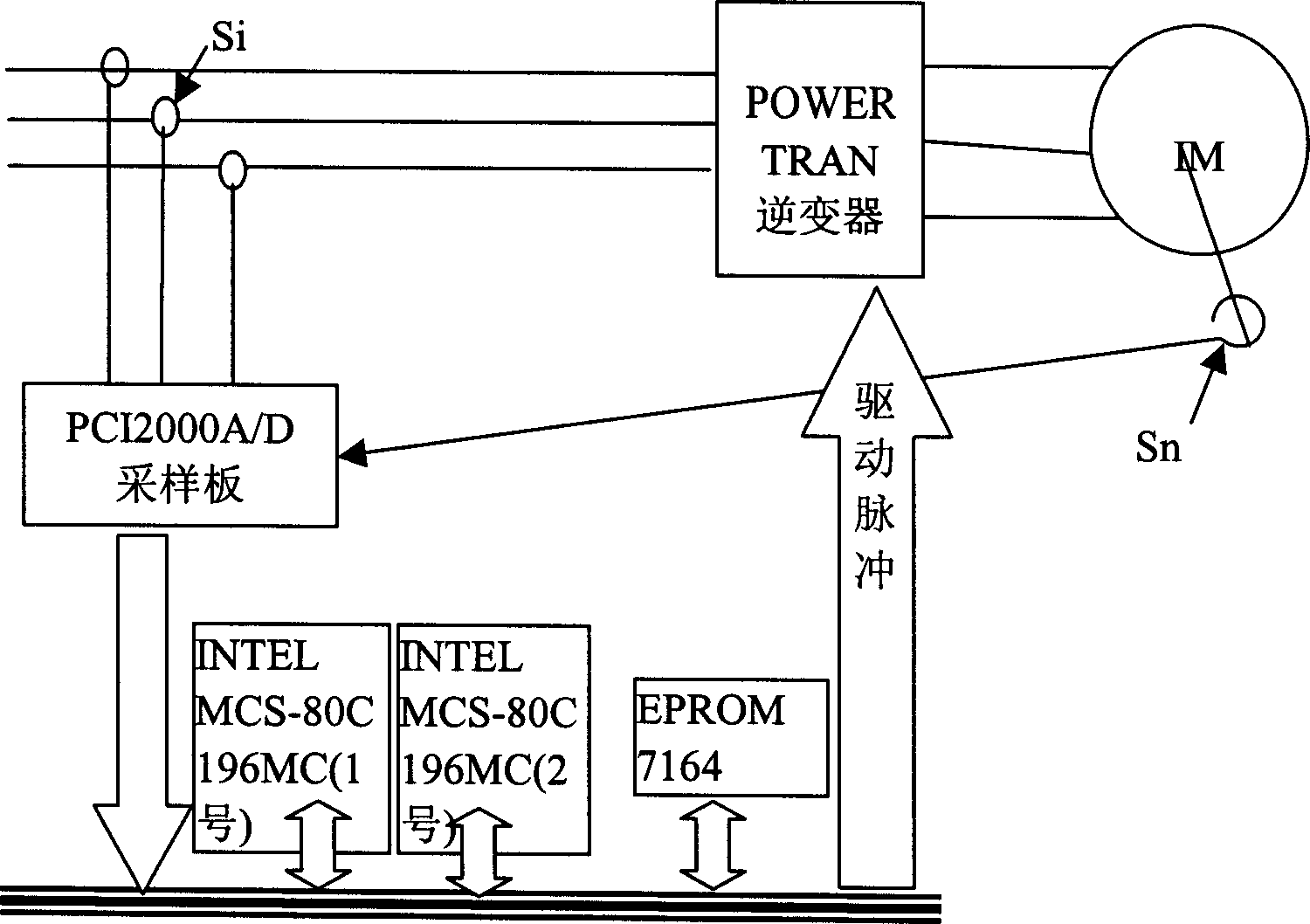
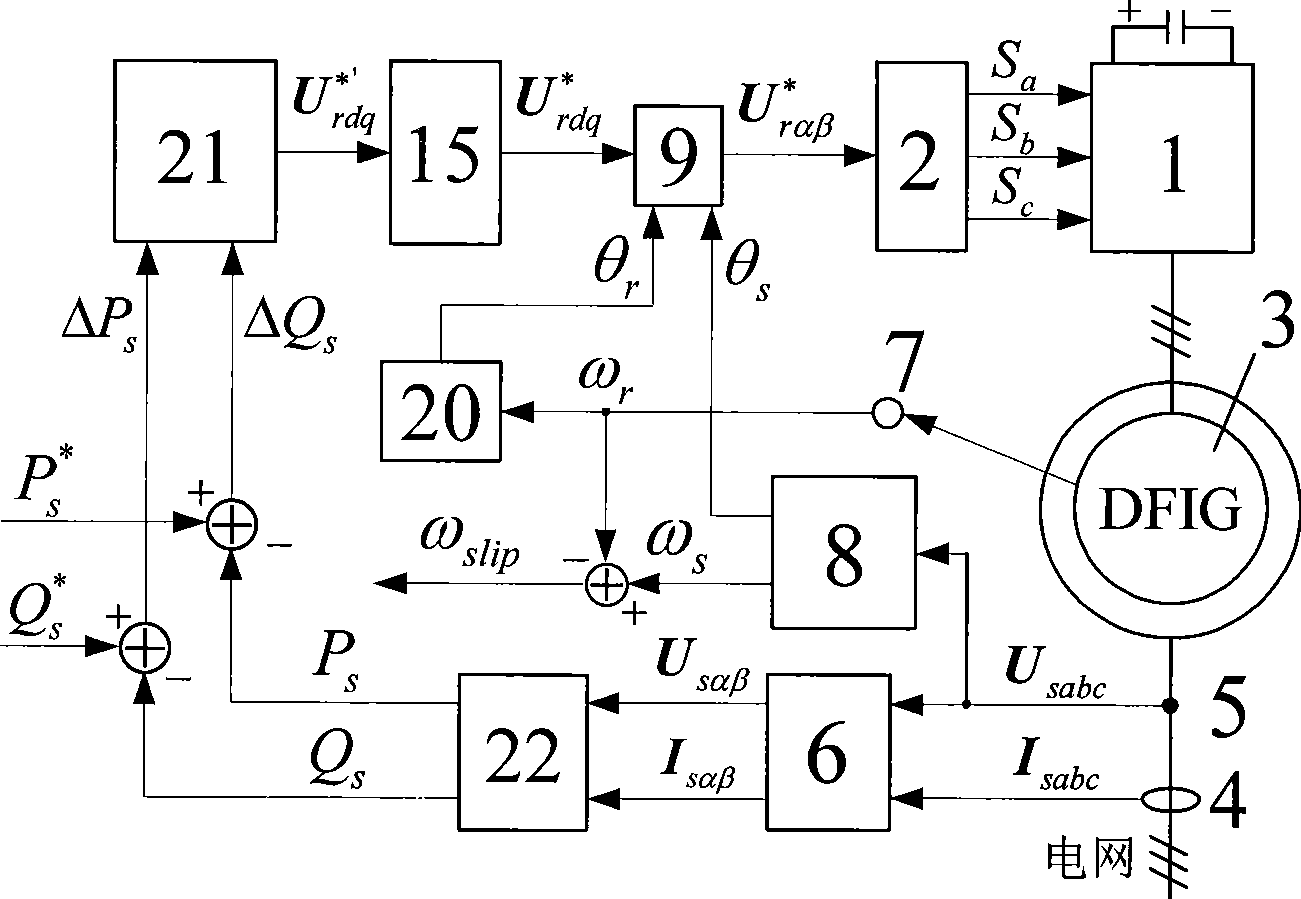
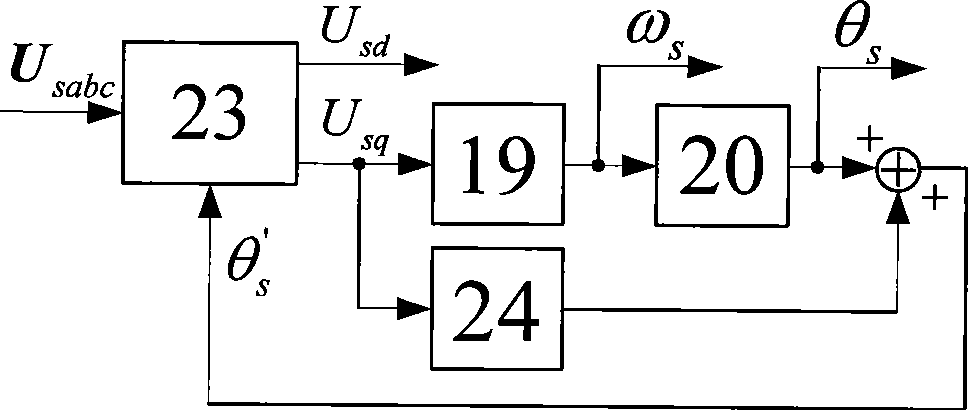
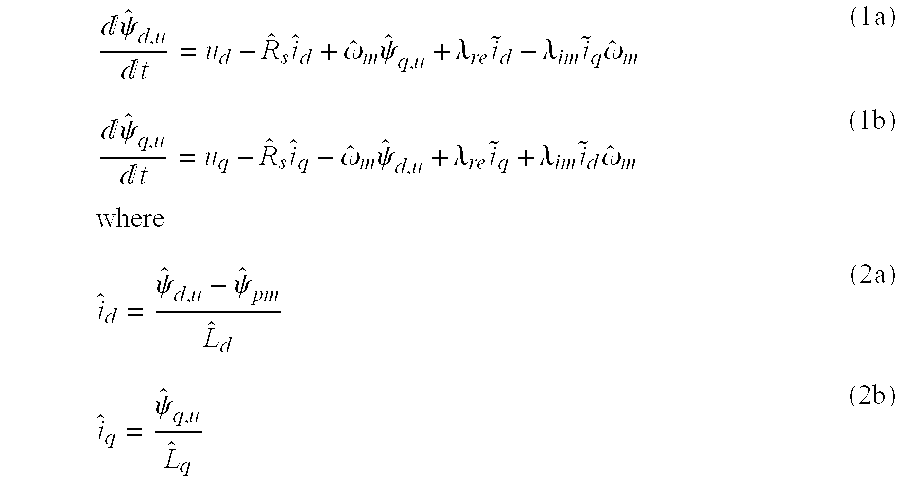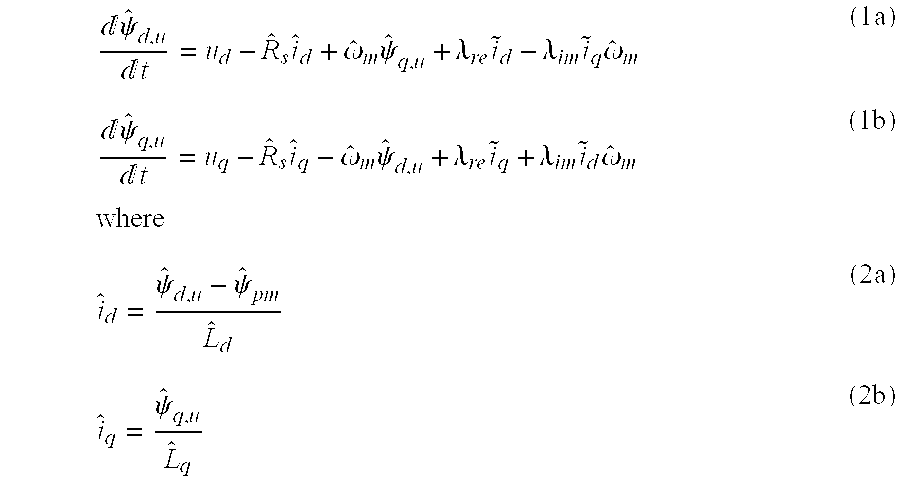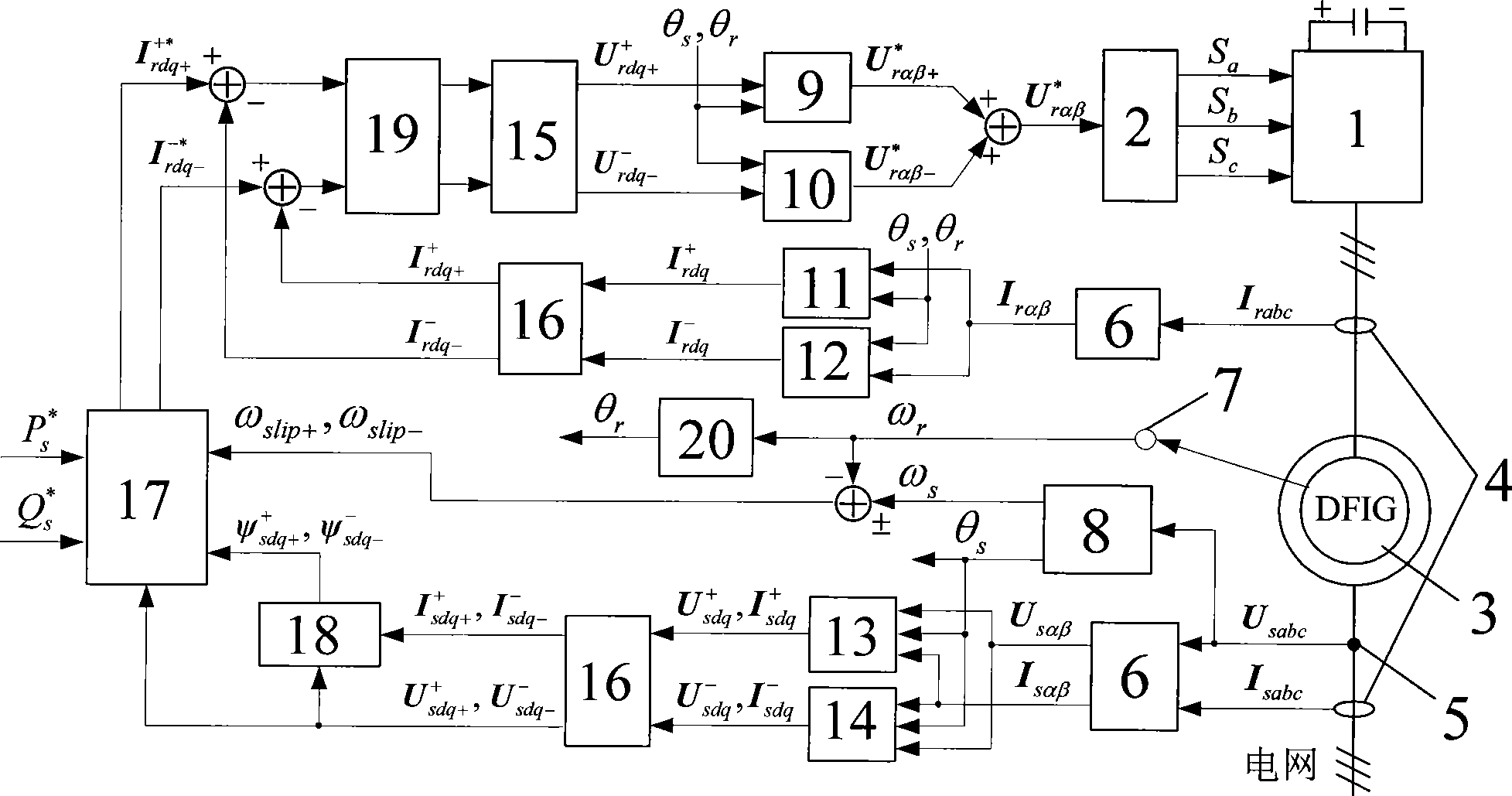Patents
Literature
751 results about "Stator voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Stator Voltage Control is a method used to control the speed of an Induction Motor. The speed of a three phase induction motor can be varied by varying the supply voltage. As we already know that the torque developed is proportional to the square of the supply voltage and the slip at the maximum torque is independent of the supply voltage.
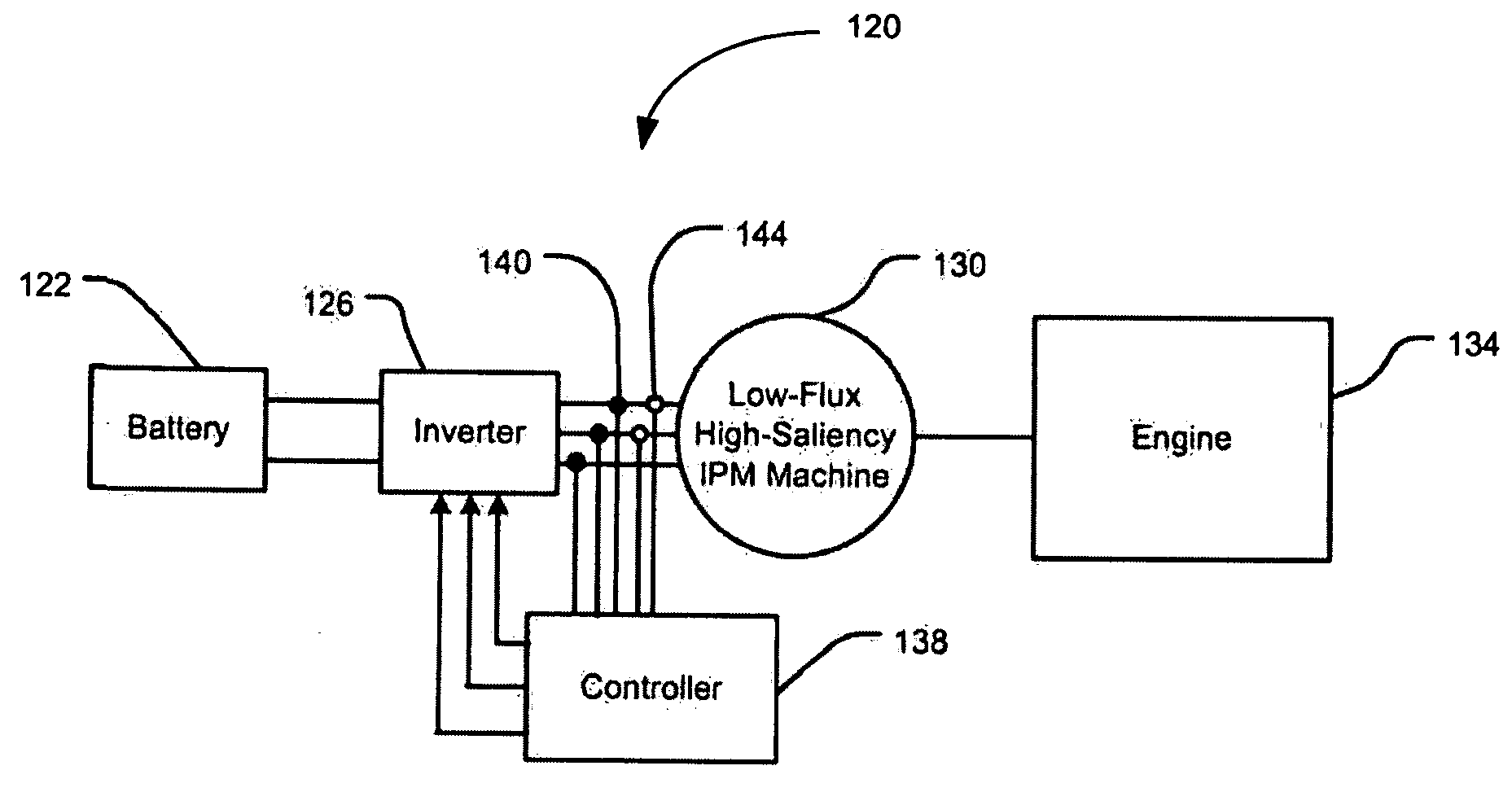
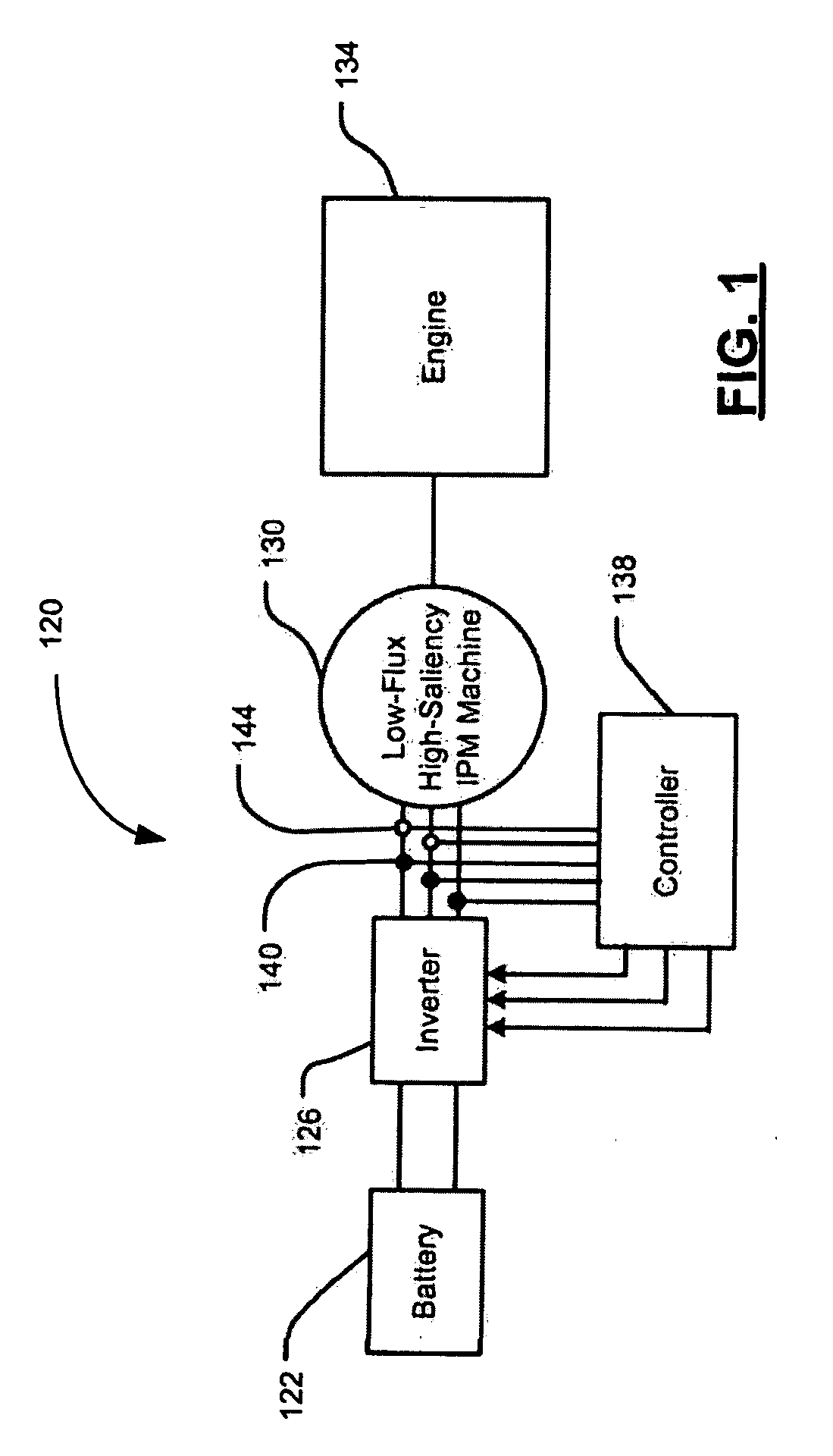
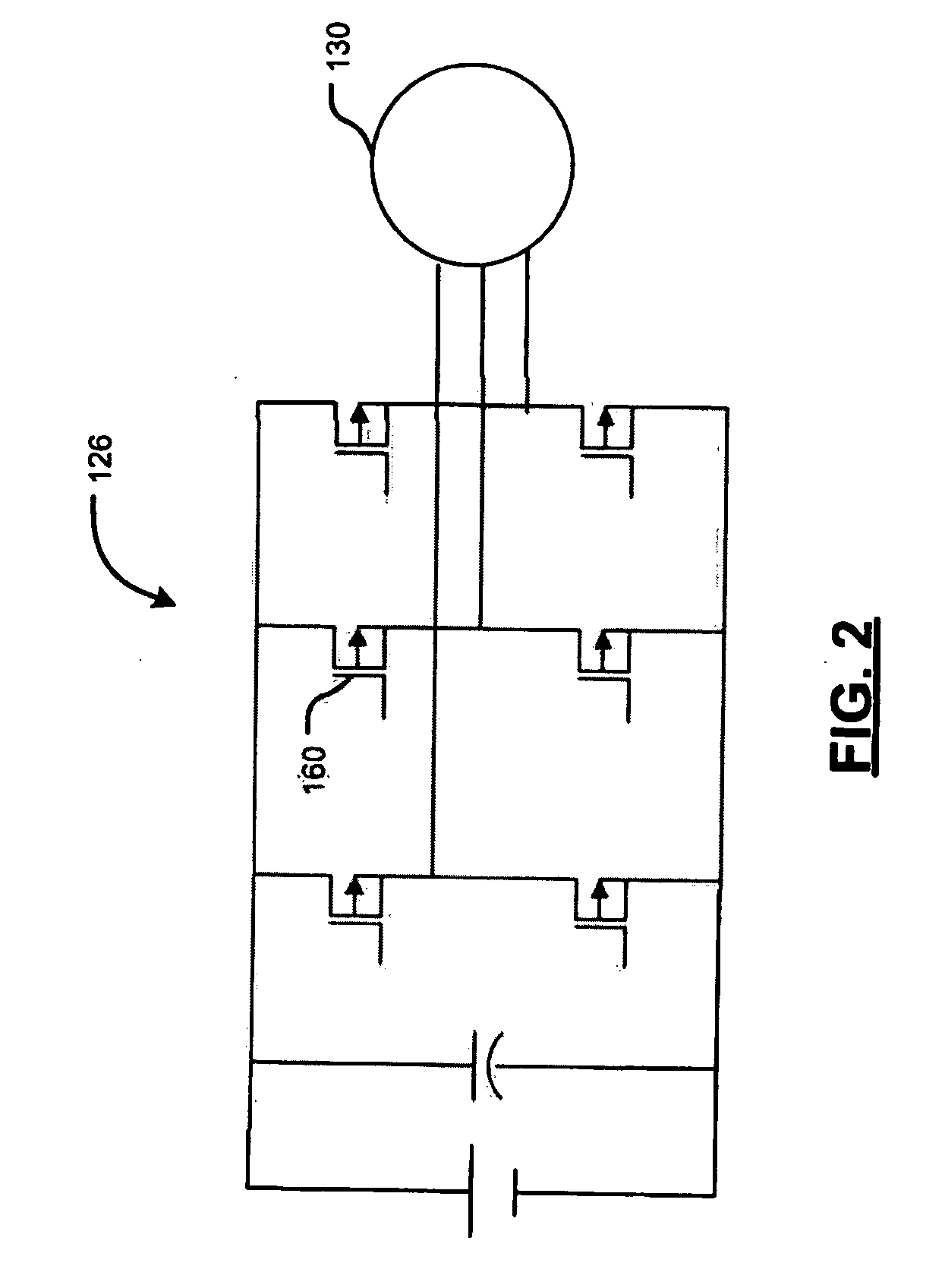
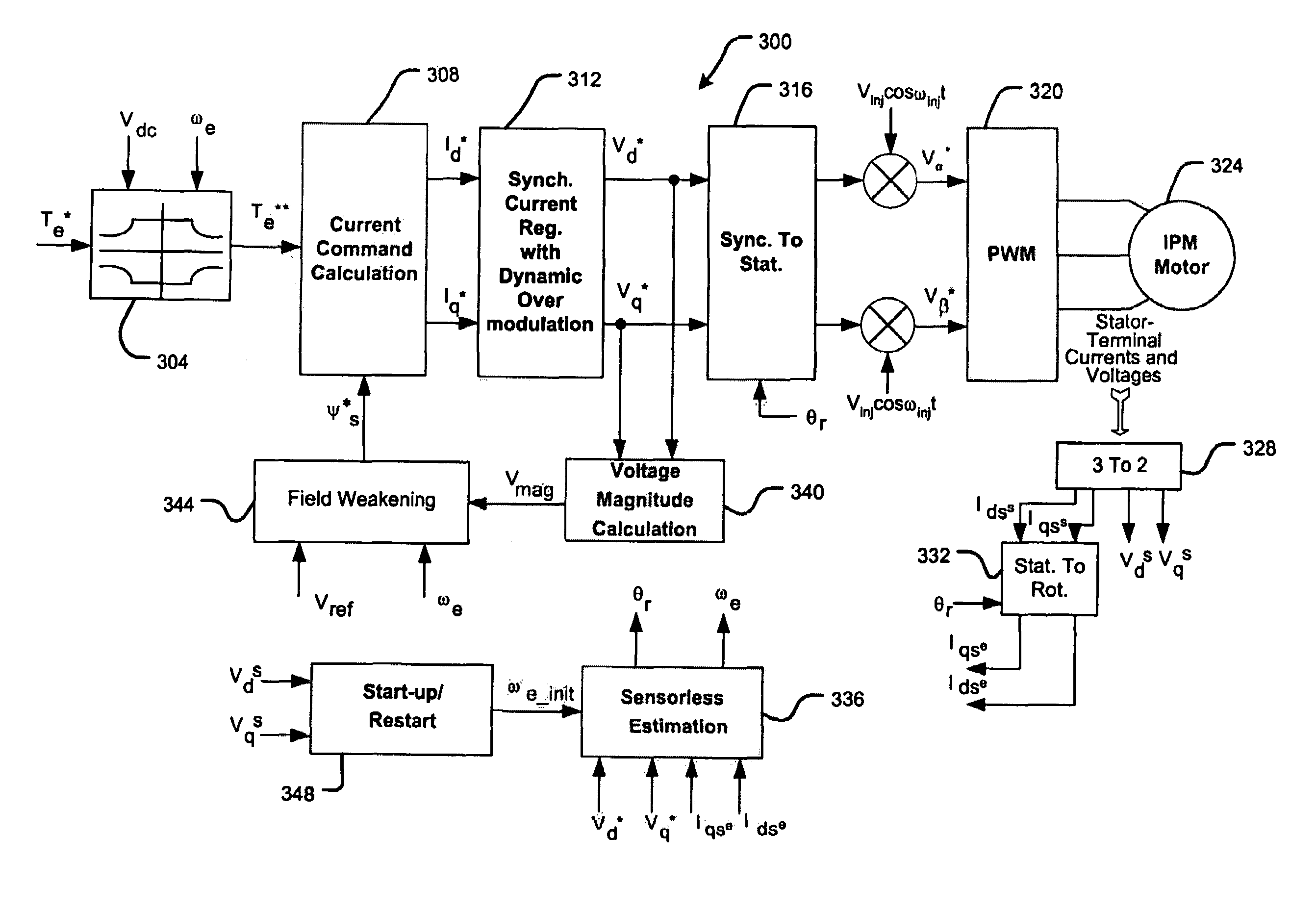
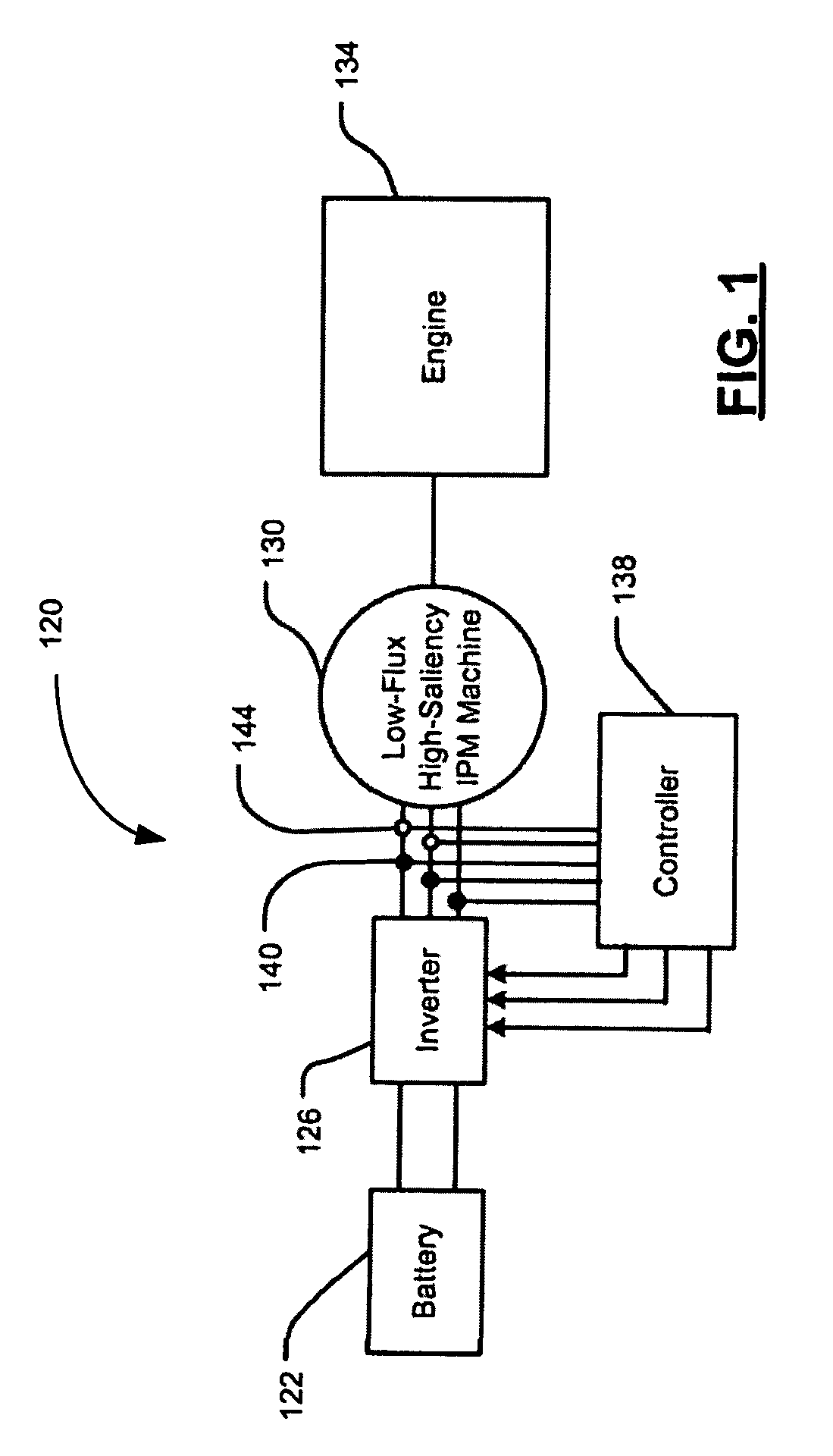
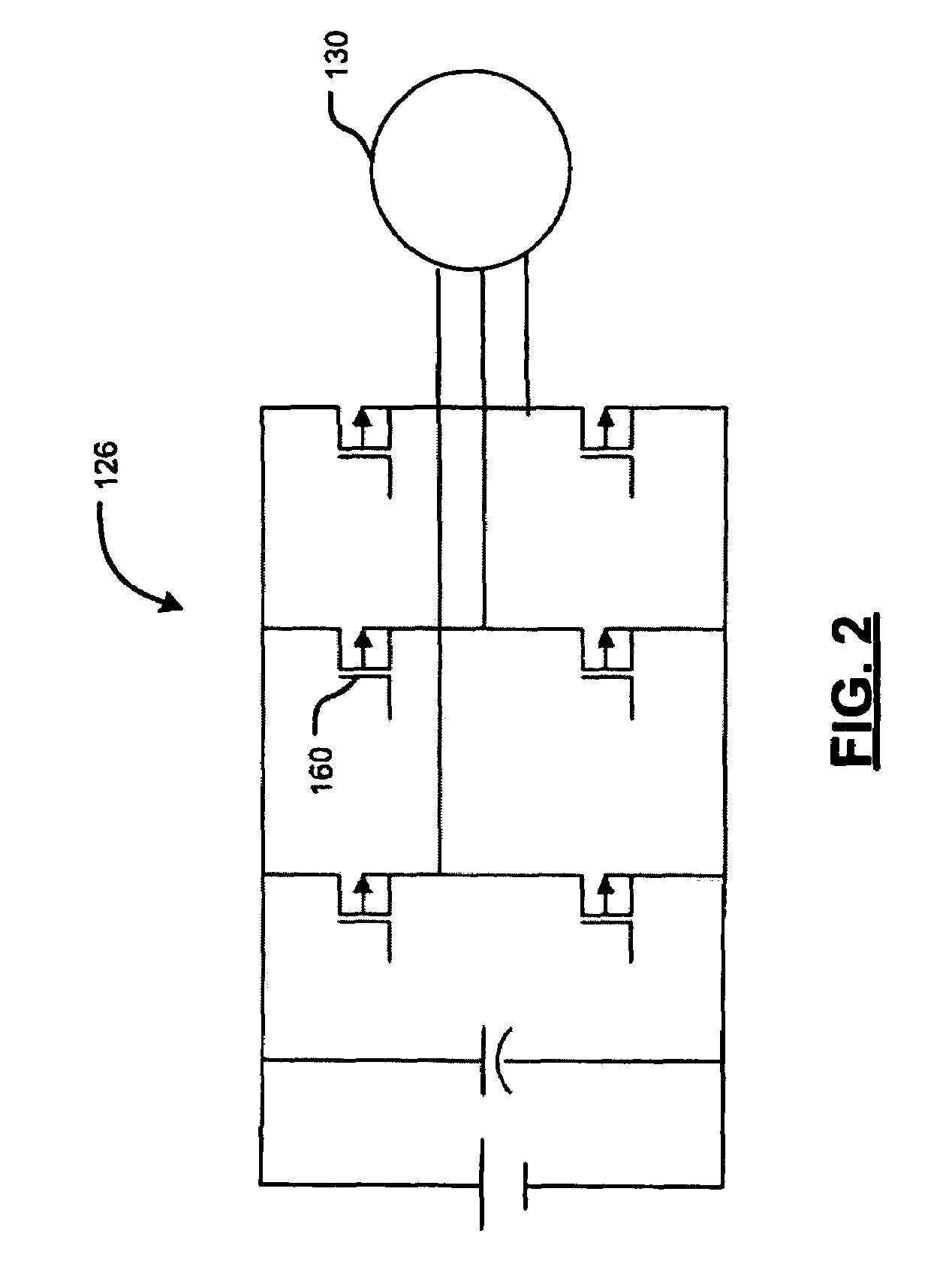
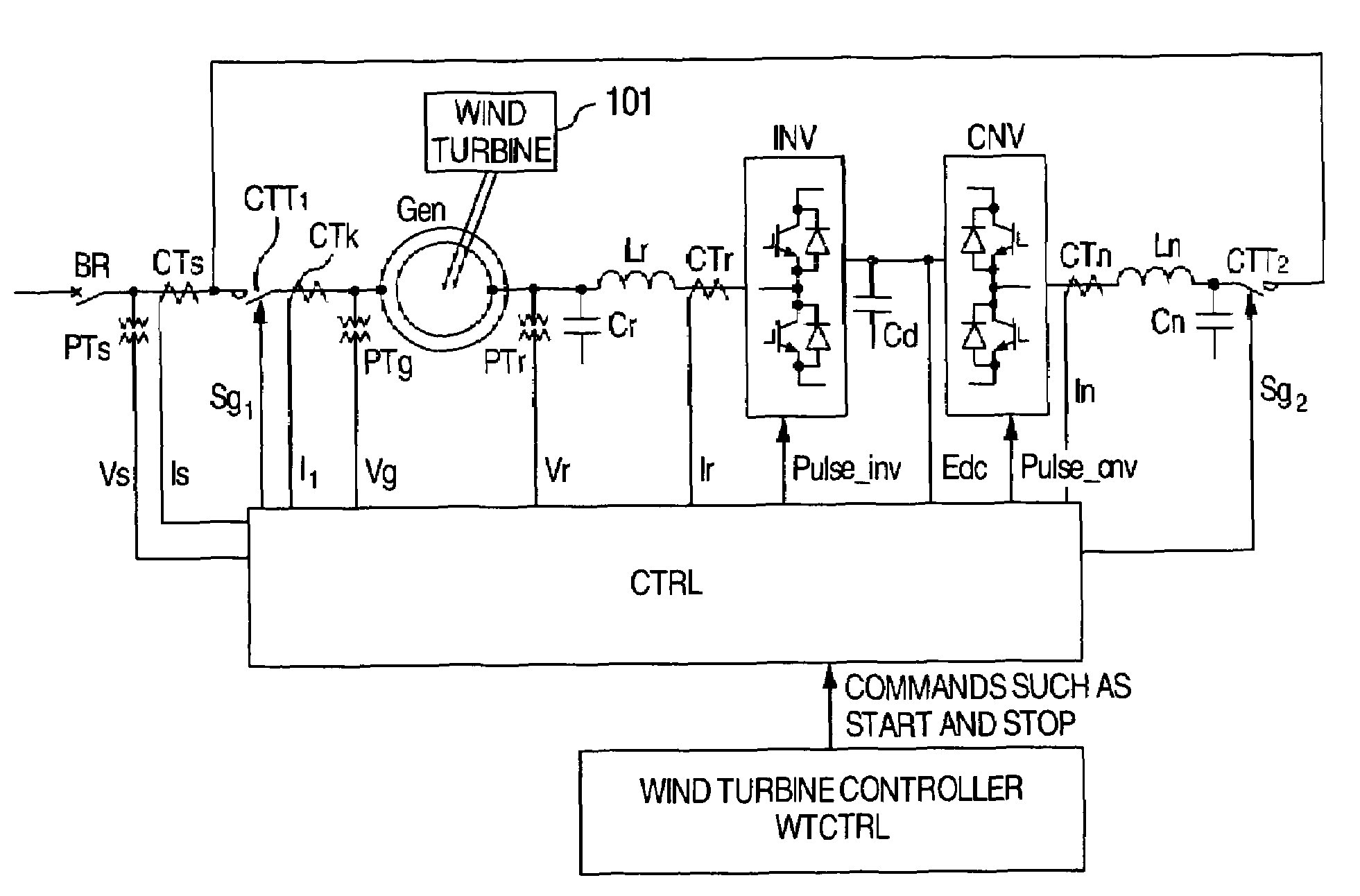
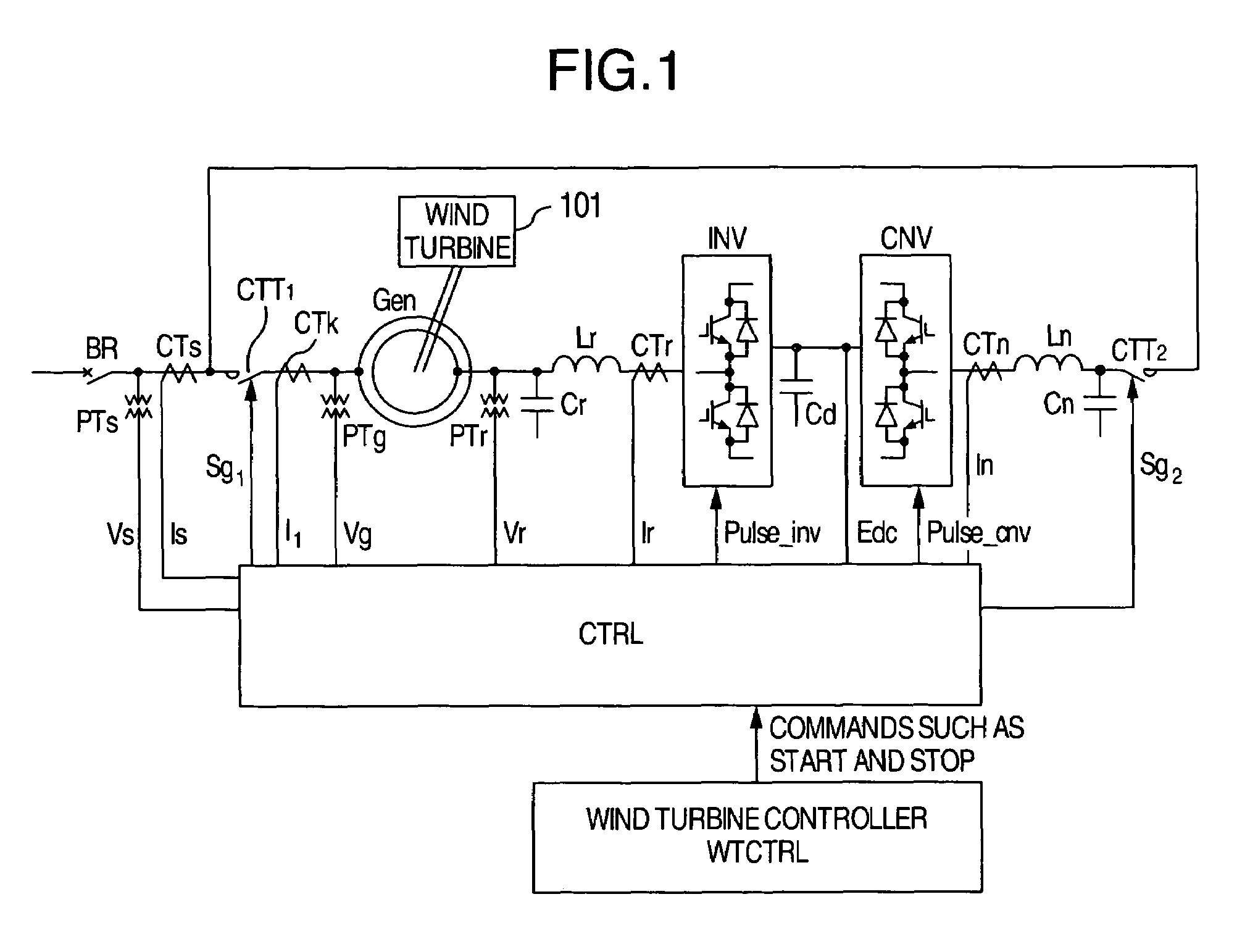
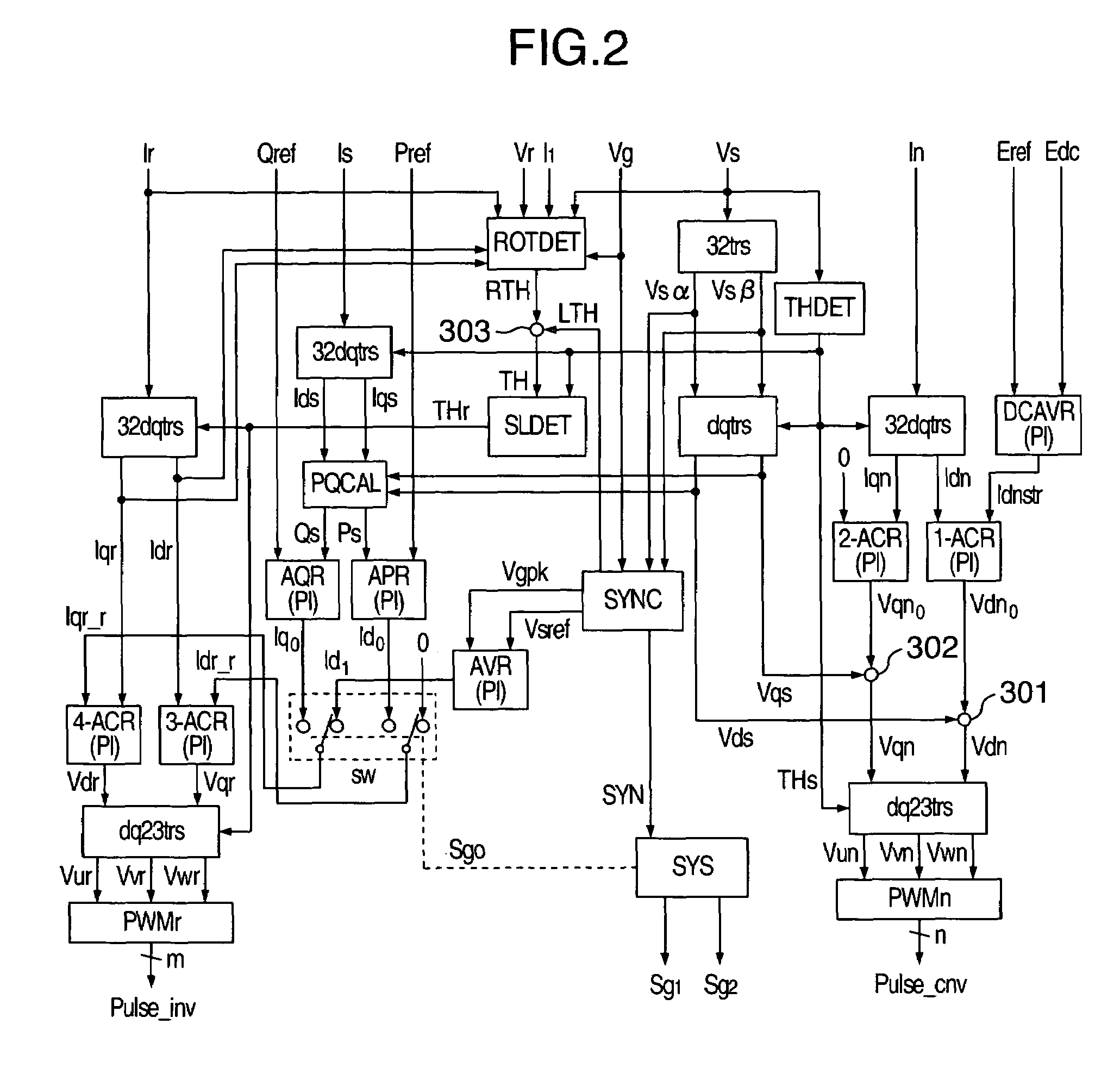
Start-up and restart of interior permanent magnet machines
ActiveUS20060097688A1Single-phase induction motor startersMotor/generator/converter stoppersStator voltageState variable
A method of starting a permanent magnet machine. A machine stator voltage in a stationary reference frame is sensed. An initial speed of a rotor of the machine is estimated based on the sensed voltage, and state variables of control algorithms are initialized based on the estimated initial speed. This method can provide smooth startup and / or restart at any speed.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
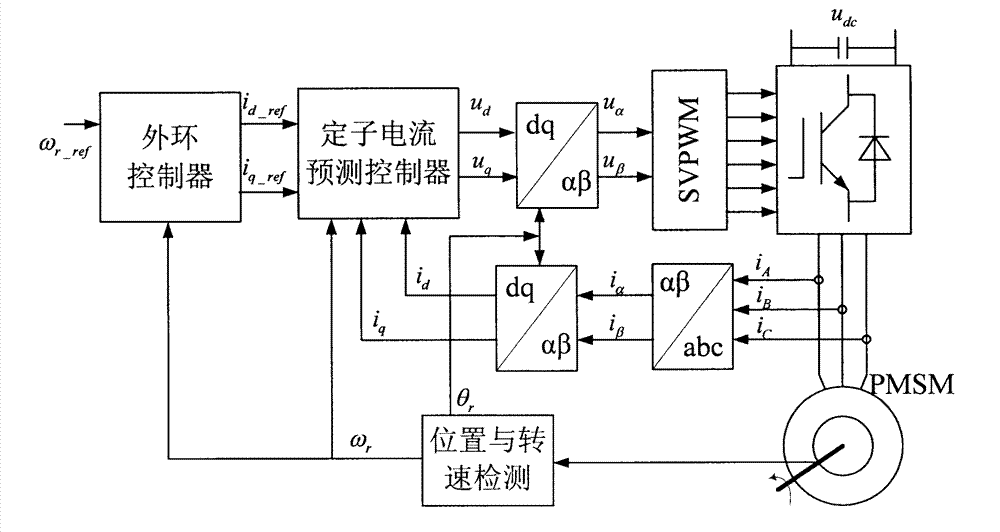
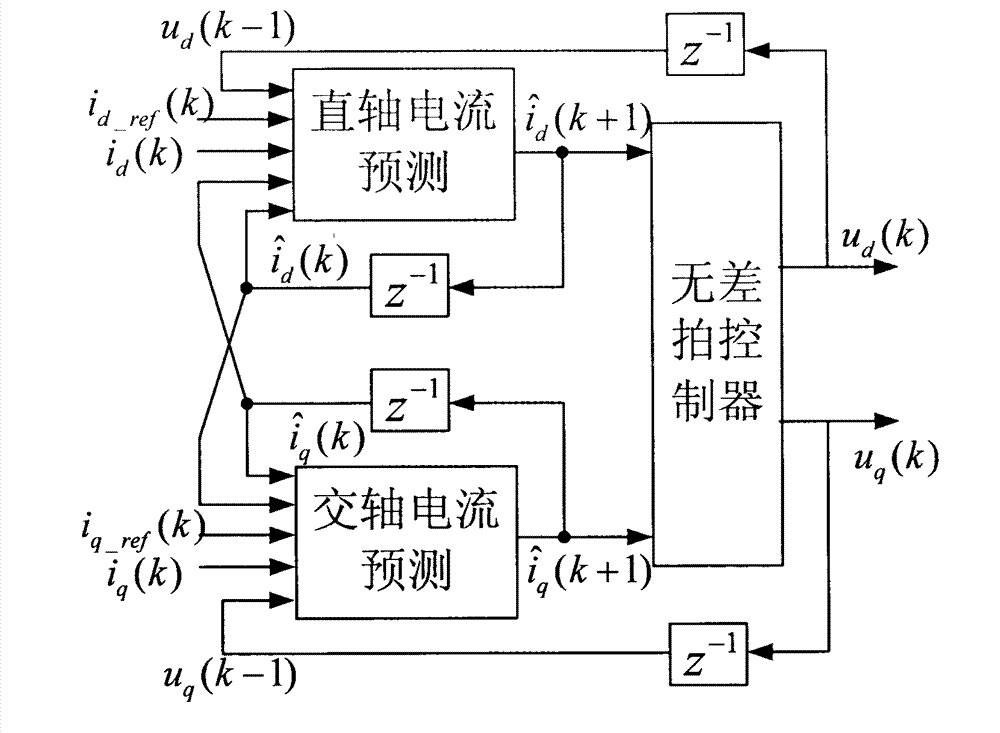
Current predictive control method of permanent magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN102904520AFast startShorten the timeElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlStator voltageControl signal
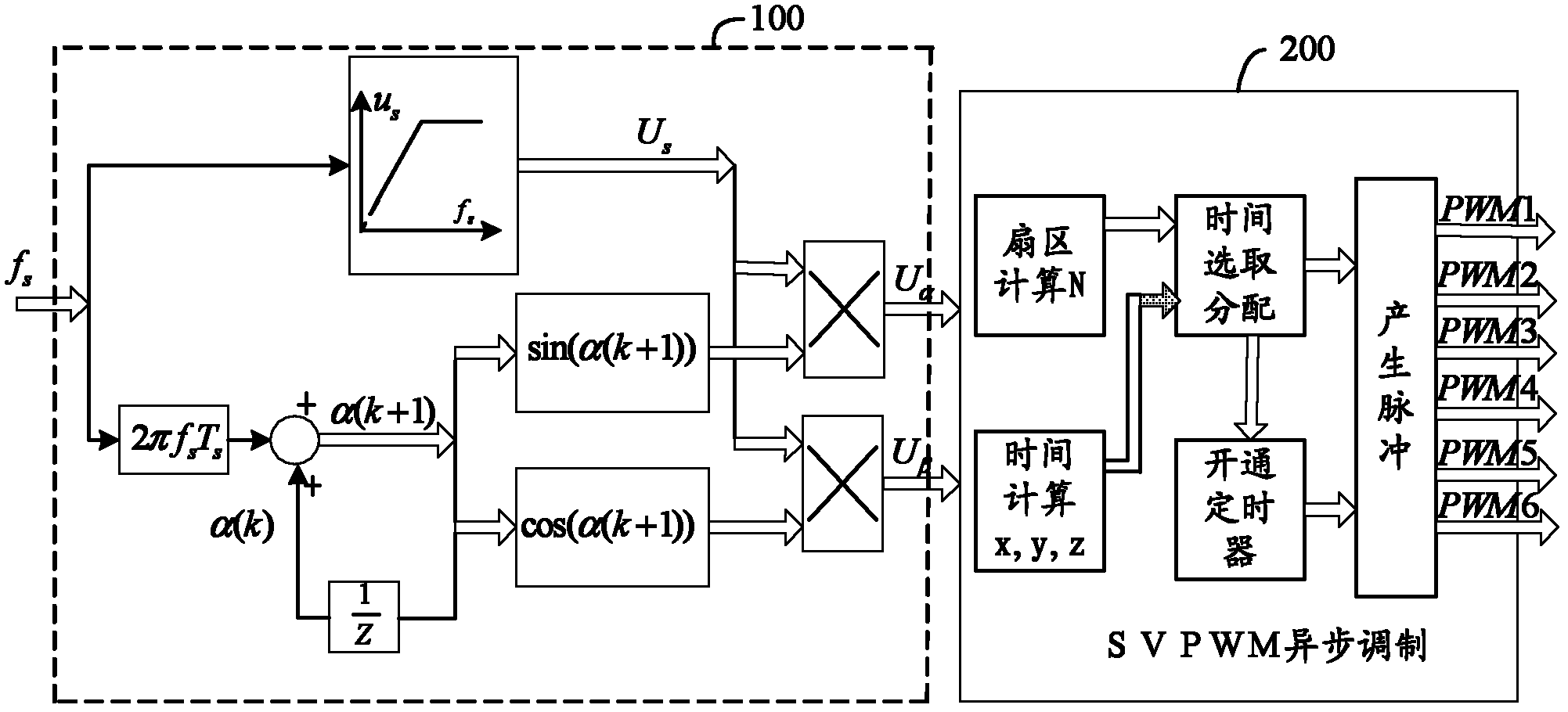
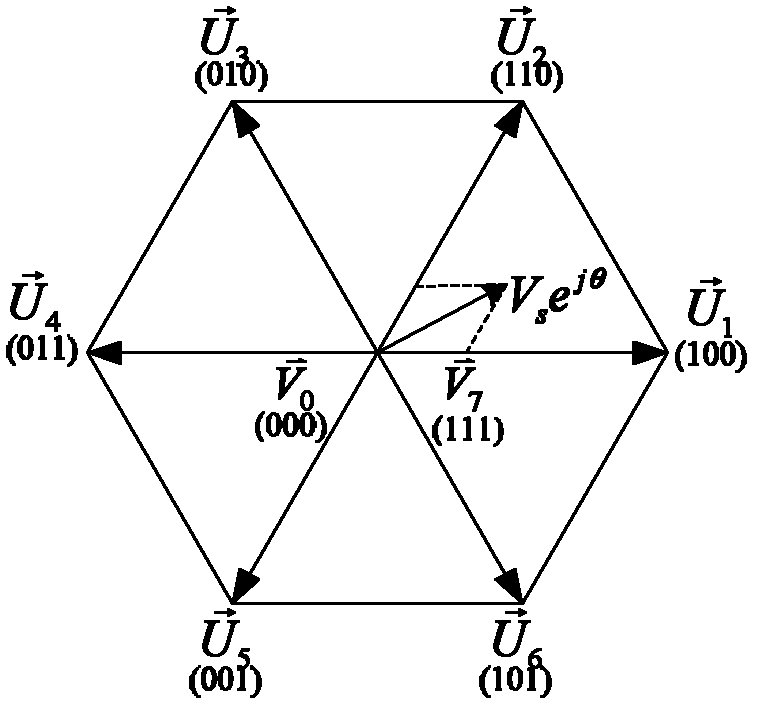
The invention relates to a current predictive control method of a permanent magnet synchronous motor, which belongs to the electric control field. The dynamic response speed and the control accuracy for the stator current control of the permanent magnet synchronous motor are improved through stator current prediction and deadbeat control, and the system delaying is compensated, so that the noise and the torque ripple of the motor in operation are reduced. The method comprises the steps as follows: obtaining a three phase stator current signal, and the electrical angle and the electrical angular speed of the motor rotor through the