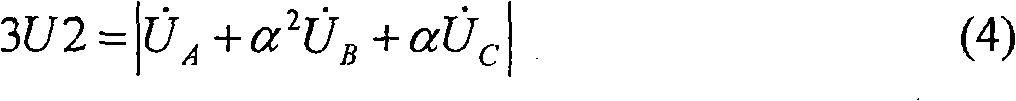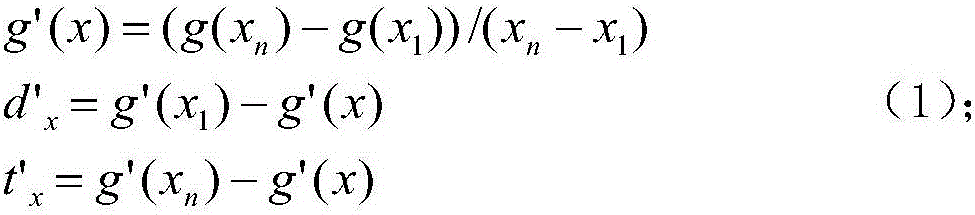Patents
Literature
63 results about "Fourier filtering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fourier filter. The Fourier filter is a type of filtering function that is based on manipulation of specific frequency components of a signal. It works by taking the Fourier transform of the signal, then attenuating or amplifying specific frequencies, and finally inverse transforming the result.
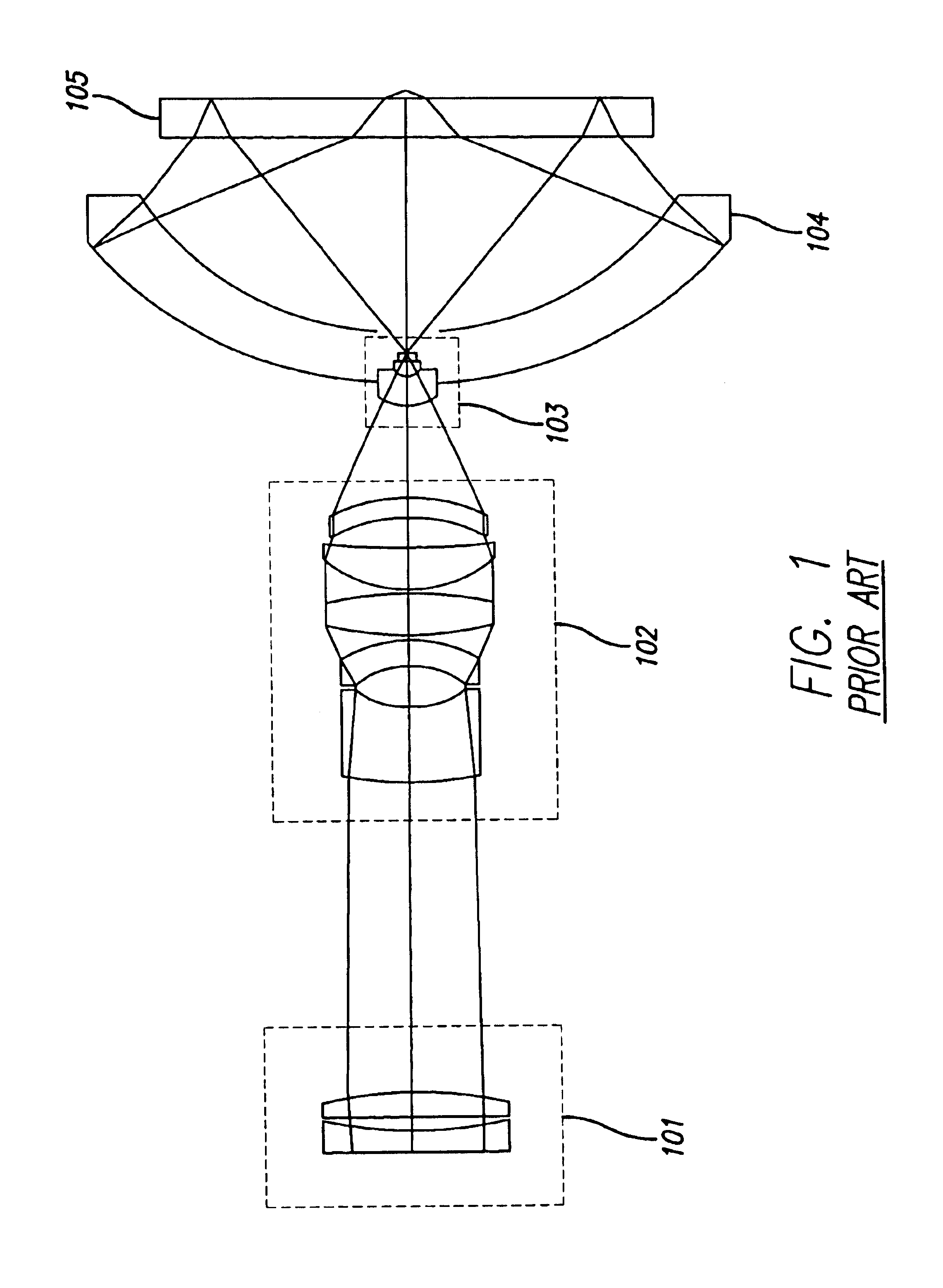
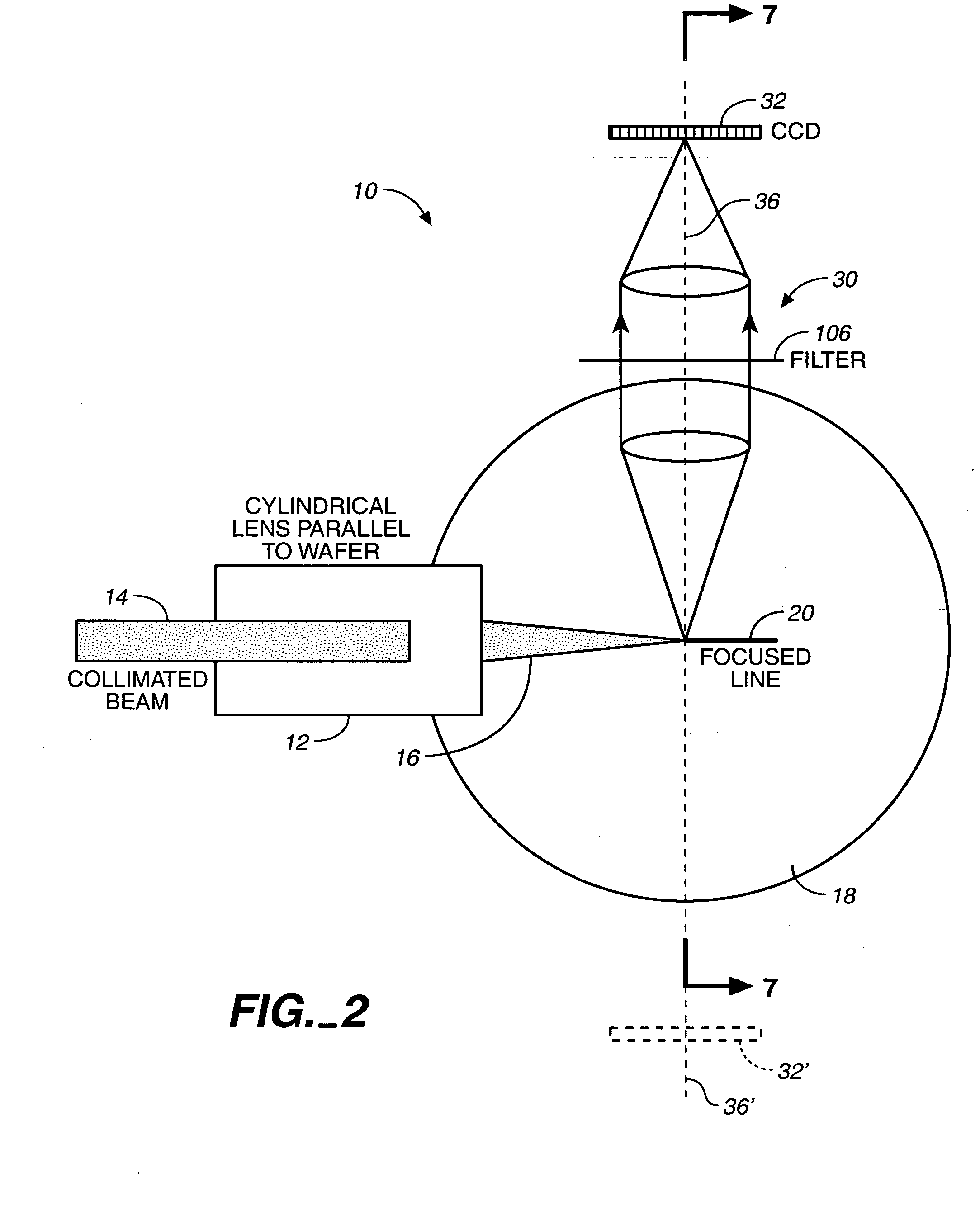
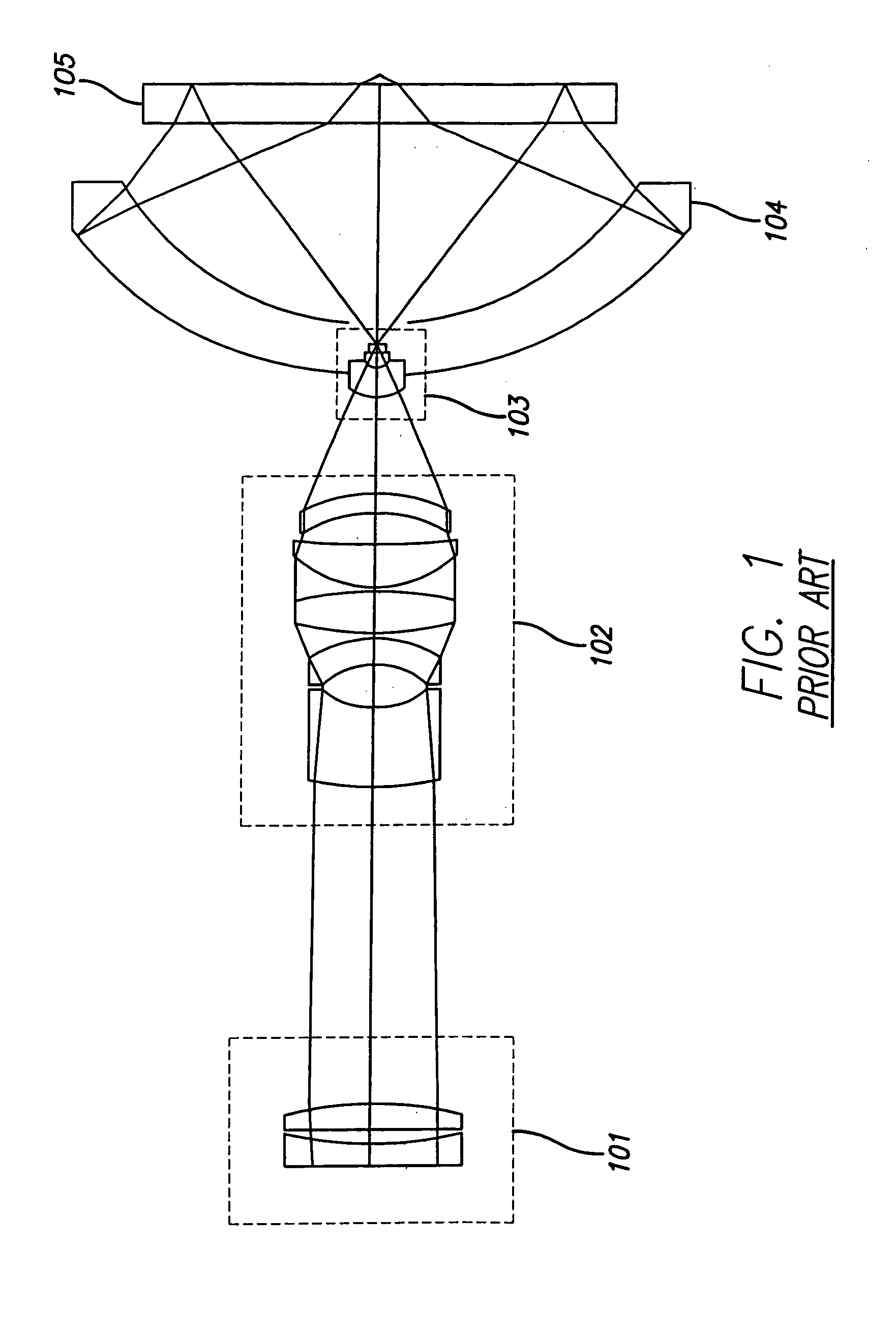
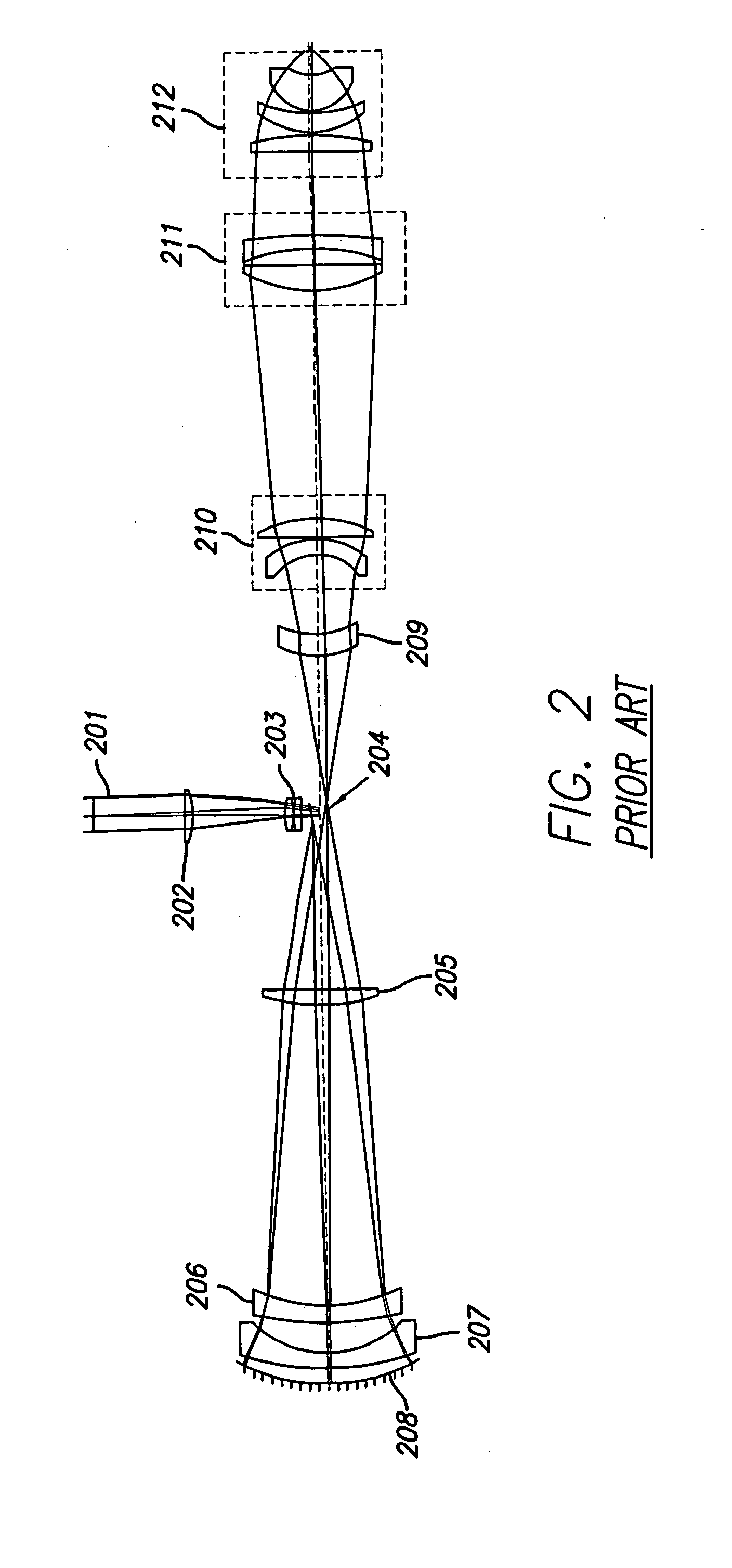
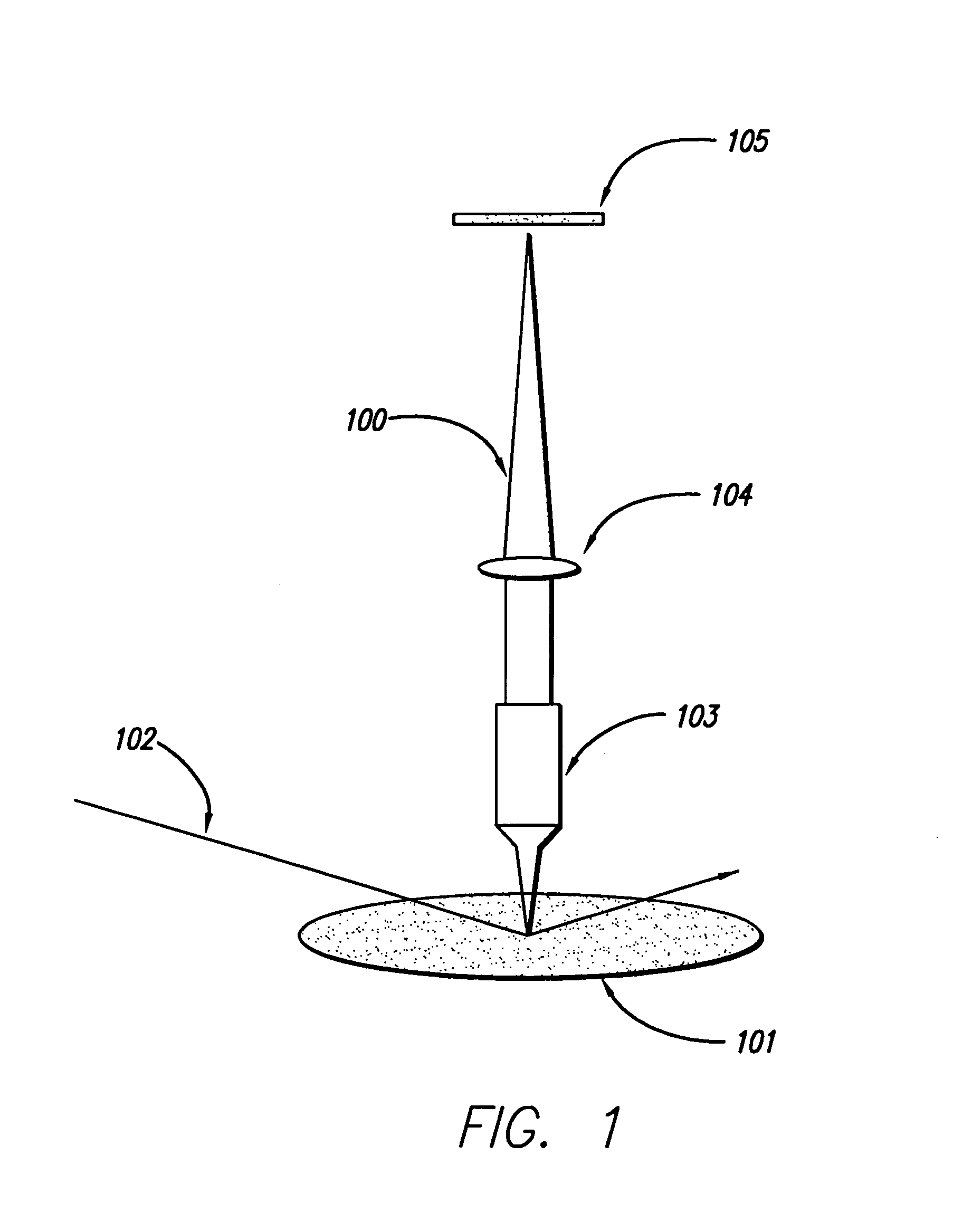
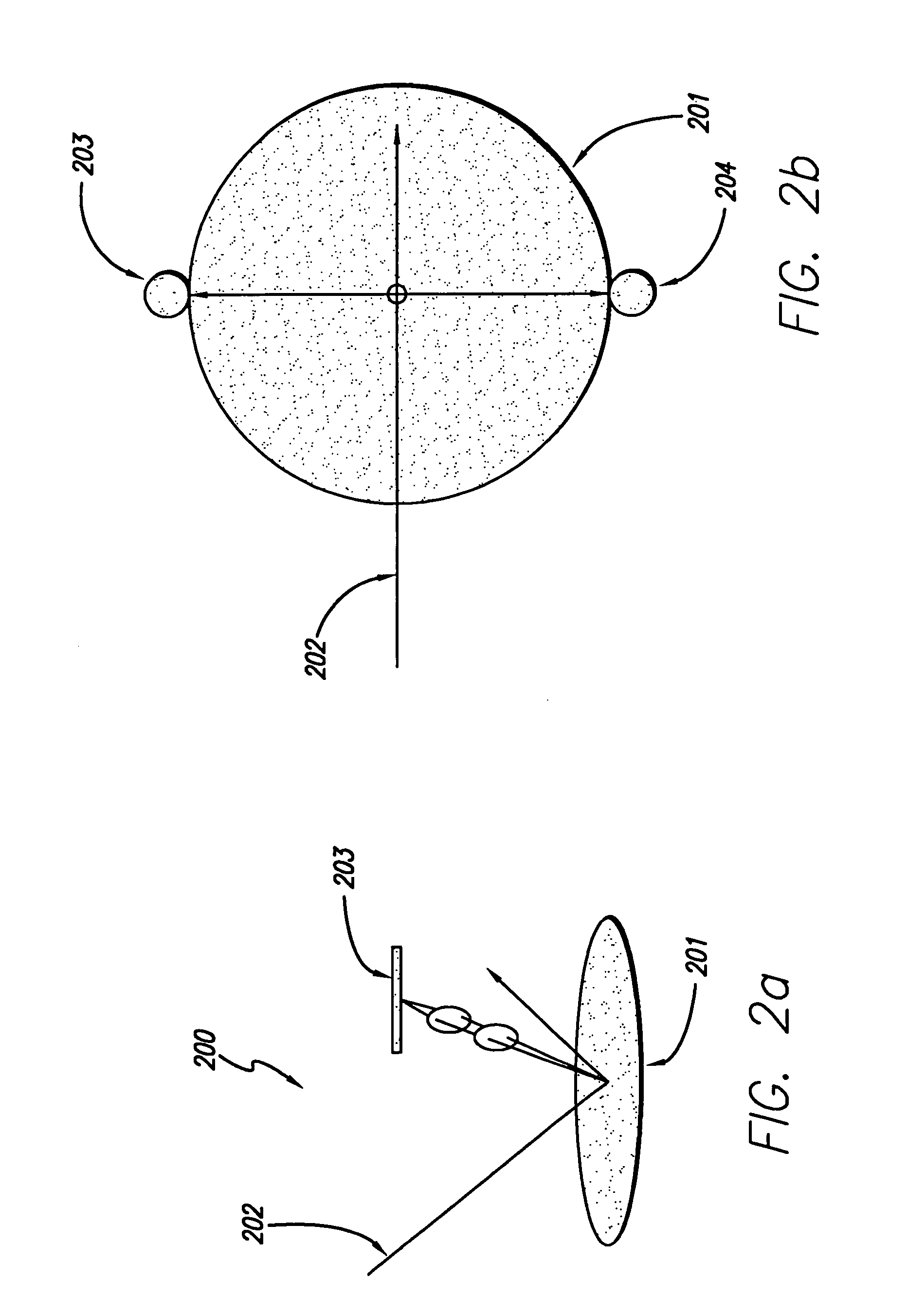
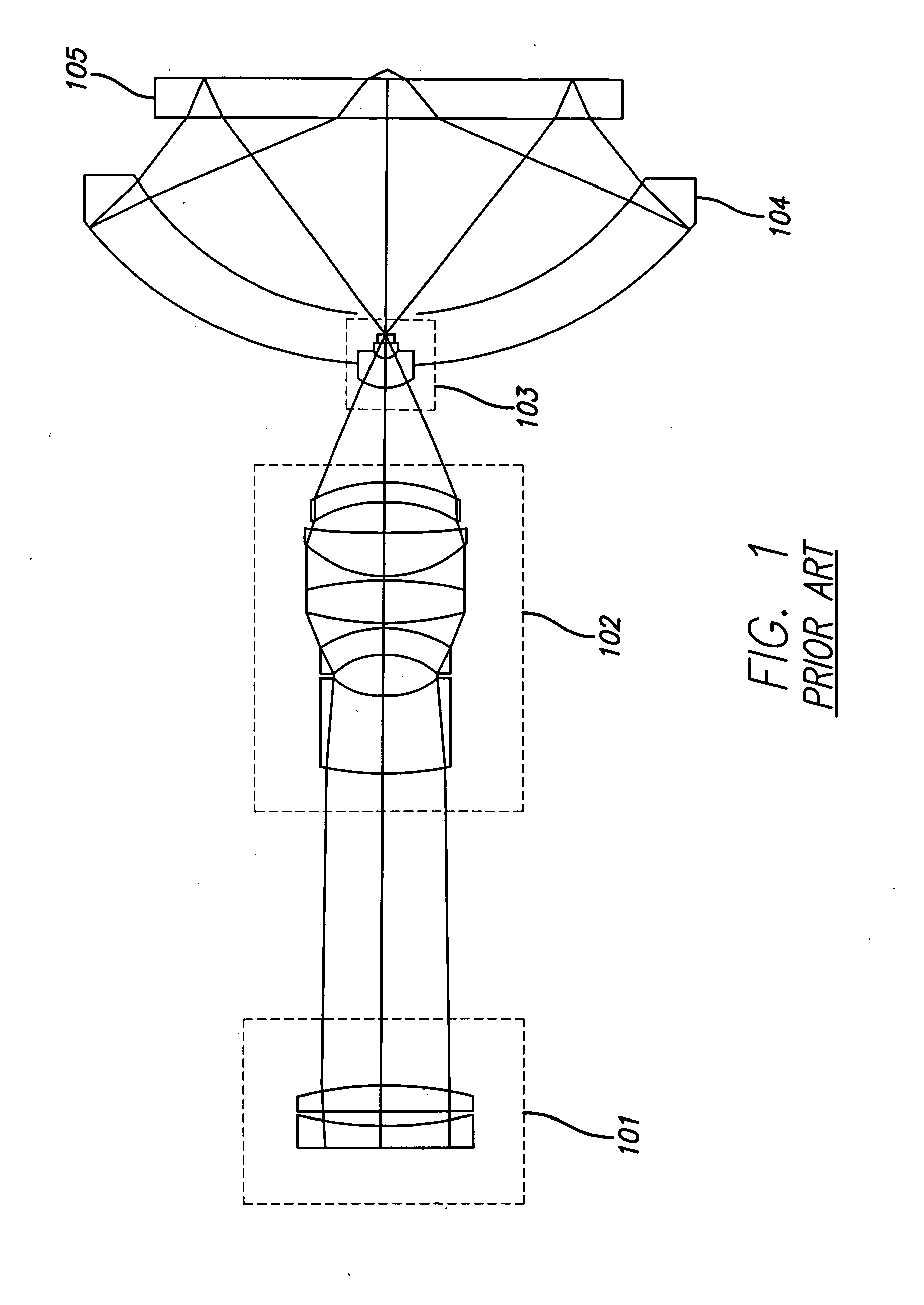
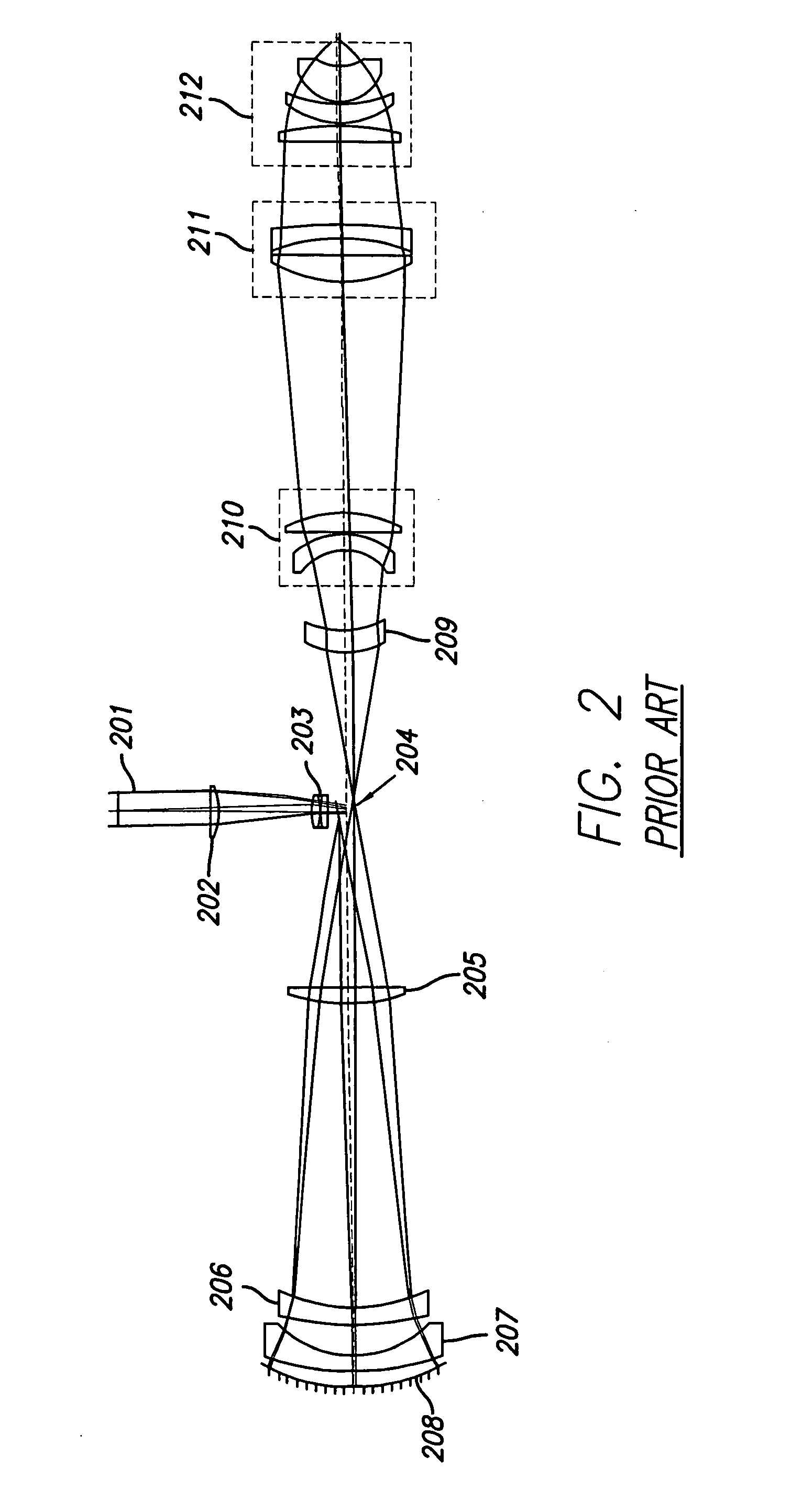
System and method for inspecting semiconductor wafers
InactiveUS6020957ALow costFaster throughputSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGratingImage subtraction
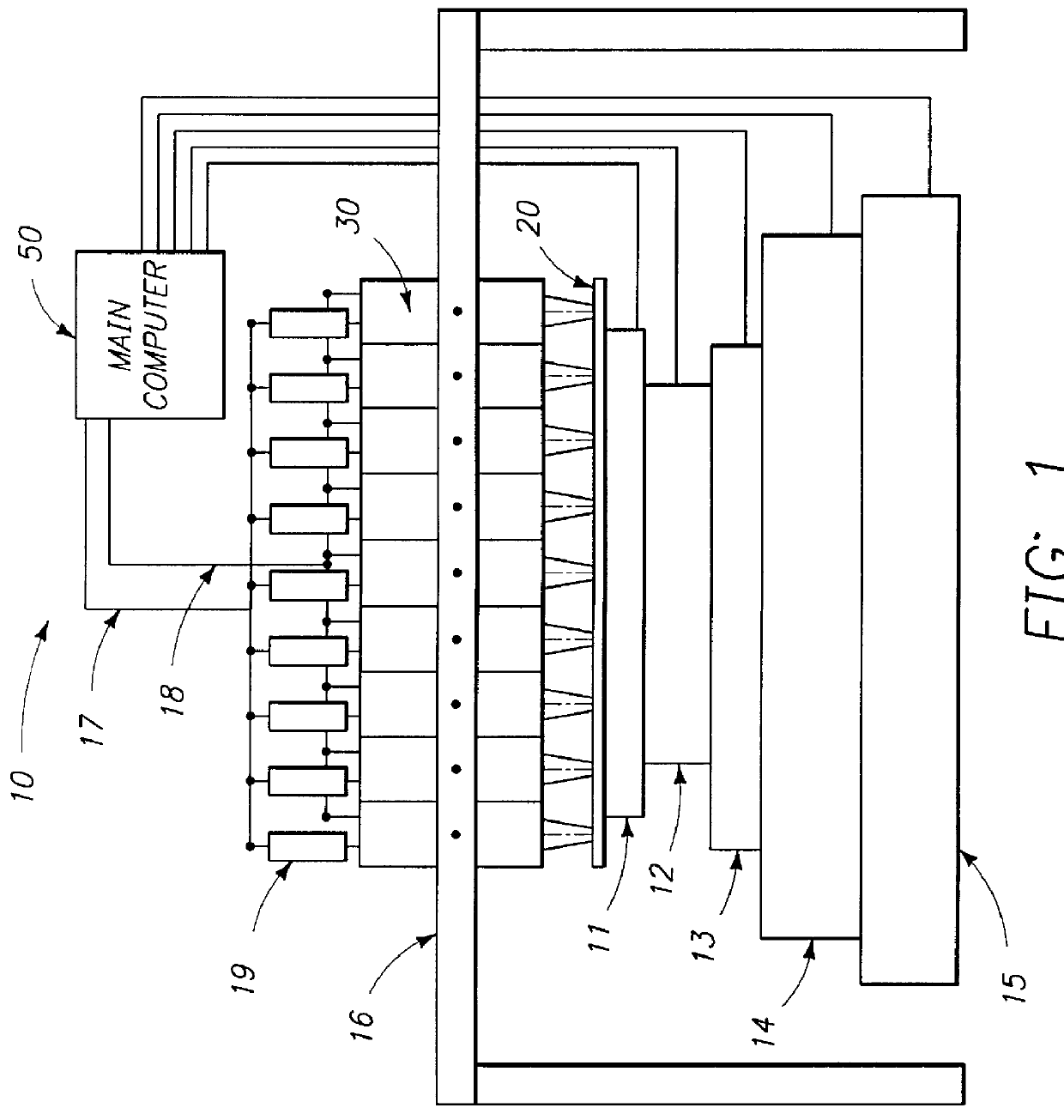
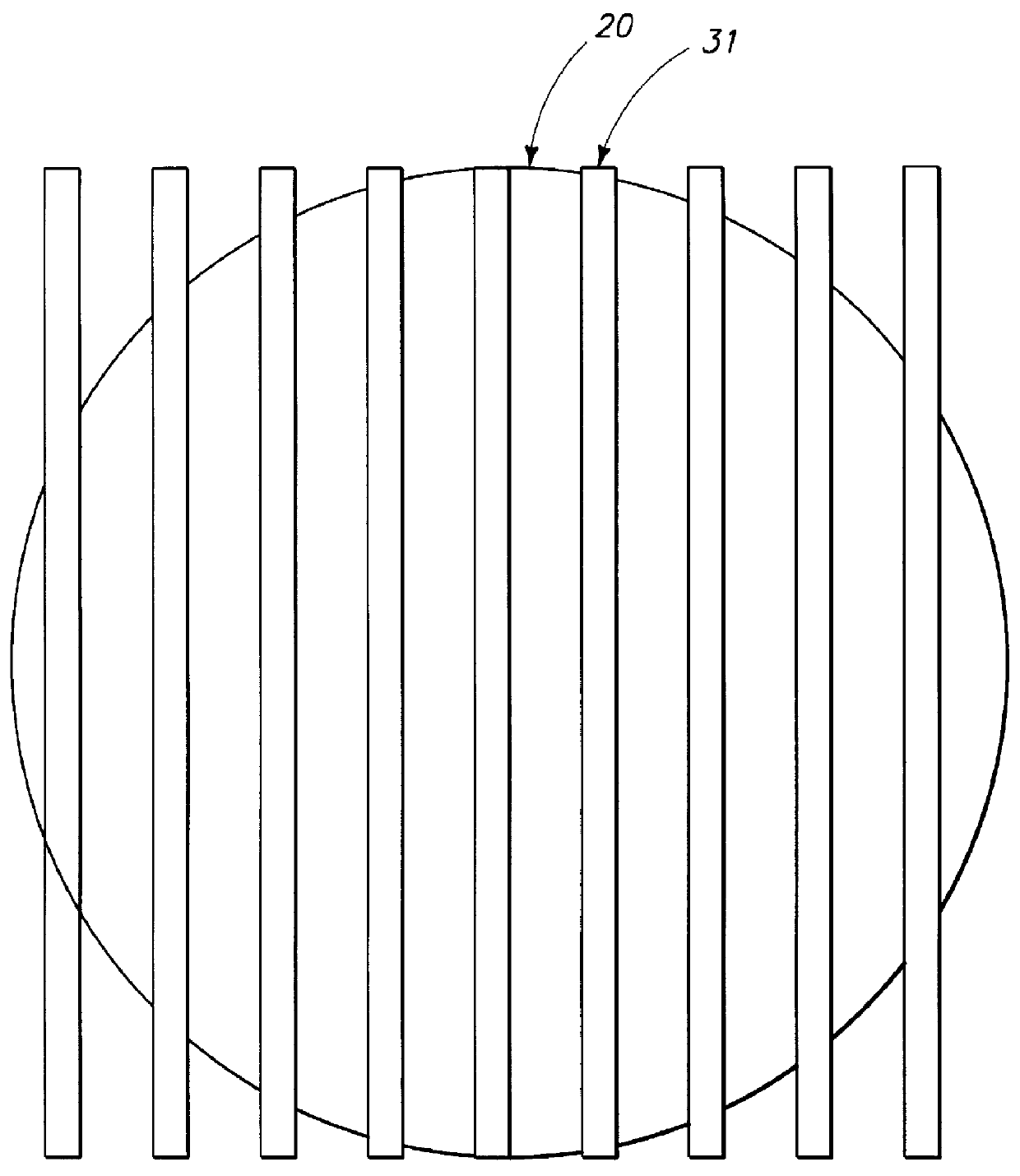
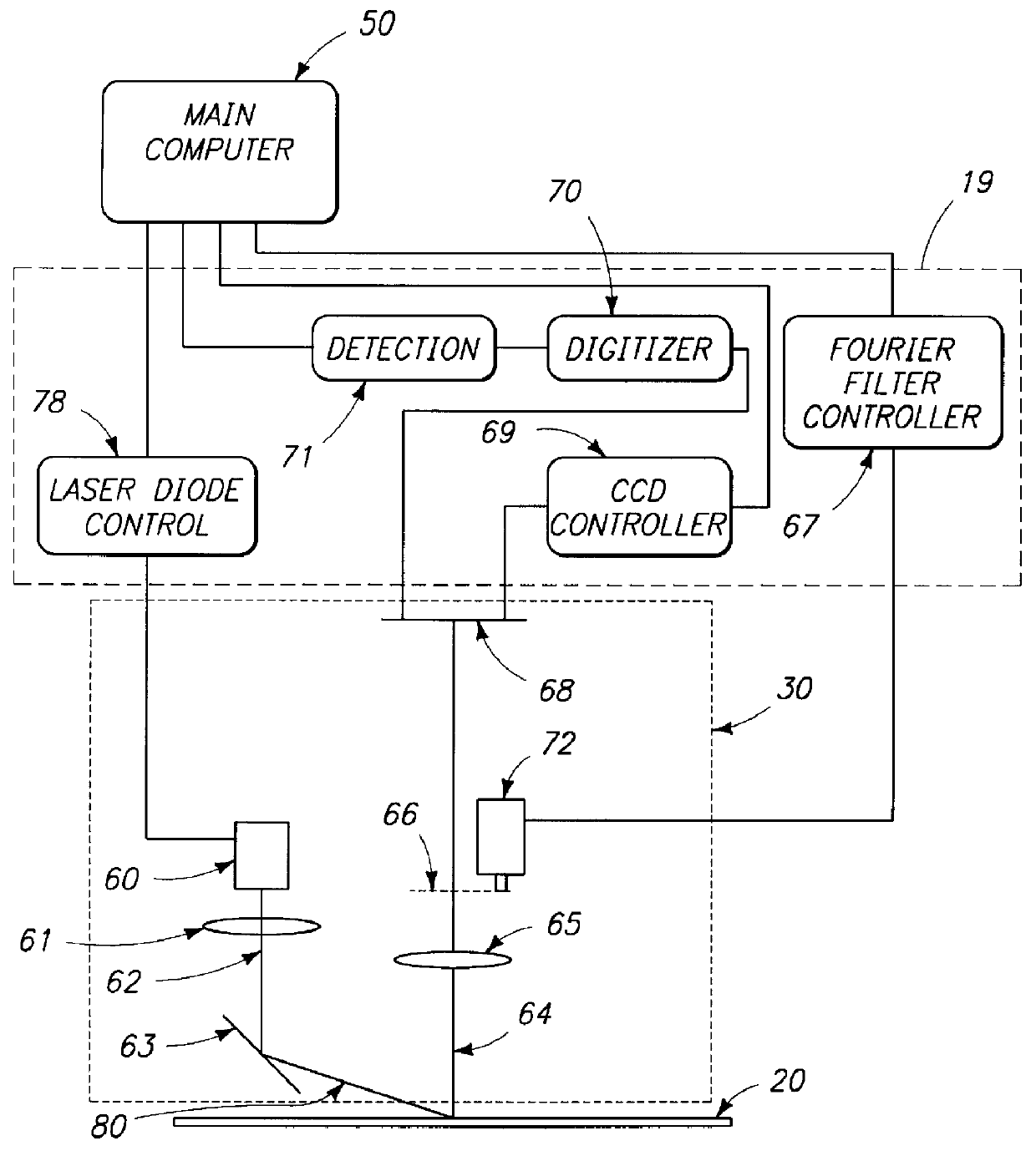
