Patents
Literature
653 results about "Optical network terminal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
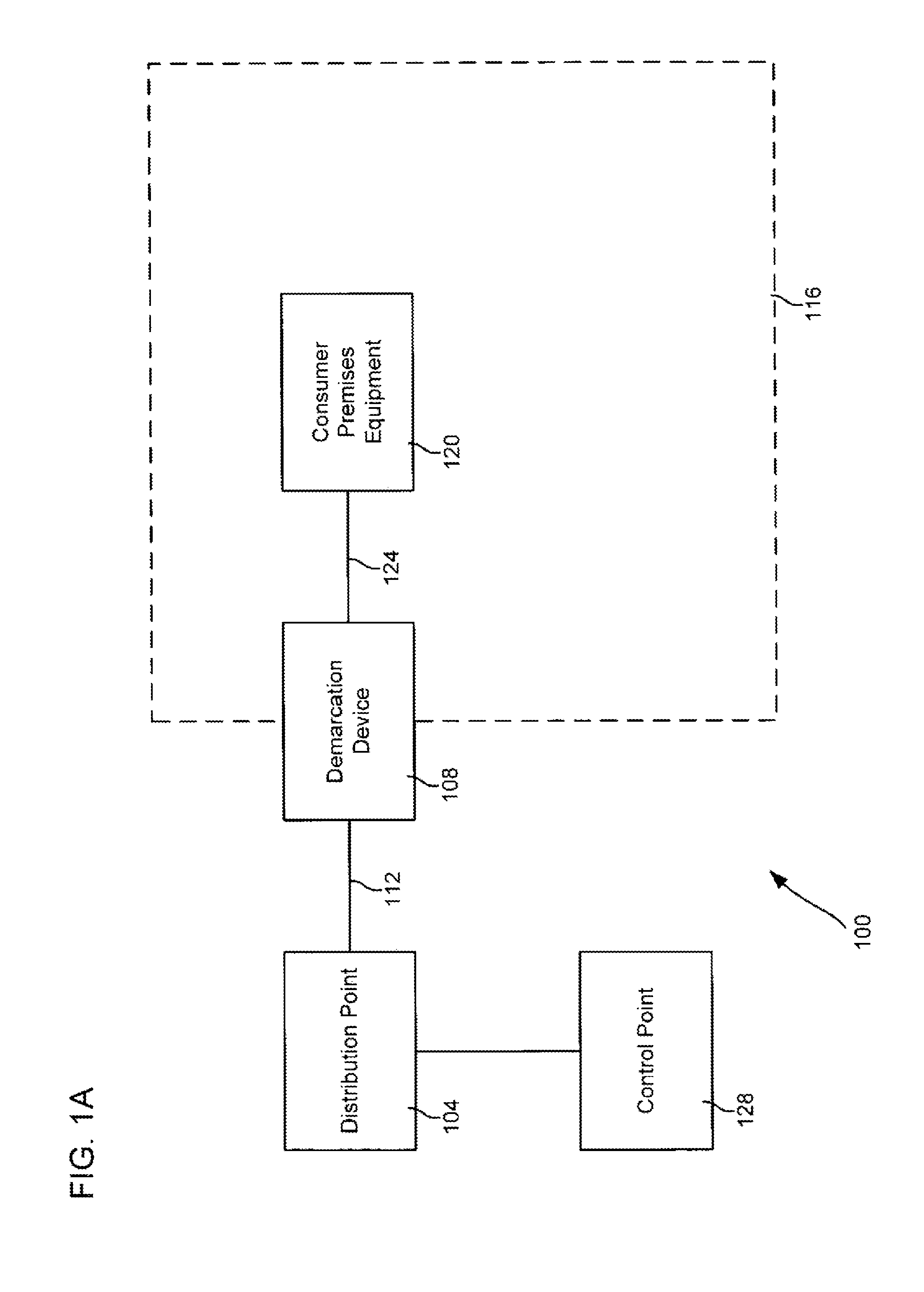
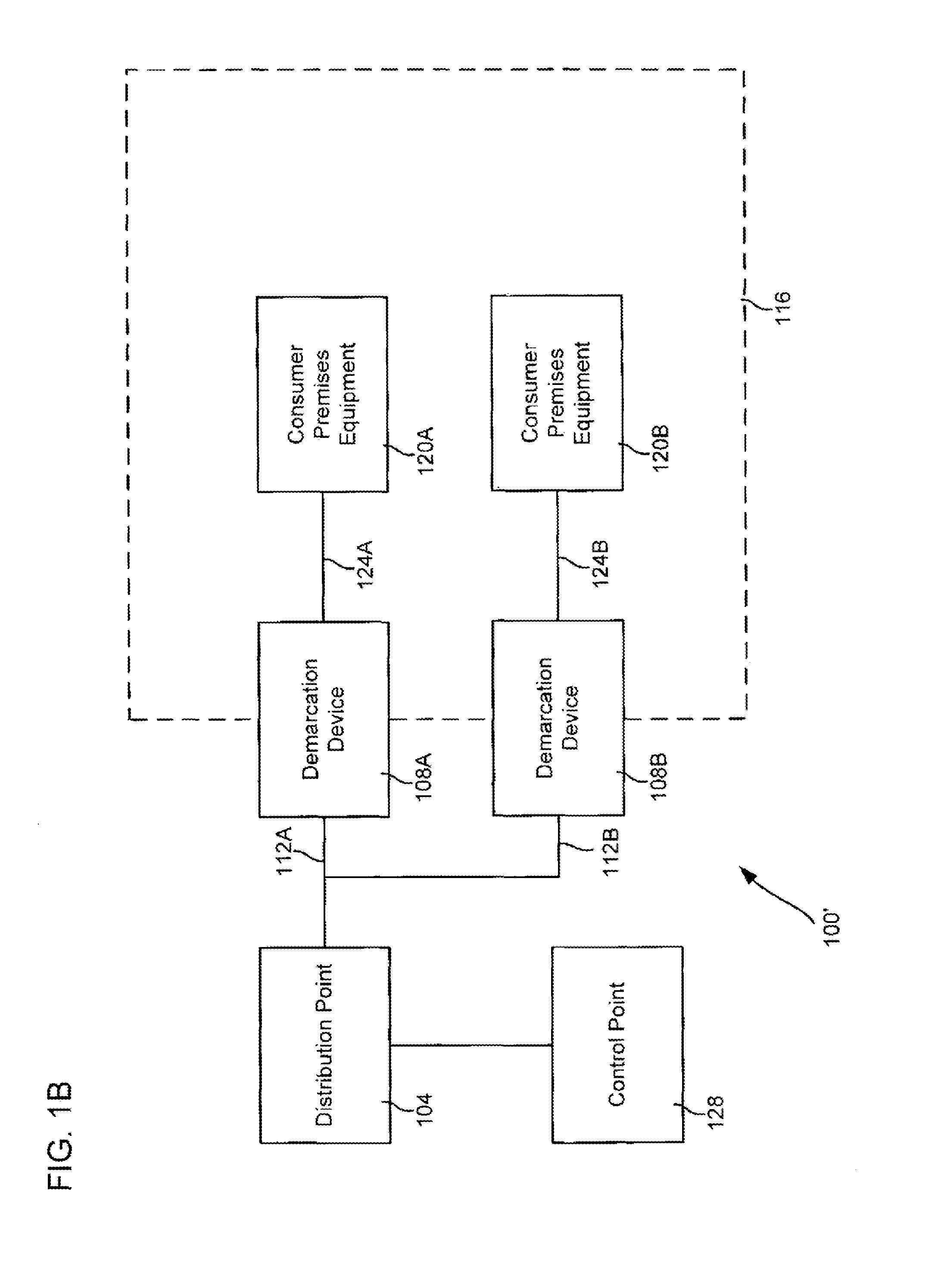
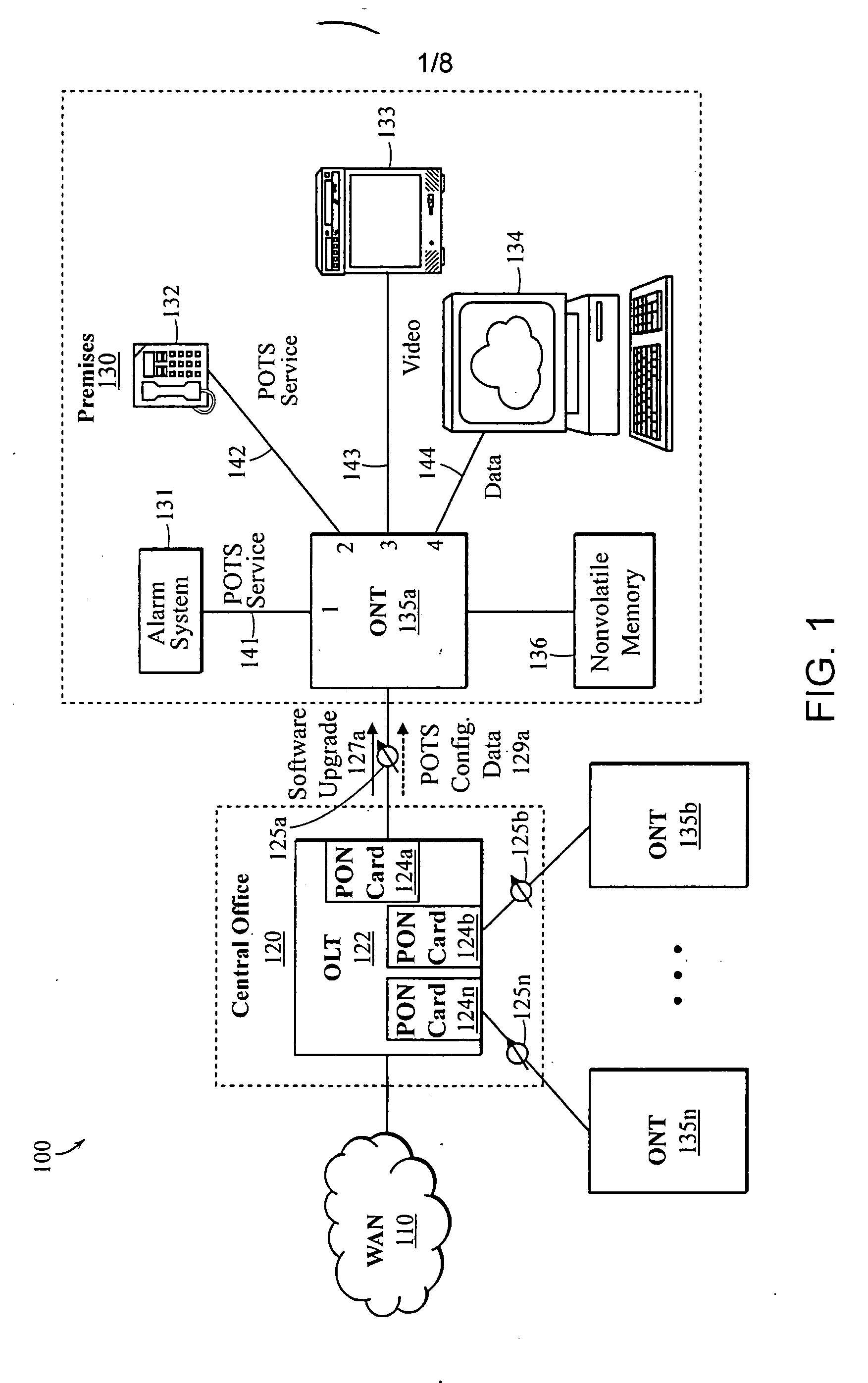
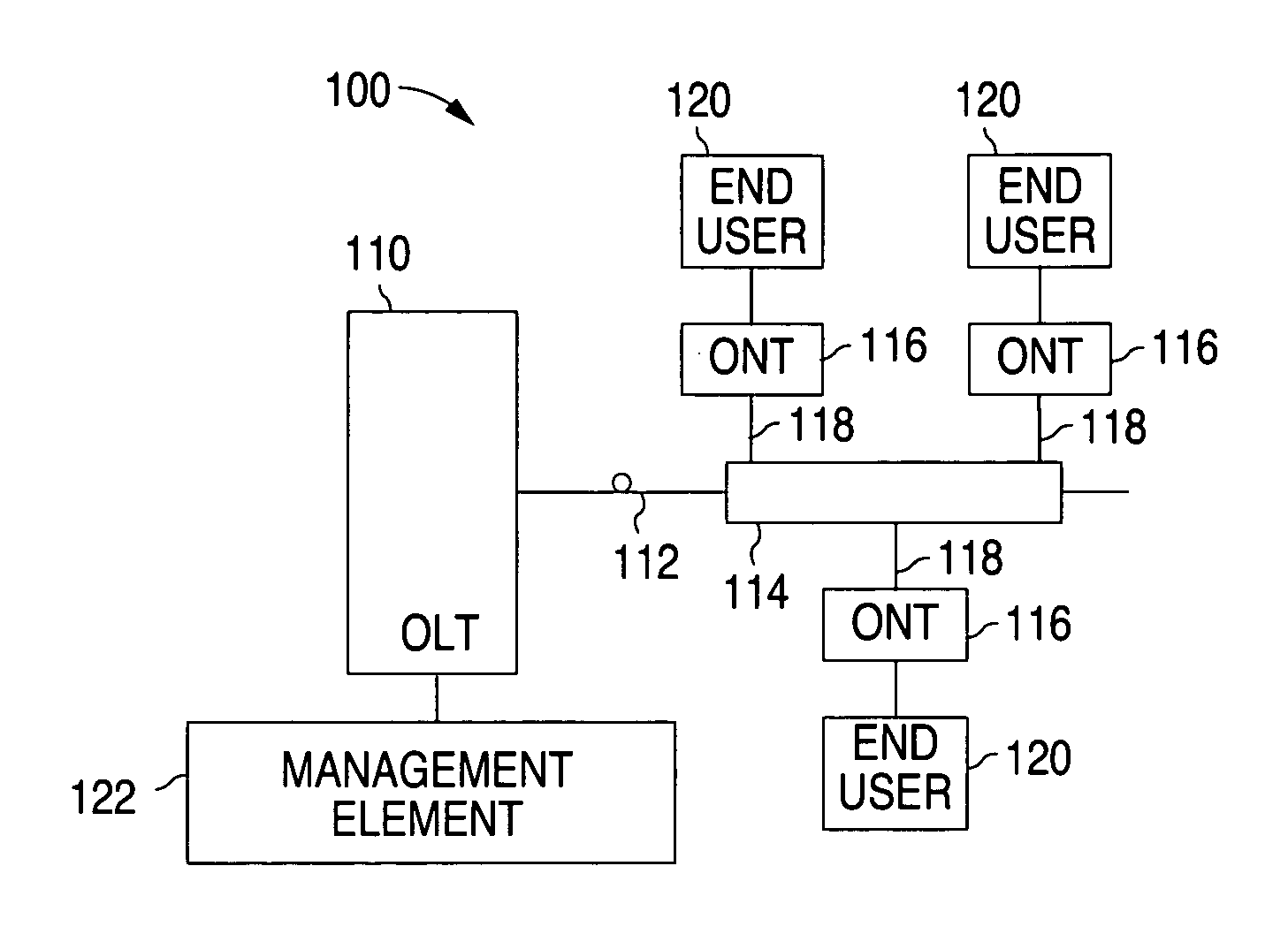
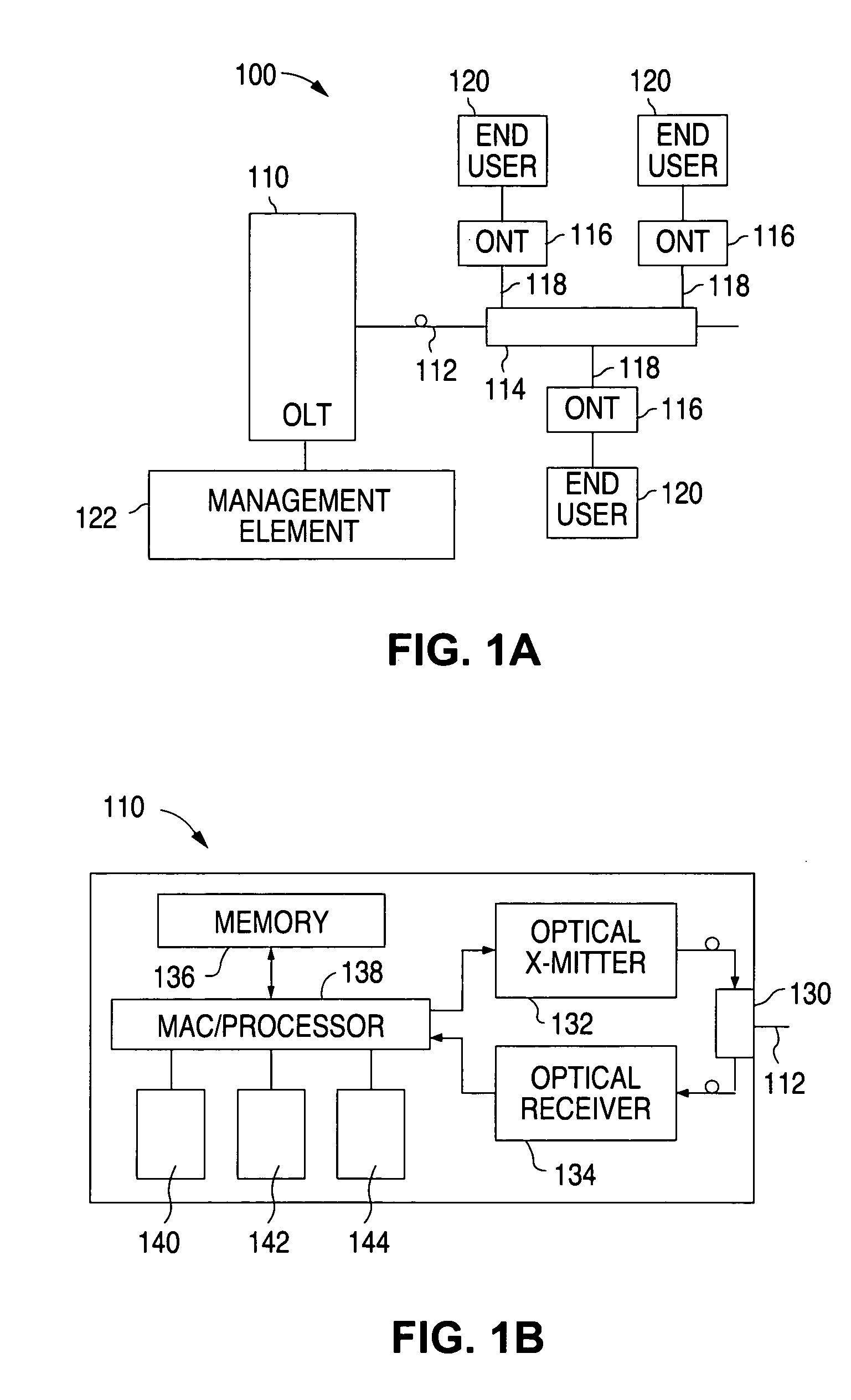
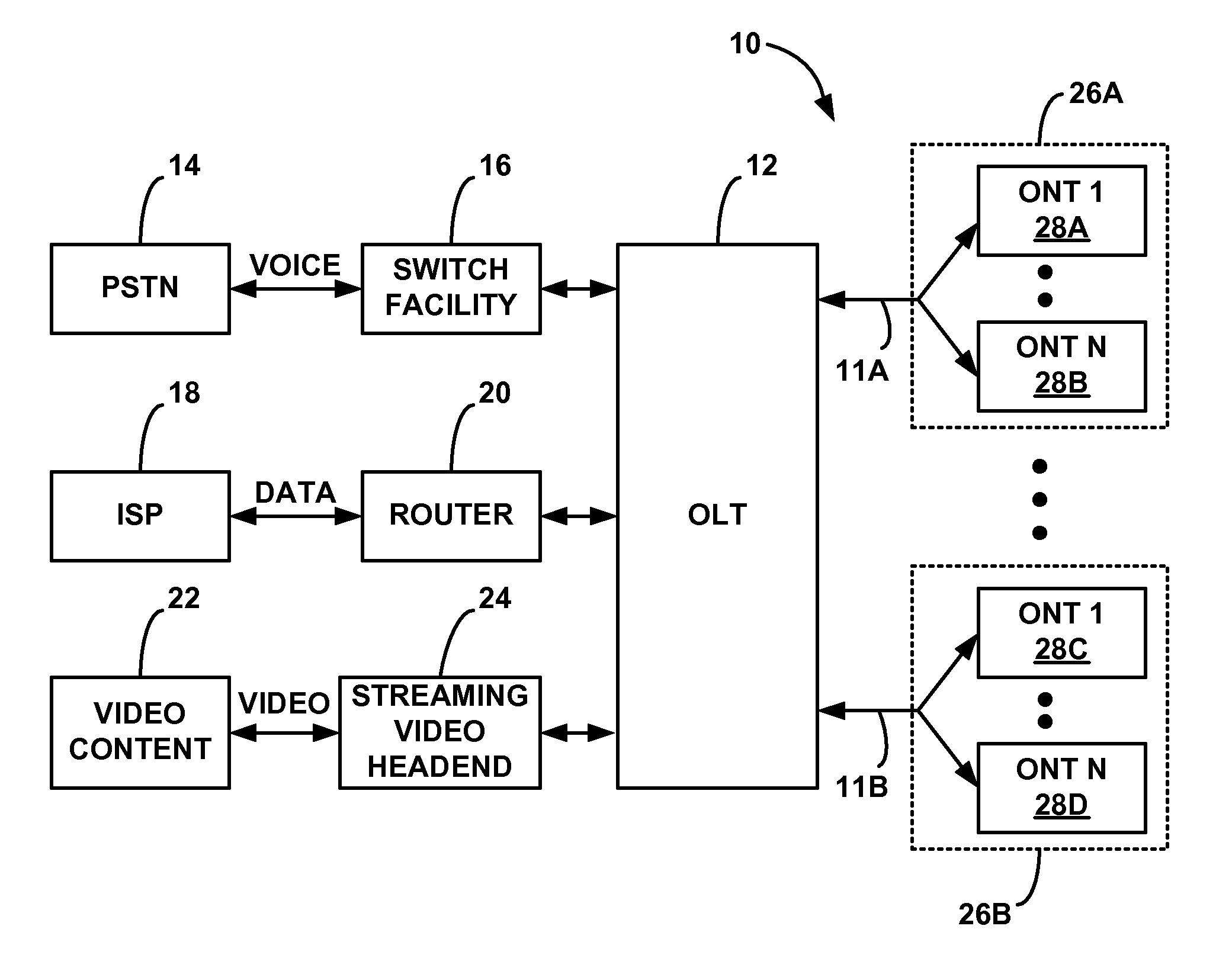
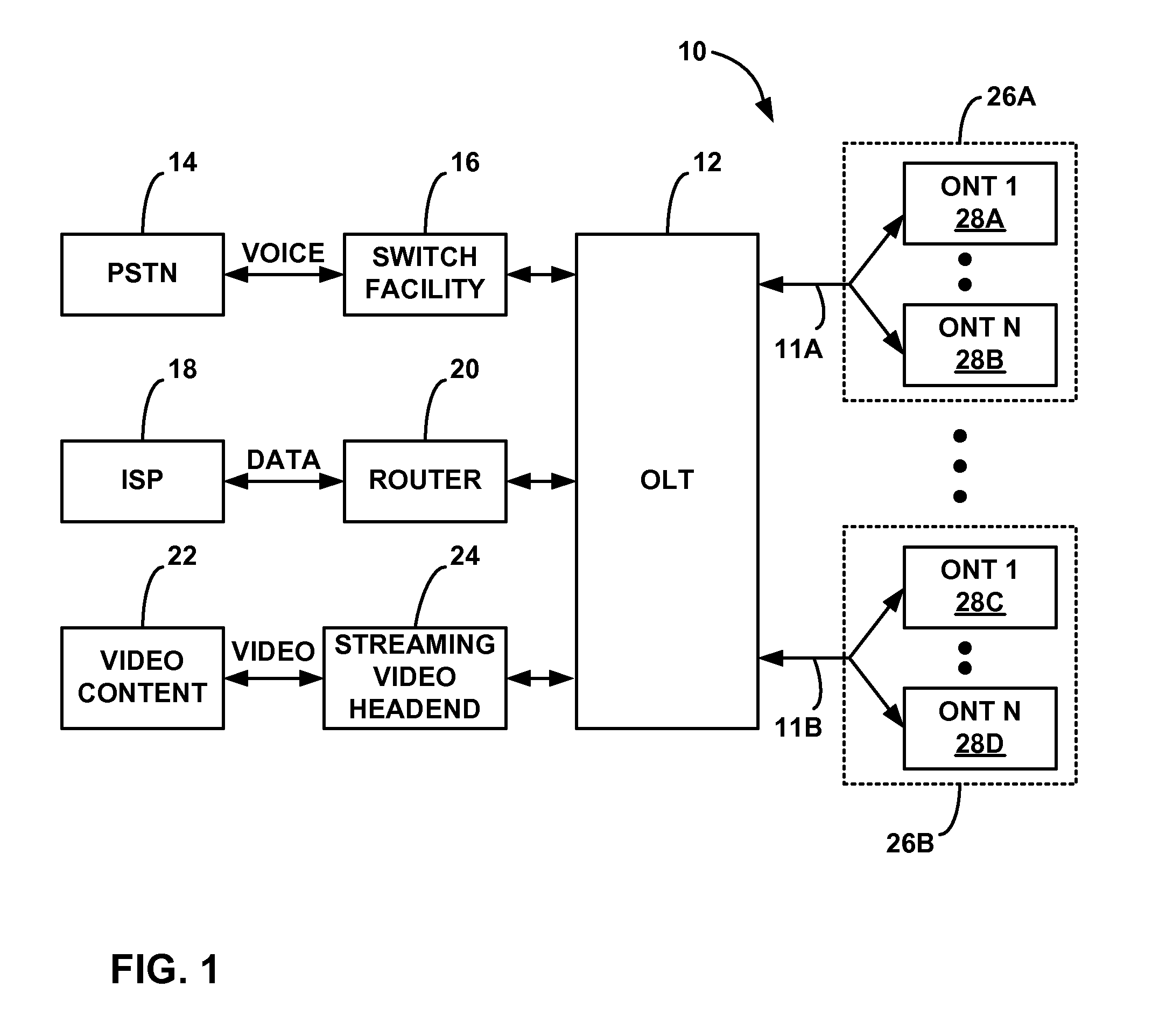
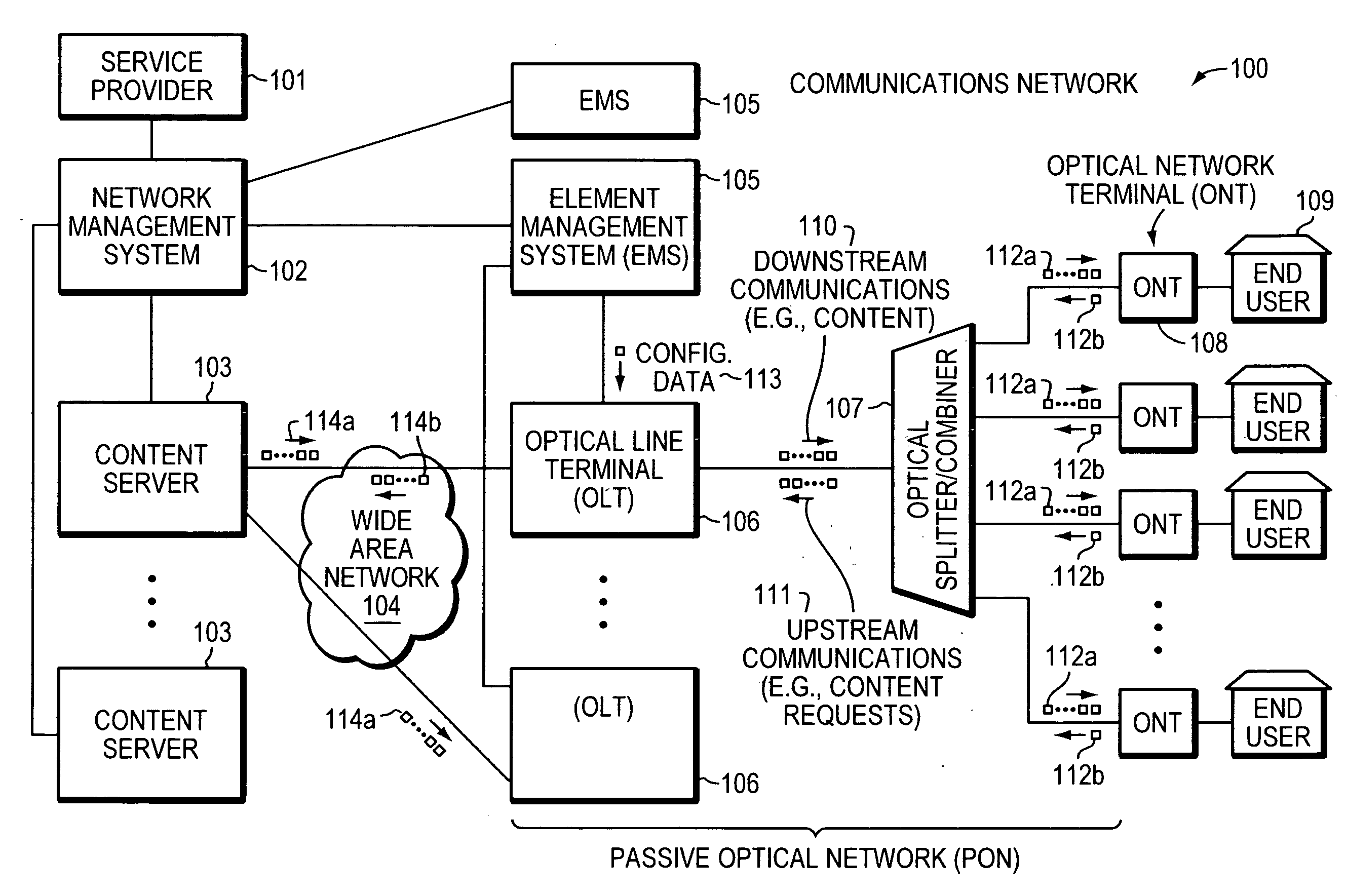
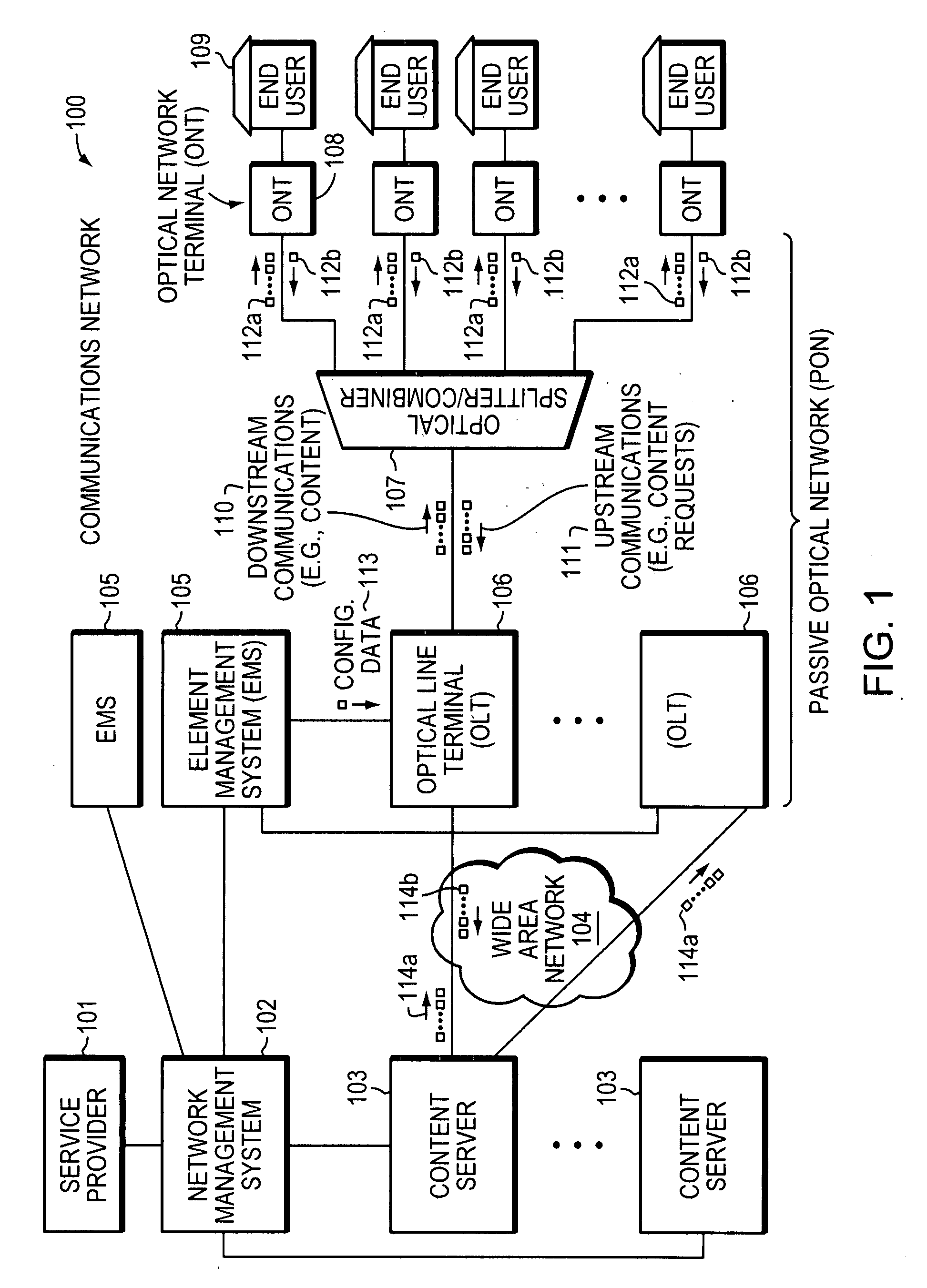
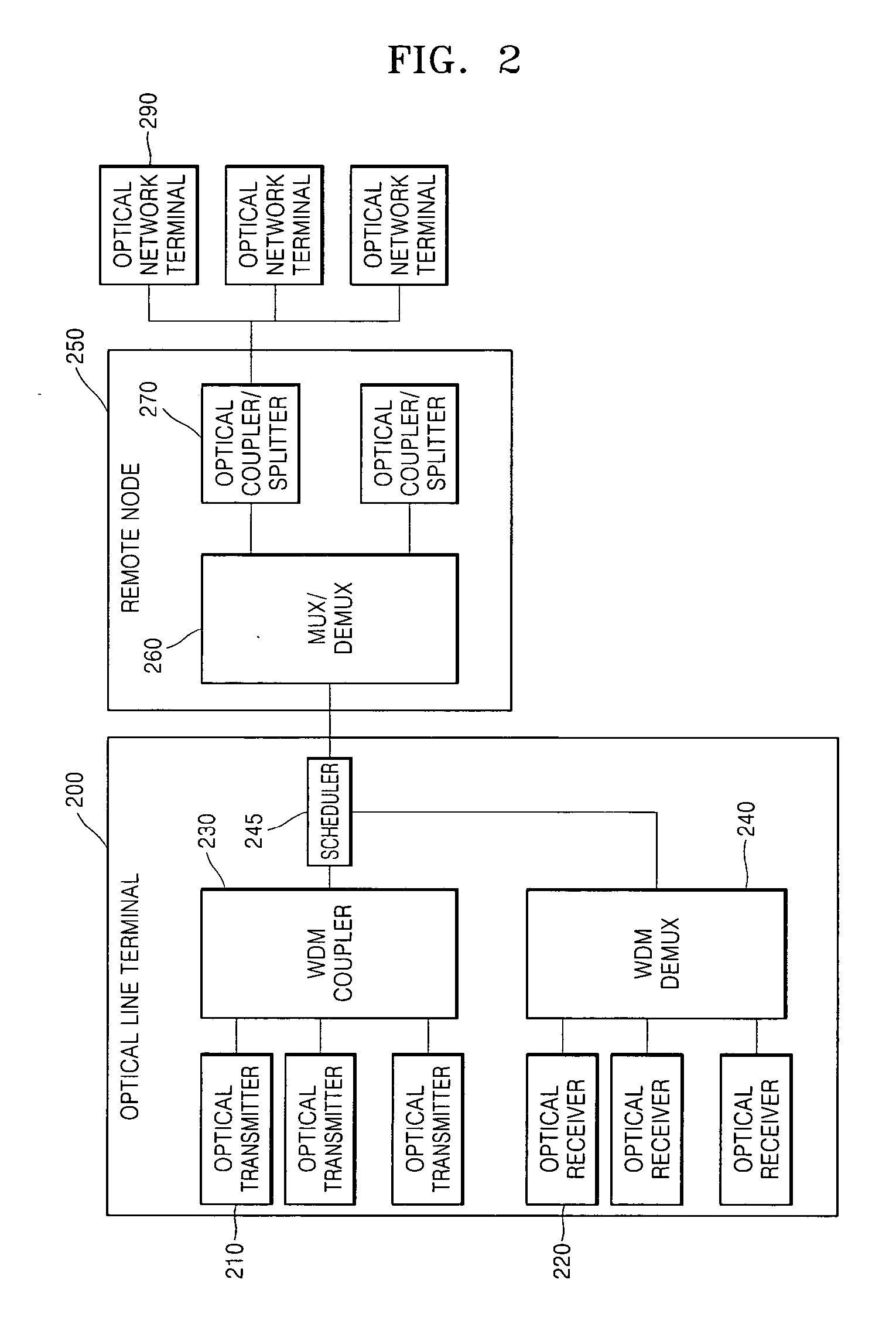
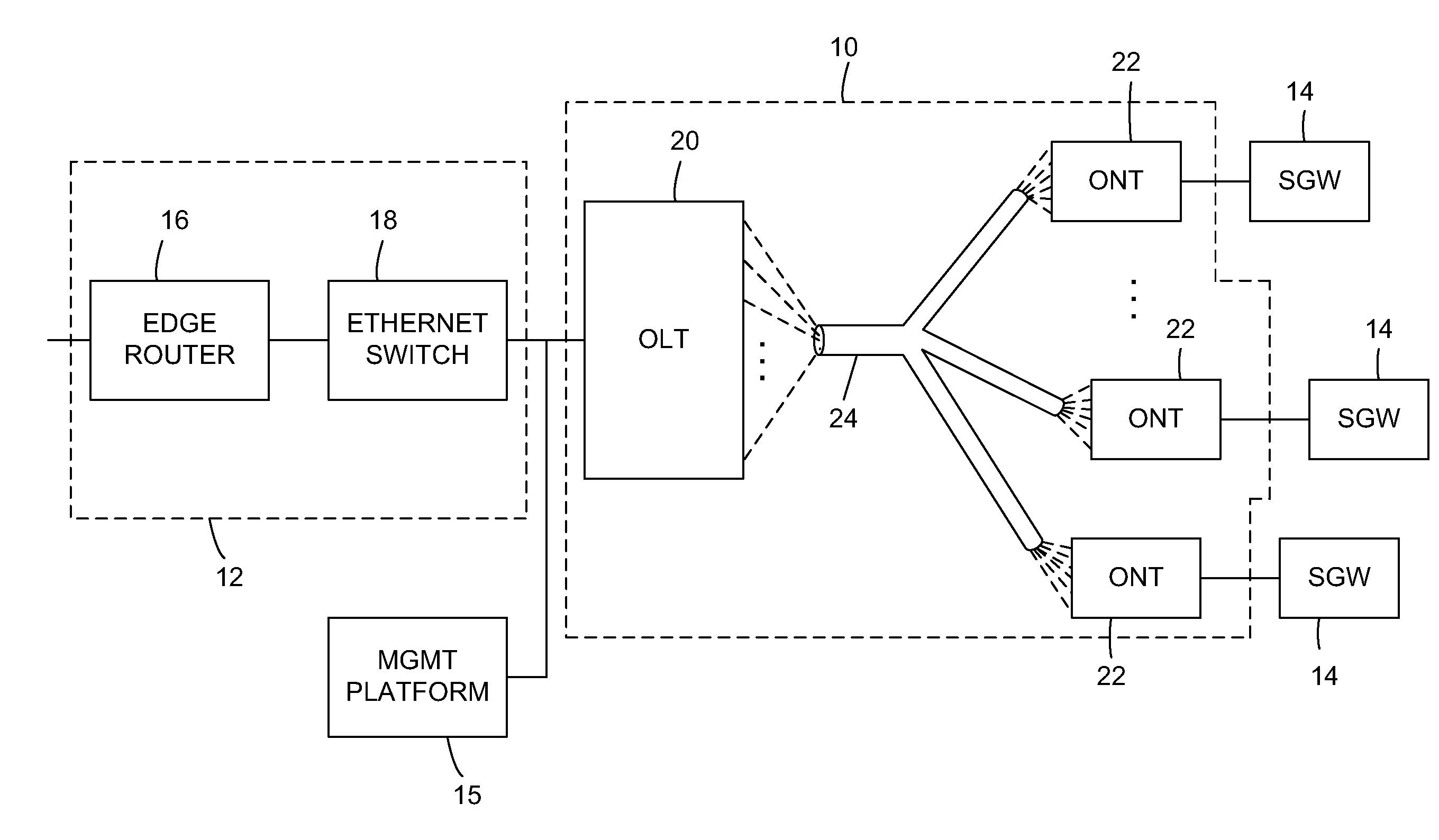
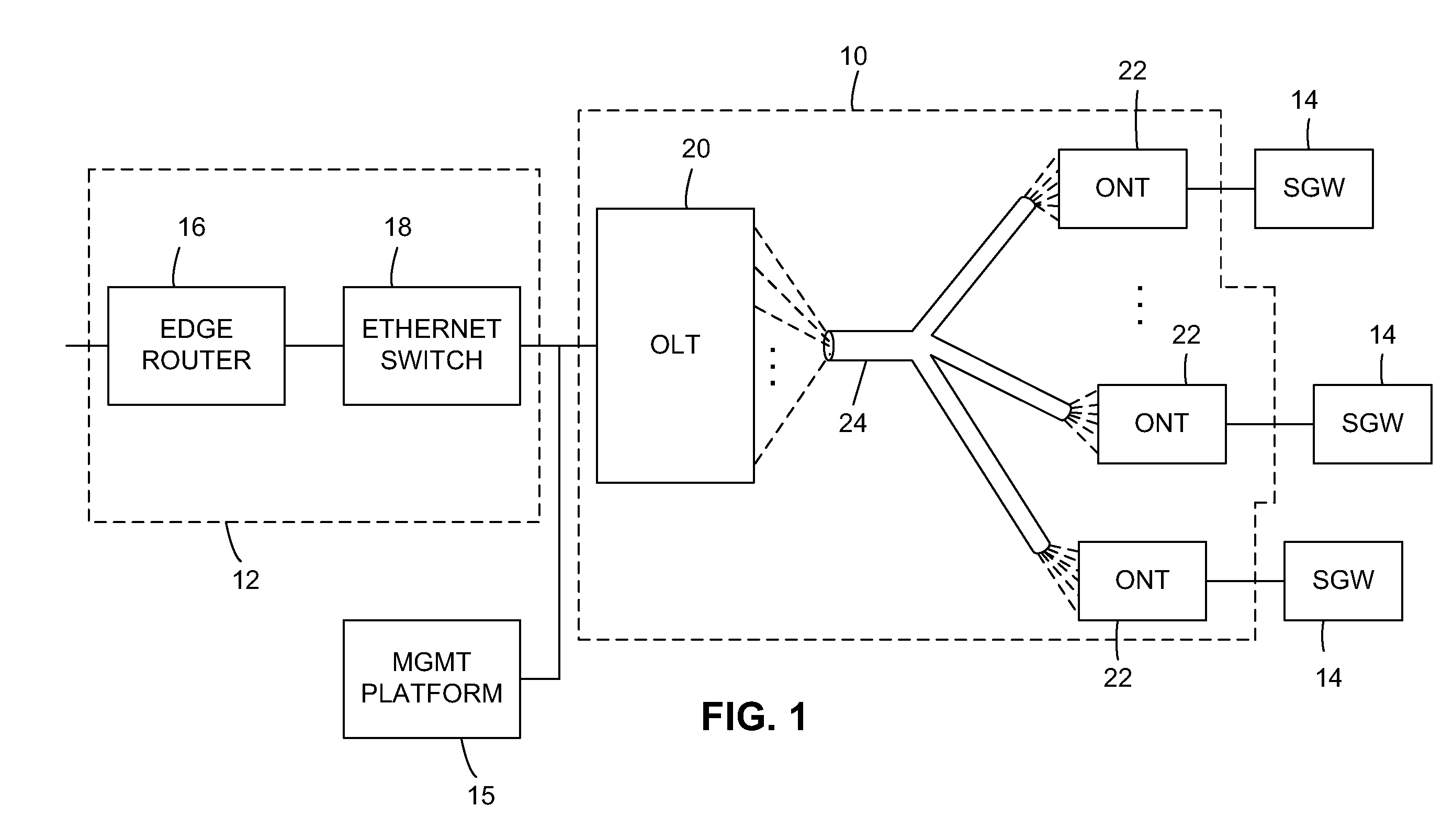
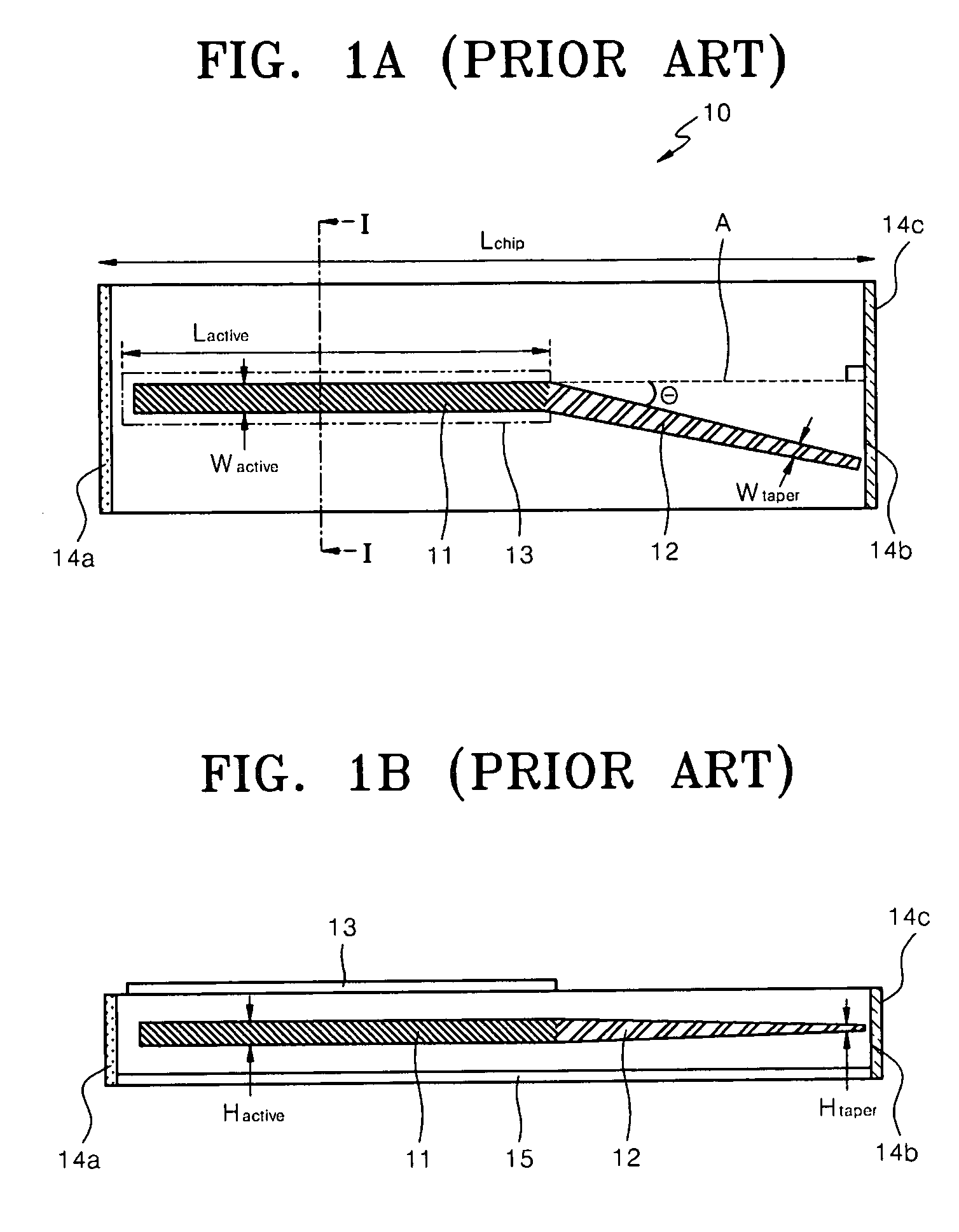
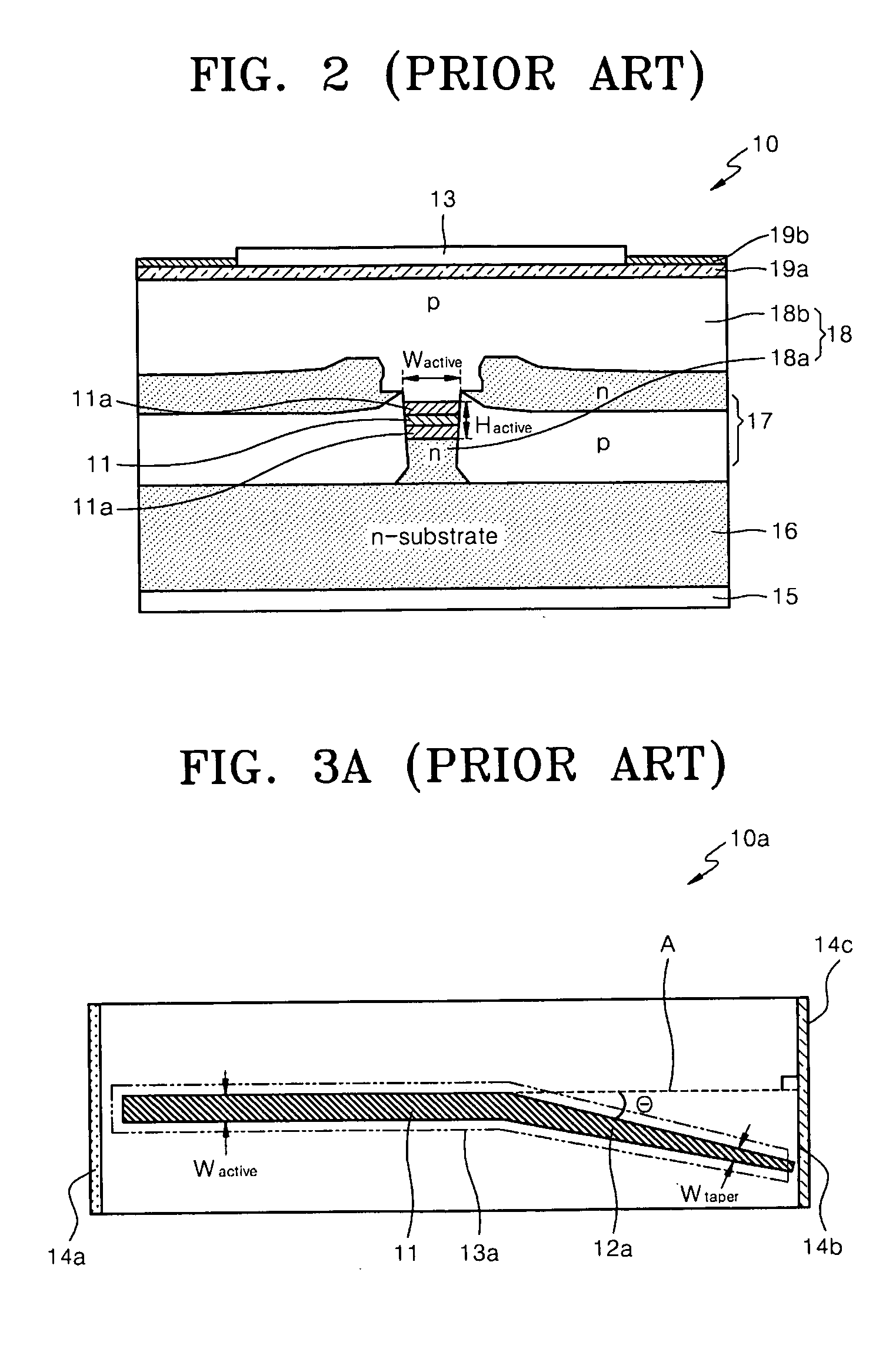
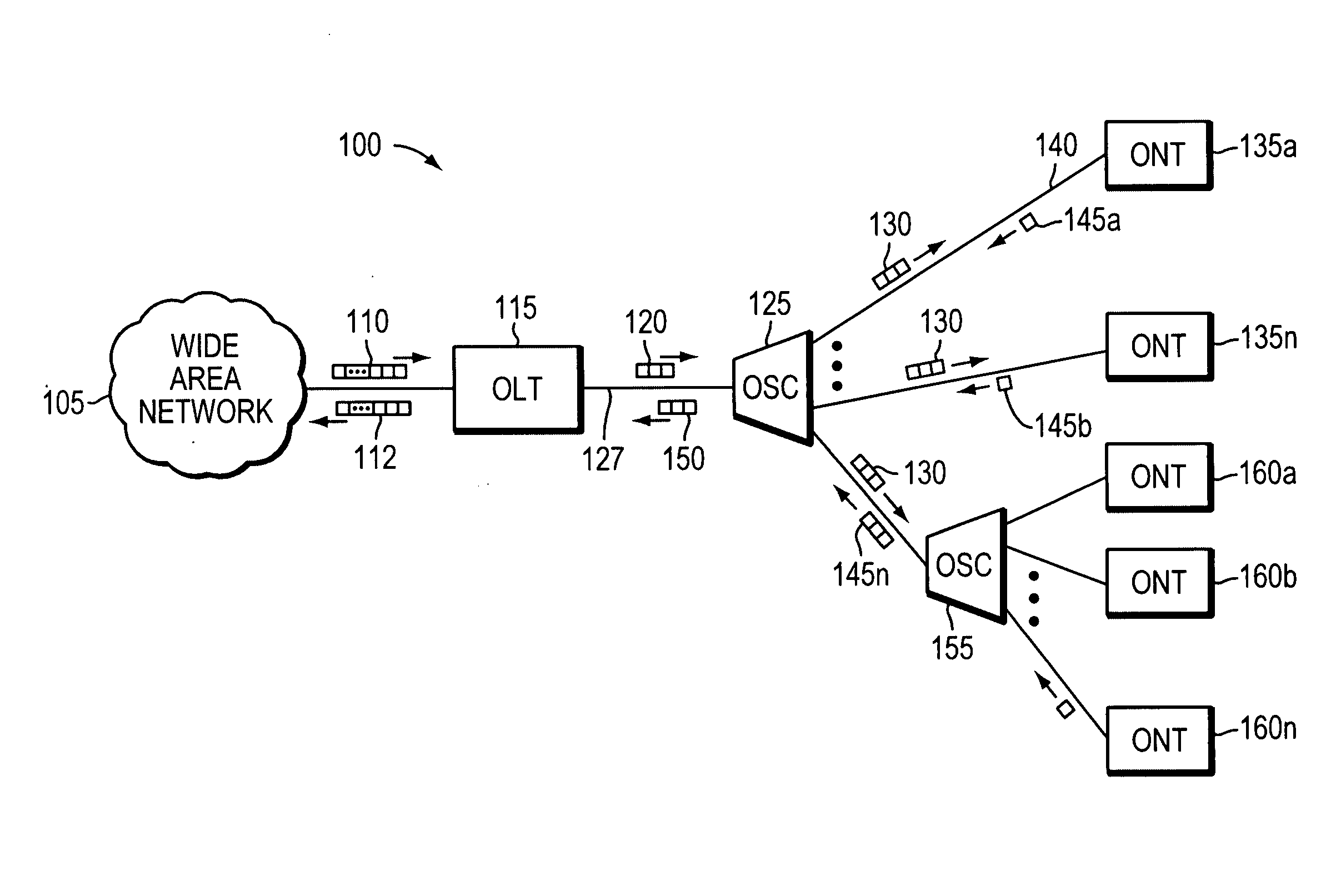
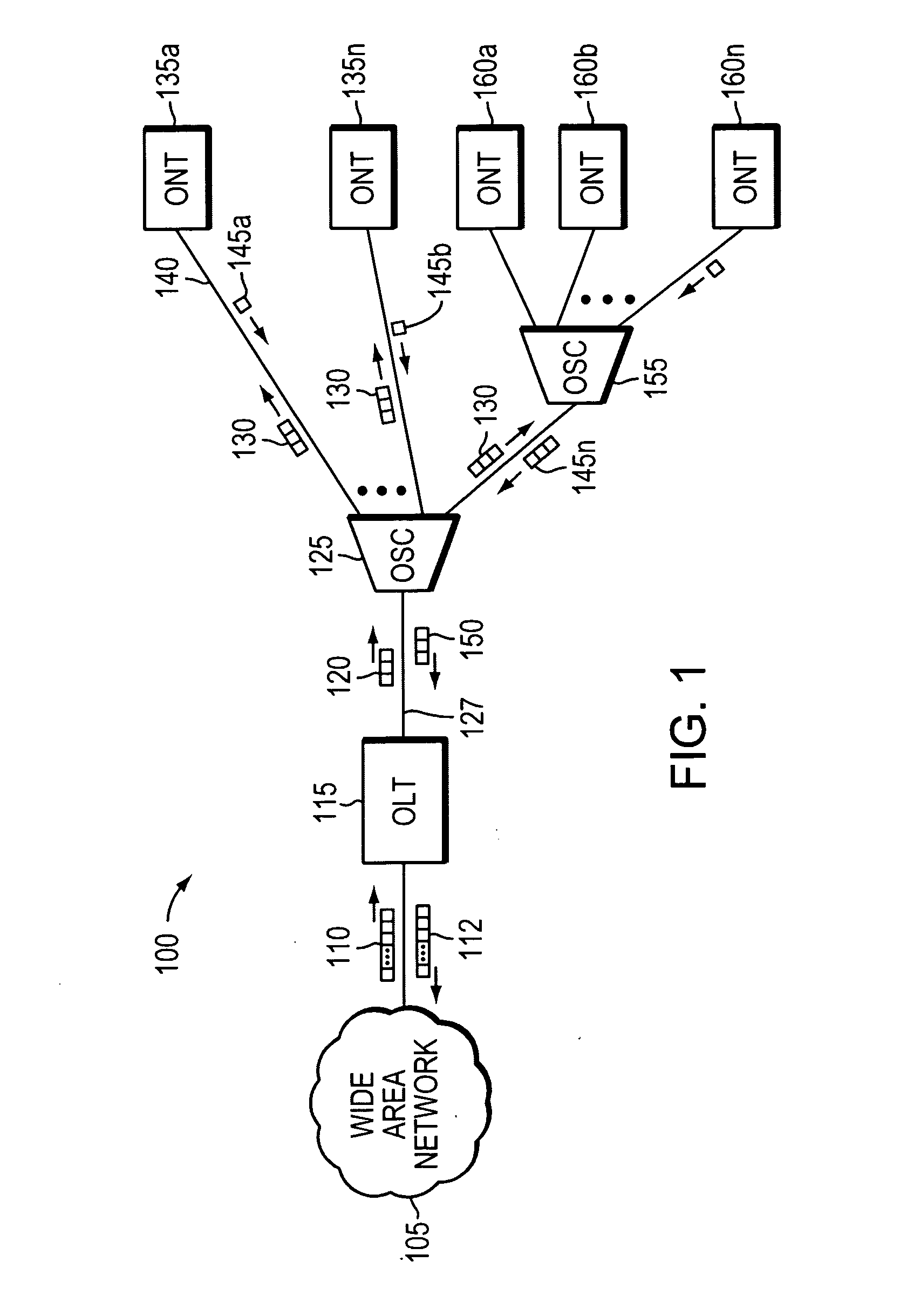
An optical network terminal (ONT) is used to terminate the fiber optic line, demultiplex the signal into its component parts (voice telephone, television, and Internet access), and provide power to customer telephones.
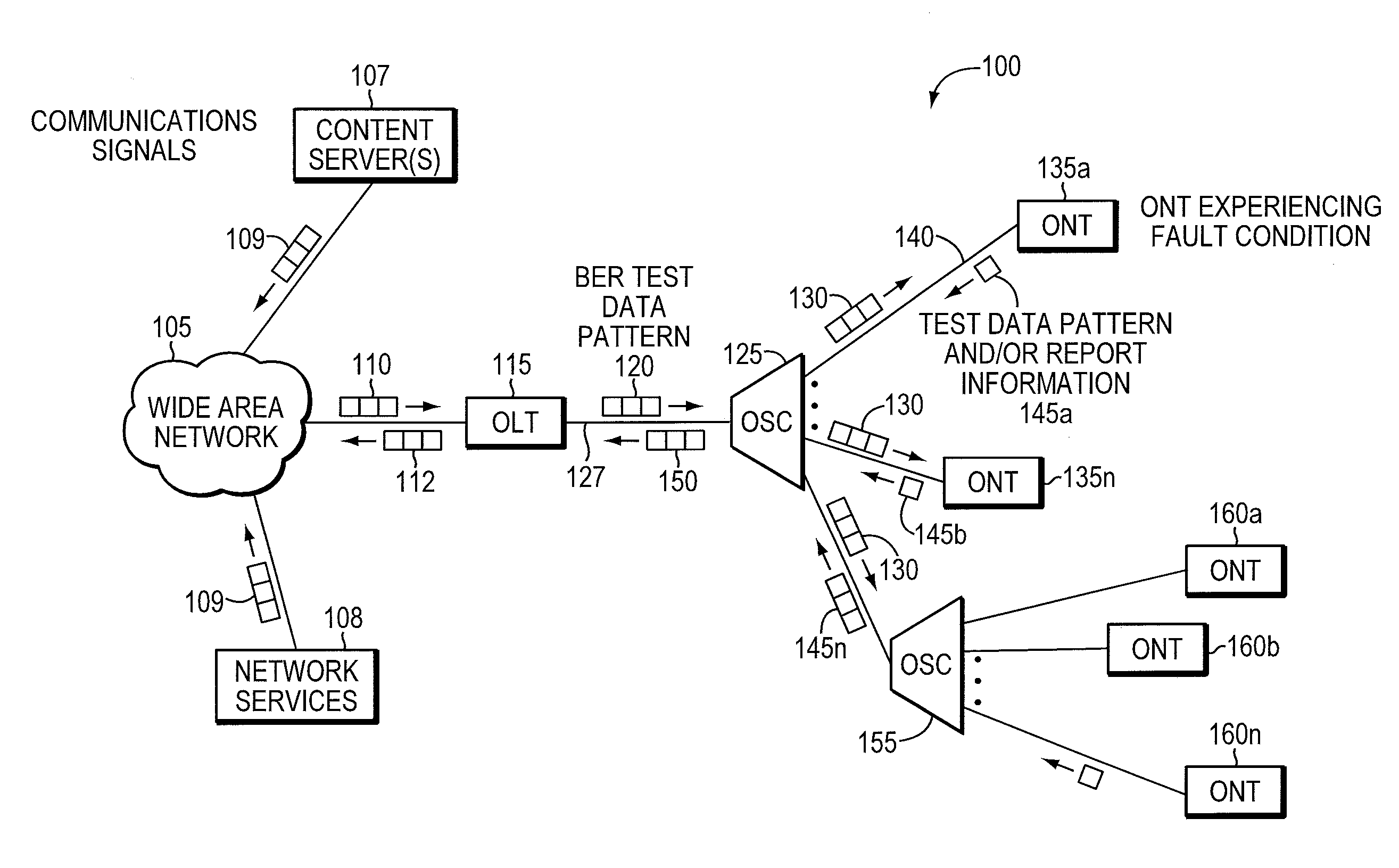
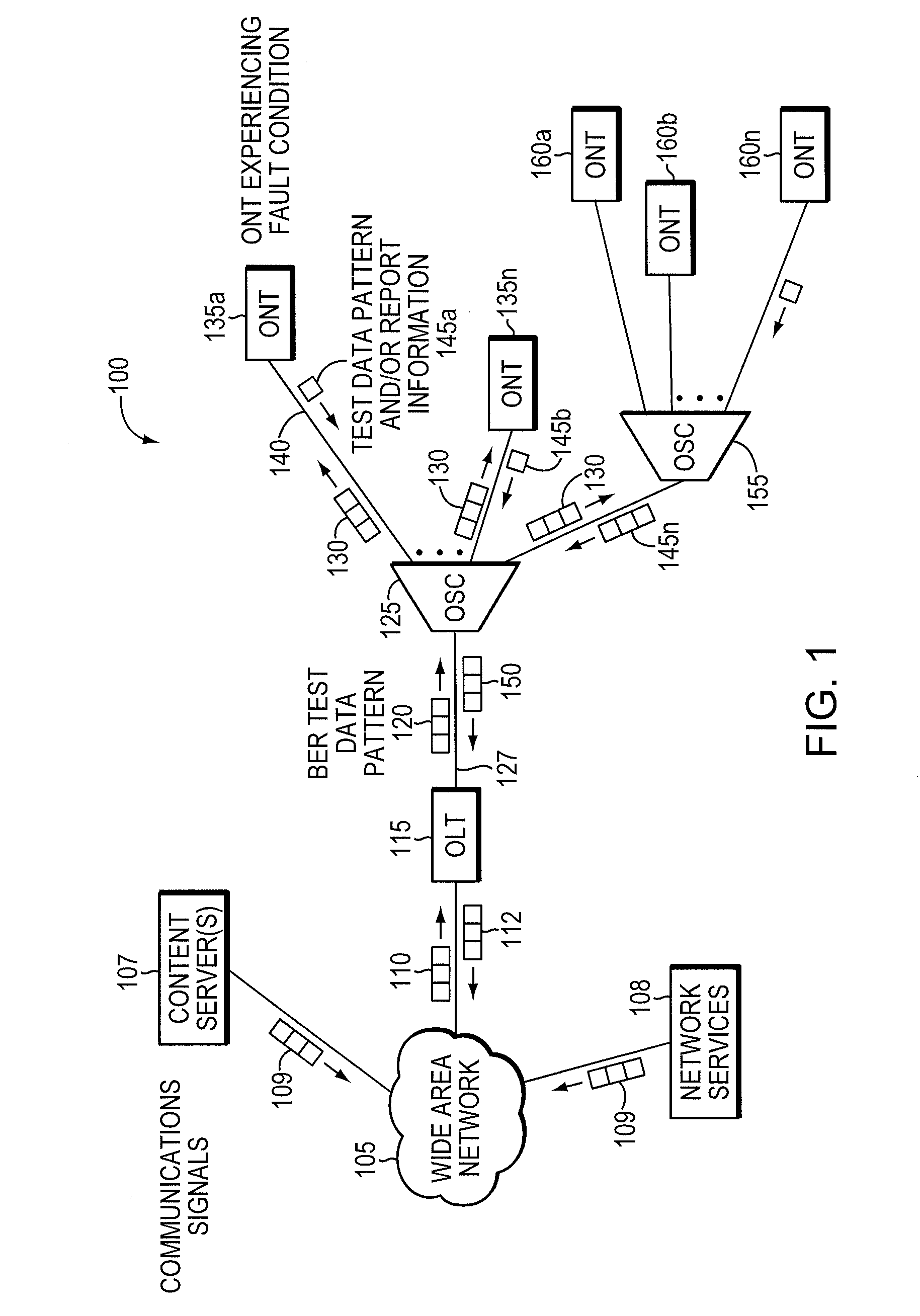
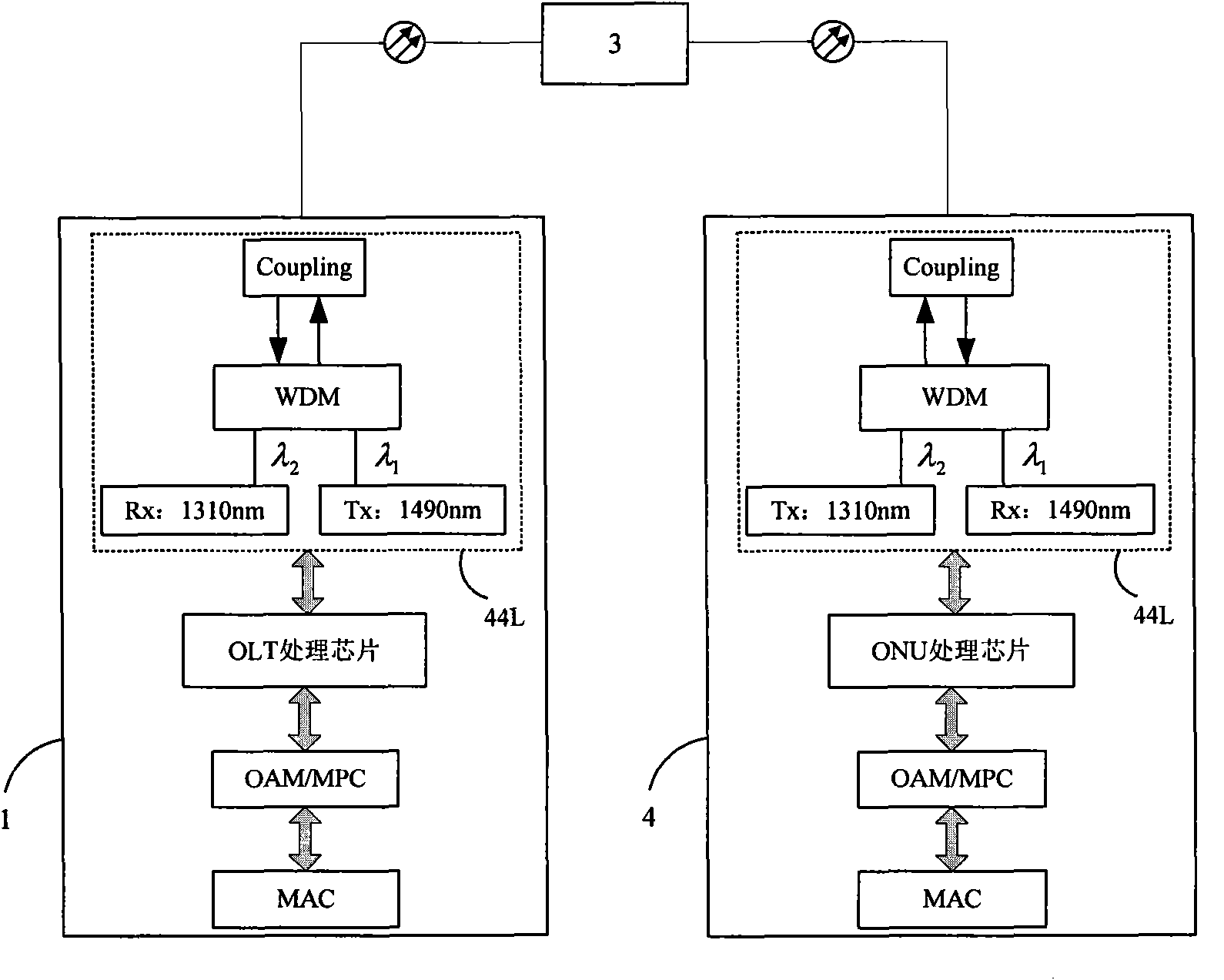
Method and apparatus for correcting faults in a passive optical network
ActiveUS8090258B2Transmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Engineering
