Patents
Literature
39results about How to "Satisfactory mechanical property" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polypropylene Composition Comprising a Propylene Homopolymer Component
InactiveUS20090018267A1Equally distributedHighly satisfactory optical propertyChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsOptical propertyPolymer science
The present invention concerns a polypropylene composition comprising a nucleated propylene homopolymer having improved optical properties.
Owner:BOREALIS TECH OY
Battery pack
InactiveUS20060057460A1Reduce material costsImprove mechanical propertiesPrimary cell to battery groupingSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsPower toolBattery cell
A battery pack for supplying power to an electrical appliance, in particular a power tool, has a housing which at least partly comprises plastic and holds at least one battery cell, wherein the plastic is a polyethylene (PE) with a density of more than 0.93 g / cm3
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Electric article comprising at least one element made from a semiconductive polymeric material and semiconductive polymeric composition
ActiveUS20110017509A1Low viscosityEasy to processRubber insulatorsNon-metal conductorsElastomerConductive polymer
An electric article, particularly an electric cable or an accessory thereof, such as a cable joint or a cable termination, includes at least one element made from a semiconductive polymeric material, wherein the at least one element is obtained by crosslinking a semiconductive polymeric composition including: (a) at least one elastomeric polymer; (b) a filler mixture including: (i) at least one first carbon black having a dibutyl phthalate (DBP) absorption number of from 250 to 600 ml / 100 g; (ii) at least one second carbon black, different from the first one, having a dibutyl phthalate (DBP) absorption number of from 80 to 250 ml / 100 g; and (c) at least one graphite having a specific surface area, measured according to the BET method, not higher than 20 m2 / g.
Owner:PRYSMIAN SPA
Polyoxyalkylene polyol or monool and polyurethane resin
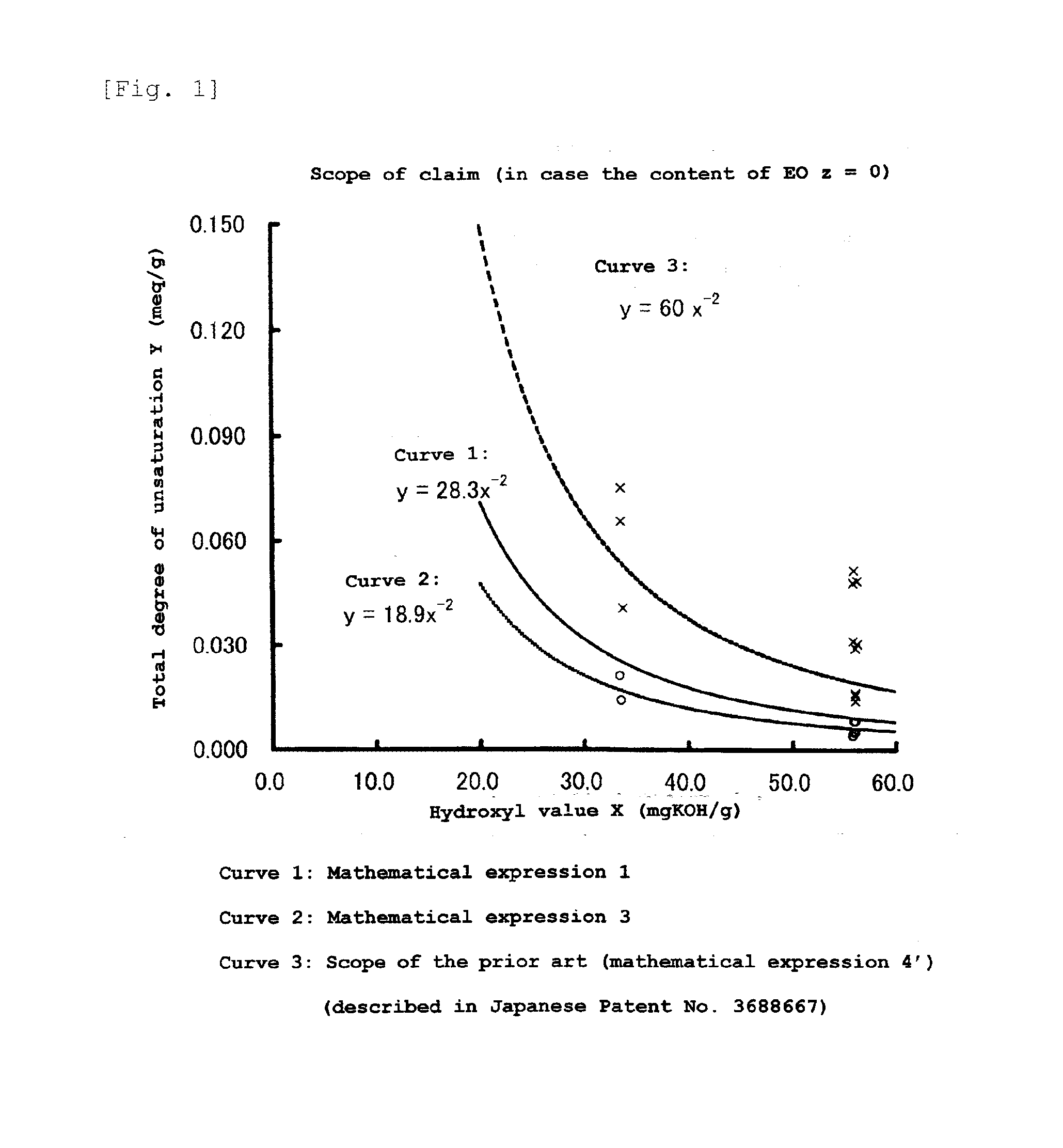
ActiveUS9388271B2Satisfactory mechanical property and moisture resistanceSufficient reactivityOrganic chemistryArylHalogen
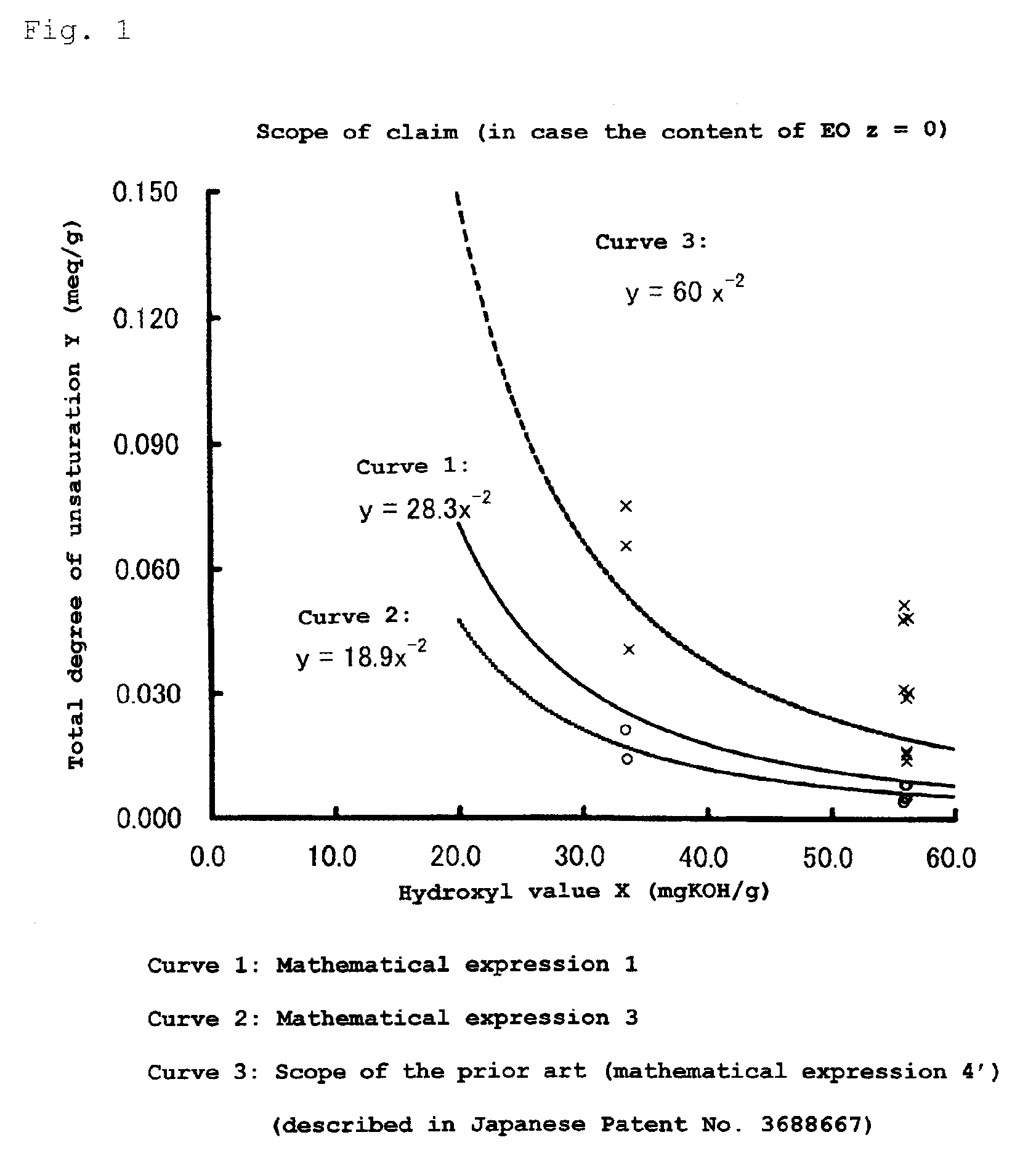
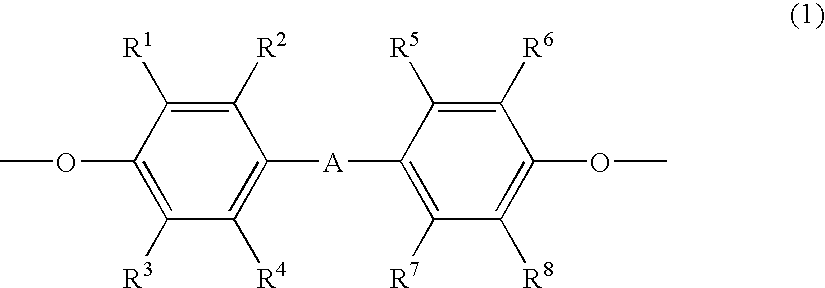
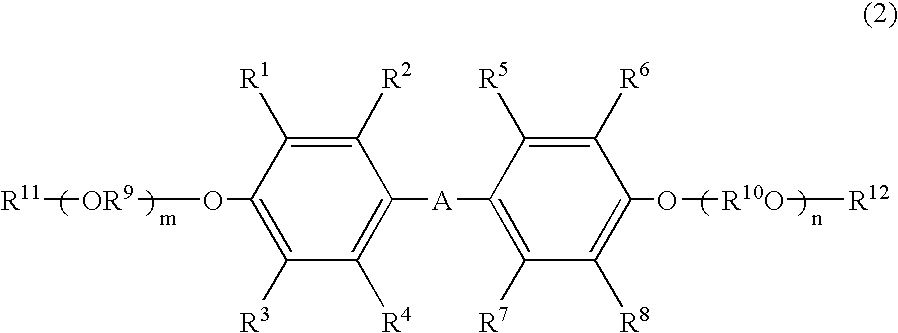
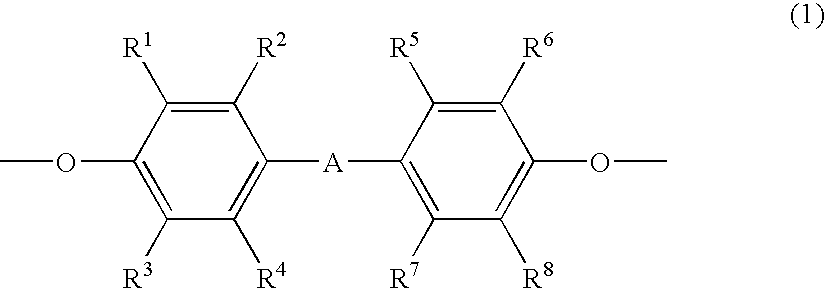
