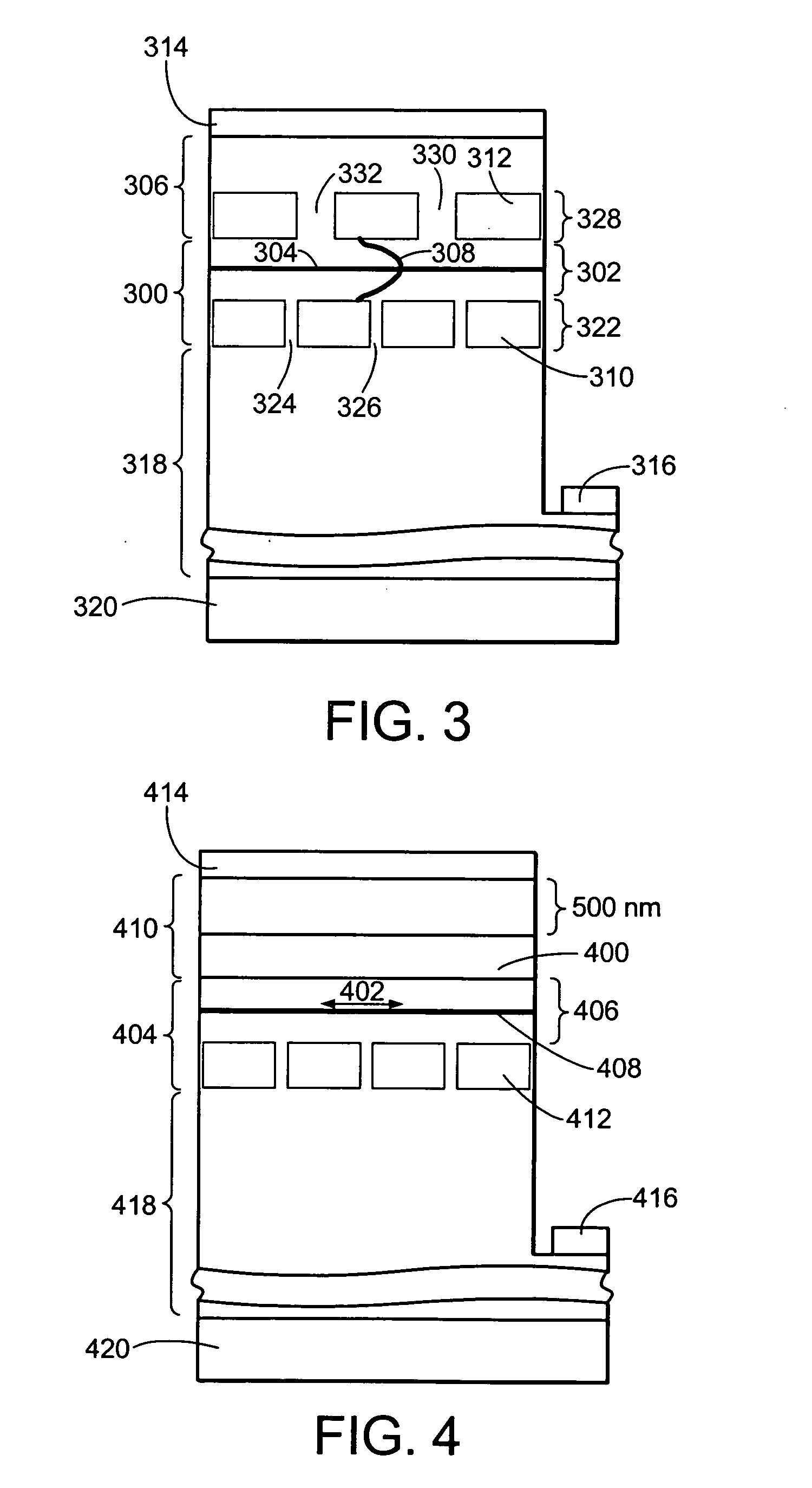
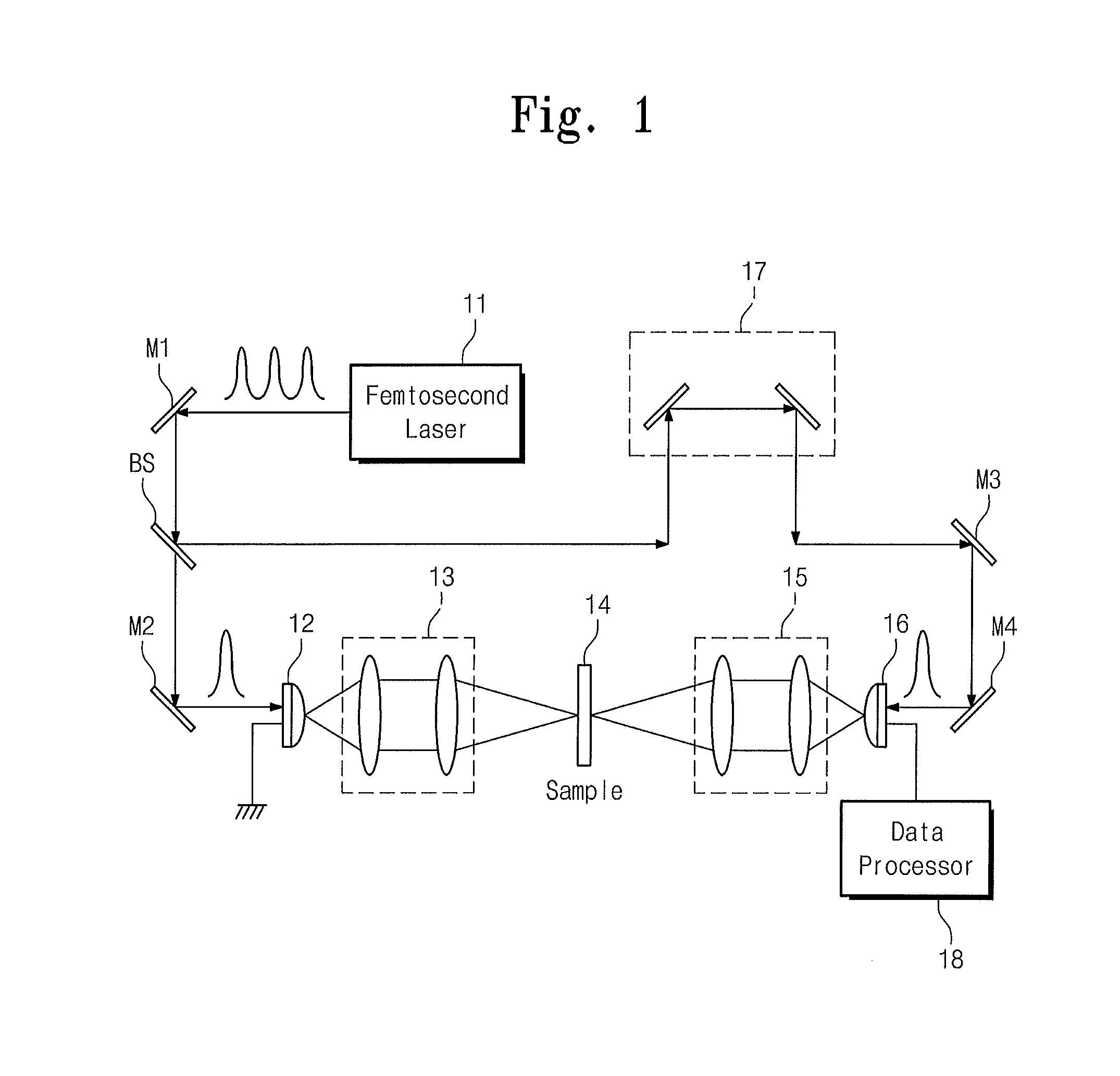
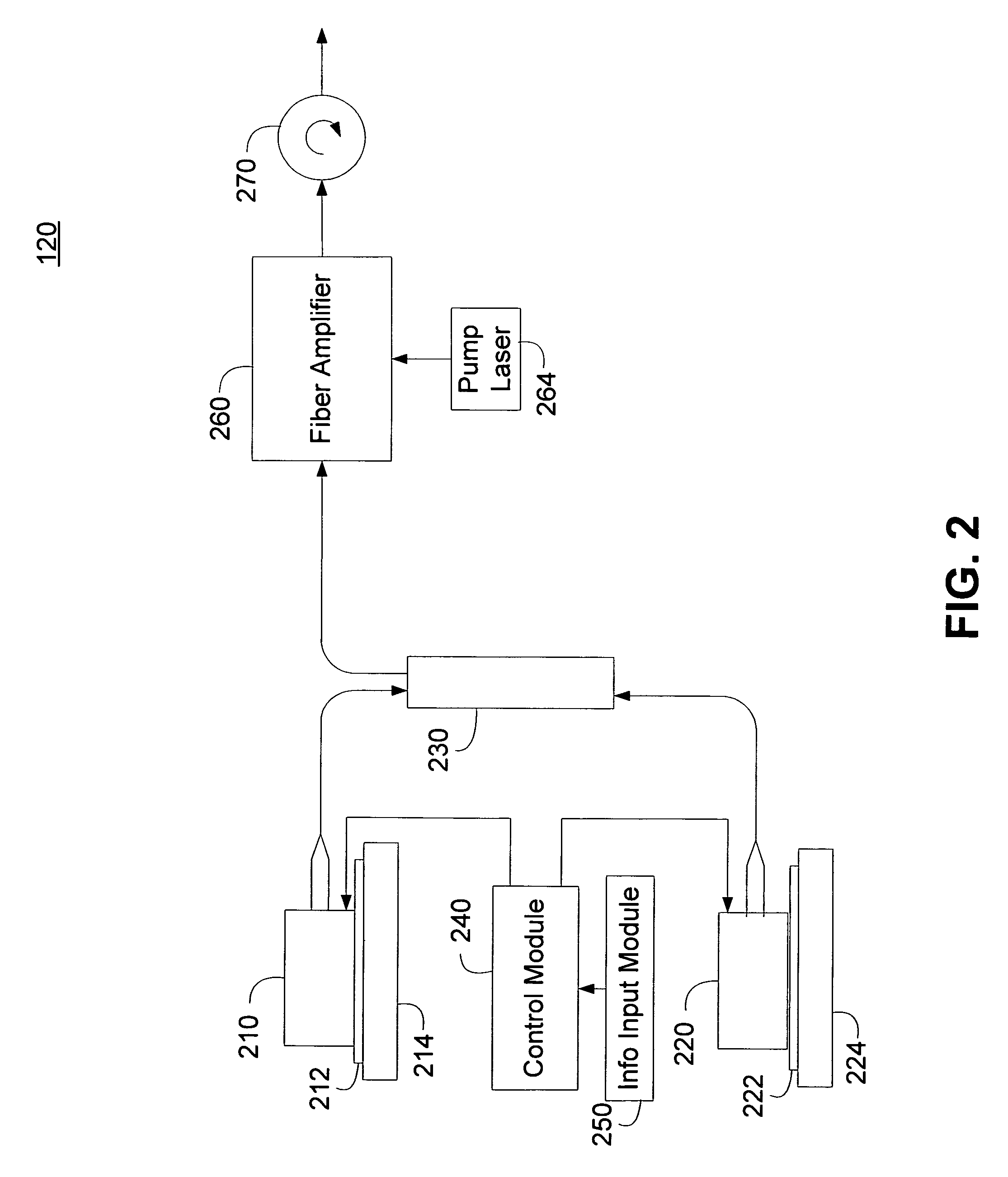
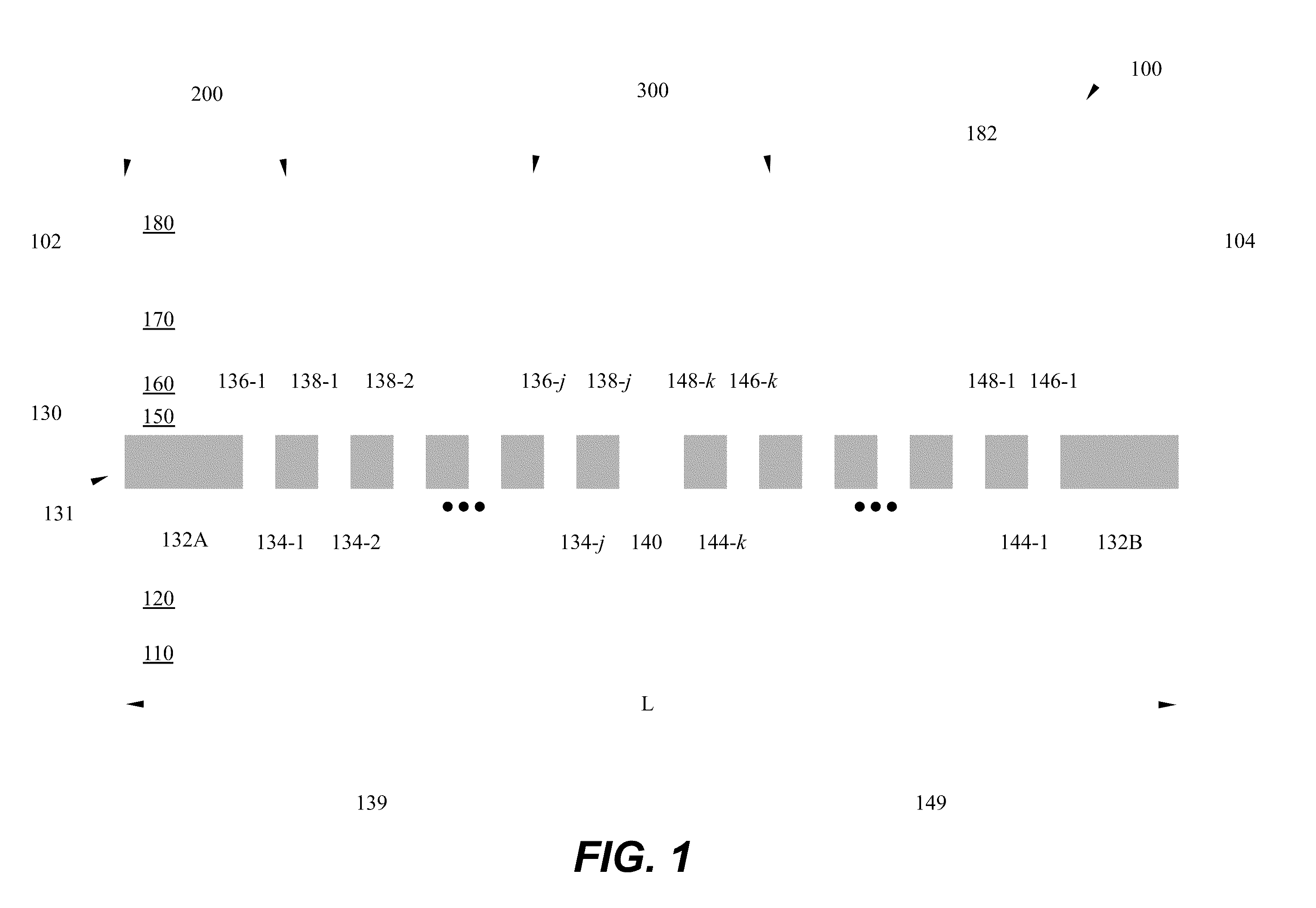
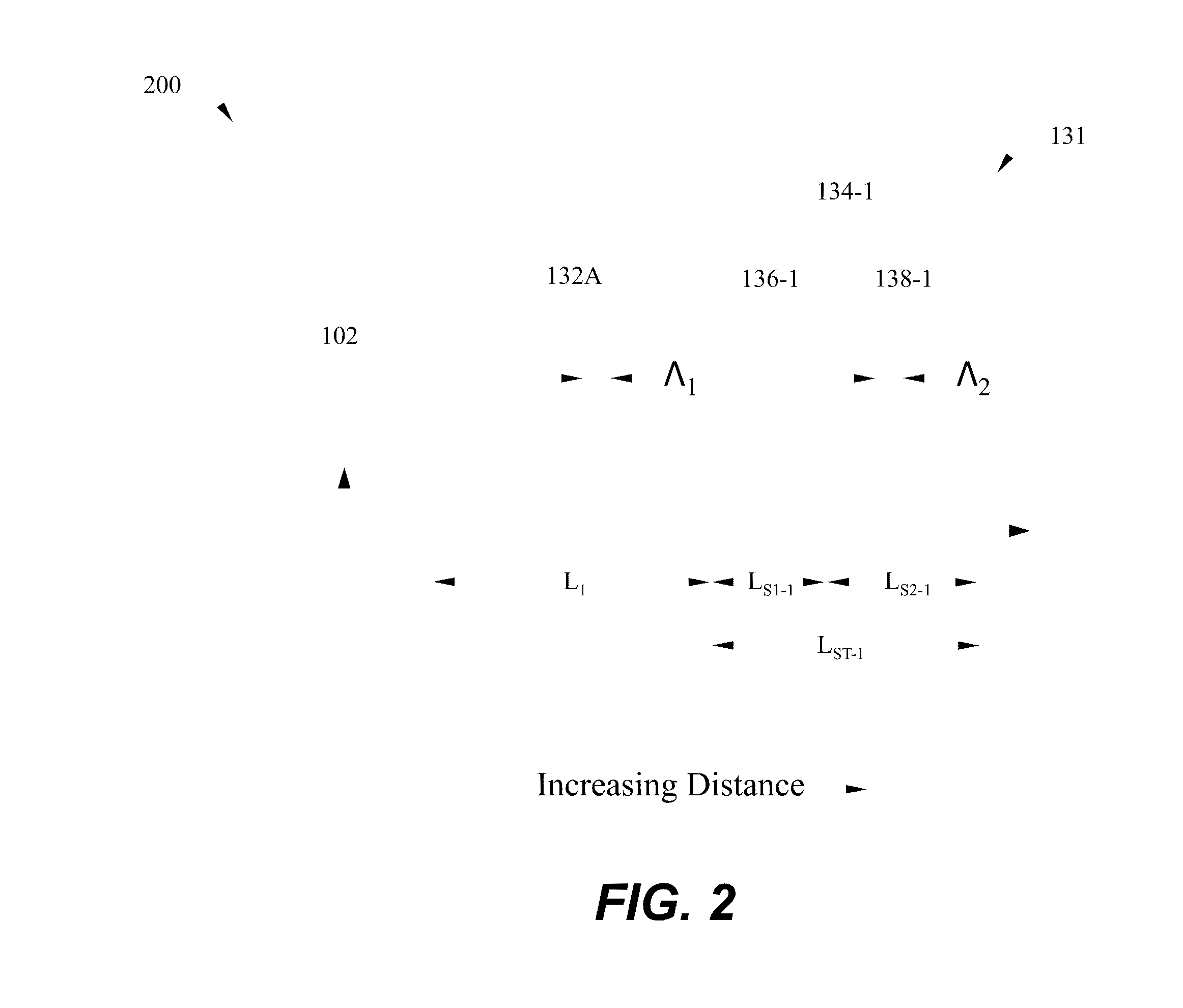
Energy assisted magnetic recording disk drive using a distributed feedback laser
A method and system for providing an energy assisted magnetic recording (EAMR) disk drive are described. The EAMR disk drive includes a media, a slider having a trailing face and an air-bearing surface (ABS), at least one distributed feedback (DFB) layer and at least one EAMR transducer on the slider. The DFB laser(s) each includes a plurality of quantum wells, a laser coupling grating, at least one reflector, and a cavity in the at least one DFB laser. The DFB laser(s) for providing energy to the media. The EAMR transducer(s) includes at least one waveguide, a write pole, at least one coil for energizing the write pole, at least one grating, and may include a near-field transducer. The grating(s) include a coupling grating for coupling the energy from the at least one DFB laser to the waveguide(s). The waveguide(s) direct the energy from the at least one grating toward the ABS.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method and system for providing energy assisted magnetic recording disk drive using a distributed feedback laser
A method and system for providing an energy assisted magnetic recording (EAMR) disk drive are described. The EAMR disk drive includes a media, a slider having a trailing face and an air-bearing surface (ABS), at least one distributed feedback (DFB) layer and EAMR transducer(s) on the slider. The DFB laser(s) each includes a plurality of quantum wells, a laser coupling grating, at least one reflector, and a cavity in the at least one DFB laser. The DFB laser(s) for providing energy to the media. The EAMR transducer(s) includes at least one waveguide, a write pole, at least one coil for energizing the write pole, at least one grating, and may include a near-field transducer. The grating(s) include a coupling grating for coupling the energy from the at least one DFB laser to the waveguide(s). The waveguide(s) direct the energy from the at least one grating toward the ABS.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Distributed feedback lasers formed via aspect ratio trapping
InactiveUS20080187018A1Large difference of refractive indexHigh optical coupling constantOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsDistributed feedback laserTrapping
Structures including dielectric diffraction gratings. In some embodiments, laser devices include diffraction gratings defined by openings formed in a dielectric material.
