Patents
Literature
31 results about "Relativistic electron beam" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Relativistic electron beams are streams of electrons moving at relativistic speeds. They are the lasing medium in free electron lasers to be used in atmospheric research conducted at entities such as the Pan-oceanic Environmental and Atmospheric Research Laboratory (PEARL) at the University of Hawaii and NASA.
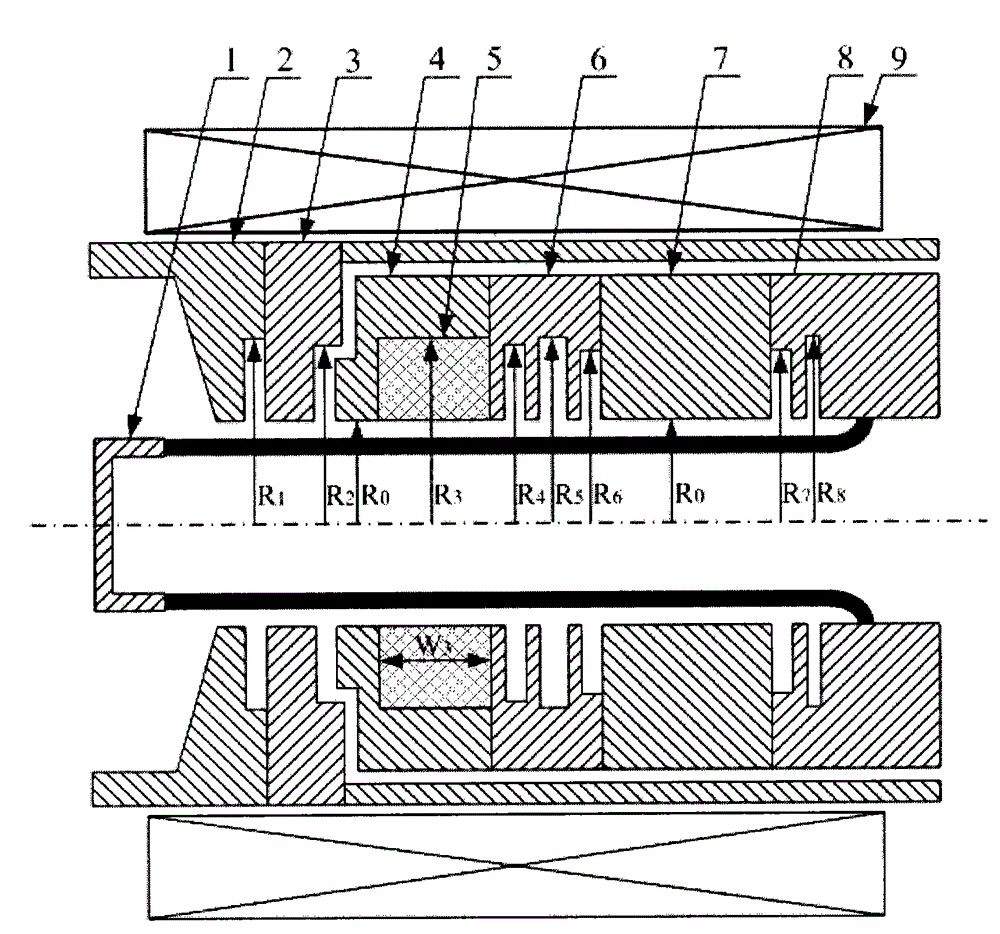
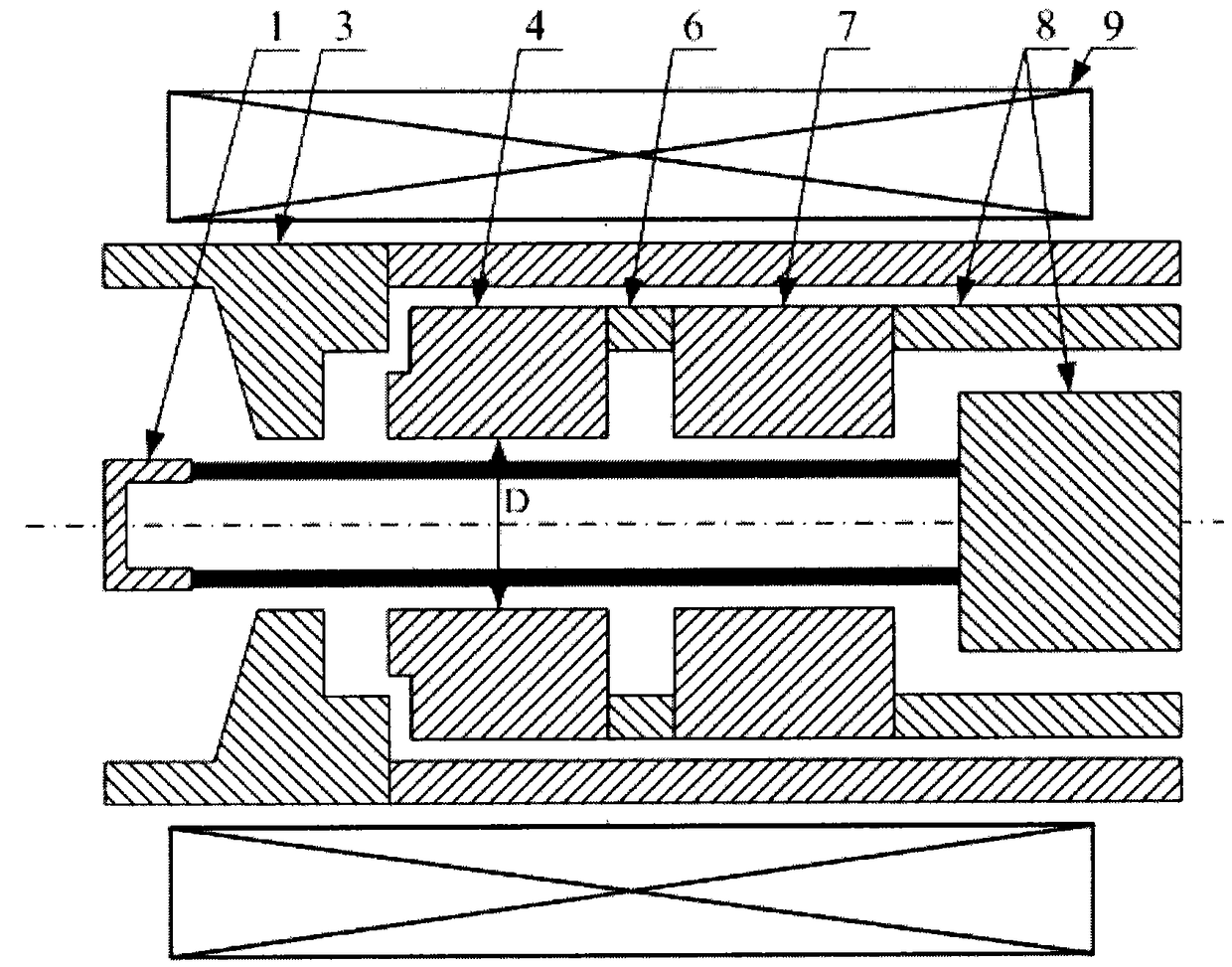
High-power coaxial structure over-mode surface wave oscillator and terahertz wave generating method
ActiveCN103516327AIncrease output powerHigh pattern purityImpedence networksTransit-time tubesWave structureWave band
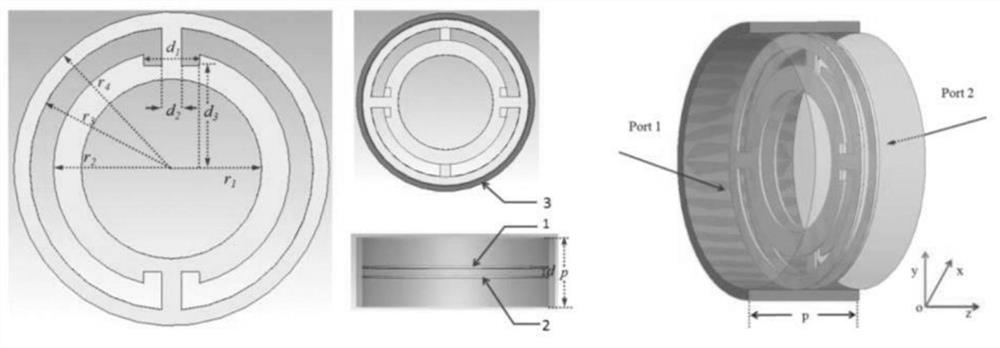
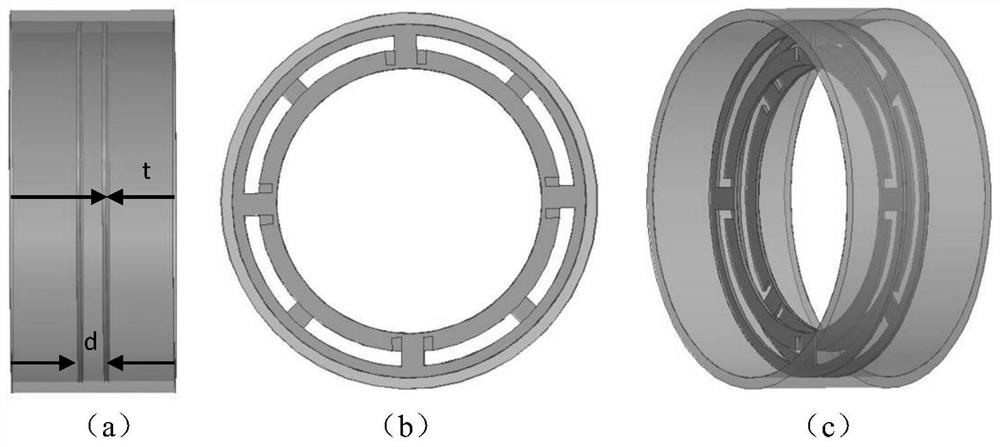
The invention discloses an axisymmetric-structure high-power coaxial over-mode surface wave oscillator which uses electromagnetic wave radiation of the terahertz wave band generated through wave-beam interaction as the basic working principle, according to high-current relativity theory electron beams and an over-mode coaxial slow wave structure, strong wave-beam interaction happens, and high-power terahertz waves are generated. The coaxial over-mode surface wave oscillator comprises a non-foil diode, the over-mode coaxial slow wave structure, a transitional wave guiding part and an output wave guiding part of a coaxial structure. The working mode of the over-mode surface wave oscillator in a wave-beam interaction zone is a TM01 mode, by mode converting of the transitional wave guiding part, transmission is carried out at an output wave guiding end of the surface wave oscillator in a TEM mode, the 0.14THz over-mode surface wave oscillator is designed through the structure, and the peak power of an output port can reach 115MW. The over-mode surface wave oscillator is suitable for generating the high-power electromagnetic waves in the terahertz wave band.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
Relativistic backward wave oscillator for generating linearly polarized TE11 mode directly
ActiveCN105280462AEnhanced interactionImprove beam conversion efficiencyTransit-tube cathodesTransit-tube circuit elementsWave structureMaser
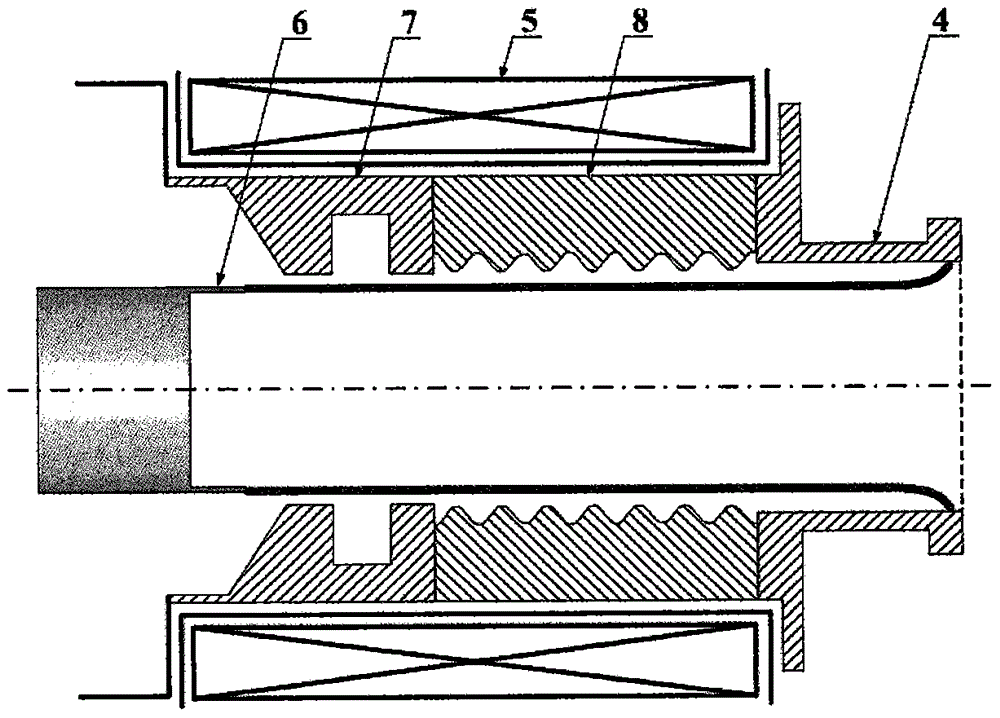
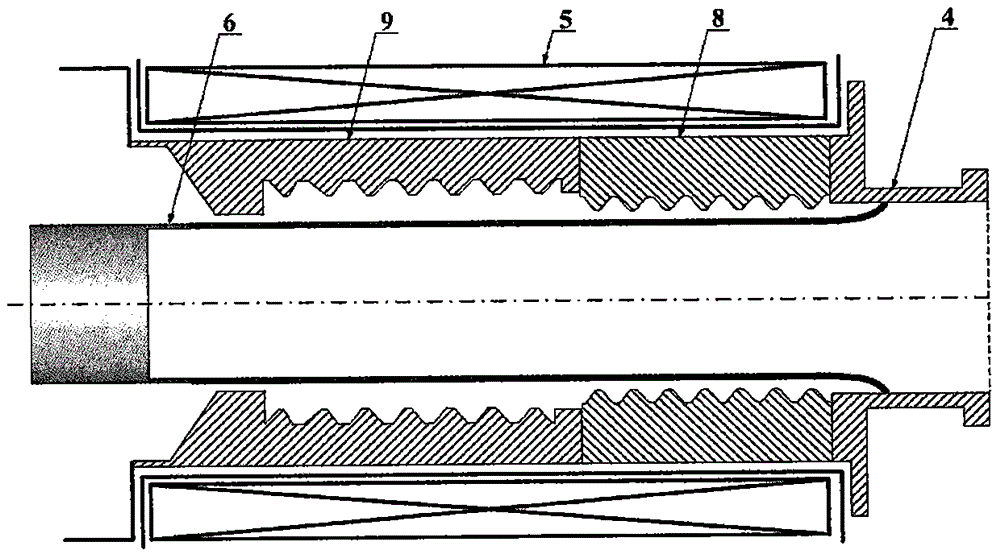
The invention, which belongs to the maser field, directly relates to a relativistic backward wave oscillator for generating a linearly polarized TE11 mode directly. The relativistic backward wave oscillator comprises an arc cathode, a reflector, an angular partition slow wave structure, an output waveguide and a magnetic field coil. The arc cathode is arranged at the front end of the relativistic backward wave oscillator; the reflector, the angular partition slow wave structure, and the output waveguide are arranged at the rear side of the arc cathode successively; and the magnetic field coil is installed at the periphery. According to the invention, with the nonaxisymmetrical arc cathode and the angular partition slow wave structure, the TE11 mode is excited directly. The reflector employs the dual-premodulation-cavity unit preferably and is used for carrying out premodulation on an arc relativistic electron beam and leaking the part of TE11 mode to enter the arc cathode zone, so that certain premodulation of the electron beam at the arc cathode zone is realized and thus the beam wave conversion efficiency is improved. Moreover, the oscillator has advantages of simple structure and high conversion efficiency; and the linearly polarized TE11 mode can be generated directly.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
X wave band over-mode relativistic klystron amplifier
The invention discloses an X wave band over-mode relativistic klystron amplifier, which comprises an annular cathode, a resonant reflector, an input cavity, a first section of drift tube, a wave absorbing material, a buncher cavity, a second section of drift tube, an output cavity and a magnetic field coil, wherein the annular cathode is arranged at the most significant end of the structure and emits annular relativistic electron beams outwards under the action of high voltage pulse, the resonant reflector, the input cavity, the first section of drift tube, the wave absorbing material, the buncher cavity, the second section of drift tube and the output cavity are sequentially arranged at rear of the annular cathode, the magnetic field coil is installed at the periphery of the whole structure, the working mode of the resonant reflector, the input cavity, the buncher cavity and the output cavity is a TM02 mode, and the first section of drift tube and the second section of drift tube can transmit a TM01 mode. The X wave band over-mode relativistic klystron amplifier can produce high power X wave band microwave.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
All-optical laser plasma accelerator-based Gamma ray source
InactiveCN103745760ALow costSimple and fast operationRadioactive sourcesTime domainHigh power lasers
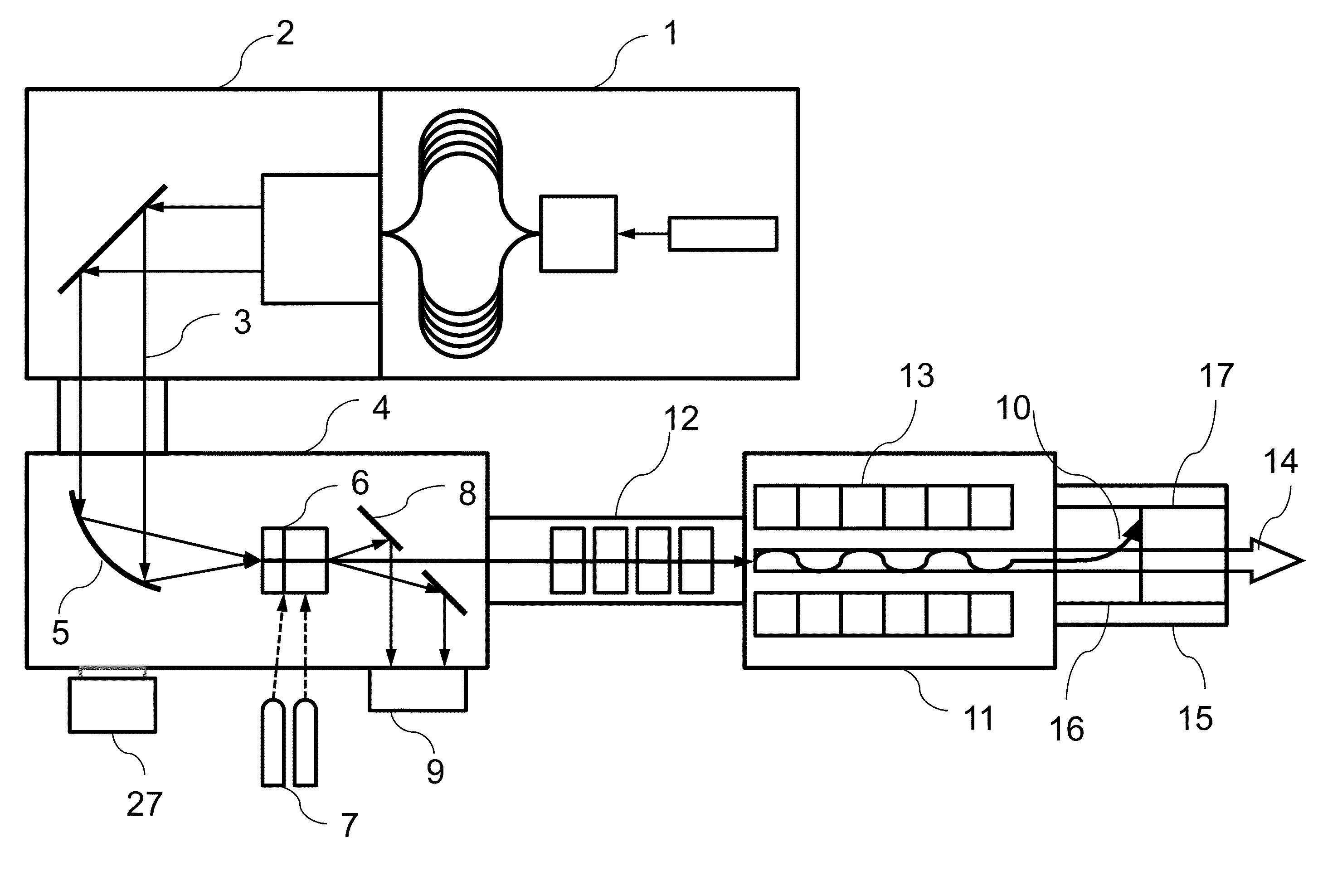
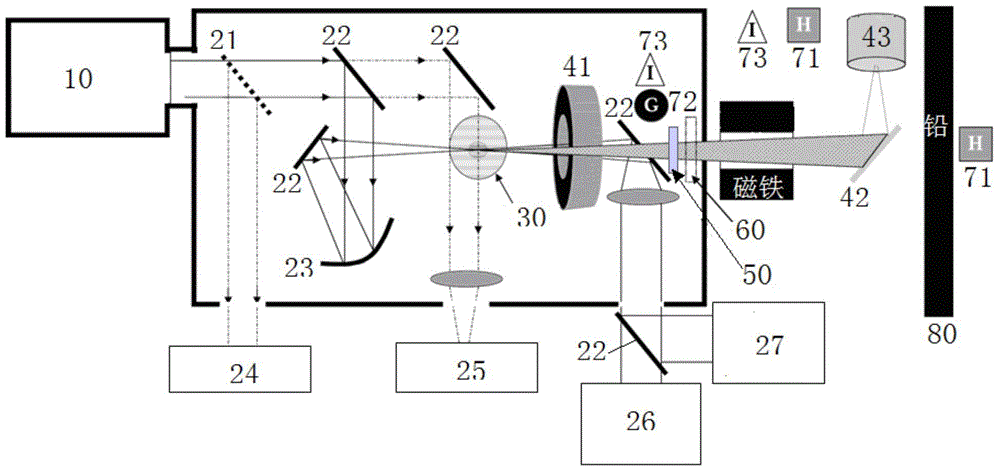
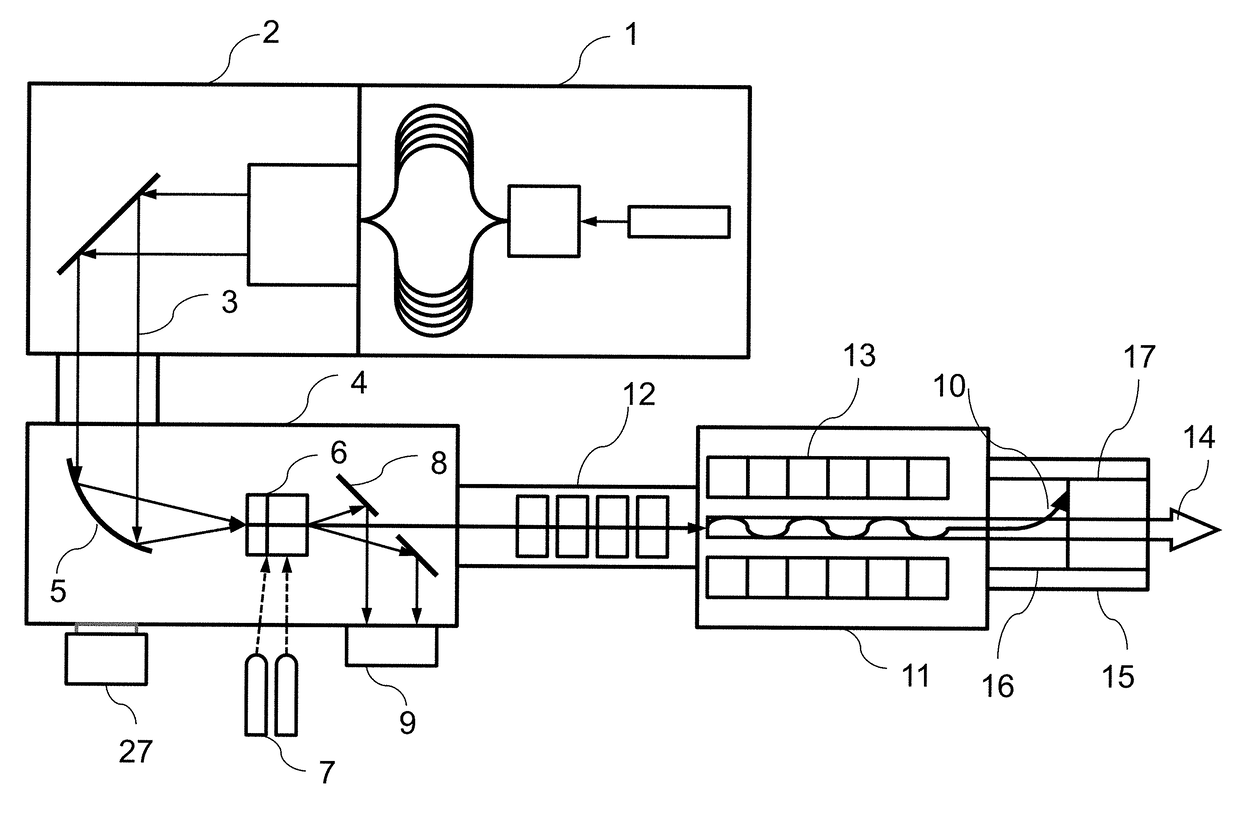
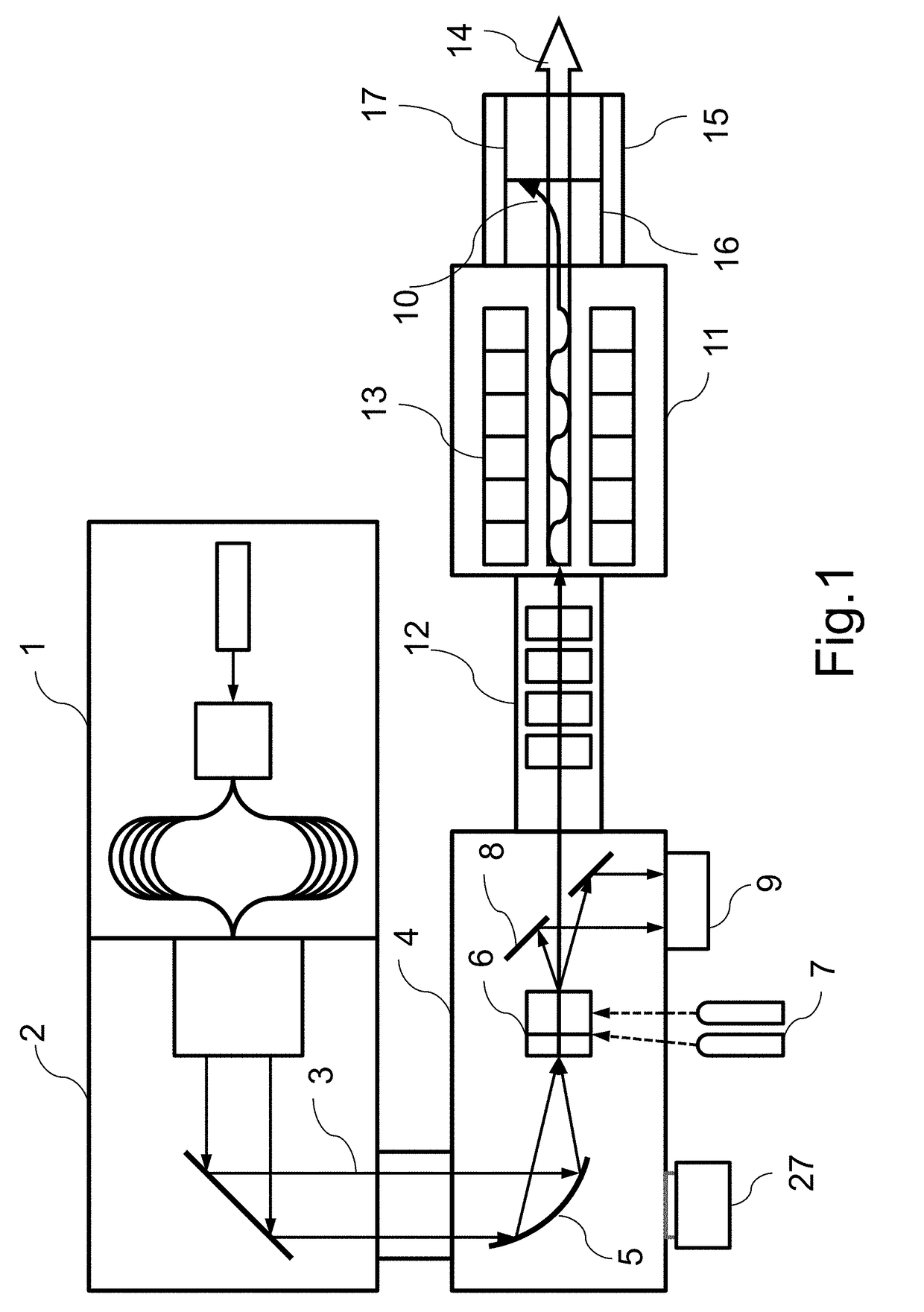
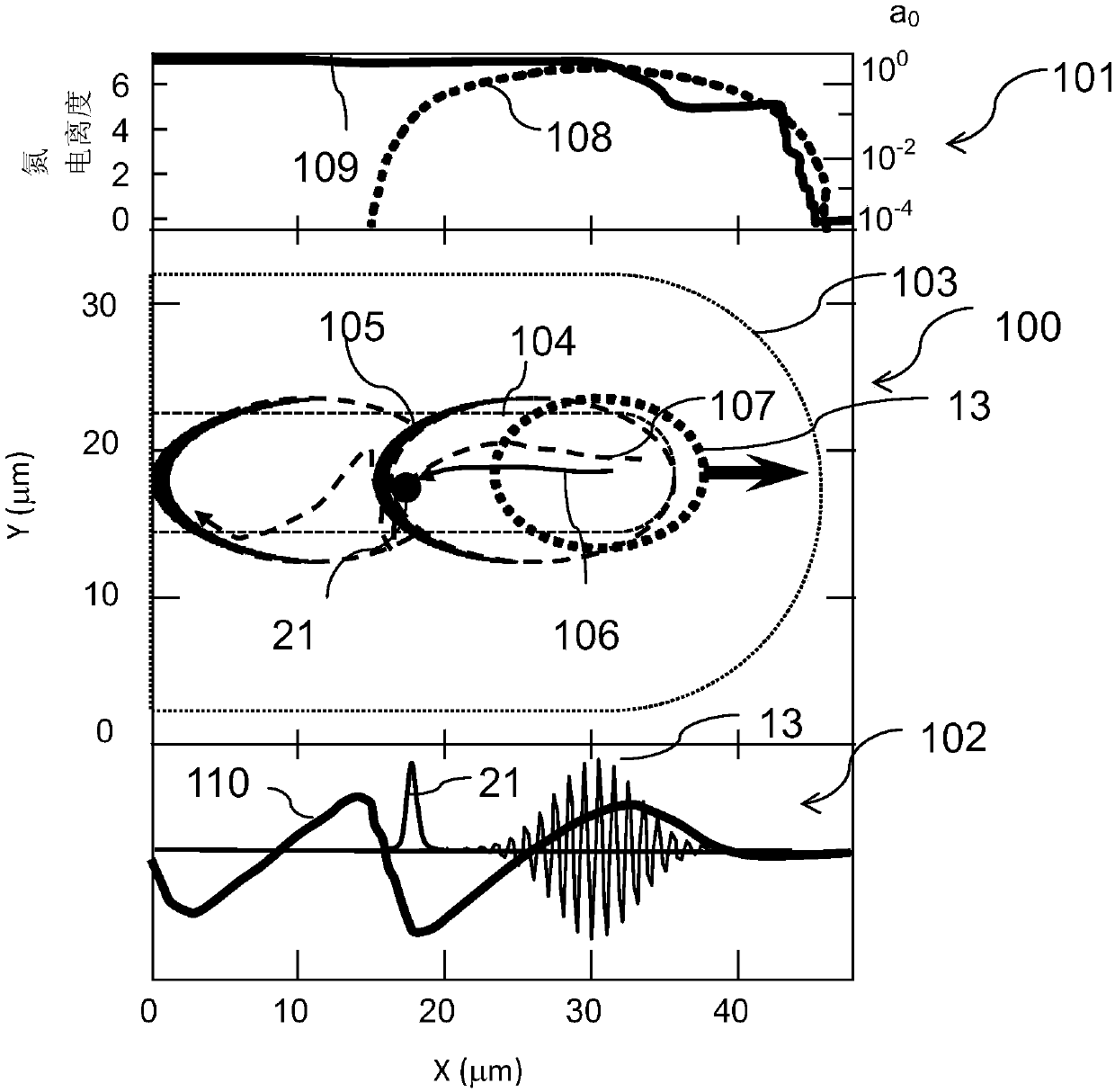
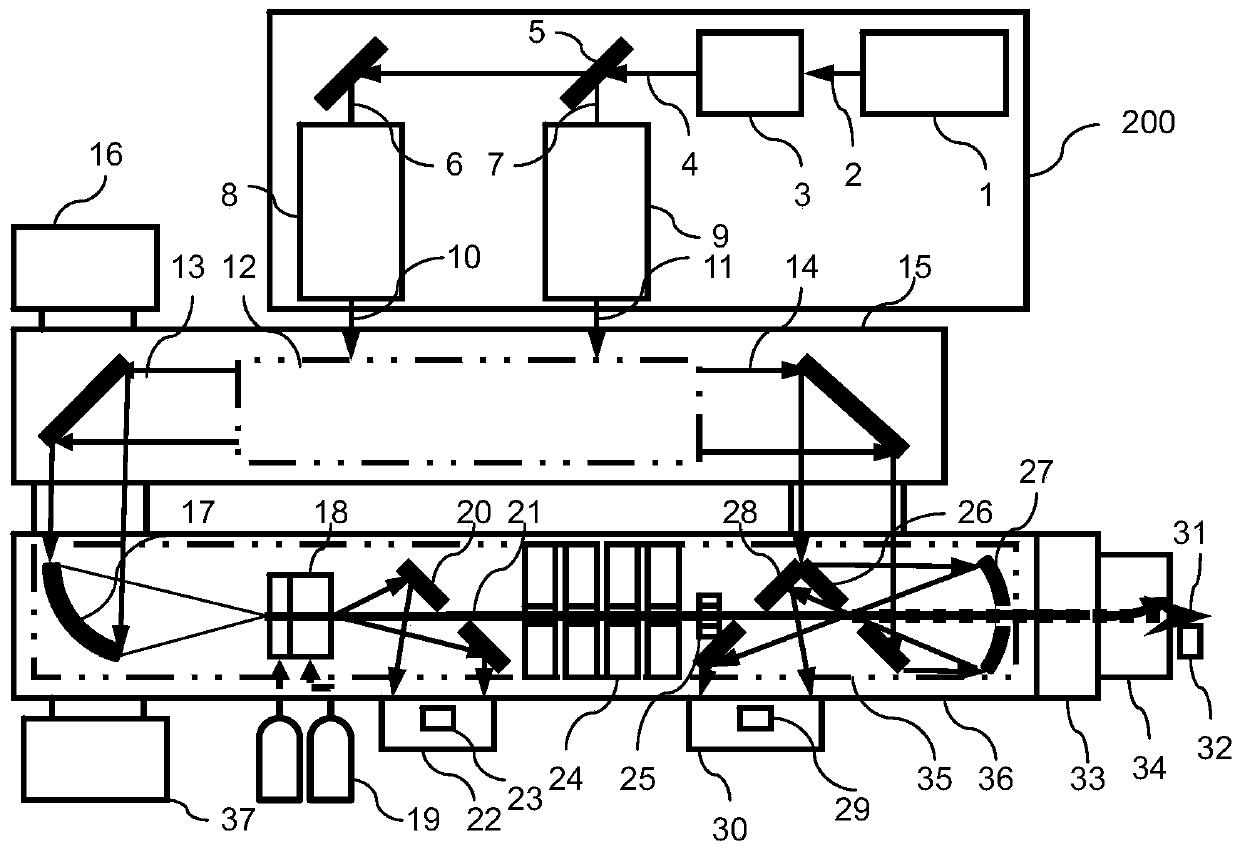
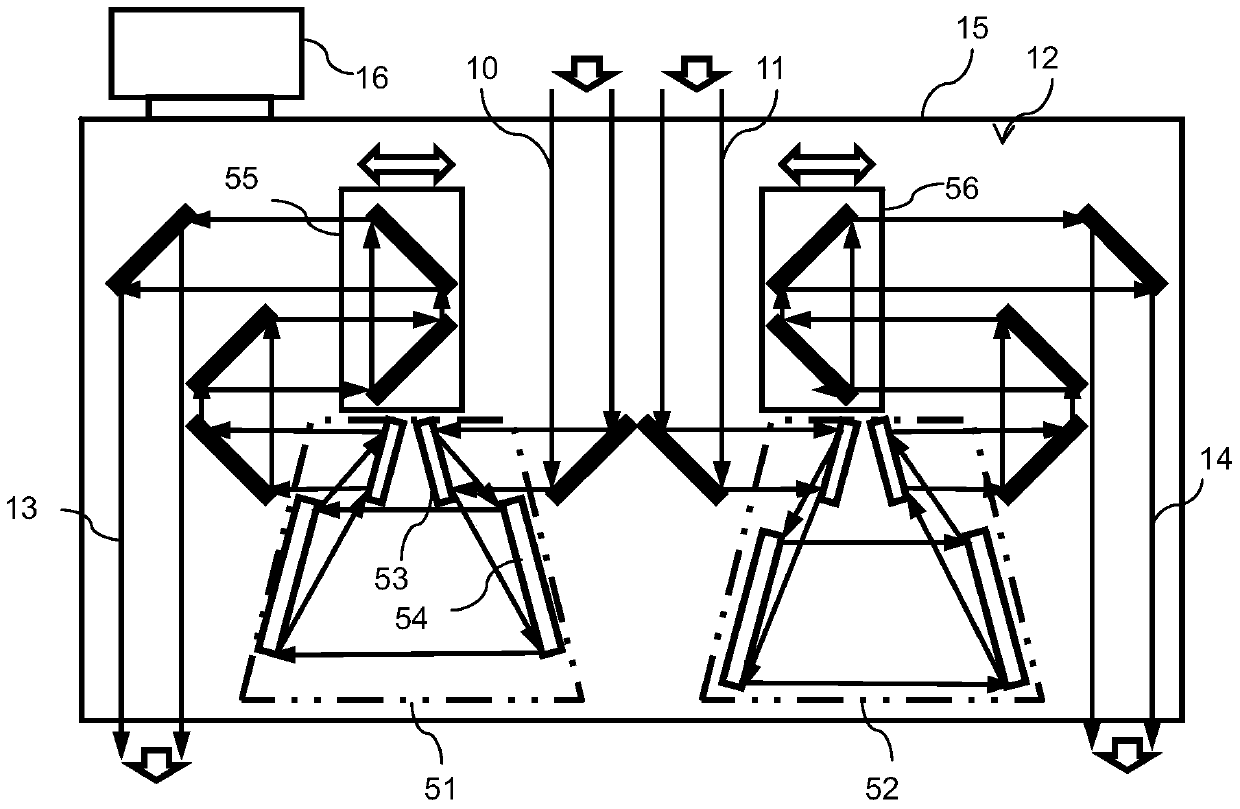