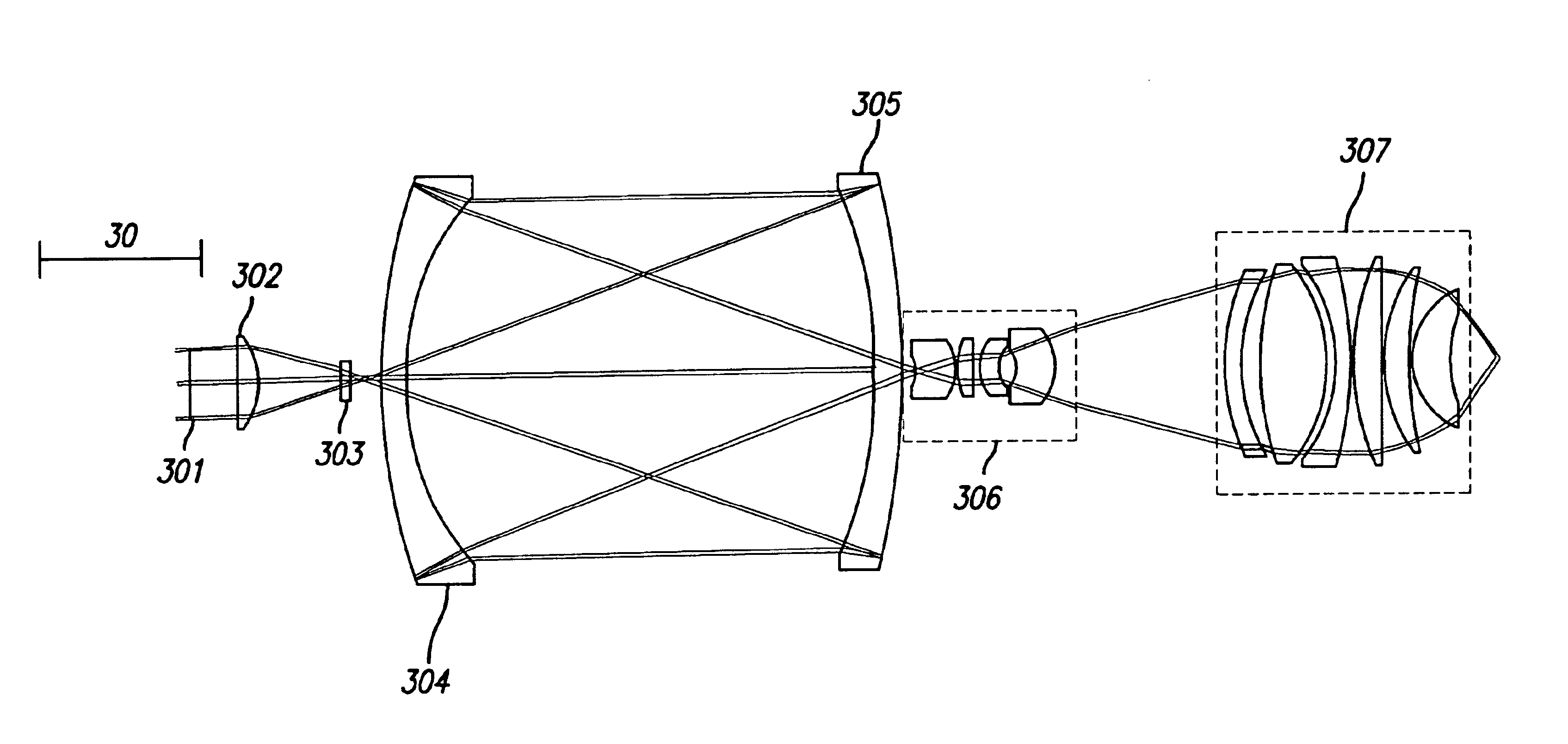
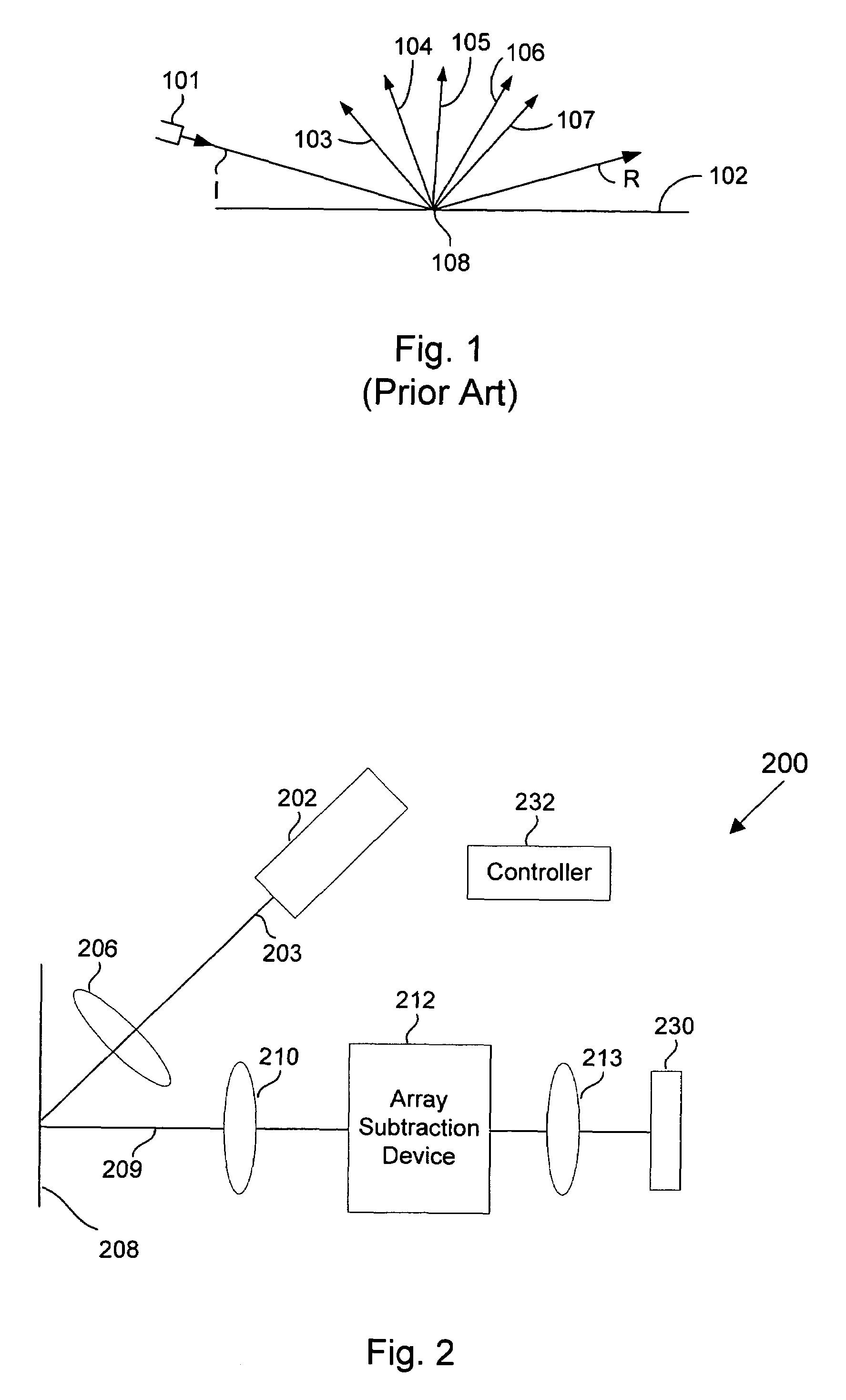
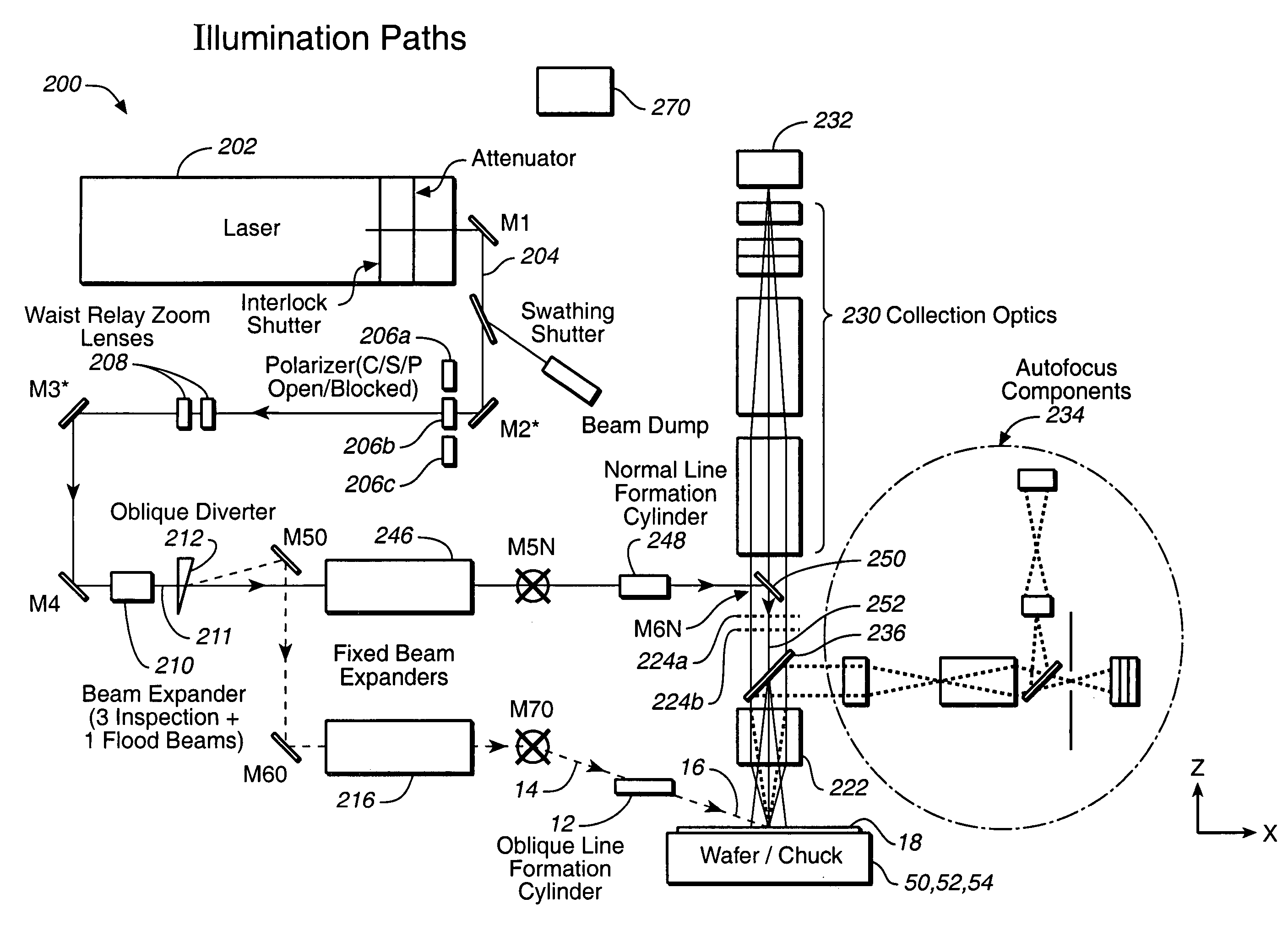
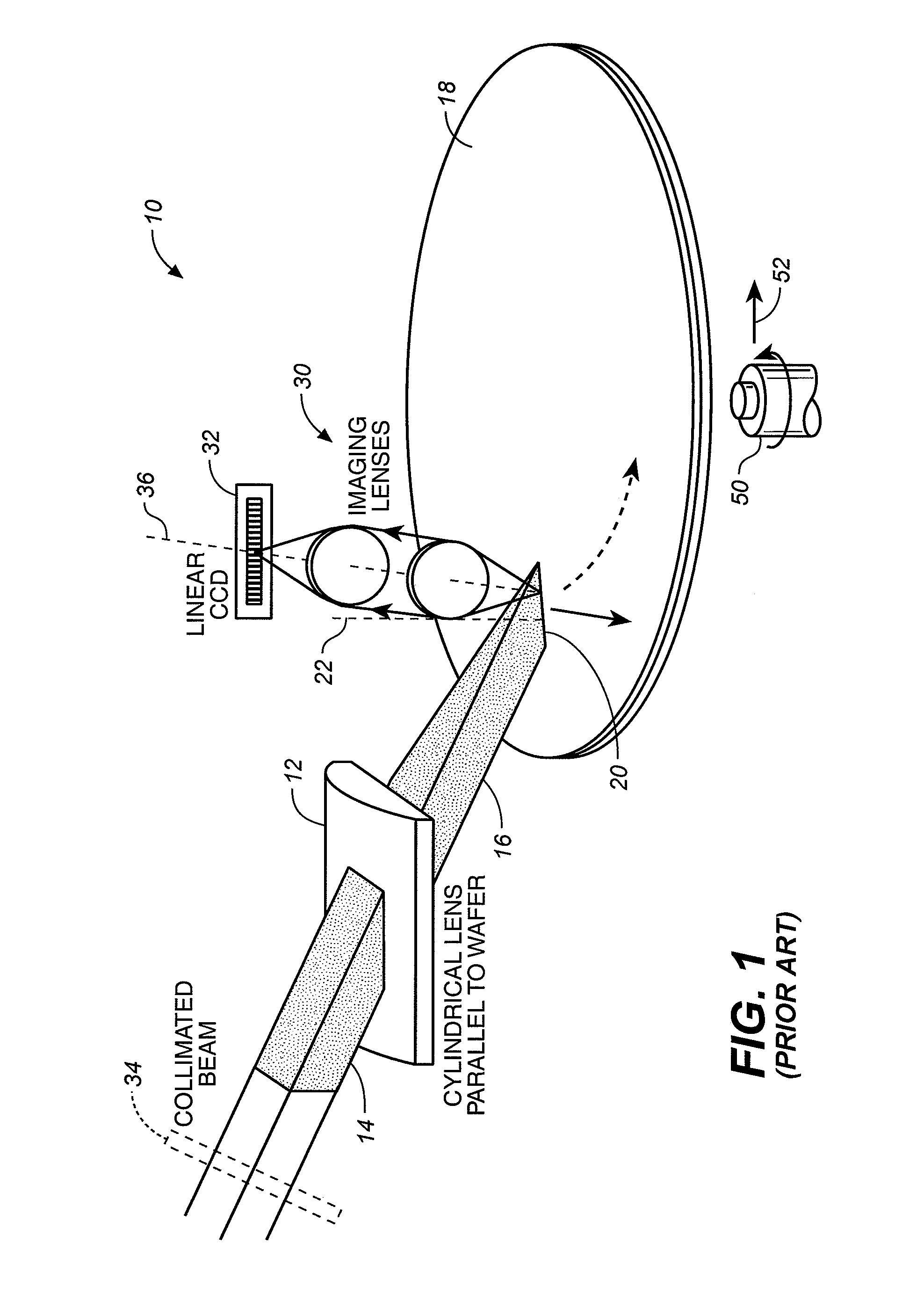
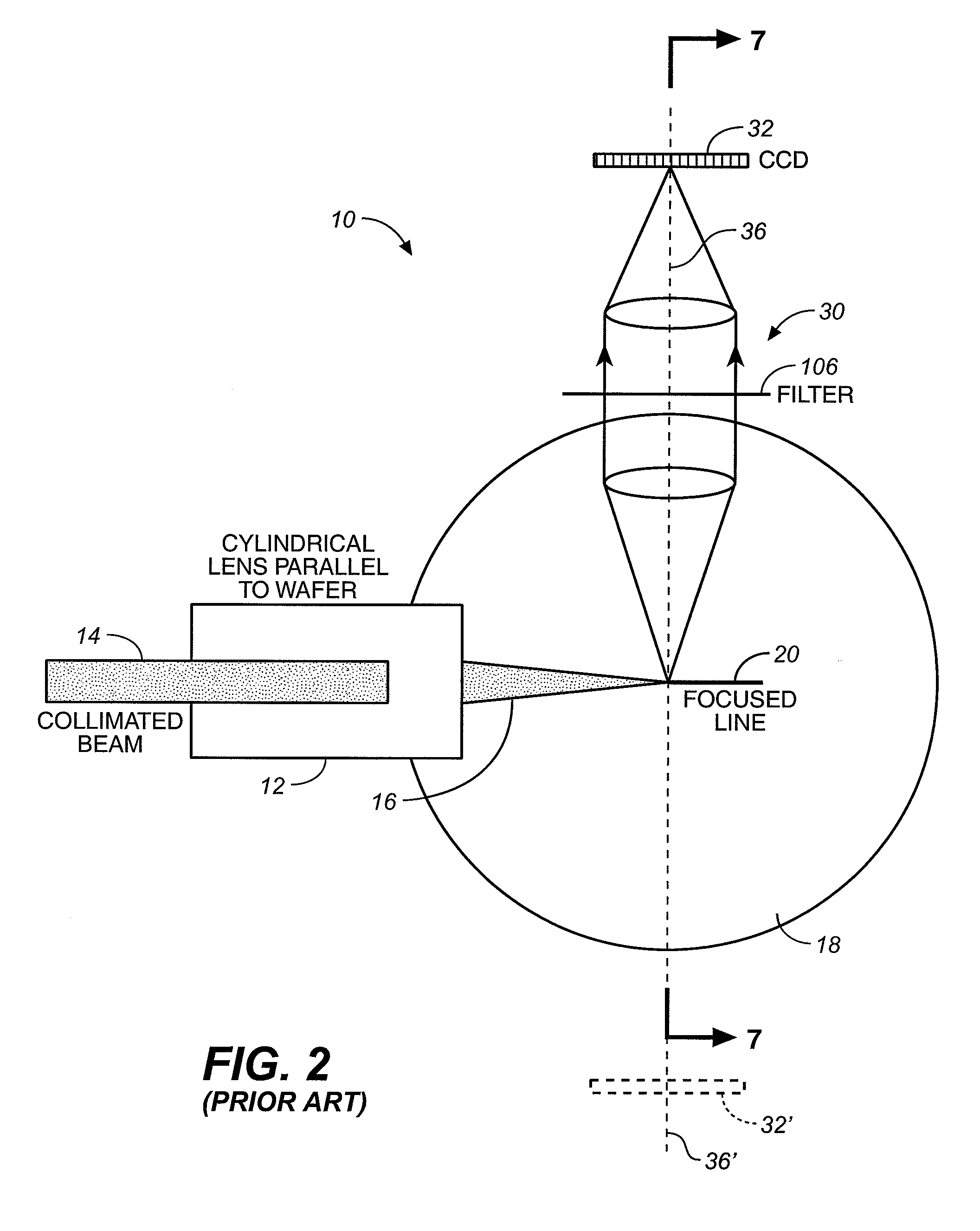
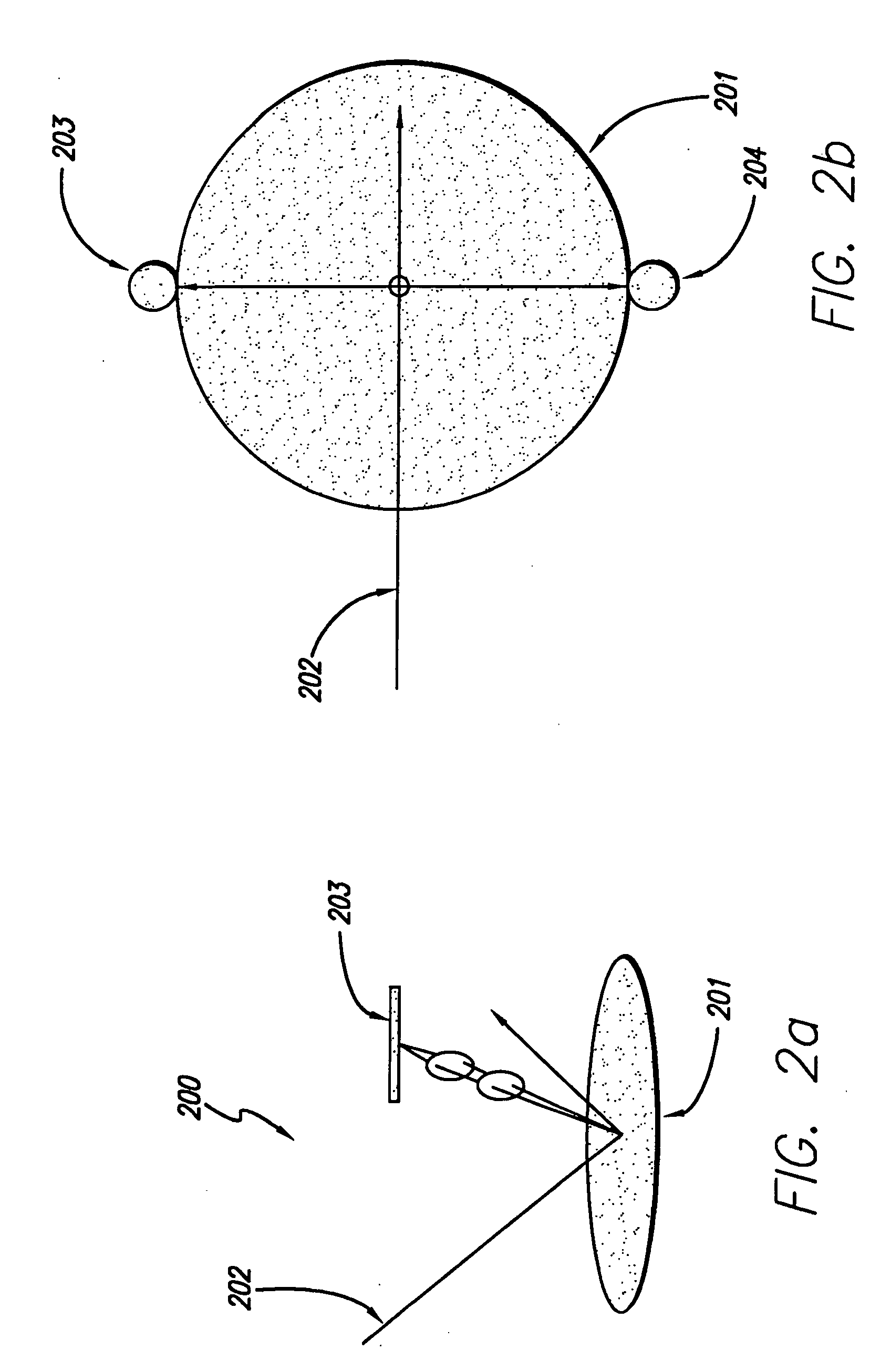
A method for inspecting semiconductor wafers is provided in which a plurality of independent, low-cost, optical-inspection subsystems are packaged and integrated to simultaneously perform parallel inspections of portions of the wafer, the wafer location relative to the inspection being controlled so that the entire wafer is imaged by the system of optical subsystems in a raster-scan mode. A monochromatic coherent-light source illuminates the wafer surface. A darkfield-optical system collects scattered light and filters patterns produced by valid periodic wafer structures using Fourier filtering. The filtered light is processed by general purpose digital-signal processors. Image subtraction methods are used to detect wafer defects, which are reported to a main computer to aid in statistical process control, particularly for manufacturing equipment.
