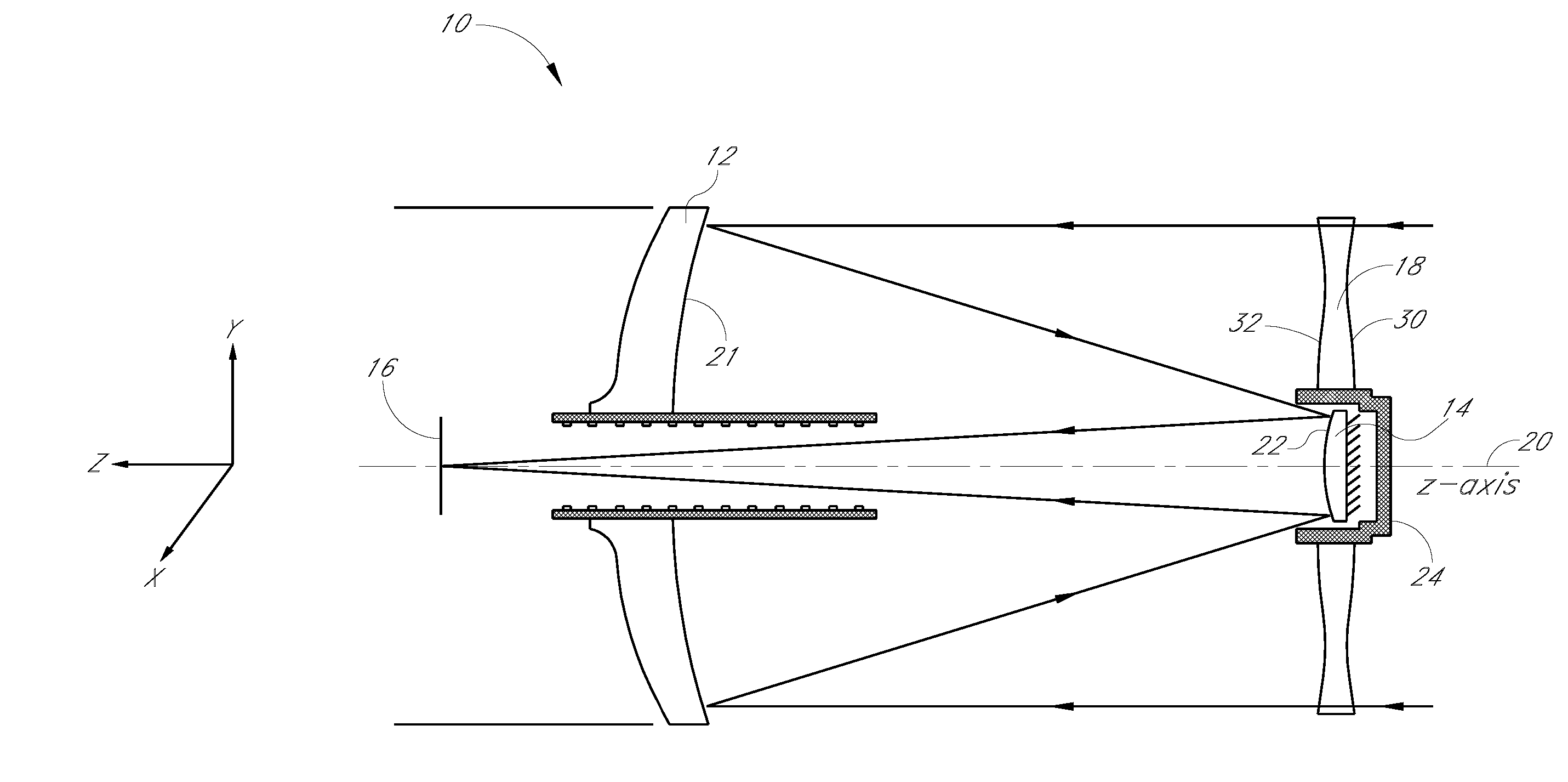
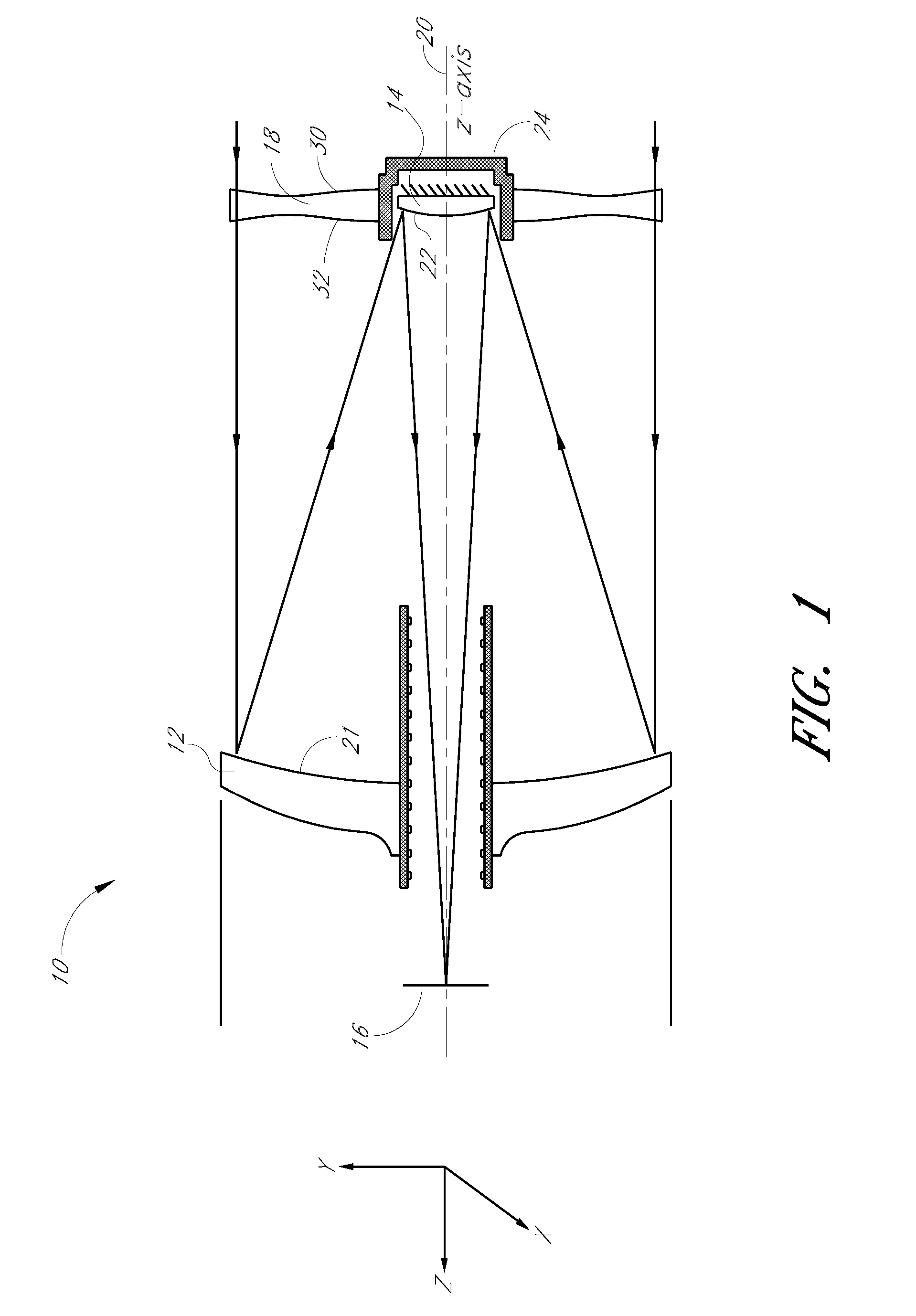
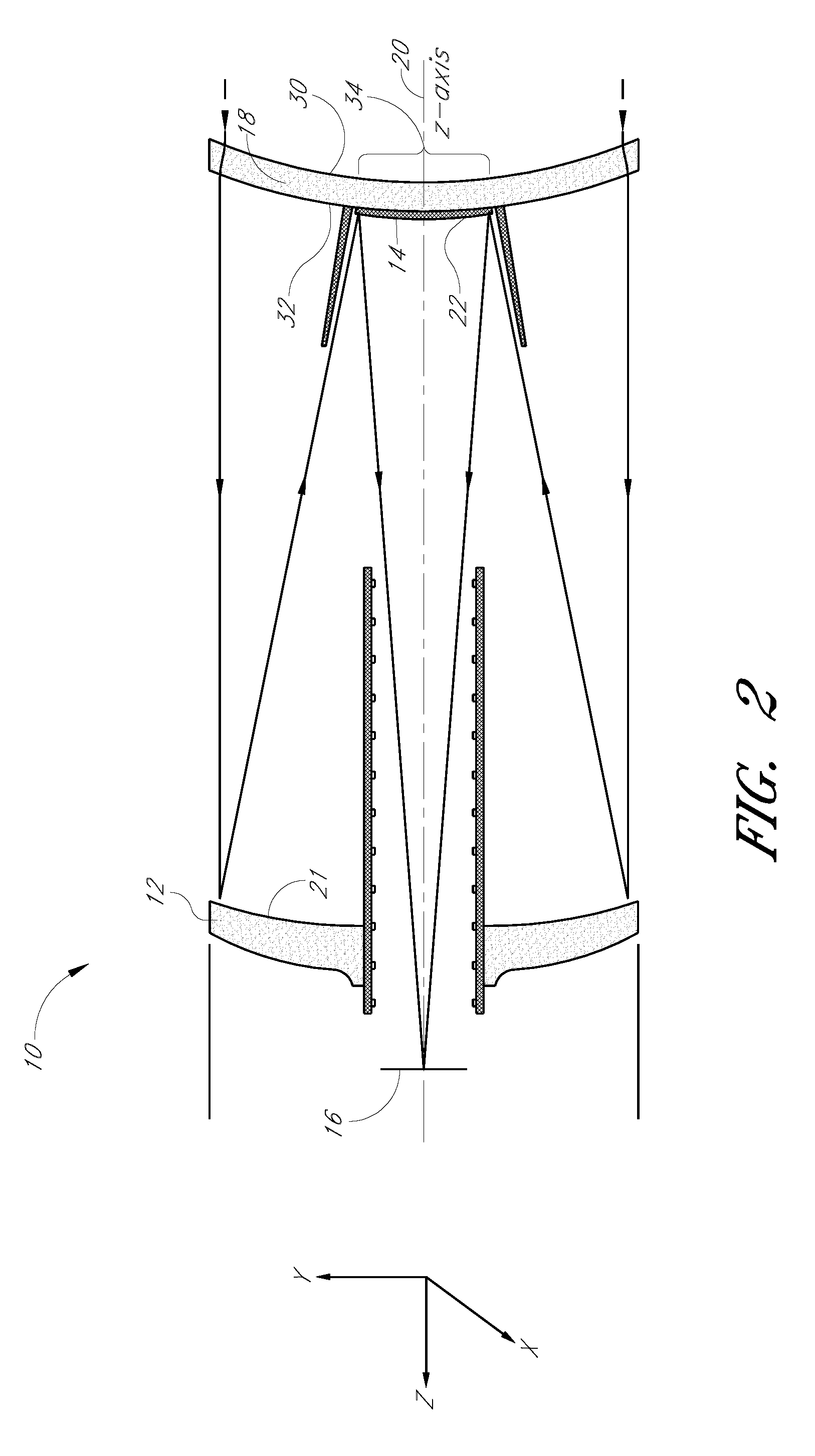
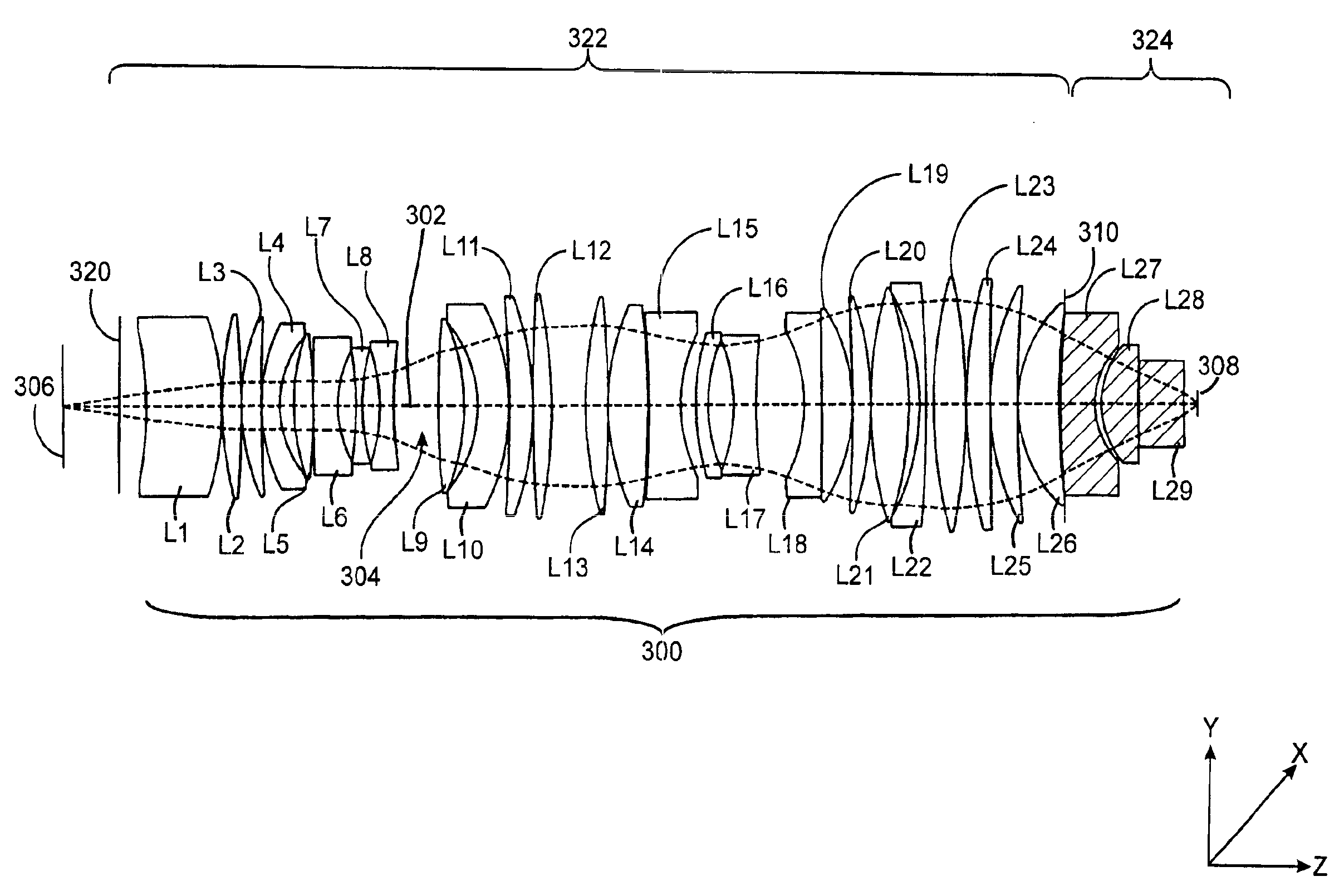
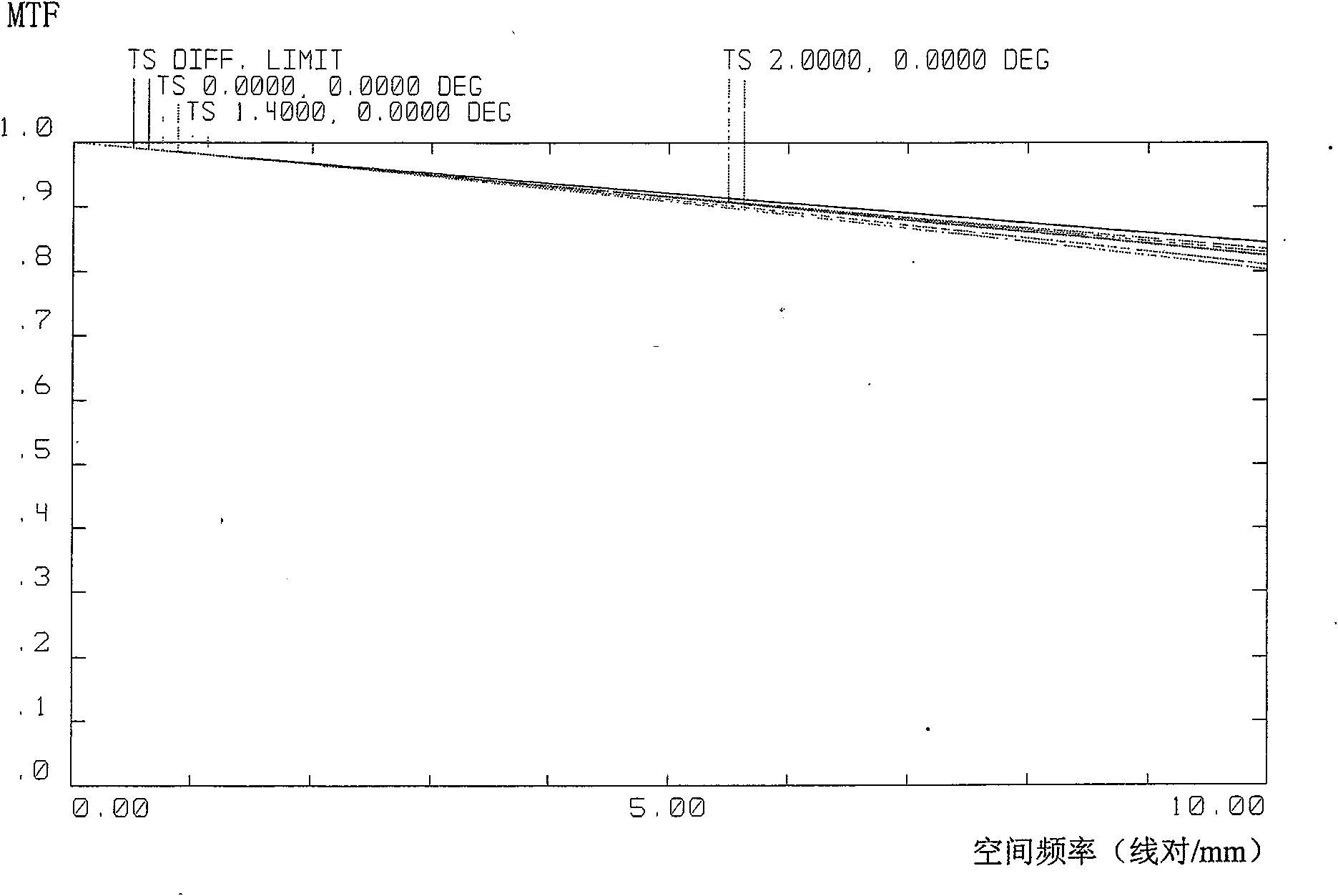
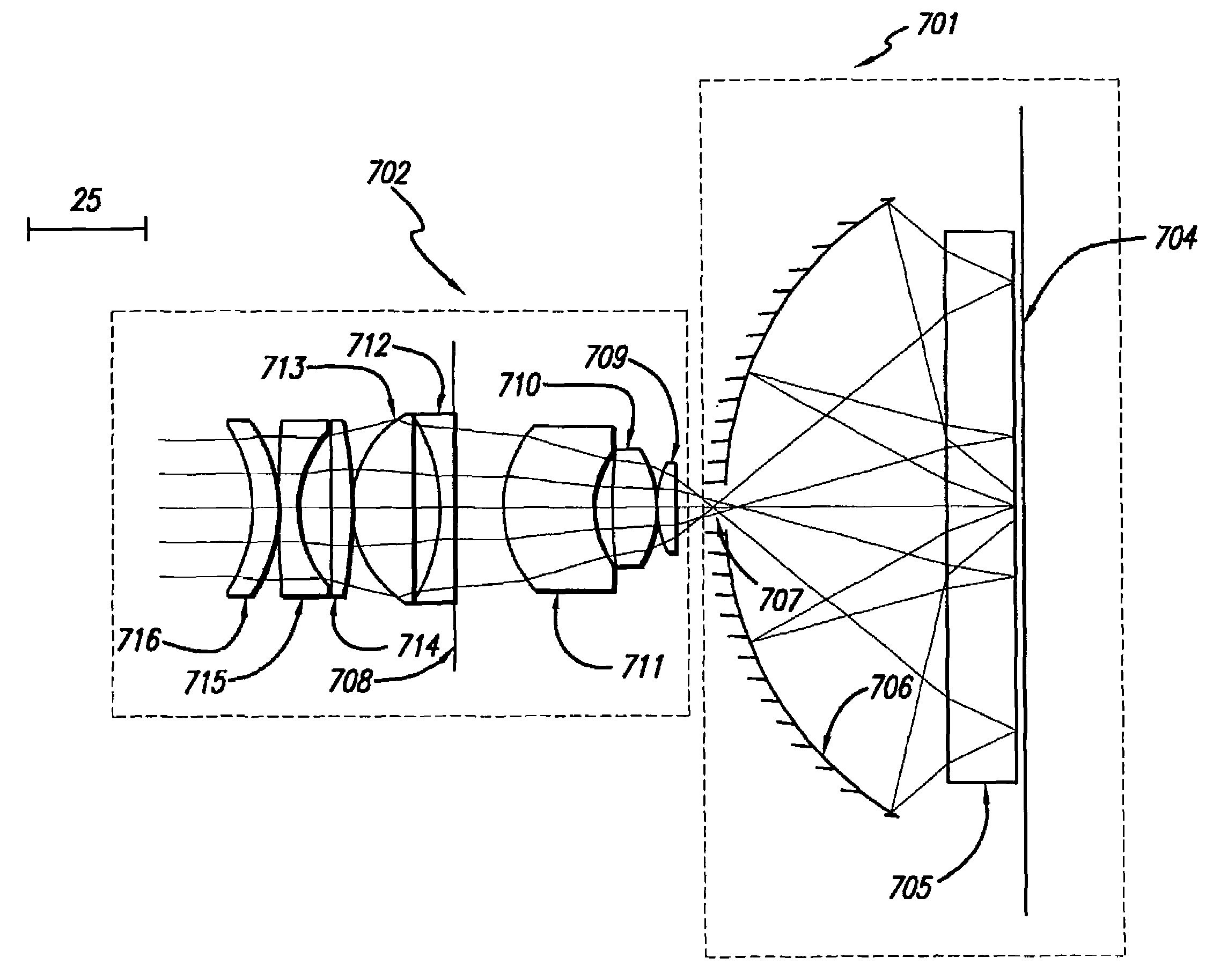
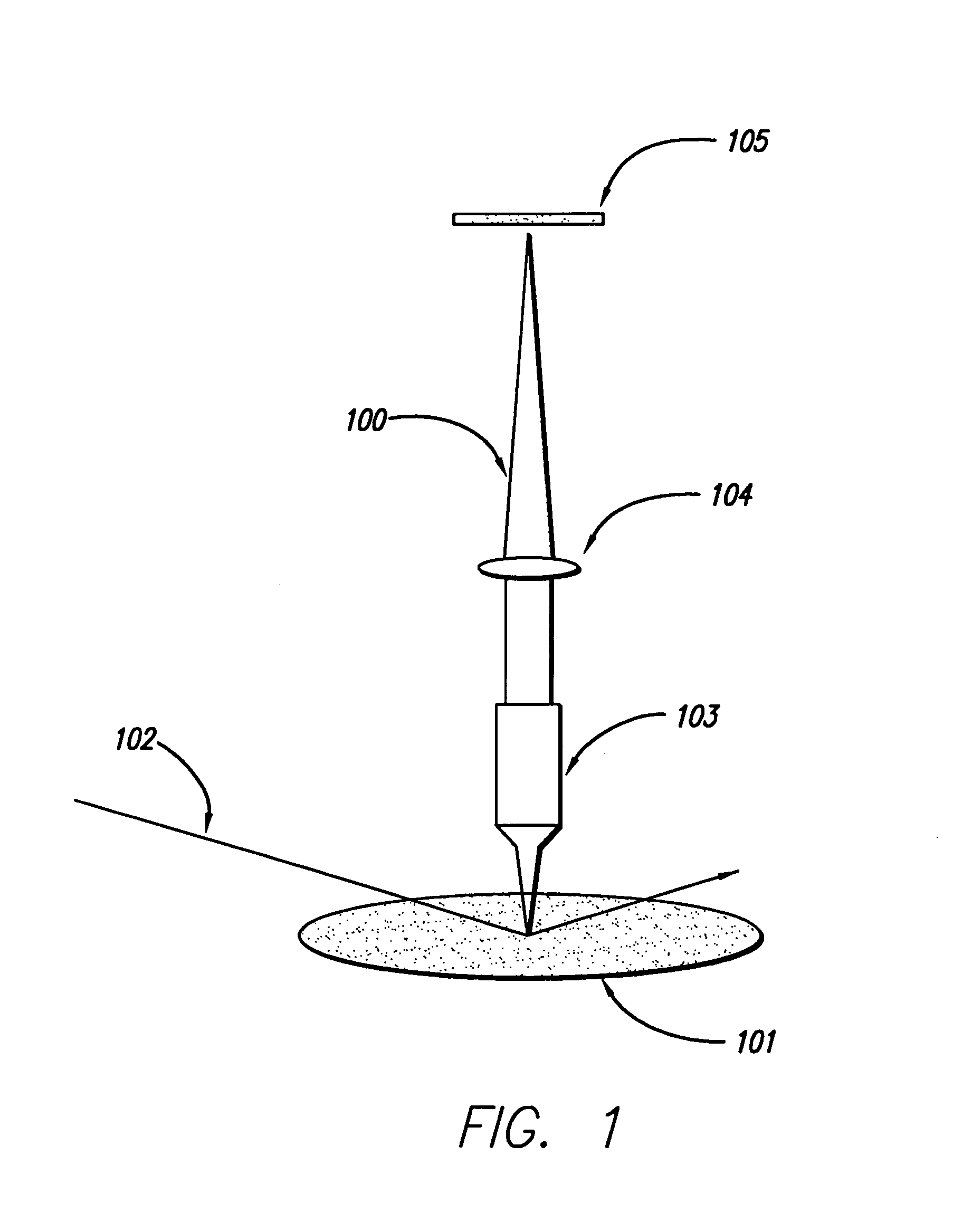
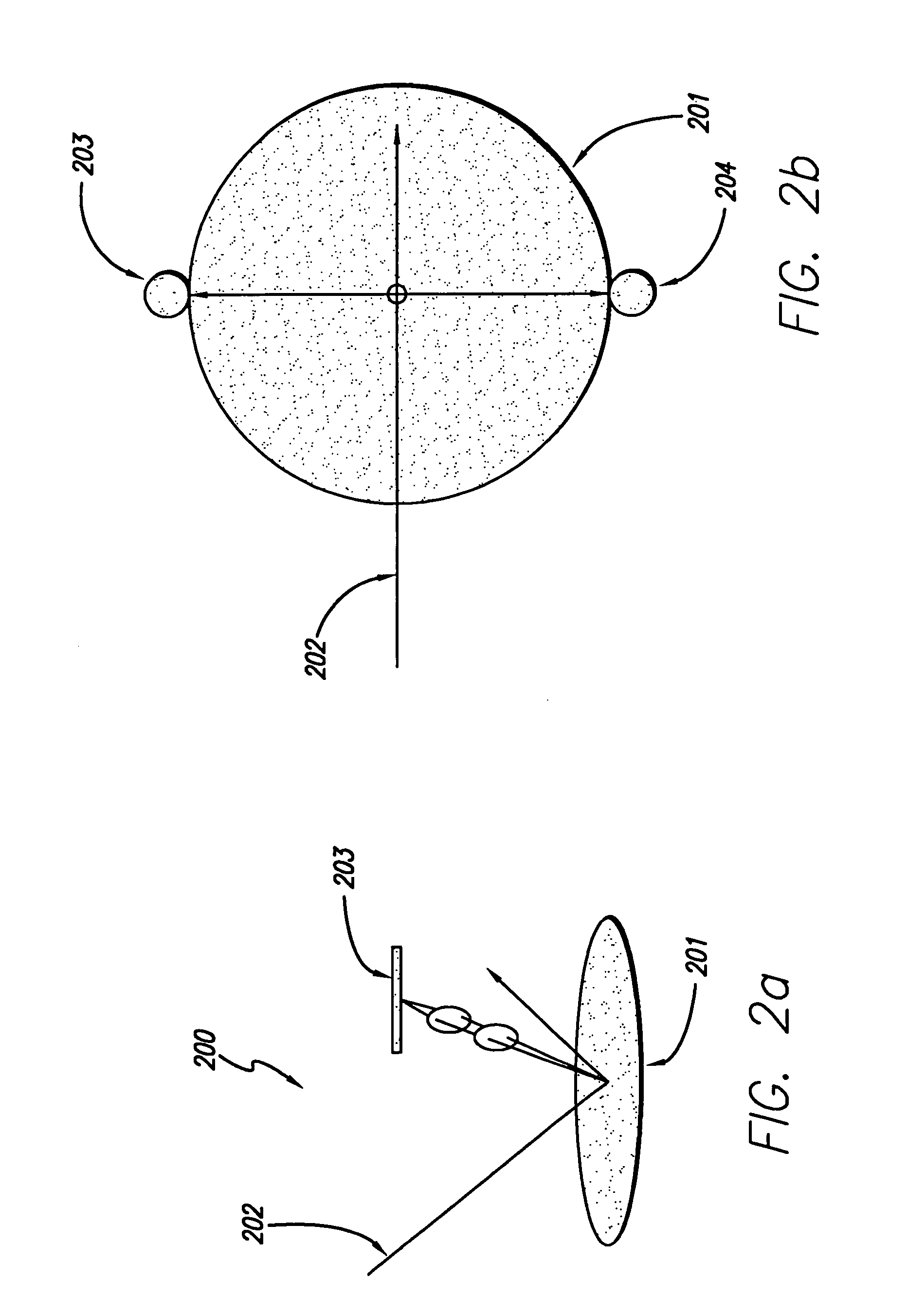
Patents
Literature
49 results about "Catadioptric system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
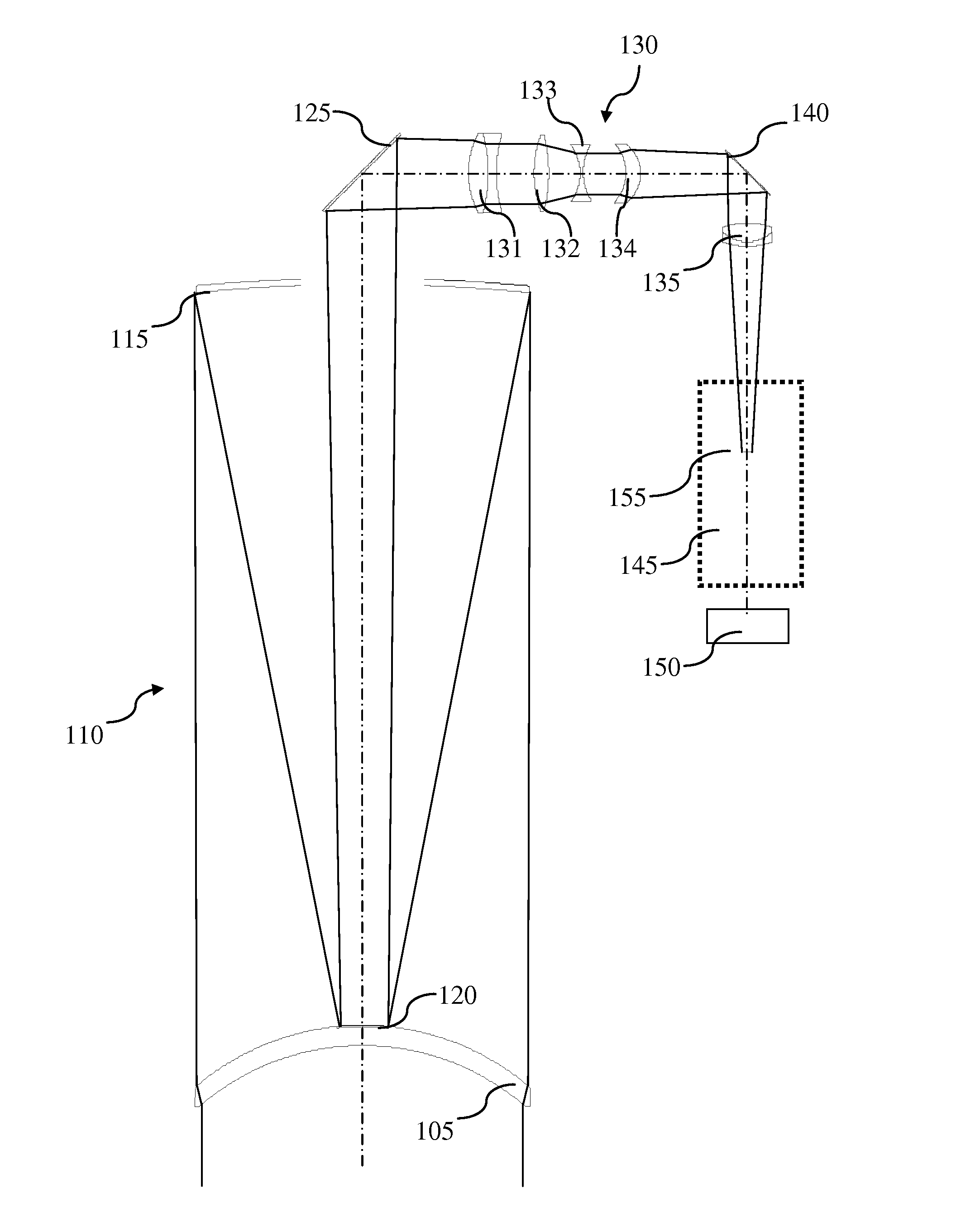
A catadioptric optical system is one where refraction and reflection are combined in an optical system, usually via lenses (dioptrics) and curved mirrors (catoptrics). Catadioptric combinations are used in focusing systems such as searchlights, headlamps, early lighthouse focusing systems, optical telescopes, microscopes, and telephoto lenses. Other optical systems that use lenses and mirrors are also referred to as "catadioptric", such as surveillance catadioptric sensors.