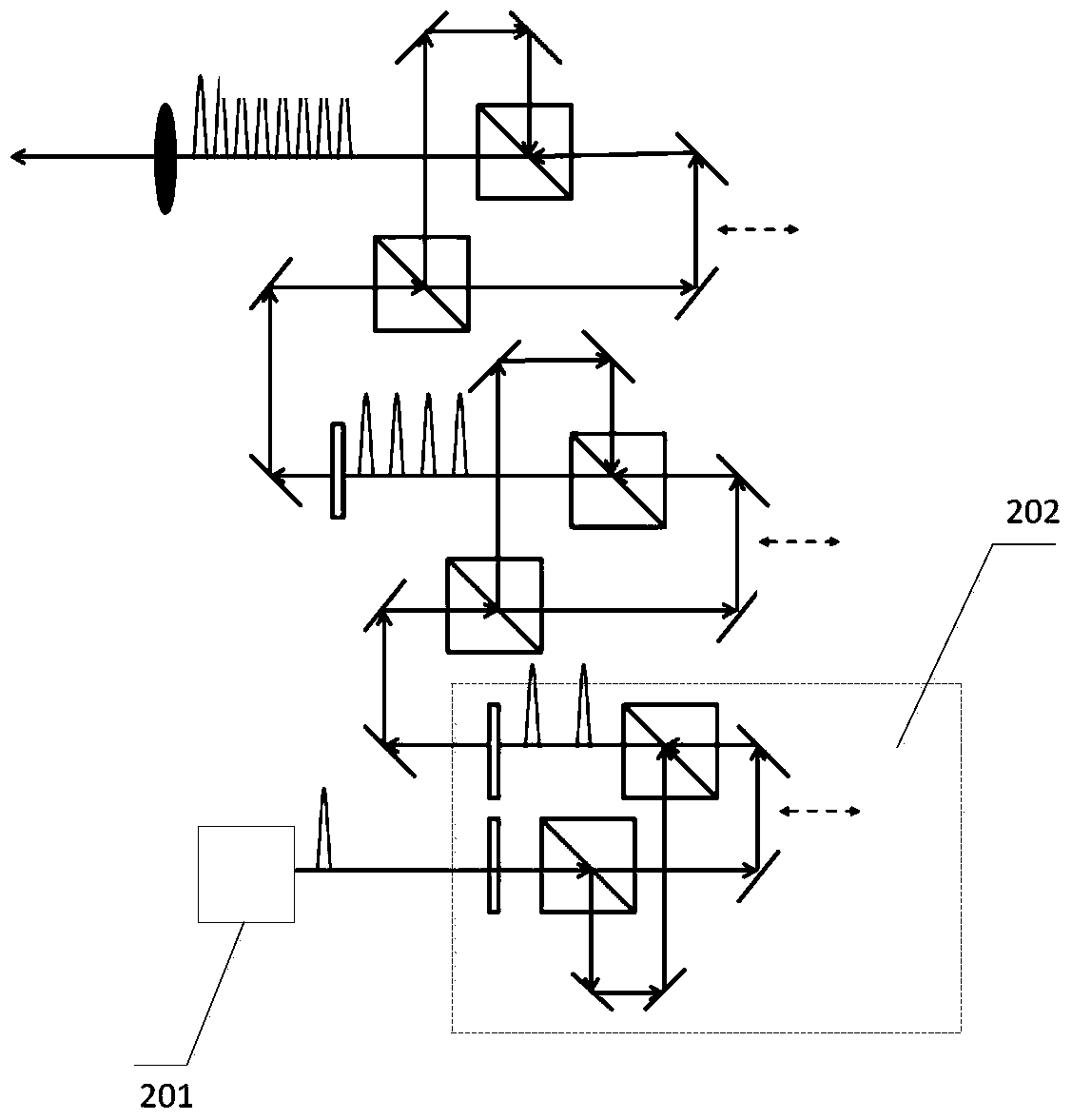
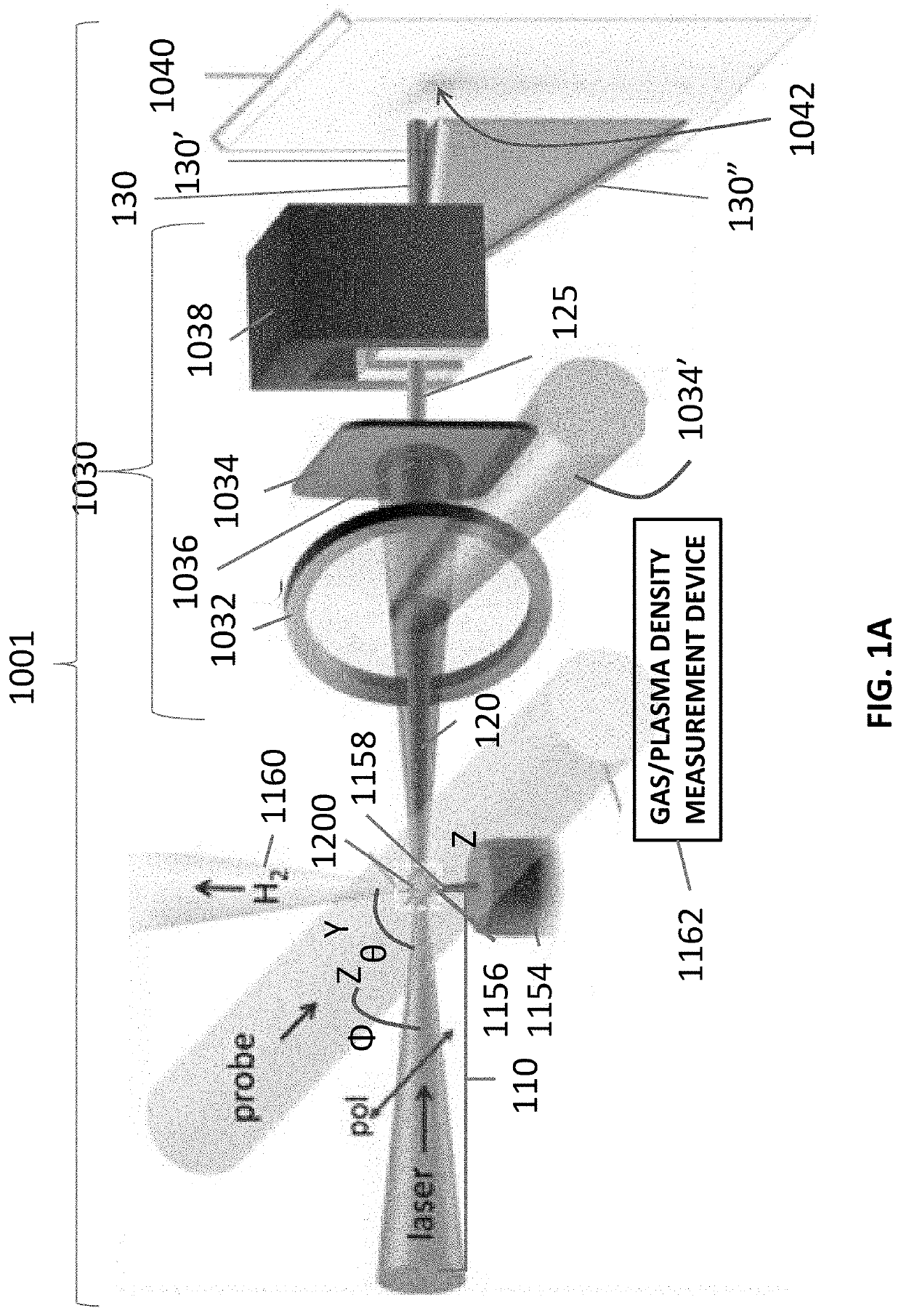
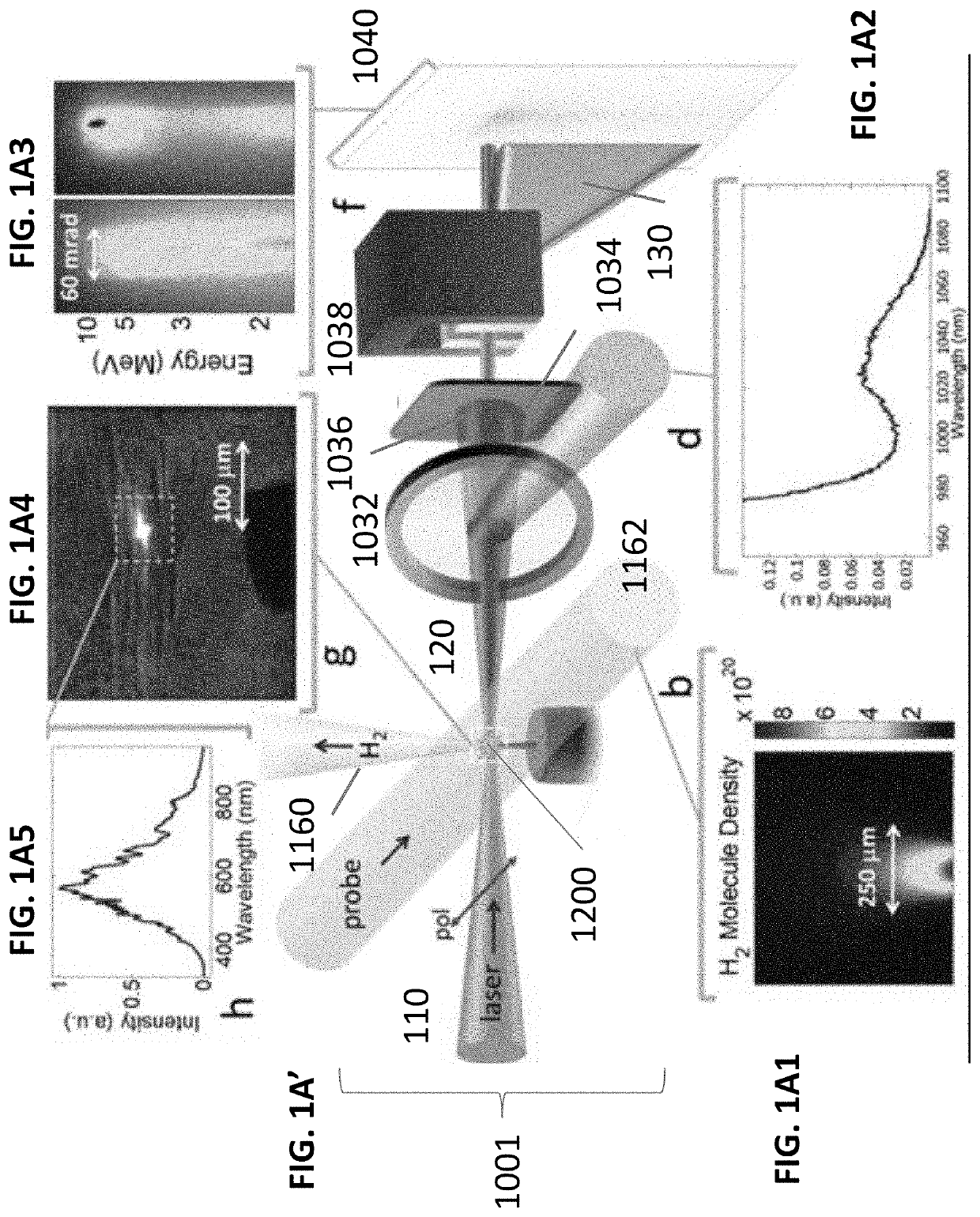
The invention provides an all-optical laser plasma accelerator-based small-sized Gamma ray source. The ray source comprises a synchronous dual-output high-power laser system (200), a double-compression-delay system (12), a laser plasma accelerator (18), a particle beam focusing system (24), a scattered light focusing mirror (27) and a particle beam separation system. A bunch of initial laser pulse is separated and amplified through the laser system (200) to generate two bunches of synchronous high-energy laser pulses (10 and 11); the two amplified laser pulses are compressed in a time domain through the double-compression-delay system (12), and proper delay is performed to form a drive pulse (13)-scattering pulse (14) pair; a drive pulse (13) passes through the laser plasma accelerator (18) to generate a relativistic electron beam (21); the particle beam focusing system (24) is used for transmitting the electron beam (21); the scattered light focusing mirror (27) is used for focusing a scattering pulse (14) to the electron beam (21) so as to generate a gamma ray 31); the separation system is used for separating the electron beam (21) from the gamma ray (31).
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Laser-driven high repetition rate source of ultrashort relativistic electron bunches
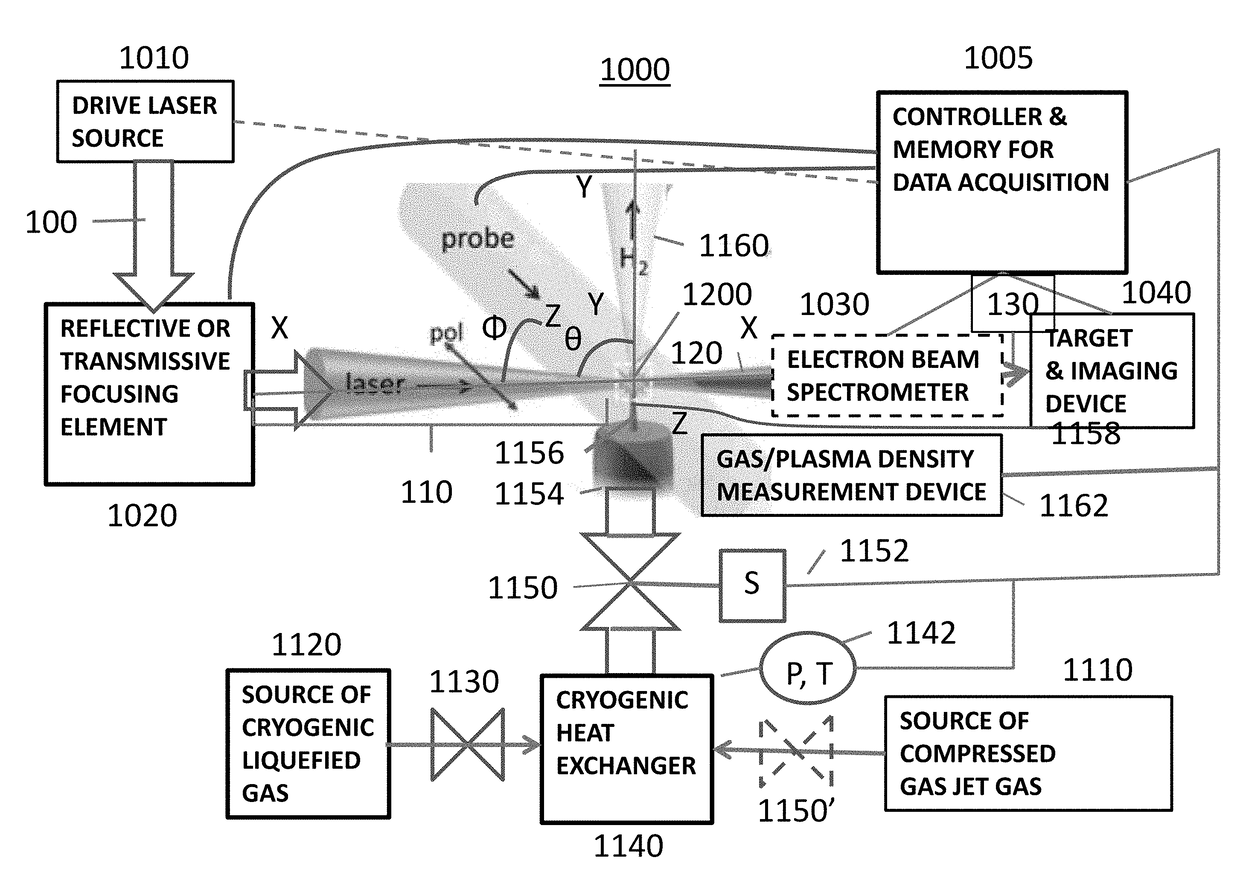
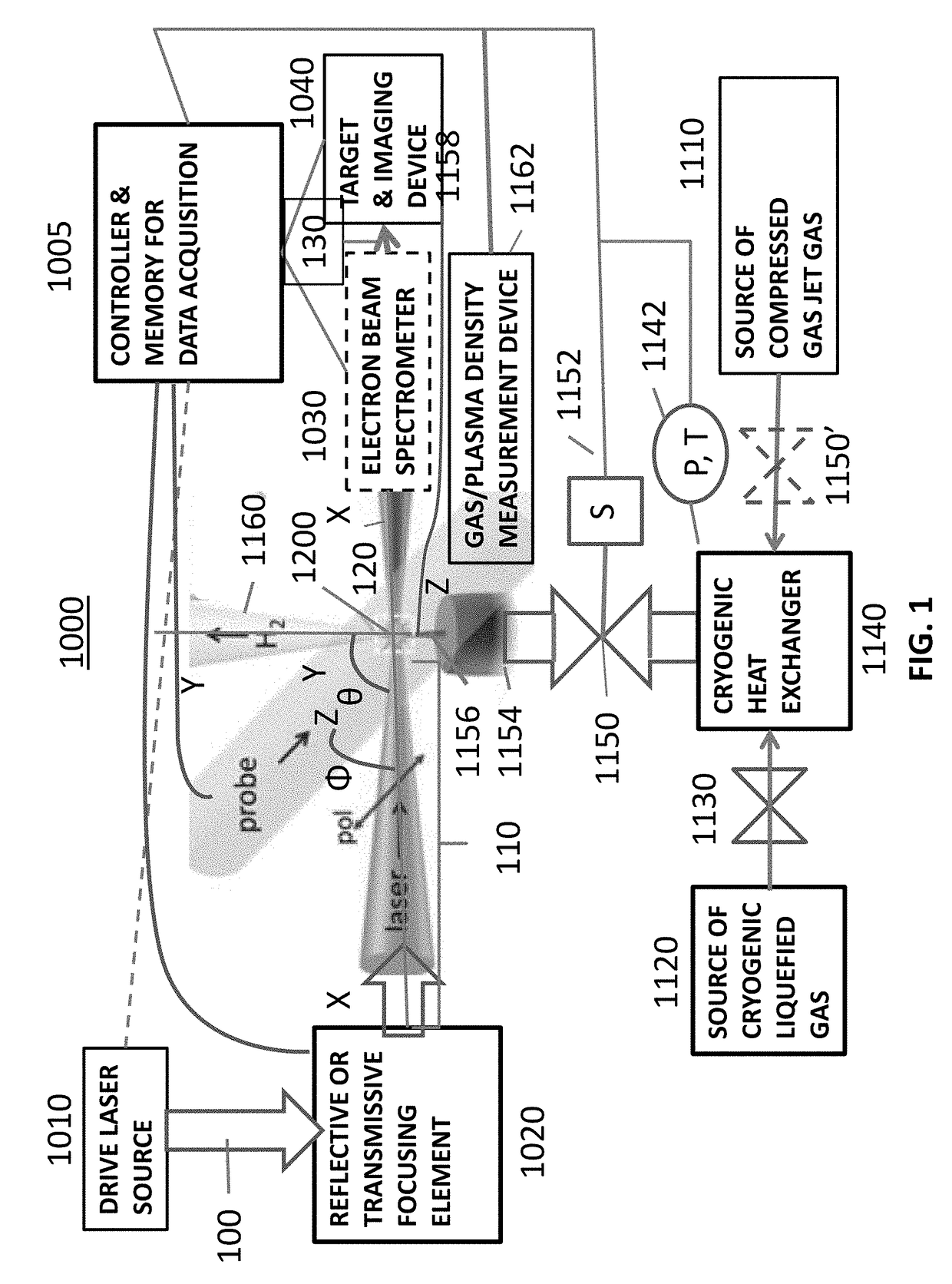
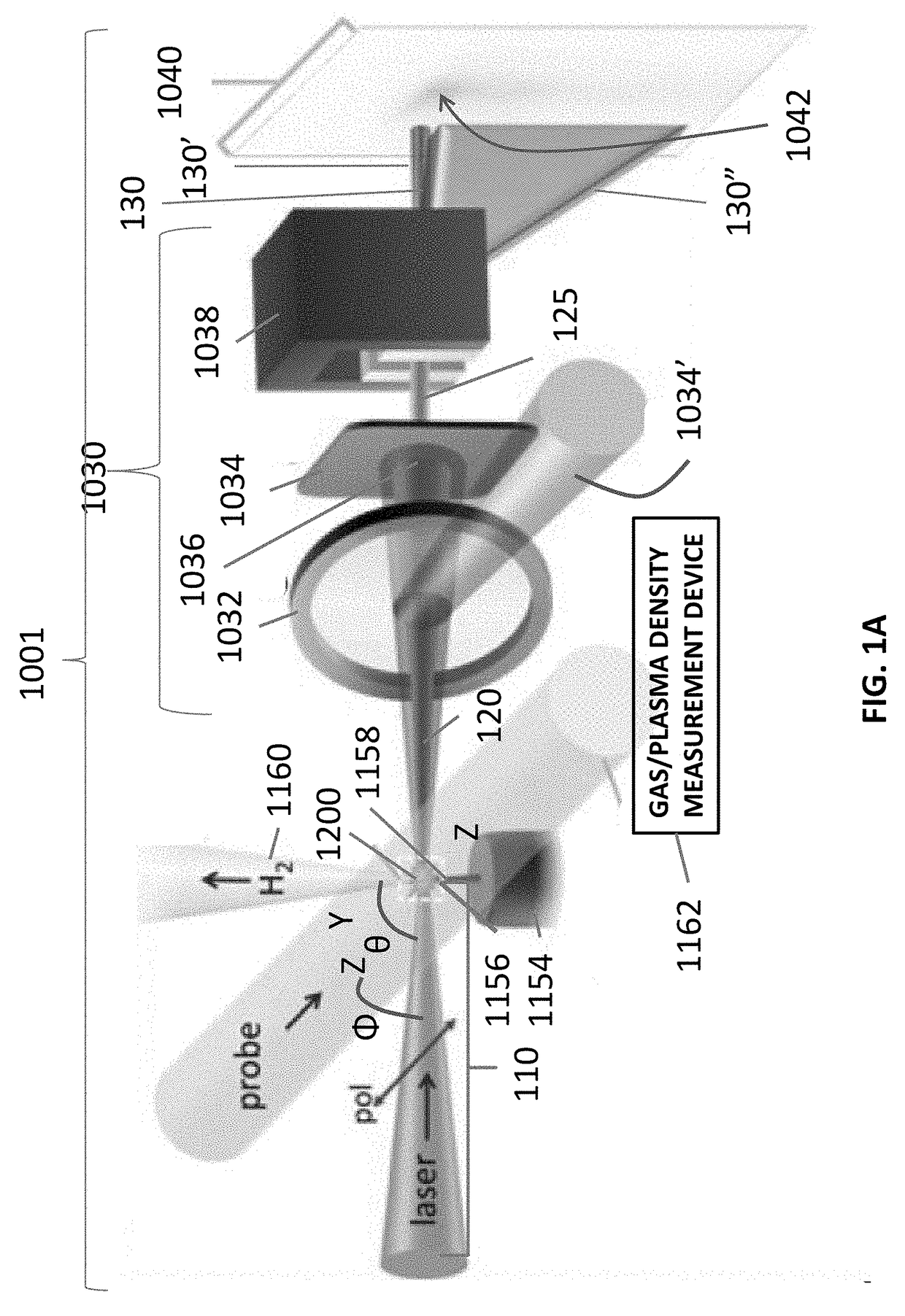
ActiveUS20170332468A1X-ray tube with very high currentCharged particle radiation pressure manipulationInfraredUltraviolet
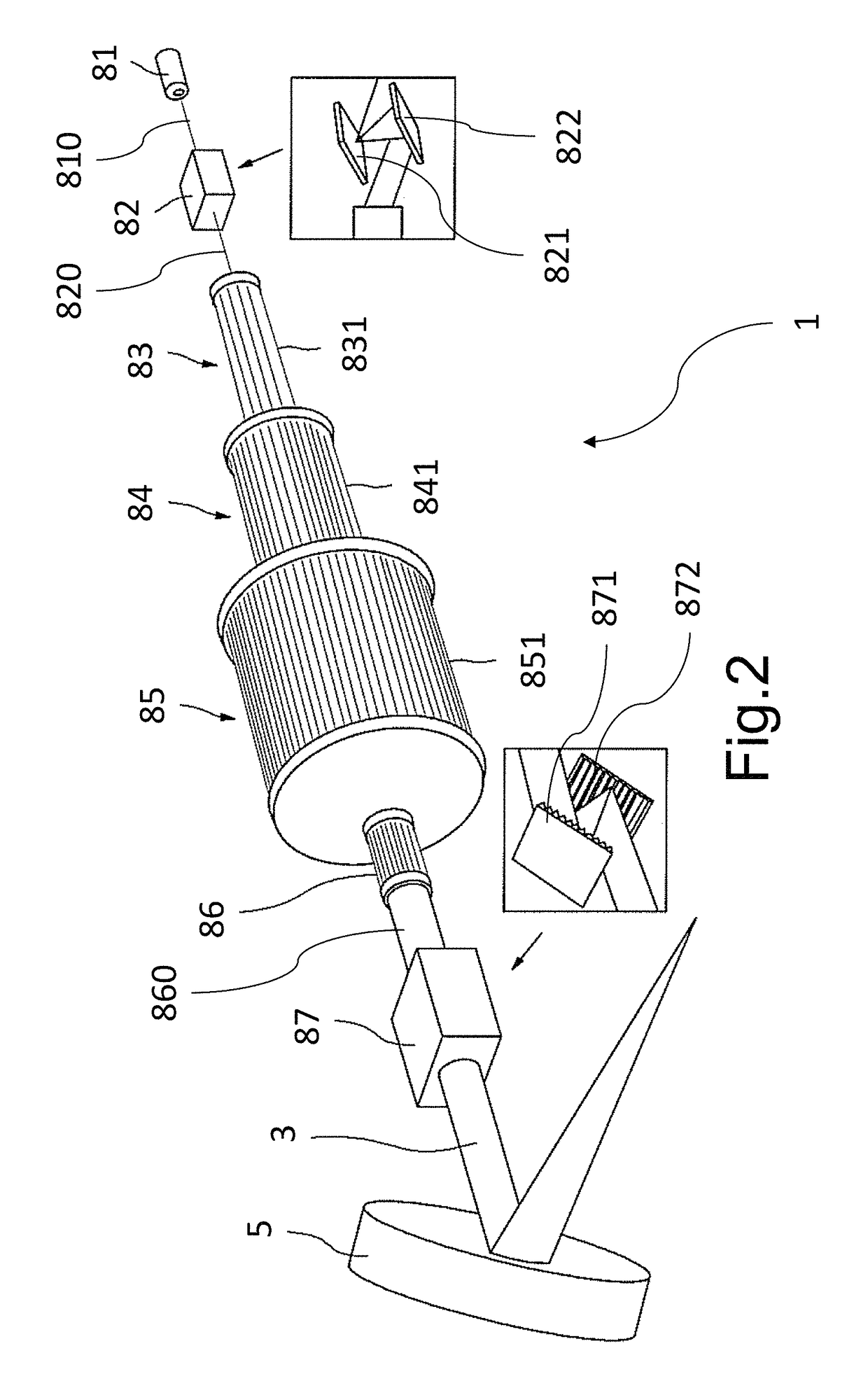
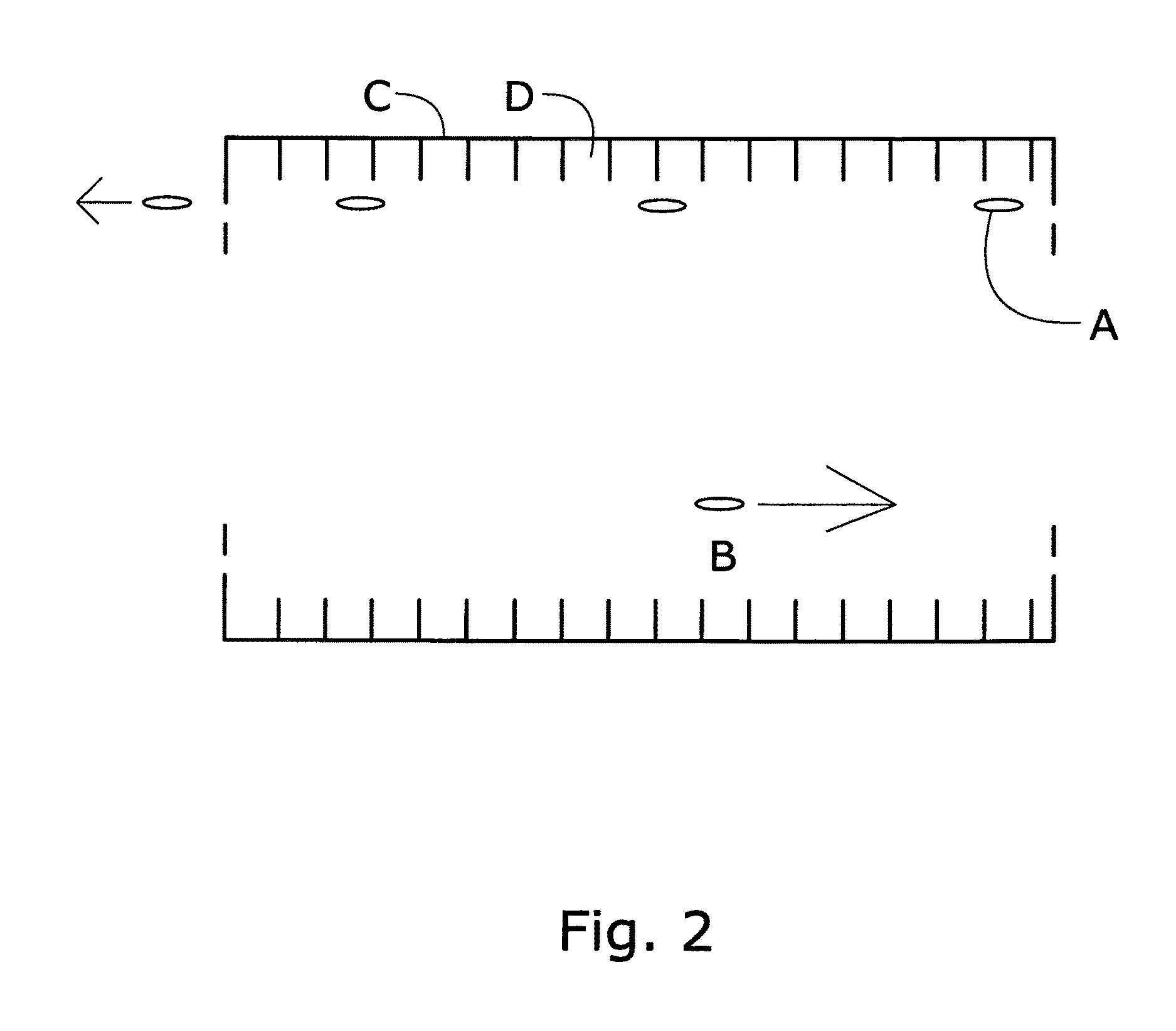
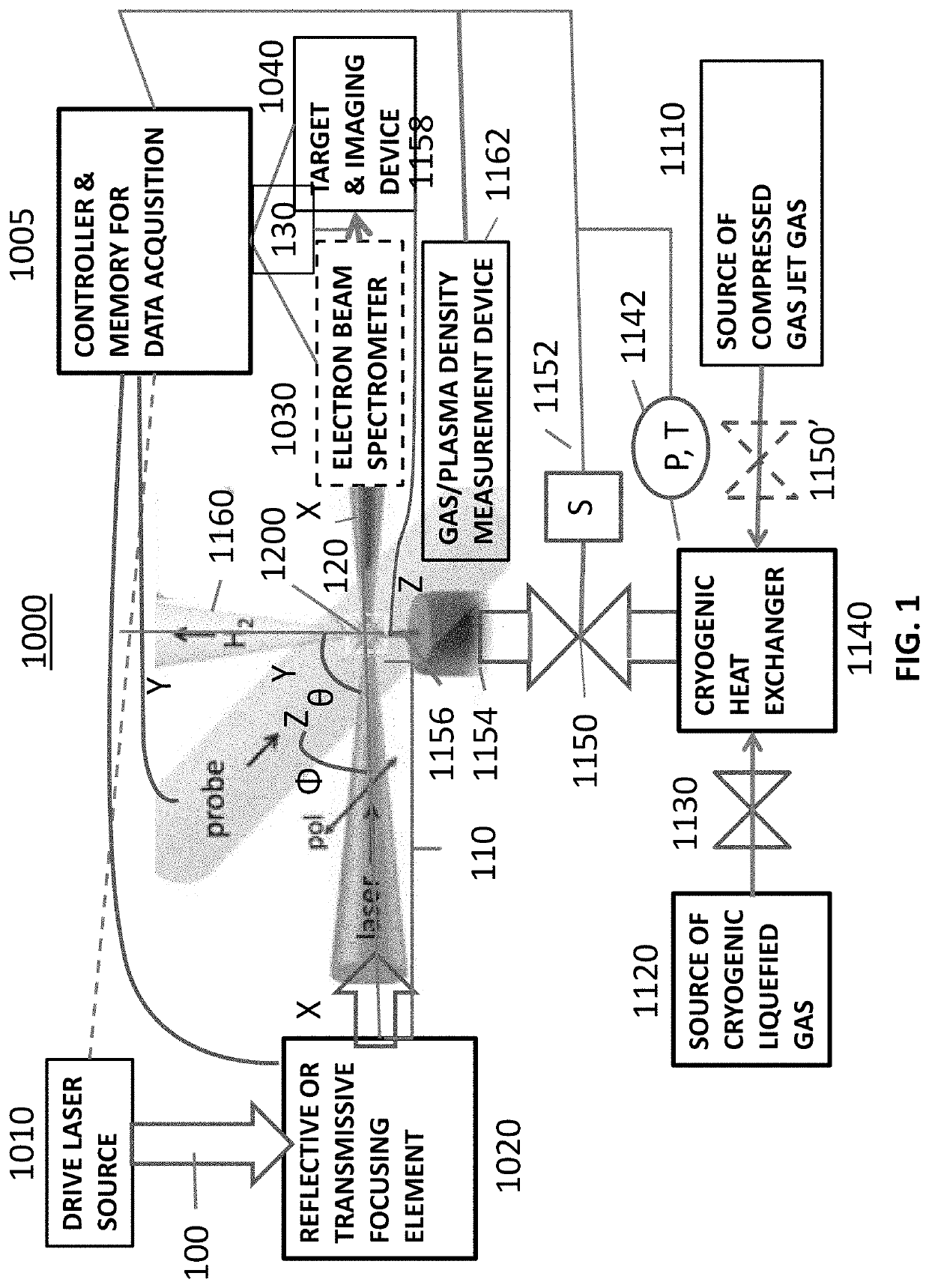
A laser-plasma-based acceleration system includes a focusing element and a laser pulse emission directing a laser beam to the focusing element to such that laser pulses transform into a focused beam and a chamber defining a nozzle having a throat and an exit orifice, emitting a critical density range gas jet from the exit orifice for laser wavelengths ranging from ultraviolet to the mid-infrared. the critical density range gas jet intersects the focused beam at an angle and in proximity to the exit orifice of the nozzle to define a point of intersection between the focused beam and the critical density range gas jet. In intersection with the critical density range gas jet, the pulsed focused beam drives a laser plasma wakefield relativistic electron beam. A corresponding method of laser-plasma-based acceleration is also described. The critical density range may include 2×1020 cm−3 to 5×1021 cm−3.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Free-electron laser driven by fiber laser-based laser plasma accelerator
ActiveUS20160226212A1High repetition rateExtreme UltraVioletExcitation process/apparatusX-ray tube with very high currentPlasma accelerationLight beam
A Free Electron Laser source includes: a fiber-based laser having a plurality of amplifying fibres wherein an initial laser pulse is distributed and amplified, and element for grouping together the elementary pulses amplified in the fibre in order to form an a single amplified global laser pulse; a laser plasma accelerator wherein the global laser pulse generates relativistic electron beams, a beam focusing system transporting electron beams from the laser plasma accelerator, an undulator wherein relativistic electron beams generate an electromagnetic beam, and a beam separator system, wherein the electron beam and the electromagnetic beam are separated.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE
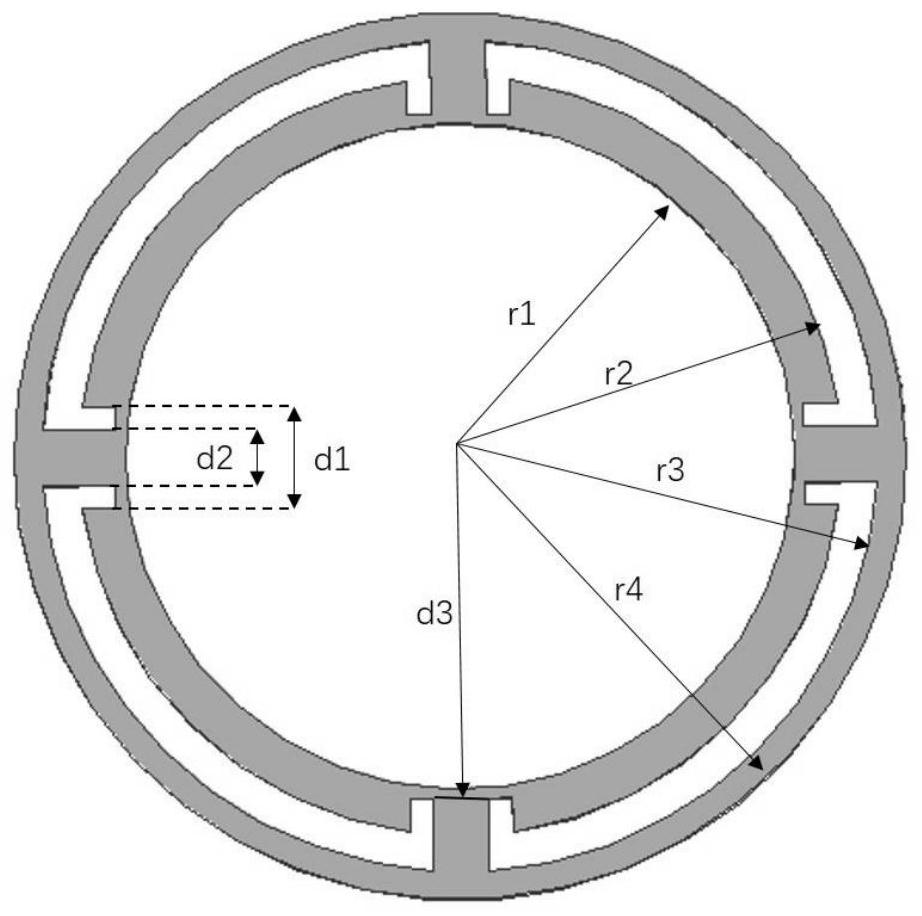
Relativistic backward wave oscillator of direct circular polarization TE11 mode
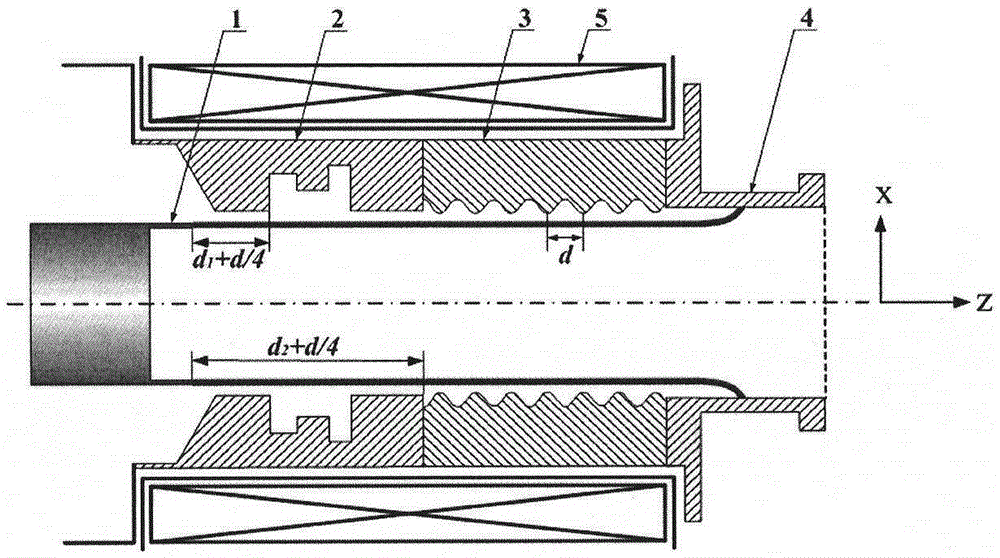
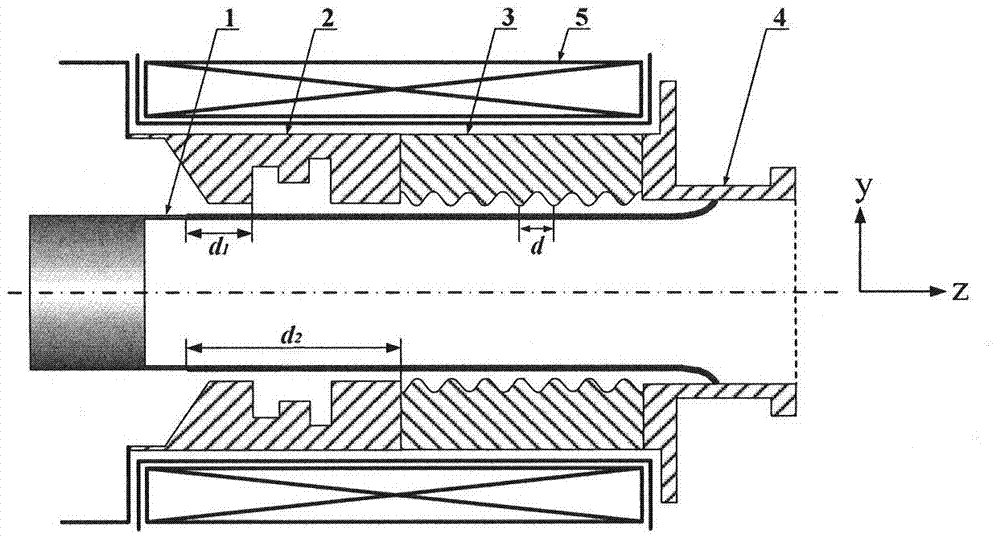
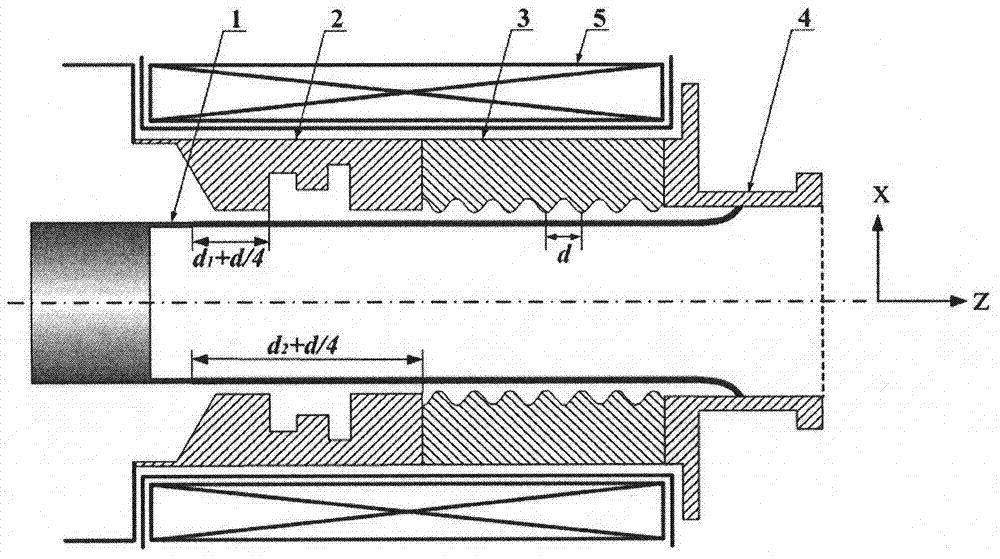
The invention belongs to the field of masers and relates to a relativistic backward wave oscillator of a direct circular polarization TE11 mode. The relativistic backward wave oscillator comprises an annular cathode, angular partition double-pre-modulation chambers, angular partition slow wave structures, an output waveguide and a magnetic field coil. The annular cathode is at the most front end of the structure and emits an annular relativistic electron beam under the effect of high voltage pulse. The angular partition double-pre-modulation chambers, the angular partition slow wave structures, and the output waveguide are orderly arranged behind the annular cathode. The magnetic field coil is at the periphery of the annular cathode, the angular partition double-pre-modulation chambers, and the angular partition slow wave structures. The angular partition double-pre-modulation chambers and the slow wave structures are employed by the invention, two linearly polarized TE11 modes with the same frequency, similar amplitude and orthogonal polarization can be generated in two groups of structure. Through the offset of d / 4 of two groups of the double-pre-modulation chambers and the slow wave structures in an axial position, thus a 90-degree phase difference is introduced between the linearly polarized TE11 modes with orthogonal polarization, and the circular polarization TE11 mode is obtained in an output waveguide.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
