Patents
Literature
240 results about "Phase conjugation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
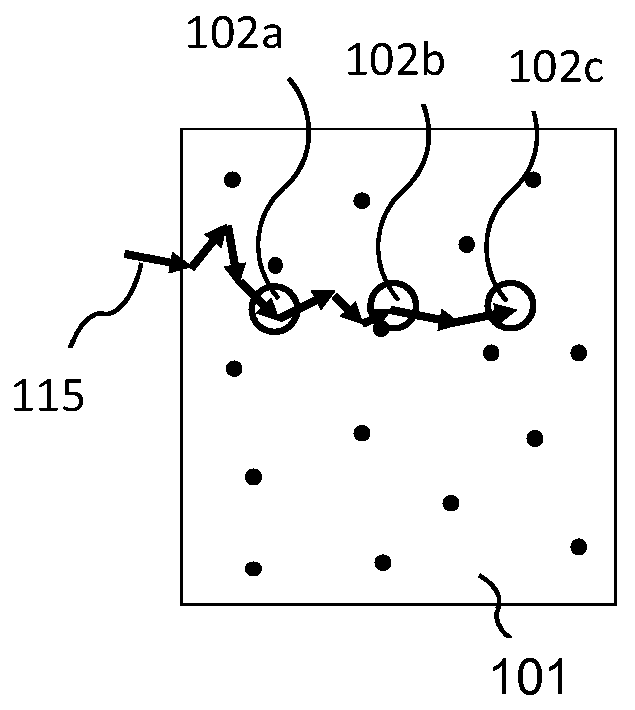
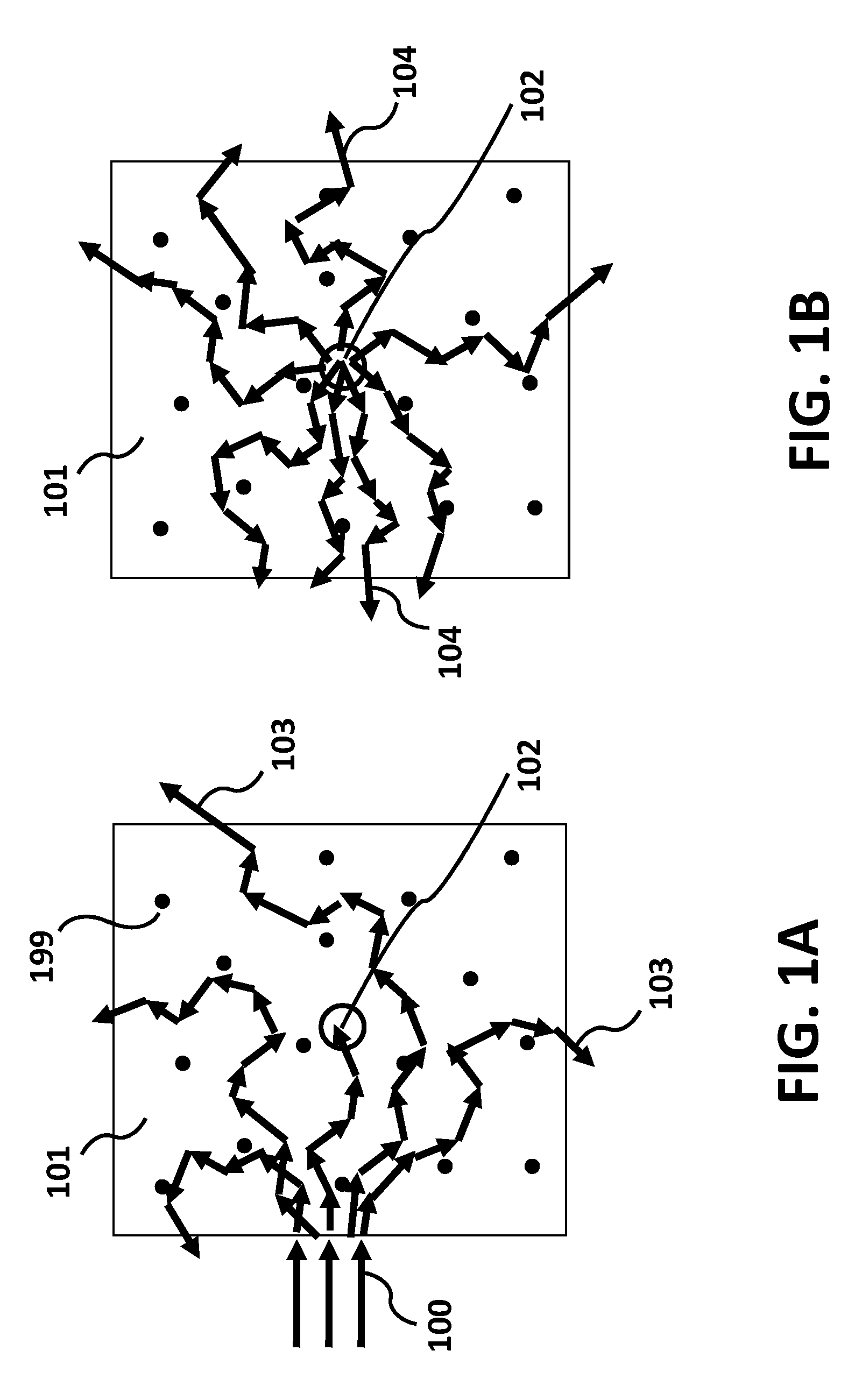
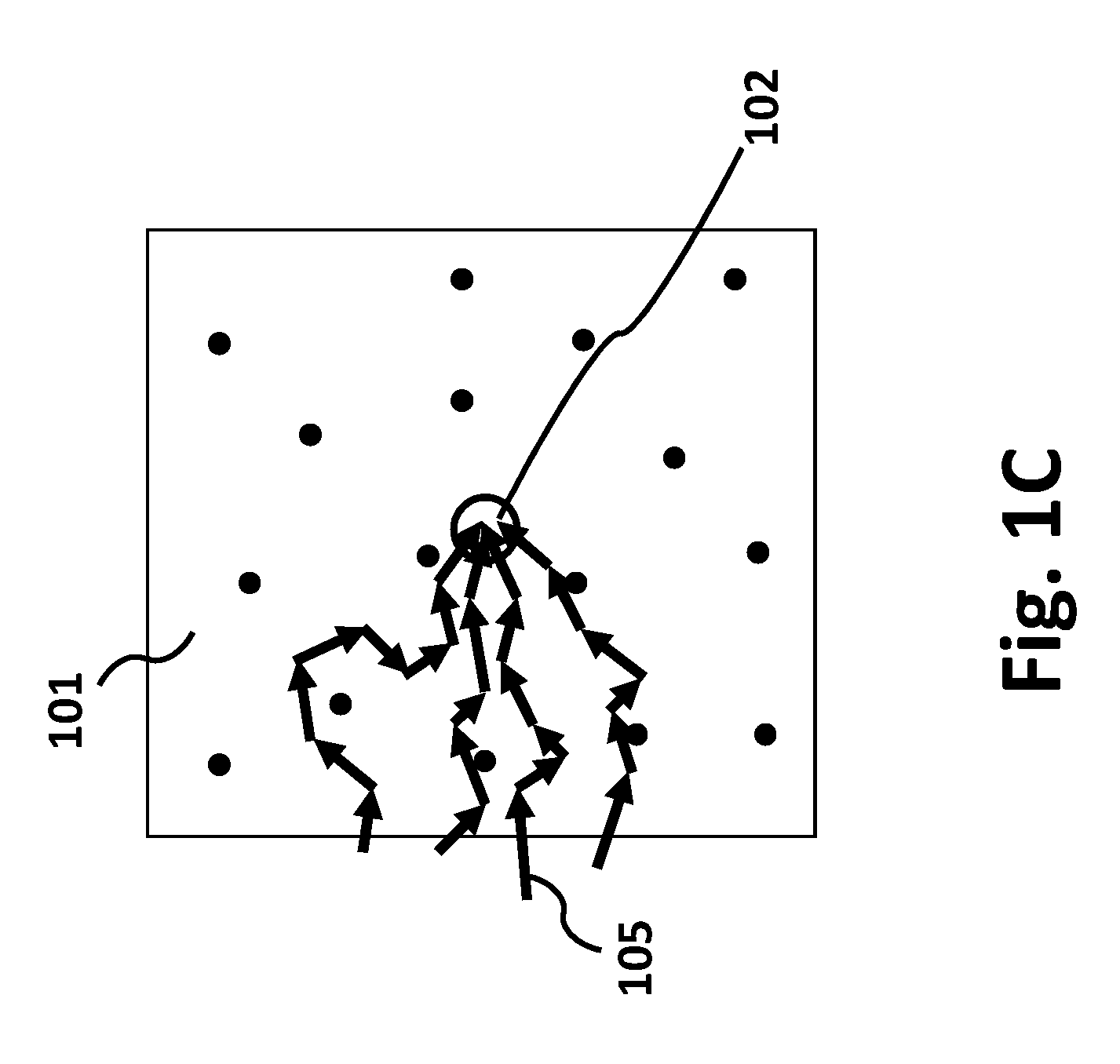
Phase conjugation is a physical transformation of a wave field where the resulting field has a reversed propagation direction but keeps its amplitudes and phases.
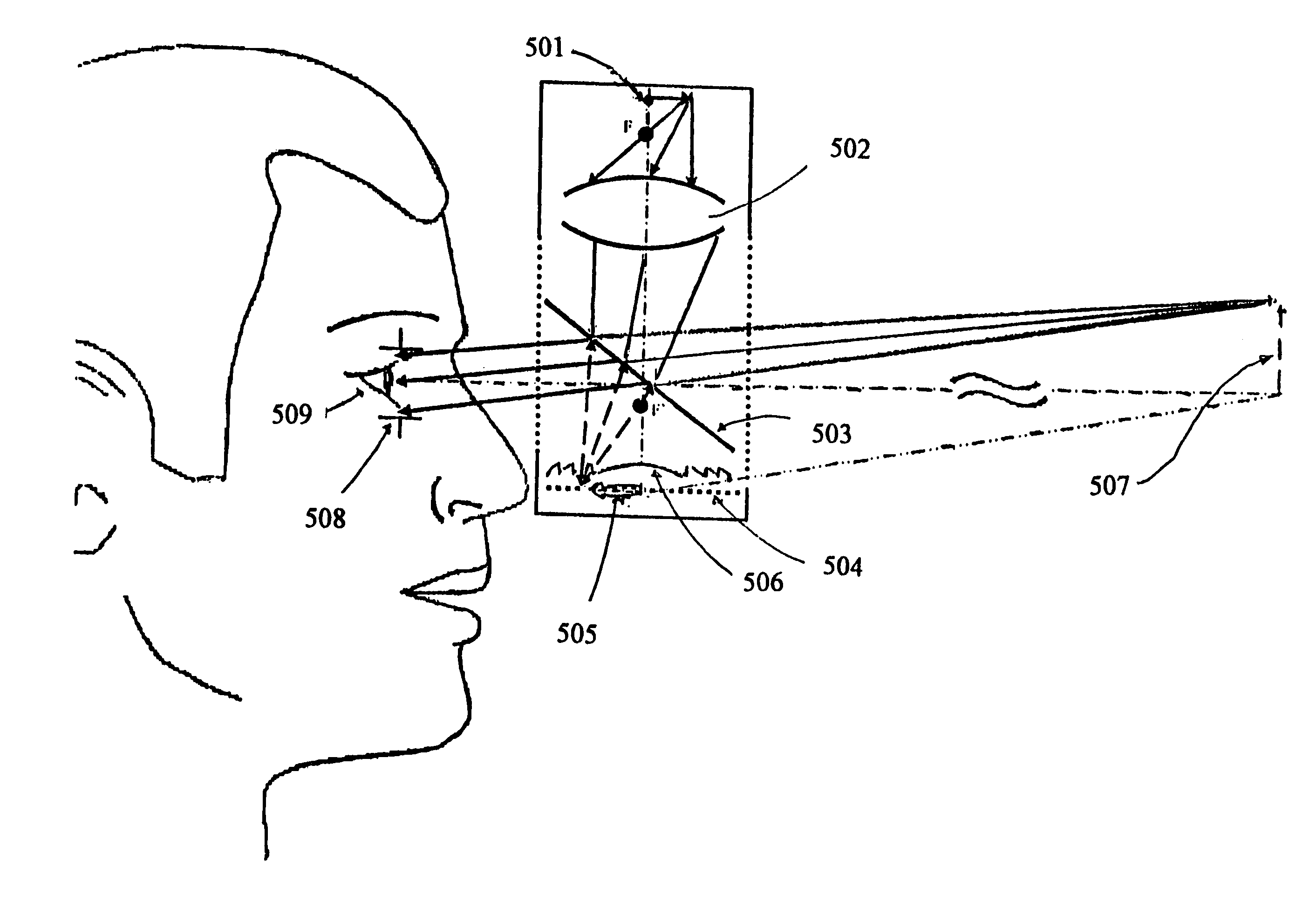
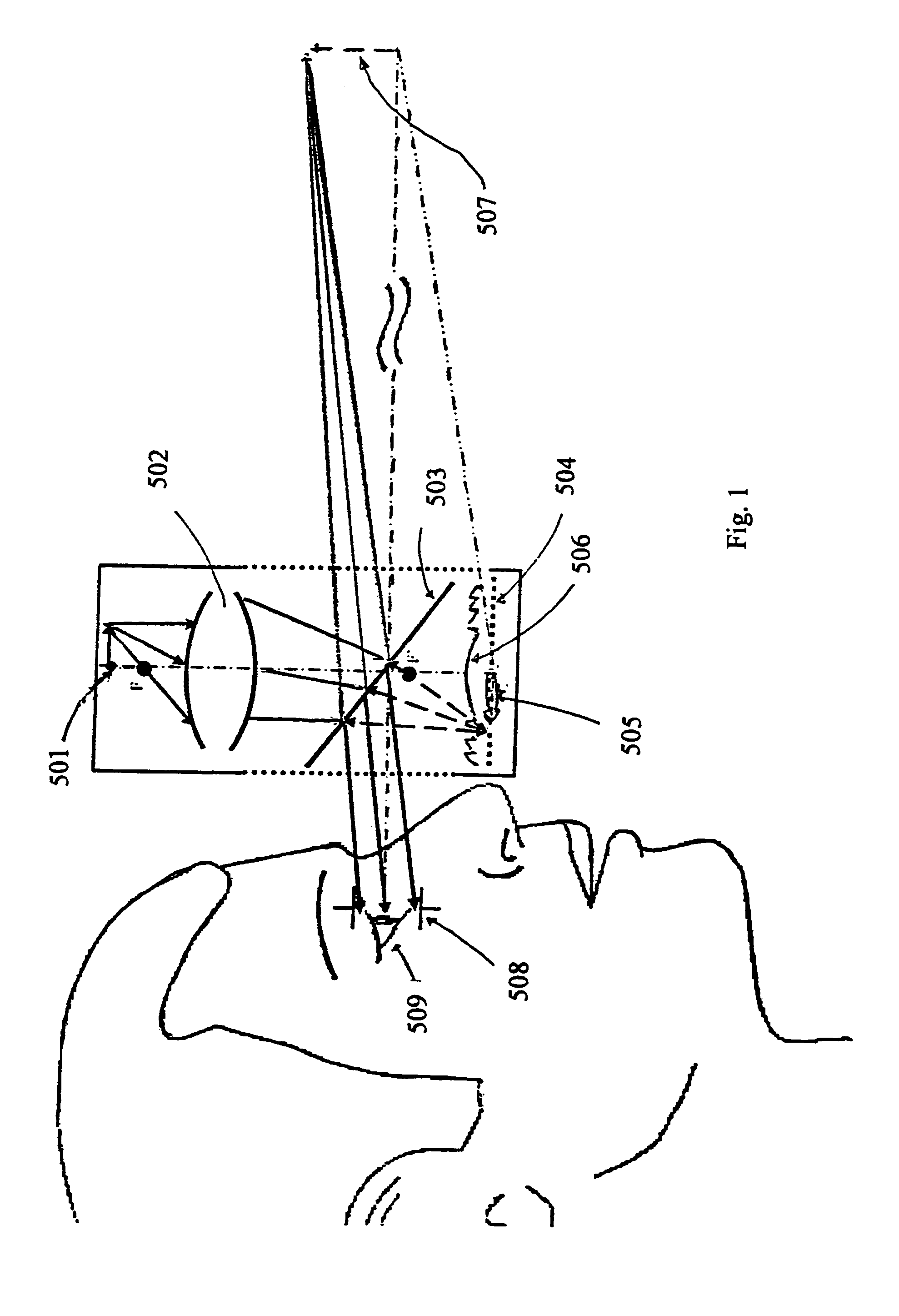
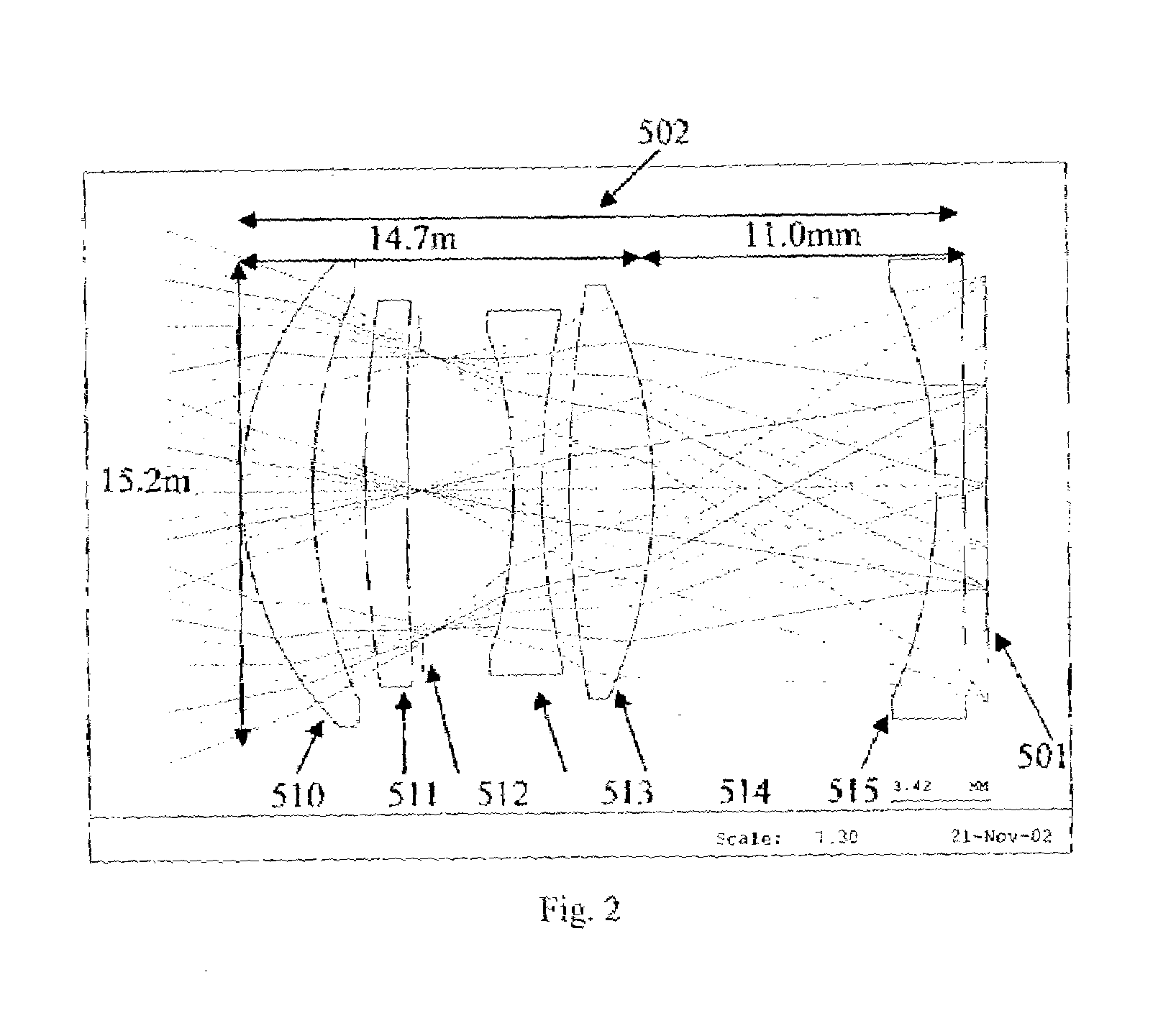
Head-mounted display by integration of phase-conjugate material
This invention has incorporated projective optics and phase conjugate material thus eliminating the requisite use of an external phase conjugate material to provide a see-through head mounted projective display. A key component of the invention is the use of optical imaging technology in combination with projective optics to make this revolutionary technology work. In previous head mounted projective displays the phase conjugate material had to be placed in the environment to display images, but in this invention one is not limited to the use of an external phase conjugate material but further extends its use to outdoor see-through augmented reality to produce images using the see-through head mounted projective display system. Furthermore, this invention extends the use of projective head mounted displays to clinical guided surgery, surgery medical, an outdoor augmented see-through virtual environment for military training and wearable computers.