Owner:AMBERWAVE SYST
Light source for swept source optical coherence tomography based on cascaded distributed feedback lasers with engineered band gaps
ActiveUS20080037608A1Laser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionDistributed feedback laserGrating
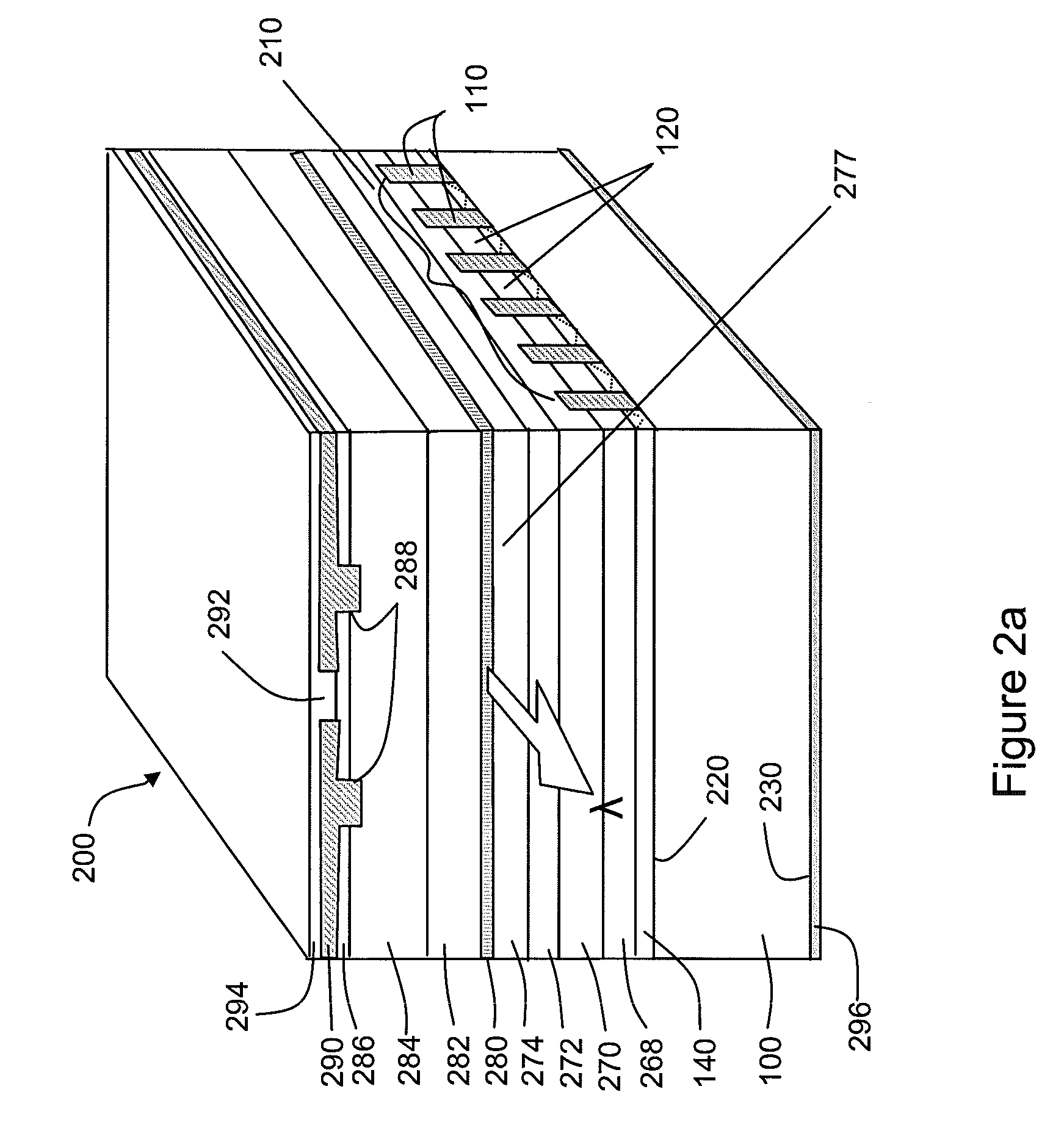
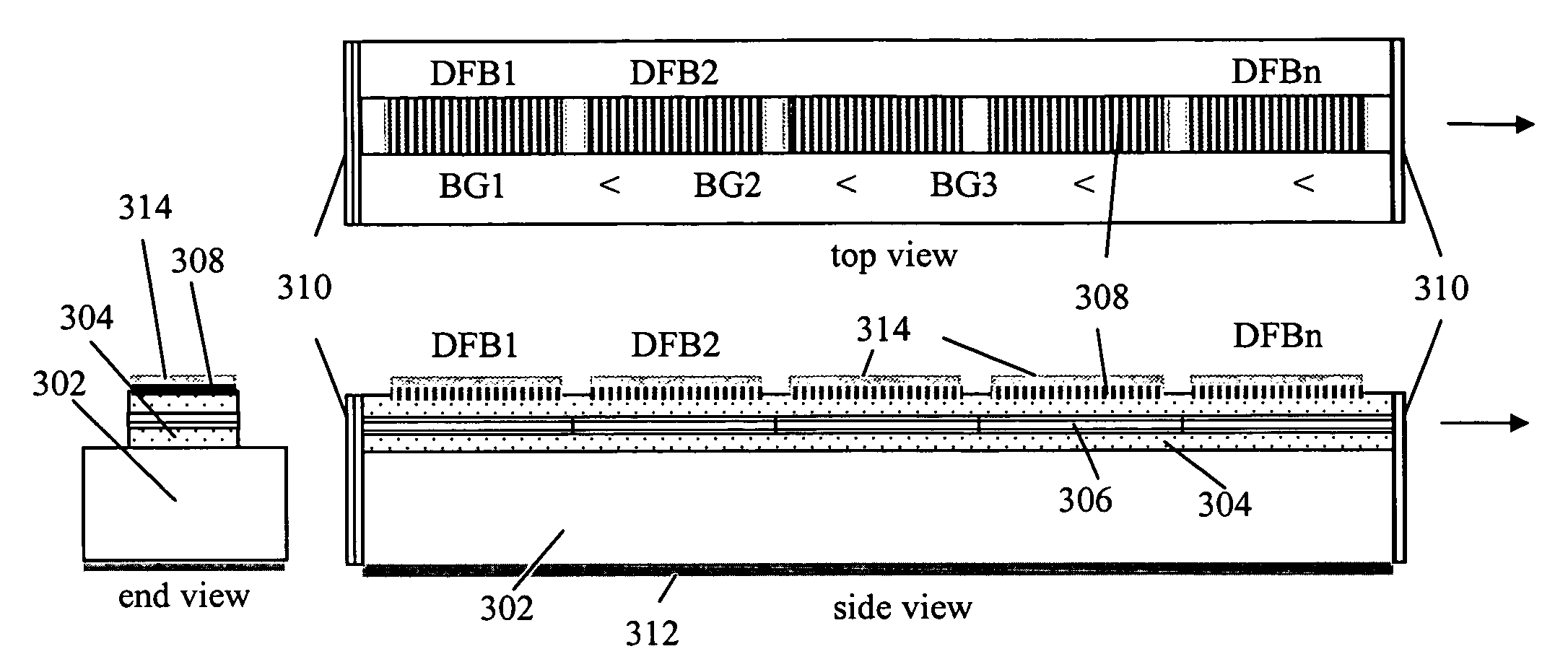
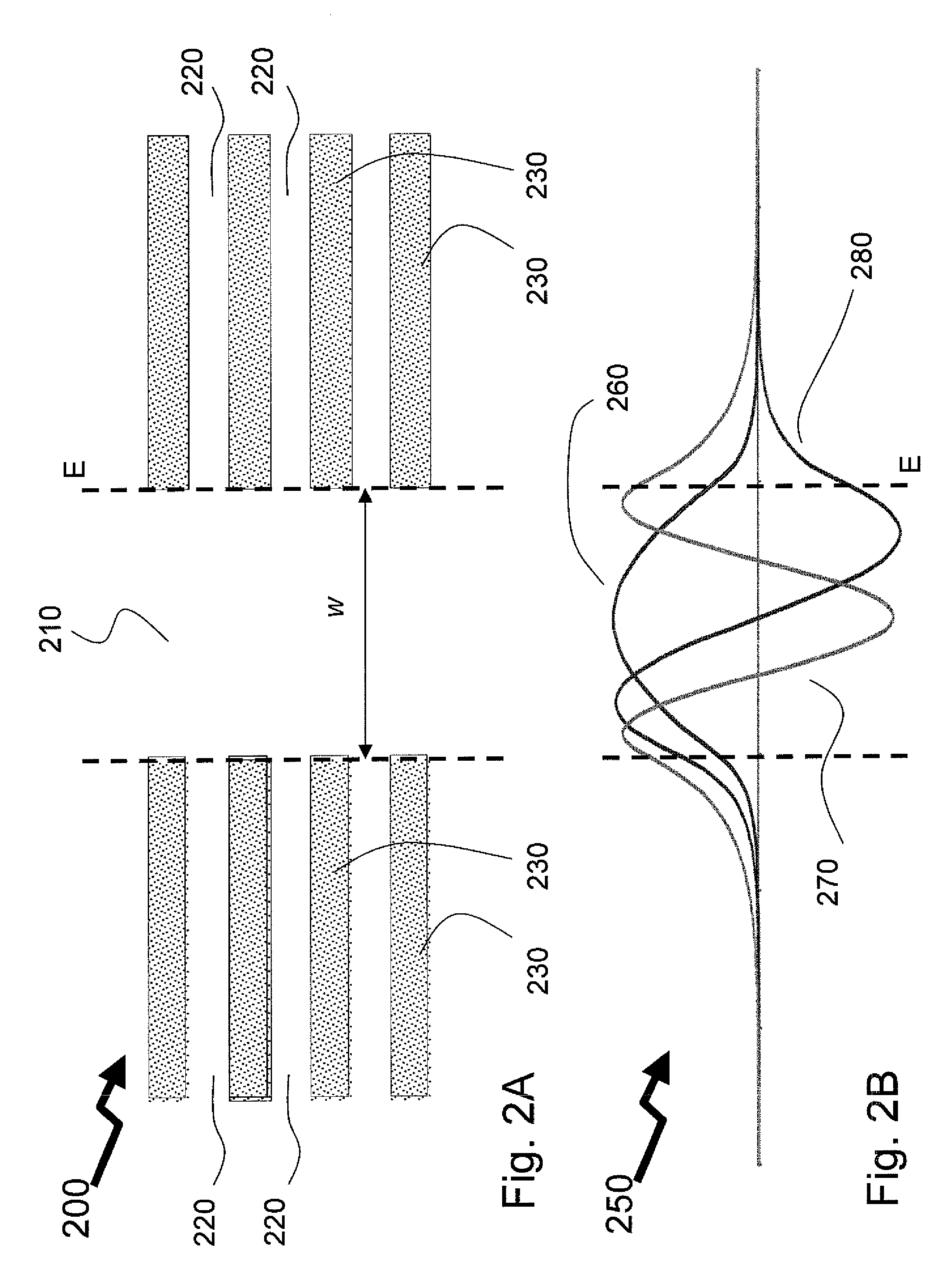
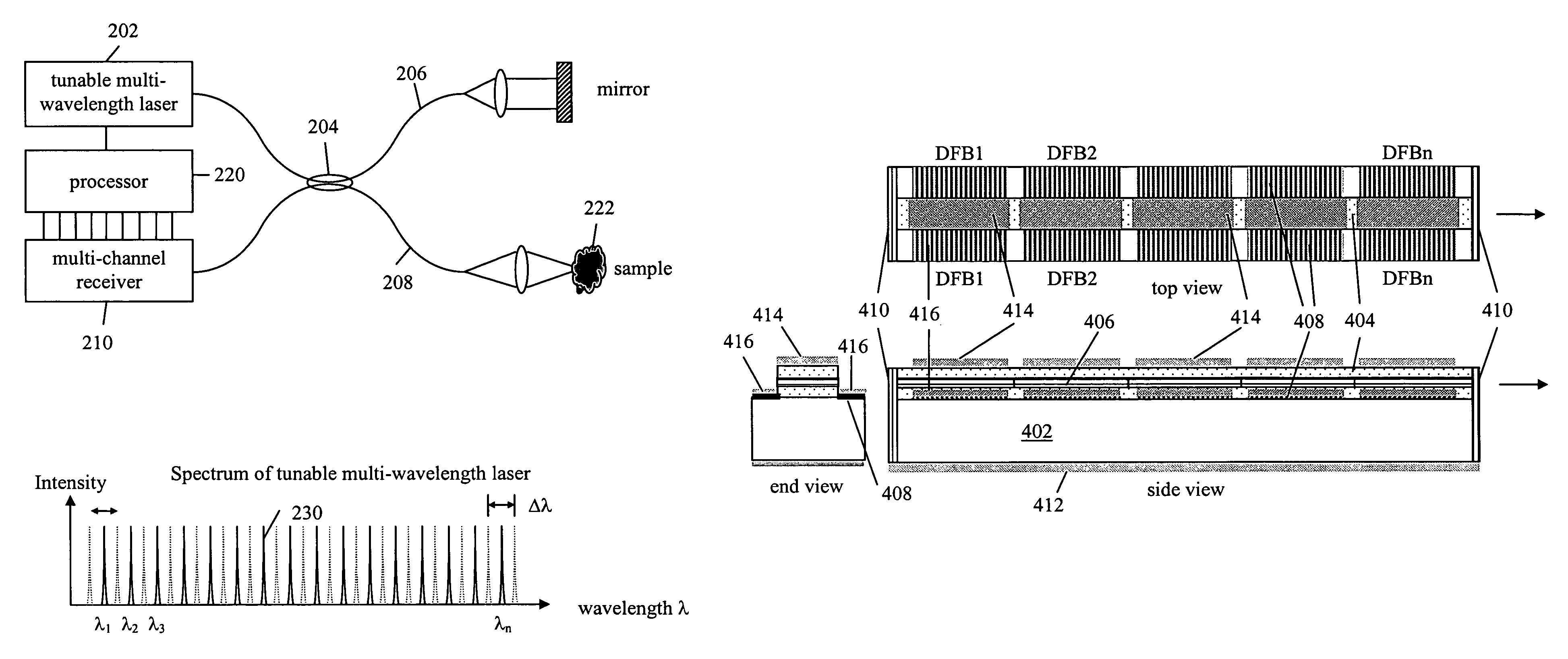
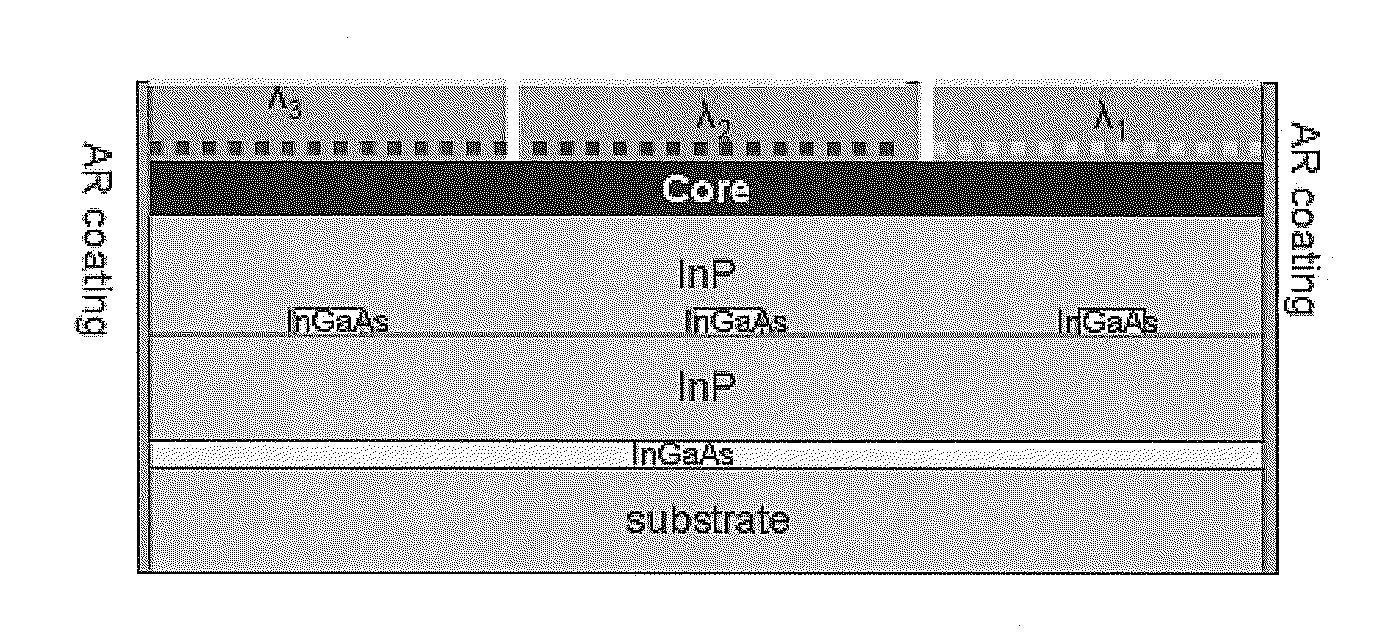
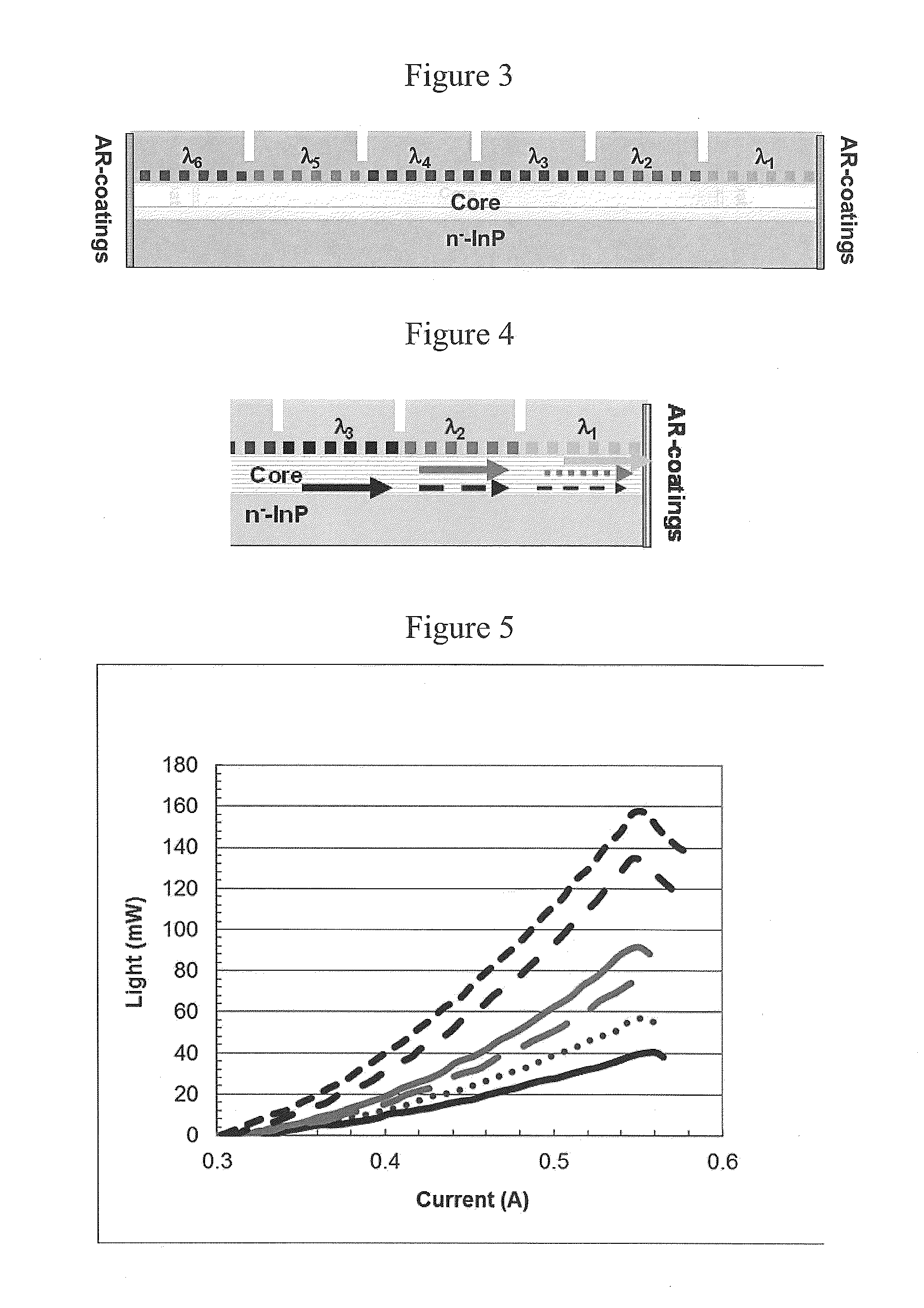
The present invention is a tunable semiconductor laser for swept source optical coherence tomography, comprising a semiconductor substrate; a waveguide on top of said substrate with multiple sections of different band gap engineered multiple quantum wells (MQWs); a multiple of distributed feedback (DFB) gratings corresponding to each said band gap engineered MWQs, each DFB having a different Bragg grating period; and anti-reflection (AR) coating deposited on at least the laser emission facet of the laser to suppress the resonance of Fabry-Perot cavity modes. Each DFB MQWs section can be activated and tuned to lase across a fraction of the overall bandwidth as is achievable for a single DFB laser and all sections can be sequentially activated and tuned so as to collectively cover a broad bandwidth, or simultaneously activated and tuned to enable a tunable multi-wavelength laser. The laser hence can emit either a single lasing wavelength or a multiple of lasing wavelengths and is very suitable for swept-source OCT applications.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
Horizontal emitting, vertical emitting, beam shaped, distributed feedback (DFB) lasers fabricated by growth over a patterned substrate with multiple overgrowth
InactiveUS20070125995A1Improve propertiesEffective limitOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionDistributed feedback laserGrating
A structure using integrated optical elements is comprised of a substrate, a buffer layer grown on the substrate, one or more first patterned layers deposited on top of the buffer layer, wherein each of the first patterned layers is comprised of a bottom lateral epitaxial overgrowth (LEO) mask layer and a LEO nitride layer filling holes in the bottom LEO mask layer, one or more active layers formed on the first patterned layers, and one or more second patterned layers deposited on top of the active layer, wherein each of the second patterned layers is comprised of a top LEO mask layer and a LEO nitride layer filling holes in the top LEO mask layer, wherein the top and / or bottom LEO mask layers act as a mirror, optical confinement layer, grating, wavelength selective element, beam shaping element or beam directing element for the active layers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
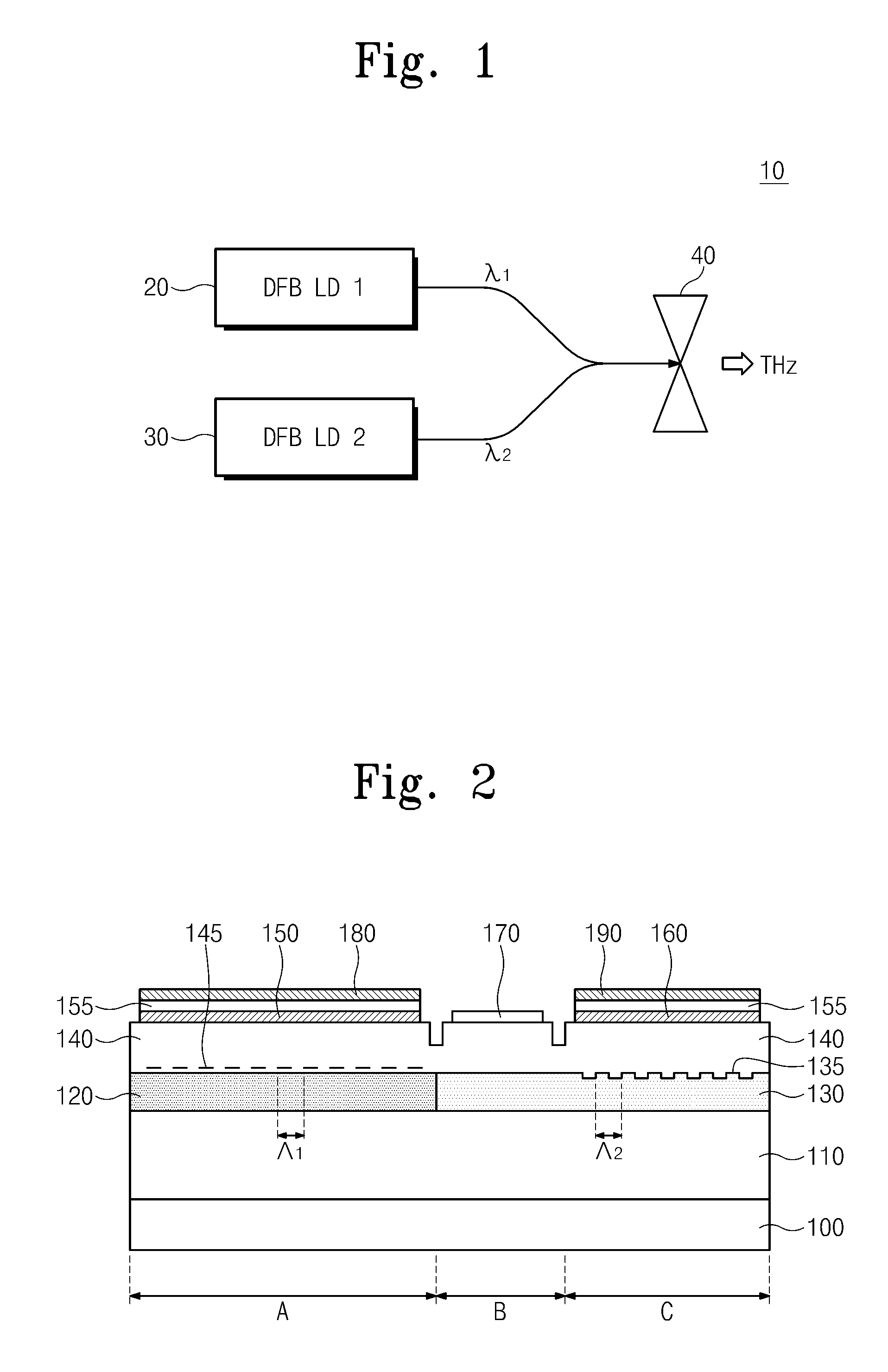
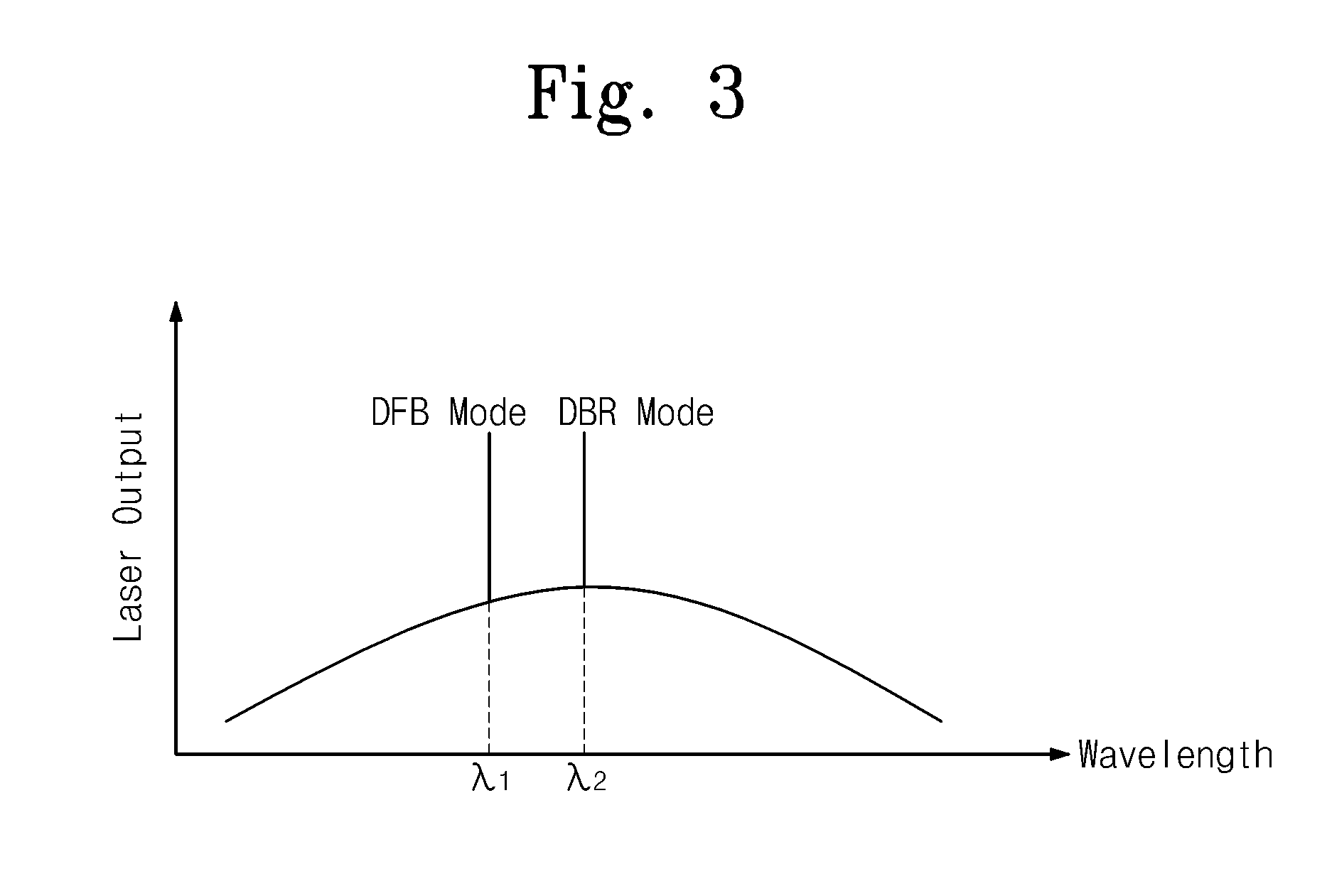
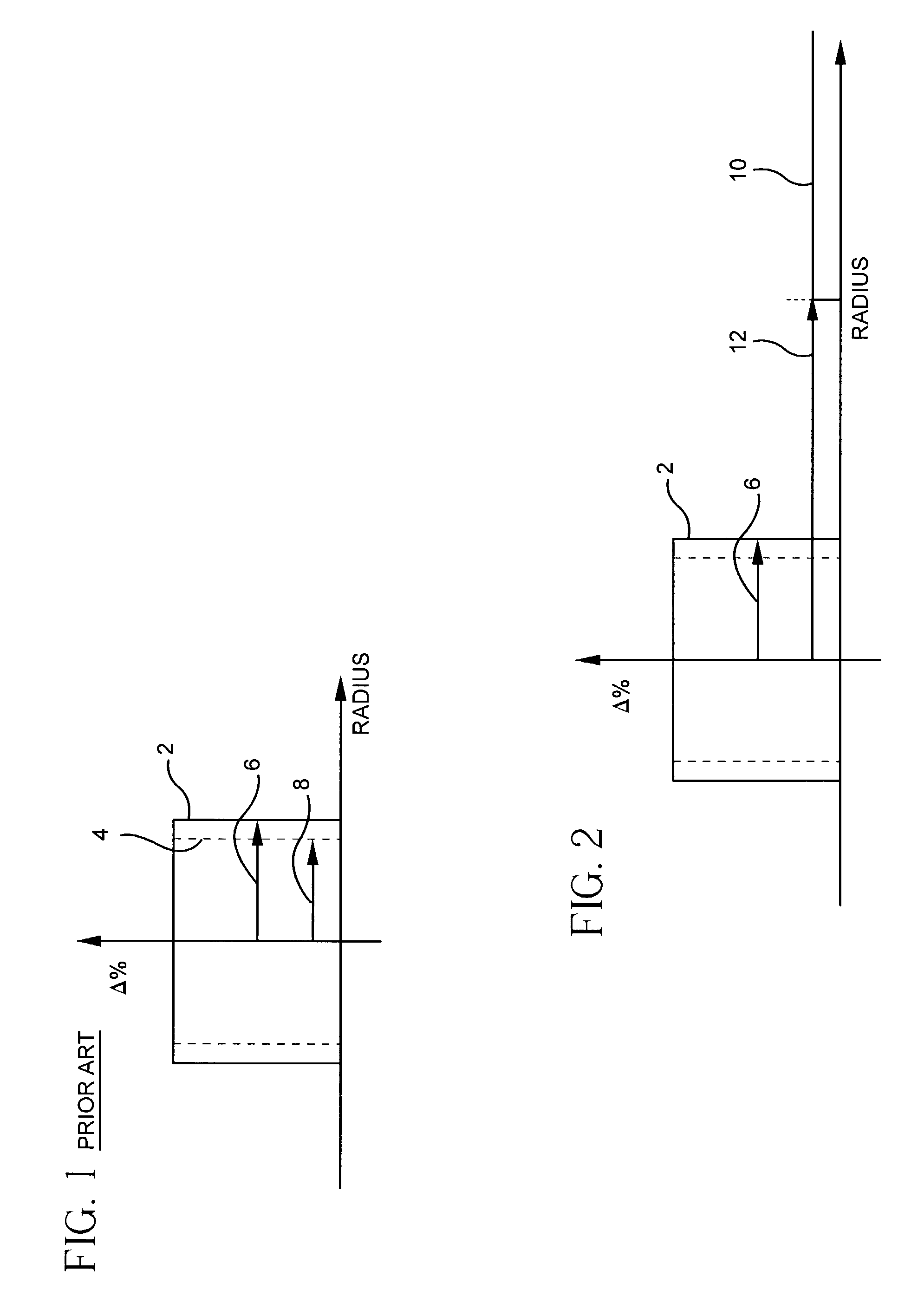
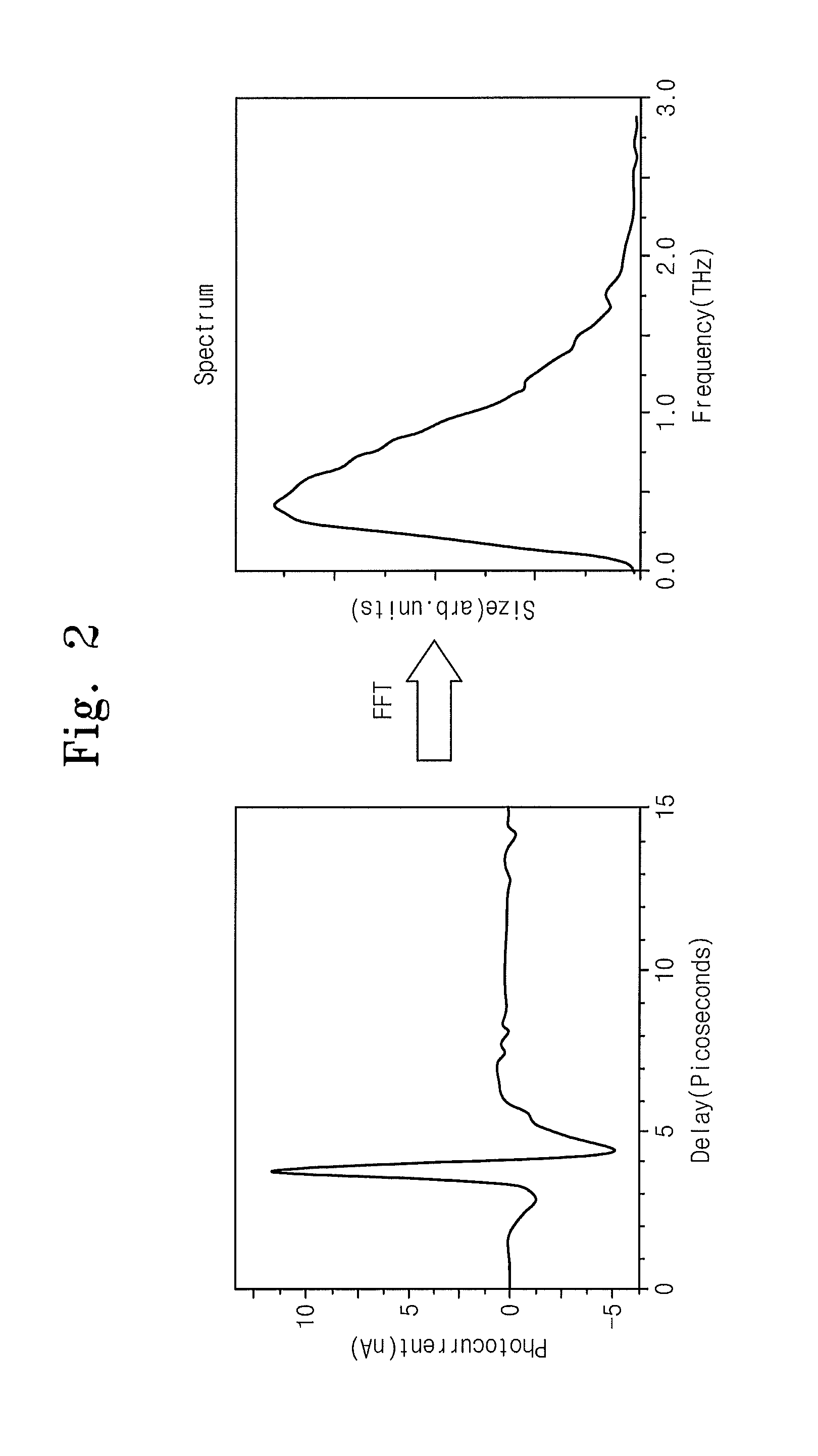
Dual mode semiconductor laser and terahertz wave apparatus using the same
InactiveUS20120051386A1Change the refractive indexOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersDistributed feedback laserDistributed Bragg reflector laser