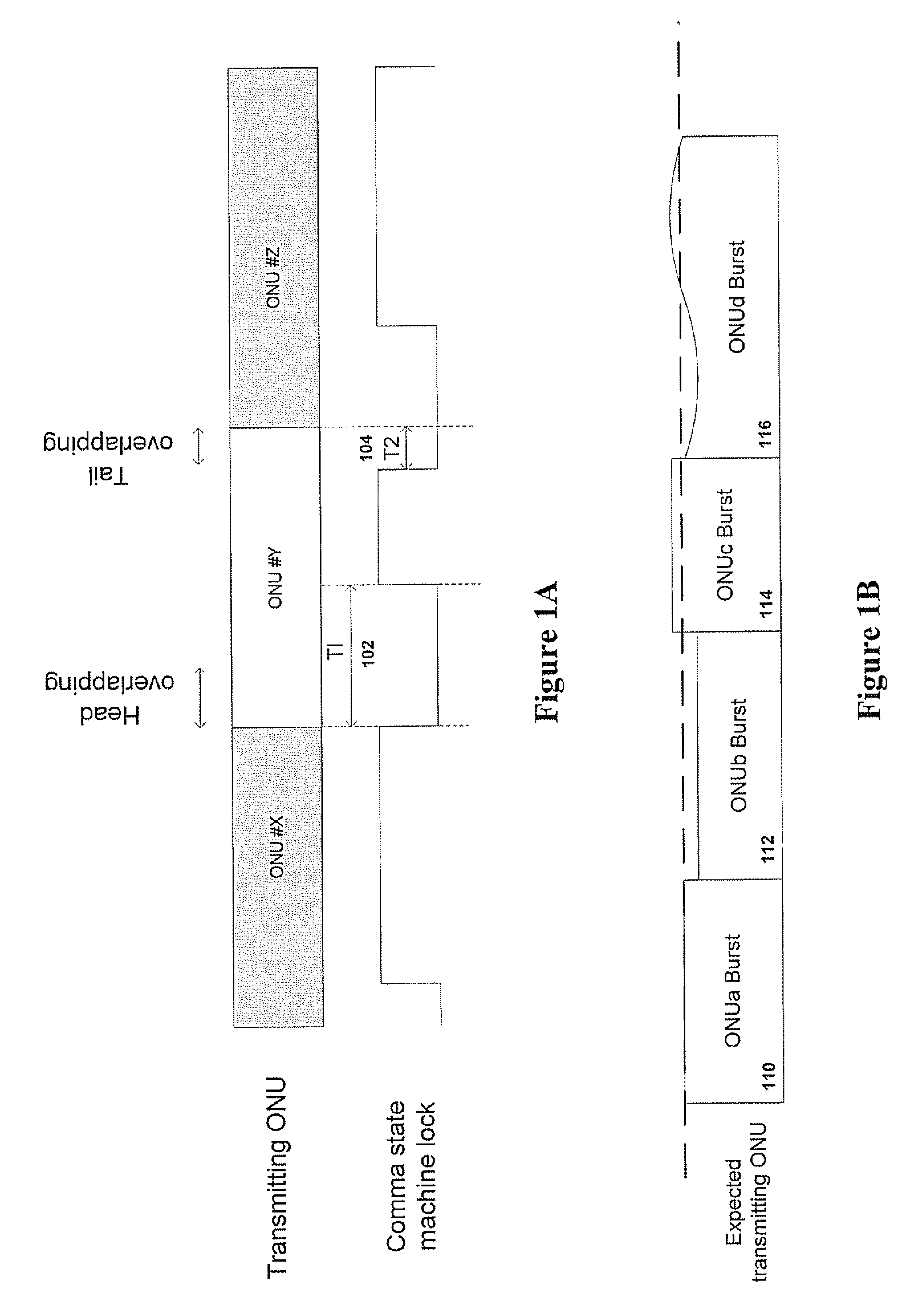
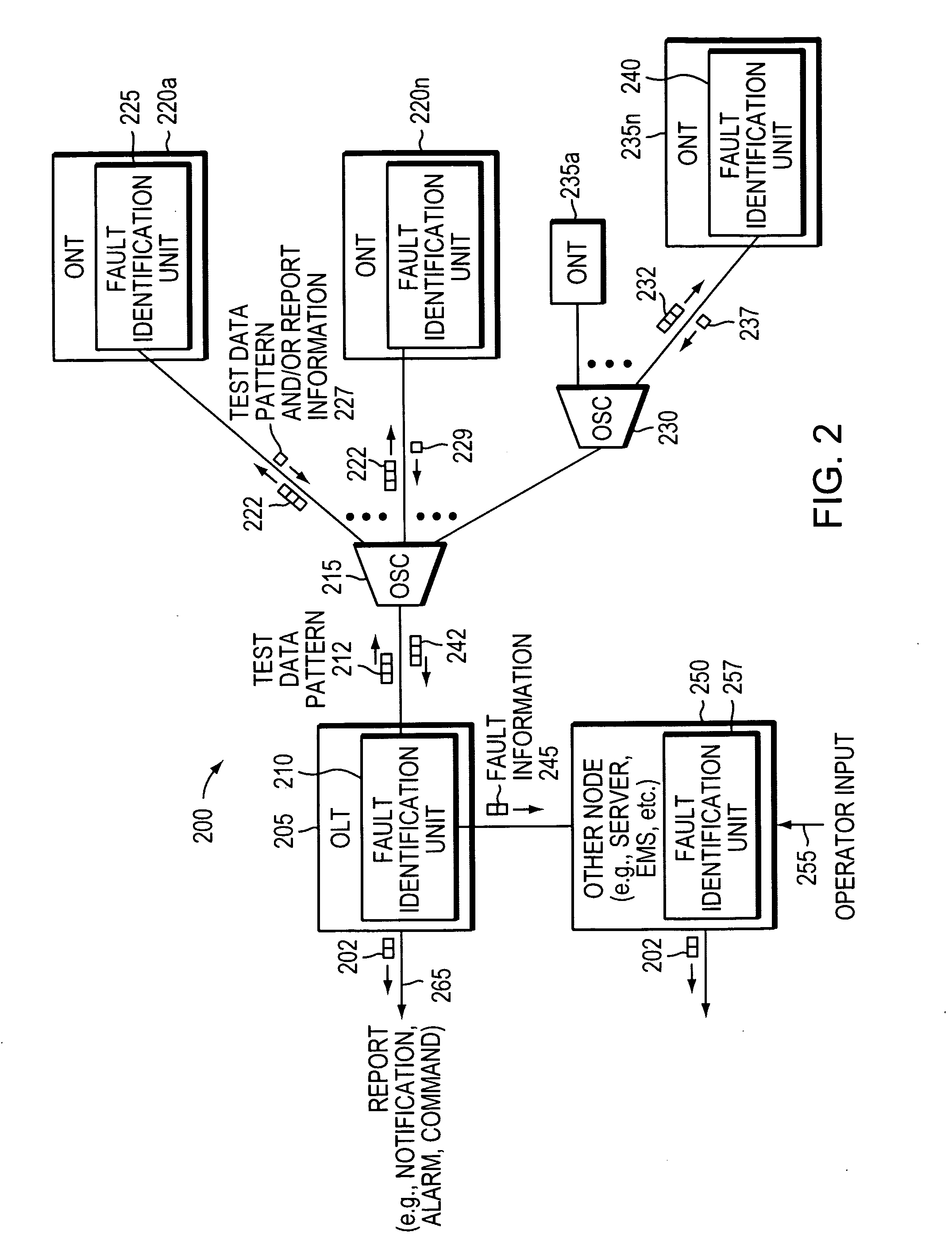
Component malfunctions in passive optical networks (PON) can increase bit error rates and decrease signal-to-noise ratio of communications signals. These faults may cause the receivers of the signals, either the optical line terminal (OLT) or optical network terminals (ONTs), to experience intermittent faults and / or may result in misinterpreted commands that disrupt other ONT's communication, resulting in a rogue ONT condition. Existing PON protocol detection methods may not detect these types of malfunctions. An embodiment of the present invention identifies faults in a PON by transmitting a test series of data patterns via an optical communications path from a first optical network node to a second optical network node. The test series is compared to an expected series of data patterns. An error rate may be calculated as a function of the differences between the test series and expected series. The error rate may be reported to identify faults in the PON. Through use of the embodiment, network faults can be identified and optionally automatically corrected, saving a network service provider from expending technician time and maintaining an operating state of the network.