technologies of sensor sampling and a photoelectric coded disc or position sensorless detection; carrying out Clarke transformation and Park transformation on the stator current signal to obtain the stator current in a synchronous revolution dq coordinate system; substituting the obtained stator current signal in the dq coordinate system into a control equation of a current predictive controller of the permanent magnet synchronous motor, carrying out deadbeat control according to the given value of the obtained stator current in the dq coordinate system in an outer ring controller to obtain a stator voltage vector in the dq coordinate system; carrying out Park inverse transformation on the obtained stator voltage vector in the dq coordinate system, to obtain a pulse-width modulation (PWM) control signal of an inverter by a space vector pulse width modulation (SVPWM) method, controlling the stator current through the inverter, and then implementing the current predictive control over the permanent magnet synchronous motor.
Owner:EAST CHINA ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN & RES INST
Speed sensorless control algorithm for direct drive permanent magnet synchronous wind power system
InactiveCN102291079AImprove stabilityImprove reliabilityElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsDifferentiatorEngineering
The invention is a control algorithm that uses detected current and voltage to estimate the real-time value of the stator resistance and speed of the wind power generator, and uses the speed estimated by the algorithm as speed feedback to control the permanent magnet synchronous wind power generator. The speed value is estimated in the following way: According to the motor stator voltage and current value obtained by detection, the stator resistance value of the wind turbine is identified online based on the model reference adaptive system (MRAS), and the estimated electrical angle and the actual electrical angle of the rotor are obtained based on the back electromotive force. Error calculation formula, the fan speed is estimated by eliminating this error. The current and voltage values in the electrical angle error calculation formula are obtained by detection, the stator resistance value that changes during generator operation is obtained by MRAS identification, and the differential term of the stator current is realized by a tracking differentiator (TD), so that it can be estimated more accurately and quickly Rotating speed.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Asynchronous motor stator winding inter-turn short circuit failure on-line detecting method and device
