Patents
Literature
198 results about "Optical index" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
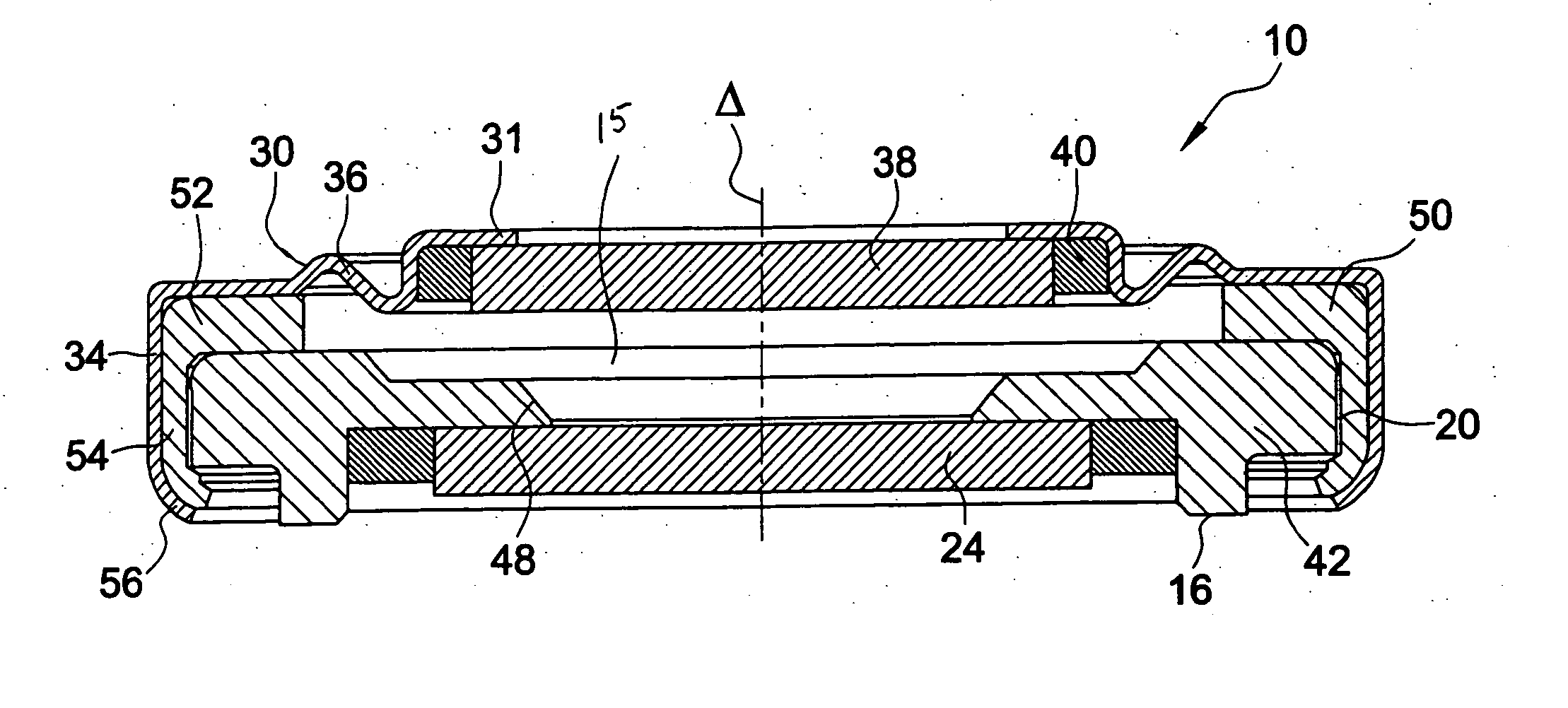
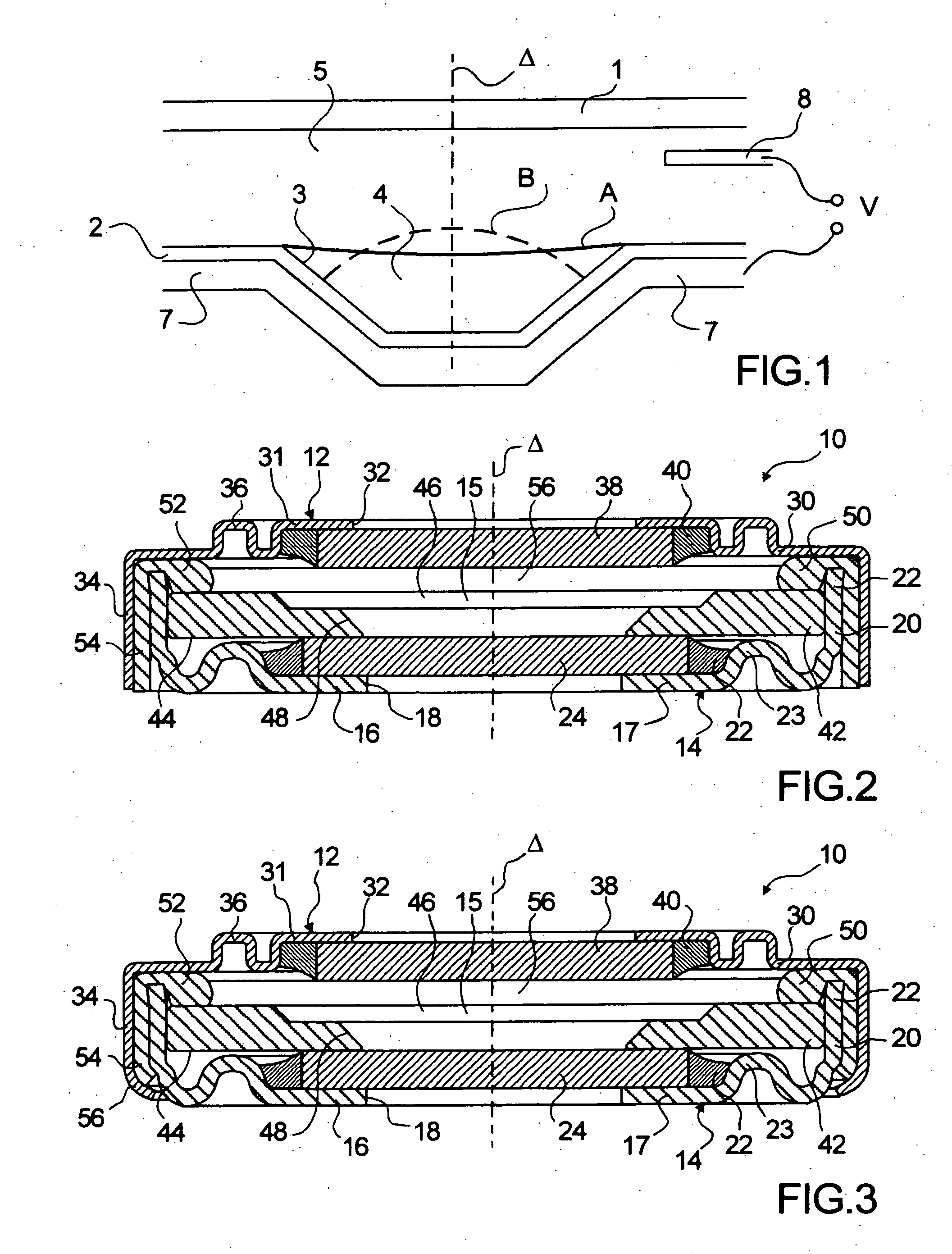
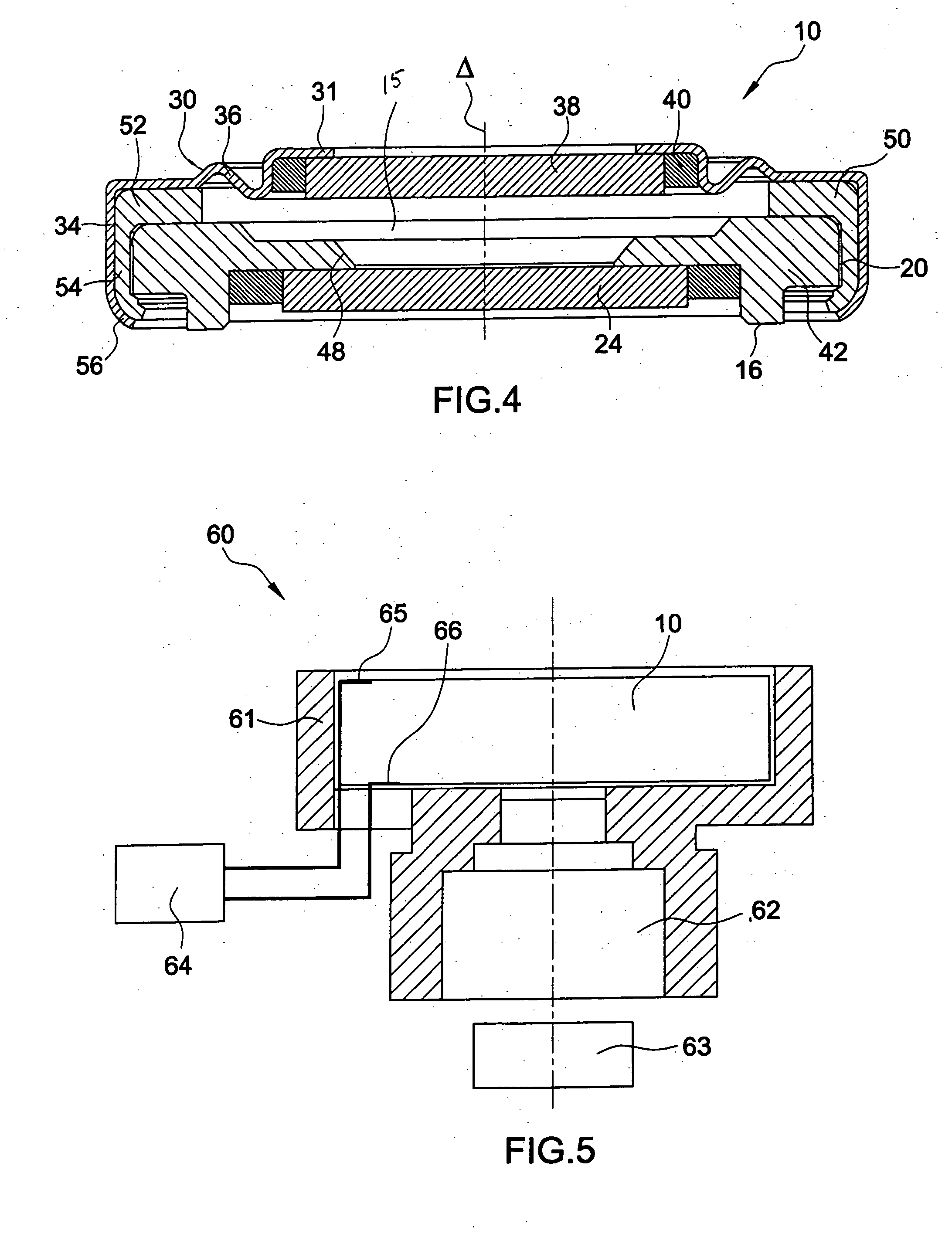
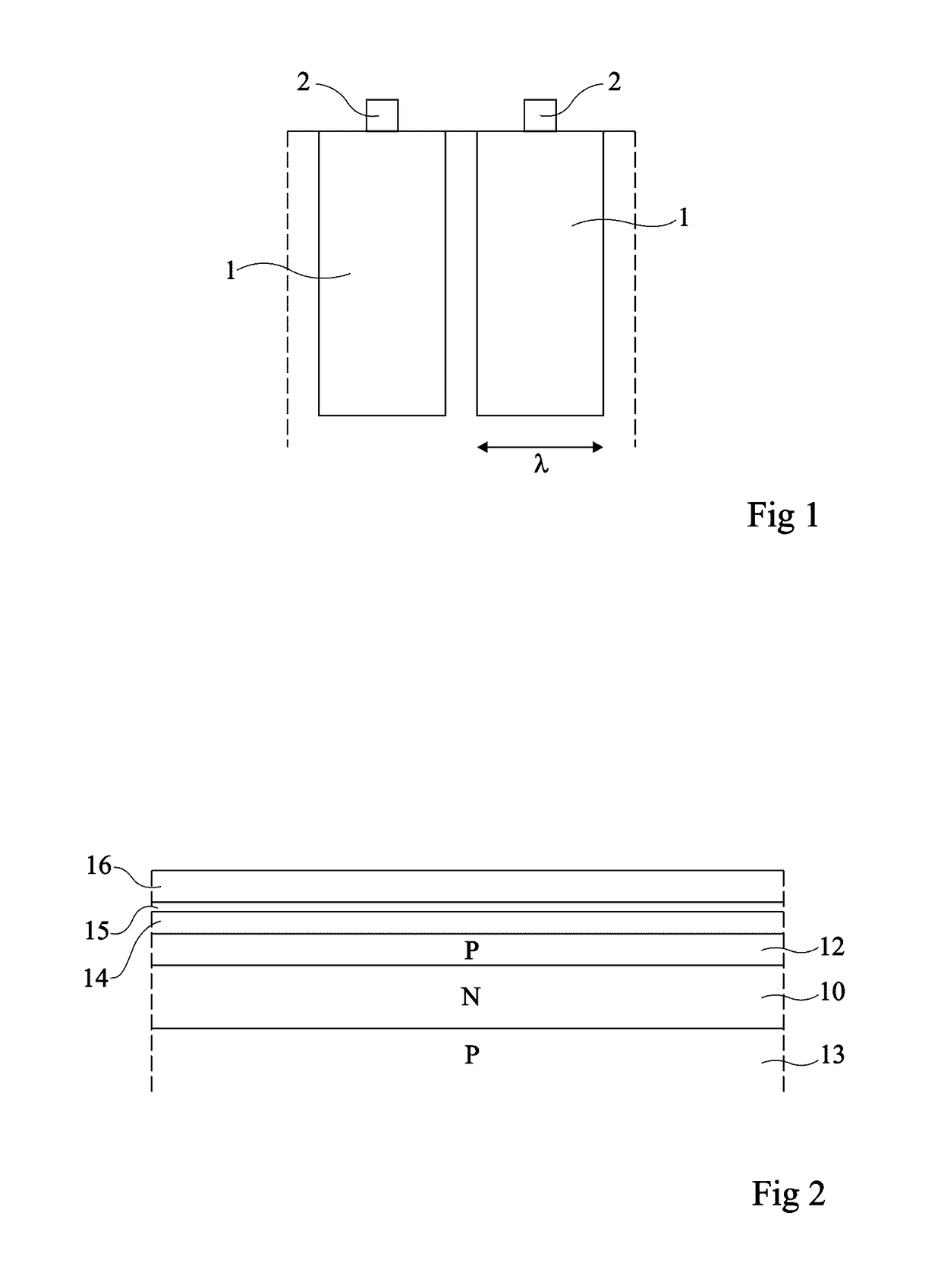
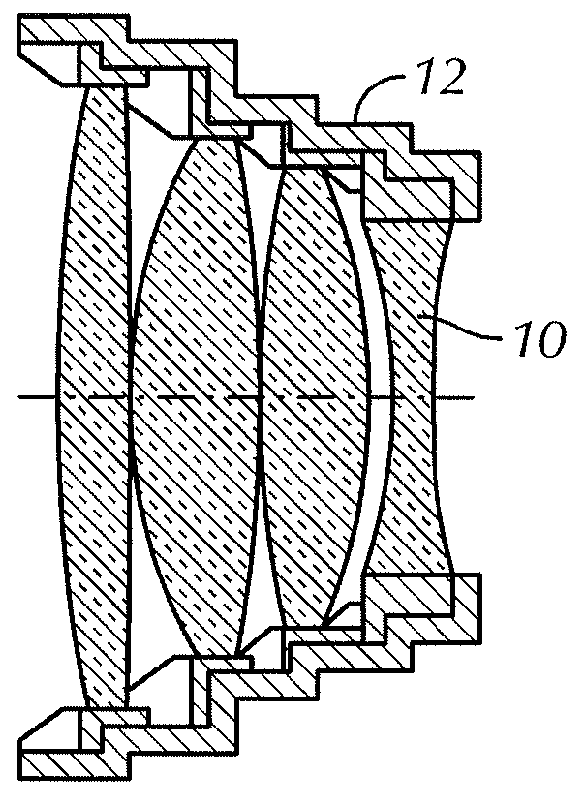
Lens of variable focal length
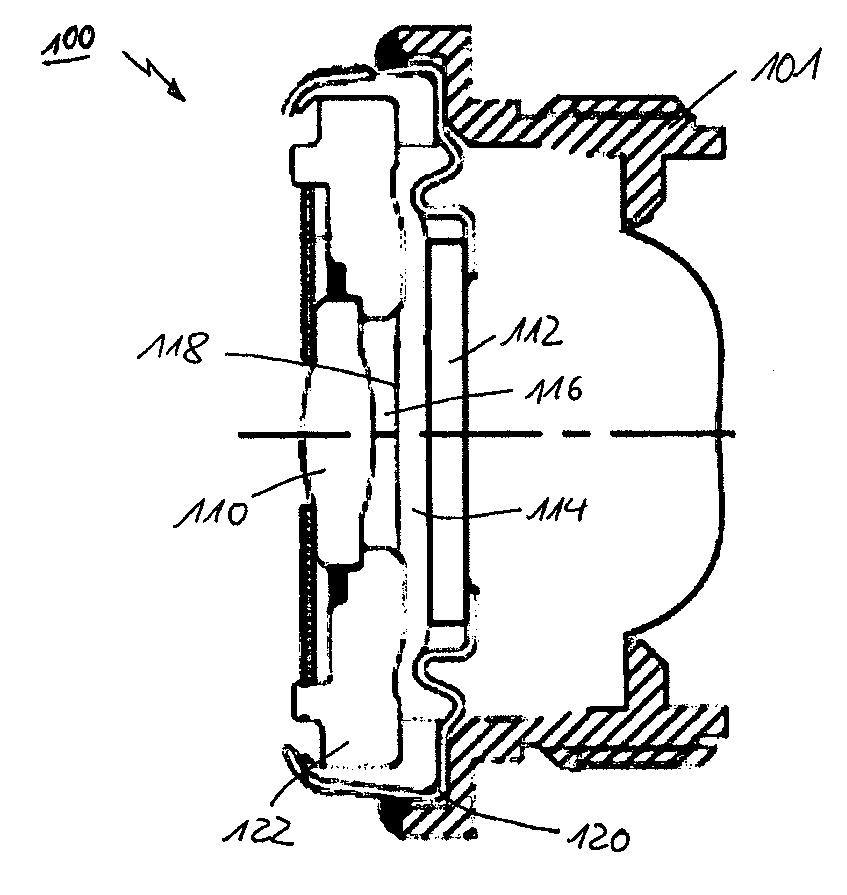
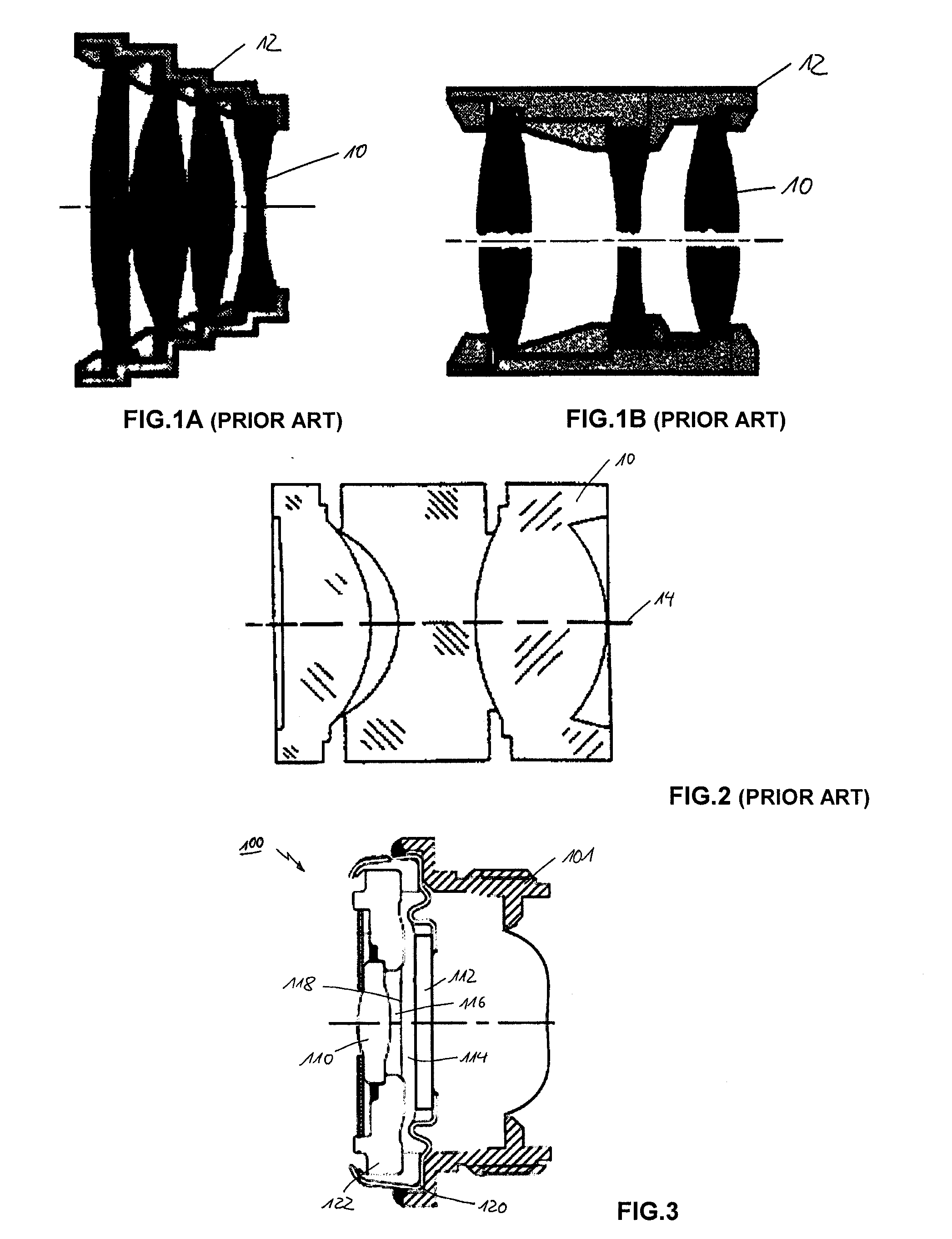
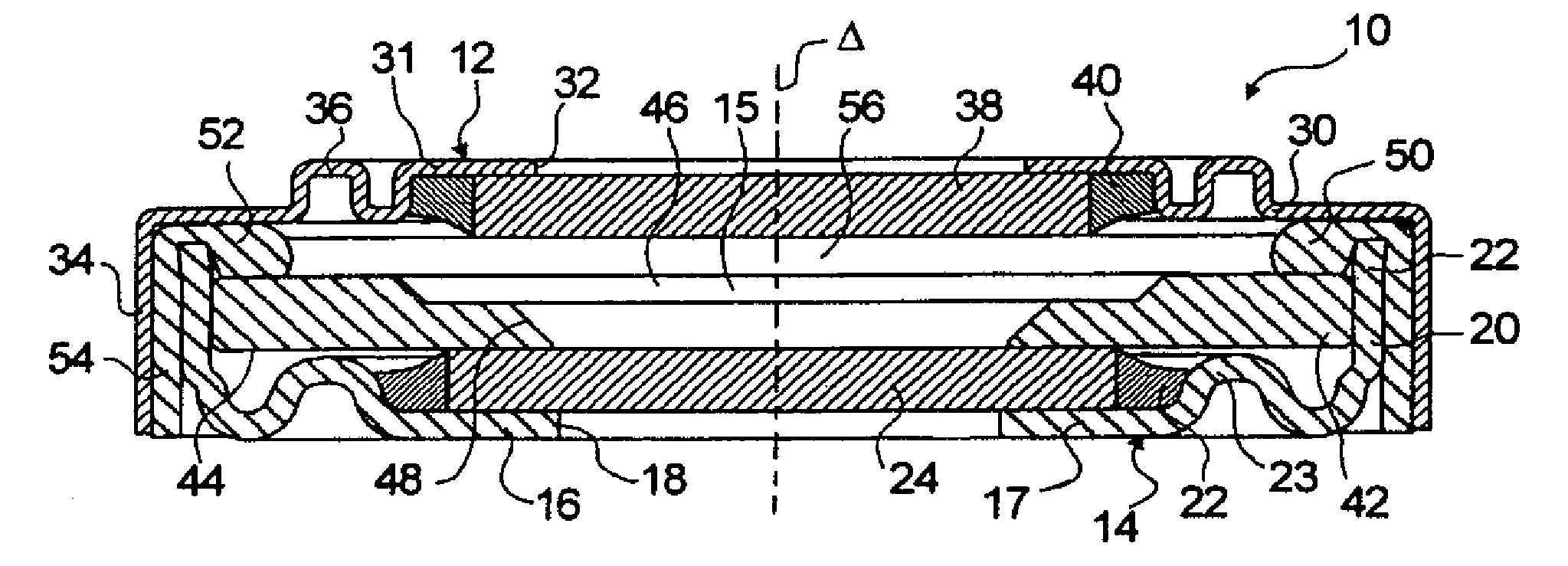
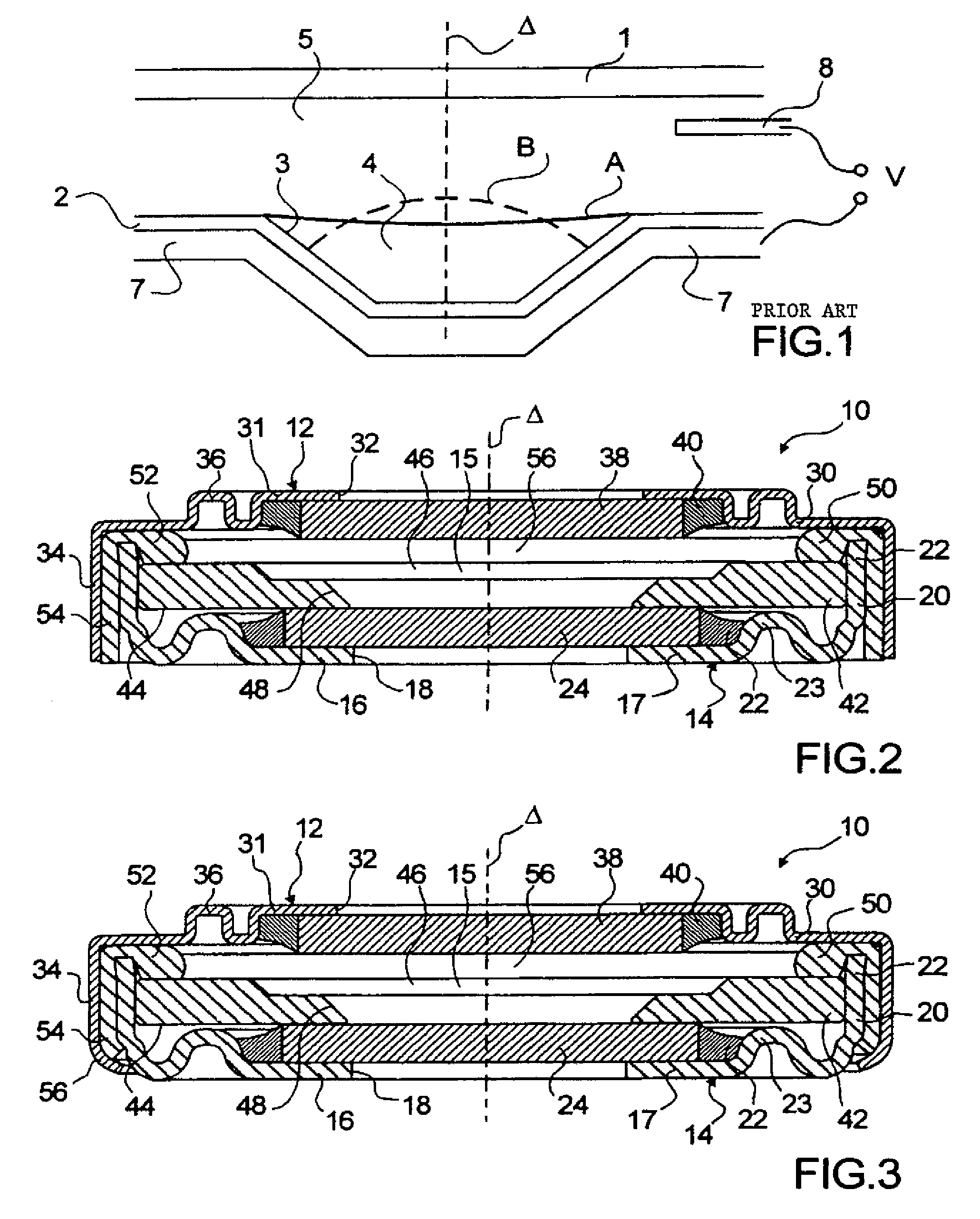
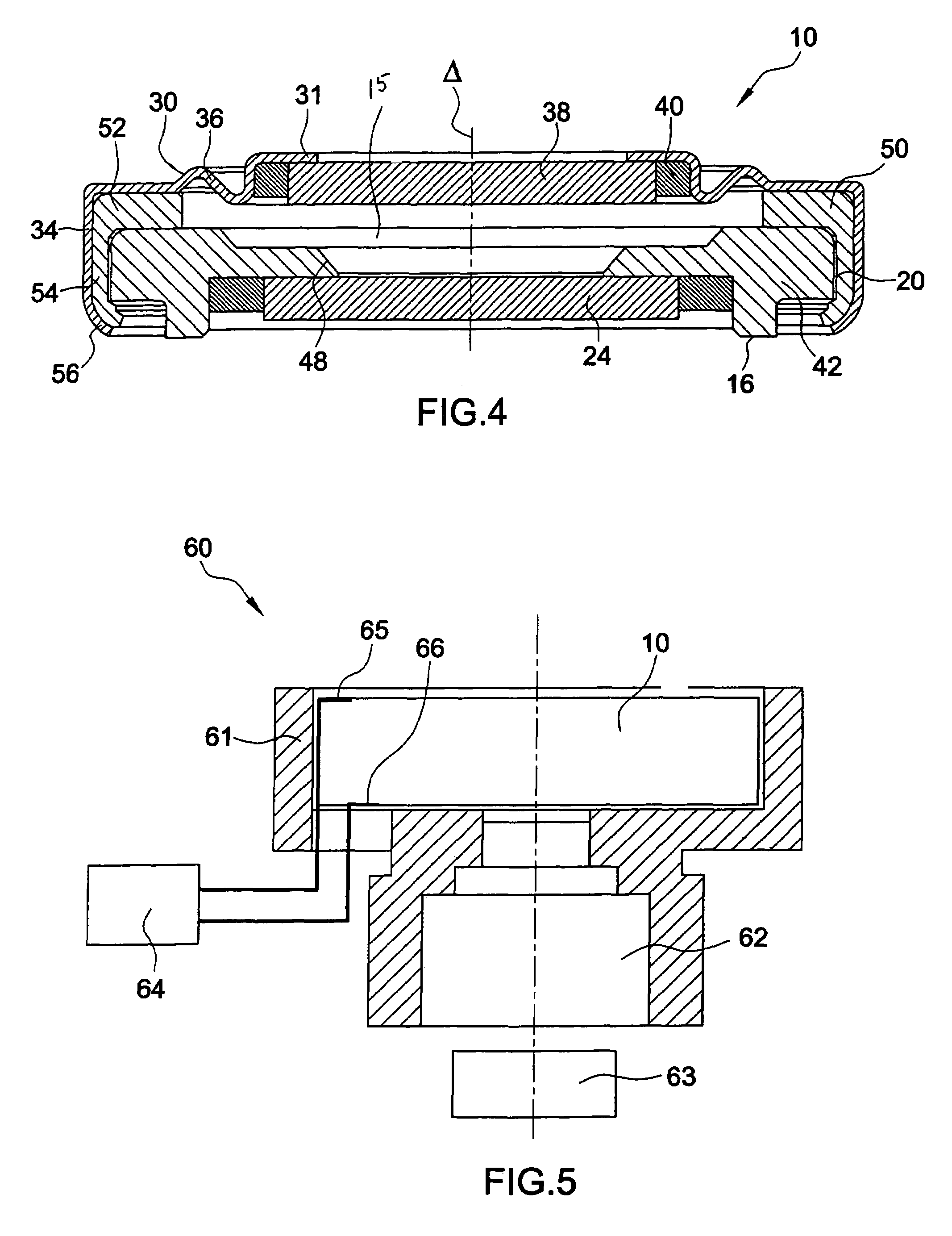
A lens assembly of variable focal length comprises two transparent plates (24, 38) at least partially facing each other and parallel to one another and delimiting, at least in part, an internal volume (15) containing two non-miscible liquids having different optical indices. The lens comprises an elastic element (36) capable of deforming in response to a change in pressure of the liquids, in such a way as to substantially maintain the optical properties of the lens assembly, e.g., in order to maintain the parallelism of the two transparent plates.
Owner:INVENIOS FRANCE SAS
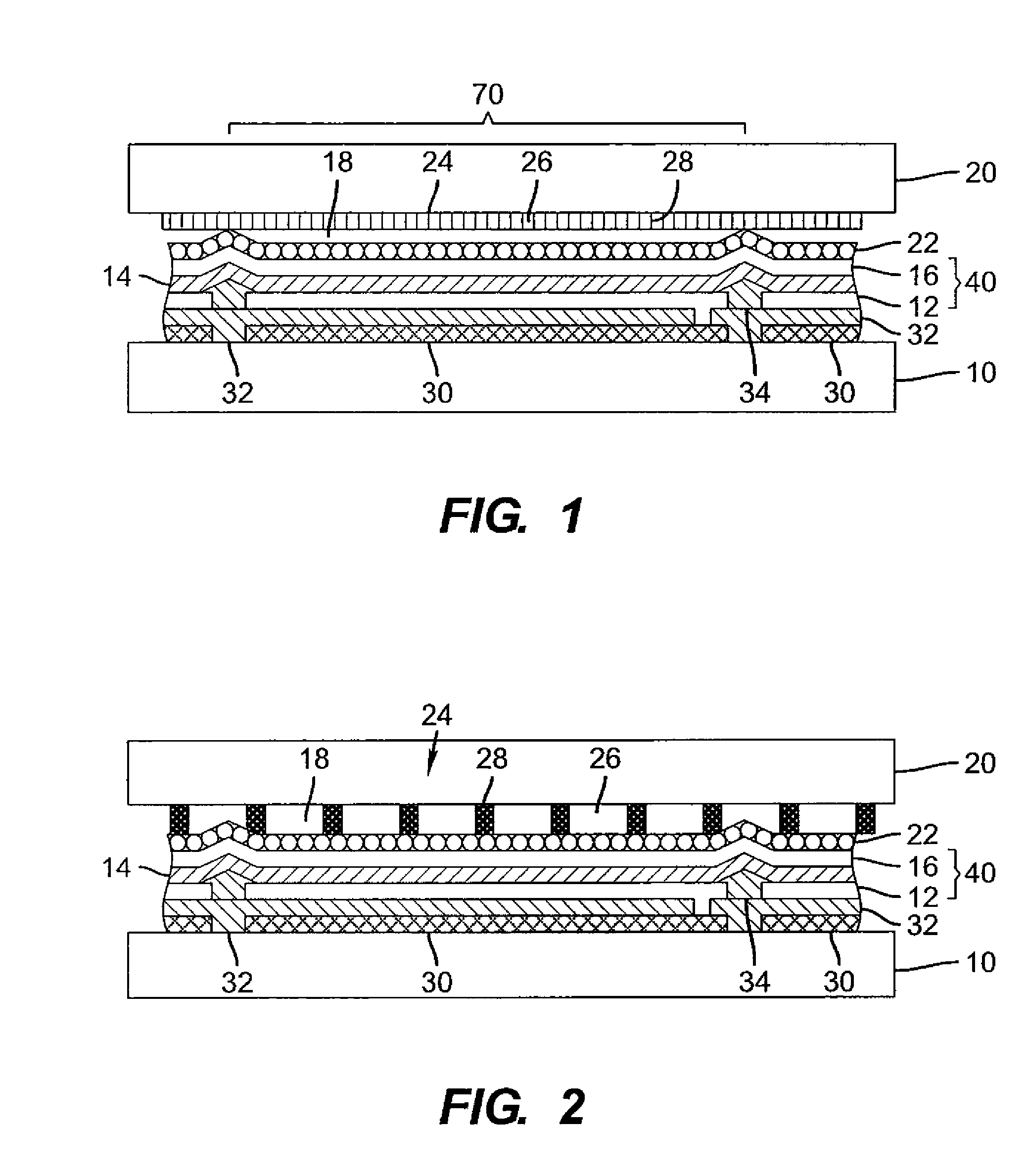
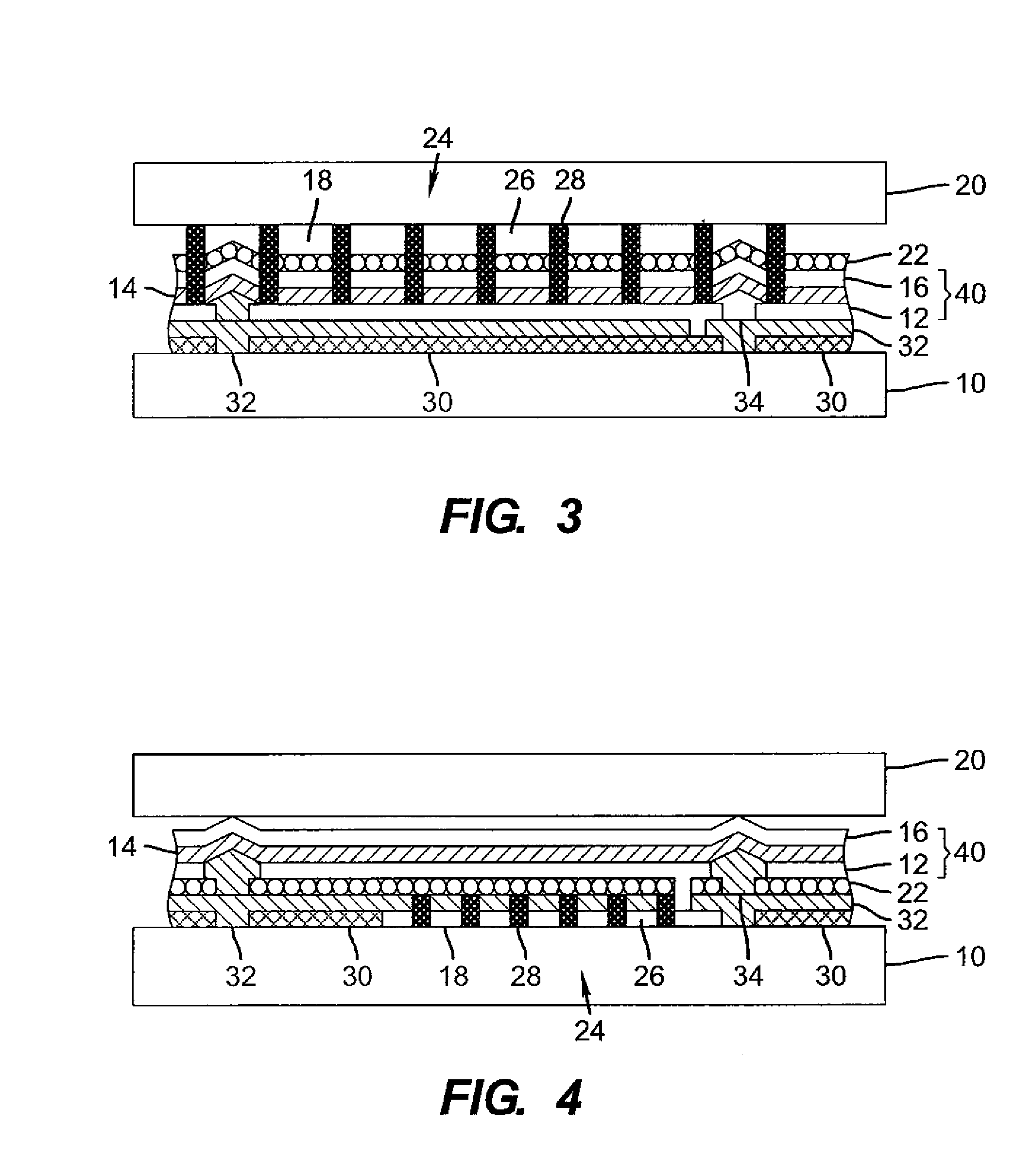
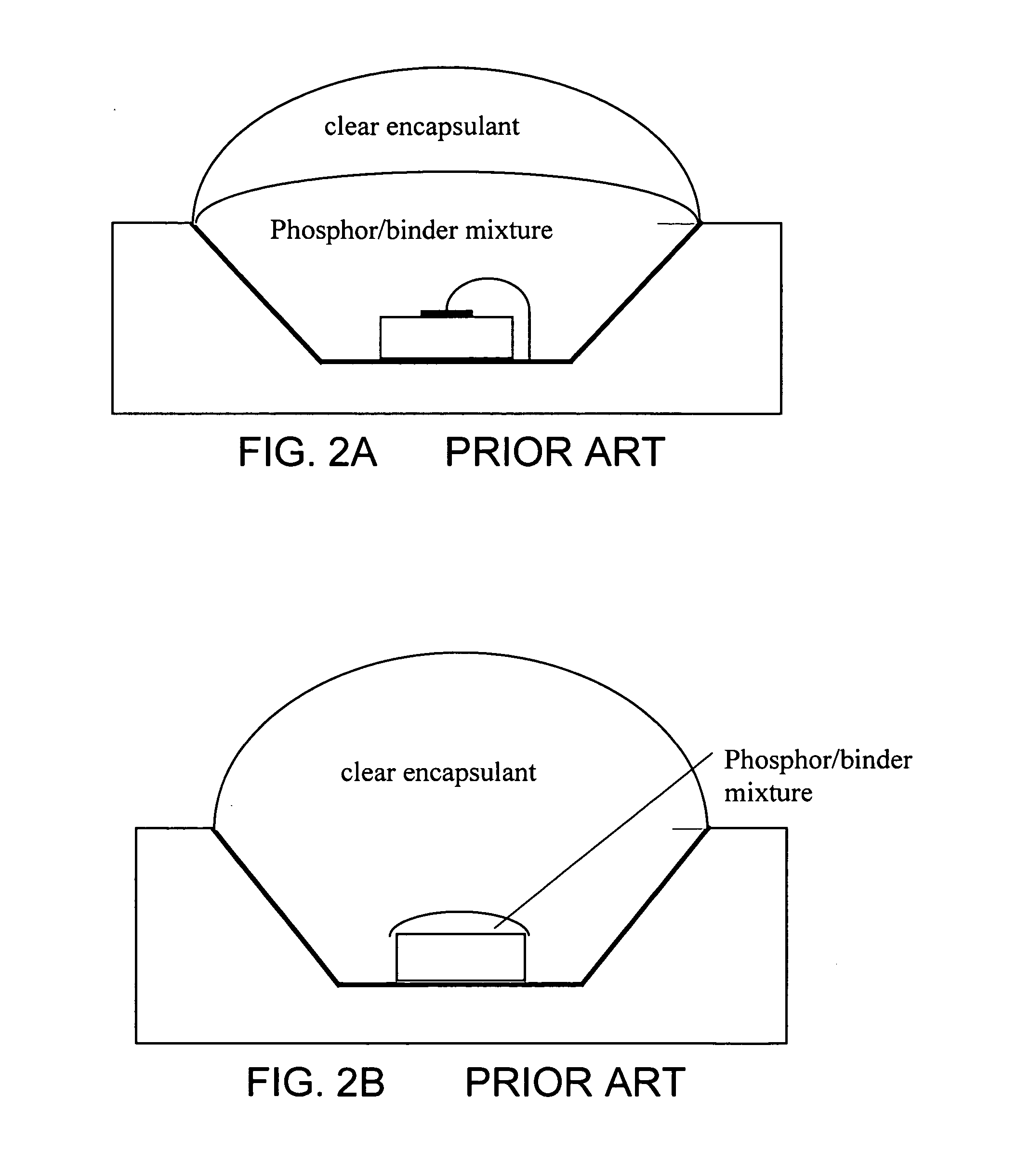
OLED device having improved output and contrast with light-scattering layer and contrast-enhancement layer
ActiveUS7466075B2Incadescent screens/filtersDischarge tube luminescnet screensRefractive indexContrast enhancement
An organic light-emitting diode (OLED) device, with an OLED formed on a substrate having a first and second electrodes and one or more light-emitting organic material layers formed between the electrodes, the organic material layer(s) having a first optical index and at least one of the electrodes patterned to define light-emitting areas; a cover formed over the OLED. The cover or substrate is transparent and has a second optical index and the light is emitted through the transparent cover or substrate; a light-scattering layer formed between the cover and substrate for scattering light; a low-index element having an optical index lower than the first and second optical indices formed between the scattering layer and the transparent cover or substrate; and a contrast-enhancement layer having a plurality of alternating light-absorbing portions and light-transmissive portions formed in the layer located between the light-scattering layer and the transparent substrate or cover through which light is emitted, wherein a plurality of light-absorbing portions and light-transmissive portions are located in each light-emitting area.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Light-emitting device having improved light output
ActiveUS20080272367A1Improve light outputConducive to environmental protectionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight emitting deviceLight scattering