Provided are a dual mode semiconductor laser and a terahertz wave apparatus using the same. The dual mode semiconductor laser includes a distributed feedback laser structure section including a first diffraction grating on a substrate and a distributed Bragg reflector laser structure section including a second diffraction grating on the substrate. A first wavelength oscillated by the distributed feedback laser structure section and a second wavelength oscillated by the distributed Bragg reflector laser structure section are different from each other, and the distributed feedback laser structure section and the distributed Bragg reflector laser structure section share the same gain medium with each other.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Optical waveguide fiber for local access
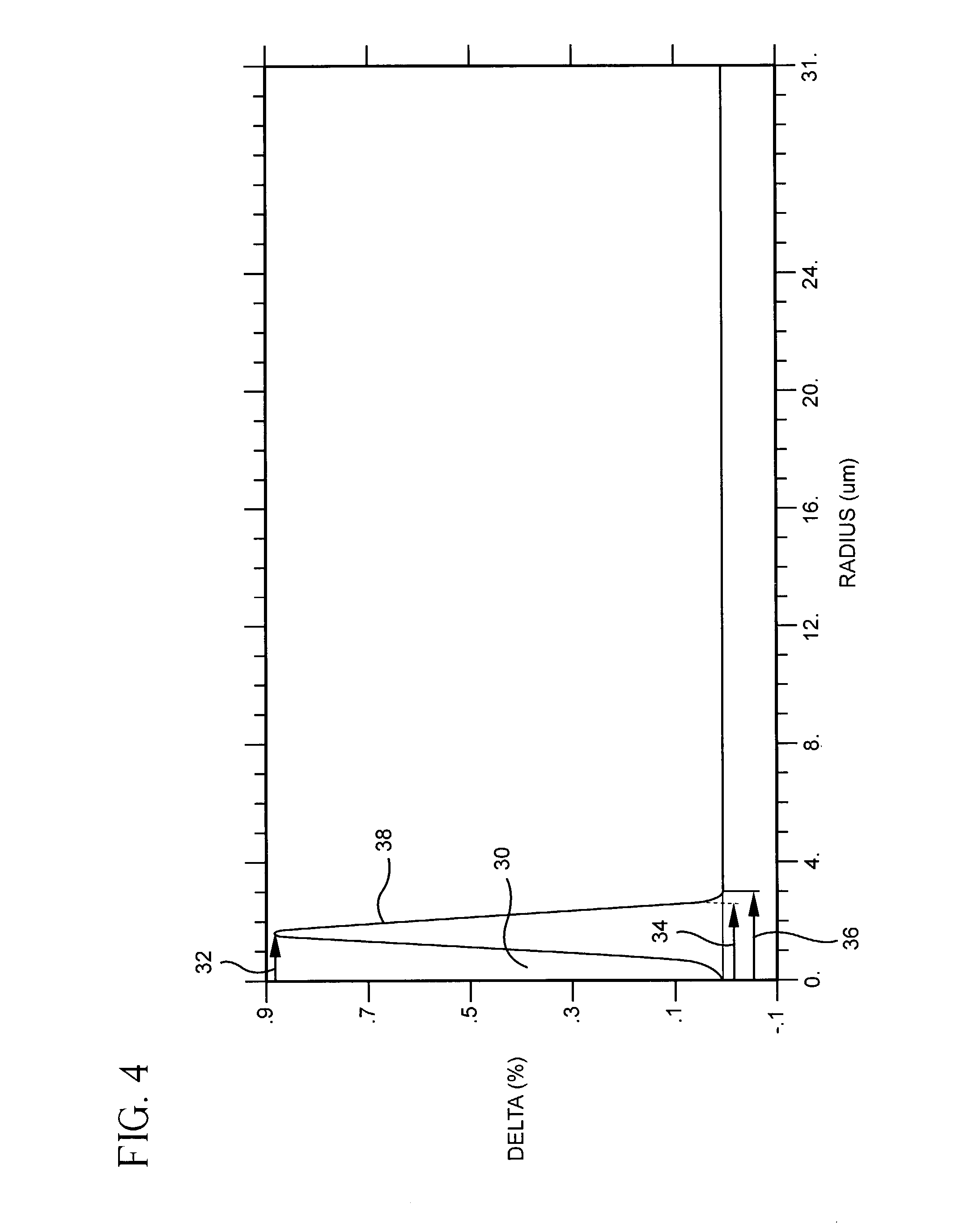
InactiveUS7043125B2Consistent performancePower Loss MinimizationLaser detailsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingDistributed feedback laserRefractive index
Disclosed is a single mode optical waveguide fiber having a low cut off wavelength, and mode field diameter and bend resistance similar to step index single mode optical waveguide fiber designed for use at 1310 nm. By including a clad region of raised refractive index spaced apart from the core region of the single mode optical waveguide fiber, the cut off wavelength can be reduced to 850 nm. The single mode optical waveguide fiber in accord with the invention may also have a core region having a reduced refractive index on centerline surrounded by a region of higher refractive index and a clad region which is substantially uniform. The single mode optical waveguide fiber is thus ideally suited for use with the low cost, reliable VCSEL operating at 850 nm, a Fabry-Perot laser operating at 1310 nm, or a distributed feedback laser operating at 1550 nm thereby enabling low cost, easily installed, home access portions of the broadband telecommunications system.
Owner:CORNING INC
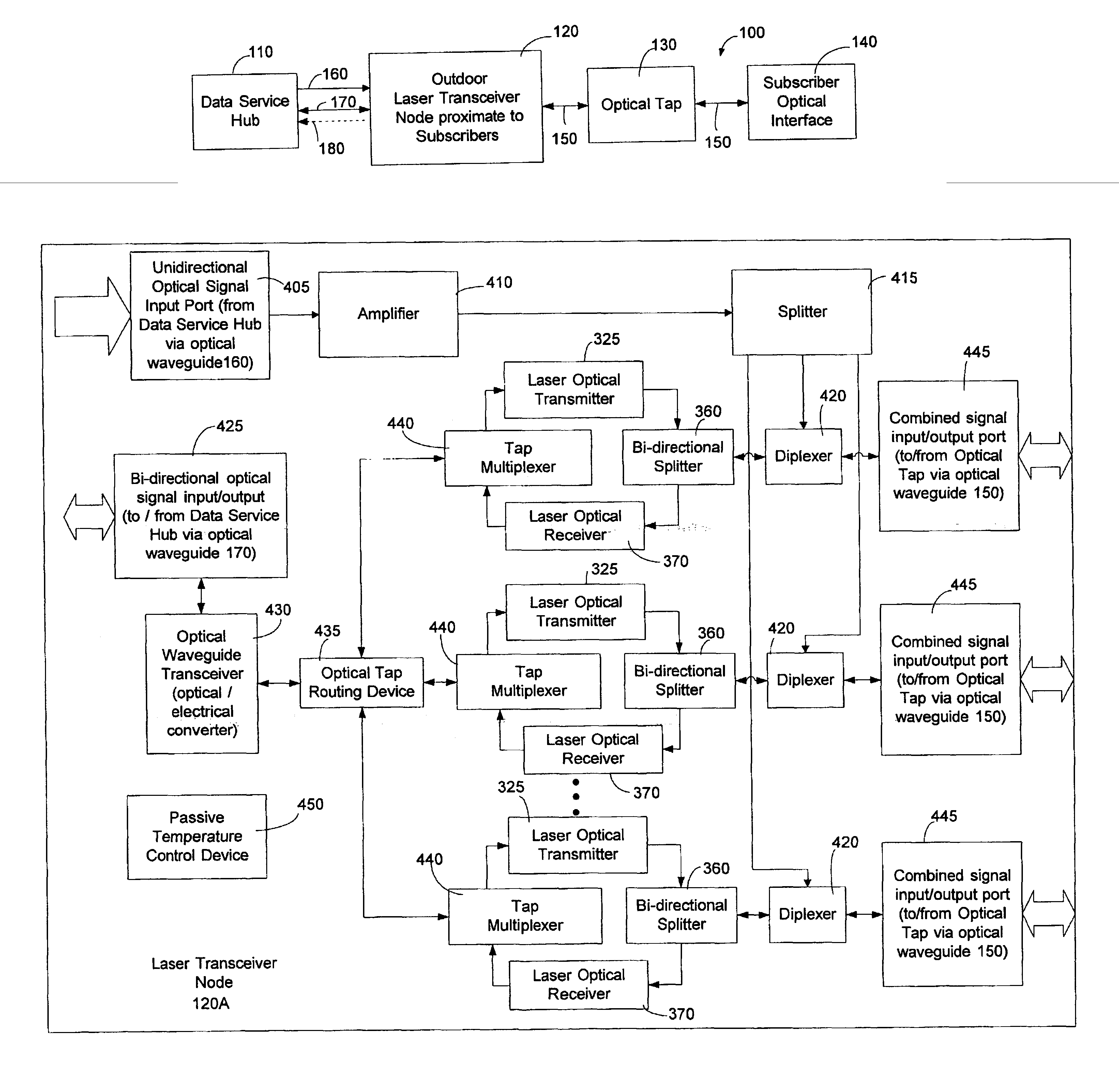
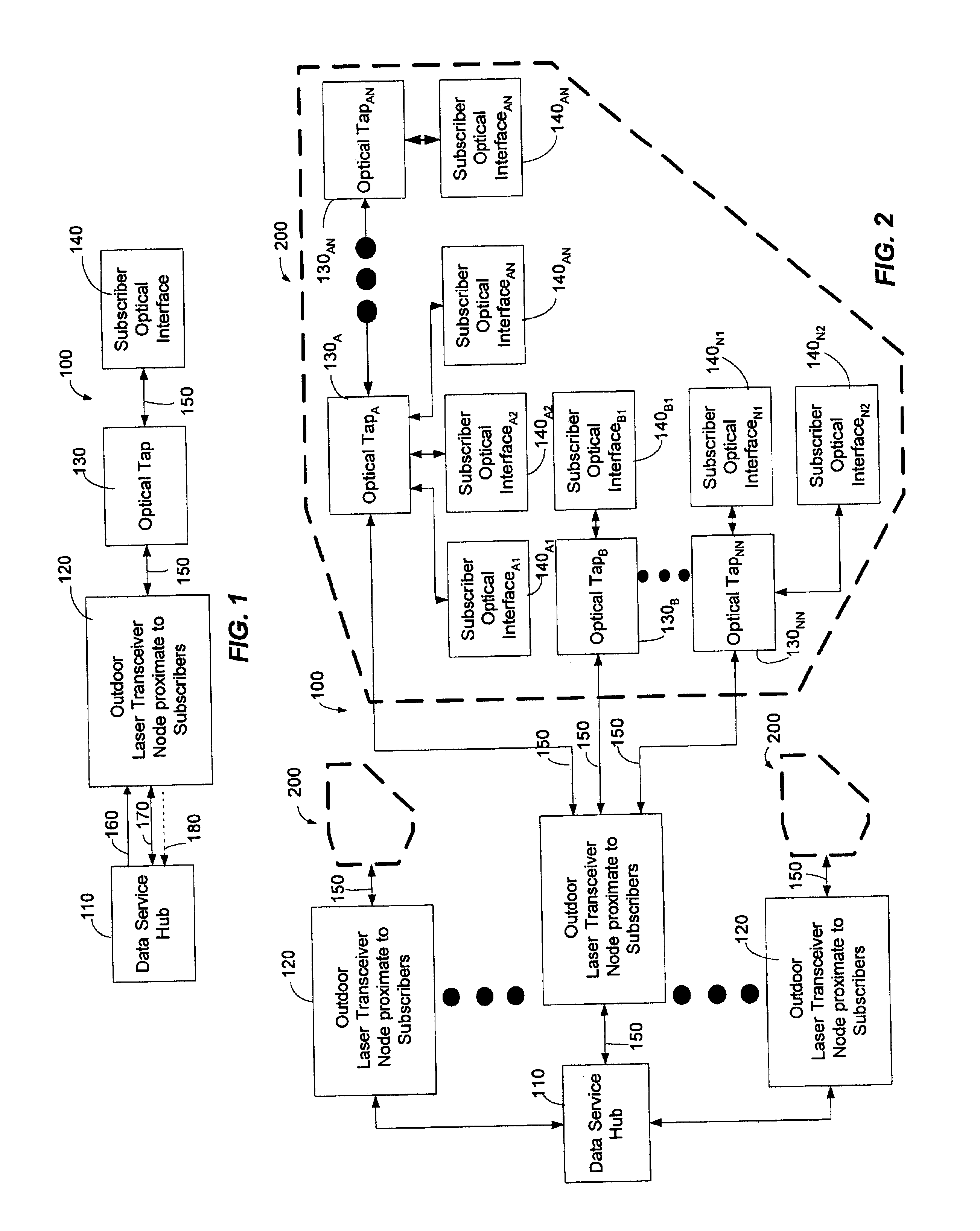
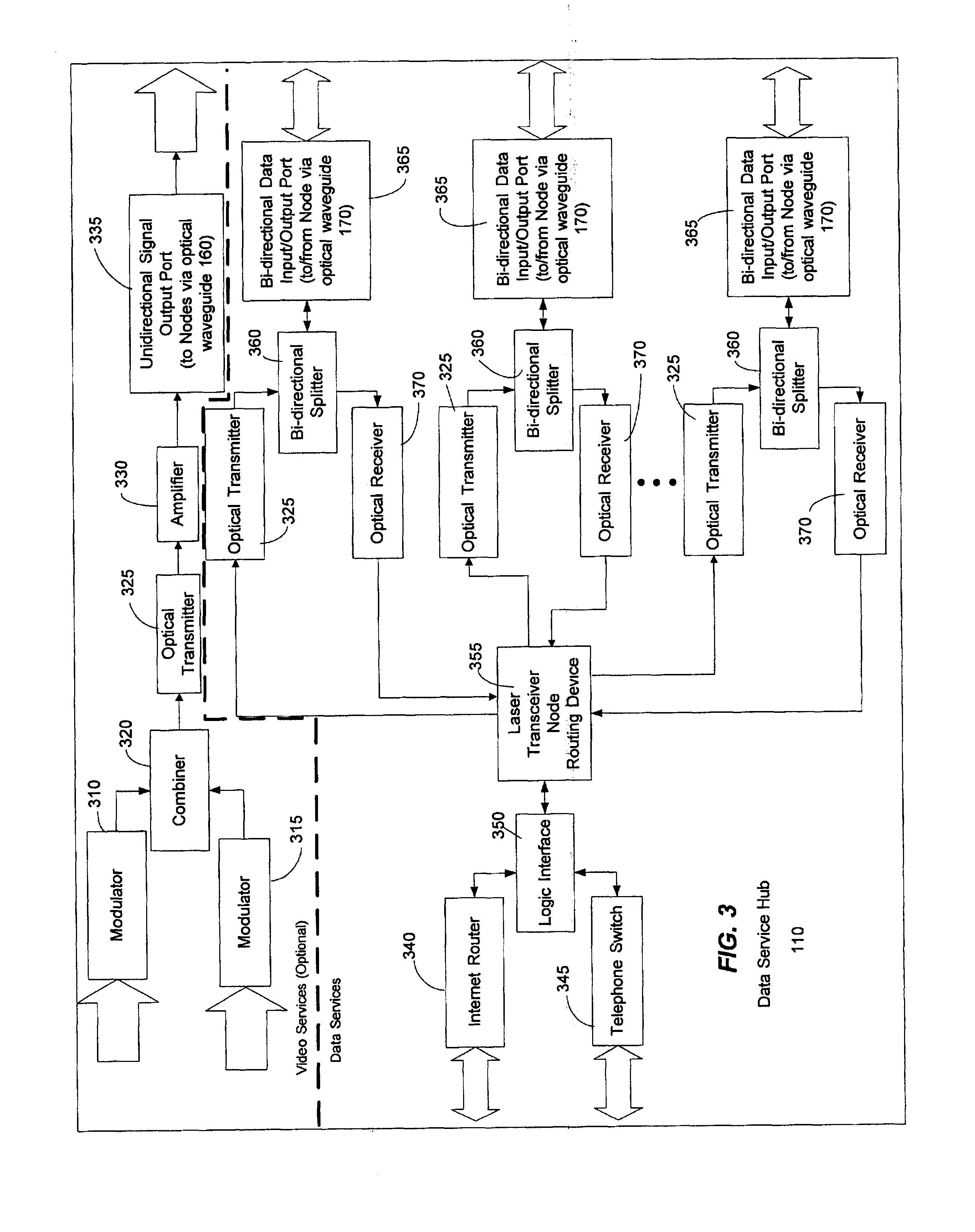
System and method for communicating optical signals between a data service provider and subscribers
InactiveUS6973271B2High speed symmetrical data transmissionReduce in quantityMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsDistributed feedback laserLaser transmitter
An optical fiber network can include an outdoor laser transceiver node that can be positioned in close proximity to the subscribers of an optical fiber network. The outdoor laser transceiver node does not require active cooling and heating devices that control the temperature surrounding the laser transceiver node. The laser transceiver node can adjust a subscriber's bandwidth on a subscription basis or on an as-needed basis. The laser transceiver node can also offer data bandwidth to the subscriber in preassigned increments. Additionally, the laser transceiver node lends itself to efficient upgrading that can be performed entirely on the network side. The laser transceiver node can also provide high speed symmetrical data transmission. Further, the laser transceiver node can utilize off-the-shelf hardware to generate optical signals such as Fabry-Perot (F-P) laser transmitters, distributed feed back lasers (DFB), or vertical cavity surface emitting lasers (VCSELs).