Owner:TELLABS PETALUMA
Antenna System and Methods for Wireless Optical Network Termination
ActiveUS20140233951A1Television system detailsOptical transmission adaptationsNetwork terminationTransport medium
Optical network termination systems, devices and methods including an optical network terminal (ONT) having a processor in communication with an external optical fiber. The ONT processors further in communication with a wireless access point and at least one electrically conductive internal transport medium, both providing for the communication of telecommunication signals with devices located within a customer premises. The wireless access point and in certain instances the processor are back powered over the electrically conductive internal transport medium from AC power within the premises. In certain embodiments, the wireless access point communicates with devices within the premises over a distributed antenna.
Owner:CENTURYLINK INTPROP
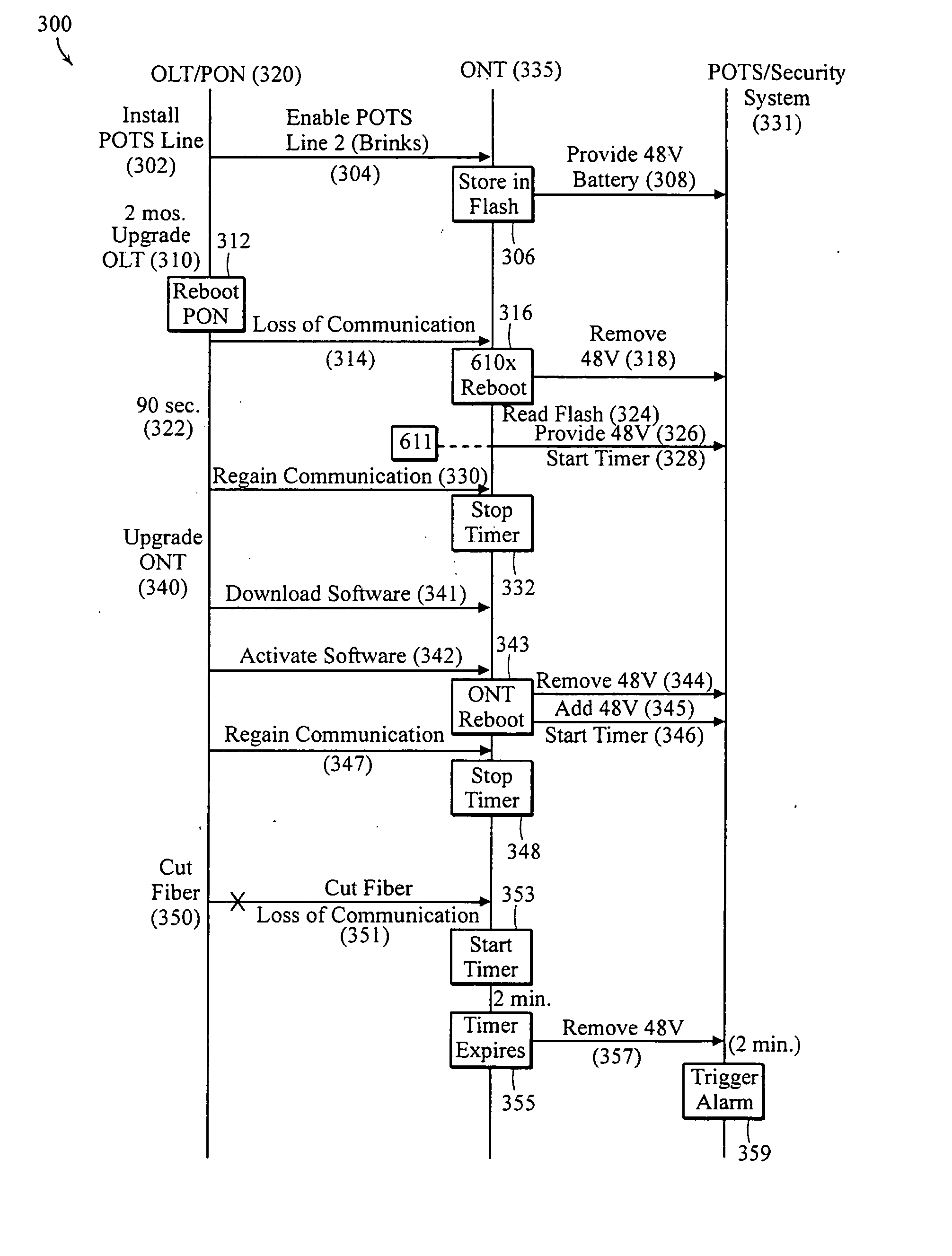
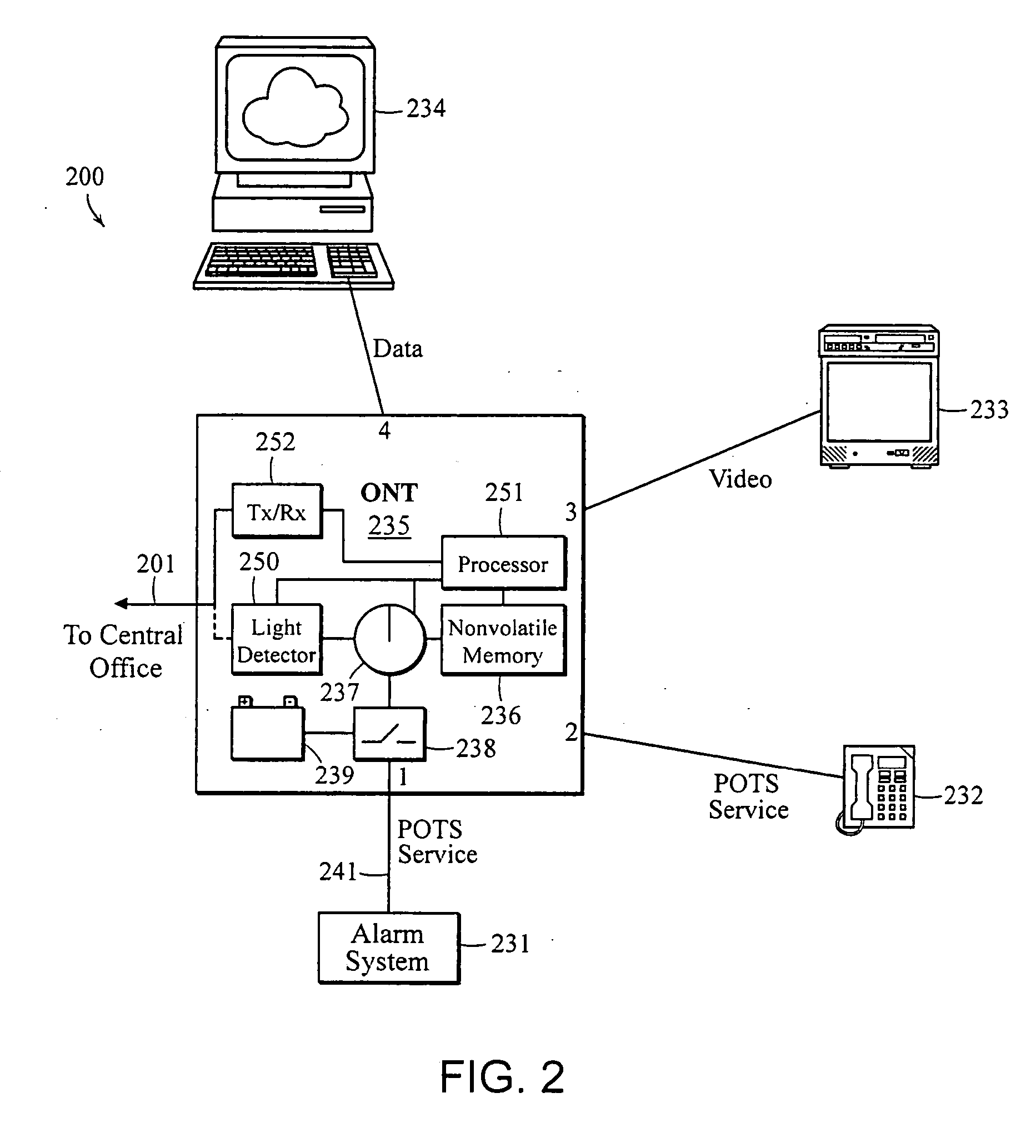
Apparatus and method of managing POTS lines in a PON network
ActiveUS20070263782A1Maintain validityMultiplex system selection arrangementsSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionEngineeringSoftware upgrade
An apparatus or corresponding method of managing Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS) lines in a Passive Optical Network (PON) to prevent an alarm system from generating an alarm during a software upgrade or maintenance of an Optical Network Terminal (ONT), Optical Line Terminal (OLT), or PON while maintaining the effectiveness of the alarm system. The ONT may store data related to a POTS line in nonvolatile memory. The ONT may activate the POTS line based on the data from the nonvolatile memory in an event of interruption in communications with an OLT prior to reestablishing communications with the OLT. The interruption in communications may be caused by an ONT reboot to complete an installation of a software upgrade. The ONT may energize the POTS line with a voltage in response to activating the POTS line to prevent the alarm system from generating the alarm.
Owner:TELLABS PETALUMA
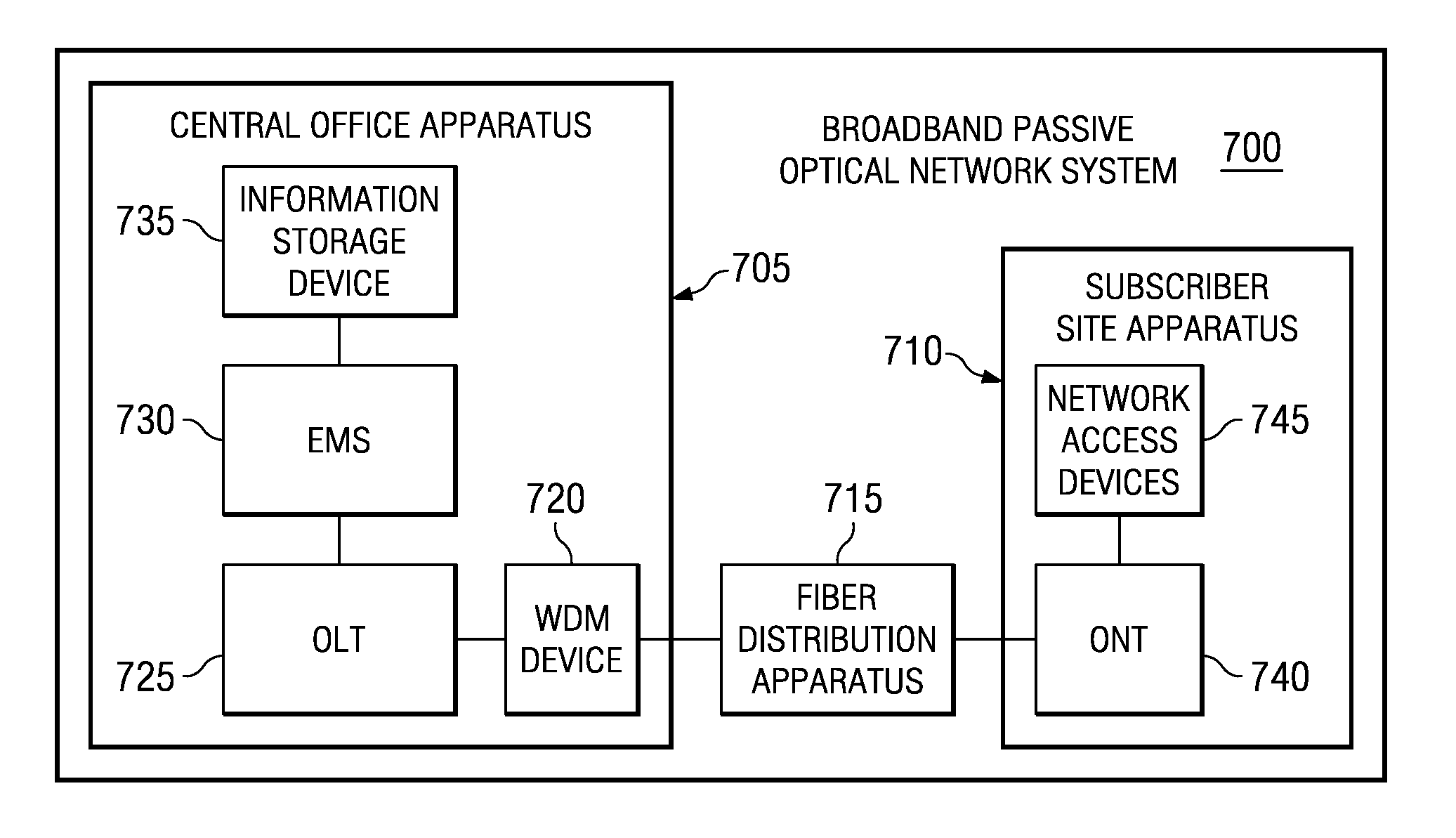
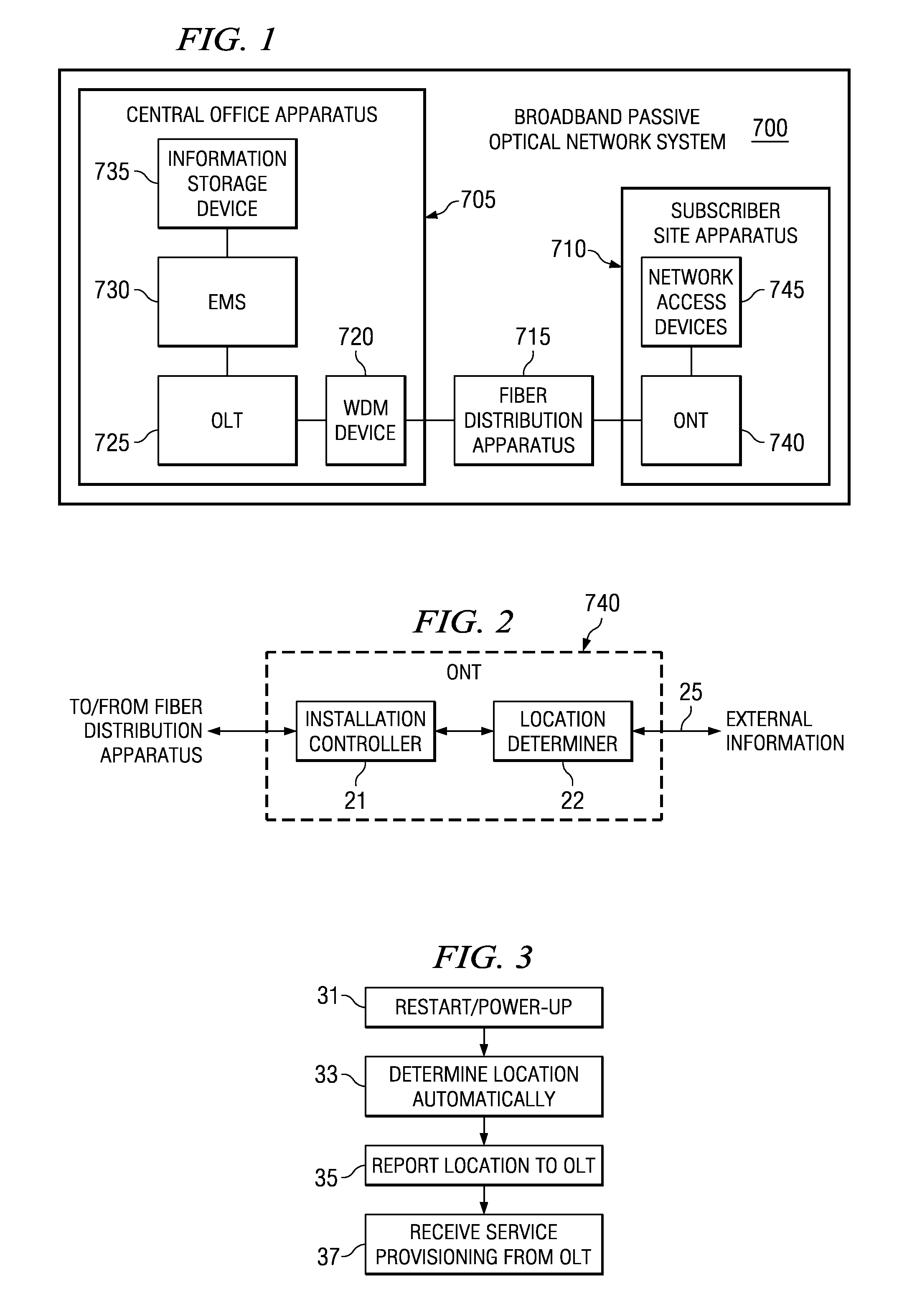
Optical network termination with automatic determination of geographic location
An optical network termination (ONT) apparatus can determine its own geographic location information automatically, thereby permitting the ONT to report its geographic location to a management entity in a passive optical network (PON) automatically, without manual intervention.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
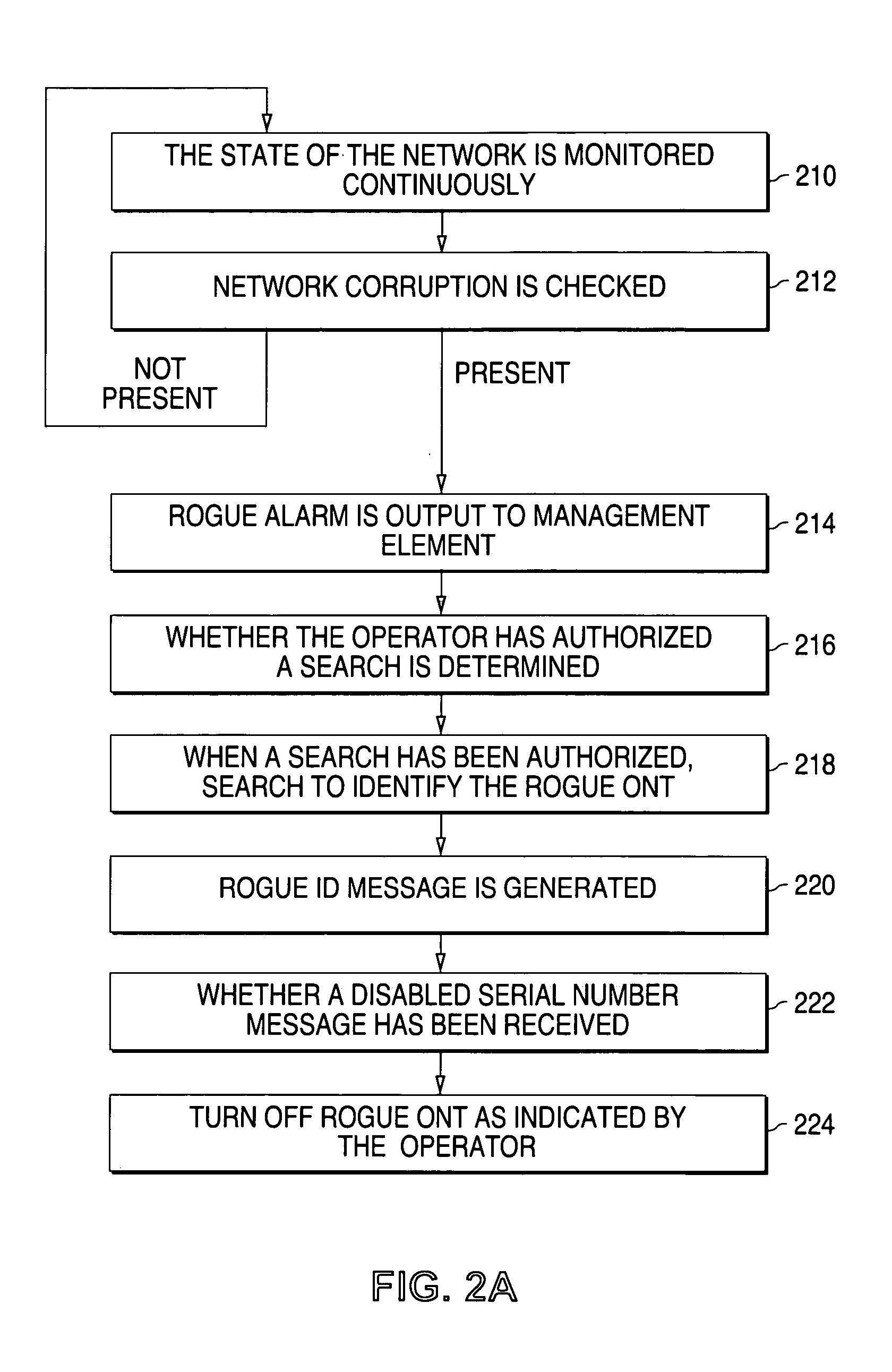
Optical network that detects and removes Rogue ONTS
InactiveUS20060093356A1Transmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsComputer networkOptical line termination
A point-to-multipoint communications network includes an optical line terminal (OLT) and a number of optical network terminals (ONTS) which each detect and remove rogue ONTs from the network. The OLT monitors transmission errors to detect the presence of a rogue ONT, and can determine the identity of the rogue. Each ONT monitors its own upstream data packets to detect the presence of a rogue, and turns itself off when a rogue is detected.
Owner:TELLABS PETALUMA
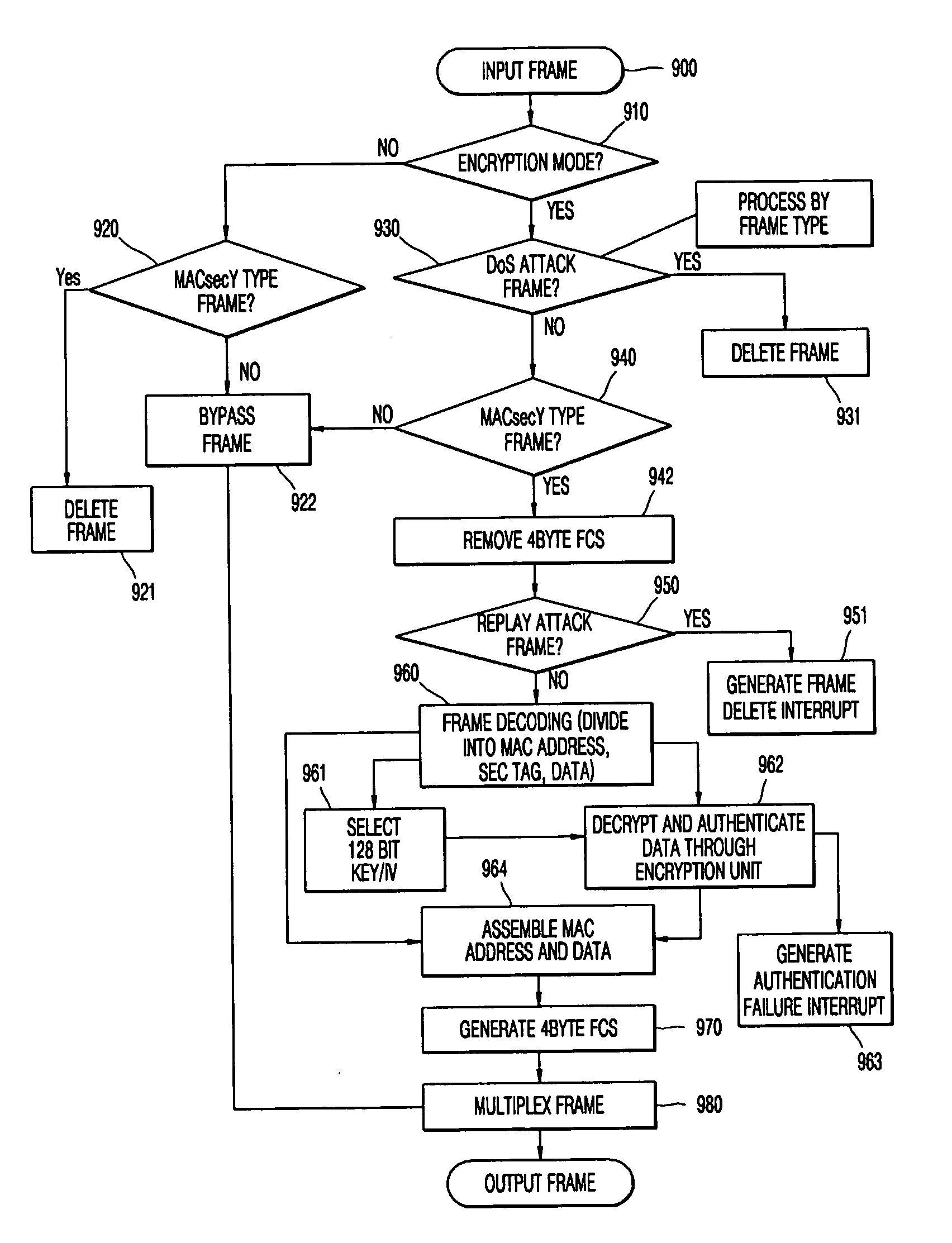
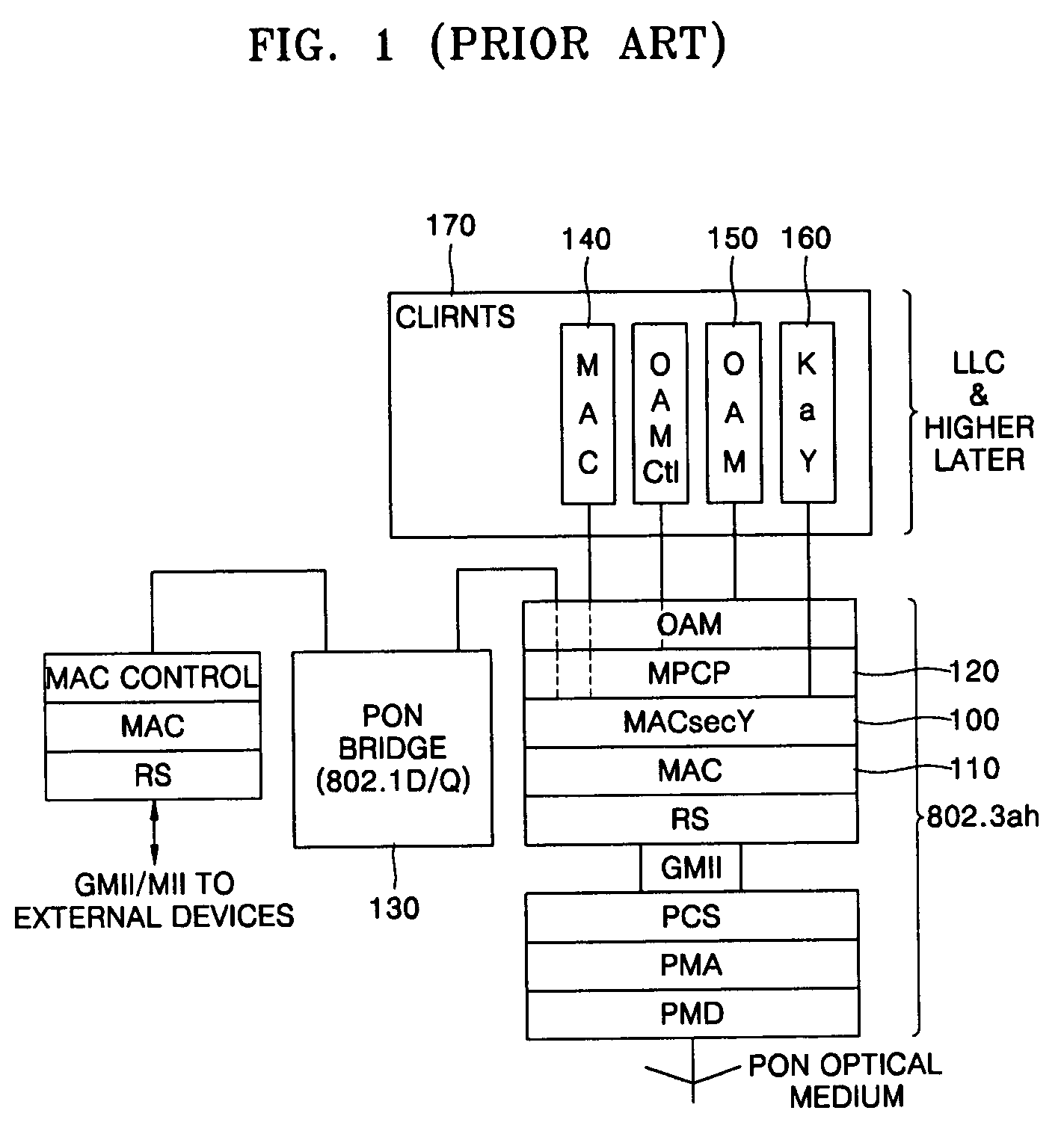
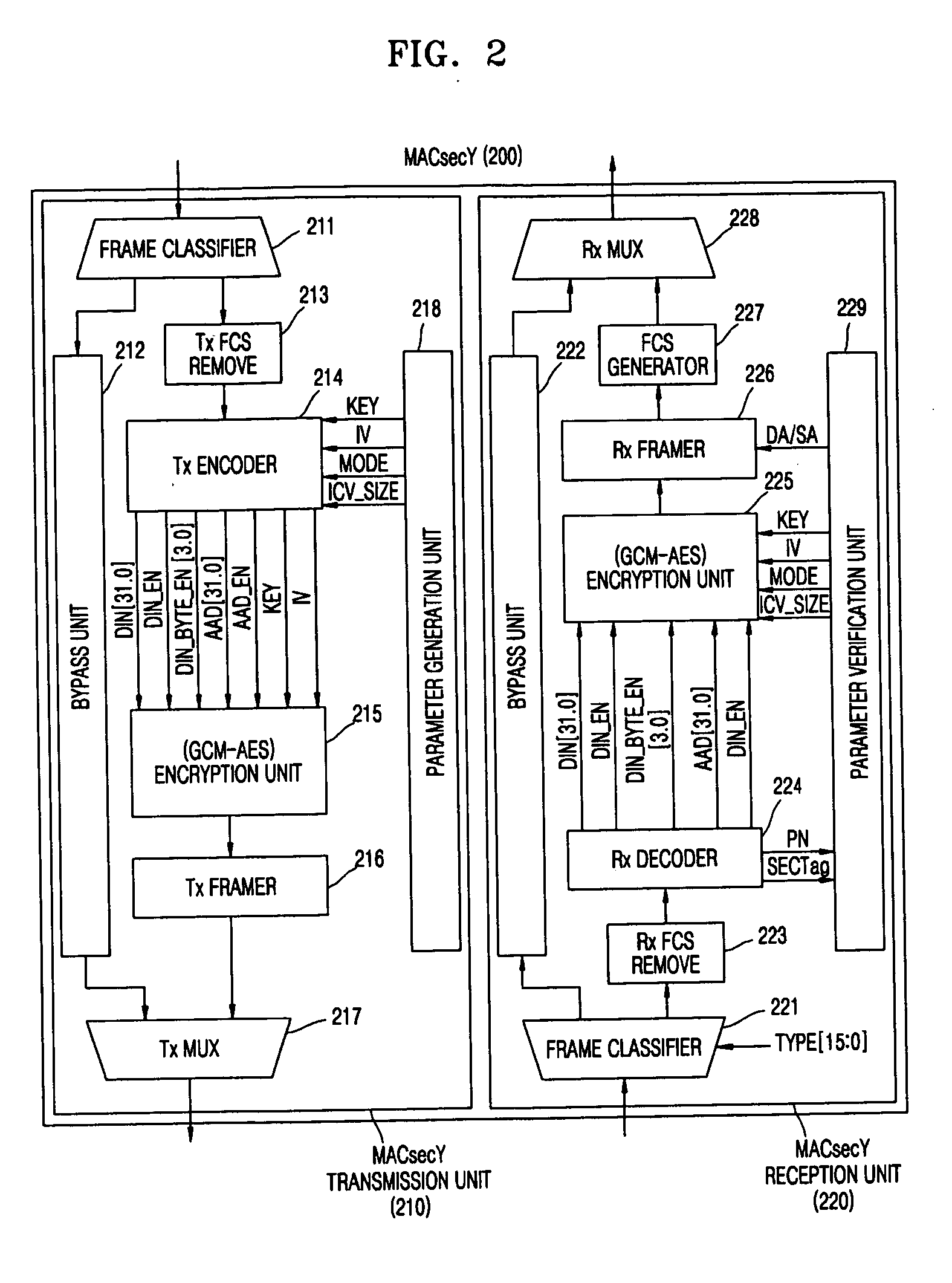
MAC security entity for link security entity and transmitting and receiving method therefor
InactiveUS20060136715A1Memory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionMedia access controlOptical network unit
An apparatus and method for providing a security function of frames transmitted between optical network terminals (OLTs) and optical network units (ONUs) in an Ethernet passive optical network (EPON) providing media access control (MAC) services are provided. The apparatus includes: a frame classifier distinguishing the type of a frame, and based on the logical link identifier (LLID) of the distinguished frame, determining whether or not the frame is a security link to which a security function is to be applied; a bypass unit delaying a no-security-function frame so that a processing time for converting the security-function-applied frame classified in the frame classifier into an encrypted frame is the same as a time for processing the no-security-function frame; and a parameter generation unit transmitting in relation to each of the LLIDs, a parameter set value including a security-function-application setting signal used in the encryption, decryption and authentication of the frame, a frame decryption signal, an encryption mode selection signal, and an authentication intensity adjustment signal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Optical network terminal and its packet processing method thereof
ActiveCN101064682AVarious operating modesEasy to operateMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksNetwork terminationEmbedded system
The invention relates to report process method of optic network terminal, report processing includes following steps: B1. ONT receives up-bound message from user network interface which is distributed with VLAN operation distribution data property; B2. the user network interface function module of ONT operates the said VLAN Tag based on VLAN operation distribution data property, said operation of VLAN Tag are divided into three types, one is operation of VLAN marking VID and VLAN PRI, two is operation to inner layer, three is operation to outer layer, the ONT executes any type of said operation or combination of said three types. The method of the invention simplifies the operation of VLAN Tag, and the operation mode of VLAN Tag can be expanded flexibly, and it is convenient to realize various operation modes of VLAN Tag.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
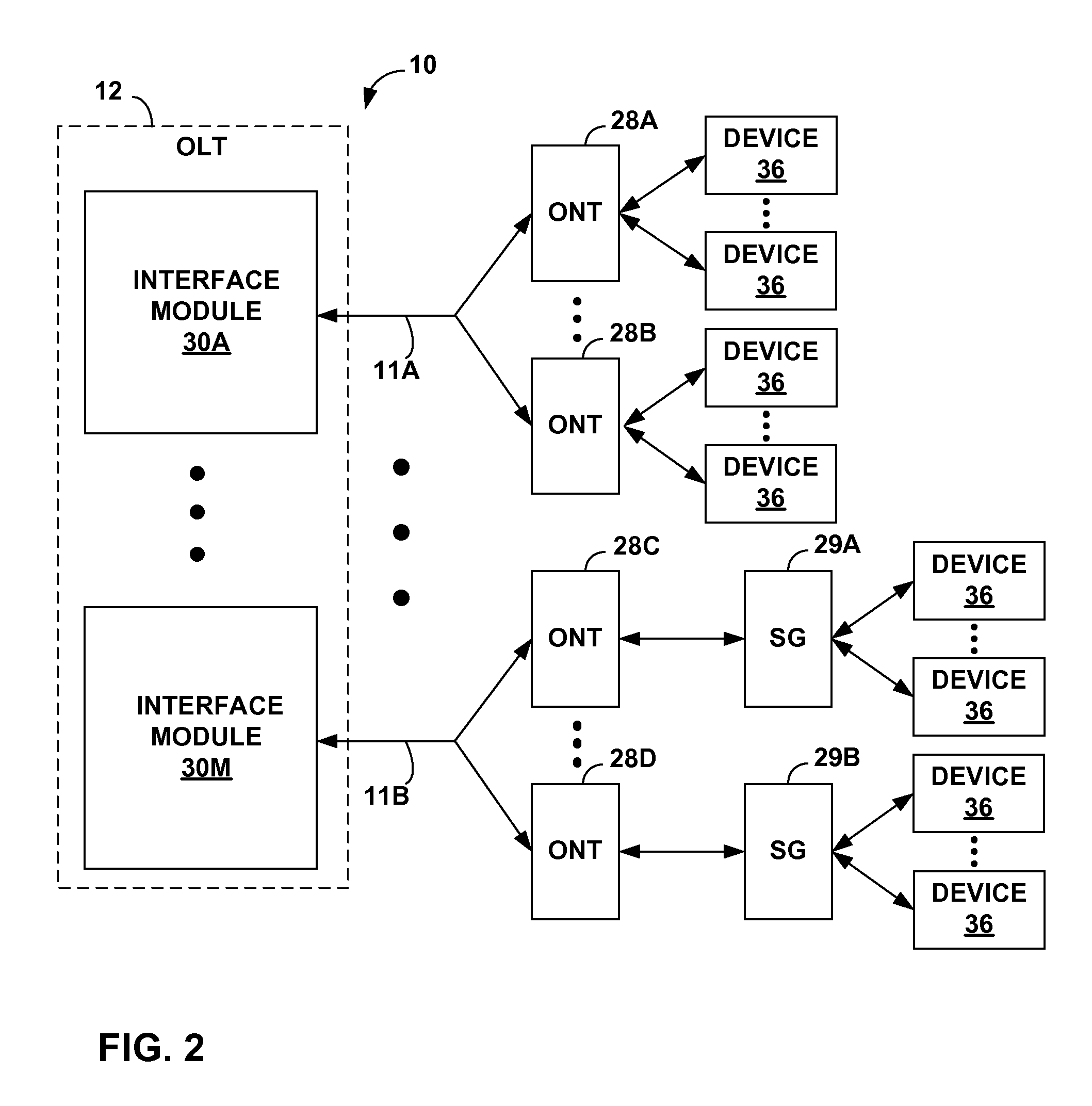
Optical network interface devices and methods
ActiveUS20090060530A1Simplifying ONT installationReduce in quantityMultiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexNetwork interface deviceEngineering
A system comprises an optical network terminal (ONT) that provides an interface to a passive optical network (PON). The ONT is coupled to a subscriber gateway device via at least one cable. The ONT may be located outside a subscriber premises while the subscriber gateway device may be located within the subscriber premises. The ONT converts optical signals received from PON to electrical signals and transmits the electrical signals to the subscriber gateway device without performing any MAC layer functions. The subscriber gateway device includes an optical media access control (MAC) unit that converts the electrical signals into MAC layer signals and a gateway unit that distributes the MAC layer signals to one or more subscriber devices. In this manner the MAC and gateway layer functions are relocated from the ONT to the subscriber gateway device.
