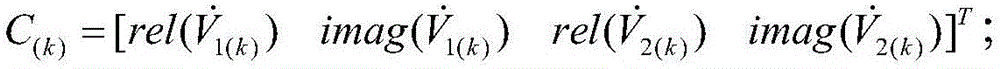Patents
Literature
121 results about "Series impedance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
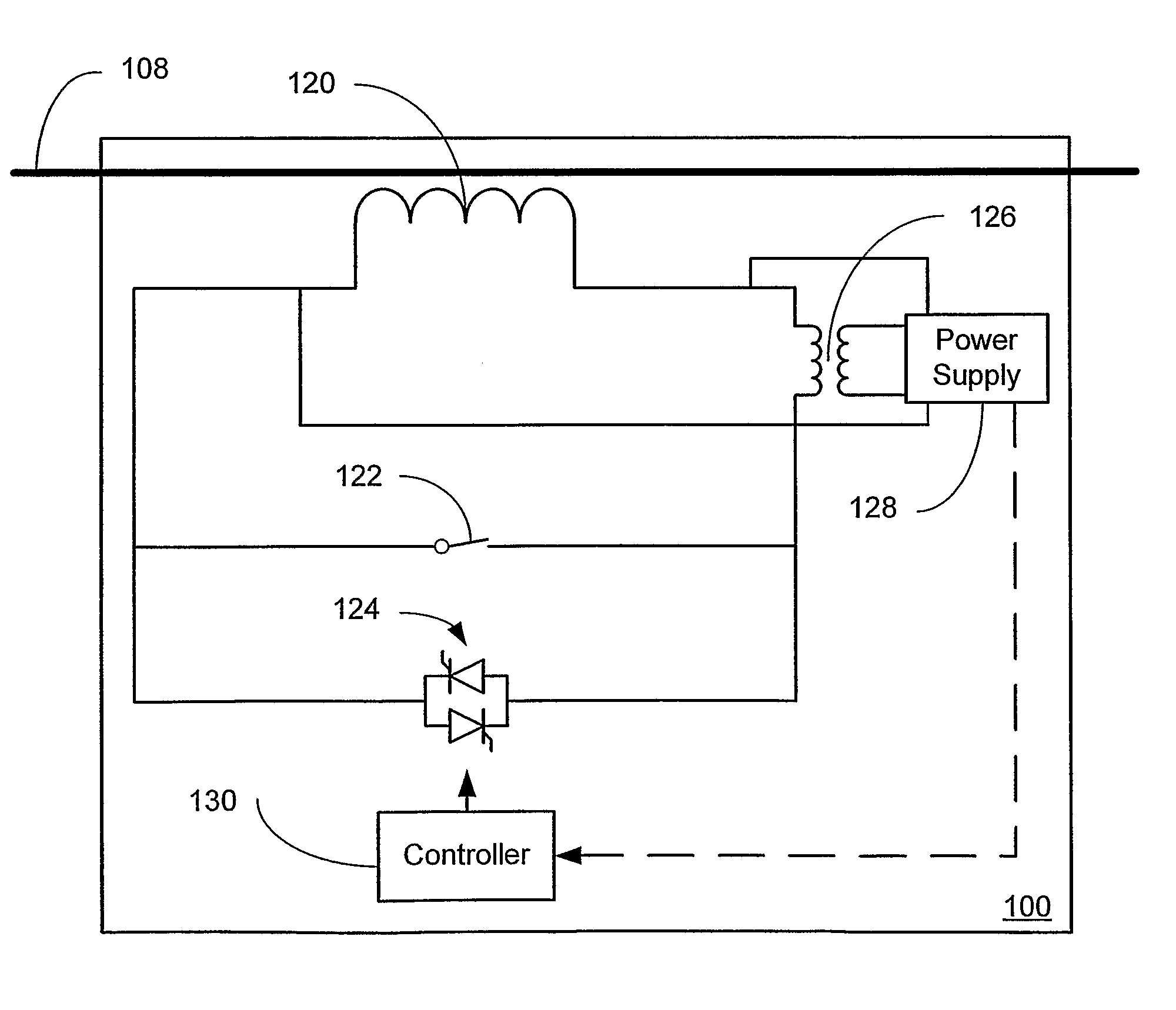
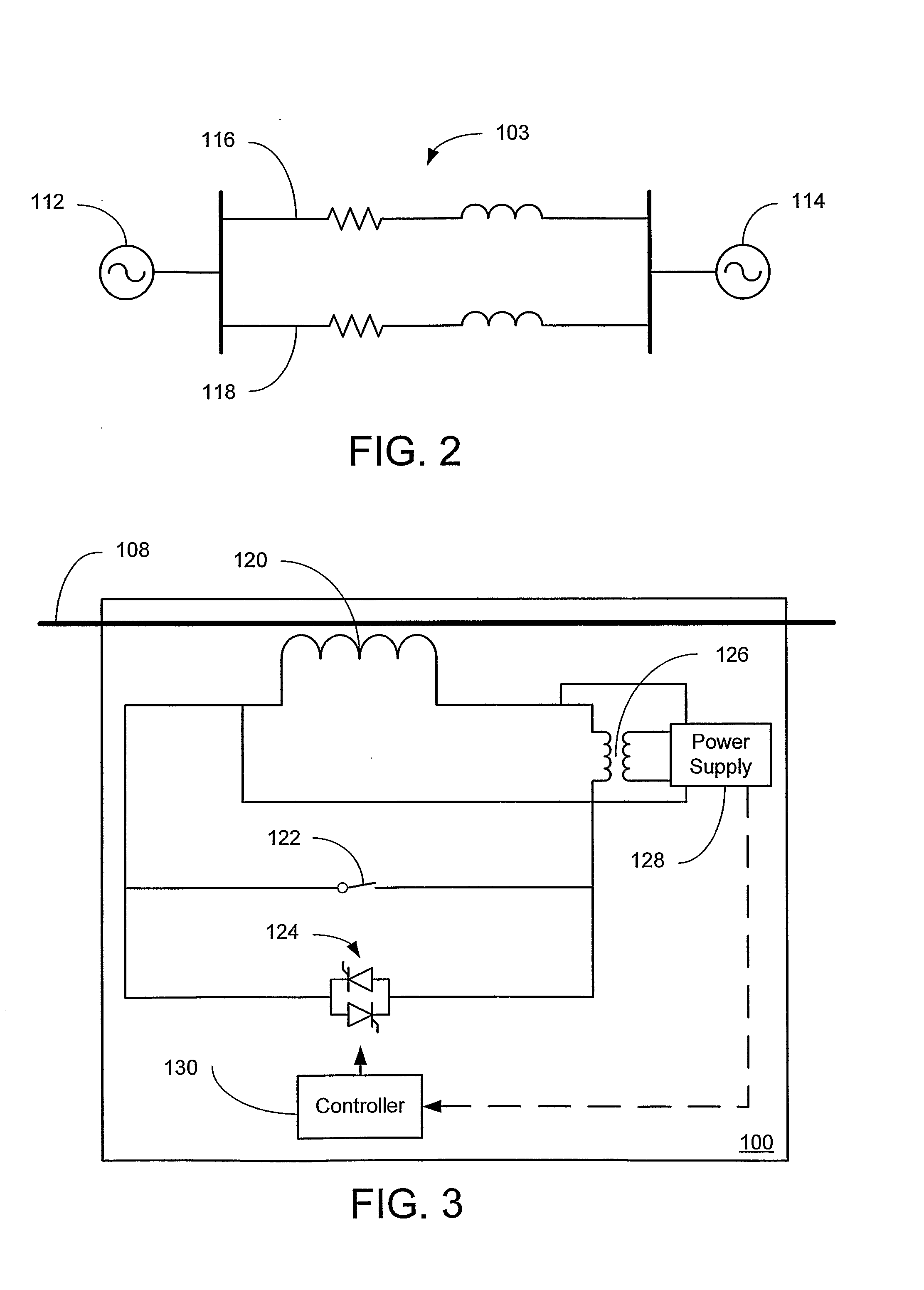
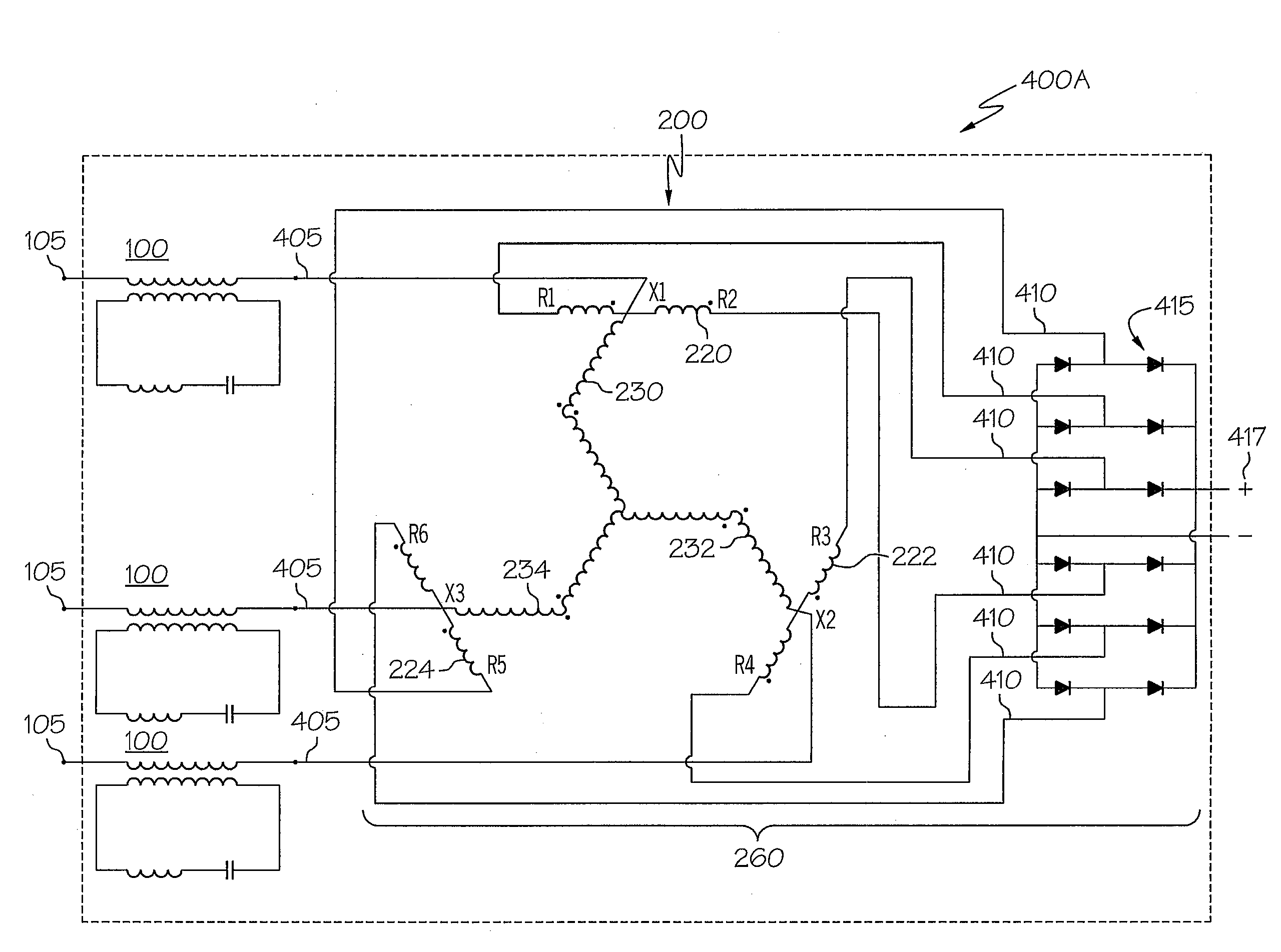
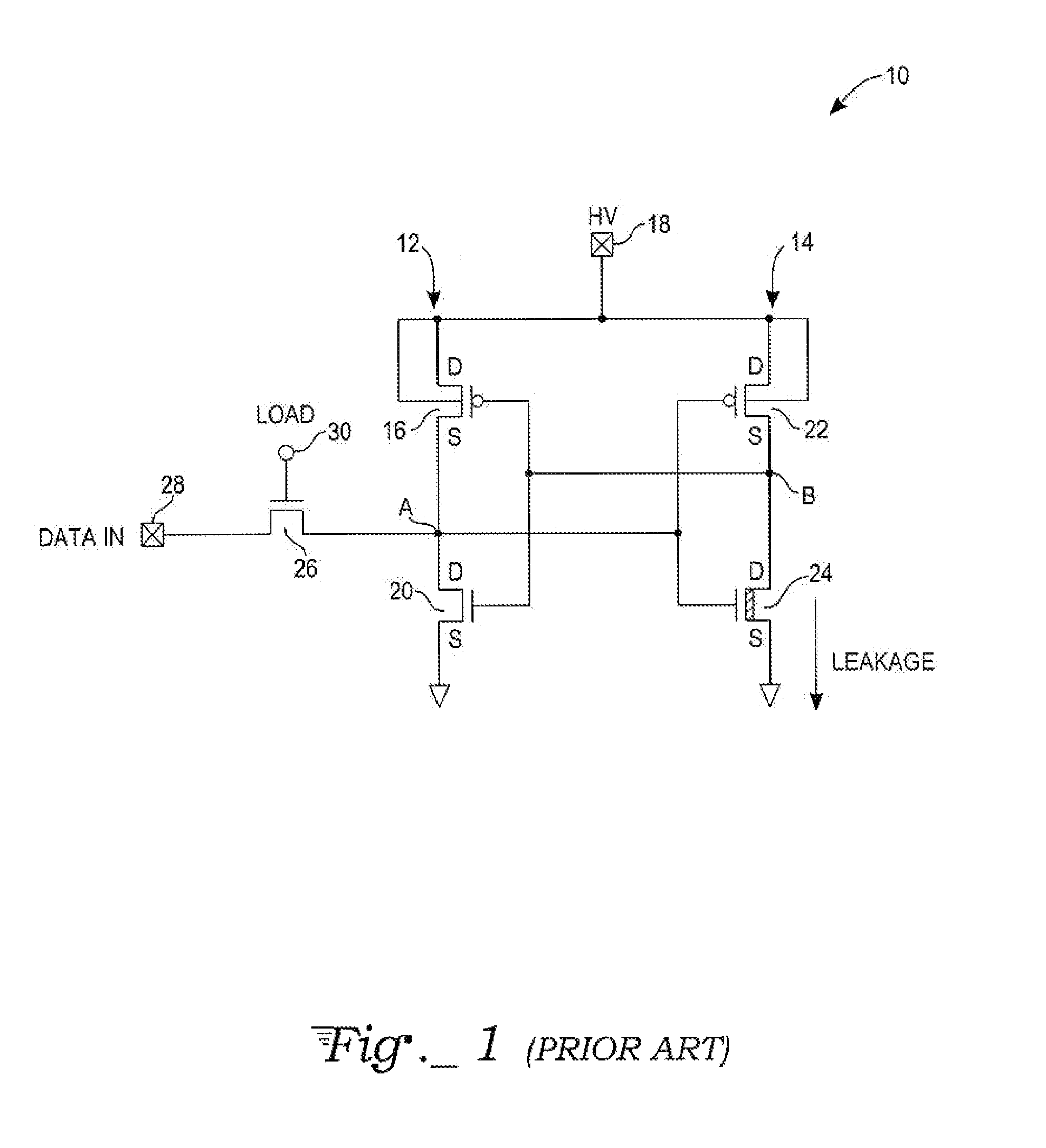
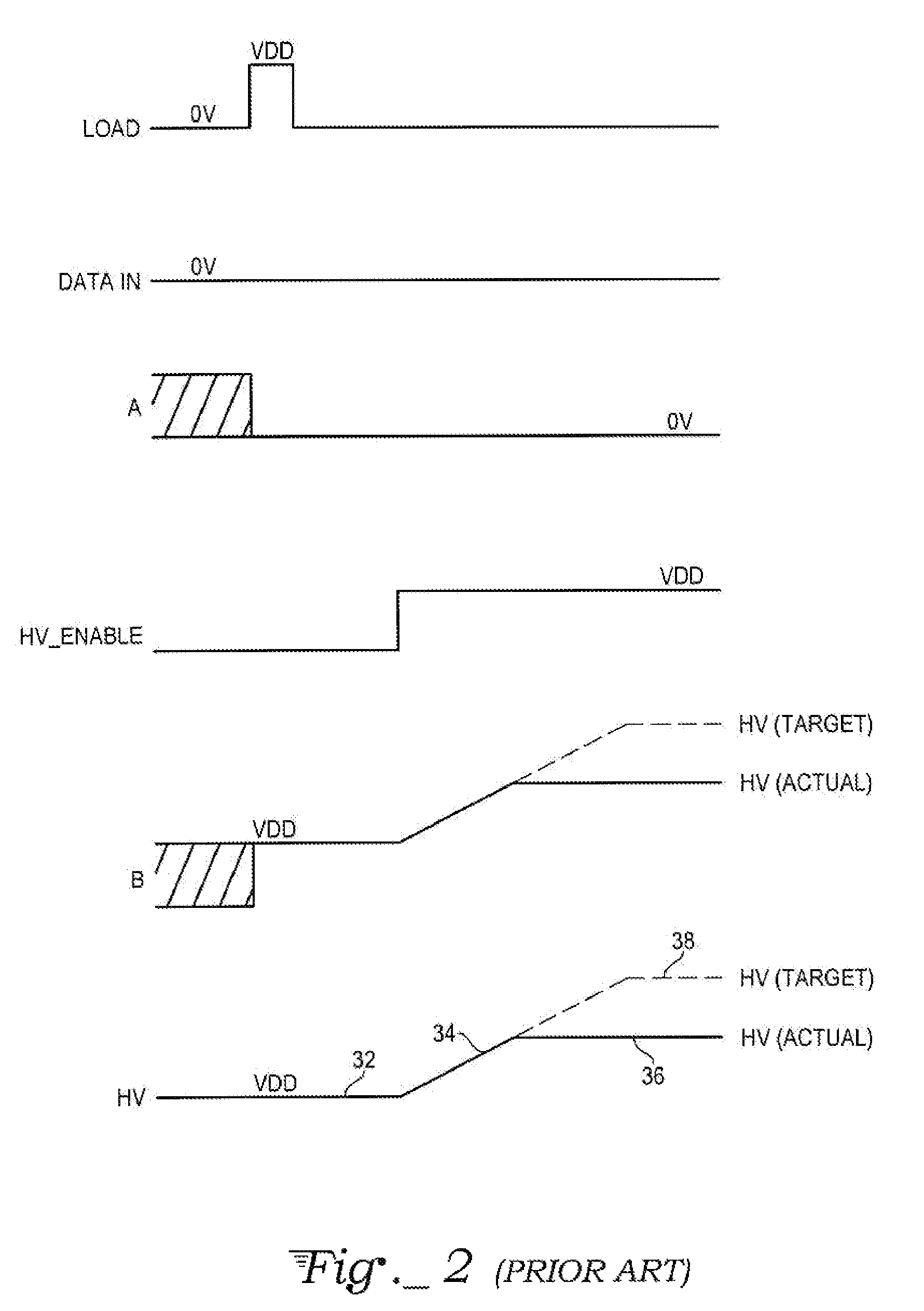
Systems and methods for distributed series compensation of power lines using passive devices
ActiveUS7835128B2Emergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentReactive power compensationElectrical conductorTransformer
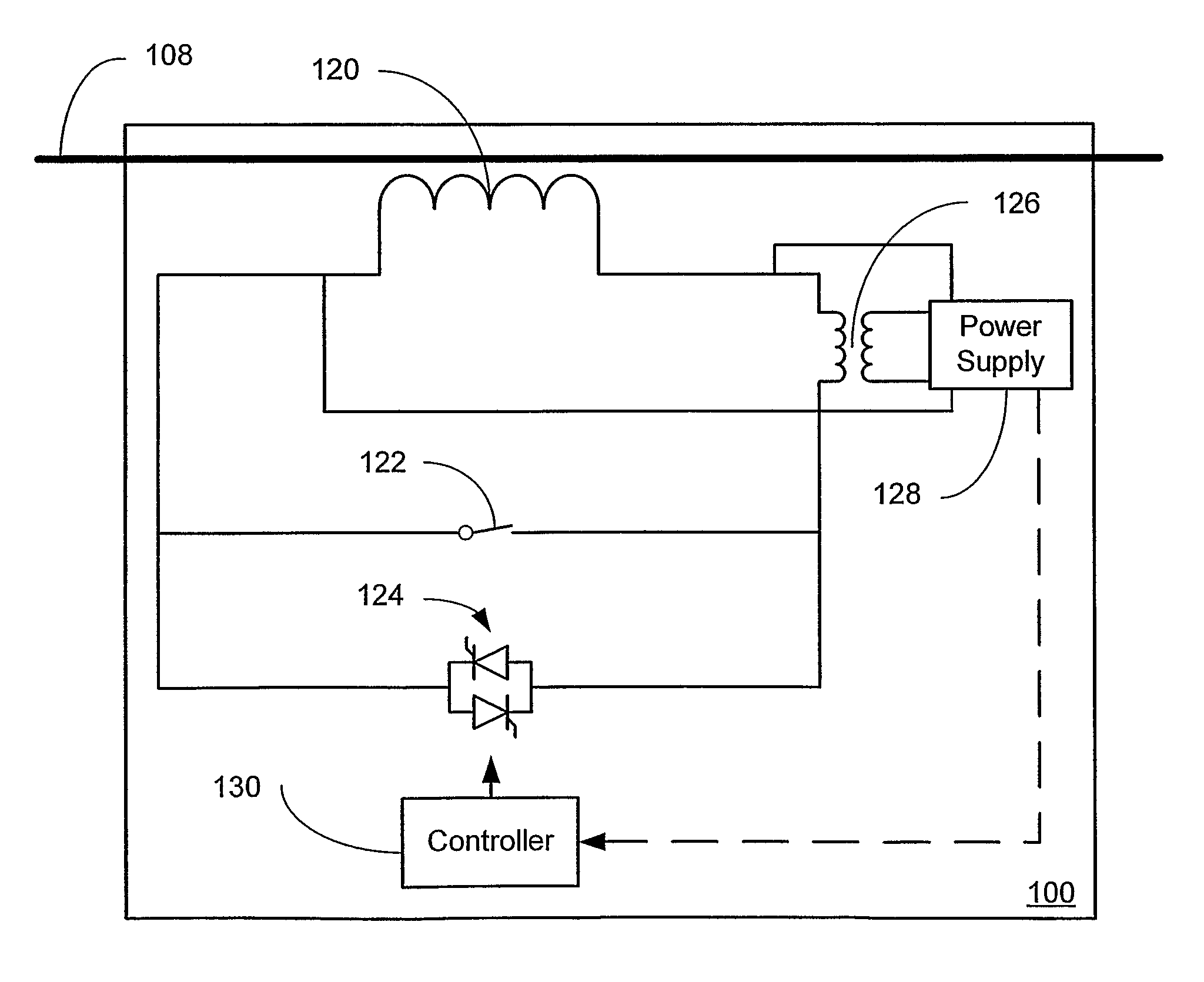
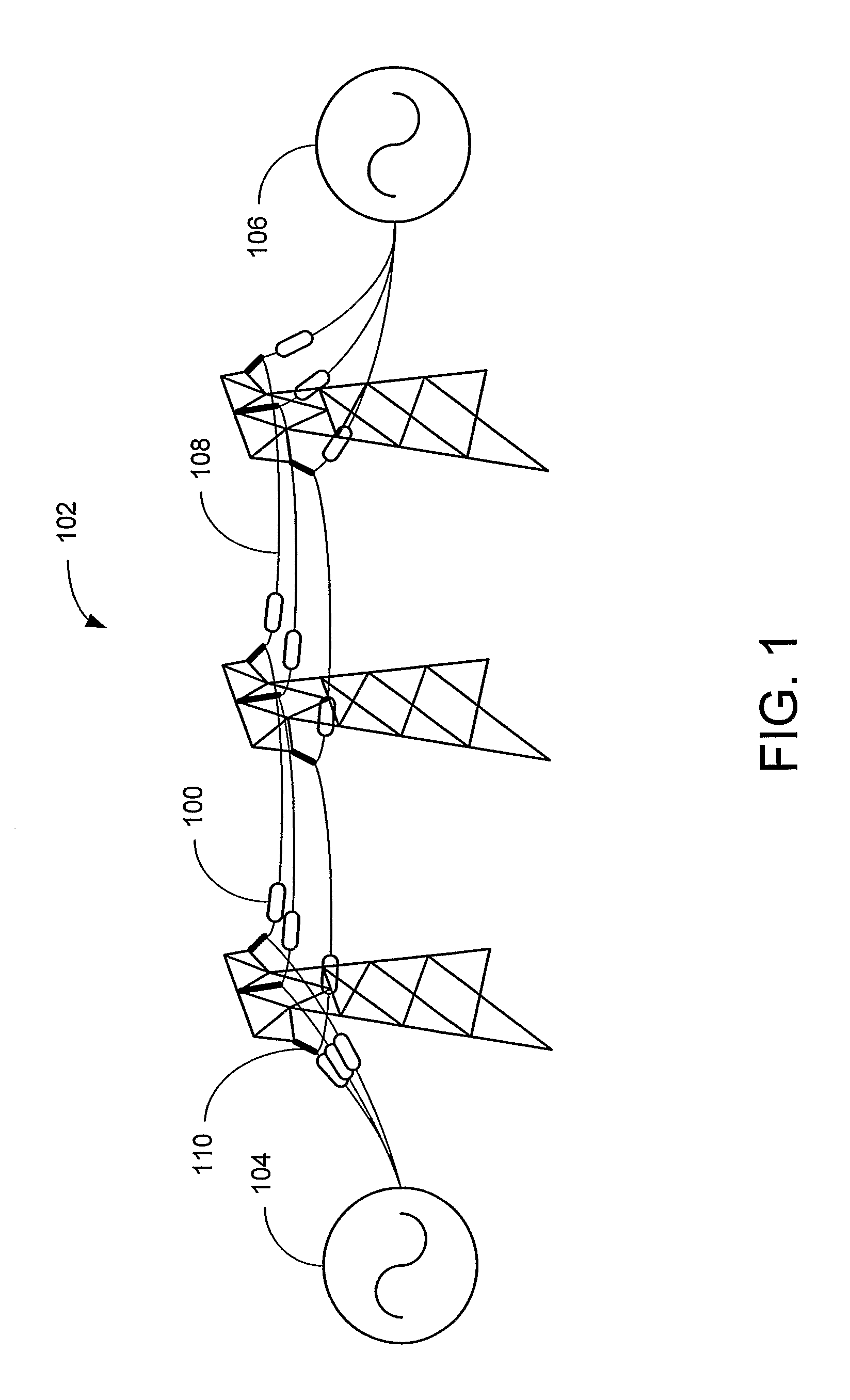
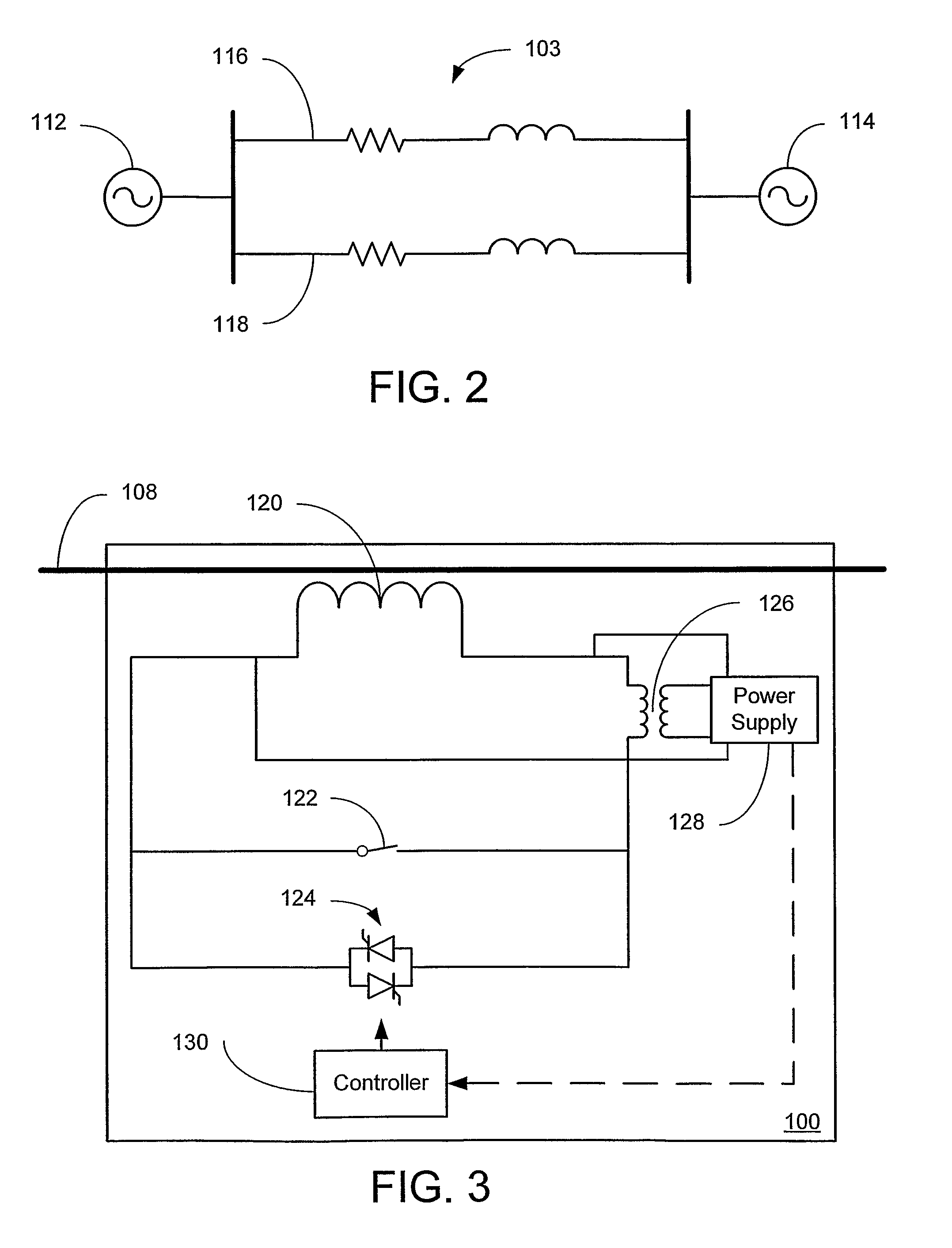
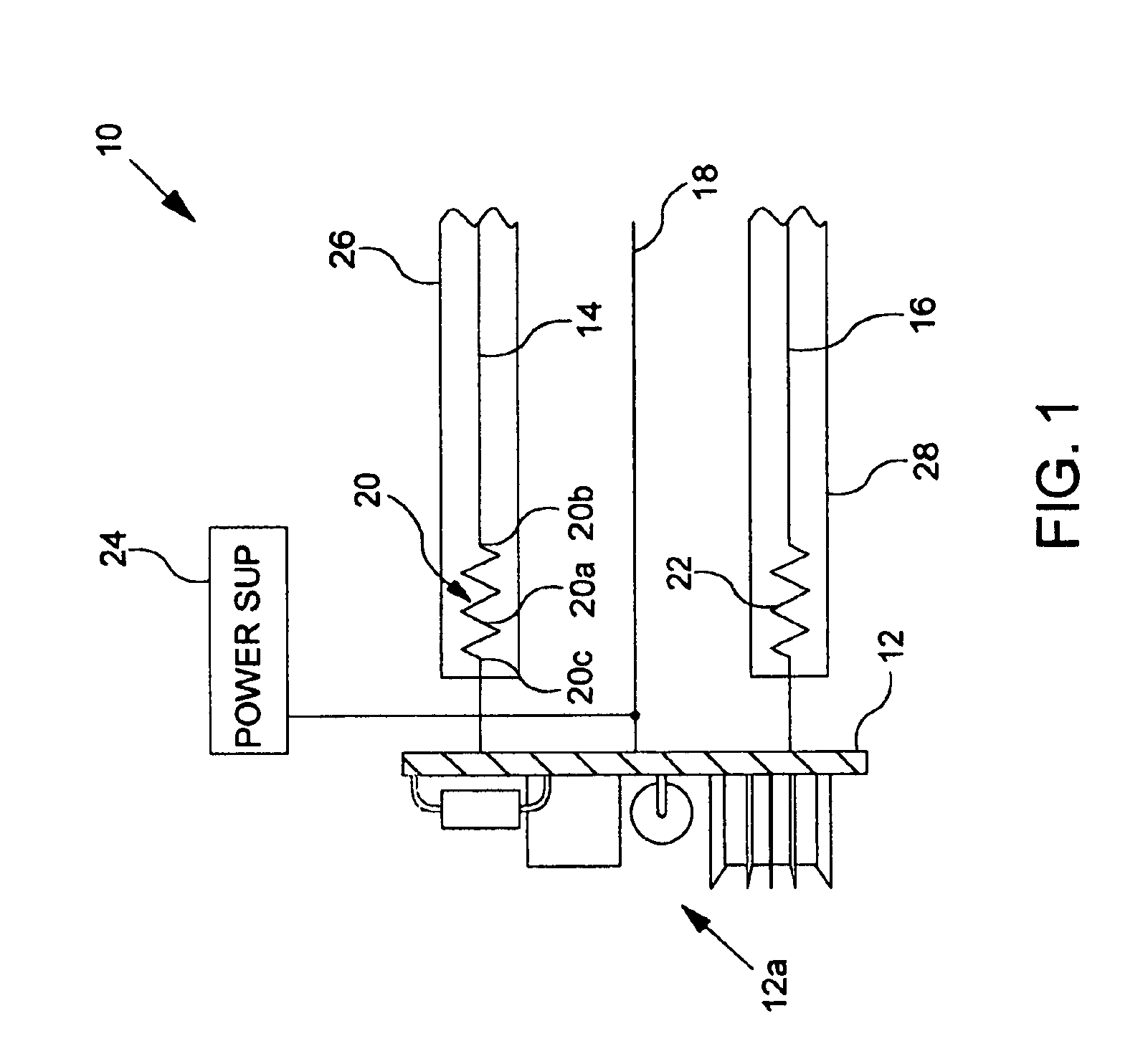
Systems and methods for implementing line overload control via providing distributed series impedance are disclosed. One system, amongst others, comprises at least one distributed series reactor (DSR). Each DSR comprises a single turn transformer (SST) comprising two split-core sections (132), a winding (120), and an air-gap (138), the air-gap designed such that a magnetizing inductance is produced when the two split-core sections (132) are clamped around a conductor (108). Each DSR further comprises a contact switch (122) that short circuits the winding when the contact switch (122) is in a closed condition, a power supply (128) that derives power from conductor line current, and a controller (130) configured to open the contact switch when the conductor line current reaches a predetermined value, thus causing insertion of the magnetizing inductance into the conductor. The controller (130) may be further configured to close the contact switch (122) when the conductor line current drops below the predetermined value.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
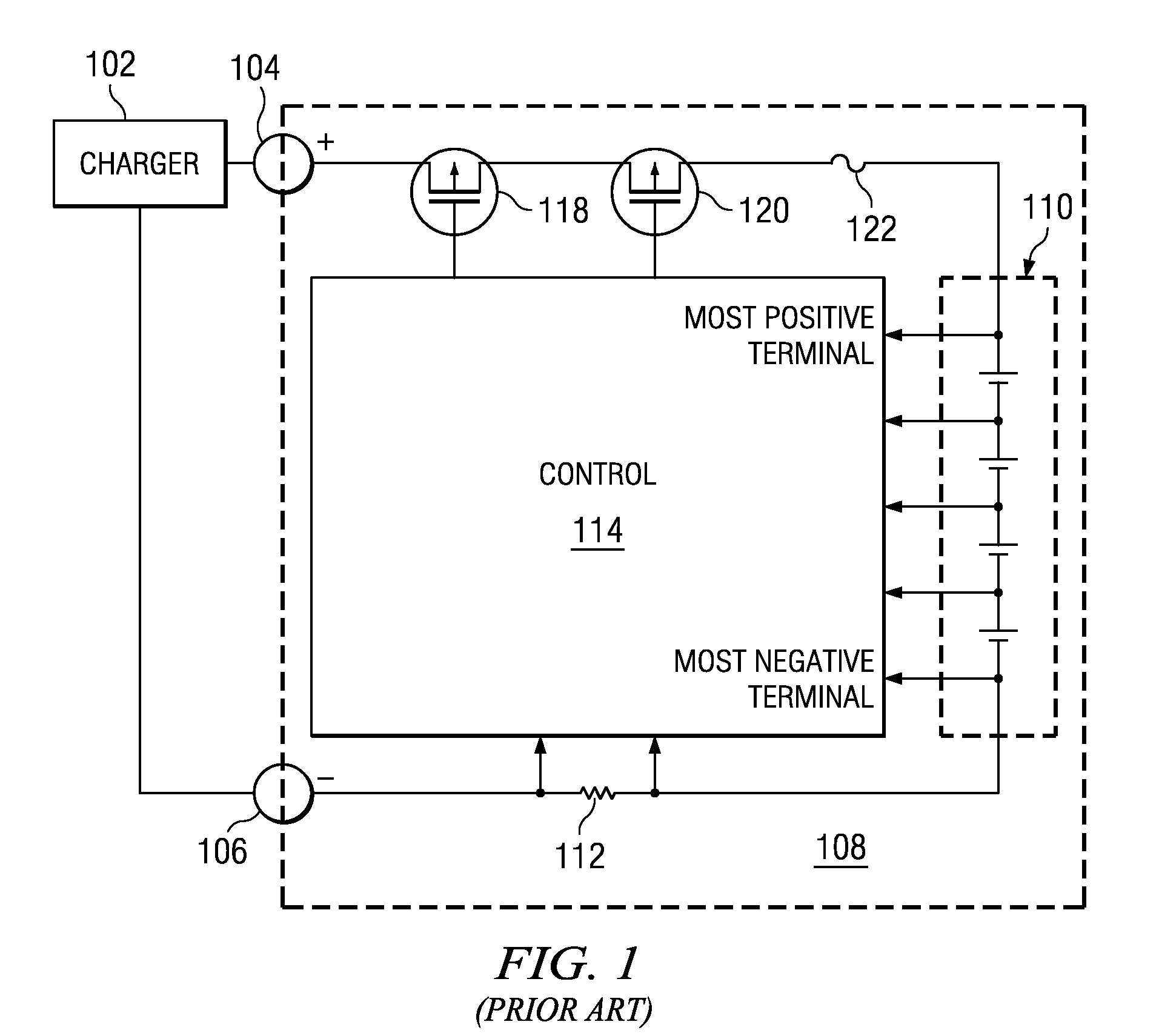
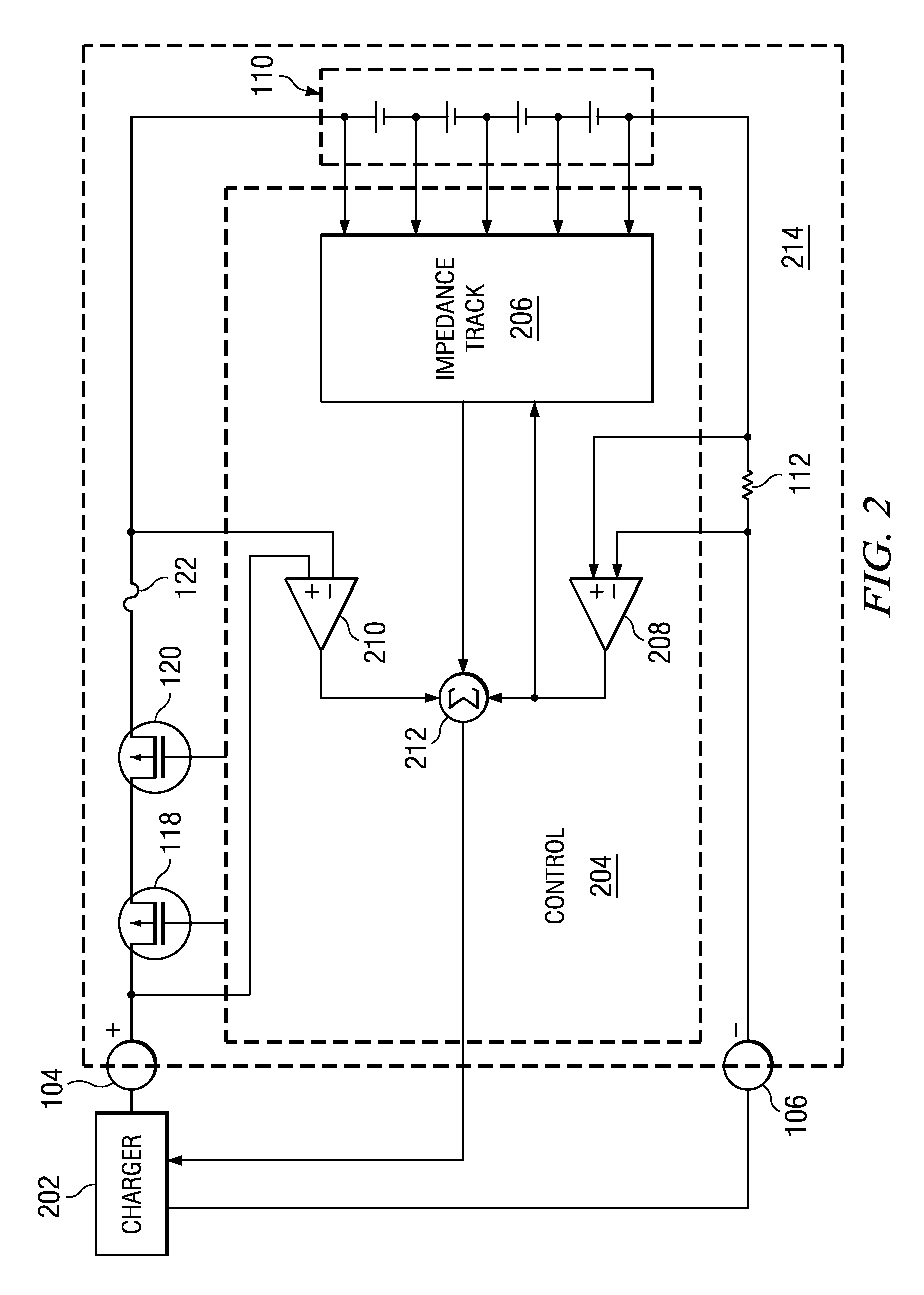
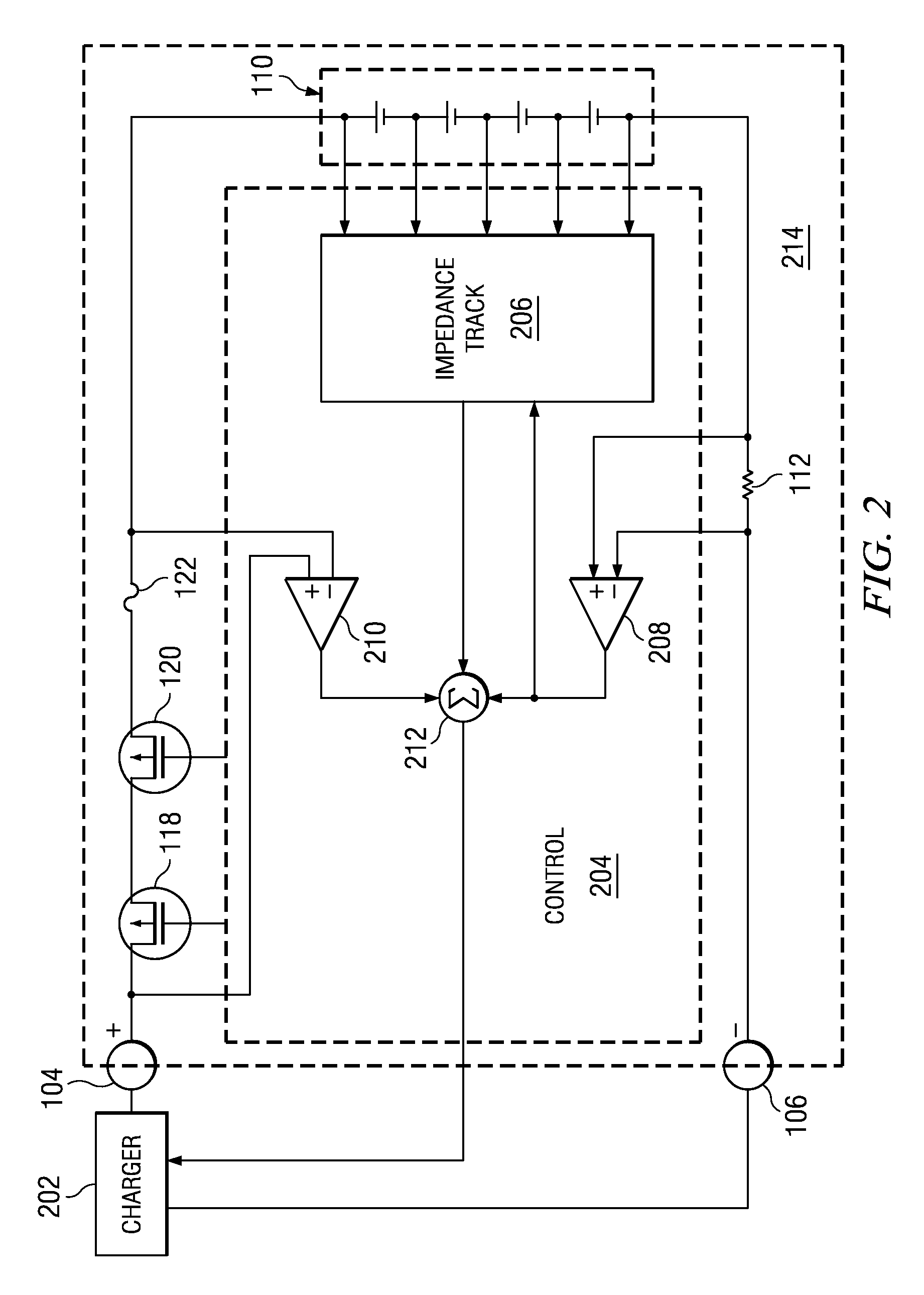
Battery charge compensation
ActiveUS20090261786A1Improve charging efficiencyImprove battery efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBattery chargeCharge current
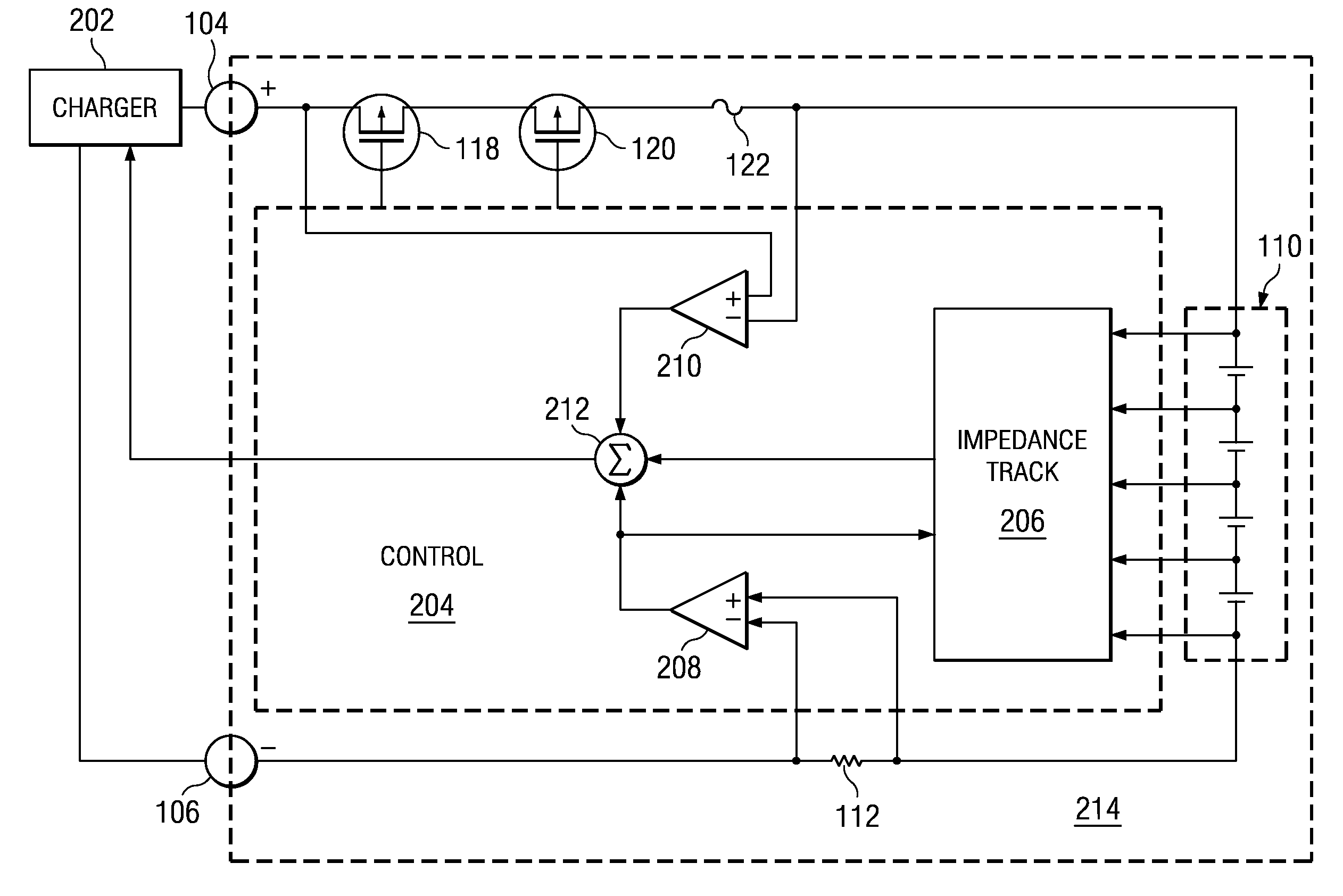