InactiveCN101025434AGuaranteed safe operationAvoid adverse effects of fault detectionDynamo-electric machine testingStator voltageInduction motor
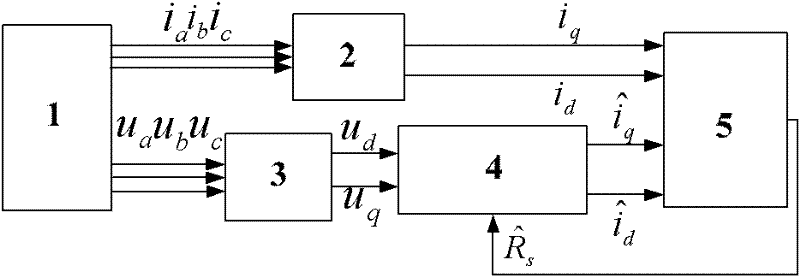
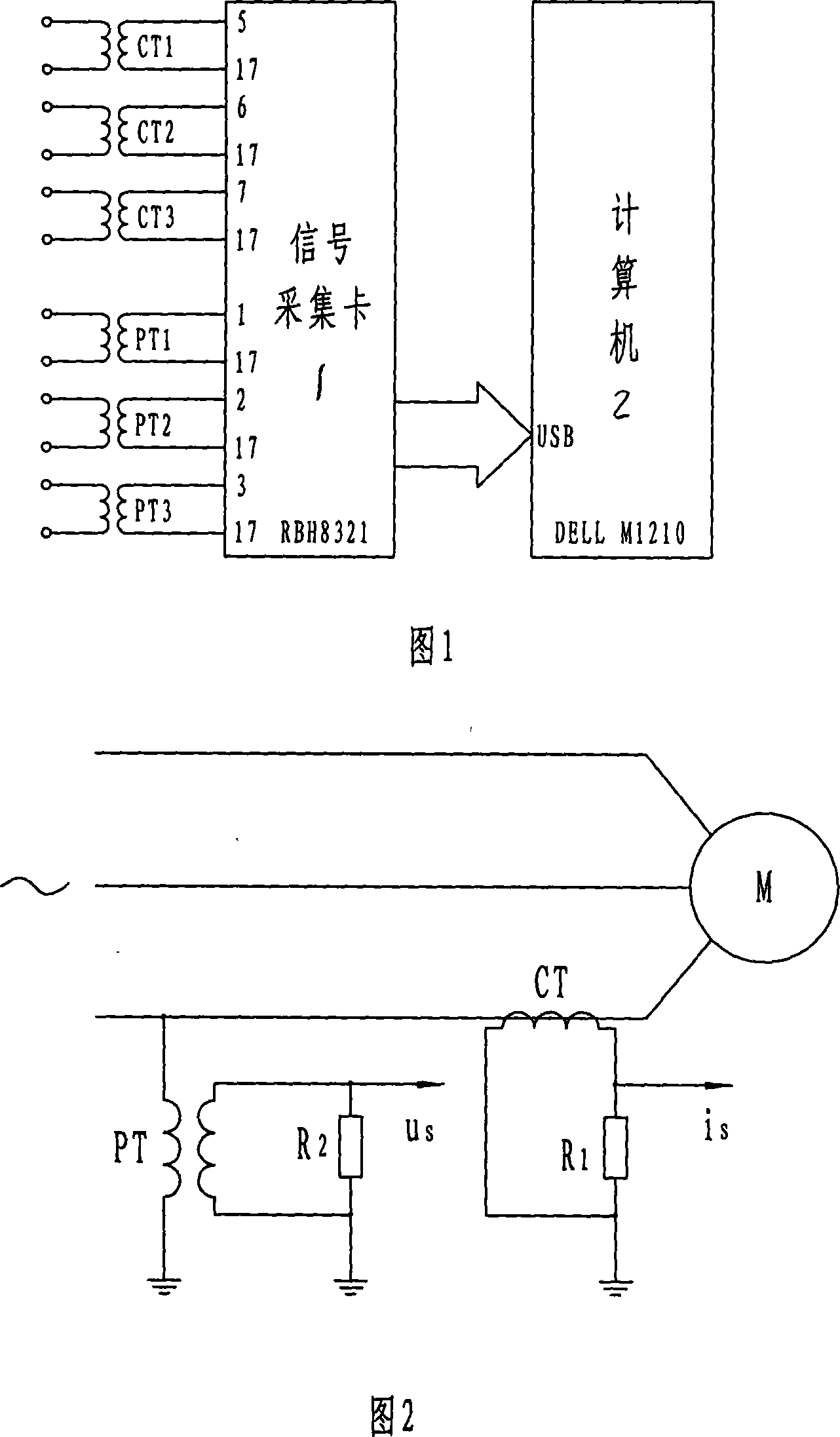
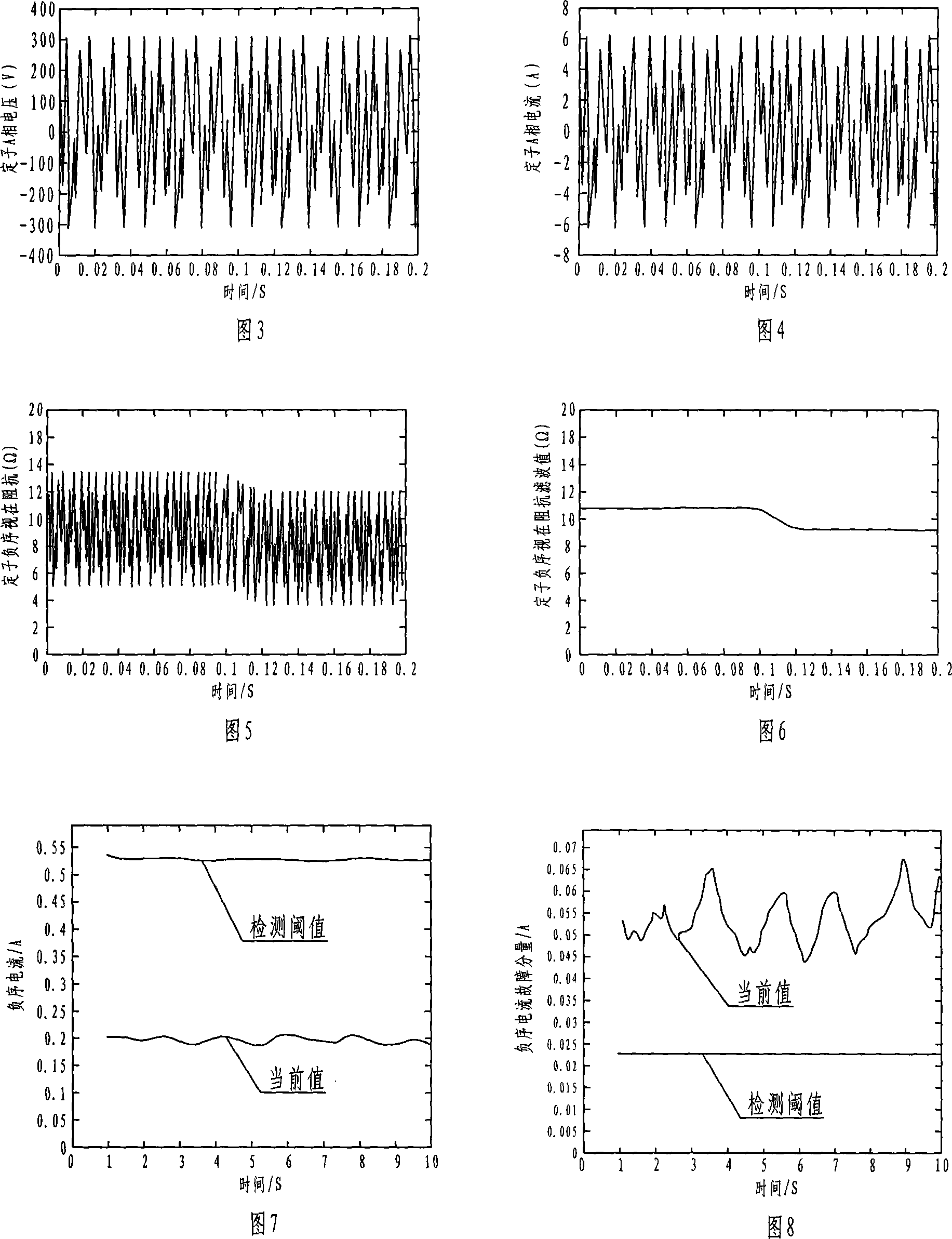
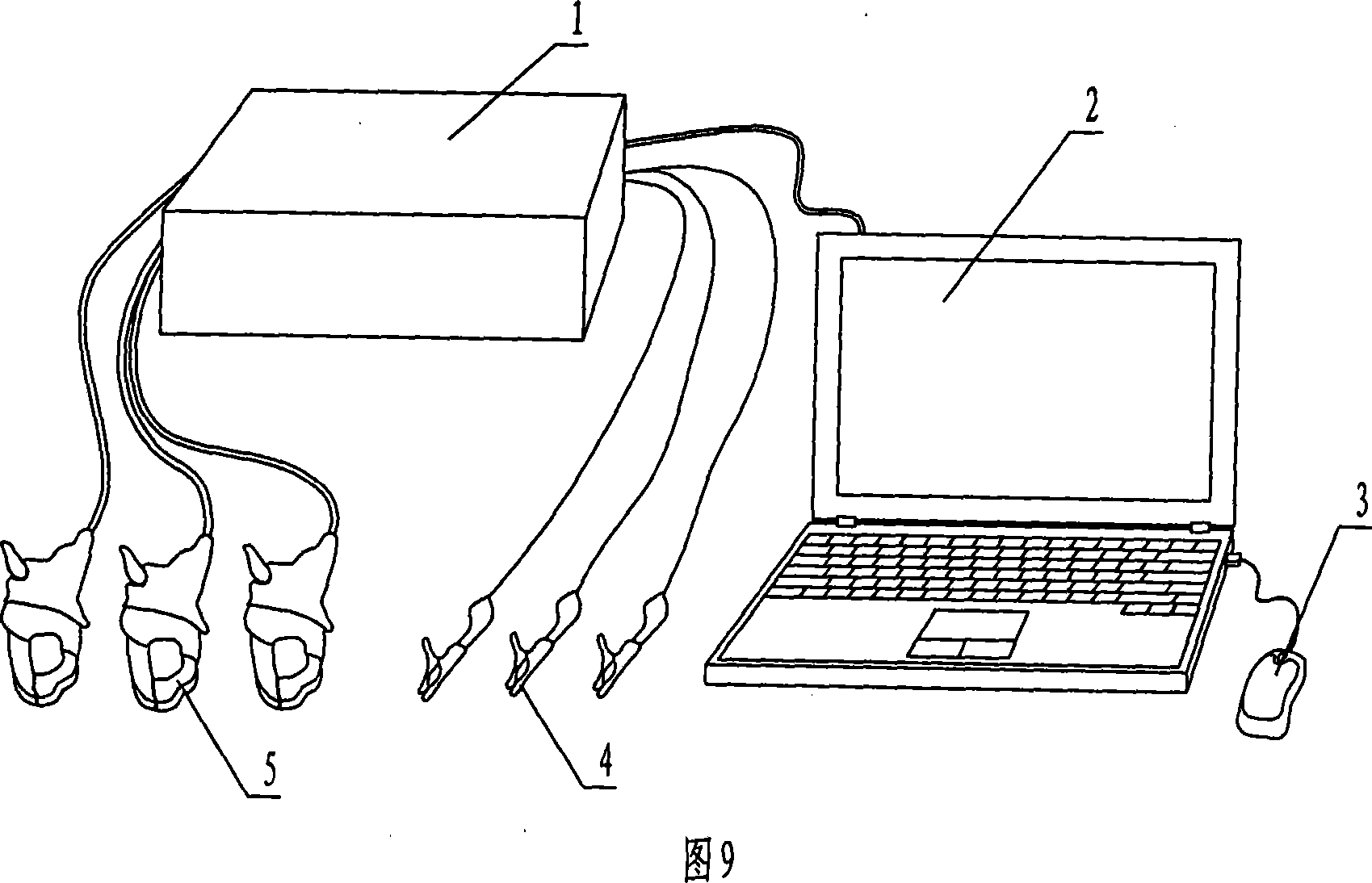
The invention relates to a online testing process for shorted fault of asynchronous motor's stator winding, which is belong to Detecting Technology. It was designed to solve the detecting problem of stator winding. The project is that it figures out the voltage and current of negative sequence and positive sequence of the stator winding by collecting three-phase stator voltage, instantaneous-current signal. Then using of normal motor sample reference document estimated the filter value of the stator negative sequence, figured out the stator negative sequence current fault component. And then base on the threshold of the stator negative sequence current fault component educe failure exponent. Finally according to the index judge whether to exist short circuit failure or not. This invention also gave corresponding detection device. Not only can high sensitivity, high reliability and on-line measurement asynchronous motor stator windings at the beginning of the early short circuit fault, but also can judge short circuit phase. This can effectively ensure the asynchronous motor operating safely.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Broad-speed-range generator variations
InactiveUS20120256422A1High energy yieldImprove global economyWindingsMagnetic circuitPower qualityDc current
A brushless generator with permanent-magnet multi-pole rotor disks and stator winding disks in their axial magnetic field includes integral electronics to efficiently generate regulated DC current and voltage from mechanical input power over a broad speed range. All power for the electronics is provided by rectifier diodes from its stator windings. Differential amplifiers provide stator voltage feedback signals. Its power rating is scalable, depending on the number of its disks. Having no iron cores and no gears, it incurs no cogging torque, and no gear friction. Integral power control electronics includes high-frequency pulse-width-modulated boost regulation, which provides regulated current at requisite voltage over its broad speed range. A main wind-powered embodiment to produce DC power for a constant voltage DC load over a broad speed range includes signal processing so output power varies according to the third power of speed. Combined boost-regulation, zero cogging torque, and no gearing, enable a wide speed range, for better power quality and higher wind energy yields.