Owner:WHITE OAK GLOBAL ADVISORS
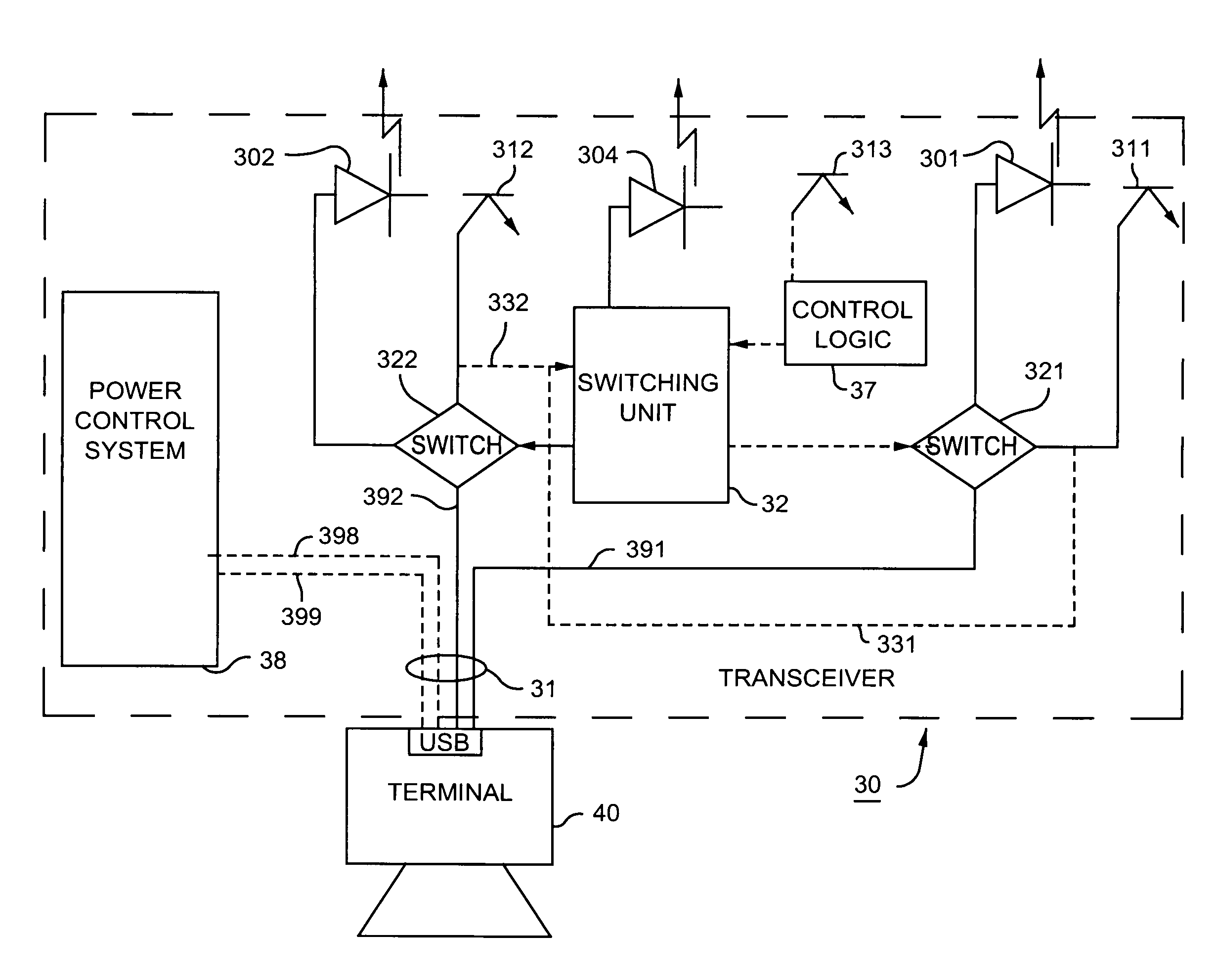
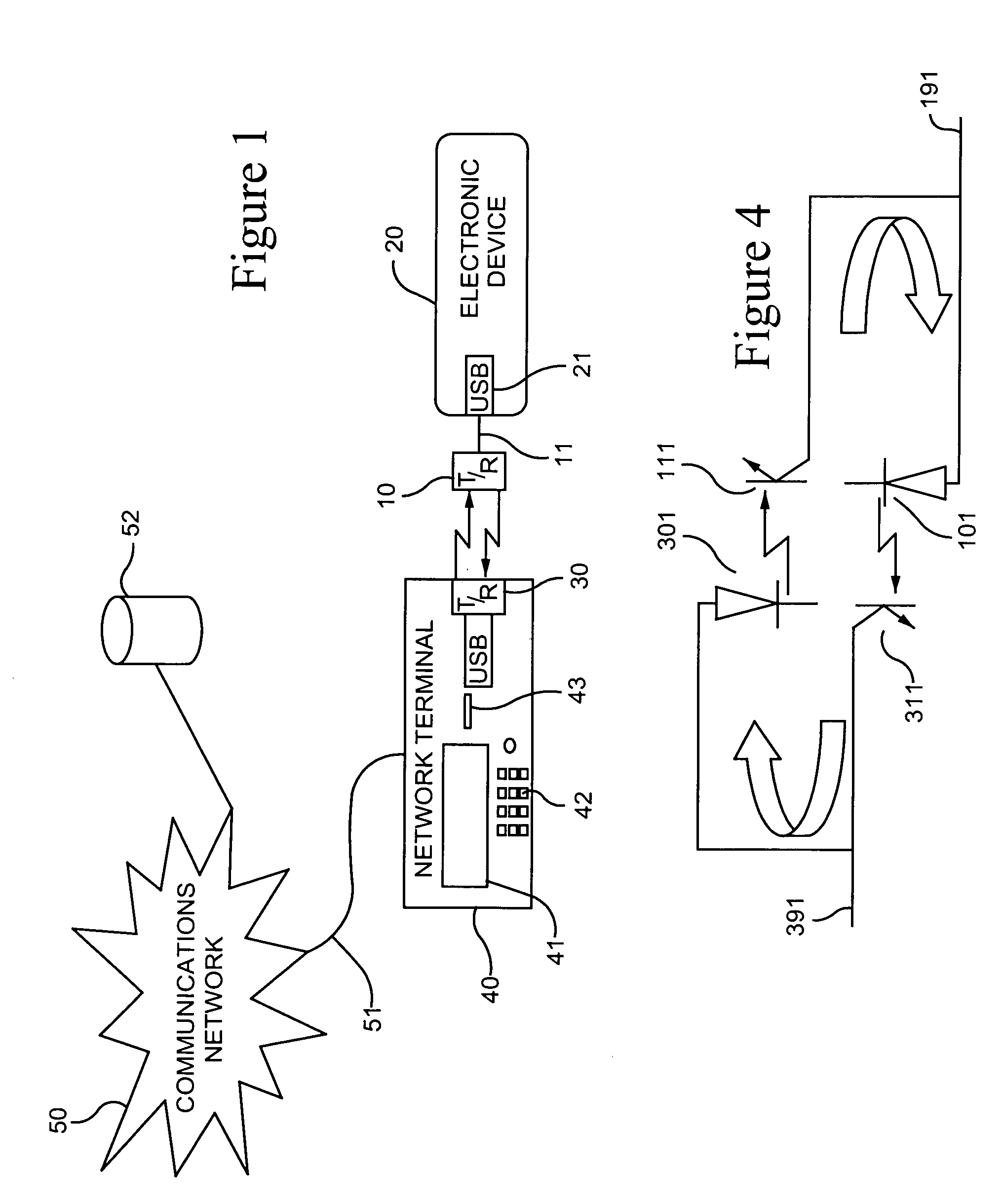
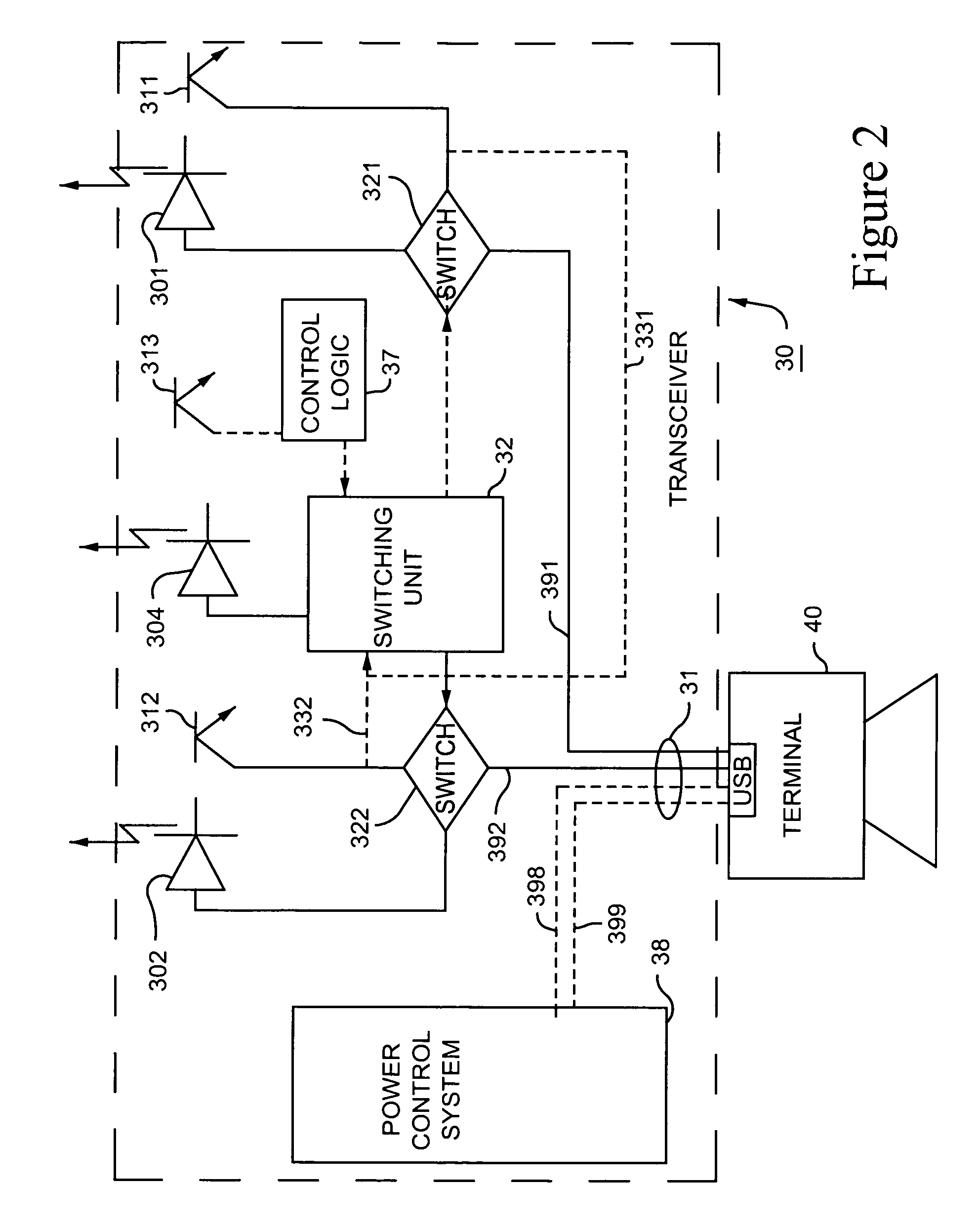
USB communication transceiver using optical link
ActiveUS7324757B2Without complexityImprove protectionActive radio relay systemsClose-range type systemsNetwork terminationTransceiver
An optical version of USB is provided to enable PDAs and digital cameras to download data and media files to remote network servers. The PDA is plugged into an optical transceiver that communicates with a complementary transceiver located in a network terminal (for example a payphone) that is in communication with the network server.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
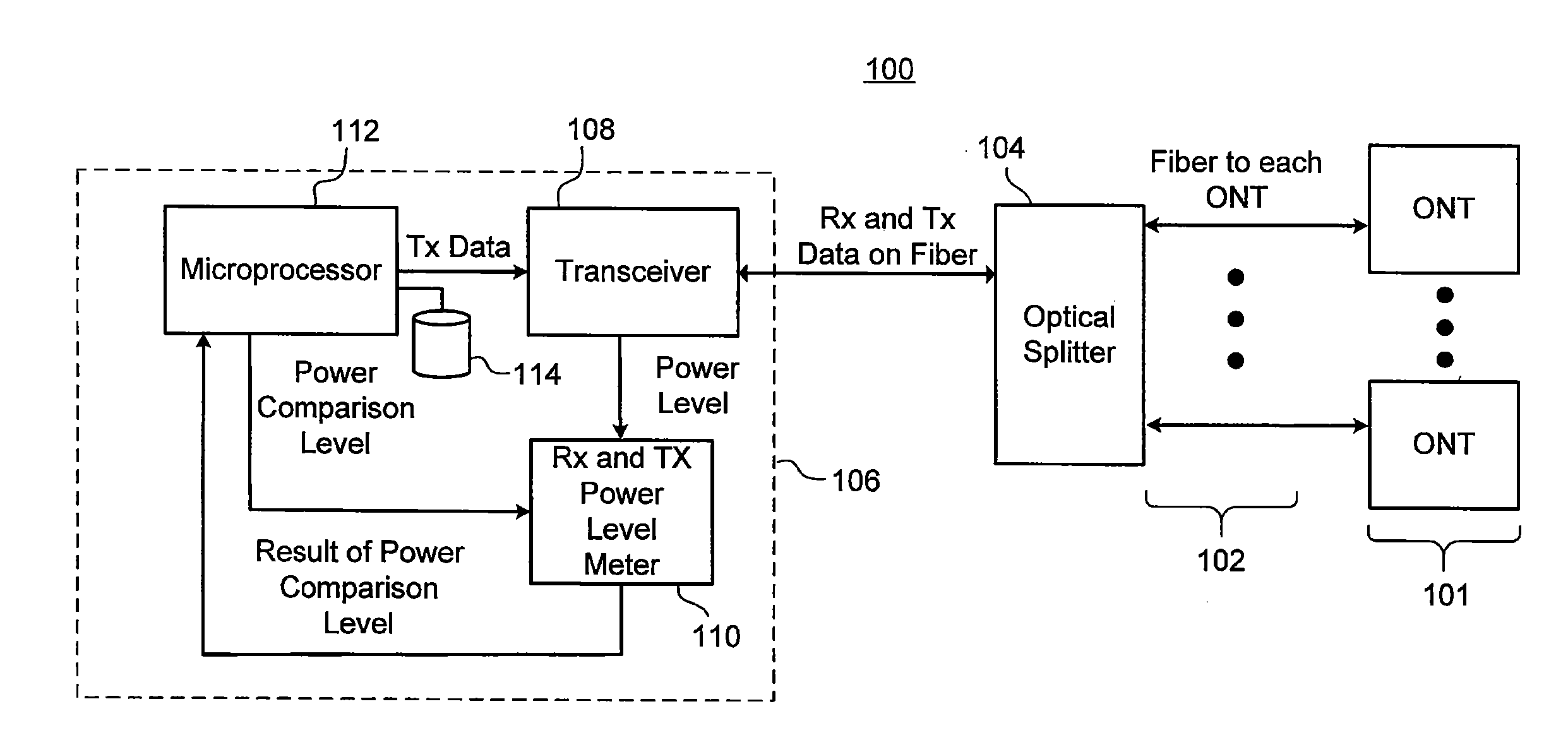
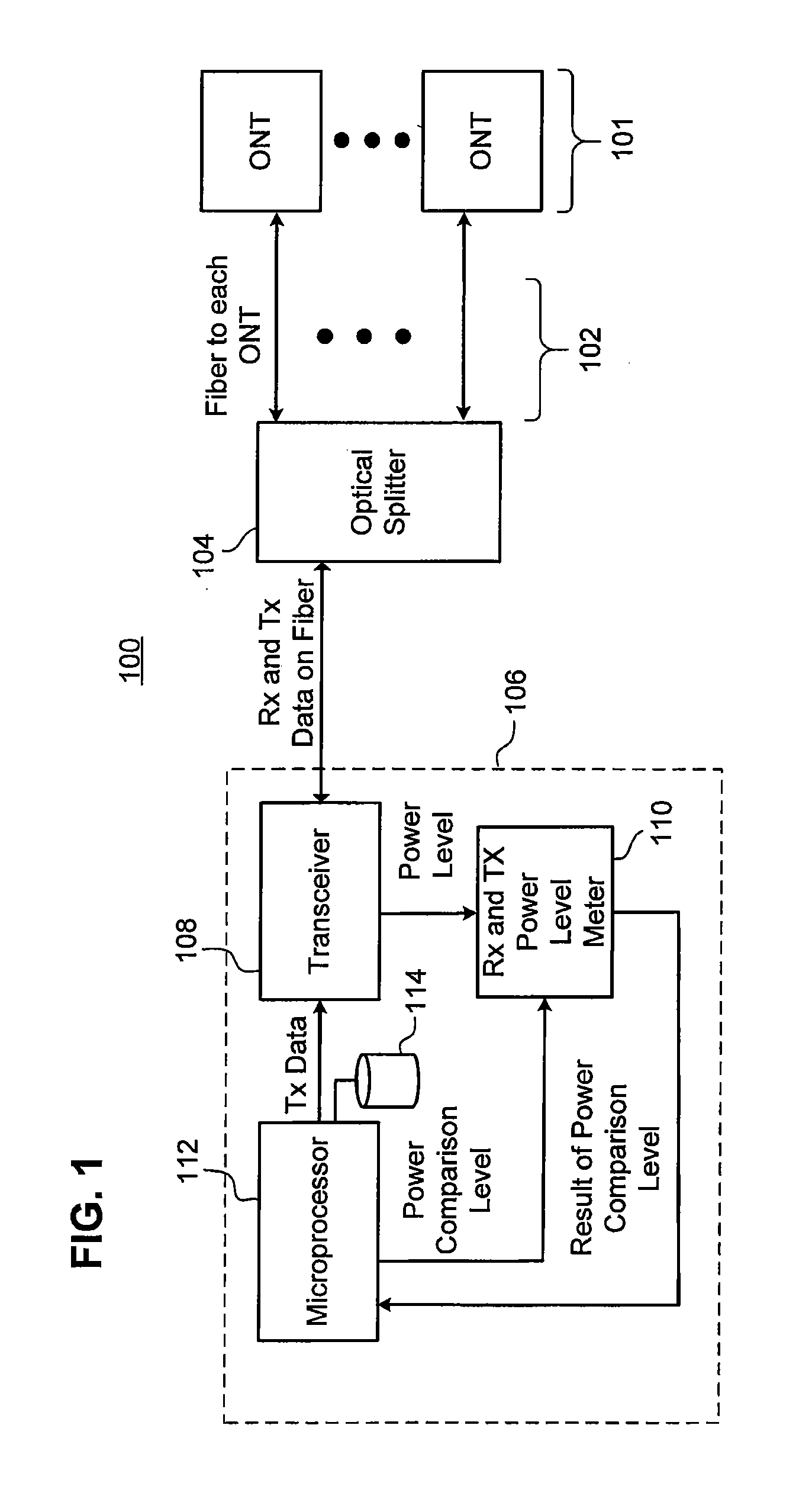
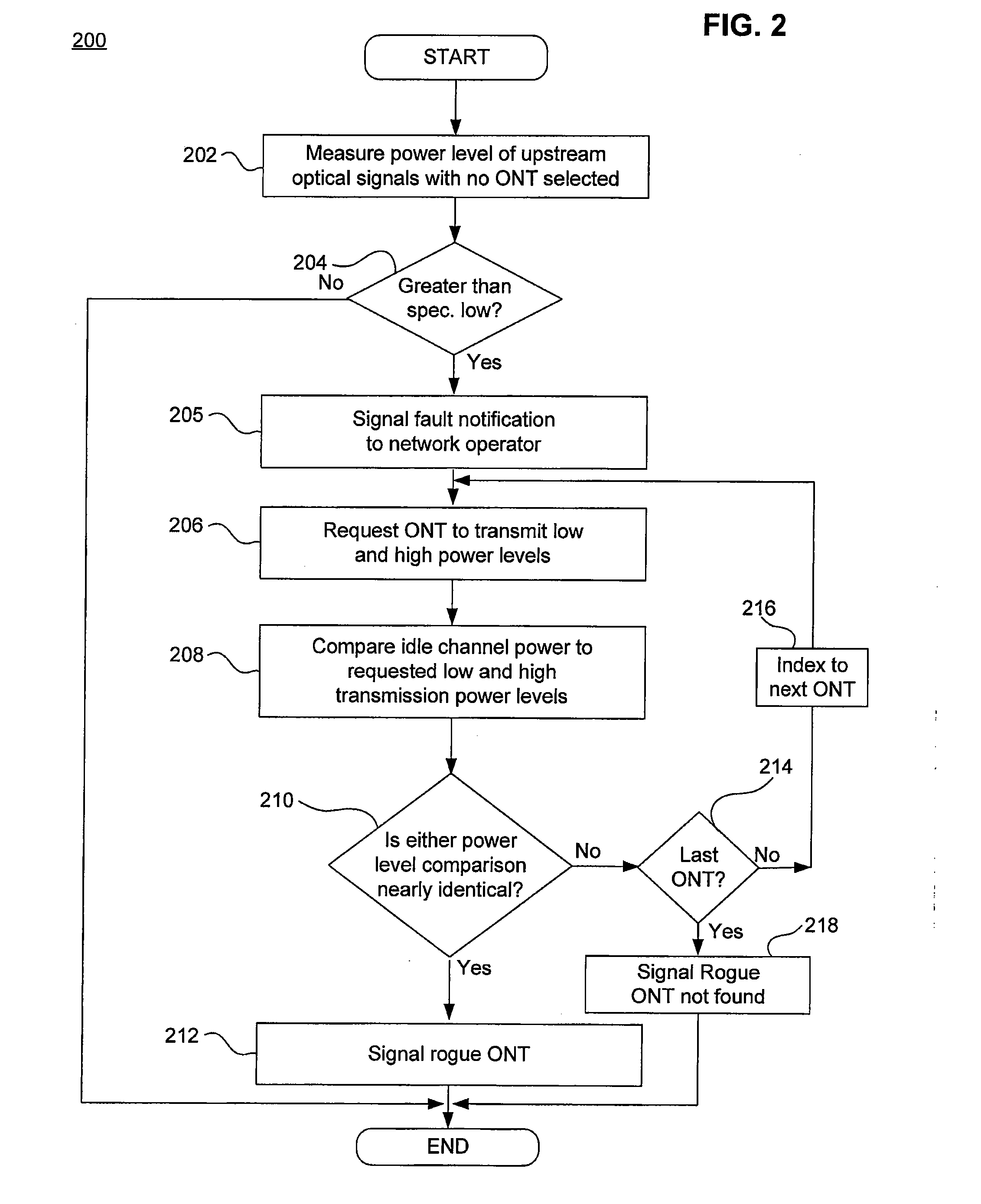
Method, apparatus, system and computer program product for identifying failing or failed optical network terminal(s) on an optical distribution network
InactiveUS20070201867A1Avoid mistakesReduced customer down timeTransmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsNetwork terminationDistribution networks
An error in a passive optical network is identified by communicating to an optical network terminal on the passive optical network a request to transmit a response signal at a predetermined power level, receiving the response signal in response to the request, and measuring a power level of the response signal. A predetermined channel power level is compared to the power level of the response signal and a status of the optical network terminal is determined based on the result of the comparison.
Owner:TELLABS PETALUMA
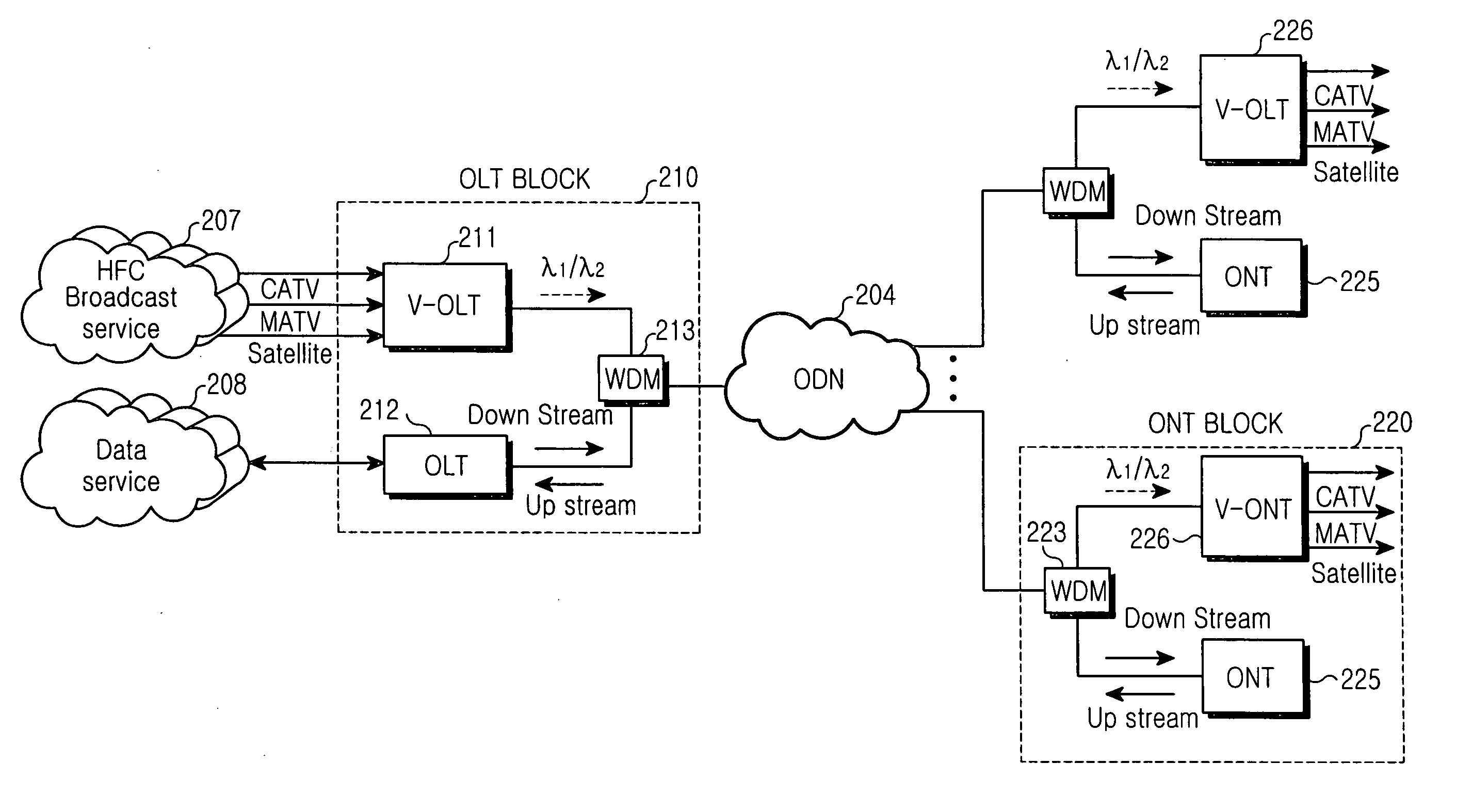
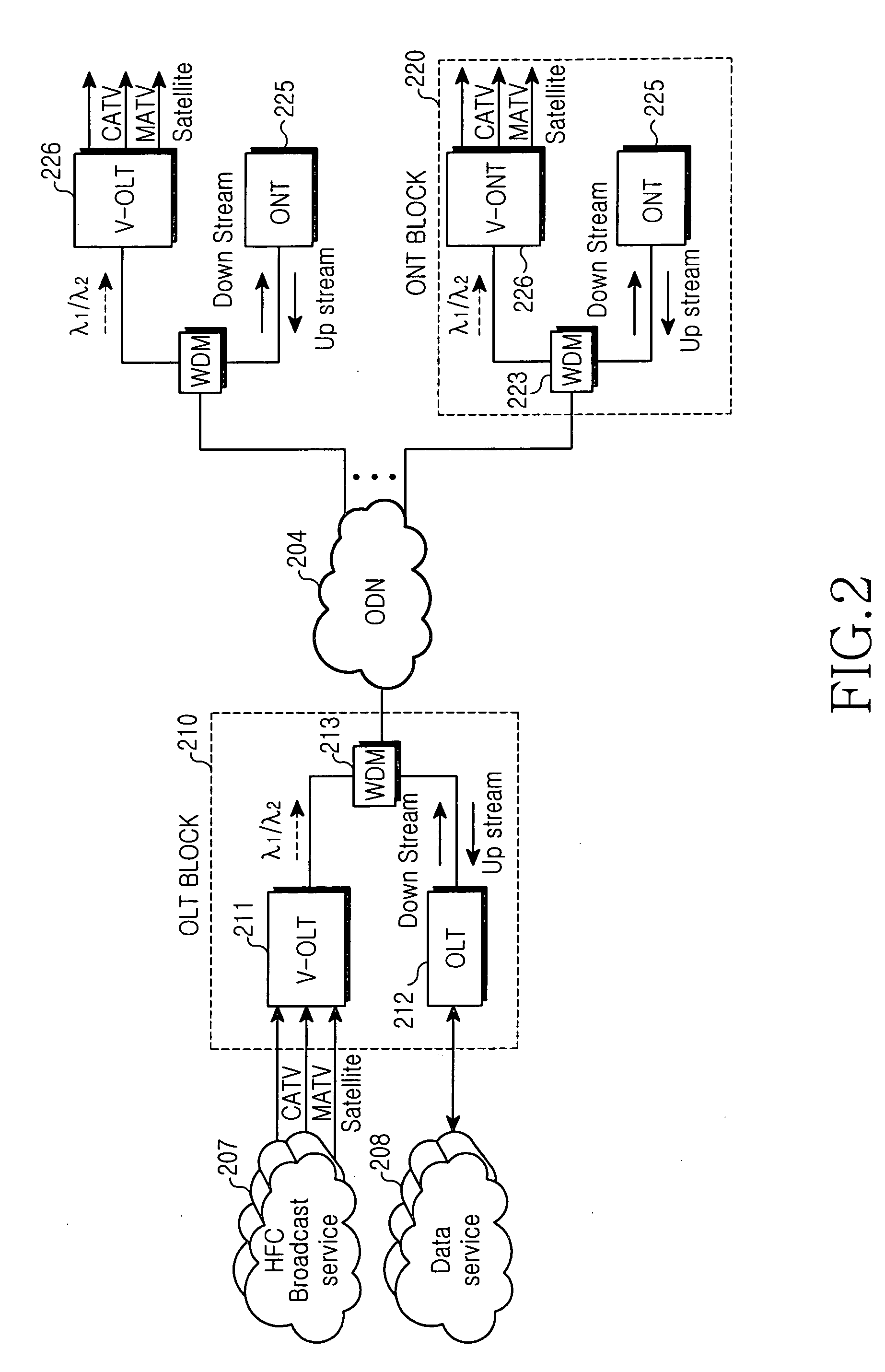
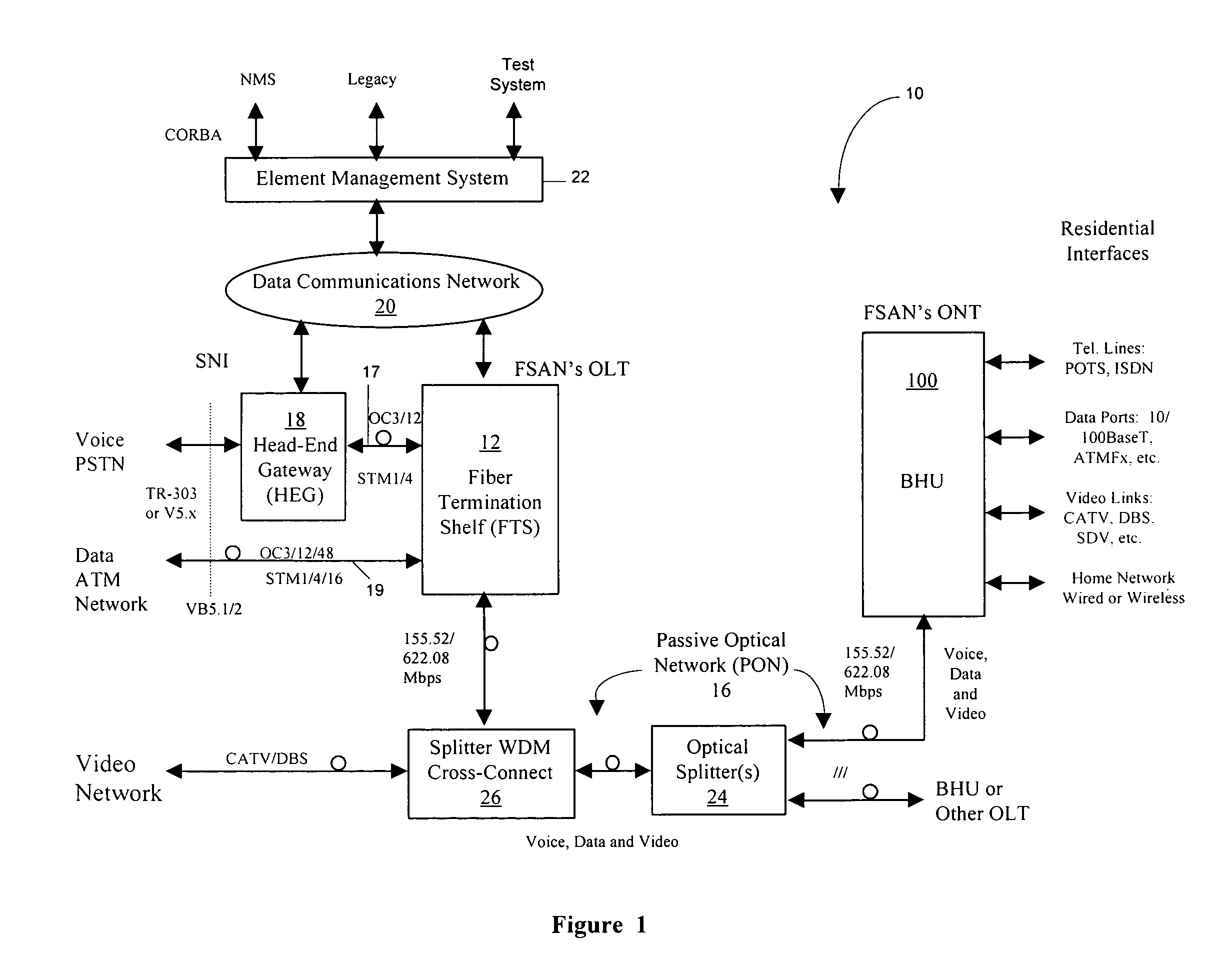
FTTH system based on passive optical network for broadcasting service
InactiveUS20050172328A1Low costWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical transmission adaptationsNetwork terminationFiber
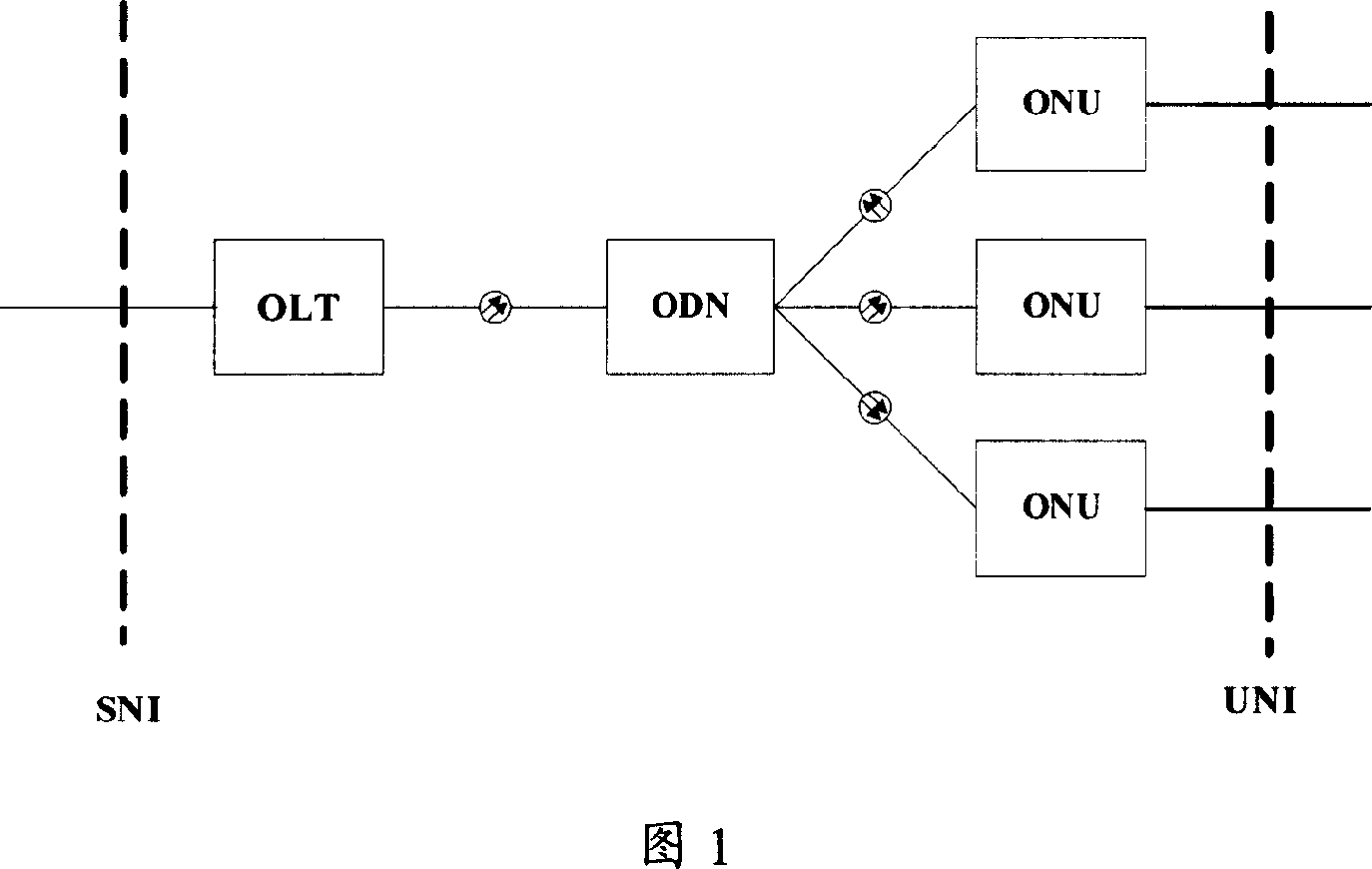
A fiber to the home (FTTH) system based on a passive optical network (PON) includes an optical line terminal (OLT) block, an optical network terminal (ONT) block, and an optical distribution network (ODN). The ONT block includes a video-optical line terminal (V-OLT) and an optical line terminal (OLT) in order to output optical signals of the video-optical line terminal (V-OLT) and the optical line terminal (OLT) by multiplexing the optical signals. The VOLT receives cable TV, master antenna TV, and satellite broadcasting optical signals inputted from a broadcasting service network so as to output received signals as a first optical signal having a predetermined wavelength band. The OLT includes a first downstream data optical transmitter and a first upstream data optical receiver and outputs a data communication signal inputted from a data service network as a second optical signal having different wavelength from the video-optical line terminal. The ONT block includes a video-optical network terminal (V-ONT) and an optical network terminal (ONT) in order to split multiplexed data communication signals, and cable TV broadcasting, master antenna TV broadcasting, and satellite broadcasting optical signals. The V-ONT processes the split cable TV broadcasting, master antenna TV and satellite broadcasting optical signals so as to provide subscribers with the split cable TV broadcasting, master antenna TV and satellite broadcasting optical signals. The optical network terminal (ONT) has an upstream data optical transmitter and a downstream data optical receiver so as to process split data communication signals. The optical distribution network (ODN) connects the optical line terminal block to the optical network terminal as an optical transmission medium.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for dynamic bandwidth allocation on PONs
InactiveUS7385995B2Low costGood broadband performanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexNetwork terminationDynamic bandwidth allocation