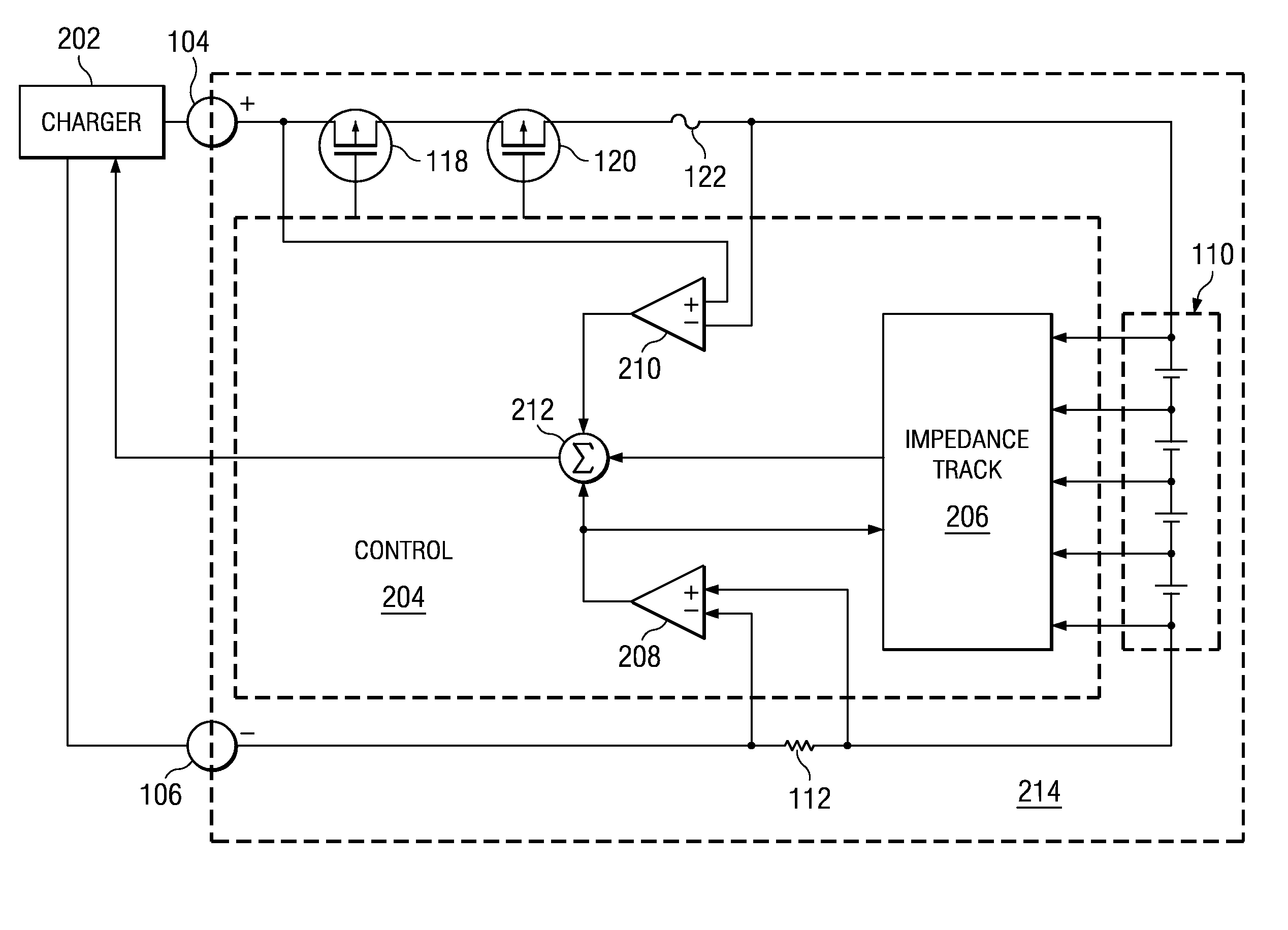
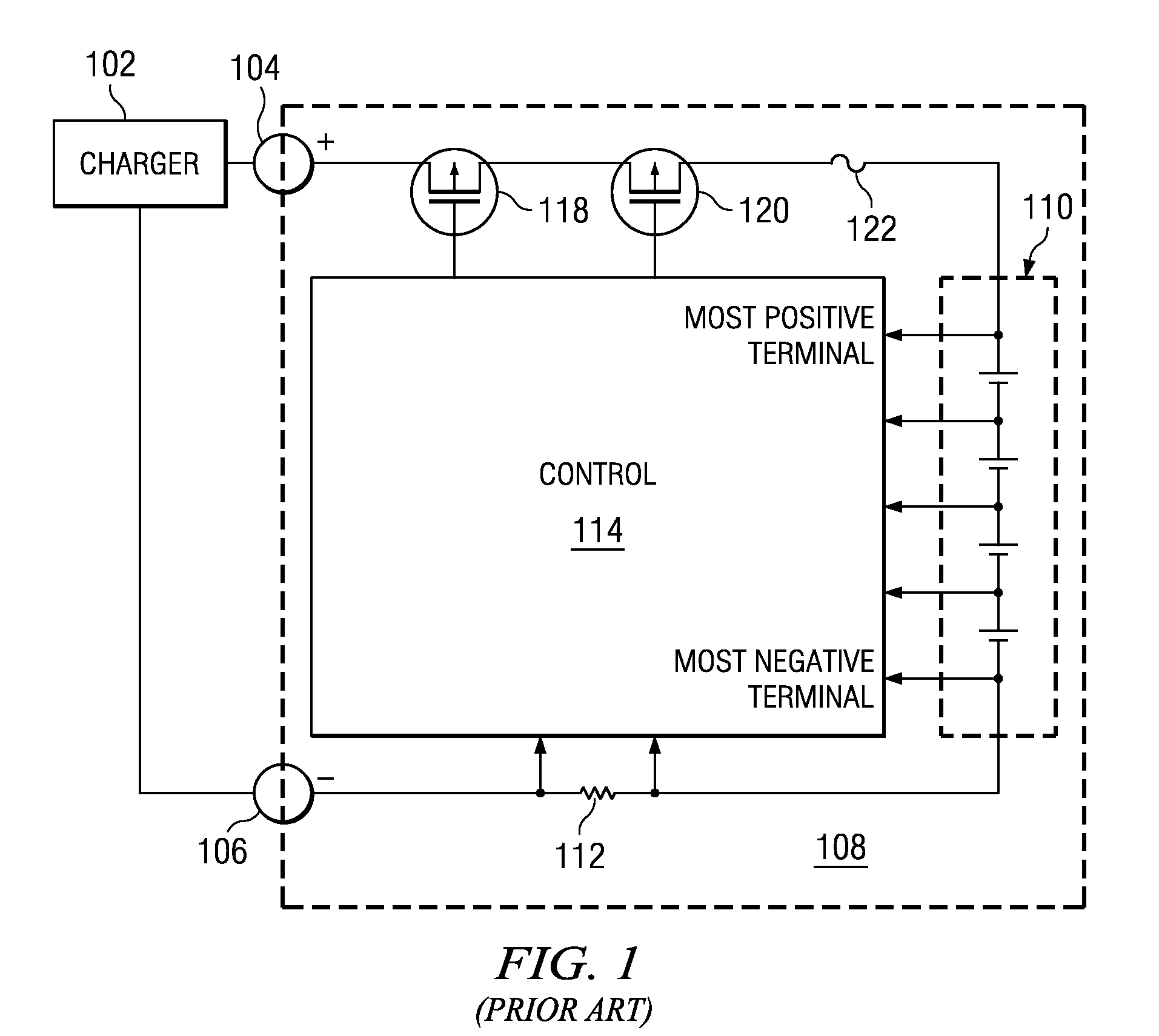
A battery charger and method for a rechargeable battery pack which includes various elements in series with the cells to be charged, including but not limited to current control FETs, a fuse, current sense resistor, and internal series impedance of the series connected cells to be charged. The charging current Ichg flowing through these series elements reduces the voltage applied to the cells, thus lengthening charging time. A compensation voltage Vcomp, which when added to the nominal charging voltage for the series connected cells overcomes these voltage drops, facilitates more efficient charging while avoiding over-voltage damage to the cells. Three voltages representing substantially all of the voltage drops reducing the charging voltage on the cells, are summed, and the result is a compensation voltage which is utilized to change the nominal charge voltage for the battery to overcome these voltage drops.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
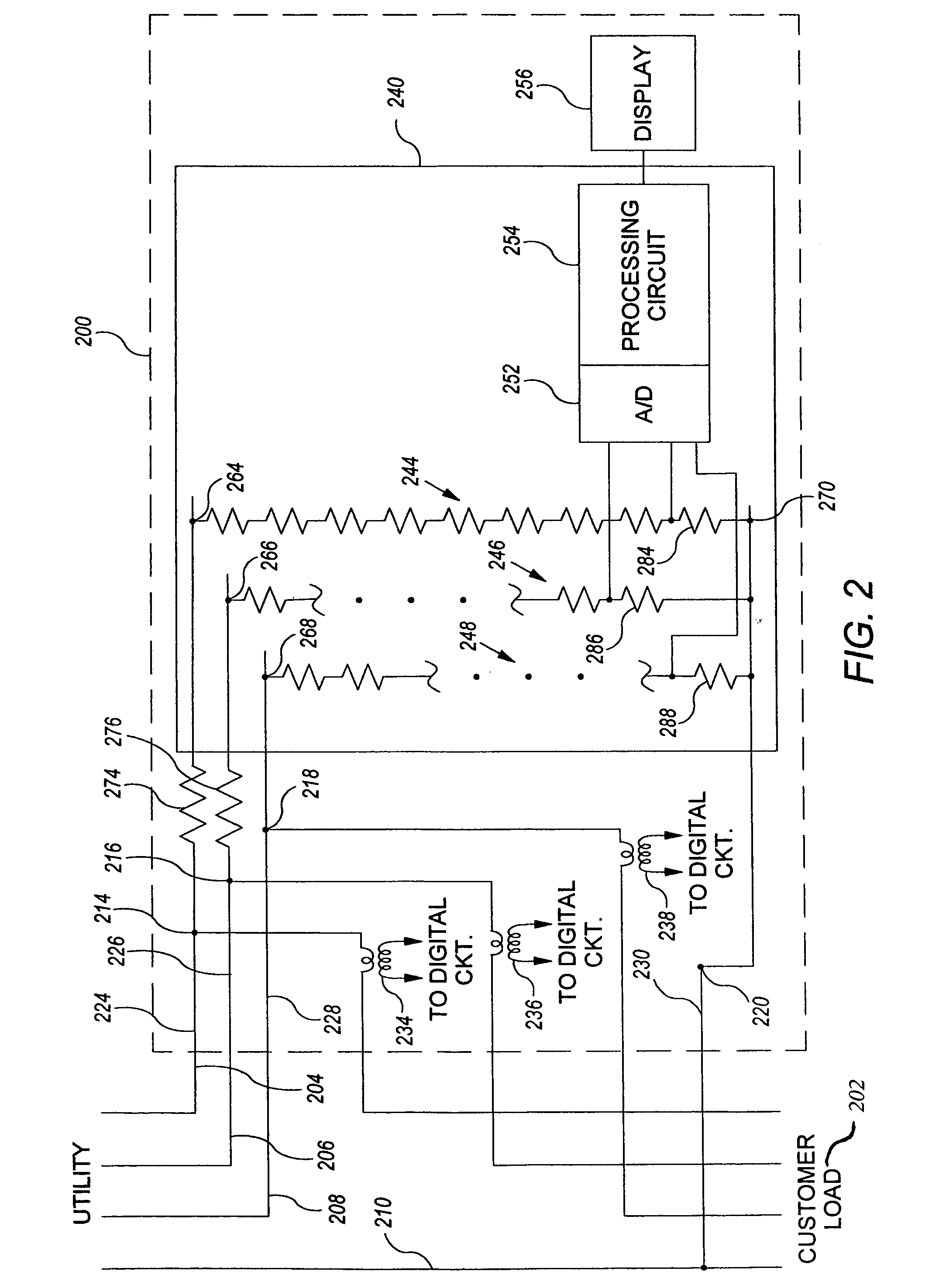
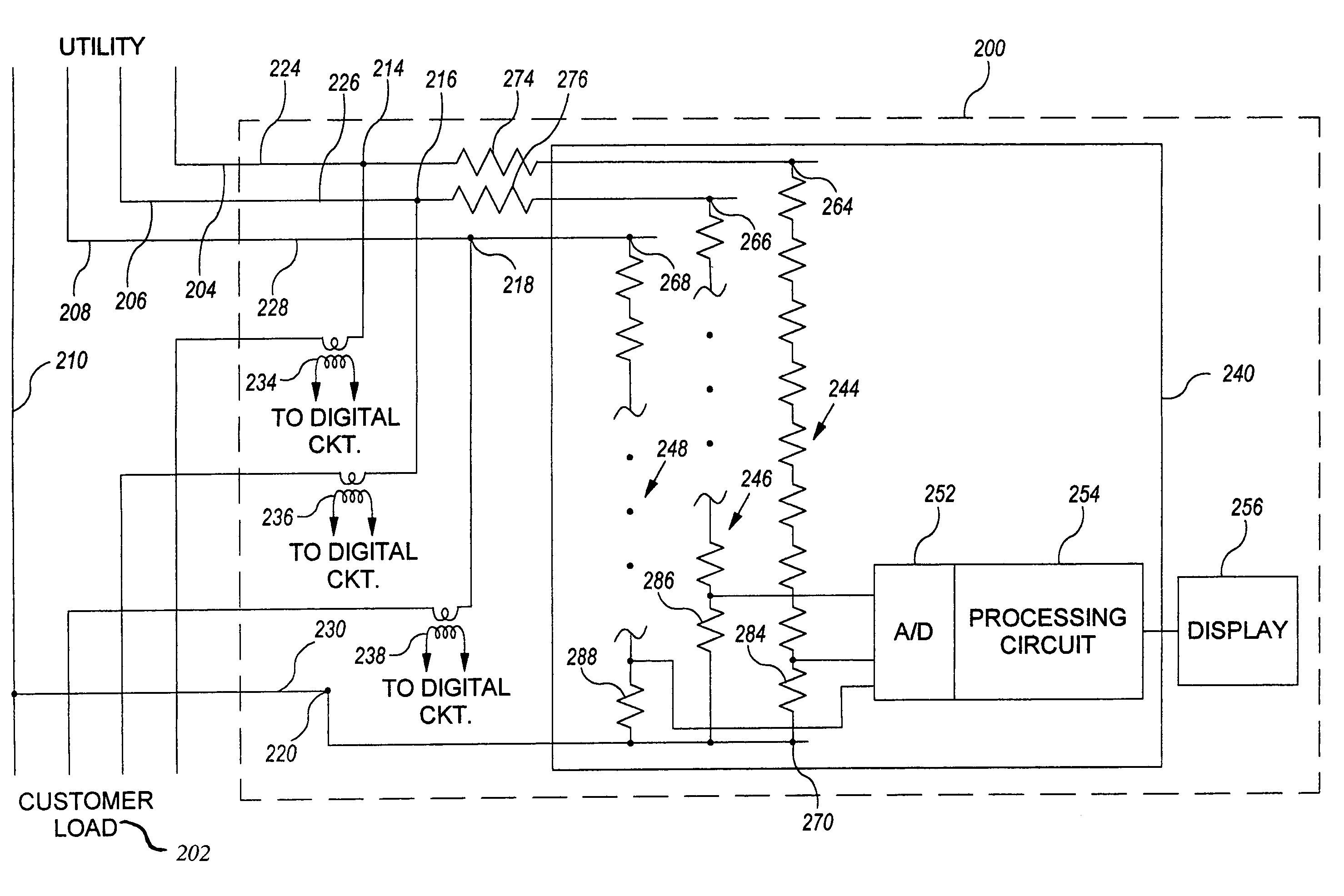
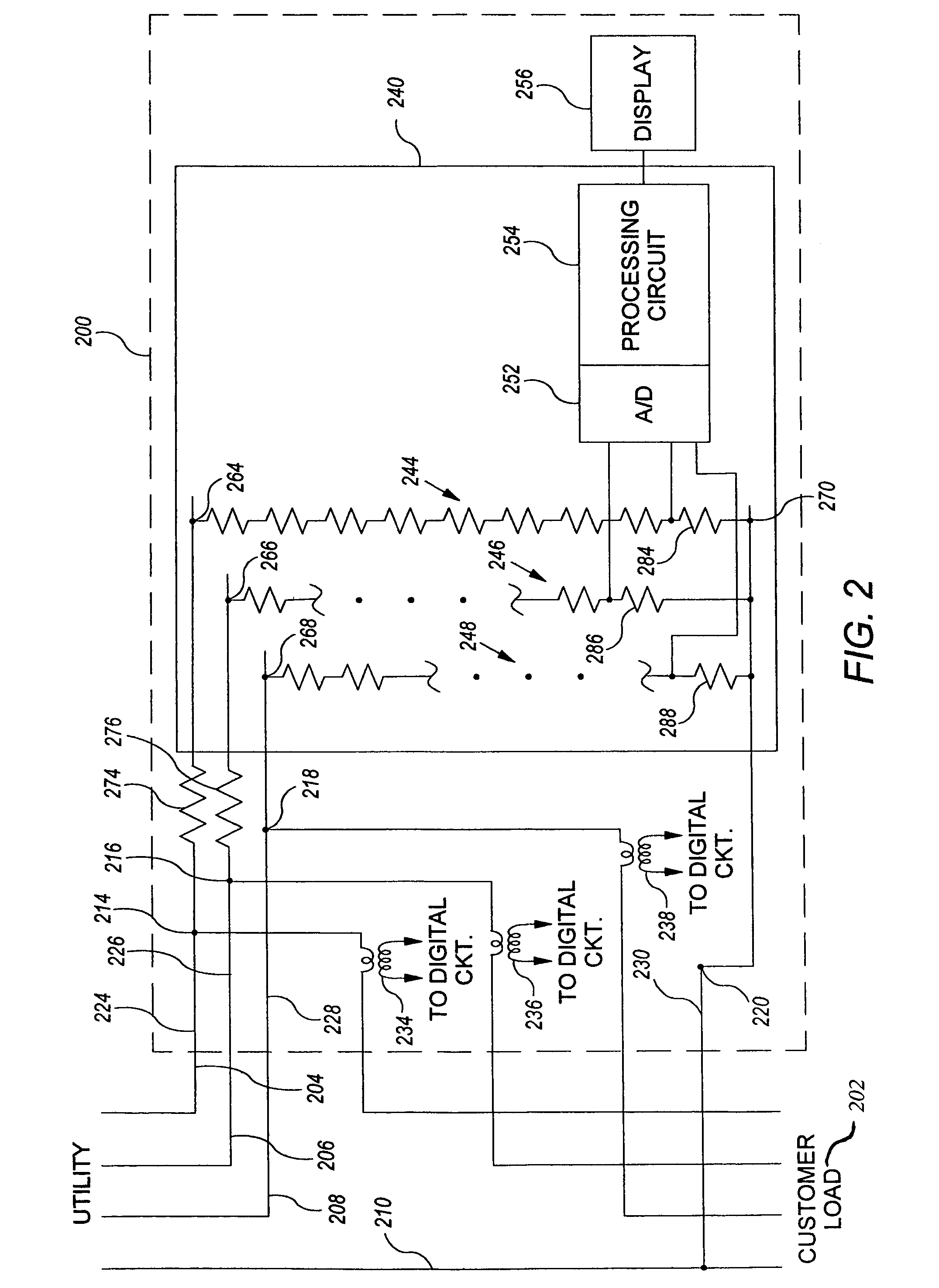
Enhanced fault protection in electricity meter
ActiveUS20050237047A1Voltage will not be measured accuratelyLower average currentCurrent/voltage measurementTime integral measurementCurrent limitingEngineering
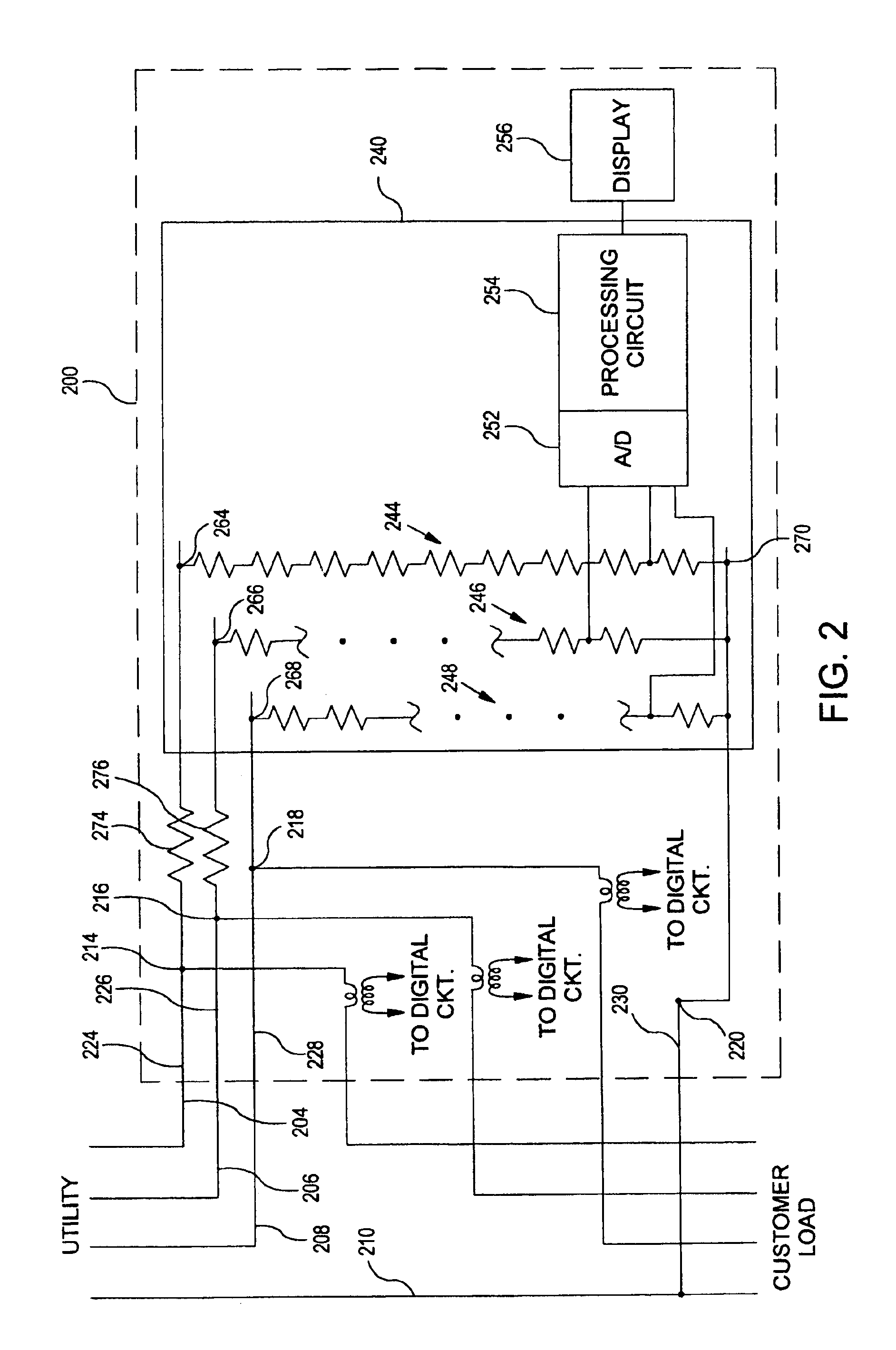
An arrangement for obtaining measurable voltage signals in a utility meter includes a first connection to a phase of a power line, a second connection to a reference of a power line, a voltage divider circuit, and a series inductor. The voltage divider circuit is disposed on a circuit board and is coupled between a first node and the second connection. The voltage divider circuit has an output configured to provide measurable voltage signals to a circuit operable to generate voltage measurement information. The series inductor is disposed apart from the circuit board and is configured for current limiting. The series impedance element is coupled between the first connection and the first node.
