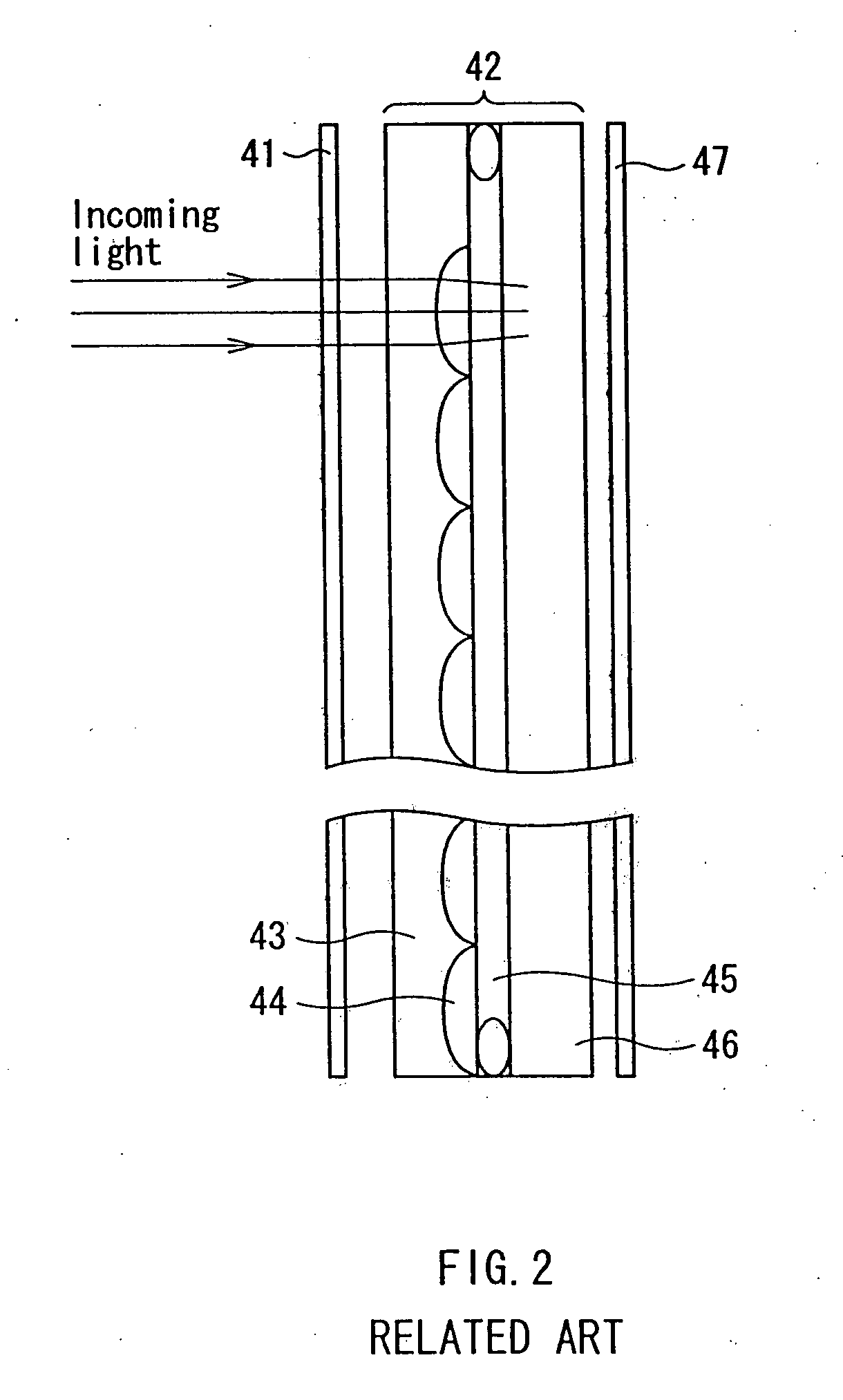
Patents
Literature
63 results about "Crystal optics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Crystal optics is the branch of optics that describes the behaviour of light in anisotropic media, that is, media (such as crystals) in which light behaves differently depending on which direction the light is propagating. The index of refraction depends on both composition and crystal structure and can be calculated using the Gladstone–Dale relation. Crystals are often naturally anisotropic, and in some media (such as liquid crystals) it is possible to induce anisotropy by applying an external electric field.
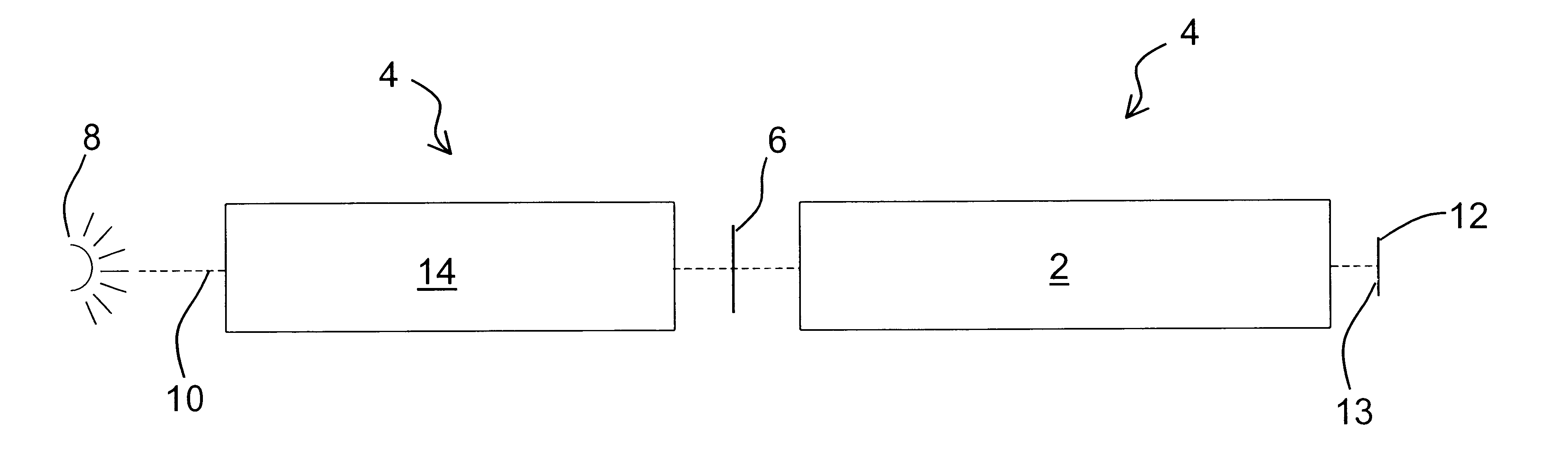
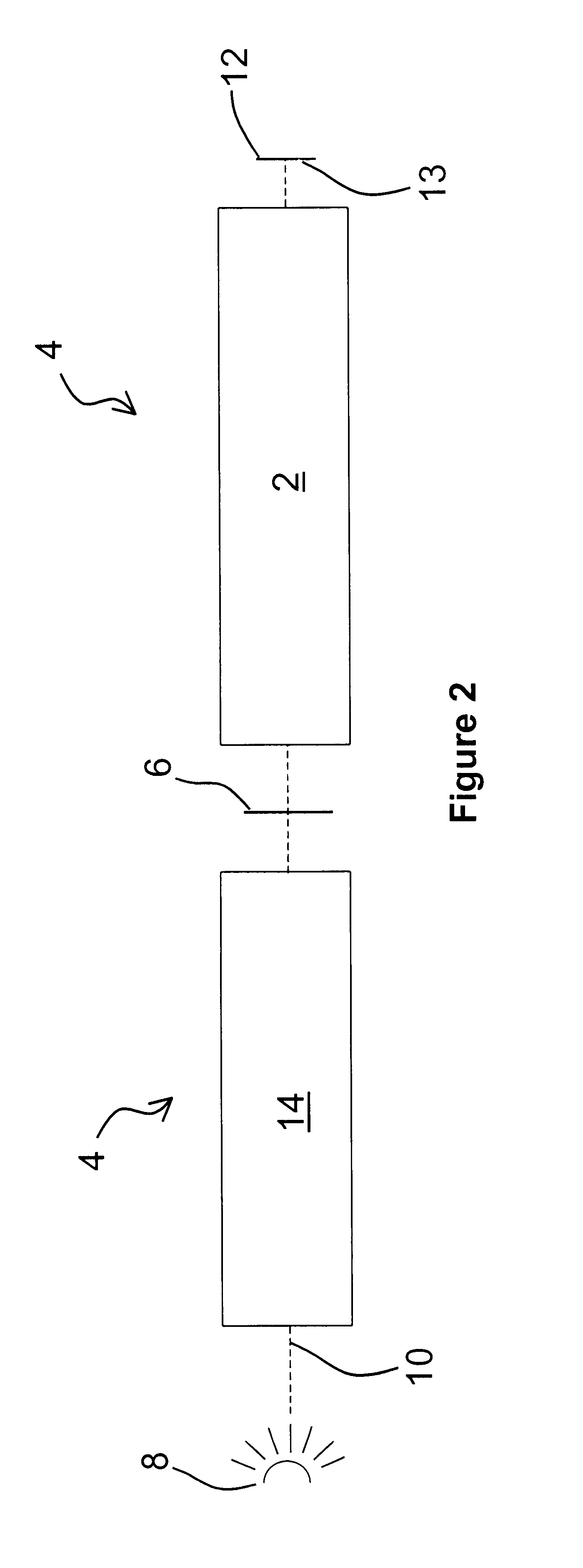
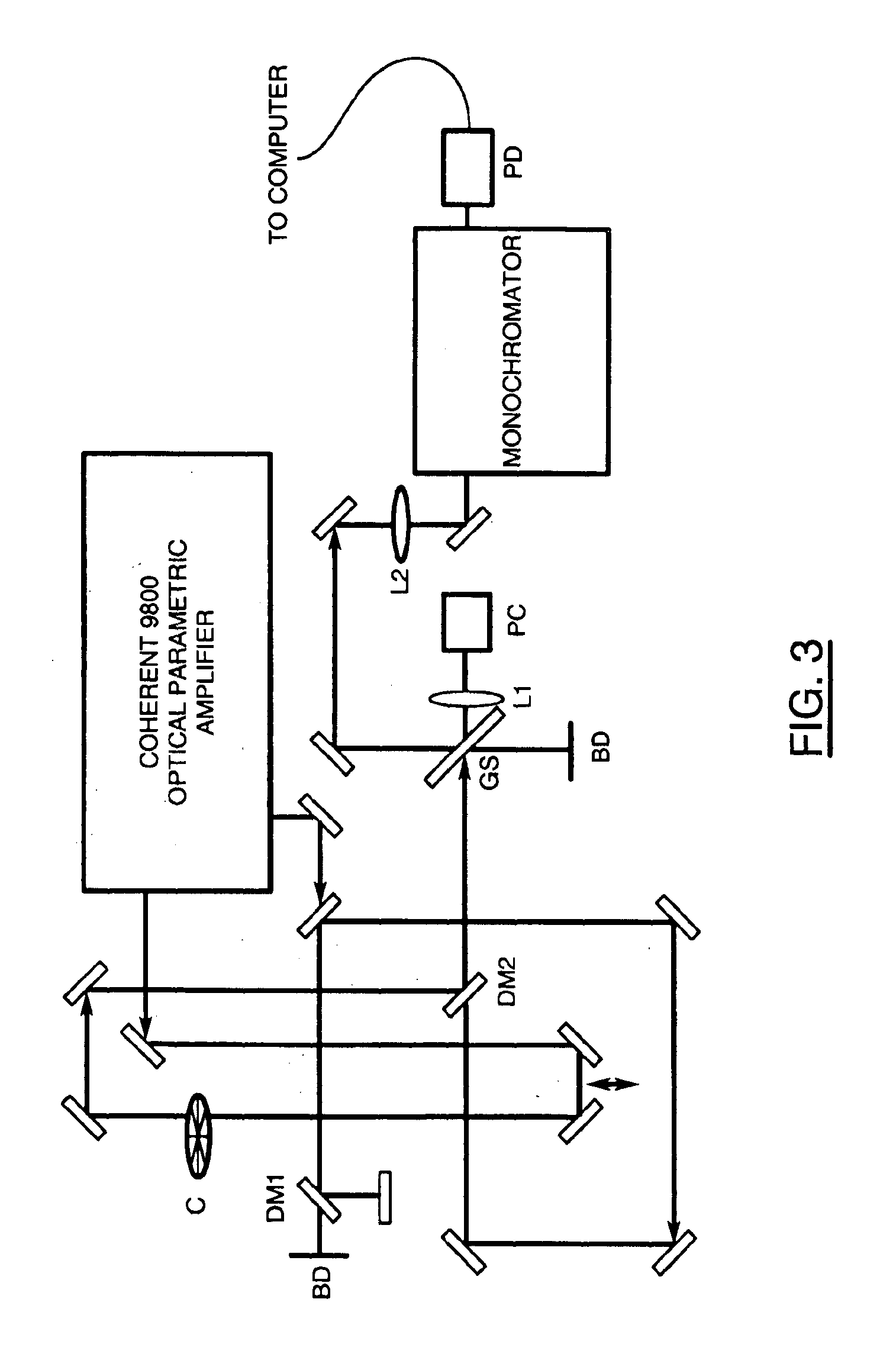
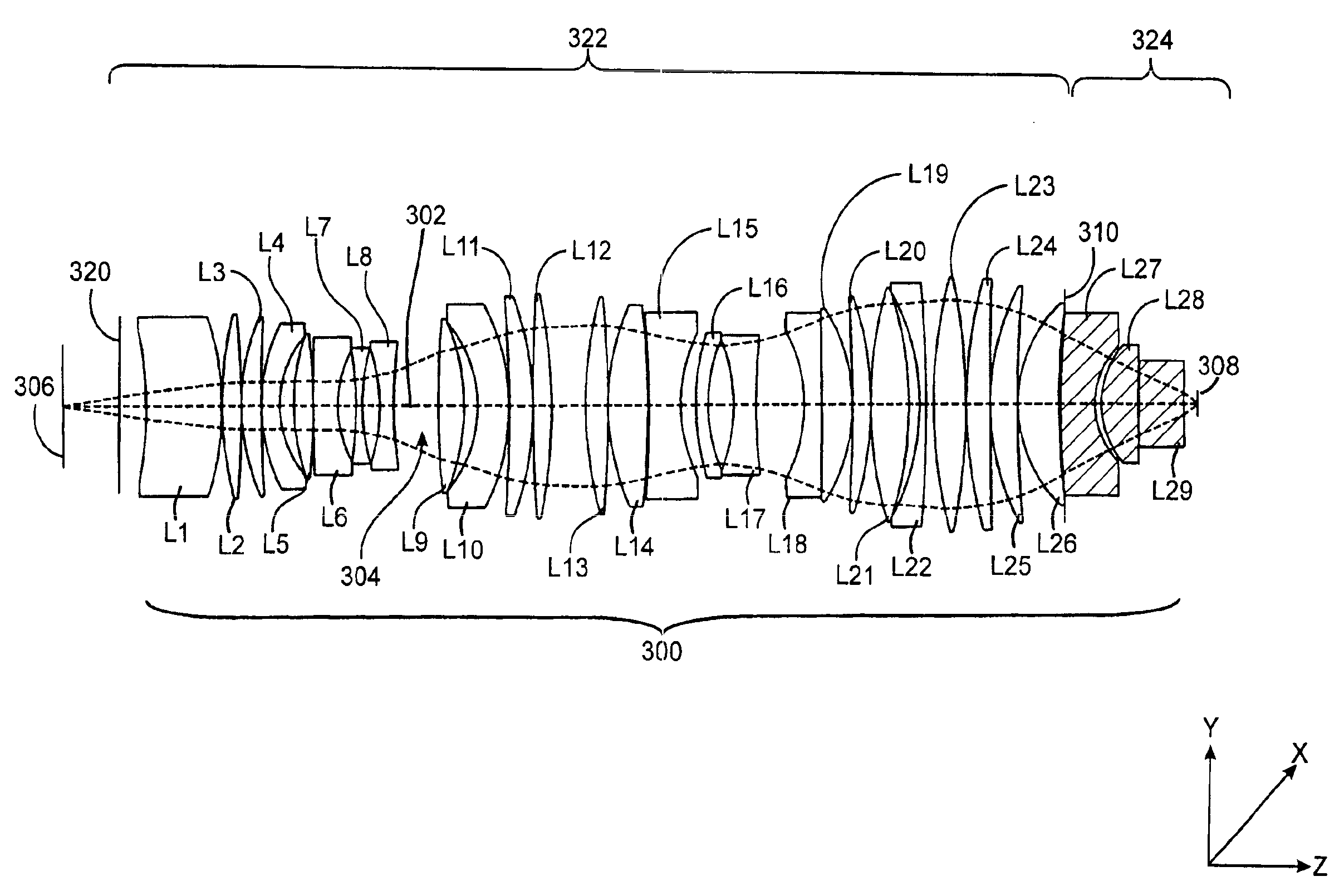
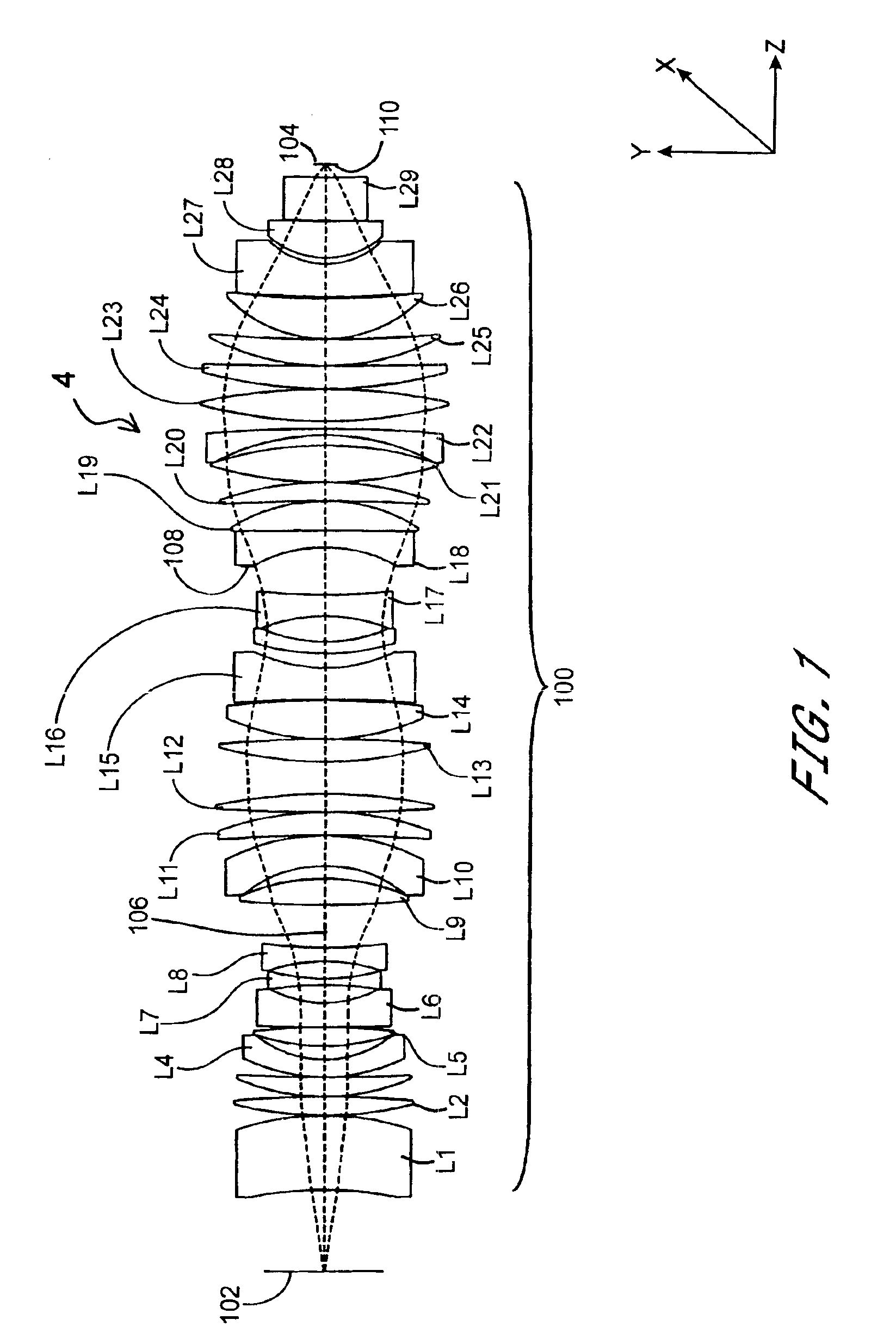
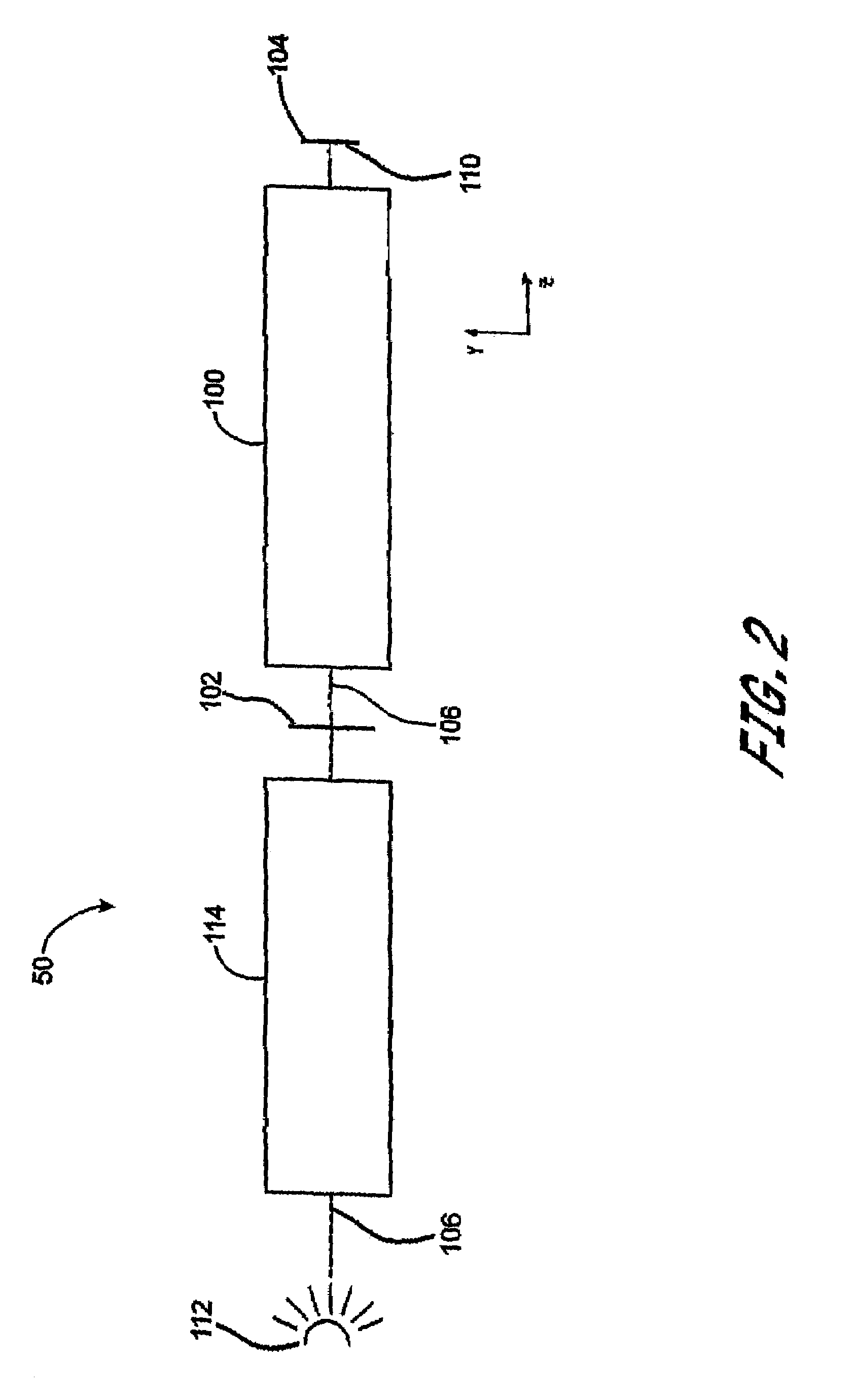
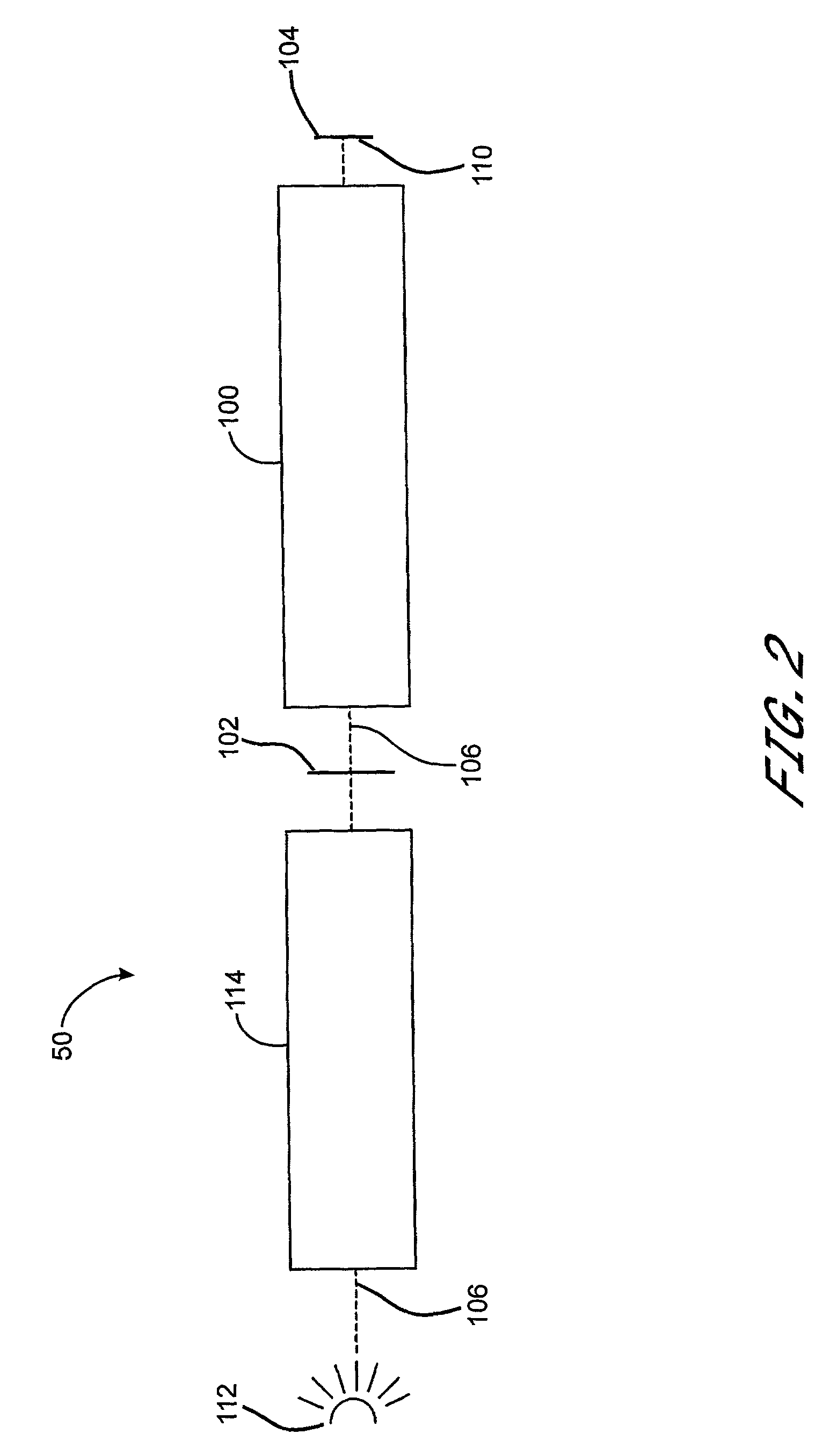
Correction of birefringence in cubic crystalline optical systems
InactiveUS6683710B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusCatadioptric systemWavefront aberration
An optical system includes multiple cubic crystalline optical elements aligned along a common optical axis and having their crystal lattices oriented with respect to each other to minimize the effects of intrinsic birefringence and produce a system with reduced retardance. The optical system may be a refractive or catadioptric system having a high numerical aperture and using light with a wavelength at or below 248 nanometers. The net retardance of the system is less than the sum of the retardance contributions of the respective optical elements as the elements are oriented such that the intrinsic birefringences of the individual elements cancel each other out. In one embodiment, two [110] cubic crystalline optical elements are clocked with respect to one another and used in conjunction with a [100] cubic crystalline optical element to reduce retardance. Various birefringent elements, wave plates, and combinations thereof provide additional correction for residual retardance and wavefront aberrations. The optical system may be used in a photolithography tool to pattern substrates such as semiconductor substrates and thereby produce semiconductor devices.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