Owner:FRADELLA RICHARD B
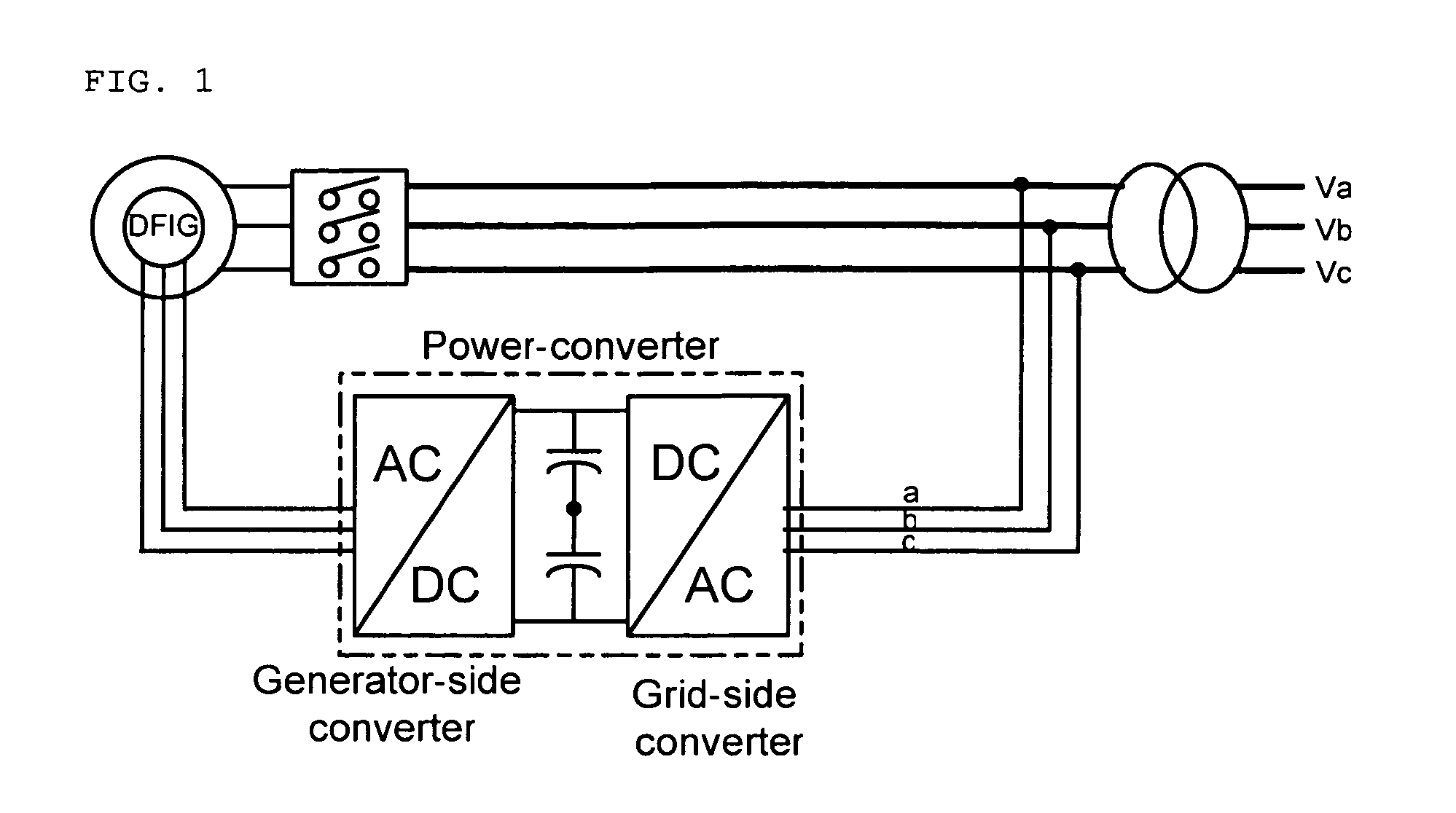
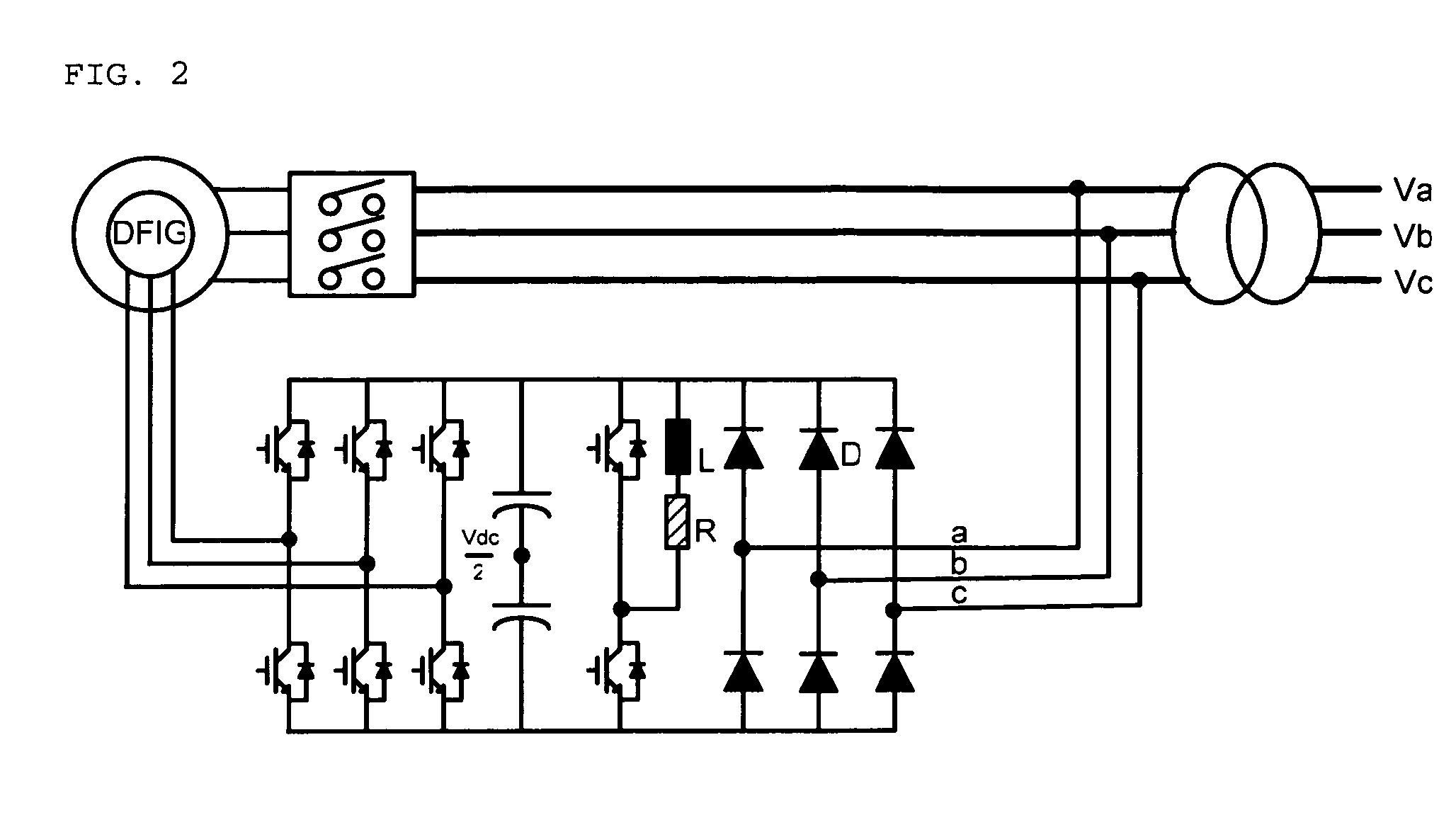
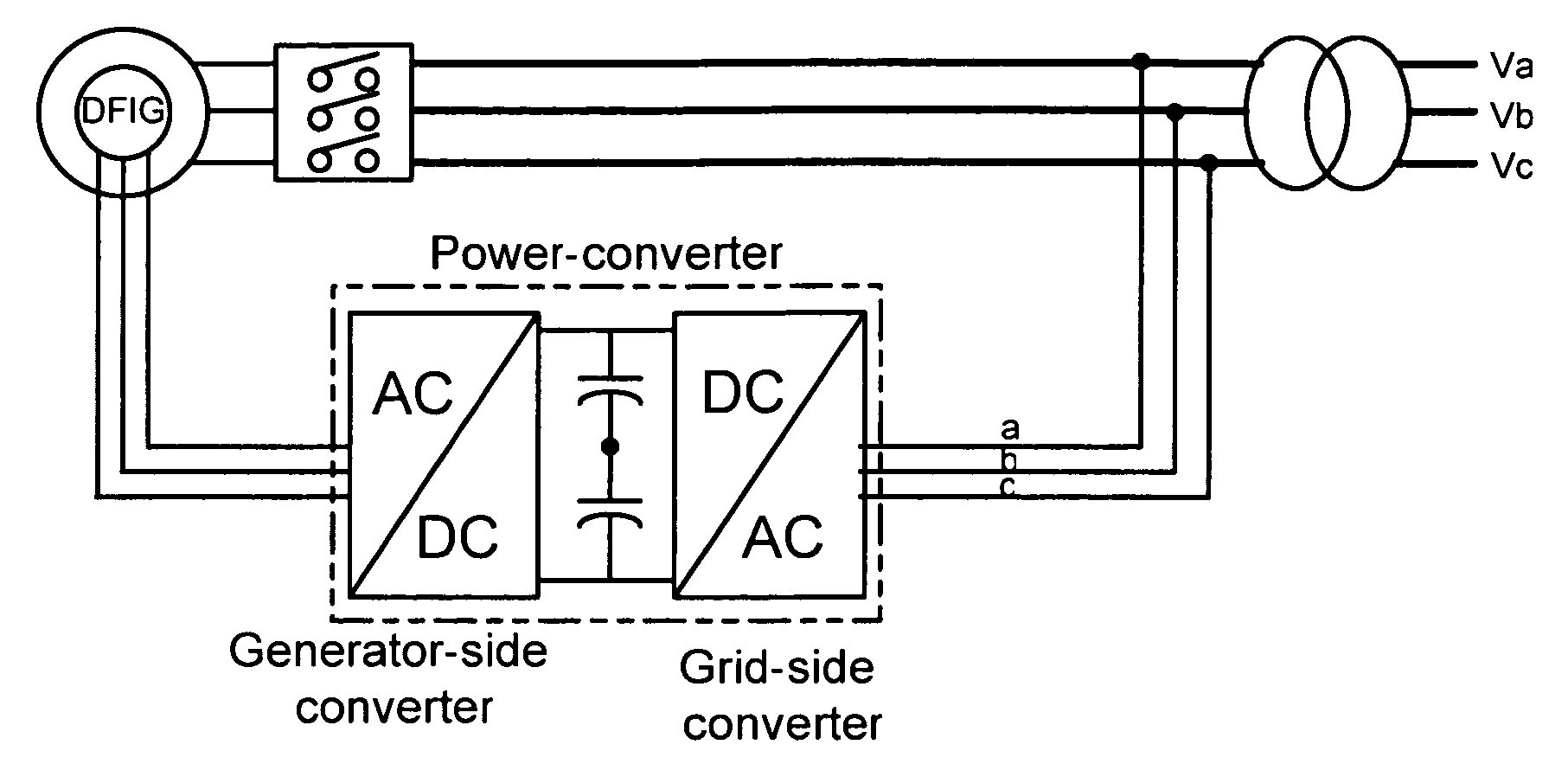
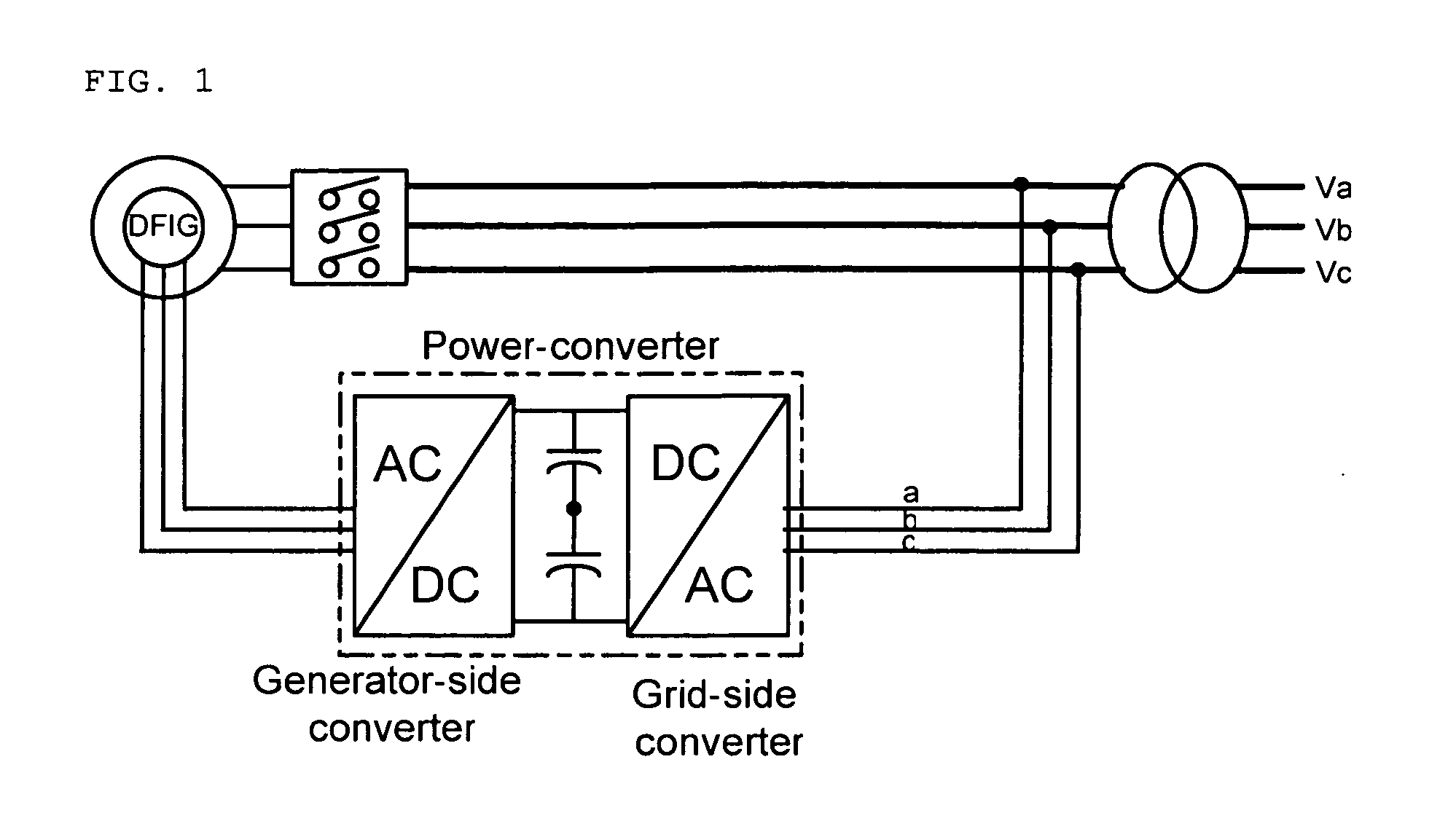
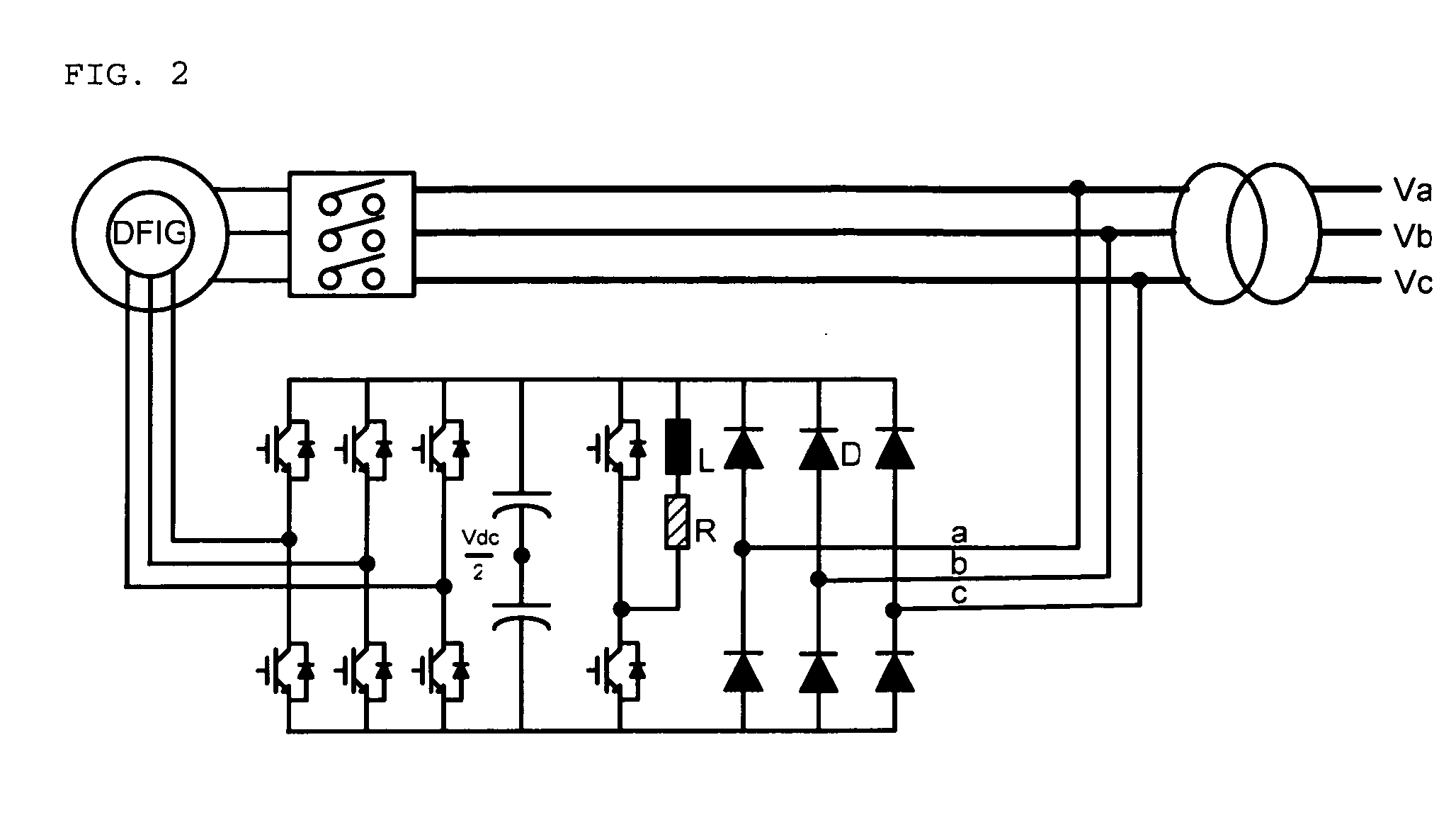
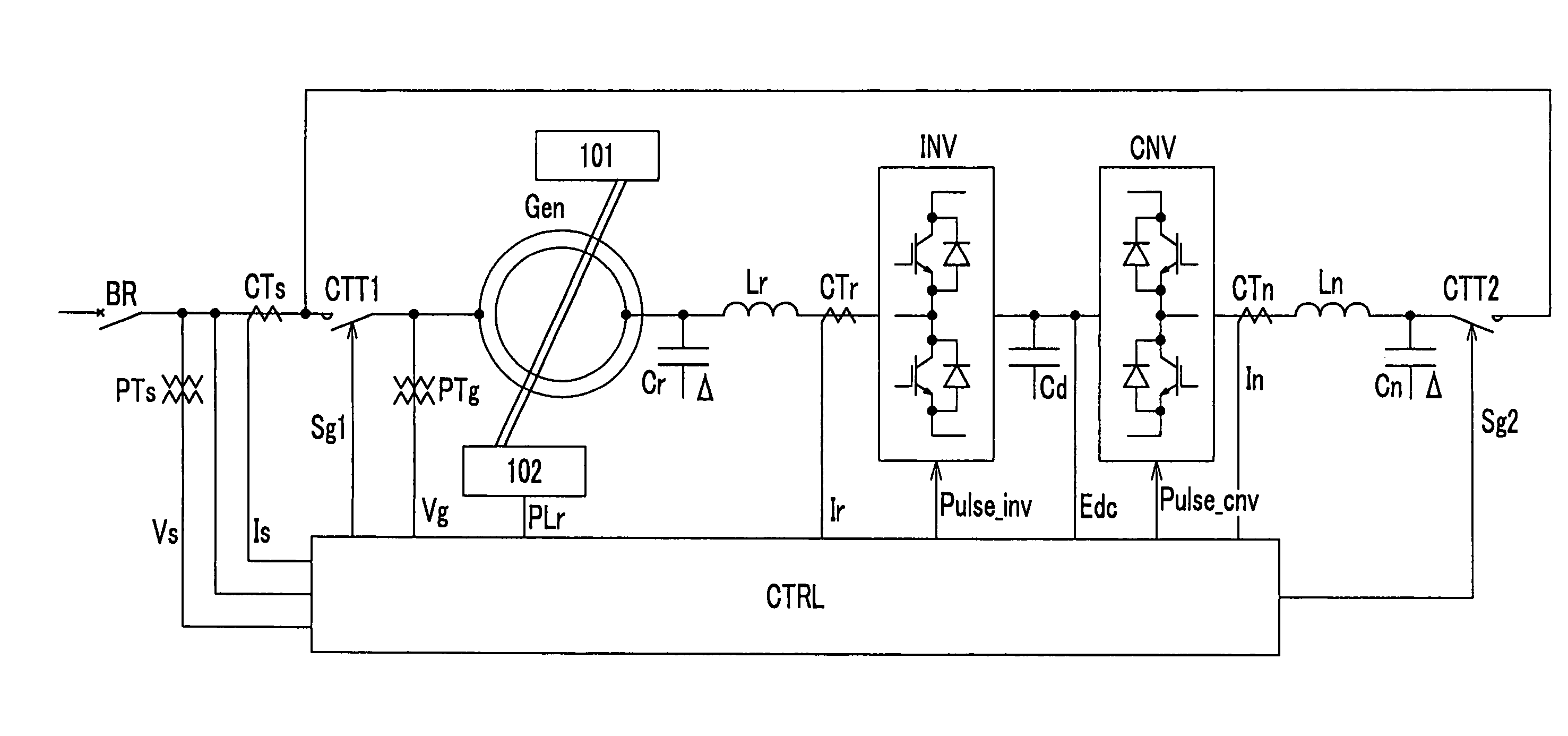
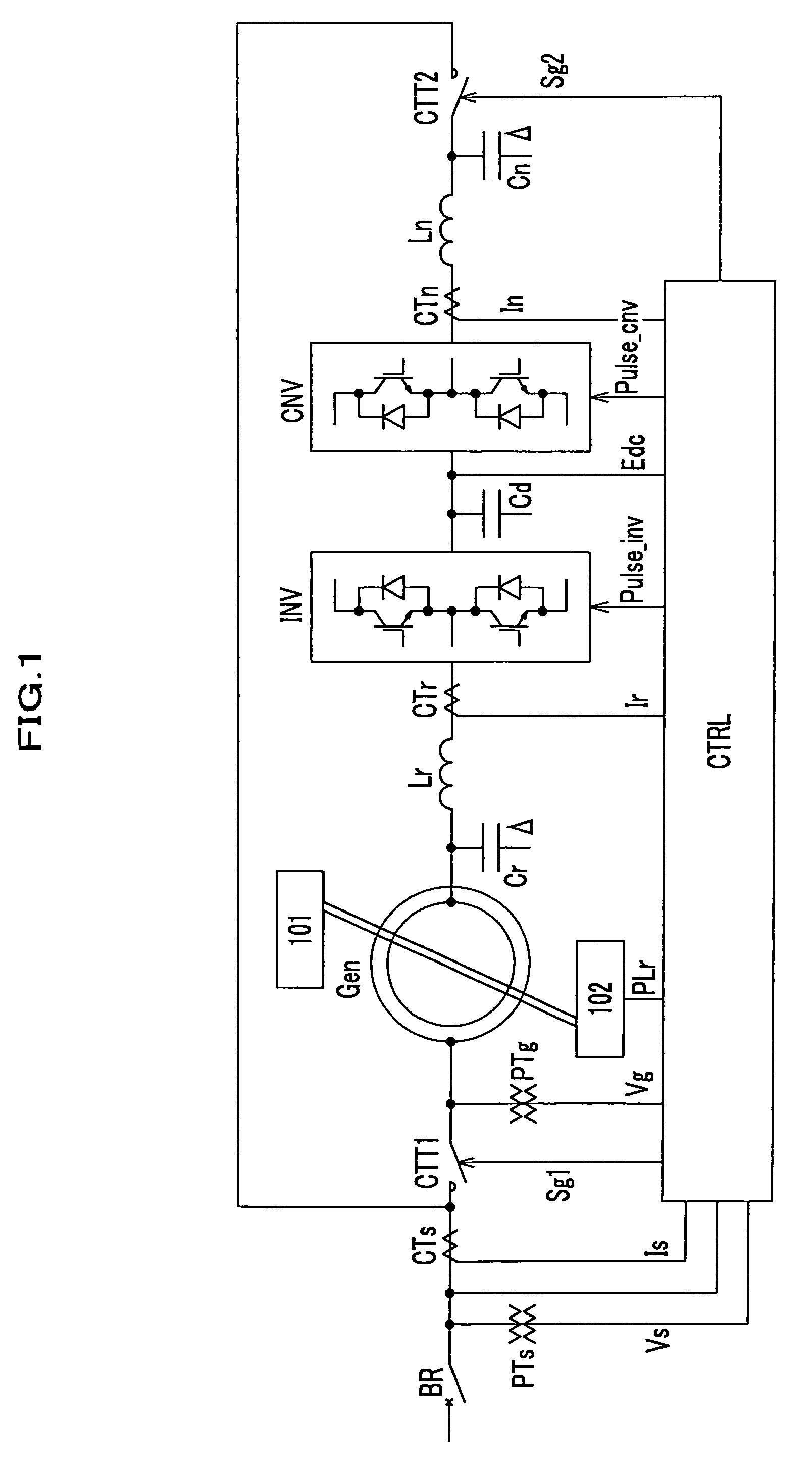
Electric power converting device and power converting method for controlling doubly-fed induction generator
ActiveUS7579702B2Generator control circuitsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectricityStator voltage
Disclosed herein is an electric power converting device and power converting method for controlling doubly-fed induction generators, which provides a synchronous generator for generating auxiliary electric power independently of a doubly-fed induction generator so as to generate electricity even in a system power-free environment, a grid-side converter is composed of a three-phase four-wire converter so as to generate a balanced voltage even in an unbalanced load condition and automatically synchronize a stator voltage of a doubly-fed induction generator and a system voltage with each other.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
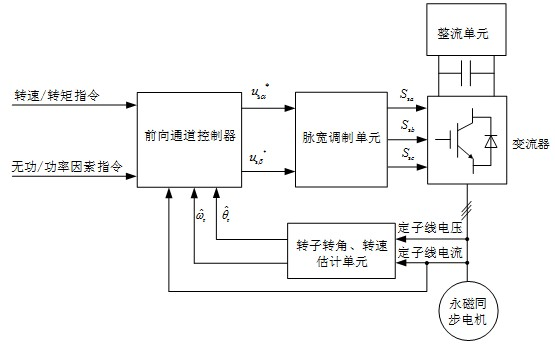
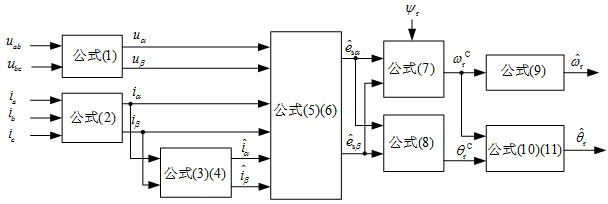
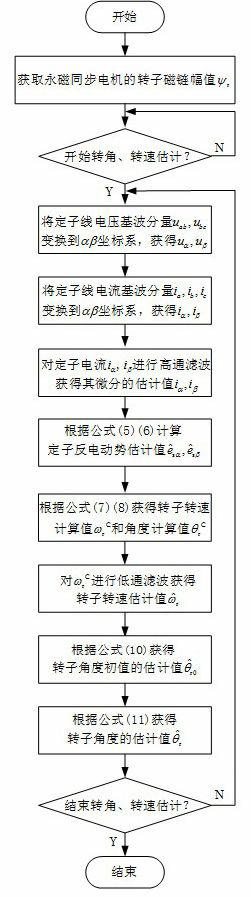
Speed sensor-less method for estimating rotor angle and revolving speed of permanent-magnet synchronous motor
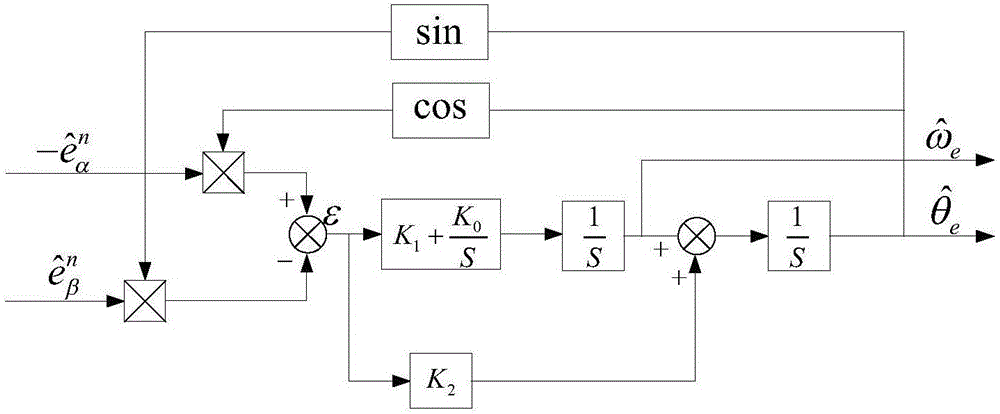
ActiveCN102437813AImprove dynamic performanceEasy to debugElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsStator voltageSynchronous motor
The invention relates to the technical field of electric transmission and control, in particular to a speed sensor-less method for estimating the rotor angle and the revolving speed of a permanent-magnet synchronous motor. The method comprises the following steps: a. obtaining the rotor flux linkage amplitude Psi<r> of a permanent-magnet synchronous motor; b. transforming a stator voltage fundamental component to be under an alpha beta coordinate system to obtain u<alpha> and u<beta>; c. transforming the stator current fundamental component to be under the alpha beta coordinate system to obtain i<alpha> and i<beta>; d. carrying out highpass filtering on stator current i<alpha> and i<beta> under the alpha beta coordinate system, and obtaining the differential estimation value sum of the stator current; e. obtaining a stator counter electromotive force estimation value; f. obtaining a rotor revolving speed calculation value omega<rC> and a rotor angle calculation value theta<rC>; g. carrying out lowpass filtering on the rotor revolving speed calculation value omega<rC> to obtain a rotor revolving speed estimation value; h. obtaining the estimation value of a rotor angle starting value; and i. obtaining a rotor angle estimation value. The method has the advantages that only forward calculation, instead of a feedback channel, exists in the method for estimating the rotor angle and revolving speed, and except filter delaying, no dynamic regulation process exists.
Owner:DONGFANG ELECTRIC CORP LTD
Electric power converting device and power converting method for controlling doubly-fed induction generator
ActiveUS20070182383A1Generator control circuitsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsStator voltageElectricity
Disclosed herein is an electric power converting device and power converting method for controlling doubly-fed induction generators, which provides a synchronous generator for generating auxiliary electric power independently of a doubly-fed induction generator so as to generate electricity even in a system power-free environment, a grid-side converter is composed of a three-phase four-wire converter so as to generate a balanced voltage even in an unbalanced load condition and automatically synchronize a stator voltage of a doubly-fed induction generator and a system voltage with each other.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
Start-up and restart of interior permanent magnet machines
ActiveUS7211984B2Single-phase induction motor startersSynchronous motors startersStator voltageState variable
A method of starting a permanent magnet machine. A machine stator voltage in a stationary reference frame is sensed. An initial speed of a rotor of the machine is estimated based on the sensed voltage, and state variables of control algorithms are initialized based on the estimated initial speed. This method can provide smooth startup and / or restart at any speed.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
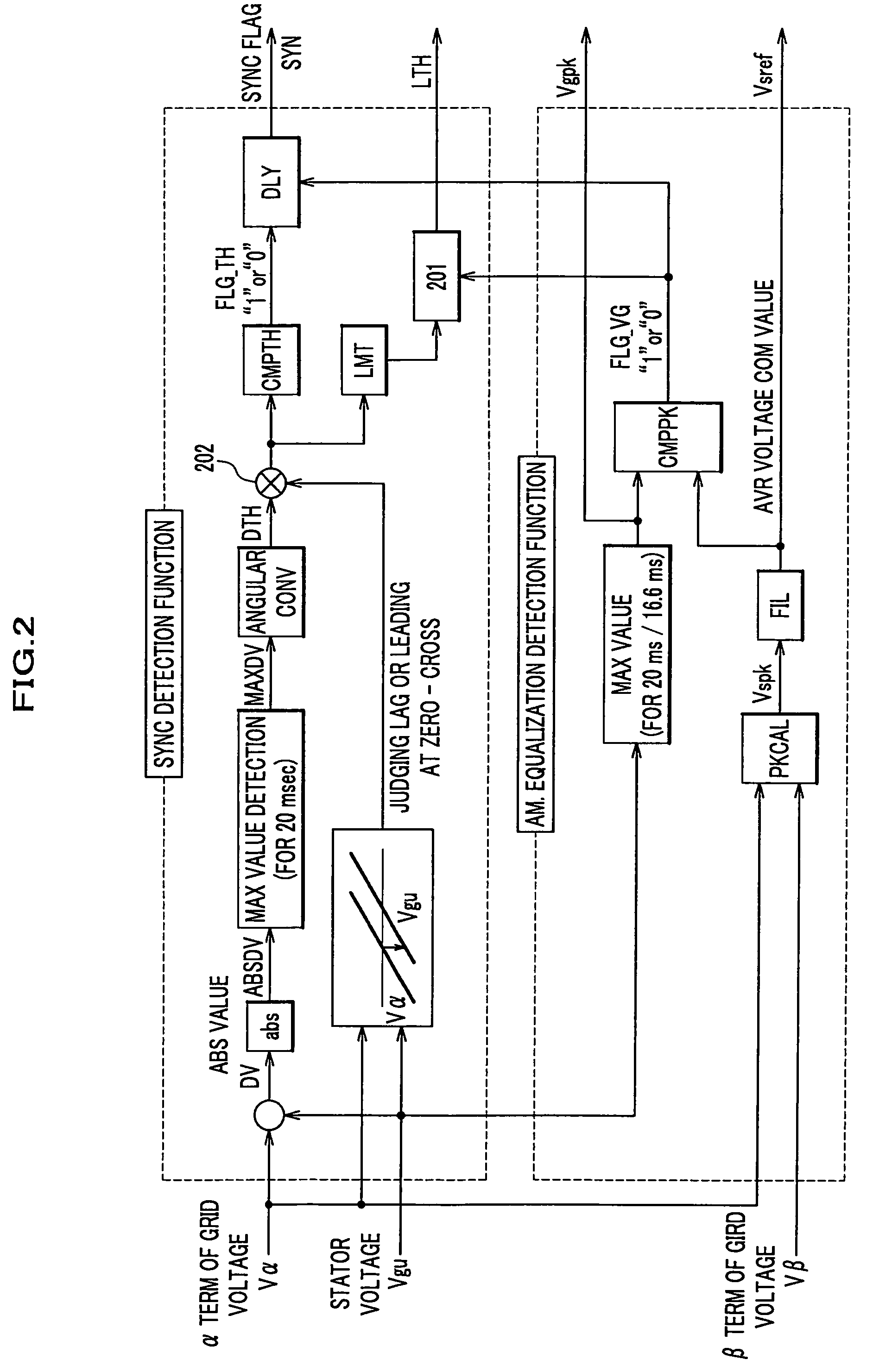
Wind turbine generator system
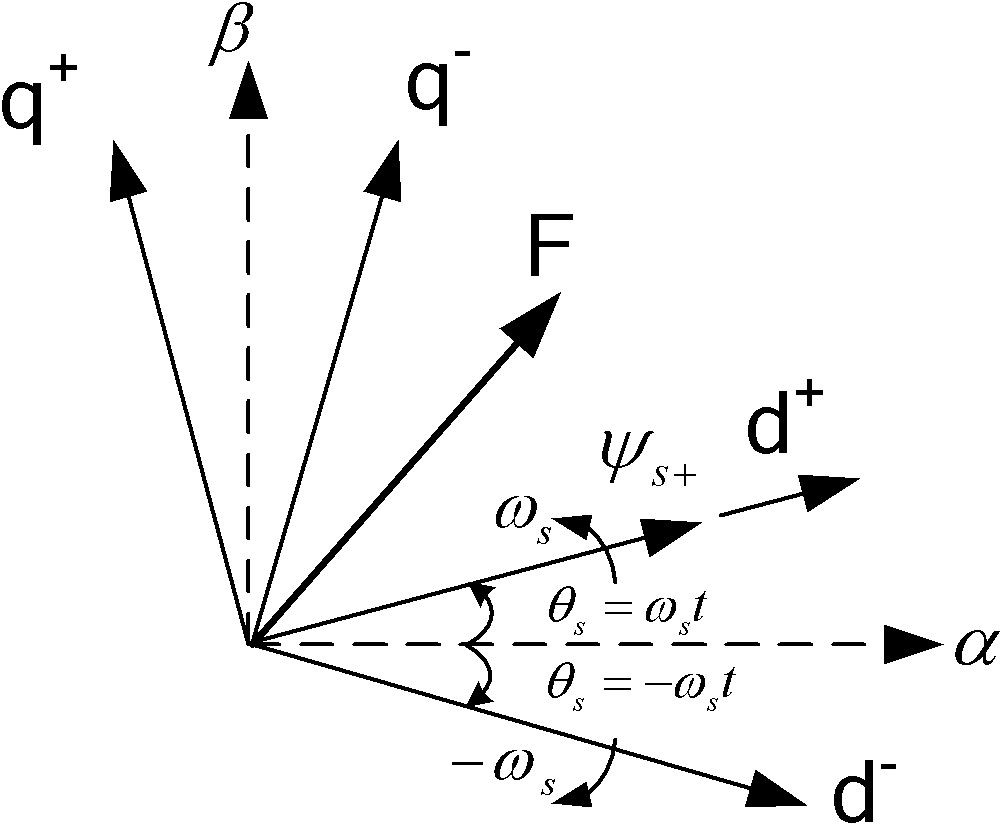
ActiveUS20050151377A1Readily enter synchronous operation with gridReduce in quantityGenerator control circuitsWind motor controlStator voltagePhase difference
To shorten a startup interval to reach a synchronizing condition, a phase difference and an amplitude difference between the grid voltage and the stator voltage of one phase of a winding are obtained. The difference in amplitude is decreased prior to or in parallel to synchronizing the stator voltage with the grid voltage. The calculated compensation phase compensation value is used as an initial value for synchronizing at the next synchronizing operation.
Owner:HITACHI IND PROD LTD
Control method of open winding permanent magnet synchronous motor system of hybrid inverter
ActiveCN103281026AImprove active voltage utilizationGuaranteed uptimeElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlConstant powerVoltage vector
The invention discloses a control method of an open winding permanent magnet synchronous motor system of a hybrid inverter. The control method comprises the following steps: after acquiring voltage and current of a three-phase stator of a motor, performing three-phase / two-phase static coordinate transformation to obtain voltage and current under a two-phase static coordinate system, thereby obtaining actual feedback values of electromagnetic torque and stator flux linkage; obtaining an initial given value of the electromagnetic torque through a PI (Proportional Integral) controller so as to obtain given values of the electromagnetic torque and the stator flux linkage; then combining output of a capacitor voltage PI controller to obtain final given voltage vectors of two inverters; finally generating a switching signal of the inverters through space vector pulse width modulation; and triggering a switching device of the hybrid inverter to realize direct torque control of the open winding permanent magnet synchronous motor. According to the control method, wide-range operation of low, medium and high speed of the open winding permanent magnet synchronous motor is realized, the electromagnetic torque in a motor acceleration process is increased, the voltage utilization rate of a direct current voltage source is improved, and high-speed constant-power operation of the permanent magnet synchronous motor is guaranteed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Judgment method of key sensor fault of double-fed wind generating set