Mechanisms for providing a subscriber-side interface with a passive optical network are described herein. An optical network termination (ONT) having an integrated broadband passive optical network processor is utilized to receive downstream data from an optical line termination (OLT) via a passive optical network and provide the contents of the downstream data to one or more subscriber devices via one or more data interfaces. Similarly, the ONT is adapted to receive and transmit upstream data from the one or more subscriber devices to the OLT via the passive optical network. The ONT preferably implements one or burst buffers for buffering upstream and / or downstream data. The ONT can be adapted to notify the OLT of the status of the burst buffer, thereby allowing the OLT to modify the bandwidth allocations.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
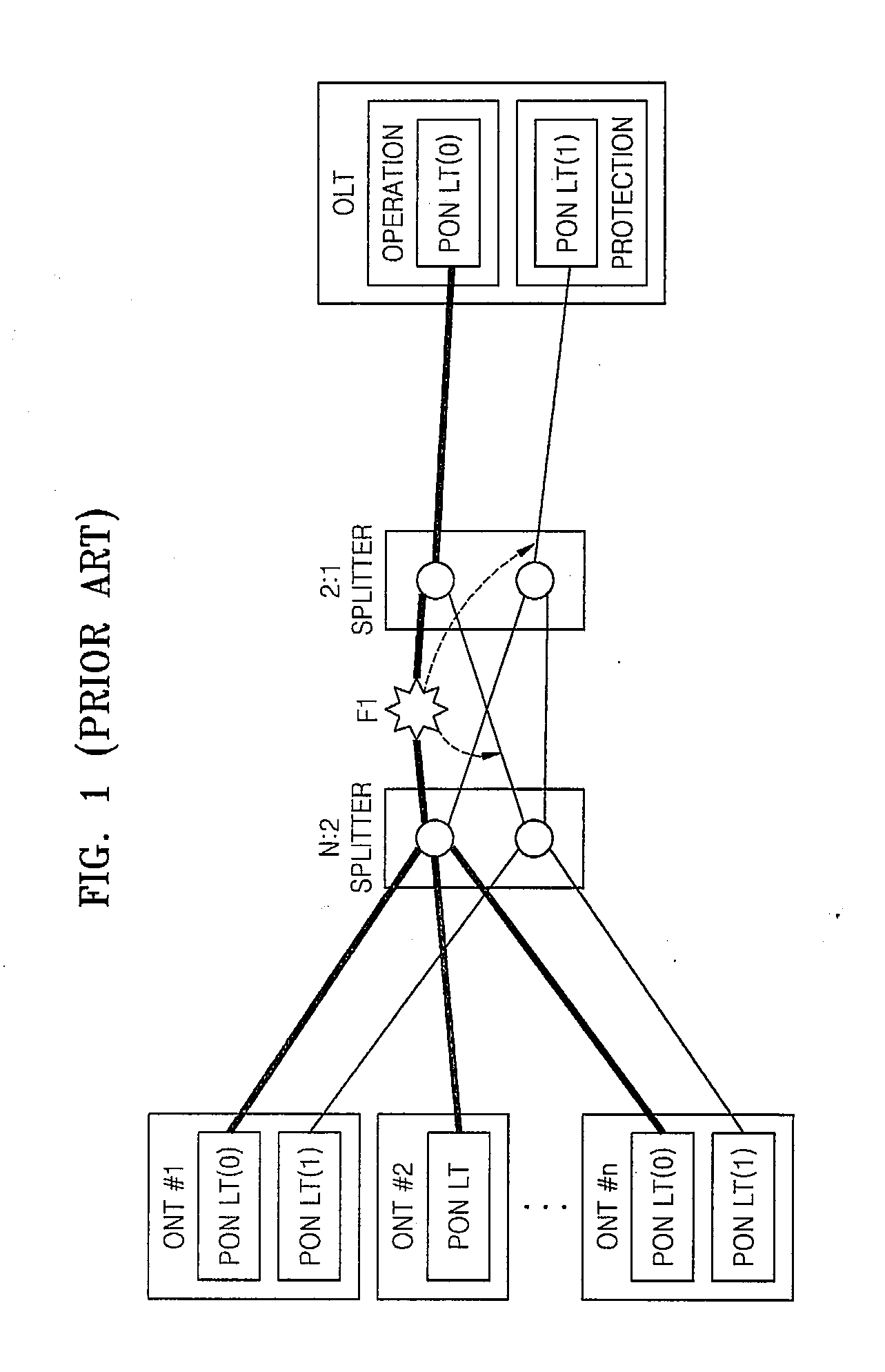
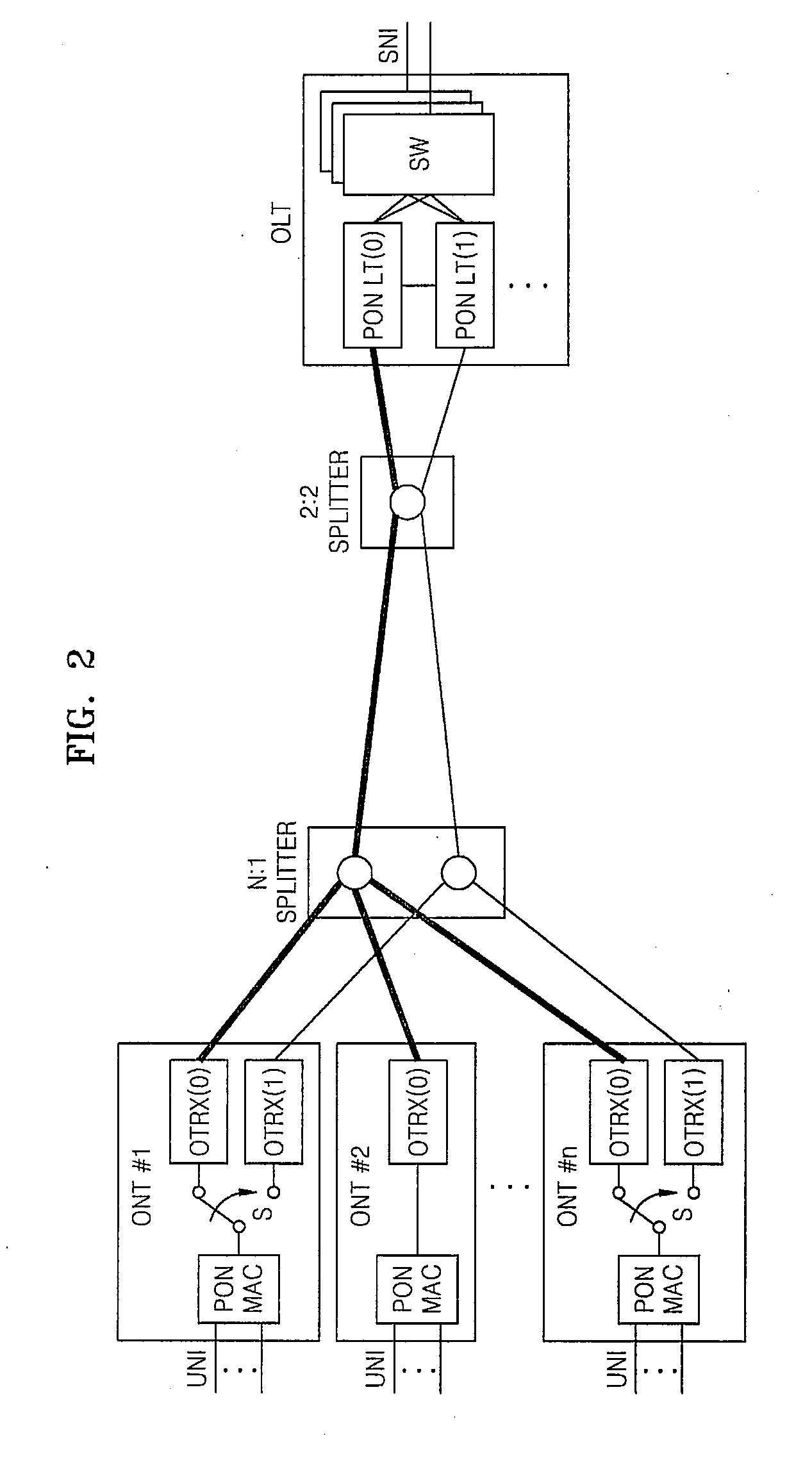
Method and apparatus for partial duplex protection switching by using single splitter in PON
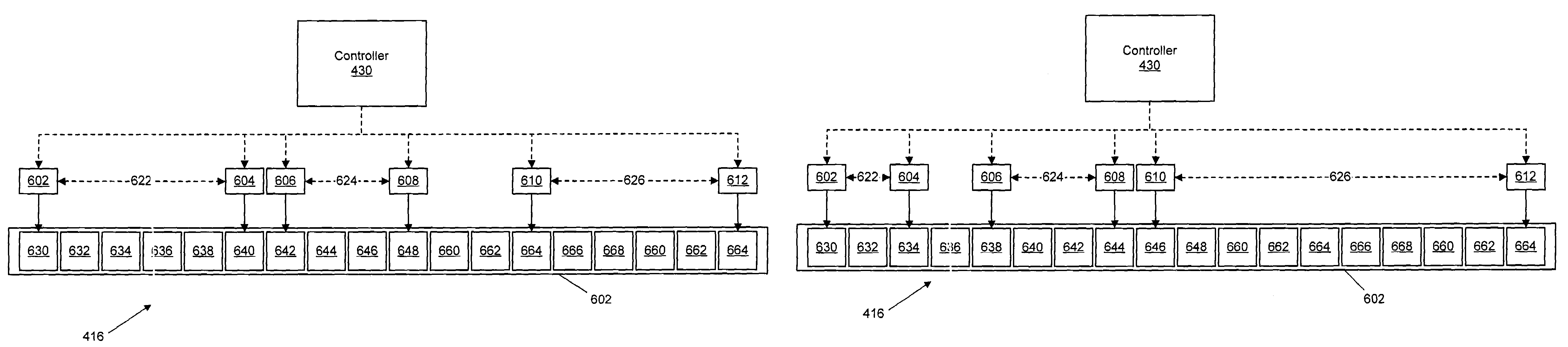
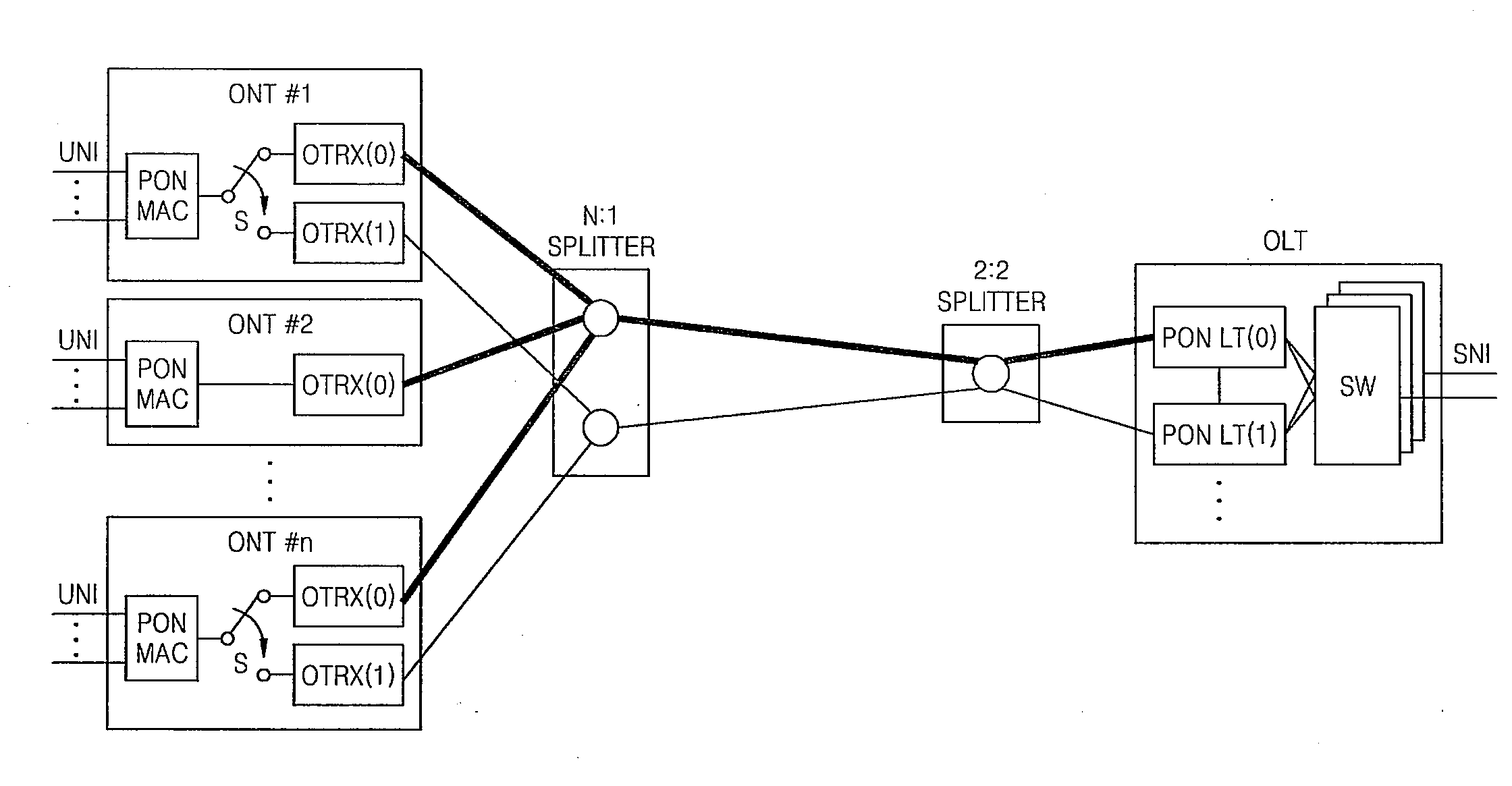
InactiveUS20080131124A1Quick switchEasy to switchMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexOptical network terminalEngineering
A method and apparatus for duplex protection switching by using a single splitter in a passive optical network (PON) are provided. The apparatus for duplex protection switching in a PON, in which a single optical line termination (OLT) and many optical network terminations (ONTs) are connected together in a multiple-access manner, includes: a 2:2 splitter connected to two PON line terminations (LTs) in the OLT; and two N:1 splitters which are connected to the 2:2 splitter, and each of which is connected to two PON LTs in the ONT. According to the method and apparatus, an economical effect can be provided in which two links, an operational link and a protection link, in the PON can provide a partial duplex function at a lower cost. Also, a protection switching time can be reduced by simplifying a restoration process so that when an error is detected, an operational state is returned by protection switching.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
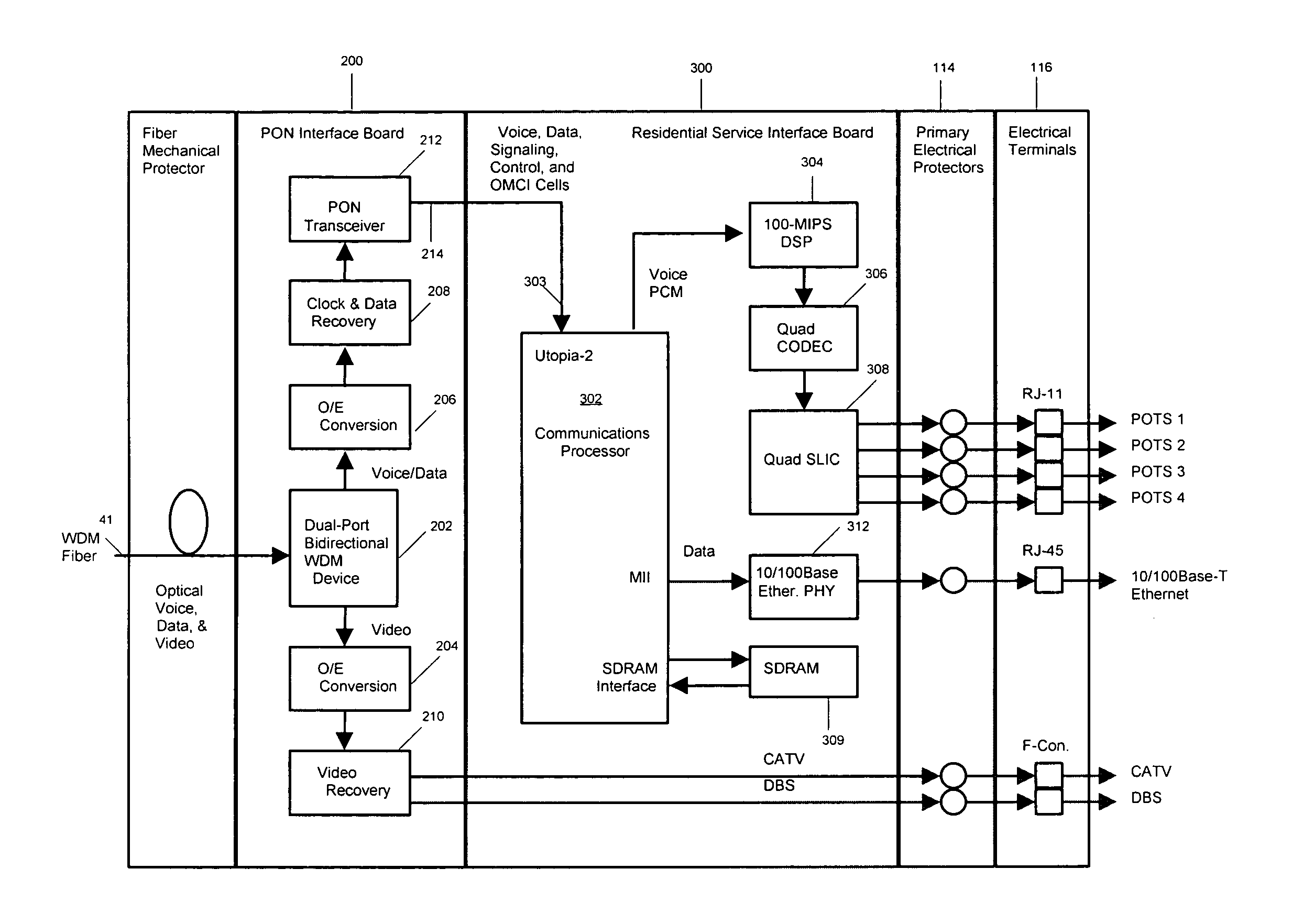
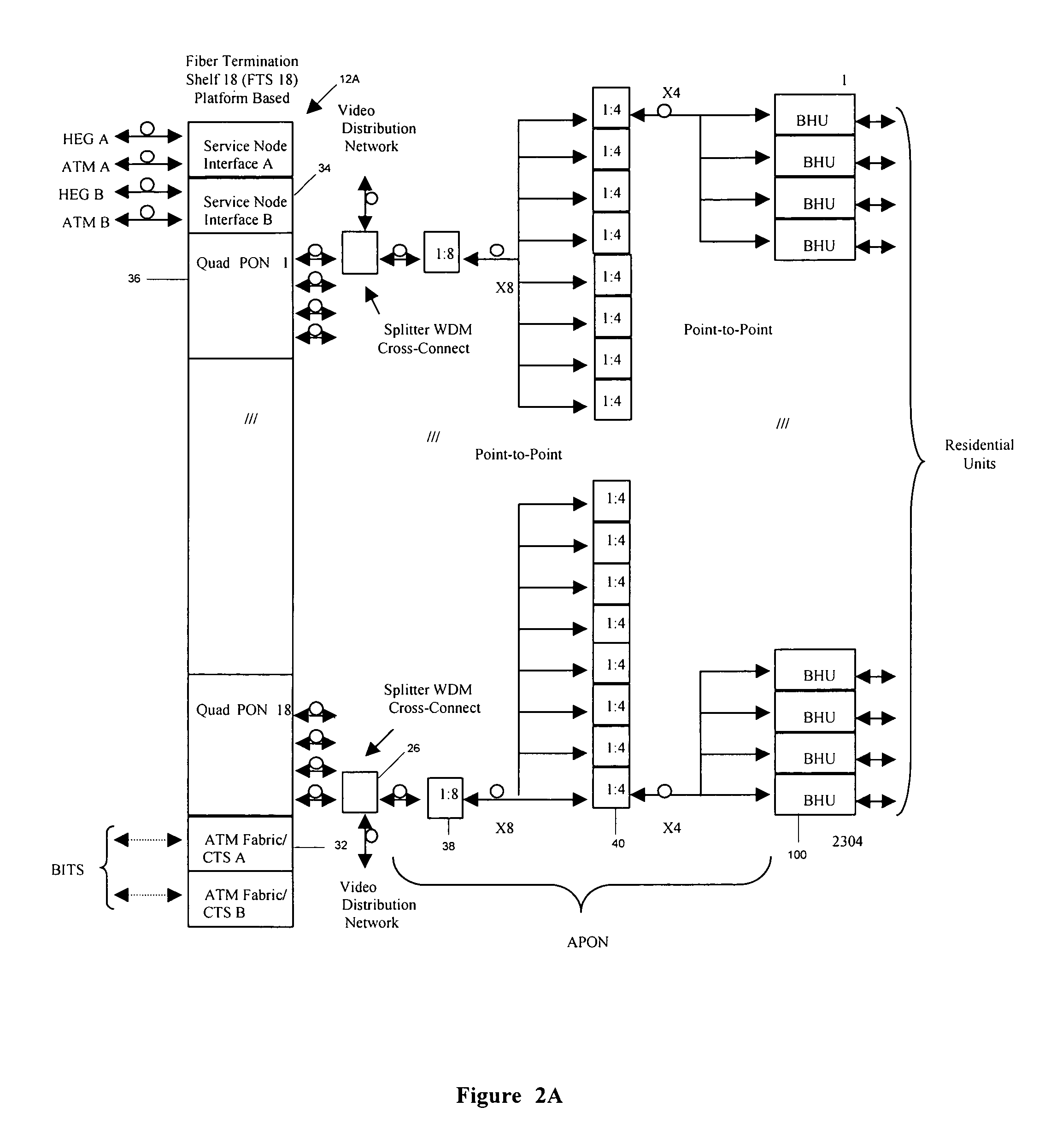
Fiber to the home broadband home unit
InactiveUS7277637B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsTime-division multiplexFiberData information
An apparatus and system are provided for delivering communication services such as video, data and telephony services to individual residential units.According to one embodiment, an optical network terminal (ONT) for providing communication services to a single residential unit comprises a passive optical network interface (PI) circuit, a residential service interface (RSI) circuit, and a power unit. The PI circuit receives optical signals from an optical fiber and transmits optical signals onto the optical fiber. The PI circuit is adapted to convert received optical signals containing voice information to electrical voice ATM cells, received optical signals containing data information to electrical data ATM cells, and received optical signals containing video signals to electrical video signals. The PI circuit is also adapted to convert electrical voice ATM cells and electrical data ATM cells to optical signals for transmission over the optical fiber;The RSI circuit that is adapted to convert the electrical voice ATM cells to a telephony format suitable for use at the residential unit and the electrical data ATM cells to a network format suitable for use at the residential unit. The RSI circuit is also adapted to convert telephony format information received from the residential unit to voice ATM cells and network format information received from the residential unit to data ATM cells.The power unit provides power for use in the PI circuit and the RSI circuit. The power unit includes an AC / DC converter for converting ac power received from the residential unit to dc power for use in the ONT and backup batteries for providing power when there is an interruption of the ac power.
