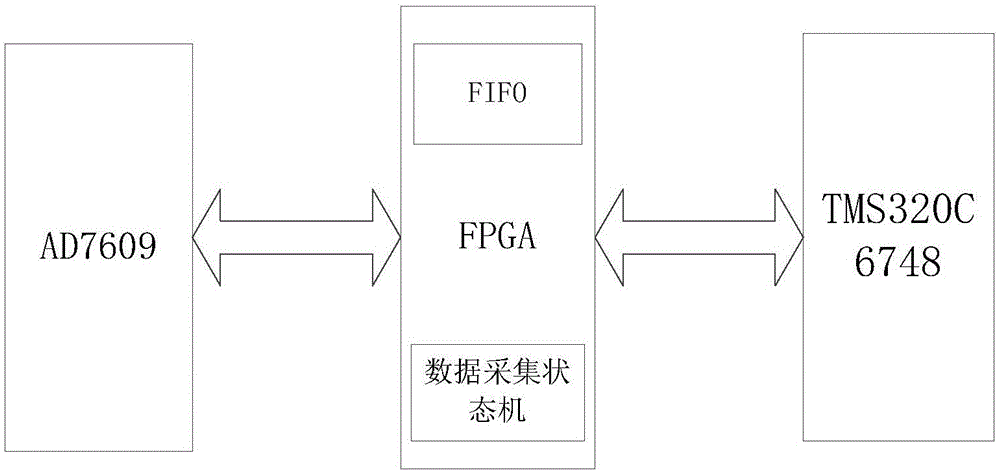
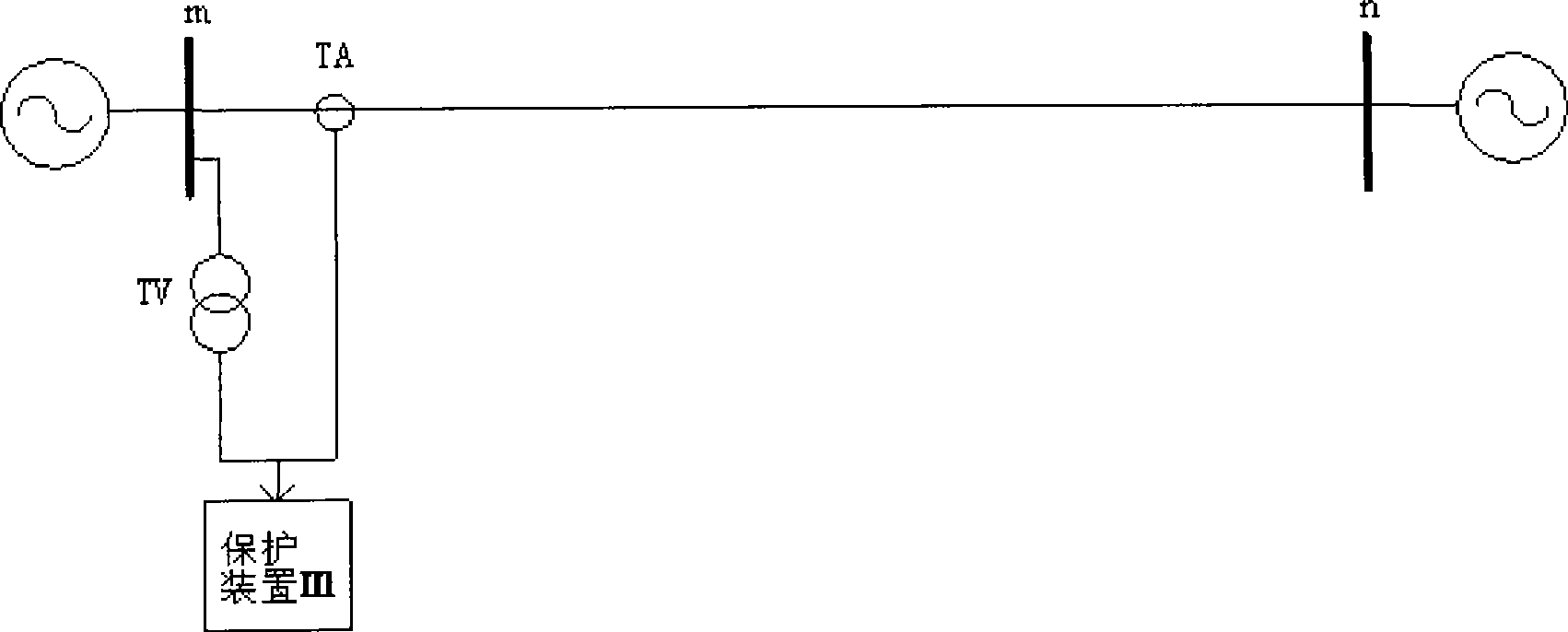
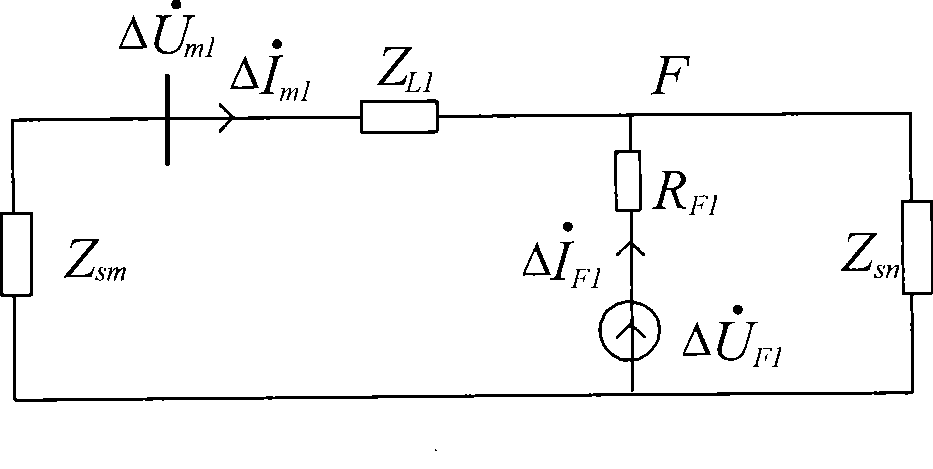
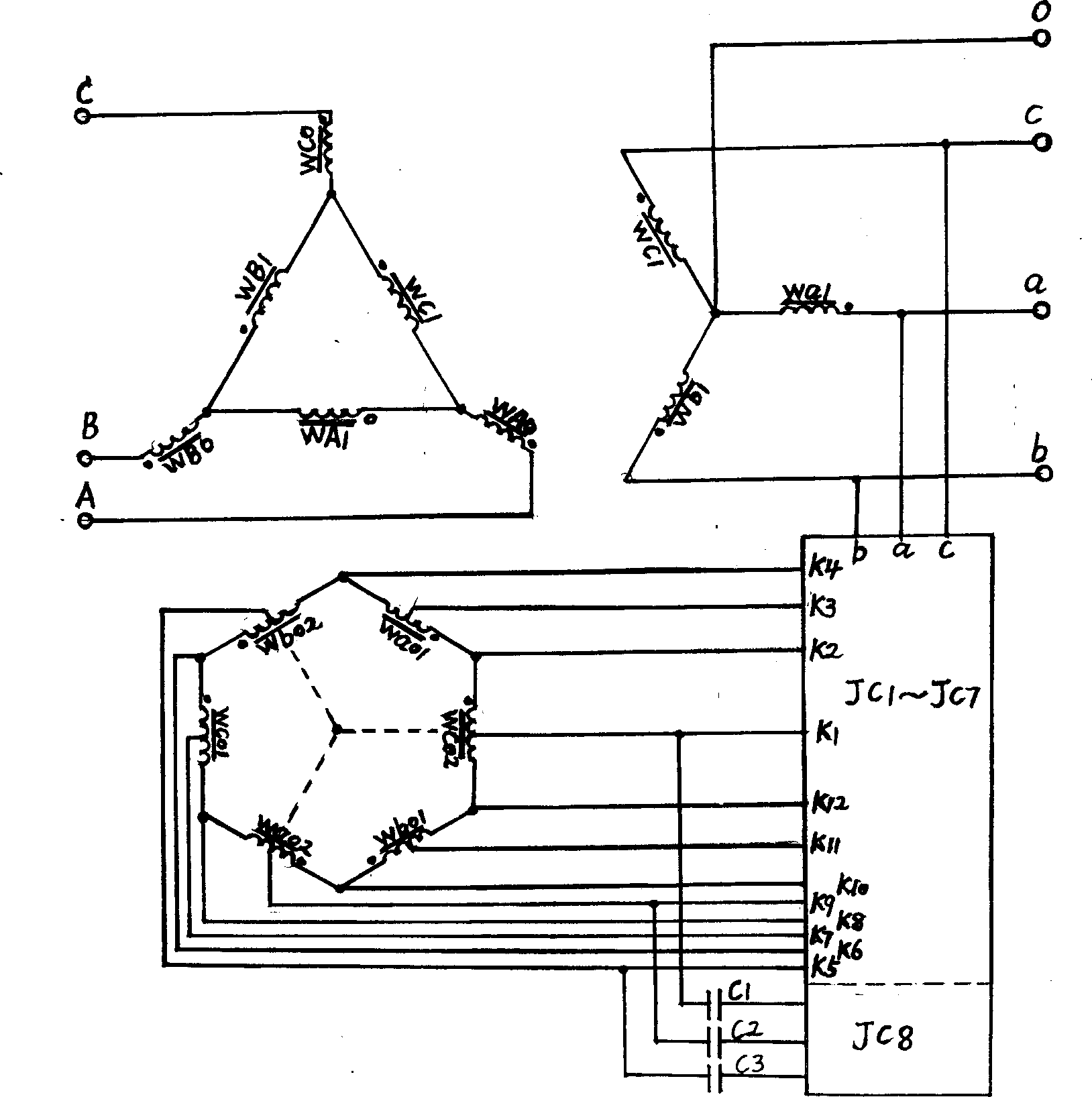
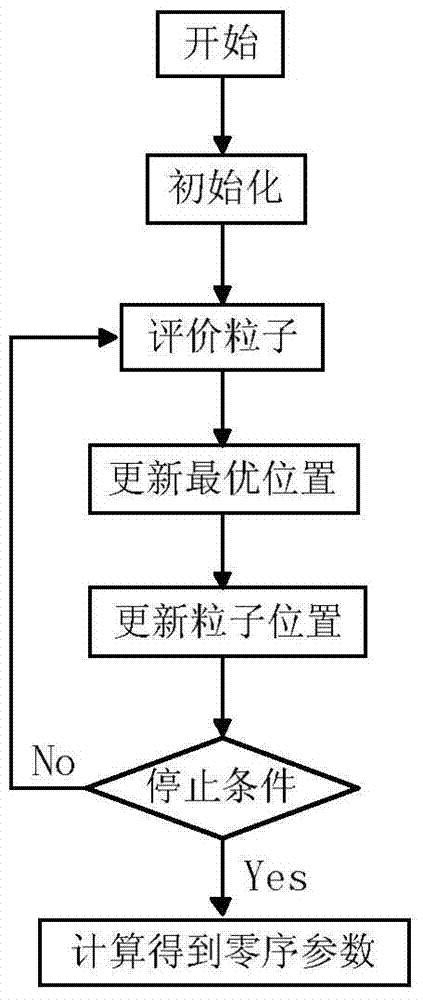
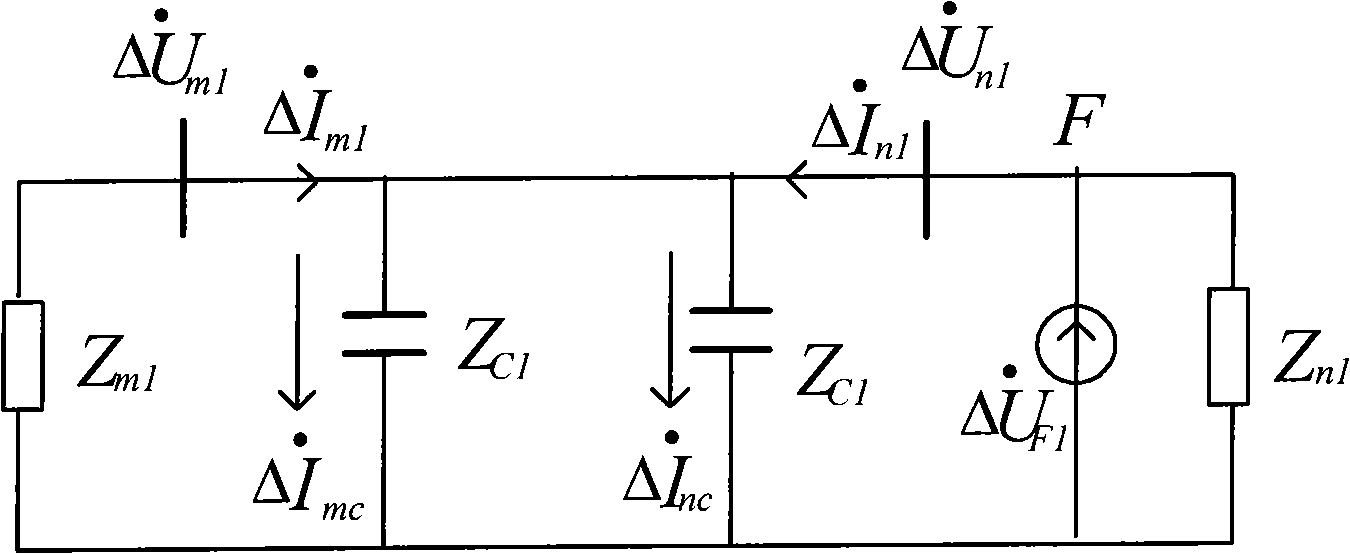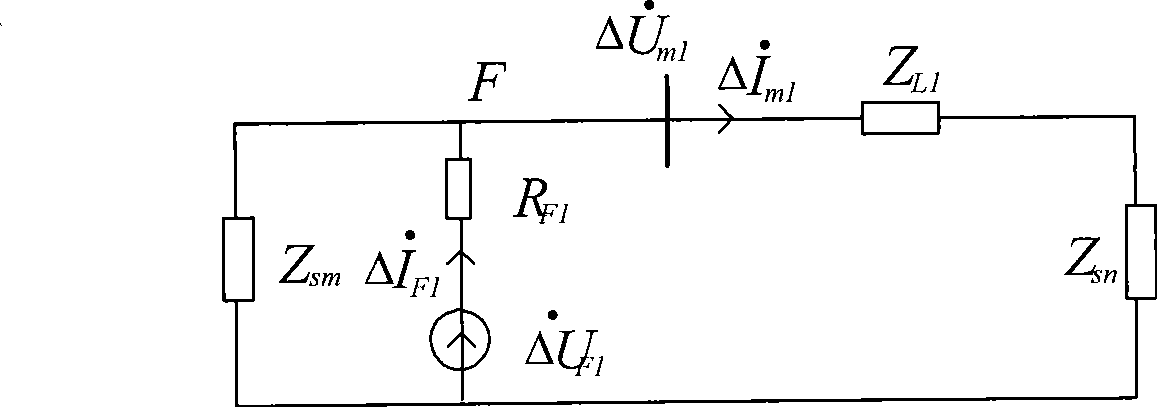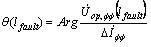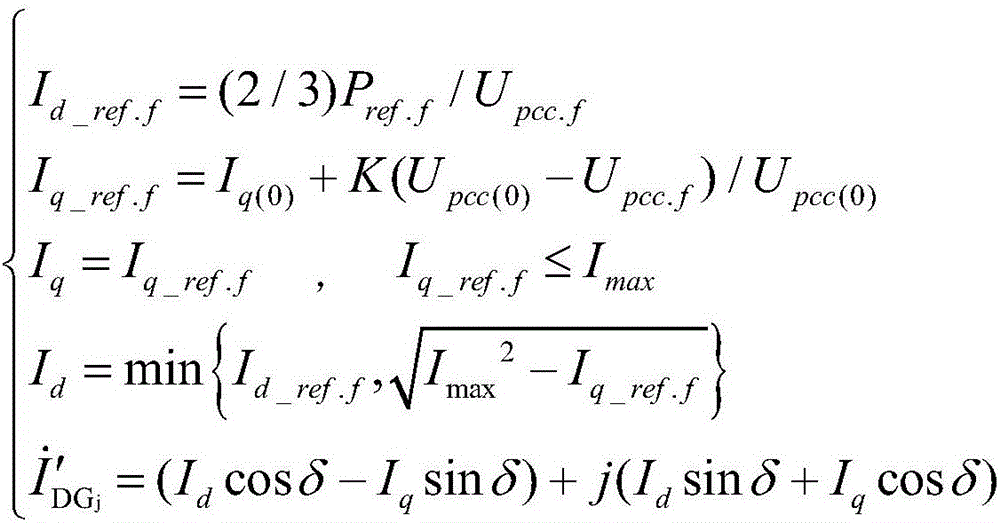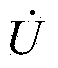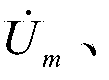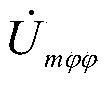Patents
Literature
298 results about "Voltage phasors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
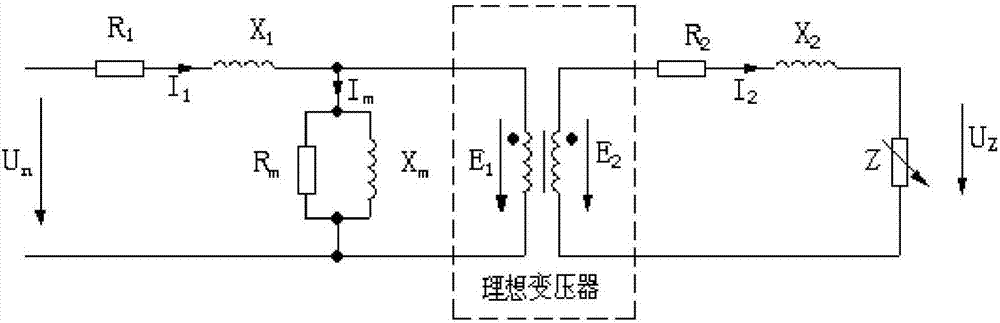
Phasor voltage represents the instantaneous value of the voltage. For example in time t the voltage may have a value of 120V and one second later it may have a voltage of 50V.