Owner:CENT FLORIDA UNIV OF
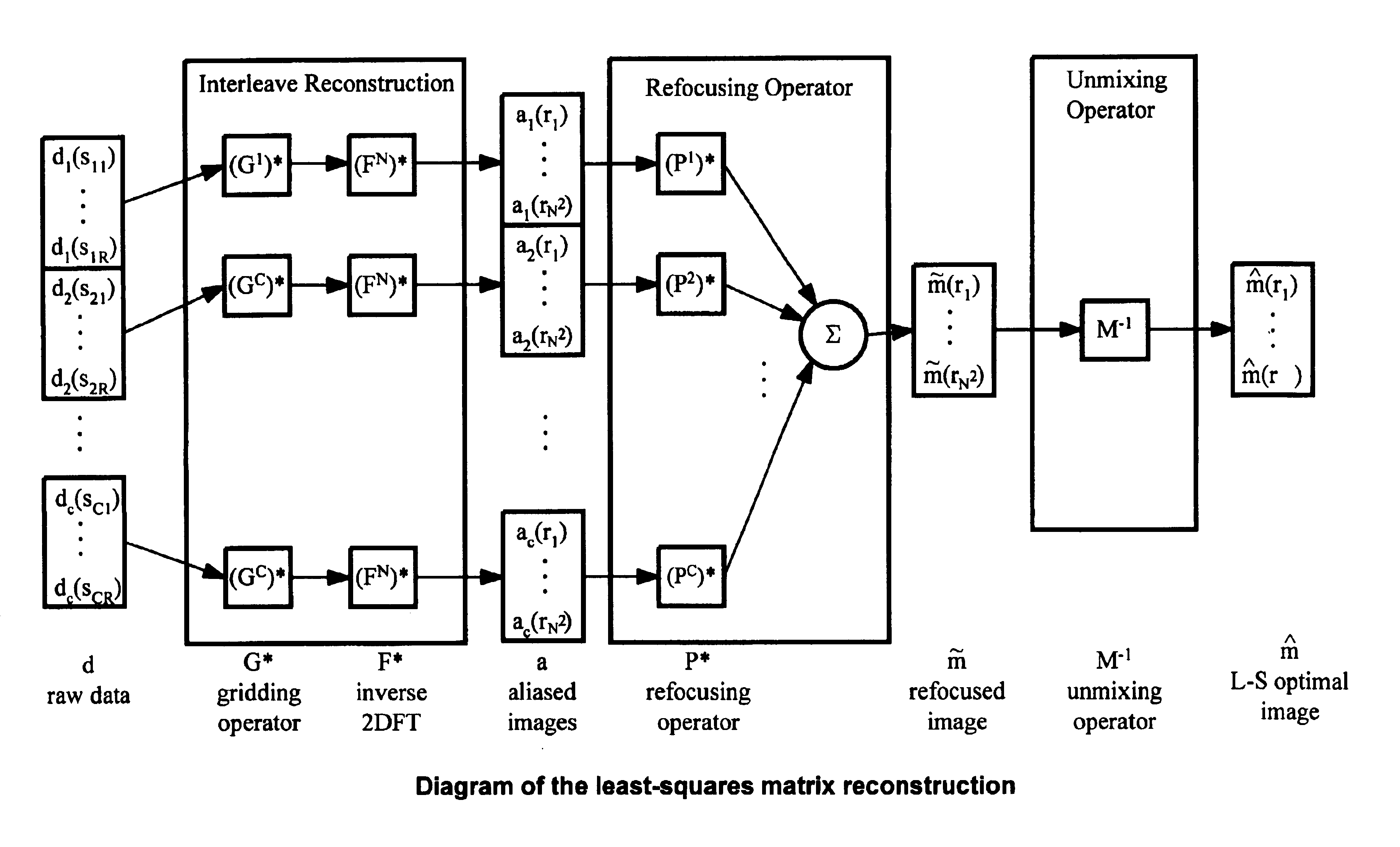
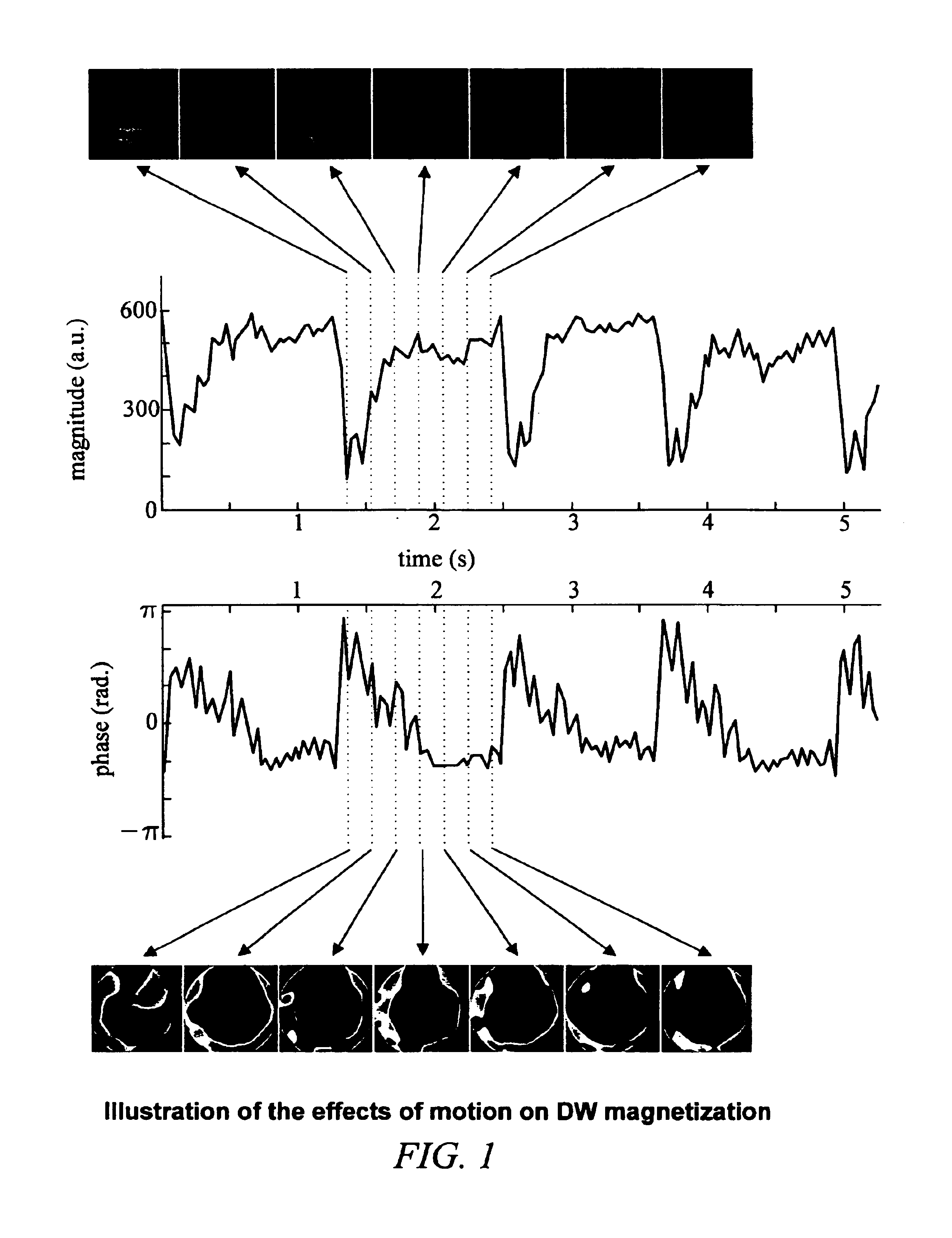
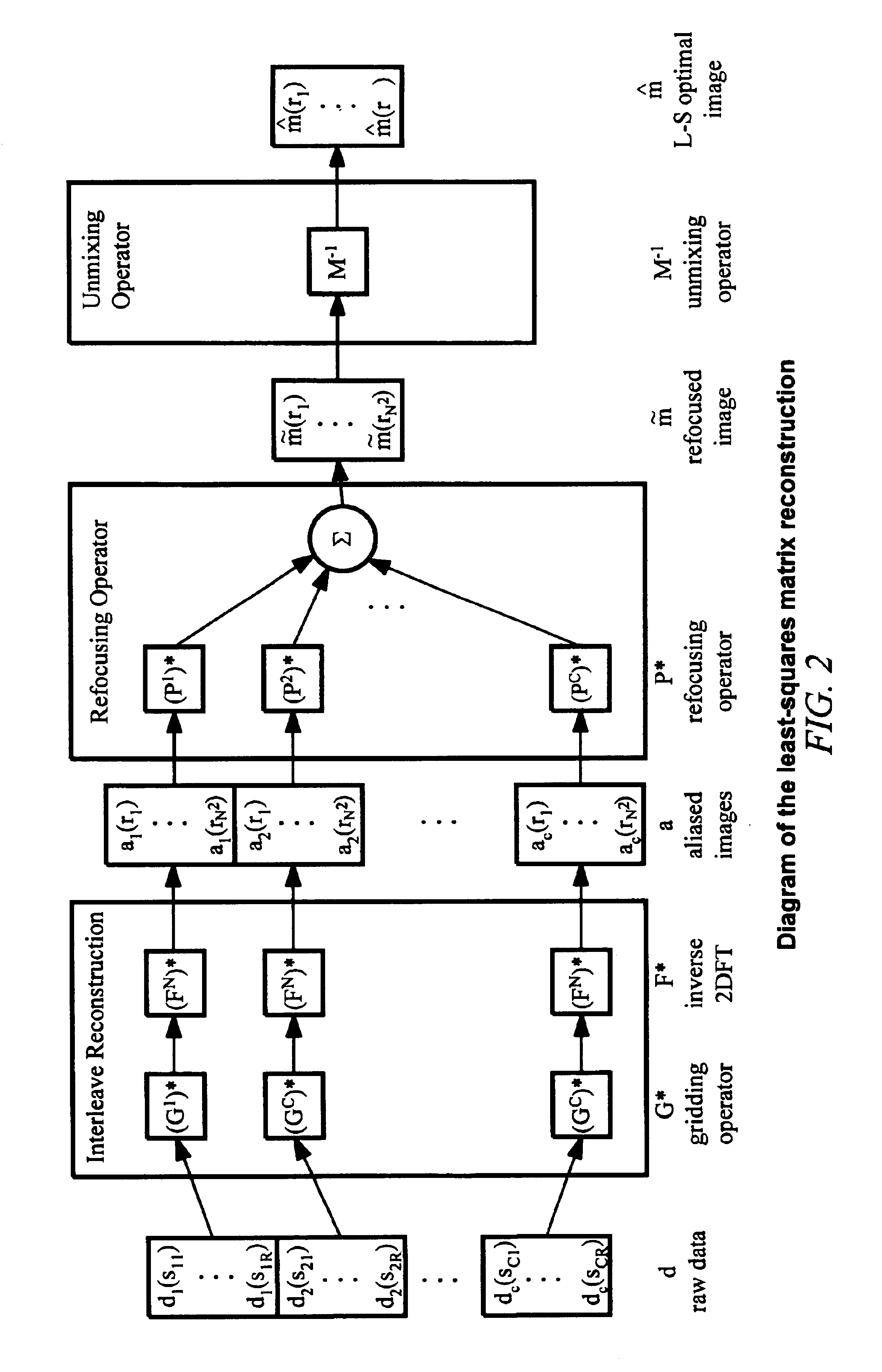
Method of removing dynamic nonlinear phase errors from MRI data
ActiveUS6853191B1Improve performanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionReconstruction methodComputer science
Disclosed is a generalized reconstruction method that corrects for non-linear phase errors based on least-squares estimation. An approximation of the least squares estimate utilizes refocusing reconstruction in which high-resolution data is multiplied by the phase conjugate of a navigator in image-space. The multiplication rephases the unaliased signal in the high-resolution data. The high-resolution data can then be added together coherently. The multiplication can be effected in k-space as a convolution using a gridding reconstruction of the high-resolution data using the low resolution navigator.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
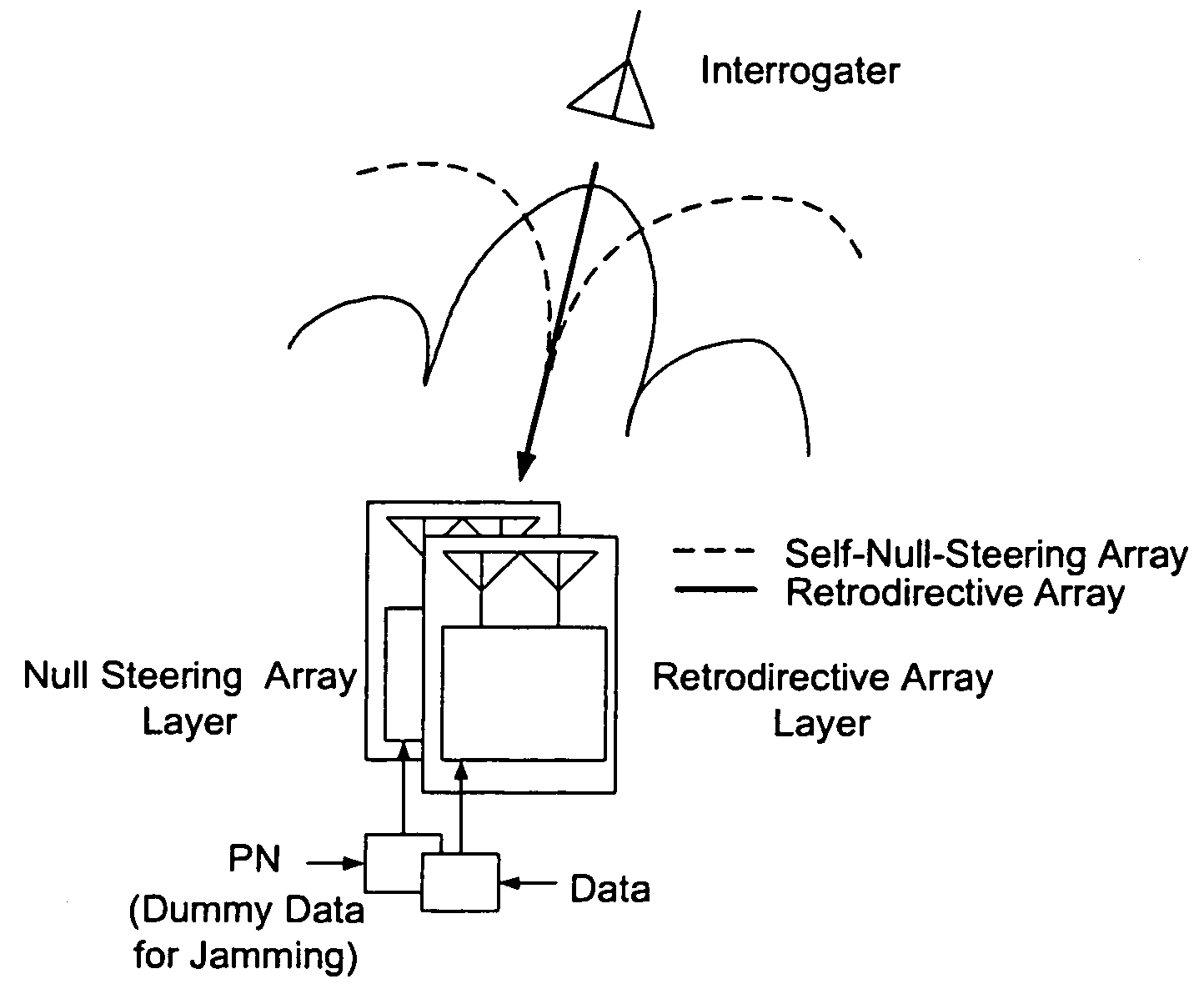
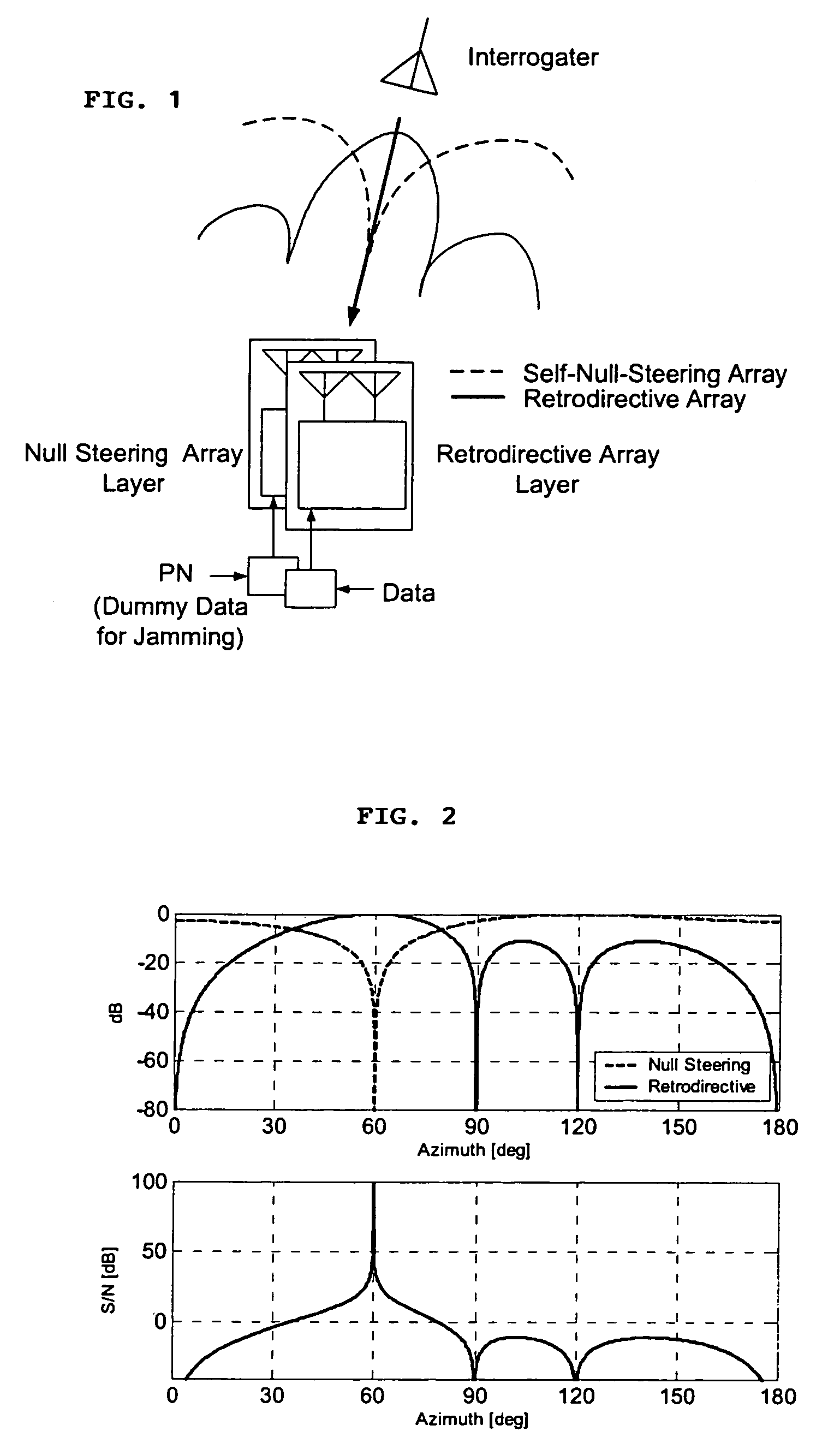
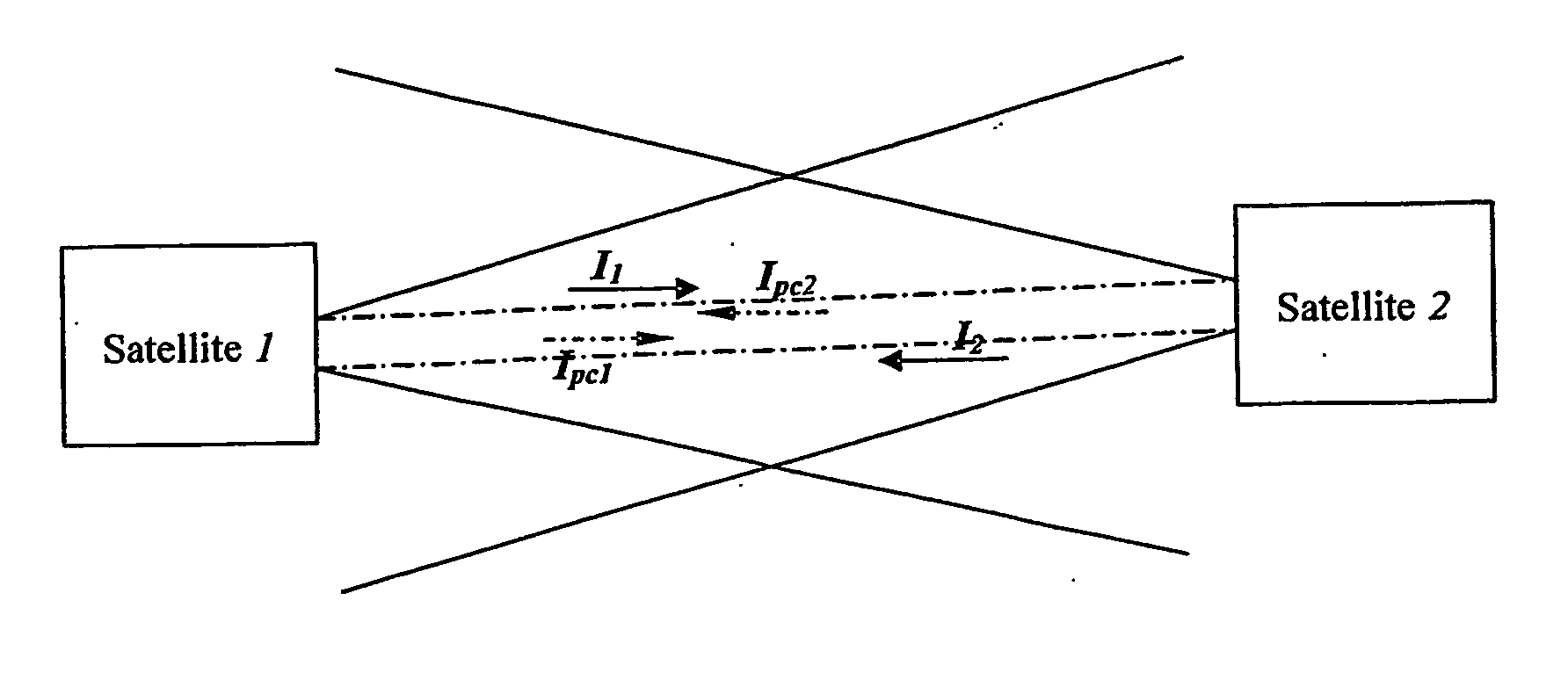
Microwave self-phasing antenna arrays for secure data transmission & satellite network crosslinks
ActiveUS7006039B2Increase user capacityImprove directivityRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsAntenna supports/mountingsTactical communicationsFrequency spectrum
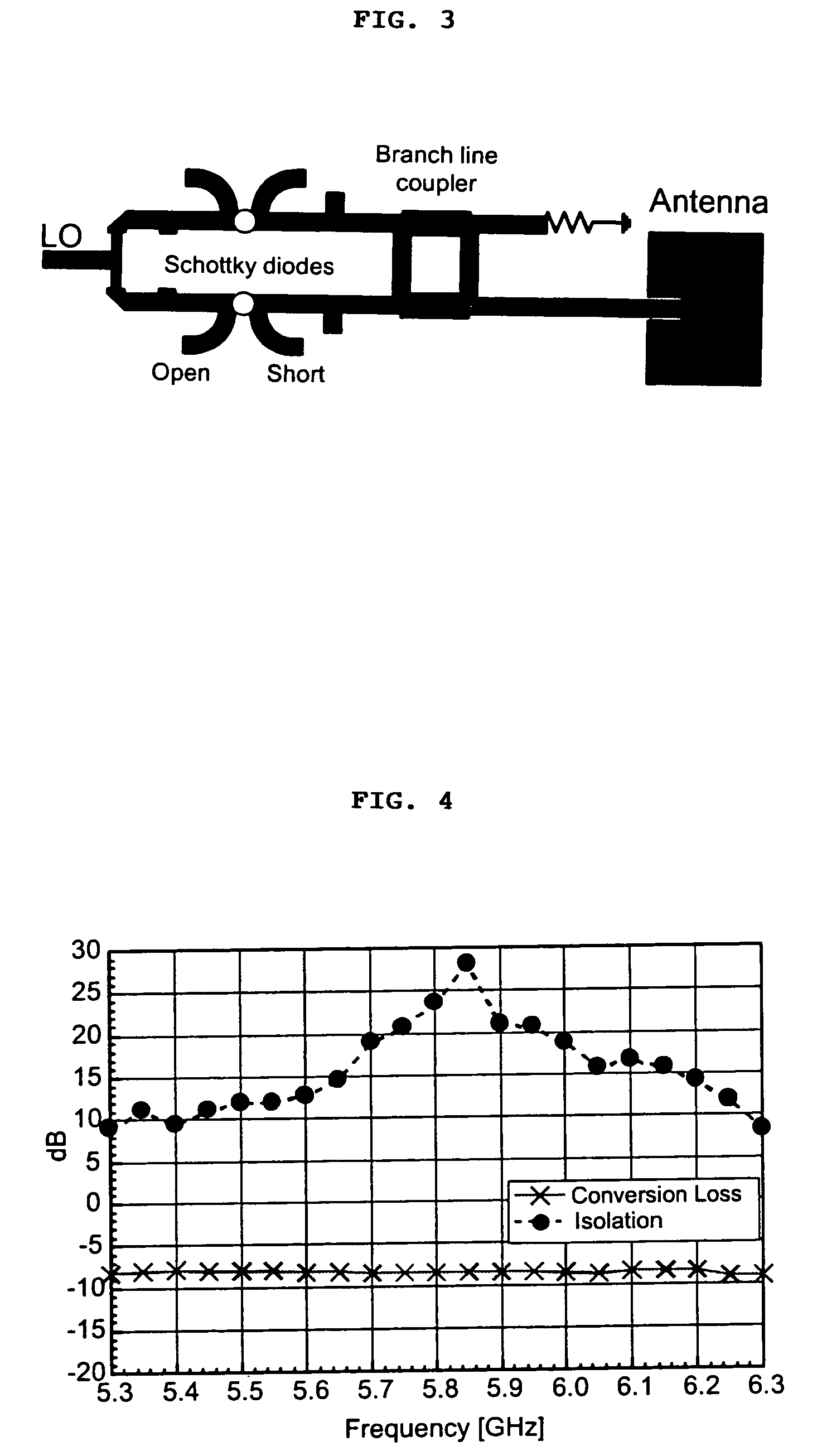
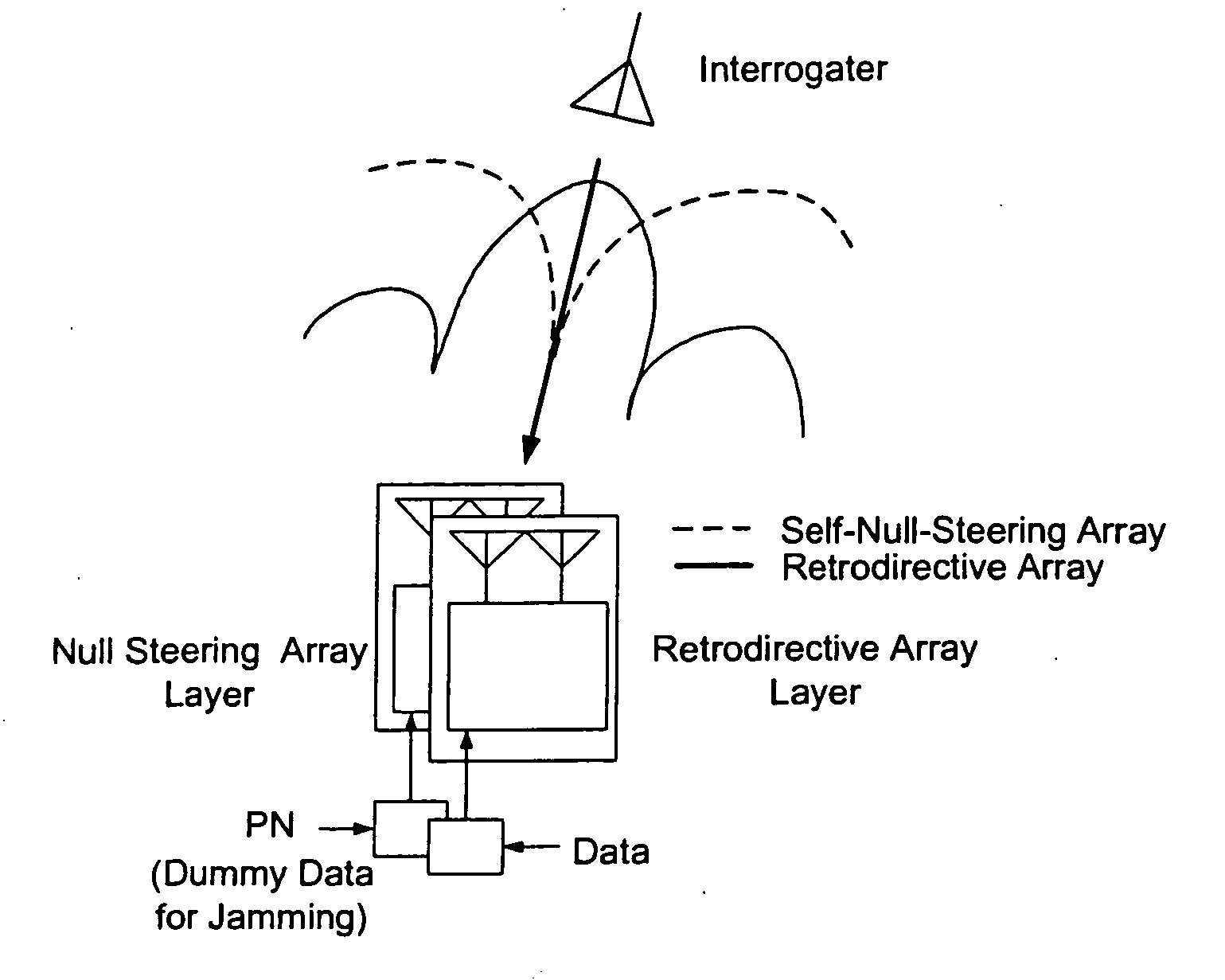
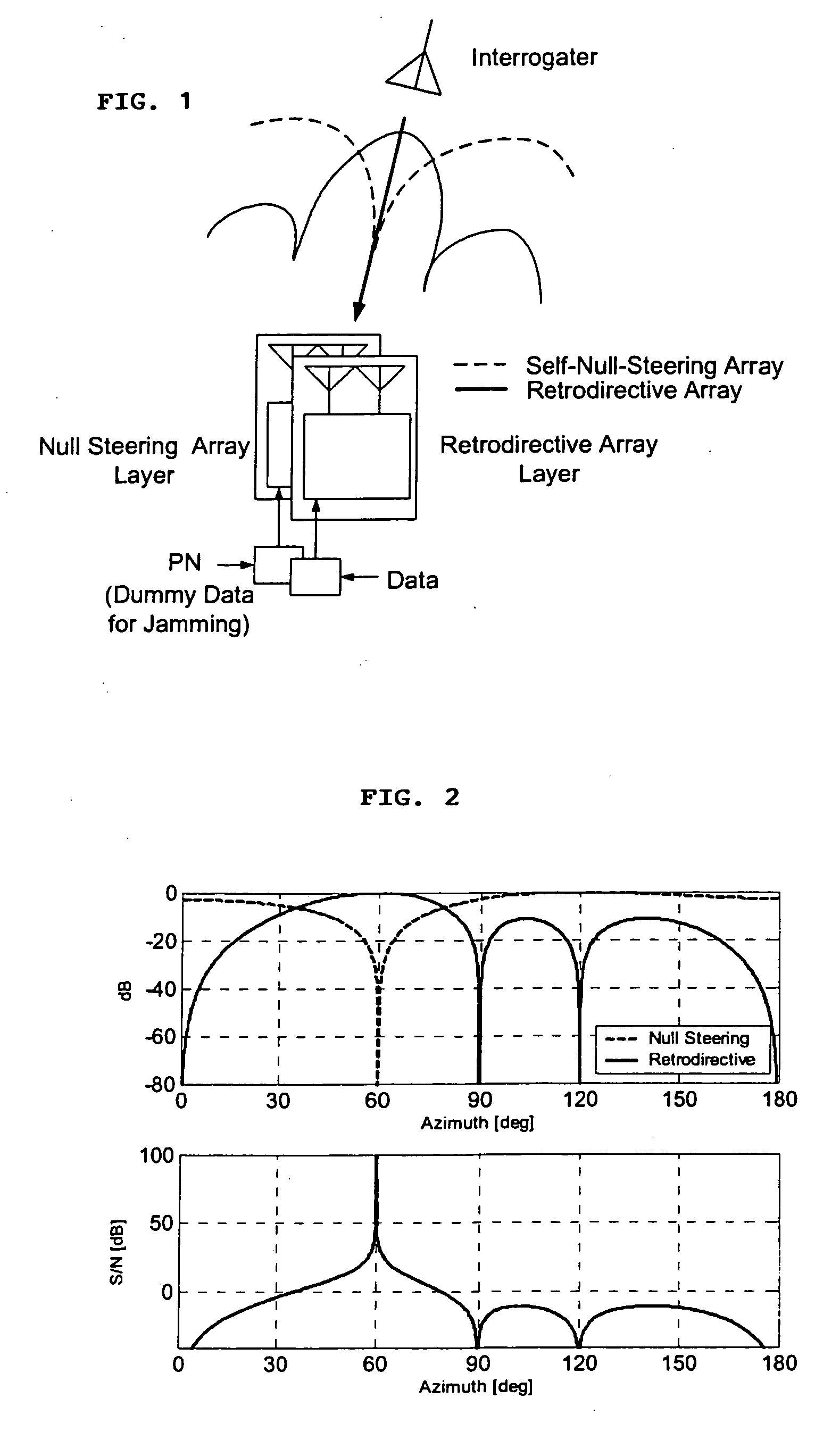
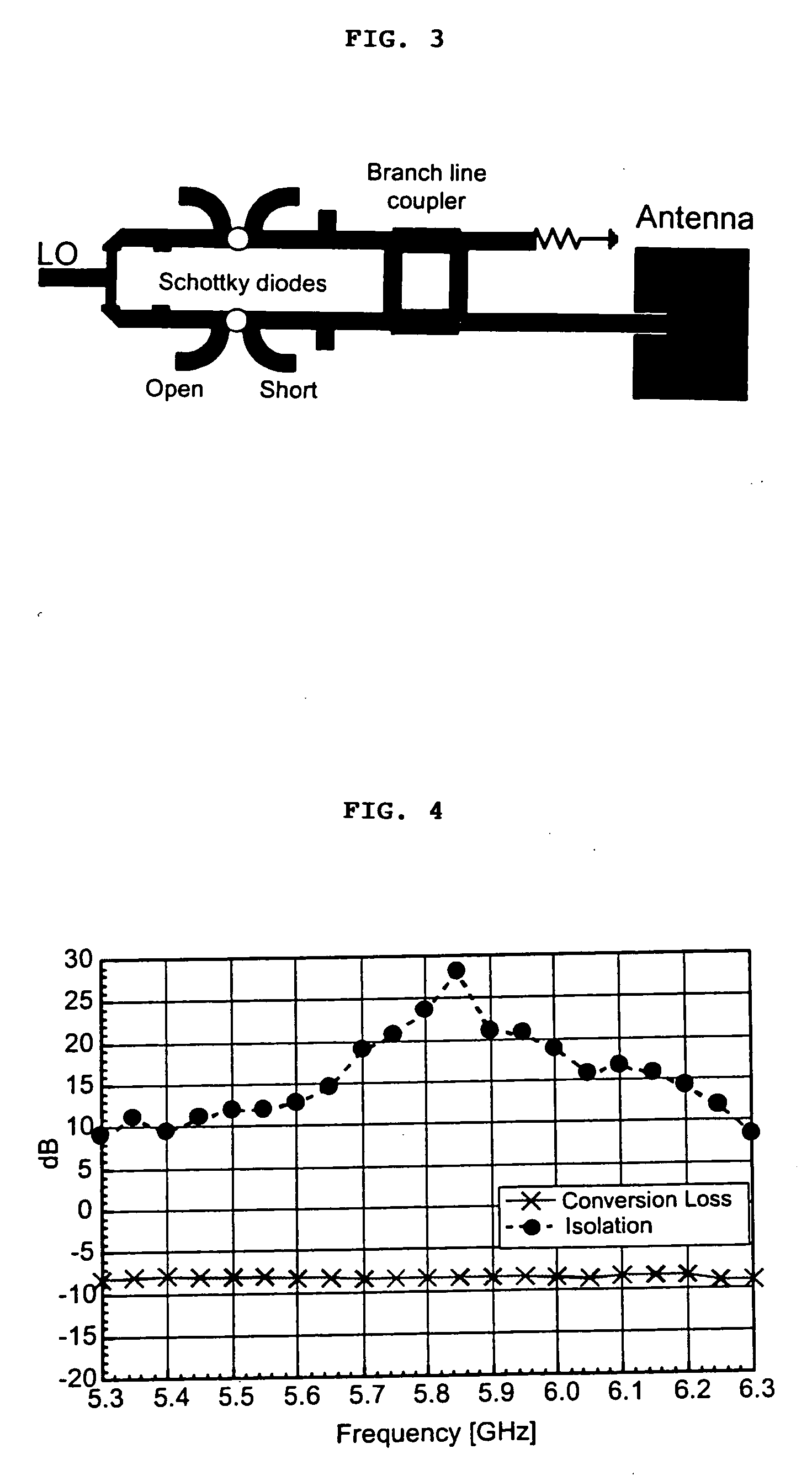
A high-directivity transponder system uses a dual system of a retrodirective array transmitting a data signal peak toward an interrogator source, and a self-null-steering array transmitting a null toward the interrogator source and a jamming signal elsewhere, resulting in high S / N reception at the interrogator source and avoidance of interception. Integrating modulators would allow each array to transmit different data while the spectra of the transmitted signals are identical, thus disabling interception. The system enables secure point-to-point communications and can be used for short-distance wireless data transmission systems such as wireless LAN and RFID servers. As another aspect, self-steering signal transmission is employed for randomly oriented satellites using circularly polarized, two-dimensional retrodirective arrays. Quadruple subharmonic mixing is used as an effective means of achieving phase