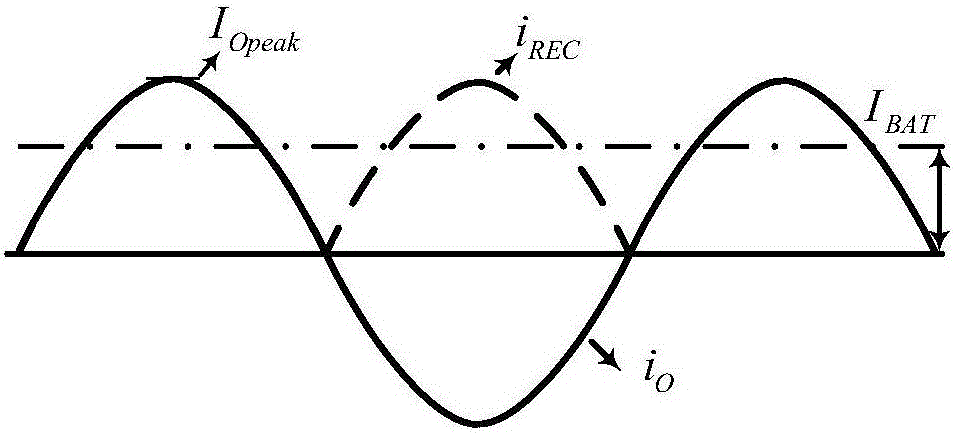
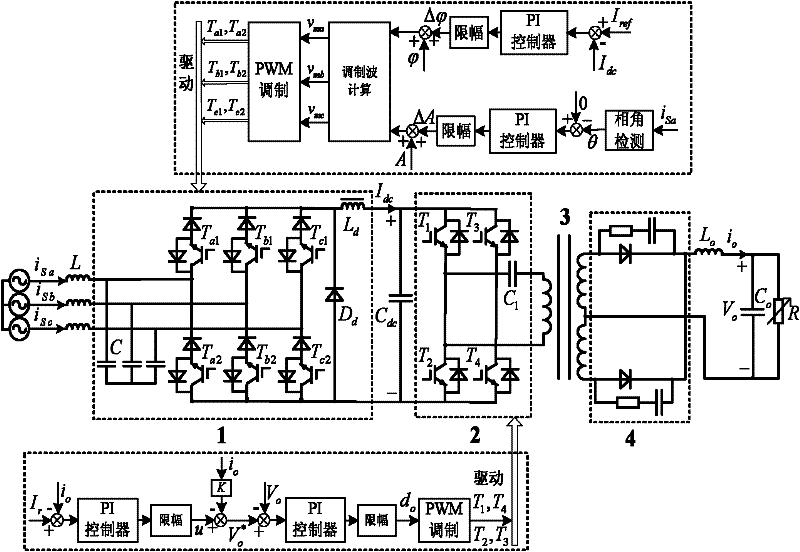
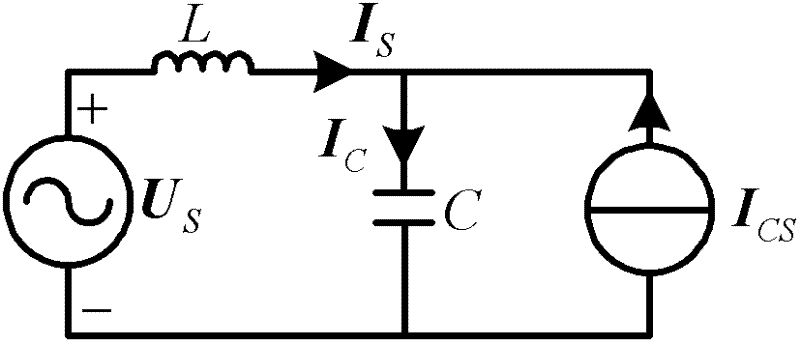
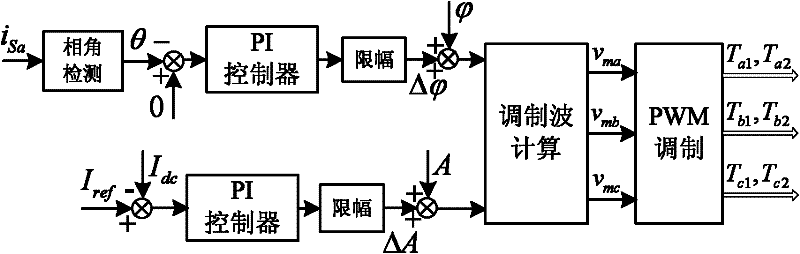
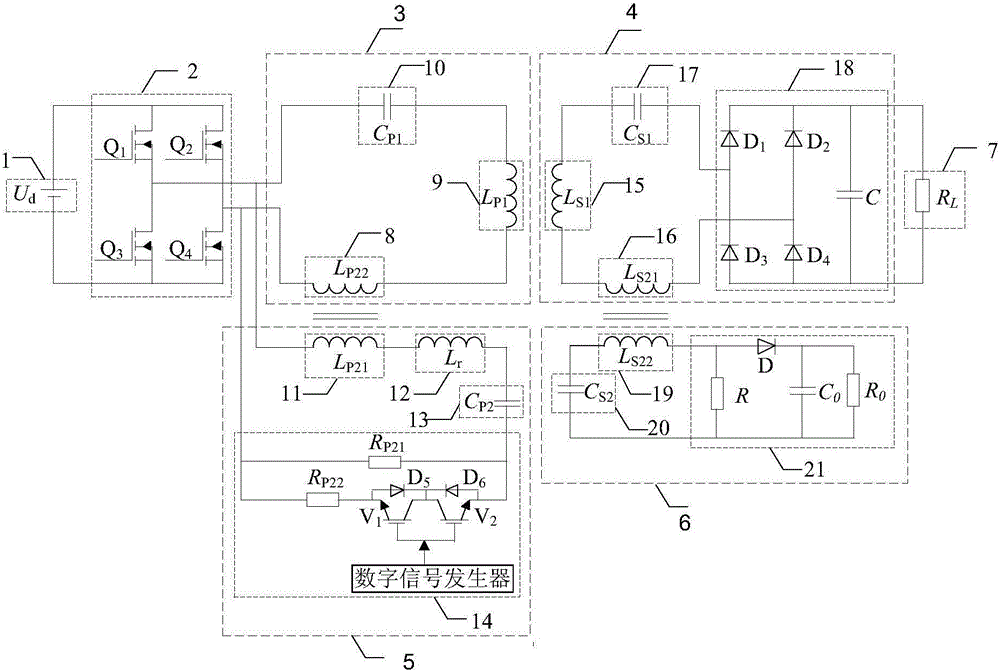
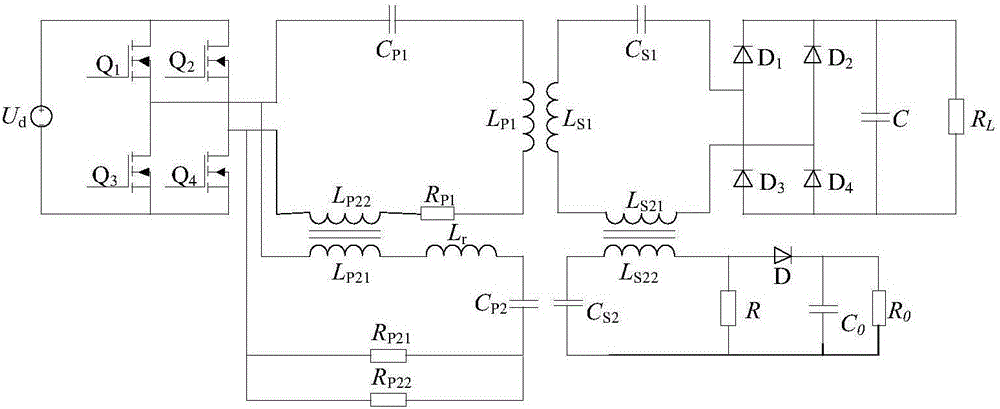
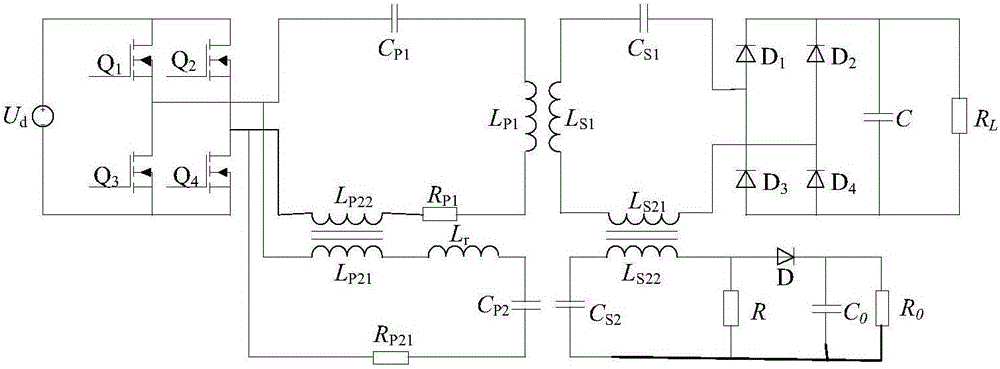
Patents
Literature
684 results about "Coupling transformer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
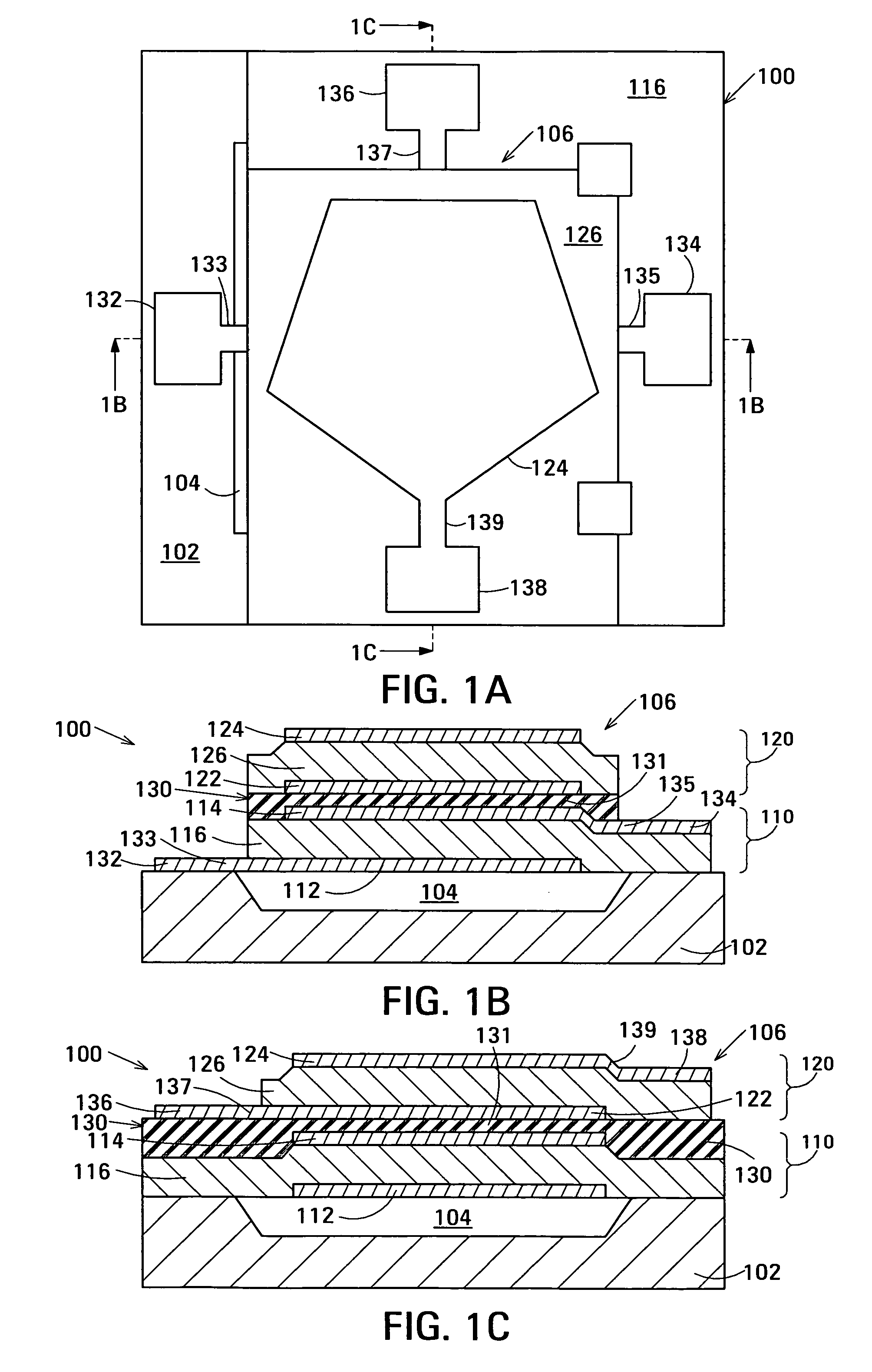
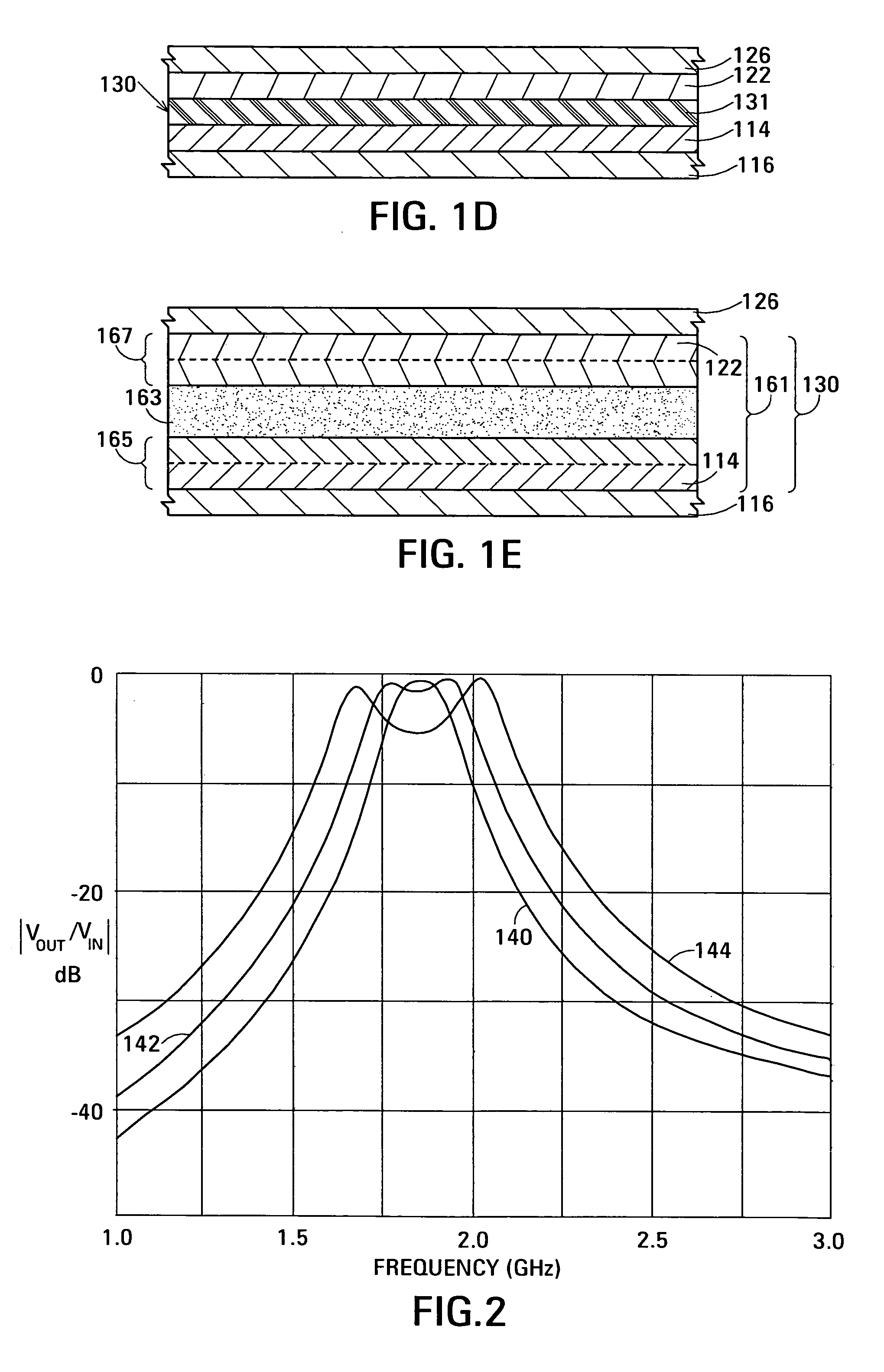
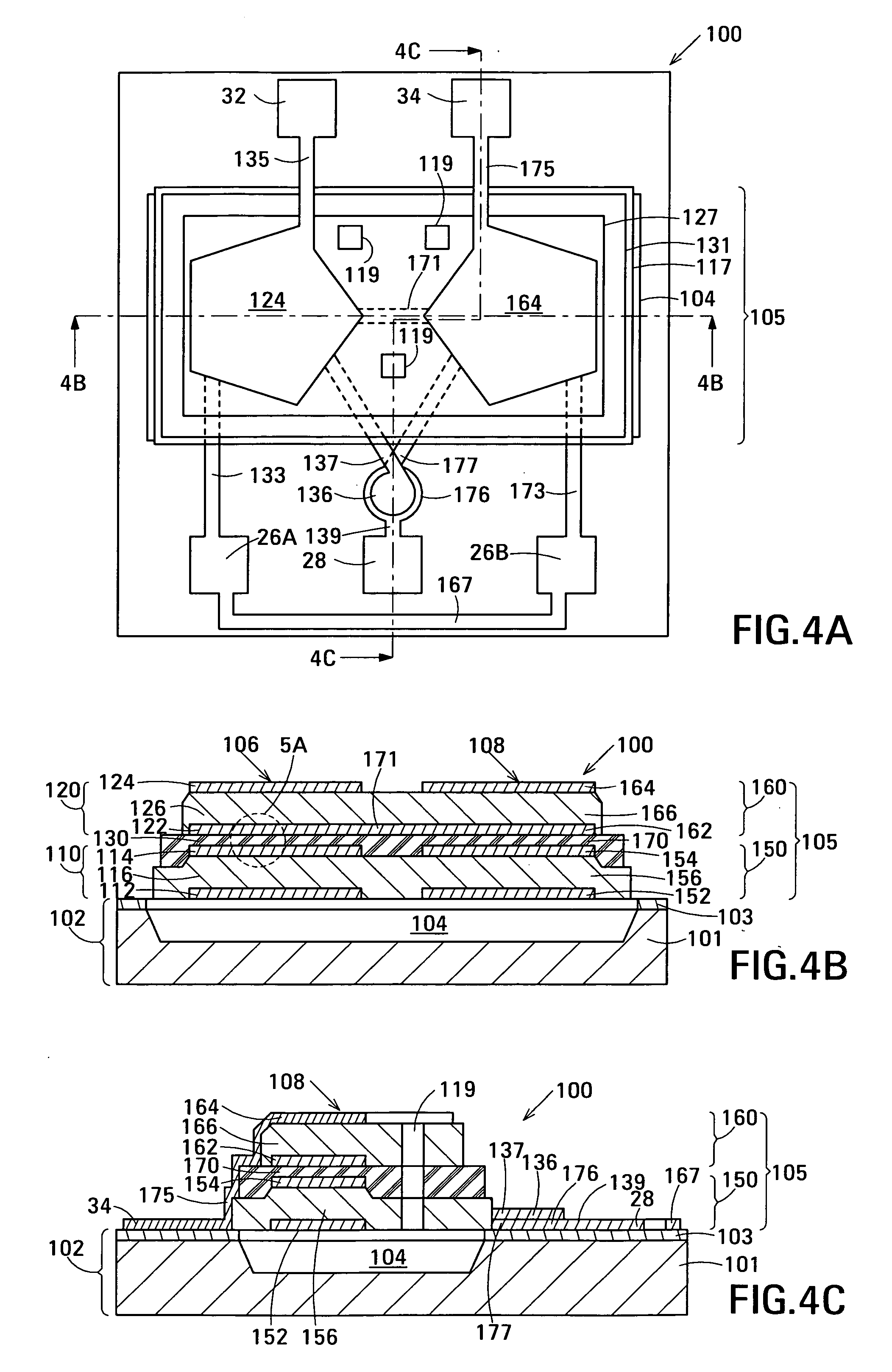
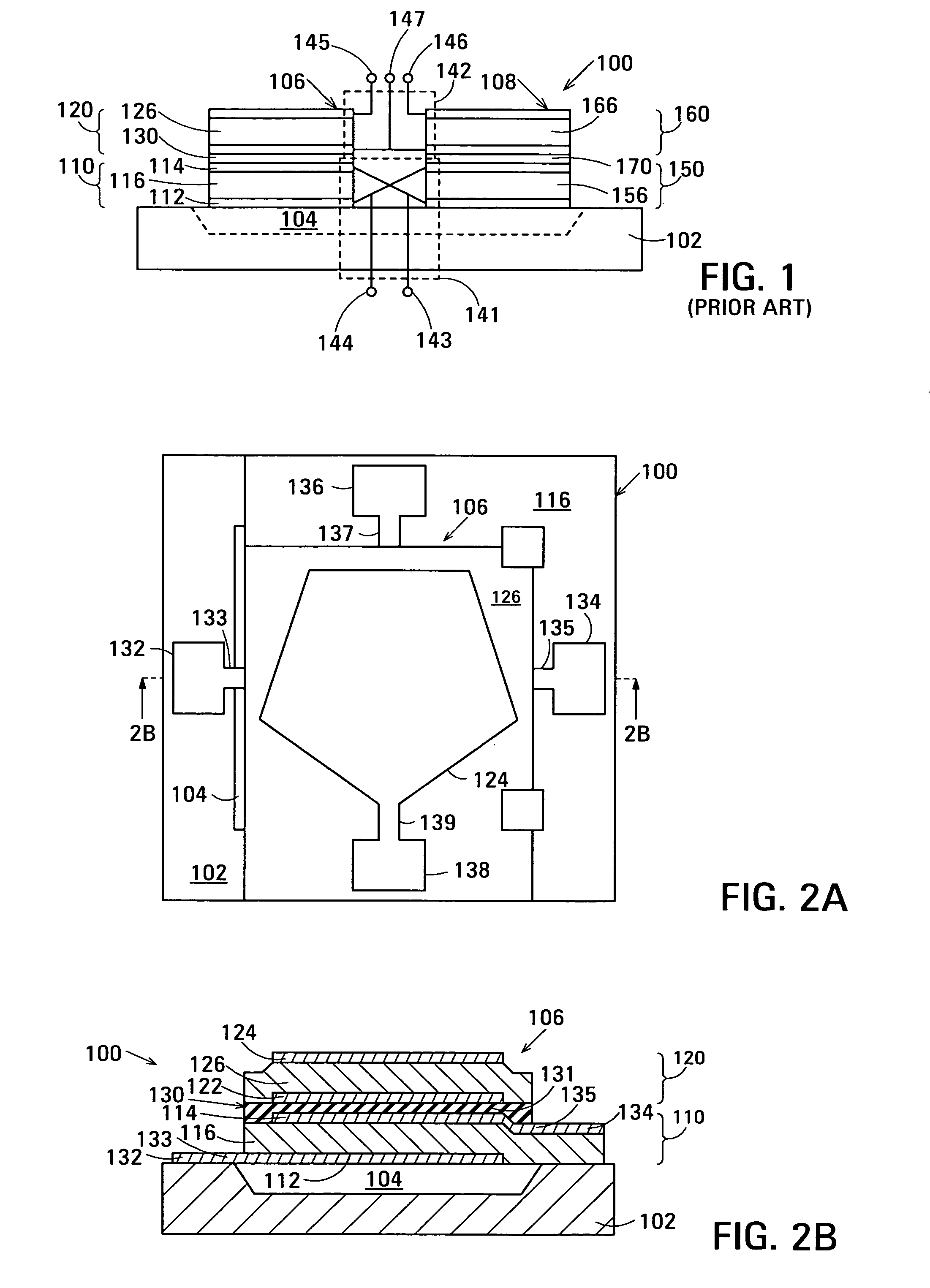
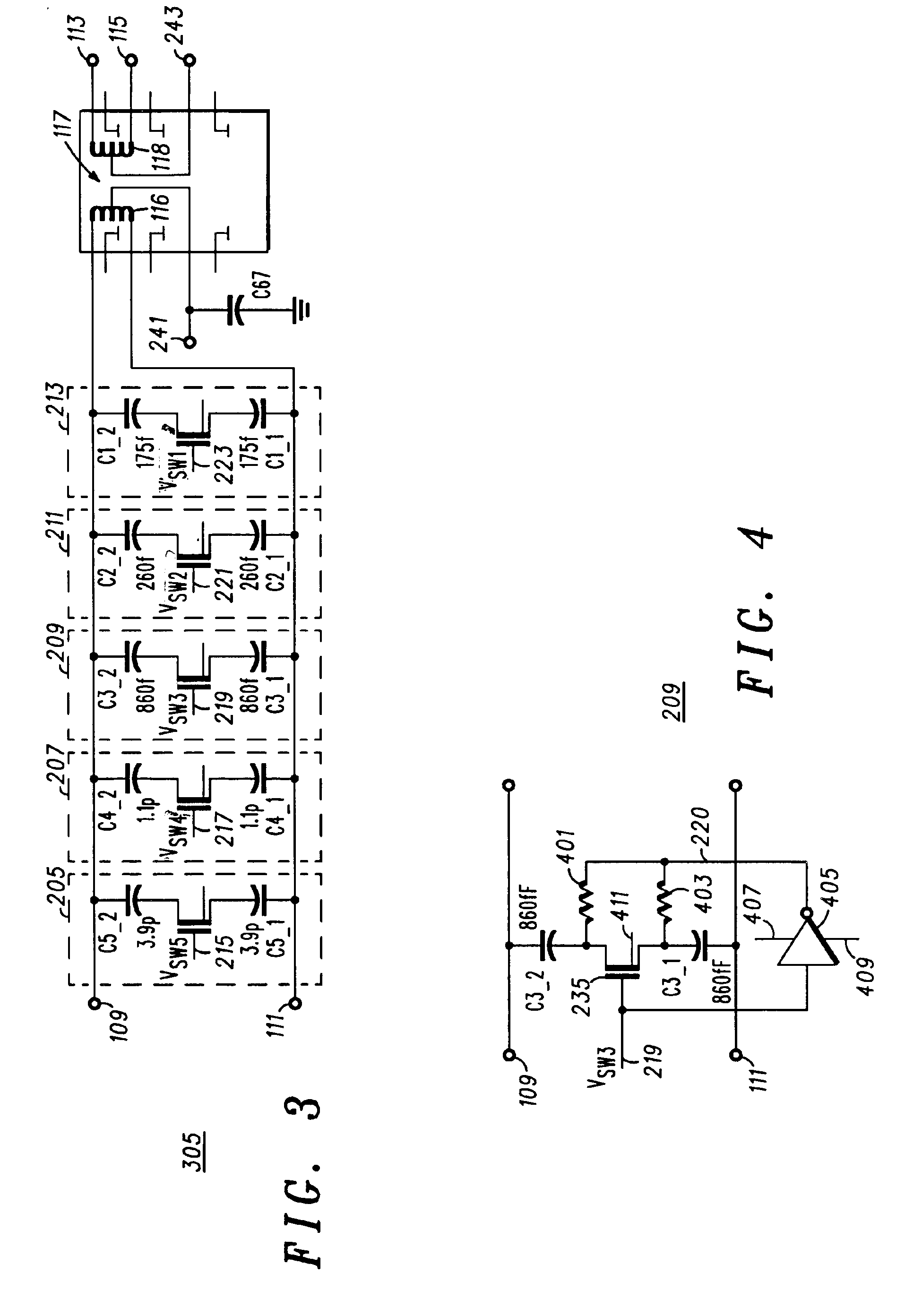
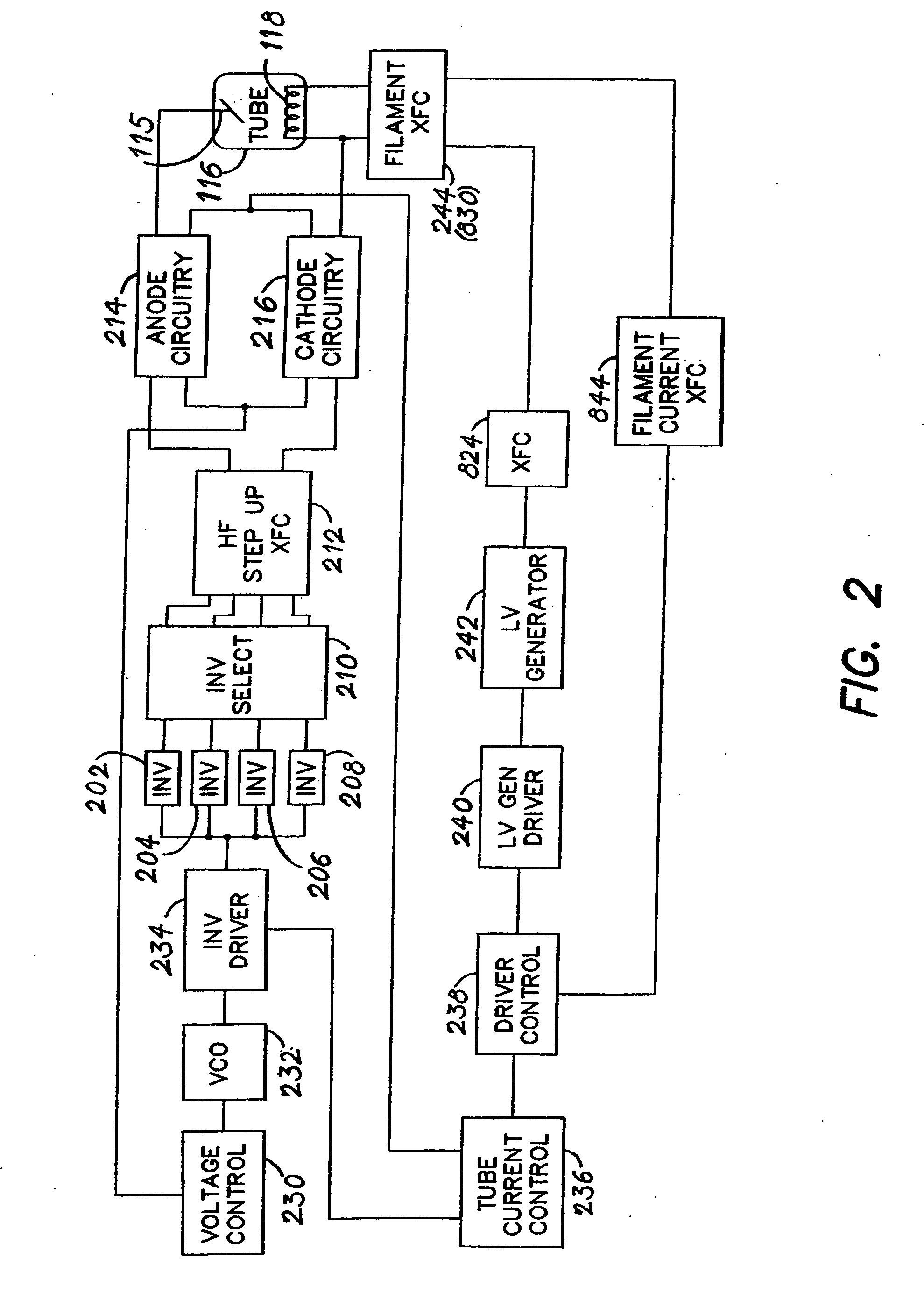
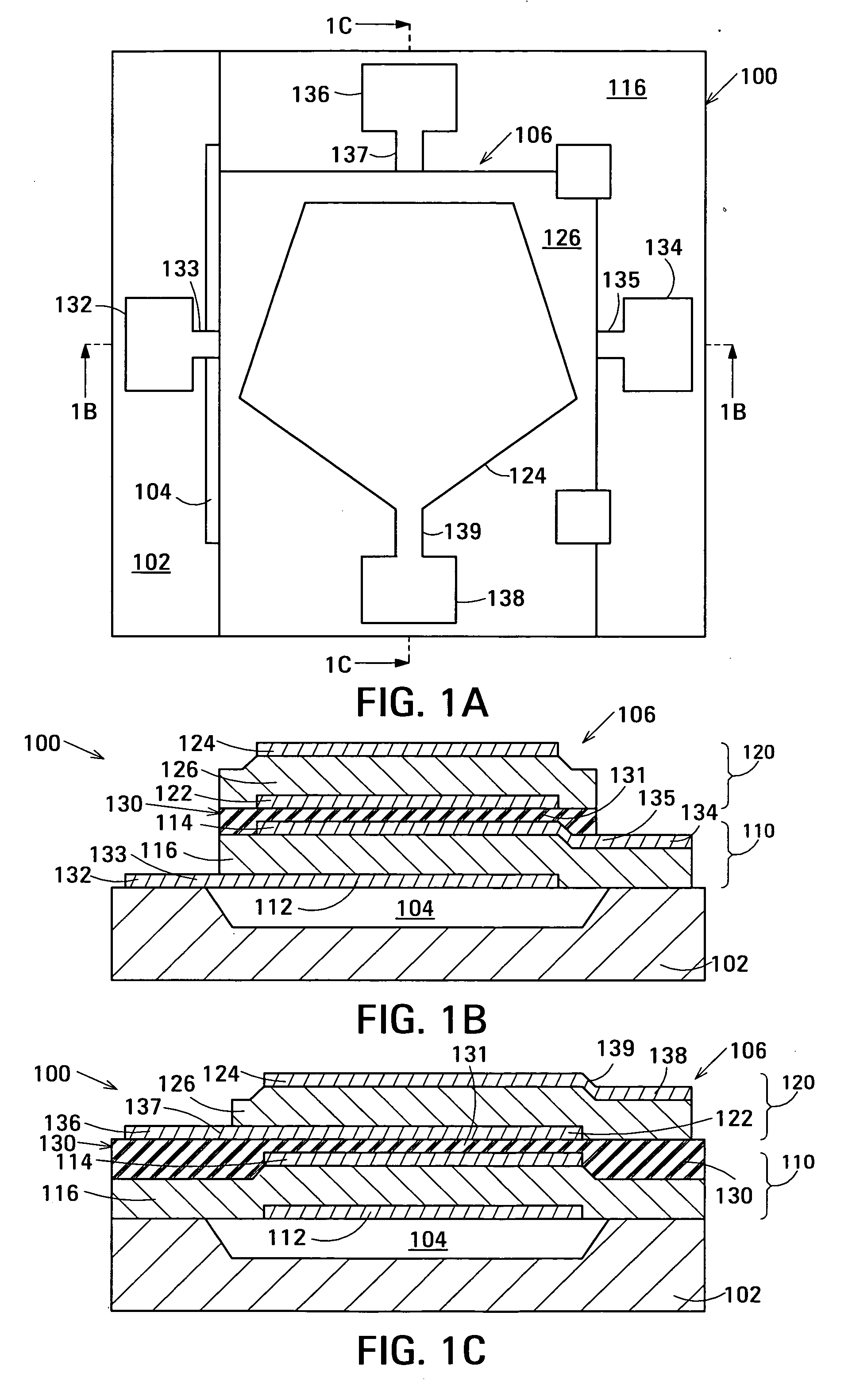
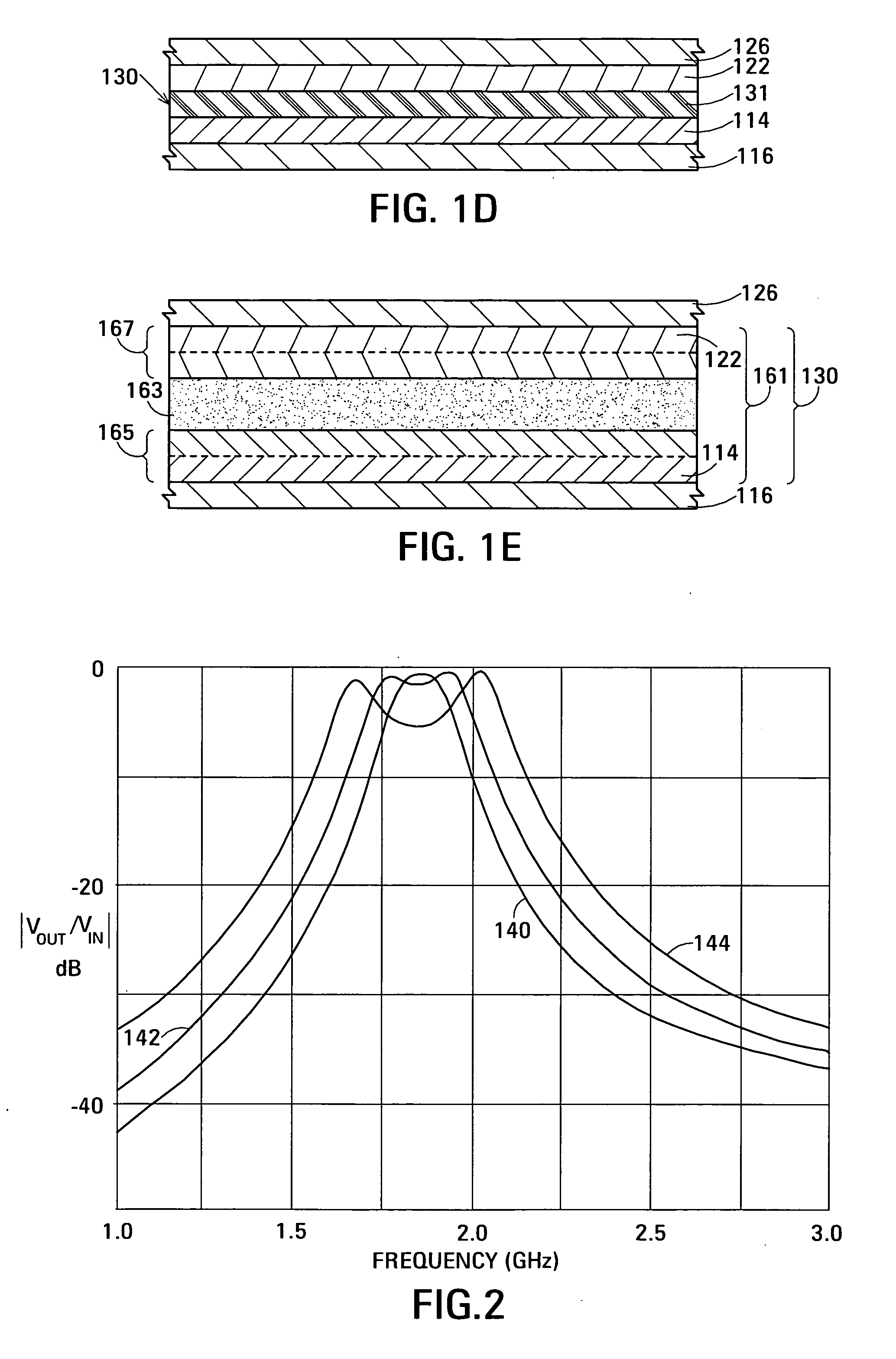
Film acoustically-coupled transformer with increased common mode rejection
ActiveUS20050093659A1Improved common mode rejection ratioRaise the ratioImpedence networksSolid-state devicesPlanar electrodeThin-film bulk acoustic resonator
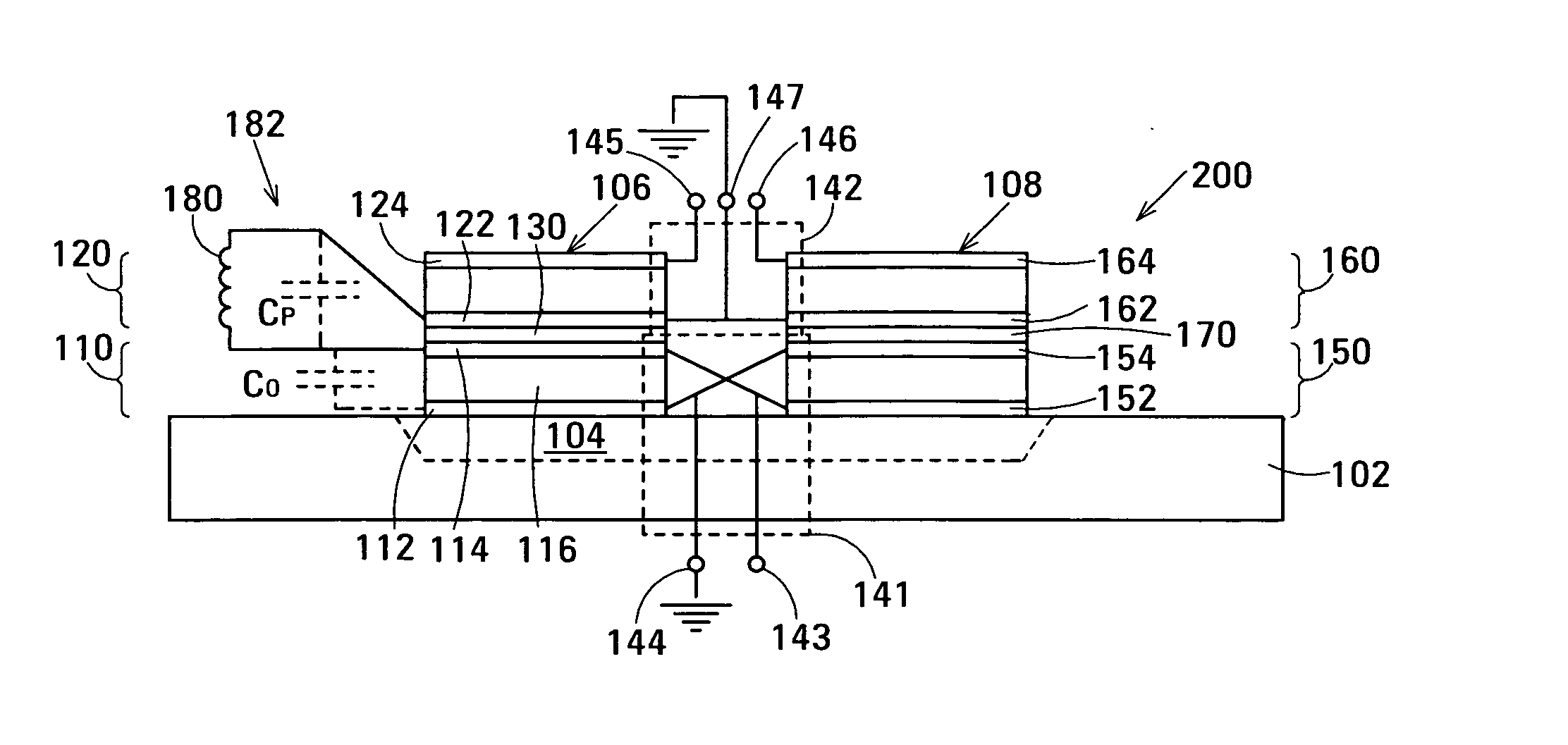
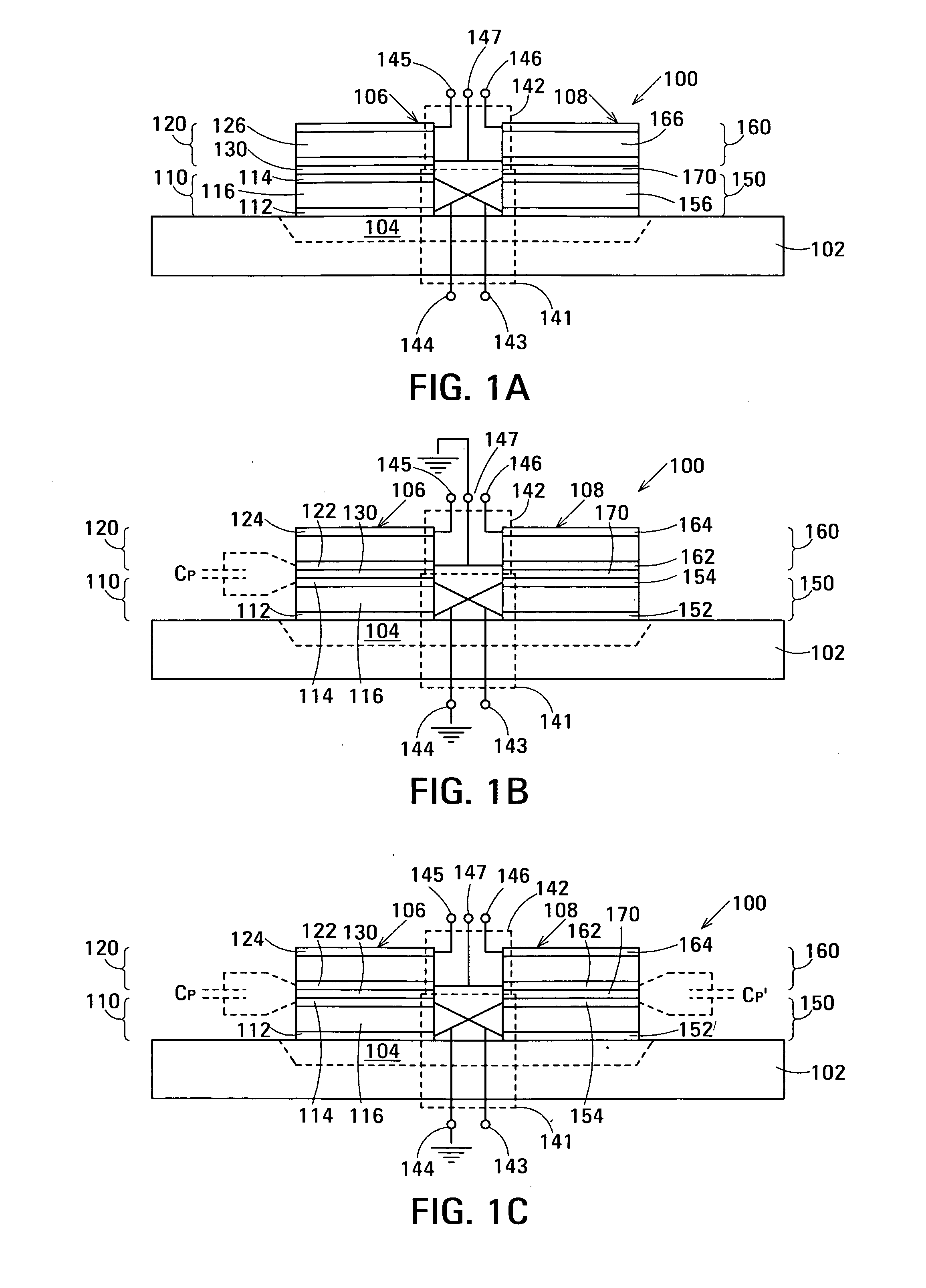
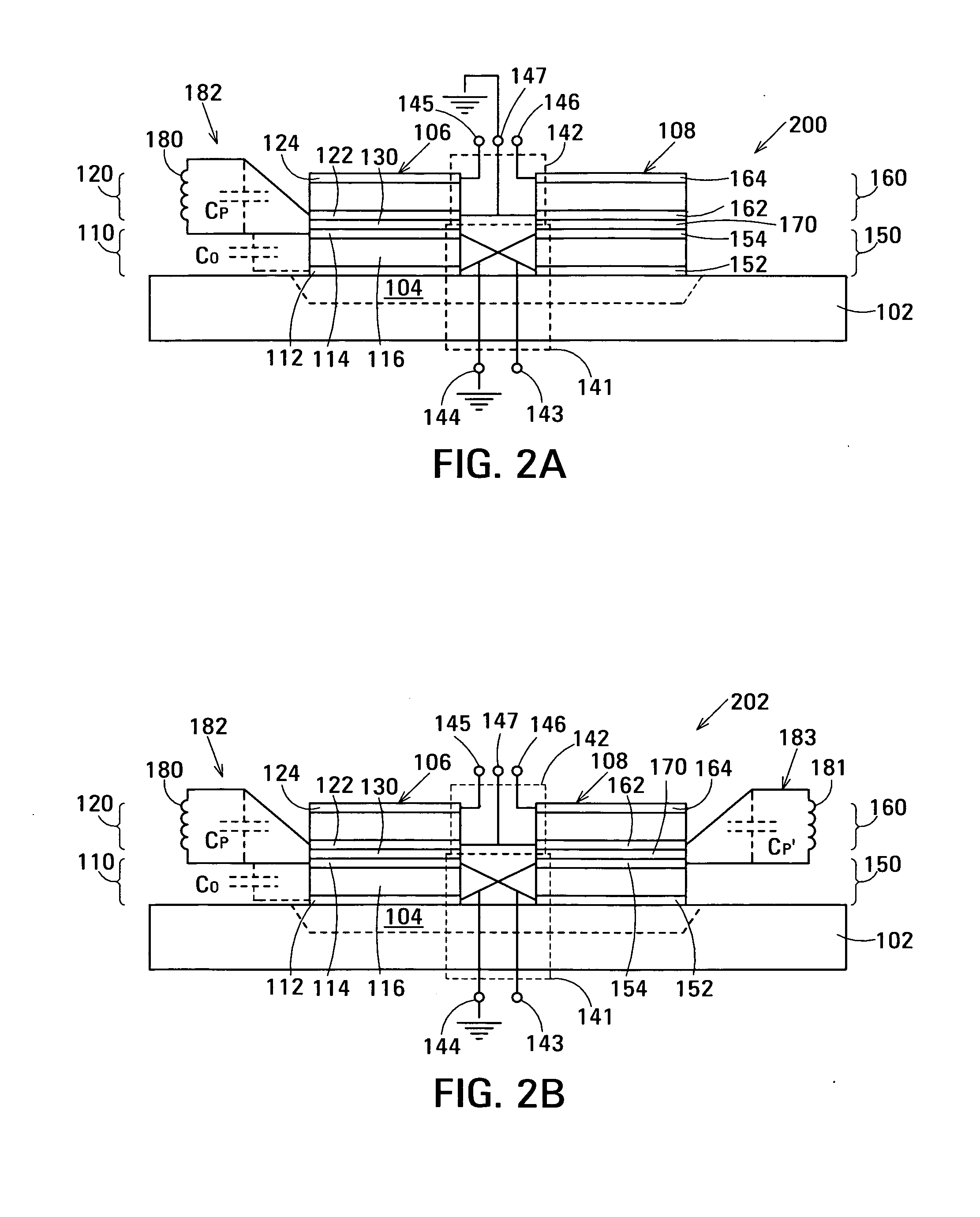
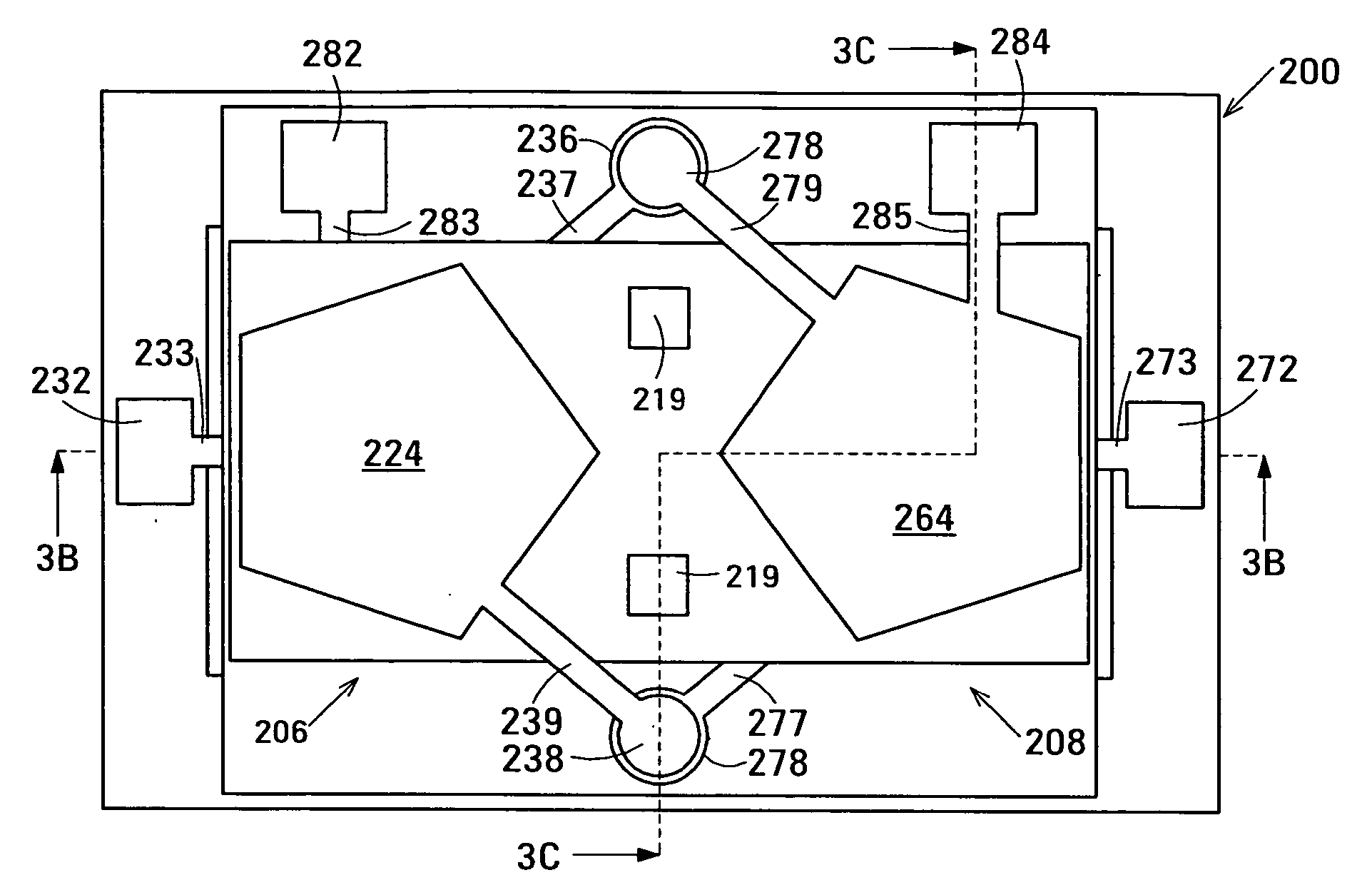
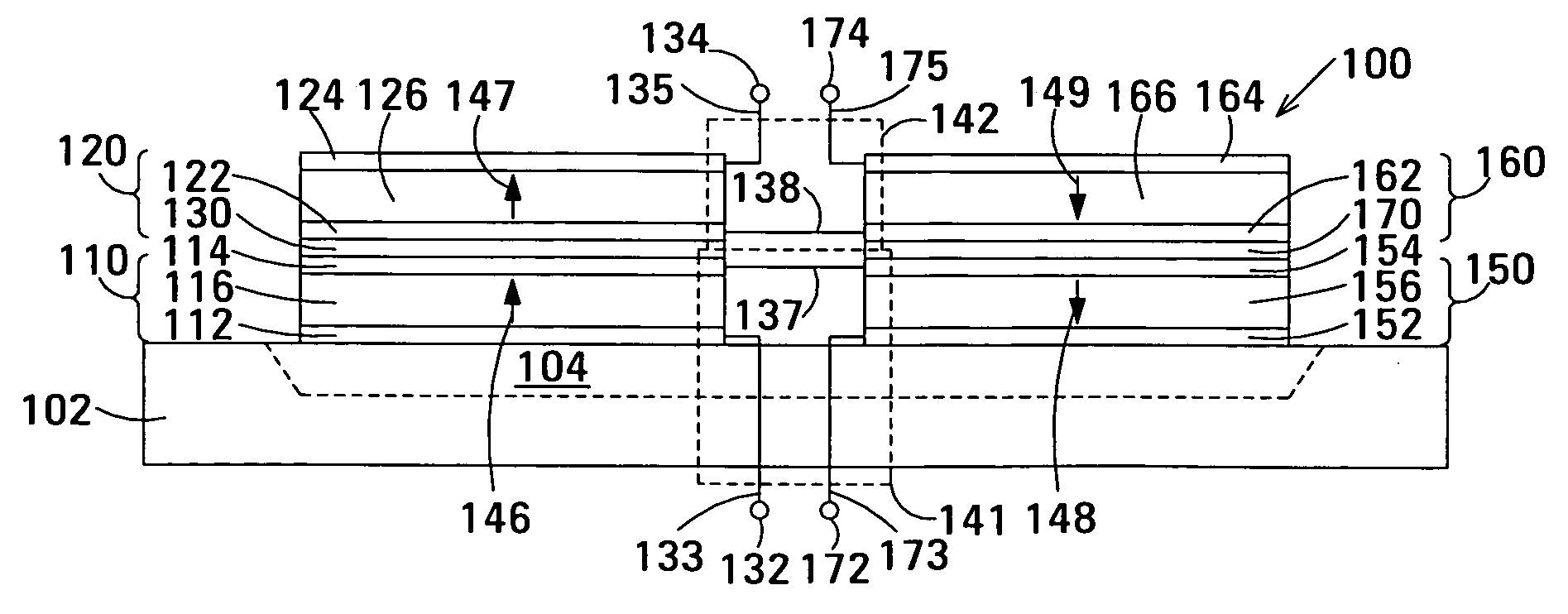
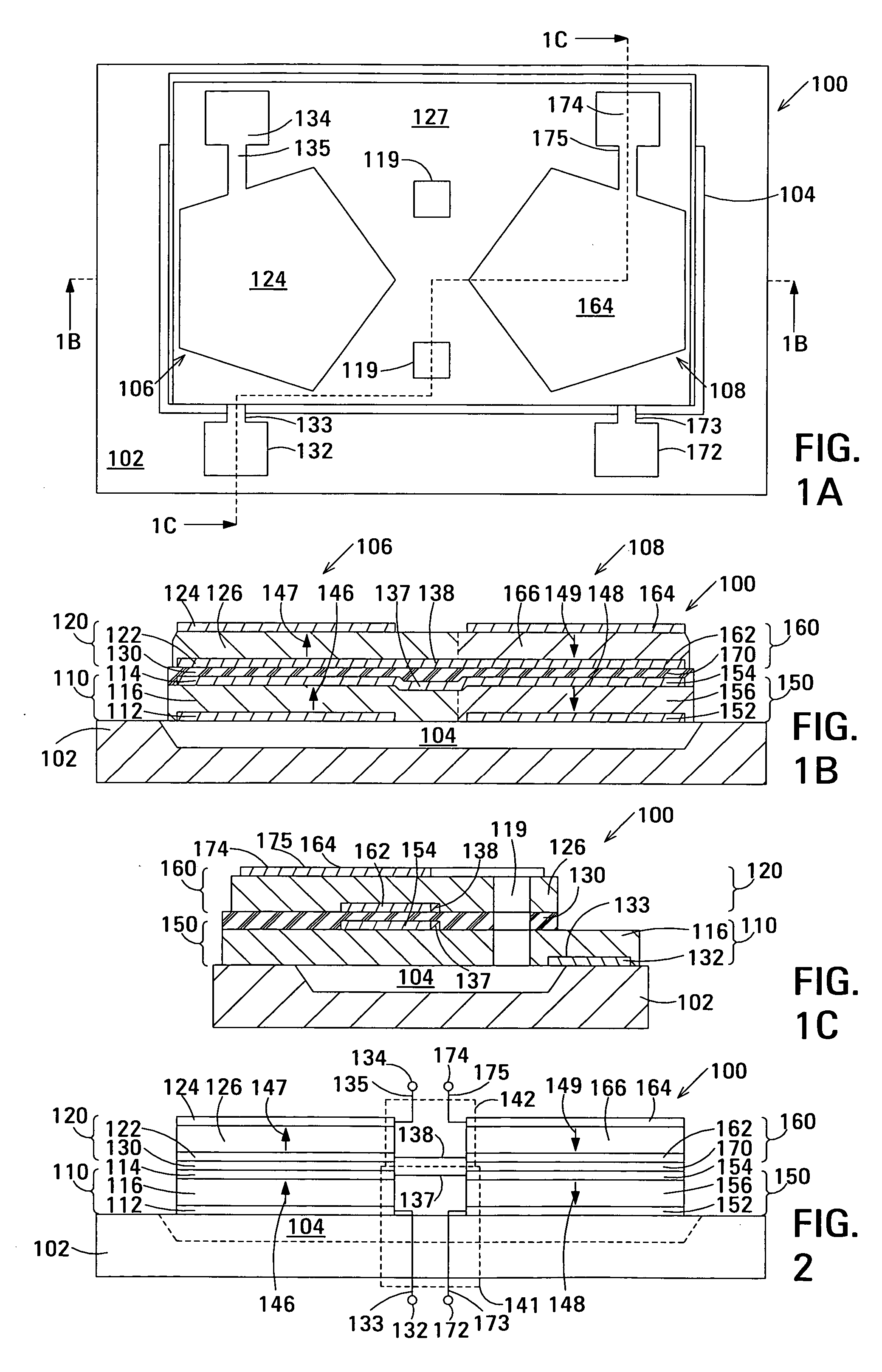
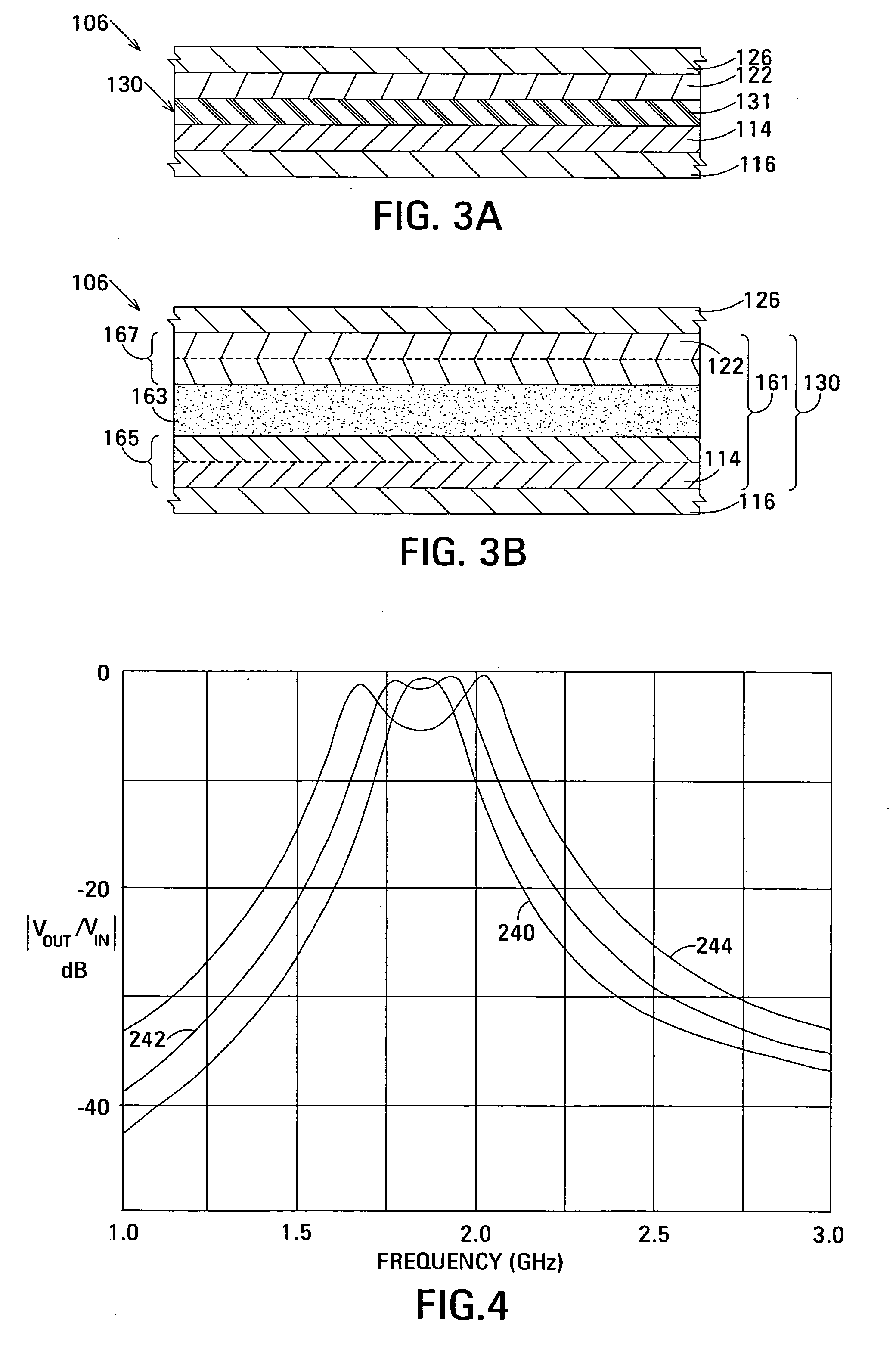
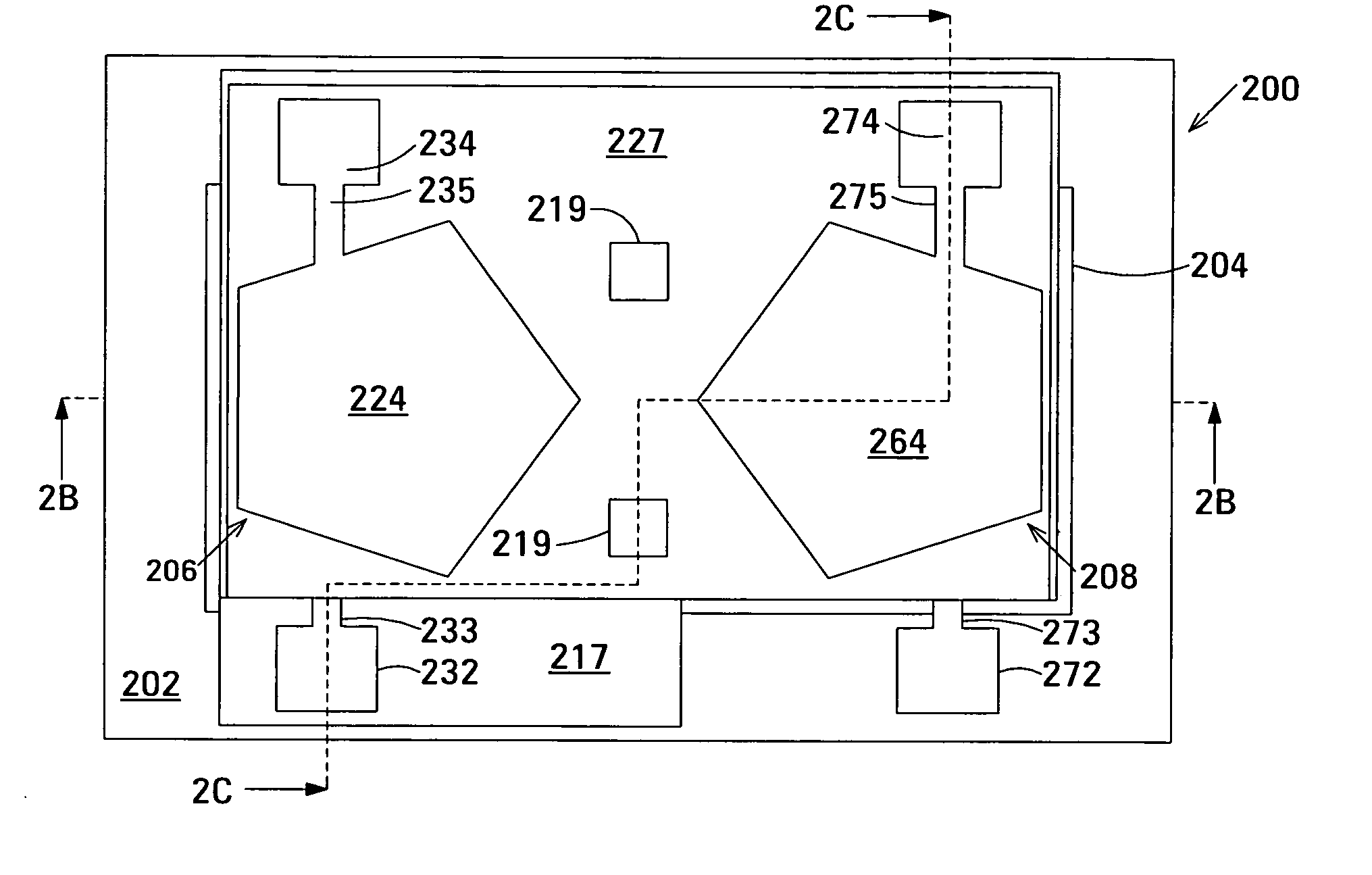
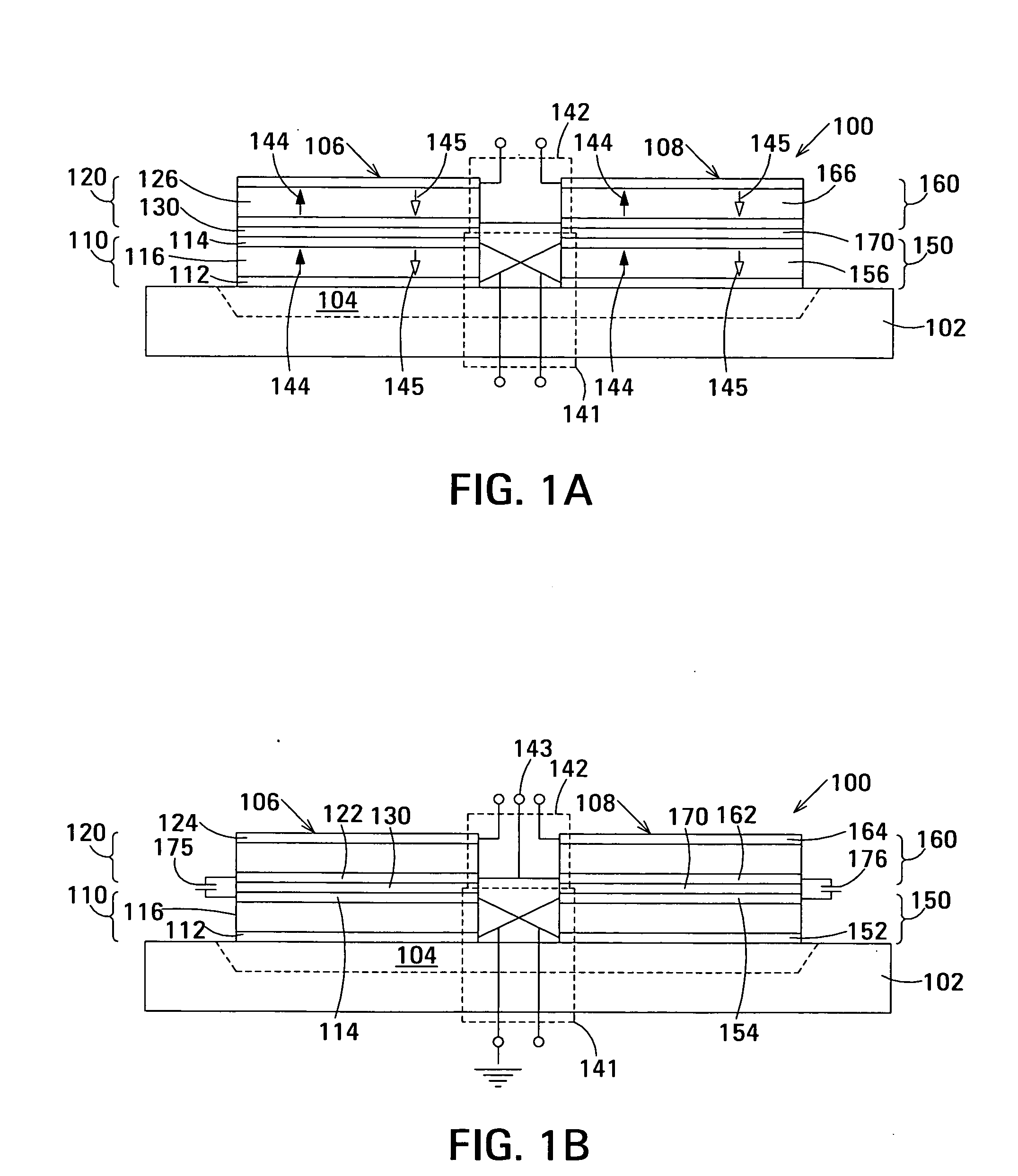
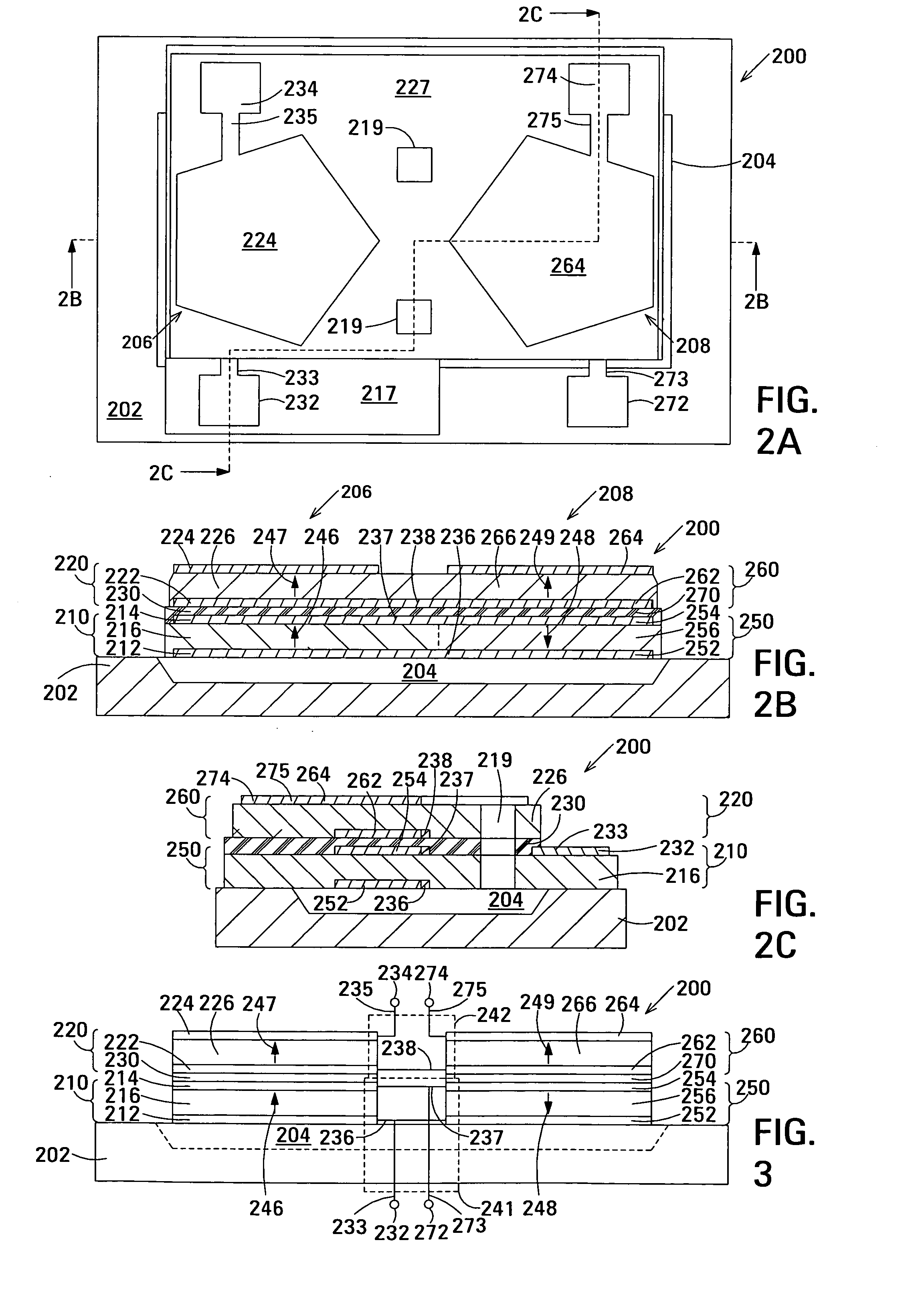
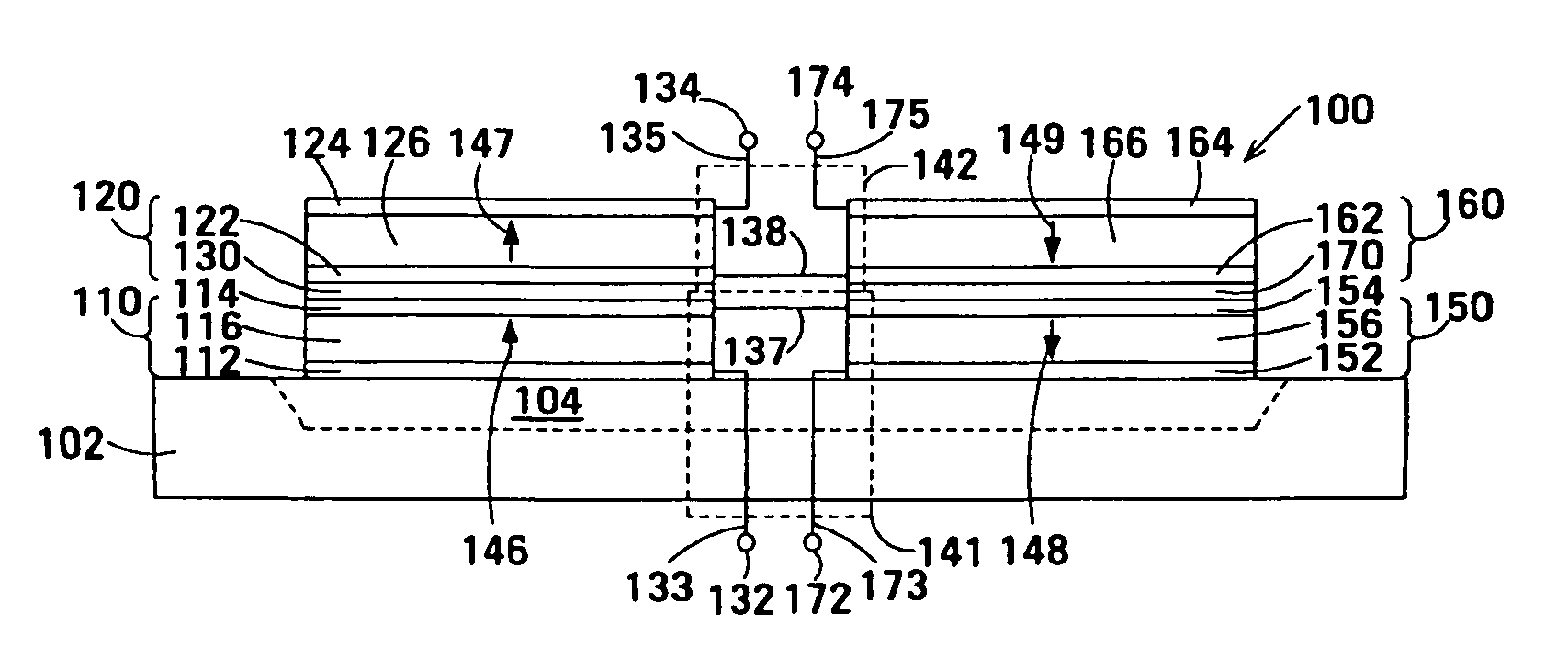
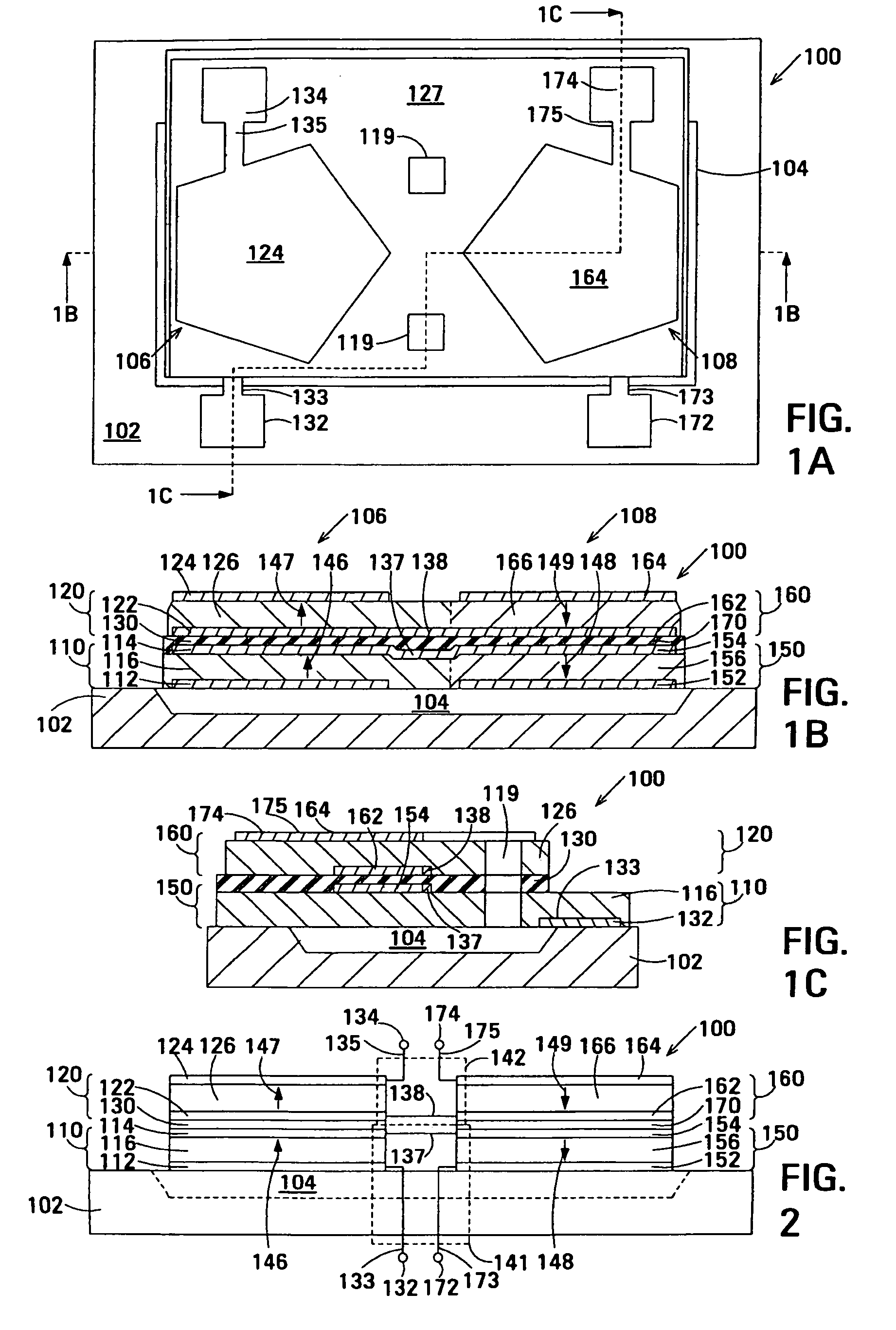
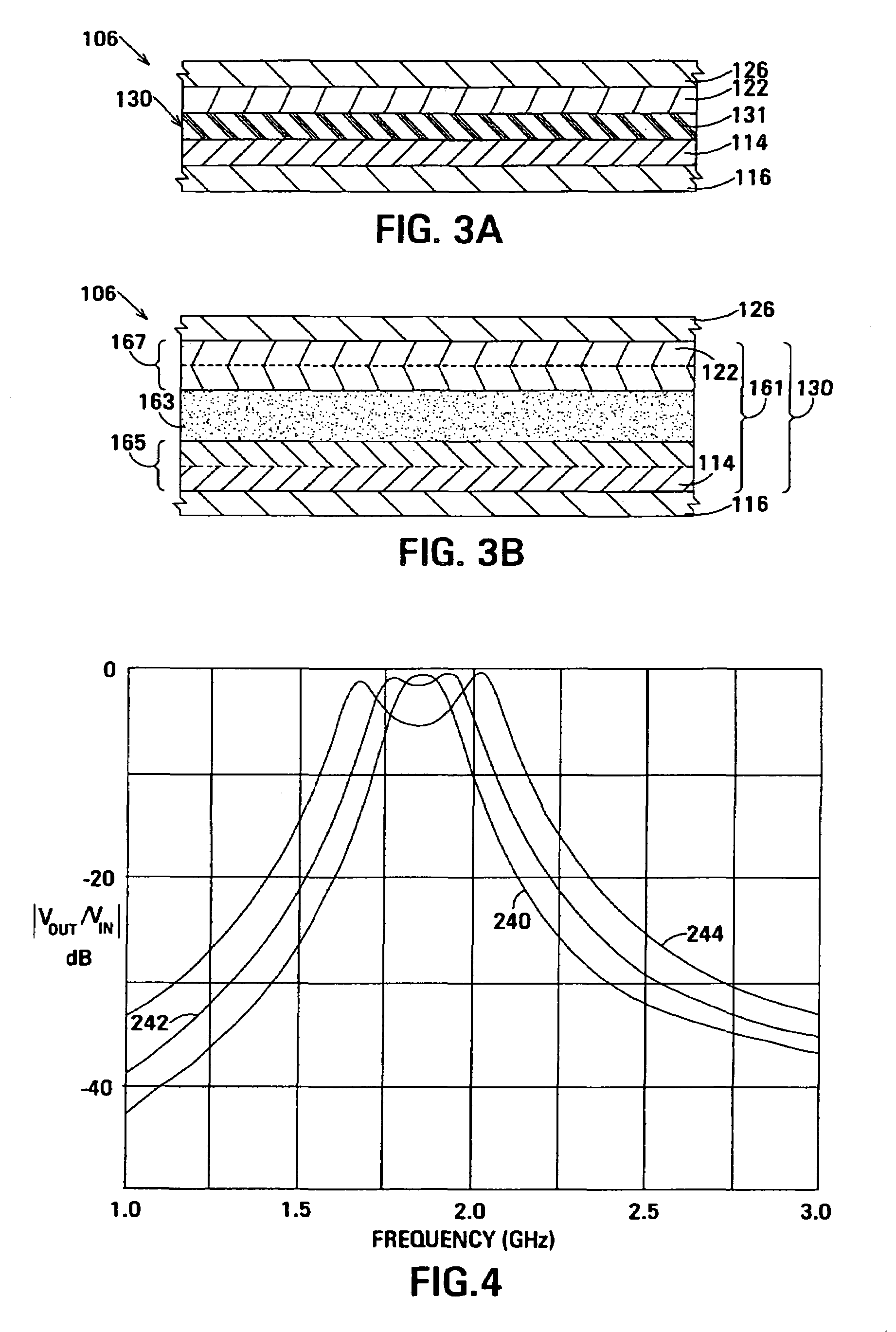
The film acoustically-coupled transformer (FACT) has a first and second decoupled stacked bulk acoustic resonators (DSBARs). Each DSBAR has a lower film bulk acoustic resonator (FBAR), an upper FBAR atop the lower FBAR, and an acoustic decoupler between them FBARs. Each FBAR has opposed planar electrodes and a piezoelectric element between the electrodes. A first electrical circuit interconnects the lowers FBAR of the first DSBAR and the second DSBAR. A second electrical circuit interconnects the upper FBARs of the first DSBAR and the second DSBAR. In at least one of the DSBARs, the acoustic decoupler and one electrode of the each of the lower FBAR and the upper FBAR adjacent the acoustic decoupler constitute a parasitic capacitor. The FACT additionally has an inductor electrically connected in parallel with the parasitic capacitor. The inductor increases the common-mode rejection ratio of the FACT.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
