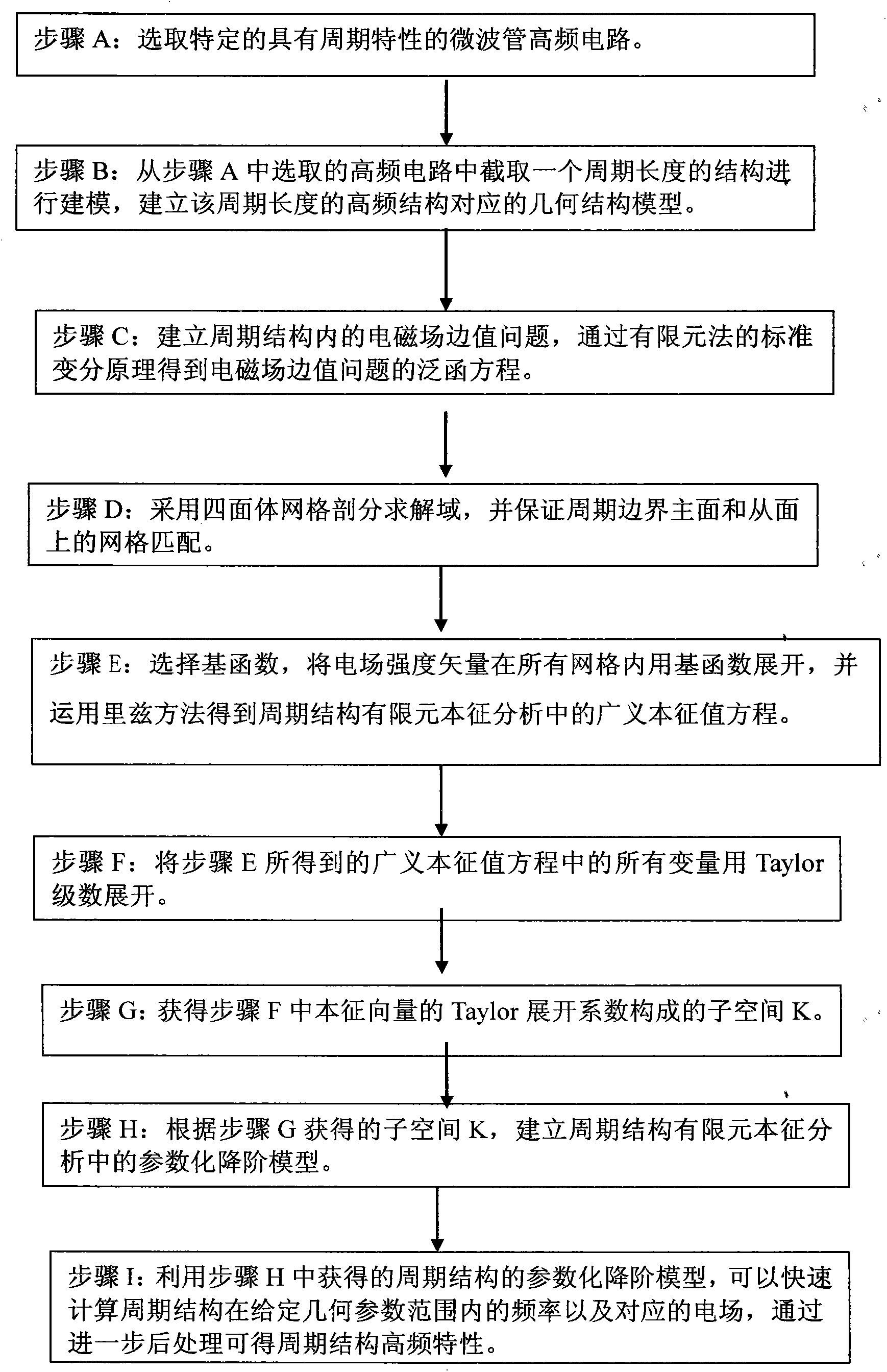
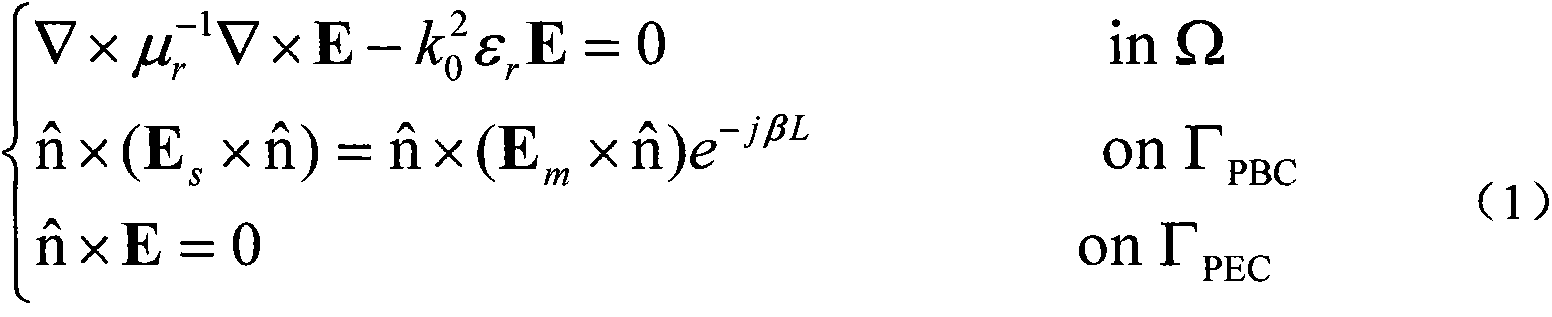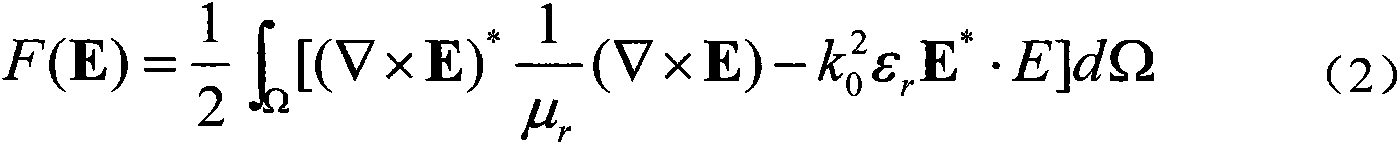Patents
Literature
953 results about "Wave structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
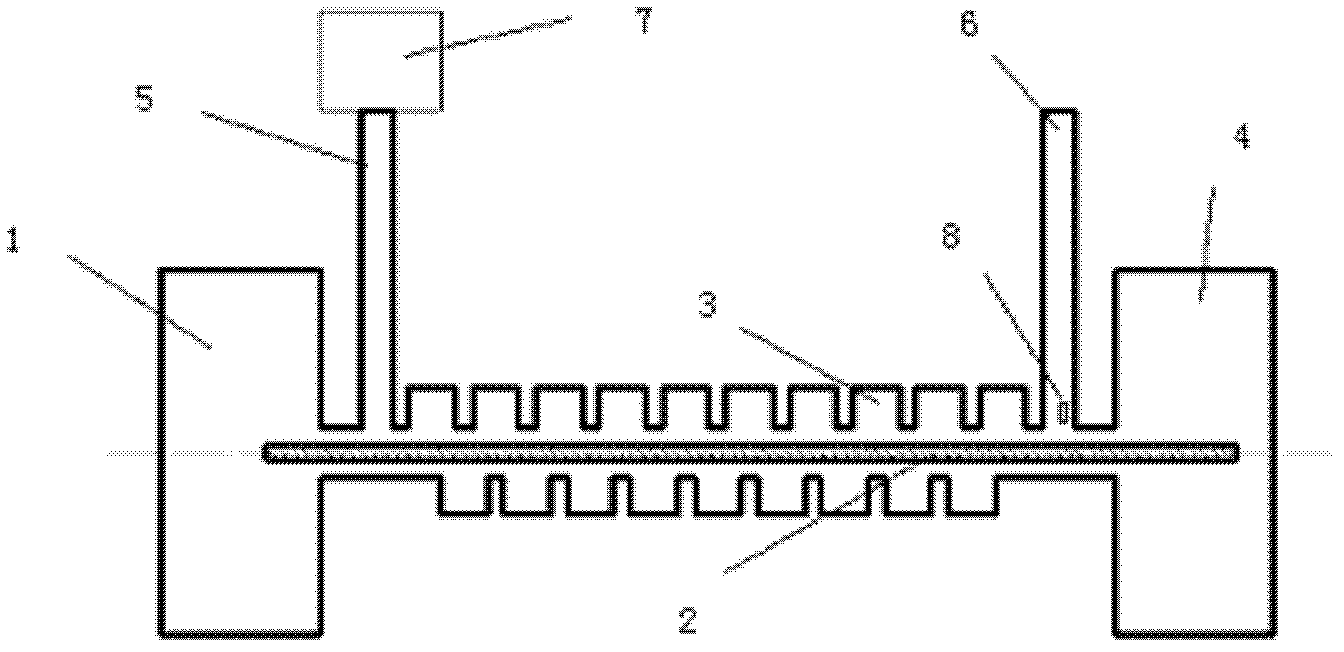
Electric field generator incorporating a slow-wave structure
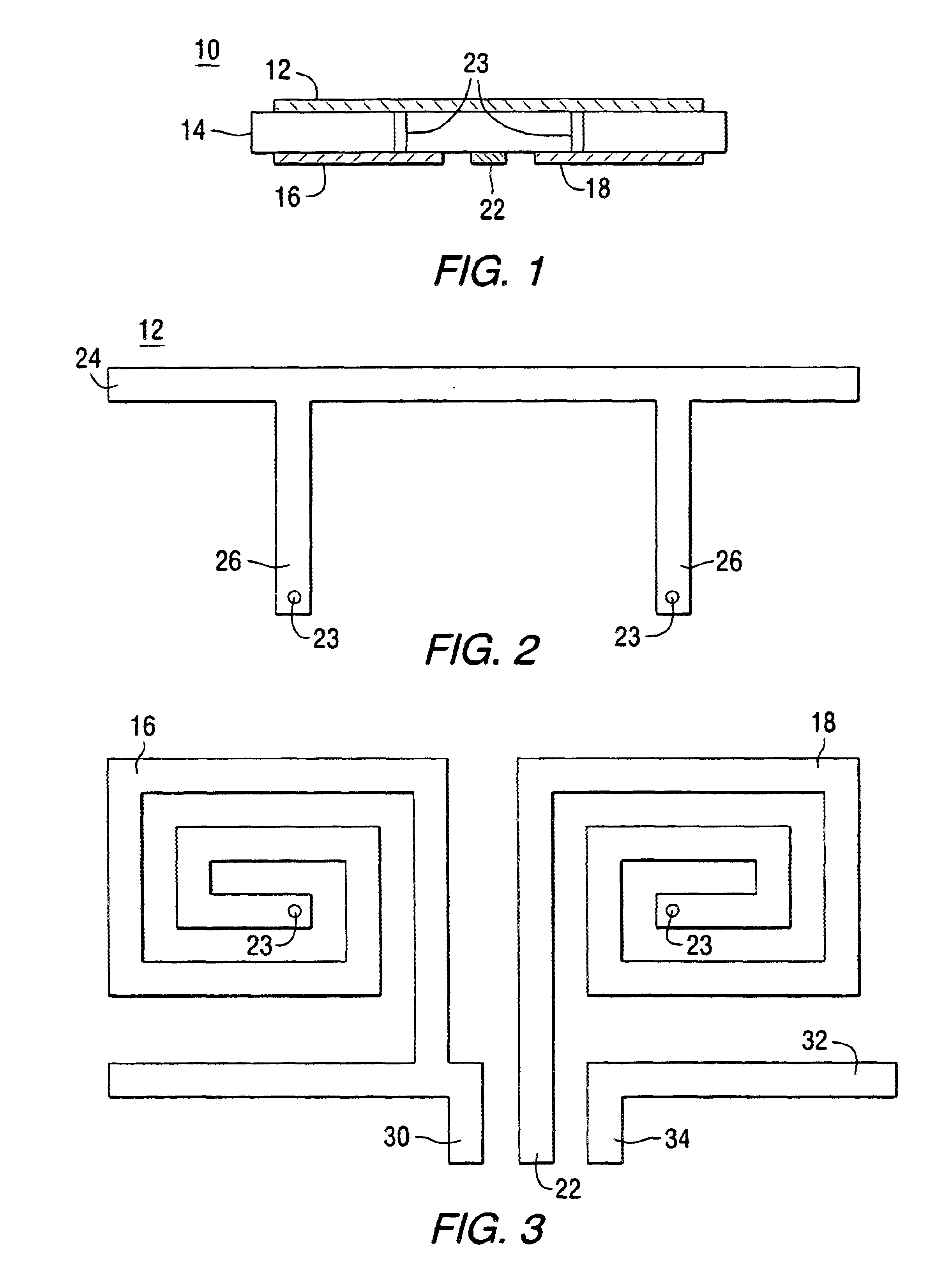
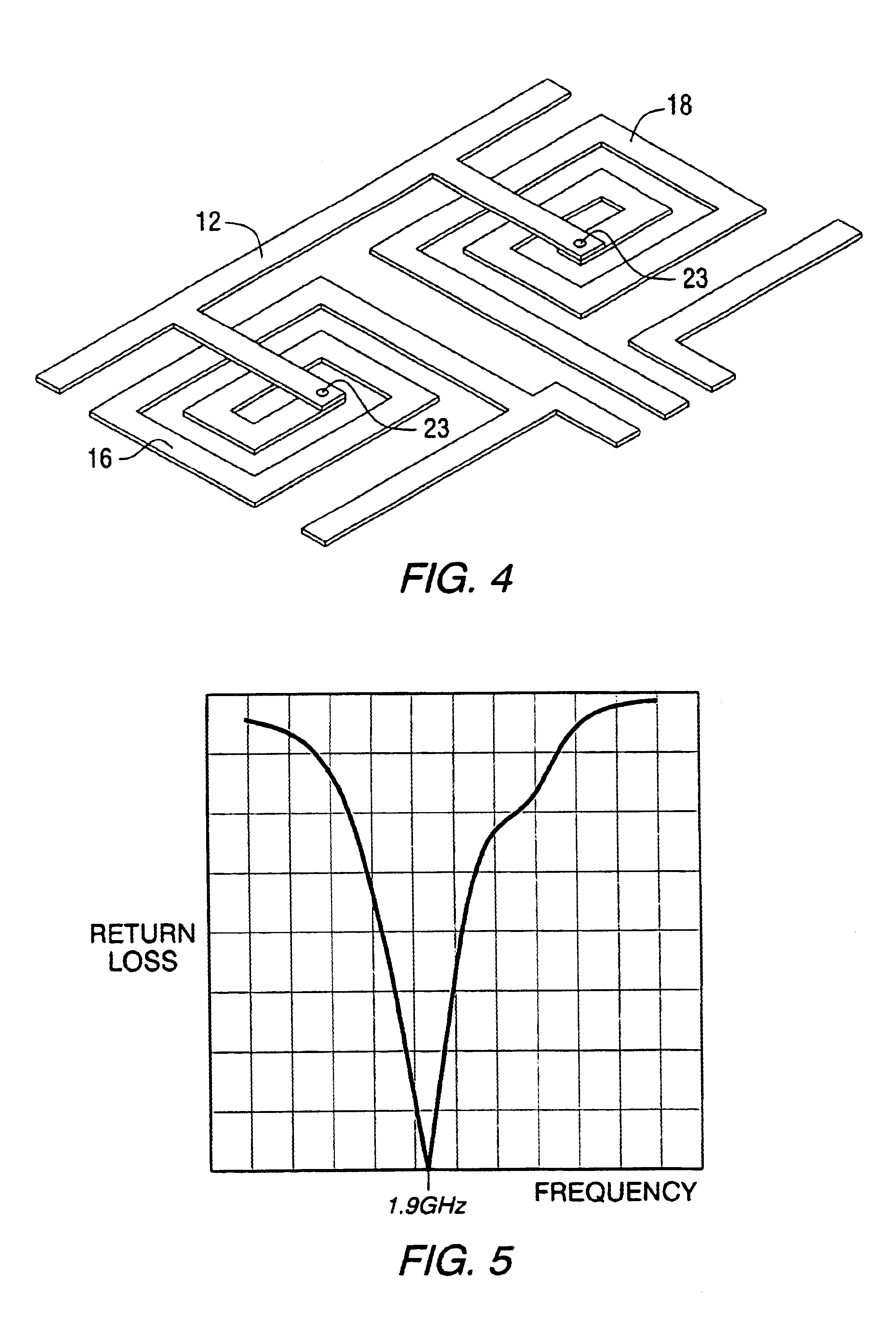
InactiveUS7656167B1Increase the lengthReduced phase velocityResistance/reactance/impedenceDelay linesWave structureEngineering
An improved E-field generator including a slow-wave transmission line structure is provided herein. In some cases, the improved E-field generator may include an inductively-loaded slow-wave transmission line structure driven by a power source at one end of the structure and terminated by a load at the other end of the structure. In other cases, the improved E-field generator may include a capacitively-loaded slow-wave transmission line structure. In either case, the improved E-field generator provides a frequency-independent, significantly increased electric field at a distance spaced from the generator without altering the dimensions of the generator and / or the input power supplied to the generator. The increase in generated field intensity is achieved by decreasing the phase velocity of the electromagnetic wave propagating along the parallel elements of the generator.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Near field antenna for object detecting device
ActiveUS20150333804A1Improve sensor sensitivityImprove sensing accuracyNear-field in RFIDMeasurement leads/probesWave structureCoaxial cable
A near field antenna adapted to an object detecting device, for sensing a plurality of units under test of at least an object under test. The near field antenna comprises a periodic guided-wave structure, a metallic reflection portion and at least two near field magnetic coupling antennas. The periodic guided-wave structure disposed below the object under test has a plurality of conductive units periodically arranged on a first plane. The metallic reflection portion is disposed under the periodic guided-wave structure to form an enclosed space. The near field magnetic coupling antennas are disposed on a second plane parallel to the periodic guided-wave structure, and are located in the enclosed space. The feed point and the ground point of each near field magnetic coupling antenna are fed by a coaxial cable with a feeding direction parallel to the periodically arranged conductive units.
