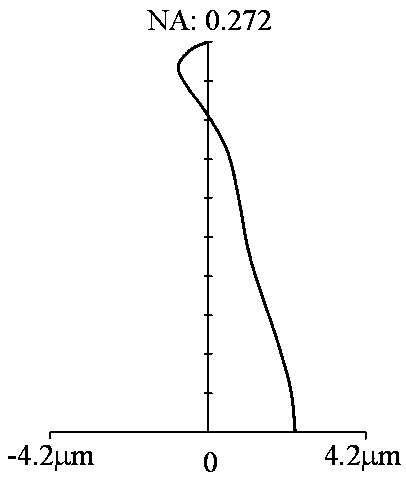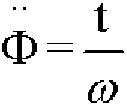Patents
Literature
57 results about "Linear dispersion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
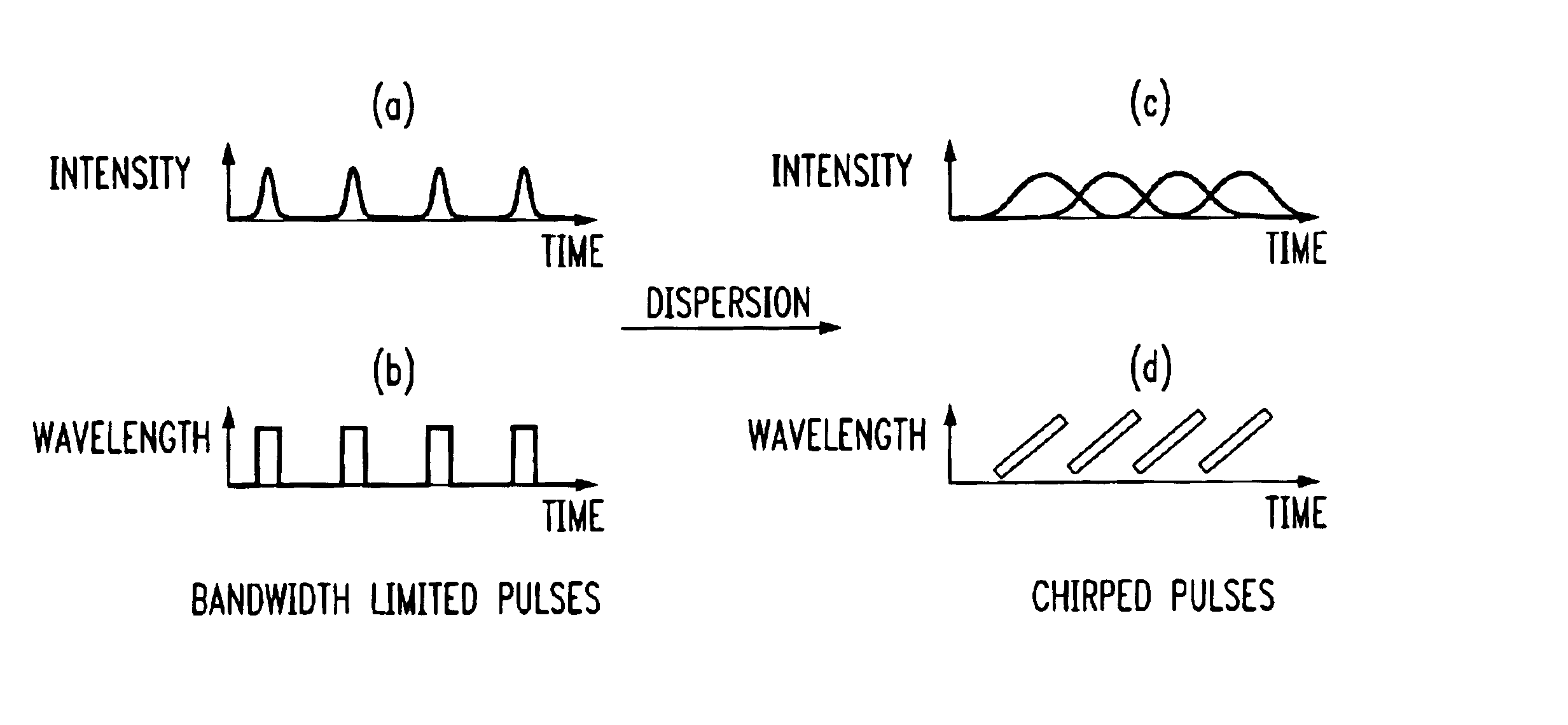
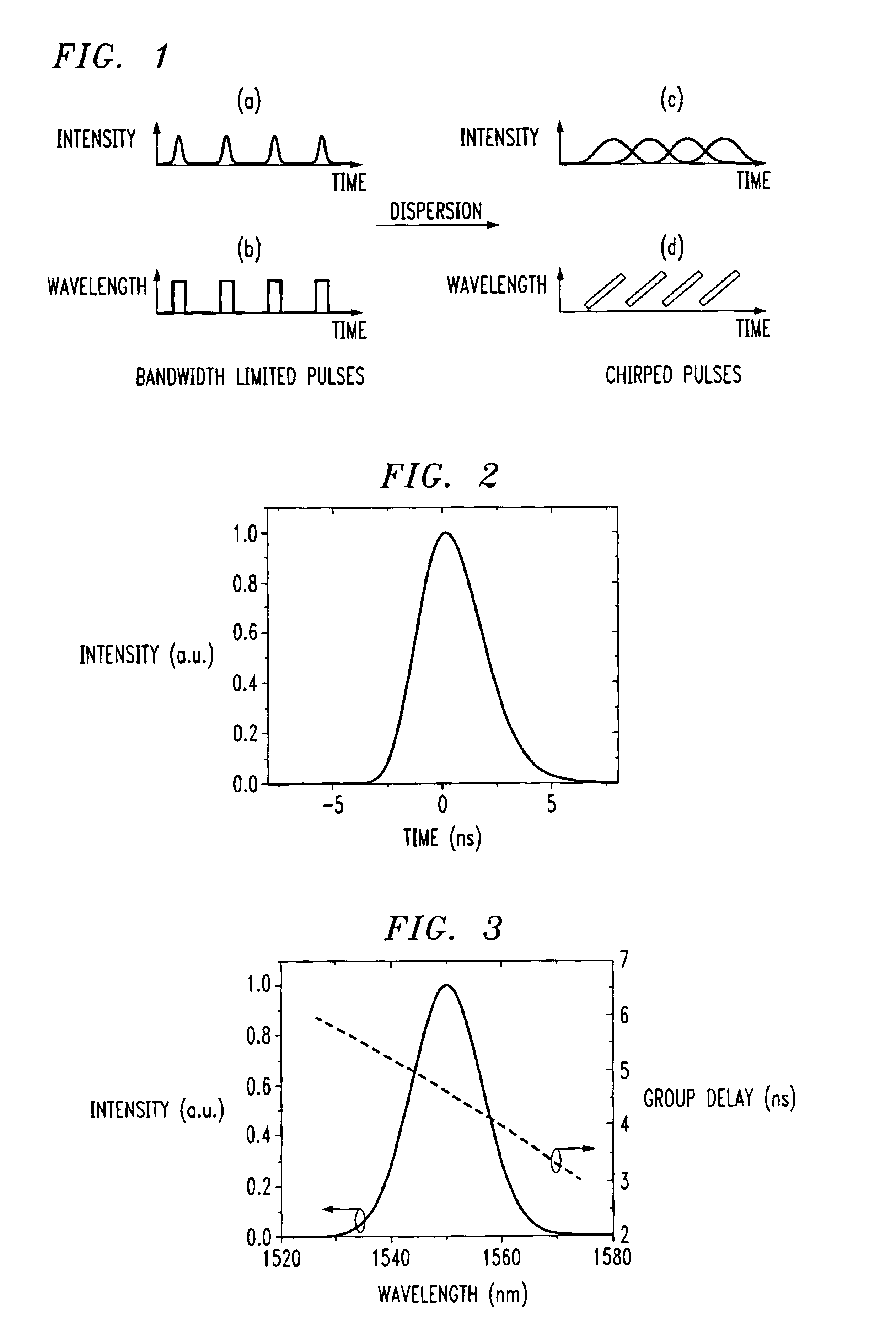
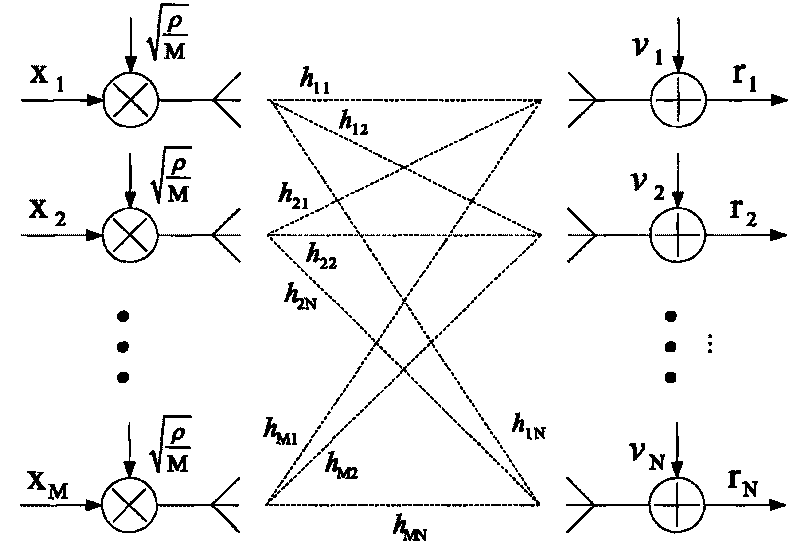
Linear dispersion in wireless communication channels distorts the transmitted signal in both time and frequency. This is accounted for by a (t, f) scattering function. In wireless communication systems with CDMA protocol, fading and multiaccess interference can be dealt with using ( t, f) processing.
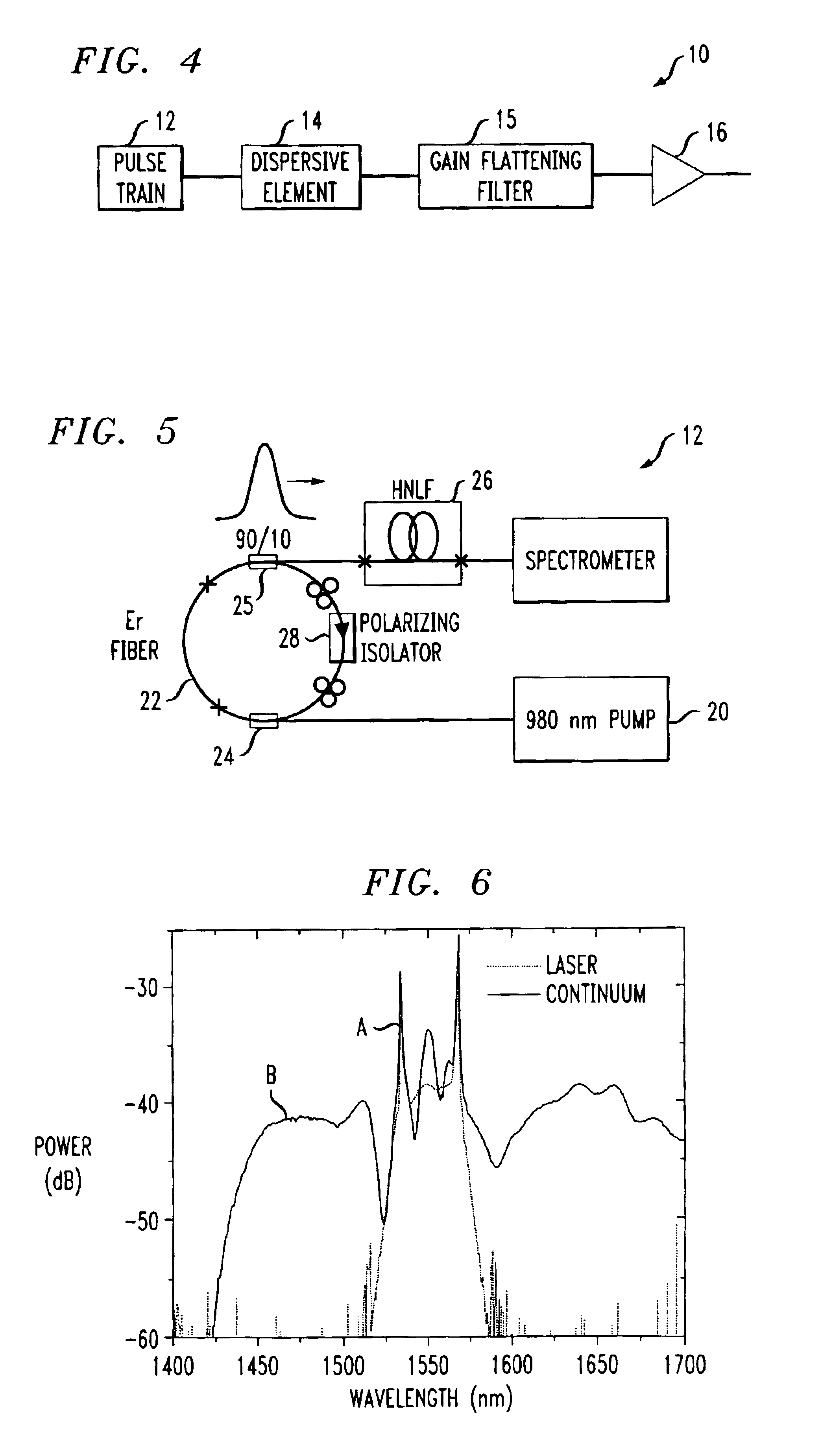
Generation of stabilized, ultra-short light pulses and the use thereof for synthesizing optical frequencies
InactiveUS6785303B1Optical measurementsMaterial analysis by optical meansLinear dispersionOptical frequencies
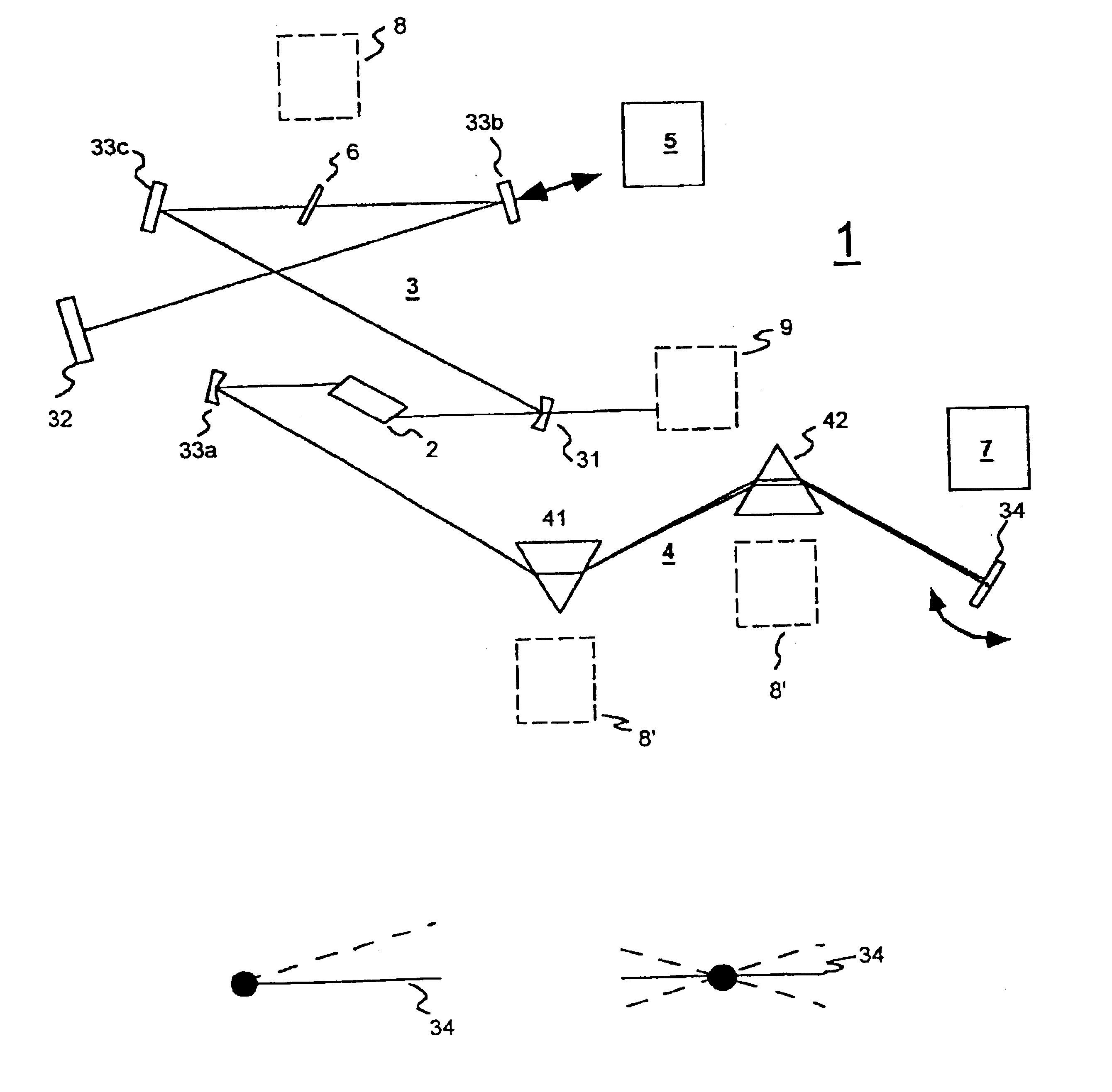
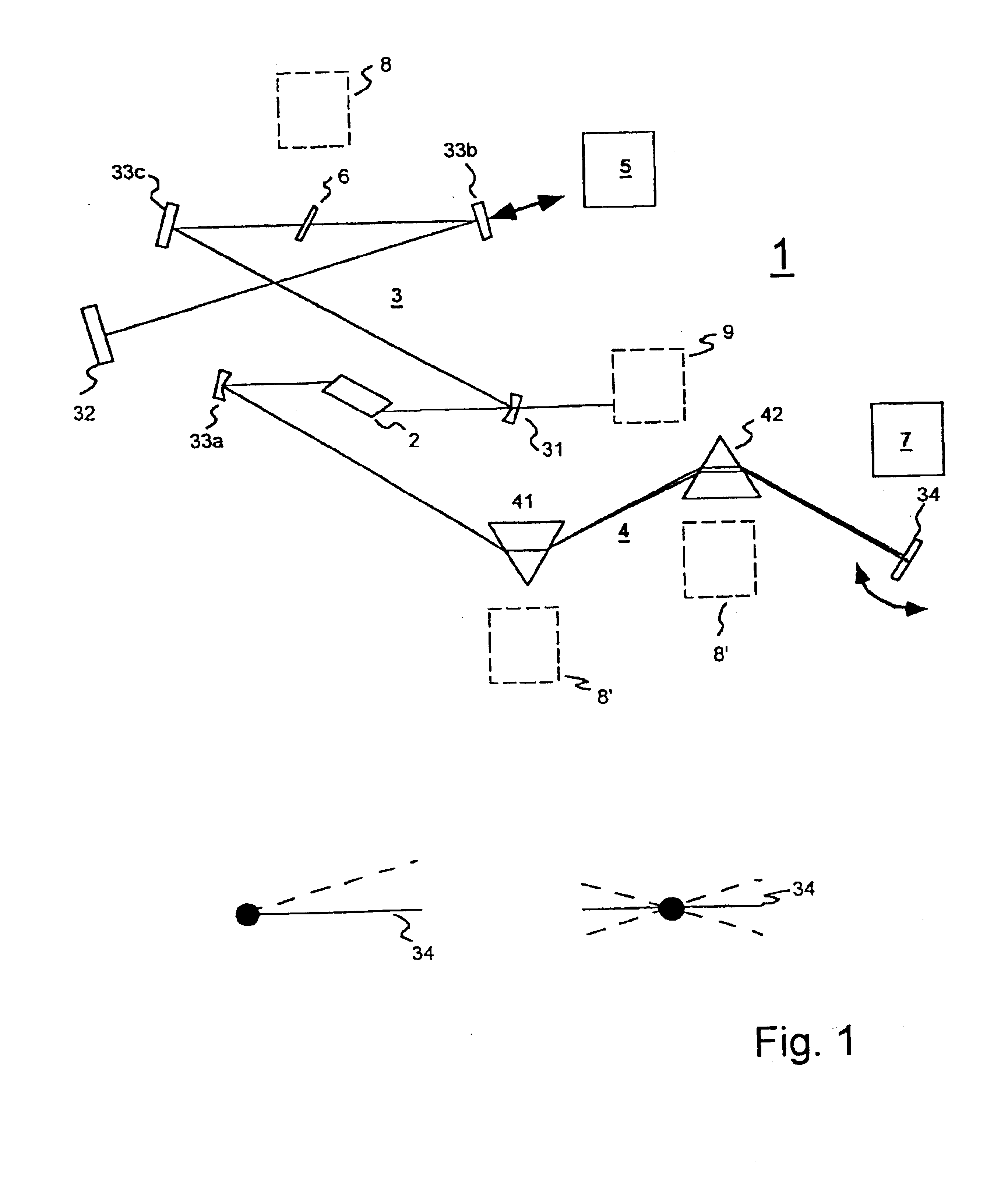
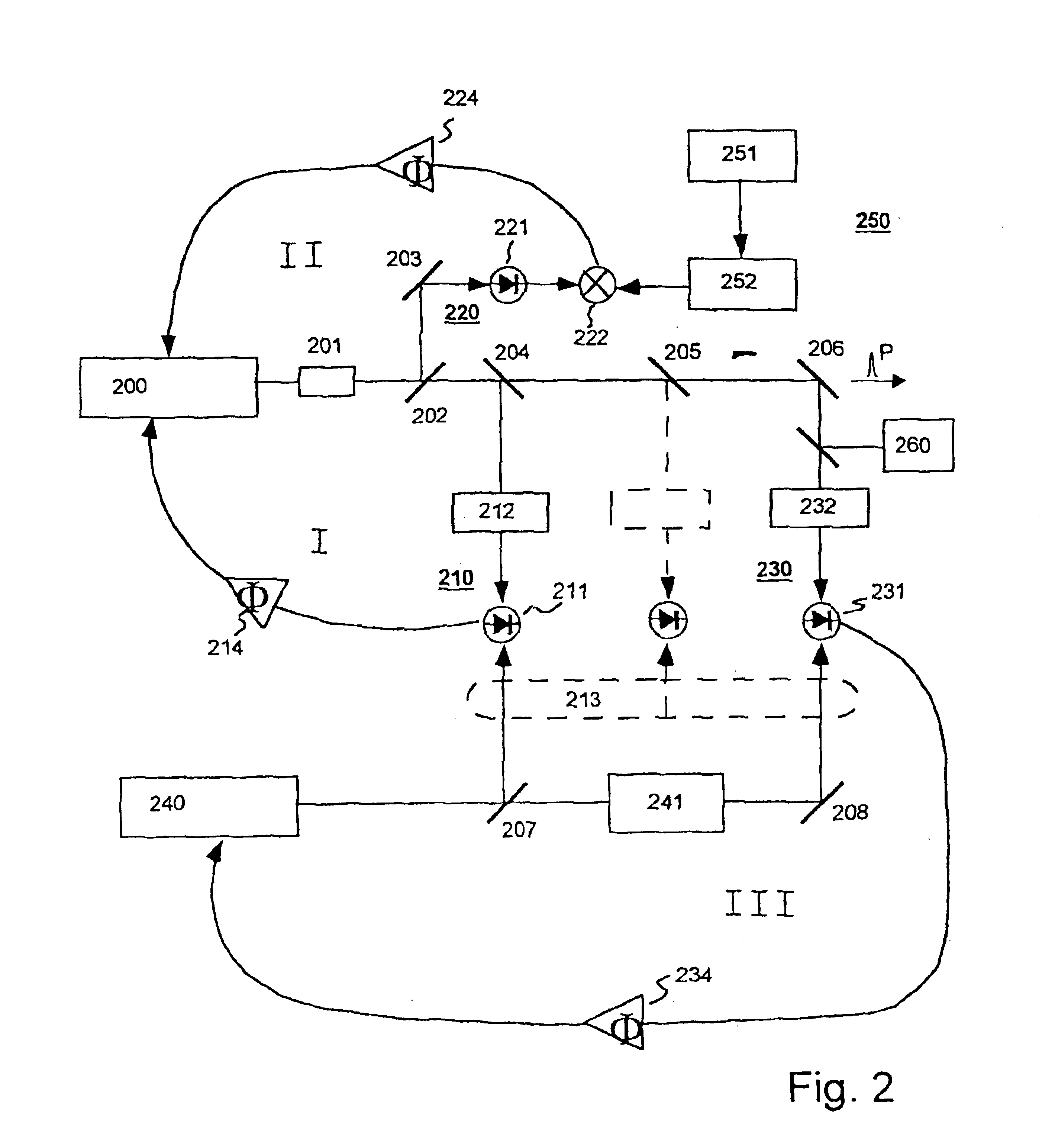
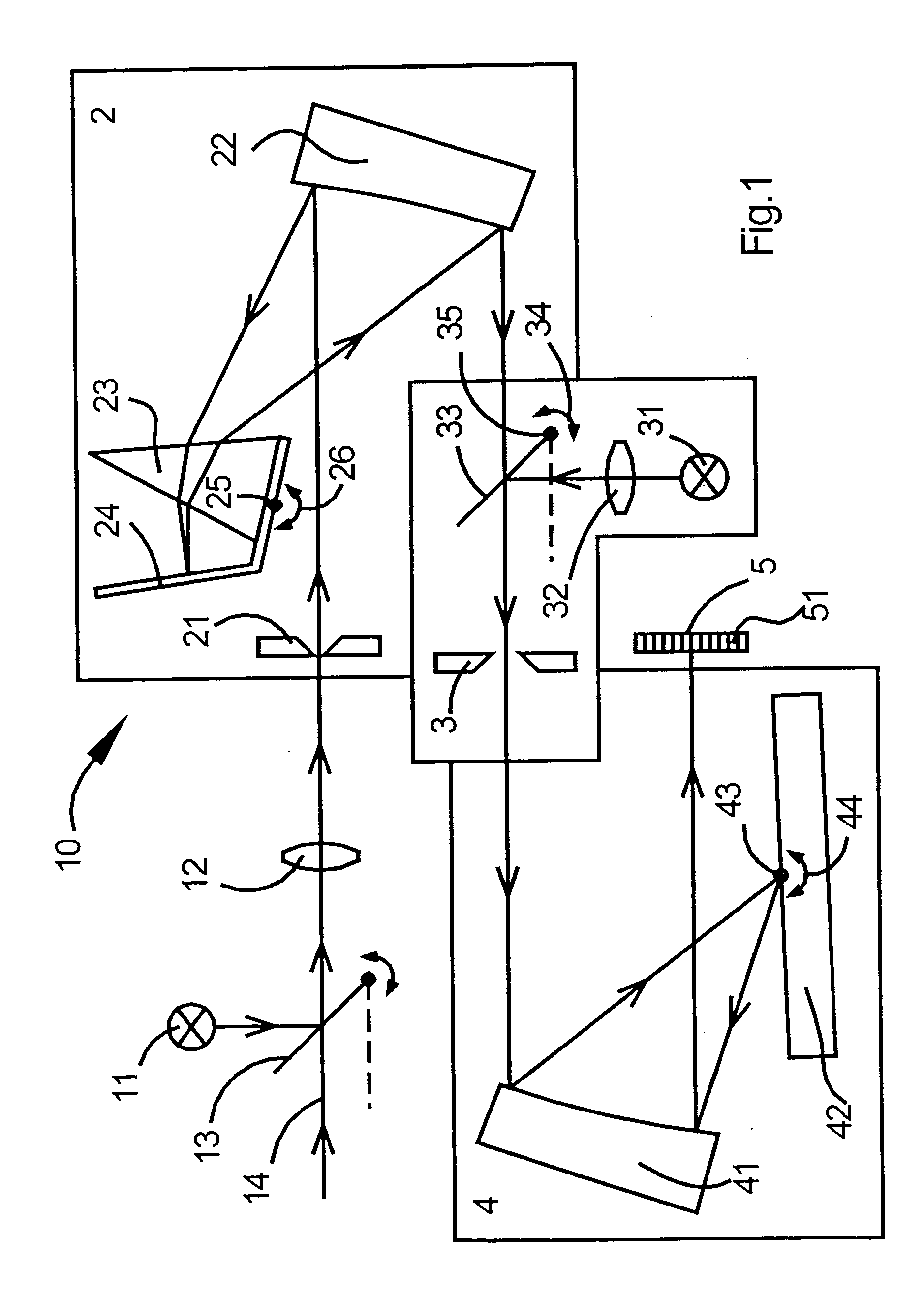
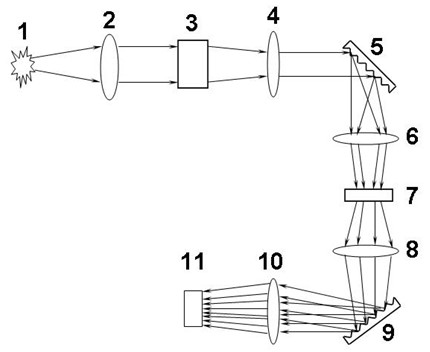
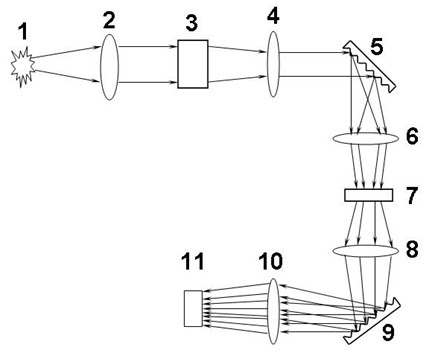
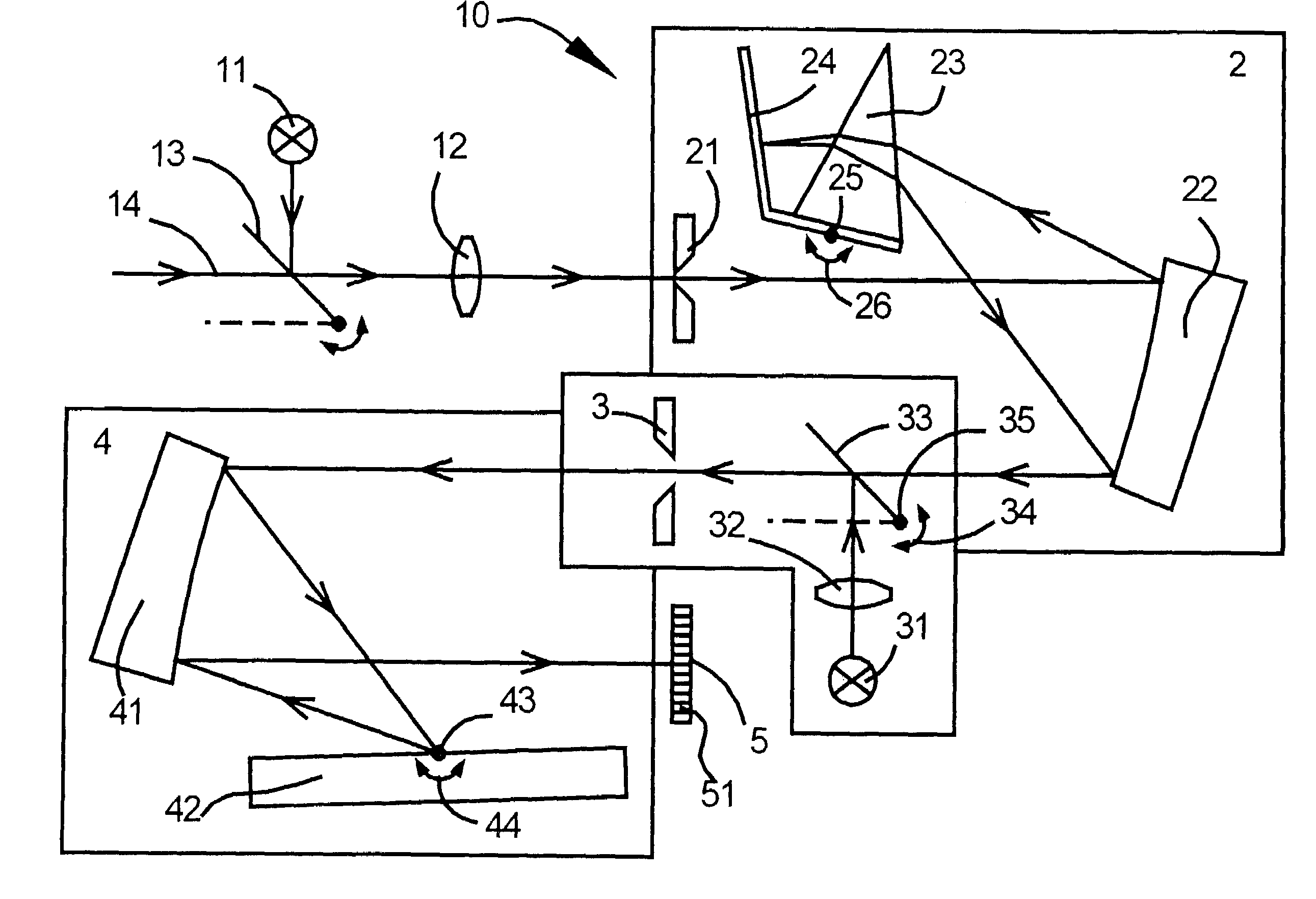
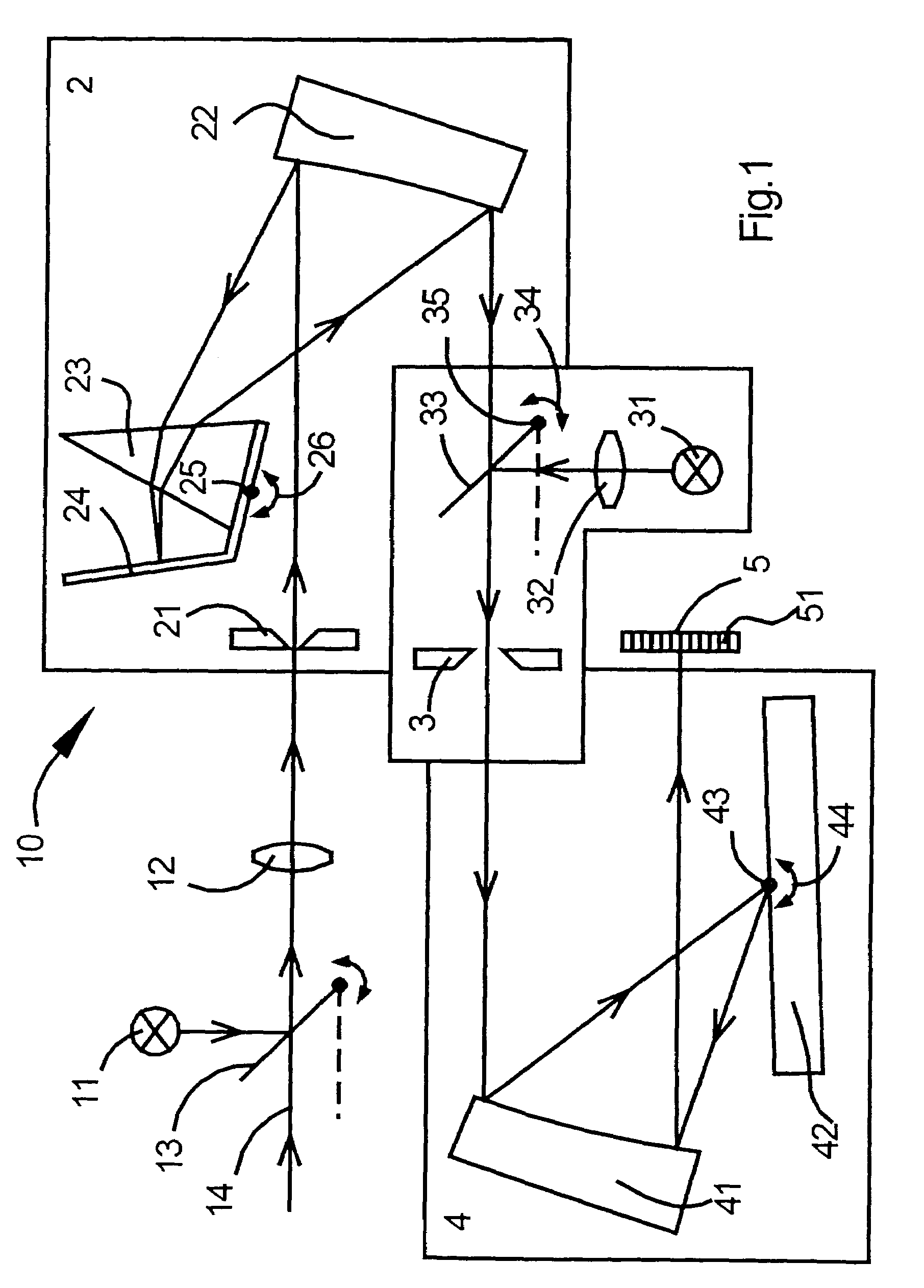
A process for operation of a laser device (1) is described, whereby circulating light pulses each comprising spectral components according to a plurality of longitudinal modes of a resonator configuration (3) are generated in the resonator configuration (3) and subjected to a compensation of group velocity dispersion, and a predetermined linear dispersion is introduced into the light path of the resonator configuration (3), so that at least one mode has a predetermined frequency and / or the mode distance between the modes has a predetermined value. Furthermore, regulations for stabilizing the laser device on the basis of this process and applications of the regulations for the generation for stabilized, ultra-short light pulses, generation of optical frequencies and in the frequency and / or time measuring technique as well as in the spectroscopy are described.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
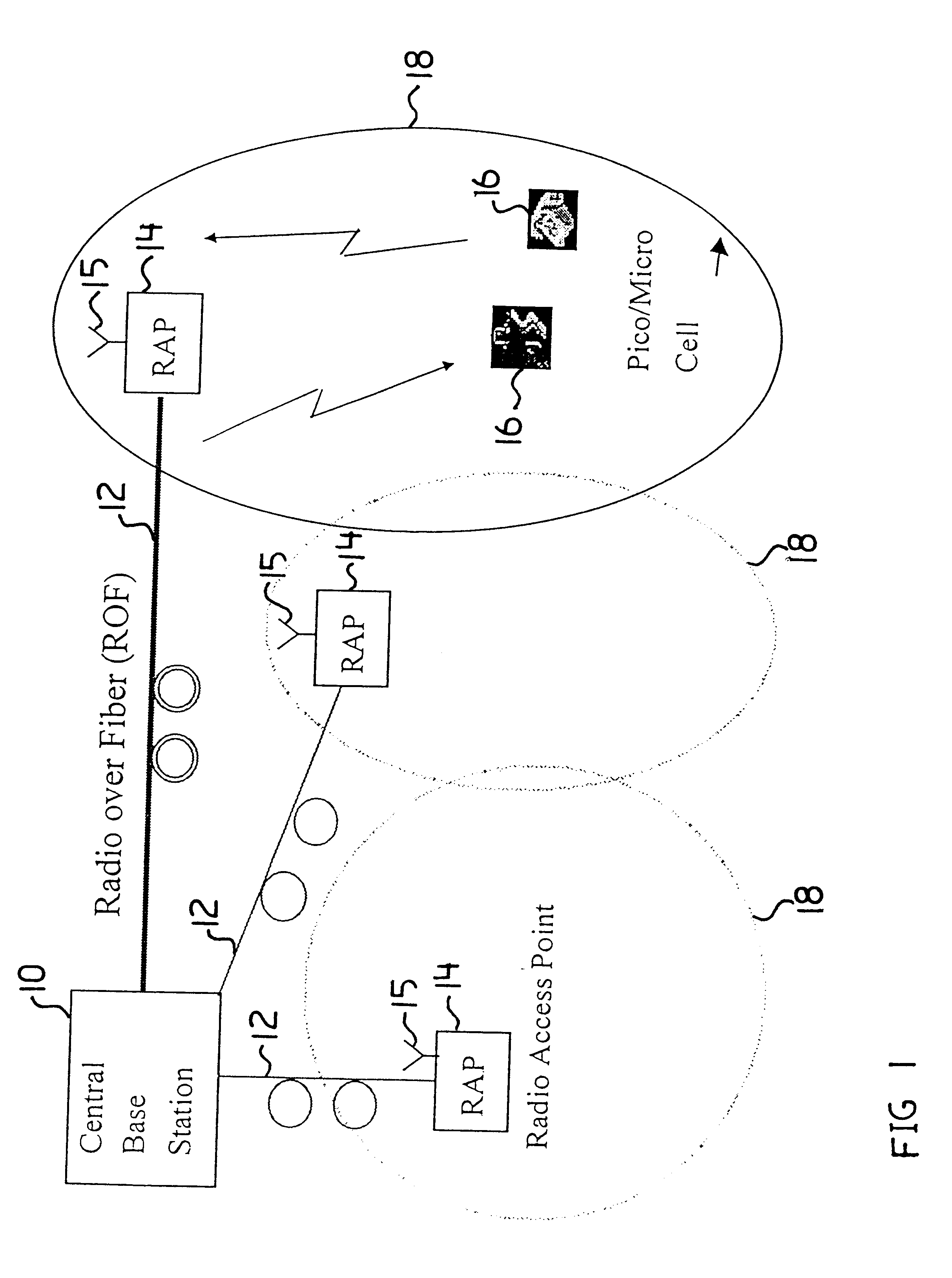
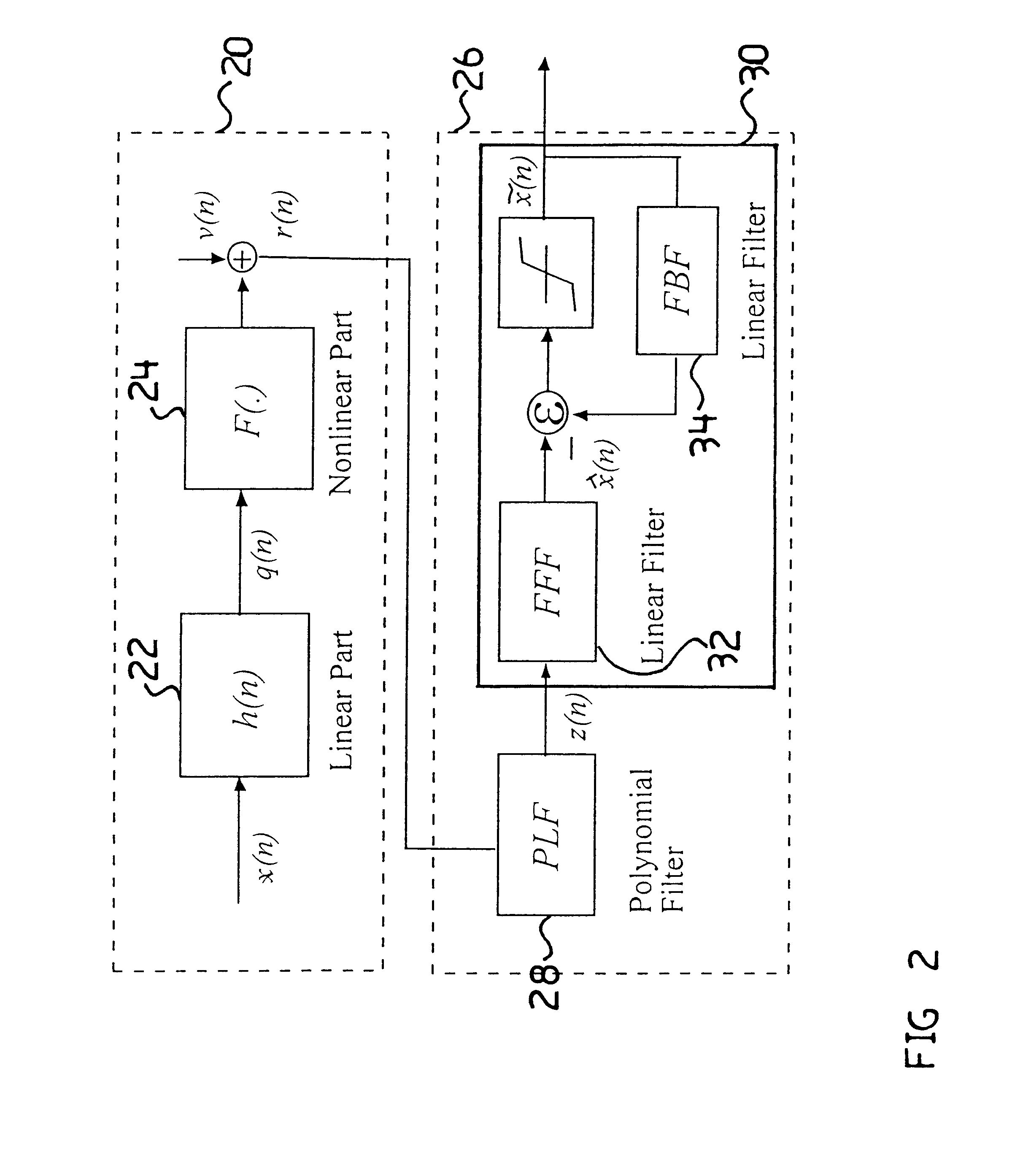
Optical fiber based on wireless scheme for wideband multimedia access
InactiveUS6889060B2Good compensationLess complexMultiple-port networksError preventionNonlinear distortionRadio over fiber
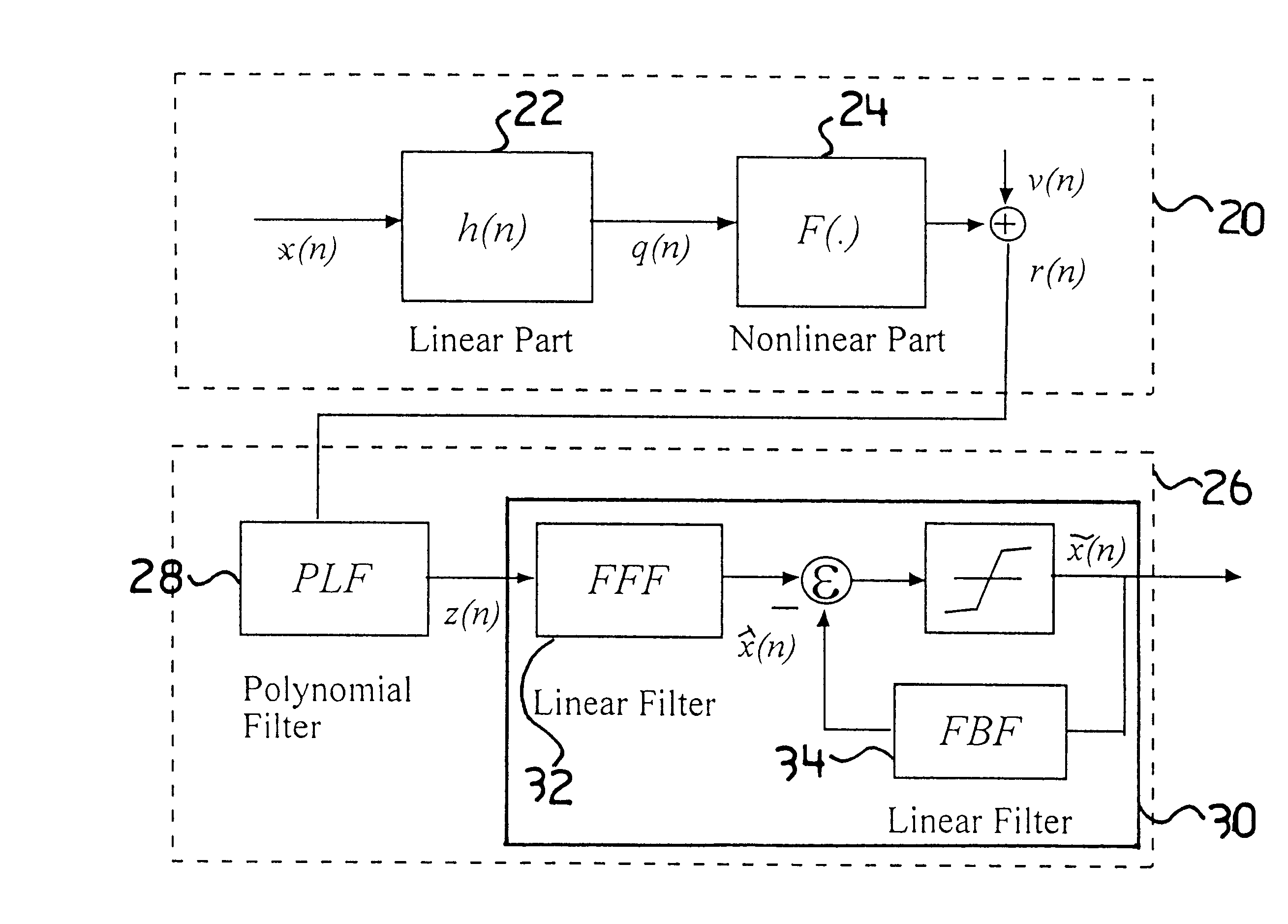
A Fiber-wireless uplink consists of a wireless channel followed by a radio-over-fiber (ROF) link. Typically, nonlinear distortion of the ROF link is the major concern when the radio frequency is only a few GHz. This especially severe in the uplink, because of the multipath fading of the wireless channel. A Hammerstein type decision feedback equalizer is described for the fiber wireless uplink, that compensates for nonlinear distortion of the ROF link as well as linear dispersion of the wireless channel. Since the linear and nonlinear parts of the receiver are separated, tracking the fast changing wireless channel is virtually independent of compensating for the relatively static nonlinearity. Analytical results show that the receiver provides excellent compensation with notably less complexity.