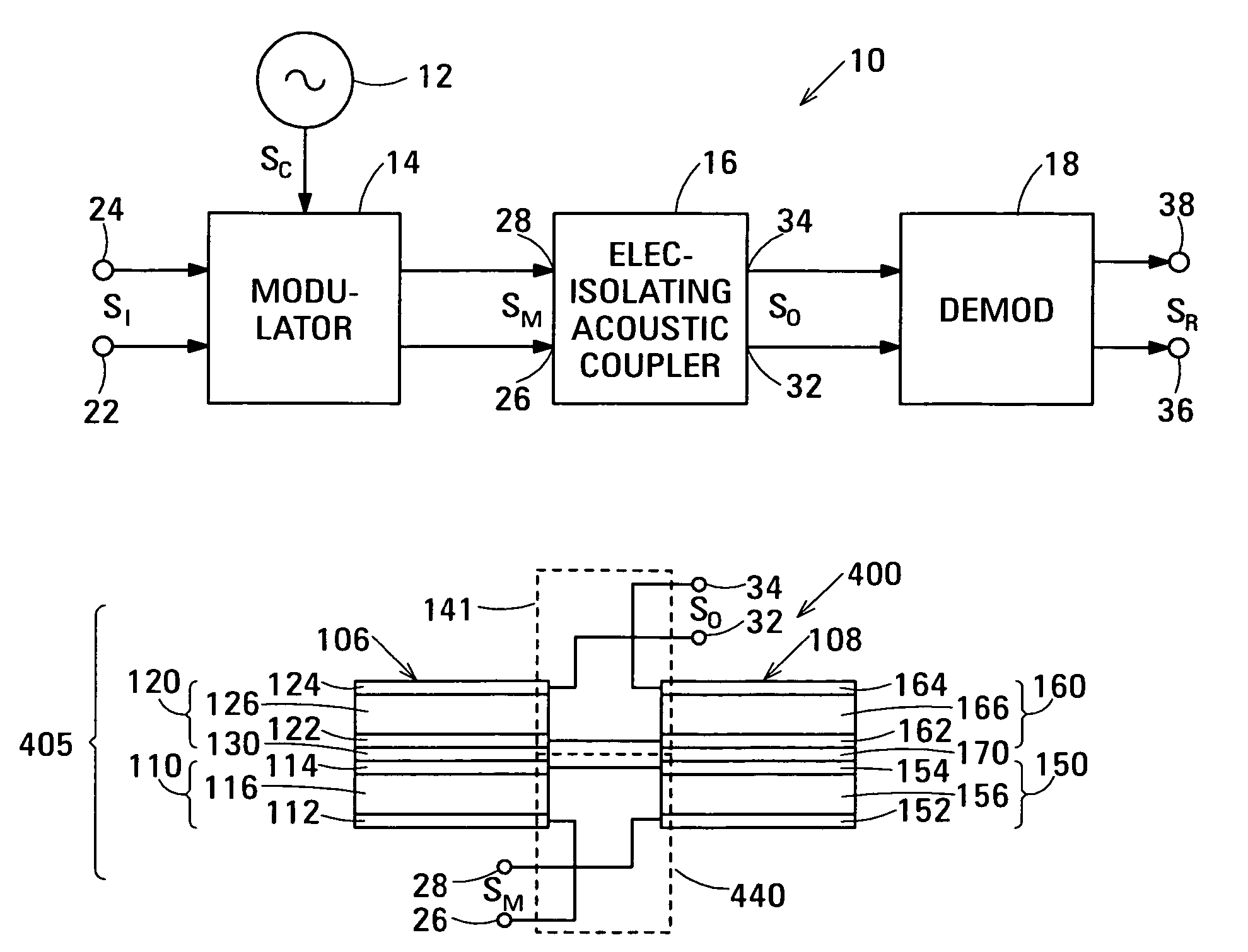
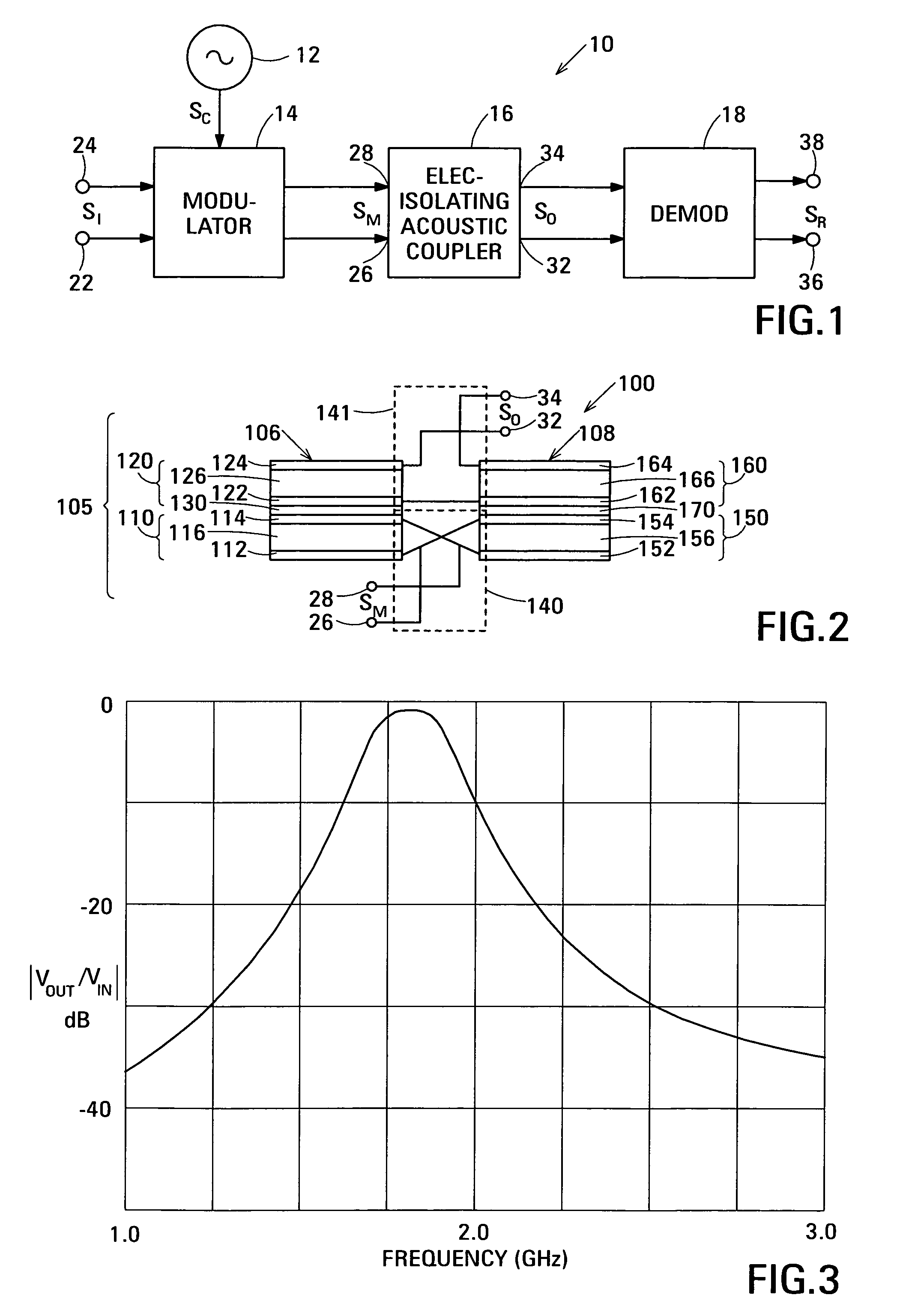
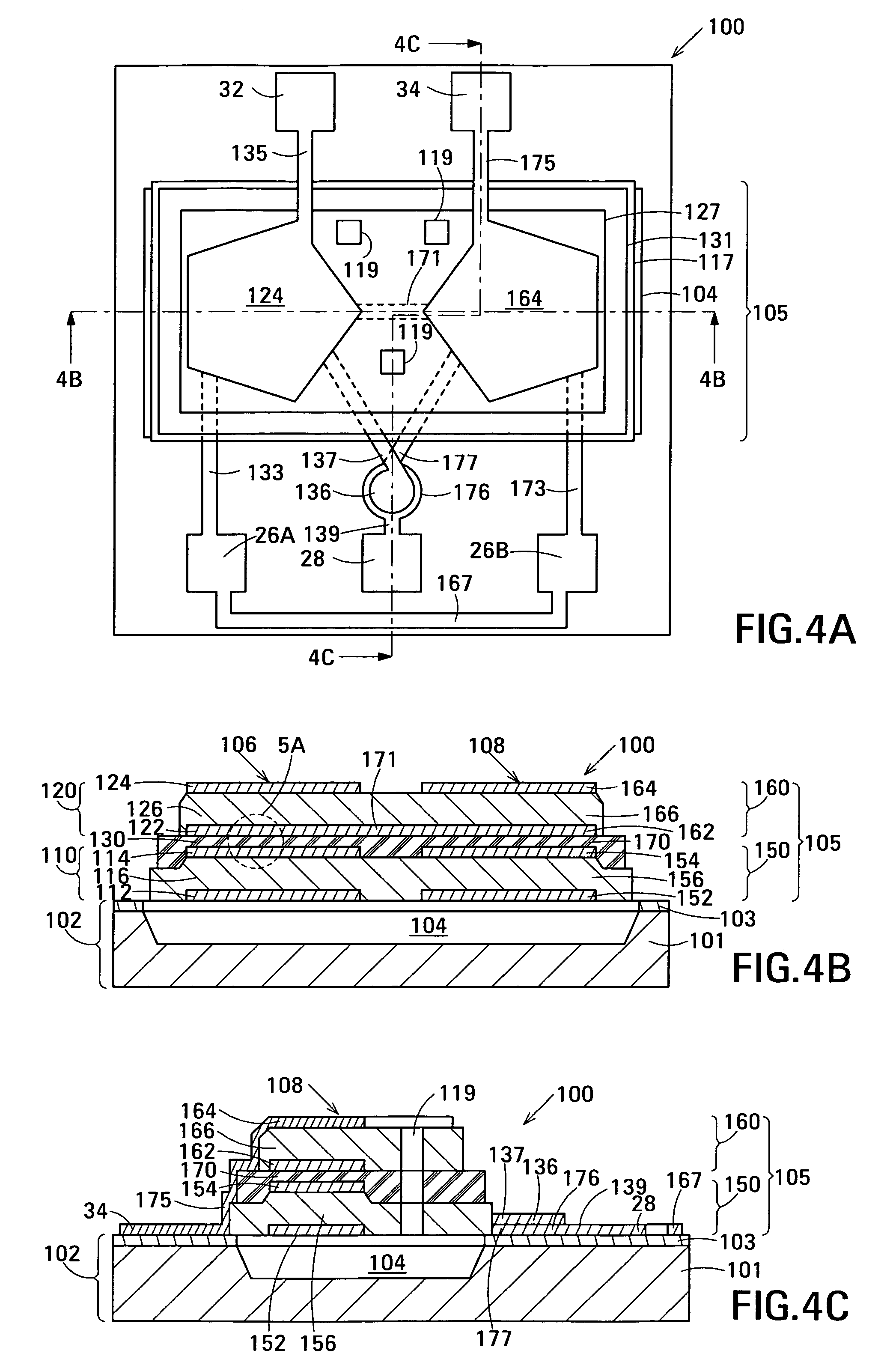
Film acoustically-coupled transformer
ActiveUS20050093655A1Multiple-port networksPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPlanar electrodeBalanced circuit
One embodiment of the film acoustically-coupled transformer (FACT) includes a decoupled stacked bulk acoustic resonator (DSBAR) having a lower film bulk acoustic resonator (FBAR) an upper FBAR stacked on the lower FBAR, and, between the FBARs, an acoustic decoupler comprising a layer of acoustic decoupling material. Each FBAR has opposed planar electrodes with a piezoelectric element between them. The FACT additionally has first terminals electrically connected to the electrodes of one FBAR and second terminals electrically connected to the electrodes of the other FBAR. Another embodiment has decoupled stacked bulk acoustic resonators (DSBARs), each as described above, a first electrical circuit interconnecting the lower FBARs, and a second electrical circuit interconnecting the upper FBARs. The FACT provides impedance transformation, can linking single-ended circuitry with balanced circuitry or vice versa and electrically isolates primary and secondary. Some embodiments are additionally electrically balanced.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
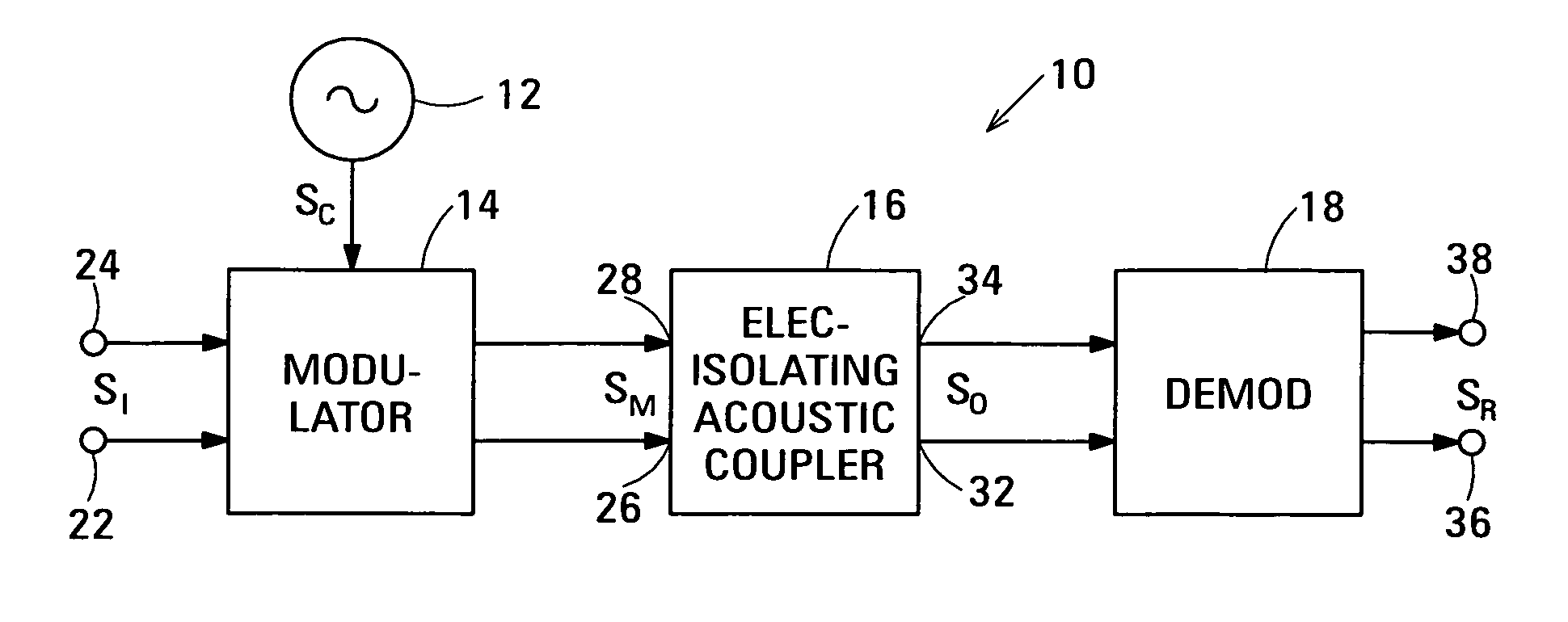
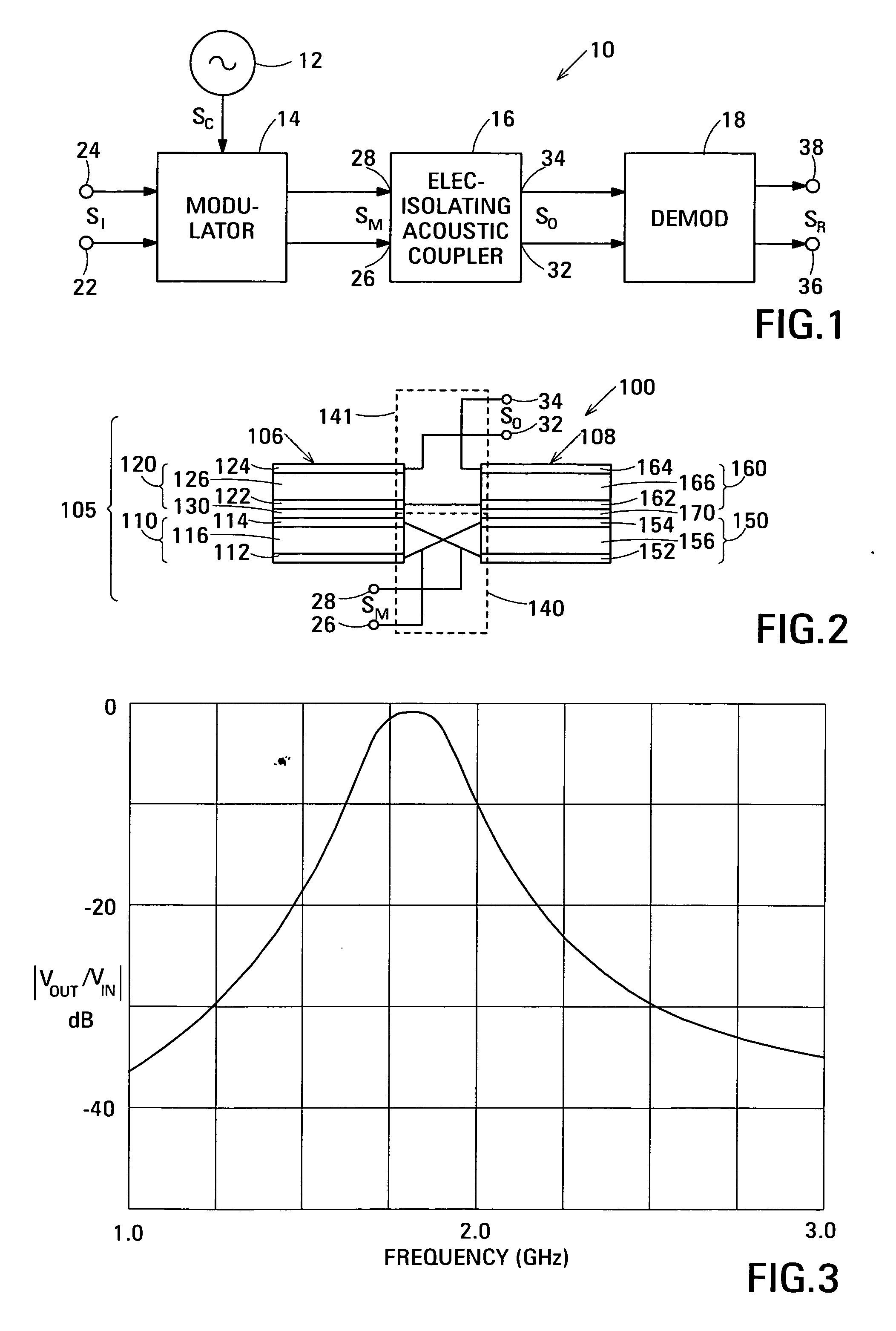
Acoustic galvanic isolator incorporating film acoustically-coupled transformer
ActiveUS20070085631A1Inexpensive to fabricateGood Common Mode RejectionImpedence networksCarrier signalEngineering
Embodiments of the acoustic galvanic isolator comprise a carrier signal source, a modulator connected to receive an information signal and the carrier signal, a demodulator, and, connected between the modulator and the demodulator, an electrically-isolating acoustic coupler comprising an electrically-isolating film acoustically-coupled transformer (FACT).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
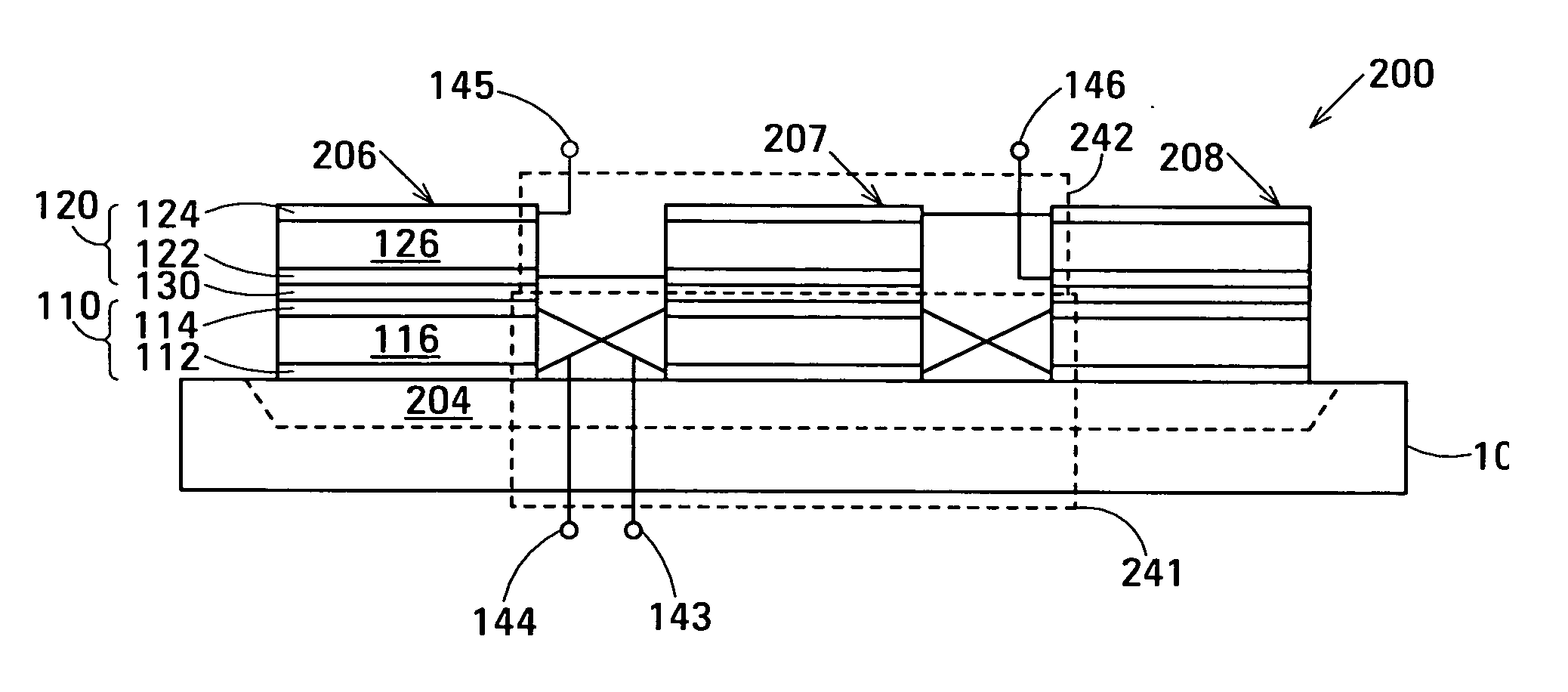
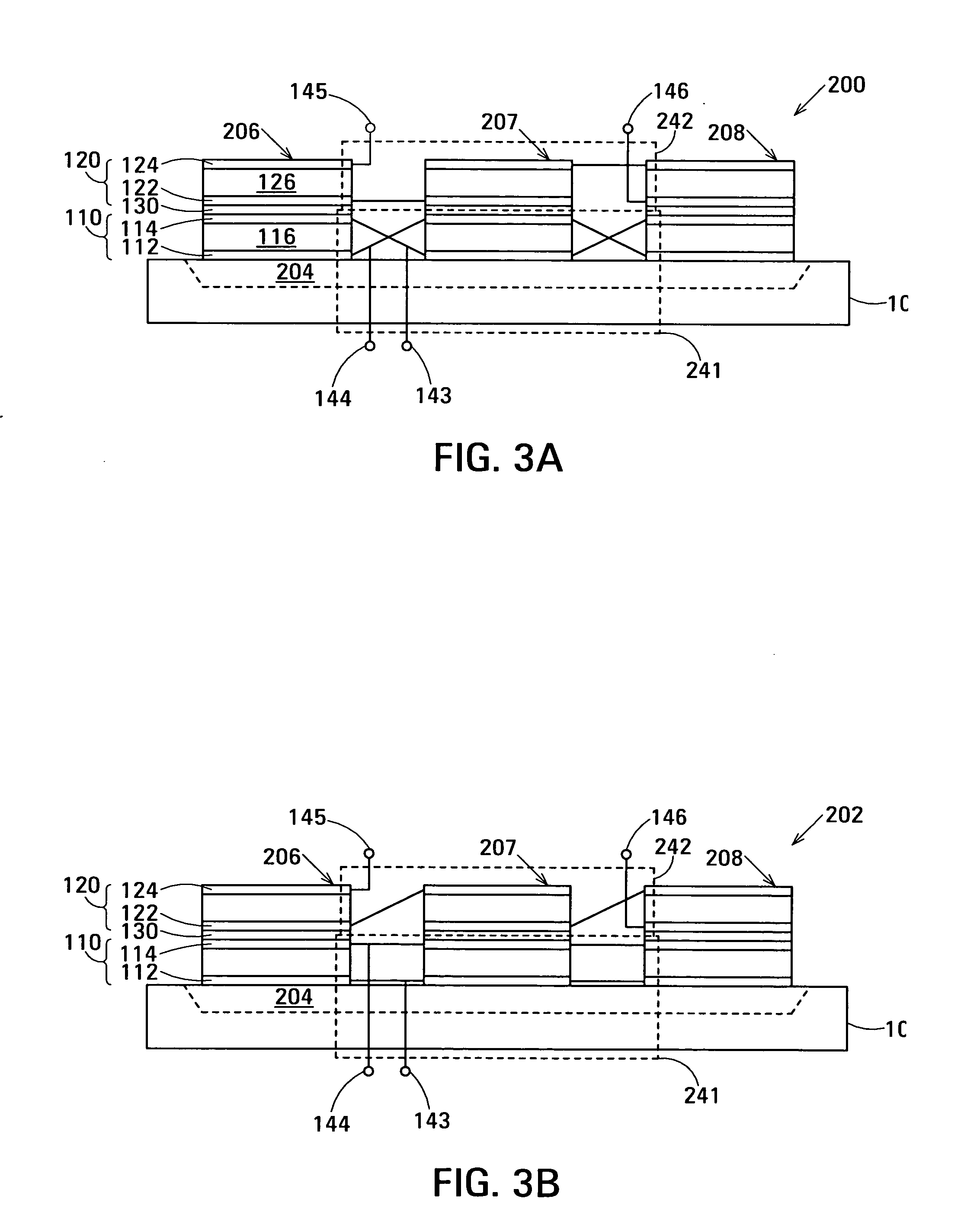
