Patents
Literature
34results about How to "Satisfactory conductivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
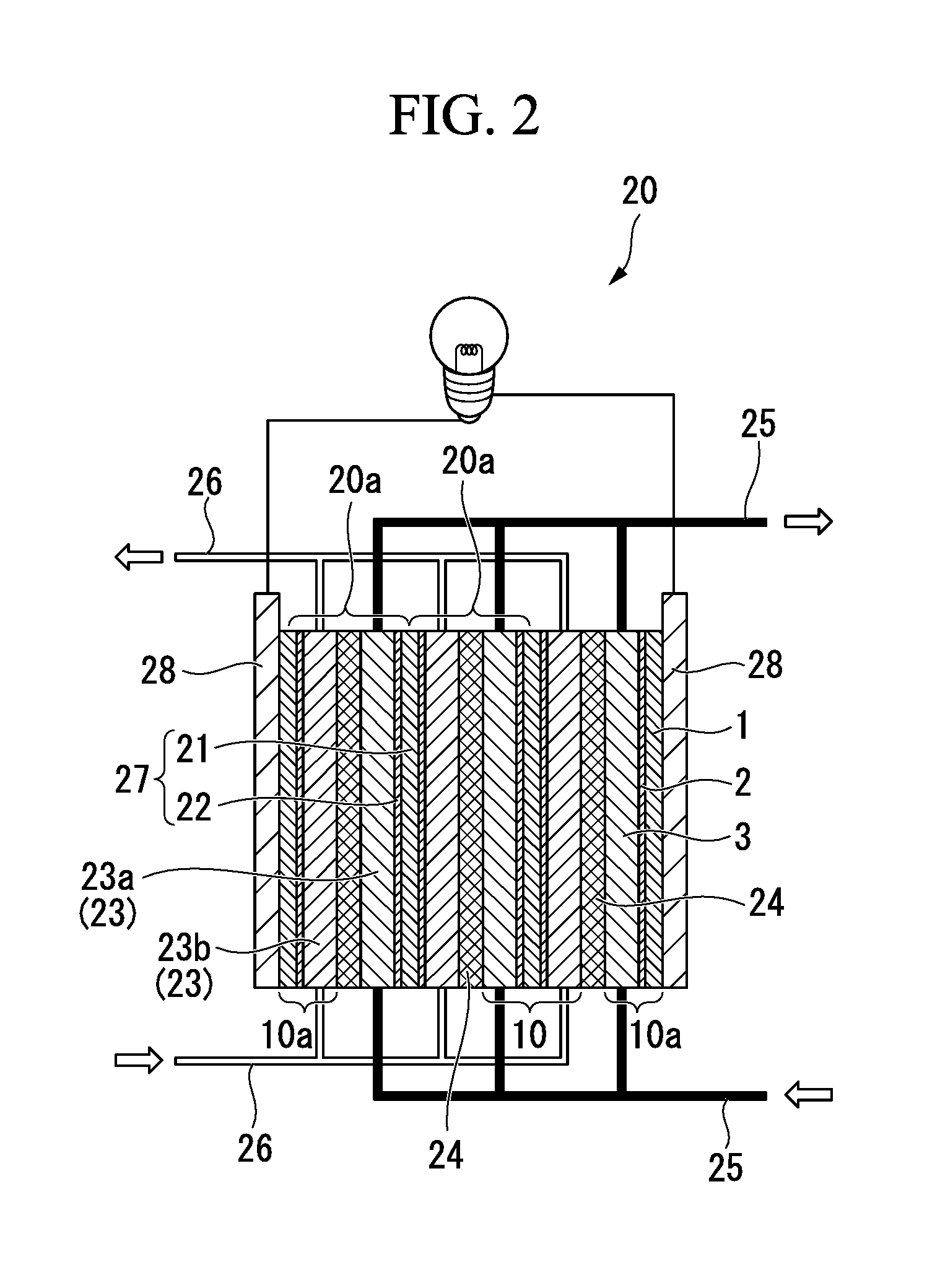
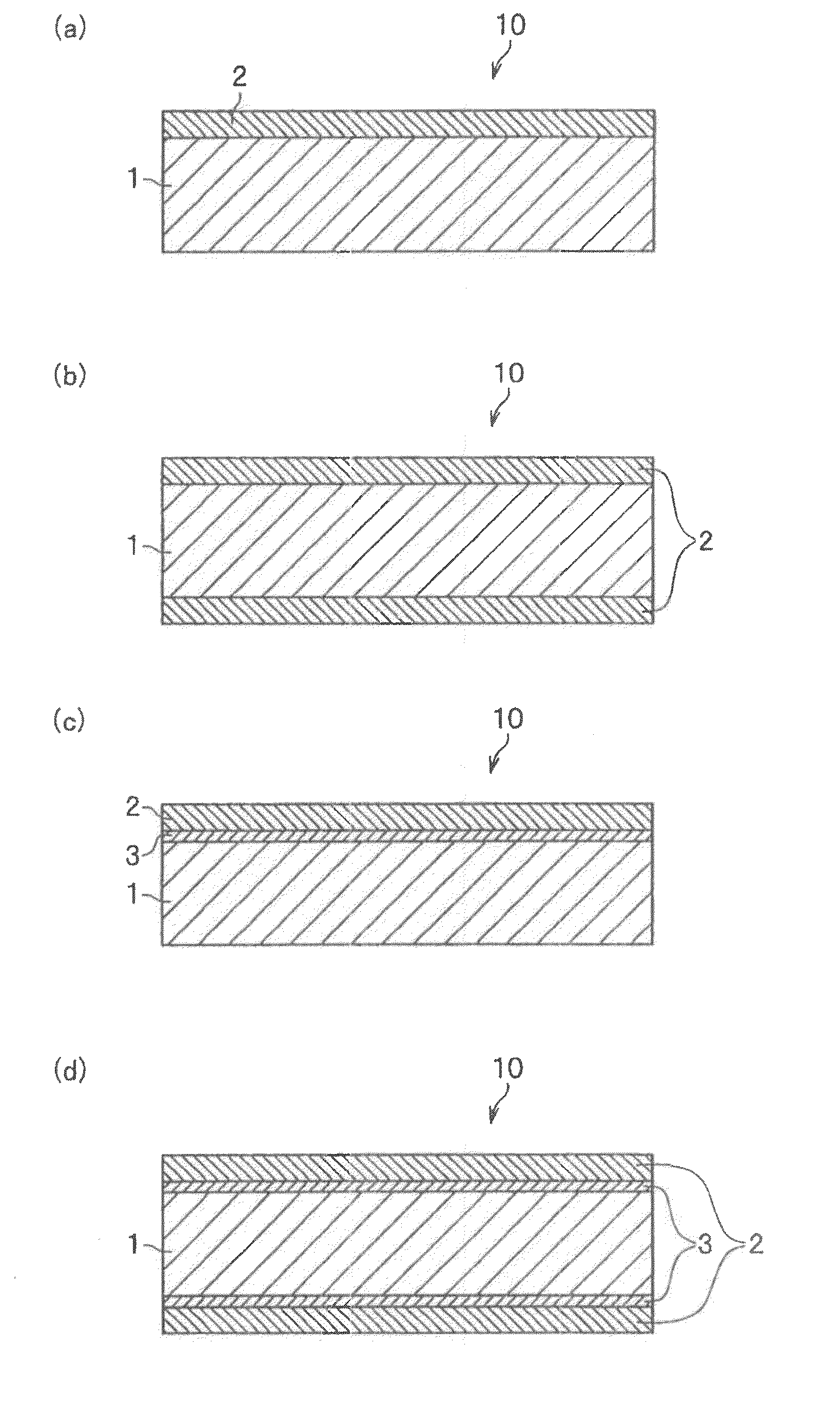
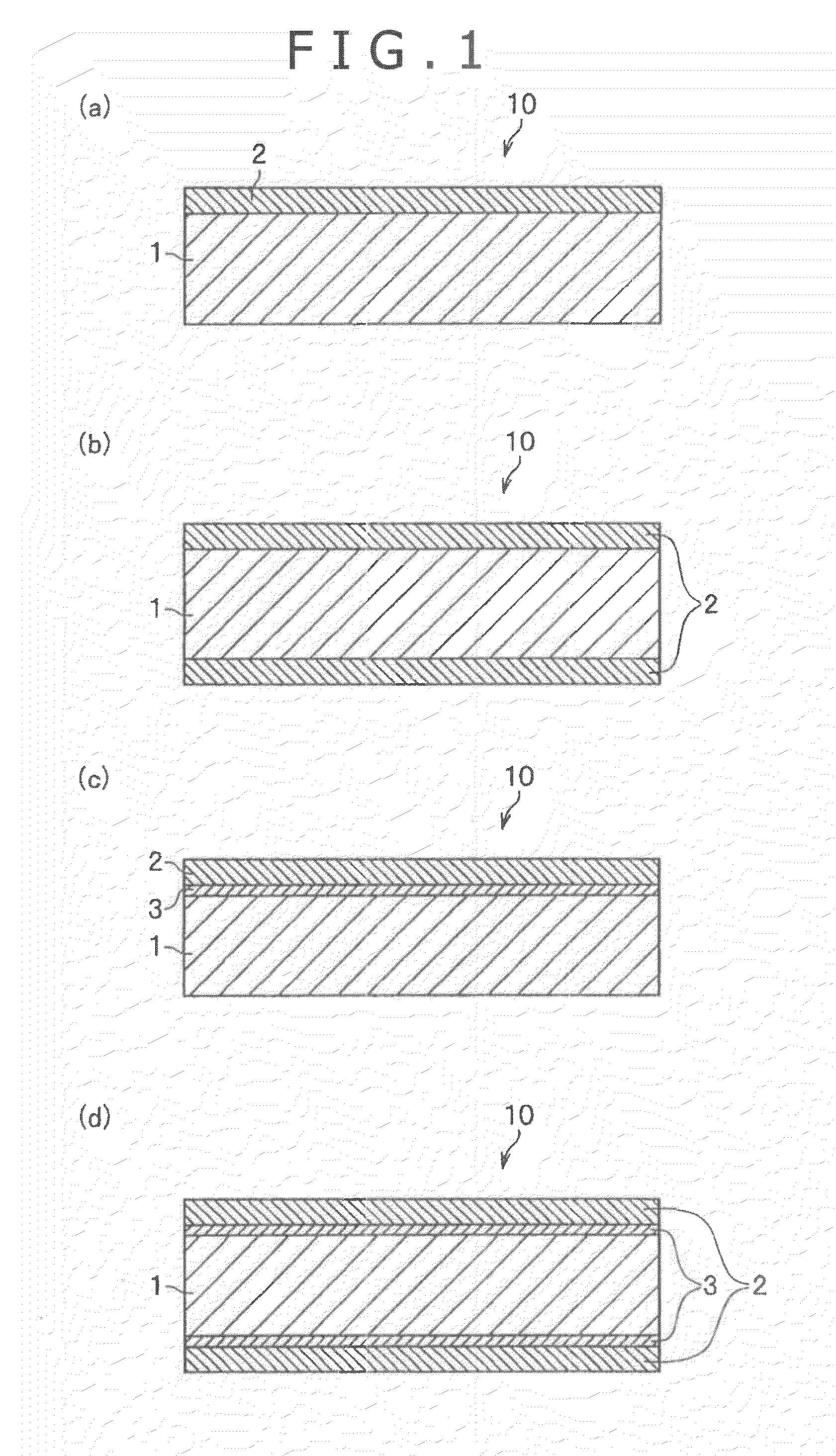
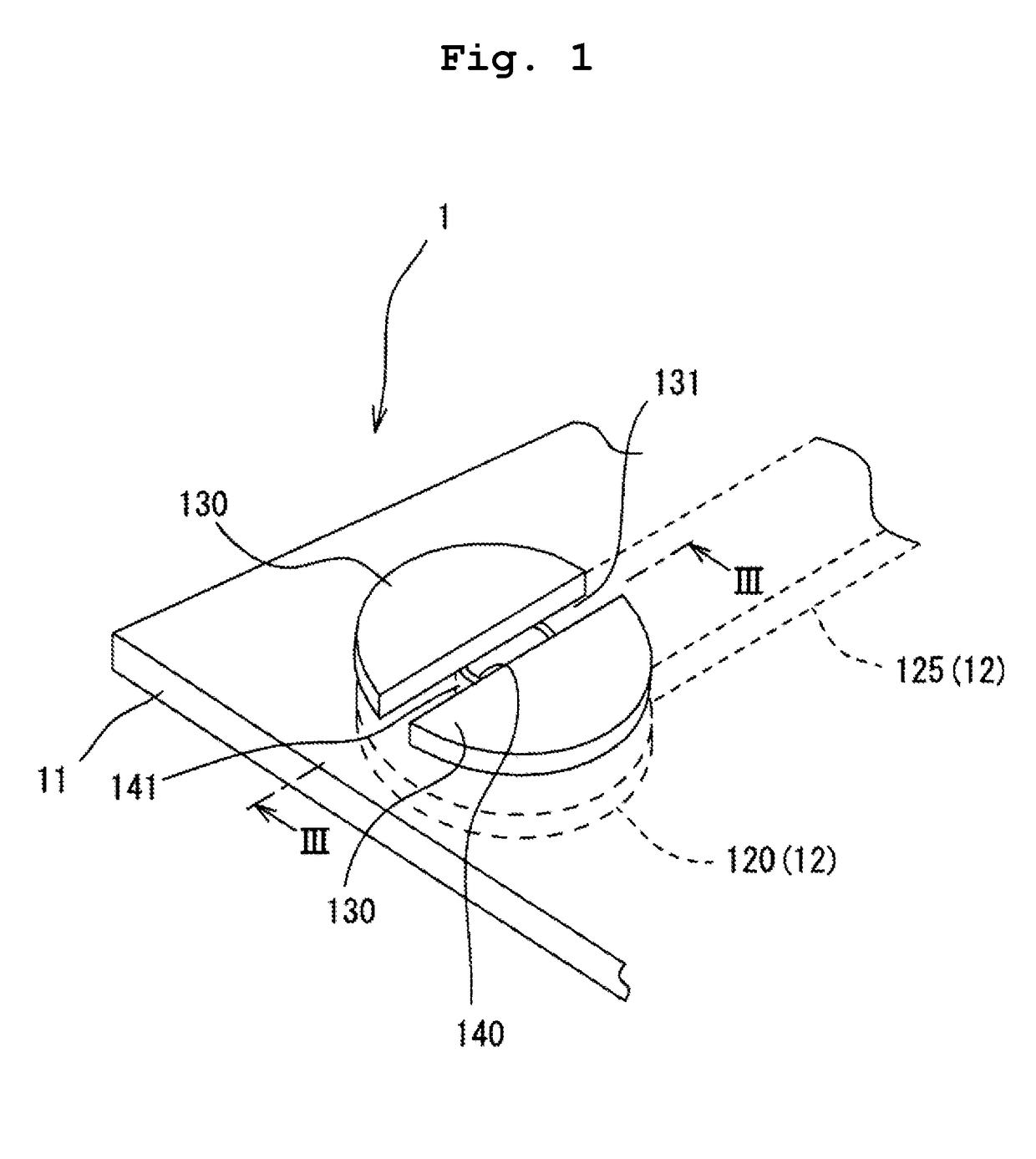
Processes for producing nano-space controlled polymer ion-exchange membranes
InactiveUS20050049320A1Increase resistanceHigh film stabilitySolid electrolytesIon-exchanger regenerationPolymer scienceFunctional monomer
A polymer film substrate is irradiated with ions to make a large number of nano-sized through-holes and the substrate is further irradiated with an ionizing radiation so that a functional monomer is grafted or co-grafted onto a surface of the film and within the holes; in addition, the sulfonic acid group is introduced into the graft chains, thereby producing a polymer ion-exchange membrane that has high oxidation resistance, dimensional stability, electrical conductivity and methanol resistance, as well as an ion-exchange capacity controlled over a wide range.