Owner:TELECOMM RES LAB
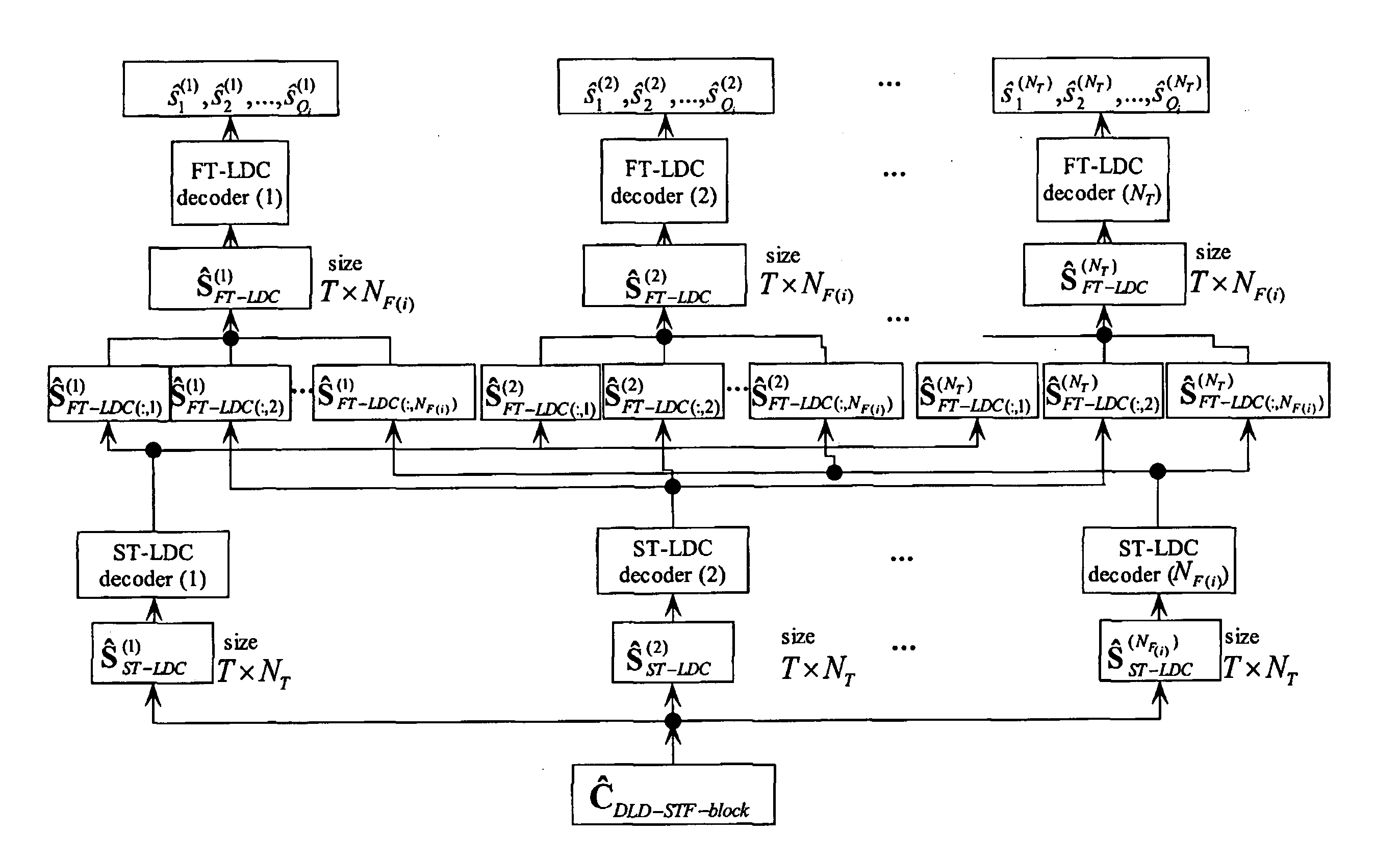
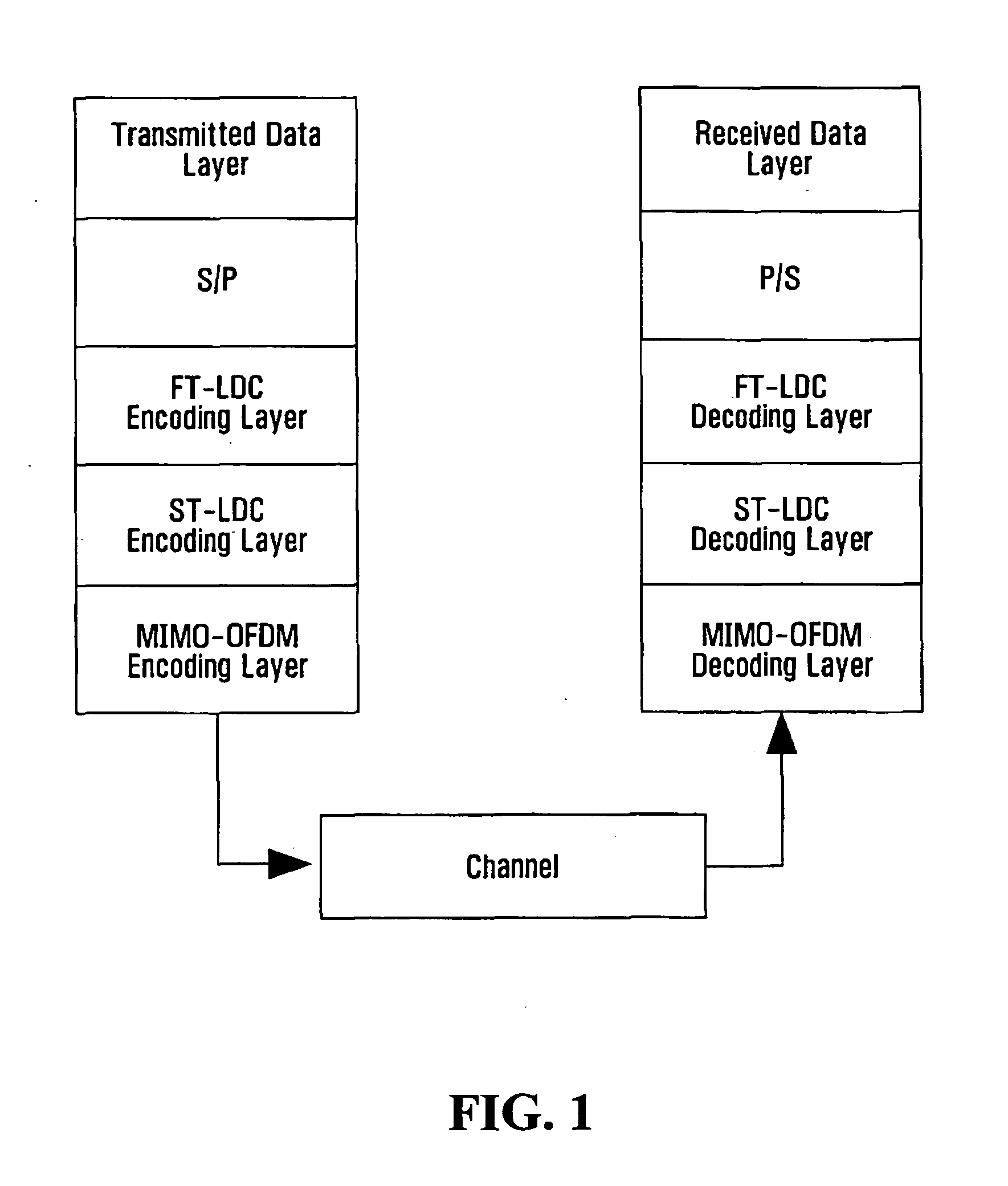
System and method employing linear dispersion over space, time and frequency
InactiveUS20070177688A1Diversity/multi-antenna systemsForward error control useLinear dispersionTwo-vector
Systems and methods for performing space time coding are provided. Two vector→matrix encoding operations are performed in sequence to produce a three dimensional result containing a respective symbol for each of a plurality of frequencies, for each of a plurality of transmit durations, and for each of a plurality of transmitter outputs. The two vector→matrix encoding operations may be for encoding in a) time-space dimensions and b) time-frequency dimensions sequentially or vice versa.
Owner:QUEENS UNIV OF KINGSTON
Mimo System Performing Hybrid Arq and Retransmission Method Thereof
InactiveUS20080256410A1Efficient retransmission gainImprove error correction performanceError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsError checkingLinear dispersion
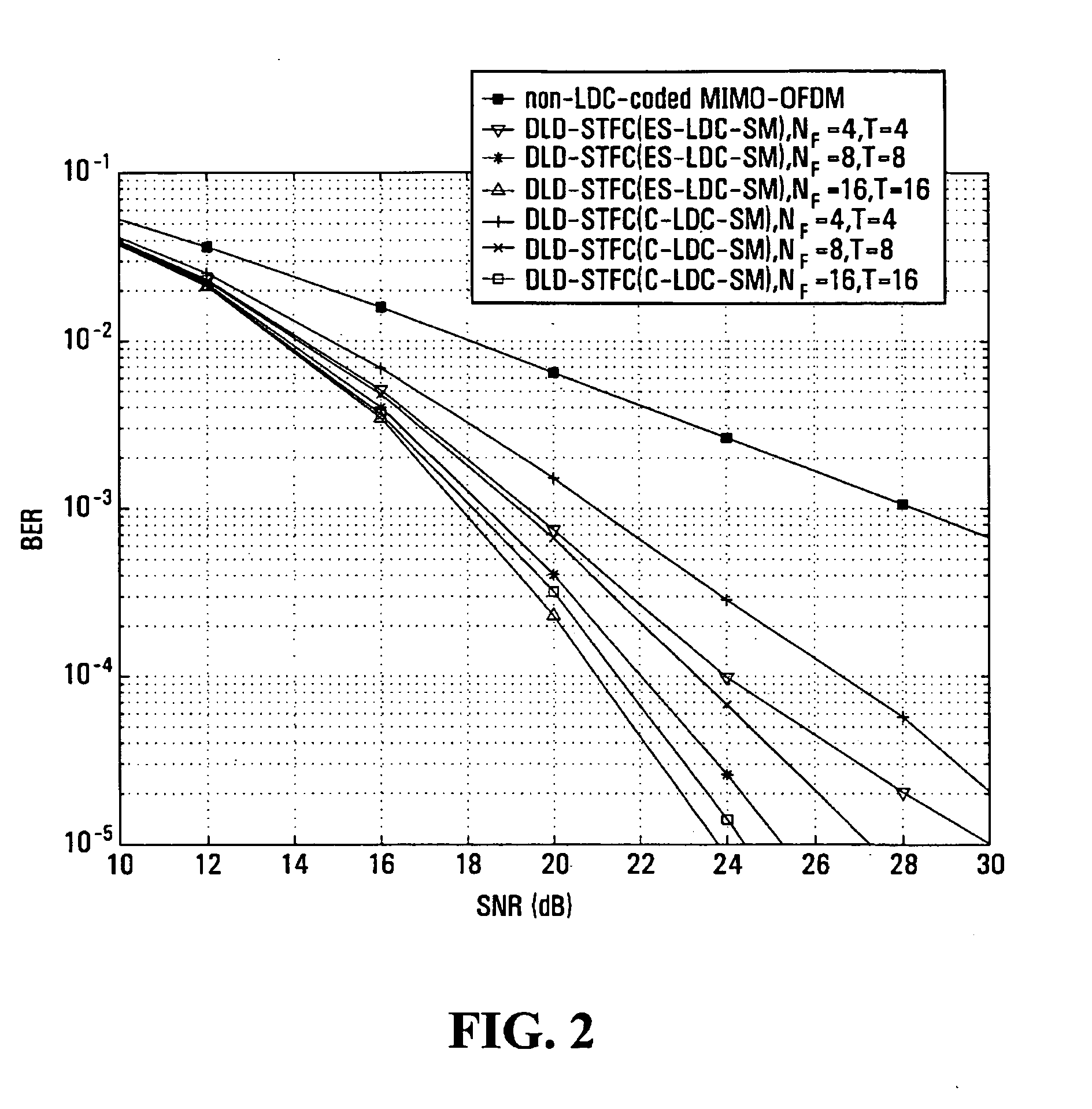
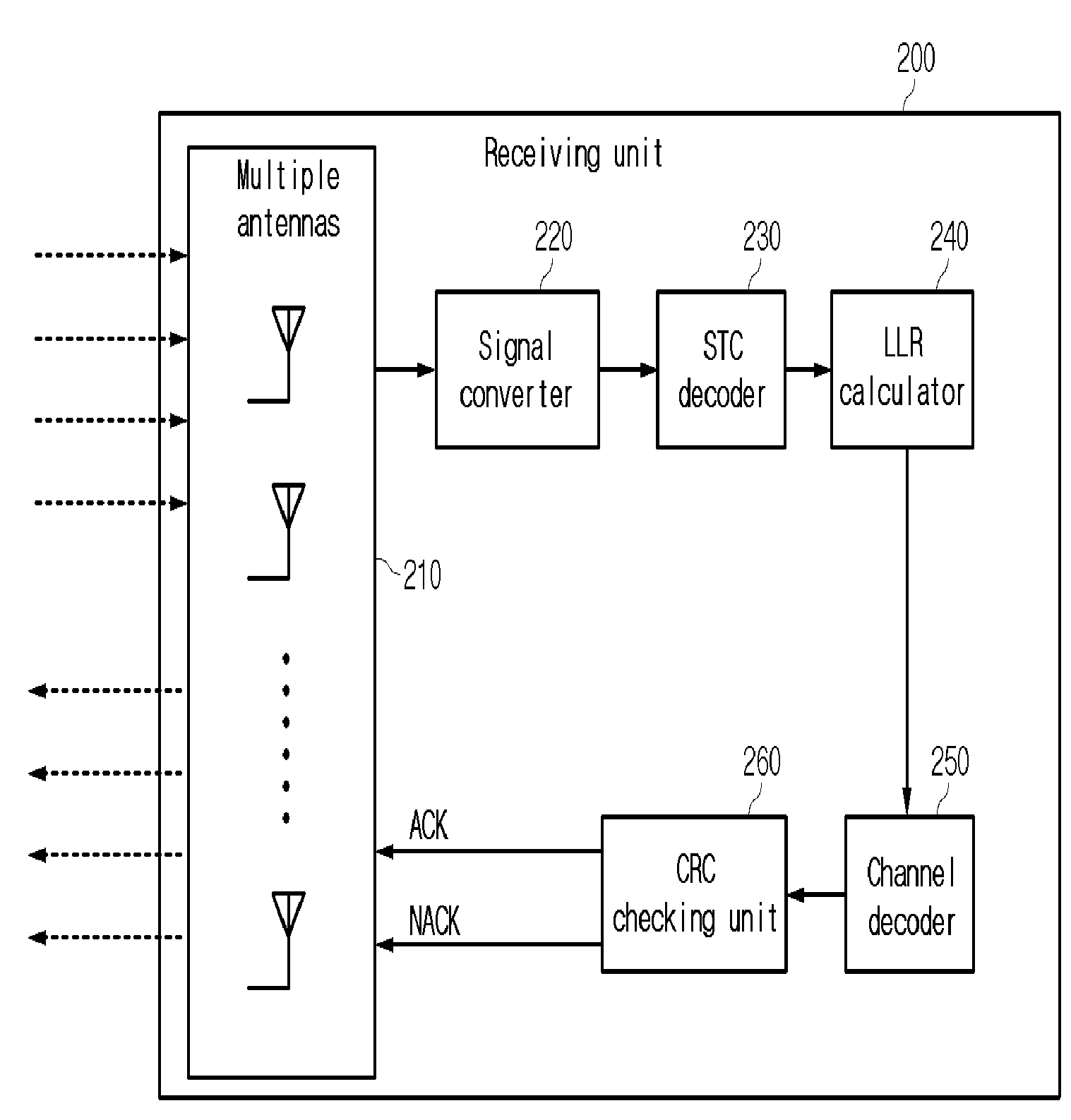
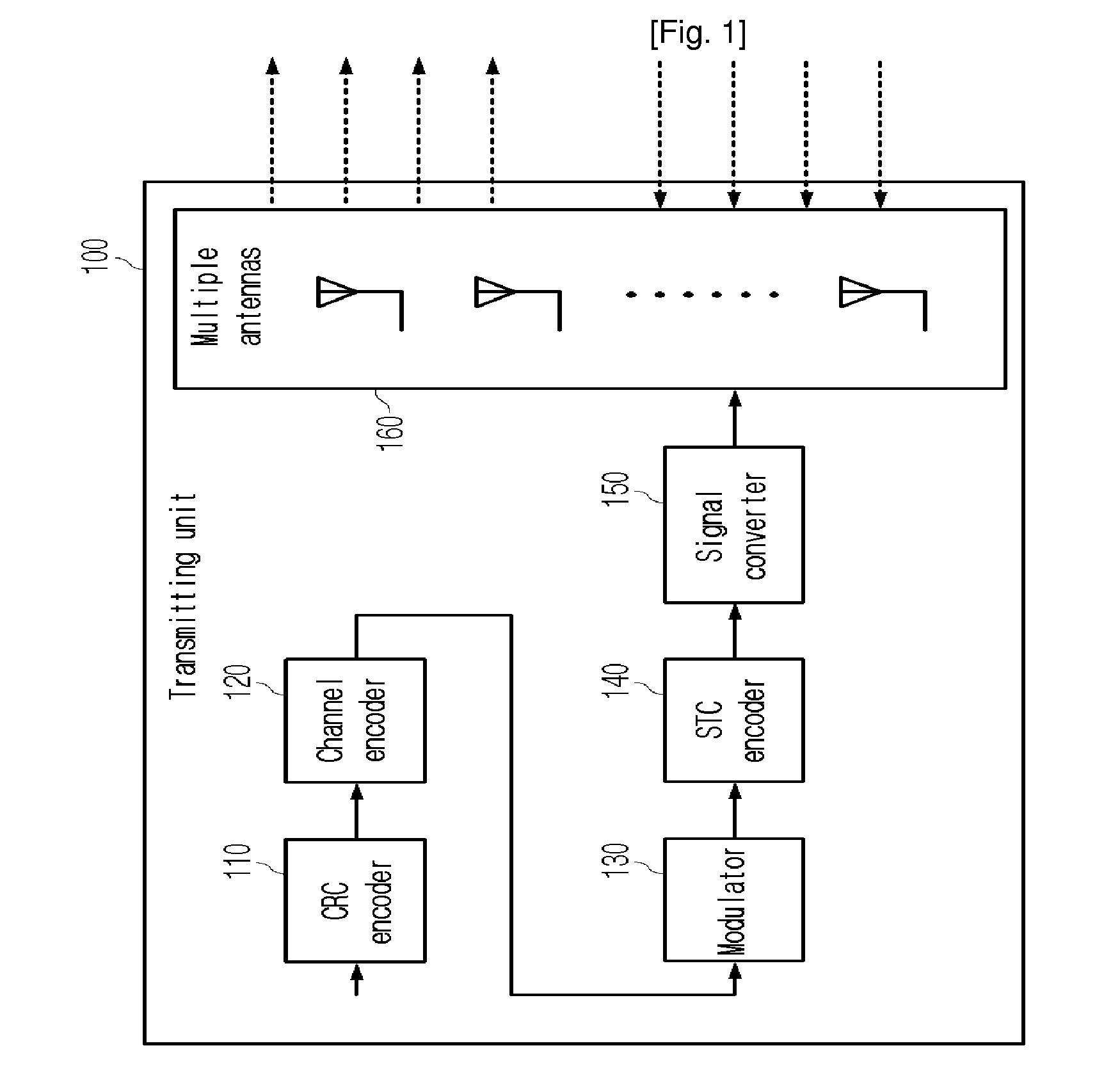
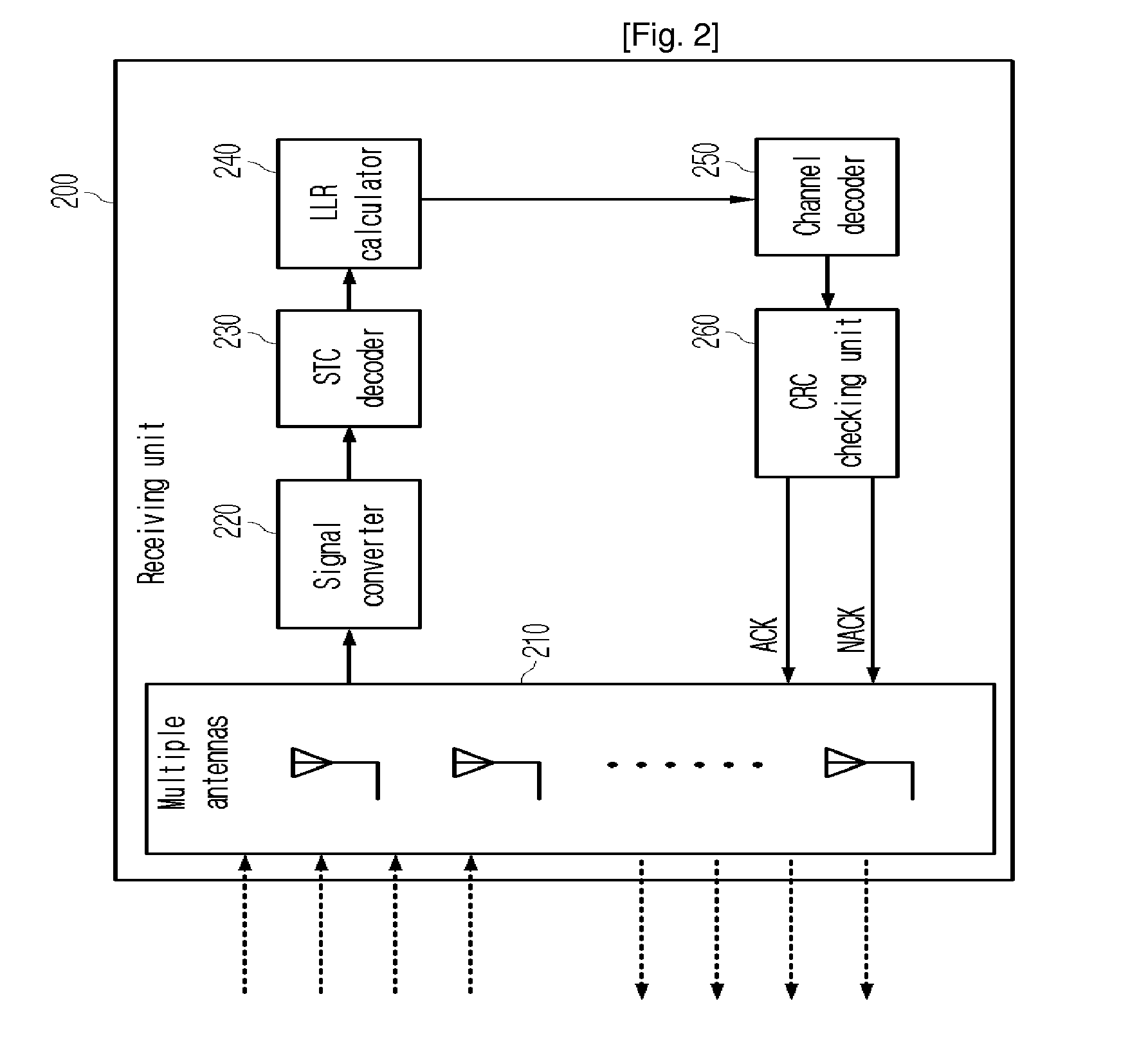
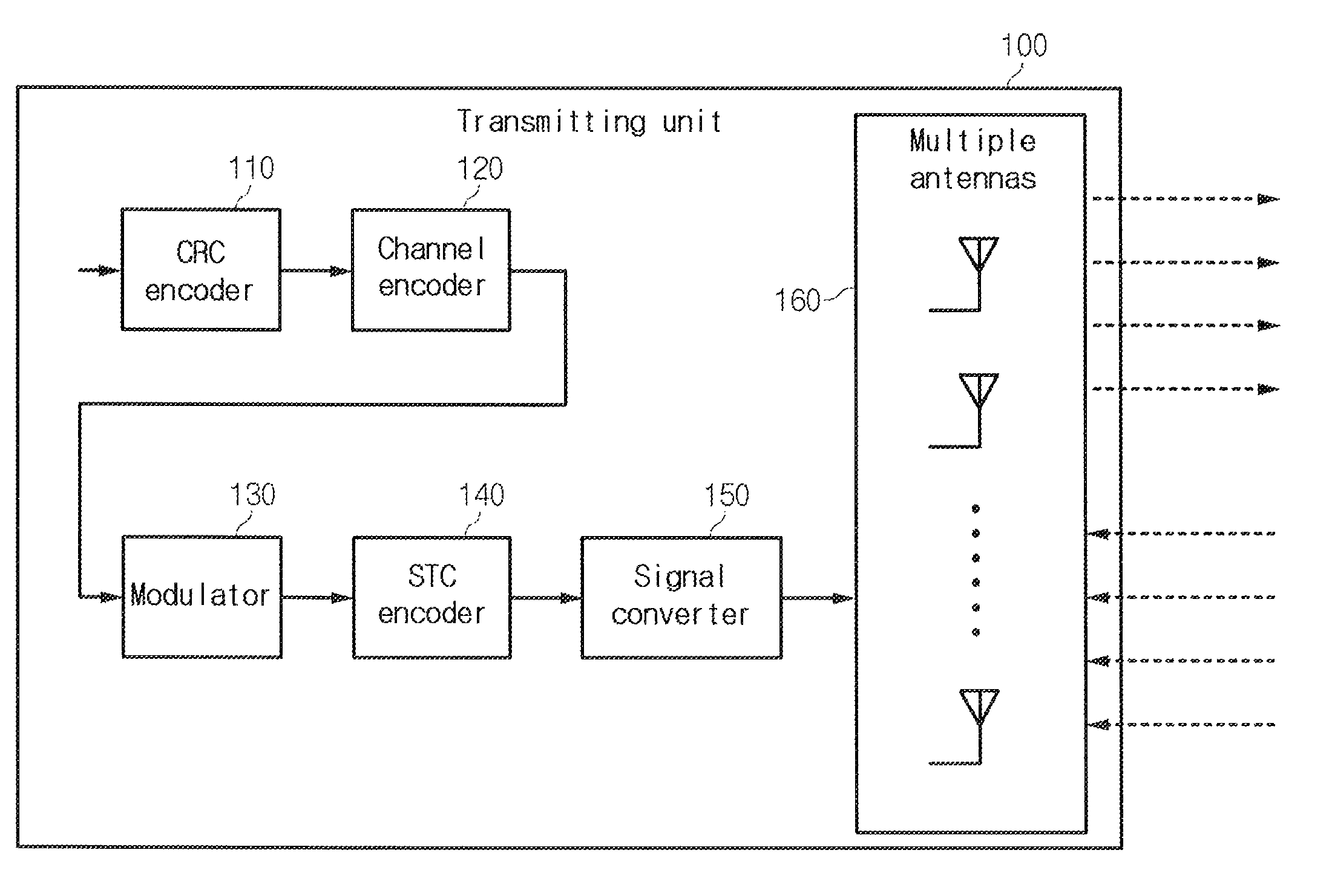
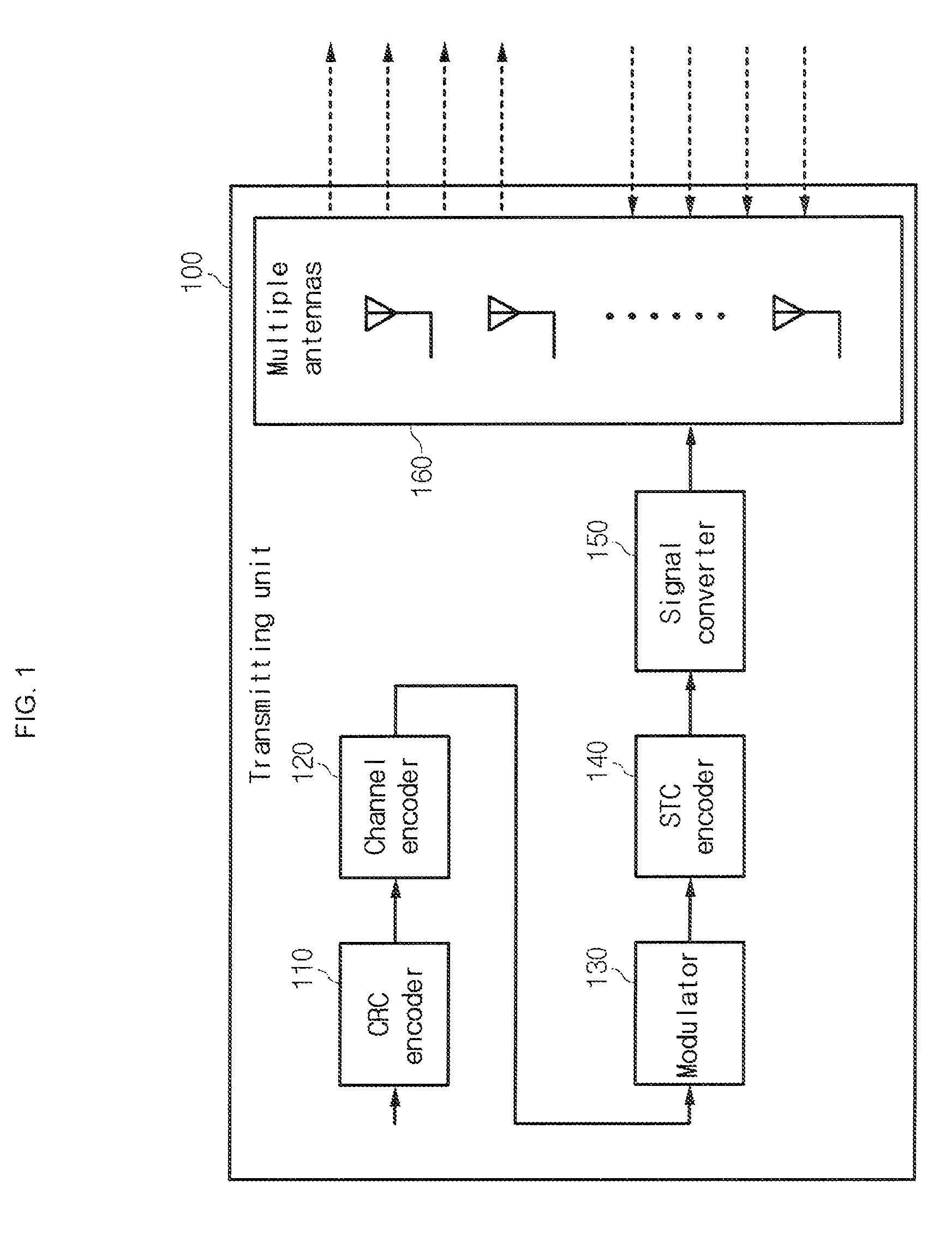
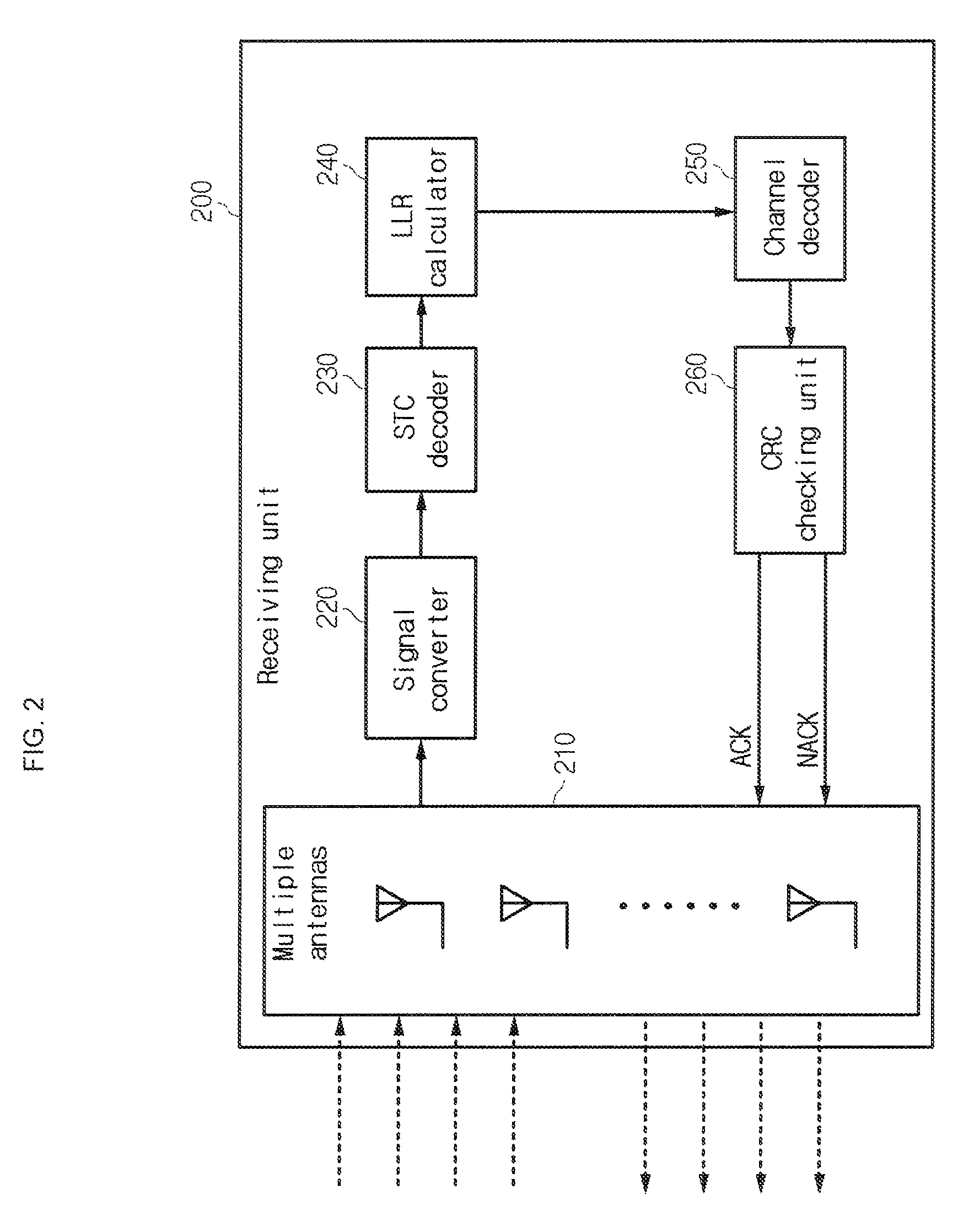
The present invention relates to a multiple antenna transmitting / receiving apparatus that performs a hybrid automatic repeat request, and a retransmission method thereof. An initial transmission signal is encoded into the form of an initial transmission matrix and transmitted to the receiving apparatus, the initial transmission matrix corresponding to a linear dispersion code, with a result of error checking performed on the initial transmission signal by the receiving apparatus. When an error is detected in the initial transmission signal, a first retransmission signal is generated by encoding the initial transmission signal in the form of a retransmission matrix and transmitted to the receiving apparatus. The retransmission matrix is formed of constituent elements of the initial transmission matrix but different from the initial transmission matrix, and corresponds to a linear dispersion code having the same capacity and diversity gain as those of the initial transmission matrix.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Hyper-spectral compression imaging method and system thereof
InactiveCN102322954AEliminate difficultiesImprove fidelitySpectrum investigationSpatial light modulatorGrating
The invention discloses a hyper-spectral compression imaging method and a system thereof. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out first dispersion after imaging and collimation of an object; focusing an optical signal after dispersion and carrying out space intensity modulation; focusing the modulated optical signal again and carrying out second dispersion; focusing the optical signal after second dispersion, carrying out detection by a detector, carrying out acquisition by a computer, carrying out data resolution, and recovering a three-dimensional data cube of a shot object; wherein the first dispersion and the second dispersion are linear dispersion which are realized by employing a Prism-Grating-Prism device, dispersion directions of the first dispersion and the second dispersion are opposite, and the space intensity modulation is realized by employing a spatial light modulator. According to the invention, data amount is reduced, realization of data resolution of high fidelity is facilitated, and miniaturization design and imaging diversification of an imaging system are facilitated.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Assembly and method for wavelength calibration in an echelle spectrometer