Owner:TELLABS BEDFORD
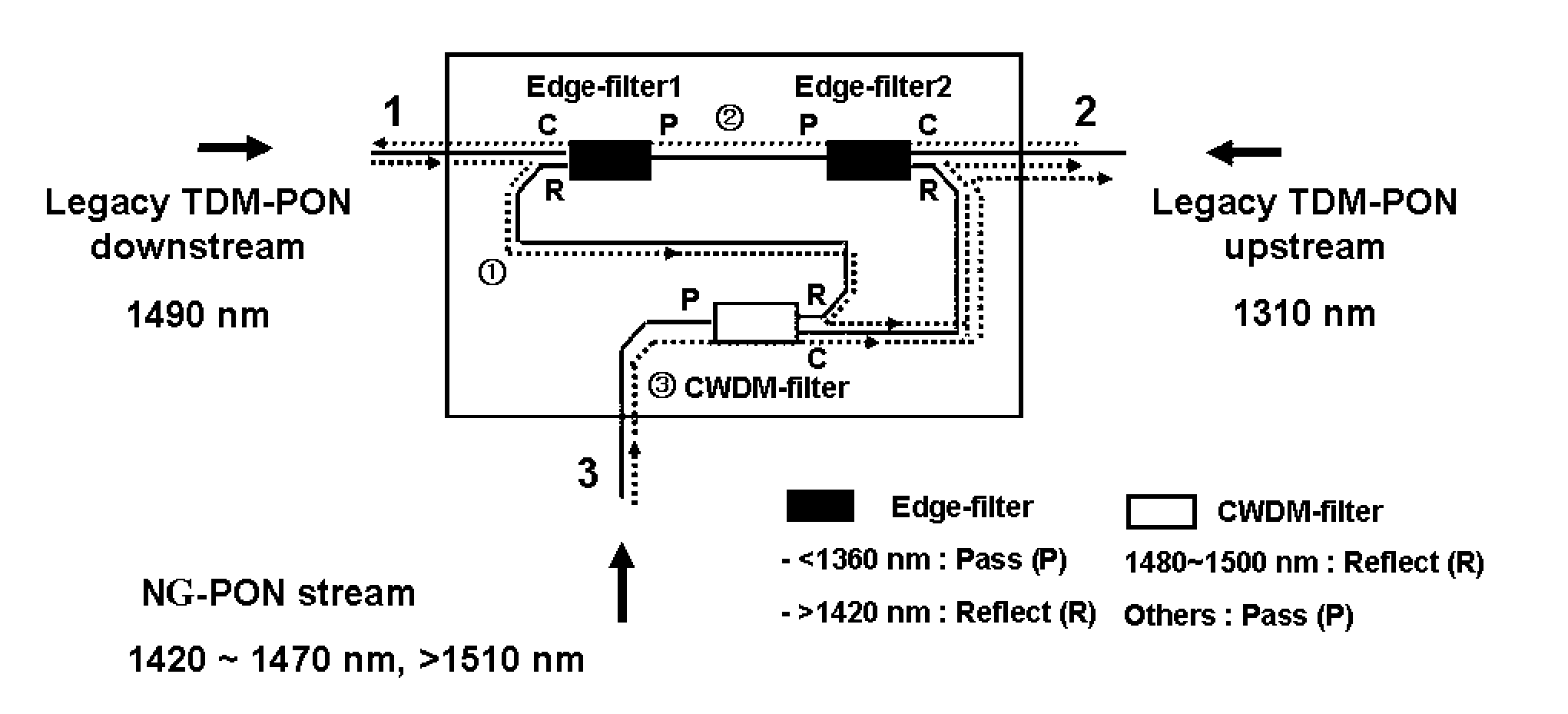
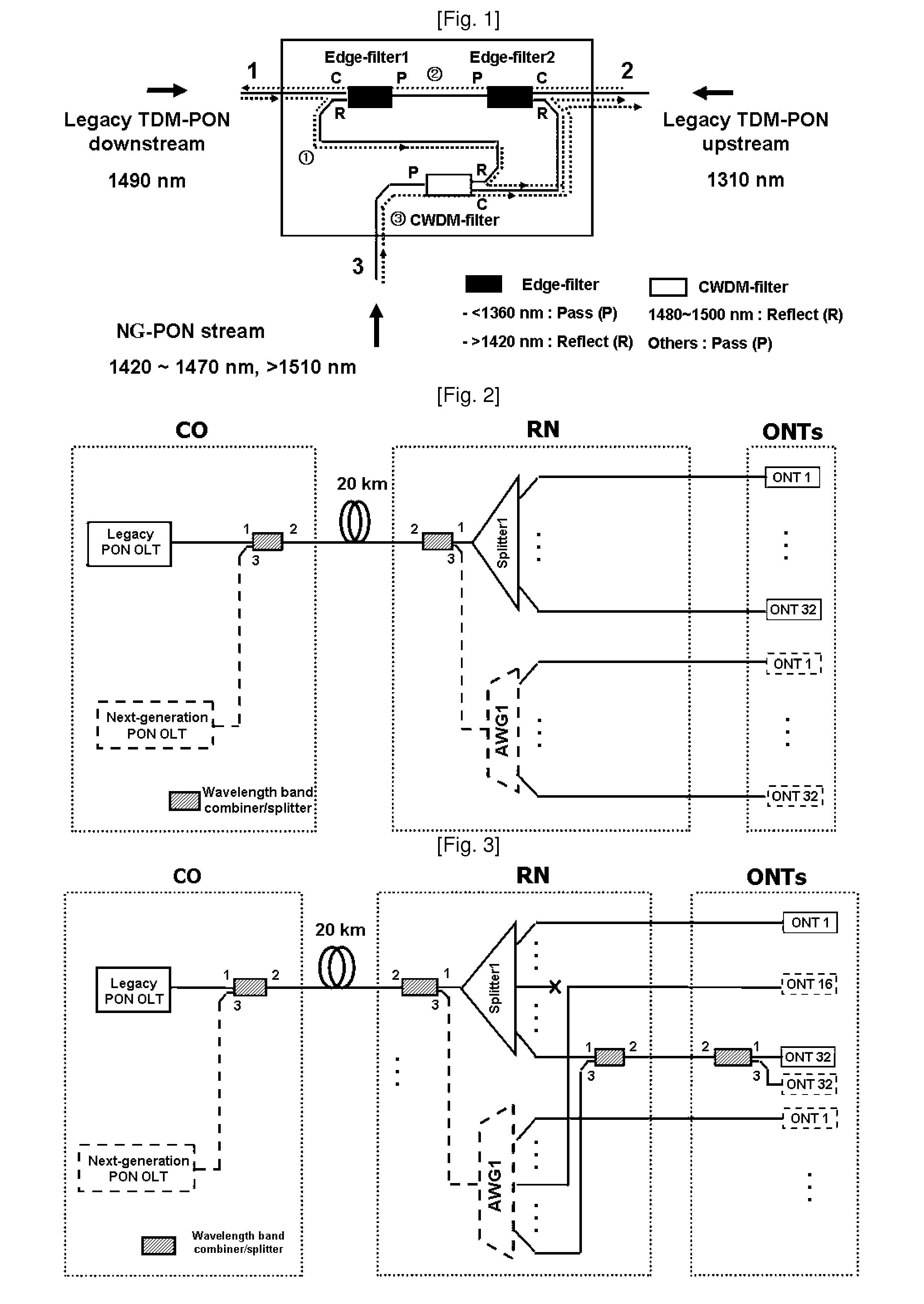
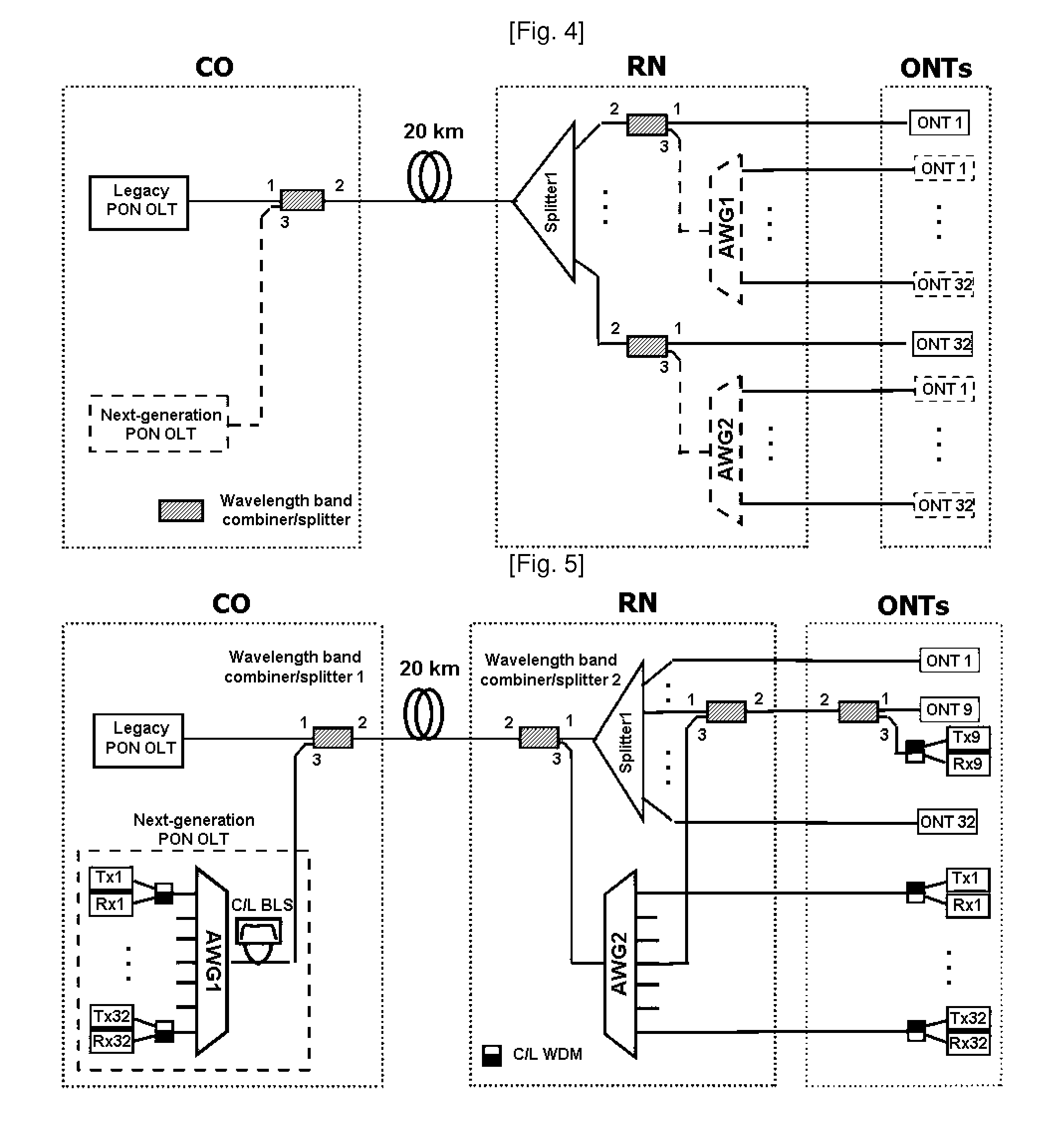
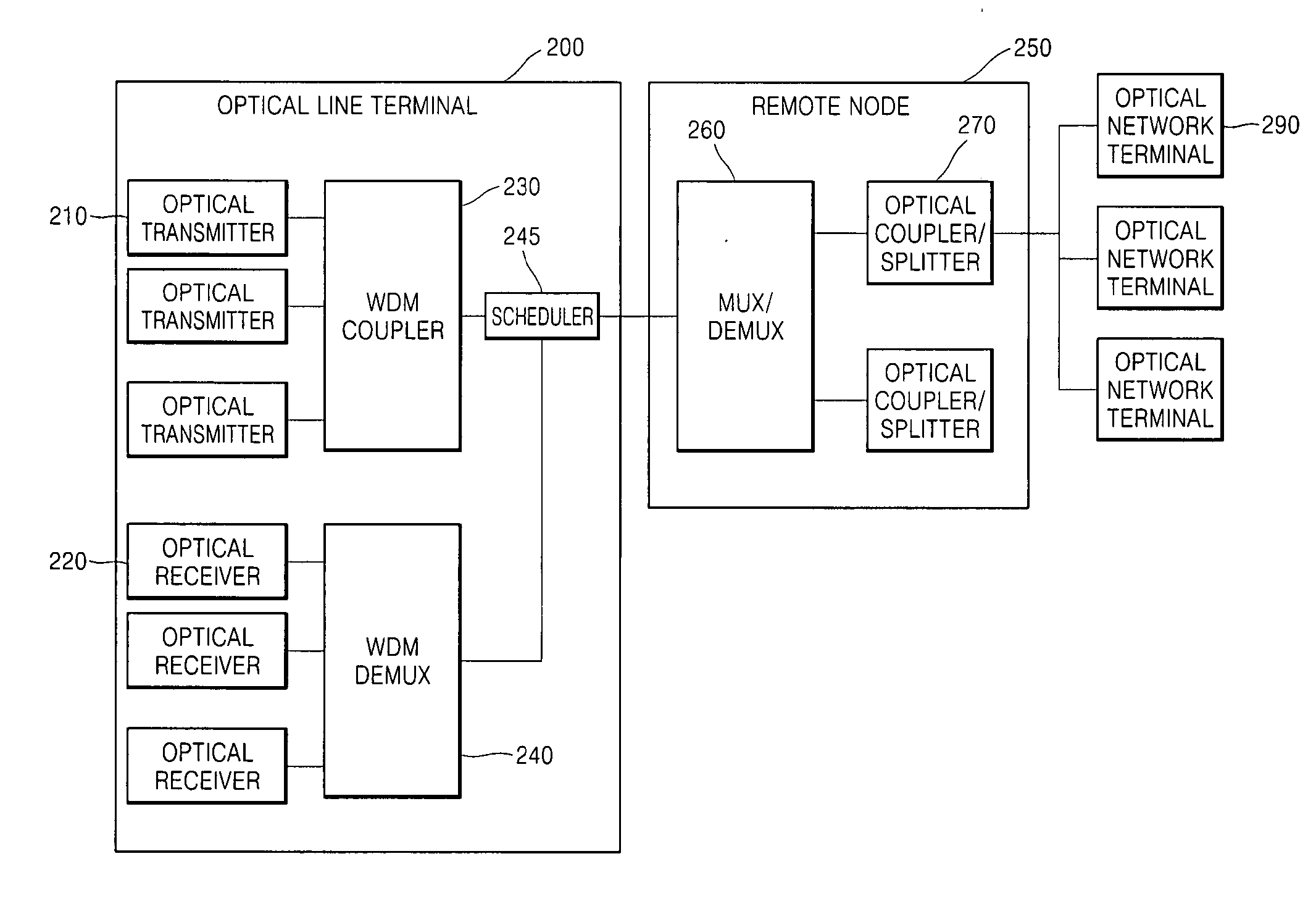
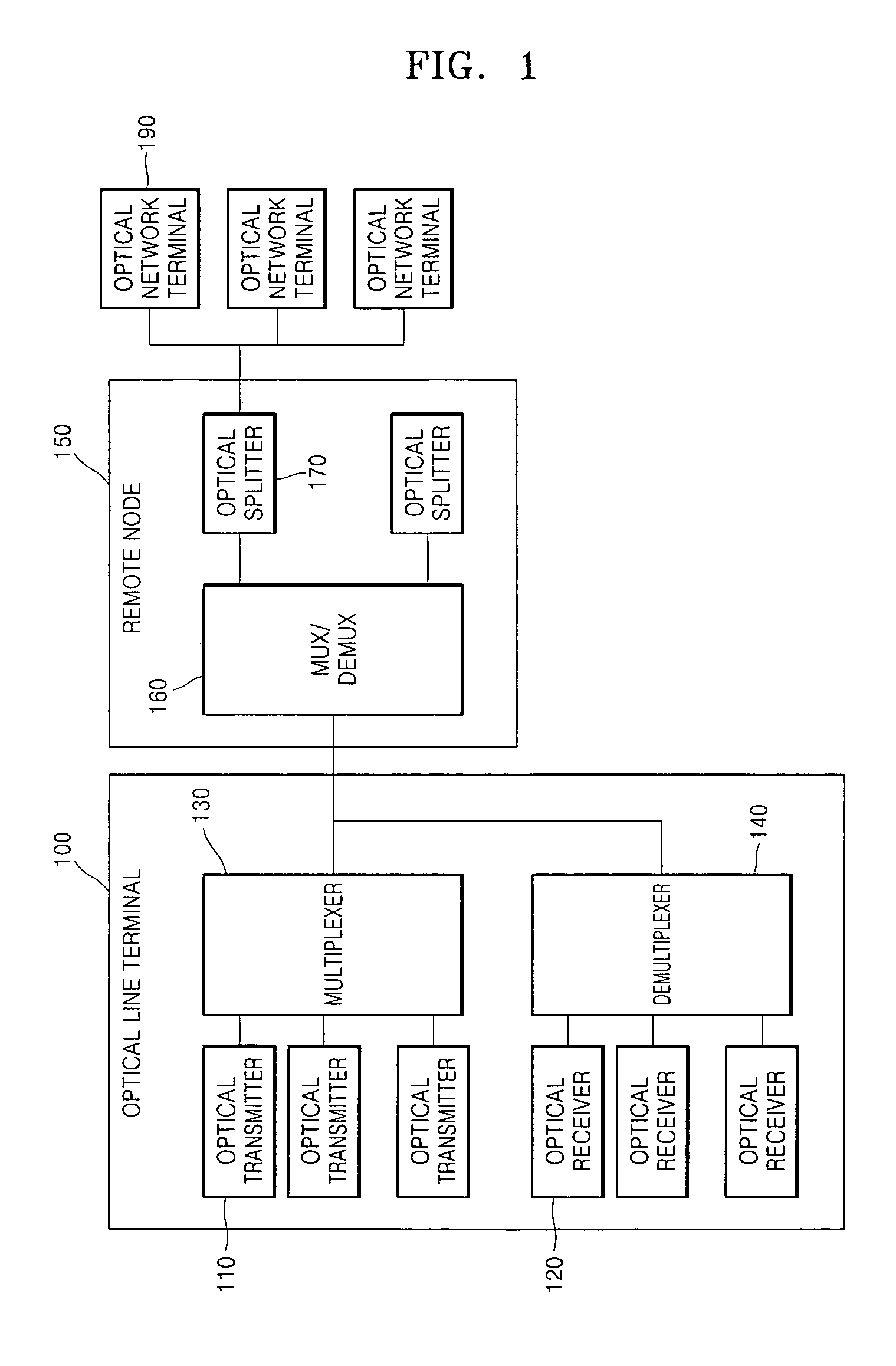
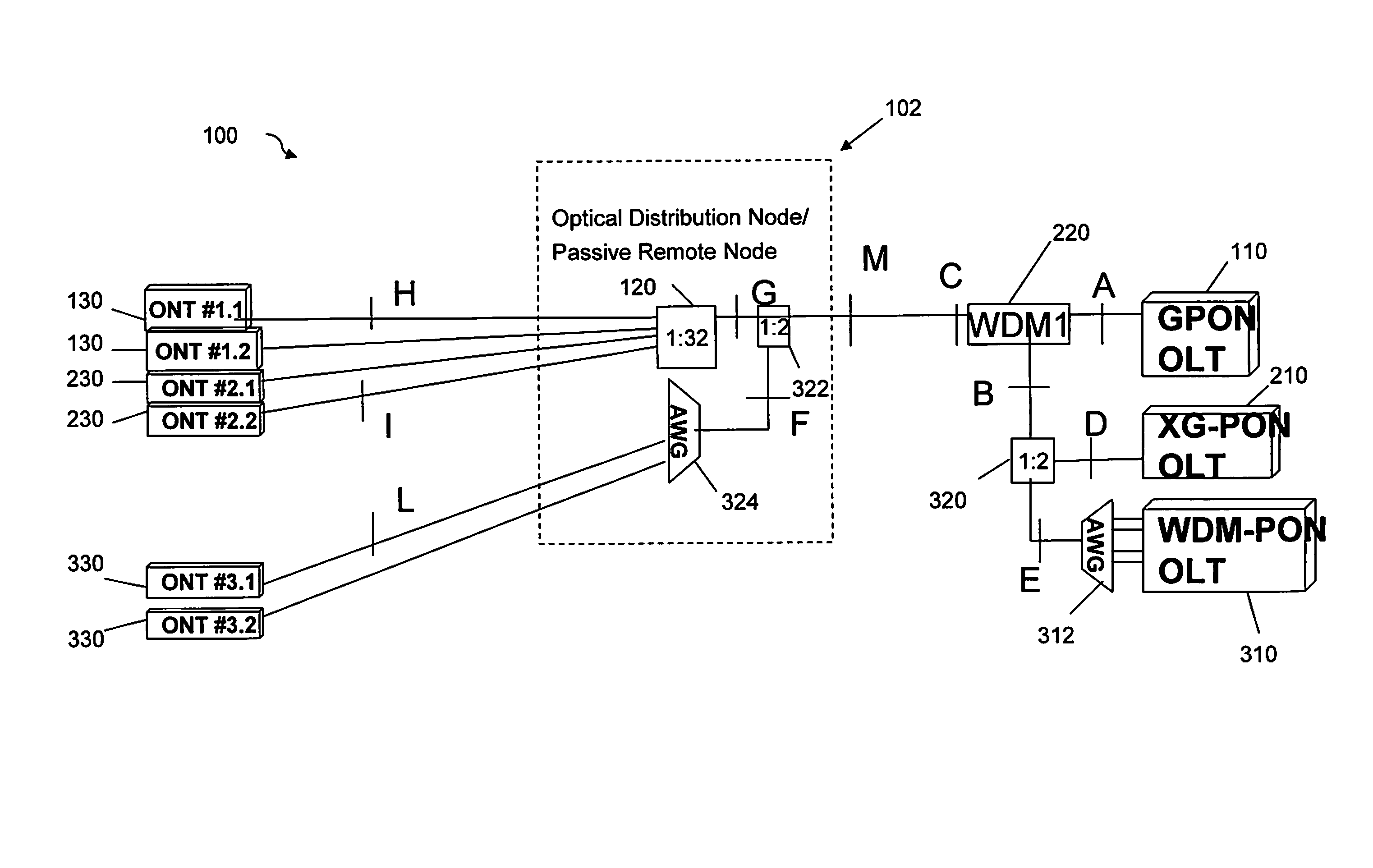
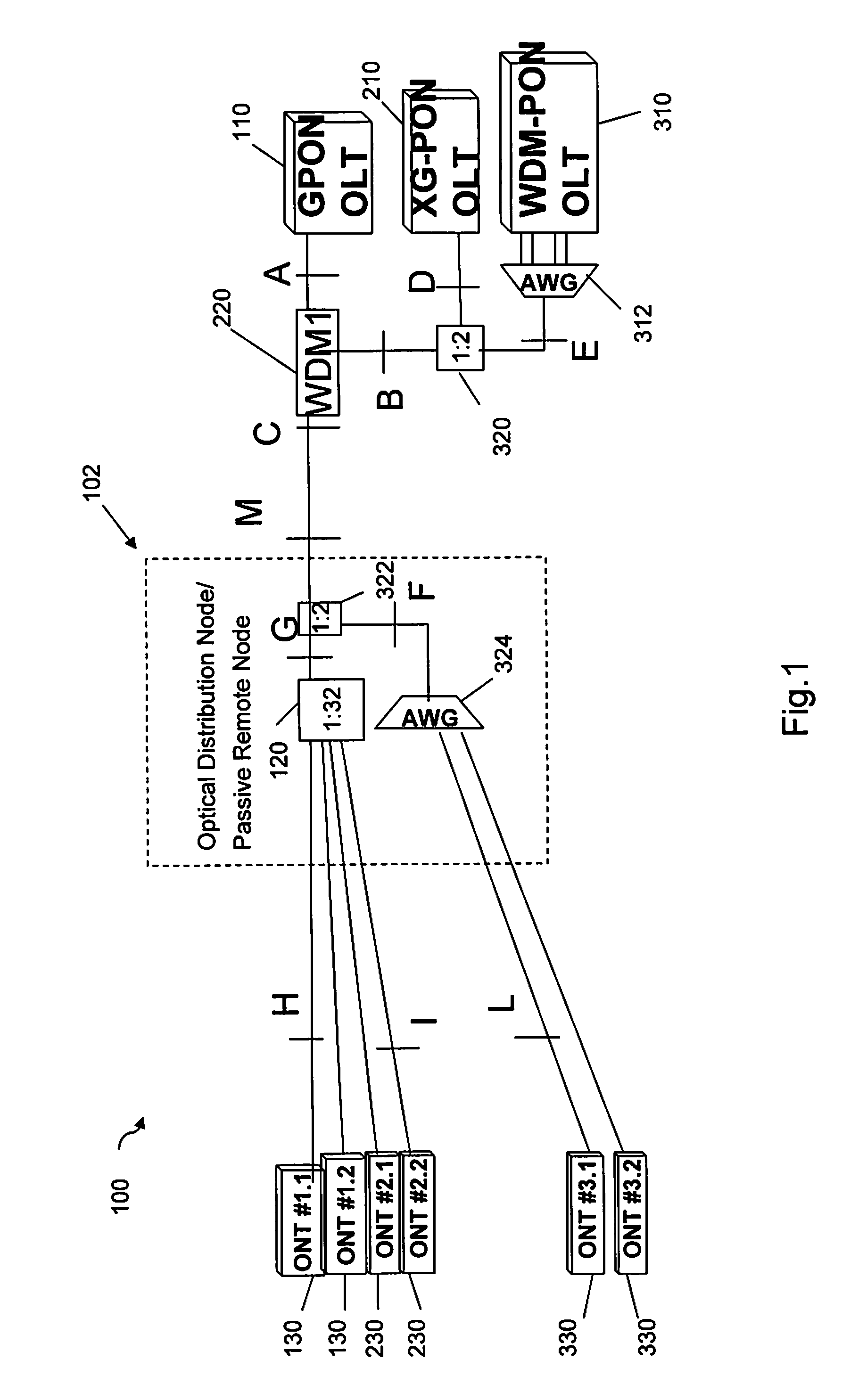
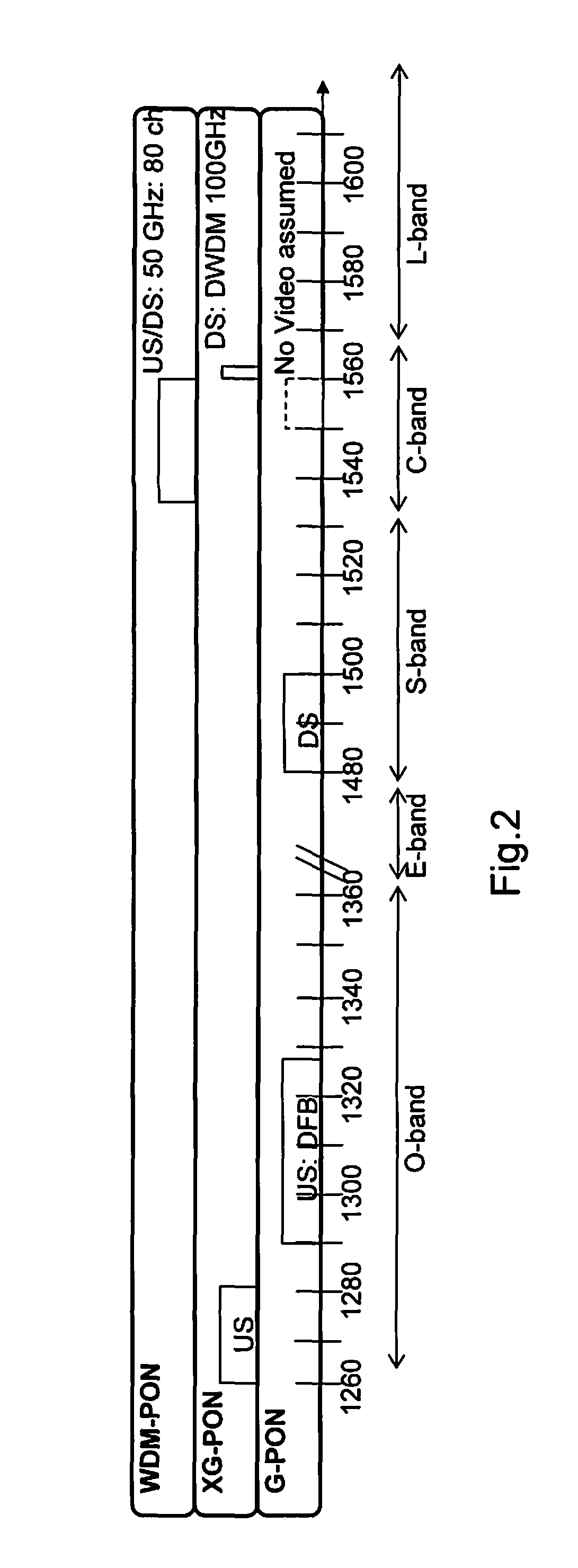
Method and network architecture for upgrading legacy passive optical network to wavelength division multiplexing passive optical network based next-generation passive optical network
InactiveUS20100054740A1Increase the number ofExpansion of bandwidthTime-division optical multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsNetwork terminationNetwork architecture
The present invention discloses a network architecture for upgrading a legacy time division multiplexing-passive optical network (TDM-PON) to a wavelength division multiplexing-passive optical network (WDM-PON) based next-generation passive optical network (next-generation PON), wherein the legacy TDM-PON comprises: a central office (CO) having a first optical line termination (OLT); a remote node (RN) having a splitter; a single mode fiber (SMF) connecting the first OLT and the splitter; and a first group of one or more optical network terminations (ONTs) being connected to the splitter by a first group of one or more distribution fibers, and wherein the network architecture further comprises: in case that the next-generation PON is a WDM-PON, a first apparatus for combining and splitting wavelength bands being positioned between the SMF and the first OLT, in order to add a second OLT to be used for the WDM-PON within the CO or within another CO which is located in a position different from the CO, while sharing the SMF; a second apparatus for combining and splitting wavelength bands being positioned at a front terminal of the splitter; and an arrayed waveguide grating (AWG) being connected to the second apparatus for combining and splitting wavelength bands within the RN, and being connected to a second group of one or more ONTs by a second group of one or more distribution fibers within the RN or within another RN which is located in a position different from the RN.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
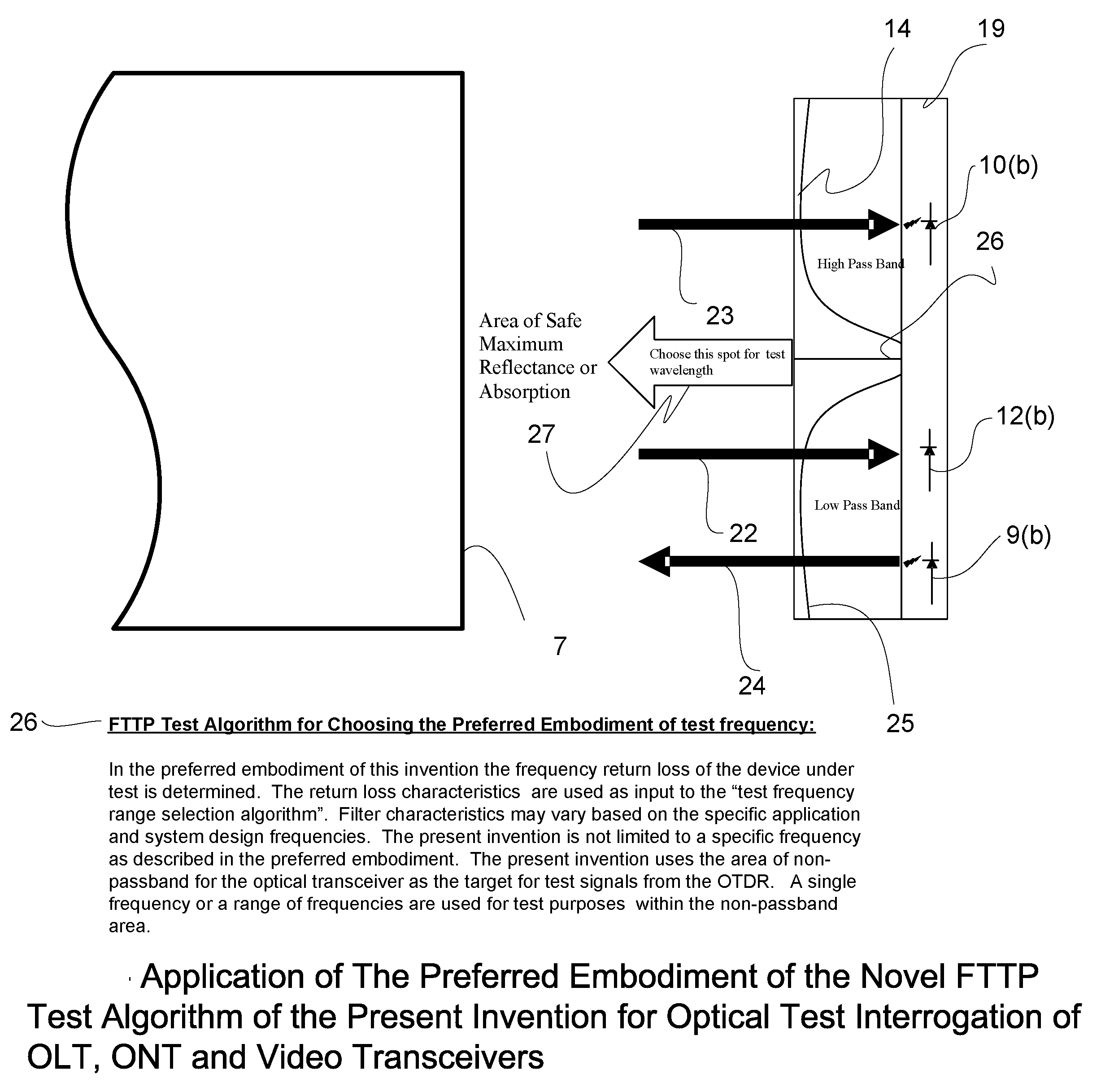
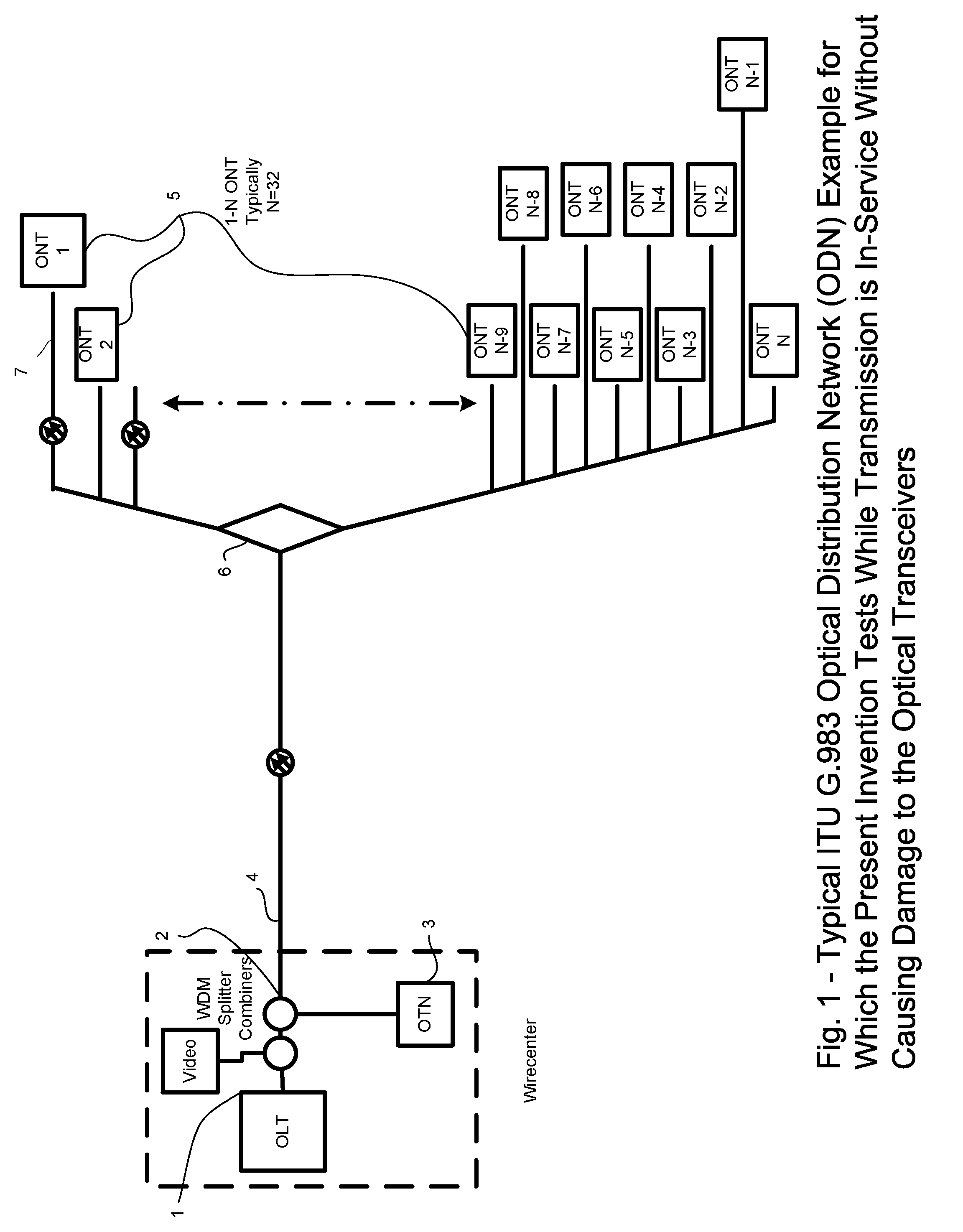
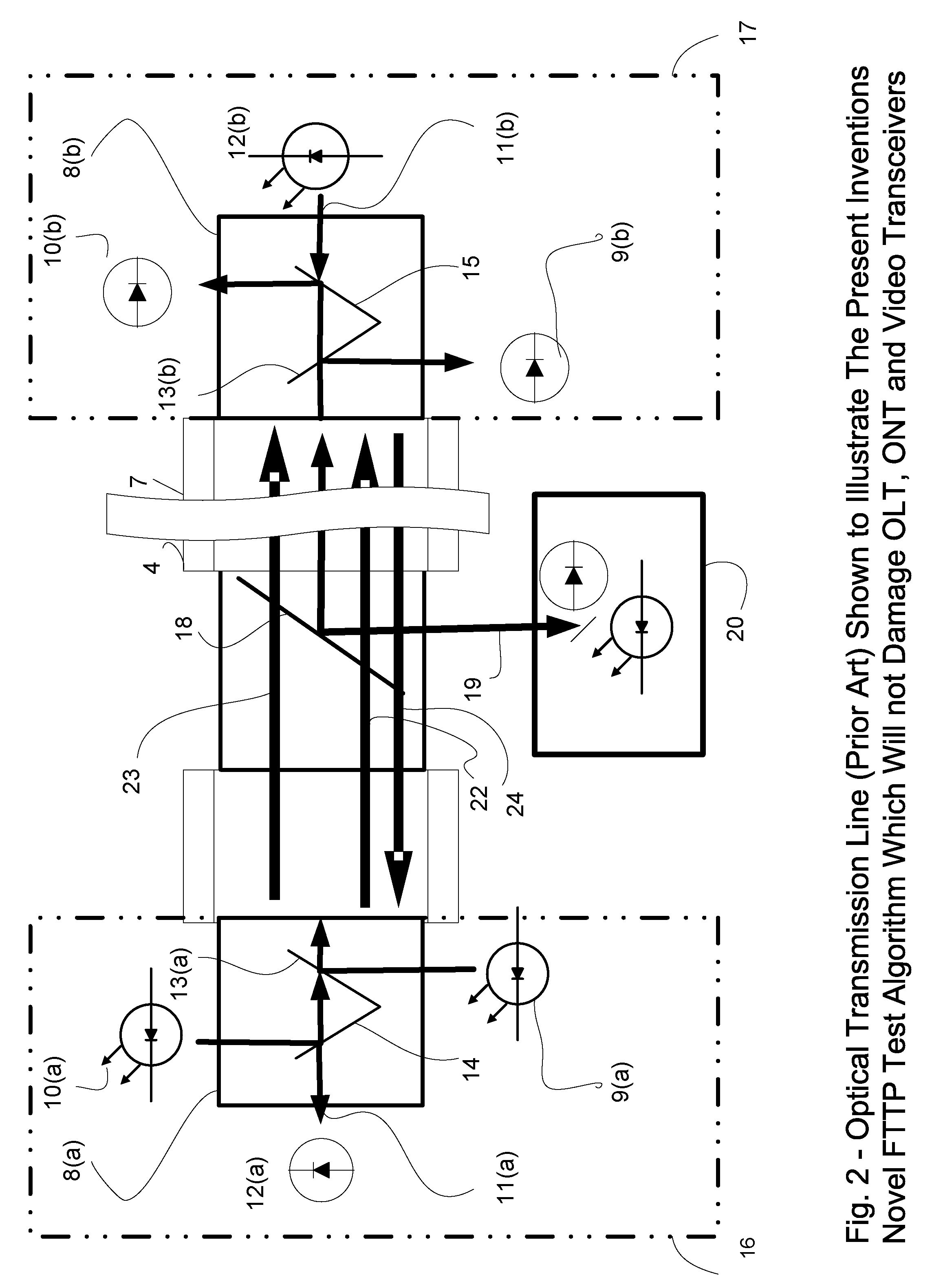
Novel Algorithm, Method and apparatus for In-Service Testing of Passive Optical Networks (PON) and Fiber to the Premise (FTTP) Networks
InactiveUS20060007426A1Test accurateMaterial analysis by optical meansElectromagnetic transmissionNetwork terminationTransceiver
Locating a fault of an optical transmission line in a system which performs bidirectional optical communication between a wire center Optical Line Terminal (OLT) and plural subscriber devices, Optical Network Terminal (ONT). In this ITU defined topology, a feeder extending from the OLT is branched by a passive (non powered) splitter / coupler device into plural legs each connected to the ONT devices. The present invention encompasses a novel test apparatus and technique for fault location on Passive Optical Networks (PON) and / or Fiber of the premise Networks (FTTP), encompassing APON, BPON and EPON allowing non-service interruptive test, without damage to the ONT or OLT transceivers. The invention provides service providers the ability to locate a fault occurring on an optical transmission line while the system is actively performing bidirectional optical communication between a OLT / head-end device and plurality of ONT / subscriber devices.
Owner:WELLER WHITNEY TURREL
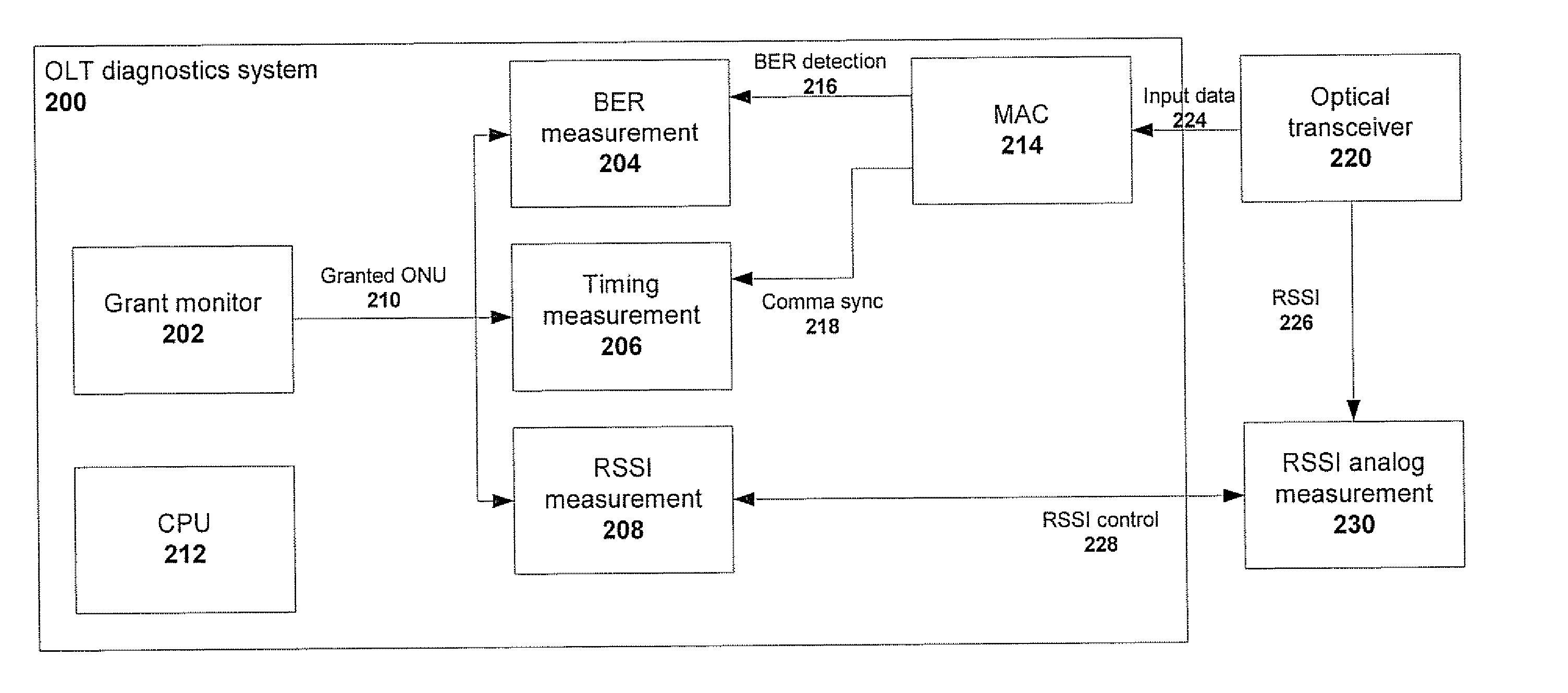
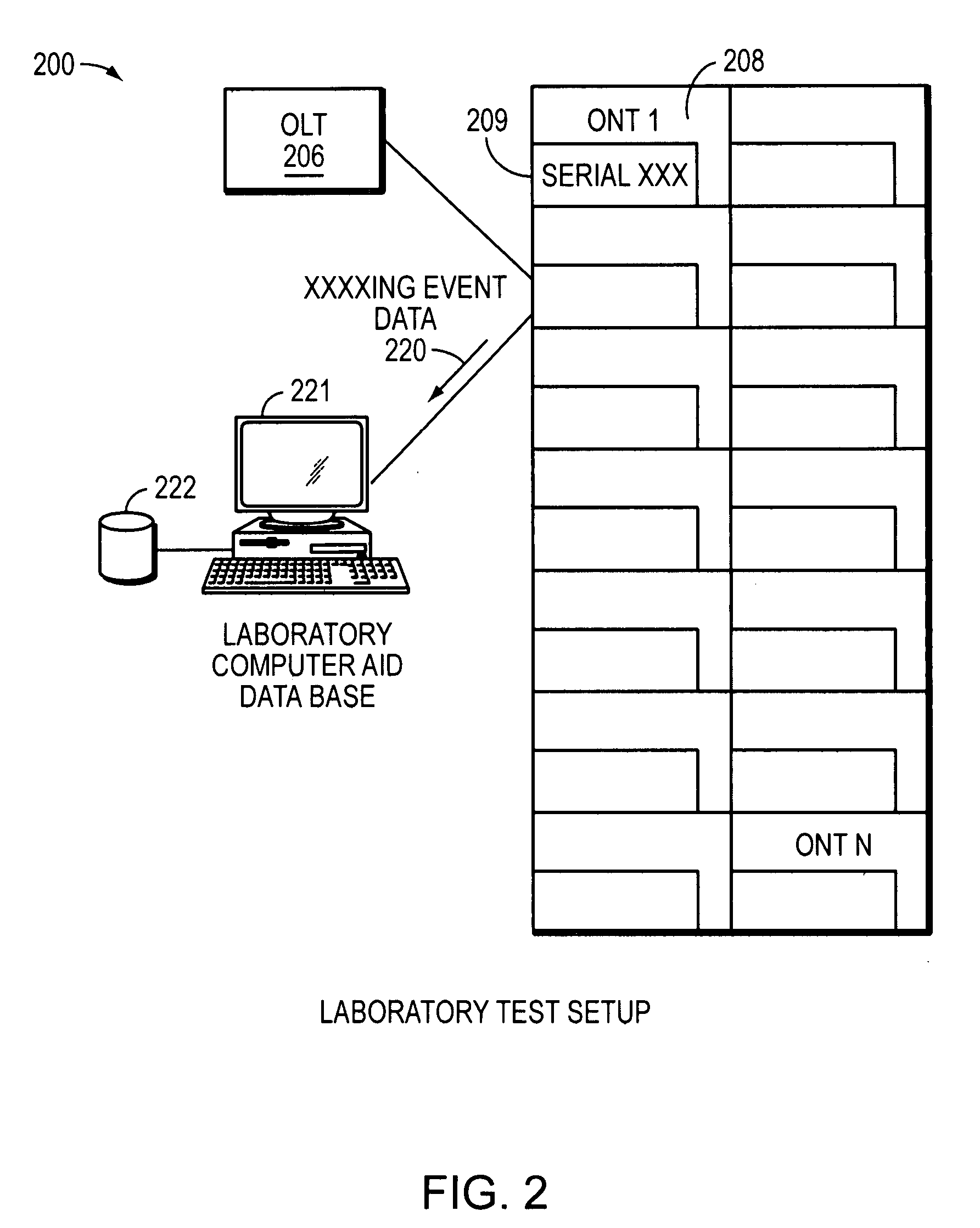
Method and system for passive optical network diagnostics
ActiveUS20070140689A1Reduce operating expensesMultiplex system selection arrangementsTransmission monitoringDigital dataProcessing element
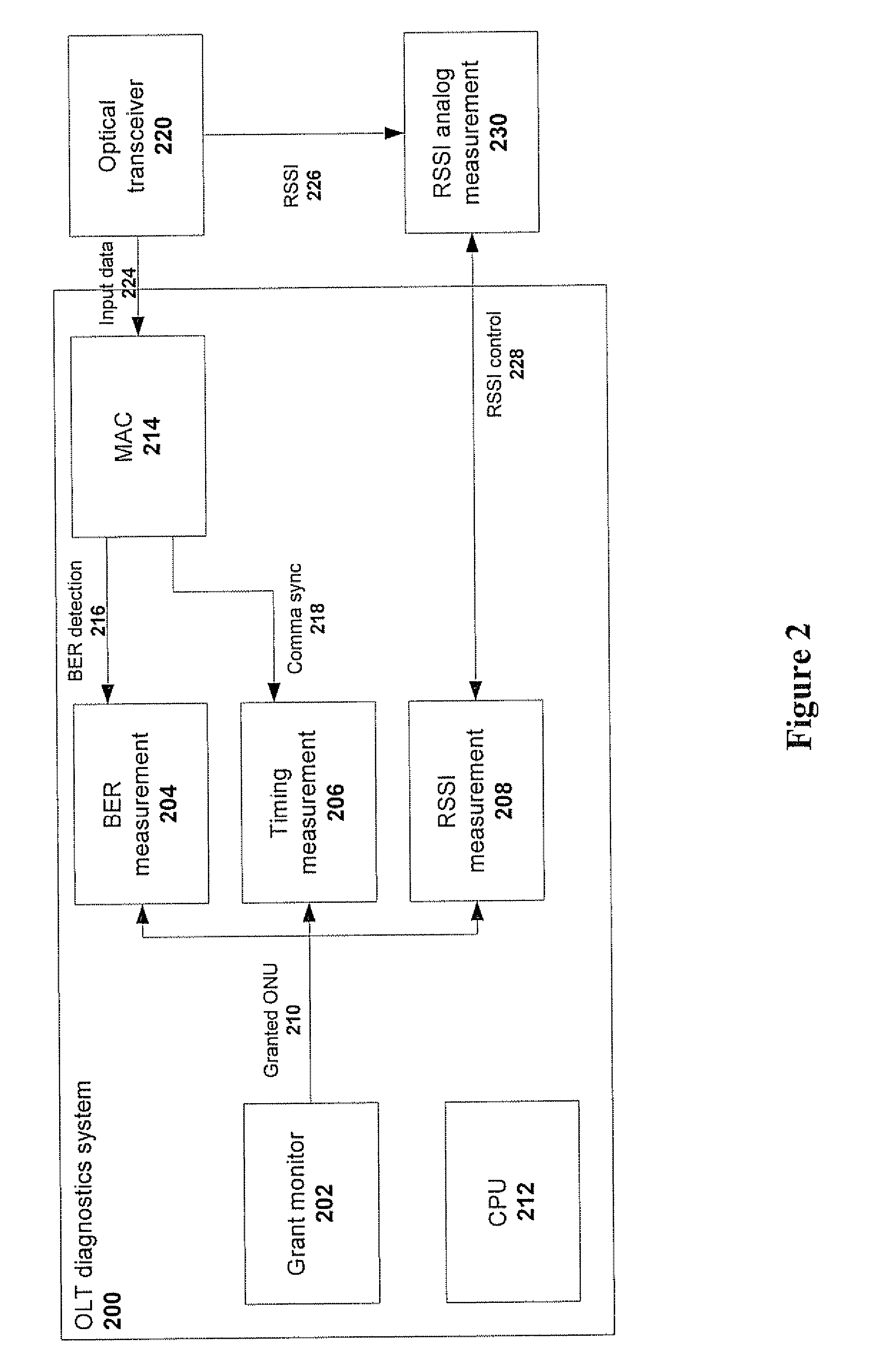
A method and system for identifying faults in a passive optical network (PON), The method comprises acquiring at an optical network terminal of the PON at least one parameter indicative of at least one malfunction in at least one optical network unit of the PON, and identifying each malfunction from the at least one parameter The parameters measured include, for each ONU, laser power, sync-lock and -unlock time and bit error rates. The information at the OLT is acquired remotely and in digital form, without use of any physical probing of any point or element in the PON. The system includes a temporal measurement module and a power laser measurement module coupled to a central processing unit that can extract fault information from digital data processed in the two modules.