InactiveCN101977008AImprove adaptabilityImprove accuracyElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsTransient stateStator voltage
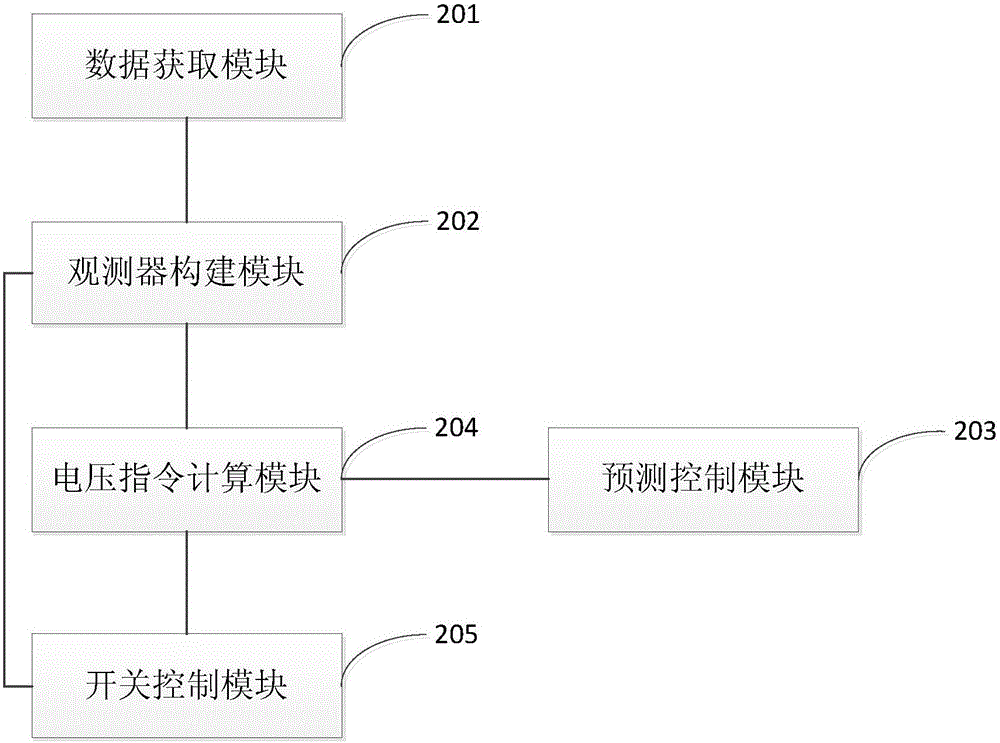
The invention provides a judgment method of a key sensor fault of a double-fed wind generating set, which realizes effective judgment of the key sensor fault by utilizing observer models, a fault detection unit and a disturbance filer unit. The judgment method comprises the following steps: constructing the observer model of stator current and rotor current and the observer model of stator voltage starting from an electromagnetic transient model of a double-fed generator; constructing the fault detection unit by an adaptive threshold method through analysis on the possible soft and hard fault types of the sensor; When the fault residual error is greater than an adaptive threshold value, constructing the disturbance filer unit by design of a timing unit; and finally completing design of the judgment models of the sensor fault based on the adaptive threshold value. The judgment method adopts an algorithm for constructing corresponding observers so as to improve the adaptability and the accuracy of the observer algorithm on fault judgment; and by combination of the adaptive threshold value and the disturbance filer unit, the false alarm rate of the sensor fault is reduced and the robustness of fault judgment is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Wind turbine generator system
ActiveUS7095130B2Readily enter synchronous operation with gridReduce in quantityGenerator control circuitsWind motor controlStator voltagePhase difference
To shorten a startup interval to reach a synchronizing condition, a phase difference and an amplitude difference between the grid voltage and the stator voltage of one phase of a winding are obtained. The difference in amplitude is decreased prior to or in parallel to synchronizing the stator voltage with the grid voltage. The calculated compensation phase compensation value is used as an initial value for synchronizing at the next synchronizing operation.
Owner:HITACHI IND PROD LTD
Method for controlling double-feed wind driven generator under imbalanced power grid voltage
InactiveCN102082543AStable controlFlexible switchingElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsWind drivenBandpass filtering
The invention belongs to the field of control over a power conversion device for a wind driven generator and relates to a method for controlling current switching of a double-feed wind driven generator rotor under an imbalanced power grid voltage. The method comprises the following steps of: calculating a stator voltage, a stator current and a rotor current under a two-phase static coordinate system; calculating stator voltages and stator currents of a d axis and a q axis under a flux linkage and a synchronous rotation coordinate system; calculating a slip angle and a slip angular velocity; calculating rotor currents of the d axis and the q axis under the rotation coordinate system; calculating stator active power, reactive power and electromagnetic torque; calculating rotor decoupling compensating voltage; naturalizing and calculating corresponding control variables, acquiring a secondary pulse actual value of a controlled variable through a bandpass filter and a lead lag link, subtracting the actual value from a secondary pulse given value, and calculating to acquire a two-time frequency compensation item through a proportional integral (PI) controller; calculating the given value of the rotor current of the d axis under the rotation coordinate system; allowing the difference of a rotation speed given value and a rotational angular velocity actual value to pass through the PI controller, and calculating to acquire the given value of the rotor current of the q axis under the rotation coordinate system; calculating to acquire reference values of rotor voltages of the d axis and the q axis under the rotation coordinate system; and calculating the rotor voltage under the rotor two-phase static coordinate system and generating switch signals which control power devices.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Power generation apparatus using AC energization synchronous generator and method of controlling the same
InactiveUS7332894B2Short timeGenerator control circuitsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsStator voltagePhase difference
In a power generation apparatus equipped with an AC energization synchronous generator, when energization of a secondary winding starts to conduct connecting to the network of the AC energization synchronous generator to a network voltage, energization of the secondary winding starts at a fixed frequency and a slip frequency is calculated from a difference between a frequency of the network voltage and a resultant stator voltage frequency. Thereafter, energization starts at the calculated slip frequency and a voltage having a frequency generally coincident with the network frequency is output to the stator to incorporate the generator to the network. A phase is adjusted to make zero a phase difference when the rotation speed changes or the phases become different.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Open-loop control method and open-loop control system of permanent magnet synchronous motor based on space vector pulse width modulation (SVPWM)
ActiveCN102843090AReduce lossImprove efficiencyElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsStator voltageConstant power
The invention discloses an open-loop control method and an open-loop control system of a permanent magnet synchronous motor based on space vector pulse width modulation (SVPWM). To each given stator power frequency, the amplitude of stator voltage corresponding to the given stator power frequency is found through searching a two-dimensional vector table of the stator voltage and the stator power frequency, wherein the two-dimensional vector table is set according to a sectional voltage / frequency ratio curve in advance, that is to say, the ratio of the stator voltage and the stator power frequency in the two-dimensional vector table disclosed by the invention is not a normal value; and the ratio is different in different interval sections. In the prior art, as the voltage / frequency ratio is a normal value, when a load changes, a motor is out of step easily so as to cause overcurrent to the system. In the method disclosed by the invention, the sectional voltage / frequency ratio can guarantee the motor to adapt to the change of the load, reduce the consumption of the motor and improve the efficiency. In a constant power area, phase compensation is introduced, so that weak magnetic control is realized by using the regulated phase, and weak magnetic speed improvement is realized.