Owner:LANDIS GYR LLC
Systems and Methods for Distributed Series Compensation of Power Lines Using Passive Devices
ActiveUS20080310069A1Emergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentReactive power compensationElectrical conductorTransformer
Systems and methods for implementing line overload control via providing distributed series impedance are disclosed. One system, amongst others, comprises at least one distributed series reactor (DSR). Each DSR comprises a single turn transformer (SST) comprising two split-core sections (132), a winding (120), and an air-gap (138), the air-gap designed such that a magnetizing inductance is produced when the two split-core sections (132) are clamped around a conductor (108). Each DSR further comprises a contact switch (122) that short circuits the winding when the contact switch (122) is in a closed condition, a power supply (128) that derives power from conductor line current, and a controller (130) configured to open the contact switch when the conductor line current reaches a predetermined value, thus causing insertion of the magnetizing inductance into the conductor. The controller (130) may be further configured to close the contact switch (122) when the conductor line current drops below the predetermined value.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
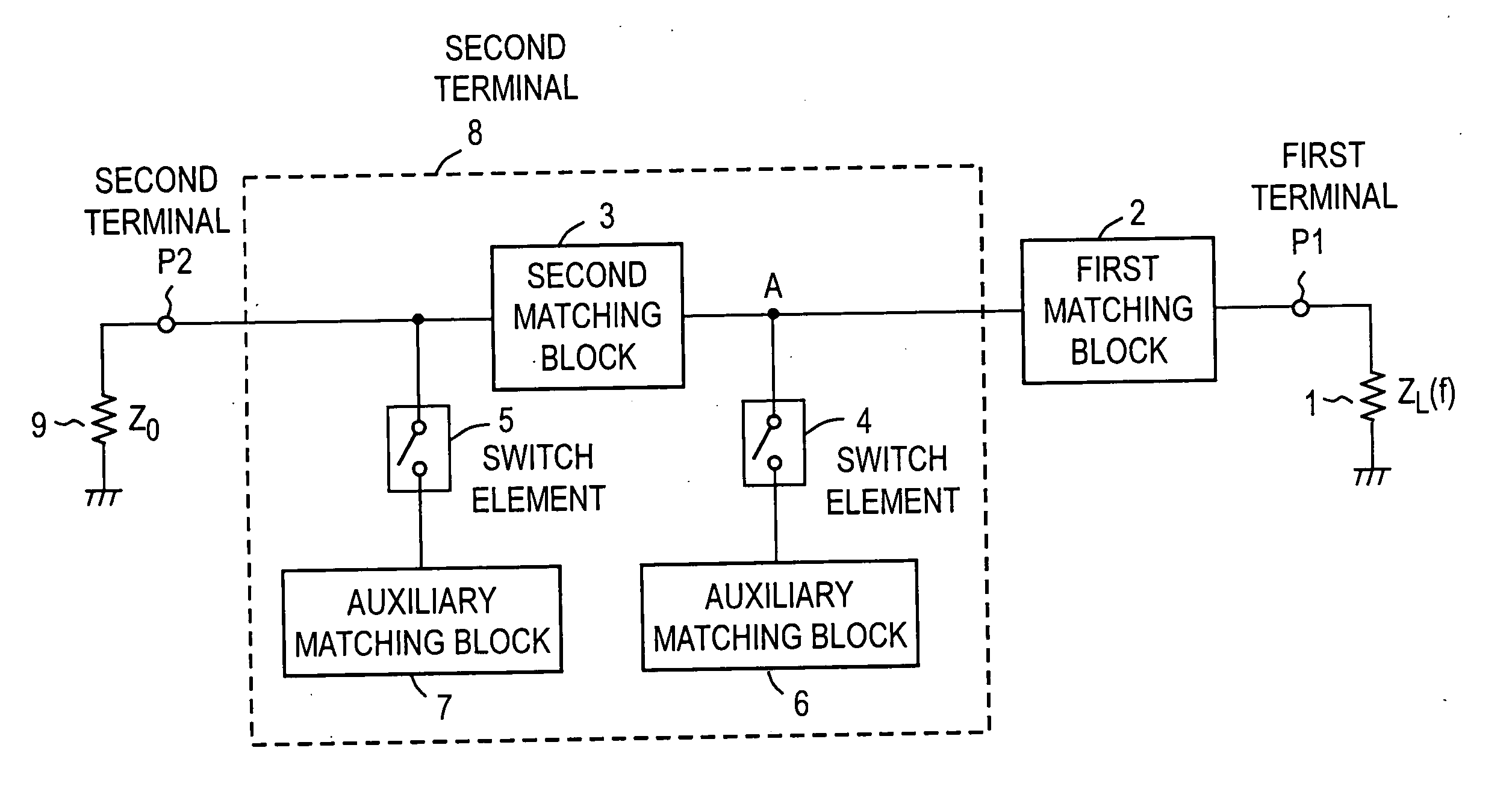
Matching circuit
InactiveUS20060261911A1Smaller-sizedMultiple-port networksTransmissionComputer scienceFrequency band
The present invention has for its object to provide a matching circuit with multiband capability which can be reduced in size, even if the number of handled frequency bands rises. The matching circuit of the present invention comprises a load having frequency-dependent characteristics, a first matching block connected with one end to the load with frequency-dependent characteristics, and a second matching block formed by lumped elements connected in series to the first matching block. And then, when a certain frequency band is used, matching is obtained with the series impedance of the first matching block and the second matching block. When a separate frequency band is used, a π-type circuit is constituted by connecting auxiliary matching blocks to both sides of the second matching block. Next, at the same frequency, by taking the combined impedance of this π-type circuit and a load whose characteristics do not depend on the frequency to be Z0, the influence of the second matching block is removed.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Enhanced fault protection in electricity meter
An arrangement for obtaining measurable voltage signals in a utility meter wherein the measurable voltage signals are representative of a power line voltage signal. Includes a first connection to a phase of a power line, a second connection to a reference of a power line, a voltage divider circuit, and a series impedance element. The voltage divider circuit is disposed on a circuit board and is coupled between a first node and the second connection. The voltage divider circuit has an output configured to provide measurable voltage signals to a circuit operable to generate voltage measurement information. The voltage divider circuit has a first impedance value. The series impedance element is disposed apart from the circuit board and is configured for current limiting. The series impedance element is coupled between the first connection and the first node and has a second impedance value.
Owner:LANDIS GYR LLC
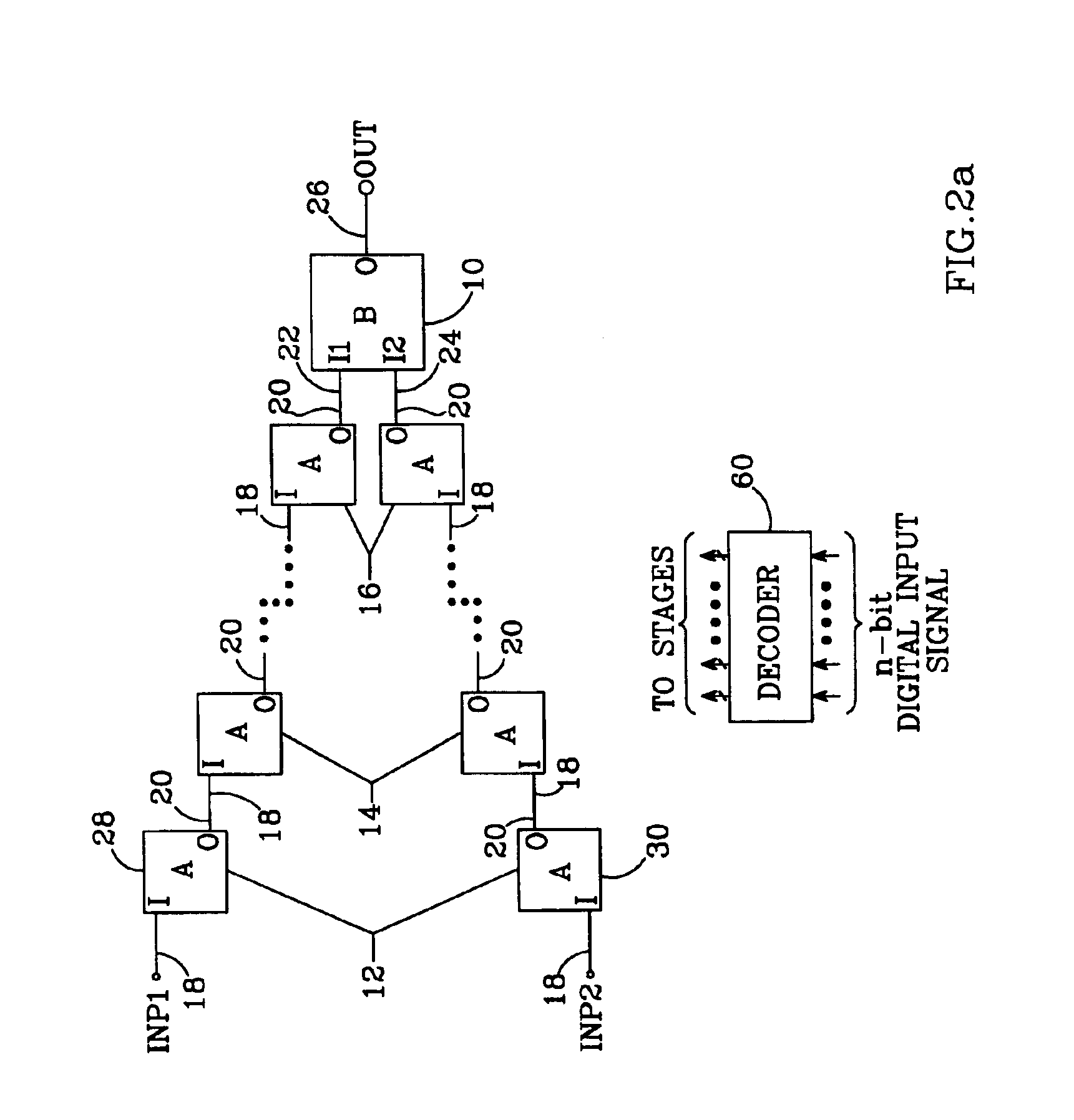
Digitally-switched impedance with multiple-stage segmented string architecture
ActiveUS6885328B1Reduce countReduce die areaElectric signal transmission systemsDigital-analogue convertorsImage resolutionDigital input
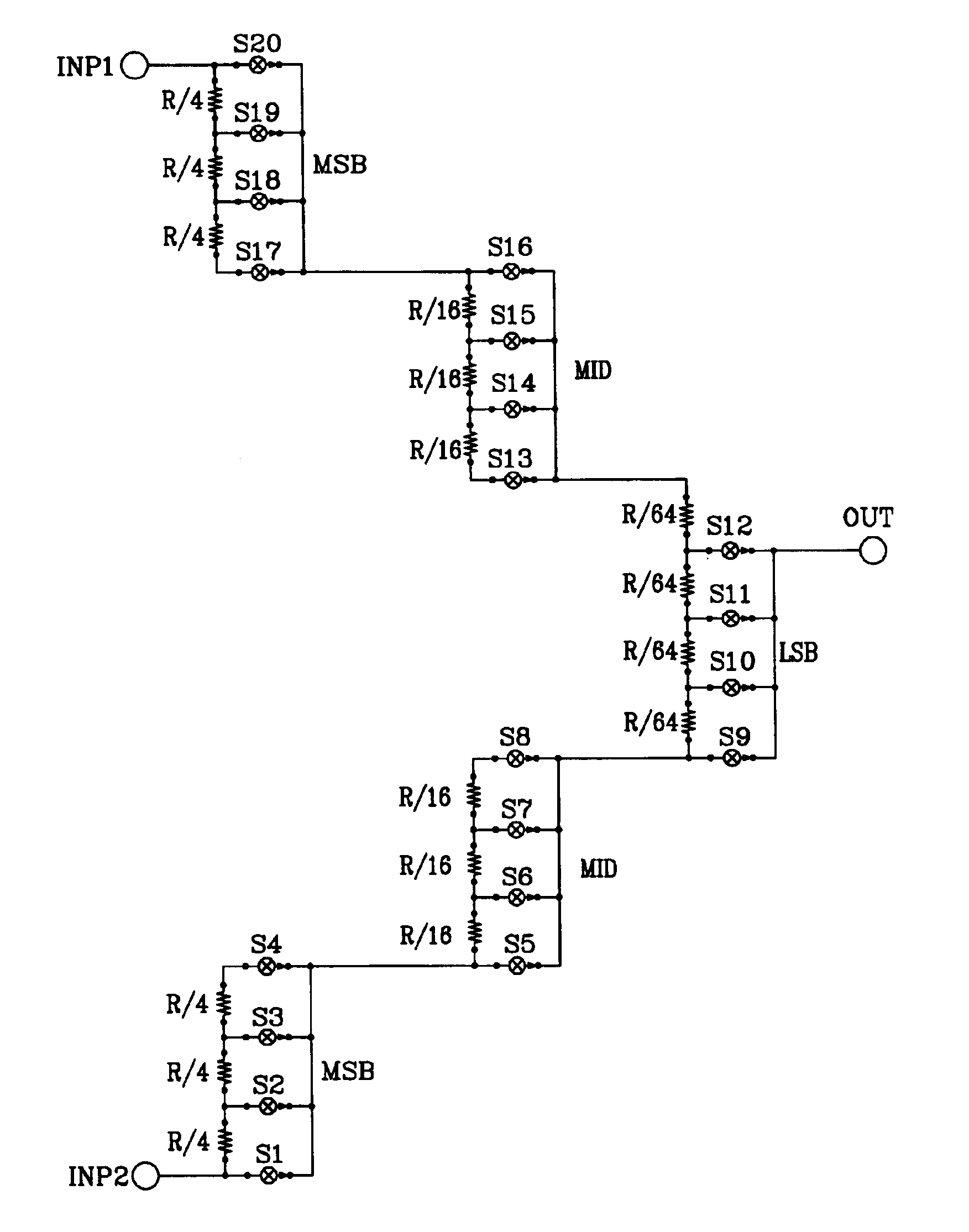
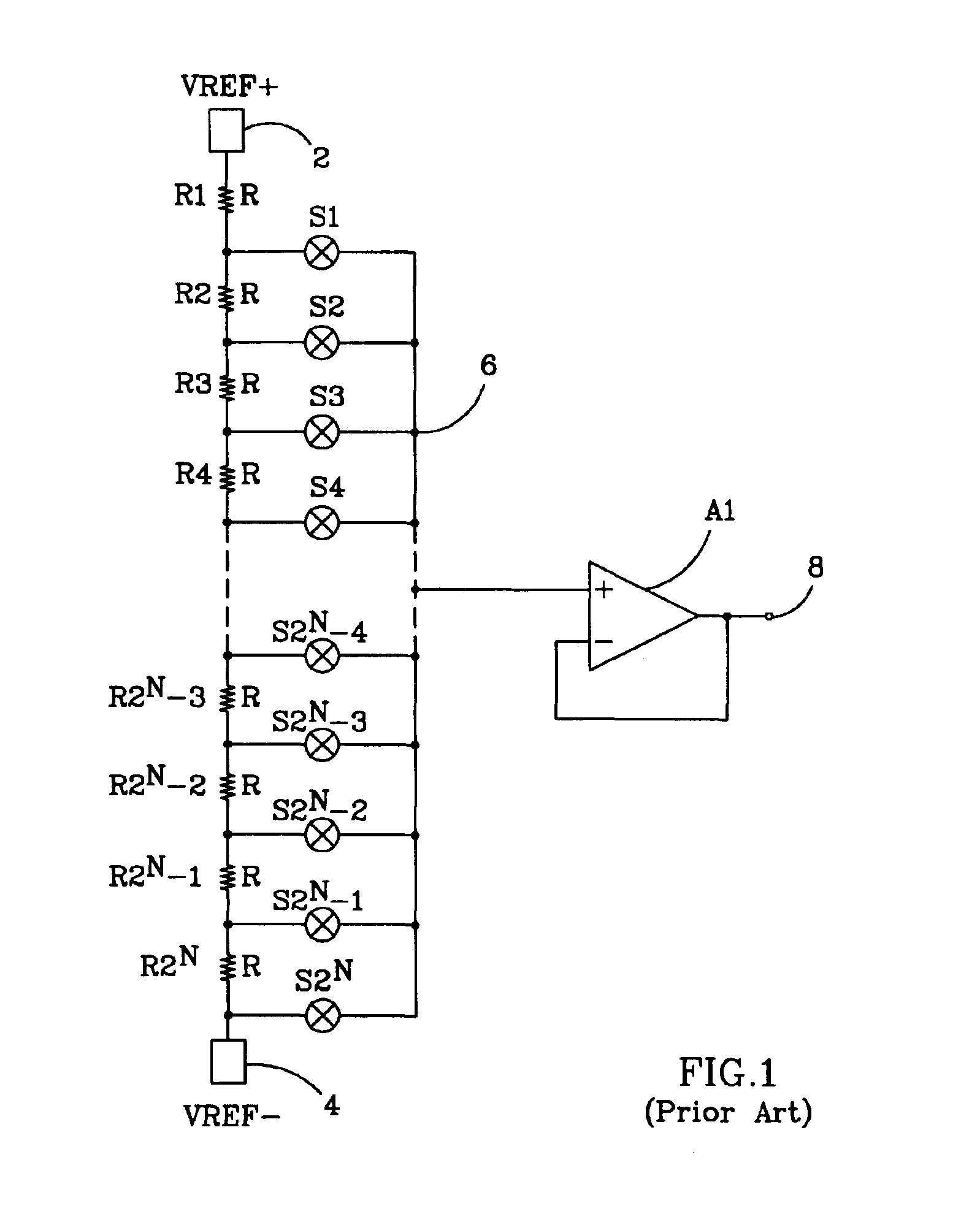
A multiple-stage digitally-switched impedance has one “type B” stage and at least two “type A” stages. The type A stages are cascaded between high and low reference nodes and the type B stage. Each stage comprises a string of series-connected impedances and a switch network. A decoder responds to an digital input signal by controlling the switch networks to switch selectable portions of the strings in the type A stages into a series connection with the type B stage's string, and to control the type B stage's switch network to tap its string at a location to provide a impedance corresponding to the n-bit digital input signal between the final output node and at least one of the high and low reference nodes. Each stage provides a portion of the impedance's n-bit resolution, and the sum of the bits of resolution provided by each stage equals the total n-bit resolution.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Enhanced fault protection in electricity meter
InactiveUS7112949B2Lower impedanceVoltage will not be measured accuratelyCurrent/voltage measurementTime integral measurementCurrent limitingInductor
An arrangement for obtaining measurable voltage signals in a utility meter includes a first connection to a phase of a power line, a second connection to a reference of a power line, a voltage divider circuit, and a series inductor. The voltage divider circuit is disposed on a circuit board and is coupled between a first node and the second connection. The voltage divider circuit has an output configured to provide measurable voltage signals to a circuit operable to generate voltage measurement information. The series inductor is disposed apart from the circuit board and is configured for current limiting. The series impedance element is coupled between the first connection and the first node.
Owner:LANDIS GYR LLC
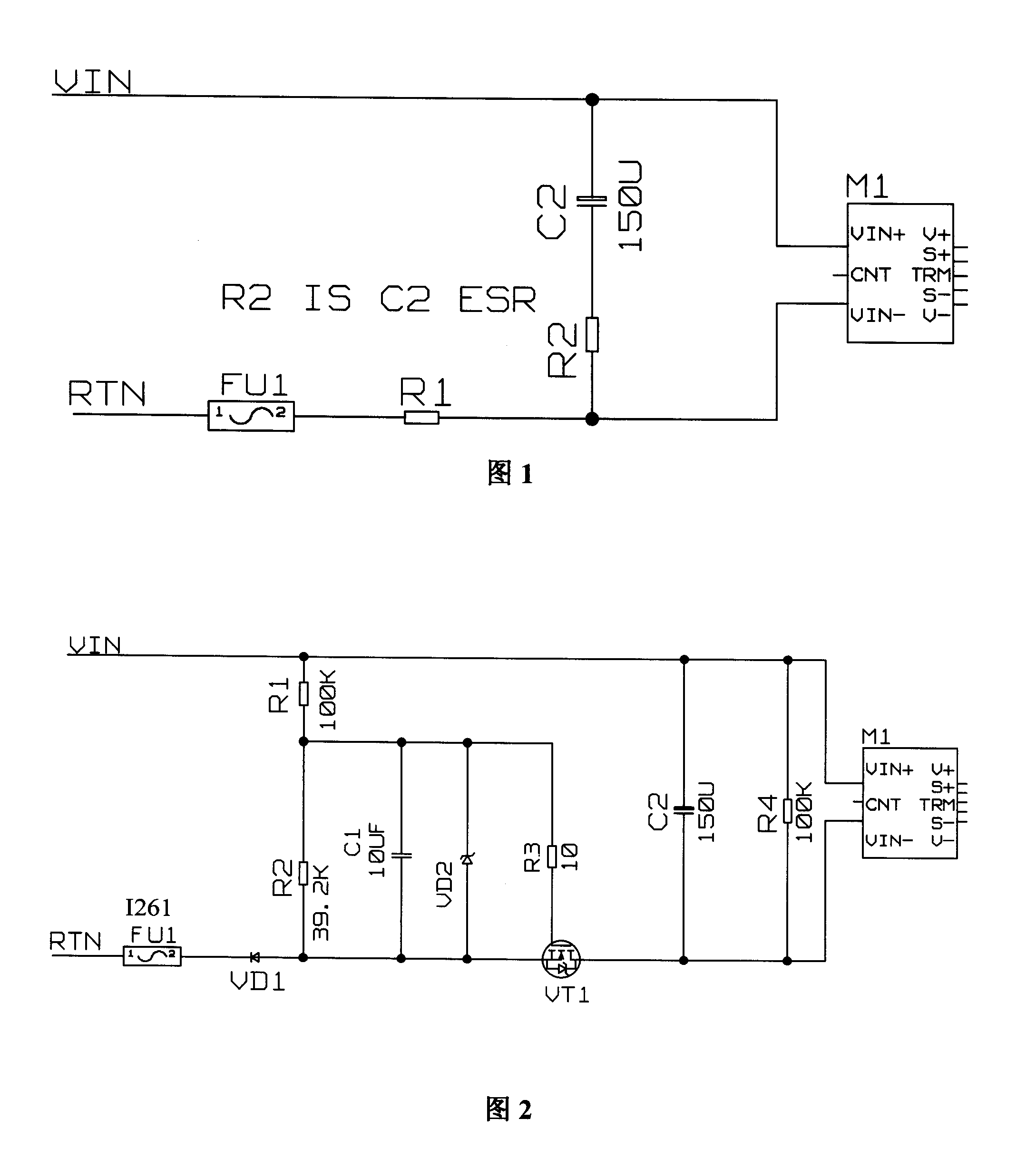
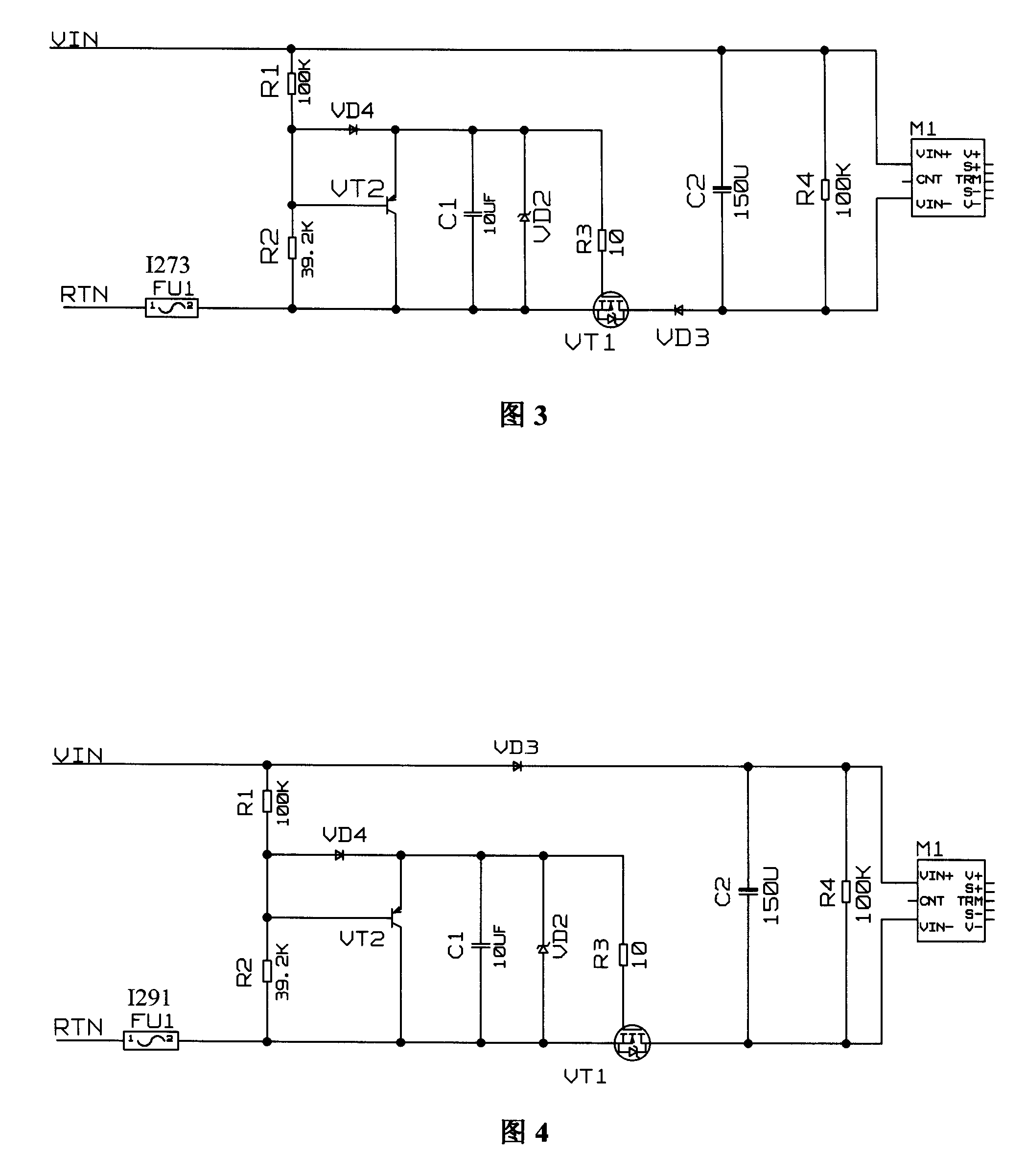
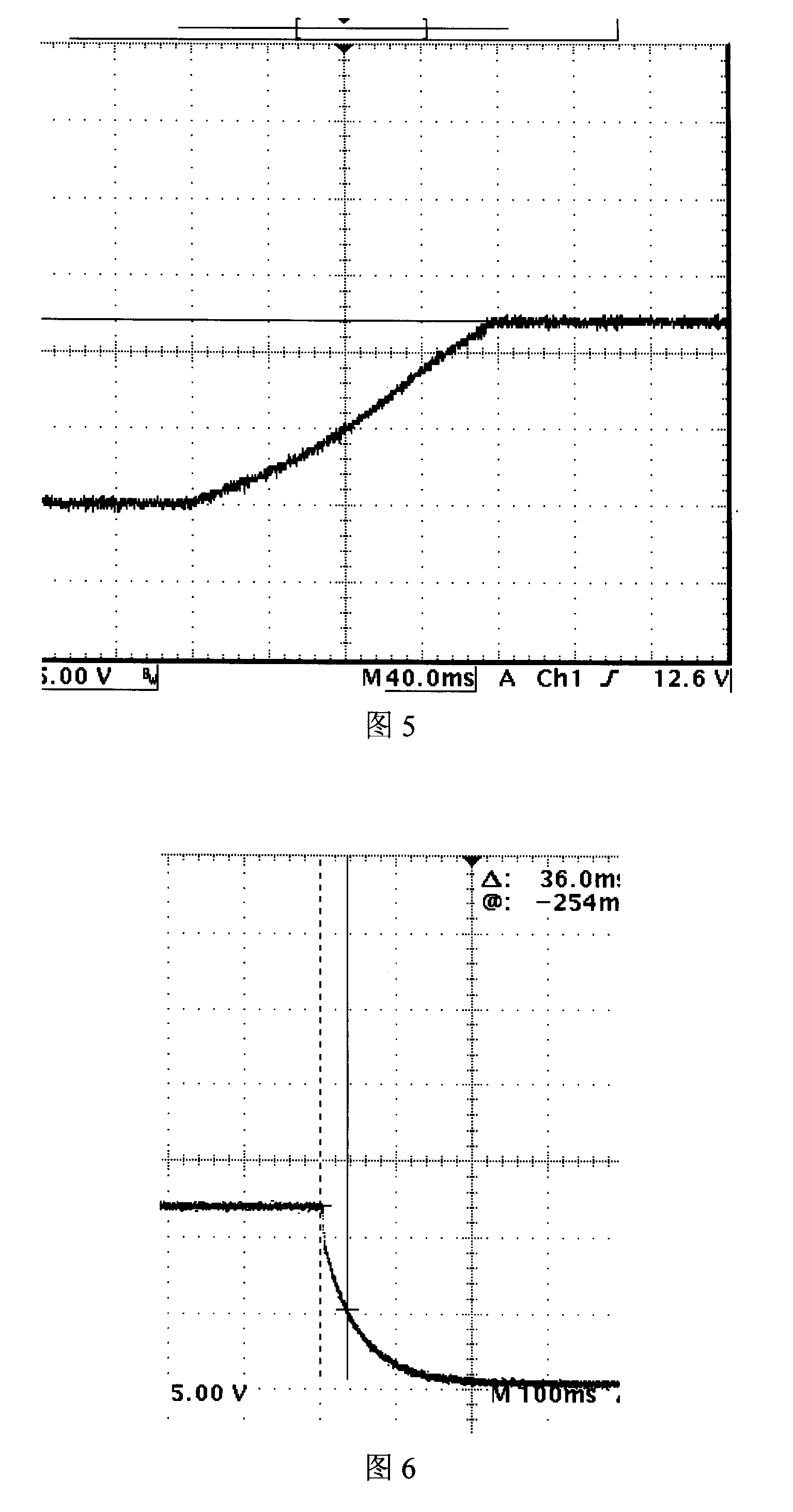
Direct-current power supply slow startup control circuit
The invention relates to a slow startup control circuit of DC electrical source, comprising a switching transistor VT1 which is connected with a negative RTN input voltage terminal in series, a bleeder circuit which is arranged between a positive VIN input voltage terminal and the negative RTN input voltage terminal, and a capacitor C1 arranged between the negative RTN input voltage terminal and the bleeder node of the bleeder circuit; wherein the control terminal of the switching transistor VT1 is connected with the bleeder node. The circuit employs a MOSFET which serves as the switching transistor to migrate from a pinch-off region to a constant-current region and at last to an ohm area, which is equivalent to that series impedances from big to small are applied to restrain impulse current so as to reach slow startup; meanwhile, a quick charge circuit is added to the control terminal to quicken the shutoff of the MOSFET after charge release; therefore the slow startup control circuit is suitable for occasions with quick and frequent swaps.