Owner:JAPAN ATOM ENERGY RES INST
Method for manufacturing semiconductor device
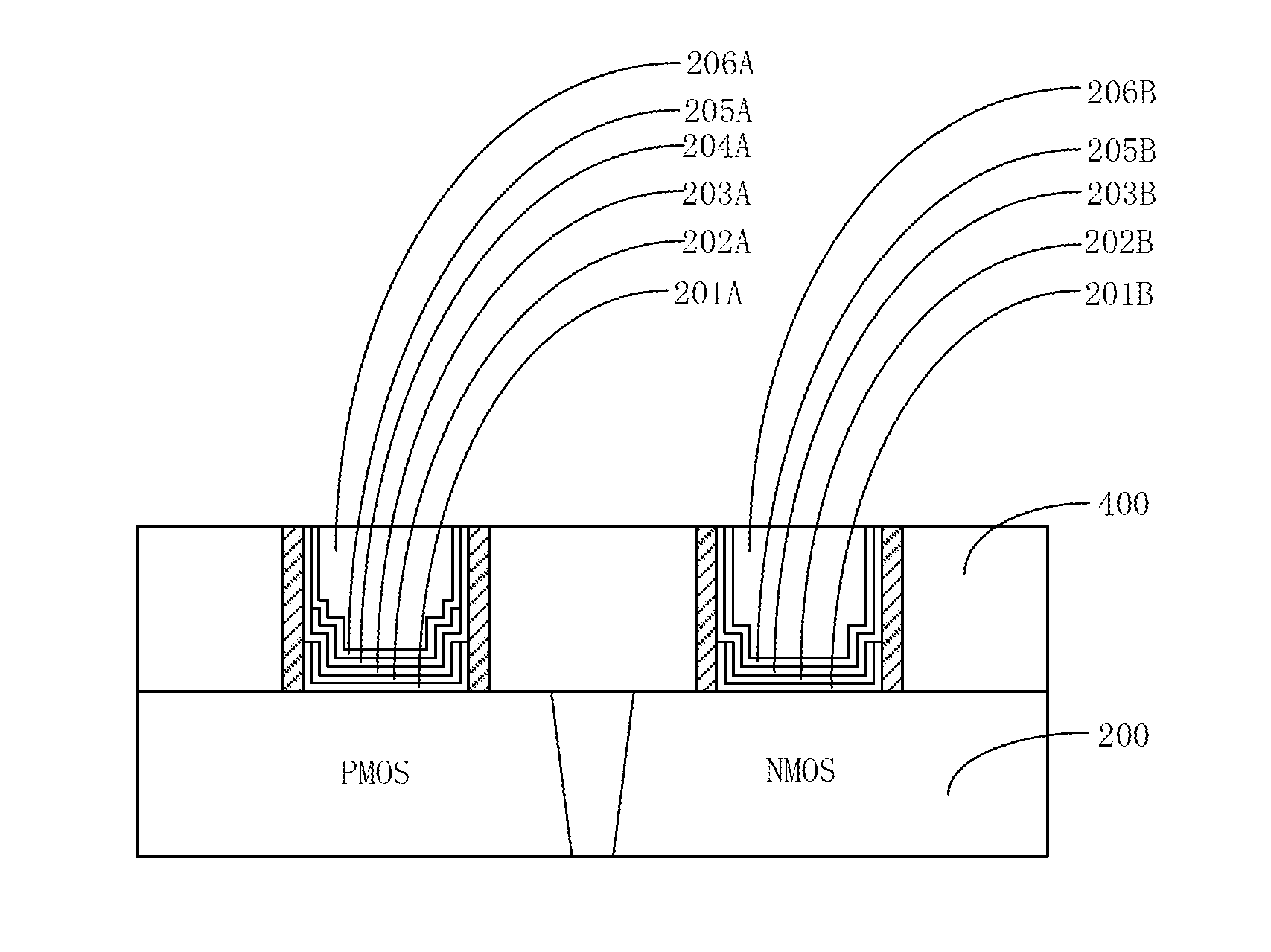
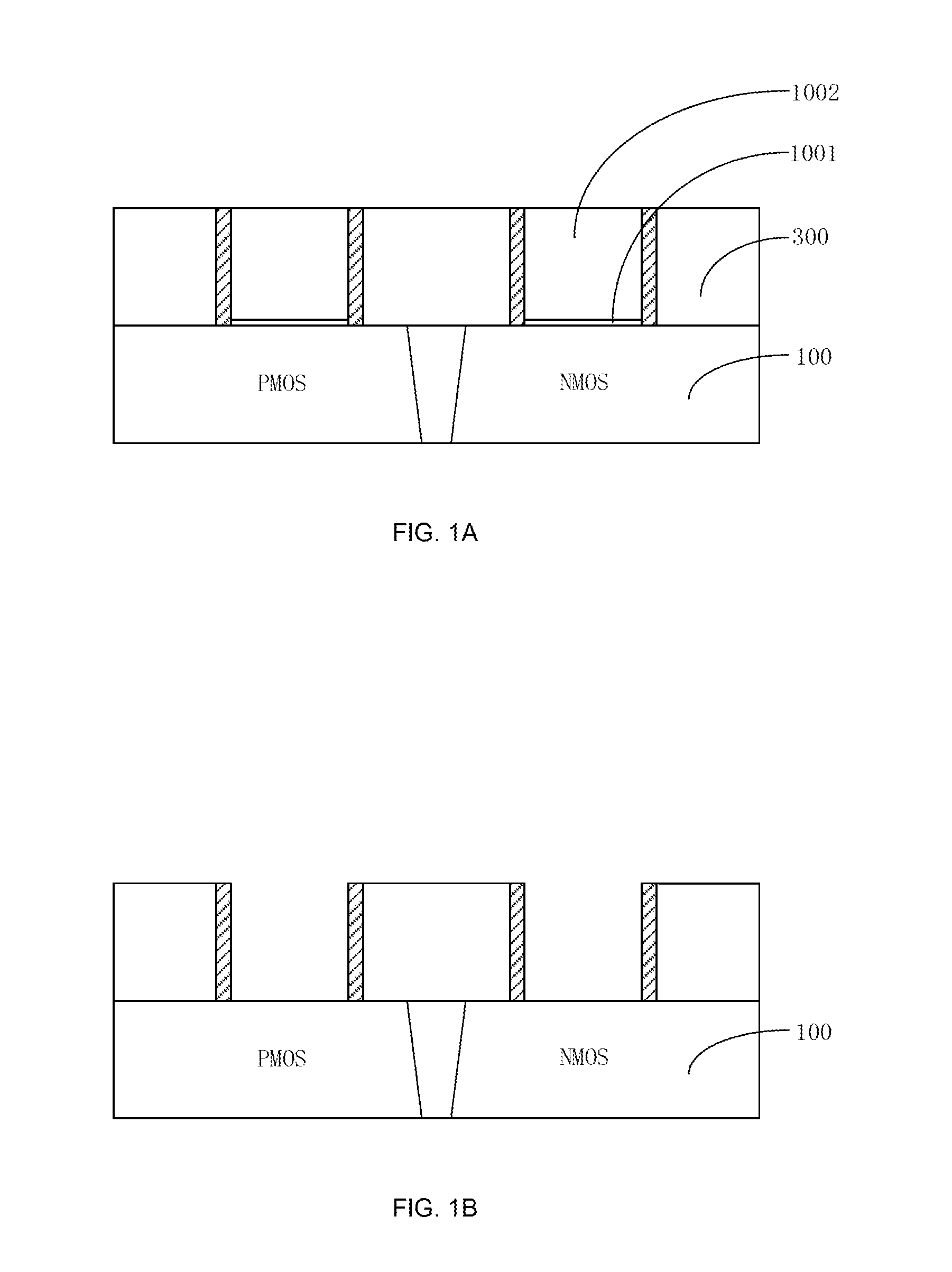
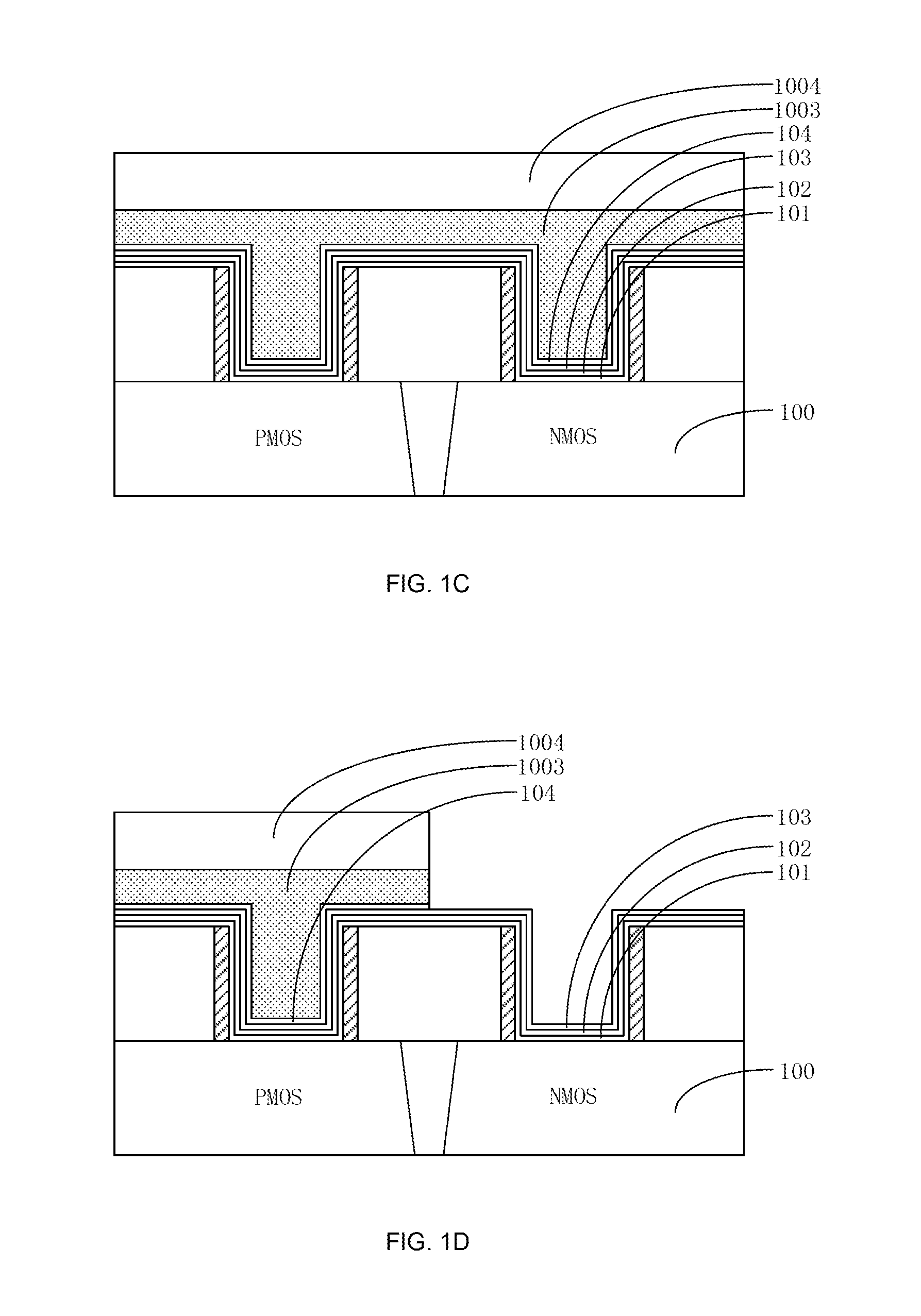
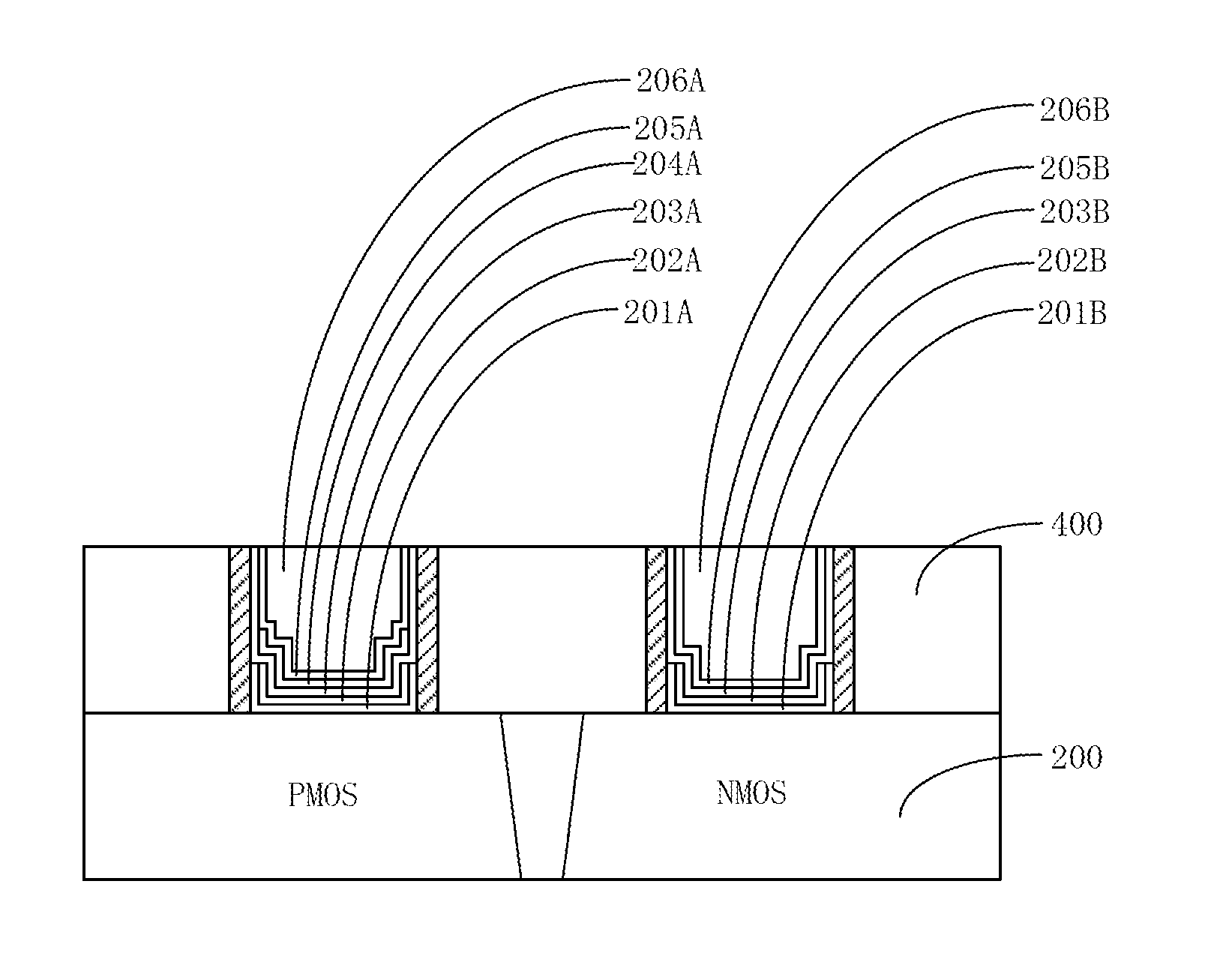
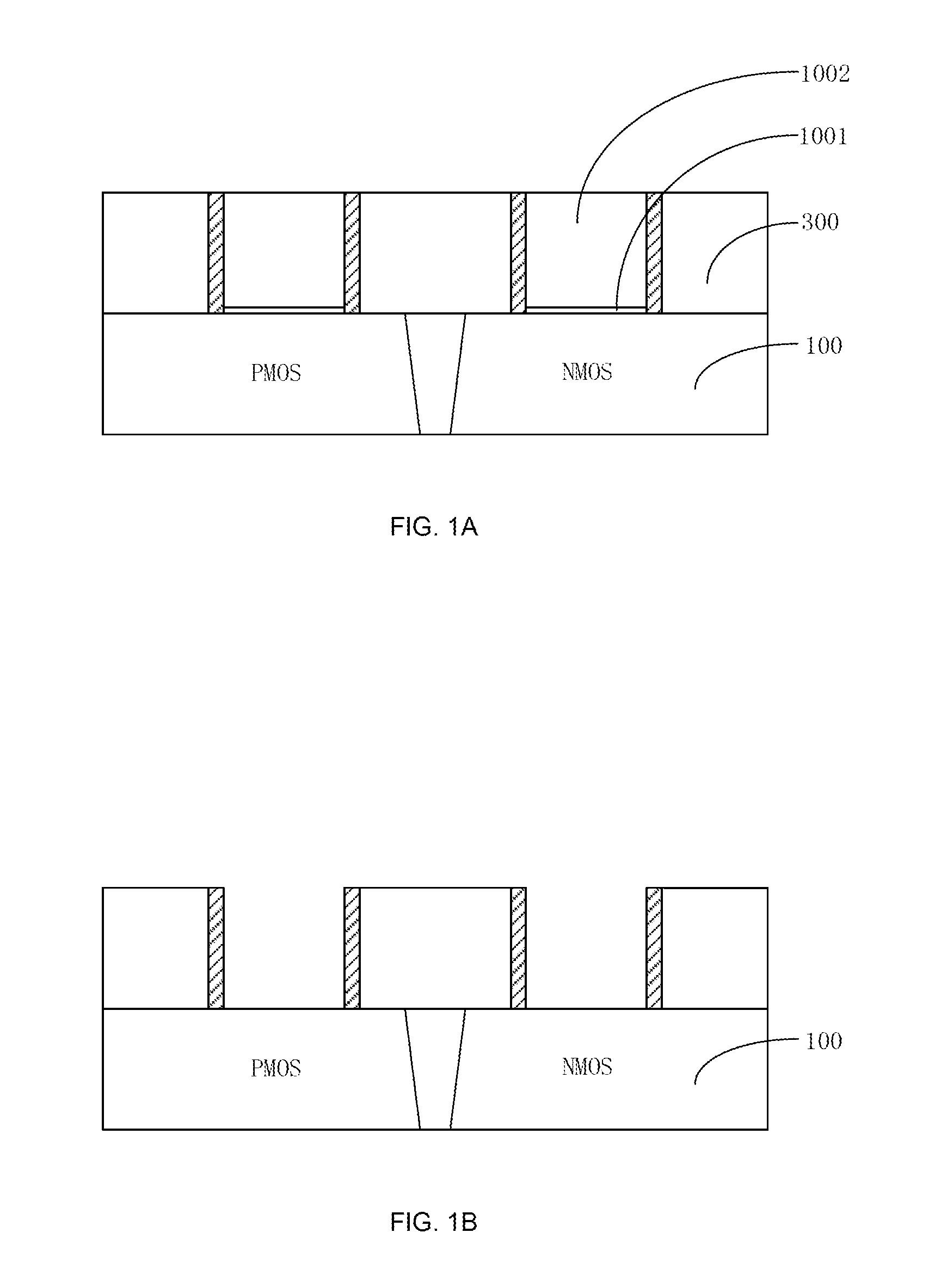
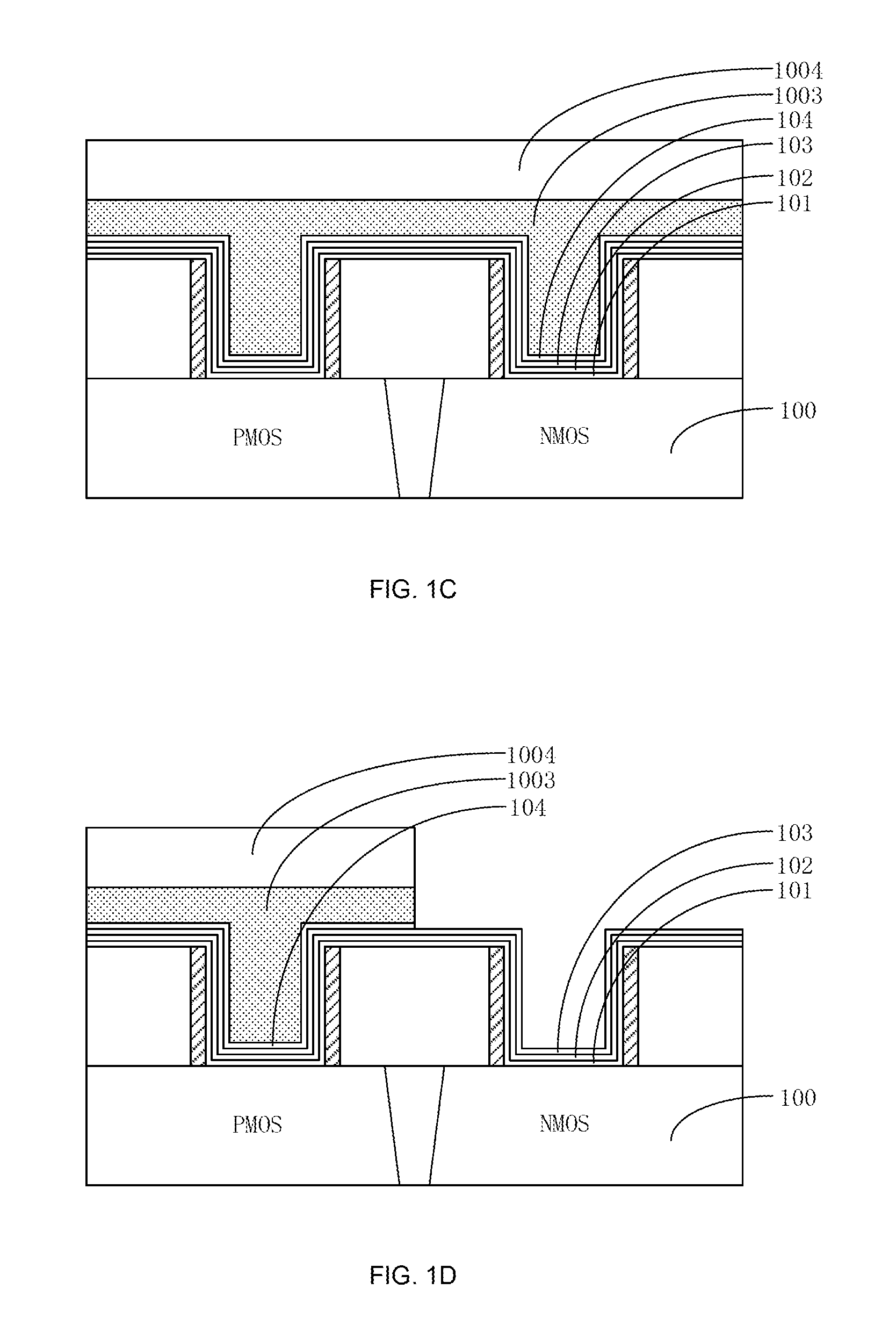
ActiveUS20150243564A1Satisfactory conductivityMinimize gate resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceDielectric layer
A method for manufacturing a semiconductor device may include the following steps: preparing a substrate having a PMOS region and an NMOS; forming a first gate trench on the PMOS region; forming a first high-k dielectric layer and a first high-k cap layer that cover a bottom and sides of the first gate trench; forming a second gate trench on the NMOS region; forming a second high-k dielectric layer and a second high-k cap layer that cover a bottom and sides of the second gate trench; removing a portion of the first high-k dielectric layer and a portion of the first high-k cap layer that are positioned on a side of the first gate trench; and removing a portion of the second high-k dielectric layer and a portion of the second high-k cap layer that are positioned on a side of the second gate trench.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Electromagnetic-shielding light diffusion sheet
InactiveCN1781034ASatisfactory conductivityGuaranteed conductivityLayered productsDiffusing elementsDiffusionSurface resistivity
An electromagnetic-shielding light-diffusing plate having good electromagnetic-shielding performance and high light transmittance is disclosed. Light diffused from the electromagnetic-shielding light-diffusing plate is uniform and has little variation in brightness. The electromagnetic-shielding light-diffusing plate is characterized in that a light-transmitting conductive layer with a surface resistivity not exceeding 105Ω / □ is formed on at least one surface of the main body of the light-diffusing plate.