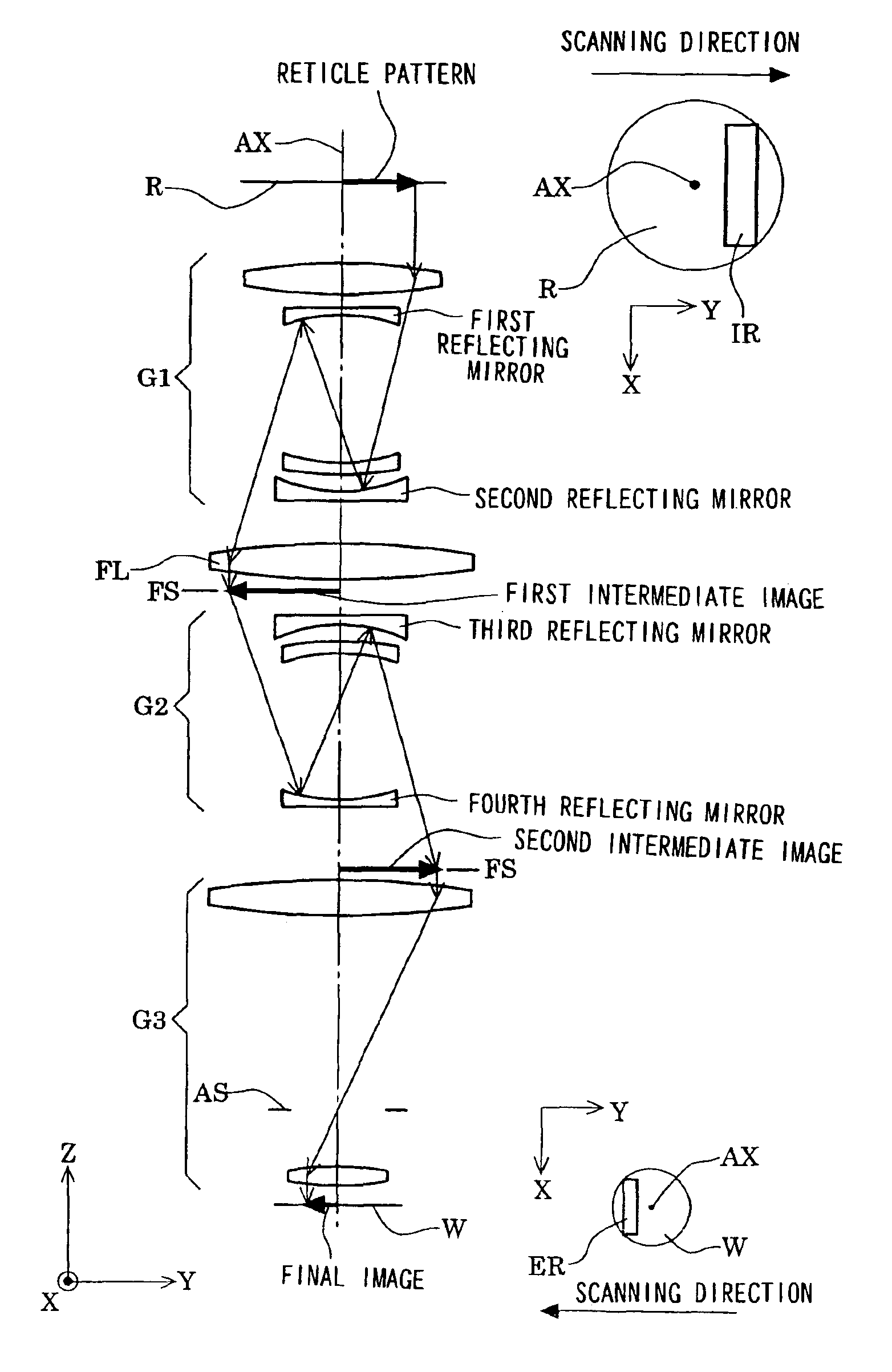
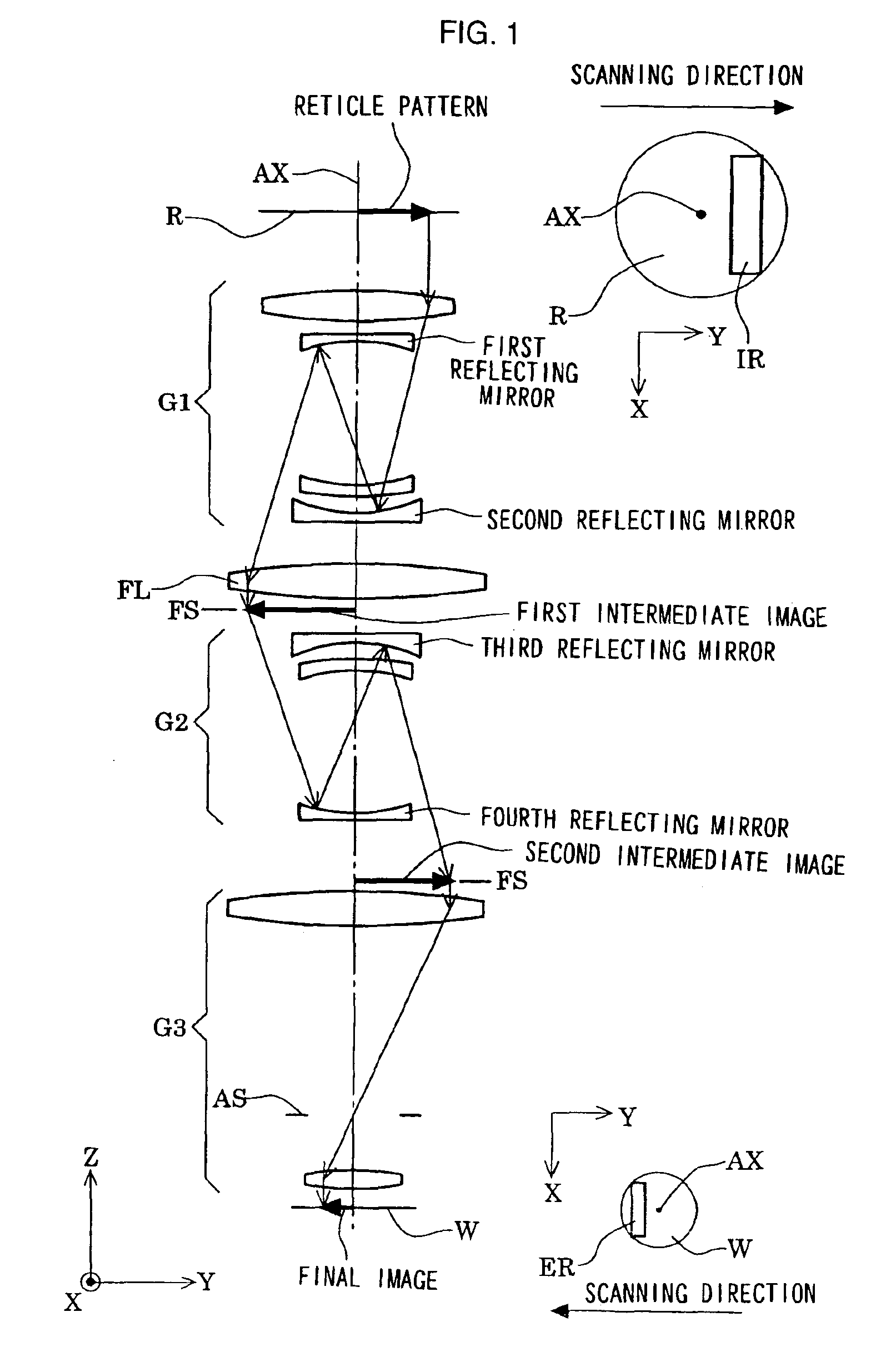
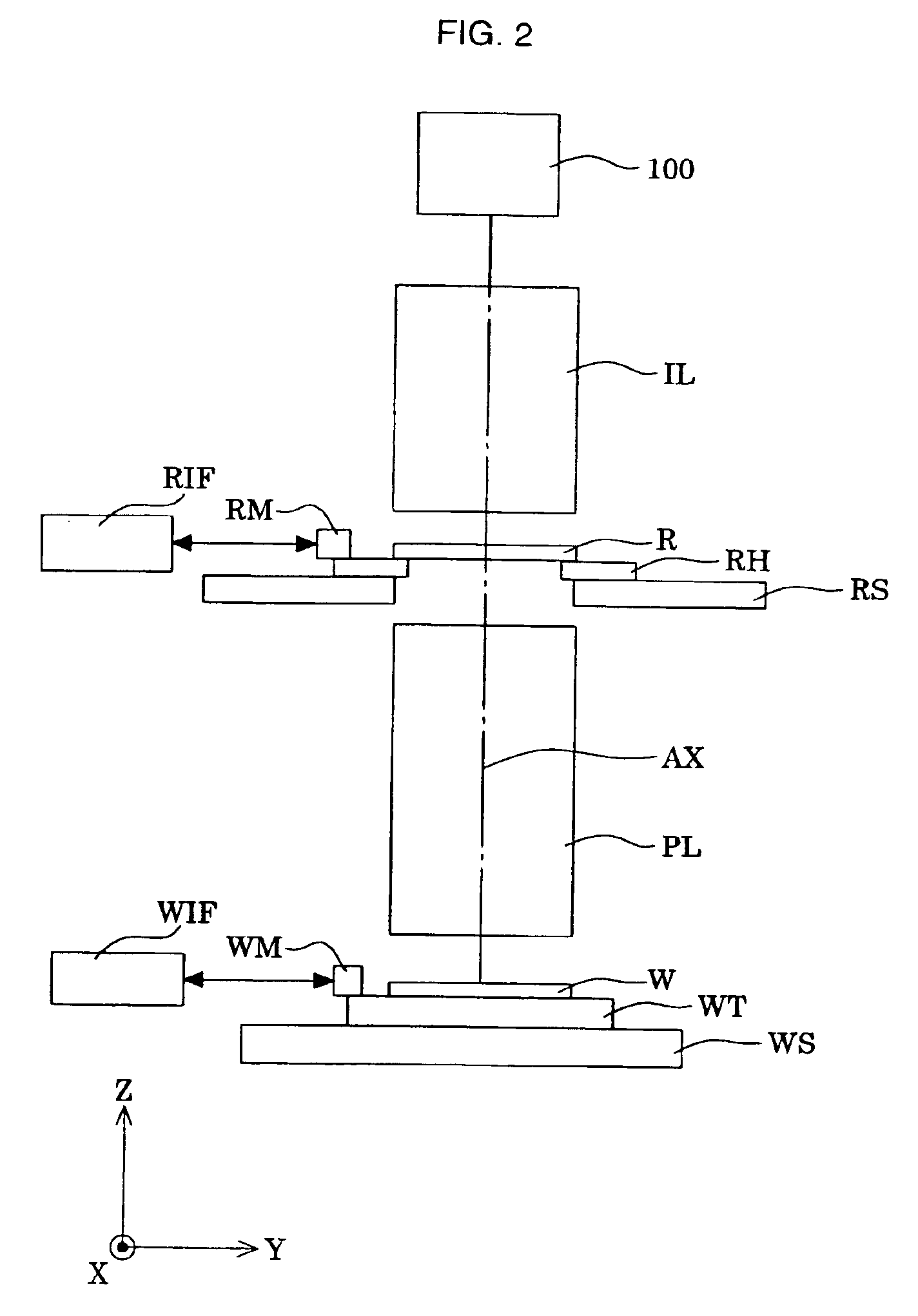
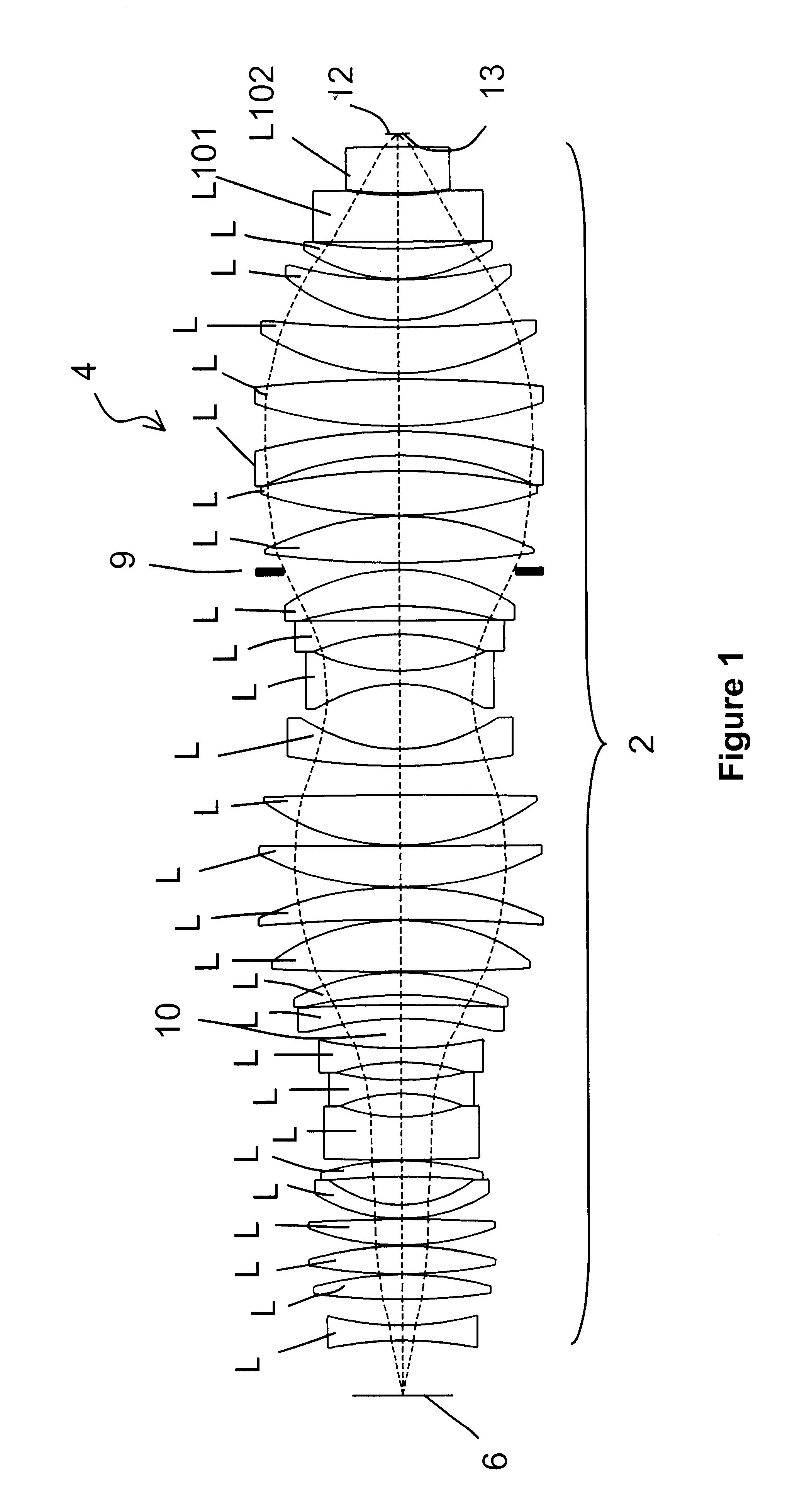
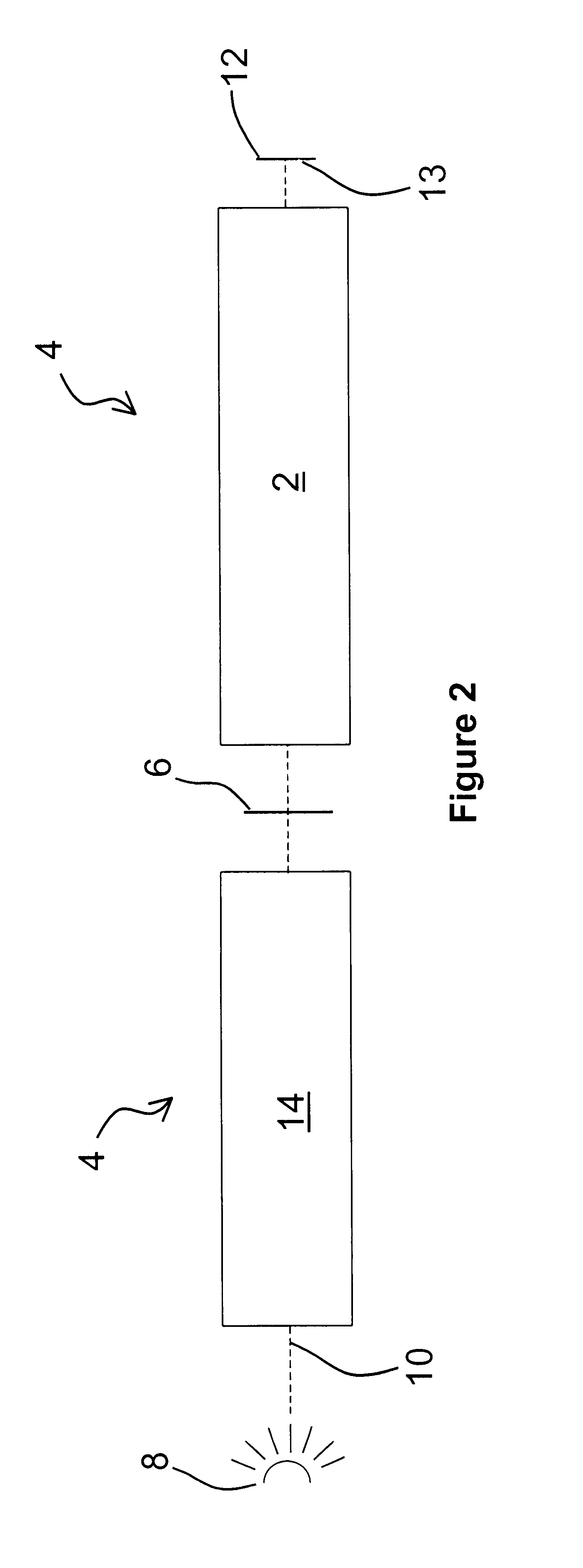
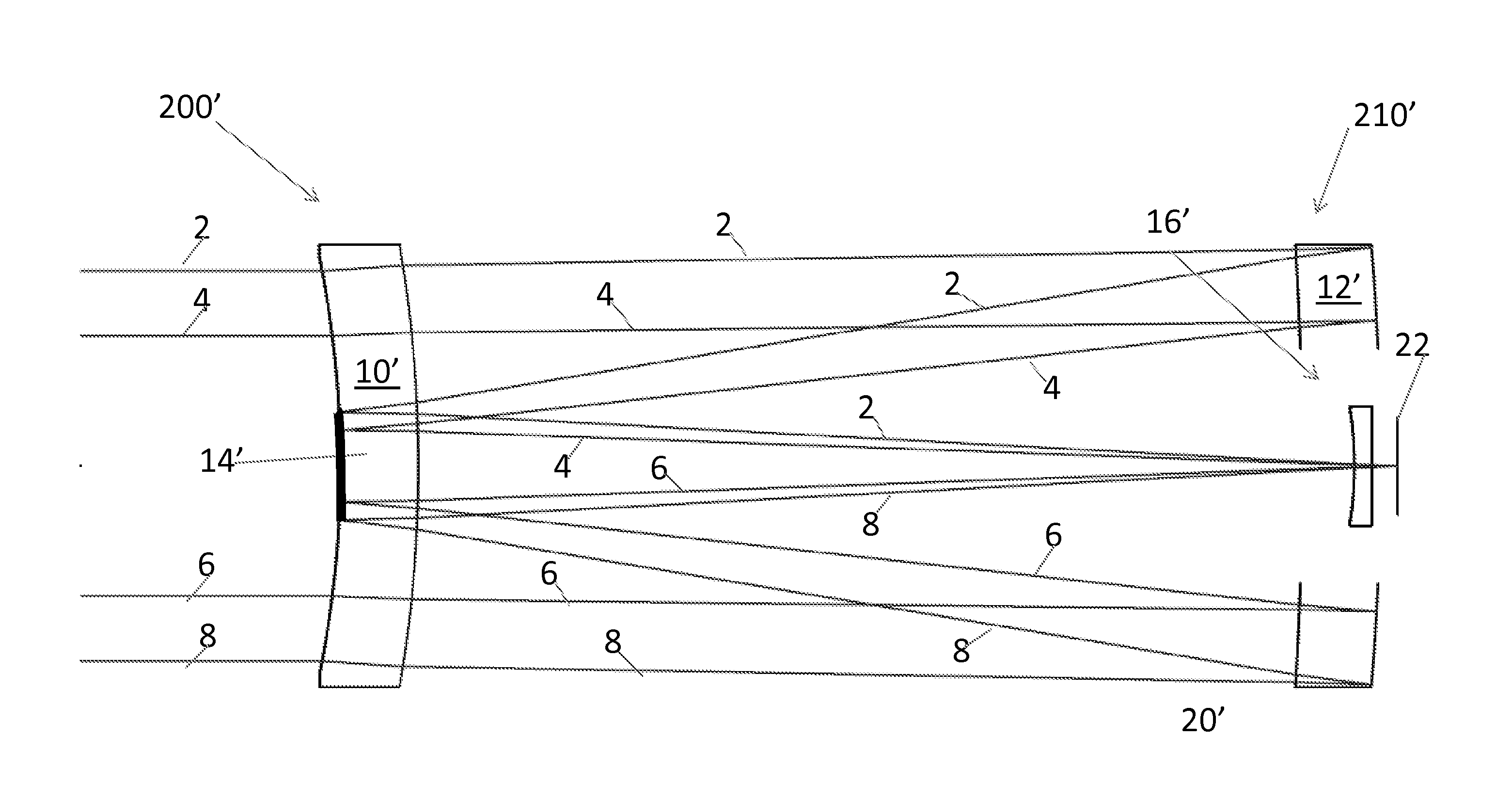
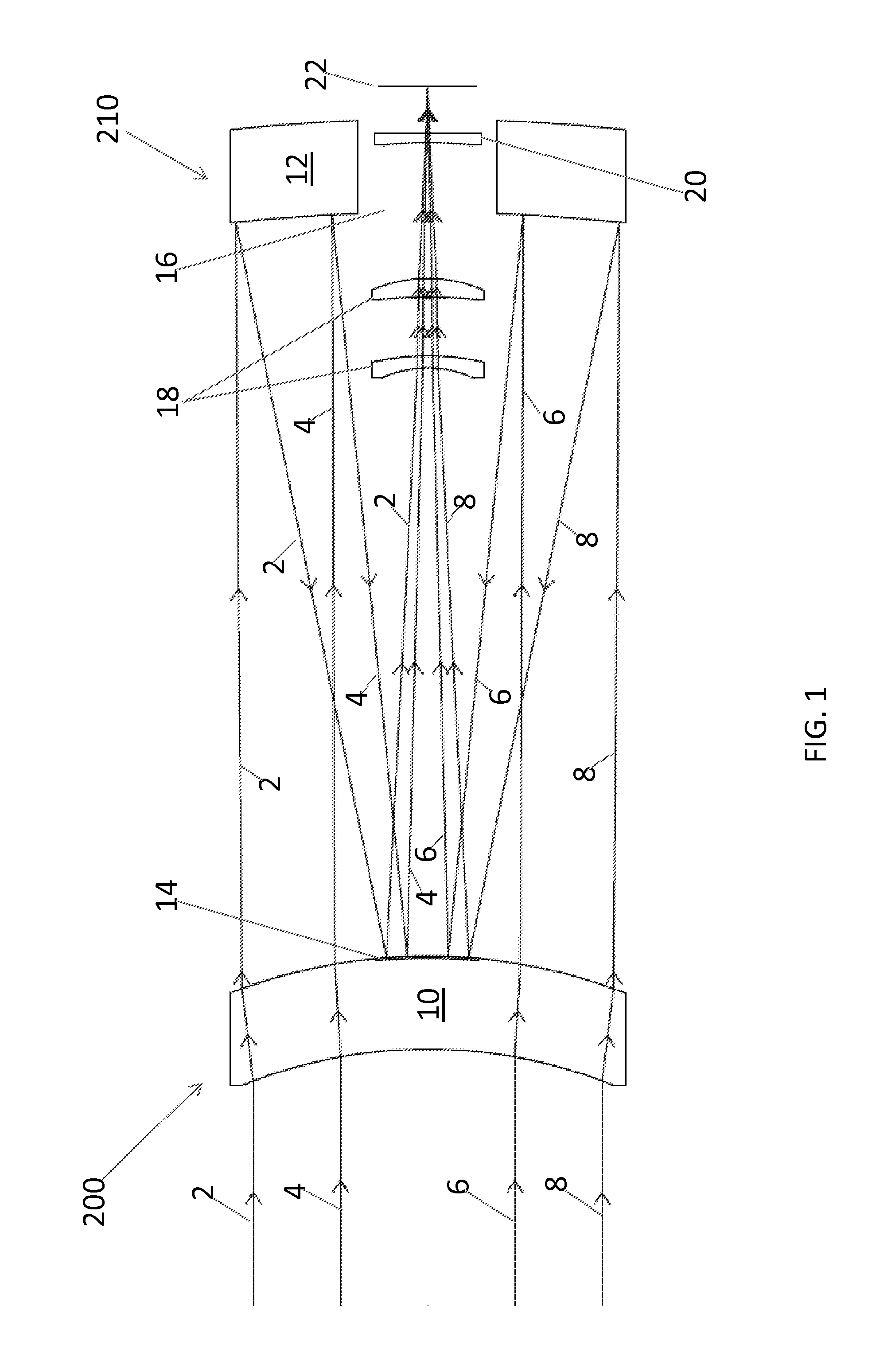
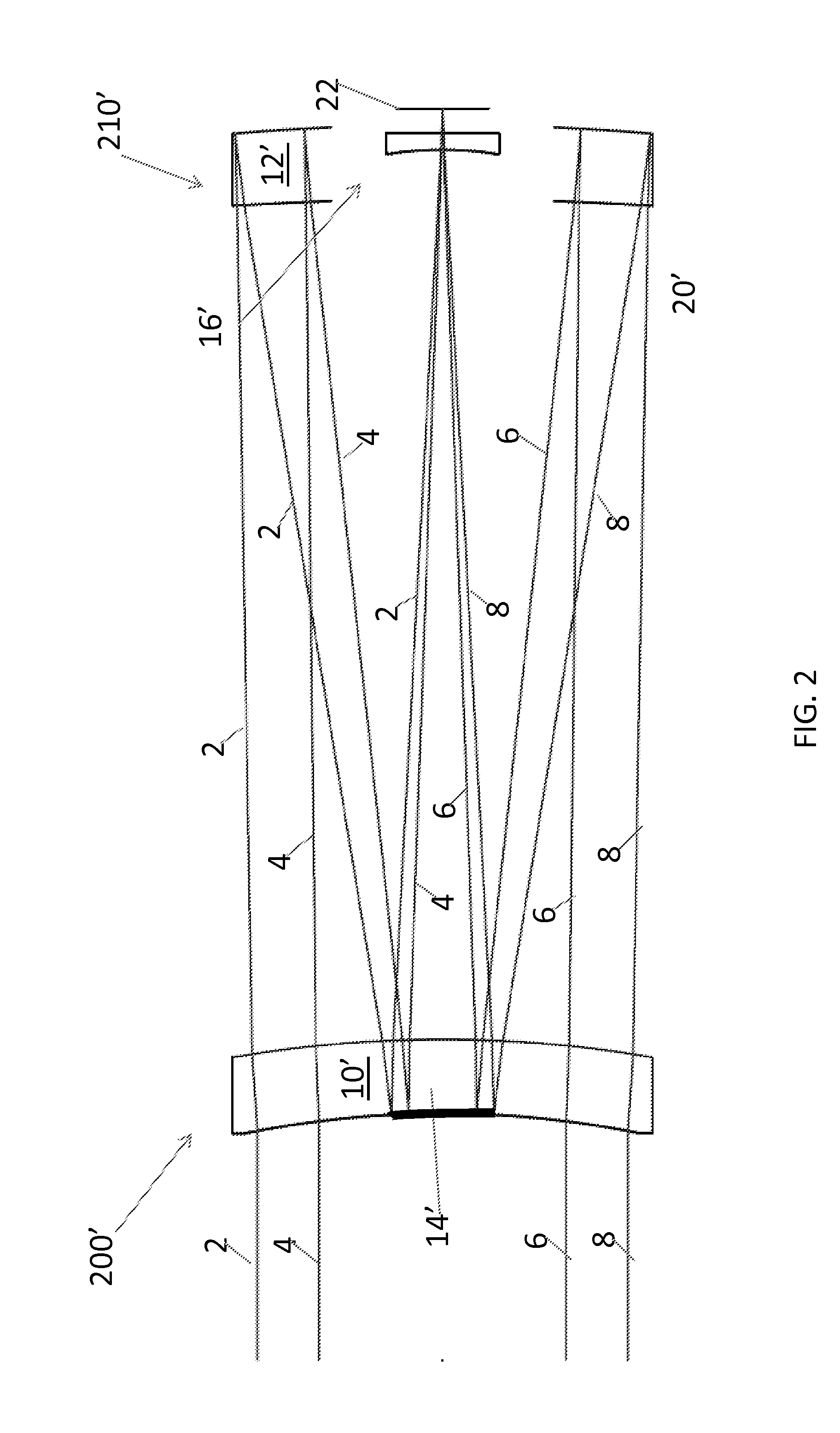
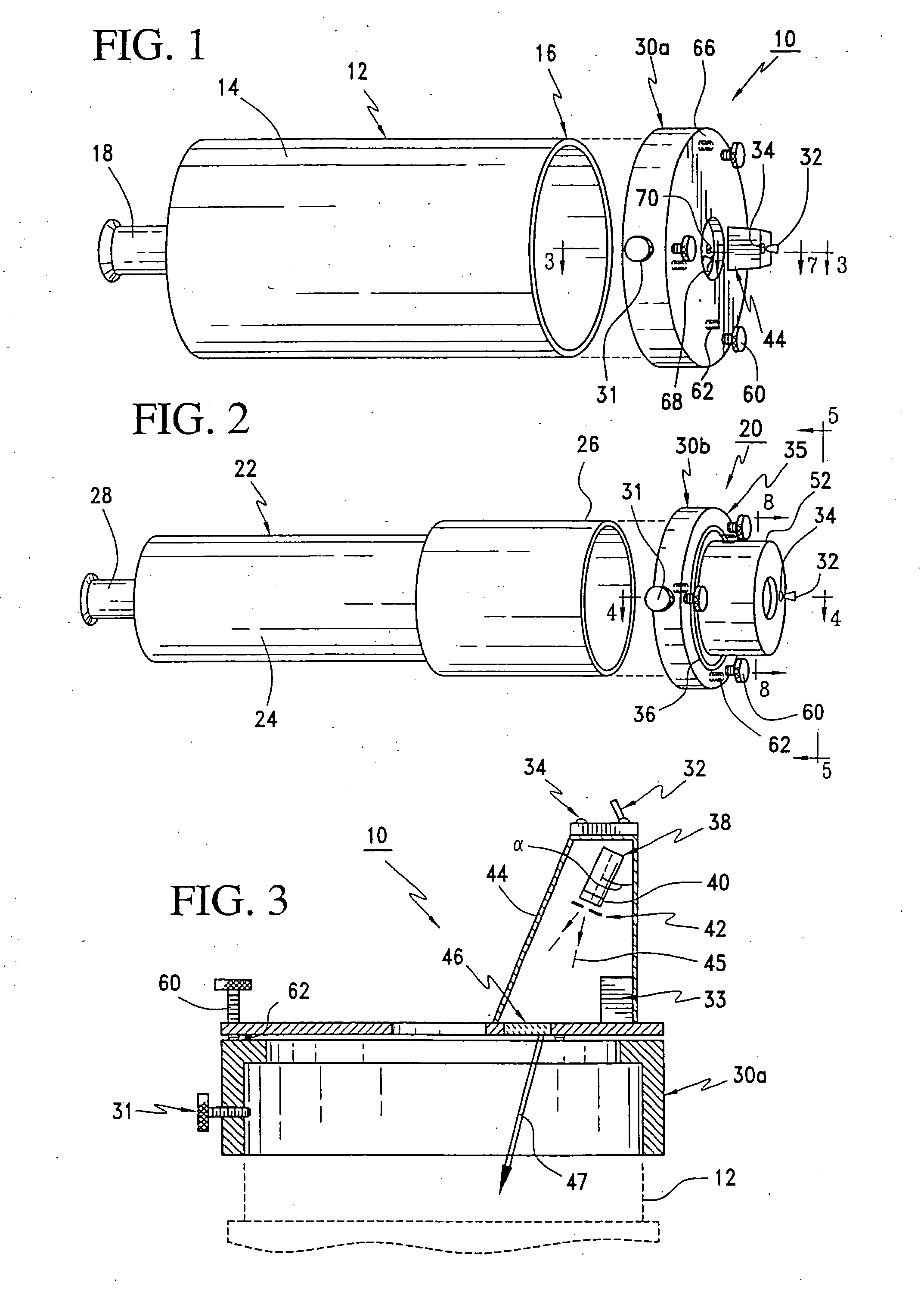
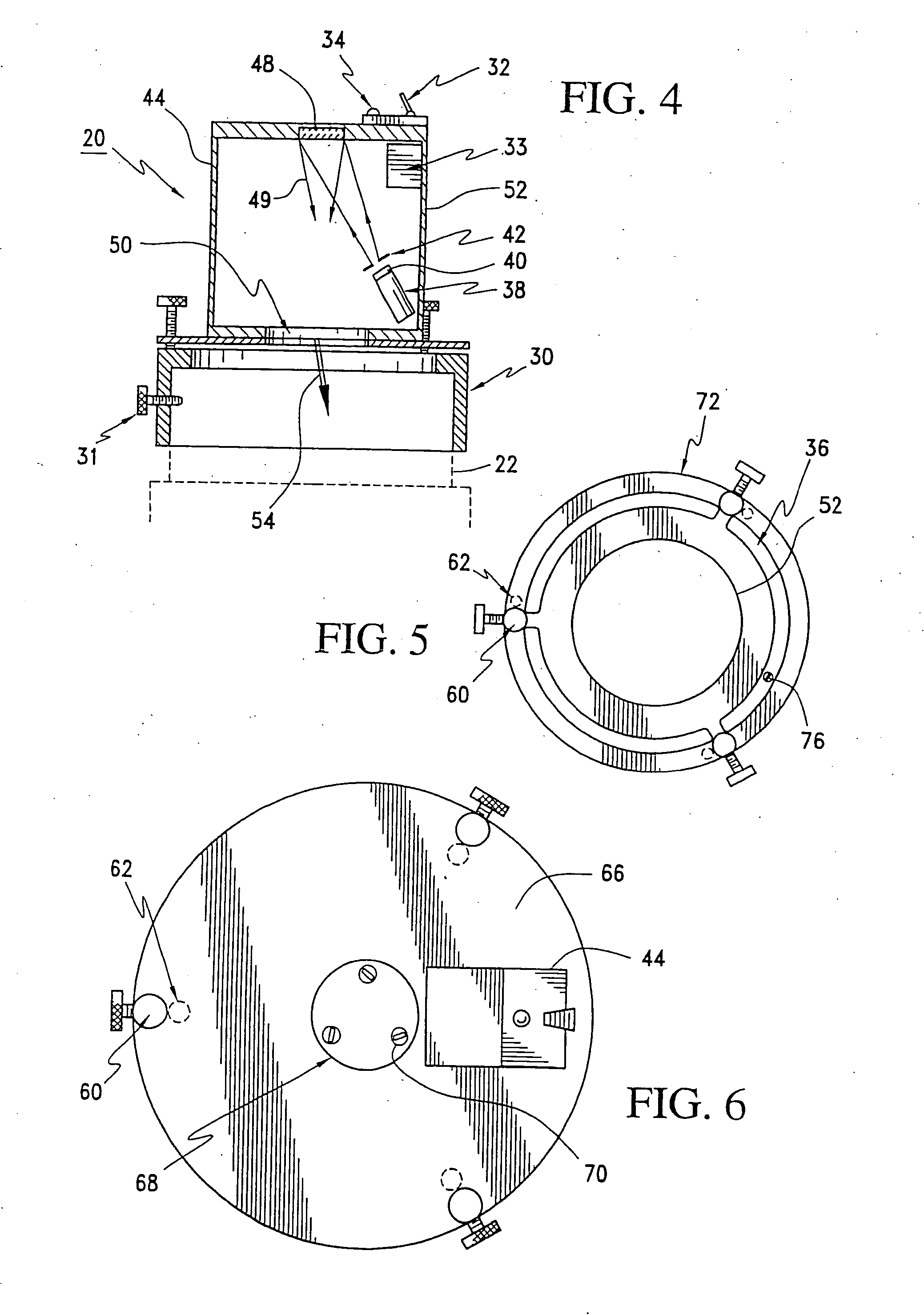
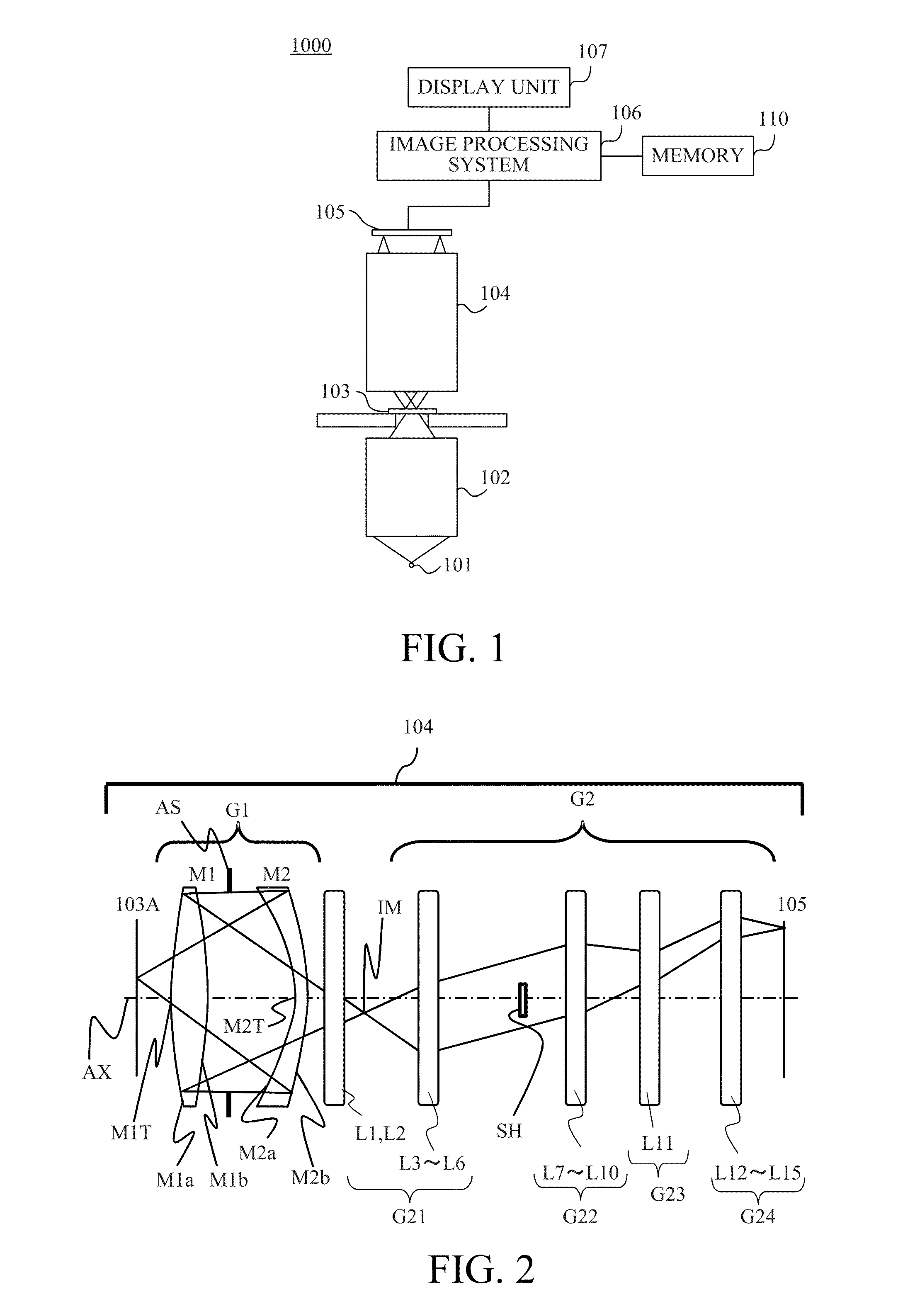
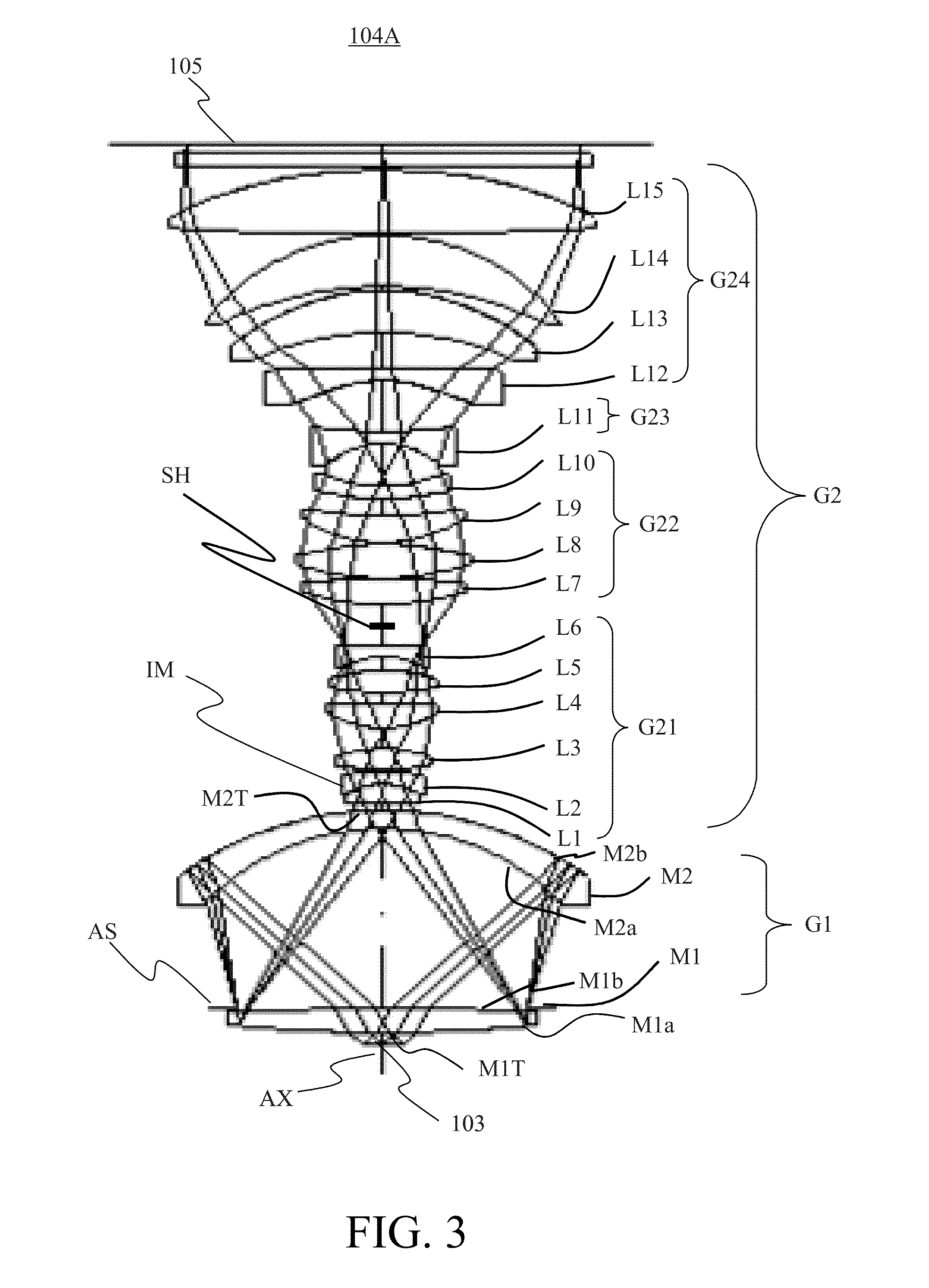
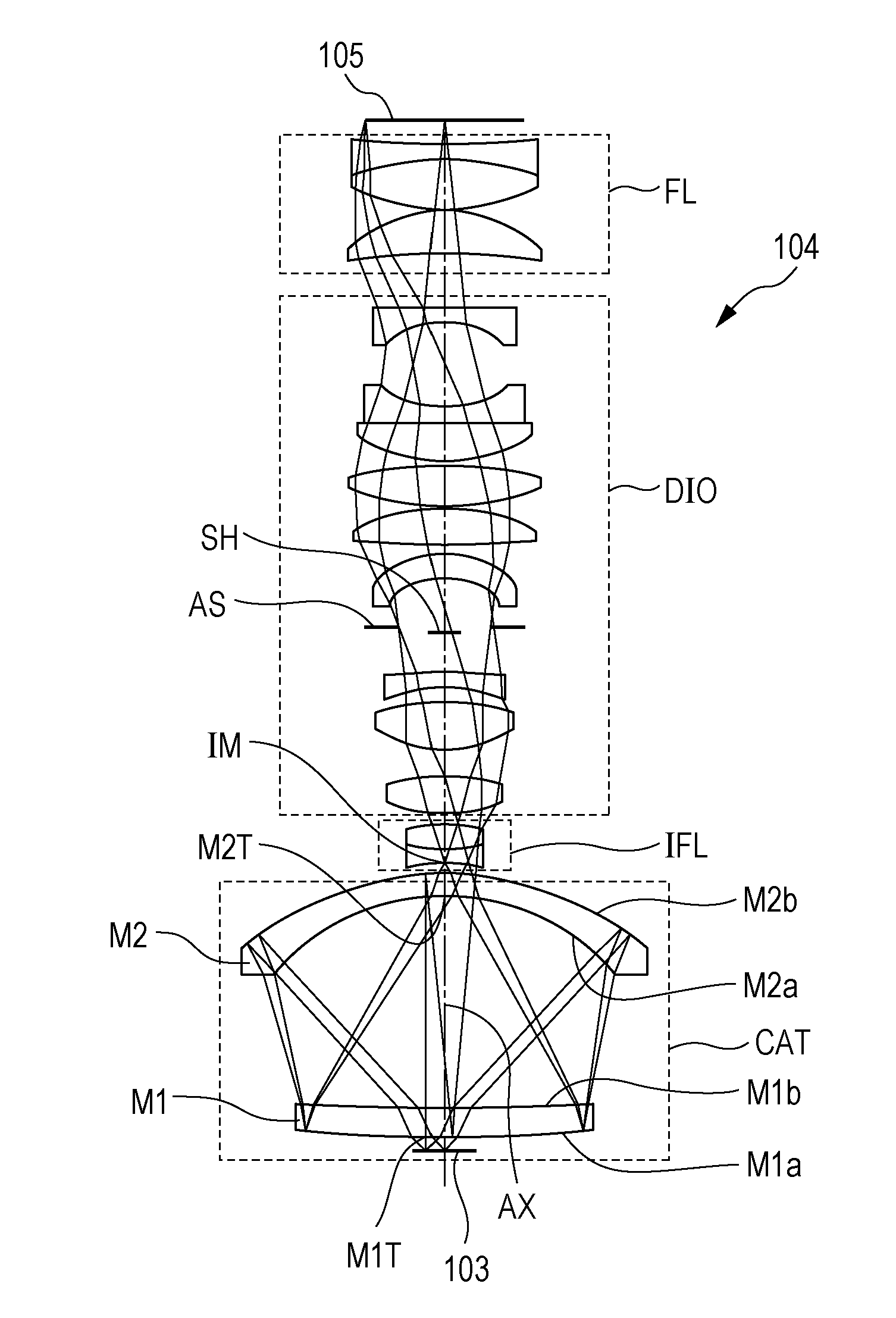
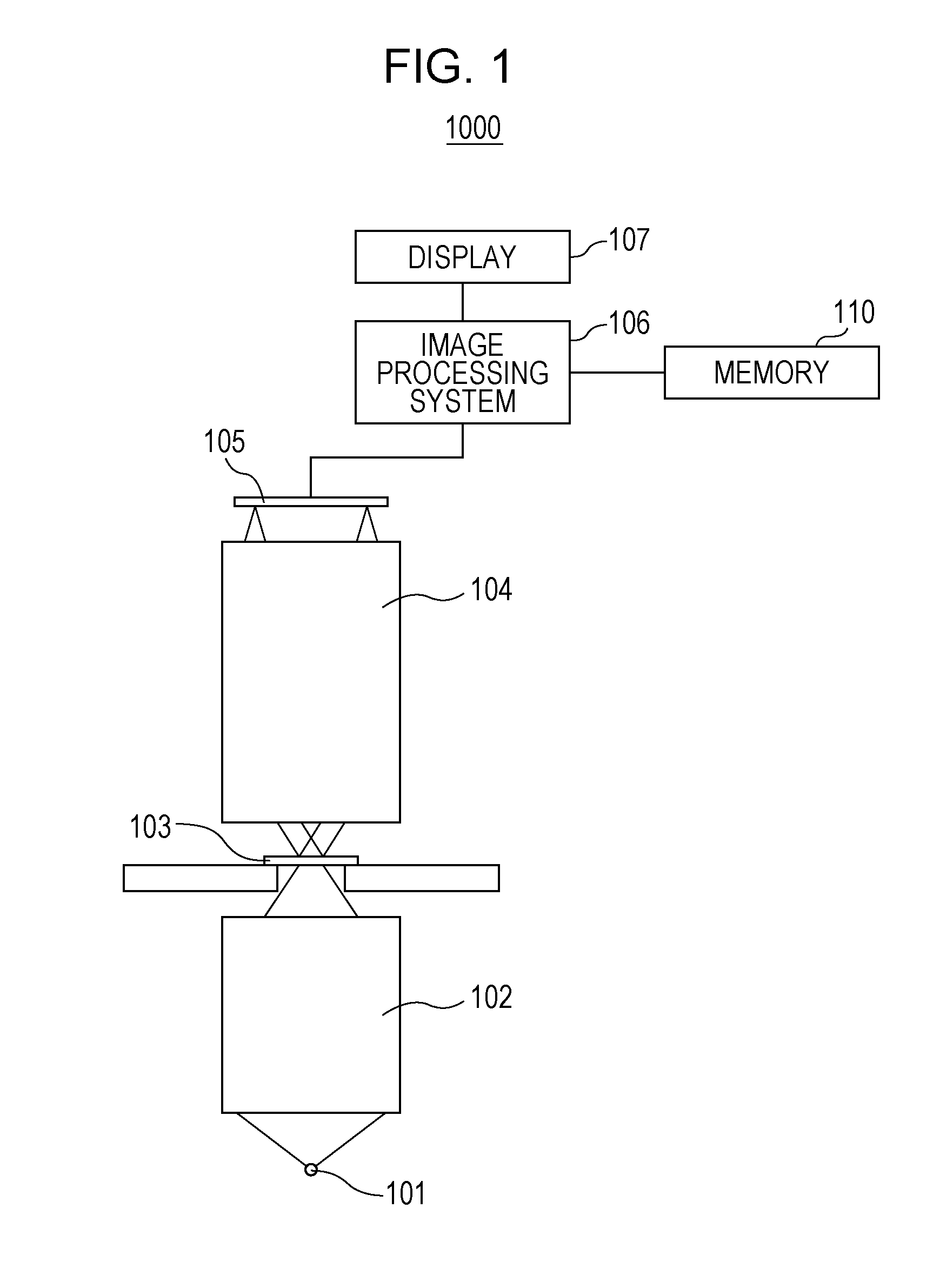
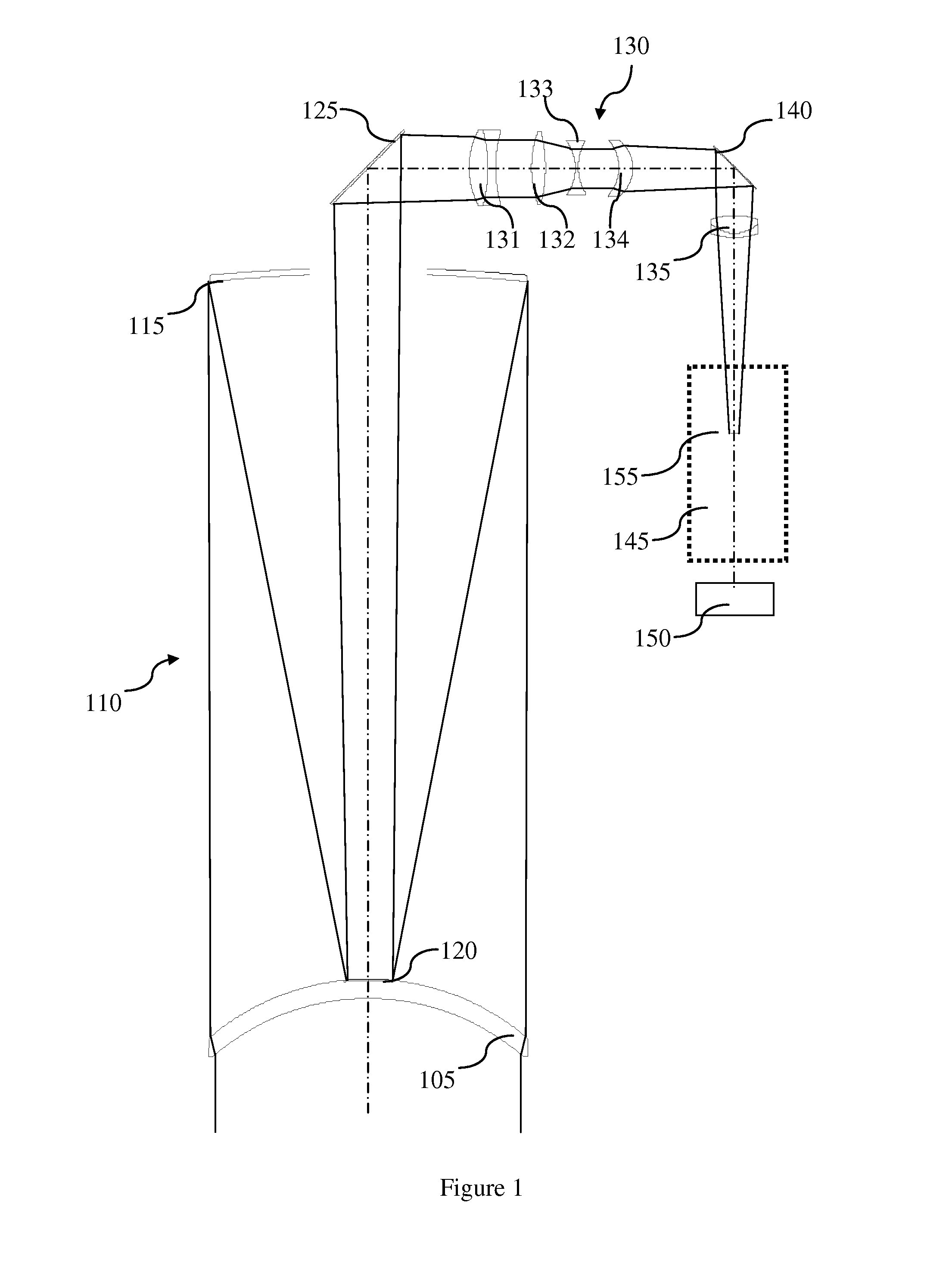
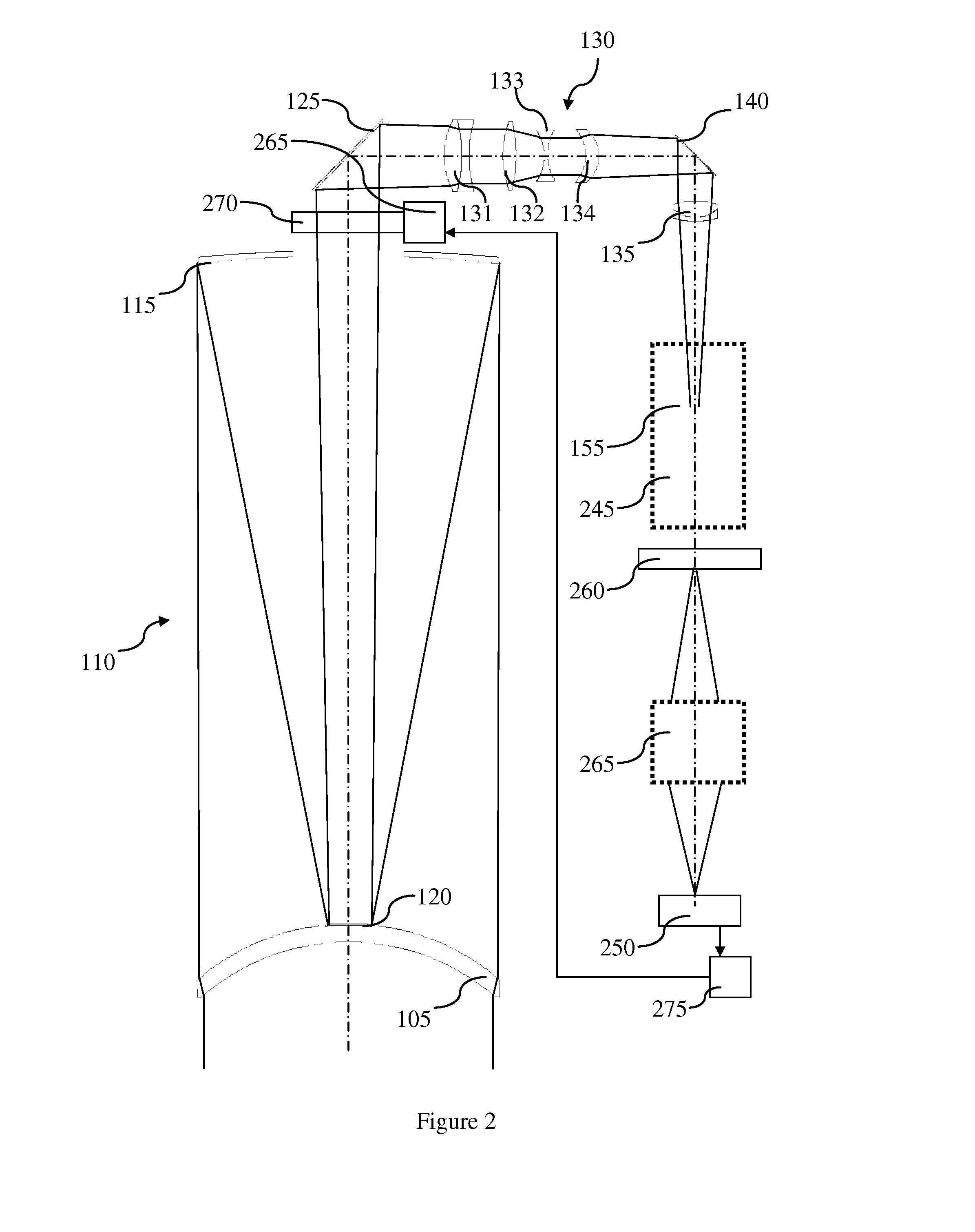
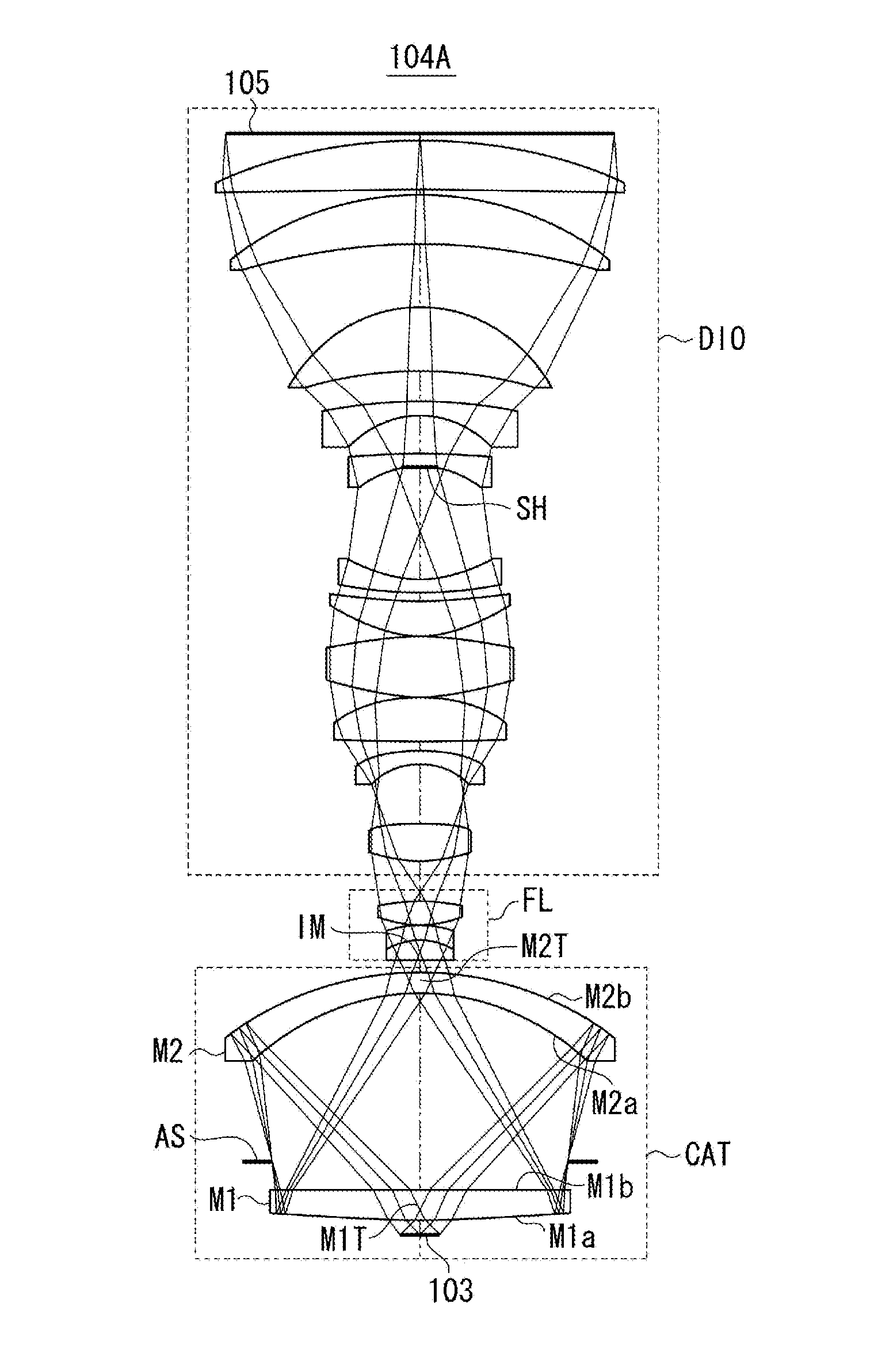
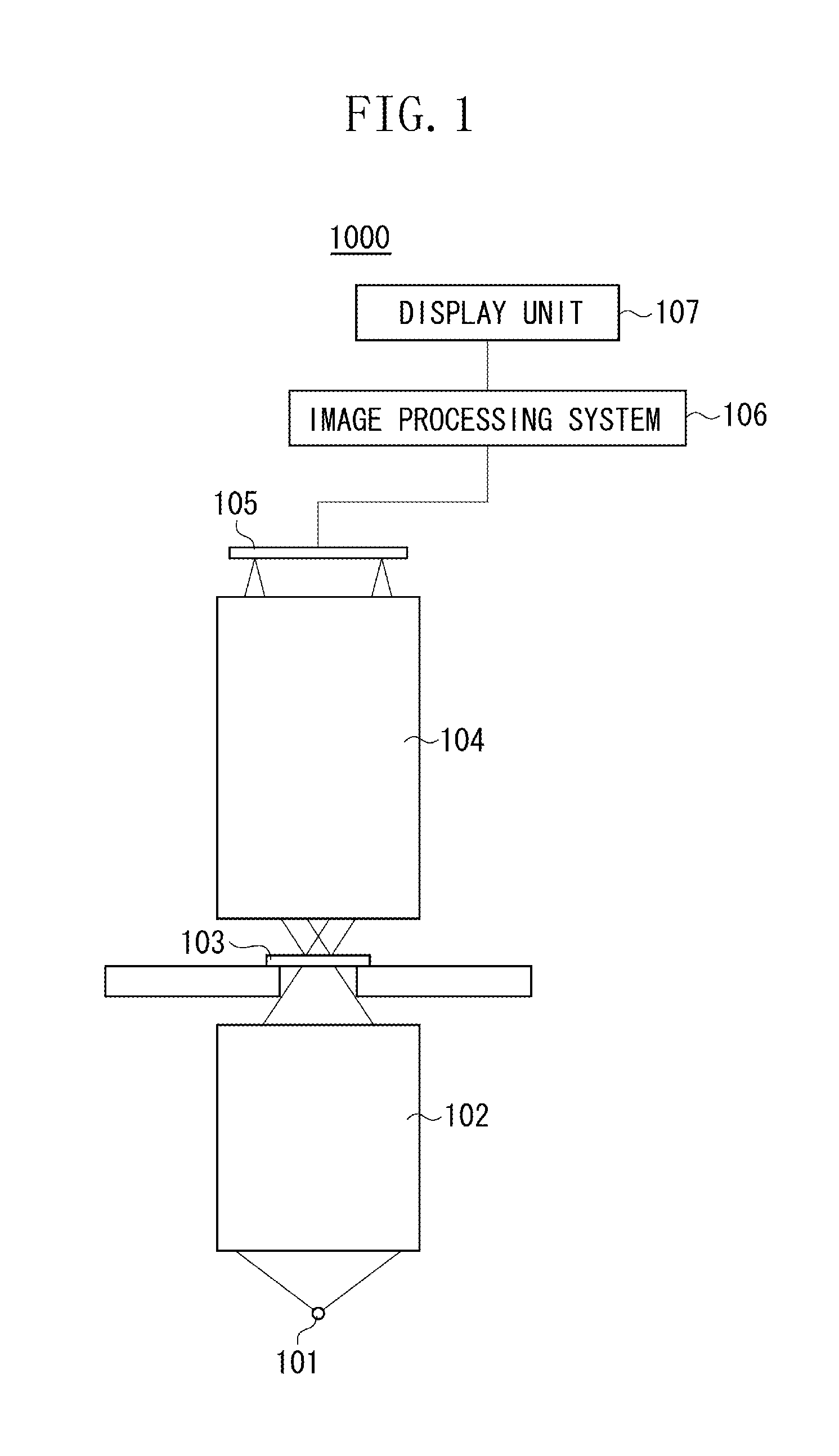
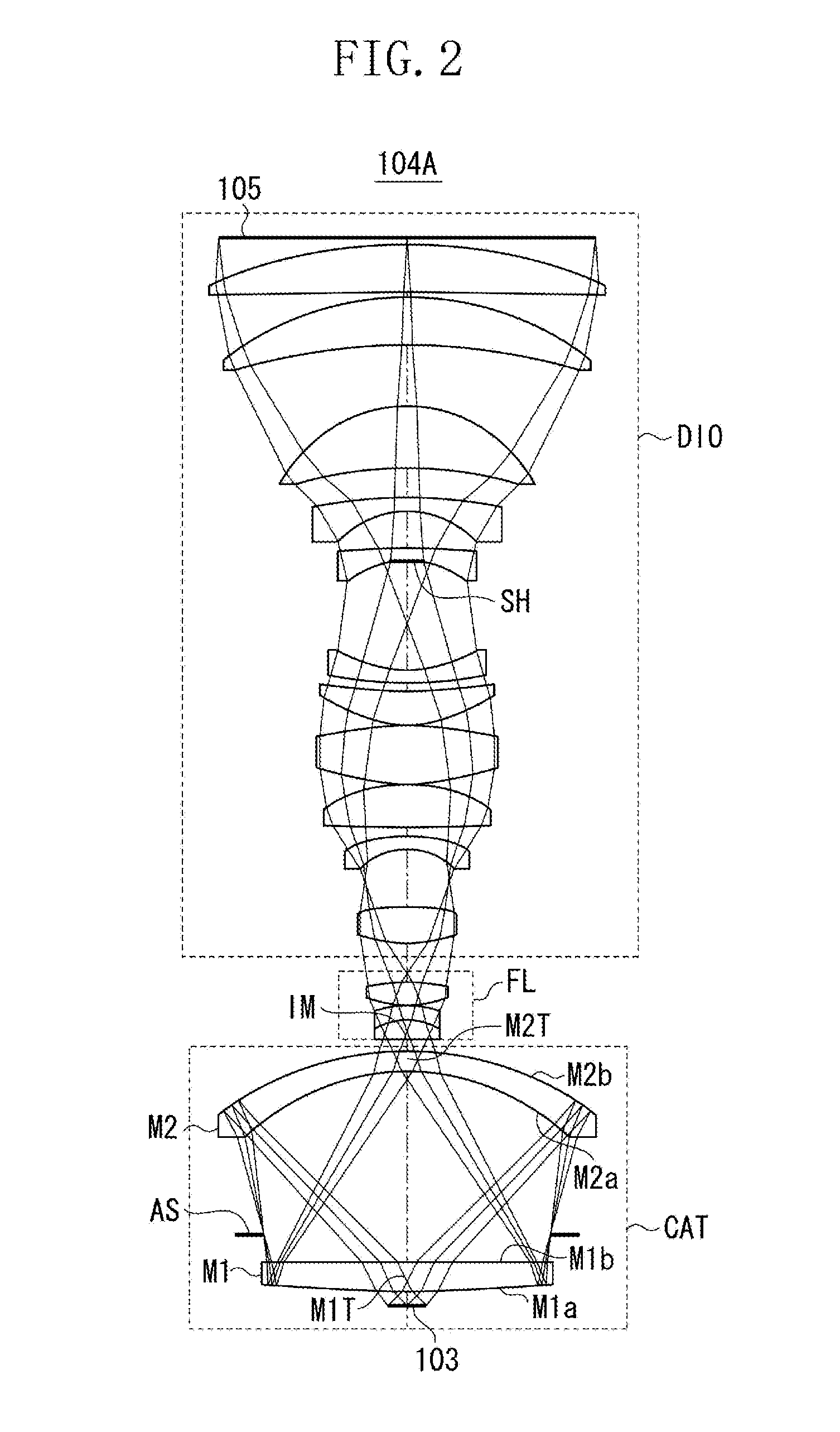
Catadioptric system and exposure device having this system
InactiveUS7030965B2Easy to adjustFacilitates high precision productionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicroscopesCatadioptric systemIntermediate image
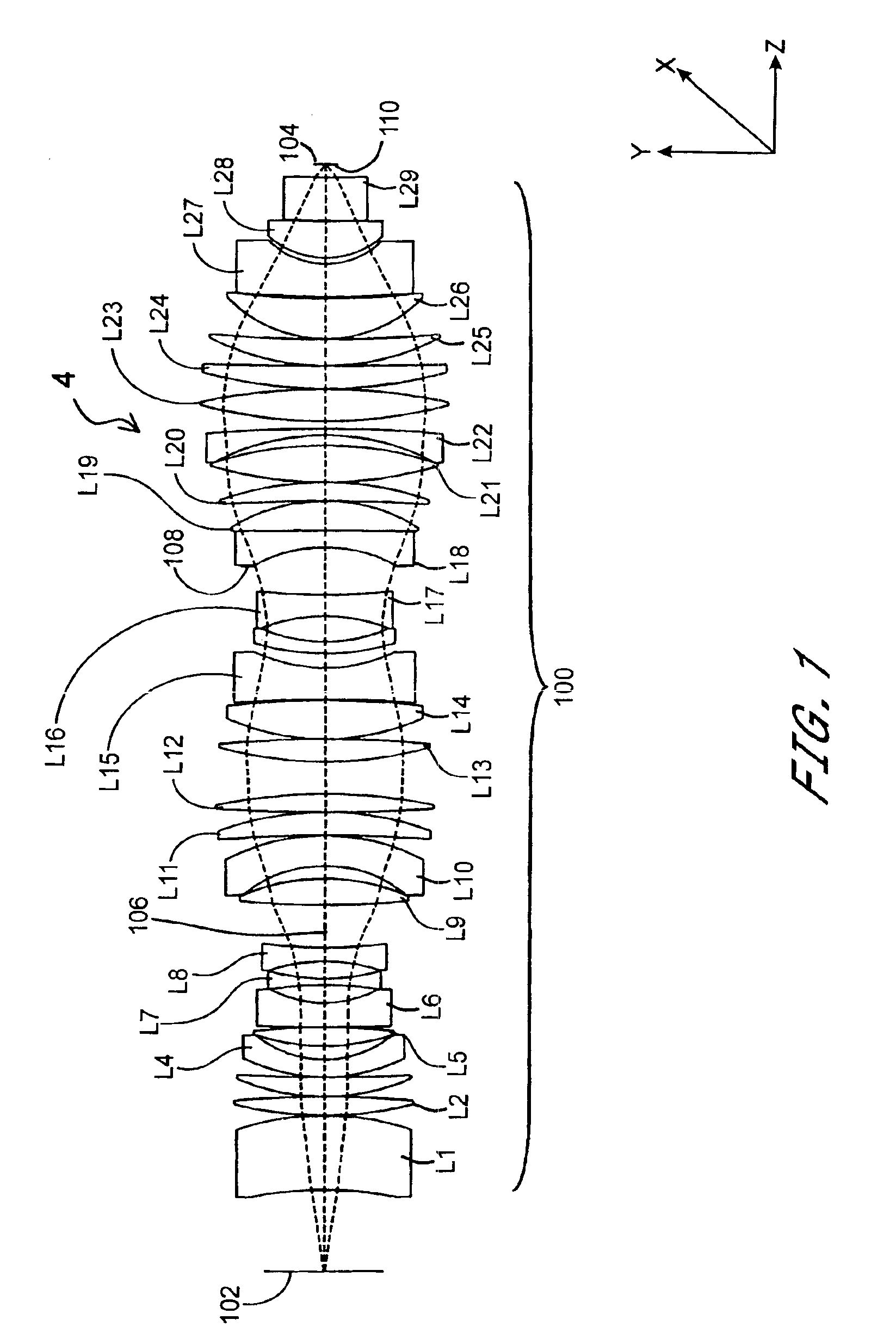
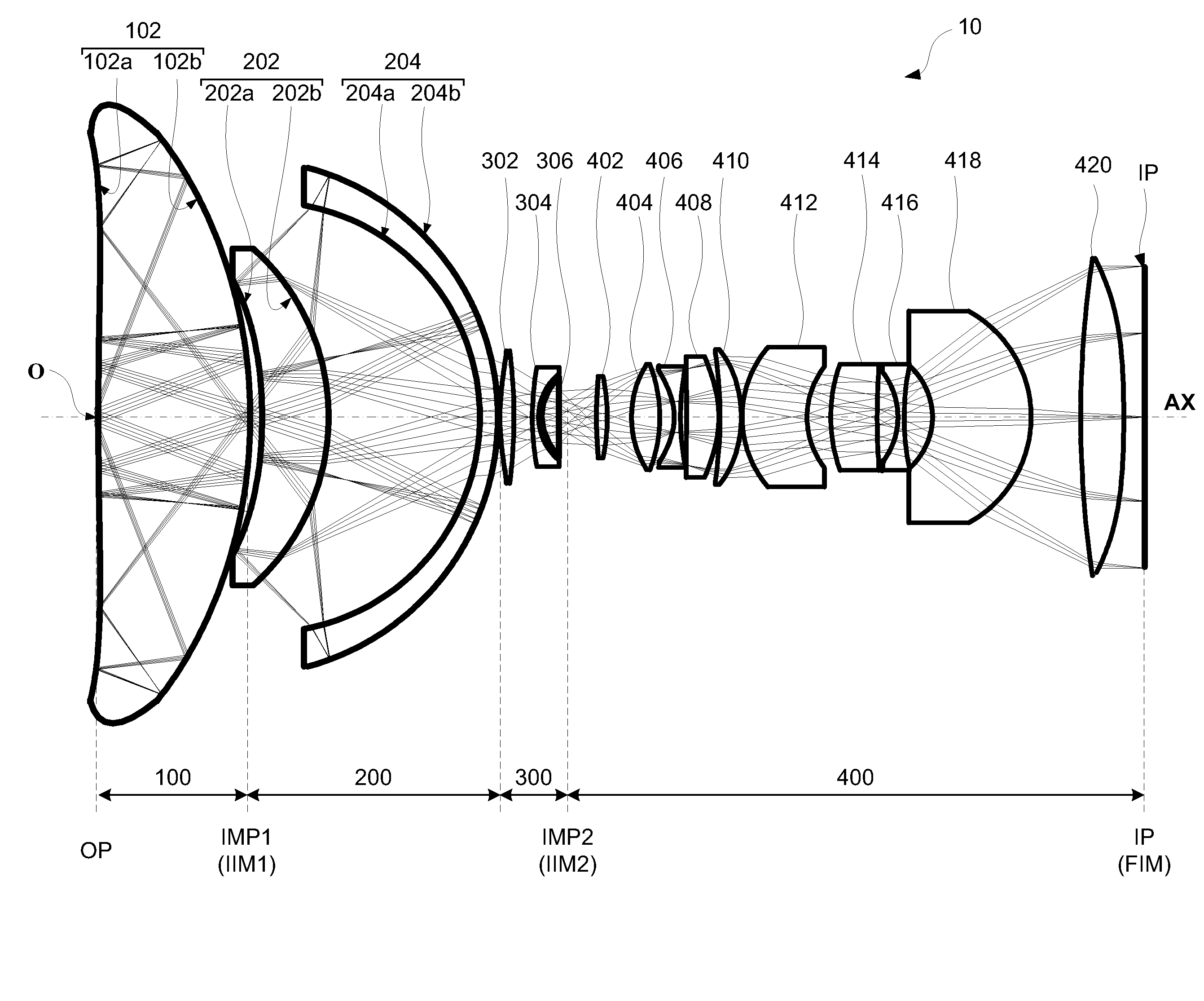
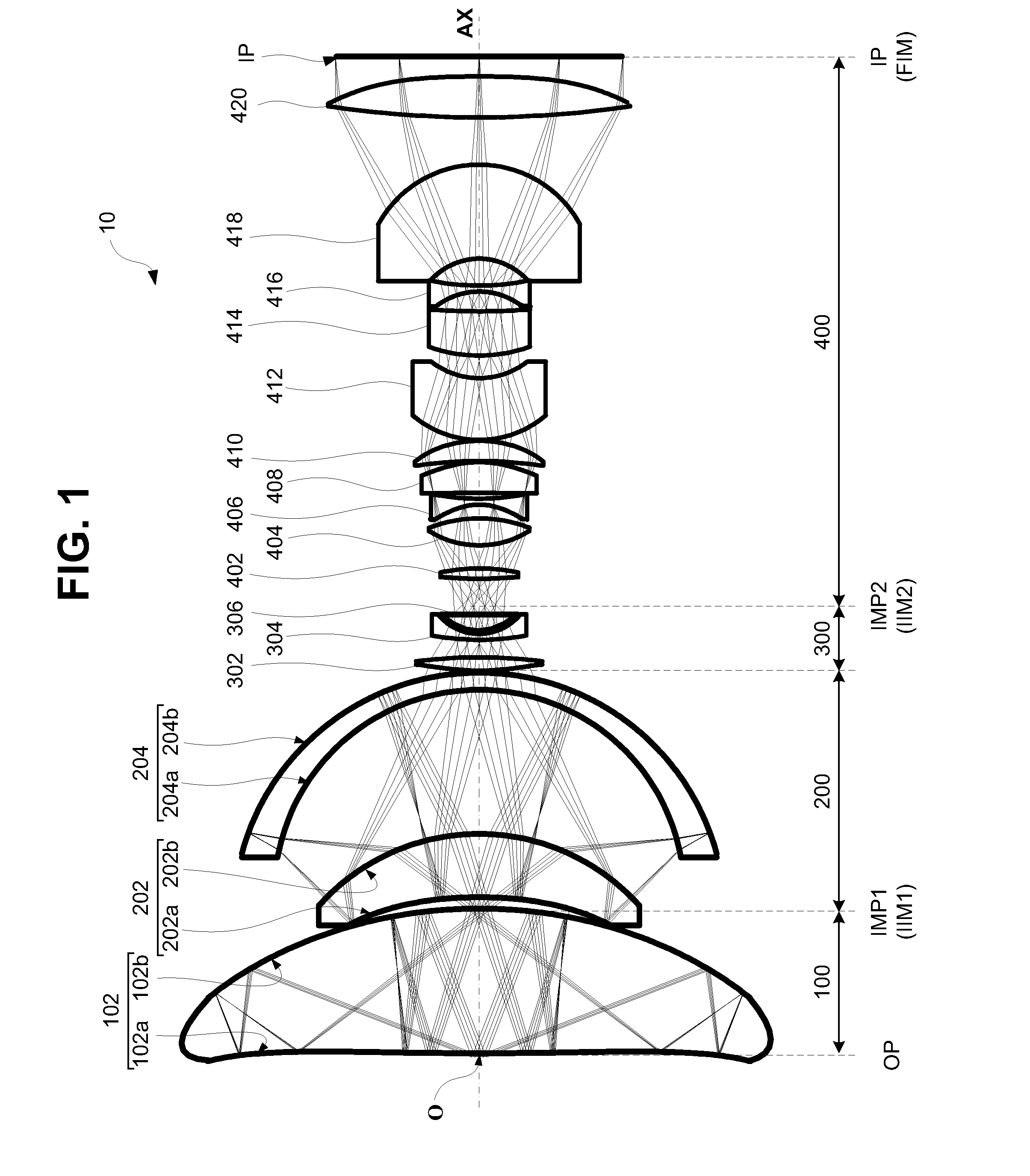
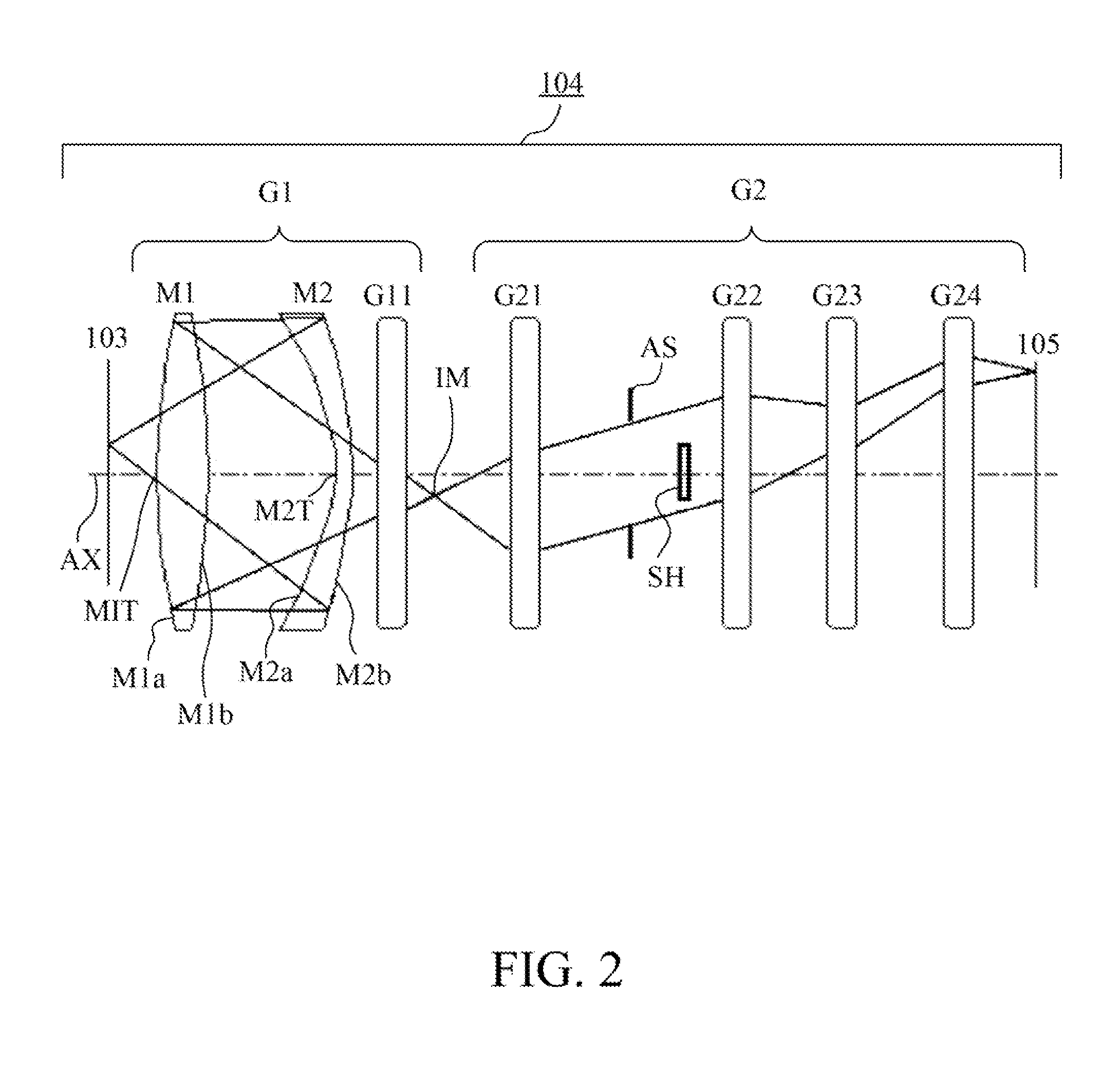
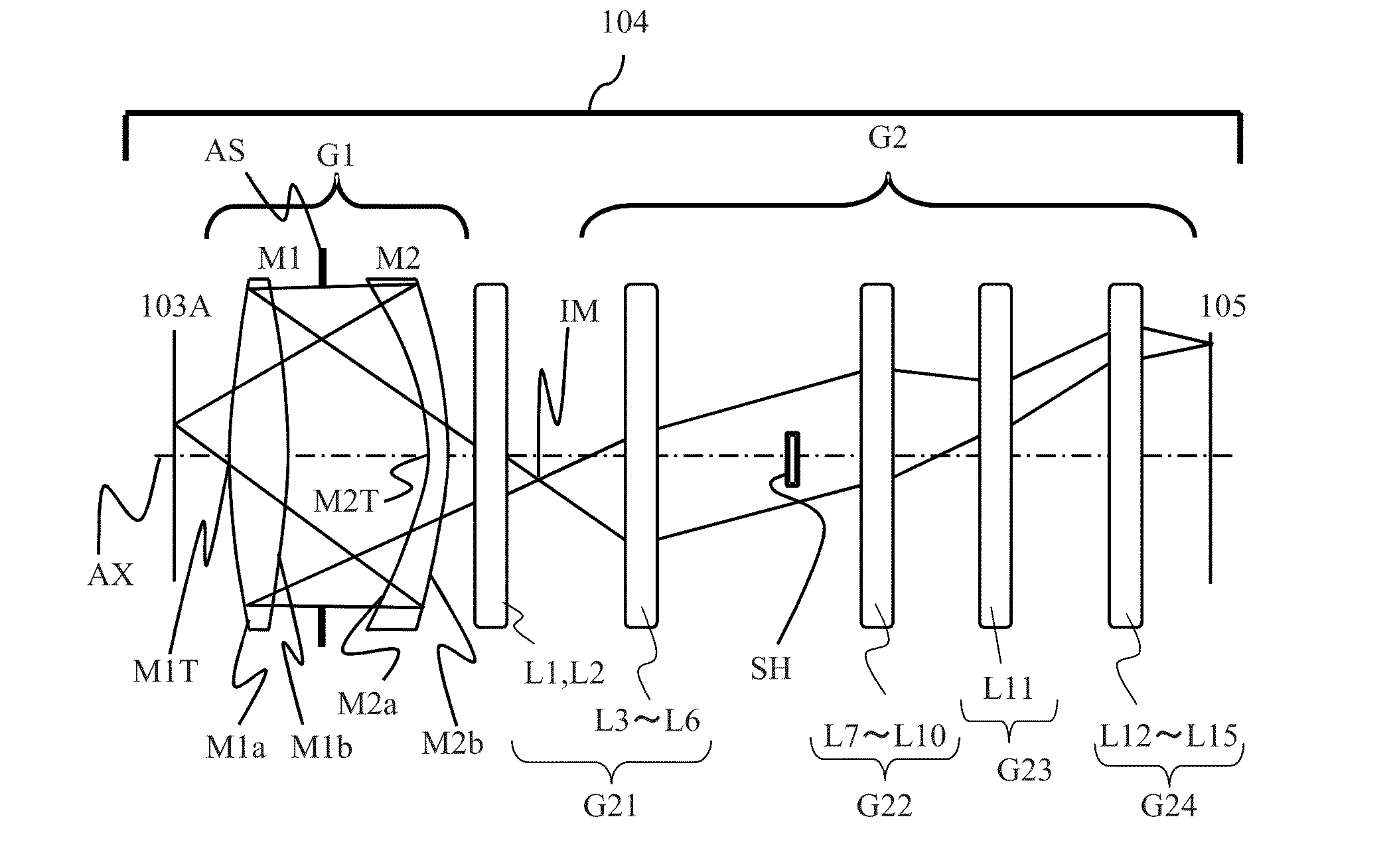
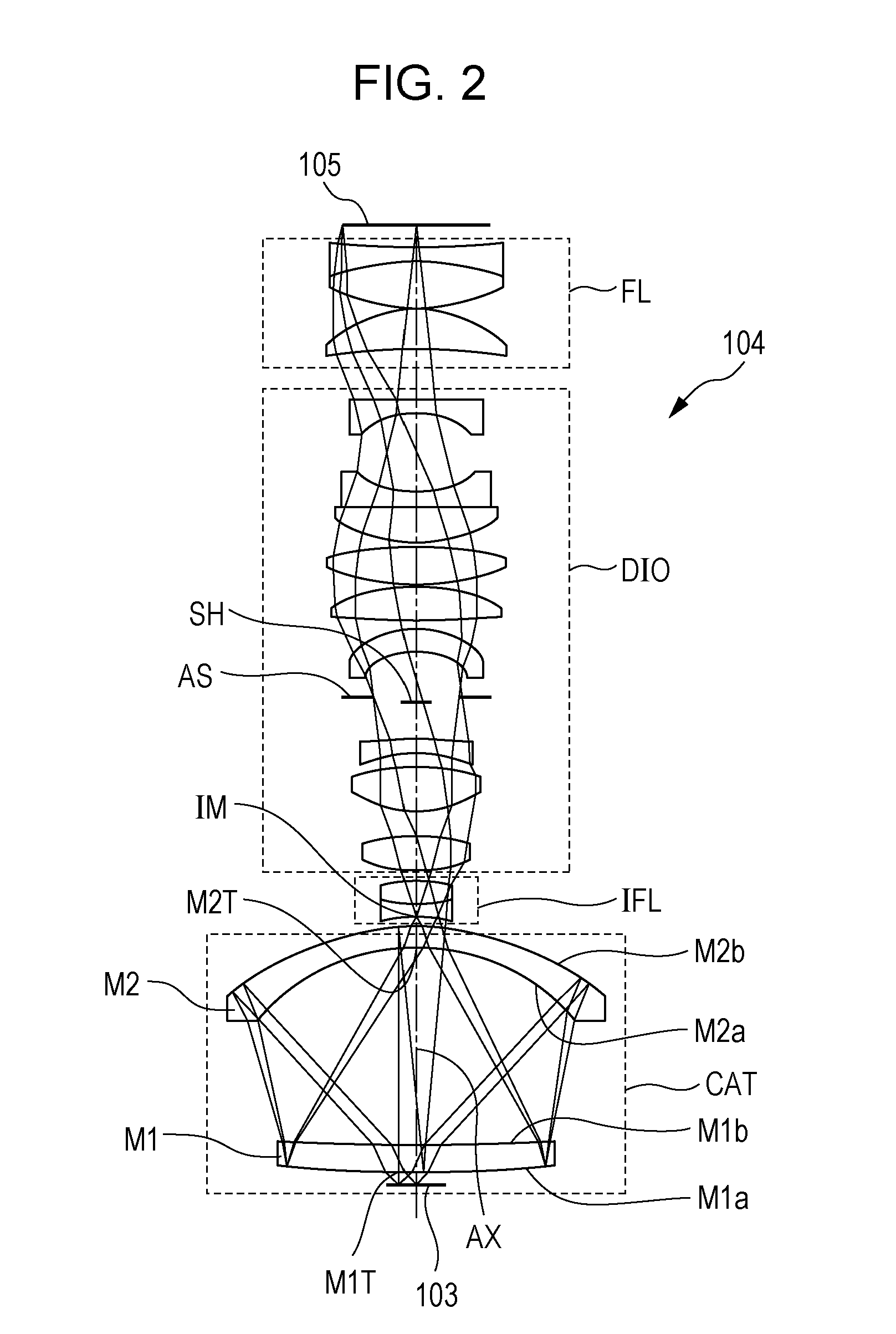
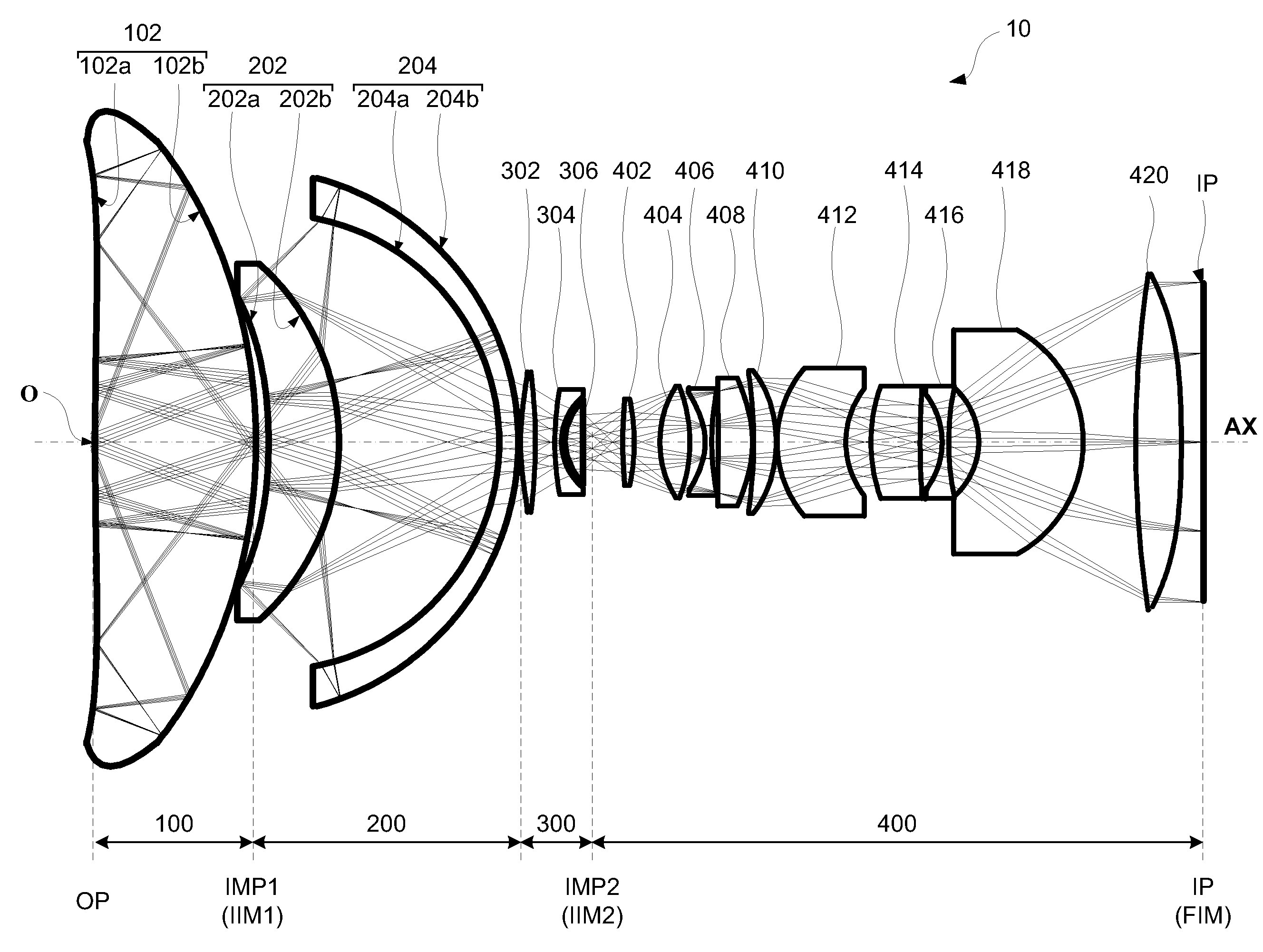
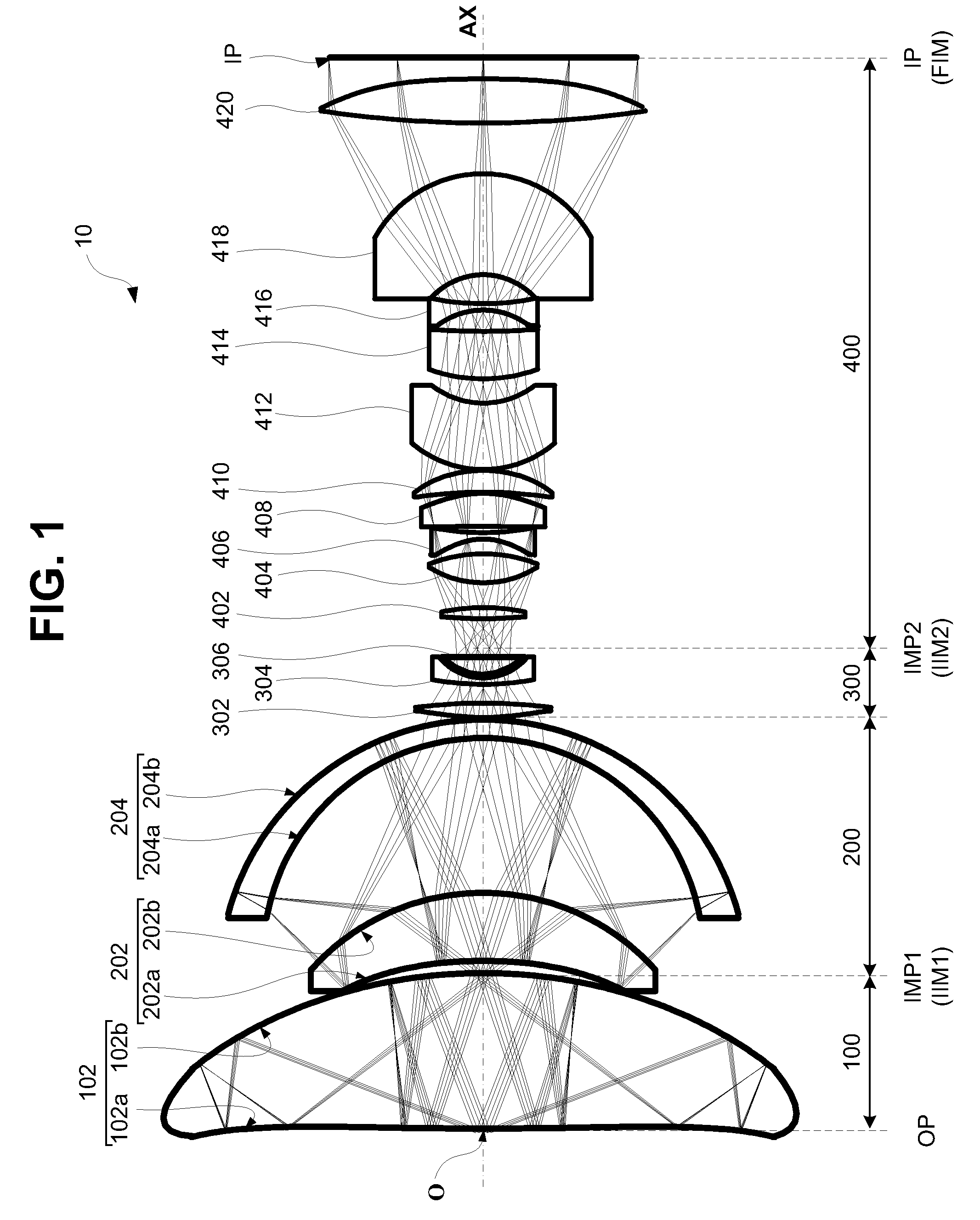
A catadioptric system includes: a first image forming optical system that includes at least two reflecting mirrors and forms a first intermediate image of a first plane with light originating from the first plane; a second image forming optical system that includes at least two reflecting mirrors and forms a second intermediate image of the first plane with light having traveled via the first image forming optical system; and a refractive type of third image forming optical system that forms a final image of the first plane onto a second plane with light having traveled via the second image forming optical system, and optical members constituting the first image forming optical system, the second image forming optical system and the third image forming optical system are all disposed along a single linear optical axis.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Correction of birefringence in cubic crystalline optical systems
InactiveUS6683710B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusCatadioptric systemWavefront aberration
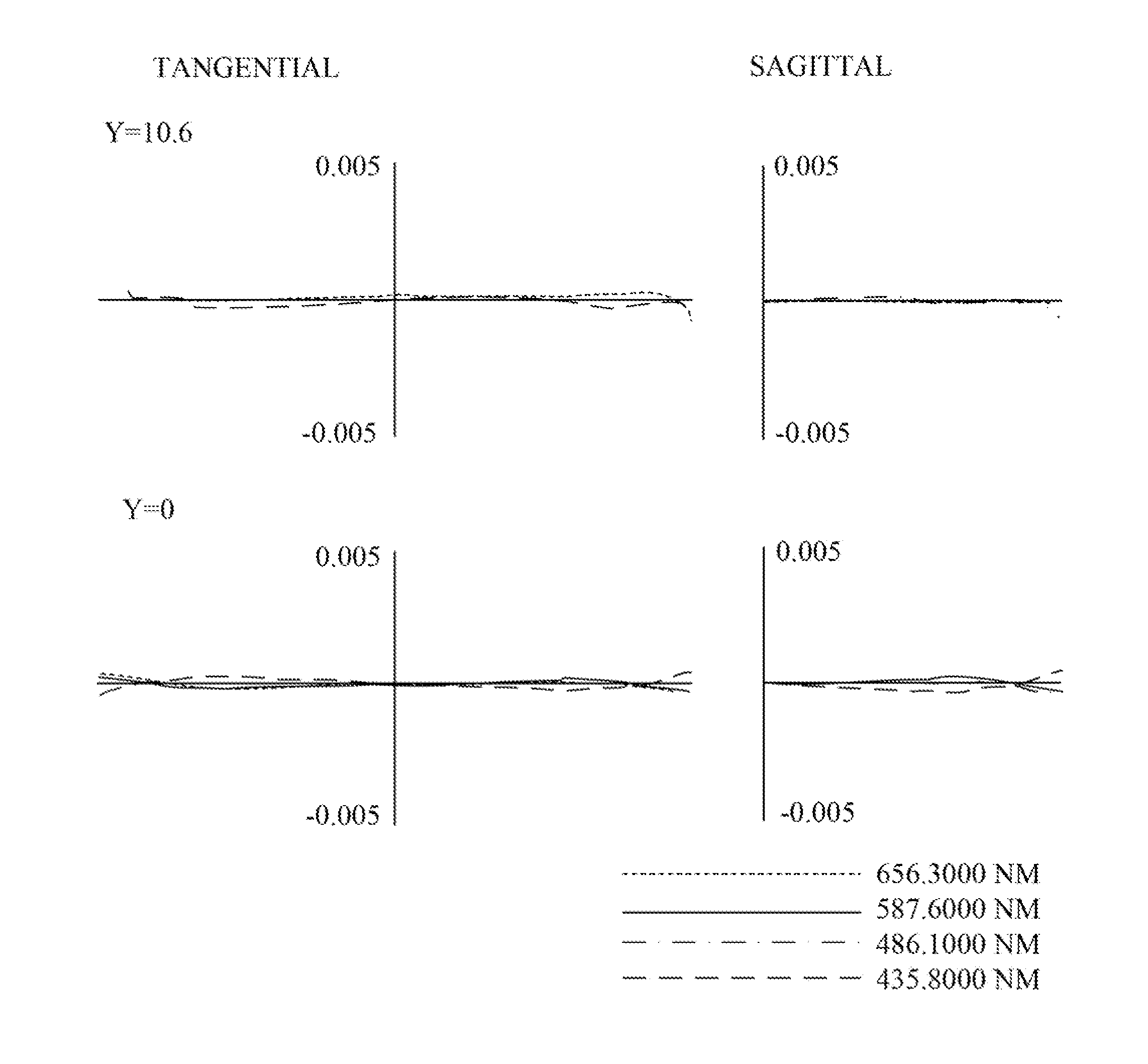