Owner:ZTE CORP
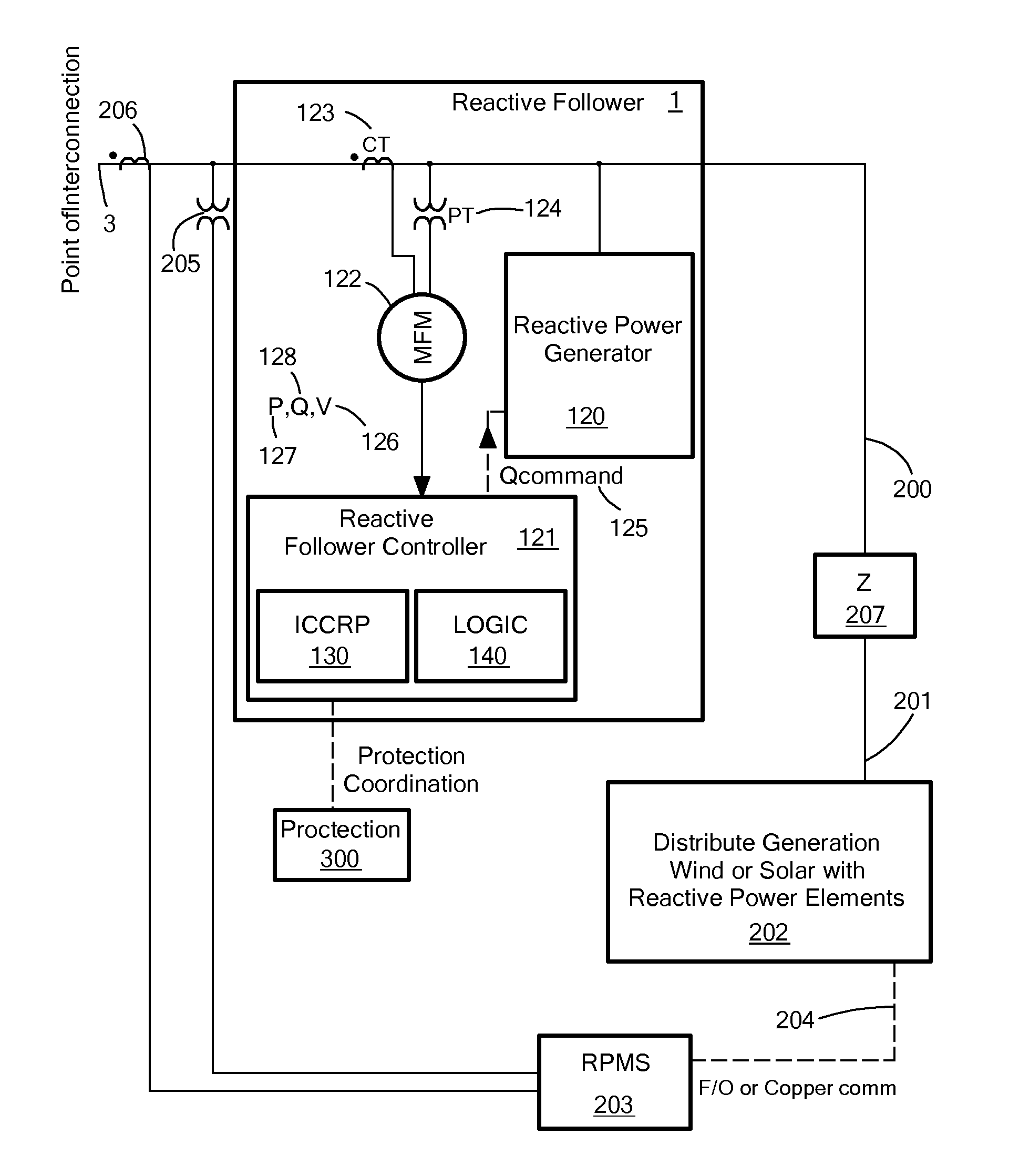
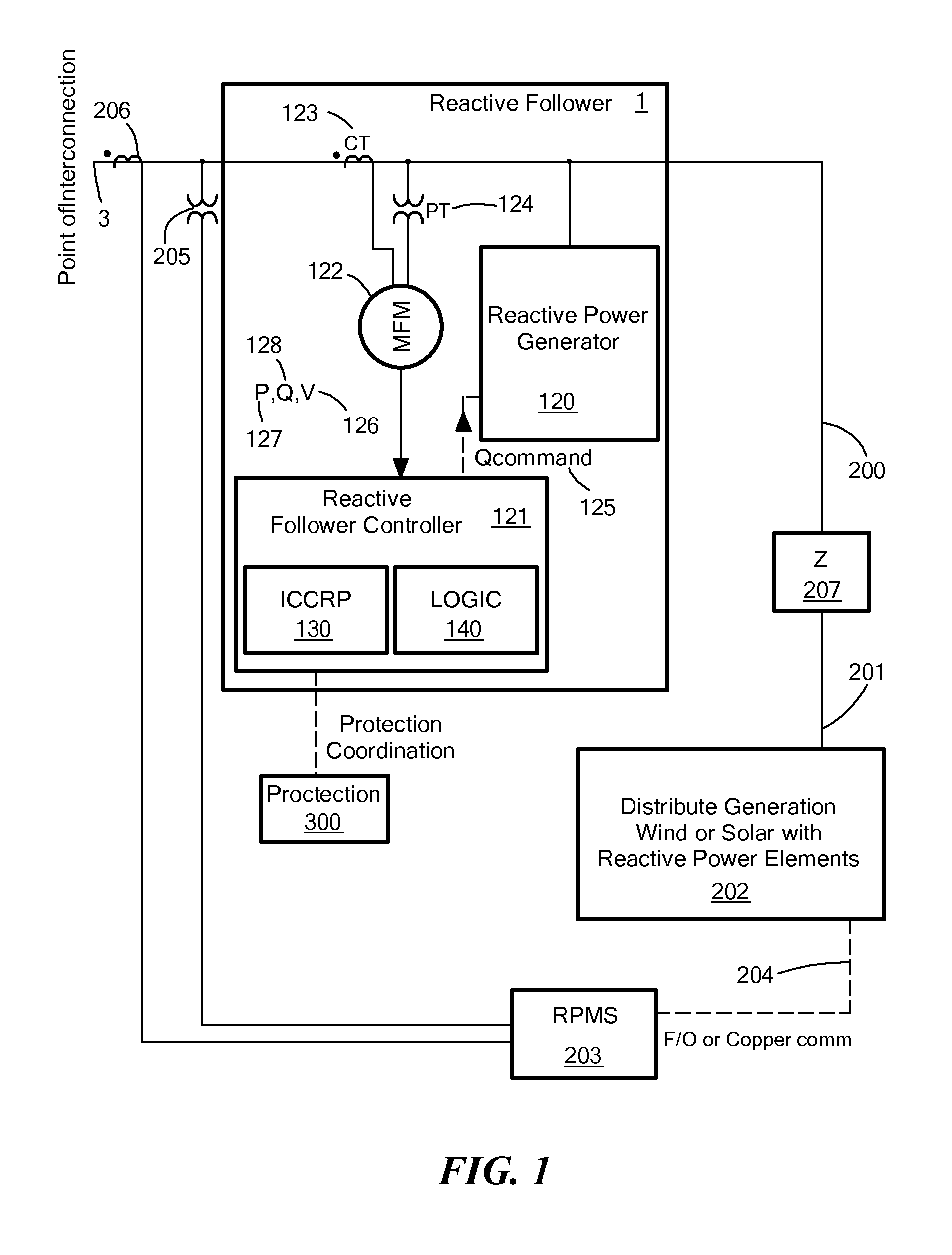
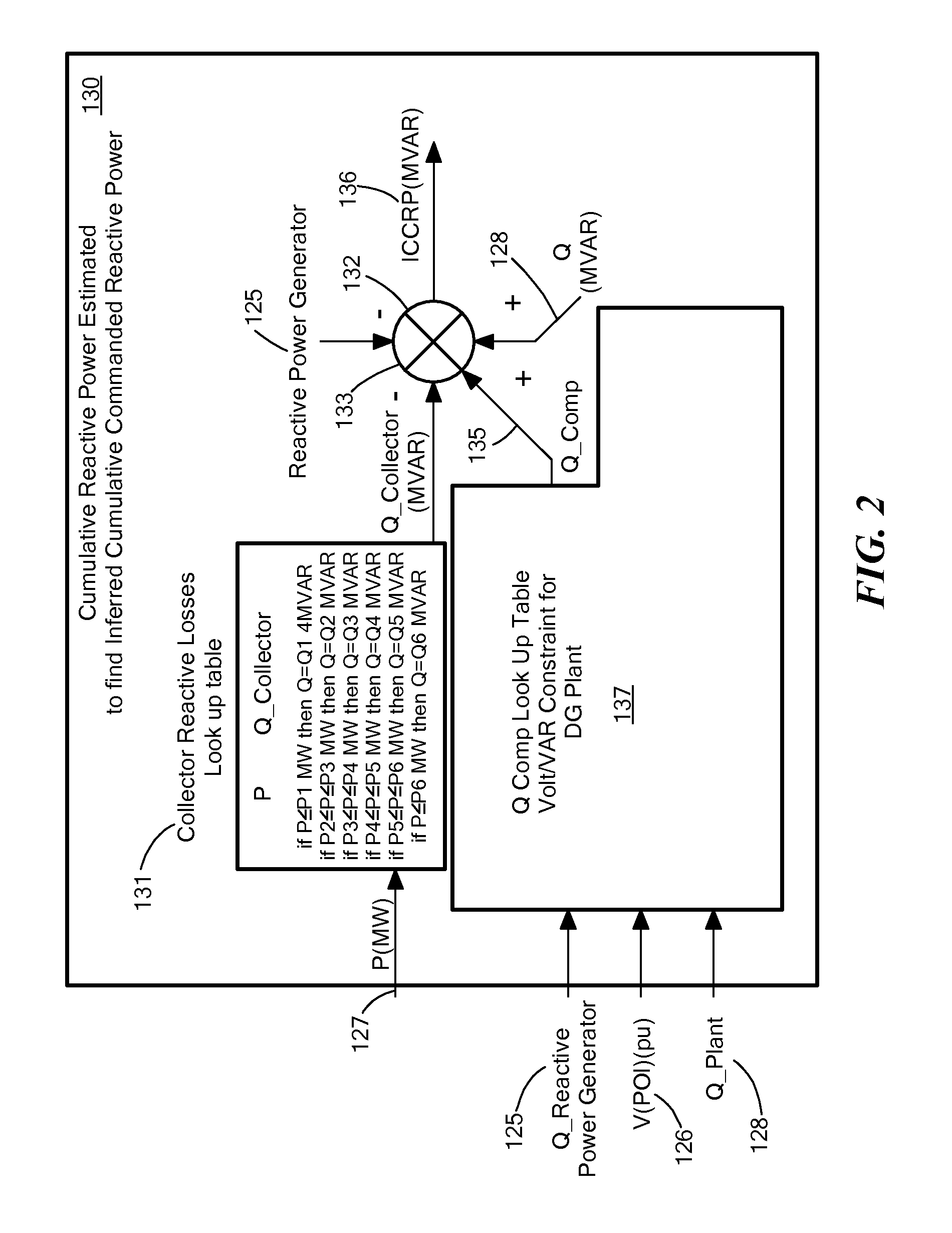
Reactive Following for Distributed Generation and Loads of Other Reactive Controller(s)
ActiveUS20130131878A1Reactive power be increaseMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlPower stationNuclear engineering
Systems and methods for providing generated power to a power grid subject to reactive power requirements. A reactive follower includes a reactive power generator coupled to a distributed power plant via a series impedance such as a step-up transformer. A reactive follower controller controls the reactive power generator on the basis of an estimated reactive power commanded by a reactive power management system and includes multi-variable control logic to determine when to increase reactive power produced by the reactive power generator based on the reactive power commanded by the distributed reactive power management system and point-of-interconnection measurements of power, reactive power, and voltage.
Owner:GRUNEWALD CHARLES +4
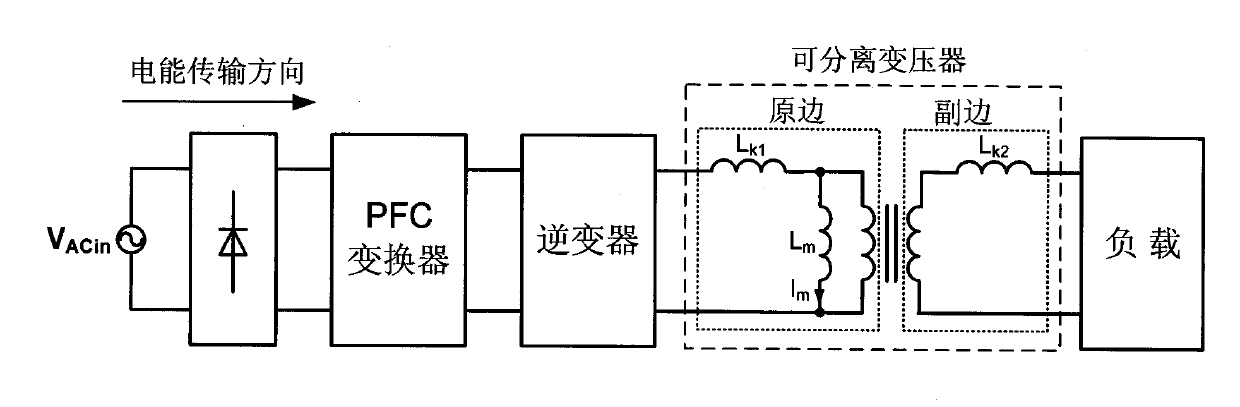
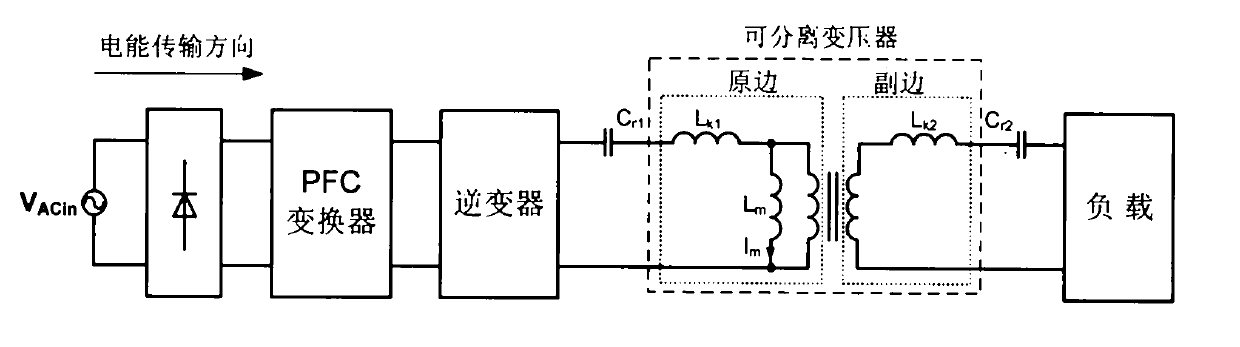
Inductive coupling type electric energy transmission device
ActiveCN101789637AImprove transmission efficiencySimple structureElectromagnetic wave systemCircuit arrangementsCapacitanceResonance
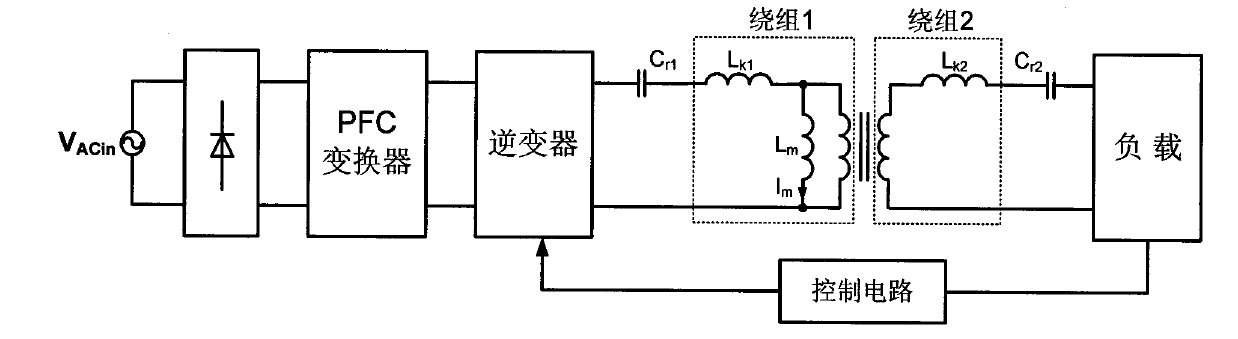
The invention discloses an inductive coupling type electric energy transmission device, which is formed by connecting an inverter in series with a separable transformer or weak coupling transformer. One ends of the primary side and secondary side of the separable transformer or weak coupling transformer are respectively connected in series with a resonance capacitor to enable the primary side and the secondary side of the separable transformer or weak coupling transformer to be subjected to the resonance, wherein Lk1 and Lk2 respectively express leakage inductance quantities of the primary side and the secondary side of the separable transformer or weak coupling transformer, and Cr2 and Cr2 respectively express capacitor values of resonance capacitors of the primary side and the secondary side of the separable transformer or weak coupling transformer. By adding the resonance capacitors, the invention ensures that the leakage inductances of the primary side and the secondary side and the series impedances of the resonance capacitors are zero when carrying out the frequency resonance, therefore, non-contact electric energy transmission efficiency is high. The invention also has the advantages of simple structure, convenient realization and easy popularization.
Owner:南京博兰得电能技术发展有限公司
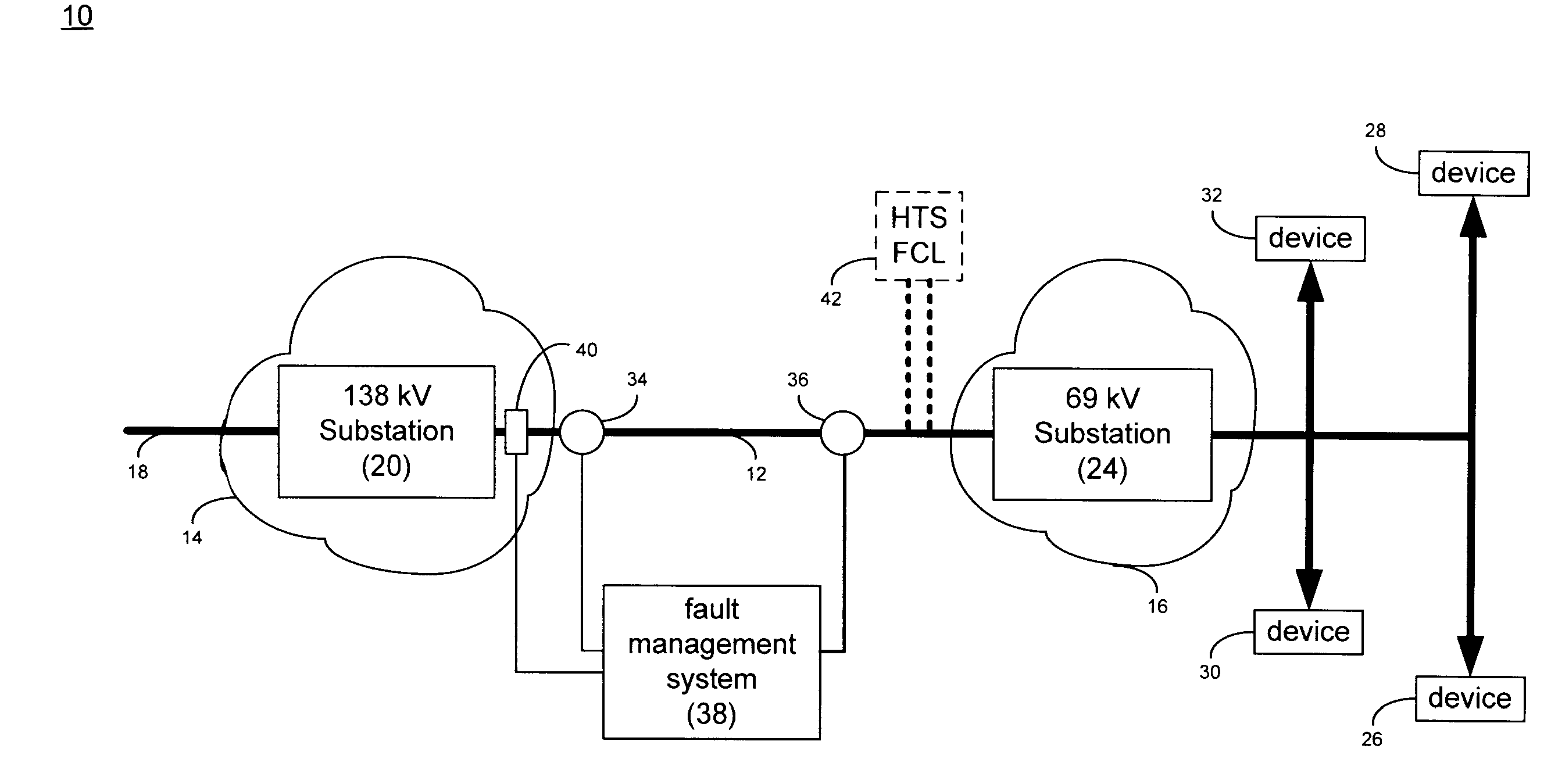
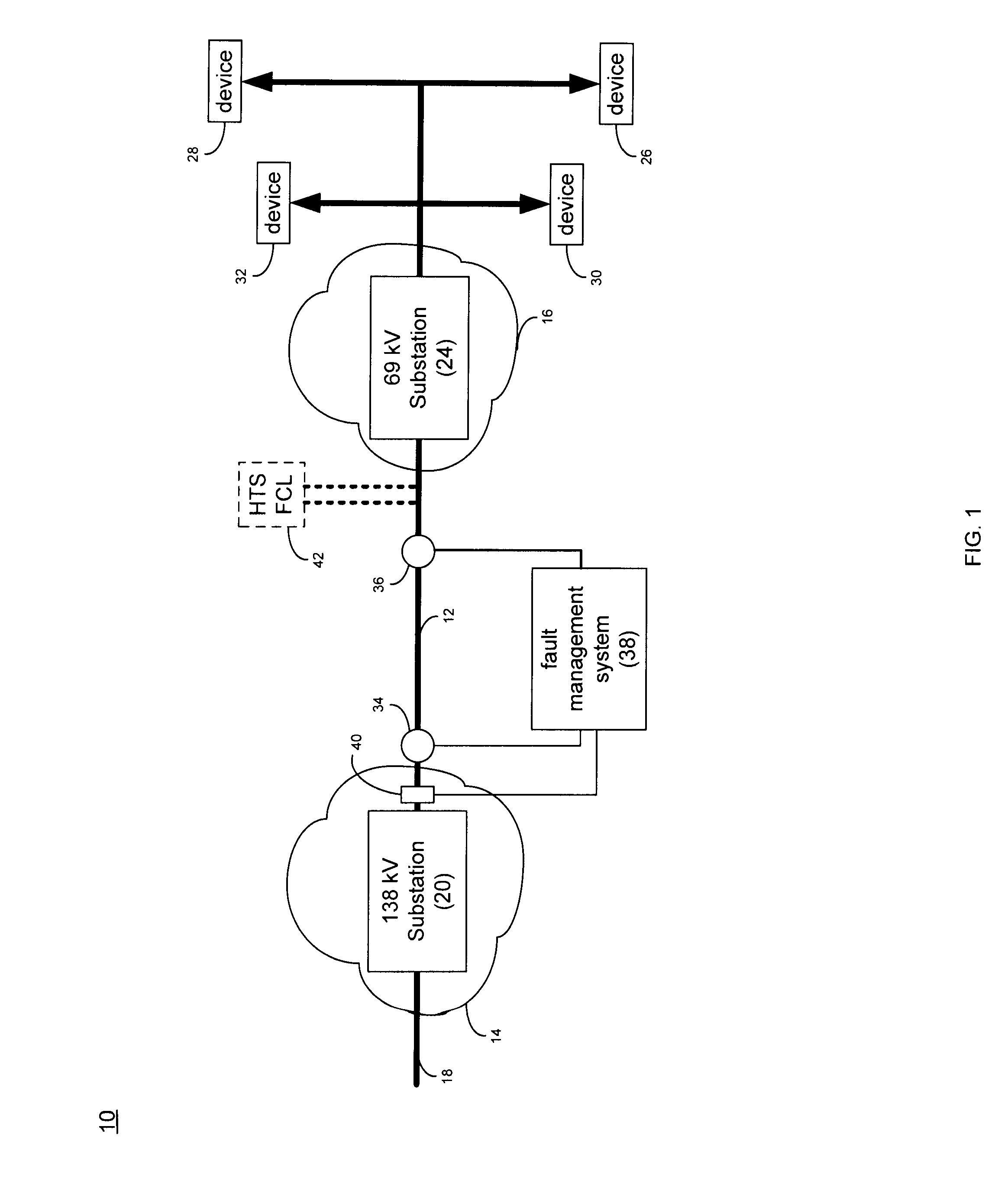
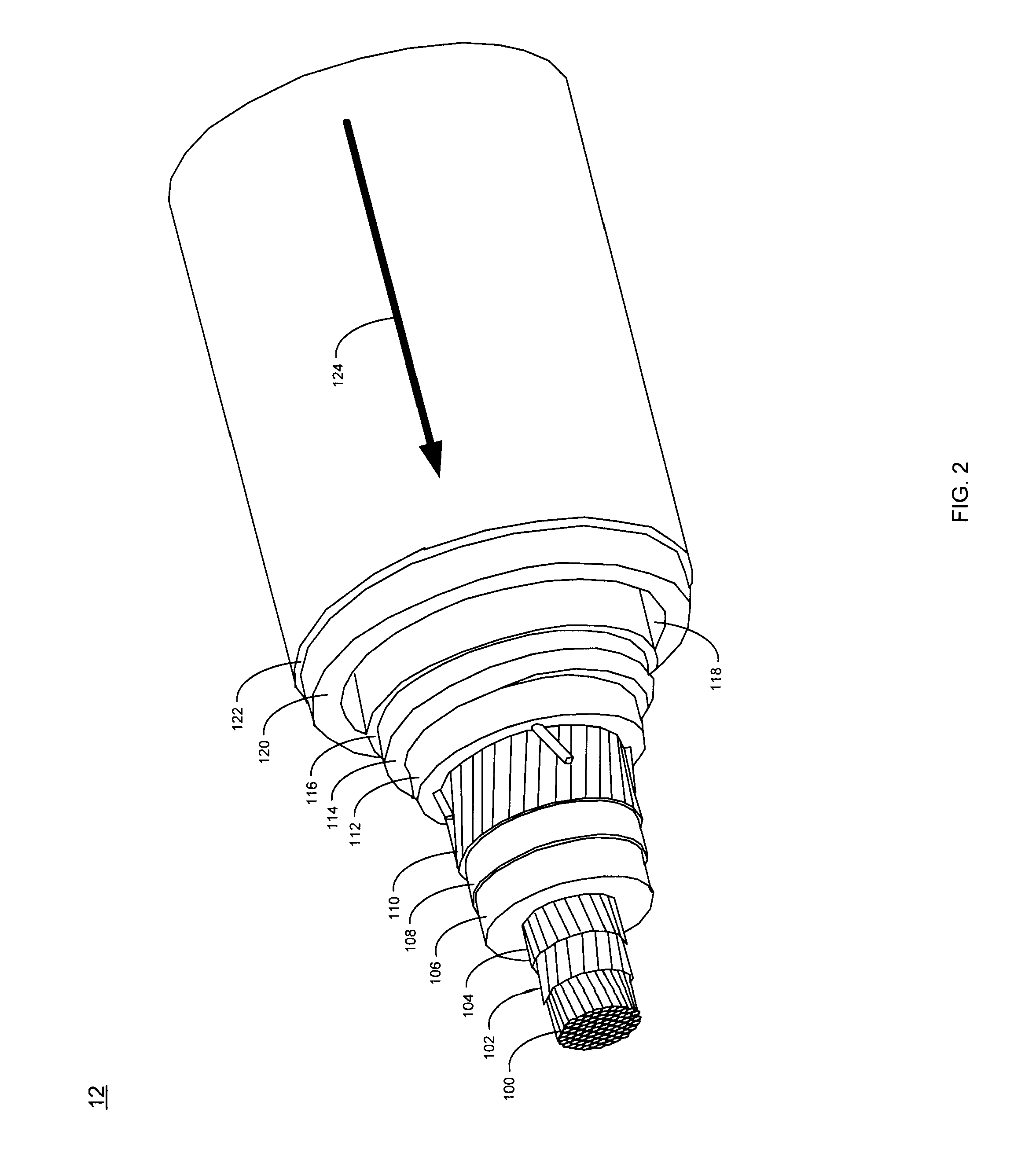
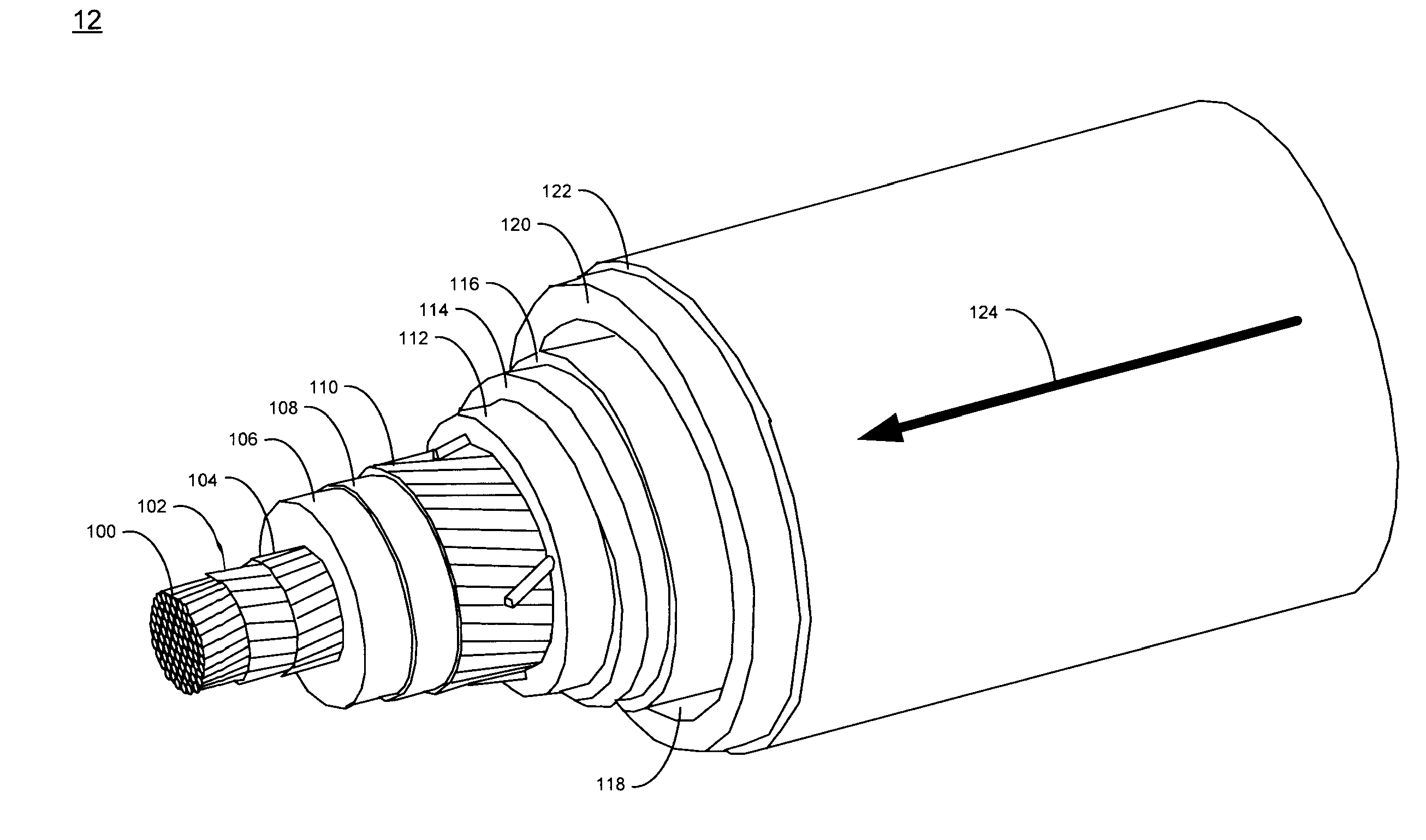
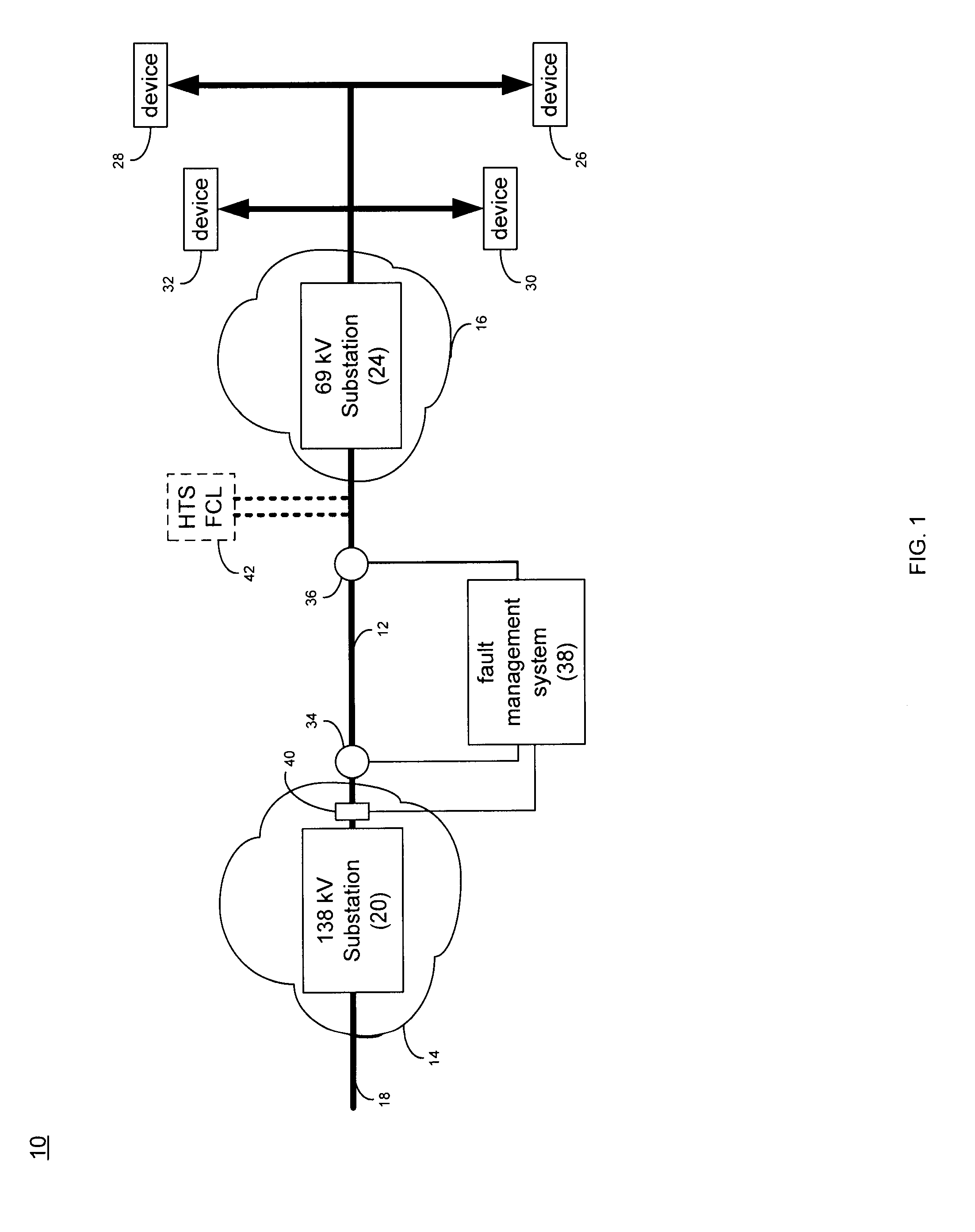
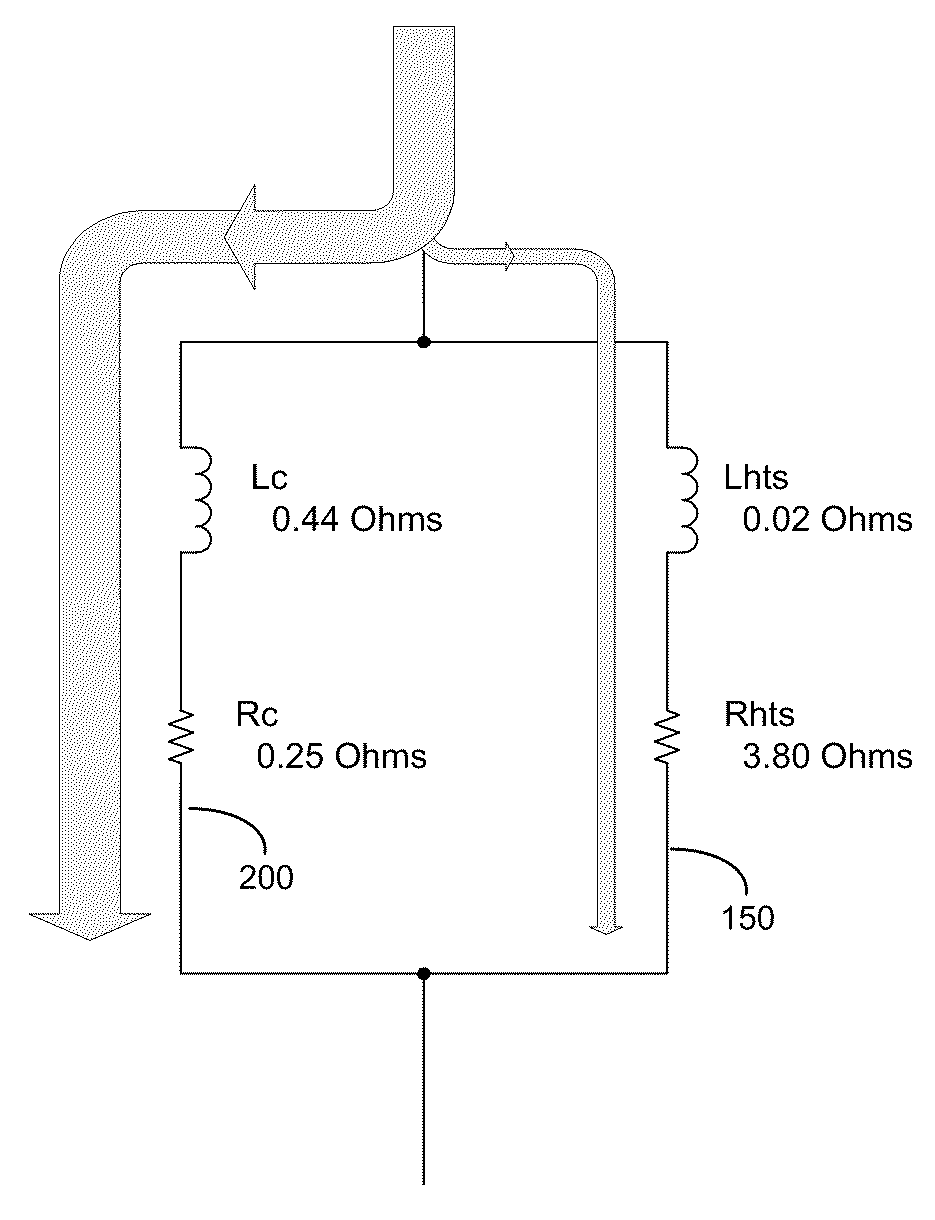
Parallel connected hts utility device and method of using same
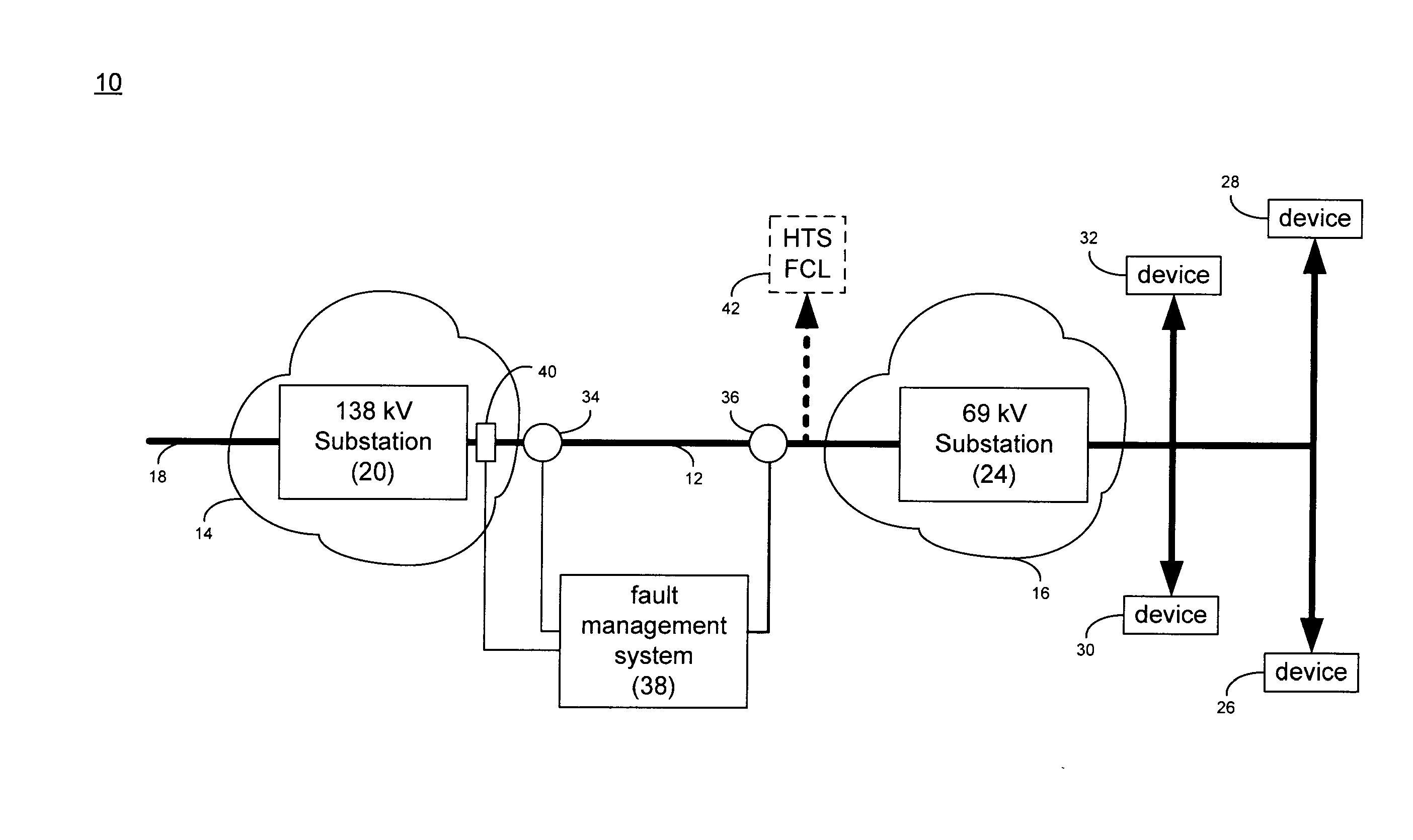
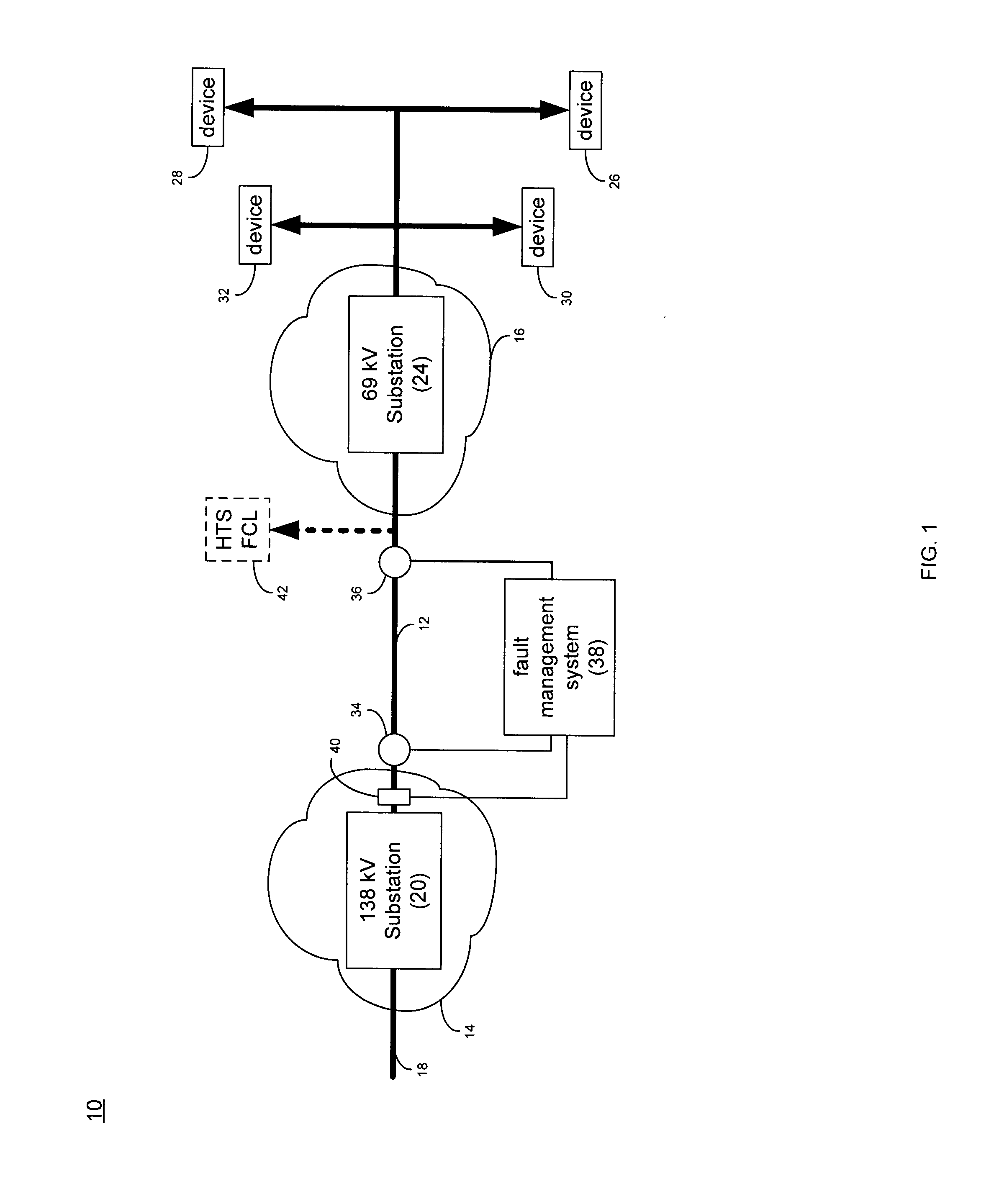
A superconducting electrical cable system is configured to be included within a utility power grid. The superconducting electrical cable system includes a superconducting electrical path interconnected between a first and a second node within the utility power grid. A non-superconducting electrical path is interconnected between the first and second nodes within the utility power grid. The superconducting electrical path and the non-superconducting electrical path are electrically connected in parallel. The superconducting electrical path has a lower series impedance, when operated below a critical current level, than the non-superconducting electrical path. The superconducting electrical path has a higher series impedance, when operated at or above the critical current level, than the non-superconductor electrical path.