Owner:ZHUZHOU CSR TIMES ELECTRIC CO LTD
Current prediction control method and apparatus for permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM)
ActiveCN105897097ASimple structureRobustElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsStator voltageElectric machine
The invention discloses a current prediction control method and apparatus for a permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM). The method comprises the steps: acquiring the motor stator current and stator voltage under two-phase rotating coordinates; constructing a current and perturbation sliding-mode observer, and predicting and obtaining the motor stator current and the parameter perturbation estimated value of the next moment; according to the principle that the practical current value of the next moment is equal to a current command value, obtaining a PMSM current prediction control expression; taking the current value, predicted by the observer, of the next beat, as current feedback, and obtaining the command voltage of a motor driver through calculation; and further adding the command voltage and the parameter perturbation estimated by the observer together, taking the sum as the final motor driver command voltage, and finally generating a pulse signal for controlling motion of a switch tube through an SVPWM device. The current prediction control method for a permanent magnet synchronous motor can predict the current of the next beat and estimate parameter perturbation at the same time, and can effectively restrain the current tracking static error and reduce the motor harmonic wave current and optimize the current control performance when a parameter mismatching problem exists.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Motor stator resistor recognition method
ActiveCN105119549AElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsStator voltageElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention discloses a motor stator resistor recognition method, and the method is used for a surface-mounted PMSM. The method comprises the steps: building a d-q coordinate system based on rotor flux linkage orientation at first; eliminating a non-resistance voltage drop part in a motor stator voltage equation in an operation process of the surface-mounted PMSM; and calculating the resistance of a stator resistor through the voltage and current of a resistor voltage drop part. The method achieves on-line recognition, also can recognize the resistance value of the stator resistor when the motor operates at different speeds, and can recognize the resistance value, which changes because of the impact of motor temperature, of the stator resistor in real time. Compared with a conventional on-line recognition method, the method just needs voltage and current signals during the calculation of the stator resistor, does not need other parameter information of the motor, is simple in algorithm, is easy to achieve through a DSP, and is higher in recognition precision.
Owner:NANJING ESTUN AUTOMATION CO LTD
Method for controlling direct torsion/ flux linkage of permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN103269191AExtended operating rangeOvercoming the crashVector control systemsSingle motor speed/torque controlPermanent magnet synchronous motorPermanent magnet synchronous generator
The invention discloses a method for controlling direct torsion / flux linkage of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. The method comprises the steps of collecting three-phase stator voltage and currents of the motor, and obtaining voltage and currents under a two-phase static coordinate system through three-phase / two-phase static coordinate conversion; calculating actual feedback value of electromagnetism torsion and stator flux linkage according to the voltage and the currents under the two-phase static coordinate system; obtaining initial given value of the electromagnetism torsion through a PI controller according to difference between given rotating speed and feedback rotating speed; obtaining given value of the electromagnetism torsion and the stator flux linkage according to a given electromagnetism torsion and stator flux linkage calculating module; obtaining given voltage on an alpha beta shaft of the two-phase static coordinate system through a given voltage calculating module; generating switching signals of an inverter through space vector pulse width modulation, triggering a switching device of the inverter, and realizing direct torsion / flux linkage control of the permanent magnet synchronous motor. The method realizes low, medium and high speed wide range operation of the permanent magnet synchronous motor, does not need to rotate coordinate conversion, and has the advantages of being convenient to calculate, quick in dynamic response, strong in robustness, and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Permanent magnet synchronous motor sliding-mode speed observer driven by two-stage matrix converter
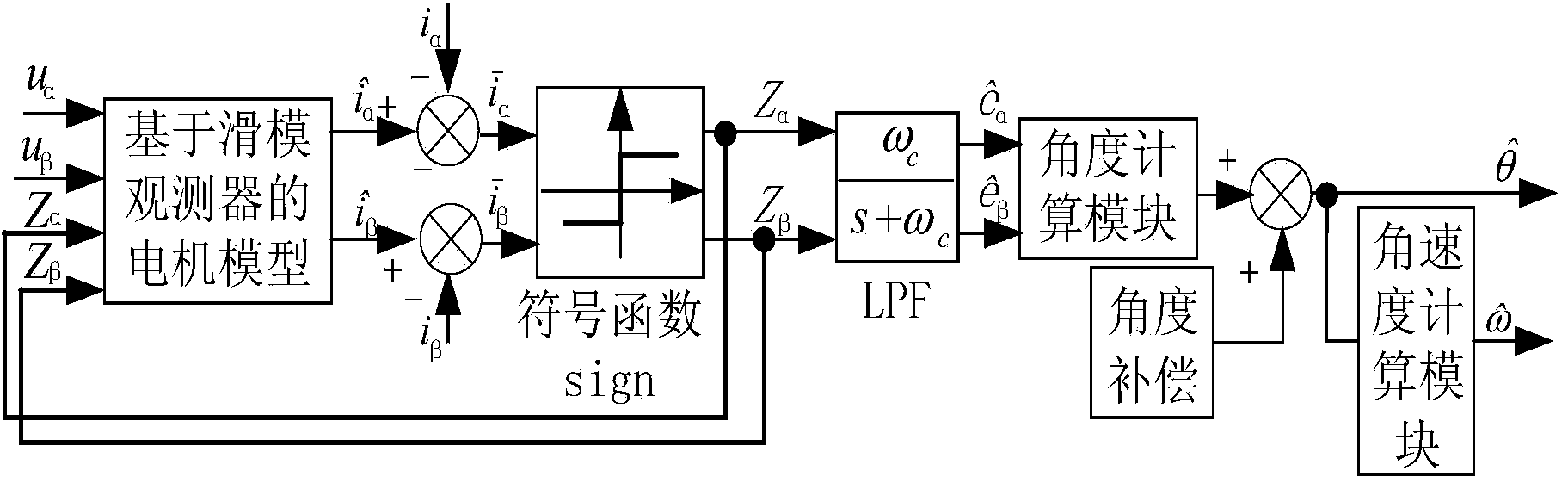
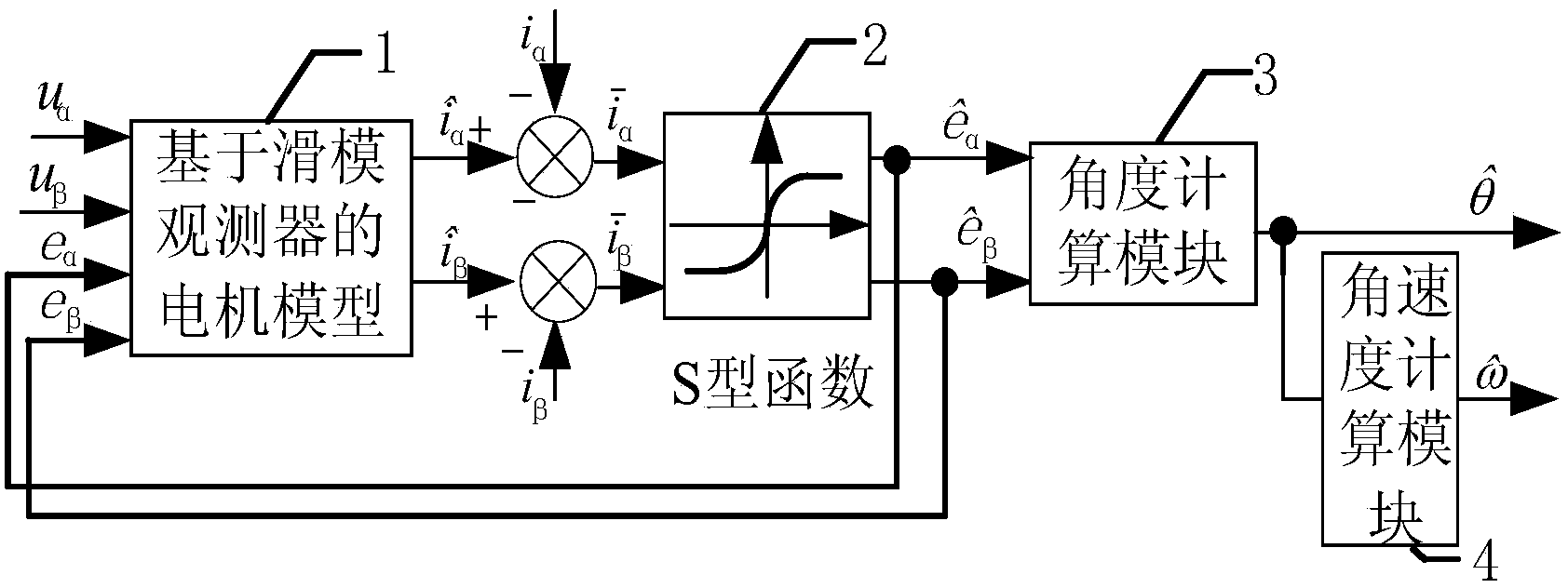
InactiveCN103715962AFix jitterResolve delayElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsMatrix convertersStator voltage
A permanent magnet synchronous motor sliding-mode speed observer driven by a two-stage matrix converter comprises a motor model based on the sliding-mode observer, an S-shaped switch function, an angle calculation module and an angular speed calculation module. Ualpha and Ubeta, obtained through the voltage reconstitution method, of stator voltages in a two-phase static coordinate system of a permanent magnet synchronous motor and the two S-shaped switch function output values (see the specification) serve as the motor model input based on the sliding-mode observer, the stator actual current values including ialpha and ibeta are subtracted from the four motor model output stator current observing values (see the specification) based on the sliding-mode speed observer, the two difference values serve as the S-shaped switch function input, the difference values are processed through the permanent magnet synchronous motor sliding-mode speed observer, then the two counter EMF estimated values in the two-phase static coordinate system are output, the rotor position is obtained through the angle calculation module, and the angular speed is obtained through the angular speed calculation module.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method in connection with permanent magnet synchronous machines
InactiveUS20060091847A1Small speedSmall position estimation errorSingle-phase induction motor startersElectronic commutation motor controlStator voltagePermanent magnet synchronous machine
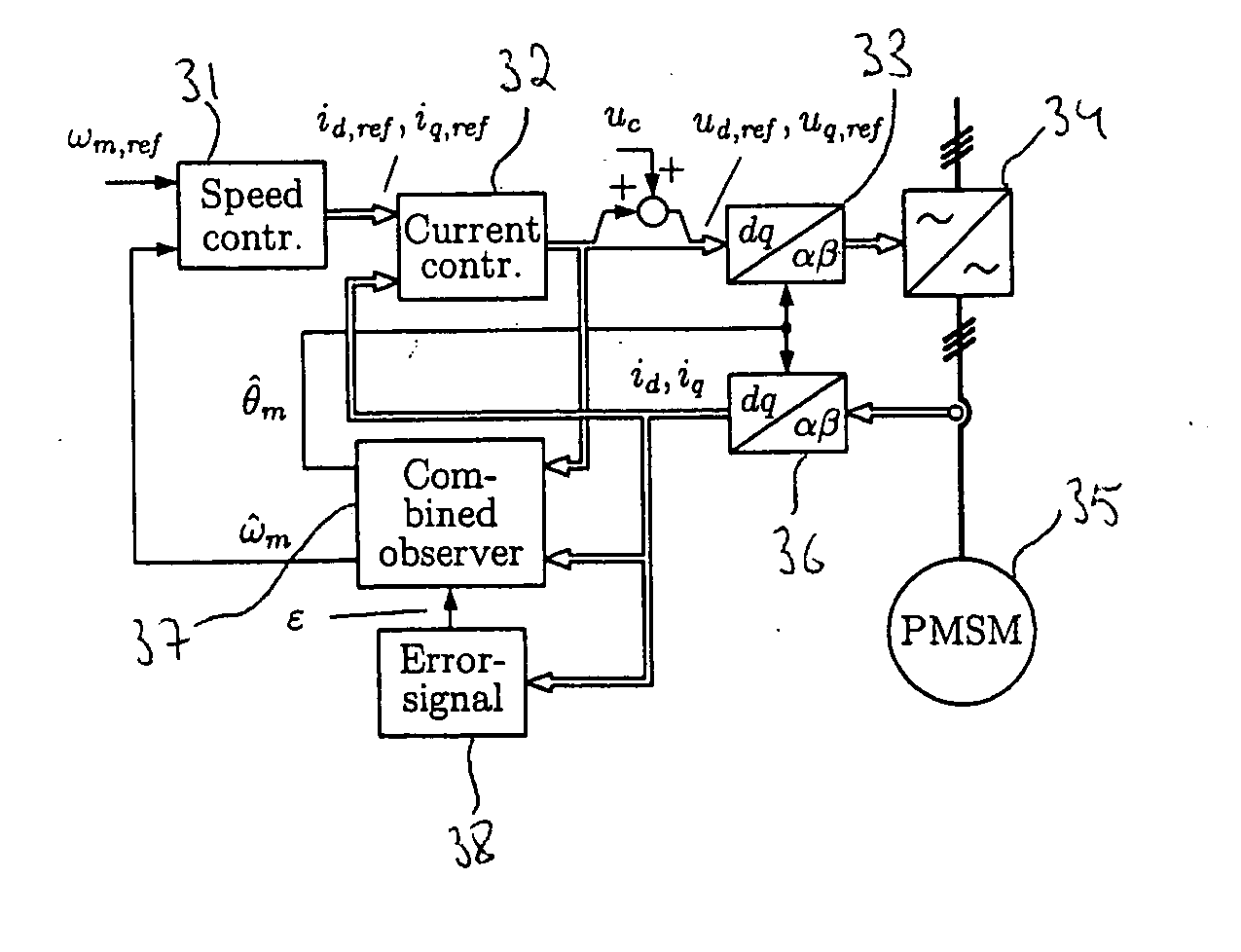
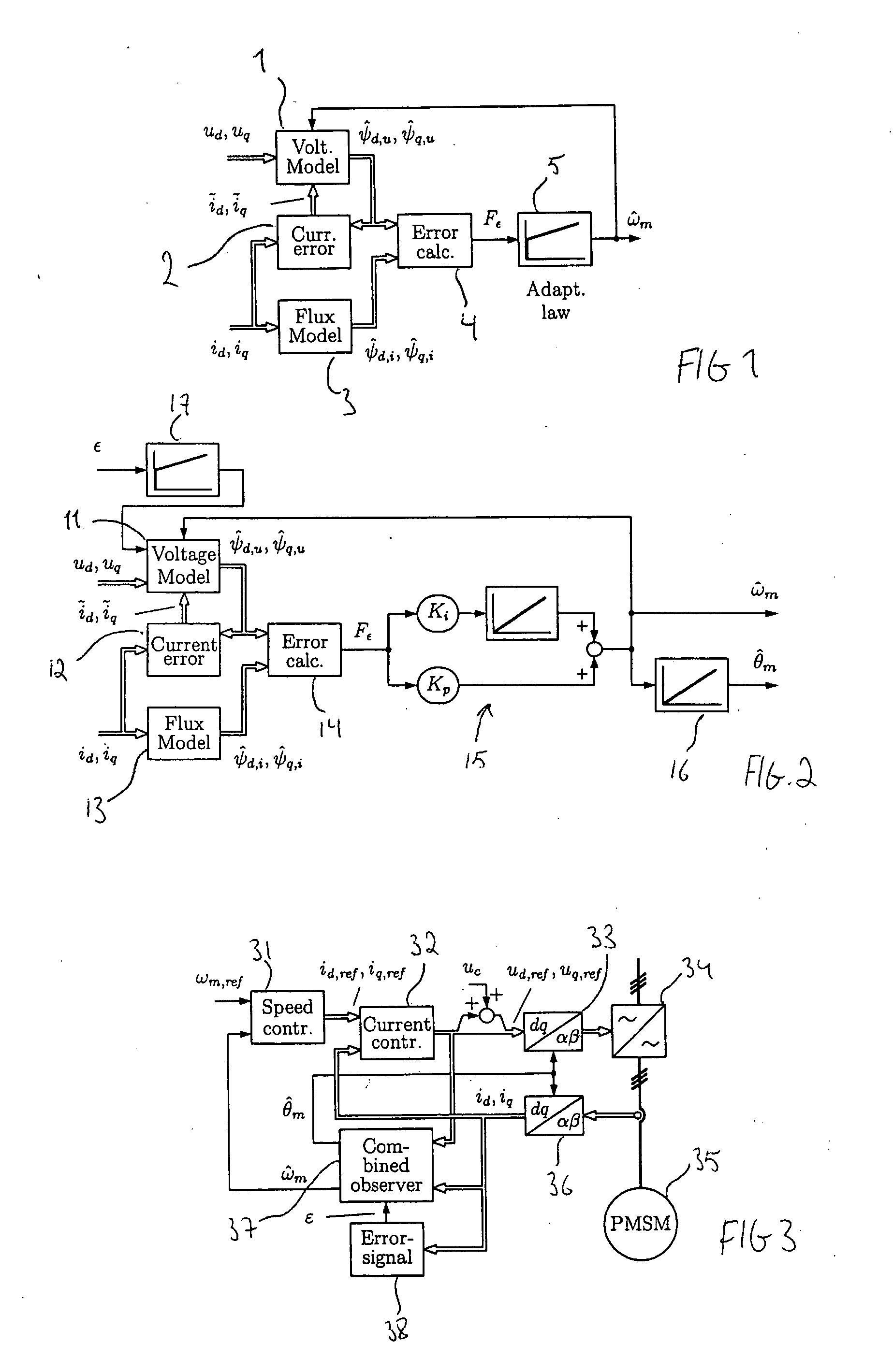
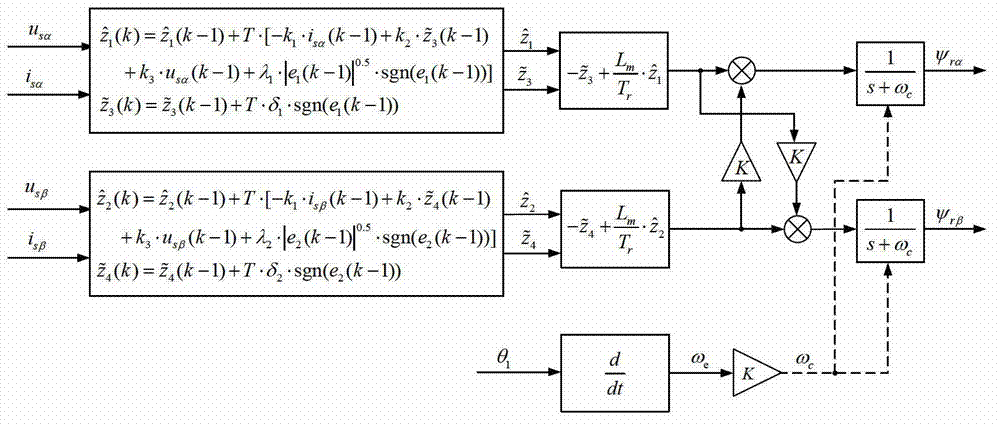
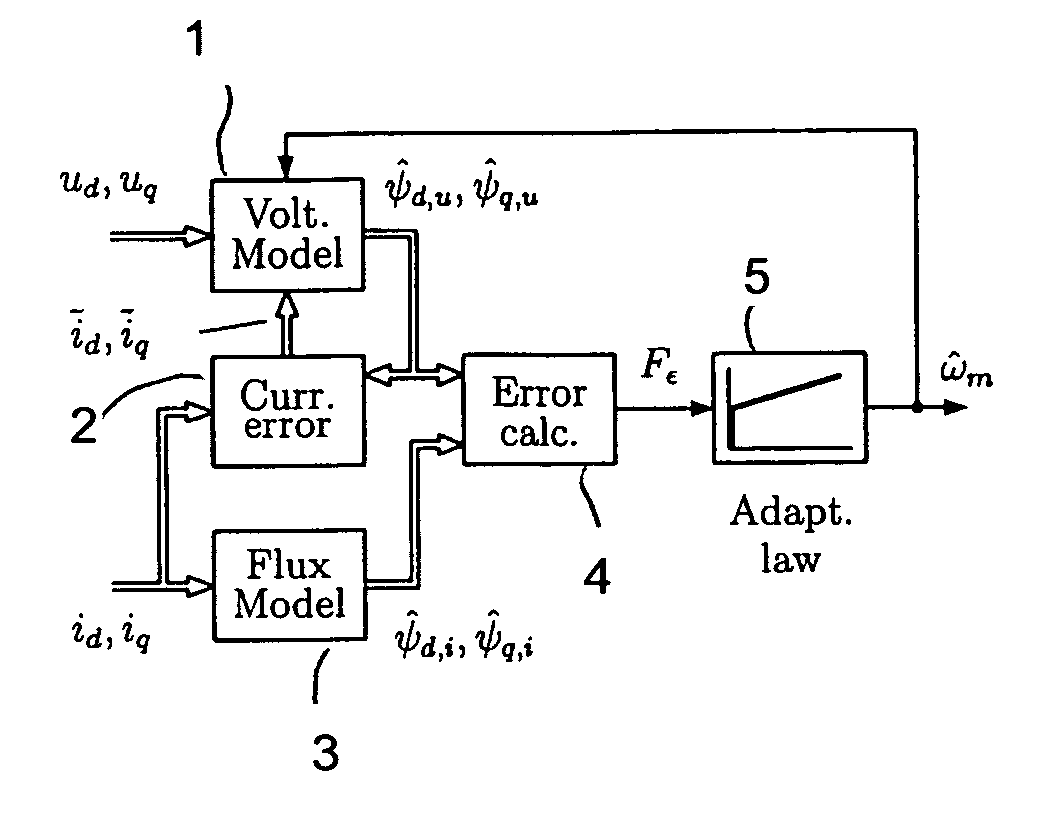
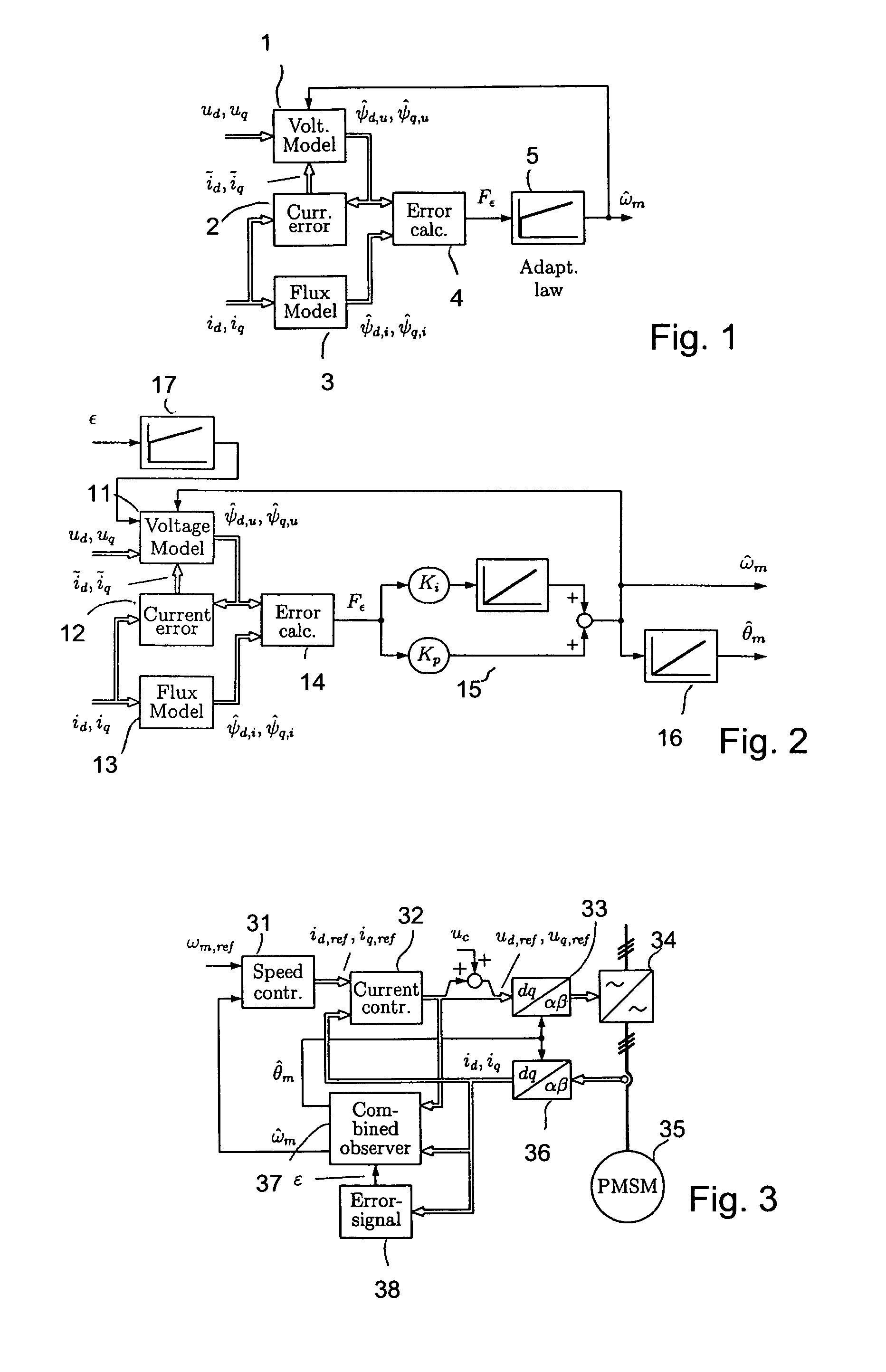
A method for sensorless estimation of rotor speed and position of a permanent magnet synchronous machine the method comprising the steps of calculating first stator flux vector estimate ({circumflex over (ψ)}d,i+j{circumflex over (ψ)}q,i) using the flux model and measured stator currents, calculating second stator flux vector estimate ({circumflex over (ψ)}d,u+j{circumflex over (ψ)}q,u) using the voltage model and measured stator voltages, comparing the directions of the first and second flux vectors to achieve a first error signal (Fε), using speed adaptation to achieve estimates for the rotor angular speed ({circumflex over (ω)}m) and angular position ({circumflex over (θ)}m) from the first error signal (Fε), injecting a known voltage signal (uc) to the stator voltage, detecting a current signal (iqc) from the stator current to form a second error (ε) signal, which is dependent on the estimation error of the rotor position, augmenting the voltage model by the second error signal (ε) to keep the first and second flux vector estimates aligned and so to correct the rotor angular speed ({circumflex over (ω)}m) and angular position ({circumflex over (θ)}m) estimates.