Medical isotope generation method and device based on laser wake-field accelerator
The invention provides a medical isotope generation method and device based on a laser wake-field accelerator. Interaction between super-strong and super-short lasers and plasma is utilized to generate a strong flow relativity electron beam. The electron beam is utilized to irradiate a high atomic number target to generate high-flow-strength bremsstrahlung gamma light. The bremsstrahlung gamma light bombards an interested object target to induce a ([gamma], xn+yp) photonuclear reaction or a ([gamma], [gamma]') optical excitation reaction, and object isotopes including gamma rays, electrons, positive electrons and [alpha] particle emitters are generated. By adopting the method provided by the invention, radio isotopes higher in activity are generated, and the cost is relatively low; in addition, the device provided by the invention is compact and convenient to carry, and the device is capable of being placed near a large-sized medical mechanism to be better applied to and serve radiation diagnosis, targeting treatment and other medical applications.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV +1
Method for thermal matching optimizing design of energy coupler
InactiveCN106777552AAccurate analysisThe result is accurate and efficientDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDielectric tensorEnergy coupling
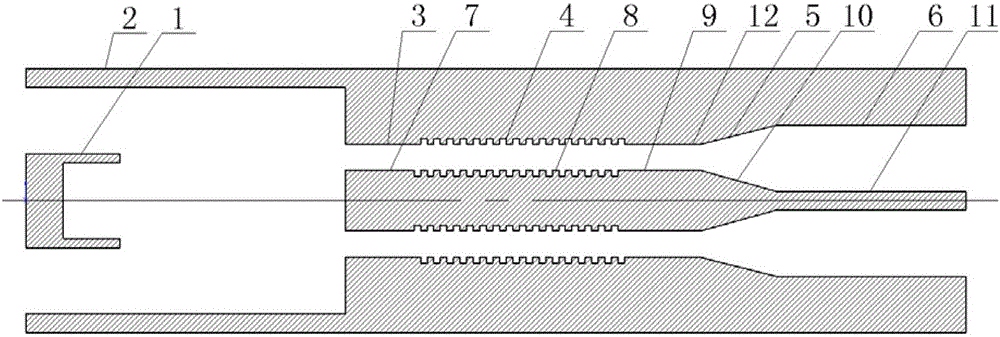
The invention belongs to the field of CAD (computer-aided design) simulation design of a microwave vacuum electronic device, and particularly relates to a method for thermal matching optimizing design of an energy coupler. The method comprises the following steps of adopting an equivalent medium treatment method of a relativistic electron beam to enable a periodic magnetic field focusing electron beam in a helix traveling wave tube to be equivalent a bi-anisotropic complicated electromagnetic medium, wherein the equivalent dielectric tensor and the magnetic conductivity tensor reflect a relativistic effect between the electron movement and an electromagnetic field; modeling the effective electron beam by sections, so as to more accurately analyze the influence of electron beam loading to the thermal matching characteristic of the helix traveling wave tube; modeling the equivalent electron beams by sections, so as to accurately reflect the fluctuating property of the electron beam in an electron beam envelope under the periodic magnetic field focusing, and the periodicity of the axial focusing magnetic field. The method has the advantages that the result is accurate and efficient, and a feasible and effective method is provided for the simulation analysis and design of the helix traveling wave tube in high-property spaces.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Bessel free electron laser device
InactiveUS7046703B2Minimal divergenceReduce power levelExcitation process/apparatusFree electron laser deviceLight beam
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Free-electron laser driven by fiber laser-based laser plasma accelerator
ActiveUS9768580B2More compactMore efficientExcitation process/apparatusX-ray tube with very high currentPlasma accelerationLight beam
A Free Electron Laser source includes: a fiber-based laser having a plurality of amplifying fibers wherein an initial laser pulse is distributed and amplified, and element for grouping together the elementary pulses amplified in the fiber in order to form an a single amplified global laser pulse; a laser plasma accelerator wherein the global laser pulse generates relativistic electron beams, a beam focusing system transporting electron beams from the laser plasma accelerator, an undulator wherein relativistic electron beams generate an electromagnetic beam, and a beam separator system, wherein the electron beam and the electromagnetic beam are separated.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE
Cold cathode capable of generating multiple cylindrical intense relativistic electron beams
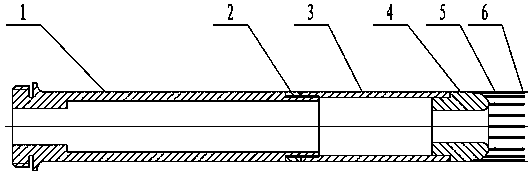
ActiveCN104332373AUniform emission densitySpatial configuration unchangedTransit-tube cathodesElectricityMetallic materials
The invention discloses a cold cathode capable of generating multiple cylindrical intense relativistic electron beams. The cold cathode comprises a cylindrical structure which is made of a metal material high in conductivity and emission threshold and has the same outer diameter, and a cathode rod, a cathode rod transition ring, a cathode rod transition section, a cathode seat, a cathode column and a cathode bulb which are all coaxial and in excellent electric connection with each other. Due to even distribution of the surface field of the cathode bulb serving as an emitting component in the cold cathode, the cold cathode has even electron emission density and the emitted multiple cylindrical electron beams are distributed symmetrically about the own centers, respectively; under the action of an appropriate guide magnetic field, the electron beams are not prone to collide with the wall of a multiple-beam drift tube due to that the electron beams rotate around the own centers in the transmission process in the drift tube; the transmission efficiency is high, the space configuration of the electron beams in the drift tube is kept unchanged, and the beam conversion efficiency is improved.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED ELECTRONICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Relativistic electron beam transmission scheme design method, device, equipment and medium