A light-emitting LED device has one or more light-emitting LED elements, including first and second spaced-apart electrodes with one or more light-emitting layers formed there-between, wherein at least one of the electrodes is a transparent electrode. Also included are a first transparent encapsulating layer having a first optical index formed over the transparent electrode opposite the light-emitting layer; a light-scattering layer formed over the first transparent encapsulating layer opposite the transparent electrode; and a second transparent encapsulating layer, having a second optical index lower than the first optical index, formed over the light-scattering layer.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Method and apparatus for spatially modulated electric field generation and electro-optical tuning using liquid crystals
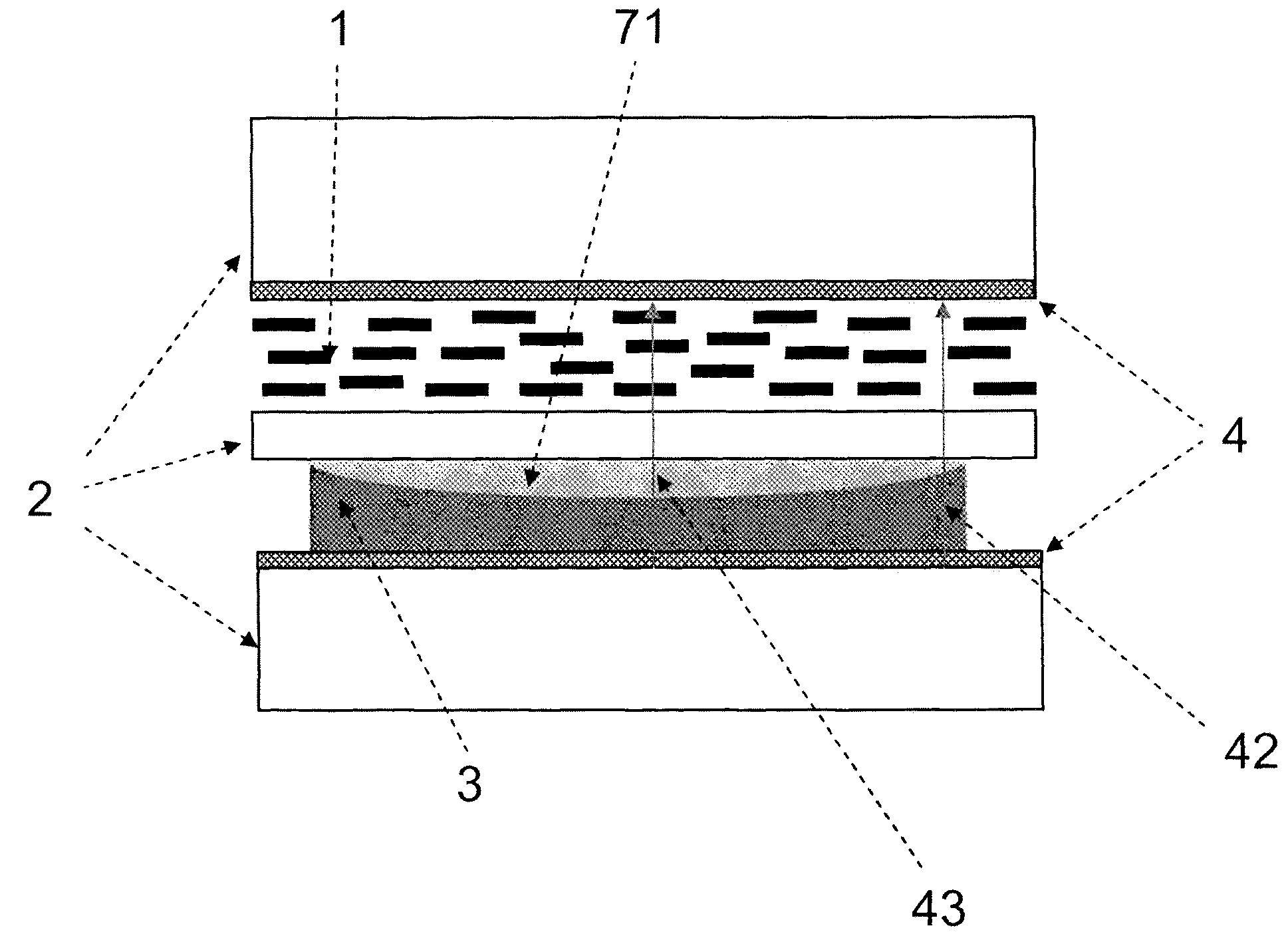
InactiveUS20070229754A1Easy to manufactureReduce lossNon-linear opticsLensDielectricElectric field modulation
A variable optical device for controlling the propagation of light has a liquid crystal layer (1), electrodes (4) arranged to generate an electric field acting on the liquid crystal layer, and an electric field modulation layer (3,71) arranged between the electrodes and adjacent the liquid crystal layer for spatially modulating said electric field in a manner to control the propagation of light passing through said optical device. The electric field modulation layer has either an optical index of refraction that is essentially spatially uniform, or a polar liquid or gel, or a very high low frequency dielectric constant material having a dielectric constant greater than 20, and preferably greater than 1000. The modulation layer can have a solid body having a first low frequency dielectric constant with a shape selected to impart a desired modulation of the electric field, and a second low frequency dielectric constant material surrounding or adjacent to the solid body such that the solid body and the second material form a layer geometry.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL +1
Lens with variable focus
InactiveUSRE39874E1Easy to manufactureEasy to useEndoscopesNon-linear opticsCamera lensElectrical conductor
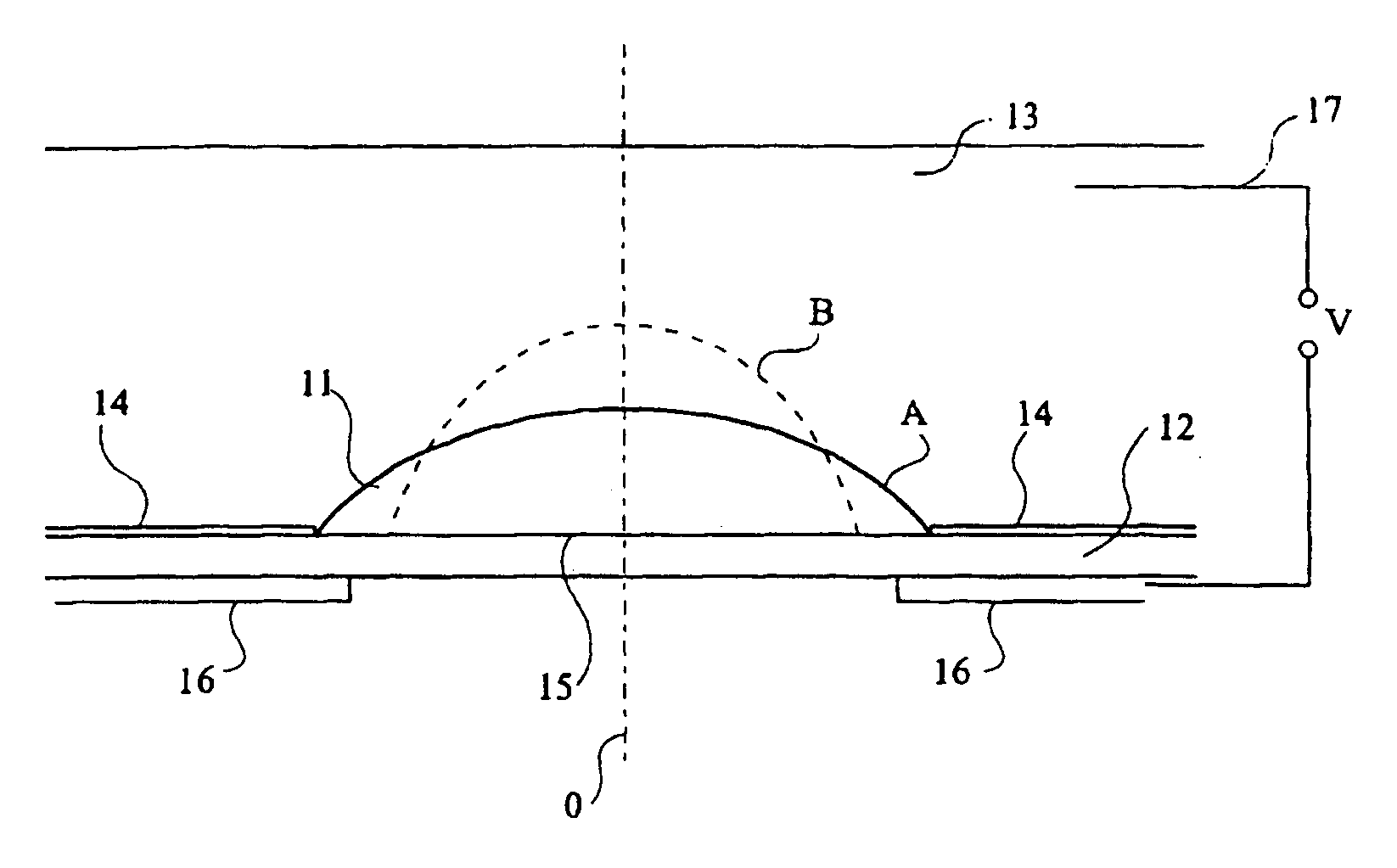
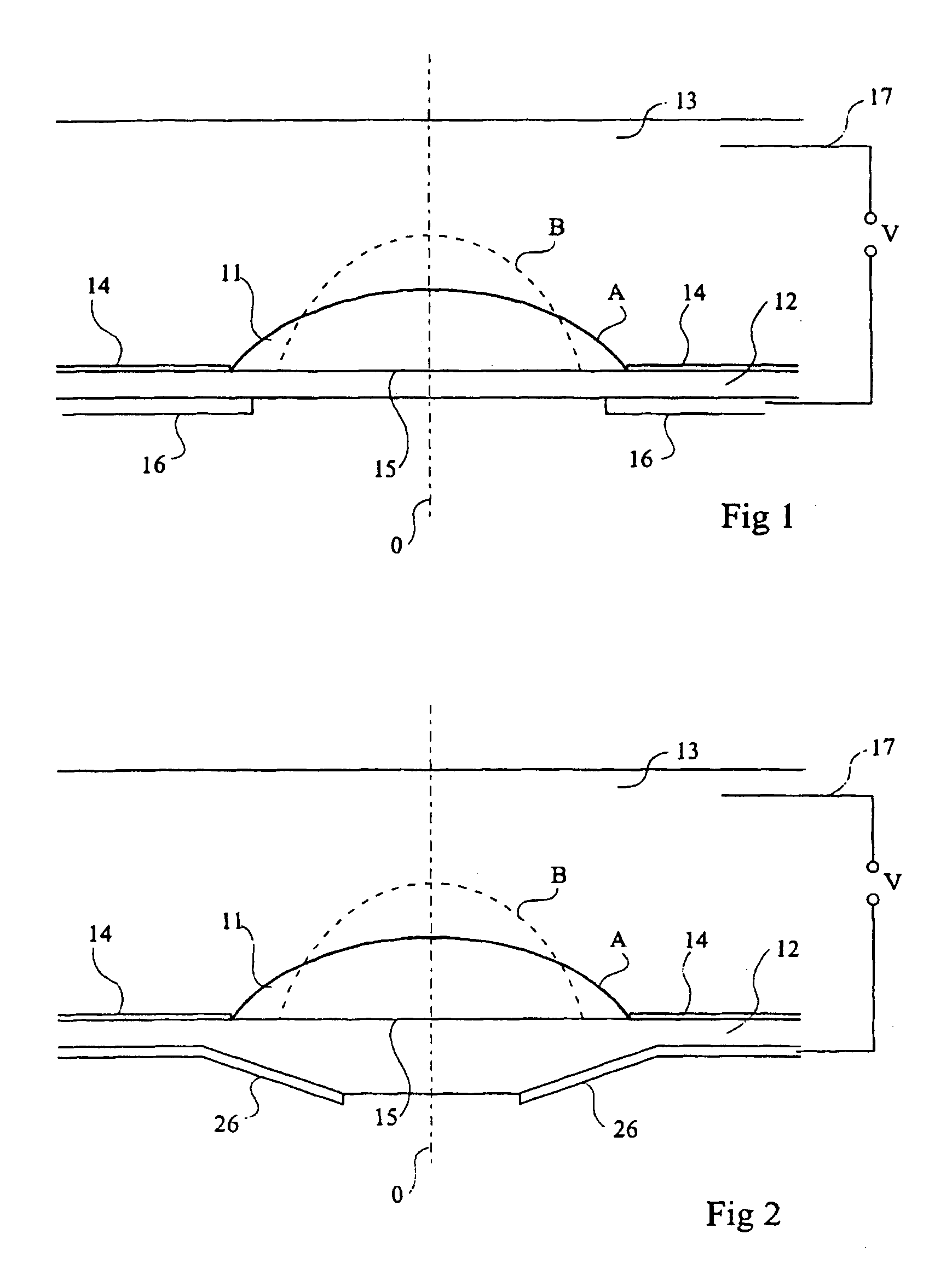
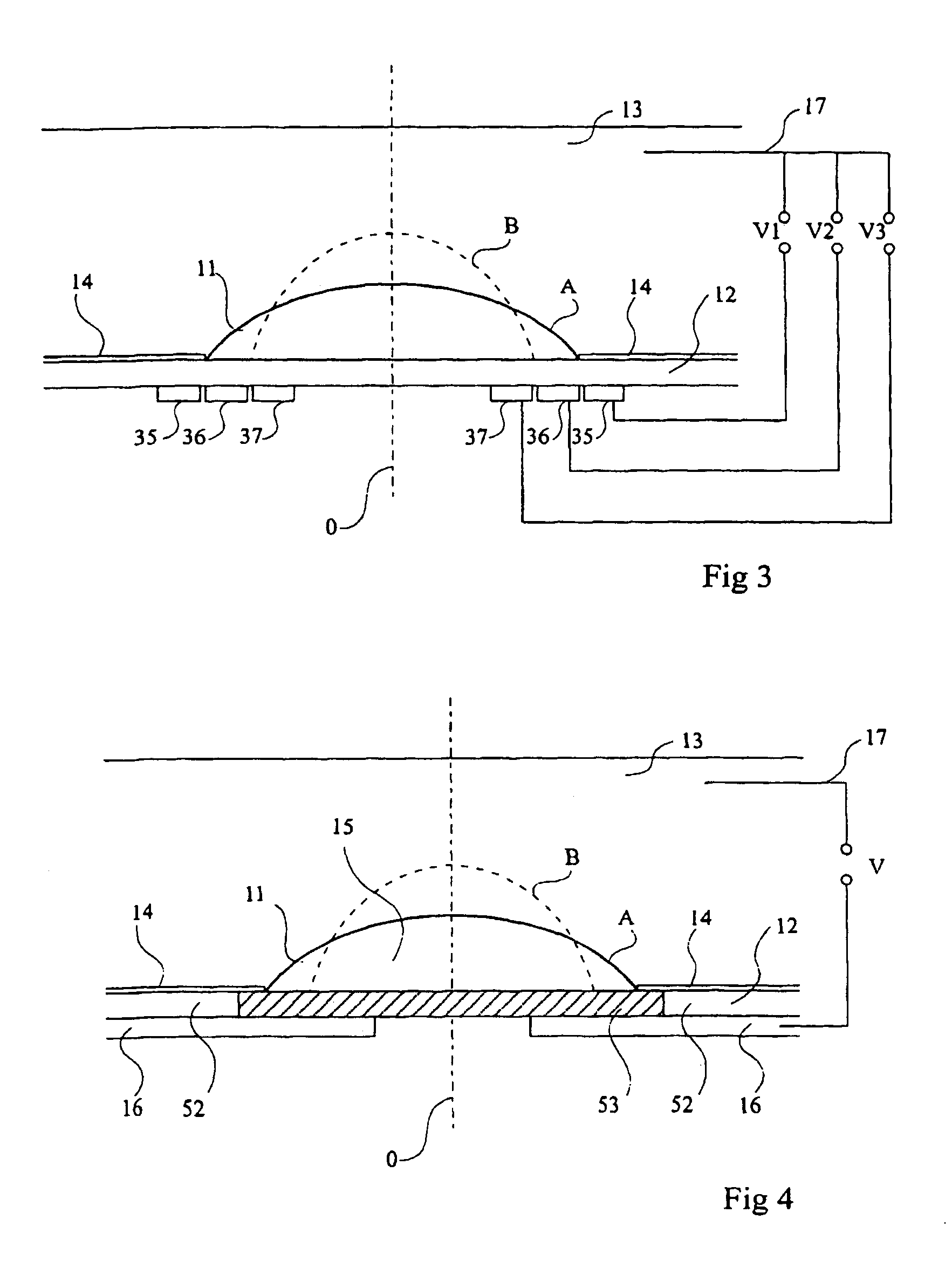
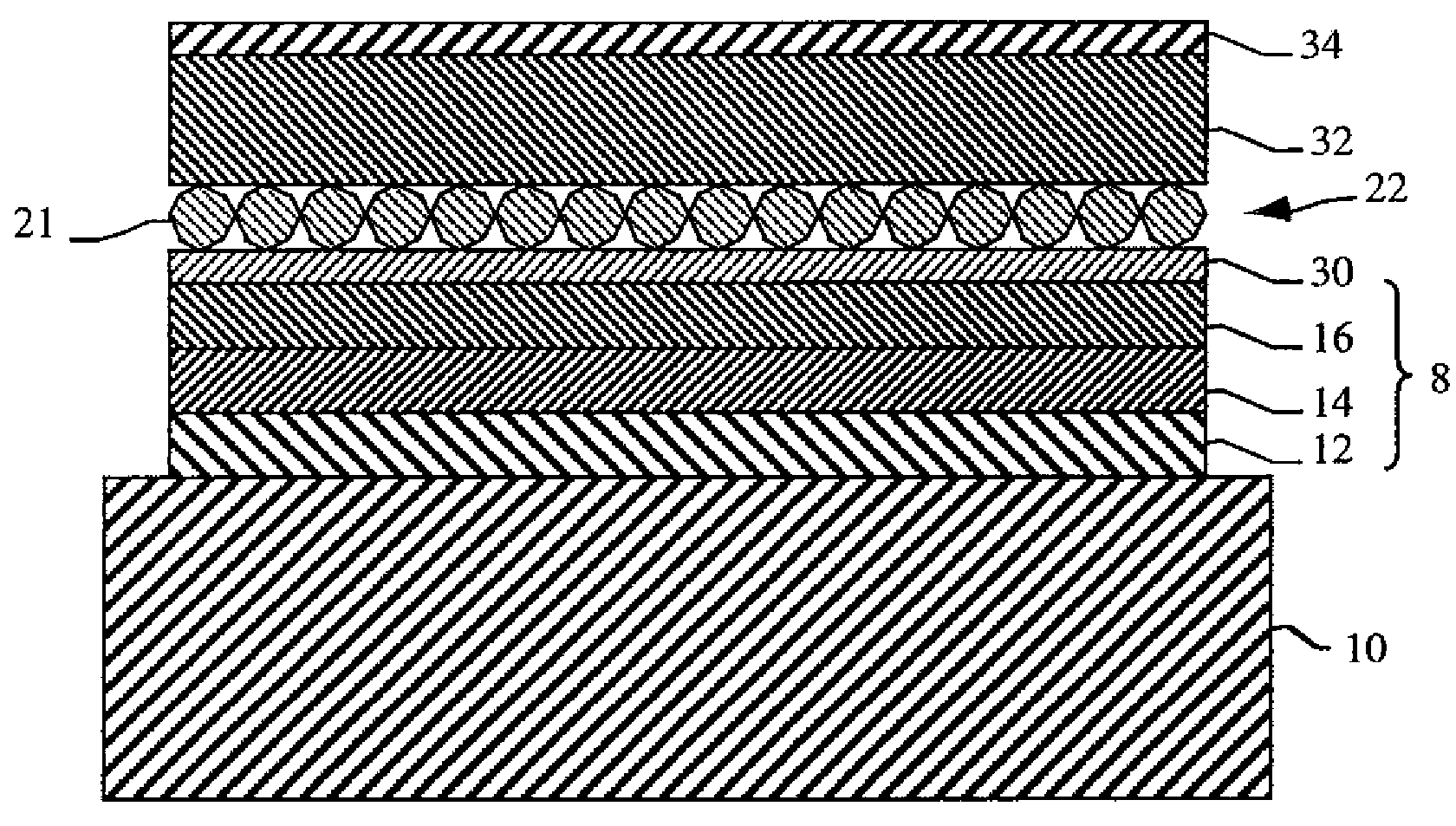
A variable focus lens comprising a chamber (12) filled with a first liquid (13), a drop of a second liquid (11) being disposed at rest on a region of a first surface of an insulating wall of the chamber, the first and second liquids being non miscible, of different optical indexes and of substantially same density. The first liquid is conductive and the second liquid is insulating. The lens further comprises means for applying a voltage between the conductor liquid and an electrode (16) placed on the second surface of said wall; and centering means for maintaining the centering of the edge of the drop while the voltage is applied and for controlling the shape thereof.
Owner:INVENIOS FRANCE SAS
Light-emitting device having improved light output
ActiveUS7560747B2Solid-state devicesOrganic semiconductor devicesLight emitting deviceLight scattering
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
High-brightness LED-phosphor coupling