Owner:AMERICAN SUPERCONDUCTOR
Low Harmonic Rectifier Circuit
A method, device, and plurality of circuit enhancements for a rectifier system that enable reduction in lower order and higher order harmonics, without substantially reducing the rectifier's direct current output voltage. The rectifier system comprises a phase shifting primary transformer subsystem and a multi-pulse rectifier. At least one series impedance path is coupled to one of three input terminals / leads of the transformer subsystem and conducts one phase of three phase currents from a power supply to the transformer subsystem. The series impedance path provides low impedance to the 1st harmonic and substantially higher, inductive impedance to higher harmonics of the power supply frequency. The impedance of the series impedance path at a selected frequency above a third harmonic of the power supply's fundamental frequency divided by the impedance at the fundamental frequency of the three phase power supply is substantially greater than the selected frequency divided by the fundamental frequency of the power supply.
Owner:HOWARD INDS
Parallel HTS Transformer Device
A superconducting transformer system is configured to be included within a utility power grid having a known fault current level. The superconducting transformer system includes a non-superconducting transformer interconnected between a first node and a second node of the utility power grid. A superconducting transformer is interconnected between the first node and the second node of the utility power grid. The superconducting transformer and the non-superconducting transformer are electrically connected in parallel. The superconducting transformer has a lower series impedance than the non-superconducting transformer when the superconducting transformer is operated below a critical current level and a critical temperature. The superconducting transformer is configured to have a series impedance that is at least N times the series impedance of the non-superconducting transformer when the superconducting transformer is operated at or above one or more of the critical current level and the critical temperature. N is greater than 1 and is selected to attenuate, in conjunction with an impedance of the non-superconducting transformer, the known fault current level by at least 10%.
Owner:AMERICAN SUPERCONDUCTOR
Parallel connected hts fcl device
InactiveUS20080190646A1Superconductors/hyperconductorsNormal-superconductive switchable devicesPower gridEngineering
A superconducting electrical cable system is configured to be included within a utility power grid having a known fault current level. The superconducting electrical cable system includes a non-superconducting electrical path interconnected between a first node and a second node of the utility power grid. A superconducting electrical path is interconnected between the first node and the second node of the utility power grid. The superconducting electrical path and the non-superconducting electrical path are electrically connected in parallel, and the superconducting electrical path has a lower series impedance than the non-superconducting electrical path when the superconducting electrical path is operated below a critical current level and a critical temperature. The superconducting electrical path is configured to have a series impedance that is at least N times the series impedance of the non-superconducting electrical path when the superconducting electrical path is operated at or above one or more of the critical current level and the superconductor critical temperature. N is greater than 1 and is selected to attenuate, in conjunction with an impedance of the non-superconducting electrical path, the known fault current level by at least 10%.