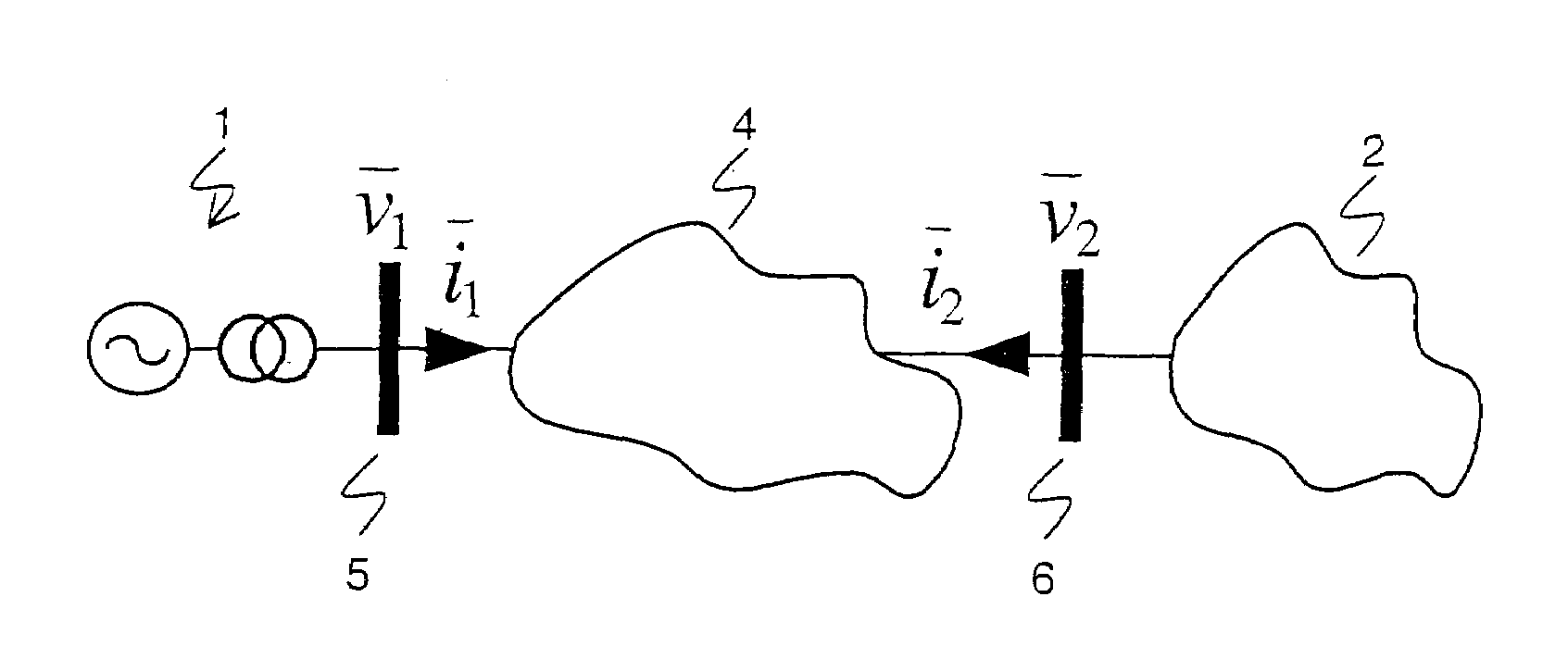
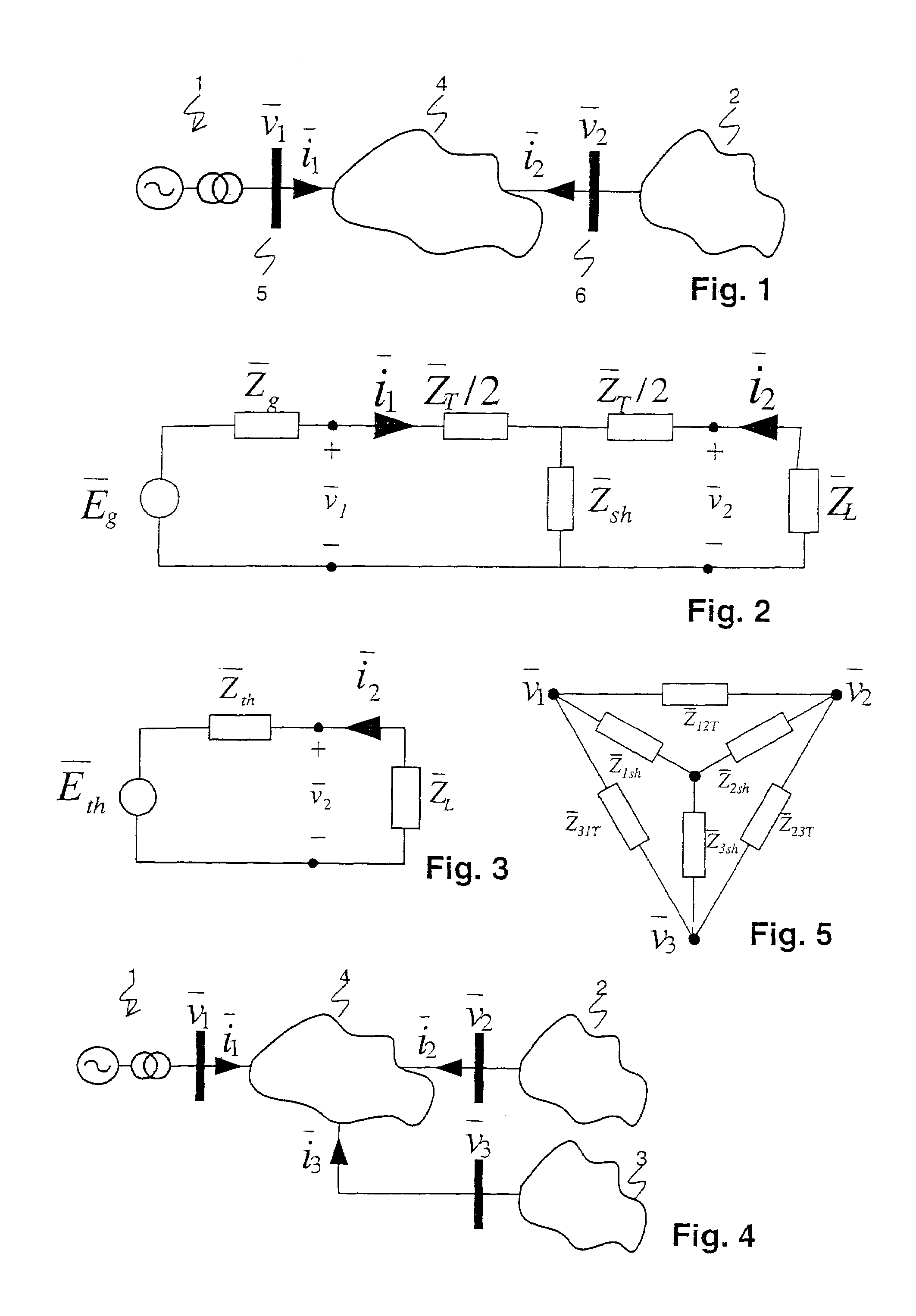
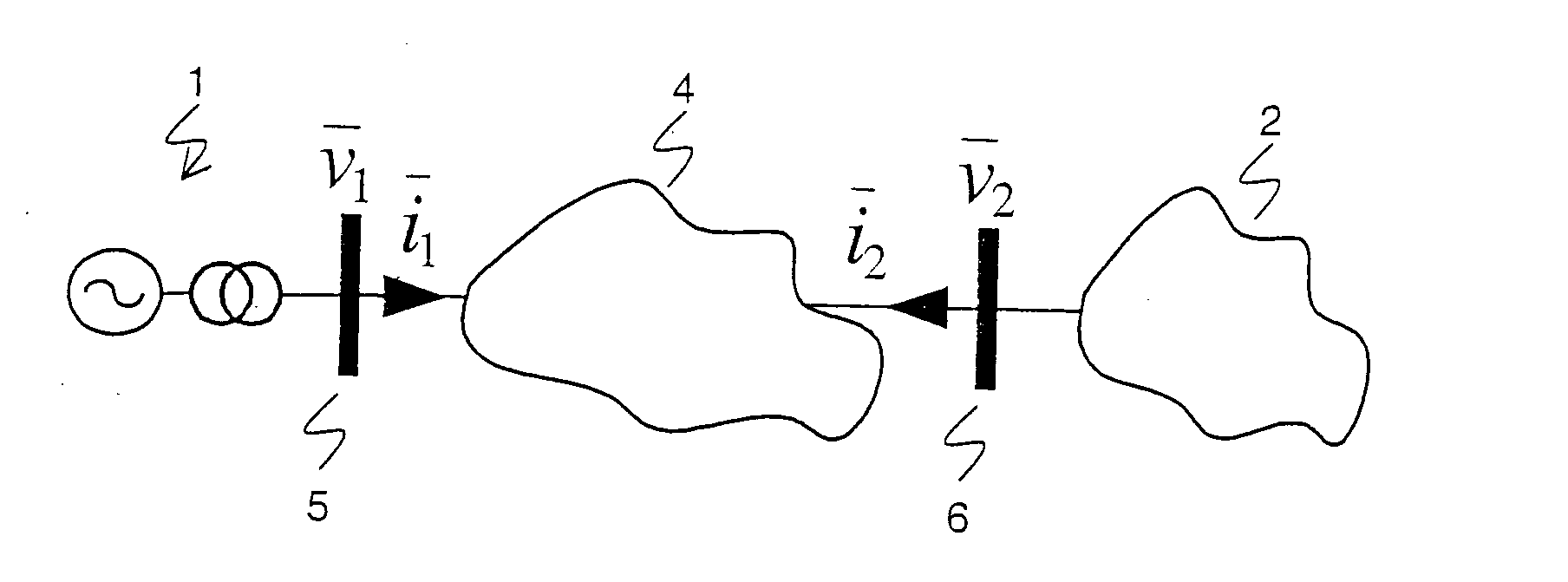
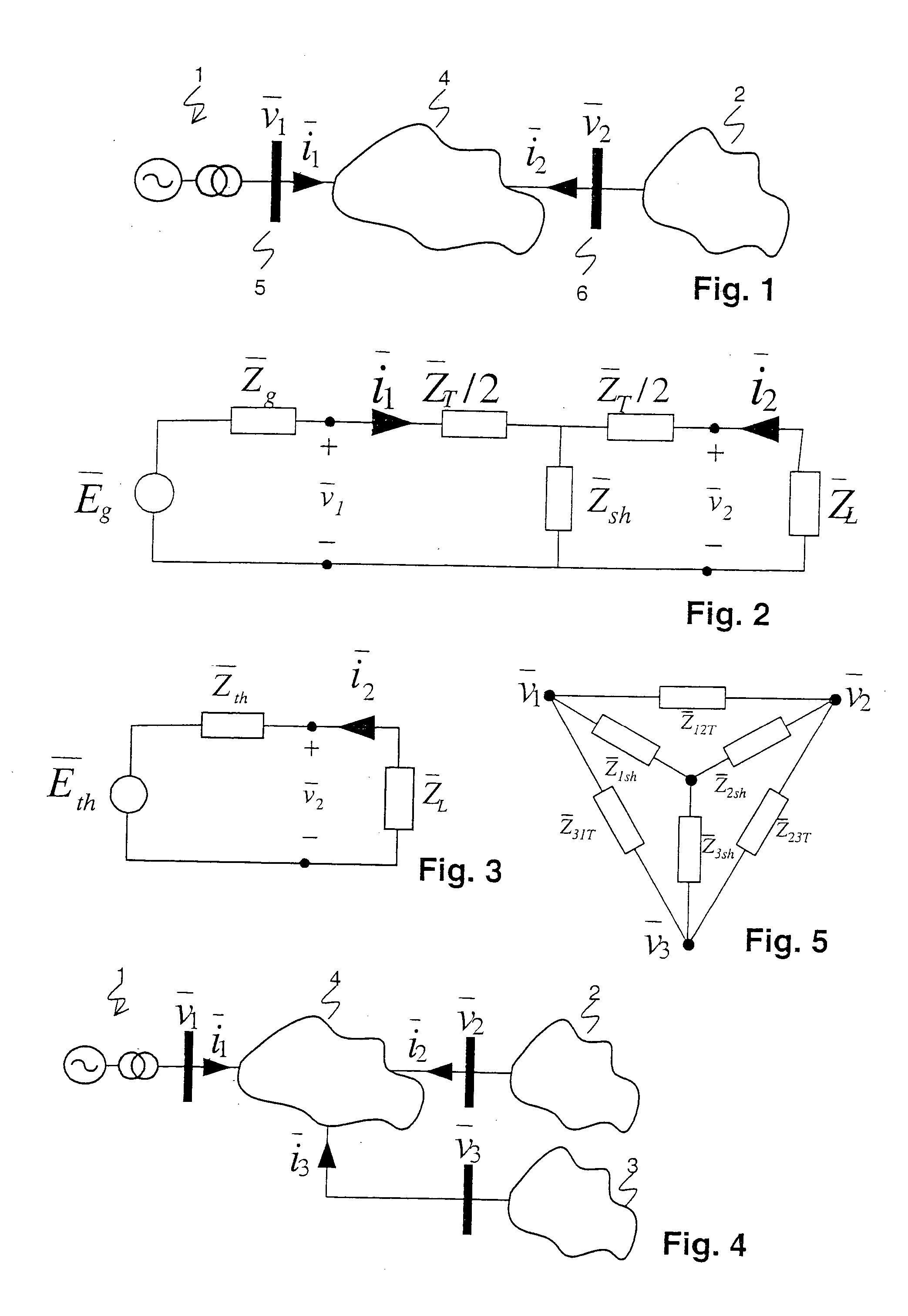
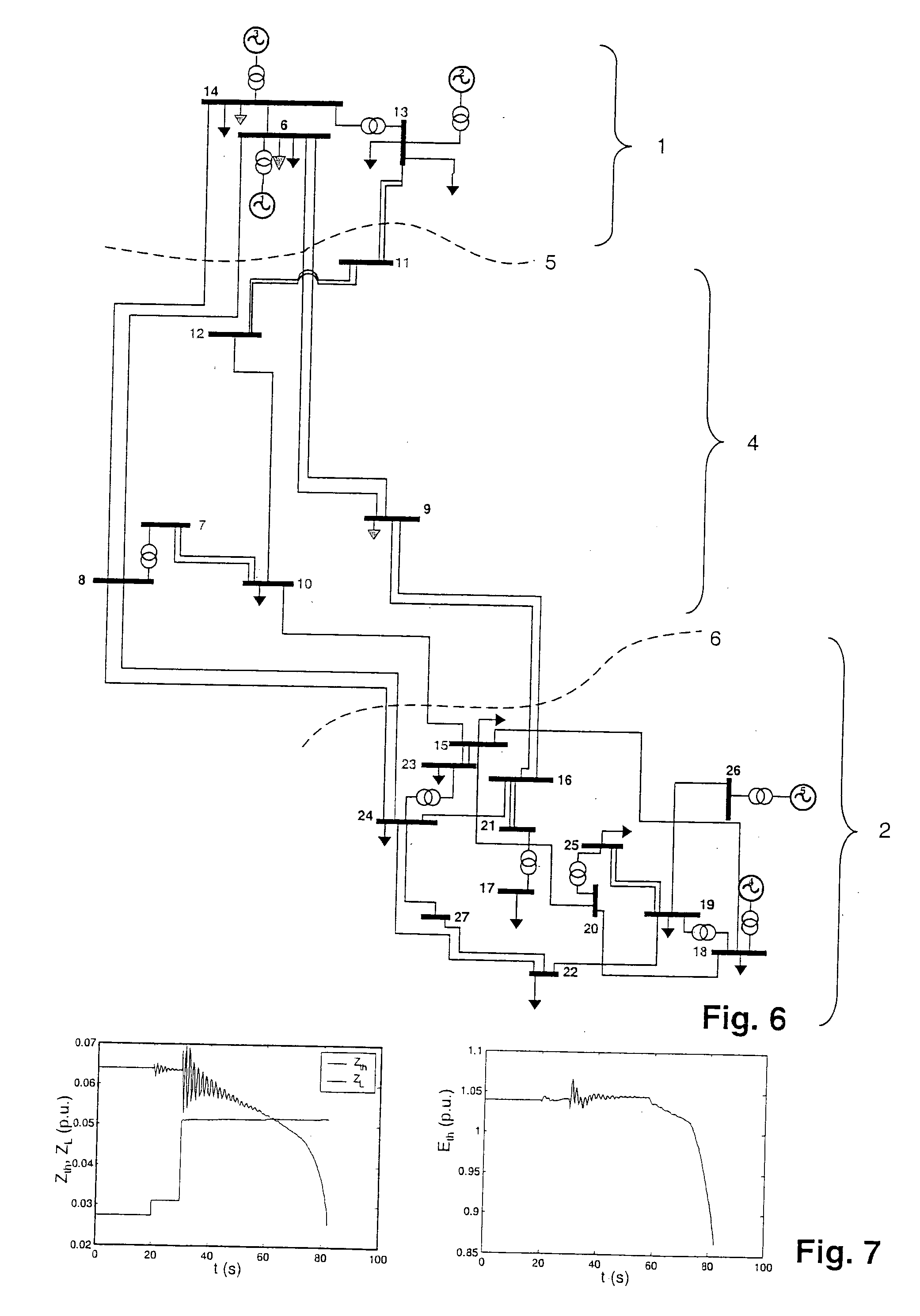
Determining parameters of an equivalent circuit representing a transmission section of an electrical network
InactiveUS7200500B2Rapid assessmentLevel controlDc circuit to reduce harmonics/ripplesPower gridVoltage phasors
A method for determining an equivalent impedance of a transmission section of an electrical network, includes representing the transmission section as having at least two interfaces with other sections of the network. For each interface, a voltage phasor and a current phasor flowing through the interface are determined from simultaneously made measurements at the interfaces. From the phasors, the equivalent impedance is calculated. The required simultaneousness of the phasor measurements is achieved by means of Phasor Measurement Units (PMUs) that are synchronized via the Global Positioning System (GPS).