conjugation when a high-frequency LO is not feasible or inapplicable. These features may be used for small-satellite communications, secure tactical communications, search and rescue, enemy location fixing and tracking, UAV command and control, forest fire detection, marine-based tracking, and many other applications requiring secure communications with high signal directivity.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII
Communication Through Phase-Conjugated Optical Variants
InactiveUS20130070786A1Improve signal qualityDegradation of bit error ratioTime-division multiplexEnergy based wastewater treatmentNonlinear distortionTransport system
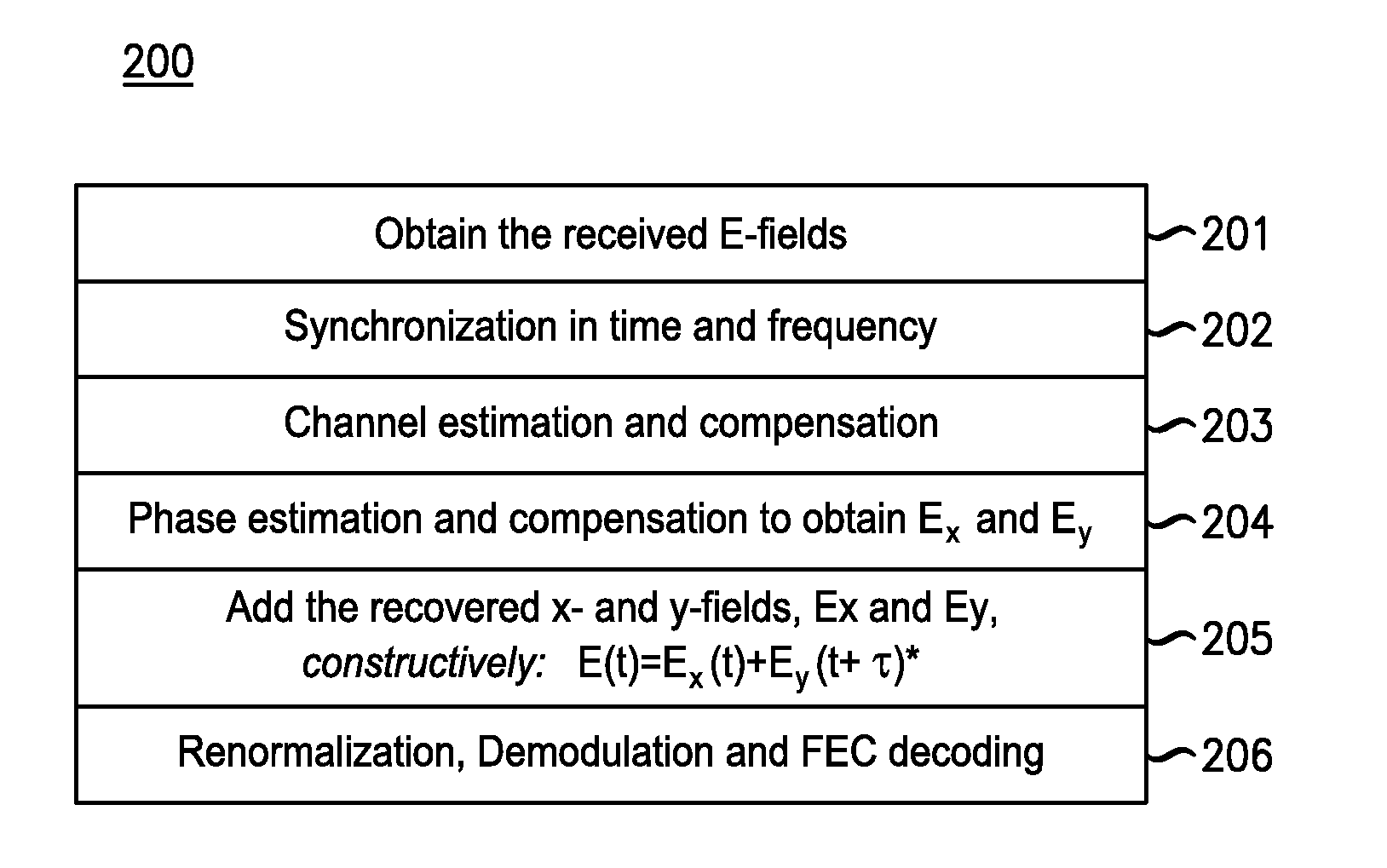
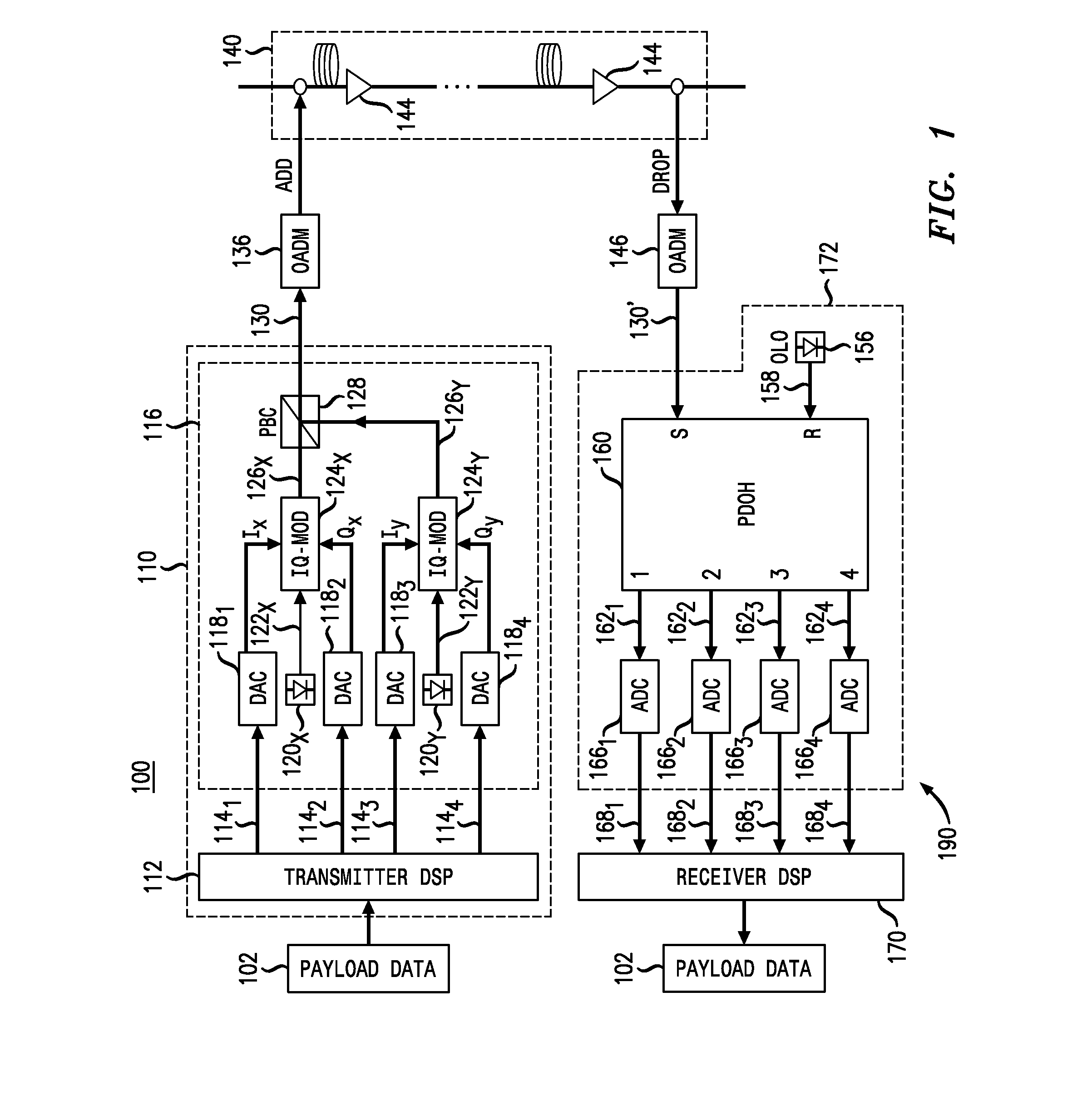
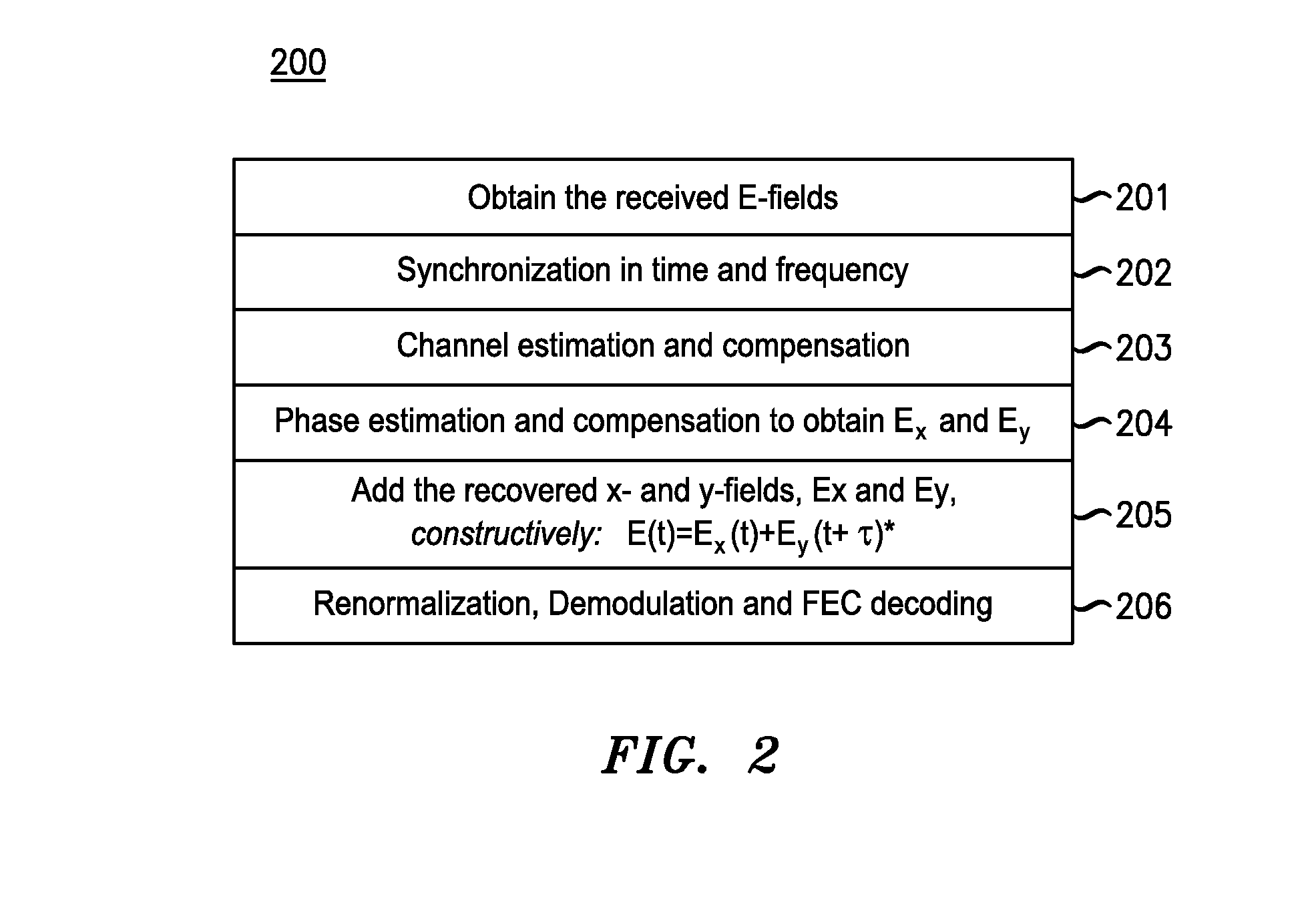
An optical transport system configured to transmit at least two phase-conjugated optical variants carrying the same modulated symbols, with the phase-conjugated optical variants in being different from one another in one or more of polarization of light, the time of transmission, spatial localization, optical carrier wavelength, and subcarrier frequency during transmission. The two phase-conjugated optical variants can be generated by a single polarization-diversity transmitter to be orthogonally polarized, and propagate through an optical transmission link with the same wavelength and spatial path. The optical variants are detected and processed at the receiver in a manner that enables coherent summation of the corresponding electrical signals prior to constellation de-mapping. The coherent summation tends to cancel out the deleterious effects of nonlinear distortions imparted on the individual phase-conjugated optical variants in an optical fiber transmission link because said nonlinear distortions tend to be opposite to each other.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Apparatus and method for irradiating a medium
InactiveUS20110071402A1Holographic light sources/light beam propertiesMaterial analysis by optical meansReference waveOptics
A method for irradiating a medium includes irradiating the medium with an electromagnetic wave which is scattered in the medium and modulated in frequency at a position in the medium; obtaining information corresponding to an interference pattern generated by interference between the modulated electromagnetic wave and a reference wave; and generating a phase conjugate wave, based on the obtained information, which irradiates the medium.