Owner:AMERICAN SUPERCONDUCTOR
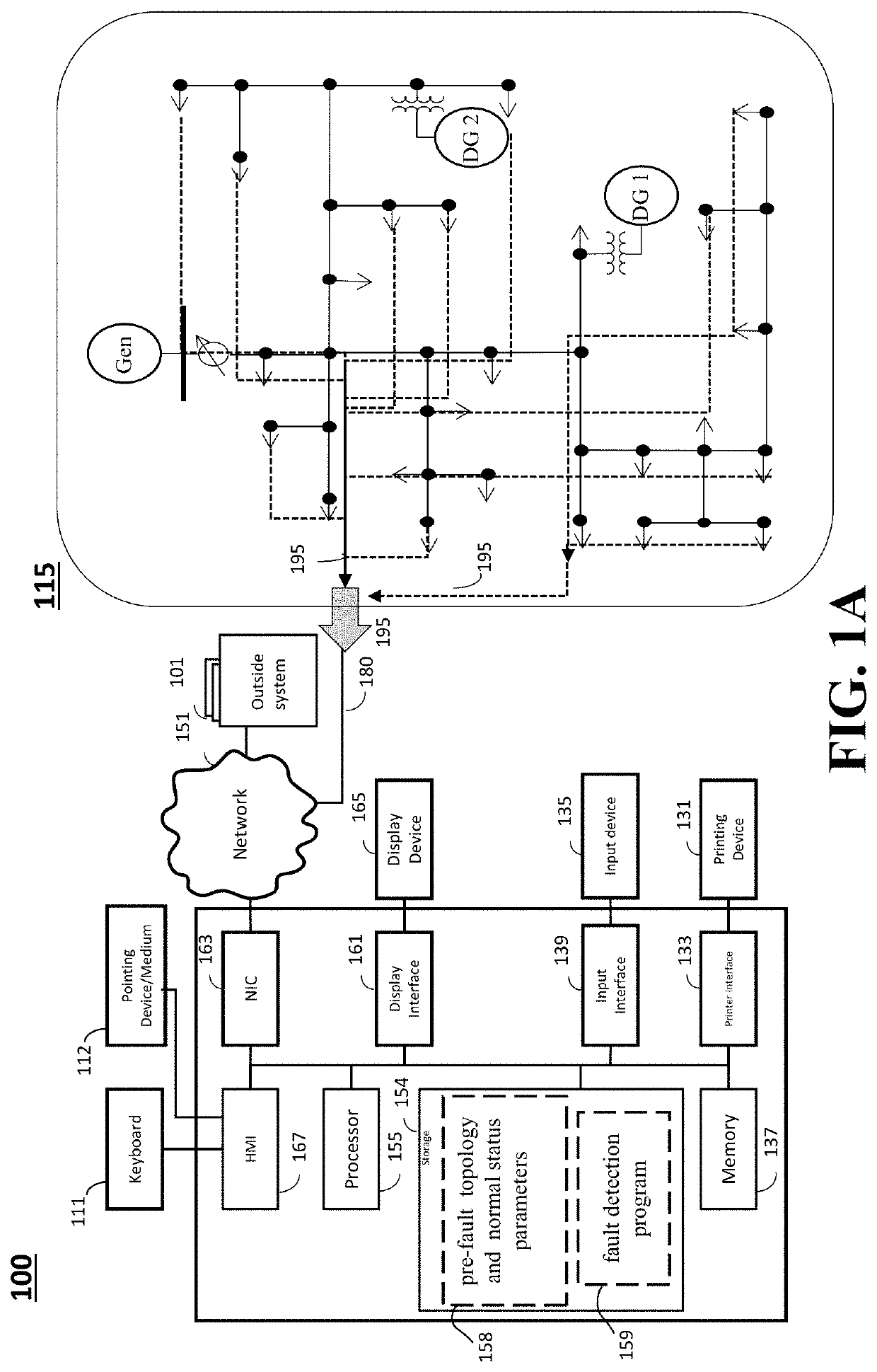
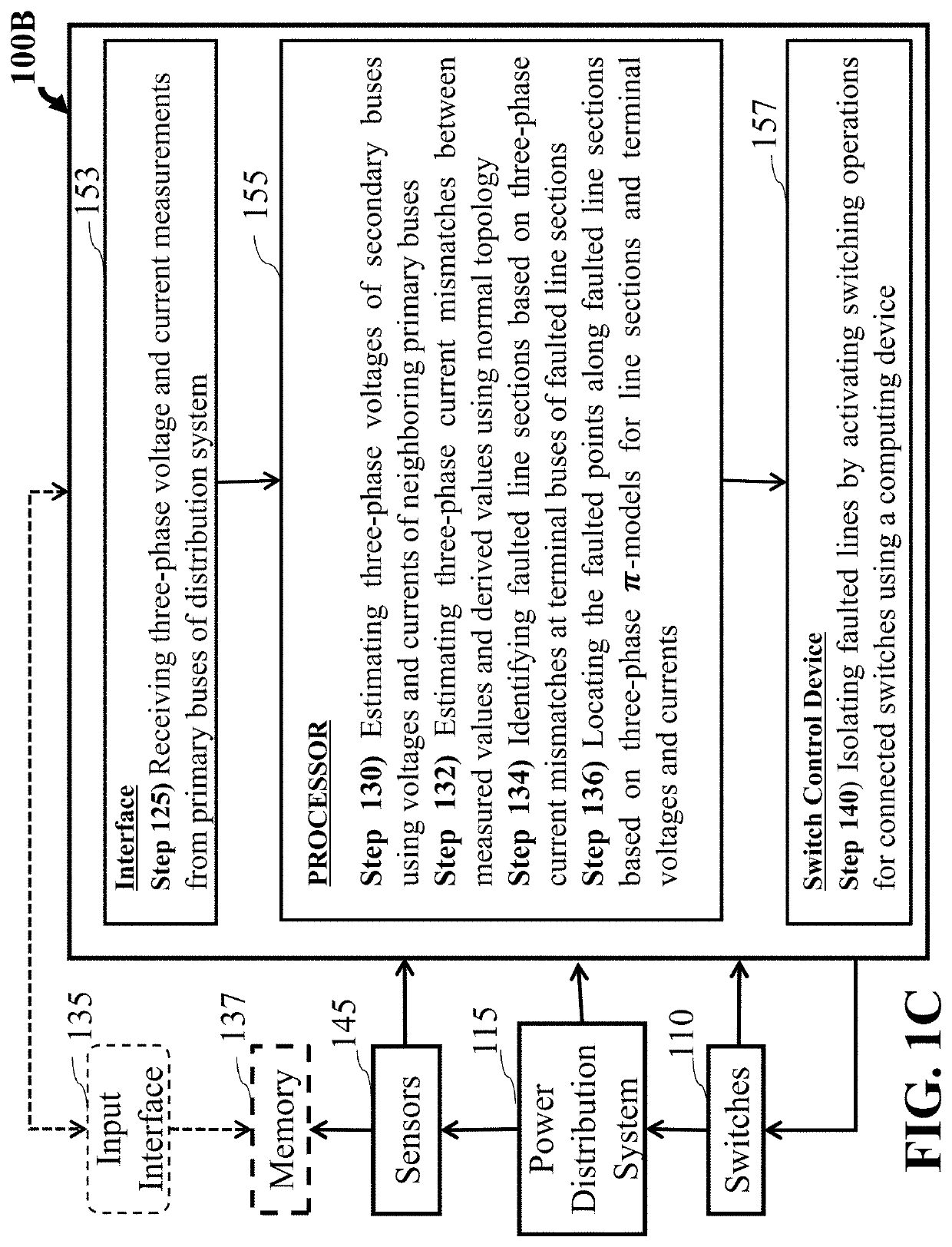
Simultaneous Fault Detection and Location of Power Distribution Systems
ActiveUS20200326363A1Quick checkReduce decreaseEmergency protection detectionFault location by conductor typesPhase currentsElectric network
Systems and methods are configured for detecting and locating simultaneous faults in a distribution network having primary and secondary buses connected with two-terminal sections. The measured three-phase voltages and currents from the primary buses are received via a communication network, and the series impedances and shunt admittances and the pre-fault connectivity topology are retrieved from the storage. Simultaneous faults are determined to occur by verifying at least one phase of at least three buses having phase current mismatches determined as the differences between the measured values and calculated values using normal topology and phase voltages that are greater than a threshold. A location for each fault is determined individually if the faults are occurring at non-adjacent sections in the distribution network, or jointly if the faults are occurring at adjacent sections in the distribution network. Faulted line sections are isolated by activating switching operations for connected switches to the faulted line sections that communicatively linked to distribution system grid via communication network.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC +1
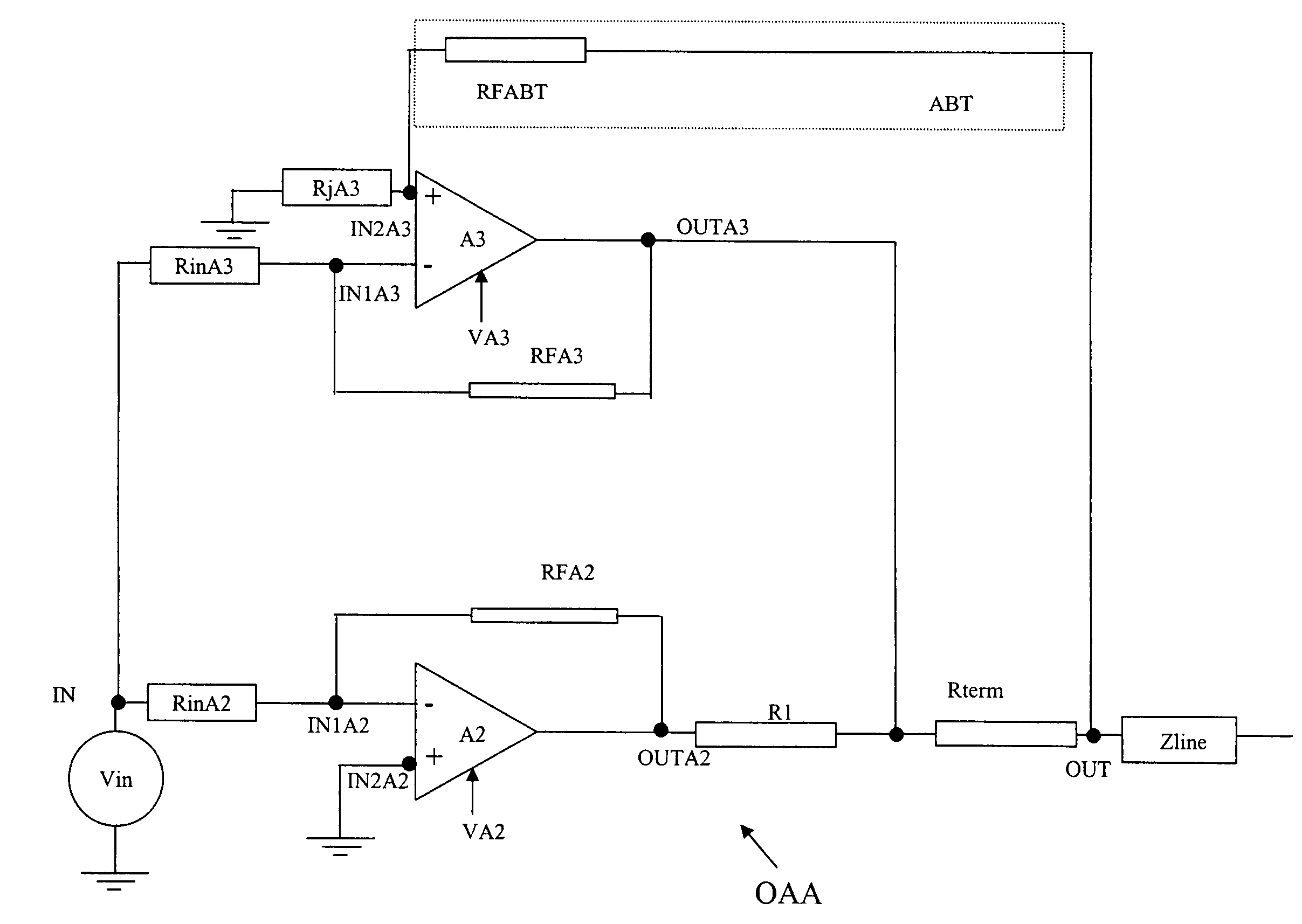
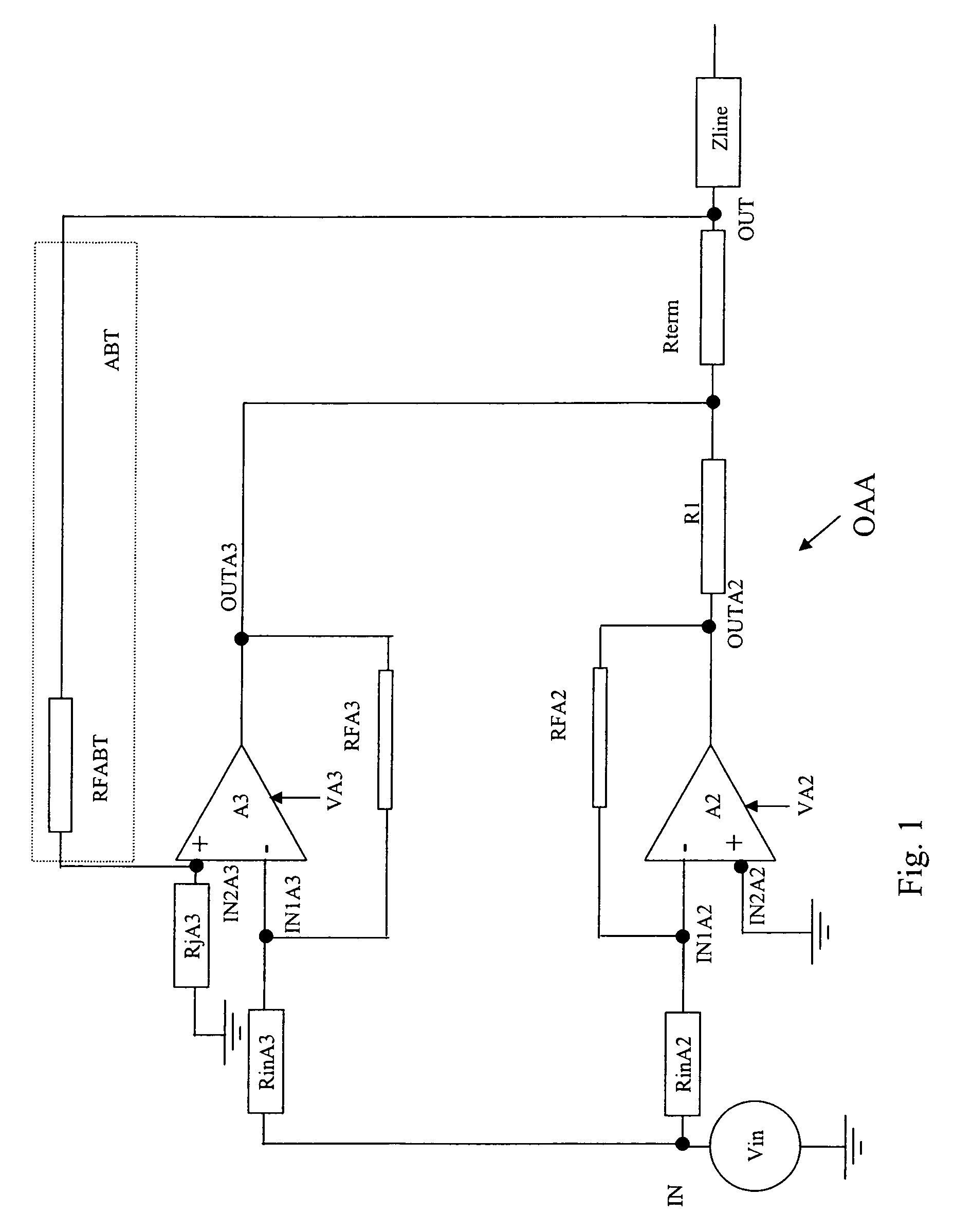
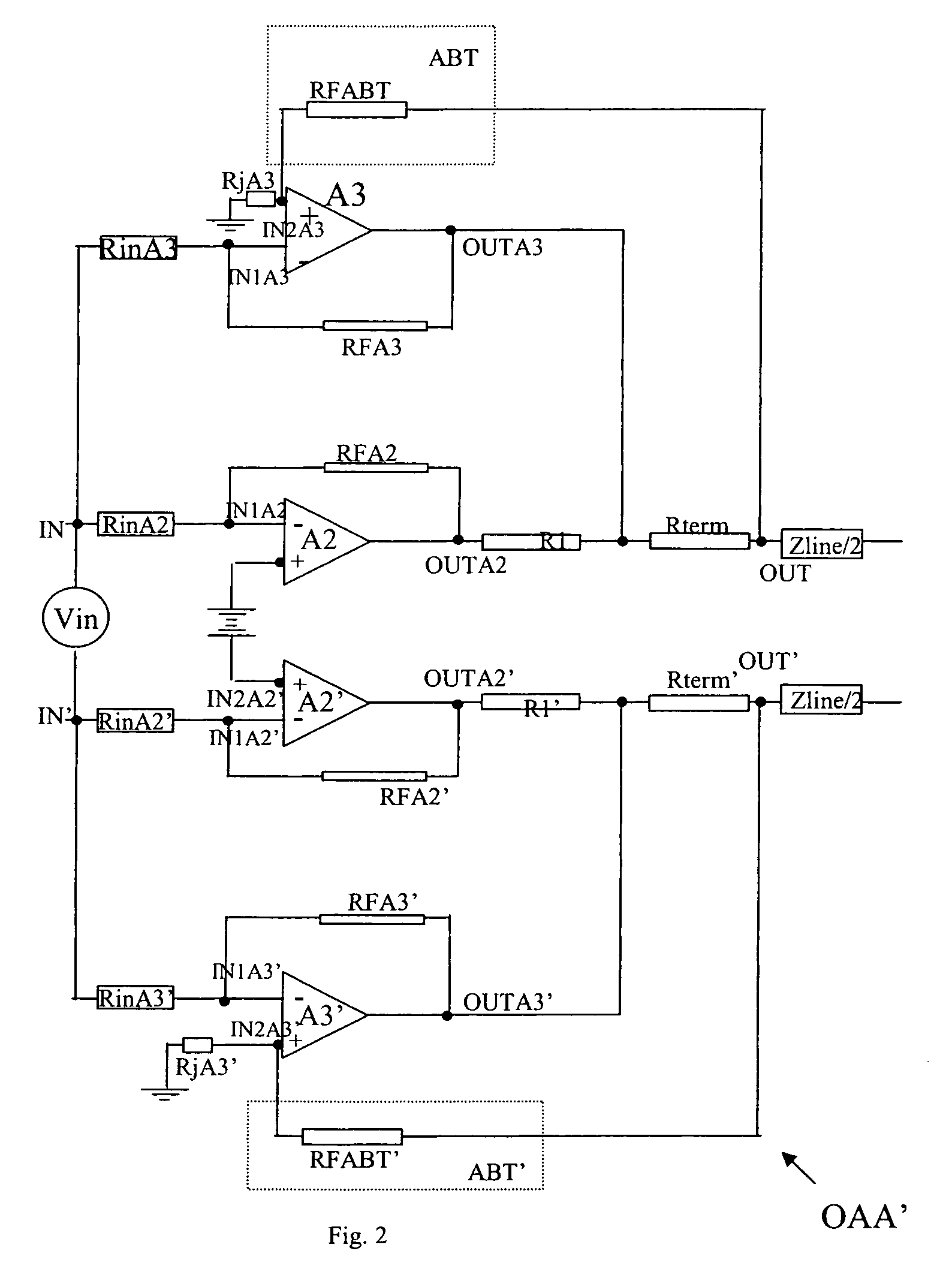
Operational amplifier arrangement
InactiveUS7042284B2Power efficient and and simpleSimple powerAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierOperational amplifier
An operational amplifier arrangement having a non-linear amplifier and a linear amplifier, both having a pair of input terminals one of which is coupled to an arrangement input terminal, and both having an output terminal that is coupled to an arrangement output terminal. The output terminal of the non-linear amplifier is further coupled to the output terminal of the linear amplifier via a series impedance. The output terminal of the linear amplifier is coupled to the arrangement output terminal via a terminating impedance. The arrangement includes an active back termination arrangement coupled between the arrangement output terminal and either one of the pair of input terminals of the linear amplifier. Preferably, the linear amplifier is receiving a supply voltage that exceeds the supply voltage received by the non-linear amplifier.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
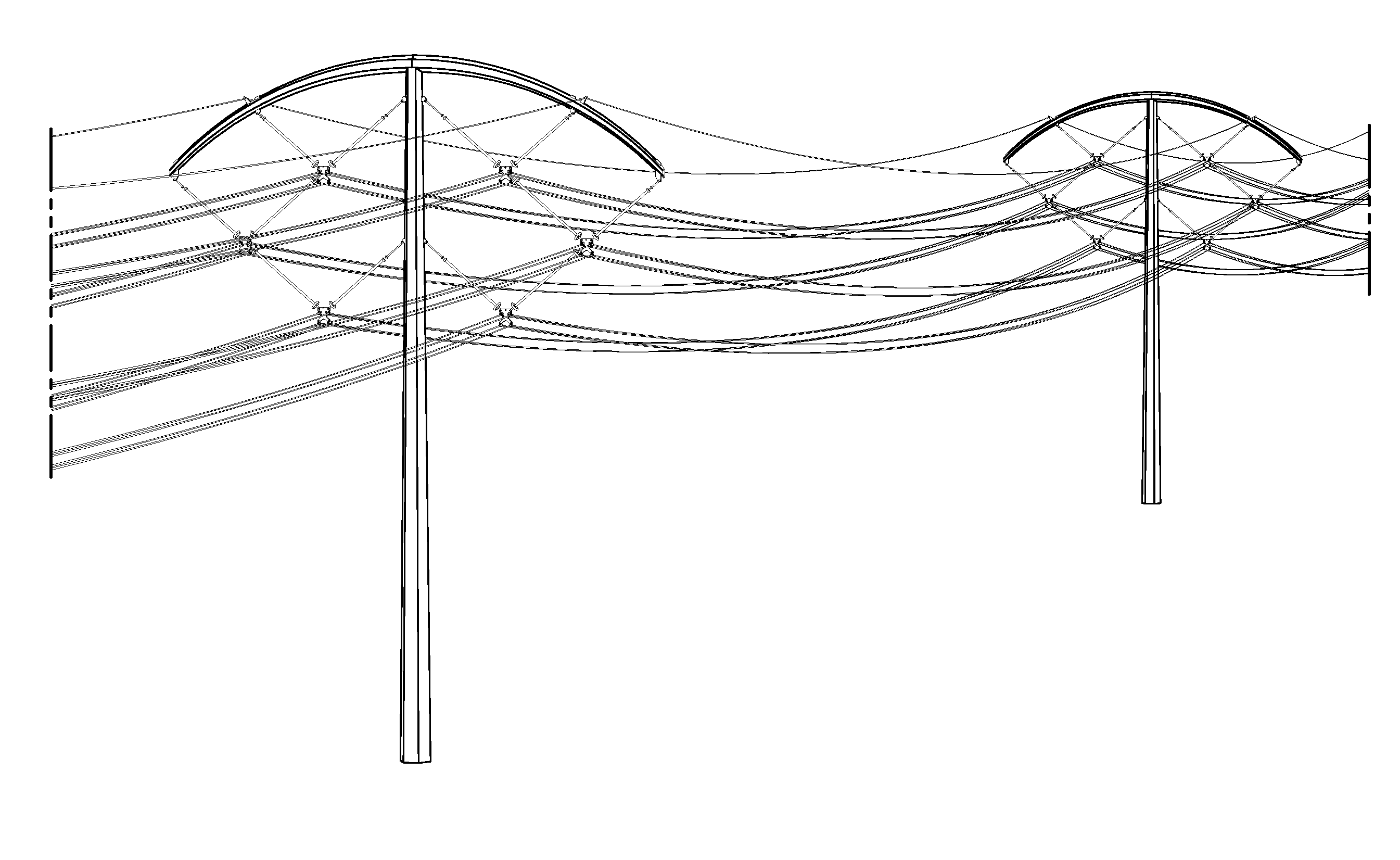
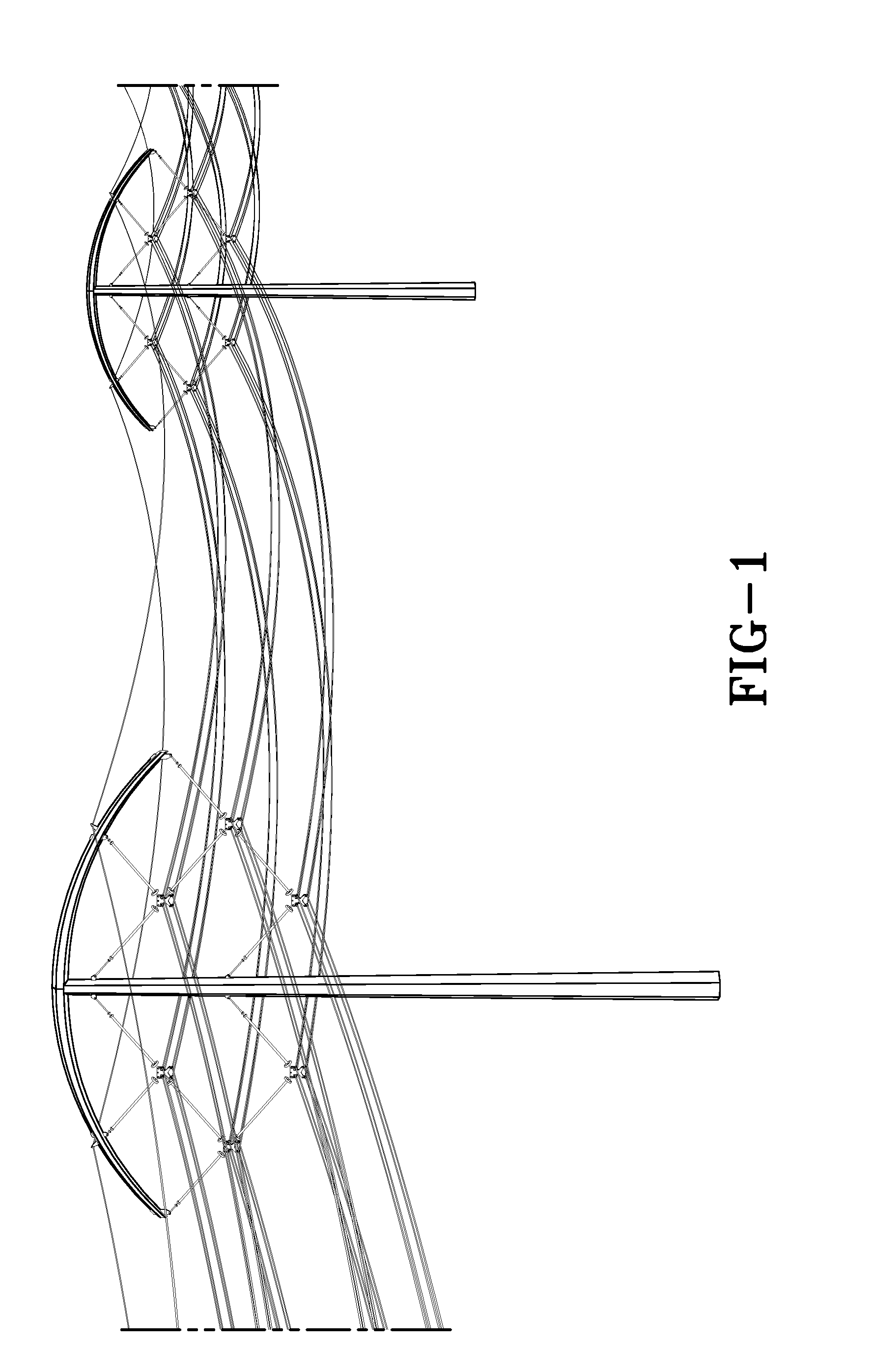
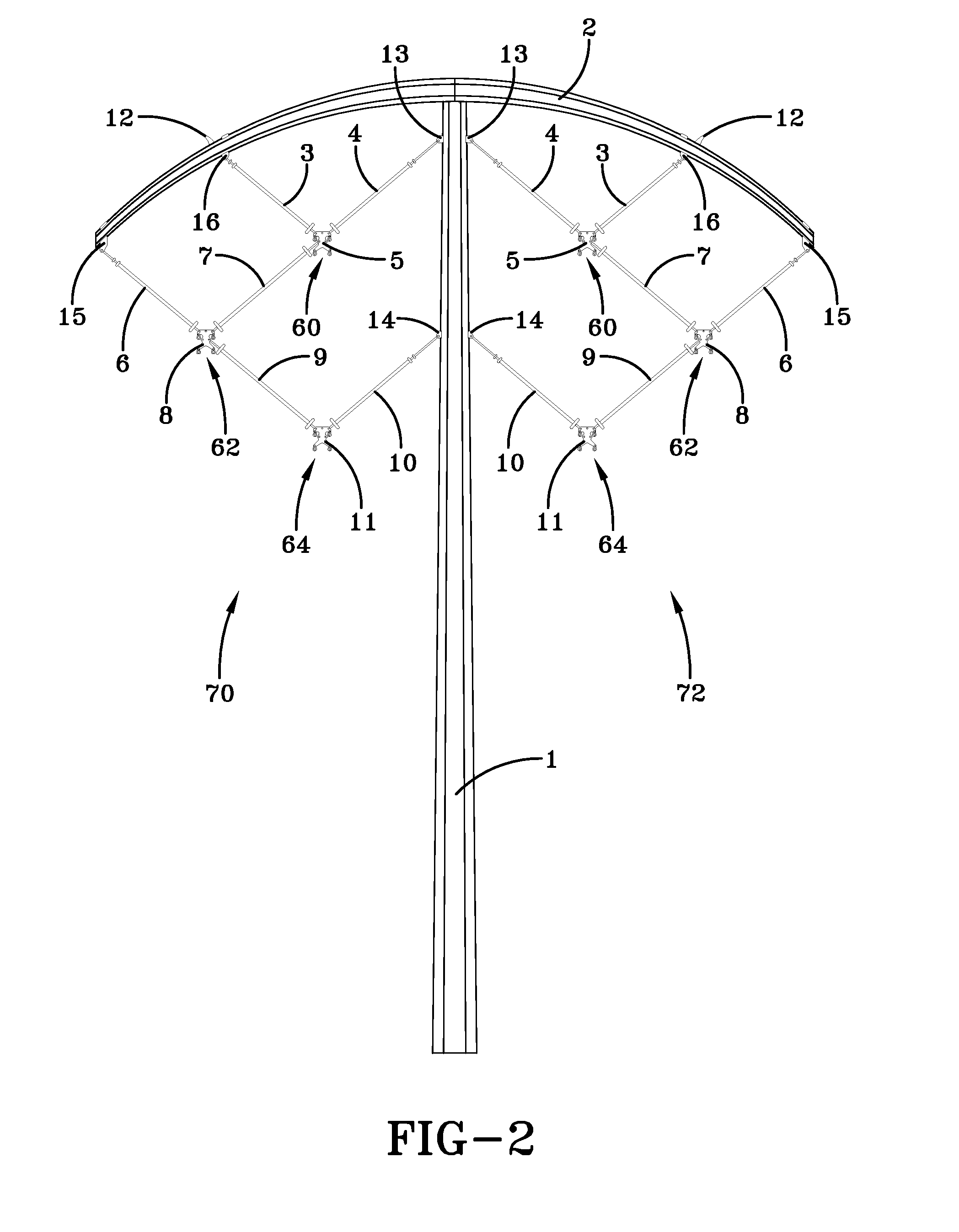
High-capacity/efficiency transmission line design
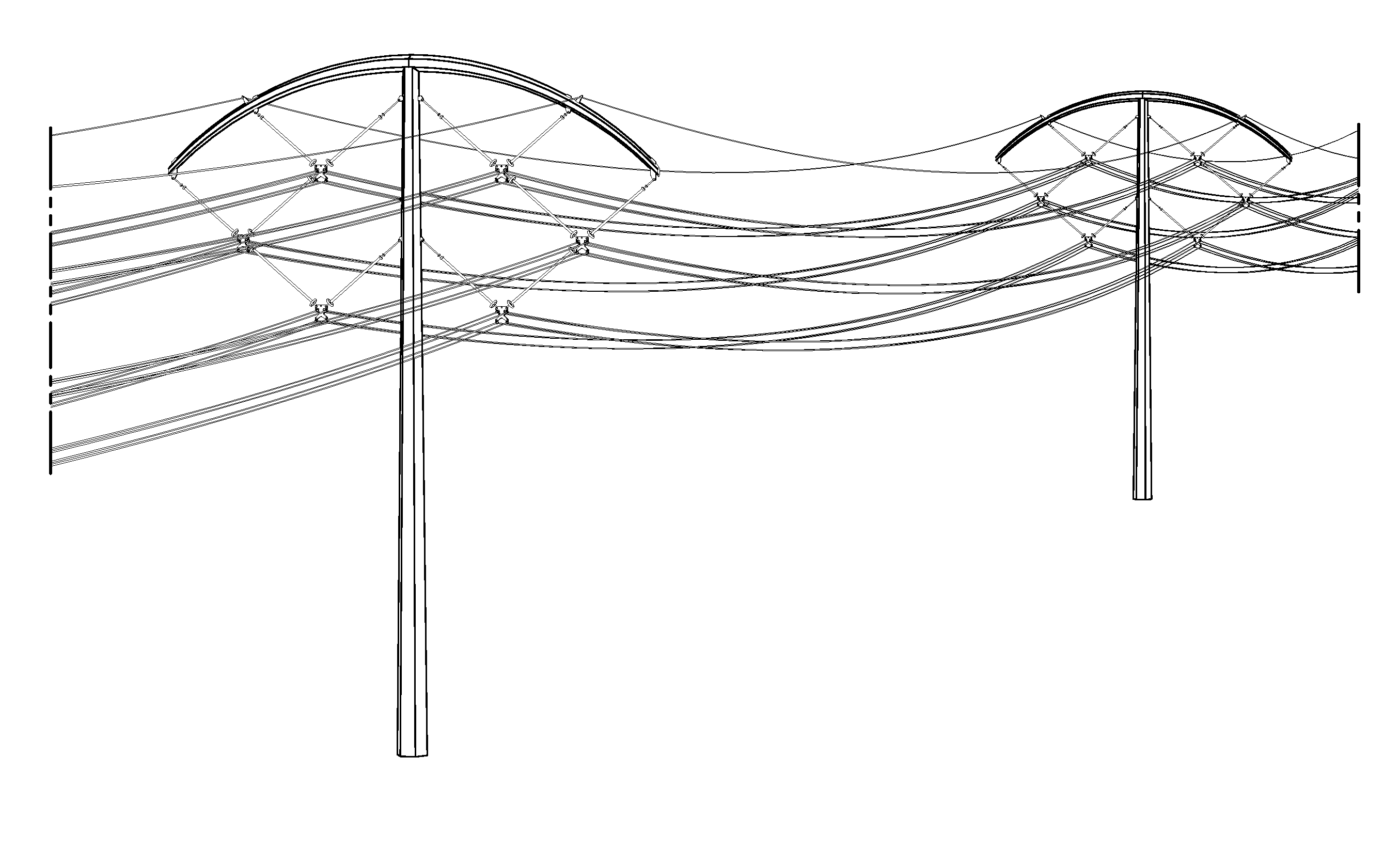
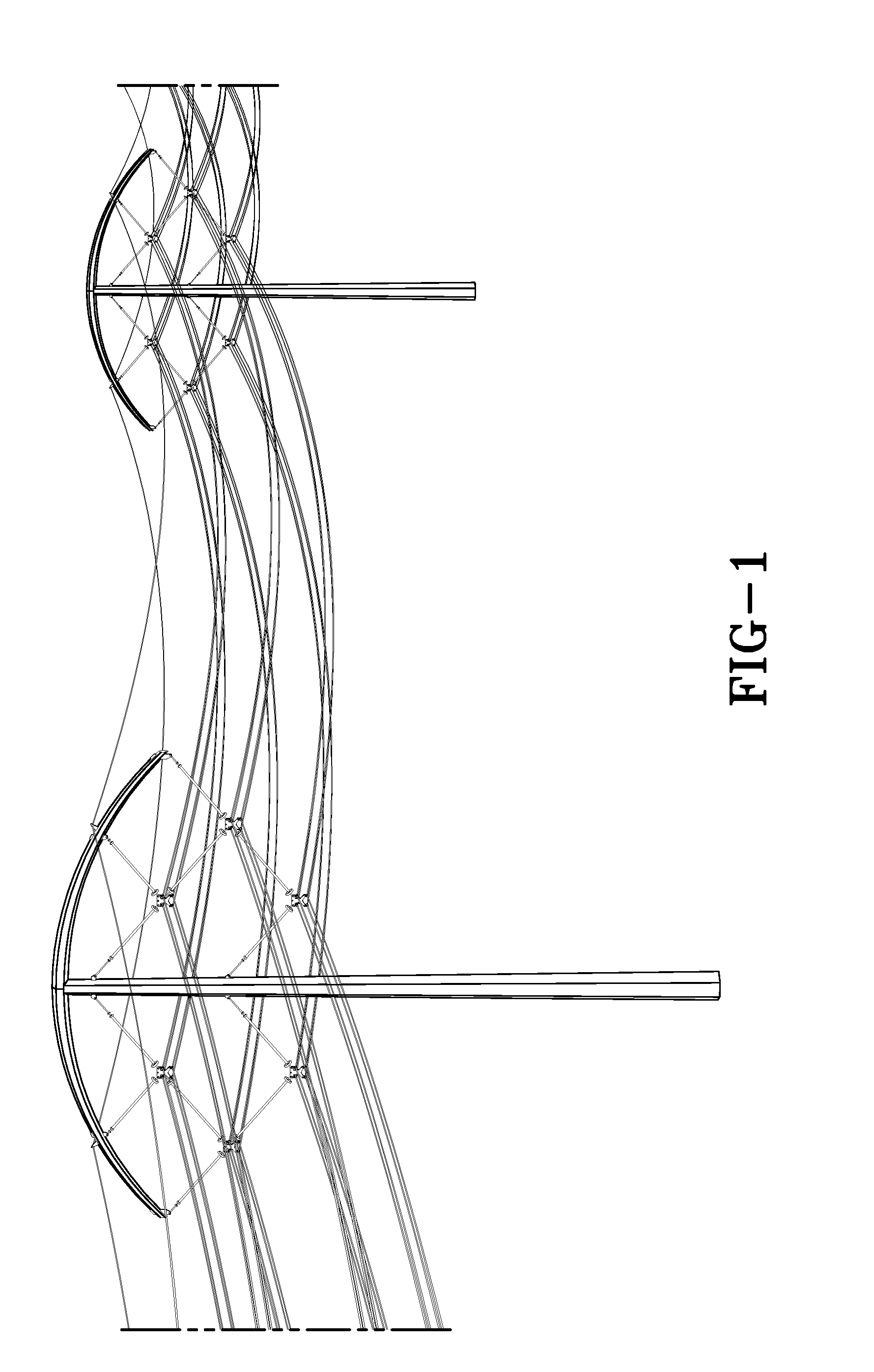
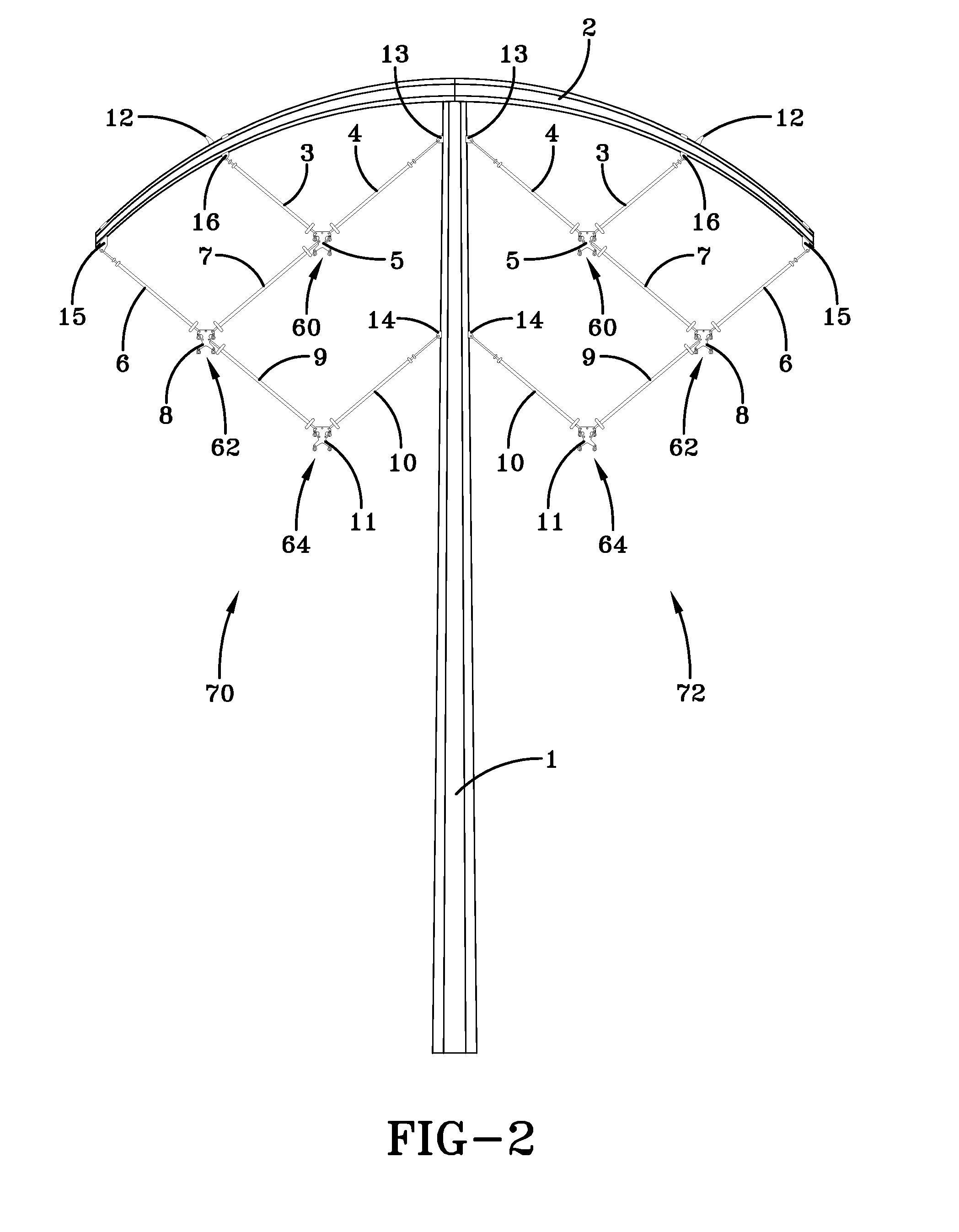
ActiveUS20130284512A1Efficient transportReduces its series impedanceTowersSpatial arrangements/dispositions of cablesTransmission towerElectrical resistance and conductance
A transmission tower structure for suspending from an arched crossarm a three phased circuit arranged in a compact delta configuration that improves the surge impedance loading (SIL) of a transmission line, reduces its series impedance, lowers both resistive and corona losses, and moderates electromagnetic fields and audible noise effects at the ground level—all achieved in a cost effective manner. The structure further has a low overall height and aesthetic appearance enhancing the public acceptance of the embodiments.