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
Determining an operational limit of a power transmision line
InactiveUS20050222808A1High resolutionTemporal resolutionSpectral/fourier analysisElectric signal transmission systemsElectric power transmissionElectrical resistance and conductance
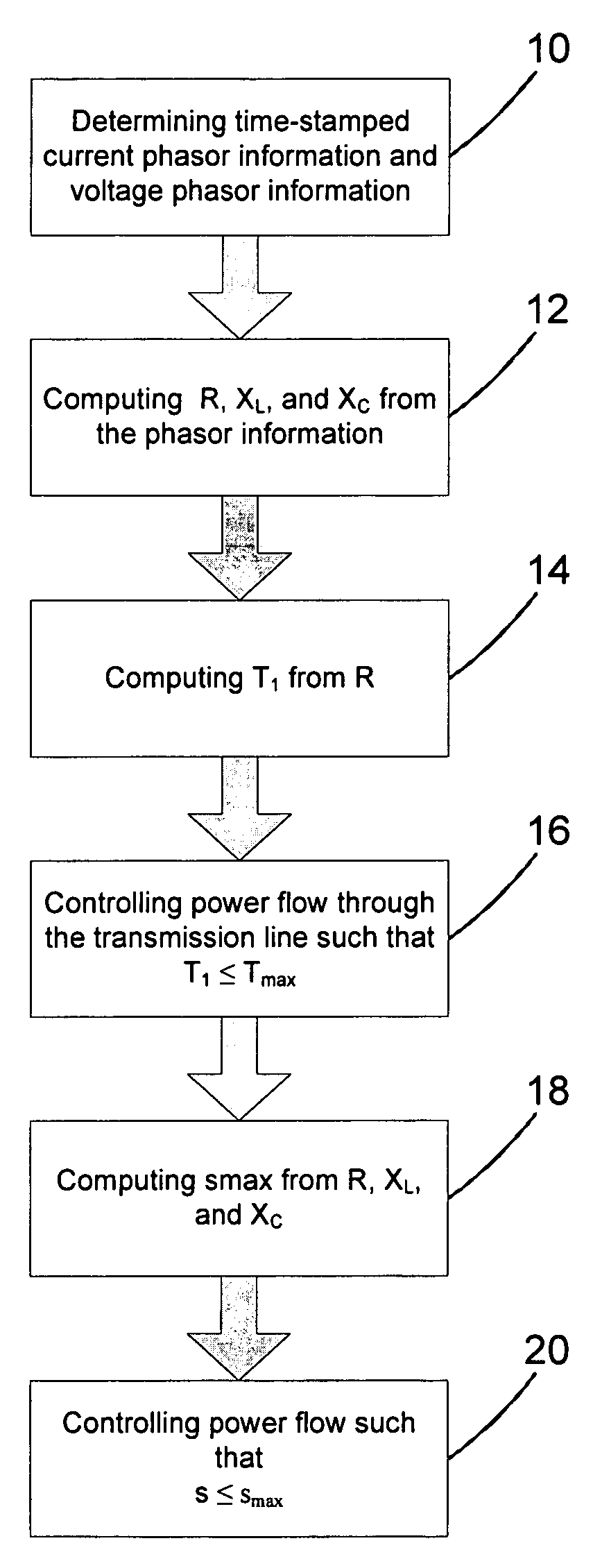
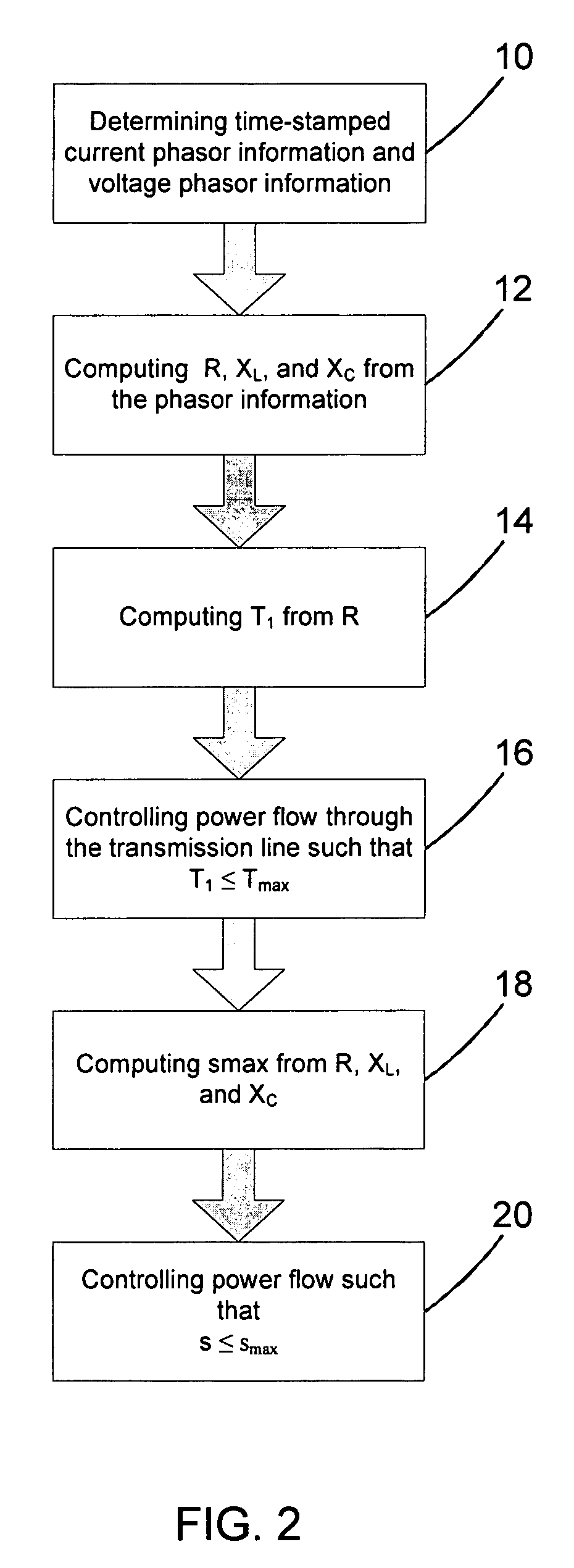
In a method, computer program and system for determining an operational limit of a power transmission line, time-stamped current phasor information and voltage phasor information for a first end and a second end of the line are determined, an ohmic resistance of the line is computed from the phasor information, and an average line temperature is computed from the ohmic resistance. This allows to determine the average line temperature without dedicated temperature sensors. The average line temperature represents the actual average temperature and is largely independent of assumptions regarding line parameters.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
Determining an operational limit of a power transmission line
InactiveUS7107162B2Good precisionClosing operationSpectral/fourier analysisDc network circuit arrangementsElectric power transmissionElectrical resistance and conductance
In a method, computer program and system for determining an operational limit of a power transmission line, time-stamped current phasor information and voltage phasor information for a first end and a second end of the line are determined, an ohmic resistance of the line is computed from the phasor information, and an average line temperature is computed from the ohmic resistance. This allows to determine the average line temperature without dedicated temperature sensors. The average line temperature represents the actual average temperature and is largely independent of assumptions regarding line parameters.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
Circuit inter-phase fault single-end ranging method
ActiveCN102175954AReduce the impactThere is no non-convergence problemFault locationPhase currentsCapacitance
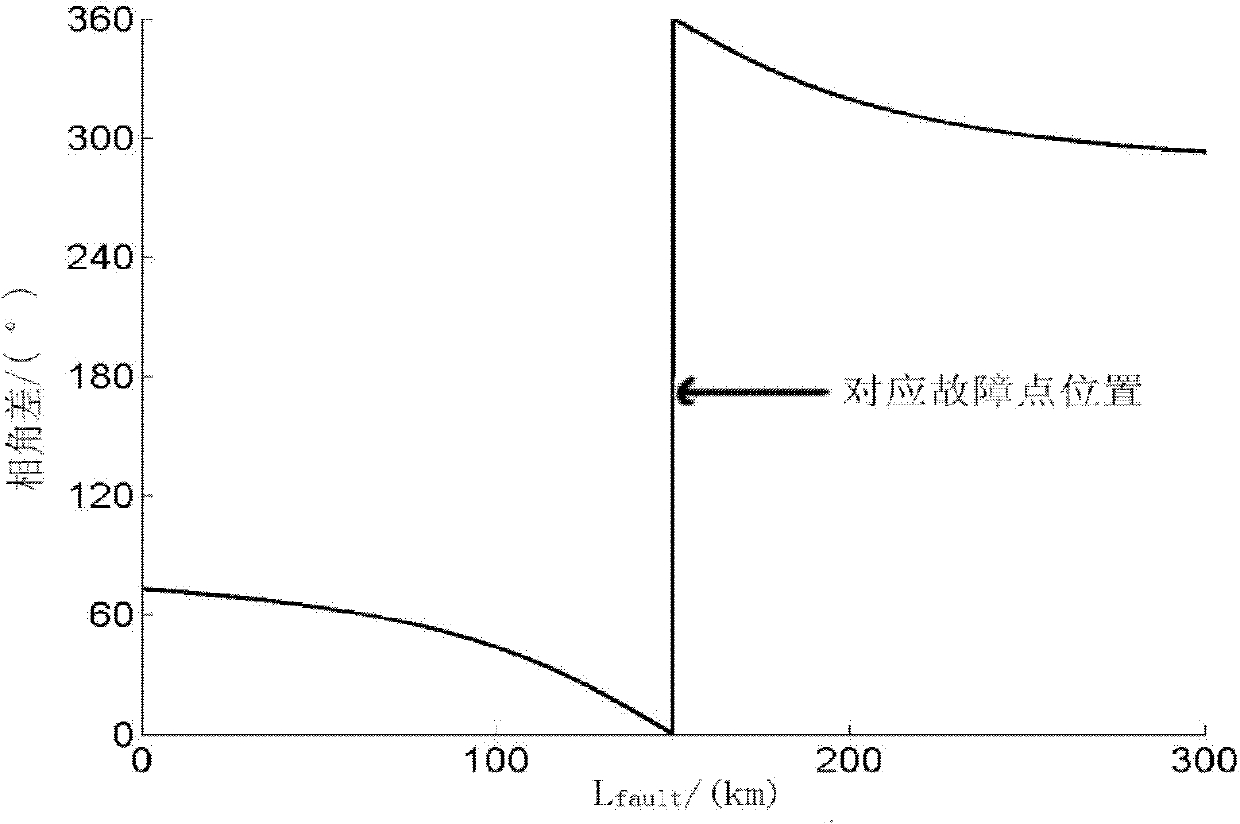
The invention discloses a circuit inter-phase fault single-end ranging method, which comprises the following steps of: measuring a fault inter-phase voltage phasor, a fault inter-phase current phasor and a fault inter-phase negative sequence current phasor serving as input quantities of a circuit at a transformer substation protection installation position; calculating the voltage phasor at a fault position by using protection measured electric quantity; sequentially calculating matching error data of each point on the circuit by gradual step length increment from the beginning end of the protected circuit till a setting range of emitting a trip signal; if the protective trip signal cannot be acquired, searching the overall length of the protected circuit; and taking the point corresponding to the minimum matching error datum value as a fault point, wherein the distance between the point and the circuit protection installation position is a fault distance. The method is not affected by distributed capacitors, load current, fault resistors and operation mode of a system, has no false root problem of solving an equation or non-convergence problem of an iteration method, and has strong practical value.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Power distribution network high voltage line single-phase line-breaking fault identification method and application
PendingCN107340455ARealize full network coverageMeet the need for protectionFault location by conductor typesInformation technology support systemLow voltageHigh pressure
The invention discloses a power distribution network high voltage line single-phase line-breaking fault identification system and method based on electric energy metering device. The power distribution network high voltage line single-phase line-breaking fault identification method comprises steps of using voltage phasor data of a two-phase line which is two-element electric energy metering device which performs high-voltage supply high-voltage metering to realize an identification function on a single-phase line-breaking fault of a 10kV power distribution line, using three-phase phase voltage phasor data measured by a high-voltage supply and low-voltage metering three-phase four-line system electric energy metering device to realize an identification function on the 10kV power distribution line single-phase line-breaking fault. In the power distribution network high voltage line single-phase line-breaking fault identification method and the application, massive electric energy metering devices having functions of single-phase line-breaking fault identification are installed, the electric energy metering devices upload the voltage phasor data and the single-phase line-breaking determination result to a remote main station for analysis, and a single-phase line-breaking fault interval of the 10kV power distribution network can be positioned according to a relative relation of installation positions.
Owner:王金泽
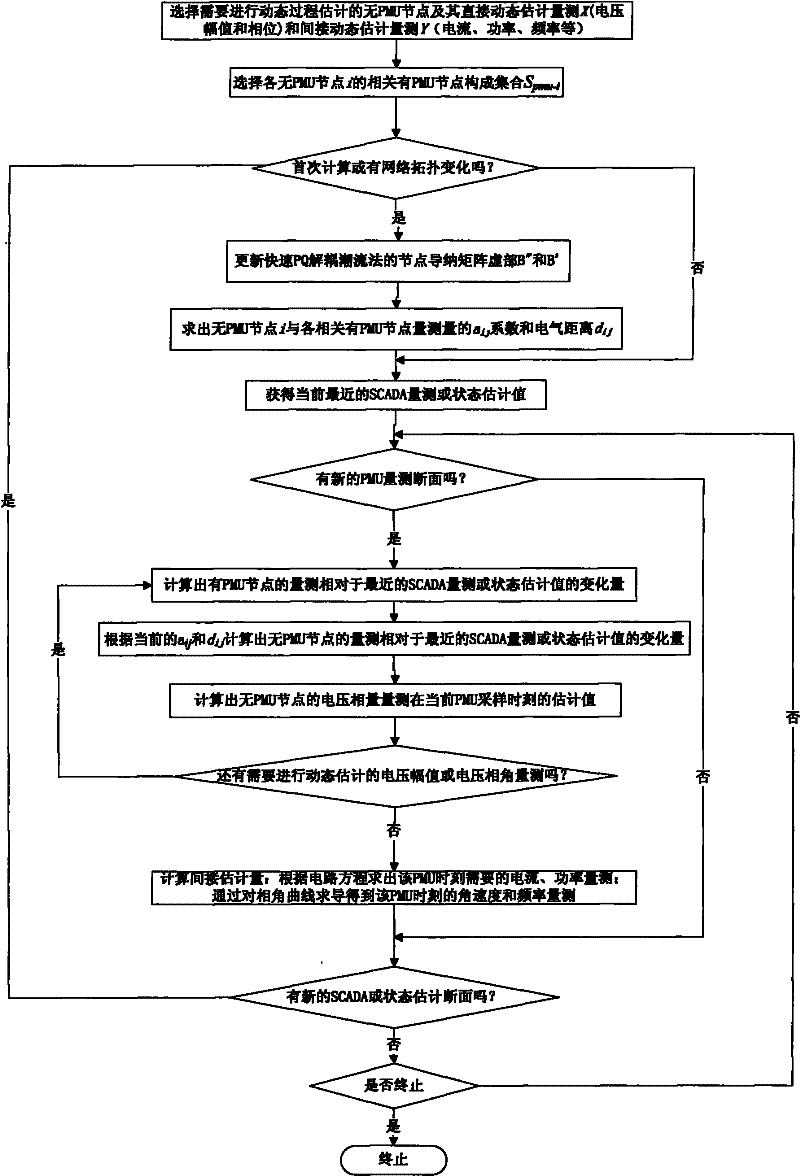
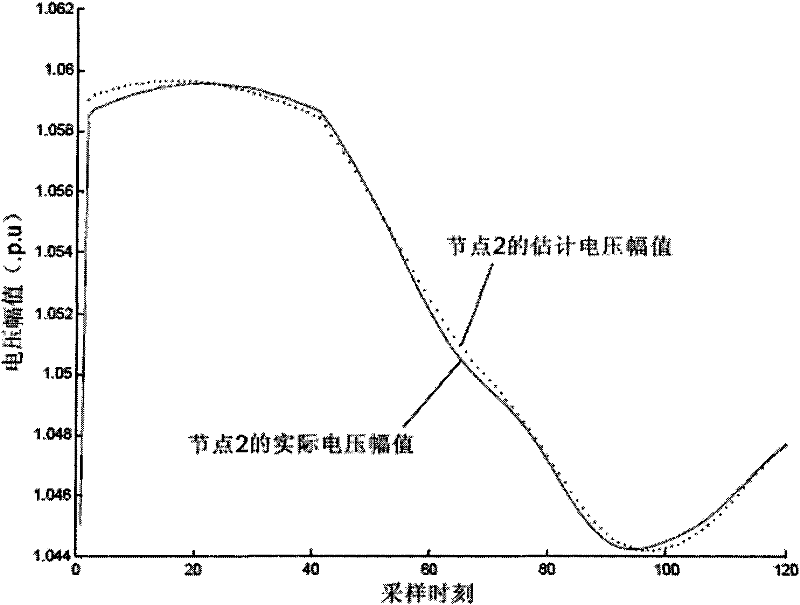
Non-PMU measure point dynamic process estimation method based on flow equation sensitiveness analysis
ActiveCN101750562AMeet the accuracy requirements of monitoringMeet the precision requirementsElectric devicesCurrent/voltage measurementElectric power systemData acquisition
The invention discloses a sensitiveness matrix of voltage phasor obtained through flow equation, and an estimation method which includes that dynamic actual measurement data and power system data acquisition and monitoring system SCADA data or state estimation data mounted with PMU nodes are adopted to estimate the dynamic process without PMU node in real-time. The method adopts the sensitiveness relationship of voltage variations among nodes derived from flow Jacobian matrix, also adopts the SCADA or initial values of state estimation and the voltage dynamic measurement values mounted with PMU nodes to estimate the dynamic variation process of other voltage phasors without PMU node. The dynamic variation processes of electric parameters such as current, power and frequency in power grid are derived according to circuit principle according to the voltage phasors and network parameters of each node. The estimation method effectively solves the difficult problem of observing the dynamic process of the non-PMU measure point when the power grid PMU is in adequate configuration situation.
Owner:STATE GRID HUBEI ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY +1
On-line positioner of small current earth fault
ActiveCN102221660ANot affected by power frequency load currentSolve the positioning problemFault locationInformation technology support systemTransformerElectric network
The invention discloses an on-line positioning method of small current earth fault and a positioner based on the positioning method. The method is suitable for a 3 to 60 kV neutral non-effective grounding electrical network. When a line is in operation with single phase earth fault, a 130 to 230 Hz (excluding power frequency of integer times of 50 Hz) AC signal is filled into a transformer station PT (potential transformer), voltage phasor of the filled signal is measured in a transformer station, current phasor of the filled signal is measured in a line, thus the section position of a fault point is determined according to the phase relationship of the filled signal voltage phasor and the filled signal current phasor. The positioner in the present invention comprises a host computer and a lower computer. The host computer is installed in the transformer station, and is used for filling 130 to 230 Hz (excluding power frequency of integer times of 50 Hz) AC signal into the transformer station PT and measuring the voltage phasor of bus filling signal. The lower computer is installed on the line, and is used for measuring current phasor of the filled signal. The lower computer uploads a measuring result to the host computer, and the host computer carries out phasor analysis and completes positioning calculation. The on-line positioning method of small current earth fault and the positioner based on the positioning method provided in the invention have the advantages of mature technology and high reliability.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING) +3
A single phase grounding failure relay protection method based on negative electrical impedance relay
ActiveCN101106047AIncreased sensitivitySwitch operated by earth fault currentsPhase currentsTransformer
The invention belongs to electric power system field, in particular to a single-phase grounding failure relay protection method based on a negative sequence reactance relay. The method includes: Measure the circuit's failure phase voltage Uphi, phase current Iphi, zero sequence voltage U0, zero sequence current I0, and negative sequence current I2 at the installation place of transformer station as the input values; calculate the residual voltage phasor of the failure point through measuring voltage, measuring current, negative sequence current at the place of protection installation, and circuit impedance angle; constitute the action voltage phasor Uop through measuring voltage, measuring current, residual voltage phasor of failure point, and impedance value within the scope of circuit protection; calculate the angle that the action voltage phasor Uop leads the negative sequence current iU2. If the angle is within the range of [180 DEG, 360 DEG], the protection action sends a signal of tripping operation; contrarily, the protection will not take any action. The method is suitable for the electricity transmission side of ultra / super high voltage electric circuit, particularly ultra / super high voltage heavy load electric circuit. The invention can meet requirements for selection, reliability, sensitivity, and speediness of relay protection.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Measuring device and method for direct current supply output impedance
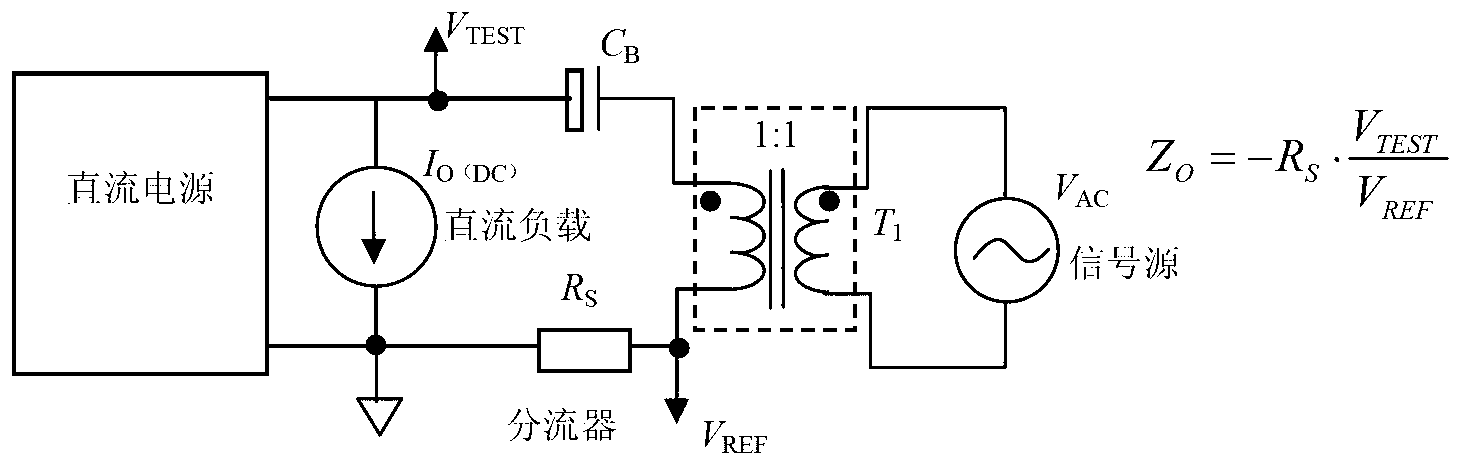
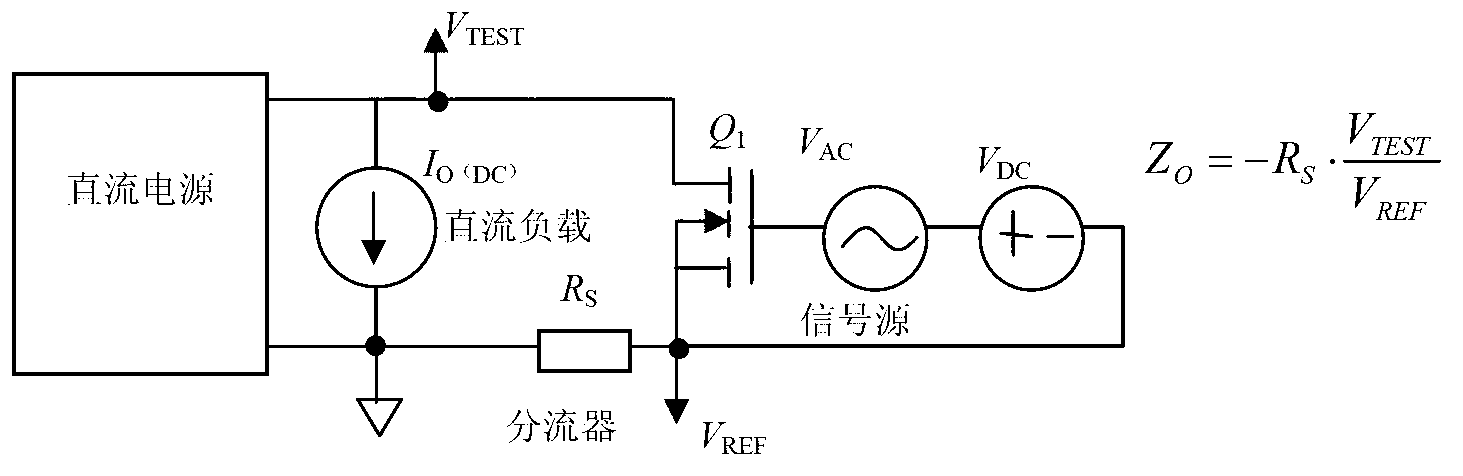
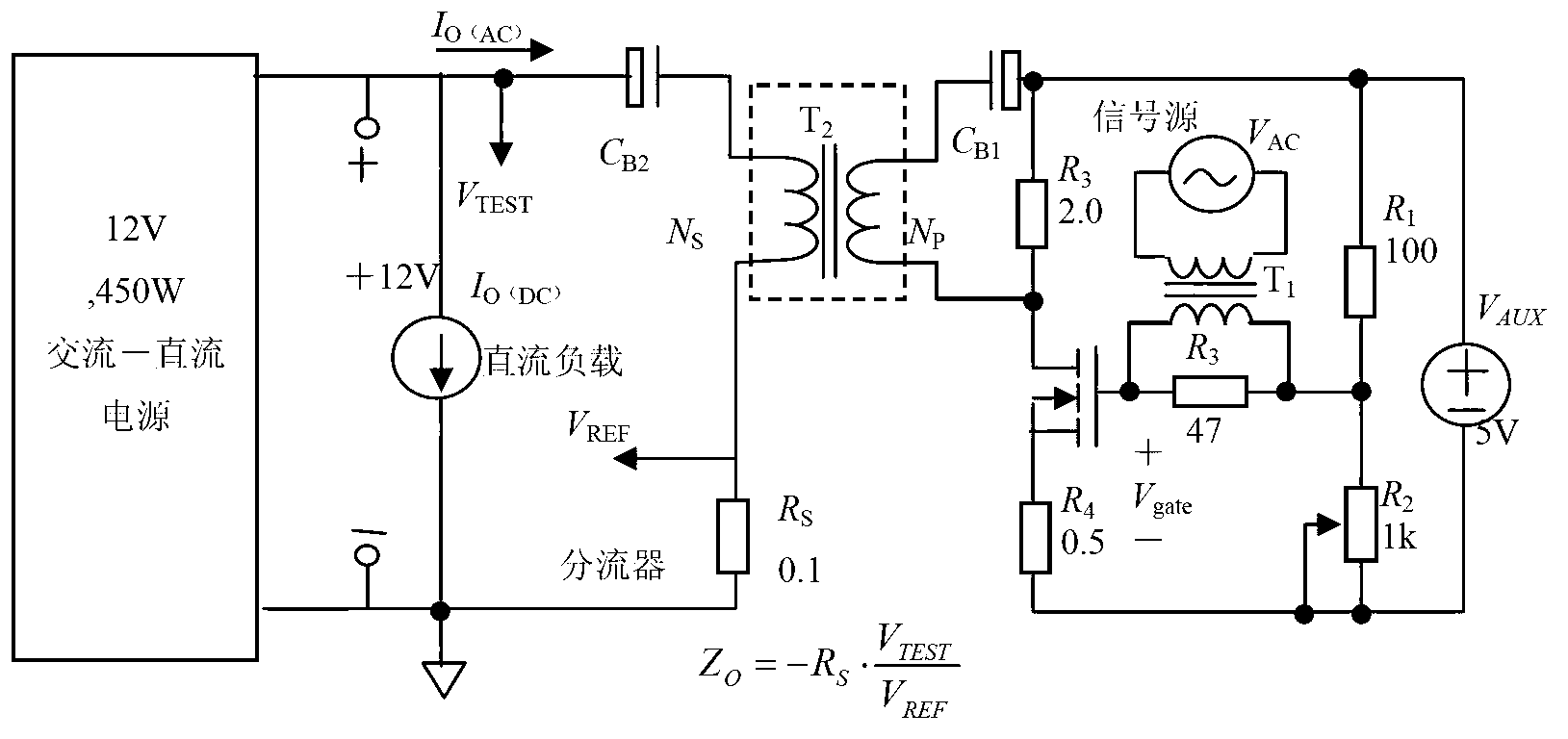
ActiveCN102841258AAvoid systematic biasReduce loadResistance/reactance/impedenceSpecific testOperating point
The invention discloses a measuring device and method for direct current supply output impedance. The measured direct current supply output impedance is defined at a specific operating point and a specific test cross section, the presented equivalent impedance is seen in the direction of the test cross section facing a power supply, and system deviation in the measuring process, caused by load input impedance, is avoided. The measuring device comprises a test frequency point voltage phasor extraction module, a test frequency point current phasor extraction module, a low-current excitation load module, a sweep frequency phasor analysis module and a control computer, wherein the test frequency point voltage phasor extraction module and the test frequency point current phasor extraction module are respectively connected with a voltage input end and a current input end of the sweep frequency phasor analysis module; the signal output end of the sweep frequency phasor analysis module is connected with the low-current excitation load module; and the sweep frequency phasor analysis module is further connected with the control computer.