Owner:AUDEN TECHNO
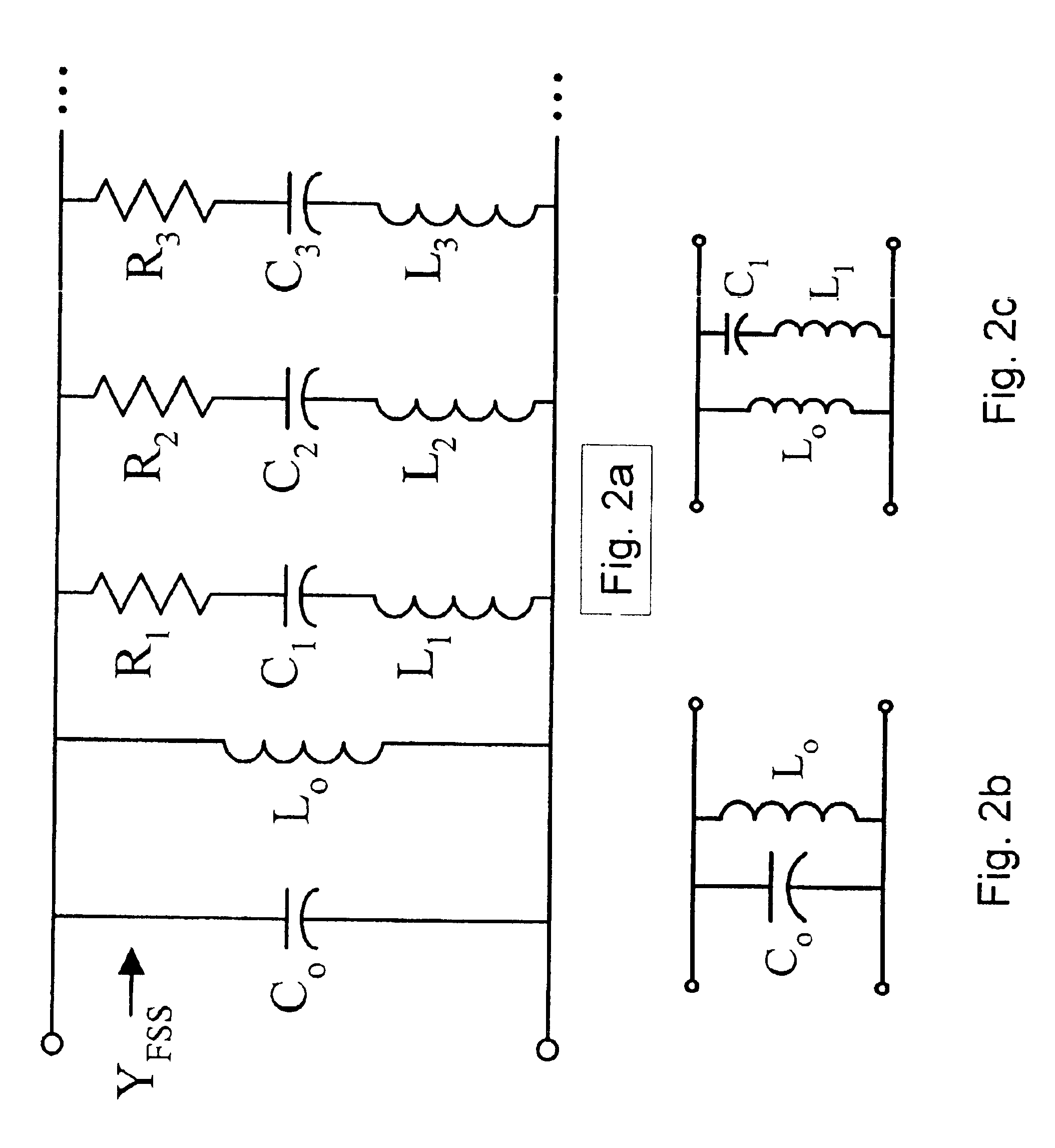
Low frequency enhanced frequency selective surface technology and applications
ActiveUS7071889B2Reduce physical sizeHigh surfaceSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsWave structureCapacitance
DC inductive FSS technology is a printed slow wave structure usable for reduced size resonators in antenna and filter applications of wireless applications. It is a dispersive surface defined in terms of its parallel LC equivalent circuit that enhances the inductance and capacitance of the equivalent circuit to obtain a pole frequency as low as 300 MHz. The effective sheet impedance model has a resonant pole whose free-space wavelength can be greater than 10 times the FSS period. A conductor-backed DCL FSS can create a DC inductive artificial magnetic conductor (DCL AMC), high-impedance surface with resonant frequencies as low as 2 GHz. Lorentz poles introduced into the DCL FSS create multi-resonant DCL AMCs. Antennas fabricated from DCL FSS materials include single-band elements such as a bent-wire monopole on the DCL AMC and multi-band (dual and triple) shorted patches, similar to PIFAs with the patch / lid being a DCL FSS.
Owner:OAE TECH INC
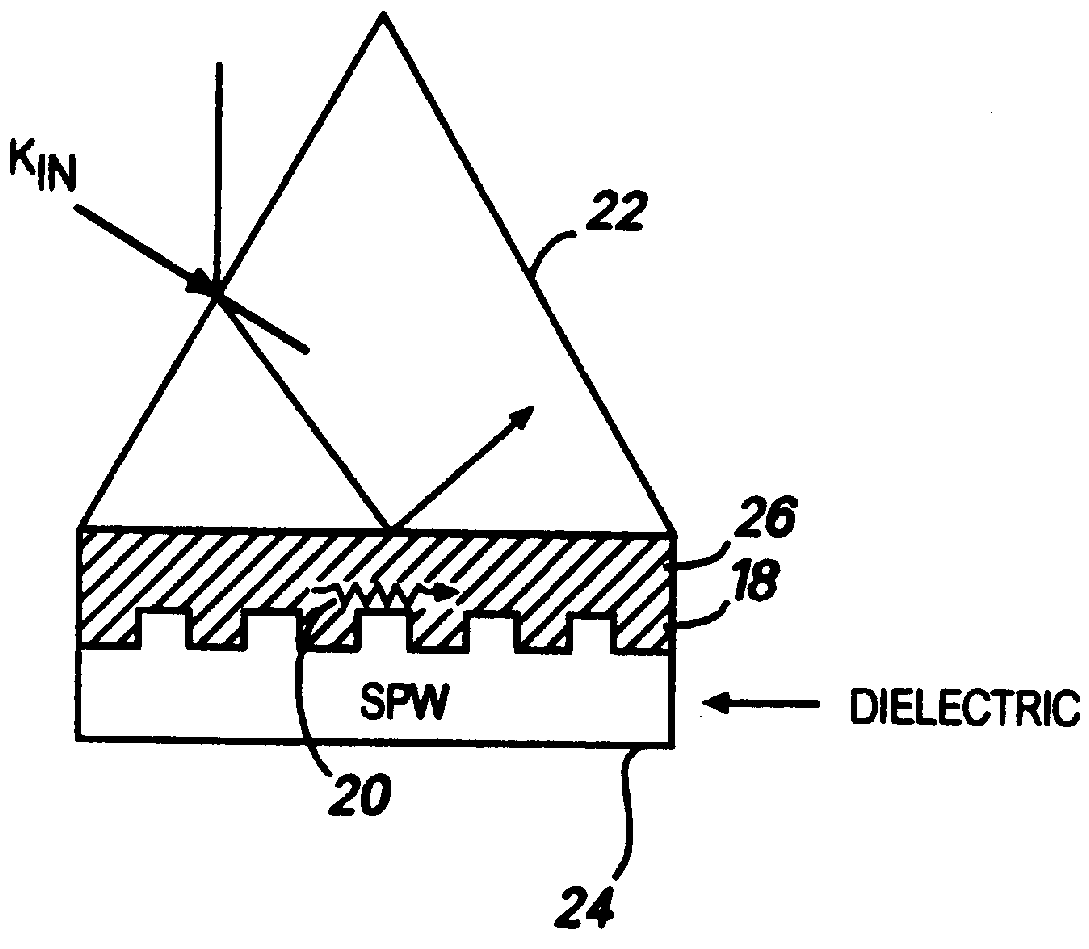
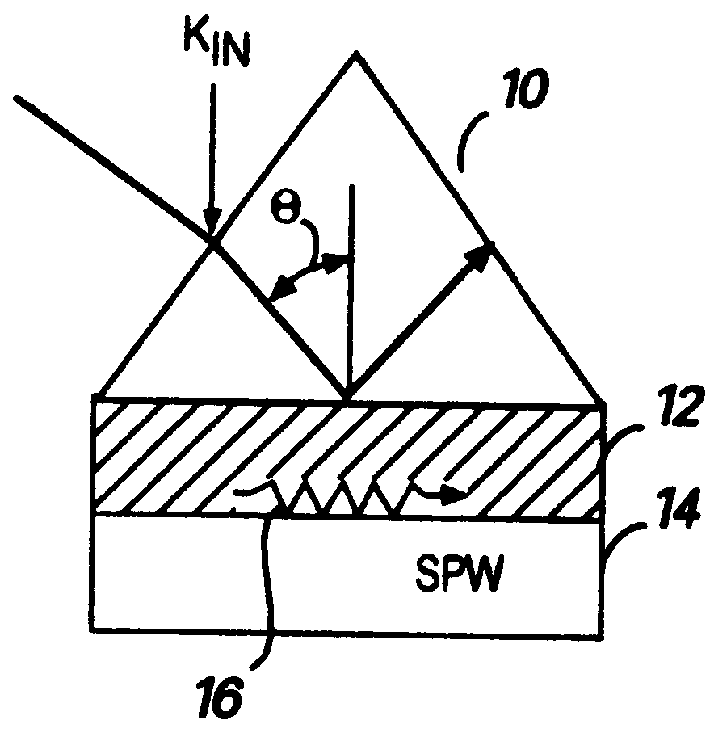
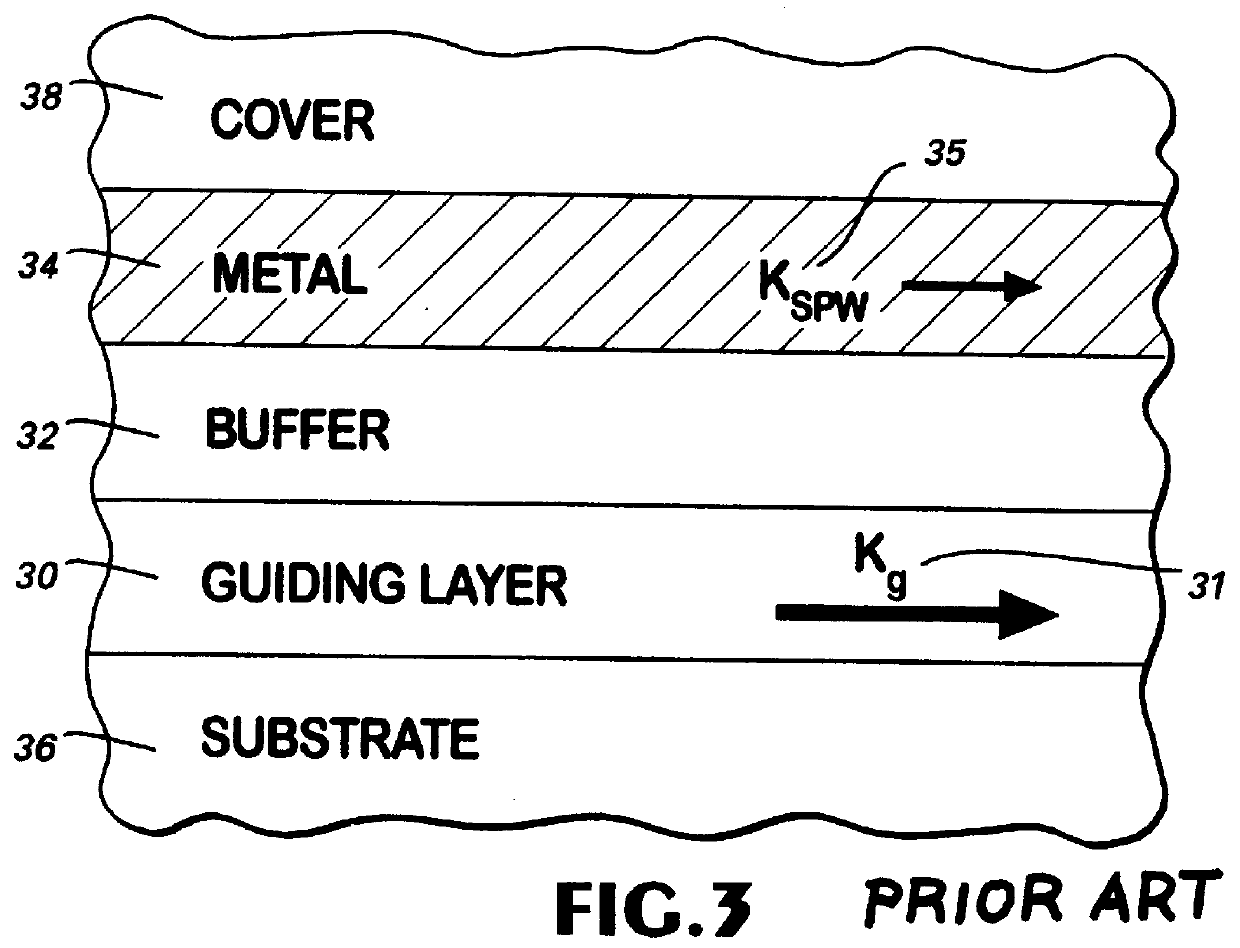
Optical plasmon-wave structures
Optical plasmon-wave attenuator and modulator structures for controlling the amount of coupling between an guided optical signal and a surface plasmon wave. Optical power coupled to the plasmon wave mode is dissipated in varying amounts producing an intensity modulation effect on the optical signal. For electrical modulation, an additional dielectric (or polymer) layer with variable refractive index in optical contact with a metal layer supporting at least one plasmon wave mode is used to perturb or vary the propagation constant of plasmon wave. Propagation constant variation results in the power coupling variation between the surface plasmon wave and the optical wave. The refractive index variation of the dielectric (or polymer) layer can be accomplished via an electro-optic traveling-wave, a lump-element, or any other integrated optics modulator configuration situated to affect the layer, thereby permitting data rates into tens of GHz. Because of the extremely small interaction lengths needed, the optical plasmon-wave modulator is a very compact device which can be implemented on the top of a fiber or as an integrated optical planar structure.