Owner:ARRIS SOLUTIONS
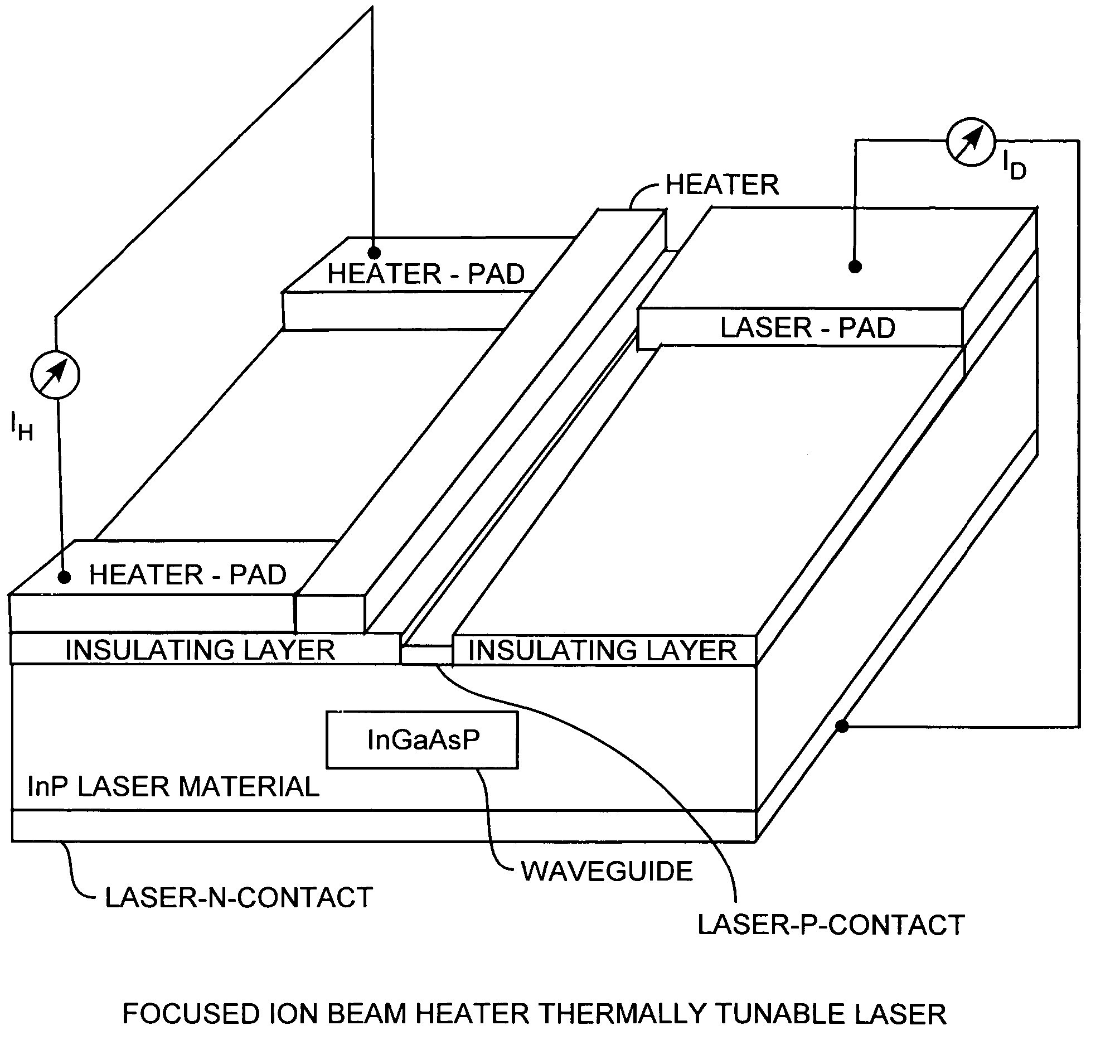
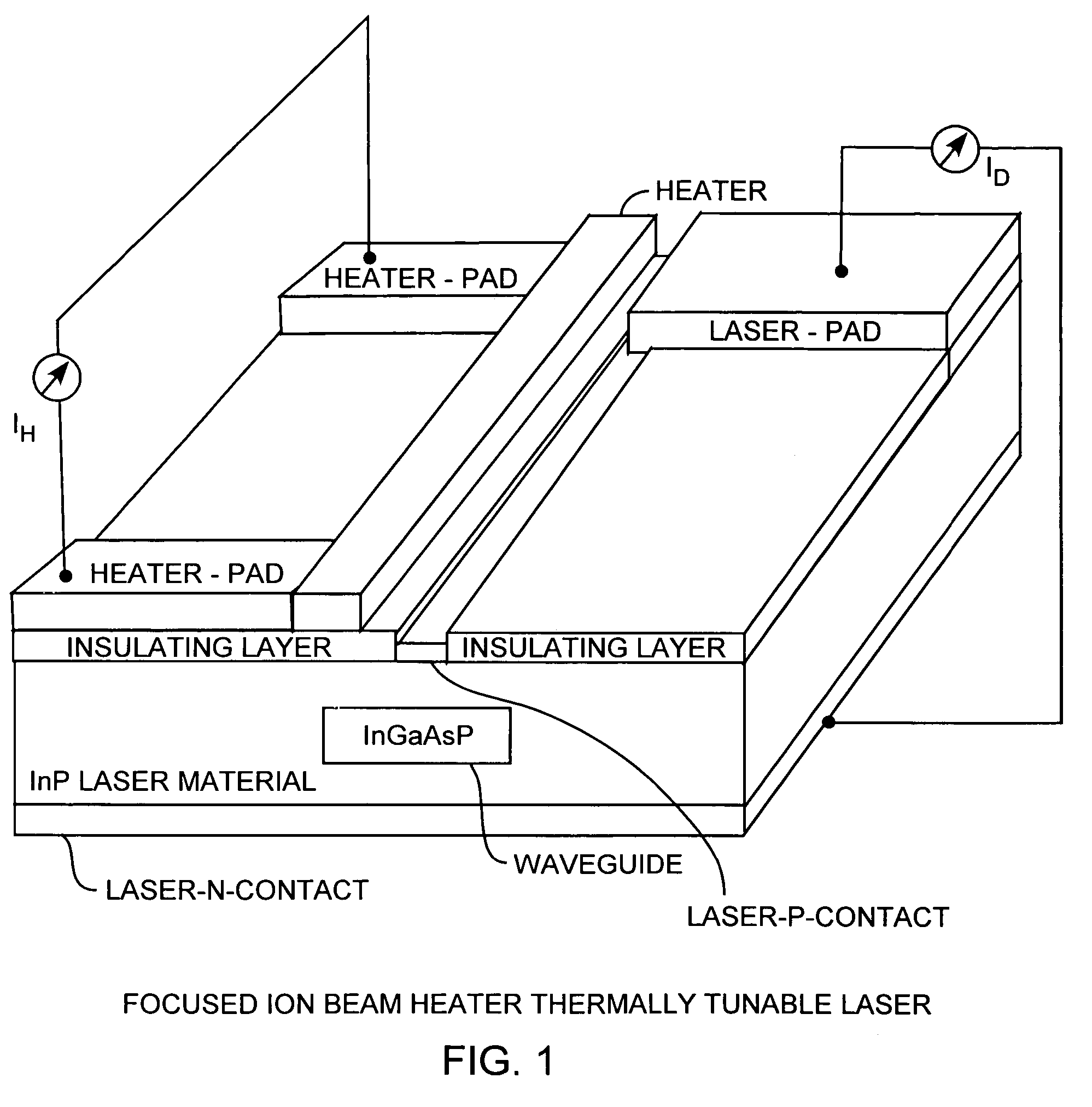
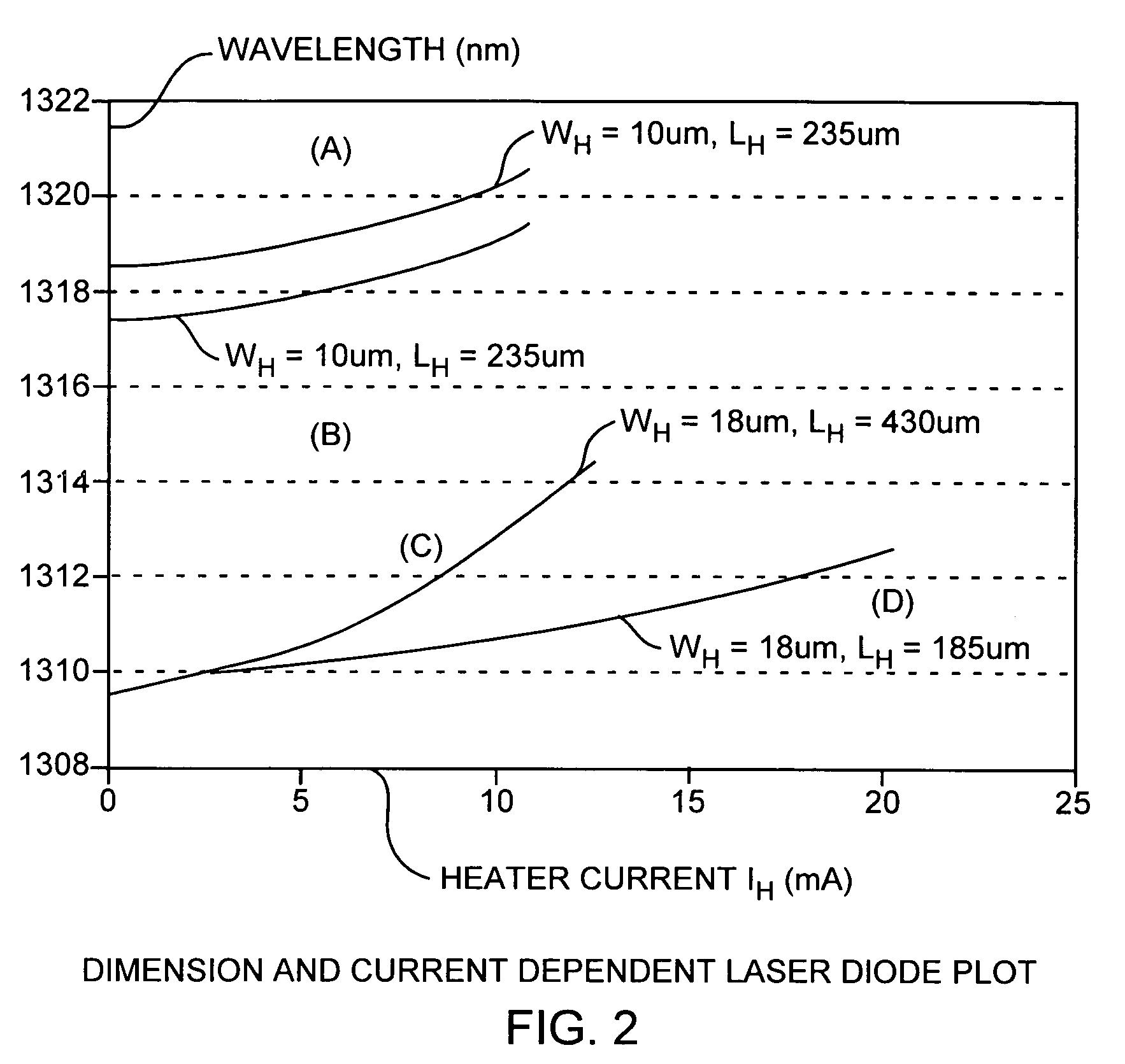
Focused ion beam heater thermally tunable laser
InactiveUS20060045147A1Laser optical resonator constructionLaser cooling arrangementsDistributed feedback laserIon beam
Platinum (Pt) thin film heaters are deposited by a focused ion beam for semiconductor manufacturing of thermally tunable distributed feedback lasers. An exemplar 1.3 μm InGaAsP / InP laser is integrated with a tuning element having a wide wavelength tuning range of 4.9 nm, that is, 857 GHz, with a small heater current of 13.0 mA.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
Article comprising a two-dimensional photonic crystal coupler and method of making the same
InactiveUS6975664B1Efficient workCladded optical fibreLaser optical resonator constructionDistributed feedback laserResonant cavity
A two-dimensional photonic crystal coupler is disclosed, together with a cross-coupled laser structure that is based on a two-dimensional photonic crystal coupler stage. Unlike traditional grating couplers, this two-dimensional photonic crystal coupler can couple light into a single or a plurality of discrete directions in the far-field, i.e., the output light may be unidirectional or discrete. The coupler can be integrated with one-dimensional lasers, a distributed feedback laser, a distributed Bragg reflector laser, and integrated on the same waveguide as the lasers. A resonant cavity coupler design improves the coupling efficiency of two-dimensional photonic crystal-based couplers.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Enhanced efficiency laterally-coupled distributed feedback laser
ActiveUS7796656B2Improve efficiencyImprove quantum efficiencyOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionDistributed feedback laserQuantum efficiency
The invention describes the method and apparatus for enhanced efficiency in a laterally-coupled distributed feedback (LC-DFB) laser. In a device featuring the effective ridge design, lateral confinement of the guided optical modes is provided by a surface etched grating, which also serves as a DFB element of the laser. Coupling and quantum efficiency of such a LC-DFB laser both improve with an increase of the lateral mode order. In accordance with this invention, a dramatic enhancement of the laser efficiency is achievable by designing it to operate in one of the higher order modes, notably the first order mode, while all the other lateral modes, including the zero order mode, are suppressed through gain-loss discrimination. In the exemplary embodiment of the invention, this enhanced efficiency technique is applied to the design of a single-mode LC-DFB laser suitable for a monolithic integration with other active and passive functional elements of photonic integrated circuits fabricated by using one-step epitaxial growth.