There is provided a polyoxyalkylene polyol or monool (S) represented by formula (2). In the formula (2), R2 represents an m-valent group in which m active hydrogens are removed from the active hydrogen-containing compound (H); Z is an alkylene group or a cycloalkylene group, and these groups are unsubstituted or substituted with a halogen atom or an aryl group. A hydroxyl value x, total degree of unsaturation y and the content of ethylene oxide z satisfy mathematical expression (3). In mathematical expression (3), x represents 5 to 280 mgKOH / g, y represents total degree of unsaturation represented by a unit meq / g, and z is from 0 to 50.R2—[—(ZO)p-(AO)q-(CH2CH2O)r-H] (2)y≦18.9×x−2×(100−z) / 100 (3)
Owner:SANYO CHEM IND LTD
Method for manufacturing wholly aromatic liquid-crystalline polyester resin
InactiveUS7335318B2Excellent toneImprove heat resistanceLiquid crystal compositionsLiquid crystallinePhosphate
The present invention provides a method for manufacturing a wholly aromatic liquid-crystalline polyester resin comprising the steps of:1) acylating the hydroxy group of major monomer components selected from the group consisting of aromatic hydroxycarboxylic acid, aromatic diol and aromatic dicarboxylic acid, with an acylating agent, provided that said major monomer components comprise at least one of aromatic hydroxycarboxylic acid and aromatic diol; and2) polycondensing said major monomer components of which hydroxy group is acylated,wherein, the polycondensation reaction is carried out in the presence of a metal dihydrogen phosphate in an amount of 1-5000 ppm based on the total monomer components, and a liquid-crystalline polyester resin manufactured by the method and a composition comprising said resin.
Owner:UENO PHARMA CO LTD
Cold working die steel
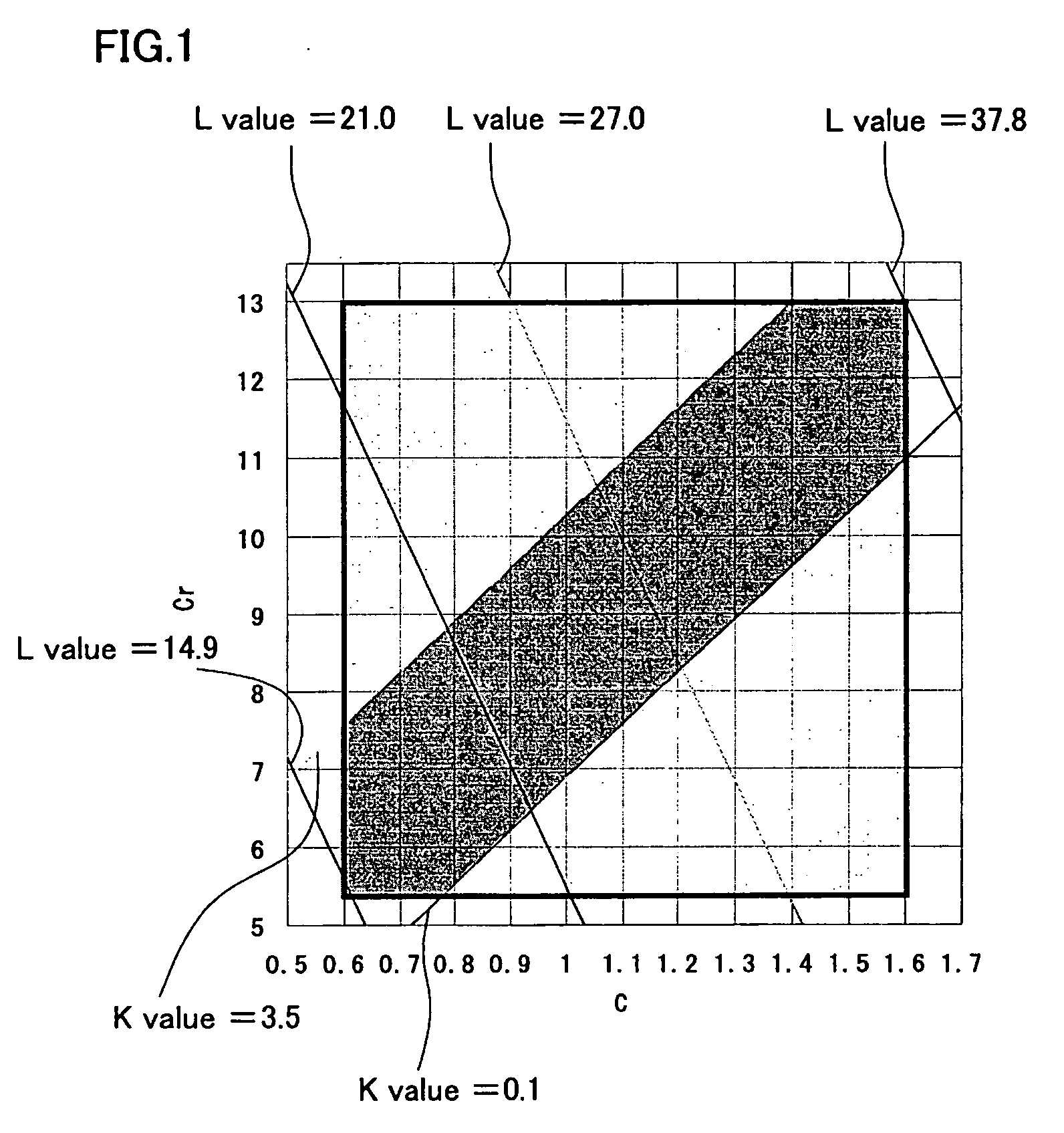
This invention is aimed at providing a cold working die steel successfully reduced in the hardness, and increased in readiness in the cold workability (forging, pressing and so forth) and machinability (milling, drilling, endmilling processing, grinding and lathe turning). A cold working die steel aimed at solving the above-described subject consists essentially of, in % by mass, 0.6%≦C≦1.60%, 0.10%≦Si≦1.20%, 0.10%≦Mn≦0.60%, 5.5%≦Cr≦13.0%, 0.80%≦Mo+0.5W≦2.10%, 0.10%≦V≦0.40%, 0.0002%≦O≦0.0080%, 0.001%≦A1≦0.10%, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities; has transformation point Ar3 in the range from 750° C. to 850° C., with both ends inclusive; has a mean circle-equivalent diameter of a carbide, which belongs to a circle-equivalent diameter range from 0.1 μm to 3 μm observed in a section of a structure obtained after spherodizing a sample that was heated at a temperature of (Ar3+50° C.) or above and 1,050° C. or below, of 0.25 μm to 0.8 μm, with both ends inclusive; has a Brinell hardness attained after the spherodizing of HB179 to HB235, with both ends inclusive; has a steel cleanliness of (dB+dC)60×400 in the group C inclusion and the group B inclusion specified by JIS G0555 of 0.05% or less; and has a K value defined as Cr(%)−6.8×C(%) of 0.1 to 3.5, both ends inclusive.