Owner:VERIFIBER TECH
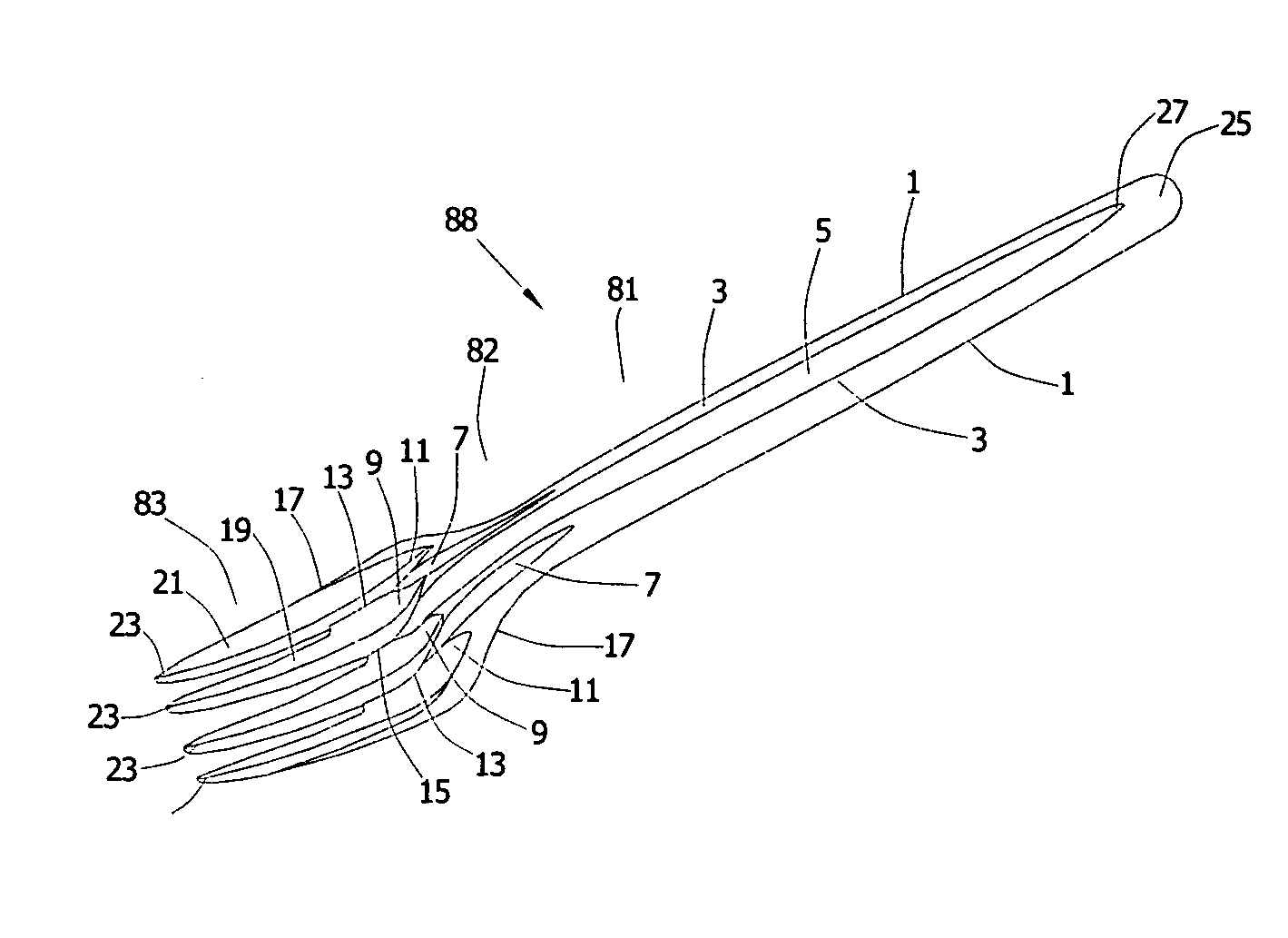
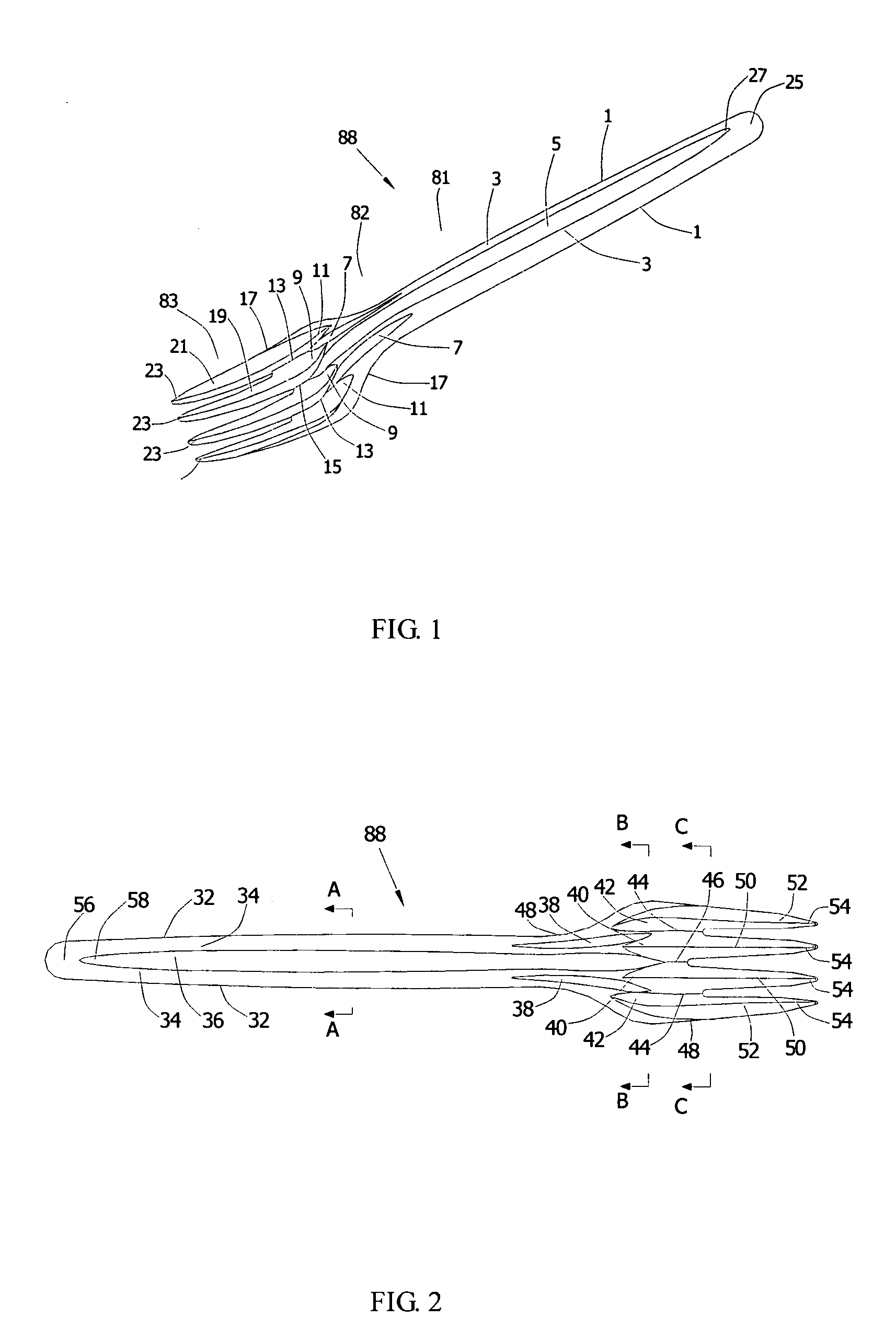
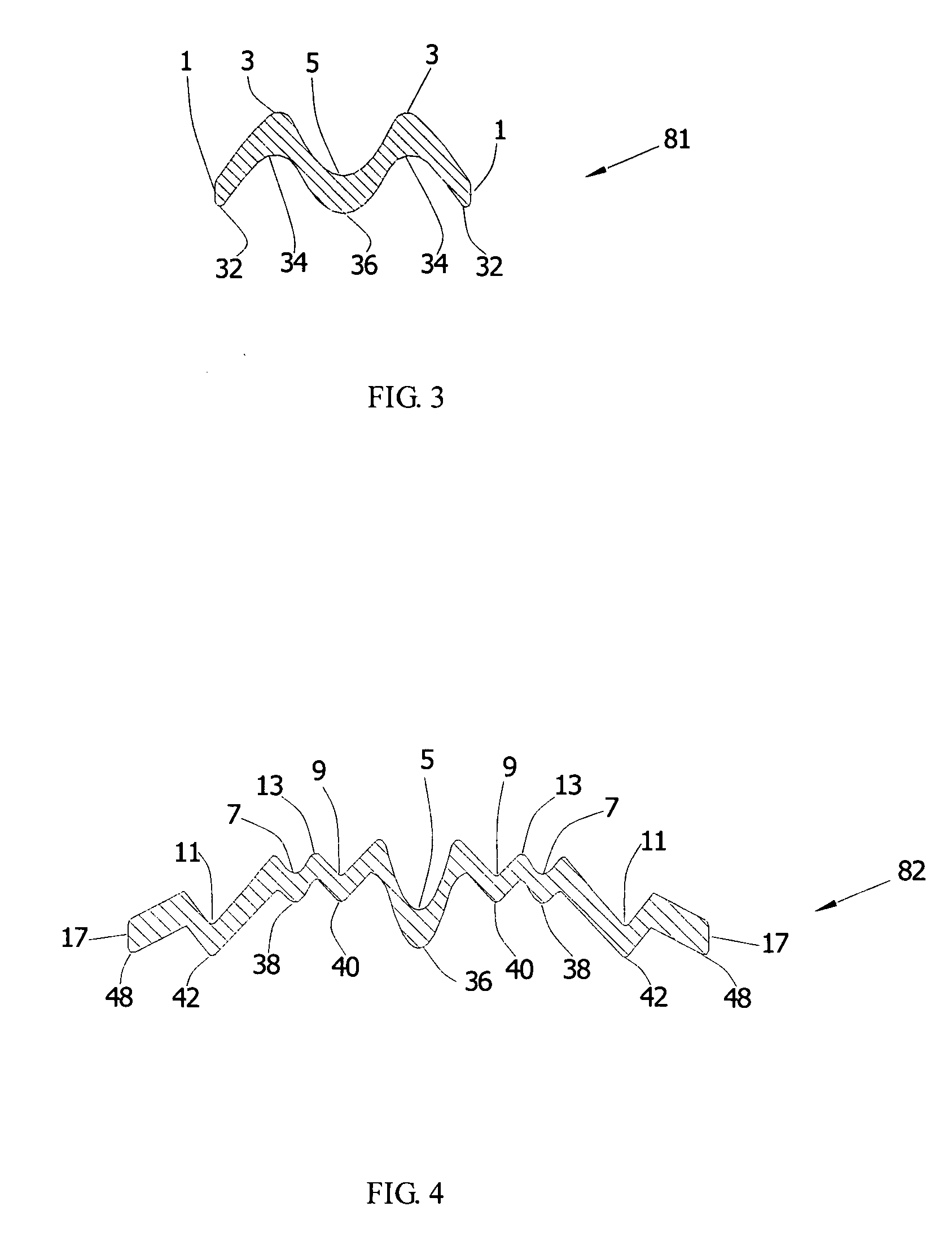
Tableware
InactiveUS20050155229A1Improve handling strengthCheap manufacturingKitchen equipmentMetal working apparatusWave structureEngineering
The present invention relates to tableware. The tableware includes a handle and a holding section connected with the handle. The cross-section of the handle is “M”-shaped, with a “V”-shaped groove extending from the middle of the handle to the holding section, and at least one V-shaped groove being positioned in the middle of the holding section. The above-mentioned parts make up the strengthened tableware. The “M”-shaped and “W”-shaped grooves strengthen the handle, the palm and the finger of the tableware. On the other hand, the manufacturing and concave points located at the “M”-shaped groove of the front surface and the “W”-shaped groove of the back surface of the tableware enable the tableware to overlap closely and steadily because of a parallel-wave structure principle. Different types or the same type of tableware can overlap closely.