Impedance transformation ratio control in film acoustically-coupled transformers
ActiveUS20050128030A1Multiple-port networksSolid-state devicesThin-film bulk acoustic resonatorPlanar electrode
The film acoustically-coupled transformer (FACT) has decoupled stacked bulk acoustic resonators (DSBARs), a first electrical circuit and a second electrical circuit. Each of the DSBARs has a lower film bulk acoustic resonator (FBAR), an upper FBAR and an acoustic decoupler. The upper FBAR is stacked on the lower FBAR and the acoustic decoupler is located between the FBARs. Each FBAR has opposed planar electrodes and a piezoelectric element between the electrodes. The first electrical circuit interconnects the lower FBARs. The second electrical circuit interconnects the upper FBARs. The FBARs of one of the DSBARs differ in electrical impedance from the FBARs of another of the DSBARs. The FACT has an impedance transformation ratio greater than 1:m2, where m is the number of DSBARs. The actual impedance transformation ratio depends on the ratio of the impedances of the FBARs.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Film acoustically-coupled transformers with two reverse c-axis piezoelectric elements
ActiveUS20050093396A1Low insertion lossSolve insufficient bandwidthImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesThin-film bulk acoustic resonatorPlanar electrode
Embodiments of an acoustically-coupled transformer have a first stacked bulk acoustic resonator (SBAR) and a second SBAR. Each of the SBARs has a lower film bulk acoustic resonator (FBAR) and an upper FBAR, and an acoustic decoupler between the FBARs. The upper FBAR is stacked atop the lower FBAR. Each FBAR has opposed planar electrodes and a piezoelectric element between the electrodes. The piezoelectric element is characterized by a c-axis. The c-axes of the piezoelectric elements of the lower FBARs are opposite in direction, and the c-axes of the piezoelectric elements of the upper FBARs are opposite in direction. The transformer additionally has a first electrical circuit connecting the lower FBAR of the first SBAR to the lower FBAR of the second SBAR, and a second electrical circuit connecting the upper FBAR of the first SBAR to the upper FBARs of the second SBAR.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Film acoustically-coupled transformer with reverse C-axis piezoelectric material