Owner:DAIDO STEEL CO LTD
Curable compositions
InactiveUS7081494B2Reduce surface tackGood coating effectSpecial tyresOrganic dyesPlasticizerSilanol
The present invention has for its object to provide a curable composition which, despite its low viscosity, gives a cured product with a high gel fraction, low residual tack, low modulus, high elongation, and good flexibility.The present invention relates to a curable composition comprising the following two components:(A) a vinyl polymer having at least one crosslinking silyl group on the average per molecule: and(B) a photocurable substance, (C) an air oxidation-curable substance, (D) a high molecular plasticizer, (E) a reactive plasticizer or (F) a compound having one silanol group in its molecule and / or a compound capable of reacting with moisture to give a compound having one silanol group in the molecule.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Polyamide resin composition comprising fiber reinforced polyamide pellet and molded article thereof
InactiveUS20170275458A1Reduce component weightSatisfactory mechanical propertyPlastic recyclingMachines/enginesPolymer scienceShell molding
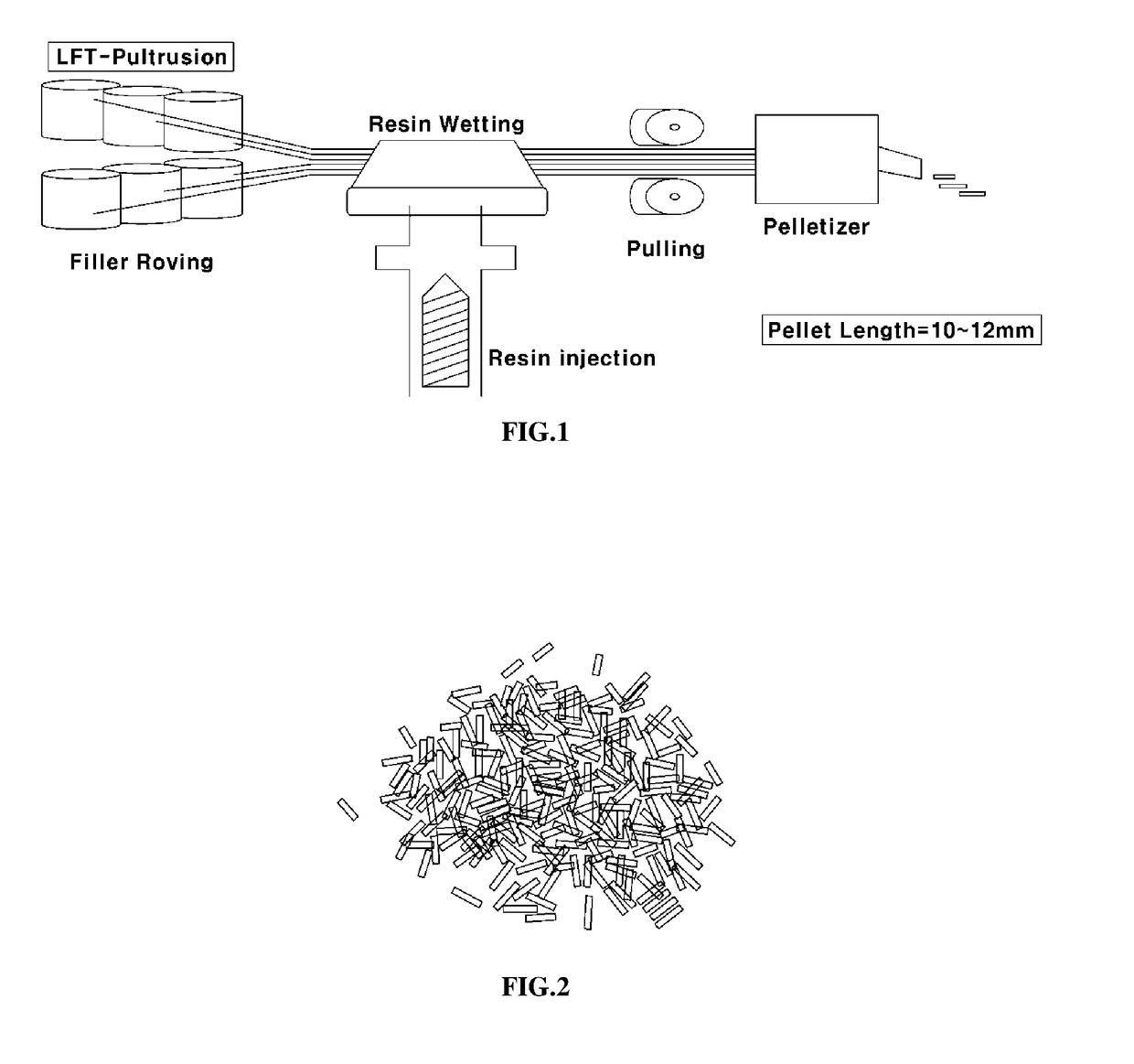
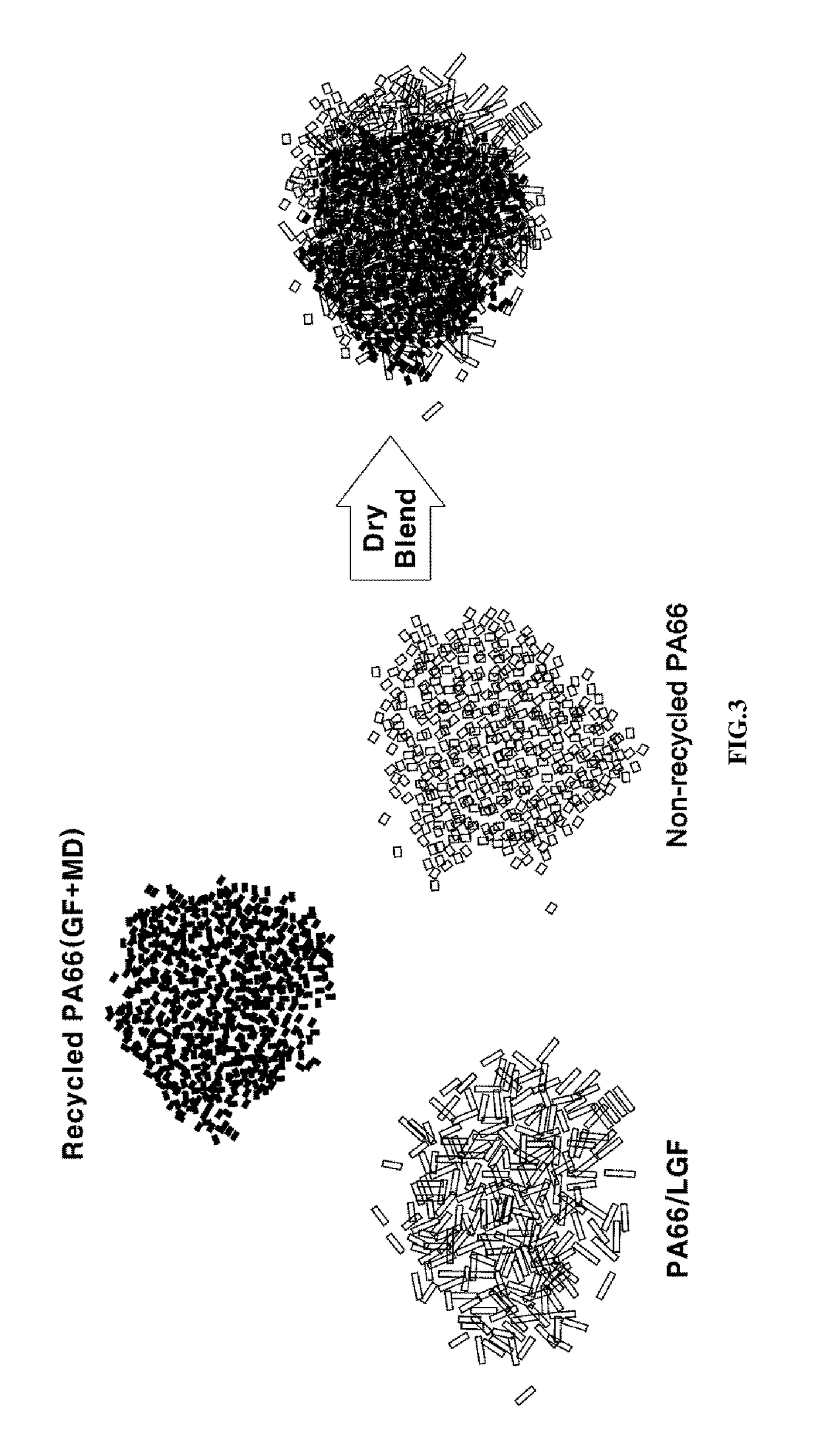
Disclosed are a polyamide resin composition comprising a fiber reinforced polyamide pellet, a molded article comprising the polyamide resin composition and a method of manufacturing the molded article. The polyamide resin composition includes the fiber reinforced polyamide pellet, which can be produced by pultrusion, such that moldability and mechanical properties of molded articles may be sufficient using the recycled polyamide 66 resin. In addition, although the polyamide resin composition contains a less amount of inorganic substance, mechanical properties of the molded article are sufficient, weight of molded articles can be reduced and production costs can be reduced.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Recycling process of a cross-linked polymeric material, in particular from electric cable coating materials
InactiveUS6127434AReduced stateSatisfactory mechanical propertyPlastic recyclingCross-linkCyclic process
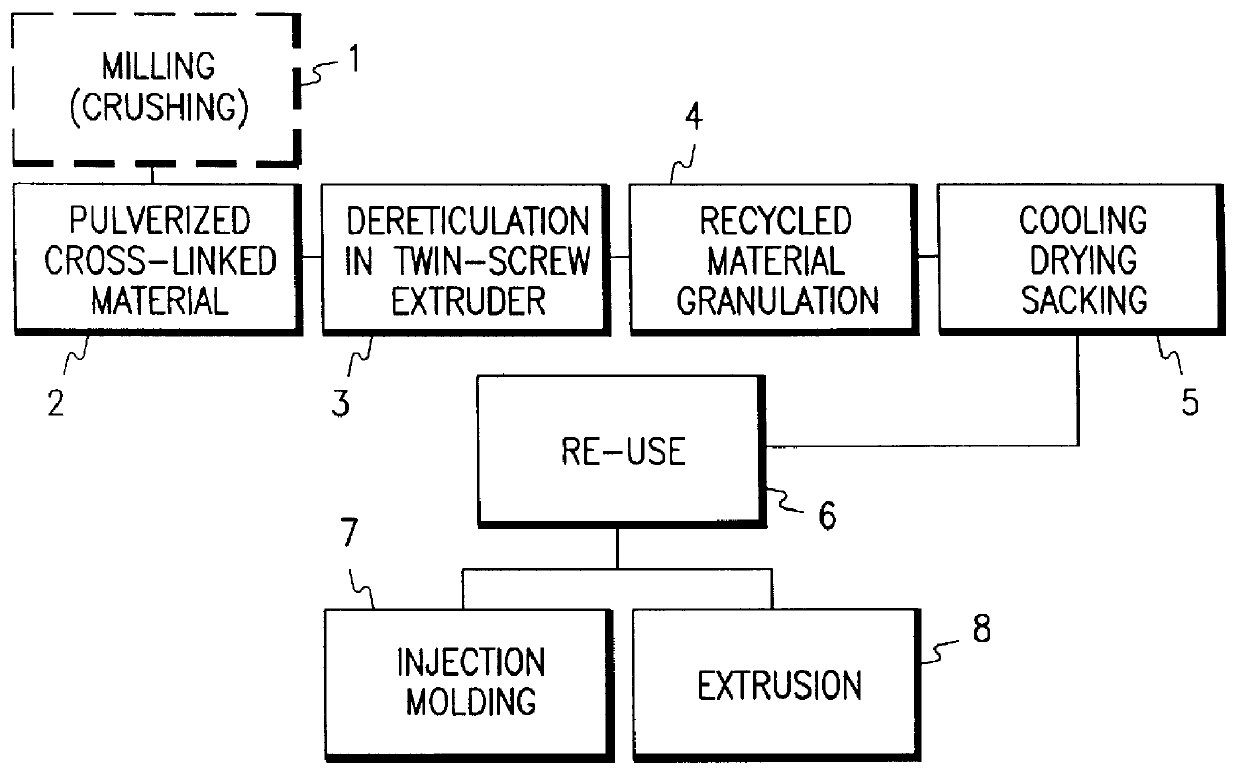
A process for dereticulating a cross-linked polymeric material, such as cross-linked polyethylene from scraps of electric cable coatings or from unused cable coatings through a mechanical mixing cycle, wherein the cross-linked material is subjected to a specific power per mass unit such as to induce shear stresses in the material itself and temperatures higher than pre-established minimum levels. At the end of this cycle the material goes back to a thermoplastic state that may be substantially regarded as thermoplastic; then, following granulation, cooling, drying and sacking, the material will be ready for re-use, either alone or mixed with virgin polymers, according to usual operating technologies for thermoplastic materials. Eventually, the mechanical mixing cycle may be preceeded by a preliminary crushing cycle of the cross-linked polymeric materials to be treated. Preferably, the mixing cycle is carried out in a twin-screw extruder with special screw and temperature profiles.
Owner:NEXANS
Gray gold alloy free of nickel and copper
ActiveUS20120114522A1Satisfactory mechanical propertyHigh whitenessFoundry mouldsFoundry coresNickelTin Element