A high brightness LED phosphor coupling device. A semiconductor light source is encapsulated by a medium of first index of refraction, a layer of phosphor surrounded by a second medium of second index of refraction of optical index less than the first index and a light coupler for redirecting most of the light from the light source to an area of the phosphor about equal to the area of the light source multiplied by the square of the ratio of the first to the second index of refraction.
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
OLED device having improved output and contrast
ActiveUS20070132378A1Improves ambient contrastHigh light efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsRefractive indexContrast enhancement
An organic light-emitting diode (OLED) device, comprising: an OLED formed on a substrate having a first and second electrodes and one or more light-emitting organic material layers formed between the electrodes, the organic material layer(s) having a first optical index and at least one of the electrodes patterned to define light-emitting areas; a cover formed over the OLED wherein the cover or substrate is transparent and has a second optical index and the light is emitted through the transparent cover or substrate; a light-scattering layer formed between the cover and substrate for scattering light; a low-index element having an optical index lower than the first and second optical indices formed between the scattering layer and the transparent cover or substrate; and a contrast-enhancement layer comprising a plurality of alternating light-absorbing portions and light-transmissive portions formed in the layer located between the light-scattering layer and the transparent substrate or cover through which light is emitted, wherein a plurality of light-absorbing portions and light-transmissive portions are located in each light-emitting area.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Electro-optic optical modulator devices and method of fabrication
ActiveUS9746743B1Small sizeOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsElectricityRefractive index
A novel electro-optic optical modulator device and a related method for creating the novel optical modulator device are disclosed. In one embodiment, the novel optical modulator comprises a high index contrast optical waveguide, a mesa region, electrical modulation electrodes, RF transmission lines, and interconnection layers. The high index contrast optical waveguide comprises an electro-optic slab core region and a high index ridge core region. A mesa section which includes the core regions can be formed, and electrical modulation electrodes are placed on etched sidewalls of the mesa section to achieve electro-optical index modulation of the electro-optic slab core region. The RF transmission lines include RF electrodes that connected to the electrical modulation electrodes. The interconnection layers connect the modulation electrodes with the RF electrodes by using etched vias. The novel optical modulator can also incorporate foldable modulation arms for poling in the electro-optic slab core region.
