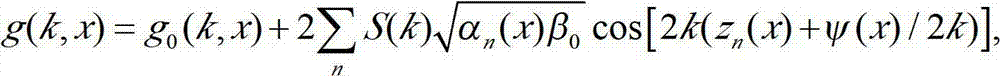Patents
Literature
32 results about "Spatial fourier transform" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
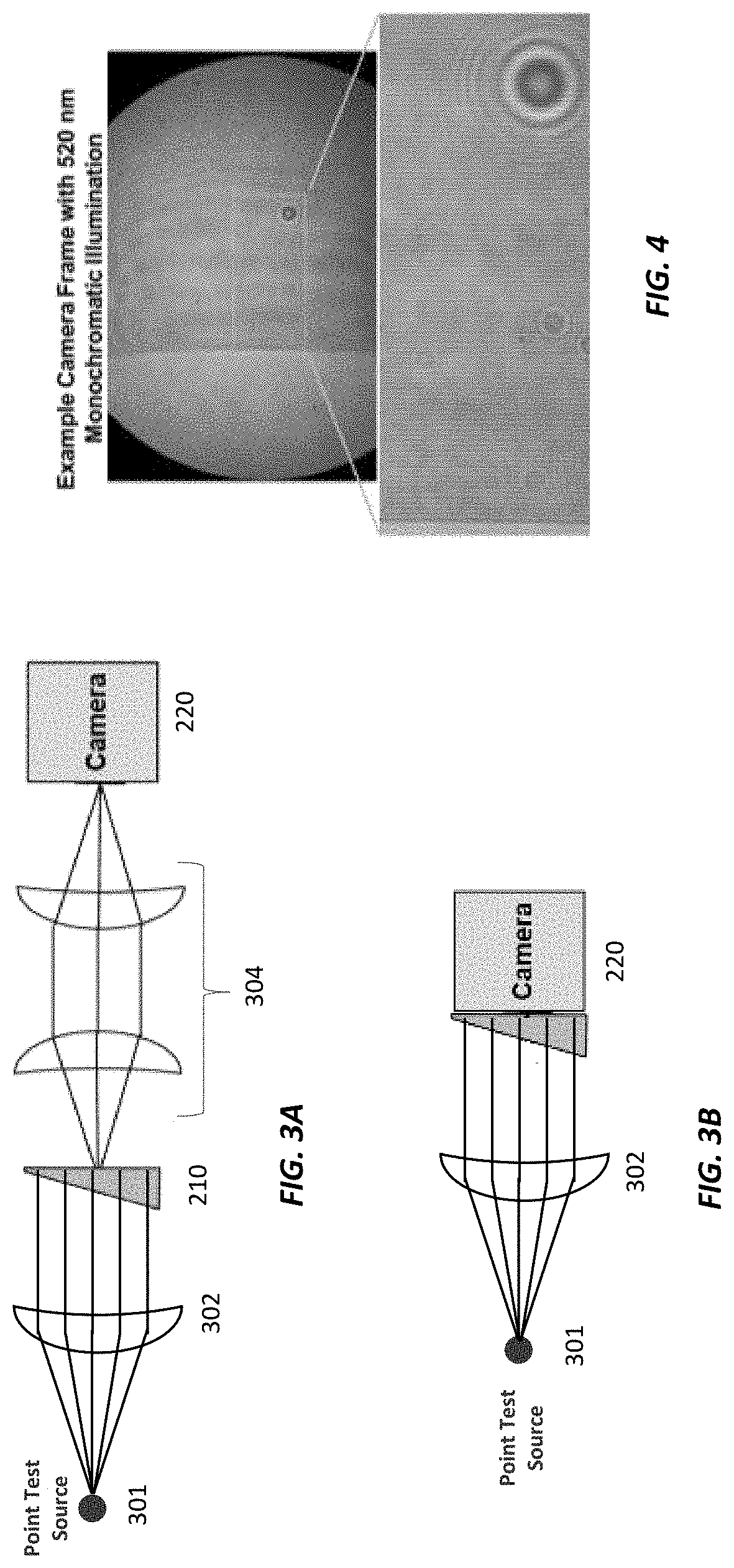
The Fourier Transform is an important image processing tool which is used to decompose an image into its sine and cosine components. The output of the transformation represents the image in the Fourier or frequency domain, while the input image is the spatial domain equivalent.
Fourier domain sensing
InactiveUS20120257197A1Photometry using reference valueRadiation pyrometrySpatial correlationLocation detection
Methods and systems are disclosed of sensing an object. A first radiation is spatially modulated to generate a structured second radiation. The object is illuminated with the structured second radiation such that the object produces a third radiation in response. Apart from any spatially dependent delay, a time variation of the third radiation is spatially independent. With a single-element detector, a portion of the third radiation is detected from locations on the object simultaneously. At least one characteristic of a sinusoidal spatial Fourier-transform component of the object is estimated from a time-varying signal from the detected portion of the third radiation.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
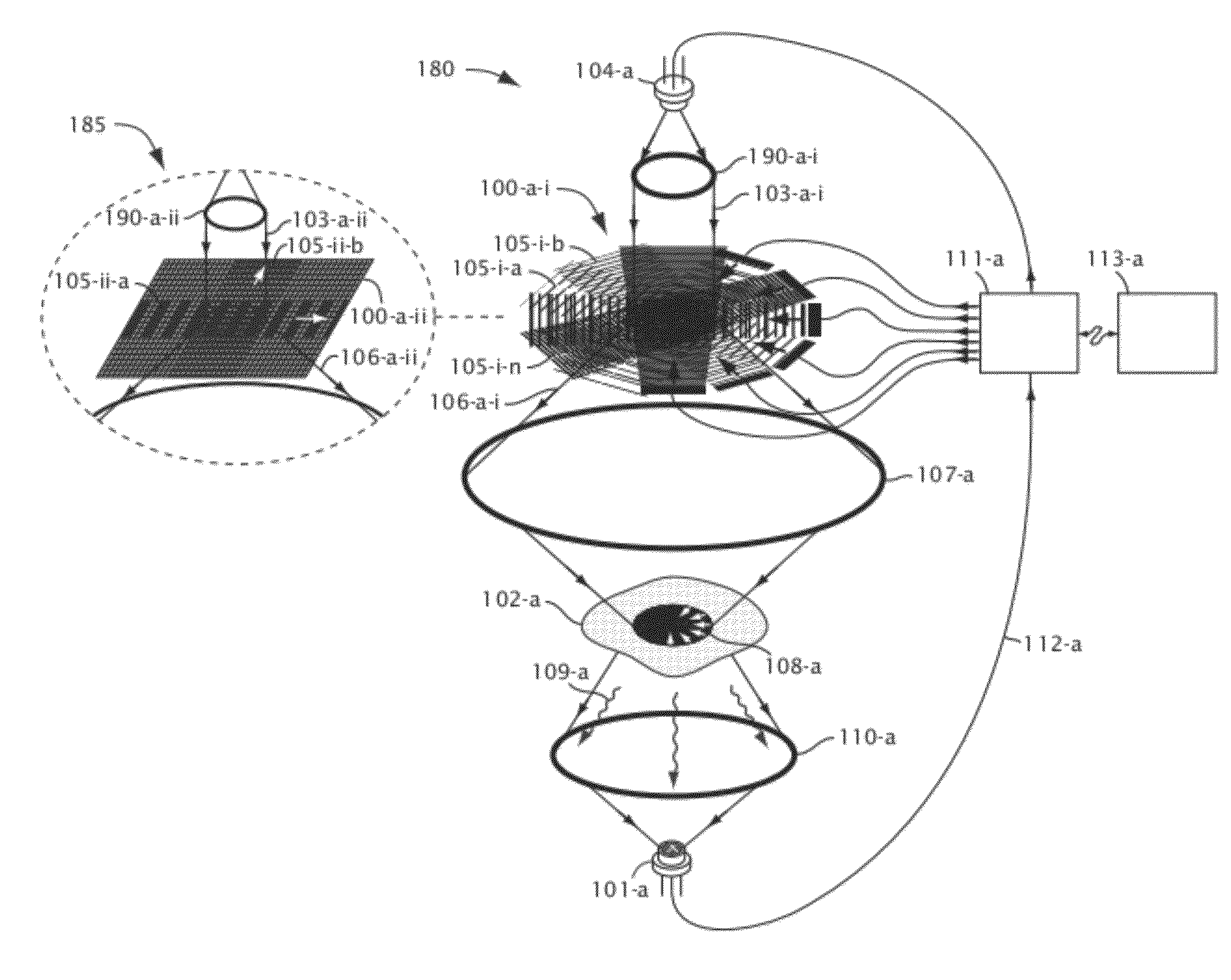
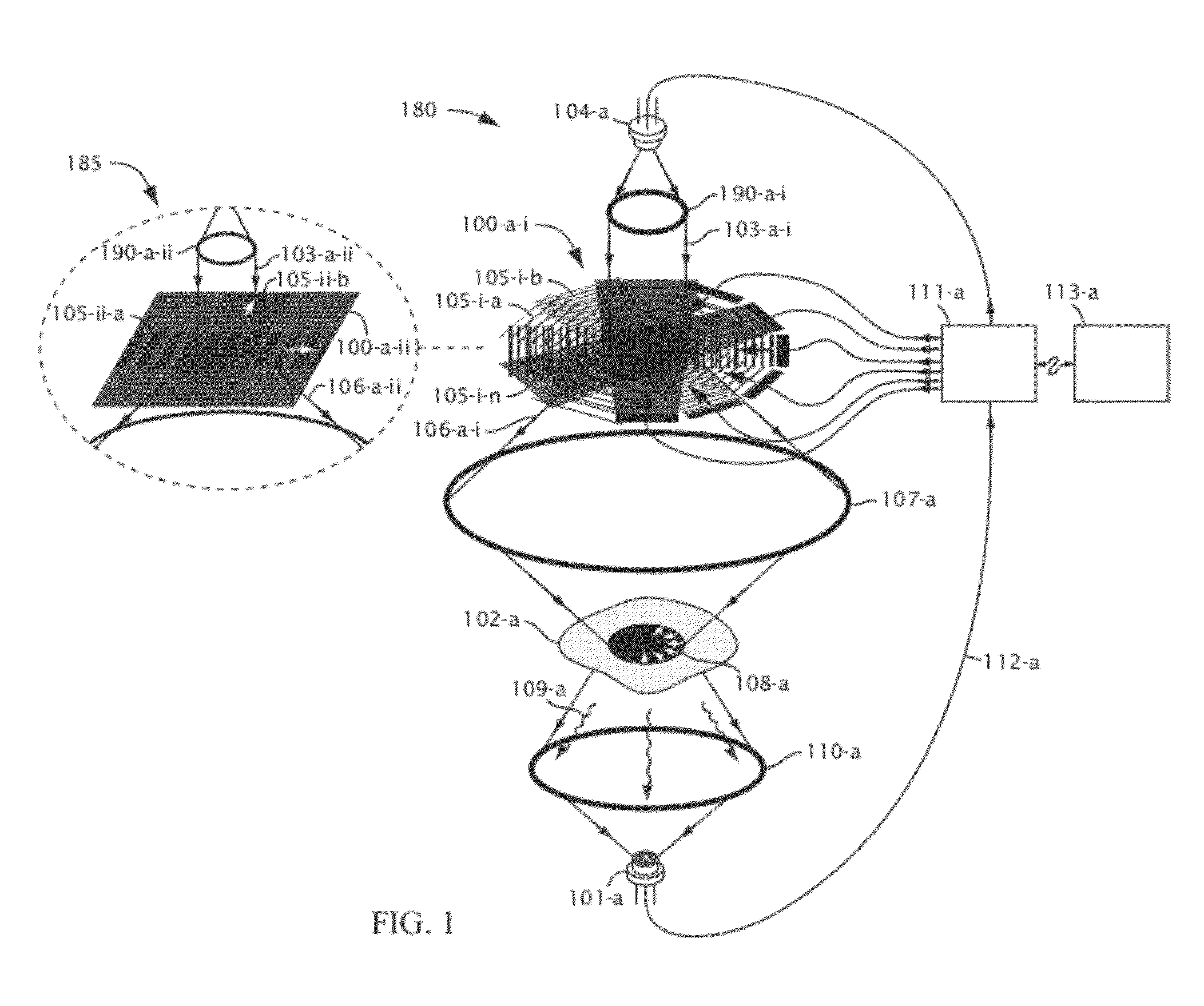
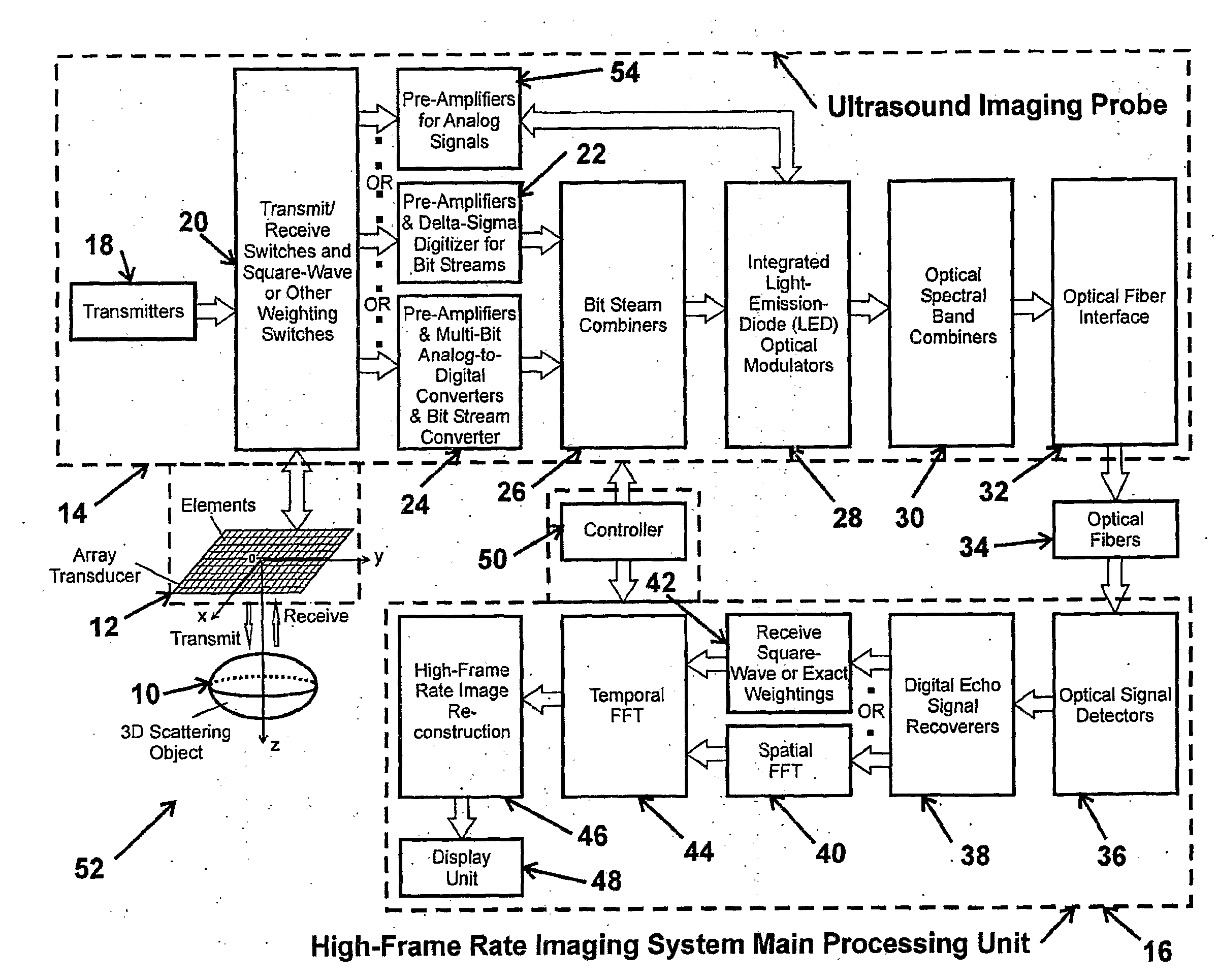
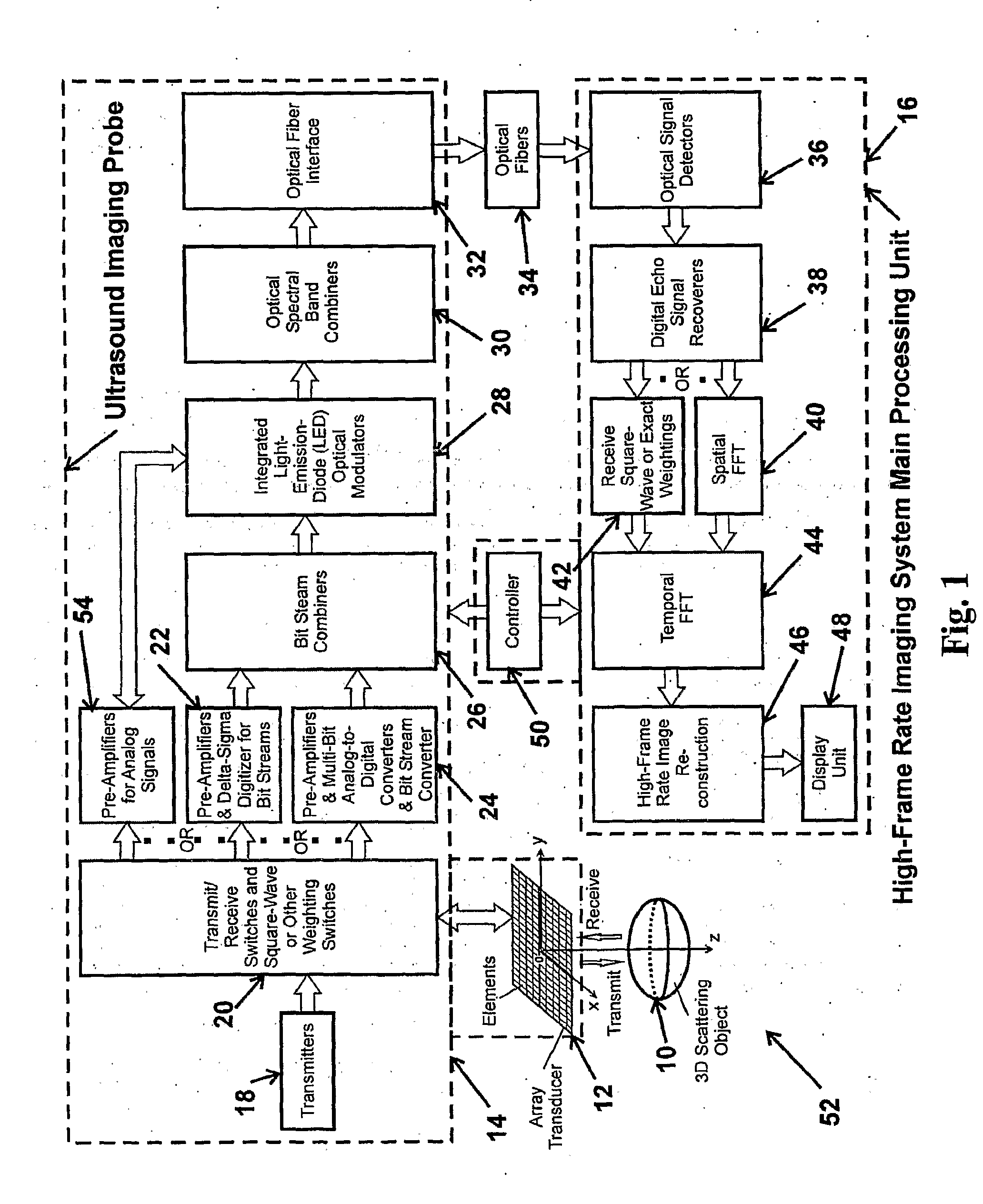
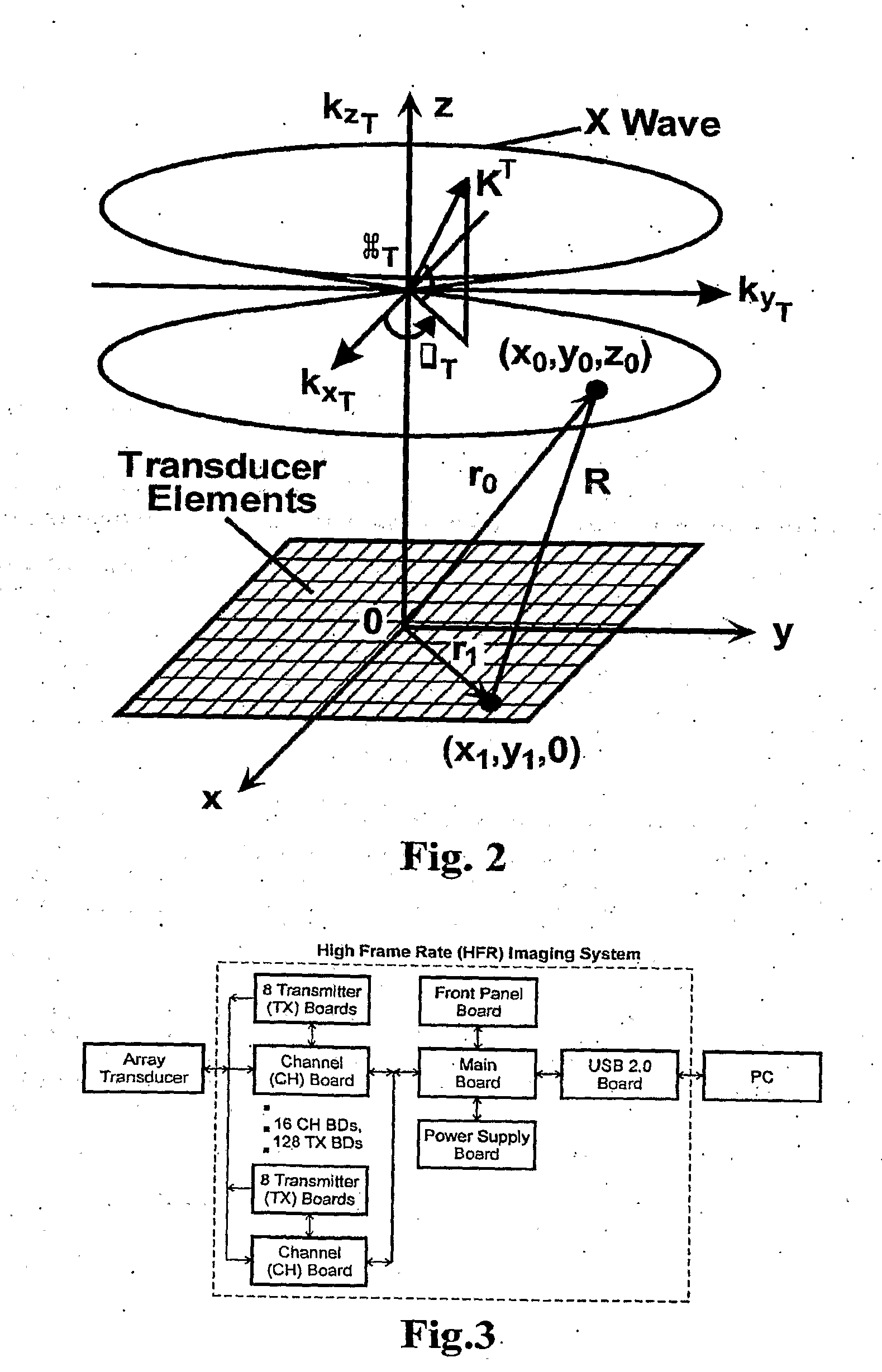
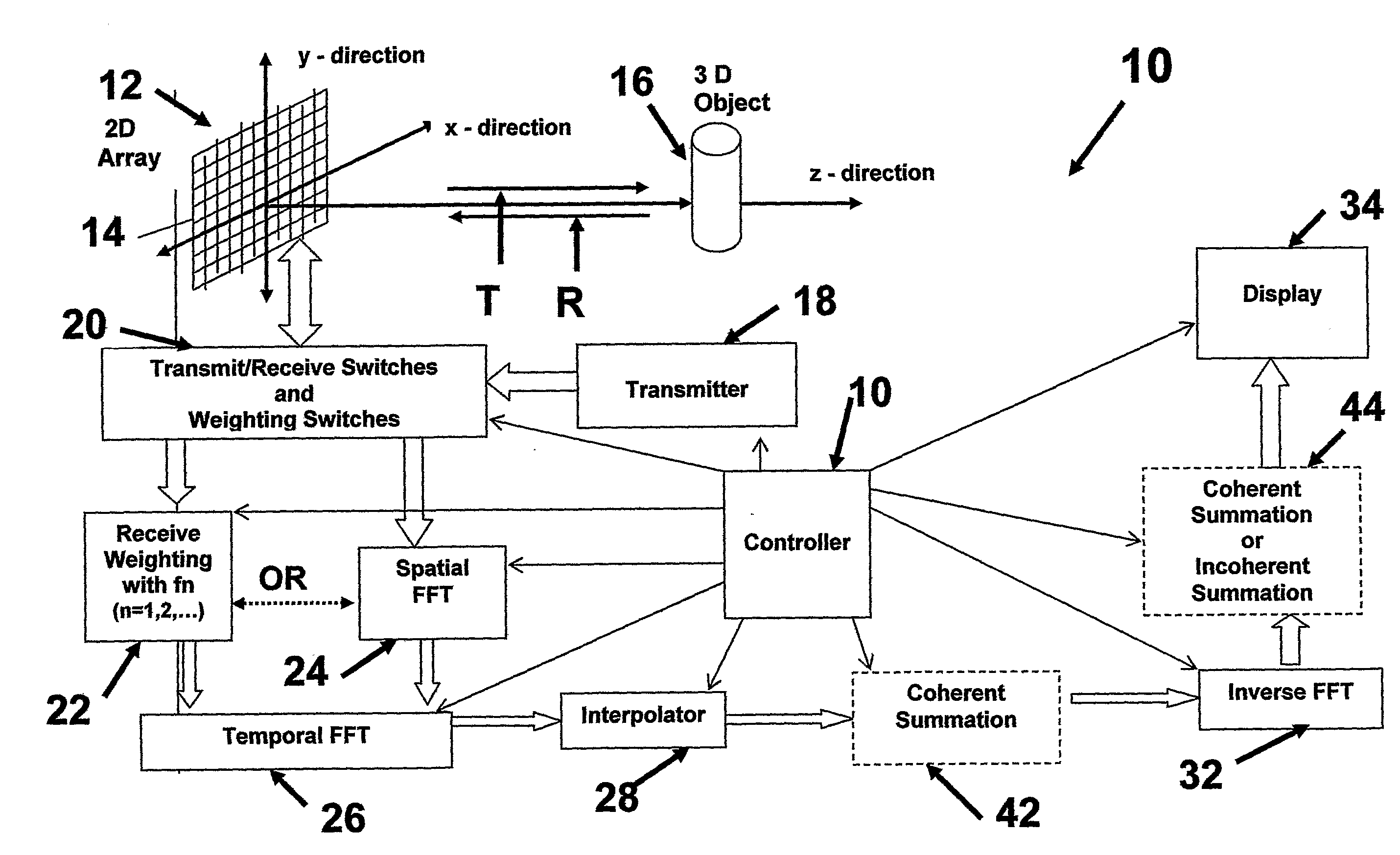
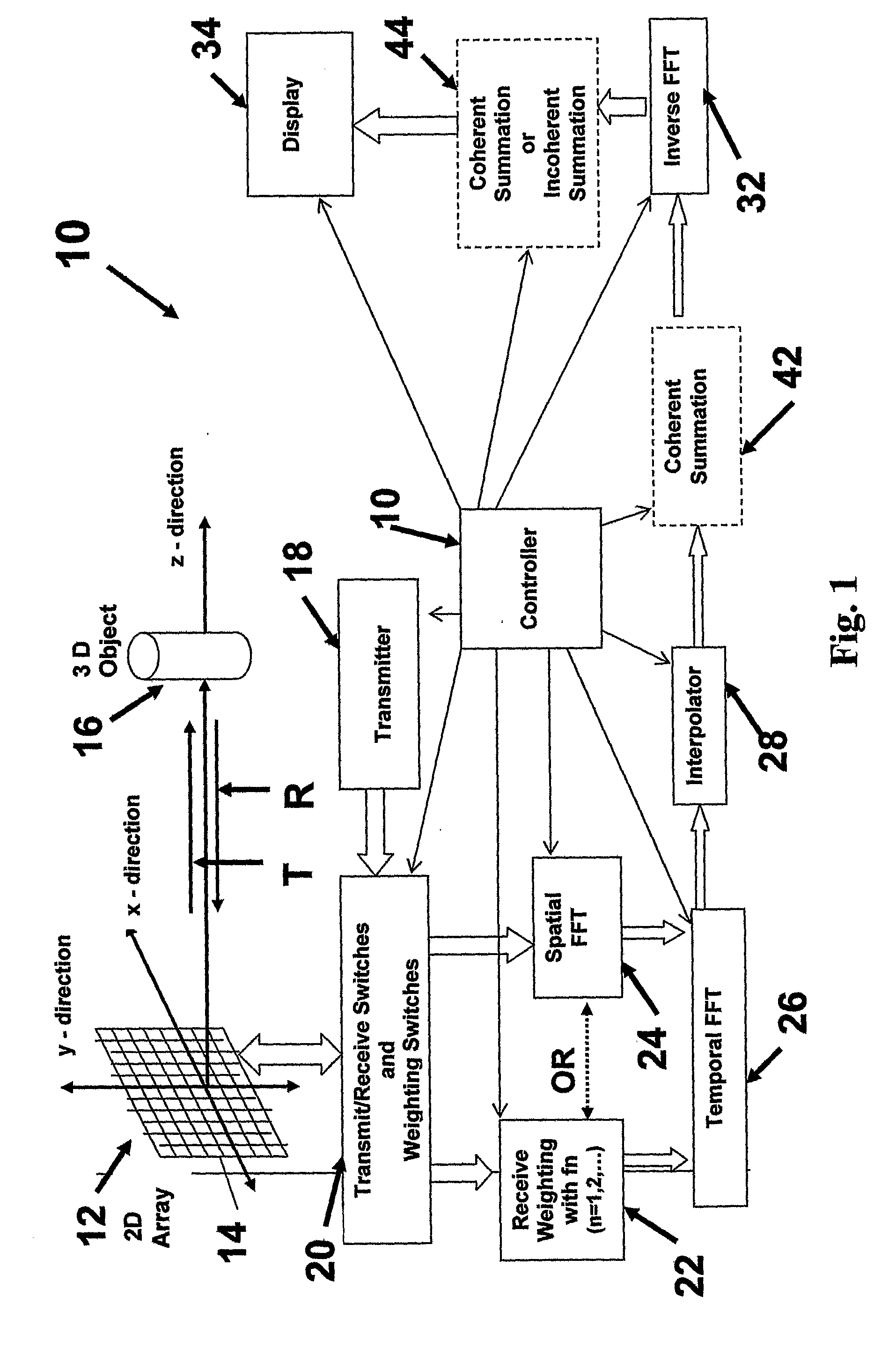
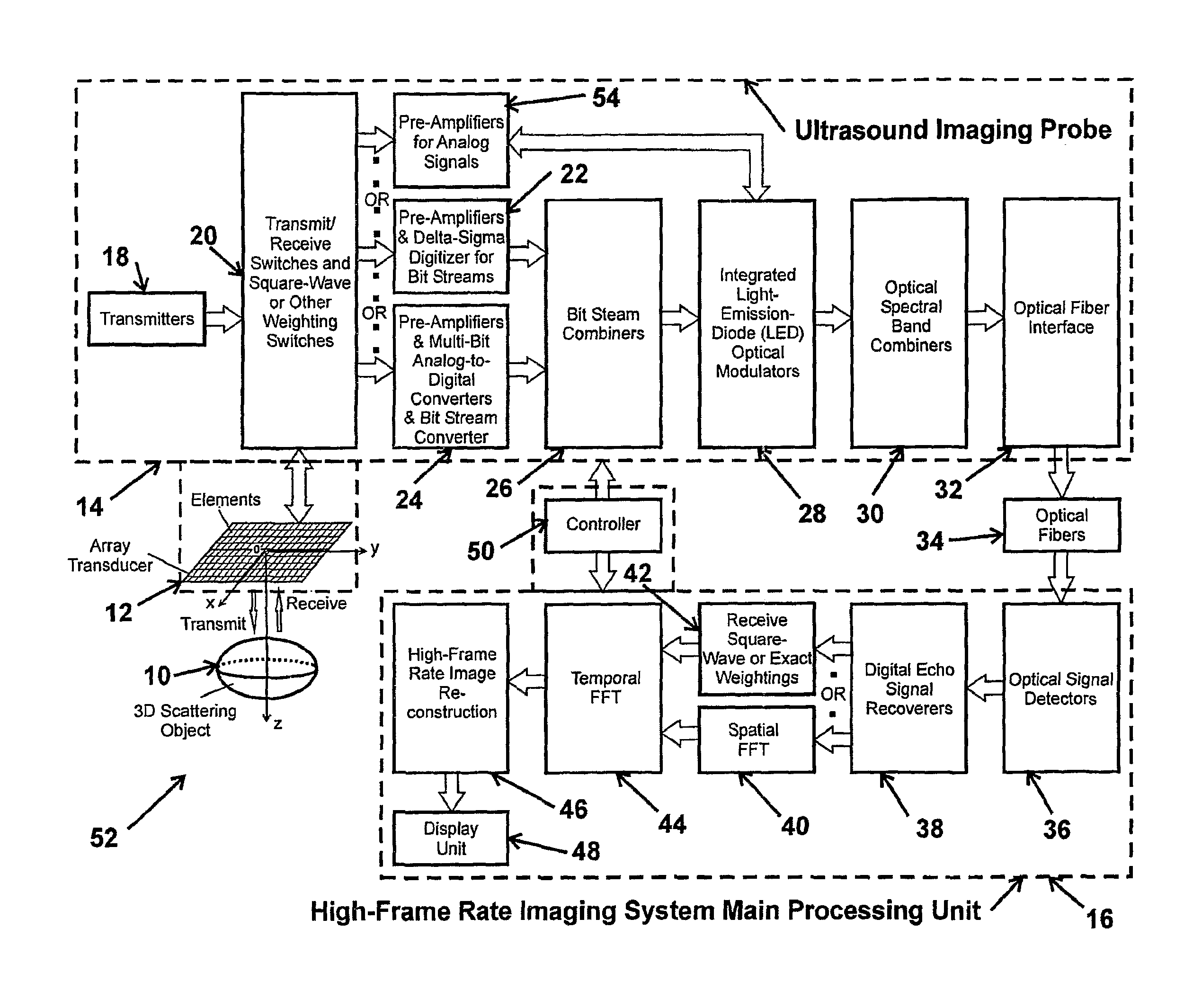
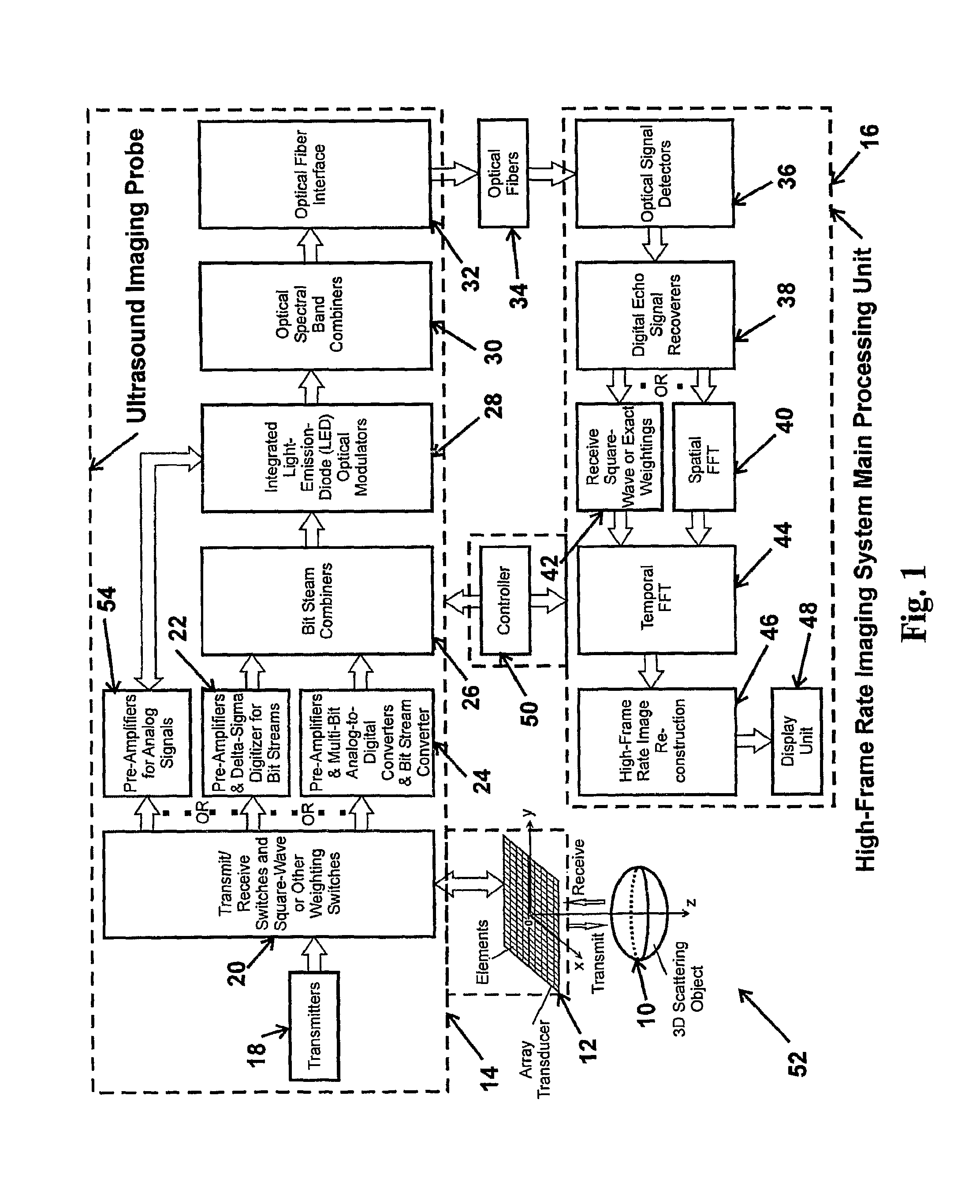
High frame rate imaging system
InactiveUS20090036772A1Increase frame rateHigh resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCharacter and pattern recognitionFast Fourier transformHigh frame rate
A system for producing an image using an imaging system includes a) transmitting at least one signal of energy toward an object to be imaged by using two transmitters having the same output amplitude but of an opposite sign, or by using one transmitter to perform the task; b) exciting at least one transducer element to produce limited-diffraction array beams or their square-wave approximations with two levels of quantitations for both sine and cosine functions, c) weighting the received signals spatially with limited-diffraction array beams, their square-wave approximations, or spatial Fourier transform, and d) digitizing and then transferring received signals through high-speed optical fibers to a system for image reconstructions.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO
System for extended high frame rate imaging with limited-diffraction beams
InactiveUS20090066727A1Character and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsHigh frame rateData set
A system for producing a high frame rate image includes transmitting a single weighted spatial frequency signal of energy toward an object to be imaged; weighting multiple receive spatial frequency signals from the object, or by performing a spatial Fourier transform; reconstructing an image data set from the single transmitted spatial frequency signal and the multiple receive spatial frequency signals; and, reconstructing the high frame rate, high resolution and high contrast image from the image data set.
Owner:TOLEDO THE UNIV OF
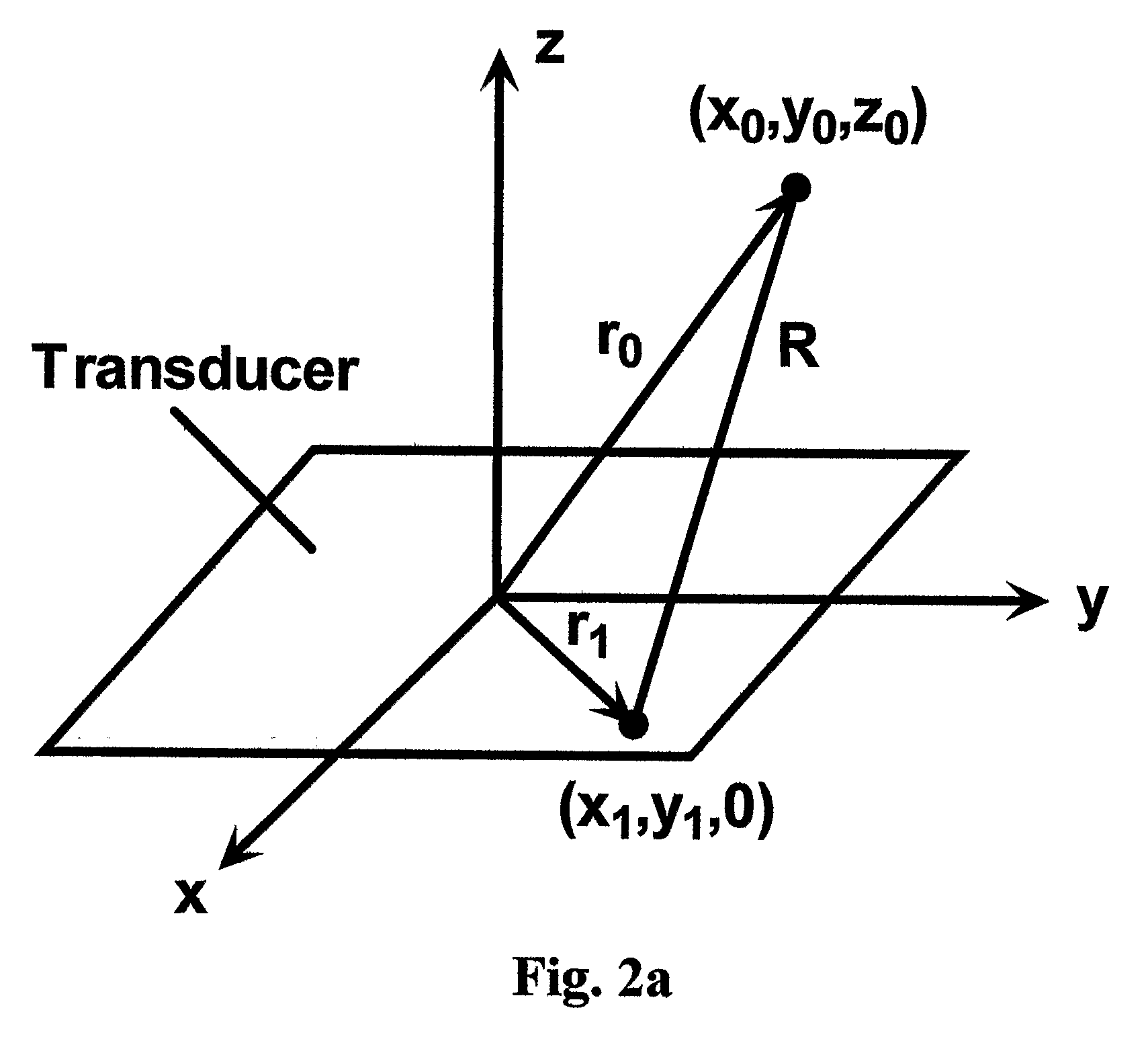
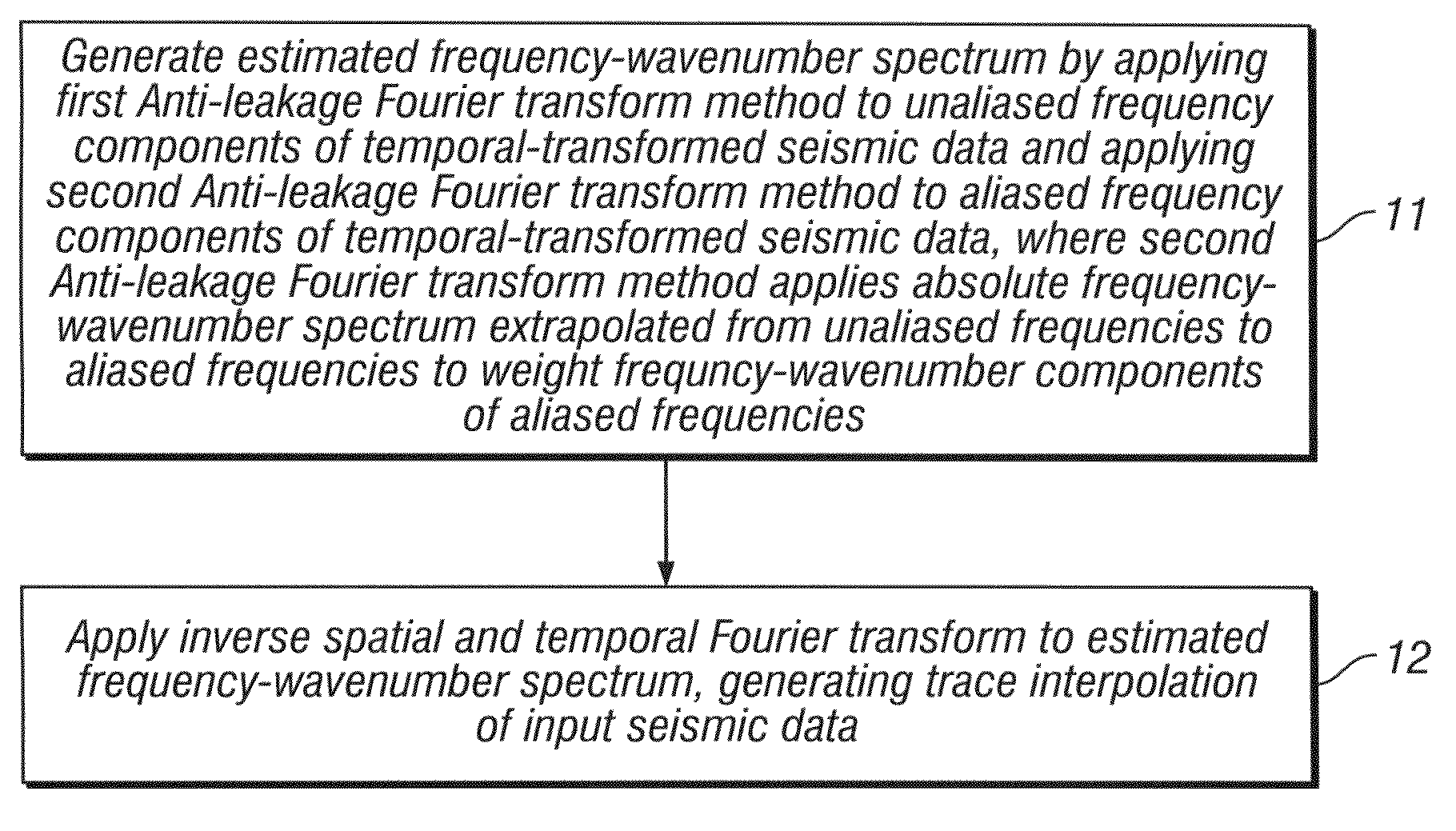
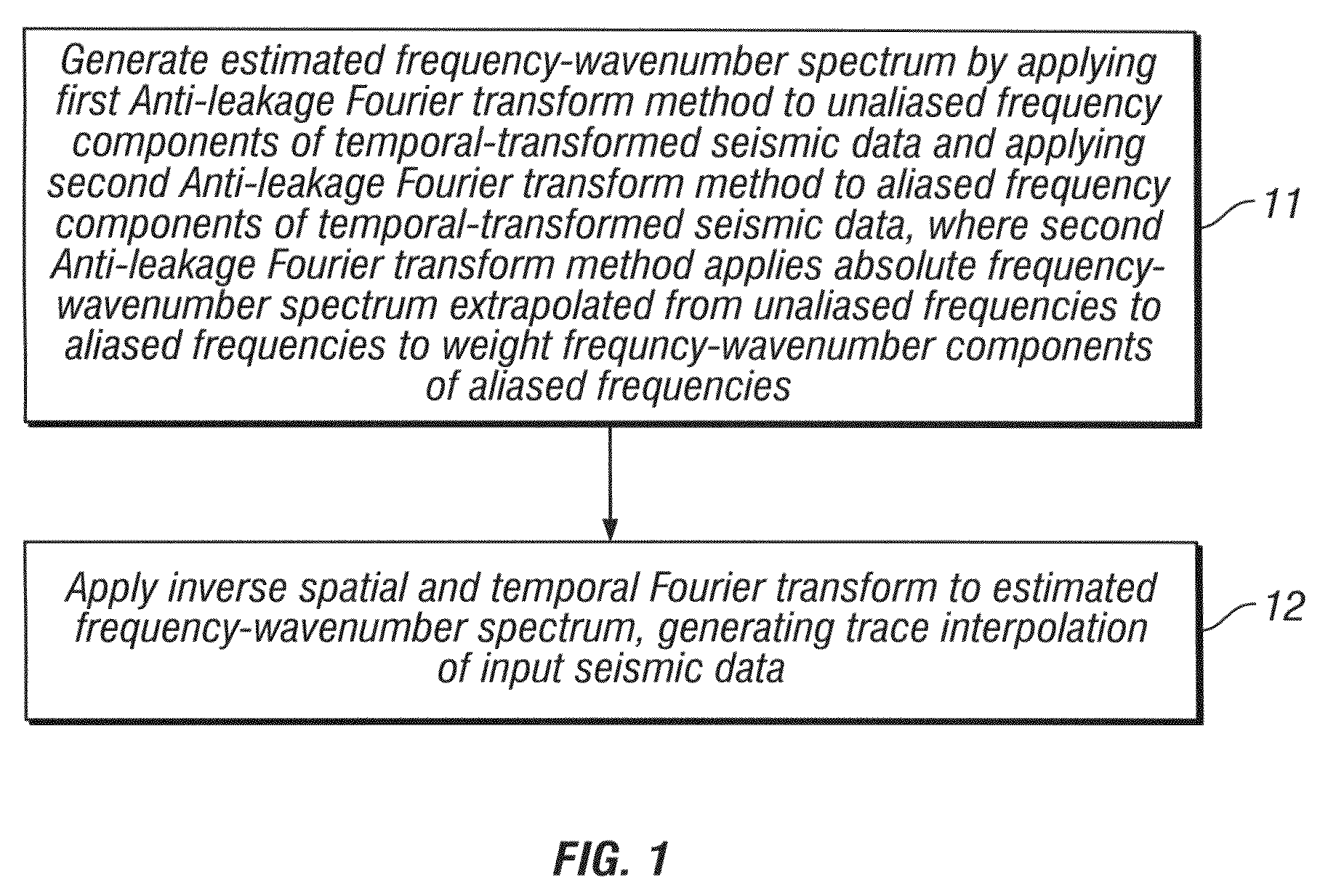
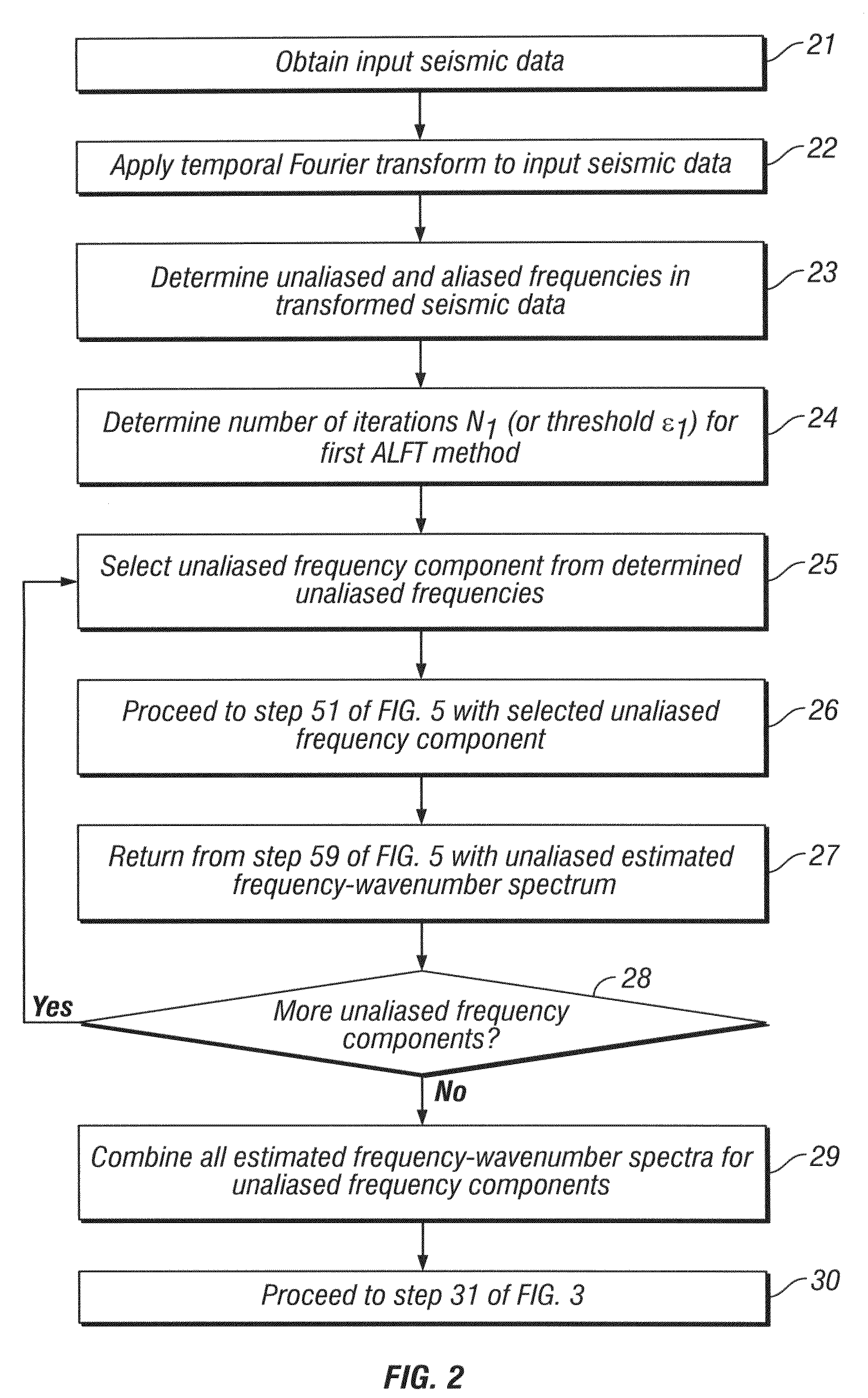
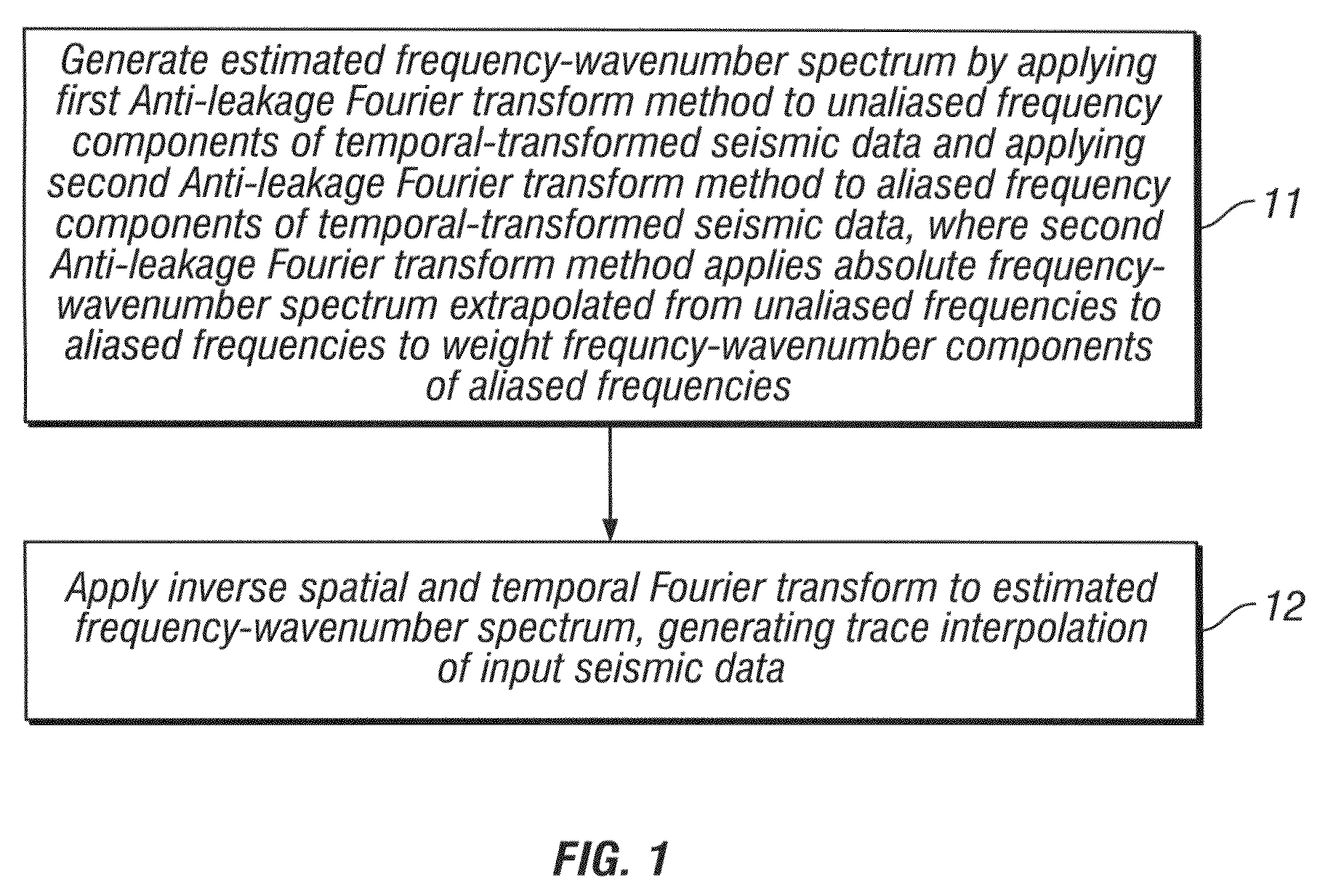
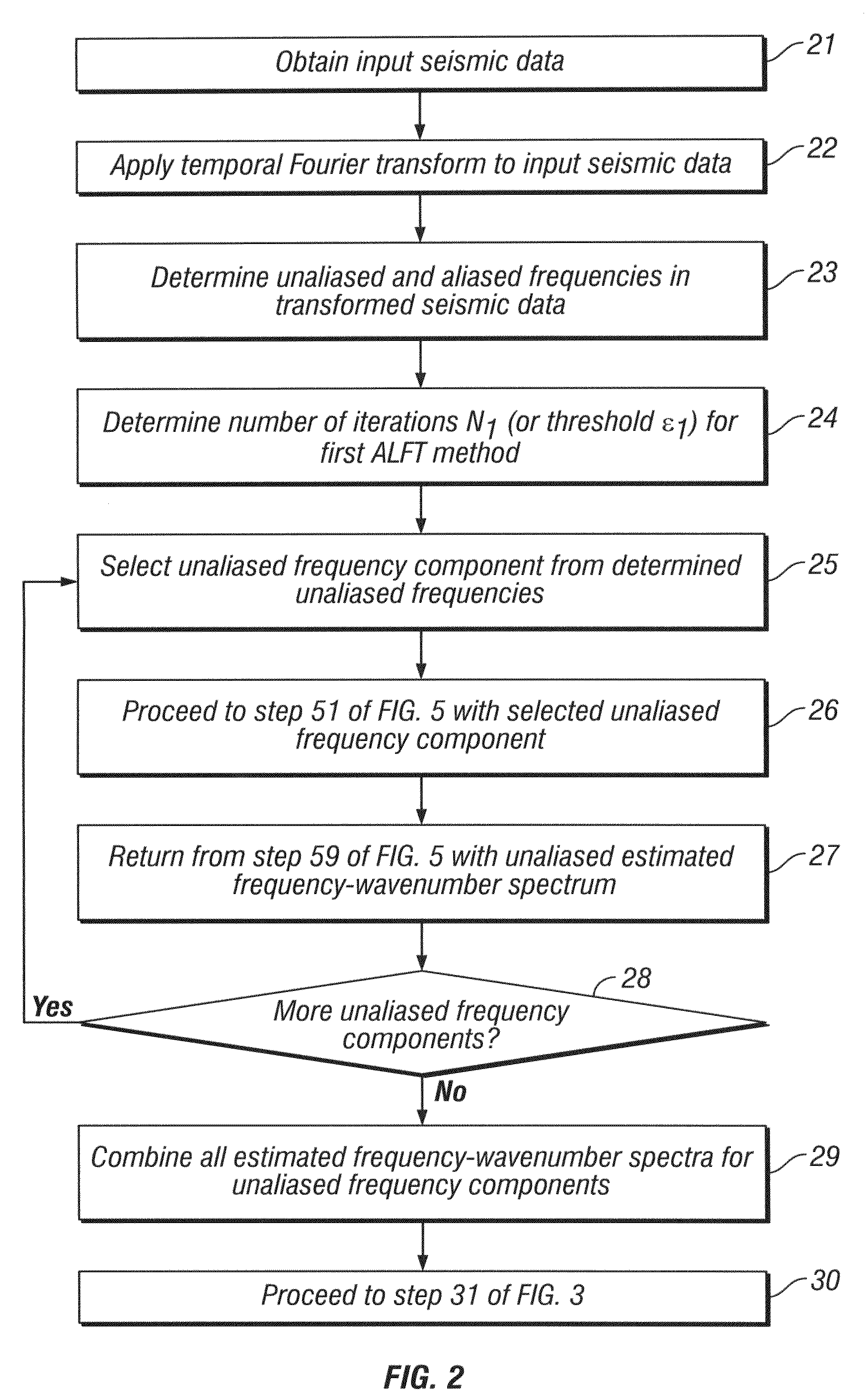
Method for interpolating seismic data by anti-alias, anti-leakage fourier transform
ActiveUS20090231956A1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsFast Fourier transformSpatial fourier transform