Owner:BEIJING DONGFANG MEASUREMENT & TEST INST
Method for positioning low-current grounding fault sections of power distribution networks on basis of transient energy analysis
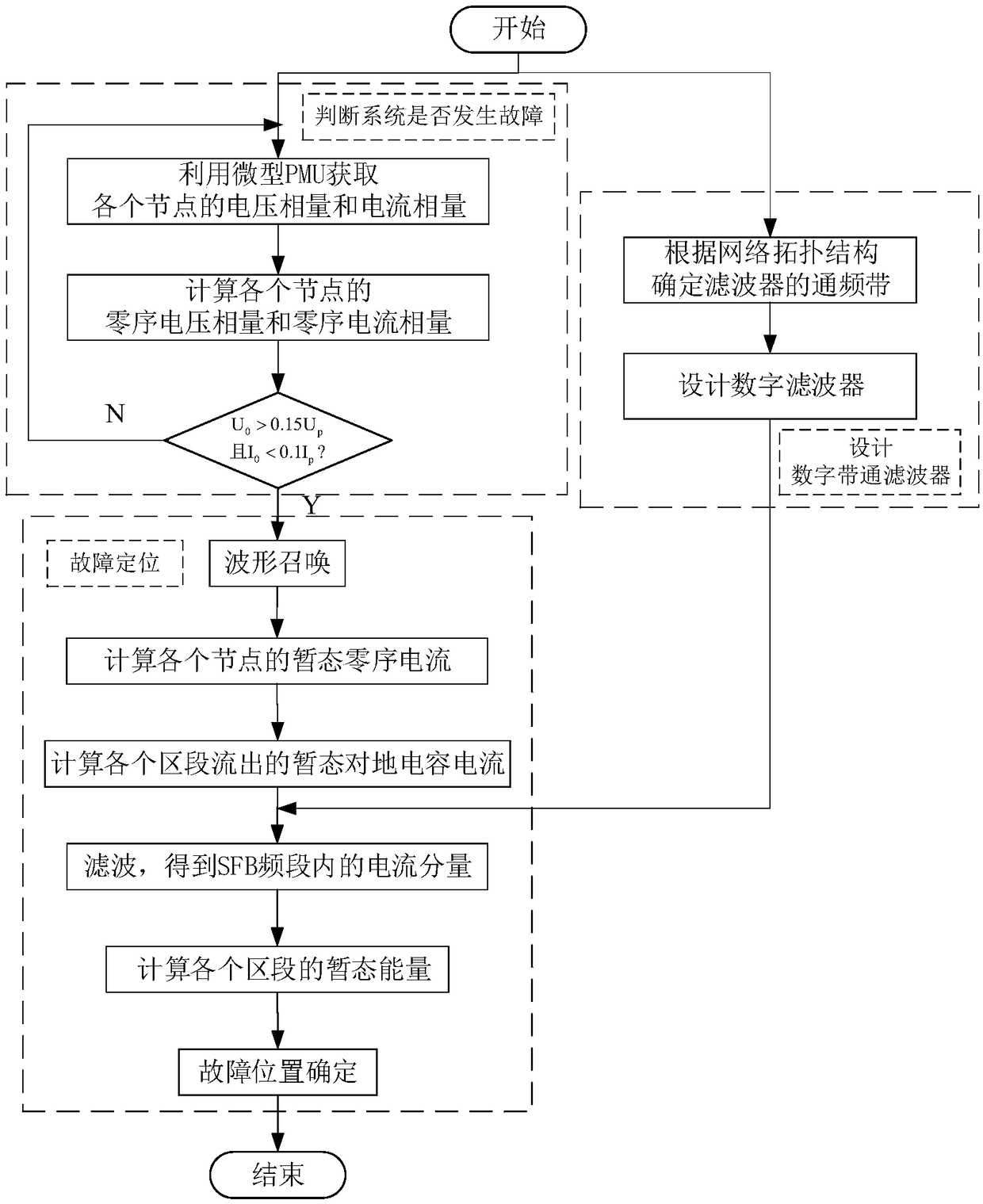
ActiveCN108254657AClear physical meaningImprove positioning accuracyFault location by conductor typesSystems intergating technologiesEngineeringResistor
The invention discloses a method for positioning low-current grounding fault sections of power distribution networks on the basis of transient energy analysis. The method includes steps of determiningpass frequency band ranges of digital filters and configuring a miniature PMU (power management unit) on each node of the power distribution networks; acquiring zero-sequence voltage phasors and zero-sequence current phasors of the various nodes of the power distribution networks by the aid of the miniature PMUs, judging whether faults of systems occur or not according to the zero-sequence voltage phasors and the zero-sequence current phasors of the various nodes, starting to position the faults if the faults occur, reading three-phase current signals recorded by the various miniature PMUs, computing transient zero-sequence currents of the various nodes by the aid of the three-phase current signals, processing the transient zero-sequence currents, computing transient energy of various sections, and determining the fault sections according to the transient energy of the various sections. The method has the advantages that physical meaning of fault features utilized by the method is clear, the method is high in positioning accuracy and reliability for the fault sections of various branch lines, and input of medium resistors connected with arc suppression coils in parallel or installation of signal injection equipment can be omitted.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV +2
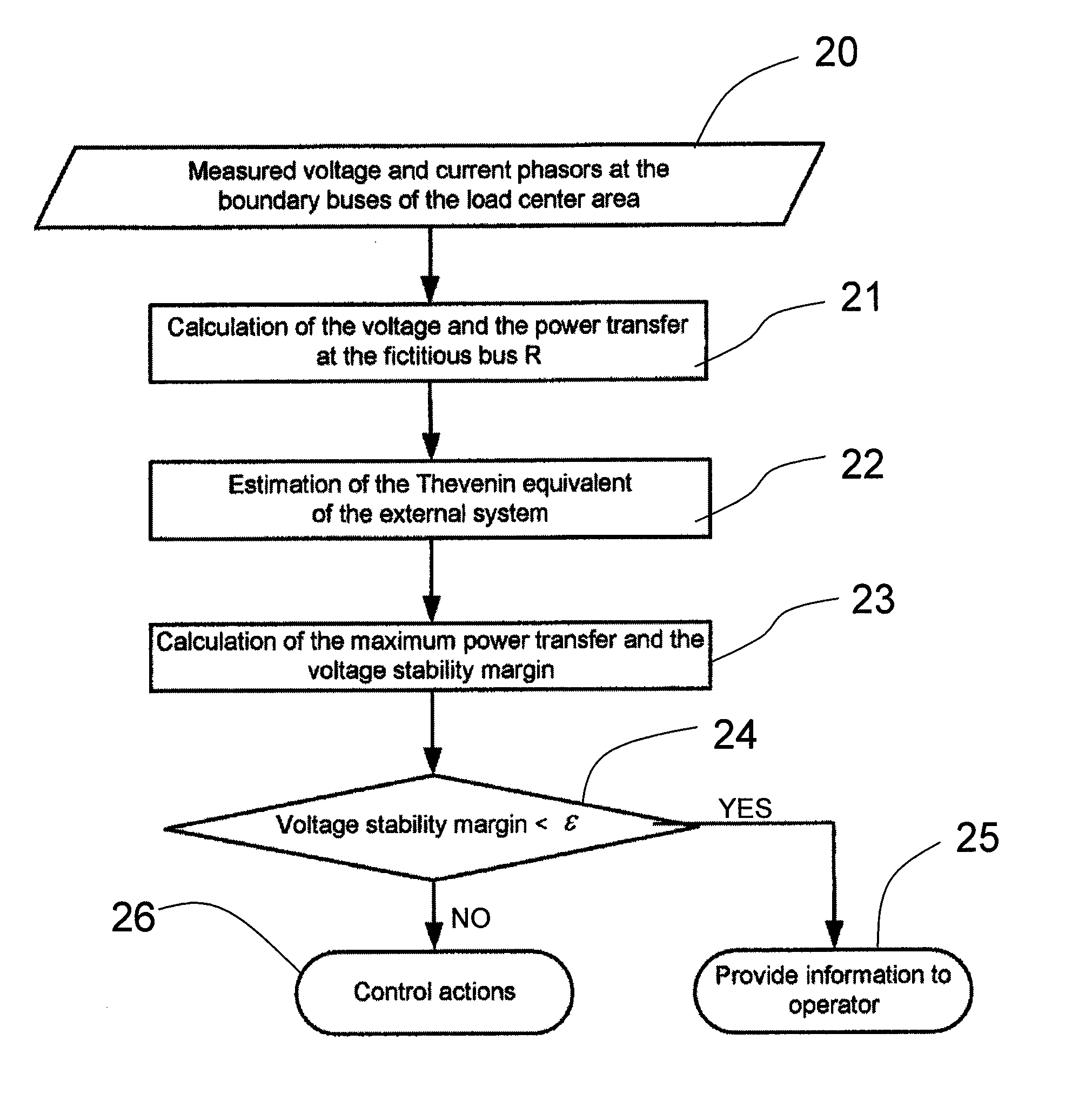
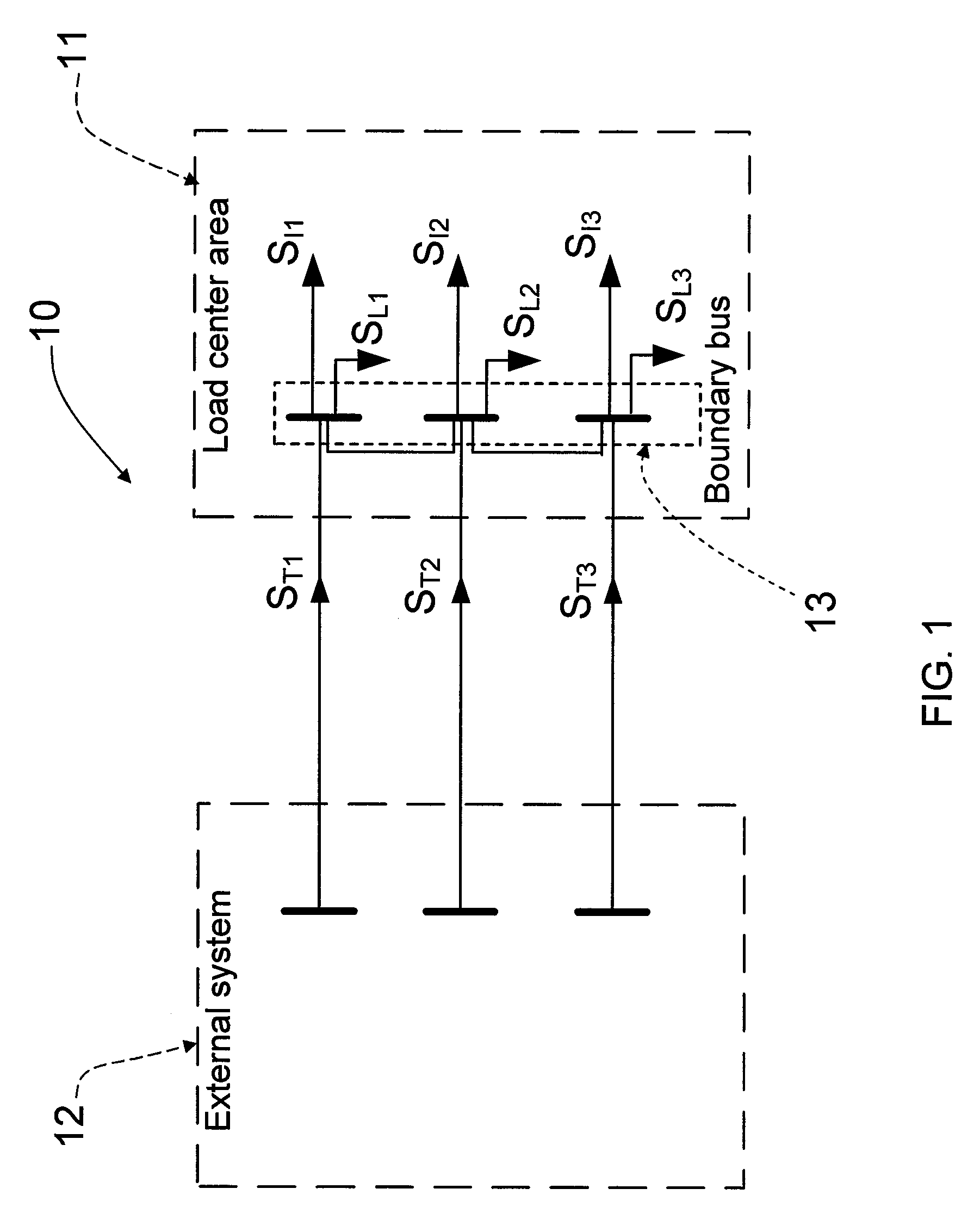
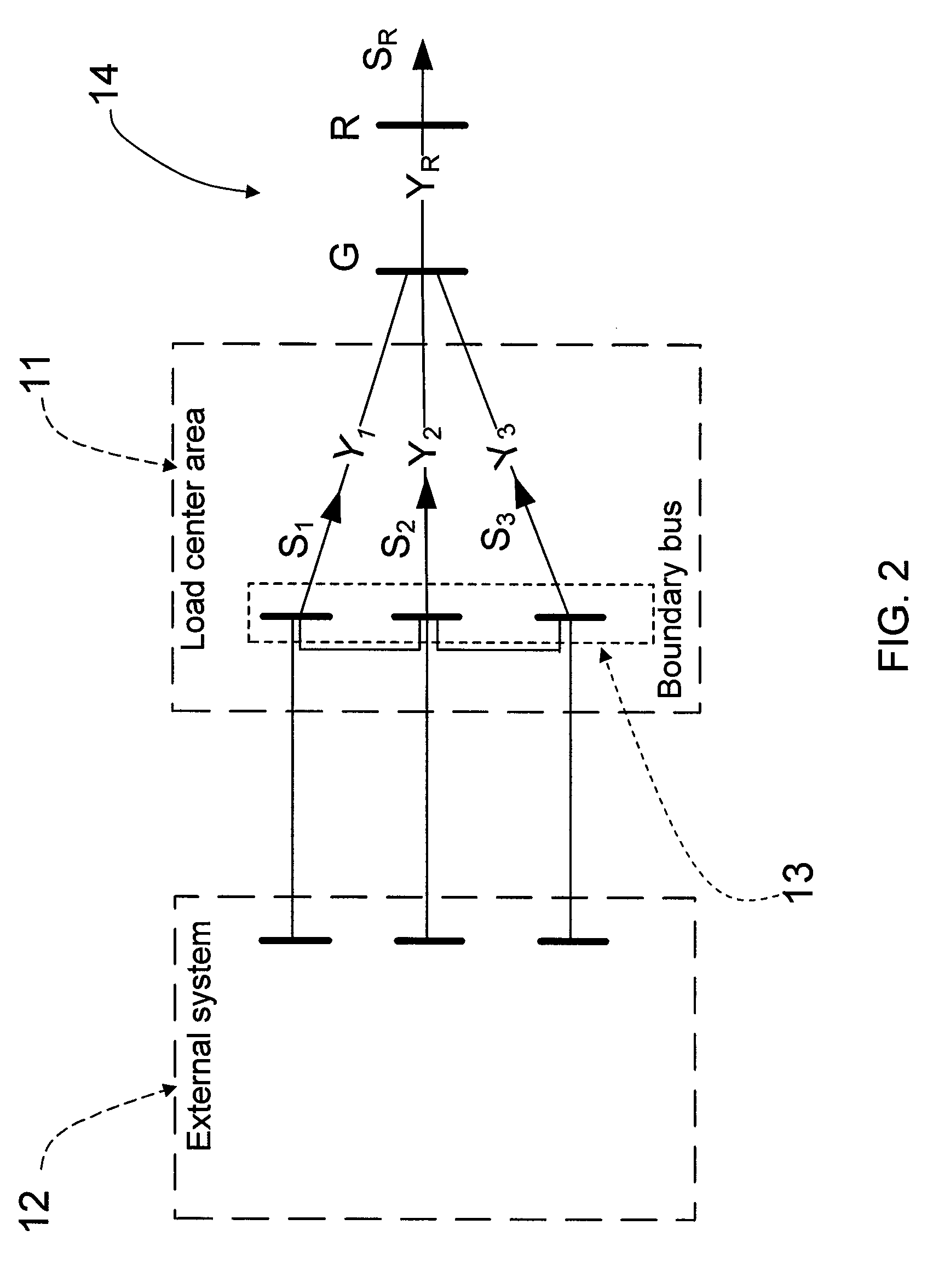
Measurement based voltage stability monitoring and control
ActiveUS20090299664A1Resistance/reactance/impedencePower network operation systems integrationEngineeringMonitoring and control
A measurement base voltage stability monitoring and control scheme having a means for measuring current and voltage phasors at a boundary bus of a load center; and an equivalent network having a fictitious bus with an aggregate load representative of all loads of the load center. The scheme further includes a computing device to calculate a voltage stability margin index based on the aggregate load of the fictitious bus and compare the voltage stability margin index to a pre-set threshold. The computing device causes an action to take place based on the comparison between the voltage stability margin index and the pre-set threshold.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST INC
Electric power line pilot protection decision method based on fault component positive sequence synthetic impedance
InactiveCN101295874AReduce trafficSmall amount of calculationEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionVoltage phasorsDecision methods
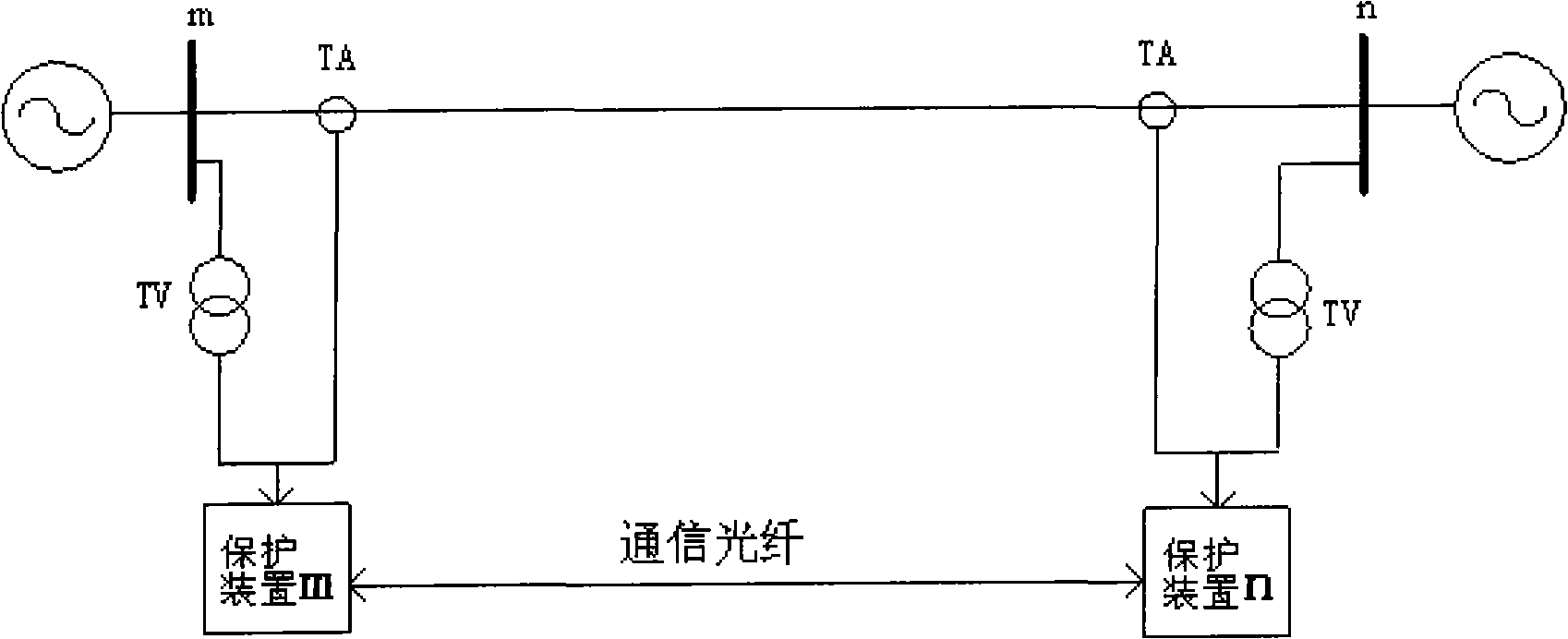
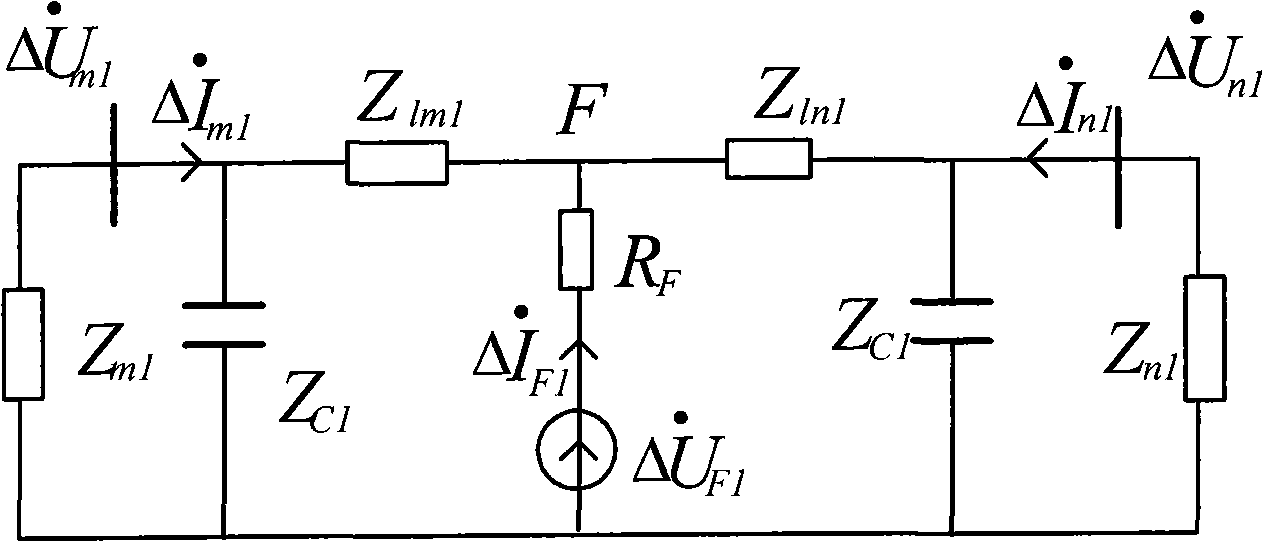
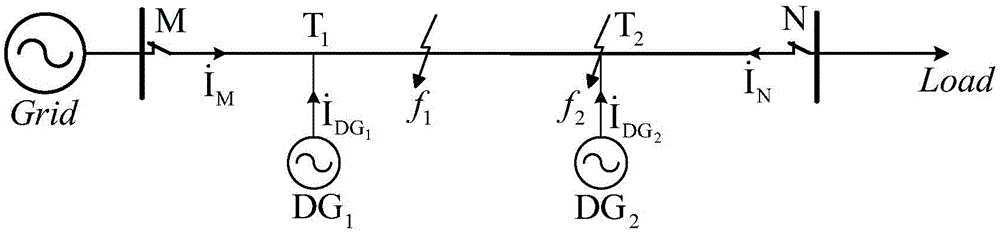
The invention discloses a judgment method for the pilot protection of a transmission line based on the synthesized impedance of a positive-sequence fault component. Two protection devices are arranged at the two sides of a protected line segment; a communication channel is arranged between the two protection devices; the voltage phasor Delta U<m1> of the positive-sequence fault component and the current phasor Delta I<m1> of the positive-sequence fault component which are at the side are calculated, and the communication channel is utilized to obtain the voltage phasor Delta U<n1> of the positive-sequence fault component and the current phasor Delta i<n1> of the positive-sequence fault component which are at the same time and at the opposite side. The synthesized impedance of the positive-sequence fault component is calculated (refer to formula (1)), wherein, Delta U<cdl> is shown in formula (2). According to the size relation between the module value and the fixed value of the synthesized impedance of the positive-sequence fault component, whether the line segment has fault is distinguished so as to control the action of the protection devices.
Owner:DONGFANG ELECTRONICS
Synchronous-phasor and electric-energy-quality integrated monitoring system and method of power distribution network
InactiveCN106226591ARealize high-precision acquisitionImprove analysis efficiencyElectrical testingSystems intergating technologiesPower qualityLow voltage