Owner:PARTOW TECH LLC
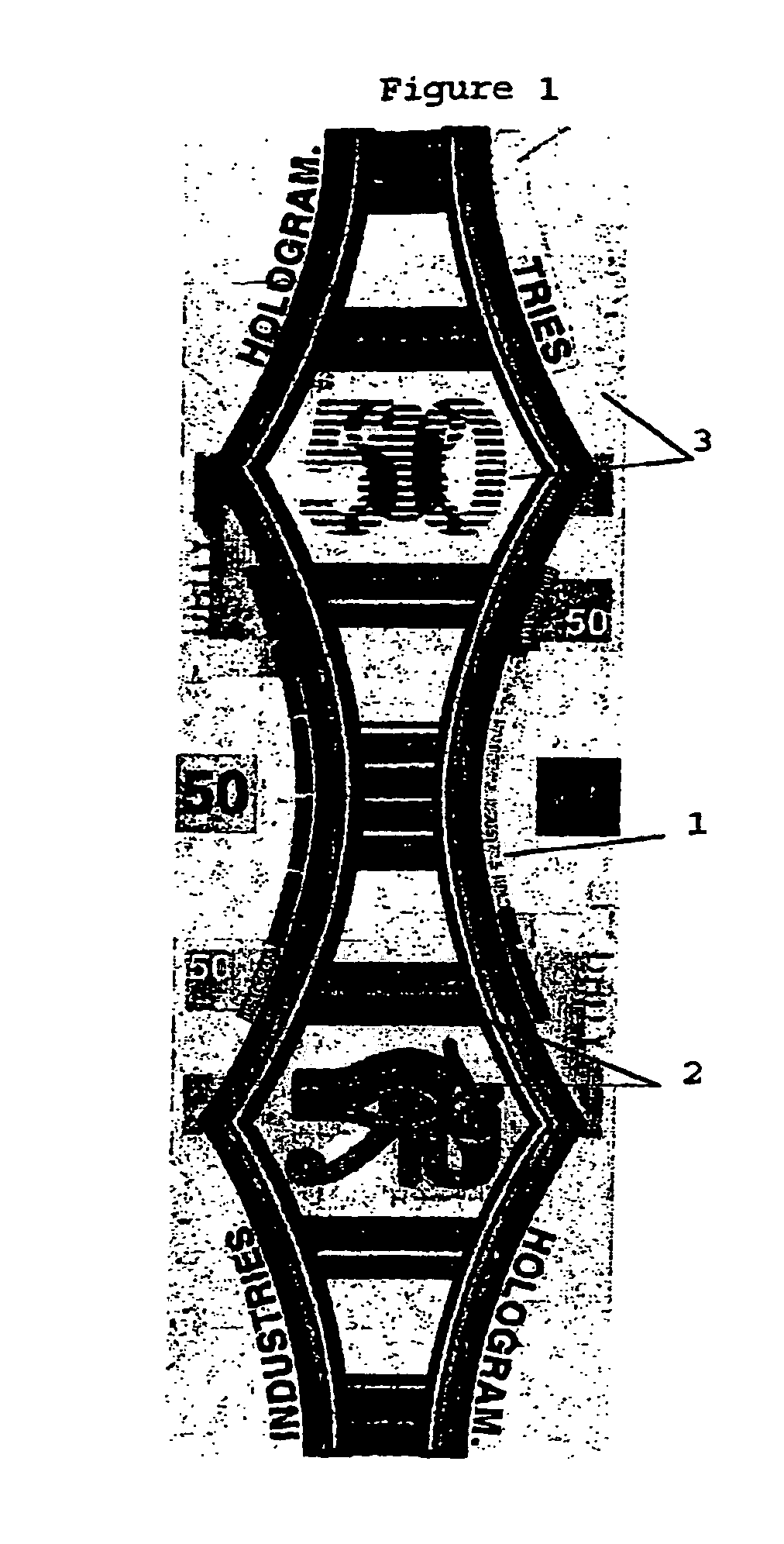
Optical security component
An optical security component for authenticating a document or a product including a transparent plastic film embossed to form an embossed surface and to have at least one diffraction grating; a layer of dielectric material of high optical index at least partially coated on the embossed surface and producing a colored effect of a first color for a first orientation of the component and a second different color for orientation perpendicular to the first orientation; a low optical index layer coated on a side opposite the viewing direction of the dielectric material; and a colored contrast layer having transparent zones and colored zones on the low optical index layer.
Owner:SURYS
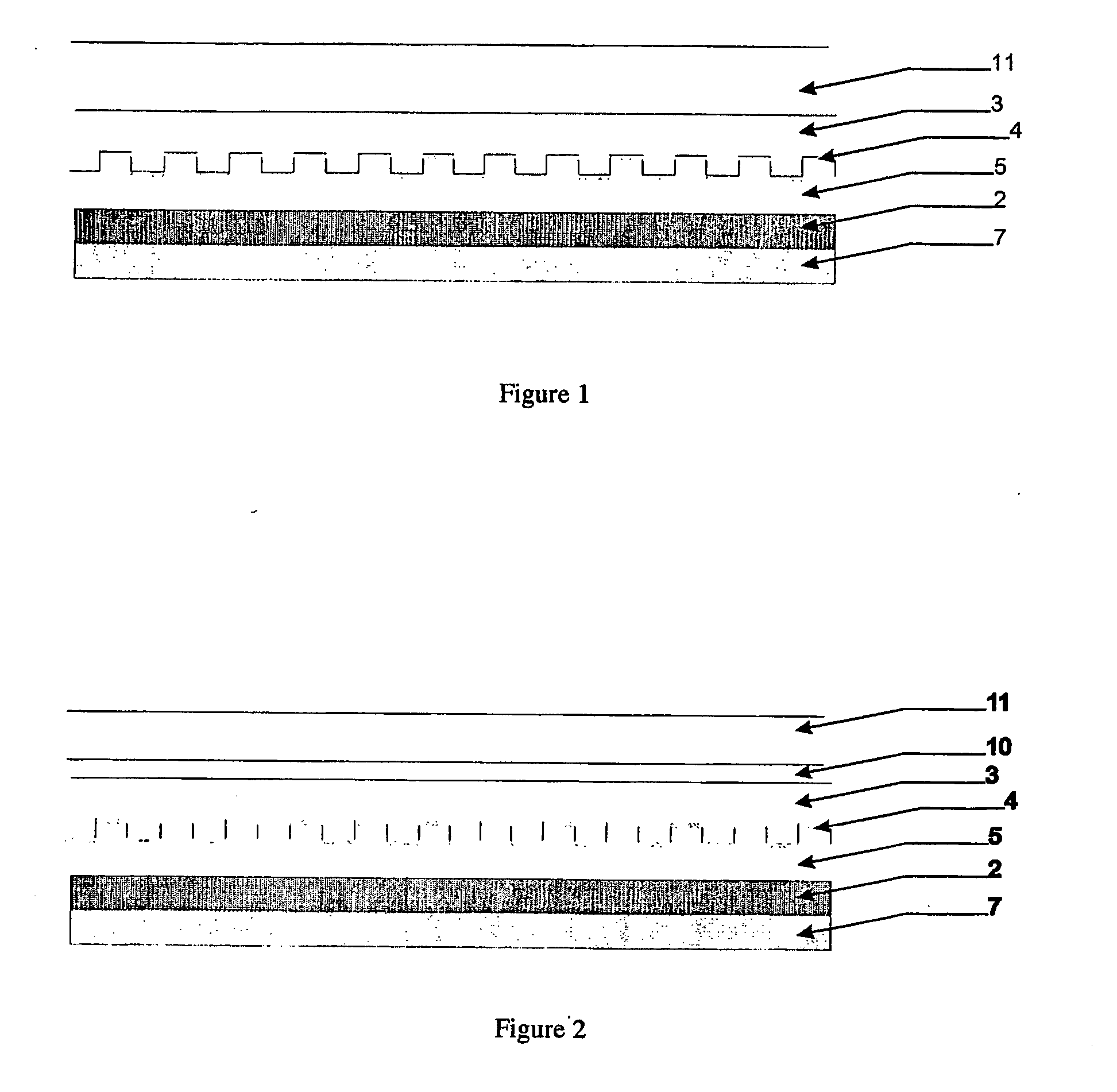
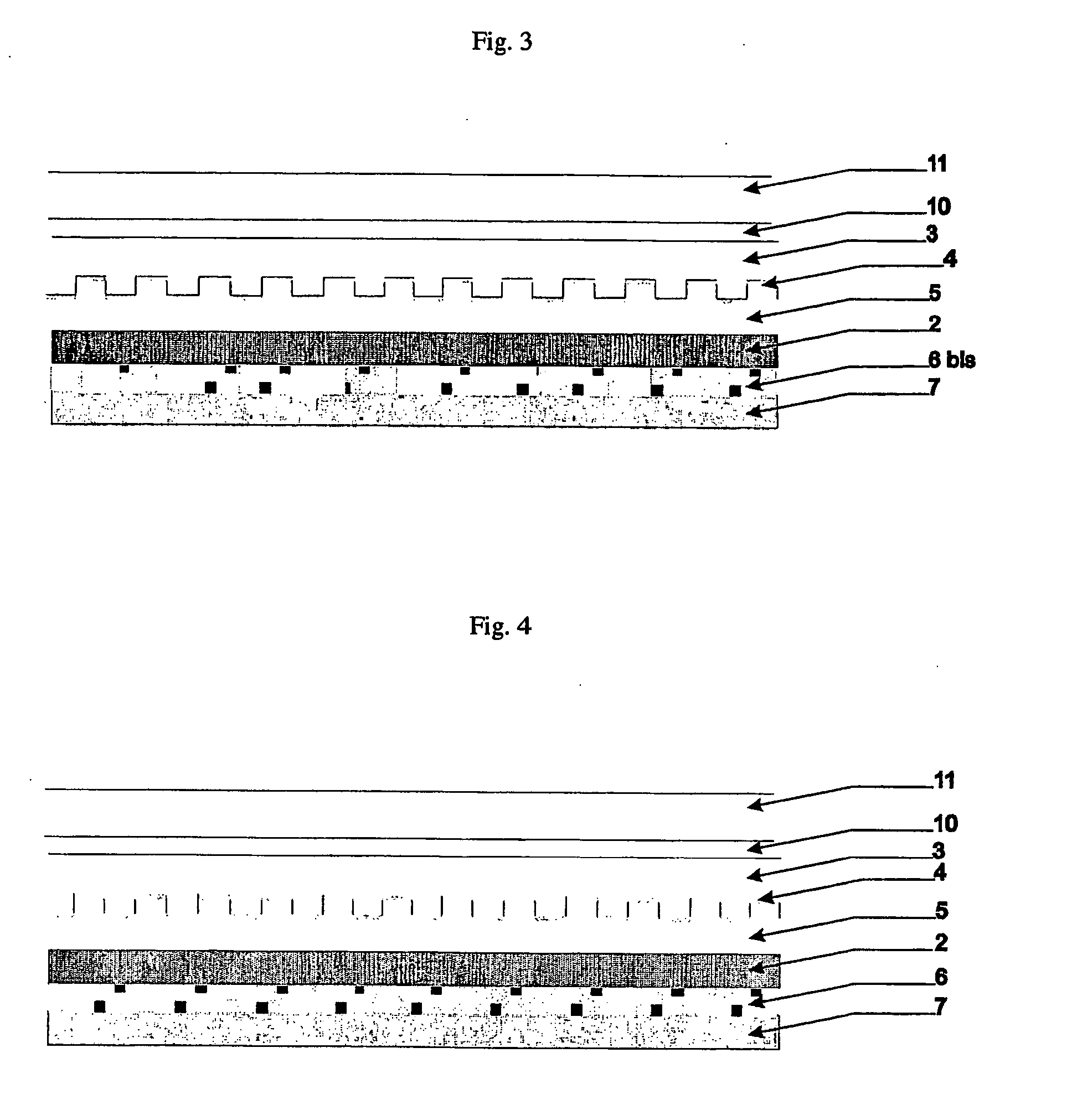
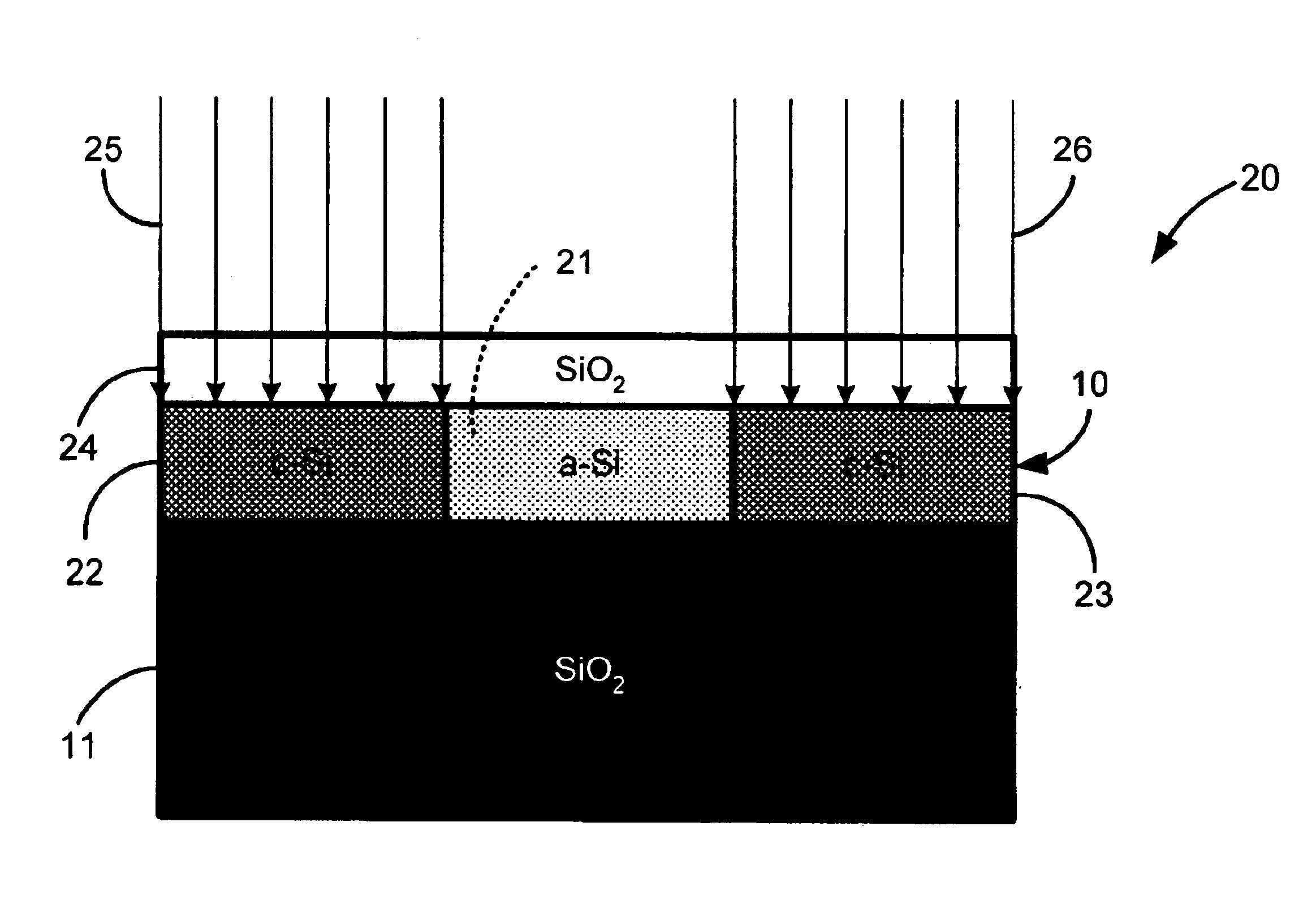
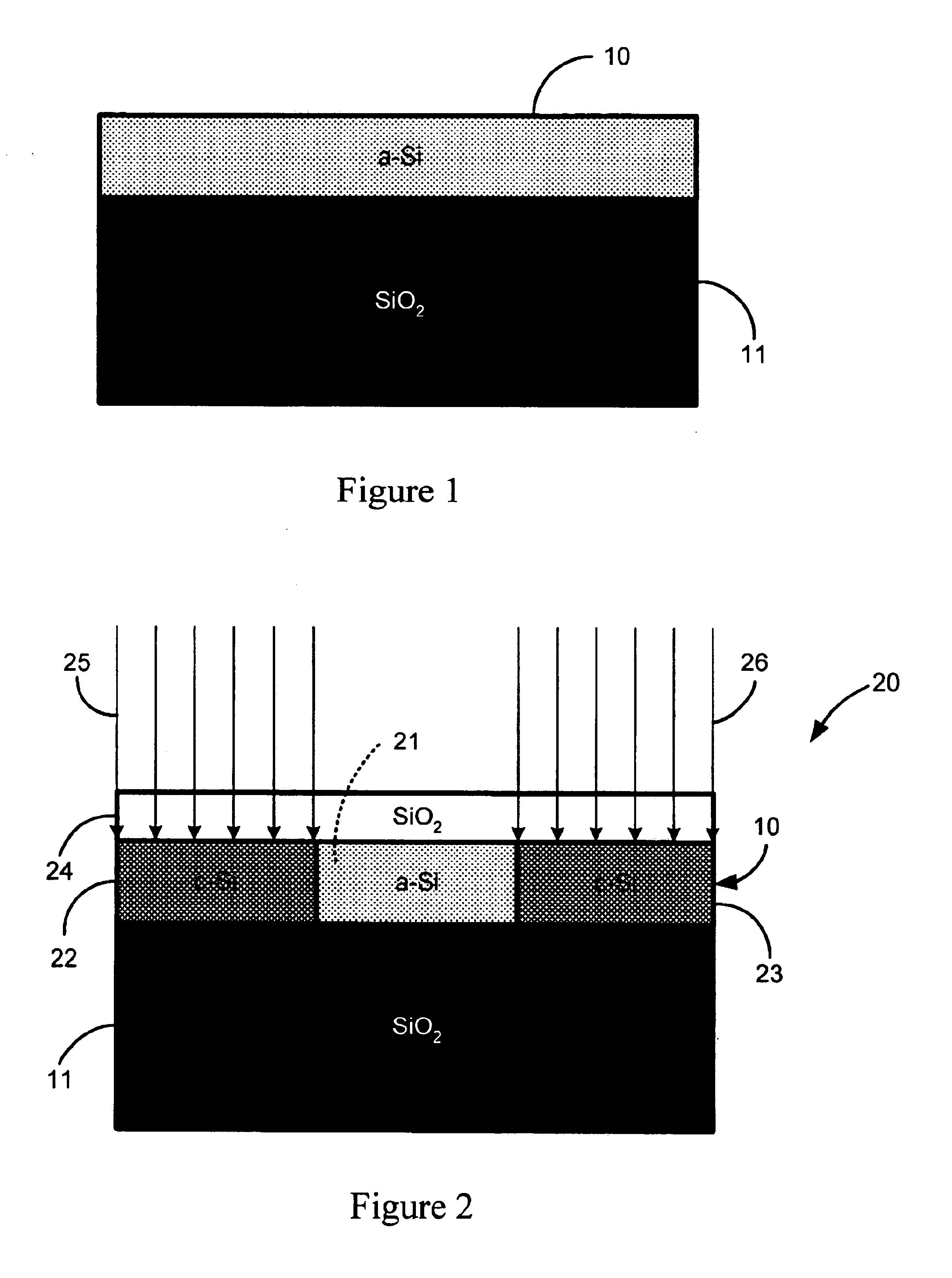
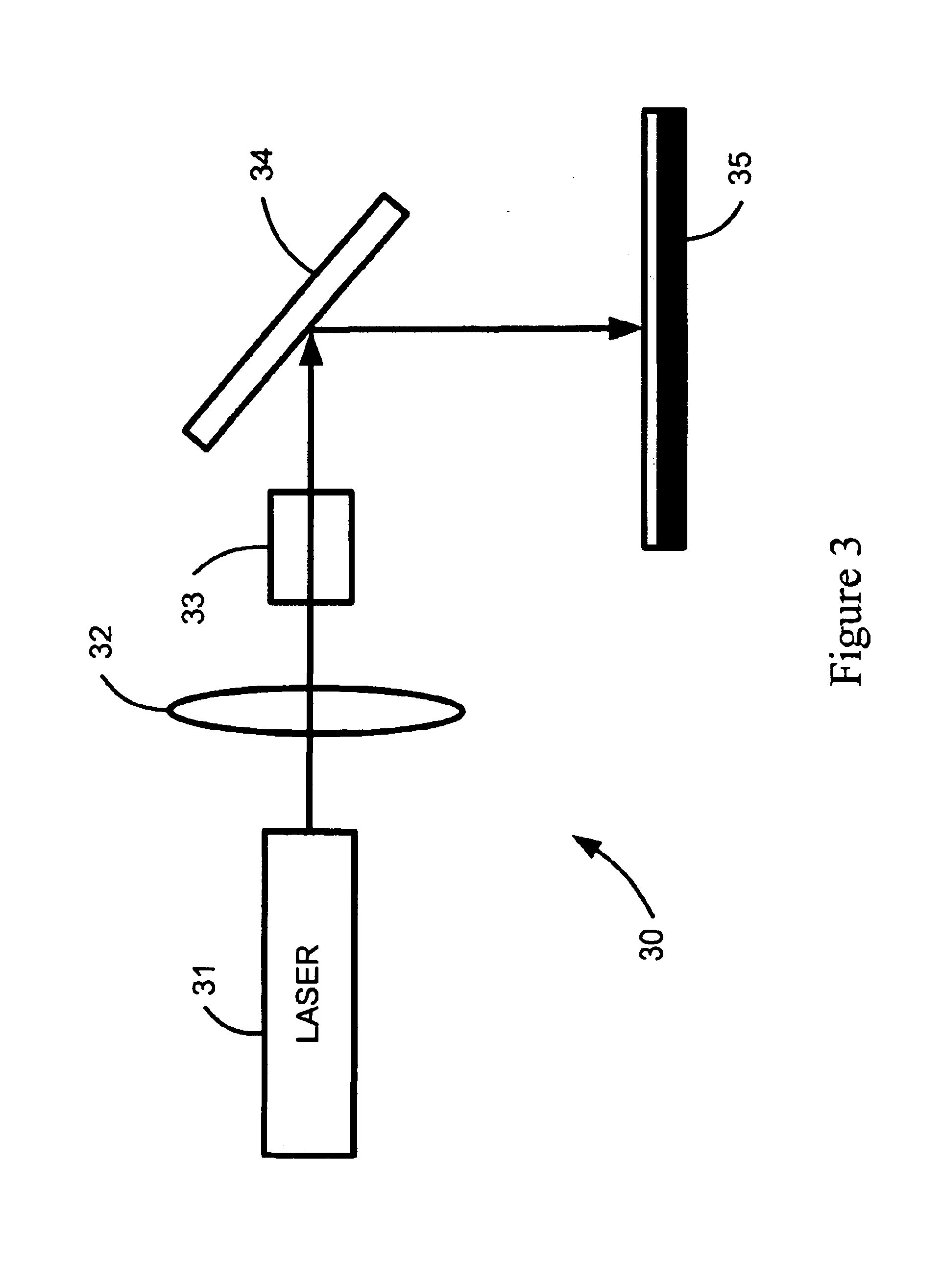
Direct-patterned optical waveguides on amorphous silicon films
InactiveUS20040240821A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical waveguide light guideWave structureRefractive index
An optical waveguide structure is formed by embedding a core material within a medium of lower refractive index, i.e. the cladding. The optical index of refraction of amorphous silicon (a-Si) and polycrystalline silicon (p-Si), in the wavelength range between about 1.2 and about 1.6 micrometers, differ by up to about 20%, with the amorphous phase having the larger index. Spatially selective laser crystallization of amorphous silicon provides a mechanism for controlling the spatial variation of the refractive index and for surrounding the amorphous regions with crystalline material. In cases where an amorphous silicon film is interposed between layers of low refractive index, for example, a structure comprised of a SiO2 substrate, a Si film and an SiO2 film, the formation of guided wave structures is particularly simple.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
High quantum efficiency photodetector
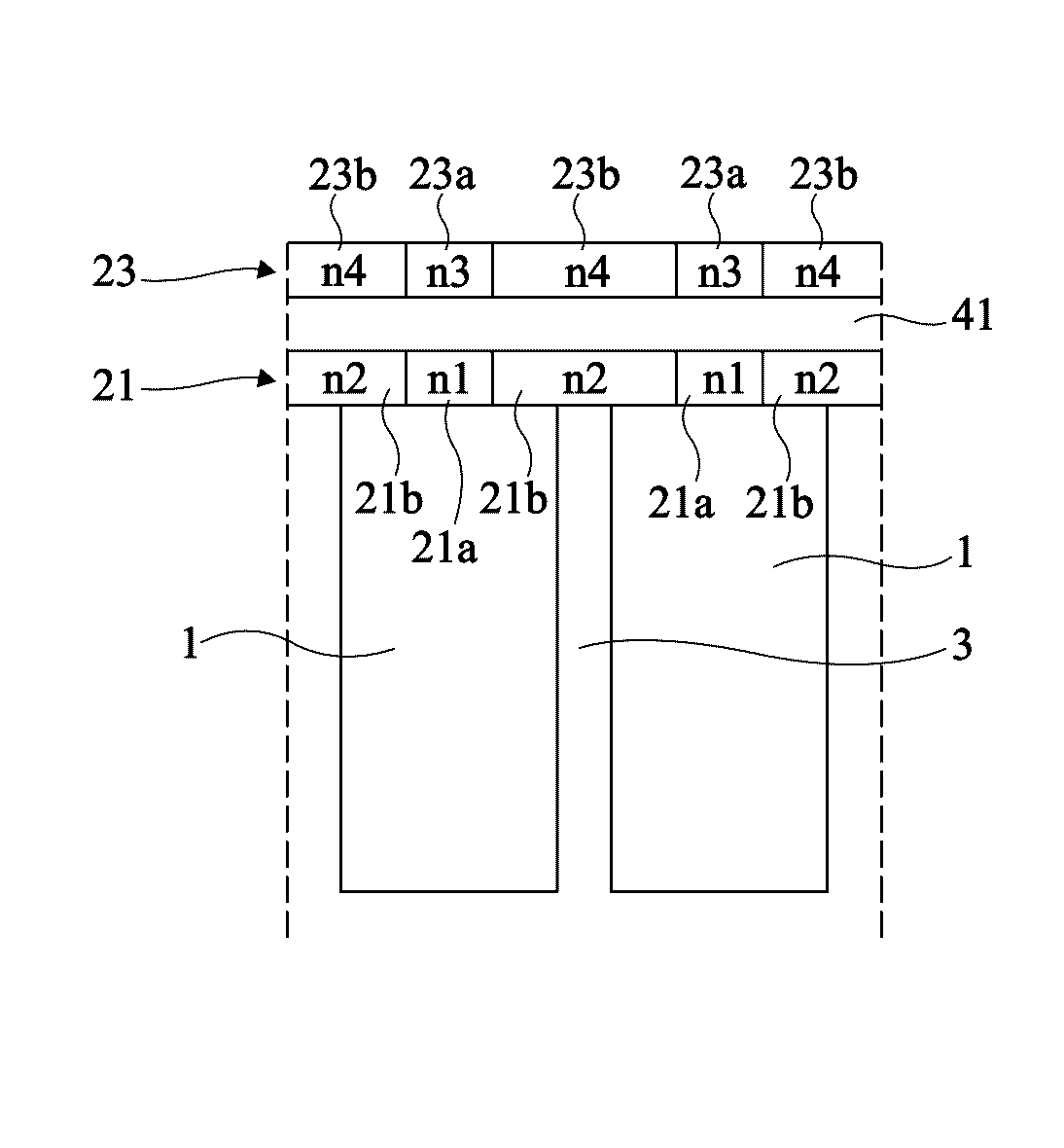
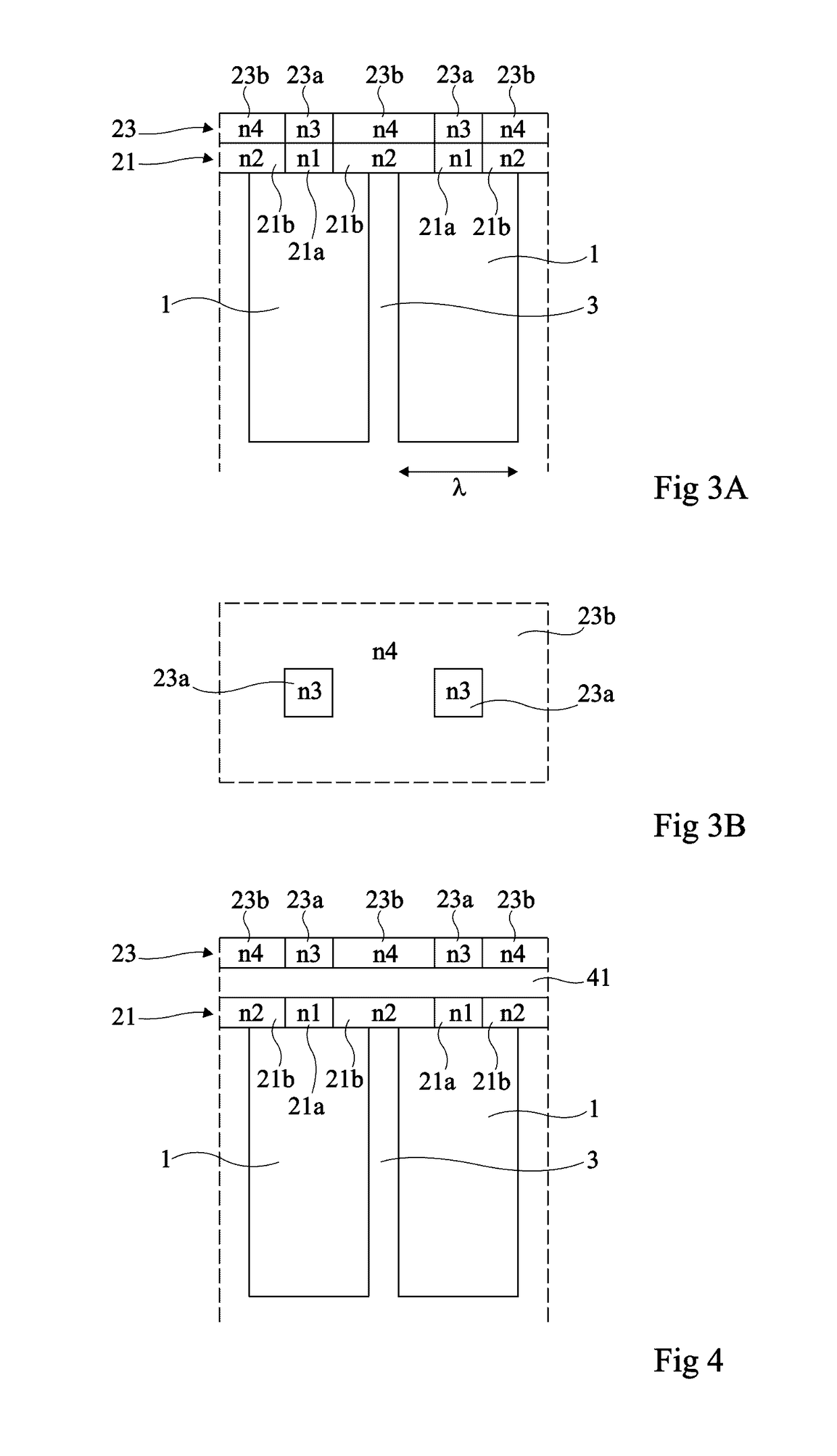
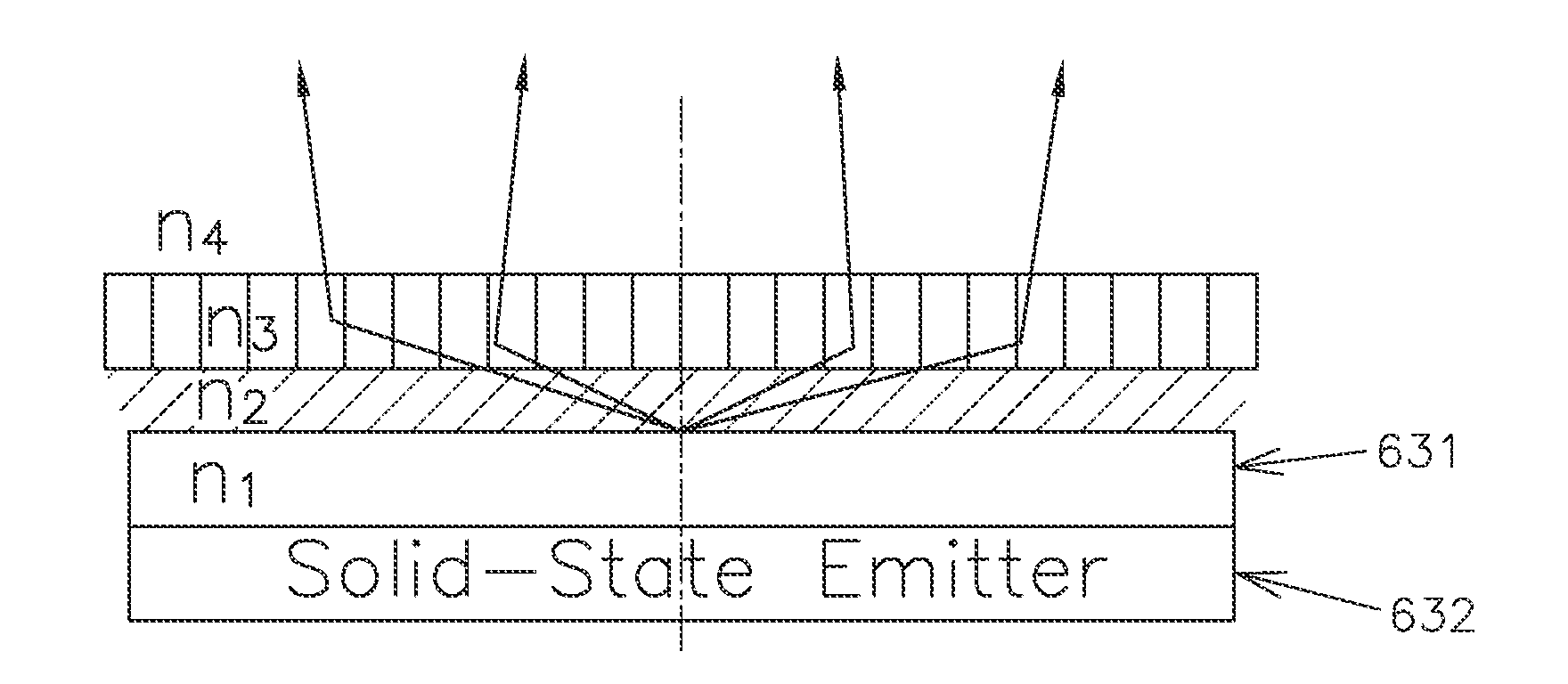
A photodetector including a photoelectric conversion structure made of a semiconductor material and, on a light-receiving surface of the conversion structure, a stack of first and second diffractive elements, the second element being above the first element, wherein: the first element includes at least one pad made of a material having an optical index n1, laterally surrounded with a region made of a material having an optical index n2 different from n1; the second element includes at least one pad made of a material having an optical index n3, laterally surrounded with a region made of a material having an optical index n4 different from n3; the pads of the first and second elements are substantially vertically aligned; and optical index differences n1−n2 and n3−n4 have opposite signs.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
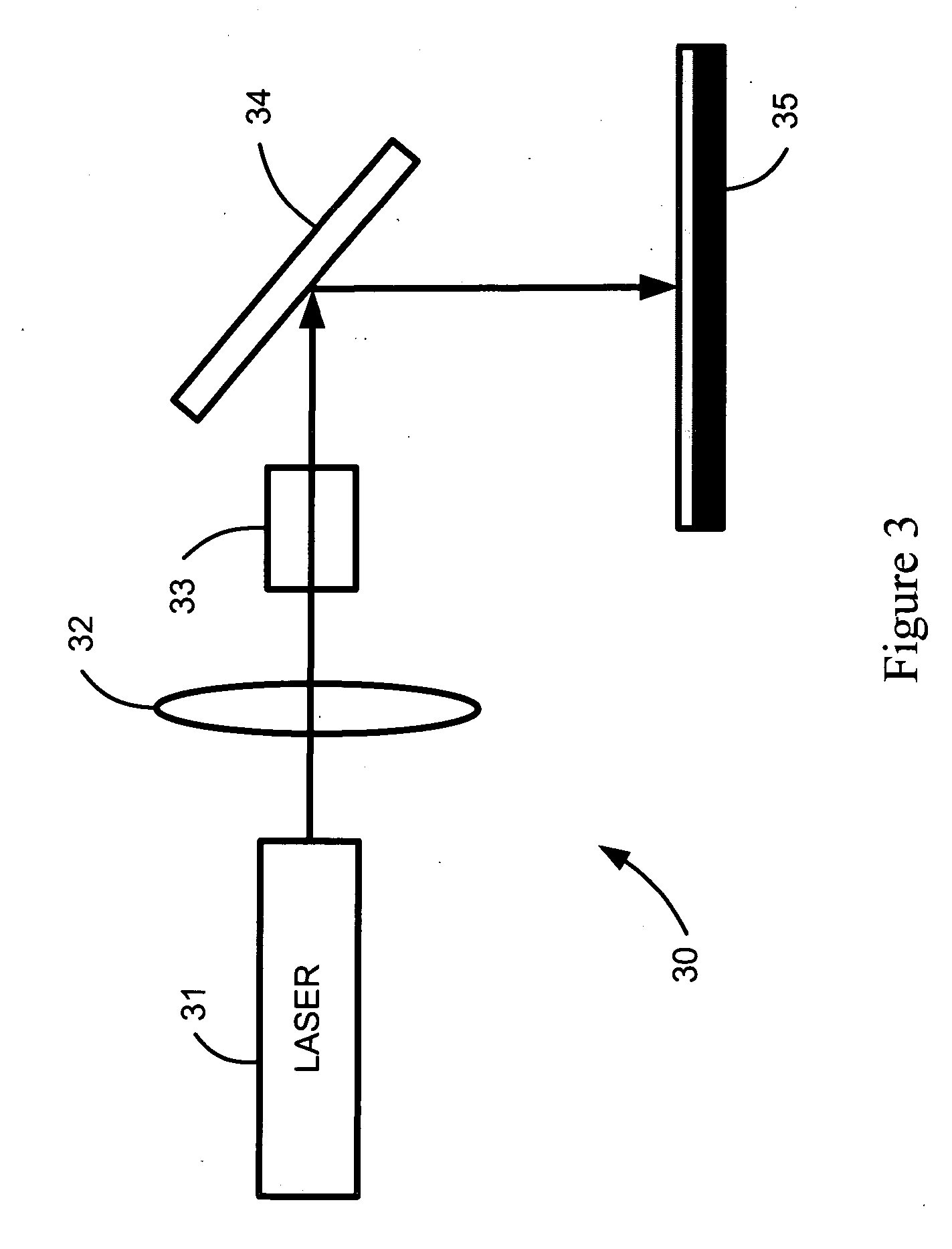
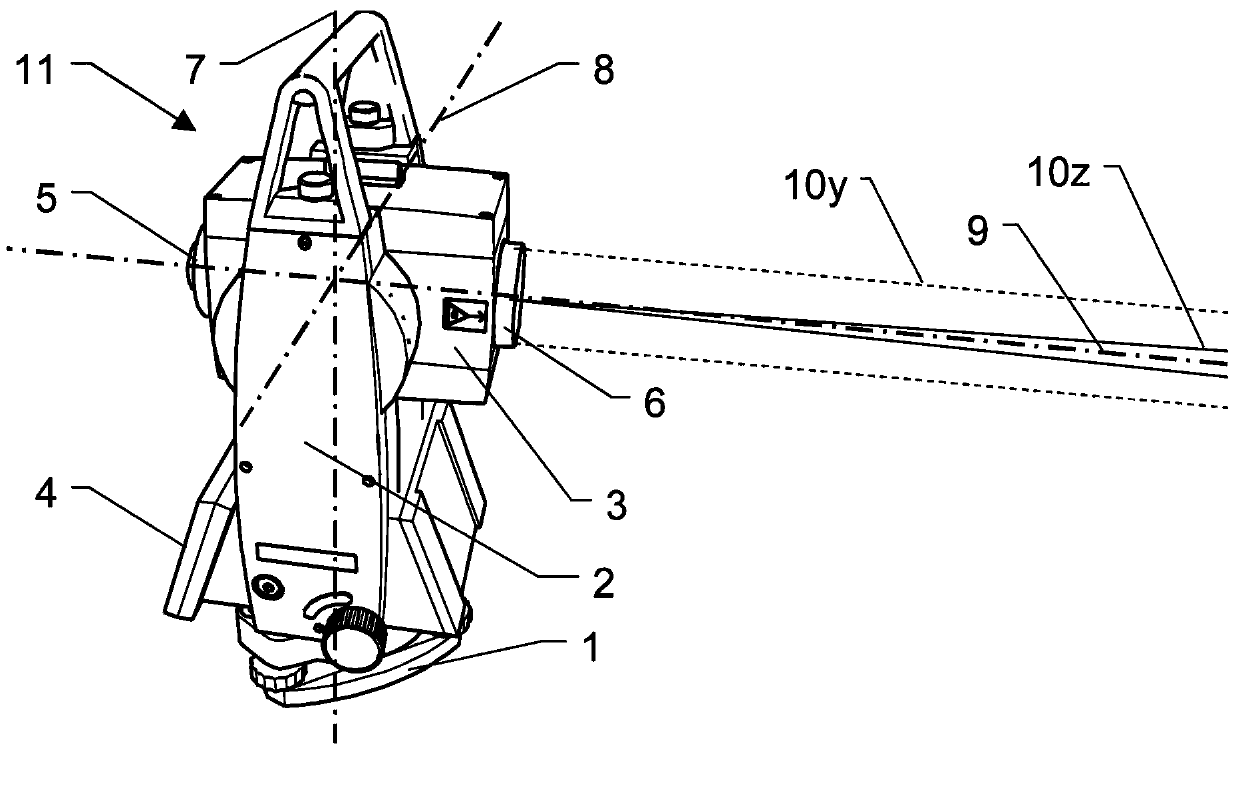
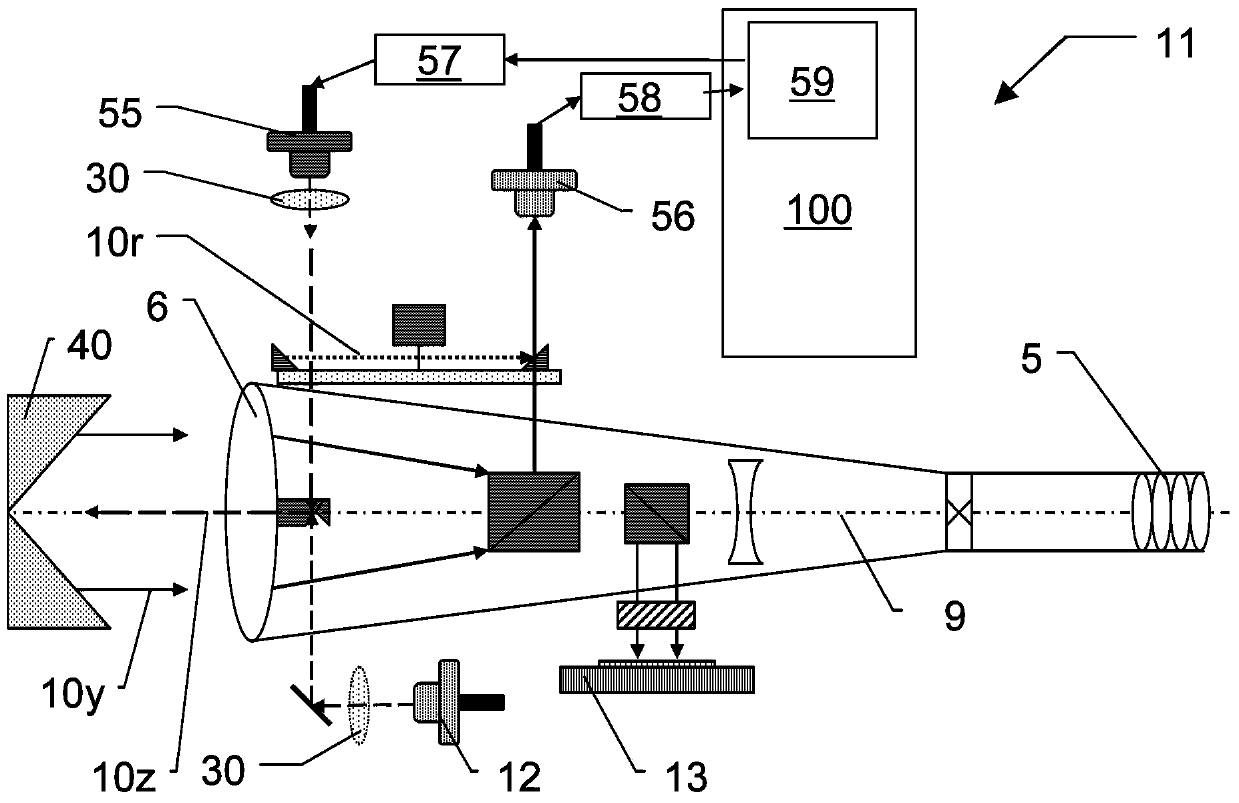
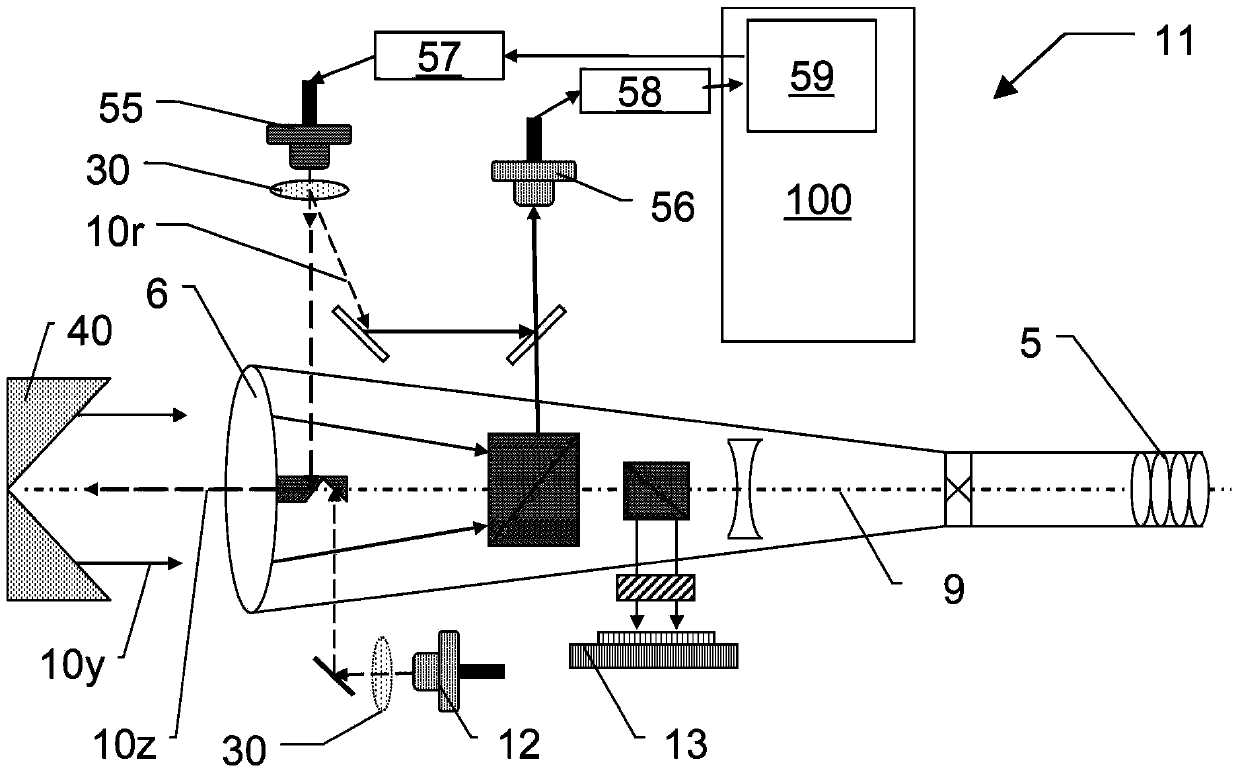
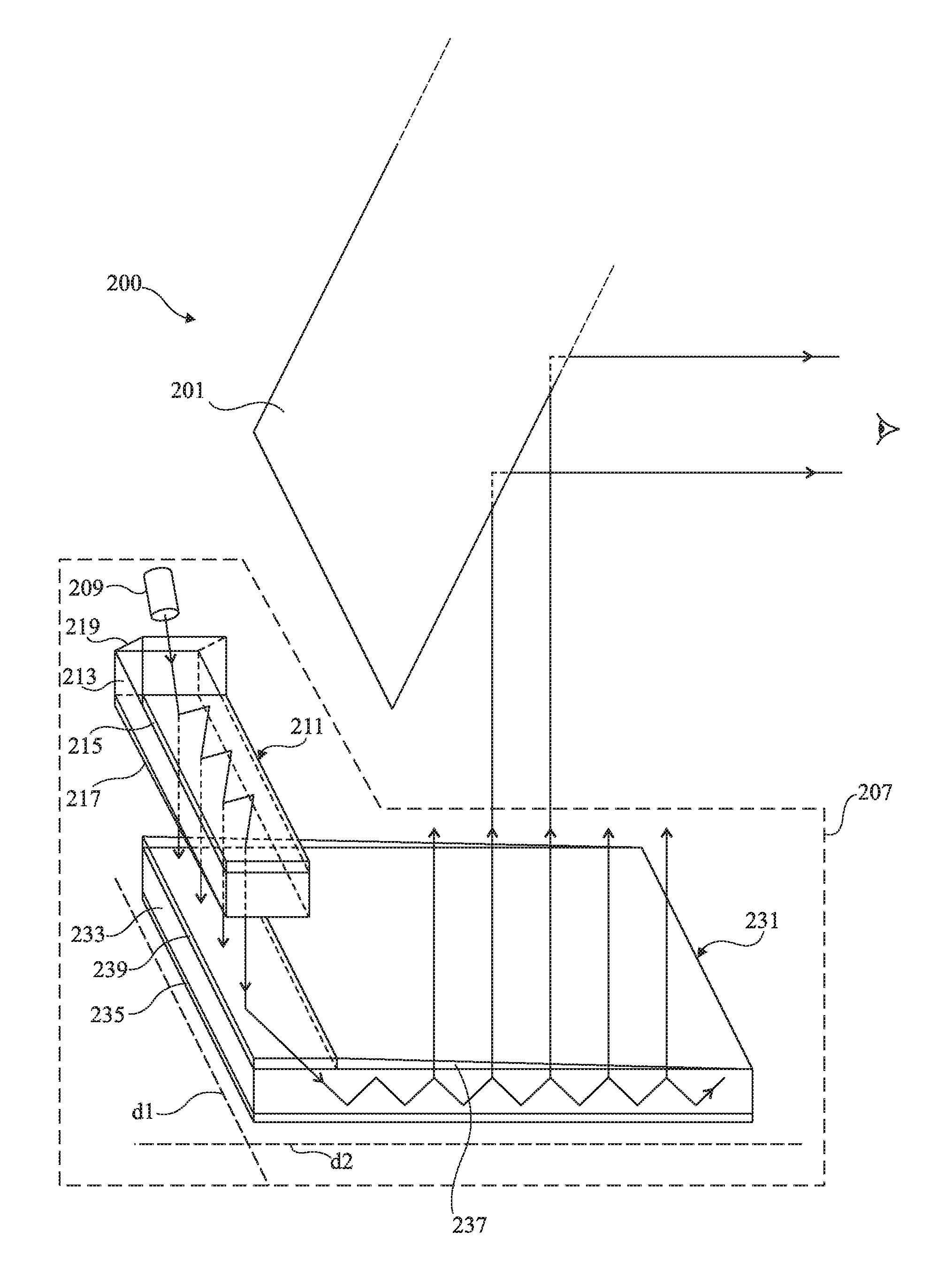
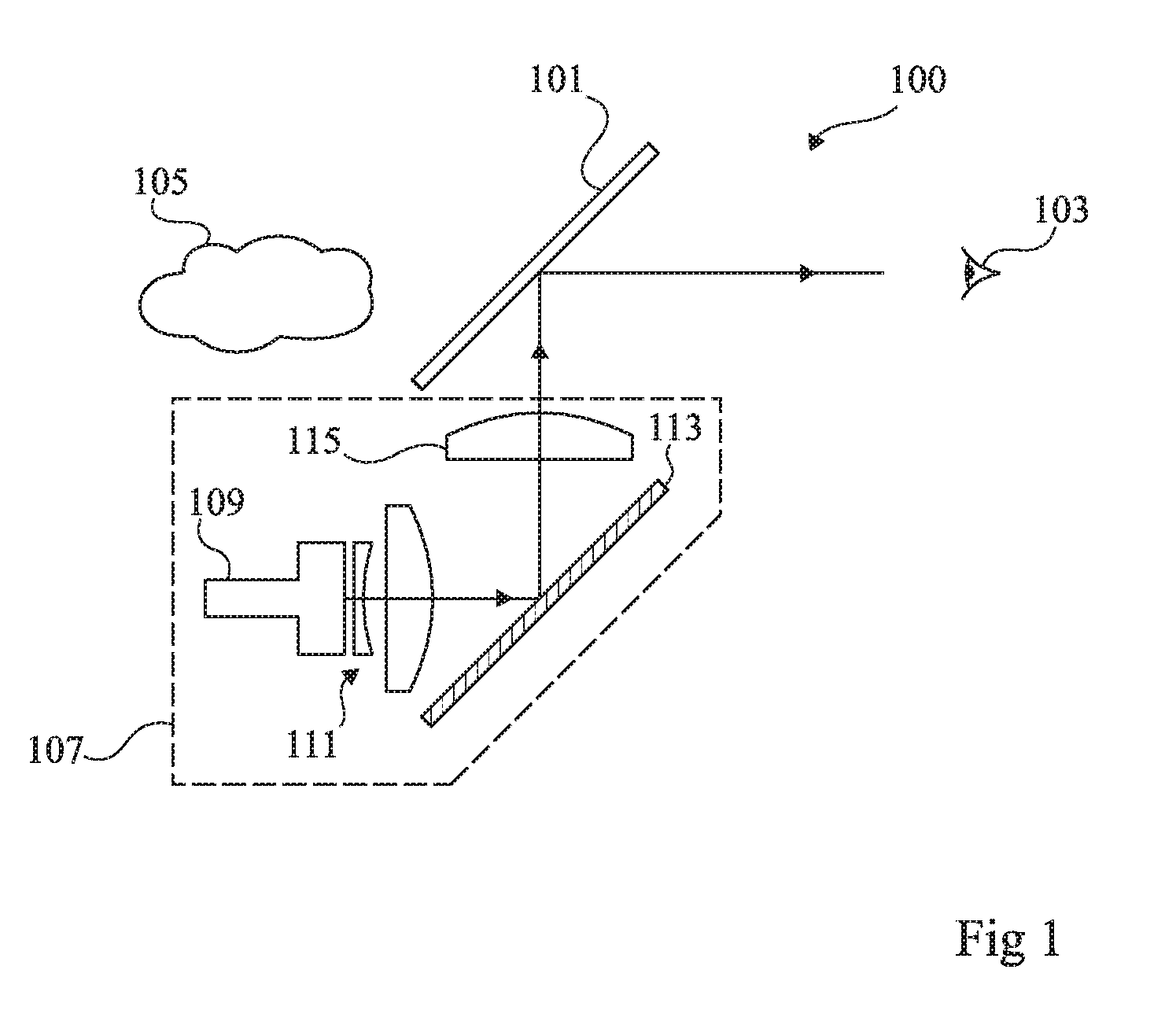
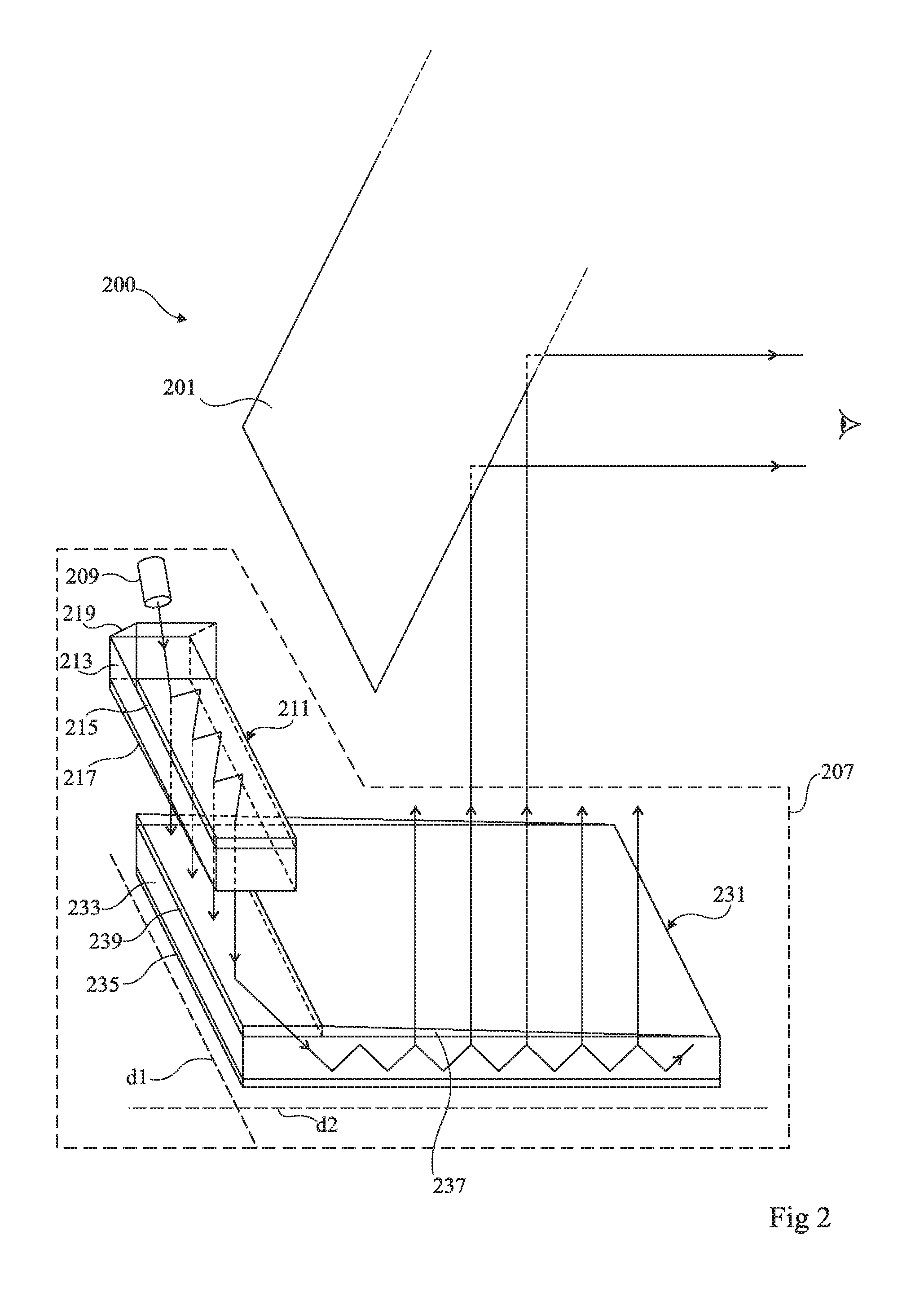
Surveying device, method for surveying target object with the survey device and computer program product
ActiveCN104101335AReference line/planes/sectorsElectromagnetic wave reradiationElectricityOptical radiation
The invention relates to a surveying device, a method for surveying a target object with the survey device and a computer program product. The surveying device has a base for setting up the surveying device and a targeting unit, which is rotatable in relation to the base about two axes, and which defines a target axis or targeting a target object to be surveyed. The targeting unit has a first beam path for emitting optical radiation in the direction of the target object to be surveyed and a second beam path for receiving a component of the optical radiation, which is reflected from the target object, by way of an optoelectronic receiving element. In some embodiments, at least one of the beam paths, has an optical element, which is implemented having an optically transparent, deformable volume body, and which has at least one interface toward a medium having an optical index of refraction deviating from the volume body. The interface makes the optical reflective performance changes on at least two different directions by deformation of a plurality of electrical activation signals.