Owner:多喜兰株式会社
Electrically conductive paste for via-hole and method of producing monolithic ceramic substrate using the same
InactiveUS6335077B1Easy to fillPrevents crack and elevation of and crackSolid-state devicesDischarge tube main electrodesCooking & bakingSoldering
As an electrically conductive paste for via-holes, an organic vehicle and an electrically conductive metal powder coated with a resin which is insoluble in the organic vehicle are prepared. Filling via-holes with the electrically conductive paste for via-holes produces a monolithic ceramic. Filling characteristics of the electrically conductive paste into via-holes are improved, and cracks and elevations of the conductive metal and cracks of the ceramic barely form during the baking step. Further, the resulting monolithic ceramic substrate can maintain excellent soldering wettability and plating characteristics.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Electroconductive Paste and Substrate Using the Same for Mounting Electronic Parts
InactiveUS20080261049A1Improve conductivityIncrease resistanceSynthetic resin layered productsConductive materialEpoxyConductive paste
The conductive paste of the invention comprises a conductive powder and a binder component, wherein the conductive powder is composed of metal powder which is copper powder or copper alloy powder partially covered on the surface with silver, and is either a mixture of roughly spherical metal powder and flat metal powder, or roughly spherical or flat metal powder alone, and wherein the binder component contains a mixture of an epoxy resin and an imidazole compound with a hydroxyl group or a mixture of an epoxy resin and an imidazole compound with a carboxyl group.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD
Substrate for an organic light-emitting device, and organic light-emitting device incorporating it
InactiveCN101960638ASatisfactory conductivityImprove conductivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductanceOrganic light emitting device
The invention relates to a substrate for an organic light-emitting device (10), comprising a transparent substrate (1) of optical index n0 bearing, on a first main face (11), a transparent or semi-transparent first electrode coating (3), called the bottom electrode, having a sheet resistance less than or equal to 6 O / square and which contains the following multilayer stack: an antireflection sublayer (2) of given optical thickness L1 and optical index n1 such that the n1 / n0 ratio is greater than or equal to 6 / 5; a first metal layer of given thickness e1; a first separating layer of given optical thickness L2; a second metal sheath, having an intrinsic electrical conductivity property, of given thickness e2; and a work-function-matching overlayer, L1 being between 20 nm and 120 nm, L2 being between 75 nm and 200 nm, and the sum of the thicknesses e1 + e2 of the first and second metal layers being less than or equal to 40 nm.
Owner:SAINT-GOBAIN GLASS FRANCE
Carbon member, carbon member manufacturing method, redox flow battery and fuel cell
InactiveUS20160064746A1Lower resistanceImprove conductivityFuel cells groupingCell electrodesFuel cellsPolyolefin
A carbon member for use as a battery member of a redox flow battery or a fuel cell, obtained by welding, into a single integrated body: a first layer including a first resin composition containing a polyolefin-based resin and having a melt flow rate of 0.01 to 10 g / 10 min, and a first carbonaceous material; a second layer including a second resin composition containing a polyolefin-based resin, having a melt flow rate of 5 to 1,000 g / 10 min that is greater than that of the first resin composition, and having a melting point that is 80° C. or higher, but is at least 10° C. lower than that of the first resin composition, and a second carbonaceous material; and a third layer, which is disposed facing the first layer with the second layer interposed therebetween, and is formed from a porous carbon material having a specified bulk density.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Titanium fuel cell separator
ActiveUS20130130153A1Good conductivity and durabilityIncreased durabilityFinal product manufactureFuel cell auxillariesCarbon layerFuel cells
Disclosed is a titanium fuel cell separator having excellent conductivity and durability. In the disclosed titanium fuel cell separator (10), a carbon layer (2) is formed on the surface of a substrate (1) formed from pure titanium or a titanium alloy. The carbon layer (2) comprises graphite which is orientated so as to be parallel to the (002) plane of the carbon layer (2). The deposition amount of the carbon layer (2) is at least 2 μg / cm2.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