The invention discloses a synchronous-phasor and electric-energy-quality integrated monitoring system and method of a power distribution network. The synchronous-phasor and electric-energy-quality integrated monitoring system comprises a synchronous-phasor and electric-energy-quality monitoring integrated machine and a master station server, and the synchronous-phasor and electric-energy-quality monitoring integrated machine is in communication with the master station server; the synchronous-phasor and electric-energy-quality monitoring integrated machine is used for carrying out synchronous measurement on main electrical variables including the voltage phasor, the current phasor and the frequency in a terminal power grid, and meanwhile completes monitoring and analysis of power grid harmonic waves and three-phase unbalance variables. The synchronous-phasor and electric-energy-quality integrated monitoring system and method have the advantages that dynamic power-grid behaviors and electric energy quality information on the low-voltage side of a power distribution network can be monitored in real time, the functions of a synchronous-phasor measuring device and the functions of an electric-energy monitoring device are integrated, the size is small, and convenience is brought to installation. More compacter and panorama stable and dynamic behavior monitoring is provided for power grid running in cooperation with a conventional synchronous phasor measuring device and an electric energy quality monitoring device of a high-voltage power grid.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Failure direction determination process for electric system AC electricity transmission line
ActiveCN101478148AHigh sensitivityAccurately determine the directionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectricityVoltage phasors
The invention discloses an electric power system alternating current transmission line fault direction judgment method, which belongs to the field of relay protection of the electric power system. The method comprises the following steps: a protection device is arranged at one side of a protected line section, the positive-sequence fault-component voltage phasor deltaU1 and the positive sequence fault-component current phasor deltaI1 at the side are calculated, then the fault-component positive-sequence impedance deltaU1 / deltaI1 is calculated out, the imaginary part is taken, i.e. the fault-component positive-sequence reactance, X1 is equal to Im (deltaU1 / deltaI1), and the fault direction is judged according to the size relationship between the fault-component positive-sequence reactance value and the fixed value.
Owner:DONGFANG ELECTRONICS
Analog circuit fault diagnosis method
InactiveCN104237770AHigh precisionImprove stabilityElectrical testingDiagnosis methodsShortest distance
The invention discloses an analog circuit fault diagnosis method. The analog circuit fault diagnosis method comprises the steps that firstly, simulation is conducted on each element under the fault-free condition and under two fault conditions respectively, so that a fault-free voltage value and two fault voltage values of a measure point are obtained, a characteristic circle corresponding to each element is obtained according to the corresponding three voltage values, the points of intersection of the characteristic circles are obtained, so that aliasing voltages are obtained, and equivalent excitation of each element is obtained; when a circuit breaks down, the shortest distances between the fault voltage and the characteristic circles are calculated, if no more than one shortest distance is smaller than a preset threshold value, the element corresponding to the minimum shortest distance is the fault element, otherwise, the aliasing voltage which is proximal to the fault voltage is found out from all the aliasing voltages, the fault circuit is excited by means of the equivalent excitation of each element, obtained response voltage phasor sequences are compared with the characteristic circles of the corresponding elements after being moved horizontally, and the element corresponding to the highest similarity is the fault element. According to the analog circuit fault diagnosis method, point diagnosis is replaced by linear diagnosis, and the accuracy, the stability and the robustness of fault diagnosis are improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
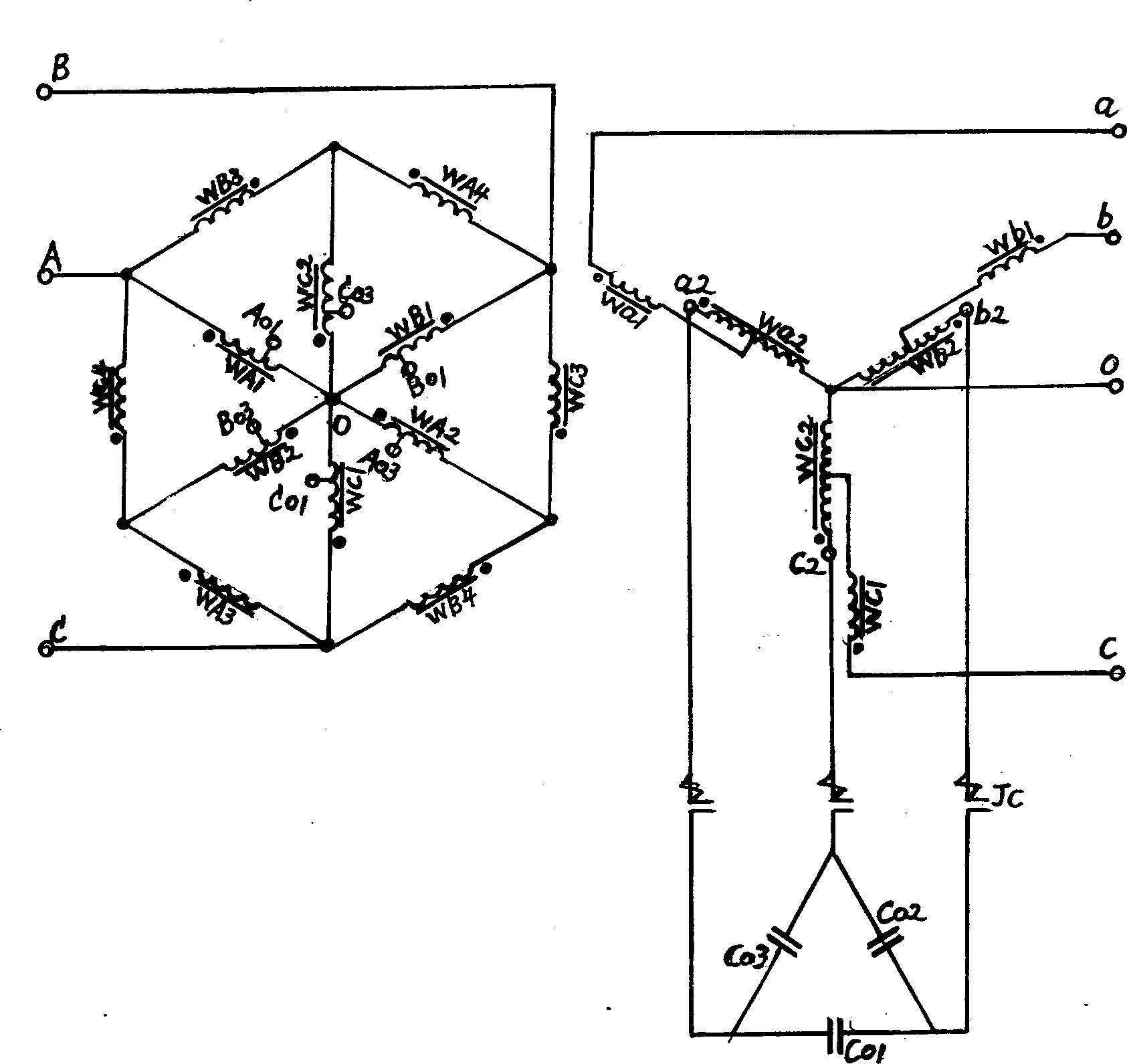
Curved compensating transformer and its phase-shift voltage regulating method
InactiveCN1375841AEasy on-load voltage regulationEasy to save energyVariable inductancesVariable transformersPhase shiftedLow voltage
This invention applies a combination structure of two three-phase iron core and double winding by switching low voltage side hexagon to regulate the winding or high voltage side six starlike ones regulate the level, so makes the voltage phasor relatively zigzag shift between the winding of the regulated sore and the host core and realizes on-load voltage regulation and the auxiliary voltage regulation by way of compensation within capacitors. It has the advantages of low cost of regulation devices, small volume of tap switching and high power factor, which is suitable for producing new type of on-load regulation voltage transformer and the reform.
Owner:刘建平
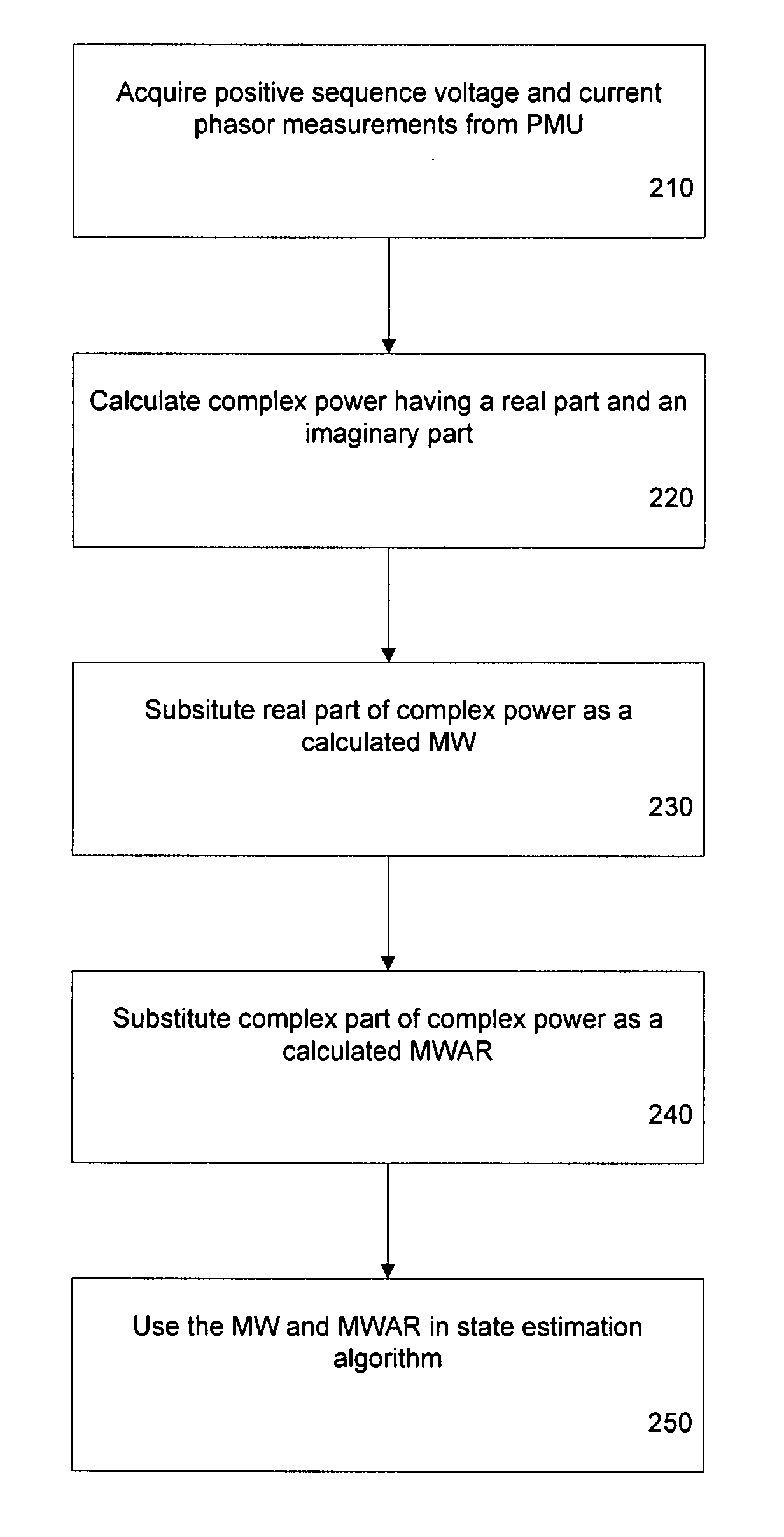
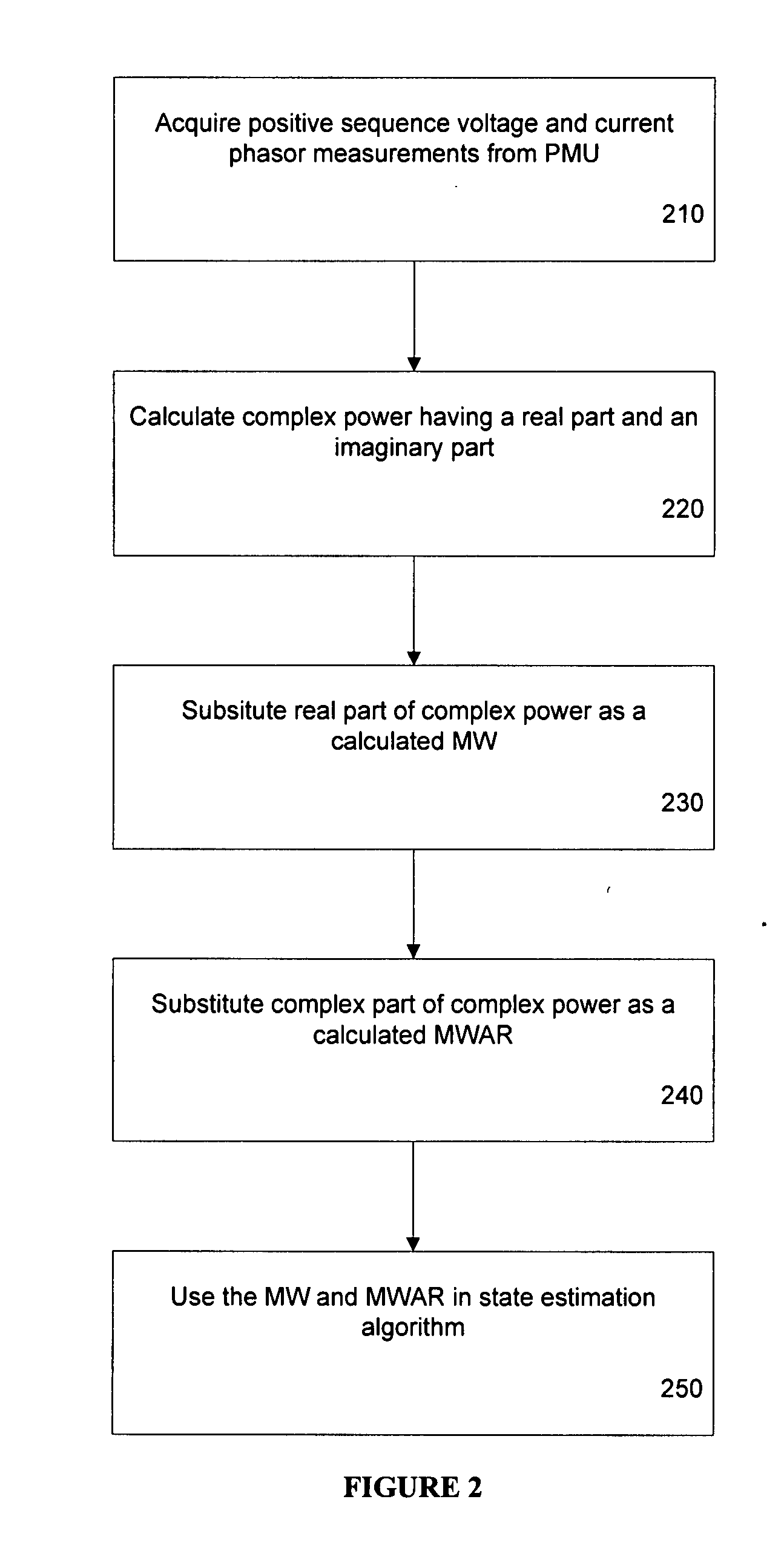
Method and system for state estimation in power systems
ActiveUS20080059088A1Easy to addDifficult to analyzeElectric devicesResistance/reactance/impedenceVoltage phasorsWatt
A method of state estimation is provided, including: (a) acquiring a plurality of positive sequence voltage and current phasor measurements; (b) designating a reference positive sequence voltage phasor measurement from the acquired phasor measurements; (c) correcting the acquired phasor measurements to account for the reference phasor measurement; (d) calculating complex power having a real component and an imaginary component, using the corrected positive sequence voltage and current phasor measurement; (e) using the real component of said complex power as a calculated mega-watt and the imaginary component of the complex power as a calculated mega-volt-ampere; and (f) using the mega-watt and mega volt-ampere calculations in a state estimation algorithm.