Owner:HEXAGON TECH CENT GMBH
Direct-patterned optical waveguides on amorphous silicon films
InactiveUS6925216B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical waveguide light guideWave structureRefractive index
An optical waveguide structure is formed by embedding a core material within a medium of lower refractive index, i.e. the cladding. The optical index of refraction of amorphous silicon (a-Si) and polycrystalline silicon (p-Si), in the wavelength range between about 1.2 and about 1.6 micrometers, differ by up to about 20%, with the amorphous phase having the larger index. Spatially selective laser crystallization of amorphous silicon provides a mechanism for controlling the spatial variation of the refractive index and for surrounding the amorphous regions with crystalline material. In cases where an amorphous silicon film is interposed between layers of low refractive index, for example, a structure comprised of a SiO2 substrate, a Si film and an SiO2 film, the formation of guided wave structures is particularly simple.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
High-brightness LED-phosphor coupling
A high brightness LED phosphor coupling device. A semiconductor light source is encapsulated by a medium of first index of refraction, a layer of phosphor surrounded by a second medium of second index of refraction of optical index less than the first index and a light coupler for redirecting most of the light from the light source to an area of the phosphor about equal to the area of the light source multiplied by the square of the ratio of the first to the second index of refraction.
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
LED device having improved output and contrast
ActiveUS7710026B2Discharge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesRefractive indexContrast enhancement
An electroluminescent (EL) device having an LED formed on a substrate with at least two electrodes formed over the substrate, and an EL unit formed between the electrodes. At least one of the electrodes is transparent. At least one of the electrodes is patterned to define independently controllable light-emitting areas. A cover is formed over the LED. The cover or substrate is transparent. A light-scattering layer is formed between the cover and substrate for scattering light. A low-index element, having an optical index lower than other optical indices, is formed between the scattering layer and the transparent cover or substrate. Additionally, a contrast-enhancement layer includes alternating light-absorbing portions and light-transmissive portions formed in the layer located between the light-scattering layer and the transparent substrate or cover through which light is emitted, wherein the light-absorbing portions and light-transmissive portions are located in each light-emitting area.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Method and apparatus for spatially modulated electric field generation and electro-optical tuning using liquid crystals
InactiveUS7859640B2Reduce lossSimple in construction and manufactureNon-linear opticsLensDielectricElectric field modulation
A variable optical device for controlling the propagation of light has a liquid crystal layer (1), electrodes (4) arranged to generate an electric field acting on the liquid crystal layer, and an electric field modulation layer (3,71) arranged between the electrodes and adjacent the liquid crystal layer for spatially modulating said electric field in a manner to control the propagation of light passing through said optical device. The electric field modulation layer has either an optical index of refraction that is essentially spatially uniform, or a polar liquid or gel, or a very high low frequency dielectric constant material having a dielectric constant greater than 20, and preferably greater than 1000. The modulation layer can have a solid body having a first low frequency dielectric constant with a shape selected to impart a desired modulation of the electric field, and a second low frequency dielectric constant material surrounding or adjacent to the solid body such that the solid body and the second material form a layer geometry.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL +1
