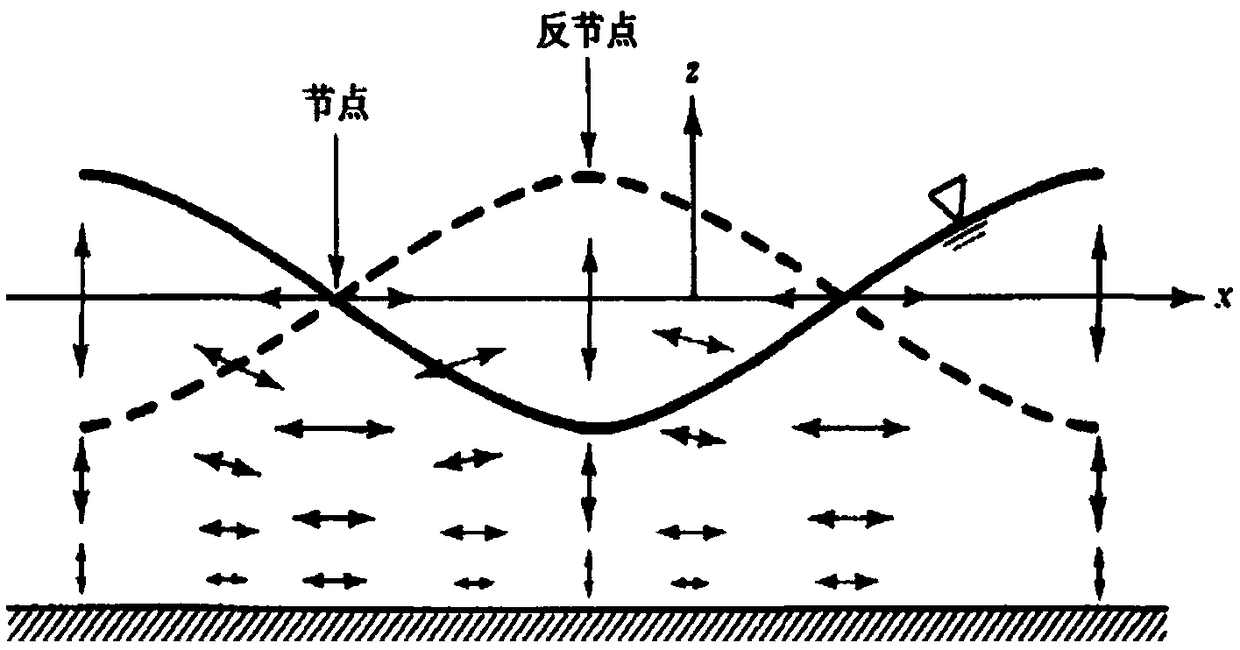
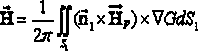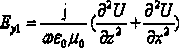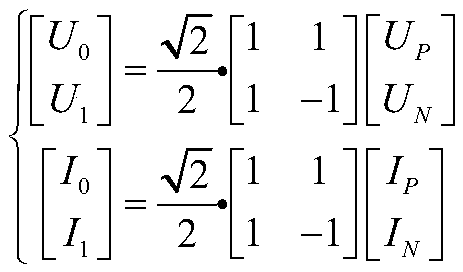Patents
Literature
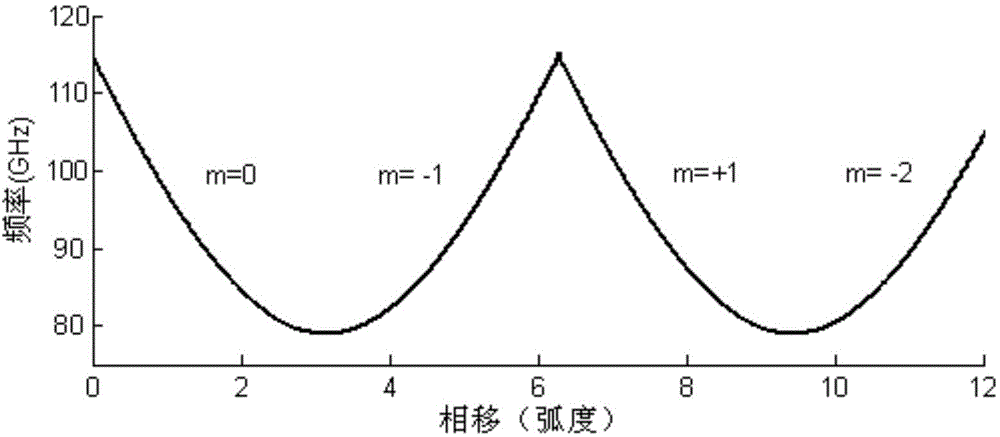
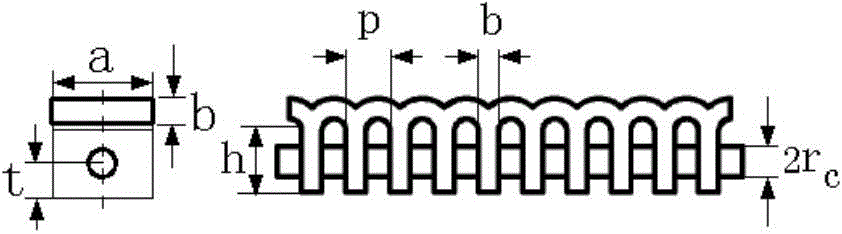
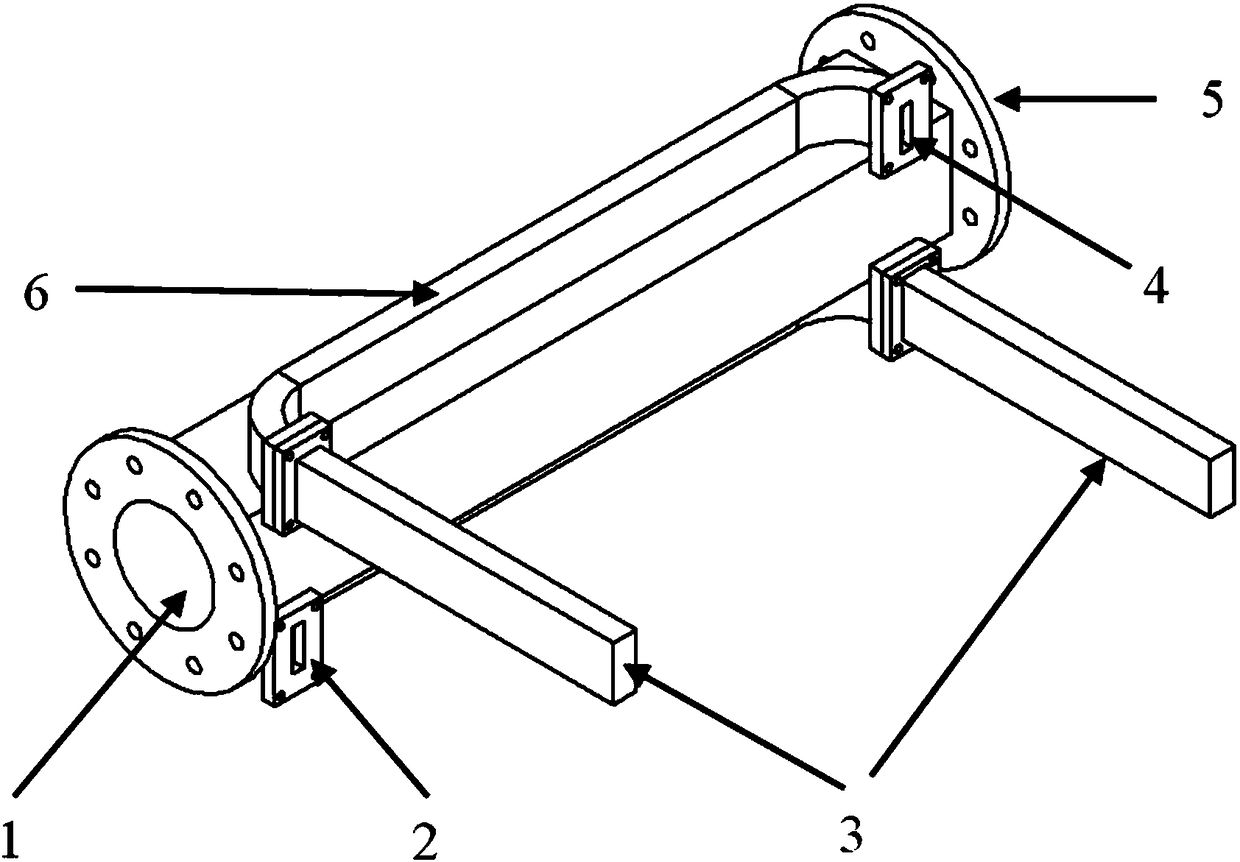
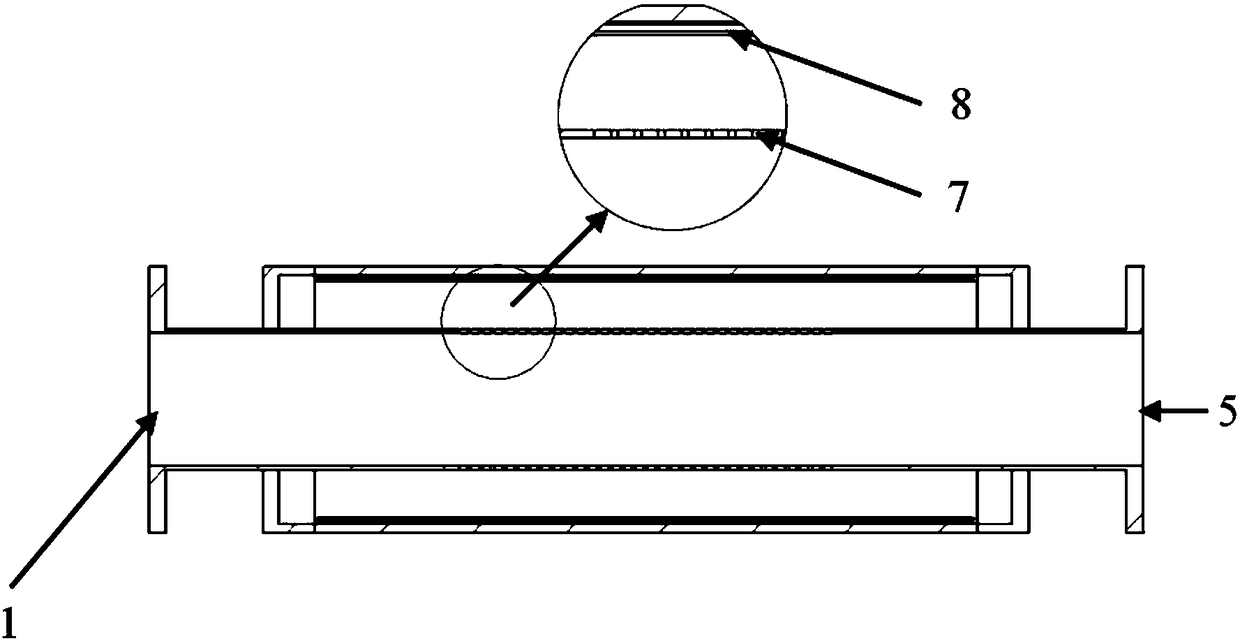
111 results about "Forward wave" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
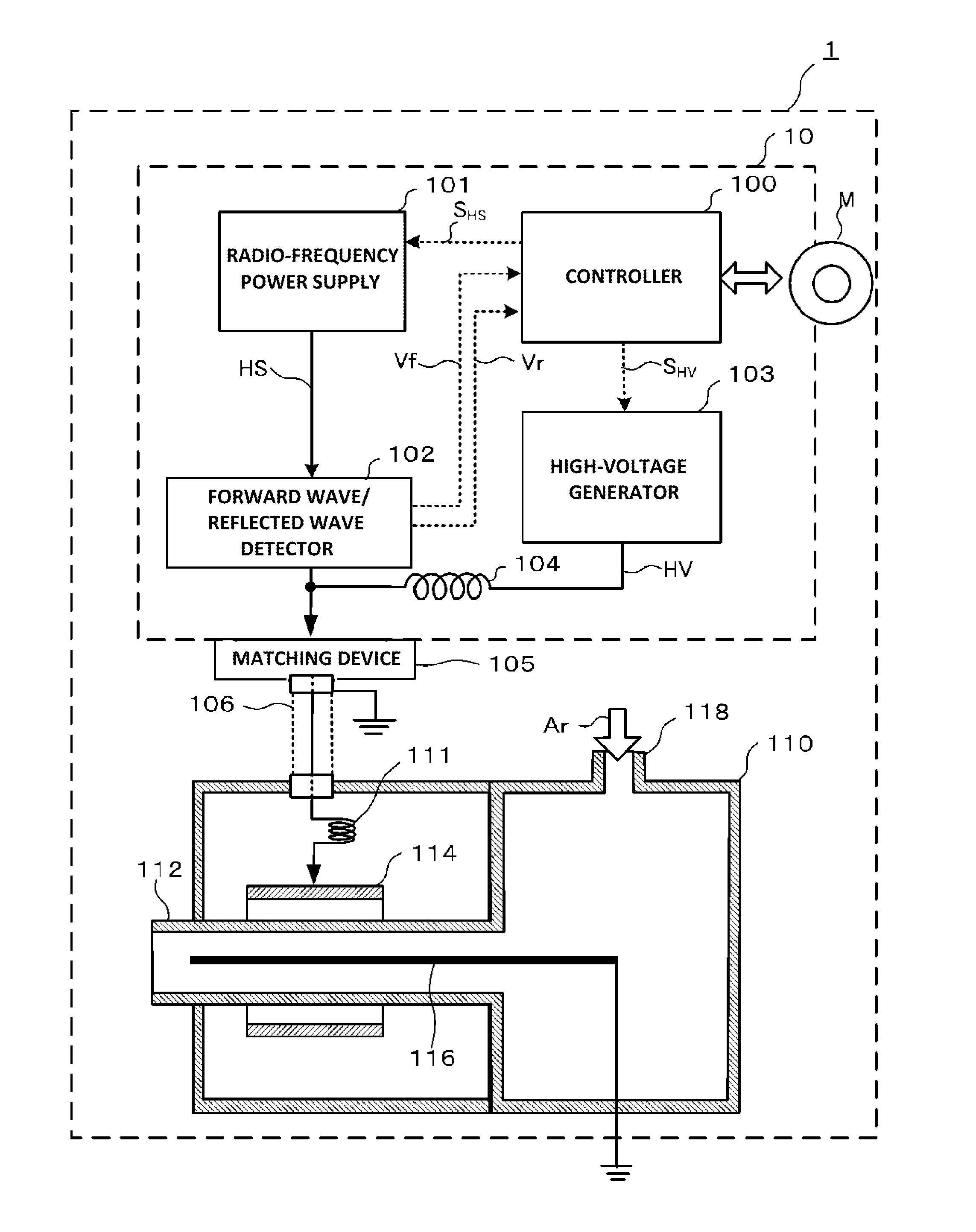
High-frequency power supply system
InactiveUS20070121267A1Multiple-port networksElectric discharge tubesDifferentiatorHigh frequency power
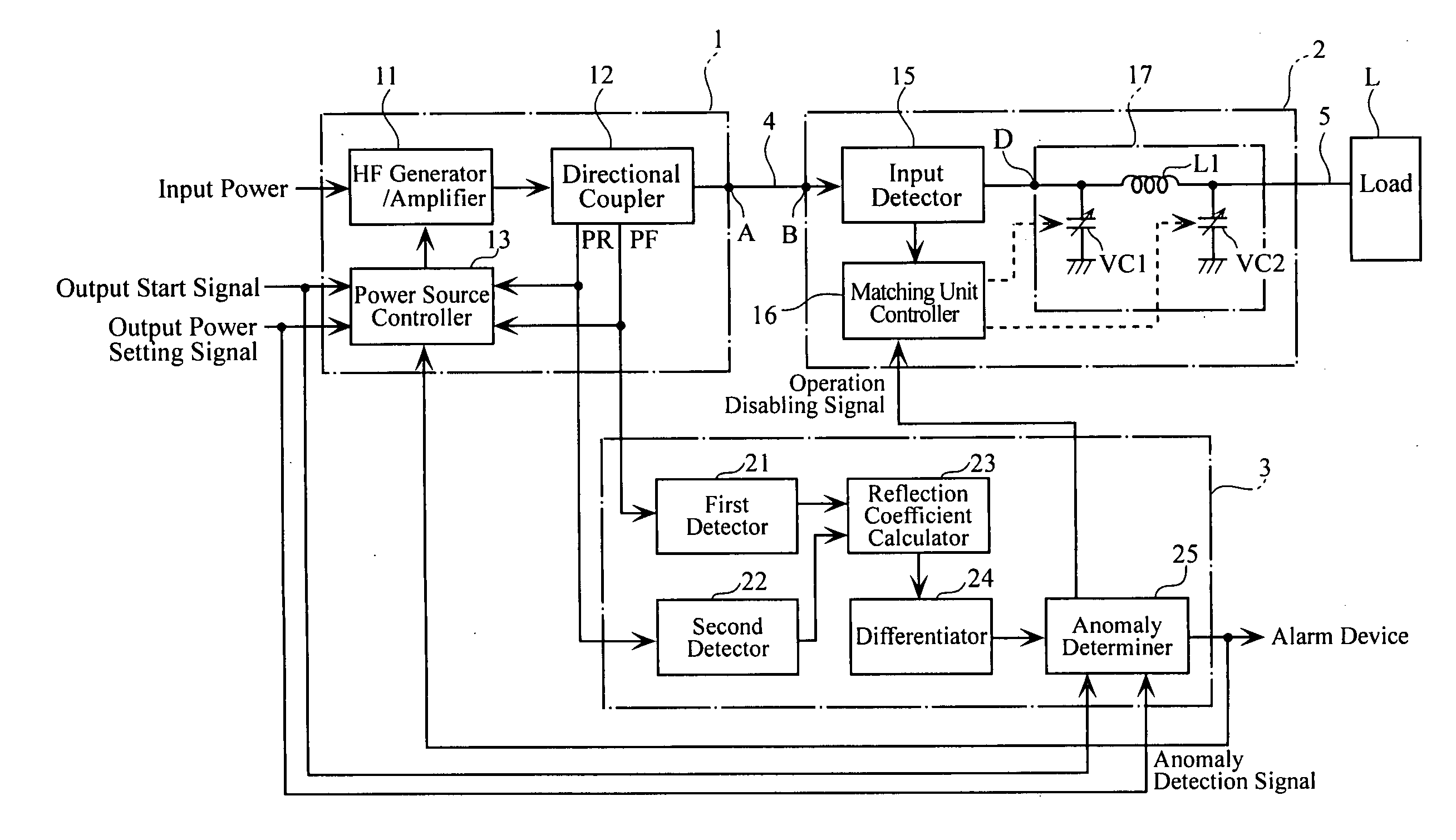
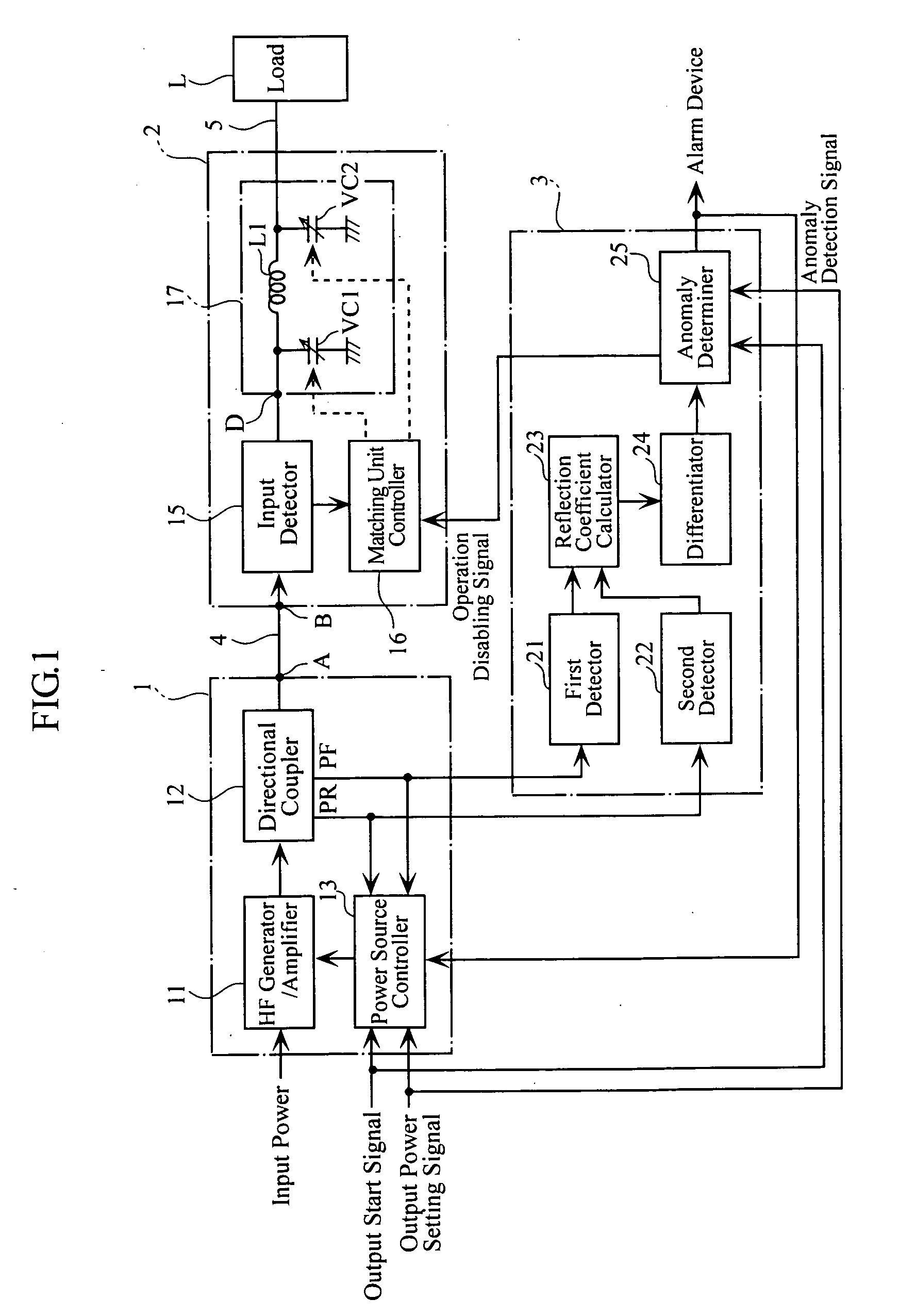
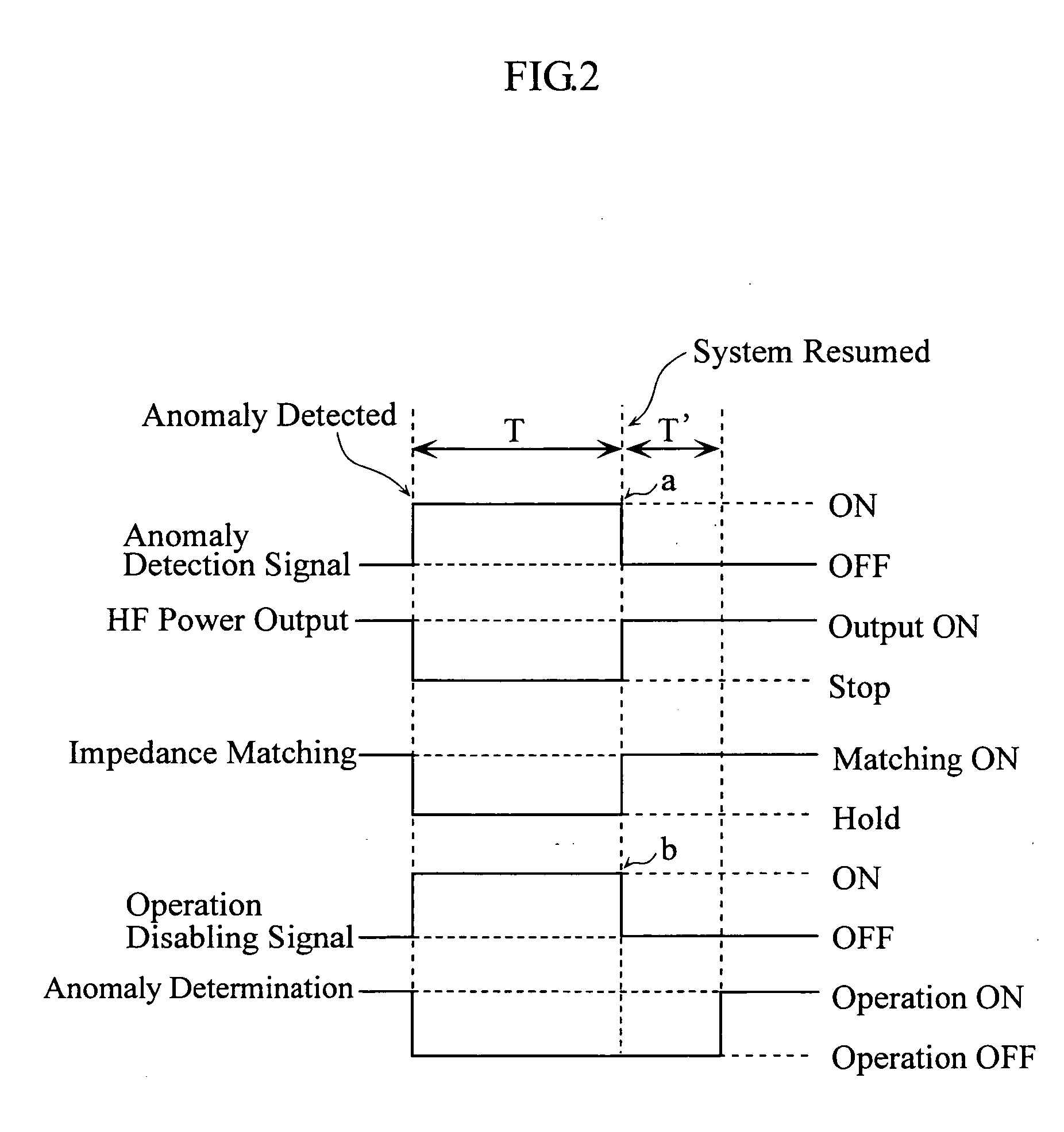
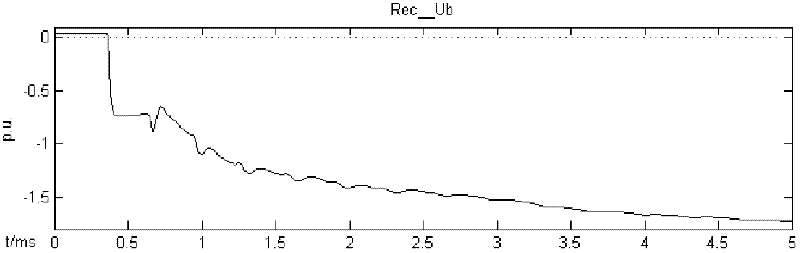
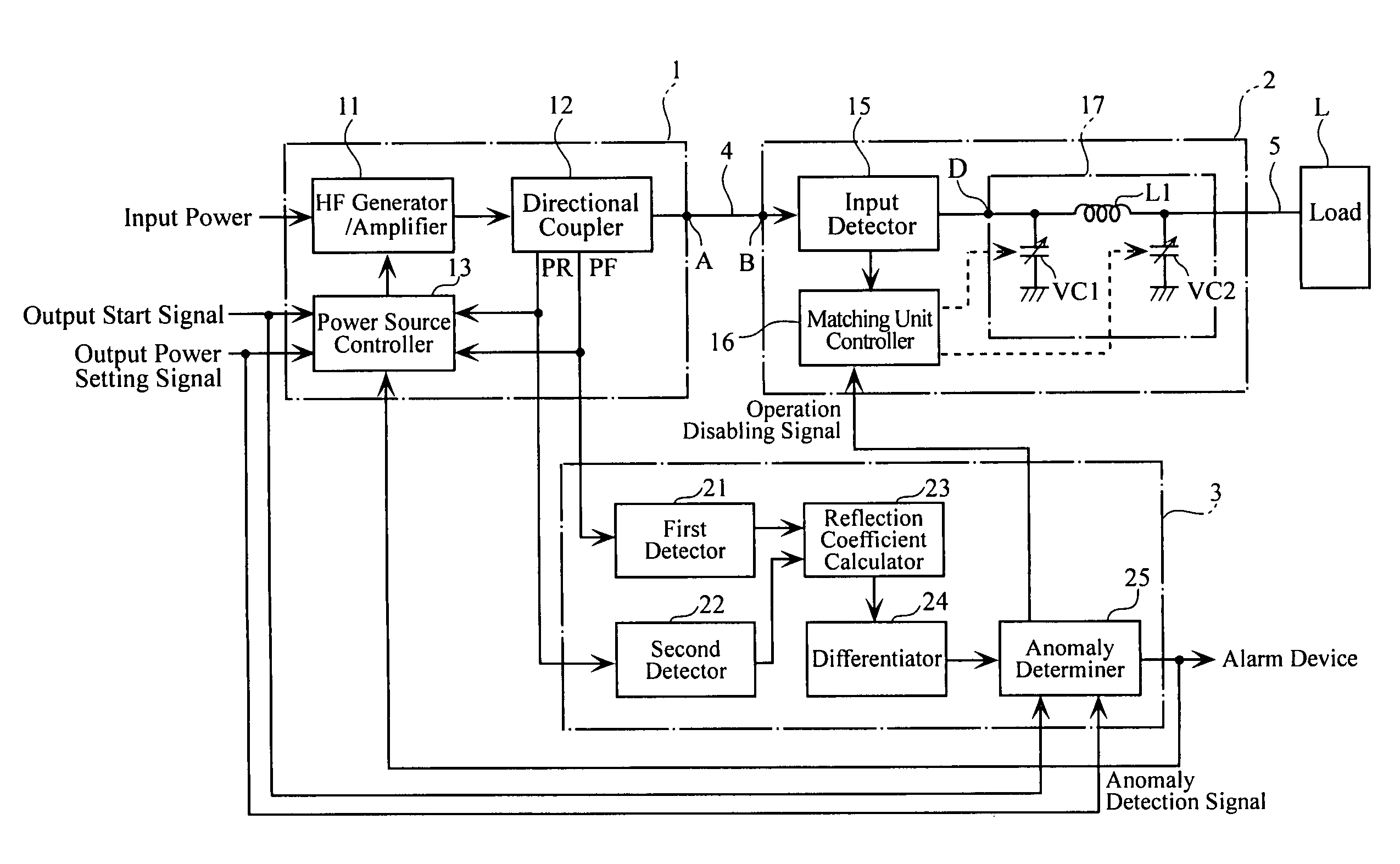
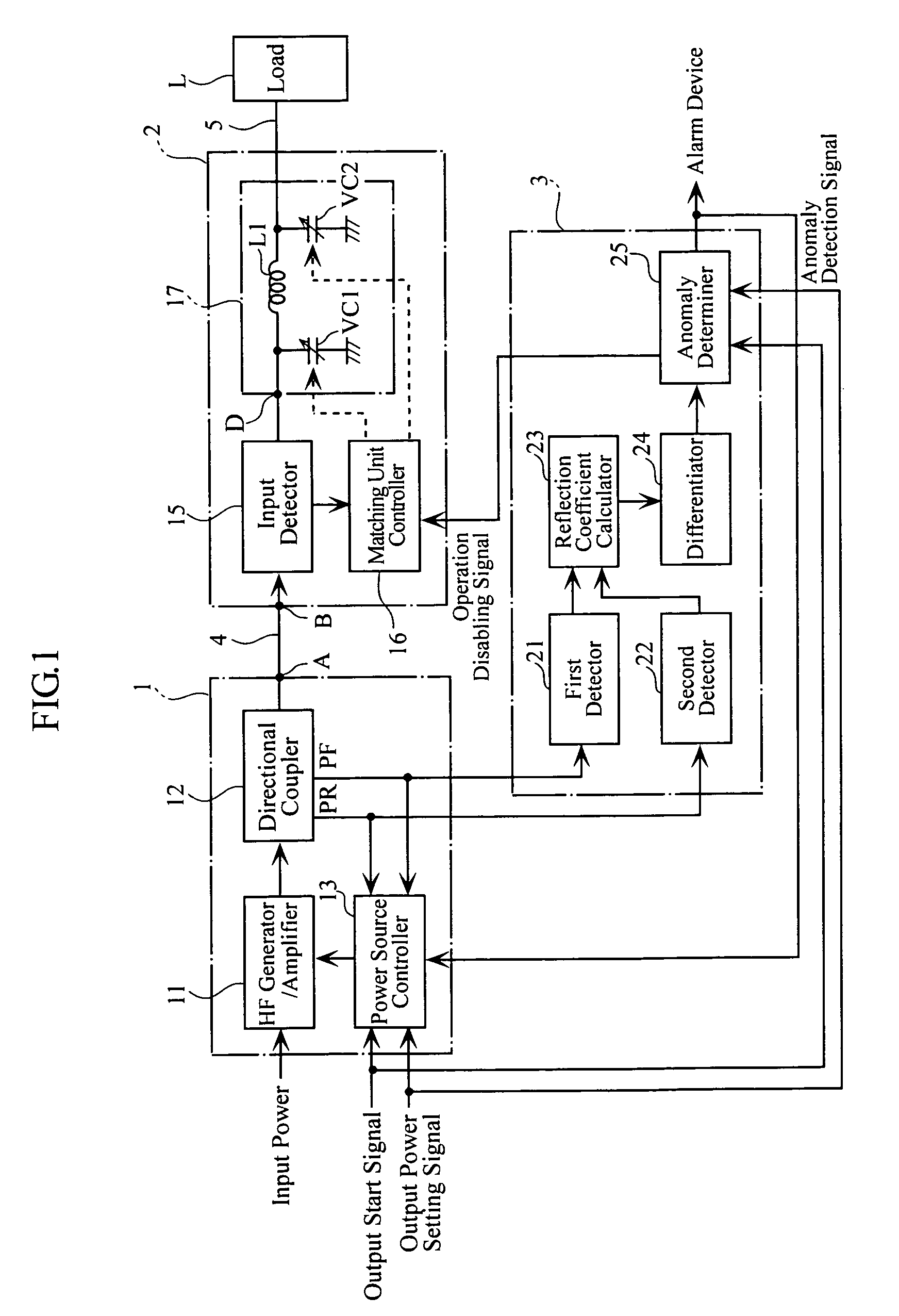
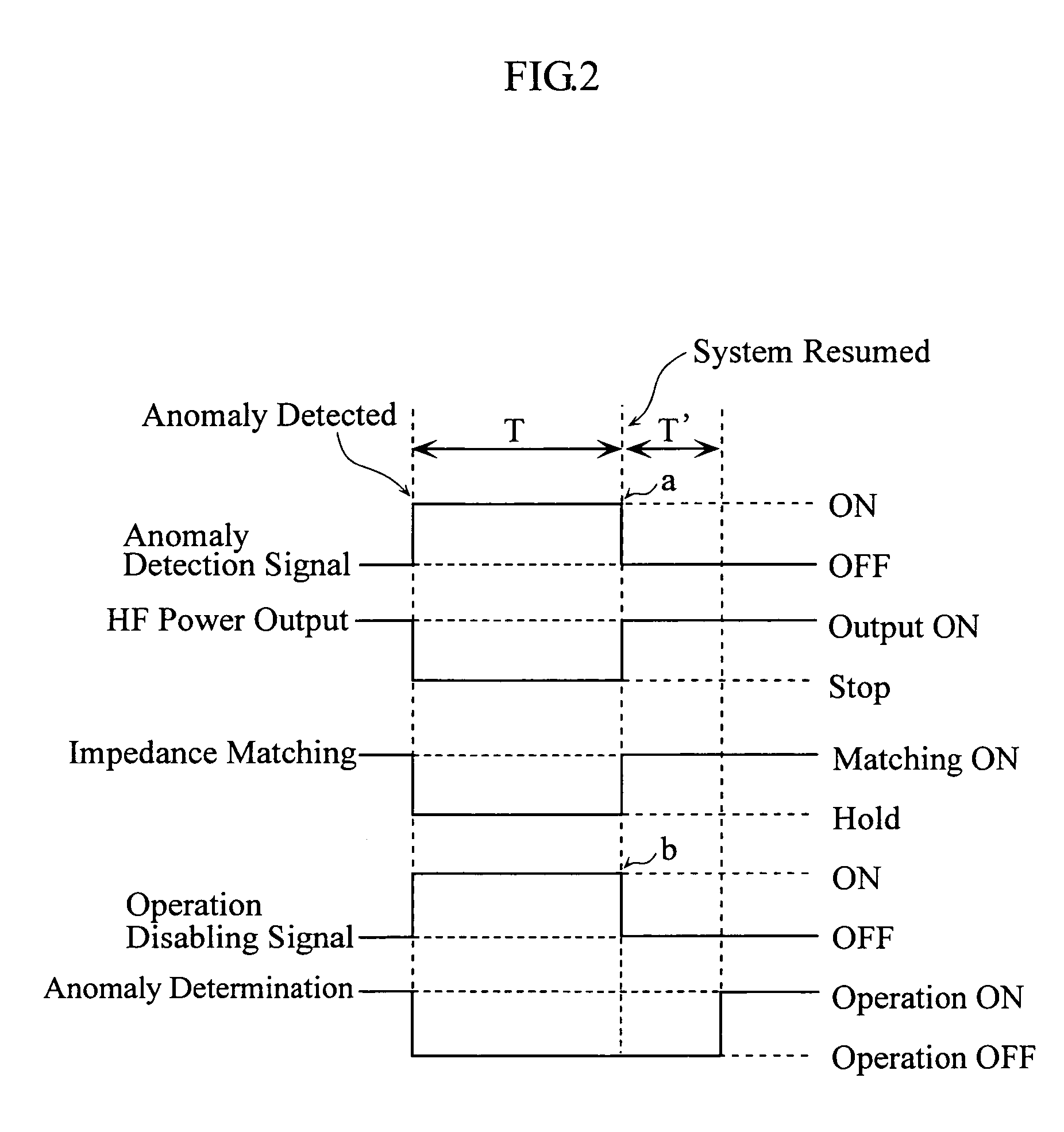
A high-frequency power supply system includes an anomaly detector 3 which detects an anomaly occurring in a circuit on the side of a load L as from an outputting end A of a high-frequency power source 1. The anomaly detector 3 includes a first detector 21 which detects a voltage value Vf of a high-frequency forward wave, a second detector 22 which detects a voltage value Vr of a high-frequency reflected wave, a reflection coefficient calculator 23 and a differentiator 24 which calculate a reflection coefficient differential value dΓ / dt from the forward wave voltage value Vf and the reflected wave voltage value Vr, and an anomaly determiner 25 which determines of an occurrence of an anomaly based on the reflection coefficient differential value dΓ / dt. When the anomaly detector 3 outputs an anomaly detection signal to the high-frequency power source 1, high-frequency power source 1 stops its power output operation.
Owner:DAIHEN CORP
Impedance matching apparatus for a plasma chamber comprising two separate storage units and calculators
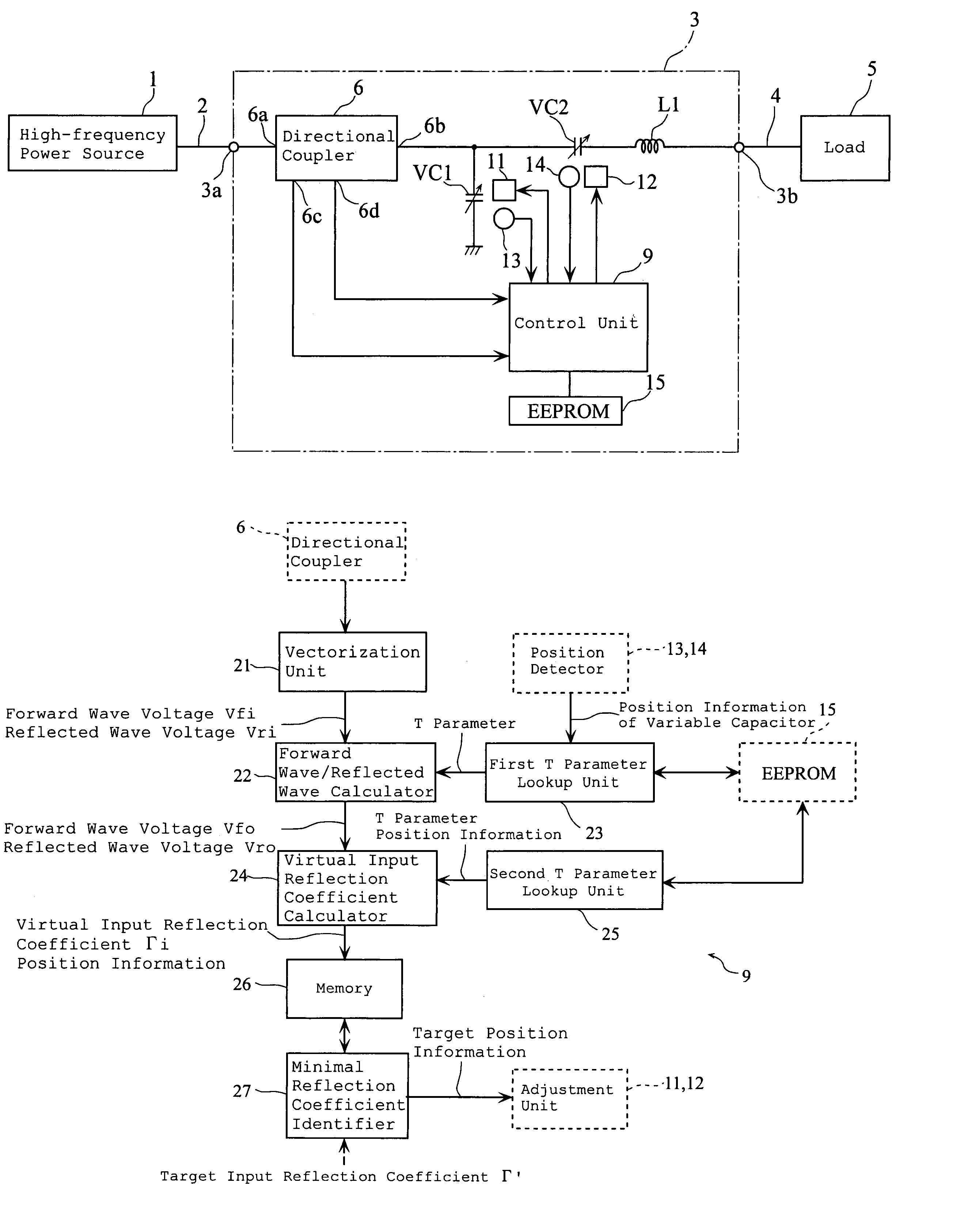
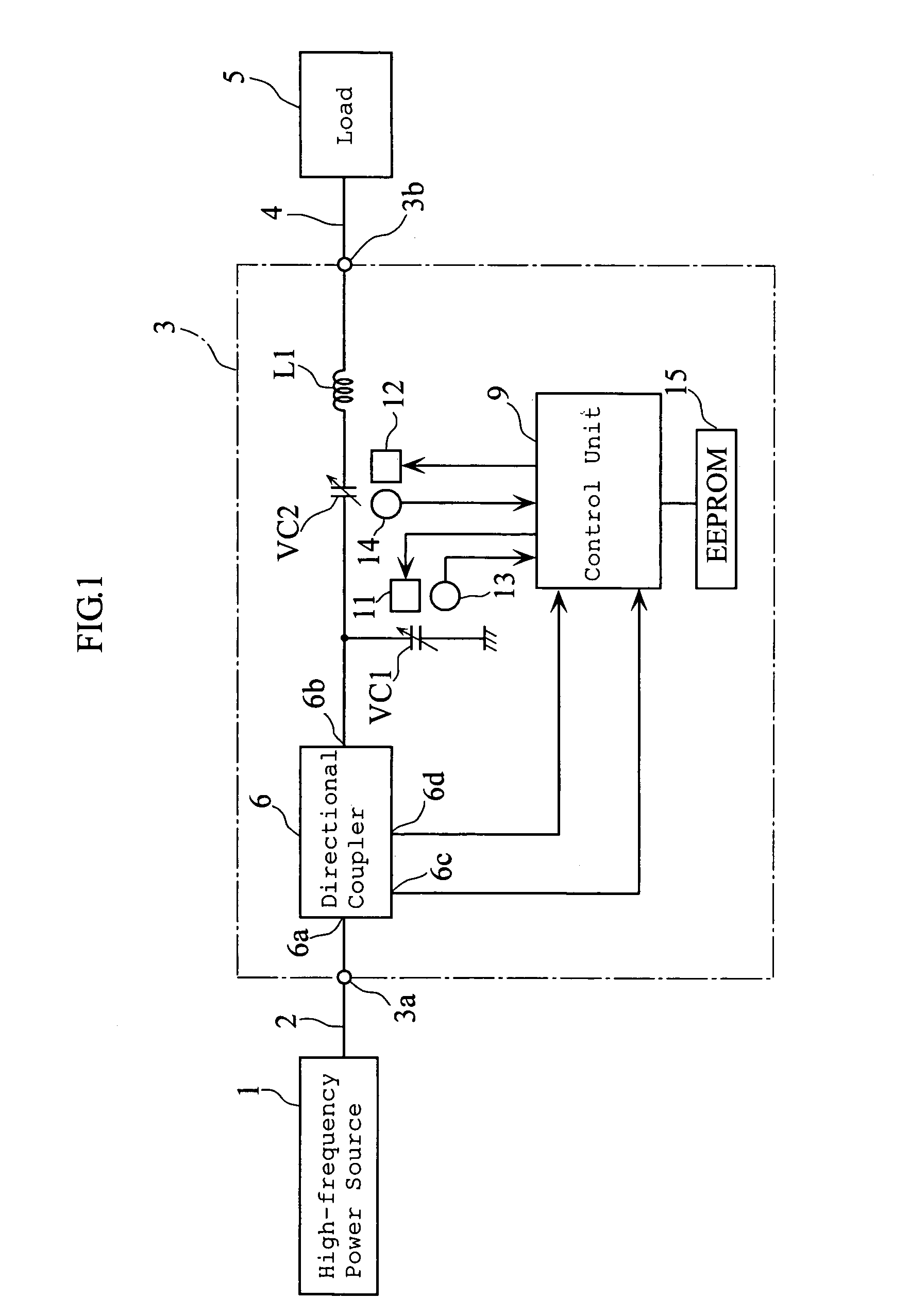
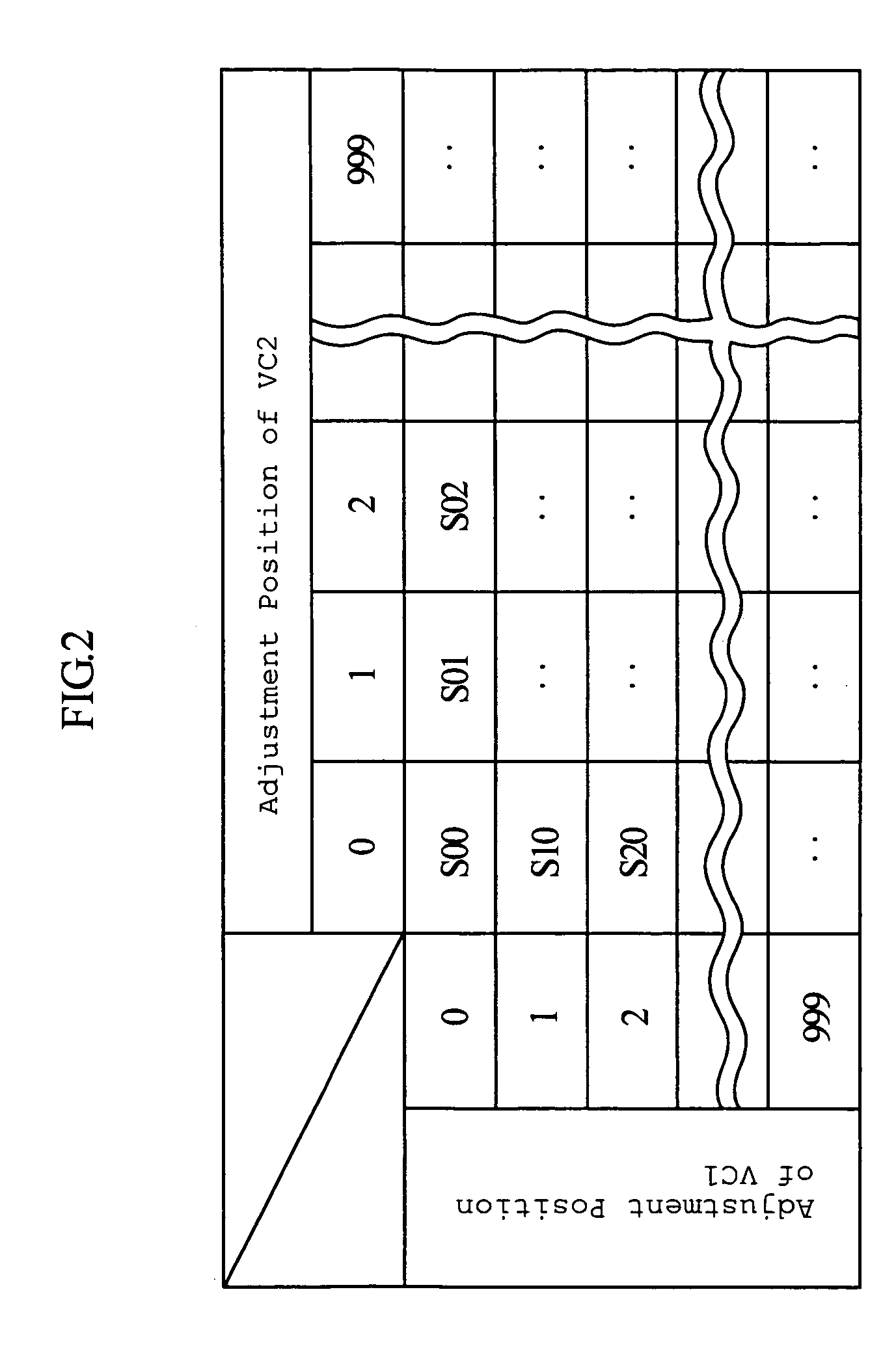
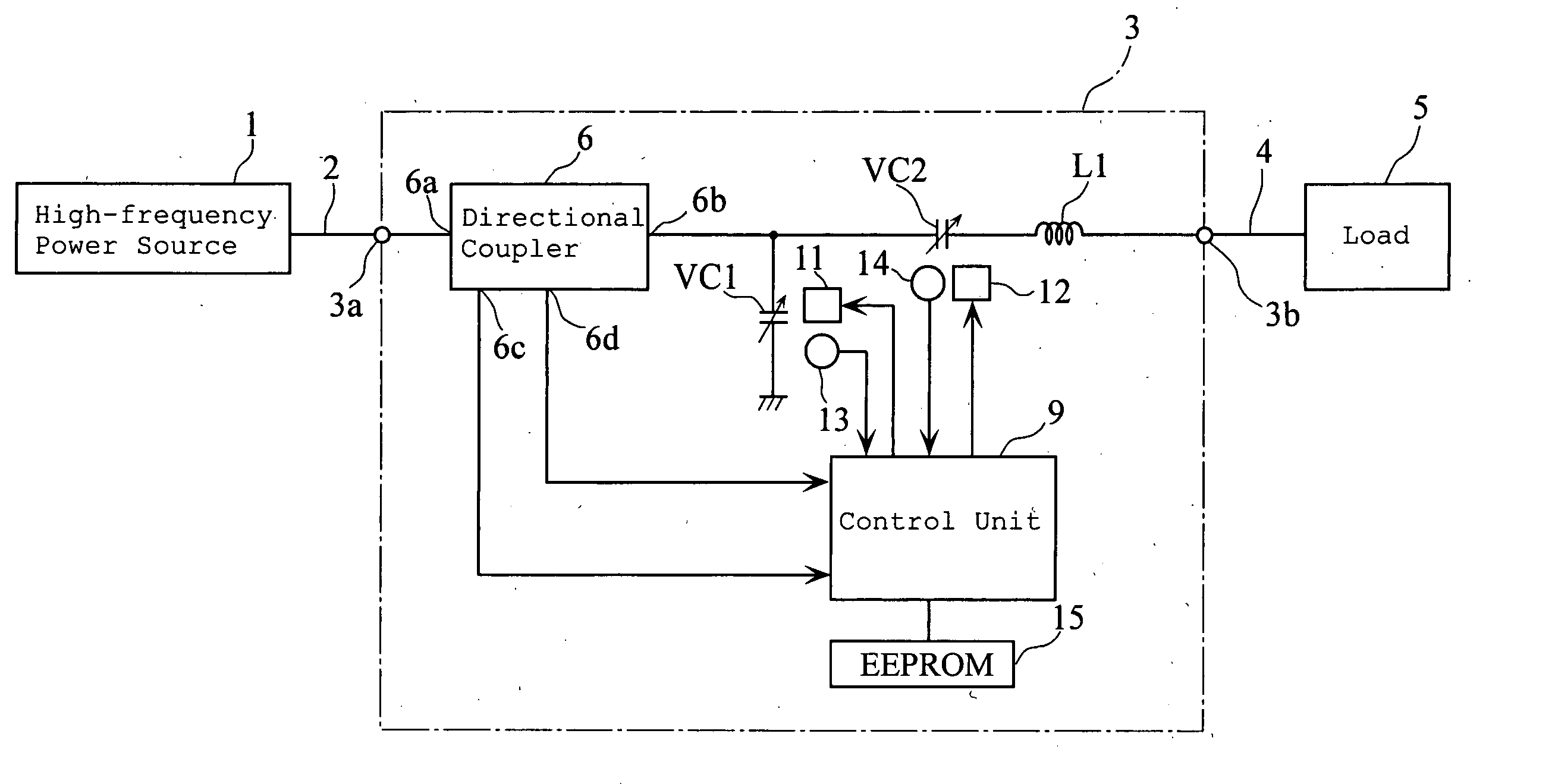
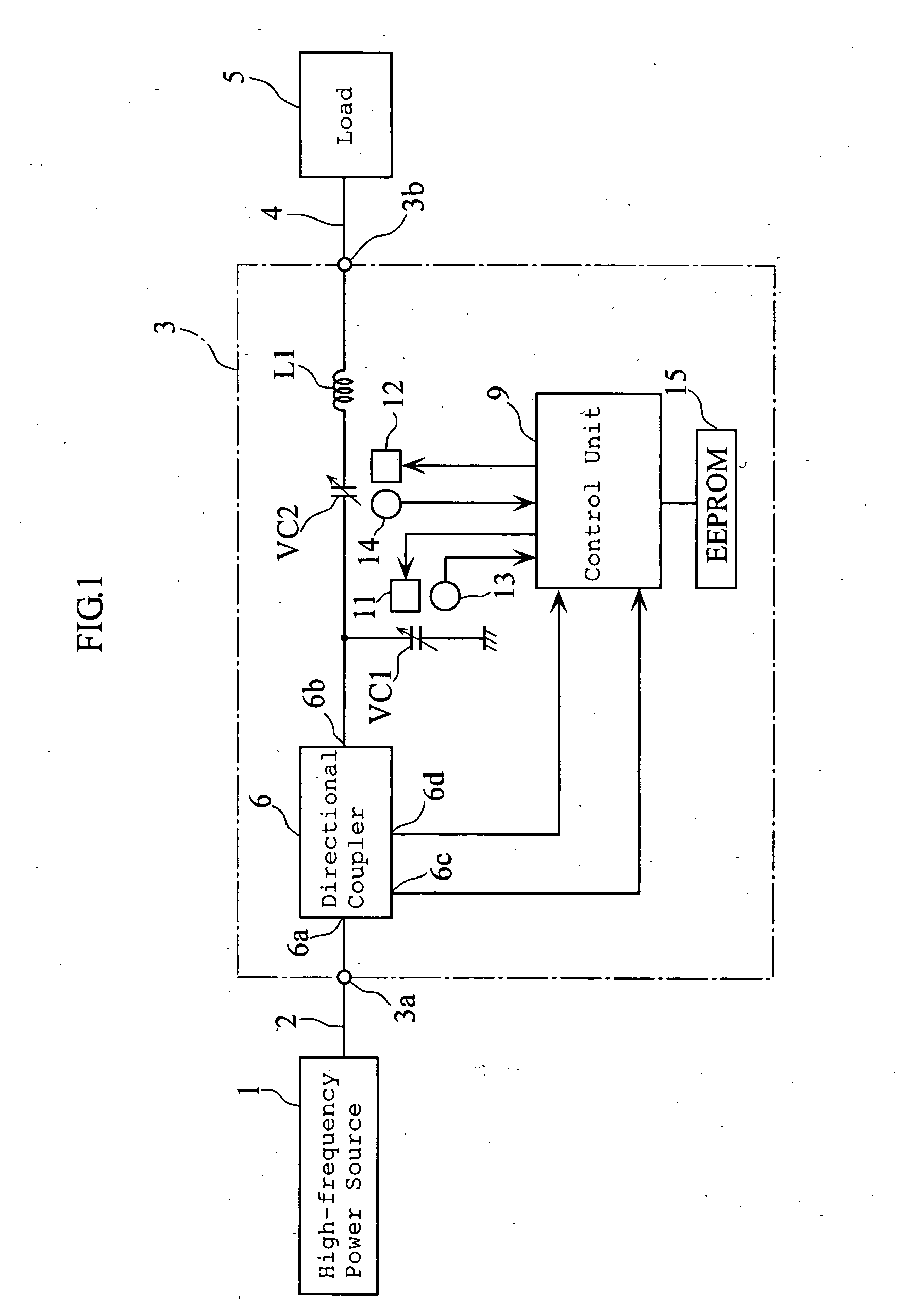
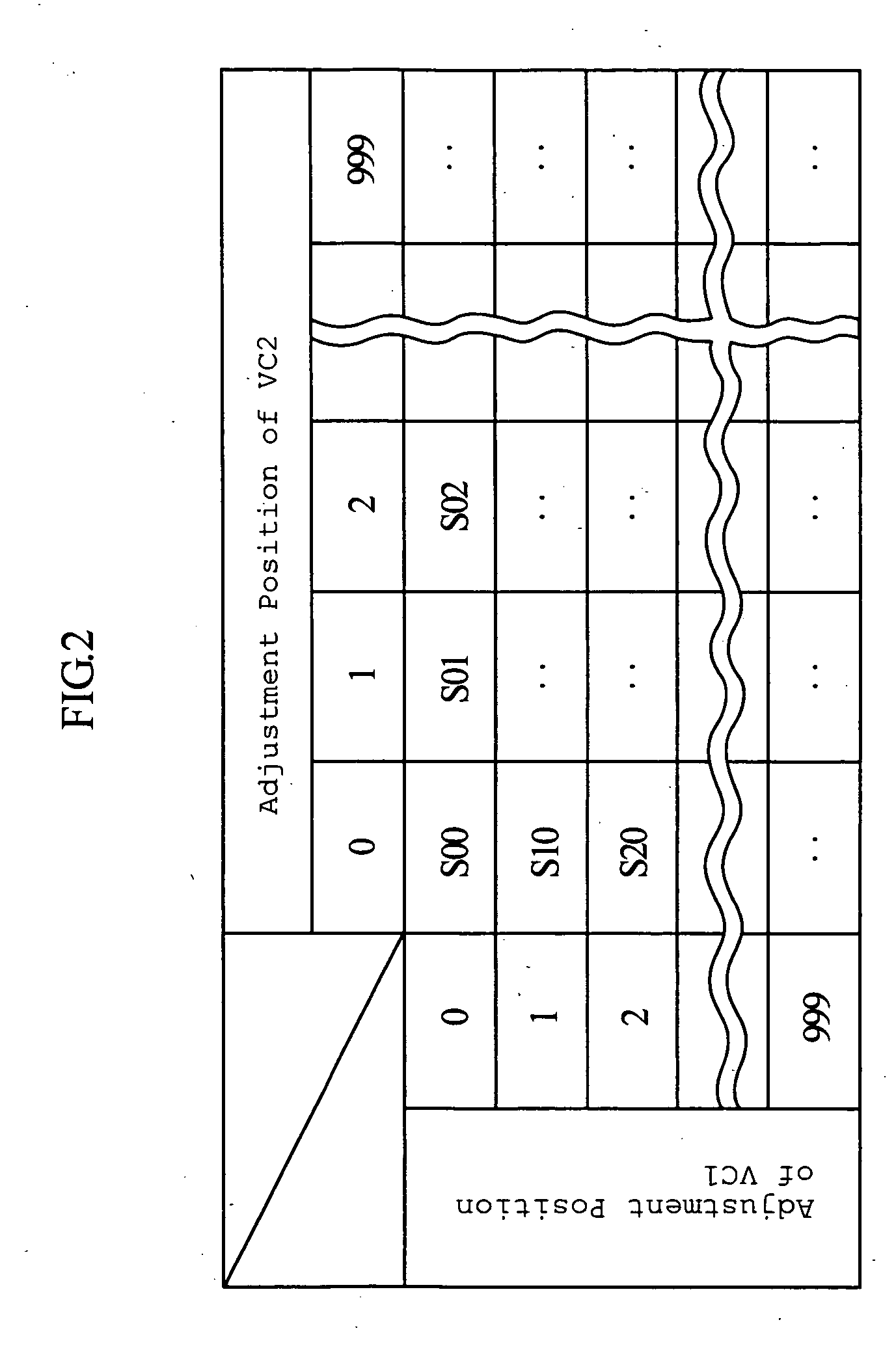
An impedance matching apparatus 3 calculates a forward wave voltage Vfo and a reflected wave voltage Vro at an output terminal 3b, based on a forward wave voltage Vfi and a reflected wave voltage Vri at an input terminal 3a, on information on variable values of variable capacitors VC1, VC2 acquired in advance through measurement, and on a T parameter of the impedance matching apparatus 3 corresponding to the information on the variable values of variable capacitors VC1, VC2. The impedance matching apparatus 3 calculates an input reflection coefficient Γi at the input terminal 3a corresponding to the information on the variable values of the variable capacitors VC1, VC2, based on the forward wave voltage Vfo, the reflected wave voltage Vro and the T parameter. The impedance matching apparatus 3 selects the lowest absolute value out of absolute values |Γi| of the input reflection coefficients corresponding to the variable values of the variable capacitors VC1, VC2, and adjusts the impedance of the variable capacitors VC1, VC2 based on the lowest value.