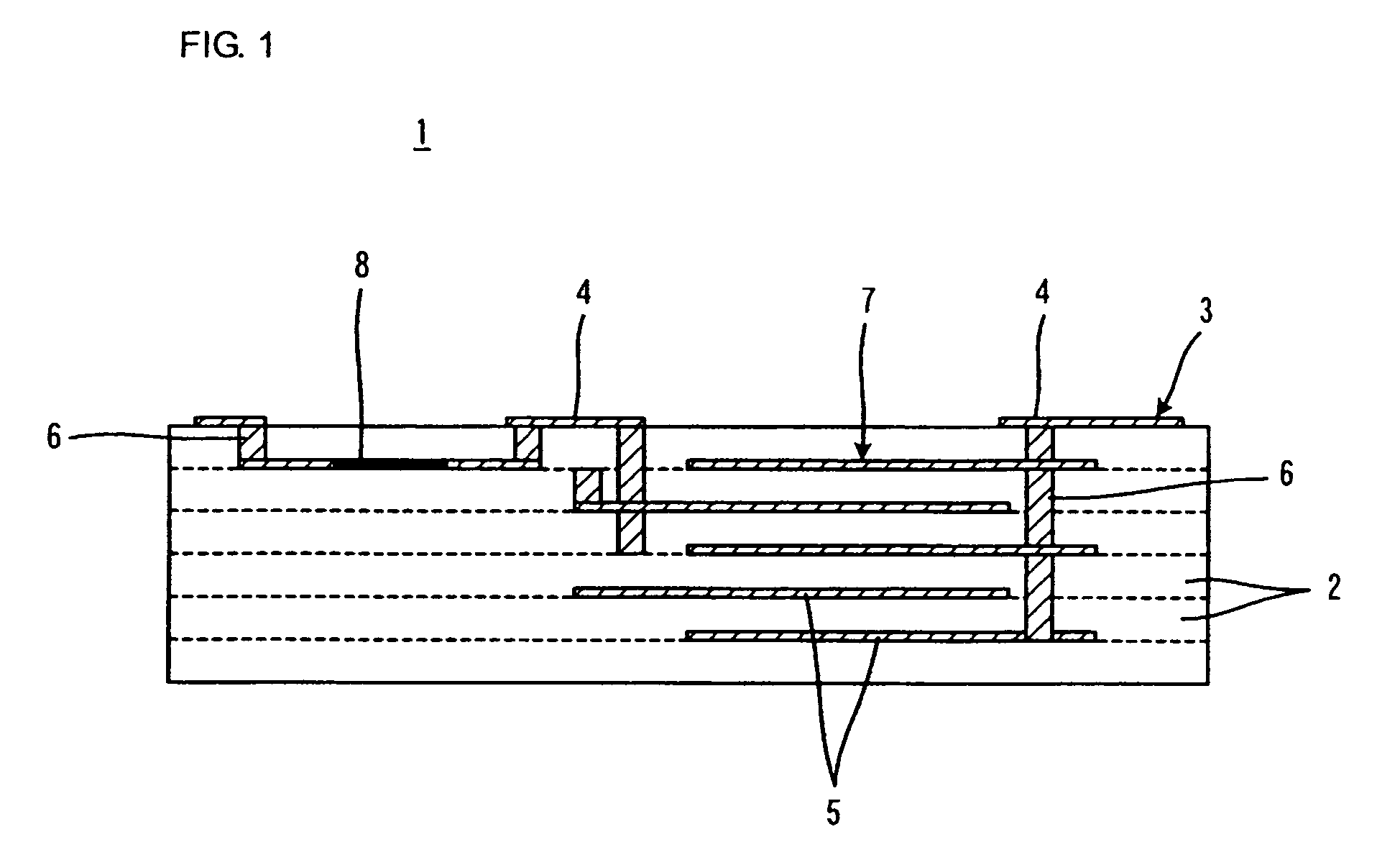
Ceramic material composition, ceramic substrate, and nonreciprocal circuit device
ActiveUS20070036996A1Satisfactory conductivityReduce areaFixed capacitor dielectricNatural mineral layered productsRare-earth elementBorosilicate glass
A ceramic material composition advantageously used as a material for a ceramic substrate containing for example a resistor such as an isolator disposed therein. includes about 10 to 45 percent by weight of a BaO—TiO2—ReO3 / 2 ceramic composition, the ceramic composition being represented by xBaO-yTiO2-zReO3 / 2 (wherein x, y, and z each represent mole percent, 8≦x≦18, 52.5≦y≦65, and 20≦z≦40, and x+y+z=100; and Re represents a rare-earth element); about 5 to 40 percent by weight of alumina; and about 40 to 65 percent by weight of a borosilicate glass composition containing about 4 to 17.5 percent by weight of B2O3, about 28 to 50 percent by weight of SiO2, 0 to about 20 percent by weight of Al2O3, and about 36 to 50 percent by weight of MO (wherein MO represents at least one compound selected from CaO, MgO, SrO and BaO), wherein the total content of the BaO—TiO2—ReO3 / 2 ceramic composition and alumina is about 35 percent by weight or more.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
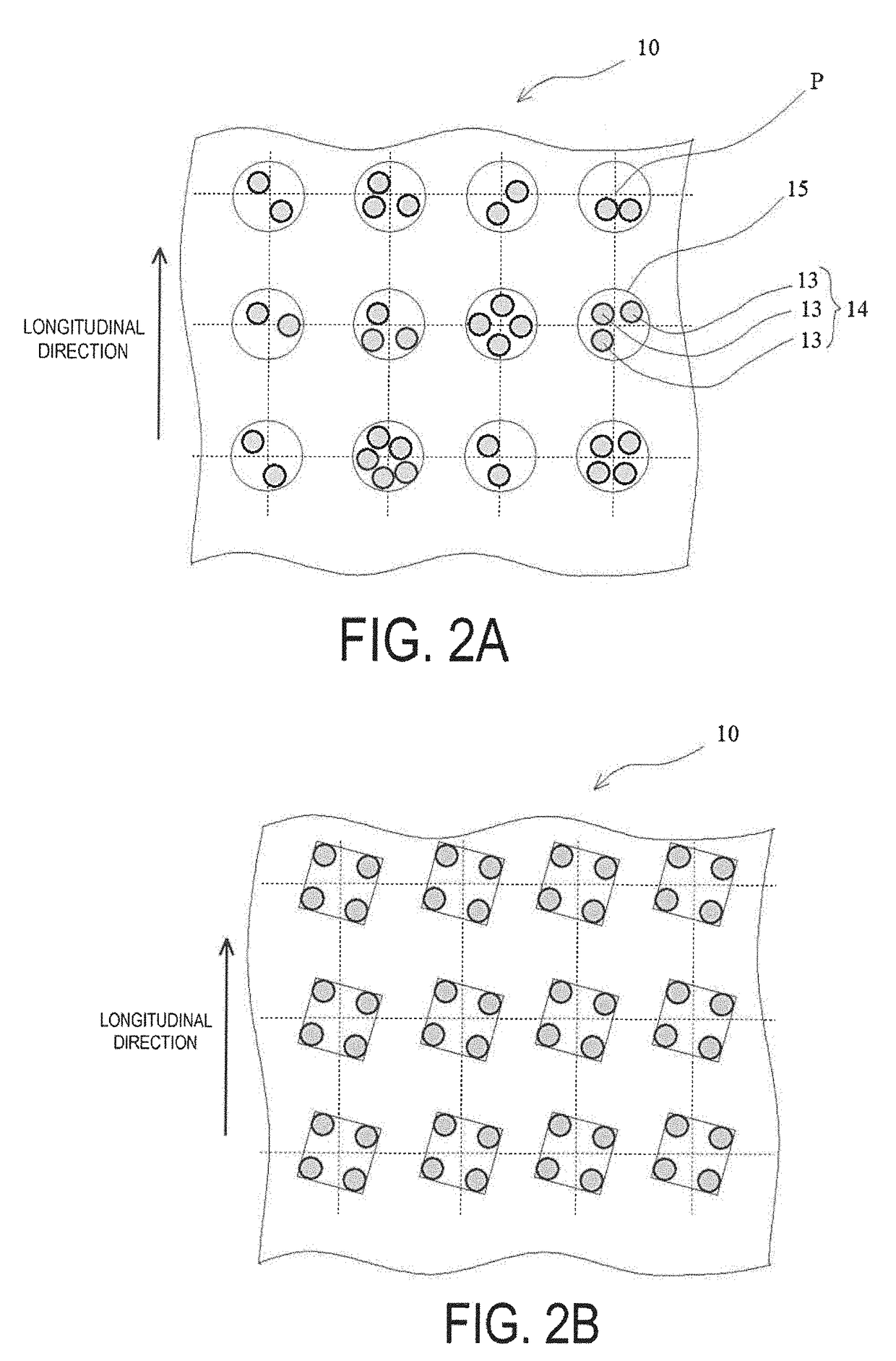
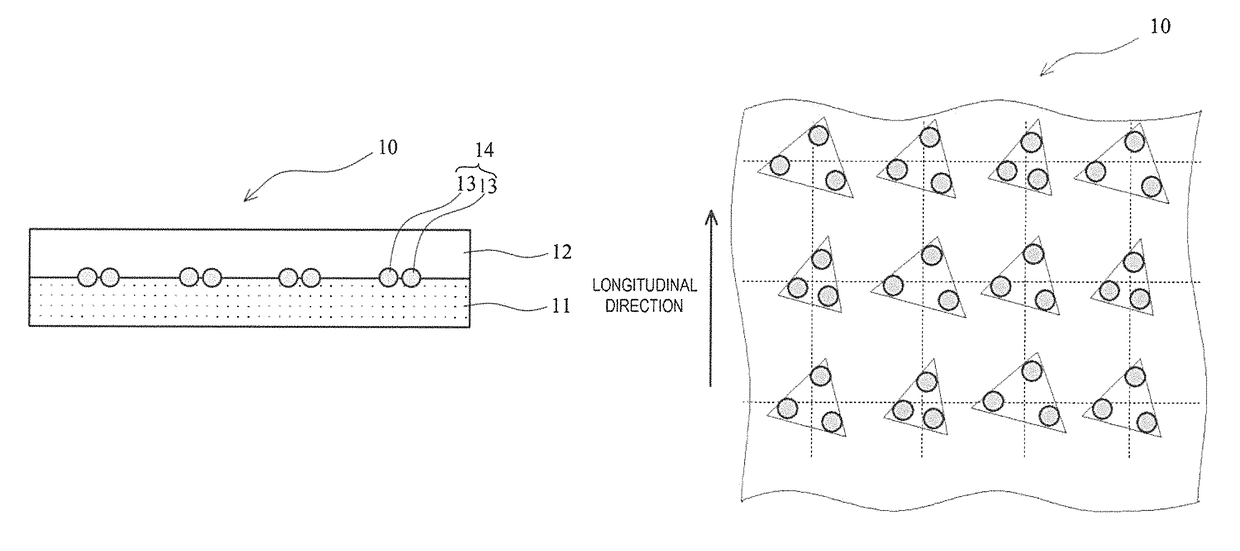
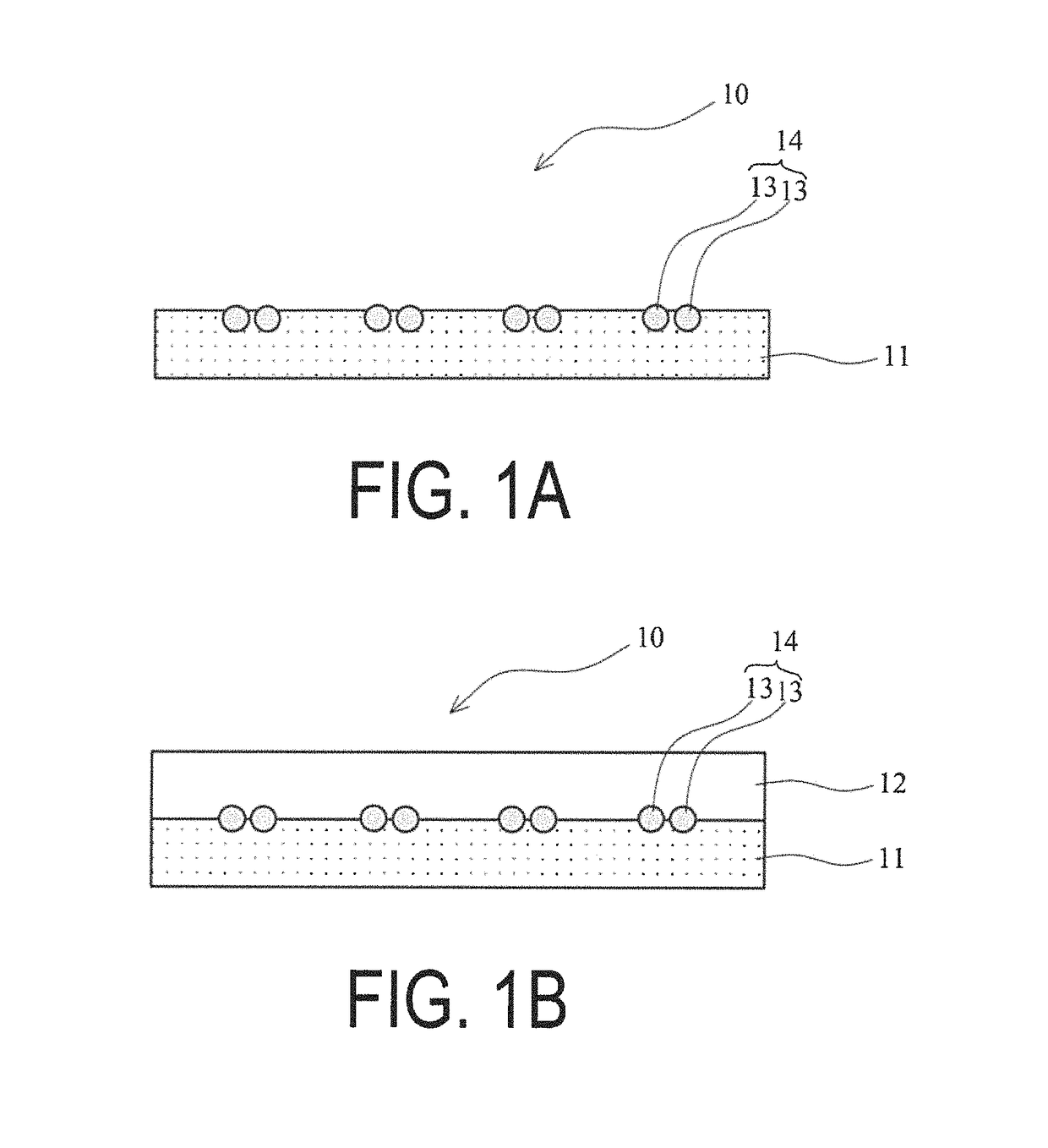
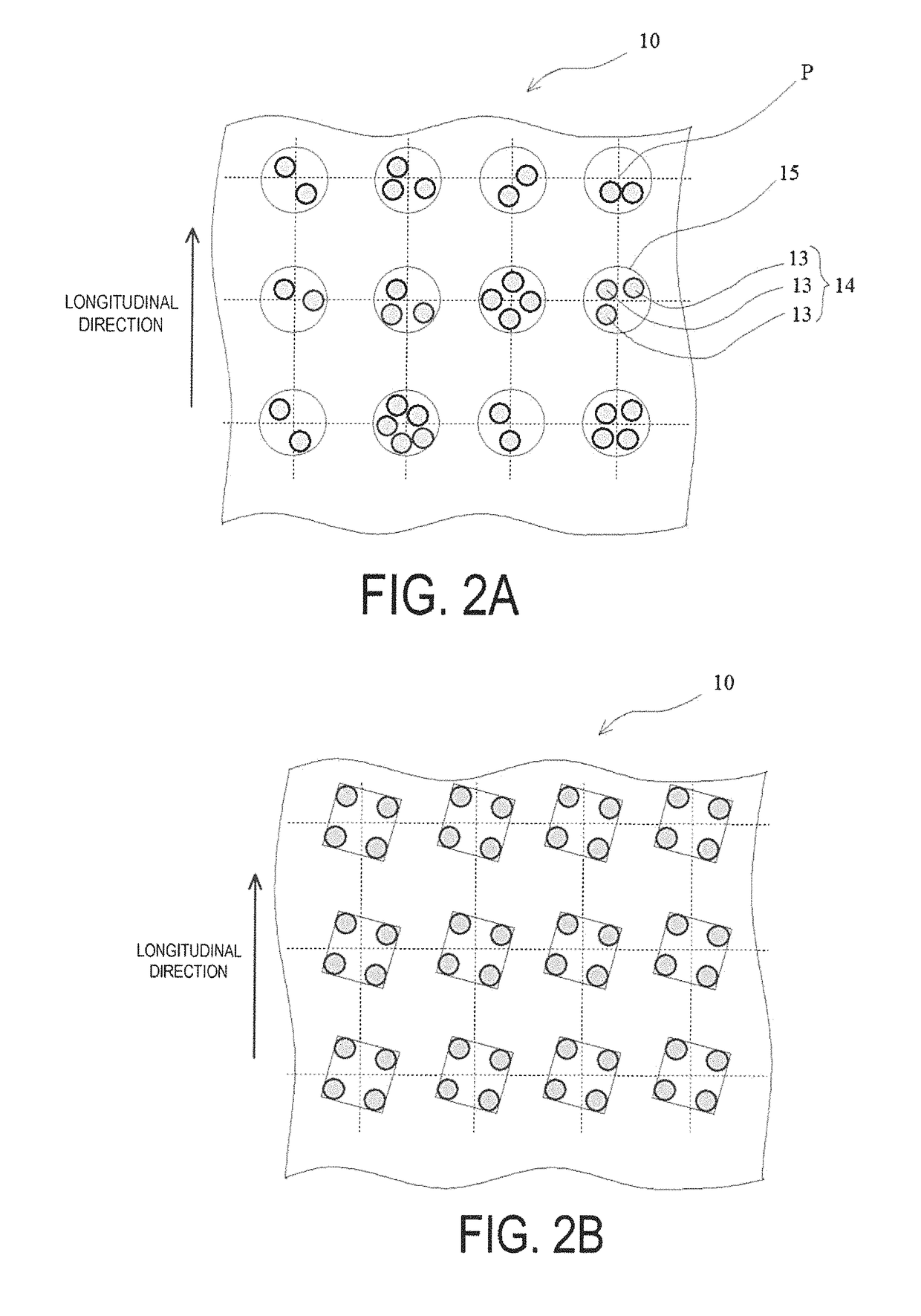
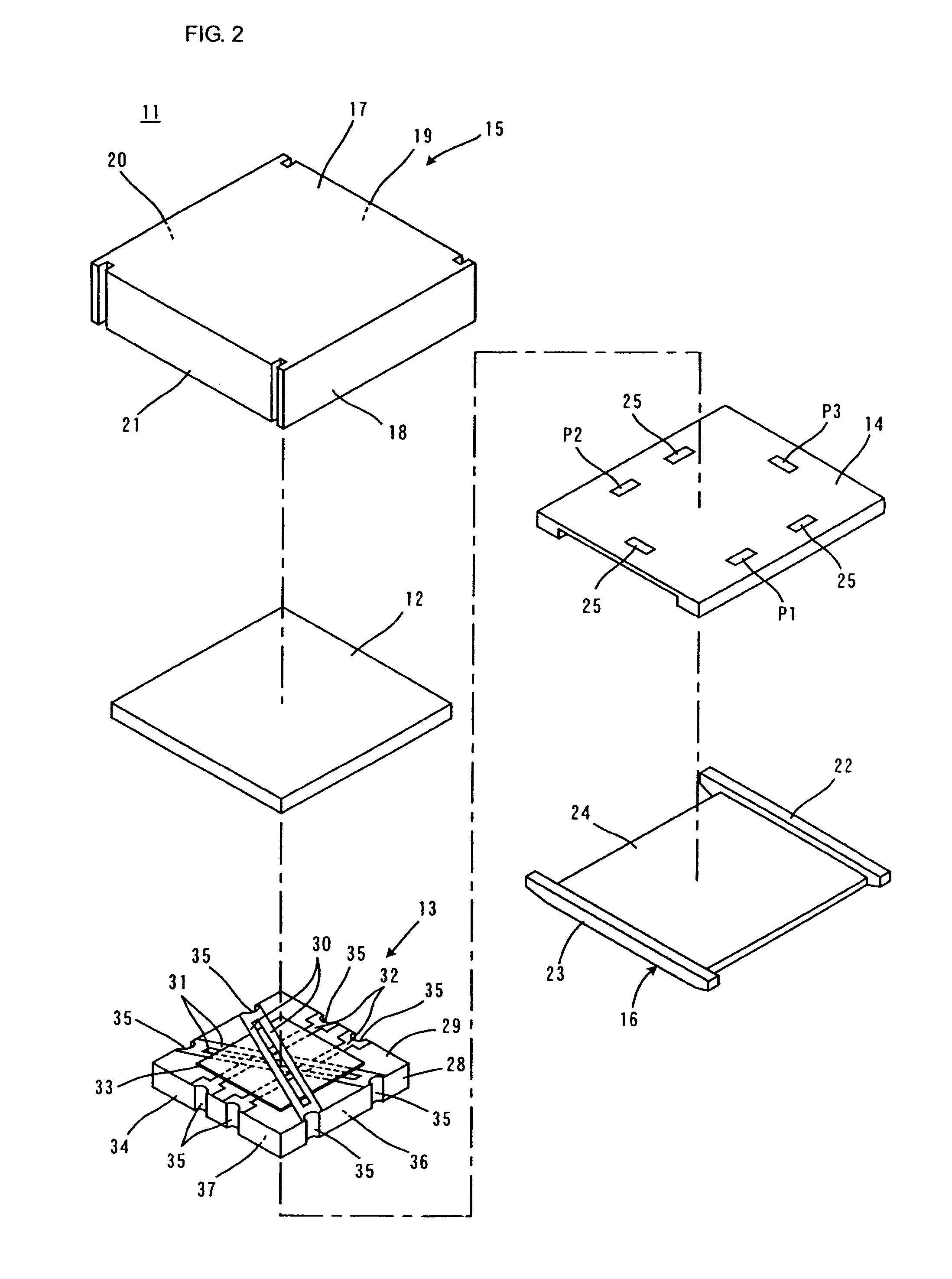
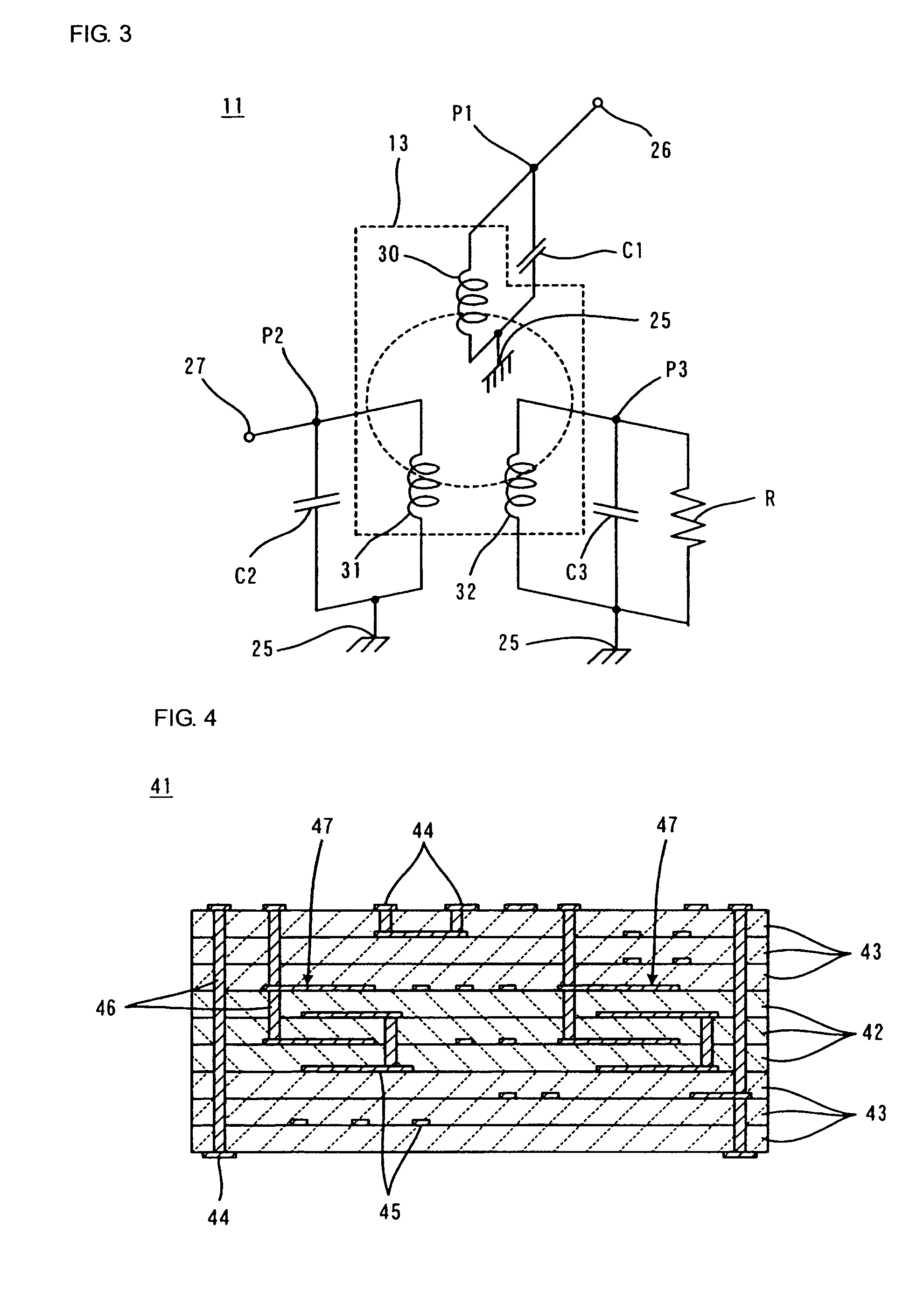
Anisotropic electrically conductive film
ActiveUS20170317047A1Satisfactory initial conductivitySatisfactory conduction reliabilityLine/current collector detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsAnisotropic conductive filmPlanar lattice
An anisotropic electrically conductive film has a structure wherein the electrically conductive particles are disposed on or near the surface of an electrically insulating adhesive base layer, or a structure wherein an electrically insulating adhesive base layer and an electrically insulating adhesive cover layer are laminated together and the electrically conductive particles are disposed near the interface therebetween. Electrically conductive particle groups configured from two or more electrically conductive particles are disposed in a lattice point region of a planar lattice pattern. A preferred lattice point region is a circle centered on a lattice point. A radius of the circle is not less than two times and not more than seven times the average particle diameter of the electrically conductive particles.
Owner:DEXERIALS CORP
Processes for producing nano-space controlled polymer ion-exchange membranes
InactiveUS7276561B2Poor dimensional stability of membraneSolve large capacitySolid electrolytesIon-exchanger regenerationPolymer scienceFunctional monomer
A polymer film substrate is irradiated with ions to make a large number of nano-sized through-holes and the substrate is further irradiated with an ionizing radiation so that a functional monomer is grafted or co-grafted onto a surface of the film and within the holes; in addition, the sulfonic acid group is introduced into the graft chains, thereby producing a polymer ion-exchange membrane that has high oxidation resistance, dimensional stability, electrical conductivity and methanol resistance, as well as an ion-exchange capacity controlled over a wide range.
Owner:JAPAN ATOM ENERGY RES INST
Anisotropic electrically conductive film
ActiveUS10026709B2InhibitionSatisfactory conductivityLine/current collector detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsAnisotropic conductive filmPlanar lattice
An anisotropic electrically conductive film has a structure wherein the electrically conductive particles are disposed on or near the surface of an electrically insulating adhesive base layer, or a structure wherein an electrically insulating adhesive base layer and an electrically insulating adhesive cover layer are laminated together and the electrically conductive particles are disposed near the interface therebetween. Electrically conductive particle groups configured from two or more electrically conductive particles are disposed in a lattice point region of a planar lattice pattern. A preferred lattice point region is a circle centered on a lattice point. A radius of the circle is not less than two times and not more than seven times the average particle diameter of the electrically conductive particles.