Owner:LEE CHING MOU
Wideband low profile spiral-shaped transmission line antenna
InactiveUS6842158B2Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsWave structureDielectric substrate
An antenna incorporating slow wave structures. The antenna comprises at least two conductive serpentine structures disposed on a dielectric substrate and further comprising an oppositely disposed conductive top plate electrically connected to the conductive serpentine structures and farther electromagnetically connected thereto. In one embodiment the antenna further comprises a ground plane below the dielectric substrate.
Owner:SKYCROSS INC
Transmission lines and components with wavelength reduction and shielding
InactiveUS6950590B2Reduce couplingReduce energy lossCoupling light guidesDelay linesWave structureMetal strips
A slow-wave transmission line component having a slow-wave structure. The slow-wave structure includes a floating shield employing one of electric and magnetic induction to set a potential on floating strips of said floating shield to about 0, thereby reducing losses caused by electric coupling to a substrate. A spacing between the strips is small to inhibit electric field from passing the metal strips to the substrate material.
Owner:CHEUNG TAK SHUN +1
Compact relativity backward wave oscillator (RBWO) with adjustable low-frequency-range frequency
ActiveCN102208315AReduce radial sizeCan be smallTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube collectorsWave structureElectrical conductor
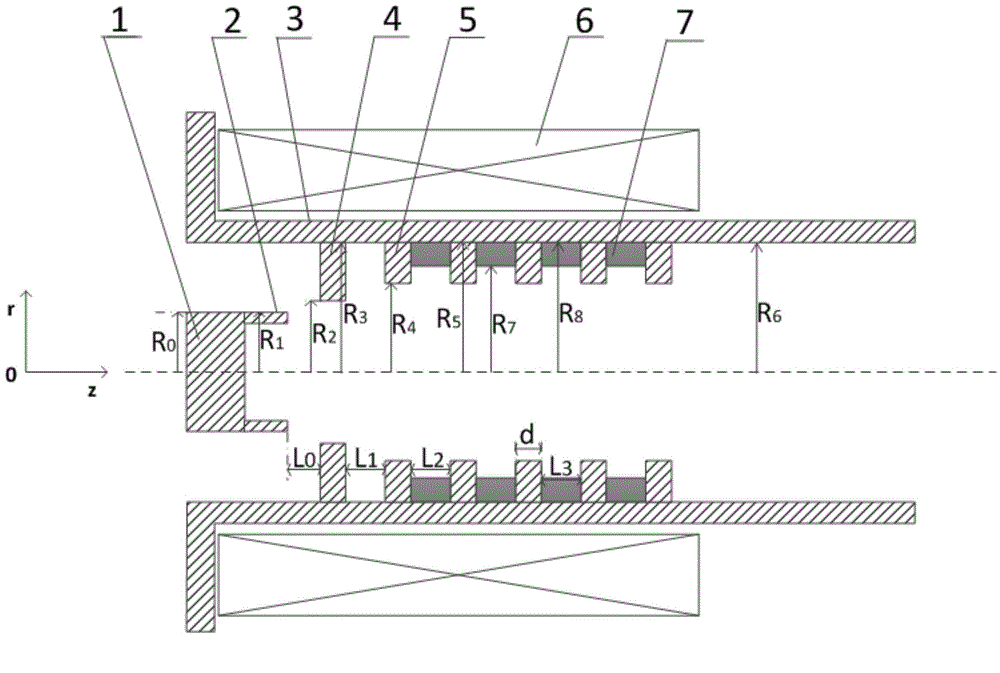
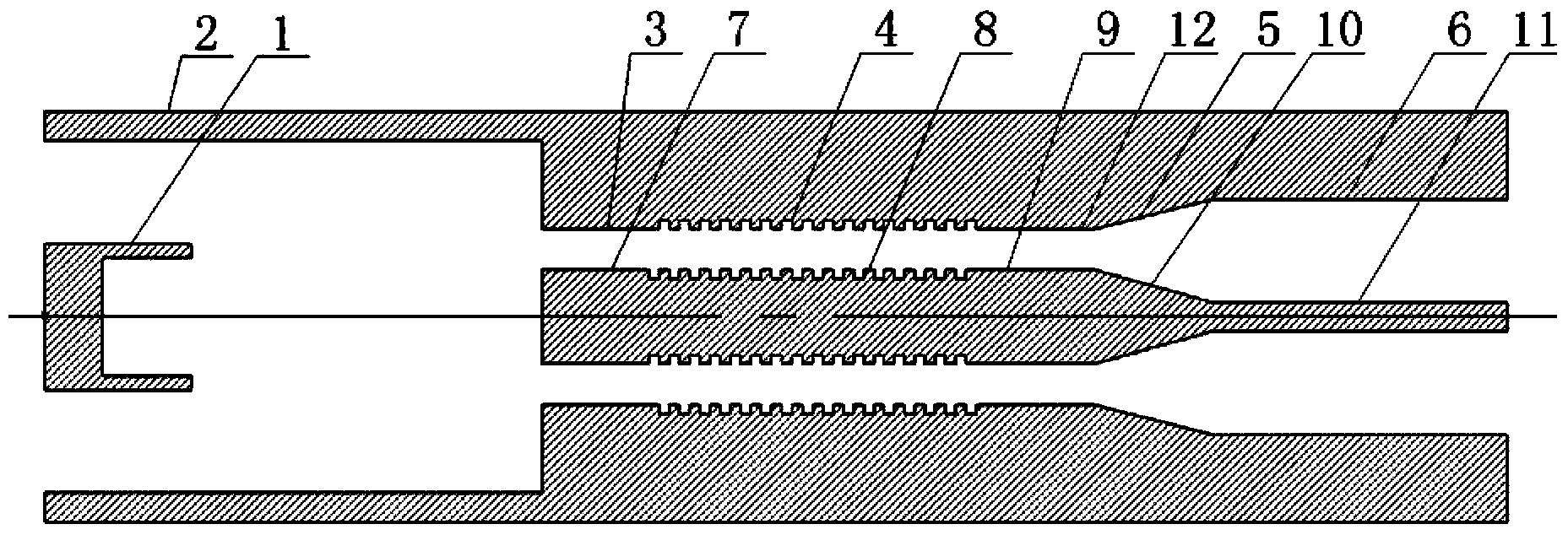
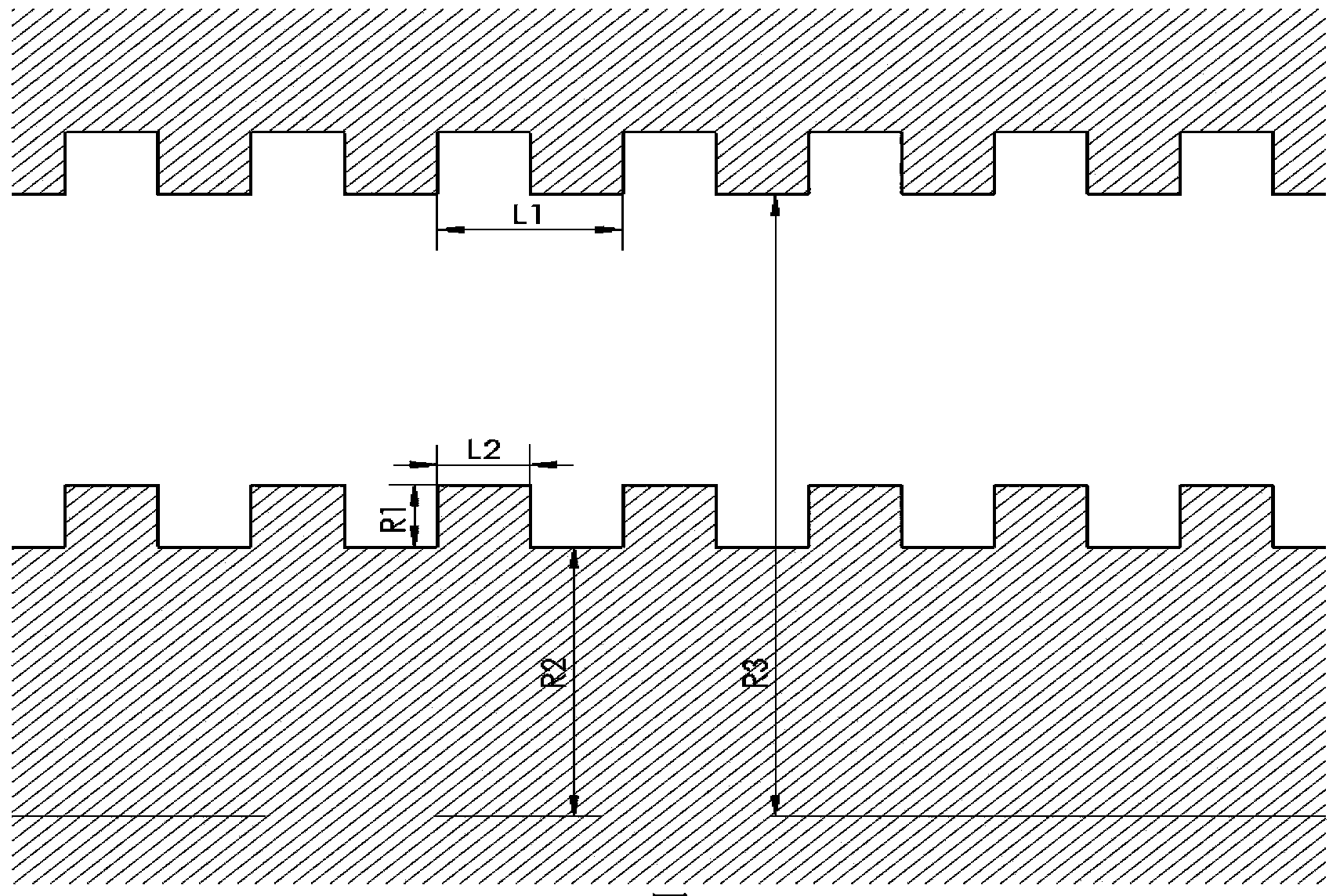
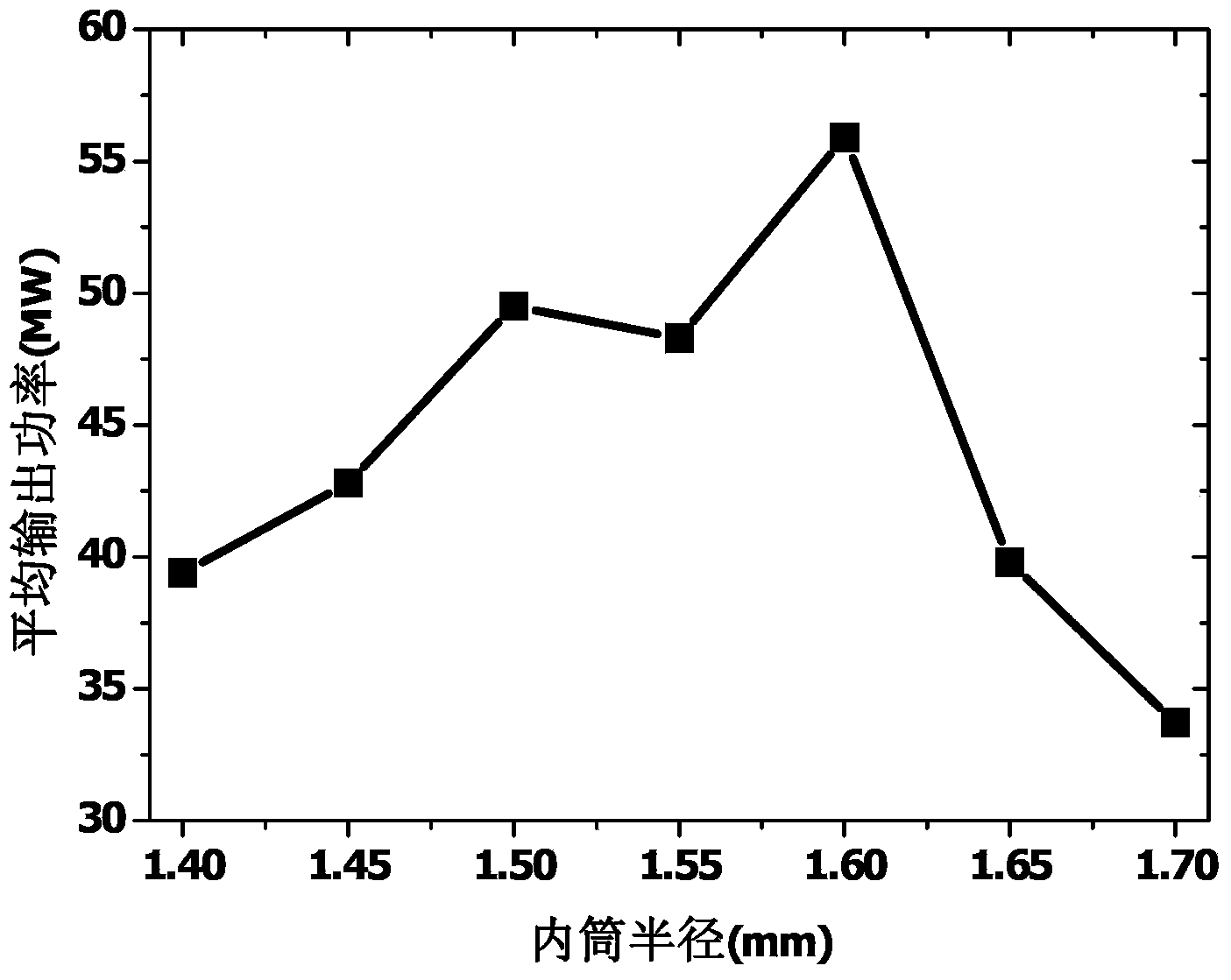
The invention discloses a compact relativity backward wave oscillator (RBWO) with an adjustable low-frequency-range frequency, and the oscillator provided by the invention is used for solving the problems that the RBWO size in a low frequency range is great, and the output microwave frequency is hard to adjust. The compact RBWO is in rotational symmetry with respect to a central axis, and composed of a cathode base, a cathode, an anode outer barrel, a stop neck, a slow wave structure, an inner conductor, a collector, a microwave output port, a solenoid field, two rows of supporting rods, a mode converter, a radiation port and a sealing plate; the slow wave structure is composed of five slow wave blades, the inner surface of each slow wave blade is in a trapezoid structure; the left end face of the collector is provided with an annular groove; the left end of the mode converter is cylindrical, and the right end of the mode converter is in a tapered structure; the radiation port is cylindrical, the left end of the radiation port is in a tapered structure and the right end of the radiation port is cylindrical; the sealing plate is pressed on the radiation port; and the frequency of the output microwave is adjusted by virtue of adjusting the semi-diameter R3 of the inner conductor. The compact RBWO has the advantages of compact structure and convenient and adjustable work frequency, thereby being beneficial to outputting a long pulse of the microwave.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Distribution terahertz oscillator
InactiveCN102403180AAppropriate generationTubes with velocity/density modulated electron streamTransit-tube circuit elementsResonant cavityKlystron
The invention discloses a distribution terahertz oscillator, which relates to technique of THz (terahertz) electromagnetic wave sources and comprises an electron gun, an interaction region and a collector. The interaction region consists of a periodic slow wave structured modulation resonant cavity and an energy extraction cavity, and the modulation resonant cavity is in a periodic slow wave structure which can be operated in a backward wave mode or a forward wave mode to be interacted with electron beams in a distributive manner, so that the electron beams can be modulated in terms of speed and density. The distribution terahertz oscillator integrates advantages of a backward wave tube and a distribution klystron, and has the advantage of suitableness for generating THz electromagnetic waves.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Wave-band-cross mechanical frequency modulation relativity back wave oscillator
ActiveCN103456587AChange lengthEasy to adjustTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube collectorsWave structureElectrical conductor