Owner:DAIHEN CORP
Distribution terahertz oscillator
InactiveCN102403180AAppropriate generationTubes with velocity/density modulated electron streamTransit-tube circuit elementsResonant cavityKlystron
The invention discloses a distribution terahertz oscillator, which relates to technique of THz (terahertz) electromagnetic wave sources and comprises an electron gun, an interaction region and a collector. The interaction region consists of a periodic slow wave structured modulation resonant cavity and an energy extraction cavity, and the modulation resonant cavity is in a periodic slow wave structure which can be operated in a backward wave mode or a forward wave mode to be interacted with electron beams in a distributive manner, so that the electron beams can be modulated in terms of speed and density. The distribution terahertz oscillator integrates advantages of a backward wave tube and a distribution klystron, and has the advantage of suitableness for generating THz electromagnetic waves.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Impedance matching apparatus
ActiveUS20060151591A1Multiple-port networksComputations using electromechanical counter-type accumulatorsCapacitanceEngineering
An impedance matching apparatus 3 calculates a forward wave voltage Vfo and a reflected wave voltage Vro at an output terminal 3b, based on a forward wave voltage Vfi and a reflected wave voltage Vri at an input terminal 3a, on information on variable values of variable capacitors VC1, VC2 acquired in advance through measurement, and on a T parameter of the impedance matching apparatus 3 corresponding to the information on the variable values of variable capacitors VC1, VC2. The impedance matching apparatus 3 calculates an input reflection coefficient Γi at the input terminal 3a corresponding to the information on the variable values of the variable capacitors VC1, VC2, based on the forward wave voltage Vfo, the reflected wave voltage Vro and the T parameter. The impedance matching apparatus 3 selects the lowest absolute value out of absolute values |Γi| of the input reflection coefficients corresponding to the variable values of the variable capacitors VC1, VC2, and adjusts the impedance of the variable capacitors VC1, VC2 based on the lowest value.
Owner:DAIHEN CORP
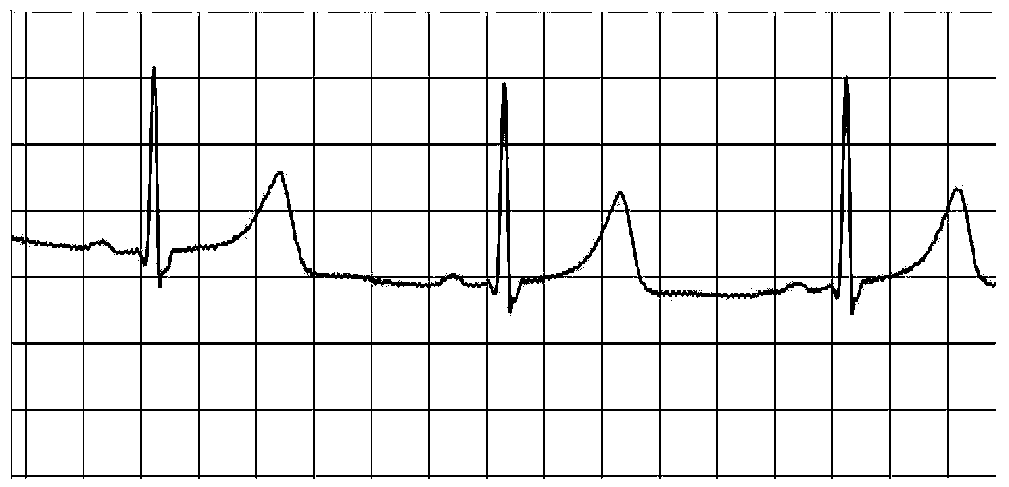
Electrocardiogram (ECG) data analysis method suitable for mobile platform
InactiveCN104173043ASimple structureImprove processing efficiencyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsS-waveT wave
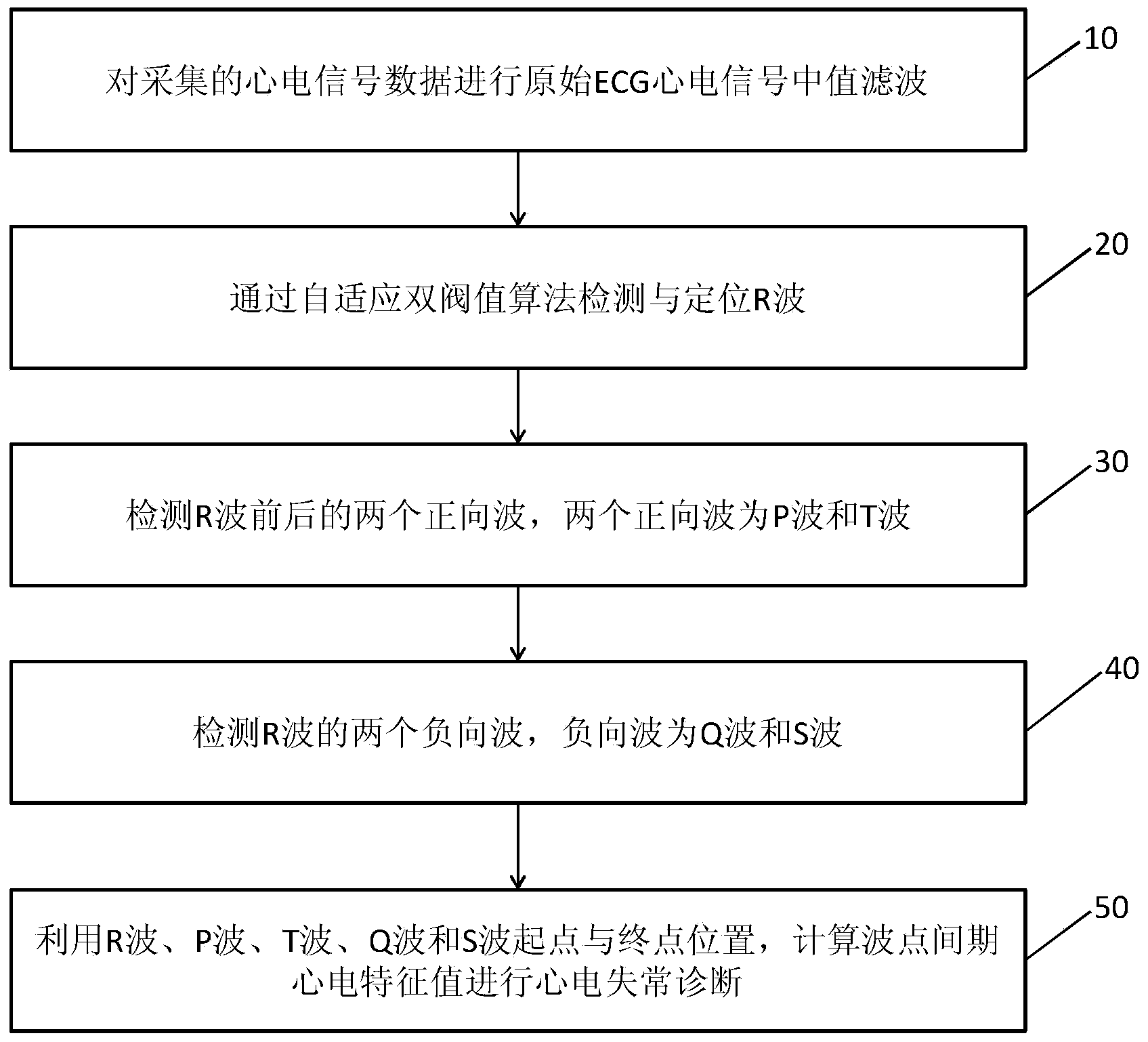
The invention discloses an electrocardiosignal (ECG) data analysis method suitable for a mobile platform. The electrocardiosignal (ECG) data analysis method includes subjecting collected electrocardiosignal data to original ECG electrocardiosignal median filtering; detecting and positioning an R wave through a self-adaption dual-threshold algorithm; detecting two forward waves before and after the R wave, wherein the two forward waves are a P wave and a T wave; detecting two negative waves on two sides of the R wave, wherein the two negative waves are a Q wave and an S wave; using starting point and terminal point positions of the R wave, the P wave, the T