Owner:DEXERIALS CORP
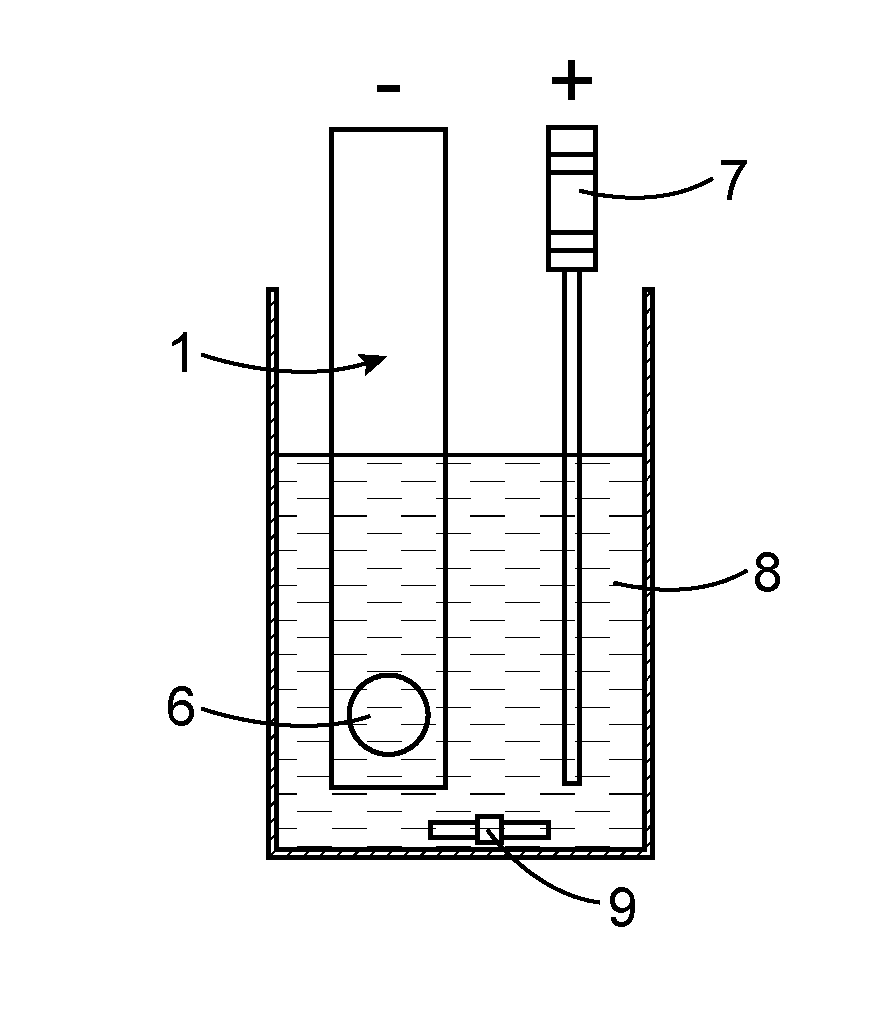
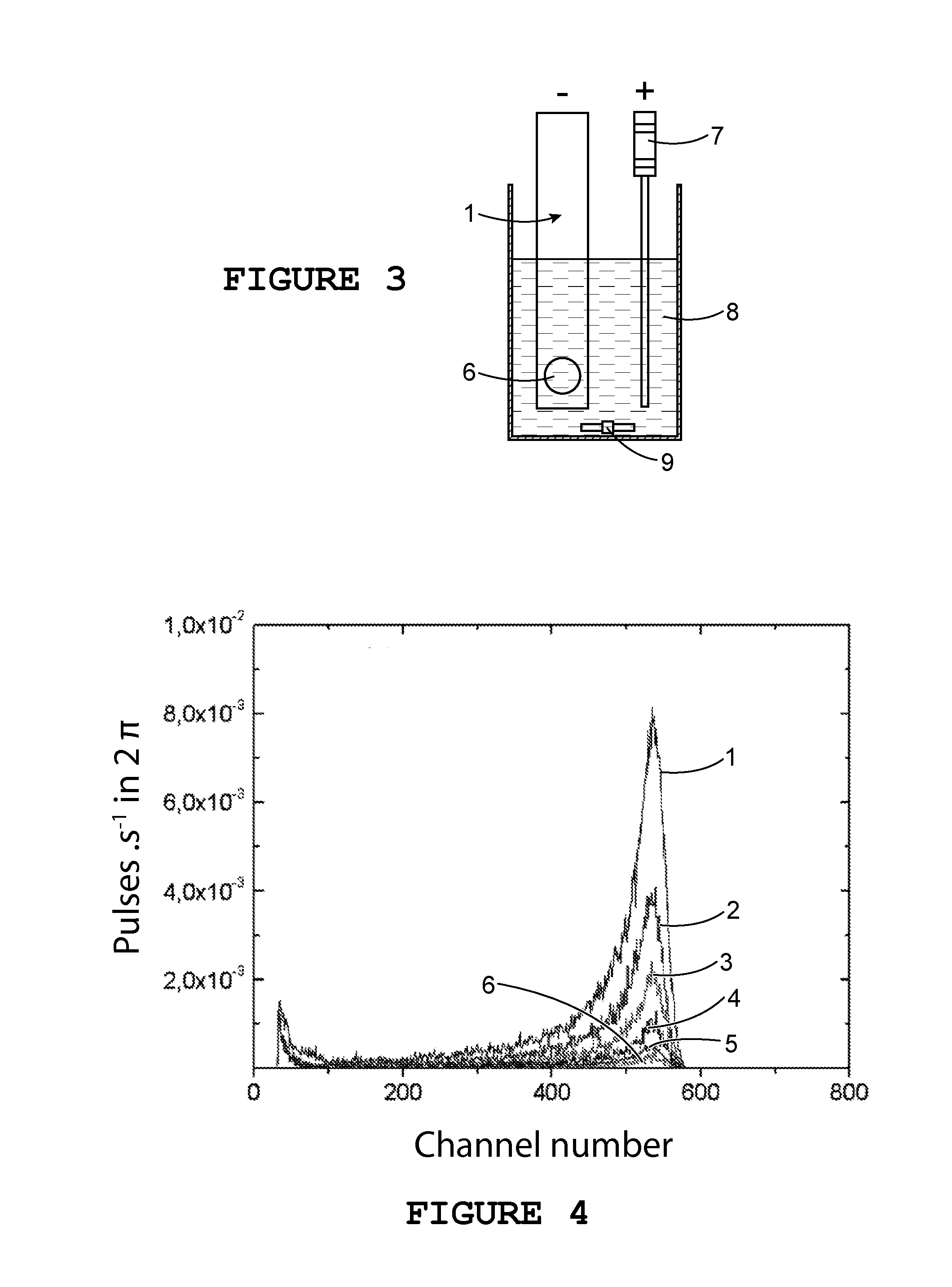
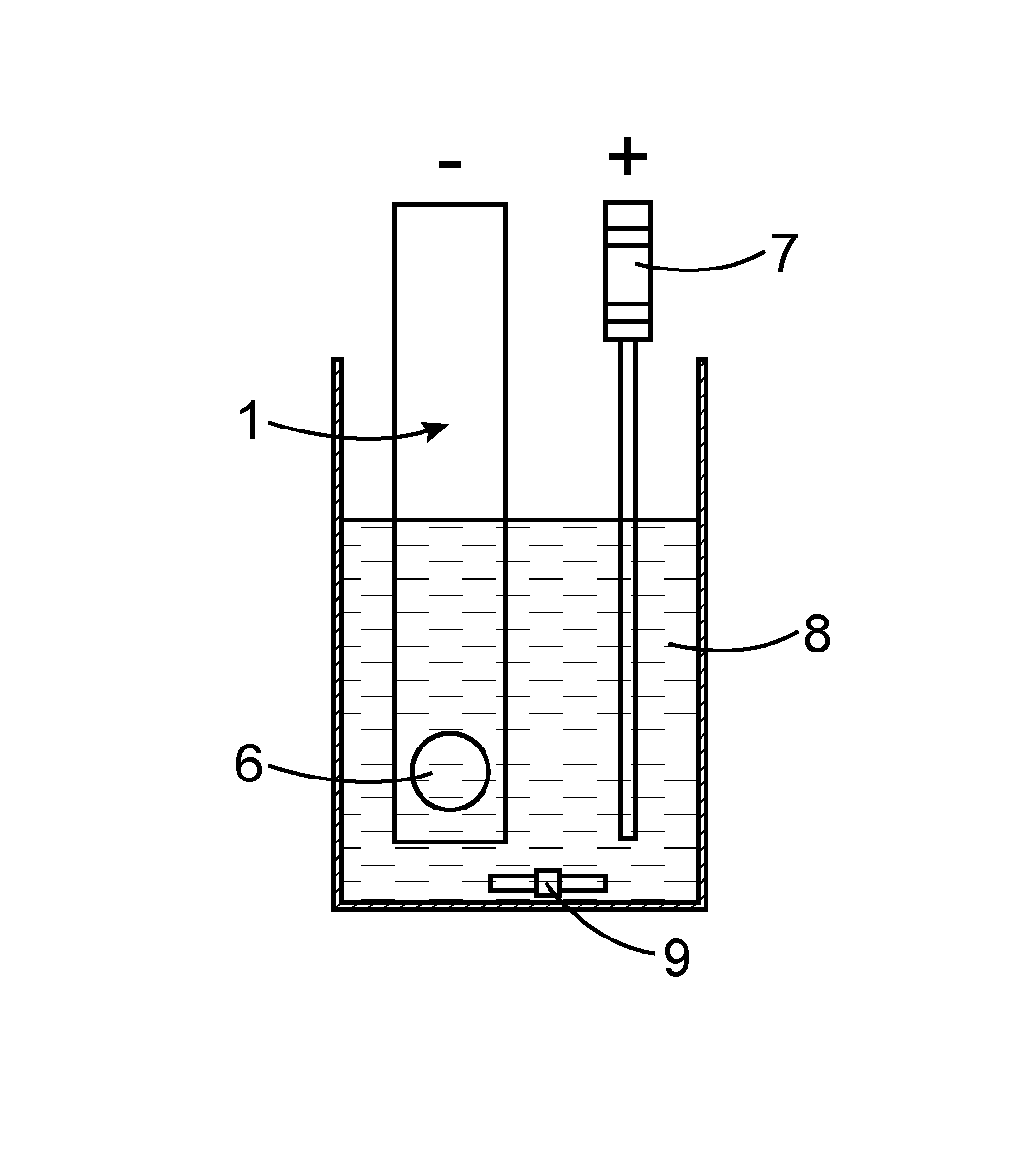
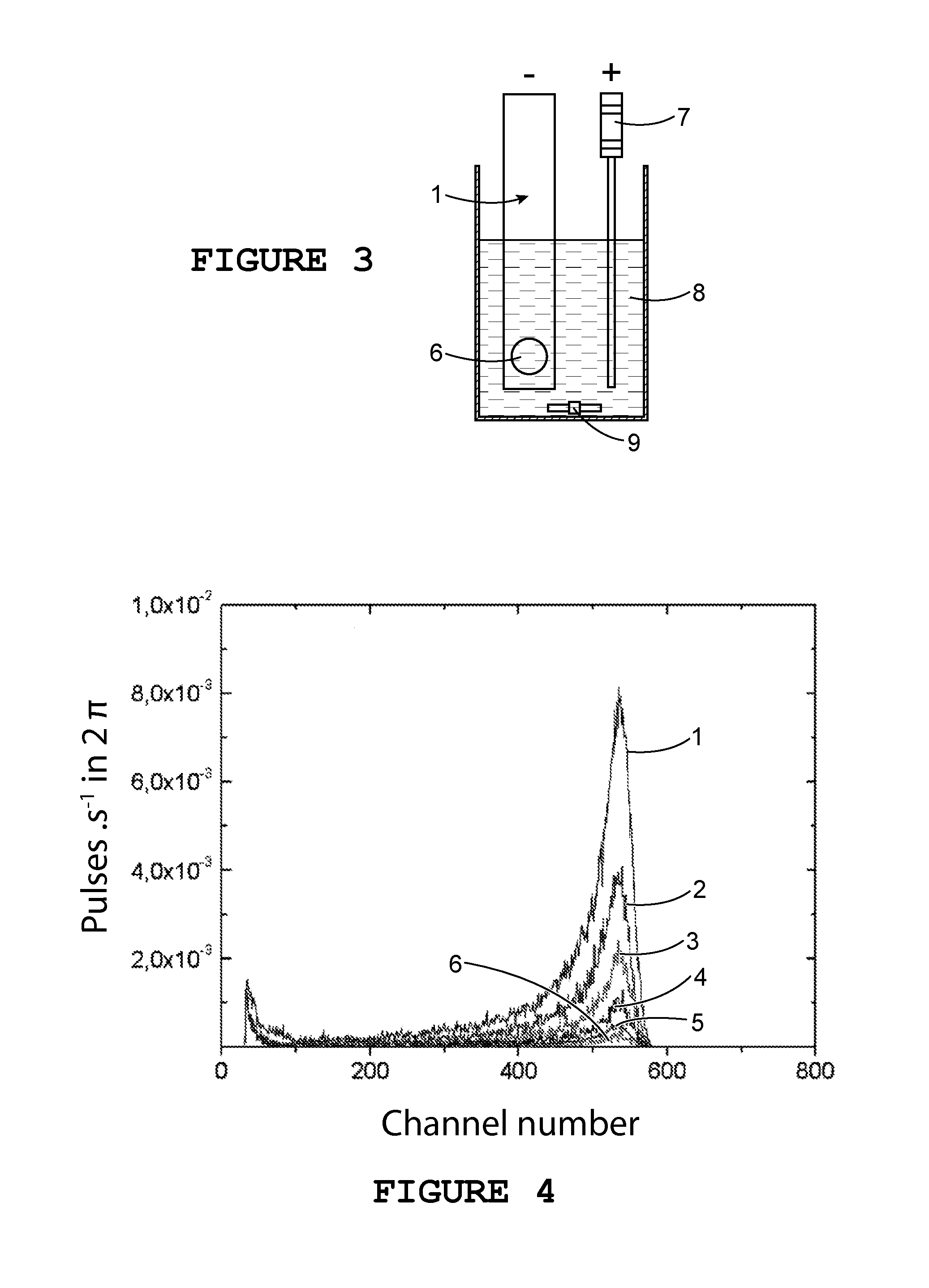
Detection method using an electrochemically-assisted alpha detector for nuclear measurement in a liquid medium
ActiveUS20130186762A1Avoid formingSatisfactory conductivityElectrolysis componentsPhotography auxillary processesElectricityPhase detector
An in situ method for detecting alpha particles contained in a liquid medium, which uses a system which includes a counter-electrode and an alpha particle detector including a substrate made of an intrinsic semiconductor material sandwiched between two electrical contacts, wherein the contact intended to be in contact with the liquid medium is made of boron-doped diamond. By forming a particular electrolyte 8 and by causing a current to flow between counter-electrode and the boron-doped diamond contact in contact with the liquid medium, actinides or polonium present in the liquid medium may be concentrated on the boron-doped diamond contact, and by this means the detection limit of the alpha emitters may be lowered.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Flexible printed circuit board
InactiveUS20170354035A1High strengthSatisfactory conductivityPrinted circuit assemblingPrinted circuit aspectsInsulation layerEngineering
Owner:MINEBEA CO LTD
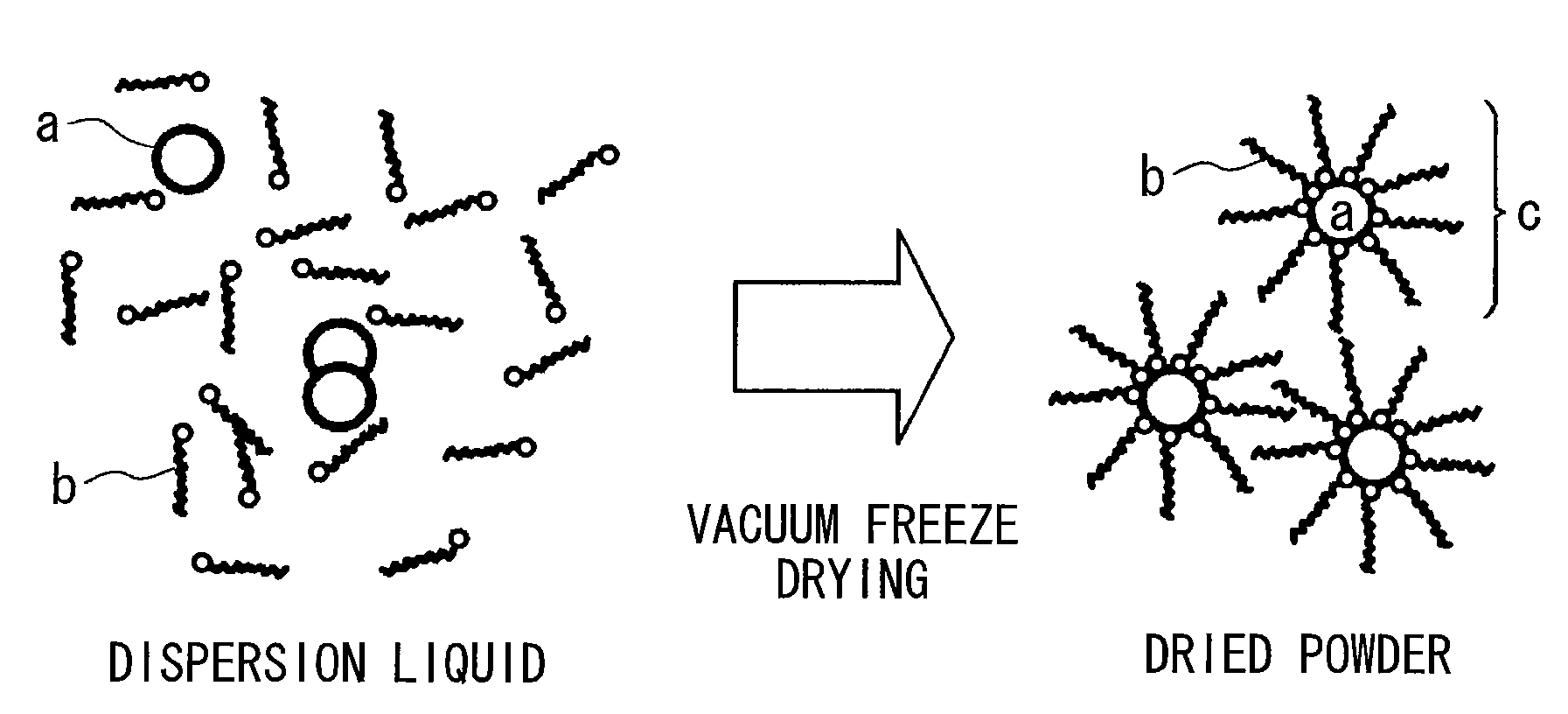
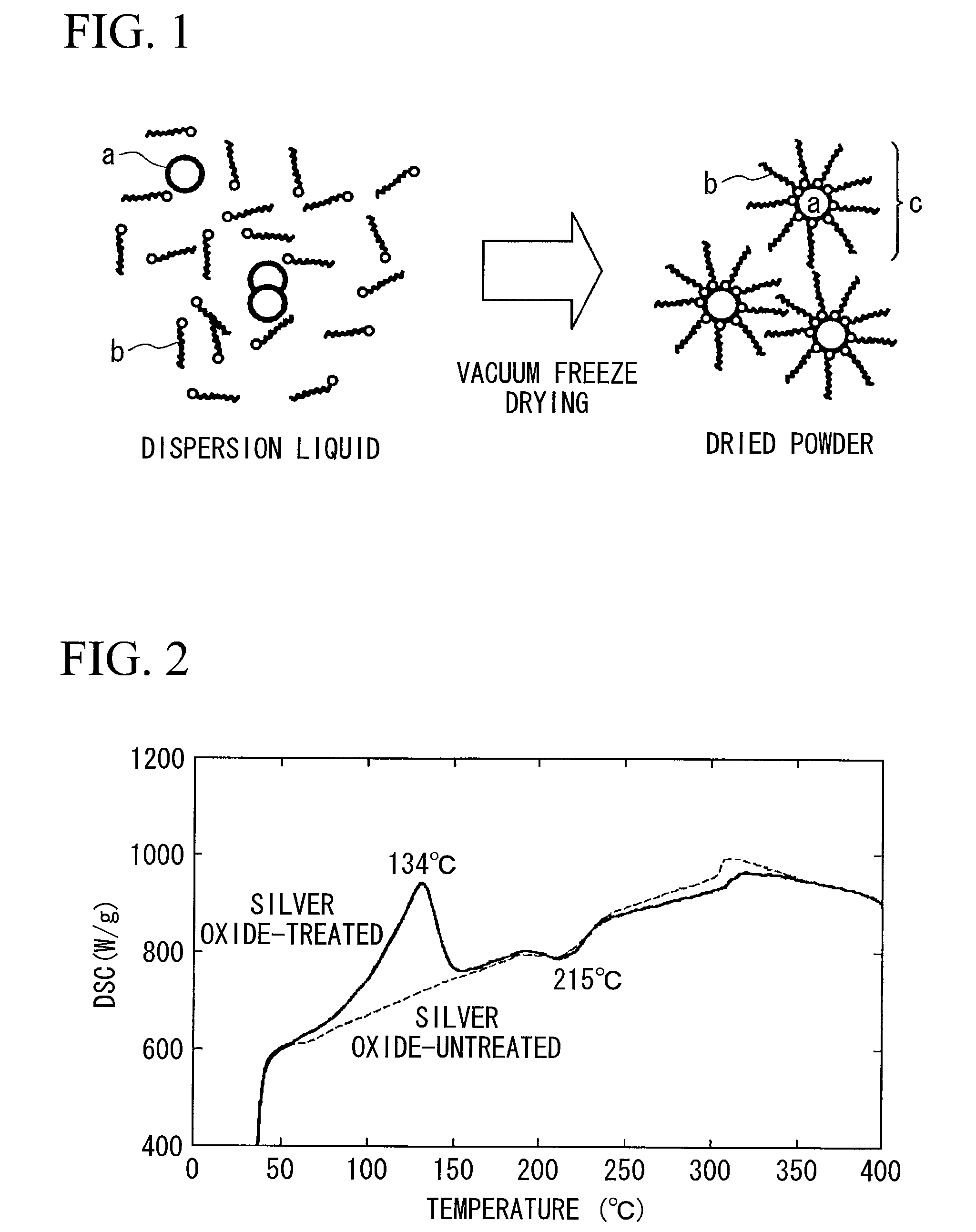
Method for producing surface-treated silver-containing powder and silver paste using surface-treated silver-containing powder
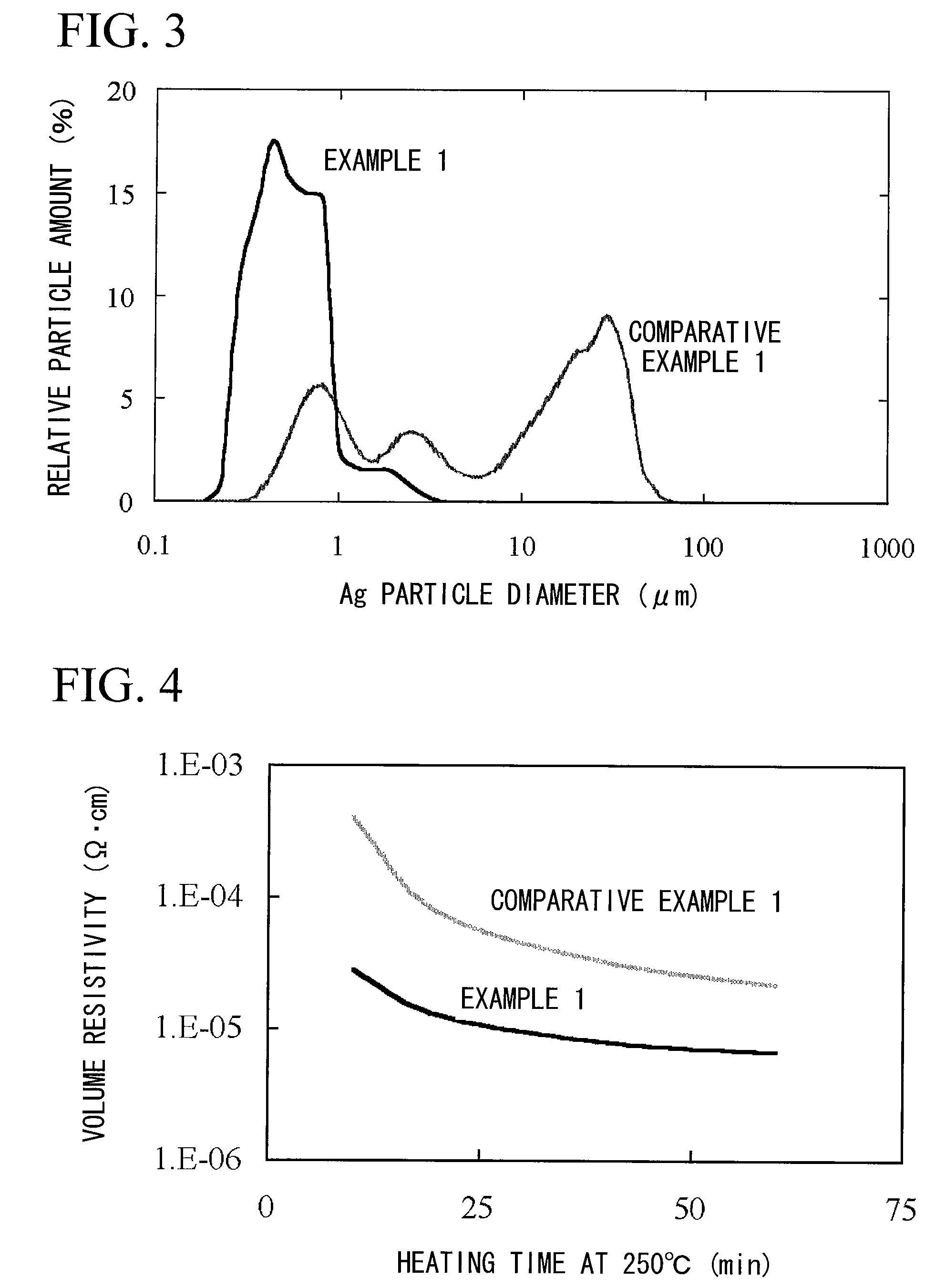
InactiveUS7771625B2Satisfactory conductivityThin line widthLiquid surface applicatorsConductive materialSilver pasteFreeze-drying
A method for producing a surface-treated silver-containing powder comprises vacuum freeze drying a dispersion liquid, which is obtained by dispersing silver or silver compound particles (a) in a solvent together with a surfactant (b) of an alkylamine type or an alkylamine salt type, or a phosphate type having a phosphorus content of 0.5 to 10% by mass so that the surfactant (b) is adsorbed in the surface of the silver or silver compound particles (a), thereby producing a silver-containing powder (c) whose surface is treated with the surfactant (b). Moreover, a silver paste is produced by dispersing the surface-treated silver-containing powder (c) in a solvent, or in a solvent with a resin.
Owner:DAINIPPON INK & CHEM INC
Carbon member, carbon member manufacturing method, redox flow battery and fuel cell
InactiveUS10109870B2Increase production capacitySatisfactory conductivityCell electrodesRegenerative fuel cellsFuel cellsPolyolefin
Owner:RESONAC HOLDINGS CORPORATION
Ceramic material composition, ceramic substrate, and nonreciprocal circuit device
ActiveUS8455381B2Satisfactory conductivityHigh dielectric constantFixed capacitor dielectricRare-earth elementChemical composition