ActiveUS20050093657A1Improved common mode rejection ratioIncreasing available choiceImpedence networksSolid-state devicesPlanar electrodeResonator
An embodiment of the acoustically-coupled transformer has first and second stacked bulk acoustic resonators (SBARs) each having a stacked pair of film bulk acoustic resonators (FBARs) with an acoustic decoupler between the FBARs. Each FBAR has opposed planar electrodes with piezoelectric material between the electrodes. A first electrical circuit connects one FBARs of the first SBAR to one FBAR of the second SBAR, and a second electrical circuit connects the other FBAR of the first SBAR to the other FBAR of the second SBAR. The c-axis of the piezoelectric material of one of the FBARs is opposite in direction to the c-axes of the piezoelectric materials of the other three FBARs. This arrangement substantially reduces the amplitude of signal-frequency voltages across the acoustic decouplers and significantly improves the common mode rejection of the transformer. This arrangement also allows conductive acoustic decouplers to be used, increasing the available choice of acoustic decoupler materials.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Magnetically shielded electrodeless light source
InactiveUS6433492B1Alternating current plasma display panelsElectric light circuit arrangementDisplay deviceConductor Coil
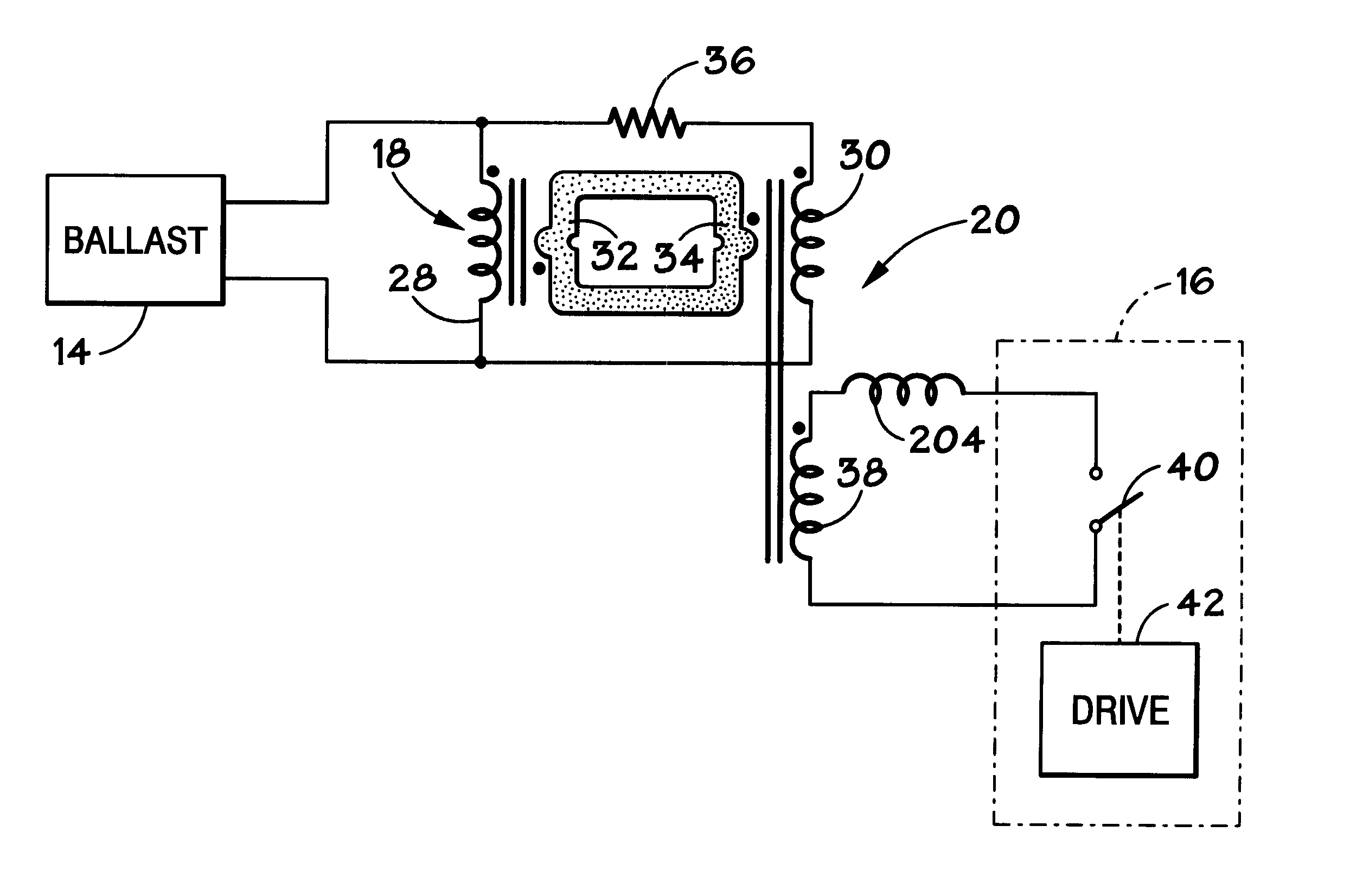
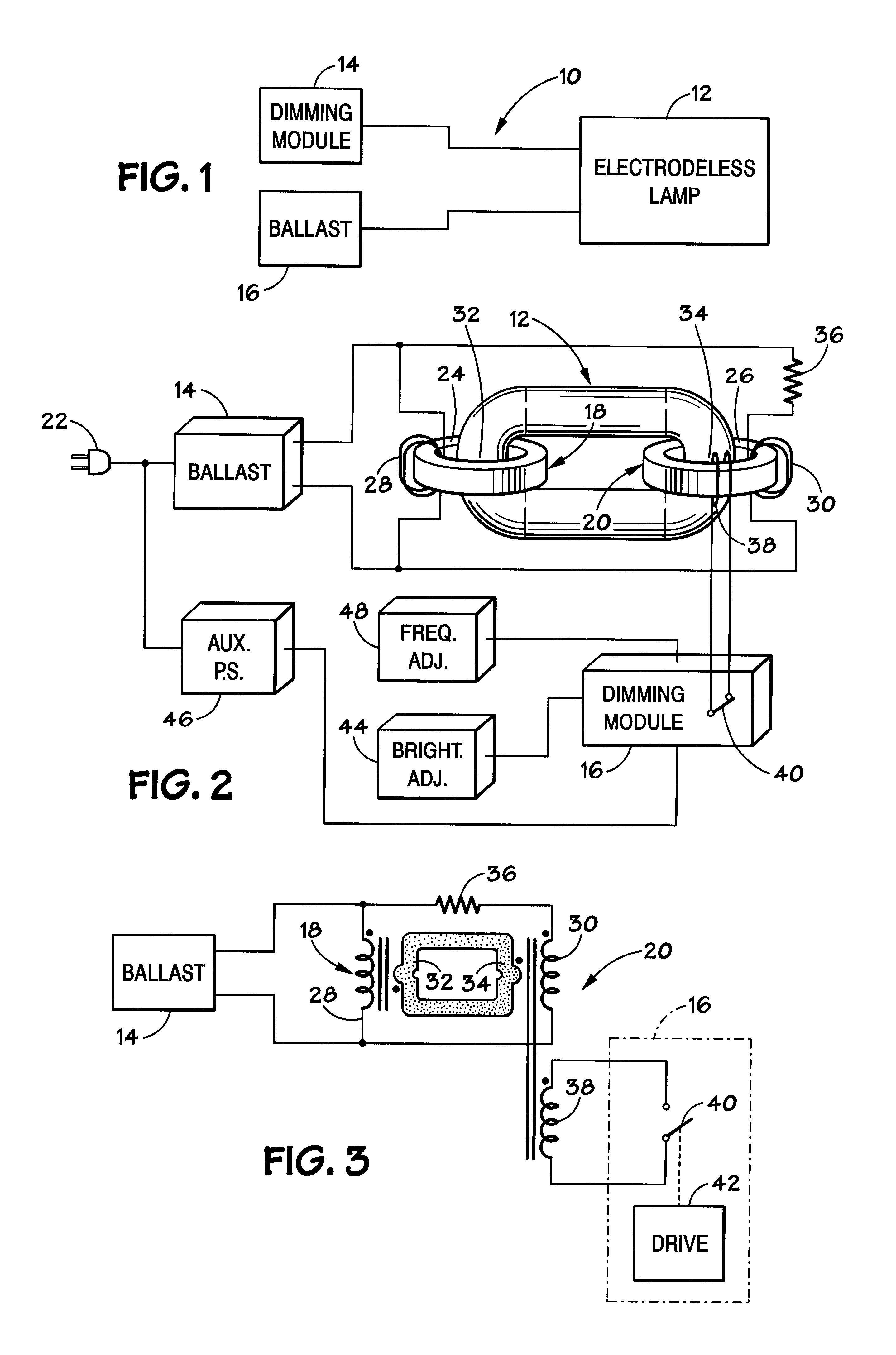
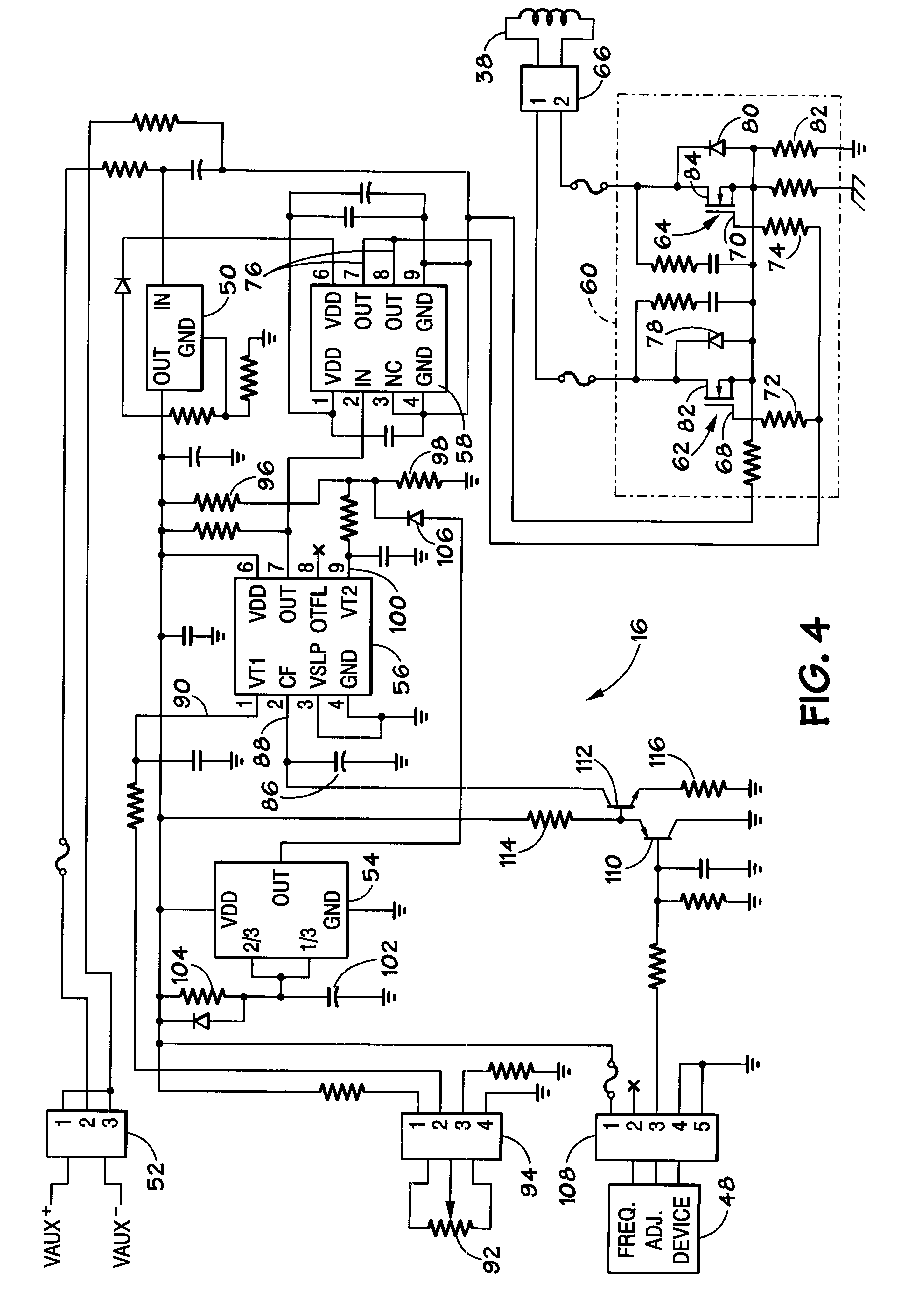
A dimmable electrodeless light source includes an electrodeless lamp, an electronic ballast and a dimming module. The light source further includes coupling transformers coupled to the electrodeless lamp for inductively coupling power to the lamp to generate light. An auxiliary winding electromagnetically coupled to the primary winding of at least one of the coupling transformers is driven by switching circuitry in the dimming module. The switching circuitry is pulse width modulated to control the average brightness of the light generated by the electrodeless lamp. An exemplary application for the dimmable electrodeless light source is as a backlight for a video display device, such as a liquid