wave, the Q wave, and the S wave to calculate ECG feature values of wave point intervals for arrhythmia diagnosis. According to the ECG data analysis method suitable for the mobile platform, the accuracy for detection of arrhythmia can reach over 92%; since an algorithm structure is concise, processing efficiency is high, only 12s is required for processing one-minute ECG data on a Cortex A8 / Android mobile platform, and the method is suitable for developing a mobile platform based portable admeasuring apparatus.
Owner:DONGGUAN UNIV OF TECH +1
Failure direction judgment element and judgment method for direct current transmission line
InactiveCN102590655AAvoid false protectionSimple calculationElectrical testingElectrical resistance and conductanceUltra high speed
The invention discloses a single-ended transient signal-based failure direction judgment element and a single-ended transient signal-based failure direction judgment method for an ultrahigh speed direct current transmission line. The element comprises a failure component calculation unit, a forward wave and backward wave energy calculation unit, and a comparison and command transmission unit. A failure direction is judged by comparing a calculated forward wave energy value with a calculated backward wave energy value, a failure is determined as a positive failure if the forward wave energy value is lower than the backward wave energy value, and on the contrary, the failure is determined as a negative failure, and a corresponding command is transmitted. A test result shows that the failure direction judgment element for the direct current transmission line can be used for accurately distinguishing the positive and negative failures of the line under different direct current transmission projects and the operating conditions of the different direct current transmission projects only by utilizing single-ended voltage and current signals of the line without the influence of a failure position and transition resistance and that only a normalized wave impedance value is required to be calculated for the protection and setting of the different direct current transmission projects so as to reduce the workload of protection workers and field operators.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
High-frequency power supply system
A high-frequency power supply system includes an anomaly detector 3 which detects an anomaly occurring in a circuit on the side of a load L as from an outputting end A of a high-frequency power source 1. The anomaly detector 3 includes a first detector 21 which detects a voltage value Vf of a high-frequency forward wave, a second detector 22 which detects a voltage value Vr of a high-frequency reflected wave, a reflection coefficient calculator 23 and a differentiator 24 which calculate a reflection coefficient differential value dΓ / dt from the forward wave voltage value Vf and the reflected wave voltage value Vr, and an anomaly determiner 25 which determines of an occurrence of an anomaly based on the reflection coefficient differential value dΓ / dt. When the anomaly detector 3 outputs an anomaly detection signal to the high-frequency power source 1, high-frequency power source 1 stops its power output operation.