Owner:CANON KK
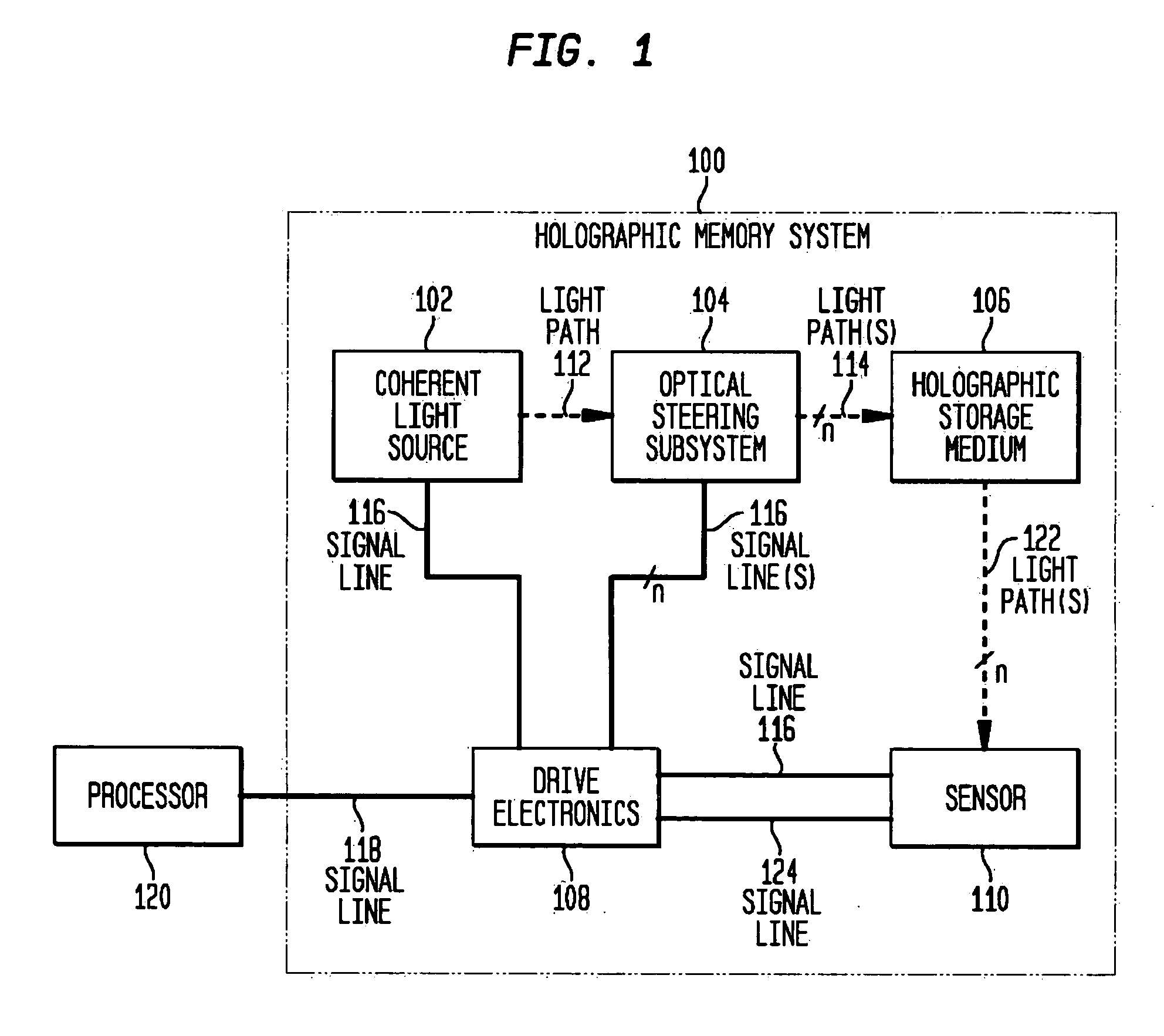
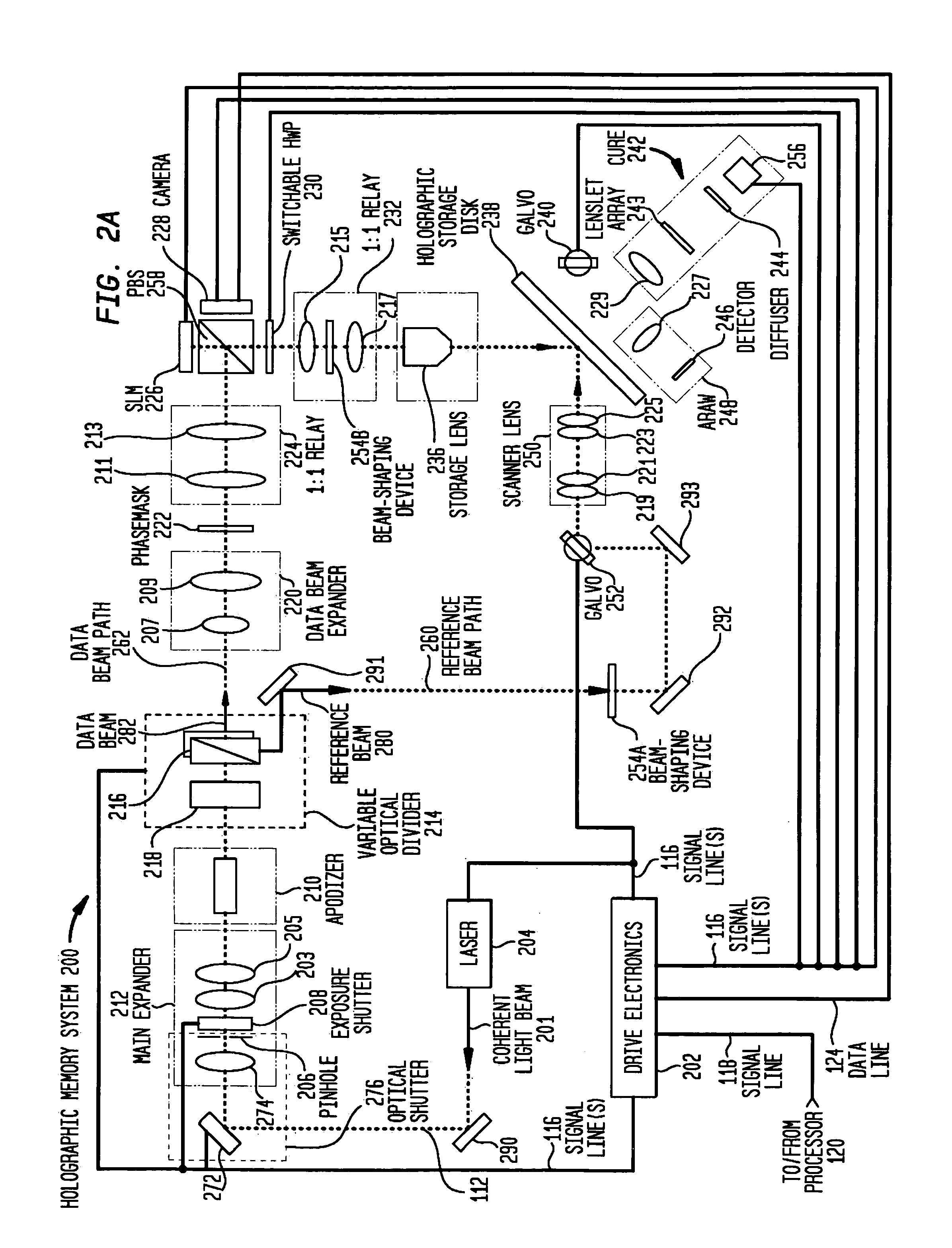
Phase conjugate reconstruction of a hologram
InactiveUS20060279823A1Holographic light sources/light beam propertiesRecording/reproducing/erasing using optical interference patternsHolographic storageLight beam
Methods and systems are provided for obtaining a phase conjugate reconstruction beam for use in retrieving holographic information from a holographic storage medium. These methods and systems include generating a coherent light beam that is a reproduction of the reference beam used in storing the holographic information in the storage medium. This coherent light beam is then directed through the holographic storage medium at the same angle and location of the reference beam during recording of the hologram. The directed coherent beam is then reflected back through the storage medium so that the reflected coherent light beam provides a phase conjugate of the reference beam and passes through the storage medium at the same angle and location that the reference beam passed through the storage medium during recordation of the hologram.
Owner:AKONIA HOLOGRAPHICS
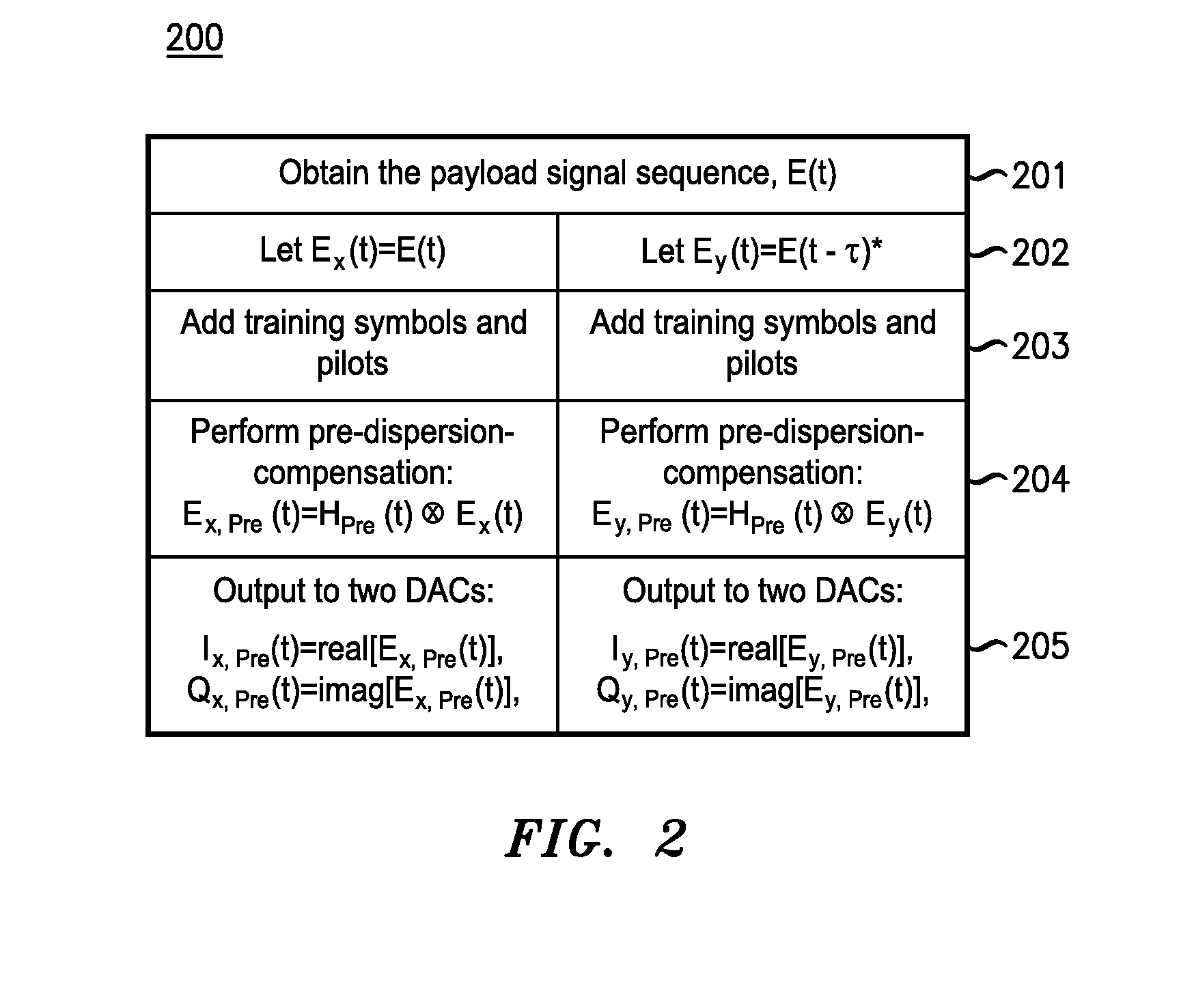
Communication through pre-dispersion-compensated phase-conjugated optical variants
ActiveUS20130071119A1Provide securityEffectively cancellingPolarisation multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersCarrier signalEngineering
An apparatus comprises an optical transmitter that comprises a processor and at least one optical modulator. The processor is configured to generate electronic representations of at least two pre-dispersion-compensated phase-conjugated optical variants carrying a same modulated payload data for transmission. The at least one optical modulator is configured to modulate the electronic representations, wherein an amount of dispersion induced on the pre-dispersion-compensated phase-conjugated optical variants depends on an accumulated dispersion (AD) of a transmission link through which the pre-dispersion-compensated phase-conjugated optical variants are to be transmitted. The amount of dispersion induced on the phase-conjugated optical variants may be approximately −AD / 2, where AD is the accumulated dispersion of the transmission link. The pre-dispersion-compensated phase-conjugated optical variants are different from one another in one or more dimensions such as the polarization of light, the time of transmission, the spatial localization, the optical carrier wavelength, or the subcarrier frequency during transmission.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
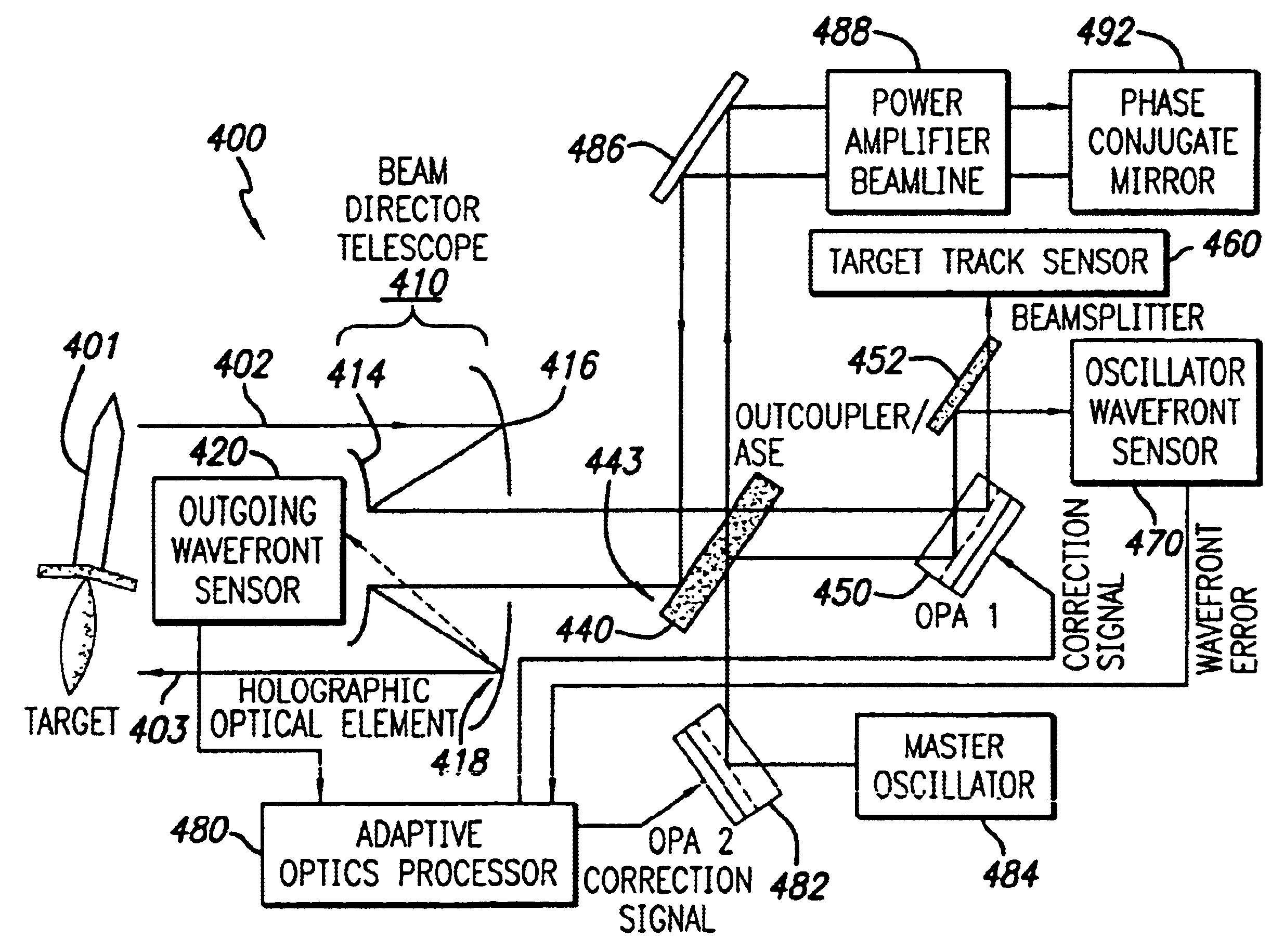
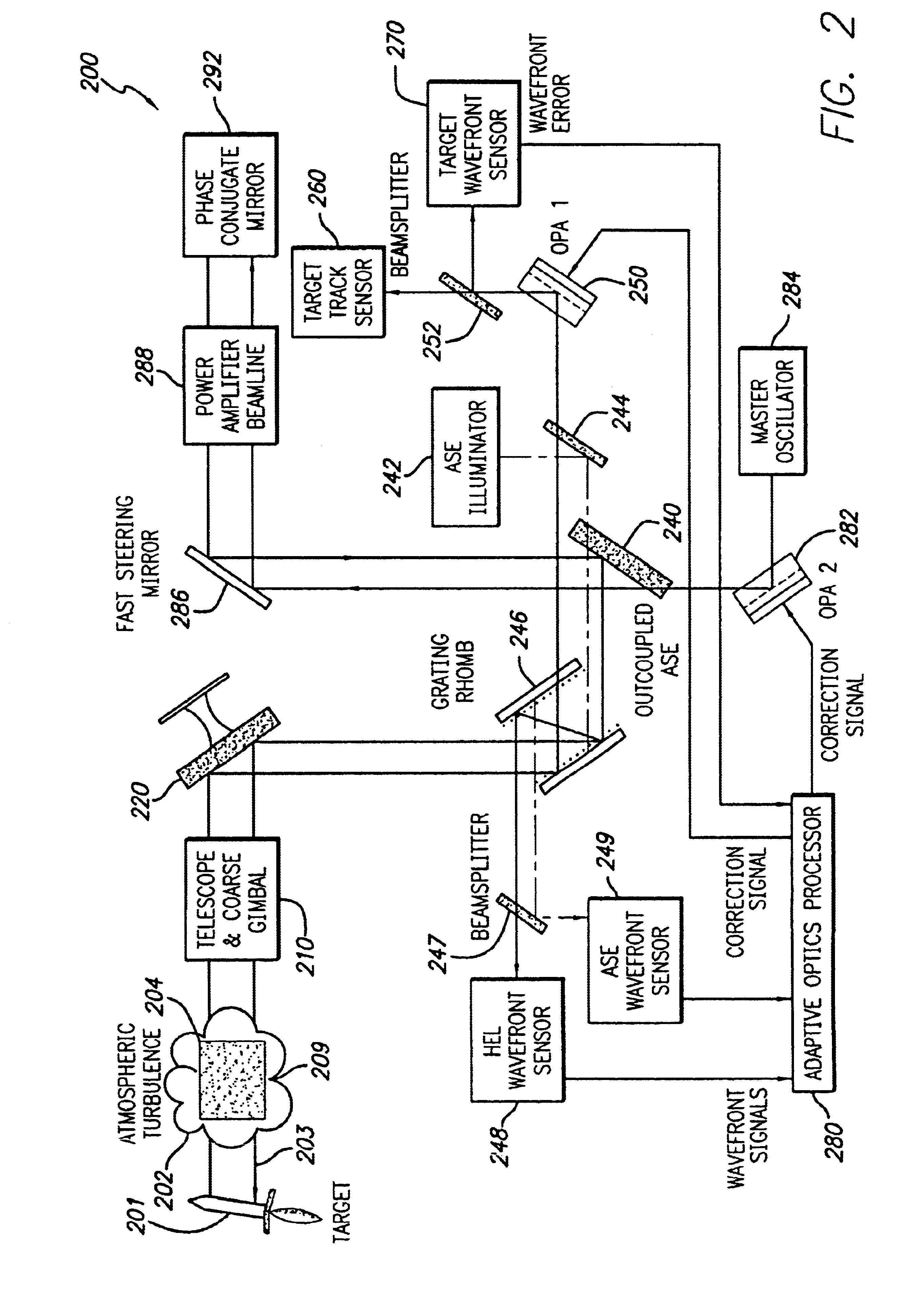
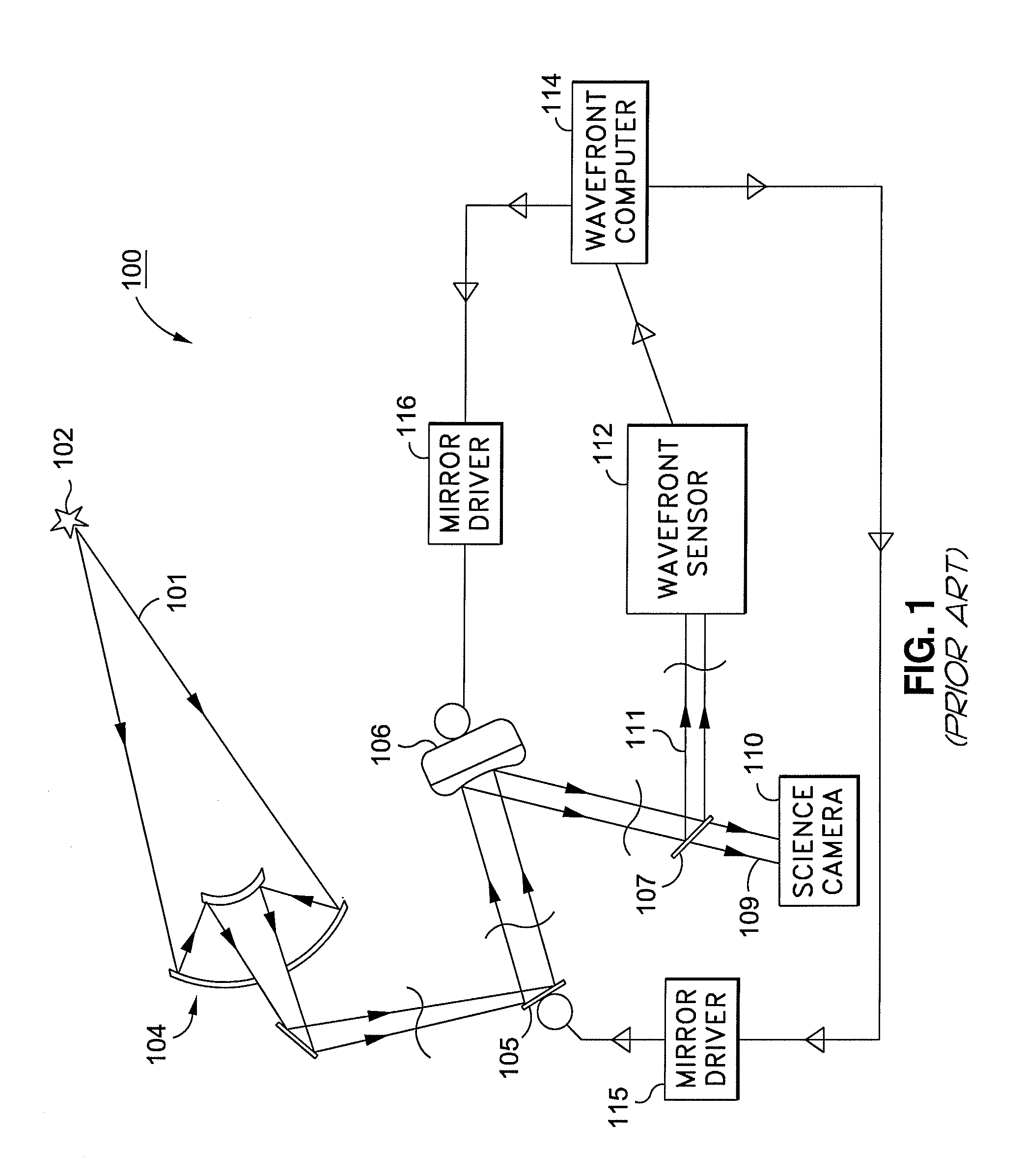
System and method for effecting high-power beam control with outgoing wavefront correction utilizing holographic sampling at primary mirror, phase conjugation, and adaptive optics in low power beam path
InactiveUS6849841B2Cancellation effectPhotometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansWavefront sensorPhased array
A beam control system and method. In an illustrative embodiment, the inventive system (500) provides a first beam of electromagnetic energy (503); samples the first beam (503) and provides a second beam (505) in response thereto; detects aberrations in the second beam (505); and corrects aberrations in the first beam (503) in response to the detected aberrations. In a specific implementation, the invention (500) includes a beam director telescope (510) having a primary mirror (516) on which a holographic optical element (518) is disposed. The holographic optical element (518) samples the output high-power beam and provides a sampled beam to a wavefront sensor (520). The wavefront sensor (520) provides signals to an adaptive optics processor (580). The adaptive optics processor (580) analyzes the sampled wavefront, detects aberrations therein and provides a correction signal to an optical phased array (550).