An optical system includes multiple cubic crystalline optical elements aligned along a common optical axis and having their crystal lattices oriented with respect to each other to minimize the effects of intrinsic birefringence and produce a system with reduced retardance. The optical system may be a refractive or catadioptric system having a high numerical aperture and using light with a wavelength at or below 248 nanometers. The net retardance of the system is less than the sum of the retardance contributions of the respective optical elements as the elements are oriented such that the intrinsic birefringences of the individual elements cancel each other out. In one embodiment, two [110] cubic crystalline optical elements are clocked with respect to one another and used in conjunction with a [100] cubic crystalline optical element to reduce retardance. Various birefringent elements, wave plates, and combinations thereof provide additional correction for residual retardance and wavefront aberrations. The optical system may be used in a photolithography tool to pattern substrates such as semiconductor substrates and thereby produce semiconductor devices.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Reducing aberration in optical systems comprising cubic crystalline optical elements
InactiveUS6844972B2Reduced polarization effectsLower latencyMaterial analysis by optical meansPolarising elementsCatadioptric systemDevice material
An optical system includes multiple cubic crystalline optical elements and one or more polarization rotators in which the crystal lattices of the cubic crystalline optical elements are oriented with respect to each other to reduce the effects of intrinsic birefringence and produce a system with reduced retardance. The optical system may be a refractive or catadioptric system having a high numerical aperture and using light with a wavelength at or below 248 nanometers. The net retardance of the system is less than the sum of the retardance contributions of the respective optical elements. In one embodiment, all cubic crystalline optical elements are oriented with identical three dimensional cubic crystalline lattice directions, a 90° polarization rotator divides the system into front and rear groups such that the net retardance of the front group is balanced by the net retardance of the rear group. The optical system may be used in a photolithography tool to pattern substrates such as semiconductor substrates and thereby produce semiconductor devices.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Correction of birefringence in cubic crystalline optical systems