Owner:DAIHEN CORP
Wave power plant
InactiveUS7411311B2Force is smallEasy to fix and locateMachines/enginesEngine componentsPower stationWave power generation
Owner:Y T ENTERPRISES +1
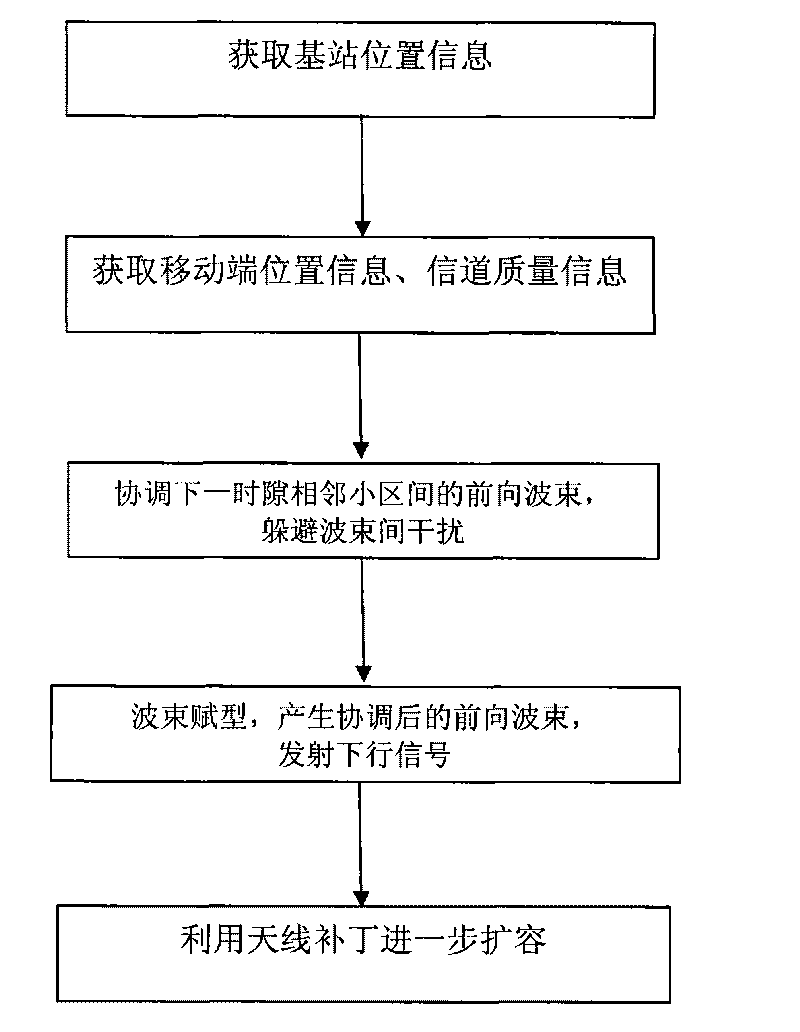
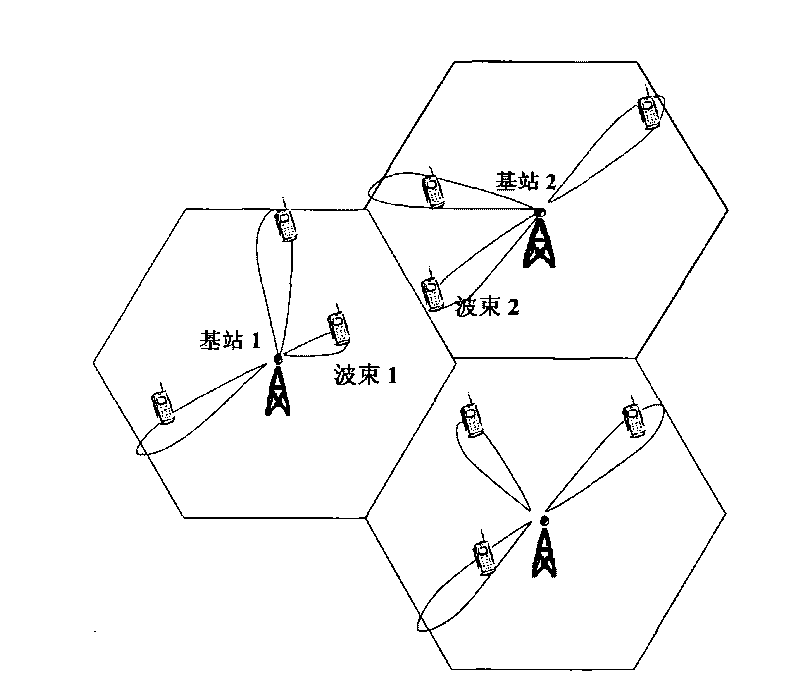
Communication system volume expansion method
InactiveCN101754477AAvoid or reduce distractionsImprove spectrum utilizationWireless communicationSignal waveFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a communication system volume expansion method, which belongs to the wireless communication field. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, determining the relative position information of each base station and adjacent base stations; determining the position information and the signal channel quality information of a mobile terminal in a subdistrict through received up-running signals; then, coordinating a forward wave beam between adjacent subdistricts at a next down-running time interval by each base station according to the relative position information, the mobile terminal position information and the signal channel quality information to avoid the interference between the forward wave beams of the adjacent subdistricts; and finally, carrying out the wave beam molding for sending the coordinated forward wave beam as the down-running signals. At the same time, the invention adds an antenna patch in the base station, and the antenna patch is used for receiving the up-running signals for further expanding the volume. Compared with the prior art, the invention can avoid the interference between the signal wave beams, can improve the frequency spectrum utilization rate and the system volume, and simultaneously realizes the transmission of the up-running and down-running data at the same frequency and the same time interval is realized through adding the antenna patch, so the system volume is further and greatly improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
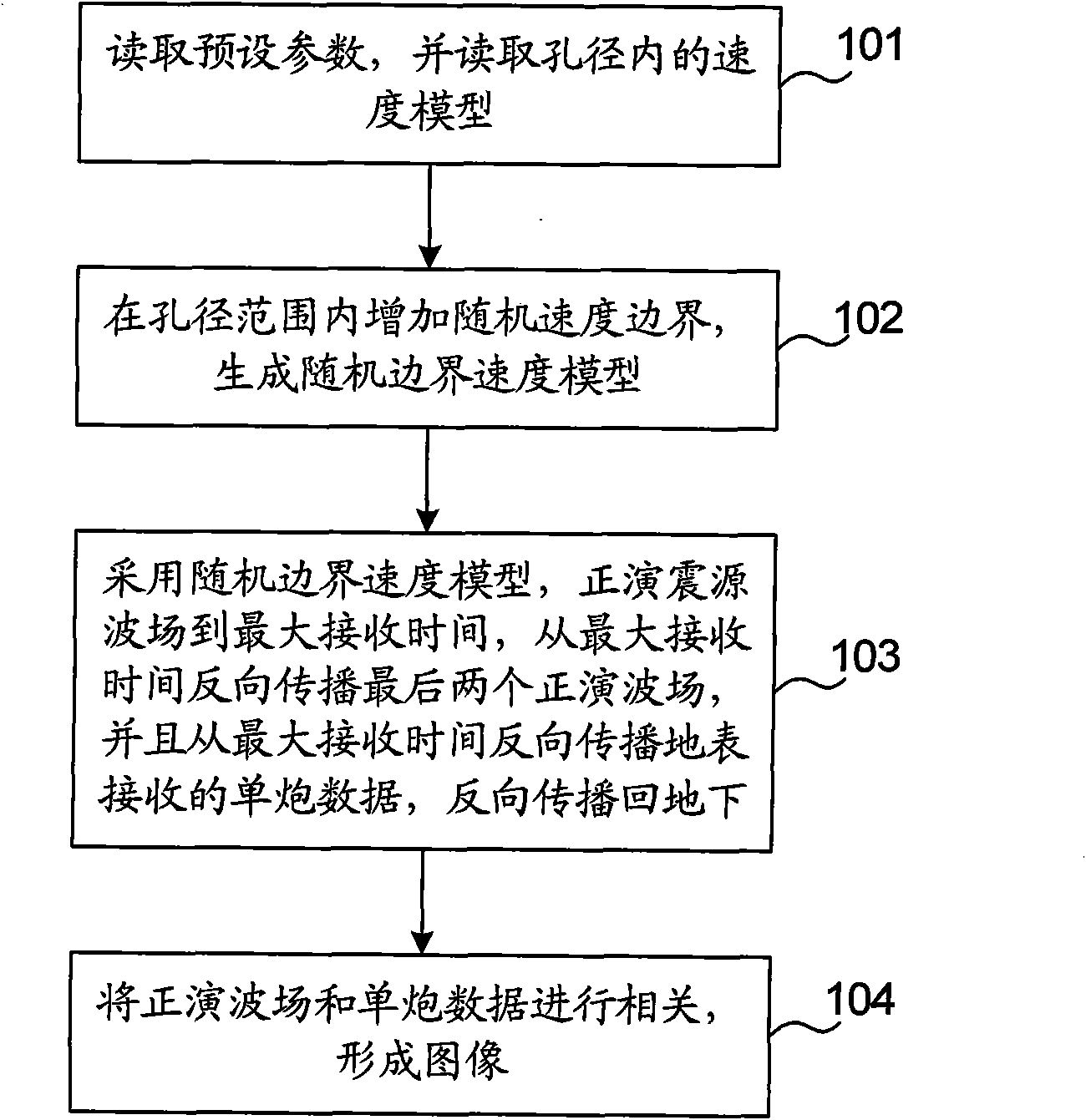
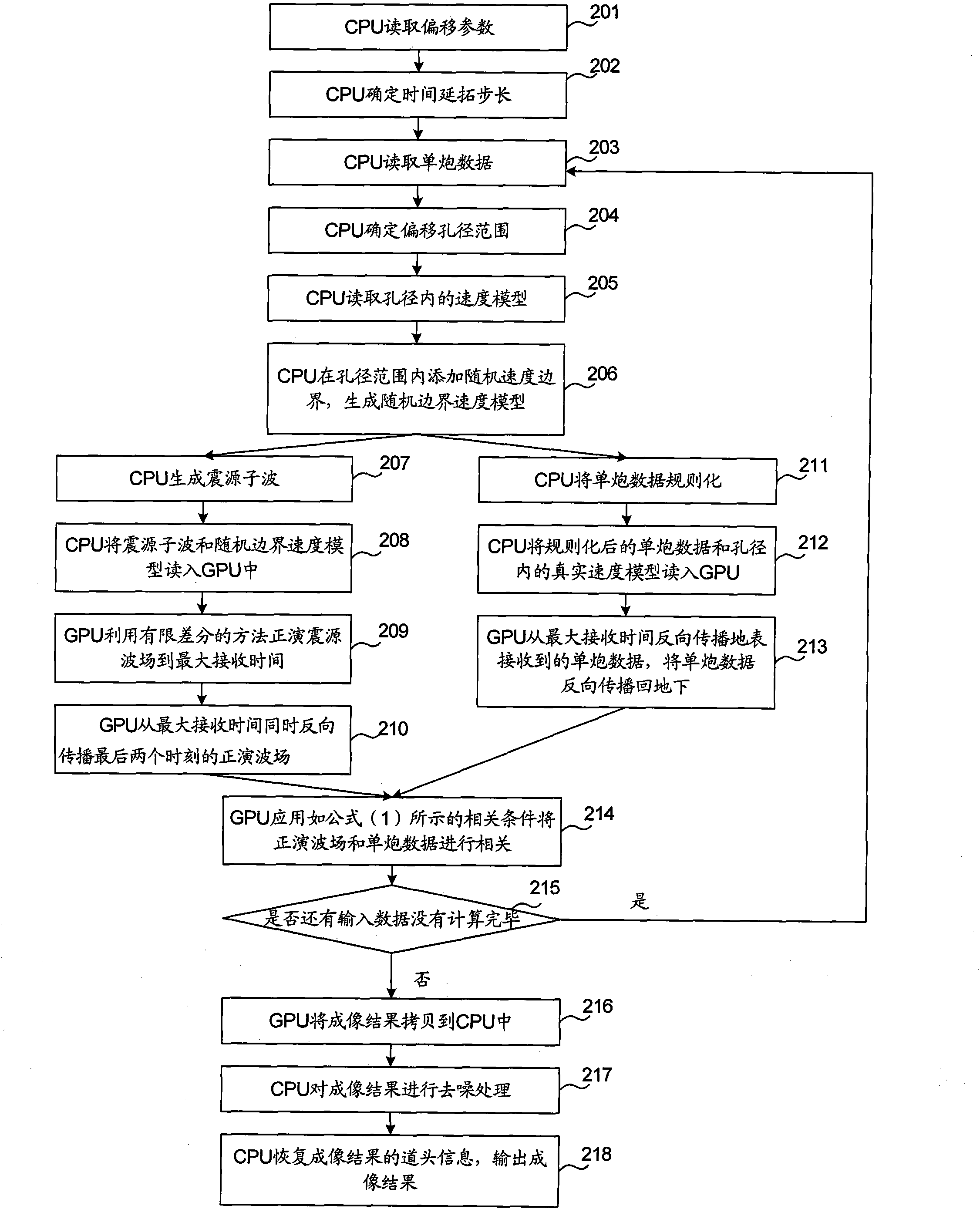
Prestack reverse time migration imaging method and device
The invention provides a prestack reverse time migration imaging method and a prestack reverse time migration imaging device. The method comprises the following steps of: increasing random speed boundaries in an aperture range to generate a random boundary speed model; forwarding a focus wave field to the maximal receiving time by using the random boundary speed model, reversely propagating the last two forwarding wave fields from the maximal receiving time, reversely propagating single shot data received by the earth surface from the maximal receiving time and reversely propagating the single shot data back to an underground place; and correlating the forwarding wave fields and the single shot data to form an image. By the method provided by the invention, the prestack reverse time migration imaging speed can be increased and the requirements on a storage space is reduced.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Over-mode circular waveguide broadband directional coupler and design method thereof
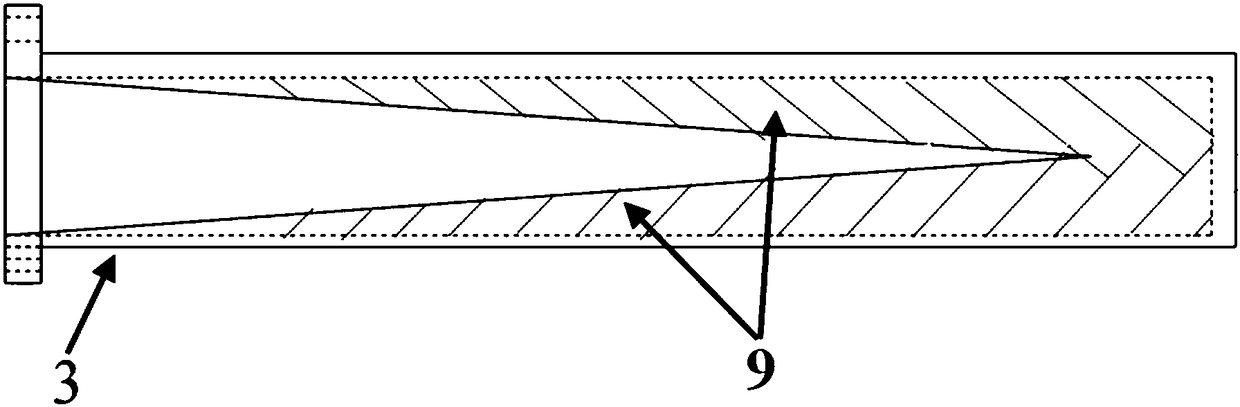
The invention provides a novel over-mode circular waveguide broadband directional coupler and a design method thereof. According to the over-mode circular waveguide broadband directional coupler and the design method thereof, a standard rectangular waveguide in the traditional over-mode circular waveguide directional coupler is replaced with a non-standard over-mode rectangular waveguide; the cutoff wave number of a basic mode TE10 of the non-standard over-mode rectangular waveguide is changed through adjusting the size of the non-standard over-mode rectangular waveguide, and the cutoff wave number of the basic mode TE10 of the non-standard over-mode rectangular waveguide is enabled to be the same as that of a working mode TEmn in an over-mode circular waveguide, so that the propagation constant of the TE10 at any frequency point is the same as that of the TEmn, then, forward waves of the coupler can meet equidirectional superposing conditions at any frequency point, and the aims of expanding the working bandwidth of the over-mode circular waveguide directional coupler and reducing in-band coupling degree fluctuation are achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Impedance matching device
ActiveUS20140354173A1Shorten the timeLow costMultiple-port networksElectric discharge tubesHigh frequency powerEngineering
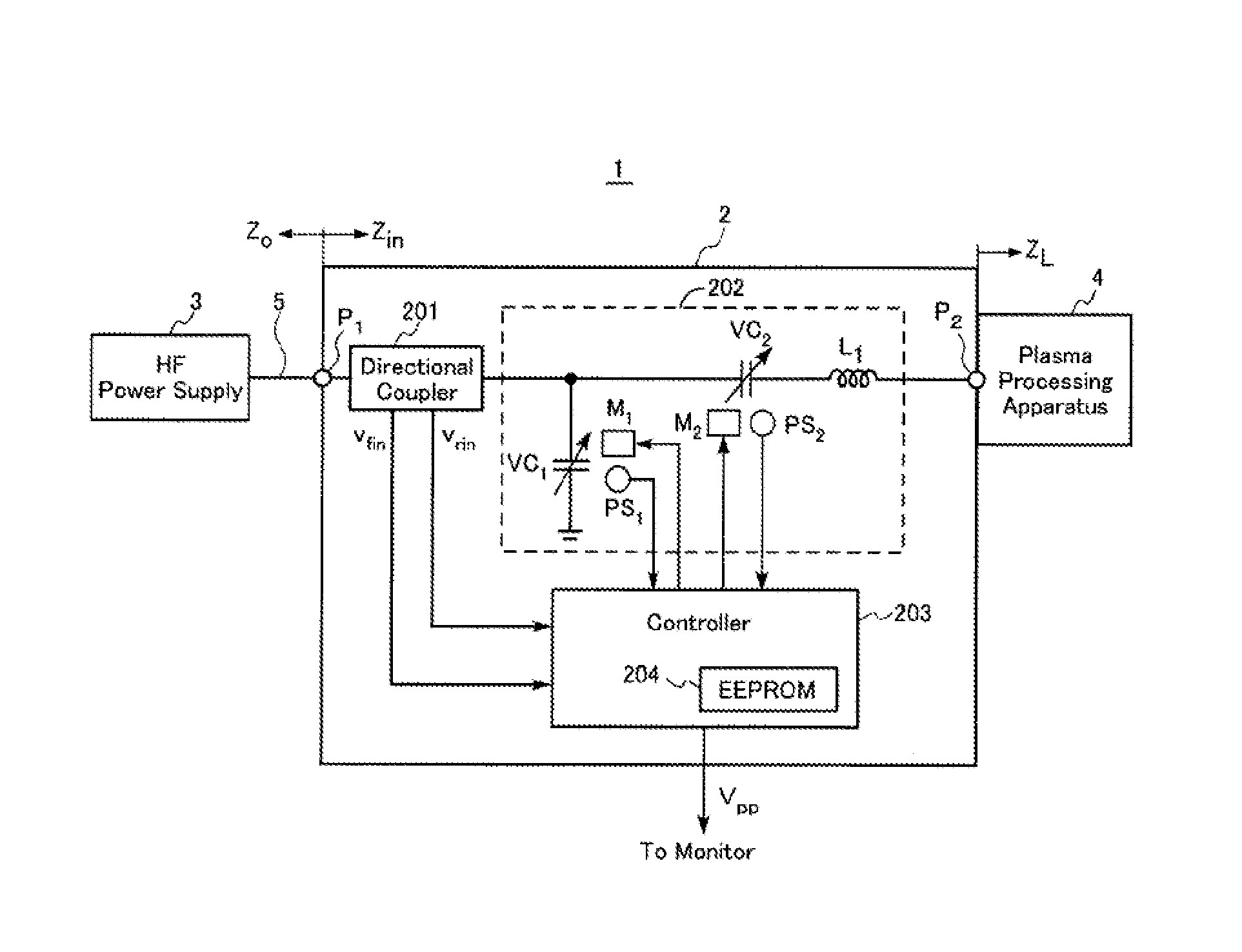
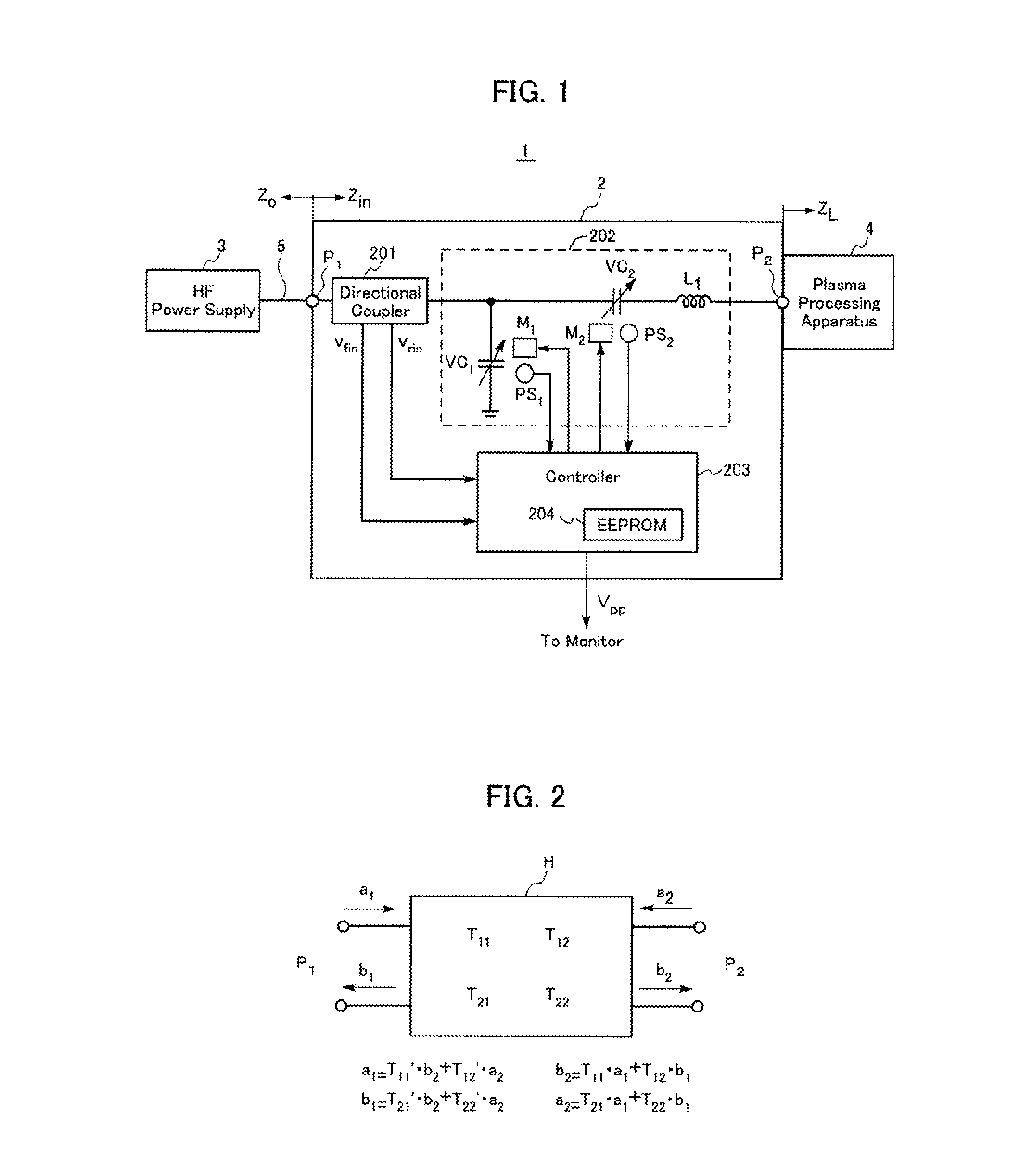
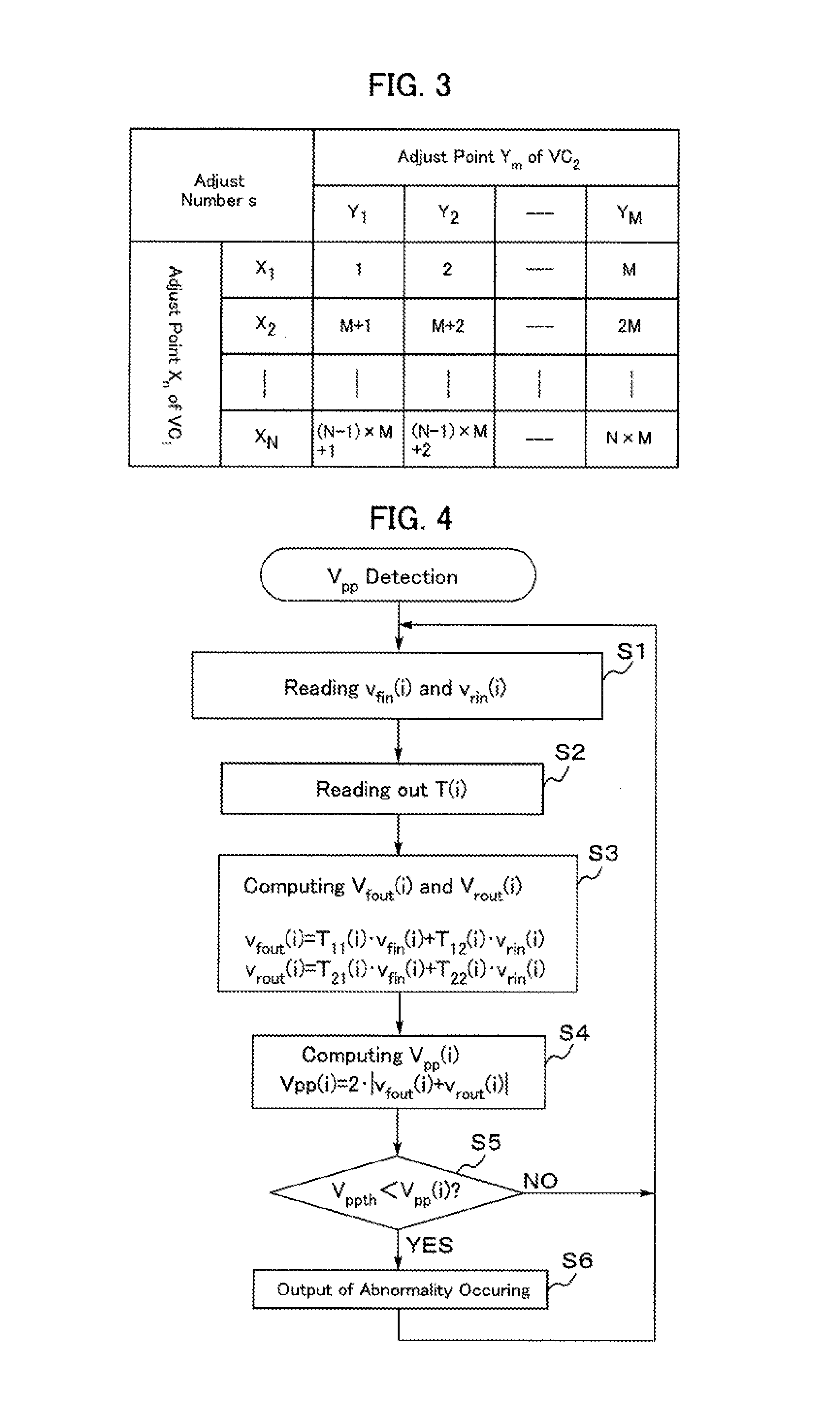
An impedance matching device includes an input port connected to a high-frequency power supply, an output port connected to a load, an impedance variable circuit, a T-parameter memory for storing sets of T-parameters in a manner such that each of the sets of T-parameters is related to a corresponding one of adjustable impedance values of the device, an input voltage detector for detecting a forward wave voltage and a reflected wave voltage at the input port, and a p-p value calculator for computation of a p-p value of a high-frequency voltage at the output port. The computation of the p-p value of the high-frequency voltage is performed by using the forward wave voltage and the reflected wave voltage detected at the input port and also using one set of the T-parameters stored in the T-parameter memory.