ActiveUS20050157293A1Reduce measurement errorReduce stray lightRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationExit planeSpatially resolved
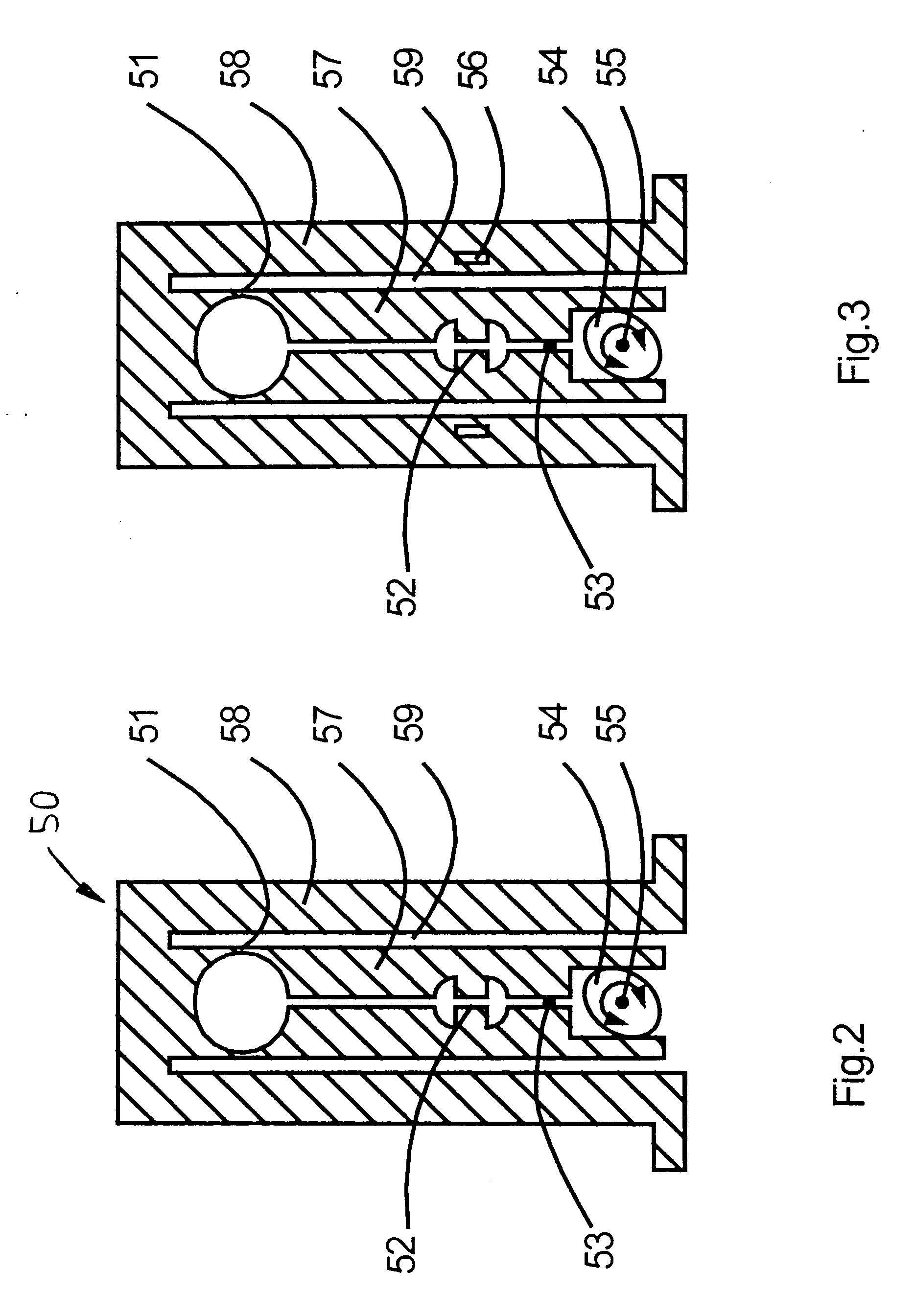
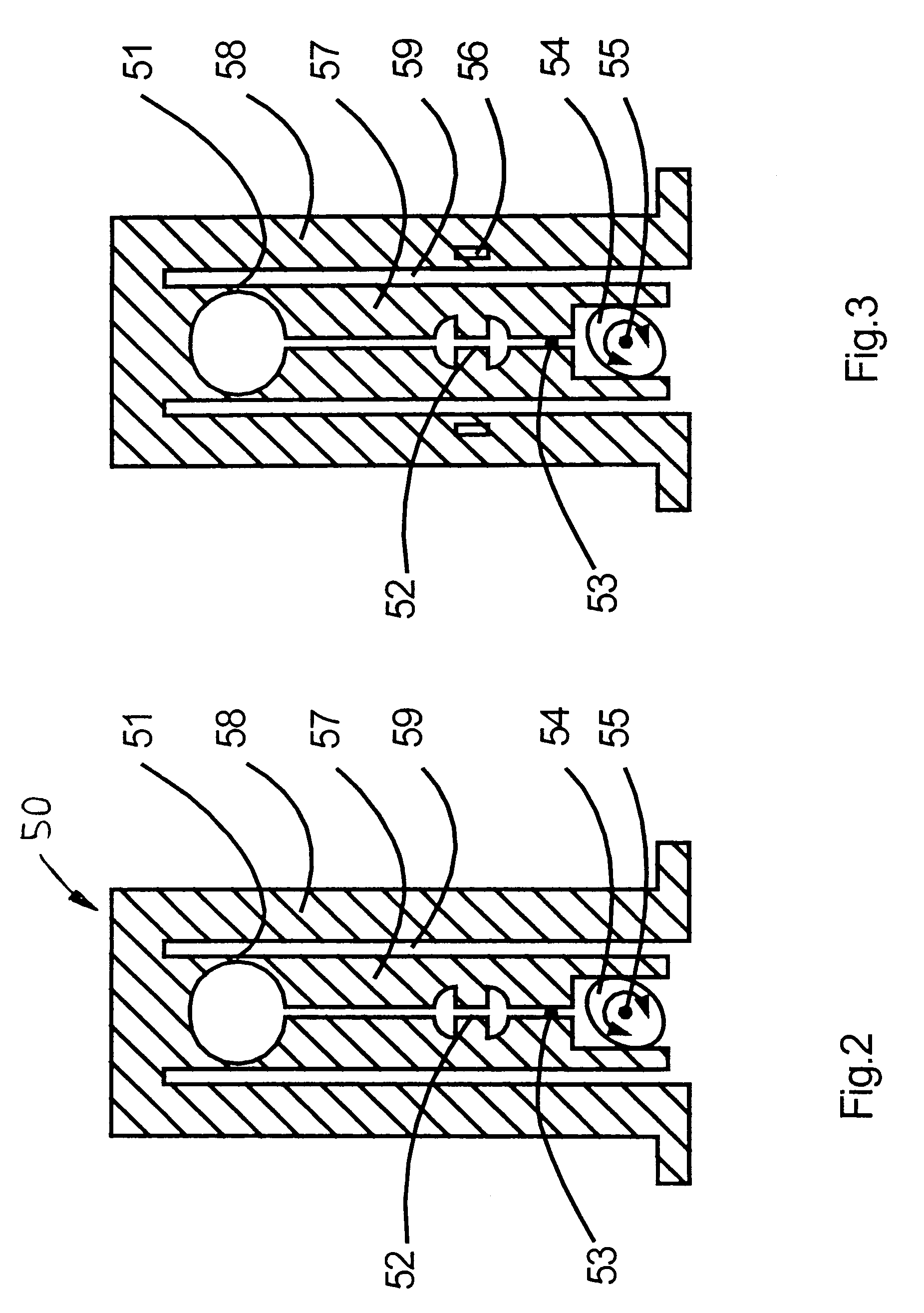
A spectrometer assembly (10) comprises a light source (11) with a continuous spectrum, a pre-monochromator (2) for generating a spectrum with a relatively small linear dispersion from which a spectral portion is selectable, the spectral bandwidth of such spectral portion being smaller than or equal to the bandwidth of the free spectral range of such order in the echelle spectrum wherein the centre wavelength of the selected spectral interval is measurable with maximum blaze efficiency, an echelle spectrometer (4) with means for wavelength calibration, an entrance slit (21) at the pre-monochromator (2), an intermediate slit assembly (50) with an intermediate slit (3) and a spatially resolving light detector (5) in the exit plane of the spectrometer for the detection of wavelength spectra. The assembly is characterised in that the width of the intermediate slit (3) is larger than the monochromatic image of the entrance slit generated by the pre-monochromator at the location of the intermediate slit, and means for calibrating the pre-monochromator are provided, which are adapted to calibrate the light of the light source with a continuous spectrum on the detector to a reference position.
Owner:LEIBNIZ - INSTITUT FUER ANALYTISCHE WISSENSCHAFTEN ISAS +1
Method for automatically forwardly/reversely tapering fiber
ActiveCN103383477AGood repetition rateHigh degree of automationCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideLinear dispersionOptical frequencies
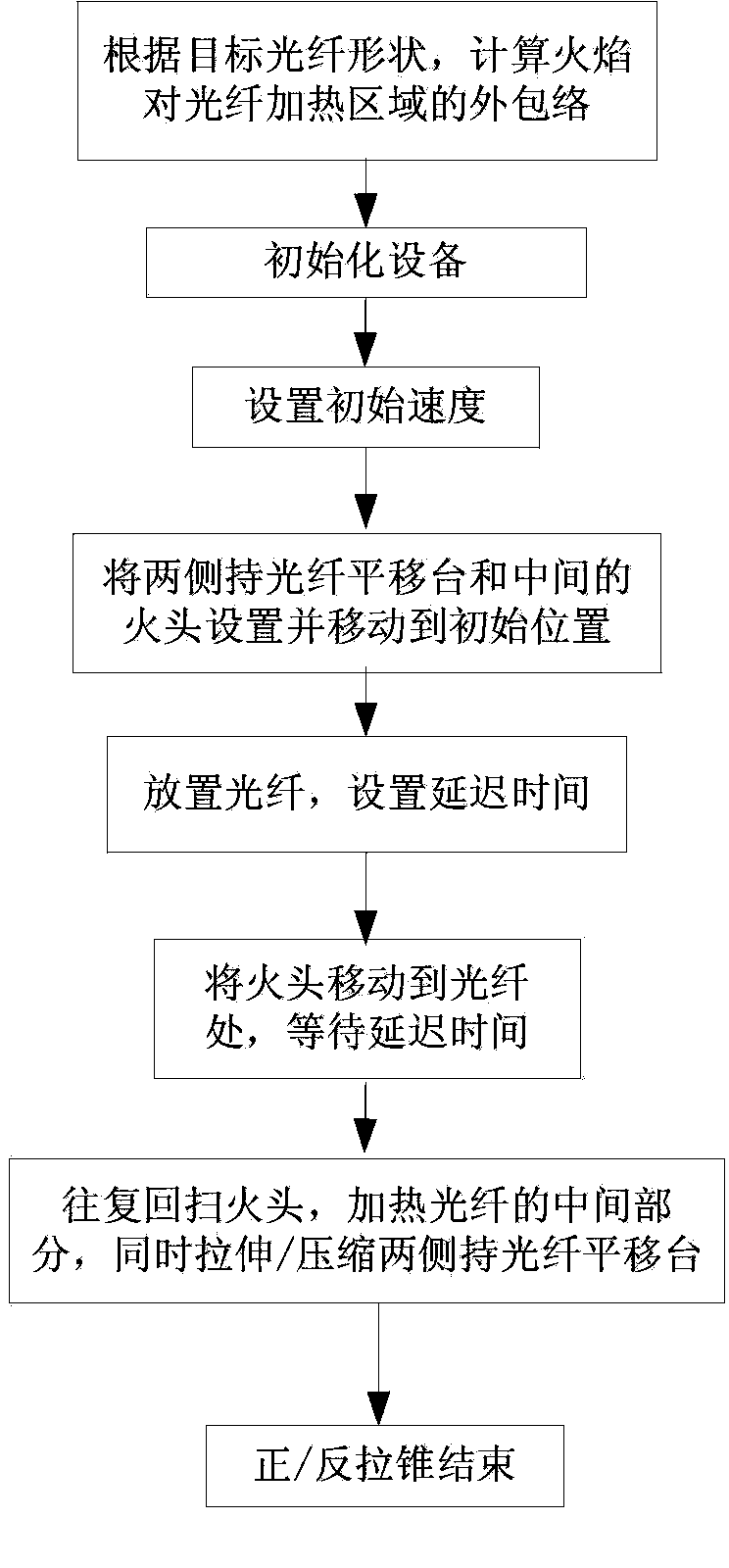
The invention provides a method for automatically forwardly / reversely tapering a fiber. According to the method, the external envelope of a flame in a fiber heating area in the tapering process is calculated according to the shape of a target fiber, and reciprocating of a flame front is controlled, so that a tapered fiber conforming to a target shape is prepared. Post-treatment of a fiber waveguide is realized by constant-speed reciprocating heating of the dotted flame and simultaneous stretch or compression of two ends of the fiber, and the movement speed of the dotted flame front and the stretch / compression speed of the two ends of the fiber can be optionally adjusted in the forward / reverse tapering process. The linear dispersion characteristic and the nonlinear Kerr characteristic of the tapered fiber can be greatly changed. The tapered fiber can be efficiently and laterally coupled with an external environment. The properties are quite widely applied to fiber optics and a plurality of fields including fiber sensing, optical frequency conversion, super-continuum broadening, quantum optics and the like.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Image compression and reconstruction method based on LCTF (liquid crystal tunable filter) hyperspectral imaging system
ActiveCN106679807AHigh spectral resolutionFast wavelength switchingSpectrum investigationImage codingLinear dispersionReconstruction method
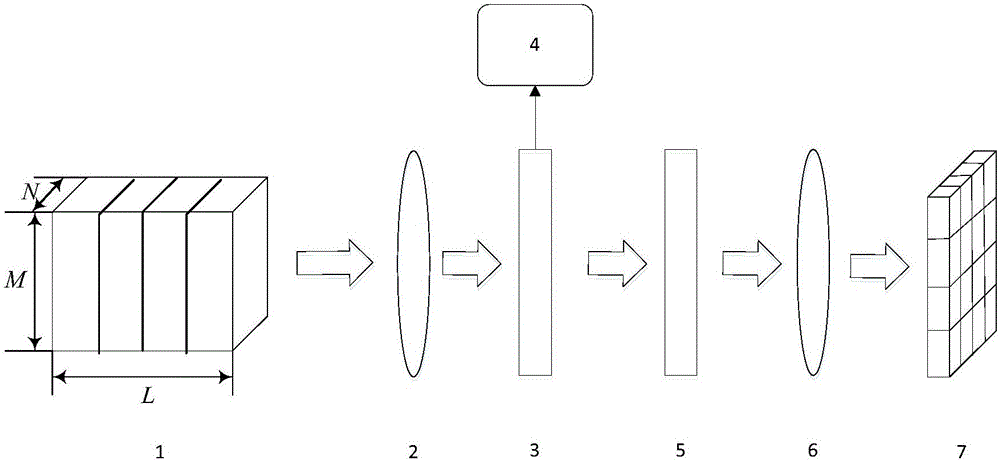
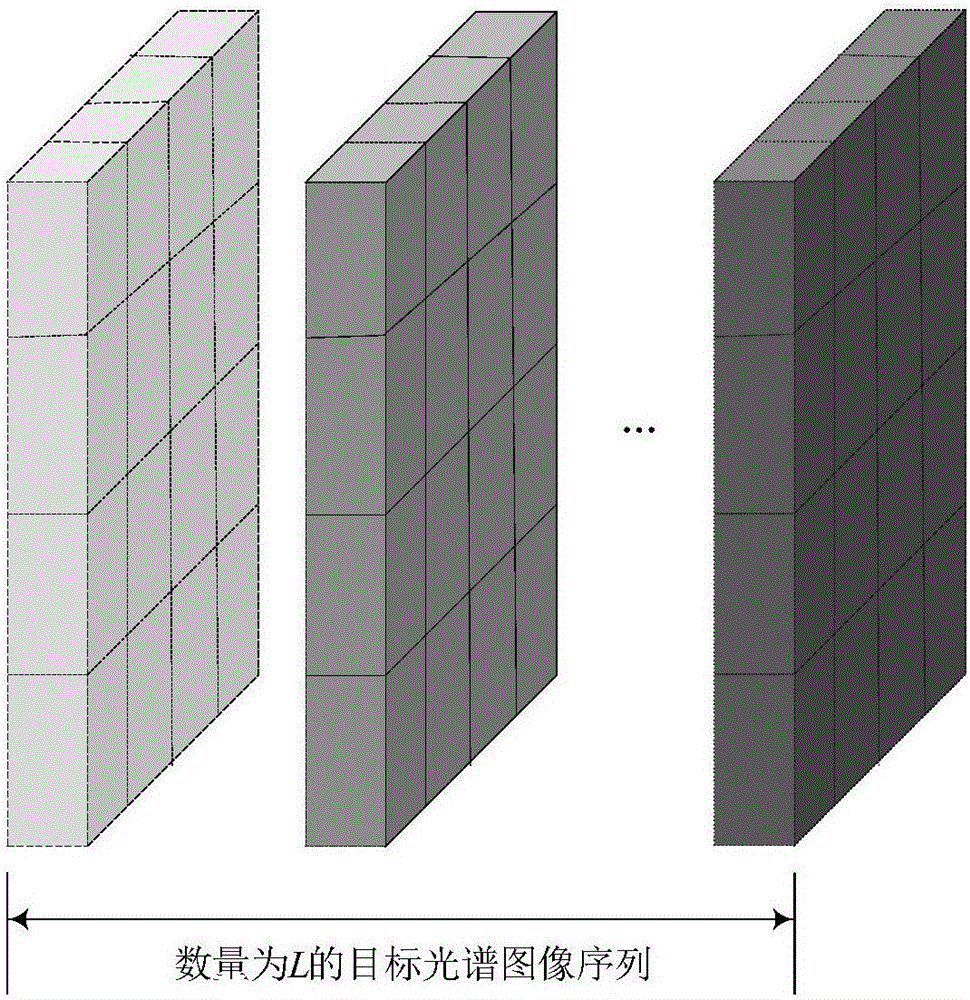
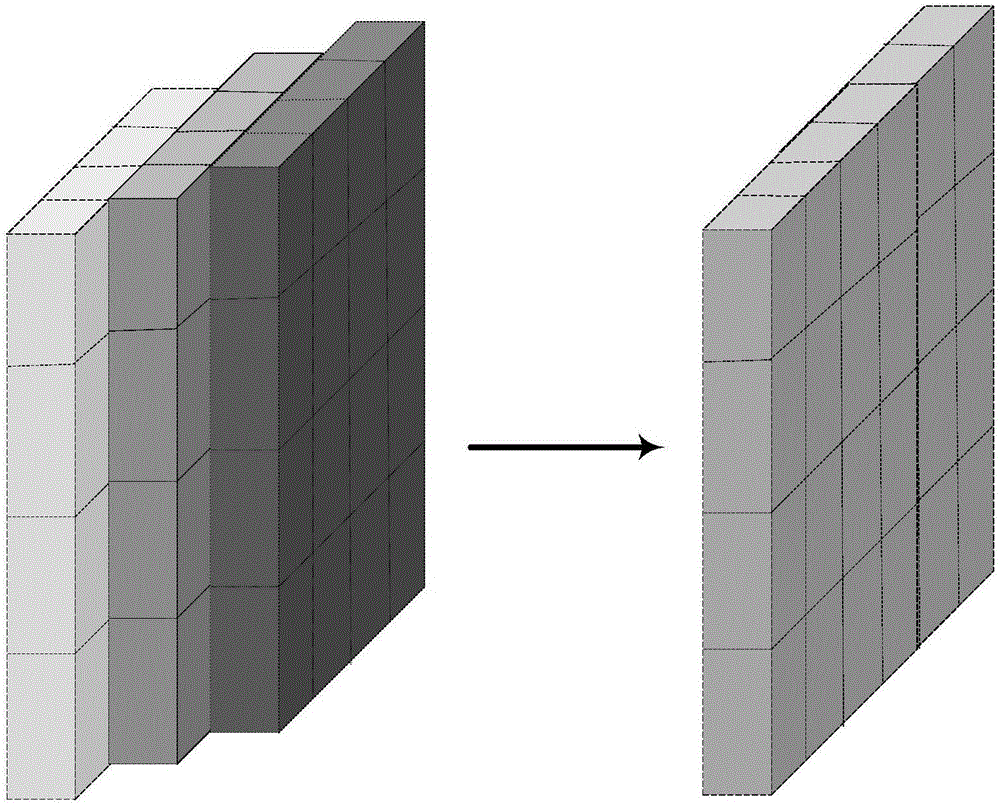