The invention relates to microwave source devices in the technical field of high-power microwaves and provides a wave-band-cross mechanical frequency modulation relativity back wave oscillator. The wave-band-cross mechanical frequency modulation relativity back wave oscillator comprises a cathode seat, a cathode, an anode outer cylinder, a cut-off neck, a slow wave structure, an inner conductor, a collector, a microwave output and a solenoidal magnetic field. The inner conductor is a cylinder, by adjusting the length of the inner conductor, the frequency of outputting microwaves can be adjusted, and outputting of wave-band-cross microwaves is achieved. An annular groove is formed in the collector, and a supporting rod is fixed on the anode outer cylinder. The wave-band-cross mechanical frequency modulation relativity back wave oscillator has the advantages that by adjusting the length of the inner conductor, frequency can jump between L wavebands and S wavebands, the adjusting manner is simple, the frequency in the wavebands can be adjusted, the bandwidth in the L-waveband frequency is adjusted by 7% or so, and the bandwidth in the S-waveband frequency is adjusted by 2% or so. The outer radius of a slow-wave vane can have a low value, and miniaturization is achieved. A groove structure is reserved at the left end of the collector, reflection of the tail end of the device can be increased, and achieving long-pulse outputting of the wavebands is facilitated.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
FM CW cable guided intrusion detection radar
Owner:SOUTHWEST MICROWAVE
Energy coupling device suitable for rectangular-crossed double-gate slow-wave structure
InactiveCN102064069APromote circulationEnhanced couplingTransit-tube coupling devicesWave structureEnergy coupling
The invention relates to an energy coupling device suitable for a rectangular-crossed double-gate slow-wave structure, belonging to the technical field of vacuum electronics. One end of the device is connected with a rectangular waveguide, and the other end is connected with a rectangular-crossed double-gate slow-wave structure; the part connected with the rectangular-crossed double-gate slow-wave structure comprises an upper row and a lower row of rectangular gate waveguide structures which are mutually staggered and distributed and have gradually changed height; the half-height positions of the rectangular gates at the upper row are in an upper datum plane (1); all half-height positions of the rectangular gates at the lower row are in a lower datum plane (2); counted from a port connected with the rectangular-crossed double-gate slow-wave structure, the heights of the upper row and the lower row of rectangular gates are gradually reduced to zero; and the maximum height of the rectangular gates does not exceed the rectangular gate height of the rectangular-crossed double-gate slow-wave structure. The invention has the advantages of favorably coupling a microwave signal into the rectangular-crossed double-gate slow-wave structure, favorably extracting the amplified microwave signal from the rectangular-crossed double-gate slow-wave structure and being easy to connect with a traditional standard waveguide device.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Zigzag slow-wave line of double ridged waveguide
InactiveCN101572205ALower cutoff frequencyWide side smallTransit-tube circuit elementsWave structureMicrowave
A zigzag slow-wave line of double ridged waveguide belongs to the technical field of microwave vacuum electron and relates to a traveling-wave tube amplifier. A slow-wave structure is formed by periodically bending the double ridged waveguide (4) along the electric field to form a right-angled zigzag line or a U-shaped zigzag line; circular through holes are arranged at the positions along the mean axis symmetric line (2) of the slow-wave structure on the waveguide wall; and the slow-wave lines are connected by the metal tubes (3) with the aperture the same with that of the circular through holes between two circular through holes of the right-angled groove or U-shaped groove in each zigzag periodic structure of the slow-wave structure to form an electron stream channel. Compared with conventional zigzag slow-wave line of waveguide, the slow-wave line has lower cut-off frequency, wider pass band range and flatter dispersion characteristics. In addition, in the event that the dispersion characteristics are approximate, the zigzag slow-wave line of double ridged waveguide has smaller cross-sectional dimension to well ensure the transfer characteristics of electron stream in traveling wave tube under the action of the same focusing magnetic field, so as to improve the integral output power and grain of the traveling wave tube.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