Owner:DAIHEN CORP
Full waveform inversionmethod and system based on gradient processing
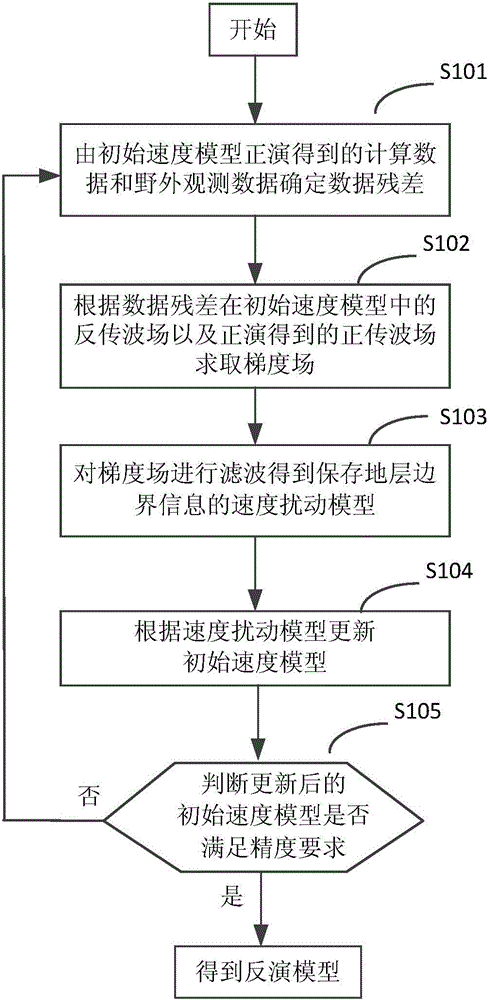
ActiveCN105445798AInversion stabilizationImprove inversion accuracySeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsObservation dataWave field
The invention discloses a full waveform inversion (FWI) method and system based on gradient processing. The method comprises a residual calculation step of determining a data residual according to calculation data and outdoor observation data obtained by the forward modeling of an initial velocity model; a gradient calculation step of solving a gradient field according to a backward wave field of the data residual in the initial velocity model and a forward wave field obtained by forward modeling; a disturbance model computing steps of filtering the gradient field to obtain a velocity disturbance model with reserved stratum boundary information; and an updating step of updating the initial velocity model according to the velocity disturbance model. The method carries out low-pass filtering and adaptive filtering on the gradient in the FWI, suppresses random noise by means of the low-pass filtering, and recovers the boundary information lost in the low-pass filtering so as to achieve boundary fidelity.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
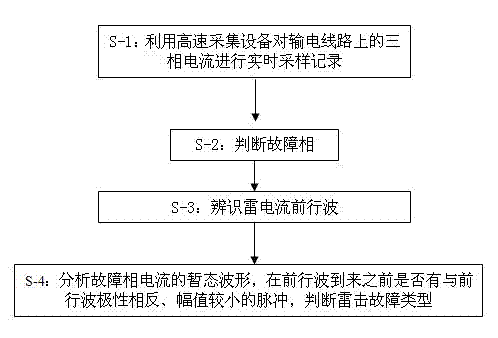
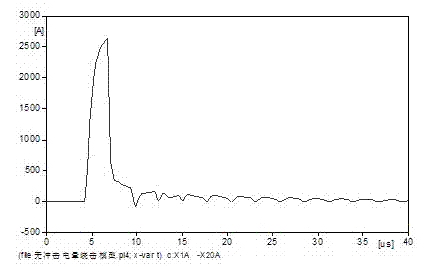
Method for distinguishing back flashover faults and lightning shielding failure faults of power transmission line
ActiveCN102645612ANo load currentSimple Waveform AnalysisCurrent/voltage measurementFault locationSmall amplitudePhase currents
The invention discloses a method for distinguishing back flashover faults and lightning shielding failure faults of a power transmission line. The method comprises the following steps of: sampling and recording three-phase transient current on the power transmission line in real time by using a high-speed acquisition device; comparing maximum amplitudes of the three-phase transient current at the same observation point, and judging fault phases; analyzing transient waveforms of fault phase current, and identifying forwarding waves of lightning current; and identifying whether pulses with the polarity opposite to that of the forwarding waves and small amplitudes exist, and determining the pulses as the back flashover faults or the lightning shielding failure faults. The method for identifying fault types by using power frequency voltage in the past is often influenced by load current, the length of a circuit and transition resistance. On the basis of characteristic differences of fault high-frequency transient signals, the method is not influenced by the load current, the length of the circuit and the transition resistance, and has the advantage of simple criterion and easiness in implementation.
Owner:GUANGDONG ELECTRIC POWER SCI RES INST ENERGY TECH CO LTD
High frequency power device
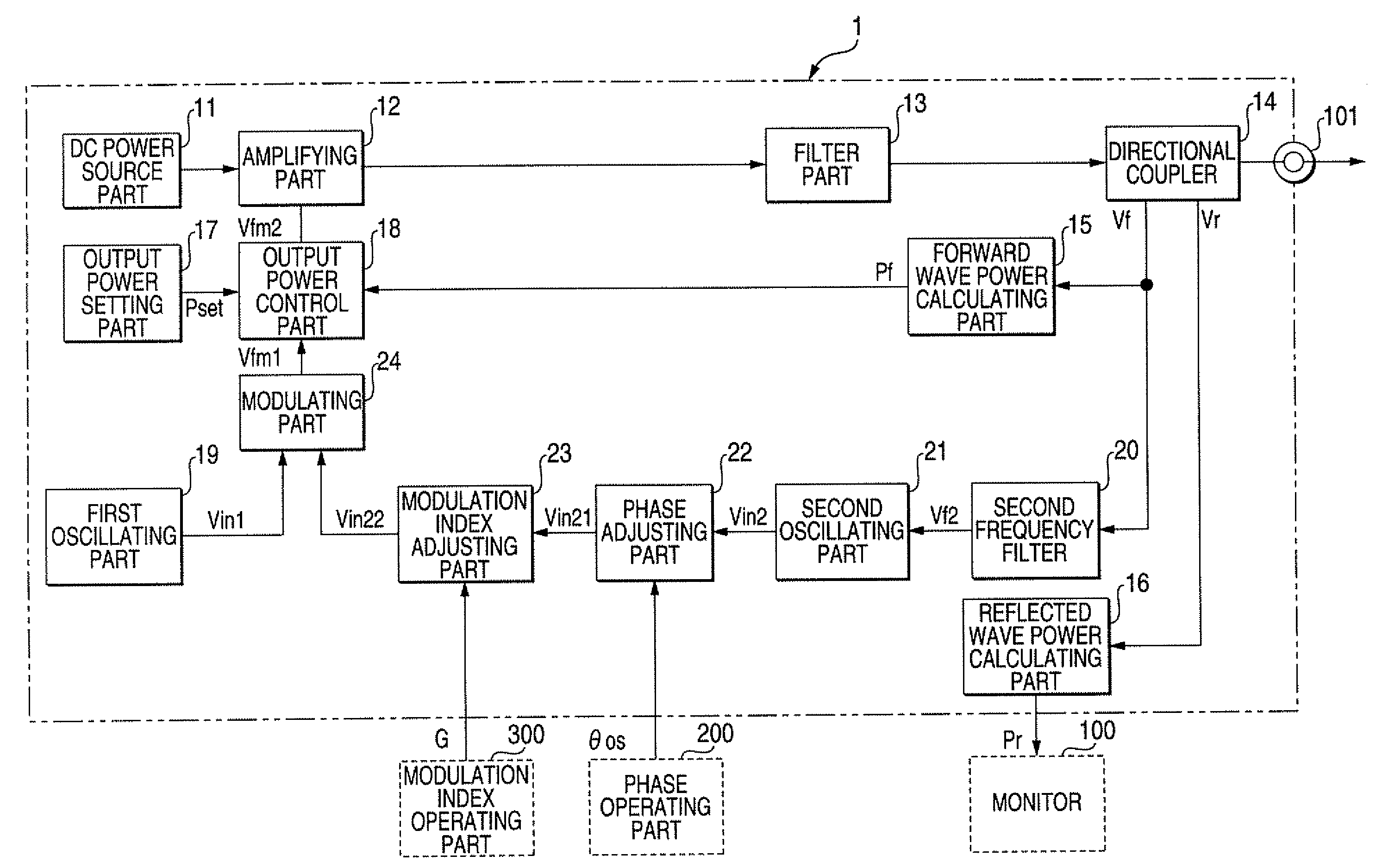
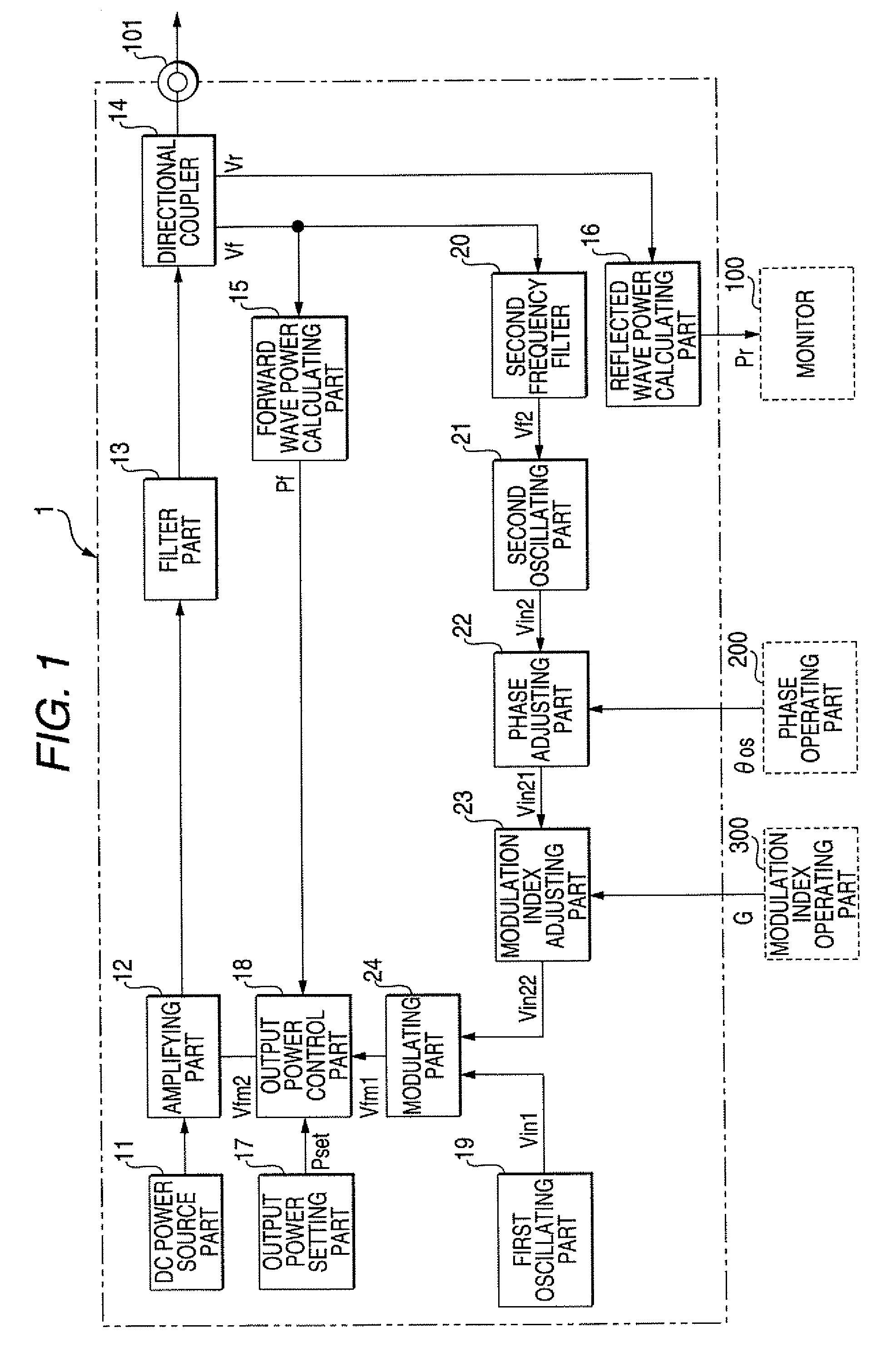
ActiveUS20070076344A1Reduce the required powerReduce outputElectric discharge tubesElectrographic process apparatusHigh frequency powerReflected waves
A high frequency power device for supplying high frequency power to a load to generate plasma, includes: a high frequency detector, detecting a forward wave voltage and a reflected wave voltage in an output end of the high frequency power device to output a forward wave signal corresponding to the forward wave voltage and a reflected wave signal corresponding to the reflected wave voltage; a first oscillator, outputting a signal oscillated by a first predetermined frequency as a first oscillating signal; a second oscillator, outputting a signal oscillated by a frequency within a second predetermined frequency band as a second oscillating signal; a phase adjuster, adjusting a phase of the second oscillating signal outputted from the second oscillator; a modulation index adjuster, adjusting a modulation index of the second oscillating signal outputted from the second oscillator; a modulator, outputting a modulated signal obtained by modulating, in frequency, the first oscillating signal by the second oscillating signal whose phase and modulation index are adjusted by the phase adjuster and the modulation index adjuster respectively; and a high frequency output unit, amplifying and outputting the modulated signal outputted from the modulator or a signal obtained by controlling the output level of the modulated signal.
Owner:DAIHEN CORP
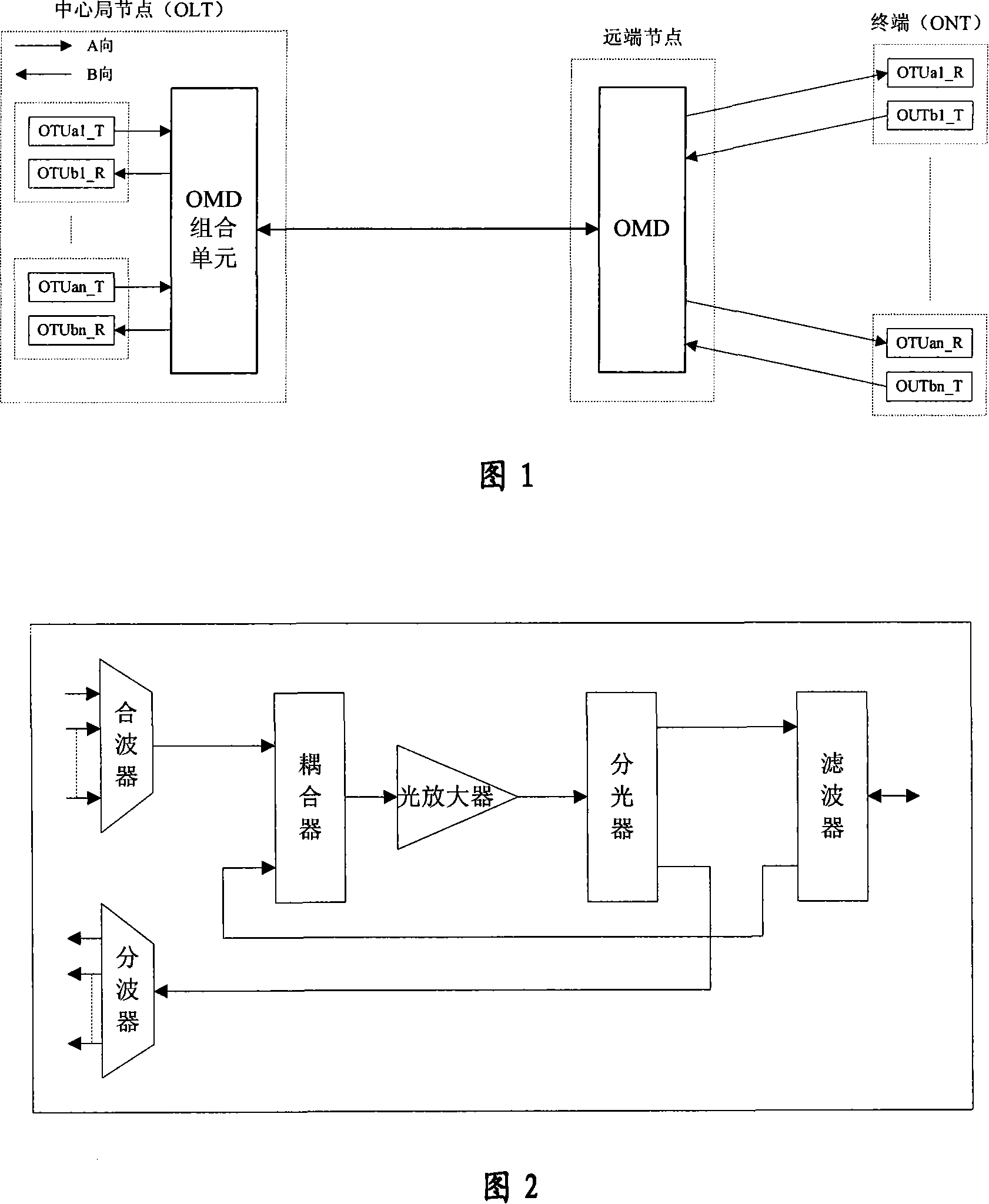
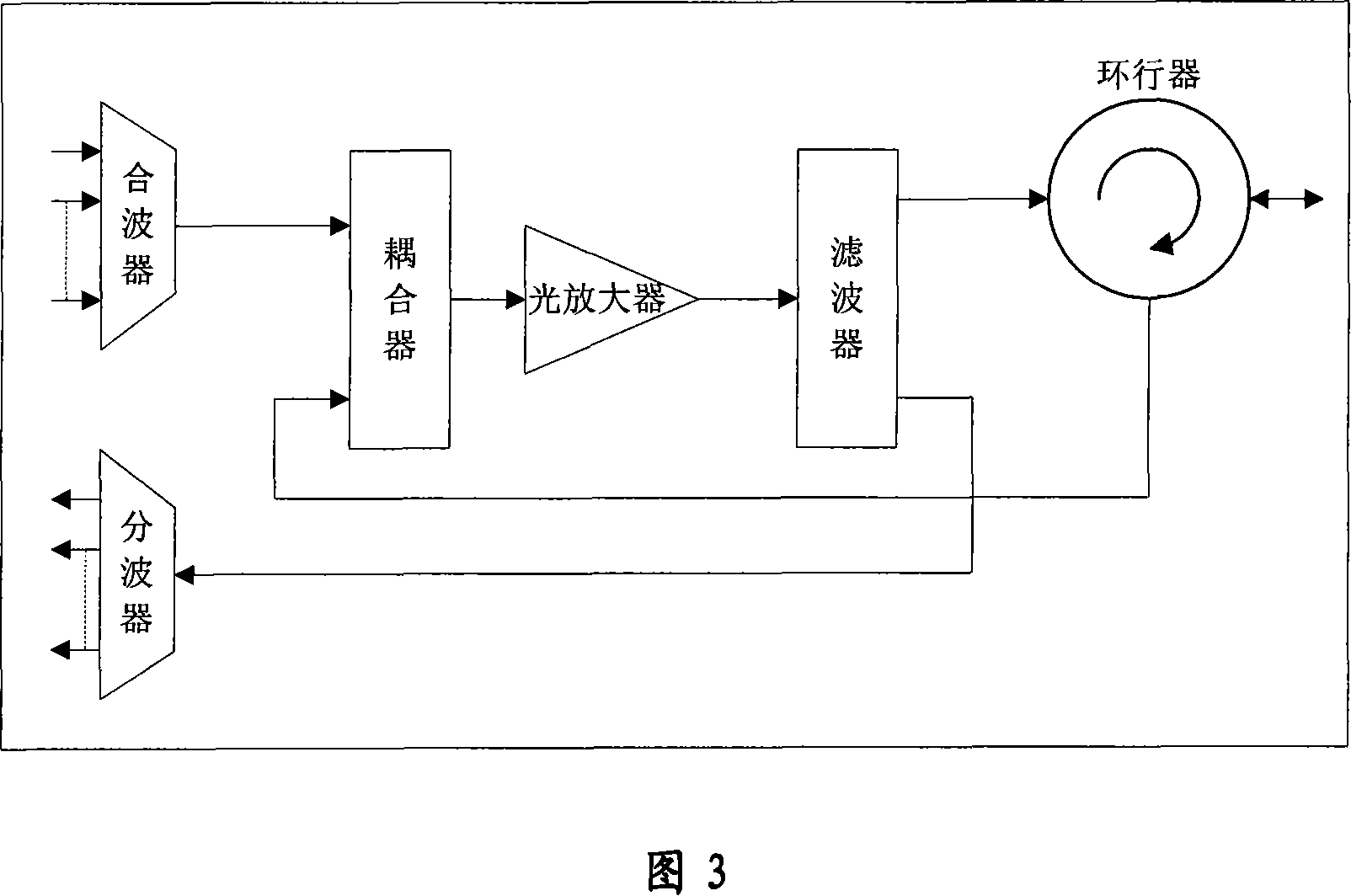
Wavelength division multiplexing passive optical network device
InactiveCN101141346ARealize long-distance transmissionIncrease available bandwidthMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationNetwork terminationInformation transmission
The utility model provides a wave division multiplex passive optical network device, which comprises a central optical link terminal, a remote terminal node passive photosynthesis component wave unit and n optical network terminals. The central optical link terminal includes a optical retransmission unit and a photosynthetic component wave module; the optical retransmission unit completes retransmission service of which the rate is 10Gbps and further comprises n groups of the OTU modules; the remote terminal node passive photosynthetic component wave unit is a heat-insulated passive module which is used to complete the wave splitting of the forward wave length and the wave coupling of the retrograding wave length. The optical network terminal includes a group of OTU modules which is correspondent to the central optical link terminal, so as to jointly complete one information transmission between the central part and the terminal. As compared with the existing technology, the utility model realizes the 10 Gbps WDM PON for the individual user and improves the available bandwidth of the system. Meanwhile, the deficient transmission range is well solved, so as to achieve the long distance transmission with 10Gbps' WDM PON.