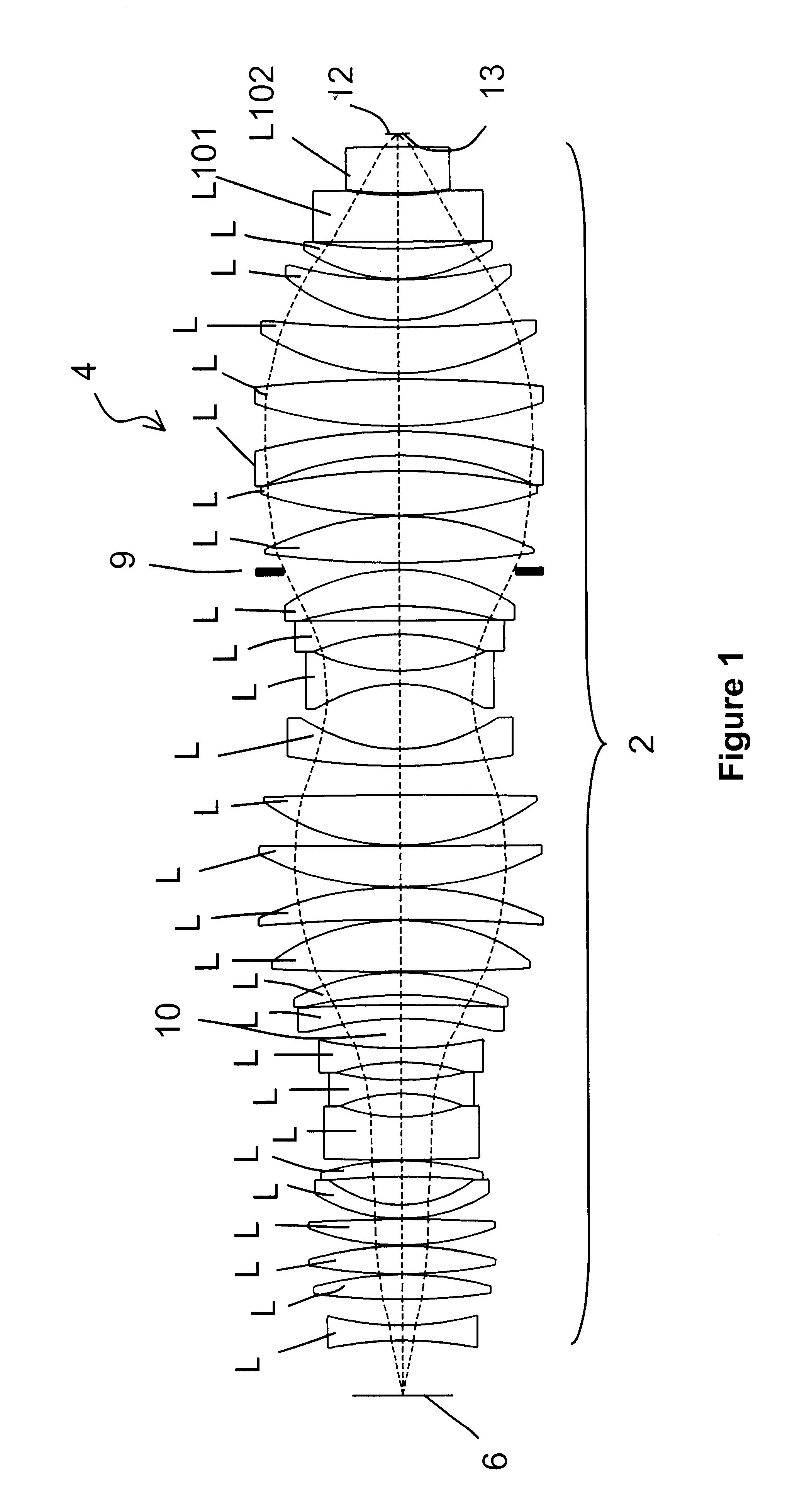
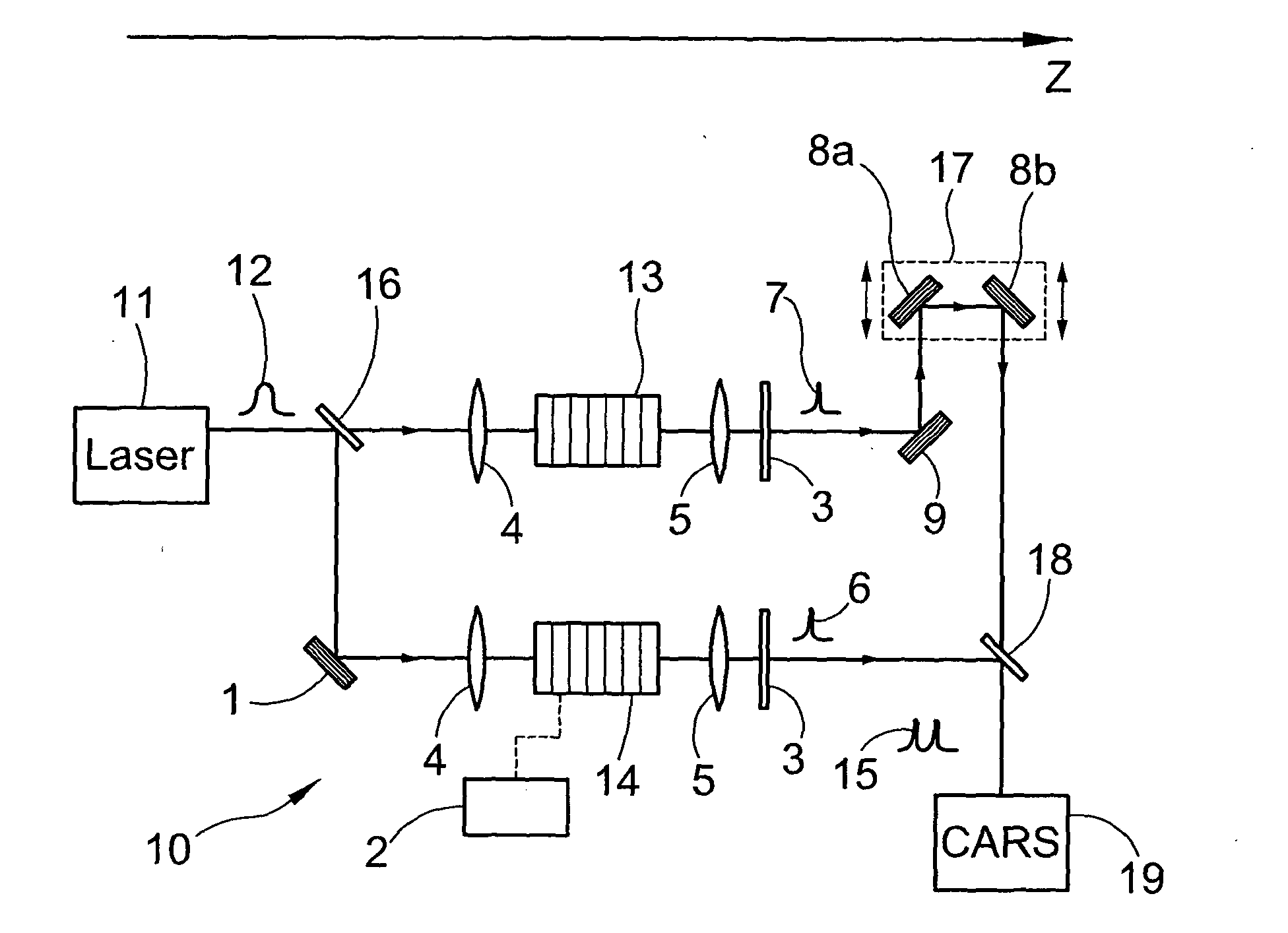
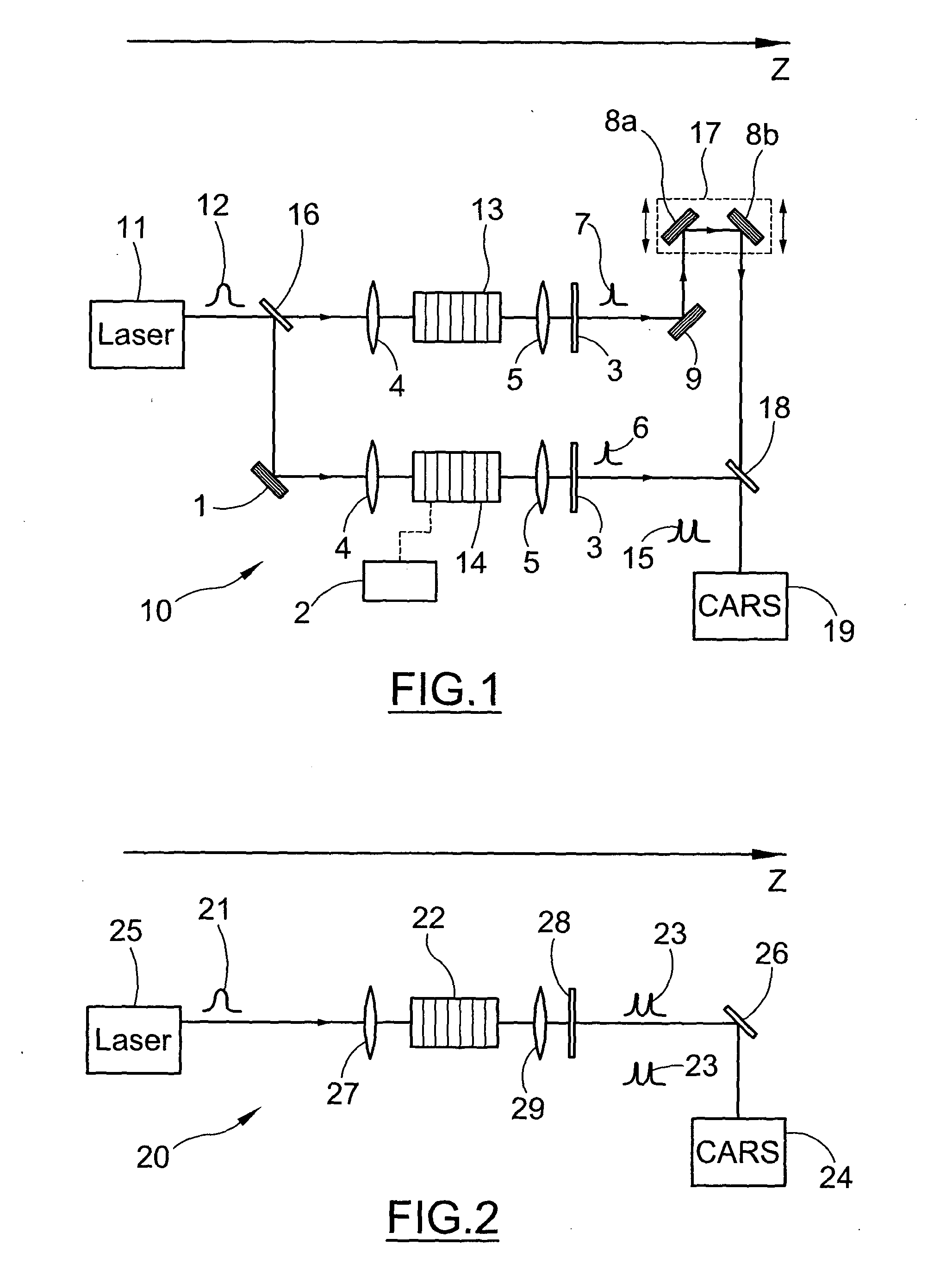
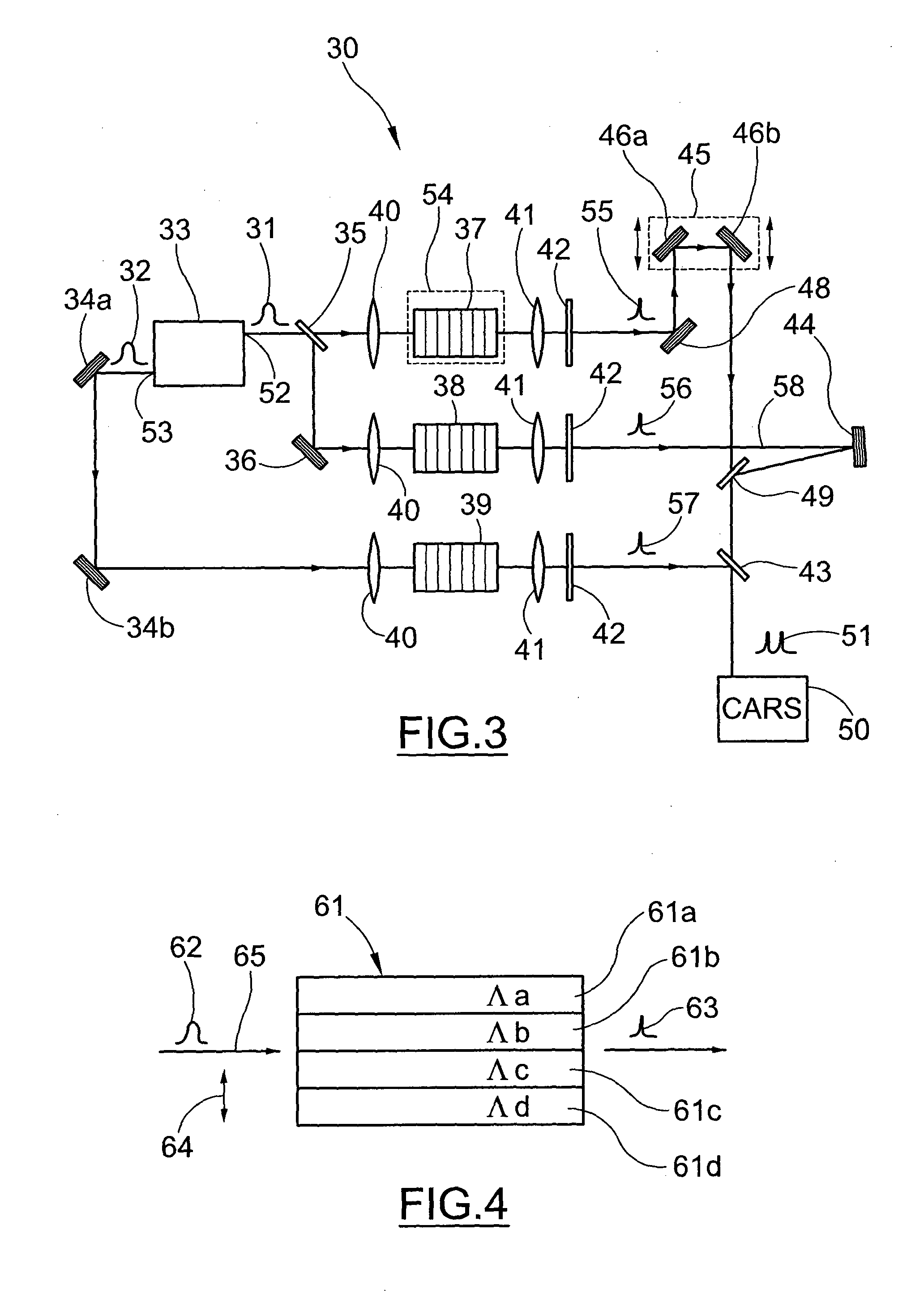
System for Generating Raman Vibrational Analysis Signals
ActiveUS20110128538A1Increased complexityImprove bulkRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringNonlinear optical crystalHarmonic
A system for generating signals for Raman vibrational analysis, particularly for a CARS microscope or spectroscope of an external specimen, the system comprising a a laser source apt to emit at least one fundamental optical pulse in a first band of fundamental frequencies comprising at least one first (ωf1) and one second (ωf2) fundamental frequencies; a second-harmonic (SH) generating system comprising at least one nonlinear optical crystal for converting said at least one fundamental optical pulse into at least two second-harmonic optical pulses, i.e. a first second-harmonic pulse at a first second-harmonic frequency (ωp) of the first fundamental frequency (ωf1) and a second second-harmonic pulse at a second second-harmonic frequency (ωs) of the second fundamental frequency (ωf2), said second second-harmonic frequency being other than the first second-harmonic frequency, and a Raman vibrational analysis apparatus apt to receive said first and second second-harmonic pulses and direct them toward said specimen.According to an embodiment, the SH system comprises two nonlinear optical crystals, each including a ferroelectric crystal with periodic space-modulation of the sign of the optical susceptibility.In a different embodiment, the SH system comprises a ferroelectric crystal with aperiodic space-modulation of the sign of nonlinear optical susceptibility, with a period varying along the optical path of said at least one fundamental optical pulse, said crystal being apt to generate said first and second second-harmonic pulses.