ActiveCN113609737AImprove stabilitySuppress instabilityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsWave fieldParticle physics
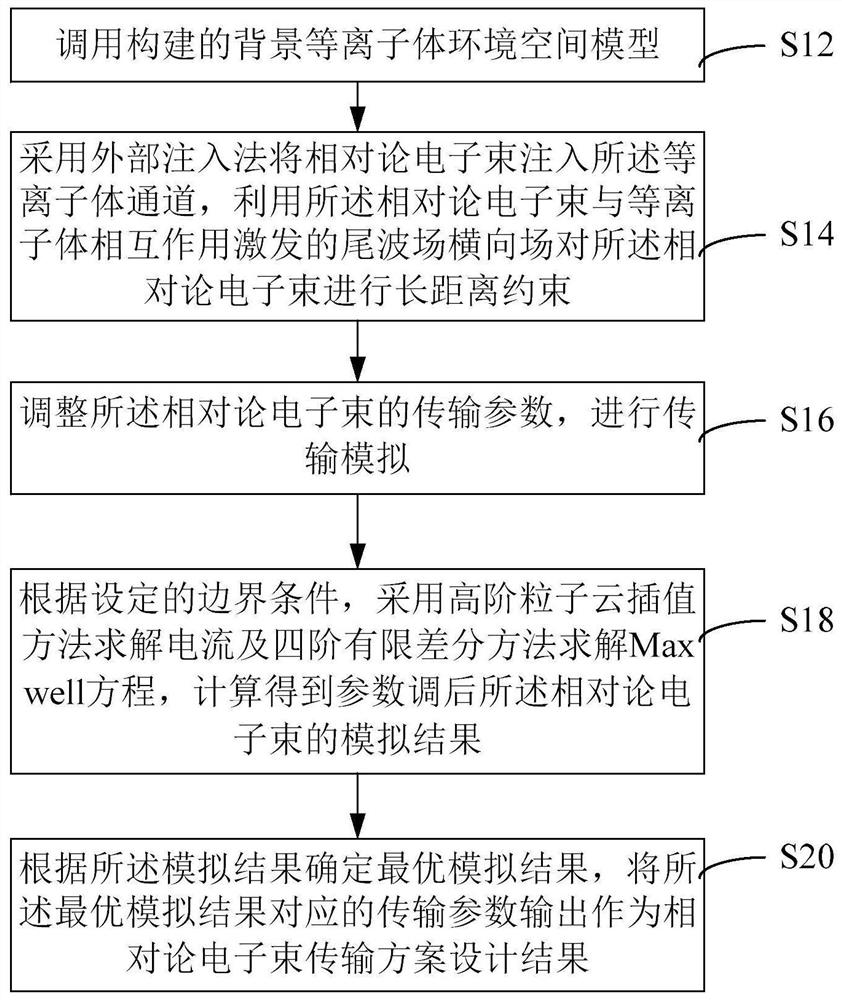
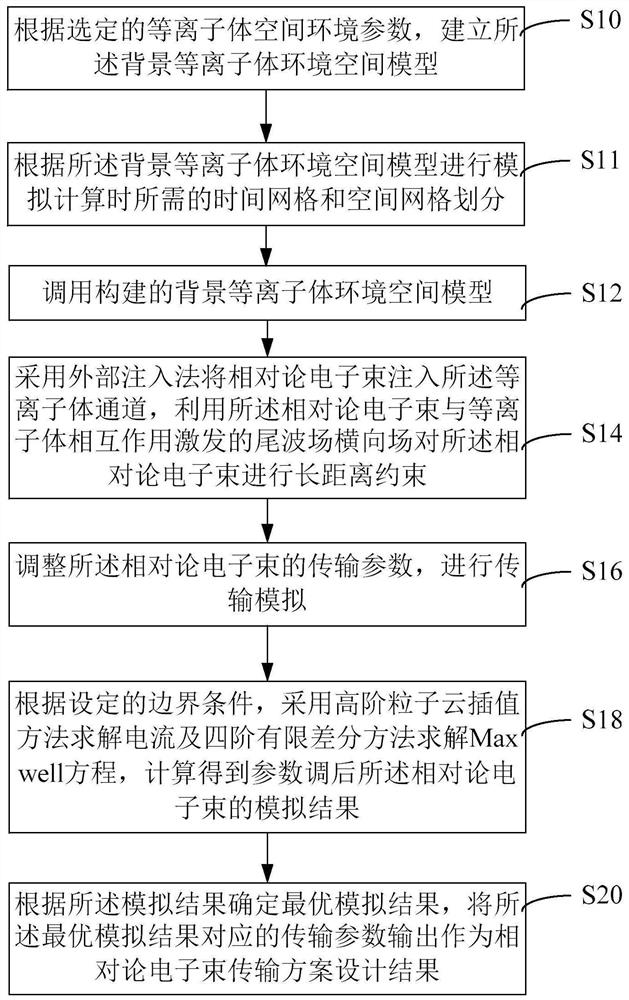
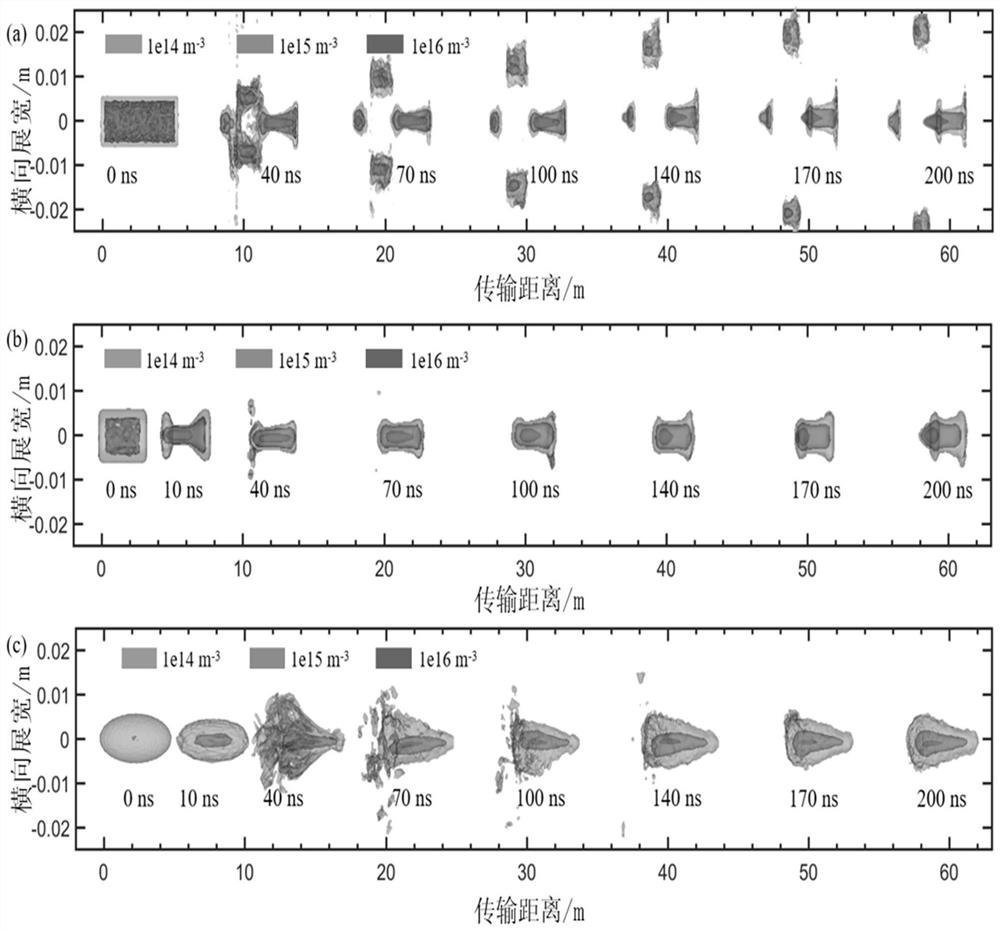
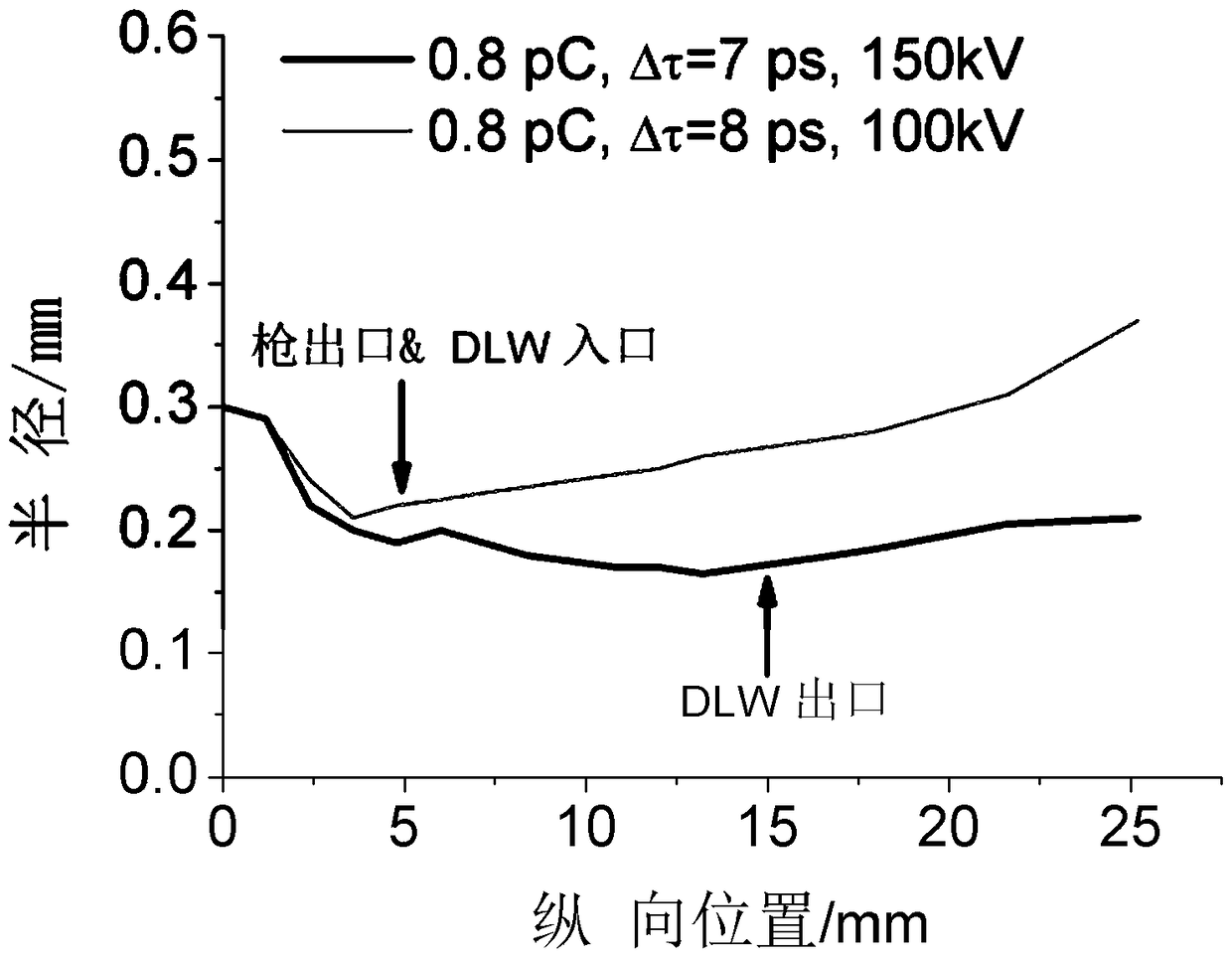
The invention relates to a relativistic electron beam transmission scheme design method and device, equipment and a medium. The method comprises the following steps: calling a background plasma environment space model; injecting the relativistic electron beam into a plasma channel by adopting an external injection method, and performing long-distance constraint on the relativistic electron beam by utilizing an excited tail wave field transverse field; adjusting transmission parameters of the relativistic electron beam, and performing transmission simulation; according to set boundary conditions, adopting a high-order particle cloud interpolation method to solve the current, adopting a fourth-order finite difference method to solve the Maxwell equation, and obtaining a simulation result of the relativistic electron beam after parameter adjustment through calculation; and determining an optimal simulation result according to the simulation result, and outputting a transmission parameter corresponding to the optimal simulation result as a relativistic electron beam transmission scheme design result, wherein the optimal simulation result is the simulation result when the beam spot of the relativistic electron beam is minimum, the energy collimation is optimal and the energy loss is minimum. The effect of efficient long-range stable transmission of relativistic electron beams is achieved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
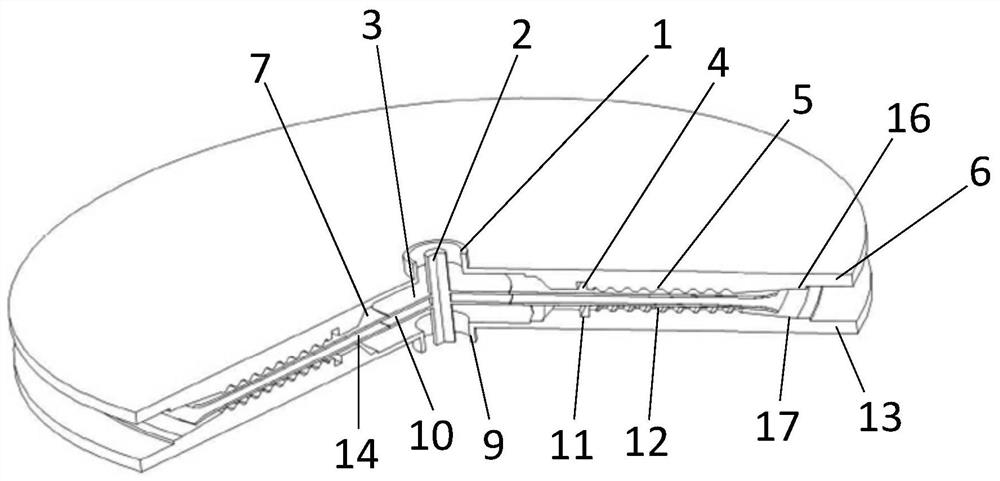
Fiber array cathode
ActiveCN105355525AImprove high temperature ablation resistanceExtend your lifeTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube cathodesGlass fiberFiber bundle
The invention relates to a fiber array cathode, and belongs to the field of a microwave source in the technical field of high-power microwaves. The fiber array cathode is formed by sleeving fiber bundle circumference arrays composed of porous array circular rings, U-shaped fiber bundles and circumference pads on a cathode substrate, wherein the two ends of each U-shaped fiber bundle are exposed at the side surface of a cathode to form a dense fiber array so as to replace velvet in a conventional cathode, the porous array circular rings have structural support and current conduction effects, and the dense fiber arrays formed by the fiber bundles mainly generate cathode plasma under the effect of a strong electric field and accordingly generate relativistic electron beams. The employed fiber bundles are generally carbon fiber bundles, glass fiber bundles or ceramic fiber bundles, or other materials with low emission thresholds and high temperature ablation resistance. Since the employed fiber bundle materials are better in high temperature ablation resistance than chemical fiber velvet in the conventional cathode, by use of the long-life fiber array cathode with the high temperature ablation resistance, the operation life of a MILO can be greatly prolonged.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
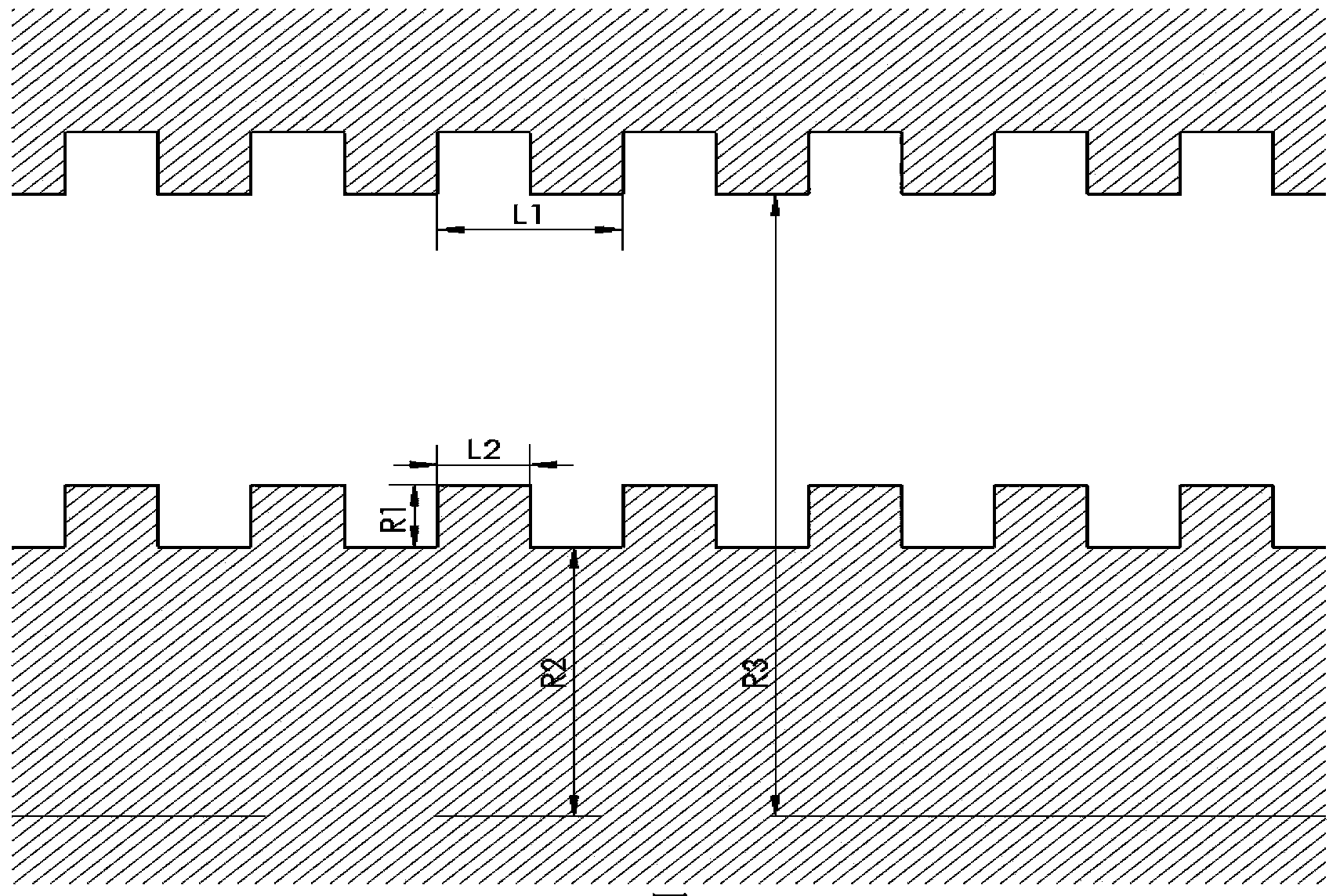
Metamaterial-based low-frequency-band slow wave structure
ActiveCN112820608AHas the advantage of horizontal miniaturizationLong slow wave structure periodTransit-tube circuit elementsWave structureLow frequency band
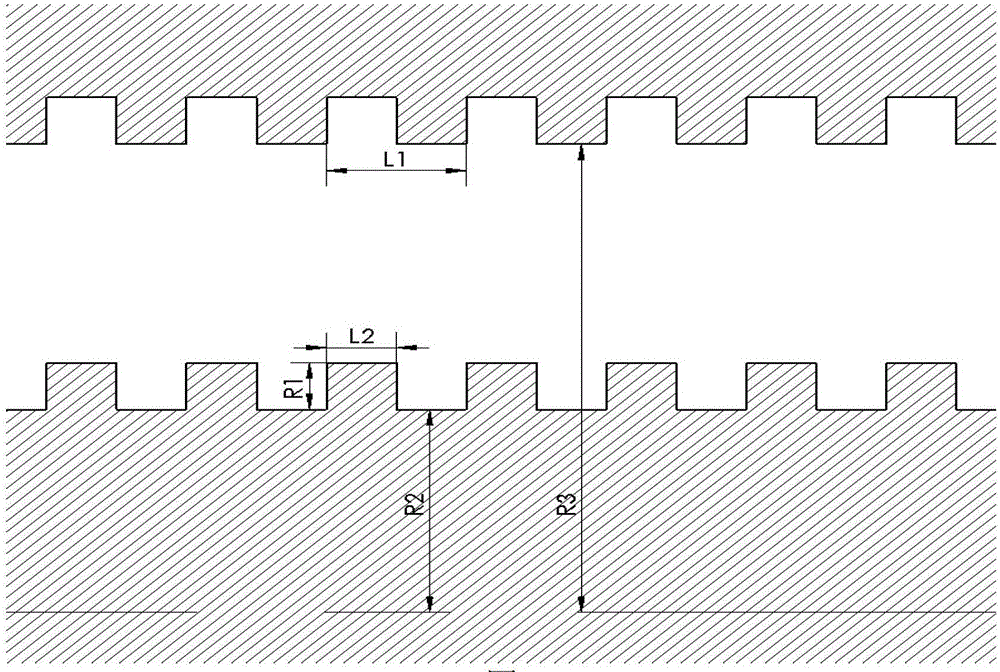
The invention relates to a microwave source device in the field of high-power microwaves, in particular to a metamaterial-based low-frequency-band slow wave structure which comprises a first metamaterial resonance unit, a second metamaterial resonance unit and a circular waveguide. The first metamaterial resonance unit and the second metamaterial resonance unit are in 45-degree rotation coupling arrangement to form a single period of the slow wave structure. The metamaterial-based low-frequency-band slow wave structurehas the following technical advantages that the metamaterial-basedslow wave structure can work below the cut-off frequency of the hollow metal circular waveguides with the same size, and has the advantage of transverse miniaturization; due to the sub-wavelength characteristic of the metamaterial, the slow wave structure is shorter in period and has the advantage of miniaturization in the axial direction; due to the local field enhancement effect of the metamaterial-based slow-wave structure, the slow-wave structure has higher coupling impedance, and a device has the advantage of higher beam-wave interaction efficiency; strong electromagnetic coupling between metamaterial slow wave structures is stronger in relativistic electron beam modulation, so that the device has shorter oscillation starting time.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