The present invention relates to a white gold alloy free of nickel and copper having a hardness that is suitable in particular for watchmakers and jewellers. Said alloy consists of (in wt %): more than 75% of Au; more than 18% to less than 24% of Pd; more than 1% to less than 6% of at least one element selected from among Mn, Hf, Nb, Pt, Ta, V, Zn and Zr; optionally, no more than 0.5% of at least one element selected from among Si, Ga and Ti; and optionally, no more than 0.2% of at least one element selected from among Ru, Ir and Re. The invention also relates to a method for preparing said alloy.
Owner:ROLEX SA
Process for calibrating a sensor, automated method for online monitoring of the changes to a liquid body and associated sensor
ActiveUS10816488B2Satisfactory mechanical propertyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial testing goodsPolyethylene terephthalate glycolPolyethylene terephthalate
A sensor for determining the overall content of a pre-determined chemical element in a liquid body uses X-ray fluorescence technology and includes an X-ray source, an X-ray detector, and a cell intended to contain a sample of lubricant to be analyzed, and is provided with a wall forming a window for passage of X-rays, the wall of the sensor cell being produced from polyethylene terephthalate, the cell also including a casing defining an internal volume for receiving the sample. A procedure for calibrating the sensor, and an automated method for online monitoring are also described and claimed.
Owner:WIKA
Polyamide resin composition and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20060058424A1Improve heat resistanceSatisfactory mechanical propertyPigmenting treatmentFilm/foil adhesivesHeat resistancePolyamide
An object of the present invention is to provide a polyamide resin composition having high mechanical properties and high heat resistance while achieving a satisfactory balance between various physical properties. A molded product made of this polyamide resin exhibits a lower warpage and excellent surface appearance. A method for producing the polyamide, resin composition is also provided. The present invention provides a polyamide resin composition containing a polyamide resin and swelling mica treated with a polyether compound having a bisphenol structure. The present invention also provides a method for making the polyamide resin composition including melt-mixing a polyamide resin with a polyether compound.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Liquid (METH)acrylic syrup, method for impregnating a fibrous substrate with said syrup, and composite material produced after polymerisation of said impregnation syrup
ActiveUS20170369618A1Easy to prepareNot to degrade mechanical performance qualityViscous liquidFiber
The invention relates to a viscous liquid (meth)acrylic syrup comprising:a) a (meth)acrylic polymer,b) a (meth)acrylic monomer,c) an initiator to start the polymerization of the (meth)acrylic monomer, said initiator being in the form of a peroxide compound that is liquid in a temperature range of between 0° and 50° C.,said syrup being characterized in that the initiator is combined with an accelerating system comprising:d) a reducing compound,e) a metal salt or a mixture of metal salts not comprising any cobalt andf) a tertiary amine.