Owner:POLITECNICO DI MILANO
Reducing aberration in optical systems comprising cubic crystalline optical elements
InactiveUS6844972B2Reduced polarization effectsLower latencyMaterial analysis by optical meansPolarising elementsCatadioptric systemDevice material
An optical system includes multiple cubic crystalline optical elements and one or more polarization rotators in which the crystal lattices of the cubic crystalline optical elements are oriented with respect to each other to reduce the effects of intrinsic birefringence and produce a system with reduced retardance. The optical system may be a refractive or catadioptric system having a high numerical aperture and using light with a wavelength at or below 248 nanometers. The net retardance of the system is less than the sum of the retardance contributions of the respective optical elements. In one embodiment, all cubic crystalline optical elements are oriented with identical three dimensional cubic crystalline lattice directions, a 90° polarization rotator divides the system into front and rear groups such that the net retardance of the front group is balanced by the net retardance of the rear group. The optical system may be used in a photolithography tool to pattern substrates such as semiconductor substrates and thereby produce semiconductor devices.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Correction of birefringence in cubic crystalline optical systems
InactiveUS20030099047A1Lower latencyMinimize changesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusCatadioptric systemOptical axis
An optical system includes multiple cubic crystalline optical elements aligned along a common optical axis and having their crystal lattices oriented with respect to each other to minimize the effects of intrinsic birefringence and produce a system with reduced retardance. The optical system may be a refractive or catadioptric system having a high numerical aperture and using light with a wavelength at or below 248 nanometers. The net retardance of the system is less than the sum of the retardance contributions of the respective optical elements as the elements are oriented such that the intrinsic birefringences of the individual elements cancel each other out. In one embodiment, two [110] cubic crystalline optical elements are clocked with respect to one another and used in conjunction with a [100] cubic crystalline optical element to reduce retardance. Various birefringent elements, wave plates, and combinations thereof provide additional correction for residual retardance and wavefront aberrations. The optical system may be used in a photolithography tool to pattern substrates such as semiconductor substrates and thereby produce semiconductor devices.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
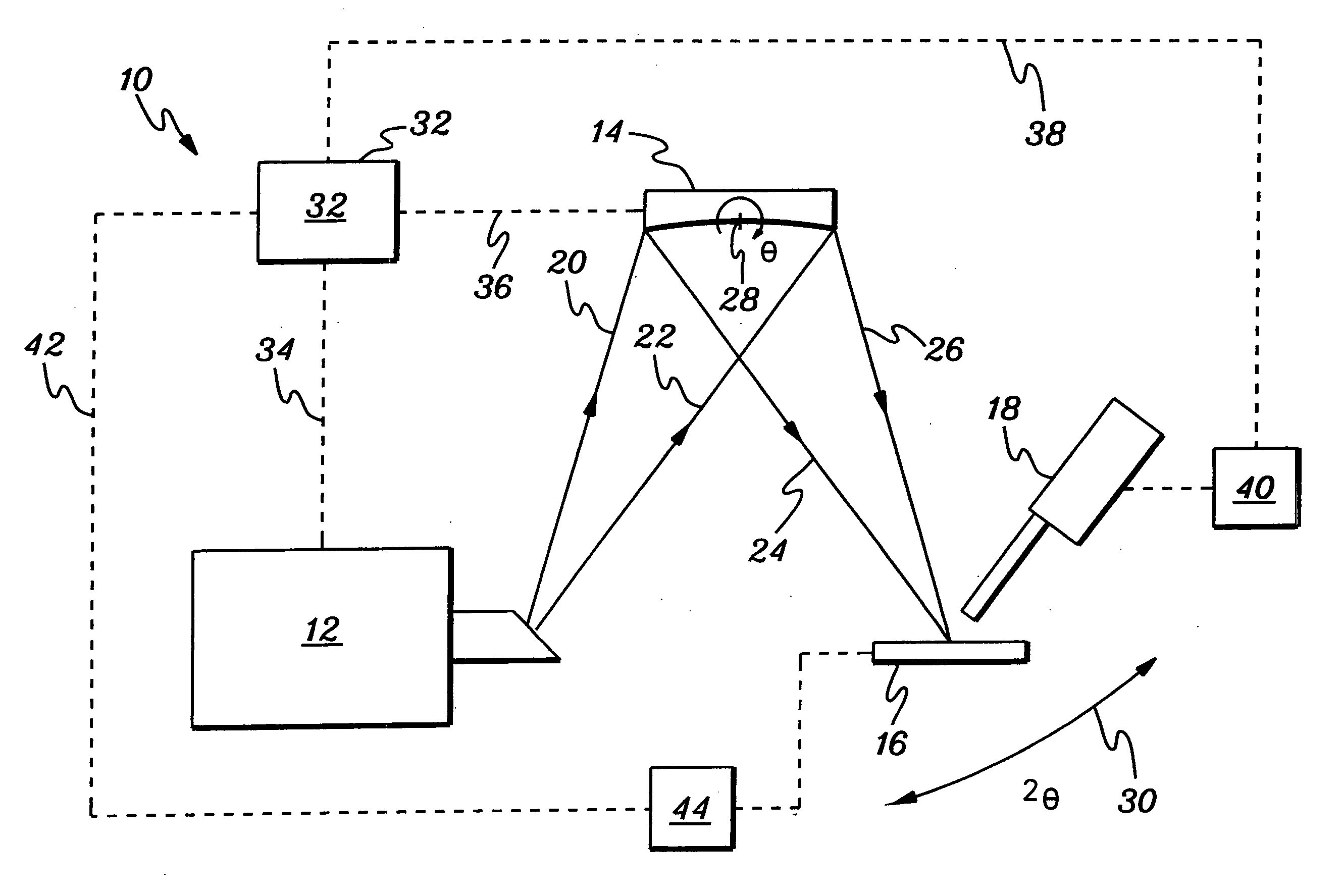
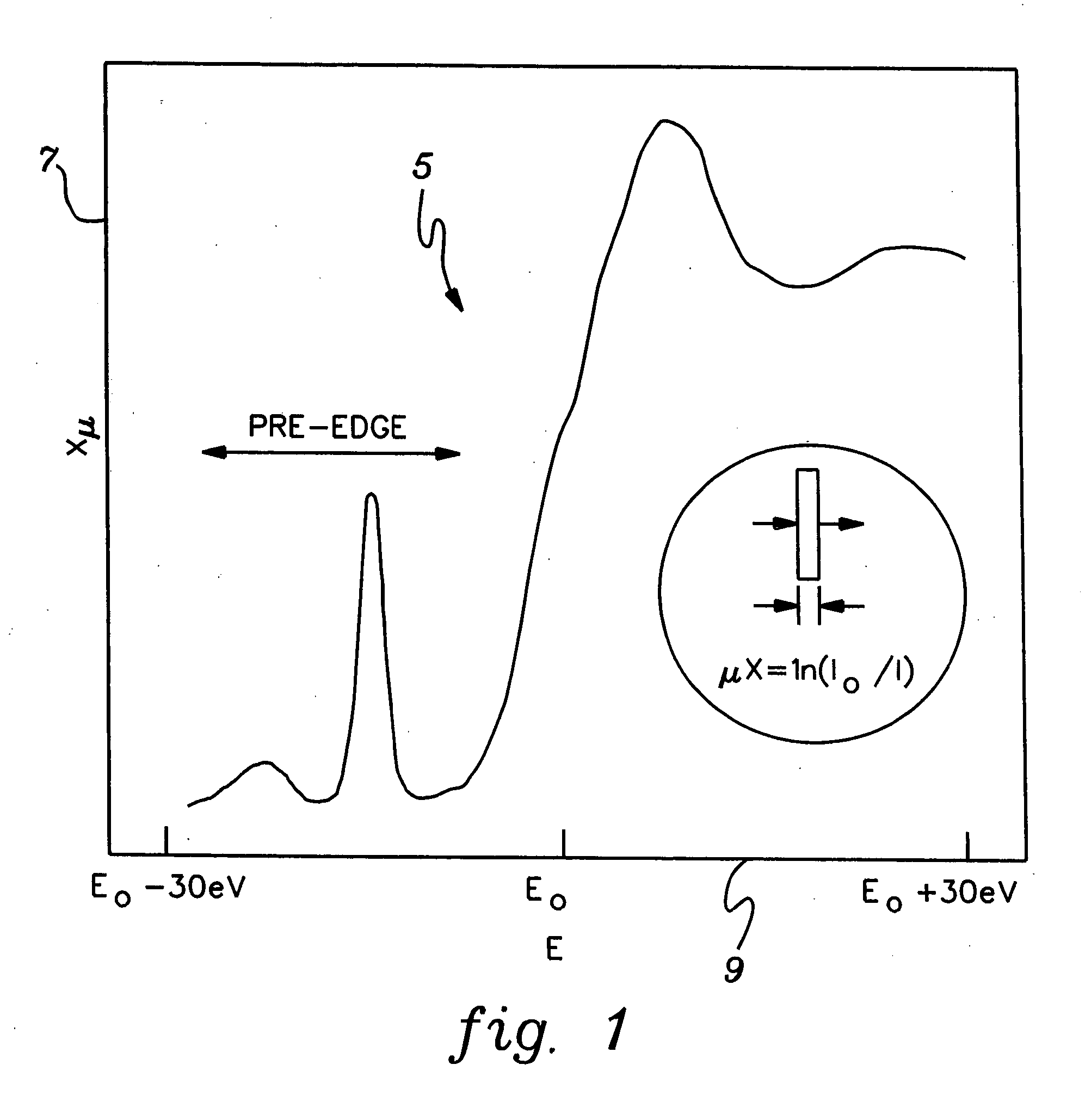
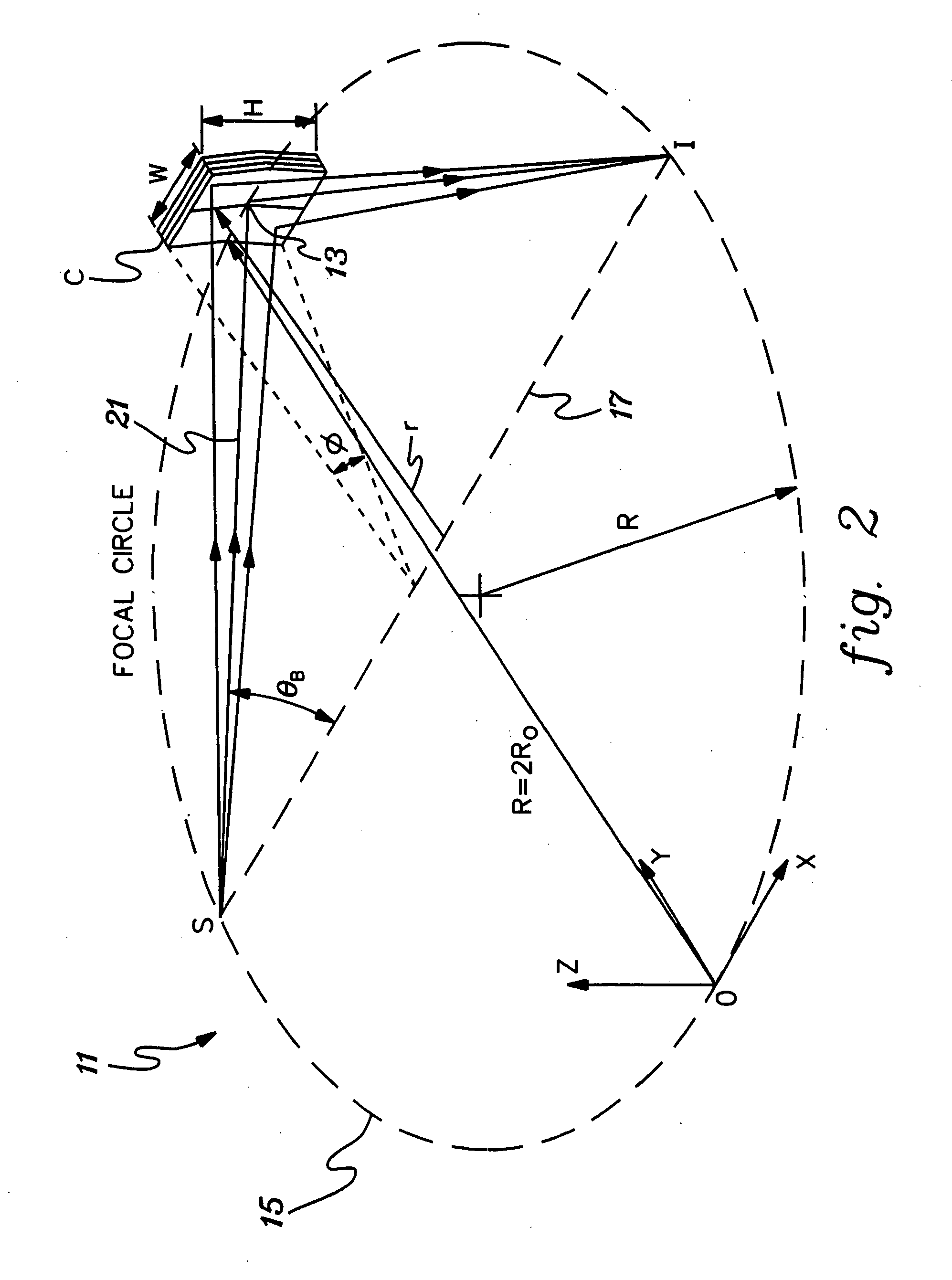
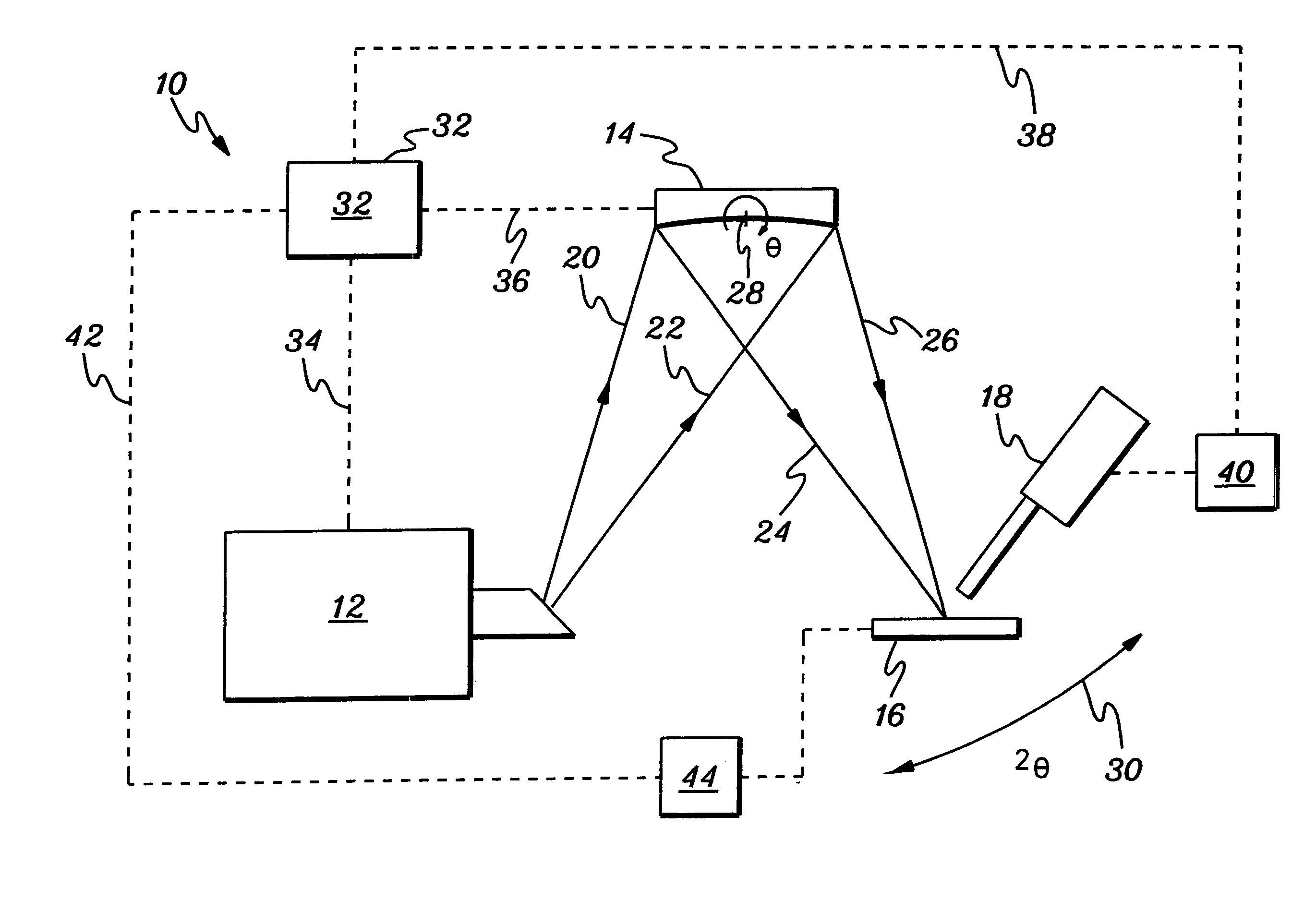
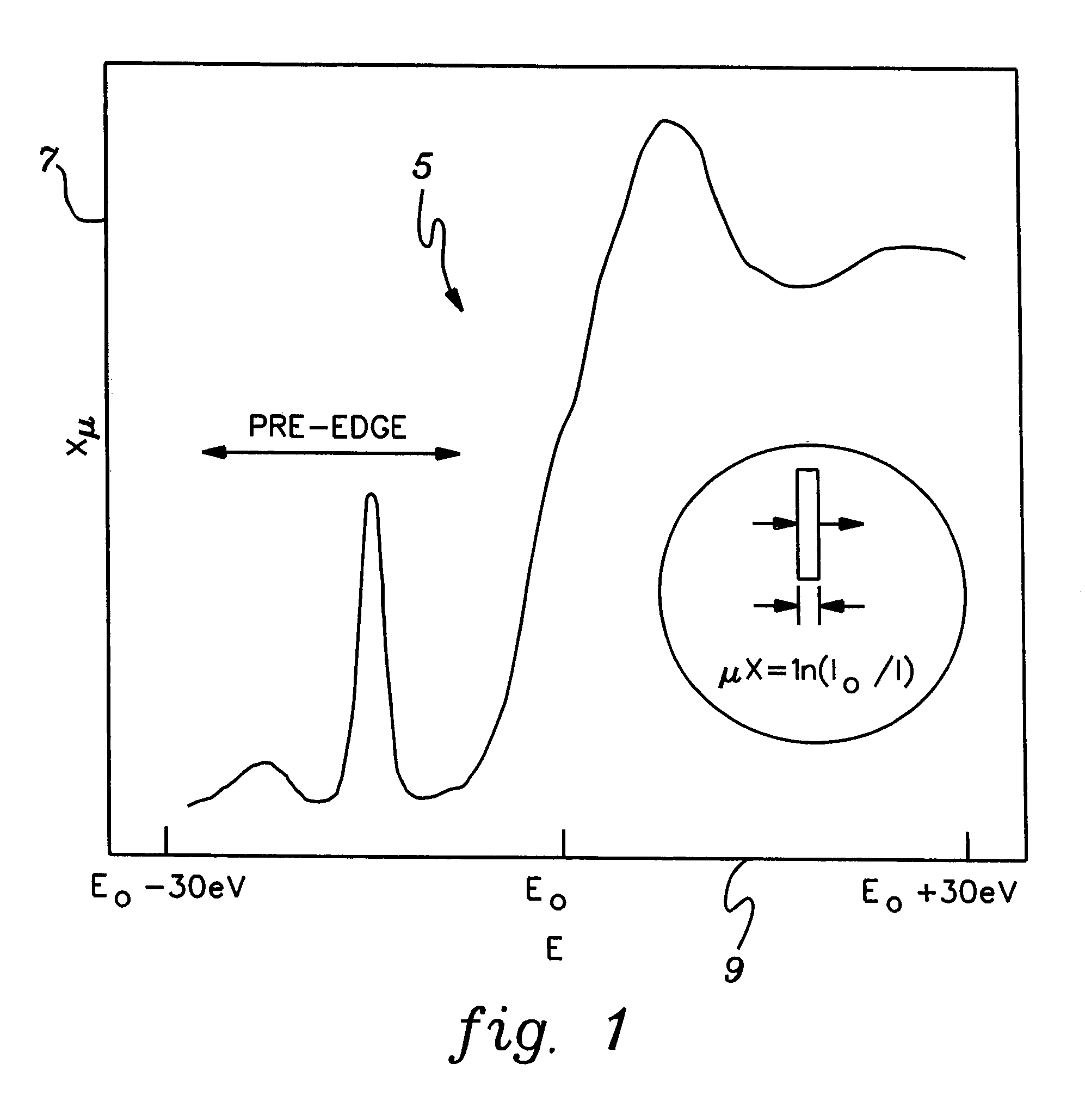
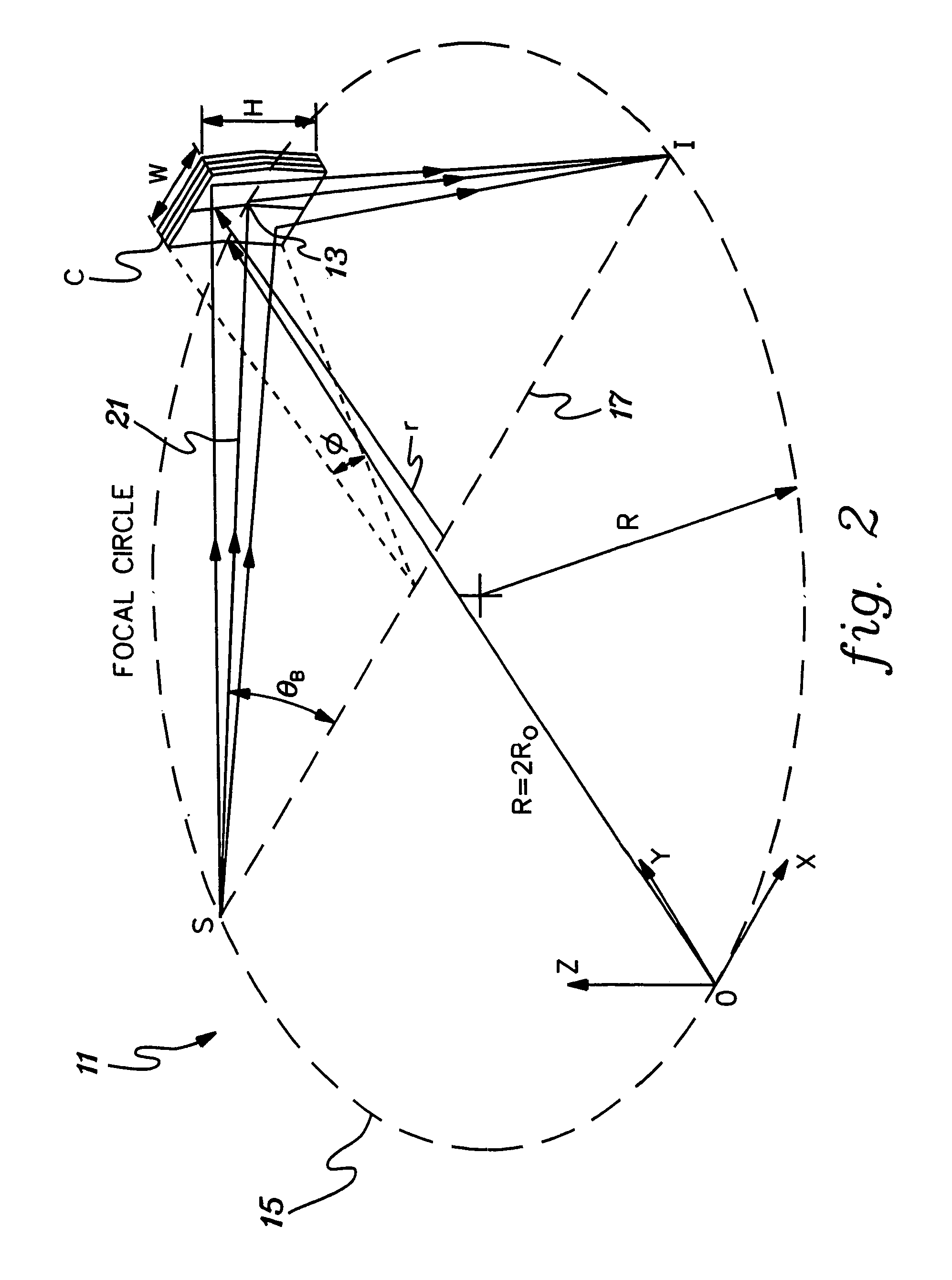
Method and apparatus for implement XANES analysis
InactiveUS20060120508A1High sensitivityLow powerVolume/mass flow measurementHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionOrganismal ProcessHigh energy
Compact, low-power-consuming systems and methods for exposing samples to high-energy radiation, for example, for exposing samples to x-rays for implementing x-ray absorption near edge analysis (XANES). The systems and methods include a low-power-consuming radiation source, such as an x-ray tube; one or more tunable crystal optics for directing and varying the energy of the radiation onto a sample under analysis; and a radiation detecting device, such as an x-ray detector, for detecting radiation emitted by the sample. The one or more tunable crystal optics may be doubly-curved crystal optics. The components of the system may be arranged in a collinear fashion. The disclosed systems and methods are particularly applicable to XANES analysis, for example, XANES analysis of the chemical state of chromium or another transition metal in biological processes.
Owner:X-RAY OPTICAL SYSTEM INC
Method and apparatus for implement XANES analysis
InactiveUS7206375B2High sensitivityLow powerVolume/mass flow measurementHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionHigh energyX-ray
Compact, low-power-consuming systems and methods for exposing samples to high-energy radiation, for example, for exposing samples to x-rays for implementing x-ray absorption near edge analysis (XANES). The systems and methods include a low-power-consuming radiation source, such as an x-ray tube; one or more tunable crystal optics for directing and varying the energy of the radiation onto a sample under analysis; and a radiation detecting device, such as an x-ray detector, for detecting radiation emitted by the sample. The one or more tunable crystal optics may be doubly-curved crystal optics. The components of the system may be arranged in a collinear fashion. The disclosed systems and methods are particularly applicable to XANES analysis, for example, XANES analysis of the chemical state of chromium or another transition metal in biological processes.