High power microwave radial line slit array antenna
InactiveCN103151620AImprove radiation efficiencyInhibitionAntenna arraysRadiating element housingsWave structureMicrowave
The invention relates to a high power microwave radial line slit array antenna which comprises a coaxial input waveguide, a radial line leaky wave waveguide and an antenna housing, wherein an output port of the coaxial input waveguide is connected with an input port of the radial line leaky wave waveguide, and an output port of the radial line leaky wave waveguide is sealed through the antenna housing. Microwaves are inputted through a coaxial over-mode waveguide in a transverse electronic and magnetic (TEM) mode, folding conversion is carried out through a double layer radial line waveguide, and microwave radial inner feedback is achieved on a waveguide upper layer. Slit unit arrays arranged on an antenna aperture cut a radial electric field, distant field same-phase superimposed circular polarization radian is achieved, the whole axial dimension is small, and the structure is compact. Due to action of a radial line slow wave structure, the wavelength of the radial line waveguide is reduced, and generation of slit array grating lobes is restrained. Due to the fact that a high order reflection mode excited by a wide slit array is restrained through a reflection offset spiral groove in a lower layer waveguide, the whole antenna has high radiant efficiency. Due to the improvement on the slit unit structure and vacuum sealing of the antenna housing, the whole radiating system has high power capacity, and application requirements in the high power microwave field can be met.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Coaxial-extraction long-pulse relativistic backward-wave oscillator
ActiveCN103137399AHigh Q valueOvercome the impact on work efficiencyTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube collectorsWave structureMicrowave
The invention relates to a microwave component in the technical field of high power microwave and provides a coaxial-extraction long-pulse relativistic backward-wave oscillator. The coaxial-extraction long-pulse relativistic backward-wave oscillator comprises a cathode base, a cathode, an anode outer cylinder, a cut-off neck, a slow wave structure, a tapered waveguide, an output waveguide, a solenoidal field, a coaxial-extraction structure and a front-arranged reflection cavity. The coaxial-extraction structure is a cylinder. The front-arranged reflection cavity is disposed between the cut-off neck and the slow wave structure. According to the coaxial-extraction long-pulse relativistic backward-wave oscillator, a cylinder is adopted as the coaxial-extraction structure, and therefore the defect that the coaxial-extraction structure with a groove generates plasma is overcome, and meanwhile in the electromagnetic wave mode, function transformation can be carried out and installation can be achieved conveniently. The front-arranged reflection cavity is utilized to replace the cut-off neck so that the resonance characteristic of the front-arranged reflection cavity can be utilized to achieve the effect of the cut-off neck, electron beam scraping or electron beam bombardment of the front-arranged reflection cavity can be avoided, and premodulation of electron beams emitted from the cathode also can be carried out. Therefore, the coaxial-extraction long-pulse relativistic backward-wave oscillator is beneficial for subsequent beam wave interaction and improves power conversion efficiency of the component.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Integrally formed 3D flyknitted vamp and making method thereof
The invention discloses an integrally formed 3D flyknitted vamp and a making method thereof.Low-melting yarn and dyed yarn are adopted as raw materials, an upper layer of double-faced jacquard vamp body and a lower layer of double-faced jacquard vamp body with the edges interwoven together are woven on a bidirectional jacquard double-faced loop transfer computer flat knitting machine, openwork figured texture weave is primary weave, different weave structures are adopted in functional zones of the vamp, and then the integrally formed 3D flyknitted vamp is made through hot pressing shaping.The temperature of hot pressing shaping ranges from 170 DEG C to 200 DEG C, and the time of hot pressing shaping ranges from 20 s to 80 s.Each double-faced jacquard vamp body comprises a dyed yarn layer and a low-smelting yarn layer which are interwoven together through yarn coils, and the integrally formed 3D flyknitted vamp is formed by bonding and combining the two layers of double-faced jacquard vamp bodies according to the wave structure of one dyed yarn layer, one low-melting yarn layer, the other low-melting yarn and the other dyed yarn layer through the upper low-melting yarn layer and the lower low-melting yarn layer in a hot pressing and melting mode.The integrally formed 3D flyknitted vamp has the advantages of being soft, comfortable, durable, colorful, attractive, low in cost and the like.