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
Fibrous preforms for use in making composite parts
ActiveUS20160311175A1Improve impact resistanceEasily fabricatedLayered productsVehicle componentsTotal thicknessFiber
Owner:HEXCEL REINFORCEMENTS SAS
Polymer electrolyte membrane, and membrane electrode assembly and polymer electrolyte fuel cell using the same
InactiveUS8597854B2Satisfactory mechanical propertyImprove antioxidant capacitySolid electrolyte fuel cellsPolymer electrolytesFuel cells
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Engineered concrete binder composition comprising mechano-chemically modified component and method of producing the same
ActiveUS20210323869A1Significant utilityImprove propertiesSolid waste managementDrilling compositionPolymer sciencePolymer chemistry
Owner:SAROD GREENBACK LLP
Polymer electrolyte membrane, and membrane electrode assembly and polymer electrolyte fuel cell using the same
InactiveUS20120107721A1Satisfactory mechanical propertyImprove antioxidant capacitySolid electrolyte fuel cellsPolymer electrolytesFuel cells
Disclosed is a fuel cell in which a membrane electrode assembly less undergoes increase in ion conduction resistance, and a polymer electrolyte membrane less undergoes deterioration. Specifically, the polymer electrolyte membrane includes a first membrane and a second membrane being two different membranes composed of polymer electrolytes having different ion-exchange capacities, in which the first membrane has an area of one surface thereof equal to or larger than an area of one surface of an anode or a cathode, and the second membrane has an area of one surface thereof smaller than that of the first membrane and is arranged in a gas inflow region on a side being in contact with the cathode. The second membrane has an ion-exchange capacity smaller than that of the first membrane or has a number-average molecular weight larger than that of the first membrane.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
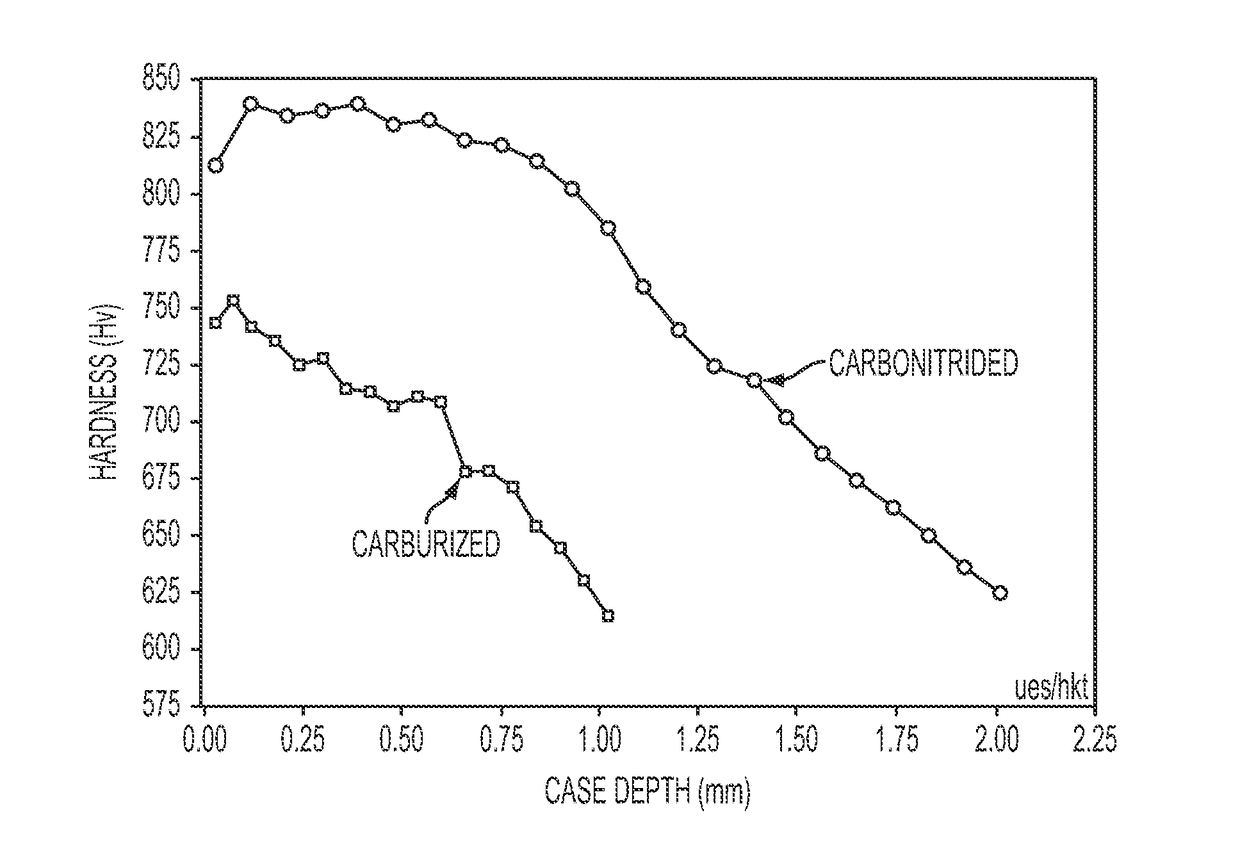
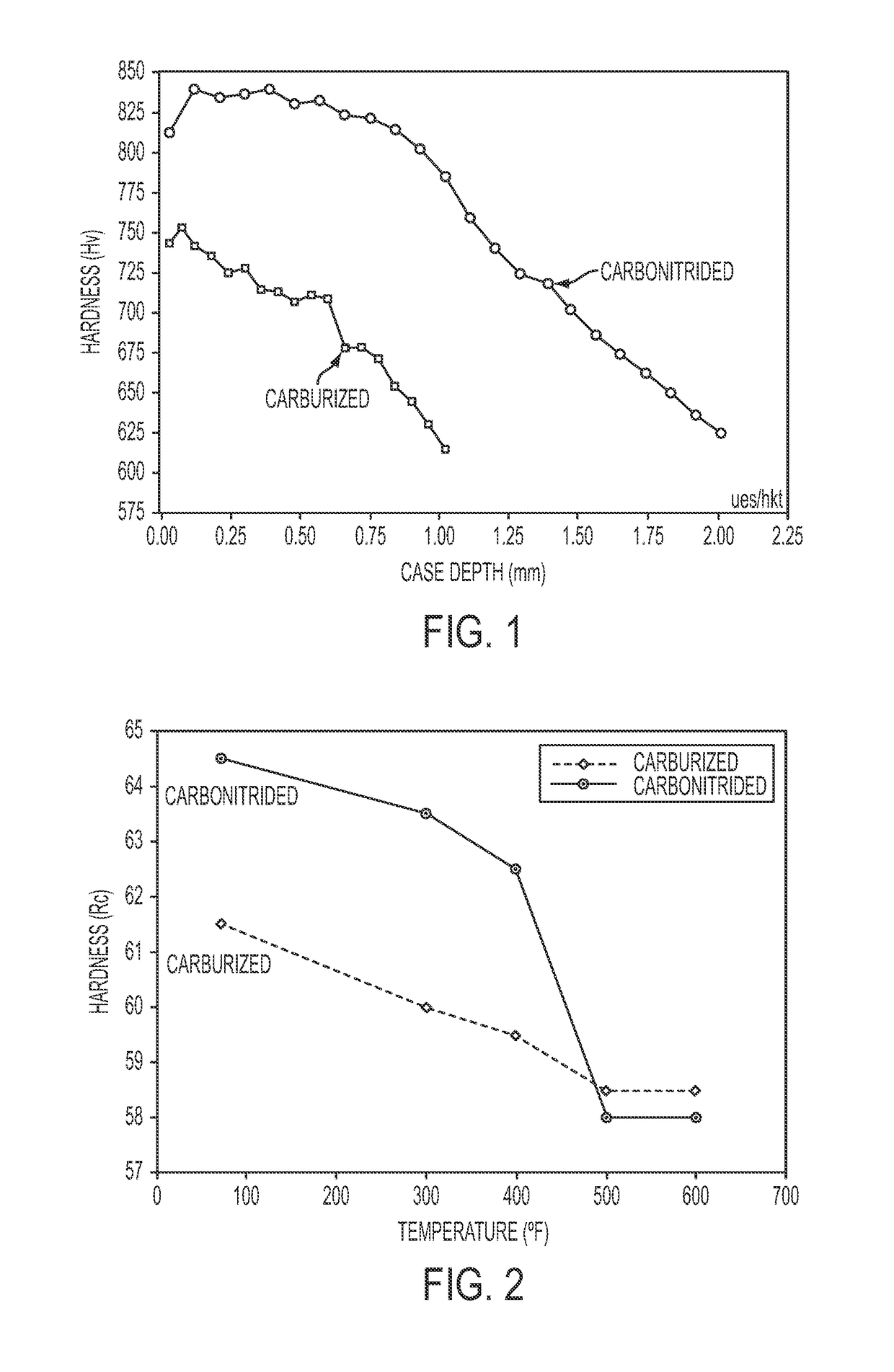
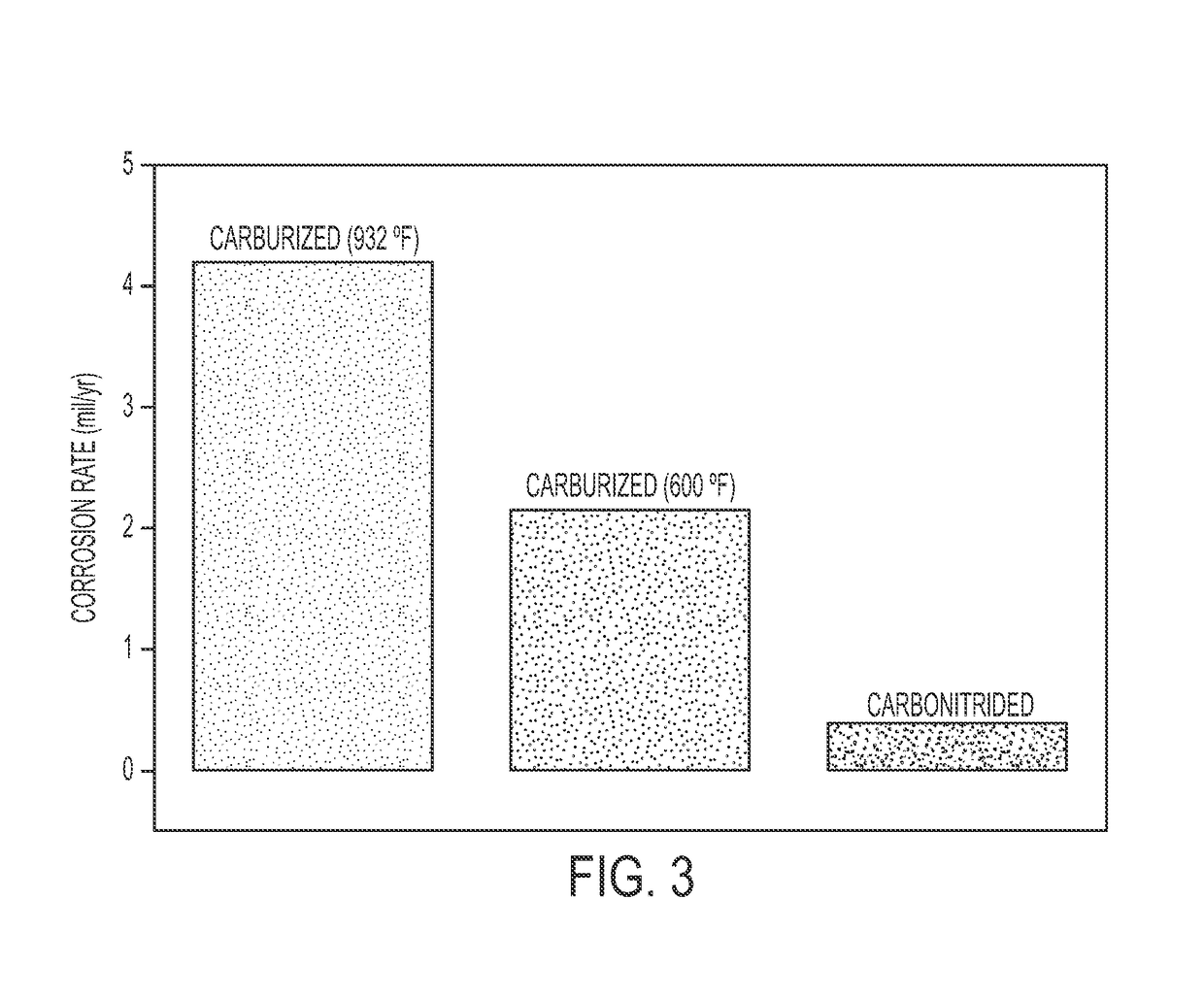
Carbo-nitriding process for martensitic stainless steel and stainless steel article having improved corrosion resistance
ActiveUS10053763B2Improve corrosion resistanceSatisfactory mechanical propertyShaftsBearing componentsMartensitic stainless steelCase hardening
Owner:RAO UES +2
Electric article comprising at least one element made from a semiconductive polymeric material and semiconductive polymeric composition
ActiveUS8383012B2Improve electrical performanceSatisfactory mechanical propertyRubber insulatorsNon-metal conductorsElastomerConductive polymer