Owner:ZTE CORP
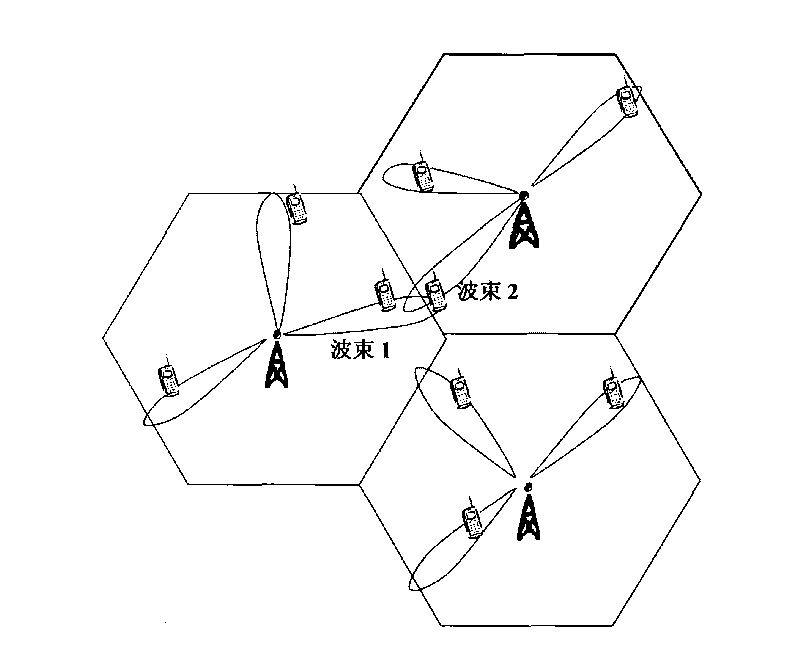
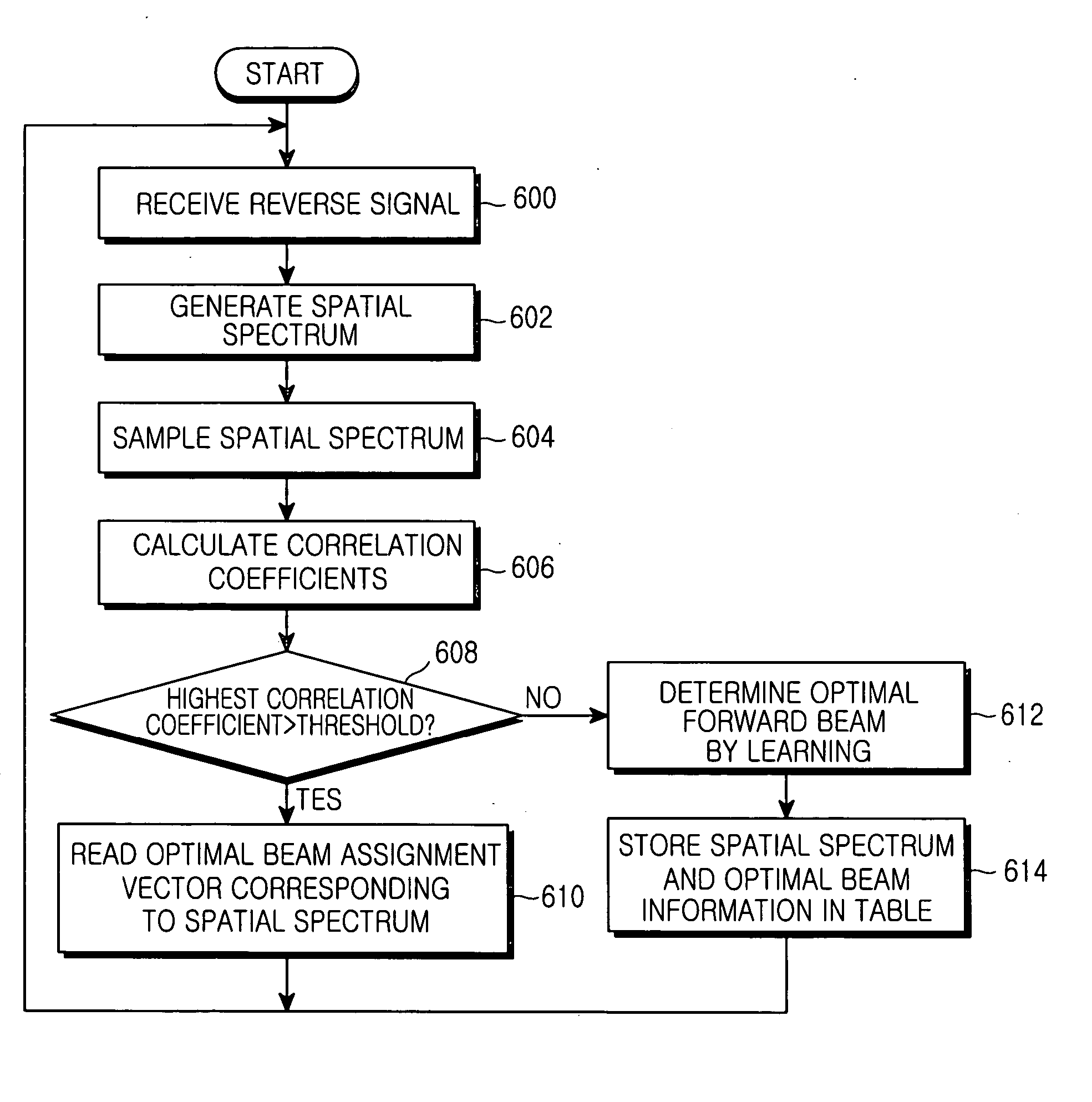
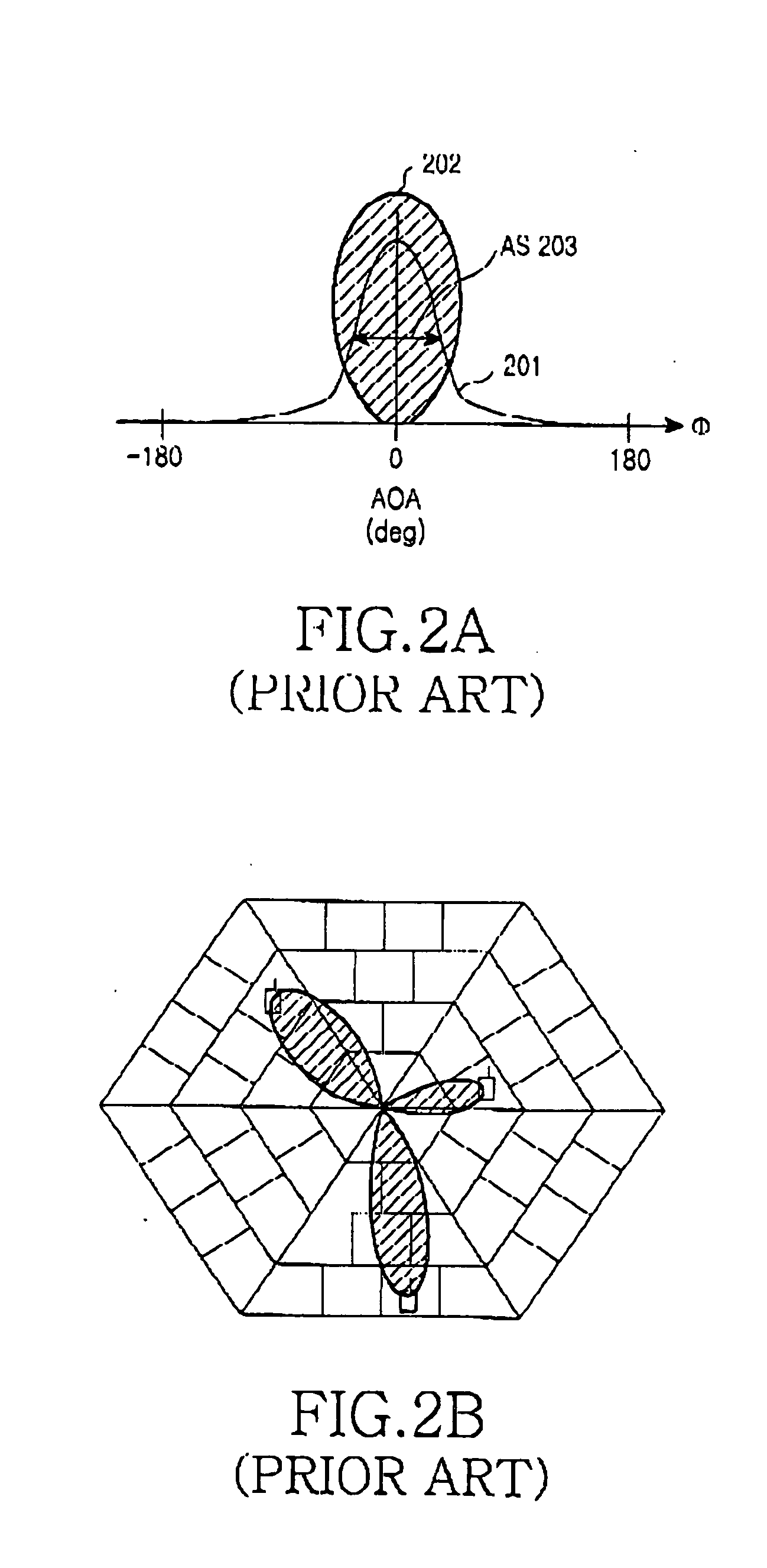
Beam assigning apparatus and method in a smart antenna system
InactiveUS20050064909A1Accurate analysisSpatial transmit diversitySubstation equipmentCorrelation coefficientSmart antenna
A method and apparatus for assigning a forward beam using a received reverse signal in a smart antenna system are provided. A reverse signal is received from a wireless terminal, the spatial spectrum of the reverse signal is detected and sampled at a predetermined sampling rate, the correlation coefficients between the sampled spectral spectrum and spatial spectrum values stored in a spatial spectrum table are calculated, a forward beam assignment vector corresponding to the highest of the correlation coefficients is detected, and a forward beam is assigned using the forward beam assignment vector.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
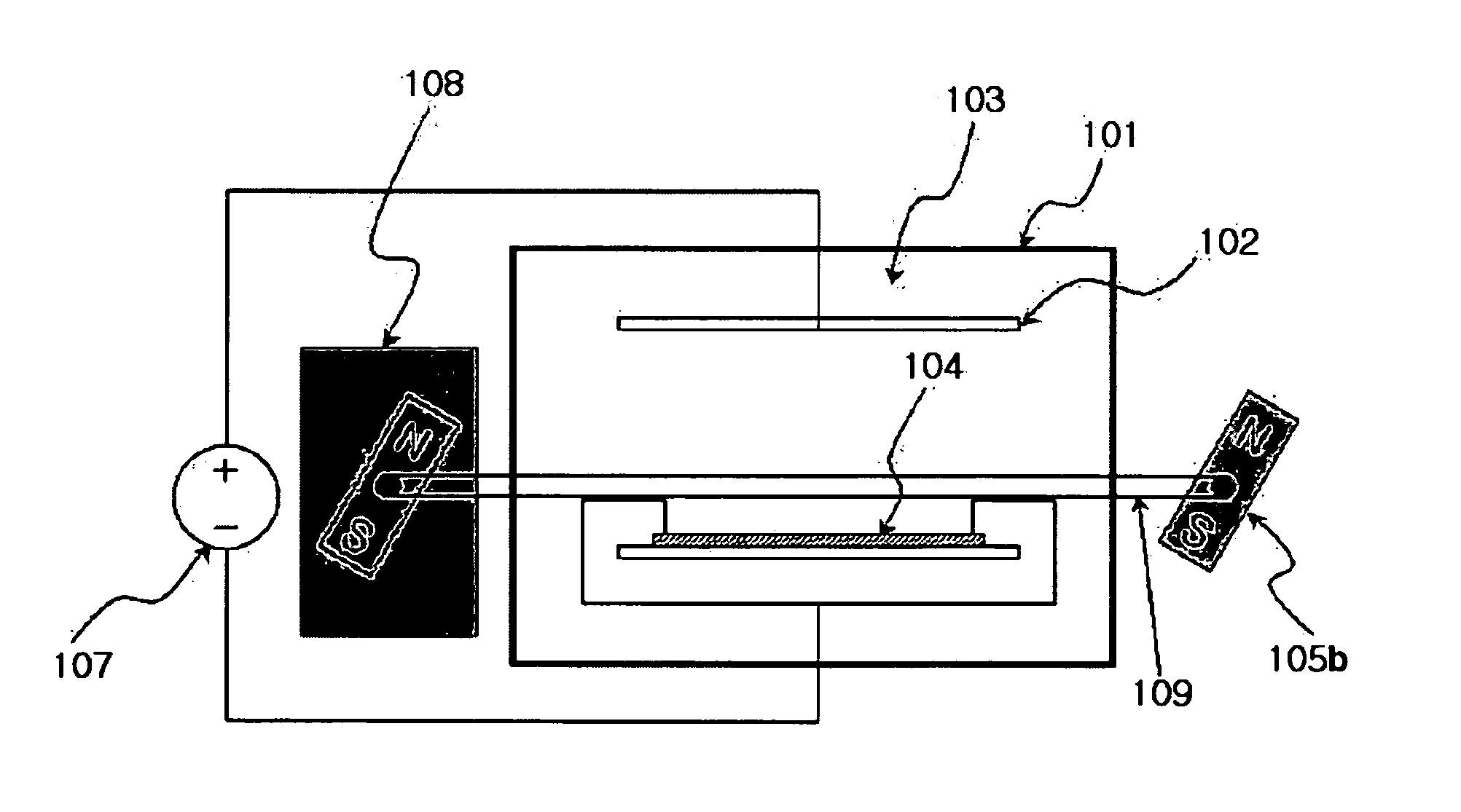
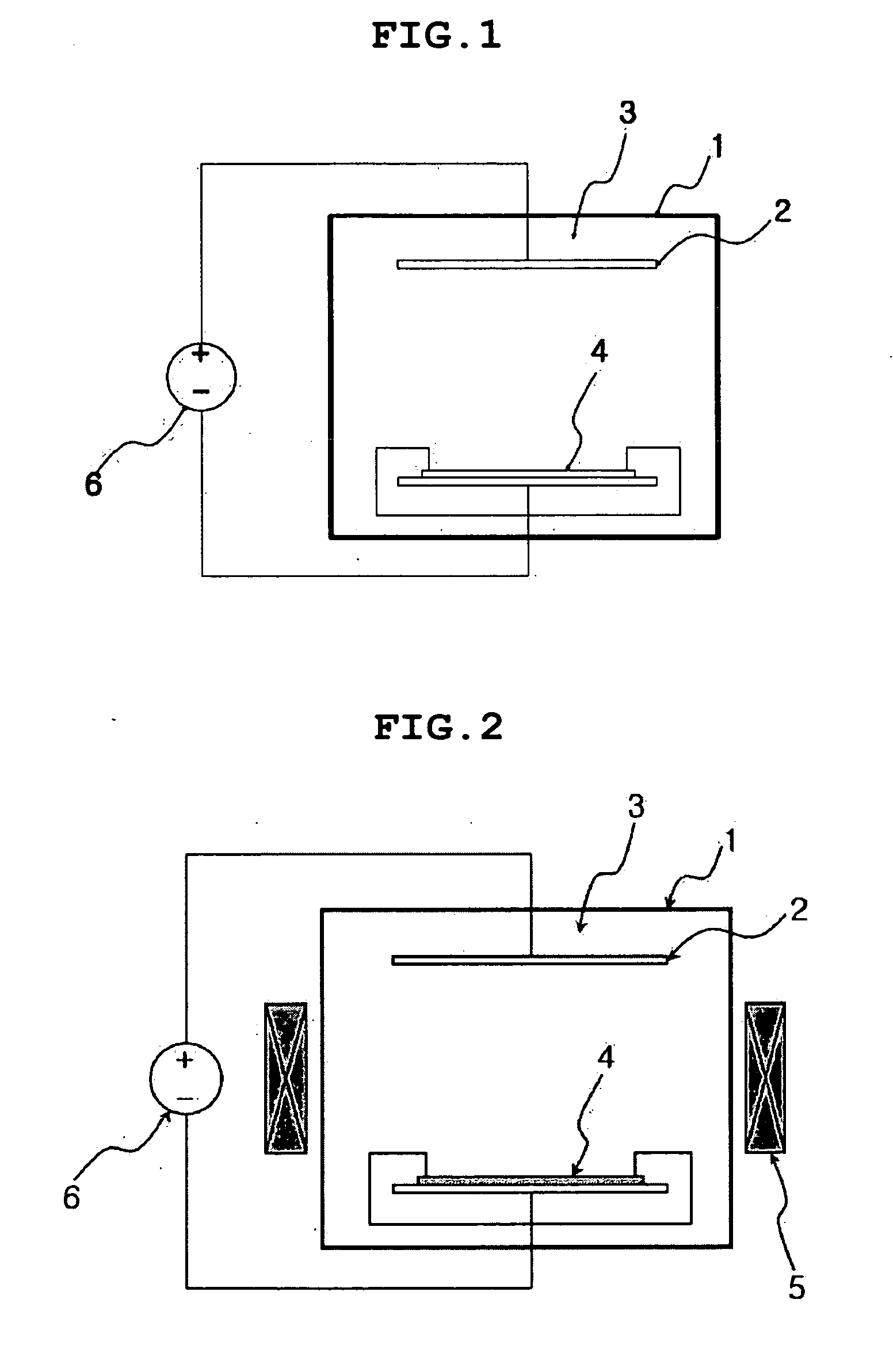
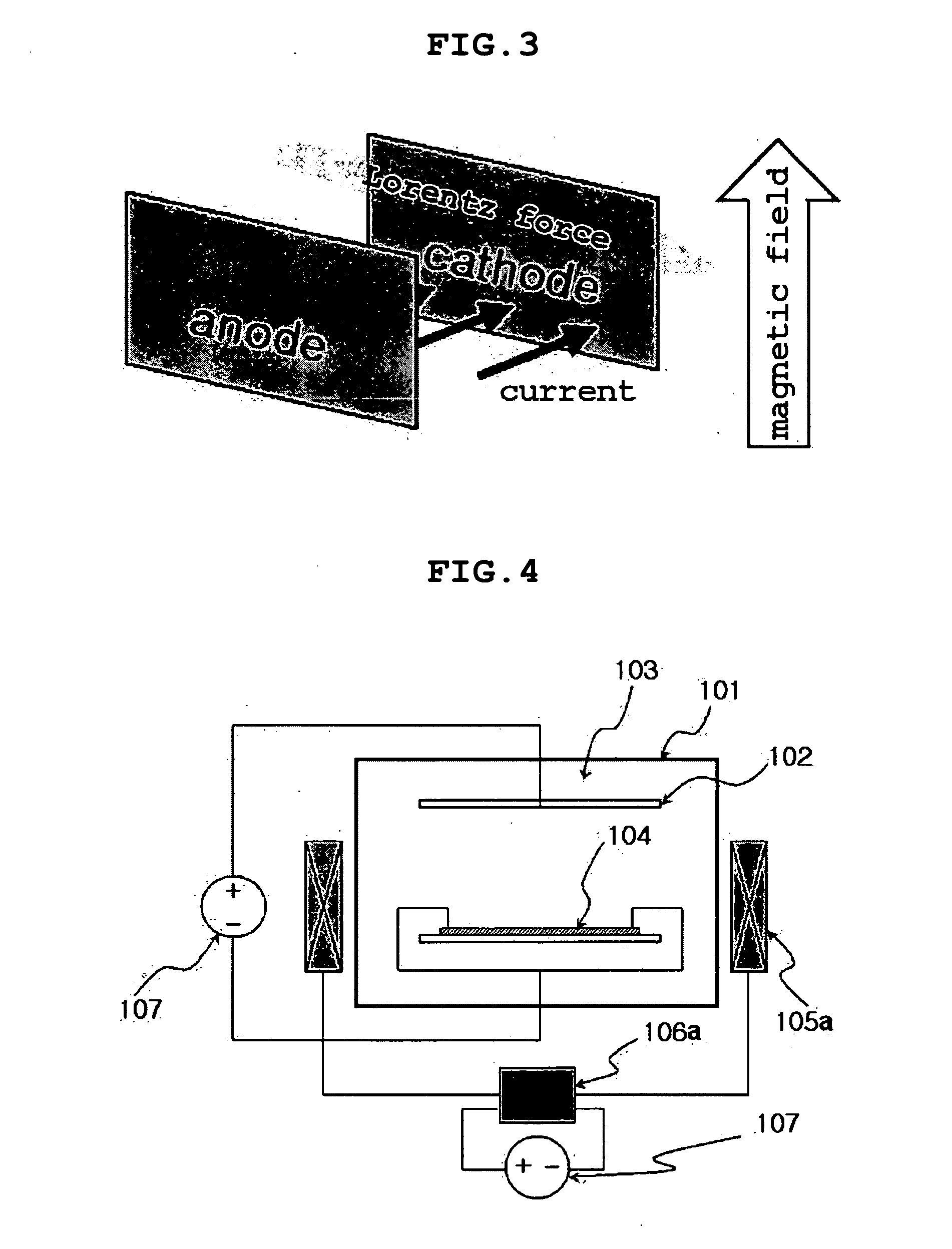
Method of electroplating printed circuit board using magnetic field having periodic directionality
InactiveUS20070062816A1High trafficReduce variationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPrinted circuit manufactureEngineeringPrinted circuit board
Disclosed is a method of electroplating a printed circuit board using a magnetic field having periodic directionality, in which the printed circuit board is electroplated using a magnetic field that is generated substantially perpendicular to a current direction and that has periodic directionality between a forward wave and a reverse wave. According to the method of the present invention, since the magnetic field having the periodic directionality is used, the aging of the plating solution may be prevented and the ionic concentration thereof may be made uniform even without the use of an external liquid flow device, and as well, the substrate may be uniformly plated.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Optical Isolator
Various optical isolator embodiments are disclosed. Embodiments comprise a waveguide section utilizing materials that induce a propagation constant shift that is propagation-direction-dependent. Embodiments are characterized by a cutoff frequency for forward propagating waves that is different than the cutoff frequency for reverse waves; the dimensions and direction of magnetization of the waveguide can be tailored so that, in a particular embodiment, the cutoff frequency for forward propagating waves is lower than the cutoff frequency for reverse waves. A particular embodiment is constructed as a single-mode waveguide on a substrate. The cross-section of the waveguide is inhomogeneous in terms of materials. At least one part of the cross-section is a non-reciprocal magneto-optic medium, which has nonzero off-diagonal permittivity tensor components. This inhomogeneity induces a propagation constant shift, which is propagation-direction-dependent. This device works as an optical isolator from the cut-off frequency of the lowest forward wave (lower frequency) to one for the lowest reverse wave (higher frequency). Various configurations consistent with the principles of the invention are disclosed.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
One-side folded waveguide slow wave structure for backward wave oscillator
ActiveCN104576266AAppropriate working voltageHigh coupling impedanceTransit-tube circuit elementsWave structureMiddle line
The invention discloses a one-side folded waveguide slow wave structure for a backward wave oscillator. Curved waveguides on one side of a folded waveguide are arranged in symmetrical positions along a midline. The one-side folded waveguide slow wave structure particularly structurally comprises a straight waveguide array consisting of a plurality of straight waveguides and a plurality of curved waveguides, wherein every two adjacent straight waveguides are connected via one curved waveguide to form a periodic structure; and an electron beam channel penetrates through the straight waveguide array. According to the one-side folded waveguide slow wave structure, the curved waveguides on one side are transferred to the symmetric positions along the midline, so that fundamental waves of the slow wave structure are forward waves; and the backward wave oscillator can achieve appropriate working voltage and higher coupling impedance simultaneously by using the one-side folded waveguide slow wave structure.