Owner:ONECHIP PHOTONICS
Light source for swept source optical coherence tomography based on cascaded distributed feedback lasers with engineered band gaps
ActiveUS7554668B2Laser optical resonator constructionMaterial analysis by optical meansDistributed feedback laserGrating
The present invention is a tunable semiconductor laser for swept source optical coherence tomography, comprising a semiconductor substrate; a waveguide on top of said substrate with multiple sections of different band gap engineered multiple quantum wells (MQWs); a multiple of distributed feedback (DFB) gratings corresponding to each said band gap engineered MWQs, each DFB having a different Bragg grating period; and anti-reflection (AR) coating deposited on at least the laser emission facet of the laser to suppress the resonance of Fabry-Perot cavity modes. Each DFB MQWs section can be activated and tuned to lase across a fraction of the overall bandwidth as is achievable for a single DFB laser and all sections can be sequentially activated and tuned so as to collectively cover a broad bandwidth, or simultaneously activated and tuned to enable a tunable multi-wavelength laser. The laser hence can emit either a single lasing wavelength or a multiple of lasing wavelengths and is very suitable for swept-source OCT applications.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
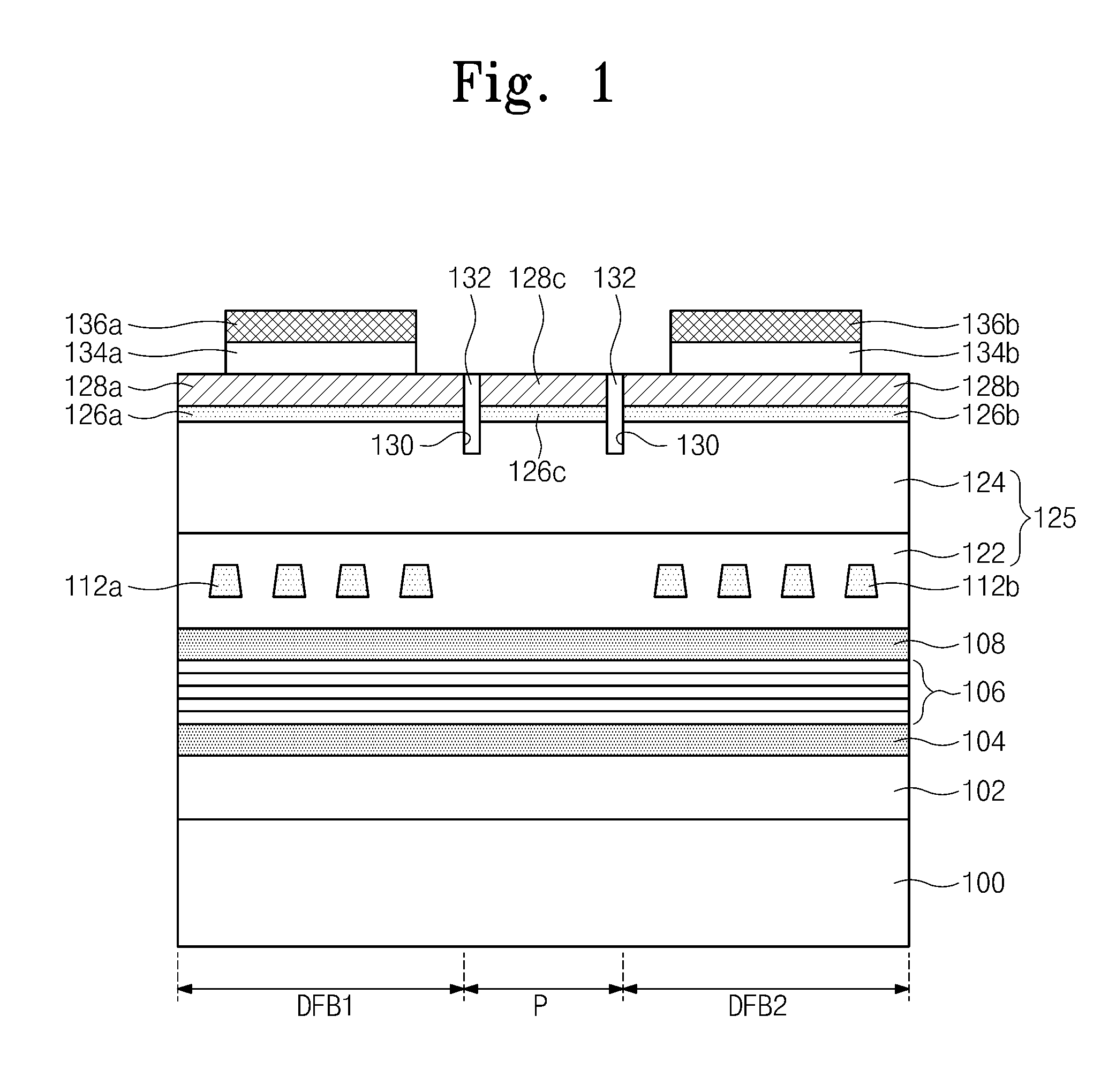
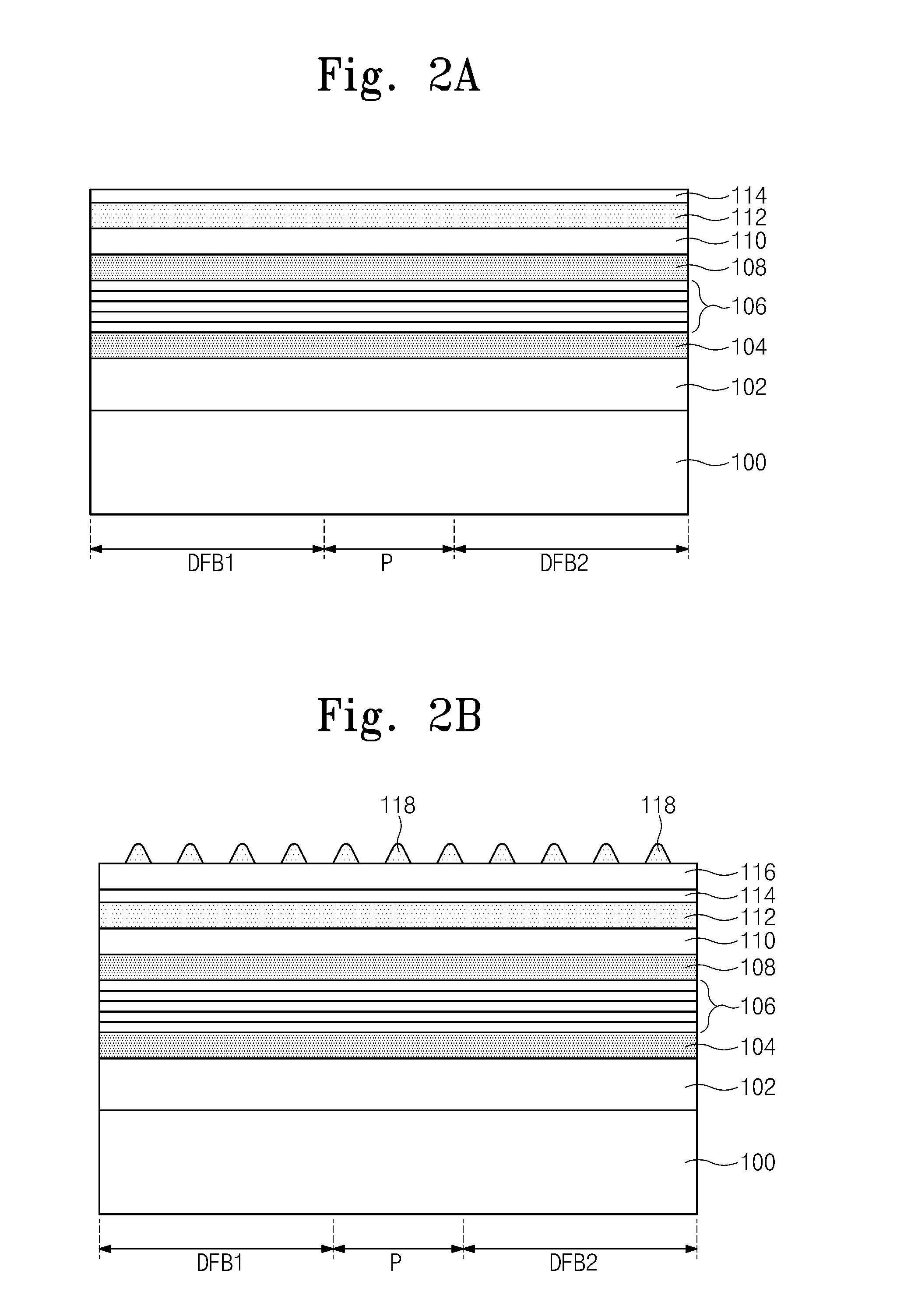
Multiple distributed feedback laser devices
ActiveUS20100142571A1Improve reliabilityImprove power generation efficiencyOptical resonator shape and constructionNanoopticsDistributed feedback laserActive layer
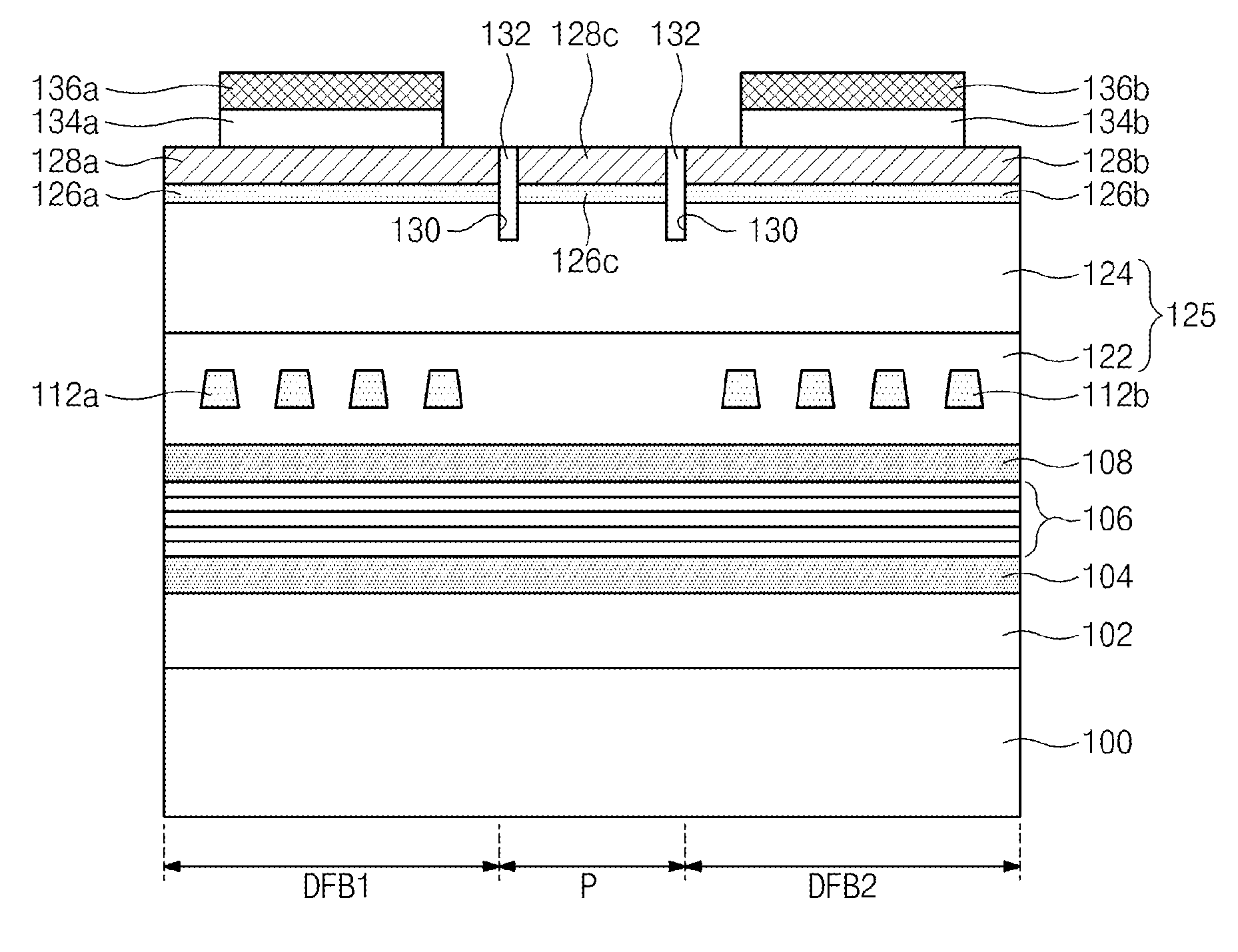
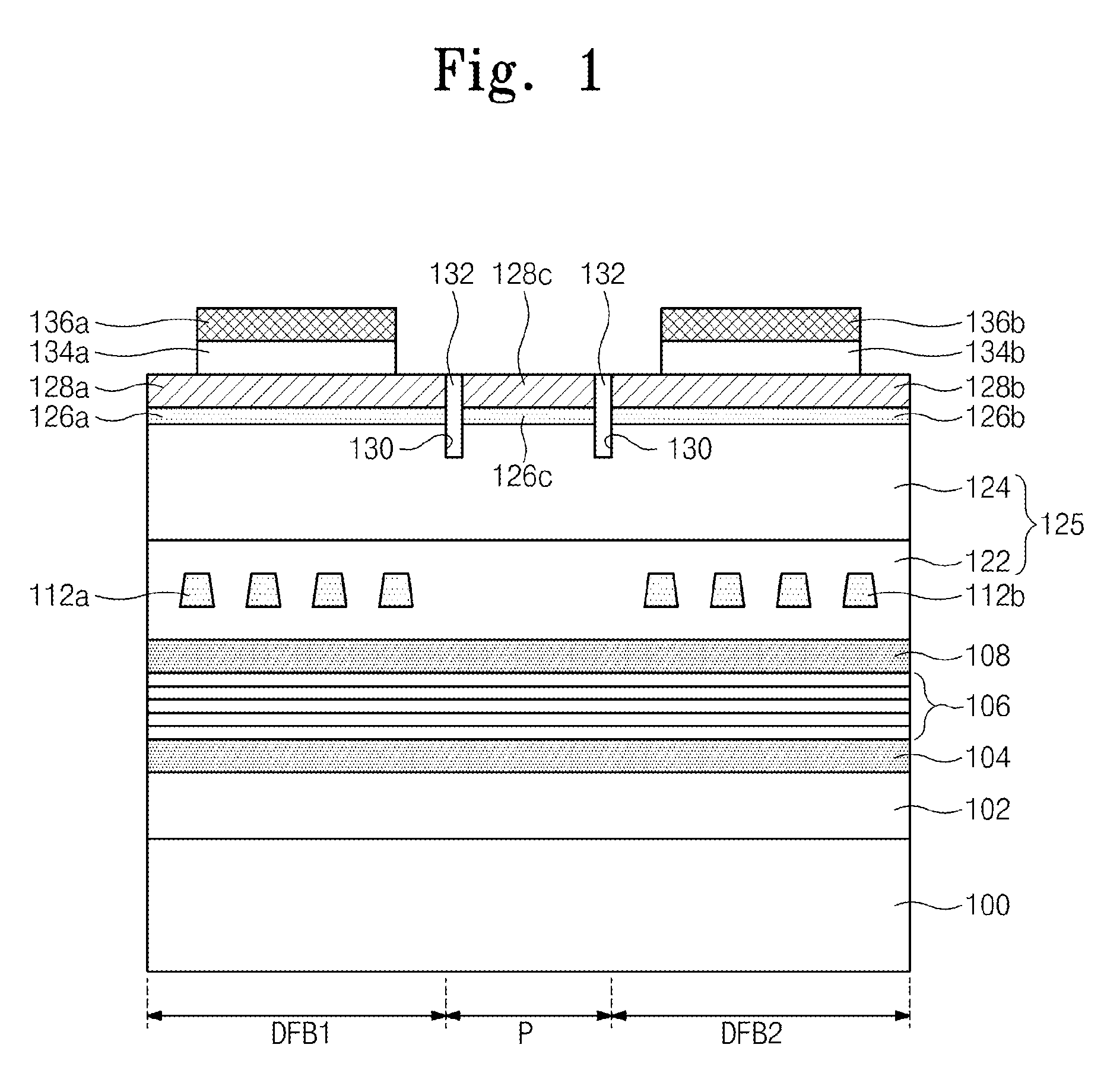
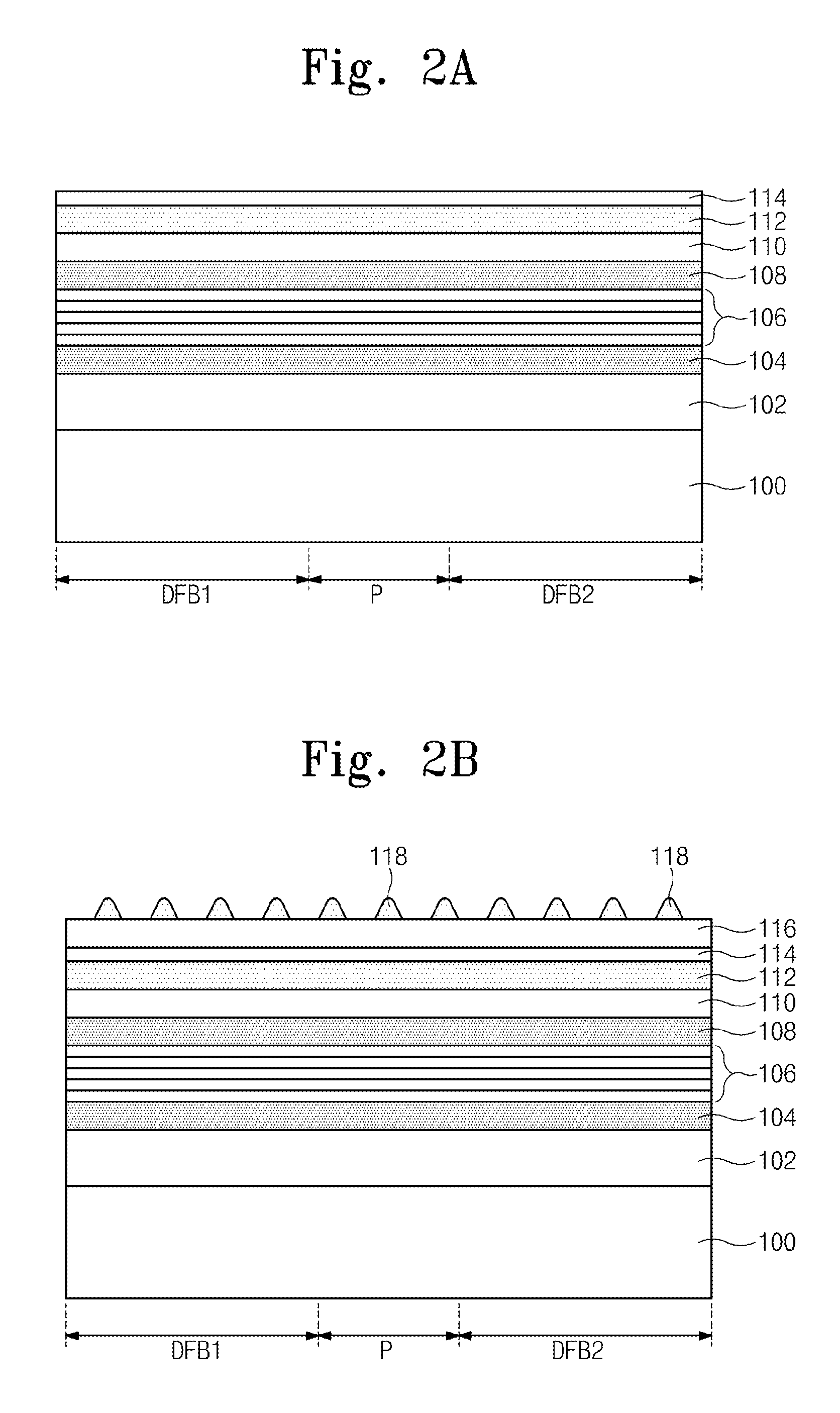
Provided is a multiple distributed feedback laser device. The laser device includes an active layer, a first diffraction grating, and a second diffraction grating. The substrate includes a first distributed feedback region, a modulation region, and a second distributed feedback region. The first diffraction grating is coupled to the active layer in the first distributed feedback region. The second diffraction grating is coupled to the active layer in the second distributed feedback region. In addition, the laser device includes a first micro heater and a second micro heater. The first micro heater supplies heat to the first diffraction grating. The second micro heater supplies heat to the second diffraction grating. The first micro heater and the second micro heater are controlled independently from each other.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Frequency tunable terahertz transceivers and method of manufacturing dual wavelength laser
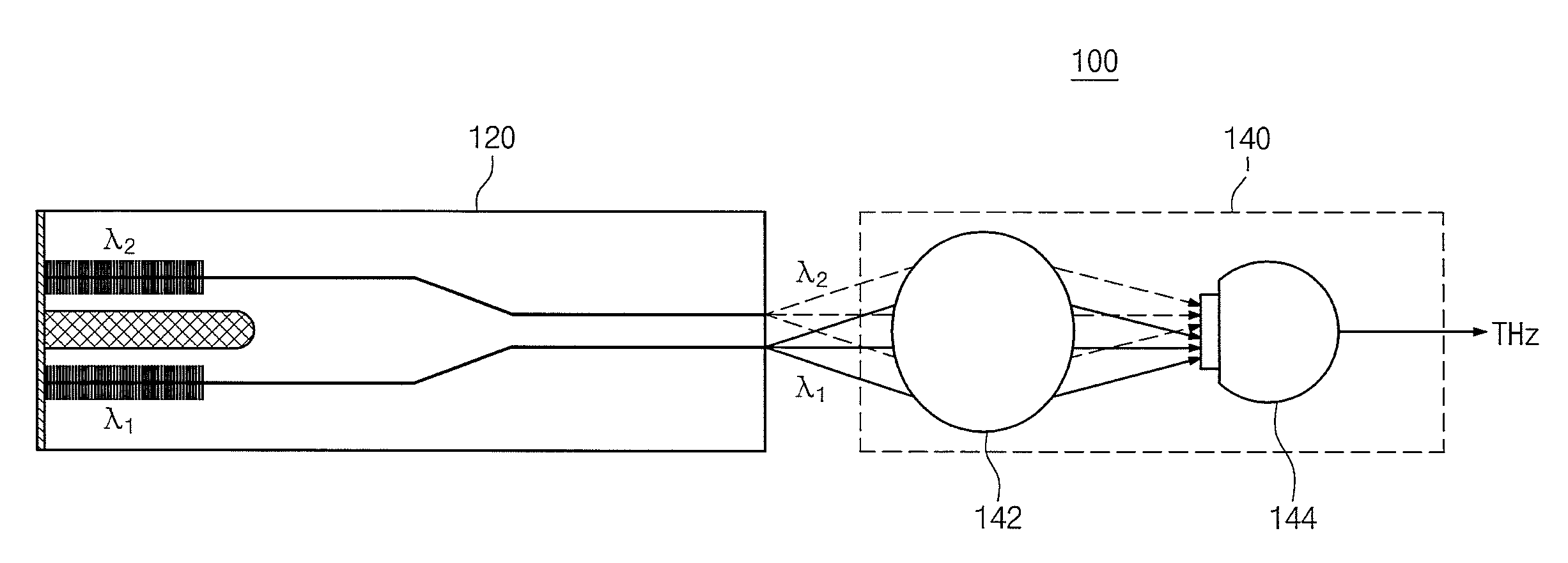
InactiveUS20120068090A1Reduce reflectivityOptical coupling efficiency improvementLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionDistributed feedback laserTransceiver
Provided are a frequency tunable terahertz transceiver and a method of manufacturing a dual wavelength laser. The frequency tunable terahertz transceiver includes: a dual wavelength laser including two distributed feedback lasers that are manufactured in one substrate and output optical signals of respectively different wavelengths; and an optical device receiving the outputted optical signals to generate a terahertz wave.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
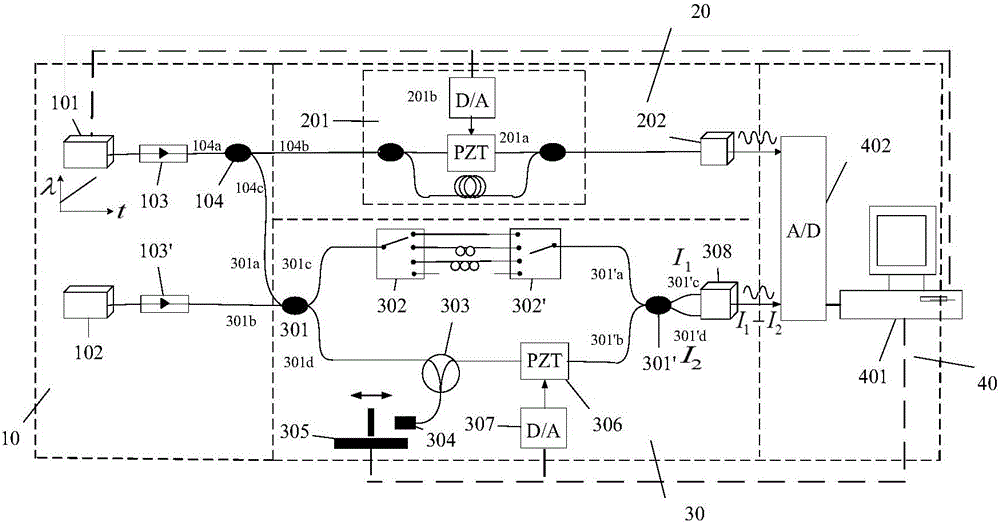
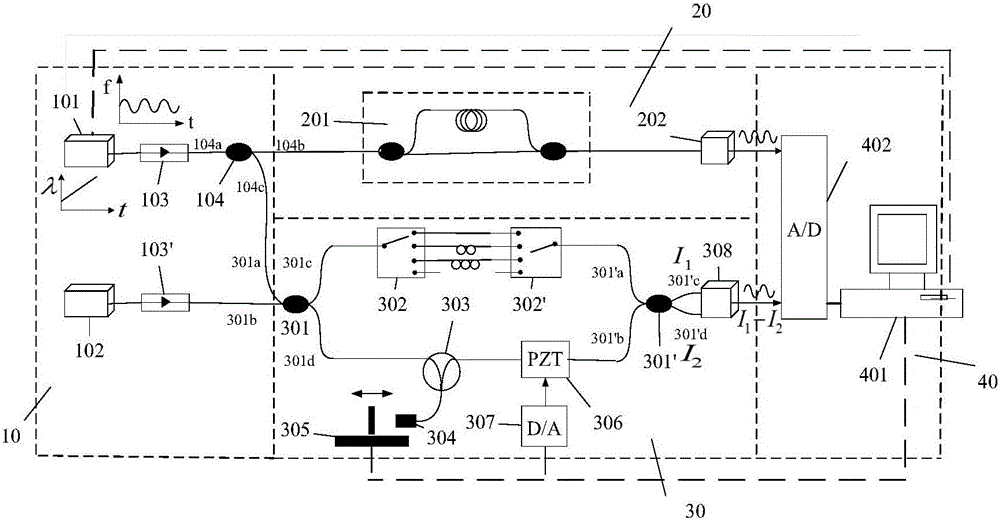
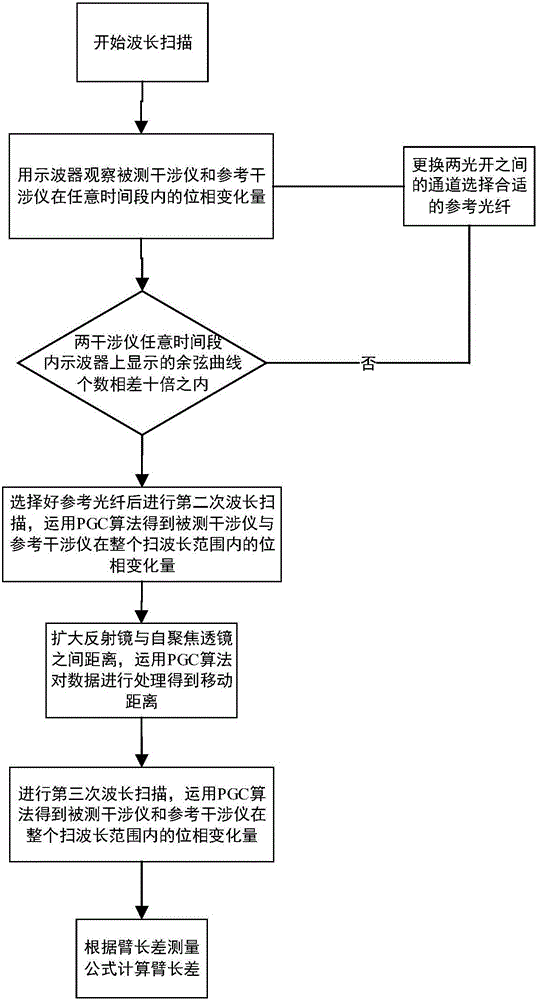
Measuring device and method for length difference between arms of optical fiber interferometer
ActiveCN105865753AHigh measurement accuracyAddressing the Effects of Length Difference MeasurementsTesting optical propertiesTesting fibre optics/optical waveguide devicesDistributed feedback laserOptical pathlength
The invention provides a measuring device and method for the length difference between arms of an optical fiber interferometer. The measuring device comprises a laser source module, a measured optical fiber interferometer module, a reference interferometer module and an acquisition and control module, wherein laser with wavelength varying linearly is emitted by a tunable laser to enter the measured optical fiber interferometer module and the reference interferometer module, a computer controls an analog quantity output board card to drive piezoelectric ceramic with optical fibers wound thereon, and accurate phase variation of the two modules is acquired after acquired signal demodulation; the optical path difference between two arms of the reference interferometer is changed, and meanwhile, the optical path difference variation is demodulated by the aid of a distributed feedback laser in the source module in combination with a PGC algorithm; the first step is repeated after the optical path difference between the two arms of the reference interferometer is changed; the length difference between arms of the measured optical fiber interferometer is calculated according to a measuring formula for the length difference between the arms. The piezoelectric ceramic, the distributed feedback laser and the like are introduced, the length difference between the arms of the measured optical fiber interferometer can be measured accurately with the PGC algorithm, and the measuring device has the advantages of high measurement accuracy, wide range, capability of automatic calibration and the like.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Temperature compensated dynamic optical tag modulator system and method
ActiveUS20060280505A1DC bias required to tune the optical modulator is reducedElectromagnetic transmissionDistributed feedback laserTelecommunications link
A dynamic optical tag system and method that allows for operation over a wide temperature range. A variable wavelength optical source, such as a dual wavelength fiber laser, is generated by combining the outputs from two distributed feedback lasers having separate operating wavelengths using a wavelength division multiplexer (WDM). A quantum well optical modulator mounted on the front surface of a retro-reflector in the remote receiver end of the communication link is biased to modulate one of the two laser wavelengths. At higher temperatures, the optical modulator can be biased to operate at the wavelength of one of the two lasers. At a lower temperature, the optical modulator can be biased to operate at the second of the two wavelengths. The DC bias required to tune the optical modulator is reduced by operating at two separate wavelengths depending on temperature.