Owner:ABB OY
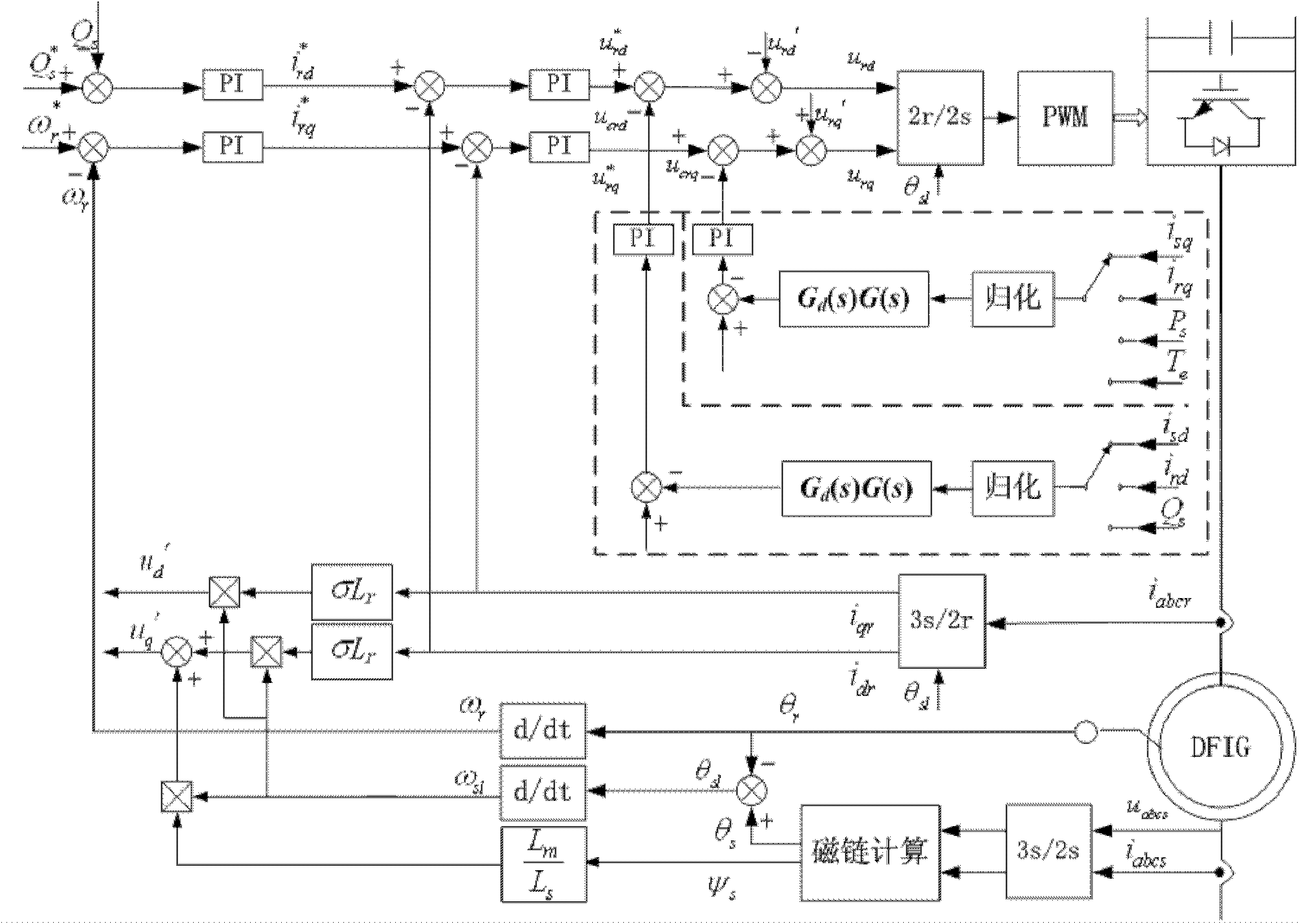
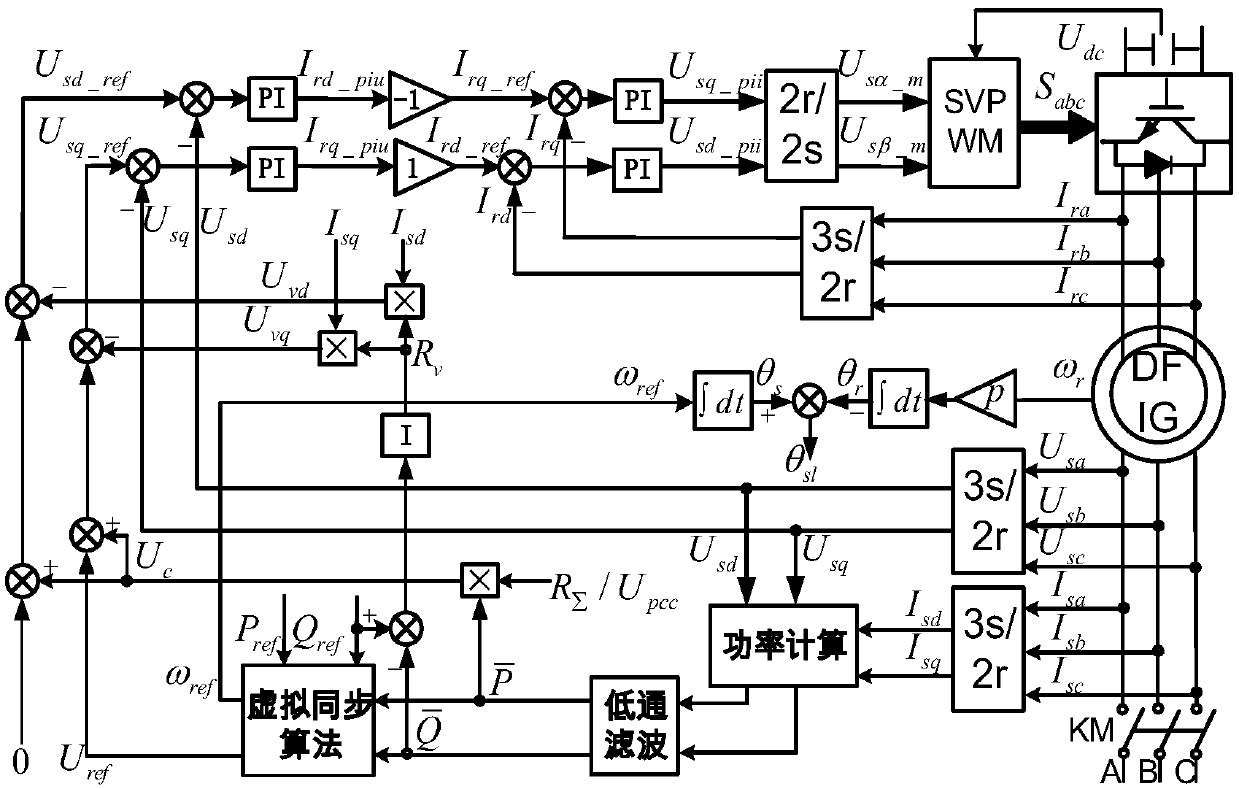
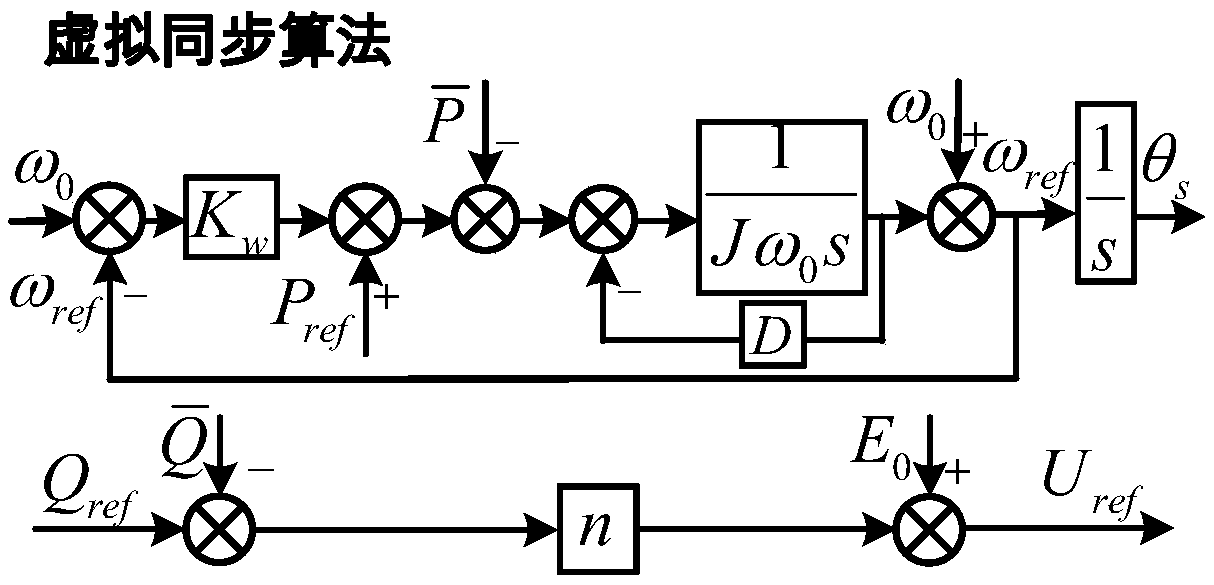
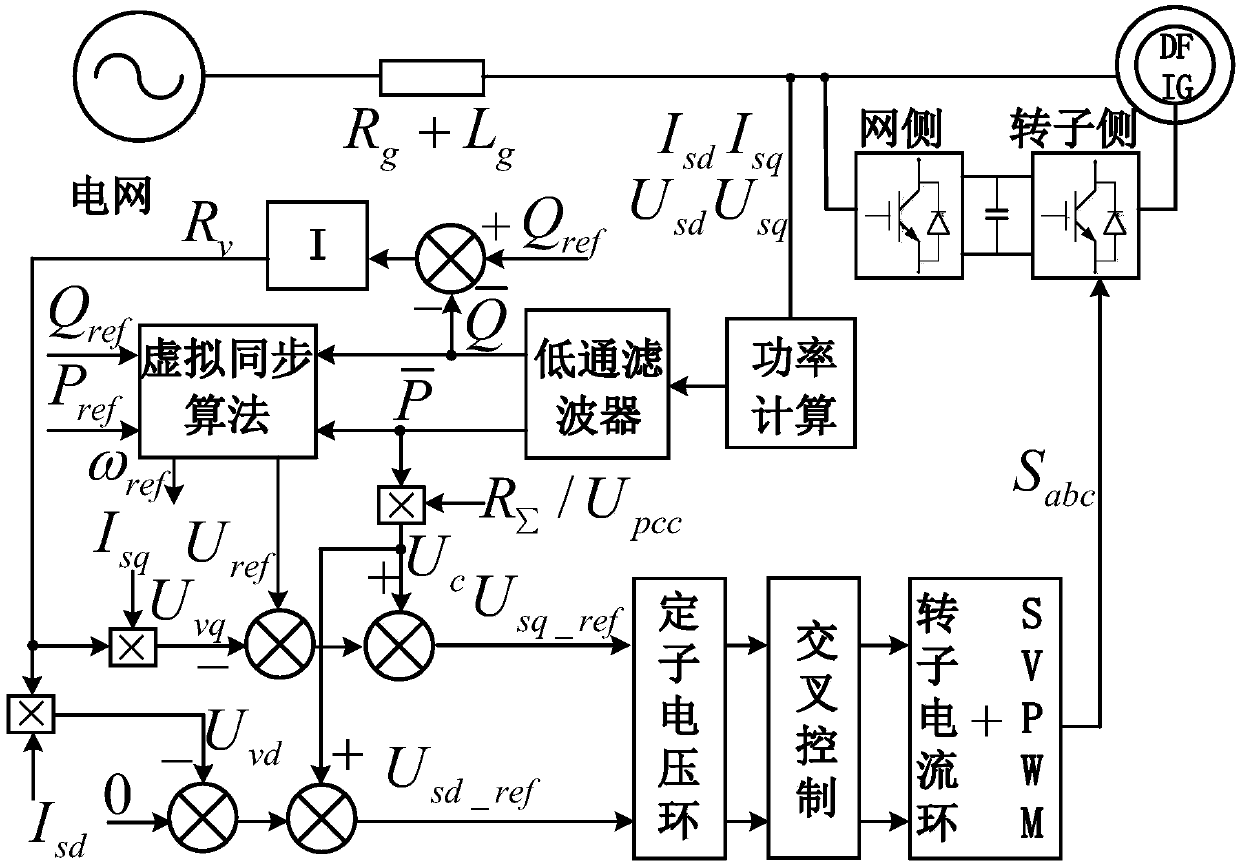
Voltage control type virtual synchronizing method of double-feed wind power generator set
ActiveCN108683198AAccurately offsets estimation errorsSpeed up the dynamic process of power regulationClimate change adaptationSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsControl mannerClosed loop
The invention discloses a voltage control type virtual synchronizing method of a double-feed wind power generator set. Through simulating inertia and a frequency-modulating and voltage-modulating characteristic of a synchronizer, the set can be different from a characteristic of no electric grid frequency change response in a traditional current control type, thereby possessing capability of supporting voltage and frequency of a weak power grid based on the voltage control type through virtual inertia. The method provides and realizes a VCT-DFIC virtual synchronous control structure of which an inner ring is controlled by an improved double-feed generator stator voltage rotor current double-closed-loop structure based on adaptive stator virtual impedance and transmission line sag voltage feedforward compensation in a control manner which includes crossed control between stator voltage and rotor current and furthermore an outer ring is controlled by a virtual synchronous realizing algorithm. The method realizes output power control in VCT-DFIG grid integration operation in a weak grid condition with any actual impedance and effective decoupling, and furthermore a designed control structure realizes higher inertia and frequency supporting capability of the double-feed generator.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
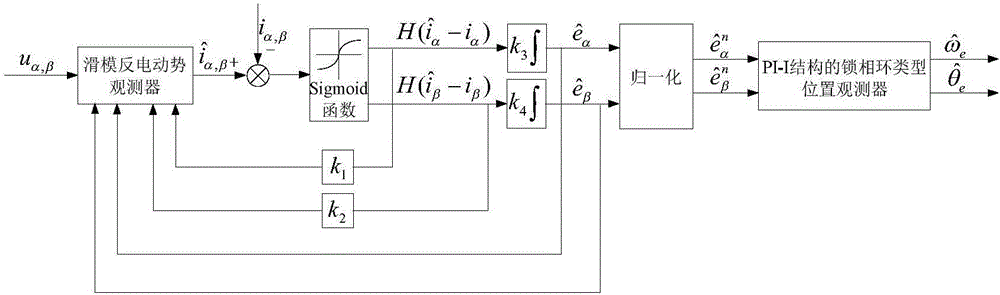
Permanent magnet synchronous motor state estimation method based on sliding mode back EMF observer
InactiveCN106487304ASuppress chatterEliminate delayElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsKaiman filterStator voltage
The invention discloses a permanent magnet synchronous motor state estimation method based on a sliding mode back EMF observer. According to stator voltage and stator current detected in real time, a sigmoid function is used to substitute a sign function, and the sliding mode back EMF observer is constructed to estimate the back EMF. The type of the sliding mode back EMF observer is characterized in that the observer is insensitive to switch noise and has a filtering characteristic, thus the filtering of the estimated back EMF through a low-pass filter is not needed. After the normalization processing of the back EMF, a rotor position and speed information are extracted through a PI-I structure phase-locked loop position observer equivalent to a simplified Kalman filter. The permanent magnet synchronous motor state estimation method of the invention has good estimation performance even in the condition of noise and motor parameter changes, the chattering phenomenon in a traditional sliding mode observer is reduced, and the dynamic tracking performance and estimation precision of the rotor position and speed are improved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method for asynchronous motor rotor flux linkage observation and rotation speed identification
InactiveCN102931906AGuaranteed observation accuracyImprove recognition accuracyElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsVector control systemFlux linkage
The invention discloses a method for asynchronous motor rotor flux linkage observation and rotation speed identification, which comprises the following steps of: according to stator voltage and current signals measured in real time, observing to obtain a rotor flux linkage through a sliding mode observer based on a super-twisting theory and using the rotor flux linkage as a reference value; using a rotor flux linkage calculated according to a rotor flux linkage current model as an adjustable value; constructing a model reference self-adaptive system (MRAS) based on the rotor flux linkages; and identifying the asynchronous motor rotation speed through the self-adaptive law. The rotation speed identification method provided by the invention has high robustness for the variation of stator resistance, and can provide accurate rotor flux linkages and rotation speed values, thereby being especially suitable for an asynchronous motor vector control system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for sensorless estimation of rotor speed and position of a permanent magnet synchronous machine
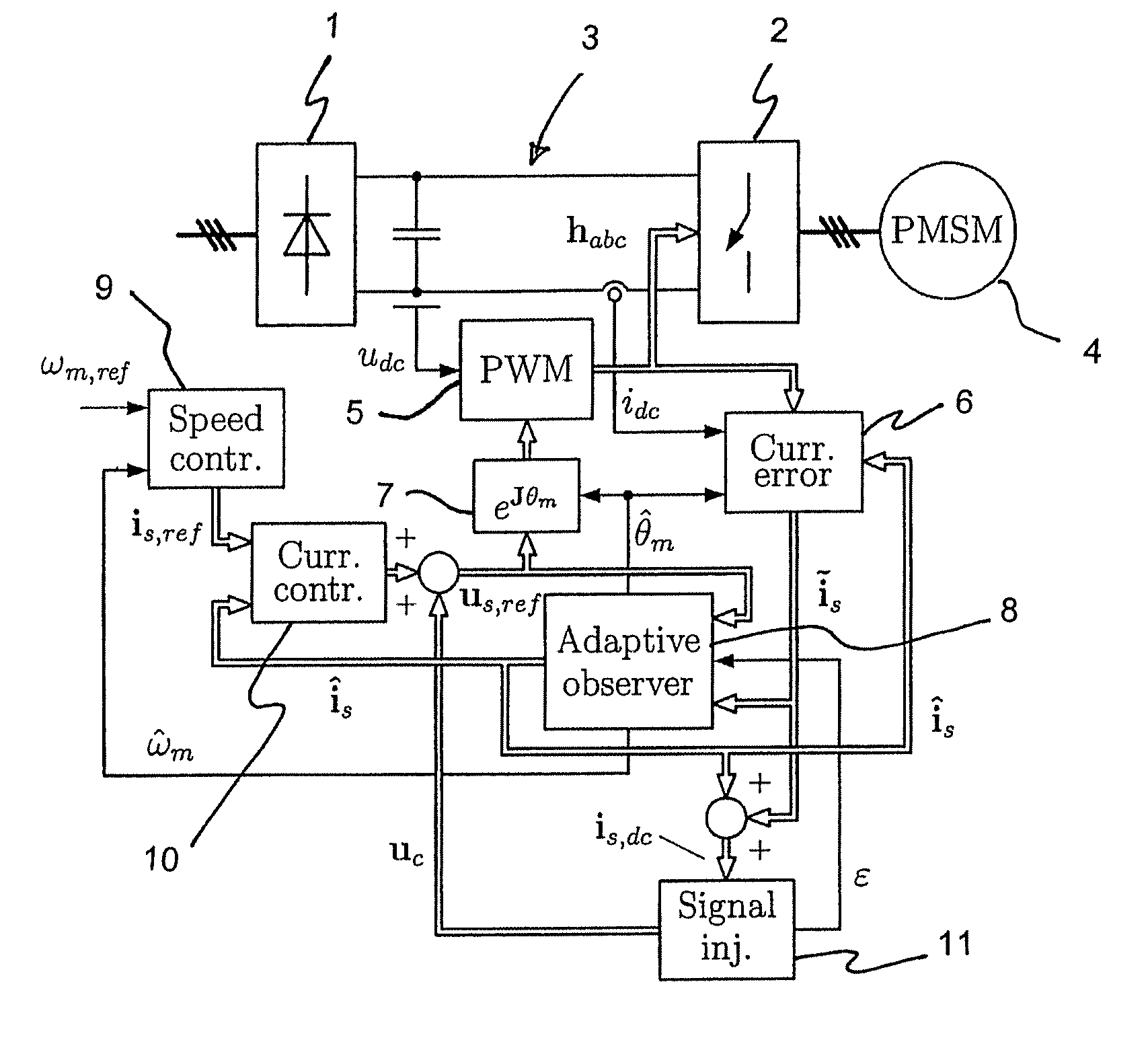
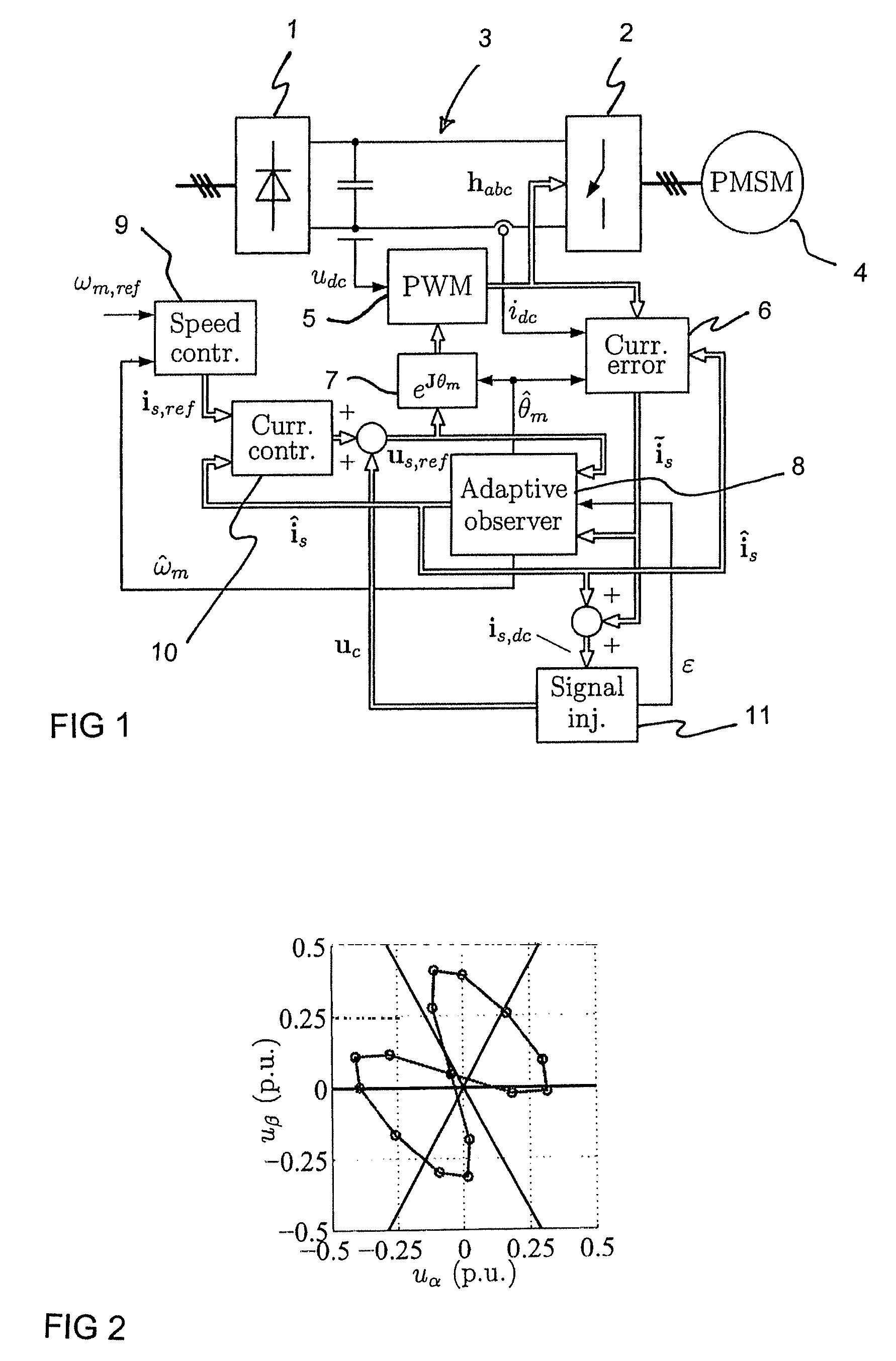
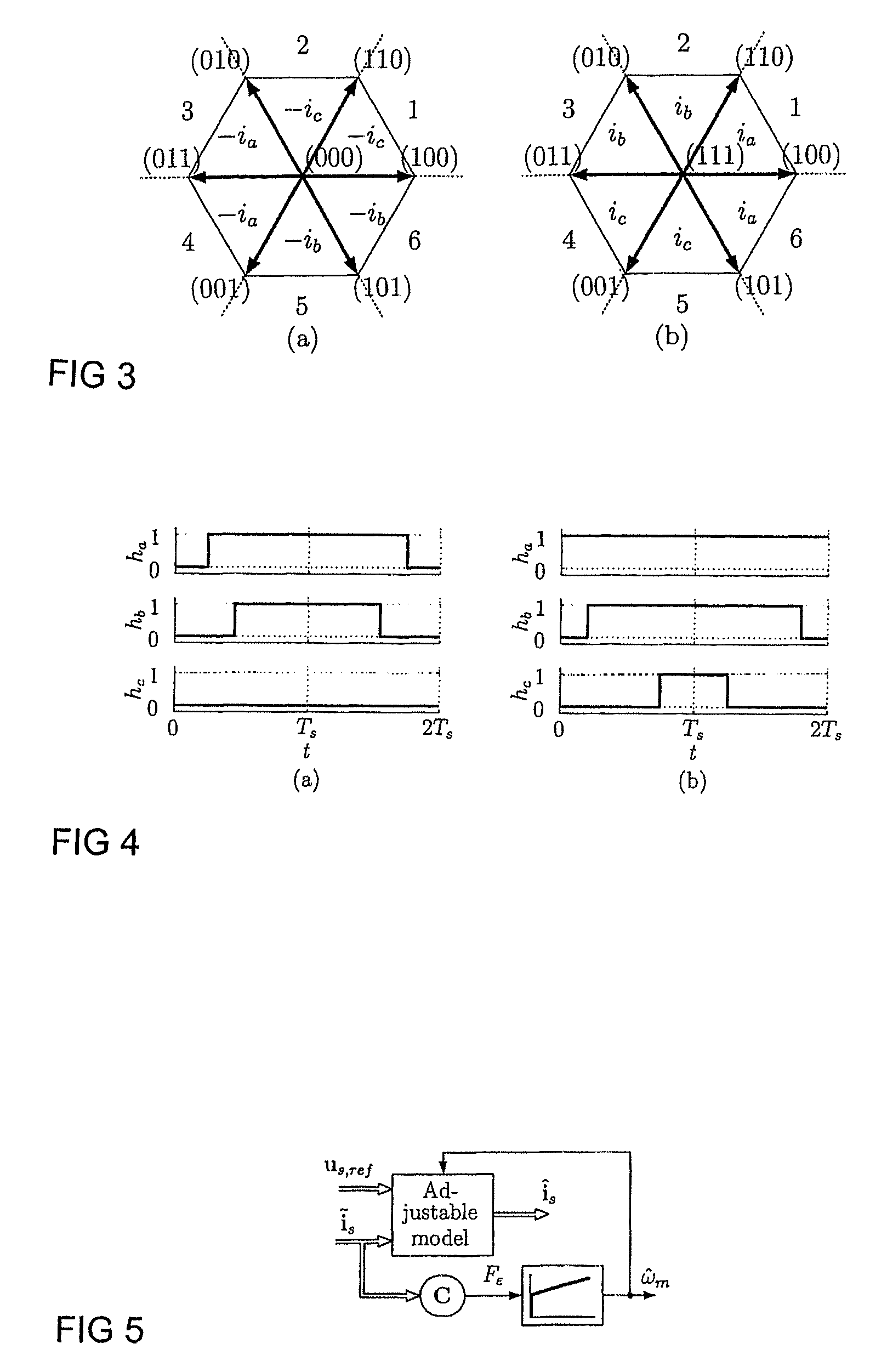
ActiveUS7759897B2Stabilize estimationGuaranteed uptimeSingle-phase induction motor startersElectronic commutation motor controlStator voltageFrequency changer
A method for sensorless estimation of rotor speed and position of a permanent magnet synchronous machine, when the permanent magnet synchronous machine is fed with a frequency converter, the method comprising the steps of forming a stator voltage reference for the permanent magnet synchronous machine, injecting a high frequency signal (uc) into the stator voltage reference, measuring a DC-link current (idc) of the frequency converter when the permanent magnet synchronous machine (4) is fed with a voltage (us,ref) corresponding to a sum of the stator voltage reference and the injected signal, calculating a stator current estimate (îs), calculating a current error (ĩs) as a difference between the stator current estimate and the measured DC-link current, and estimating a rotor speed ({circumflex over (ω)}m) and position ({circumflex over (θ)}m) of the permanent synchronous machine based on the current error. The injected high frequency signal (uc) comprises a direct axis component and a quadrature axis component, the direct axis component having a first frequency and the quadrature axis component having a second frequency, the first and second frequencies being different.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Method in connection with permanent magnet synchronous machines
InactiveUS7098623B2Improve dynamic performanceSmaller positionSingle-phase induction motor startersElectronic commutation motor controlStator voltagePermanent magnet synchronous machine