Owner:BRITISH COLUMBIA HYDRO & POWER AUTHORITY
Method for accurately positioning single-phase earth fault of generator stator
ActiveCN105116279AMeet the engineering requirements of accurately locating ground fault pointsThe principle is simpleElectrical testingDistribution characteristicVoltage phasors
The invention discloses a method for accurately positioning the single-phase earth fault of a generator stator. The method includes the steps of forming potential phasor distribution characteristics of each turn of stator windings gathered to phase potential according to the developed view of the stator winding, calculating the inductive electrodynamic potential of each turn of the three-phase stator windings before failure under current working conditions and the voltage phasor from any point of the stator winding to a neutral point through the voltage and current measured value at the machine end of a generator, and searching and determining the accurate position of a failure point based on the voltage phasor from the failure point to the neutral point and the potential phasor distribution characteristics of each turn of the stator windings before failure.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Single-ended phase-to-phase fault location method for distributed capacitance current and fault resistance resistant line
ActiveCN102129011AOvercoming the effects of transition resistancePracticalFault locationCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention discloses a single-ended phase-to-phase fault location method for a distributed capacitance current and fault resistance resistant line. The method comprises the following steps of: calculating the angle of a fault phase-to-phase action voltage phasor ahead of a fault phase-to-phase current break variable of each point on the line in turn from the starting end of a protected line by a method of increasing a step length successively until a setting range for sending a tripping signal; if a protection tripping signal cannot be obtained, searching the overall length of the protected line; and taking the angle of the fault phase-to-phase action voltage phasor ahead of the fault phase-to-phase current break variable lying within the interval of [180 degrees, 360 degrees] at a certain point and the angle of the fault phase-to-phase action voltage phasor ahead of the fault phase-to-phase current break variable laying within the interval of [0 degree, 180 degrees] at a point adjacent to the point, wherein the middle position between the two points is a fault point; and the distance from the fault point to a line installation position is fault distance. The method is not influenced by distributed capacitance, fault resistance and a load current and has a very high practical value.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Generator stator winding single-phase earth fault position locating method
The invention provides a generator stator winding single-phase earth fault position locating method. According to the method, firstly the single-phase earth fault is simulated on the generator end andcharacteristic parameters are calculated; then the fundamental voltage phasor of each winding bar and the fundamental voltage phasor of the tail end of each winding bar are calculated according to the stator winding connection diagram; then when the stator winding single-phase earth fault actually occurs, the three-phase fundamental voltage and the zero sequence voltage of the generator end are measured and calculated and the fault phase is judged; and supposing that the earth fault occurs on the tail end of each winding bar, the fundamental zero sequence voltage under the fault conditions iscalculated and compared with the fundamental zero sequence voltage under the condition of actual fault so as to judge the fault position. According to the method, the workload of actual parameter measurement is low, implementation is easy and the method is accurate.
Owner:TECH INNOVATION CENT OF CHINA HUANENG GROUP +3
Fault positioning method used for power distribution network and comprising multiple T-connection inversion distributive power sources
ActiveCN107064736ARealize the solutionRealize fault locationFault location by conductor typesElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
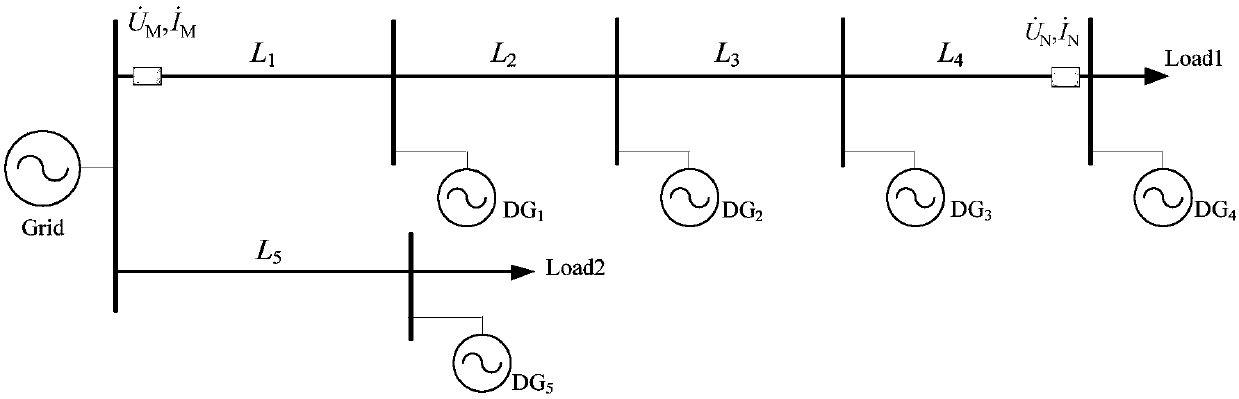
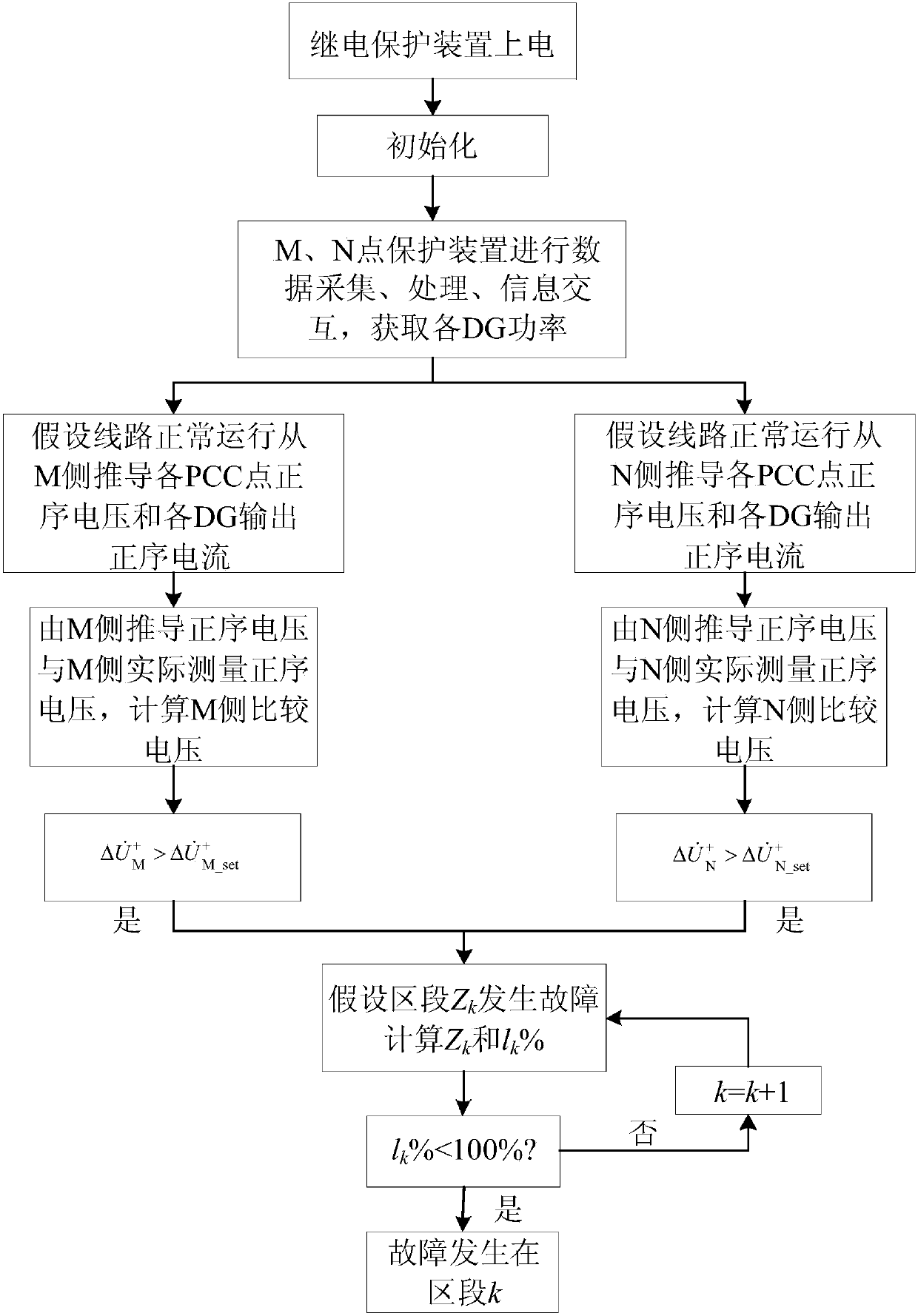
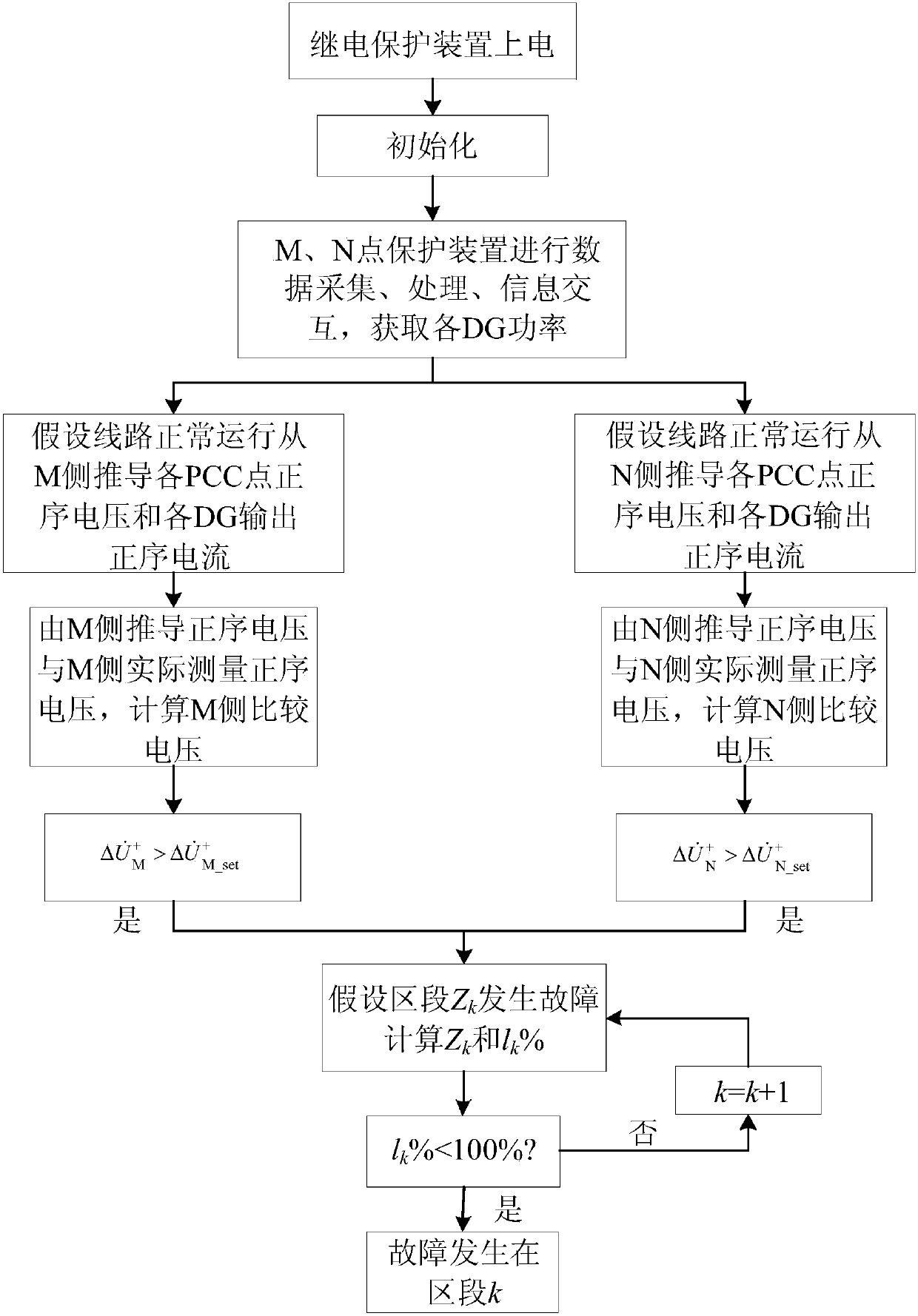
The invention discloses a fault positioning method used for a power distribution network and comprising multiple T-connection inversion distributive power sources. The method includes steps of electrifying a relay protection device; initiating circuit parameters; acquiring power of the distributive power sources; acquiring voltage phasor and current phasor on two sides of a feed line; calculating output current of the distributive power sources; calculating the magnitudes of comparison voltage on two sides of the feed line; if the comparison voltage is greater than a setting value, determining faults within a feed line zone and starting a fault positioning algorithm; if the faults occur in a specific section, calculating a measurement distance percentage, and determining the faults within the section if the measurement distance percentage is smaller than 100%. By adopting the method, problems in relay protection and fault positioning when the multiple distributive power sources are in T-connection with the circuit can be solved effectively. Besides, the method is insusceptible to influence by connection number and connection position of the distributive power sources, fault types and transition resistors, and is high in adaptability and engineering practicality.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Pilot protection method containing multi-T-connection inverter interfaced distributed generation power distribution network
ActiveCN105762777AReduce adverse effectsImprove applicabilityEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionPower control systemResistor
The invention discloses a pilot protection method containing multi-T-connection inverter interfaced distributed generation power distribution network. The pilot protection method includes the following steps: electrifying a relay protection device; initializing line parameters; setting the practical rated power capacity; setting a constant value Iset for pilot current differential protection; acquiring a voltage phasor and a current phasor; acquiring an active power; calculating the sum of the output power of the distributed generation; calculating an active reference power for a distributed generation control system; calculating the positive sequence voltage of a point of common coupling PCC to acquire the practical output current; according to the current phasor, calculating the sum of the practical output current, and calculating a total differential current Delta I of the line; determining whether the Delta I is greater than Iset; and determining that a fault in the area occurs and starting a protective action if so, or expressing that no fault occurs in the area if not. The pilot protection method containing multi-T-connection inverter interfaced distributed generation power distribution network is suitable for a line containing an arbitrary number of T distributed generation, and is not influenced by a fault type, a transition resistor, distributed generation capacity and other factors, thus being high in applicability and reliability and having high practicability during the engineering practice process.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Steady-state harmonic wave analyzing method for line terminal synchronous measurement signal multi-bus micro-grid
ActiveCN103091554AAvoid Monitoring Power QualityLess investmentSpectral/fourier analysisHarmonicPower grid
The invention relates to a steady-state harmonic wave analyzing method for a line terminal synchronous measurement signal multi-bus micro-grid. The fact of additionally installing detecting devices on all buses of the micro-grid is avoided and a large amount of investment is saved. The steady-state harmonic wave analyzing method comprises the steps of collecting voltage and current synchronous signals of a micro-grid line terminal detecting point and obtaining line impedance information between the detecting point and a bus adjacent to the detecting point; according to obtained amplitude and initial phase of the voltage and current synchronous signals and by combining the impedance information between the line terminal detecting point and the bus adjacent to the line terminal detecting point, calculating the voltage phasor of the bus adjacent to the line terminal detecting point by the utilization of the Kirchhoff law; by combining voltage phasors of two adjacent buses and line impedance information between the buses, calculating the current phasor in a bus connecting line according to the Ohm law; by combining the voltage and current phasors of all the buses, obtaining effective values of fundamental waves and all sub-harmonic waves and calculating the harmonic wave situations of all the buses by the utilization of the calculation formula of harmonic wave voltage ratio, harmonic wave current ratio, voltage harmonic wave total distortion rate, and current harmonic wave total distortion rate.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY +1
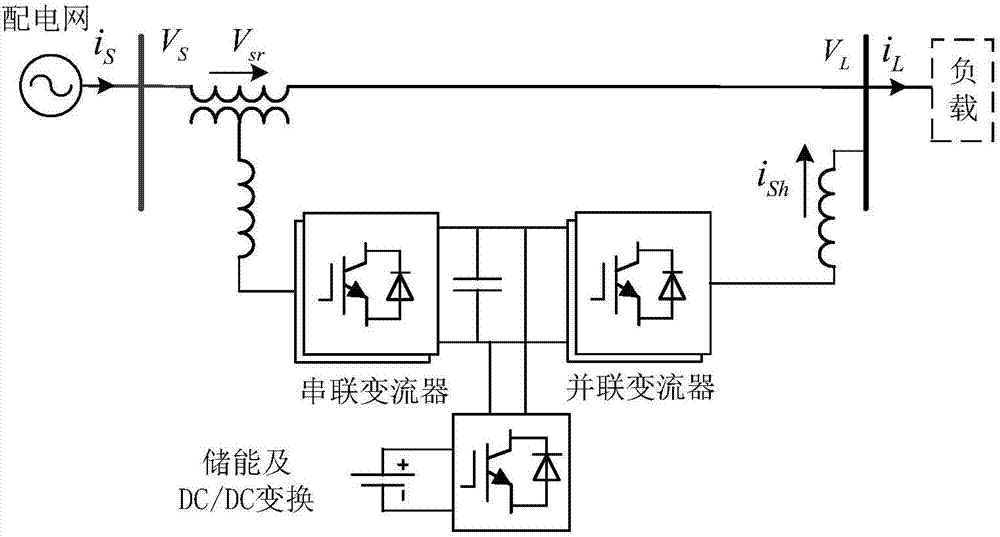
UPQC control method and device based on coordinated power allocation
ActiveCN107425529AEliminate Active CirculationGuaranteed uptimeAc network voltage adjustmentReactive power compensationAbsorbed energyCirculating current
The invention provides a UPQC control method and device based on coordinated power allocation. The invention first proposes a UPQC power control strategy based on the principle of capacity equalization, so that series and parallel converters share the load power equally, thereby giving full play to the series converter. At the same time, considering that when the voltage of a power supply drops too much, an active circulating current of a system increases, thereby increasing the capacity load and loss of the series and parallel converters, the invention further proposes a UPQC power control strategy based on reactive compensation in the case where the voltage of the power supply drops too much, a compensation voltage phasor of the series converter is controlled to be always perpendicular to a power supply current phasor so that the series converter only emits reactive power, the parallel converter absorbs energy from a DC side energy storage unit and shares the load active power with the power supply, the purpose of eliminating the active circulating current is thus achieved, and at this time, the reactive power output by the series and parallel converters still follows the principle of equalization.