Owner:CUBIC CORPORATION
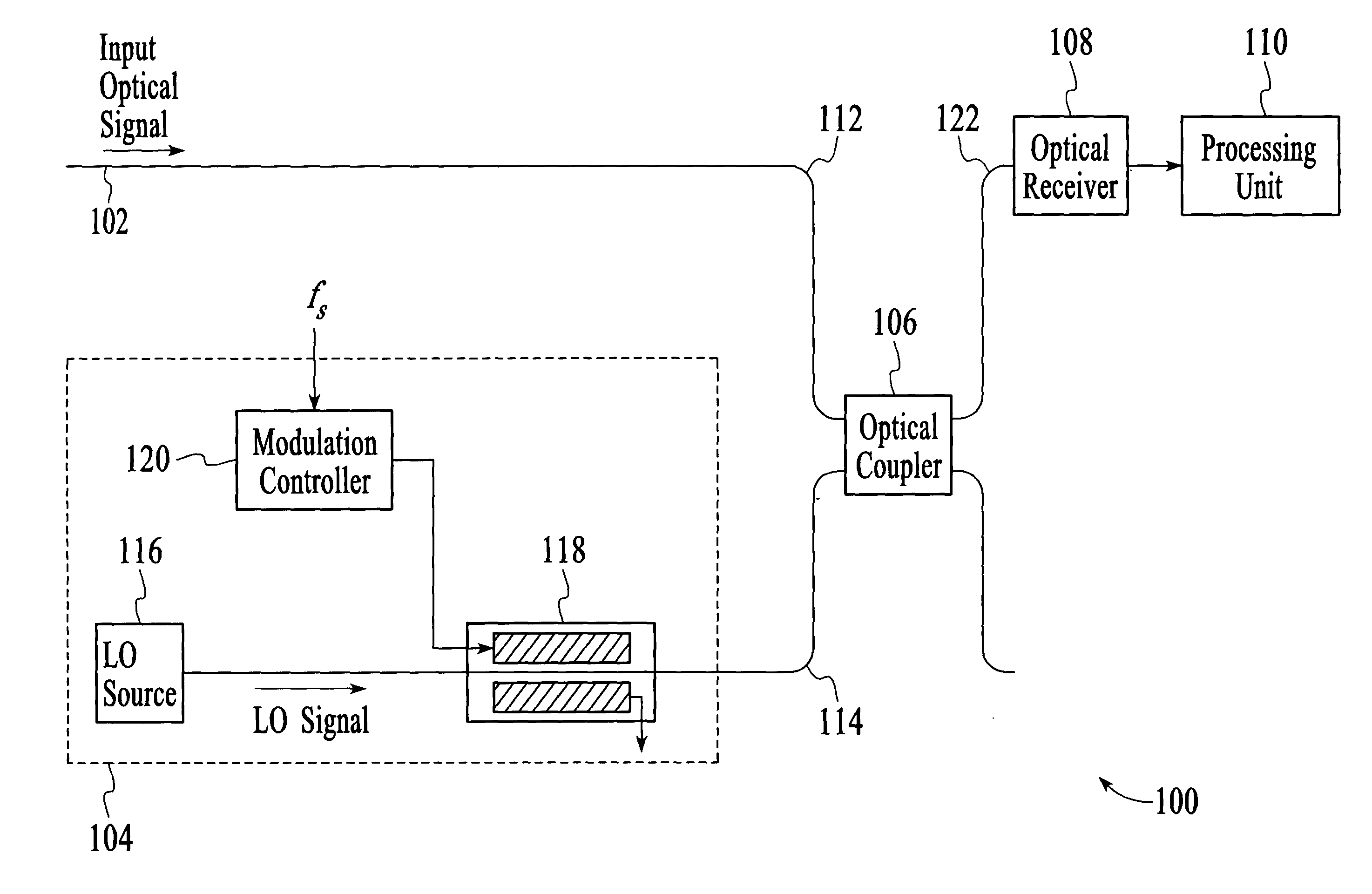
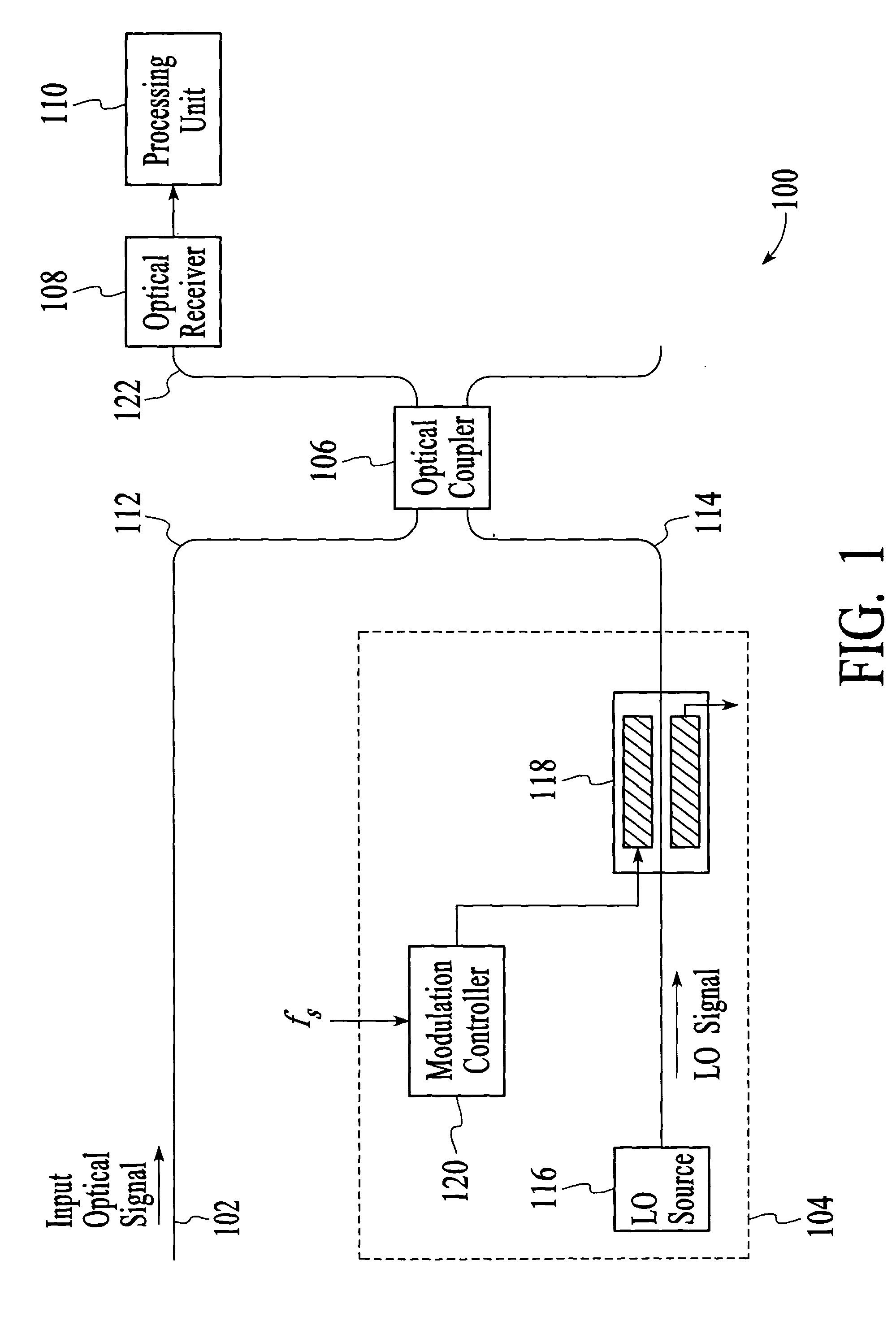
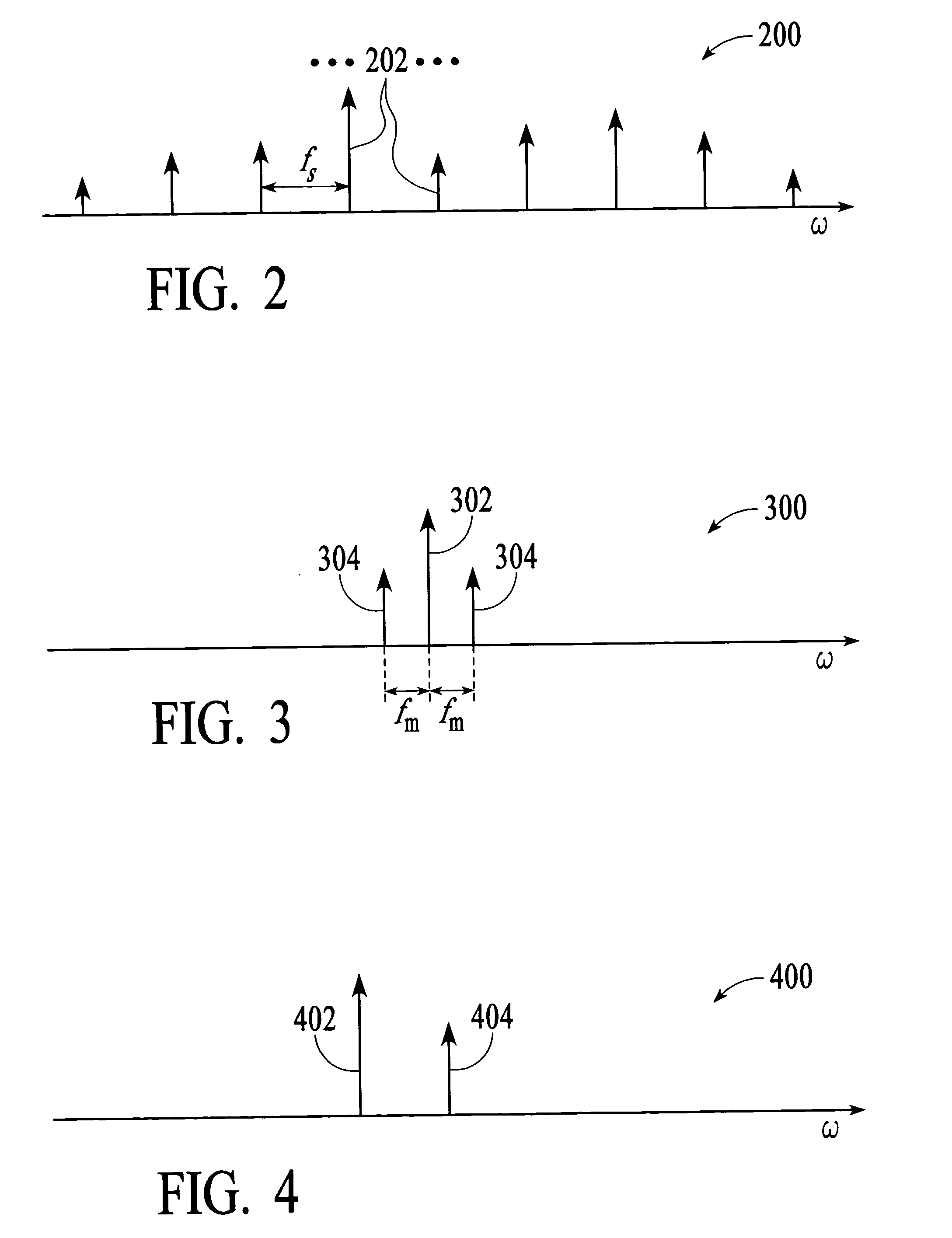
Optical analyzer and method for measuring spectral amplitude and phase of input optical signals using heterodyne architecture
InactiveUS20050012934A1Calculation is complexOptical measurementsRadiation pyrometryDistributed feedback laserFrequency spectrum
An optical analyzer and method for measuring optical properties of optical signals utilizes a heterodyne architecture to measure spectral amplitude and phase of a periodically modulated input optical signal, such as an optical signal from a periodically modulated distributed feedback (DFB) laser. The spectral amplitude and phase measurements are derived from a heterodyne signal, which is produced by combining and mixing the input optical signal and a local oscillator (LO) signal. The optical spectrum that is reconstructed from the heterodyne signal includes “inner” spectral peaks that contain phase information of the input optical signal. The inner spectral peaks may be produced by an optical or electrical mixing technique. The spectral phase of the input optical signal is recovered from the inner spectral peaks of the reconstructed optical spectrum.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
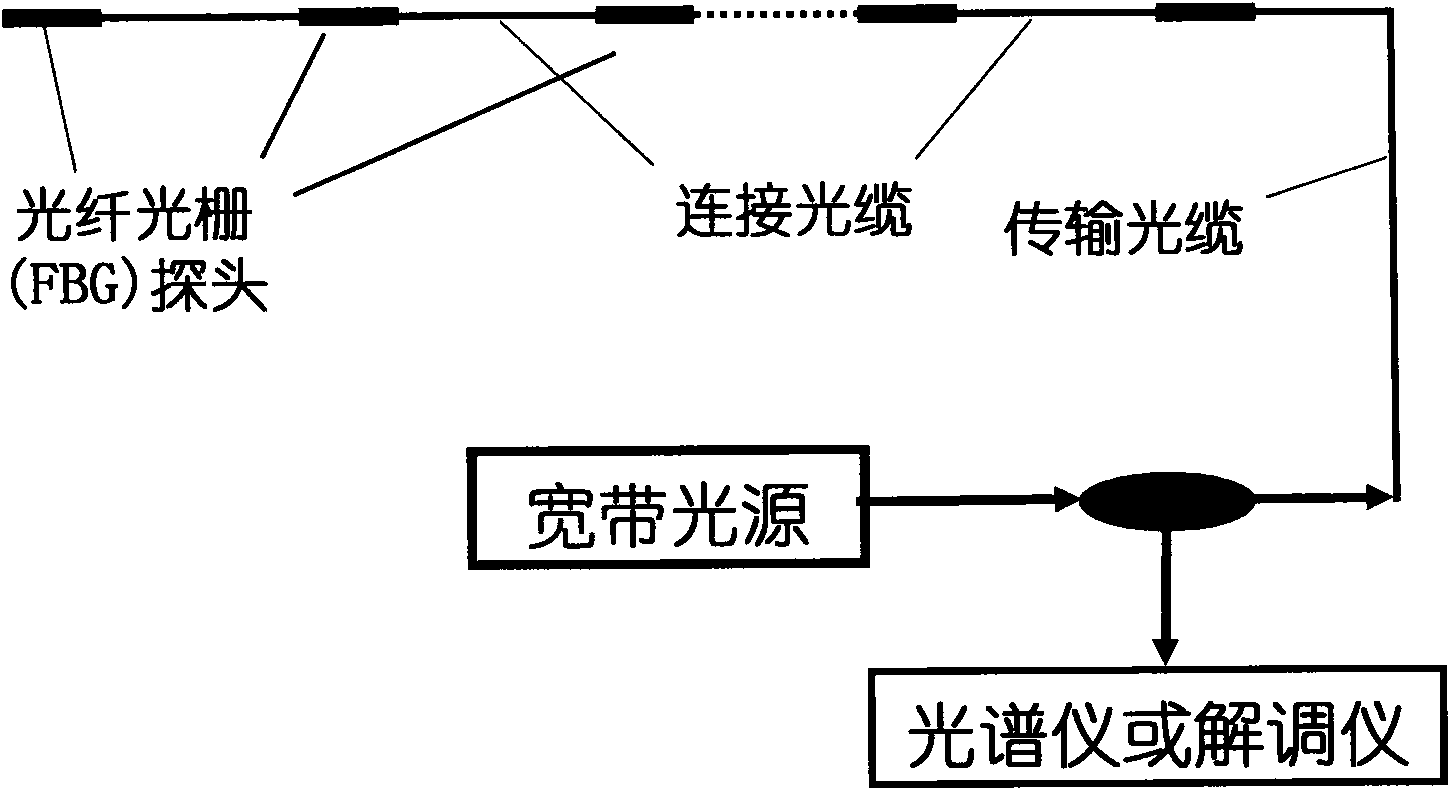
Narrow-band distributed feedback laser wavelength scanning fiber bragg grating sensing device
InactiveCN101852626AChange the output wavelengthAchieve temperatureForce measurement by measuring optical property variationThermometers using physical/chemical changesDistributed feedback laserFiber
The invention discloses a narrow-band distributed feedback laser wavelength scanning fiber bragg grating sensing device, which senses and detects external physical quantities in the following way that: the device comprises a current-driven distributed feedback laser controlled by a temperature control circuit; light emitted from the laser enters a sensing fiber bragg grating through an optical isolation unit; the light passing through the fiber bragg grating enters an opto-electric receiving unit and then enters a control analysis unit in a form of electrical signal; the output wavelength of the distributed feedback laser can be regulated by changing a control temperature; and a grating reflection centre wavelength and a corresponding external physical quantity are reckoned according to an extremum output by the opto-electric receiving unit when the output wavelength of the laser is matched with the fiber bragg grating reflection centre wavelength by temperature scanning. Compared with a conventional structure where sensing is realized by performing wavelength demodulation at the output end of the fiber bragg grating with a broadband light source, the narrow-band distributed feedback laser wavelength scanning fiber bragg grating sensing device has the characteristics of great production cost reduction, and miniature and low-cost engineering.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Temperature compensated dynamic optical tag modulator system and method
ActiveUS7603041B2DC bias required to tune the optical modulator is reducedElectromagnetic transmissionDistributed feedback laserTelecommunications link
Owner:CUBIC CORP
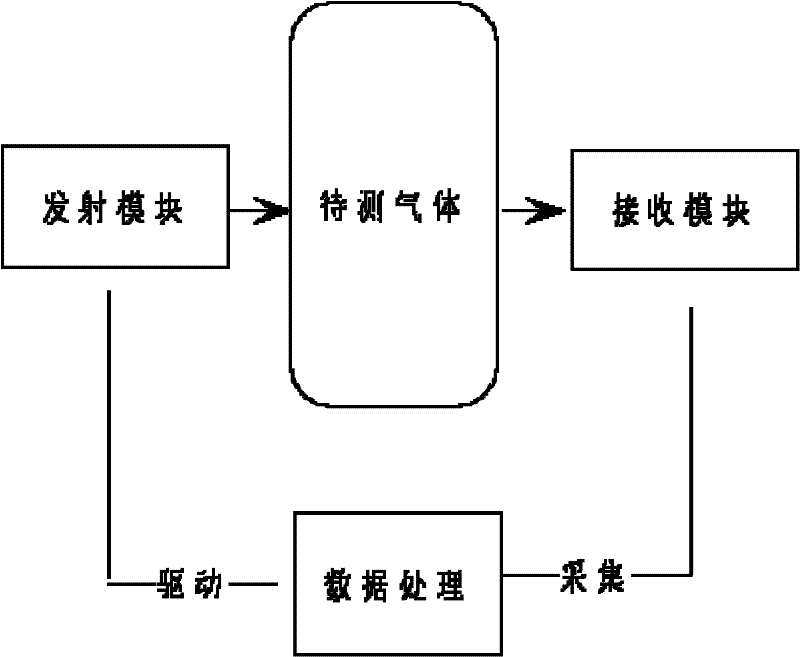
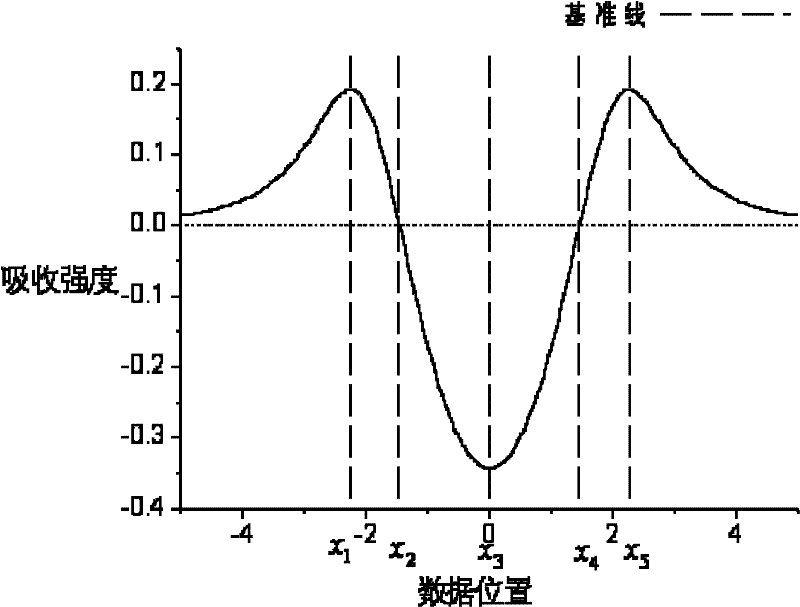
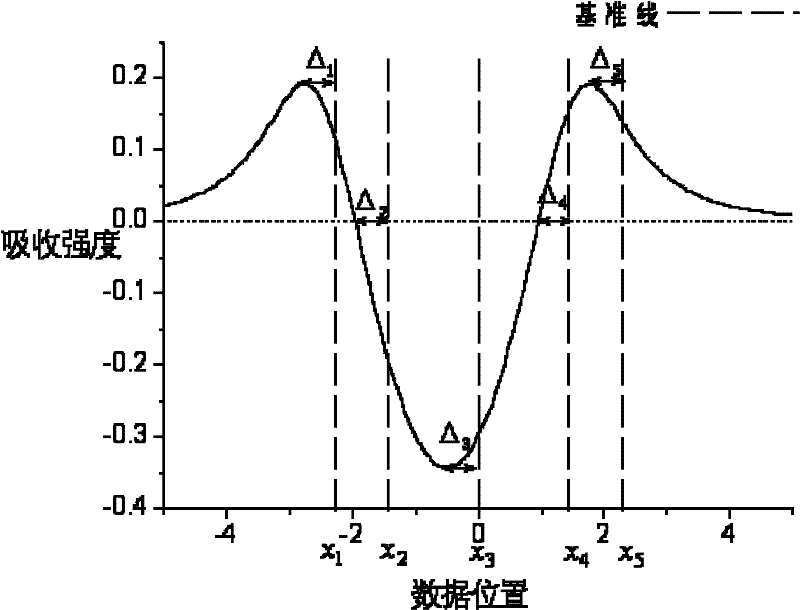
Wavelength drift compensation method for laser gas analyzer
InactiveCN102252982ASolve the problem of wavelength shiftColor/spectral properties measurementsTemperature controlDistributed feedback laser
The invention discloses a wavelength drift compensation method for a laser gas analyzer. The wavelength drift compensation method for the laser gas analyzer is mainly used for compensating the central wavelength drift of a distributed feedback laser (DFB). In the method, the absorption peak position of a signal to be tested is detected and the absorption peak offset is fed back to a laser temperature control module, so that the central wavelength drift of the laser can be compensated. A multi-characteristic-point measurement method is adopted, so that the deviation of noises such as optical interference fringes and the like from the monitoring of the laser central wavelength offset can be reduced, the offset of the laser central wavelength can be measured precisely, and the whole system is credible.