InactiveUS20030099047A1Lower latencyMinimize changesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusCatadioptric systemOptical axis
An optical system includes multiple cubic crystalline optical elements aligned along a common optical axis and having their crystal lattices oriented with respect to each other to minimize the effects of intrinsic birefringence and produce a system with reduced retardance. The optical system may be a refractive or catadioptric system having a high numerical aperture and using light with a wavelength at or below 248 nanometers. The net retardance of the system is less than the sum of the retardance contributions of the respective optical elements as the elements are oriented such that the intrinsic birefringences of the individual elements cancel each other out. In one embodiment, two [110] cubic crystalline optical elements are clocked with respect to one another and used in conjunction with a [100] cubic crystalline optical element to reduce retardance. Various birefringent elements, wave plates, and combinations thereof provide additional correction for residual retardance and wavefront aberrations. The optical system may be used in a photolithography tool to pattern substrates such as semiconductor substrates and thereby produce semiconductor devices.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Catadioptric telescopes
Certain embodiments described herein comprise a telescope comprising primary and secondary mirrors and a corrector. The primary mirror has a first curved reflecting surface having a non-hyperbolic shape. The second secondary mirror has a second curved reflecting surface having a hyperbolic shape. The corrector comprises substantially optically transmissive material. The primary mirror, the secondary mirror, and the corrector are disposed along an optical path such that light propagates through the corrector to the primary mirror and from the primary mirror to the secondary mirror. In certain embodiments, the shapes of the first and second curved reflecting surfaces of the primary and second mirrors, respectively, and the shape and the index of refraction of the optically transmissive material of the corrector are such that the telescope is aplanatic.