Owner:KLA TENCOR CORP
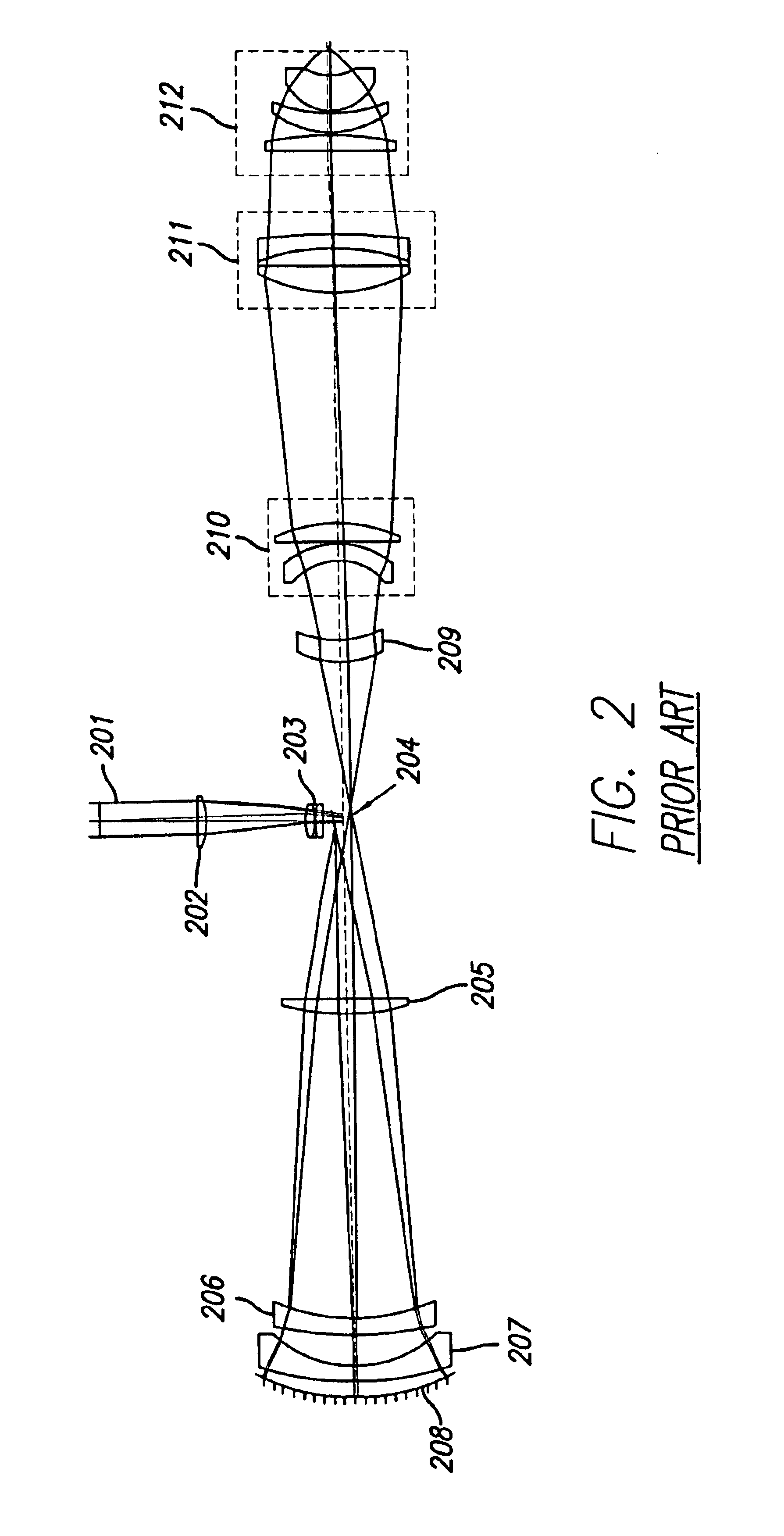
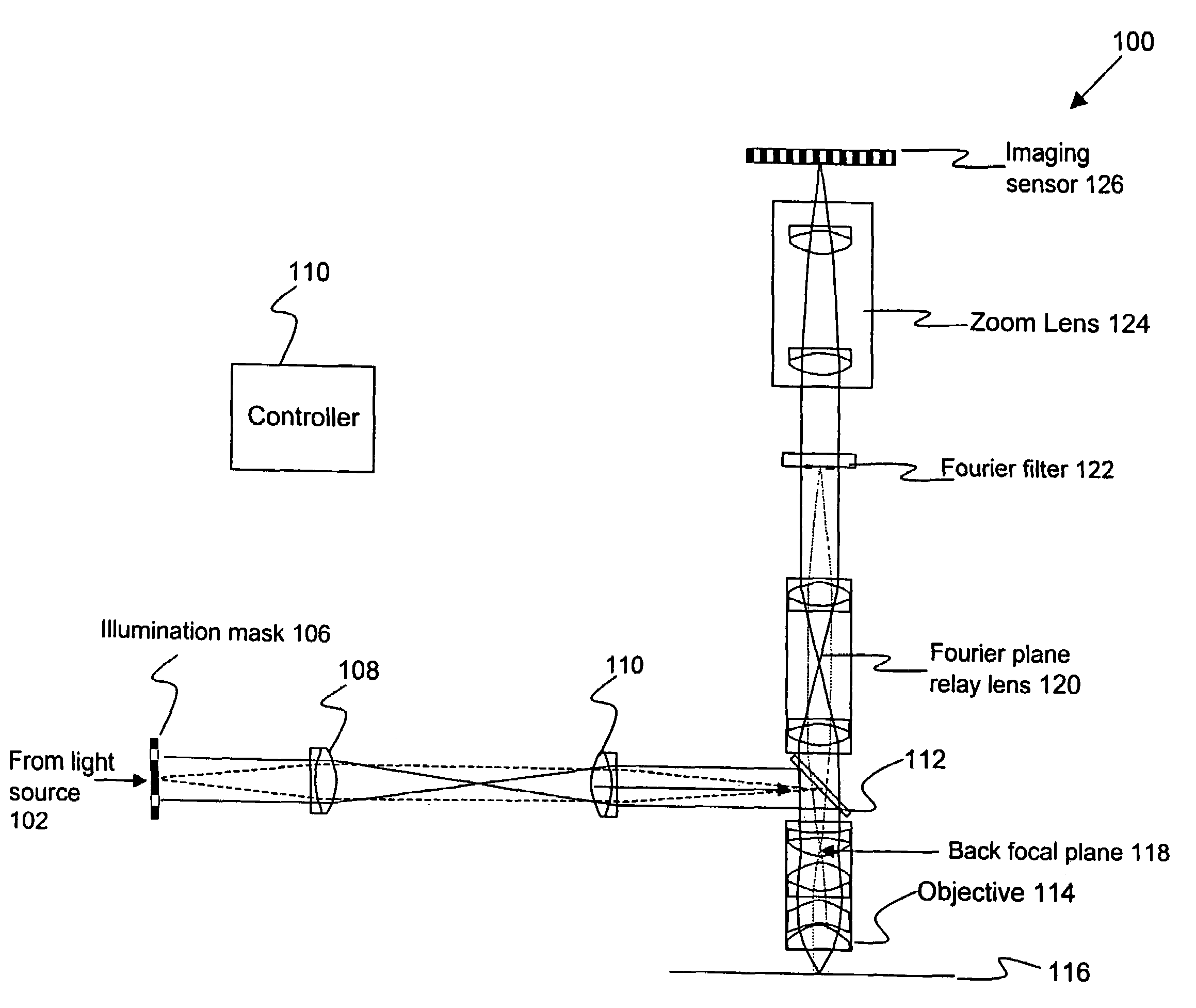
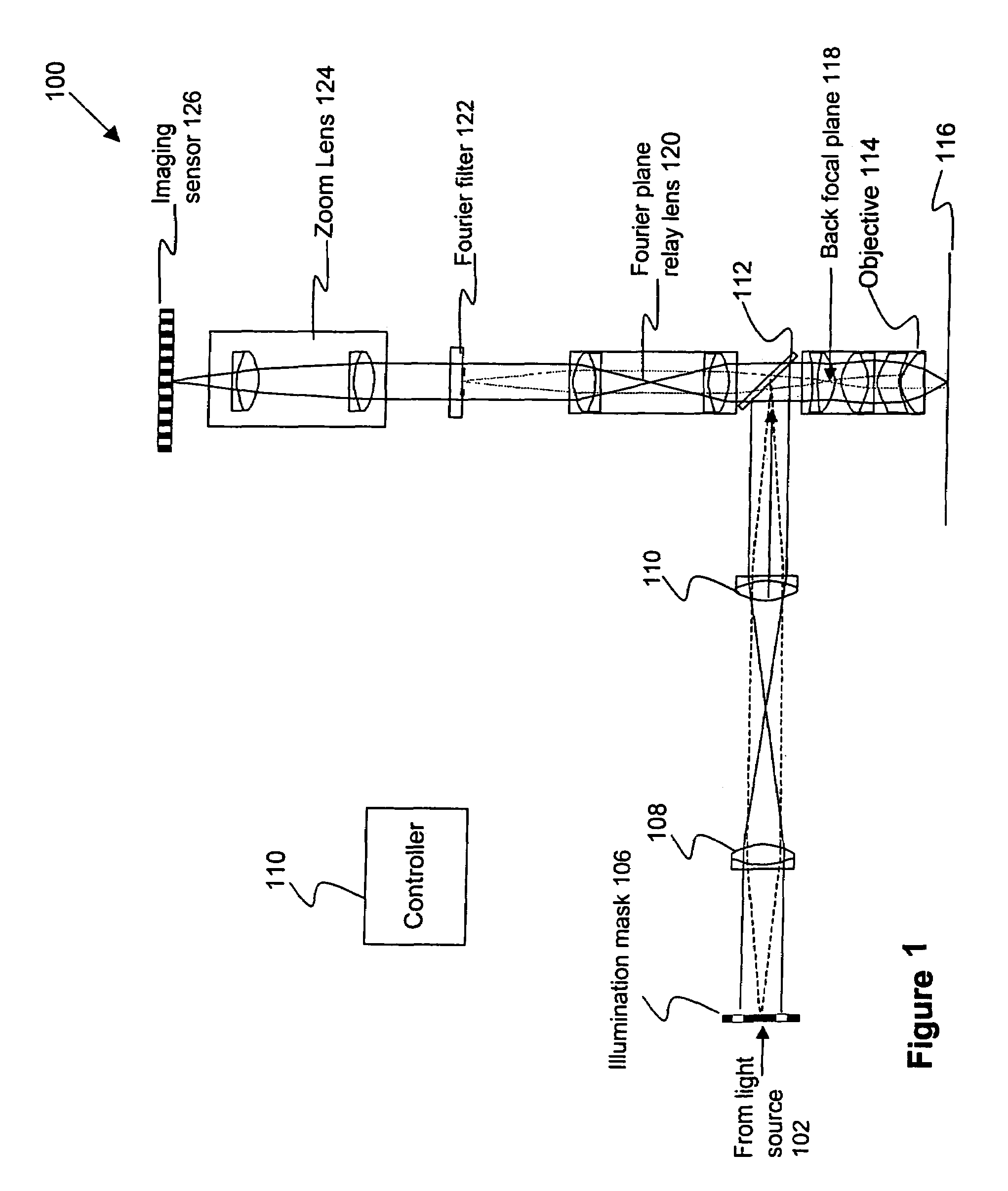
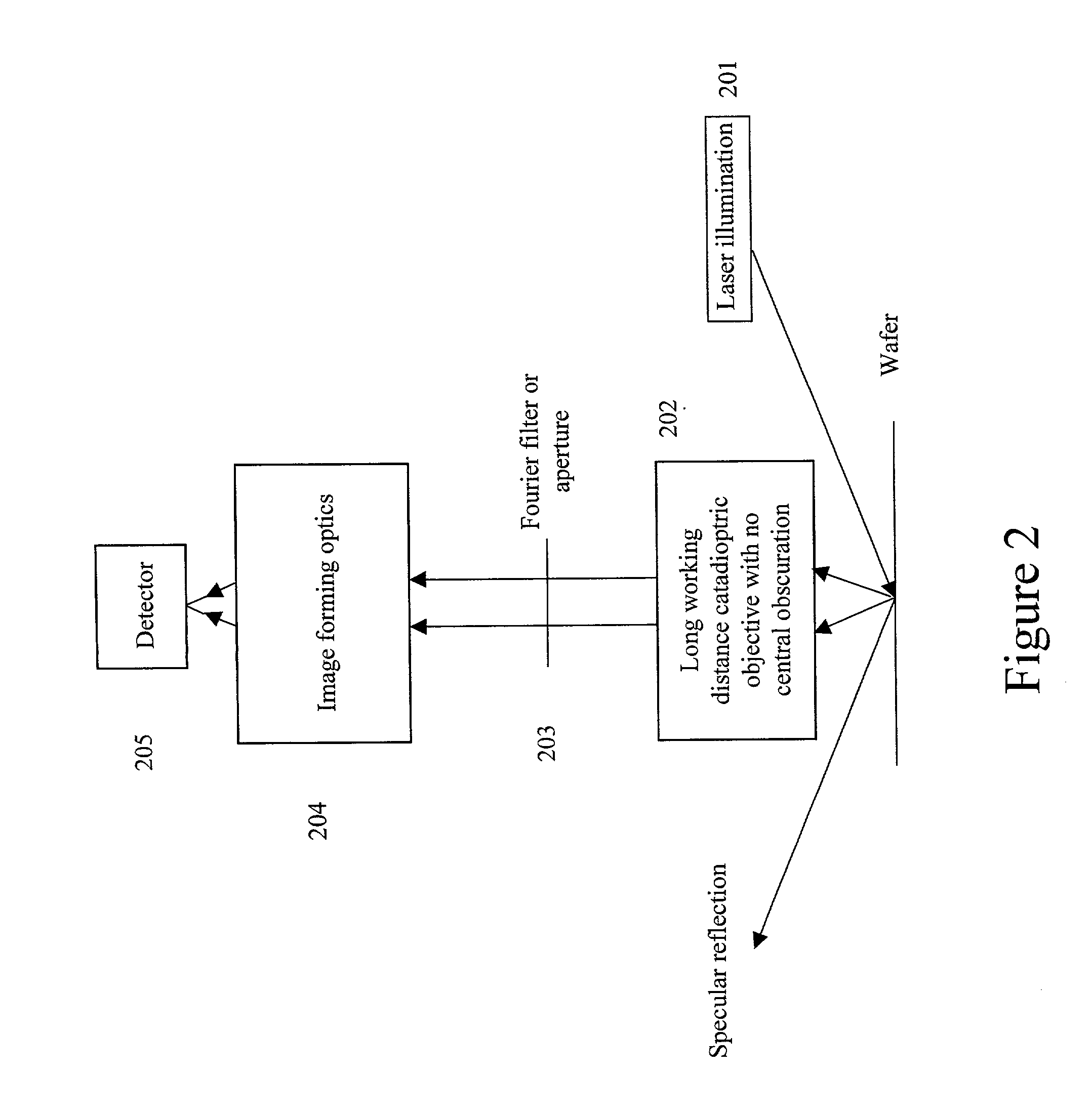
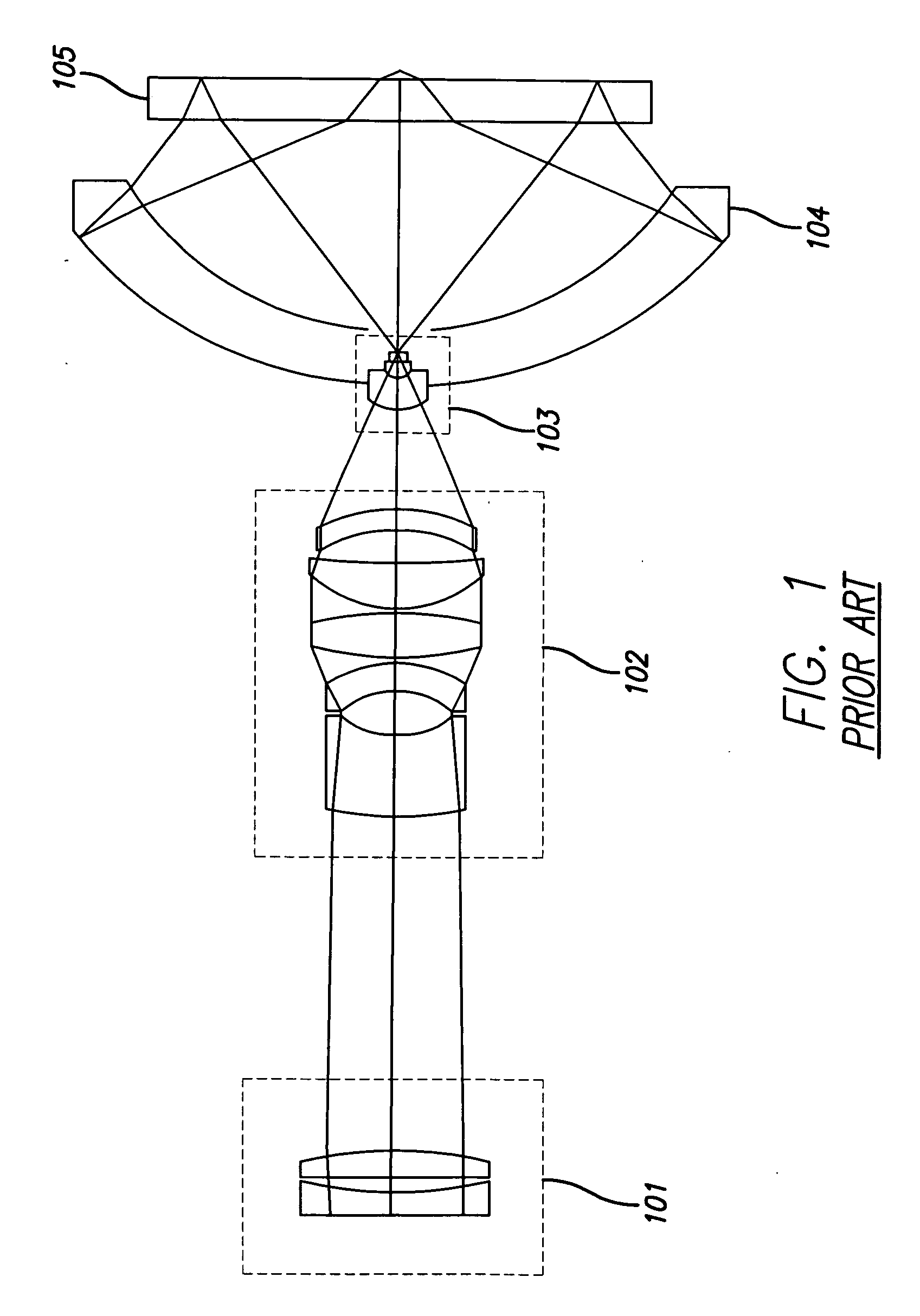
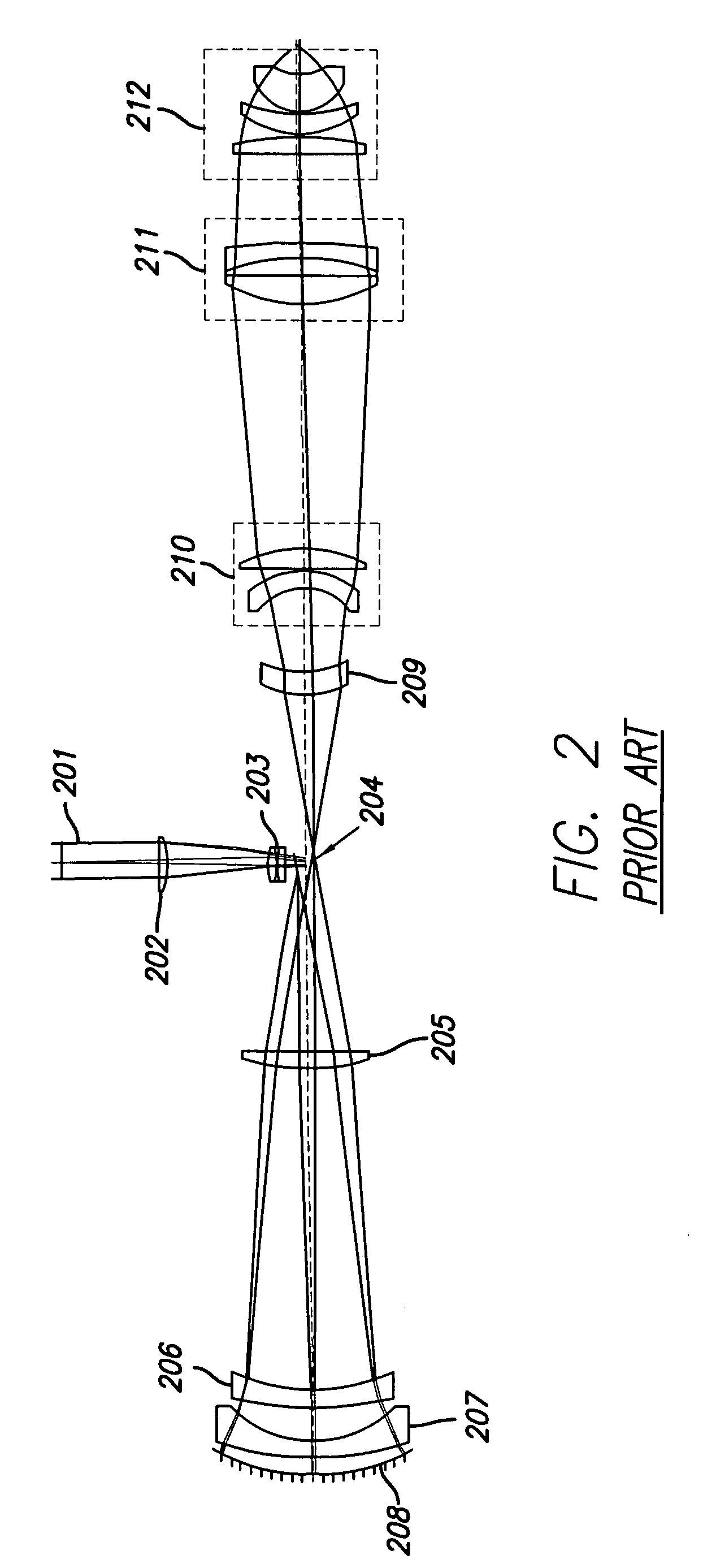
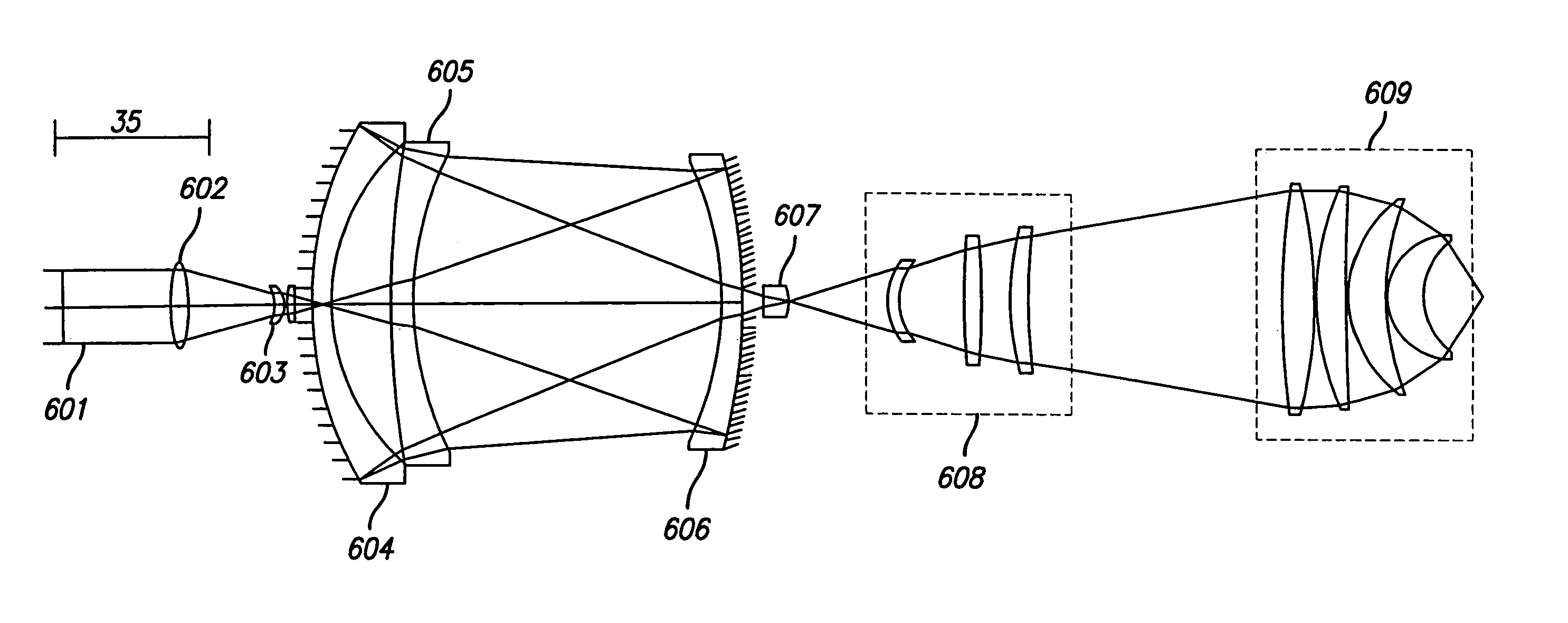
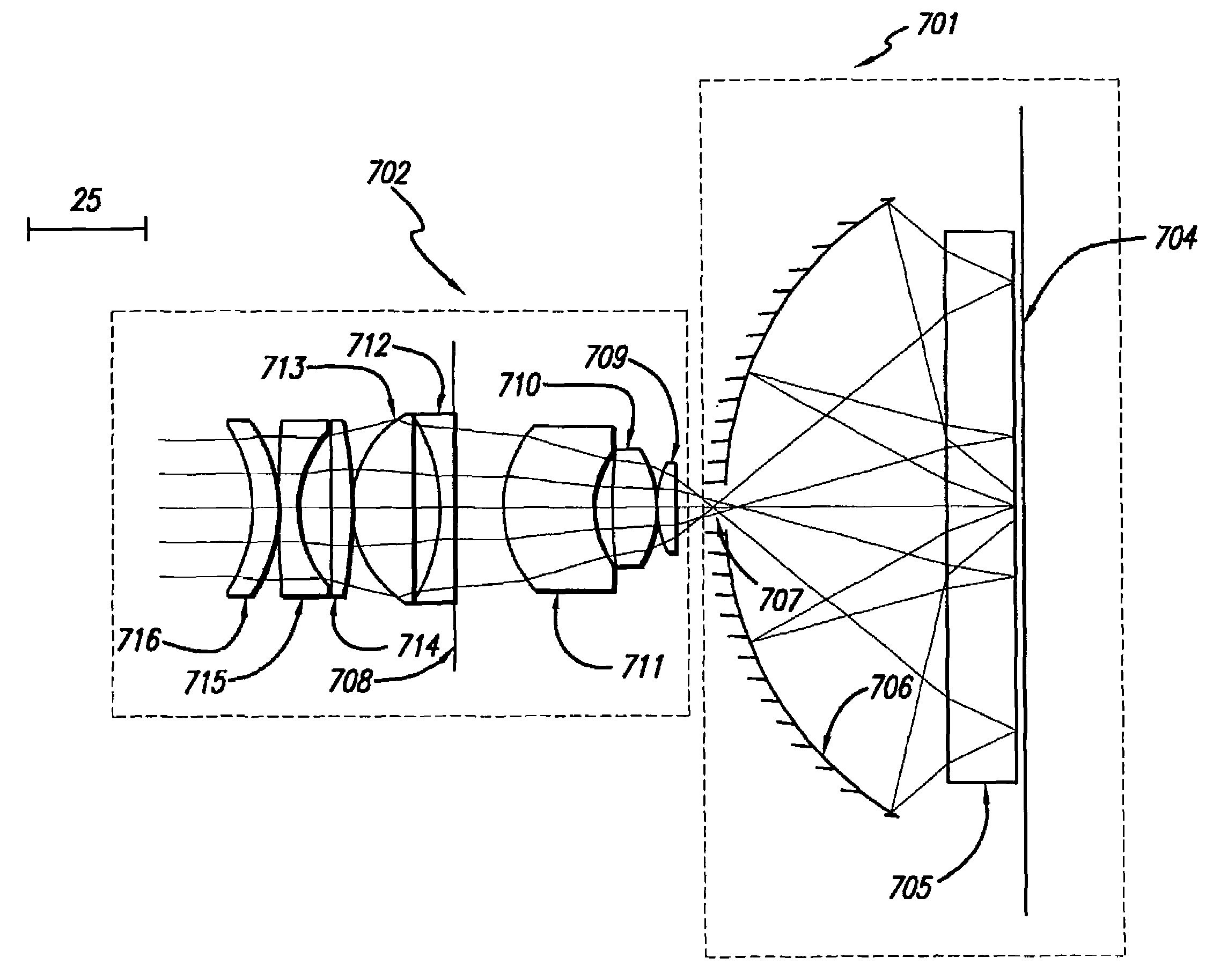
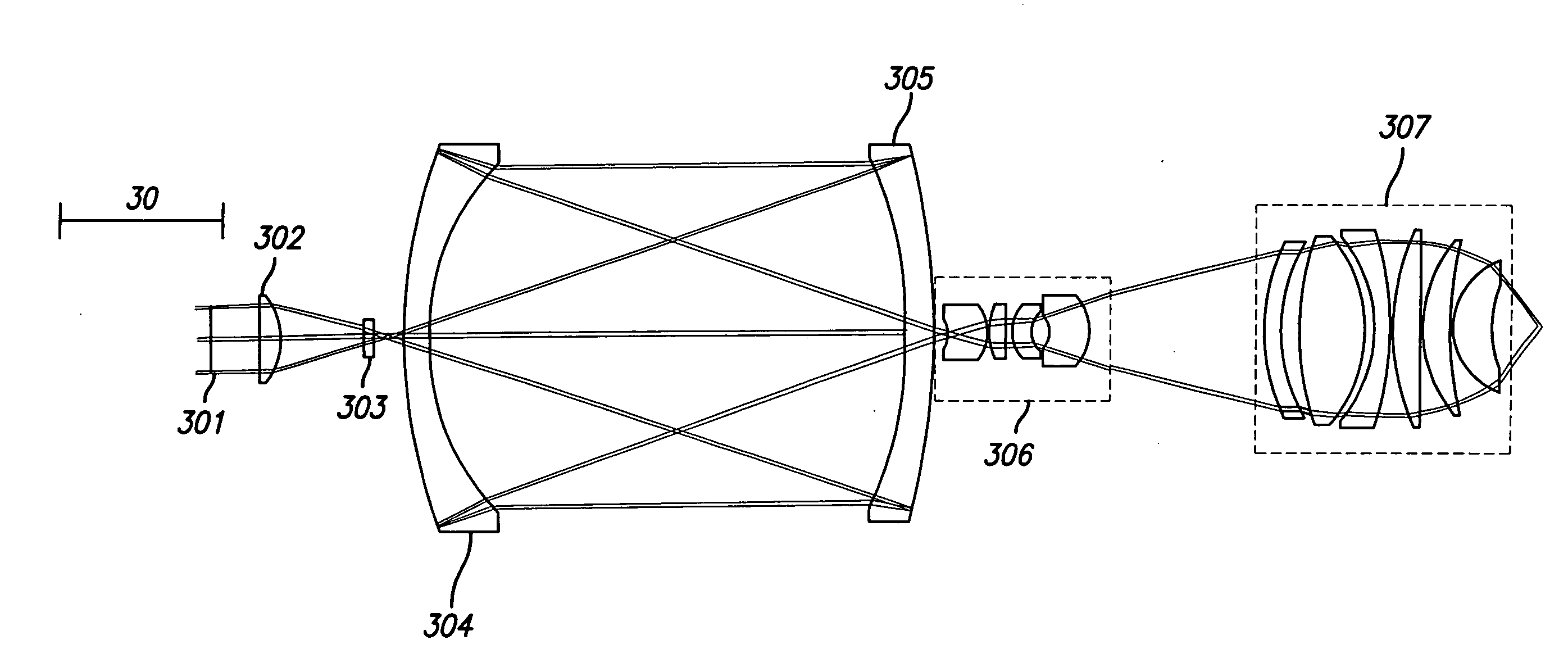
Broad band DUV, VUV long-working distance catadioptric imaging system
InactiveUS6842298B1Long free working distanceMinimize central obscurationMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusPupilLength wave
A high performance objective having very small central obscuration, an external pupil for apertureing and Fourier filtering, loose manufacturing tolerances, large numerical aperture, long working distance, and a large field of view is presented. The objective is preferably telecentric. The design is ideally suited for both broad-band bright-field and laser dark field imaging and inspection at wavelengths in the UV to VUV spectral range.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
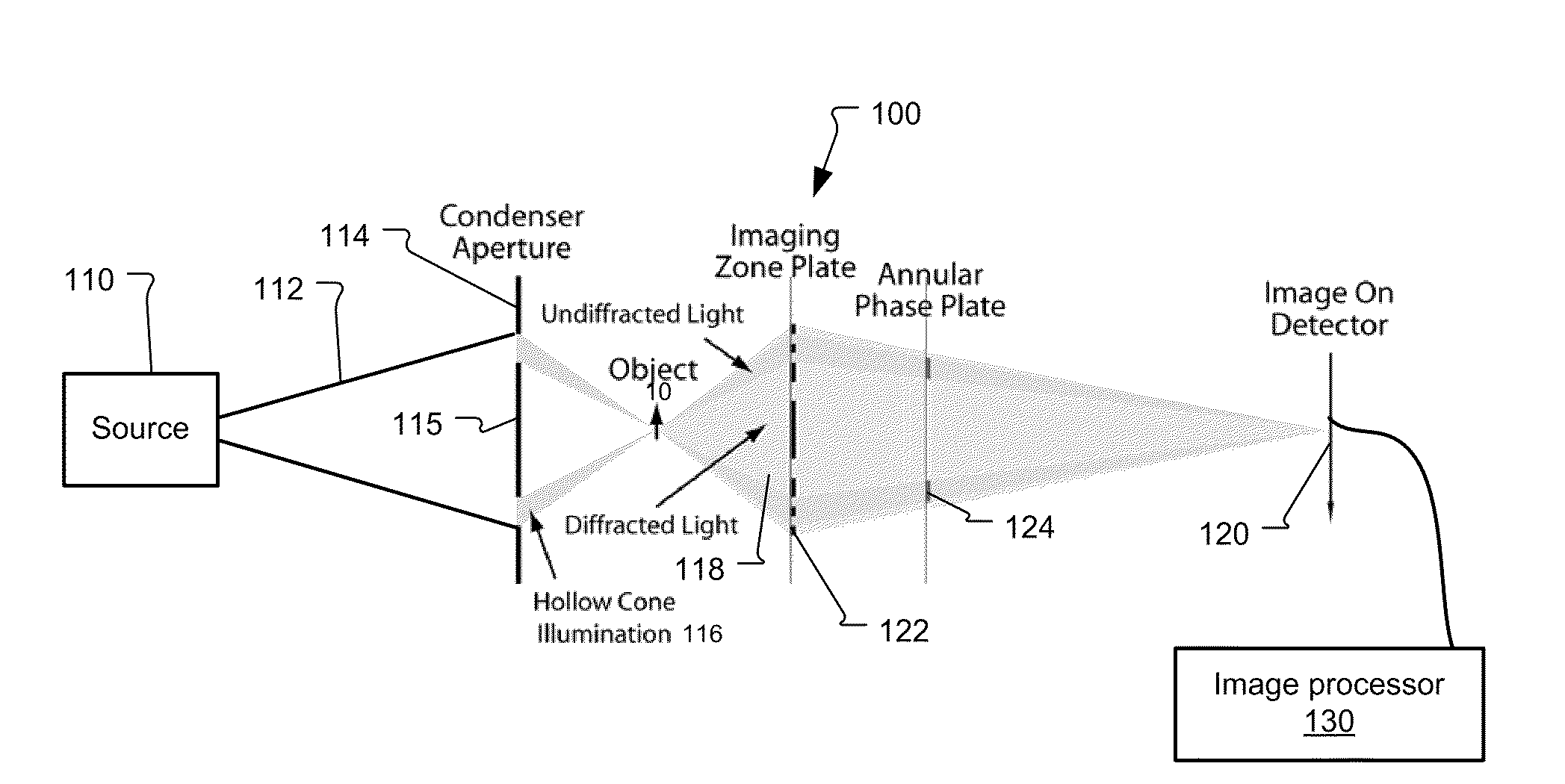
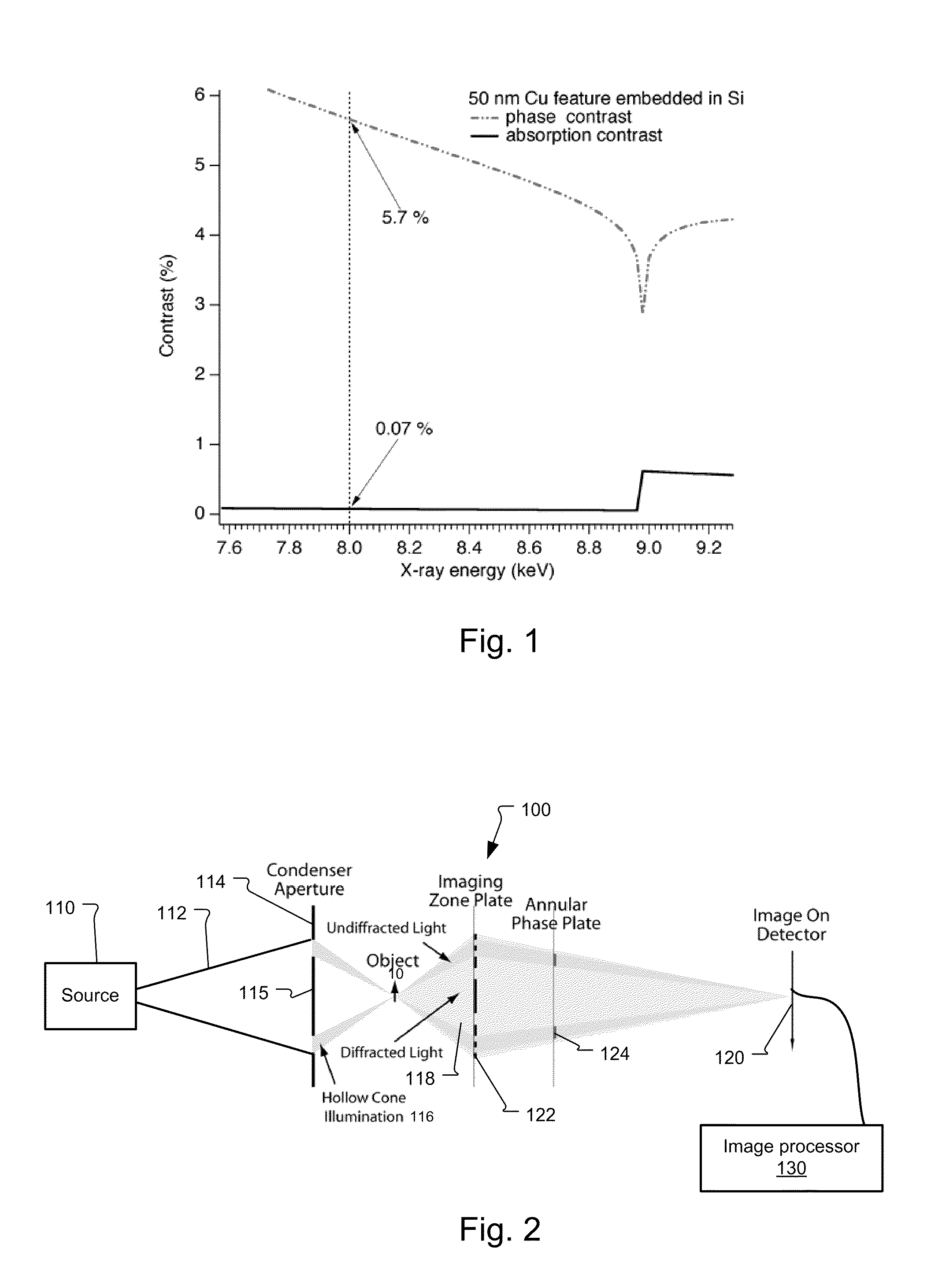
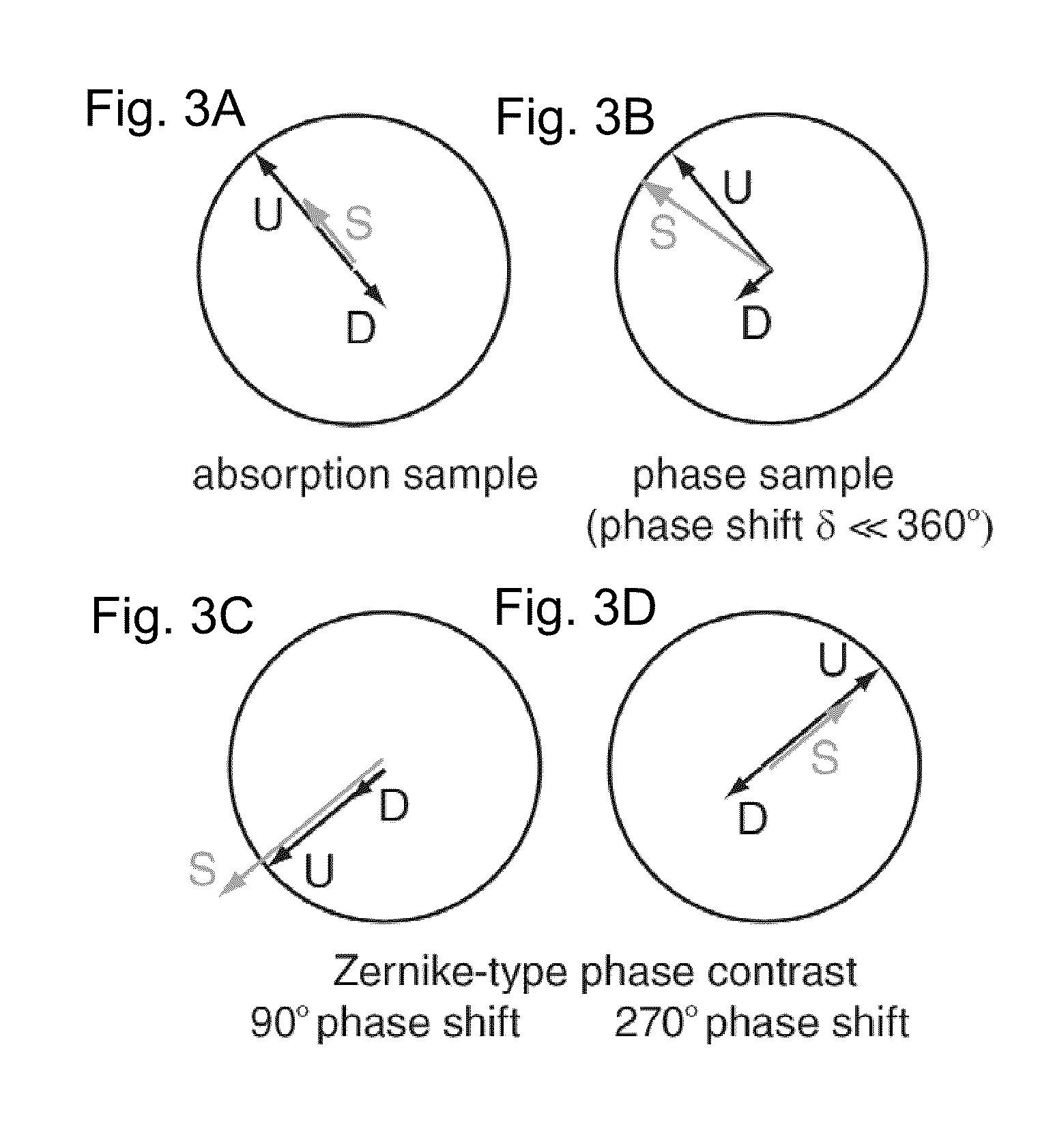
System and method for quantitative reconstruction of Zernike phase-contrast images
ActiveUS7787588B1Reduce artifactsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationGamma-ray/x-ray microscopesContrast transfer functionFull field
The principle of reciprocity states that full-field and scanning microscopes can produce equivalent images by interchanging the roles of condenser and detector. Thus, the contrast transfer function inversion previously used for images from scanning systems can be applied to Zernike phase contrast images. In more detail, a full-field x-ray imaging system for quantitatively reconstructing the phase shift through a specimen comprises a source that generates x-ray radiation, a condenser x-ray lens for projecting the x-ray radiation onto the specimen, an objective x-ray lens for imaging the x-ray radiation transmitted through the specimen, a phase-shifting device to shift the phase of portions of x-ray radiation by a determined amount, and an x-ray detector that detects the x-ray radiation transmitted through the specimen to generate a detected image. An image processor then determines a Fourier filtering function and reconstructs the quantitative phase shift through the specimen by application of the Fourier filtering function to the detected image. As a result, artifacts due to absorption contrast can be removed from the detecting image. This corrected image can then be used in generating three dimensional (3D) images using computed tomography.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
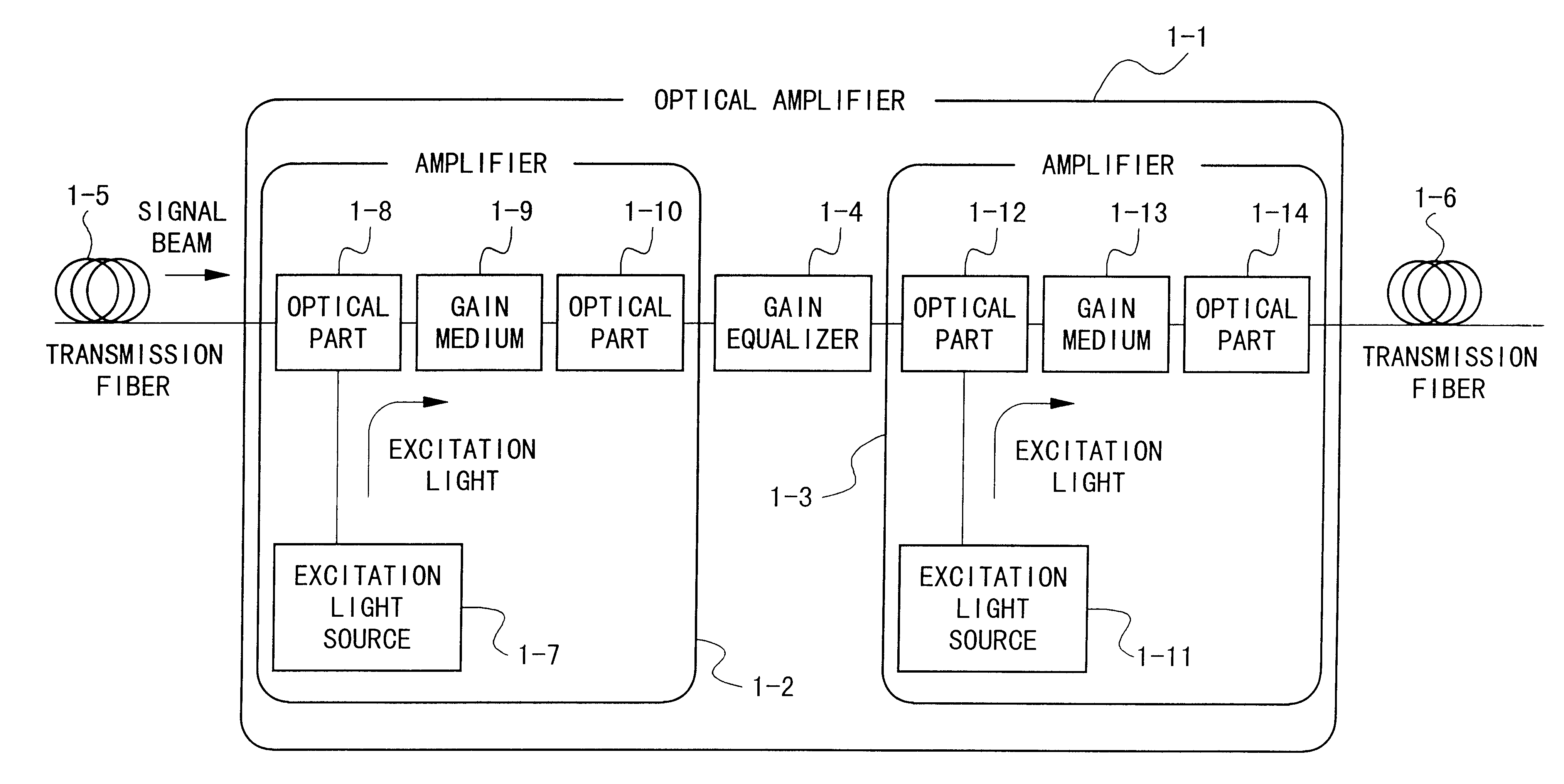
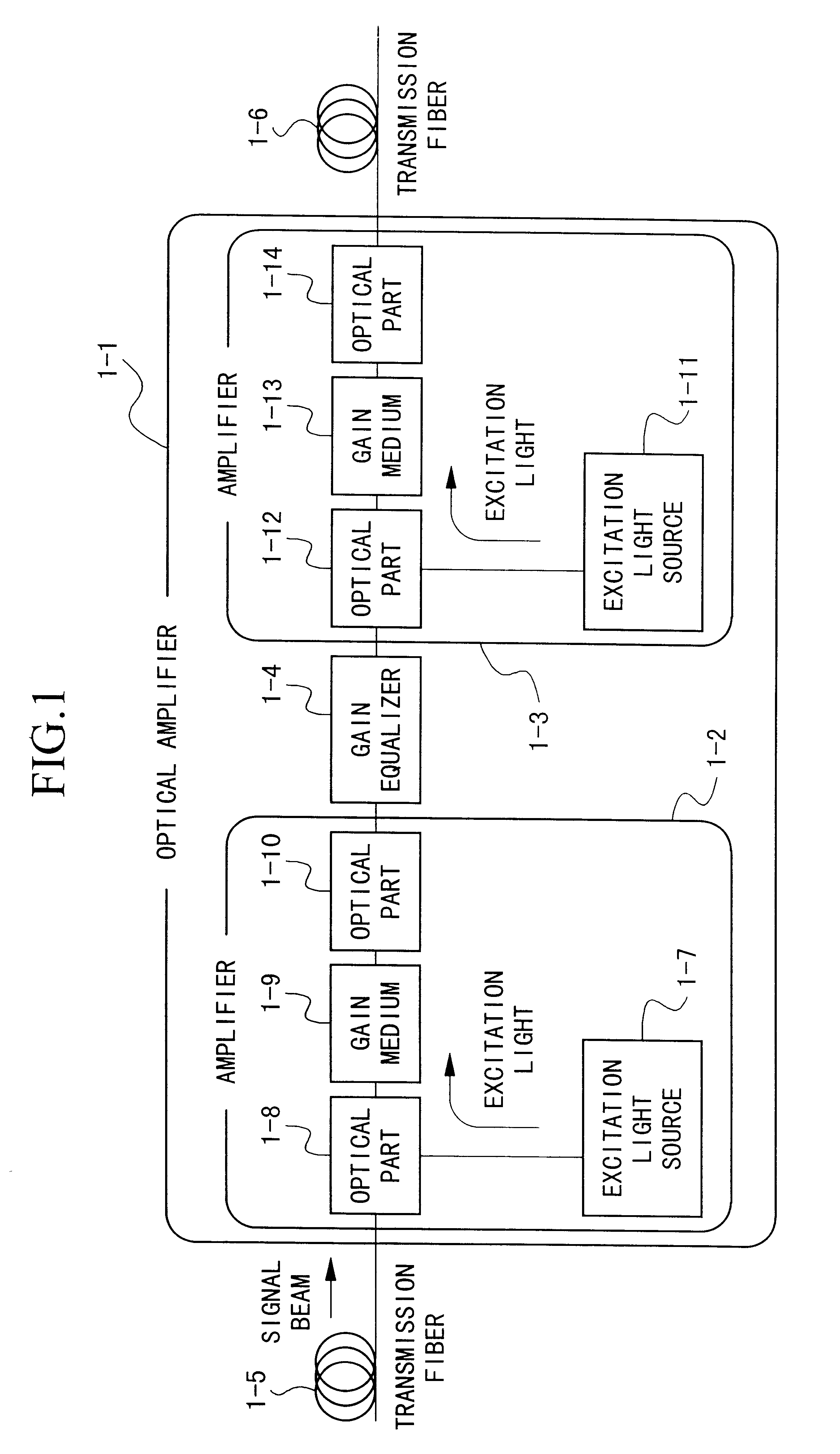
Optical amplifier and transmission system using the same
InactiveUS6172803B1Laser using scattering effectsOptical transmission with multiple stagesFiberErbium doping
An optical amplifier having a two-stage construction using an erbium doped fiber (EDF) as a gain medium. The erbium dopant concentration is 1000 ppm, and the unsaturated absorption coefficient of the signal beam at 1550 nm is 1 dB / m. The length of the EDF 14-8 is 10 m, and the length of the EDF 14-12 is 70 m. The excitation light sources 14-6 and 14-10 are semiconductor lasers of 1.53 mum, and the excitation light power is 100 mW. Multiplexers 14-7 and 14-11 are inductive multi-layer film filters, and the gain equalizer 14-4 is a Fourier filter. The peak loss of the Fourier filter is 17 dB. The gain of the EDF 14-8 is 25 dB, and the gain of the EDF 14-12 is 15 dB. Two optical isolators are installed on a pre-stage amplifier, and one on a post-stage amplifier in order to prevent laser oscillation.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
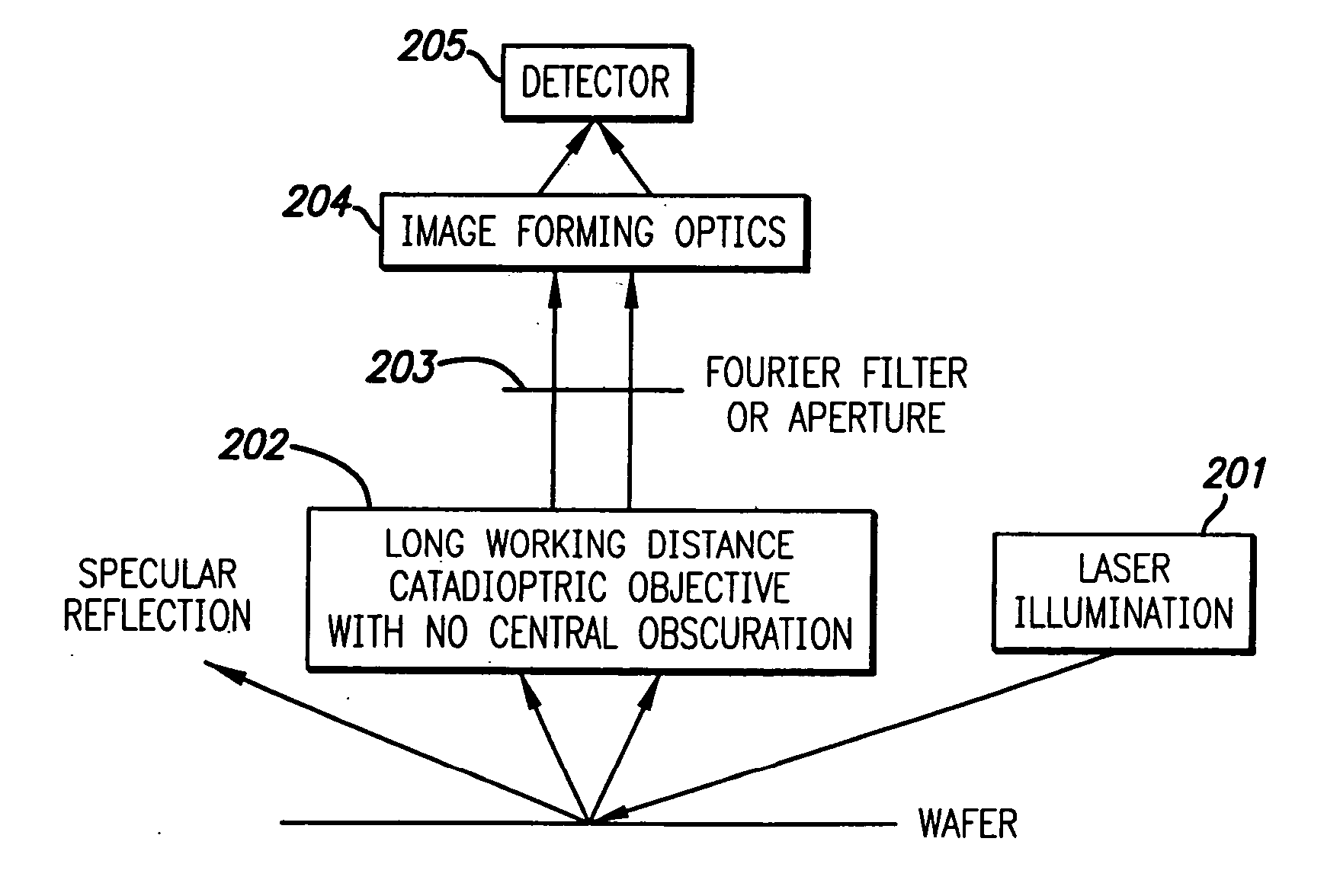
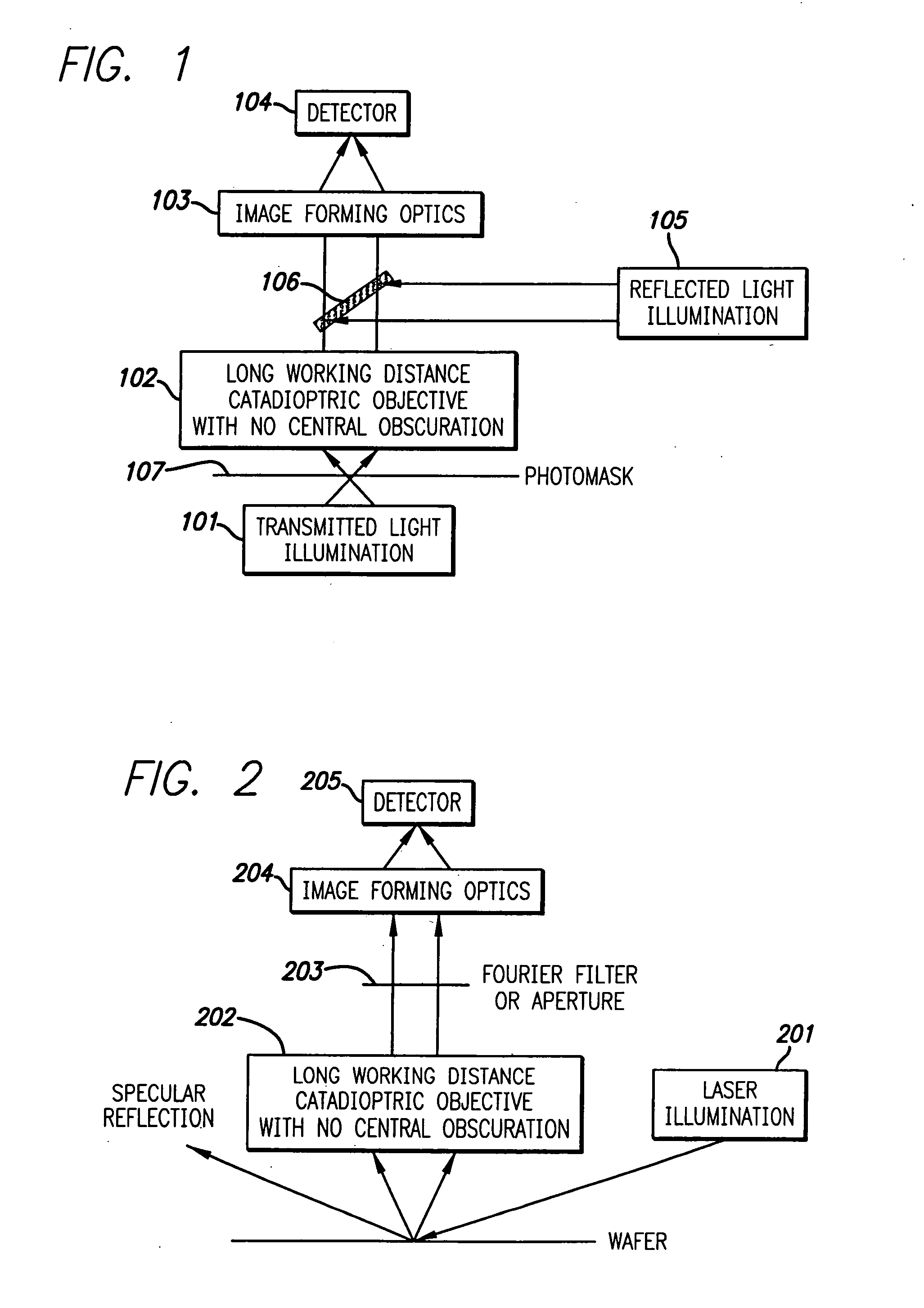
Methods and apparatus for inspecting a sample
ActiveUS7295303B1Increase contrastEliminate the effects ofMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesCombined useLight beam