γ-ray source based on all-optical laser plasma accelerator
The invention provides a small gamma ray source based on an all-optical laser plasma accelerator. The ray source includes a synchronous dual-output high-power laser system (200), a dual compression-delay system (12), a laser plasma accelerator (18), a particle beam focusing system (24), a scattered light focusing mirror (27) and a particle beam separate system. Wherein, an initial laser pulse is separated and amplified by the laser system (200) to generate two synchronous high-energy laser pulses (10, 11), and the two amplified laser pulses pass through a double compression-delay system (12) at Compressed in the time domain and appropriately delayed to form a pair of driving pulses (13)-scattering pulses (14), the driving pulses (13) pass through a laser plasma accelerator (18) to generate relativistic electron beams (21), particle beams The focusing system (24) is used to transmit the electron beam (21), the scattered light focusing mirror (27) is used to focus the scattered pulse (14) on the electron beam (21) to generate gamma rays (31), and the separation system is used to The electron beams (21) and gamma rays (31) are separated.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
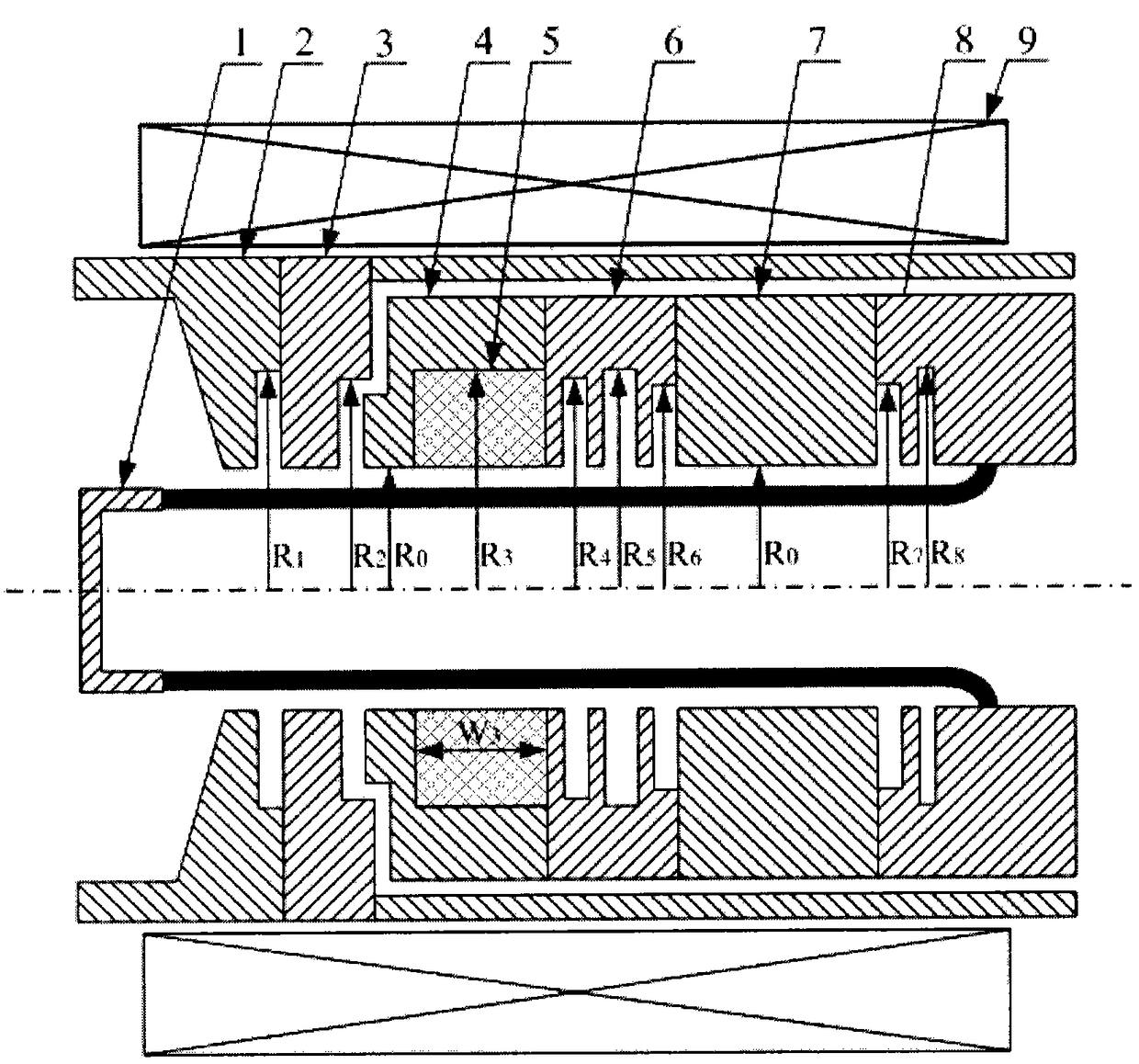
High-current diode based on gradient magnetic field and gradient magnetic field device
PendingCN113921357ASmall sizeSufficient magnetic field strengthTubes with magnetic controlTubes with electrostatic and magnetic controlElectrical conductorEngineering
The invention discloses a gradient magnetic field device which comprises a guiding magnetic field for guiding transmission of a high-current relativistic electron beam; the guide magnetic field comprises a solenoid coil; the solenoid coil is wound around the high-current diode so as to form a gradient magnetic field enabling the high-current relativistic electron beam to generate radial deflection, and the solenoid coil comprises a first sub-coil, a second sub-coil and a third sub-coil; the first sub-coil is wound on the outer side of an anode of the high-current diode, the second sub-coil is wound on the outer side of an outer conductor of the high-current diode, and the third sub-coil is wound on the outer side of the second sub-coil; the guide magnetic field further comprises an adjusting magnetic field; and the adjusting magnetic field is fixedly arranged between the first sub-coil and the second sub-coil, is wound around the high-current diode and is used for adjusting the radius change speed of the high-current relativistic electron beam. The invention further discloses a high-current diode based on the gradient magnetic field. The high-current diode comprises the gradient magnetic field device. The problem that the size of a high-impedance diode is difficult to reduce can be solved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Terahertz radiation source based on non-relativistic electron beam excitation of dielectric waveguide
The invention discloses a non-relativistic electron beam induced dielectric waveguide-based terahertz radiation source. The non-relativistic electron beam induced dielectric waveguide-based terahertz radiation source includes a pulse laser light source used for emitting a laser pulse string, a frequency adjusting device used for adjusting the repetition frequency of the laser pulse string, an electron gun and a dielectric waveguide; the cathode of the electron gun is used for absorbing the laser pulse string and transmitting an electron beam cluster string; a size-adjustable electric field formed between the cathode and anode of the electron gun is used for accelerating the emitting of the electron beam cluster string into the dielectric waveguide; the dielectric waveguide is excited by the electron beam cluster string to form terahertz radiation; and the repetition frequency of the laser pulse string and the radiation frequency of the dielectric waveguide form resonance. With the non-relativistic electron beam induced dielectric waveguide-based terahertz radiation source adopted, energy conversion efficiency between the electrons and radiations of the terahertz radiation source can be effectively improved, radiation power can be improved, radiation frequency is adjustable. The cost of the terahertz radiation source can be reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
High-power coaxial structure overmode surface wave oscillator and terahertz wave generation method
ActiveCN103516327BIncrease output powerHigh pattern purityImpedence networksTransit-time tubesWave structurePeak value
The invention discloses an axisymmetric-structure high-power coaxial over-mode surface wave oscillator which uses electromagnetic wave radiation of the terahertz wave band generated through wave-beam interaction as the basic working principle, according to high-current relativity theory electron beams and an over-mode coaxial slow wave structure, strong wave-beam interaction happens, and high-power terahertz waves are generated. The coaxial over-mode surface wave oscillator comprises a non-foil diode, the over-mode coaxial slow wave structure, a transitional wave guiding part and an output wave guiding part of a coaxial structure. The working mode of the over-mode surface wave oscillator in a wave-beam interaction zone is a TM01 mode, by mode converting of the transitional wave guiding part, transmission is carried out at an output wave guiding end of the surface wave oscillator in a TEM mode, the 0.14THz over-mode surface wave oscillator is designed through the structure, and the peak power of an output port can reach 115MW. The over-mode surface wave oscillator is suitable for generating the high-power electromagnetic waves in the terahertz wave band.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