An estimated frequency-wavenumber spectrum is generated by applying a first Anti-leakage Fourier transform method to aliased frequency components in temporal-transformed seismic data and applying a second Anti-leakage Fourier transform method to unaliased frequency components in the temporal-transformed seismic data. The second Anti-leakage Fourier transform method applies an absolute frequency-wavenumber spectrum extrapolated from unaliased frequencies to aliased frequencies to weight frequency-wavenumber components of the aliased frequencies. An inverse temporal and spatial Fourier transform is applied to the estimated frequency-wavenumber spectrum, generating trace interpolation of the seismic data.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
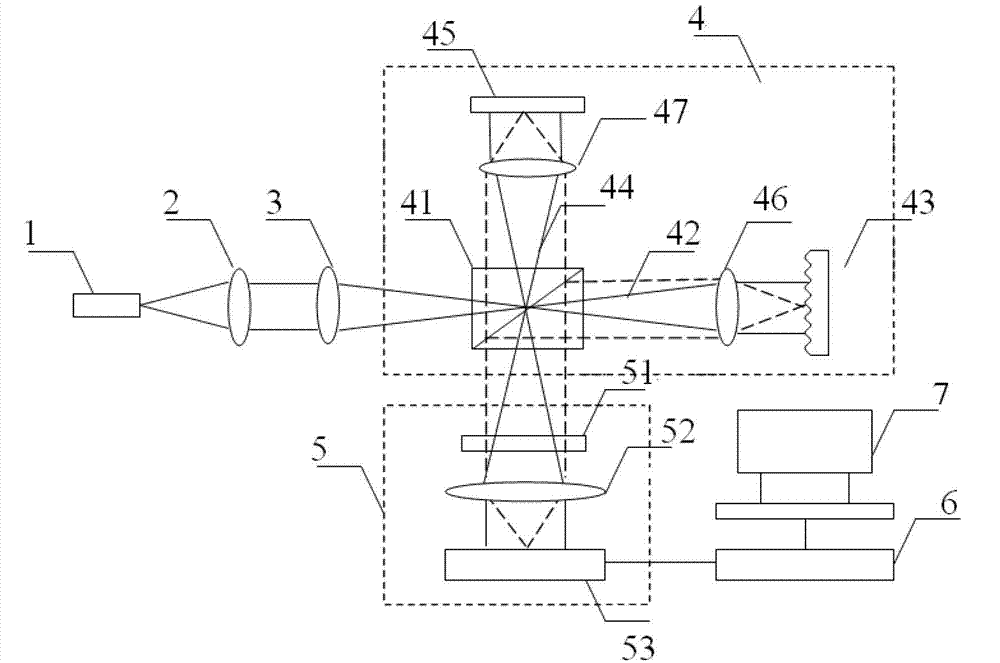
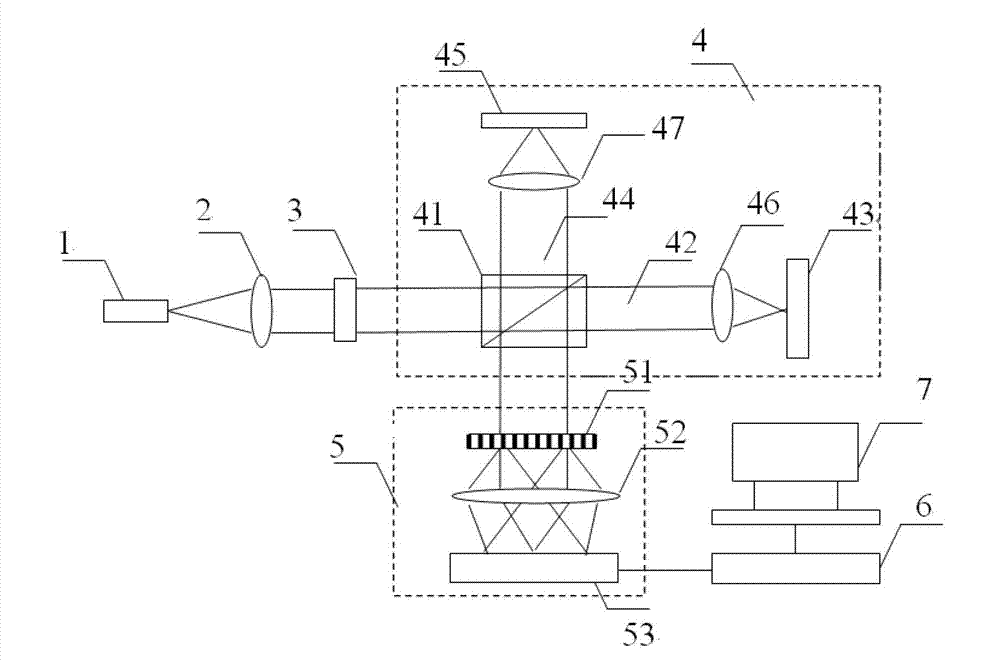
Sinusoidal phase modulation parallel complex frequency domain optical coherence tomography imaging system and method
ActiveCN102818786AEliminate self-coherent noiseImprove signal-to-noise ratioPhase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansSpatial fourier transformDetector array
The invention relates to a sinusoidal phase modulation parallel complex frequency domain optical coherence tomography imaging system and a method. The method and the system are characterized in that on the basis of the parallel frequency domain optical coherence tomography imaging system and method, a reflective space sinusoidal phase modulation device is used for replacing a reference plane reflecting mirror of an interference reference arm, two-dimensional frequency domain interference fringes obtained on a two-dimensional photoelectric detector array are introduced into a space to be subjected to sinusoidal phase modulation, i.e. spatial carriers are introduced into the two-dimensional frequency domain interference fringes; and then, the two-dimensional frequency domain interference fringes containing the spatial carriers are subjected to spatial Fourier transform analysis, two-dimensional complex frequency domain interference fringes are obtained, and finally, the chromatographic profile of samples to be measured is obtained through the inverse Fourier transform in the optical frequency direction. The system and the method have the characteristics that the structure is simple, the imaging speed is high, the sensitivity on the motion blur is low, and the samples to be measured are always in a region with higher sensitivity. The chromatographic profile of samples to be measured can be obtained only through once exposure.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for interpolating seismic data by anti-alias, anti-leakage Fourier transform
ActiveUS7751277B2Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsSpatial fourier transformAbsolute frequency
An estimated frequency-wavenumber spectrum is generated by applying a first Anti-leakage Fourier transform method to unaliased frequency components in temporal-transformed seismic data and applying a second Anti-leakage Fourier transform method to aliased frequency components in the temporal-transformed seismic data. The second Anti-leakage Fourier transform method applies an absolute frequency-wavenumber spectrum extrapolated from unaliased frequencies to aliased frequencies to weight frequency-wavenumber components of the aliased frequencies. An inverse temporal and spatial Fourier transform is applied to the estimated frequency-wavenumber spectrum, generating trace interpolation of the seismic data.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Fourier domain sensing
Methods and systems are disclosed of sensing an object. A first radiation is spatially modulated to generate a structured second radiation. The object is illuminated with the structured second radiation such that the object produces a third radiation in response. Apart from any spatially dependent delay, a time variation of the third radiation is spatially independent. With a single-element detector, a portion of the third radiation is detected from locations on the object simultaneously. At least one characteristic of a sinusoidal spatial Fourier-transform component of the object is estimated from a time-varying signal from the detected portion of the third radiation.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Three-dimensional imaging sonar wave beam forming method and implementation method on multi-core processor