Owner:MEADE INSTRUMENTS
Structures and methods for reducing aberration in integrated circuit fabrication systems
InactiveUS6970232B2Reduced polarization effectsLower latencyInvestigating moving sheetsPolarising elementsCatadioptric systemWavelength
An optical system includes multiple cubic crystalline optical elements and one or more polarization rotators in which the crystal lattices of the cubic crystalline optical elements are oriented with respect to each other to reduce the effects of intrinsic birefringence and produce a system with reduced retardance. The optical system may be a refractive or catadioptric system having a high numerical aperture and using light with a wavelength at or below 248 nanometers. The net retardance of the system is less than the sum of the retardance contributions of the respective optical elements. In one embodiment, all cubic crystalline optical elements are oriented with identical three dimensional cubic crystalline lattice directions, a 90° polarization rotator divides the system into front and rear groups such that the net retardance of the front group is balanced by the net retardance of the rear group. The optical system may be used in a photolithography tool to pattern substrates such as semiconductor substrates and thereby produce semiconductor devices.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
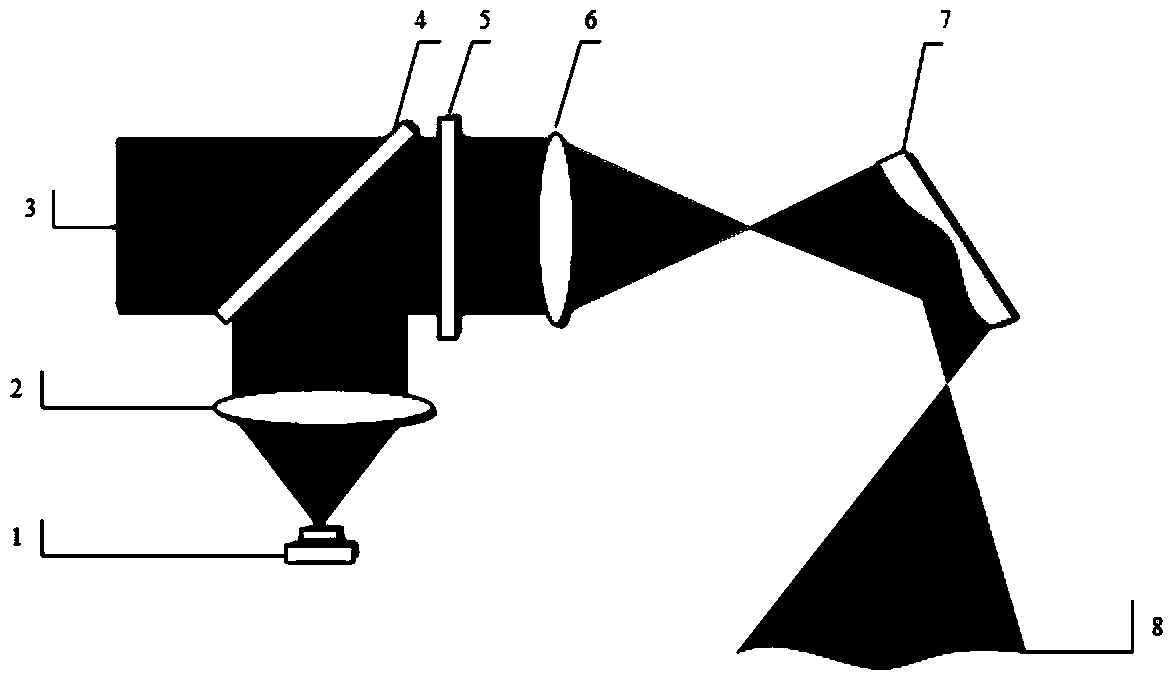
Catadioptric type off-axis three-reflector long-wave infrared optical system
InactiveCN101672978ARelatively large apertureNo increase in difficultyWave based measurement systemsOptical elementsCatadioptric systemOptoelectronics
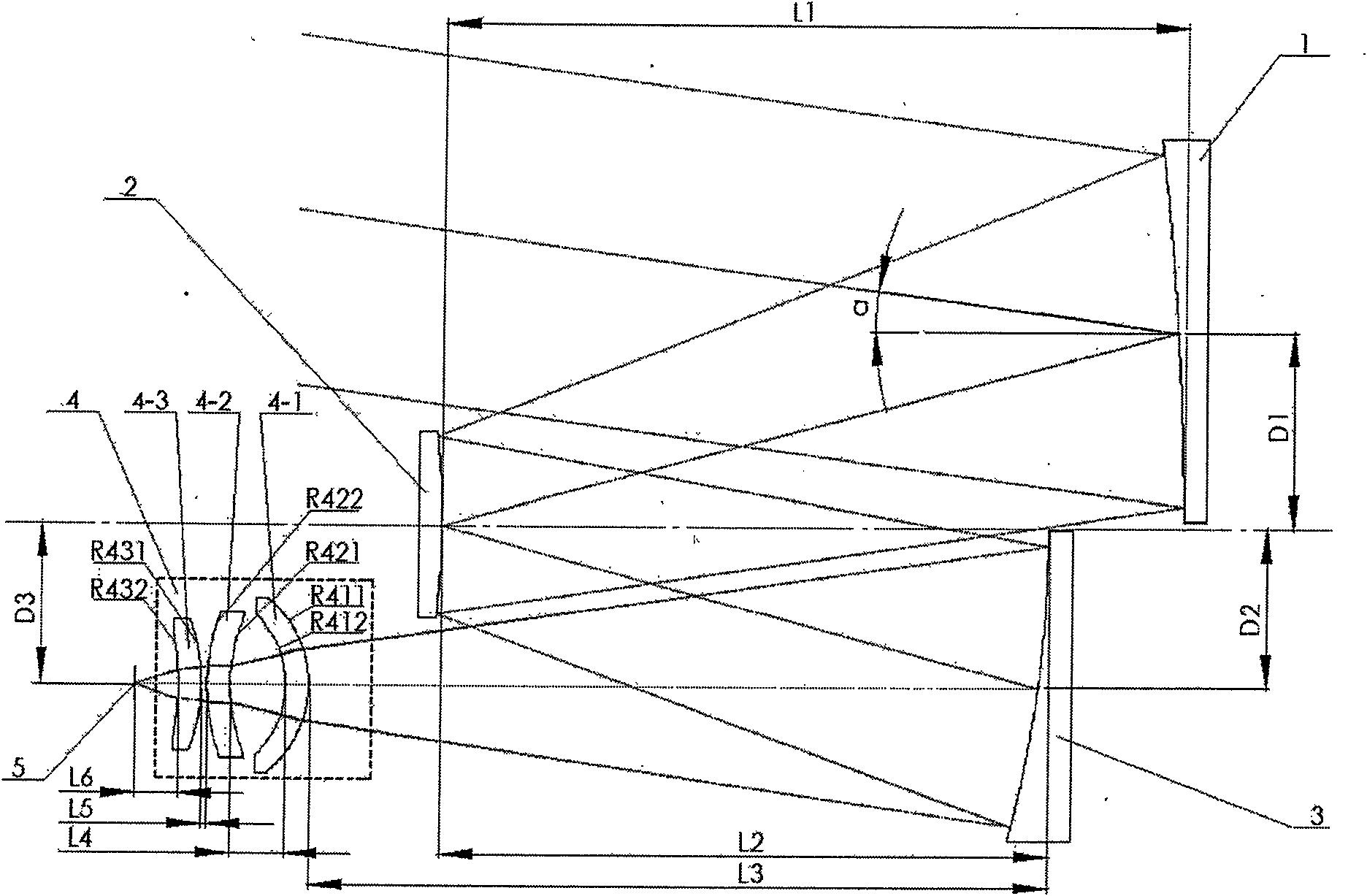
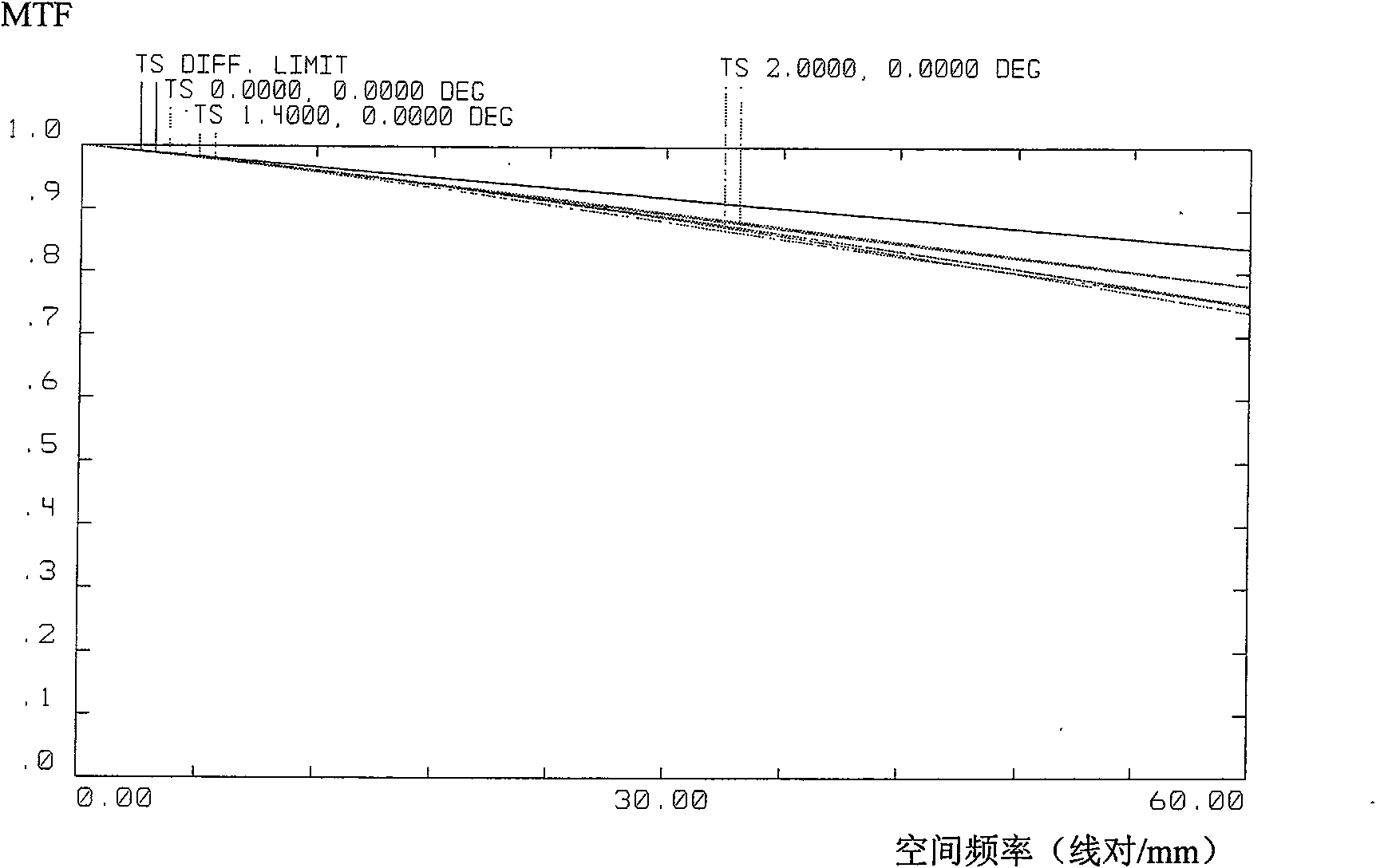
The invention discloses a catadioptric type off-axis three-reflector long-wave infrared optical system for spaceborne or airborne ground observation. The optical system comprises an off-axis three-reflector system and a convertible lens group 4, wherein the off-axis three-reflector system comprises a concave reflector 1, a convex reflector 2 and a concave reflector 3; the three off-axis reflectorscan perfectly image, and the focus of each reflector is longer than the focus of the system; the convertible lens group is achromatic, and the amplification factor beta of the convertible lens groupis larger than or equal to 0.35 and less than or equal to 1; the focus of each of the three off-axis reflectors is shortened; and the relative aperture of the system is enlarged. The invention has simple structure and is mainly applied to long-wave infrared cameras in airborne or spaceborne ground imaging instruments.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High NA system for multiple mode imaging
InactiveUS7035001B2Increased field sizeTelevision system detailsX-ray/infra-red processesCatadioptric systemPupil shape
A system for multiple mode imaging is disclosed. The catadioptric system has an NA greater than 0.65, and preferably greater than 0.9, highly corrected for low and high order monochromatic aberrations. The system employs unique illumination entrances and optics to collect reflected, diffracted, and scattered light over a range of angles. Multiple imaging modes are possible by varying the illumination geometry and apertures at the pupil plane. Illumination can enter the catadioptric optical sytems using an auxiliary beamsplitter or mirror, or through the catadioptric elements at any angle from 0 to 85 degrees from vertical. The system may employ a relayed pupil plane, used to select different imaging modes, provide simultaneous operation of different imaging modes, Fourier filtering, and other pupil shaping operations.
Owner:KLA TENCOR CORP
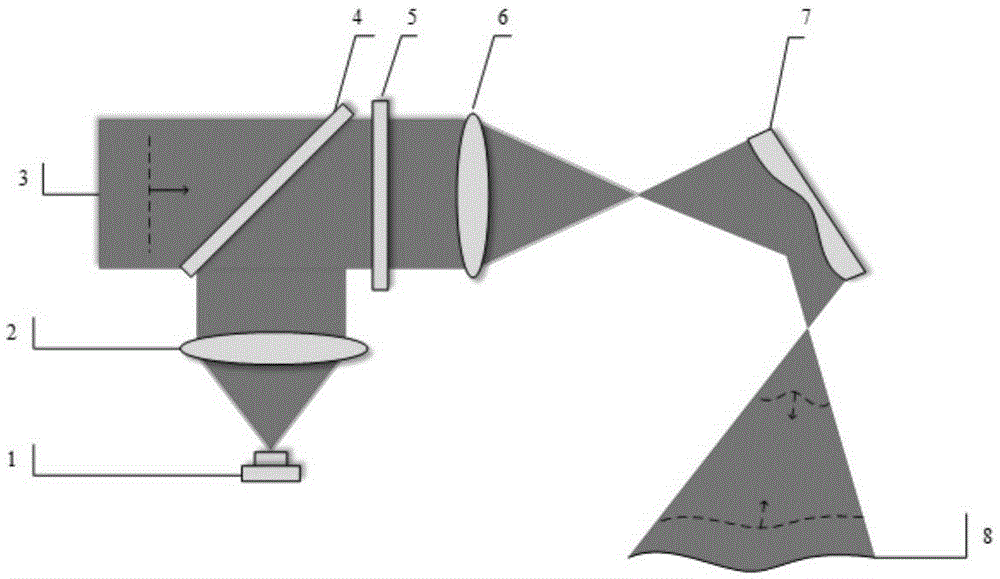
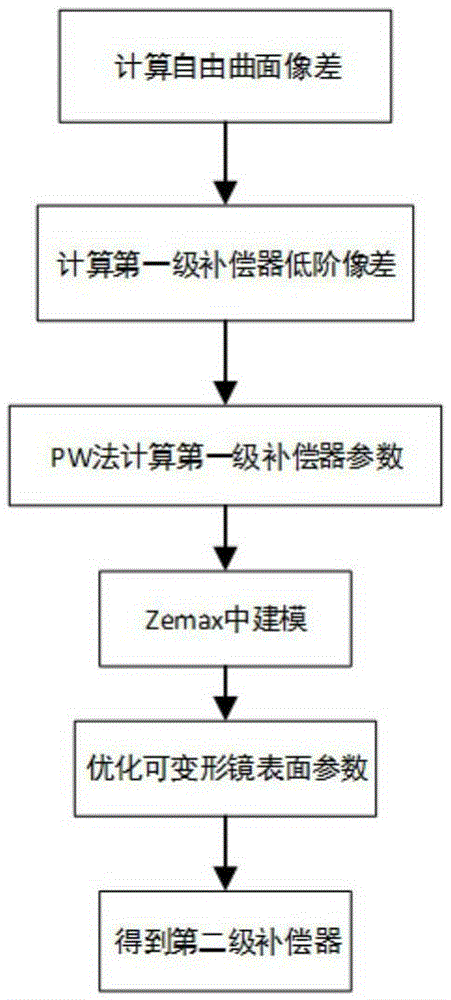
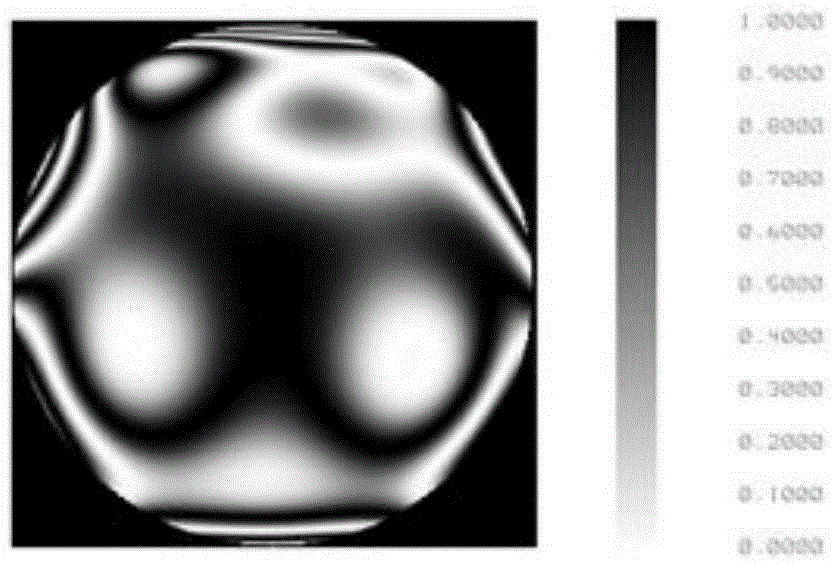
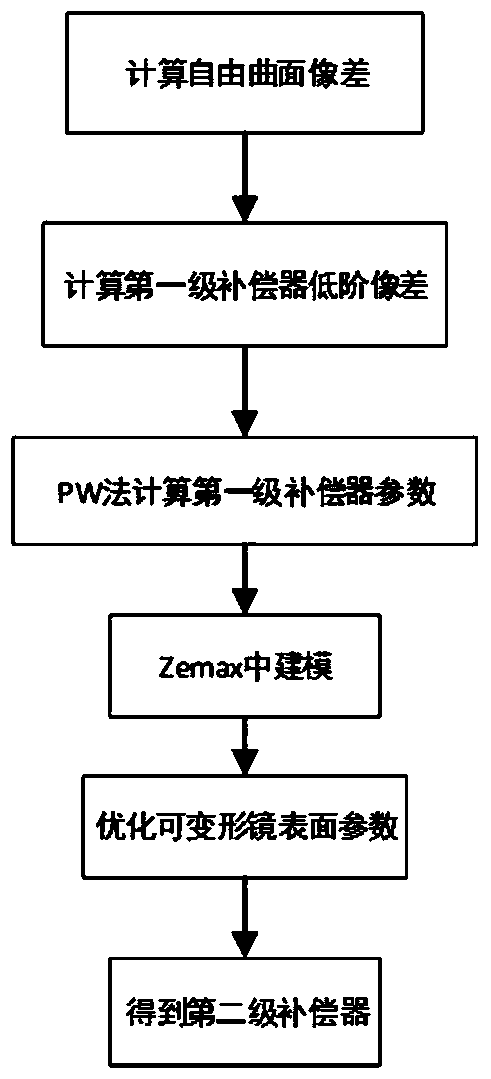
Universal compensation mirror based on deformable mirror and design method
ActiveCN105352451AReduce design difficultyReduce processing costsUsing optical meansCatadioptric systemLaser interference
The invention relates to a universal compensation mirror based on a deformable mirror and a design method, aims to detect surface morphology of a free curved surface through laser interference and belongs to the photoelectric detection field. The compensation mirror comprises a first level compensator and a second level compensator. Through the design method, low-order aberration of the detected free curved surface is calculated by firstly utilizing a primary Seidel aberration formula, parameters of the first level compensator are acquired through employing an aberration matching and paraxial formula algorithm; a catadioptric system is established by utilizing software, and residual high-order aberration can be compensated as much as possible by utilizing the second level compensator. According to the compensation mirror and the design method, the deformable mirror is taken as the second level compensator and is for surface morphology detection on the free curved surface, so one compensator can be utilized to detect free curved surfaces in multiple types, design difficulty and processing fee of compensators can be reduced to a maximum degree, moreover, through the compensation detection method, the structure is simple, introduced error sources are reduced, early-stage calibration adjustment is easy, and instantaneous and high precision surface morphology measurement can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
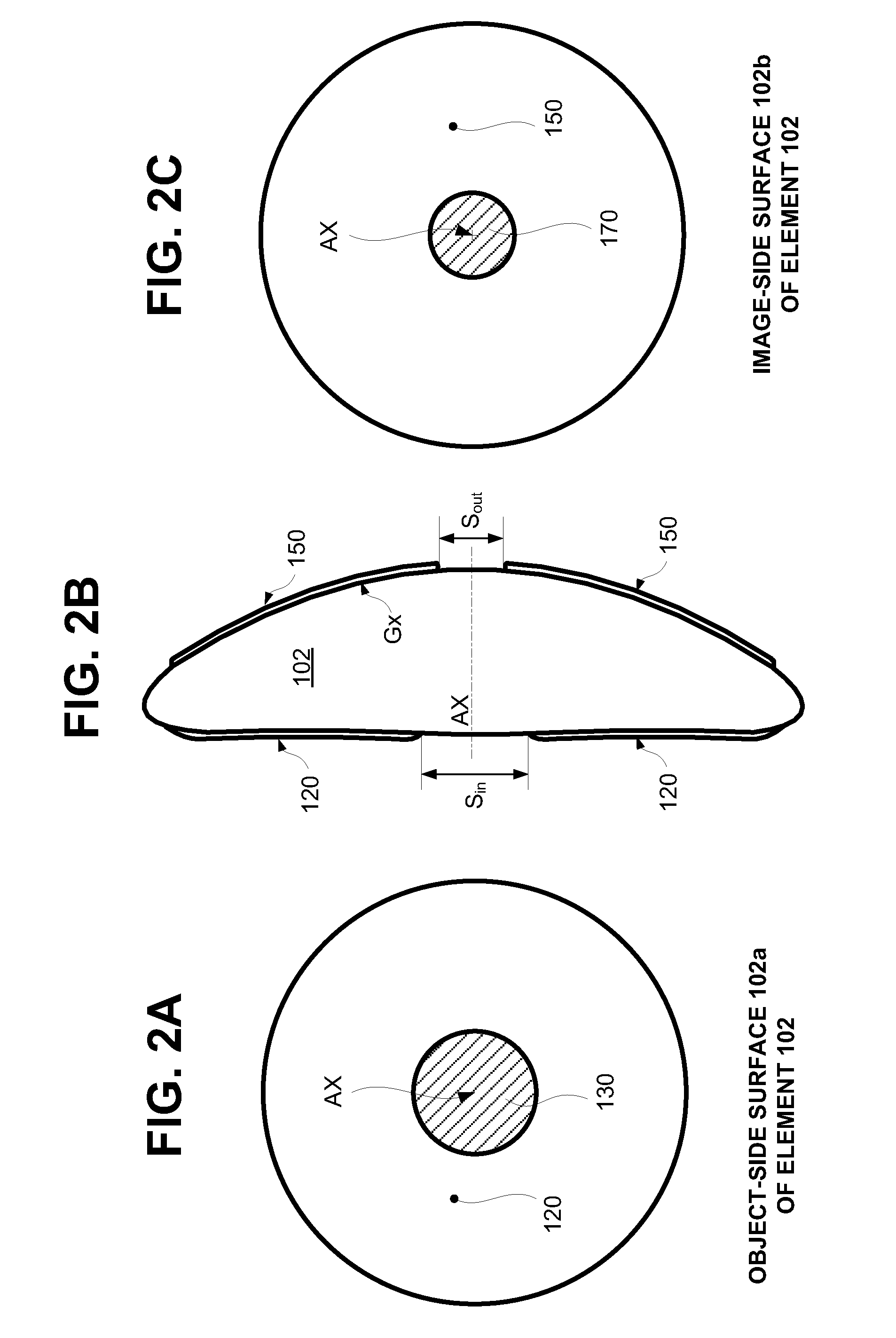
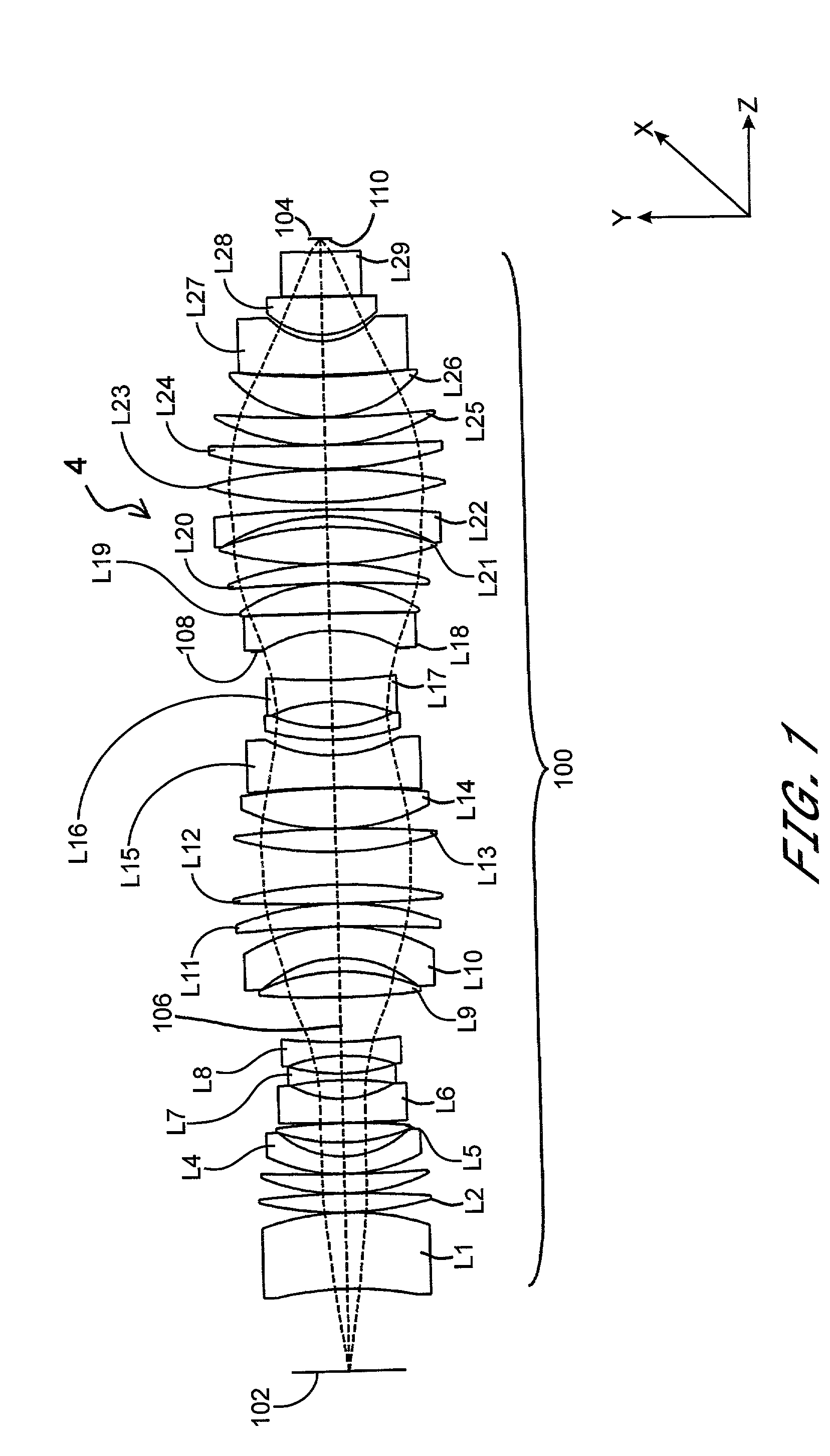
Catadioptric optical system with multi-reflection element for high numerical aperture imaging
A catadioptric system includes a first catadioptric group, a second catadioptric group, and a lens group disposed in axial alignment with each other. The first catadioptric group includes a solid lens having an input surface, a primary reflective surface, secondary reflective surface and an exit surface. The primary reflective surface is a curved surface concave towards the secondary reflective surface. A light flux entering through the input surface undergoes more than two reflections between the primary and secondary reflective surfaces, prior to exiting through the exit surface. At least one of the primary reflective surface and secondary reflective surface has a continuous and smooth topological profile.
Owner:CANON KK +1
Methods for reducing aberration in optical systems
InactiveUS6995908B2Reduced polarization effectsLower latencyPolarising elementsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusCatadioptric systemHigh numerical aperture
An optical system includes multiple cubic crystalline optical elements and one or more polarization rotators in which the crystal lattices of the cubic crystalline optical elements are oriented with respect to each other to reduce the effects of intrinsic birefringence and produce a system with reduced retardance. The optical system may be a refractive or catadioptric system having a high numerical aperture and using light with a wavelength at or below 248 nanometers. The net retardance of the system is less than the sum of the retardance contributions of the respective optical elements. In one embodiment, all cubic crystalline optical elements are oriented with identical three dimensional cubic crystalline lattice directions, a 90° polarization rotator divides the system into front and rear groups such that the net retardance of the front group is balanced by the net retardance of the rear group. The optical system may be used in a photolithography tool to pattern substrates such as semiconductor substrates and thereby produce semiconductor devices.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
High NA system for multiple mode imaging
InactiveUS20060279837A1Easy alignmentEasy to operateTelevision system detailsX-ray/infra-red processesCatadioptric systemIntermediate image
A system for multiple mode imaging is disclosed herein. The system is a catadioptric system preferably having an NA greater than 0.9, highly corrected for low and high order monochromatic aberrations. This system uses unique illumination entrances and can collect reflected, diffracted, and scattered light over a range of angles. The system includes a catadioptric group, focusing optics group, and tube lens group. The catadioptric group includes a focusing mirror and a refractive lens / mirror element. The focusing optics group is proximate to an intermediate image, and corrects for aberrations from the catadioptric group, especially high order spherical aberration and coma. The tube lens group forms the magnified image. Different tube lens groups can be used to obtain different magnifications, such as a varifocal tube lens group to continuously change magnifications from 20 to 200×. Multiple imaging modes are possible by varying the illumination geometry and apertures at the pupil plane. Imaging modes include bright-field, full sky, ring dark-field, inverted ring dark-field, directional dark-field, double dark-field, Manhattan geometry, confocal bright-field, confocal dark-field, conoscopic, etc. Illumination can enter the catadioptric optical system using an auxiliary beamsplitter or mirror, or through the catadioptric group at any angle from 0 to 85 degrees from vertical. Multiple beams at multiple angles may be used for illumination. The high NA catadioptric system can also have a relayed pupil plane, used to select different imaging modes, providing simultaneous operation of different imaging modes, Fourier filtering, and other pupil shaping operations.
Owner:KLA CORP
Telescope and telescope array for use in spacecraft
ActiveUS20140300959A1Customization can be easily and inexpensivelyHigh-resolution imageTelescopesCatadioptric systemOptoelectronics
A catadioptric telescope is a modified version of a conventional Maksutov-Cassegrain optical telescope. In accordance with the invention, the reflecting surfaces of the primary mirror and the secondary spot mirror are on the second surfaces of the primary mirror and correcting lens, respectively. In further accordance with the invention, two of these telescopes can be joined together to form a binocular telescope array. The array can be easily customized to suit different remote sensing / satellite applications.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Artificial star generation apparatus and method for telescope systems
InactiveUS20050195456A1Eliminate the effects ofHigh precision collimation for focusing the telescopeTelescopesCatoptricsCatadioptric system
This invention describes an apparatus and method for generating artificial stars for the simple collimation of catoptric, dioptric, and catadioptric telescopes using a light source along with an appropriate hologram and housing to generate collimated laser beams that enter the front aperture of the telescope. The apparatus of this invention can be fastened to the outside of the telescope aperture. In addition, this invention allows the apparatus position to be adjusted at its tip and tilt axis to center an artificial star under the view of the ocular. The light source illuminates the hologram from some off axis position. Once the hologram is illuminated, the collimated beam emanates from the hologram with a slightly different angle. When these beams are then viewed with the telescope they appear as artificial stars.
Owner:LASERMAX
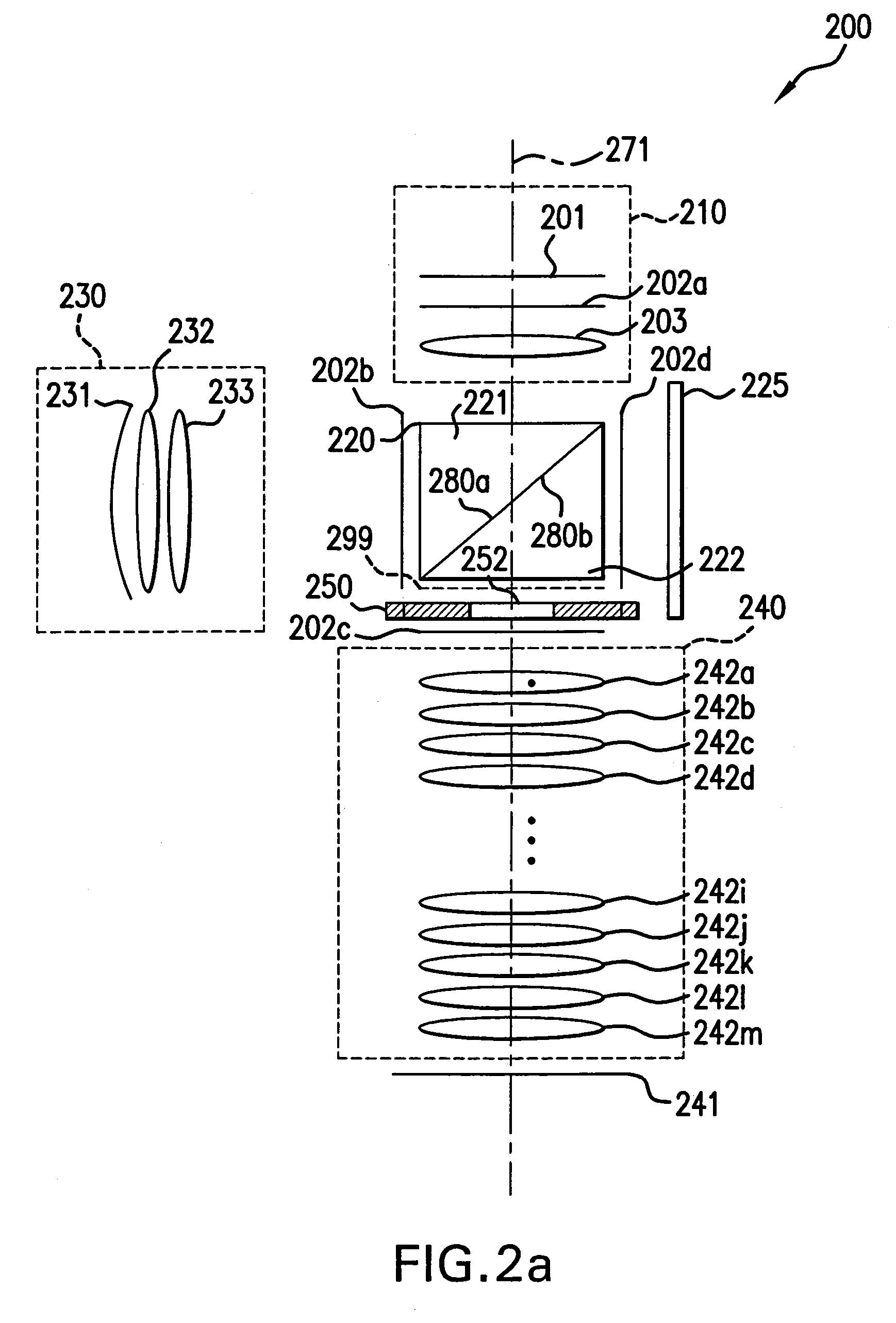
Catadioptric system and image pickup apparatus
InactiveUS20120320187A1Good both-side telecentric propertyHigh resolutionColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsIntermediate imageCatadioptric system
The catadioptric system includes a first optical imaging system (catadioptric part) causing a light flux from an object to form an intermediate image and a second optical imaging system (dioptric part) causing the light flux from the intermediate image to form an image. In the first optical imaging system, the light flux sequentially passes a first transmissive portion, a second reflective portion, a first reflective portion and a second transmissive portion. In the second optical imaging system, consecutive four lens surfaces among plural lens surfaces placed between an aperture stop and an image surface have a negative combined refractive power, and a condition of −0.52<φ4n<sub2>—< / sub2>max·Ymax<−0.14 is satisfied, φ4n<sub2>—< / sub2>max represents a maximum value of the negative combined refractive power, and Ymax represents a maximum object height in a field-of-view of the catadioptric system at the object.
Owner:CANON KK
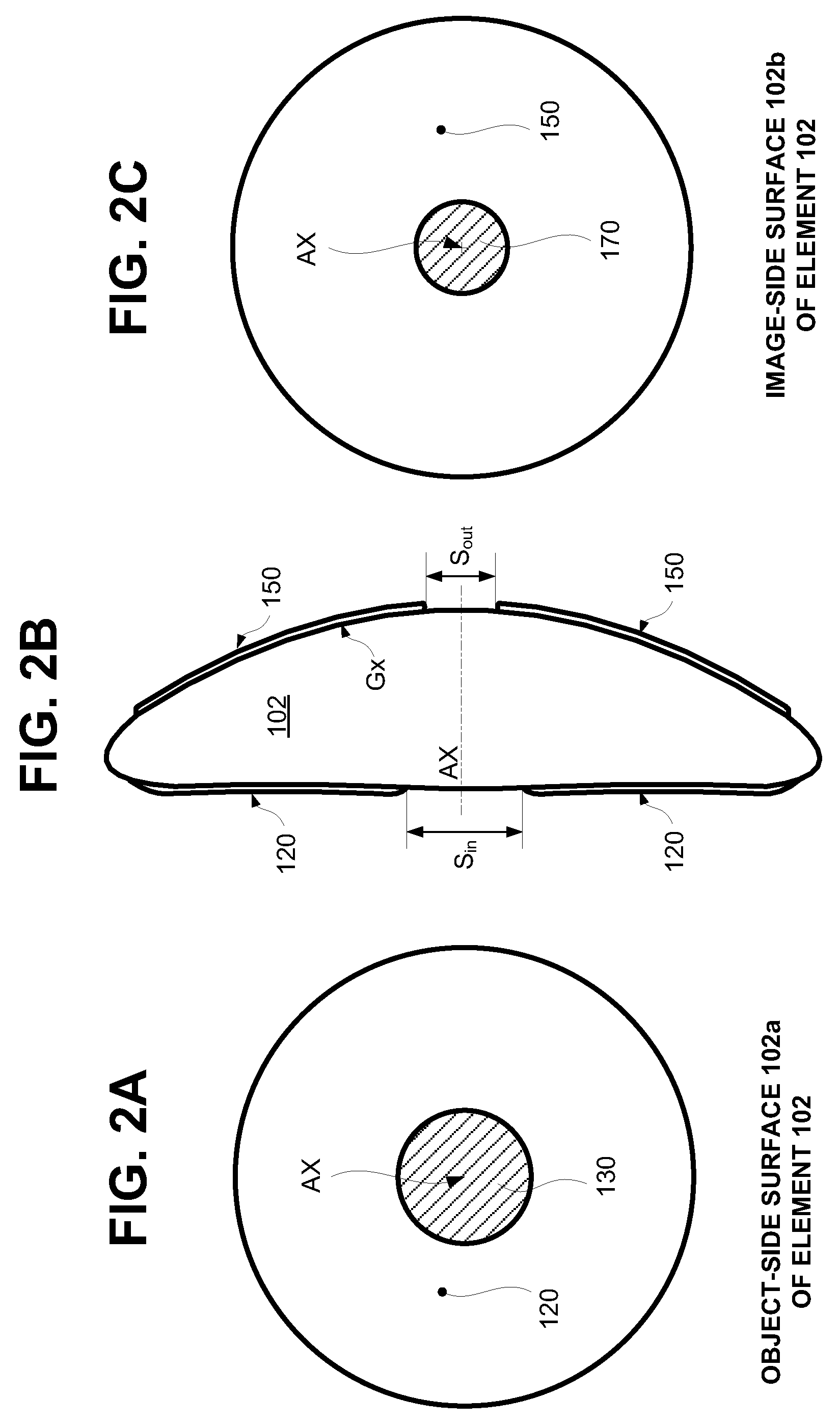
Panoramic optical lens and image acquisition device
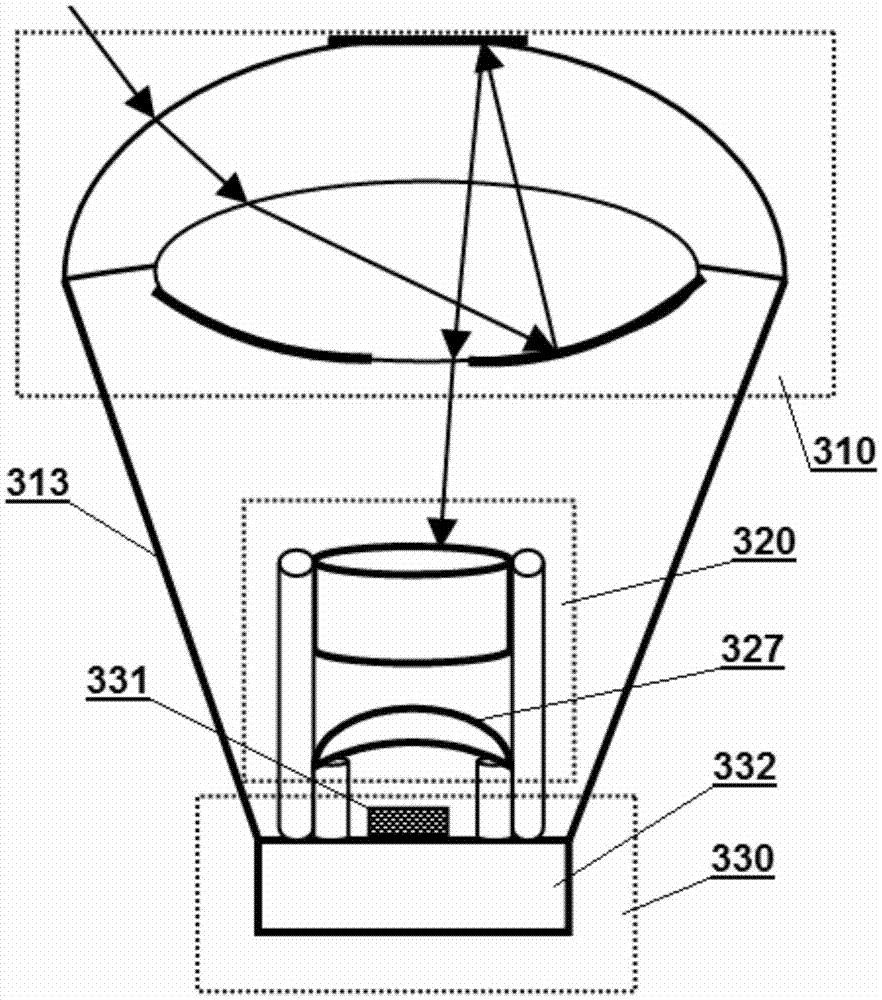
InactiveCN106908936AHigh-resolutionEasy for optical designPanoramic photographyOptical elementsCamera lensCatadioptric system
The invention relates to a panoramic optical lens and an image acquisition device. The panoramic optical lens comprises a catadioptric lens group (110) and a lens group (120). The catadioptric lens group comprises two catadioptric lenses which are glued together; the central area of the front surface of the first catadioptric lens is a reflection area, and other areas are transmission areas; the central area of the rear surface of the second catadioptric lens is a transmission area, and other areas are reflection areas; and the lens group is arranged on the optical path behind the catadioptric lens group. The catadioptric lens group combining refraction and reflection is employed to collect incident light, light is refracted, then reflected, then refracted and then reflected between the two catadioptric lenses and is converged for many times, the resolution of the edge of the field of view can be effectively increased, the imaging quality is improved, and the image acquisition device is designed more compactly.