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for inspecting or imaging a sample, such as a semiconductor wafer or reticle. In general, an optical inspection or microscopy tool that has a complex Fourier filter positioned in the Fourier plane of the radiation beam output from the sample in response to an incident beam striking the sample is provided. Use of such Fourier filter is also disclosed. In one implementation, the complex Fourier is designed to alter a phase, and possibly amplitude, of the scattered spatial portions of the output beam relative to the specular spatial portions of the output beam so as to enhance the contrast between the two. In another implementation, the complex Fourier serves to filter the effects of repeating structures on the sample from the output beam. The complex Fourier filter is used in conjunction with a complementary illumination aperture.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
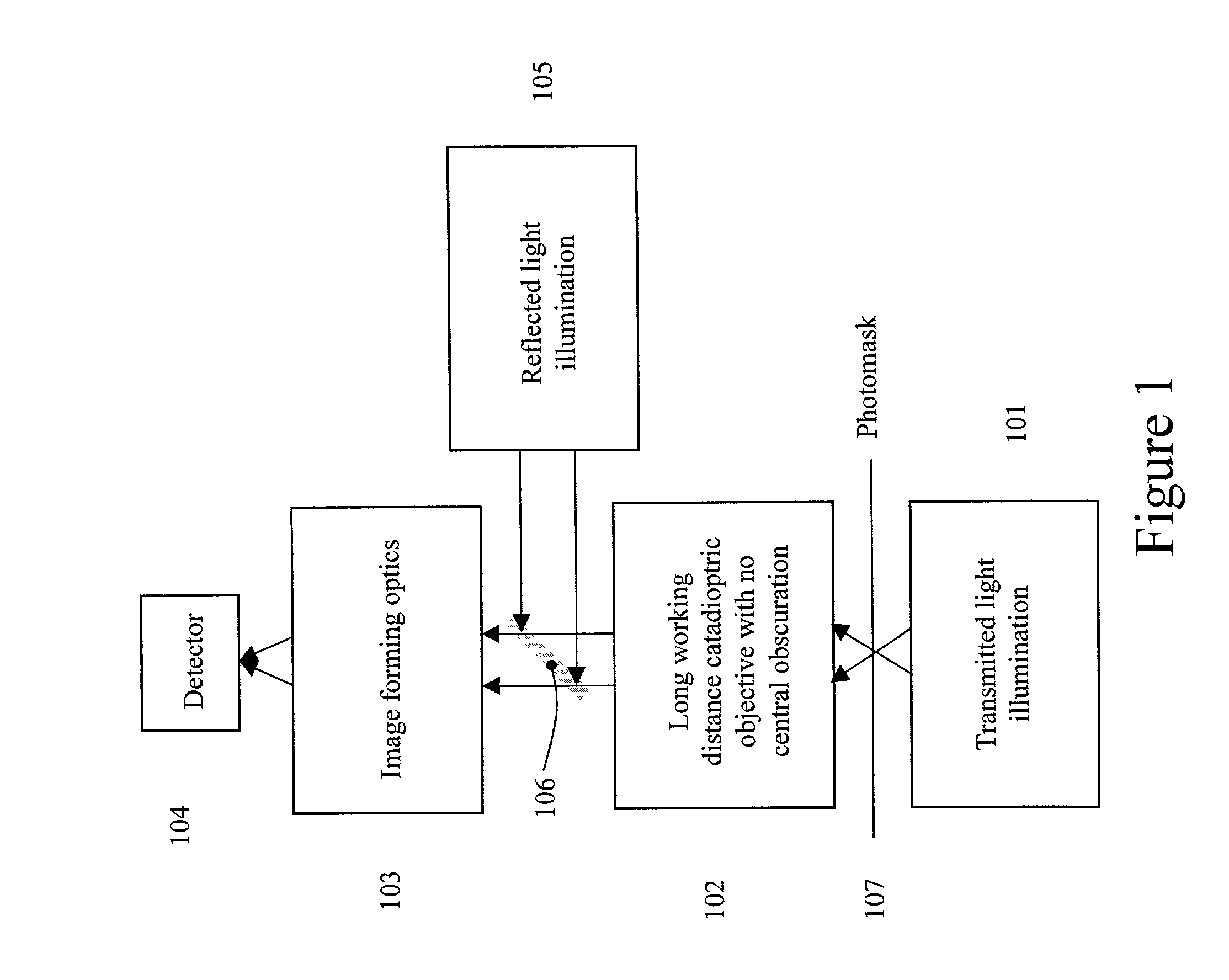
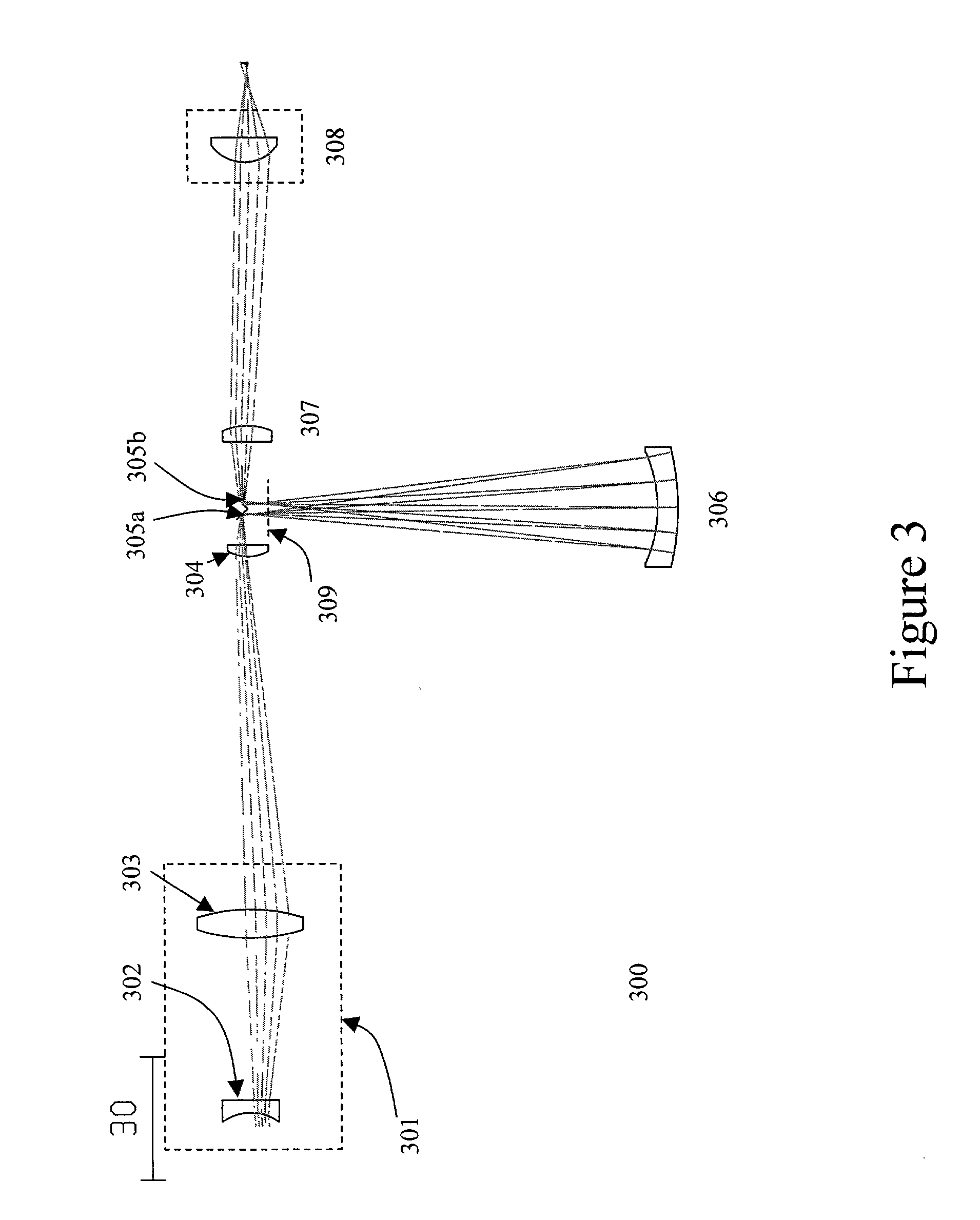
Broad band deep ultraviolet/vacuum ultraviolet catadioptric imaging system
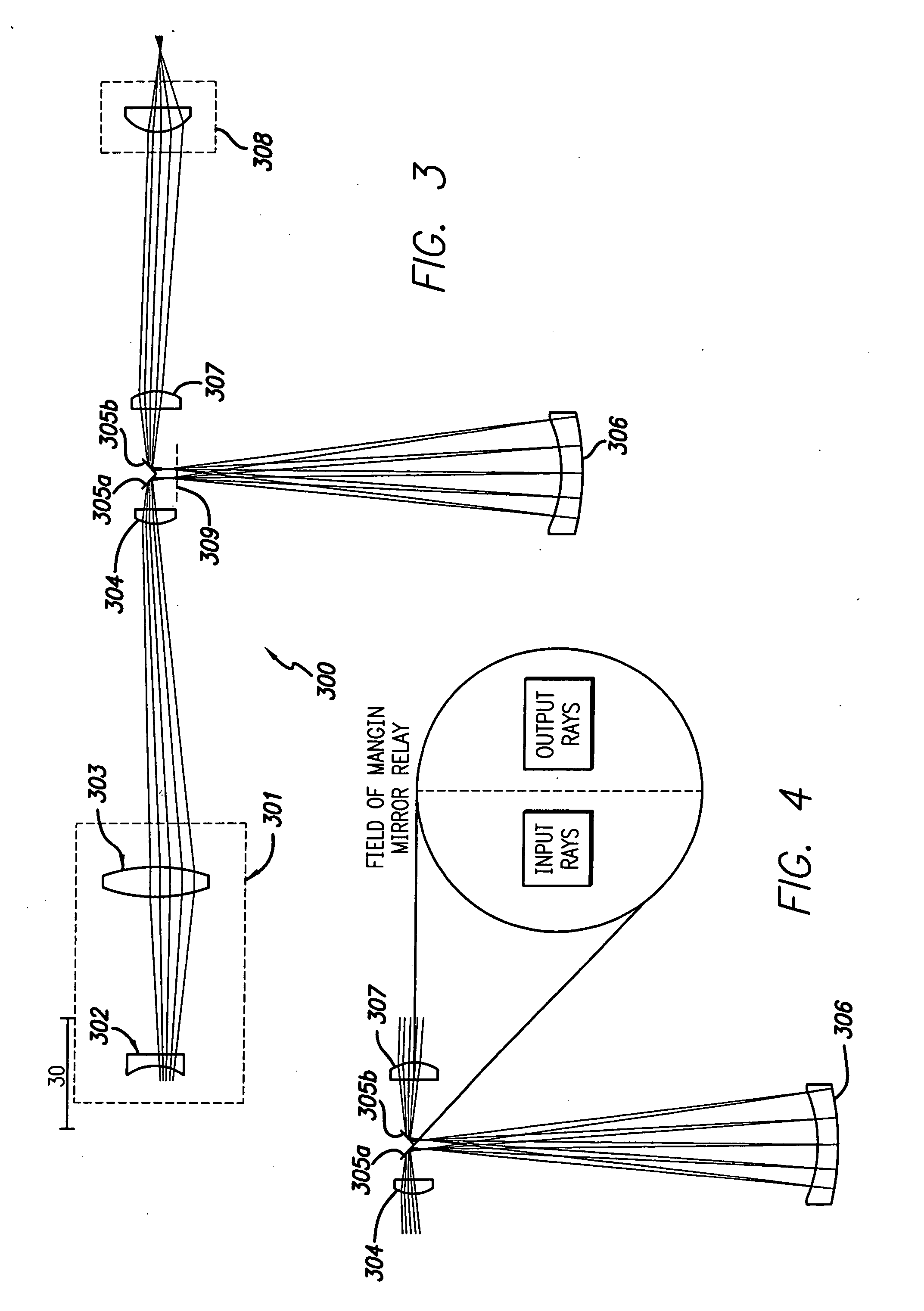
InactiveUS20010040722A1Increase spectral bandwidthRelaxed manufacturing toleranceMirrorsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMangin mirrorUltraviolet
A design for inspecting specimens, such as photomasks, for unwanted particles and features such as pattern defects is provided. The system provides no central obscuration, an external pupil for aperturing and Fourier filtering, and relatively relaxed manufacturing tolerances, and is suited for both broad-band bright-field and laser dark field imaging and inspection at wavelengths below 365 nm. In many instances, the lenses used may be fashioned or fabricated using a single material. Multiple embodiments of the objective lensing arrangement are disclosed, all including at least one small fold mirror and a Mangin mirror. The system is implemented off axis such that the returning second image is displaced laterally from the first image so that the lateral separation permits optical receipt and manipulation of each image separately. The objective designs presented have the optical axis of the Mangin mirror image relay at ninety degrees to the optical axis defined by the focusing lenses, or an in-line or straight objective having one ninety degree bend of light rays.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
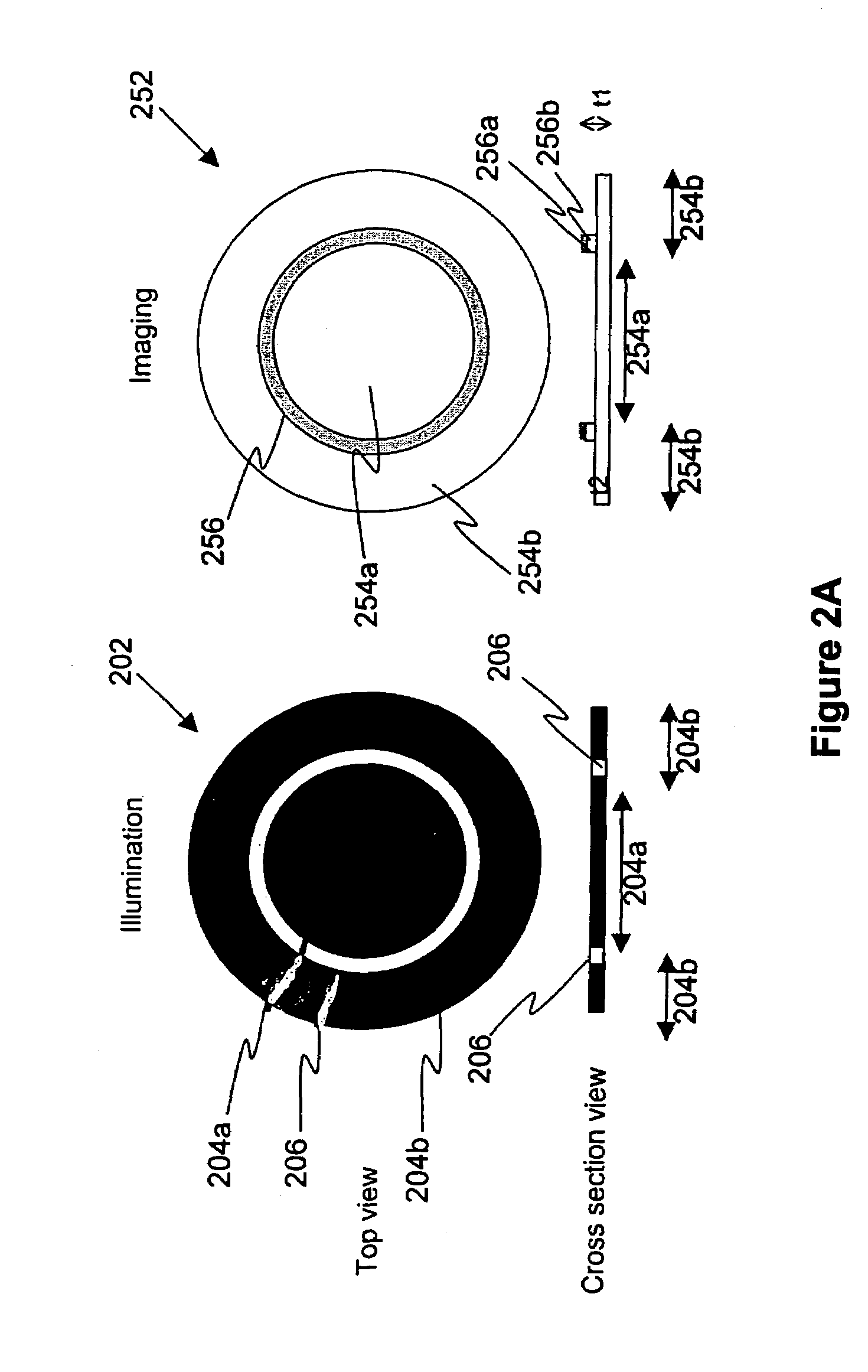
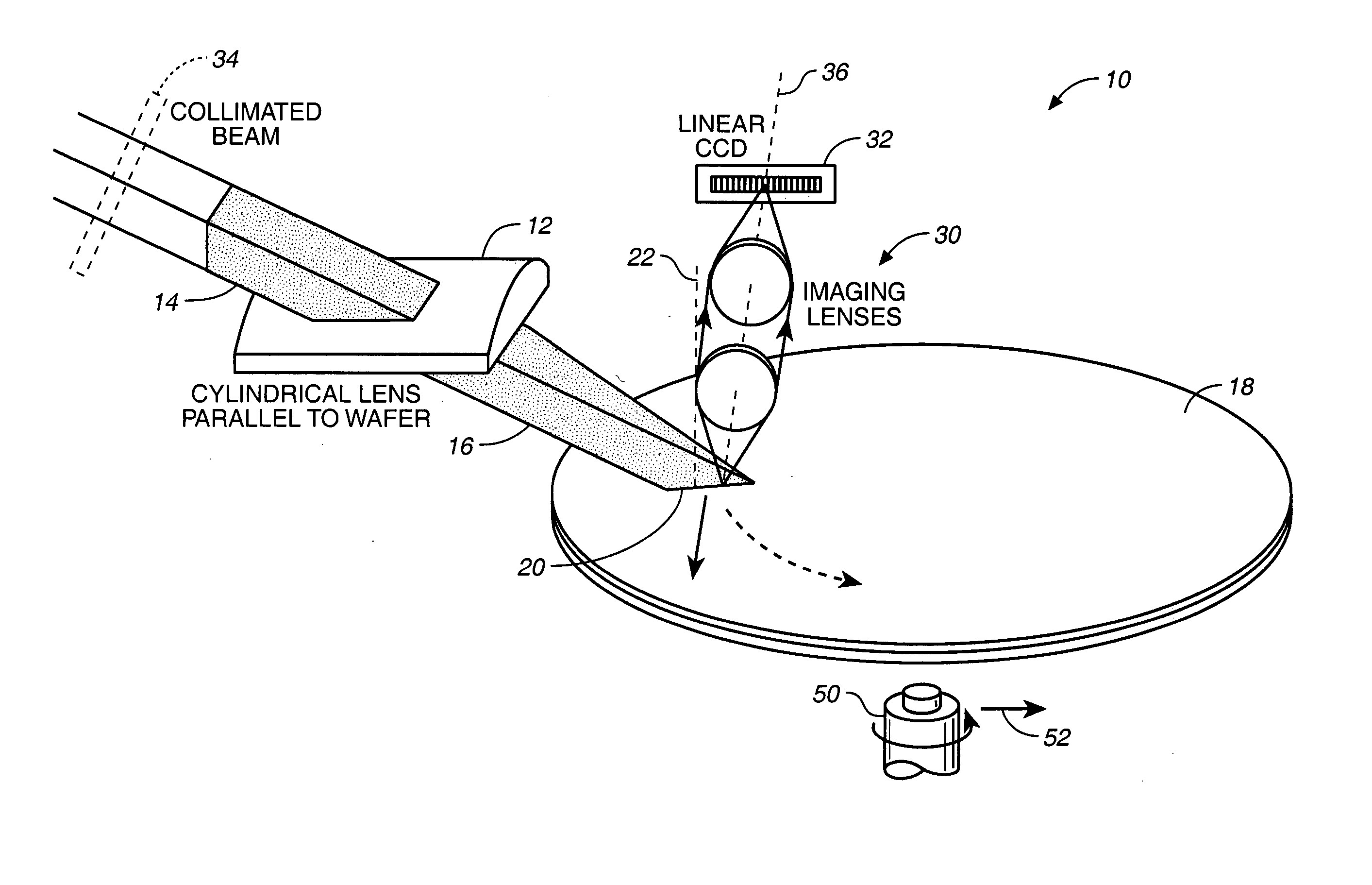
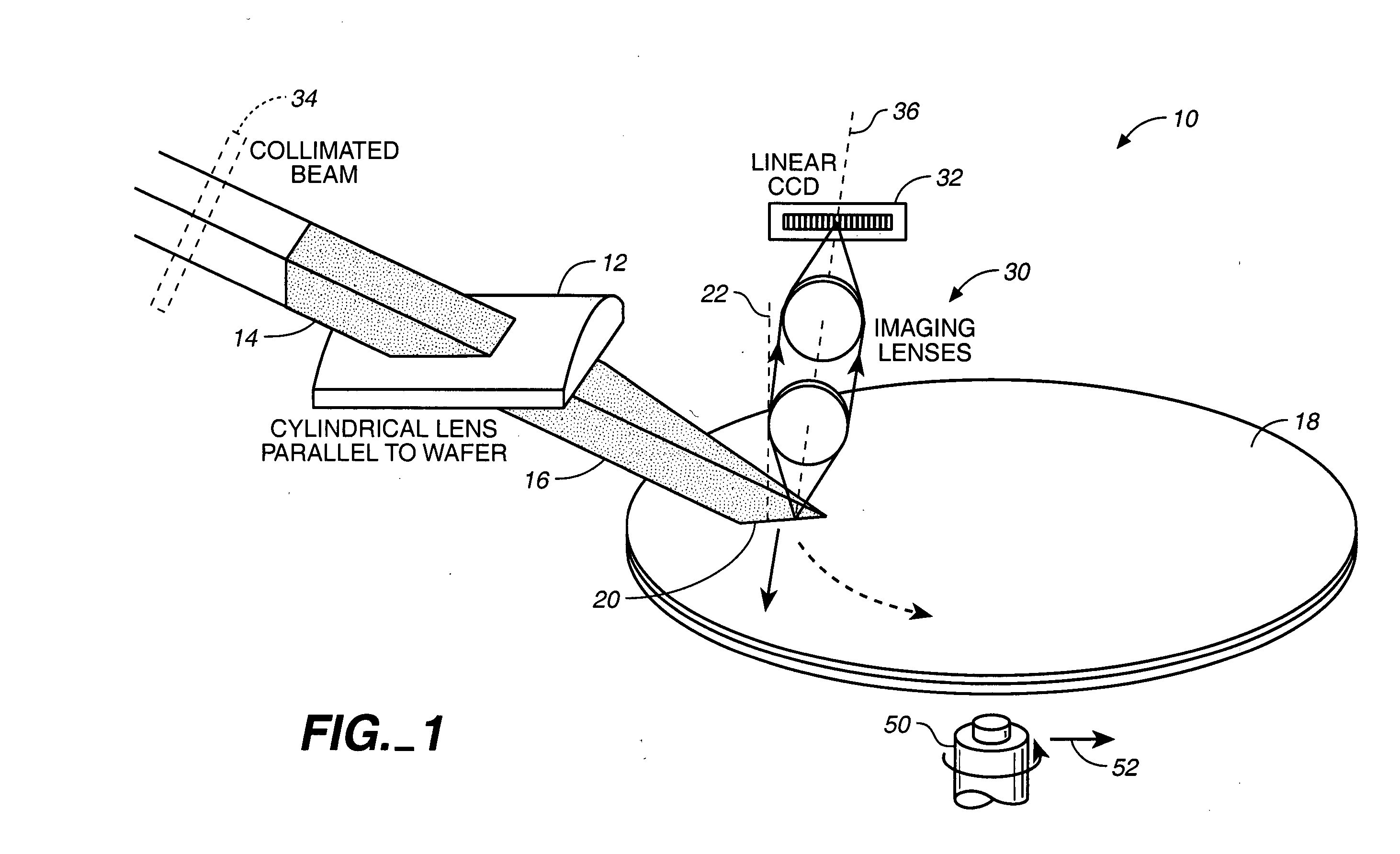
Optical system for detecting anomalies and/or features of surfaces
ActiveUS20050052644A1High detection sensitivityImprove throughputScattering properties measurementsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationDetector arrayRelative motion
A surface inspection of the system applies a first oblique illumination beam and may also apply a second illumination beam to illuminate a surface either sequentially or simultaneously. Radiation reflected or scattered is collected by preferably three collection channels and detected by three corresponding detector arrays, although a different number of channels and detector arrays may be used. One or both illumination beams are focused to a line on the surface to be inspected and each line is imaged onto one or more detector arrays in the up to three or more detection and collection channels. Relative motion is caused between the lines and the surface inspected in a direction perpendicular to the lines, thereby increasing throughput while retaining high resolution and sensitivity. The same detection channels may be employed by detecting scattered or reflected radiation from both illumination beams. Fourier filters may be employed to filter out diffraction at one or more different spatial frequencies.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
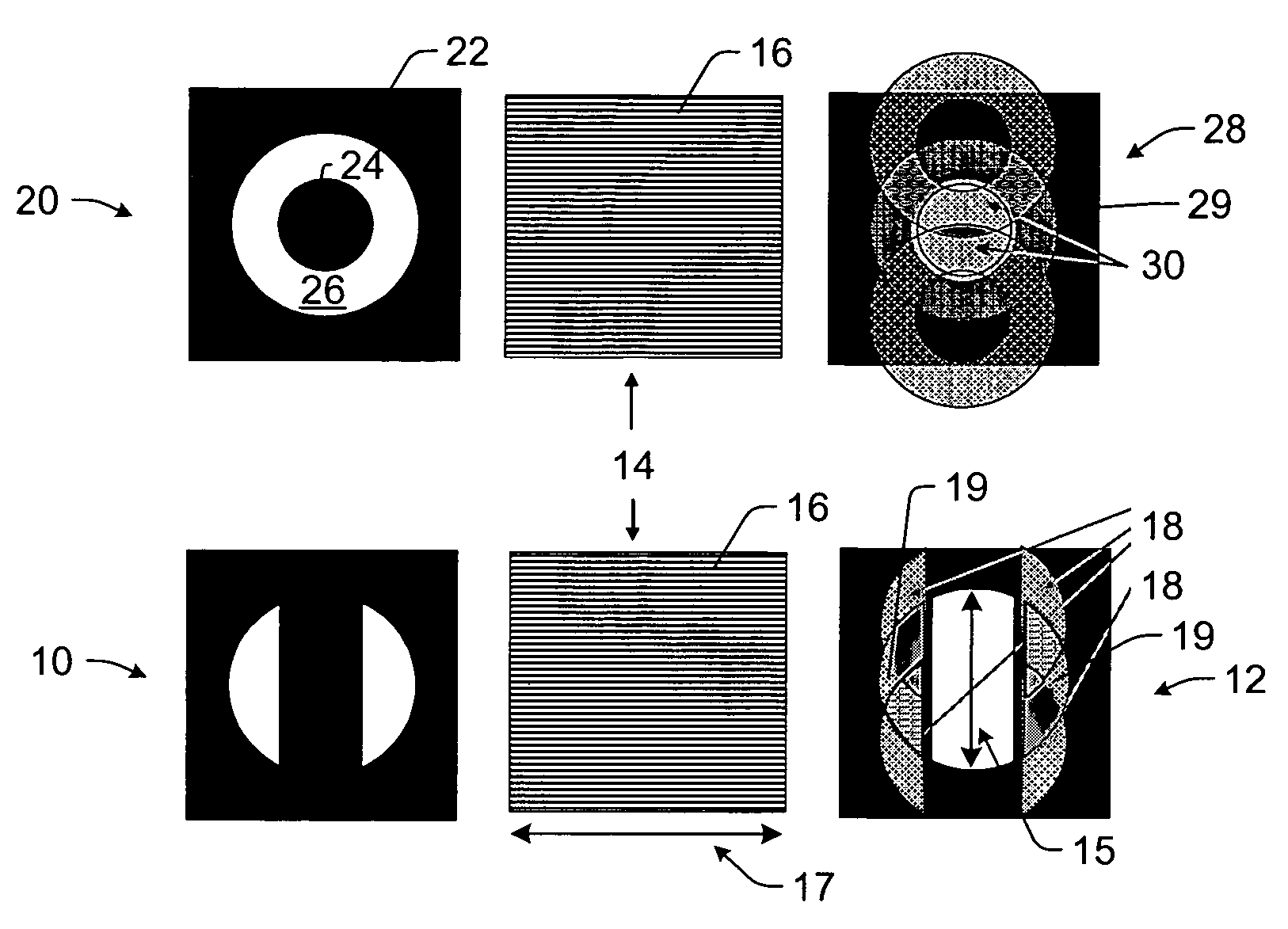
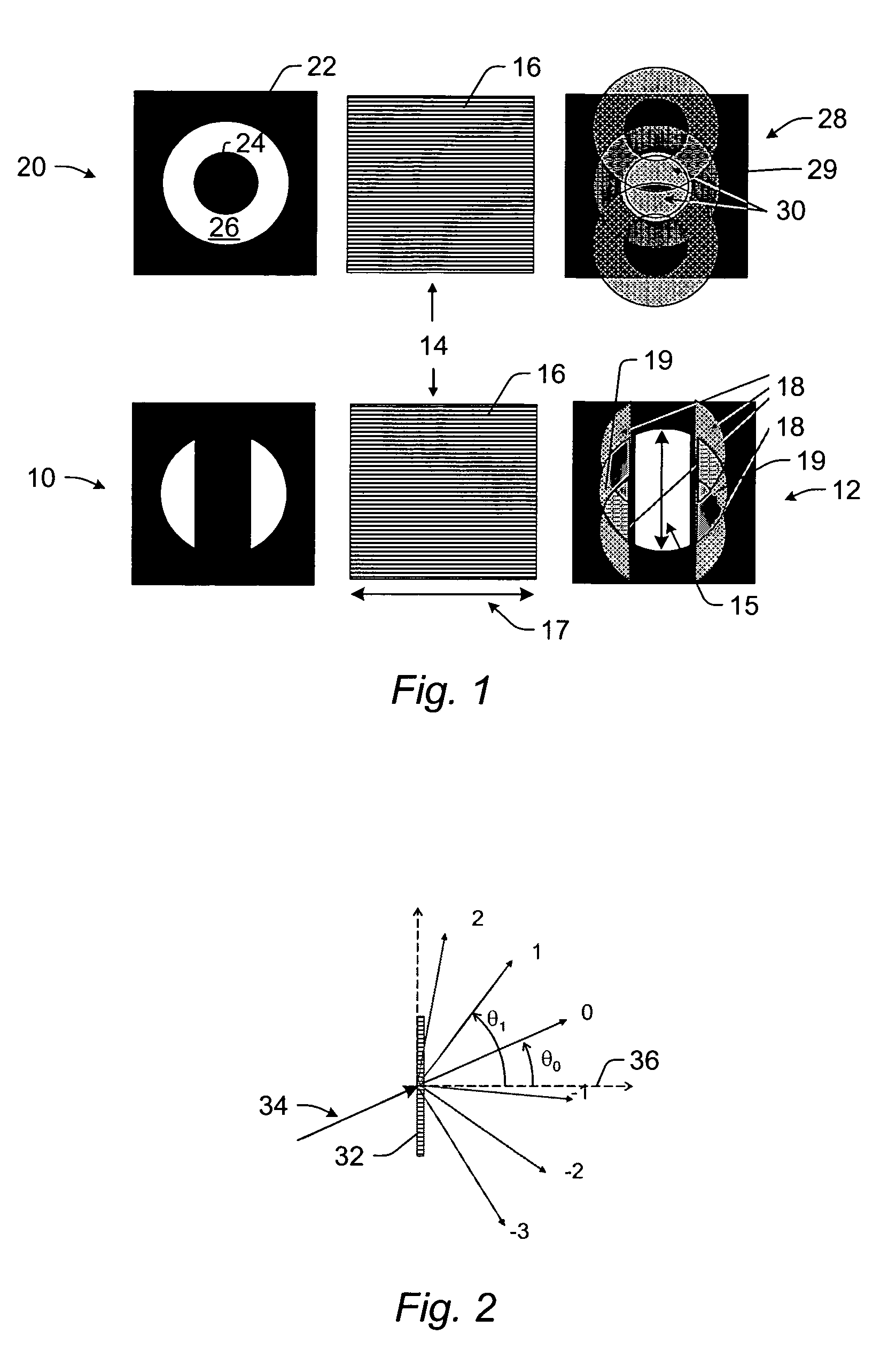
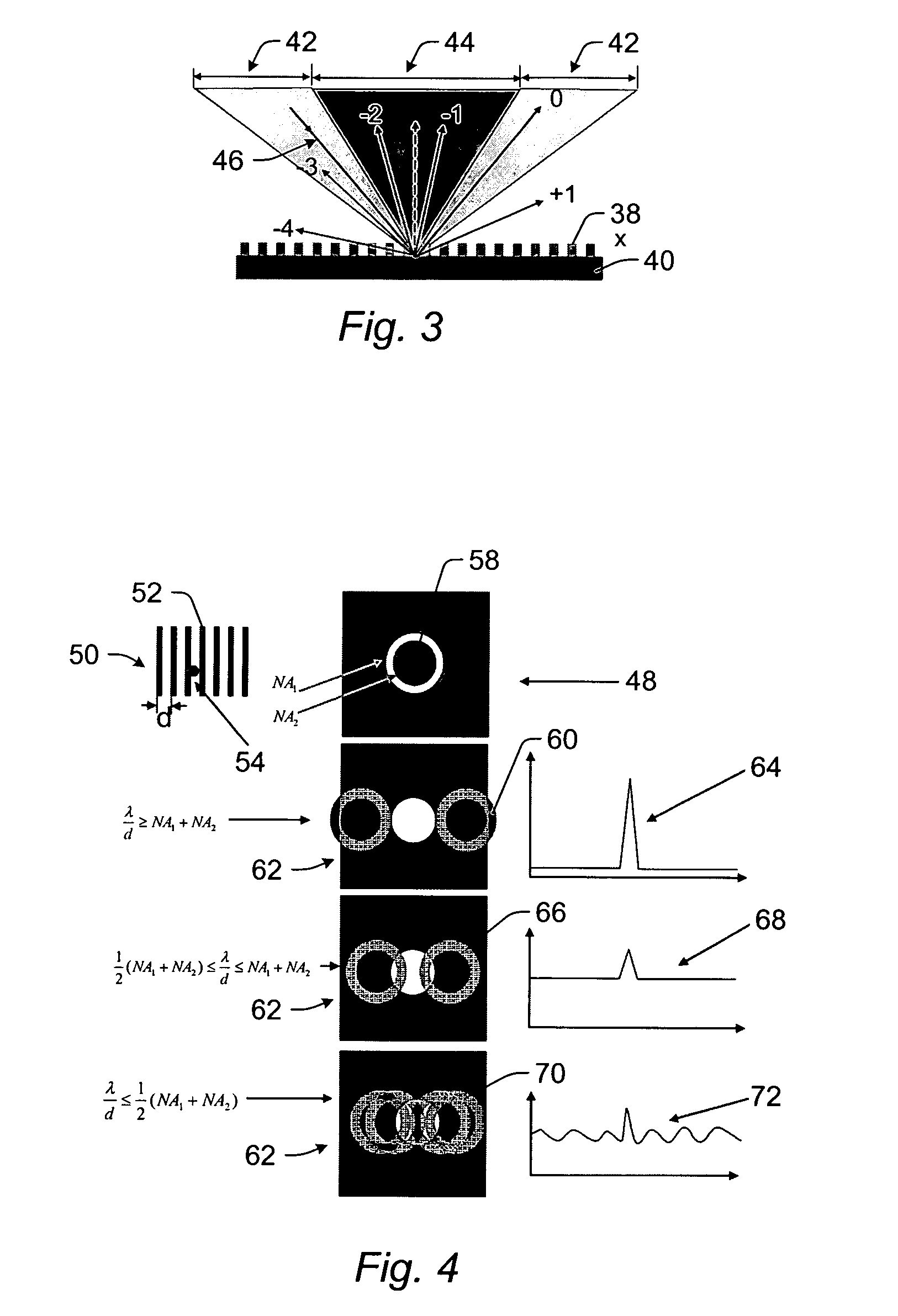
Fourier filters and wafer inspection systems