Owner:XUJI GRP +4
Double-circuit fault single-ended positioning system and positioning method based on distribution parameters
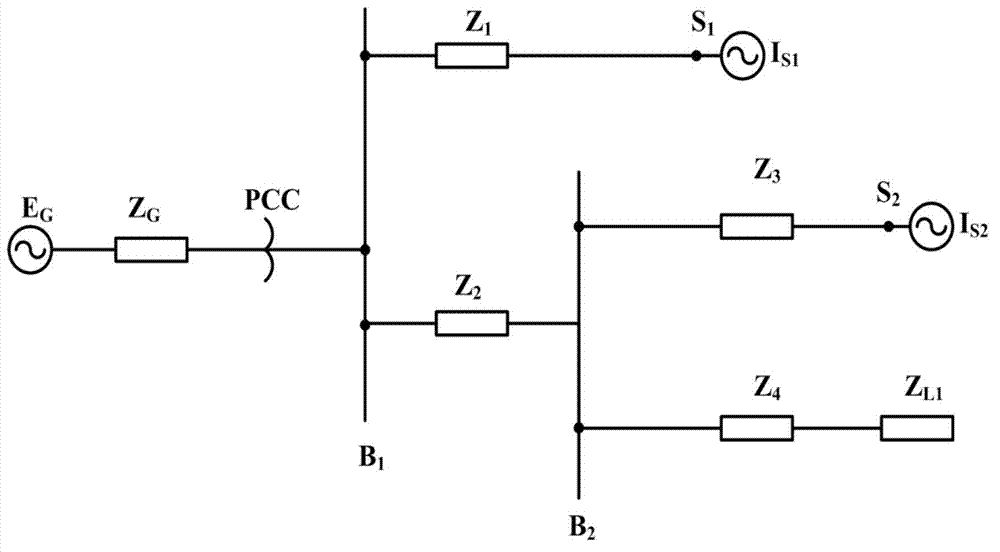
ActiveCN103954885ASmall fault locationThe influence of factors such as transition resistance is smallFault locationInformation technology support systemVoltage amplitudeElectric power system
The invention discloses a double-circuit fault single-ended positioning system and a positioning method based on distribution parameters in the technical field of electric power system line fault positioning. The system comprises a data acquisition module, a compensation voltage solution module, a fault-position voltage solution module and a fault positioning module. The method comprises the steps of acquiring voltage phasor and current phasor at any end of a double-circuit fault line, solving a unidirectional zero sequence compensation factor function, a reverse-direction zero sequence compensation factor function and a compensation voltage function of the double-circuit fault line; solving reverse-direction sequence current at the fault position, calculating voltage phase at the fault position according to the reverse-direction sequence current at the fault position, solving a voltage amplitude value at the fault position, establishing a fault positioning function and recognizing the fault position by solving a phase mutation point of the fault positioning function. The double-circuit fault single-ended positioning system and the positioning method are suitable for various double-circuit faults, only acquire single-ended power information without information of other transformer substations, and is small in influence of the fault positions, transition resistance and other factors, high in positioning accuracy and easy to achieve.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Visualization method for real-time state monitoring of synchronous phasor of power distribution network
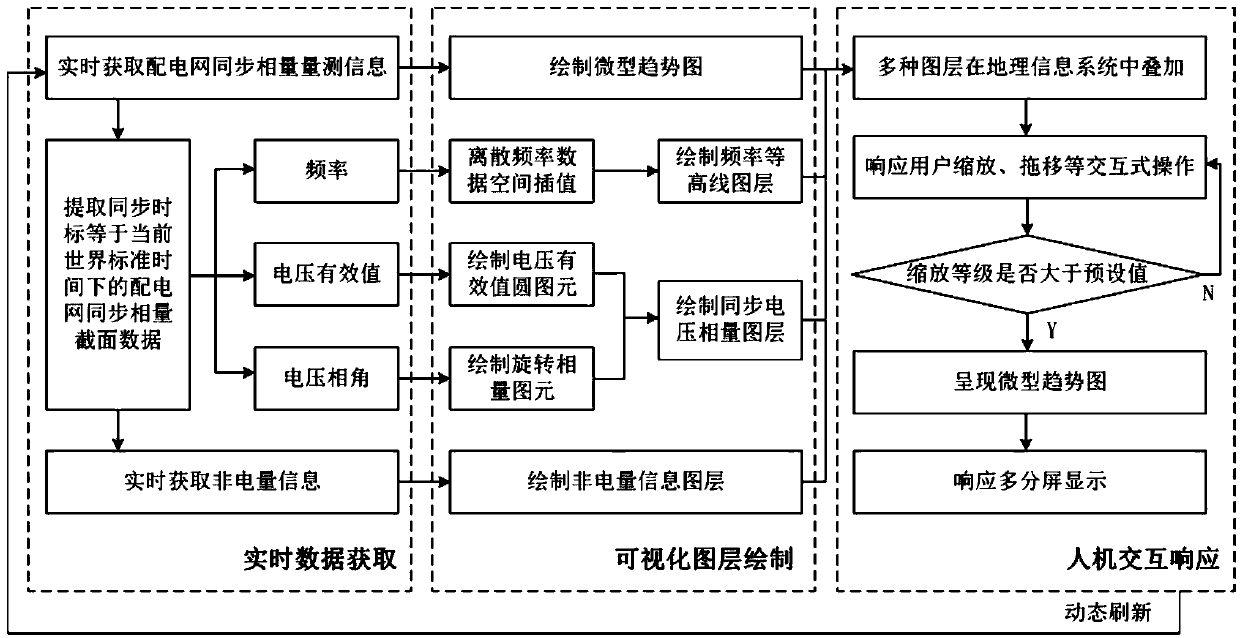
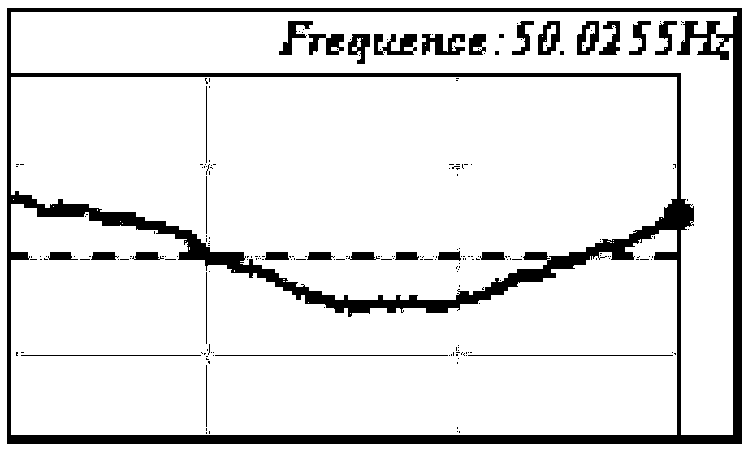
ActiveCN108802540ARealize the display effectEasy to grasp status characteristicsElectrical testingInformation layerSimulation
The invention discloses a visualization method for real-time condition monitoring of synchronous phasor of power distribution network, which comprises: acquiring synchronous phasor measurement information of power distribution network in real time, and drawing a micro trend graph according to the measurement information; extracting synchronous phasor cross-section data at the current moment and obtaining non-electric quantity information corresponding to the cross-section data in real time; performing spatial interpolation processing on the frequency data in the synchronous phasor cross-section data to draw a frequency contour line layer; drawing a valid voltage value circular primitive based on the valid voltage data in the synchronous phasor cross-section data, drawing a rotating phasorprimitive based on the voltage phase angle data in the synchronous phasor cross-section data, drawing a synchronous voltage phasor layer based on the rotating phasor primitive and the valid voltage value circular primitive; drawing a non-electric quantity information layer based on real-time acquired non-electric quantity information; superimposing the frequency contour line layer, a synchronous voltage phasor layer, a non-electric quantity information layer, and a micro trend graph in a geographic information system; the display and multi-screen display of the micro trend graph are achieved by human-computer interaction response.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV +2
Voltage longitudinal protective method of power distribution network with inversion type distributed power supplies
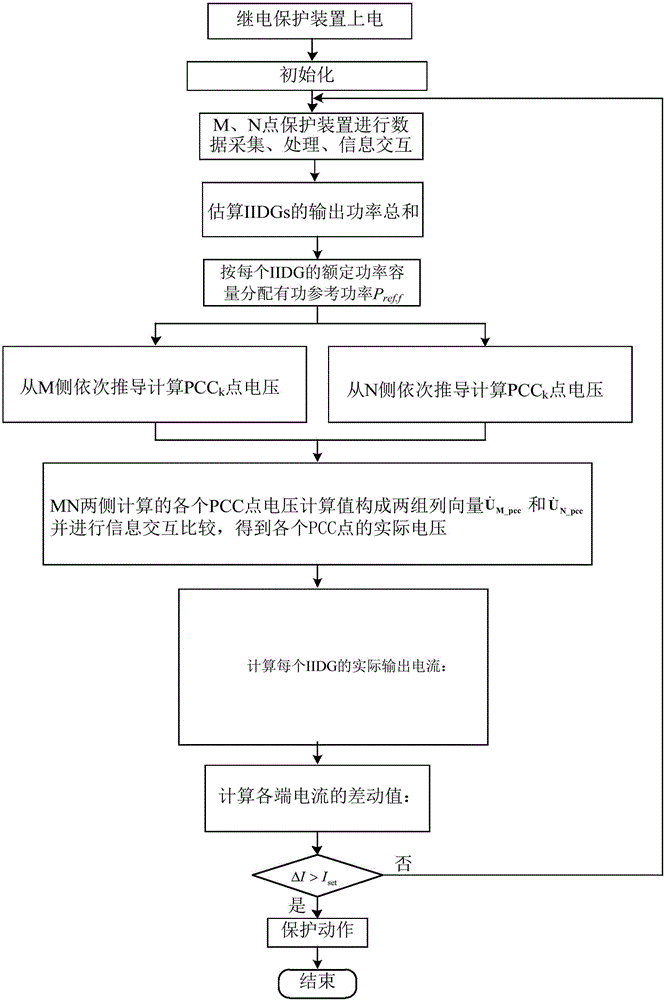
ActiveCN107104421ANumber of protected accessesReduce adverse effectsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsNameplate capacityVoltage phasors
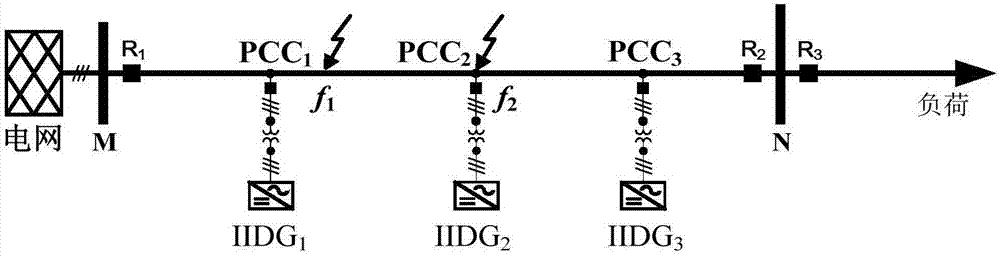
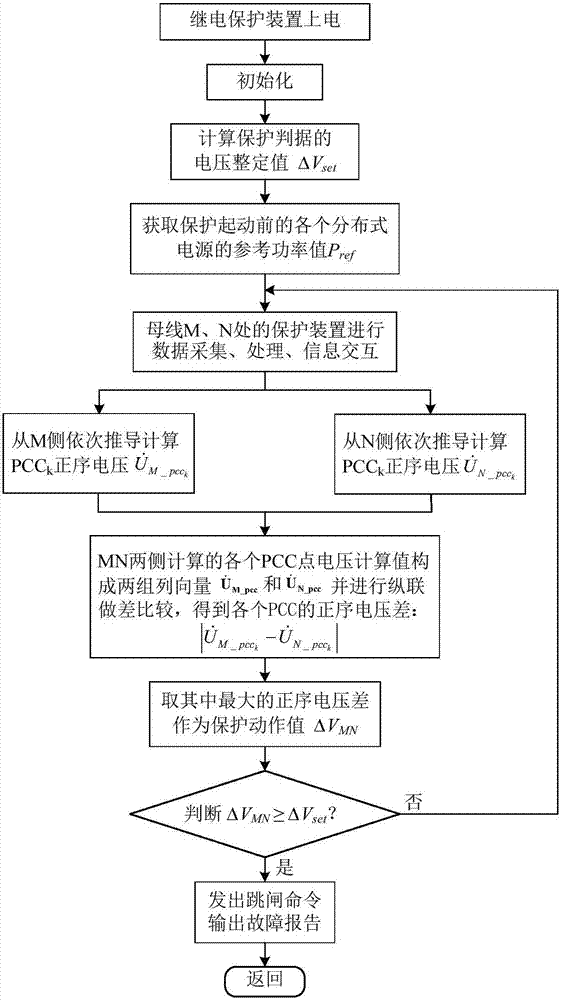
The invention relates to a voltage longitudinal protective method of a power distribution network with inversion type distributed power supplies. The method comprises the steps that a protective relaying device is electrified; line parameters are initialized; a practical rated capacity of each distributed power supply is initialized; a voltage setting value is calculated; latest active power reference values, collected before start of the protection, of the distributed power supplies collected before start of the protection are obtained; positive-sequence voltage phasor U<M_pcc0> and current phasor I<M> of a bus M as well as positive-sequence voltage phasor U<N_pccn+1> and current phasor I<N> of a bus N are obtained; positive-sequence voltage calculated values U<M_pcck> and U<N_pcck> of each common joint point PCC are calculated; the positive-sequence voltage difference between the positive-sequence voltage calculated values U<M_pcck> and U<N_pcck> is calculated; a maximal positive-sequence voltage difference of n+2 nodes is selected as an action value of protection; whether the action value of protection is greater than a voltage setting value is determined; and if YES, a fault in the area is determined, and protection action is implemented. Thus, the distributed power supplies can be connected to the power distribution network in a flexible and scattered way needless of extra longitudinal channels, and the method has the advantages of high applicability, reliability and practicality in engineering practice.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for measuring power frequency parameters of superhigh/extrahigh-voltage alternating-current (direct-current) power transmission circuit