A fiber array cathode
ActiveCN105355525BImprove high temperature ablation resistanceExtend your lifeTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube cathodesGlass fiberFiber bundle
The invention relates to a fiber array cathode, and belongs to the field of a microwave source in the technical field of high-power microwaves. The fiber array cathode is formed by sleeving fiber bundle circumference arrays composed of porous array circular rings, U-shaped fiber bundles and circumference pads on a cathode substrate, wherein the two ends of each U-shaped fiber bundle are exposed at the side surface of a cathode to form a dense fiber array so as to replace velvet in a conventional cathode, the porous array circular rings have structural support and current conduction effects, and the dense fiber arrays formed by the fiber bundles mainly generate cathode plasma under the effect of a strong electric field and accordingly generate relativistic electron beams. The employed fiber bundles are generally carbon fiber bundles, glass fiber bundles or ceramic fiber bundles, or other materials with low emission thresholds and high temperature ablation resistance. Since the employed fiber bundle materials are better in high temperature ablation resistance than chemical fiber velvet in the conventional cathode, by use of the long-life fiber array cathode with the high temperature ablation resistance, the operation life of a MILO can be greatly prolonged.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Light periodic magnetic field coil applied to high-power microwave source
The invention discloses a light periodic magnetic field coil applied to a high-power microwave source, the high-power microwave source comprises a radial transit time oscillator, and the periodic magnetic field coil comprises a plurality of magnet exciting coils which are uniformly arranged on the outer wall of a beam wave interaction area of the radial transit time oscillator at intervals; each excitation coil comprises multiple layers of densely wound solenoids oppositely arranged on the two sides of the outer wall of the beam-wave interaction area, the solenoids located on the same side of the beam-wave interaction area are linearly arranged, and an insulator is arranged between every two adjacent solenoids located on the same side of the outer wall of the beam-wave interaction area; superposed magnetic fields B (r) generated in the electron beam channel of the beam wave interaction area after the solenoids are electrified are in cosine distribution; wherein the peak value B0 of the superimposed magnetic field is times of the Brillouin magnetic field Bb of the electron beam under the corrected relativistic condition, and the magnetic field parameter alpha of the superimposed magnetic field B (r) is 0-0.66 or 1.72-3.76. On the premise of ensuring the stable transmission of the radial high-current relativistic electron beam, the weight of the external magnetic field coil can be reduced.
Owner:NAVAL UNIV OF ENG PLA
Directly produce circular polarization te 11 relativistic return wave tube
The invention belongs to the field of masers and relates to a relativistic backward wave oscillator of a direct circular polarization TE11 mode. The relativistic backward wave oscillator comprises an annular cathode, angular partition double-pre-modulation chambers, angular partition slow wave structures, an output waveguide and a magnetic field coil. The annular cathode is at the most front end of the structure and emits an annular relativistic electron beam under the effect of high voltage pulse. The angular partition double-pre-modulation chambers, the angular partition slow wave structures, and the output waveguide are orderly arranged behind the annular cathode. The magnetic field coil is at the periphery of the annular cathode, the angular partition double-pre-modulation chambers, and the angular partition slow wave structures. The angular partition double-pre-modulation chambers and the slow wave structures are employed by the invention, two linearly polarized TE11 modes with the same frequency, similar amplitude and orthogonal polarization can be generated in two groups of structure. Through the offset of d / 4 of two groups of the double-pre-modulation chambers and the slow wave structures in an axial position, thus a 90-degree phase difference is introduced between the linearly polarized TE11 modes with orthogonal polarization, and the circular polarization TE11 mode is obtained in an output waveguide.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
Directly generate linearly polarized te 11 relativistic return wave tube
ActiveCN105280462BEnhanced interactionImprove beam conversion efficiencyTransit-tube cathodesTransit-tube circuit elementsWave structureMaser