Owner:BOLY MEDIA COMM SHENZHEN
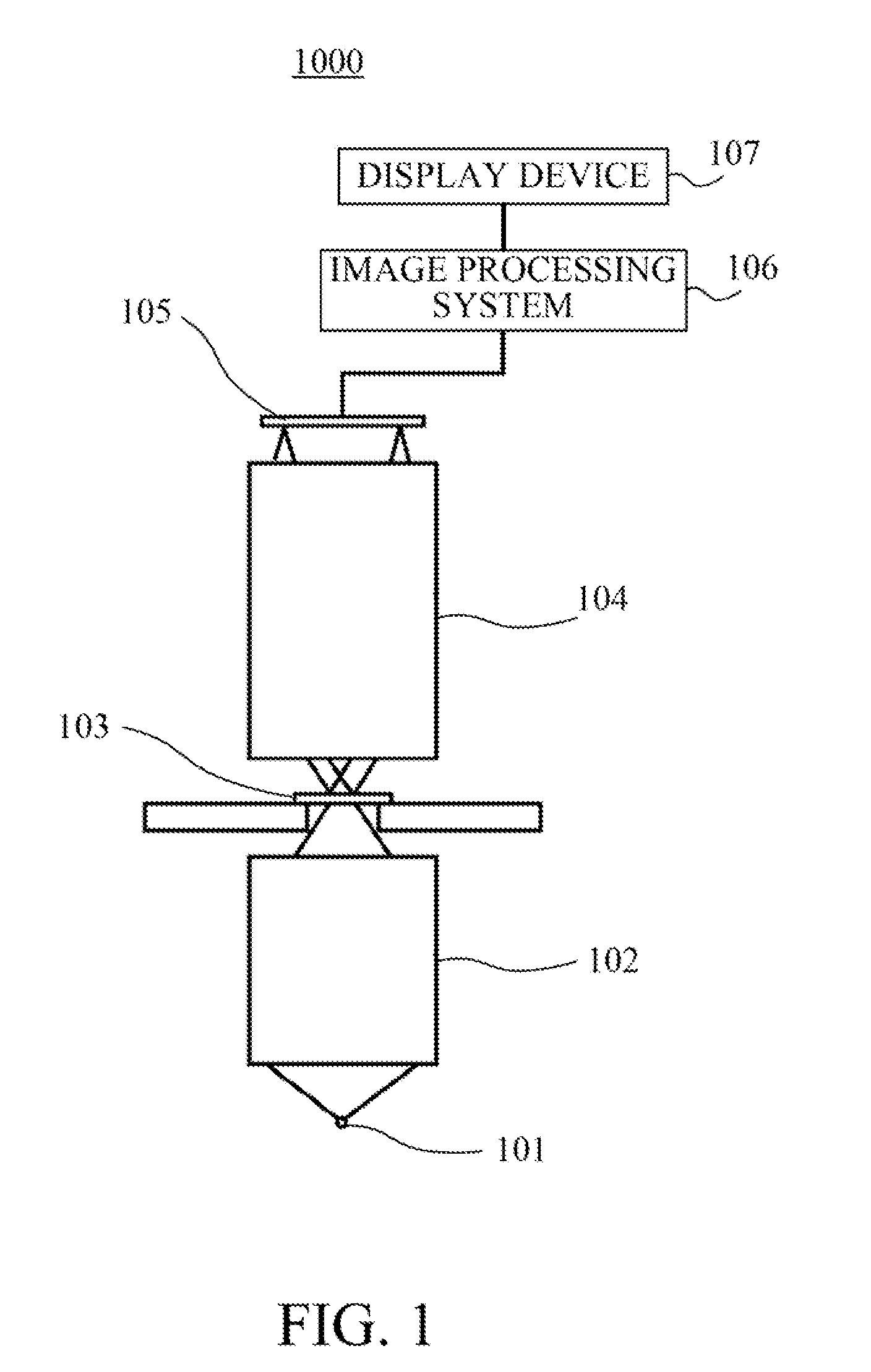
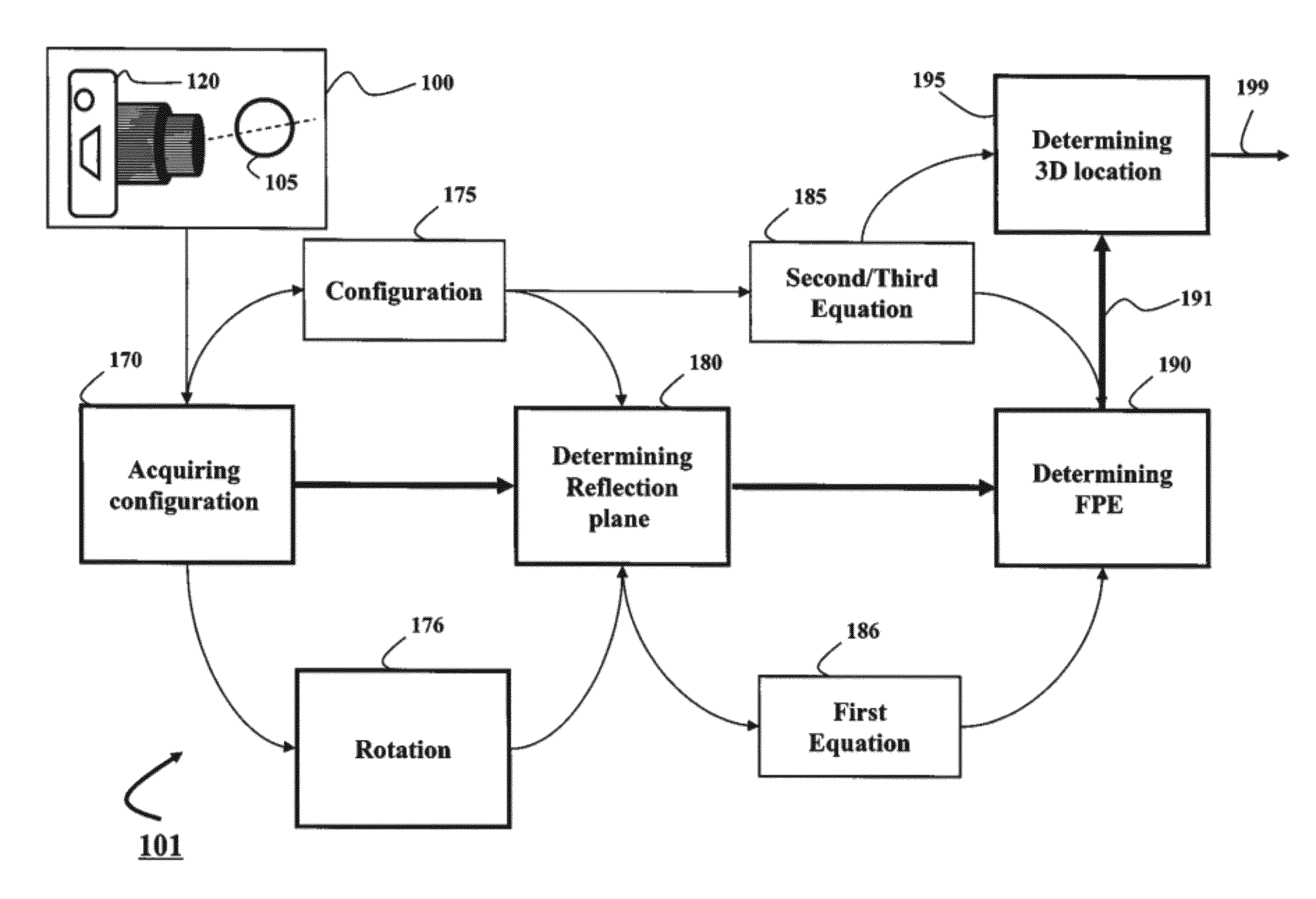
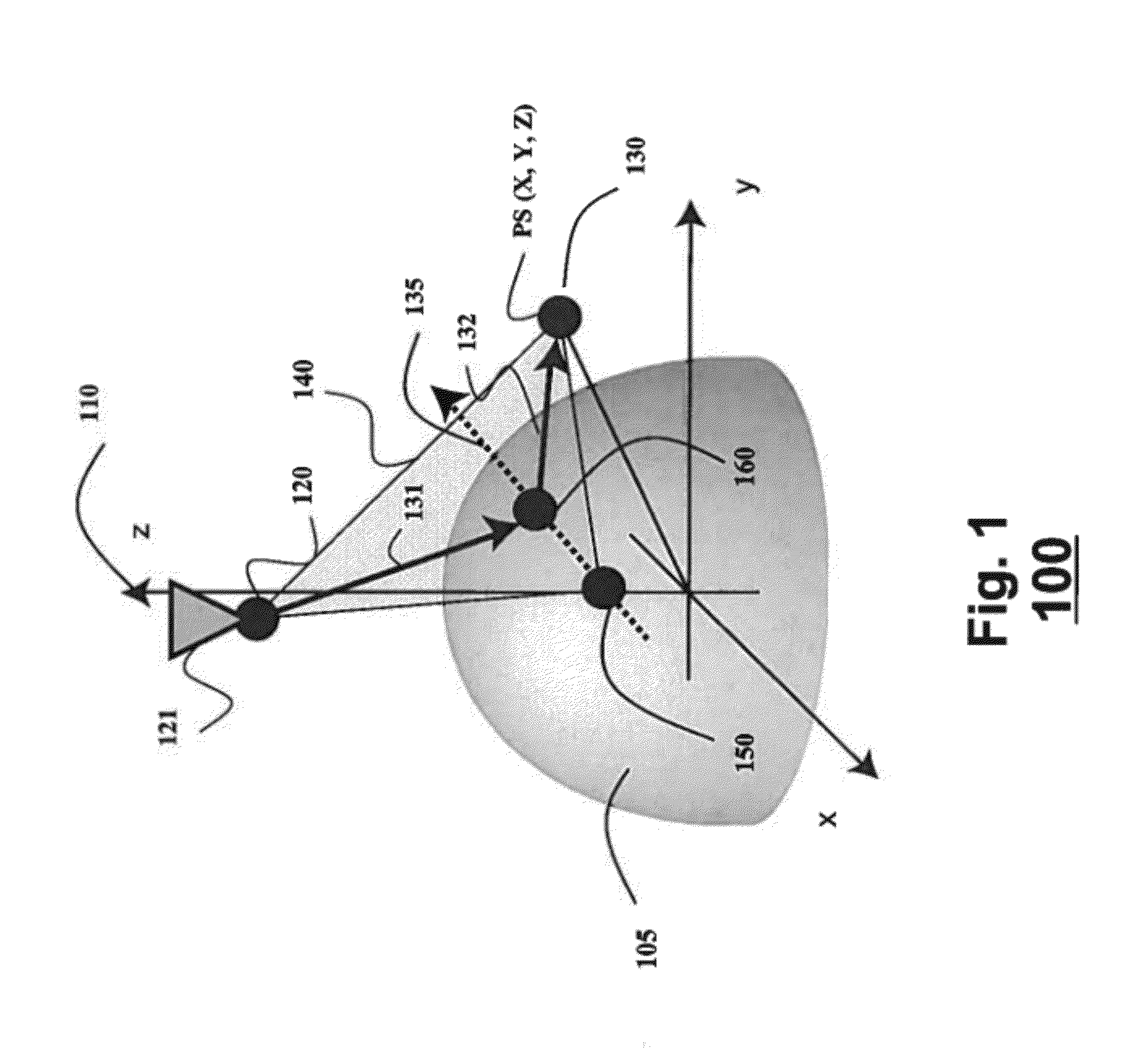
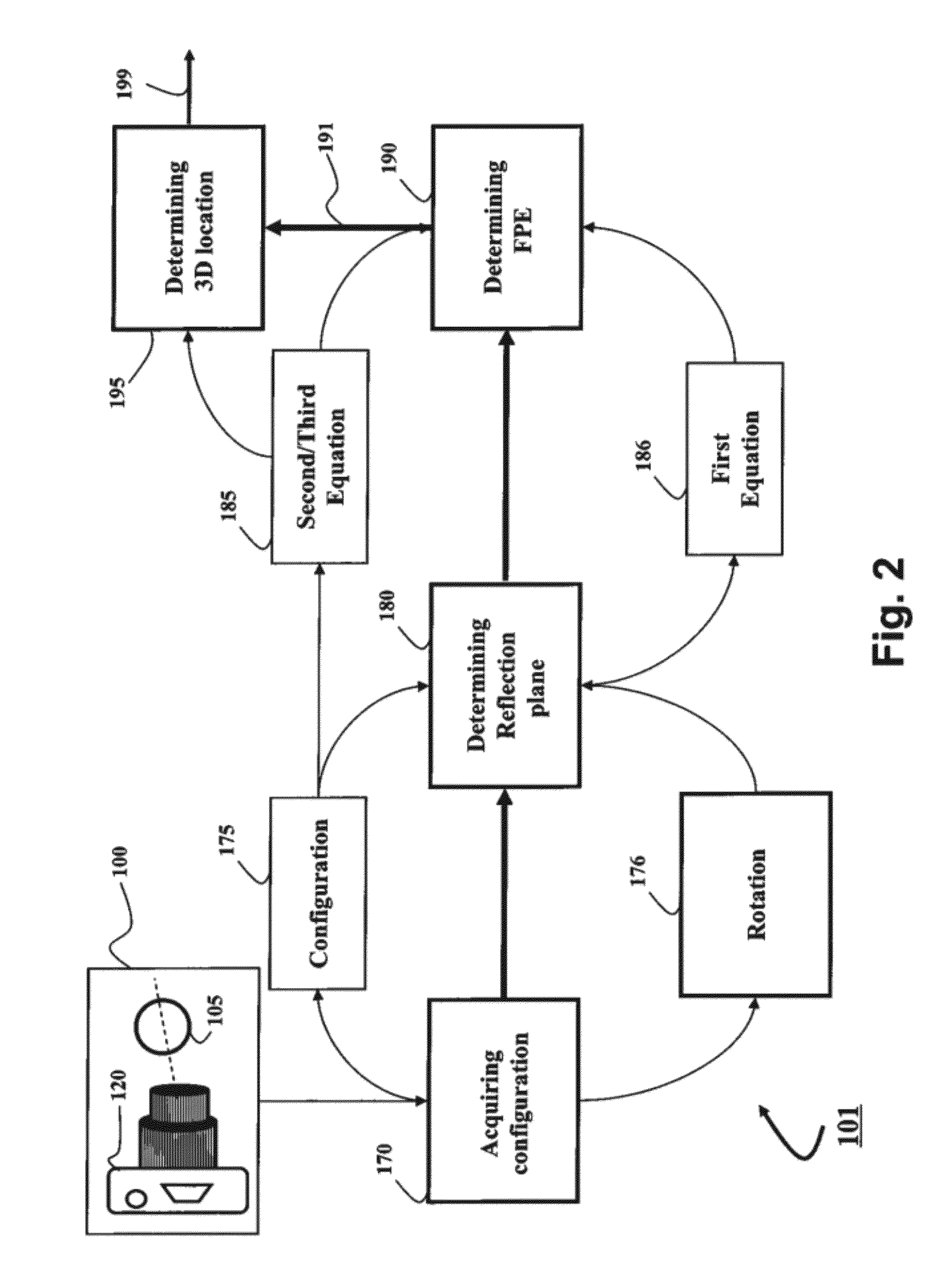
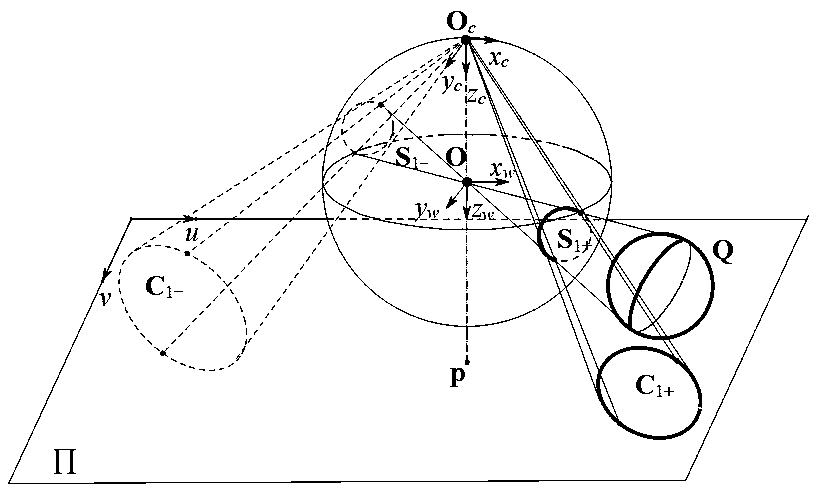
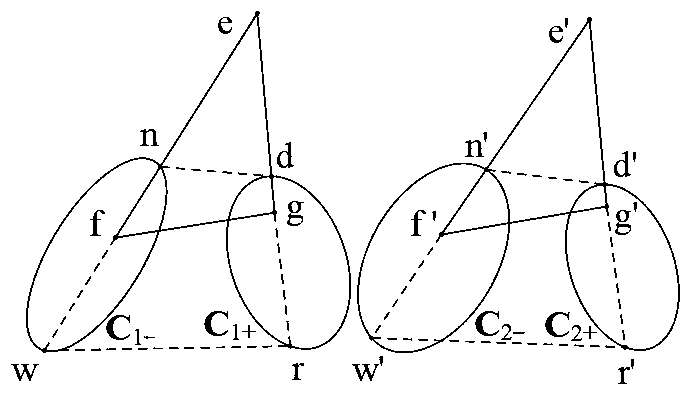
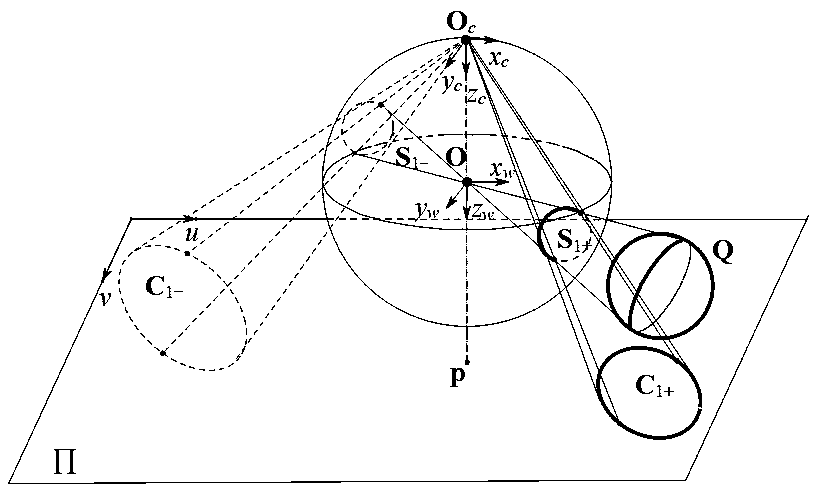
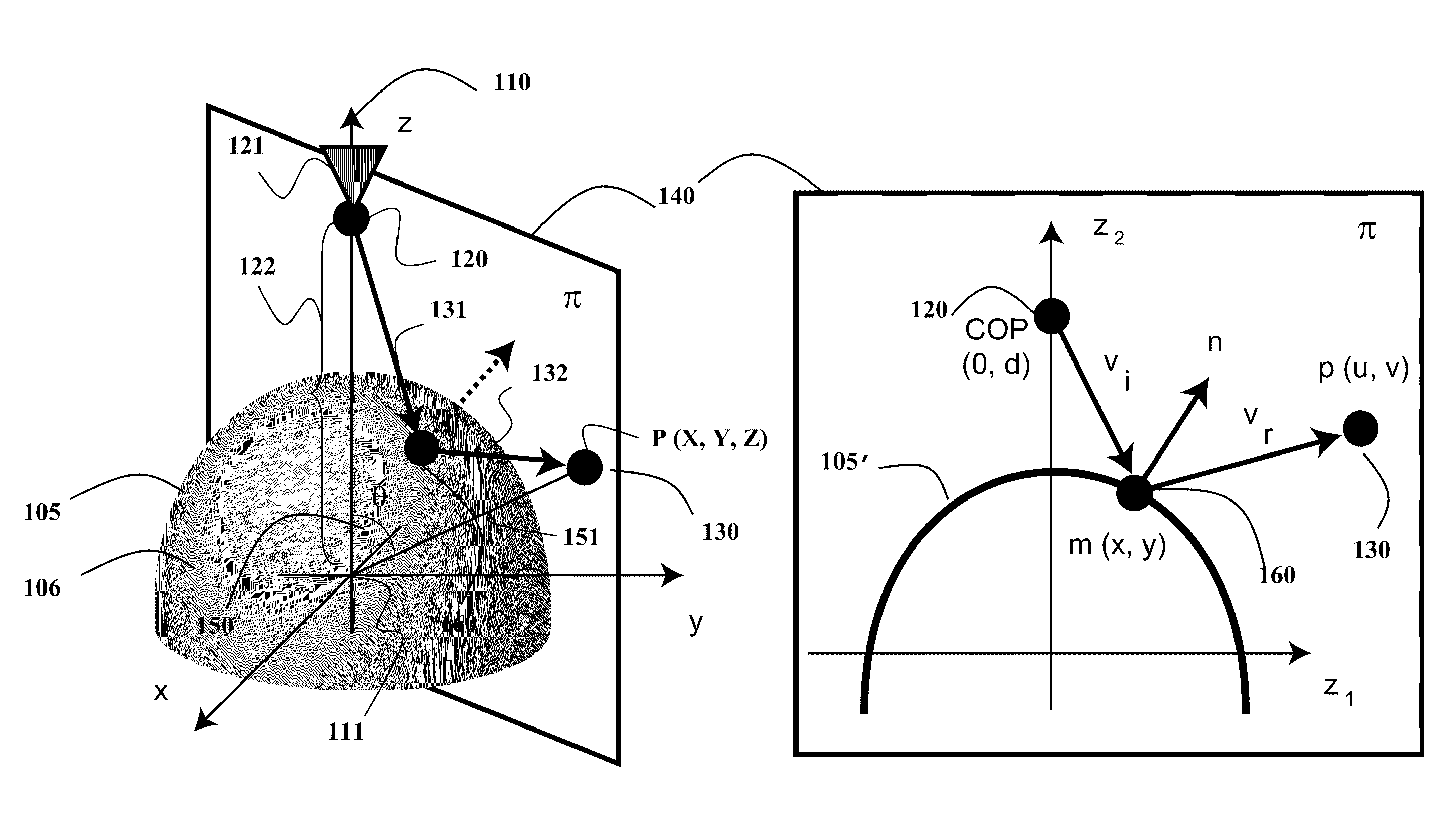
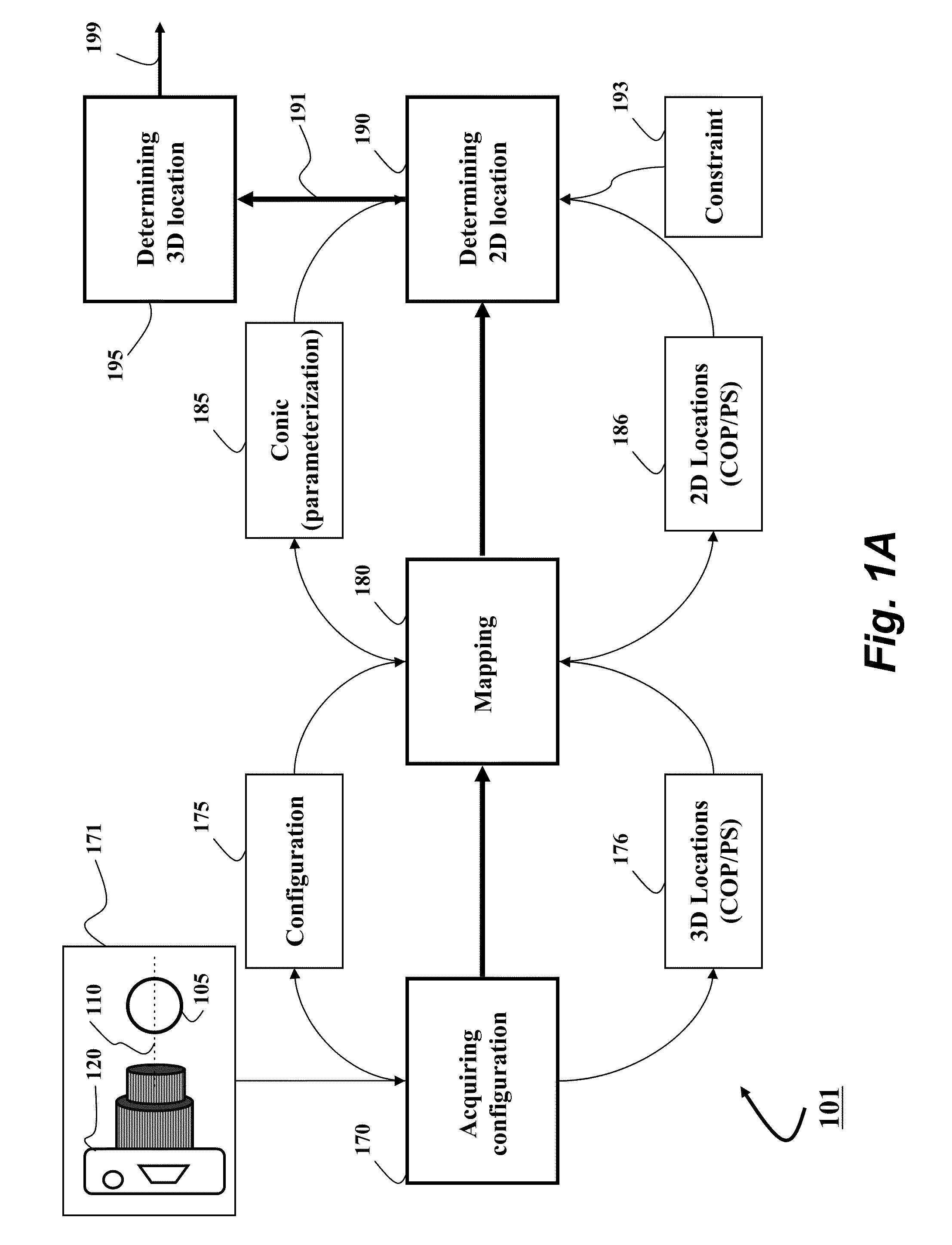
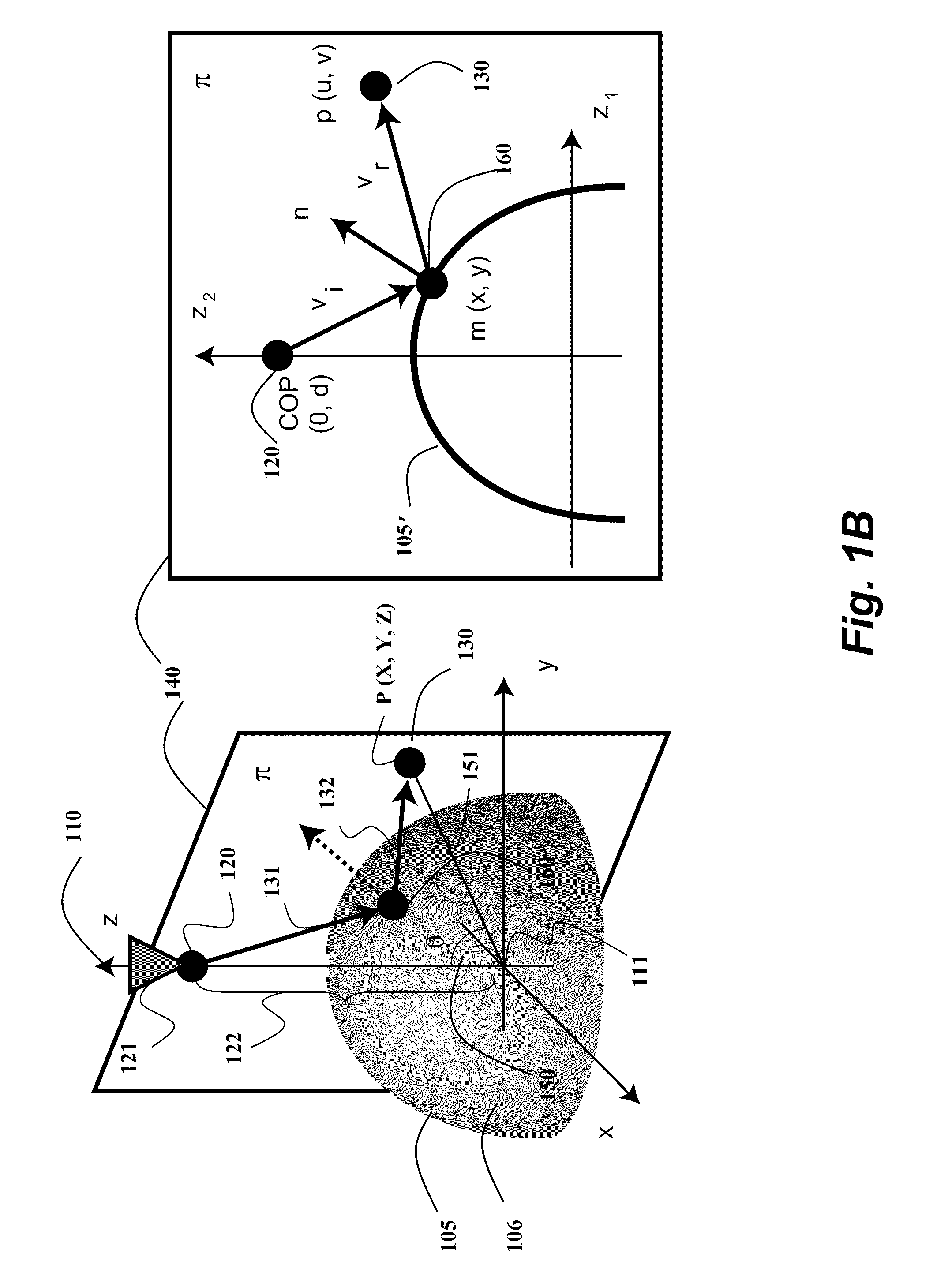
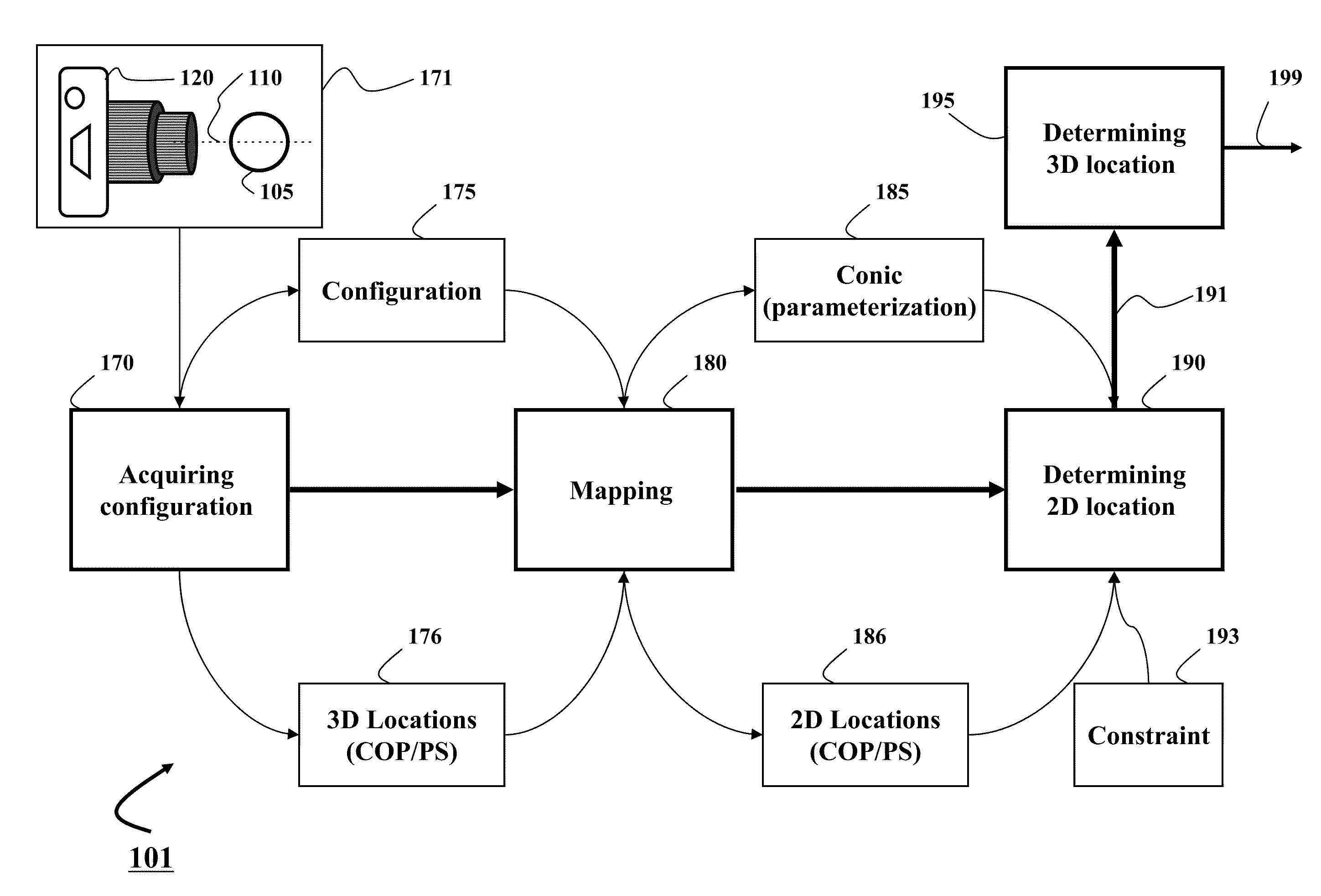
Method and System for Determining Projections in Non-Central Catadioptric Optical Systems
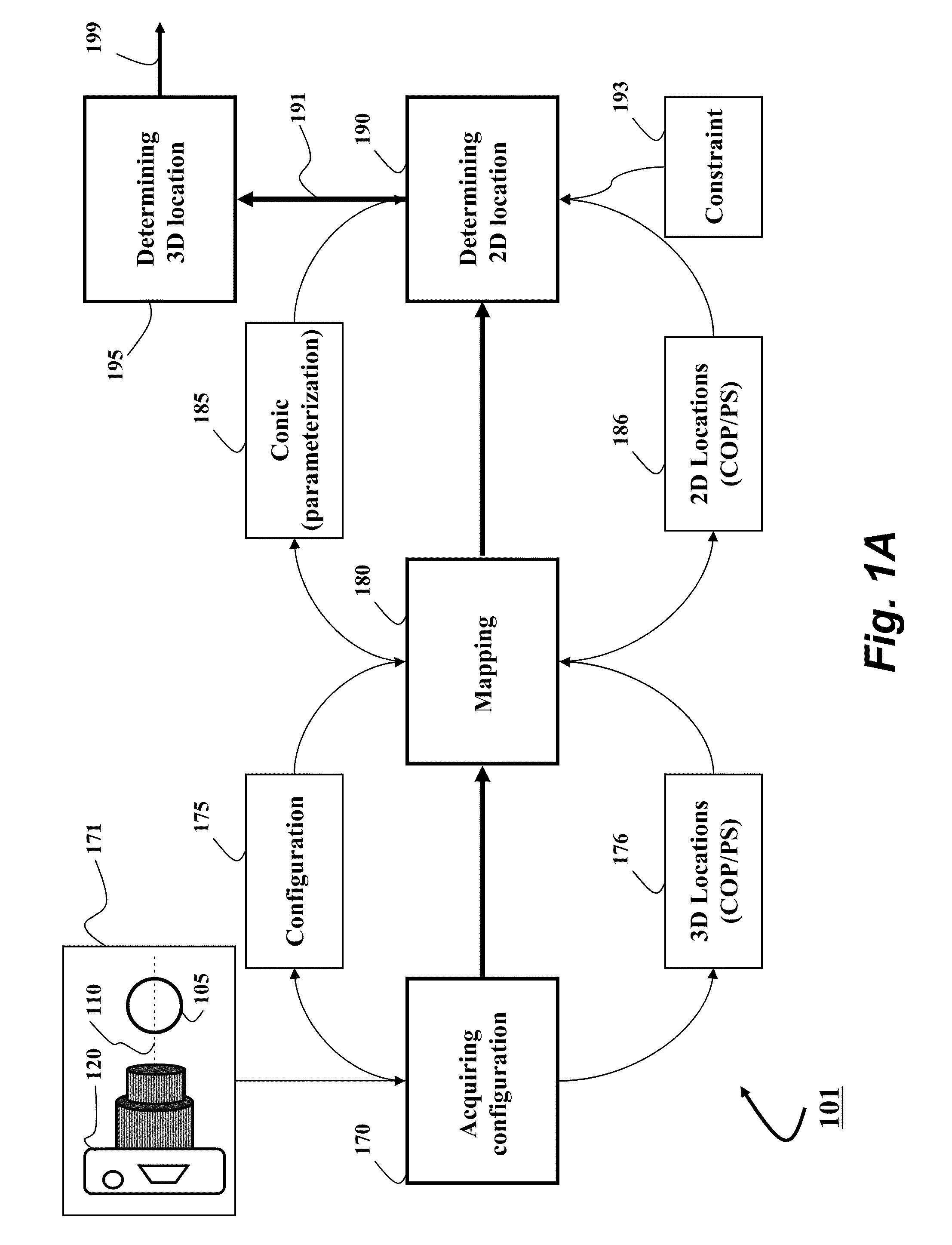
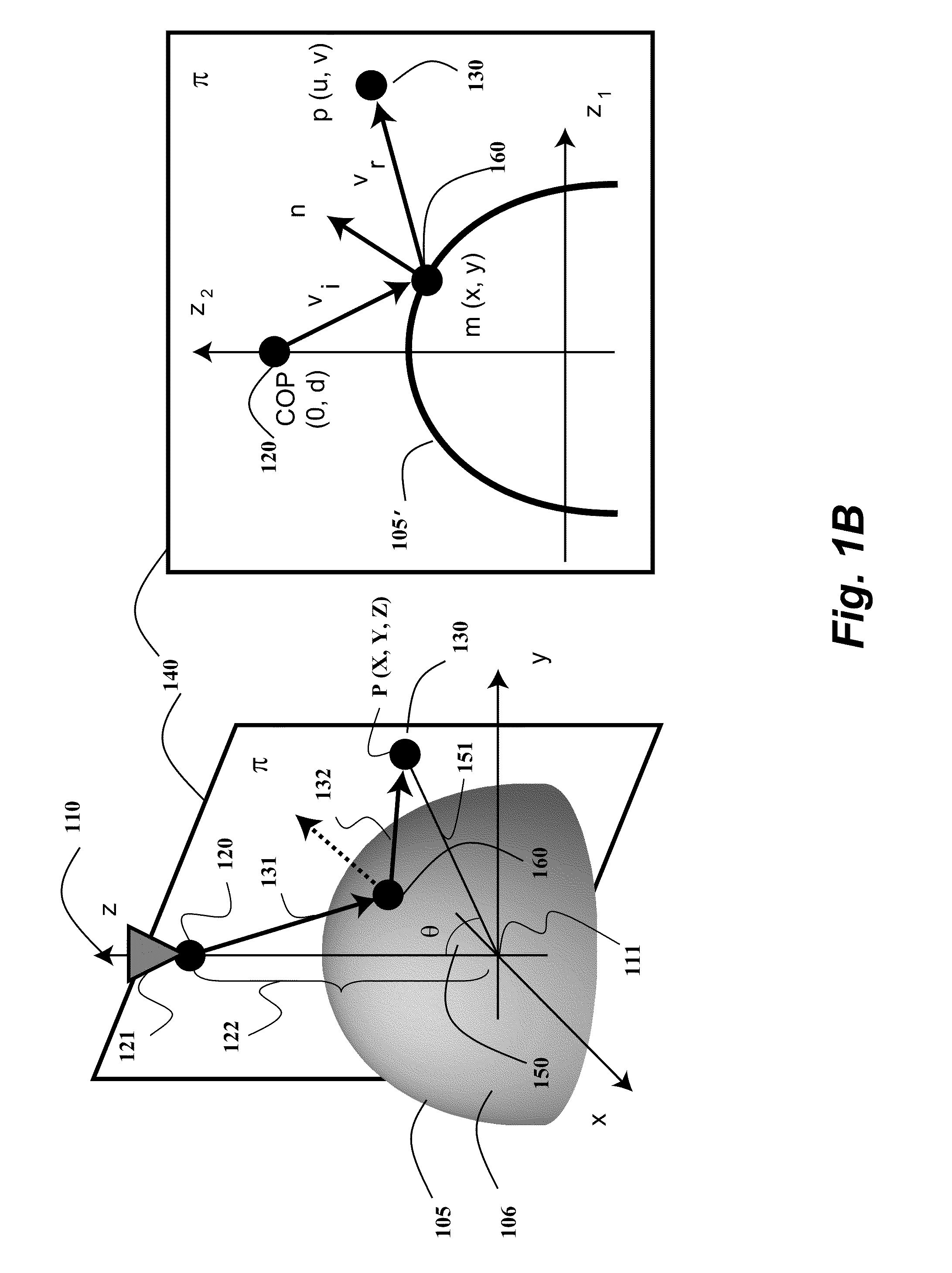
InactiveUS20120250977A1Degree of reductionImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionCatadioptric systemAxis of symmetry
A three-dimensional (3D) location of a reflection point of a ray between a point in a scene (PS) and a center of projection (COP) of a camera of a catadioptric system is determined. The catadioptric system is non-central and includes the camera and a reflector, wherein a surface of the reflector is a quadric surface rotationally symmetric around an axis of symmetry. The 3D location of the reflection point is determined based on a law of reflection, an equation of the reflector, and an equation describing a reflection plane defined by the COP, the PS, and a point of intersection of a normal to the reflector at the reflection point with the axis of symmetry.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Catadioptric system and image pickup apparatus
ActiveUS20130033635A1Good image side telecentricityGood optical performanceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCatadioptric systemIntermediate image
The catadioptric system includes a first imaging optical system collecting light from an object and a second imaging optical system causing the light from the first imaging optical system to form an intermediate image and to cause the light from the intermediate image to form an optical image. The first imaging optical system includes a first optical element including a first light transmissive portion and a first back reflective portion, and a second optical element including a second light transmissive portion and a second back reflective portion. The first light transmissive portion, the second back reflective portion, the first back reflective portion and the second light transmissive portion introduce the light from the object to the second imaging optical system. The second imaging optical system includes an aspheric lens having a negative refractive power on and around the optical axis and a positive refractive index in its peripheral portion.