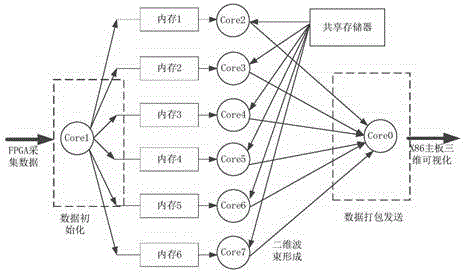
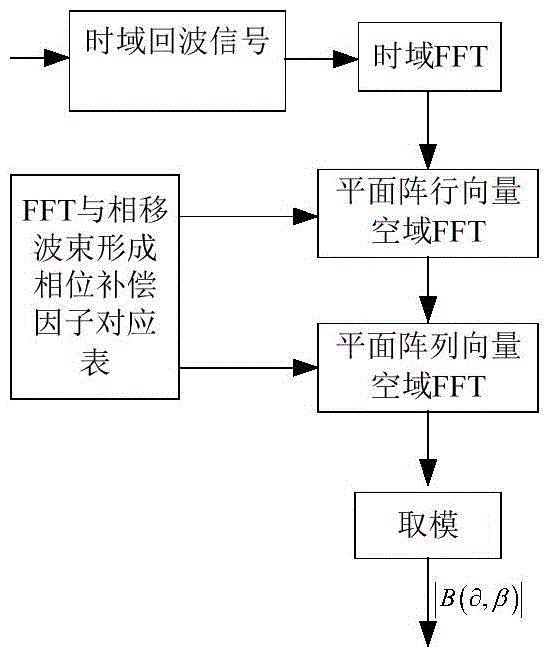
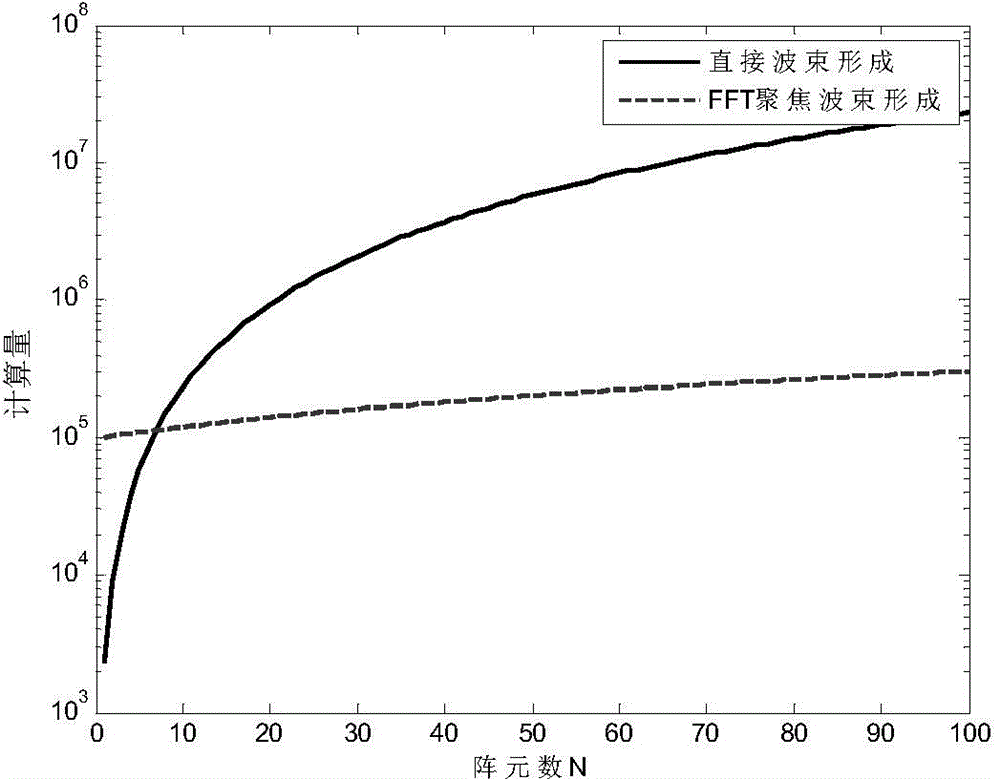
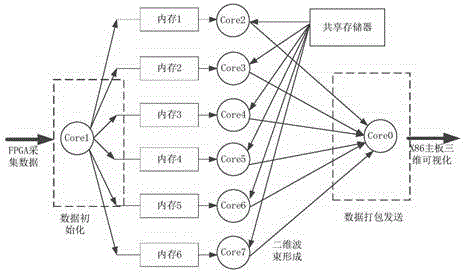
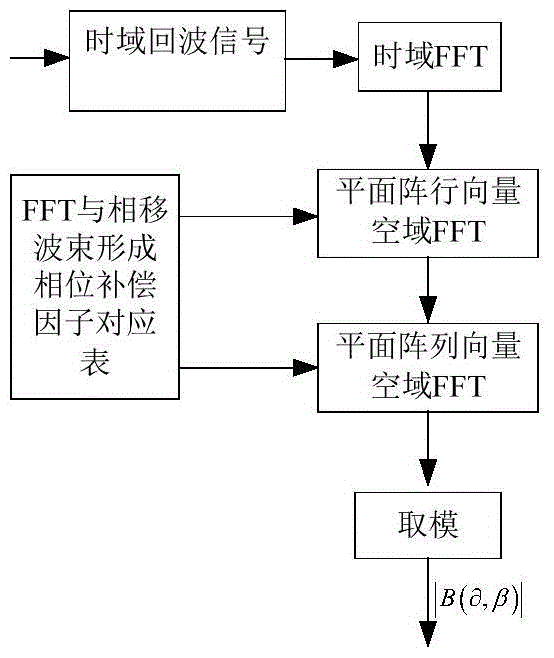
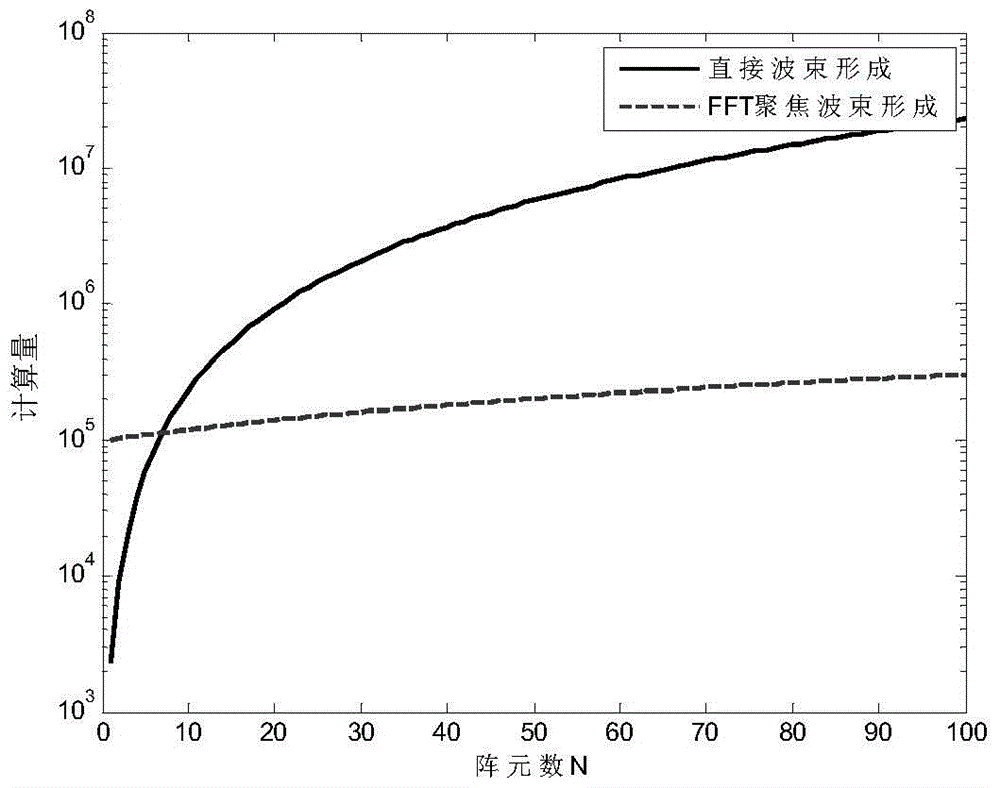
ActiveCN104656073ASmall amount of calculationImprove real-time performanceWave based measurement systemsSpatial fourier transformFourier transform on finite groups
The invention relates to a three-dimensional imaging sonar wave beam forming method applied to uniformly-distributed plane arrays in three-dimensional detection sonar. The method comprises the following steps: receiving and collecting time domain echo signals; carrying out time domain Fourier transform on the time domain echo signals, then judging whether the result obtained by the time domain Fourier transform meets the far-field condition or not, compensating distance influence items of a time delay calculation formula in a near-field wave beam forming expression formula, and then carrying out the next step if the result shows that the near-field wave beams are formed; directly carrying out the next step if the result shows that far-field wave beams are formed; carrying out spatial Fourier transform on row vectors of the plane arrays of the signals; carrying out spatial Fourier transform on line vectors of the plane arrays of the signals; performing a modulus on the obtained spatial two-dimensional Fourier transform result to obtain a final two-dimensional wave beam forming result.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optically Monitoring and Controlling Nanoscale Topography
ActiveUS20140093986A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpatially resolvedGrating
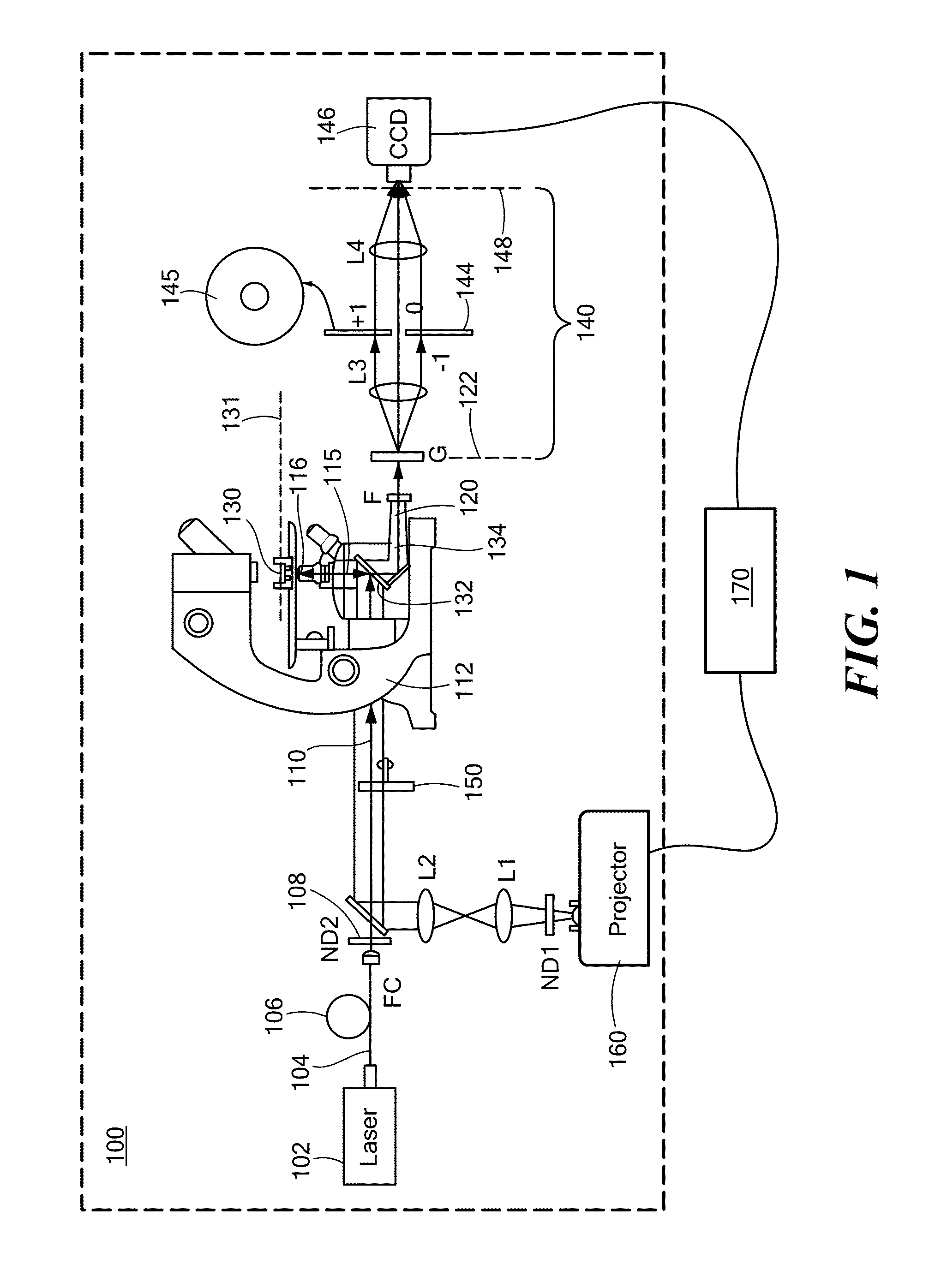
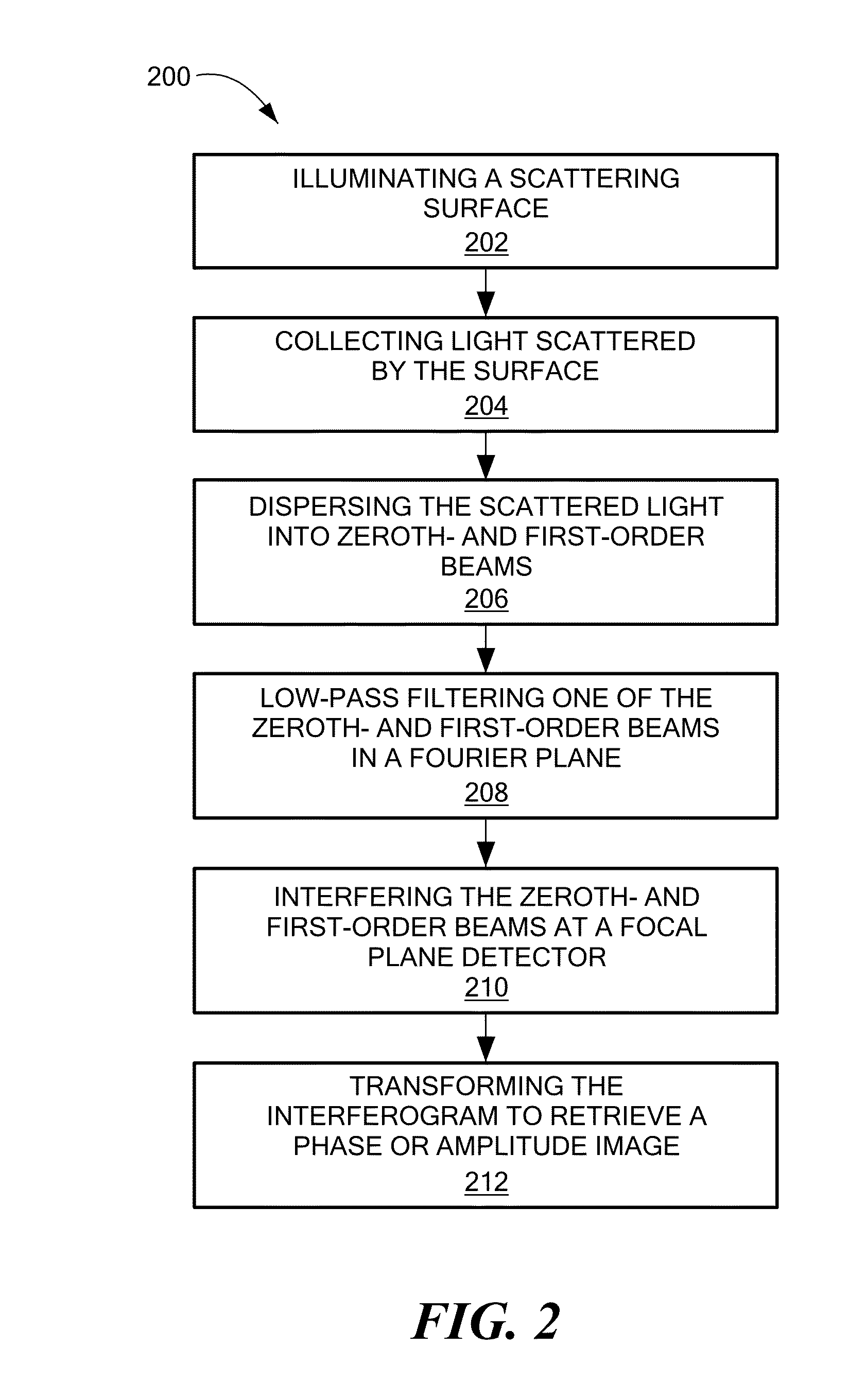
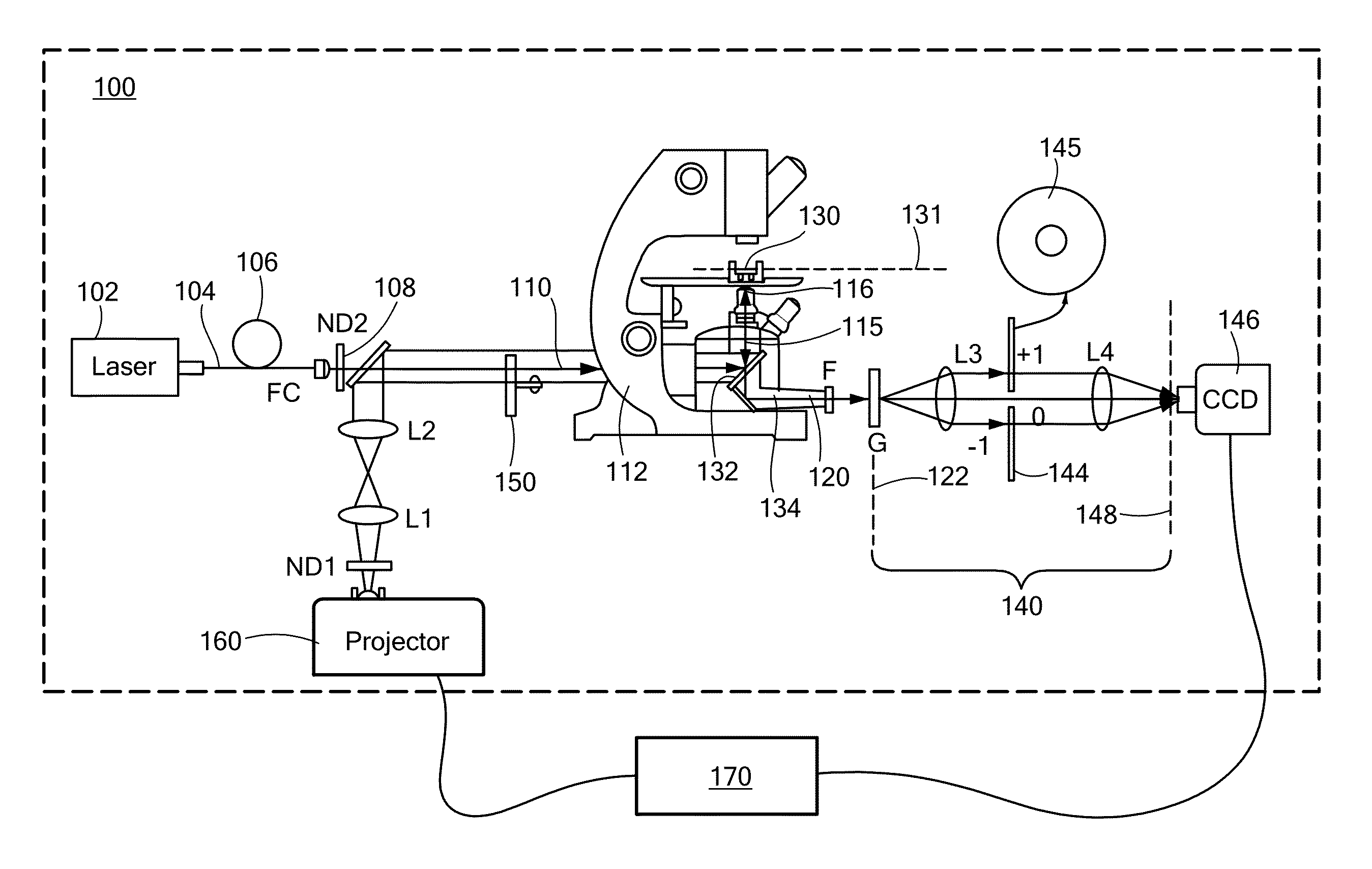
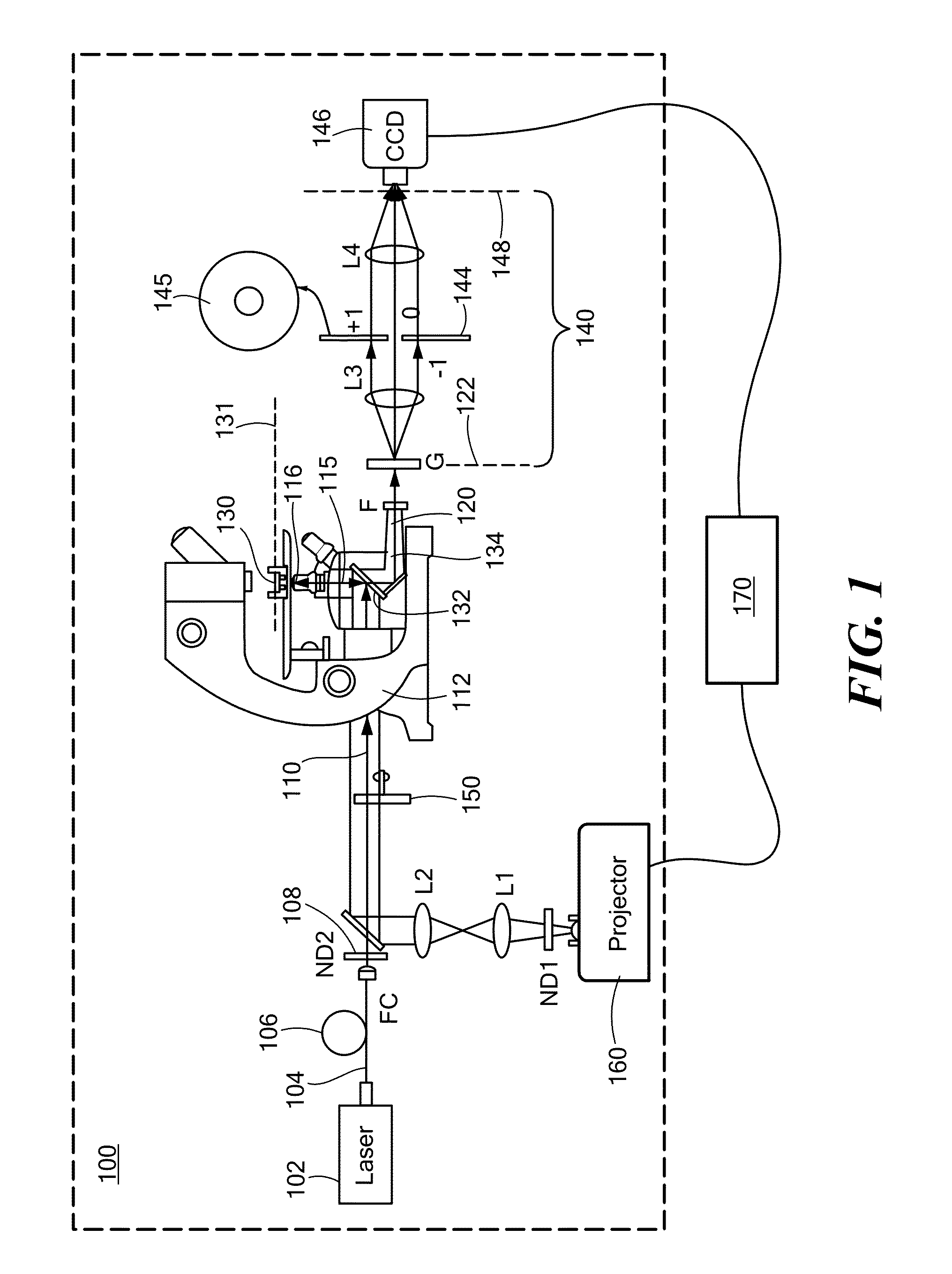
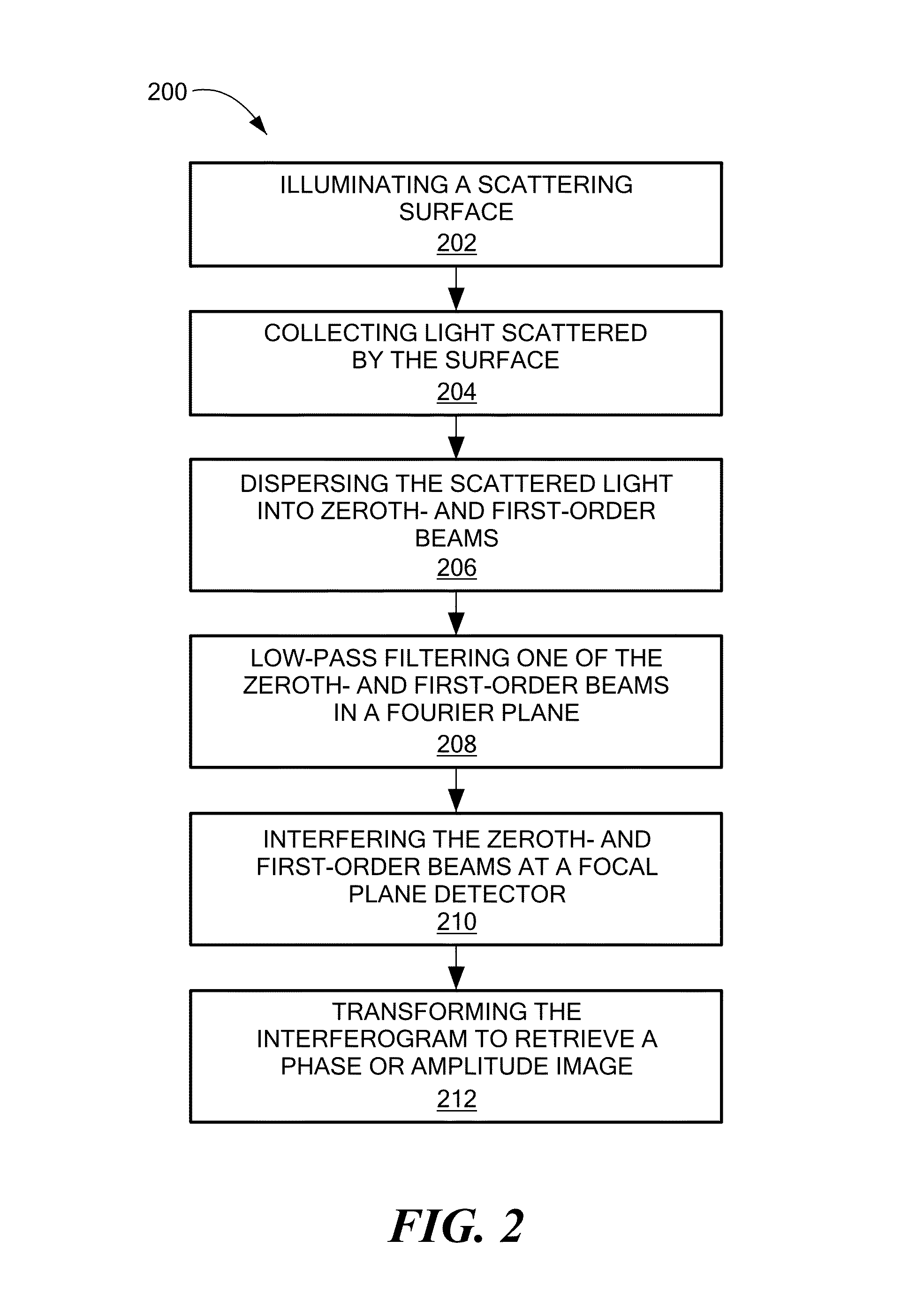
Methods and apparatus for method for characterizing a height profile of a scattering surface relative to a fiducial plane. The scattering surface, which may be an interface between distinct solid, liquid, gaseous or plasma phases, is illuminated with substantially spatially coherent light, and light scattered by the scattering surface is collected and dispersed, such as by a grating, into zeroth- and first-order beams. A spatial Fourier transform of the zeroth- and first-order beams is created, and one of the beams is low-pass filtered. The beams are interfered at a focal plane detector to generate an interferogram, which is transformed to retrieve a spatially resolved quantitative phase image and / or an amplitude image of the scattering surface. Imaging may be performed during an etching process, and may be used to adaptively control a photoetching process in a feedback loop.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Method and apparatus for high-throughput inspection of large flat patterned media using dynamically programmable optical spatial filtering
InactiveUS20060186361A1Reduce resolutionAutomatic control devicesBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsSpatial light modulatorSpatial fourier transform
In an inspection system for planar objects having periodic structures, programmable optical Fourier filtering in the focal plane of a telecentric lens system is used to directly identify physical phenomena indicative of non-periodic defects. Lens assemblies and a coherent optical source are used to generate and observe a spatial Fourier transform of a periodic structure in the Fourier plane. Optical Fourier filtering (OFF) is performed in the focal plane using an electrically programmable and electrically alignable spatial light modulator. The spatial light modulator with high signal to noise ratio is electrically reconfigurable according to a feedback-driven, filter construction and alignment algorithm. The OFF enhances any non-periodic components present in the Fourier plane and final image plane of the object. A system having a plurality of inspection channels provides high-throughput inspection of objects with small non-periodic defects while maintaining high detection sensitivity.