The invention, which belongs to the maser field, directly relates to a relativistic backward wave oscillator for generating a linearly polarized TE11 mode directly. The relativistic backward wave oscillator comprises an arc cathode, a reflector, an angular partition slow wave structure, an output waveguide and a magnetic field coil. The arc cathode is arranged at the front end of the relativistic backward wave oscillator; the reflector, the angular partition slow wave structure, and the output waveguide are arranged at the rear side of the arc cathode successively; and the magnetic field coil is installed at the periphery. According to the invention, with the nonaxisymmetrical arc cathode and the angular partition slow wave structure, the TE11 mode is excited directly. The reflector employs the dual-premodulation-cavity unit preferably and is used for carrying out premodulation on an arc relativistic electron beam and leaking the part of TE11 mode to enter the arc cathode zone, so that certain premodulation of the electron beam at the arc cathode zone is realized and thus the beam wave conversion efficiency is improved. Moreover, the oscillator has advantages of simple structure and high conversion efficiency; and the linearly polarized TE11 mode can be generated directly.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
A method and device for generating medical isotopes based on a laser wakefield accelerator
The invention provides a medical isotope generation method and device based on a laser wake-field accelerator. Interaction between super-strong and super-short lasers and plasma is utilized to generate a strong flow relativity electron beam. The electron beam is utilized to irradiate a high atomic number target to generate high-flow-strength bremsstrahlung gamma light. The bremsstrahlung gamma light bombards an interested object target to induce a ([gamma], xn+yp) photonuclear reaction or a ([gamma], [gamma]') optical excitation reaction, and object isotopes including gamma rays, electrons, positive electrons and [alpha] particle emitters are generated. By adopting the method provided by the invention, radio isotopes higher in activity are generated, and the cost is relatively low; in addition, the device provided by the invention is compact and convenient to carry, and the device is capable of being placed near a large-sized medical mechanism to be better applied to and serve radiation diagnosis, targeting treatment and other medical applications.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV +1
Beam-driven short wavelength undulator
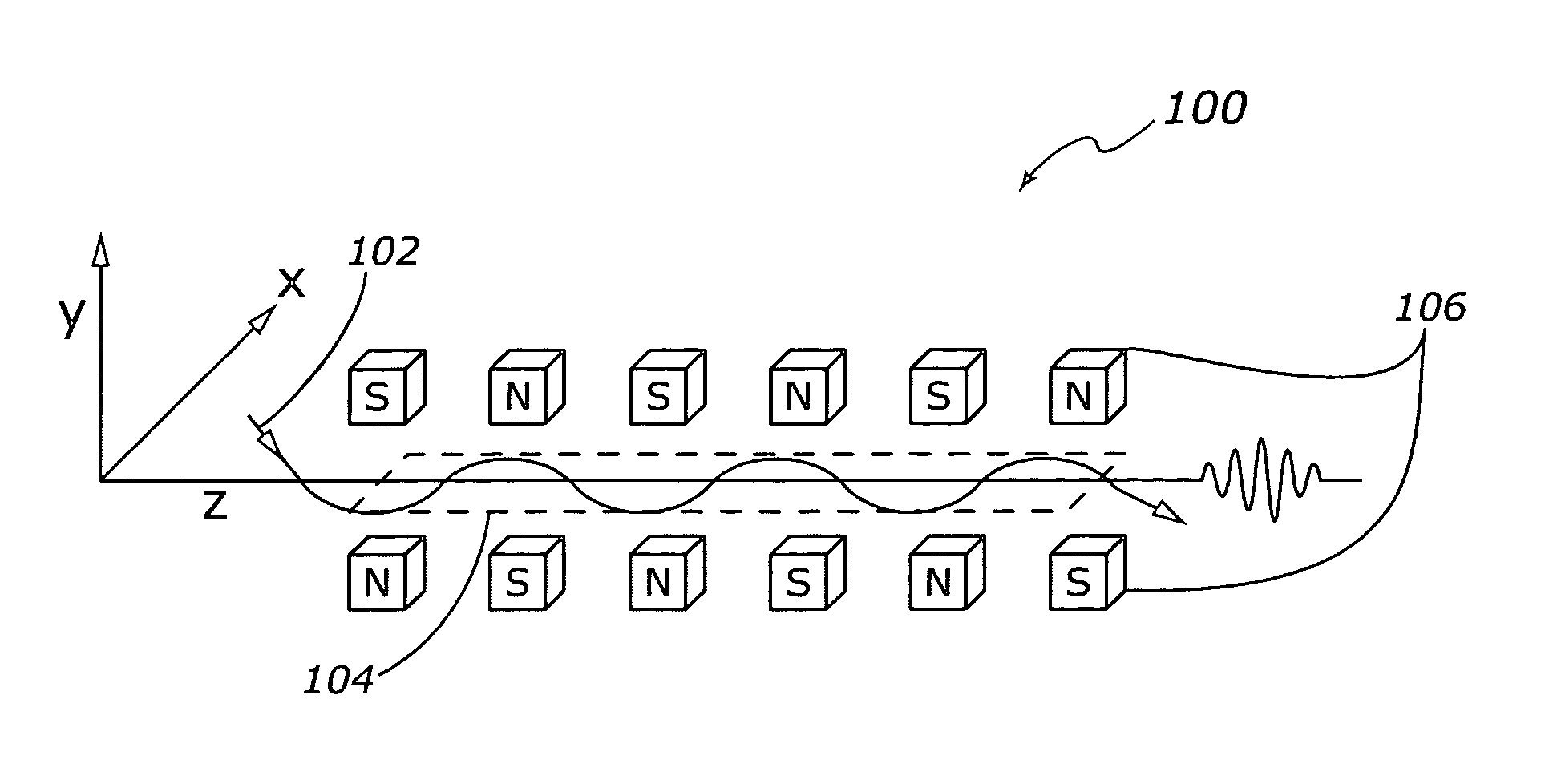
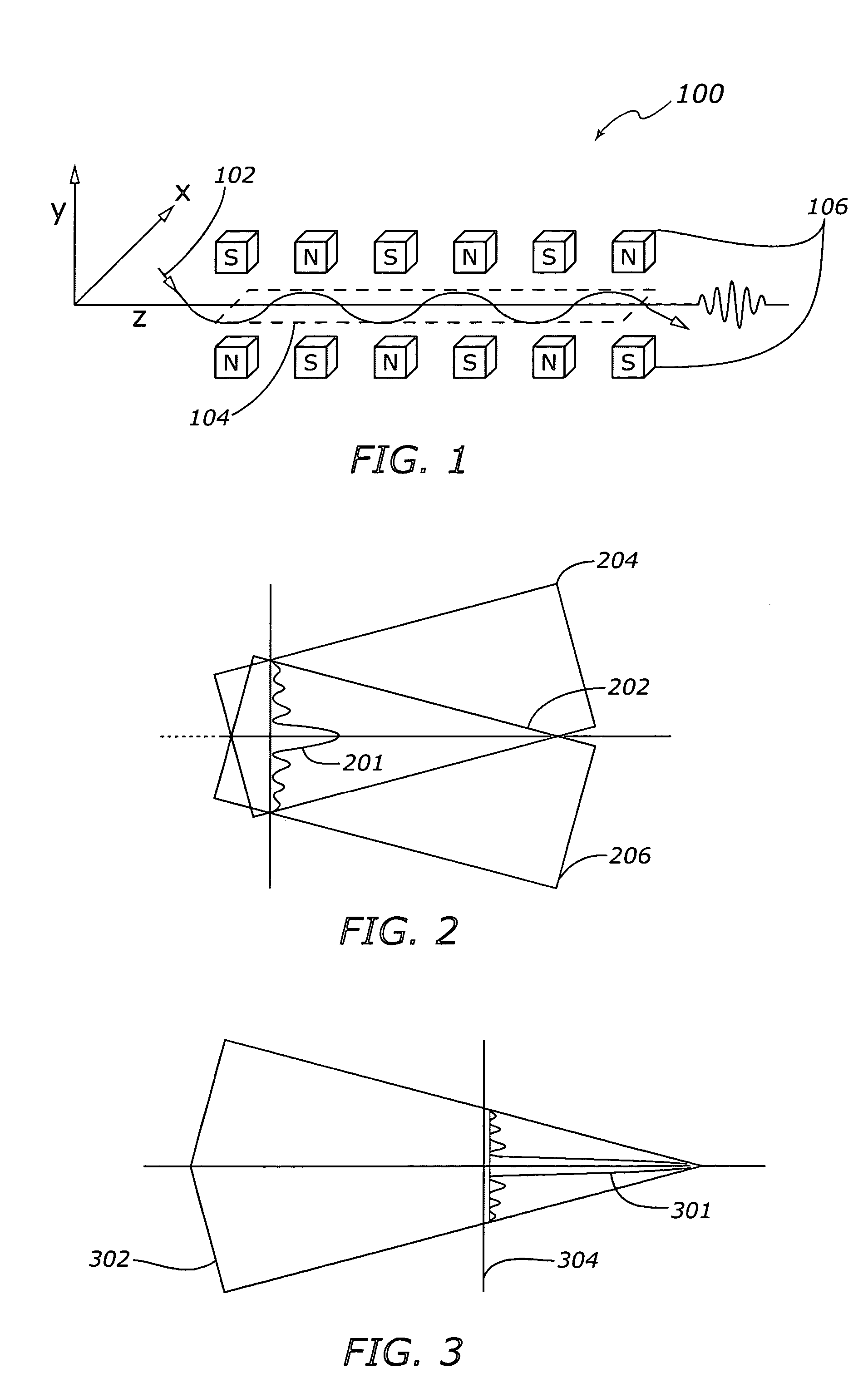
A technique for producing a coherent beam of hard X-rays is provided. This technique is based on a short wavelength undulator that uses the fields of an electromagnetic wave to deflect a relativistic electron beam along a sinusoidal trajectory in order to cause it to emit X-rays. The undulator consists of a slow-wave structure that is energized by a second counterpropagating electron beam. Cylindrical and planar structure configurations are provided and also a mechanism for electrical and mechanical tuning to allow control over the wavelength of the emitted X-ray beam.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC +1
A Cold Cathode for Generating Cylindrical Multiple Intense Relativistic Electron Beams
ActiveCN104332373BUniform emission densitySpatial configuration unchangedTransit-tube cathodesMetallic materialsCold cathode
The invention discloses a cold cathode capable of generating multiple cylindrical intense relativistic electron beams. The cold cathode comprises a cylindrical structure which is made of a metal material high in conductivity and emission threshold and has the same outer diameter, and a cathode rod, a cathode rod transition ring, a cathode rod transition section, a cathode seat, a cathode column and a cathode bulb which are all coaxial and in excellent electric connection with each other. Due to even distribution of the surface field of the cathode bulb serving as an emitting component in the cold cathode, the cold cathode has even electron emission density and the emitted multiple cylindrical electron beams are distributed symmetrically about the own centers, respectively; under the action of an appropriate guide magnetic field, the electron beams are not prone to collide with the wall of a multiple-beam drift tube due to that the electron beams rotate around the own centers in the transmission process in the drift tube; the transmission efficiency is high, the space configuration of the electron beams in the drift tube is kept unchanged, and the beam conversion efficiency is improved.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED ELECTRONICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Laser-driven high repetition rate source of ultrashort relativistic electron bunches
ActiveUS10524344B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray tube with very high currentUltravioletElectron bunches