Owner:MICROSEMI ISRAEL STORAGE SOLUTIONS LTD
Mine mobile communication system
InactiveCN101790179AImprove anti-interference abilityStrong emergency communication capabilitiesMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpatial transmit diversityNetwork terminationAccess network
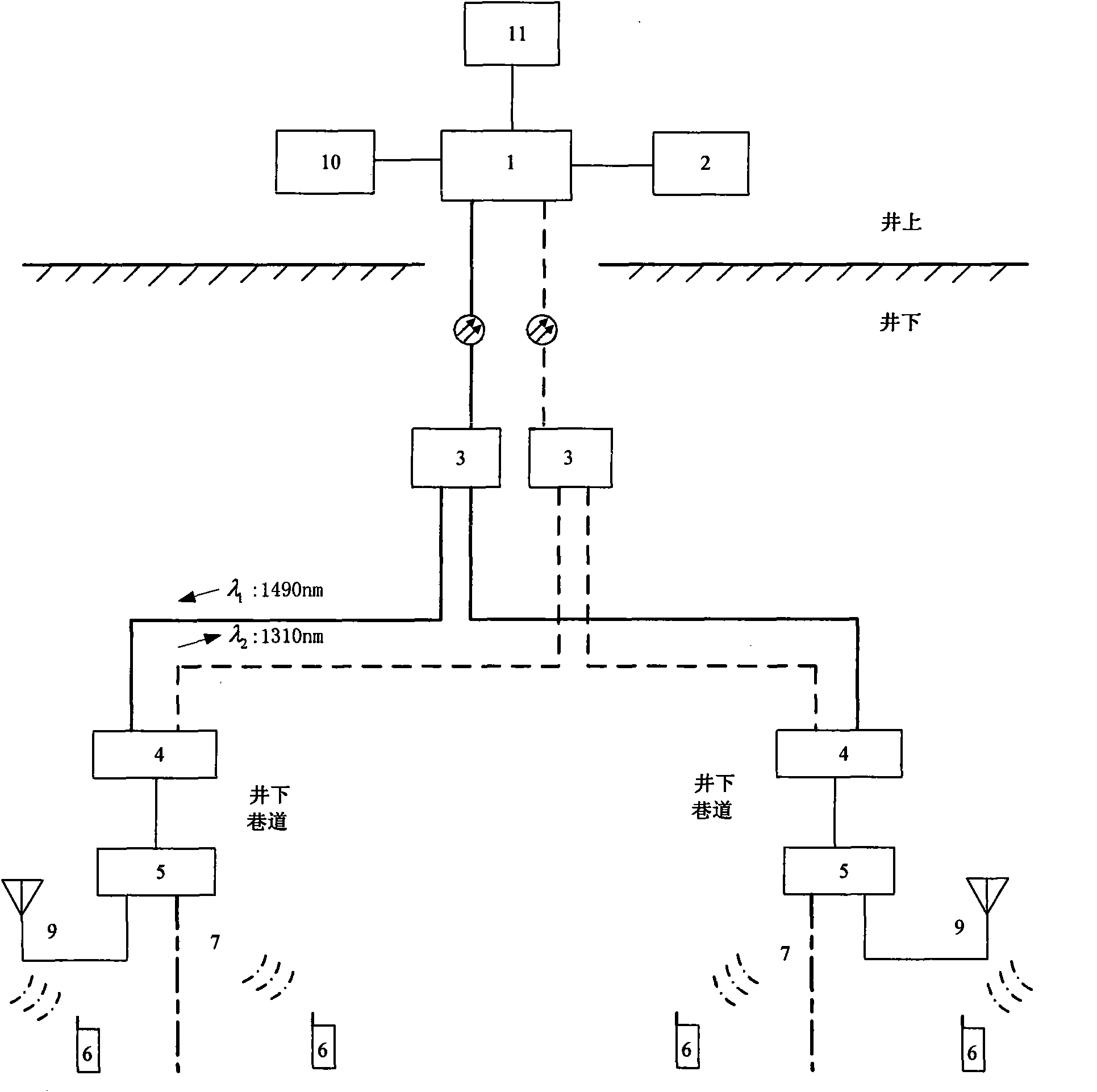
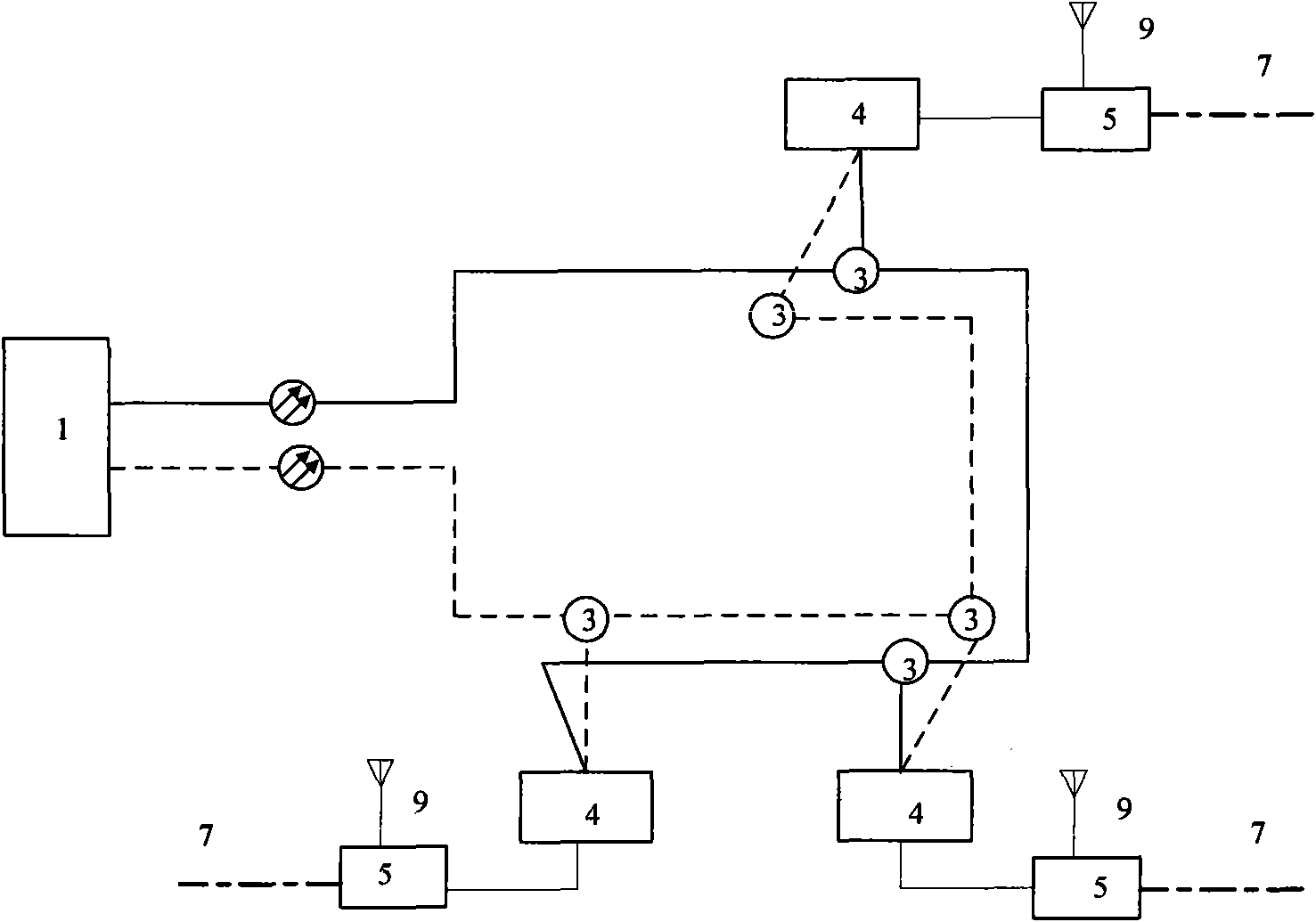
The invention discloses a mine mobile communication system, which consists of an Ethernet passive optical network of a double-bus or double-loop structure, a wireless access network, a control system and an explosion-proof mobile station. The system comprises an optical link terminal, a base station controller, a ground base station, office-end equipment, passive optical splitters, explosion-proof optical network terminals, an underground explosion-proof base station, leakage antennae, base station antennae, distributed antennae and the explosion-proof mobile station, wherein the optical link terminal is connected with the ground base station and the base station controller; the explosion-proof optical network terminals are connected with the underground explosion-proof base station; the underground explosion-proof base station is connected with the leakage antennae, the base station antennae and the distributed antennae; and the explosion-proof mobile station is connected with the underground explosion-proof base station and the ground base station through a wireless interface. The mine mobile communication system has the characteristics of simple structure, flexible deployment, convenient maintenance, relatively lower cost, strong disaster resistance and anti-jamming capacity, capability of eliminating dead zones in communication and meeting requirements on a specific service environment and security for mining, and suitability for underground mobile communication in a coal mine.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
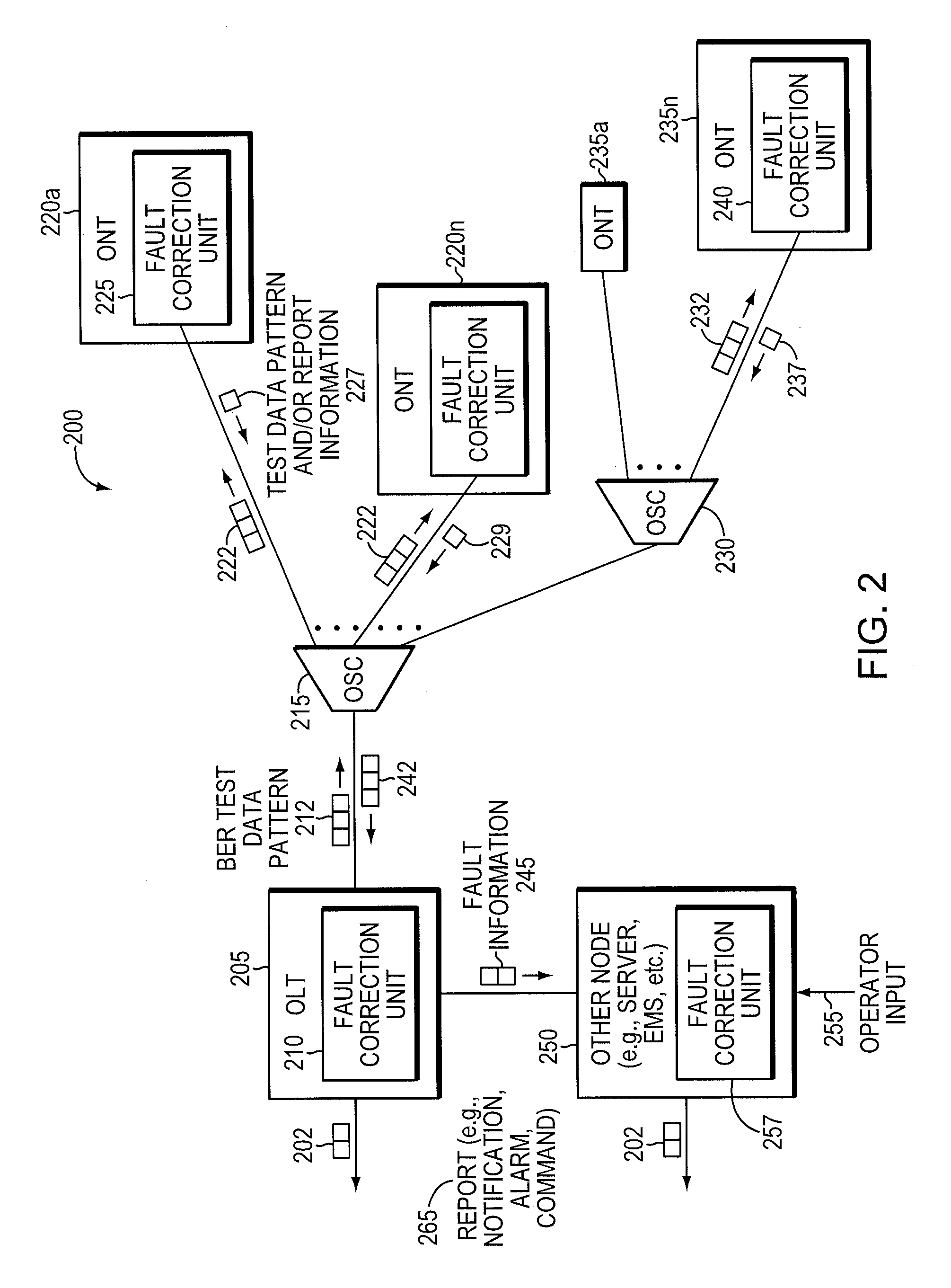
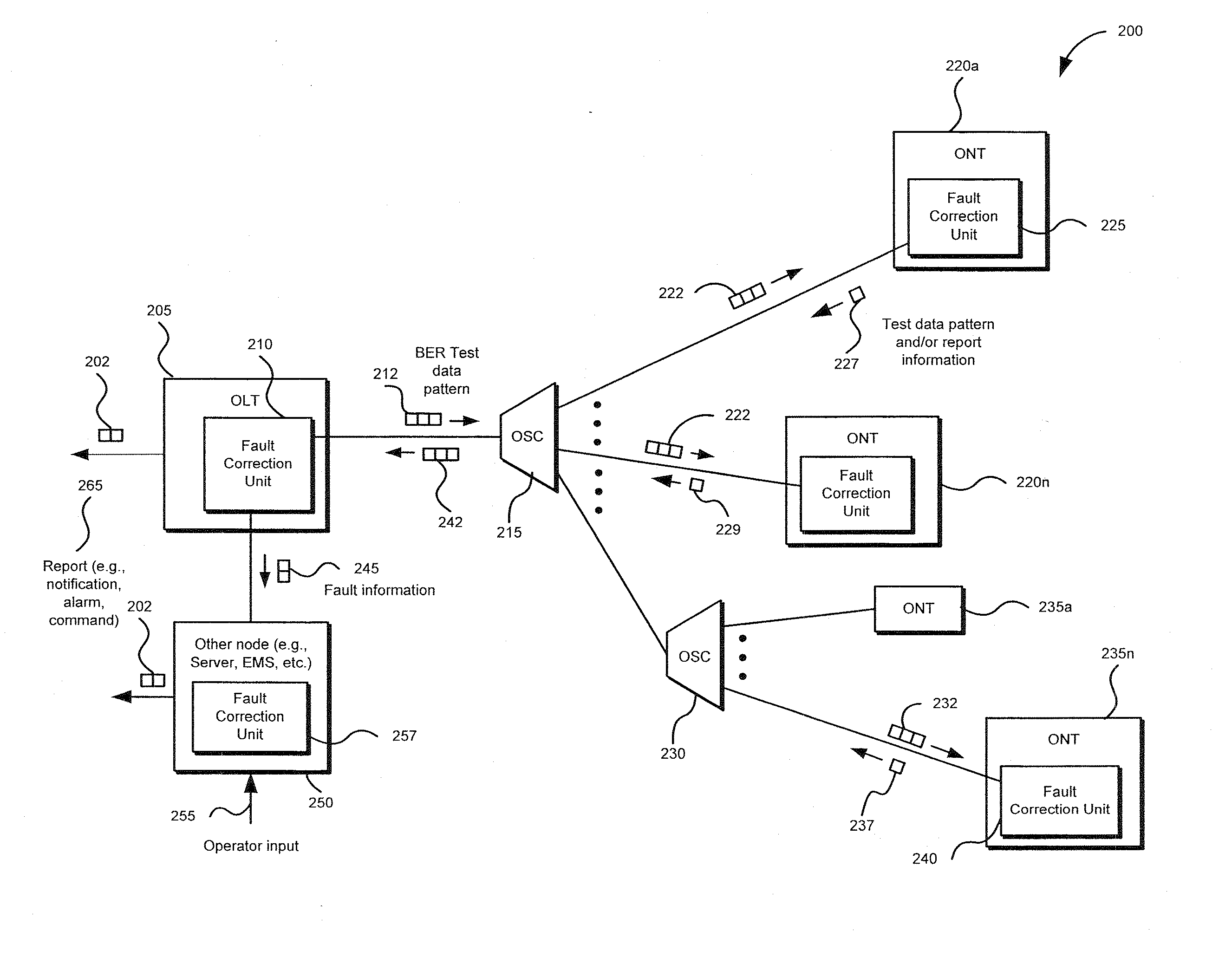
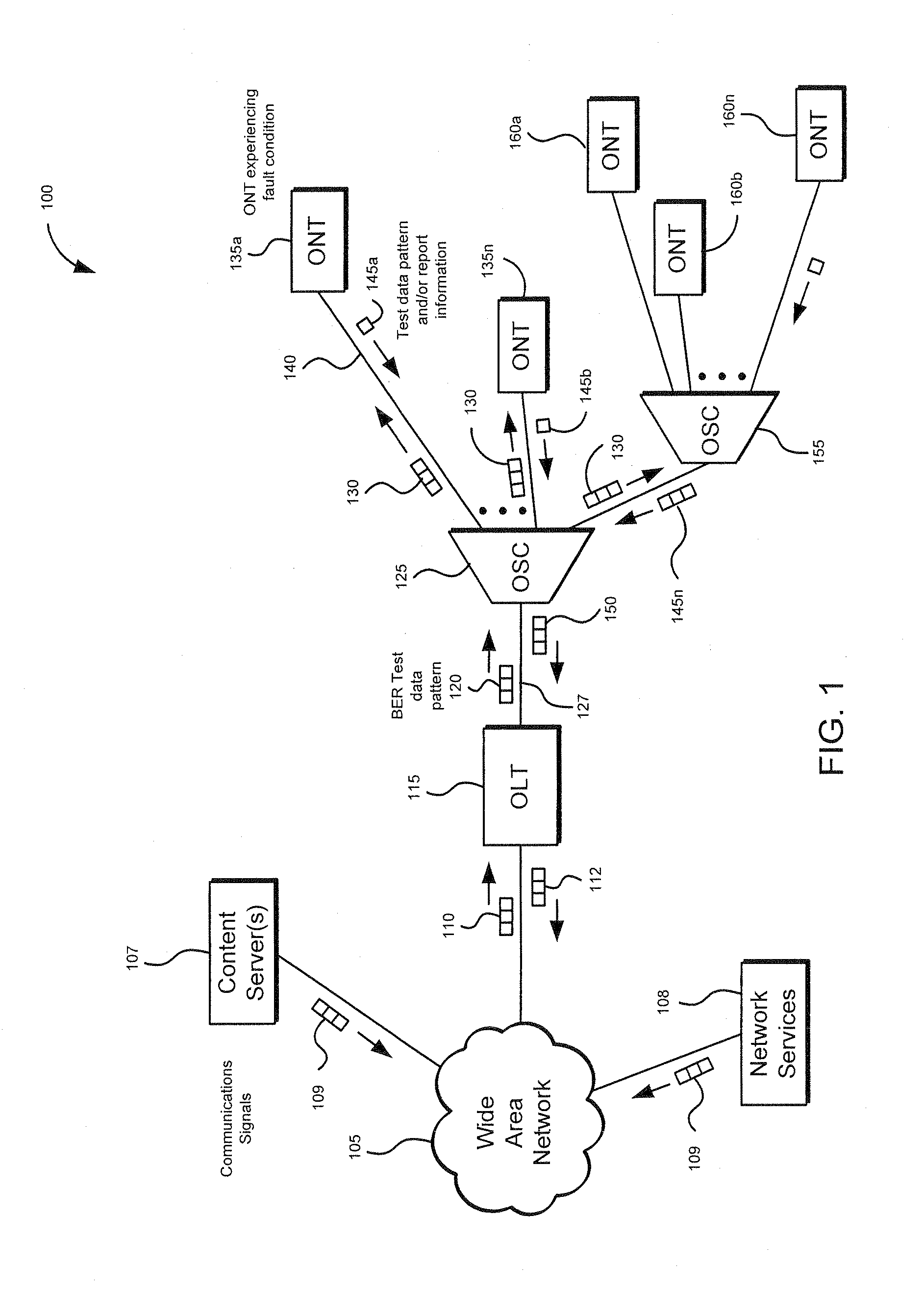
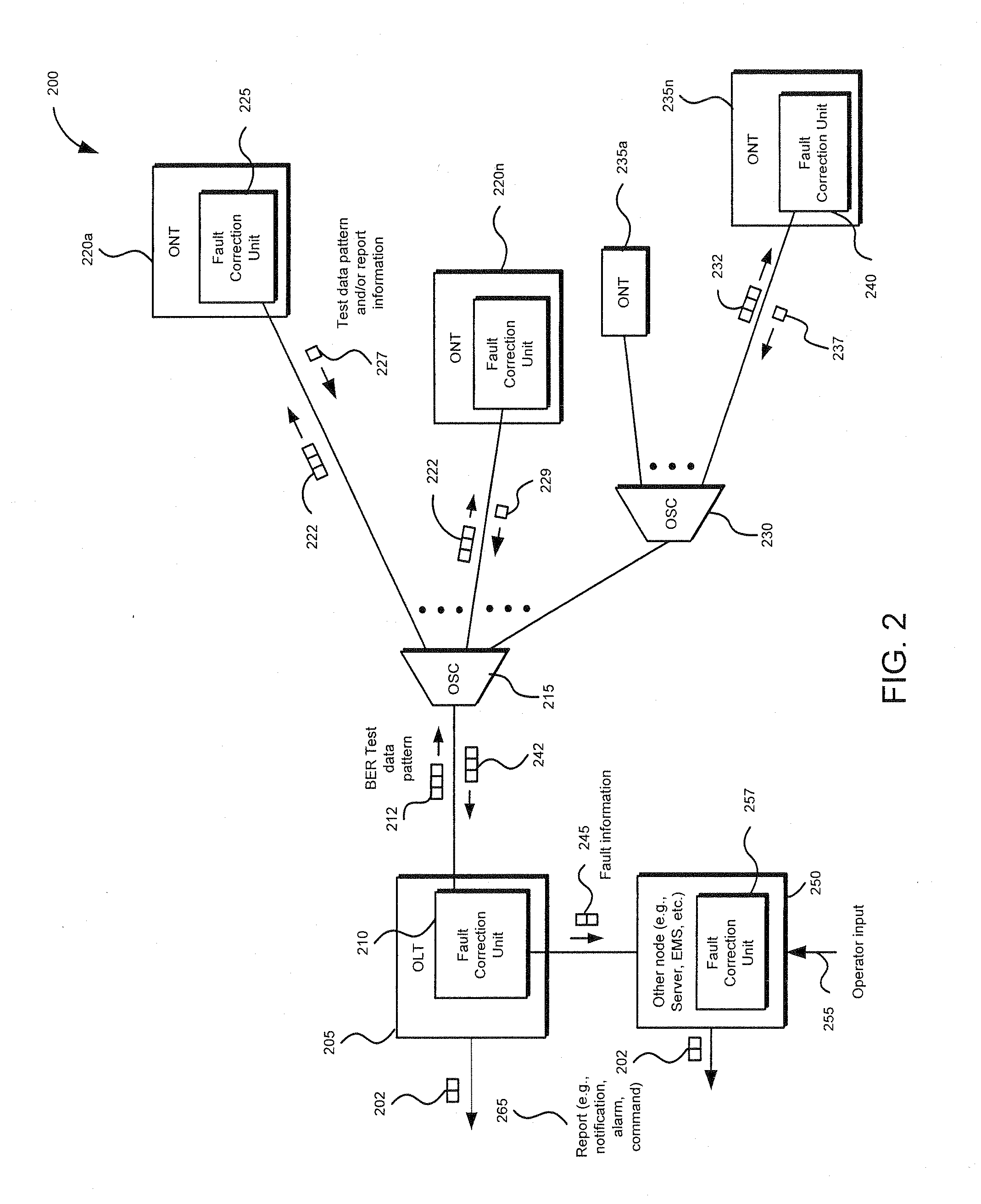
Method and apparatus for correcting faults in a passive optical network
ActiveUS20100074614A1Transmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsEngineeringOptical communication
Component malfunctions in passive optical networks (PON) can increase bit error rates and decrease signal-to-noise ratio of communications signals. These faults may cause the receivers of the signals, either the optical line terminal (OLT) or optical network terminals (ONTs), to experience intermittent faults and / or may result in misinterpreted commands that disrupt other ONT's communication, resulting in a rogue ONT condition. Existing PON protocol detection methods may not detect these types of malfunctions. An embodiment of the present invention identifies faults in a PON by transmitting a test series of data patterns via an optical communications path from a first optical network node to a second optical network node. The test series is compared to an expected series of data patterns. An error rate may be calculated as a function of the differences between the test series and expected series. The error rate may be reported to identify faults in the PON. Through use of the embodiment, network faults can be identified and optionally automatically corrected, saving a network service provider from expending technician time and maintaining an operating state of the network.
Owner:TELLABS PETALUMA
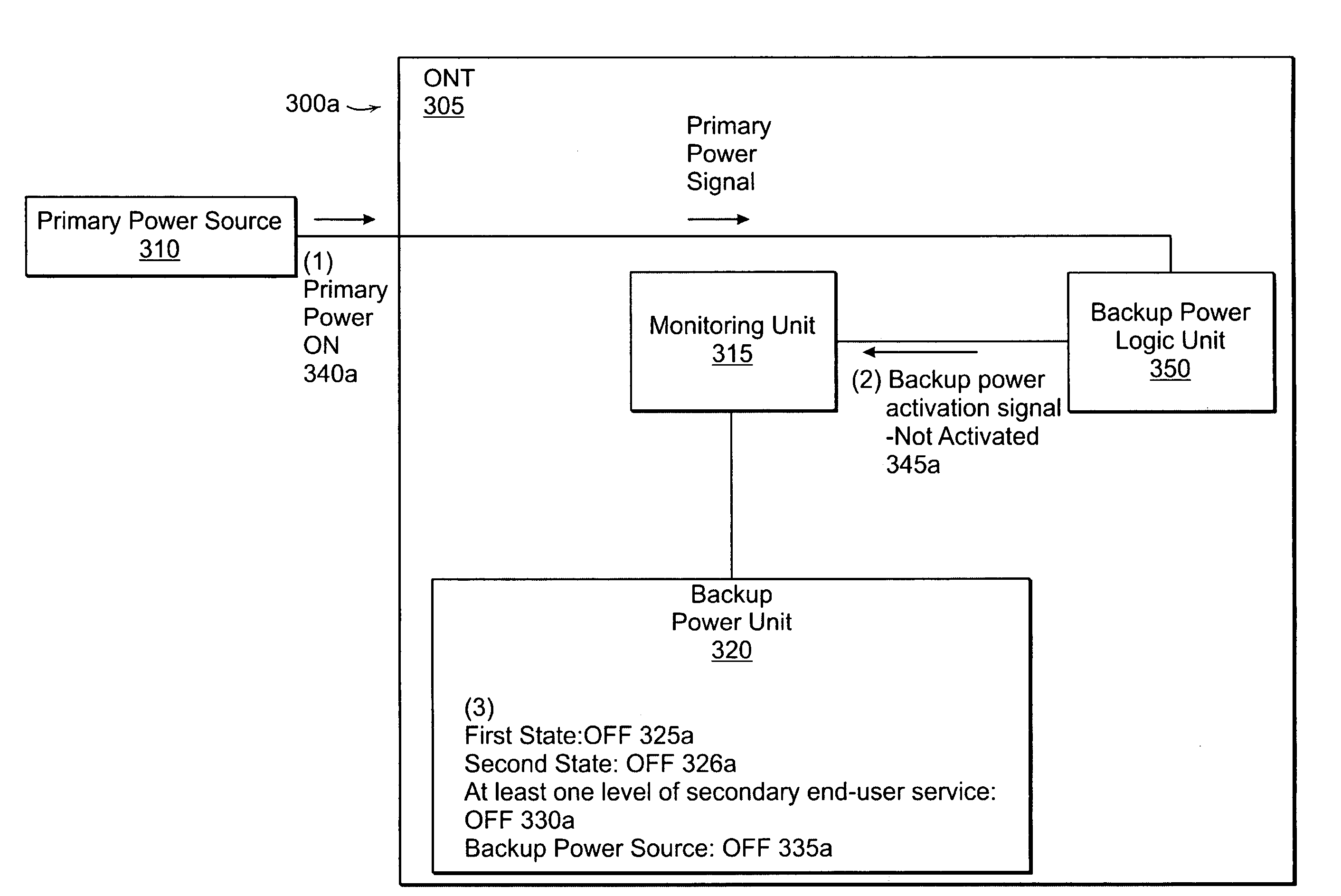
Method and apparatus for providing on-demand backup power for an optical network terminal
InactiveUS20080195881A1Complete banking machinesMultiplex system selection arrangementsElectrical batteryStandby power
There is demand in the marketplace for smaller optical network devices, such as Optical Network Terminals (ONTs). As a result of decreasing the ONT's size, the size of the backup power source, such as the batteries that power the ONT during periods of back-up power usage, may also have to be reduced. To extend energy usage of the backup power source, methods and corresponding apparatus for providing backup power for a network device are provided. An example method includes entering a first state of backup power in an event of a loss of primary power to an ONT, monitoring a state of a backup power activation signal enabled to be activated in the event of the loss of primary power to the ONT, and causing the ONT to enter a second state of backup power in response to the backup power activation signal being in an active state.