The invention discloses a method for measuring power frequency parameters of superhigh / extrahigh-voltage alternating-current (direct-current) power transmission circuit. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of synchronously measuring zero-sequence voltage and zero-sequence current on the head end and the tail end of the power transmission circuit, obtaining a power-frequency zero-sequence voltage phasor and a power-frequency zero-sequence current phasor by utilizing a Fourier filtering method, solving the power-frequency zero-sequence parameters of the power transmission circuit on the basis of a differential equation model and particle swarm optimization of the power transmission circuit, considering the influence of electromagnetic coupling between a distributive capacitor and the circuit on the power transmission circuit on the measurement of the power-frequency zero-sequence parameters, so that the precision of the power-frequency zero-sequence parameter measurement result of the power transmission circuit can be improved. The method is not only suitable for measuring the power-frequency zero-sequence parameter of a single-circuit and a multi-circuit superhigh / ultrahigh voltage alternating-current power transmission circuit, particularly suitable for measuring the power-frequency zero-sequence parameters of a double-circuit and four-circuit superhigh / ultrahigh voltage alternating-current power transmission circuit of a same tower and also suitable for remotely measuring the power-frequency parameters of the superhigh / ultrahigh voltage direct-current power transmission circuit.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
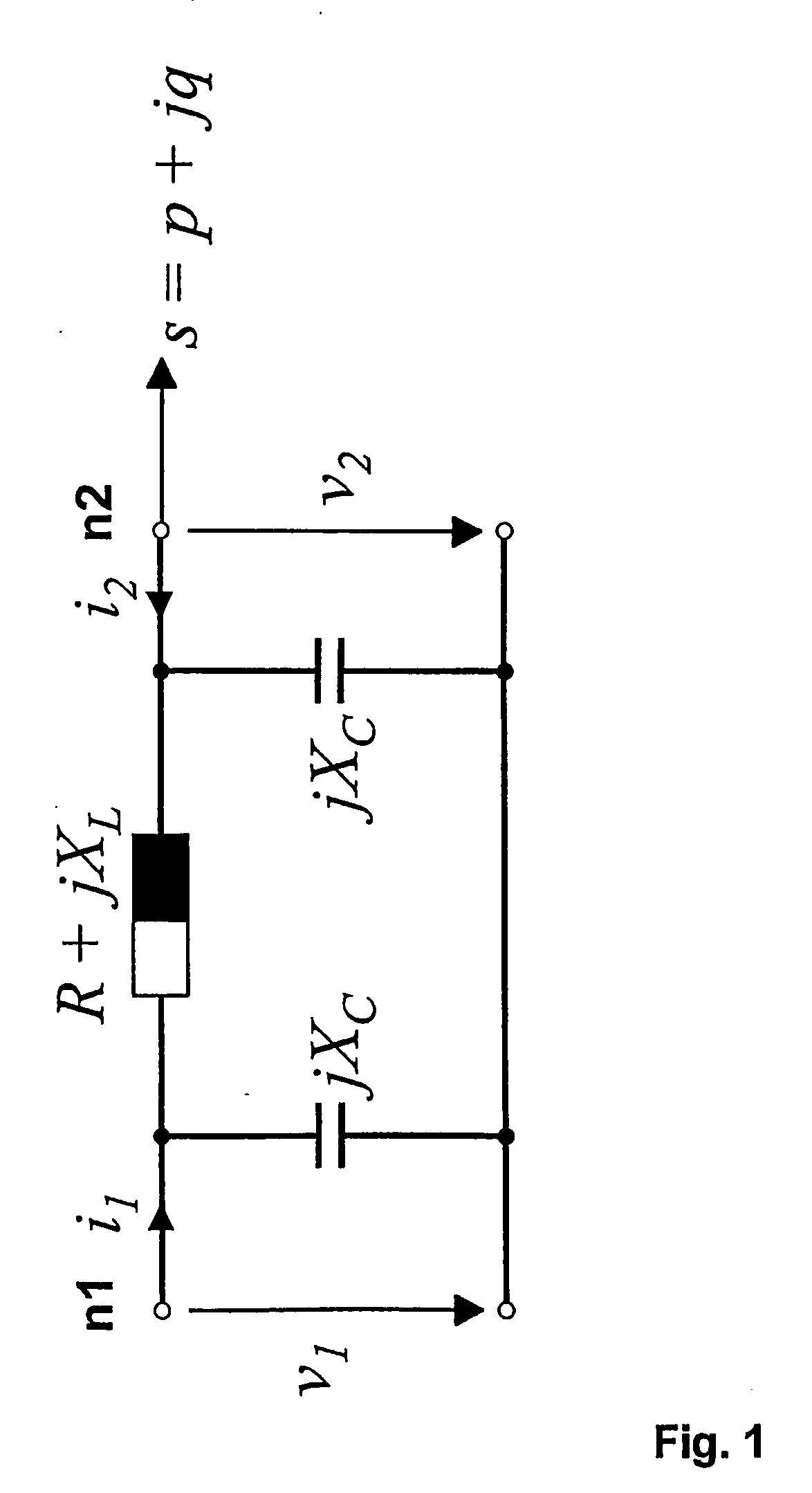
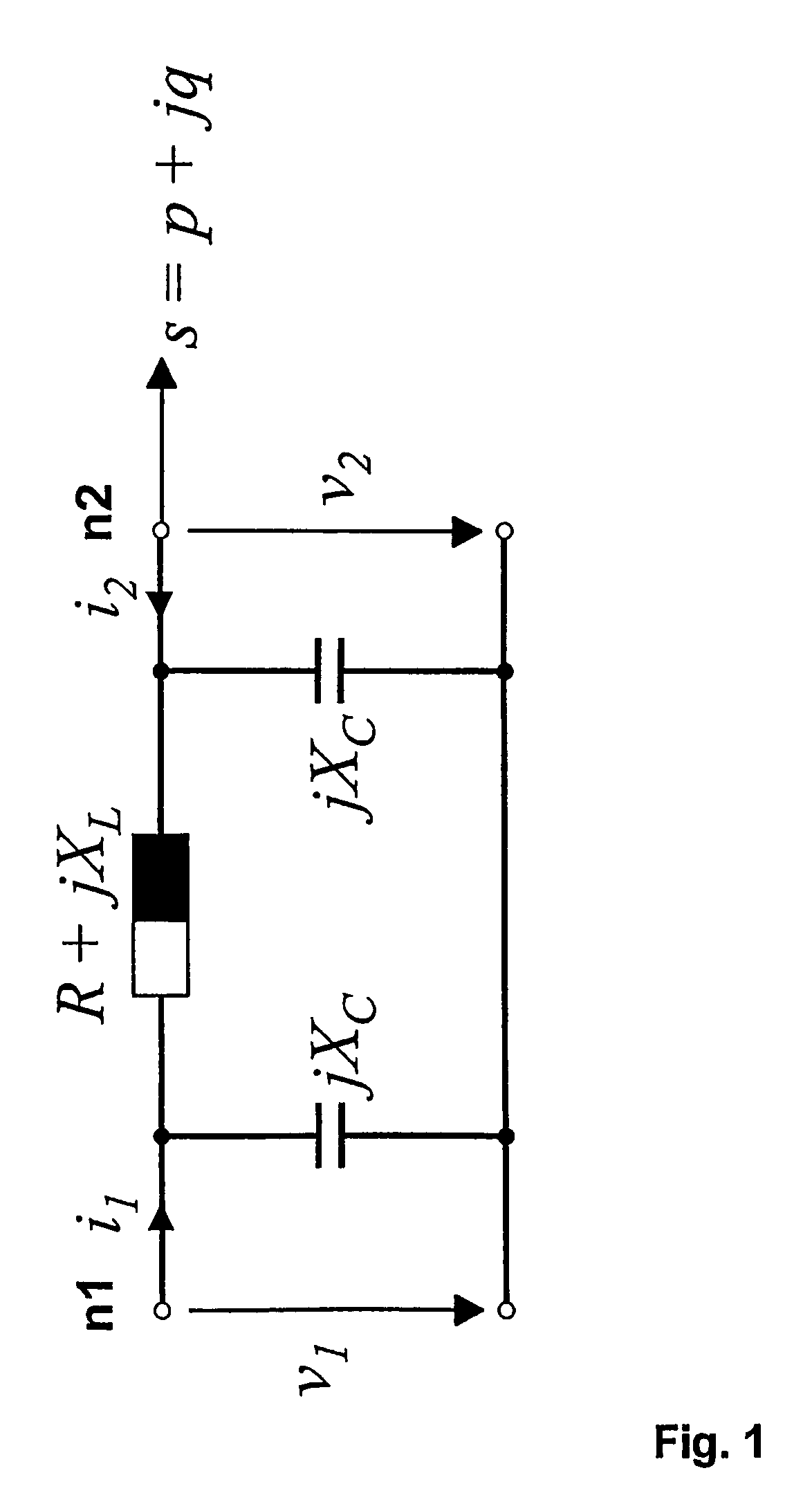
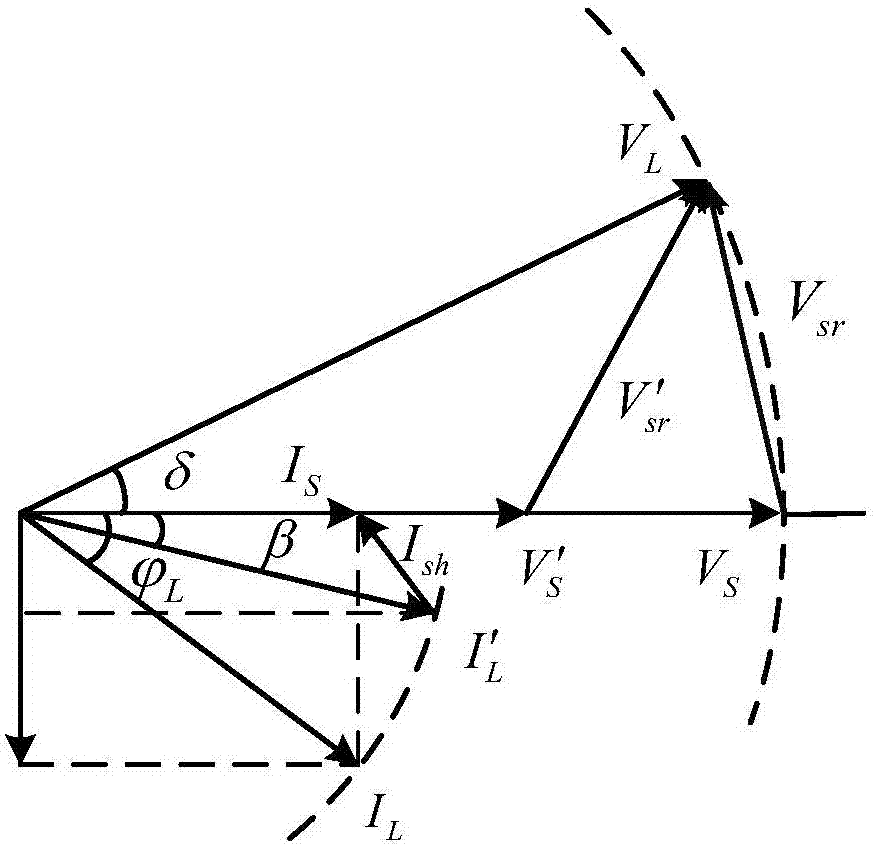
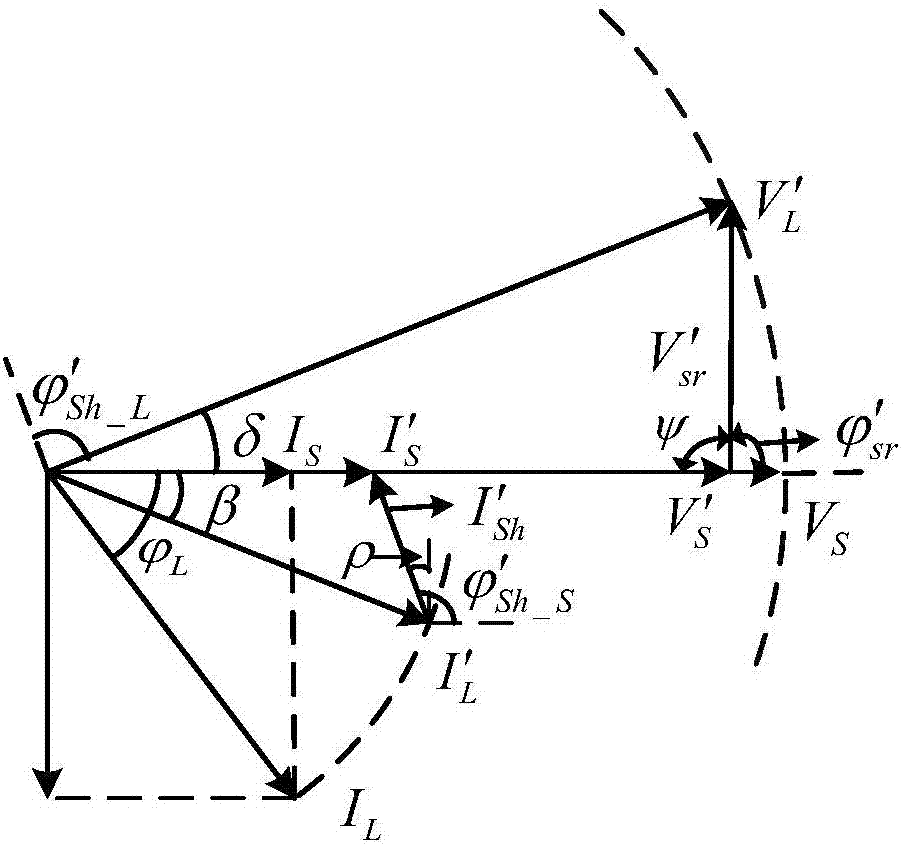
Determining parameters of an equivalent circuit representing a transmission section of an electrical network
In a method, computer program and apparatus for determining parameters of an equivalent circuit representing a transmission section of an electrical network, the transmission section (4) is representable as having at least two interfaces (5,6,7) with other sections (1,2,3) of the network, and the method comprises the steps of a) determining, for each of the interfaces (5,6,7), a voltage phasor ({overscore (v1,{overscore (v2,{overscore (v3) at the interface (5,6,7) and a phasor of a current ({overscore (i1,{overscore (i2,{overscore (i3) flowing through the interface (5,6,7), the measurements at the different interfaces (5,6,7) being made essentially simultaneously, and b) computing, from said voltage ({overscore (v1,{overscore (v2,{overscore (v3) and current ({overscore (i1, {overscore (i2,{overscore (i3)phasors, values of impedances ({overscore (ZT,{overscore (Zsh) constituting the equivalent circuit. This allows determining the equivalent circuit from a single set of essentially simultaneous measurements.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
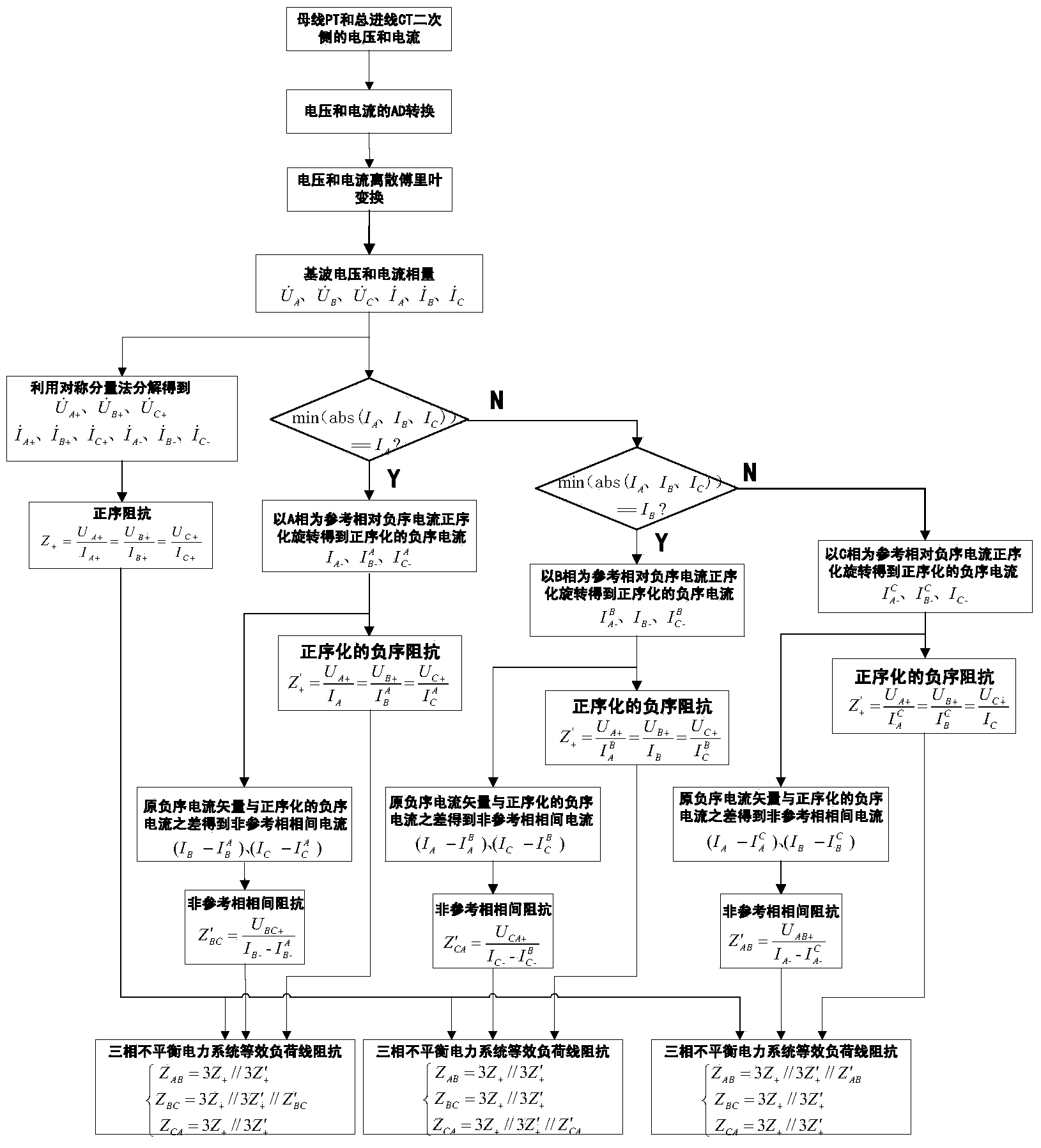
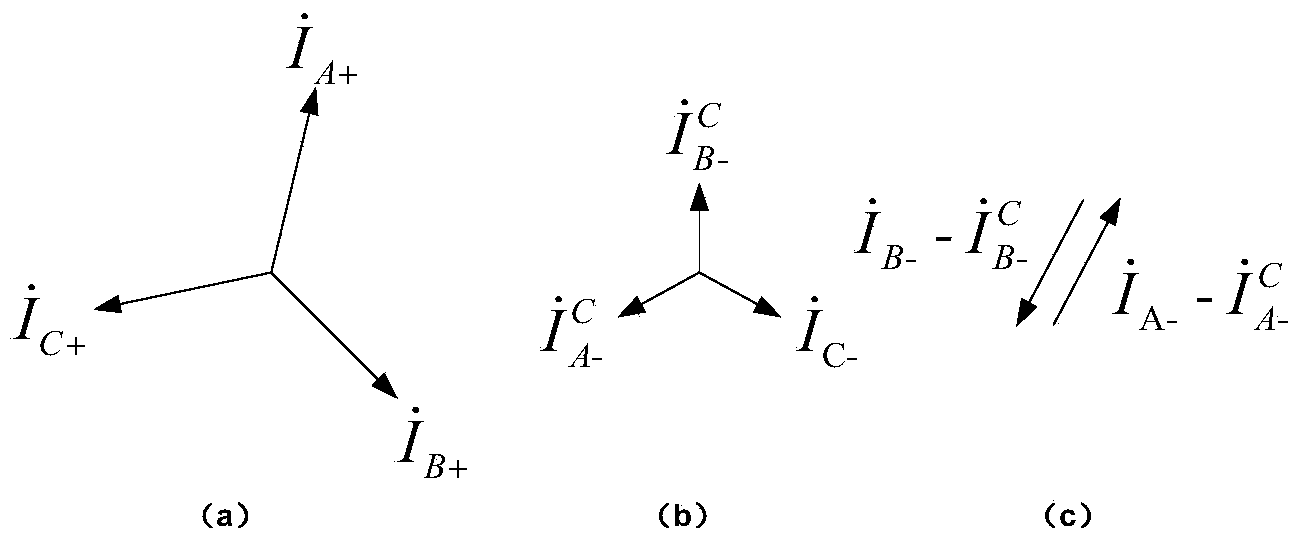
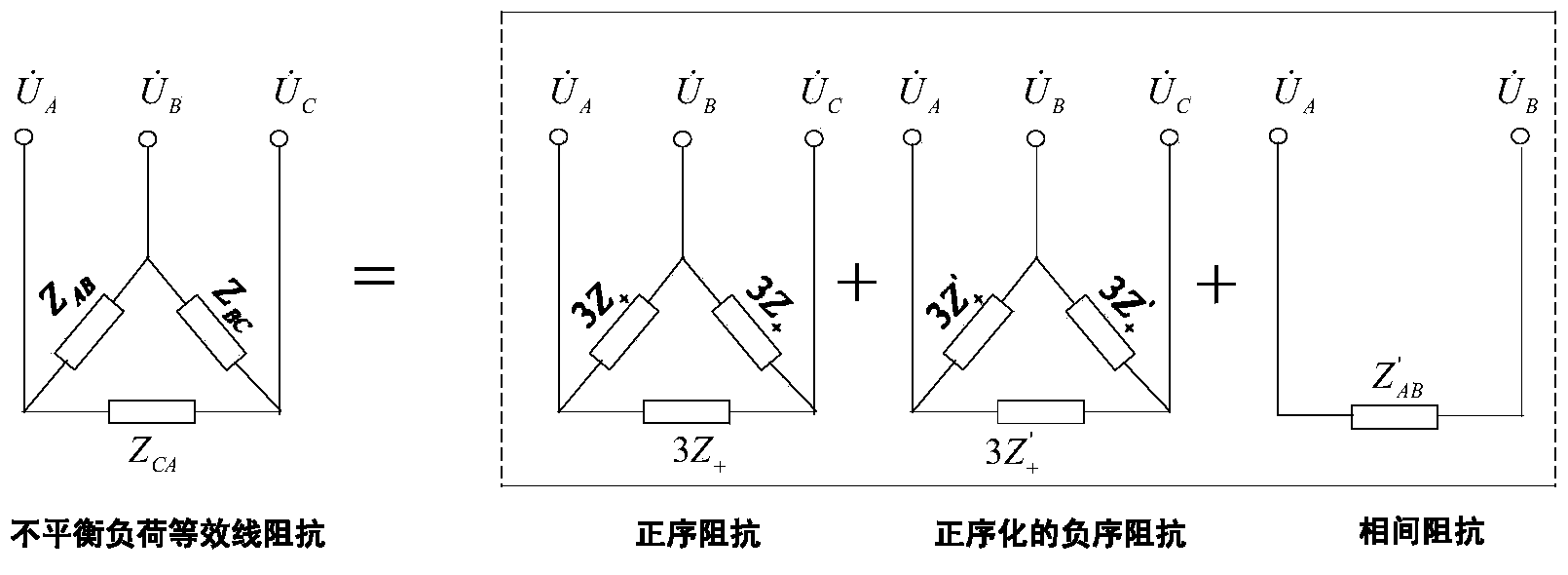
Method for calculating equivalent load line impedance of three-phase three-wire system unbalanced system
The invention discloses a method for calculating equivalent load line impedance of a three-phase three-wire system unbalanced system. The method includes the steps that firstly, a bus voltage phasor and a general incoming line current phasor of a three-phase unbalanced power system are acquired, the voltage phasor and the current phasor are resolved according to a symmetrical component method, and therefore a bus voltage positive-sequence component, a general incoming line current positive-sequence component and a general incoming line current negative-sequence component of the three-phase unbalanced power system are acquired; secondly, the minimum phase of a general incoming line current phasor module value serves as a reference phase, and the general incoming line current negative-sequence component is rotated in the positive sequence, so that the general incoming line current negative-sequence component in the positive sequence is acquired; the general incoming line current negative-sequence component in the positive sequence is subtracted from an original general incoming line current negative-sequence component of a non-reference phase, so that a current component passing through the non-reference interphase is acquired; thirdly, the bus voltage positive-sequence component, the general incoming line current positive-sequence component, the general incoming line current negative-sequence component in the positive sequence and the interphase current component are used for calculation, so that positive-sequence impedance, negative-sequence impedance in the positive sequence and interphase impedance of the non-reference phase of a load are acquired, the positive-sequence impedance and the negative-sequence impedance in the positive sequence of the load are equivalently converted in an angle joint mode and combined with the interphase impedance together, and therefore the equivalent load line impedance of the three-phase three-wire system unbalanced system can be calculated through a impedance parallel formula.
Owner:安徽安大清能电气科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com