Fourier filters and wafer inspection systems are provided. One embodiment relates to a one-dimensional Fourier filter configured to be included in a bright field inspection system such that the bright field inspection system can be used for broadband dark field inspection of a wafer. The Fourier filter includes an asymmetric illumination aperture configured to be positioned in an illumination path of the inspection system. The Fourier filter also includes an asymmetric imaging aperture complementary to the illumination aperture. The imaging aperture is configured to be positioned in a light collection path of the inspection system such that the imaging aperture blocks light reflected and diffracted from structures on the wafer and allows light scattered from defects on the wafer to pass through the imaging aperture.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Dark field inspection apparatus and methods
ActiveUS7436503B1Reducing and eliminating long range ringing responseLong responseMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesAtomic physicsIncident beam
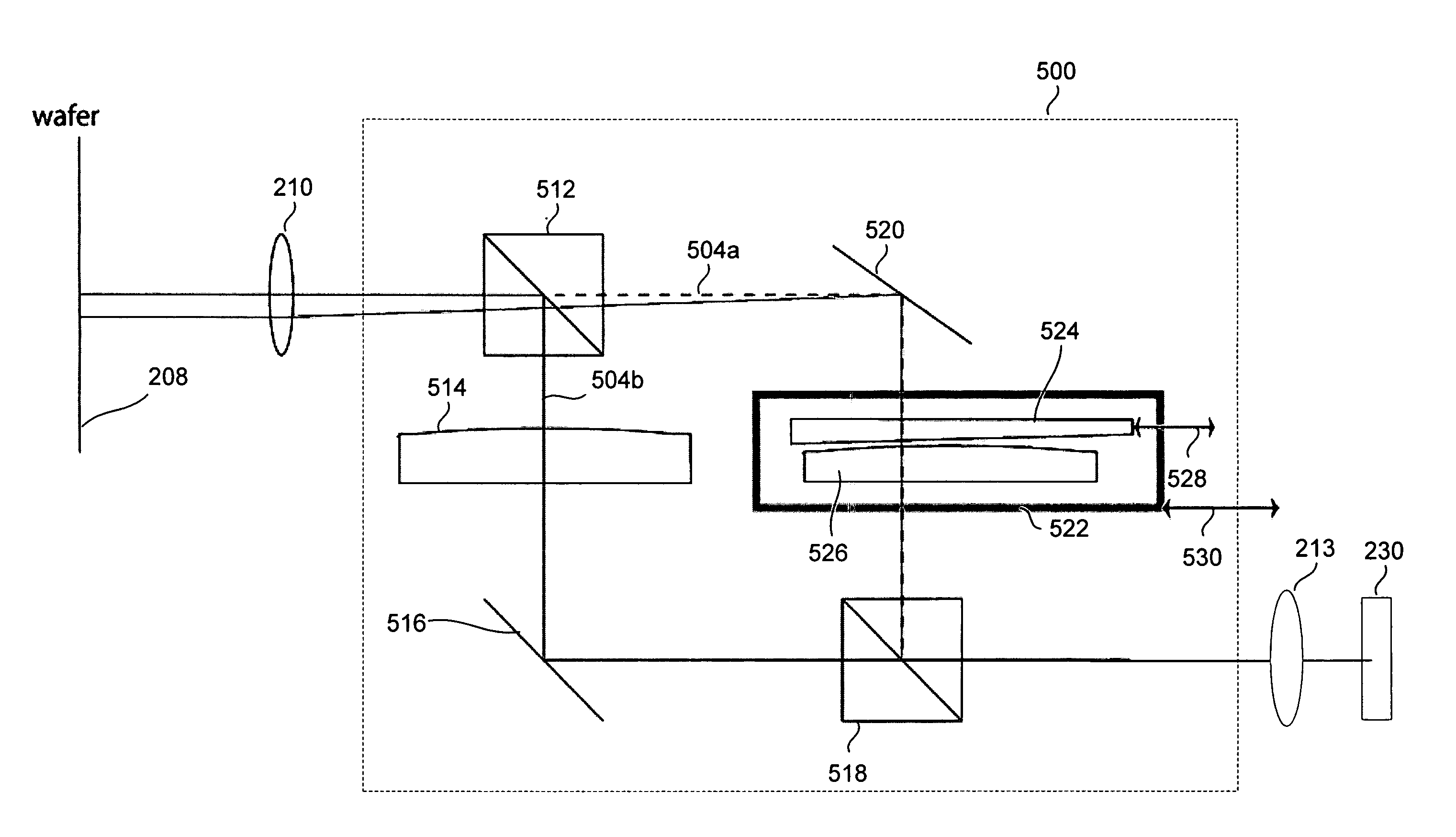
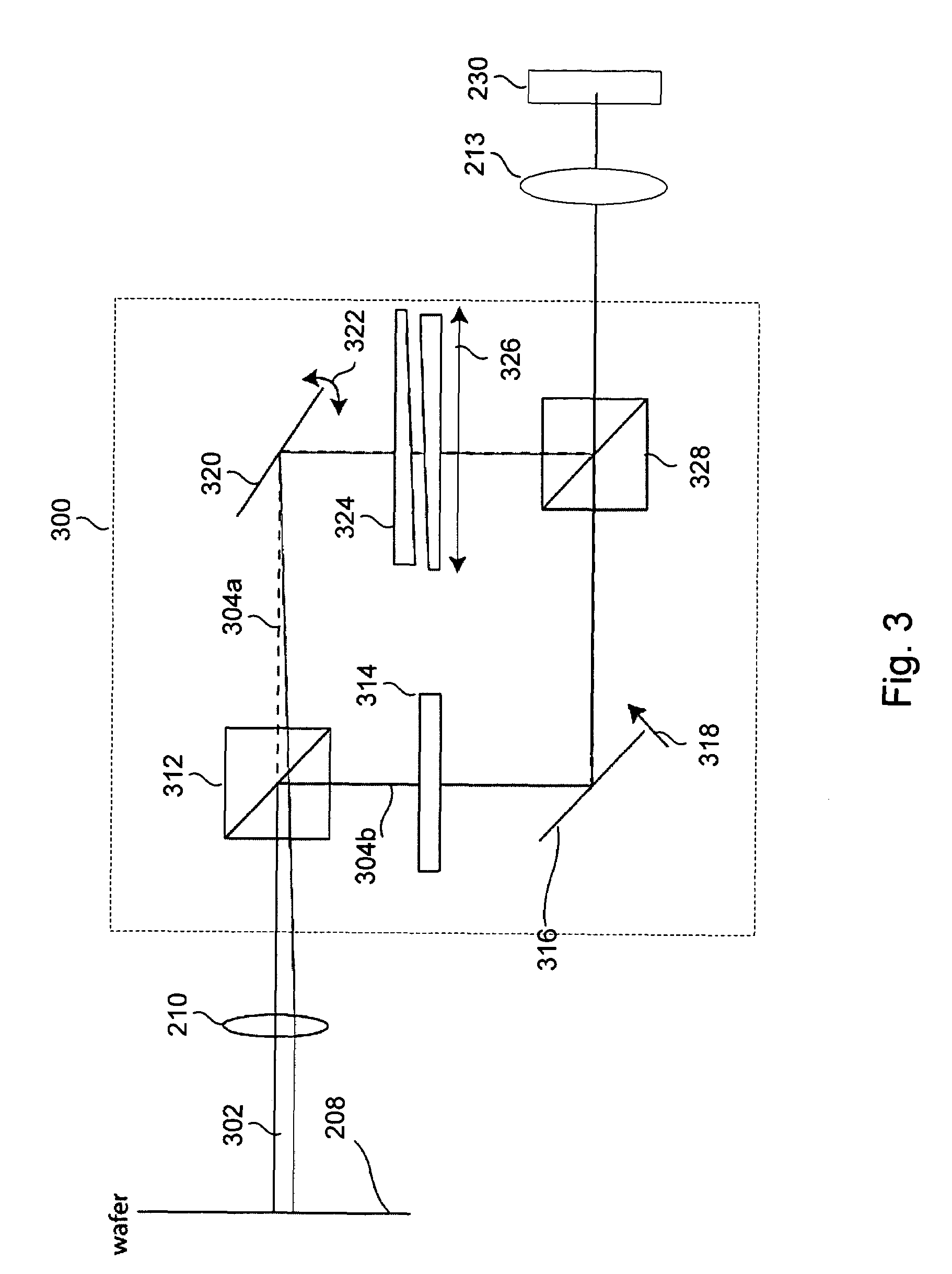
Accordingly, the present invention provides methods and apparatus for performing a darkfield inspection on a specimen having periodic structures thereon while substantially reducing or eliminating the long range ringing response, which is typically produced by a traditional Fourier filter mask used to eliminate the diffraction caused by the periodic structures. In one embodiment, an apparatus for inspecting a specimen by detecting optical beams scattered from the specimen. The apparatus includes a beam generator for providing and directing an incident beam towards a specimen and an array subtraction device for substantially subtracting a periodic component from an output beam scattered from the specimen in response to the incident beam. The periodic component corresponds to at least one periodic structure on the specimen, and the subtraction is performed so as to substantially reduce or eliminate a ringing response from the output beam. The subtraction is also performed so as to substantially prevent subtracting any actual defect components from the output beam. The apparatus further includes a detector for receiving the output beam and generating an output image or signal based on the output beam.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Broad band DUV, VUV long-working distance catadioptric imaging system
InactiveUS20070171547A1Long distanceMinimize central obscurationMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusPupilLength wave
A high performance objective having very small central obscuration, an external pupil for apertureing and Fourier filtering, loose manufacturing tolerances, large numerical aperture, long working distance, and a large field of view is presented. The objective is preferably telecentric. The design is ideally suited for both broad-band bright-field and laser dark field imaging and inspection at wavelengths in the UV to VUV spectral range.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Broad band deep ultraviolet/vacuum ultraviolet catadioptric imaging system
InactiveUS20050111081A1High degreeImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMangin mirrorUltraviolet
A design for inspecting specimens, such as photomasks, for unwanted particles and features such as pattern defects is provided. The system provides no central obscuration, an external pupil for aperturing and Fourier filtering, and relatively relaxed manufacturing tolerances, and is suited for both broad-band bright-field and laser dark field imaging and inspection at wavelengths below 365 nm. In many instances, the lenses used may be fashioned or fabricated using a single material. Multiple embodiments of the objective lensing arrangement are disclosed, all including at least one small fold mirror and a Mangin mirror. The system is implemented off axis such that the returning second image is displaced laterally from the first image so that the lateral separation permits optical receipt and manipulation of each image separately. The objective designs presented have the optical axis of the Mangin mirror image relay at ninety degrees to the optical axis defined by the focusing lenses, or an in-line or straight objective having one ninety degree bend of light rays.