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Method for employing multipath propagation in wireless radio communications
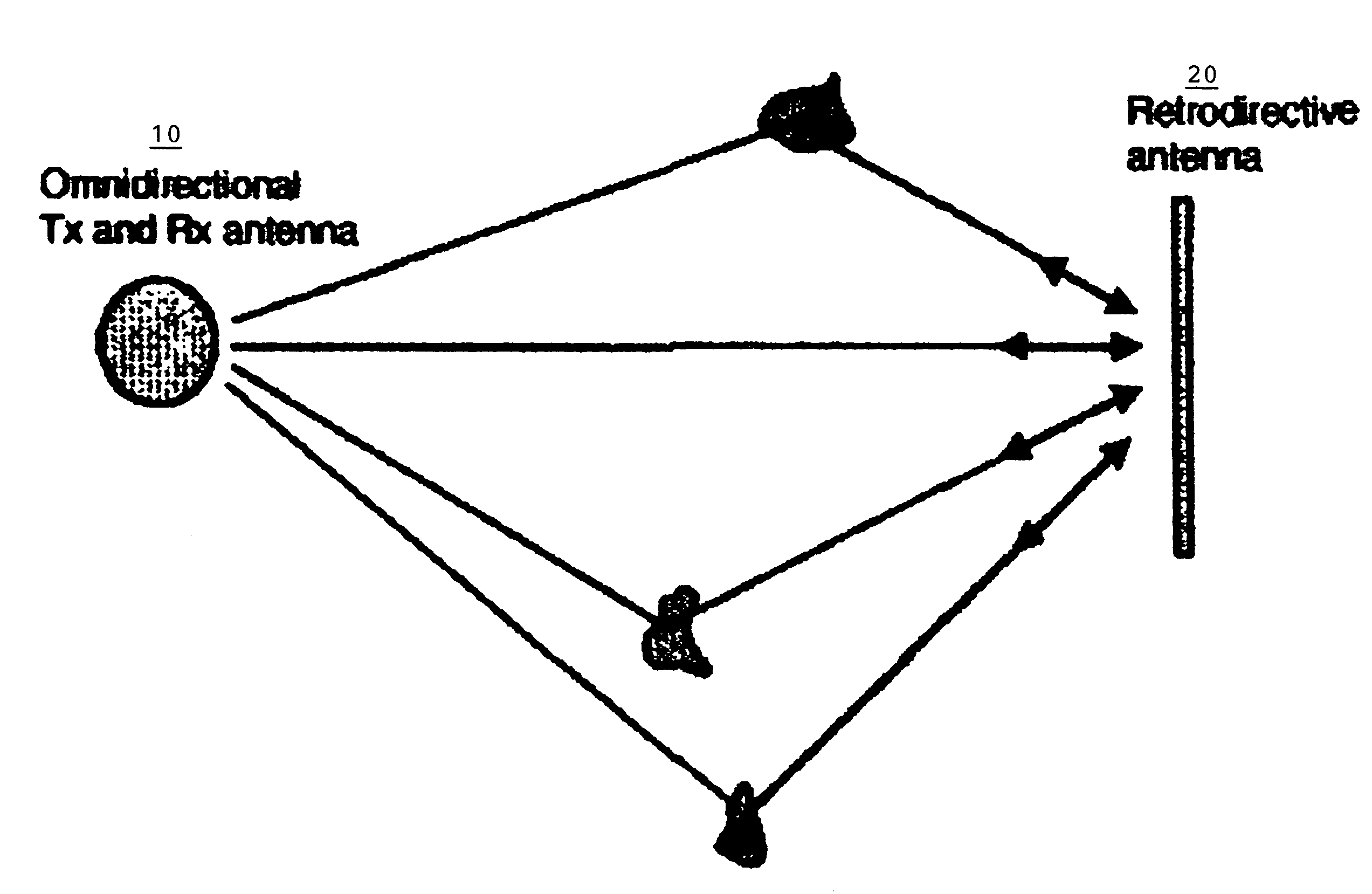
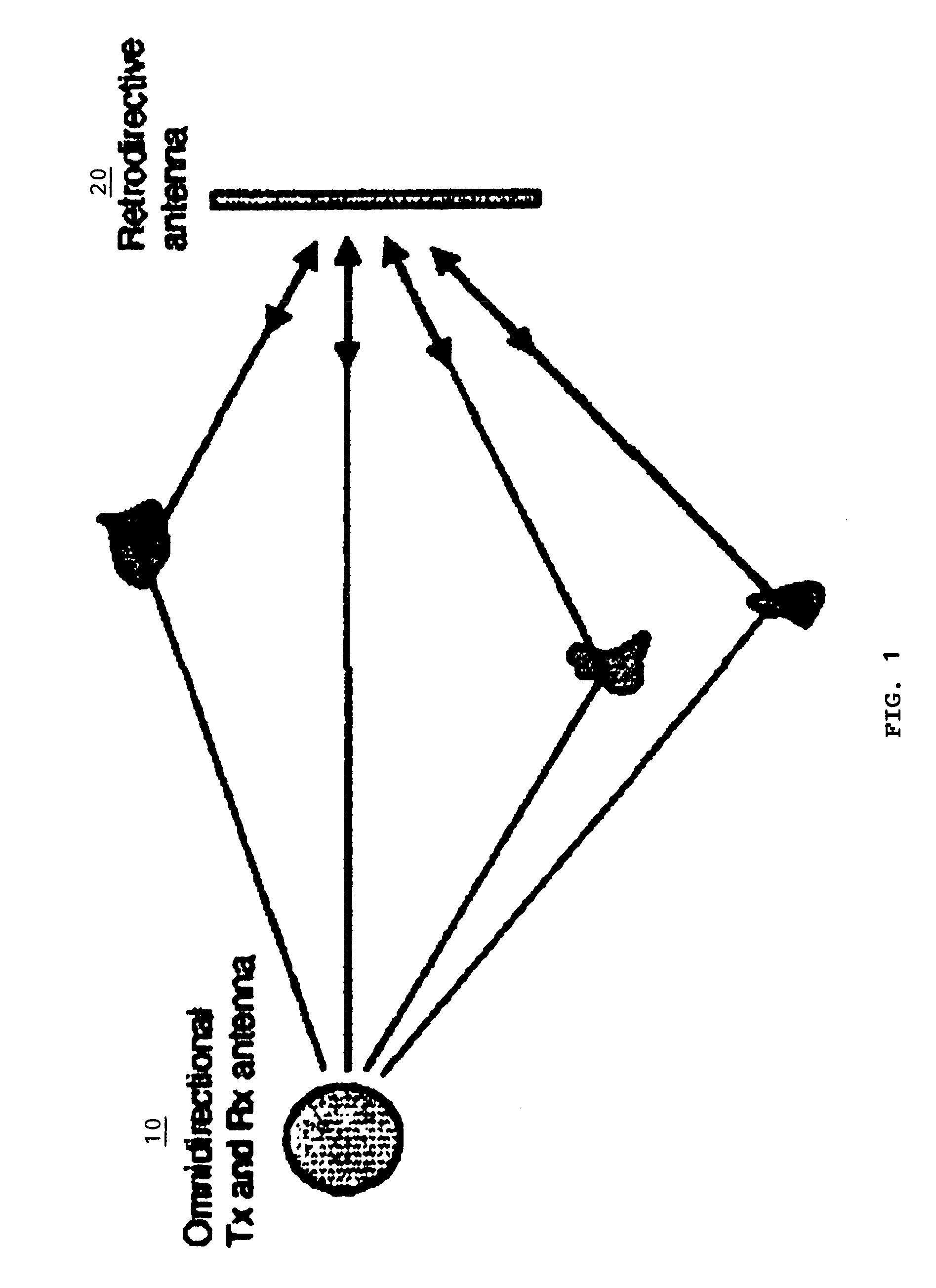
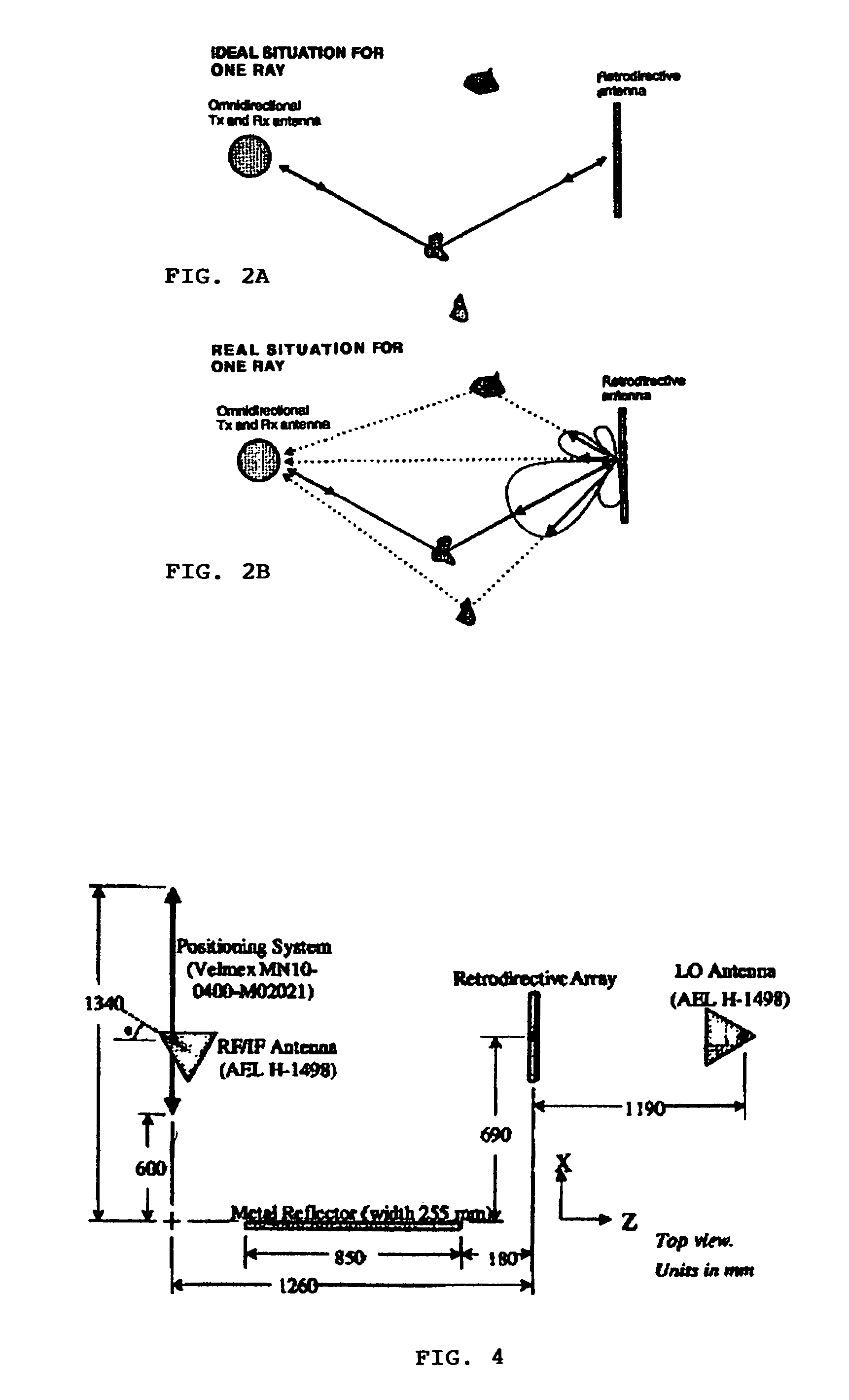
InactiveUS7440766B1Reduce negative impactAntenna supports/mountingsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsOmnidirectional antennaSimplex communication
A method of employing multipath propagation in wireless radio communications uses an omnidirectional transmitting / receiving antenna at one end of a transmission link to send an interrogating signal across an environment subject to multipath disturbances to a phase-conjugating retrodirective antenna, and the retrodirective antenna returns a communication signal along the multiple pathways taken by the interrogating signal to the omnidirectional antenna despite the multipath disturbances. In a simplex communication mode, the retrodirective antenna sends a return signal mixed with a communication signal to the omnidirectional antenna. In a duplex communication mode, both an omnidirectional antenna and a phase-conjugating retrodirective antenna are operated in tandem at each end of the transmission link to provide effective two-way wireless radio transmissions.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII
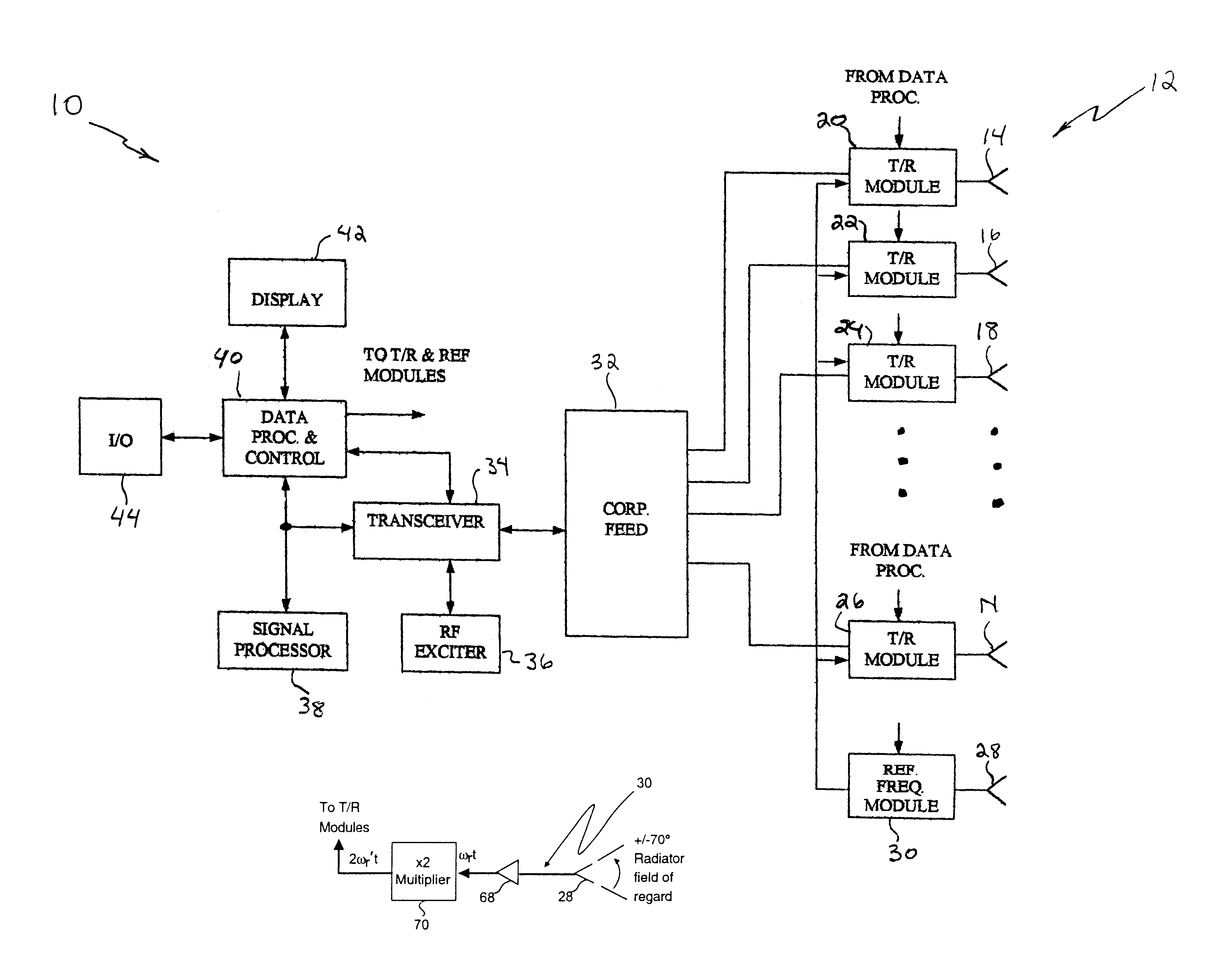
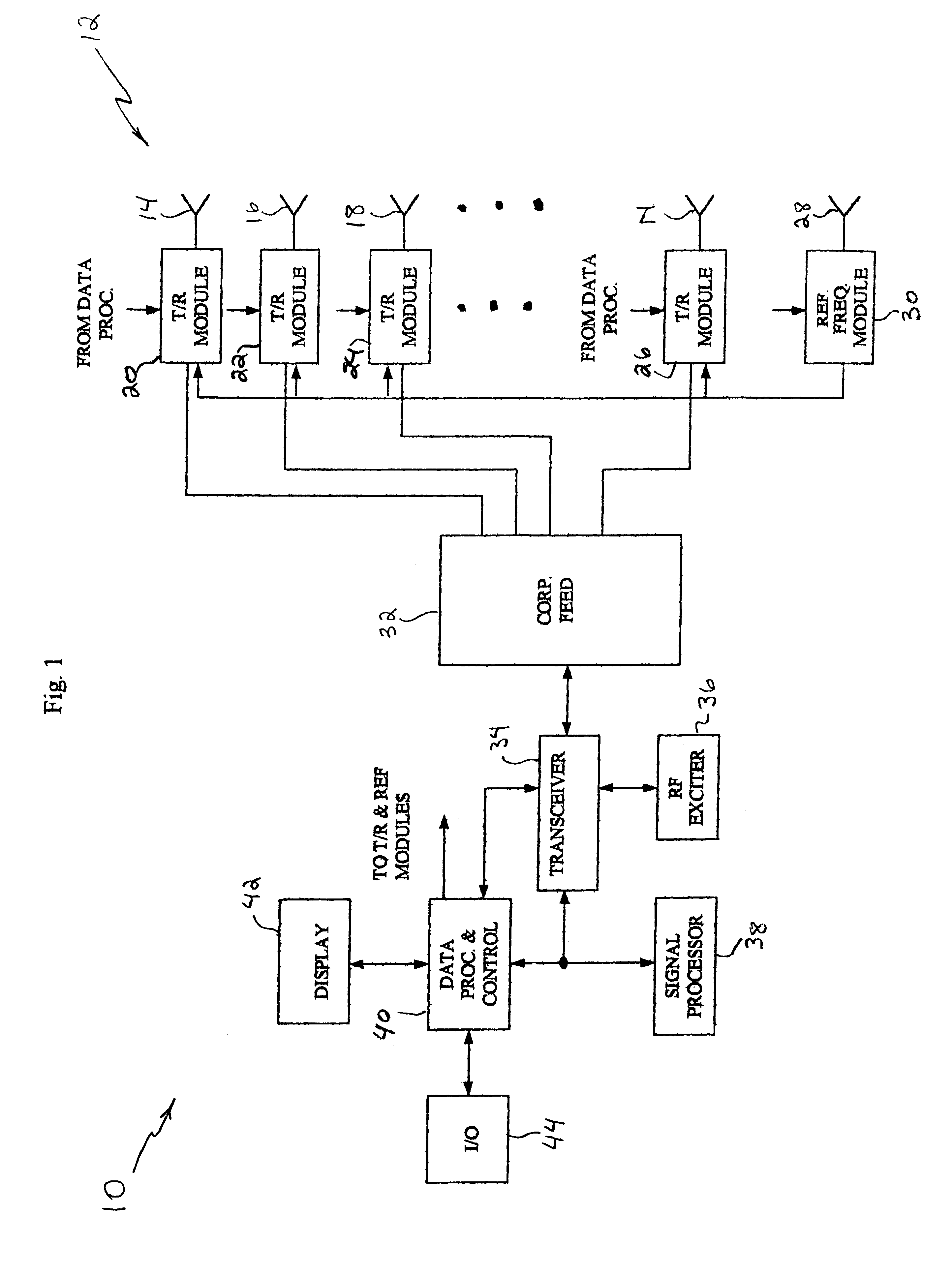
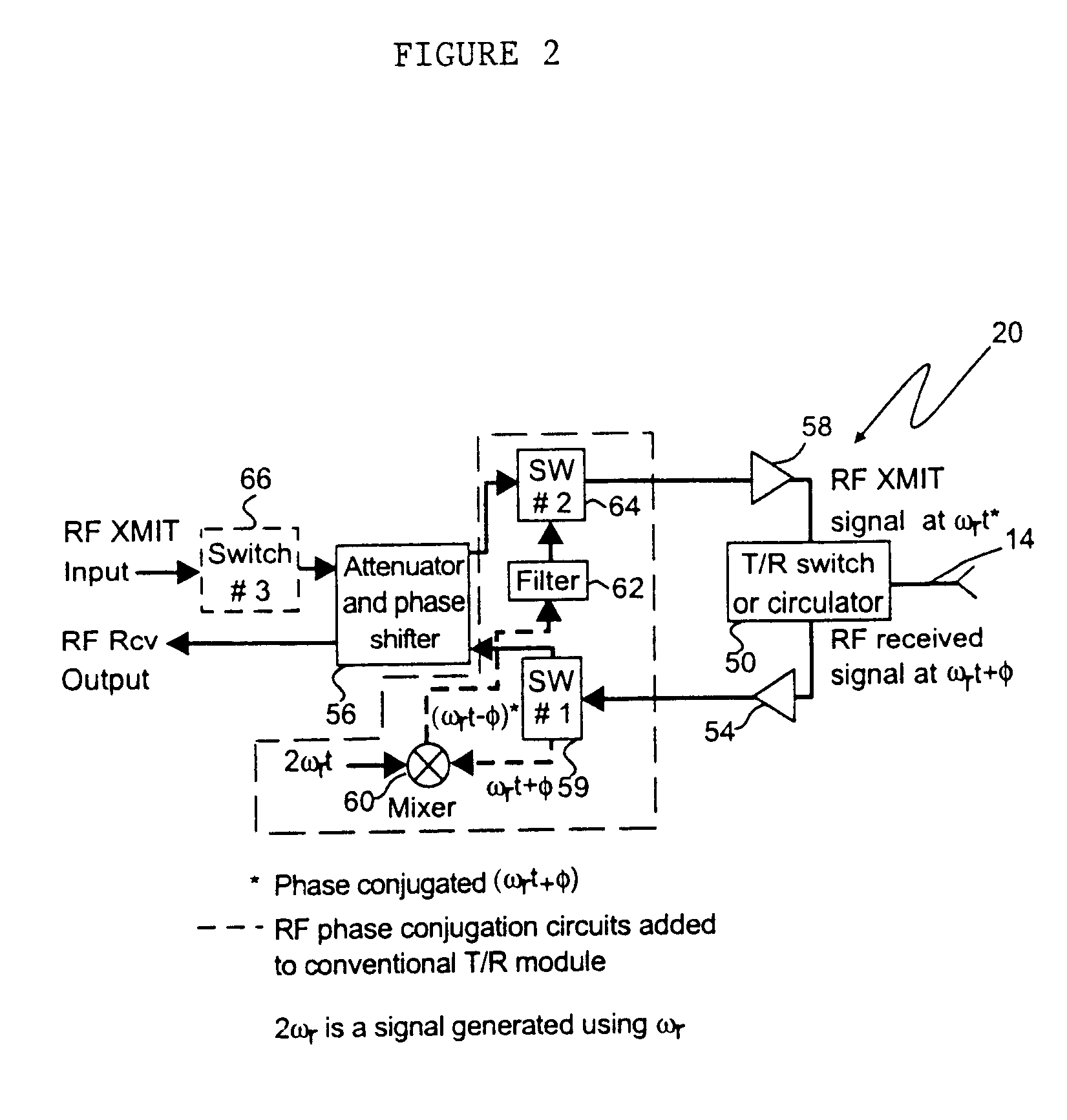
System and method for redirecting a signal using phase conjugation
A system and method for automatically generating a return beam in the direction of a received beam. The inventive system (10) includes a phased array antenna (12) for receiving a radio frequency signal having a first wavefront from a first direction. In response to this signal, the invention (10) provides a second signal having a second wavefront. The second signal is a phase conjugate of the first signal and is transmitted in a reverse direction relative to the direction of the first signal. In the illustrative embodiment, the invention includes a plurality of phase conjugators each of which are disposed in a transmit / receive module and coupled to an associated radiating element. Each of the phase conjugators includes a mixer (60) having the input signal as a first input thereto. The input signal has a first frequency and a first phase. A second signal having a frequency equal to twice the first frequency is input to each mixer (60) from a reference frequency module (30) such that the output of the mixer includes a component representative of the negative of the first phase. The output of each mixer (60) is filtered to extract a signal component having a negative phase relative to the input signal. These signal components are then transmitted as the phase conjugated wavefront. This process will occur for each signal when multiple signals are received within the field of regard of the phased array antenna (12).
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
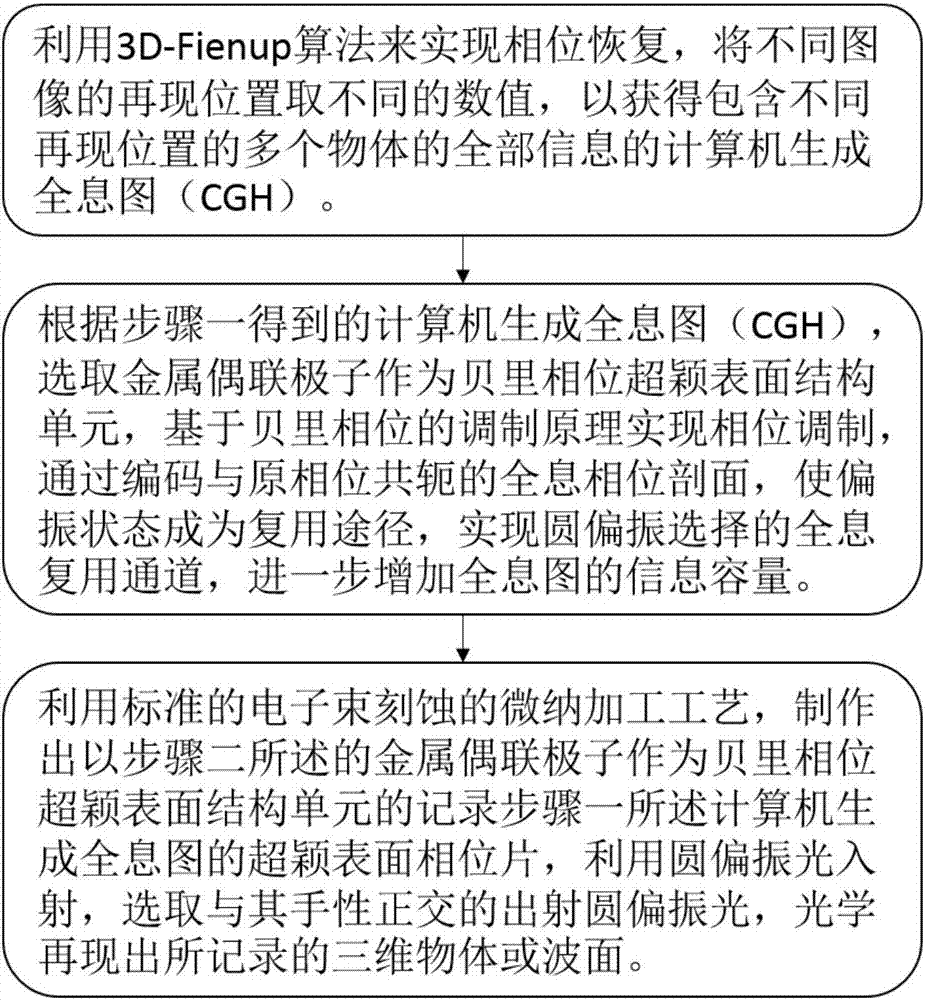
Berry phase metasurface-based multi-plane holographic multiplexing method