Owner:PHOTON DYNAMICS
Finite space plane near-field acoustic holography measurement method based on spatial Fourier transform
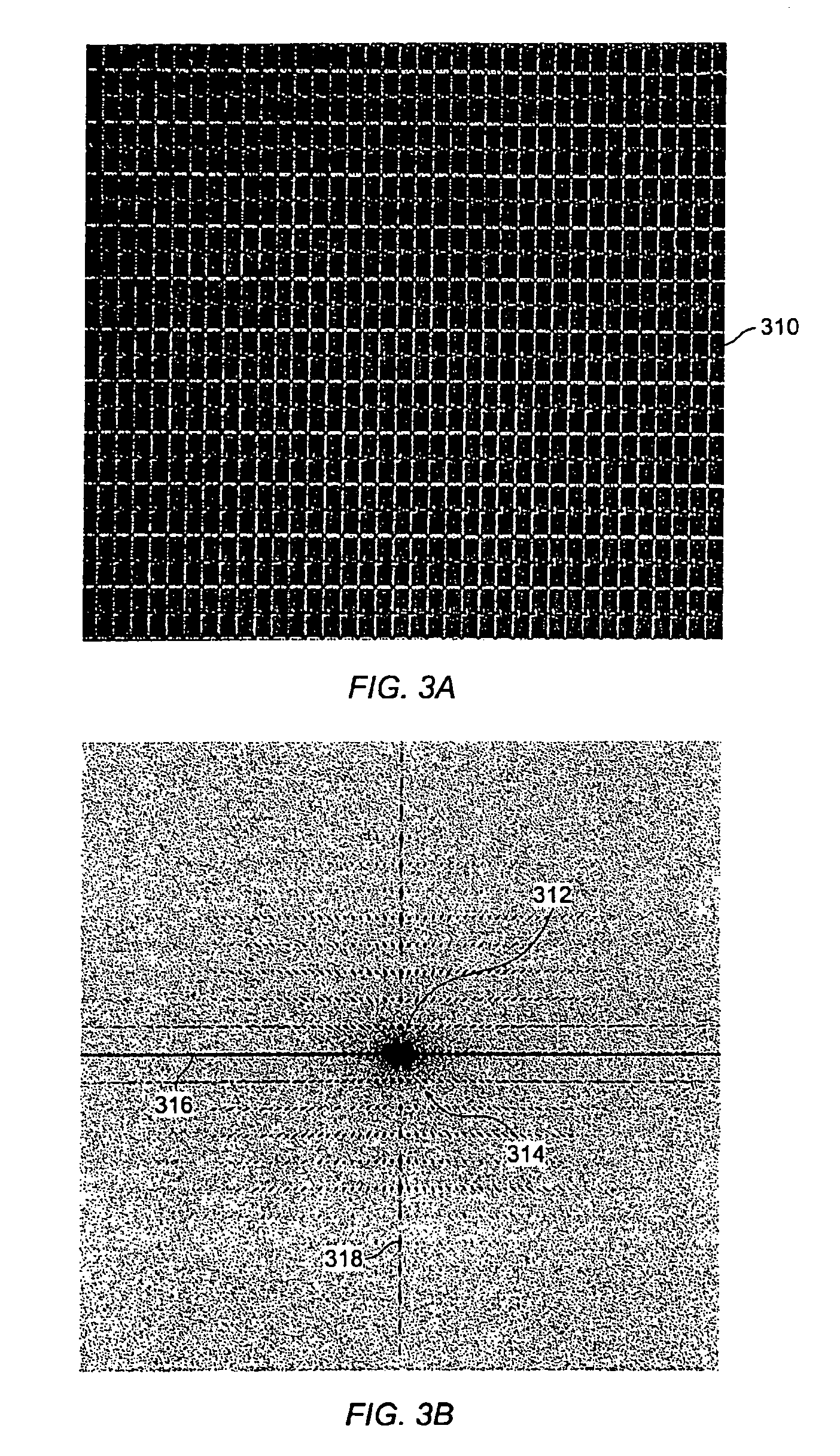
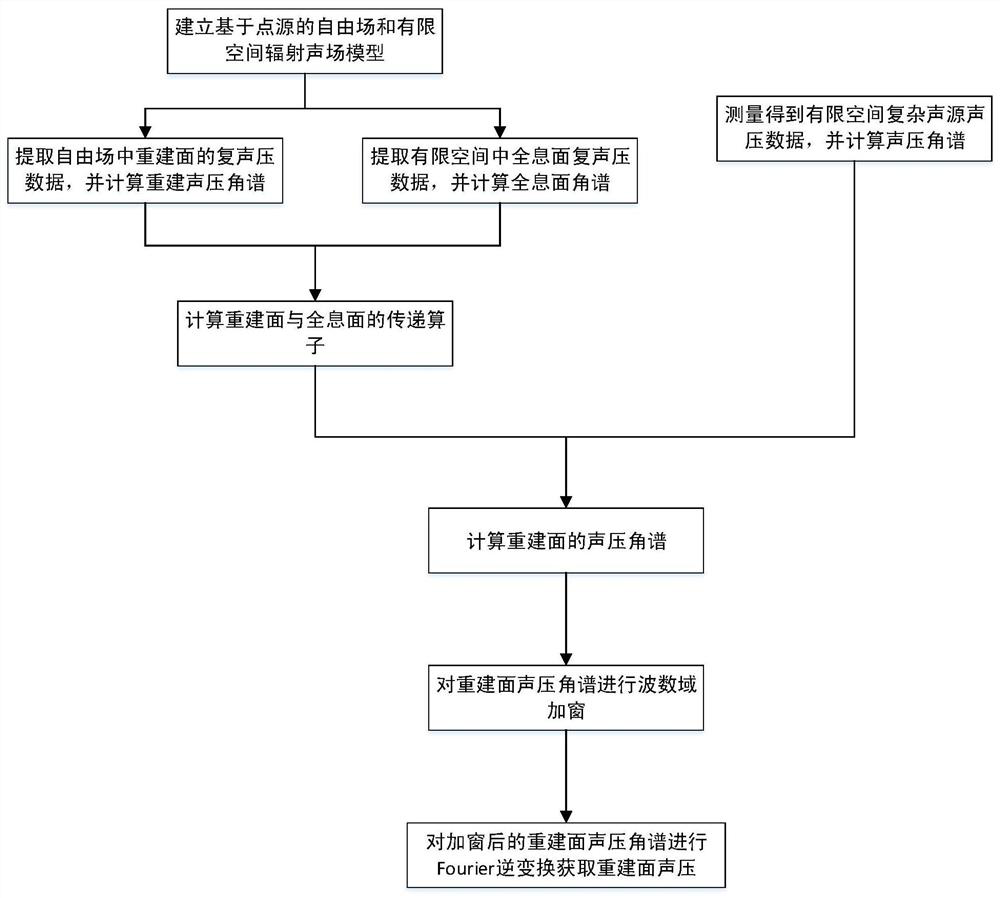
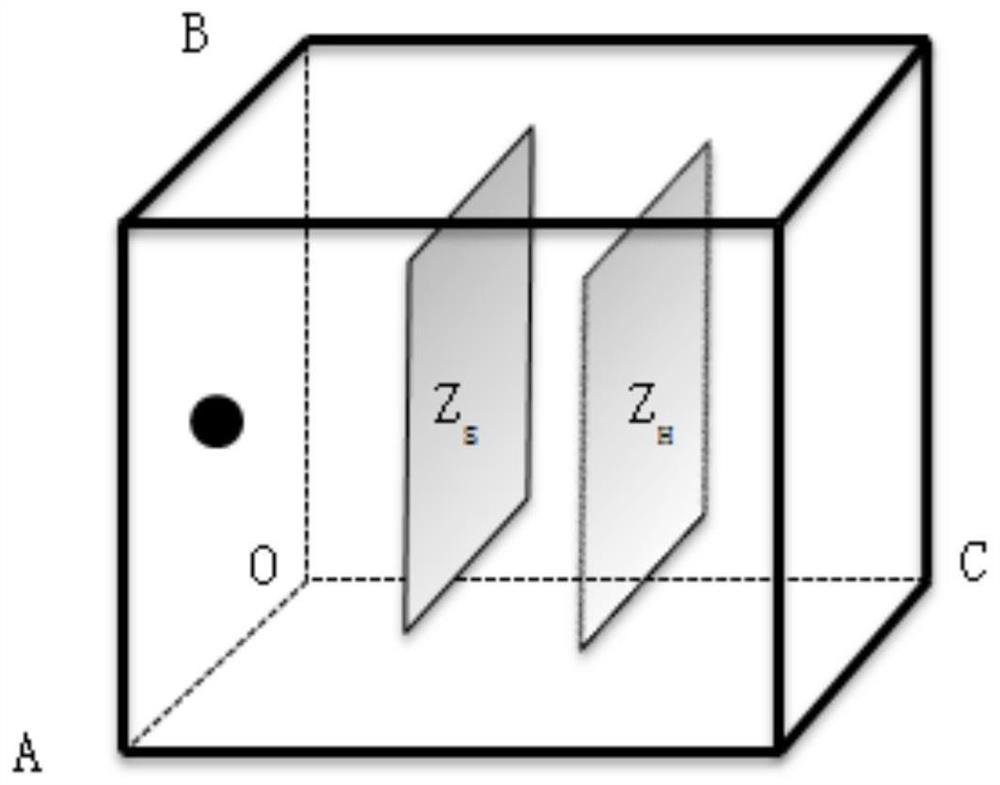
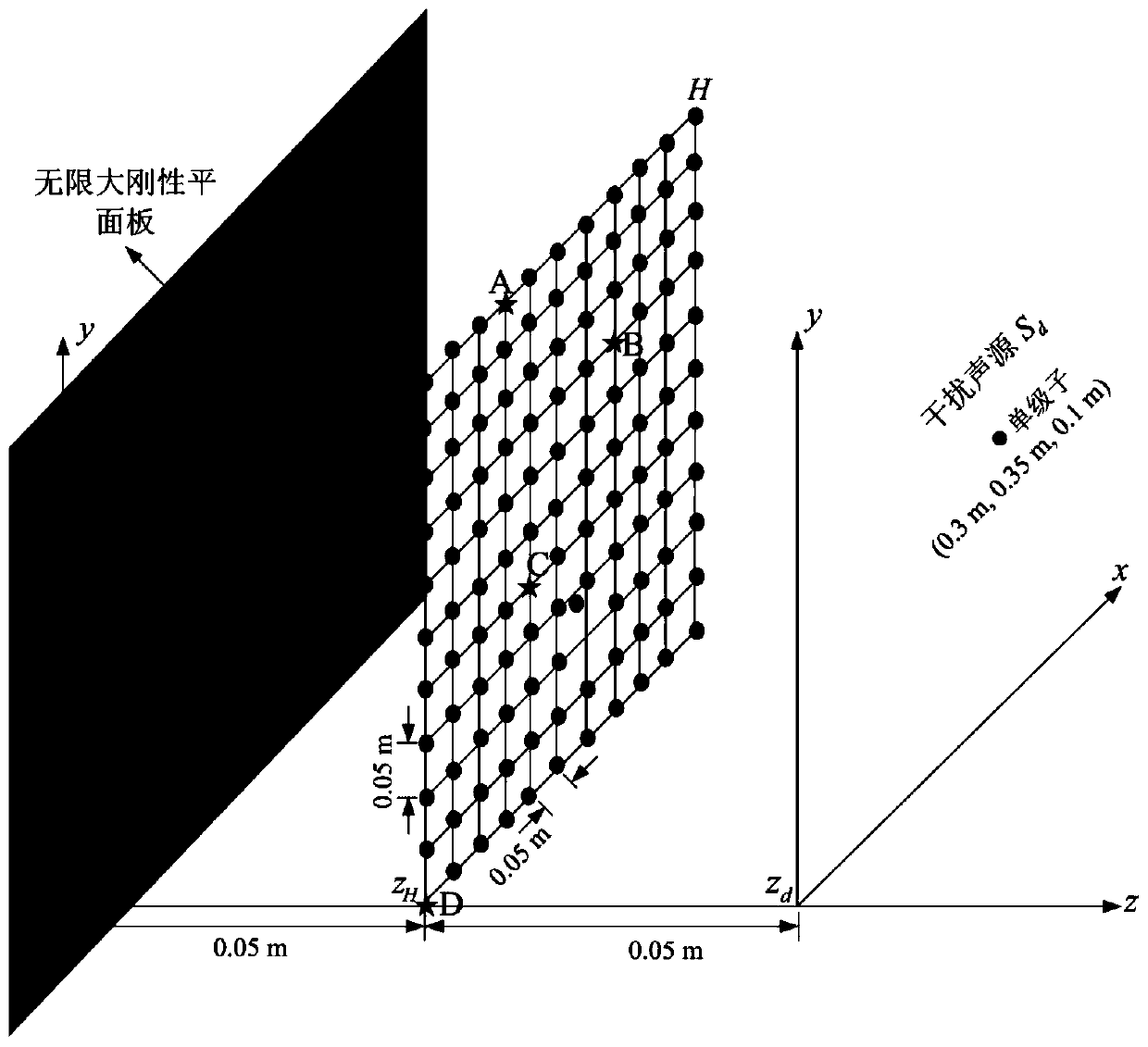
ActiveCN112577592AImprove reconstruction accuracySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementSound sourcesSpatial fourier transform
The invention discloses a finite space plane near-field acoustic holography measurement method based on spatial Fourier transform, which comprises the following steps: 1, establishing a free field andfinite space radiation sound field model based on a point sound source, and extracting complex sound pressure of a point sound source reconstruction surface in the free field and complex sound pressure data on a holographic surface in a finite space; 2, calculating a sound pressure angle spectrum of a point source reconstruction surface in a free field and a point source holographic surface in afinite space, and calculating a transfer operator G-1 of the reconstruction surface and the holographic surface; 3, measuring to obtain complex sound pressure data on the holographic surface with thereconstructed sound source in the limited space; and calculating a holographic surface sound pressure angle spectrum; 4, multiplying the holographic surface sound pressure angle spectrum in the step 3by the transfer operator G-1 in the step 2 to obtain a sound pressure angle spectrum on the reconstruction surface; and 5, performing wave number domain windowing on the sound pressure angle spectrumof the reconstruction surface; and performing Fourier inverse transformation on the windowed reconstructed sound pressure angular spectrum to obtain reconstructed surface sound pressure. According tothe method, the finite space test environment is considered, and the reconstruction precision is improved by solving the transfer operator in the free field and the finite space.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
High frame rate imaging system
InactiveUS8496585B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCharacter and pattern recognitionFast Fourier transformSquare waveform
A system for producing an image using an imaging system includes a) transmitting at least one signal of energy toward an object to be imaged by using two transmitters having the same output amplitude but of an opposite sign, or by using one transmitter to perform the task; b) exciting at least one transducer element to produce limited-diffraction array beams or their square-wave approximations with two levels of quantitations for both sine and cosine functions, c) weighting the received signals spatially with limited-diffraction array beams, their square-wave approximations, or spatial Fourier transform, and d) digitizing and then transferring received signals through high-speed optical fibers to a system for image reconstructions.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO
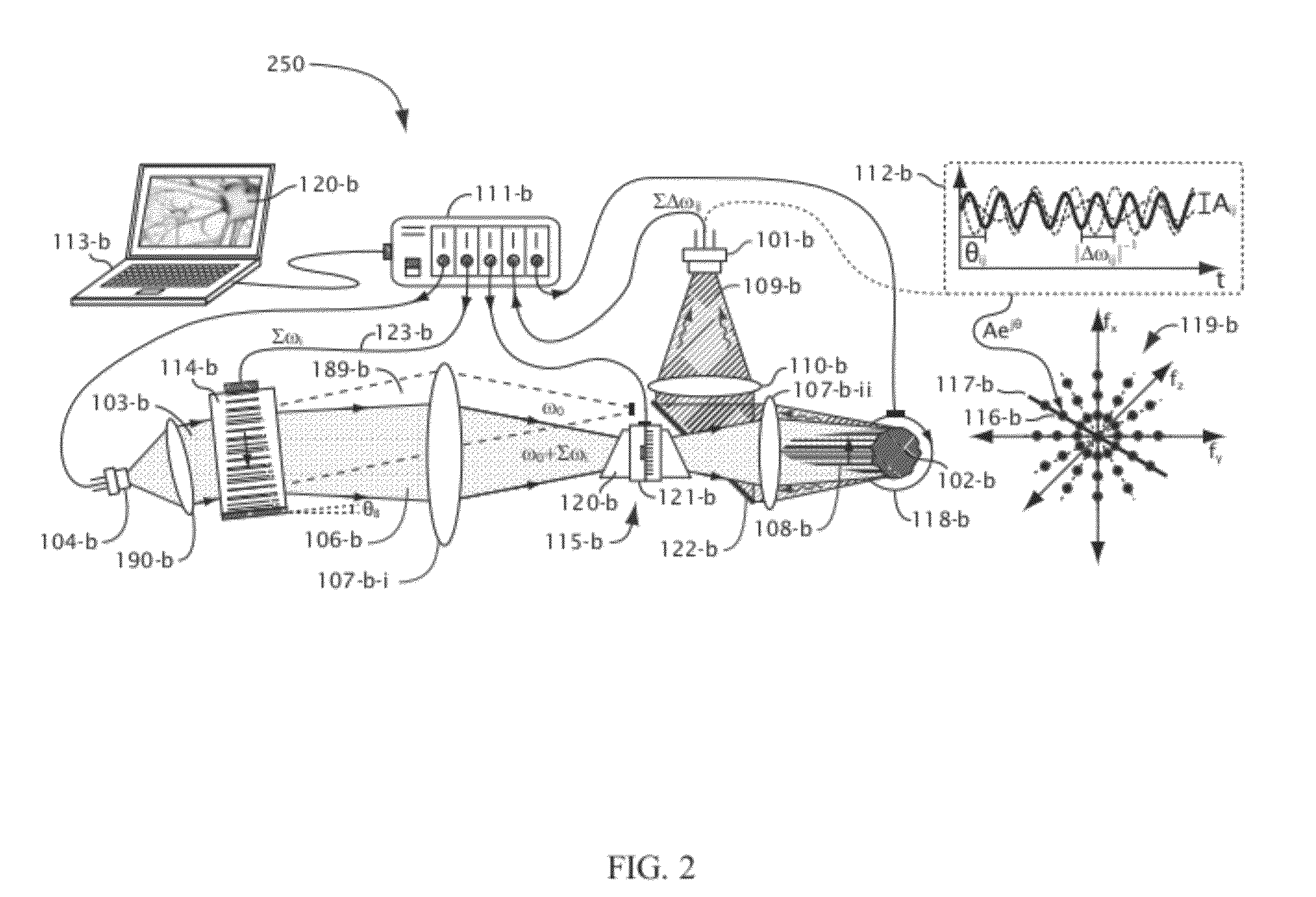
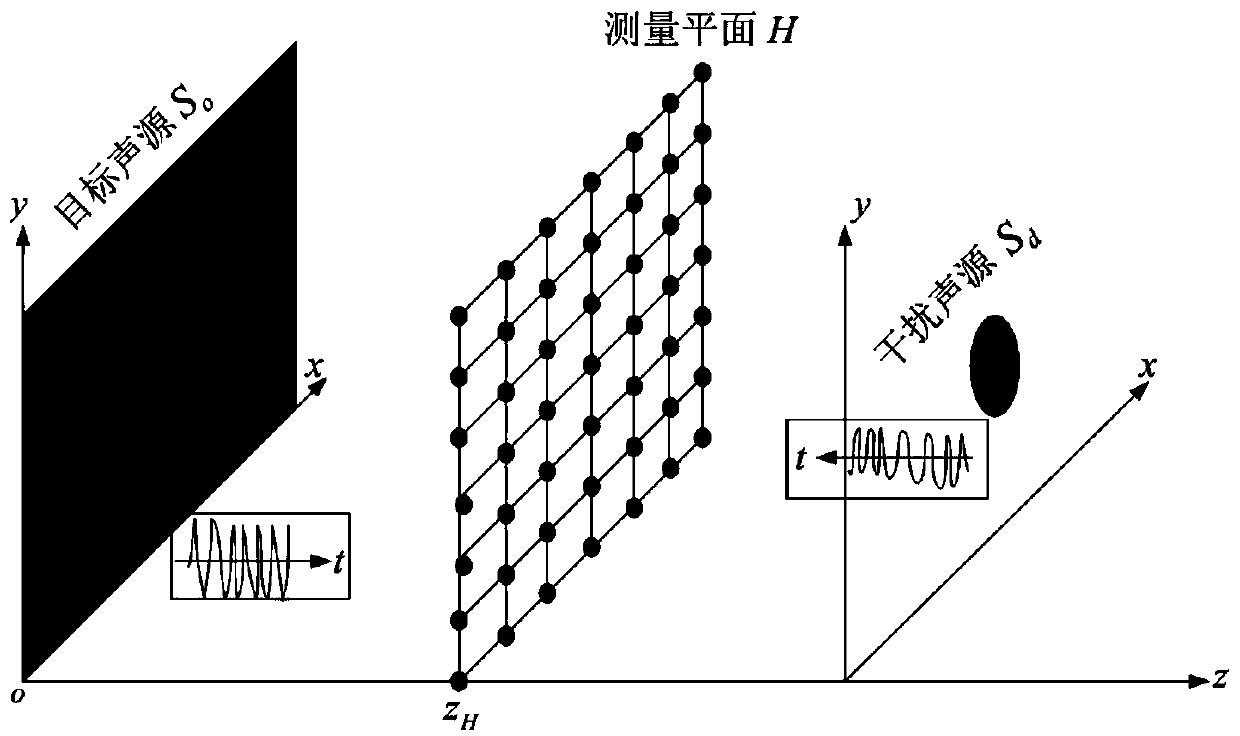
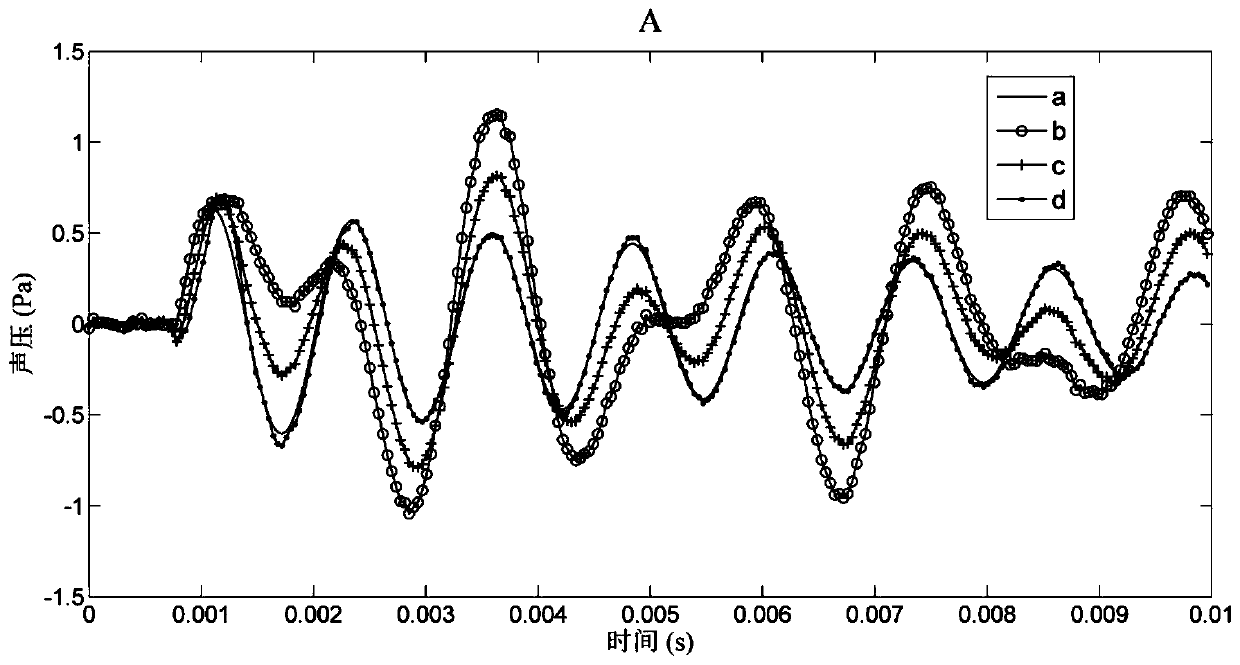
Unsteady-state free-field reduction method using single-sided sound pressure and mass point vibration velocity measurement
InactiveCN110487393AReduce computing timeImprove stabilitySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementSound sourcesSpatial fourier transform