A ceramic material composition advantageously used as a material for a ceramic substrate containing for example a resistor such as an isolator disposed therein.includes about 10 to 45 percent by weight of a BaO—TiO2—ReO3 / 2 ceramic composition, the ceramic composition being represented by xBaO-yTiO2-zReO3 / 2 (wherein x, y, and z each represent mole percent, 8≦x≦18, 52.5≦y≦65, and 20≦z≦40, and x+y+z=100; and Re represents a rare-earth element); about 5 to 40 percent by weight of alumina; and about 40 to 65 percent by weight of a borosilicate glass composition containing about 4 to 17.5 percent by weight of B2O3, about 28 to 50 percent by weight of SiO2, 0 to about 20 percent by weight of Al2O3, and about 36 to 50 percent by weight of MO (wherein MO represents at least one compound selected from CaO, MgO, SrO and BaO), wherein the total content of the BaO—TiO2—ReO3 / 2 ceramic composition and alumina is about 35 percent by weight or more.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Method for manufacturing CMOS device with high-k dielectric layers and high-k cap layers formed in different steps
ActiveUS9299619B2Minimize gate resistanceSatisfactory conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCMOSDielectric layer
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
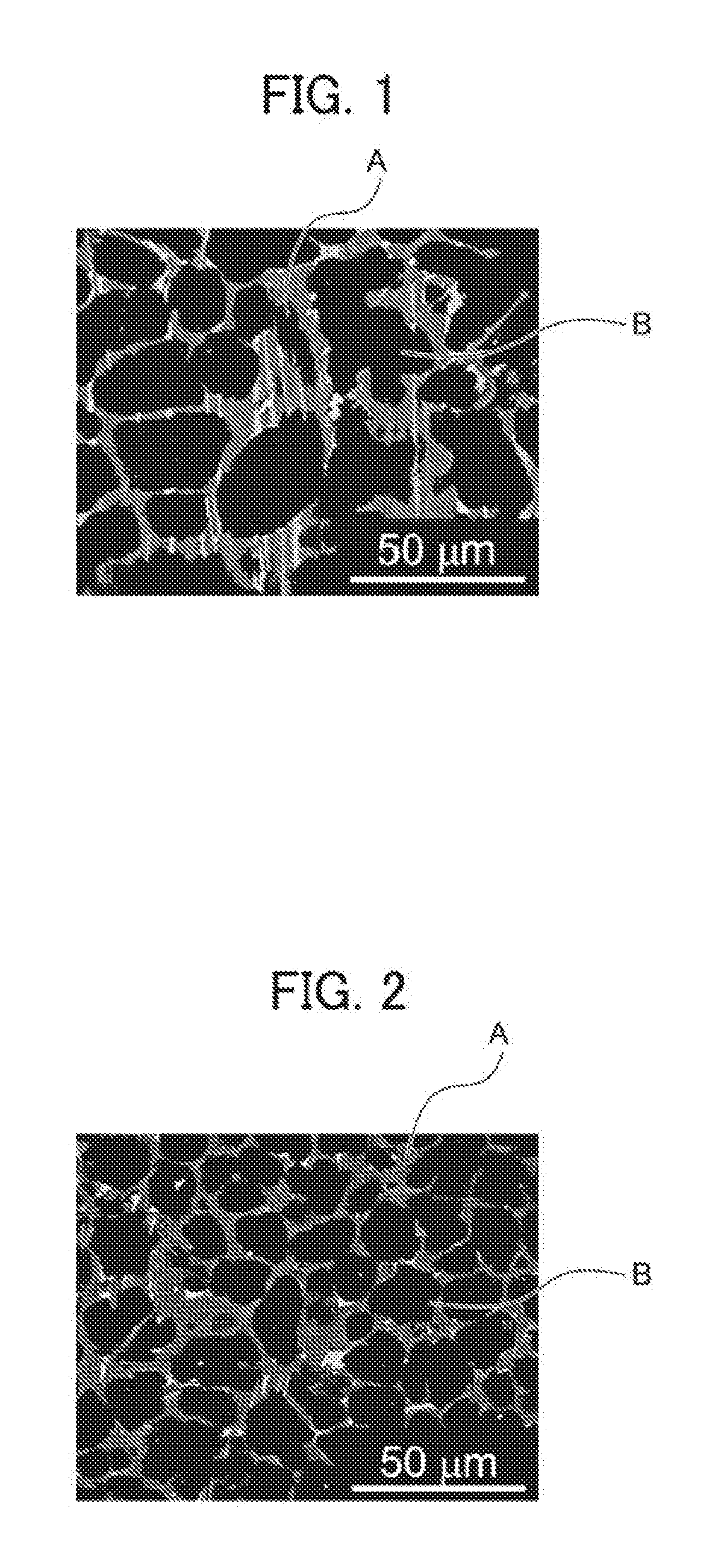
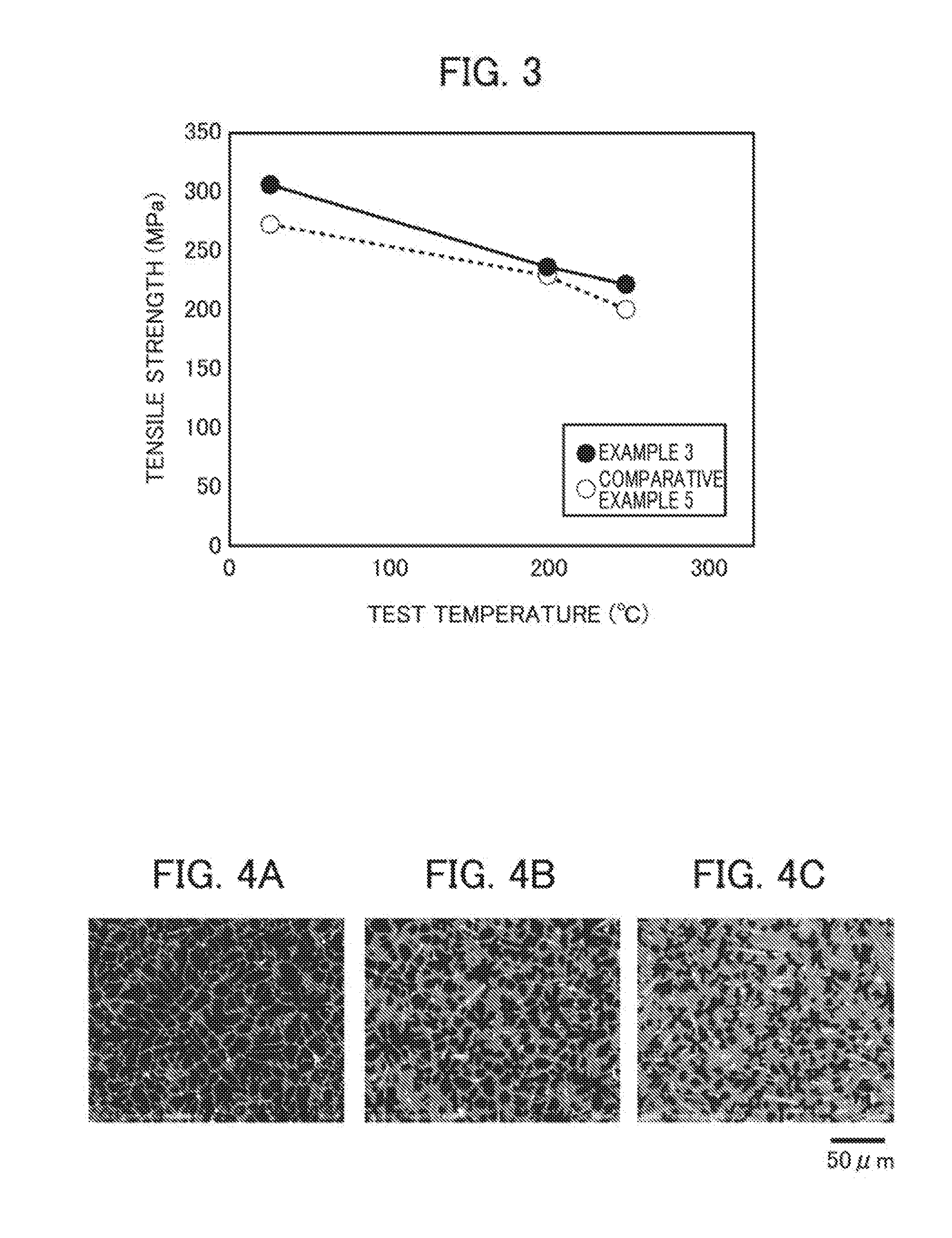
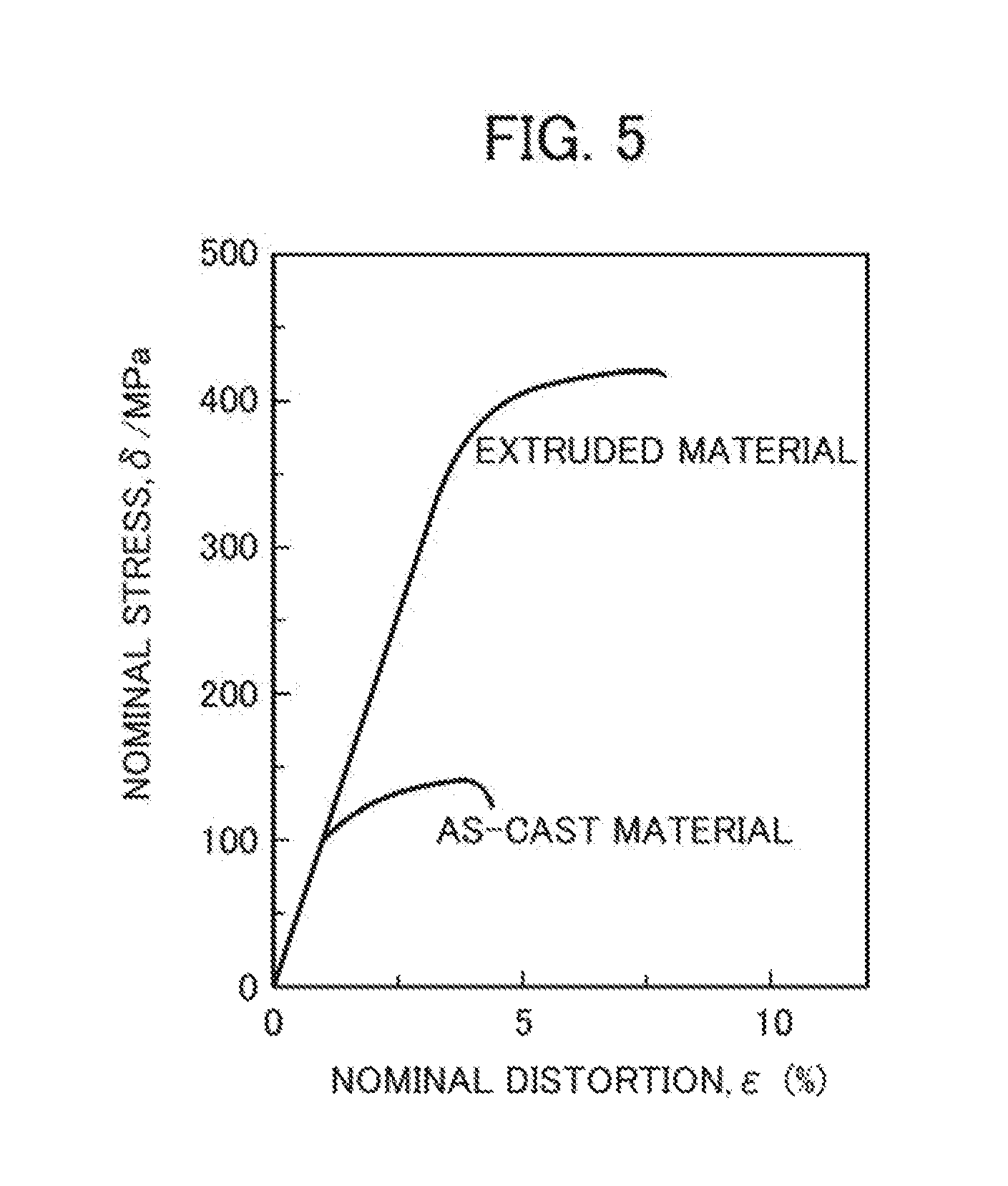
Magnesium alloy and method of manufacturing same
ActiveUS20160348217A1Satisfactory mechanical propertySatisfactory thermal conductivityRare earthMechanical property
A magnesium alloy is provided which does not contain a rare earth and which achieves, in a high-temperature region of about 200° C., both satisfactory mechanical properties and thermal conductivity. A magnesium alloy including Mg, Ca, Al and Si,where a content of Ca is less than 9.0 mass %,a content of Al is equal to or snore than 0.5 mass % but less than 5.7 mass %,a content of Si is equal to or less than 1.3 mass % and Al+8Ca≧20.5%.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Processes for producing nano-space controlled polymer ion-exchange membranes
InactiveUS20080033069A1Poor dimensional stability of membraneSolve large capacitySolid electrolytesIon-exchanger regenerationPolymer scienceFunctional monomer
Owner:JAPAN ATOM ENERGY RES INST
Magnesium casting alloy and method of manufacturing same
ActiveUS20160348218A1Satisfactory mechanical propertySatisfactory thermal conductivityAlloyMechanical property
A magnesium casting alloy is provided in which unlike an extruded alloy, a large amount of energy and a large cost are not needed for plastic processing, and in which in a high-temperature region of about 200 to 250° C., both mechanical properties and thermal conductivity are achieved. A magnesium casting alloy including Mg, Zn and Y, where a content of Zn is equal to or more than 1.2 atomic % but equal to or less than 4.0 atomic %, a content of Y is equal to or more than 1.2 atomic % but equal to or less than 4.0 atomic %, a composition ratio Zn / Y of Zn to Y is equal to or more than 0.65 but equal to or less than 1.35 and an Mg purity of an Mg mother phase is equal to or more than 97.0%.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
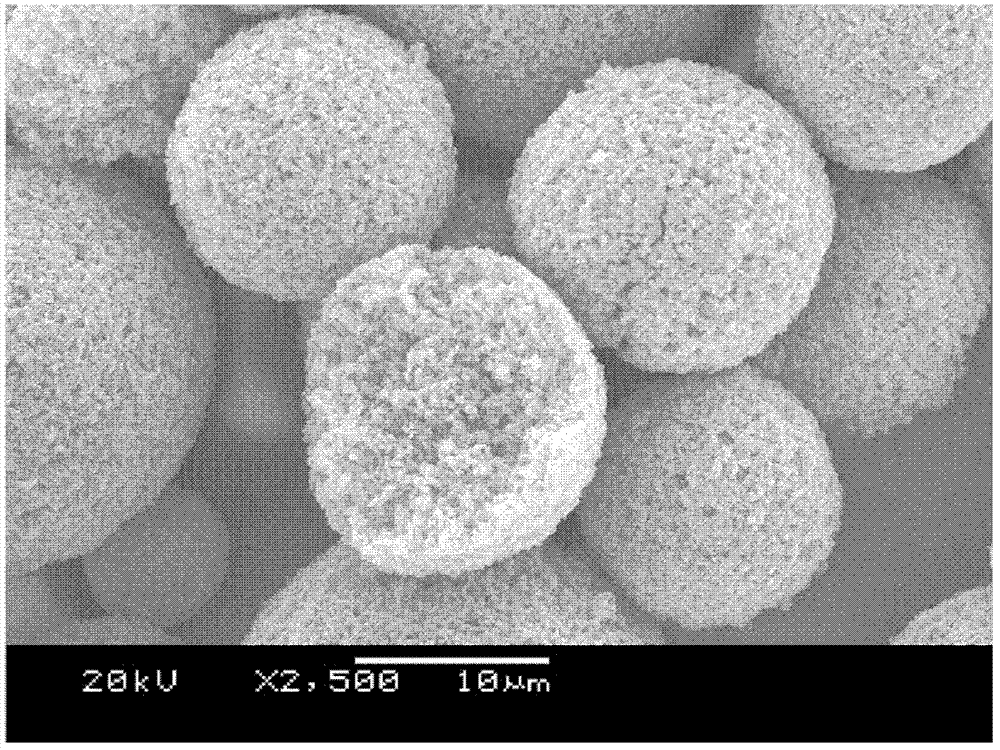
LiFePO4 (lithium iron phosphate) positive electrode material with specific morphology and structure and lithium secondary battery
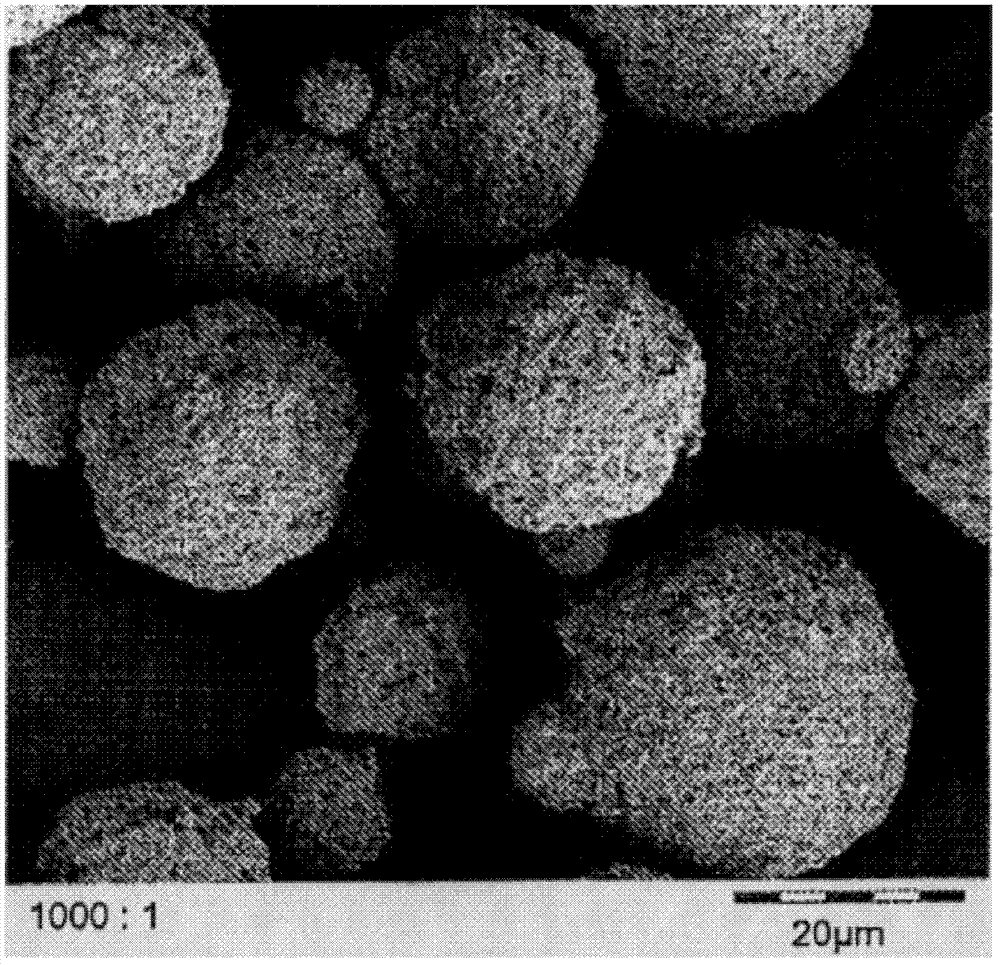
ActiveCN102509790BEasy to makeImprove high current charge and discharge performanceMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesCarbon layerLithium iron phosphate