Owner:TELLABS VIENNA
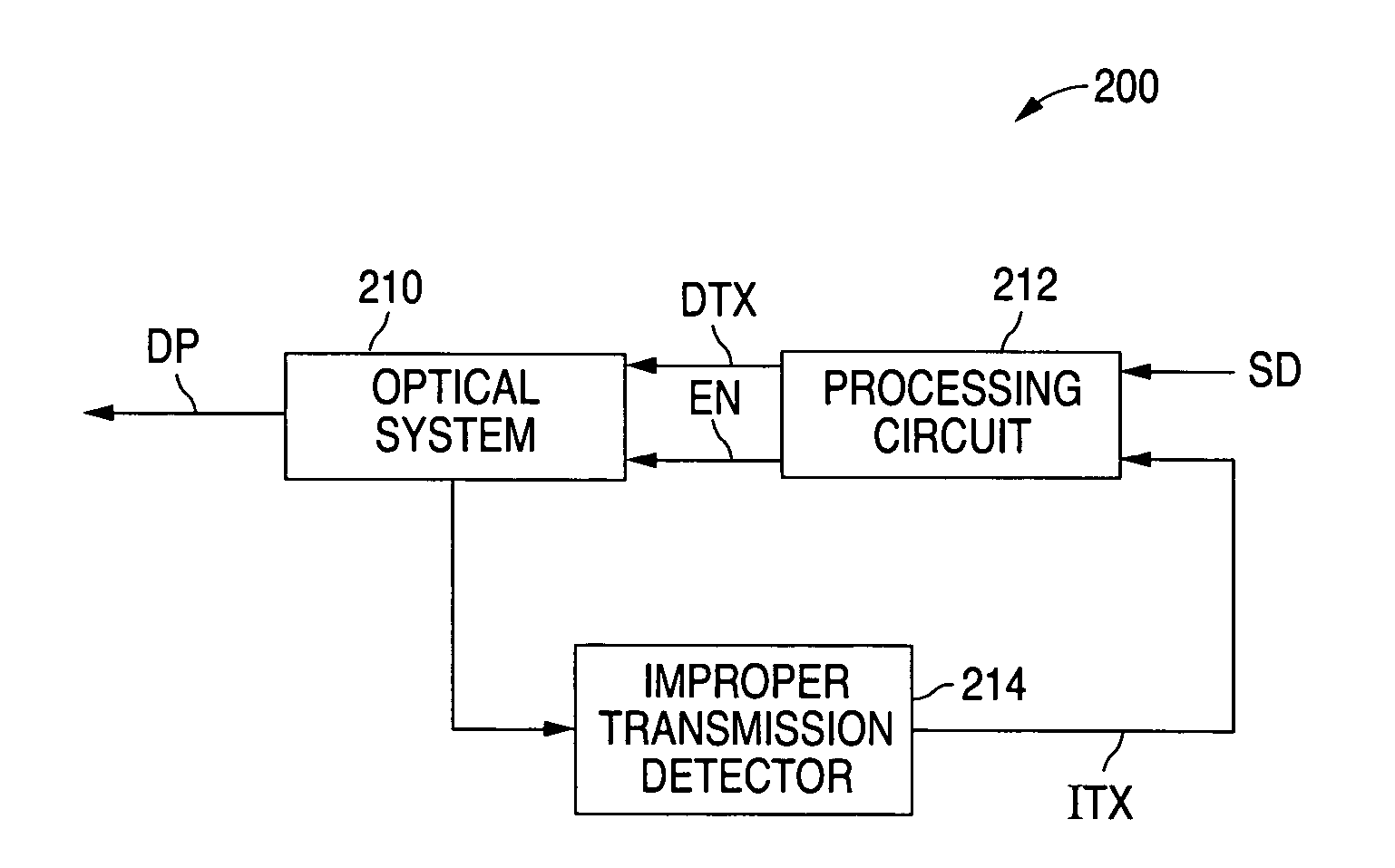
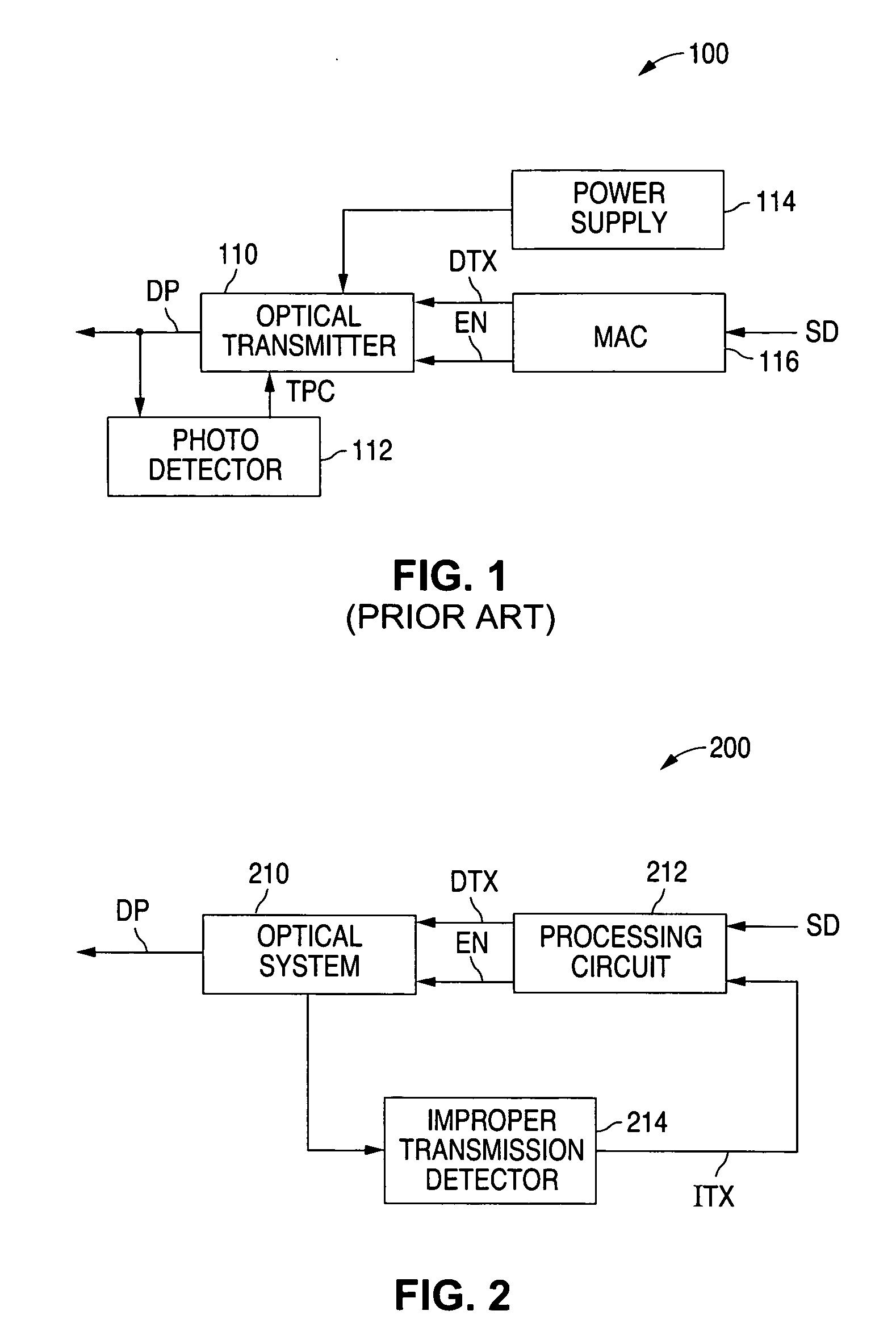
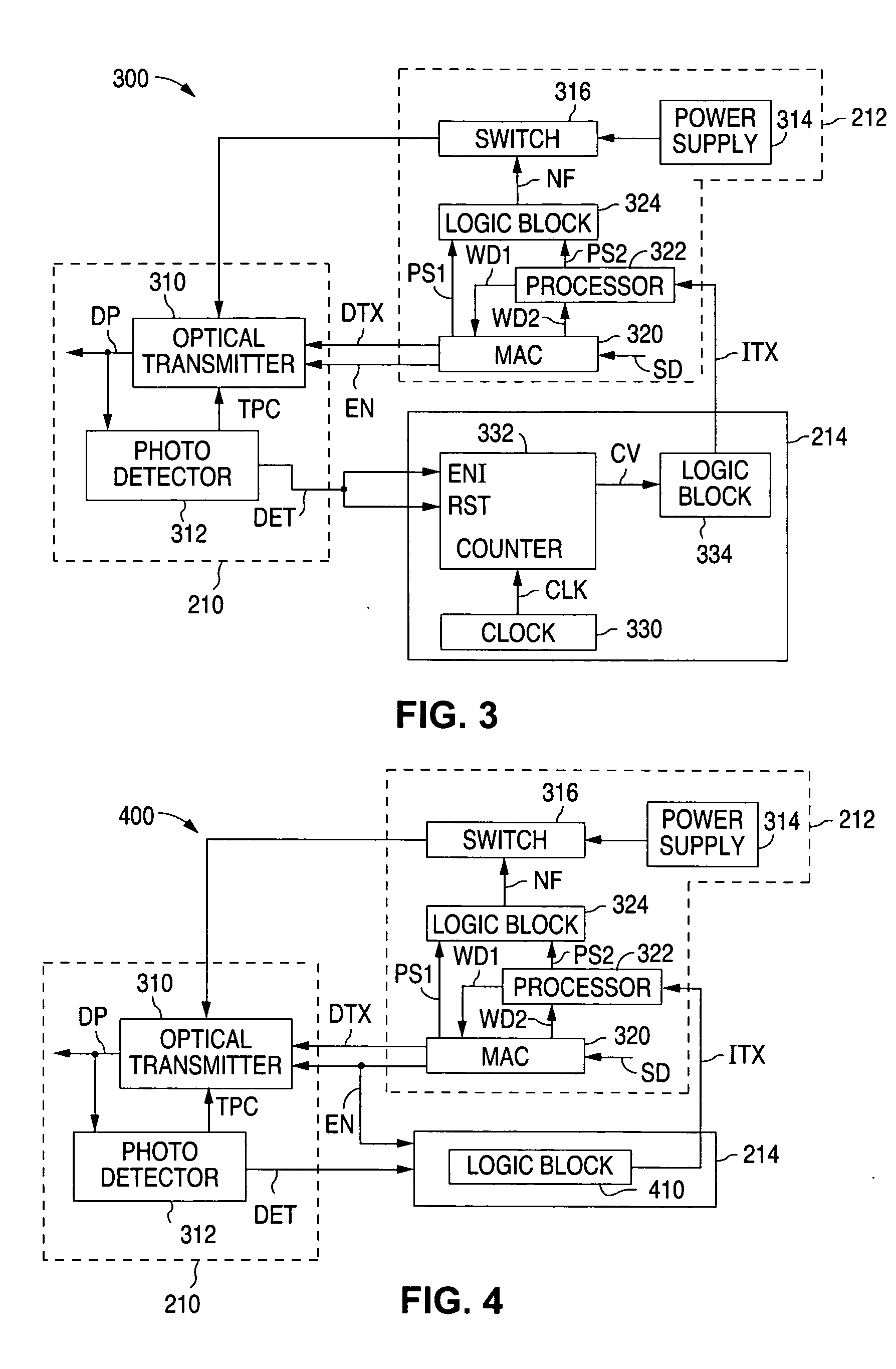
Optical network terminal with illegal transmission detection circuitry
ActiveUS20060198635A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringEngineeringOptical transmitter
An optical network terminal, which includes an optical transmitter, monitors the status of the optical transmitter, such as the output or the power consumption of the optical transmitter, to determine when the optical transmitter is illegally transmitting. When an illegal transmission is detected, the optical network terminal removes power from the optical transmitter.
Owner:TELLABS PETALUMA
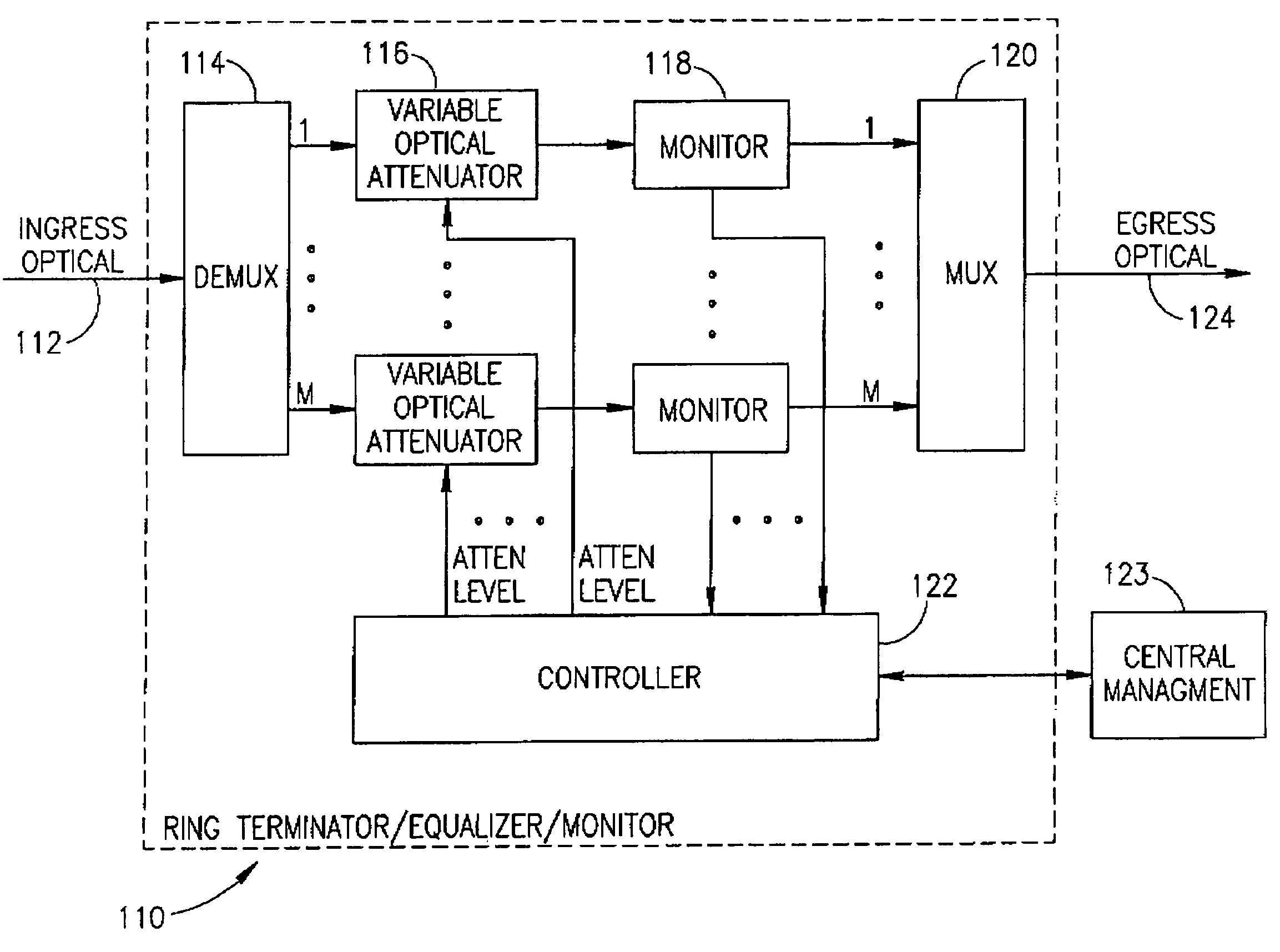
Optical network terminator
InactiveUS7106969B1Removing unwanted noiseEliminate the problemWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringAudio power amplifierFiber Bragg grating
An optical network terminator for terminating and reducing the accumulated noise in optical networks, particularly ring based networks. The terminator eliminates problems of noise accumulation from amplifier spontaneous emission (ASE), thermal noise, etc., while providing bi-directional communications in the optical network. The optical network may have any topology including ring, star, mesh, point-to-point, etc. In the case of an optical ring, the ring is broken and an optical terminator is placed in line therewith. The optical network terminator includes a filer such as an optical demultiplexer / multiplexer or Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG) based filter. Each individual wavelength of light is filtered and a multi-wavelength optical output is generated whereby the noise accumulation is removed. Each channel is adapted to only pass a band-limited signal around the center frequency corresponding to the wavelengths supported by the particular optical ring network. Channel equalization uses variable optical attenuators and monitors in line with each channel. Channels currently not in use may be disconnected from the ring remotely by setting the corresponding optical attenuator to a low enough level.
Owner:VENTURE LENDING & LEASING III
Method for mapping service flow to service transmission path and optical network terminal
ActiveCN101005445AGuarantee the QOS requirements of subdivided servicesMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksService flowProtocol processing
The method comprises: optical network terminal saves message features of different services, and after receiving service stream, maps the service stream matching the message feature into the appointed service transmission channel, or maps the service stream into the appointed service transmission channel and meanwhile re-labels the priority of the service stream, or re-labels the priority of service stream; according to the re-labeled priority, the optical network terminal maps the service stream into the service transmission channel. The optical network terminal thereof comprises: an optical network protocol processing module comprising a universal service stream mapping module and a service processing module.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and system for enabling diagnosing of faults in a passive optical network
InactiveUS20090060496A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexFiberInstability
In a passive optical network (PON), multiple optical network terminals (ONTS) transmit data to an optical line terminal (OLT) using a common optical wavelength and fiber optical media. Various components of the PON, including the OLT and ONT(s), can malfunction. Centralized techniques for maintaining or diagnosing fault conditions may be ineffective in large networks or in relatively small networks because of vast amounts of information and limited storage capacity for the information. Thus, fault conditions may occur and not be diagnosed due to lost or overwritten information. Therefore, a distributed approach based on information related to ranging of ONTs within the PON is employed in an example embodiment of the invention. This distributed approach can improve monitoring and diagnosis of fault conditions that may lead to instability of the PON.
Owner:TELLABS VIENNA
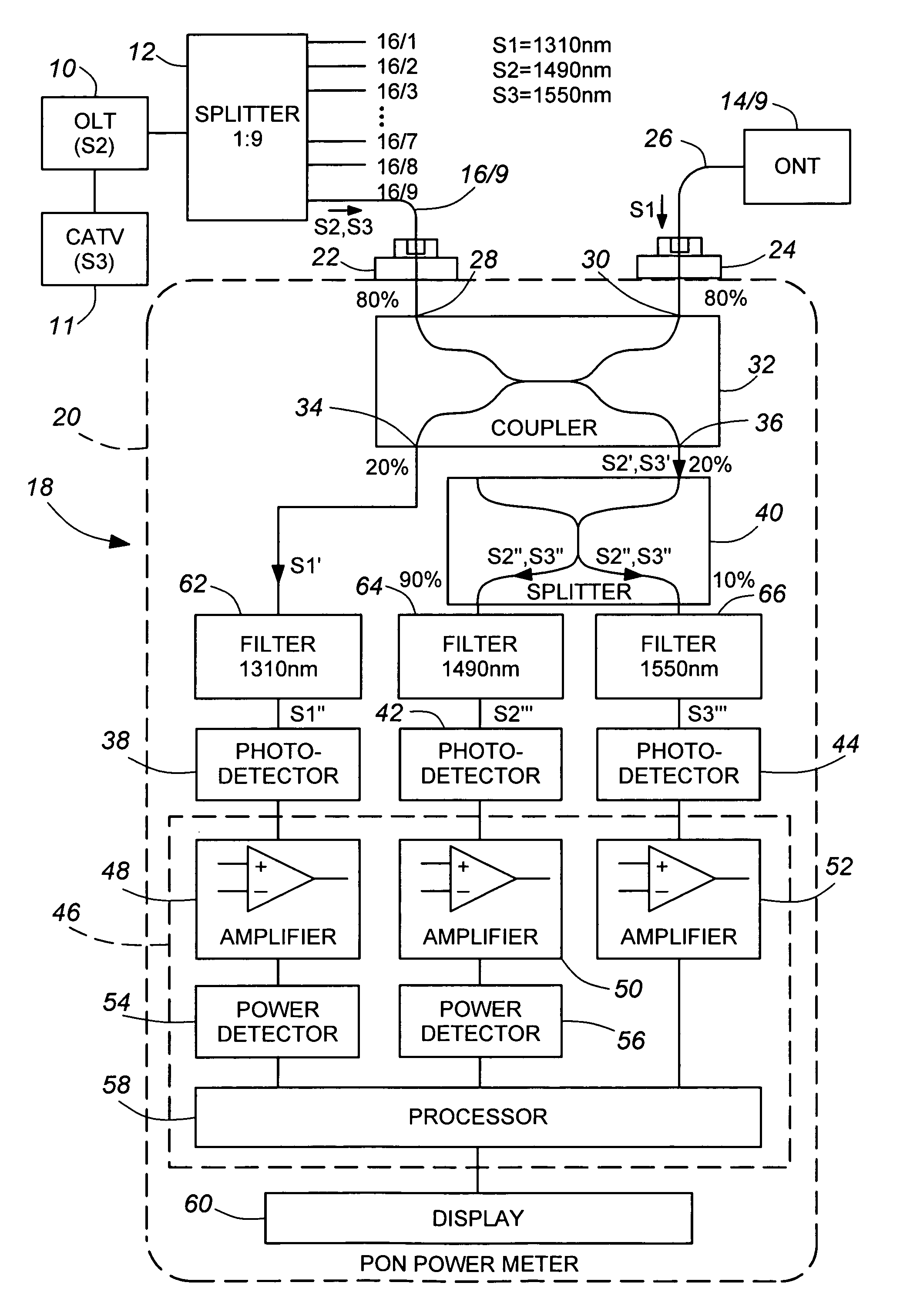
Method and apparatus for testing optical networks
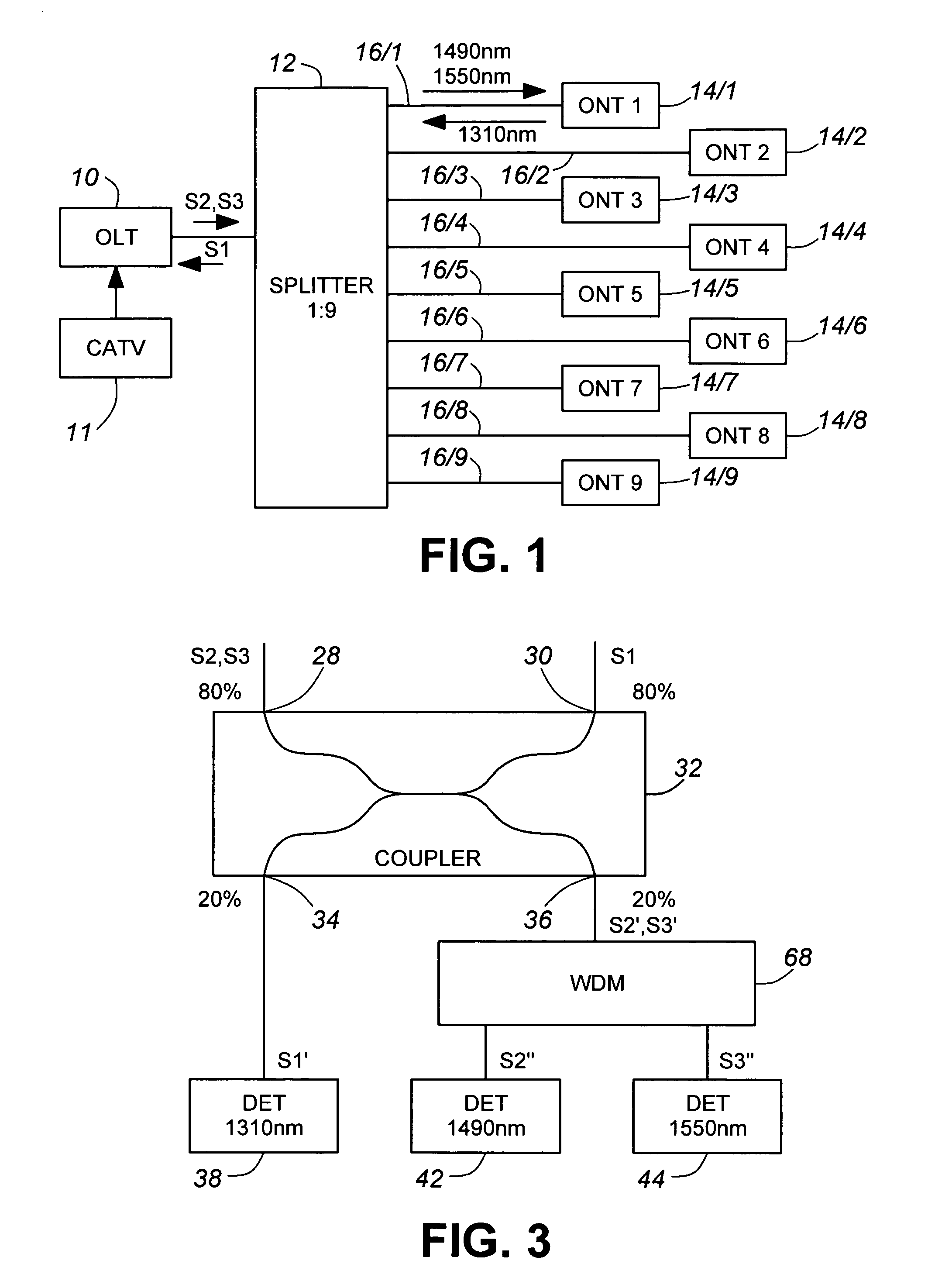
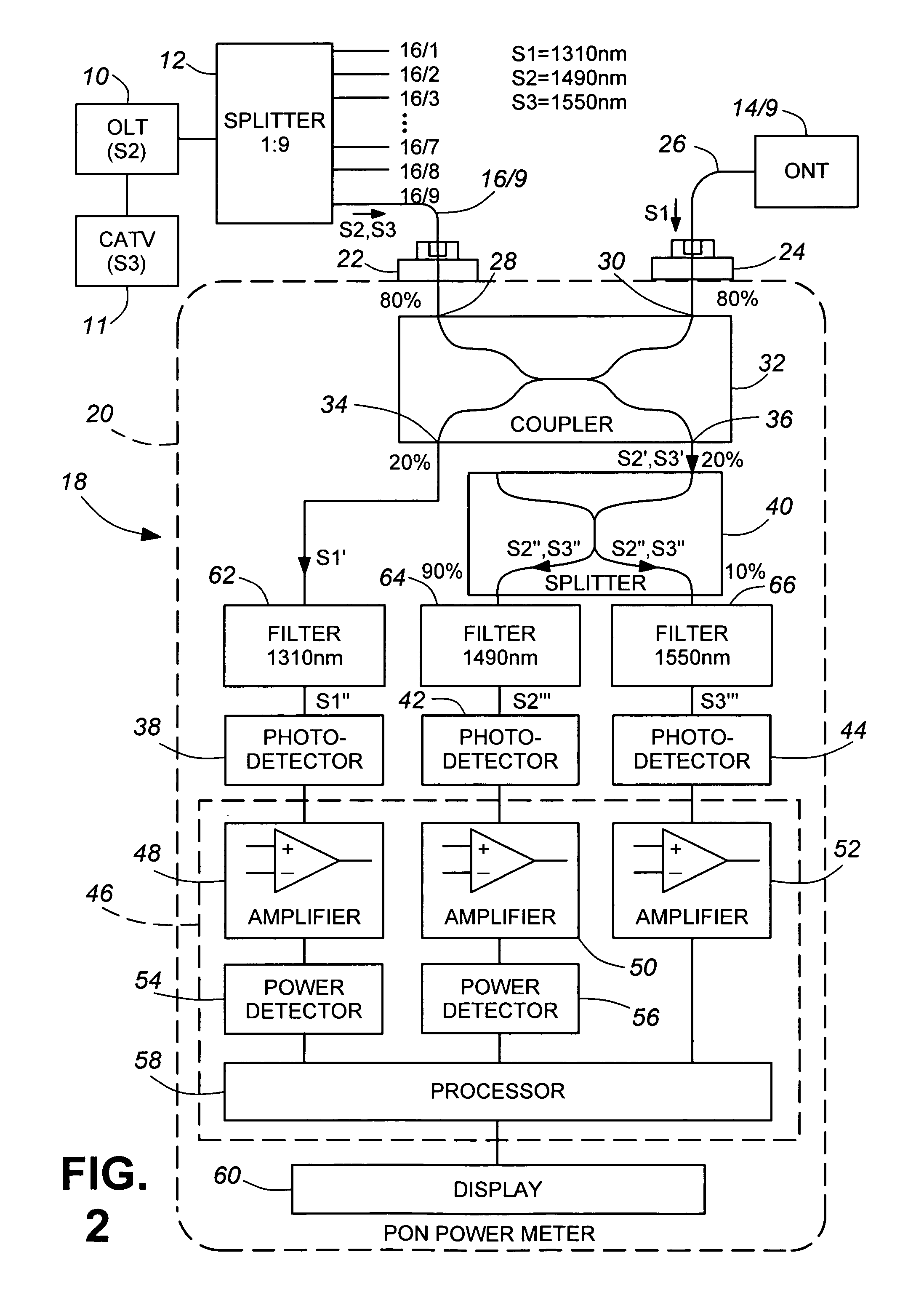
InactiveUS7187861B2Reduce disadvantagesMultiplex system selection arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansTelecommunicationsOptical line termination
An instrument for measuring bidirectional optical signals propagating in an optical transmission path between elements one of which will not transmit if continuity of the transmission path is not maintained, for example a branch path between a central offices optical line terminal (OLT) and an end-user's optical network terminal (ONT), comprises first and second connector receptacles for connecting the instrument into the path, a 2×2 coupler (32) having first and second ports (28, 30) connected to the first and second connectors (22, 24), respectively, for completing the optical transmission path, a third port (36) for, outputting a portion of each optical signal received via the first port (28) and a fourth port (34) for outputting a portion of each optical signal received via the second port (30) Detectors (38, 42, 44) coupled to the third and fourth ports convert the optical signal portions into corresponding electrical signals, which are processed to provide the desired measurements. The measurement results may be displayed by a suitable display unit (60) Where the ÖLT transmits signals at two different wavelengths, the instrument may separate parts of the corresponding optical signal portion according to wavelength and process them separately.
Owner:EXFO ELECTRO OPTICAL ENG
Extendable loop-back type passive optical network and scheduling method and apparatus for the same
InactiveUS20070154217A1Low costMaintained and upgradedWavelength-division multiplex systemsTime-division multiplexLength waveOptical transmitter
Provided are extendable loop-back passive optical network (PON) and scheduling method and apparatus for the same. The loop-back type PON includes an OLT (optical line terminal) including a wavelength-tunable optical transmitter and a wavelength-locked optical receiver, and an RN (remote node) including an optical coupler / splitter, the optical coupler / splitter receiving optical signals from the wavelength-tunable optical transmitter and splitting the optical signals by wavelength so as to transmit the optical signals to corresponding ONTs (optical network terminals). Each of the ONTs transmits upstream data to the OLT using the same wavelength as the wavelength of the optical signal received from the OLT through the RN. Since the optical network makes use of the TDM and WDM communication schemes, the optical network can be maintained and upgraded at lower cost.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Optical network
InactiveUS20110158650A1Easy to useNetwork maintenanceWavelength-division multiplex systemsNetwork terminationAudio power amplifier
An optical network and a method of provisioning an optical network are described. The optical network includes a first passive optical network optical line terminal arranged to transmit a first optical signal at a first wavelength, coupled to a first port of a first optical filter arrangement, and a second passive optical network optical line terminal arranged to transmit a second optical signal at a second, different wavelength, coupled to a second port of the first optical filter arrangement. An optical coupler is connected between the second passive optical network line terminal and the second port of the first optical filter arrangement, for coupling a plurality of optical signals at a predetermined set of wavelengths from a third optical line terminal into the second port. A passive optical distribution node, for connection to a plurality of optical network terminations, is coupled to a third port of the first optical filter arrangement for distribution of optical signals between the optical line terminals and the plurality of optical network terminations. The first optical filter arrangement is arranged to pass optical signals at the first wavelength between the first port and the third port and to block optical signals at the second wavelength and the predetermined set of wavelengths between the first port and the third port, and the first optical filter arrangement is further arranged to pass optical signals at the second wavelength and the predetermined set of wavelengths between the second port and the third port and to block optical signals at the first wavelength between the second port and the third port. The second optical signal is at a faster rate than the first optical signal, and the second wavelength and the predetermined set of wavelengths are within an amplification band of a doped fibre amplifier.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
GPON OAM USING IEEE 802.1ag METHODOLOGY
ActiveUS20080279105A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionNetwork connectionEngineering
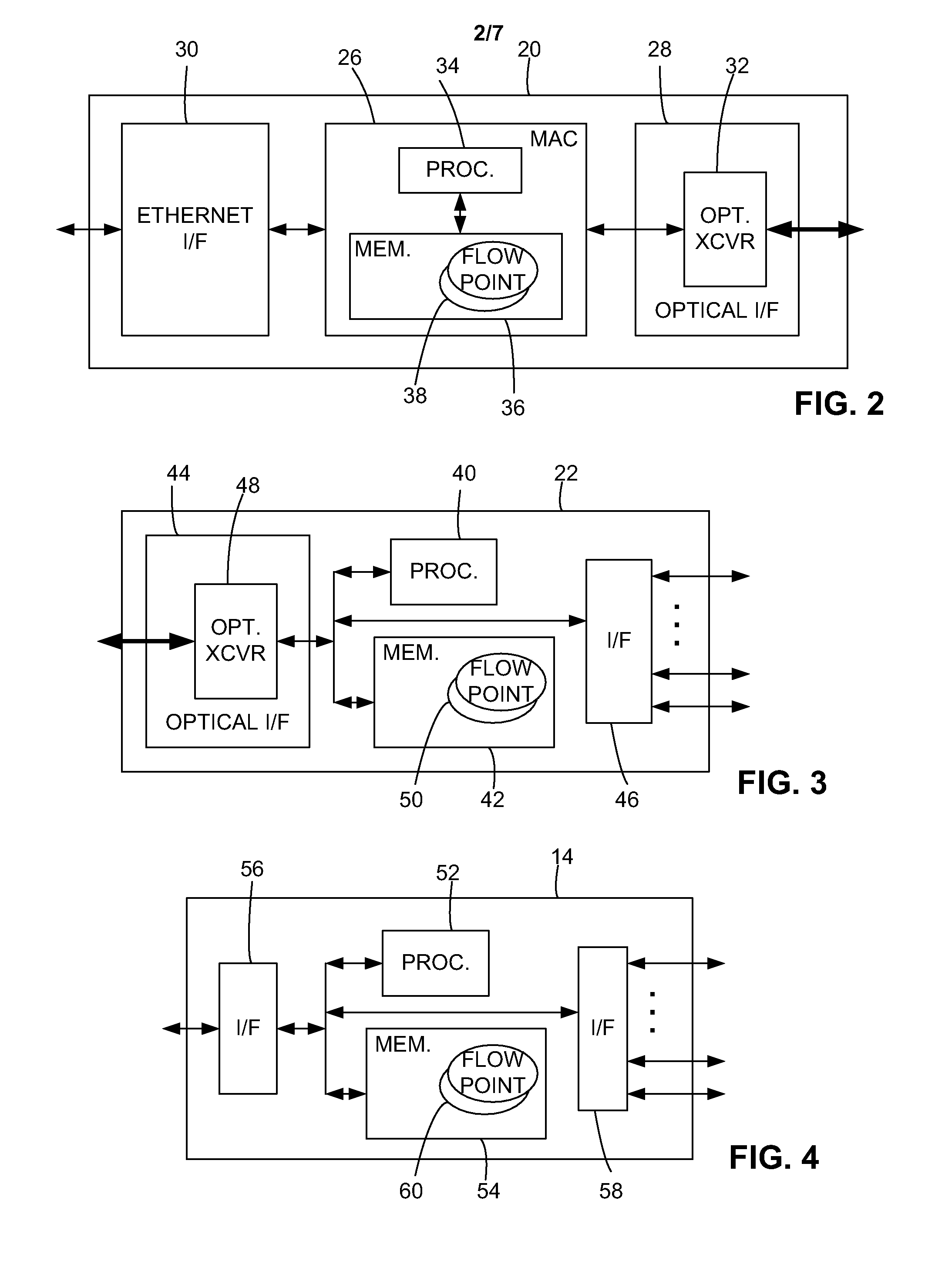
Operations, administration and management (OAM) functions in a passive optical network (PON) can be performed by providing a system of flow points (i.e., software entities), such as those along the lines of the Maintenance End Points (MEPs) and Maintenance Intermediate Points (MIPs) described in the IEEE 801.1ag specification, which communicate connectivity fault test messages with each other. The flow points can be provided in the Optical Line Terminal (OLT) and Optical Network Terminator (ONT). Alternatively or in addition, flow points can be provided in a subscriber gateway coupled to the ONT. The flow points issue test messages, to which other flow points can respond with information regarding the state of network connectivity.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
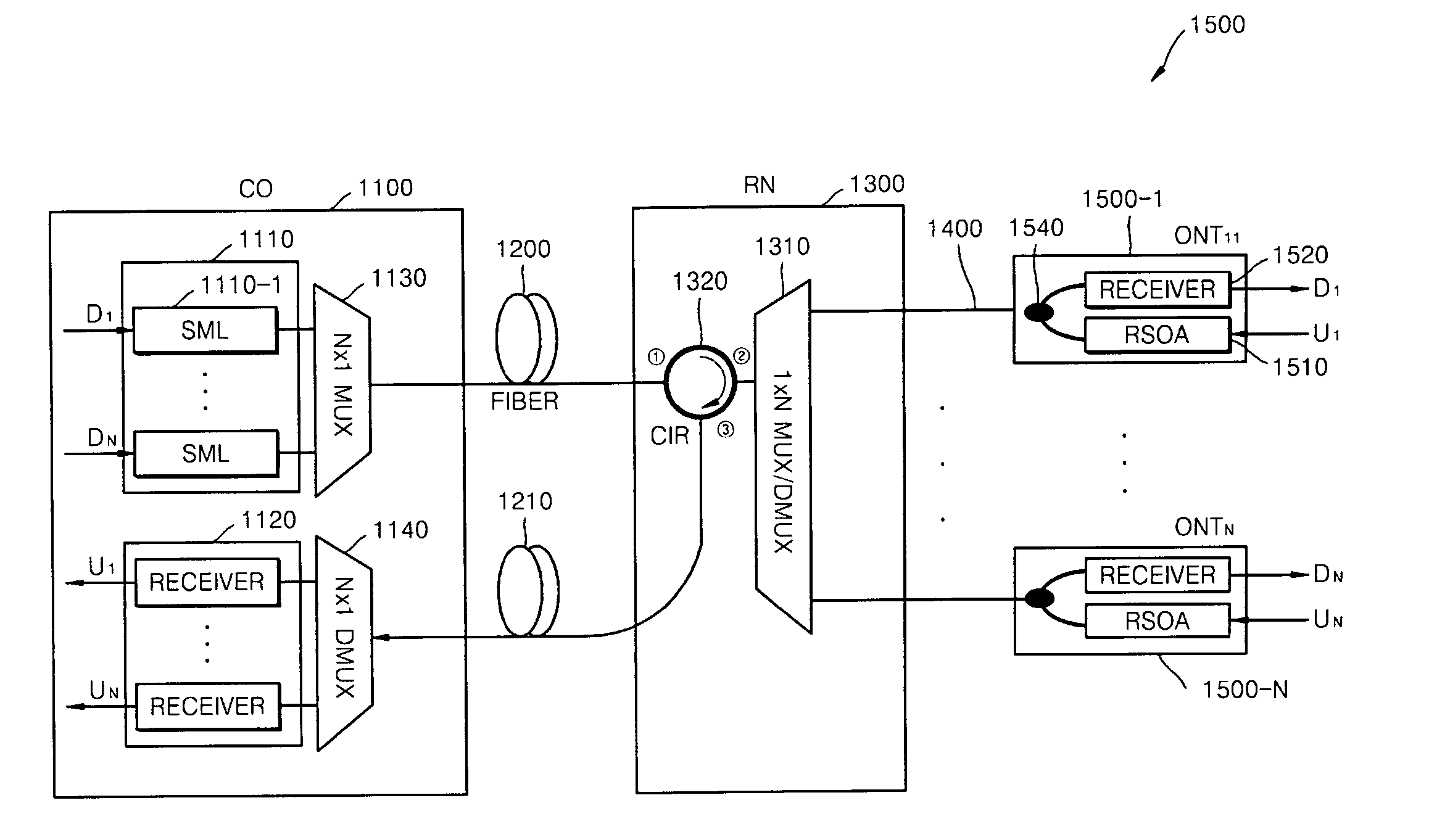
Reflective semiconductor optical amplifier (RSOA), RSOA module having the same, and passive optical network using the same
InactiveUS20070133990A1Reduce light lossImproving polarization dependencyLaser detailsLaser active region structureAudio power amplifierOptical power
A Reflective Semiconductor Optical Amplifier (RSOA) for compensating for light loss in an optical link, an RSOA module for improving polarization dependency using the RSOA, and a Passive Optical Network (PON) for increasing economical efficiency and practical use of a bandwidth using the RSOA are provided. The PON includes a central office comprising a plurality of optic sources transmitting a downstream signal and a plurality of first receivers receiving an upstream signal; at least one optical network terminal (ONT) including a second receiver receiving the downstream signal and an RSOA which receives the downstream signal, remodulates the downstream signal into the upstream signal, and transmits the upstream signal in loopback mode; and a remote node interfacing the central office with the ONT. The upstream signal and the downstream signal are transmitted between the remote node and the ONT via a single optical fiber. The remote node includes an optical power splitter at its port connected to the ONT.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method and apparatus for identifying faults in a passive optical network
InactiveUS20090010643A1Transmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsOptical communicationSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
Component malfunctions in passive optical networks (PON) can increase bit error rates and decrease signal-to-noise ratio in communications signals. These faults may cause the receivers of the signals, either the optical line terminal (OLT) or optical network terminals (ONTs), to experience intermittent faults and / or may result in misinterpreted commands that disrupt other ONT's communication, resulting in a rogue ONT condition. Existing PON protocol detection methods may not detect these types of malfunctions. An embodiment of the present invention identifies faults in a PON by transmitting a test series of data patterns via an optical communications path from a first network node to a second network node. The test series is compared to an expected series of data patterns. An error rate may be calculated as a function of the differences between the test series and expected series. The error rate may be reported to identify faults in the PON.
Owner:TELLABS PETALUMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com