The invention discloses an unsteady-state free-field reduction method using single-sided sound pressure and mass point vibration velocity measurement. Two-dimensional spatial Fourier transform is carried out on a time-domain sound pressure and time-domain mass point velocity that are measured directly on a measurement plane H to obtain sound pressure and mass point vibration velocity time-domain wavenumber spectrums on the plane H; and with the sound pressure and mass point vibration velocity time-domain wavenumber spectrums on the plane H, known sound pressure and mass point vibration velocities, a time-domain impulse response function between the sound pressures, and a surface reflection coefficient of a target sound source, a free-field reduction formula is derived and a time-varying sound pressure signal radiated on the plane H under the free field condition of the target sound source is reduced in real time. According to the disclosed method, only with one measurement plane, the input amount does not need to be obtained by approximate calculation and the reduction formula is calculation of the forward convolution sum; no unrolling and inversion processing is needed; and the influence of the unsteady-state scattered sound field is eliminated in real time. The method can be applied to field analysis of the time-varying radiation characteristic and vibration characteristic ofthe target sound source in an actual sound field environment.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
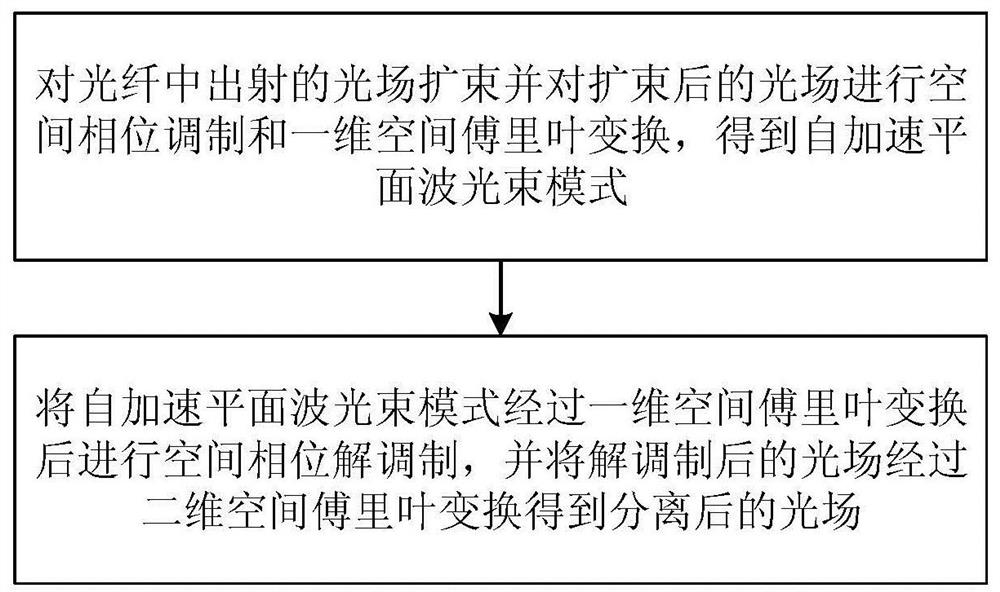
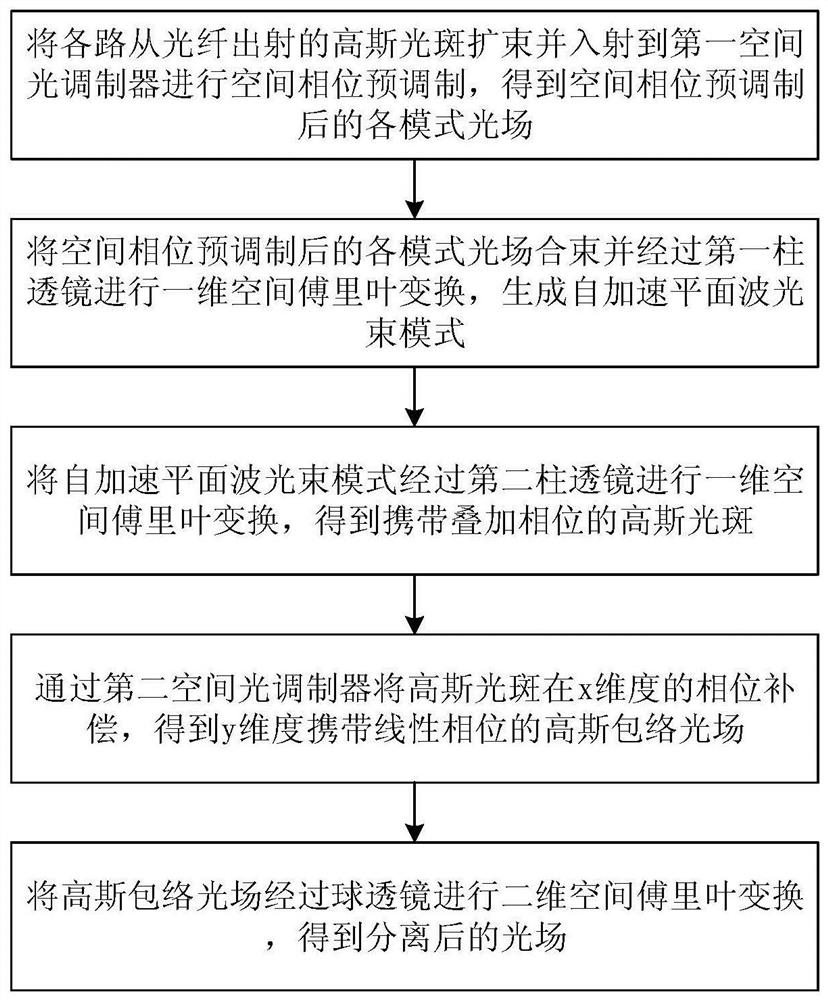
Space division multiplexing and demultiplexing method and system based on self-acceleration plane wave light beam
ActiveCN111756449AIncrease the number of channelsImprove capacity utilizationOptical mode multiplex systemsMultimode transmissionSpatial fourier transformLight beam
The invention discloses a space division multiplexing and demultiplexing method based on a self-acceleration plane wave light beam, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the beam expansionof a light field emitted from an optical fiber, carrying out the spatial phase modulation and one-dimensional spatial Fourier transform on the light field subjected to beam expansion so as to obtain aself-acceleration plane wave light beam mode; carrying out one-dimensional spatial Fourier transform on the self-acceleration plane wave beam mode, then carrying out spatial phase demodulation, and carrying out two-dimensional spatial Fourier transform on the demodulated light field to obtain a separated light field. The system comprises a multiplexing module and a demultiplexing module. According to the invention, the communication capacity and the space utilization rate can be improved. The space division multiplexing and demultiplexing method and system based on the self-acceleration planewave light beam can be widely applied to the field of optical communication application.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Ultrasound method and device for representing the propagation of ultrasound waves in a guide of linearly variable thickness
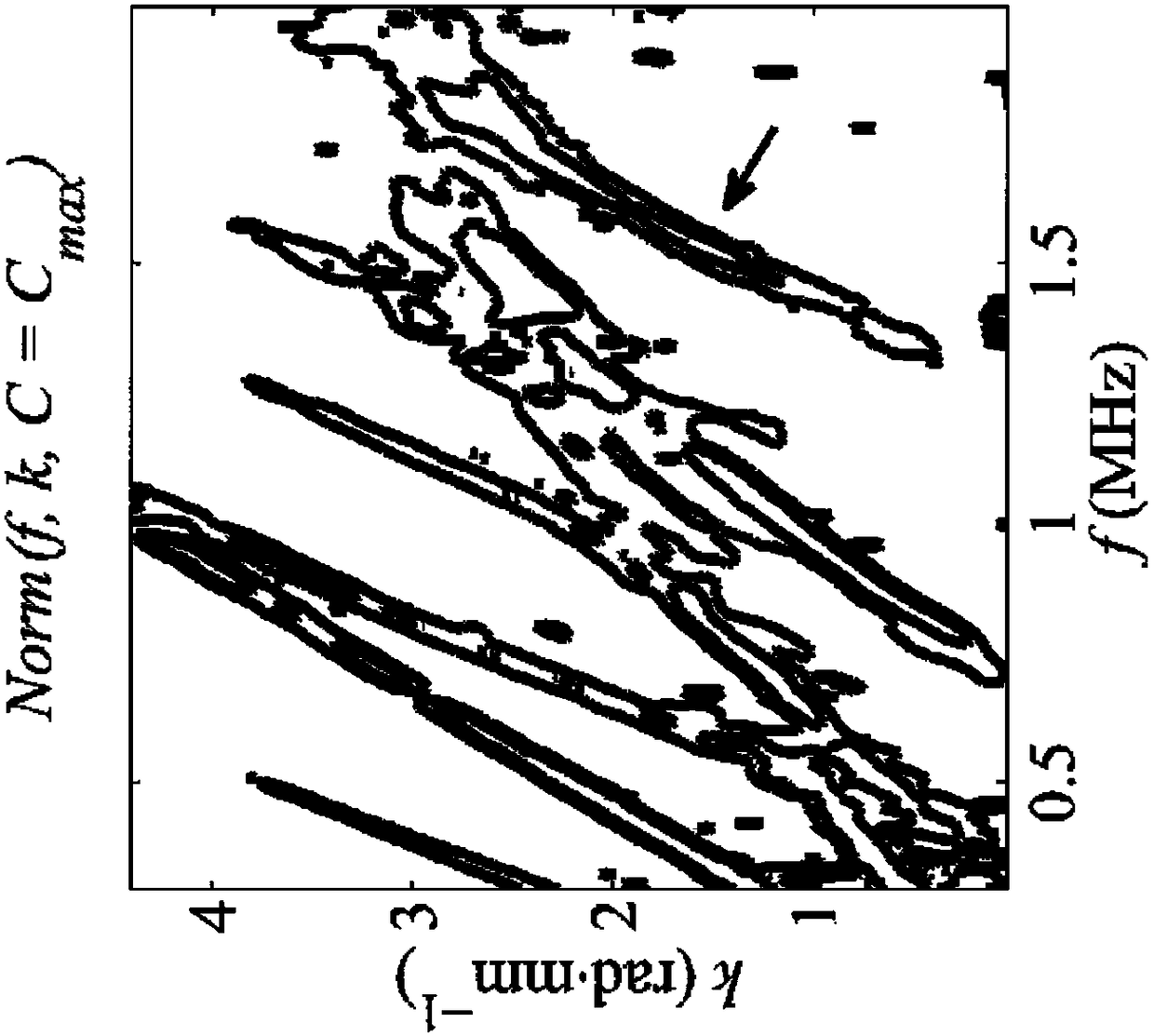
InactiveCN105518451AAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesOrgan movement/changes detectionVariable thicknessSonification
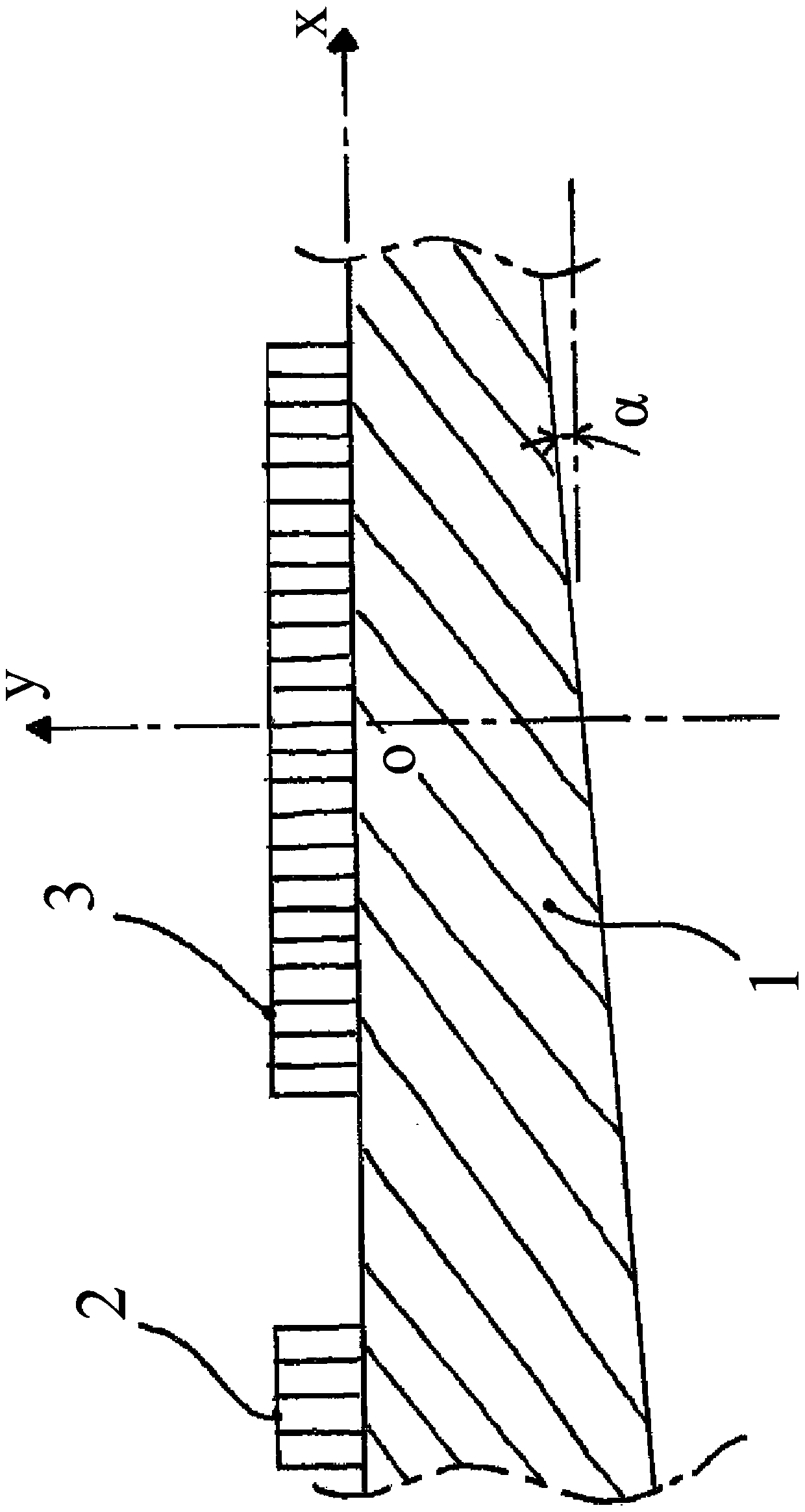
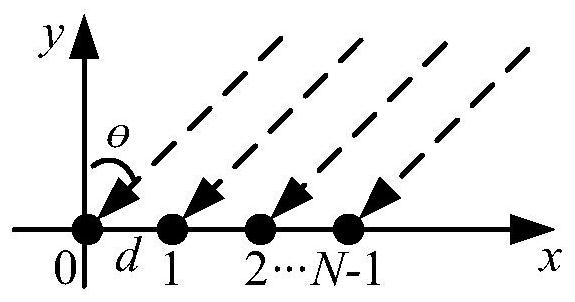
Device for the representation, in a frequency-wave number reference frame f-k, of the propagation of an ultrasound wave in a dihedral guide (1), which comprises ultrasound emitters (2) referenced by 'Ej ' with j an integer varying between 1 and N, N a strictly positive integer and ultrasound receivers (3) referenced by 'Ri ' with i an integer varying between 1 and M, M a strictly positive integer, the receivers being disposed spatially over a first segment of a straight line according to a regular pitch 'A ', which comprises means for processing the signal received by the receivers, originating from the emitters, and in which the processing means comprise means for calculating a modified discrete spatial Fourier transform, for a spatial integration variable 'x ', centred in the middle of said first segment and running through the receivers in the direction of increasing x, and for a wave vector k(x) equal to a product k.P(x), with k a constant coefficient in x and included between 0 and 2*Pi / A, and with P(x) a polynomial in x, of coefficient of degree 0 in x equal to 1 and of coefficient 'C ' of degree 1 in x such that C.A lies between -1 / 10 and +1 / 10.