Owner:KLA CORP
Judgment method of line breakage of special TV for inter-turn protection of generator
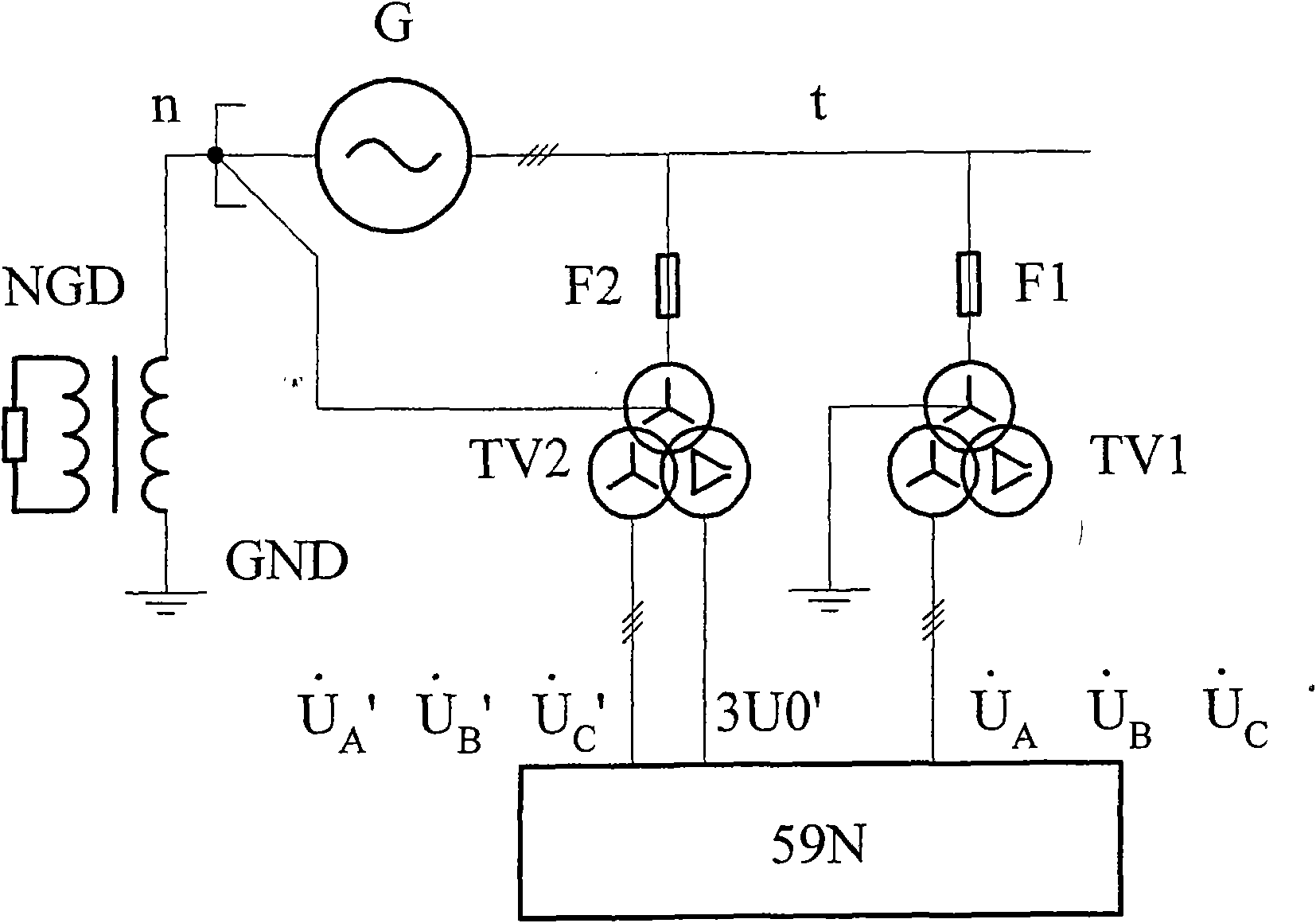
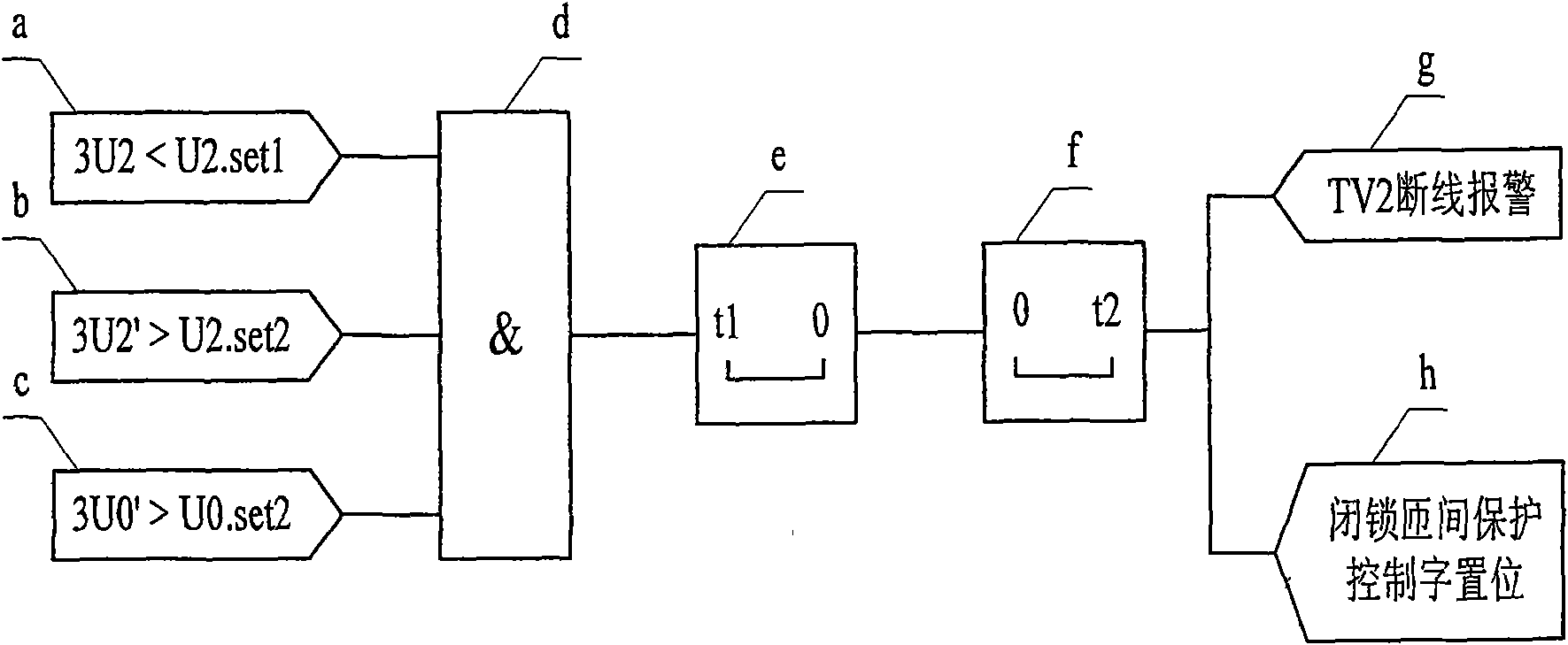
ActiveCN101651329AAvoid false protectionCriterion is simpleEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric machine testingEngineeringSecondary side
A judgment method of line breakage of a special TV for inter-turn protection of a generator comprises the following steps: a generator terminal is provided with a general voltage transformer TV1 and aspecial voltage transformer TV2 for inter-turn protection; a protection device is used for sampling secondary side voltages of the voltage transformers, thus respectively obtaining negative sequencevoltage 3U2 of the TV1, negative sequence voltage 3U2' and foundational wave zero sequence voltage 3U0' of the TV2 based on holocycle Fourier filtering and calculation; and fixed values U2.set1, U2.set2 and U0.set2 are preset inside the protection device, wherein, 3U2 is smaller than U2.set1(1), 3U2' is greater than U2.set2 (2) and 3U0' is greater than U0.set2 (3). When meeting inequations (1)-(3)simultaneously, a line breakage alarm signal of the TV2 is generated after short delay t1, and the inter-turn protection is locked; and if the TV2 has no line breakage later, that is, that is, the inequations (1)-(3) can not be met simultaneously, line breakage alarm of the TV2 is canceled after long delay t2, and longitudinal fundamental wave zero voltage inter-turn protection is re-started.
Owner:NR ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
Broad band DUV, VUV long-working distance catadioptric imaging system
InactiveUS7136234B2Long distanceMinimize central obscurationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicroscopesPupilLength wave
A high performance objective having very small central obscuration, an external pupil for apertureing and Fourier filtering, loose manufacturing tolerances, large numerical aperture, long working distance, and a large field of view is presented. The objective is preferably telecentric. The design is ideally suited for both broad-band bright-field and laser dark field imaging and inspection at wavelengths in the UV to VUV spectral range.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Low coherent interference demodulation method based on chromatic dispersion characteristic and envelopment peak value
ActiveCN103267536ANo increase in computationImprove demodulation accuracyLight demodulationConverting sensor output opticallyRefractive indexThree dimensional shape
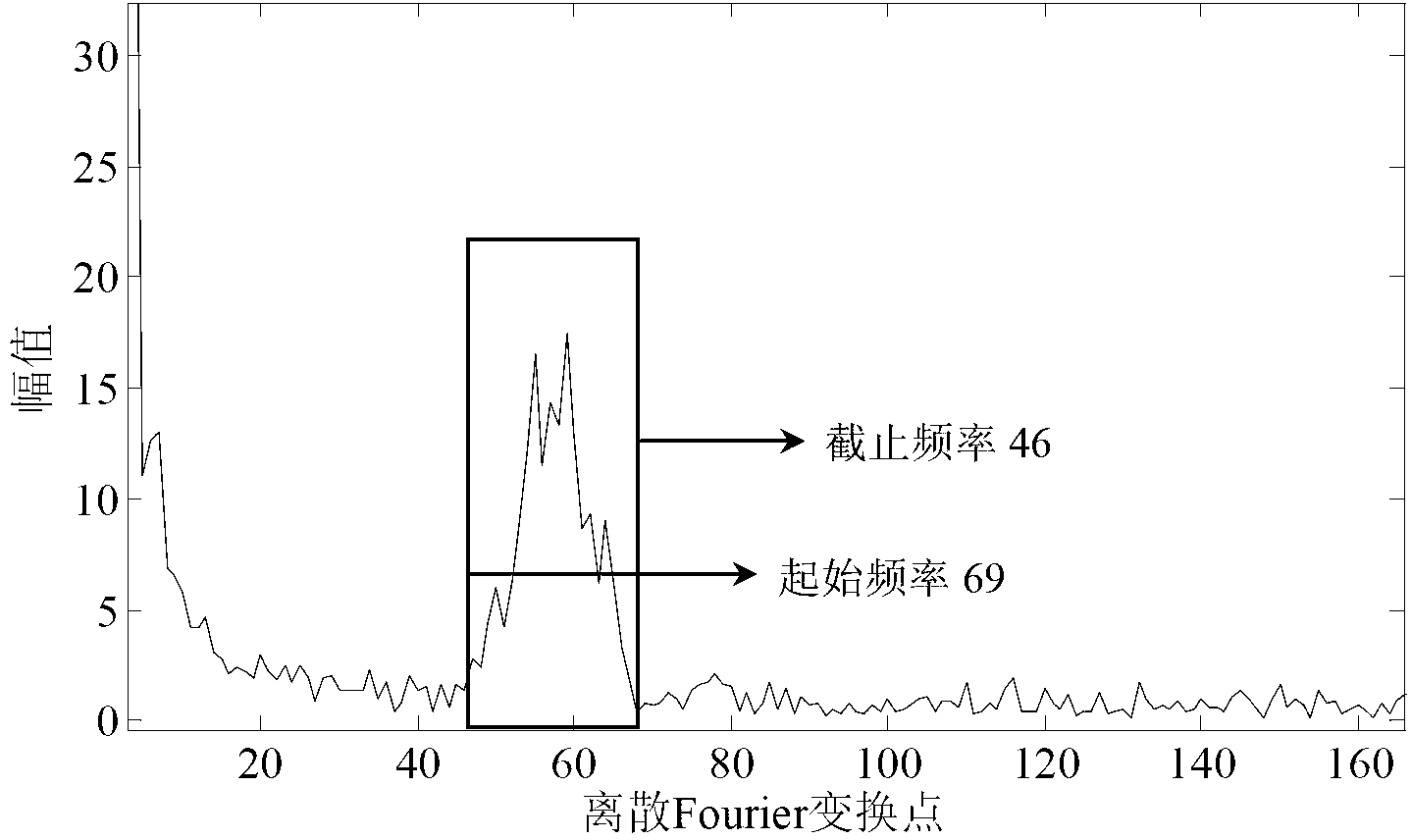
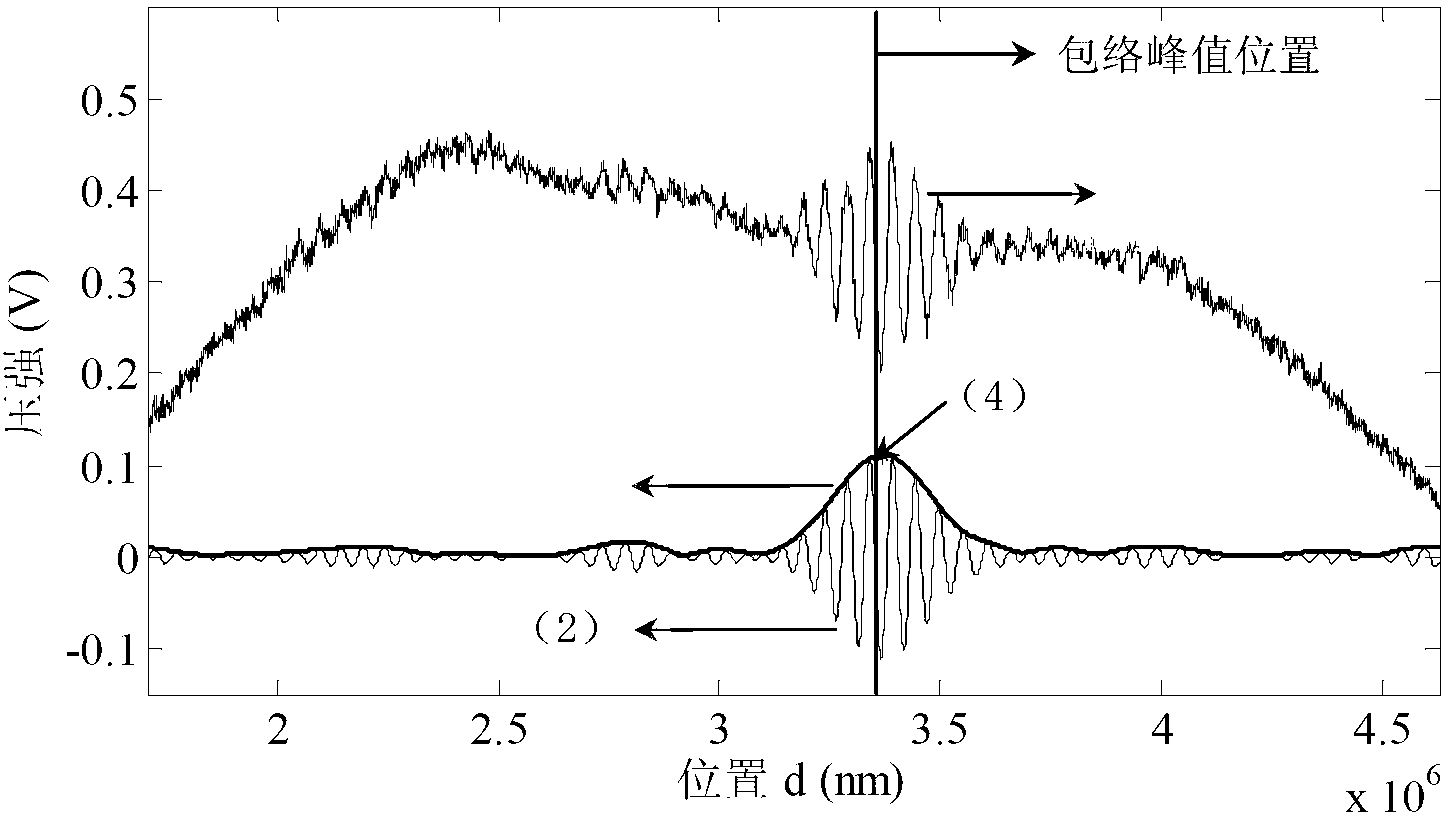
The invention discloses a low coherent interference demodulation method based on a chromatic dispersion characteristic and an envelopment peak value. According to the method, an F-p sensor is chosen to serve as a sensing element, a double refraction optical wedge serves as an optical path difference space scanning element, an interference fringe is formed in a zero optical path difference local area, an F-P cavity length is demodulated according to the interference fringe, and therefore atmospheric pressure is felt. According to the method, firstly, Fourier filtering is carried out on an interference signal; then a low precision distance corresponding to a peak value position according to a peak value position obtained by the envelopment peak value method and a cluster refractive index of a low coherent interference system dispersion element is obtained; finally, a theoretical phase position is calculated by the utilization of the peak value position chromatic dispersion characteristic, and the distance error of the envelopment peak value method is determined according to the theoretical phase position and a measured phase position and high-precision demodulation is achieved. Under the condition that prior information is not needed, the system chromatic dispersion characteristic and the envelopment peak value are utilized to achieve wide-range high-precision measurement of low coherent interference. The low coherent interference demodulation method is applied to the optical fiber sensing filed, the three-dimensional shape detecting and optical chromatographic technique, and other distance measurement fields.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
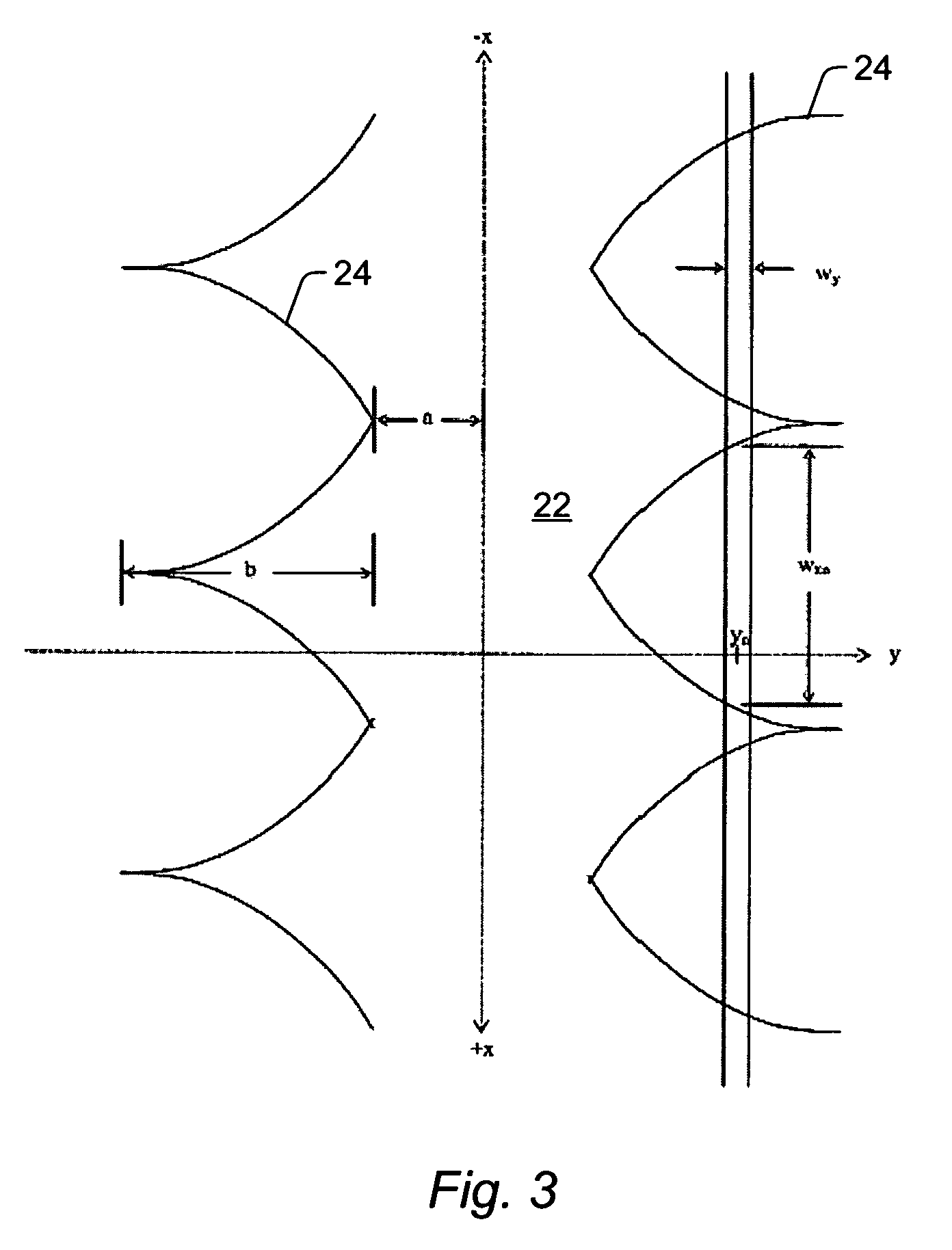
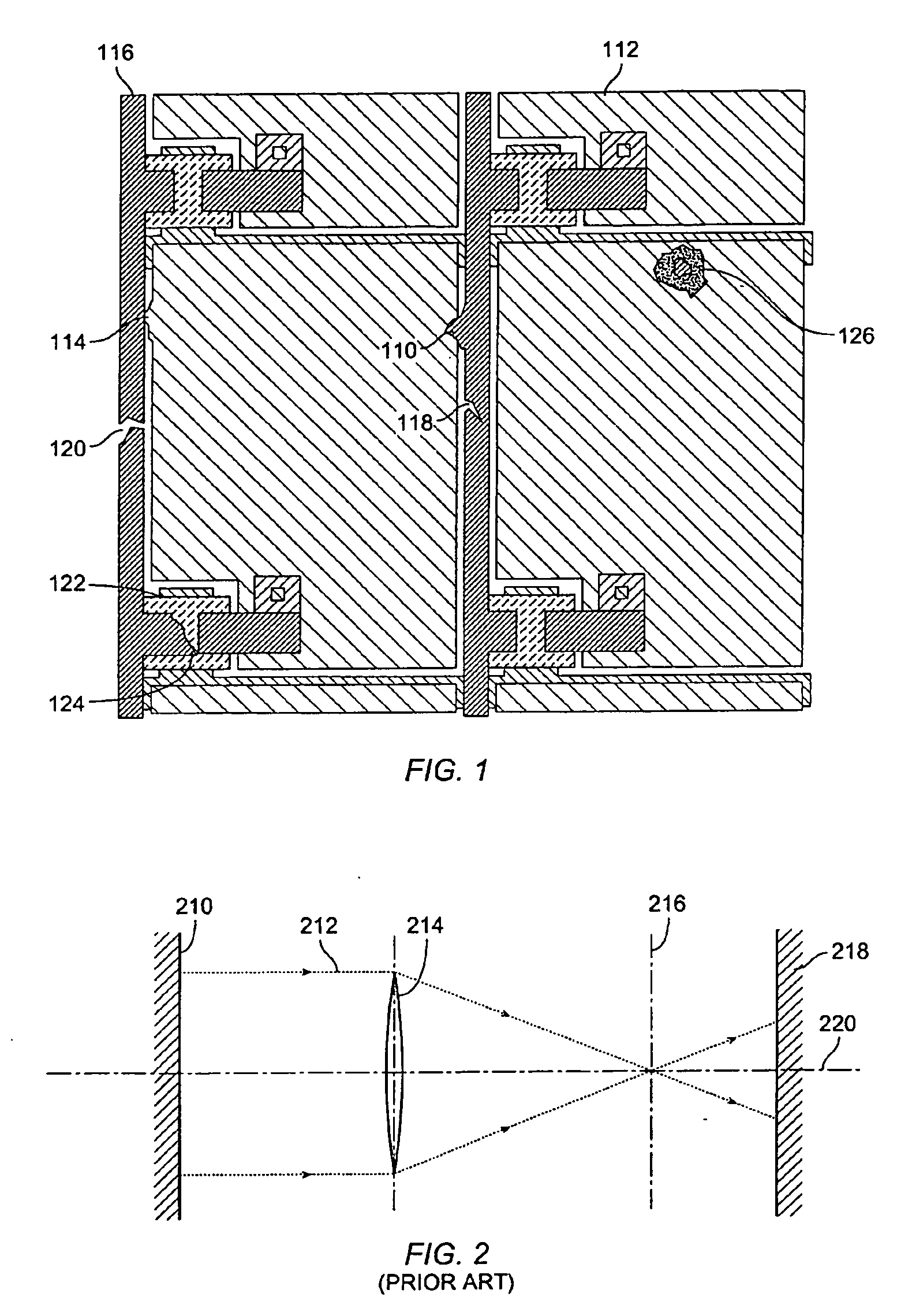
Serrated Fourier filters and inspection systems
ActiveUS7397557B2Smooth changeDiffraction reductionMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical elementsTransmittanceEngineering
Serrated Fourier filters and inspection systems are provided. One Fourier filter includes one or more blocking elements configured to block a portion of light from a wafer. The Fourier filter also includes periodic serrations formed on edges of the one or more blocking elements. The periodic serrations define a transition region of the one or more blocking elements. The periodic serrations are configured to vary transmission across the transition region such that variations in the transmission across the transition region are substantially smooth. One inspection system includes a Fourier filter configured as described above and a detector that is configured to detect light transmitted by the Fourier filter. Signals generated by the detector can be used to detect the defects on the wafer.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
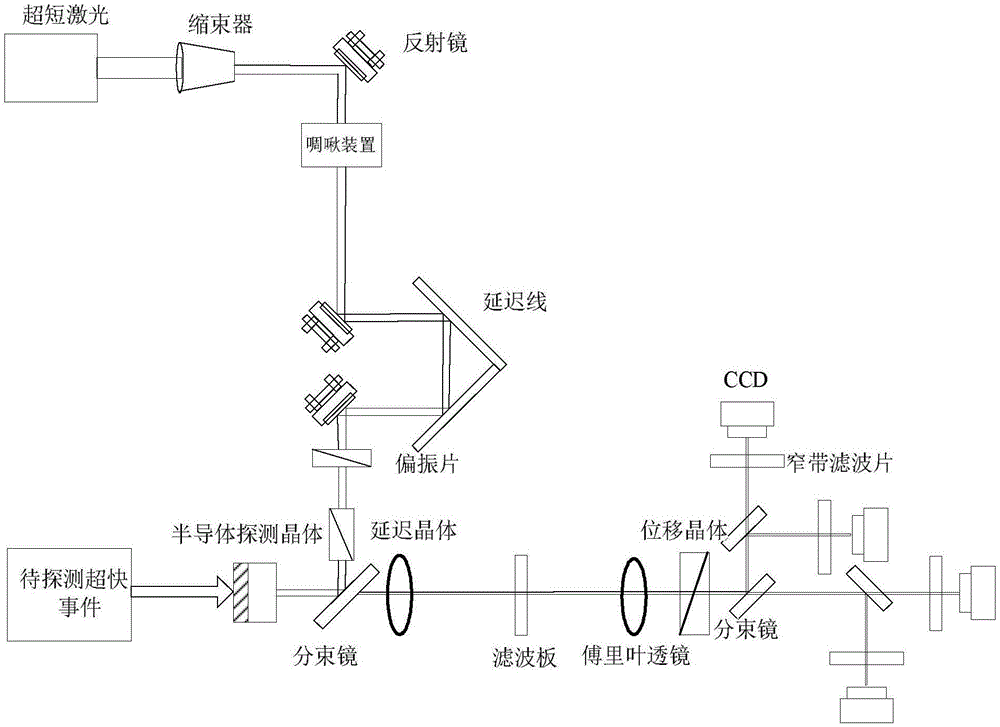
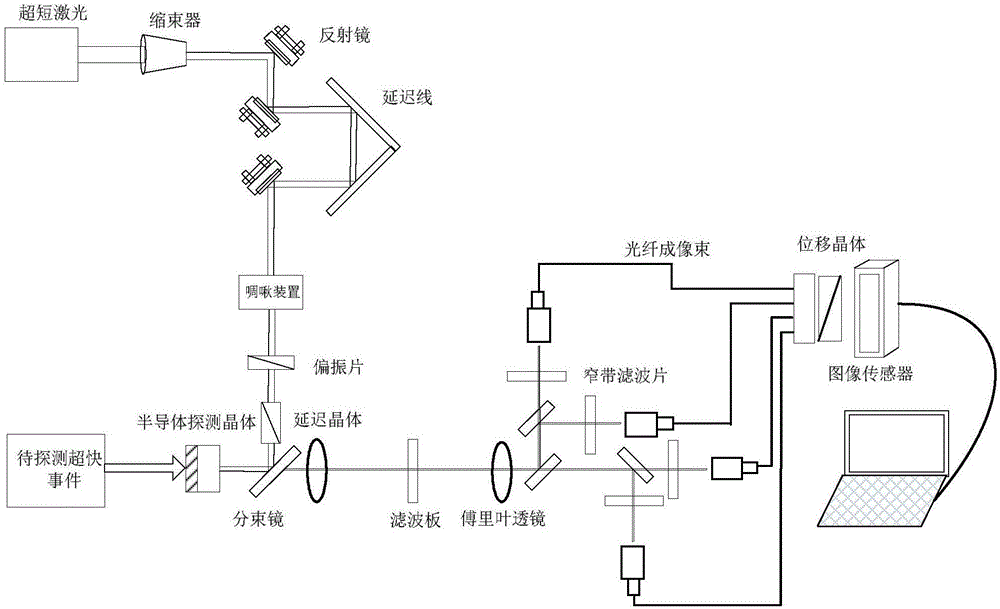
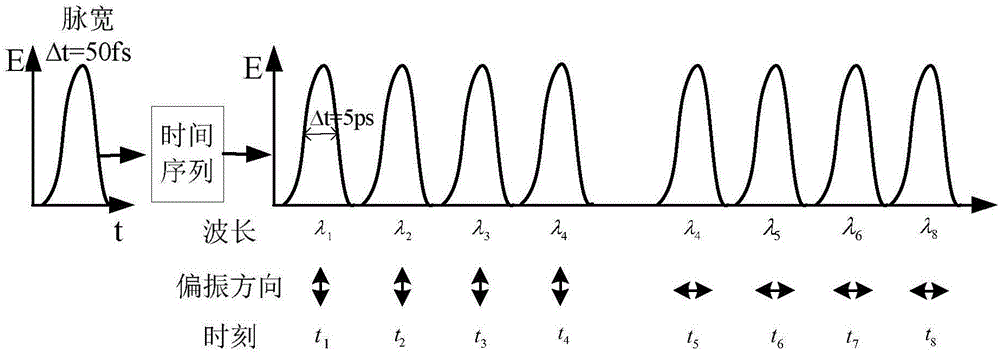
Multi-framing optical imaging device with high temporal-spatial resolution and imaging method
ActiveCN106406019AHigh time resolutionHigh spatial resolutionHigh-speed photographyOptical elementsTemporal resolutionTime delays
The invention discloses a multi-framing optical imaging device with a high temporal-spatial resolution and an imaging method. The device comprises a femtosecond-magnitude ultra-short pulse laser system, a time delay system, a spatial shaping system, a time serialization system, a semiconductor detector, a Fourier filtering system, a spatial framing unfolding system and an imaging recording system, wherein signal light enters the semiconductor detector from a front side; ultra-short pulse laser light is subjected to time delay, spatial shaping and time serialization to form probe light, and the probe light enters the semiconductor detector from a back side; changed image information caused by the signal light is modulated onto serial light pulses of the probe light; and after the modulated probe light is subjected to Fourier filtering and spatial framing unfolding, images at different moments are unfolded spatially and recorded by the imaging recording system. Through adoption of the device, multi-framing imaging with a high temporal resolution and a high spatial resolution can be realized; the spatial resolution is larger than 30lp / mm; the temporal resolution is higher than 5ps; and the framing number is not less than eight images.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
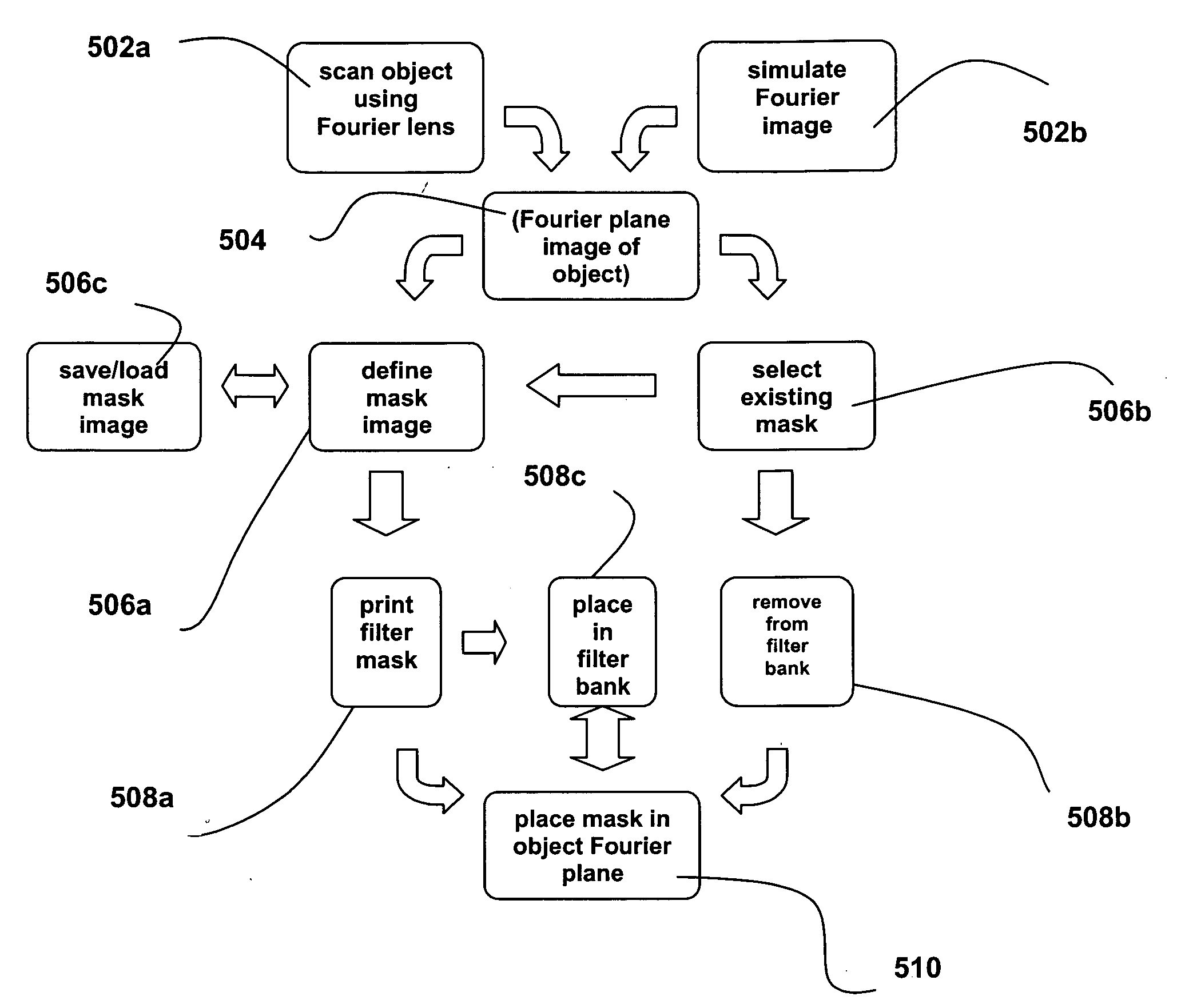
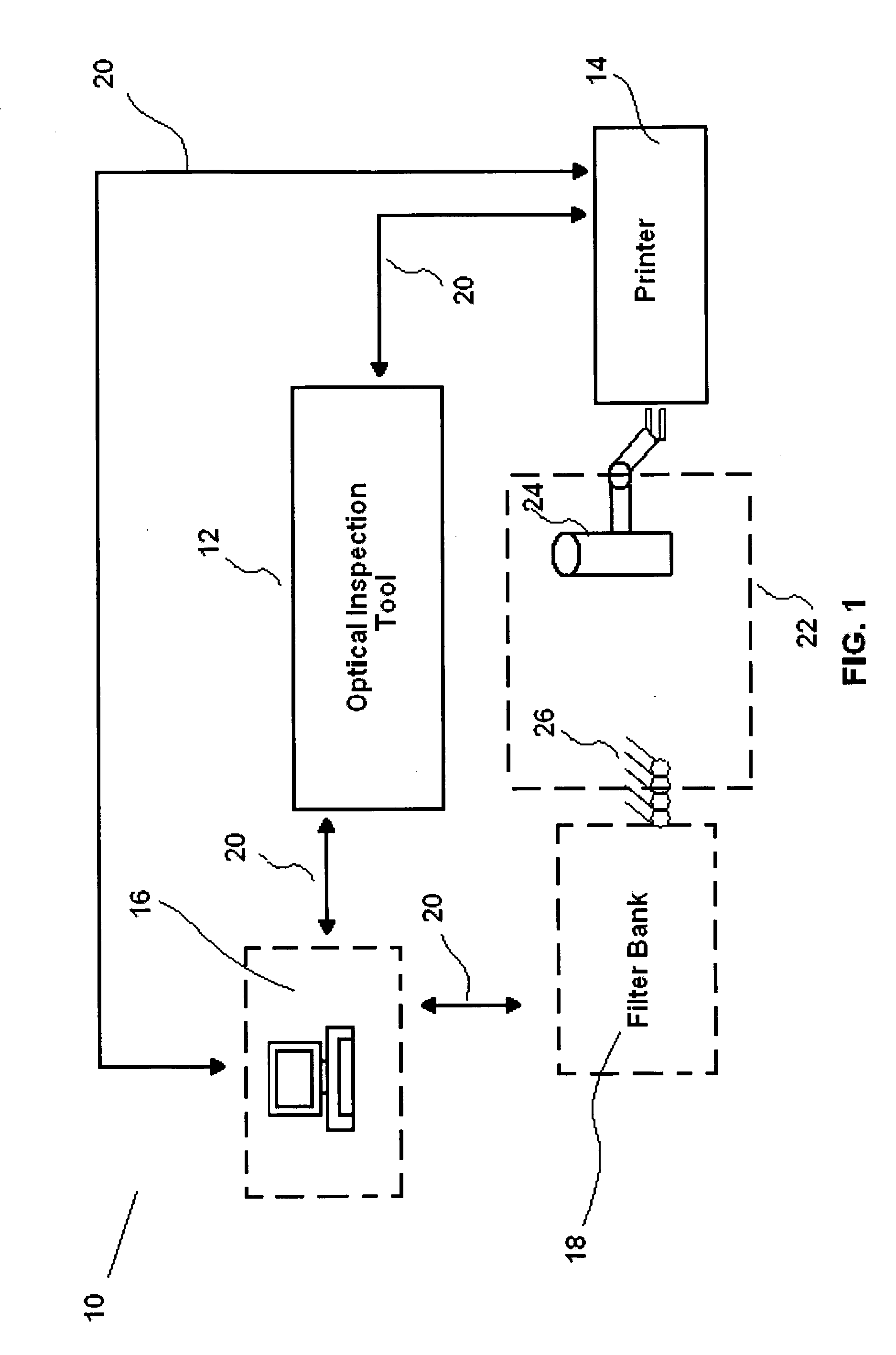
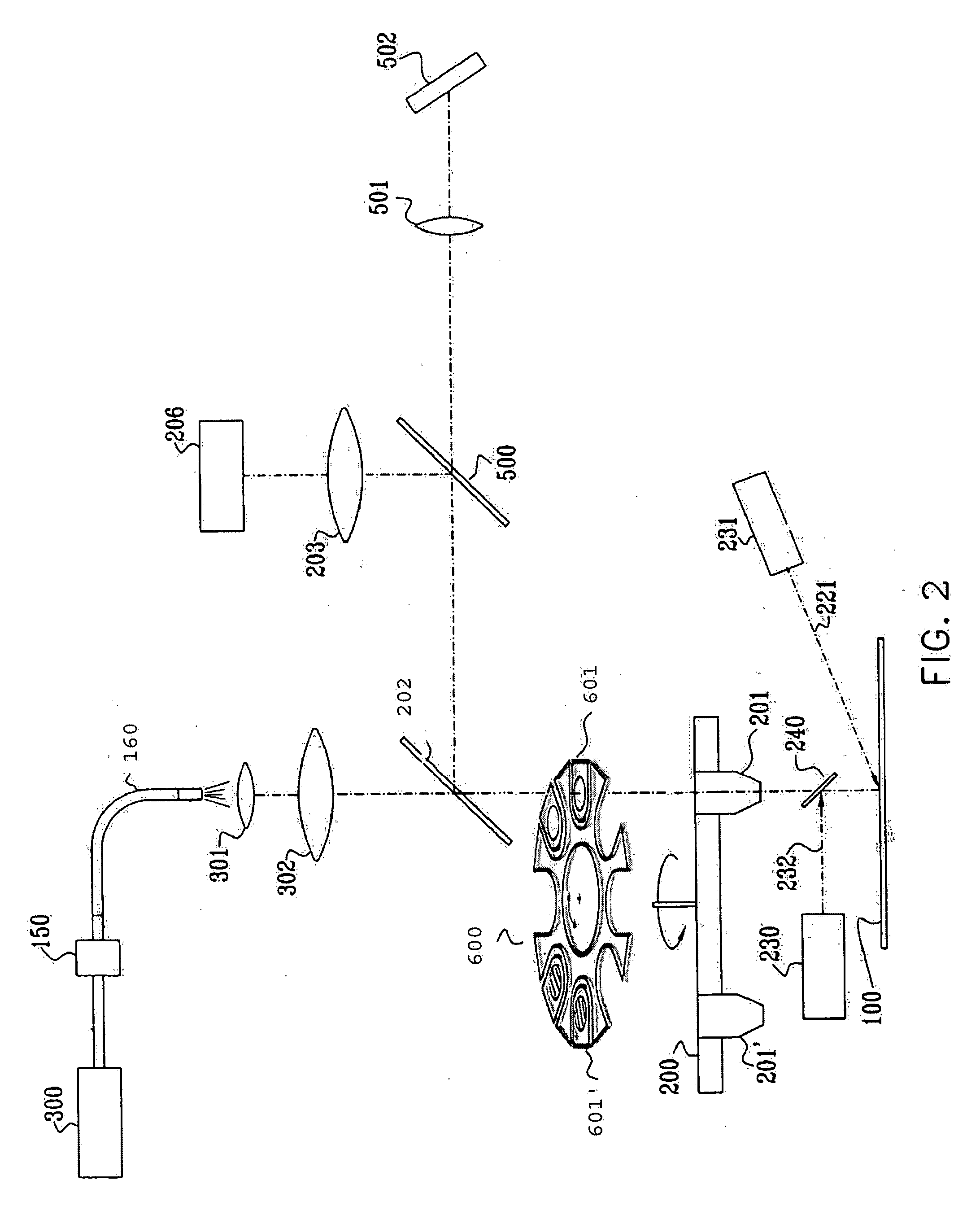
Printed fourier filtering in optical inspection tools
ActiveUS20070247668A1Material analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionLight filterComputer science