Owner:X-RAY OPTICAL SYSTEM INC
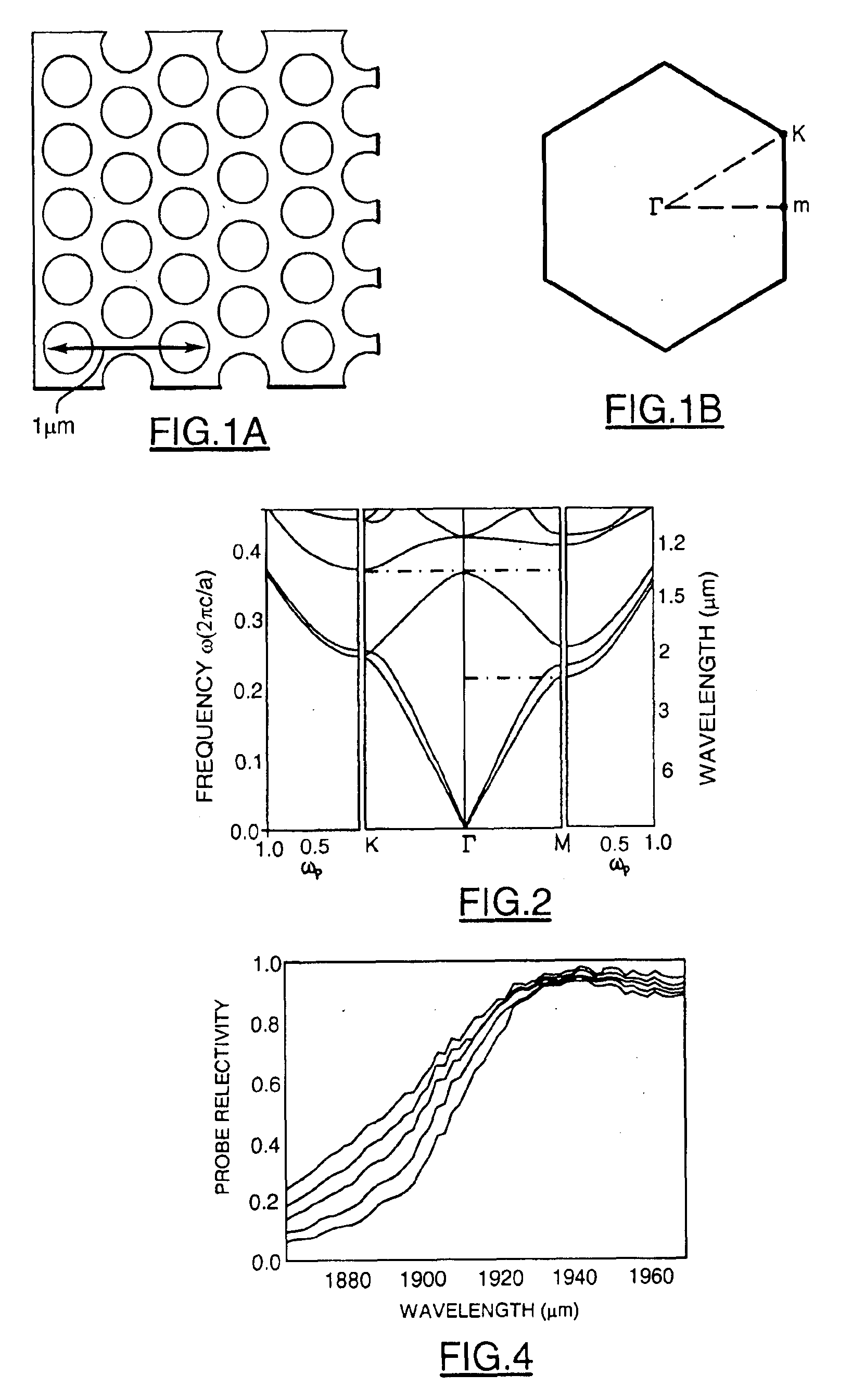
Method of varying optical properties of photonic crystals on fast time scales using energy pulses
InactiveUS6870970B2Reduce reflectivitySmall shiftNanoopticsCoupling light guidesPhotonic bandgapGain
The present invention provides a method for fast switching of optical properties in photonic crystals using pulsed / modulated free-carrier injection. The results disclosed herein indicate that several types of photonic crystal devices can be designed in which free carriers are used to vary dispersion curves, stop gaps in materials with photonic bandgaps to vary the bandgaps, reflection, transmission, absorption, gain, or phase. The use of pulsed free carrier injection to control the properties of photonic crystals on fast timescales forms the basis for all-optical switching using photonic crystals. Ultrafast switching of the band edge of a two-dimensional silicon photonic crystal is demonstrated near a wavelength of 1.9 μm. Changes in the refractive index are optically induced by injecting free carriers with 800 nm, 300 fs pulses. Band-edge shifts have been induced in silicon photonic crystals of up to 29 nm that occurs on the time-scale of the pump pulse. The present invention also provides a method of producing a virtual or temporary photonic crystal using free carrier injection into pure semiconductors, bulk or thin film, in which the carriers are generated in patterns which create a patterned refractive index contrast used to steer light beams in the semiconductor while it is being pulsed.
Owner:LEONARD STEPHEN W +5
Apparatus and method for displaying image
InactiveUS6885422B2Improve the display effectHigher-contrast imagePicture reproducers using projection devicesNon-linear opticsPhase differenceCrystal optics
Provided is a projection type liquid crystal display apparatus, which can improve black-level display and thus can display a higher-contrast image as compared to the related art. An optical compensator is located on the light exit side with respect to the liquid crystal display device so as to compensate for the optical phase difference caused by liquid crystal molecules in a light-entry-side region of the liquid crystal layer. As the optical compensator is located on the light exit side with respect to the liquid crystal display device, birefringence, caused by the liquid crystal molecules present in the light-entry-side region, is compensated for without being influenced by a microlenses provided in the liquid crystal plane. Consequently, the apparatus can improve the black-level display and thus can display a higher-contrast image as compared to the related art. Further, a phase difference caused by the birefringence of the nematic liquid crystal molecule is compensated for by using a substance having properties optically opposite to the positive crystal, namely, a substance having birefringence equivalent to birefringence of a negative crystal.
Owner:SONY CORP
Structures and methods for reducing aberration in integrated circuit fabrication systems
InactiveUS6970232B2Reduced polarization effectsLower latencyInvestigating moving sheetsPolarising elementsCatadioptric systemWavelength
An optical system includes multiple cubic crystalline optical elements and one or more polarization rotators in which the crystal lattices of the cubic crystalline optical elements are oriented with respect to each other to reduce the effects of intrinsic birefringence and produce a system with reduced retardance. The optical system may be a refractive or catadioptric system having a high numerical aperture and using light with a wavelength at or below 248 nanometers. The net retardance of the system is less than the sum of the retardance contributions of the respective optical elements. In one embodiment, all cubic crystalline optical elements are oriented with identical three dimensional cubic crystalline lattice directions, a 90° polarization rotator divides the system into front and rear groups such that the net retardance of the front group is balanced by the net retardance of the rear group. The optical system may be used in a photolithography tool to pattern substrates such as semiconductor substrates and thereby produce semiconductor devices.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
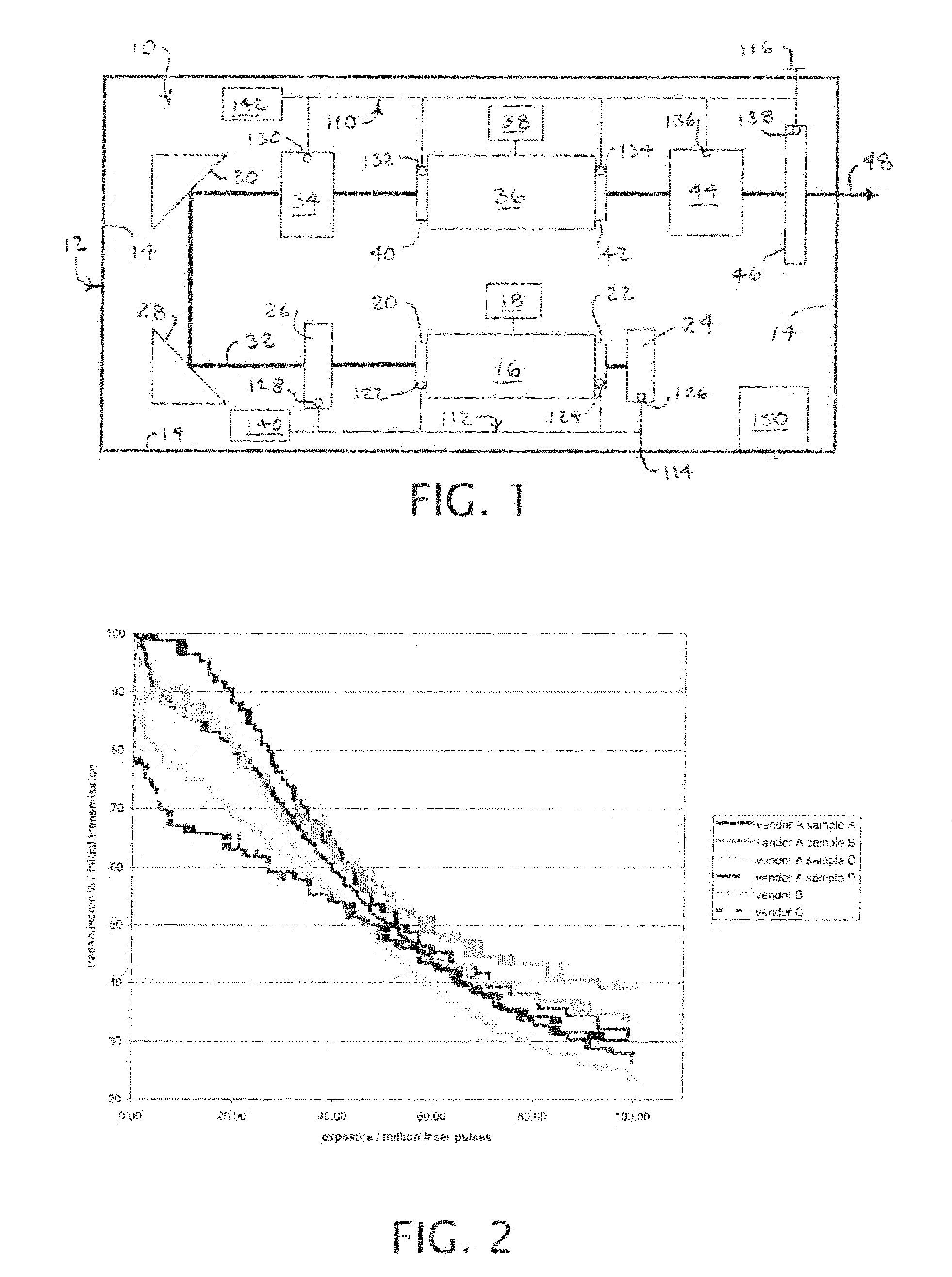
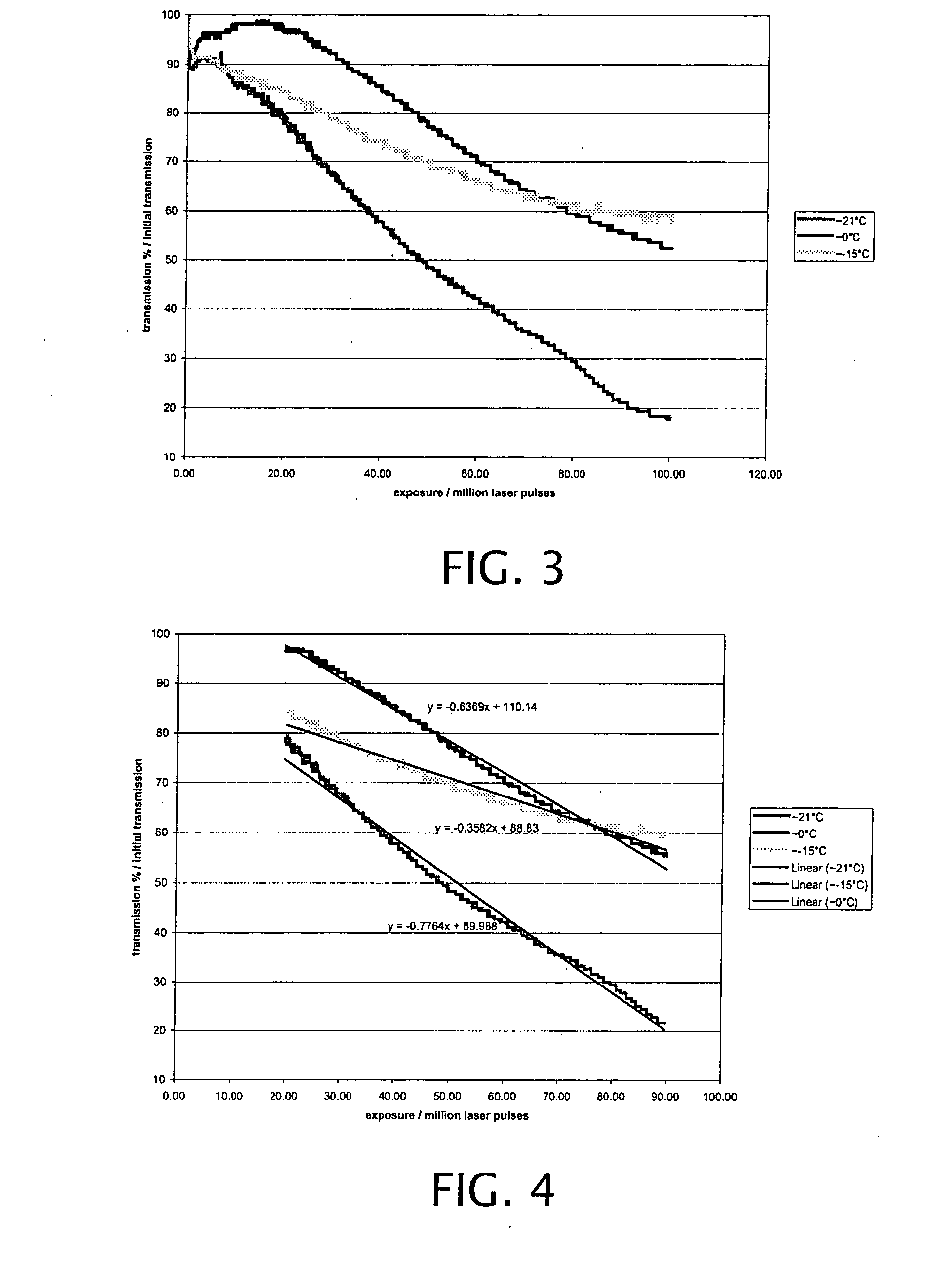
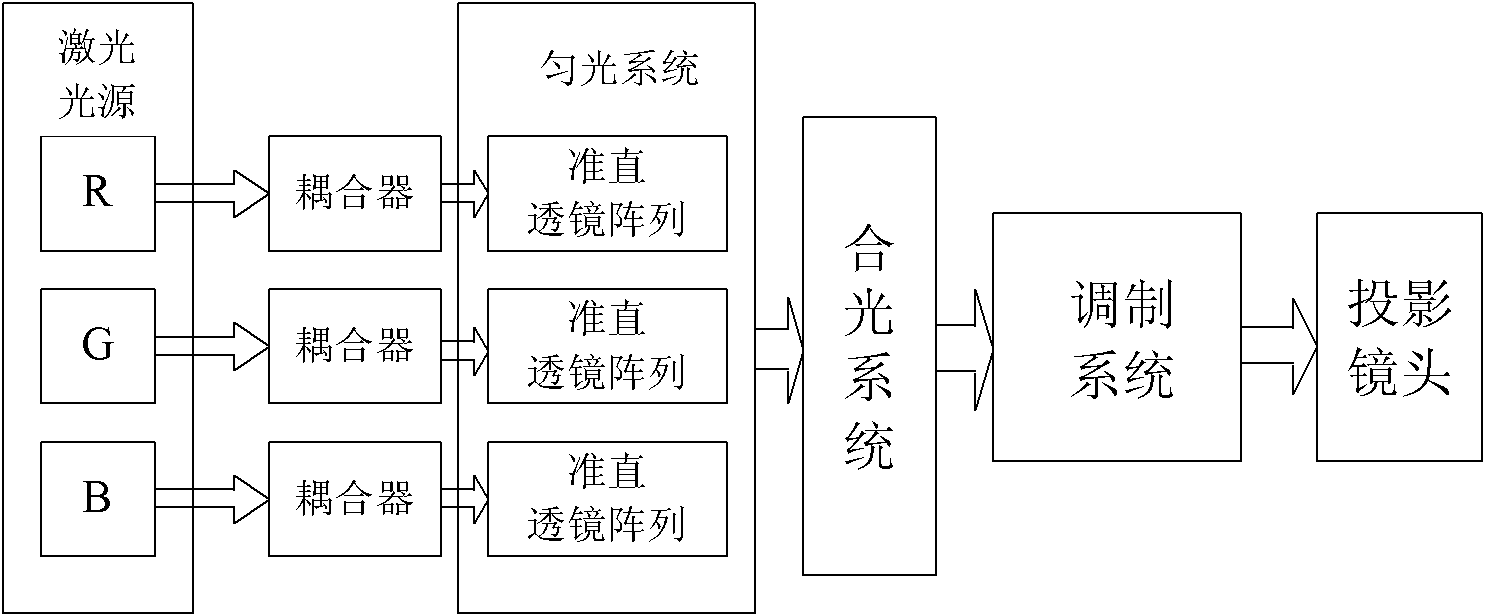
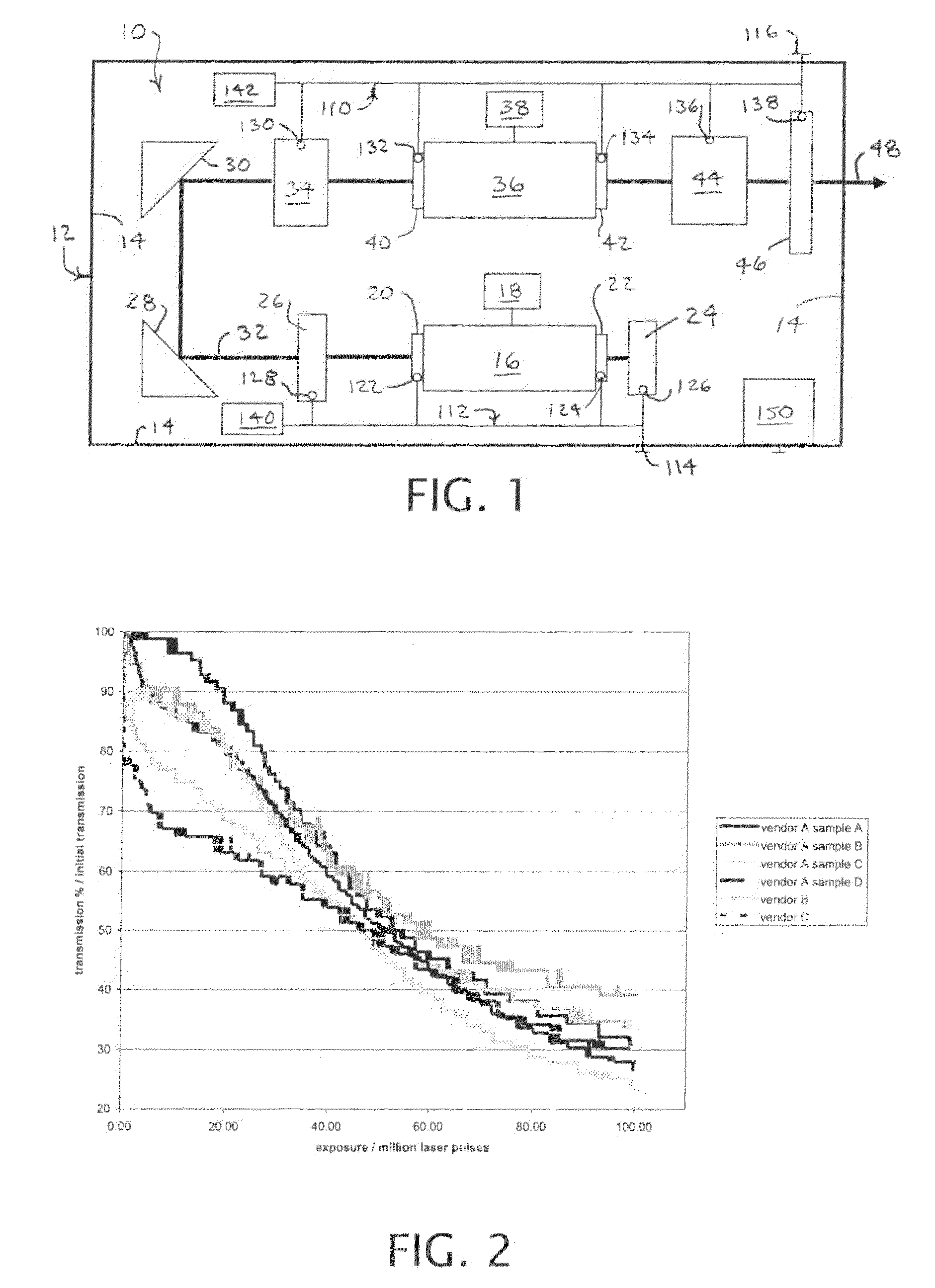
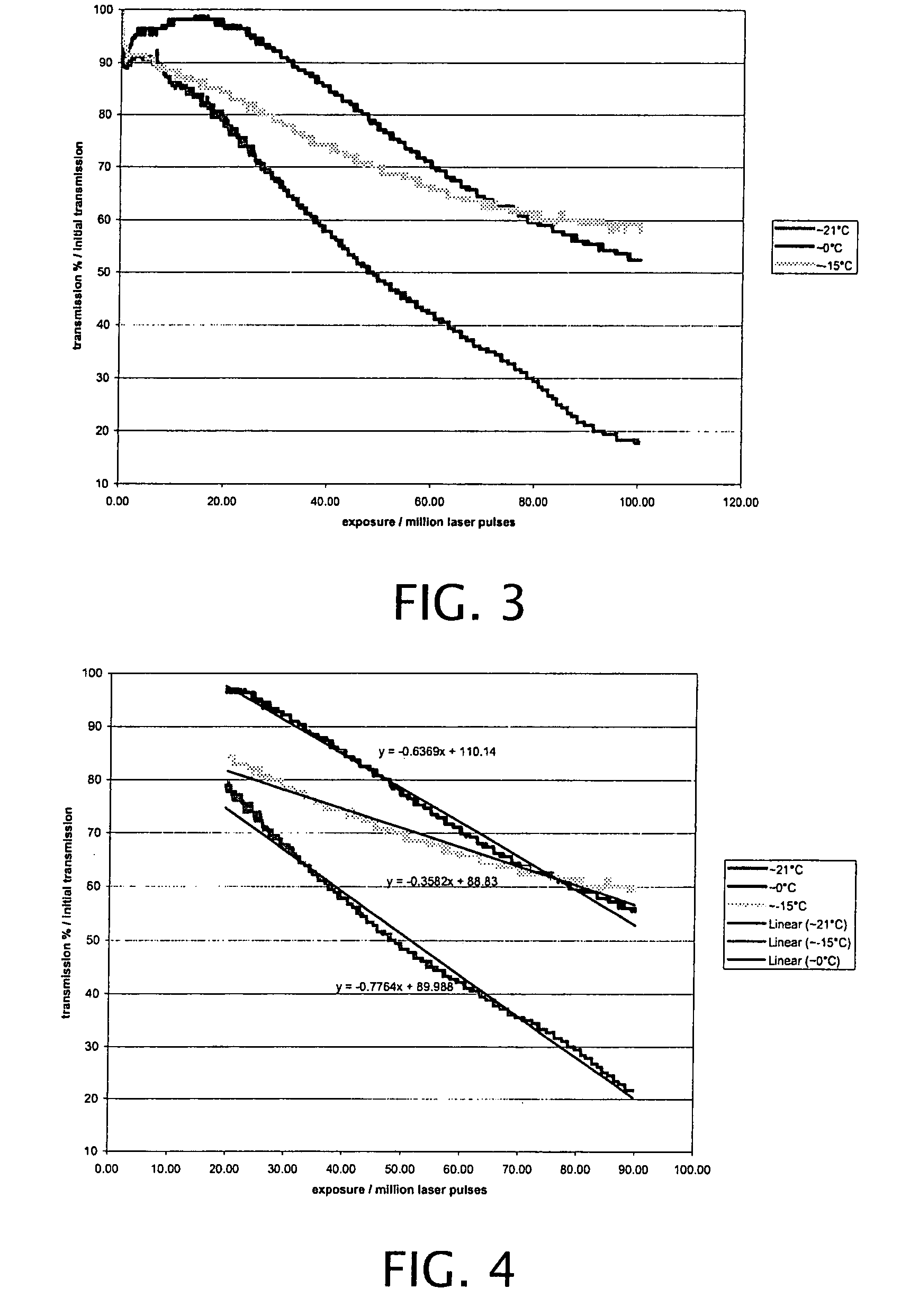
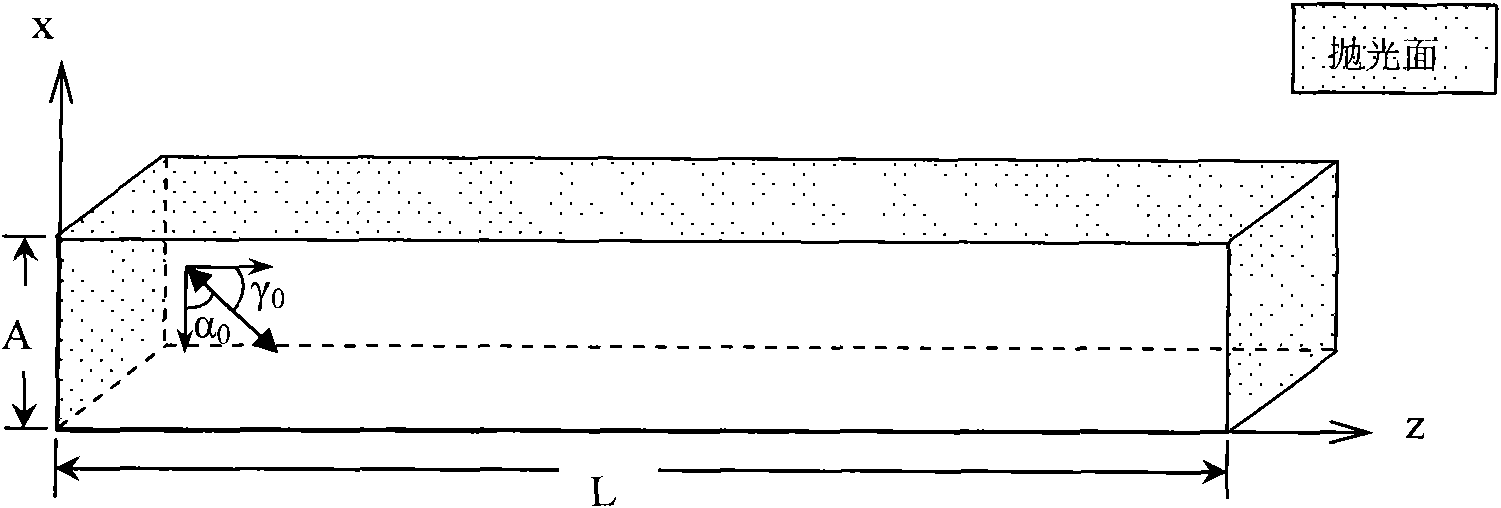
Active cooling of crystal optics for increased laser lifetime
InactiveUS20080198882A1Reduce degradationLow costPhotomechanical apparatusMountingsActive coolingTransmittance
A laser beam is generated and transmitted within an enclosed pathway through at least one crystal optic at a power density that progressively degrades transmissivity of the crystal optic with accumulating fluence. The crystal optics are cooled below normal operating temperatures to slow the progressive degradation in the transmissivity of the crystal optics with the accumulating fluence or to accommodate a higher power density without correspondingly increasing the progressive degradation in transmissivity.