Owner:厦门翔鹭化纤股份有限公司
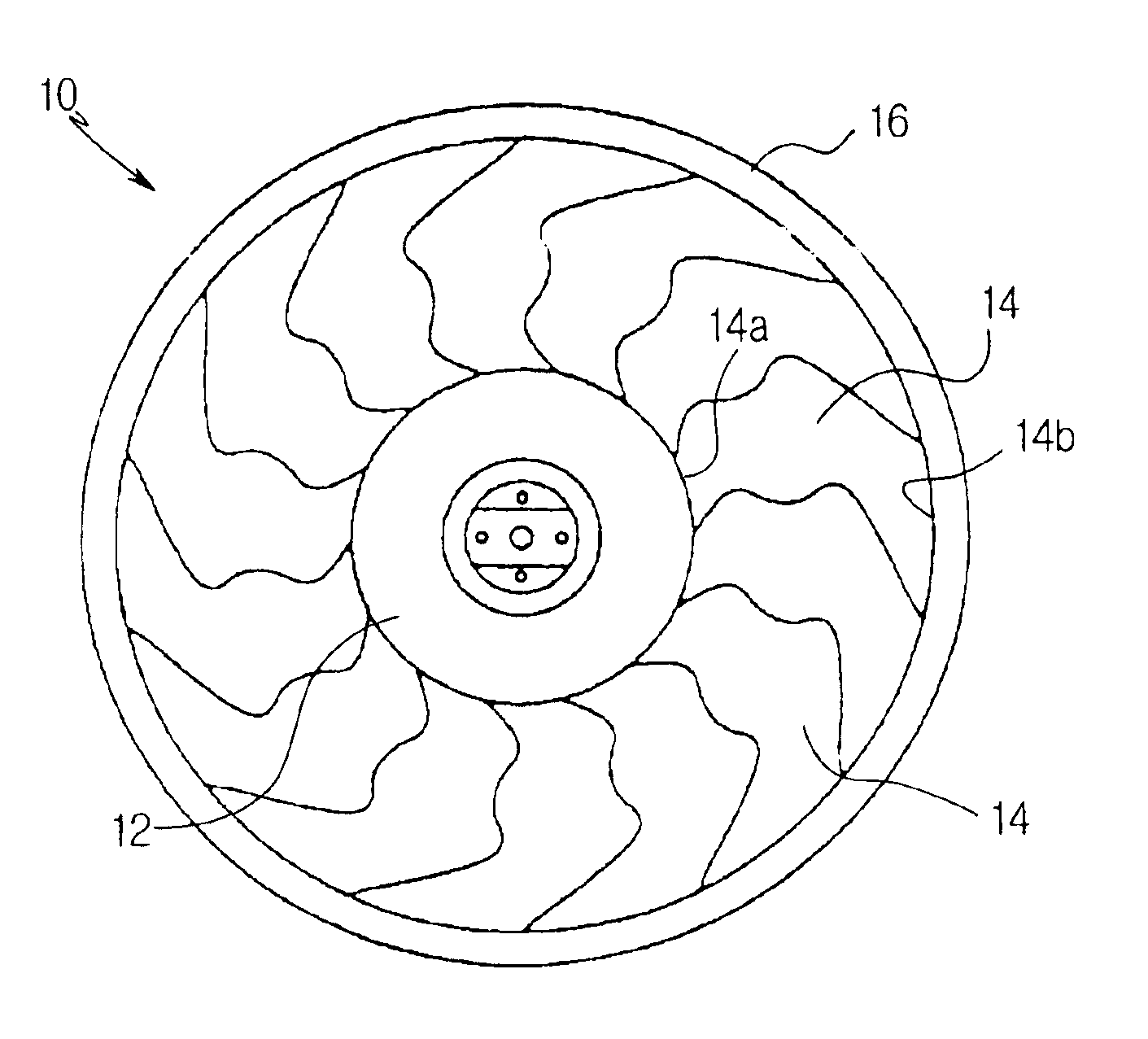
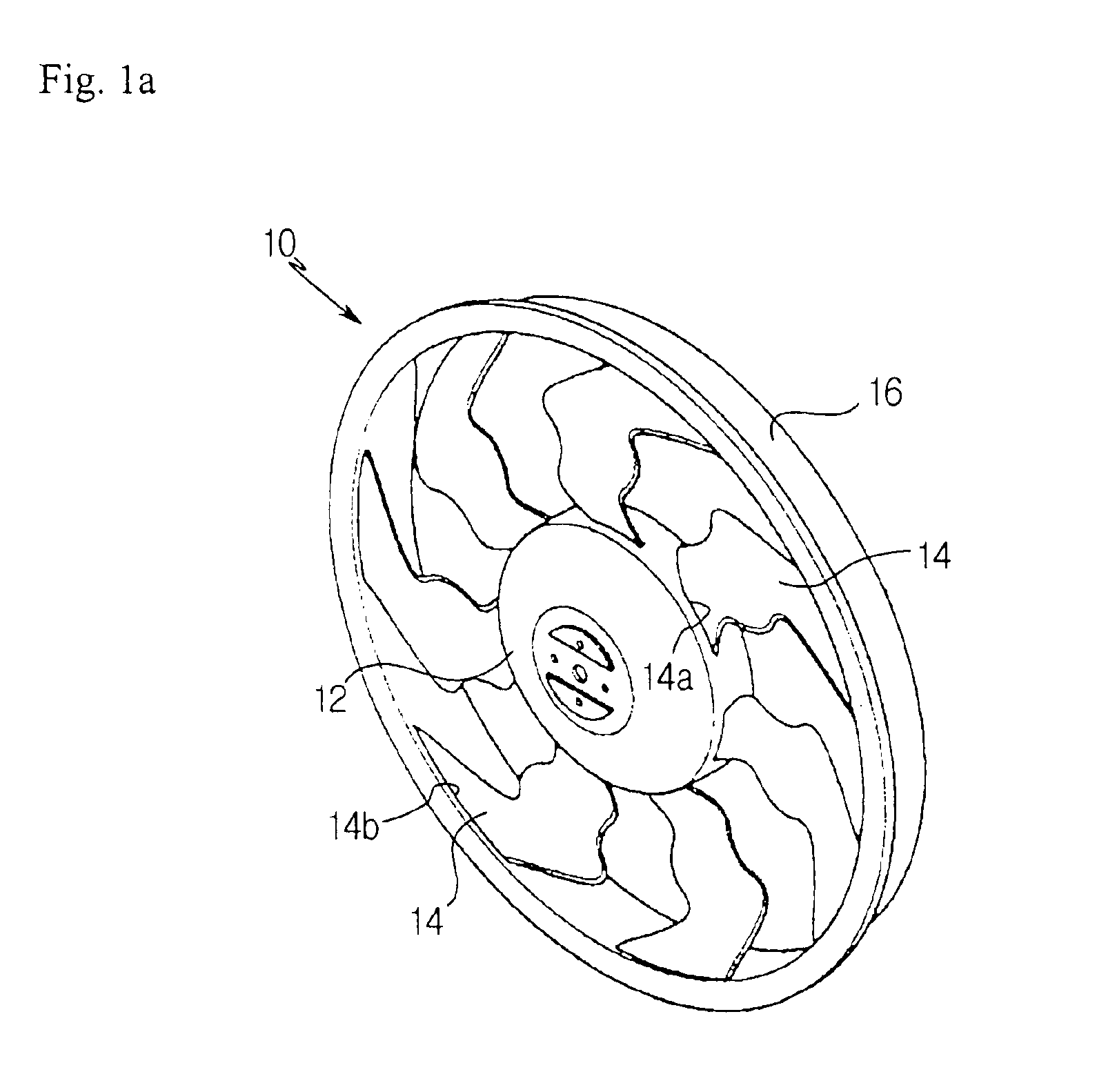
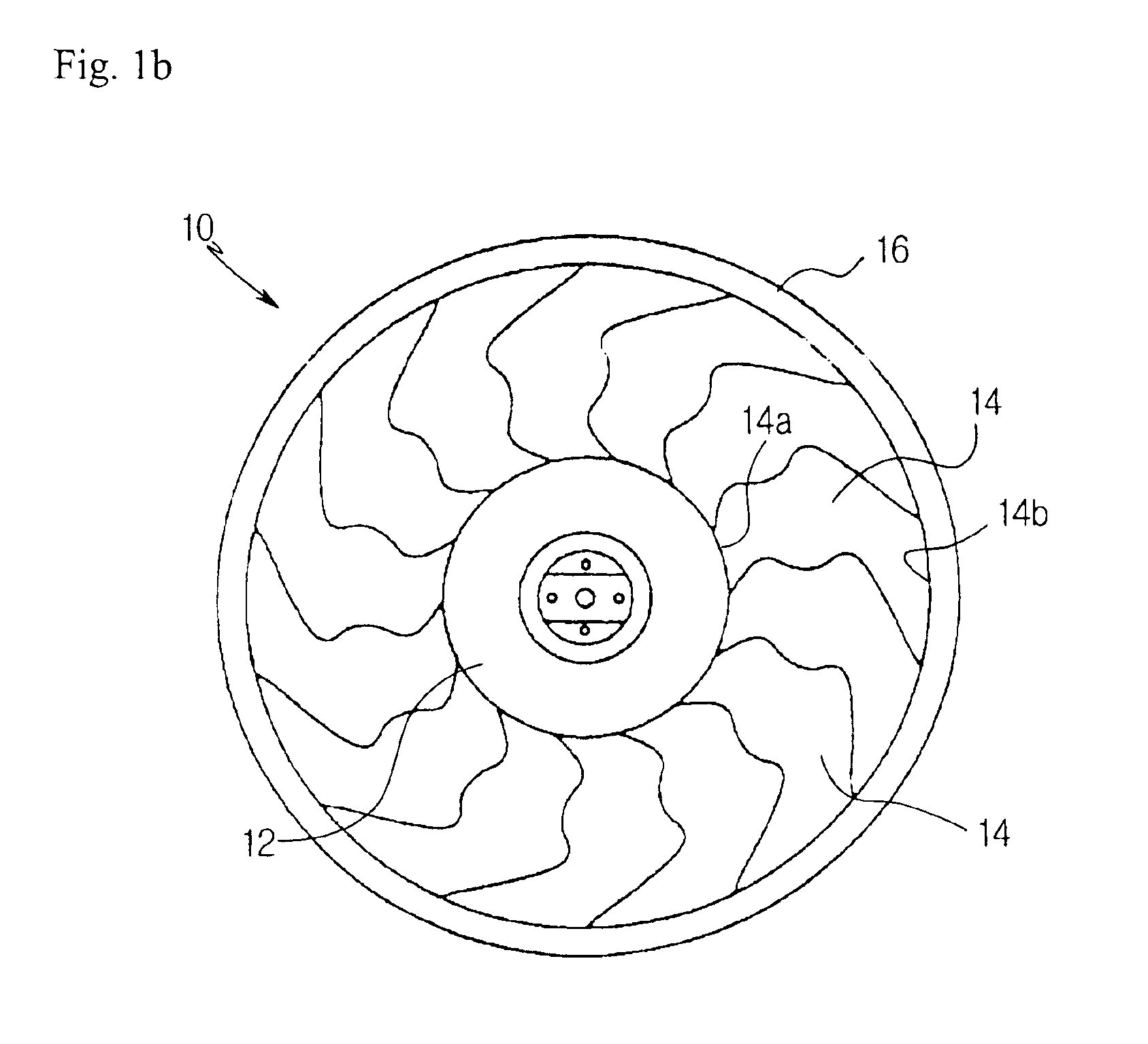
Axial flow fan
InactiveUS6908287B2Reduce blowing noiseImprove blowing efficiencyPropellersRotary propellersLeading edgeWave structure
Disclosed is an axial flow fan capable of achieving reduction of noise while having a high blowing efficiency compared to the power consumption of a motor adapted to drive the axial flow fan. The axial flow fan includes a hub, and a plurality of blades extending radially around the hub. Each blade has a sweep angle varying gradually from a backward angle at a root of the blade connected to the hub to a forward angle at a tip of the blade, while having a flow dispersion region having a plurality of regions where the sweep angle is alternately changed, at a region defined between a backward sweep angle region at the root of the blade and a forward sweep angle region at the tip of the blade. Each blade has a longitudinal cross section curved to have a wave structure between the root of the blade and the tip of the blade. The axial flow fan may further include a fan band connecting tips of the blades. The axial flow fan achieves reduction of blowing noise by receiving air in a dispersed state at the leading edge of each blade, discharging air in a dispersed state at the trailing edge of each blade, and offsetting turbulent flows of air by virtue of the wave-shaped longitudinal cross-sectional structure of each blade.
Owner:HANON SYST
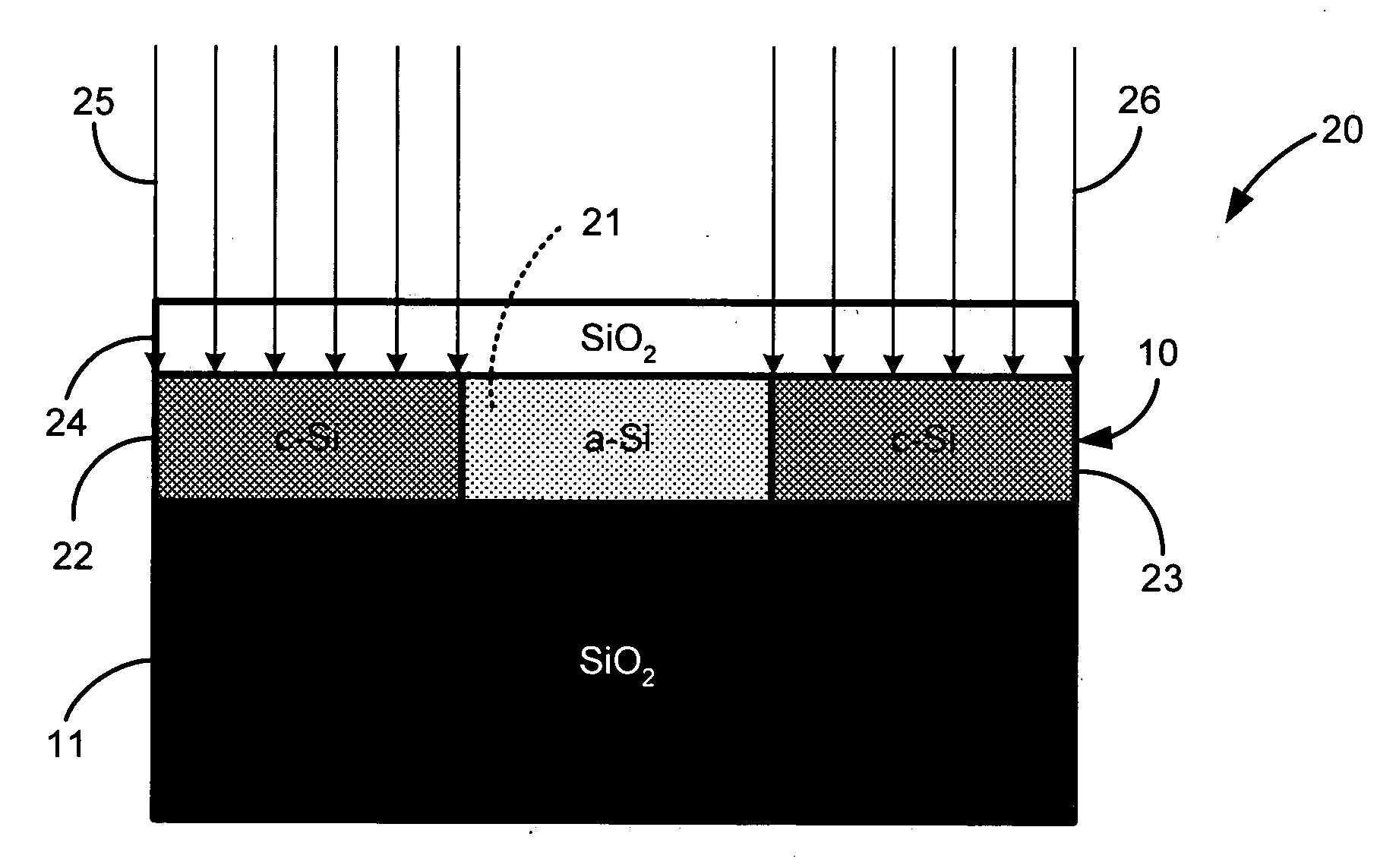
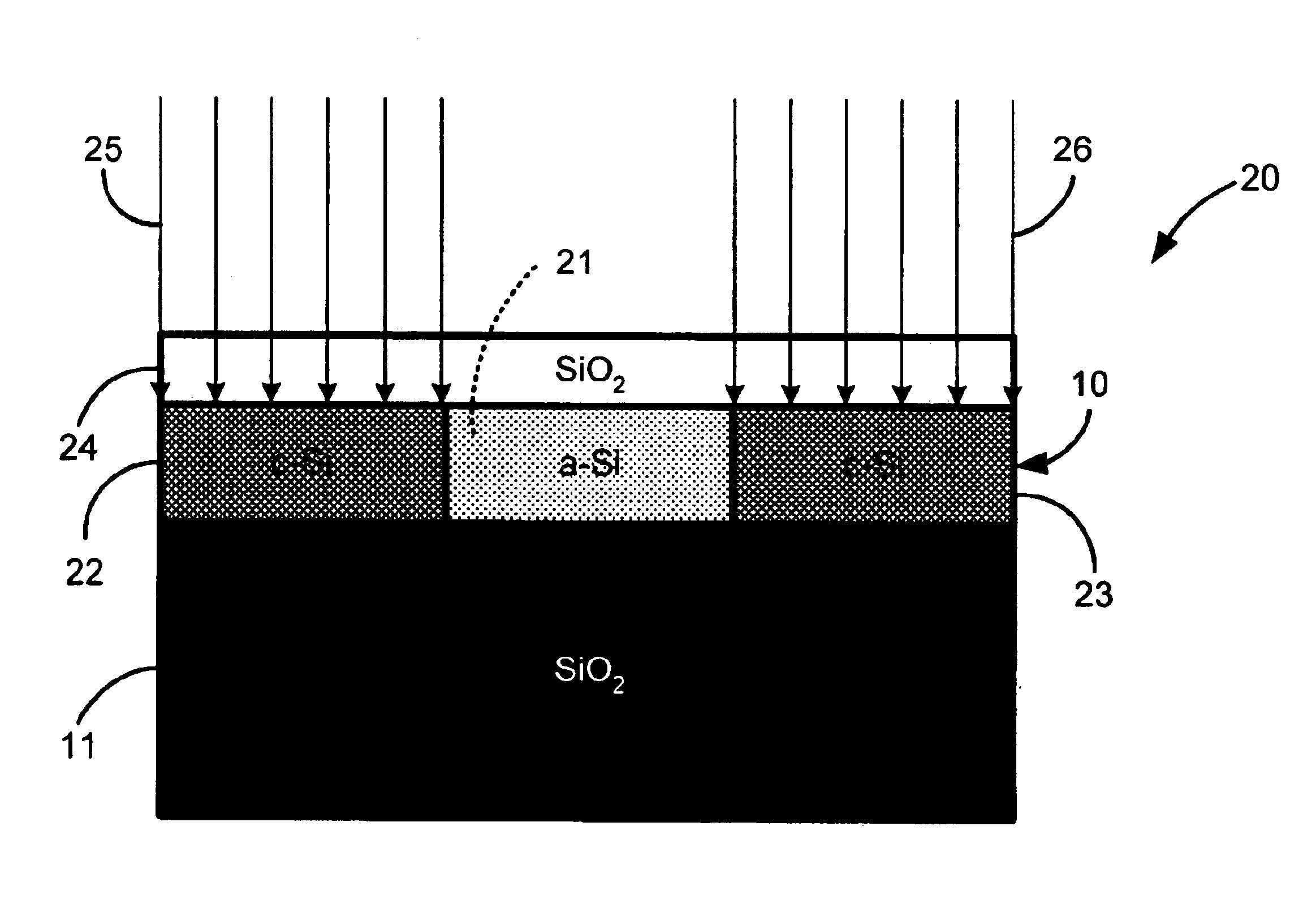
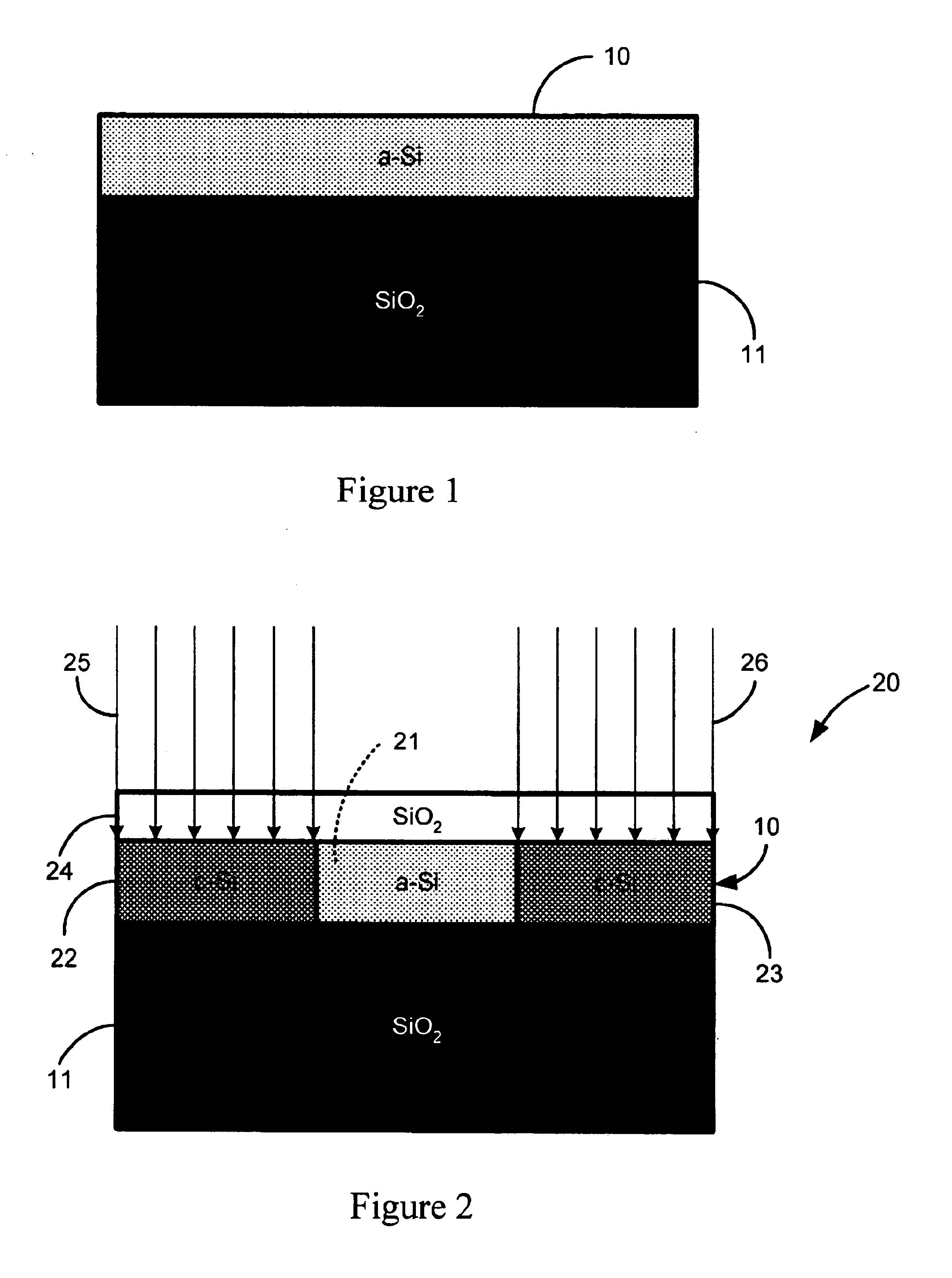
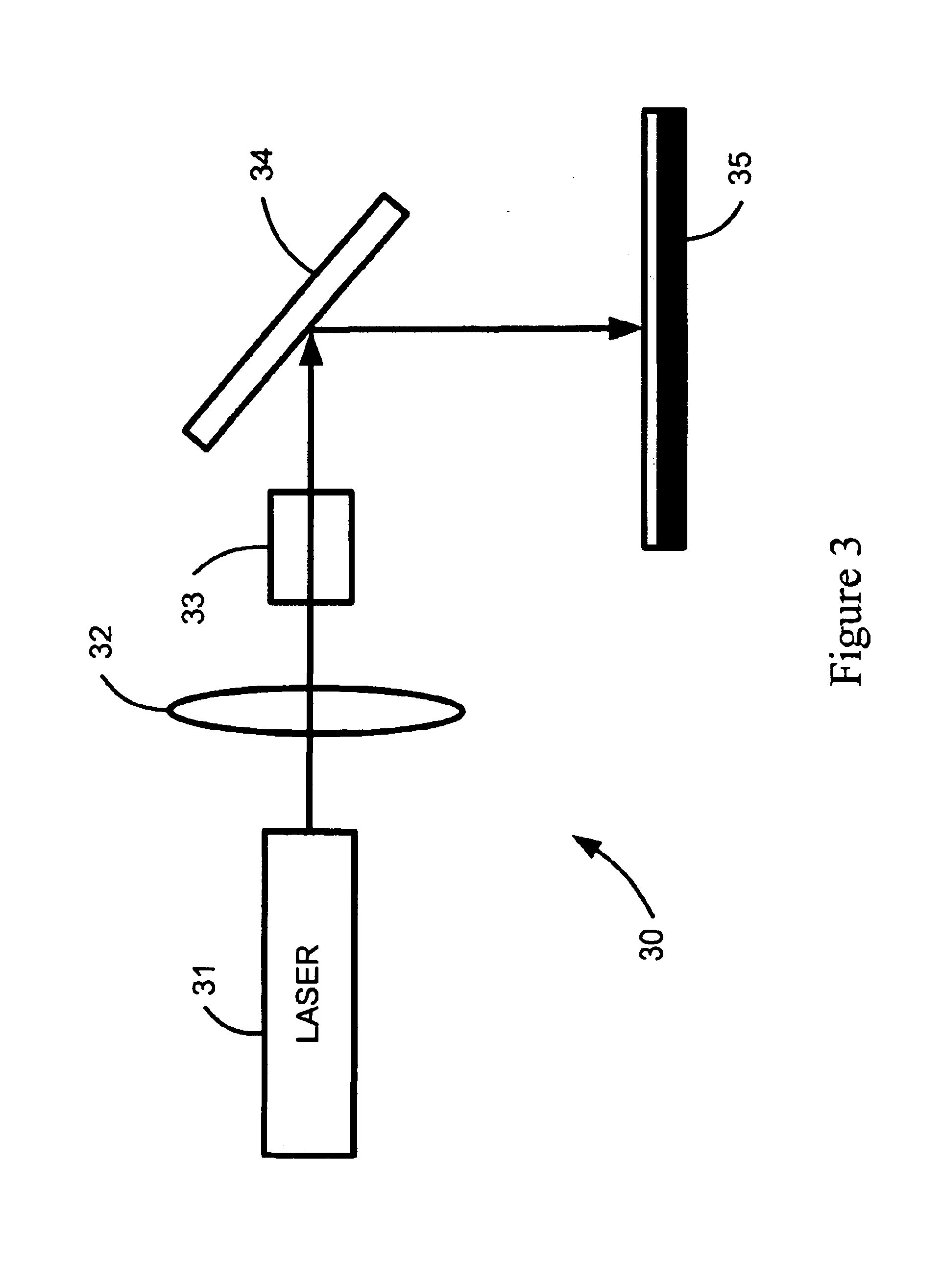
Direct-patterned optical waveguides on amorphous silicon films
InactiveUS20040240821A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical waveguide light guideWave structureRefractive index
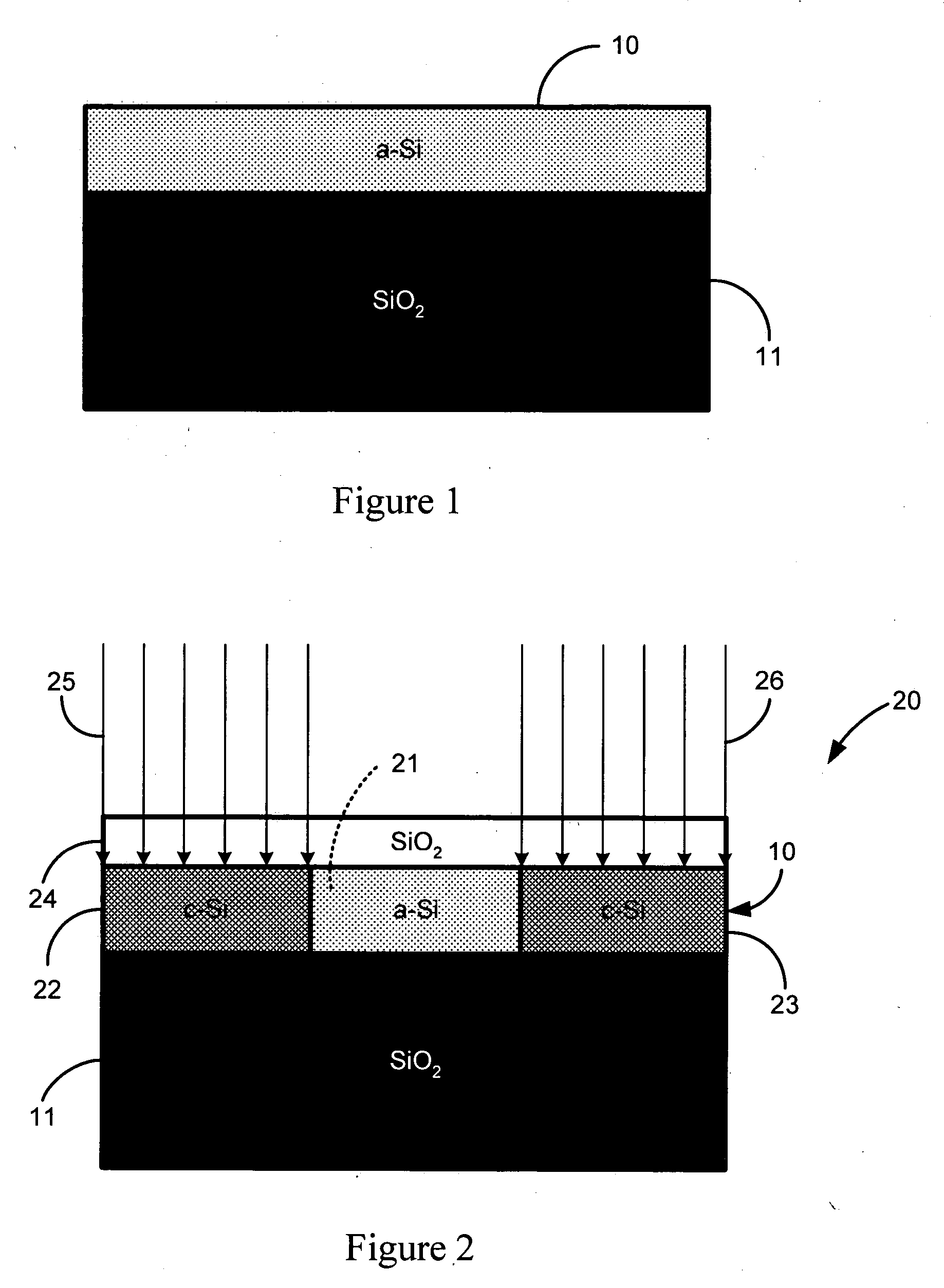
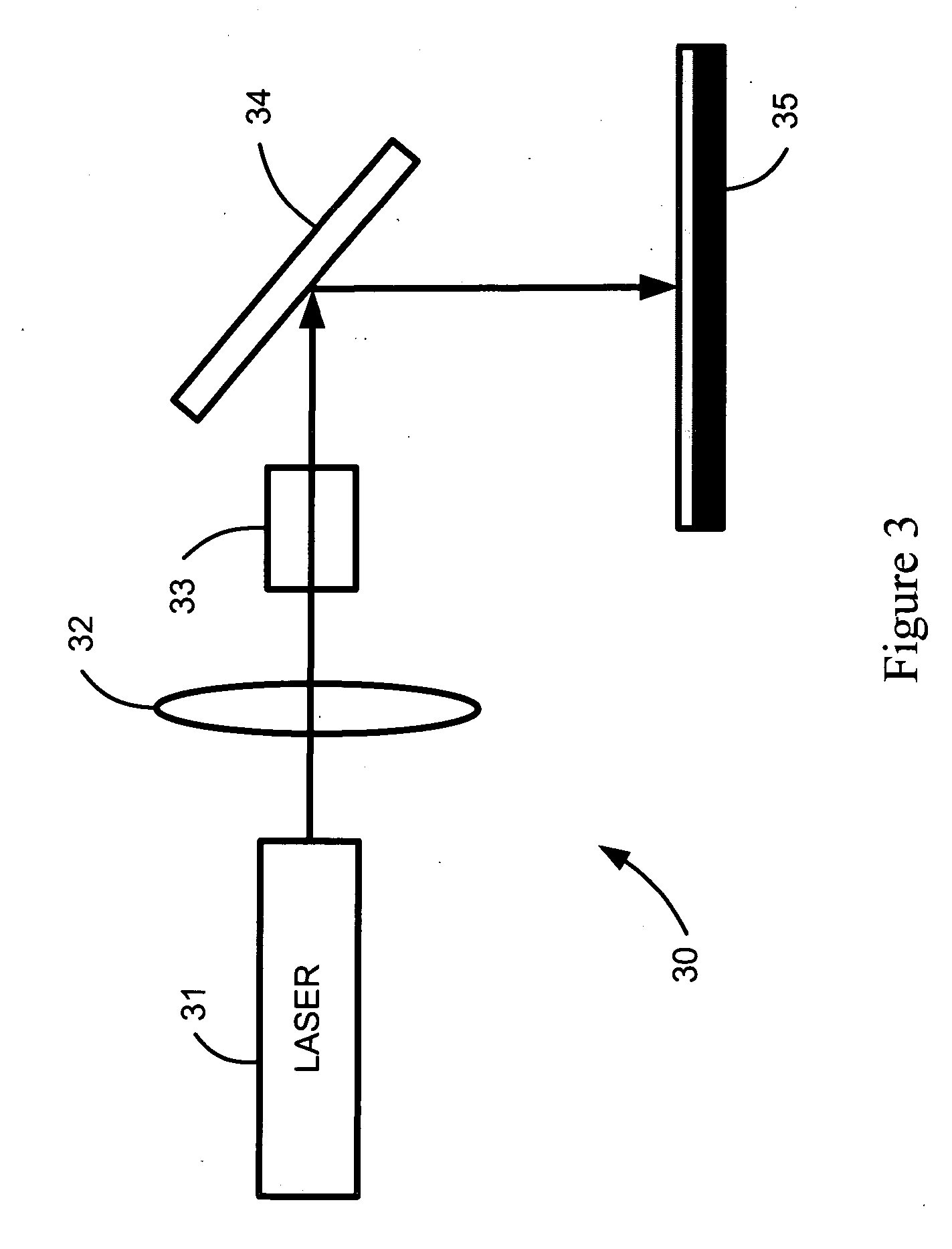
An optical waveguide structure is formed by embedding a core material within a medium of lower refractive index, i.e. the cladding. The optical index of refraction of amorphous silicon (a-Si) and polycrystalline silicon (p-Si), in the wavelength range between about 1.2 and about 1.6 micrometers, differ by up to about 20%, with the amorphous phase having the larger index. Spatially selective laser crystallization of amorphous silicon provides a mechanism for controlling the spatial variation of the refractive index and for surrounding the amorphous regions with crystalline material. In cases where an amorphous silicon film is interposed between layers of low refractive index, for example, a structure comprised of a SiO2 substrate, a Si film and an SiO2 film, the formation of guided wave structures is particularly simple.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Arc-shaped curve boundary folding waveguide slow wave structure
The invention relates to a microwave vacuum electronic device, in particular to an arc-shaped curve boundary folding waveguide slow wave structure, and belongs to the technical field of microwave vacuum electrons. The novel folding waveguide slow wave structure is a periodic structure of a series of straight waveguides and arc-shaped boundary curve waveguides, inner boundaries Cin and / or outer boundaries Cout of the curve waveguides are non-semicircles, and the positions (Yin and / or Yout) of arc circle centers (Oin and / or Oout) and radius sizes (Rin and / or Rout) are adjusted to increase the widths of the curve waveguides to strengthen electron beam direction electromagnetic fields of gaps of the straight waveguides. By means of the arc-shaped curve boundary folding waveguide slow wave structure, under the condition that the technology complexity and accuracy are not improved, the coupled impedance is improved, and the arc-shaped curve boundary folding waveguide slow wave structure is suitable for the improvement of gains and efficiency of short millimeter waves and terahertz devices.