crystal display unit. The dimmable electrodeless light source further includes a magnetic shield device that is operably positioned with respect to the electrodeless lamp. The magnetic shield device produces a magnetic field that substantially opposes, and cancels, the magnetic field that is produced by the electrodeless lamp when energized. In an alternative embodiment, the magnetic shield device produces a magnetic field which, when combined with the lamp magnetic field, results in a total magnetic field that is substantially constant regardless of the energization level of the lamp (e.g., totally energized or dimmed). The magnetic shield thus reduces visual artifacts that might otherwise appear on a video display unit due to a variation of the magnetic field produced by the lamp.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
Method of making an acoustically coupled transformer
InactiveUS7367095B2Low insertion lossSolve insufficient bandwidthPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyImpedence networksPlanar electrodeHemt circuits
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Non-Contact Power Transmission Device
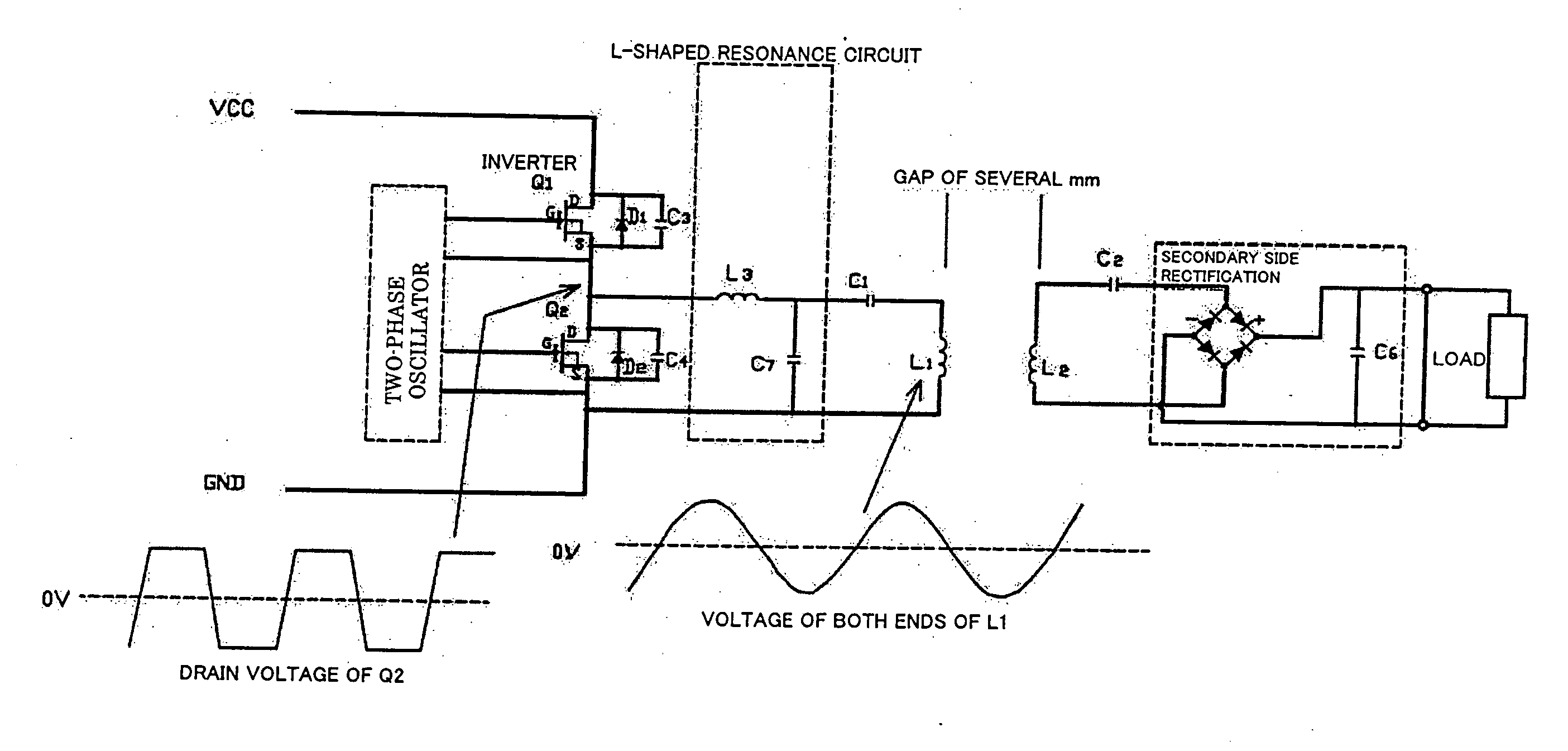
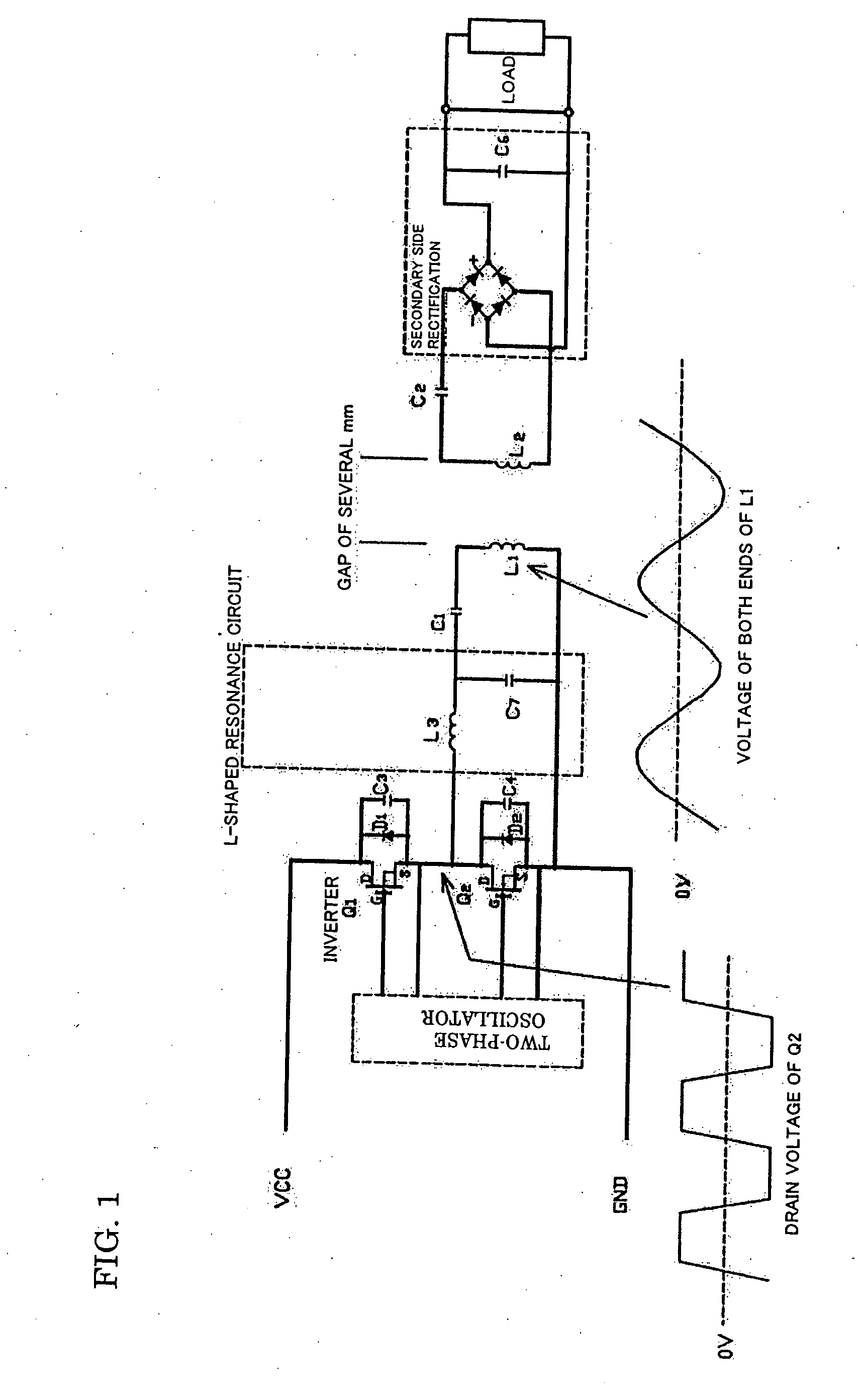
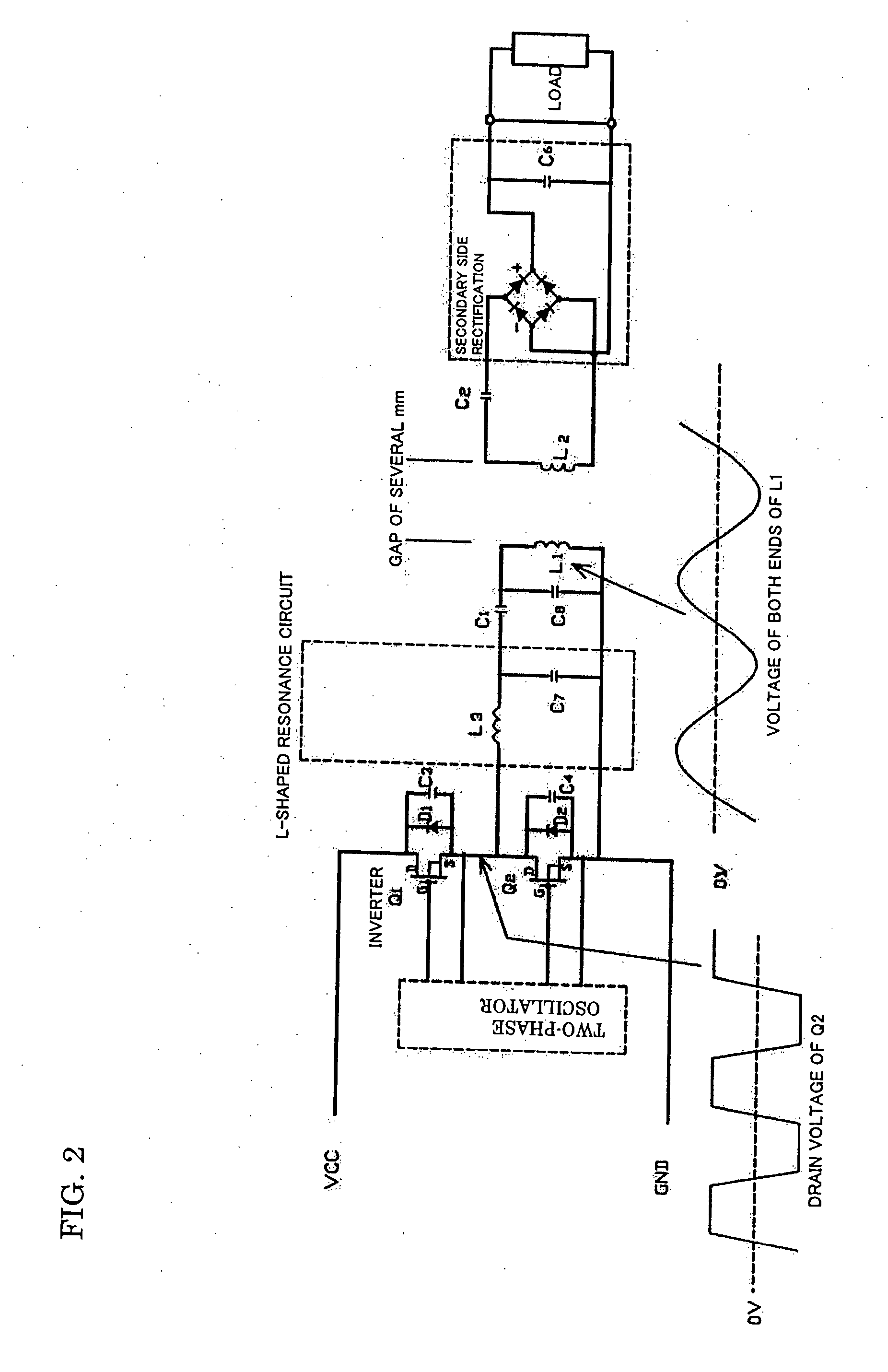
InactiveUS20070252441A1Improve transmission efficiencyReduce device sizeTransformersEfficient power electronics conversionHarmonicEngineering
A non-contact power transmission device, which is capable of efficiently reducing the device size and reducing unnecessary radiation of a harmonic component from a primary side coil, is provided. The non-contact power transmission device which includes a primary side unit and a secondary side unit which house a primary side and a secondary side of a coupling transformer individually and can be separated from each other, a capacitor C1 which resonates with a primary side coil L1 is connected to the primary side coil L1 in series so that a primary side series resonance circuit is formed, an L-shaped resonance circuit which has a coil L3 and a capacitor C7 resonating with the coil L3 is inserted between the primary side series resonance circuit and a driving circuit, and the L-shaped resonance circuit is connected to the primary side series resonance circuit in series.