The invention discloses an image compression and reconstruction method based on LCTF (liquid crystal tunable filter) hyperspectral imaging system; the method prevents the precision of a reconstructed image from being affected by nonlinear dispersion of the original CASSI (coded aperture snapshot spectral imaging) system, the problem that coded aperture is unmatched with pixel size of a detector is solved by means of calculating synthetic aperture size, and spatial resolution of the constructed image is improved. The minimum pixel size of the hyperspectral imaging system is the pixel size of the detector; a target spectral image sequence is acquired through the LCTF hyperspectral imaging system; shift is manually added to each single image in the target spectral image sequence, and the shifted image sequences are superposed in order to obtain a mixed image. The use of the method according to the invention is equivalent to linear dispersion, the correspondence between coded aperture pixel and detector pixel can be analyzed, and the precision of a reconstructed mage can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Rapid K-space linear frequency sweep laser source
InactiveCN102969651AQuick scanAchieve wavenumber linear effectLaser output parameters controlLinear dispersionGrating
The invention discloses a rapid K-space linear frequency sweep laser source. The laser source comprises a semiconductor optical amplifier, two polarization controllers, a dispersion control delay line, a circulator, a tuned filter and an output optical fiber coupler, wherein radiation light emitted from the semiconductor optical amplifier is transmitted to the dispersion control delay line through a polarization controller I; the middle port of the circulator is connected to the tuned filer through a first port of the circulator; returned signals are connected to the optical fiber coupler after passing through a third port of the circulator; one path of the optical fiber coupler outputs frequency sweep laser through a 60% port, and the other path of the optical fiber coupler is connected to the polarization controller II and then returns to a ring laser oscillation cavity; the tuned filter mainly comprises two dispersion elements, namely a grating and a prism, and a rotary polygonal mirror; and the linearity of a wave number space is achieved through combination of linear dispersion of the grating and non-linear dispersion of the prism as well as selection on the angles and directions of the prism. The rapid K-space linear frequency sweep laser source can be used for outputting the rapid K-space linear frequency sweep laser, and can obtain the signals of the linearity of the wave number space directly without calibration when being applied to an OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography) imaging system.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
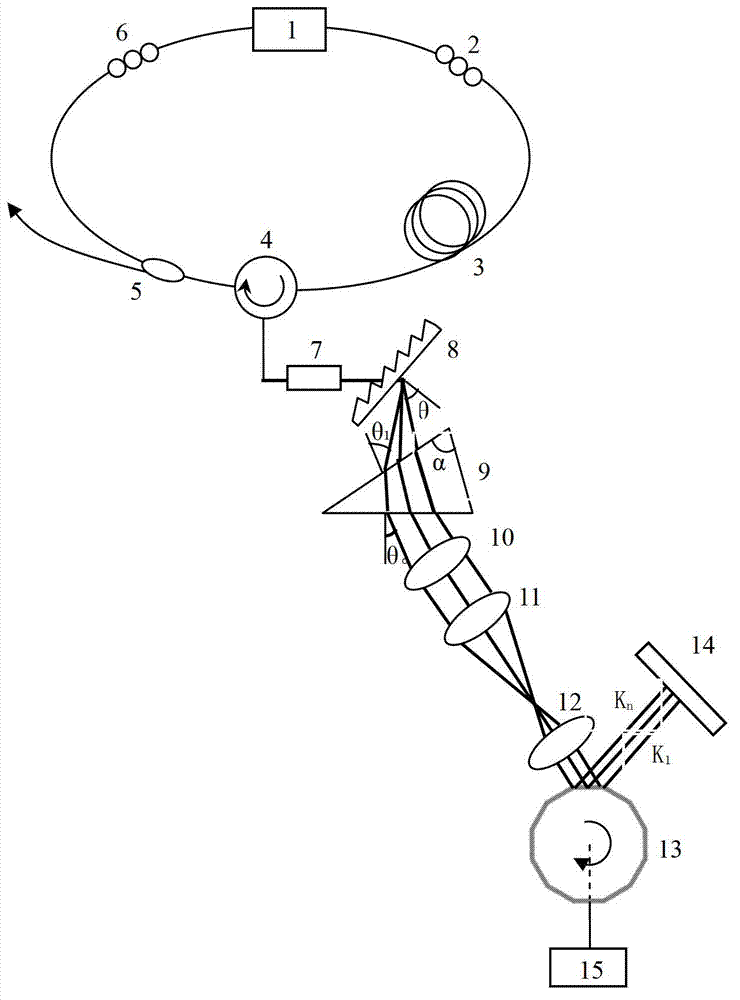
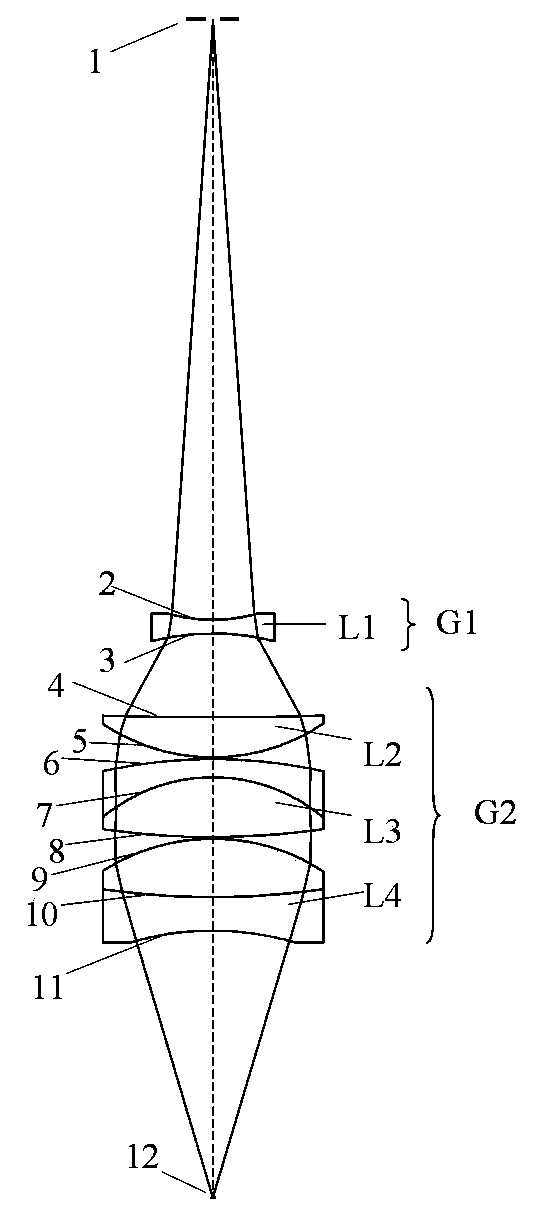
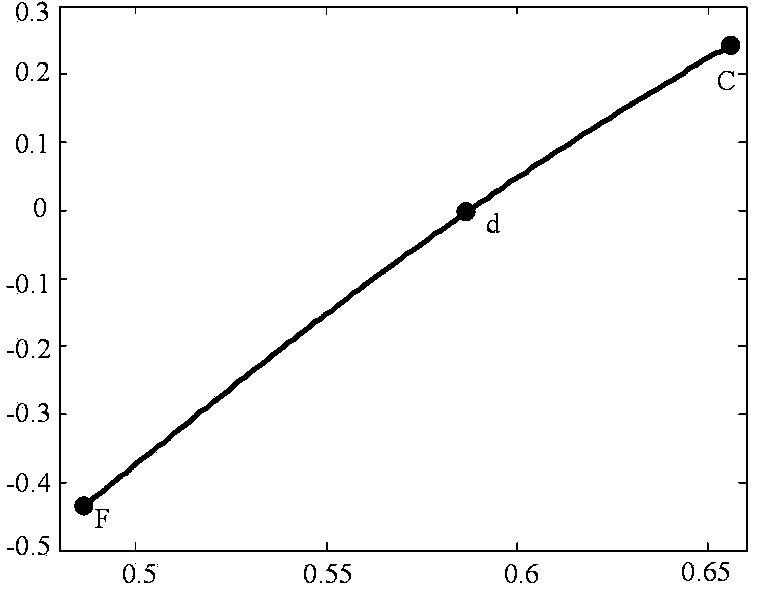
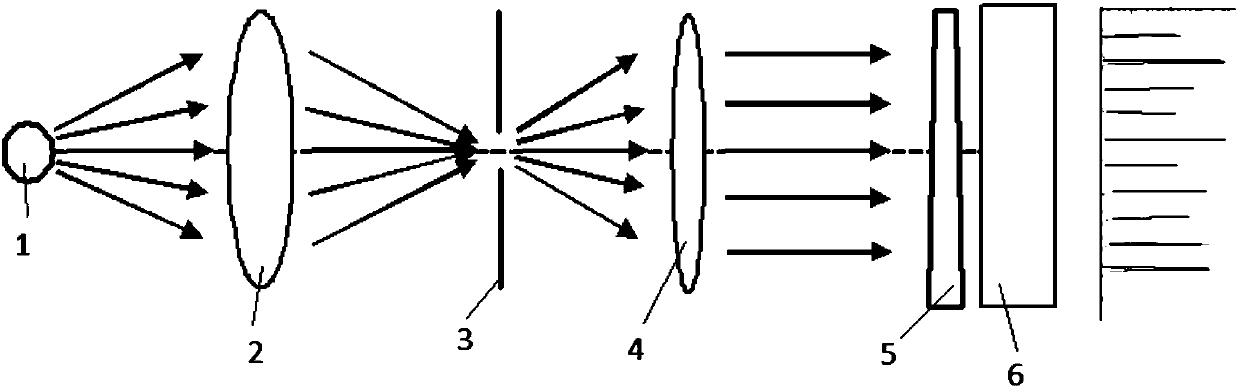
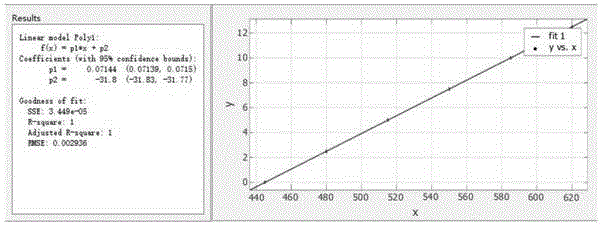
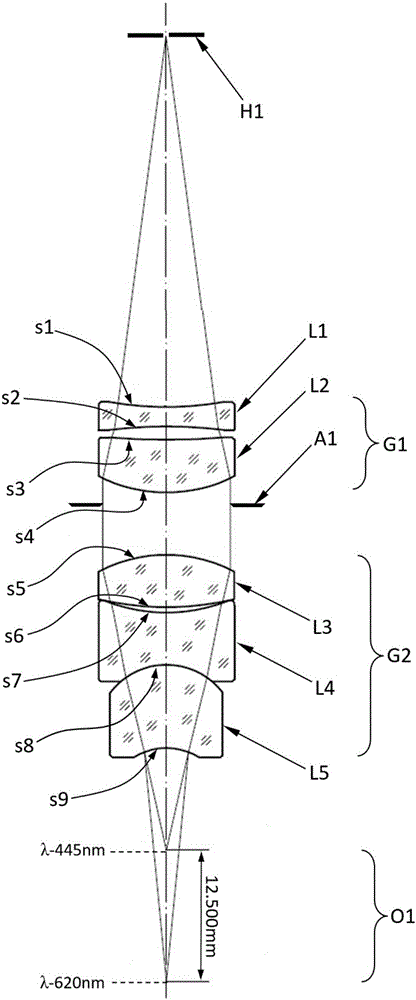
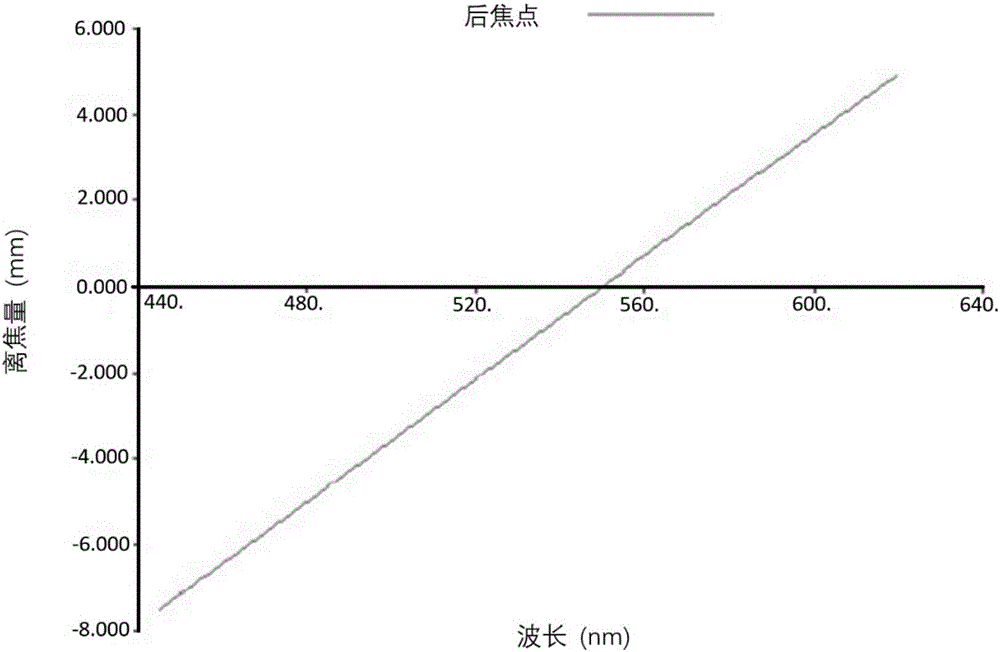
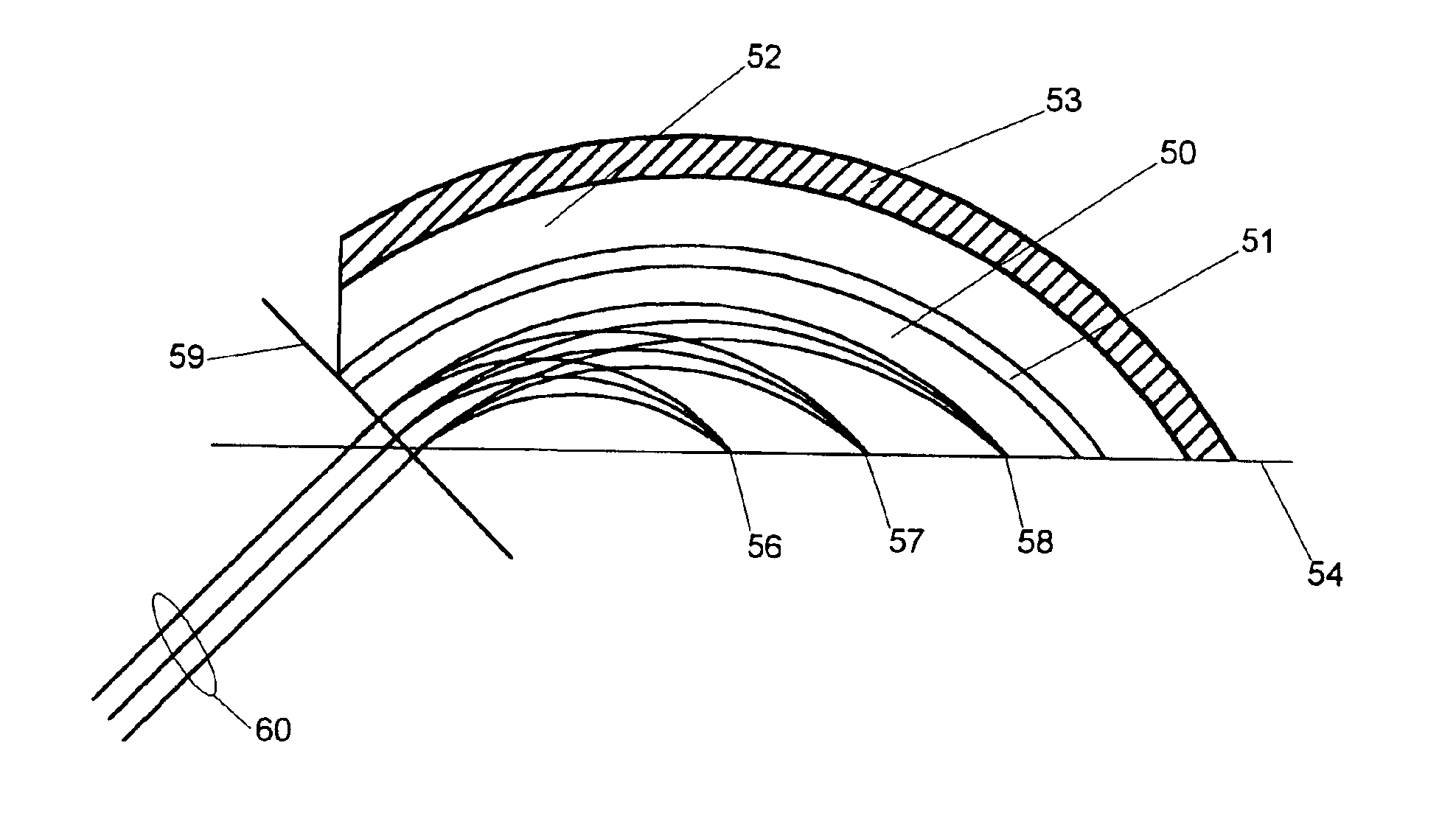
Linear dispersion objective lens
The invention provides a linear dispersion objective lens. Axial dispersion and the wave length approximately form a linear relation within the wavelength range from light F to light C. The linear dispersion objective lens has large dispersion, long working distance and small spherical aberration. The linear dispersion objective lens is composed of a positive lens assembly and a negative lens assembly, wherein the negative lens assembly is close to a needle hole and integrally has negative power, and the positive lens assembly is close to an object and integrally has the positive power. The surface, closest to the object, of the objective lens is a concave face, and the materials of the positive lens assembly and the materials of the negative lens assembly meet the certain dispersion correcting relation. The linear dispersion objective lens can provide large design freedom degree, is used for a spectrum confocal device, effectively improves the whole performance of the device, and is mainly applied to detection of displacement, the transparent element thickness, the micro three-dimensional structure and surface roughness and the like.