A spatial mask printer may be used in conjunction with an optical inspection tool. The tool can be used to obtain a Fourier image of an inspected object, and a filter mask image can be designed to block certain aspects of the object's image in the Fourier plane corresponding to repetitive aspects of the imaged object. The filter mask image can then be printed and used in the tool during the inspection process. The mask image may be designed by hand or by computer and may be stored for later use. Filters may be automatically placed into the optical path of the inspection tool by a filter wheel, or may be housed in other filter banks. The printer may be configured to operate in a clean room environment, and may be integrated into the optical inspection tool.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS SOUTH EAST ASIA PTE +1
Method for measuring power frequency parameters of superhigh/extrahigh-voltage alternating-current (direct-current) power transmission circuit
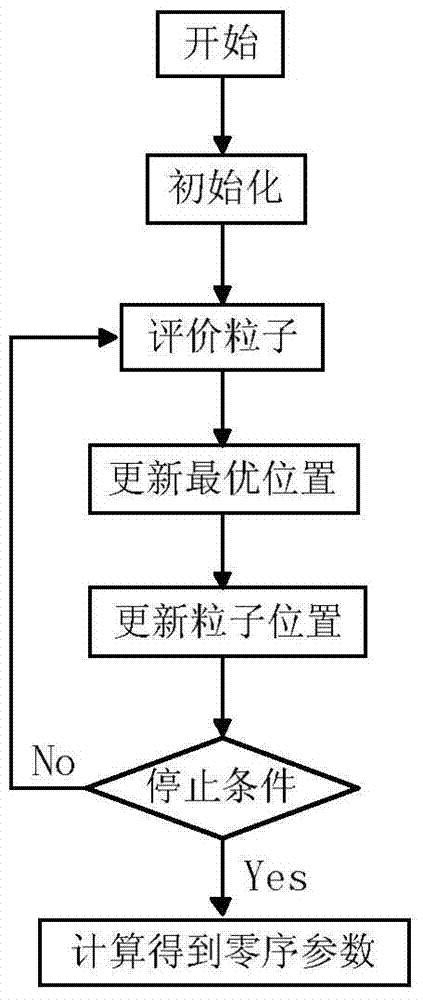
The invention discloses a method for measuring power frequency parameters of superhigh / extrahigh-voltage alternating-current (direct-current) power transmission circuit. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of synchronously measuring zero-sequence voltage and zero-sequence current on the head end and the tail end of the power transmission circuit, obtaining a power-frequency zero-sequence voltage phasor and a power-frequency zero-sequence current phasor by utilizing a Fourier filtering method, solving the power-frequency zero-sequence parameters of the power transmission circuit on the basis of a differential equation model and particle swarm optimization of the power transmission circuit, considering the influence of electromagnetic coupling between a distributive capacitor and the circuit on the power transmission circuit on the measurement of the power-frequency zero-sequence parameters, so that the precision of the power-frequency zero-sequence parameter measurement result of the power transmission circuit can be improved. The method is not only suitable for measuring the power-frequency zero-sequence parameter of a single-circuit and a multi-circuit superhigh / ultrahigh voltage alternating-current power transmission circuit, particularly suitable for measuring the power-frequency zero-sequence parameters of a double-circuit and four-circuit superhigh / ultrahigh voltage alternating-current power transmission circuit of a same tower and also suitable for remotely measuring the power-frequency parameters of the superhigh / ultrahigh voltage direct-current power transmission circuit.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Optical system for detecting anomalies and/or features of surfaces
ActiveUS7365834B2High detection sensitivityImprove throughputScattering properties measurementsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationDetector arrayLight beam
A surface inspection of the system applies a first oblique illumination beam and may also apply a second illumination beam to illuminate a surface either sequentially or simultaneously. Radiation reflected or scattered is collected by preferably three collection channels and detected by three corresponding detector arrays, although a different number of channels and detector arrays may be used. One or both illumination beams are focused to a line on the surface to be inspected and each line is imaged onto one or more detector arrays in the up to three or more detection and collection channels. Relative motion is caused between the lines and the surface inspected in a direction perpendicular to the lines, thereby increasing throughput while retaining high resolution and sensitivity. The same detection channels may be employed by detecting scattered or reflected radiation from both illumination beams. Fourier filters may be employed to filter out diffraction at one or more different spatial frequencies.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
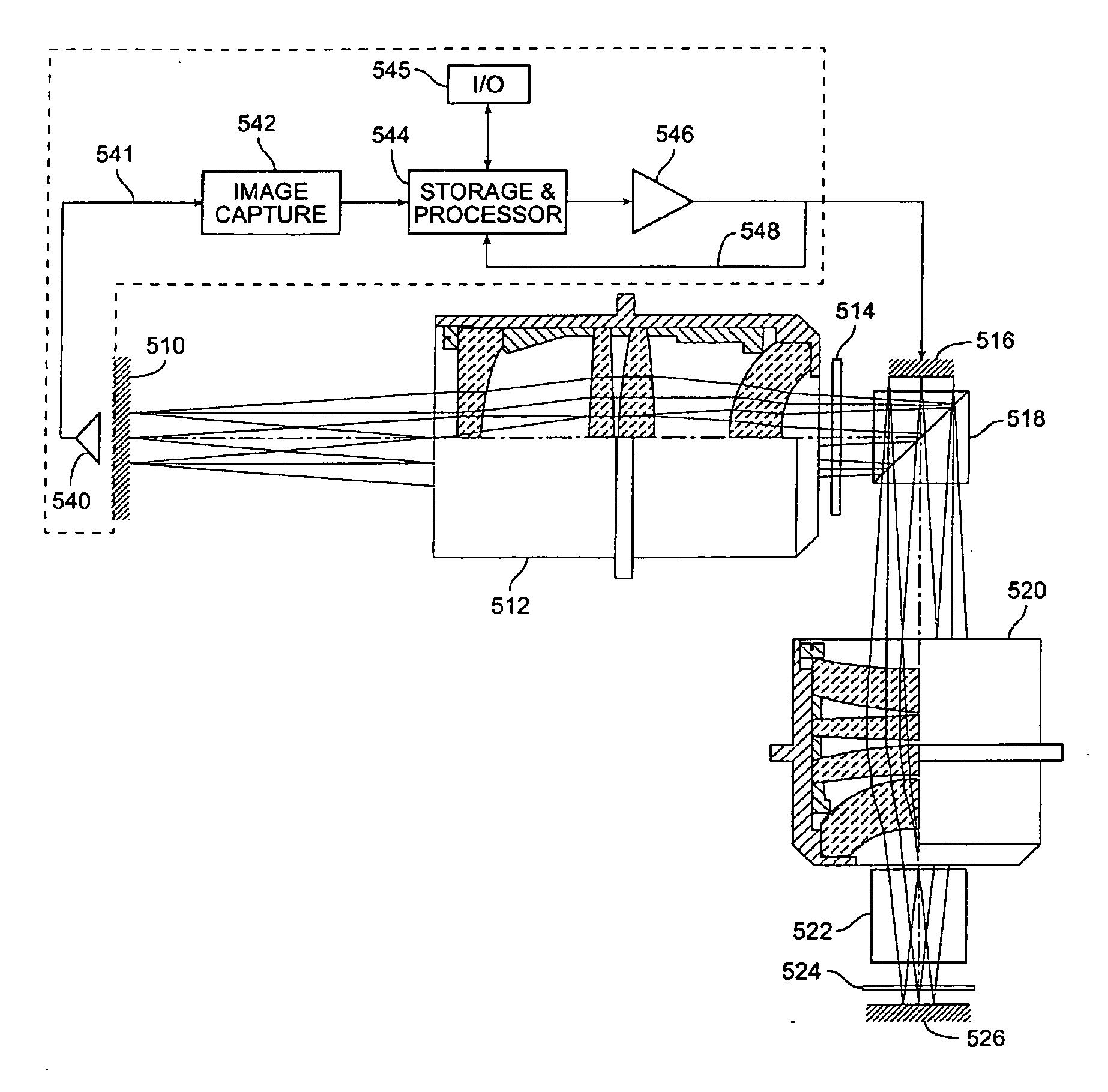
High NA system for multiple mode imaging
InactiveUS7035001B2Increased field sizeTelevision system detailsX-ray/infra-red processesCatadioptric systemPupil shape
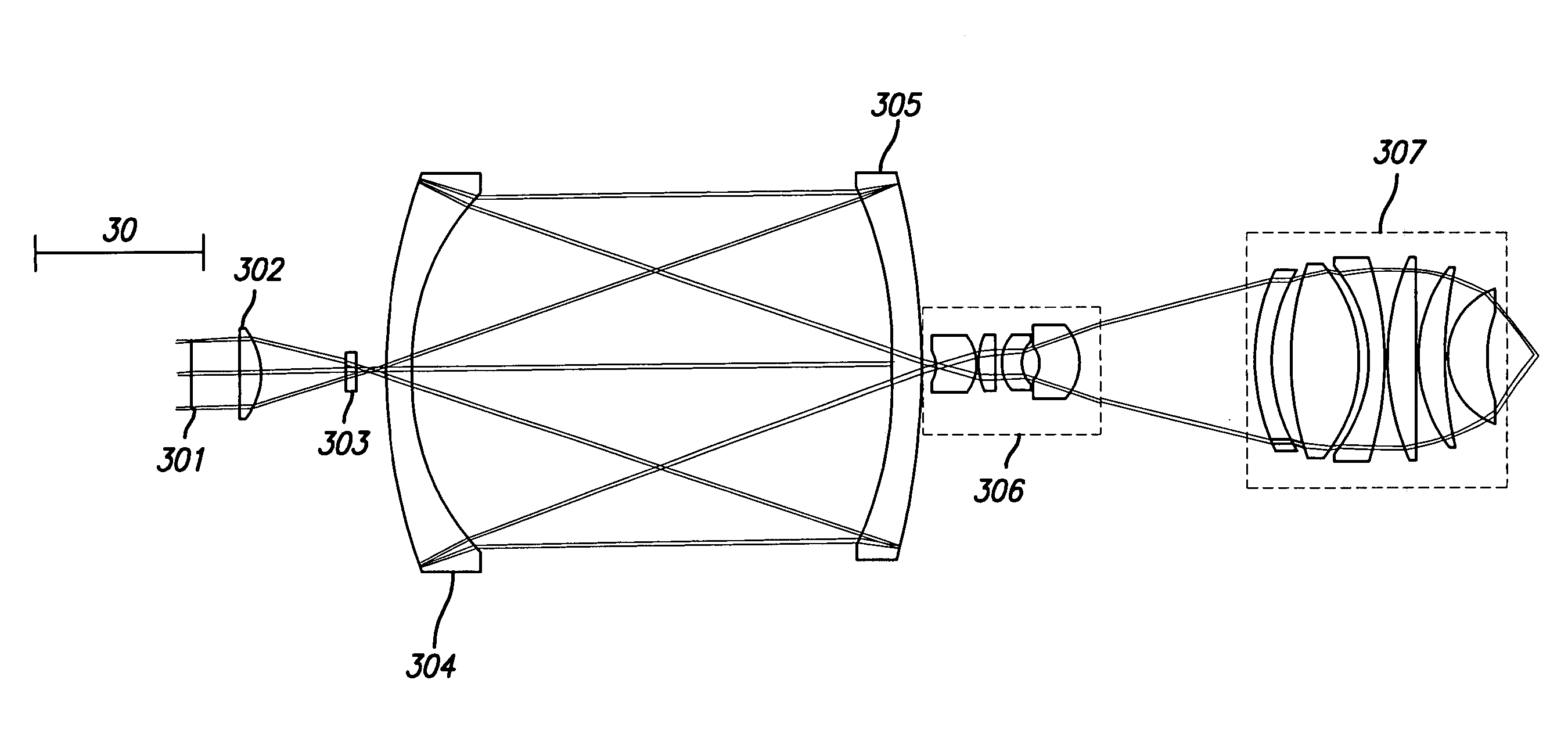
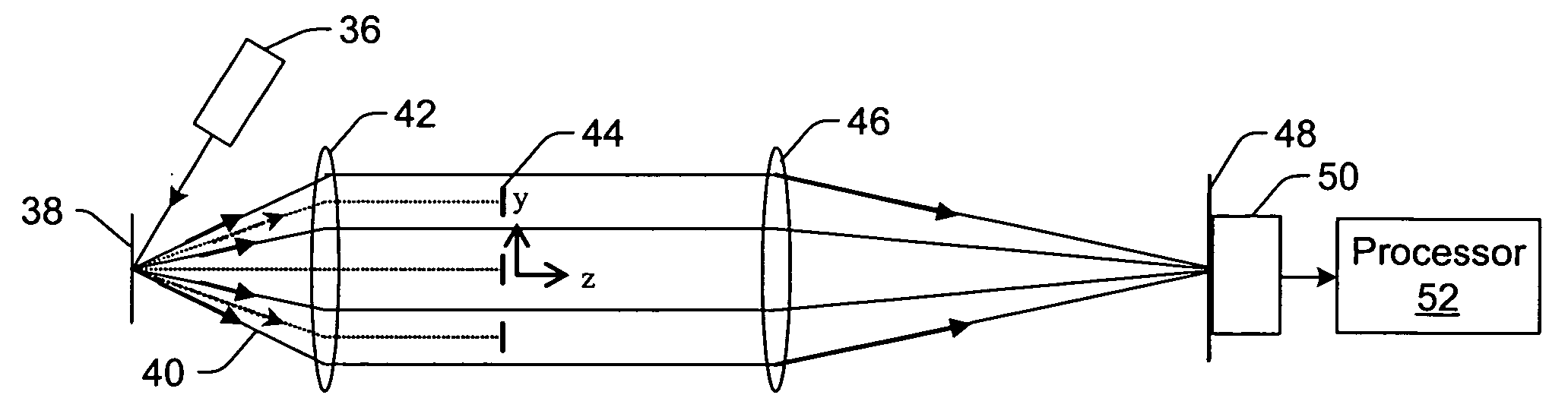
A system for multiple mode imaging is disclosed. The catadioptric system has an NA greater than 0.65, and preferably greater than 0.9, highly corrected for low and high order monochromatic aberrations. The system employs unique illumination entrances and optics to collect reflected, diffracted, and scattered light over a range of angles. Multiple imaging modes are possible by varying the illumination geometry and apertures at the pupil plane. Illumination can enter the catadioptric optical sytems using an auxiliary beamsplitter or mirror, or through the catadioptric elements at any angle from 0 to 85 degrees from vertical. The system may employ a relayed pupil plane, used to select different imaging modes, provide simultaneous operation of different imaging modes, Fourier filtering, and other pupil shaping operations.
Owner:KLA TENCOR CORP
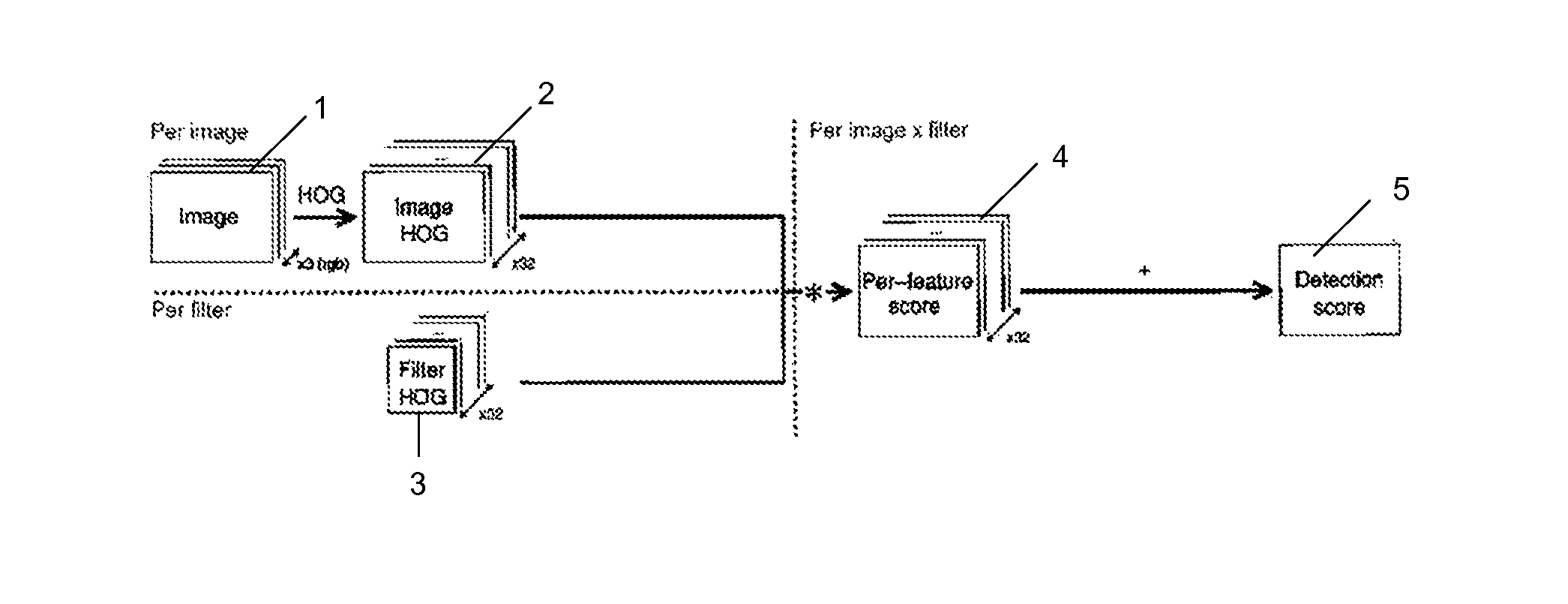
Object detection method, object detector and object detection computer program
ActiveUS20140089365A1Reduce computing timeReduces further the computation timeDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionObject detectionComputer program
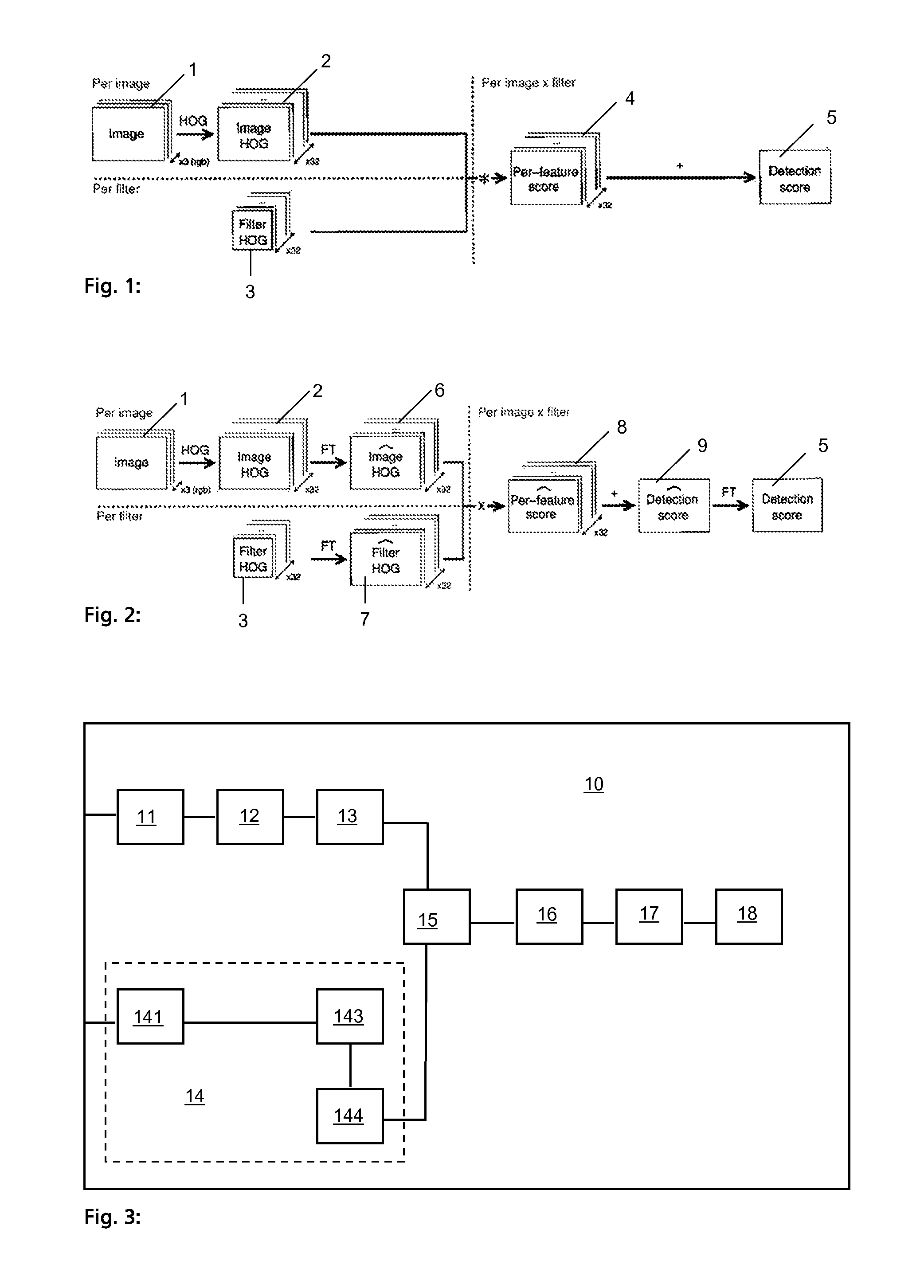
Object detection receives an input image to detect an object of interest. It determines feature matrices based on the received image, wherein each matrix represents a feature of the received image. The plurality of matrices are Fourier transformed to Fourier feature matrices. Fourier filter matrices are provided, each representing a feature of an object transformed in Fourier space. Each filter matrix is point-wise multiplied with one of the feature matrices corresponding to the same feature. The plurality of matrices are summed, resulting by point-wise multiplying each Fourier filter matrix with the corresponding Fourier feature matrix to obtain a Fourier score matrix. An inverse Fourier transform of the Fourier score matrix is performed, resulting in a score matrix, which is used to detect the object in the input image.
Owner:FOND DE LINST DE RECH IDIAP
High NA system for multiple mode imaging
InactiveUS20060279837A1Easy alignmentEasy to operateTelevision system detailsX-ray/infra-red processesCatadioptric systemIntermediate image
A system for multiple mode imaging is disclosed herein. The system is a catadioptric system preferably having an NA greater than 0.9, highly corrected for low and high order monochromatic aberrations. This system uses unique illumination entrances and can collect reflected, diffracted, and scattered light over a range of angles. The system includes a catadioptric group, focusing optics group, and tube lens group. The catadioptric group includes a focusing mirror and a refractive lens / mirror element. The focusing optics group is proximate to an intermediate image, and corrects for aberrations from the catadioptric group, especially high order spherical aberration and coma. The tube lens group forms the magnified image. Different tube lens groups can be used to obtain different magnifications, such as a varifocal tube lens group to continuously change magnifications from 20 to 200×. Multiple imaging modes are possible by varying the illumination geometry and apertures at the pupil plane. Imaging modes include bright-field, full sky, ring dark-field, inverted ring dark-field, directional dark-field, double dark-field, Manhattan geometry, confocal bright-field, confocal dark-field, conoscopic, etc. Illumination can enter the catadioptric optical system using an auxiliary beamsplitter or mirror, or through the catadioptric group at any angle from 0 to 85 degrees from vertical. Multiple beams at multiple angles may be used for illumination. The high NA catadioptric system can also have a relayed pupil plane, used to select different imaging modes, providing simultaneous operation of different imaging modes, Fourier filtering, and other pupil shaping operations.