Owner:NO 12 RES INST OF CETC
Two-stage serial-connection terahertz slow wave structure
ActiveCN103346056AReduce current densitySimple structureTransit-tube circuit elementsWave structureChannel width
The invention discloses a two-stage serial-connection terahertz slow wave structure which comprises two stages of slow wave structure bodies. The two stages of the slow wave structure bodies are different in period and tooth space width and are equal in length, depth, channel width and electronic beam channel height. The period and the tooth space width of the first stage of slow structure body are smaller than that of the second stage of slow wave structure body, transition gradient structures are arranged at the electronic beam input ends and the electronic beam output ends of the two stages of slow wave structure bodies, the electronic beam input ends of the two stages of the slow wave structure are in serial connection, and two rectangular holes are formed in the connection position between the two stages of the slow wave structures to be used for banding electrons to enter the slow wave structure bodies. The two-stage serial-connection terahertz slow wave structure is simple in main body structure, easy to process, low in high-frequency loss, good in frequency stability and completely suitable for terahertz wave bands and uses banding electrons to work. By means of the two electronic beams, homogeneous tube work current is improved under the same cathode emission density, and power output is improved. Under the same homogenous tube work current, the current density of the banding beams is reduced, and the electronic efficiency is improved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Electromagnetic method and apparatus for the measurement of linear position
ActiveUS7216054B1High sensitivityReduce operating frequencyAcceleration measurementDevices using time traversedWave structurePhase shifted
Owner:NYCE DAVID S
Dielectric filled compact type relativistic backward wave oscillator
ActiveCN104362060AReduce microwave frequencyReduce radial sizeTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube circuit elementsWave structureDielectric
The invention discloses a dielectric filled compact type relativistic backward wave oscillator and belongs to the technical field of high-power microwave. The dielectric filled compact type relativistic backward wave oscillator is rotationally symmetrical relative to the central axis and consists of a cathode seat, a cathode, an anode outer barrel, a cut-off neck, a slow wave structure and a solenoidal field coil. The slow wave structure is a disk loaded waveguide type slow wave structure and consists of five slow wave blades, wherein the inner surface of each slow wave blade is of a rectangular structure. During dielectric filling, an original structure of the RBWO is not needed to be changed, and only dielectric materials are needed to be filled among all blades of the slow wave structure. The problem that a low-frequency relativistic backward wave oscillator is too large in size and weight can be solved, and the dielectric filled compact type relativistic backward wave oscillator has wide application prospect and important scientific research value on research of small-sized compact type relativistic backward wave oscillators, promotion of engineering application process of high-power microwave systems and expansion of the RBWO application field.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
High-power coaxial structure over-mode surface wave oscillator and terahertz wave generating method
ActiveCN103516327AIncrease output powerHigh pattern purityImpedence networksTransit-time tubesWave structureWave band
The invention discloses an axisymmetric-structure high-power coaxial over-mode surface wave oscillator which uses electromagnetic wave radiation of the terahertz wave band generated through wave-beam interaction as the basic working principle, according to high-current relativity theory electron beams and an over-mode coaxial slow wave structure, strong wave-beam interaction happens, and high-power terahertz waves are generated. The coaxial over-mode surface wave oscillator comprises a non-foil diode, the over-mode coaxial slow wave structure, a transitional wave guiding part and an output wave guiding part of a coaxial structure. The working mode of the over-mode surface wave oscillator in a wave-beam interaction zone is a TM01 mode, by mode converting of the transitional wave guiding part, transmission is carried out at an output wave guiding end of the surface wave oscillator in a TEM mode, the 0.14THz over-mode surface wave oscillator is designed through the structure, and the peak power of an output port can reach 115MW. The over-mode surface wave oscillator is suitable for generating the high-power electromagnetic waves in the terahertz wave band.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
Parameterized reduced model based three-dimensional electromagnetic field simulation method of periodic structure
ActiveCN103412989AAccurately obtainedSpecial data processing applicationsWave structureReduced model
The invention discloses a parameterized reduced model based three-dimensional electromagnetic field simulation method of a periodic structure. Geometric parameters, needing optimization, of the periodic structure are set to be variables, finite-element eigen analysis of the microwave-tube periodic structure is performed after a group of data is fetched in a geometric parameter variation range for modeling, and then all high-frequency characteristic curves of the microwave-tube periodic structure in variation ranges of multiple geometric parameters such as pitch of a helix slow-wave structure, internal diameter of a helix and clamping rod width can be acquired rapidly and accurately, so that quick optimized simulation of the microwave-tube periodic structure is realized.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Graded transmitted wave structure in microwave sintering and method for preparing ceramic material using the same
The invention relates to a gradient wave-transmitting structure used for microwave sintering and a method used for preparing ceramic materials, which are characterized in that: (1) when a material with high dielectric property is sintered, at least a transition layer is added into the exterior of the material and the transition layer is composed of high-efficient wave absorption material with certain concentration and a microwave transparent thinner; when a multilayered structure is used as the transition layer, the concentration of the high-efficient wave absorption material increases from exterior to interior in sequence; (2) when a material with low dielectric and relatively poor wave absorption properties is sintered, the multilayered structure is adopted for an exothermic material ora coat, wherein, the concentration of the high-efficient wave absorption material increases from exterior to interior in sequence and then decreases so as to be favorable for transmitting microwave. In the invention, energy consumption caused by a plurality of times of reflection and wave-absorbing and heat-emitting of a thermal insulating layer are reduced by improving the efficiency of being sintered and wave absorption, thus being capable of effectively realizing the purpose of increasing sintering temperature. In addition, the gradient thermal insulating structure can help materials sintered to obtain an even temperature field and better sintering quality.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Relativistic backward wave oscillator for generating linearly polarized TE11 mode directly
ActiveCN105280462AEnhanced interactionImprove beam conversion efficiencyTransit-tube cathodesTransit-tube circuit elementsWave structureMaser
The invention, which belongs to the maser field, directly relates to a relativistic backward wave oscillator for generating a linearly polarized TE11 mode directly. The relativistic backward wave oscillator comprises an arc cathode, a reflector, an angular partition slow wave structure, an output waveguide and a magnetic field coil. The arc cathode is arranged at the front end of the relativistic backward wave oscillator; the reflector, the angular partition slow wave structure, and the output waveguide are arranged at the rear side of the arc cathode successively; and the magnetic field coil is installed at the periphery. According to the invention, with the nonaxisymmetrical arc cathode and the angular partition slow wave structure, the TE11 mode is excited directly. The reflector employs the dual-premodulation-cavity unit preferably and is used for carrying out premodulation on an arc relativistic electron beam and leaking the part of TE11 mode to enter the arc cathode zone, so that certain premodulation of the electron beam at the arc cathode zone is realized and thus the beam wave conversion efficiency is improved. Moreover, the oscillator has advantages of simple structure and high conversion efficiency; and the linearly polarized TE11 mode can be generated directly.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
Relativistic backward-wave oscillator with collector shaped as Chinese character chang
ActiveCN106449337ALow densityReduce the impactTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube circuit elementsWave structureChinese characters
The present invention relates to a microwave source of the high-power microwave technology field, and provides a relativistic backward-wave oscillator with a collector shaped as a Chinese character chang. The relativistic backward-wave oscillator comprises a cathode base, a cathode, an anode outer cylinder, a cut-off neck, a slow wave structure, a tapered waveguide, a reflector, an output waveguide and a solenoidal magnetic field. The collector shaped as the Chinese character chang is arranged behind the tapered waveguide, a stepped reflection cavity is arranged between the cut-off neck and the slow wave structure, and double extraction cavities are also arranged between the tail end of the slow wave structure and the tapered waveguide. The relativistic backward-wave oscillator of the present invention overcomes the disadvantage that the conventional relativistic backward-wave oscillator is difficult to consider the long output microwave pulse width and the high power conversion efficiency simultaneously, solves the problem that a coaxial extraction structure is easy to generate the plasmas to thereby influence the working efficiency, and realizes the microwave output that the pulse width is greater than 100 ns, the efficiency is greater than 40%, and the power is 6 GW, on the condition of using less slow wave blades. Moreover, a high-power microwave source is compact in structure, and is easy for the repeated frequency operation.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Electric control scanning waveguide leaky-wave antenna based on liquid crystal
ActiveCN105006656AEasy to primeSimple control mechanismLeaky-waveguide antennasWave structureSpecial design
The invention provides an electric control scanning waveguide leaky-wave antenna based on liquid crystal, belongs to the technical field of microwave antenna engineering, and aims at solving problems that a conventional electric control scanning leaky-wave antenna based on a varactor and other conventional electrically controlled elements is difficult to work at a microwave high-frequency band, and existing liquid crystal electric control scanning leaky-wave antennas require the special design of a bias circuit. The electric control scanning waveguide leaky-wave antenna comprises a top part dielectric plate layer, a metal layer, an insulation paste layer, a liquid crystal layer and a bottom part waveguide slot. The metal layer is arranged at the lower surface of the top part dielectric plate layer. The metal layer has a leaky-wave structure with etching of periodic transverse seams. Equivalent series inductance of electromagnetic wave is enabled to be increased by the periodic transverse seams when electromagnetic wave is transmitted between the bottom part waveguide slot and the metal layer. The metal layer is provided with N periodic seam units. Seam unit spacing distance p is from lambdag / 2 to lambdag. The seams of the middle part are main radiation units. Seam length l of the main radiation unit is from lambdag / 4 to lambdag / 2. The former four and the latter four seams are auxiliary radiation units.
Owner:北京超材信息科技有限公司
Internal-feedback-type terahertz traveling wave tube oscillator
InactiveCN103021770AReduce volumeIncrease powerTransit-tube circuit elementsTransit-tube coupling devicesWave structurePhase shifted
The invention discloses an internal-feedback-type terahertz traveling wave tube oscillator, and relates to a terahertz electromagnetic wave source technique. Based on a traveling wave tube, a feedback mechanism is introduced so as to form an oscillator. Compared with the existing traveling wave tube, the structure is characterized in that 1. a tuning device is added at an input port of the oscillator, and is a variable short circuit device; and 2. an output port is designed with a special method, so that the oscillator has certain reflection in a working frequency band, and the reflection coefficient is about 0.2. According to the oscillator provided by the invention, a feedback loop of an electromagnetic wave is introduced into the structure, the phase shift of the electromagnetic wave through the feedback loop is integral multiples of 2*pi, and under the condition that a slow wave structure provides sufficient gain, the device is oscillated, and one or a plurality of electromagnetic waves with specific frequency is / are output. Because the tuning device can introduce phase shift variations through methods of mechanical tuning and the like in the feedback loop, the frequency of a start oscillation electromagnetic wave also varies to meet the condition that the total phase shift of the feedback loop is integral multiples of 2*pi, so that the tunable characteristic is realized.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Direct-patterned optical waveguides on amorphous silicon films
InactiveUS6925216B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical waveguide light guideWave structureRefractive index
An optical waveguide structure is formed by embedding a core material within a medium of lower refractive index, i.e. the cladding. The optical index of refraction of amorphous silicon (a-Si) and polycrystalline silicon (p-Si), in the wavelength range between about 1.2 and about 1.6 micrometers, differ by up to about 20%, with the amorphous phase having the larger index. Spatially selective laser crystallization of amorphous silicon provides a mechanism for controlling the spatial variation of the refractive index and for surrounding the amorphous regions with crystalline material. In cases where an amorphous silicon film is interposed between layers of low refractive index, for example, a structure comprised of a SiO2 substrate, a Si film and an SiO2 film, the formation of guided wave structures is particularly simple.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com