A method for sensorless estimation of rotor speed and position of a permanent magnet synchronous machine the method comprising the steps of calculating first stator flux vector estimate ({circumflex over (ψ)}d,i+j{circumflex over (ψ)}q,i) using the flux model and measured stator currents, calculating second stator flux vector estimate ({circumflex over (ψ)}d,u+j{circumflex over (ψ)}q,u) using the voltage model and measured stator voltages, comparing the directions of the first and second flux vectors to achieve a first error signal (Fε), using speed adaptation to achieve estimates for the rotor angular speed ({circumflex over (ω)}m) and angular position ({circumflex over (θ)}m) from the first error signal (Fε), injecting a known voltage signal (uc) to the stator voltage, detecting a current signal (iqc) from the stator current to form a second error (ε) signal, which is dependent on the estimation error of the rotor position, augmenting the voltage model by the second error signal (ε) to keep the first and second flux vector estimates aligned and so to correct the rotor angular speed ({circumflex over (ω)}m) and angular position ({circumflex over (θ)}m) estimates.
Owner:ABB OY
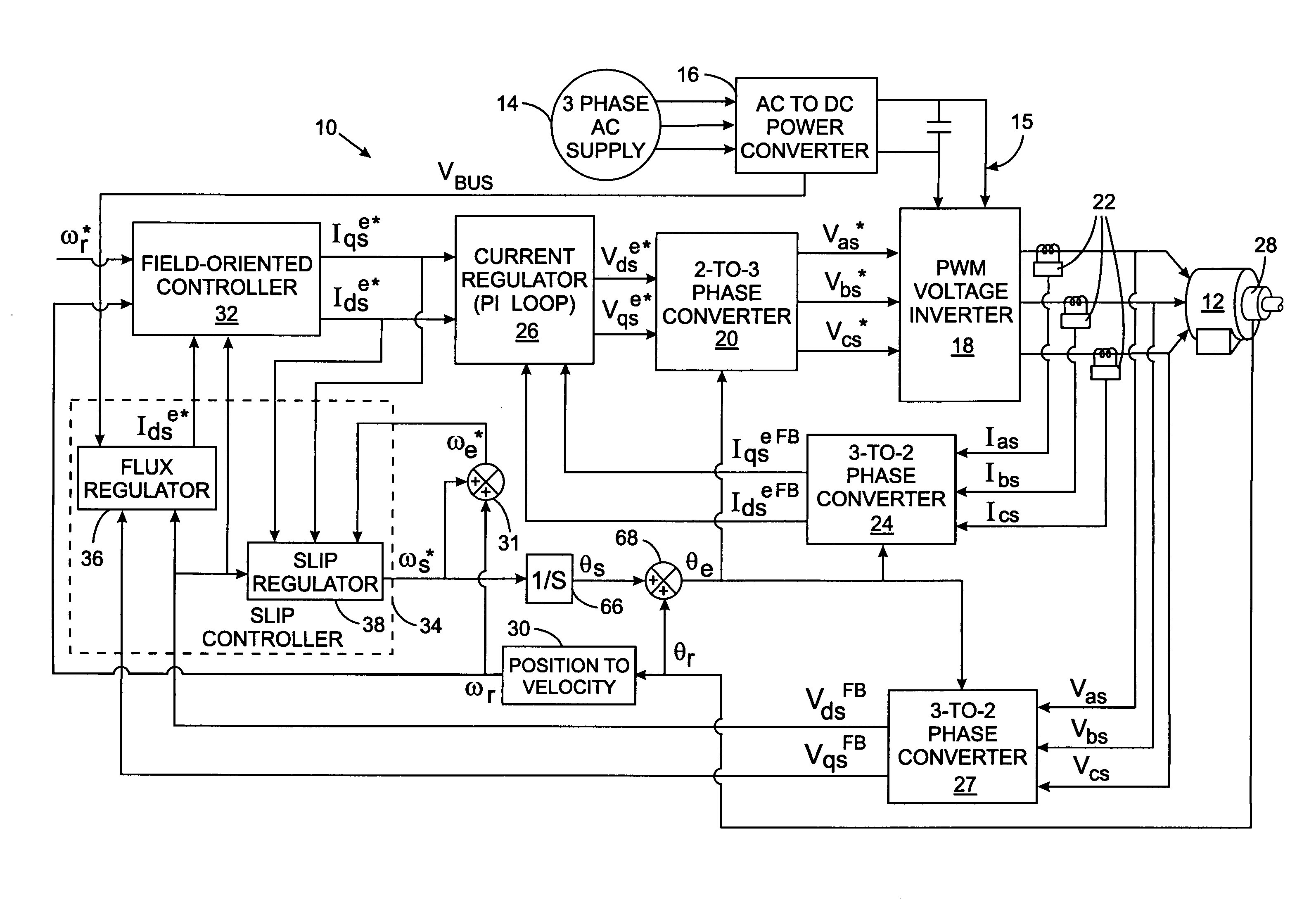
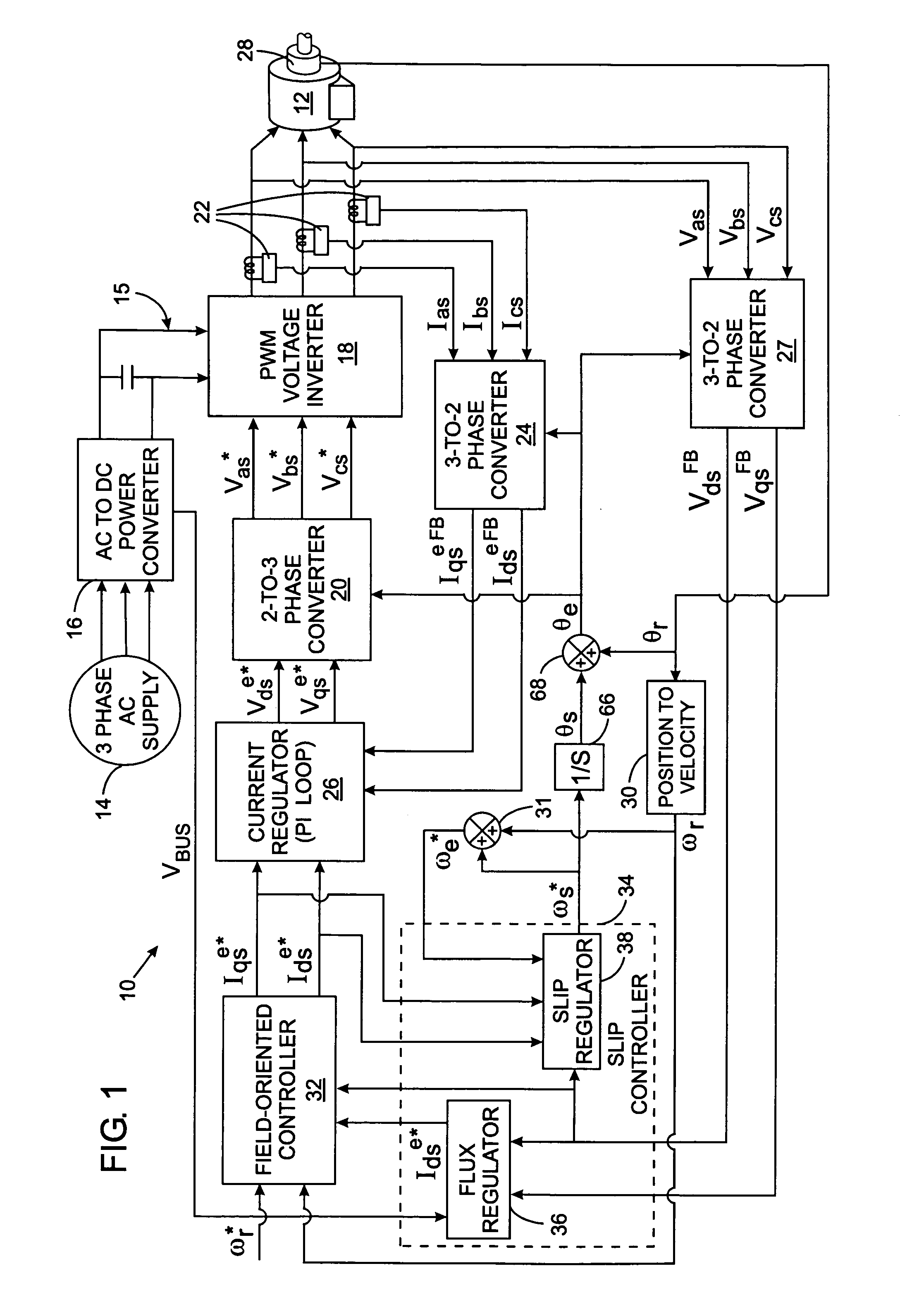
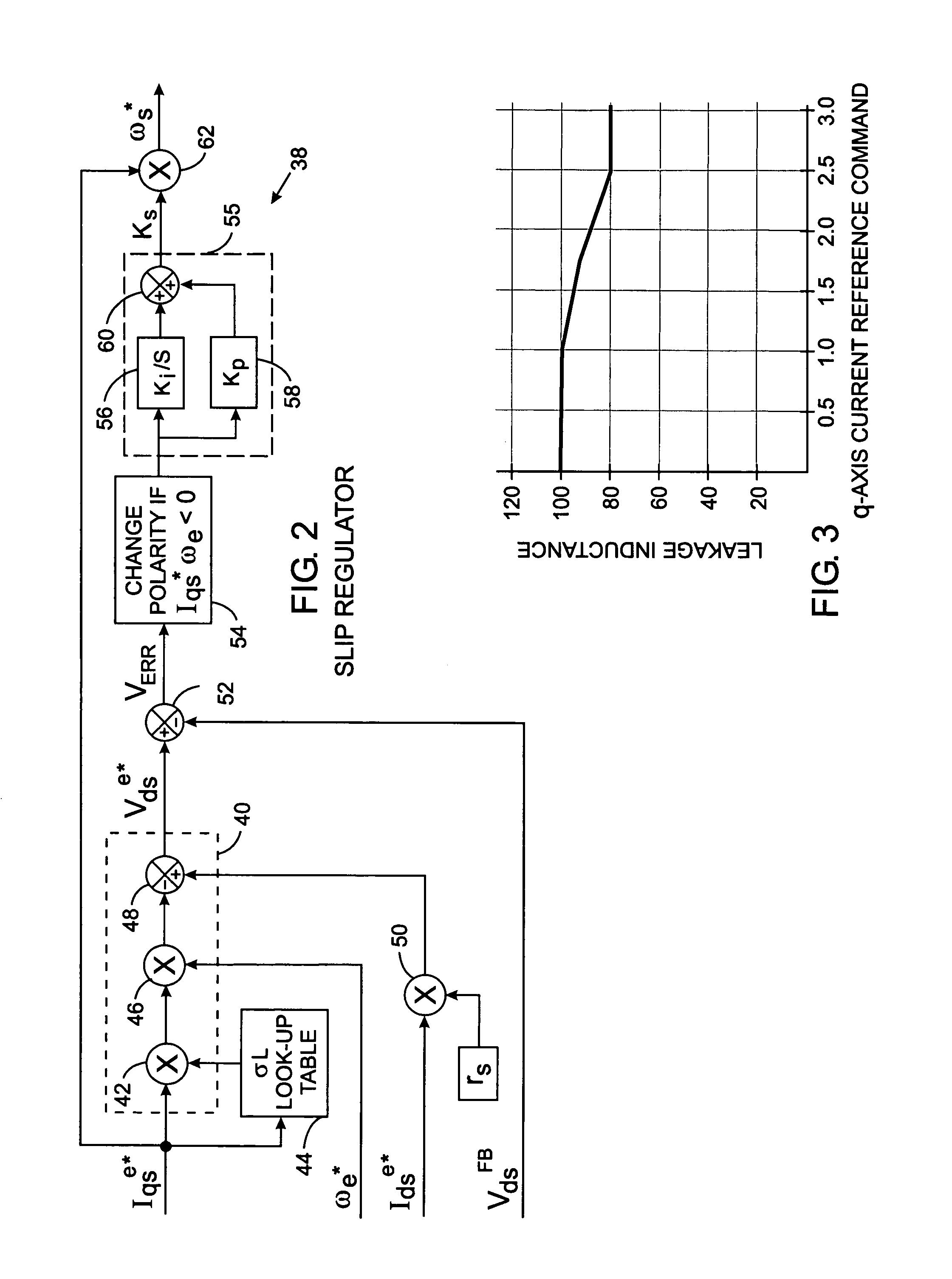
Leakage inductance saturation compensation for a slip control technique of a motor drive
ActiveUS7187155B2Single-phase induction motor startersSynchronous motors startersStator voltageControl vector
An electronic drive for vector control of an induction motor controls slip and operating frequency in response to changes in stator voltage. The drive includes a torque control loop, a flux control loop and a frequency control loop. The control is based on a commanded stator current that is resolved into a torque-producing, or q-axis, current component and a flux-producing, or d-axis, current component that are in quadrature. The frequency control loop includes slip control in which a slip frequency command is produces based on a value for the leakage inductance of the motor. The leakage inductance value dynamically varies as a function of the q-axis current reference command.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Asynchronous motor optimizing excitation control method based on magnetic-field saturated non-linear motor model
InactiveCN1404215AImprove performanceIncrease output torqueElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsMaximum torqueStator voltage
The present invention belongs to the field of asynchronous motor exciting speed-regulating technology and features the exciting speed-regulating method of optimizing stator-exciting current to regulate rotor magnetic linkage. It MT coordinate system, the finite element analysis to asynchronous motor magnetic field is performed to obtain the effect of saturated motor magnetic field on motor parameters and the stator and rotor magnetic linkage via solving non-linear equation. The magnetic linkage table is optimized to obtain optimized exciting table and maximum torque vs rotation speed table. By means of PI control method to obtain optimized exciting current and reference value of torque current, comparison to practical exciting current and torque current and PI regulation and voltage decoupling, final stator voltage in MT coordinate system is obtained for the control of the inverter.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Asymmetric direct power control method for dual feed asynchronous wind power generator
InactiveCN101505131AEliminate current control loopEnhanced Control ObjectivesElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlDecompositionTime delays
The invention discloses a method for controlling asymmetric direct power of doubly-fed asynchronous wind power generators. The method comprises the following steps that: by collecting voltage and current signals of a three-phase stator of a DFIG, instantaneous active power and reactive power output by the DFIG stator are calculated; error signals between the instantaneous active / reactive power of the stator and given active / reactive power are regulated by utilizing a proportional regulator and two resonant regulators; output signals of the three regulators are added and then decoupled through feedback compensation so as to obtain a reference voltage signal of a rotor in a rotor-speed rotational coordinate system; a switching signal of the operation of a rotor-side converter is generated through space vector pulse-width modulation so as to control the operation state of the DFIG; and the method can eliminate fundamental-frequency fluctuation and double-frequency fluctuation in the output power of the stator, which are caused by voltage asymmetry of power networks, and does not need to decompose positive / negative-sequence components, thereby avoiding introducing decomposition time delay and errors. Therefore, the method can enhance the capability of controlling wind power generating sets under the circumstance that the power networks have asymmetric faults, and improve the uninterrupted operation capability of the wind power generation systems with the faults.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Alternating-current asynchronous motor frequency converter without speed sensor
InactiveCN102111103AElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlFrequency changerAlternating current
The invention relates to an alternating-current asynchronous motor frequency converter without a speed sensor. In the frequency converter, a personal computer (PC)-based frequency converter online debugging and monitoring software, a communication mechanism, parameter identification of an alternating-current asynchronous motor, and alternating-current asynchronous motor rotating speed identification are involved, wherein the PC-based frequency converter online debugging and monitoring software can set related parameters of the frequency converter, distribute a control command, dynamically display the related parameters of the frequency converter and an alternating-current asynchronous motor in a literary form, and dynamically display the waveforms of a rotating speed, a torque, a stator voltage and a stator current of the alternating-current asynchronous motor in a graphical form; the communication mechanism is on the basis of any one serial bus of Ethernet / a universal serial bus (UBS) / a recommend standard 485 (RS485) / a recommend standard 232 (RS232) and realizes bidirectional data communication between the debugging software and the frequency converter; the parameter identification of the alternating-current asynchronous motor comprises stator resistance, rotor resistance, stator leakage inductance, rotor leakage inductance, stator and rotor mutual inductance and total leakage inductance; and the alternating-current asynchronous motor rotating speed identification is on the basis of a model reference adaptive theory.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com