Owner:ANHUI WAYEE SCI & TECH CO LTD
Distributed feedback laser array
InactiveCN102638003AEasy to makeEasy to manufactureLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsDistributed feedback laserWave structure
The invention discloses a distributed feedback laser array composed of distributed feedback lasers which are arranged in parallel and made on an epitaxial wafer of a same semiconductor. The epitaxial wafer of the semiconductor at least comprises an upper coating layer, an active layer, a spacing layer, a refractive index control layer, a lower coating layer and a substrate. The active layer or the refractive index control layer is internally provided with bragg gratings forming distributed feedback. All layers above the refractive index control layer form upper table-boards of the distributed feedback lasers. The refractive index control layer forms guided wave structures of the distributed feedback lasers, and the widths of the guided wave structures of all the distributed feedback lasers in the array are different. Any distributed feedback laser in the distributed feedback laser array is composed of an upper electrode, an upper table-board, a guided wave structure, a substrate and a lower electrode. Due to the adoption of the guided wave structures with different widths, each distributed feedback laser is provided with the bragg gratings with the same period, and meanwhile, the lasing wavelength has a certain excursion. The array can be used as a multi-wavelength laser and a tunable laser.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Distributed feedback laser with short cavity length
InactiveCN104993375AImprove direct modulation bandwidthImprove slope efficiencyOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsDistributed feedback laserGrating
The invention relates to the technical field of semiconductor lasers, and provides a distributed feedback laser with a short cavity length. The laser contains two parts, i.e., a gain region and a reflection region; a metal electrode exists in the gain region, current needs to be injected to provide a gain for the laser; a grating layer of the gain region is a distributed feedback Bragg grating containing a lambda / 4 phase shift region; one end of the gain region is the reflection region which contains a core layer structure which is the same as that of the gain region, i.e., a waveguide transmission layer is also an active quantum well material, but current is not injected to the region; a grating layer of the reflection region is formed by evenly distributed Bragg gratings; an outer end face of the reflection region is plated with an antireflection film or adopts an antireflection structure to reduce reflection; and the other end of the gain region is an output end face of the laser, and the end face is plated with an antireflection film to reduce reflection. The scheme of the laser can enable the laser to still have a relatively low threshold gain and a good side-mode suppression ratio when the cavity length is relatively short, and the laser has the characteristic of small manufacture difficulty at the same time.
Owner:宁波元芯光电子科技有限公司
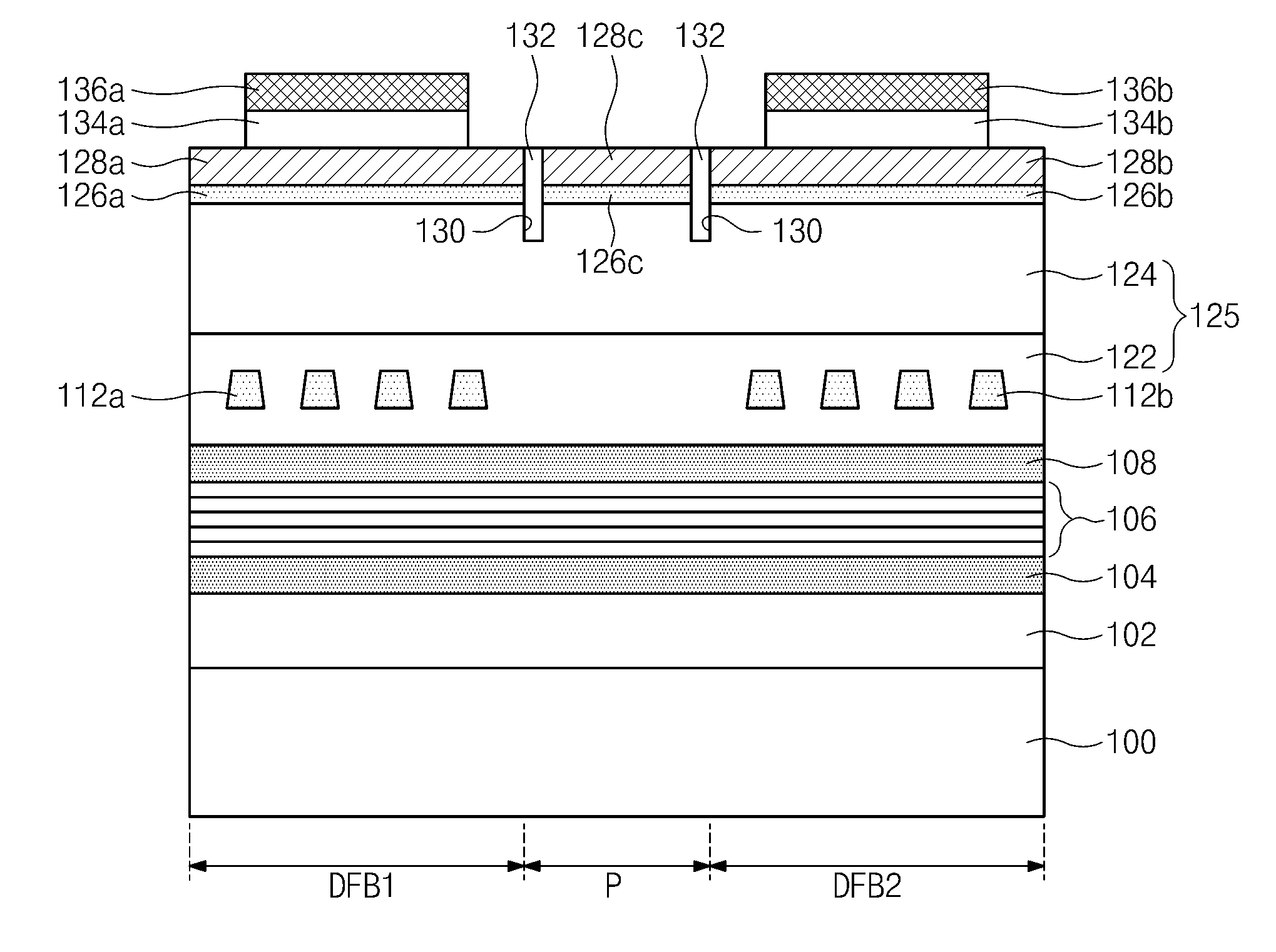
Distributed feedback laser and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102738701AAvoid the use of secondary epitaxyStable light outputLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionDistributed feedback laserLower limit
The invention provides a distributed feedback laser and a preparation method thereof. The distributed feedback laser comprises the following layers deposited on a substrate from bottom to top: a lower limit layer, a lower waveguide layer, an active region, an upper waveguide layer, an upper limit layer and an ohmic contact layer; the two sides of the middle part of the distributed feedback laser are etched with grooves, and the bottoms of the grooves are formed in any positions between the ohmic contact layer and the active region; and a ridge type waveguide structure is formed between the two grooves in the middle of the distributed feedback laser, and two side faces of the ridge type waveguide structure are provided with distributed feedback gratings. When the distributed feedback laser is used, the times of extension can be reduced, and errors caused by multiple extensions can be avoided.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
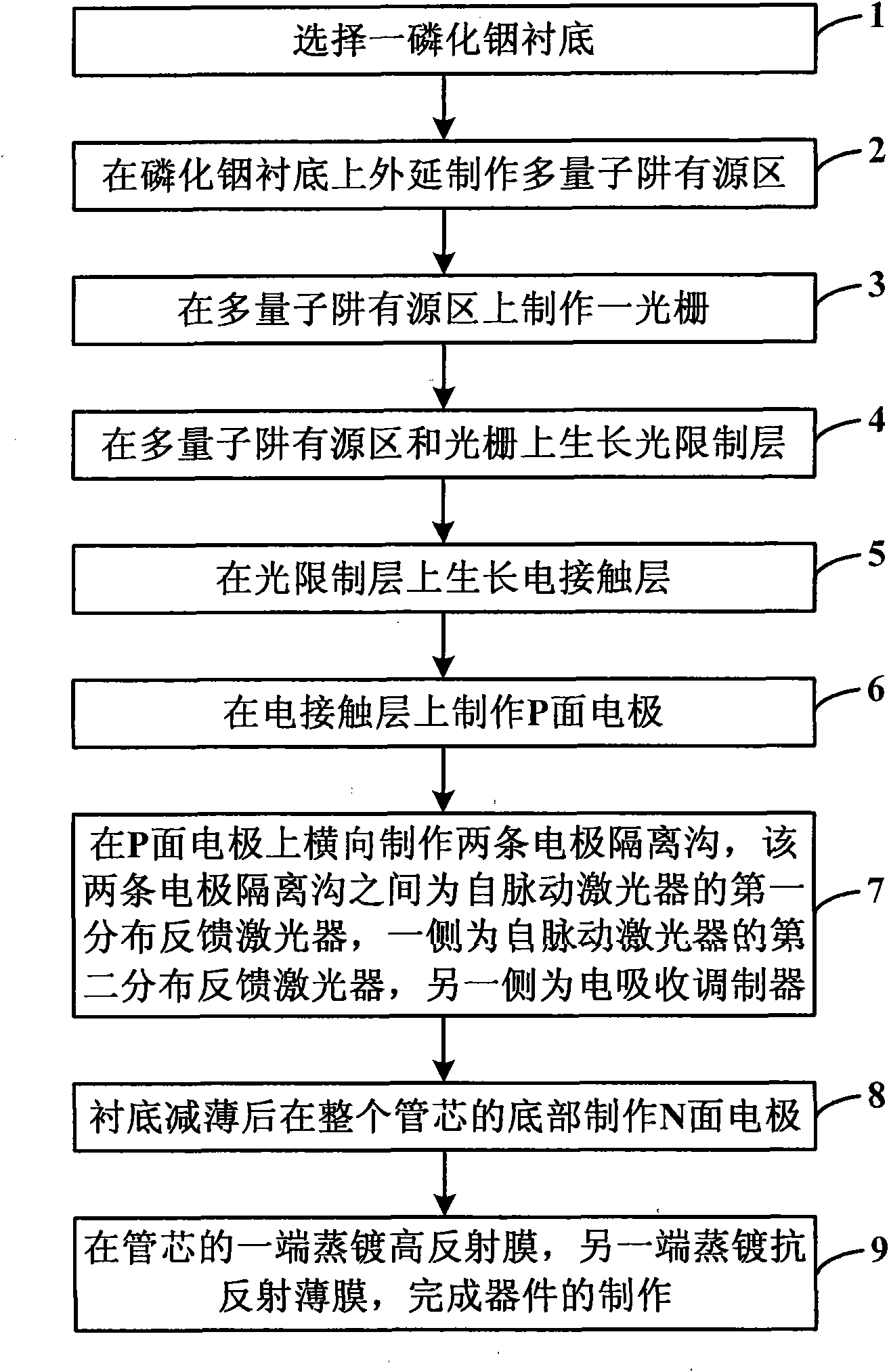
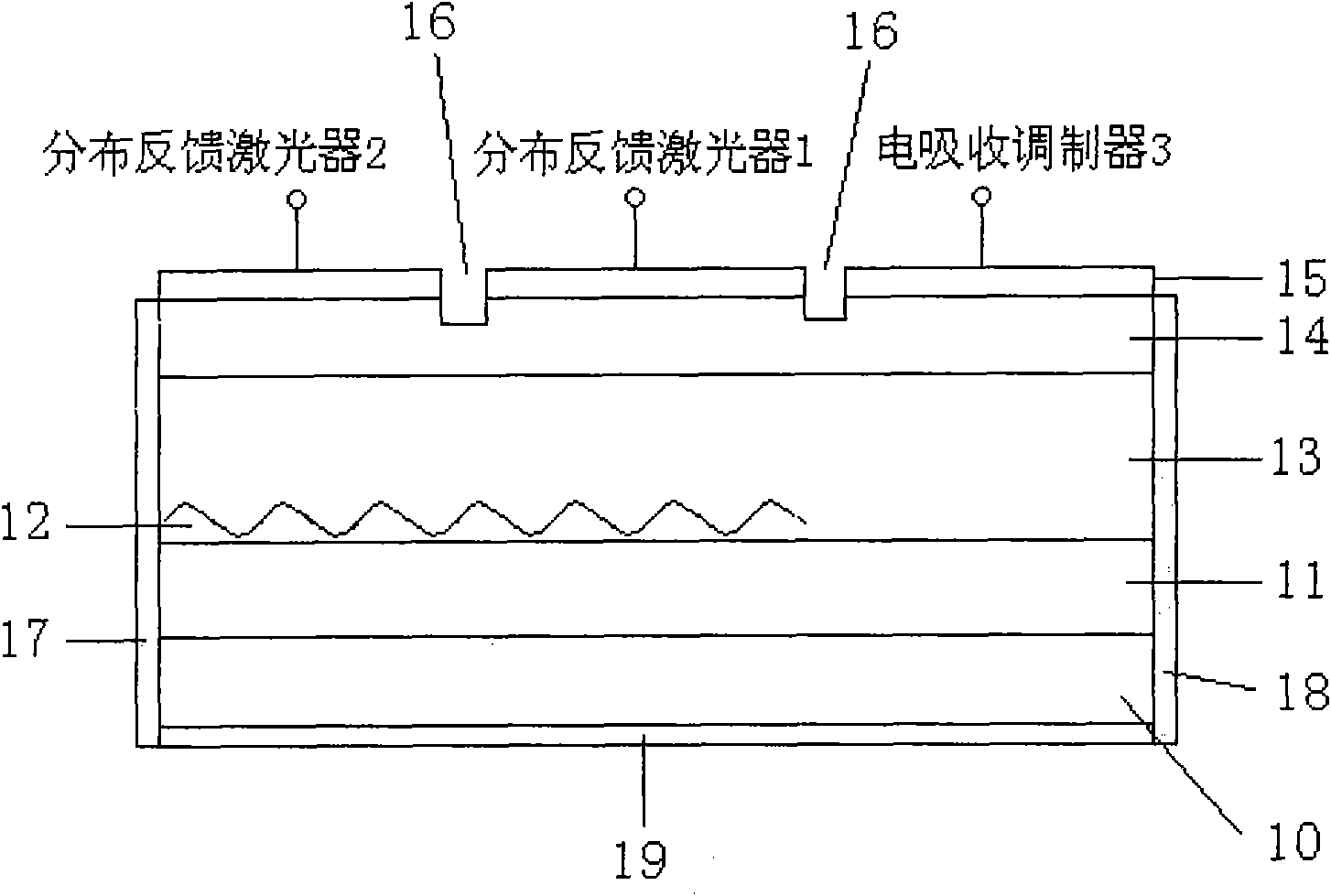
Manufacturing method for monolithic integrated device of electrical absorption modulator and self-pulsation laser
ActiveCN101826699AReduce loss costReduce manufacturing costLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsDistributed feedback laserElectro-absorption modulator
The invention discloses a manufacturing method for a monolithic integrated device of an electrical absorption modulator and a self-pulsation laser, which comprises the steps of: selecting an indium phosphide substrate; manufacturing a multiple-quantum-well active region on the extension of the indium phosphide substrate; manufacturing a grating on the multiple-quantum-well active region; growing optical limiting layers on the multiple-quantum-well active region and the grating; growing electrical contact layers on the optical limiting layers; manufacturing P-surface electrodes on the electrical contact layers; transversely manufacturing two electrode isolating channels on the P-surface electrodes; installing a first distributing feedback laser of the self-pulsation laser between the two electrode isolating channels; installing a second distributing feedback laser of the self-pulsation laser on one side; installing the electrical absorption modulator on the other side; thinning the substrate; manufacturing N-surface electrodes on the bottom of a whole pipe core; evaporating and plating a high-reflection film on one end of the pipe core; and evaporating and plating an anti-reflection film on the other end to finish the manufacture of the device. The invention reduces the power loss and the manufacturing cost of a ROF (Rate Of Fire) system emitter, and enhances system stability.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
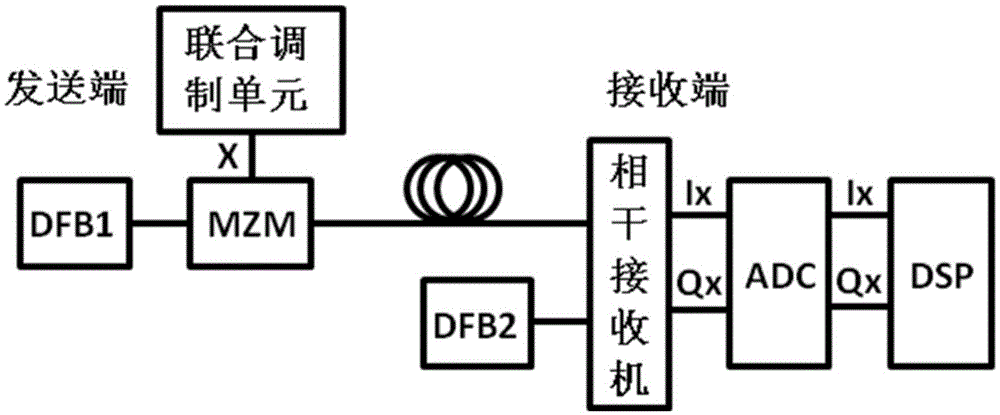
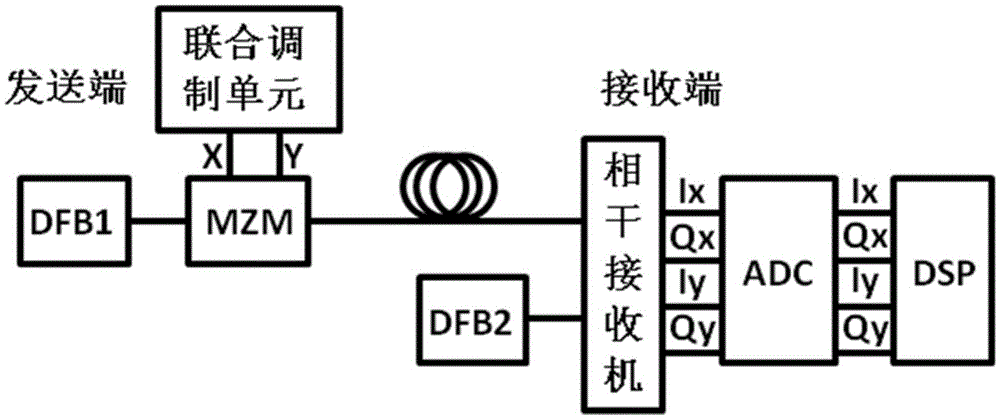
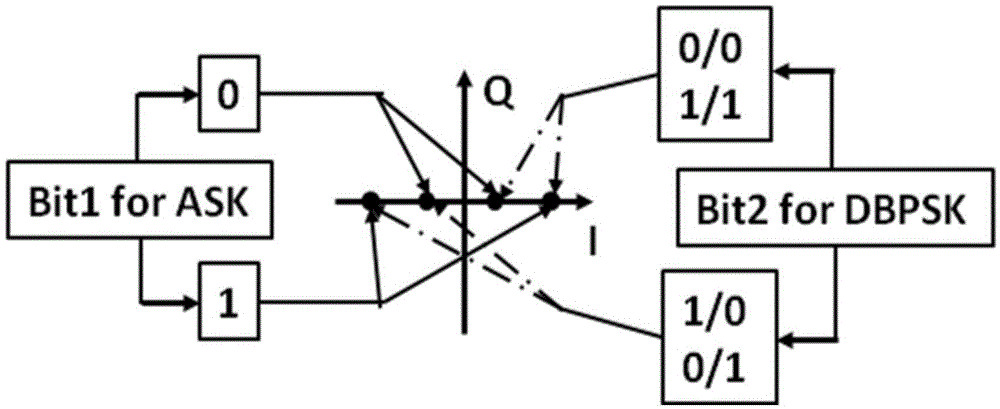
Intensity modulation coherent detection system and method based on ASK (Amplitude Shift Keying) and DBPSK (Differential Binary Phase Shift Keying)
ActiveCN105530054ALow costReduce power consumptionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsElectromagnetic transmittersDistributed feedback laserDigital signal processing
The invention discloses an intensity modulation coherent detection system and method based on ASK and DBPSK relating to the coherent detection field. The system comprises a sending end and a receiving end. The first DFB (Distributed Feedback Laser) laser of the sending end sends optical carriers; united modulation is carried out to electric signals by a united modulation unit basing on ASK and DBPSK; an MZM (Mach-Zehnder Modulator) modulator loads the electric signals after united modulation to the optical carriers to obtain polarization signals; the polarization signals are sent to the receiving end; the second DFB laser of the receiving end sends local oscillation light; a coherent receiver carries out coherent receiving to the polarization signals sent by the MZM modulator basing on the local oscillation light; the real parts and imaginary parts of the polarization signals are respectively generated; the polarization signals are converted into digital signals through an ADC (Analog-Digital Converter); digital signal processing is carried out by a DSP (Digital Signal Processor). According to the invention, the cost of the system is reduced; the receiving sensitivity of the system is effectively improved; the spectrum efficiency is remarkably improved; and the power consumption of the system is reduced.