Owner:CORNING INC
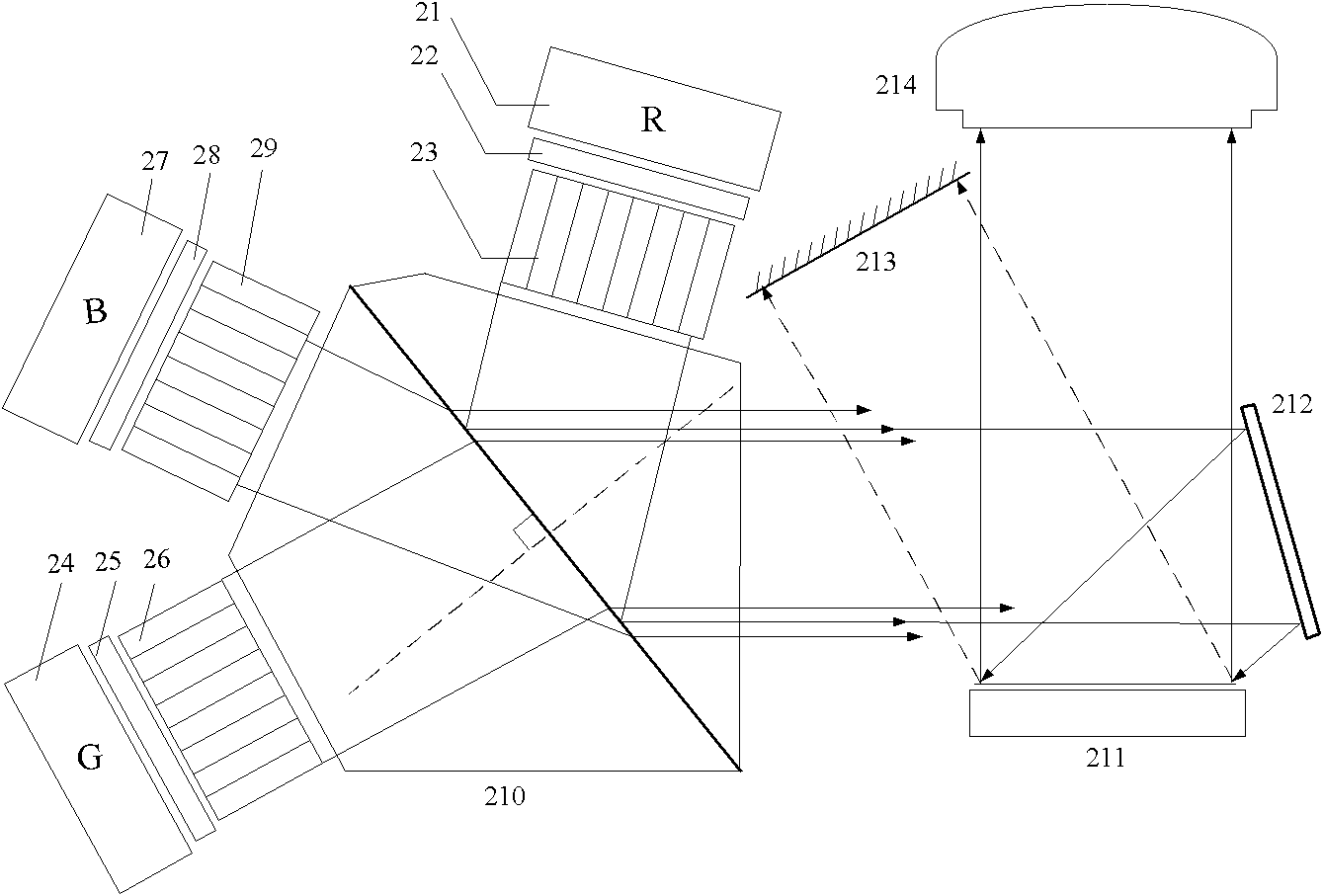
Optical engine for projector
The invention relates to an optical engine for a projector, belonging to the technical field of projection display. Three light beam couplers respectively output three groups of array light by processing laser light generated by an RGB (three primary colors: red, green and blue) laser light source; a light-equaling system comprises three collimation lens arrays; each collimation lens array consists of gradient reflective index lens units with a quarter of pitch of optical length; the three groups of array light are respectively output by the three collimation lens arrays to form three groups of parallel light with even energy distribution; and the parallel light can be merged by a merging and modulating system, and then can be output to a projection lens. In the optical engine, the light-equaling system adopts the collimation lens arrays consisting of the gradient reflective index lens units and can simultaneously realize light equaling, reshaping and collimation; the energy of emergent light spots of the light-equaling system are equally distributed, so as to realize higher utilization rate of light energy; simultaneously, the light-equaling system has the characteristic of a simple structure, is beneficial to reducing the volume of the optical engine and realizes miniaturization of a complete machine. A light merging system can adopt a Wollaston prism; based on related principles of crystal optics and polarization optics, the light merging structure is innovated, so as to further increase the utilization rate of light energy.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Structures and methods for reducing polarization aberration in integrated circuit fabrication systems
InactiveUS6958864B2Polarising elementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialCrystal optics
An optical system includes multiple cubic crystalline optical elements and one or more uniaxial birefringent elements in which the crystal lattices of the cubic crystalline optical elements are oriented with respect to each other to reduce the effects of intrinsic birefringence and produce a system with reduced retardance. The net retardance of the system is reduced by the cancellation of retardance contributions from the multiple cubic crystalline optical elements and the uniaxial birefringent element. The optical system may be used in a photolithography tool to pattern substrates such as semiconductor substrates and thereby produce semiconductor devices.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Light-diffusing ink composition and light guide panel using same
The present invention relates to a light-diffusing ink composition and to a light guide panel and display unit using same, wherein the light-diffusing ink composition comprises: an ink binder made of one or more selected from a group consisting of acrylic resin and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) copolymer; polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) particles for forming a crystal optical pattern; and a solvent for ink. According to the present invention, light from a light source is converted into a crystal optical pattern and outputted, thus producing aesthetic and sensuous light, and lighting with an aesthetic design can be achieved by means of the light guide panel using the composition.
Owner:KSCB
Optical wavelength conversion element having a cesium-lithium-borate crystal
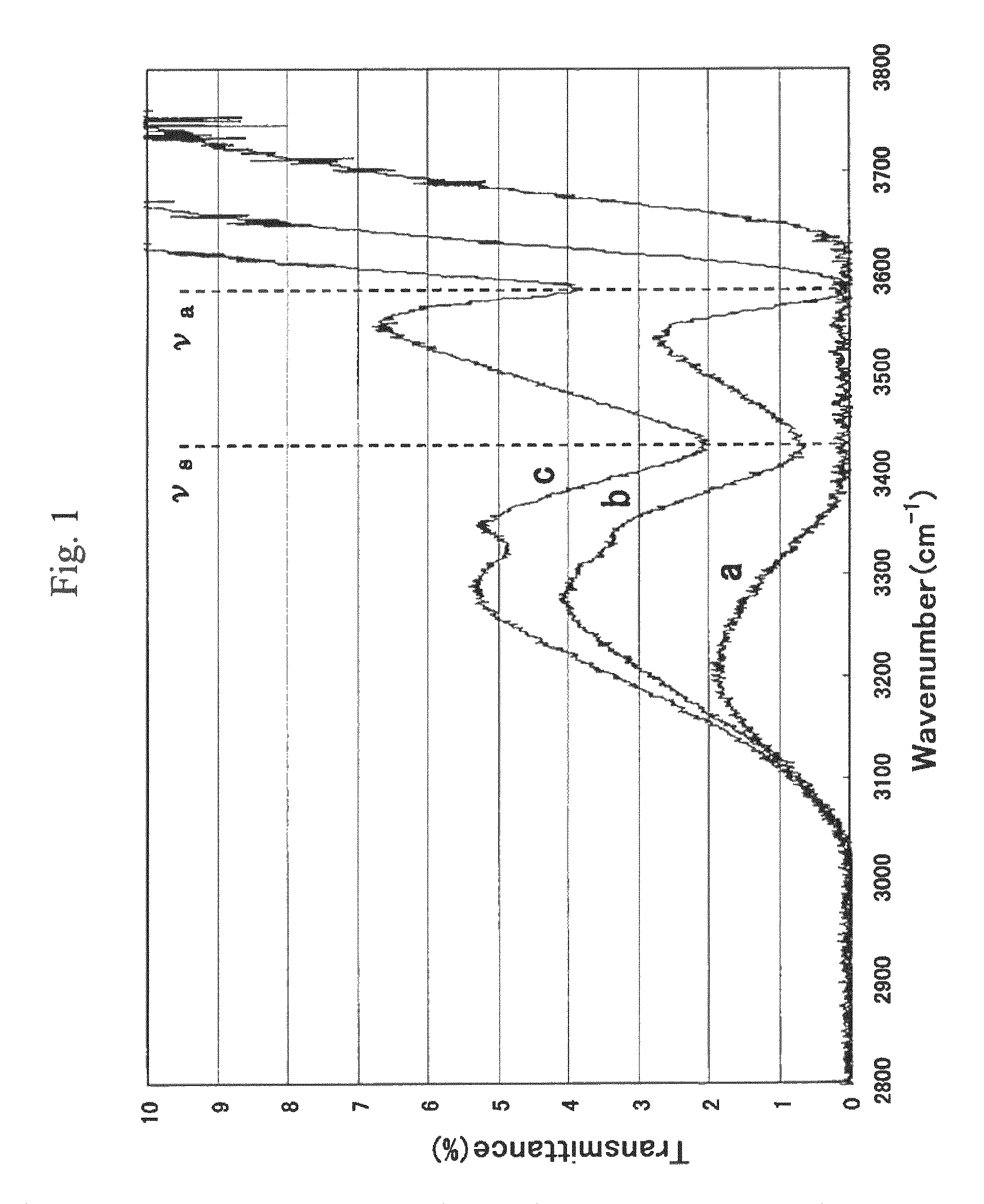
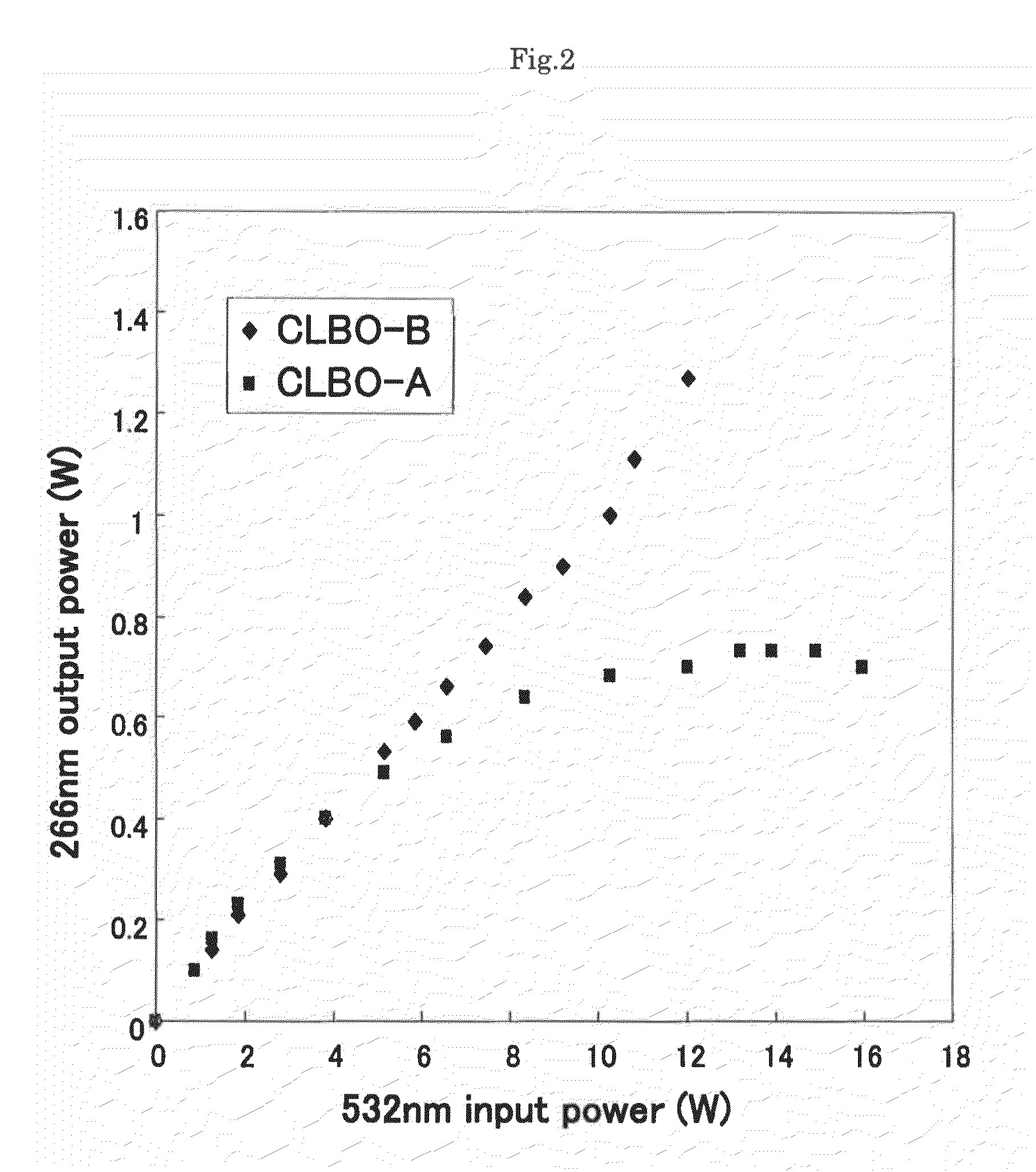
ActiveUS7948673B2Increase output powerImprove performanceLaser detailsLight demodulationFourth harmonicNd:YAG laser
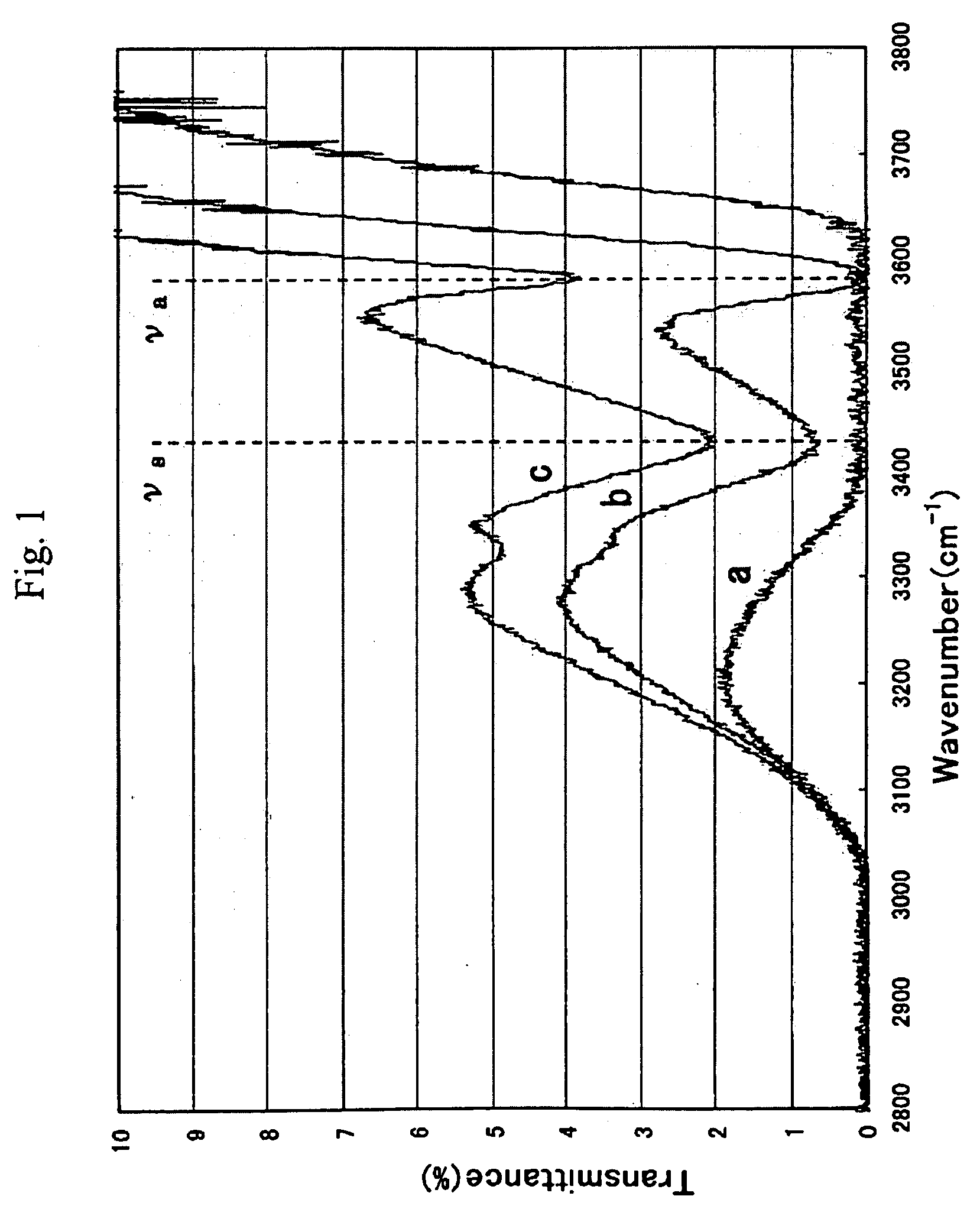
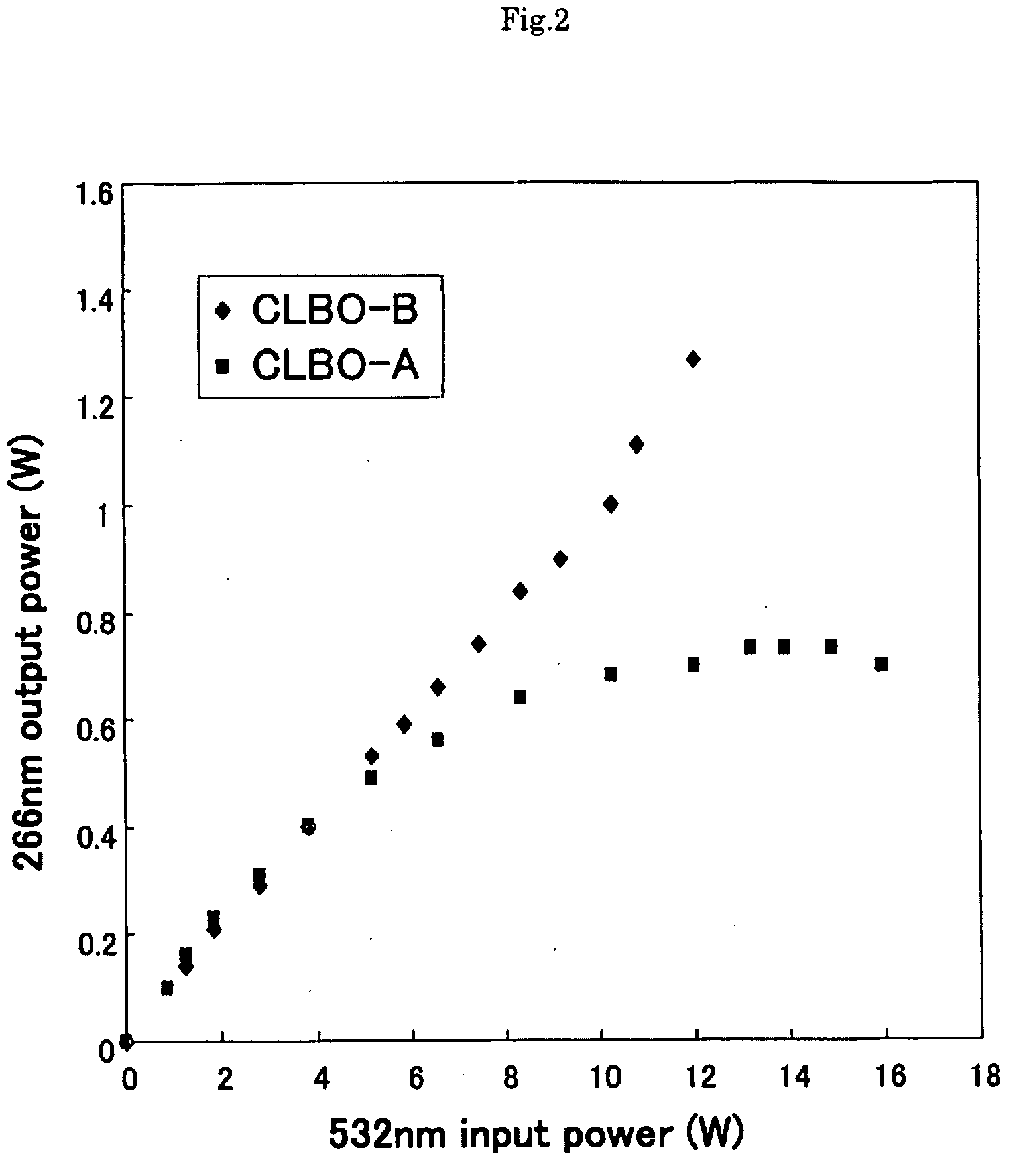
An optical wavelength conversion element includes a cesium-lithium-borate crystal processed into a 10-mm long optical element cut in an orientation that allows a fourth harmonic of a Nd:YAG laser to be generated. A transmittance (Ta) at 3589 cm−1 in an infrared transmission spectrum of the optical element is used as an index that indicates a content of water impurities in the crystal and is independent of a polarization direction. An actual measurement of the transmittance Ta is at least 1%, without taking into account loss at an optically polished surface of the crystal. A wavelength conversion device, a ultraviolet laser irradiation apparatus, a laser processing system, and a method of manufacturing an optical wavelength conversion element are also described.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV +1
Methods for reducing polarization aberration in optical systems
InactiveUS7072102B2Reduce phase delayPolarising elementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCrystal opticsOptic system
An optical system includes multiple cubic crystalline optical elements and one or more uniaxial birefringent elements in which the crystal lattices of the cubic crystalline optical elements are oriented with respect to each other to reduce the effects of intrinsic birefringence and produce a system with reduced retardance. The net retardance of the system is reduced by the cancellation of retardance contributions from the multiple cubic crystalline optical elements and the uniaxial birefringent element. The optical system may be used in a photolithography tool to pattern substrates such as semiconductor substrates and thereby produce semiconductor devices.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
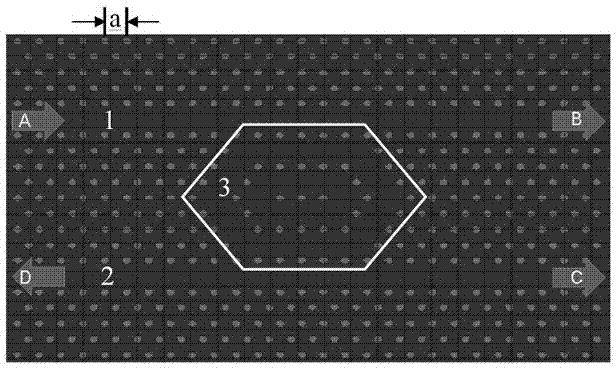