Multi-channel intelligent optical testing device
ActiveCN103647600AFreely configure the number of channelsFree configuration of test indicatorsFibre transmissionTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsControl cellDetector array
The invention discloses a multi-channel intelligent optical testing device which comprises a light source, a light source control circuit, a wavelength calibration monitoring module and an optical switch which are sequentially connected. One output end of the optical switch is sequentially connected with a polarization controller, a 2*2 shunt and a 1*N optical splitter. One output end of the 2*2 shunt is connected with a first optical power detector, and one input end of the 2*2 shunt is connected with a second optical power detector. The other output end of the optical switch is connected with an N*N shunt, and output ends of the N*N shunt are connected with array optical power detectors in a one-to-one correspondence mode. The light source control circuit, the wavelength calibration monitoring module, the optical switch, the polarization controller, the first optical power detector, the second optical power detector and the array optical power detectors are connected with a control unit. The testing device can test optical indexes of a multi-channel module.
Owner:GUANGXUN SCI & TECH WUHAN
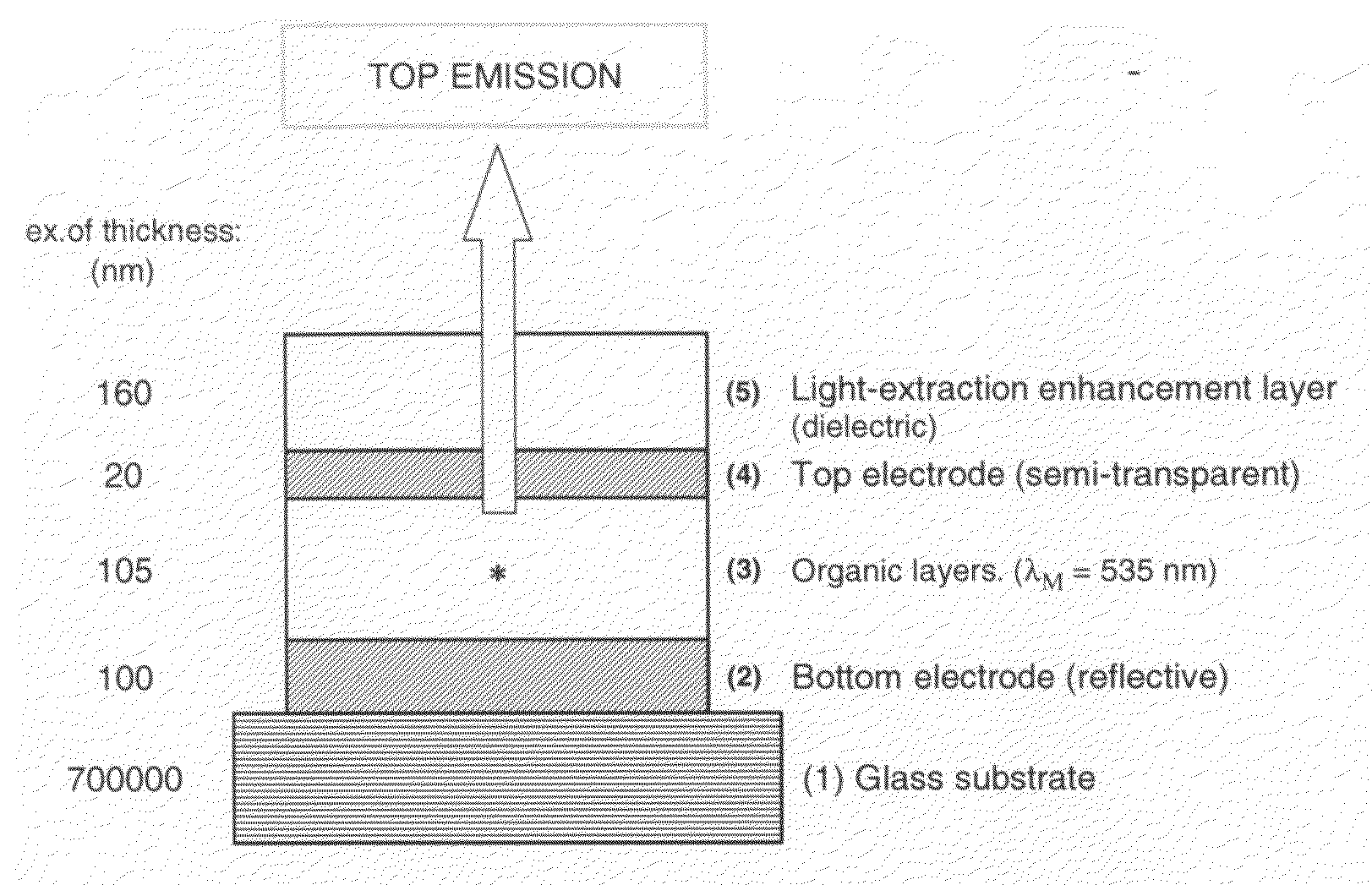
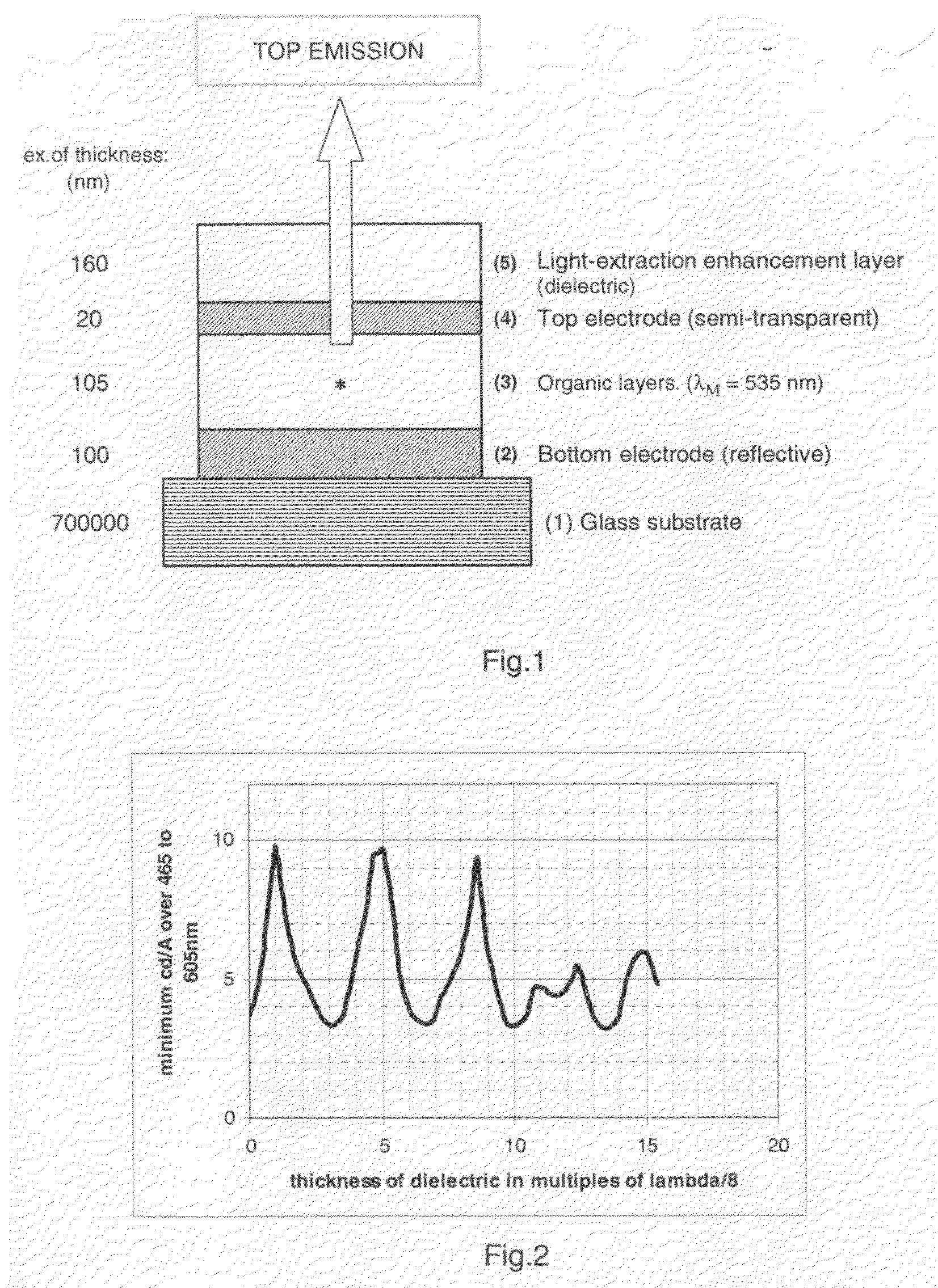
Oled or group of adjacent oleds with a light-extraction layer efficient over a large range of wavelengths
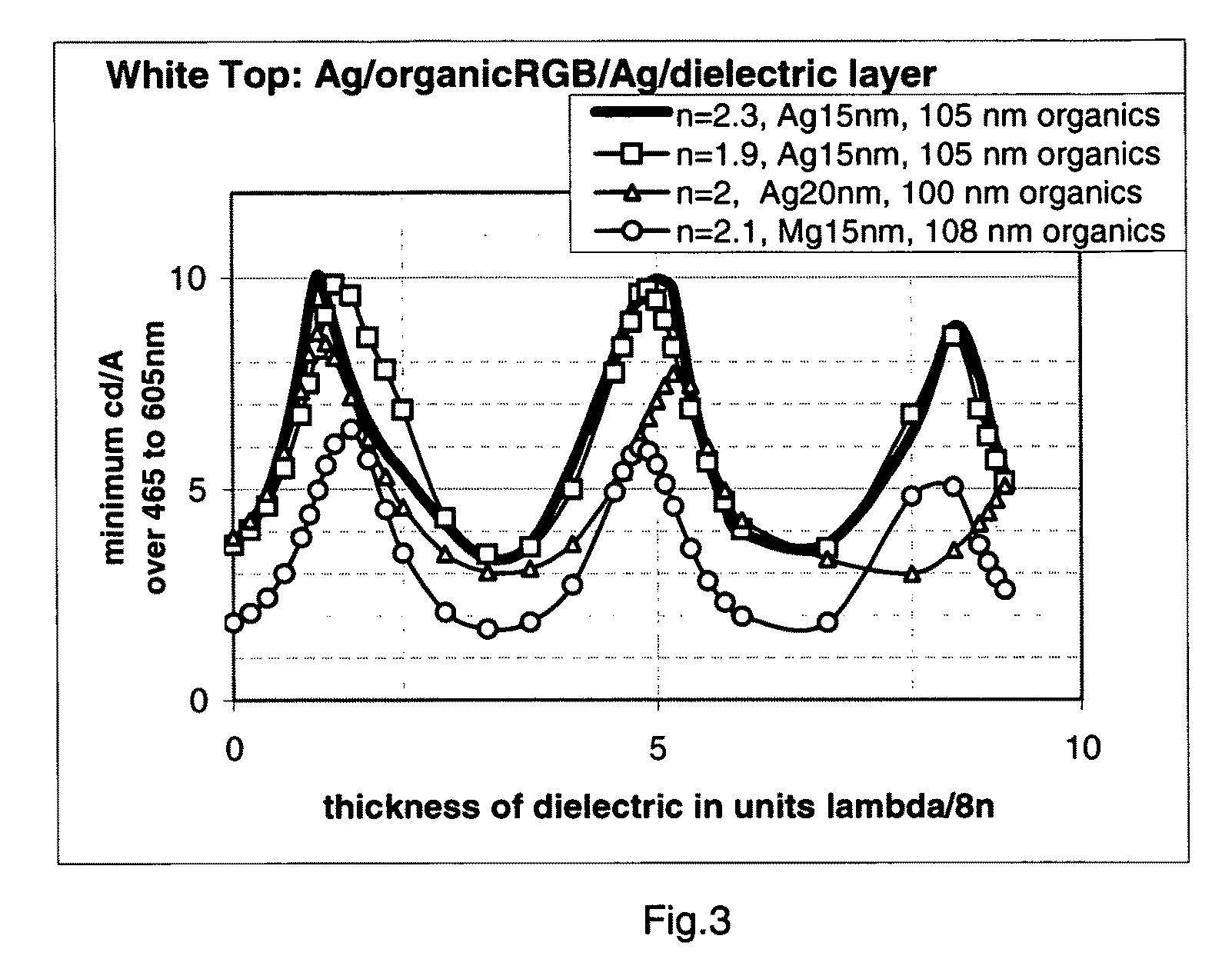
ActiveUS20100084677A1Improve light extractionIncrease heightSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricLength wave
An organic light emitting diode comprises, between a bottom electrode and a top electrode, an organic light-emitting layer and a light-extraction enhancement layer made of a dielectric material. According to the invention, if nD, is the optical index of said dielectric material, and if λM is the center of the range of wavelengths of the emitted light, the thickness of the light-extraction enhancement layer is approximately equal to 5.λM / 8.nD. Thank to the invention, light extraction is enhanced in a range of wavelengths superior or equal to 150 nm.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
Waveguide display
An optical waveguide system includes a generally planar waveguide (1) arranged so that light can be injected by a projector (2) into one edge at a range of out-of-plane angles. The waveguide (1) is tapered so that different out-of-plane angles, after being totally internally reflected for a certain distance, leave the waveguide at different respective points along the waveguide. This expands the image in the direction of propagation along the waveguide. Meanwhile the image is expanded transversely by a parallel-sided input waveguide (3). A large-area flat-panel display is thus created, or the planar waveguide can be used as a planar collimating light source or, using layers of controllable optical index, an optical switch.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE FLAT PROJECTION DISPLAY
Nano-Structured Lens for Collimating Light from Surface Emitters
ActiveUS20170017091A1Improve efficiencyReduce power usageMicroscopesSpectral modifiersRefractive indexNanostructure
A light source for providing light comprises a light emitting layer and a lens comprising a periodic structure therein that is periodic along at least one direction in a plane. The structure includes or is formed from at least two optically transparent materials of different optical indices. The lens is separated from the light emitting layer, and the radiation propagating from the light emitting layer within an angle to a line normal to the plane will be transmitted by the lens to a far field in an index-guided mode. The separation between the light emitting layer and the lens is such that near field radiation propagating from the light emitting layer towards the lens not within said angle to the line will be scattered and redirected by the first lens to the far field to thereby collimate the radiation propagating from the light emitting layer to the far field.