Owner:爱莎莉 +2
Optically monitoring and controlling nanoscale topography
ActiveUS9255791B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementUsing optical meansSpatially resolvedGrating
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
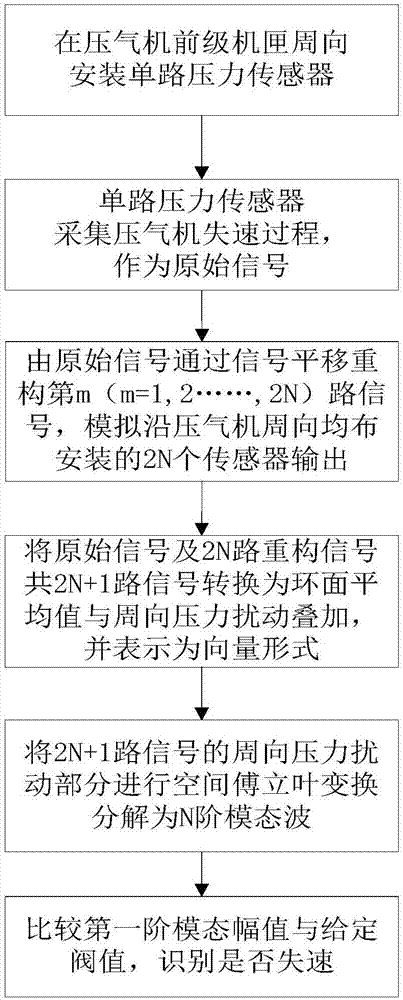
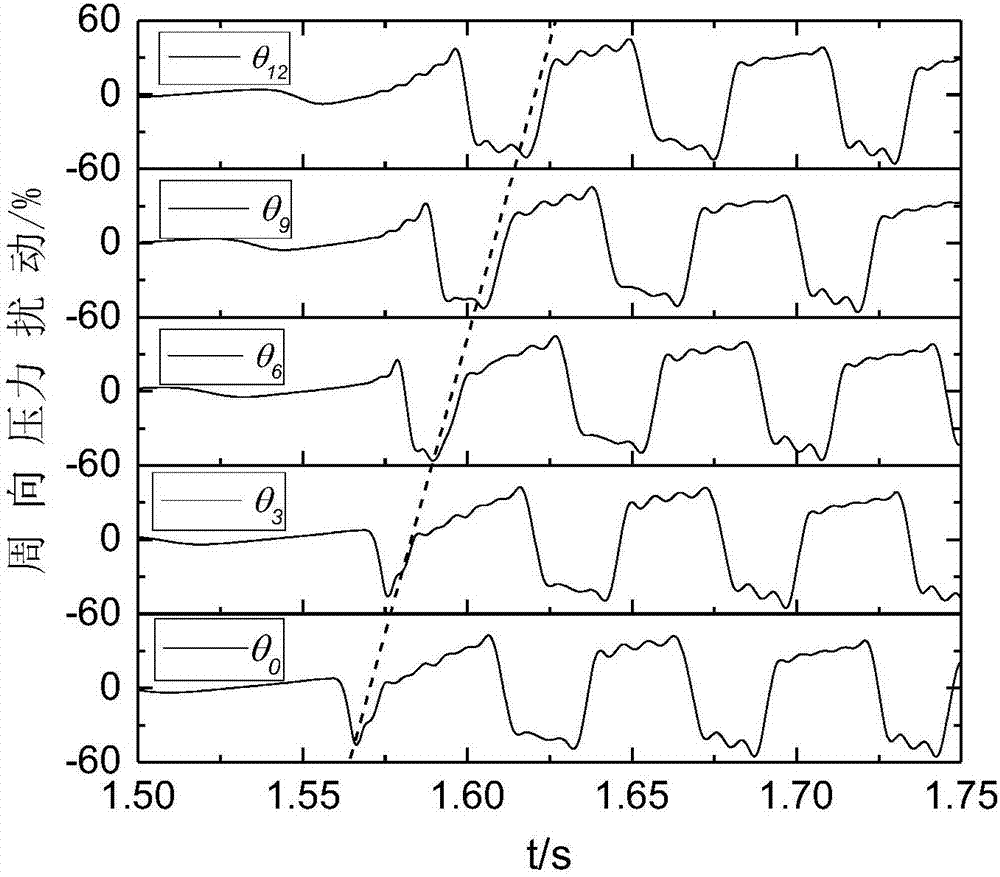
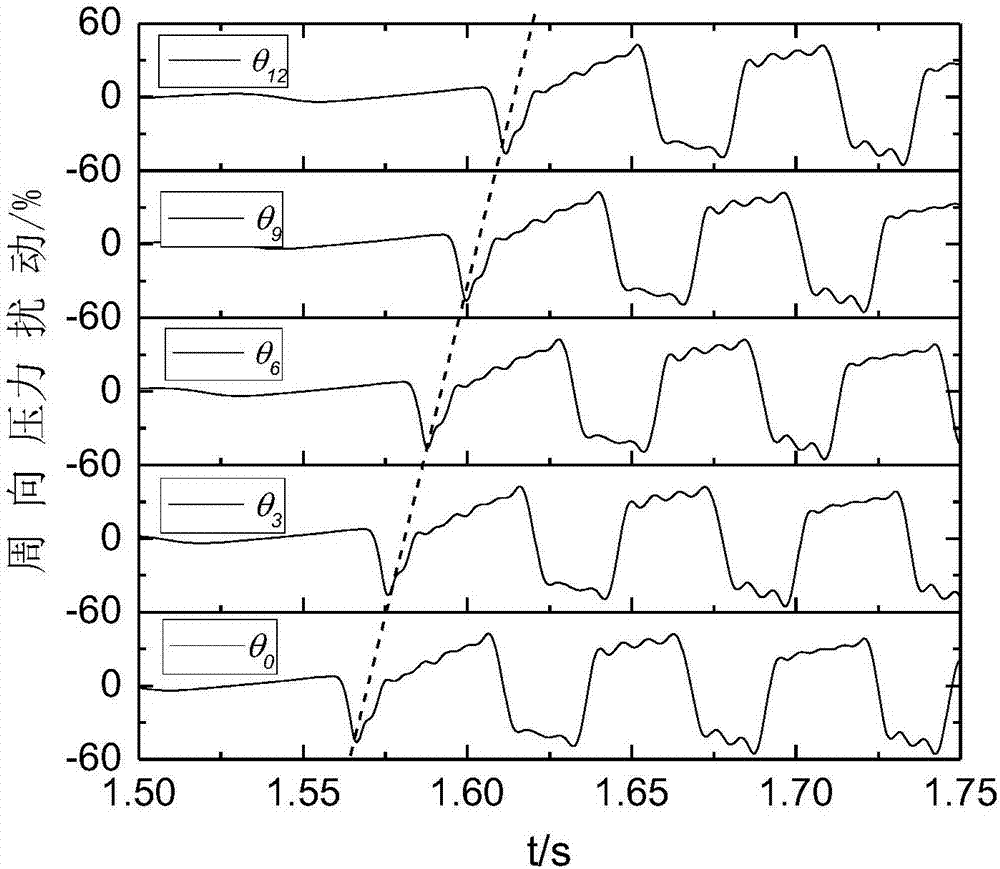
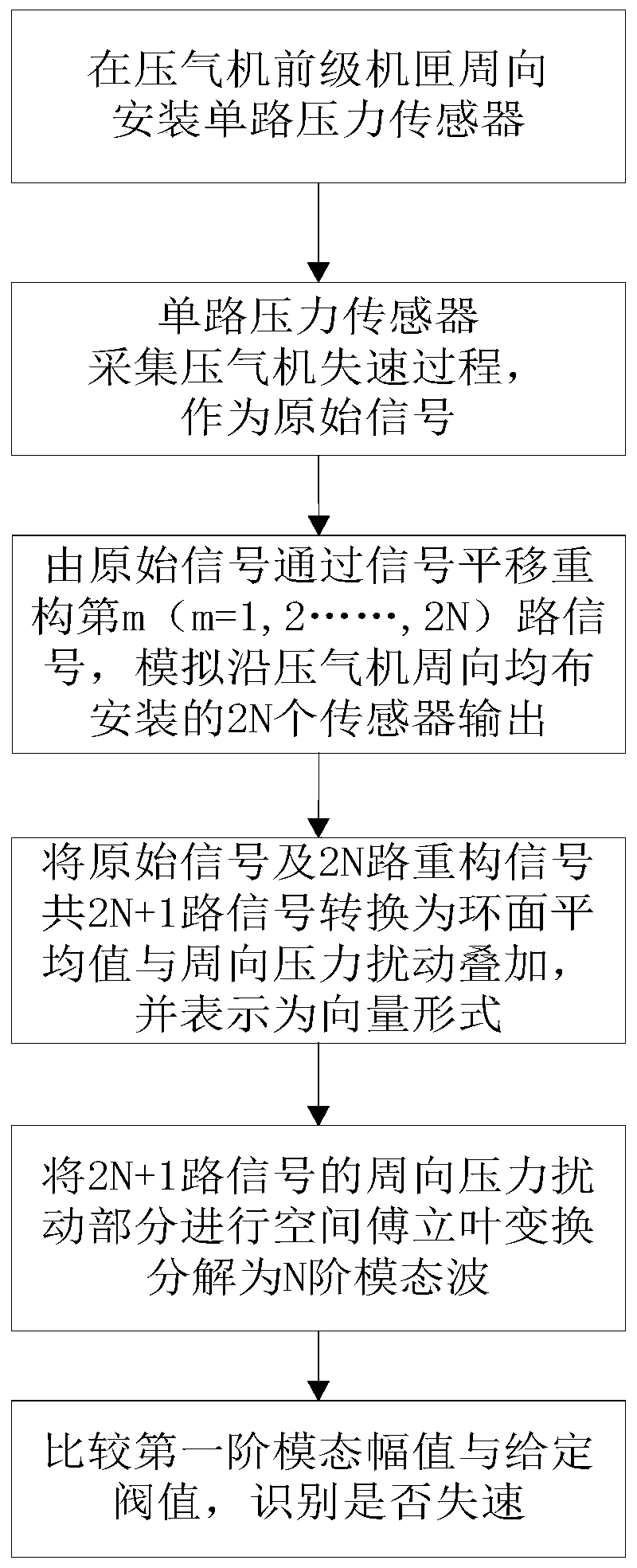
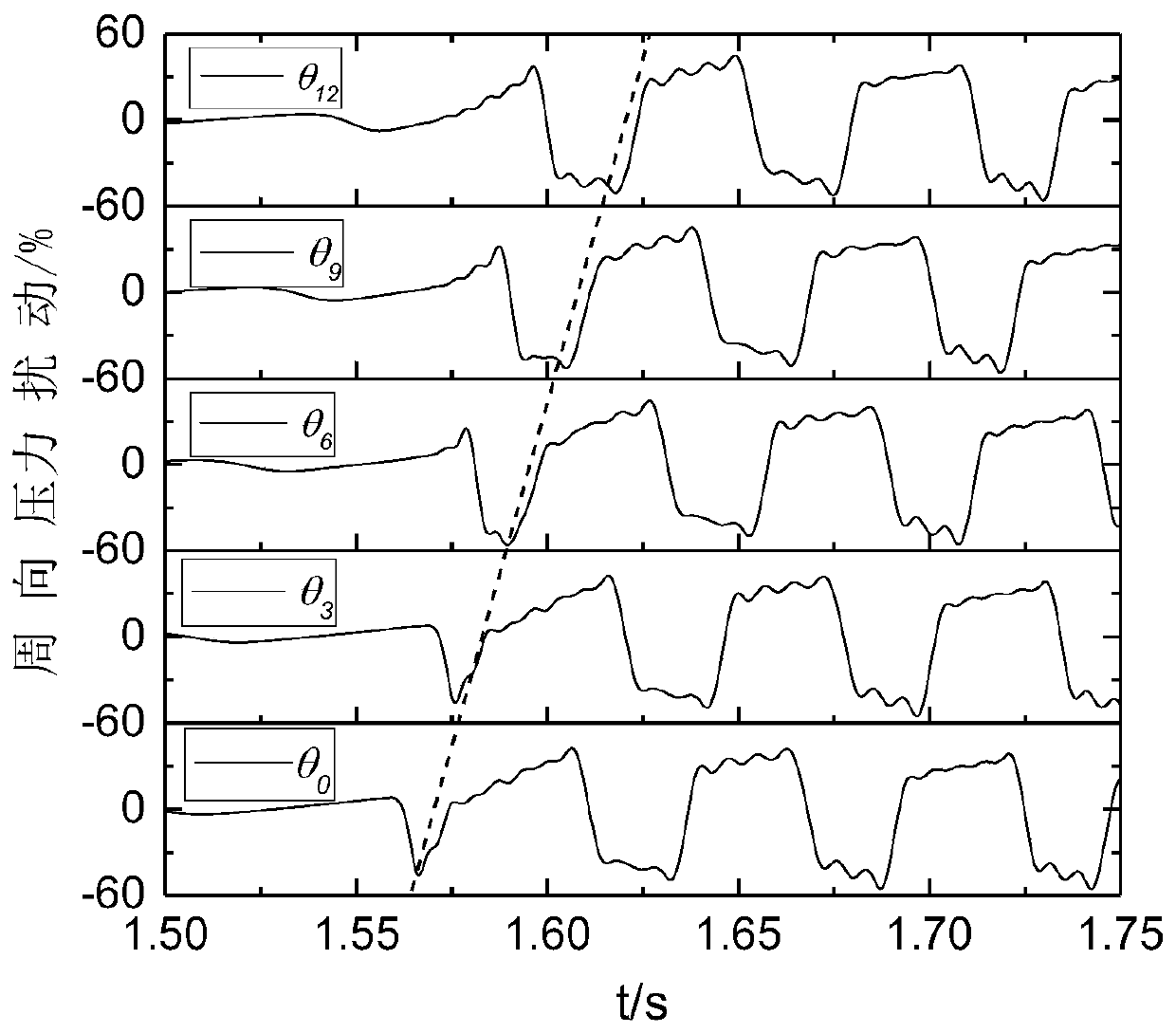
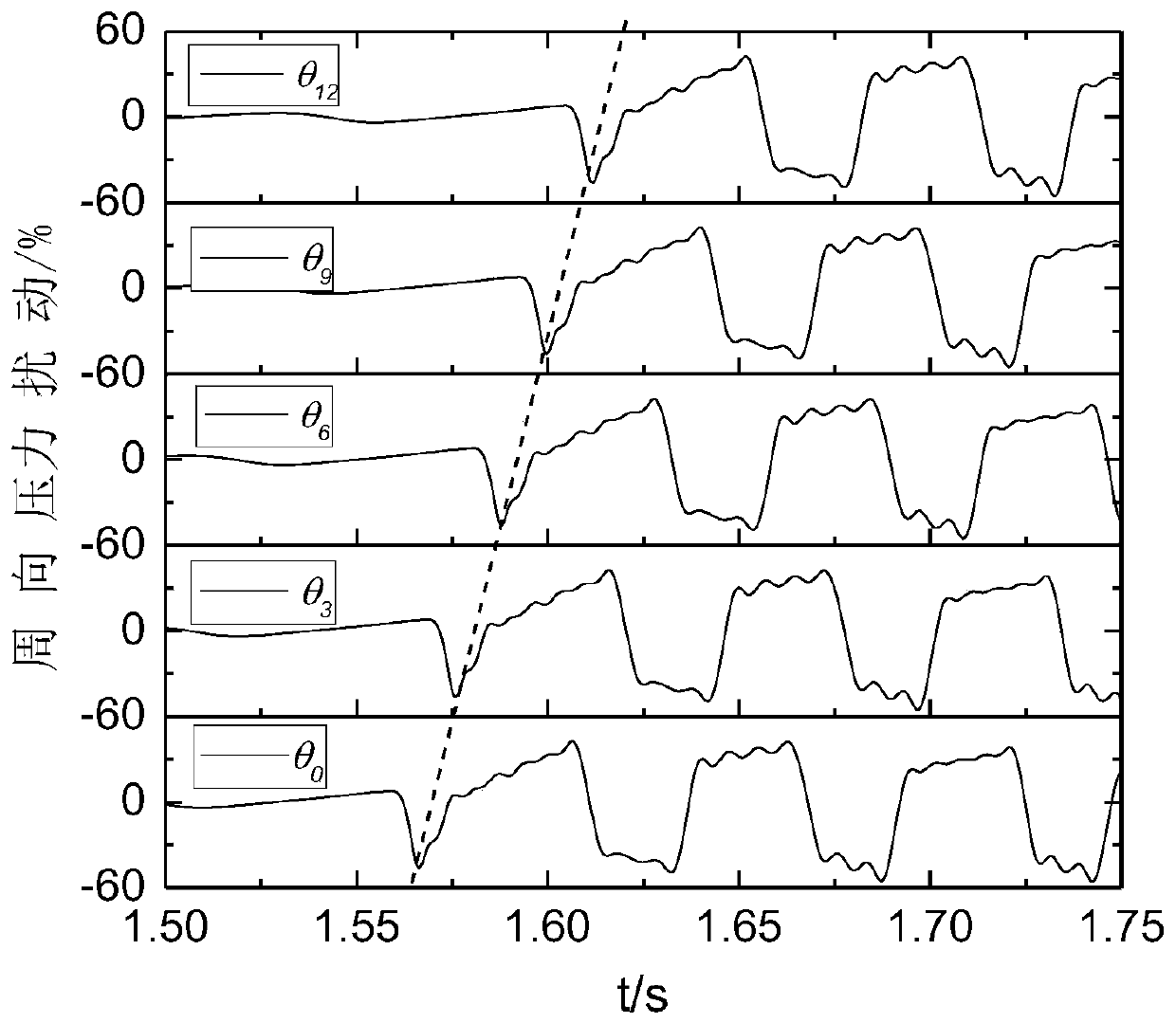
Compressor stall pre-warning signal reconstruction and identification method based on single-path sensor signal
ActiveCN107576445AAvoid the disadvantage of installing a large number of sensorsHigh engineering application valueGas-turbine engine testingRapid change measurementSpatial fourier transformFourier transform on finite groups
The invention provides a compressor stall pre-warning signal reconstruction and identification method based on a single-path sensor signal. The method includes obtaining the pressure signal through asingle-path sensor installed in the circumferential direction of a front-stage case of a compressor; and then according to the rotation characteristic of the compressor stall pre-warning signal, simulating the output of a multi-path sensor in the circumferential direction by adopting a signal translation method, and realizing the multi-path stall pre-warning signal reconstruction of the compressor. The reconstructed multi-path stall pre-warning signal is expressed as the superposition of the torus average and the circumferential pressure disturbance in the vector form, and the circumferentialpressure disturbance vector is subjected to the spatial Fourier transform to be decomposed into the superposition of multi-order modal waves; the first-order modal amplitude is compared with the set threshold value, and the stall is considered to occur when the threshold value is exceeded, and the identification of the stall pre-warning signal is realized. A single sensor can be used to replace aplurality of sensors, so that the defect that a plurality of sensors are installed is overcome, and the method has a large engineering application value.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
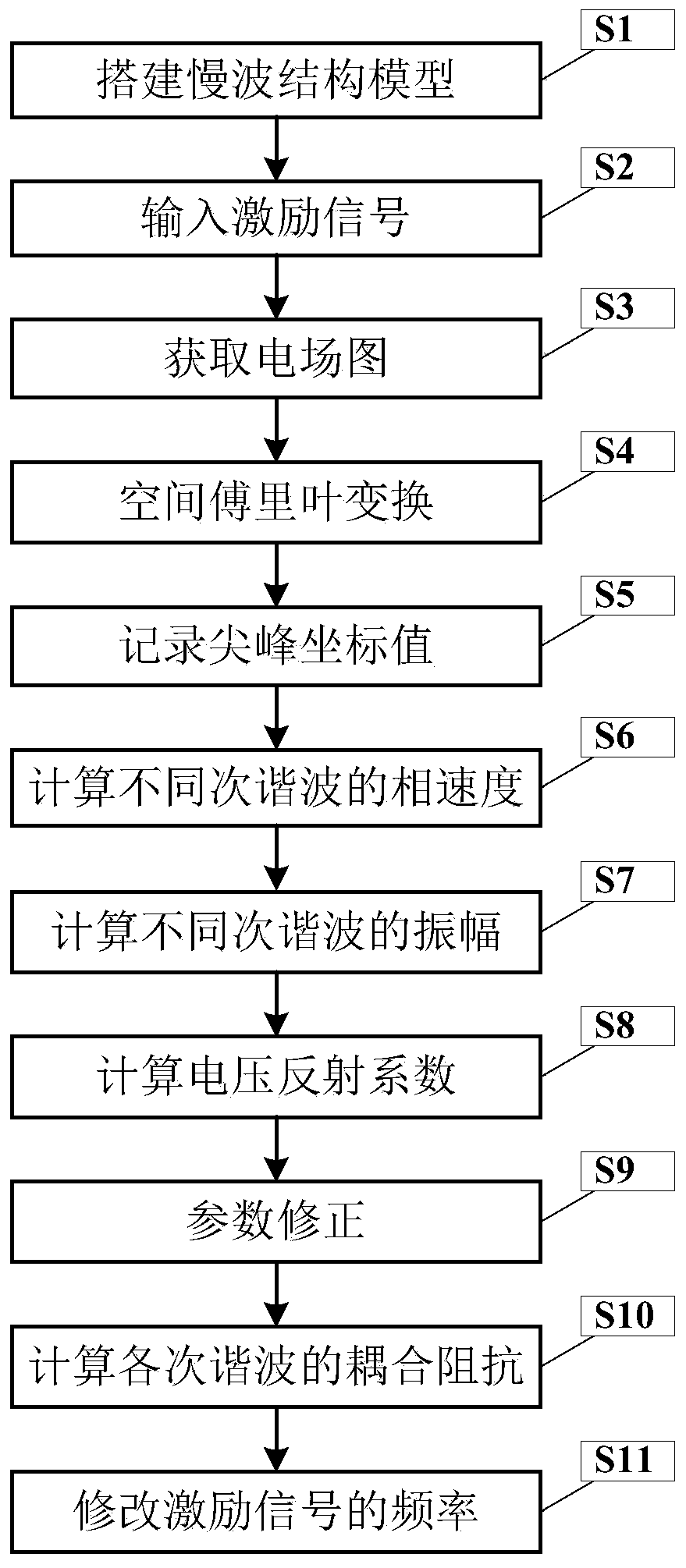
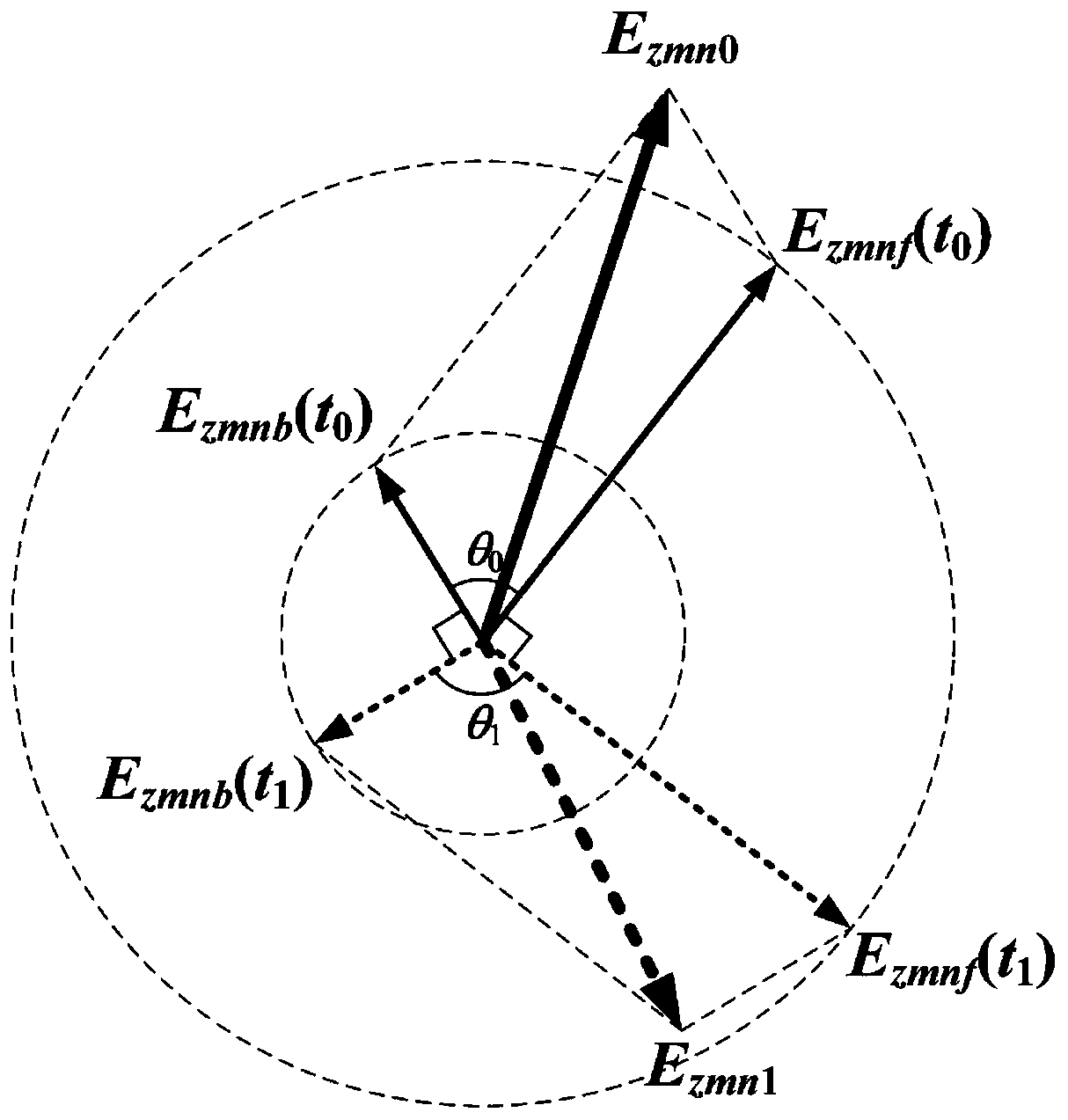
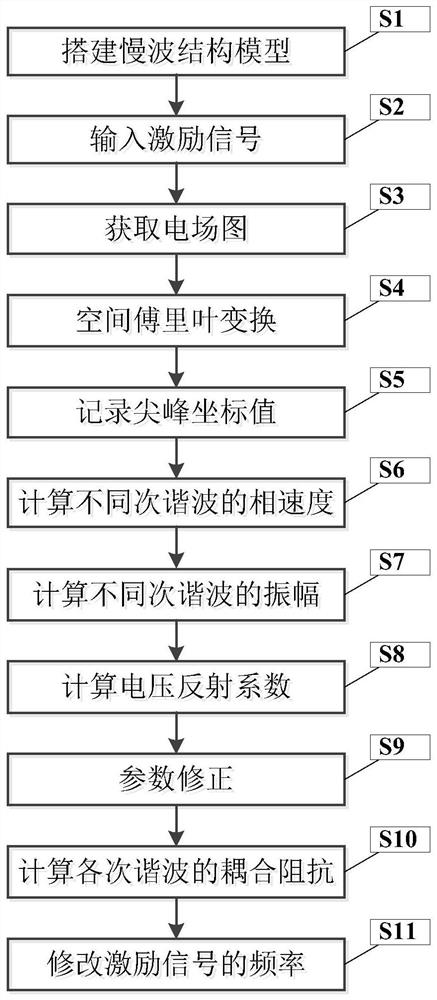
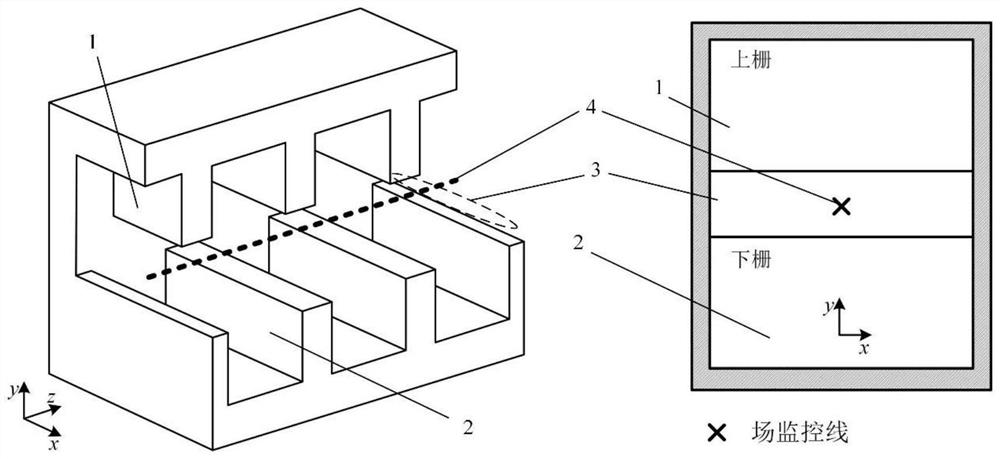
Method for obtaining dispersion characteristics and coupling impedance of slow wave structure
ActiveCN110909515AImprove accuracyAvoid schema confusion problemsComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainWave structure
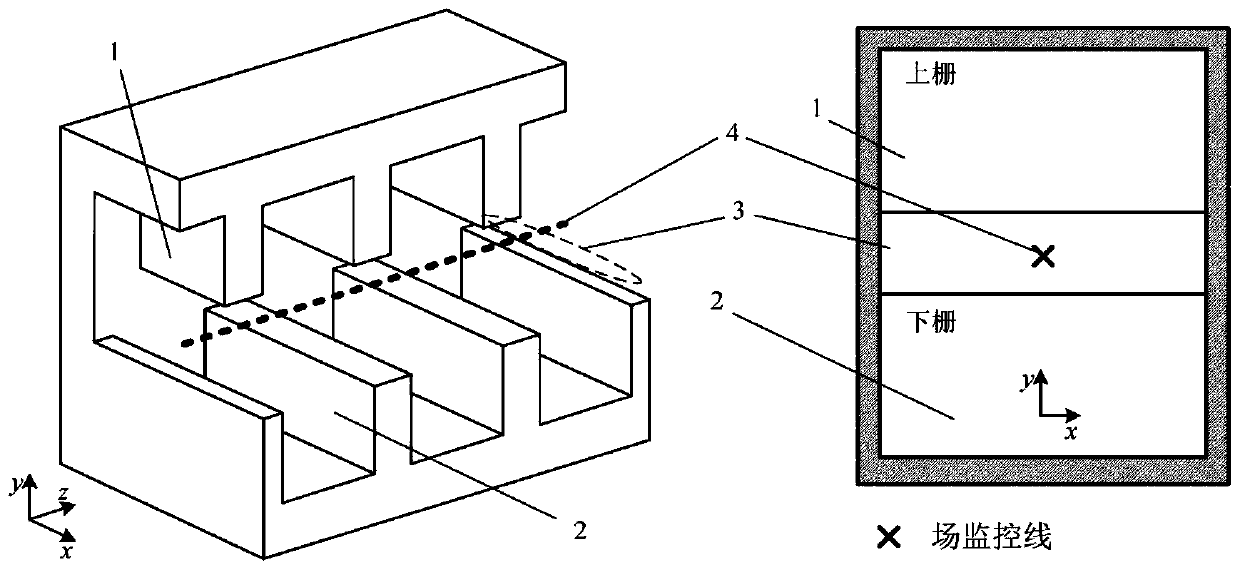
The invention discloses a method for obtaining dispersion characteristics and coupling impedance of a slow wave structure. Firstly, a lossless slow wave structure model to be processed is established;relevant parameters of the slow wave structure model are set; sinusoidal excitation signals are input, when the energy of the slow wave structure model is stabilized at the t0 moment, a time domain field monitor extracts electric field distribution on a field monitoring line to obtain an electric field graph, then spatial Fourier transform is carried out on the electric field graph, parameter correction is carried out, and finally the dispersion characteristic and the coupling impedance of the slow wave structure are calculated.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Compressor Stall Premonition Signal Reconstruction and Recognition Method Based on Single Sensor Signal
ActiveCN107576445BAvoid the disadvantage of installing a large number of sensorsHigh engineering application valueGas-turbine engine testingRapid change measurementSpatial fourier transformFourier transform on finite groups
The invention provides a compressor stall pre-warning signal reconstruction and identification method based on a single-path sensor signal. The method includes obtaining the pressure signal through asingle-path sensor installed in the circumferential direction of a front-stage case of a compressor; and then according to the rotation characteristic of the compressor stall pre-warning signal, simulating the output of a multi-path sensor in the circumferential direction by adopting a signal translation method, and realizing the multi-path stall pre-warning signal reconstruction of the compressor. The reconstructed multi-path stall pre-warning signal is expressed as the superposition of the torus average and the circumferential pressure disturbance in the vector form, and the circumferentialpressure disturbance vector is subjected to the spatial Fourier transform to be decomposed into the superposition of multi-order modal waves; the first-order modal amplitude is compared with the set threshold value, and the stall is considered to occur when the threshold value is exceeded, and the identification of the stall pre-warning signal is realized. A single sensor can be used to replace aplurality of sensors, so that the defect that a plurality of sensors are installed is overcome, and the method has a large engineering application value.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
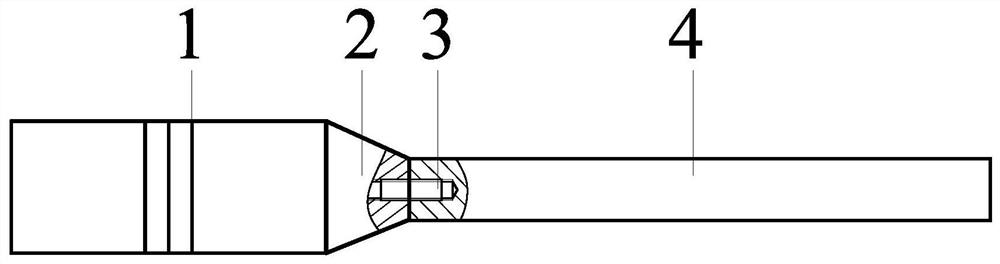
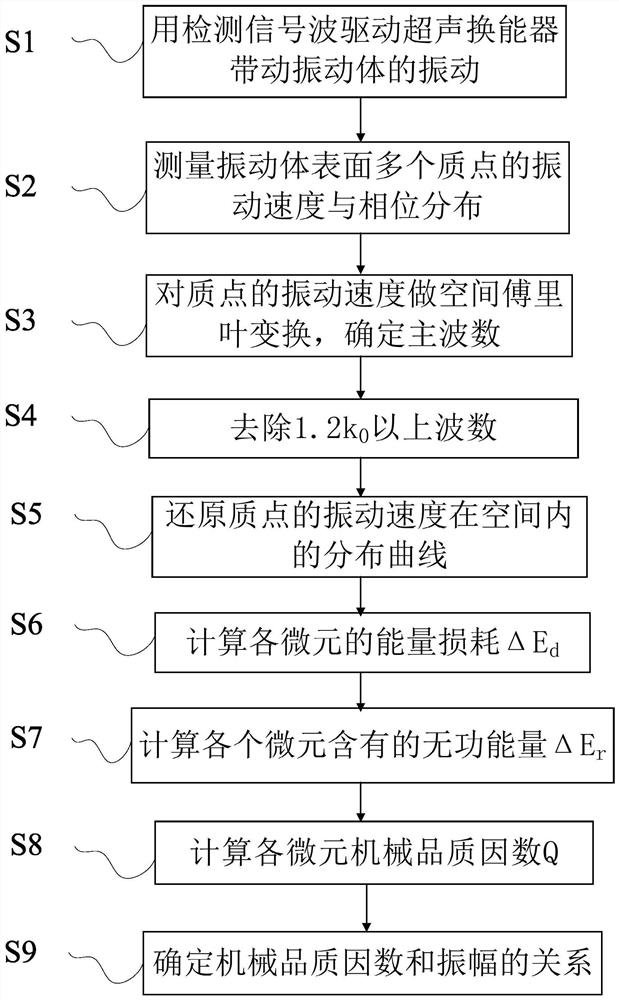
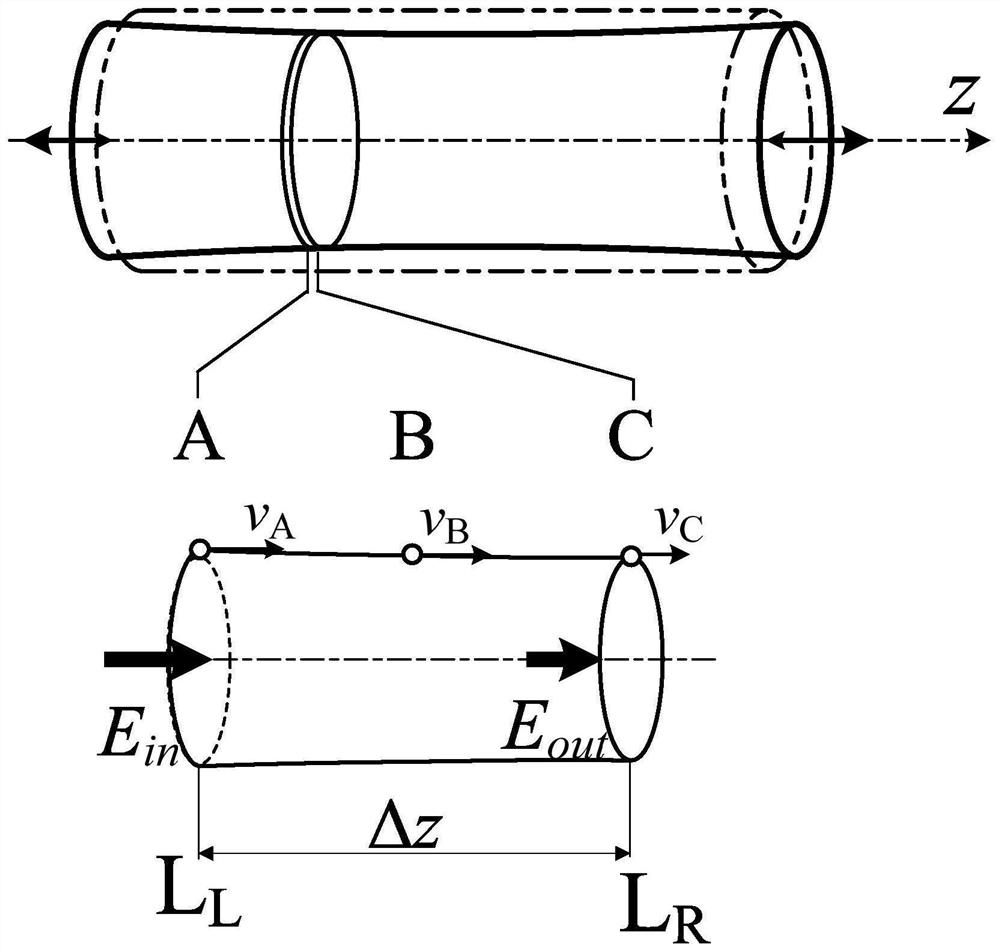
Measuring system and method for mechanical quality factor of vibrating body
ActiveCN111504586BGuaranteed measurement accuracySimple calculationVibration testingVibration amplitudeSignal wave
The invention belongs to the technical field of mechanical quality factor measurement, and in particular relates to a measurement method and a measurement system for the mechanical quality factor of a vibrating body. Use the detection signal wave to drive the ultrasonic transducer to excite the vibration of the vibrating body, move the vibration measuring device along the axial direction of the vibrating body, measure the vibration velocity and phase of multiple particles at the ΔZ microelement spacing on the surface of the vibrating body, and measure the vibration of the particle on the vibrating body Do spatial Fourier transform of the velocity to obtain the frequency spectrum in the wavenumber space and determine the dominant wavenumber k 0 , remove 1.2k 0 For the above wave number, restore the distribution curve of the vibration velocity of the particle in space, and calculate the energy loss ΔE of the microelement d and the reactive energy ΔE of the element r , the corresponding relationship between the mechanical quality factor of the vibrating body and the amplitude of the vibrating body is obtained; the invention avoids the influence of the energy loss of the connector on the measurement result in principle, and ensures the measurement accuracy. The overall approach makes the whole calculation process simple and can be applied on a large scale.