Owner:CANON KK
Catadioptric system and image pickup apparatus including the system
InactiveUS20150043063A1High resolutionWide range of fieldsMicroscopesTelescopesCatadioptric systemIntermediate image
A catadioptric system includes: a catadioptric unit configured to form an intermediate image of an object; a refracting portion configured to form an image of the intermediate image; a first field lens configured to guide optical flux from the catadioptric unit to the refracting portion; and a second field lens configured to guide the optical flux from the refracting portion toward an image side. The first and the second field lenses each include a positive lens and a negative lens adjacent to each other, and wherein where νIFLp1 and νIFLn1 are respectively Abbe numbers of materials of the positive lens and the negative lens of the first field lens, and νFLp1 and νFLn1 are respectively Abbe numbers of materials of the positive lens and the negative lens of the second field lens, conditions20<νIFLp1−νIFLn1 and20<νFLp1−νFLn1are satisfied.
Owner:CANON KK
A method for homography estimation by using a common autopolar triangle of a spherical image
The invention relates to a method for homography estimation by using a public autopolar triangle of a spherical image, which comprises the following steps of: taking a sphere in space as a target, shooting two images of the sphere in the space from different positions under a parabolic catadioptric system, and fitting a mirror surface contour projection equation, a target projection equation and an antipodal sphere image equation; Secondly, respectively calculating a characteristic value and a characteristic vector of a matrix formed by the spherical image and the antipodal spherical image inthe two images; then, by matching characteristic values, three pairs of line correspondence are obtained, and the three pairs of line correspondence are three pairs of corresponding edges of the public self-polar triangle; then, connecting the intersection points of the public self-polar triangle and the quadratic curve to obtain a fourth pair of line correspondence which is correspondingly positioned in the public self-polar triangle; and finally, the four pairs of lines are correspondingly subjected to SVD decomposition to obtain a homography matrix.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method and system for determining projections in non-central catadioptric optical systems
InactiveUS8134786B2Reduce complexityCharacter and pattern recognitionComputation using non-denominational number representationAxis of symmetryCatadioptric system
Embodiment of invention discloses a system and a method for determining a three-dimensional (3D) location of a folding point of a ray between a point in a scene (PS) and a center of projection (COP) of a camera of a catadioptric system. One embodiment maps the catadioptric system, including 3D locations of the PS and the COP on a two-dimensional (2D) plane defined by an axis of symmetry of a folding optical element and the PS to produce a conic and 2D locations of the PS and COP on the 2D plane, and determines a 2D location of the folding point on the 2D plane based on the conic, the 2D locations of the PS and the COP. Next, the embodiment determines the 3D location of the folding point from the 2D location of the folding point on the 2D plane.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Method and System for Determining Projections in Non-Central Catadioptric Optical Systems
InactiveUS20120002304A1Reduce complexitySolve the blockageCharacter and pattern recognitionComputation using non-denominational number representationAxis of symmetryCatadioptric system
Embodiment of invention discloses a system and a method for determining a three-dimensional (3D) location of a folding point of a ray between a point in a scene (PS) and a center of projection (COP) of a camera of a catadioptric system. One embodiment maps the catadioptric system, including 3D locations of the PS and the COP on a two-dimensional (2D) plane defined by an axis of symmetry of a folding optical element and the PS to produce a conic and 2D locations of the PS and COP on the 2D plane, and determines a 2D location of the folding point on the 2D plane based on the conic, the 2D locations of the PS and the COP. Next, the embodiment determines the 3D location of the folding point from the 2D location of the folding point on the 2D plane.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
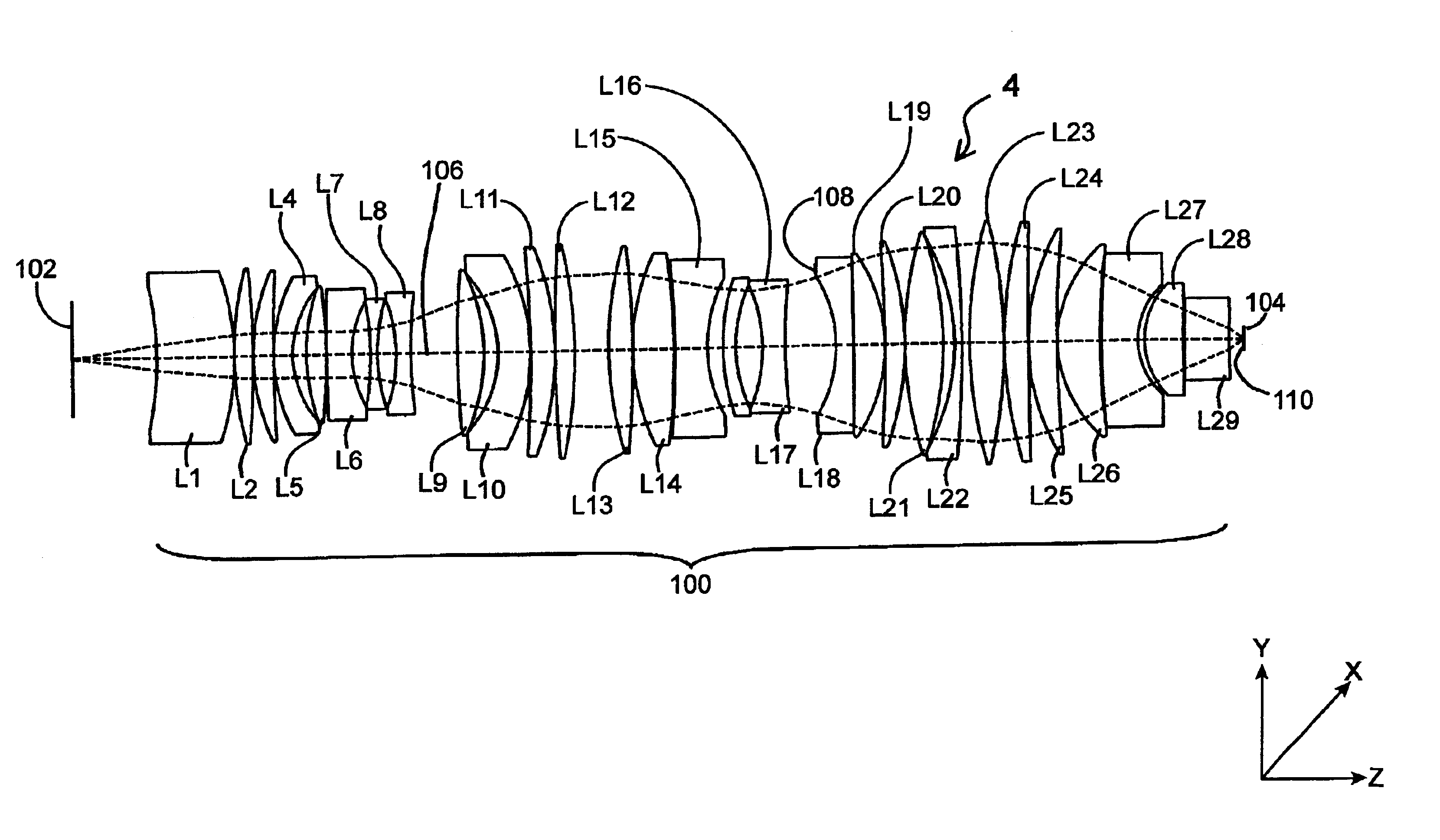
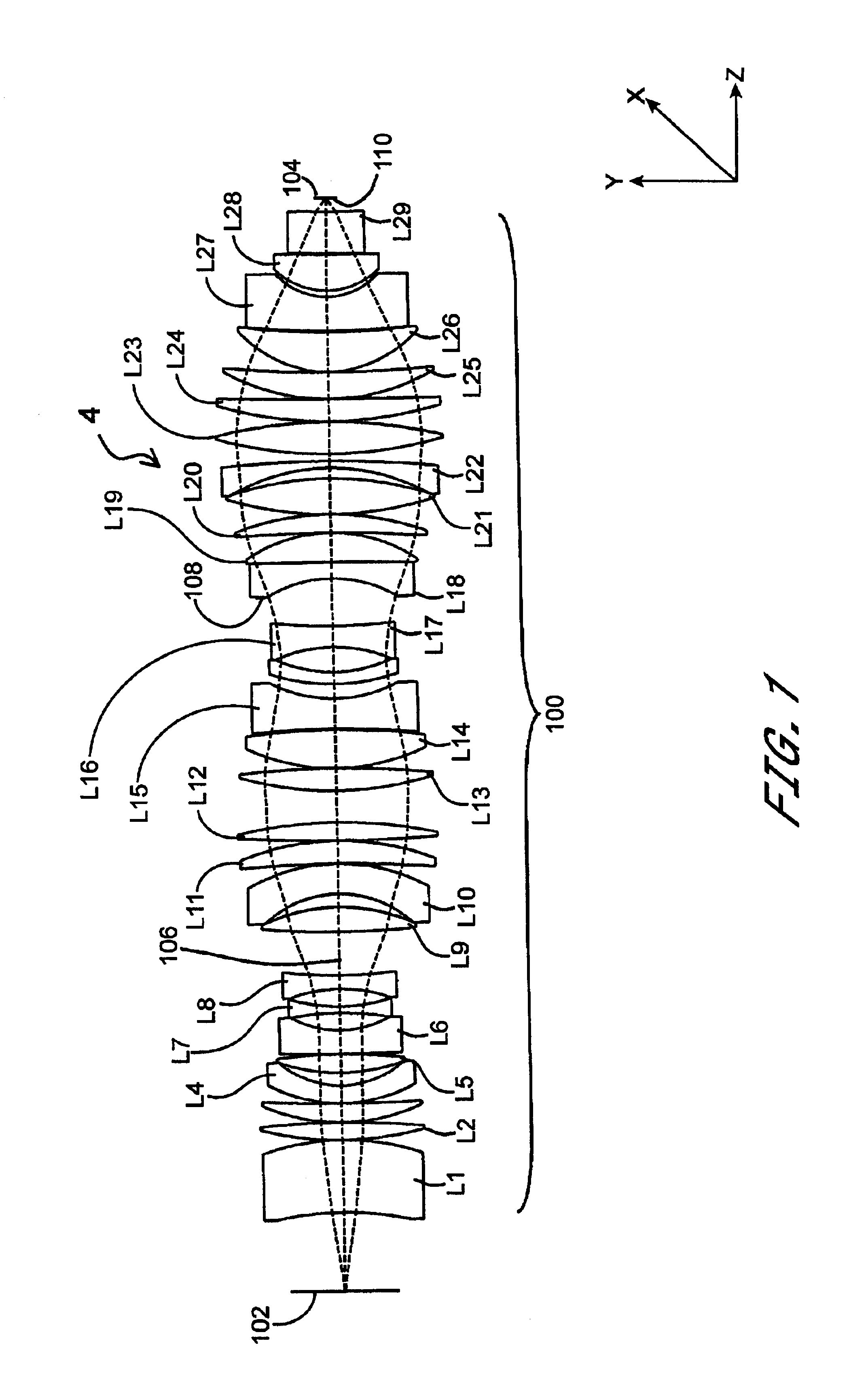
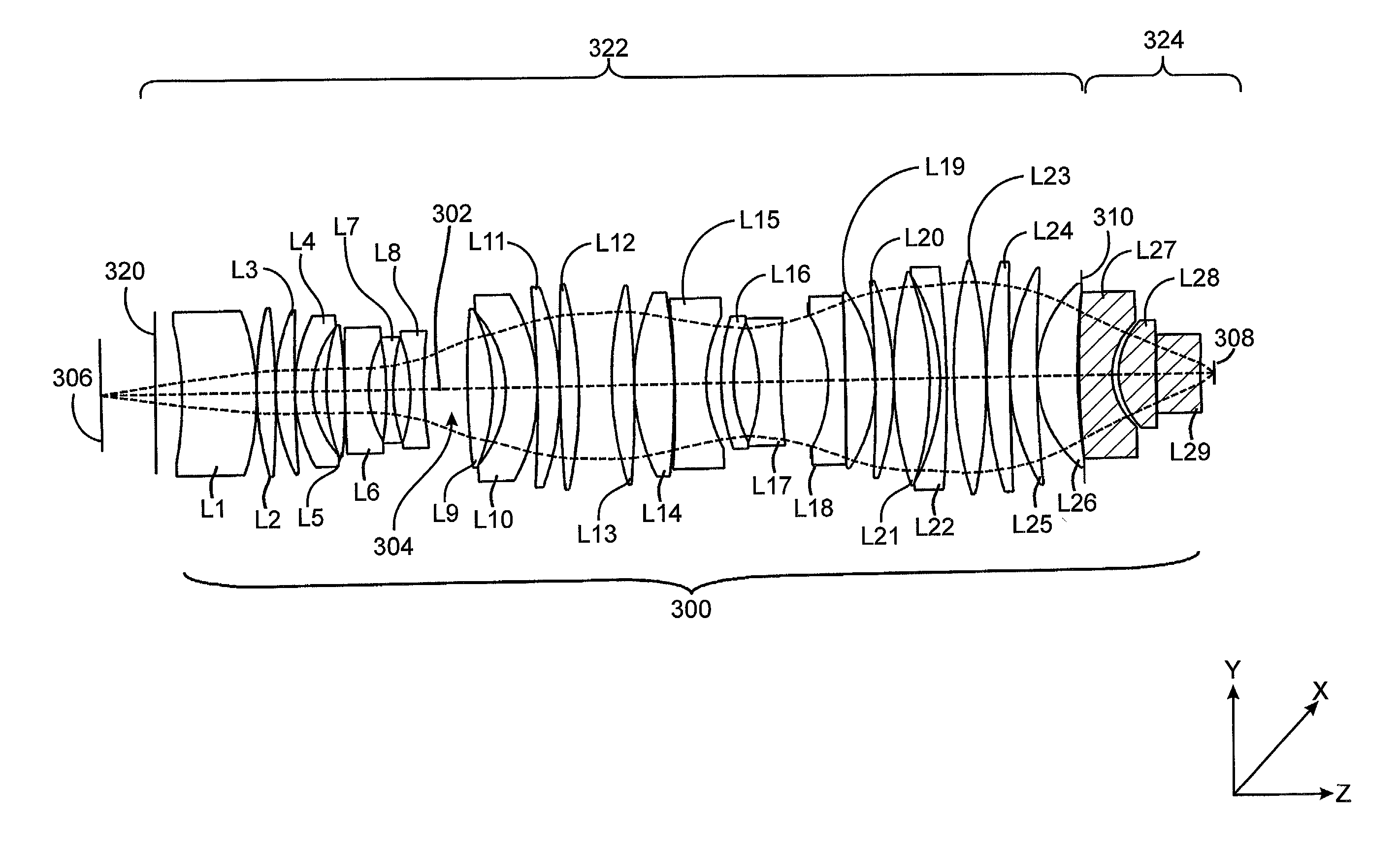
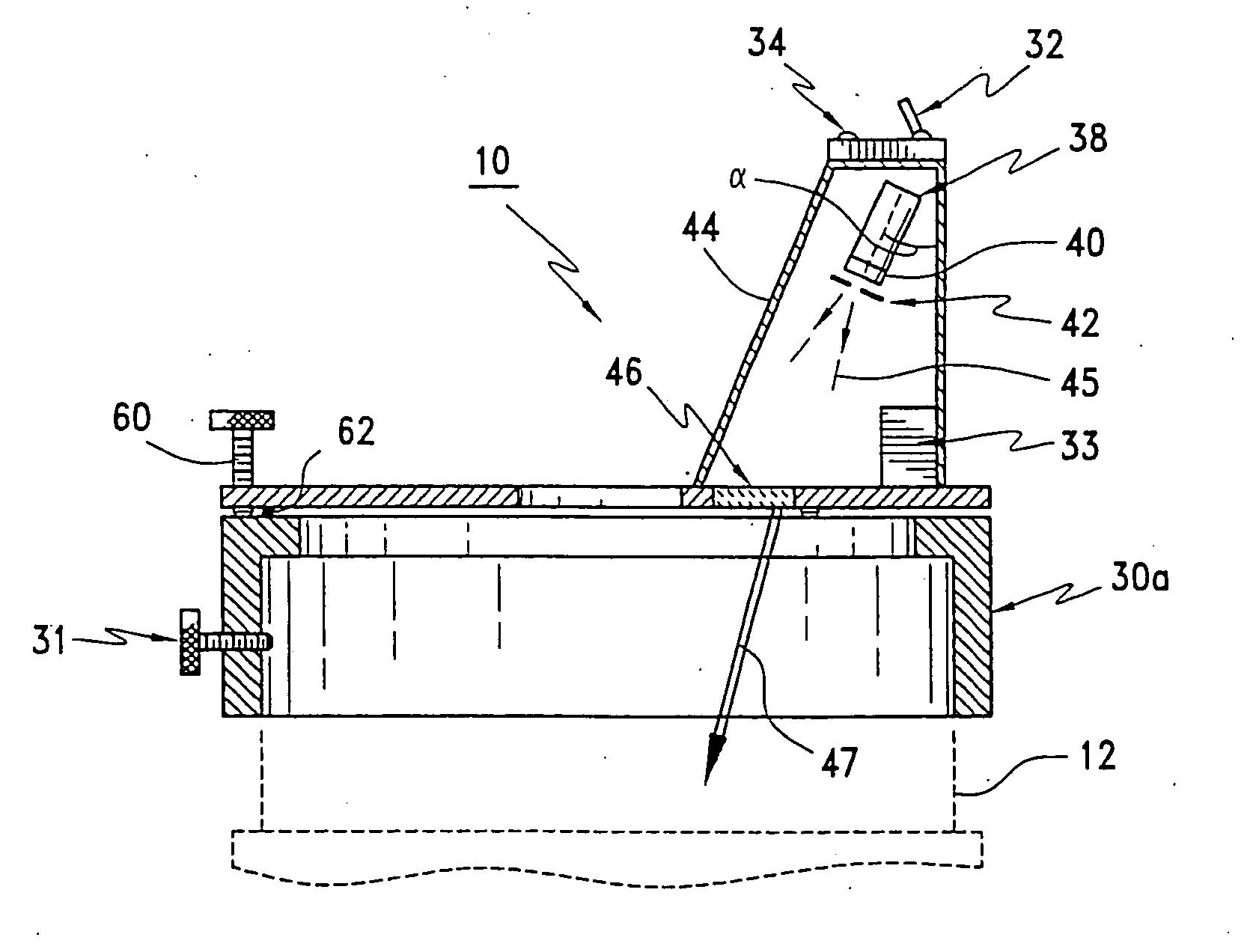
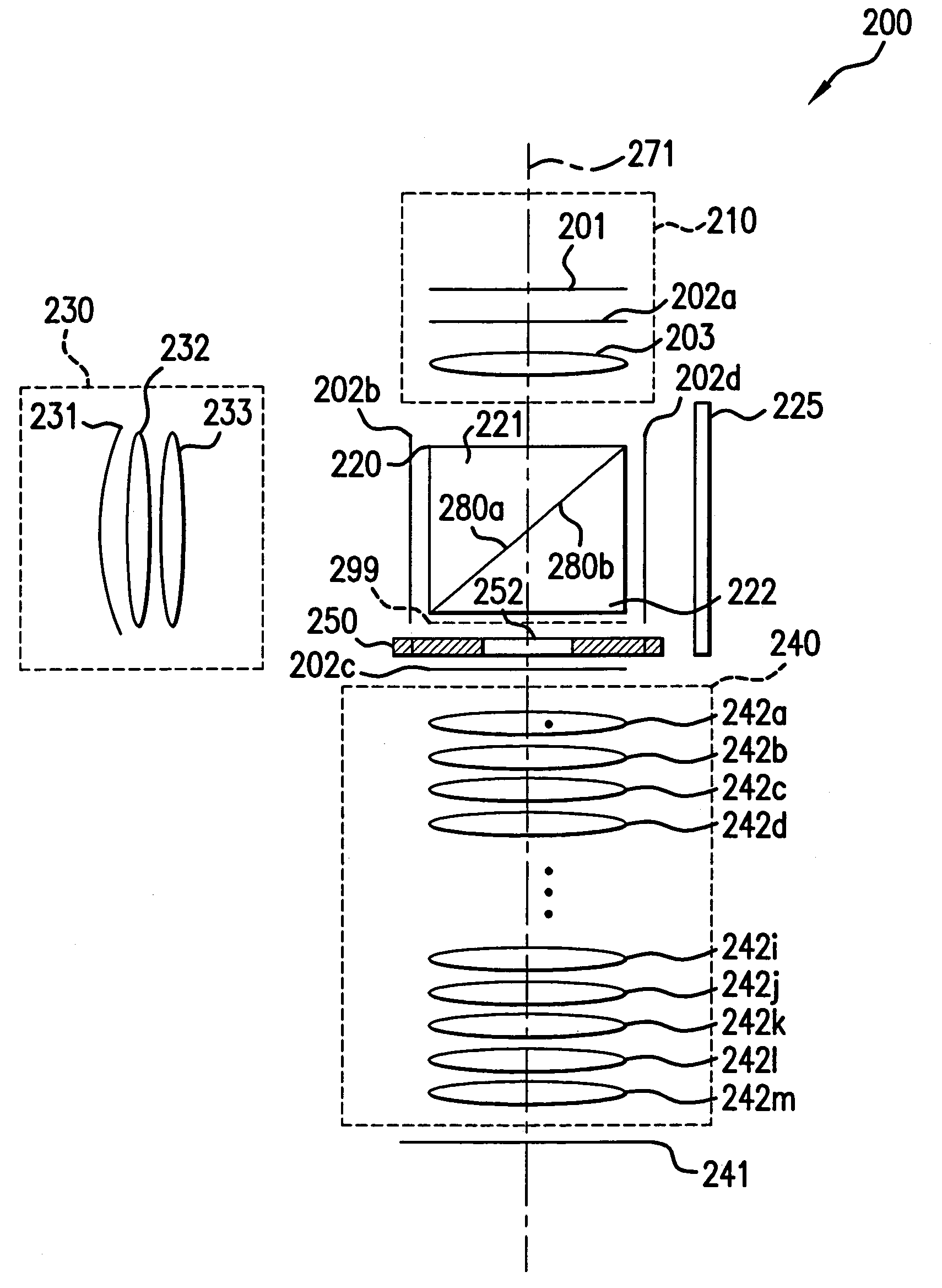
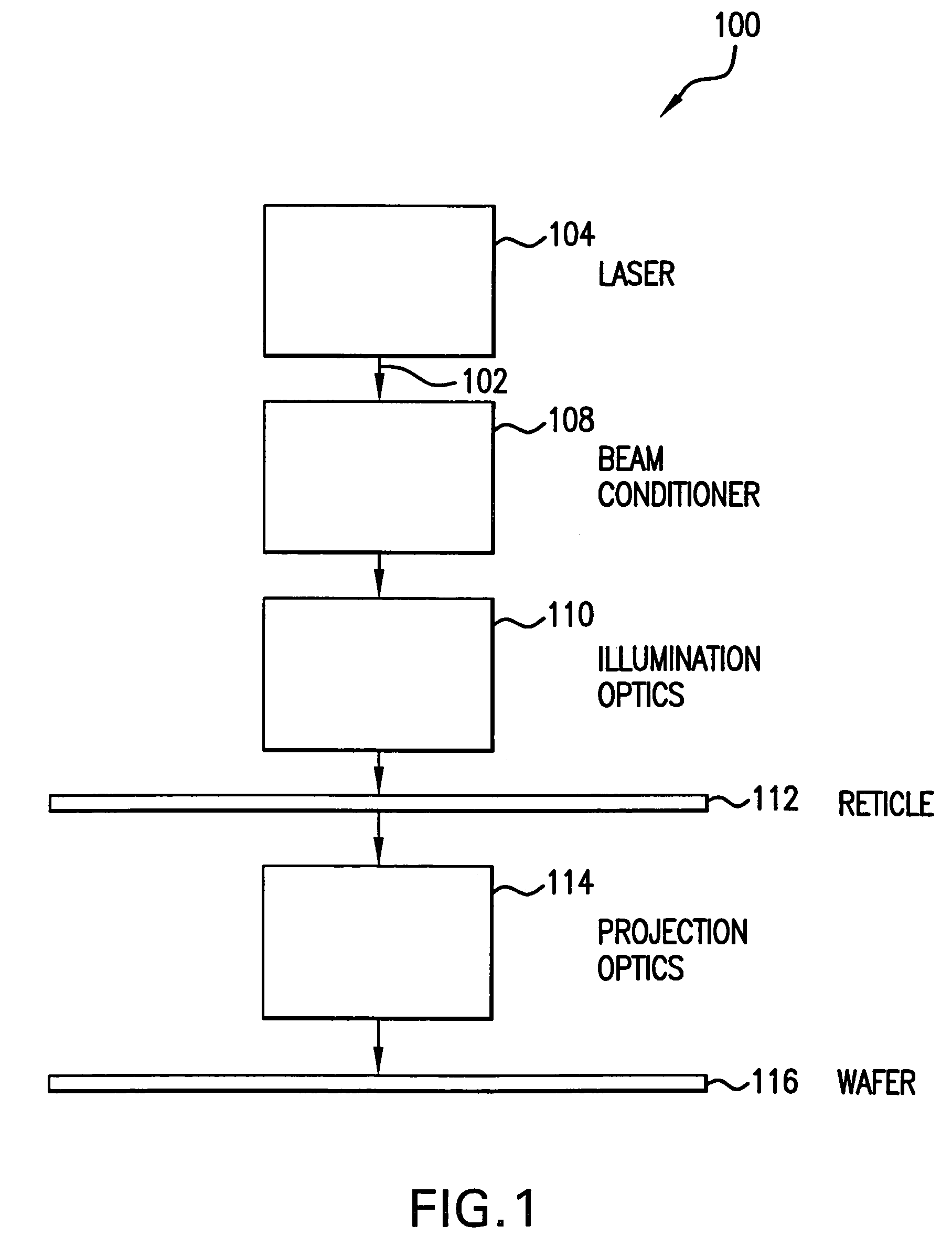
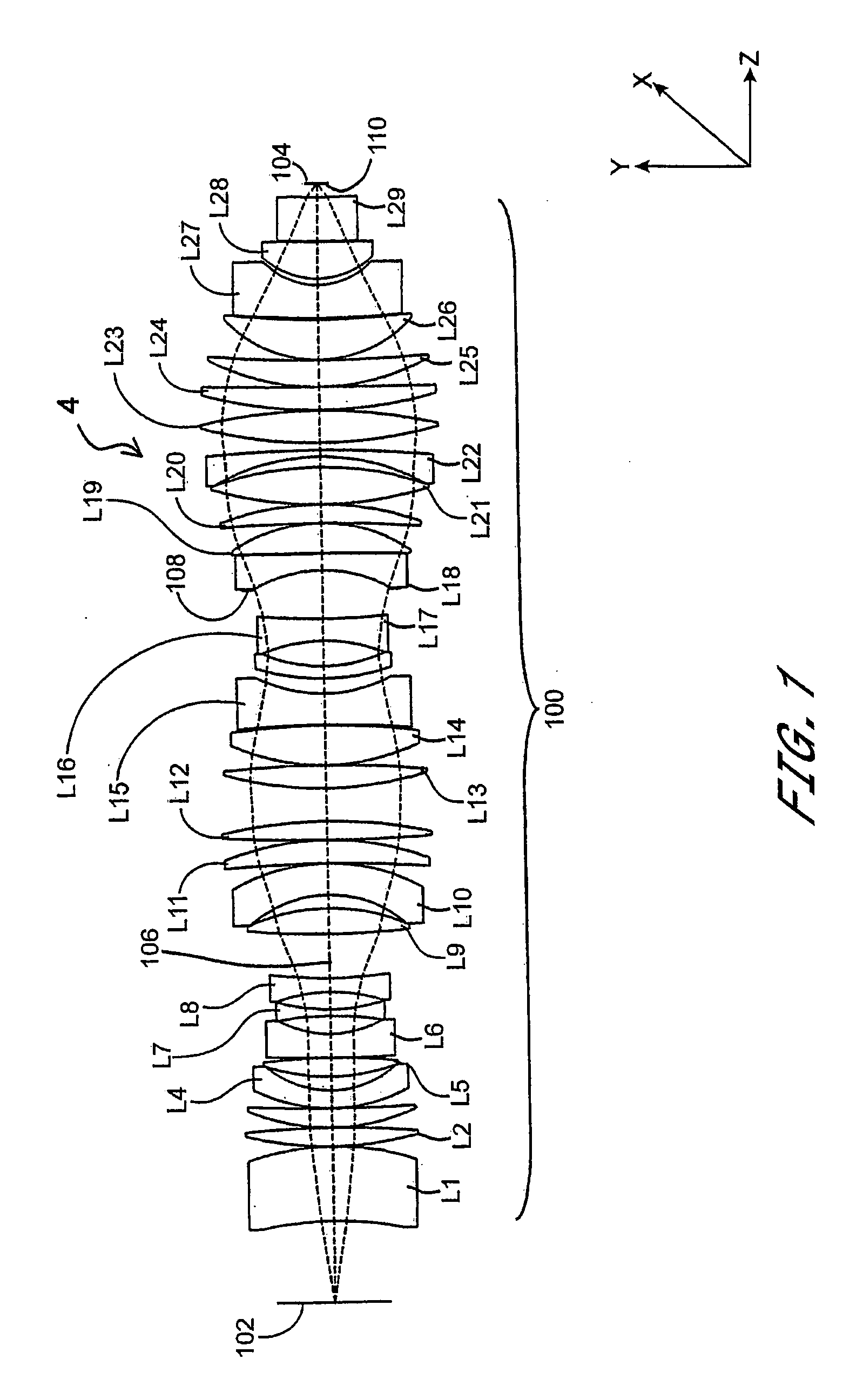
Beam-splitter optics design that maintains an unflipped (unmirrored) image for a catadioptric lithographic system
InactiveUS6972830B2Even heat distributionReduce the burden onSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPackaging automatic controlBeam splitterCatadioptric system
The present invention is a catadioptric system having a reticle optical group, a beam splitter, an aspheric mirror, a baffle plate, a folding mirror and a semiconductor wafer optical group. The reticle optical group, the beam splitter and the semiconductor wafer optical group are placed on the same beam axis, different from aspheric mirror and folding mirror axis. The light passes through an image pattern on the reticle and is reflected by the beam splitter onto the aspheric mirror. The aspheric mirror reflects the light back through the beam splitter onto the folding mirror. The folding mirror reflects the light back to the beam splitter. The beam splitter reflects the light onto the semiconductor wafer optical group. A plurality of quarter wave plates can be placed in optical paths between optical elements of the present invention to change polarization of an incoming light. Before light passes through the semiconductor wafer optical group, it passes through the baffle plate, which prevents any background scattered light caused by internal reflections within the beam splitter from entering the semiconductor wafer optical group. In another embodiment, a spacer plate is inserted into the beam splitter. The spacer plate creates an offset between reticle optical group beam axis and semiconductor wafer optical group beam axis. This reduces direct passage of light from reticle optical group to semiconductor wafer optical group.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
Structures and methods for reducing aberration in optical systems
InactiveUS20090103180A1Reduced polarization effectsLower latencyPolarising elementsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusCatadioptric systemHigh numerical aperture
An optical system includes multiple cubic crystalline optical elements and one or more polarization rotators in which the crystal lattices of the cubic crystalline optical elements are oriented with respect to each other to reduce the effects of intrinsic birefringence and produce a system with reduced retardance. The optical system may be a refractive or catadioptric system having a high numerical aperture and using light with a wavelength at or below 248 nanometers. The net retardance of the system is less than the sum of the retardance contributions of the respective optical elements. In one embodiment, all cubic crystalline optical elements are oriented with identical three dimensional cubic crystalline lattice directions, a 90° polarization rotator divides the system into front and rear groups such that the net retardance of the front group is balanced by the net retardance of the rear group. The optical system may be used in a photolithography tool to pattern substrates such as semiconductor substrates and thereby produce semiconductor devices.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