Owner:INST OF MACHINERY MFG TECH CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Filter spectrometer with adjustable linear dispersion rate
InactiveCN107677368ADispersion rate adjustableMiniaturizationSpectrum investigationSpectrum generation using diffraction elementsLinear dispersionSpectrometer
The invention relates to a filter spectrometer with adjustable linear dispersion rate. Light beams emitted by a light source enter a converging lens. The converging lens converges the light beams to aslit in the focus position of a collimating lens. The light beams going out of the slit are changed into parallel light after passing through the collimating lens, and the parallel light is incidenton the surface of a linear gradient filter. A light-splitting spectrum is detected by a linear array CCD detector according to spectrum information obtained through light splitting by the linear gradient filter, and is transmitted to a computer for processing. The linear array CCD detector is fixed on a rotary adjustable bracket. With the direction in which the resonant cavity layer of the filterchanges thickness fastest as a reference direction, the linear array CCD detector is rotated in such a way that there is an included angle between the length direction of the detector and the reference direction. Then, the transmitted light of the filter is detected, and the dispersion rate can be changed. The linear array CCD detector can move in a two-dimensional direction to measure light within different wavelength ranges. The filter spectrometer has the advantages of simple structure, convenience of use and adjustable linear dispersion rate.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Chromatic dispersion compensation by sub-band
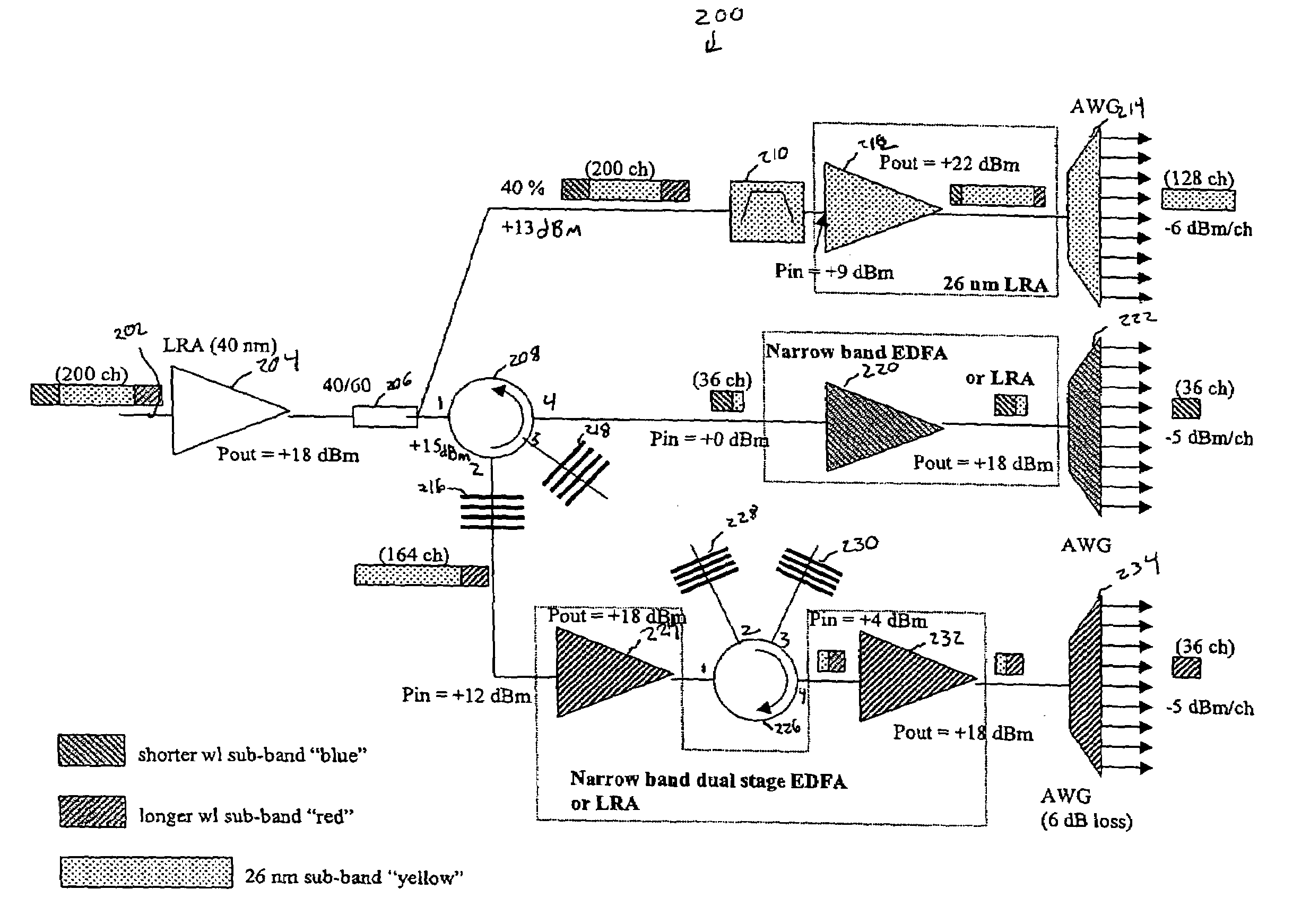
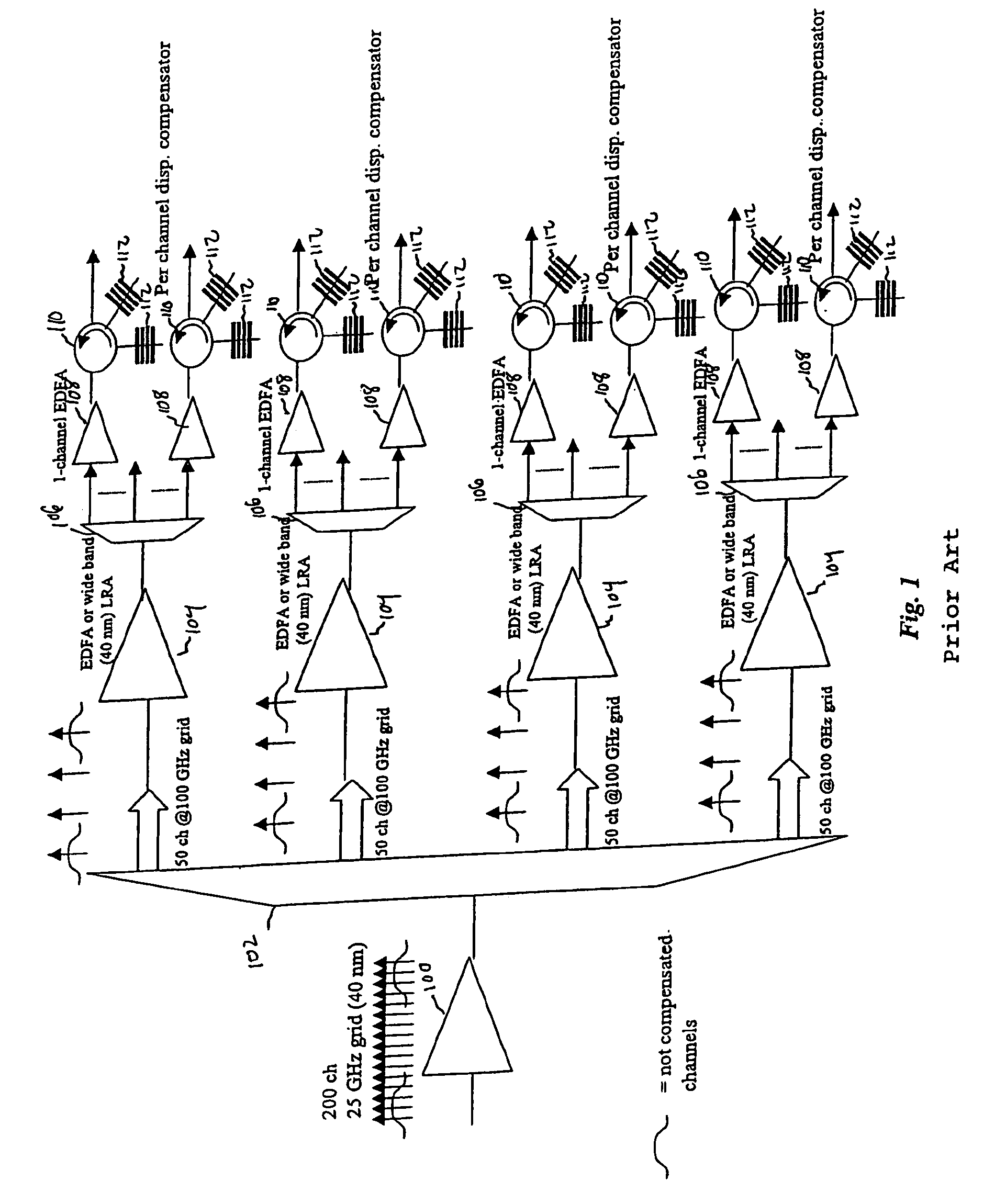
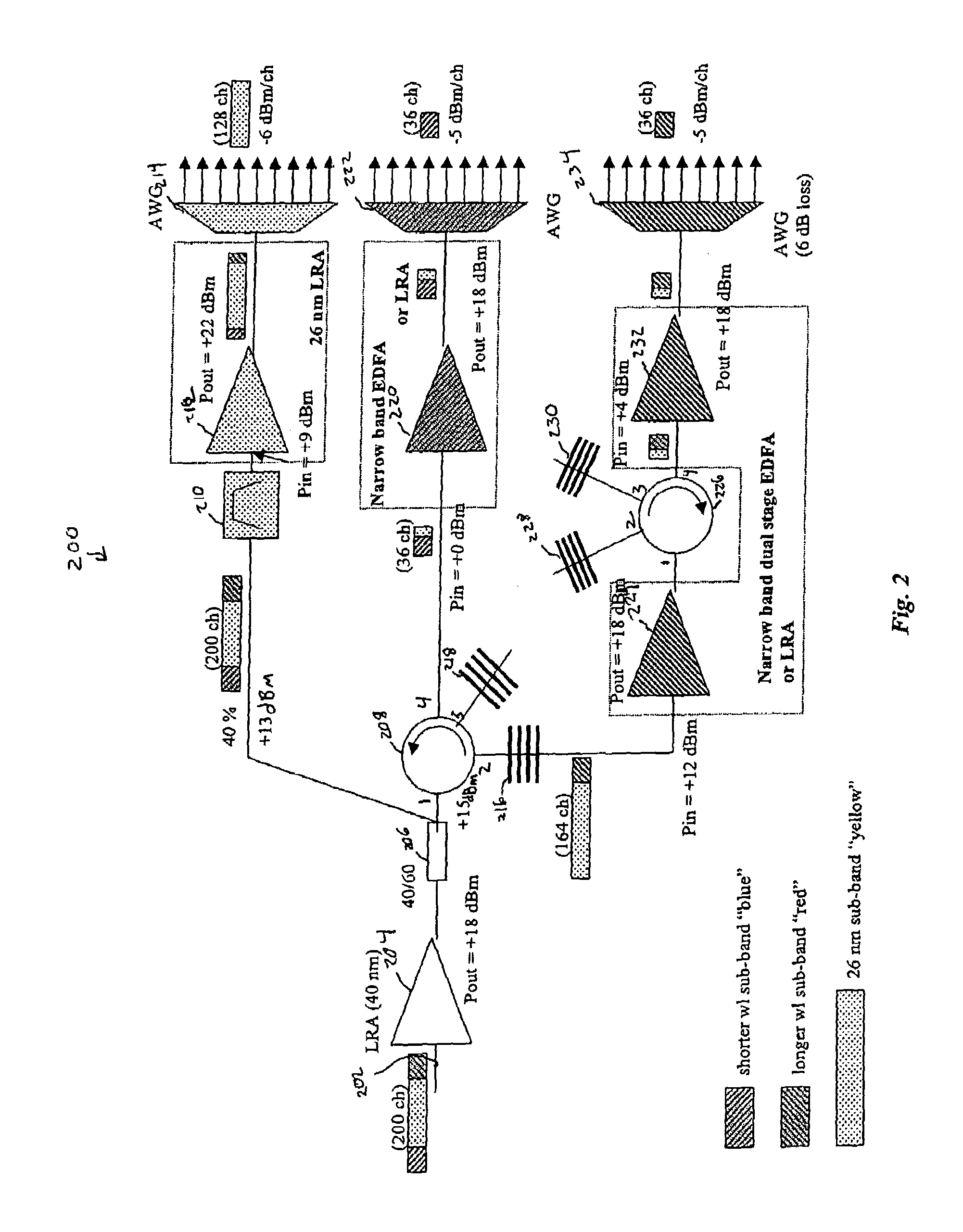
InactiveUS7031613B1Low costSave volumeWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesGratingLinear dispersion
End of line dispersion compensation is applied on a sub-band by sub-band basis. Adequate end-of-line dispersion compensation may be provided for high data rate WDM systems even for optical link lengths of 1000 km or more. Dispersion compensating gratings (DCGs) may be used as the dispersion compensating components. There is a great savings in cost and package volume compared to per-channel compensation schemes.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method for broadband radio-frequency signal correlation detection based on time-spectrum convolution principle
ActiveCN103326795AAvoid offline processingAvoid immediate measurementsTransmission monitoringFrequency spectrumLinear dispersion
The invention relates to a method for broadband radio-frequency signal correlation detection based on the time-spectrum convolution principle. The method is used for filtering and matching broadband radio signals and comprises the following steps that step 1, a laser device is used for generating a multi-wavelength laser light source; step 2, the spectrum forming technology is used by generated lasers through an optical filter so that an amplitude-frequency response envelope conjugated with a detected broadband radio-frequency signal time domain waveform can be generated; step 3, the received detected broadband radio-frequency signals are loaded on the lasers after spectrum forming through an electro-optic strength modulator; step 4, the modulated optical signals are introduced to chromatic dispersion delay through a linear chromatic dispersion component; step 5, the optical signals are connected to a photoelectric detector for photovoltaic conversion and an output signal is a detected electric pulse signal after a correlation operation. The method for broadband radio-frequency signal correlation detection based on the time-spectrum convolution principle can effectively avoid offline processing of data and achieve immediate measurement of the broadband radio-frequency signals.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Polarization and hyper-spectral compression imaging method and system
InactiveCN102155992AReduce data volumeEasy to createRadiation pyrometryPolarisation spectroscopyLinear dispersionData information
The invention discloses a polarization and hyper-spectral compression imaging method and system. The polarization and hyper-spectral compression imaging system is provided with an objective lens, a polarization modulator, a collimating lens, a first linear dispersion device, a first convex lens, a spatial modulation mask plate, a second convex lens, a second linear dispersion device, a lens and adetector in sequence along the direction of light transmission, wherein the objective lens is used for imaging a target on the polarization modulator. The polarization and hyper-spectral compression imaging method comprises the following steps: imaging the target on the polarization modulator, collimating the emergent light, carrying out first dispersion on the collimated emergent light, carryingout spatial modulation on the dispersed light signal, carrying out second dispersion, projecting the light on the detector, collecting data by using a computer, completing data calculation, and restoring four-dimensional data information of the target. The invention realizes the hyper-spectral instantaneous compression imaging of three-dimensional data cubes in a certain vision field under the control of polarization modulation, greatly reduces the quantity of data received by the detector, improves the signal-to-noise ratio of the system and is especially beneficial to the target imaging of weak light intensity and strong dispersion.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
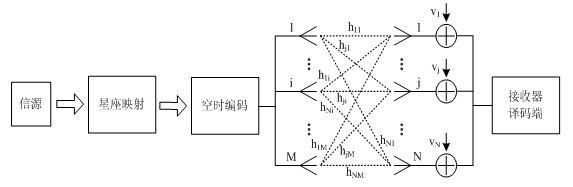
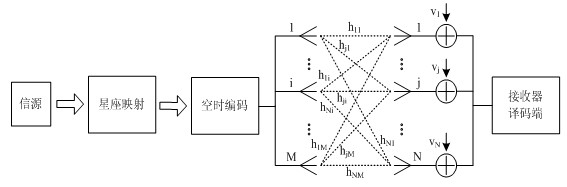
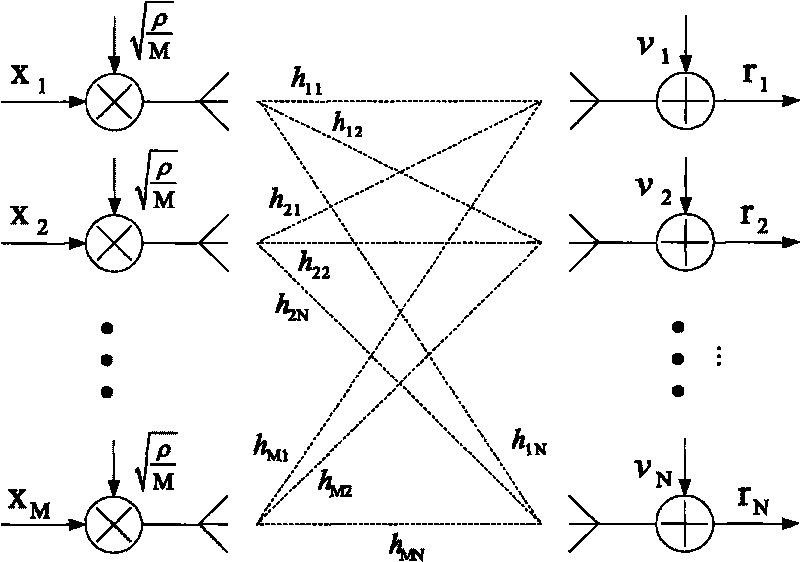
Space-time coding for communication systems
ActiveCN107949997AReduce decoding complexityCode conversionRadio transmissionDigital dataCommunications system
The invention relates to space-time coding for communication systems. There is provided a method of generating a space-time block code (STBC) for encoding a digital data sequence comprising a set of independent symbols to be transmitted through a transmission channel in a communication system, the space-time block code being represented by a set of linear dispersion matrices in a linear dispersionrepresentation, each linear dispersion matrix comprising components having complex values, the method comprising, generating at least some of the linear dispersion matrices depending on component-wise conditions related to a set of selected pairs of the linear dispersion matrices, each pair comprising a first linear dispersion matrix and a second linear dispersion matrix, said component-wise conditions comprising a component-wise condition between the components of the first linear dispersion matrix and the components of the second linear dispersion matrix.
Owner:INST MINES TELECOM
Swept wavelength broadband Raman pump source
ActiveUS6967767B2High repetition rateLaser using scattering effectsFibre transmissionFiberLinear dispersion
A swept wavelength source for broad bandwidth Raman pump applications includes a source of ultrashort (e.g., picosecond) optical pulses. The pulse train output from the source is then applied as an input to a linear dispersive element (such as a section of negative dispersion-shifting fiber) which functions to “stretch” the ultrashort pulses, causing the pulses to become separated in time, with a continuous shift in the wavelength through the length of the pulse.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Large axial chromatic aberration linear dispersion object lens
ActiveCN106405803AIt has the effect of collimating first and then focusingSmall sizeUsing optical meansOptical elementsLinear dispersionOptical axis
The embodiment of the invention provides a large axial chromatic aberration linear dispersion object lens. The object lens comprises a collimating lens group with positive focusing luminosity and a focusing lens group with positive focusing luminosity, the collimating lens group and the focusing lens group are arranged along the optical axis in order between a light source pinhole and measured object, the collimating lens group is close to the light source pinhole, and the focusing lens group is close to the measured object. The object lens system comprehensively considers the balance of the linearity of the dispersion object lens and the system aberration correction, and the collimating lens group and the focusing lens group are both positive lens groups and have the effect of collimation first and then focusing. The collimating lens group includes an aspheric lens to allow the ratio of the axial direction dispersion range of the linear dispersion object lens and the system focal length to be larger than 0.2 so as to entirely reduce the size of the object lens, reduce the processing difficulty and allow the object lens to have excellent linearity; and moreover, an additional arrival aperture diaphragm can limit the incident ray angle, prevent the adjustment process from being difficult because the structure of the dispersion object lens is complicated, and improve the processing precision.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ADVANCED LASER TECH
Space time collaboration diversity method in OFDMA system
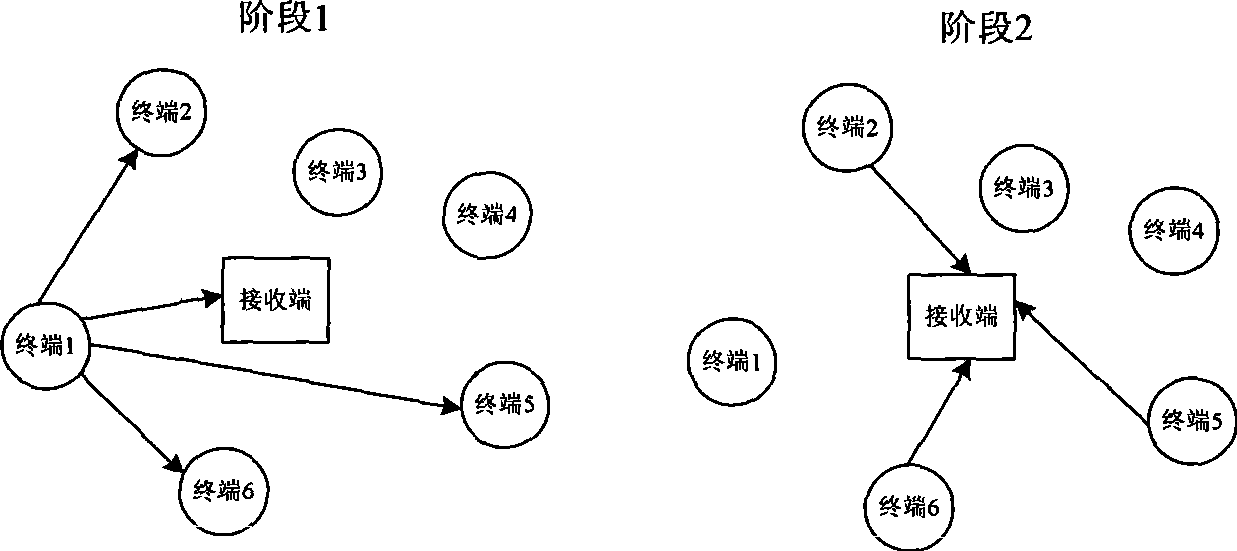
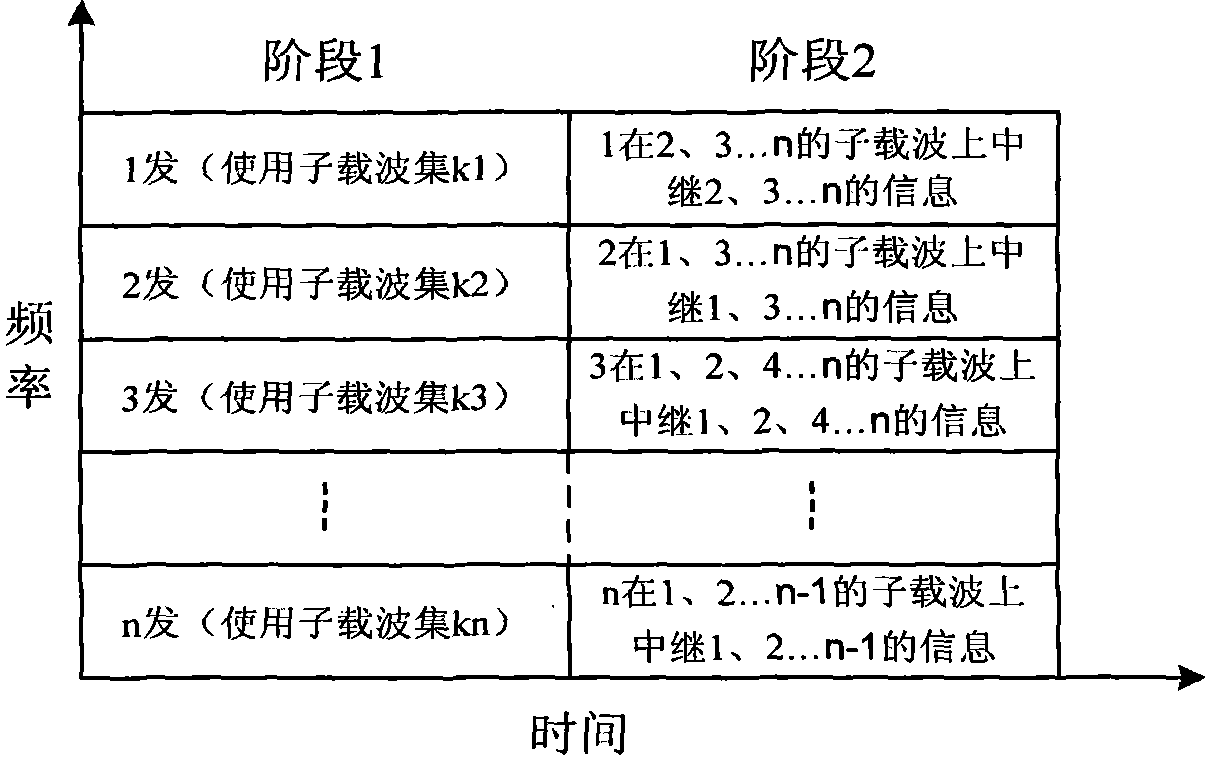
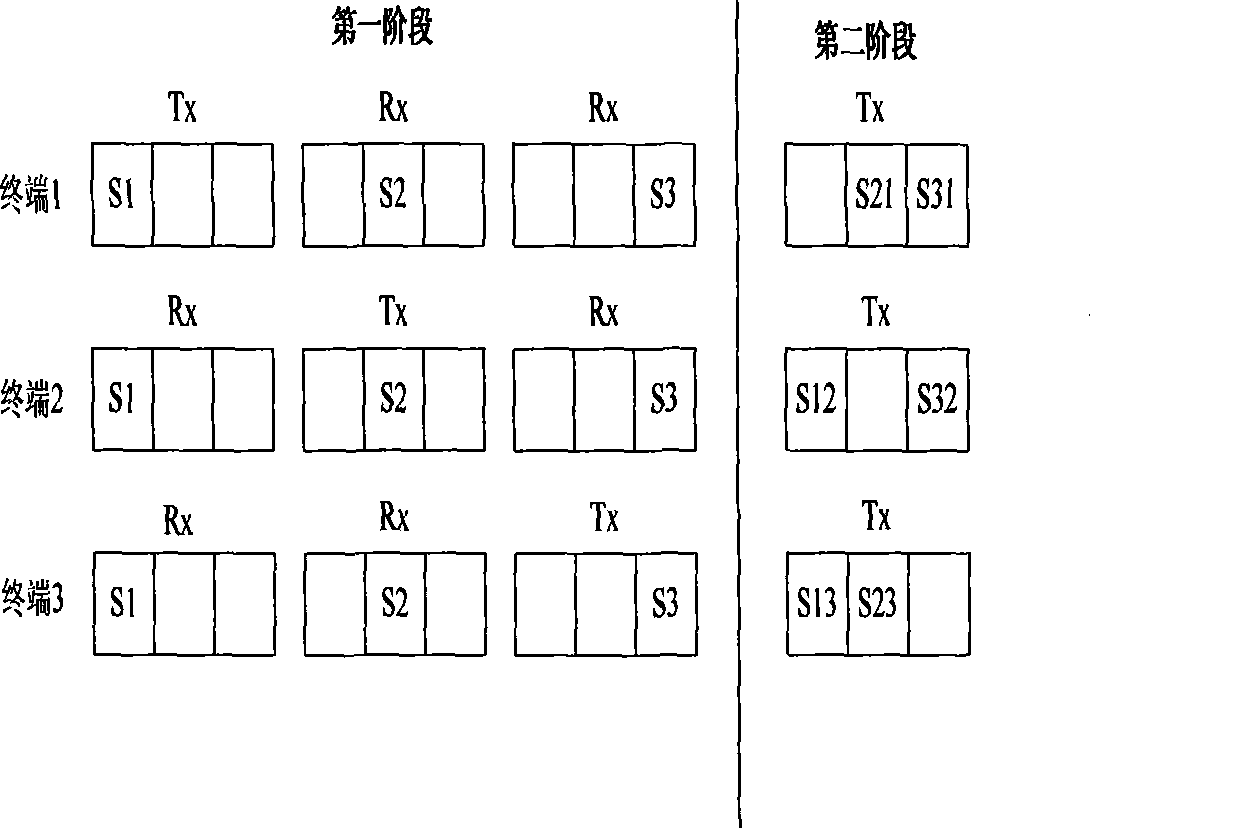
InactiveCN101394259AReduce bit error rateMulti-frequency code systemsError prevention/detection by diversity receptionLinear dispersionTelecommunications
The invention discloses a space-time cooperation diversity method of an OFDMA system, which mainly solves the problem of low performance of the system. The method comprises the following steps: 1. the number of terminals participating in cooperation is determined and a linear dispersion code used in cooperation is appointed; 2. subcarriers in the first stage and the second stage are allocated to every terminal; 3. in the first stage of cooperation, LDC code words are sent to other terminals and a receiving terminal by a terminal n on the allocated subcarriers; 4. the LDC code word information sent by the terminal n is received by a terminal m and whether the receiving is correct is checked, if correctly receiving the information of the terminal n, the terminal m reports system to participate in the cooperation, and otherwise, the terminal m does not participate in the cooperation; 5. the terminals participating in the cooperation and LDC code word line components sent by every terminal are determined; 6. in the second period of cooperation, respective cooperation information is sent by the terminals participating in the cooperation to the receiving terminal; and 7. the received information in the first stage and the received information in the second stage are merged and then decoded by the receiving terminal. The invention has the advantages of low bit error rate and is used for cooperation communication in a wireless network.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
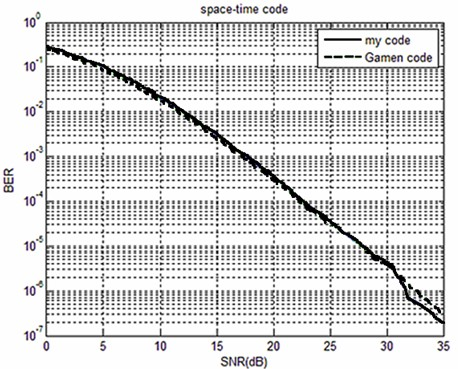
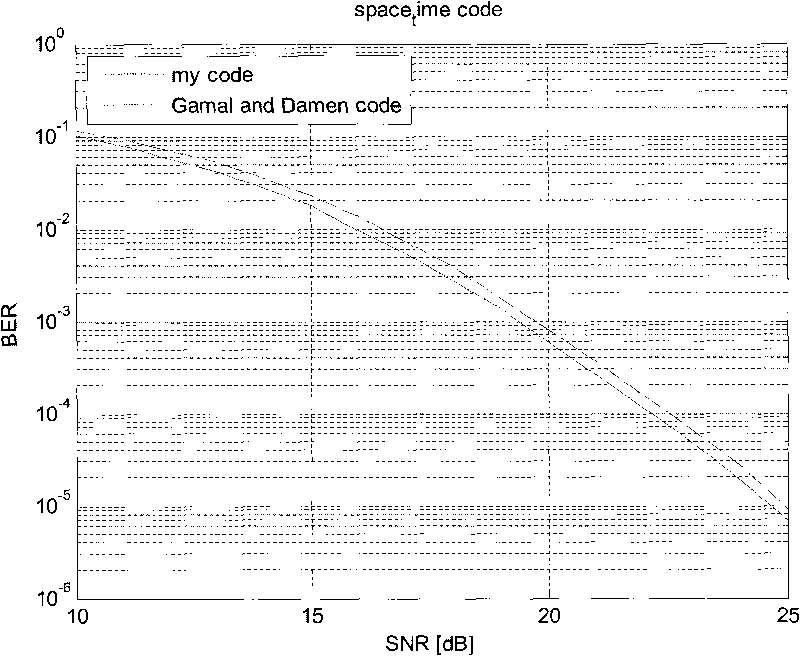
Linear dispersion space-time coding method applicable to any antenna number
InactiveCN102035630ABER Accurate ResponseBER responseError prevention/detection by diversity receptionCode moduleLinear dispersion
The invention relates to a linear dispersion space-time coding method applicable to any antenna number. The method comprises the following steps of: determining a time length of a coding module and an information symbolic number to be transmitted; randomly generating MT complex vectors u1, u2, ..., uMT, and converting each complex vector into a Hermite matrix; generating an MT-order diagonal matrix D, multiplying D rightwards by the Hermite matrix to acquire a new MT-order square matrix U, randomly selecting L column vectors from the matrix U, and rearranging each column vector from top to bottom and from left to right to form an M*T matrix; and finally calculating L singular values for constructing the matrix respectively, solving sum of square and sum of biquadrate of each group of singular values to acquire two groups of sequences, and finishing coding until the two groups of sequences accord with set conditions. The method is applicable to application occasions of any number of transmitting antennas and receiving antennas and can freely set coding transmission rate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for determining linear dispersion space-time codes for receiving antenna numberless than transmitting antenna number
InactiveCN101702643ASimple Coding Design ComplexityGood coding performanceSpatial transmit diversityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionLinear dispersionOrthogonal method
The invention relates to a method for determining linear dispersion space-time codes when the receiving antenna number is less than the transmitting antenna number. Large limitation exists in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, determining channel using times T (T is not less than M) and constructing layered matrices C1-CN; then constructing N stepped matrices U1-UN in T*T; constructing q=NT encoding matrices Aj, K in M*T, wherein the j is equal to 1 to T, the k is equal to 1 to N, the M is the transmitting antenna number, the N is the receiving antenna number, Aj, k is equal to P.Ck.diag (Uk(:, j)).Q, NT encoding matrices Aj, k are obtained together, and then the linear dispersion space-time codes are determined. The method adopts a trace orthogonal method to achieve approximately optimal channel volume and uses an algebraic method to obtain full set gains. The linear dispersion space-time codes determined in the method of the invention have simple encoding design complexity and simultaneously provide favorable encoding properties.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Magnetic separator for linear dispersion and method for producing the same
InactiveUS6906333B2Improve magnetic circuit efficiencyOverall light weightThermometer detailsSpectrometer detectorsLinear dispersionMagnetic separator
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
MIMO system performing hybrid ARQ and retransmission method thereof
InactiveUS8347161B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsError checkingLinear dispersion
The present invention relates to a multiple antenna transmitting / receiving apparatus that performs a hybrid automatic repeat request, and a retransmission method thereof. An initial transmission signal is encoded into the form of an initial transmission matrix and transmitted to the receiving apparatus, the initial transmission matrix corresponding to a linear dispersion code, with a result of error checking performed on the initial transmission signal by the receiving apparatus. When an error is detected in the initial transmission signal, a first retransmission signal is generated by encoding the initial transmission signal in the form of a retransmission matrix and transmitted to the receiving apparatus. The retransmission matrix is formed of constituent elements of the initial transmission matrix but different from the initial transmission matrix, and corresponds to a linear dispersion code having the same capacity and diversity gain as those of the initial transmission matrix.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Assembly and method for wavelength calibration in an echelle spectrometer
ActiveUS7215422B2Reduce stray lightMinimum driftRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationExit planeSpatially resolved
A spectrometer assembly (10) is disclosed. The assembly includes a light source (11) with a continuous spectrum. A pre-monochromator (2) generates a spectrum with a relatively small linear dispersion from which a spectral portion is selectable, the spectral bandwidth of the spectral portion being smaller than or equal to the bandwidth of the free spectral range of the order in the echelle spectrum. The centre wavelength of the selected spectral interval is measurable with maximum blaze efficiency. The assembly also includes an echelle spectrometer (4) with means for wavelength calibration, an entrance slit (21) at the pre-monochromator (2), an intermediate slit assembly (50) with an intermediate slit (3) and a spatially resolving light detector (5) in the exit plane of the spectrometer for the detection of wavelength spectra.