Owner:吴疆
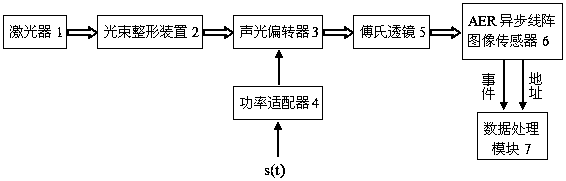
An acousto-optic real-time signal analyzer based on asynchronous detection
ActiveCN104808057BHigh bandwidthImprove dynamic performanceSpectral/fourier analysisSpatial fourier transformFourier transform on finite groups
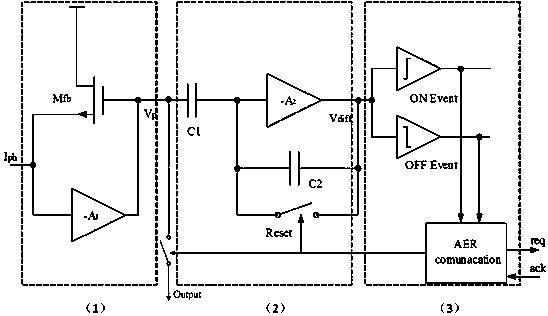
The invention discloses an acousto-optic real-time signal analyzer based on asynchronous detection, which includes a laser, a beam shaping device, an acousto-optic deflector, a power adapter, a Fourier lens, an AER asynchronous line array image sensor and a data processing module; the AER asynchronous line The output of the array image sensor is connected to the data processing module; each diffracted beam output by the acousto-optic deflector completes the spatial Fourier transform through the Fourier lens, and is incident on the pixel of the AER asynchronous linear array image sensor; the data processing module controls the AER asynchronous linear array The spatial position of each pixel output by the image sensor and the magnitude of the photocurrent induced by the pixel are processed, converted into time-frequency domain parameters corresponding to the measured signal, and stored and displayed. The invention has large bandwidth, high sensitivity and large dynamic performance. High time precision, effectively realize transient signal monitoring; fundamentally solve the problem of data redundancy; can process parallel signals in real time, and have strong adaptability to different types of signals.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP NO 26 RES INST
Ultrasonic method and apparatus for characterizing the propagation of ultrasonic waves in waveguides of linearly variable thickness
InactiveCN105518451BAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesOrgan movement/changes detectionFrequency waveSpatial fourier transform
Device for the representation, in a frequency-wave number reference frame f-k, of the propagation of an ultrasound wave in a dihedral guide (1), which comprises ultrasound emitters (2) referenced by “Ej” with j an integer varying between 1 and N, N a strictly positive integer and ultrasound receivers (3) referenced by “Ri” with i an integer varying between 1 and M, M a strictly positive integer, the receivers being disposed spatially over a first segment of a straight line according to a regular pitch “A”, which comprises means for processing the signal received by the receivers, originating from the emitters, and in which the processing means comprise means for calculating a modified discrete spatial Fourier transform, for a spatial integration variable “x”, centered in the middle of said first segment and running through the receivers in the direction of increasing x, and for a wave vector k(x) equal to a product k.P(x), with k a constant coefficient in x and included between 0 and 2*Pi / A, and with P(x) a polynomial in x, of coefficient of degree 0 in x equal to 1 and of coefficient “C” of degree 1 in x such that C.A lies between − 1 / 10 and + 1 / 10
Owner:爱莎莉 +2
A Method for Obtaining Dispersion Characteristics and Coupling Impedance of Slow-wave Structure
ActiveCN110909515BImprove accuracyAvoid schema confusion problemsComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainWave structure
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
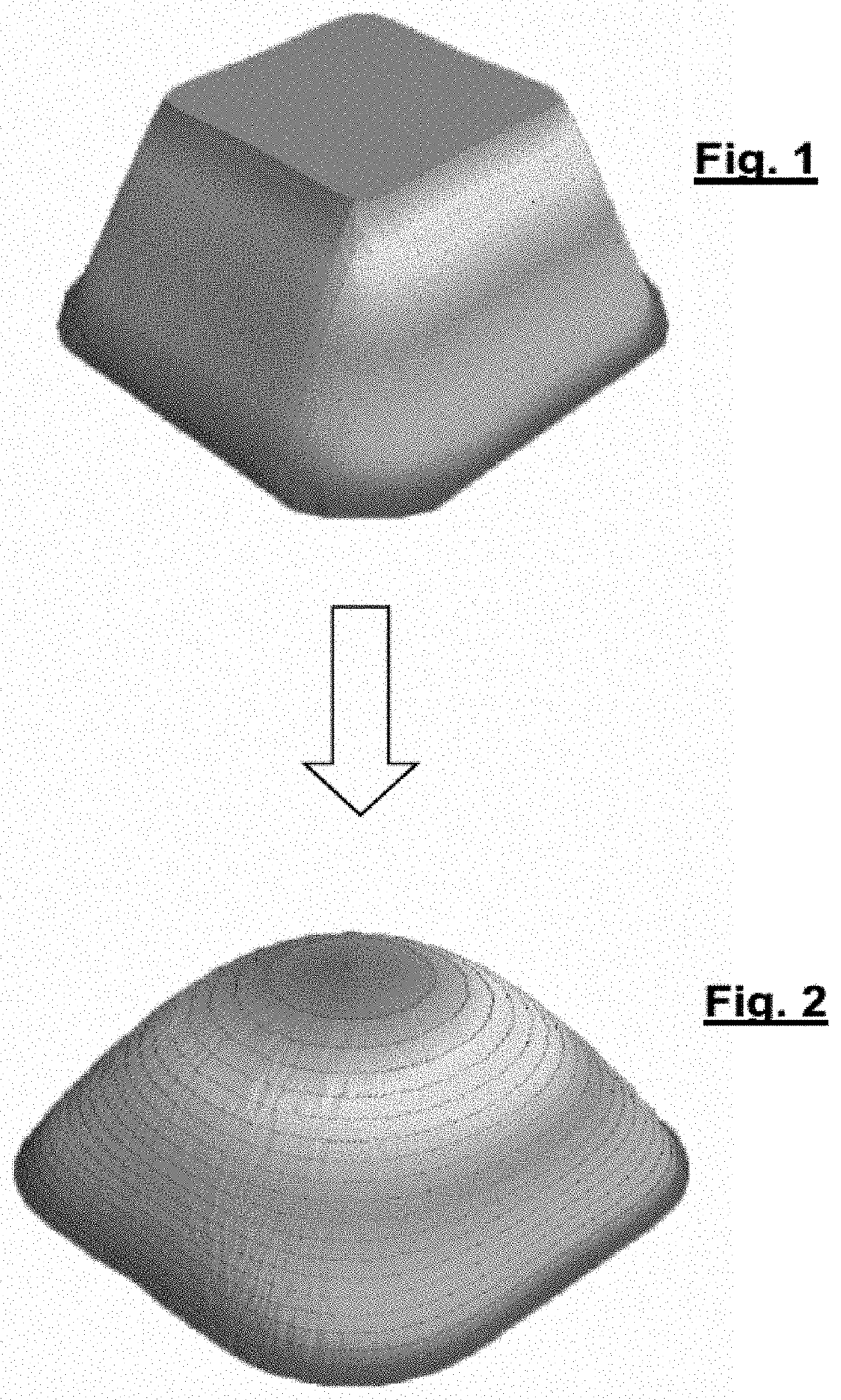
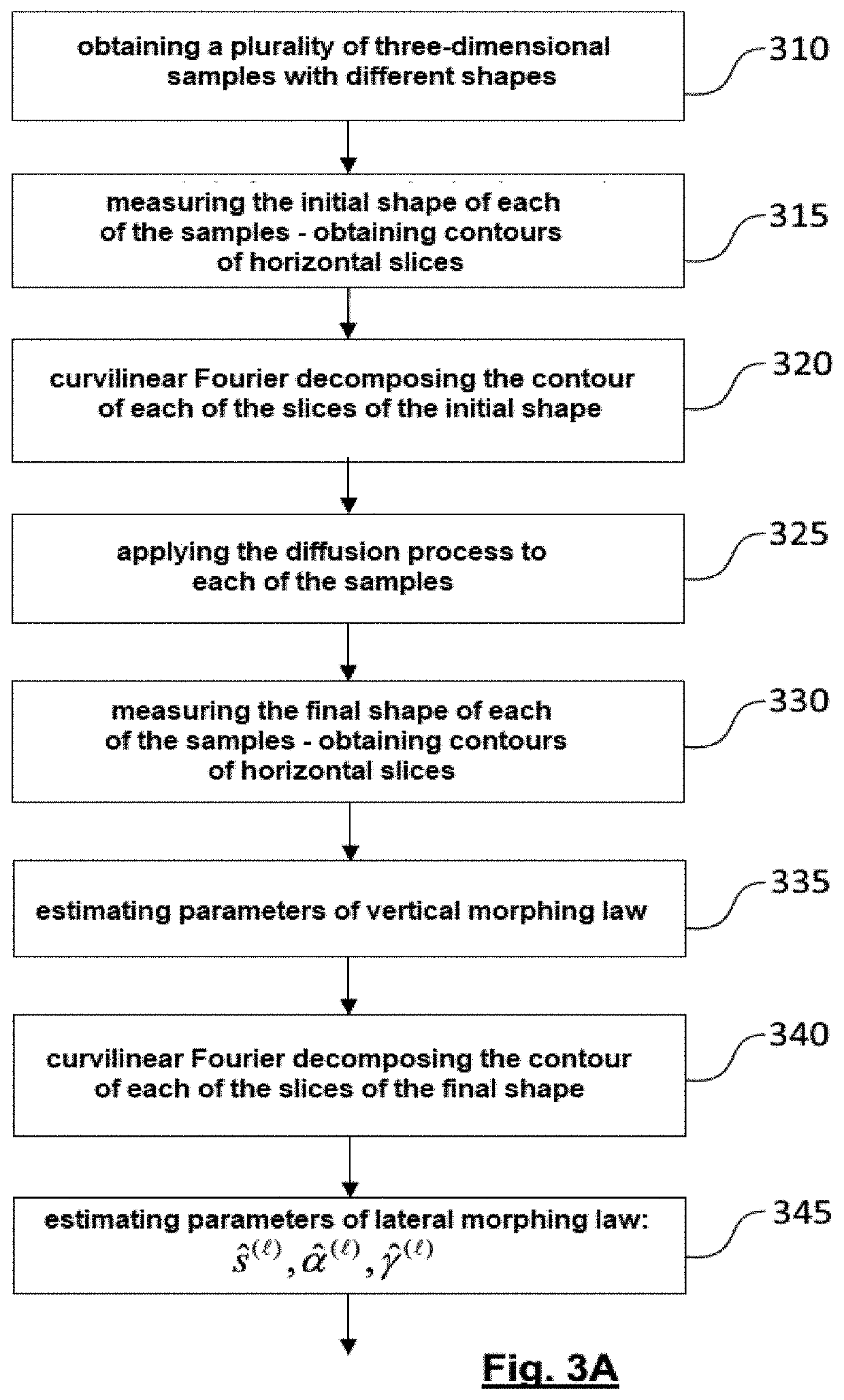
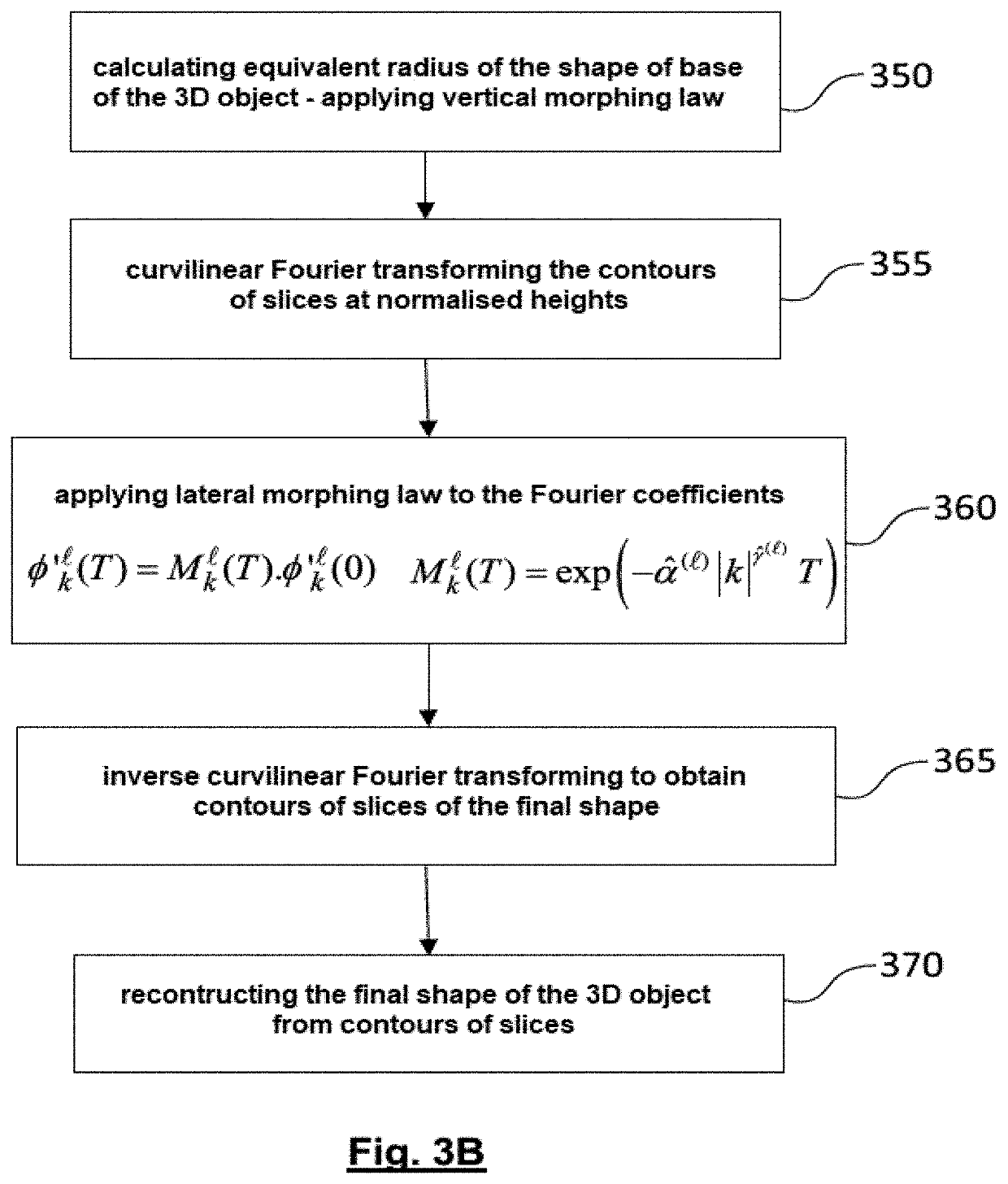
Predicting the shape of a three-dimensional object which is subjected to a diffusion process
The present invention relates to a method for predicting the shape of a three-dimensional object which has been subjected to a diffusion process for a predetermined duration. The prediction method uses a law of vertical morphing and a law of lateral morphing. The law of lateral morphing applies to a description of the contours of different slices of a sample at standardised heights. The description of the contour of a slice is obtained by a curvilinear Fourier transform of the contour or by a two-dimensional spatial Fourier transform of a contour line approximating said contour. The present invention also relates to the manufacture of a three-dimensional object of a given material and a given nominal shape.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
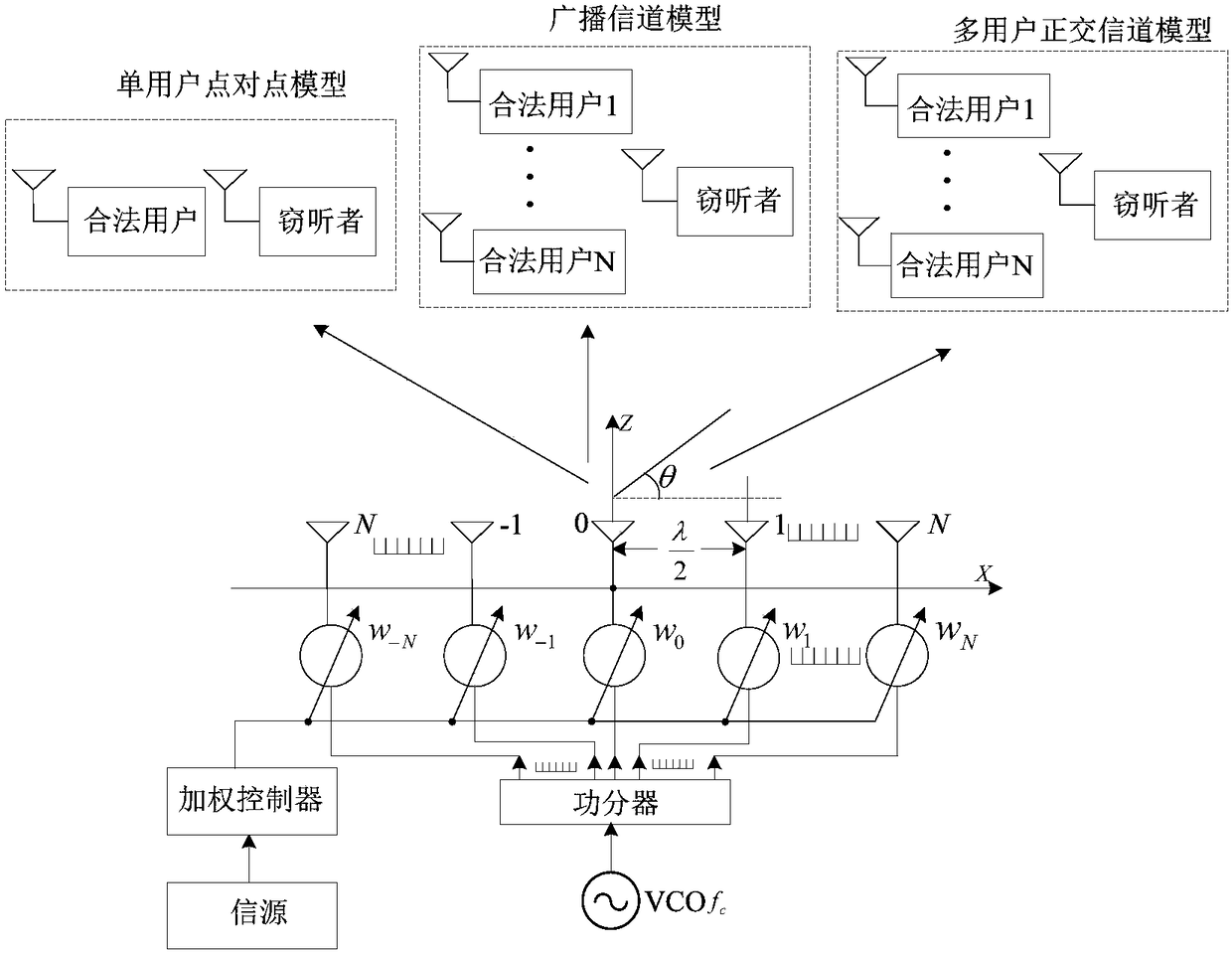
Design method of direction modulation signal based on spatial Fourier transform
ActiveCN105049399BSimple design methodEasy to implementSpatial transmit diversityMultiple carrier systemsSpatial fourier transformArray element
The invention provides a directional modulation signal design method based on spatial Fourier transformation. The method comprises the following steps of establishing desired phase wave beam spatial coverage functions in ideal conditions relative to different communication models; and acquiring a phased array element weighted value according to the spatial Fourier transformation pair relation among phase wave beams and the array element weighted value of a phased array in a directional modulation signal transmitter to achieve a directional modulation signal design in different communication models. By using the directional modulation signals designed by the method, valid users can normally demodulate received directional modulation signals through common digital signal receivers. As to wiretappers in undesirable directions, their wiretapping receivers cannot demodulate useful communication information from received signals due to the relative phase relationship distortion of constellation points in a received signal constellation diagram. The invention provides a safe transmission method for transmitting communication information in wireless channels.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
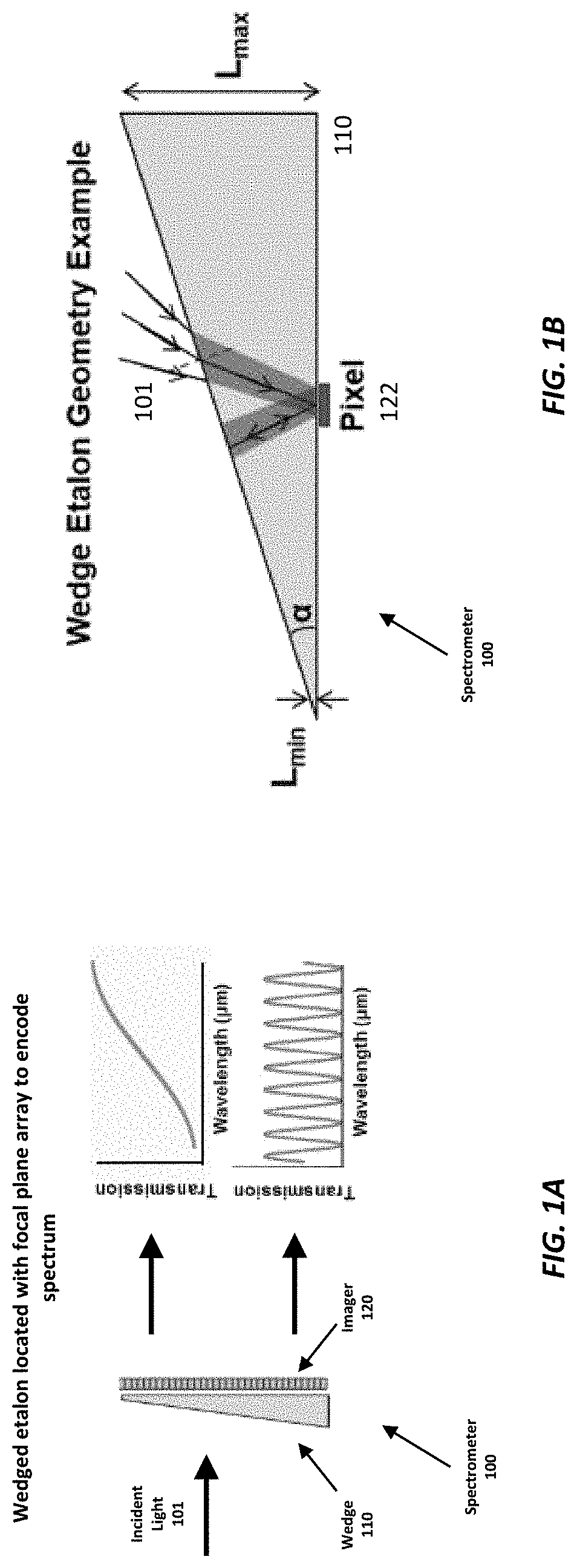
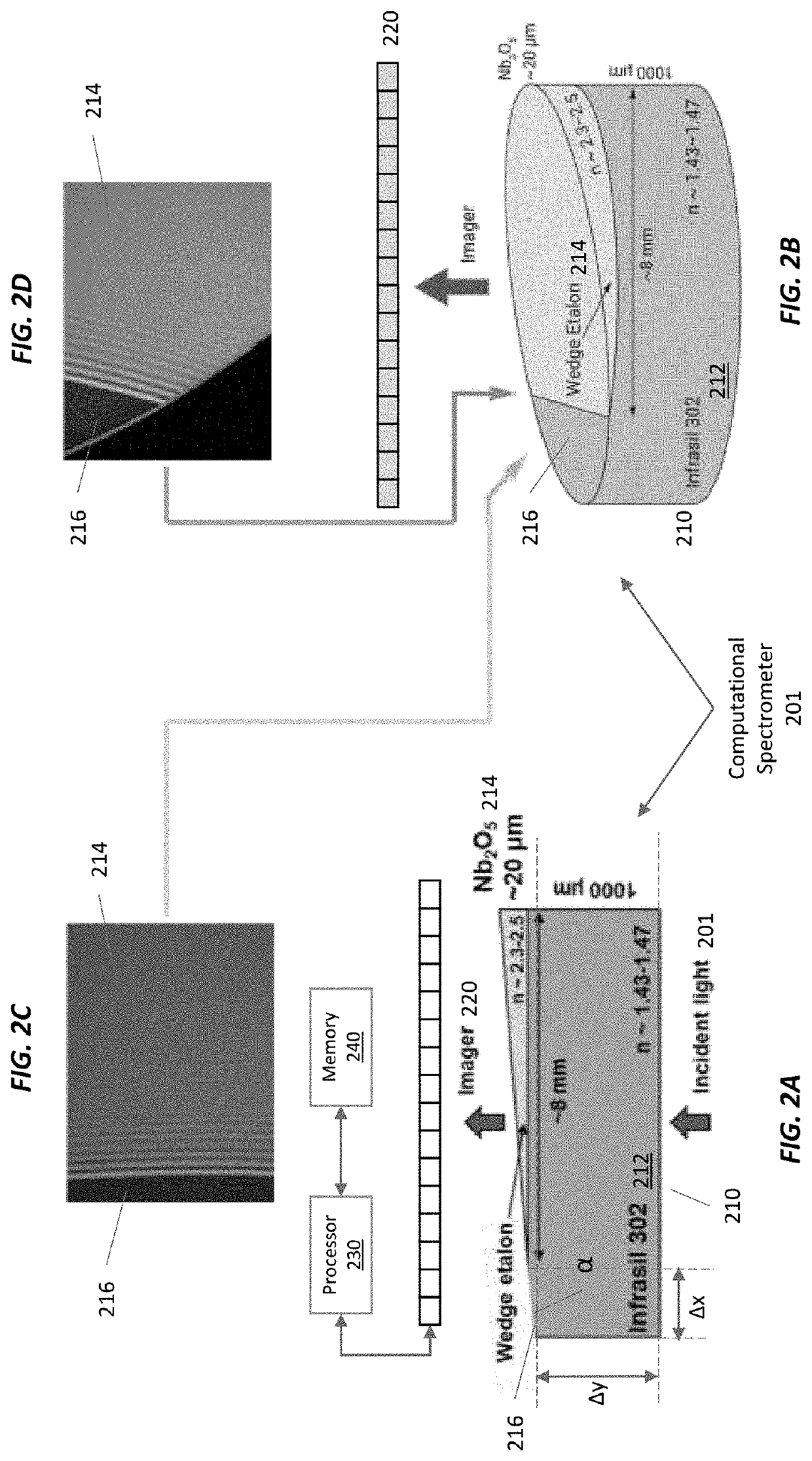
Compact Computational Spectrometer Using Solid Wedged Low Finesse Etalon
ActiveUS20220252452A1High spectral resolutionFew spectral artifactRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometrySpatial fourier transformFitting algorithm