ActiveCN107065490AIncrease information capacityHigh reproduction qualityInstrumentsWavelengthChirality
The invention discloses a berry phase metasurface-based multi-plane holographic multiplexing method, and belongs to the field of micronano optical and holographic multiplexing application. The berry phase metasurface-based multi-plane holographic multiplexing method comprises the steps of achieving phase recovery by a 3D-Fienup algorithm, taking different numerical values of reproduction positions of different images, and acquiring a computer generation holographic diagram containing all information; selecting a metal coupling polaron as a berry phase metasurface structure unit, achieving phase modulation based on a berry phase modulation principle, and enabling a polarization state to become a multiplexing path by coding a holographic phase profile conjugated with an original phase to achieve a holographic multiplexing passage selected by circular polarization; making a metasurface phase sheet for recording the computer generation holographic diagram, selecting an emergent circular polarization light orthogonal to chirality of the polarization stat, and optically reproducing a three-dimensional object or a wave surface which is recorded. The holographic multiplexing method with sub-wavelength pixel of visible light and near-infrared bands, ultrathinness, large visual angle and large capacity is provided by the invention; and moreover, the crosstalk can be effectively reduced, and the holographic multiplexing of circular polarization selectivity is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
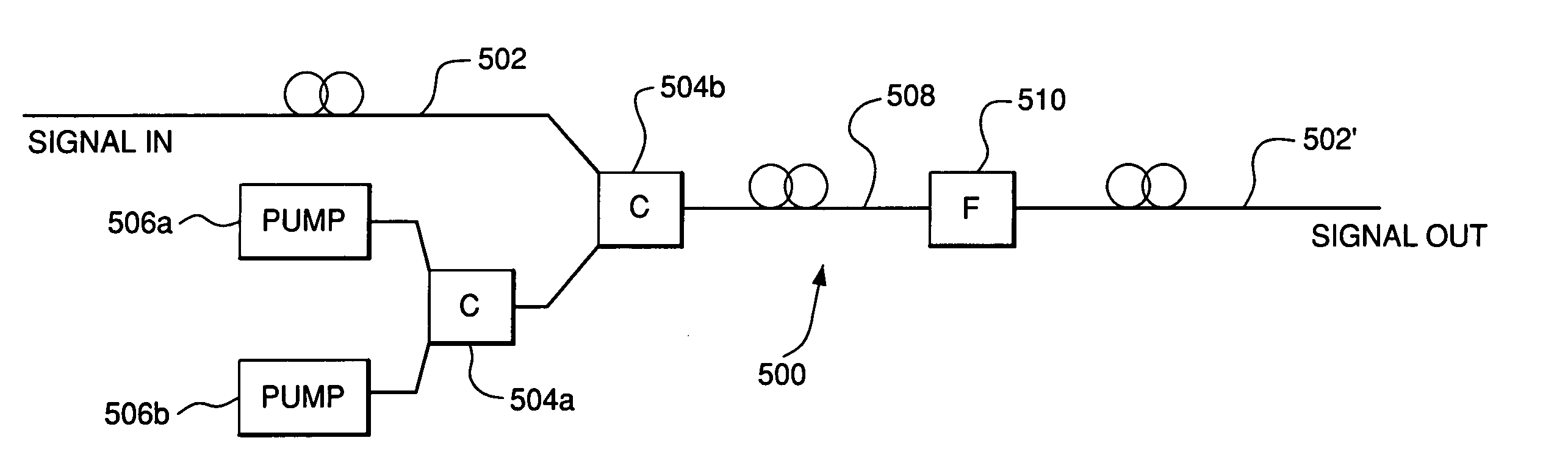
Phase-sensitive amplification in a fiber
A method of and device for generating an amplified optical signal directly in an optical fiber by way of phase-sensitive amplification based on one or more four-wave mixing (FWM) processes. In one embodiment, an input signal and two pump waves are applied to a highly nonlinear fiber (HNLF). The input signal is amplified in the HNLF due to energy transfer from the pump waves to the input signal via a degenerate phase-conjugation (PC) process. In another embodiment, an input signal and first and second pump waves are applied to a first HNLF to generate, via a Bragg scattering (BS) process, an idler signal corresponding to the input signal. The second pump wave is then filtered out and the first pump wave, a third pump wave, and the input and idler signals are applied to a second HNLF, where they interact via a non-degenerate PC process to produce an amplified output signal.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
Microwave self-phasing antenna arrays for secure data transmission & satellite network crosslinks
InactiveUS20060238414A1Increase user capacityImprove directivityDirection finders using radio wavesAntenna supports/mountingsTactical communicationsCommunications security
A high-directivity transponder system uses a dual system of a retrodirective array transmitting a data signal peak toward an interrogator source, and a self-null-steering array transmitting a null toward the interrogator source and a jamming signal elsewhere, resulting in high S / N reception at the interrogator source and avoidance of interception. Integrating modulators would allow each array to transmit different data while the spectra of the transmitted signals are identical, thus disabling interception. The system enables secure point-to-point communications and can be used for short-distance wireless data transmission systems such as wireless LAN and RFID servers. As another aspect, self-steering signal