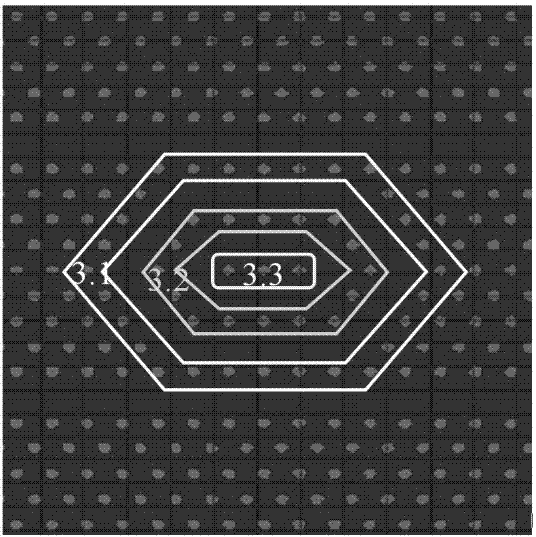
Two-dimensional photonic-crystal optical router based on nested ring cavity structure
The invention relates to a two-dimensional photonic-crystal optical router based on a nested ring cavity structure. A two-dimensional photonic crystal, which is a triangular lattice medium column structure, is formed by one ring cavity including one large non-equilateral hexagon and one small non-equilateral hexagon which are nested, wherein the ring-shaped cavity is guided in two horizontal input and output waveguides. Several medium columns are distributed in the ring cavity in a central symmetry mode, and the whole structure is distributed symmetrically. An appropriate structure parameter is selected. The router can simultaneously realize forward bottom route and backward bottom route functions of a single wavelength input light wave, the forward bottom route and backward bottom route functions of two wavelength input light waves, and a function of exchanging forward and backward bottom route directions of two wavelengths. Compared to the two-dimensional photonic-crystal optical router of a single ring cavity structure, by using the router of the invention, a bottom route effect is obviously increased and can reach 100%. The router possesses characteristics that the structure is simple; manufacturing is easy; a size is small; cost is low; stability is high; and flexible functions are possessed and so on. The router can be mainly applied to an all-optical integrated loop network.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
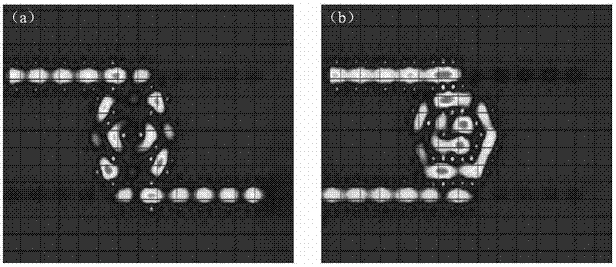
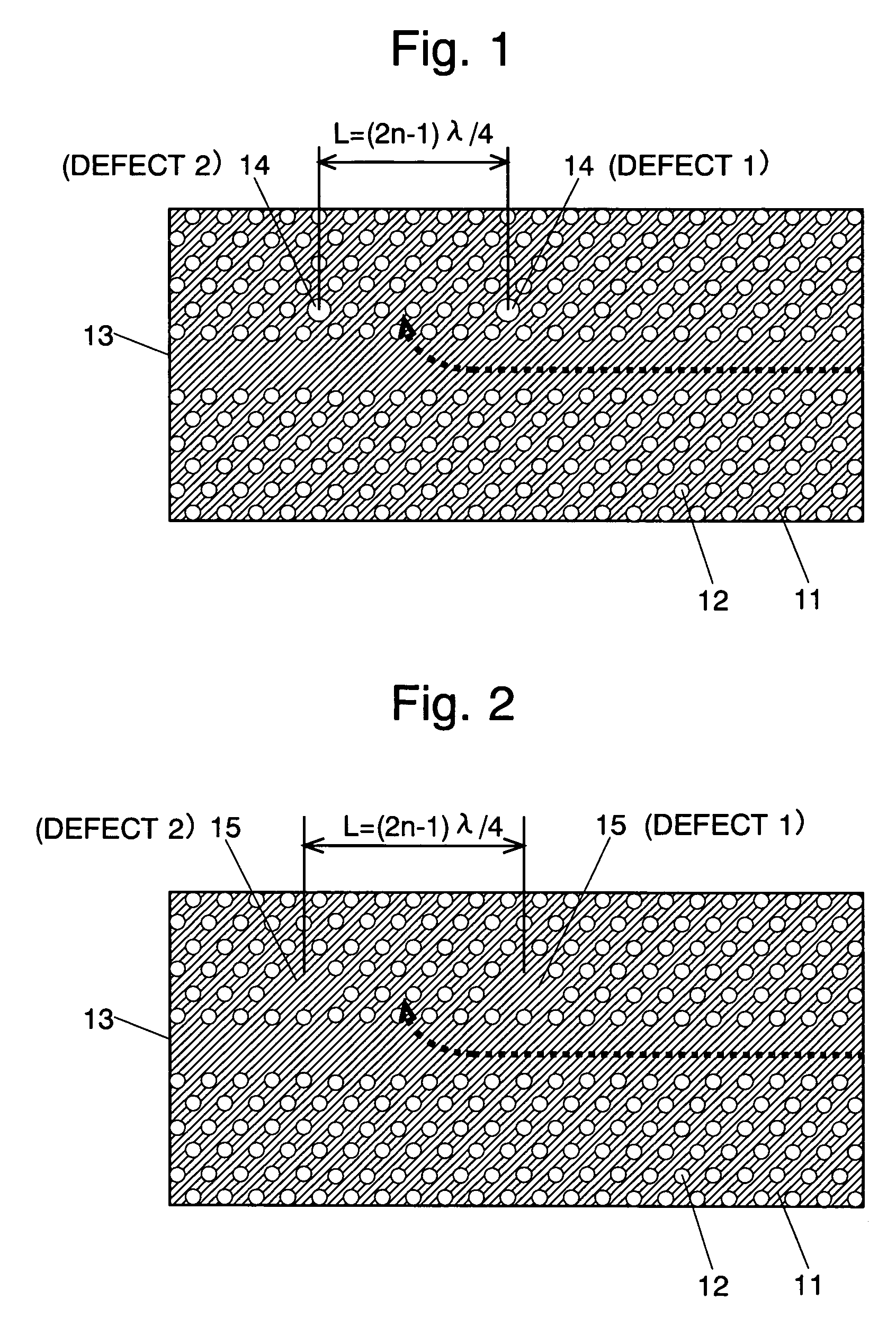
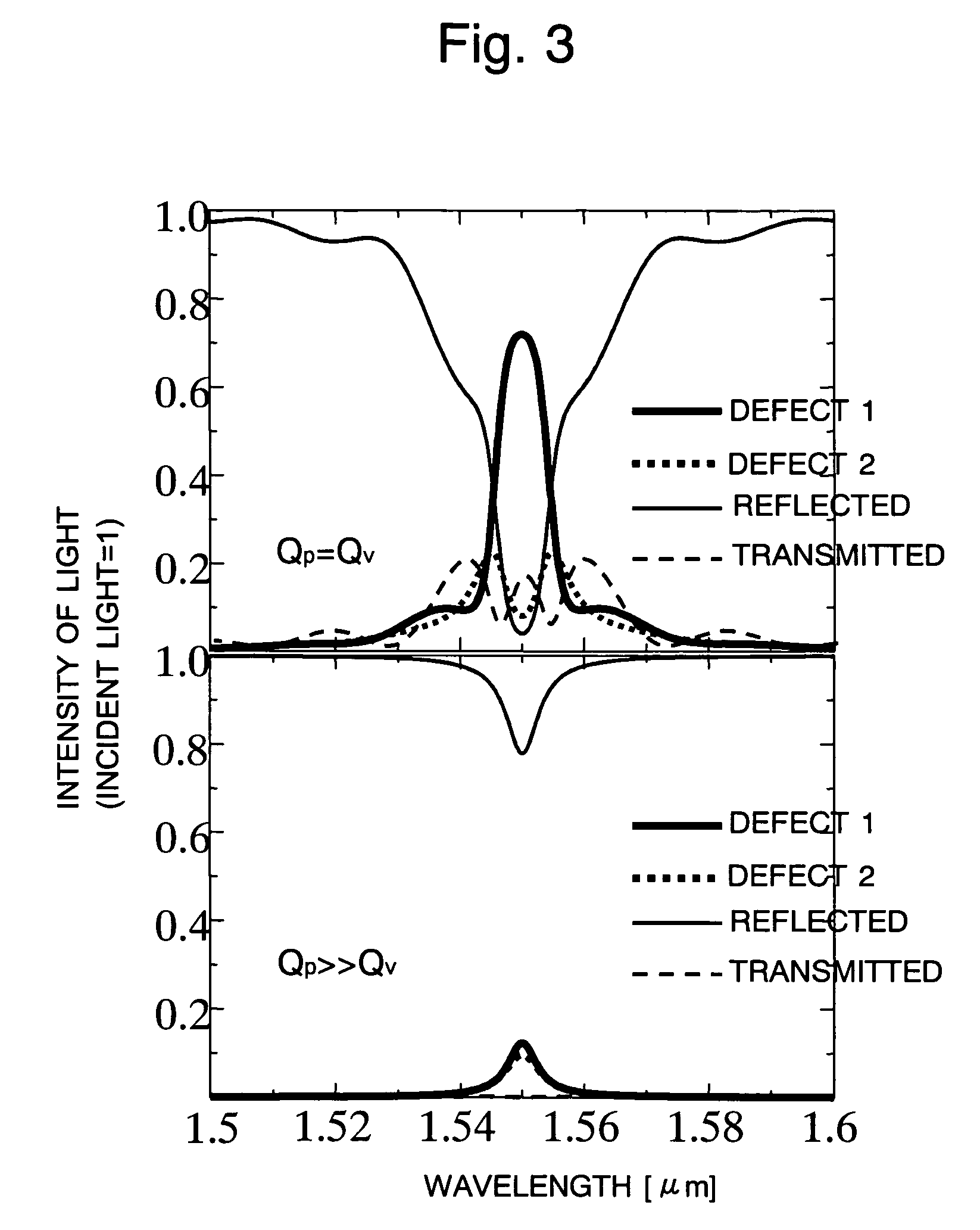
Two-dimensional photonic crystal optical resonator and optical reflector using interference between point defects
InactiveUS20050147371A1Effective reflectionImprove efficiencyLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionOptical reflectionPhotonic crystal
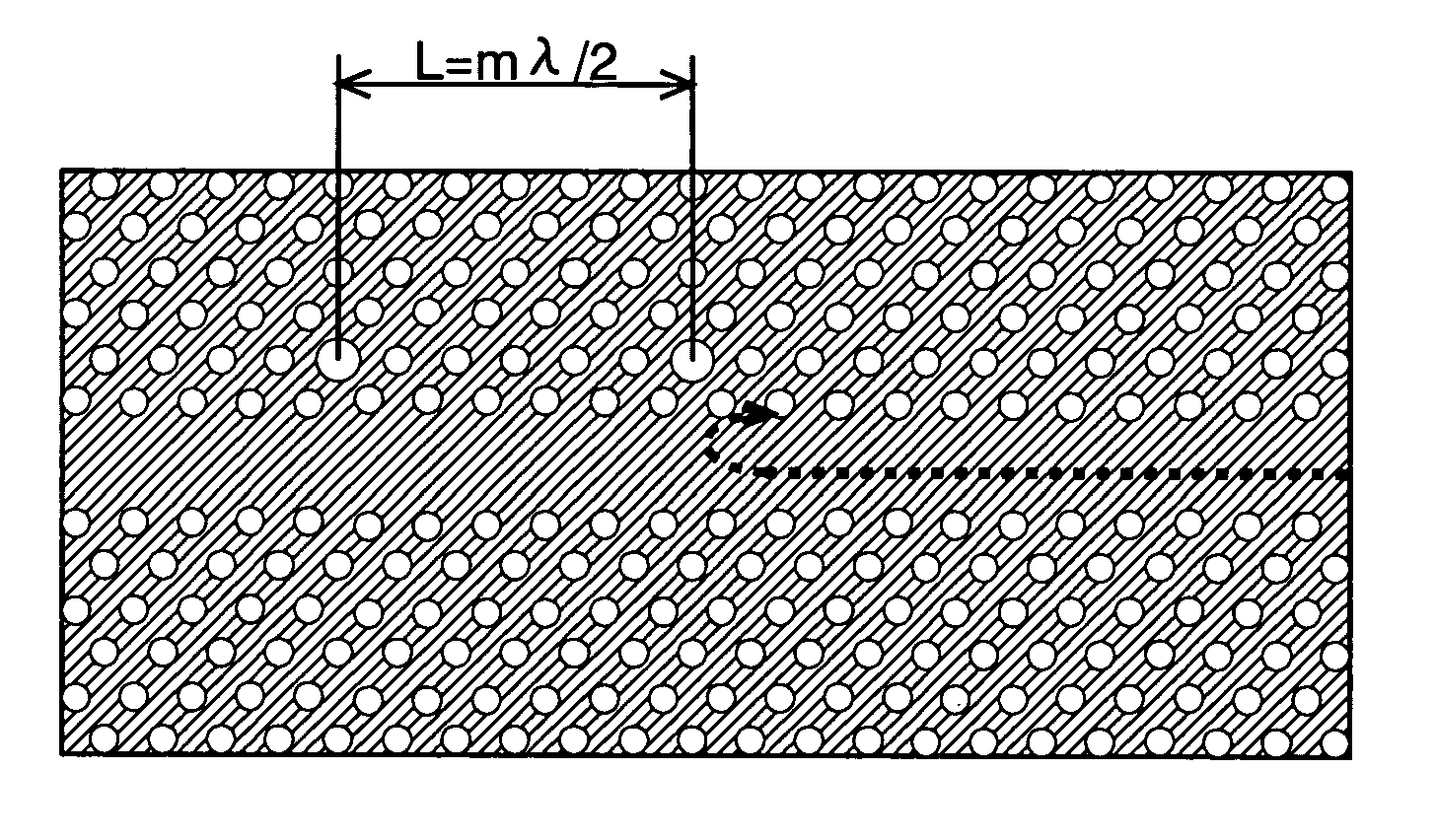
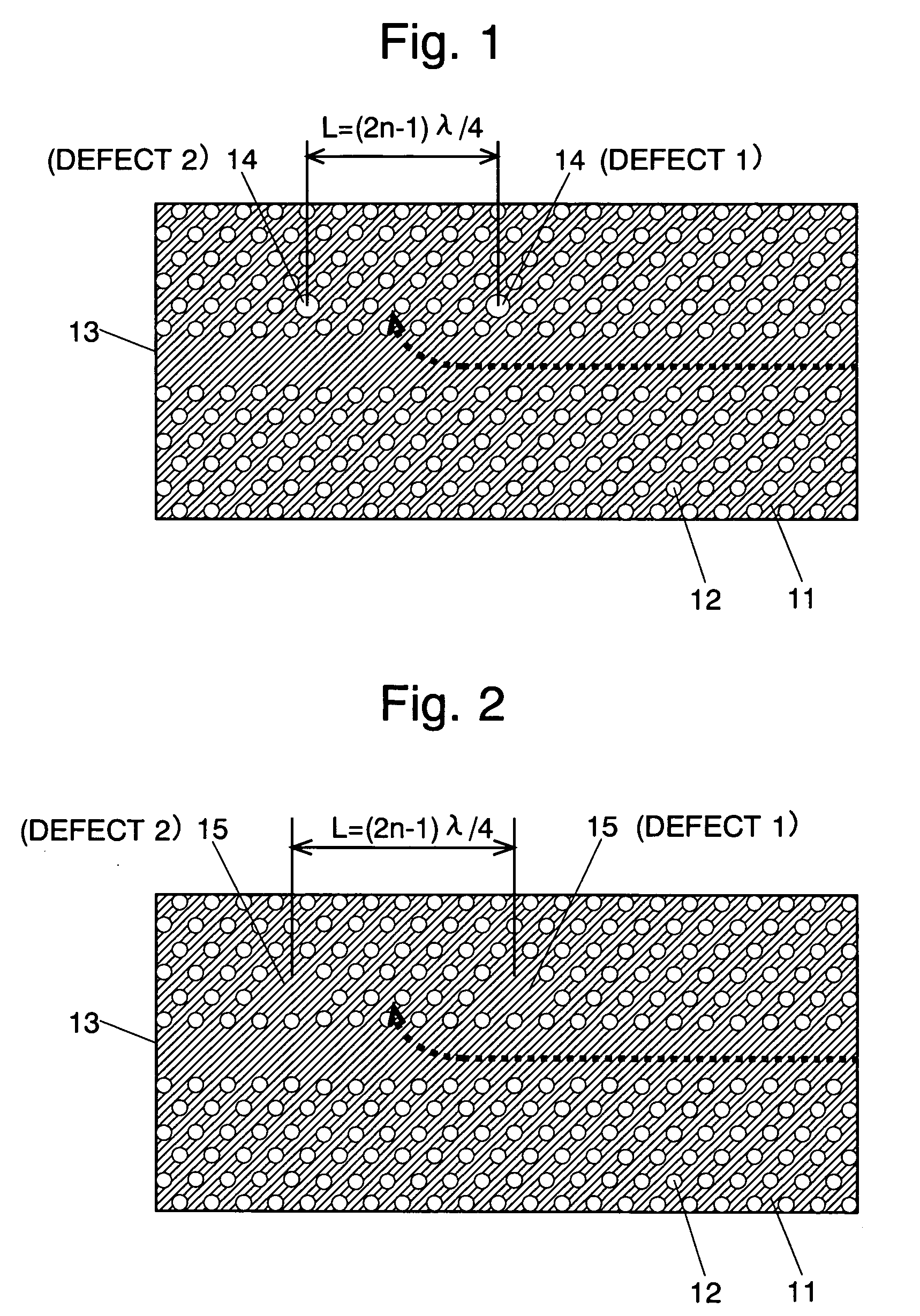
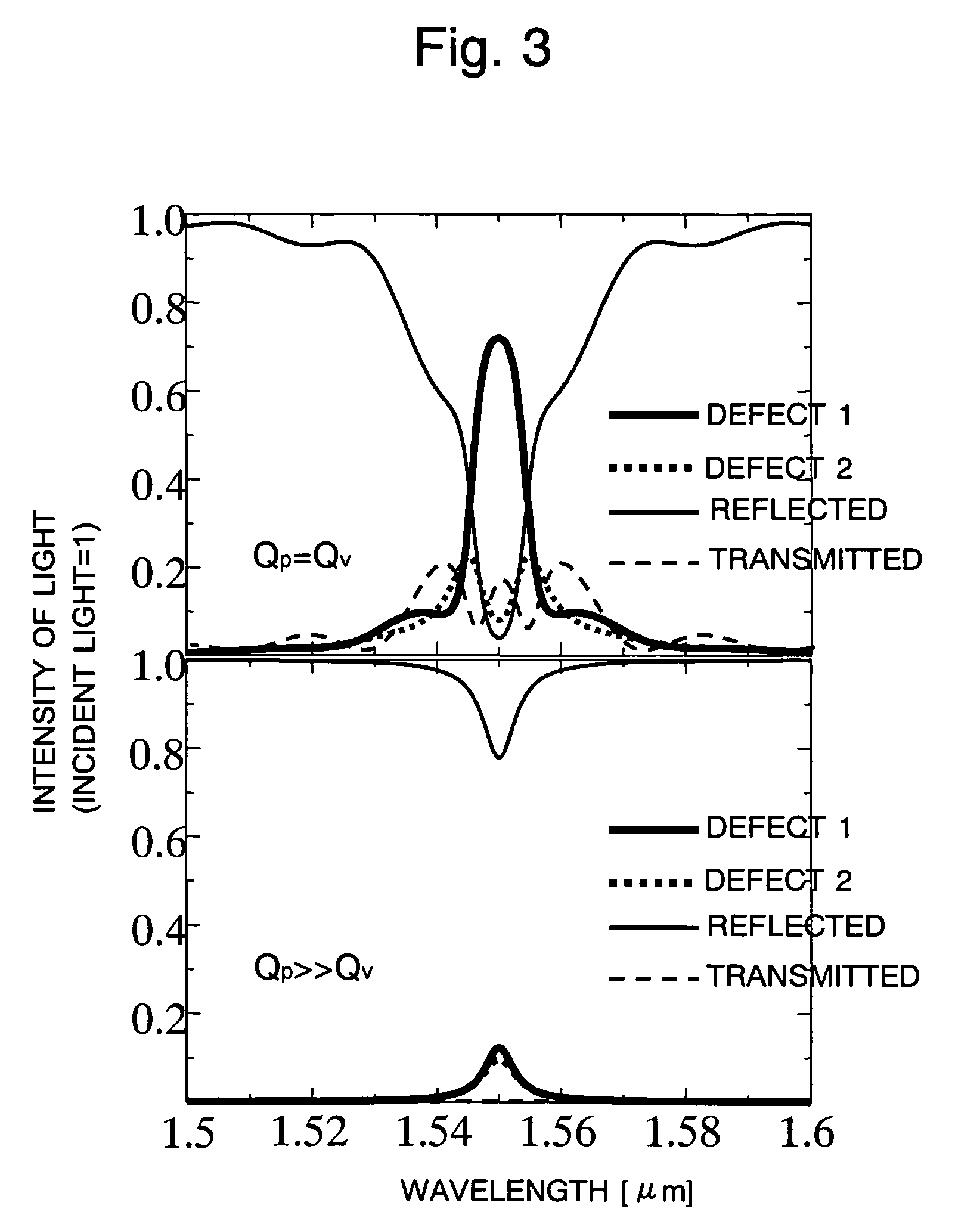
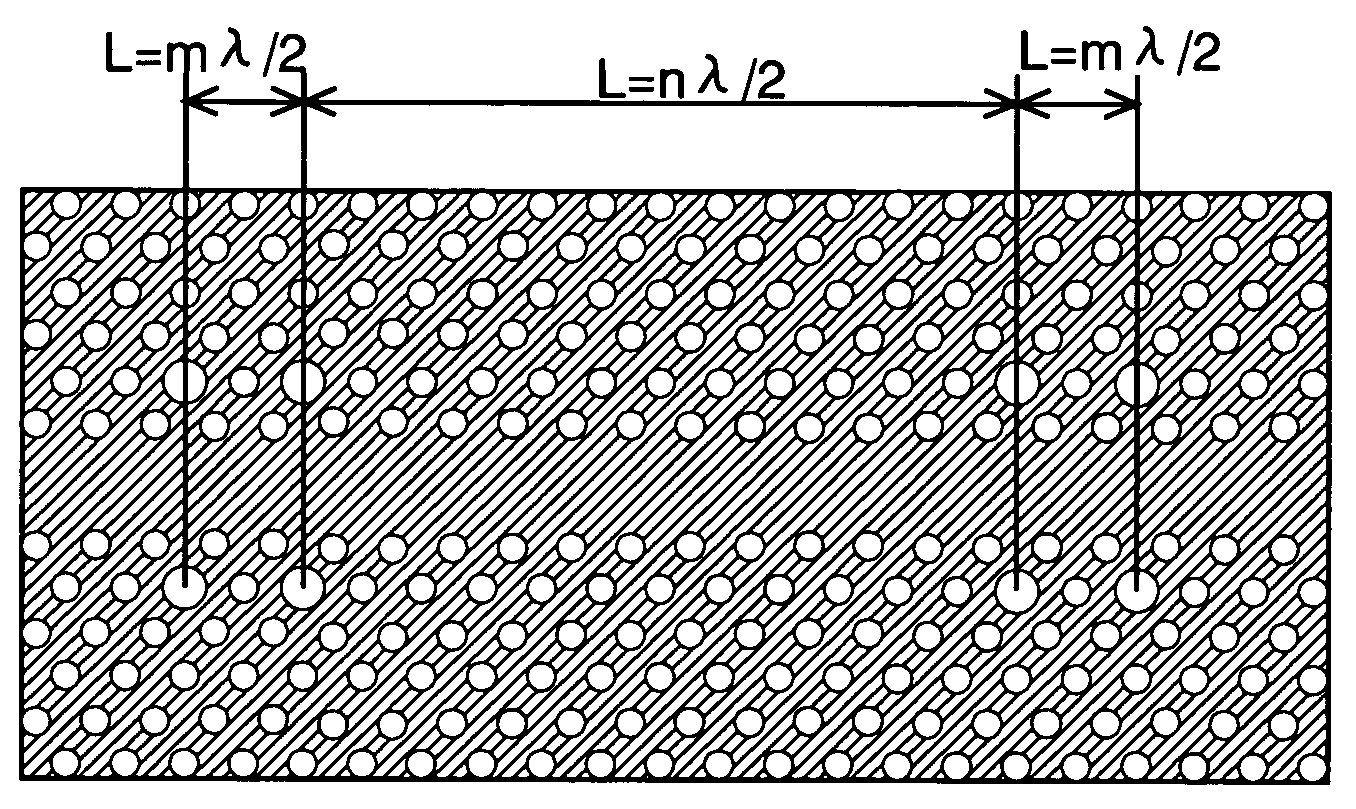
The present invention has been devised to provide a two-dimensional photonic crystal optical resonator and optical reflector having high light-extracting efficiency. This is achieved by the following construction. A two-dimensional photonic crystal consisting of a slab-shaped body 11 is created by periodically arranging areas (or holes) 12 having a refractive index different from that of the body 11. A waveguide 13 is formed by providing a linear zone where no hole 12 is bored. Two acceptor type point defects 14 are formed by enlarging two holes 12 spaced apart from each other by a distance L in the longitudinal direction of the waveguide. In this construction, an appropriate selection of the distance L suppresses the reflection and transmission of light at the point defects 14, allowing an efficient extraction of light resonating at the point defects 14. An appropriate selection of the distance L will increase the reflectivity of light at the point defects 14. This allows the body 11 to be used as an optical resonator for producing a resonance of light between the two point defects 14 or an optical reflector for reflecting light at the two point defects 14.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Two-dimensional photonic crystal optical resonator and optical reflector using interference between point defects
InactiveUS6996319B2Low refractive indexImprove the level ofLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionOptical reflectionLinear region
The present invention provides a two-dimensional photonic crystal optical resonator and reflector having high light-extracting efficiency. A two-dimensional photonic crystal consisting of a slab-shaped body is created by periodically arranging holes having a refractive index different from that of the body. A waveguide is formed by providing a linear zone where no hole is bored. Two acceptor type point defects are formed by enlarging two holes spaced apart from each other by a distance L in the longitudinal direction of the waveguide. An appropriate selection of the distance L suppresses or increases the reflection and transmission of light at the point defects, allowing an efficient extraction of light resonating at the point defects. This allows the body to be used as an optical resonator for producing a resonance of light between the two point defects or optical reflector for reflecting light at the two point defects.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Methods for reducing aberration in optical systems
InactiveUS6995908B2Reduced polarization effectsLower latencyPolarising elementsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusCatadioptric systemHigh numerical aperture
An optical system includes multiple cubic crystalline optical elements and one or more polarization rotators in which the crystal lattices of the cubic crystalline optical elements are oriented with respect to each other to reduce the effects of intrinsic birefringence and produce a system with reduced retardance. The optical system may be a refractive or catadioptric system having a high numerical aperture and using light with a wavelength at or below 248 nanometers. The net retardance of the system is less than the sum of the retardance contributions of the respective optical elements. In one embodiment, all cubic crystalline optical elements are oriented with identical three dimensional cubic crystalline lattice directions, a 90° polarization rotator divides the system into front and rear groups such that the net retardance of the front group is balanced by the net retardance of the rear group. The optical system may be used in a photolithography tool to pattern substrates such as semiconductor substrates and thereby produce semiconductor devices.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Green coherent light generating device using even nonlinear crystals