Owner:HOKUSHIN ELECTRIC
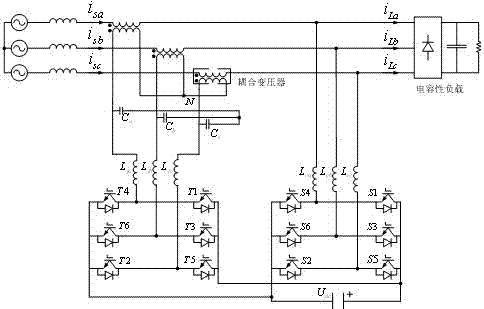
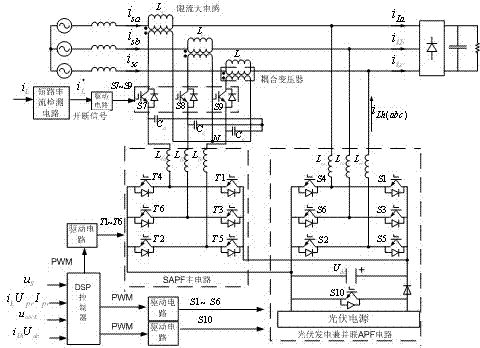
Control method of quality control system of micro source internetworking electric energy
ActiveCN102832642AImprove power qualityImprove power supply reliabilityActive power filteringEnergy industryCapacitanceQuality control system
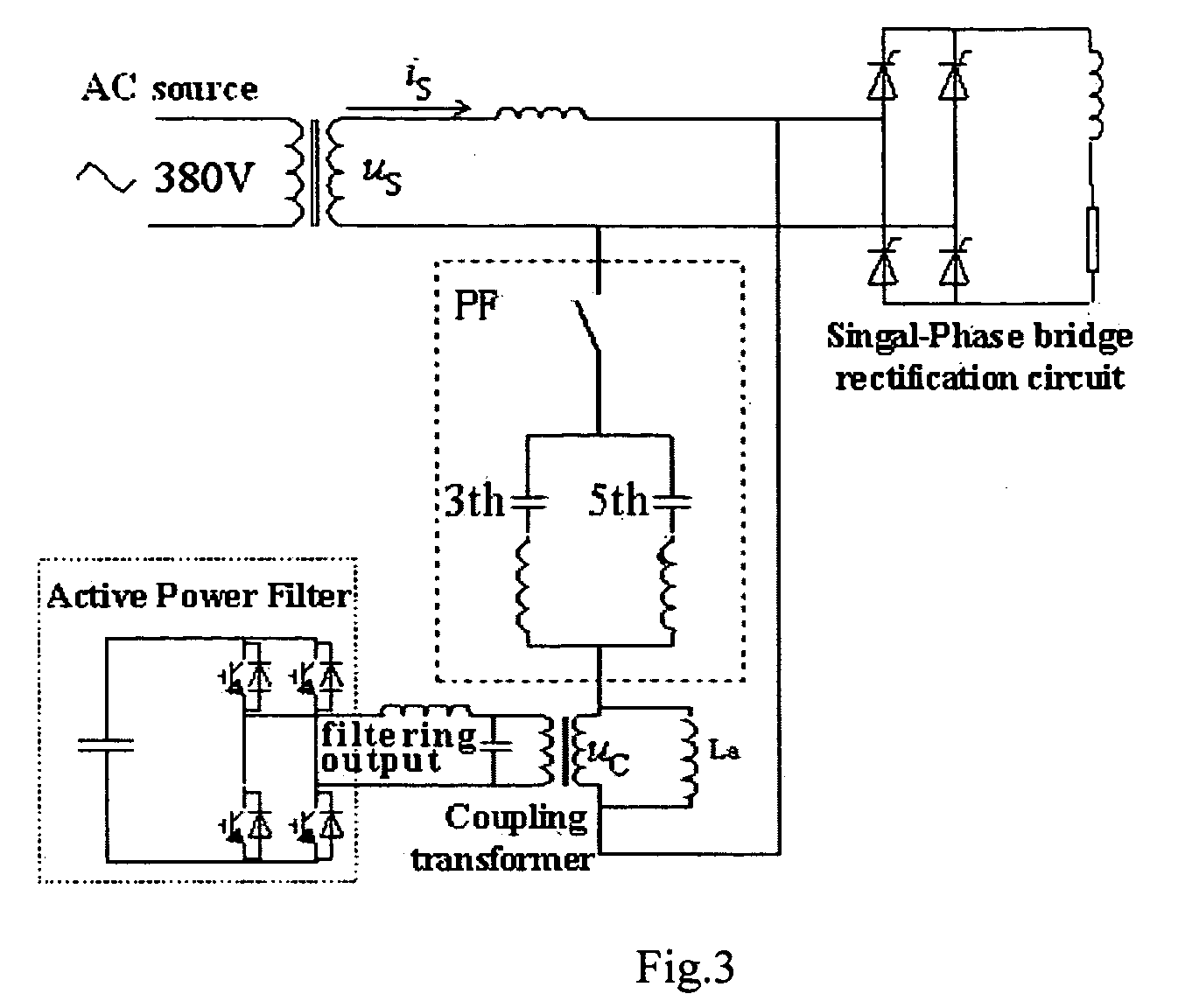
The invention discloses a control method for a quality control system of micro source internetworking electric energy. A primary side of the coupling voltage transformer on a serial active power filter side of a UPQC (unified power quality controller) is connected with a larger current-limiting inductor in parallel, and a direct-current large-capacitance side of the UPQC is connected with a photovoltaic generating power supply in parallel. Due to effects of cooperative control, the photovoltaic power supply is internetworked for power generation during normal operation, active power is provided for a power grid by the parallel active power filter of the UPQC, and the harmonic current from a load side and the voltage fluctuation and harmonic voltage from the power grid side are governed and compensated by the UPQC. In the case of short-circuiting failure on the load side, the main circuit of the UPQC stops operating, a secondary side of the coupling voltage transformer is subjected to high impedance, and the current can be limited by the parallel current-limiting large inductor. By adopting the method, the functions of failure current limitation, harmonic treatment, voltage support, photovoltaic power generation and the like can be realized during micro grid internetworking operation, and the optimized protection and operation of the quality of electric energy in micro grid internetworking can also be realized.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
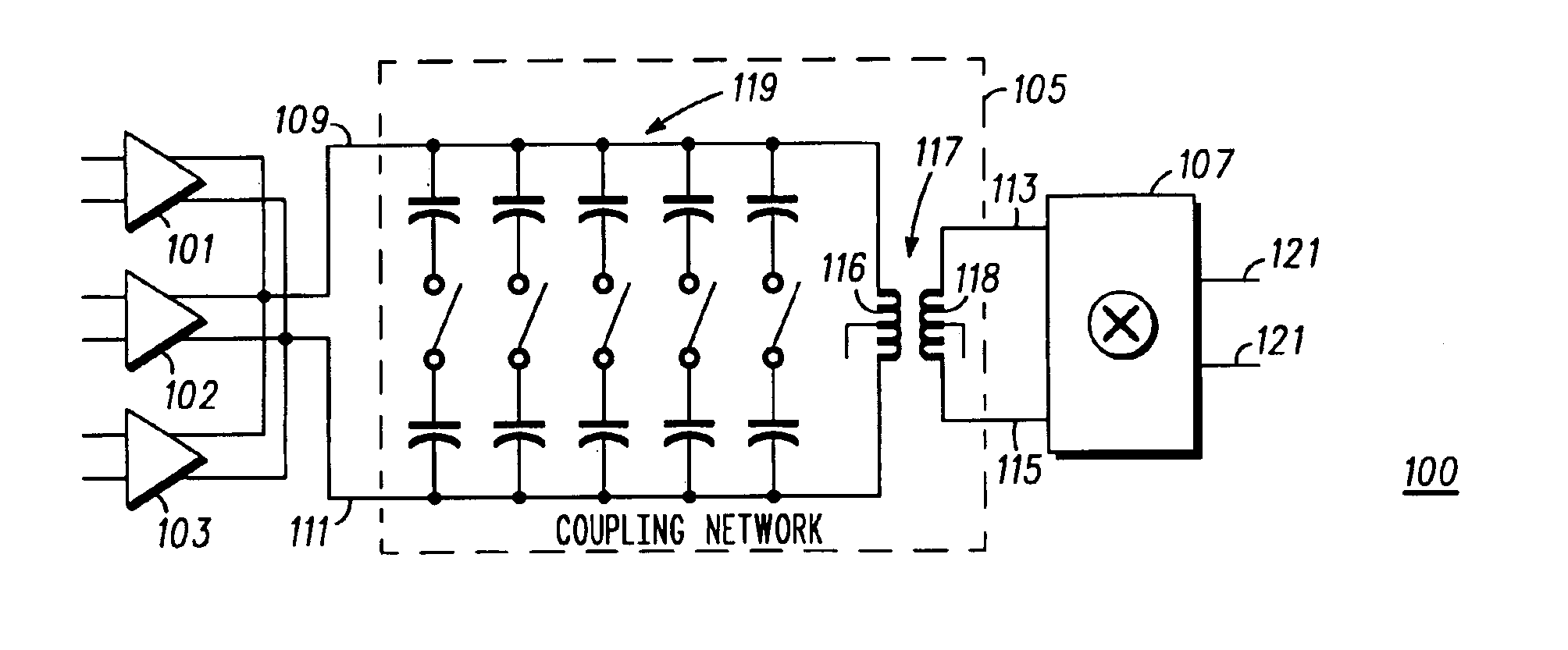
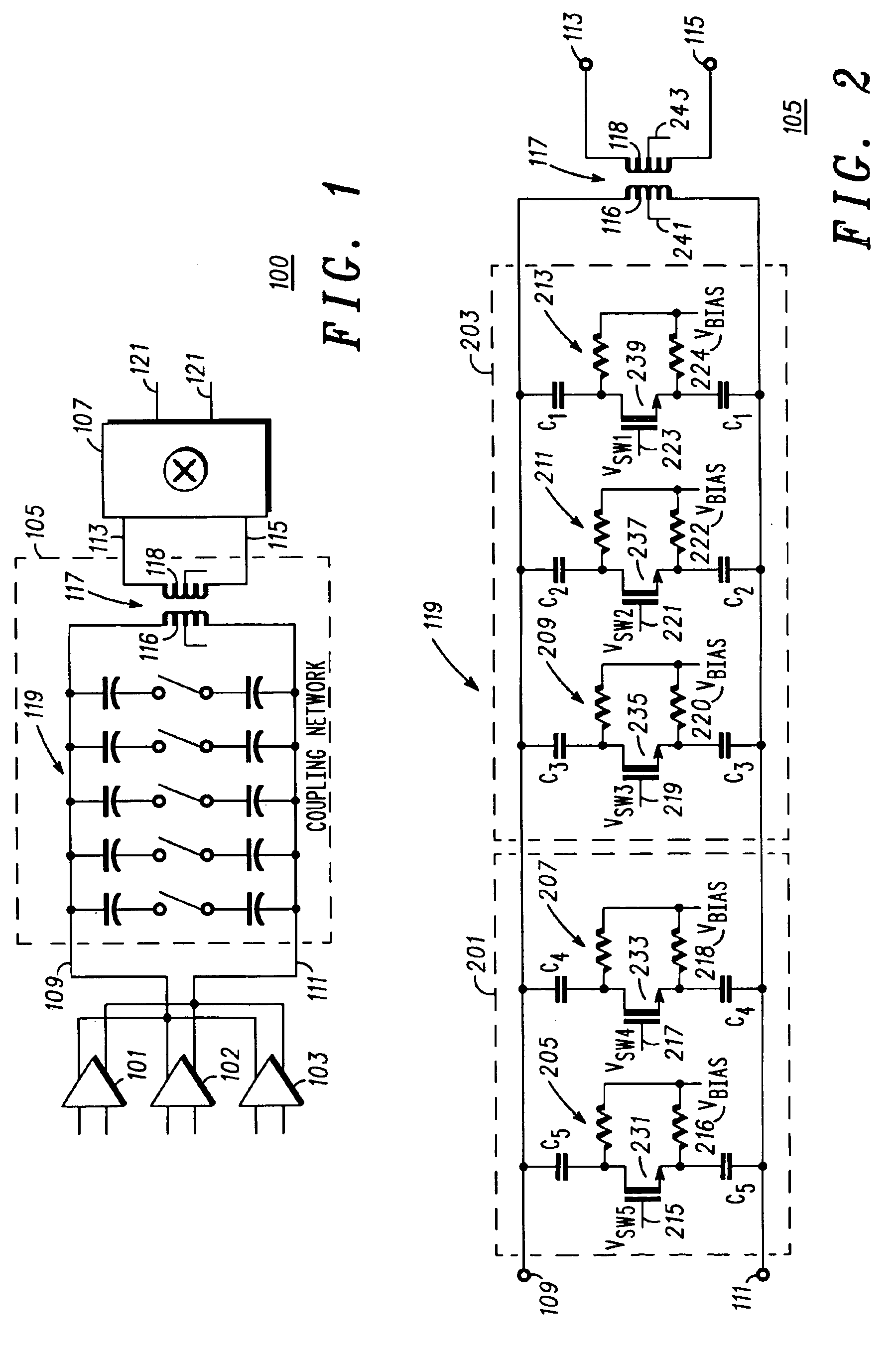
Integrated frequency selectable resonant coupling network and method thereof
InactiveUS6889036B2Reduce noiseDiscontnuous tuning with seperate pretuned circuitsTransmissionCouplingConductor Coil
An integrated center frequency selectable resonant coupling network suited for use in an integrated circuit is disclosed. The network includes an integrated coupling transformer having a secondary winding for coupling to a load and a primary winding for coupling to a source; a first integrated capacitive circuit controllably coupled across one of the primary and secondary windings and when so coupled operable to resonate with the integrated coupling transformer at a frequency in a first frequency band; and a second integrated capacitive circuit coupled across a second one of the primary and the secondary windings that is operable to resonate with the integrated coupling transformer at a frequency in a second frequency band. The method is in an IC and includes providing and coupling an input signal within alternatively a first frequency band and a second frequency band to a primary winding of an integrated coupling transformer; controlling an integrated switched capacitor network, coupled to the transformer, to provide a coupling network that is alternatively and respectively resonant at a first and second frequency within the first and second frequency band thus selectively providing an output signal at a secondary winding of the transformer; and down converting the output signal.
Owner:APPLE INC
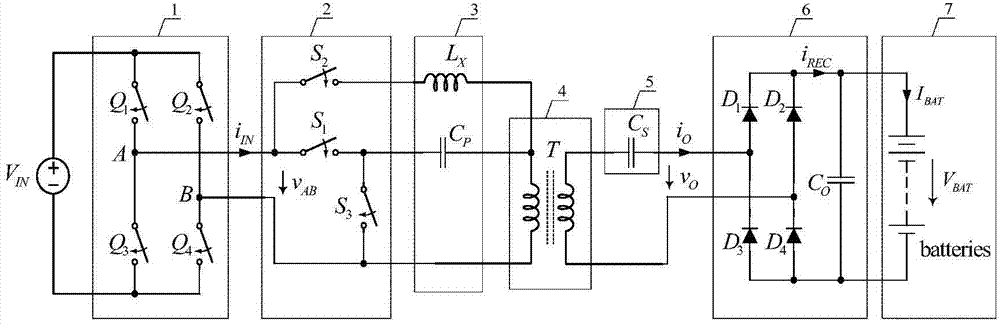
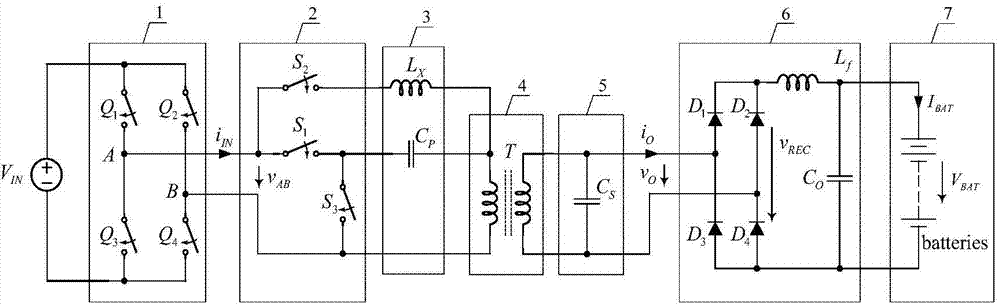
Constant current-constant voltage composite topological sensing type charging system
ActiveCN104753152ASimple structureImprove efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionConstant frequencyConstant current
The invention relates to a constant current-constant voltage composite topological sensing type charging system which satisfies the charging feature of constant current first and constant voltage later and is adaptive to wireless charging occasions of electric cars, mobile phones and the like. The constant current-constant voltage composite topological sensing type charging system comprises a high-frequency inverter circuit, a constant current-constant voltage mode switching network, a primary side compensation capacitor, an additional inductor, a loosely-coupled transformer, a secondary side compensation capacitor and a rectifying and filter circuit. The constant current-constant voltage composite topological sensing type charging system has the advantages that during a whole charging process, a mode switching switch is simply controlled to directly provide constant currents and constant voltage required by battery charging without changing working frequency, using of extra last-stage converters, output features are irrelevant with loads, input impedance is pure resistive in the whole constant current-constant voltage charging process, so that the topological system can use simple constant-frequency duty ratio control, the zero voltage on and off of a high-frequency inverter switch are guaranteed, converter efficiency is increased, reactive power is avoided, device stress is reduced, and efficiency is further increased.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
False-detection resistant annular coil vehicle detector
InactiveCN101833862AImprove frequency stabilityHigh harmonic impedance is smallRoad vehicles traffic controlMicrocontrollerControl system
The invention discloses a false-detection resistant annular coil vehicle detector comprising an oscillating circuit module, a parameter setting module, a frequency measuring module, a central processing module, an RS-232 communication module and the like. The annular coil is connected with the oscillating circuit module of a vehicle detector through a coupling transformer of 1:1 to form a high-frequency oscillating circuit; the frequency measuring module is used for carrying out shaping and frequency division on an oscillating signal and feeding the finally-calculated signal frequency valve to a singlechip control system; a singlechip is used for sampling a measuring value of the frequency measuring module at regular time; the measuring value is subjected to filter processing and is detected by an embedded vehicle detection algorithm; a detection state is displayed by an LED; and the detection result can be output by a pulse manner or transmitted to an upper computer through an RS-232 bus. The invention improves the design of a threshold detection algorithm, uses a single threshold method for detecting the arrival of the vehicle and uses a flatness determination method for detecting the leaving of the vehicle. In addition, by adopting the invention, the arrival and leaving moments of the vehicle can be accurately detected, the phenomena of false detection caused by multiple false triggers are reduced, and the stability of the system is enhanced.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