The present invention relates to a lithium iron phosphate anode material with specific morphology and structure and a secondary battery using the same. The carbon-coated lithium iron phosphate anode material with specific morphology and structure of the present invention is characterized in that: the material contains spherical or spherical-like secondary particles prepared from sheet-shaped primary particles through conglomeration. A space exists among the primary particles; the average particle size of the secondary particles is 12 microns to 28 microns; the primary particles are sheet-shaped carbon-coated lithium iron phosphate particles; and the average particle size and average thickness of the primary particles in the two-dimensional plane are respectively 0.2 microns to 1 micron and 60 nanometers to 90 nanometers. The carbon layer evenly coated on the surface of the primary particles of the lithium iron phosphate anode material with specific morphology and structure of the present invention can ensure the conductive capability of the active material, maximally utilize the capacity of the active material, and improve large-current charge-discharge property of the material. In addition, the form of secondary particles performs excellently in aspects such as the active substance utilization rate, the large-current charge-discharge capability, and the capacity retention ratio of the electrode material with circulation.
Owner:天齐锂业(江苏)有限公司 +2
Detection method using an electrochemically-assisted alpha detector for nuclear measurement in a liquid medium
ActiveUS8888981B2Avoid formingSatisfactory conductivityCellsPhotography auxillary processesLiquid mediumActinide
An in situ method for detecting alpha particles contained in a liquid medium, which uses a system which includes a counter-electrode and an alpha particle detector including a substrate made of an intrinsic semiconductor material sandwiched between two electrical contacts, wherein the contact intended to be in contact with the liquid medium is made of boron-doped diamond. By forming a particular electrolyte 8 and by causing a current to flow between counter-electrode and the boron-doped diamond contact in contact with the liquid medium, actinides or polonium present in the liquid medium may be concentrated on the boron-doped diamond contact, and by this means the detection limit of the alpha emitters may be lowered.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
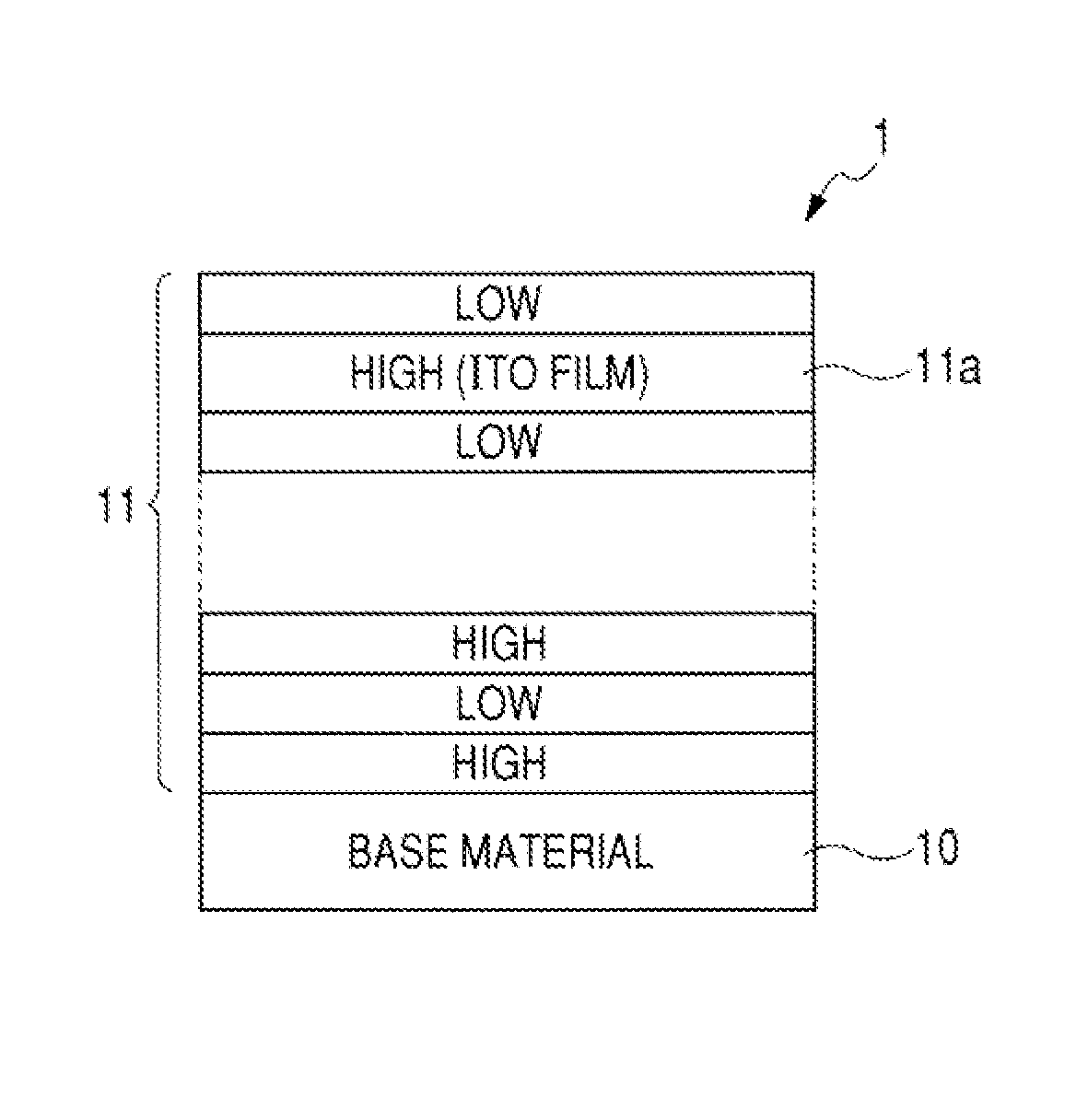
Optical low-pass filter
ActiveUS8437084B2Effectively prevent attachmentCost containmentTelevision system detailsMirrorsBand-pass filterConductive materials
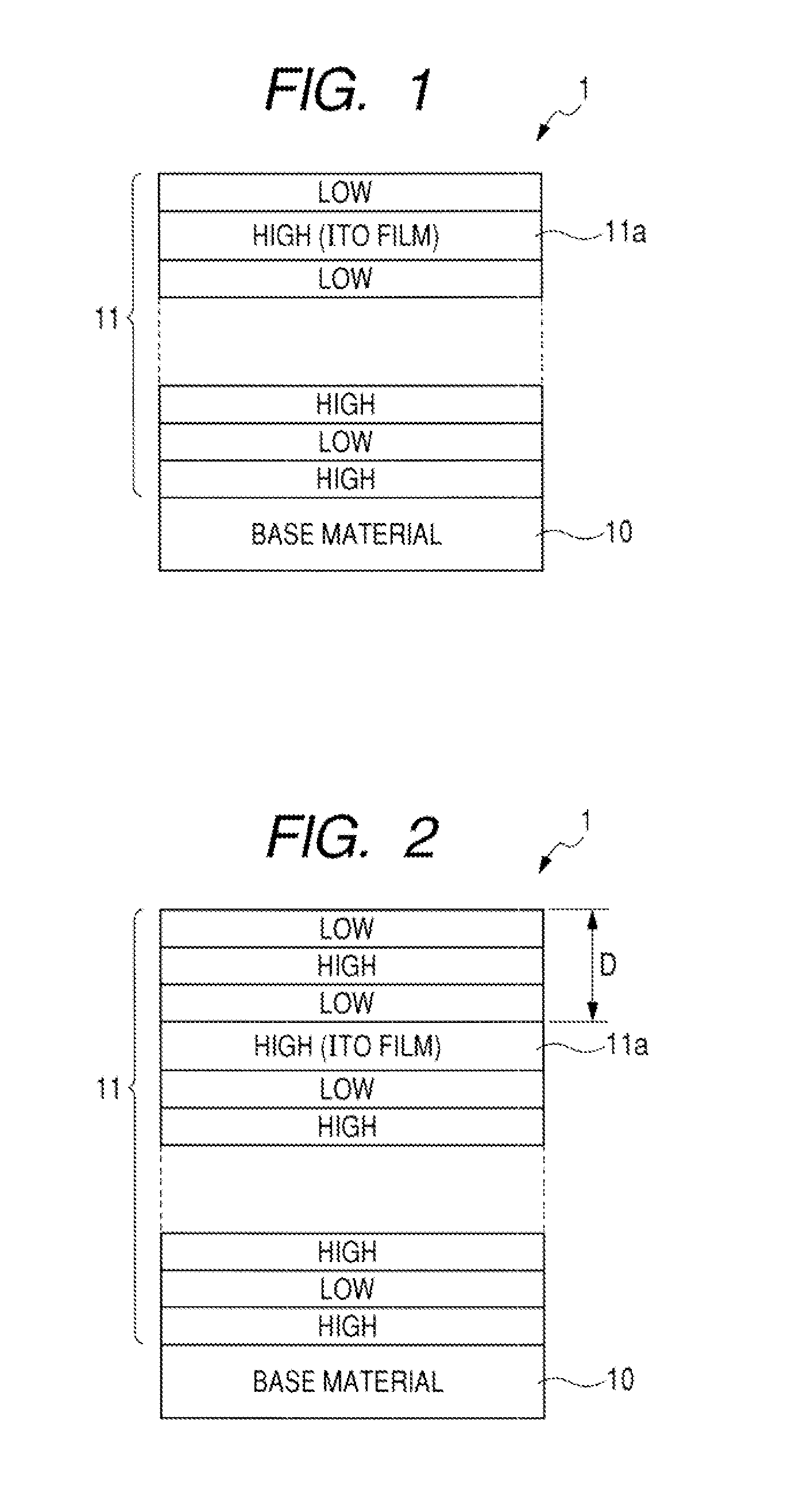
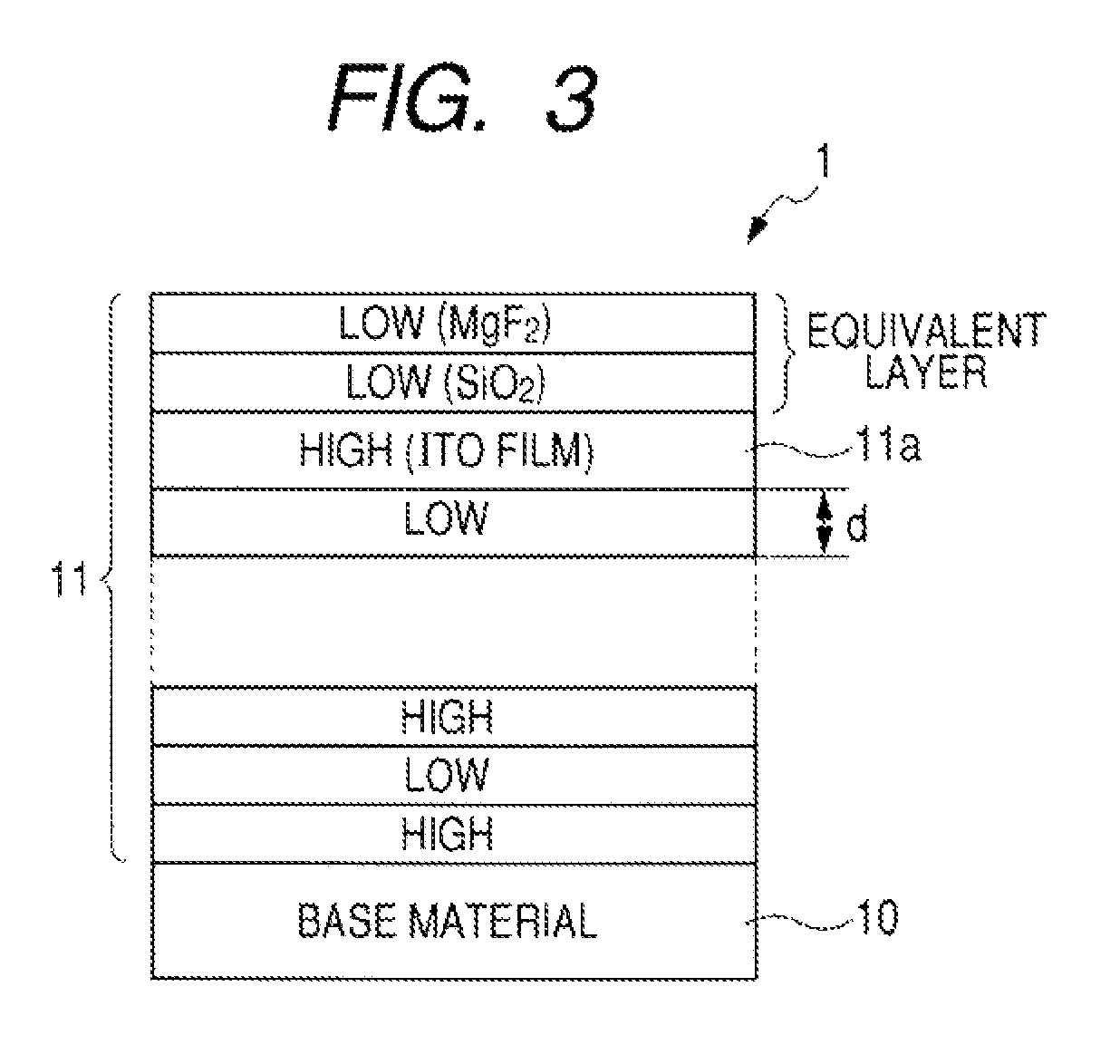
On the light-entering surface side of a base material 10, a coating layer 11 in which a high-refractive layer and a low-refractive layer are sequentially disposed alternately on one on the other is provided for blocking infrared radiation. One of the high-refractive layers is configured by an ITO film 11a so that the conductivity is increased on the surface of the coating layer. Herein, in view of preventing, to a further extent, the attachment of dirt and dust by providing the conductivity to the surface of the coating layer, it is desirable if the outermost high-refractive layer is made of a transparent conductive material. Moreover, it is desirable if the total layer thickness is 140 nm or smaller for the refractive layers formed outside of the high-refractive layer made of the transparent conductive material.