Owner:WUHAN POST & TELECOMM RES INST CO LTD
Multiple distributed feedback laser devices
ActiveUS20110090932A1Improve reliabilityImprove power generation efficiencyOptical resonator shape and constructionNanoopticsDistributed feedback laserActive layer
Provided is a multiple distributed feedback laser device which includes a first distributed feedback region, a modulation region, a second distributed feedback region, and an amplification region. An active layer is disposed on the substrate of the first distributed feedback region, the modulation region, the second distributed feedback region, and the amplification region. A first diffraction grating is disposed in the first distributed feedback region to be coupled to the active layer in the first distributed feedback region. A second diffraction grating is disposed in the second distributed feedback region to be coupled to the active layer in the second distributed feedback region. The multiple distributed feedback laser device further includes a first micro heater configured to supply heat to the first diffraction grating and a second micro heater configured to supply heat to the second diffraction grating.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
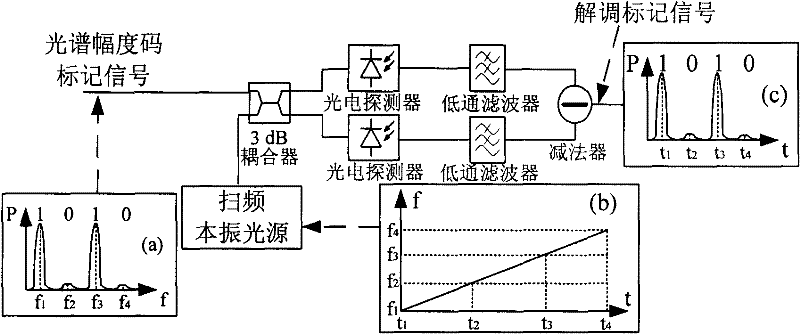
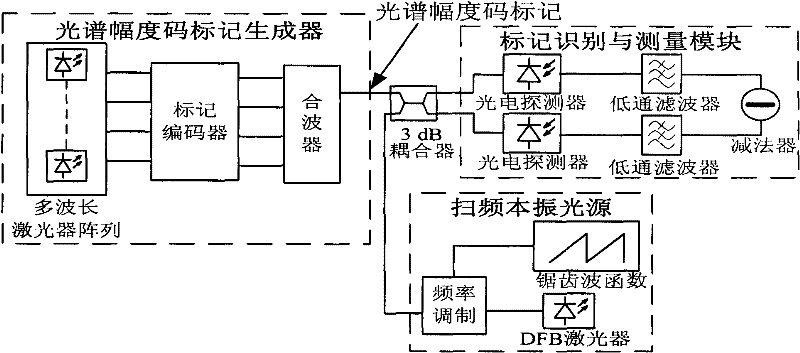
Device and method for recognizing spectrum amplitude code mark through frequency sweeping coherent detection
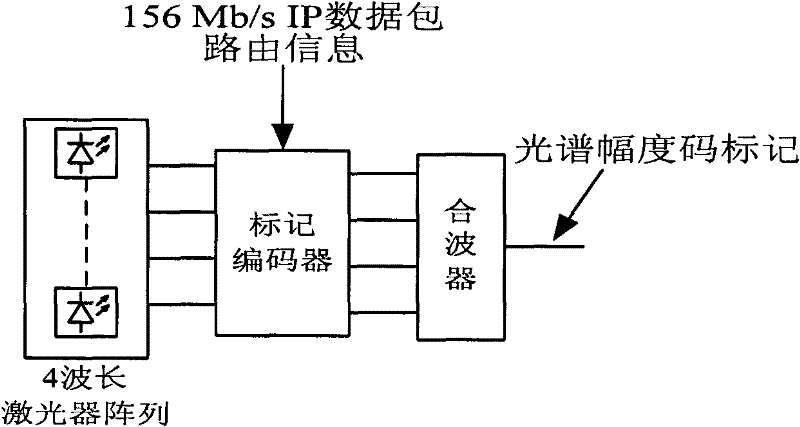
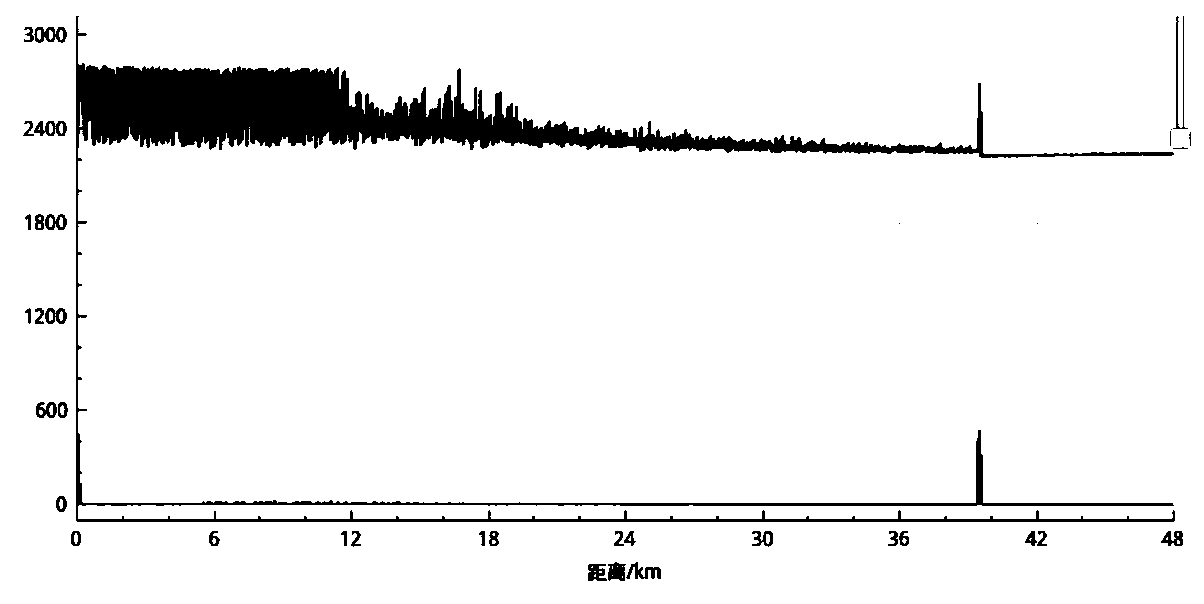
InactiveCN102231646AReduce complexityLower implementation costsMultiplex system selection arrangementsTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsDistributed feedback laserOperability
The invention discloses an information treatment device which is mainly used for the generation, demodulation and reception of optical mark information in an optical mark exchange system, wherein the information treatment device comprises a mark generator, a frequency sweeping local oscillation light source and a mark detection and reception part. The frequency sweeping local oscillation light source mainly realizes the coherent detection recognition of a spectrum amplitude code mark via a distributed feedback laser with frequency demodulated through a sawtooth wave function and receives the mark through a balanced detection method. The spectrum amplitude code mark is recognized through the method, thus a recognition unit structure of the traditional spectrum amplitude code mark can be greatly simplified and the receiving quality of marked signals is improved, and the spectral loss of the system can be reduced effectively and the actual operability of the system is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Buried optical cable fault point positioning system combining breakpoint detection and vibration detection
PendingCN110011728AAchieve positioningElectromagnetic transmissionDistributed feedback laserEngineering
The invention relates to a photoelectric detection system, in particular to a buried optical cable fault point positioning system combining breakpoint detection and vibration detection, which comprises a distributed feedback laser, a narrow-band laser, an optical switch, an acousto-optic modulator, a driver, a circulator, a detected buried optical cable, a photoelectric detector, an acquisition card and a computer, the beneficial effects of the invention are that an optical time domain reflection test technology and a phase-sensitive optical time domain reflection test technology are multiplexed during an optical cable fault point position test; and according to the sequence of optical cable fault point positioning and optical cable vibration position positioning, the buried optical cablefault point positioning is realized by searching the ground position where the ground knocking position and the fault point position coincide.
Owner:昆仑杰信(北京)科技有限责任公司
Waveguide structure for mid-ir multiwavelength concatenated distributed-feedback laser with an active core made of cascaded stages
Concatenated distributed feedback lasers having novel waveguides are disclosed. The waveguides allow for coupling of the laser beam between active and passive waveguide structures and improved device design and output efficiency. Methods of making along with methods of using such devices are also disclosed.
Owner:THORLABS QUANTUM ELECTRONICS
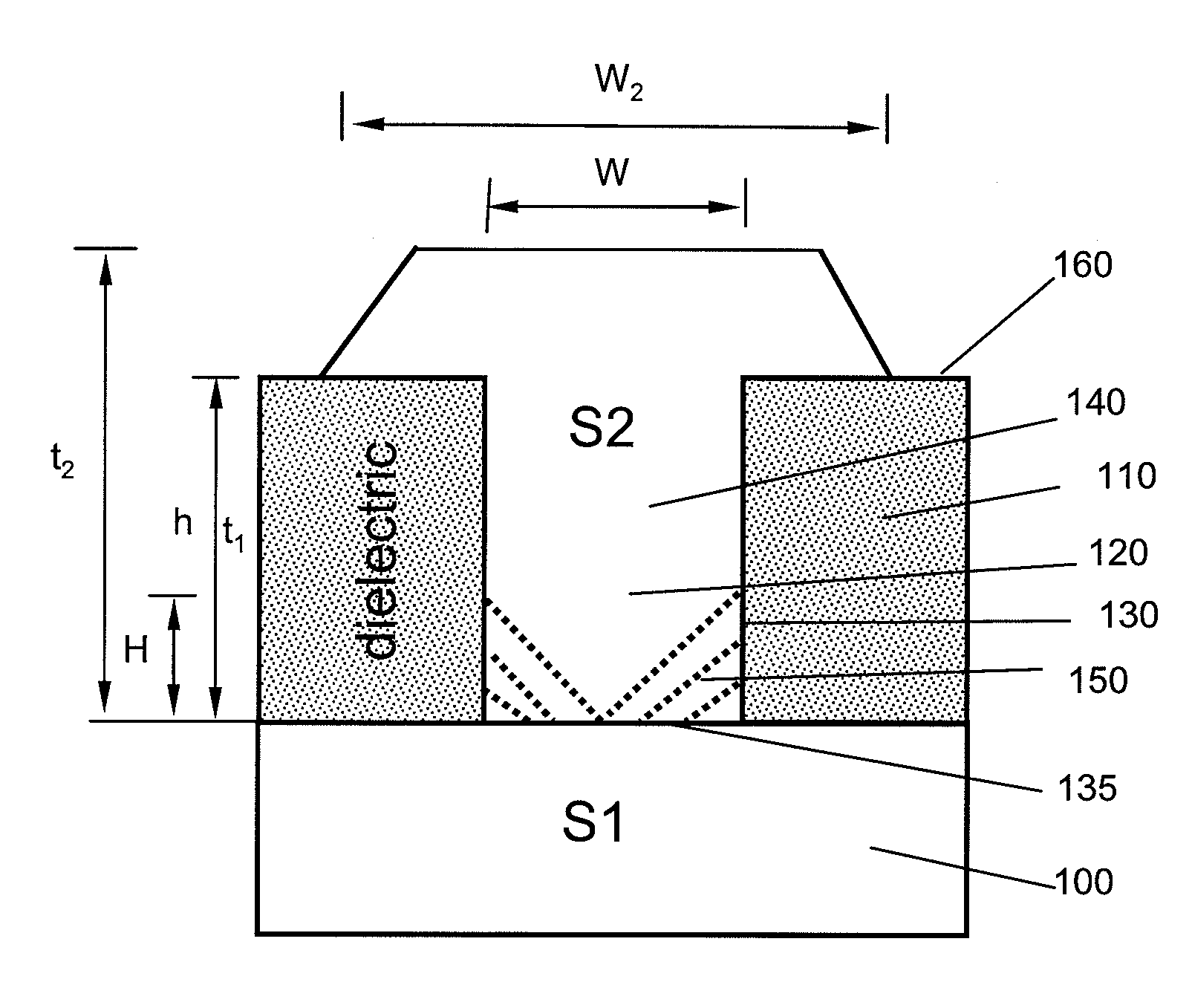
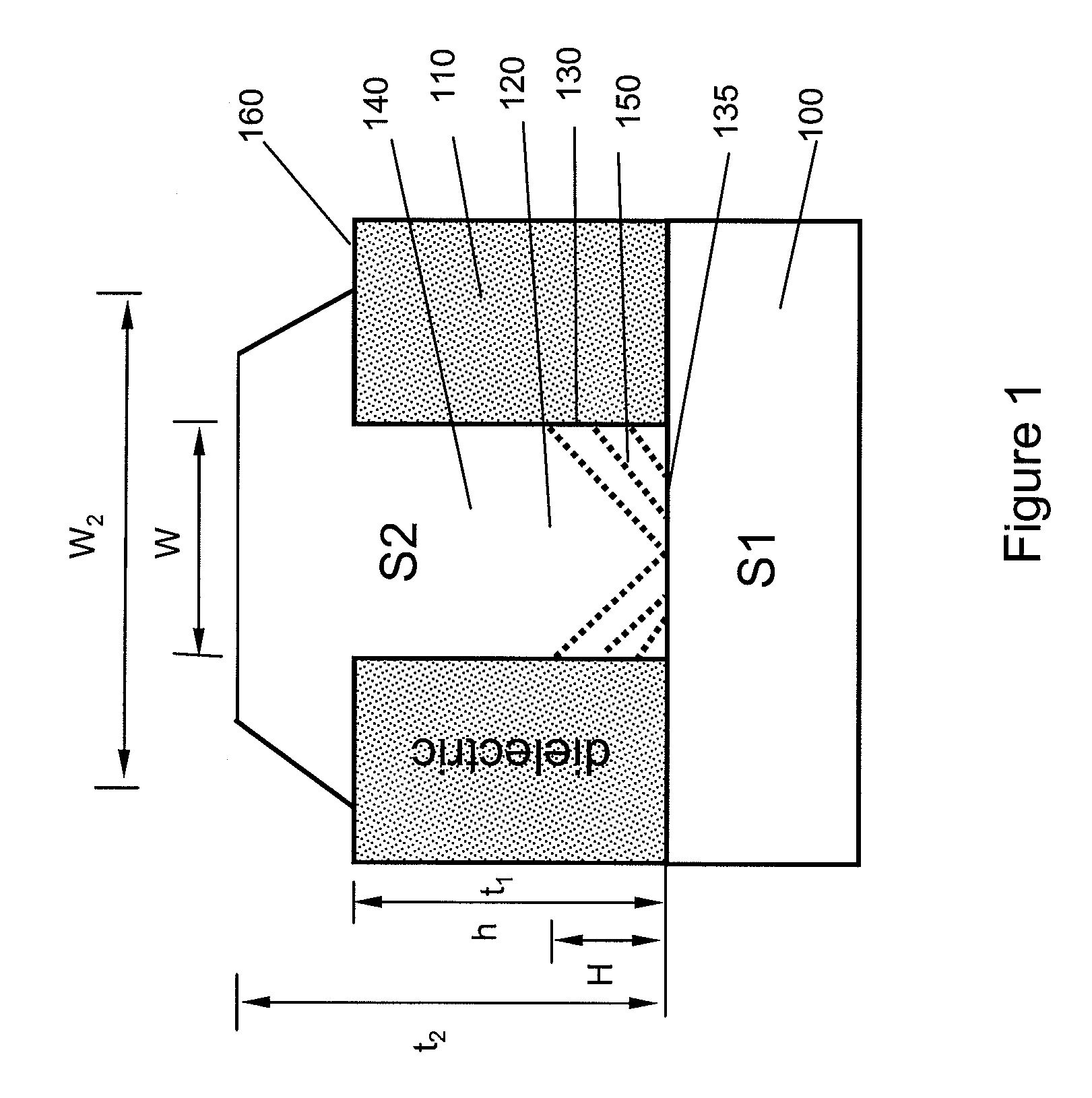
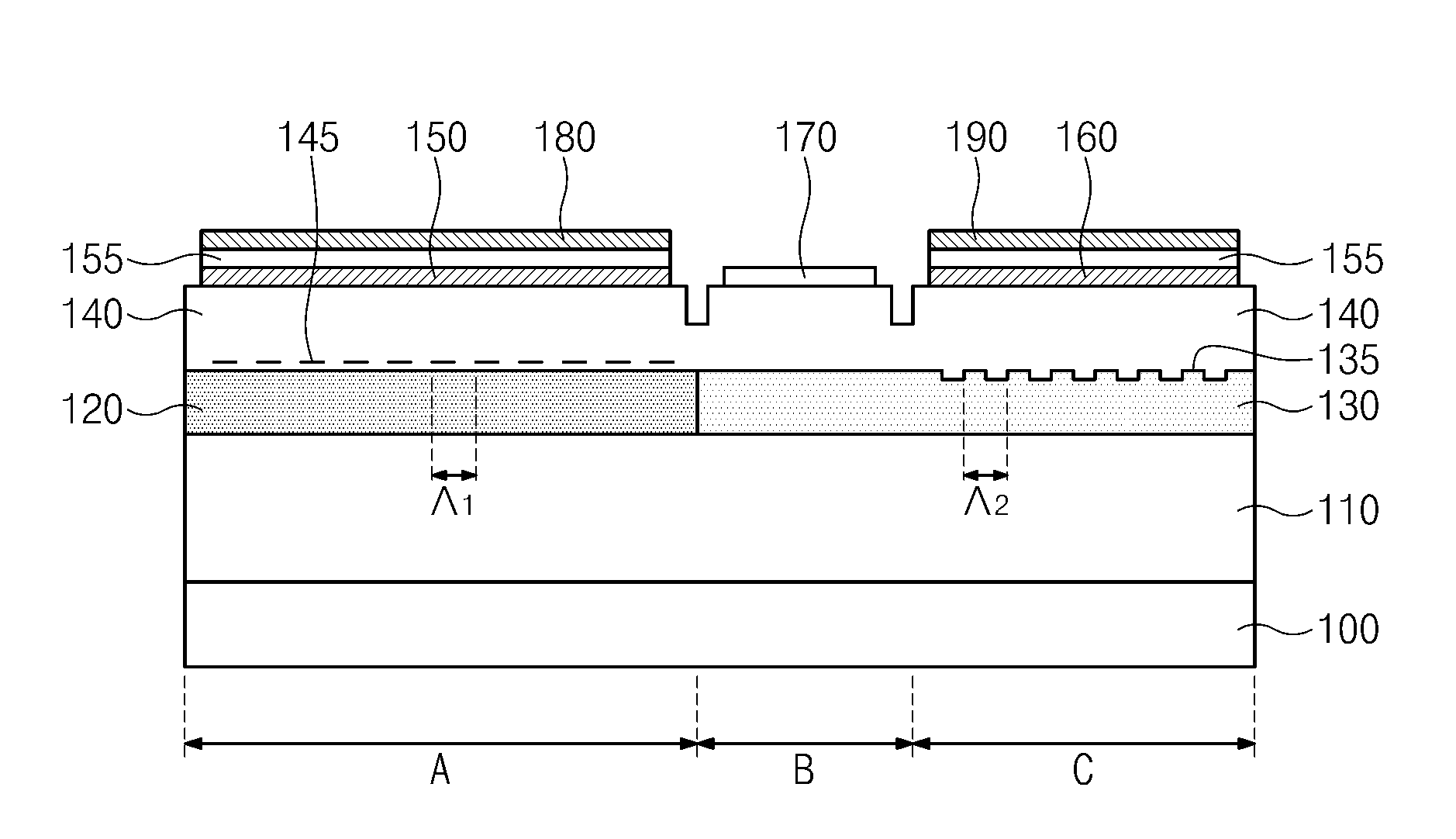
Segmented distributed feedback laser
ActiveUS20110243175A1Laser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionDistributed feedback laserGrating
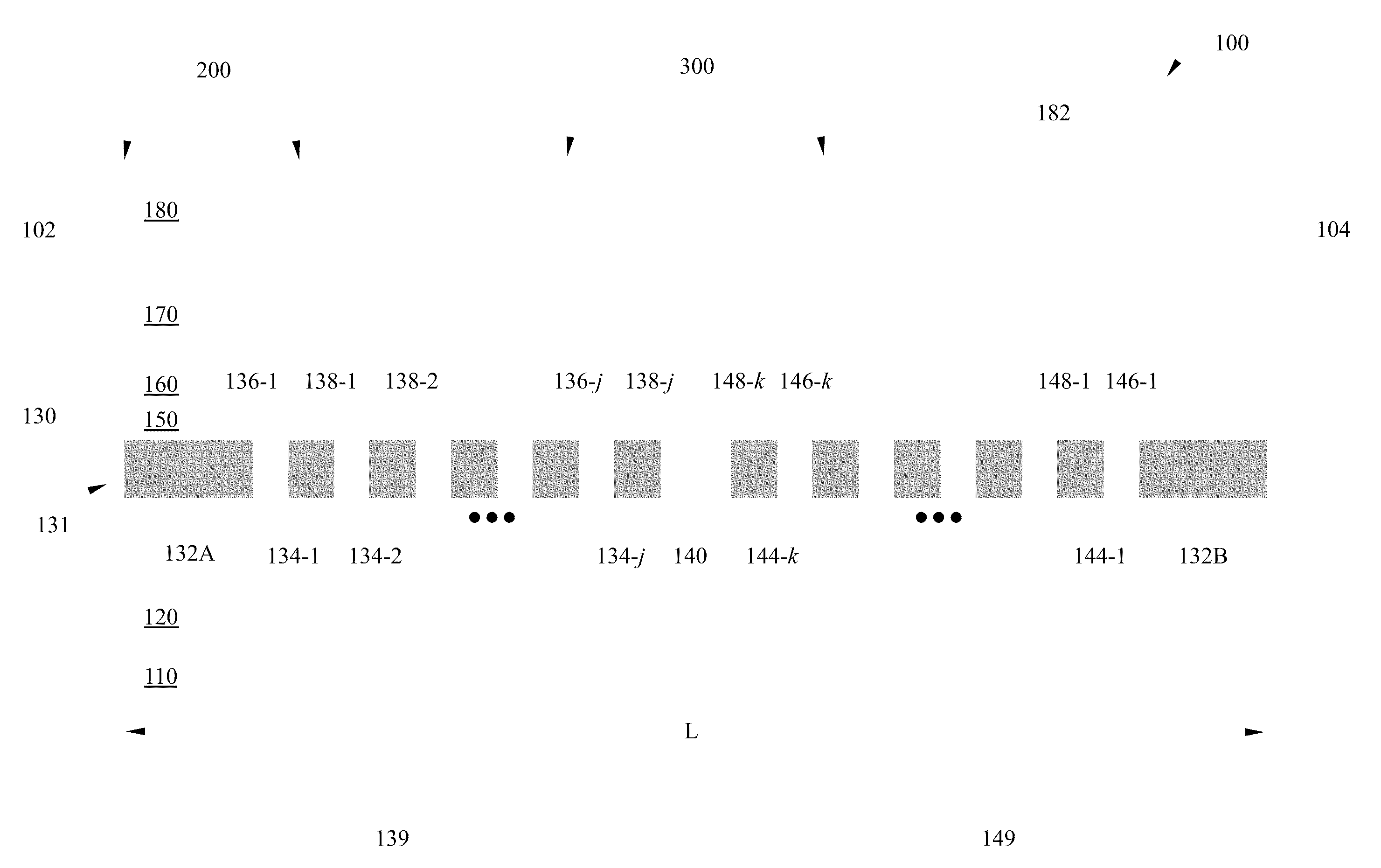
The present invention provides for a semiconductor laser having a narrow linewidth and low power consumption for optical communication applications. According to various embodiments of the invention, a semiconductor laser is provided which includes a grating layer comprising a plurality of segmented gratings, each including a non-grating portion and a grating portion. The segmented gratings are configured to enhance a fundamental mode of the semiconductor laser while sufficiently suppressing modes other than the fundamental mode, providing a narrow linewidth for example. The segmented gratings are also configured to provide an effective length longer than an actual length of the semiconductor laser, leading to smaller device areas and corresponding lower power consumption. A photonic integrated circuit is also provided which includes a plurality of semiconductor lasers, consistent with the present invention, as well as additional optical elements, all provided on a single substrate.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com