Owner:NO 12 RES INST OF CETC
Wideband circular waveguide directional coupler used for measuring microwave power
ActiveCN108172962AReduce coupling fluctuationSmall coupling fluctuationsCoupling devicesCouplingClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a wideband circular waveguide directional coupler used for measuring a microwave power, and relates to the technical field of a microwave / millimeter-wave device. Compared witha traditional over-mode circular waveguide directional coupler, the wideband circular waveguide directional coupler has the advantages that a novel non-standard over-mode rectangular waveguide is introduced to substitute a standard rectangular waveguide in the traditional over-mode circular waveguide direction coupler, the cutoff wave number of a fundamental mode TE10 is changed by adjusting the size of the non-standard over-mode rectangular waveguide, so that the cutoff wave number of the fundamental mode TE10 of the non-standard over-mode rectangular waveguide is same as the cutoff wave number of a working mode TEmn in the over-mode waveguide, a propagation (phase) constant of the TE10 mode at an arbitrary frequency point is same as a propagation constant of the working mode TEmn, a forward wave of the coupler can conform to the same-direction superpose condition at the arbitrary frequency point, and the purposes of expanding the working bandwidth of the over-mode circular polarization directional coupler and reducing fluctuation of in-band coupling degree are achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Quasi-optical phase correction surface designing method
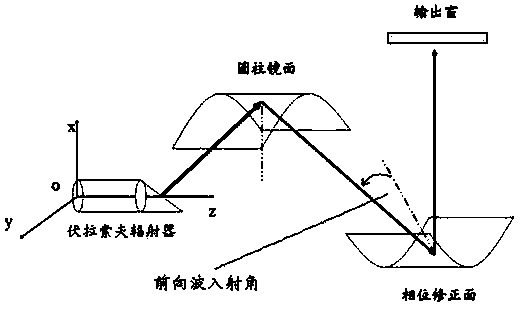
InactiveCN103412983AAccurate phase reflectorSpecial data processing applicationsPhase correctionGaussian beam
A quasi-optical phase correction surface designing method comprises a designing method of X-direction perturbation delta X of a quasi-optical phase correction surface. The quasi-optical phase correction surface designing method is characterized in that the perturbation delta X is equal to a quotient obtained by dividing the difference of phi Ey1 and phi Ey2 by 2k0cosine alpha, wherein phi Ey1 is the phase of a reverse Gaussian wave beam electric field Y-direction component in the position of the phase correction surface, phi Ey2 is the phase of a forward wave beam electric field Y-direction component in the position of the phase correction surface, k0 represents the wave number, alpha represents a forward wave beam incident angle, the phi Ey2 represents the forward wave beam electric field Y-direction component phase calculated with a vector diffraction theory, phi Ey1 is a Gaussian beam function, that is, phi Ey1 is equal to phi Ey1 (U), and U represents Gaussian beam. The adopted quasi-optical phase correction surface designing method which is used for designing a phase reflection surface with a vector diffraction theory is different from a scalar diffraction theory method, and the phase reflection surface is more accurate while compared with a phase reflection surface designed with a scalar diffraction theory.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
High frequency design method for ultra-wideband helix traveling wave tube
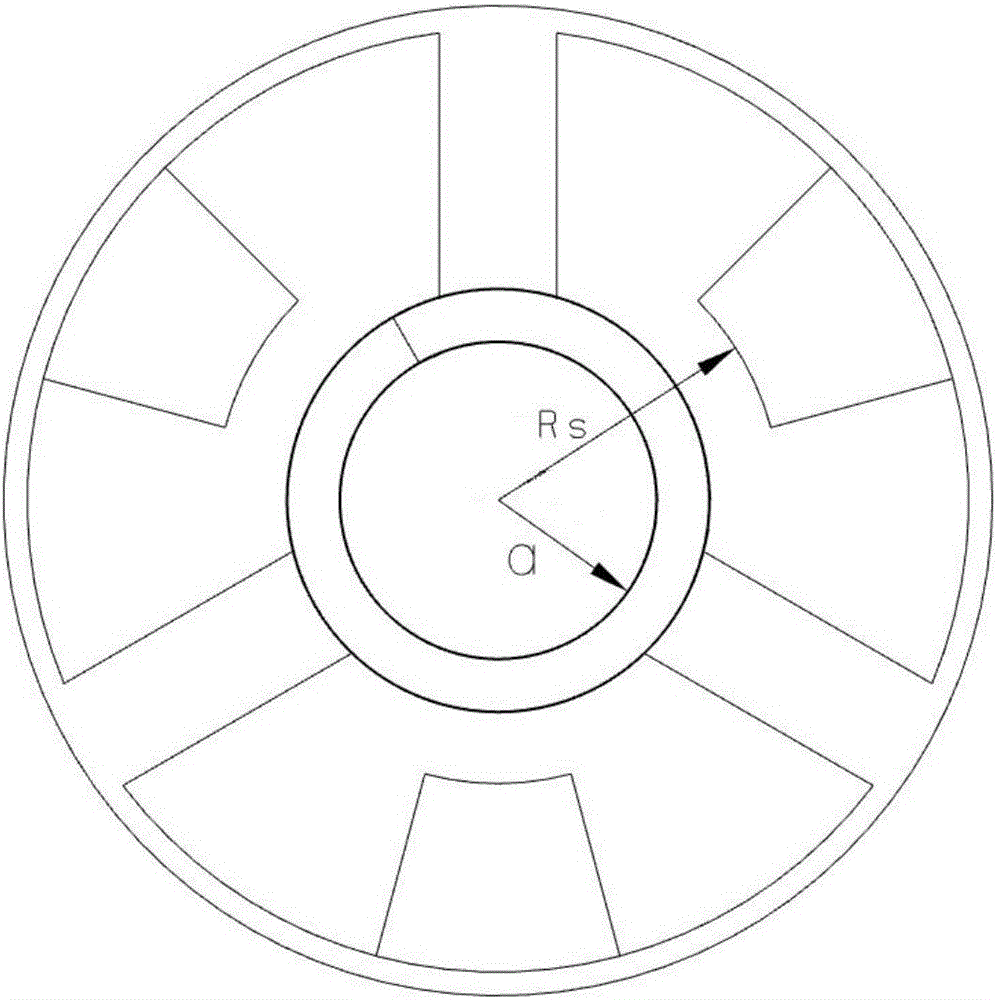
ActiveCN106024554AHigh degree of synchronizationIncrease output powerTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube circuit elementsUltra-widebandHelical line
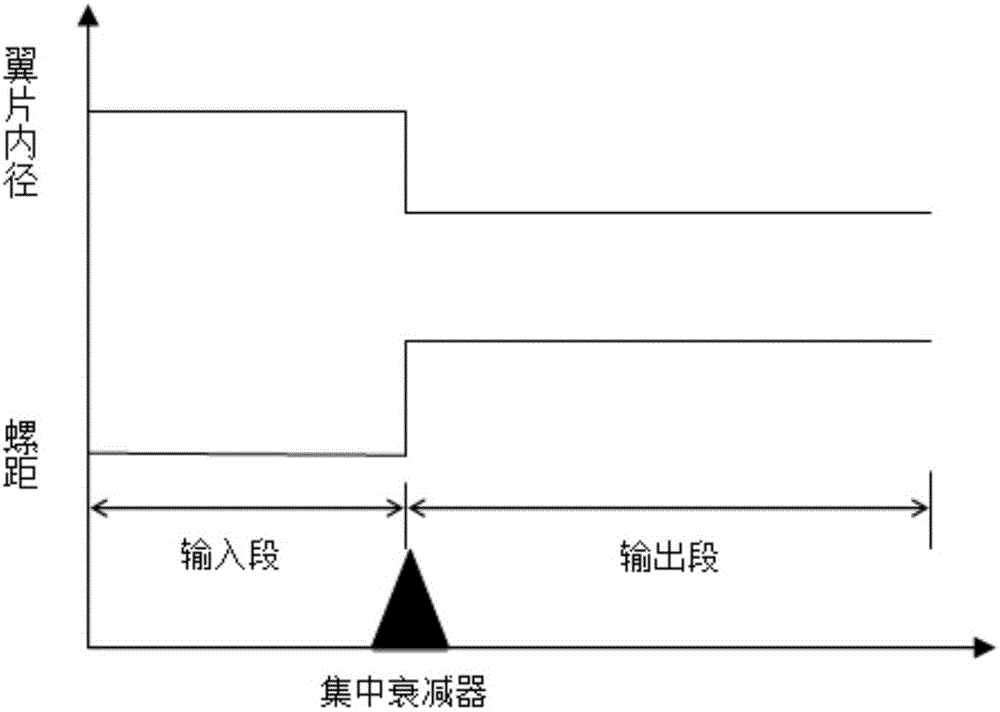
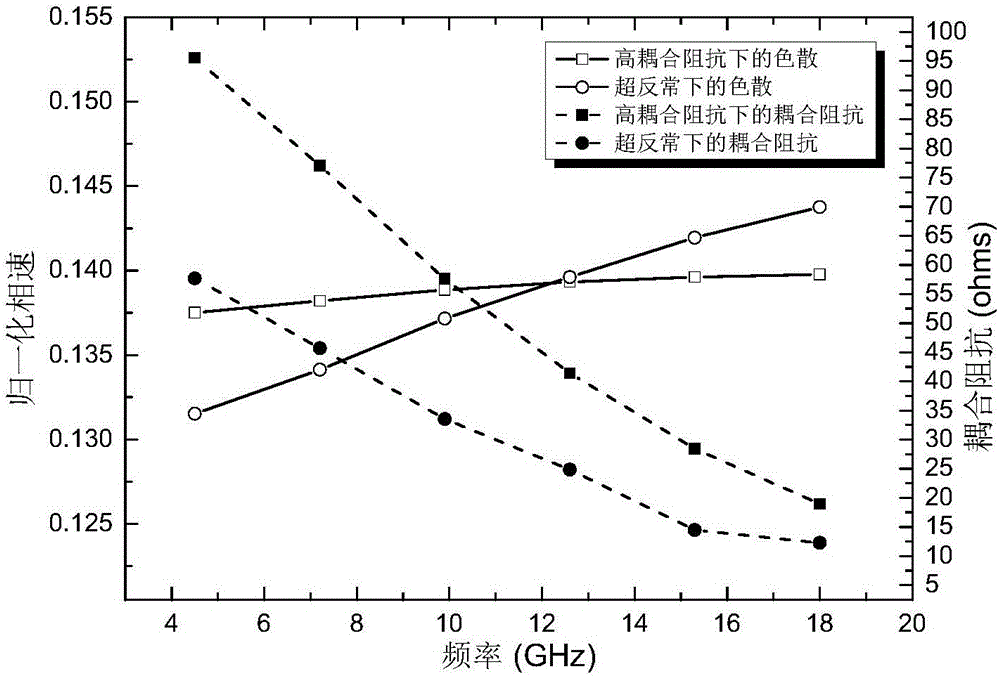
The invention relates to a high-frequency structure design method for an ultra-wide band helix traveling wave tube, belonging to the technical field of ultra-wideband traveling wave tubes. The method comprises the following steps: firstly determining the inside diameter of a helical line; then, under the premise that the inside diameter remains unchanged and through the adjustment of the pitch and the inside diameter of a wing sheet, making high coupling impedance one of the high-frequency characteristics of an input section and enabling dispersion characteristic of an output section to realize super anomalous dispersion so that the pitches and the inside diameters of wing sheets of the input section and the output section can be determined respectively. For the characteristic of high coupling impedance, a helical forward wave can be more synchronized with an electronic beam, greatly increasing the output power. For the characteristic of super anomalous dispersion at the output section, the synchronization between a higher harmonic wave and an electronic beam is destroyed, thus achieving a better harmonic suppression effect. The high frequency structure of the invention can improve the output power and suppress harmonic waves, and the output power is more than 115W in the frequency range of 4.5 to 18GHz and the second harmonic wave at 4.5GHz is less than -5dBc.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Direct-current power distribution network fault line selection method, device and system based on direction traveling waves
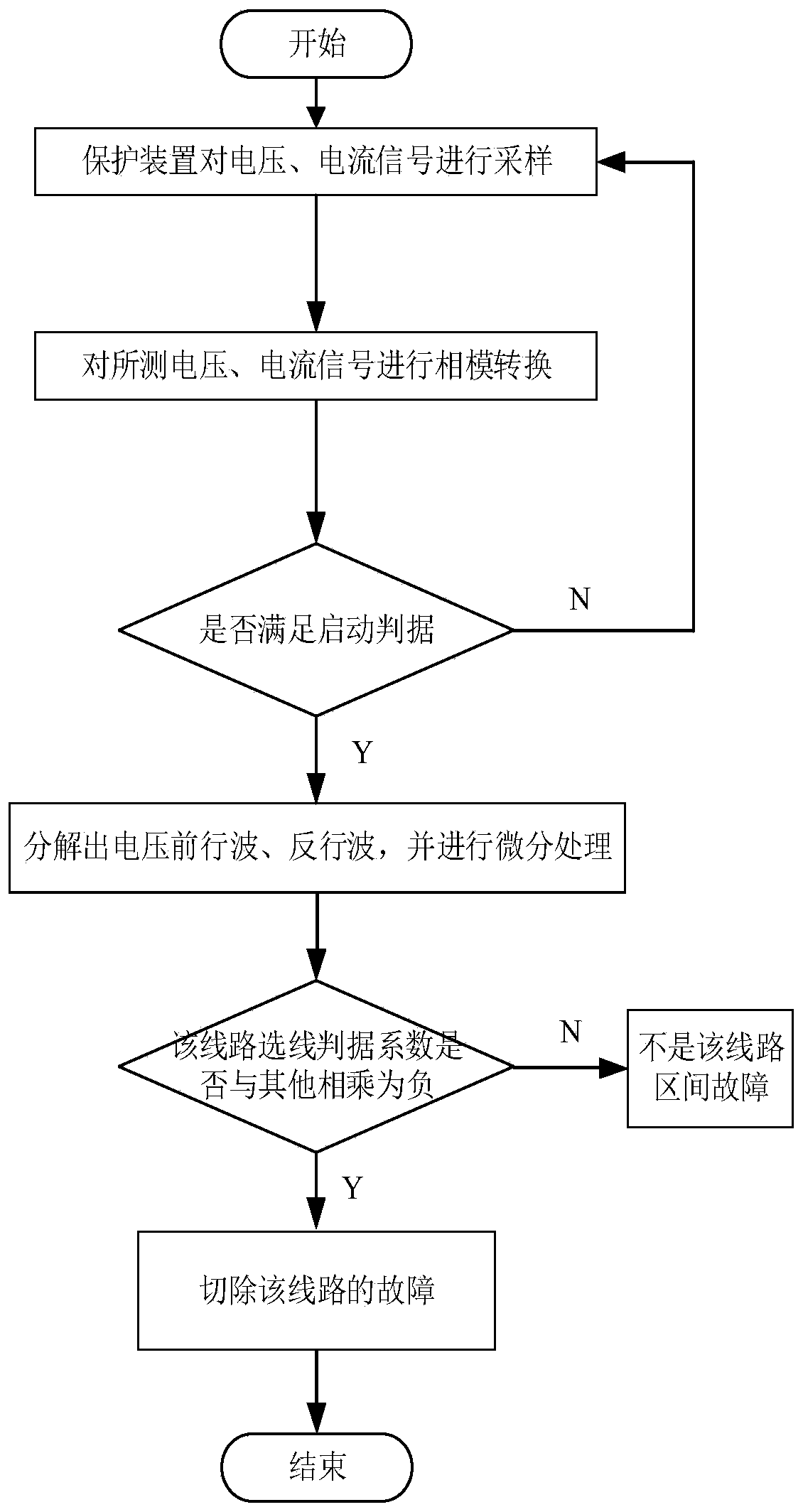
ActiveCN110907751AImprove recognition accuracyImprove the speed of removing faulty linesFault location by conductor typesInformation technology support systemCurrent distributionControl theory
The invention discloses a direct-current power distribution network fault line selection method, device and system based on direction traveling waves. The method comprises the following steps: (1) extracting a voltage traveling wave signal and a current traveling wave signal; (2) acquiring voltage and current traveling wave line mode components; (3) when the micro-component continuous multiple points of the voltage or current traveling wave line mode component are greater than a starting criterion setting value, starting a fault protection action; (4) decomposing a voltage forward wave and a voltage reverse wave of each direct-current distribution line; (5) processing to obtain forward wave and reverse wave fault line selection criterion coefficients of each DC distribution line; and (6) multiplying the forward wave line selection criterion coefficient of a certain line by the forward wave line selection criterion coefficients of other lines in pairs, if the multiplying results are allnegative numbers, judging that the line has a fault, and cutting off the line. The differential component of the directional traveling wave is used as the protection criterion quantity, so that effective identification and accurate judgment of the faulty line can be realized, and the faulty line identification accuracy and the faulty line removal speed are improved.
Owner:STATE GRID JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER CO ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +4
SPH wave simulation method applied to helicopter ditching
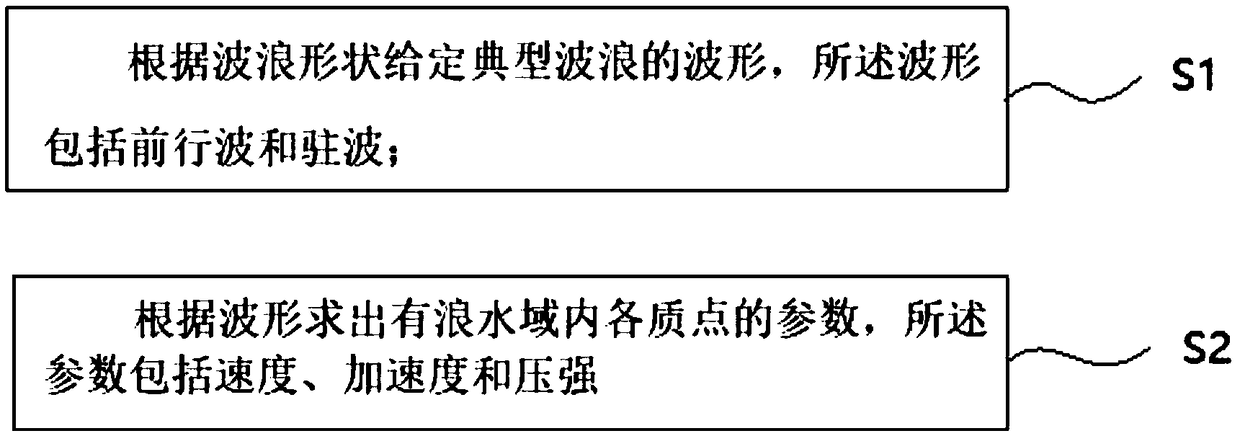
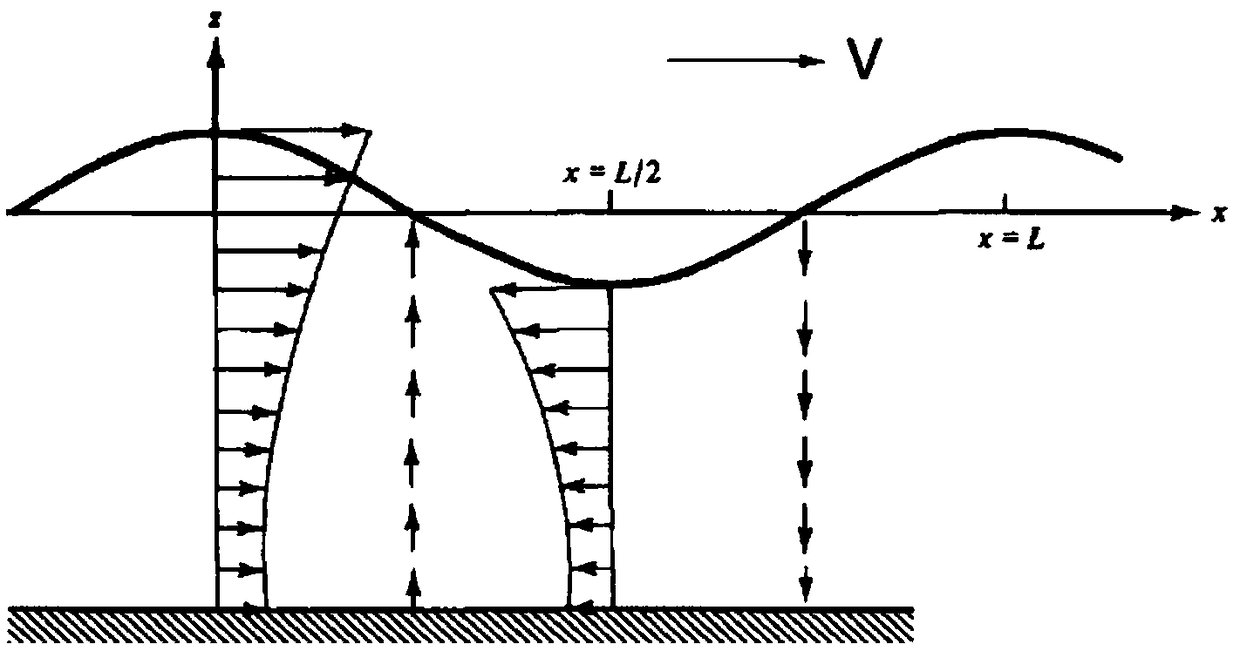
PendingCN108846225ATo achieve the wave effectReduce computing timeDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsWave shapeClassical mechanics
The invention relates to a PSH wave simulation method applied to helicopter ditching, and belongs to the technical field of the helicopter simulation experiment. The method comprises the following steps: giving waveform of classical wave according to wave shape, wherein the waveform comprises forward wave and standing wave; solving parameters of various particles in a choppy water area, wherein the parameters comprise speed, acceleration and pressure intensity. Through the SPH wave simulation method applied to helicopter ditching disclosed by the invention, the movement and kinetic parameter of various particles in the wave shape can be directly computed according to hydrodynamics rule; the time-consumed previous wave generation computation is unnecessary, the effect of pushing plate for wave-making can be achieved, and the time consumed for computation can be greatly reduced.