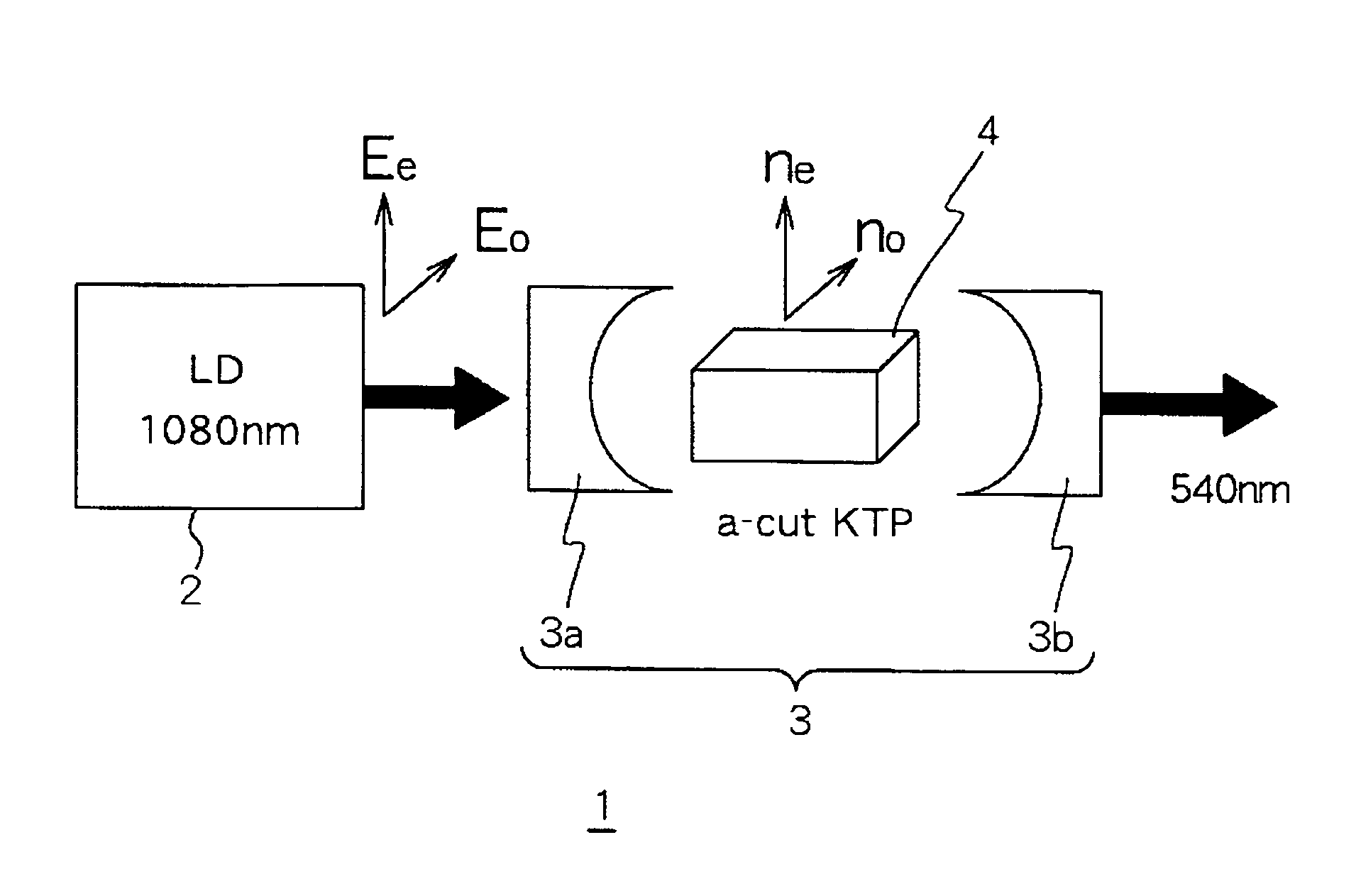
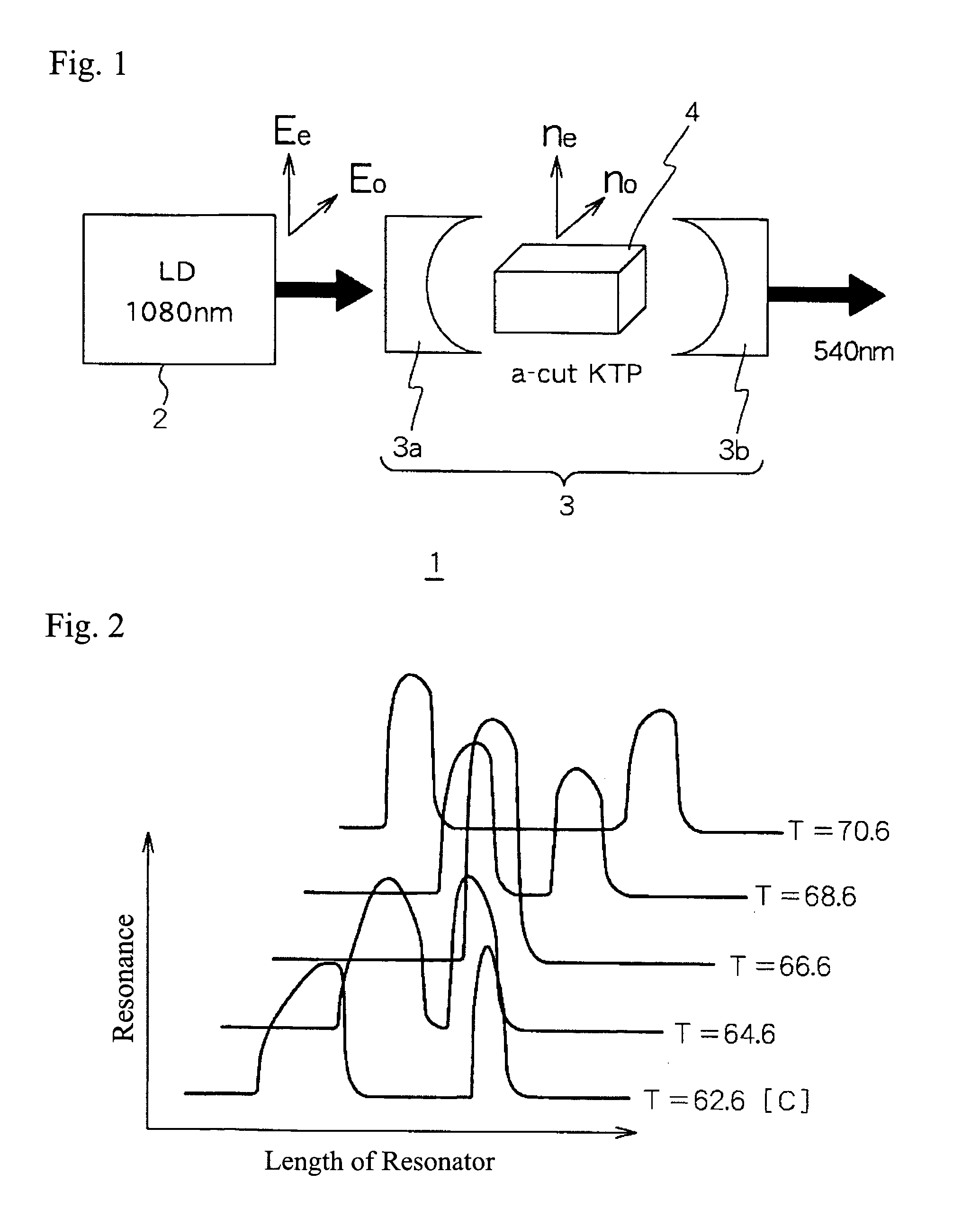
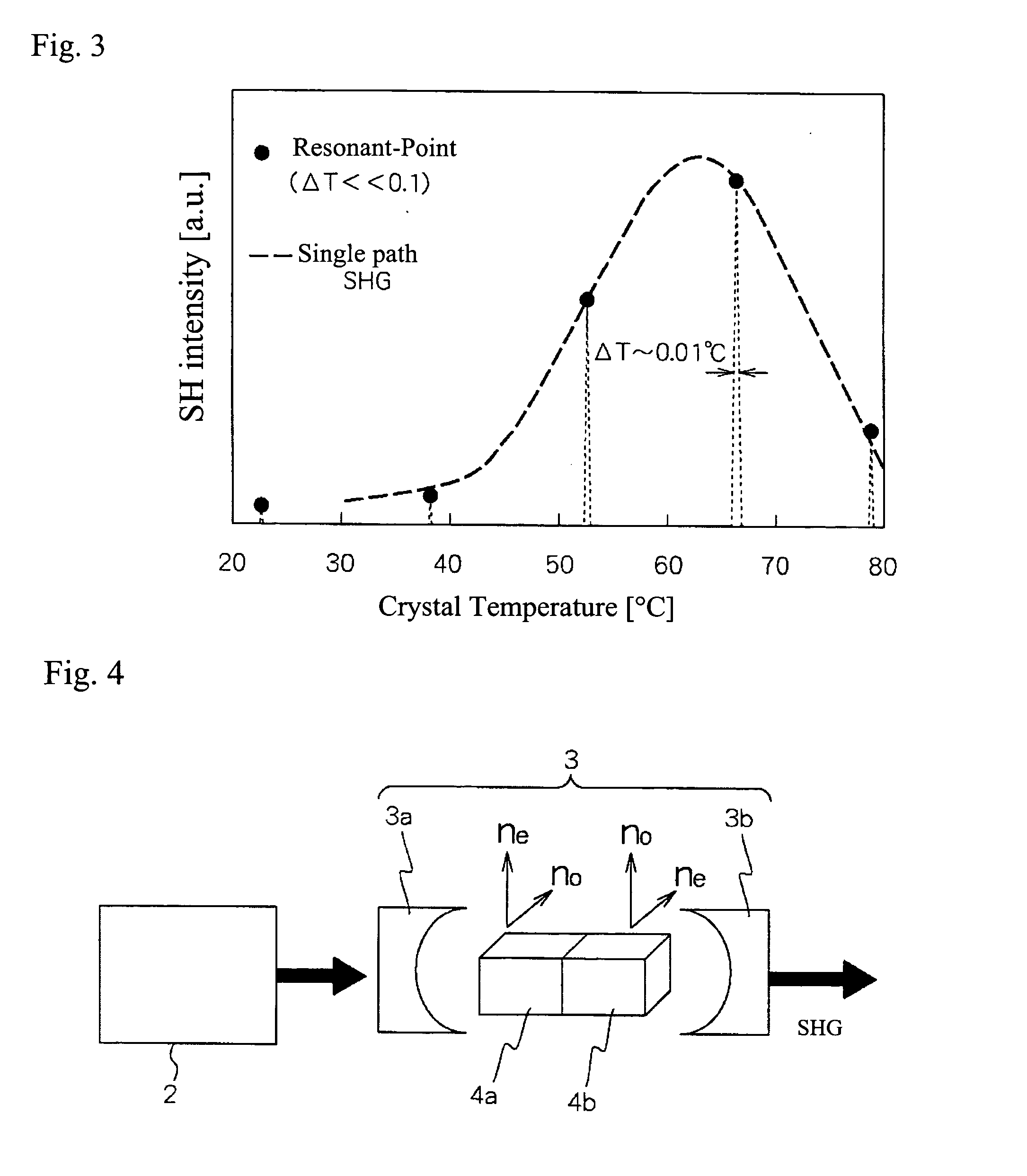
InactiveUS20050141572A1Quality improvementLarge outputLaser detailsLight demodulationHarmonicLight beam
An object of the present invention is to provide a comparatively small-scale device, that is a second harmonic generating device of a laser beam with which high-quality and large output light is obtained efficiently and stably. Specifically, the second harmonic generating device of a laser beam source includes a laser beam source, an optical resonator into which the said laser beam is injected, and KTP crystals provided in the said optical resonator. The KTP crystals in the optical resonator are a first a-axis-cut KTP crystal in which a beam of light carries out a-axis propagation and a second a-axis-cut KTP crystal, which is the same length as the first a-axis-cut KTP crystal and is rotated 90 degrees on the a-axis with respect to the first a-axis-cut KTP crystal.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
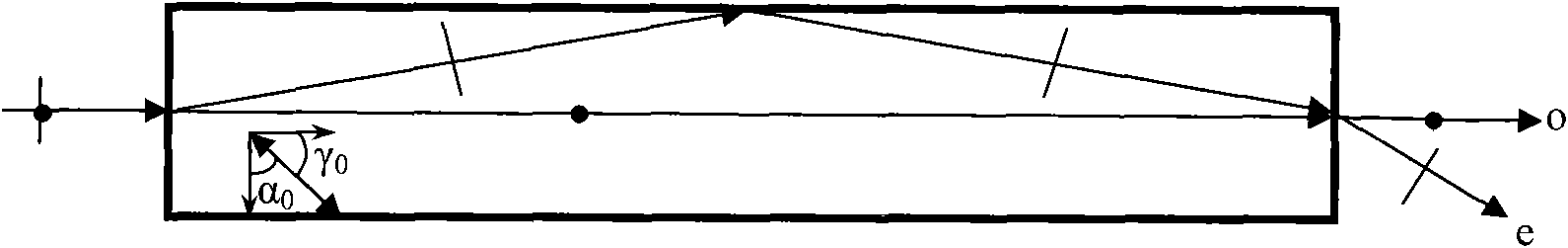
Test method of crystal optical uniformity and detection device thereof
PendingCN107228828AOptical uniformity avoidsSimple methodPolarisation-affecting propertiesPhase-affecting property measurementsRefractive indexInterferometric imaging
The invention relates to a test method of crystal optical uniformity and a detection device thereof. The method comprises the following effective steps of a, performing collimation and polarizing treatment on a selected coherent light source to obtain a detection light source required for detection; b, emitting incident light sent by the detection light source onto a crystal to be tested subjected to detective polishing treatment; regulating the position relationship of the incident light polarization direction and the crystal axial direction so that the crystal axial direction is vertical to the axial direction of the incident light; c, performing polarization inspection on the path of the incident light passing through the crystal to be tested to realize the polarization interference imaging; d, performing receiving display on the polarization interference imaging subjected to polarization inspection for further obtaining the crystal optical refractive index of the crystal in the crystal axial direction. The polarization interference imaging principle of the crystal in different axial directions is utilized; through the analysis and the comparison, the blank of a crystal device is subjected to primary inspection; inspected products with the qualified optical uniformity directly enter the precise processing work procedure; the occurrence of rejection products with unqualified optical uniformity in finished products is avoided.
Owner:济南快谱光电技术有限公司
Preparation method for three-dimensional crystal optics echo wall micro-cavity
ActiveCN103738915AIncrease varietyIncrease roughnessMicrostructural devicesLaser beam welding apparatusSurface finishTotal internal reflection
The invention provides a preparation method for a three-dimensional crystal optics echo wall micro-cavity. The preparation method comprises the steps: carrying out femtosecond laser selective ablation on crystals soaked in liquid and grinding the lateral wall of the micro-cavity by using a focused ion beam. The three-dimensional crystal optics echo wall micro-cavity prepared by adopting the method provided by the invention can be used for limiting light through continuous total internal reflection of the cavity and an outside face, and has the advantages of extremely high surface smoothness, small mode volume and high quality factor. The preparation method is applicable to various crystal materials, glass and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Apparatus and method for displaying image
InactiveUS20050157235A1Improve the display effectHigher-contrast imagePicture reproducers using projection devicesNon-linear opticsPhase differenceCrystal optics
Provided is a projection type liquid crystal display apparatus, which can improve black-level display and thus can display a higher-contrast image as compared to the related art. An optical compensator is located on the light exit side with respect to the liquid crystal display device so as to compensate for the optical phase difference caused by liquid crystal molecules in a light-entry-side region of the liquid crystal layer. As the optical compensator is located on the light exit side with respect to the liquid crystal display device, birefringence, caused by the liquid crystal molecules present in the light-entry-side region, is compensated for without being influenced by a microlenses provided in the liquid crystal plane. Consequently, the apparatus can improve the black-level display and thus can display a higher-contrast image as compared to the related art. Further, a phase difference caused by the birefringence of the nematic liquid crystal molecule is compensated for by using a substance having properties optically opposite to the positive crystal, namely, a substance having birefringence equivalent to birefringence of a negative crystal.