A laser-plasma-based acceleration system includes a focusing element and a laser pulse emission directing a laser beam to the focusing element to such that laser pulses transform into a focused beam and a chamber defining a nozzle having a throat and an exit orifice, emitting a critical density range gas jet from the exit orifice for laser wavelengths ranging from ultraviolet to the mid-infrared. the critical density range gas jet intersects the focused beam at an angle and in proximity to the exit orifice of the nozzle to define a point of intersection between the focused beam and the critical density range gas jet. In intersection with the critical density range gas jet, the pulsed focused beam drives a laser plasma wakefield relativistic electron beam. A corresponding method of laser-plasma-based acceleration is also described. The critical density range may include 2×1020 cm−3 to 5×1021 cm−3.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
A low-frequency slow-wave structure based on metamaterials
ActiveCN112820608BHas the advantage of horizontal miniaturizationLong slow wave structure periodTransit-tube circuit elementsWave structureLow frequency band
The invention relates to a microwave source device in the field of high-power microwaves, and is a low-frequency slow-wave structure based on metamaterials, comprising a first metamaterial resonance unit, a second metamaterial resonance unit and a circular waveguide; the first metamaterial resonance unit and the The second metamaterial resonant unit is arranged in a 45-degree rotational coupling to form a single period of the slow-wave structure; the present invention has the following technical advantages: using a metamaterial-based slow-wave structure, it can work below the cut-off frequency of a hollow metal circular waveguide of the same size , has the advantage of lateral miniaturization; due to the sub-wavelength characteristics of metamaterials, the slow-wave structure has a shorter period and has the advantage of miniaturization in the axial direction; due to the local field enhancement effect of the metamaterial slow-wave structure, the slow-wave structure has a higher coupling impedance, The device has the advantage of higher beam-wave interaction efficiency; the strong electromagnetic coupling between the slow-wave structures of metamaterials has a strong modulation of the relativistic electron beam, which makes the device have a shorter start-up time.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
X-Band Overmode Relativistic Klystron Amplifier
The invention discloses an X wave band over-mode relativistic klystron amplifier, which comprises an annular cathode, a resonant reflector, an input cavity, a first section of drift tube, a wave absorbing material, a buncher cavity, a second section of drift tube, an output cavity and a magnetic field coil, wherein the annular cathode is arranged at the most significant end of the structure and emits annular relativistic electron beams outwards under the action of high voltage pulse, the resonant reflector, the input cavity, the first section of drift tube, the wave absorbing material, the buncher cavity, the second section of drift tube and the output cavity are sequentially arranged at rear of the annular cathode, the magnetic field coil is installed at the periphery of the whole structure, the working mode of the resonant reflector, the input cavity, the buncher cavity and the output cavity is a TM02 mode, and the first section of drift tube and the second section of drift tube can transmit a TM01 mode. The X wave band over-mode relativistic klystron amplifier can produce high power X wave band microwave.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
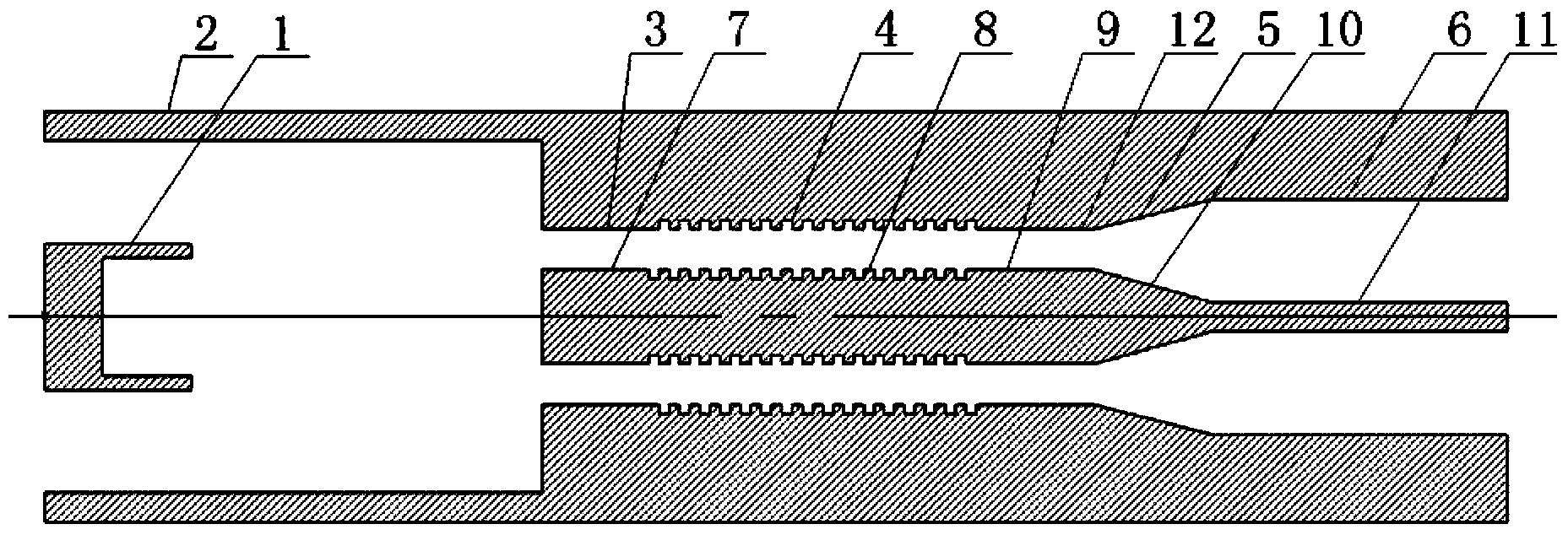
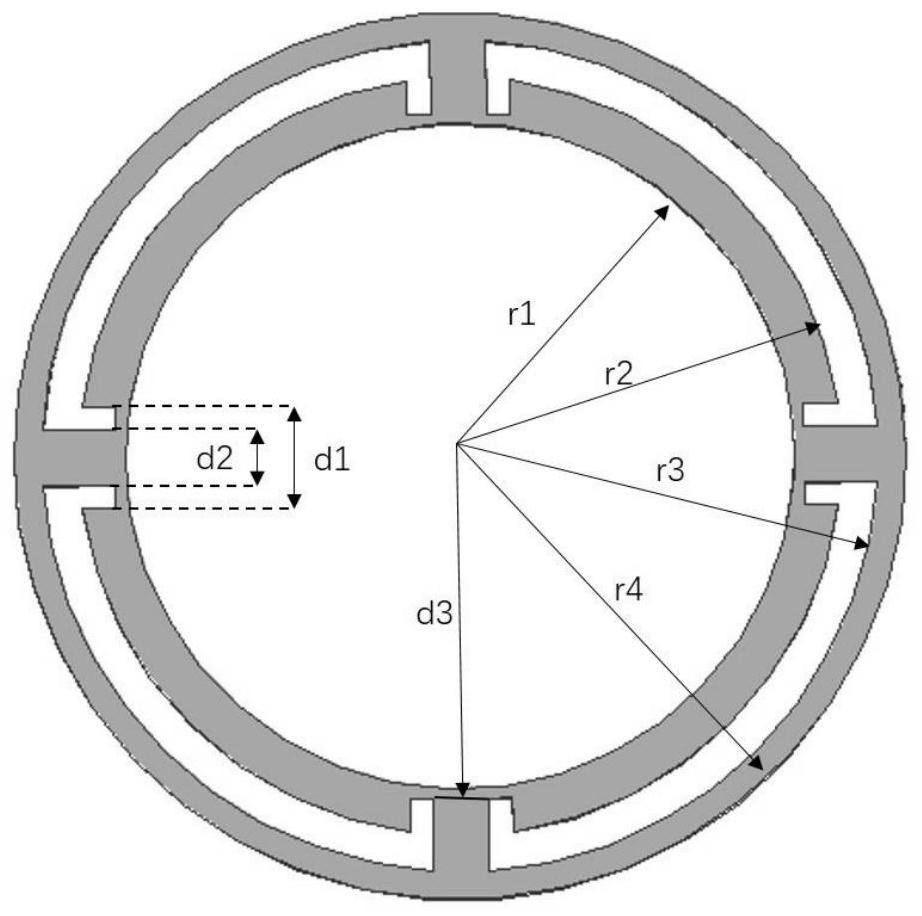
Double-electron-beam relativistic backward wave tube with radial structure
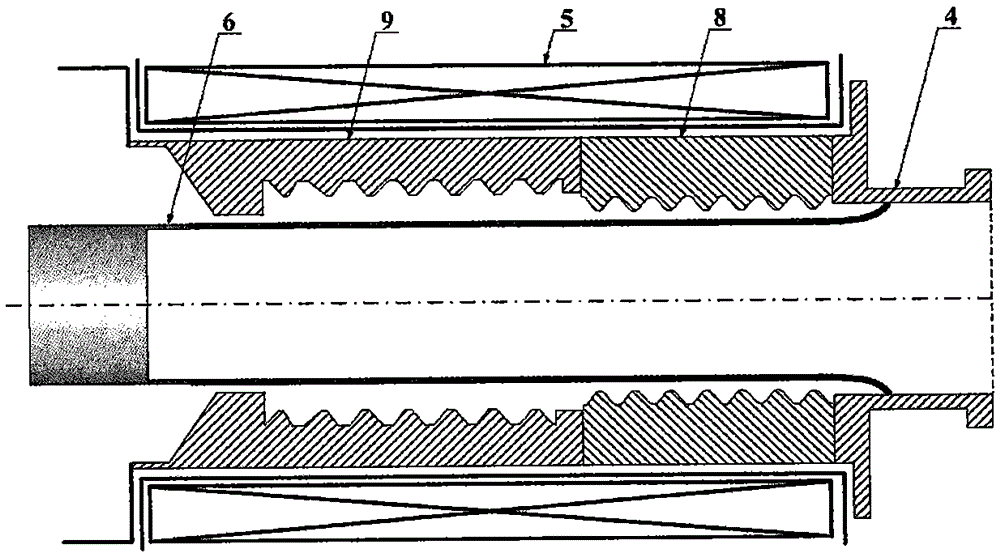
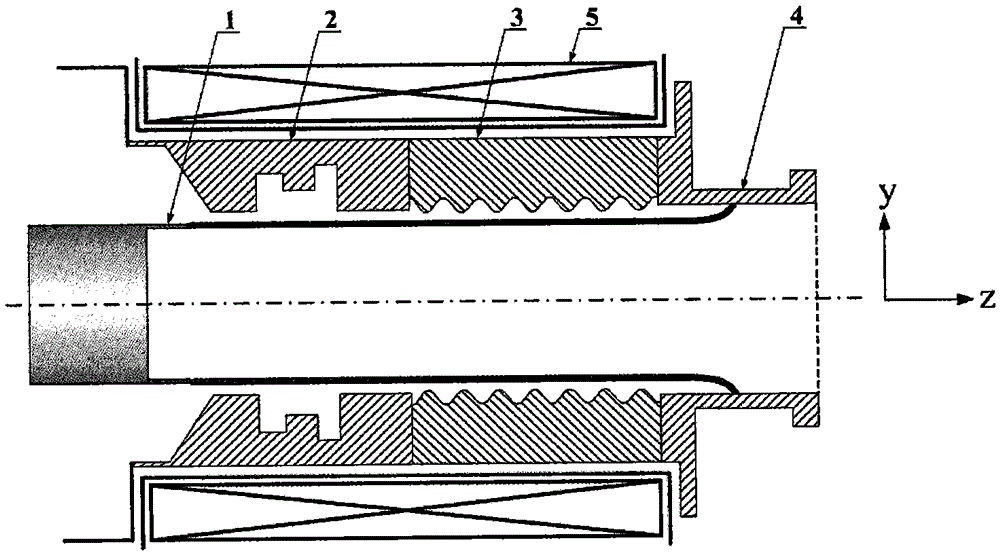
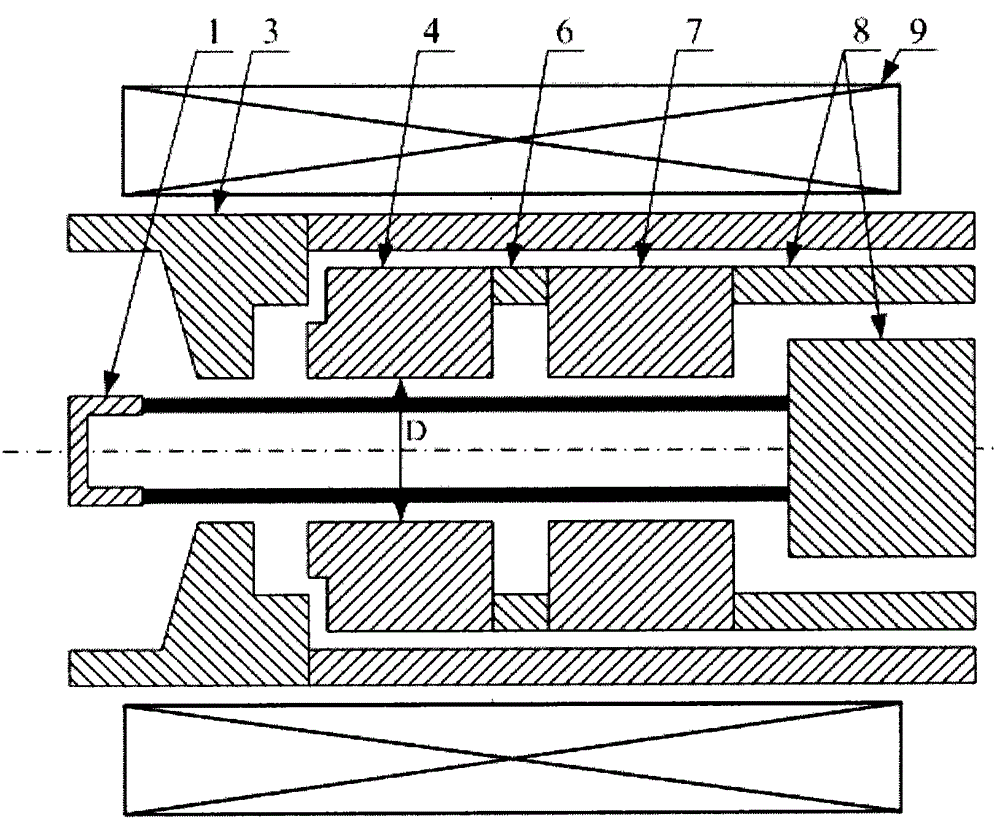
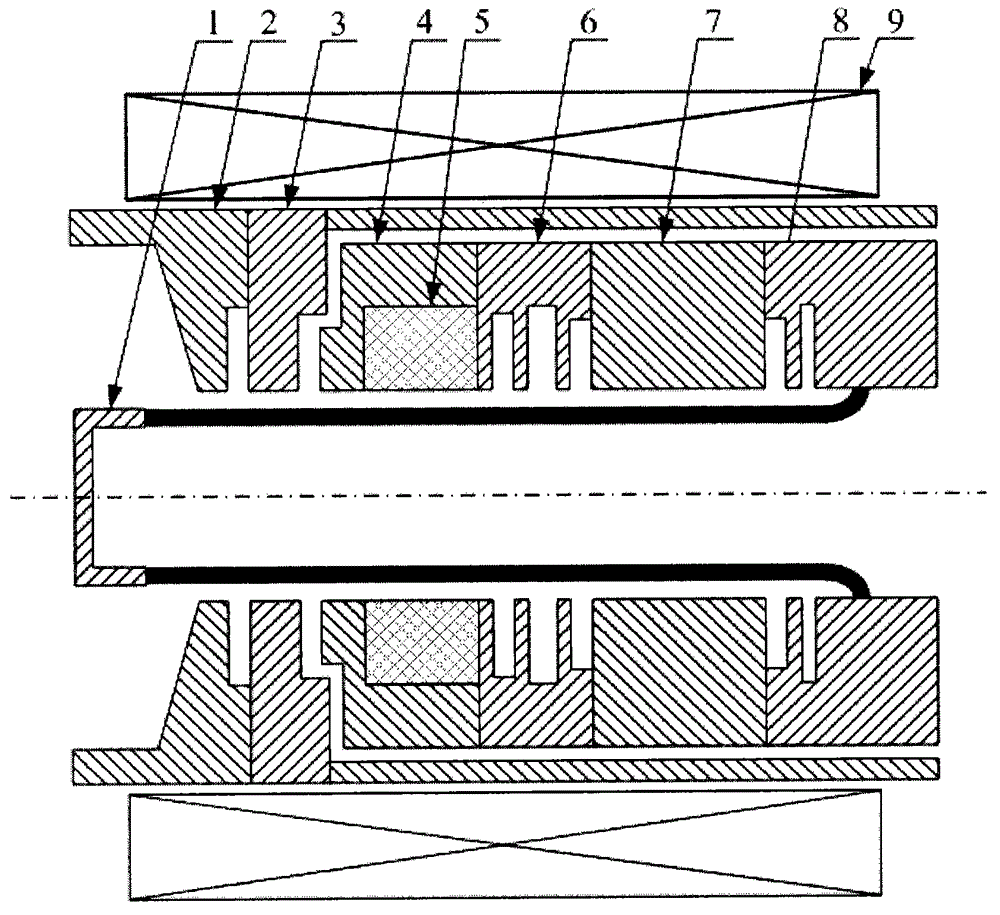
ActiveCN113628946AIncrease output powerIncrease currentTravelling-wave tubesNuclear energy generationParticle physicsQuantum electrodynamics
The invention relates to a double-electron-beam relativistic backward wave tube with a radial structure, and aims to solve the technical problem that related devices of an existing relativistic backward wave tube are difficult to meet higher and higher output power requirements on high-power microwave devices at present. According to the invention, an upper anode, a lower anode, a cathode of a high-voltage diode structure, an upper guide magnetic field generation device and a lower guide magnetic field generation device are utilized to form a double-electron-beam relativistic backward wave tube of a radial structure, and the backward wave tube is of an up-down mirror symmetry structure and also of a rotational symmetry structure. The upper anode and a lower anode adopt plate-shaped structures which are parallel to each other and are arranged in a mirror symmetry manner, a gap between the upper anode and the lower anode serves as an electron beam-electromagnetic wave channel a, a double-electron-beam working mode that a cathode of a high-voltage diode structure generates two relativistic electron beams which are transmitted in the radial direction is adopted, compared with a single electron beam, the double-electron-beam cathode can double the generated current by doubling the injection wave power of the backward wave tube, so that the output power of the backward wave tube is improved.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com