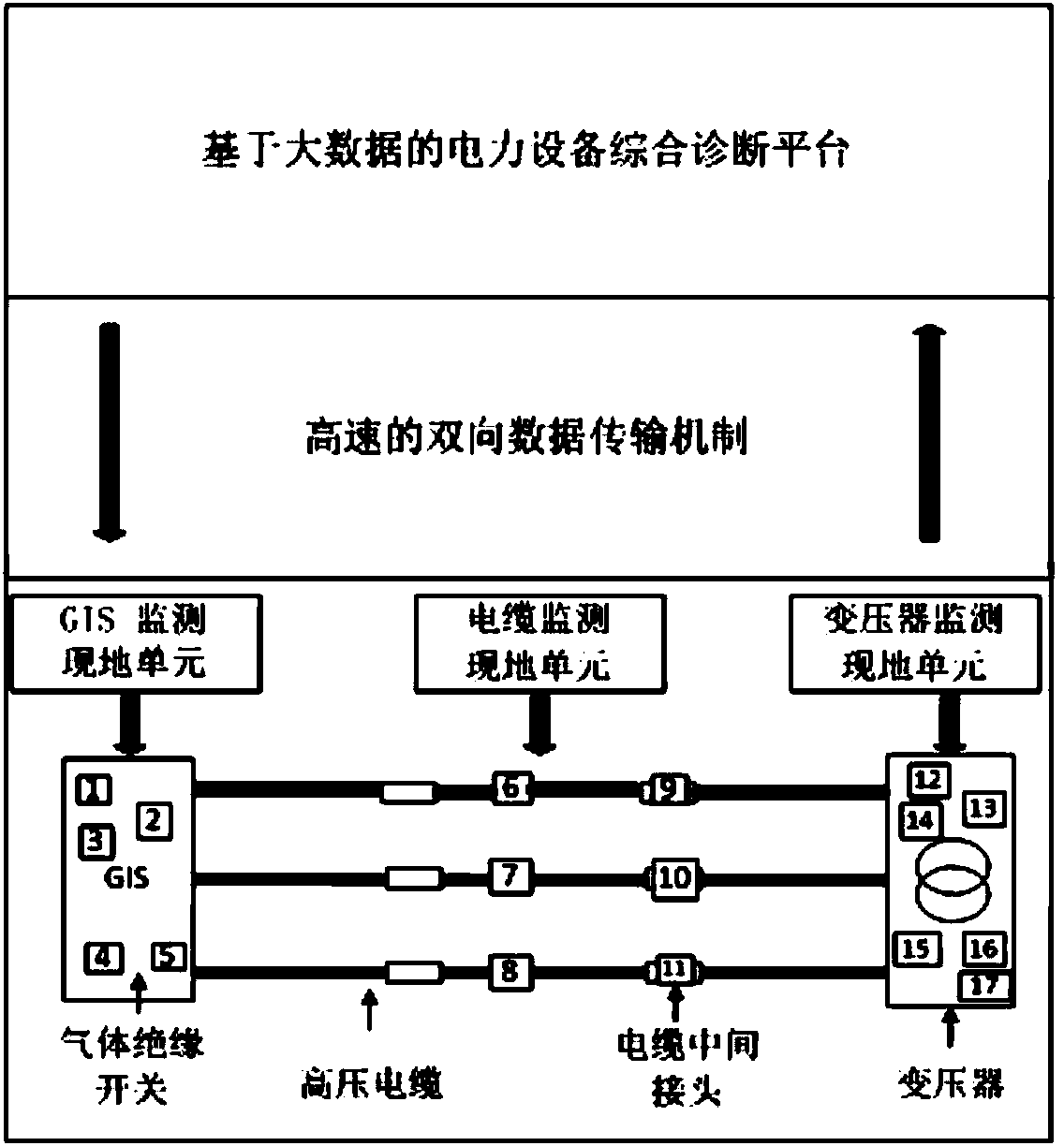
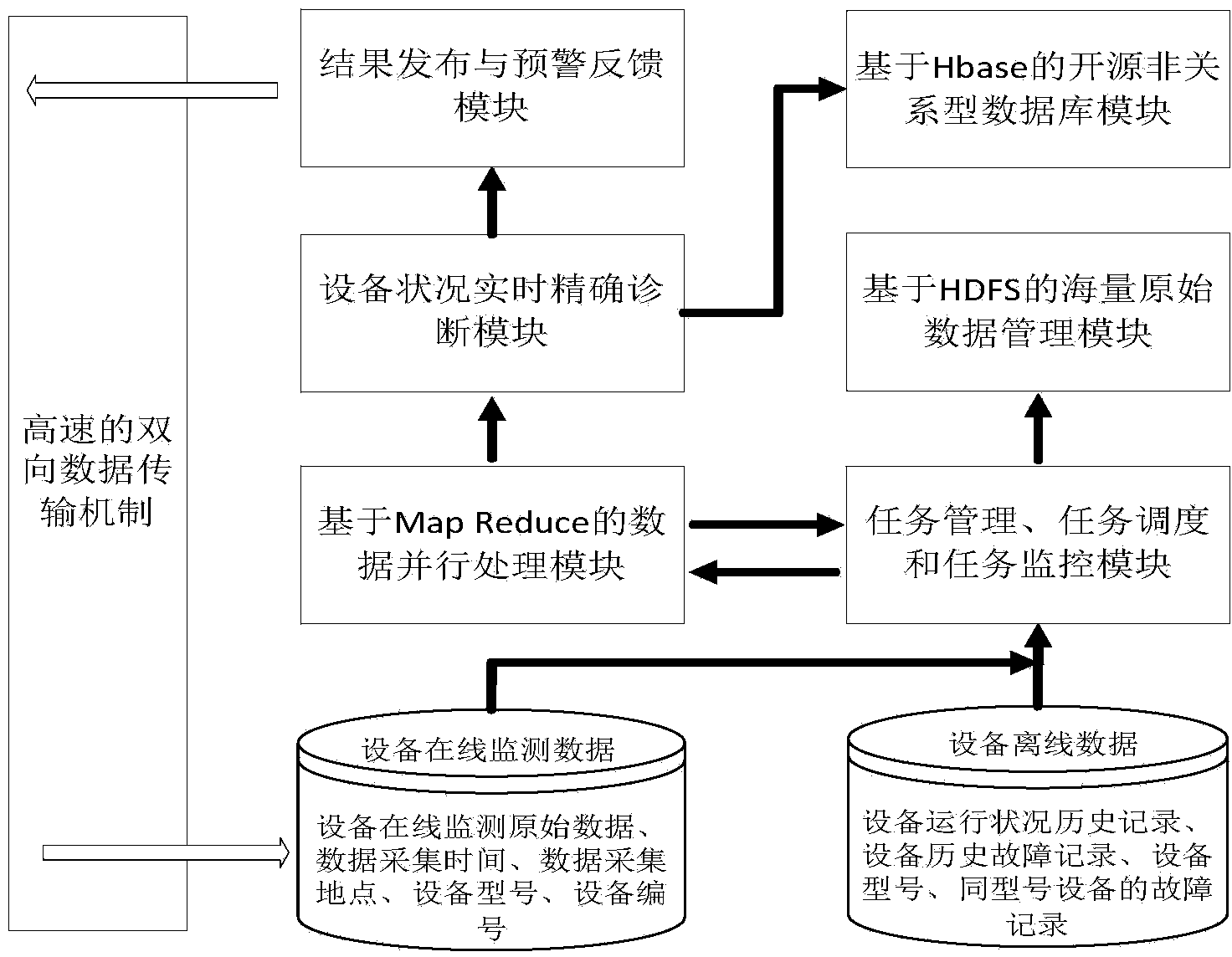
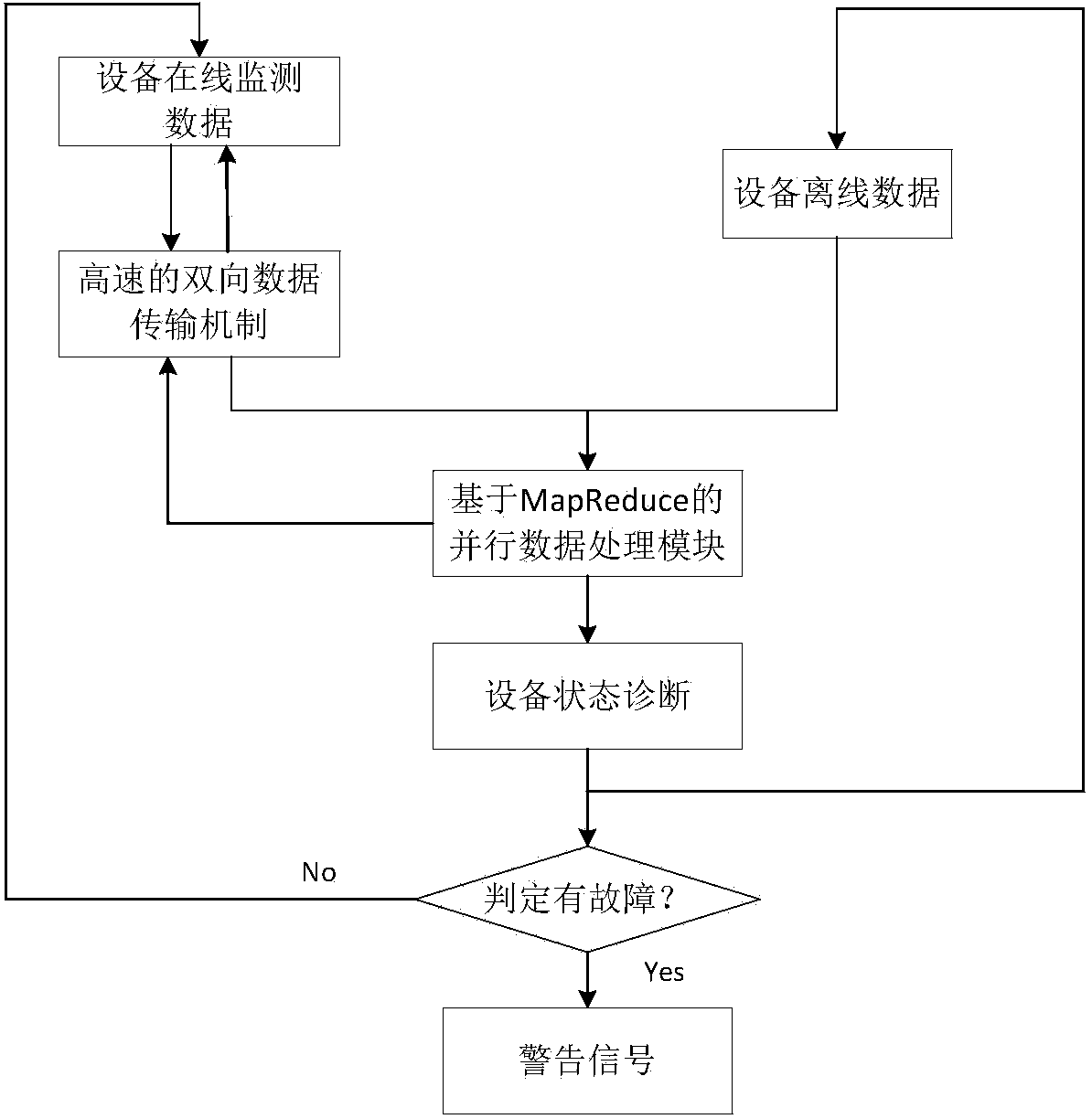
Power equipment integrated monitoring and early warning system based on big data and analysis method thereof
InactiveCN104283318AImprove accuracyRealize feedback early warningPower network operation systems integrationCircuit arrangementsMultiple sensorPower equipment
The invention discloses a power equipment integrated monitoring and early warning system based on big data and an analysis method of the power equipment integrated monitoring and early warning system. The system comprises a sensor group, a monitoring unit group and a power equipment integrated diagnosis platform, wherein the sensor group comprises multiple sensors used for obtaining monitoring parameters of a coupling transformer, a power cable and a GIS; the monitoring unit group comprises monitoring units used for monitoring the monitoring parameters of the coupling transformer, the power cable and the GIS, and each monitoring unit is connected with the corresponding sensor; the power equipment integrated diagnosis platform is connected with the monitoring unit group and used for achieving storage and management of multi-target power equipment monitoring data based on an HDFS, diagnosis based on the MapReduce technology and a fault sample bank, and real-time storage of monitoring index quantity and diagnosis results based on the NoSQL database technology; through a high-speed two-way data transmission mechanism, uploading of mass data monitored by multi-target power equipment in real time to a monitoring center is achieved on one hand, and feedback and early warning of the diagnosis results are achieved on the other hand.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
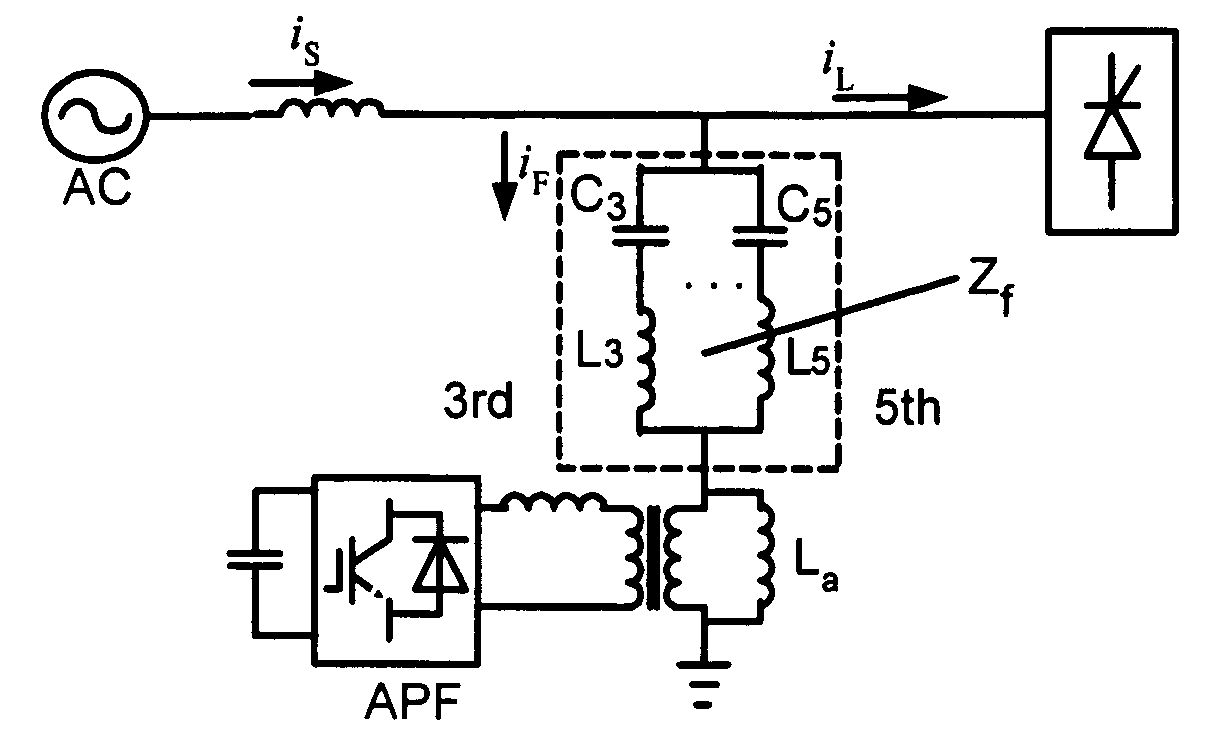
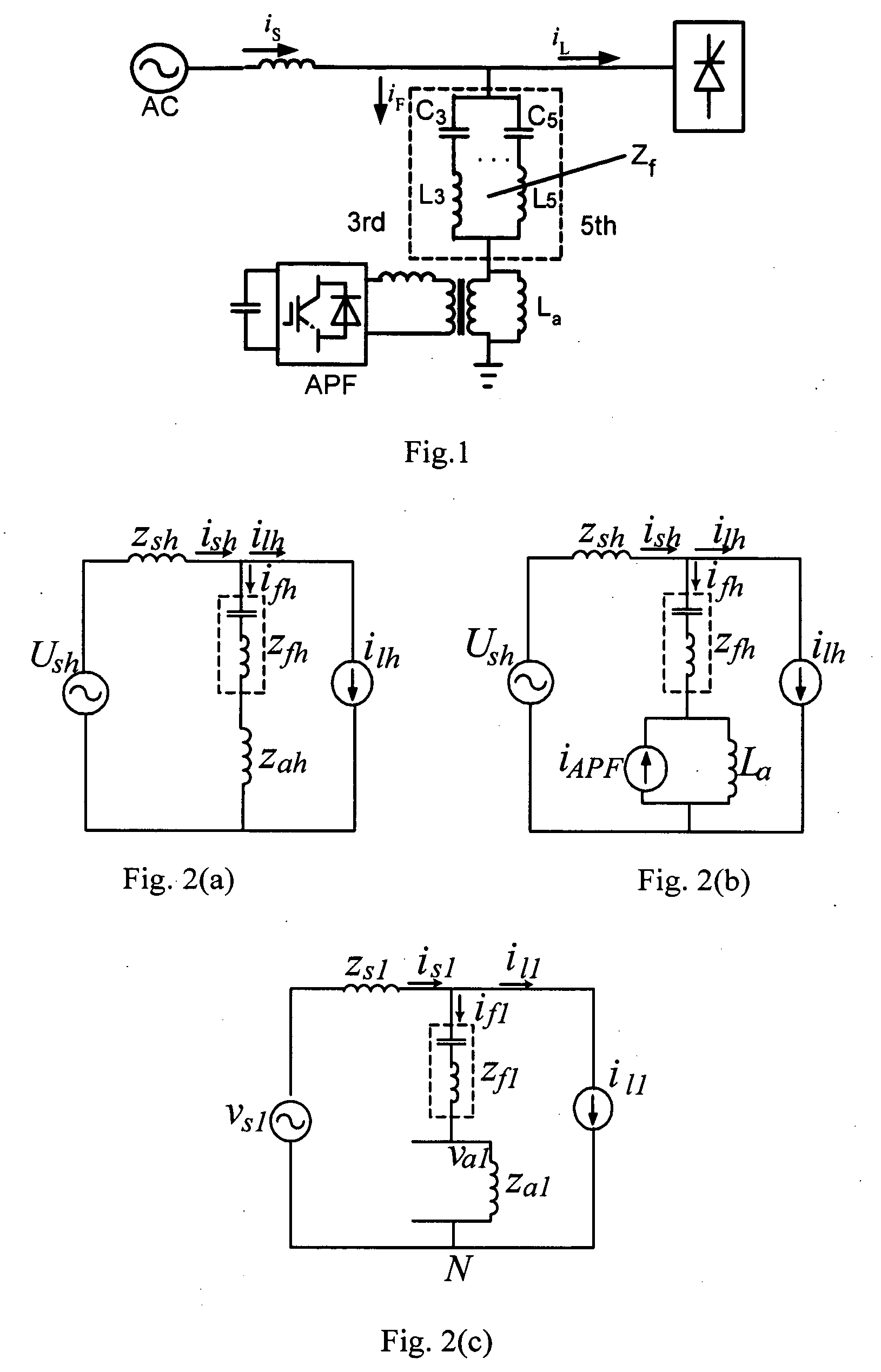
Hybrid parallel active power filter for electrified railway system
InactiveUS20050083627A1Add significant costImprove filtering resultInterference suppressionActive power filteringGrid impedanceControl manner
An exemplary parallel hybrid power filter apparatus for the electrified railway is described. The apparatus may include a group of LC reactive filter being purely tuned, an additional inductance, an active power filter and a coupling transformer. The active power filter may be controlled, e.g., as a current source in a composite control manner and can be connected in parallel to the additional inductance via the coupling transformer. The power filter can be connected to the reactive filter in series to form the parallel hybrid filtering system, and may be connected to the power grid via the circuit breaker or a thyristor. This exemplary system can be installed either in the traction substations or in the locomotives directly, or performed by ameliorating the original reactive filter. The active power filter does not add significant amount of cost, and may be simple and reliable in a control manner for the capacity of the APF is so small as to be less than one percent of that of the harmonics source. The power filter can also inhibit the impact of the “background harmonics” of the electrified railway on the reactive filter, and prevent the reactive filter and the grid impedance from resonance.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Power supply device and vehicle lamp
InactiveUS20050269968A1Minimize switchingSignificant valueElectroluminescent light sourcesEmergency protective circuit arrangementsControl circuitMagnetic flux
A power supply device includes: a regulator transformer; a primary switch for selectively supplying a current to the regulator transformer; a control circuit for reducing to 0, following each election made at the primary switch, the minimum value of a current output by the secondary side of the regulator transformer; and a coupling transformer for magnetically coupling routes along which a plurality of loads are connected in parallel to the secondary side of the regulator translator in a direction in which magnetic flux along each of the routes is offset by a current change. In this case, the control circuit increases the maximum value of the output current on the secondary side larger than twice of the target value of the current supplied to the loads.
Owner:KOITO MFG CO LTD
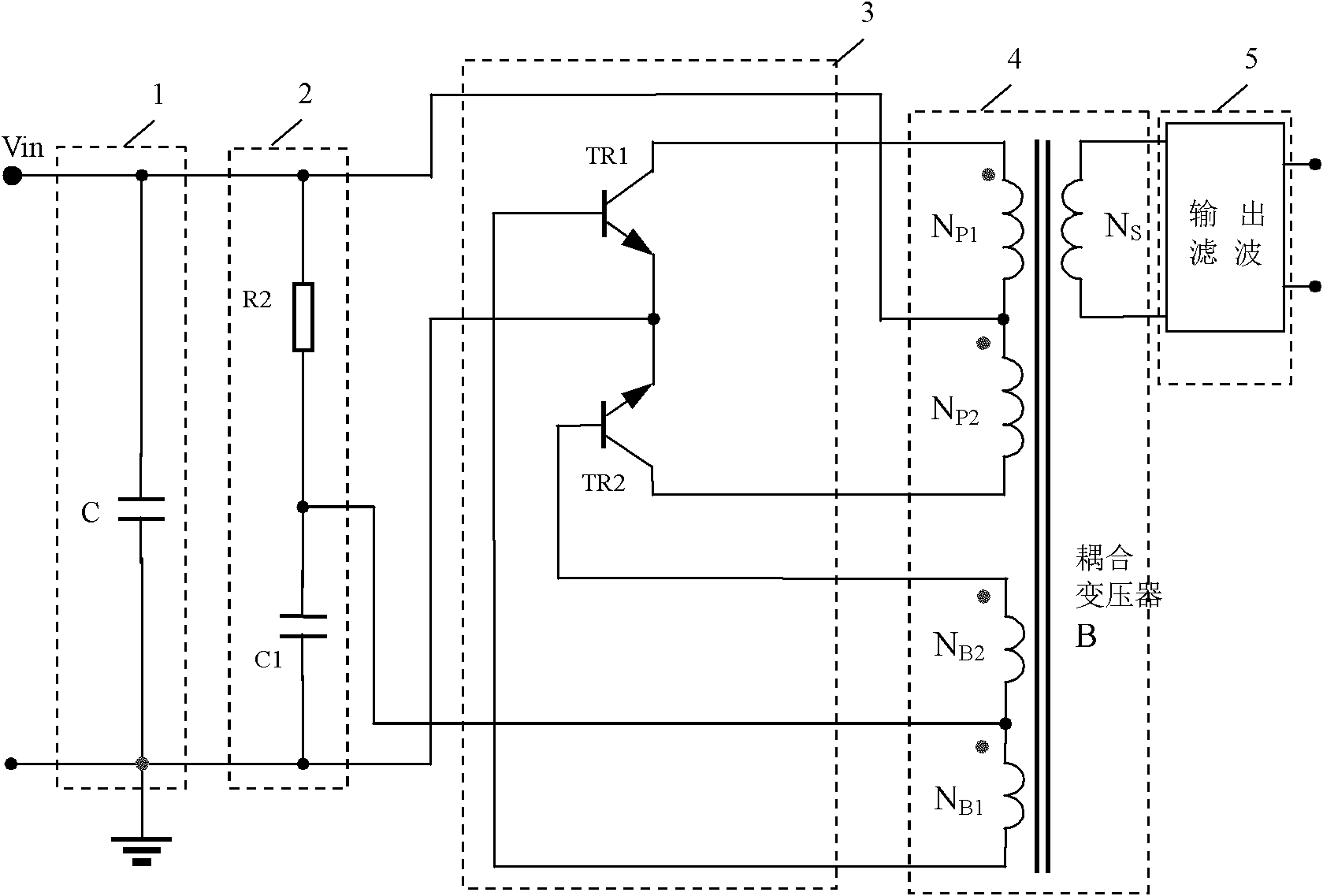
Self-exited push-pull converter
The invention discloses a self-exited push-pull converter, comprising an input soft starting circuit, a bipolar push-pull circuit, a coupling transformer and an output filter circuit, wherein the input soft starting circuit, the bipolar push-pull circuit, the coupling transformer and the output filter circuit are connected in order; the bipolar push-pull circuit comprises two triodes and a high frequency self-exited suppression circuit, wherein the two triodes are in push-pull connection; the emitters of the two triodes are grounded; the bases of the two triodes are respectively connected with two ends of a feedback winding of the coupling transformer; the collectors of the two triodes are connected with two ends of a primary winding of the coupling transformer; the high frequency self-exited suppression circuit is used for removing sine vibration generated due to high characteristic frequency when the triodes are electrified; and the high frequency self-exited suppression circuit is connected in the bipolar push-pull circuit. The self-exited push-pull converter can effectively control high frequency vibration.
Owner:MORNSUN GUANGZHOU SCI & TECH
Computed tomography systems
InactiveUS20110002446A1Reduce maintenance costsReduce manufacturing costMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPower inverterComputed tomography
A power delivery system for computed tomography includes at least one transformer (e.g., an isolation transformer, a coupling transformer, an adaptation transformer), a rotary transformer, and at least two power inverters. The rotary transformer includes a stationary winding disposed on a stationary side and a rotational winding disposed on a rotating side. The isolation or adaptation transformer is coupled to the stationary winding or the rotating winding of the rotary transformer. At least two power inverters are constructed and arranged to provide power to the primary winding of the rotary transformer. The high-voltage unit is disposed on the rotating side and connected to receive power from the rotational winding and constructed to provide power to an X-ray source.