An electric article, particularly an electric cable or an accessory thereof, such as a cable joint or a cable termination, includes at least one element made from a semiconductive polymeric material, wherein the at least one element is obtained by crosslinking a semiconductive polymeric composition including: (a) at least one elastomeric polymer; (b) a filler mixture including: (i) at least one first carbon black having a dibutyl phthalate (DBP) absorption number of from 250 to 600 ml / 100 g; (ii) at least one second carbon black, different from the first one, having a dibutyl phthalate (DBP) absorption number of from 80 to 250 ml / 100 g; and (c) at least one graphite having a specific surface area, measured according to the BET method, not higher than 20 m2 / g.
Owner:PRYSMIAN SPA
Magnesium alloy and method of manufacturing same
ActiveUS20160348217A1Satisfactory mechanical propertySatisfactory thermal conductivityRare earthMechanical property
A magnesium alloy is provided which does not contain a rare earth and which achieves, in a high-temperature region of about 200° C., both satisfactory mechanical properties and thermal conductivity. A magnesium alloy including Mg, Ca, Al and Si,where a content of Ca is less than 9.0 mass %,a content of Al is equal to or snore than 0.5 mass % but less than 5.7 mass %,a content of Si is equal to or less than 1.3 mass % and Al+8Ca≧20.5%.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Flow body for an aircraft having a solid trailing-edge component
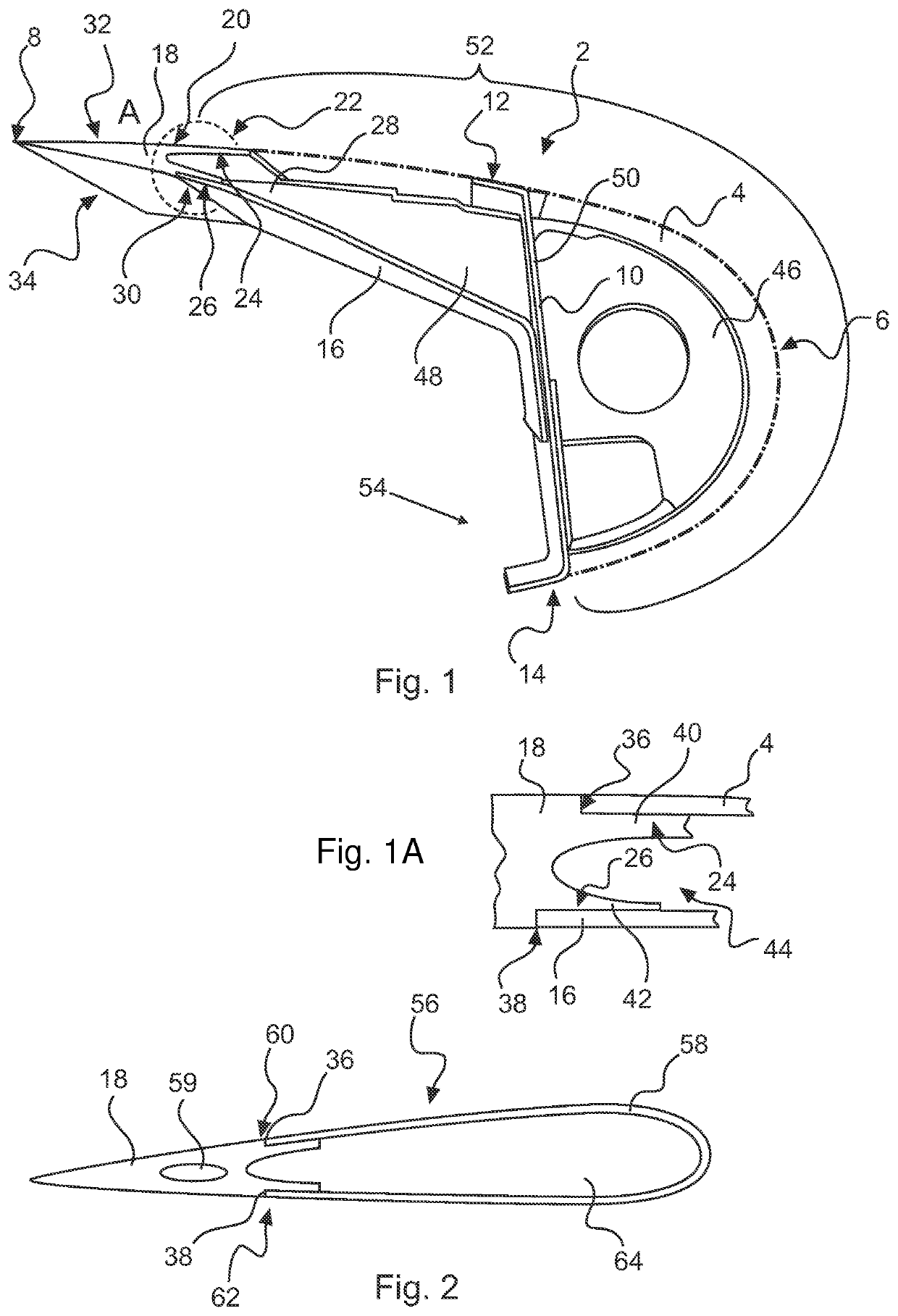
PendingUS20220119093A1Increase manufacturing costCost-efficient designAircraft controlDe-icing equipmentsLeading edgeFlight vehicle
A flow body for an aircraft, in particular for a wing leading edge device, is proposed, the flow body having a curved front skin having a leading edge and at least one trailing-edge component coupled with at least one spanwise edge of the front skin, wherein the trailing-edge component comprises a constant cross-sectional profile that tapers in a chordwise direction to form two spanwise flow surfaces that end in a trailing edge, and wherein the trailing-edge component is designed for providing a flush transition between the front skin and at least one of the two spanwise flow surfaces.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
A method of fabricating a ceramic from a chemical reaction
ActiveUS20180370859A1Flat surfaceIncrease ratingsBlade accessoriesMachines/enginesChemical reactionGas phase
A method of fabricating a ceramic material, the method including forming a ceramic material by performing a first chemical reaction at least between a first powder of an intermetallic compound and a reactive gas phase, a liquid phase being present around the grains of the first powder during the first chemical reaction, the liquid gas phase being obtained from a second powder of a metallic compound by melting the second powder or as a result of a second chemical reaction between at least one element of the first powder and at least one metallic element of the second powder, a working temperature being imposed during the formation of the ceramic material, which temperature is low enough to avoid melting the first powder.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