Owner:BOLD TRANSMISSION LLC
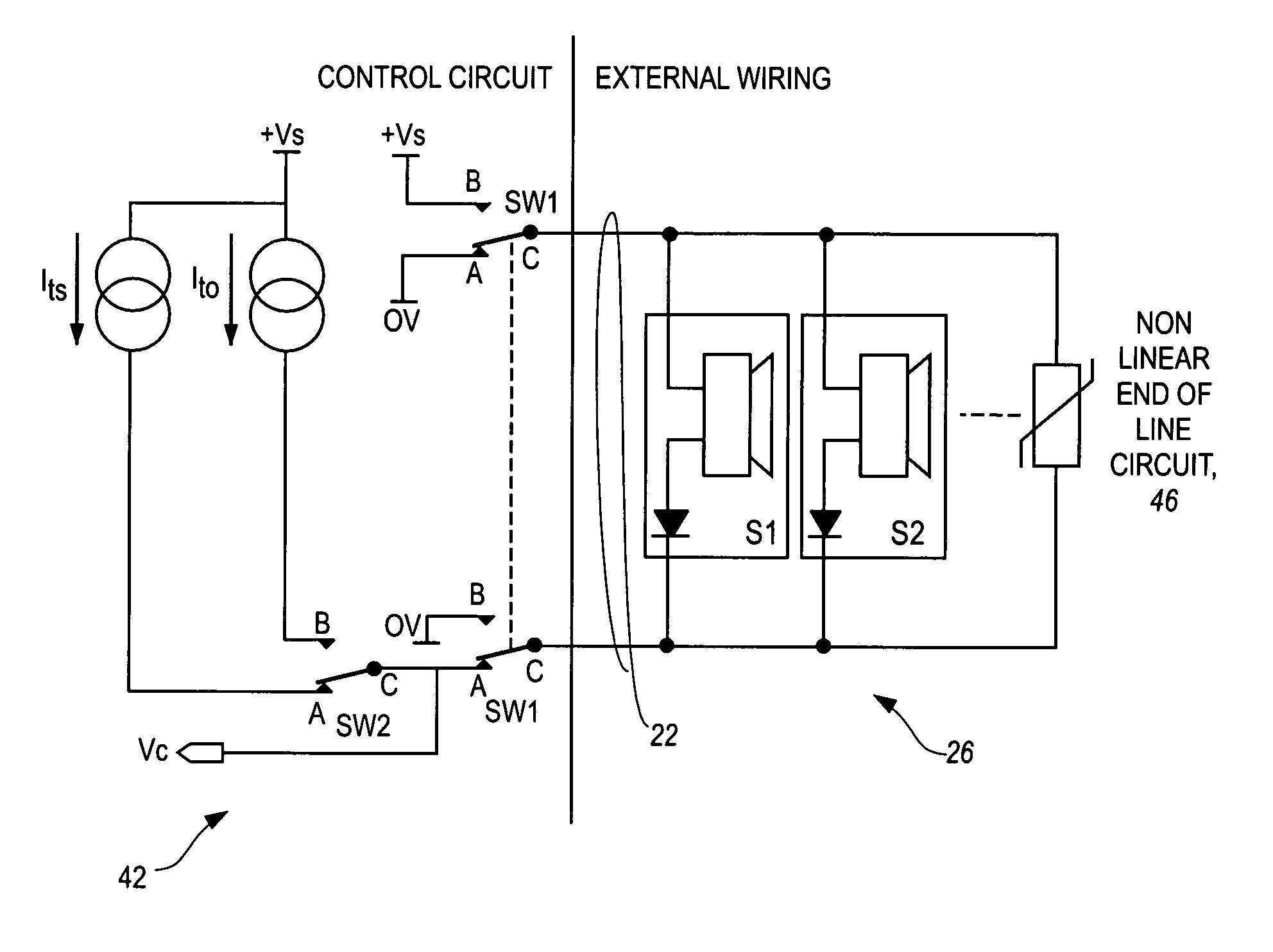
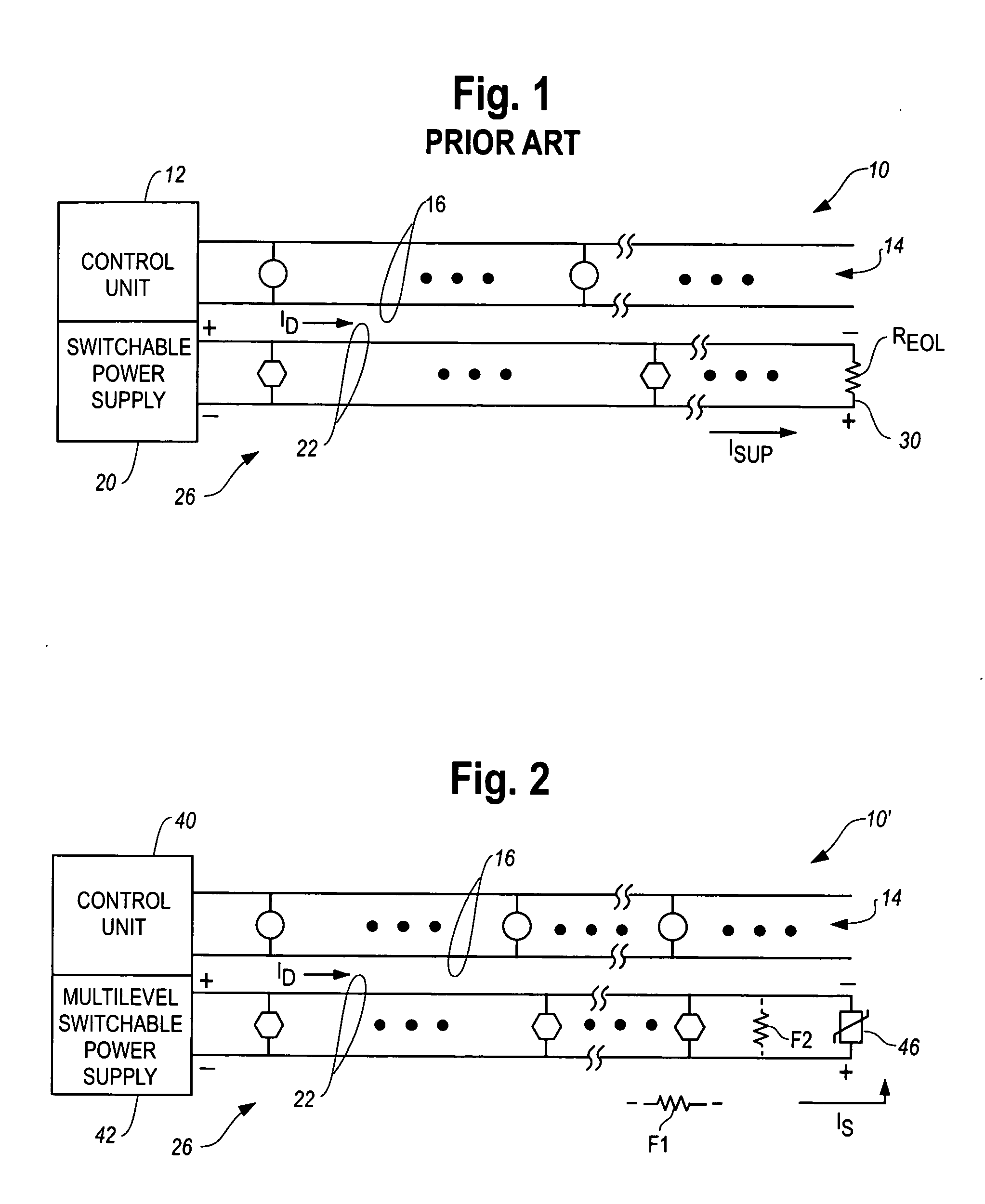
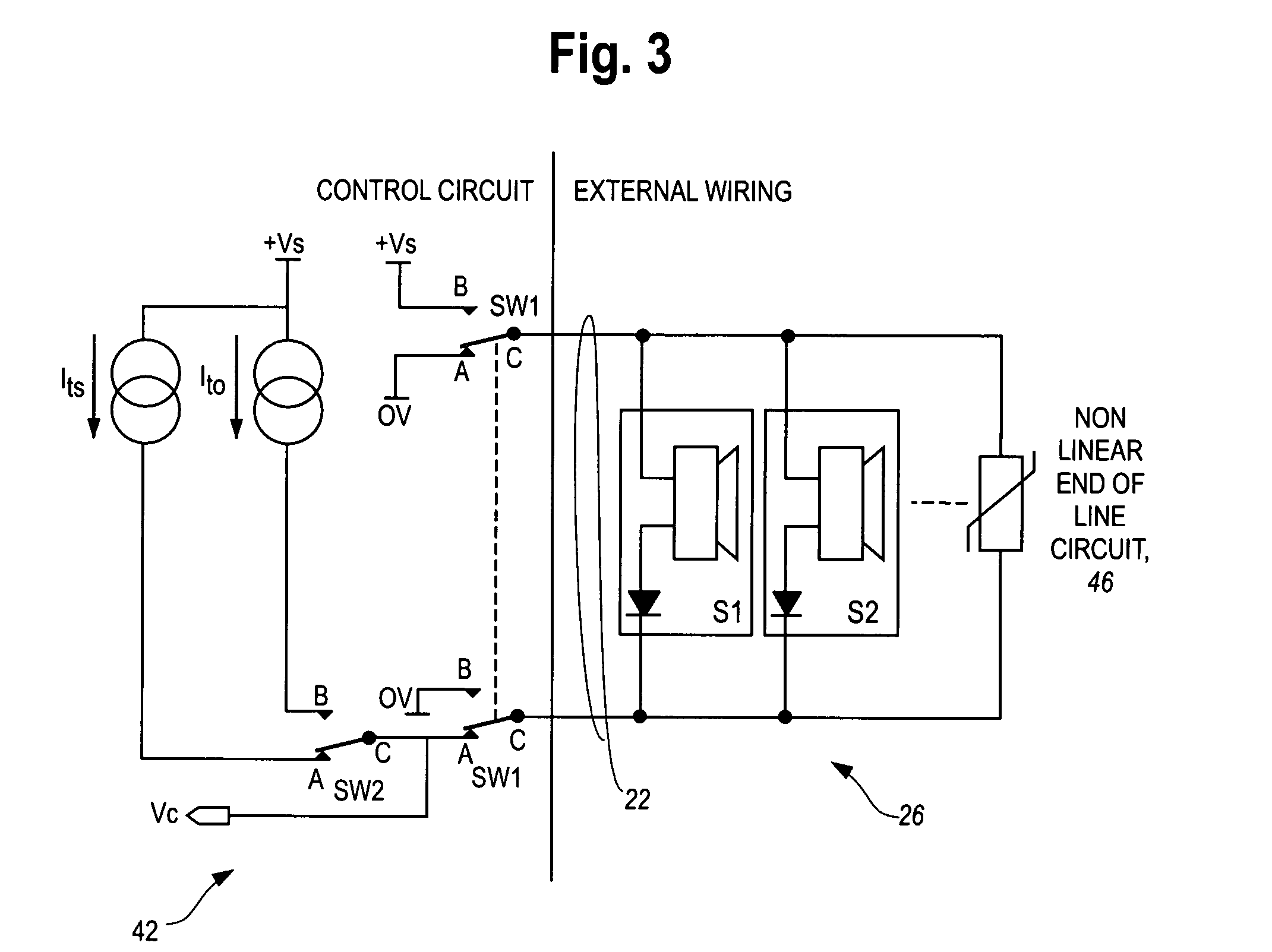
Monitoring of alarm system wiring
A supervisory method and apparatus provide for detection of “partial fault” conditions such as a relatively high series impedance in the wiring, or a relatively low parallel impedance across the wiring. A non-linear element, such as a semiconductor diode, can be used as an end of line element. The element functions as a current controlled dynamic impedance such that currents through the element can be used to detect low parallel leakage currents. Higher currents through the element can be used to detect partial open circuits.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
High-capacity/efficiency transmission line design
ActiveUS8952251B2Easy constructionLow costAdjusting/maintaining mechanical tensionSpatial arrangements/dispositions of cablesTransmission towerElectrical resistance and conductance
A transmission tower structure for suspending from an arched crossarm a three phased circuit arranged in a compact delta configuration that improves the surge impedance loading (SIL) of a transmission line, reduces its series impedance, lowers both resistive and corona losses, and moderates electromagnetic fields and audible noise effects at the ground level—all achieved in a cost effective manner. The structure further has a low overall height and aesthetic appearance enhancing the public acceptance of the embodiments.
Owner:BOLD TRANSMISSION LLC
Low-Voltage Dips Generator Device
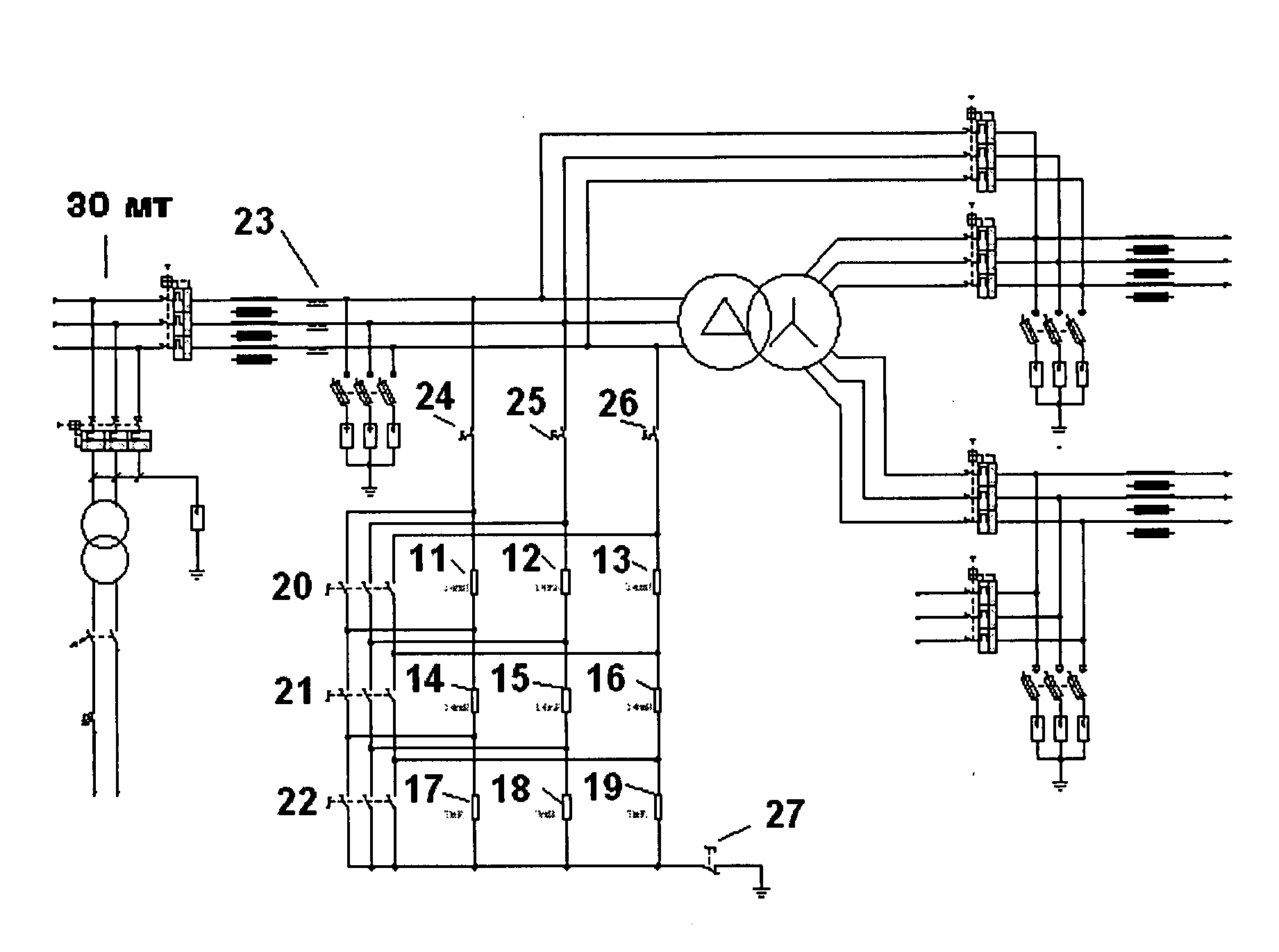
InactiveUS20090066166A1Machines/enginesEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionOutput transformerControl engineering
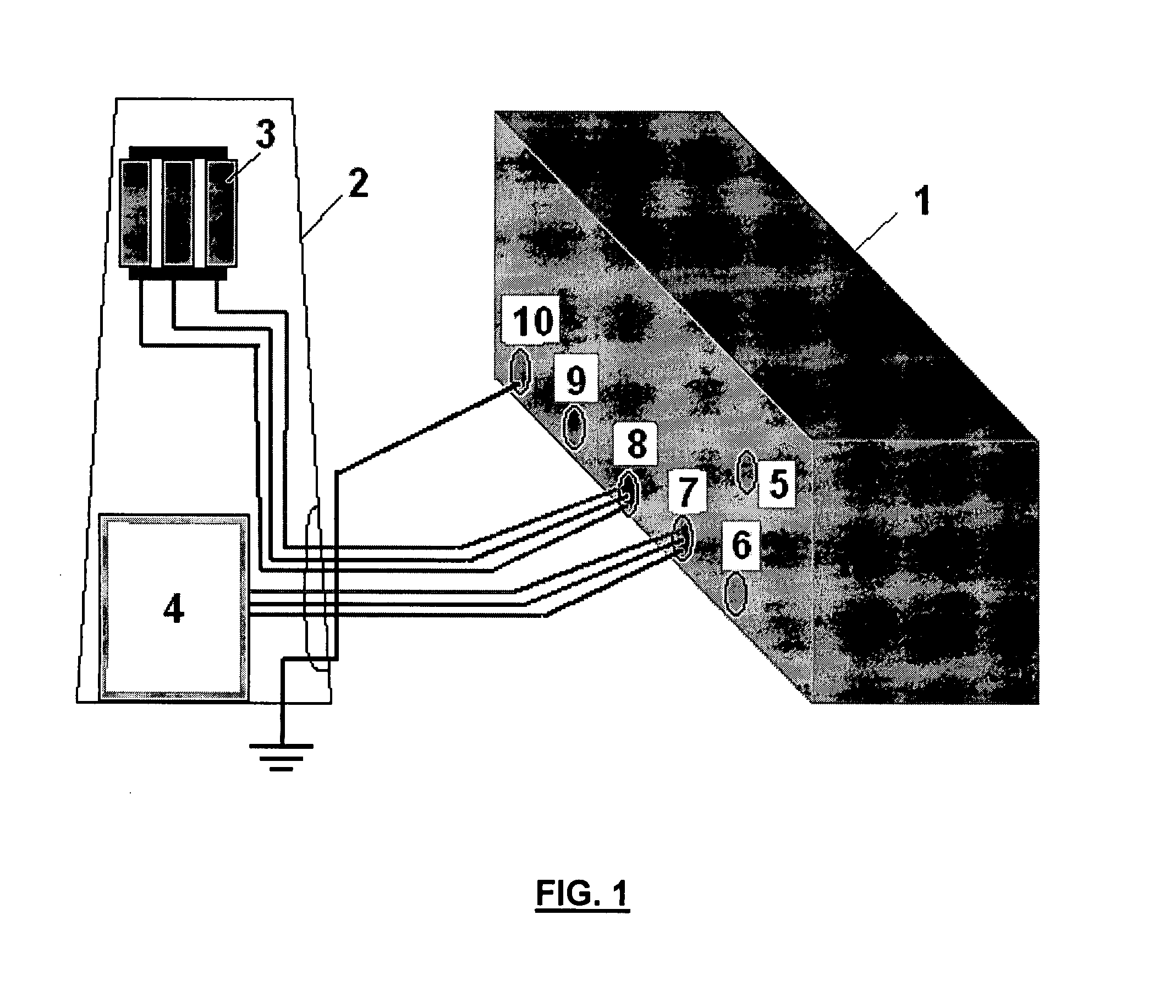
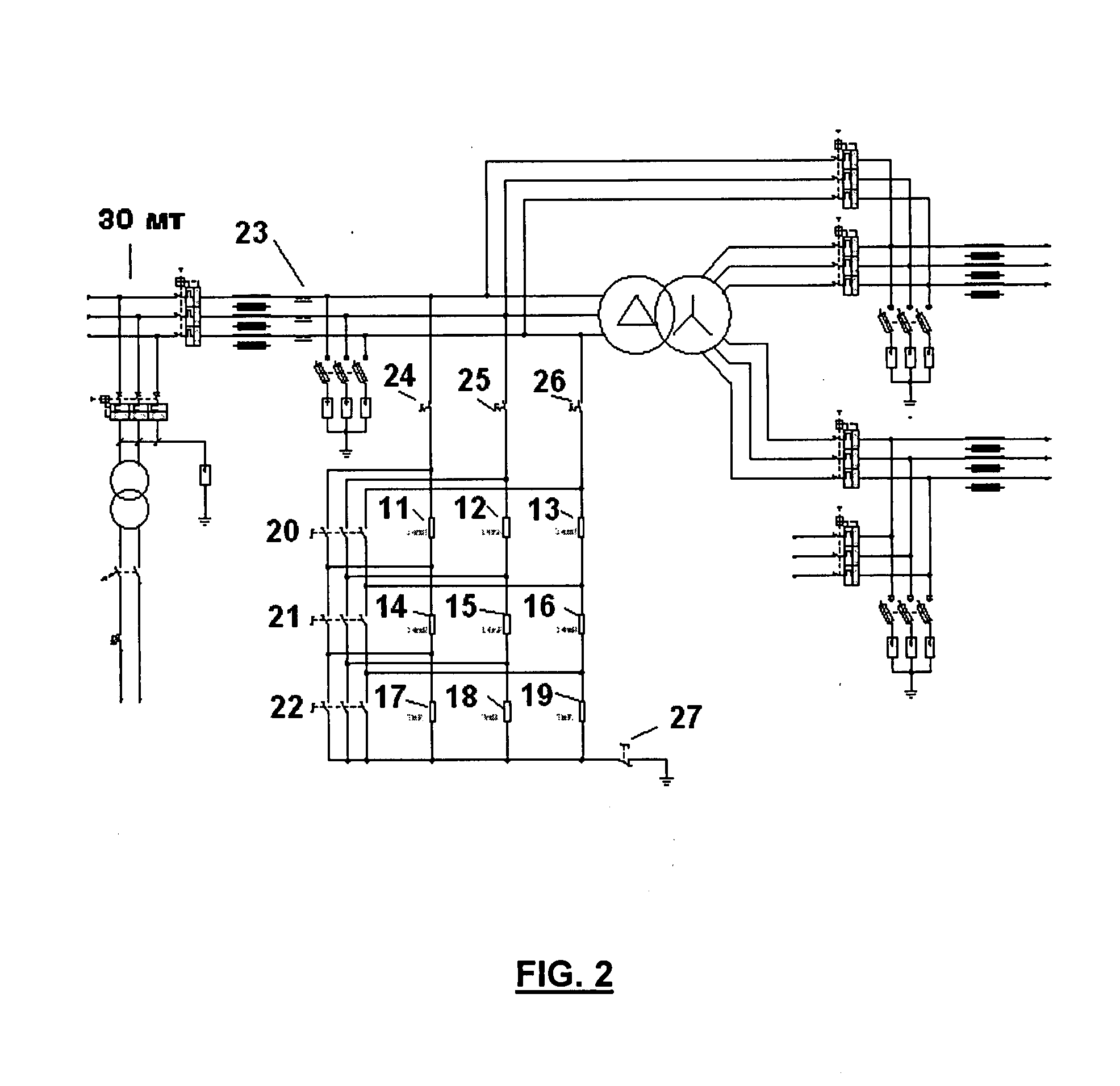
The invention relates to a device for generating low-voltage dips in an electrical power generator (2), particularly an aerogenerator, consisting of: a circuit which is disposed between the control cabinet (4) of the generator and the output transformer (3) to the network (30), comprising a transformer (31) and a plurality of in-series impedances (11, 14, 17; 12, 15, 18; 13, 16, 19) for each phase, having switches (24, 25, 26; 20, 21, 22; 27) associated therewith; and short-circuit generator means, selectively actuating the switches as a function of the type of voltage dip required.
Owner:GAMESA INNOVATION & TECH SA
Battery charge compensation
ActiveUS8421416B2Improve charging efficiencyImprove battery efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrical batteryEngineering
A battery charger and method for a rechargeable battery pack which includes various elements in series with the cells to be charged, including but not limited to current control FETs, a fuse, current sense resistor, and internal series impedance of the series connected cells to be charged. The charging current Ichg flowing through these series elements reduces the voltage applied to the cells, thus lengthening charging time. A compensation voltage Vcomp, which when added to the nominal charging voltage for the series connected cells overcomes these voltage drops, facilitates more efficient charging while avoiding over-voltage damage to the cells. Three voltages representing substantially all of the voltage drops reducing the charging voltage on the cells, are summed, and the result is a compensation voltage which is utilized to change the nominal charge voltage for the battery to overcome these voltage drops.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
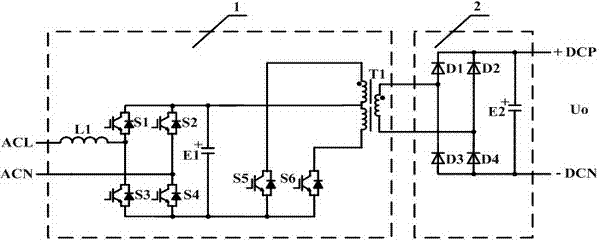
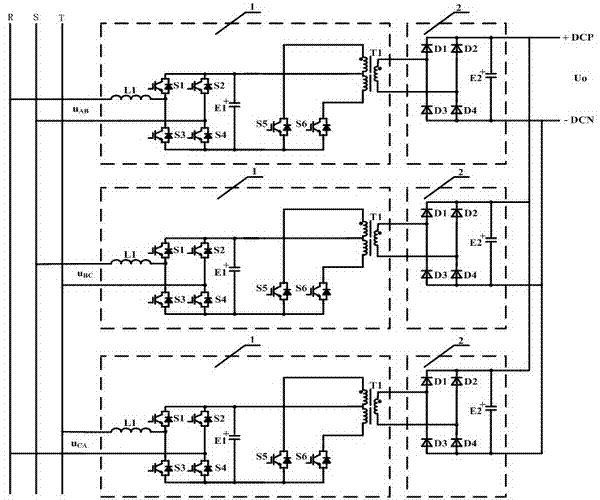
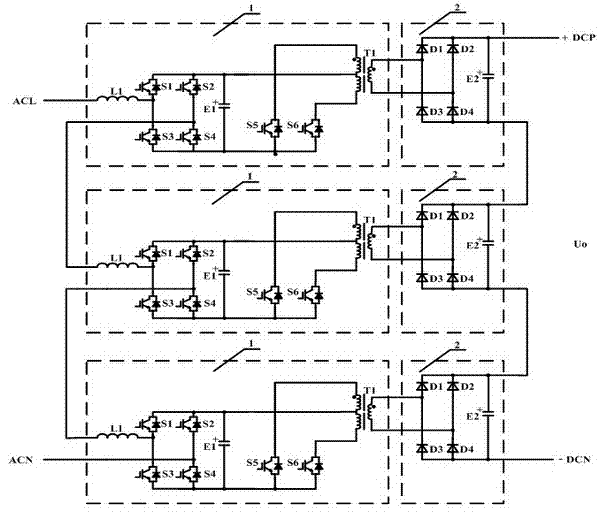
Full-bridge rectification-DC push-pull inverter ac-dc converter
InactiveCN102291019ASimple structureReduce manufacturing costAc-dc conversion without reversalDc-dc conversionCapacitanceFull bridge
The invention discloses a full-bridge rectification-DC push-pull inverter AC-DC converter in the technical field of power electronic conversion, which includes a step-down circuit and a rectifier circuit connected in series in sequence, and the step-down circuit converts the high voltage through a single-phase full-control rectification circuit The power frequency AC voltage is converted into high-voltage DC voltage, and then converted into high-voltage and high-frequency pulsed AC voltage through a push-pull converter, and the voltage is stepped down by a transformer to obtain low-voltage and high-frequency pulsed AC voltage; the rectifier circuit rectifies the low-voltage and high-frequency pulsed AC voltage, The low-voltage DC voltage is obtained, and then filtered by the output filter capacitor to obtain a stable DC output. The latter stage of the circuit can be connected in series with an impedance conversion circuit to obtain a linear input impedance, and after reflection to the high-voltage AC power grid, the linear input impedance and unit input power factor of the grid side can be obtained. The invention realizes the conversion of high-voltage AC voltage to low-voltage DC voltage through a step-down circuit and a rectifier circuit, and has the advantages of fewer power devices, simple overall structure and more perfect overall performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Low impedance series coupled radio frequency directional power detector
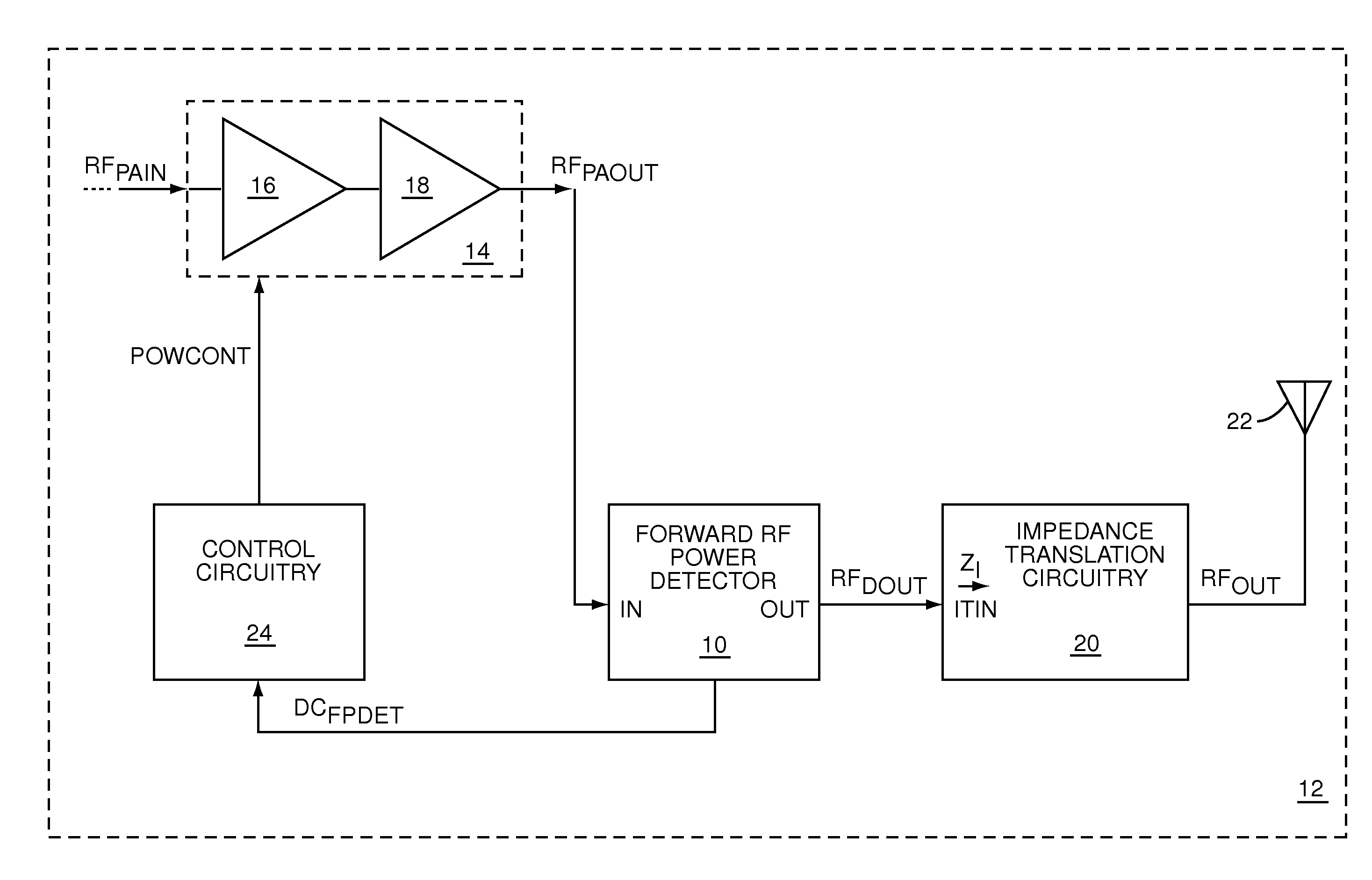
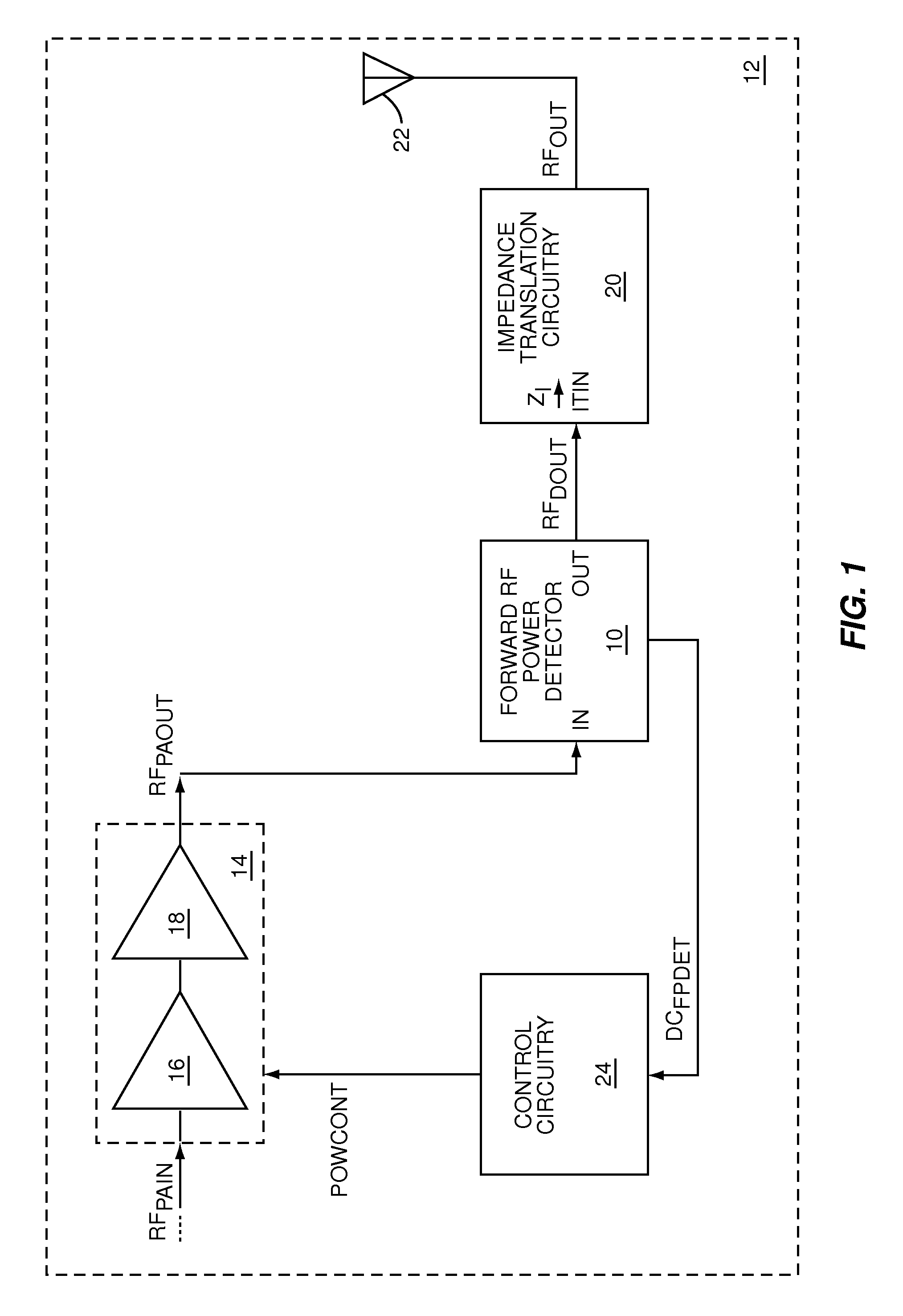
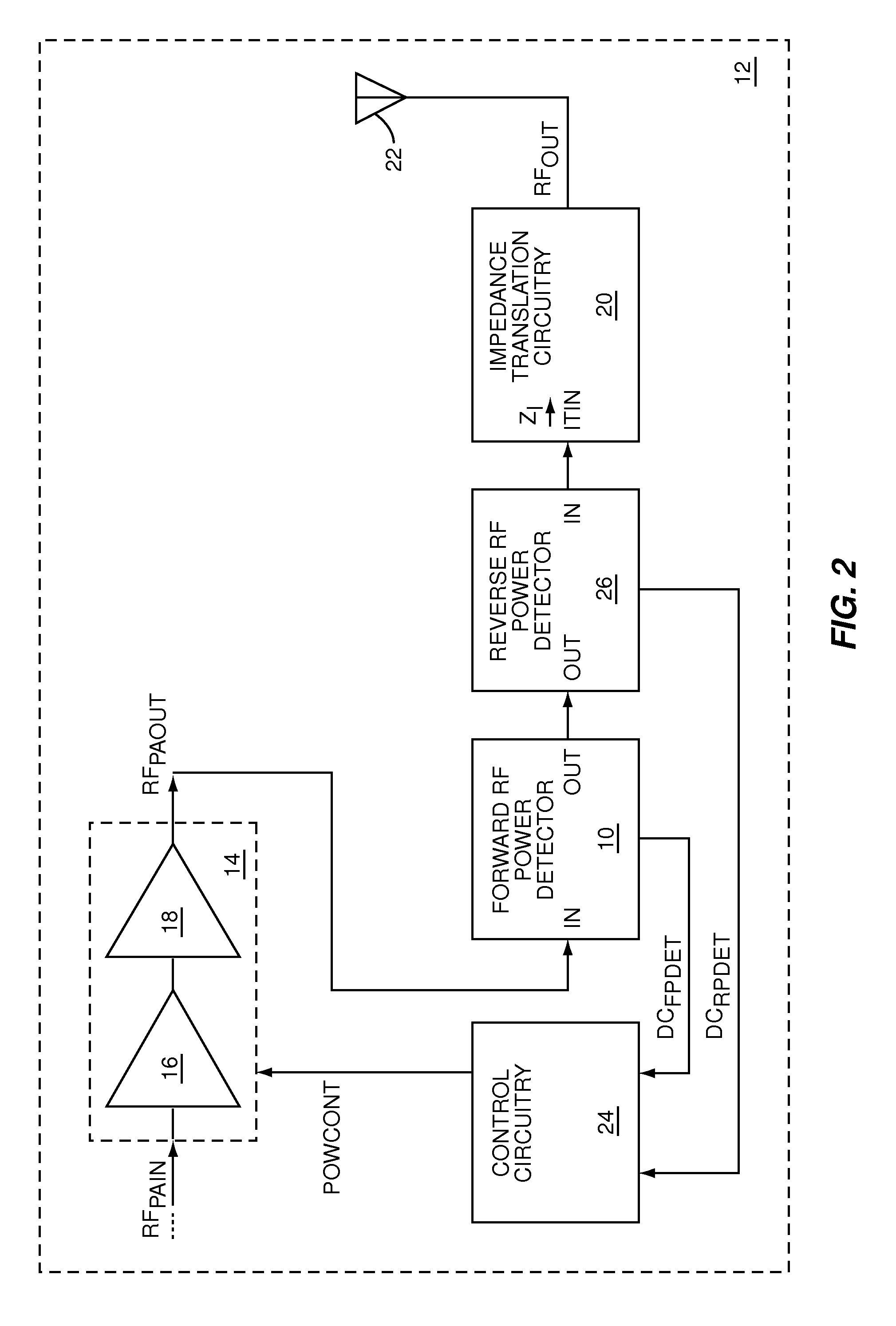
ActiveUS7977947B1Resonant long antennasNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsPhase shiftedPower detector
The present invention is a low series impedance directional power detector, which may be used to measure either forward or reverse power in a radio frequency (RF) circuit. The directional power detector includes current detection circuitry to directionally measure current, voltage detection circuitry to measure voltage, and combining circuitry to combine the directional RF current measurements and the RF voltage measurements into a combined RF measurement, which is indicative of directional power. The current detection circuitry and voltage detection circuitry apply any phase-shifts that are needed to detect power in the direction of interest and ignore power in the opposite direction when the directional power detector is presented with a complex load.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Parallel HTS transformer device
A superconducting transformer system is configured to be included within a utility power grid having a known fault current level. The superconducting transformer system includes a non-superconducting transformer interconnected between a first node and a second node of the utility power grid. A superconducting transformer is interconnected between the first node and the second node of the utility power grid. The superconducting transformer and the non-superconducting transformer are electrically connected in parallel. The superconducting transformer has a lower series impedance than the non-superconducting transformer when the superconducting transformer is operated below a critical current level and a critical temperature. The superconducting transformer is configured to have a series impedance that is at least N times the series impedance of the non-superconducting transformer when the superconducting transformer is operated at or above one or more of the critical current level and the critical temperature. N is greater than 1 and is selected to attenuate, in conjunction with an impedance of the non-superconducting transformer, the known fault current level by at least 10%.