Owner:BELAND ROBERT
Acoustic galvanic isolator incorporating film acoustically-coupled transformer
ActiveUS7423503B2Inexpensive to fabricateGood rejectionImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionCarrier signalEngineering
Embodiments of the acoustic galvanic isolator comprise a carrier signal source, a modulator connected to receive an information signal and the carrier signal, a demodulator, and, connected between the modulator and the demodulator, an electrically-isolating acoustic coupler comprising an electrically-isolating film acoustically-coupled transformer (FACT).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Wireless electric energy transmission system compensation topological structure
InactiveCN106533185AIncrease flexibilityEasy and fast commissioningEfficient power electronics conversionCircuit arrangementsCapacitanceEngineering
The invention provides a wireless electric energy transmission system compensation topological structure, relates to the wireless electric energy transmission system compensation topological structure, and aims at solving the problems that the existing wireless electric energy transmission system compensation topological structure is high in the number of compensation devices, high in system cost and low in power density. The S / CLC compensation topology comprises a primary series compensation capacitor, a loosely coupled transformer, a secondary parallel compensation capacitor, a secondary series compensation inductor and a phase shifting capacitor. The primary series compensation capacitor is connected with a full-bridge inverter. The primary series compensation capacitor is connected with the primary self-inductor of the loosely coupled transformer. The primary self-inductor of the loosely coupled transformer is connected with the full-bridge inverter. The secondary self-inductor of the loosely coupled transformer is connected with the secondary parallel compensation capacitor and the secondary series compensation inductor. The secondary self-inductor of the loosely coupled transformer is connected with the secondary parallel compensation capacitor, the phase shifting capacitor and a full-wave rectifier. The secondary series compensation inductor is connected with the phase shifting capacitor and the full-wave rectifier. The wireless electric energy transmission system compensation topological structure is used for wireless electric energy transmission.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Thin-film acoustically-coupled transformer
ActiveUS20050093656A1High Common Mode Rejection RatioHigh impedancePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksPlanar electrodeBalanced circuit
One embodiment of the acoustically-coupled transformer includes a stacked bulk acoustic resonator (SBAR) having a stacked pair of film bulk acoustic resonators (FBARs) with an acoustic decoupler between them. Each FBAR has opposed planar electrodes with piezoelectric material between them. The transformer additionally has first terminals electrically connected to the electrodes of one FBAR and second terminals electrically connected to the electrodes of the other FBAR. Another embodiment includes first and second stacked bulk acoustic resonators (SBARs), each as described above, a first electrical circuit connecting one FBARs of the first SBAR to one FBAR of the second SBAR, and a second electrical circuit connecting the other FBAR of the first SBAR to the other FBAR of the second SBAR. The transformer provides impedance transformation, can linking single-ended circuitry with balanced circuitry or vice versa and electrically isolates primary and secondary. Some embodiments are additionally electrically balanced.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Battery wireless charging system for secondary side composite type compensation network
ActiveCN106532845AEasy to switchAvoid complex communicationBatteries circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionSoft switchingBattery charge
The invention relates to a battery wireless charging system for a secondary side composite type compensation network, for providing constant current and constant voltage output required by a battery charging process in sequence. Two kinds of novel composite topological structures, including SS / S-LCL and LCL-LCL / LCL-S are provided; and each novel composite topological structure comprises a high-frequency full-bridge inversion circuit, a primary side compensation network, a loosen coupling transformer, a secondary side compensation network, a constant current-constant voltage switching voltage, and a full-bridge rectifying and filtering circuit separately. Based on the intrinsic characteristic of a circuit, a constant current or a constant voltage irrelevant to a load is realized at specific frequency; conversion of two kinds of modes is realized through the constant current-constant voltage switching network; in addition, approximate zero reactive ring current of the circuit and soft switching of a switching device are realized concurrently, so that the efficiency is improved while the device stress is reduced; and the constant current-constant voltage switching network is placed on the secondary side, so that complex communication between a transmitting end and a receiving end of the wireless charging system is avoided, the control is simplified, and the reliability is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Comprehensive control method for high-power efficient energy consuming high-frequency switching power supply
ActiveCN102255529ARealize self-balancing current controlRealize constant voltage and constant current outputAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionFull bridgeLow voltage
The invention discloses a comprehensive control method for a high-power efficient energy consuming high-frequency switching power supply. The high-power efficient energy consuming high-frequency switching power supply comprises a three-phase current inverter and a high-frequency DC / DC (Direct Current to Direct Current) converter, wherein the high-frequency DC / DC converter consists of a single-phase full-bridge inverter, a high-frequency coupling transformer and a low-voltage rectifier which are connected in series in sequence; the input end of the three-phase current inverter is connected with a group of three-phase capacitors connected in a Y form, and is connected with a power grid through a three-phase inductor L; and the three-phase current inverter is connected with the single-phase full-bridge inverter of the high-frequency DC / DC converter. According to the method, quick response of a system is realized, change of a load is tracked quickly, efficient power consumption of the system is realized, and the voltage and current distortion factors of the system are decreased.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Noncontact electric energy and signal synchronous transmission system and control method thereof
InactiveCN105846684AReduce volumeImprove efficiencyDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationLoose couplingEnergy conversion efficiency
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
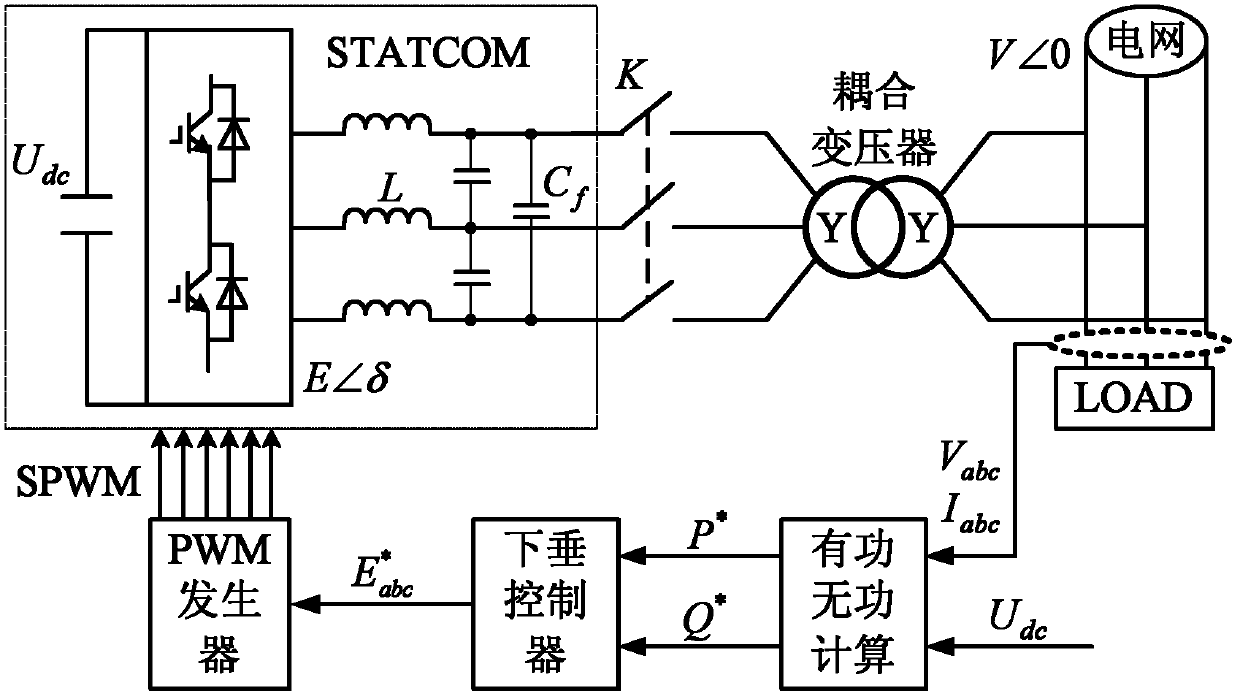
STATCOM (static synchronous compensator) control system adopting droop control strategy and control method thereof
InactiveCN102222922APrevent fallingAvoid lossFlexible AC transmissionReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationCapacitanceTime signal
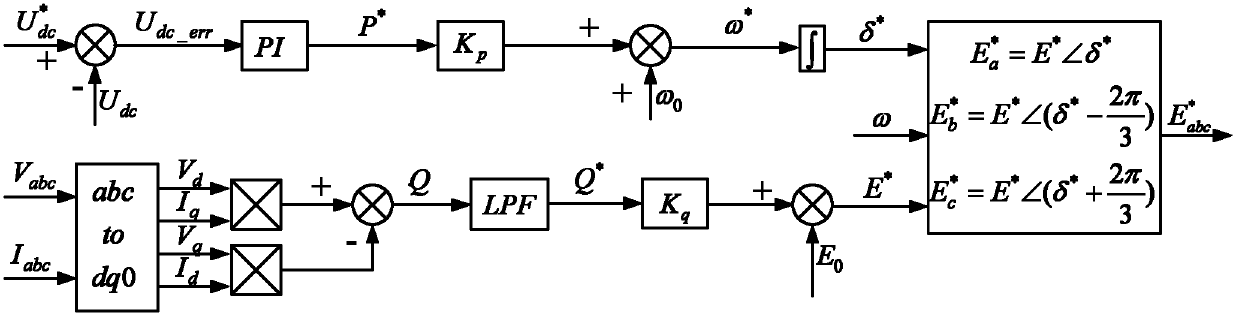
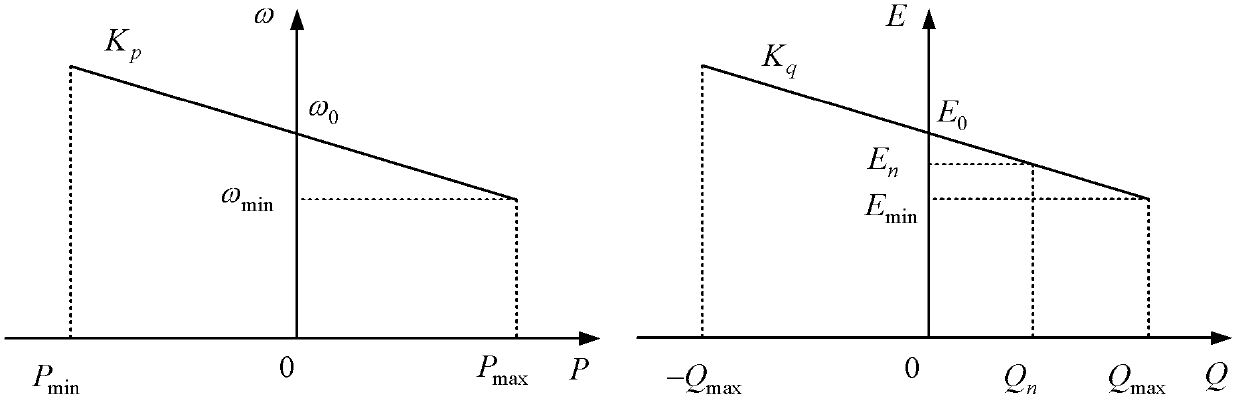
The invention discloses a STATCOM (static synchronous compensator) control system adopting a droop control strategy and a control method thereof. The STATCOM control system adopting the droop control strategy comprises a direct-current side capacitor, a three-phase inverter bridge and an inductance-capacitance filter, wherein the direct-current side capacitor and the three-phase inverter bridge are connected in parallel and then connected with the inductance-capacitance filter, and the inductance-capacitance filter is connected to a PCC (Point of Common Coupling) of a power grid by a three-phase switch K through a coupling transformer T. The control method disclosed by the invention comprises the steps of real-time signal collection, computation of active power reference value P*, computation of reactive power reference value Q*, computation of frequency reference value omega* and voltage modulation amplitude reference value E*, computation of phase reference value Delta* and computation of voltage modulation signals; and only one PI (proportional integral) regulator and two droop control coefficients need to be regulated, thus the whole control method is easy to realize, and further the power system can better supply power to users safely, excellently and economically.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV +1
Inductive coupling type electric energy transmission device
ActiveCN101789637AImprove transmission efficiencySimple structureElectromagnetic wave systemCircuit arrangementsCapacitanceResonance
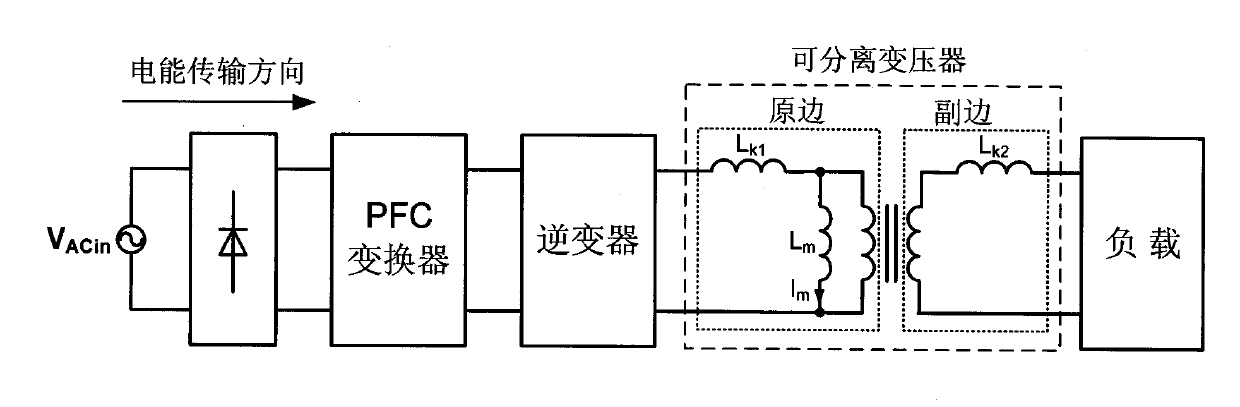
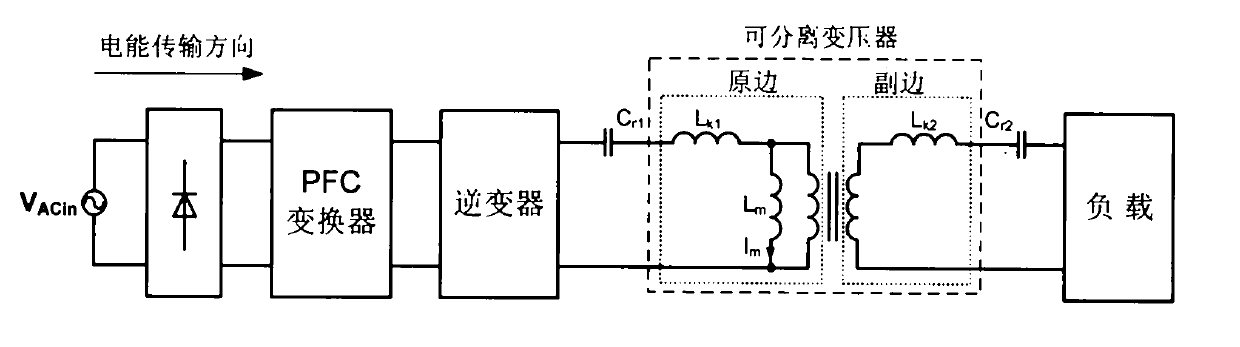
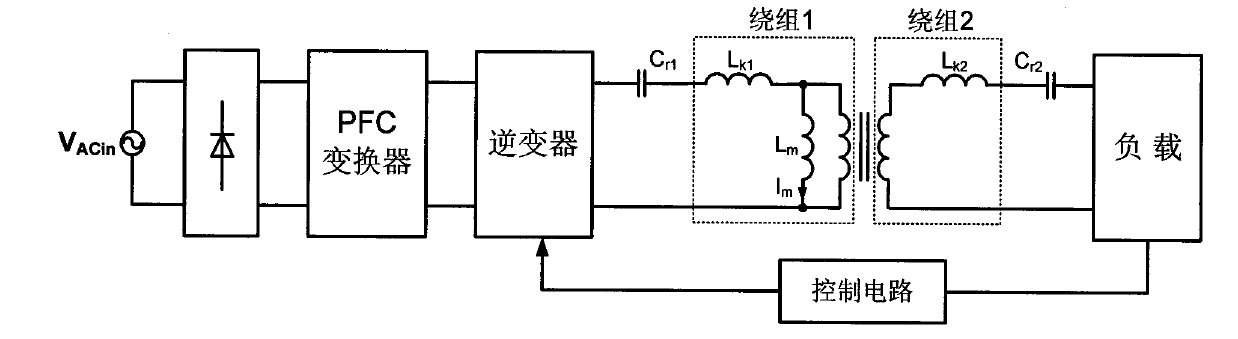
The invention discloses an inductive coupling type electric energy transmission device, which is formed by connecting an inverter in series with a separable transformer or weak coupling transformer. One ends of the primary side and secondary side of the separable transformer or weak coupling transformer are respectively connected in series with a resonance capacitor to enable the primary side and the secondary side of the separable transformer or weak coupling transformer to be subjected to the resonance, wherein Lk1 and Lk2 respectively express leakage inductance quantities of the primary side and the secondary side of the separable transformer or weak coupling transformer, and Cr2 and Cr2 respectively express capacitor values of resonance capacitors of the primary side and the secondary side of the separable transformer or weak coupling transformer. By adding the resonance capacitors, the invention ensures that the leakage inductances of the primary side and the secondary side and the series impedances of the resonance capacitors are zero when carrying out the frequency resonance, therefore, non-contact electric energy transmission efficiency is high. The invention also has the advantages of simple structure, convenient realization and easy popularization.
Owner:南京博兰得电能技术发展有限公司
Constant current-constant voltage composite topology-based deviation-resistant battery wireless charging system
ActiveCN109617190AEnsure constant power outputStrong anti-offset abilityBatteries circuit arrangementsCharging stationsConstant powerFull bridge
The invention discloses a constant current-constant voltage composite topology-based deviation-resistant battery wireless charging system. First constant current output and then constant voltage output, which are required by the battery charging process, are provided, and the constant current-constant voltage composite topology-based wireless charging system is applicable to a wireless charging occasion of an electric vehicle battery. The system comprises a high-frequency full-bridge inversion circuit, a primary compensation network, a loose coupling transformer, a secondary compensation network, a constant current-constant voltage switching network and a full-bridge rectification filtering circuit. The composite topology is used for performing constant current-contact voltage mode conversion by the constant current-constant voltage switching network placed at a secondary side, first deviation-resistant constant current output and then deviation-resistant constant voltage output in irrelevant to a load are achieved under a special frequency, complicated communication between an emission end and a receiving end of the wireless charging system is prevented, control is simplified, nearly-zero reactive power circulation of the circuit and soft switch of a switch device are achieved, the constant power output is maintained, and the wireless charging system has favorable deviation-resistant capability.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
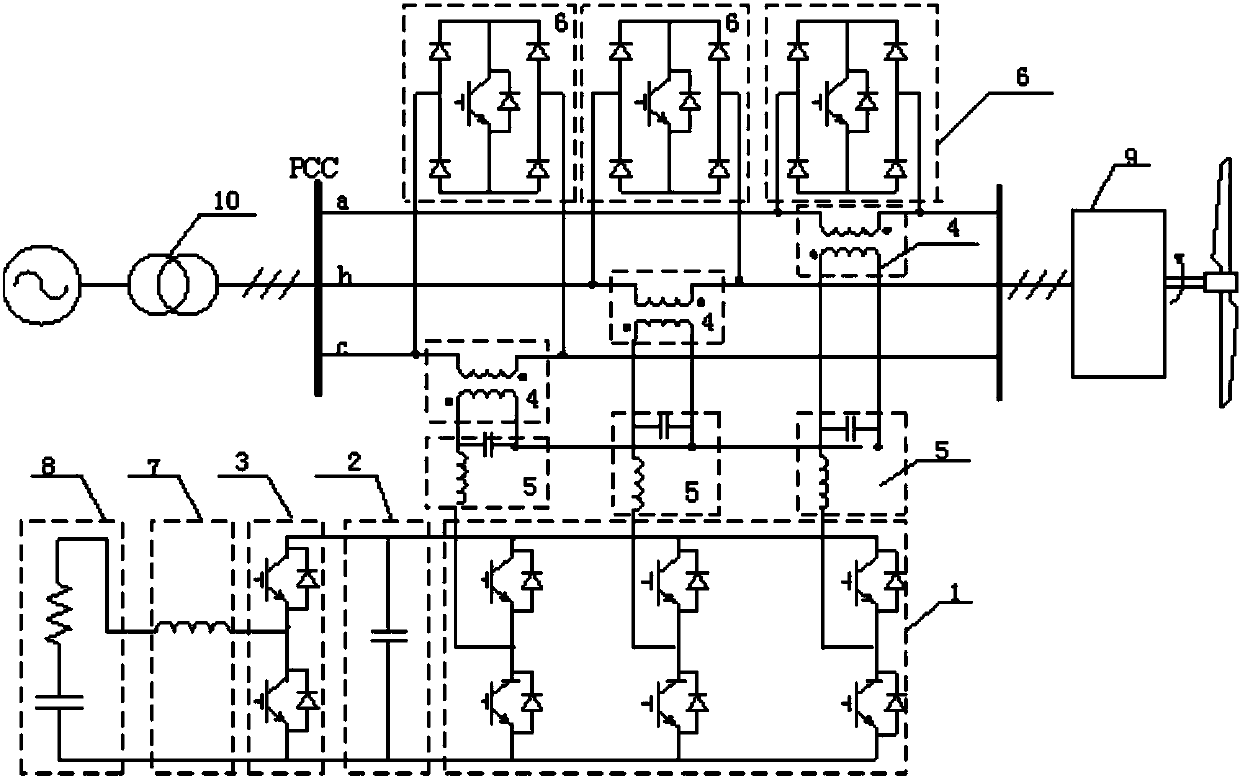
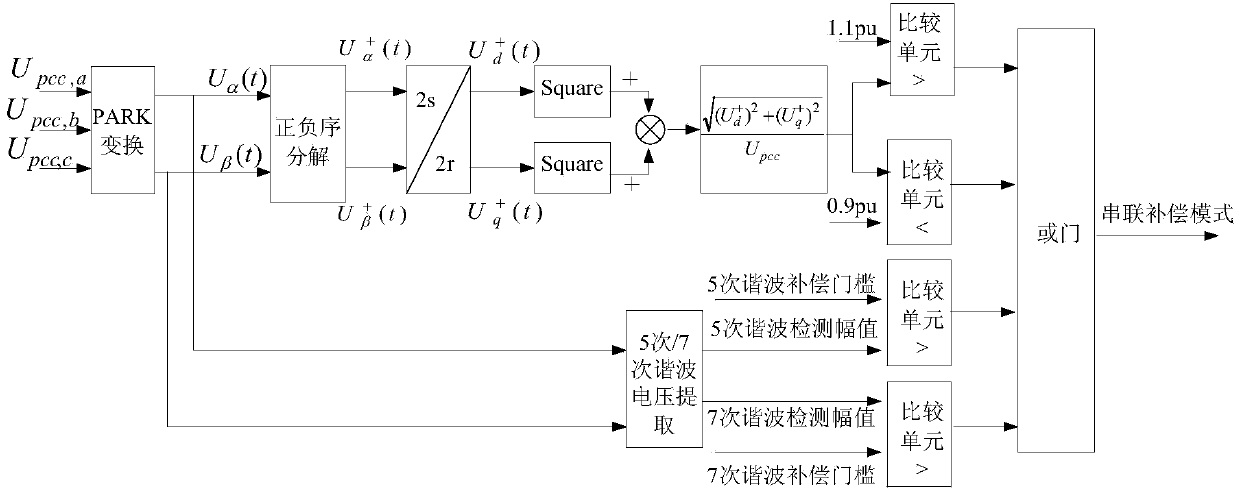
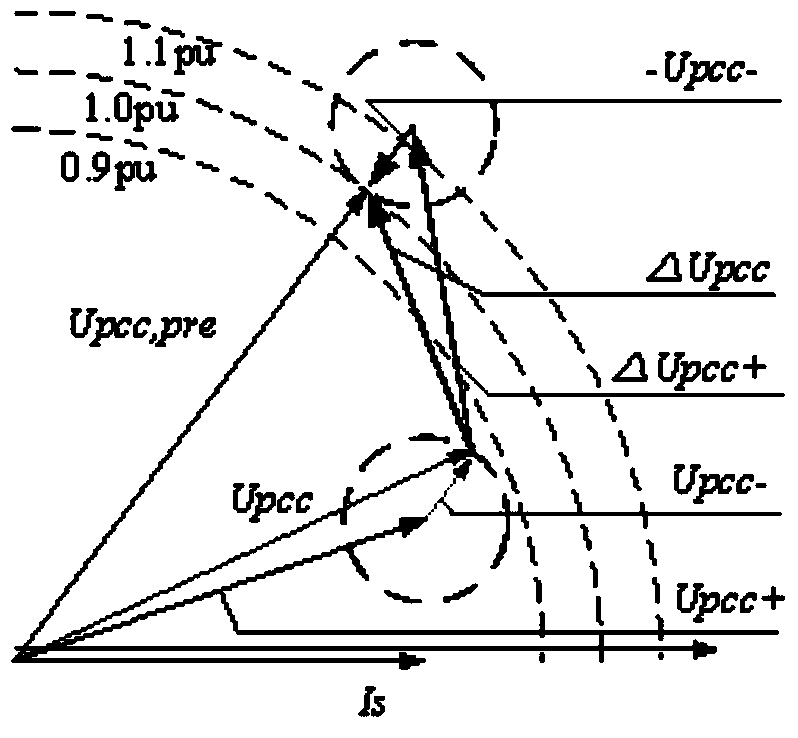
Comprehensive series compensation voltage ride-through device of wind turbine generator and control method
ActiveCN103390901AEasy to installVoltage does not dropAc network load balancingHarmonic reduction arrangementCapacitanceWind driven
The invention discloses a comprehensive series compensation voltage ride-through device of a wind turbine generator. The comprehensive series compensation voltage ride-through device of the wind turbine generator is mounted on a three-phase circuit between a wind driven generator and a control device of the wind driven generator and a PCC (point of common coupling) of a power grid, and comprises a three-phase standard transducer, a series coupling transformer, a two-way charge-discharge circuit, a DC bus capacitor and a by-pass switch. With the adoption of a dynamic voltage restorer, a chopper circuit and a super capacitor with high-capacity energy storage in the power electronic technology, low voltage ride through, high voltage ride through and harmonic compensation are realized under the condition that generator terminal voltage drops off during power grid fault, generator terminal voltage rises due to excessive reactive power of the power grid and the harmonic content of the power grid is overlarge, the wind turbine generator is prevented from being separated from the grid, and harmful effects of harmonic are prevented; and moreover, a conventional wind turbine generator is not required to be transformed, and the device can be taken as an independent control module and added at the stator output port of the wind turbine generator and is convenient to mount.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
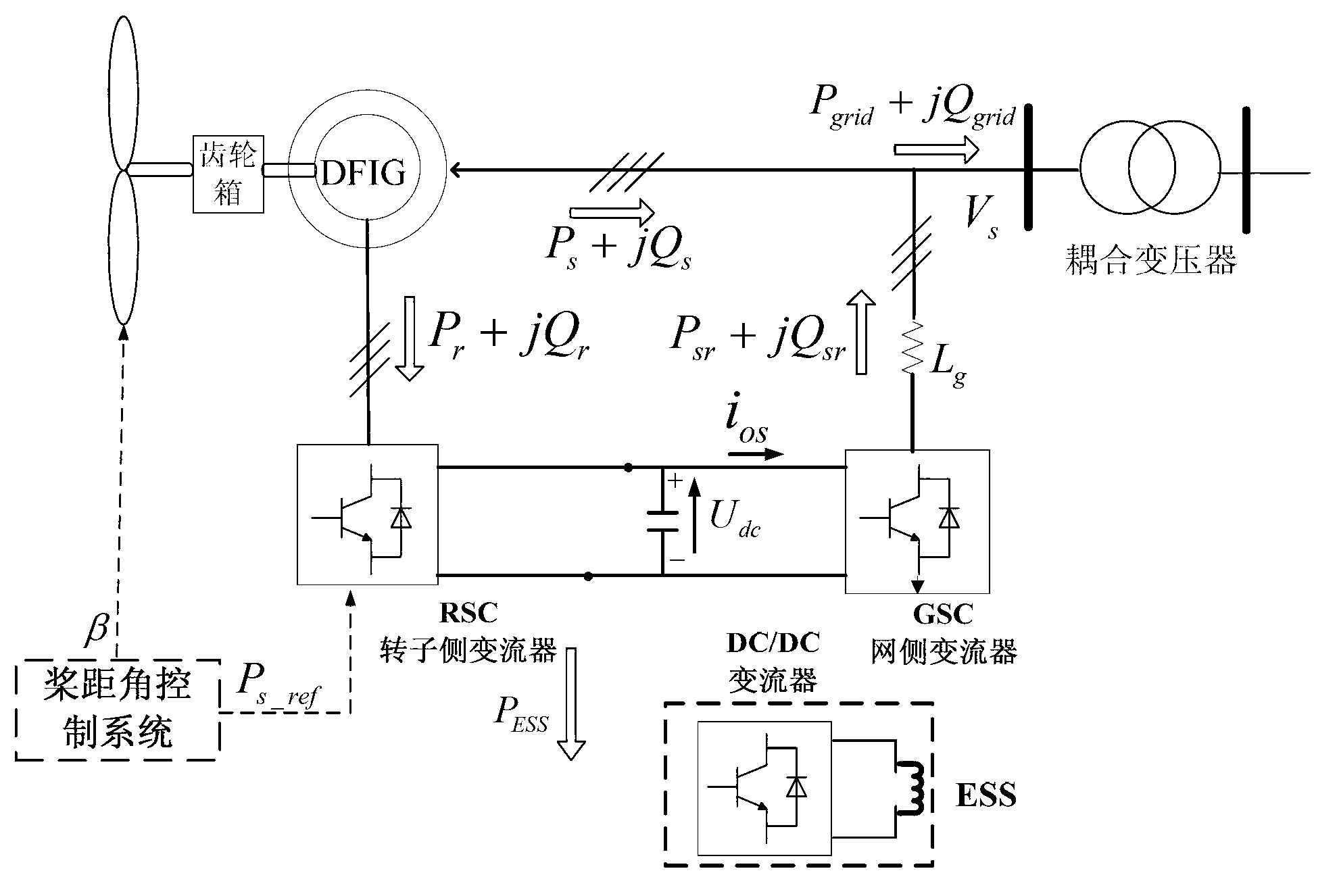
Low-voltage ride through control system and method for capacity-optimal energy-storage type double-fed motor
ActiveCN103078339AGuaranteed not to run offlineStable supportSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsEnergy storageCapacitanceWind power generation
The invention relates to a low-voltage ride through control system and a low-voltage ride through control method for a capacity-optimal energy-storage type double-fed motor. The low-voltage ride through control system comprises a power grid, a coupling transformer, a double-fed induction generator (DFIG), a grid-side converter, a rotor-side converter, a DC (Direct Current)-side capacitor, a geared head and a fan, wherein one path of the power grid is directly connected with the DFIG through the coupling transformer, and another path of the power grid passes through the grid-side transformer, the DC-side capacitor and the rotor-side converter in sequence and is connected with the DFIG; a DC-side energy storage device is connected with the DC-side capacitor through a bidirectional DC / DC converter; and the DFIG is connected with the fan through the geared head. The low-voltage ride through control system and method have the advantages of improving the low-voltage ride through capability of a DFIG wind power generation system when the voltage of the power grid sharply drops, ensuring the fault ride-through of the DFIG, improving the supporting capability of the DFID wind power generation system on the voltage of the power grid during fault, providing a measure for reducing the requirement of the DFIG on the capacity of the energy-storage device in the process of realizing the low-voltage ride through and greatly reducing the cost of the energy storage device.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
High-power induction charging converter of electric vehicle and control method thereof
InactiveCN102157973AImprove power factorHarmonic reductionBatteries circuit arrangementsElectromagnetic wave systemCapacitanceCoupling transformer
The invention provides a high-power induction charging converter of an electric vehicle and a control method thereof. The converter comprises a three-phase fully-controlled bridge rectifying circuit, a full-bridge inverter circuit and an inductive coupling circuit which are connected in sequence, wherein each phase at the alternating current (AC) side of the three-phase rectifying circuit is connected with a reactor (1), the three-phase rectifying circuit is a three-phase fully-controlled bridge rectifying circuit (2), and the positive end and the negative end of the direct current (DC) side of the three-phase rectifying circuit are connected with one DC storage capacitor (3); an inverter circuit is a full-bridge inverter circuit (4), an input end of the full-bridge inverter circuit (4) is connected with two ends of the DC storage capacitor (3), and an output end of the full-bridge inverter circuit (4) is connected with the primary side of a loosely-coupled transformer (6) in the inductive coupling circuit; and a serial compensation capacitor (5) of the inductive coupling circuit is connected with the primary side of the loosely-coupled transformer (6), and the secondary side of the loosely-coupled transformer (6) is connected with a secondary compensation capacitor (7) in parallel, thus storage batteries are charged by converting AC into DC via a secondary rectifier bridge (8). The converter is used for a charging station so as to finish a high-power non-contact induction charging function of the electric vehicle.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com