A quasi-universal compensating mirror based on deformable mirror and its design method
ActiveCN105352451BReduce design difficultyReduce processing costsUsing optical meansCatadioptric systemLaser interference
The invention relates to a universal compensation mirror based on a deformable mirror and a design method, aims to detect surface morphology of a free curved surface through laser interference and belongs to the photoelectric detection field. The compensation mirror comprises a first level compensator and a second level compensator. Through the design method, low-order aberration of the detected free curved surface is calculated by firstly utilizing a primary Seidel aberration formula, parameters of the first level compensator are acquired through employing an aberration matching and paraxial formula algorithm; a catadioptric system is established by utilizing software, and residual high-order aberration can be compensated as much as possible by utilizing the second level compensator. According to the compensation mirror and the design method, the deformable mirror is taken as the second level compensator and is for surface morphology detection on the free curved surface, so one compensator can be utilized to detect free curved surfaces in multiple types, design difficulty and processing fee of compensators can be reduced to a maximum degree, moreover, through the compensation detection method, the structure is simple, introduced error sources are reduced, early-stage calibration adjustment is easy, and instantaneous and high precision surface morphology measurement can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
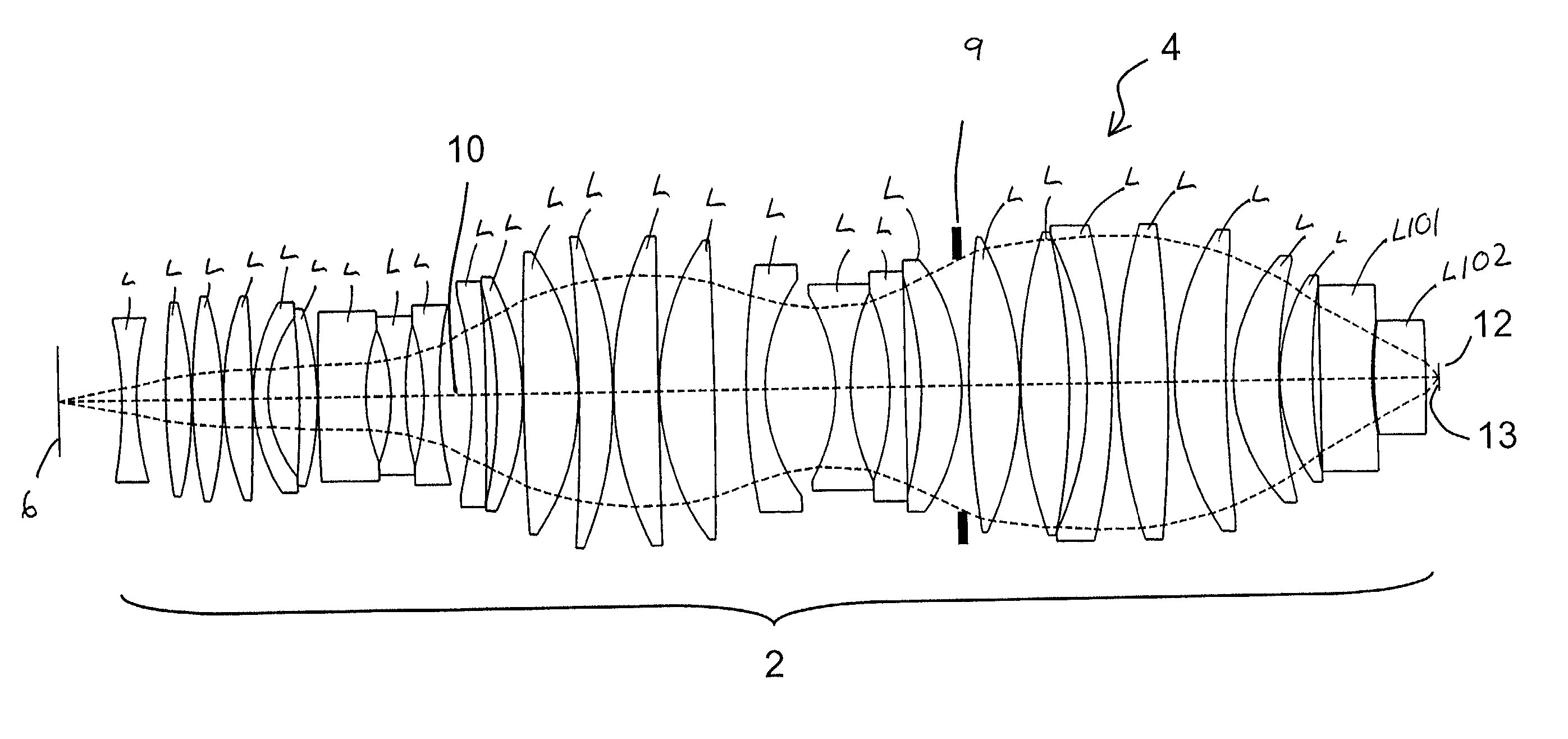
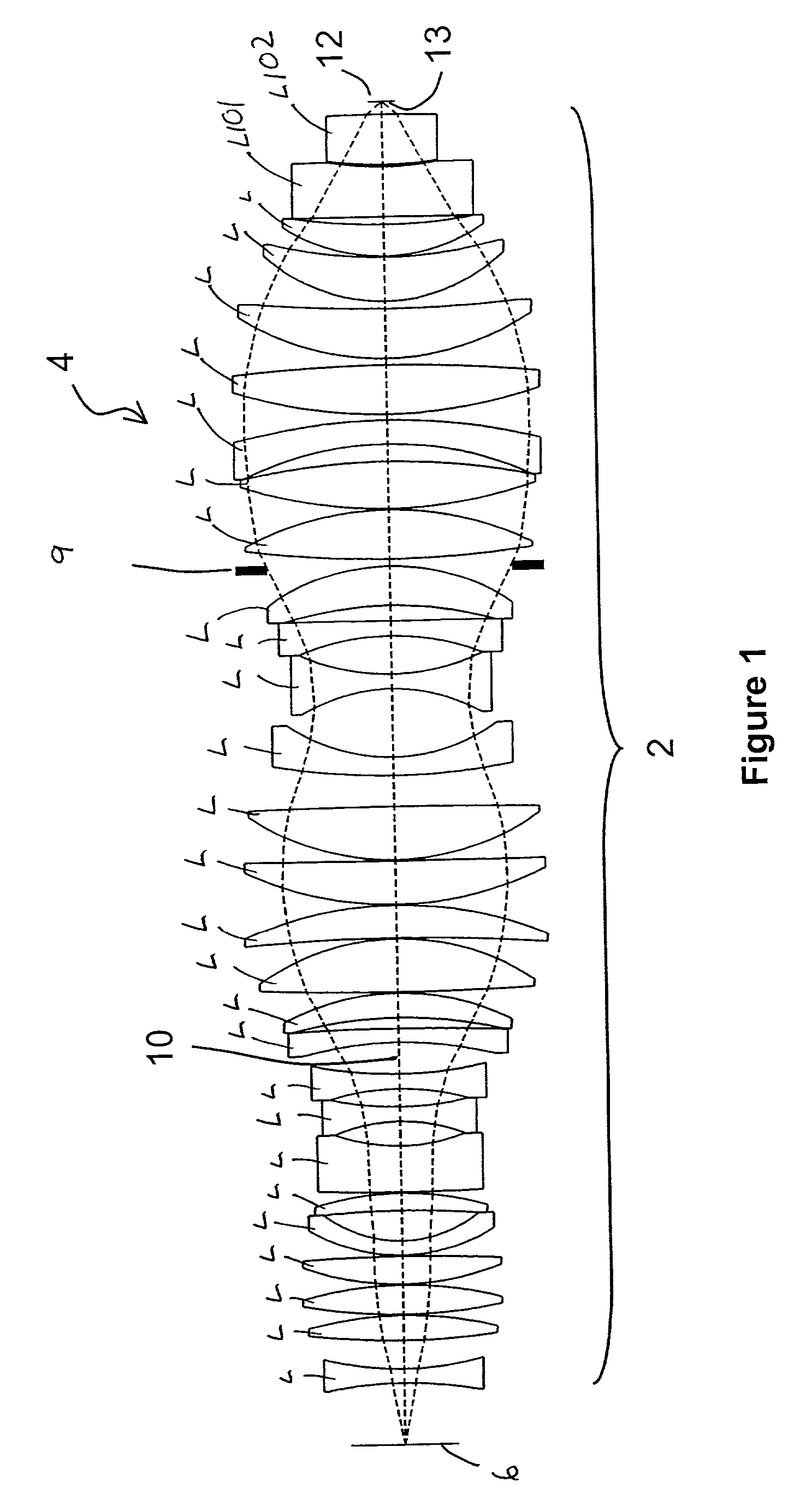
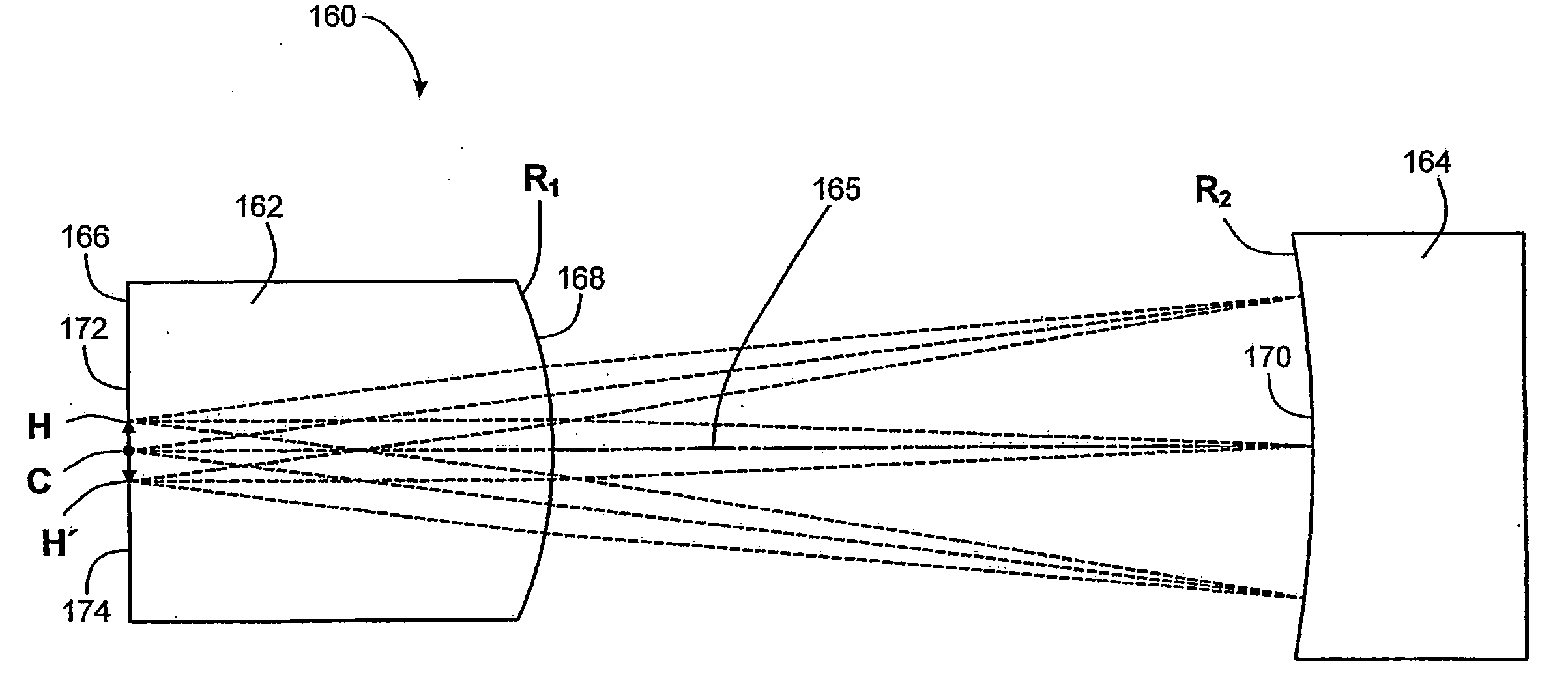
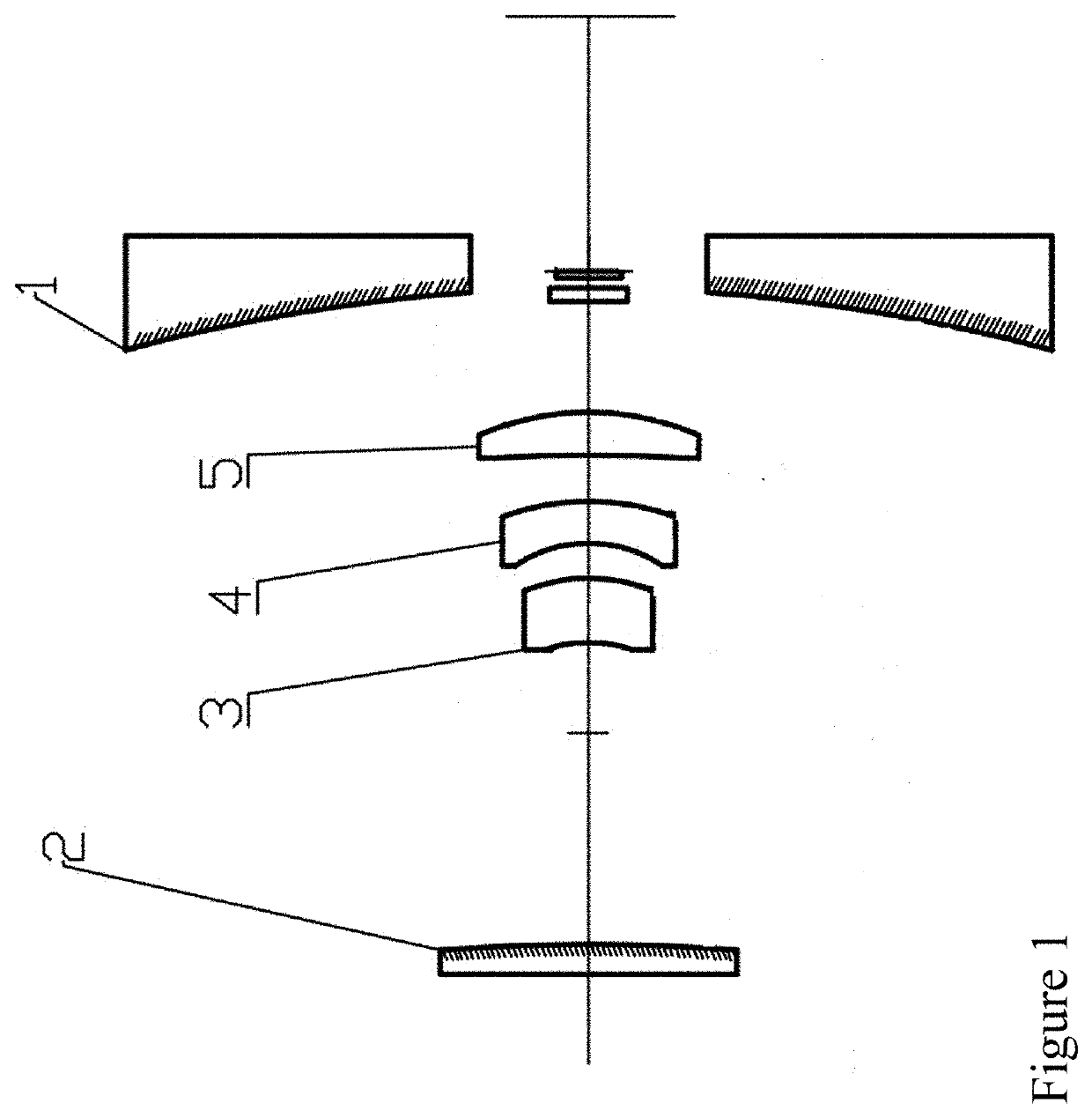
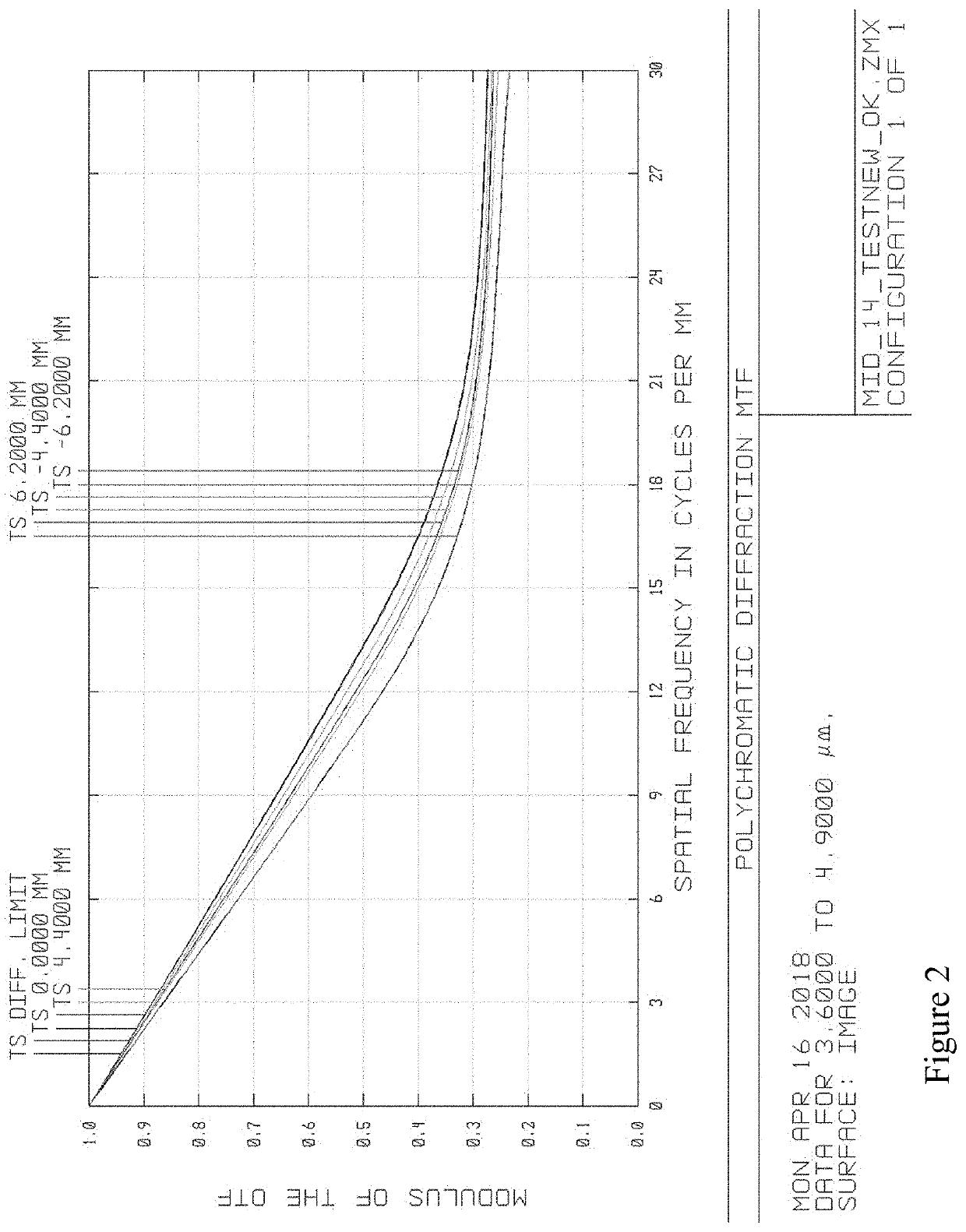
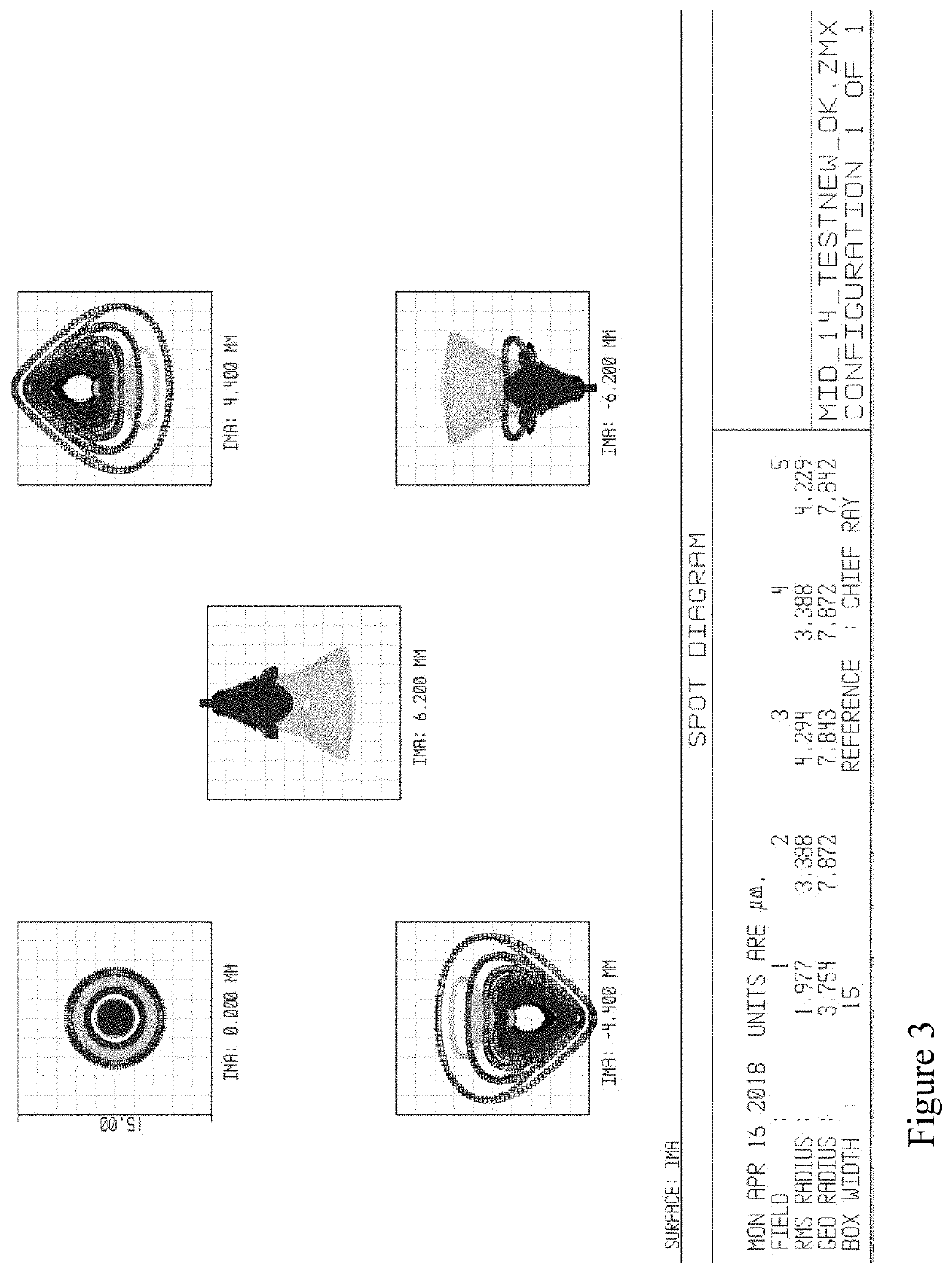
Catadioptric System for Mid-Wave Thermal Imaging Equipment
The invention proposed the catadioptric system, which consists of two main components: the first component comprising the two reflective mirrors, in which surface distortion of mirror 1 is parabolic, surface distortion of mirror 2 is aspheric; the second component is a relay consisting of three lenses: lens 1, lens 2, and lens 3 arranged after the medial image plane correspondingly; it plays an important role in fixing the pupil's position to match the position of the cold shield of the sensor and eliminating absolutely the aberration to ensure receiving good quality image at the sensor plane.
Owner:VIETTEL GRP
Catadioptric optical system with multi-reflection element for high numerical aperture imaging
A catadioptric system includes a first catadioptric group, a second catadioptric group, and a lens group disposed in axial alignment with each other. The first catadioptric group includes a solid lens having an input surface, a primary reflective surface, secondary reflective surface and an exit surface. The primary reflective surface is a curved surface concave towards the secondary reflective surface. A light flux entering through the input surface undergoes more than two reflections between the primary and secondary reflective surfaces, prior to exiting through the exit surface. At least one of the primary reflective surface and secondary reflective surface has a continuous and smooth topological profile.
Owner:CANON KK +1
Device for taking long-distance images
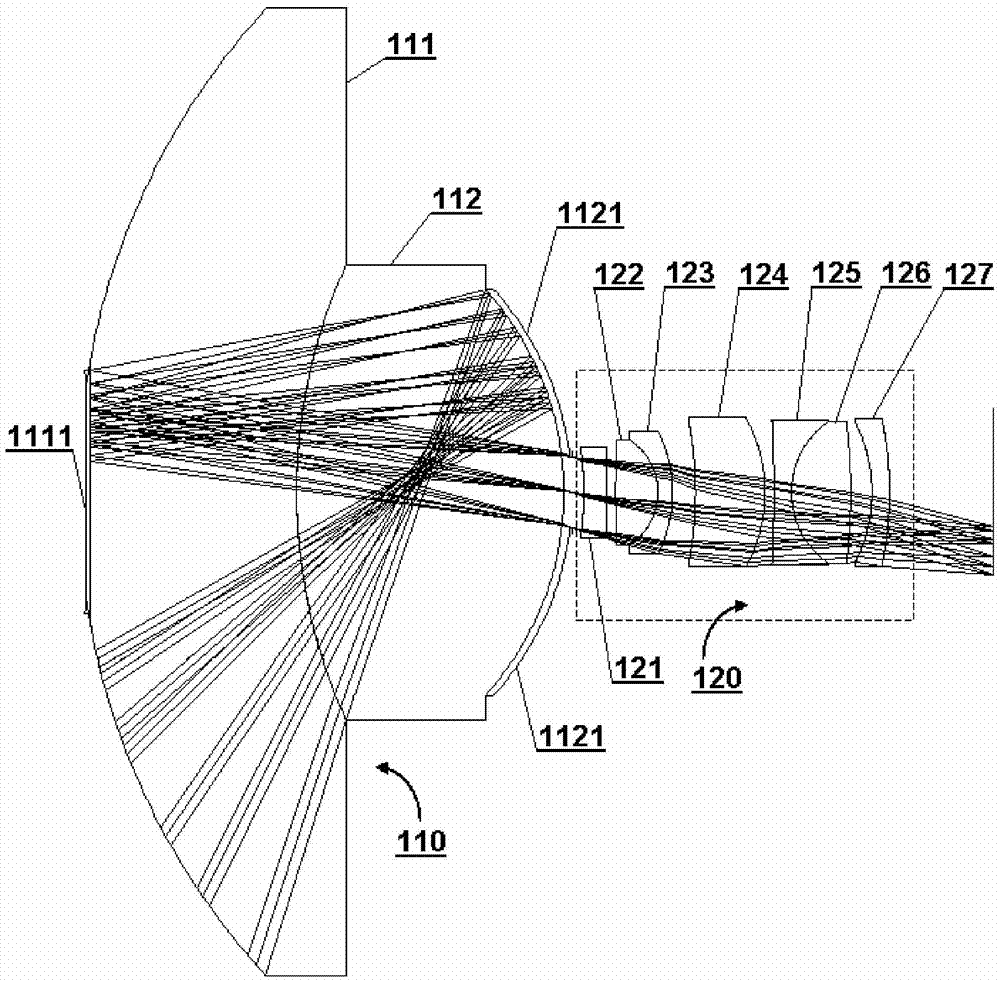
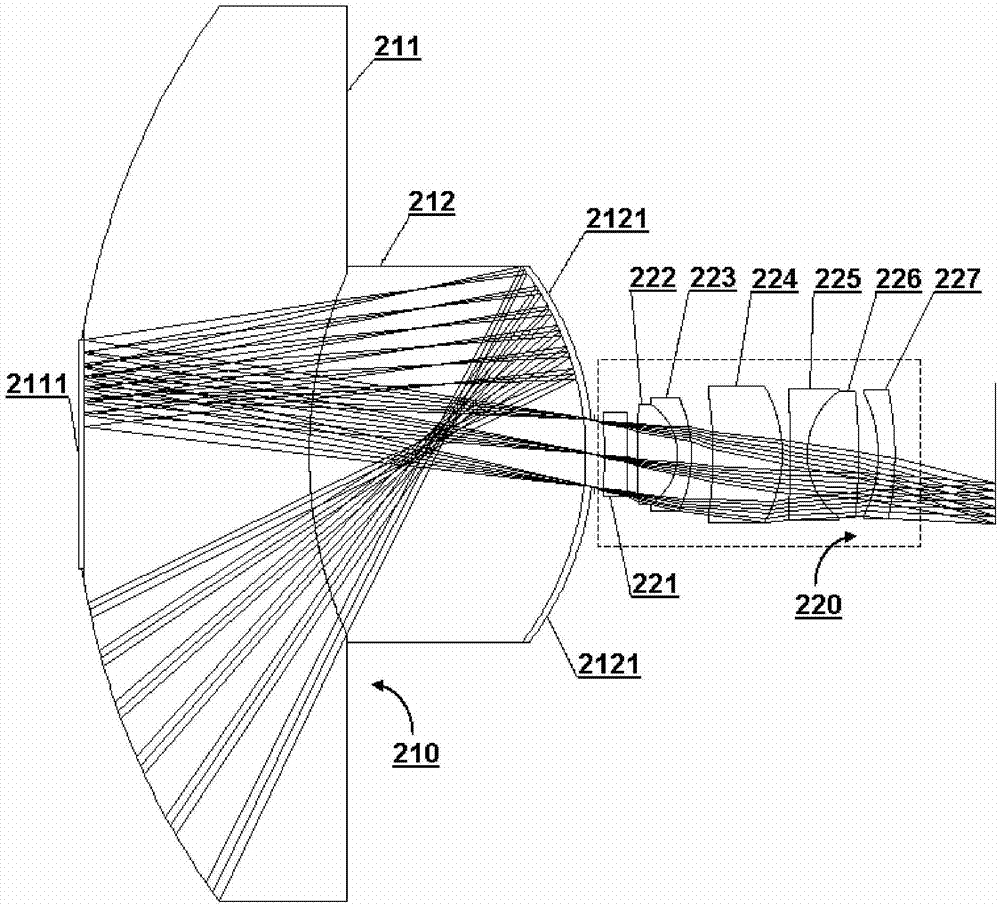
ActiveUS20130141608A1Reduce axial sizeLong focal lengthTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCatadioptric systemLight beam
A device for taking long-distance images includes, successively: a catadioptric optical system and an optical system to shape the beam positioned close to the first image generated by the catadioptric system, which adjusts the exit aperture of the catadioptric system on a second image of the aperture in an image space of a variable focal length optical system. The catadioptric optical system and the optical system to shape the beam generates a third image of the observed scene. A focal plane is superposed over an image plane of the catadioptric optical system and the optical system to shape the beam. A projection lens receives the light beam output by the variable focal length system and forms a fourth image of the observed scene at the focal plane of the projection lens. An image sensor is positioned at the focal plane of the projection lens.
Owner:SYT TECH
Catadioptric system and image pickup apparatus equipped with same
InactiveUS20130063650A1Television system detailsColor television detailsCatadioptric systemOptical axis
A catadioptric unit includes, in order from an object side to an image side, a first optical element including a first transmissive unit having positive refractive power disposed in the vicinity of an optical axis and, on the object side thereof, a first reflective unit disposed at an outer circumference relative to the first transmissive unit and having a reflective surface; and a second optical element including a second transmissive unit having negative refractive power in the vicinity of the optical axis and, on the image side thereof, a second reflective unit disposed at an outer circumference relative to the second transmissive unit and having a reflective surface. Radii of curvature of object-side and image-side surfaces of the second optical element, a thickness along the optical axis and a refractive index of a material of the second optical element are set to satisfy predetermined conditions.
Owner:CANON KK
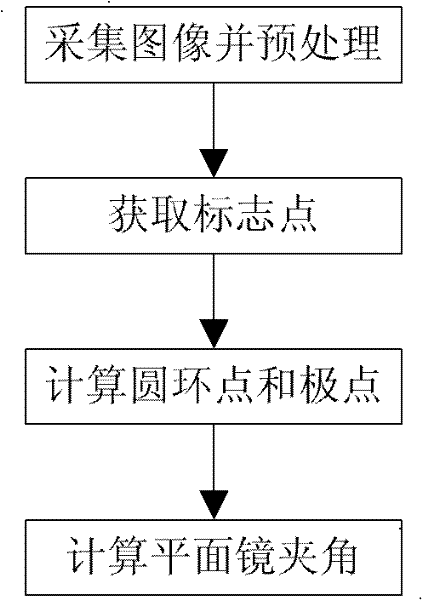
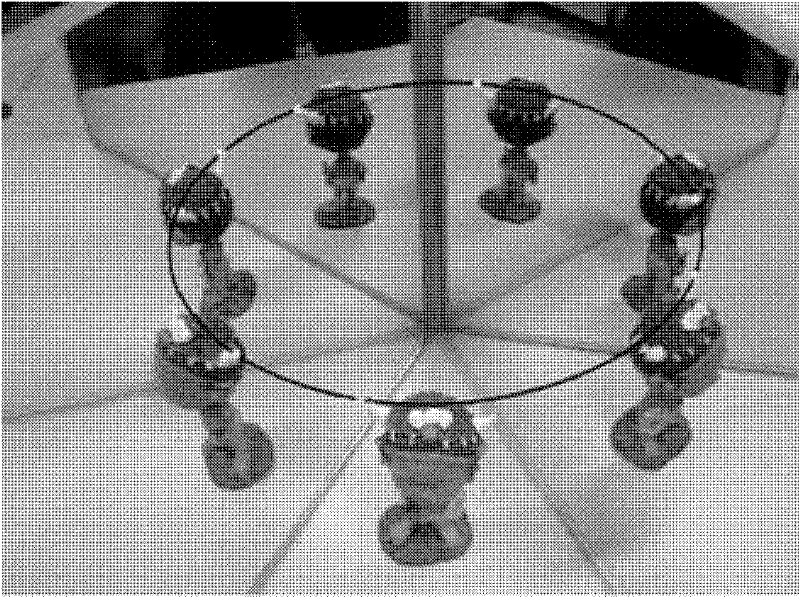
Measurement method of plane mirror included angle in multiplane-mirror catadioptric system
InactiveCN102226691ASolve the problem of difficult angle measurementHigh precisionUsing optical meansCatadioptric systemPlane mirror
The invention provides a measurement method of a plane mirror included angle in a multiplane-mirror catadioptric system. Technical schemes of the invention comprise the following steps: by using the multiplane mirrors and a monocular camera, establishing a data acquisition system, calibrating a shooting angle and a diaphragm of a real camera and collecting data of an object in a shooting area; acquiring marking points through adopting a threshold method; acquiring center positions of the marking points by using an area gap filling method; elliptically fitting the obtained marking points; calculating the position of circle points by using an ellipse; calculating pole positions by using a limit-restraint technology; finally acquiring the plane mirror included angle by using the poles and the circle points. In the traditional multiplane-mirror catadioptric system, the plane mirror included angle is difficult to be measured because of utilization of a plurality of plane mirrors. By using the method of the invention, the above problem can be solved, calibration precision of the monocular camera can be raised so that accuracy of three-dimensional scene reconstruction and stability of system can be improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com