Owner:DICON FIBEROPTICS
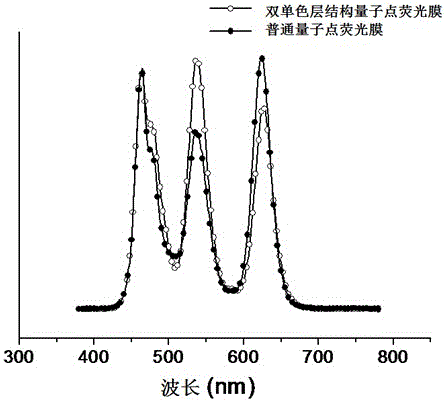
Quantum dot fluorescent film with double-monocolor-layer structure and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN105856763AHigh optical strengthReduce dosageSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationFluorescenceQuantum dot
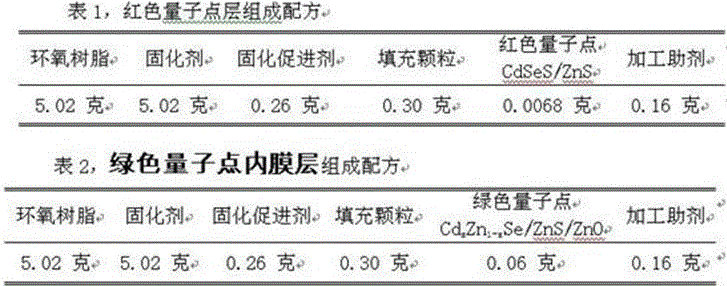
The embodiment of the invention provides a quantum dot fluorescent film with a double-monocolor-layer structure and a manufacturing method thereof; the quantum dot fluorescent film with the double-monocolor-layer structure includes two layers of substrates laminated together; the substrates are PET films, and the opposite inner surfaces of the two-side substrates are respectively provided with a green quantum dot inner film layer made of a green quantum dot composite colloid and a red quantum dot inner film layer made of a red quantum dot composite colloid. According to the embodiment of the invention, the PET films as the substrates are respectively coated with red and green monocolor quantum dot composite colloids, and then two monocolor quantum dot films are laminated to obtain the quantum dot fluorescent film with the double-monocolor-layer structure. With the same amount of quantum dots, the quantum dot fluorescent film with the double-monocolor-layer structure provided by the embodiment of the invention has higher optical intensity, thereby obviously reducing the amount of the quantum dots needed to realize same optical indexes.
Owner:北京北达双圆高分子技术有限公司
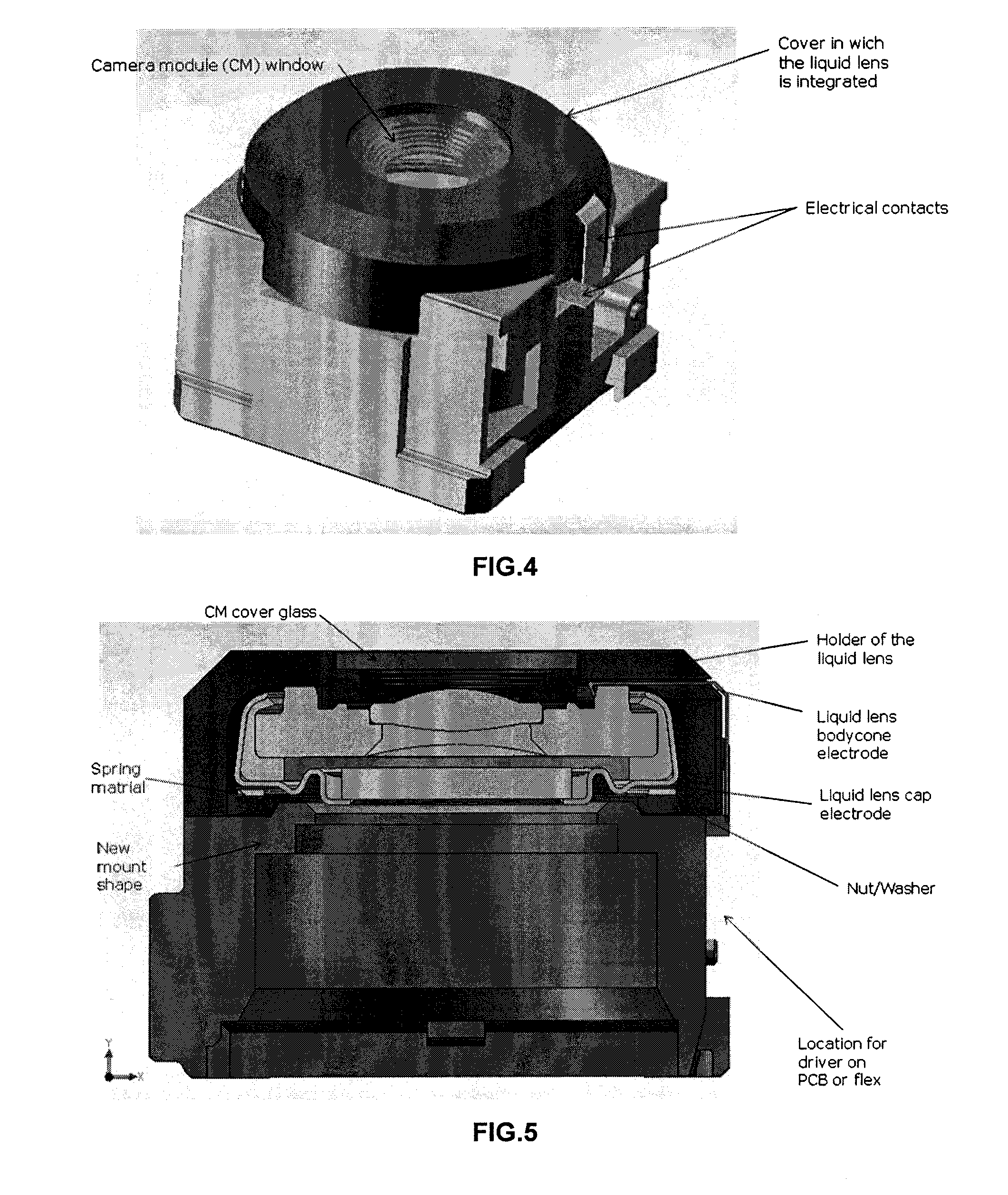
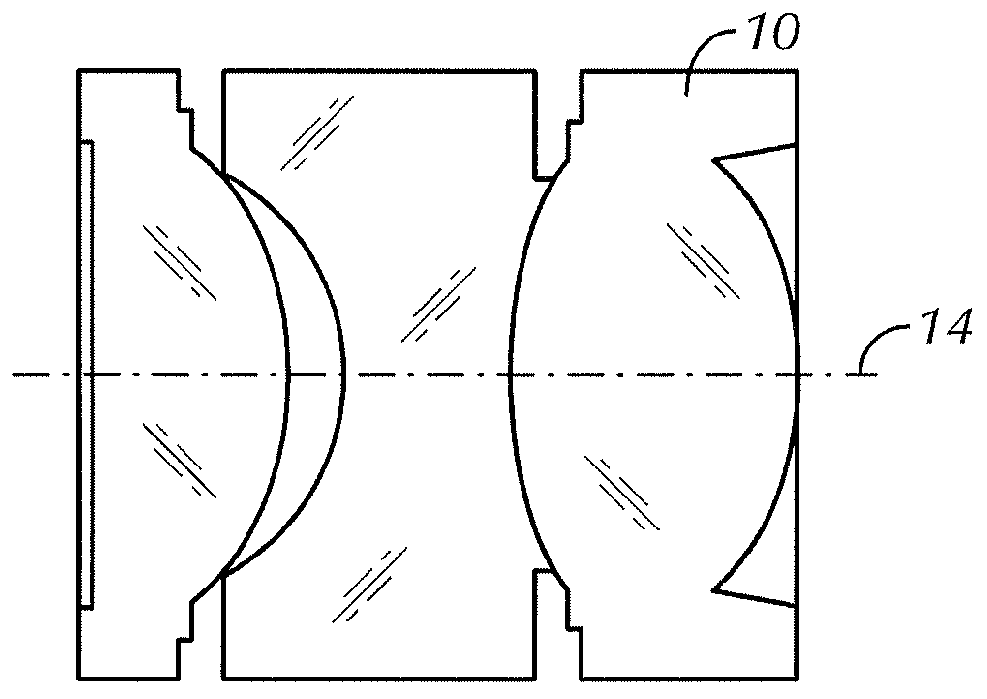
Optical device for high quality and compact camera module
An optical device for a lens assembly of a camera module is disclosed. The optical device includes a liquid lens having at least one fixed lens and a transparent window, facing each other and delimiting, at least in part, an internal volume containing two immiscible liquids having different optical indices, and a first and a second electrode. The liquids form an interface moveable by application of a voltage between said electrodes. The optical device also includes a liquid lens holder, wherein the liquid lens holder has at least one electrical contact for contacting one electrode of the liquid lens, and at least one Z reference datum for aligning the fixed lens of the liquid lens with other optical elements of the lens assembly.
Owner:INVENIOS FRANCE SAS
Lens of variable focal length
A lens assembly of variable focal length comprises two transparent plates (24, 38) at least partially facing each other and parallel to one another and delimiting, at least in part, an internal volume (15) containing two non-miscible liquids having different optical indices. The lens comprises an elastic element (36) capable of deforming in response to a change in pressure of the liquids, in such a way as to substantially maintain the optical properties of the lens assembly, e.g., in order to maintain the parallelism of the two transparent plates.
Owner:INVENIOS FRANCE SAS
Process producing an optical security component
A process for producing an optical security component including stamping a transparent film with a matrix having a first type of zone whose surface state is matte, and a second type of zone whose surface state has cuttings / slits for forming a diffraction network; depositing a layer of dielectric material with a high optical index on an entire surface, under a vacuum, on the film; partial metallization of the film by depositing a layer of metal on only part of the zones of each types whereas the other part remains transparent; and applying an adhesion layer.
Owner:HOLOGRAM INDUSTRIES
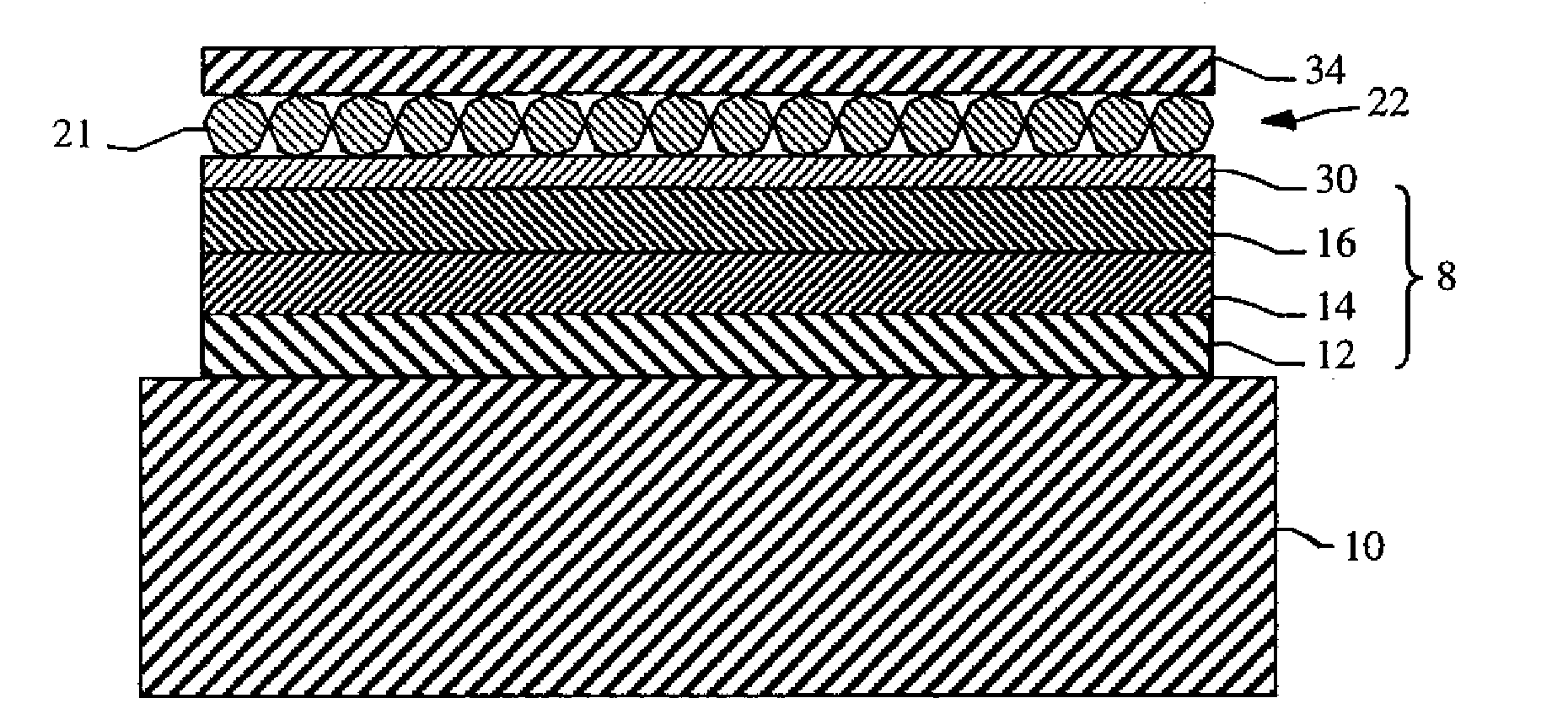
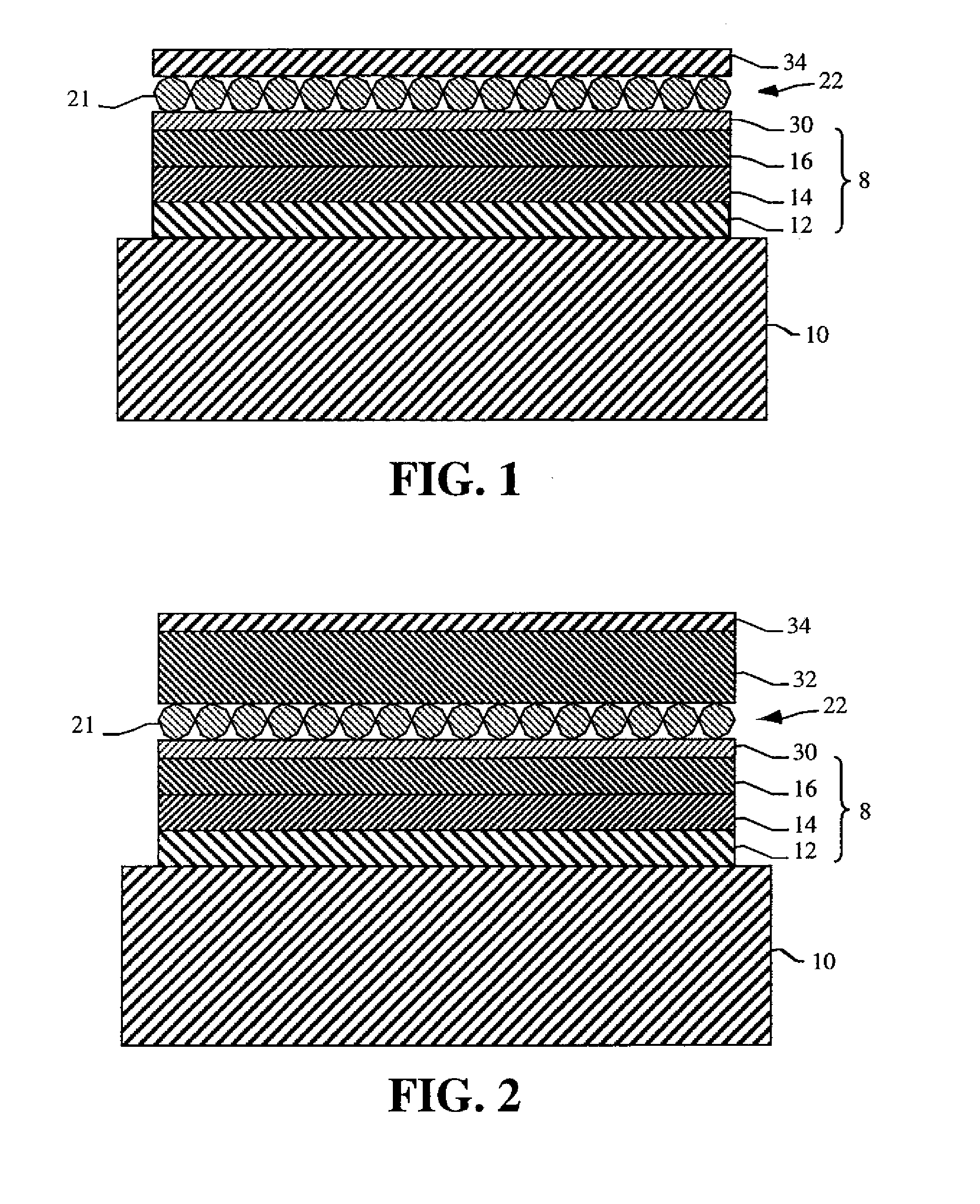
Tiled electroluminescent device with filled gaps
ActiveUS20100277064A1Improve uniformity of light emissionReduce reflectionDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsOblique angleLight emission
A tiled electroluminescent device that improves light-emission uniformity and reduces reflection from ambient light includes a first and a second electroluminescent device tile, a portion of the edge of the first device tile abutted with a portion of the edge of the second device tile leaving a gap between the first and second device tile edges, each device tile including a substrate, having an optical index and a level of transparency, and an electroluminescent diode for emitting light according to a distribution that is substantially Lambertian, whereby light is directed along an oblique angle to the surface of the substrate of the first tile and through the edge of the first device tile; and a filler located in the gap between the abutting edges of the first and second device tiles, the filler having an optical index and a level of transparency matched to the substrates.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