transmission is employed for randomly oriented satellites using circularly polarized, two-dimensional retrodirective arrays. Quadruple subharmonic mixing is used as an effective means of achieving phase conjugation when a high-frequency LO is not feasible or inapplicable. These features may be used for small-satellite communications, secure tactical communications, search and rescue, enemy location fixing and tracking, UAV command and control, forest fire detection, marine-based tracking, and many other applications requiring secure communications with high signal directivity.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII
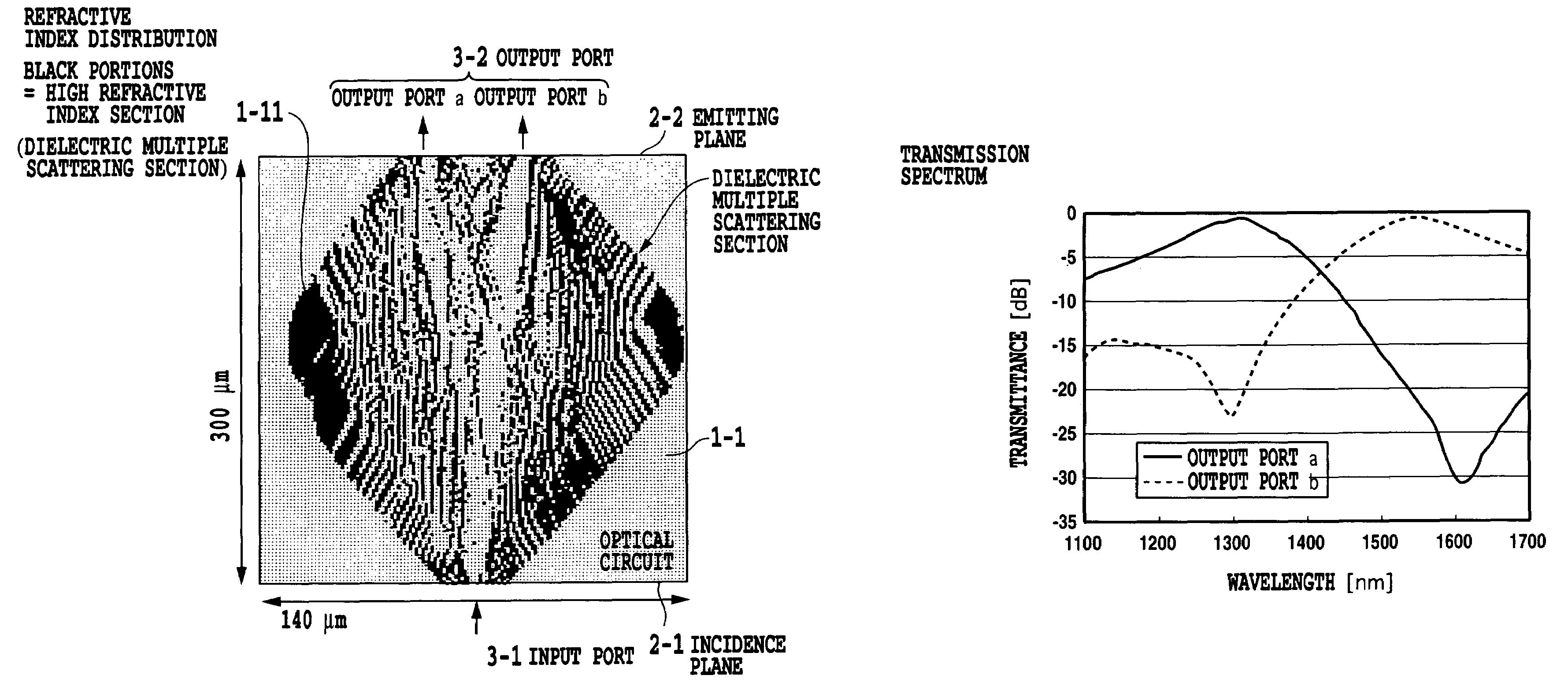
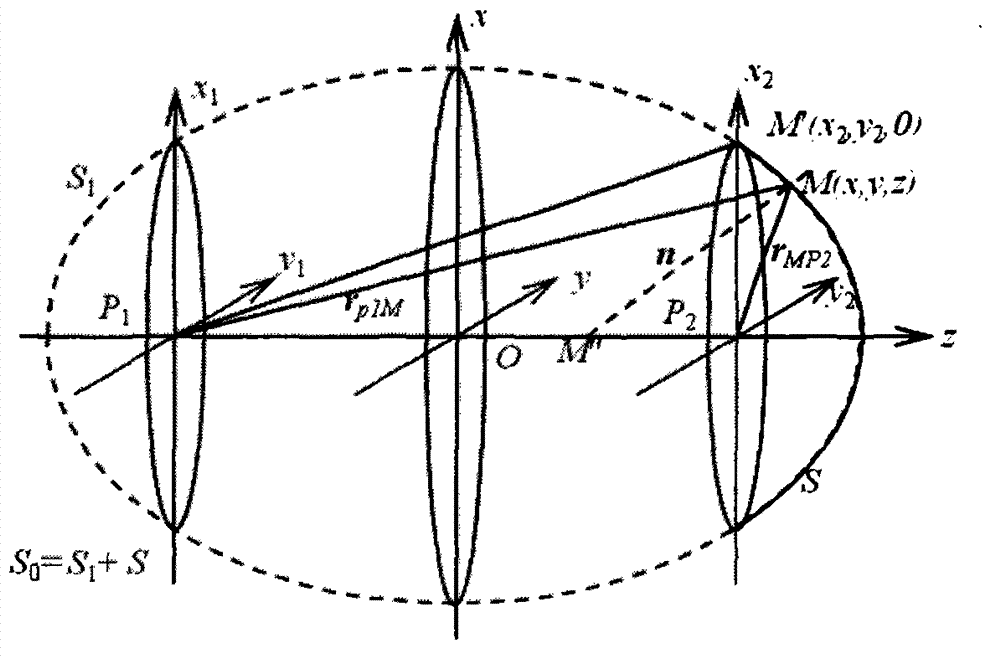
Wave transmission medium and waveguide circuit
ActiveUS20060126992A1Effective controlImprove efficiencyCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guidePhase differenceForward propagation
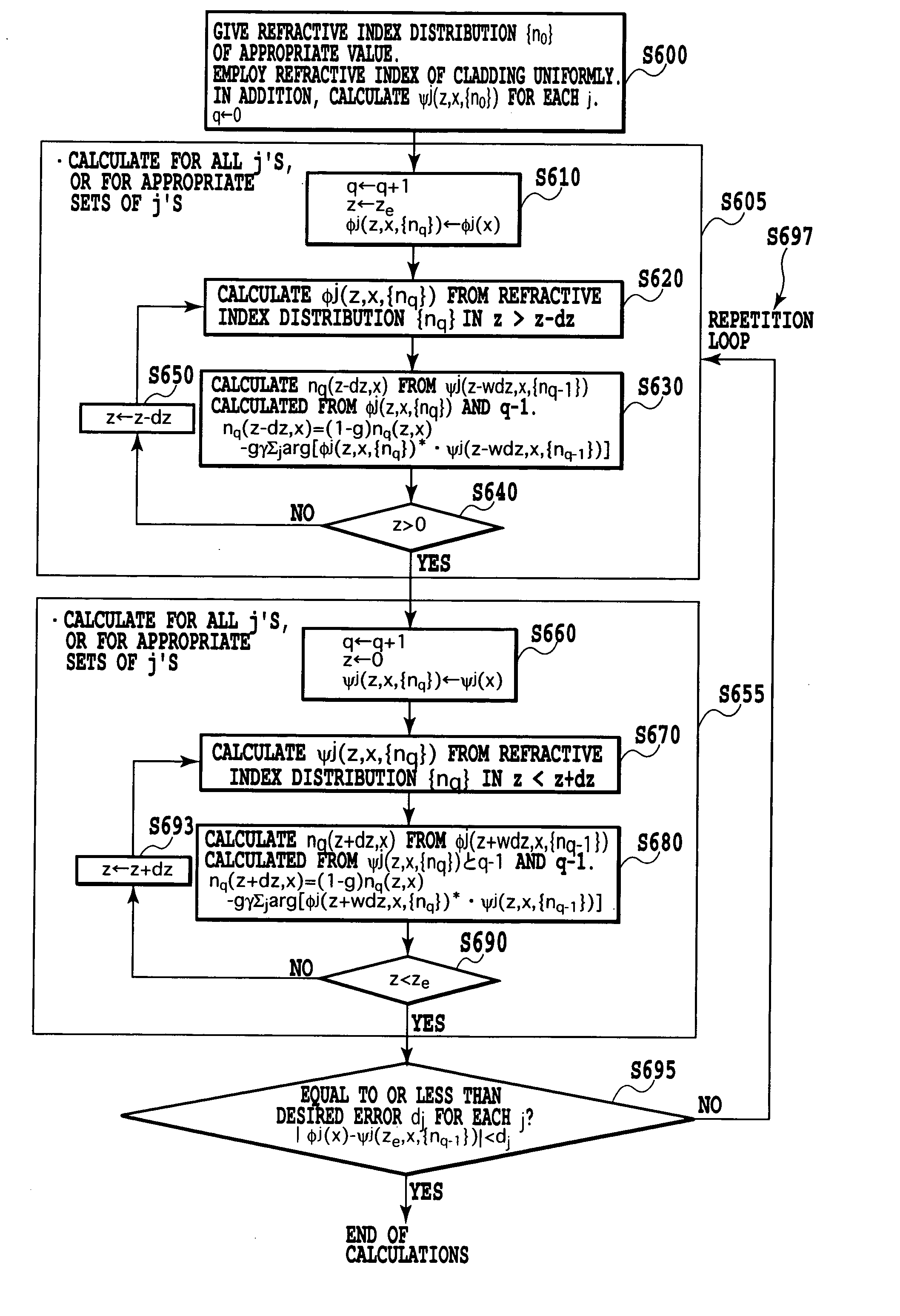
A wave transmission medium includes an input port 3-1 and an output port 3-2. A field distribution 1 and a field distribution 2 are obtained by numerical calculations. The field distribution 1 is a field distribution of the propagation light (forward propagation light) launched into the input port 3-1. The field distribution 2 is a field distribution of the phase conjugate light (reverse propagation light) resulting from reversely transmitting from the output port side an output field that is expected to be output from the output port 3-2 when an optical signal is launched into the input port 3-1. According to the field distributions 1 and 2, a spatial refractive index distribution is calculated such that the phase difference between the propagation light and reverse propagation light is eliminated at individual points (x, z) in the medium.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Distributed self-adaptive optical system based on optical fibers
ActiveCN104037606ASimple structureIncrease control bandwidthActive medium shape and constructionBeam splitterLaser array
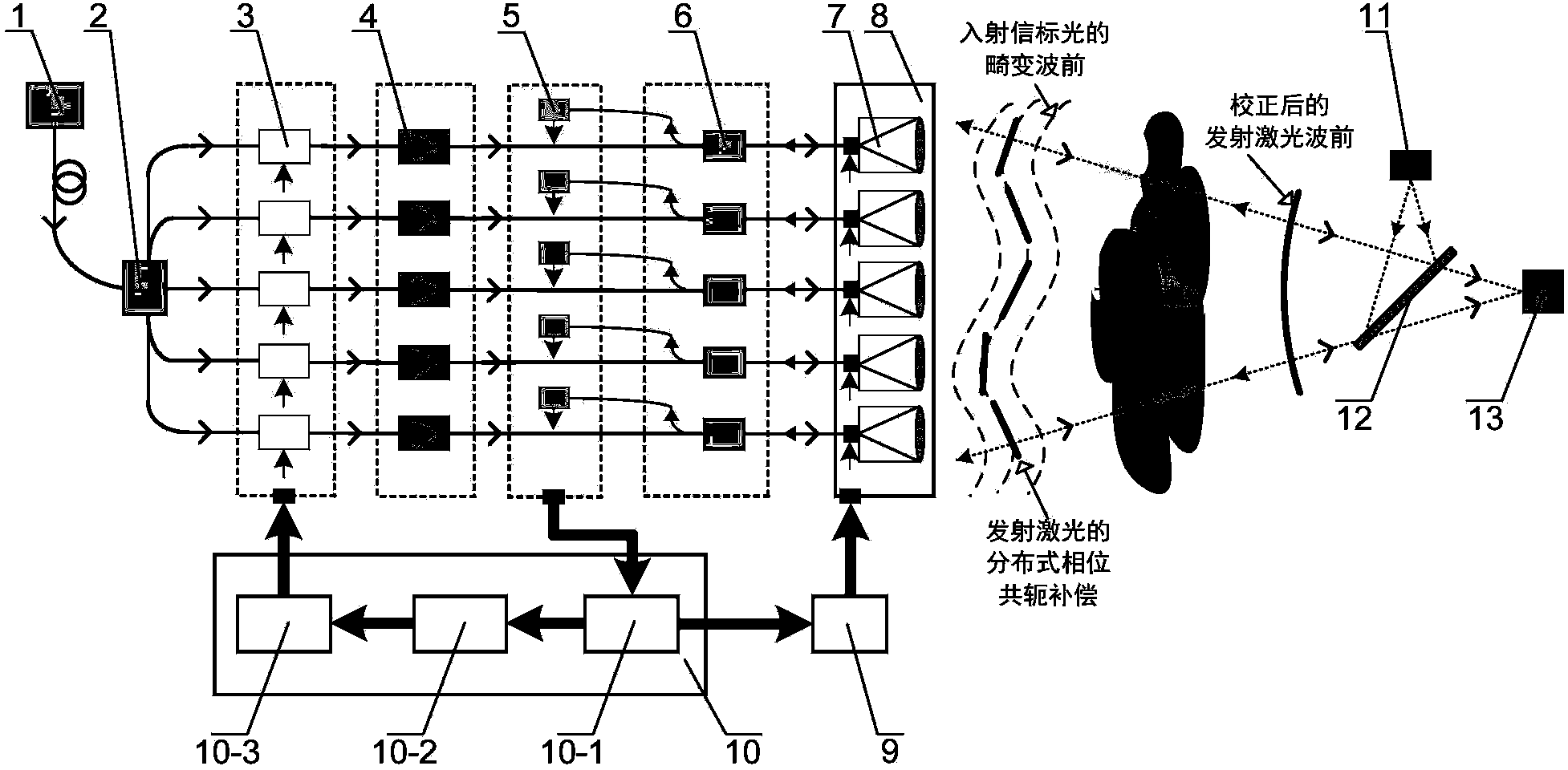
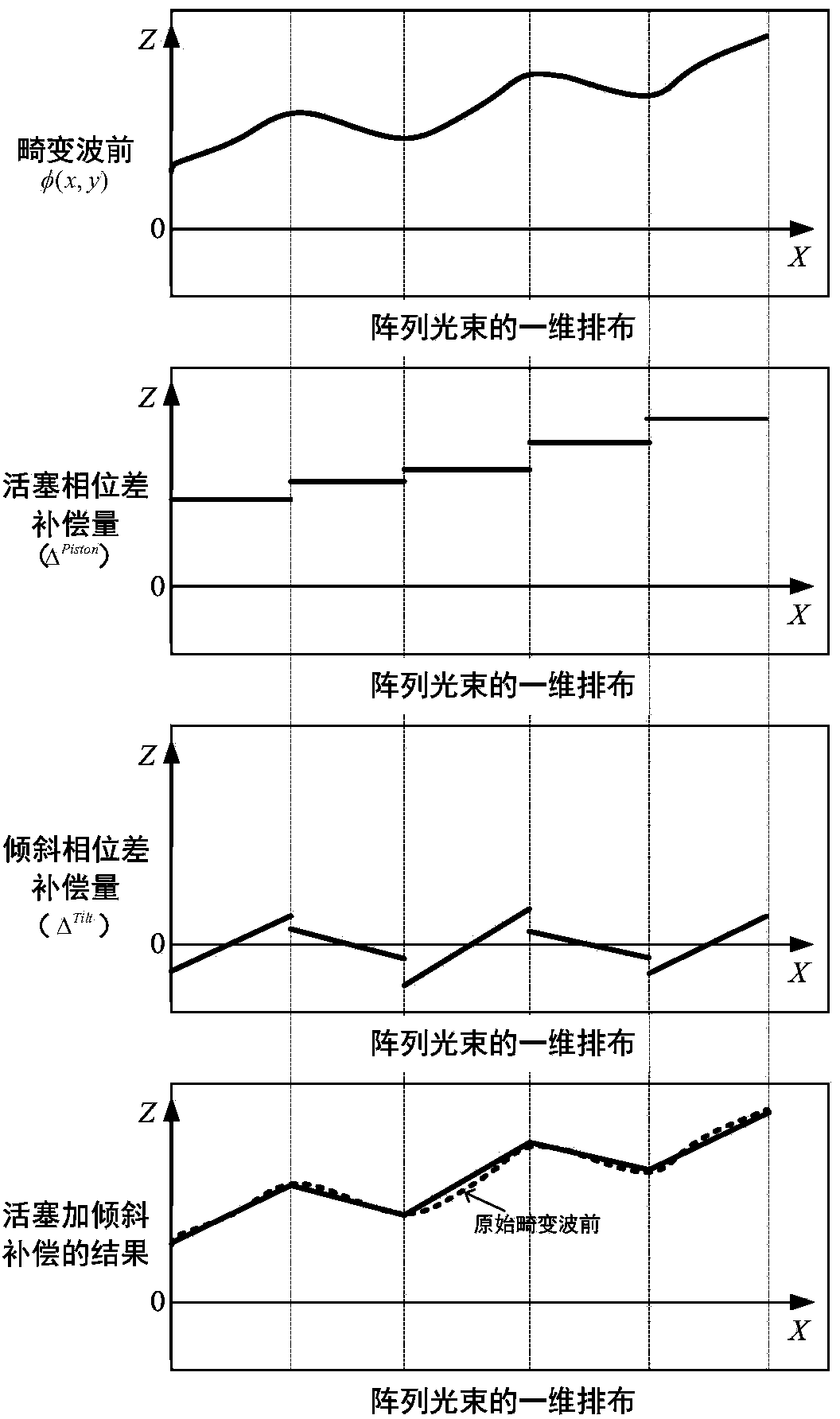
The invention provides a distributed self-adaptive optical system based on optical fibers. The distributed self-adaptive optical system based on the optical fibers comprises an emitting laser, an optical fiber beam splitter, an optical fiber phase modulator, an optical fiber laser amplifier, a photoelectric detector, a three-port optical fiber circulator, a self-adaptive optical fiber collimator and coupler array, an integrated device, a multi-channel high-voltage amplifier, a wavefront controller as well as a beacon light source, a spectroscope and a far field target. The distributed self-adaptive optical system is based on the fiber laser technology in combination with a plurality of optical fiber devices, and is characterized in that a beacon light beam is divided by use of the self-adaptive optical fiber collimator and coupler array, the wavefront error of beacon light is measured in real time and the error is decomposed to each light sub-beam in a laser array, a piston for emitting the light sub-beams and a tilting phase are controlled independently and in parallel according to the principle of phase conjugation, and the influence of atmospheric turbulence effect on the quality of the light beam at the far field target is relieved. The distributed self-adaptive optical system based on the optical fibers has important application prospects in the fields such as laser atmospheric transmission, free space laser communication and laser radar.