Owner:CHINA HELICOPTER RES & DEV INST
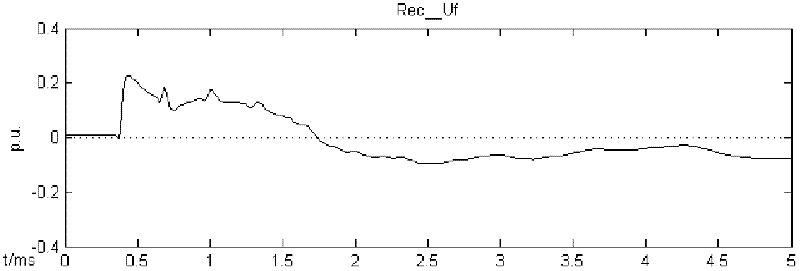
Design Support System, Design Support Method and Design Support Program
InactiveUS20160157355A1Reduce electromagnetic radiationSimple designComputer designed circuitsComputer aided designPower flowDesign support system
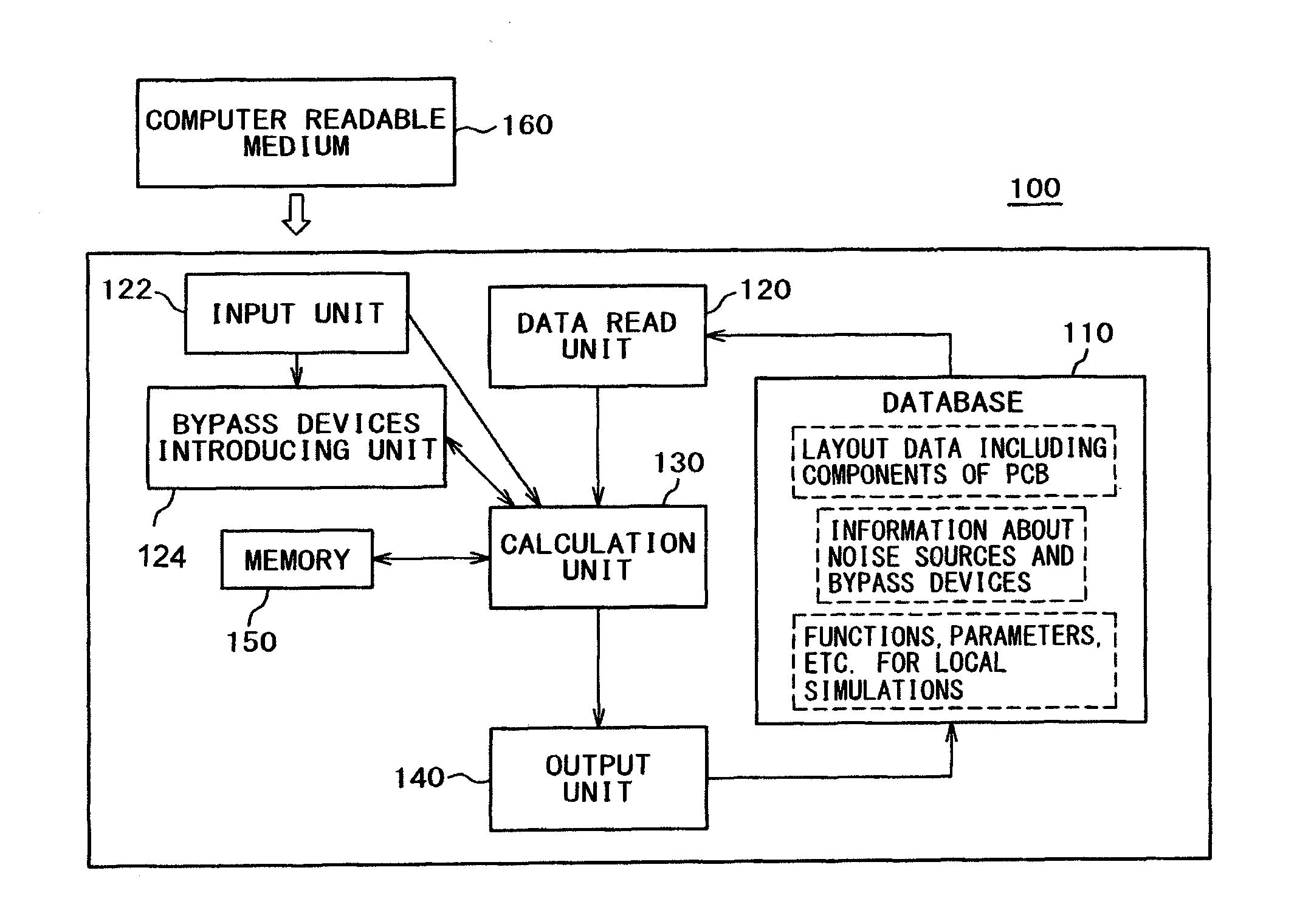
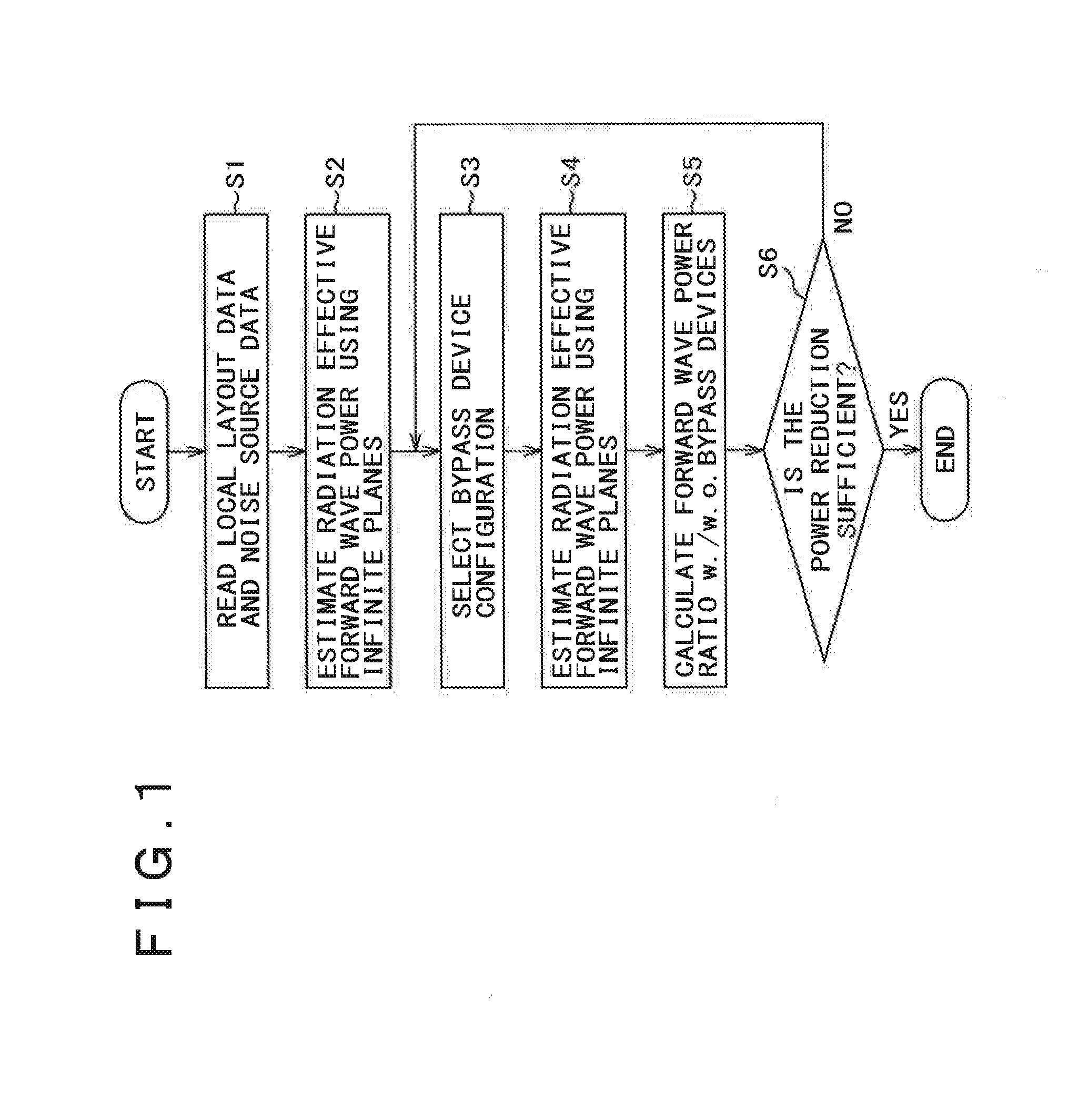
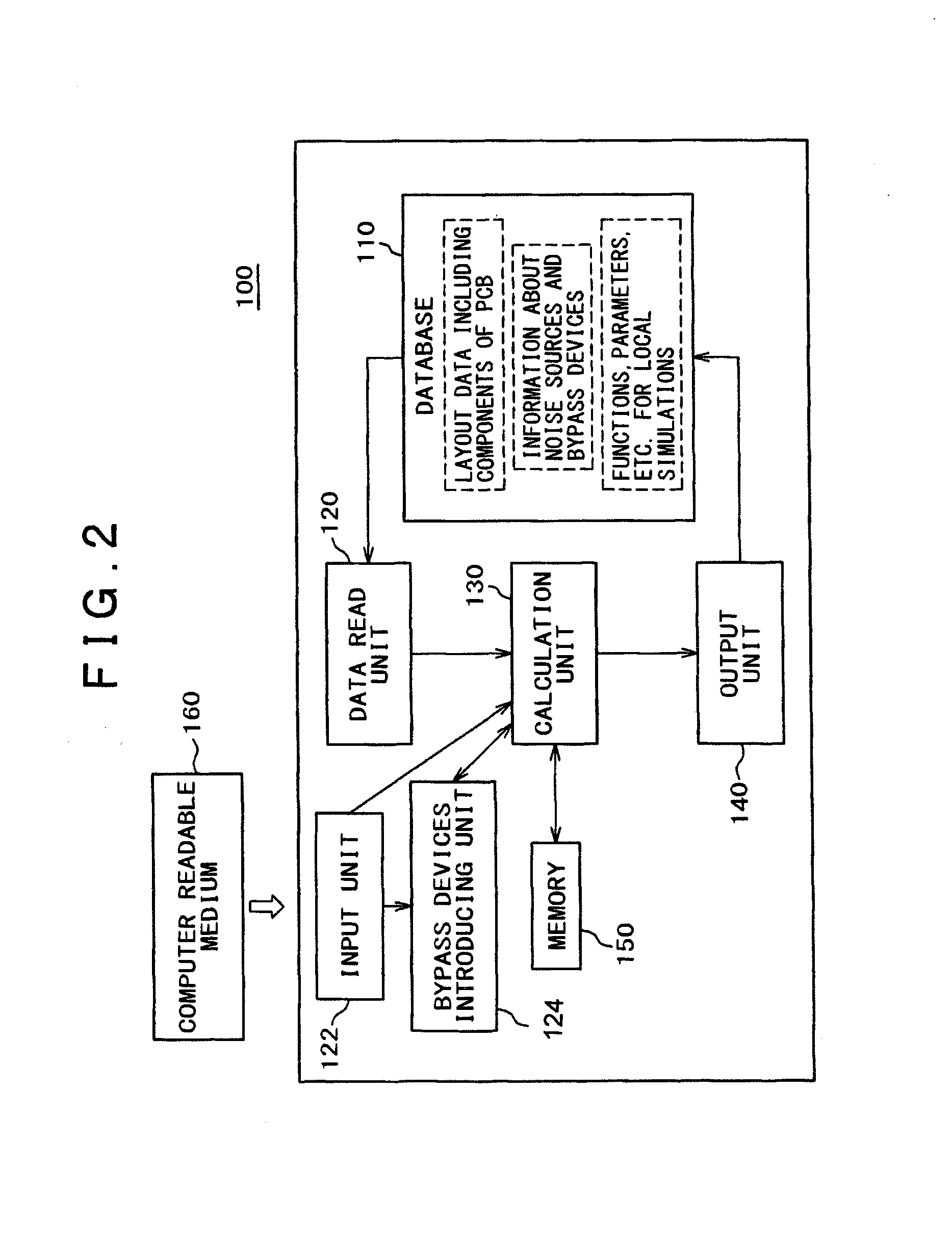
A design support system for designing a printed circuit board, comprising: a database for storing layout data, noise source data of the printed circuit board, and calculation results; a data reading unit for reading noise source data and local layout data of a local area around the noise source from the database; a bypass devices introducing unit for introducing current bypass devices to the local area, and a calculation unit for estimating the radiation effective forward wave power injected into assumed infinite power supply planes of the printed circuit board from the noise source without and with current bypass devices, and for calculating their ratio.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
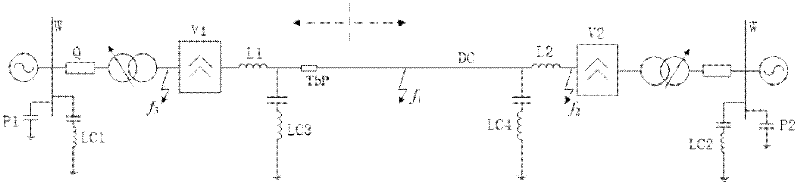
Transient traveling wave time domain calculating method of same-tower double-circuit DC power transmission line
ActiveCN106646129ASolve decouplingImprove calculation accuracyFault location by conductor typesTransient stateTime domain
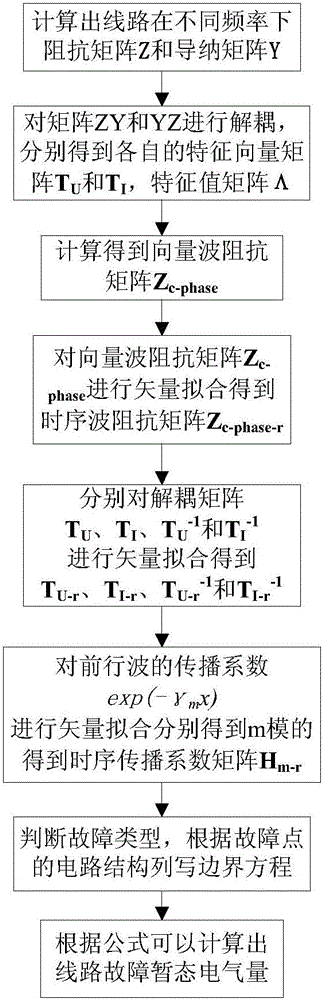
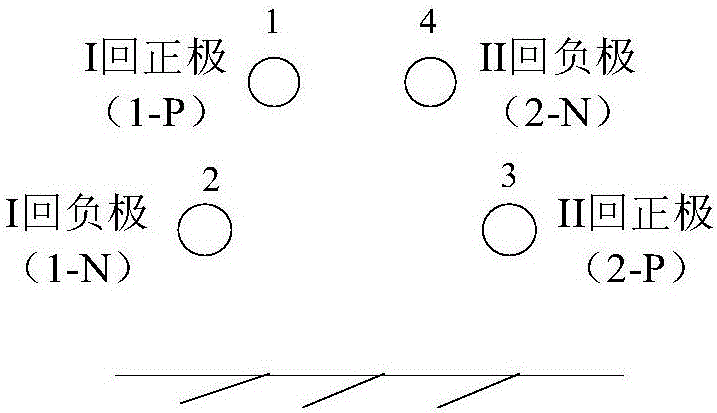
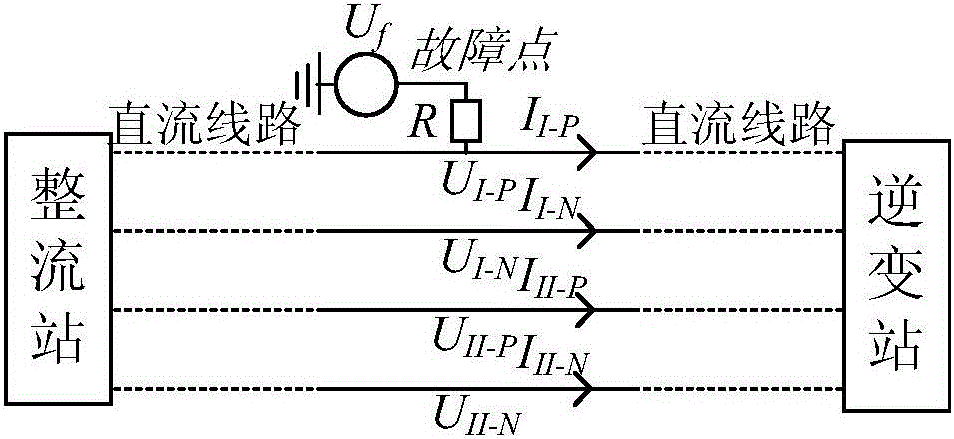
The invention discloses a transient traveling wave time domain calculating method of a same-tower double-circuit DC power transmission line. The method includes the following steps of calculating the series impedance matrix Z and the parallel impedance matrix Y of the line at different frequencies, the eigenvector matrixes TU, TI of the matrixes ZY and YZ, and an eigenvalue matrix Lambda; calculating the vector wave impedance matrix Zc-phase and the sequential wave impedance matrix Zc-phase-r according to the matrixes Y, TI, and Lambda; performing vector fitting on the matrixes TU, TI, TU-1, and TI-1 to obtain TU-r, TI-r, TU-r-1, and TI-r-1; performing vector fitting on the propagation coefficients exp (-gamma Mm) of the forward wave of different moduli to obtain a sequential propagation coefficient matrix Hm-r of the corresponding m mold; determining the fault type according to the circuit structure of the fault points to write the boundary equation; and calculating the line fault transient electrical amount. The method takes into account the influence of the frequency variation of the line parameters, and solves the problem of the line decoupling caused by the unbalanced same-tower double-circuit DC line.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
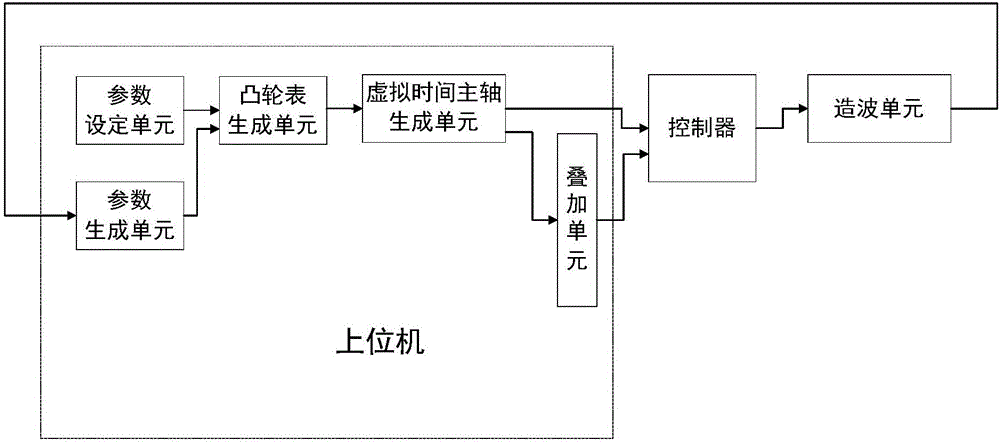
Wave maker movement control method and system
The invention relates to the field of wave simulation, in particular to a wave maker movement control method and system. According to the control method, made forward wave shapes and target wave shapes are compared, so that the forward wave shapes are regulated; finally, forward waves or inclined waves meeting user requirements are obtained. The wave making mode is simple; the wave making speed is high; the control precision is high; a corresponding control system uses a host computer and a controller for controlling a wave making unit; the cost performance is high; distribution wires are saved; the control structure is optimized; the energy consumption is reduced; the communication is faster and more stable; the control precision is higher; the requirements of synchronism and real-time performance of a wave making control system are met.
Owner:PHASE MOTION CONTROL SOLUTION WUHAN CO LTD
Forward wave directional coupler based on microstrip lines and substrate integrated waveguide structure
ActiveCN112164853ALow costSuitable for large-scale batch applicationsCoupling devicesEngineeringMillimetre wave
The invention relates to a forward wave directional coupler based on microstrip lines and a substrate integrated waveguide structure, which comprises a double-sided substrate, two microstrip lines arearranged on the surface of the double-sided substrate, the two microstrip lines are parallel to each other, and a plurality of substrate integrated waveguides are arranged between the two microstriplines. A triangular micro-strip transition section is arranged between the end part of the micro-strip substrate integrated waveguide and the adjacent micro-strip line; a plurality of substrate integrated waveguide short-circuit via holes are formed in the edges of the two sides of the substrate integrated waveguide; and an input port, a straight-through port, a coupling port and an isolation portare respectively formed at the end parts of the two microstrip lines. According to the forward wave directional coupler based on the microstrip line and the substrate integrated waveguide structure,millimeter wave energy coupling covering a specified frequency band can be achieved through manufacturing of a double-sided PCB, and reduction of the cost of large-scale commercial application is facilitated.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
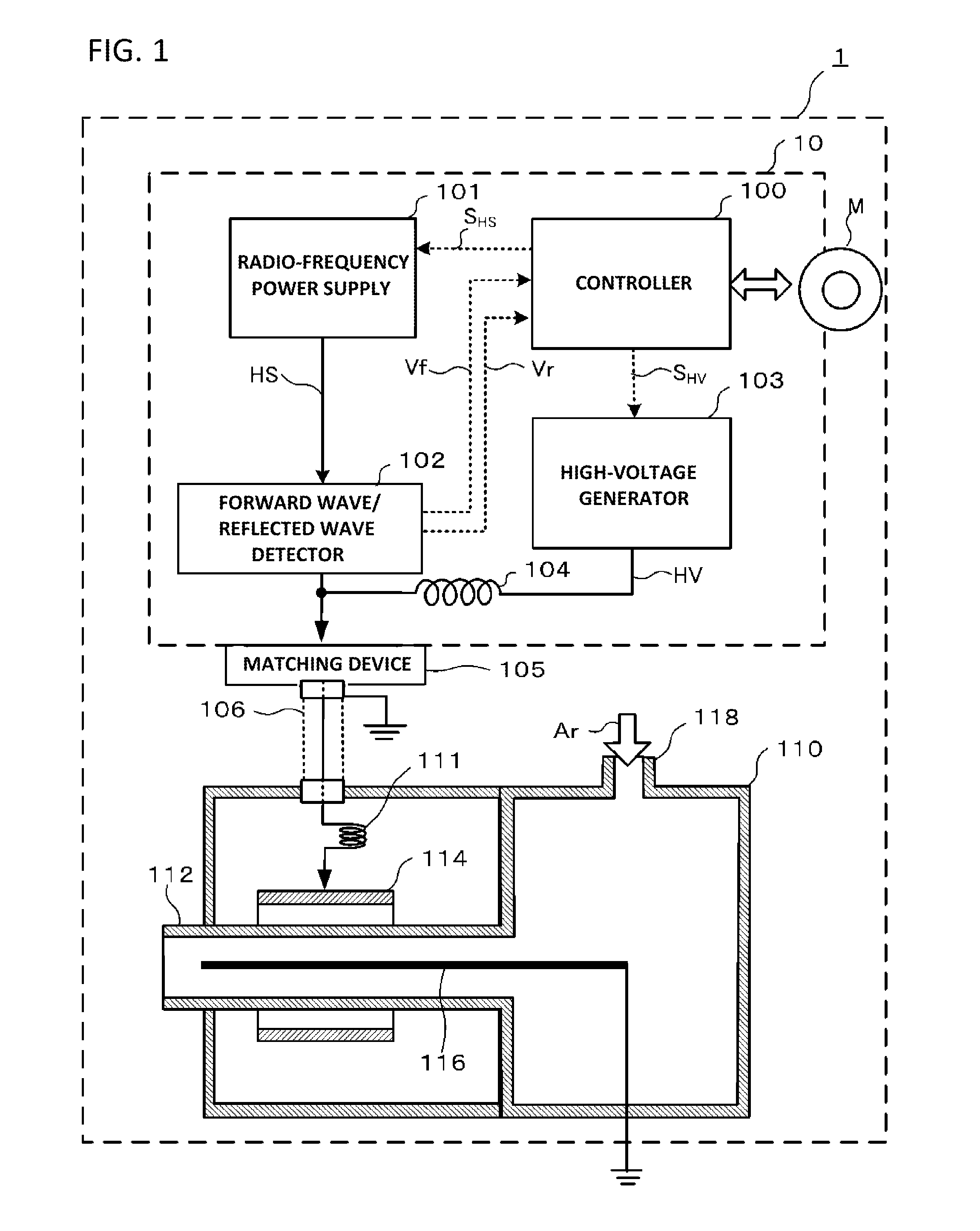
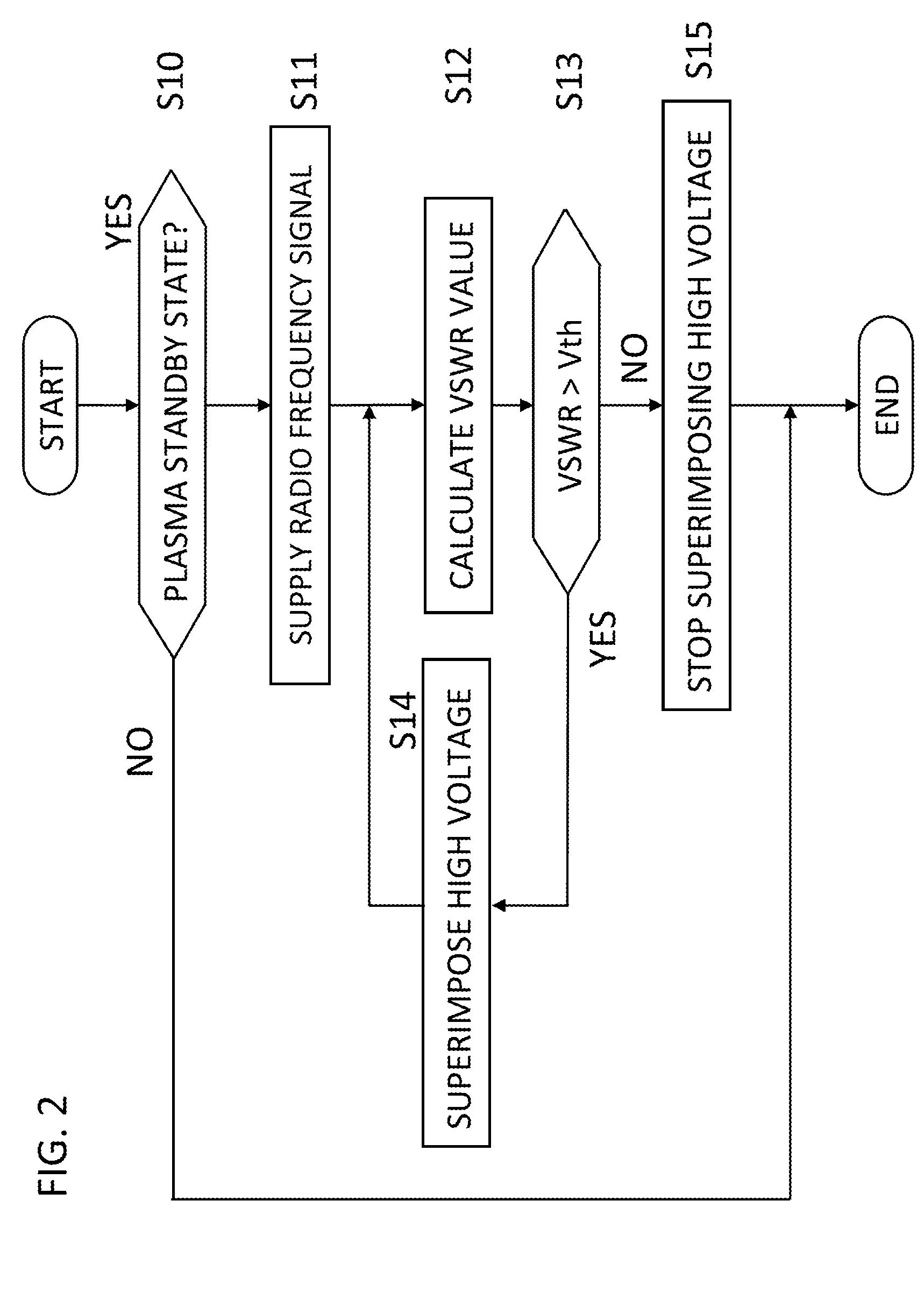
Plasma ignition system, plasma ignition method, and plasma generating apparatus
ActiveUS8716939B2Easy and reliable ignitionElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsReflected wavesEngineering
Owner:SHINKAWA CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com