Owner:LEIBNIZ INST FUER ANALYTISCHE WISSENSCHAFTEN ISAS EV +1
Method and apparatus for spatial-shift wavelength multiplexing in communication systems
InactiveUS6763163B1Efficient spatial shiftingProcess economyCoupling light guidesMultiplexingLinear dispersion
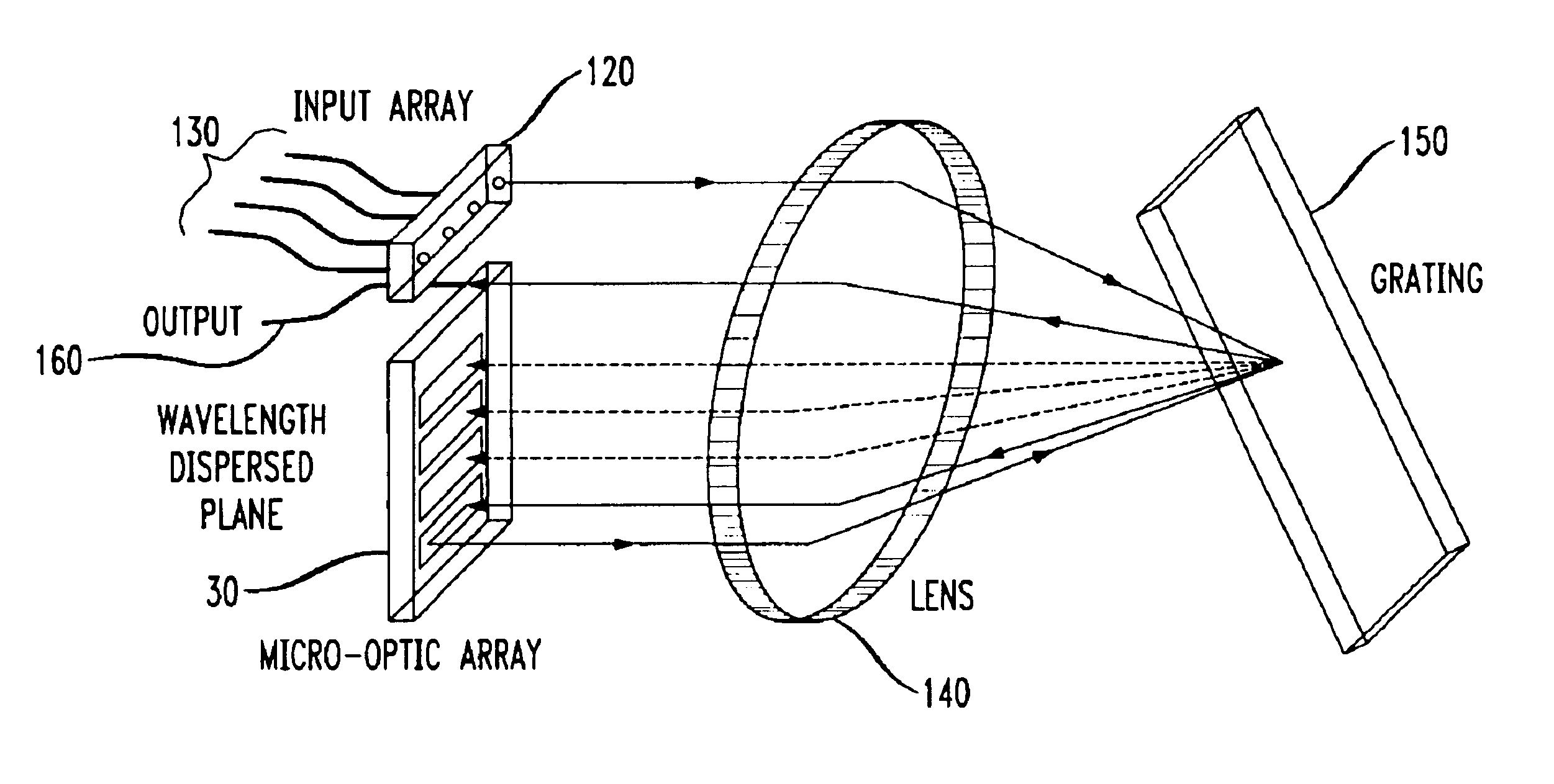
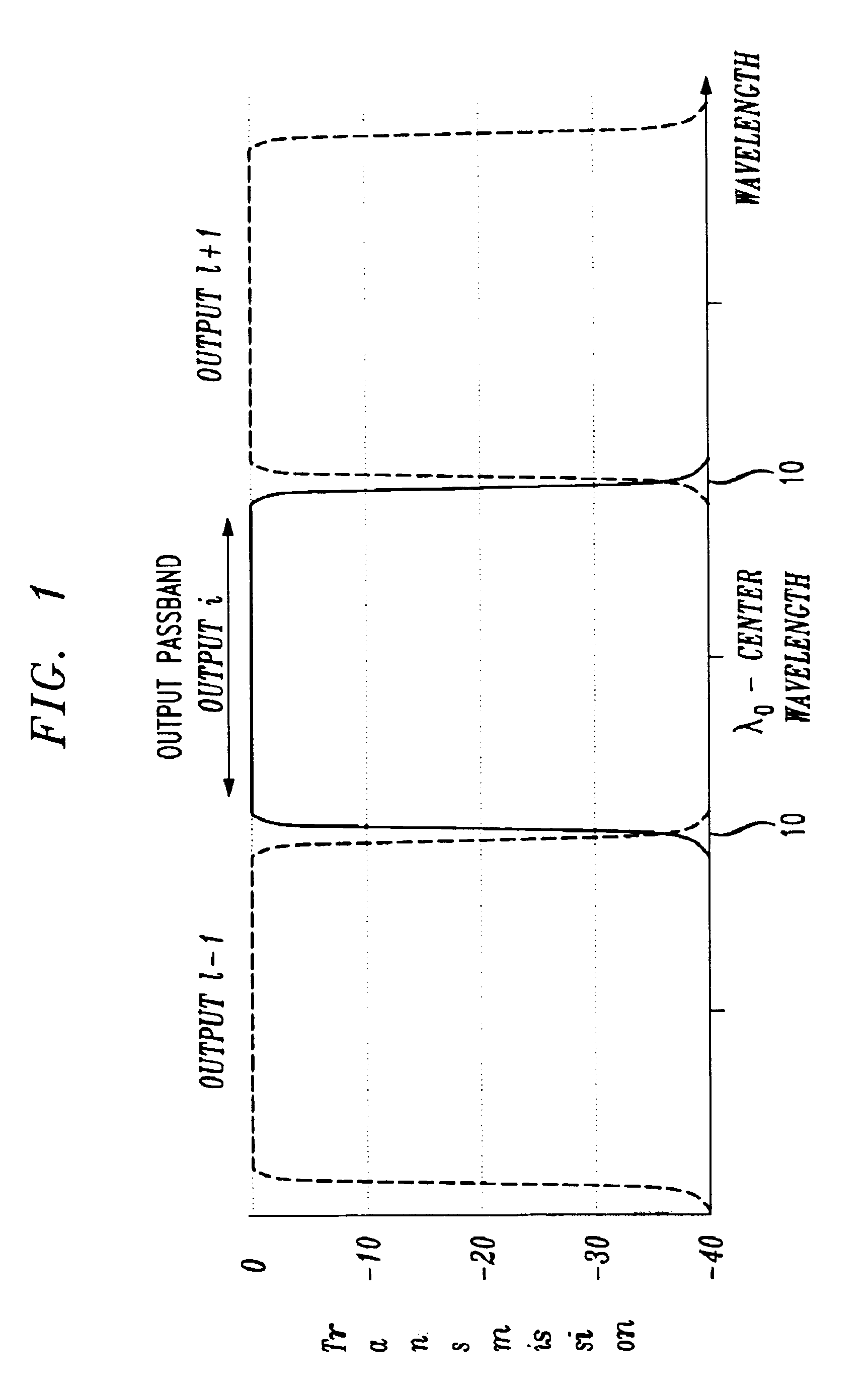
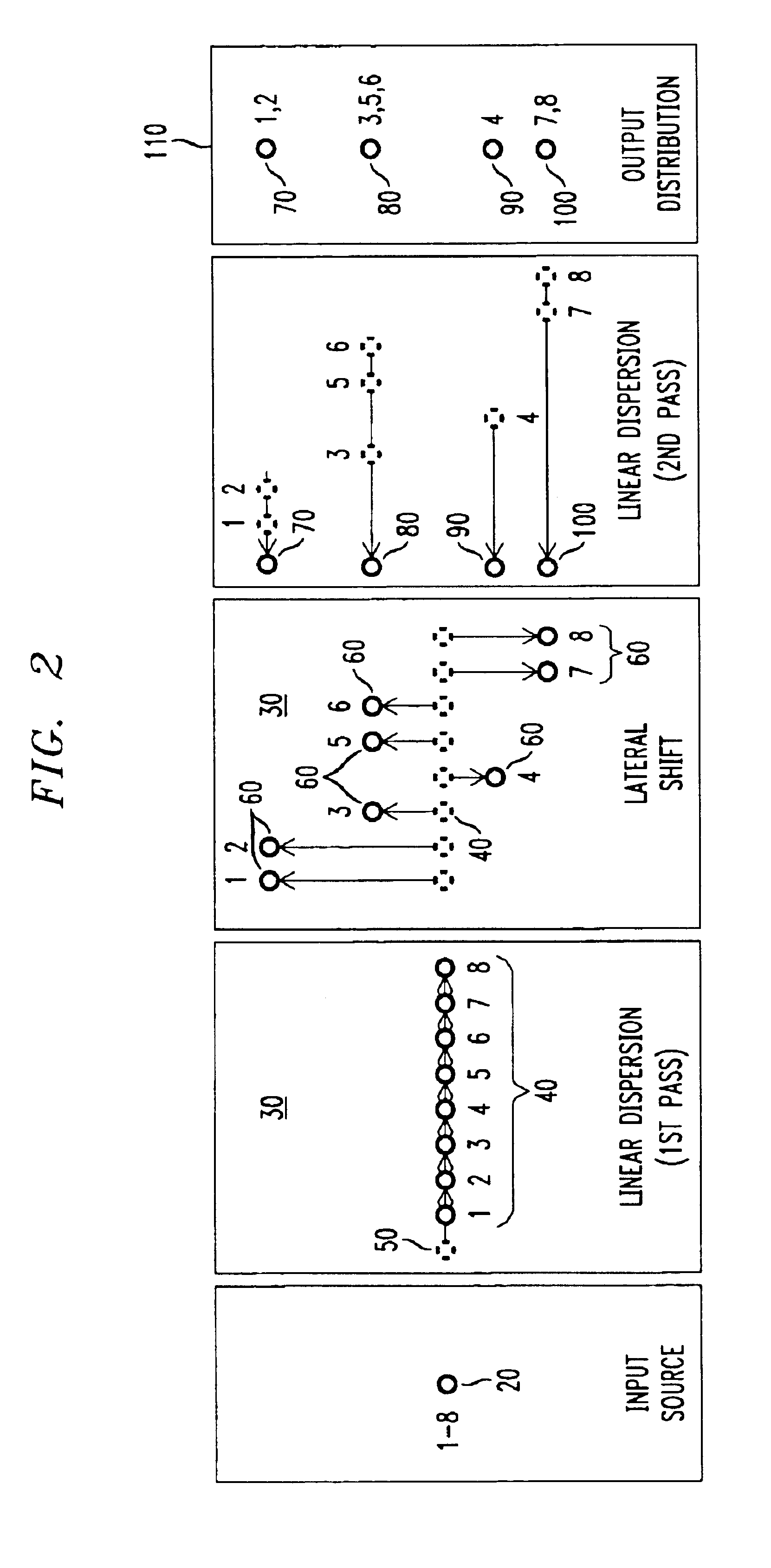
Methods and apparatus for spatially-shifting and multiplexing optical signals for transmission in a wavelength division multiplexed or dense wavelength division multiplexed optical communication system linearly disperse the optical signals and then spatially, laterally shift the signals. The spatially shifted, dispersed signals are thereafter re-imaged to remove the linear dispersion so that the spatially shifted signals can then be transmitted through the optical communication system. The spatially-shifted, multiplexed signals have a flat passband with sharp transition points so that the transmitted signals are routed through the optical communication system with low loss and high integrity.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Method for suppressing self-phase modulating effect in over long-distance optical transmission system
InactiveCN1489321AInhibition of SPM effectImprove performanceWavelength-division multiplex systemsMicroscopesLinear dispersionComputer module
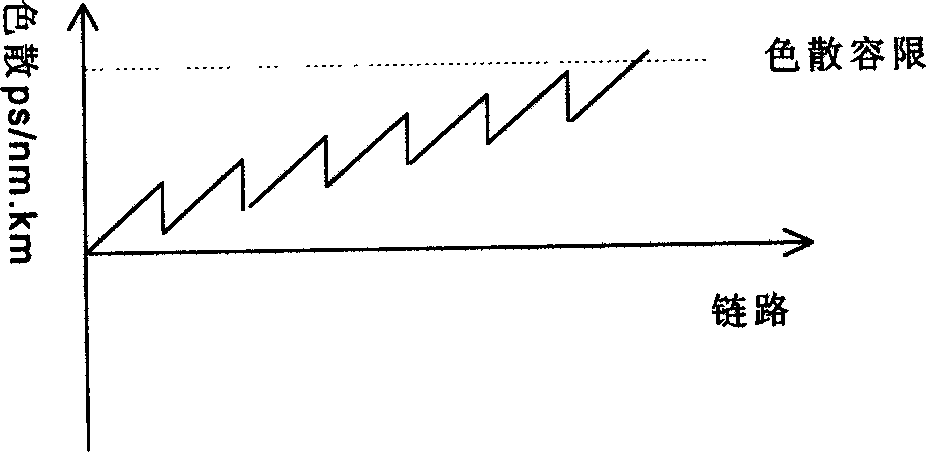
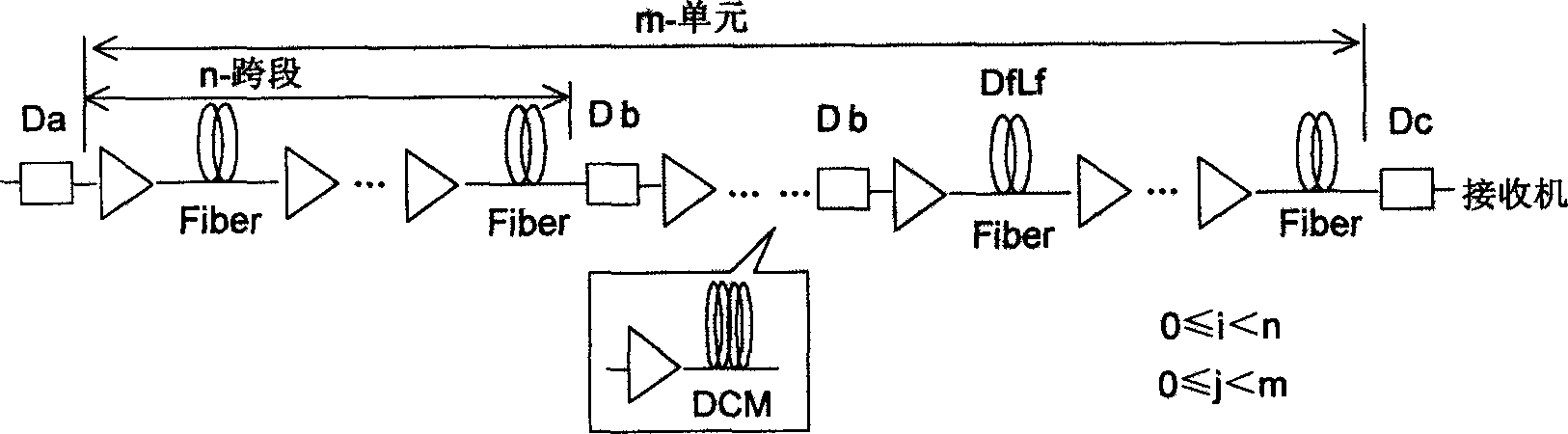
Dispersion compensation module is utilized in each chain to carry out distributivity full compensation for dispersion. Position and dispersion quantity of dispersion compensation module in chain are adjusted. With input point of optical signal power as the reference point, accumulated dispersion quantity from any reference point to front of receiver is positive. Total dispersion of system is within dispersion tolerance of receiver. Interaction between effect of self phase modulation (SPM) and dispersion is created to compress expanded pulse. The method is suitable to DWDM system, possible to control the accumulated total residual dispersion. Thus, transmission distance is not limited by linear dispersion. Under current technical condition of dispersion compensation, without need of adding any new part, SPM effect in ultralong distance transmission can be solved in entire C-BAND. The method is reliable through emulation, simulation, experiments and applicable test.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Measuring system of N2 molecule vibration-rotation Raman spectrum
ActiveCN105928922AAppropriate rangeAppropriate spectral resolving powerRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringGratingLinear dispersion
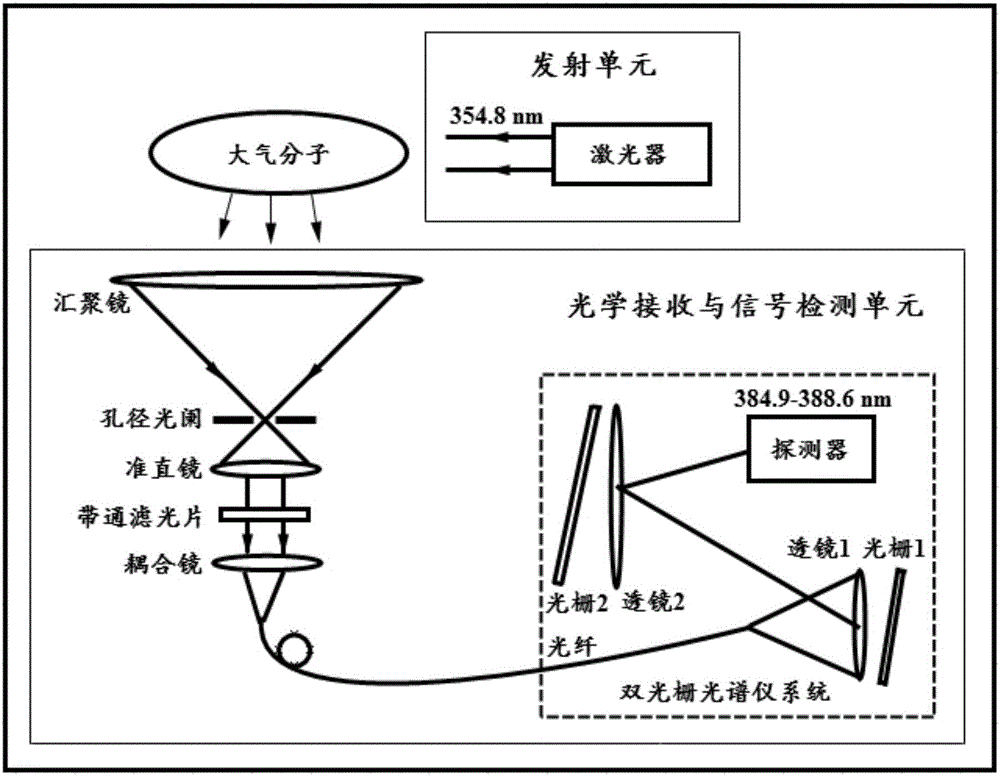
The invention discloses a measuring system of N2 molecule vibration-rotation Raman spectrum. The system comprises an emission unit and an optics reception and signal detection unit. The emission unit irradiates the atmospheric molecules by using the ultraviolet laser with extremely narrow linewidth of 354.8 nm outputted by a seed-injected solid-state laser. The optics reception and signal detection unit collects the signal of the vibration-rotation Raman spectrum produced by the N2 molecule, uses a double grating dispersion system to disperse the light in a range of 384.9-388.6 nm in space with a linear dispersion of 8.3 mm / nm, uses a linear array detector having 32 channels to distinguish and record discrete spectral line signals of O branch (rotation quantum number J=16-2) and S branch (rotation quantum number J=0-14) of N2 molecule vibration-rotation Raman spectrum, and produces inhibition better than 13 order of magnitude for the light near 354.8 nm. The system realizes the distinction and record of N2 molecule Stokes vibration-rotation Raman spectrum, and can obtain temperature information.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Creating large bandwidth line defects by embedding dielectric waveguides into photonic crystal slabs
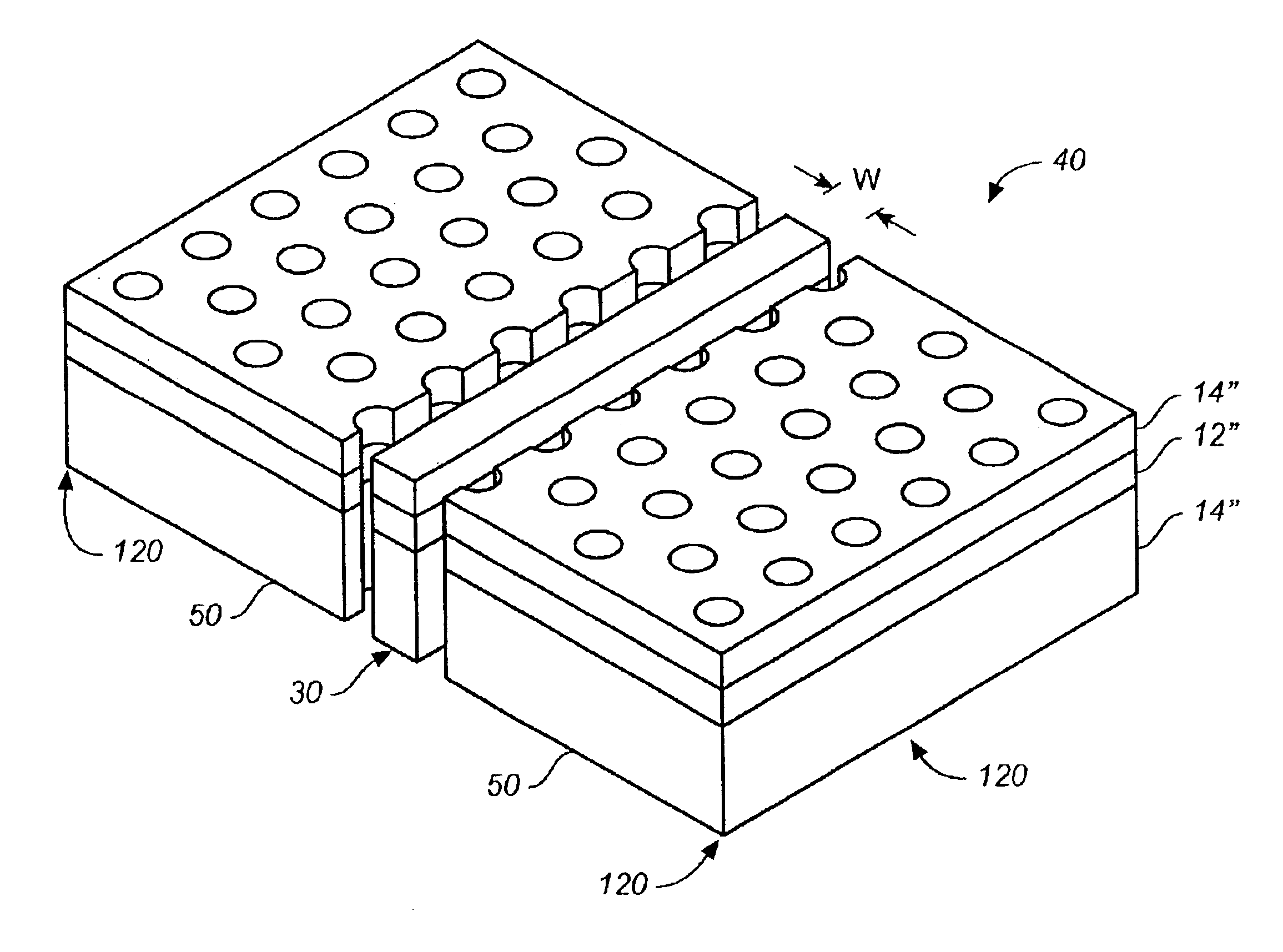
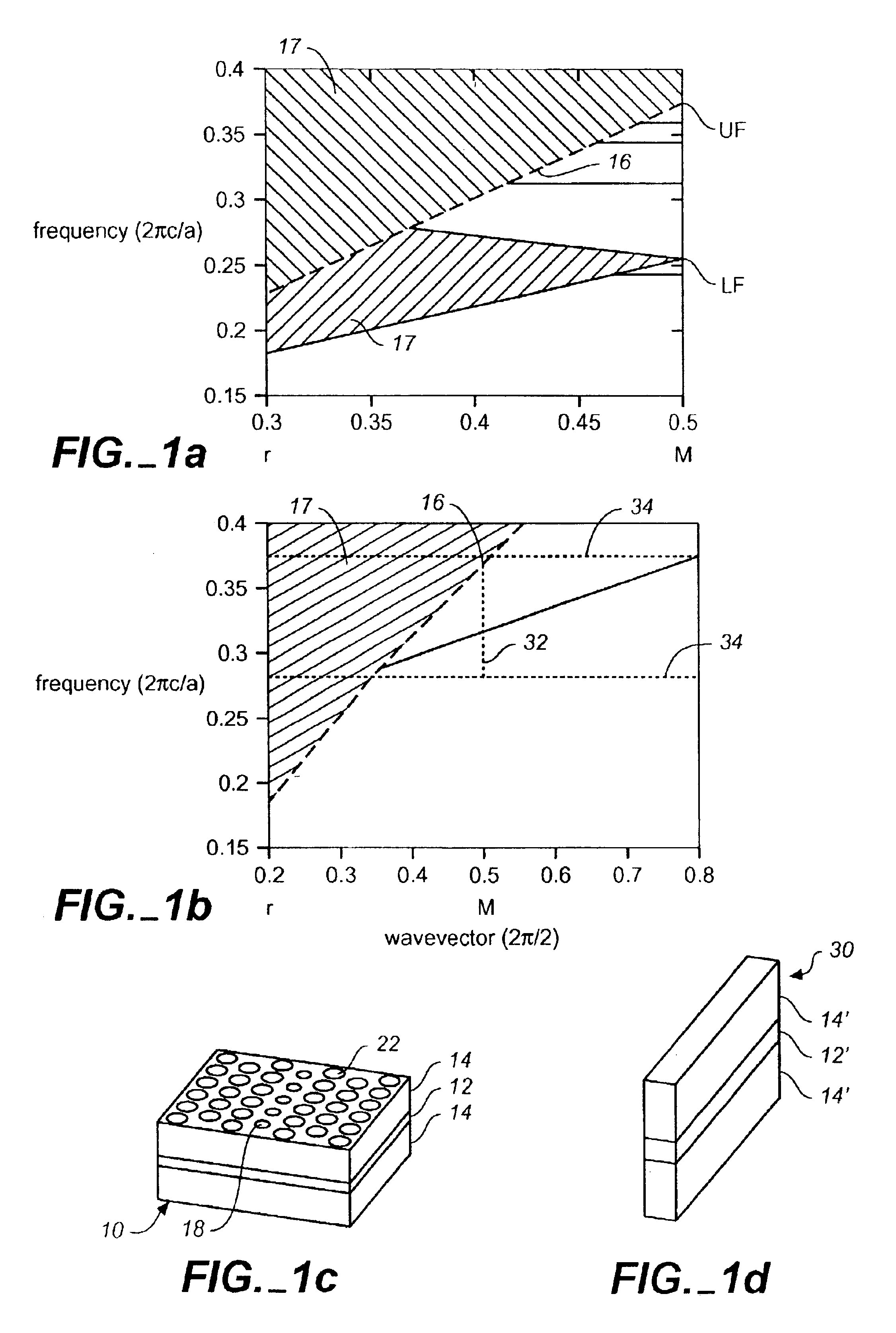
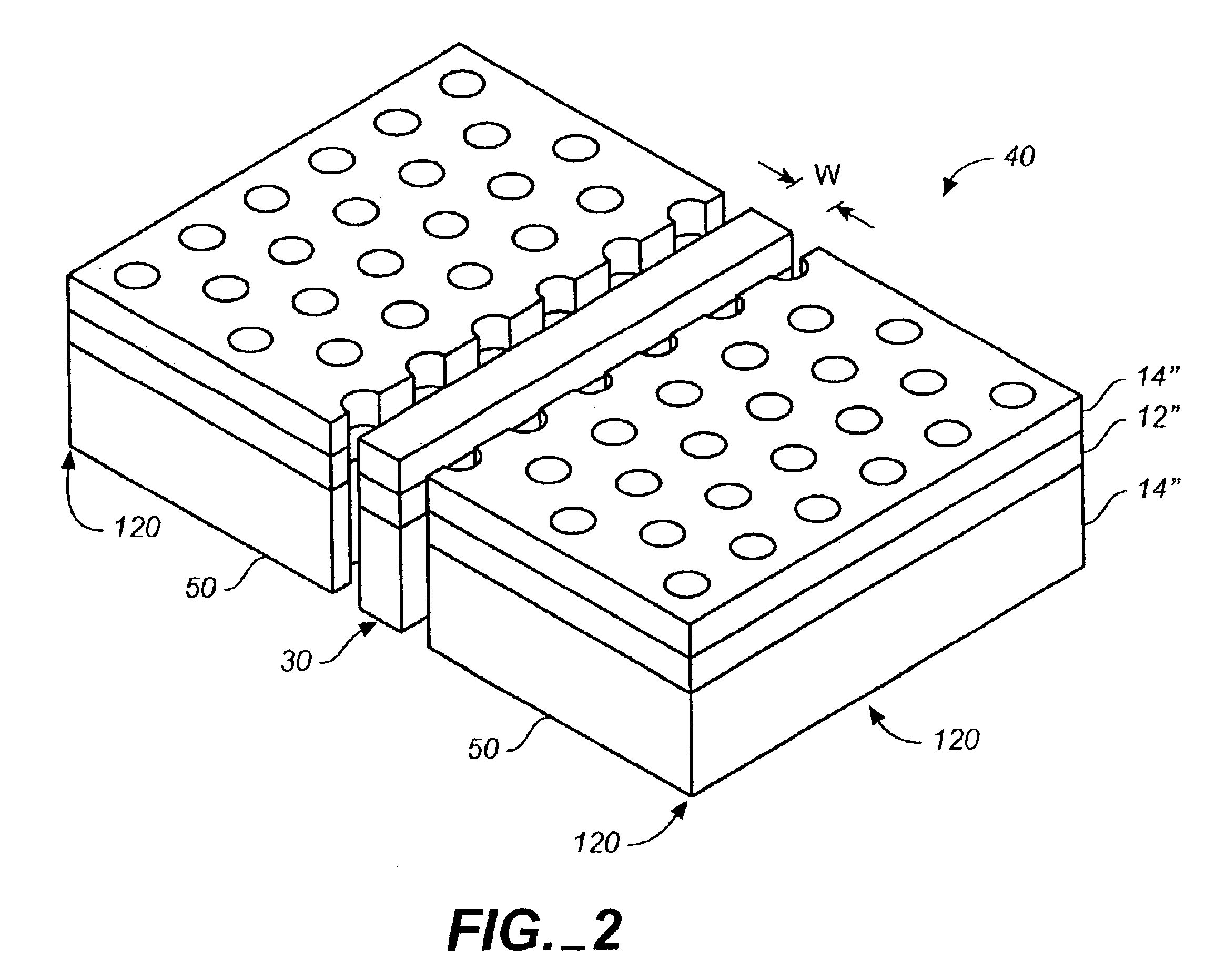
InactiveUS6957003B2Relatively large bandwidthHigh bandwidthCladded optical fibreNanoopticsLinear dispersionPhotonic bandgap