Owner:SONY CORP
Trapezoidal structure based crystal optical electric field sensor
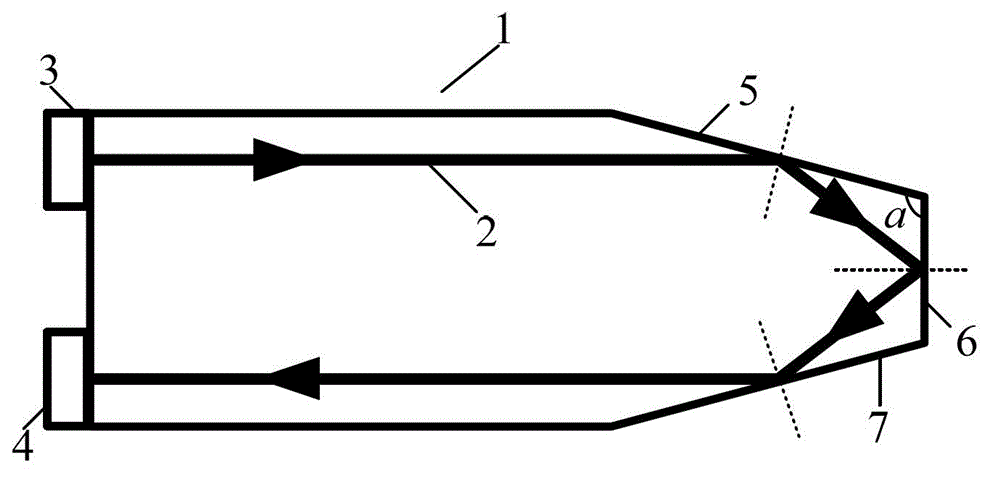
ActiveCN102914702ASimple structureImprove temperature stabilityElectrostatic field measurementsTime domainElectric field sensor
The invention relates to a trapezoidal structure based crystal optical electric field sensor, belonging to the technical field of electric field measurement. The electric field sensor comprises a crystal, a polarizer and a polarization analyzer, wherein one end part of the crystal is trapezoidal while the other end part of the crystal is rectangular; the polarizer is stuck to a laser incidence place of the rectangular end part of the crystal; the polarization analyzer is stuck to a laser emission place of the rectangular end part of the crystal; and a top angle a of the trapezoidal end part of the crystal and optical polarization points of the electric field sensor satisfy a certain relationship. Three total reflection of the end face of the electro-optical crystal is utilized to generate optical polarization points, and a special trapezoidal top angle is selected to remove 1 / 4 wave plate of the optical polarization points, so that the trapezoidal structure based crystal optical electric field sensor, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages of simplifying a sensor structure and improving temperature stability of the sensor. The optical electric field sensor, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages of not only measuring the amplitude value of the electric field, but also measuring information such as frequency and phase position of the electric field, and is a time domain electric field sensor.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
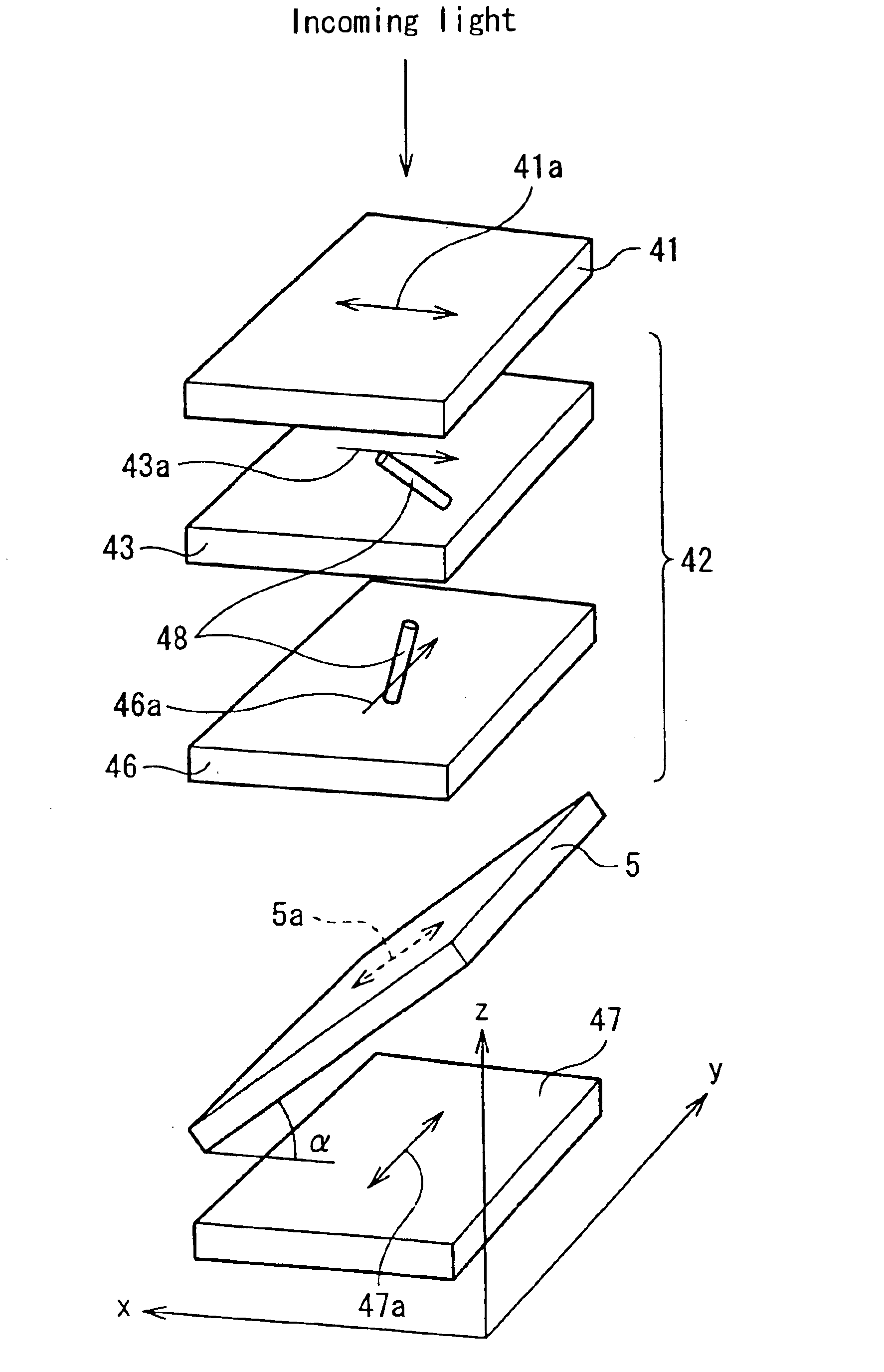
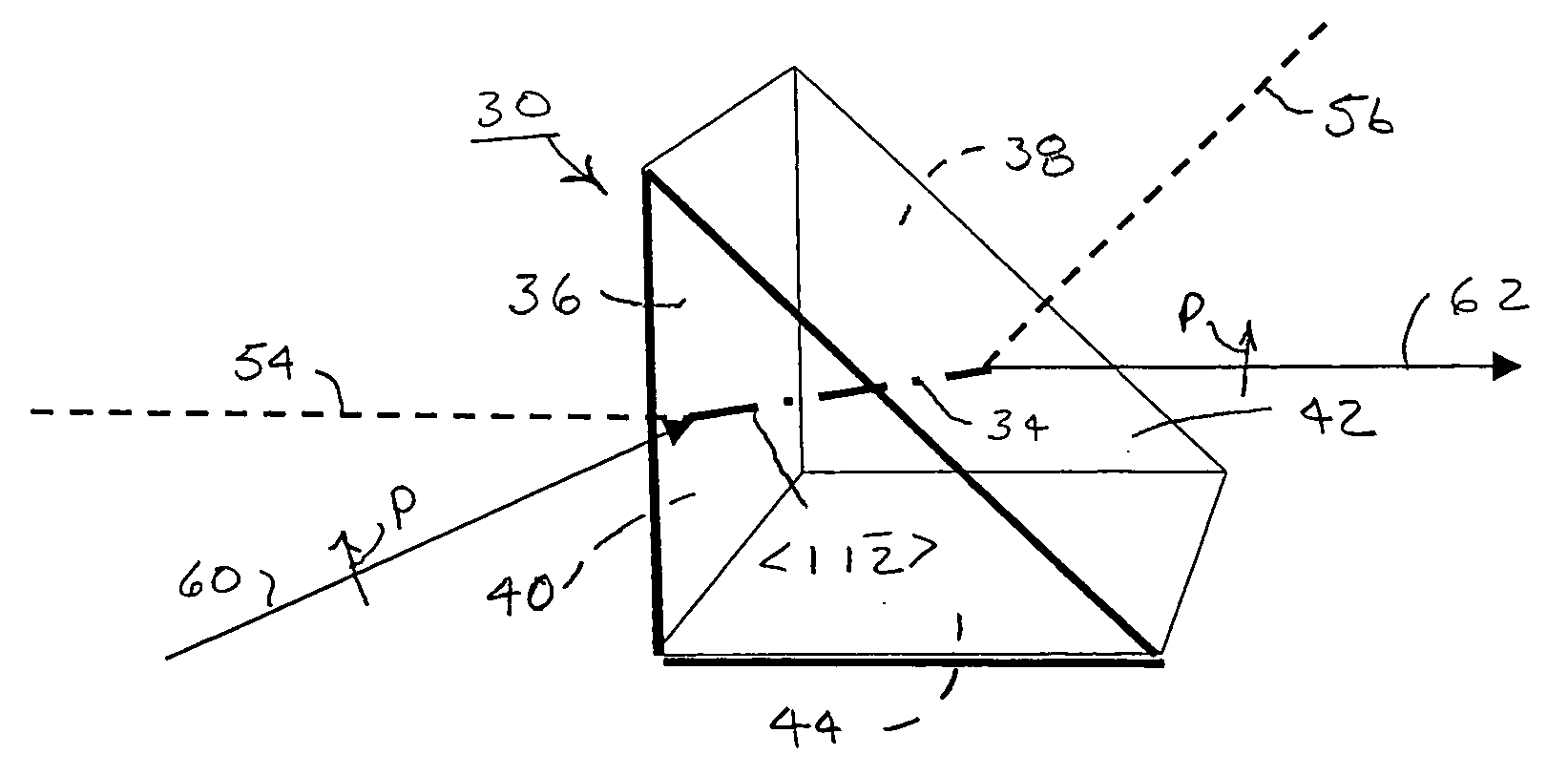
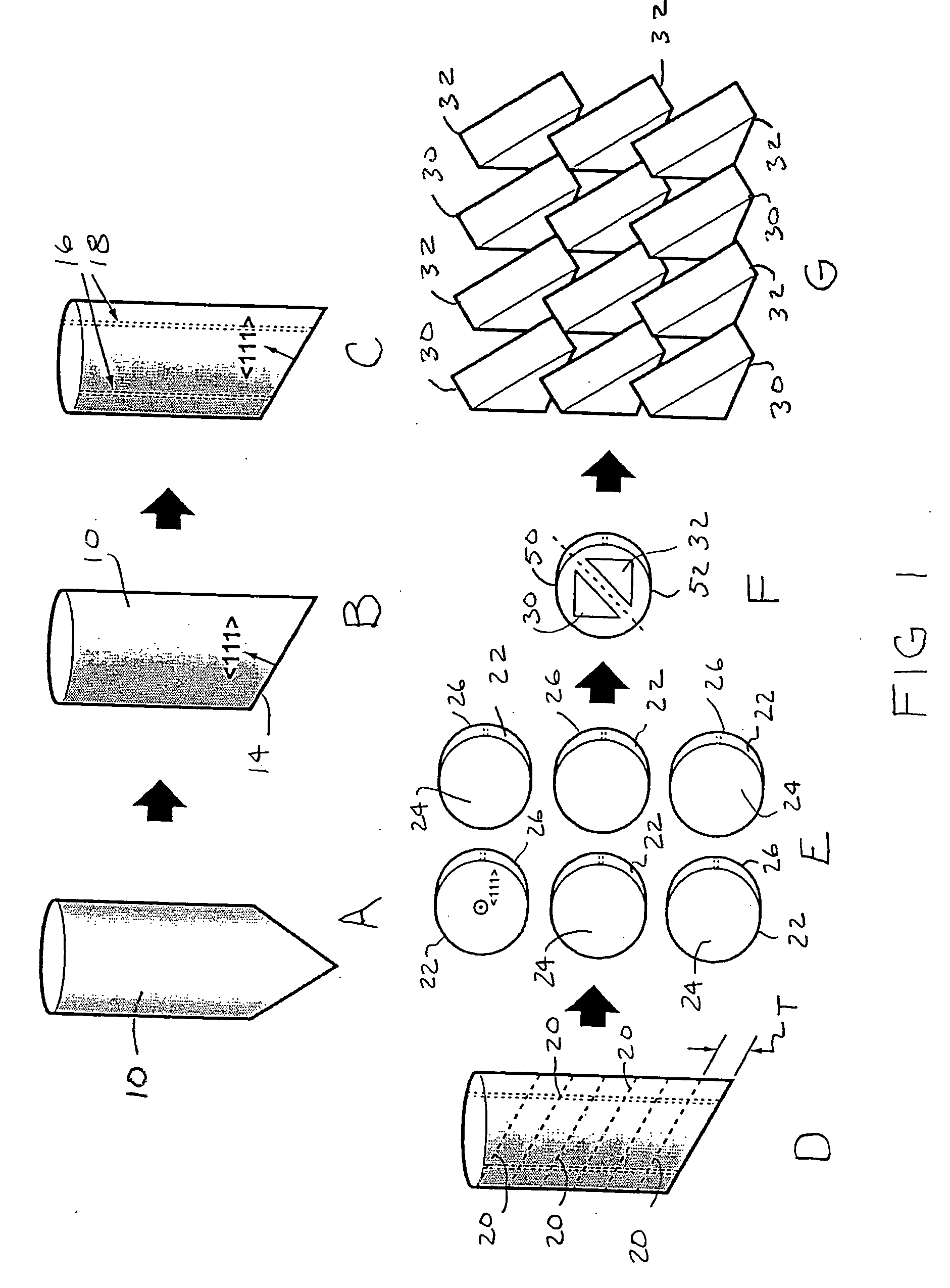
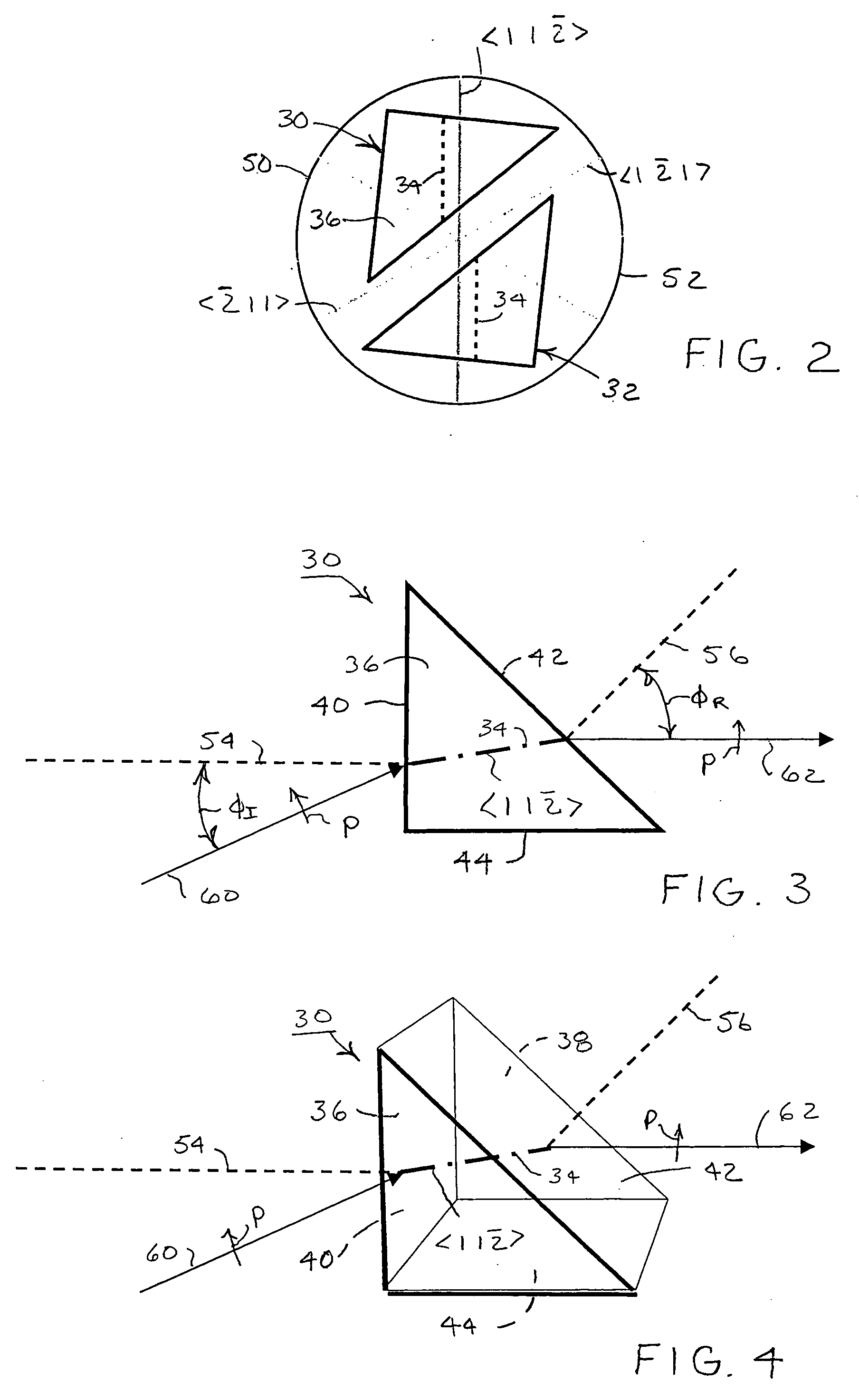
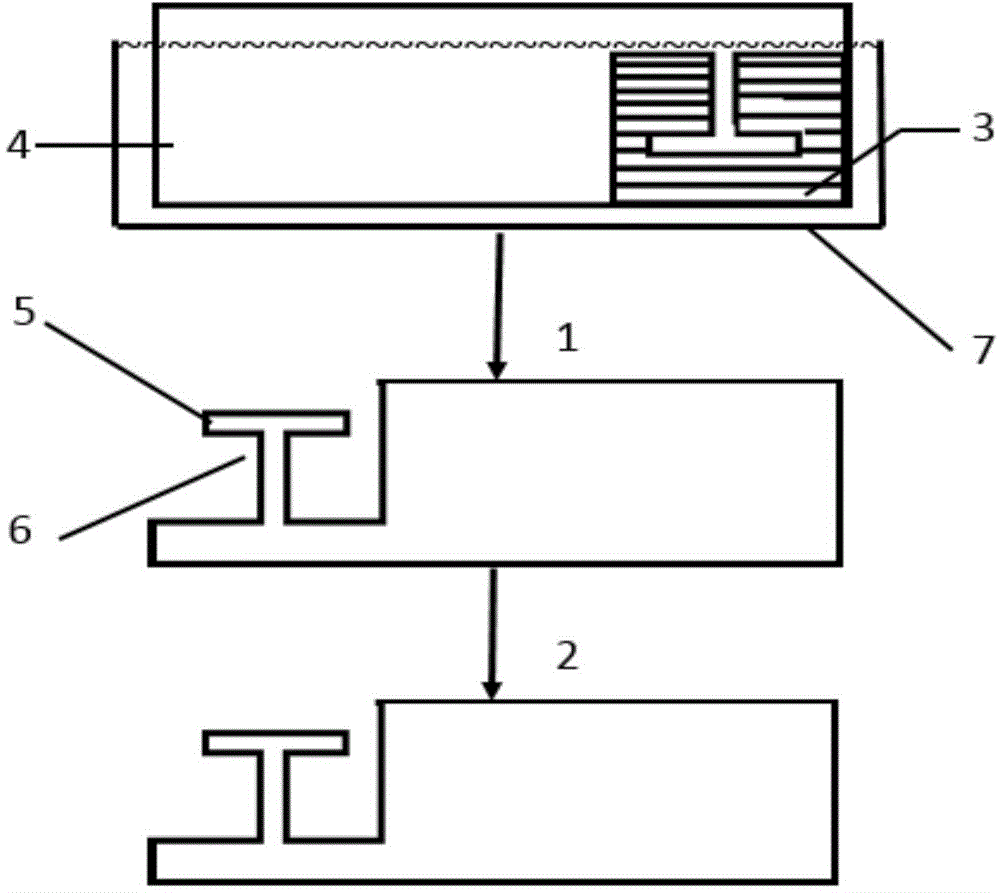
Increased yield of cubic crystalline optical elements by crystal orientation
ActiveUS20060061864A1Increase productionMirrorsDecorative surface effectsCrystal orientationCrystal plane
Increased yield of optical elements from cubic crystal rods, such as made of calcium fluoride, is made possible by orienting the optical elements for supporting the propagation of light along one of the <1 1 {overscore (2)}>, <1 2 1>, or <{overscore (2)} 1 1> alternative crystal axis, which extend perpendicular to a main <1 1 1> crystal axis. A cleave is taken through the crystal rod along a primary crystal plane {1 1 1} normal to the <1 1 1> main axis. One of the <1 1 {overscore (2)}>, <1 {overscore (2)} 1>, or <{overscore (2)} 1 1> alternative crystal axes is located by optical inspection and indicated on the crystal rod with an orientation label. Additional cuts are taken parallel to the {1 1 1} primary crystal plane to divide the crystal rod into disks each containing a portion of the orientation label. The disks can be cut again and sides formed perpendicular to the {1 1 1} primary crystal plane with regard to the orientation labels for forming optical elements, such as prisms, oriented for supporting the propagation of polarized light along one of the <1 1 {overscore (2)}>, <1 {overscore (2)} 1>, and <{overscore (2)} 1 1 > alternative crystal axes.
Owner:CORNING INC
Wavelength conversion optical element, method for fabricating wavelength conversion optical element, wavelength conversion device, ultraviolet laser irradiator and laser material processing system
ActiveUS20090080475A1Increase output powerImprove performanceLaser detailsLight demodulationFourth harmonicNd:YAG laser
An optical wavelength conversion element includes a cesium-lithium-borate crystal processed into a 10-mm long optical element cut in an orientation that allows a fourth harmonic of a Nd:YAG laser to be generated. A transmittance (Ta) at 3589 cm−1 in an infrared transmission spectrum of the optical element is used as an index that indicates a content of water impurities in the crystal and is independent of a polarization direction. An actual measurement of the transmittance Ta is at least 1%, without taking into account loss at an optically polished surface of the crystal. A wavelength conversion device, a ultraviolet laser irradiation apparatus, a laser processing system, and a method of manufacturing an optical wavelength conversion element are also described.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV +1
Structures and methods for reducing aberration in optical systems
InactiveUS7453641B2Lower latencyReduced polarization effectsPolarising elementsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusOptical axisCrystal optics
An optical system includes at least one cubic crystalline optical element aligned along an optical axis, the at least one cubic crystalline optical element being birefringent and imparting retardance on a beam of light propagating through the optical system along the optical axis, and polarization rotation optics inserted along the optical axis and selected to rotate the polarization of the beam of light to at least partially reduce the retardance.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Preparation method of three-dimensional crystal optical whispering gallery microcavity
ActiveCN103738915BIncrease varietyIncrease roughnessMicrostructural devicesLaser beam welding apparatusSurface finishWhispering gallery
The invention provides a preparation method for a three-dimensional crystal optics echo wall micro-cavity. The preparation method comprises the steps: carrying out femtosecond laser selective ablation on crystals soaked in liquid and grinding the lateral wall of the micro-cavity by using a focused ion beam. The three-dimensional crystal optics echo wall micro-cavity prepared by adopting the method provided by the invention can be used for limiting light through continuous total internal reflection of the cavity and an outside face, and has the advantages of extremely high surface smoothness, small mode volume and high quality factor. The preparation method is applicable to various crystal materials, glass and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Active cooling of crystal optics for increased laser lifetime
InactiveUS7903351B2Reduce degradationLow costPhotomechanical apparatusLaser constructional detailsActive coolingTransmittance
A laser beam is generated and transmitted within an enclosed pathway through at least one crystal optic at a power density that progressively degrades transmissivity of the crystal optic with accumulating fluence. The crystal optics are cooled below normal operating temperatures to slow the progressive degradation in the transmissivity of the crystal optics with the accumulating fluence or to accommodate a higher power density without correspondingly increasing the progressive degradation in transmissivity.
Owner:CORNING INC
Unit extraordinary refraction rochon prism and extraordinary refraction polarized beam splitting method
InactiveCN101782690AAvoids effects of polarization beam splitting processRealize functionOptical elementsBirefringent crystalBeam splitting
The invention relates to a unit extraordinary refraction rochon prism, comprising a single cuboid made of iceland crystals. A value of a crystal optic axial angle alpha can be selected in the range of 46.6 degrees to 46.3 degrees according to using wavelength. The range of applicable wavelength of the prism is from 300 nm to 1800 nm, and an extinction ratio excels 10 to 5. The extraordinary refraction polarized beam splitting method comprises the steps of: shooting beams into a unit uniaxial birefringent crystal prism, enabling o light to directly pass through the crystal prism, and keeping the o light in the same direction with the refraction beams after emergence; performing total reflection of e light with extraordinary refraction in an incident end face in the internal surface of the crystal prism, and performing extraordinary reflection again when reaching an emergence end face; and generating a beam splitting angle after the emergence of the two beams of light in the emergence end face. The invention is the polarizing beam splitting method and the unit extraordinary refraction rochon prism with higher technical index and the realization of multiple functions. The characteristic of beam splitting of the prism indicate the prism has multiple functions of polarized beam splitting, adjustable beam splitting angles with incidence angles, polarization and analysis. The invention has very important practical significance in the application technical fields such as laser technology, optical test, optical modulation, and the like.
Owner:QUFU NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com