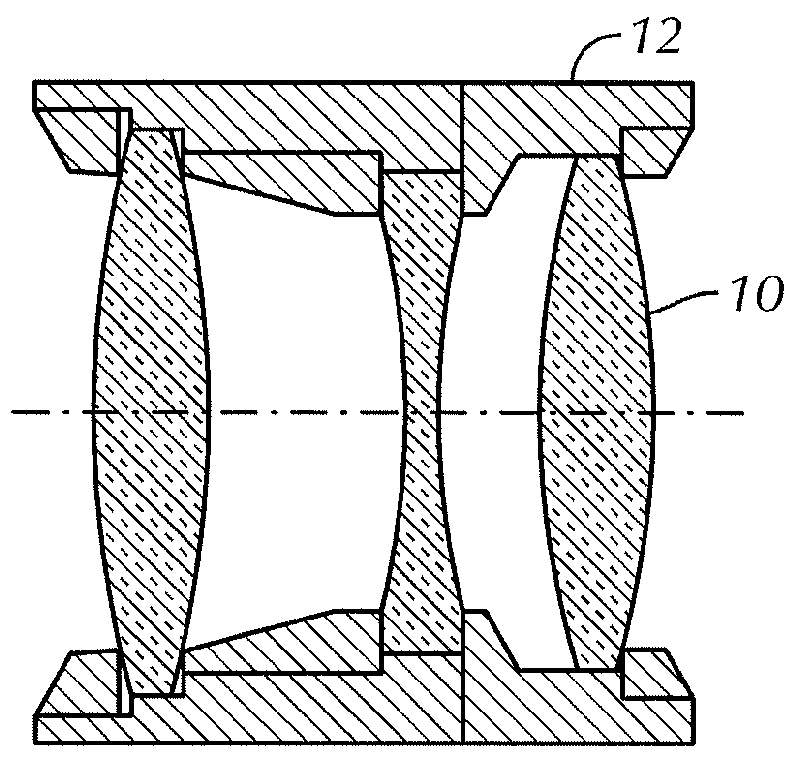
Lens with variable focal length and symmetry
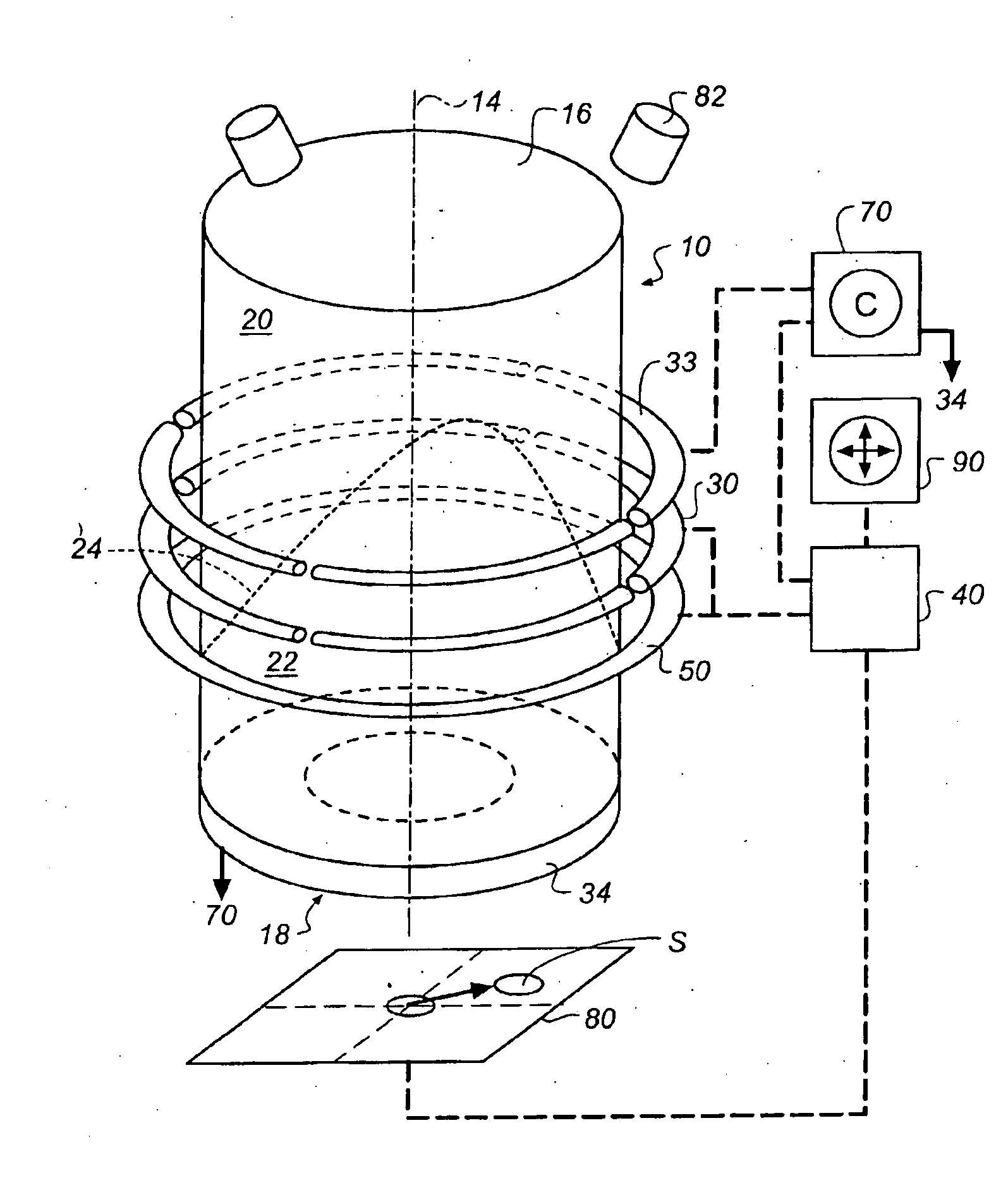
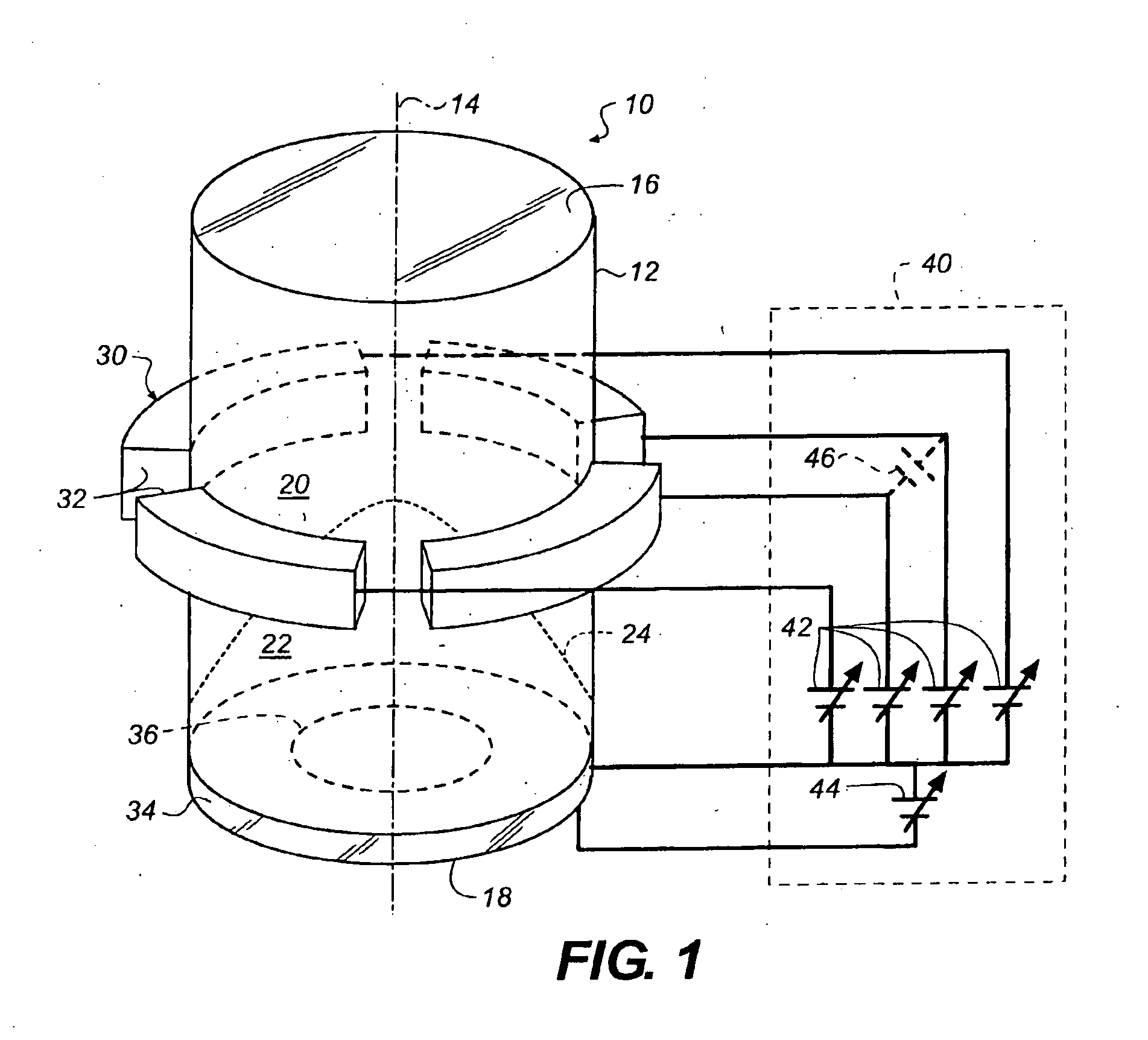
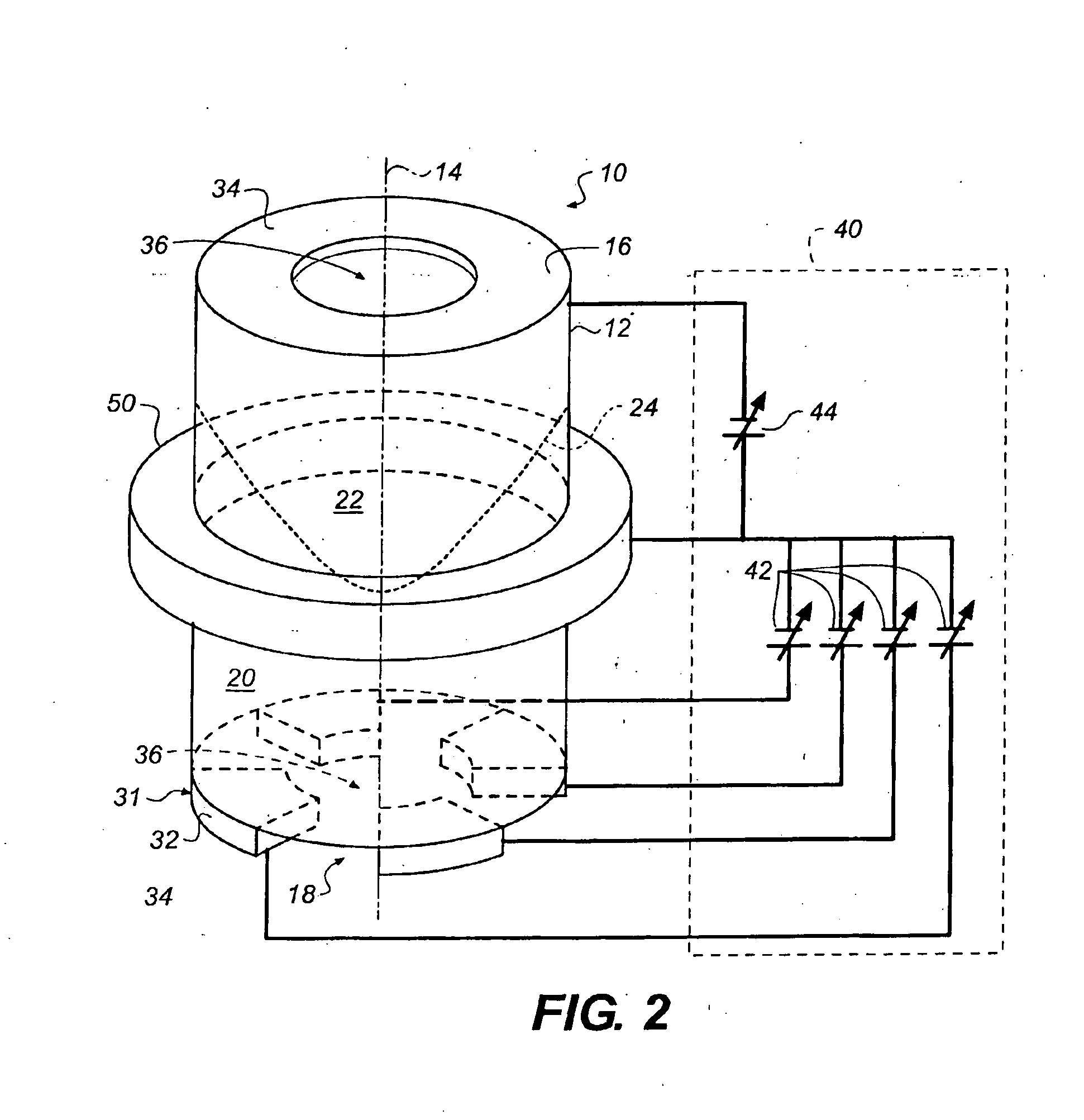
The invention relates to a variable focal length lens with a chamber (10) having symmetry of revolution around an axis (14) and containing one first transparent fluid (20) and one second transparent fluid (22) that have different optical indices and are immiscible, so as to form a meniscus (24), and that have different electrical conductivities, and means (30, 40) to modify the curvature of the meniscus.According to the invention, the means to modify the curvature of the meniscus comprises means of applying an electric field dissymmetrical in relation to the axis of said chamber.The invention has applications in the production of cameras.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
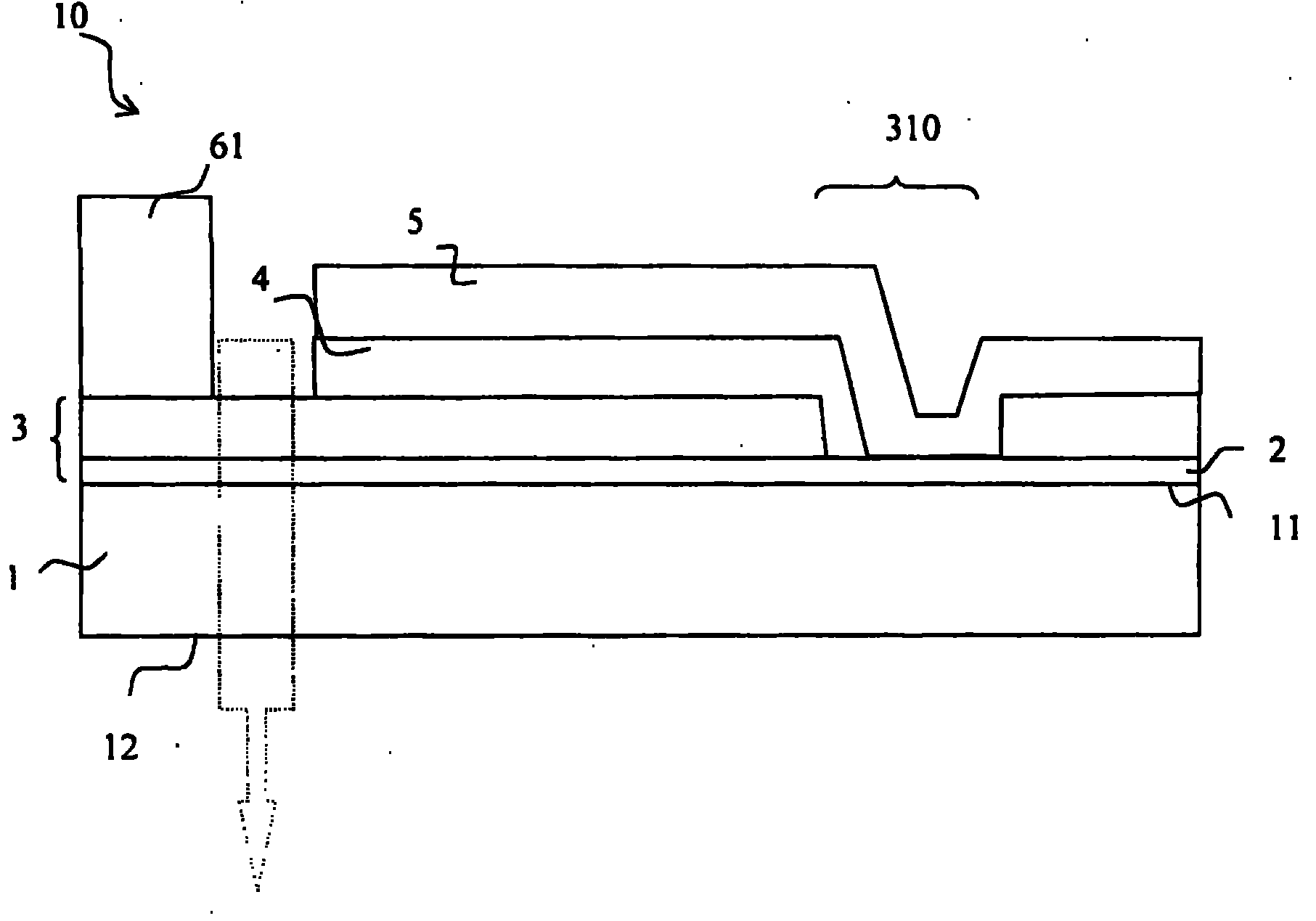
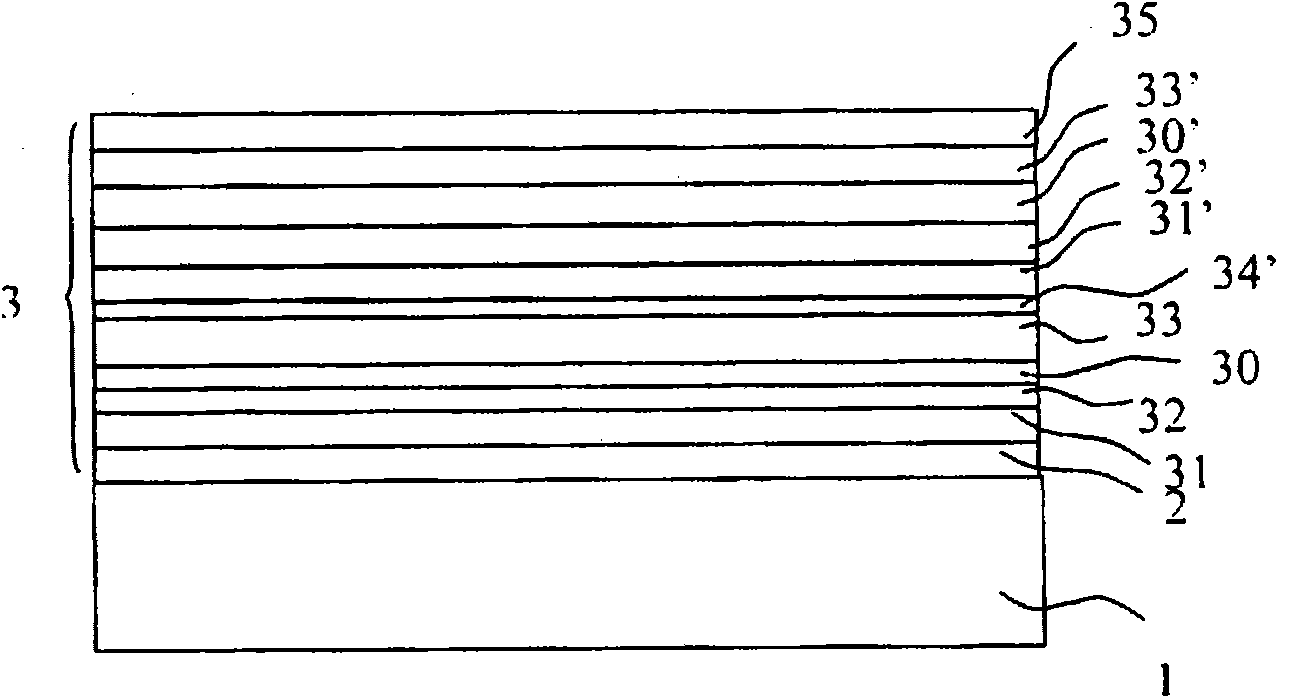
Substrate for an organic light-emitting device, and organic light-emitting device incorporating it
InactiveCN101960638ASatisfactory conductivityImprove conductivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductanceOrganic light emitting device
The invention relates to a substrate for an organic light-emitting device (10), comprising a transparent substrate (1) of optical index n0 bearing, on a first main face (11), a transparent or semi-transparent first electrode coating (3), called the bottom electrode, having a sheet resistance less than or equal to 6 O / square and which contains the following multilayer stack: an antireflection sublayer (2) of given optical thickness L1 and optical index n1 such that the n1 / n0 ratio is greater than or equal to 6 / 5; a first metal layer of given thickness e1; a first separating layer of given optical thickness L2; a second metal sheath, having an intrinsic electrical conductivity property, of given thickness e2; and a work-function-matching overlayer, L1 being between 20 nm and 120 nm, L2 being between 75 nm and 200 nm, and the sum of the thicknesses e1 + e2 of the first and second metal layers being less than or equal to 40 nm.
Owner:SAINT-GOBAIN GLASS FRANCE
Optical device for high quality and compact camera module
An optical device for a lens assembly of a camera module is disclosed. The optical device includes a liquid lens having at least one fixed lens and a transparent window, facing each other and delimiting, at least in part, an internal volume containing two immiscible liquids having different optical indices, and a first and a second electrode. The liquids form an interface moveable by application of a voltage between said electrodes. The optical device also includes a liquid lens holder, wherein the liquid lens holder has at least one electrical contact for contacting one electrode of the liquid lens, and at least one Z reference datum for aligning the fixed lens of the liquid lens with other optical elements of the lens assembly.
Owner:CORNING INC
Device for extending the exit pupil and head up display comprising said device
InactiveUS20170031161A1Simpler and more compactPlanar/plate-like light guidesHead-up displayExit pupil
An optical device comprises a transparent blade the first surface of which is reflective; a first partially reflective and partially transmissive layer covering a second surface of the transparent blade opposite the first surface, and a second layer covering the surface of the first layer opposite the transparent blade, wherein the second layer is made of a material having an optical index which differs from the optical index of the transparent blade by less than 10% and preferably by less than 5%, and the second layer comprises, on the surface thereof opposite the first layer, structures forming a diffraction grating suitable for promoting the extraction of light towards the outside of the transparent blade.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com