Owner:KLA CORP
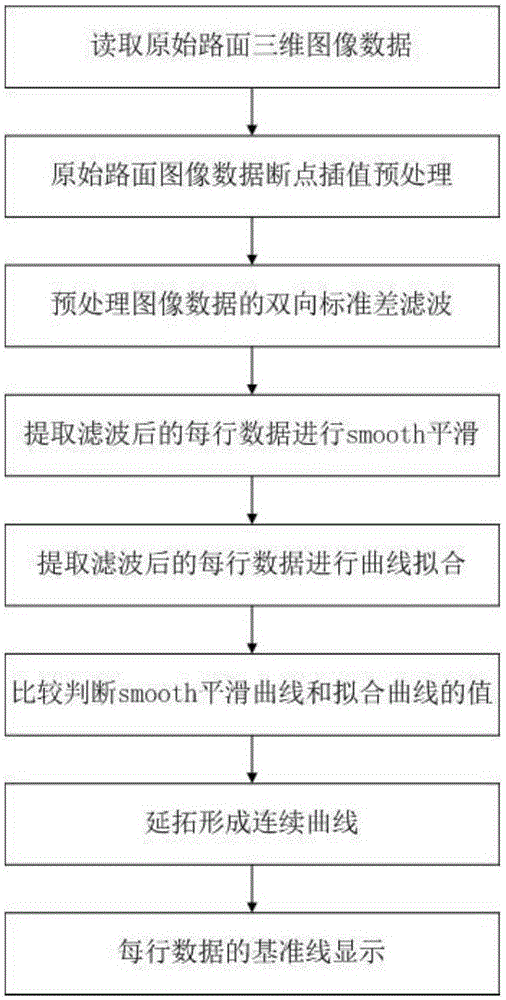
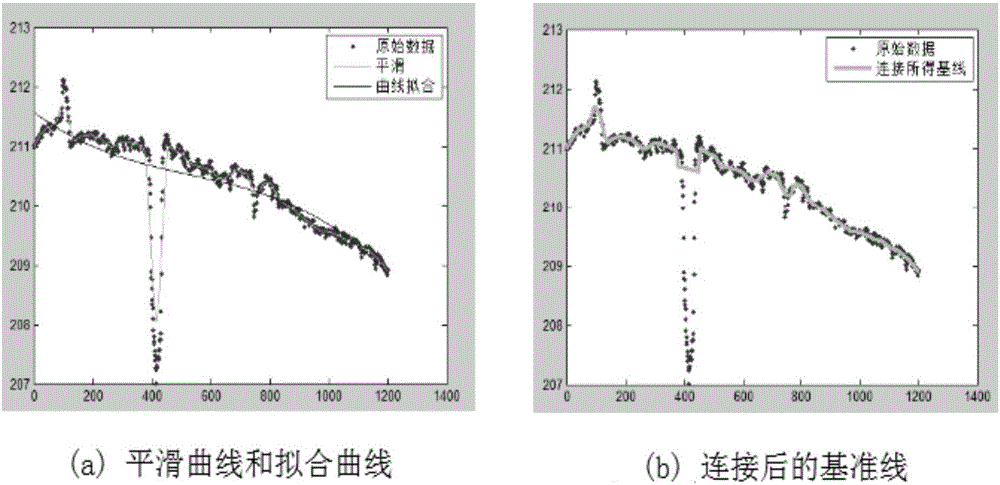
Smooth curve and fitted curve-based road surface crack extraction algorithm
The invention discloses a smooth curve and fitted curve-based road surface crack extraction algorithm. The algorithm specifically comprises the following steps of storing acquired road surface three-dimensional image data in an image data matrix AmXn, and first preprocessing the matrix AmXn by using a breakpoint interpolation algorithm with a gradually changed slope to obtain a processed data matrix A'mXn; then performing bidirectional standard deviation filtration processing on the preprocessed road surface data matrix A'mXn to obtain a filtered road surface three-dimensional image data matrix A''mXn; and finally extracting each row of data of the image data matrix A''mXn, performing smoothing and curve fitting processing separately, and extracting a contour line of a road surface crack according to a smooth curve and a fitted curve, thereby extracting the crack. The algorithm is low in complexity and short in runtime, and no artificial participation is required; and compared with an algorithm used for improving a basic line and proposed according to Fourier filtering, the extraction algorithm has the advantages that a reference line obtained by the extraction algorithm is continuous and smooth, so that the crack can be treated later more conveniently.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
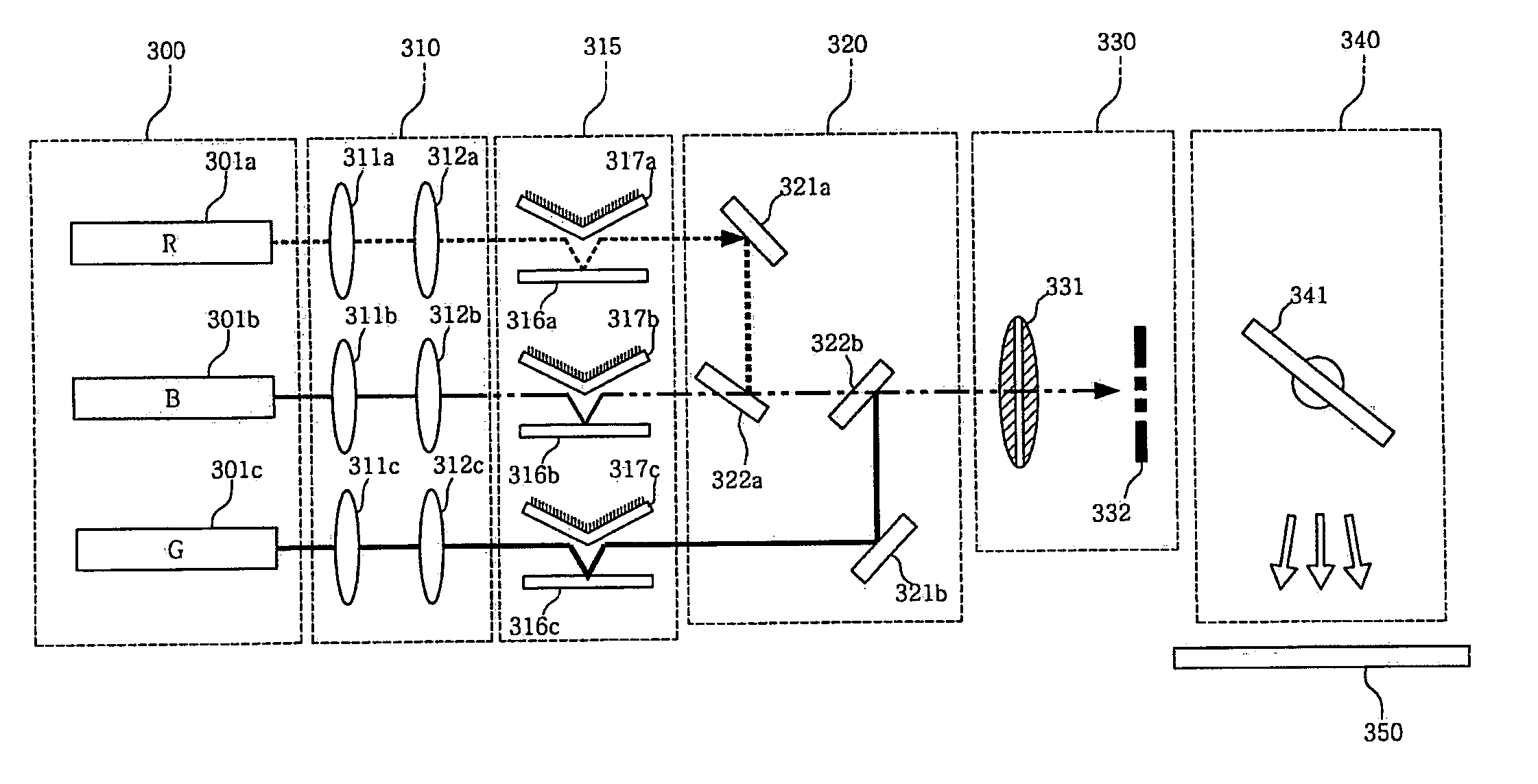
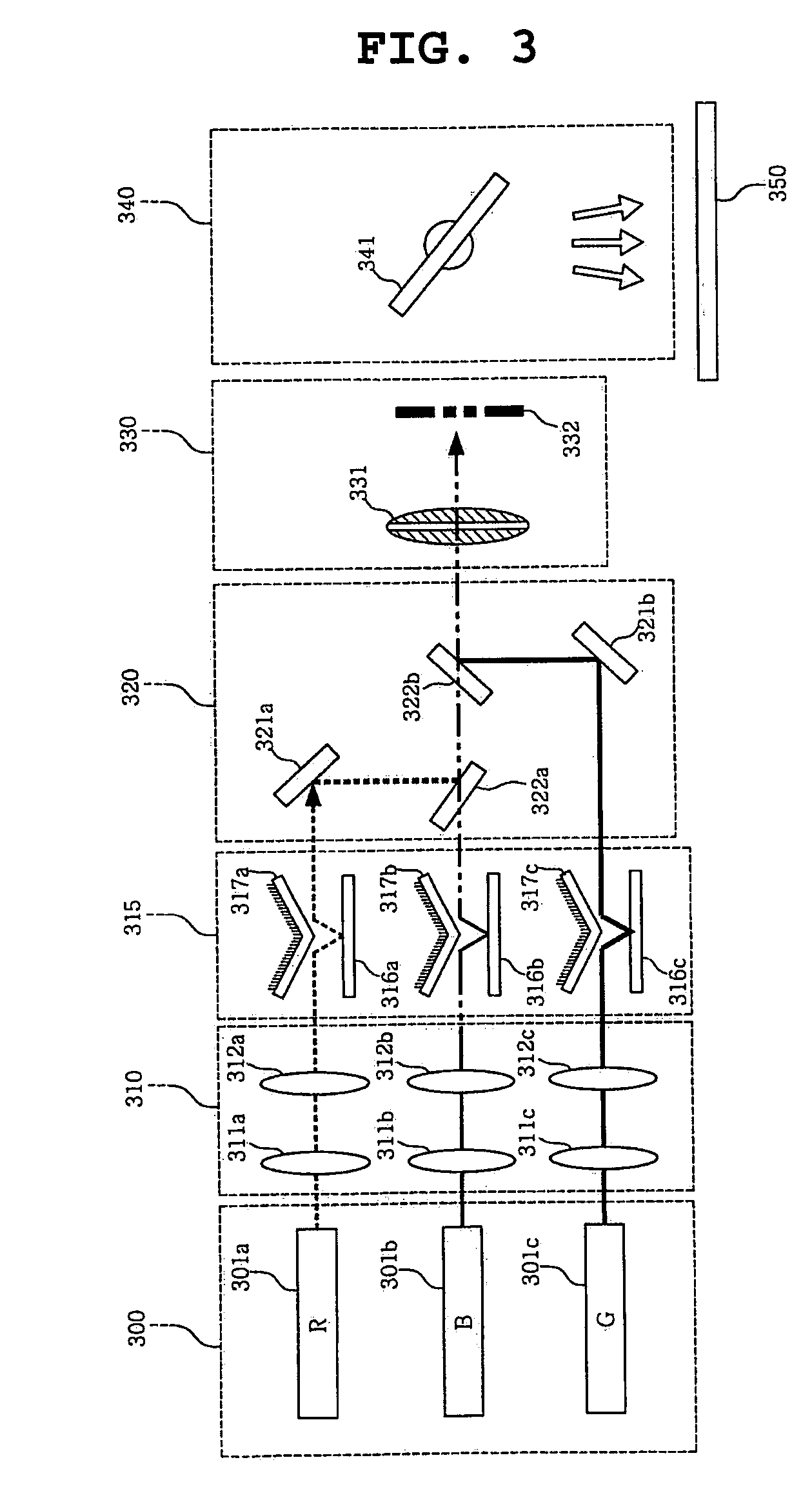
Color display device using dichroic filter
A color display device is disclosed. The color display device includes an illumination lens system, a diffractive light modulation system, a combining system, a Fourier filter system, and a projection system. The illumination lens system converts a plurality of light beams into linear parallel light beams. The diffractive light modulation system produces a plurality of diffracted light beams having a plurality of diffraction orders by modulating each of the plurality of parallel light beams that are almost perpendicularly incident from the illumination lens system, The combining system focuses the plurality of diffracted light beams having the plurality of diffraction orders. The Fourier filter system selects diffracted light beams having desired diffraction orders using a dichroic filter. The projection system focuses the diffracted light beams on an object, and allowing the focused diffracted light beams to scan the object.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Broad band DUV, VUV long-working distance catadioptric imaging system
InactiveUS20050153559A1Long free working distanceMinimize central obscurationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicroscopesPupilLength wave
A high performance objective having very small central obscuration, an external pupil for apertureing and Fourier filtering, loose manufacturing tolerances, large numerical aperture, long working distance, and a large field of view is presented. The objective is preferably telecentric. The design is ideally suited for both broad-band bright-field and laser dark field imaging and inspection at wavelengths in the UV to VUV spectral range.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
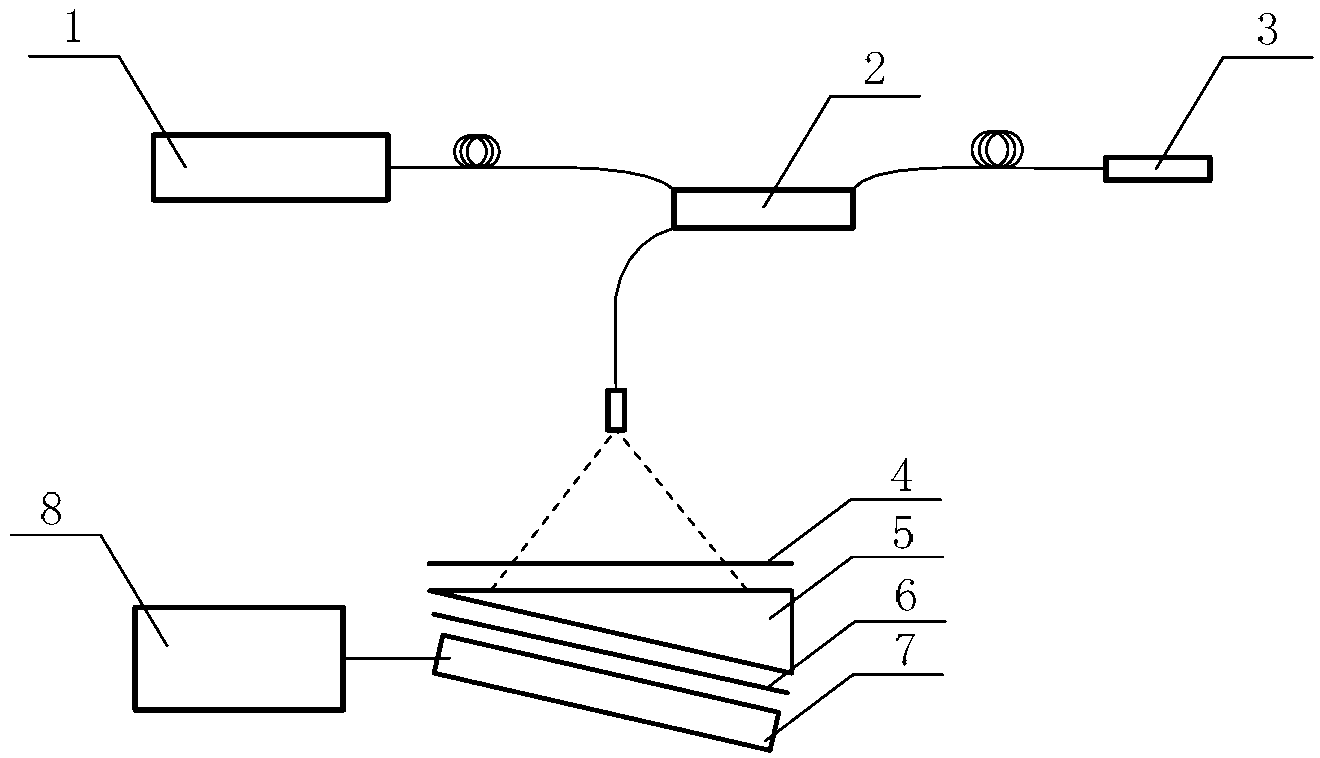
Method and apparatus for high-throughput inspection of large flat patterned media using dynamically programmable optical spatial filtering
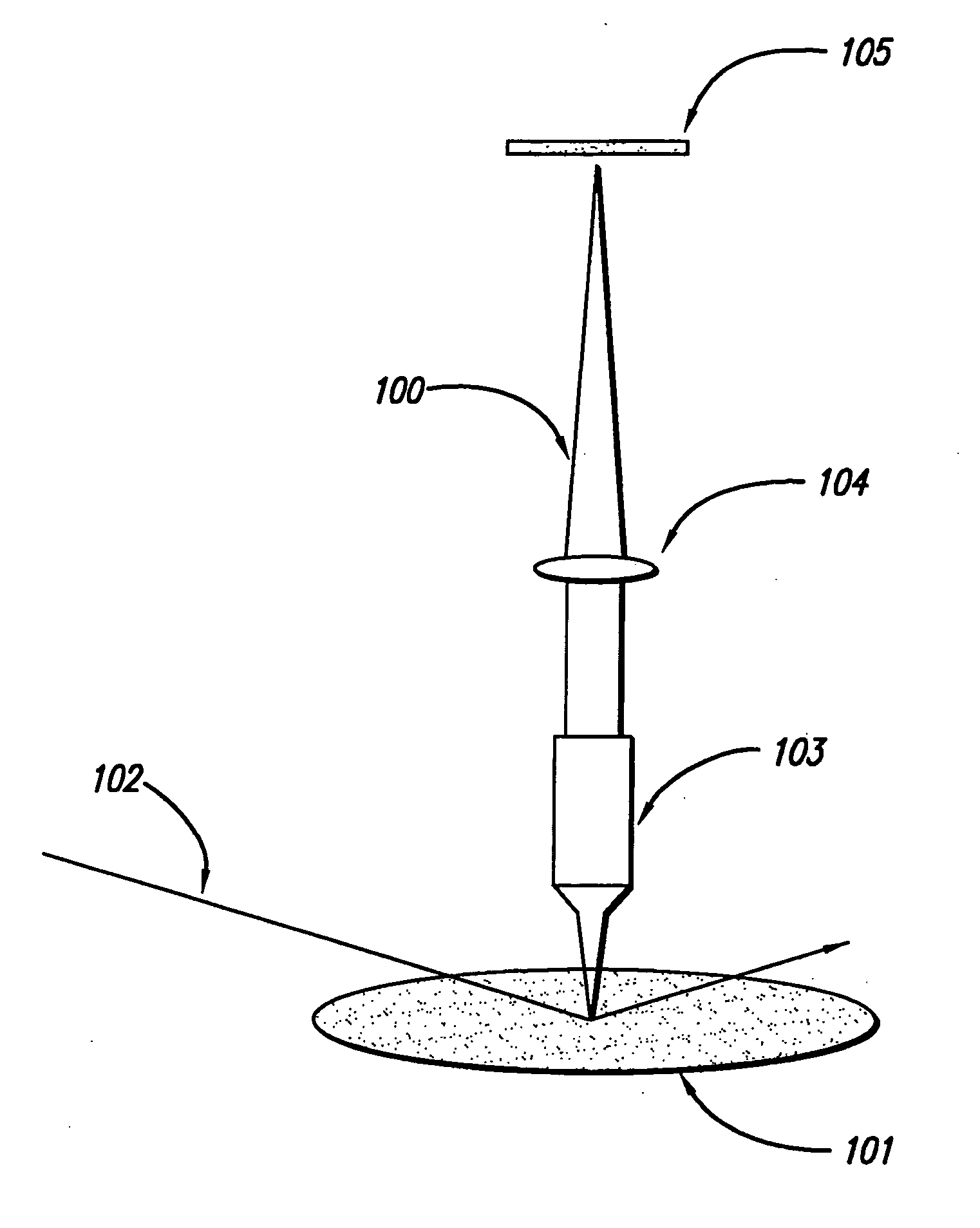
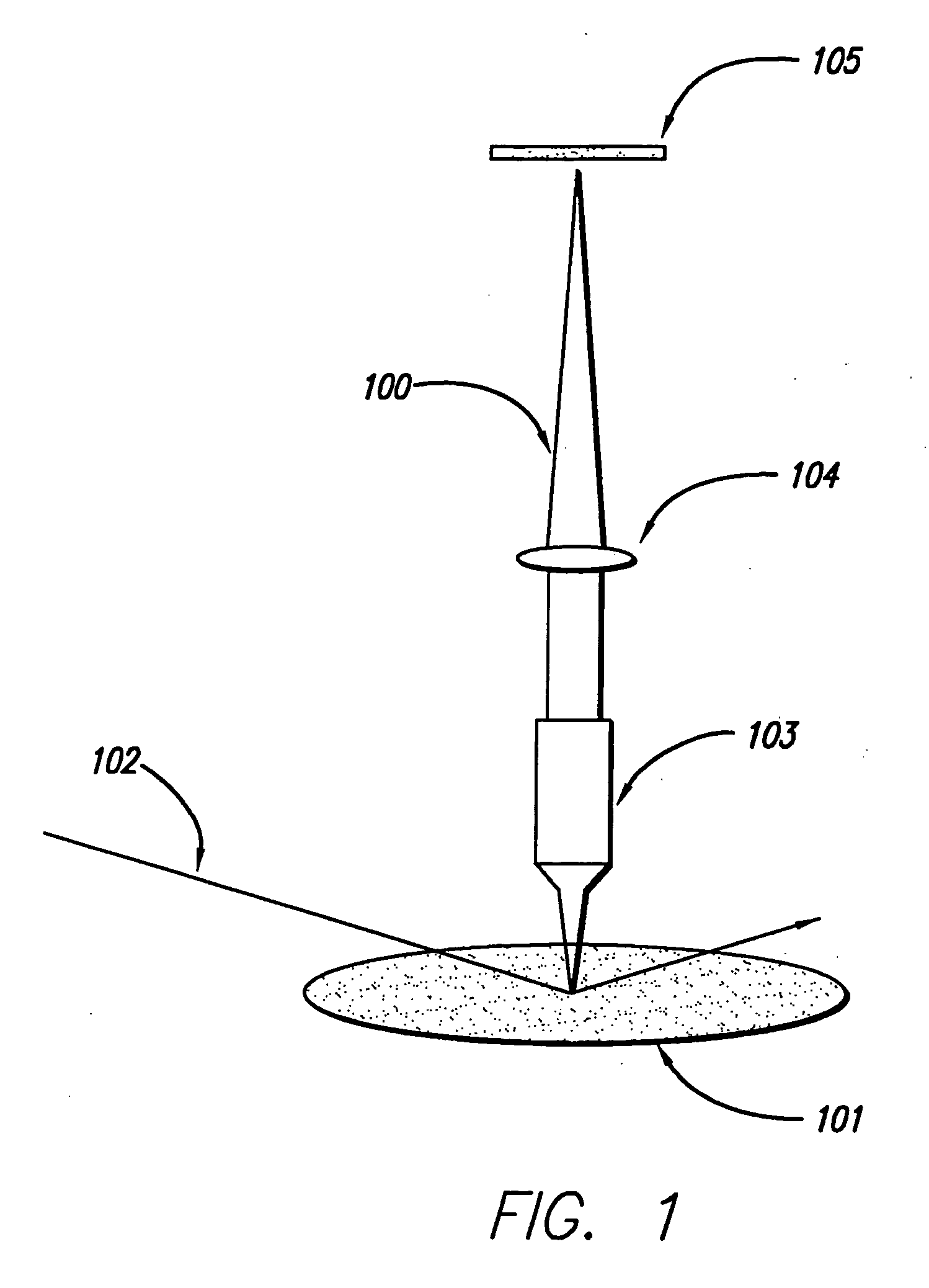
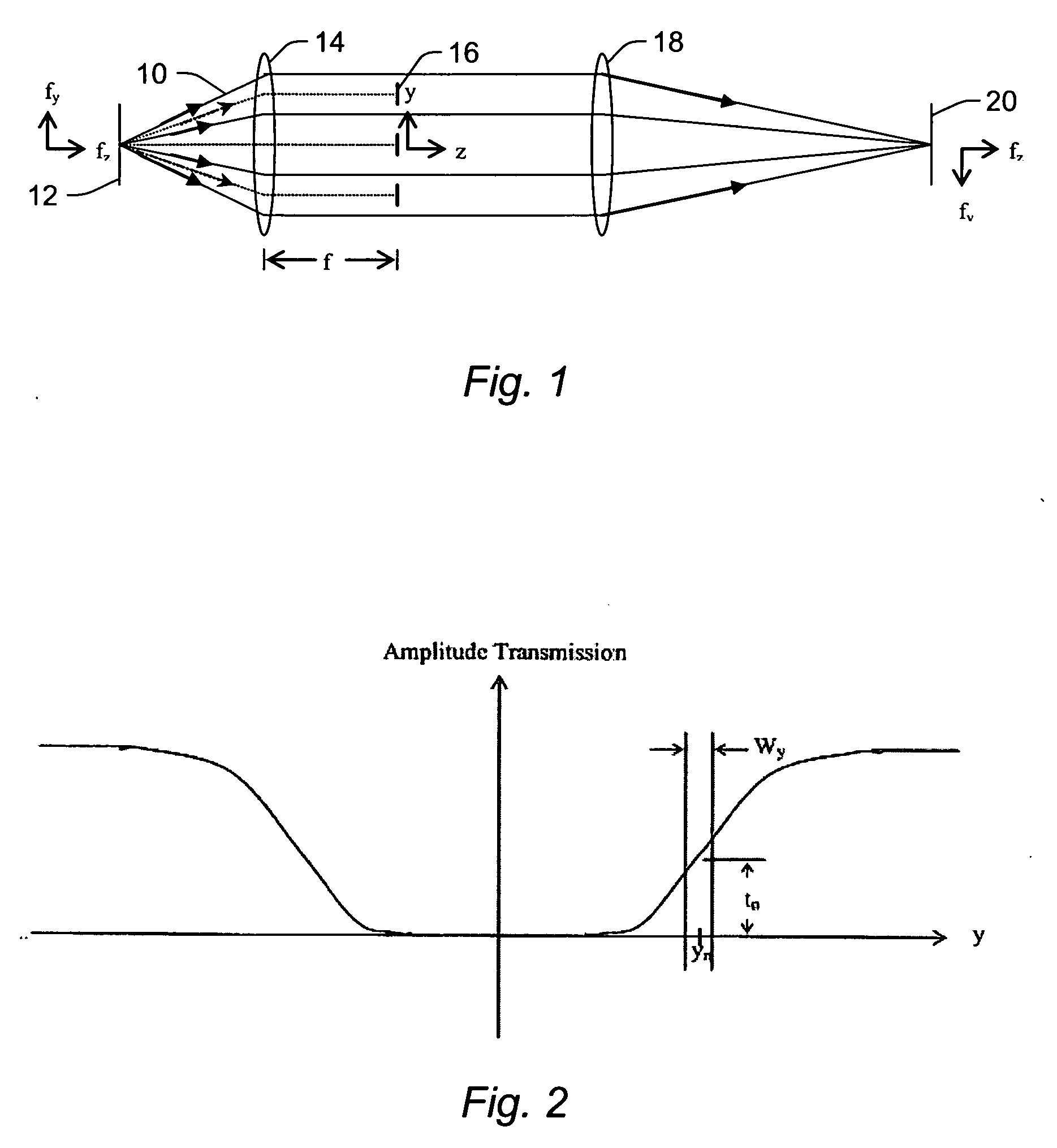
InactiveUS20060186361A1Reduce resolutionAutomatic control devicesBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsSpatial light modulatorSpatial fourier transform
In an inspection system for planar objects having periodic structures, programmable optical Fourier filtering in the focal plane of a telecentric lens system is used to directly identify physical phenomena indicative of non-periodic defects. Lens assemblies and a coherent optical source are used to generate and observe a spatial Fourier transform of a periodic structure in the Fourier plane. Optical Fourier filtering (OFF) is performed in the focal plane using an electrically programmable and electrically alignable spatial light modulator. The spatial light modulator with high signal to noise ratio is electrically reconfigurable according to a feedback-driven, filter construction and alignment algorithm. The OFF enhances any non-periodic components present in the Fourier plane and final image plane of the object. A system having a plurality of inspection channels provides high-throughput inspection of objects with small non-periodic defects while maintaining high detection sensitivity.
Owner:PHOTON DYNAMICS
Fourier plane analysis and refinement of slm calibration
ActiveUS20090008580A1Photometry using reference valuePhotomechanical apparatusZeroth orderPhase sensitive
The present disclosure relates to phase-sensitive calibration of an SLM system. In particular, it relates to selecting among local calibrations when there is more than one calibration that satisfies a calibration intensity criteria. It utilizes information available before Fourier filtering, from non-zeroth order diffraction components to counter drift among alternative local calibrations.
Owner:MICRONIC LASER SYST AB
Mask inspection with fourier filtering and image compare
InactiveUS9041903B2Easy defect detectionHigh detection sensitivityUsing optical meansOriginals for photomechanical treatmentMask inspectionImage resolution
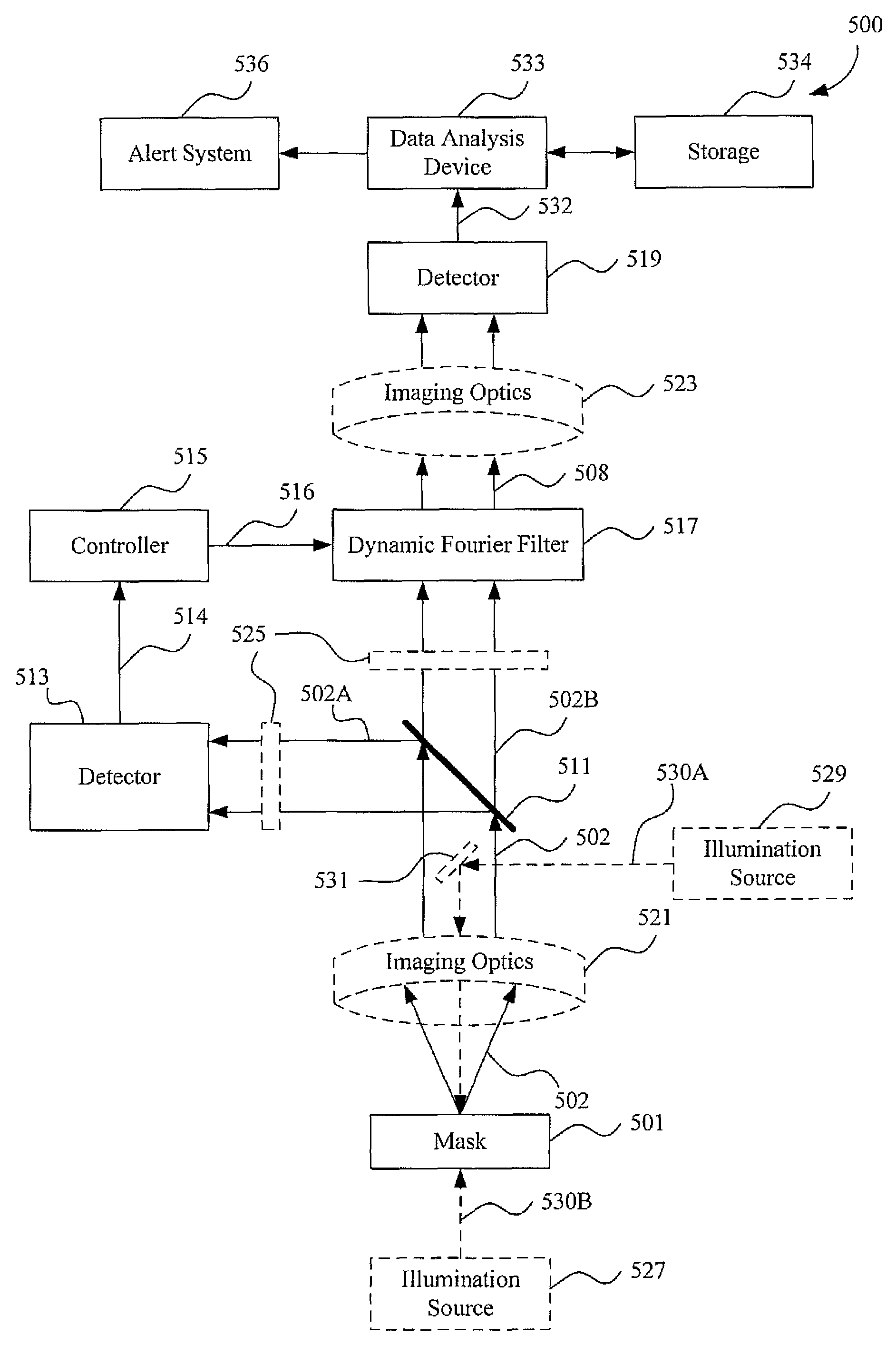
A mask inspection system with Fourier filtering and image compare can include a first detector, a dynamic Fourier filter, a controller, and a second detector. The first detector can be located at a Fourier plane of the inspection system and can detect a first portion of patterned light produced by an area of a mask. The dynamic Fourier filter can be controlled by the controller based on the detected first portion of the patterned light. The second detector can detect a second portion of the patterned light produced by the section of the mask and transmitted through the dynamic Fourier filter. Further, the mask inspection system can include a data analysis device to compare the second portion of patterned light with another patterned light. Consequently, the mask inspection system is able to detect any possible defects on the area of the mask more accurately and with higher resolution.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
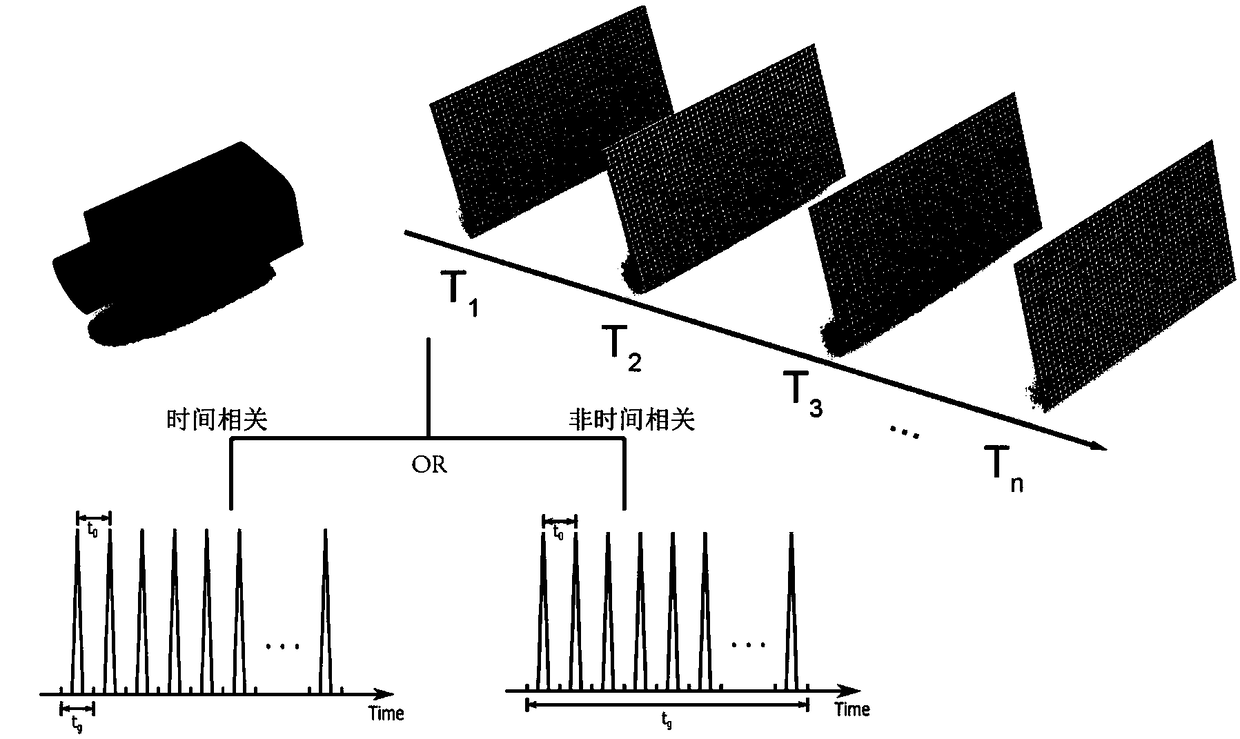
Photon-level spatial mapping correlation measurement method based on single photon imaging device
The invention provides a photon-level spatial mapping correlation measurement method based on a single photon imaging device. The quantum variables in the target space are converted into the positionvariables of photons by the detection device. The correlation of the target spatial variables is transformed into the correlation of the position spatial variables. Performing photographing frame by frame according to the time sequence by the detection device and performing division according to the time interval, and the temporal correlations events in the division are recorded in the correlationmatrix so as to construct the time-related correlation matrix. In the position space, the spatial correlation of the photons is obtained by using the detection device, and temporal correlation measurement and non-temporal correlation measurement of the target spatial variables are realized indirectly. The gate width time of the imaging system is set, the temporal correlation and non-temporal correlation information is measured and the continuity is recovered by using the Fourier filtering mode.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAODA INTELLECTUAL PORPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Serrated fourier filters and inspection systems
ActiveUS20060274305A1Smooth changeDiffraction reductionOptically investigating flaws/contaminationOptical elementsTransmittanceEngineering
Serrated Fourier filters and inspection systems are provided. One Fourier filter includes one or more blocking elements configured to block a portion of light from a wafer. The Fourier filter also includes periodic serrations formed on edges of the one or more blocking elements. The periodic serrations define a transition region of the one or more blocking elements. The periodic serrations are configured to vary transmission across the transition region such that variations in the transmission across the transition region are substantially smooth. One inspection system includes a Fourier filter configured as described above and a detector that is configured to detect light transmitted by the Fourier filter. Signals generated by the detector can be used to detect the defects on the wafer.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com