Hardened martensitic steel having a low or zero content of cobalt, method for producing a component from this steel, and component obtained in this manner
ActiveUS9045806B2Satisfactory mechanical propertyImprove fatigue performanceSolid state diffusion coatingQuenching agentsRare earthCobalt
Owner:AUBERT & DUVAL FR
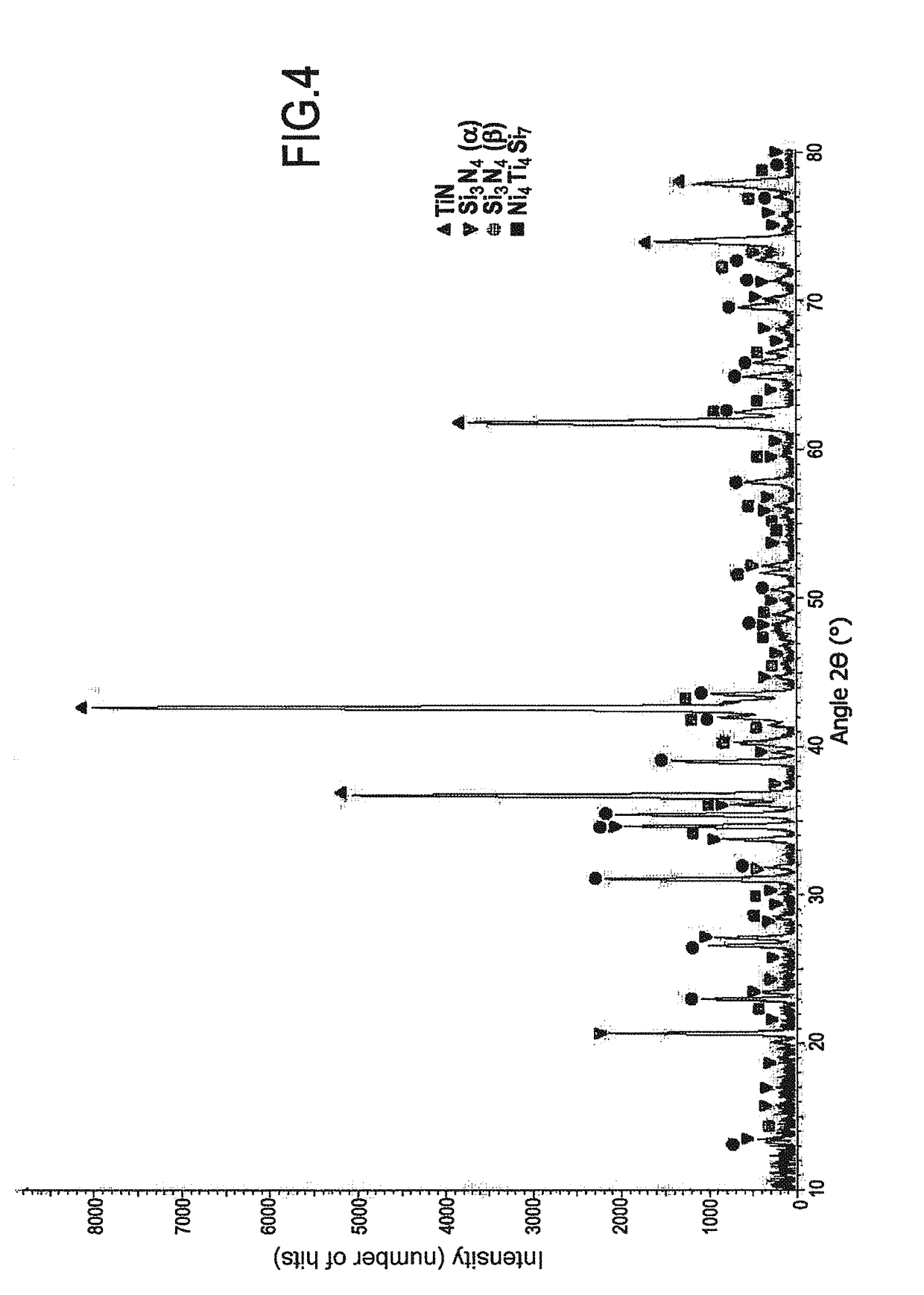
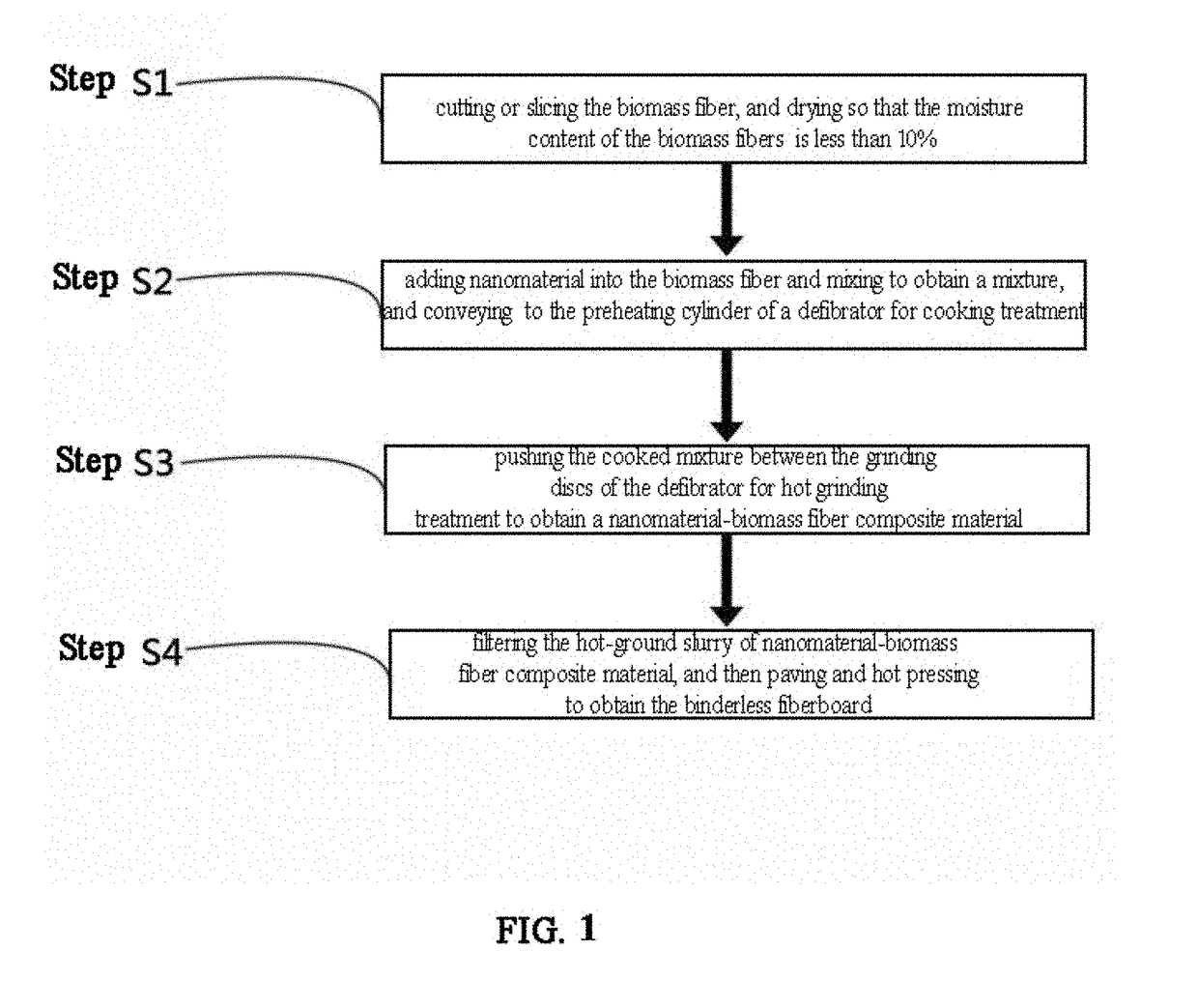
Nanomaterial-biomass fiber composite and preparation method thereof
A nanomaterial-biomass fiber composite and preparation method thereof. The biomass fibers are cut or sliced, and then dried. The dried biomass fibers are mixed with a nanomaterial and conveyed to the preheating cylinder of a defibrator for cooking treatment. The cooked mixture is pushed between the grinding discs of the defibrator for hot grinding treatment. The resulting material is then hot pressed to obtain the nanomaterial-biomass fiber composite material. The preparation method benefits from simple operation, low cost, low energy consumption, suitability for industrialized production, and wide application prospect in the field of production of binderless fiberboard.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Polyoxyalkylene polyol or monool and polyurethane resin
ActiveUS20120016049A1Satisfactory mechanical property and moisture resistanceSufficient reactivityEther preparation from oxiranesMoisture resistanceOxygen
An object of the present invention is to provide a polyoxyalkylene polyol and a polyoxyalkylene monool, capable of producing a urethane elastomer and a urethane foam which are sufficiently excellent in mechanical properties and moisture resistance.The present invention is directed to a polyoxyalkylene polyol or monool (S), which is an alkylene oxide adduct of an active hydrogen-containing compound (H), wherein 40% or more of hydroxyl groups located at the terminal are primary hydroxyl group-containing groups represented by the general formula (1) shown below, and a hydroxyl value x, the total degree of unsaturation y and the content of ethylene oxide z satisfy a relationship of the mathematical expression (1).[In the general formula (1), R1 represents a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group having 1 to 12 carbon atoms, a cycloalkyl group or a phenyl group, each of which may be substituted with a halogen atom or an aryl group.]y≦28.3×x−2×(100−z) / 100 (1)[In the mathematical expression (1), x represents a hydroxyl value, y represents the total degree of unsaturation, and z is the content of ethylene oxide based on the weight of (S) and is from 0 to 50% by weight.