Owner:AMERICAN SUPERCONDUCTOR
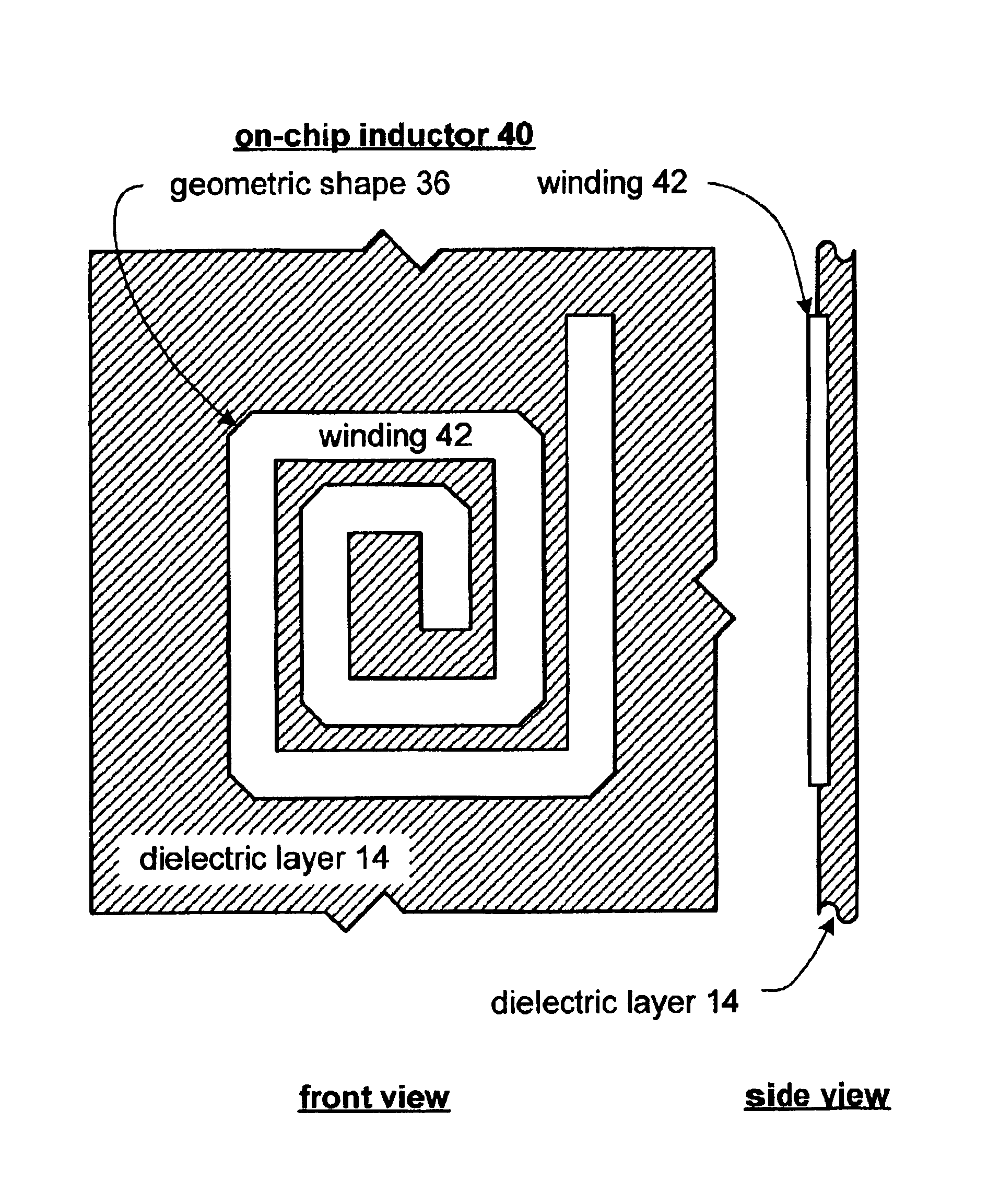
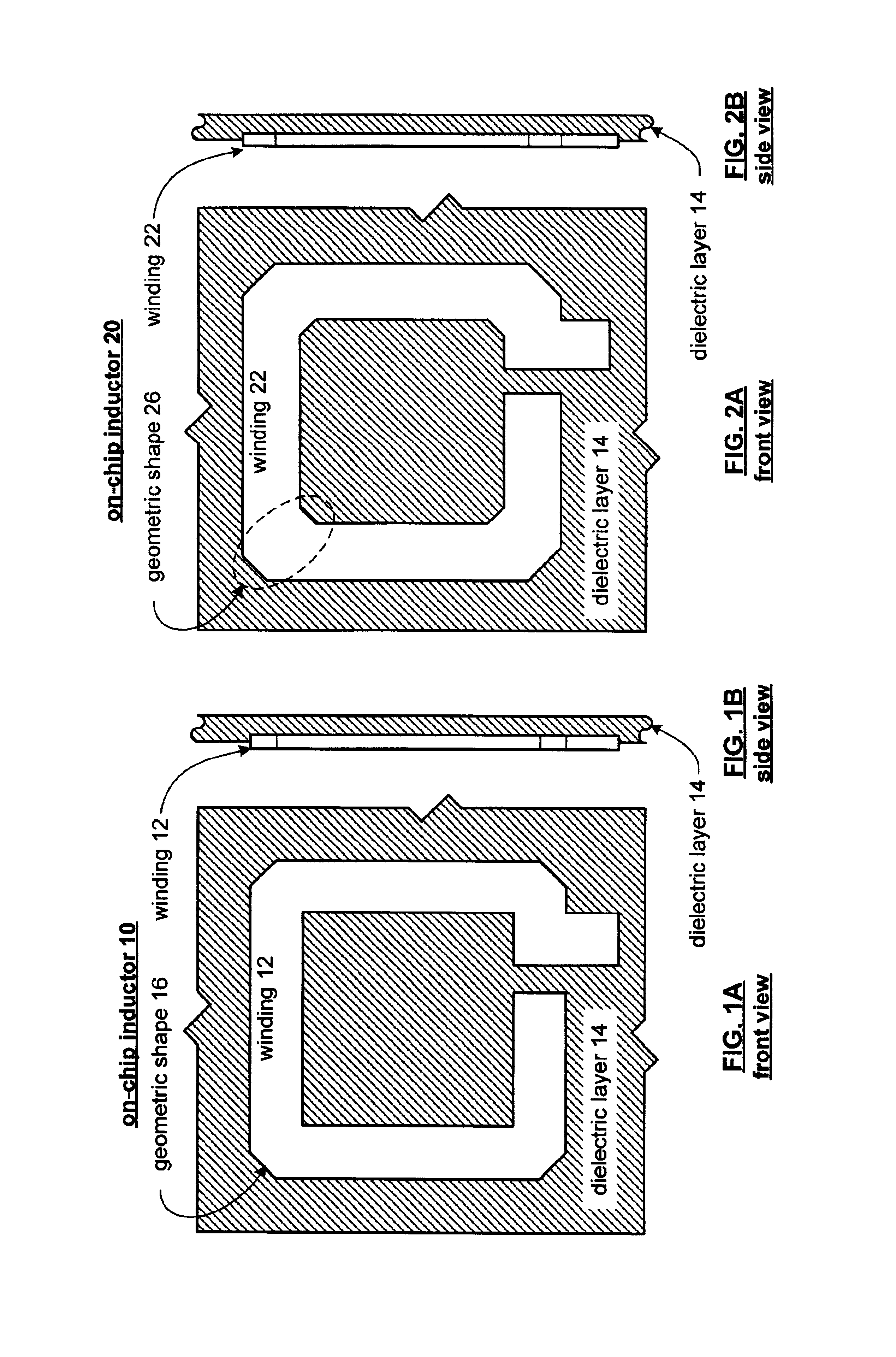
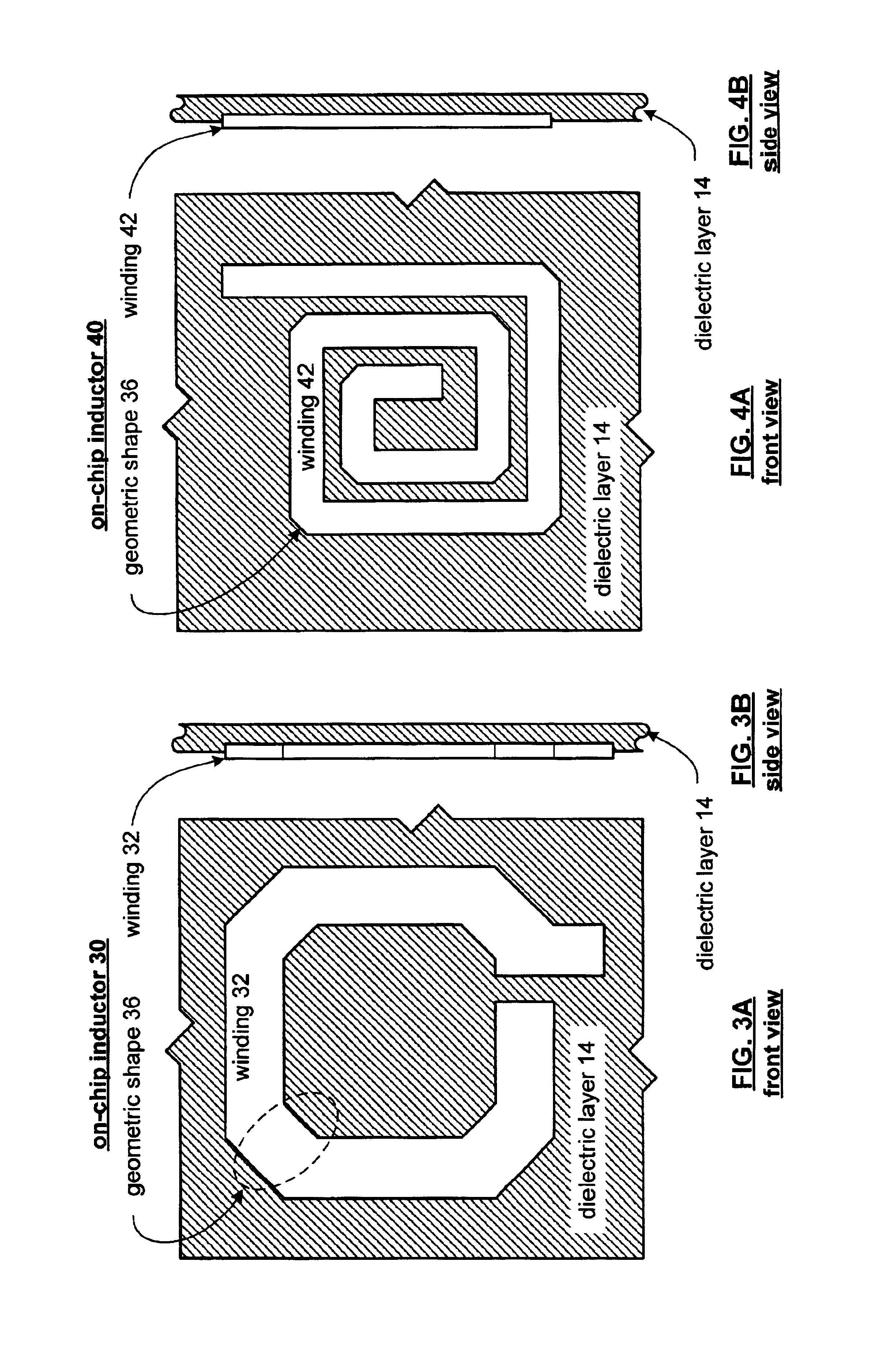
On-chip inductor having a square geometry and high Q factor and method of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS6937128B2Lower impedanceReduce capacitanceTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsSolid-state devicesTransformerEngineering
An on-chip inductor and / or on-chip transformer includes at least one dielectric layer and at least one conductive winding on the at least one dielectric layer. The conductive winding has a substantially square geometry and has at least its exterior corners geometrically shaped to reduce impedance of the conductive winding at a particular operating frequency. Since the quality factor of an on-chip inductor is inversely proportional to the effective series impedance of an inductor at an operating frequency, by reducing the effective series impedance, the quality factor is increased.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Parallel Connected HTS Utility Device and Method of Using Same
ActiveUS20100149707A1Superconductors/hyperconductorsNormal-superconductive switchable devicesElectricityPower grid
A method of controlling fault currents within a utility power grid is provided. The method may include coupling a superconducting electrical path between a first and a second node within the utility power grid and coupling a non-superconducting electrical path between the first and second nodes within the utility power grid. The superconducting electrical path and the non-superconducting electrical path may be electrically connected in parallel. The superconducting electrical path may have a lower series impedance, when operated below a critical current level, than the non-superconducting electrical path. The superconducting electrical path may have a higher series impedance, when operated at or above the critical current level, than the non-superconductor electrical path.
Owner:AMERICAN SUPERCONDUCTOR
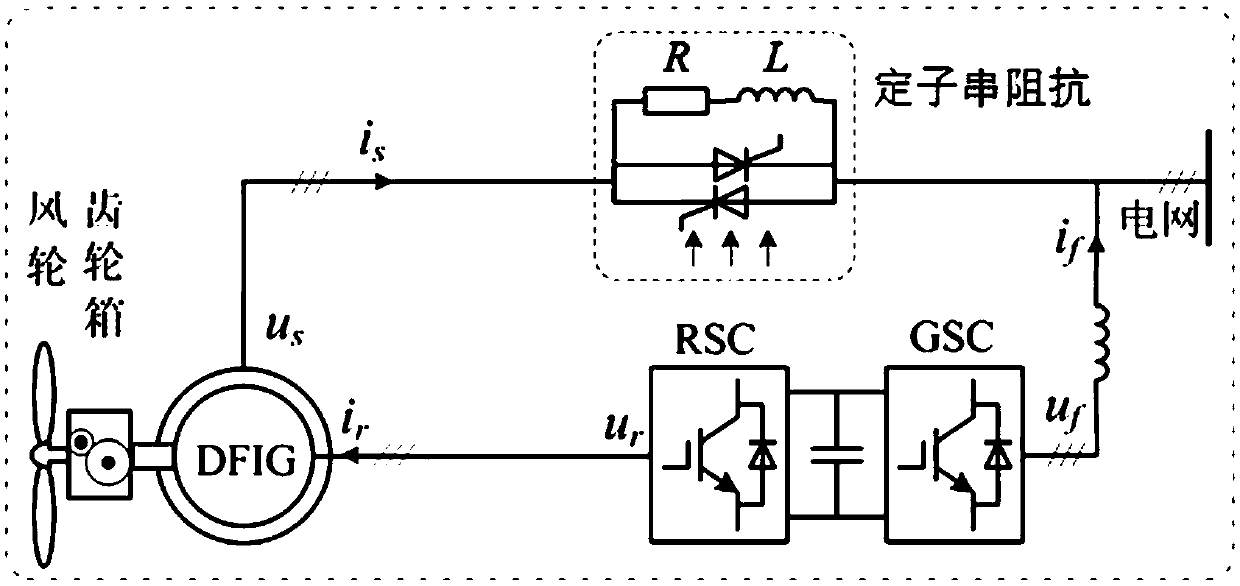
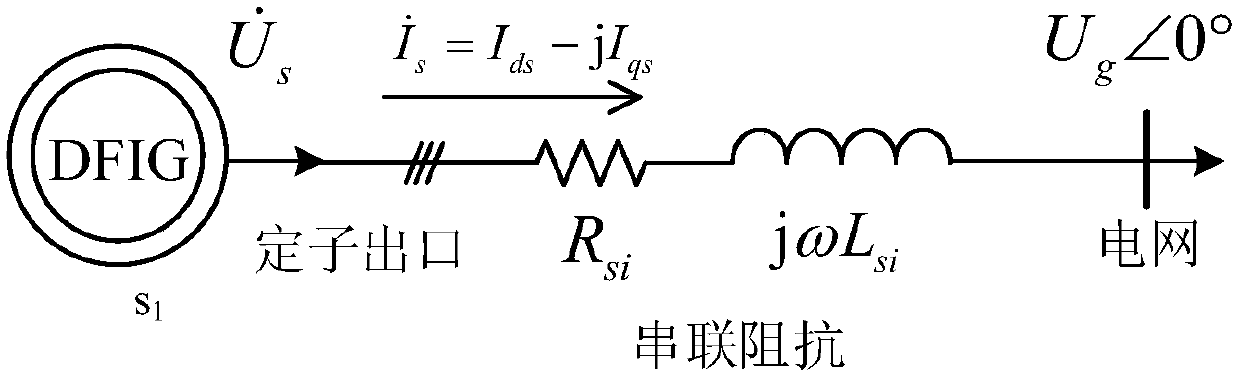
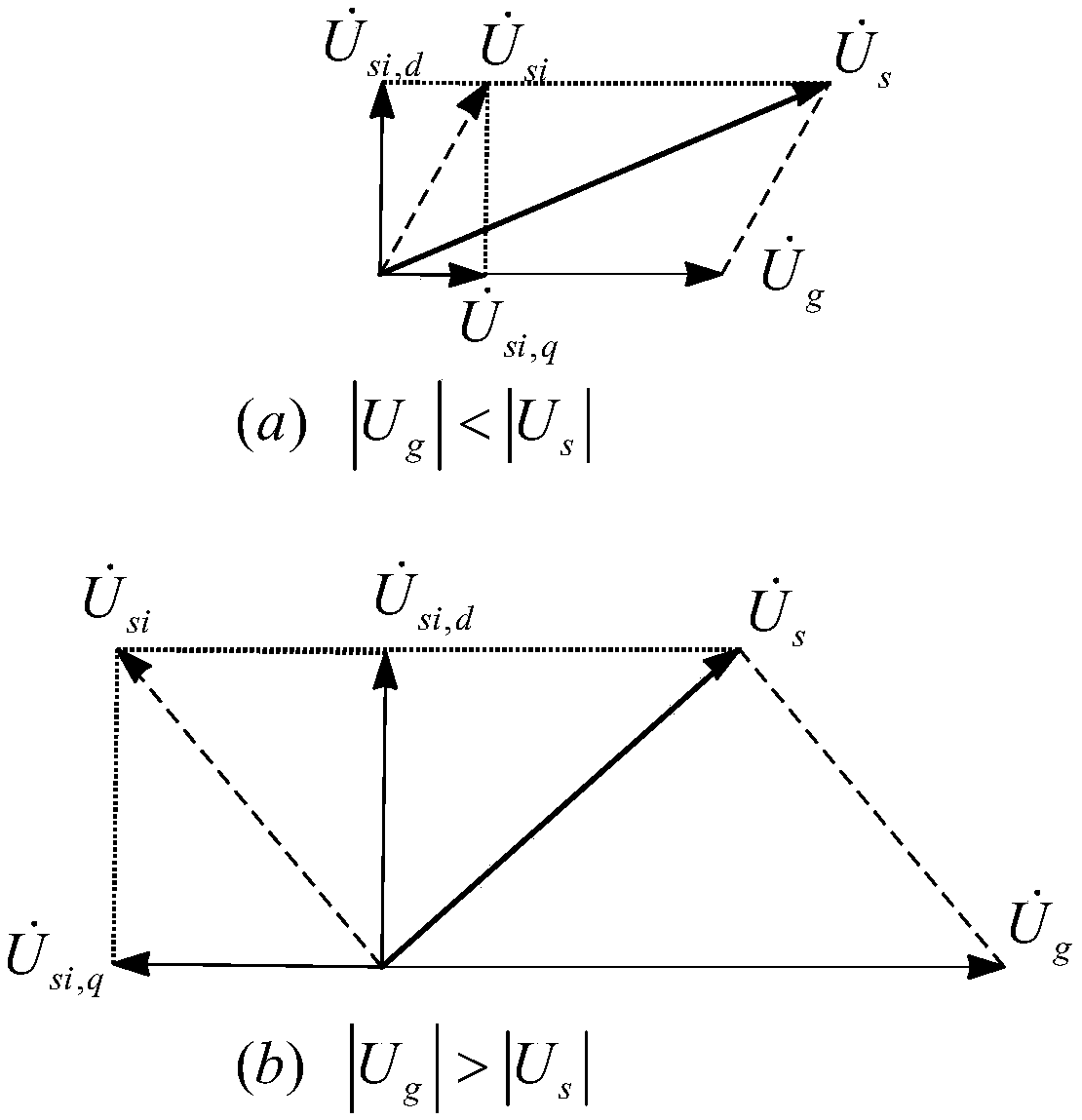
Stator series impedance-based double-fed wind generation set high/low voltage ride through system and method
ActiveCN109617125AAddressing Synthetic Fault Ride-ThroughGuaranteed availableSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
The invention provides a stator series impedance-based double-fed wind generation set high / low voltage ride through system and method. The system comprises a DFIG stator loop connected with a power grid, wherein the DFIG stator loop comprises a filter inductor, a network side converter, a rotor side converter and a double-fed wind generation set, which are connected in sequence; a serial impedanceprotection circuit is arranged between the double-fed wind generation set and the filter inductor; the serial impedance protection circuit comprises a rapid switch and an impedance branch, which areconnected in parallel; the impedance branch comprises an impedance inductor and an impedance resistor, which are connected in series. According to the system and method, power grid comprehensive faultride through comprising high / low-voltage faults of DFIG is solved, complete compensation of DFIG stator voltage during faults is realized, the DFIG is enabled to satisfy rated working conditions, andtotal-power stator reactive support problem caused to power grids by DFIG during high / low-voltage faults is solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
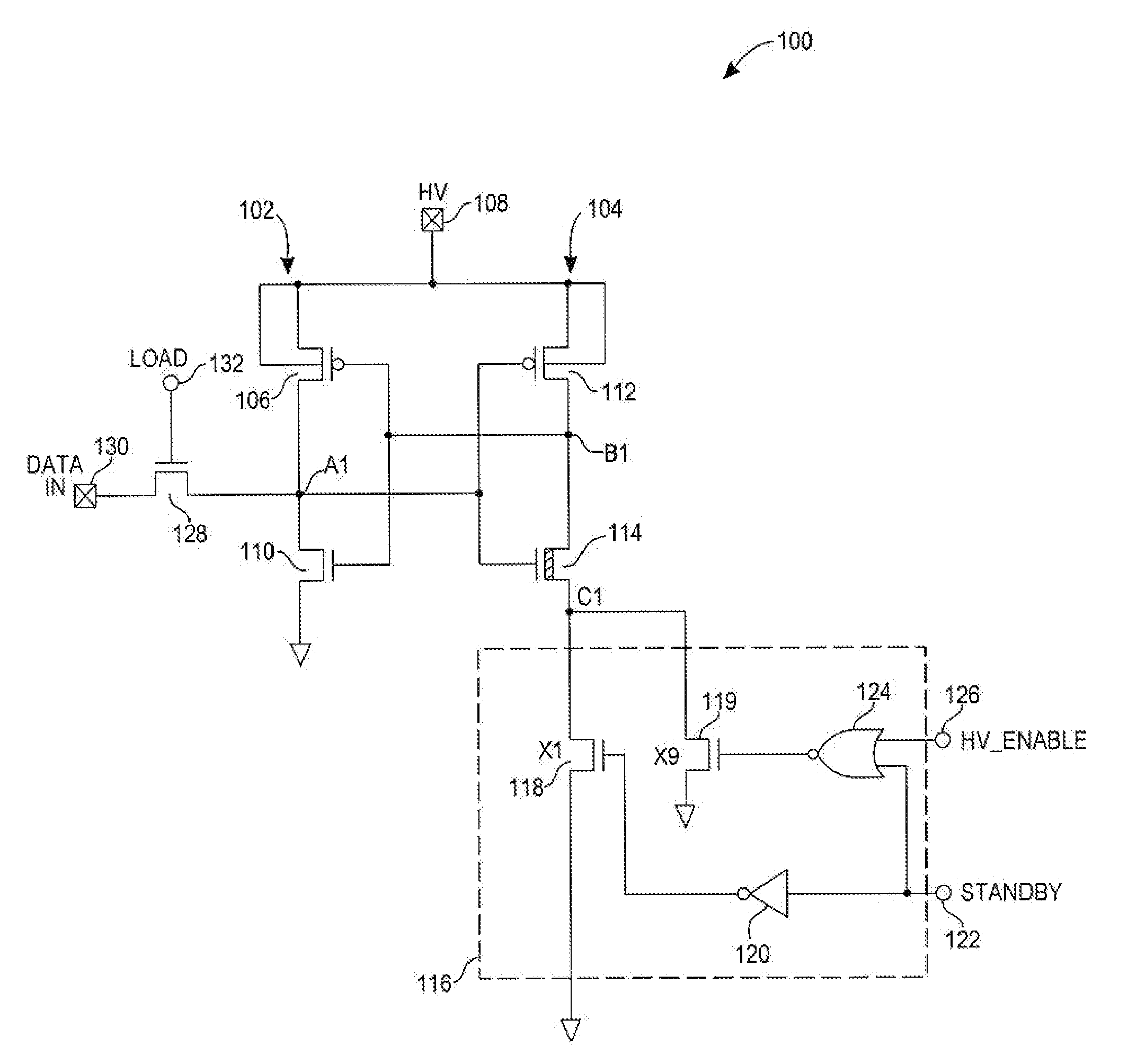
Method and apparatus to prevent high voltage supply degradation for high-voltage latches of a non-volatile memory
ActiveUS7369446B2Limit leakage currentHigh impedanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageCMOSHigh pressure
An improved cross-coupled CMOS high-voltage latch that is used for storing data bits to be written to memory cells of a non-volatile memory is provided with a switching circuit that, during writing of data bits into the memory cells of the latch, provides a high series impedance between one leg of the latch and ground to limit leakage current. A large number of latches are connected in parallel and their accumulated leakage currents are limited by the switching circuit to prevent overload of a high-voltage generator, such as a charge pump circuit, for the high-voltage latch, so that data can be properly written in the memory cells of the non-volatile memory.
Owner:SONRAI MEMORY LTD
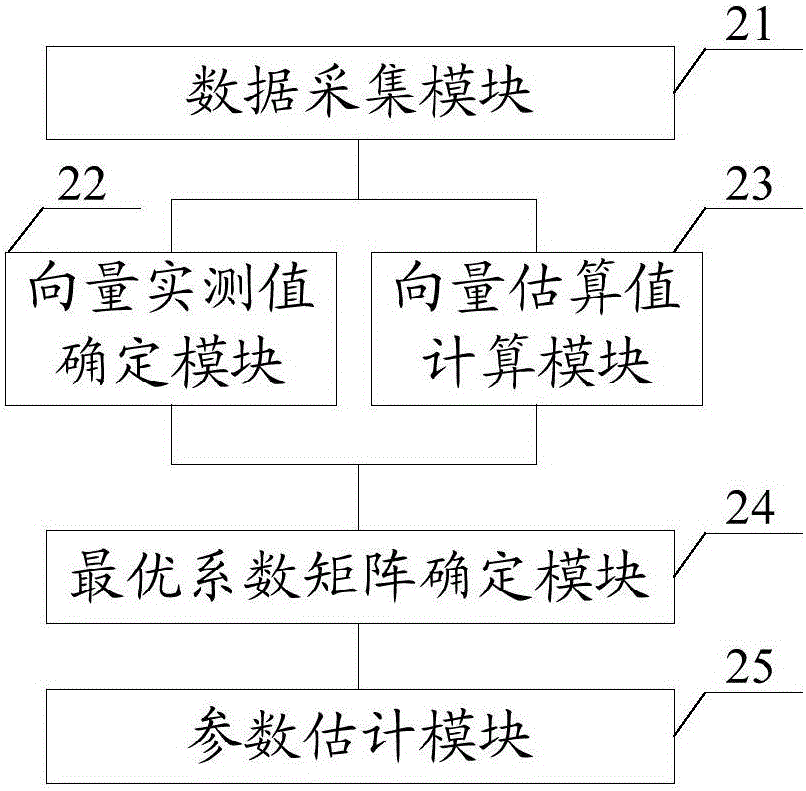
Power transmission line parameter estimation method and system and electric power system
The application discloses a power transmission line parameter estimation method and system and an electric power system. The method comprises the following steps: via a multi-period PMU, voltages and currents of two ends of a power transmission line are collected, and a corresponding phasor quantity and a corresponding current phasor quantity are obtained; via the voltage phasor quantity, an actual measured value of a voltage magnitude phase angle vector is correspondingly determined; via the current phasor quantity and a pre-estimated object coefficient matrix, a mathematical estimated value of the voltage magnitude phase angle vector is calculated; a residual absolute value between the actual measured value and the mathematic estimated value is calculated; when the residual absolute value is smaller than or equal to a preset residual threshold value, the object coefficient matrix is determined as an optimal coefficient matrix; via the optimal coefficient matrix, series impedance and parallel admittance on the power transmission line are estimated. According to the power transmission line parameter estimation method and system and the electric power system, the preset residual threshold value which is obtained based on the voltage magnitude phase angle vector cannot be affected by heavy loads and light loads of the power transmission line, and therefore power transmission line parameter estimation error is reduced.
Owner:GUANGDONG POWER GRID CORP ZHAOQING POWER SUPPLY BUREAU
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com