We introduce a general designing procedure that allows us, for any given photonic crystal slab, to create an appropriate line defect structure that possesses single-mode bands with large bandwidth and low dispersion within the photonic band gap region below the light line. This procedure involves designing a high index dielectric waveguide that is phase matched with the gap of the photonic crystal slab, and embedding the dielectric waveguide as a line defect into a crystal in a specific configuration that is free of edge states within the guiding bandwidth. As an example, we show a single mode line defect waveguide with a bandwidth approaching 13% of the center-band frequency, and with a linear dispersion relation throughout most of the bandwidth.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
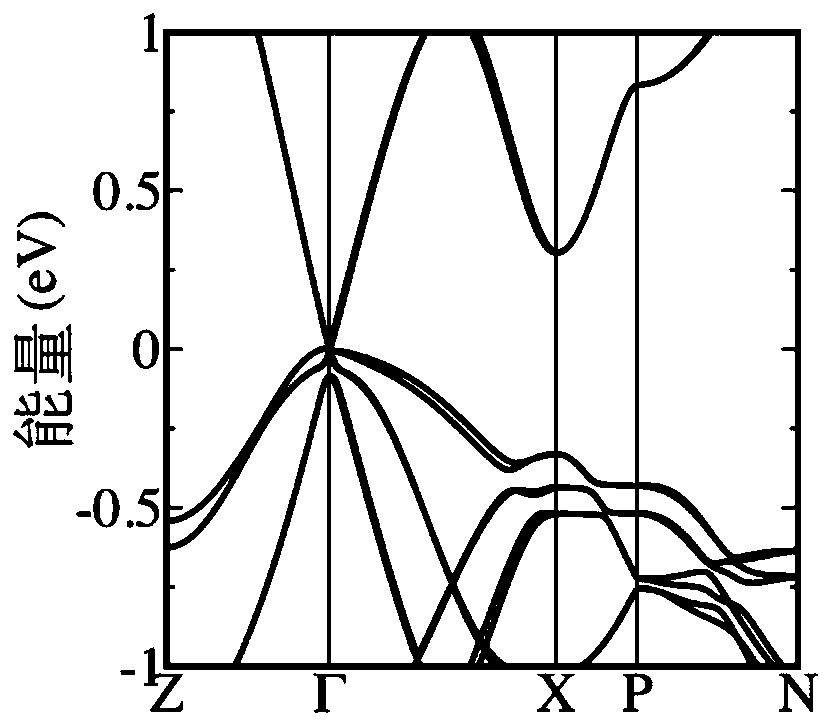
Ideal Dirac semimetal Cu2HgSnSe4 crystal and growth method and application thereof
ActiveCN111118605AReduce lossHigh precisionPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsCrystal systemSpace group
The invention discloses an ideal Dirac semimetal Cu2HgSnSe4 crystal. The Cu2HgSnSe4 crystal is characterized in that the Cu2HgSnSe4 crystal belongs to a tetragonal system; the space group of the crystal is (No. 121); and a conduction band and a valence band of the Cu2HgSnSe4 crystal are asymmetric in an energy band structure diagram, only Dirac fermion exists in the conduction band, and Schrodinger fermion and the Dirac fermion coexist in the valence band. If Fermi energy is located in the conduction band, transport properties are mainly derived from the Dirac fermion. Such a system is helpfulfor people to obtain relatively clean transportation experiment data, so the novel transportation property of a topological quantum state can be explored. Meanwhile, the linear dispersion relation ofelectrons near a Dirac point is always kept within the energy range of about 400 mV, and a Dirac cone energy band structure of linear dispersion has large-range frequency nonlinear response to lightwaves. The crystal has important academic value and potential application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
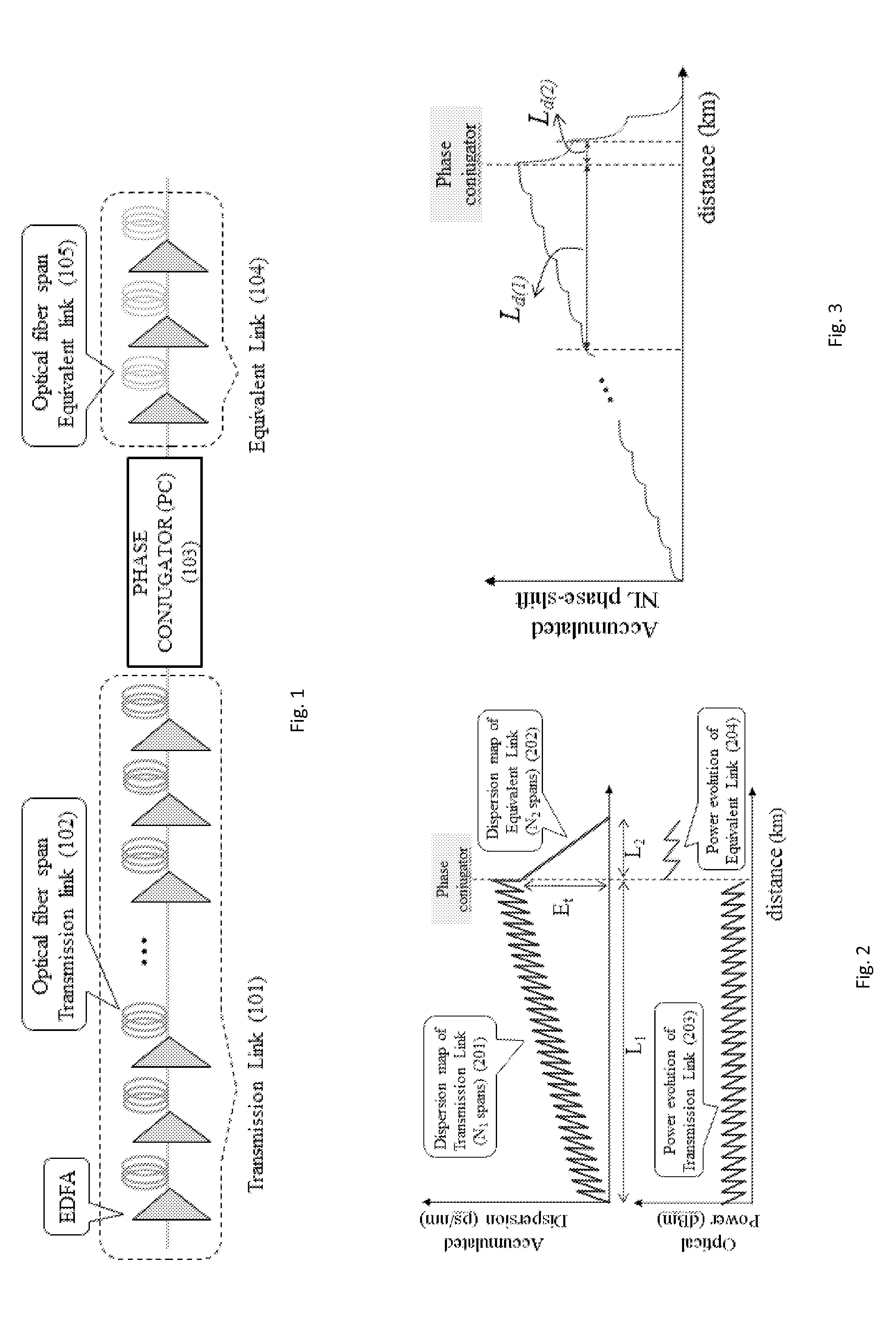
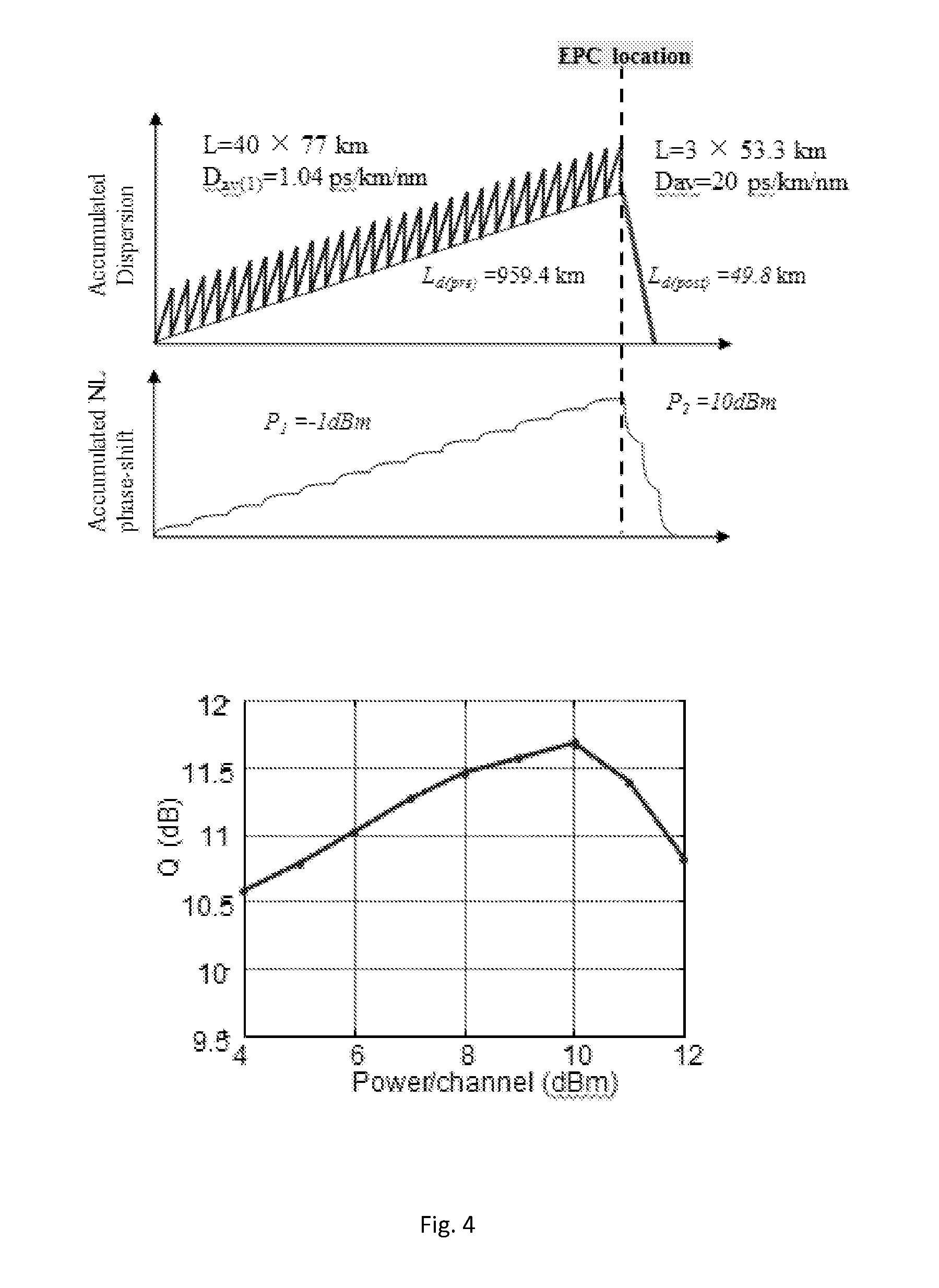
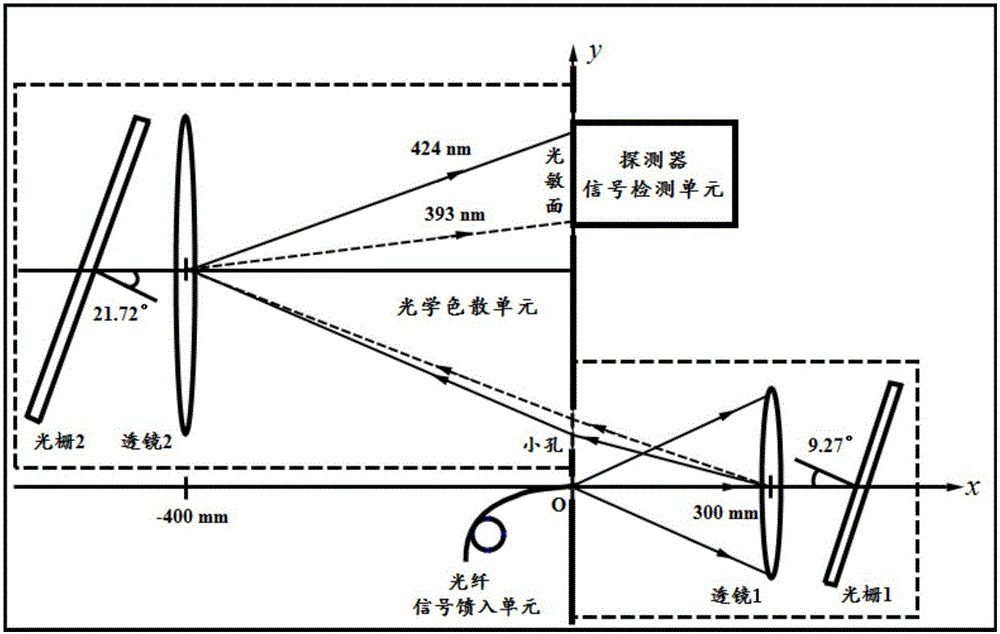
Method for the Compensation of Nonlinear Impairments in Dispersion-Managed Optical Fiber Links Using Phase Conjugation and Equivalent Optical Link
ActiveUS20130077963A1Transmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsLinear dispersionOptical link
A method for nonlinearity compensation for an optical transmission link includes determining a dispersion effect of a transmission link; applying a phase conjugation to the transmission link, the phase conjugation responsive to an input wave over the transmission link and providing a conjugated version of the input wave; and configuring an optimum equivalent link responsive to the phase conjugation after the transmission link to compensate for a non-linear dispersion effect from said transmission link
Owner:NEC CORP
Double-grating spectrometer system capable of detecting three-phase-state water Raman spectral signals simultaneously
ActiveCN105928618AFlexible and convenient optical accessFlexible and easy wayRadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsUv laserLinear dispersion
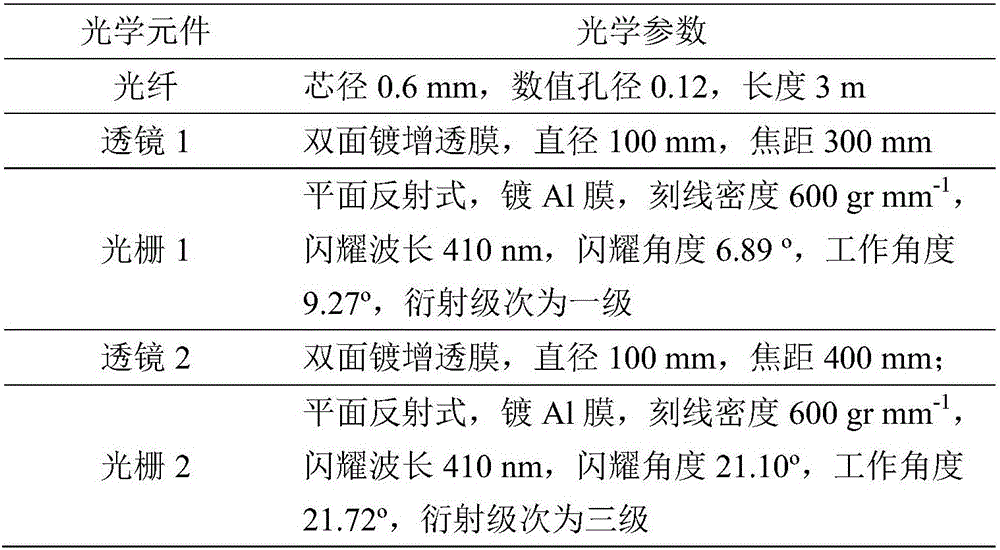
The invention discloses a double-grating spectrometer system capable of detecting three-phase-state water Raman spectral signals simultaneously. The system comprises a signal feed-in unit, an optical dispersion unit and a signal detection unit. The signal feed-in unit uses a fiber in the core diameter of 0.6mm and numerical aperture of 0.12 to feed conducted signal light into the optical dispersion unit; the optical dispersion unit comprises two cascaded grating dispersion systems of quasi-Littrow structural layout, can transmit and disperse passband signal light in the range 393.0-424.0nm in the focal plane efficiently in the linear dispersion rate of 1.0mm nm <-1>, and generates inhibition superior to 6 magnitude orders for outband light near 354.8nm; and the signal detection unit can distinguish and record the passabnd signal light after dispersion in the spectral precision of 0.8nm. In 354.8nm UV laser radiation, vibration-rotation Raman spectral regions of gas-sate, liquid-state and solid-state water correspond to the ranges of 395-409nm, 396-410nm and 401-418nm respectively; the passband spectral range covers the vibration-rotation Raman spectral regions of the three-phase-state water, the three-phase-state water Raman spectral signals are detected simultaneously, and substantial inhibition is generated for optical signals near 354.8nm.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com