Owner:SANYO CHEM IND LTD
Electrical apparatus for breaking an electric current in air comprising an improved extinguishing gas filtering device
ActiveUS10020143B2Effective protectionSatisfactory mechanical propertyDispersed particle filtrationMembrane filtersElectricityFiltration
An electrical apparatus for breaking an electric current includes an electrical arc extinguishing chamber, for extinguishing an electrical arc formed on the separation of electric contacts, provided with an extinguishing gas exhaust orifice and an extinguishing gas filtration system, placed at the output of the exhaust orifice and including a filter and a gas diffusor. The gas diffuser includes, superposed between them, a central layer and two outer layers arranged on either side of the central layer. The central layer is provided with first through holes. Each outer layer is provided with second through holes. The first holes are misaligned relative to the second holes so that each of the second holes emerges on a solid portion of the central layer without any first hole.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC IND SAS
Polyamide composition comprising a specific co-polyamide comprising caprolactam monomer, a semi-crystalline polyamide and a reinforcing filler with enhanced gloss performance
Described herein is a composition including a) at least one co-polyamide including caprolactam monomer or the corresponding amino acid, at least one aromatic diacid co-monomer and at least one cycloaliphatic diamine co-monomer; b) at least one semi-crystalline polyamide; and c) at least one reinforcing filler. The a) at least one co-polyamide has a crystallization temperature (Tc) of 150° C. or less and the difference between the melting temperature (Tm) and Tc of 50° C. or more.
Owner:BASF SE +1
Cleaning of additively manufactured objects by vacuum cycling nucleation
InactiveUS20220266518A1Easy to cleanSatisfactory mechanical propertyAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresPolymer scienceData file
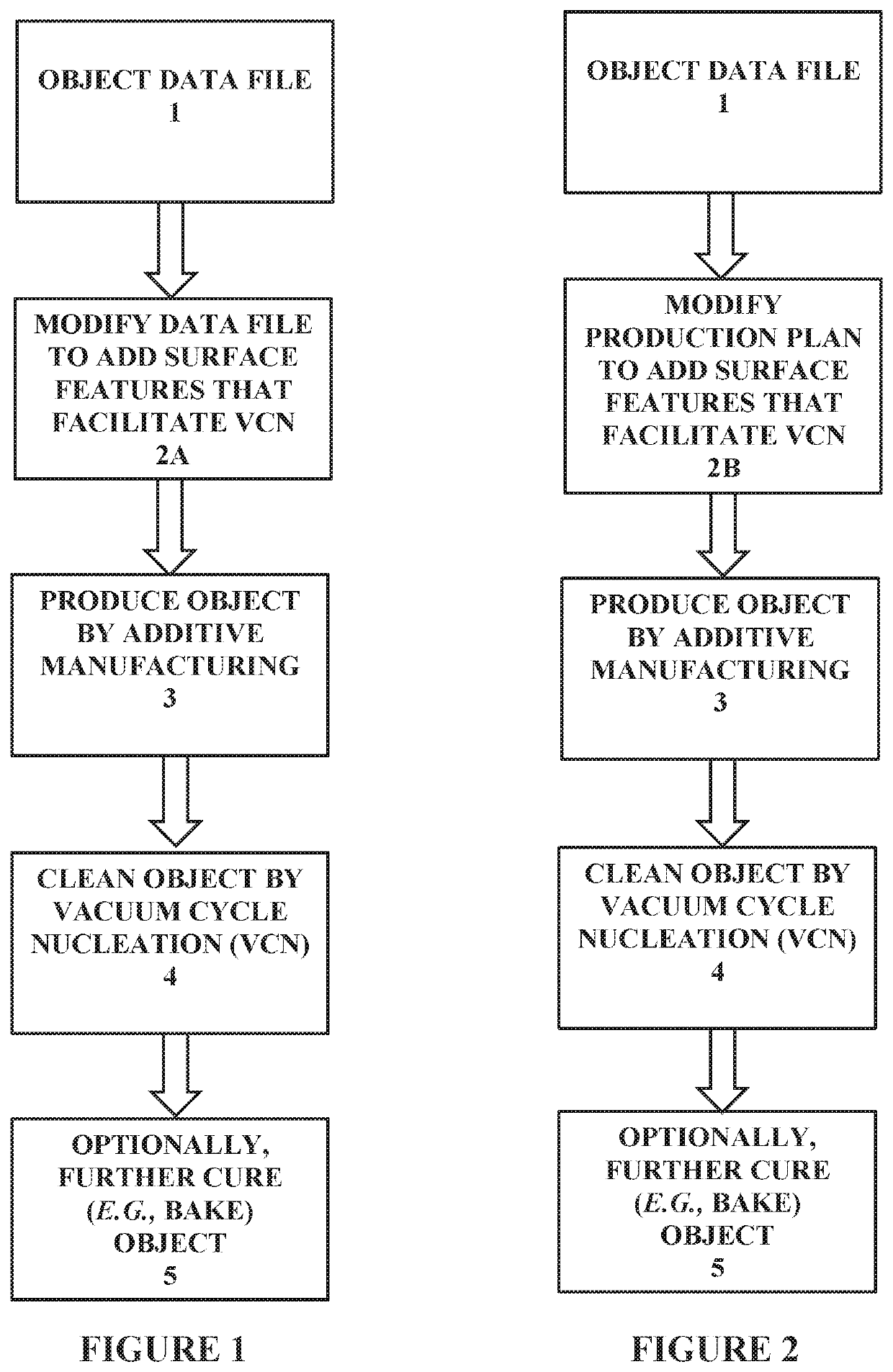
A method of making an object from a data file and a light polymerizable resin by additive manufacturing includes the steps of: (a) optionally modifying the data file to add additional vacuum cycling nucleation (VCN) nucleation sites to surfaces of the object (2A); (b) producing the object from the data file and the resin by light polymerization in an additive manufacturing process (3), optionally under conditions in which additional VCN nucleation sites are added to surfaces of the object, the object having residual resin adhered to the surface thereof; and then (c) cleaning the residual resin from the object with a wash liquid by vacuum cycling nucleation (4).
Owner:CARBON INC
Fibrous preforms for use in making composite parts
ActiveUS10059063B2Satisfactory mechanical propertyEasy to implementLayered productsVehicle componentsFiberCarbon fibers
The present invention concerns preforms made with a new intermediate material composed of a unidirectional layer of carbon fibers with a weight of 100 to 280 g / m2, associated on each of its faces, with a web of thermoplastic fibers having a thickness of 0.5 to 50 microns, preferably 3 to 35 microns, the intermediate material having a total thickness of 80 to 380 microns, preferably from 90 to 320 microns, and a process for manufacturing composite parts from such preforms and the resulting composite parts.
Owner:HEXCEL REINFORCEMENTS SAS
Gasket for alkaline battery and method for manufacturing same
ActiveUS20200091471A1Satisfies long lifetime and mechanicalHard surfaceAlkaline accumulatorsCell sealing materialsPhysical chemistryPolyamide
The present invention provides a gasket for an alkaline battery which enables such a long lifetime that liquid leakage due to carbides of a polyamide resin raw material does not occur, surface wrinkles are hardly generated because of excellent fluidity during molding, and a thin wall portion serving as an explosion-proof safety valve can be normally ruptured until the lifetime of an alkaline battery expires, and a method for manufacturing the same. The gasket for an alkaline battery is formed by injection molding a resin composition, and has a thin wall portion in part. The resin composition is a polyamide 610 resin composition containing a polyamide 610 resin as a main component and a molding aid such as a release agent and a crystal nucleating agent, the polyamide 610 resin having a viscosity number in a range of 80 ml / g or more and 145 ml / g or less.
Owner:SHINSEI KAGAKU INDS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com