A two-layer hybrid solid wedged etalon was fabricated and combined with a traditional imager to make a compact computational spectrometer. The hybrid wedge was made of Nb2O5 and Infrasil 302 and was designed to operate from 0.4-2.4 μm. Initial demonstrations used a CMOS imager and operated from 0.4-0.9 μm with spectral resolutions<30 cm−1 from single snapshots. The computational spectrometer operates similarly to a spatial Fourier Transform infrared (FTIR) spectrometer with spectral reconstruction using a non-negative least squares fitting algorithm based on analytically computed wavelength response vectors determined from extracted physical thicknesses across the entire two-dimensional wedge. This computational technique resulted in performance and spectral resolutions exceeding those that could be achieved from Fourier techniques. With an additional imaging lenses and translational scanning, the system can be converted into a hyperspectral imager.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
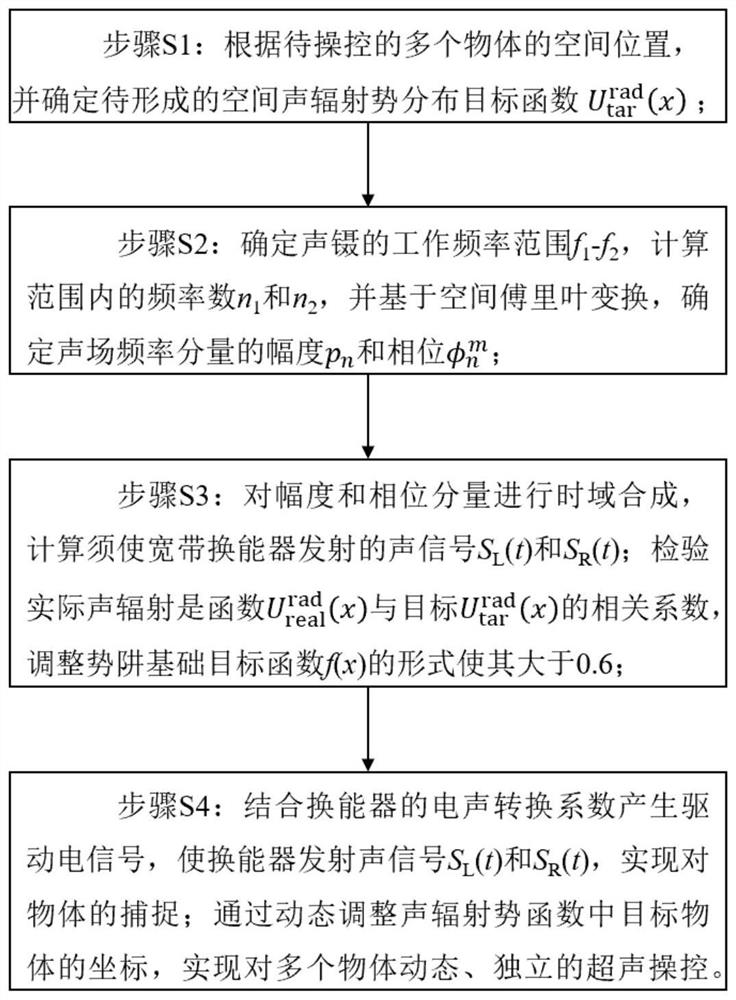
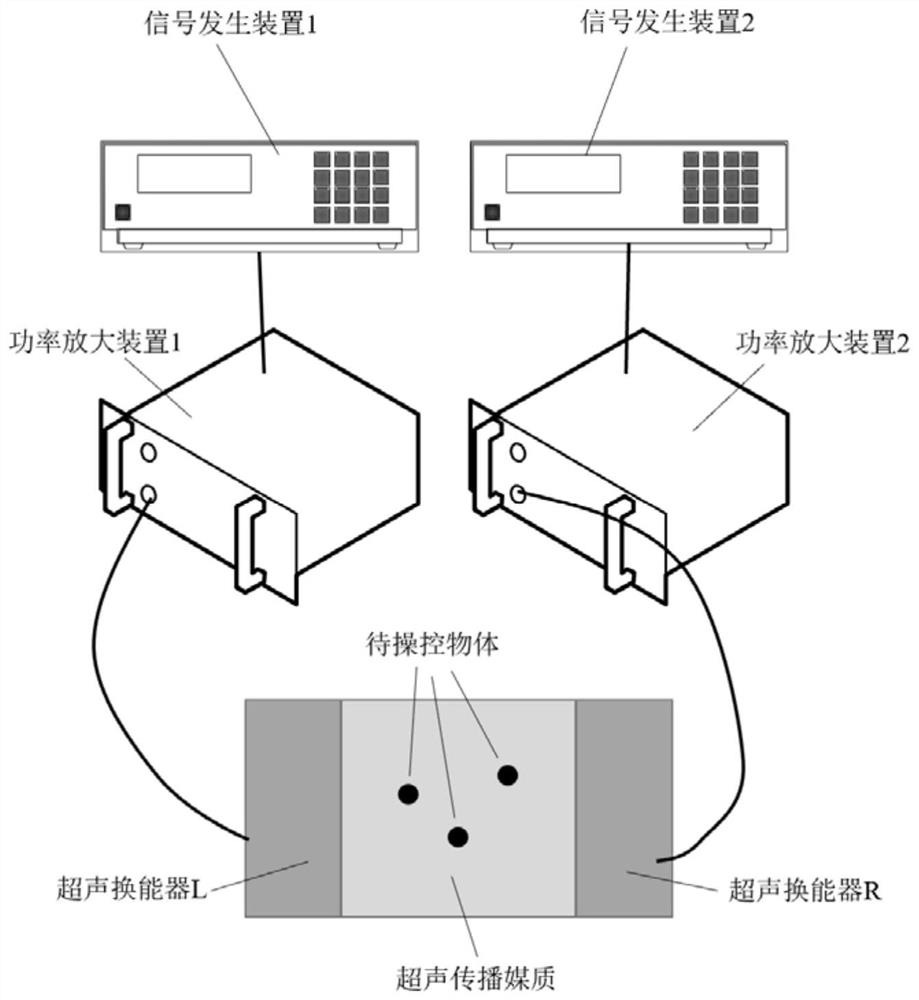
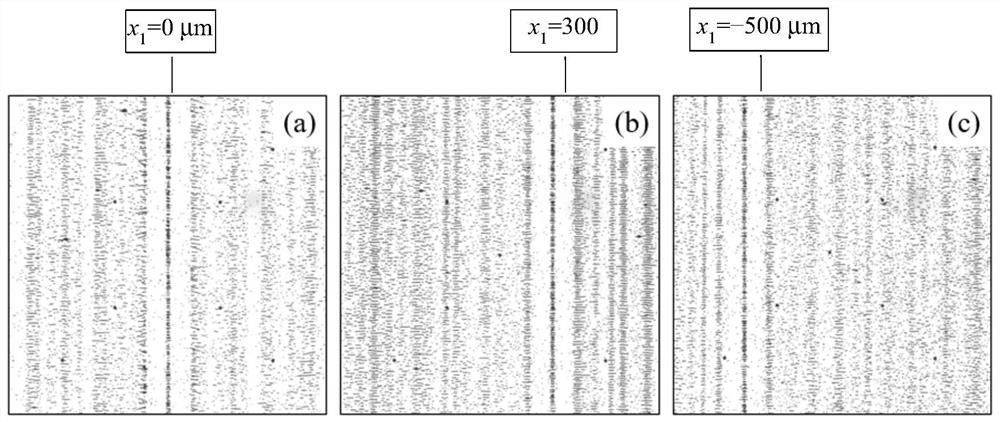
Acoustic tweezers implementation method and system based on spatial Fourier transform
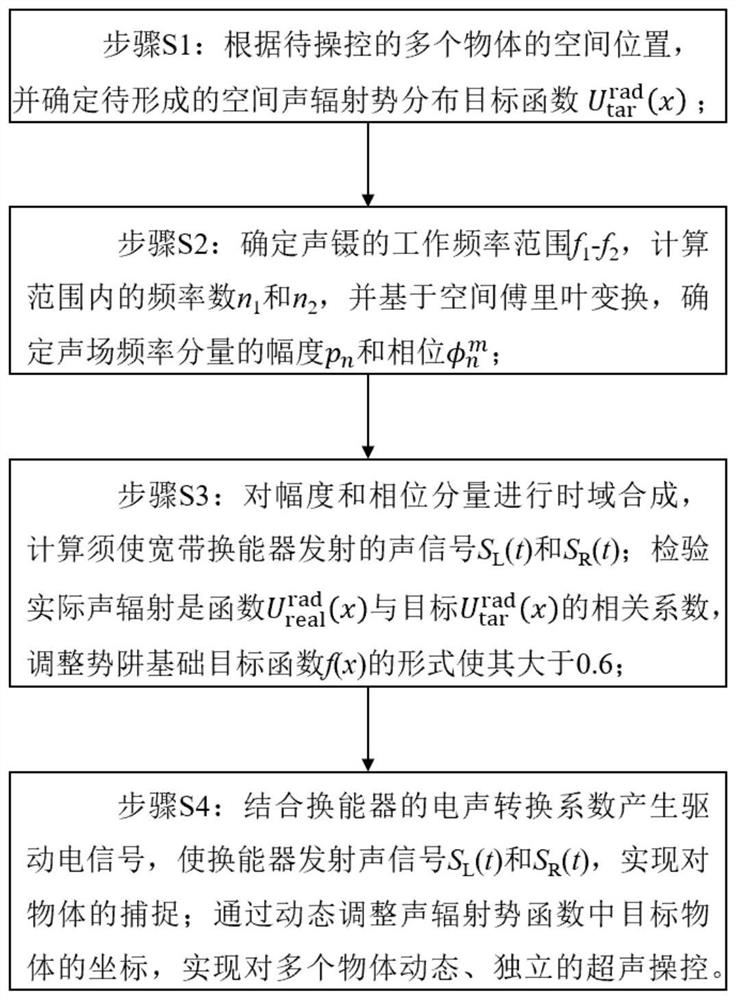
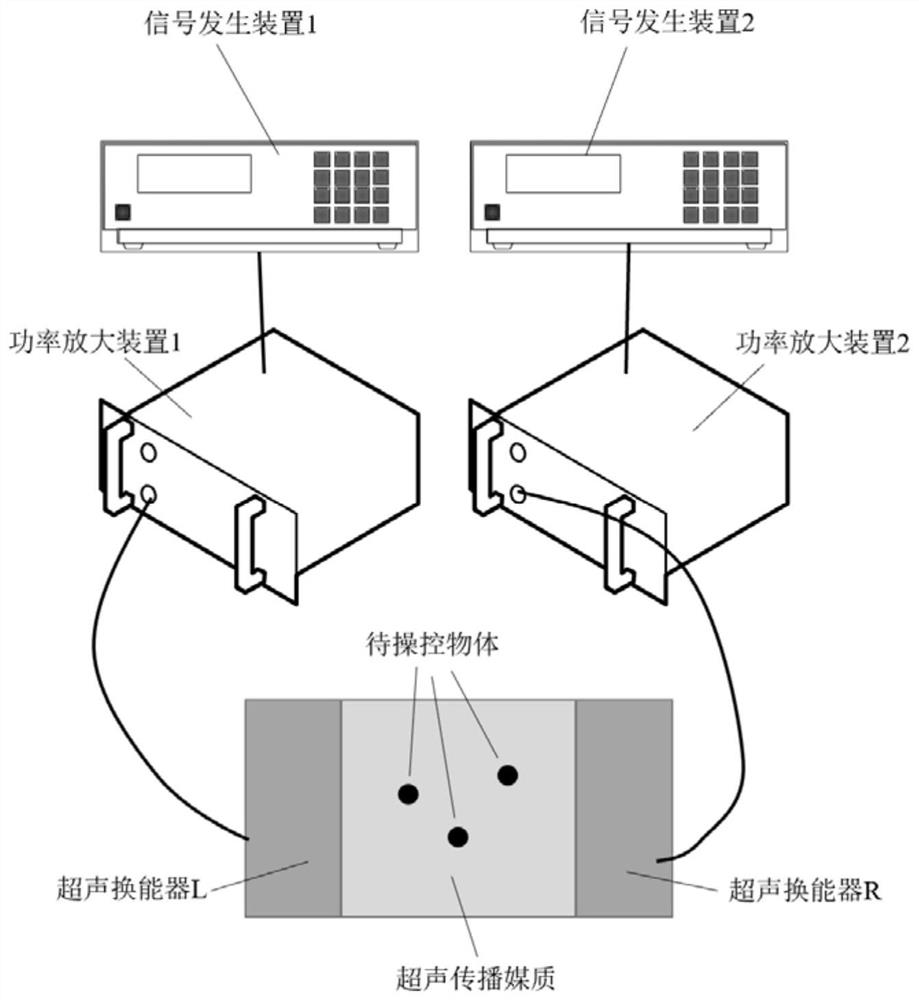
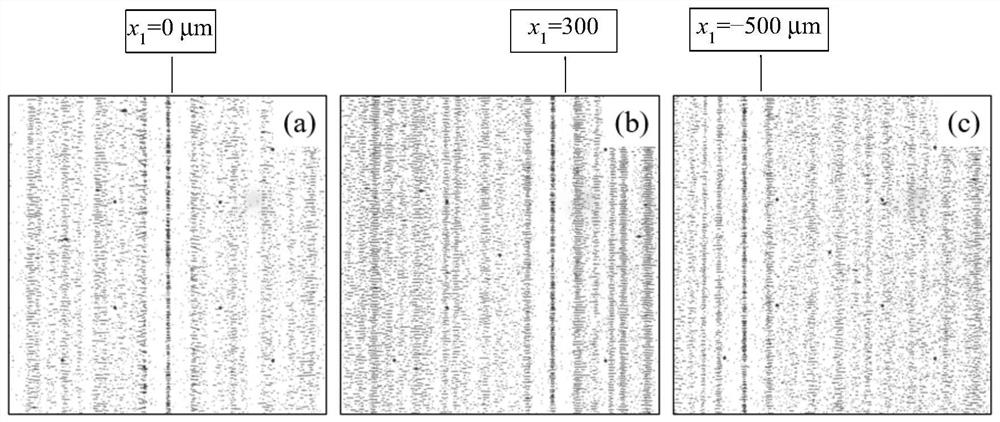
ActiveCN112169729AAchieve captureOvercome the lack of independent controlLaboratory glasswaresEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesAuditory radiationSpatial fourier transform
The invention discloses an acoustic tweezers implementation method and a system based on spatial Fourier transform, and belongs to the technical field of acoustic control. In order to solve the problem that in the prior art, in single-frequency standing wave acoustic tweezers, acoustic radiation potential well distribution which can be defined at will cannot be formed in the space, and therefore multiple target objects cannot be independently controlled, the invention provides the acoustic tweezers implementation method and the system based on spatial Fourier transform. According to the method, the orthogonality of a trigonometric function is used for decomposing the acoustic radiation potential distribution expected to be formed in the spatial domain into superposition of the acoustic radiation potential on a plurality of frequency components, and determining an electric signal for driving the two transducers according to the amplitudes and phases of the obtained components; and eachfrequency component of the acoustic radiation potential based on the control requirements is adjusted to realize dynamic adjustment of a plurality of independent acoustic radiation potential traps. The defect that existing single-frequency standing wave acoustic tweezers cannot independently control a plurality of target objects is overcome, and the control flexibility of the acoustic tweezers isgreatly improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
A method and system for implementing acoustic tweezers based on spatial Fourier transform
ActiveCN112169729BAchieve captureOvercome the lack of independent controlLaboratory glasswaresEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesAuditory radiationPotential well
The invention discloses an acoustic tweezers realization method and system based on spatial Fourier transform, and belongs to the technical field of acoustic manipulation. Aiming at the problem that in the single-frequency standing wave acoustic tweezers existing in the prior art, an acoustic radiation potential well distribution that can be defined arbitrarily cannot be formed in space, so that multiple target objects cannot be independently manipulated, the present invention provides a spatial Fourier-based The acoustic tweezers implementation method and system of leaf transformation, using the orthogonality of trigonometric functions, decomposes the acoustic radiation potential distribution expected to be formed in the space domain into the superposition of the acoustic radiation potential on multiple frequency components, and the amplitude of the obtained components The sum and phase determine the electrical signals used to drive the two transducers; the frequency components of the acoustic radiation potential are adjusted based on the control requirements to realize the dynamic adjustment of multiple independent acoustic radiation potential wells. It overcomes the deficiency that the existing single-frequency standing wave acoustic tweezers cannot independently control multiple target objects, and greatly improves the flexibility of the acoustic tweezers.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Three-dimensional imaging sonar beamforming method and its implementation on multi-core processor
ActiveCN104656073BSmall amount of calculationImprove real-time performanceWave based measurement systemsSpatial fourier transformTime delays
The invention relates to a three-dimensional imaging sonar wave beam forming method applied to uniformly-distributed plane arrays in three-dimensional detection sonar. The method comprises the following steps: receiving and collecting time domain echo signals; carrying out time domain Fourier transform on the time domain echo signals, then judging whether the result obtained by the time domain Fourier transform meets the far-field condition or not, compensating distance influence items of a time delay calculation formula in a near-field wave beam forming expression formula, and then carrying out the next step if the result shows that the near-field wave beams are formed; directly carrying out the next step if the result shows that far-field wave beams are formed; carrying out spatial Fourier transform on row vectors of the plane arrays of the signals; carrying out spatial Fourier transform on line vectors of the plane arrays of the signals; performing a modulus on the obtained spatial two-dimensional Fourier transform result to obtain a final two-dimensional wave beam forming result.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
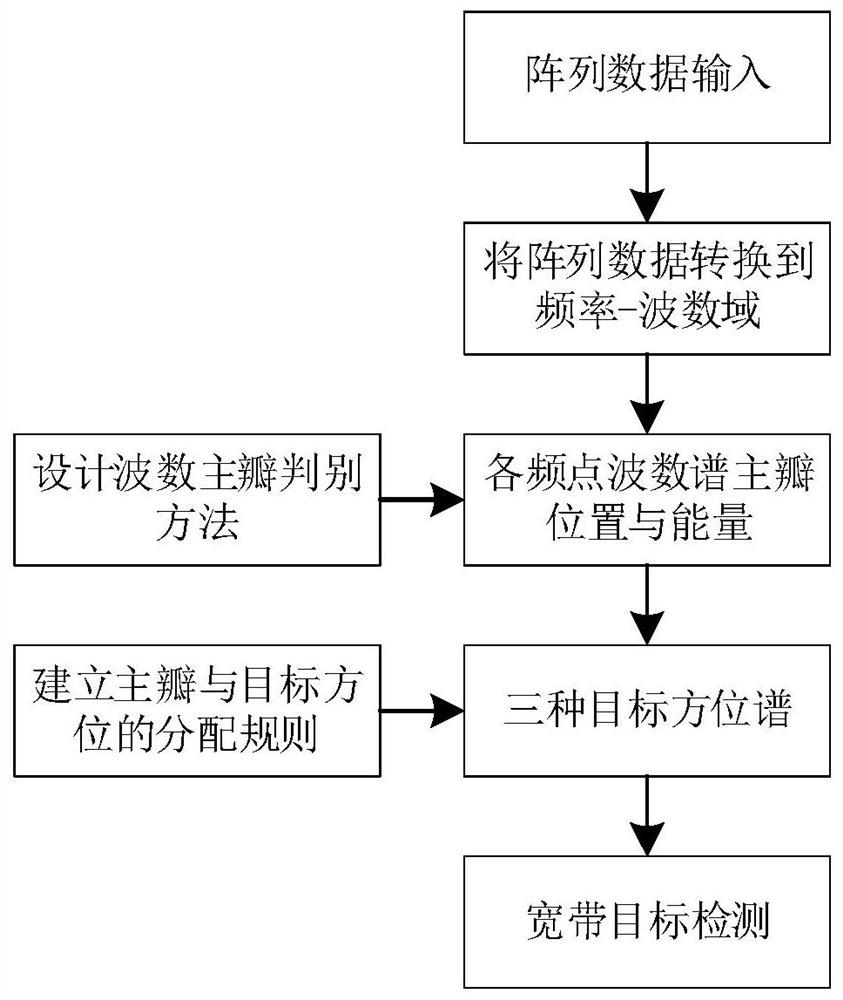
A broadband target detection method in a complex environment with strong interference
ActiveCN114114222BEfficient detectionBoth stableWave based measurement systemsSpatial fourier transformEngineering
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com