Owner:SONY CORP
Fluorescent member, its manufacturing method, and light-emitting apparatus
ActiveUS20210317367A1Satisfactory conductivitySatisfactory propertyOptical filtersLuminescent compositionsFluorescencePhosphor
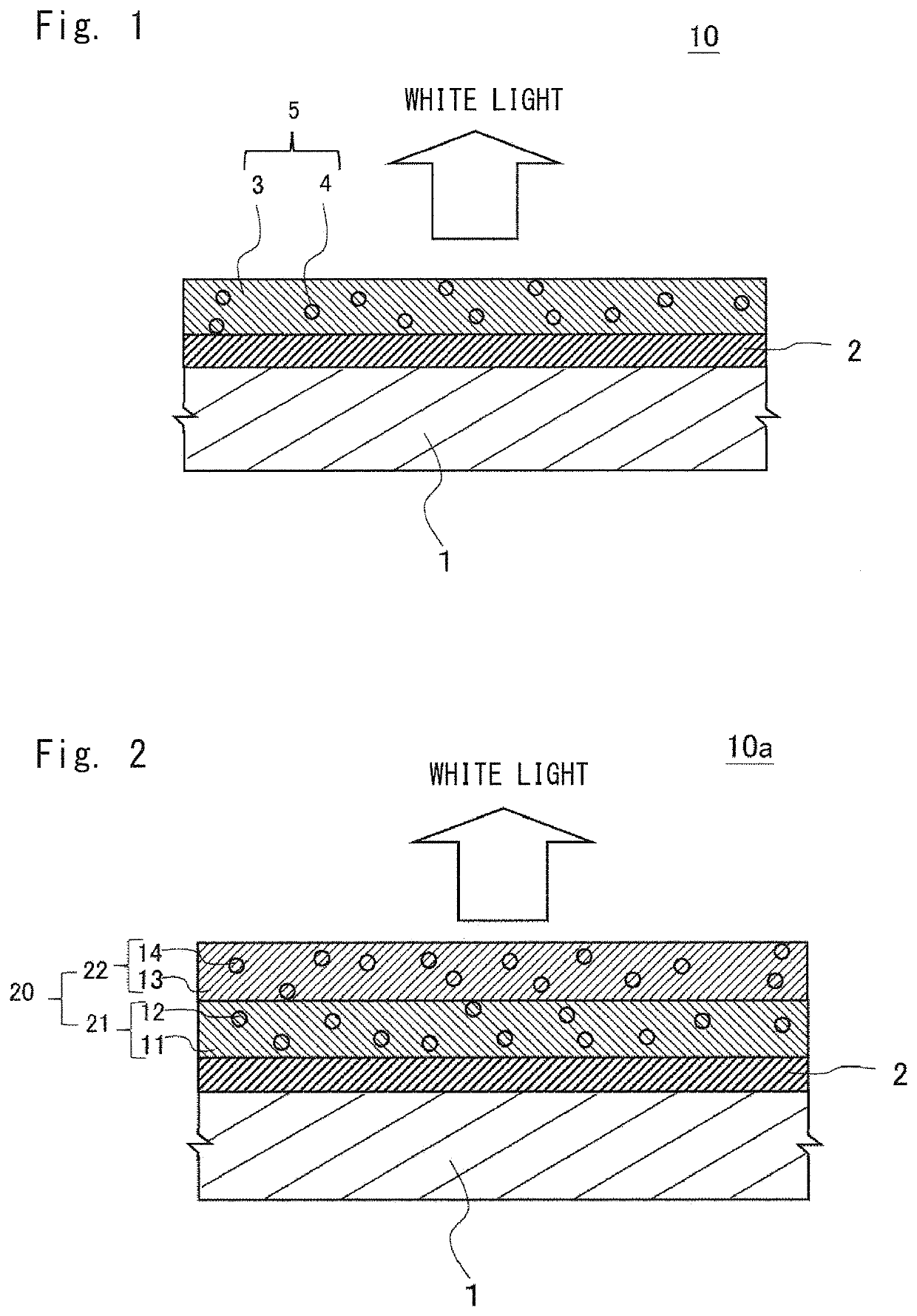
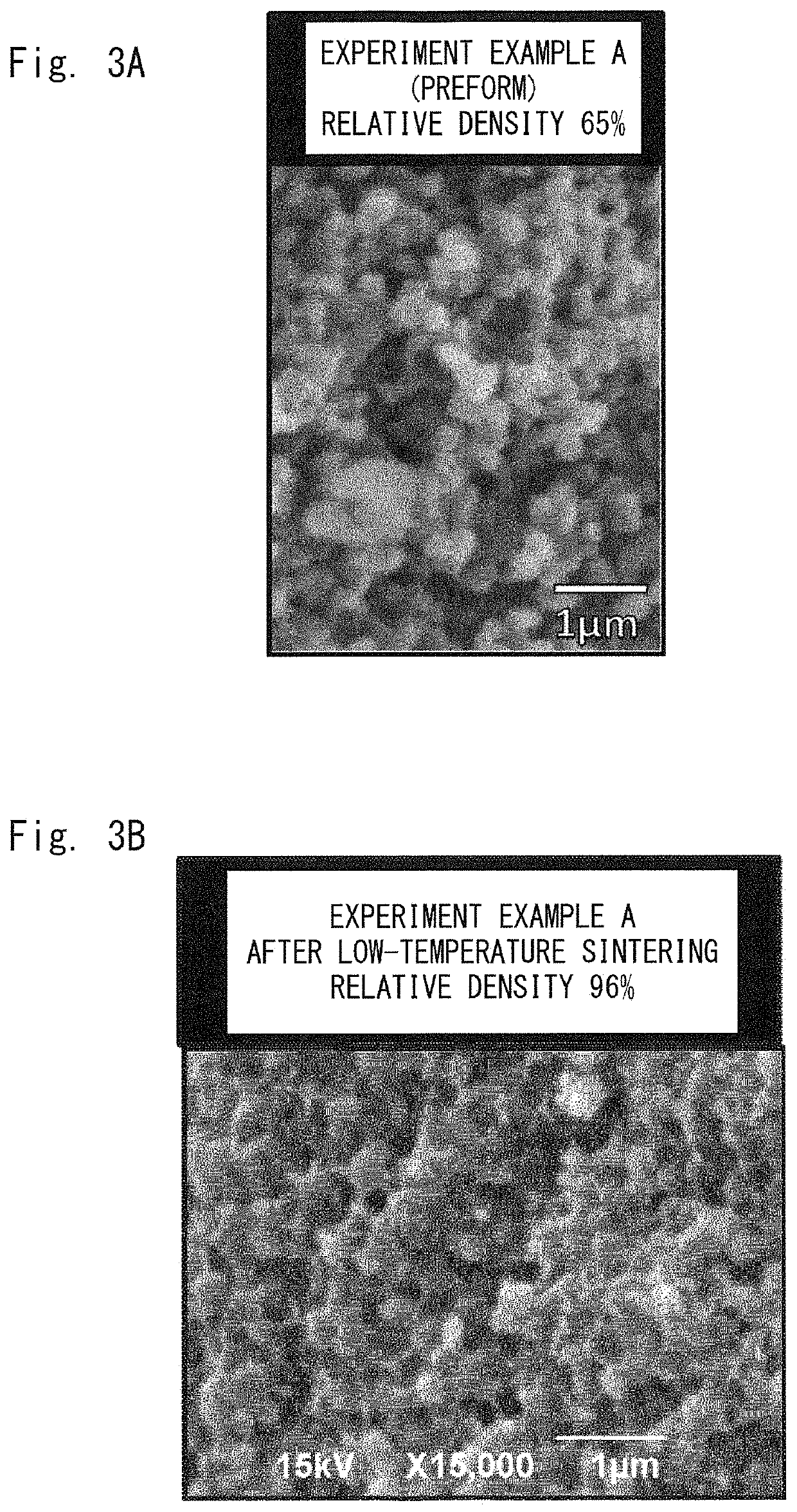
A fluorescent member according to present invention is composed of a sintered body for wavelength conversion containing a matrix containing magnesium oxide and magnesium hydroxide as main components, and phosphor particles dispersed in the matrix. A thermal conductivity of the fluorescent member is preferably 5 W / (m·K) or higher. A fluorescent member having both a satisfactory thermal conductivity and a satisfactory fluorescent property is provided without requiring a high-temperature sintering process (a high-temperature process at a temperature higher than 250° C.). Further, a method for manufacturing such a fluorescent member and a light-emitting apparatus using such a fluorescent member are provided.
Owner:KANAGAWA INST OF IND SCI & TECH
Working electrolyte of aluminum electrolytic capacitor with voltage lower than 63V
InactiveCN111627711AReduce hydrationReduced characteristic degradationElectrolytic capacitorsElectrolytic agentPhysical chemistry
The invention belongs to the field of capacitors, and particularly relates to a working electrolyte of an aluminum electrolytic capacitor of which the voltage is lower than 63V, and the electrolyte comprises the following components in parts by mass: 40-56 parts of a main solvent, 10-20 parts of an auxiliary solvent, 15-30 parts of a solute and 4-6 parts of a sparking voltage improver. The workingelectrolyte of the aluminum electrolytic capacitor is high in high-temperature stability, relatively high in sparking voltage, wide in working temperature range, high and stable in conductivity afterbeing heated, and good in application prospect and market prospect.
Owner:HUNAN CITY UNIV
Semiconductive shielding composite material, preparation method thereof and application thereof in power cables
ActiveCN111440378AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove interface compatibilityCompression moldingPower cable
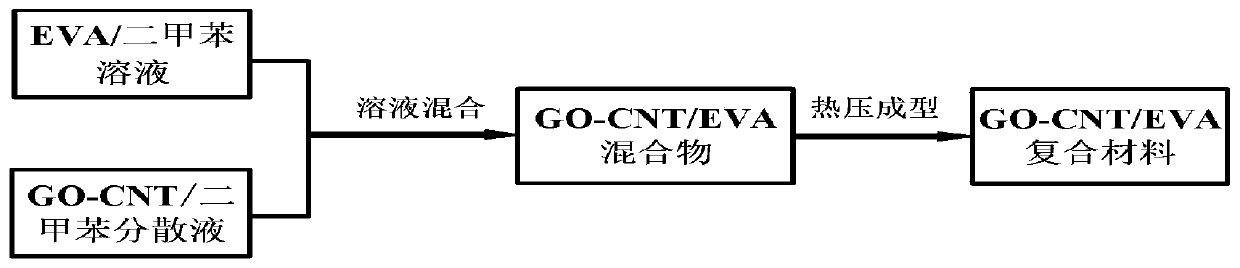
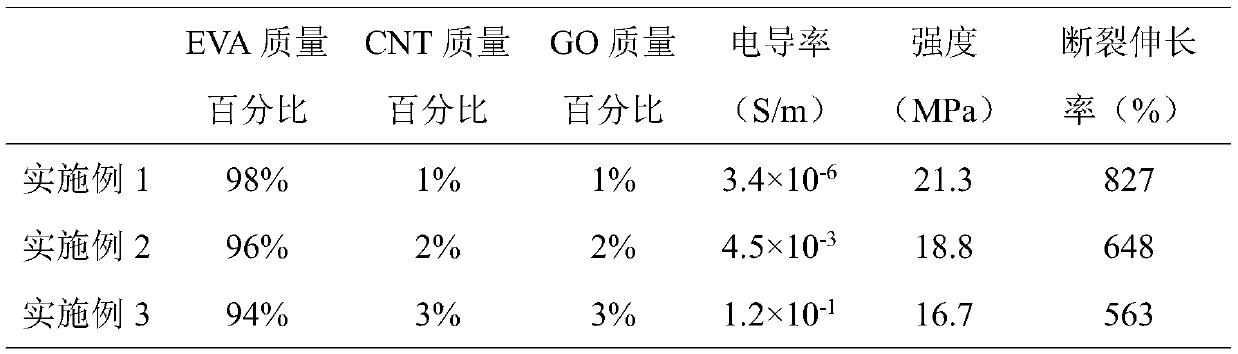
The invention relates to the technical field of semiconductive shielding composite materials, in particular to a semiconductive shielding composite material for a power cable, and the method comprisesthe following components in parts by weight: 94-98% of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA), 1-3% of carbon nanotube (CNT) and 1-3% of graphene oxide (GO). The preparation process comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a GO-CNT / EVA mixture; and (2) performing compression molding. According to the invention, the high-conductivity CNT is used as a conductive filler, the EVA is used as a matrix material, and the GO is used as a CNT and EVA matrix interface improver, so that an efficient conductive network is constructed under the condition of low CNT content, and the semiconductive shielding composite material with good conductivity and mechanical properties is obtained. The semiconductive shielding composite material for the power cable is simple to prepare, low in production cost and easy to realize mass production in industry.
Owner:STATE GRID HUNAN ELECTRIC POWER +2
Piezoelectric driving device, motor, robot, and pump
ActiveUS10580960B2Improve reliabilitySatisfactory conductivityProgramme-controlled manipulatorPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectric machineryElectrical and Electronics engineering
A piezoelectric driving device includes a vibrating plate, a first electrode, a piezoelectric layer, a second electrode layer provided above the vibrating plate. An active section is formed in a portion where the first electrode layer, the piezoelectric layer, and the second electrode layer overlap one another. The active section has a longitudinal direction and a latitudinal direction in plan view. At both ends in the latitudinal direction, ends of the first electrode layer are disposed in the same positions as ends of the wiring layer or further on the outer side than the ends, ends of the second electrode layer are disposed in the same positions as the ends of the wiring layer or further on the inner side than the ends, and the ends of the first electrode layer are disposed further on the outer side than the ends of the second electrode layer.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Fluorescent member, its manufacturing method, and light-emitting apparatus
ActiveUS11447696B2Satisfactory conductivitySatisfactory propertyOptical filtersLuminescent compositionsFluorescencePhosphor
A fluorescent member according to present invention is composed of a sintered body for wavelength conversion containing a matrix containing magnesium oxide and magnesium hydroxide as main components, and phosphor particles dispersed in the matrix. A thermal conductivity of the fluorescent member is preferably 5 W / (m·K) or higher. A fluorescent member having both a satisfactory thermal conductivity and a satisfactory fluorescent property is provided without requiring a high-temperature sintering process (a high-temperature process at a temperature higher than 250° C.). Further, a method for manufacturing such a fluorescent member and a light-emitting apparatus using such a fluorescent member are provided.
Owner:KANAGAWA INST OF IND SCI & TECH
Magnesium casting alloy and method of manufacturing same
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com