Owner:北京鸿羚科技有限公司
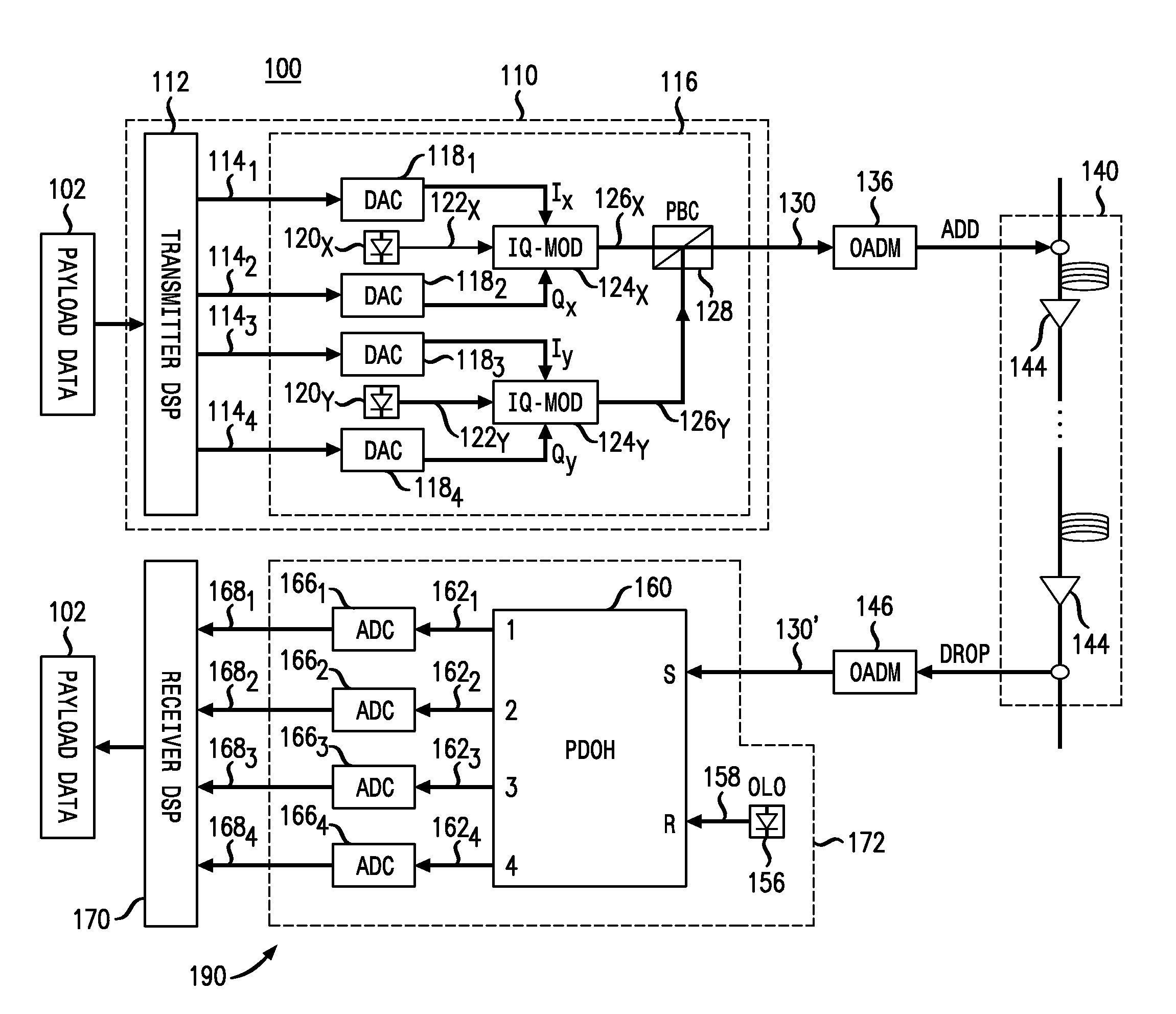
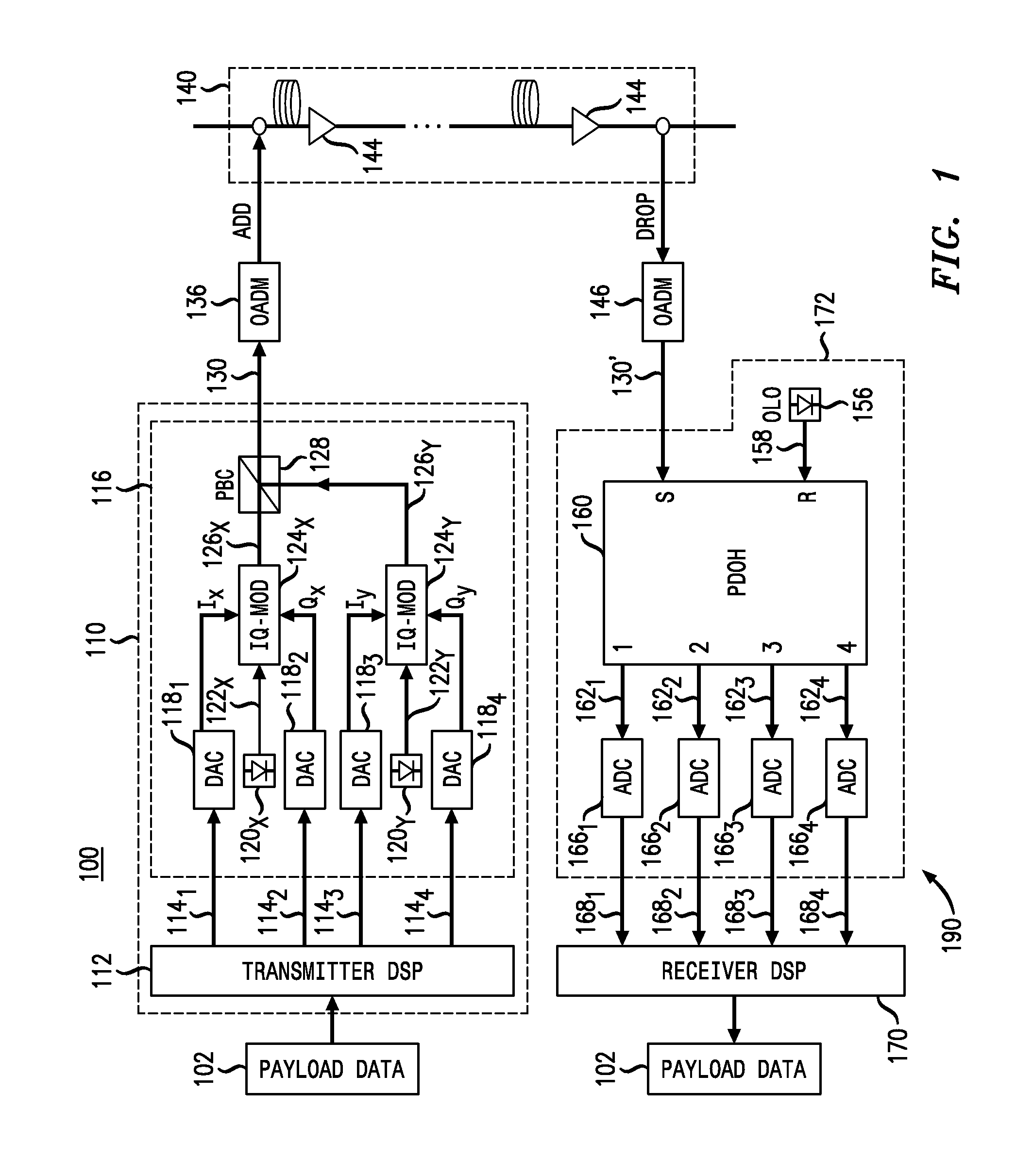
Electronic phase conjugation for impairment compensation in a fiber communication system
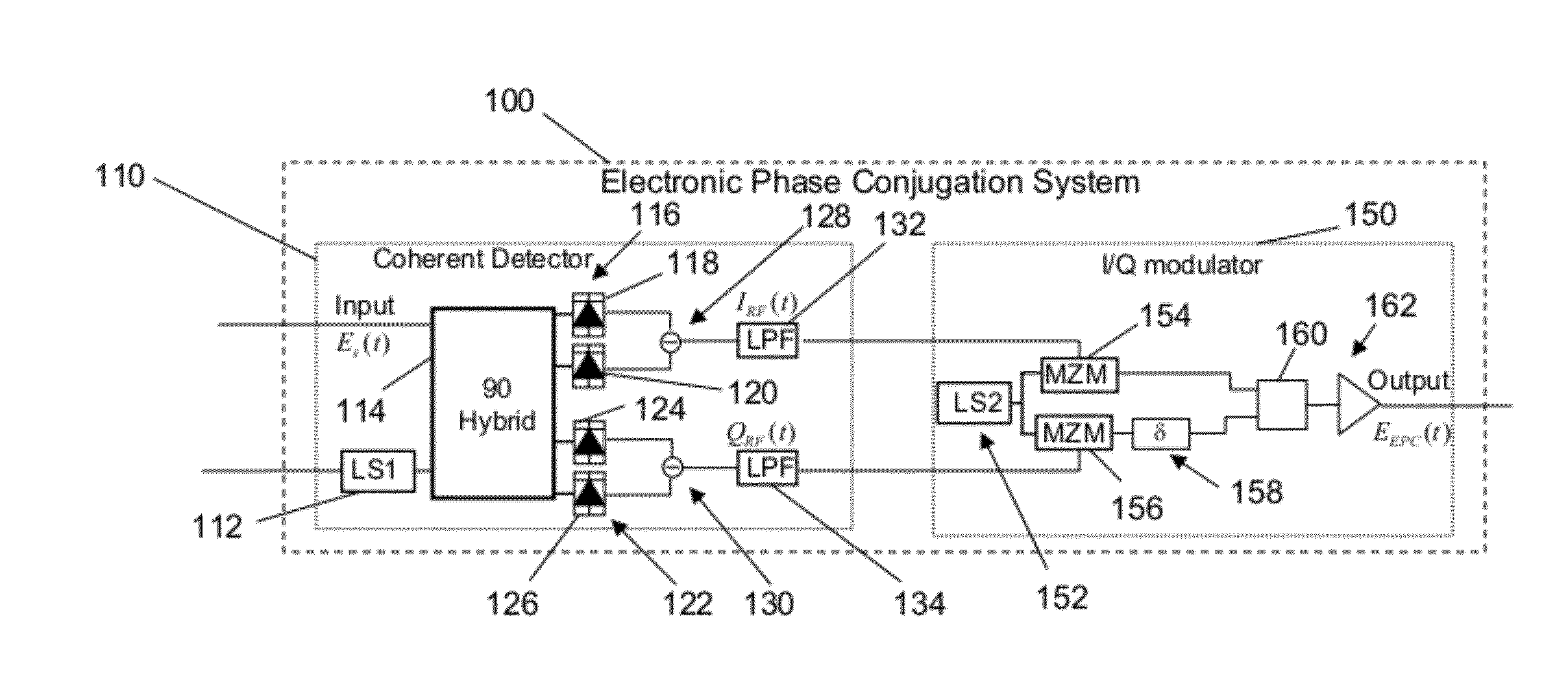
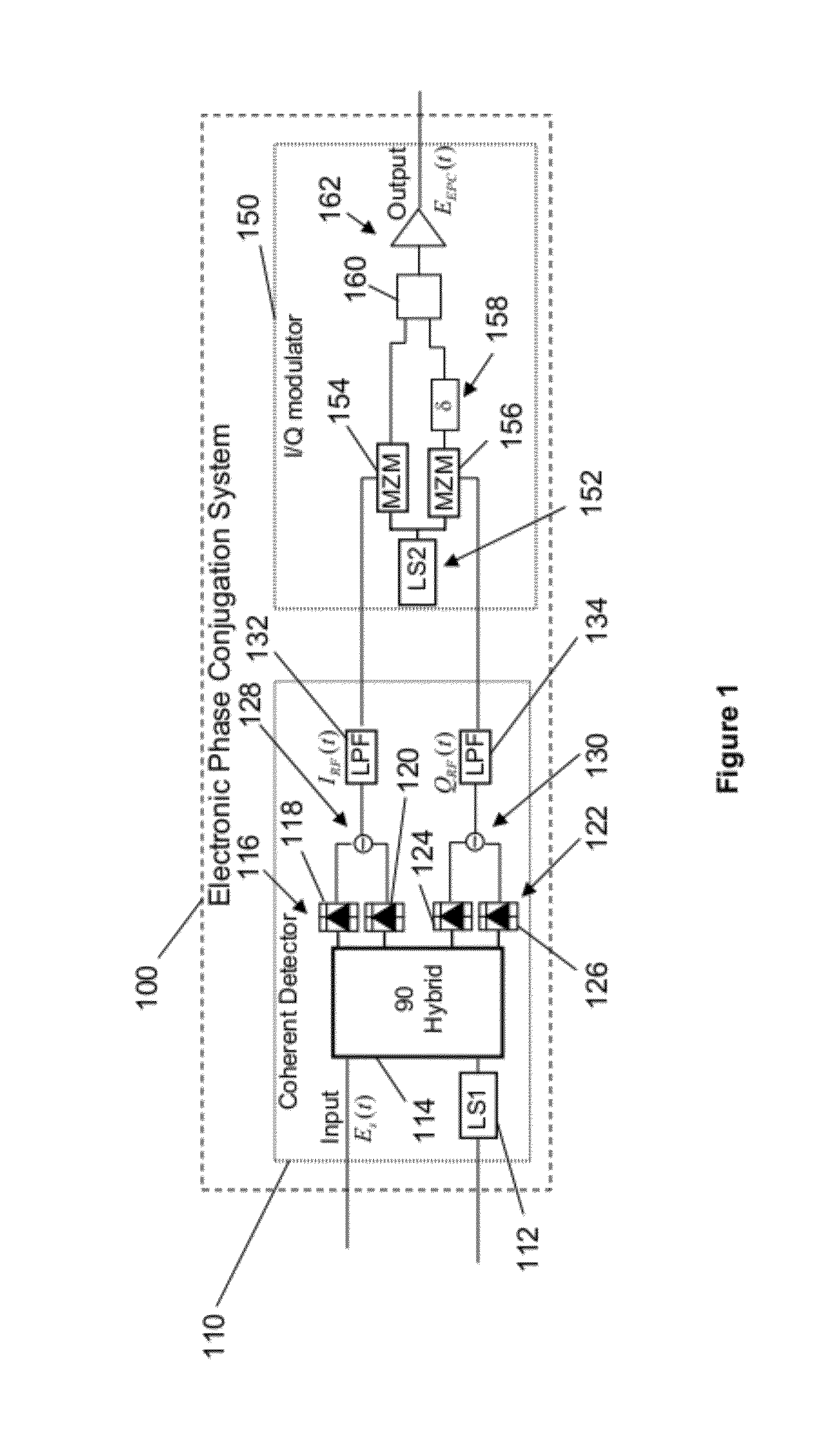
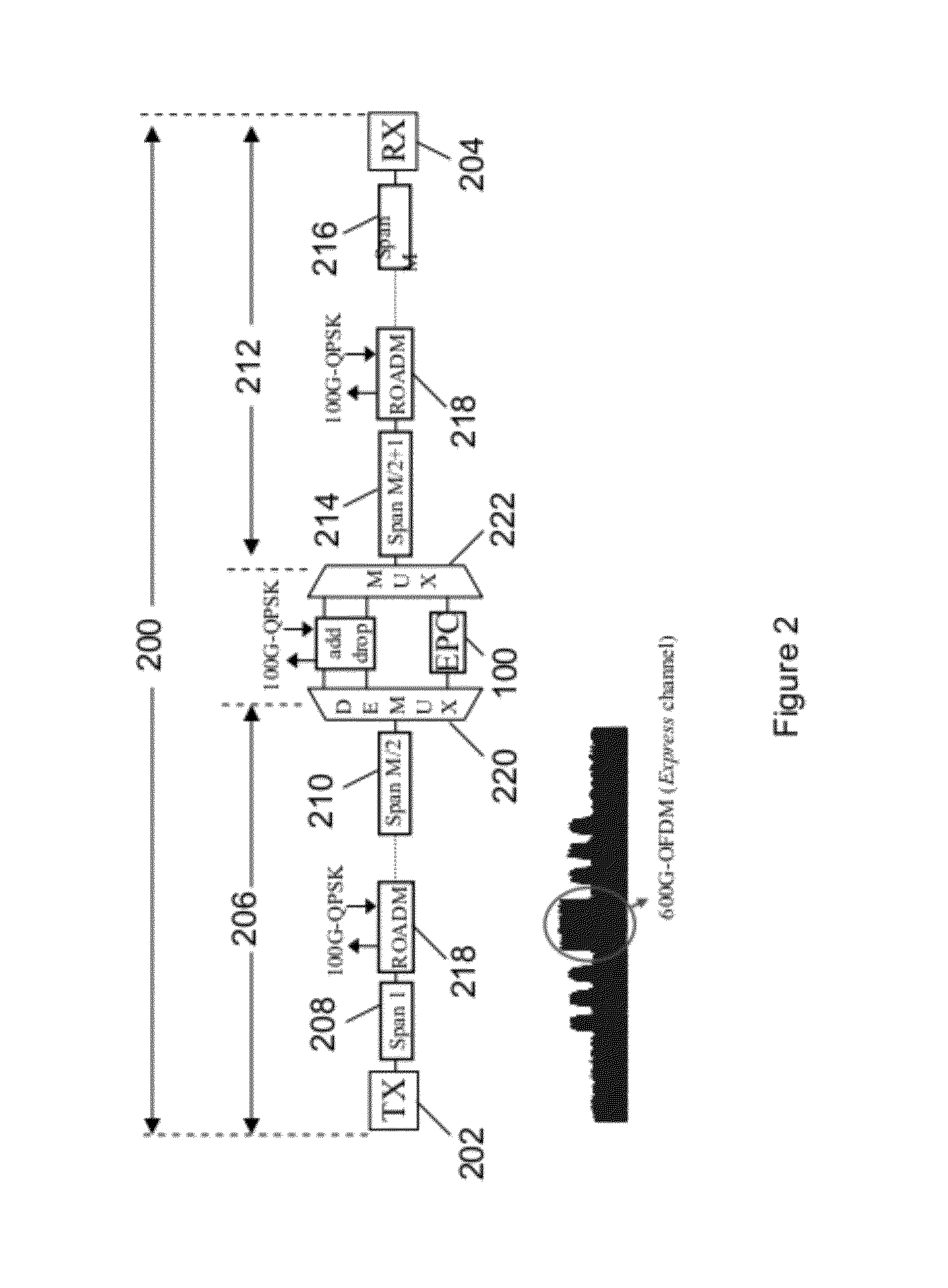
ActiveUS20120177386A1Promote disseminationDistortion/dispersion eliminationElectromagnetic receiversFiberCommunications system
Exemplary embodiments include a method and systems for impairment compensation in a communication system. The systems can include an electronic phase conjugation system that receives an incoming optical signal from a first section of a fiber optic link, converts the incoming optical signal to an in-phase electric signal and a quadrature electrical signal, and generates a phase conjugated outgoing optical signal from the in-phase and quadrature electrical signals. The phase conjugated outgoing optical signal compensates for impairment of the fiber in the communication system.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Apparatus and method for irradiating a medium
InactiveUS8954130B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesReference waveOptics
A method for irradiating a medium includes irradiating the medium with an electromagnetic wave which is scattered in the medium and modulated in frequency at a position in the medium; obtaining information corresponding to an interference pattern generated by interference between the modulated electromagnetic wave and a reference wave; and generating a phase conjugate wave, based on the obtained information, which irradiates the medium.
Owner:CANON KK
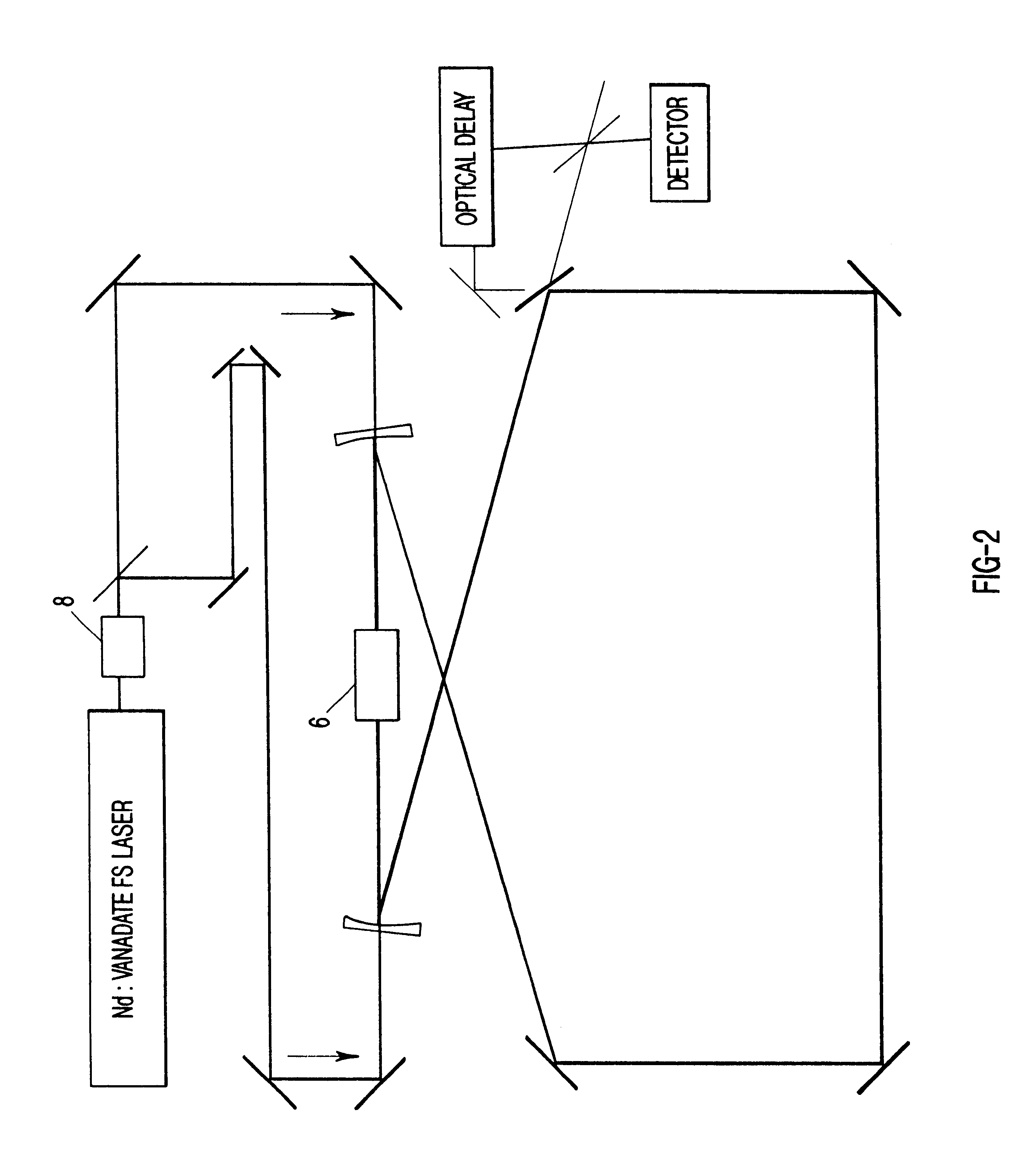
Bi-directional short pulse ring laser
InactiveUS6650682B1Reduce noiseOptical resonator shape and constructionSagnac effect gyrometersMagnetic susceptibilityRefractive index
A bi-directional pulsed ring laser that produces bi-directional light pulses that interact in such a way that they are phase conjugated. A nonlinear substance, such as a nonlinear crystal or fluid, that has an index of refraction that is dependent upon light intensity is located near a beam waist of the laser cavity to provide a self-lensing effect. Methods for reducing dead band beyond observable limits are also provided. The increased sensitivity of the bi-directional pulsed ring laser provides application in detecting magnetic susceptibility by detecting the change in phase between the arrival times of the bi-directional pulses at a modulator and the electrical signal of the modulator to determine the change in frequency of a coil that has magnetic susceptibility.
Owner:STC UNM
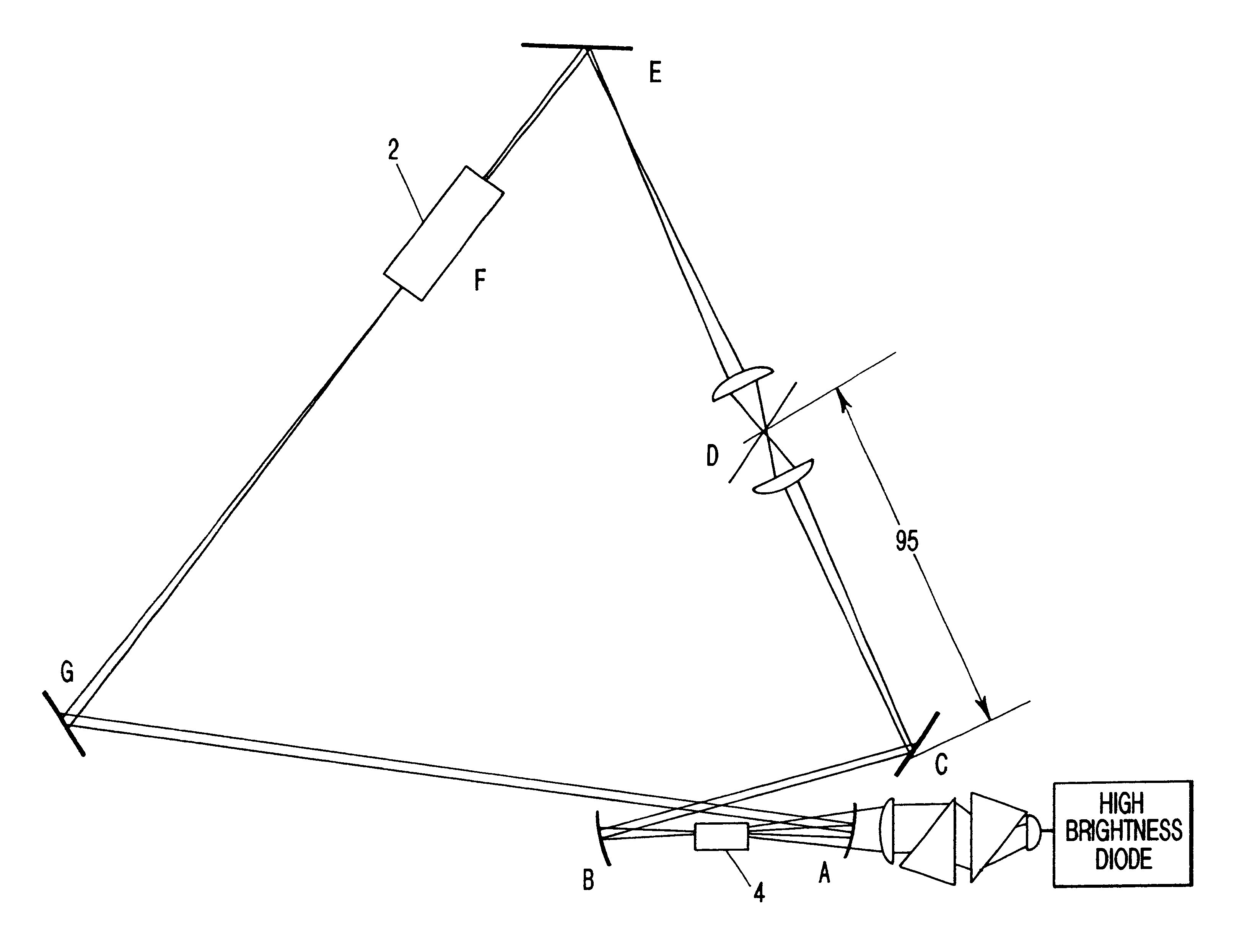
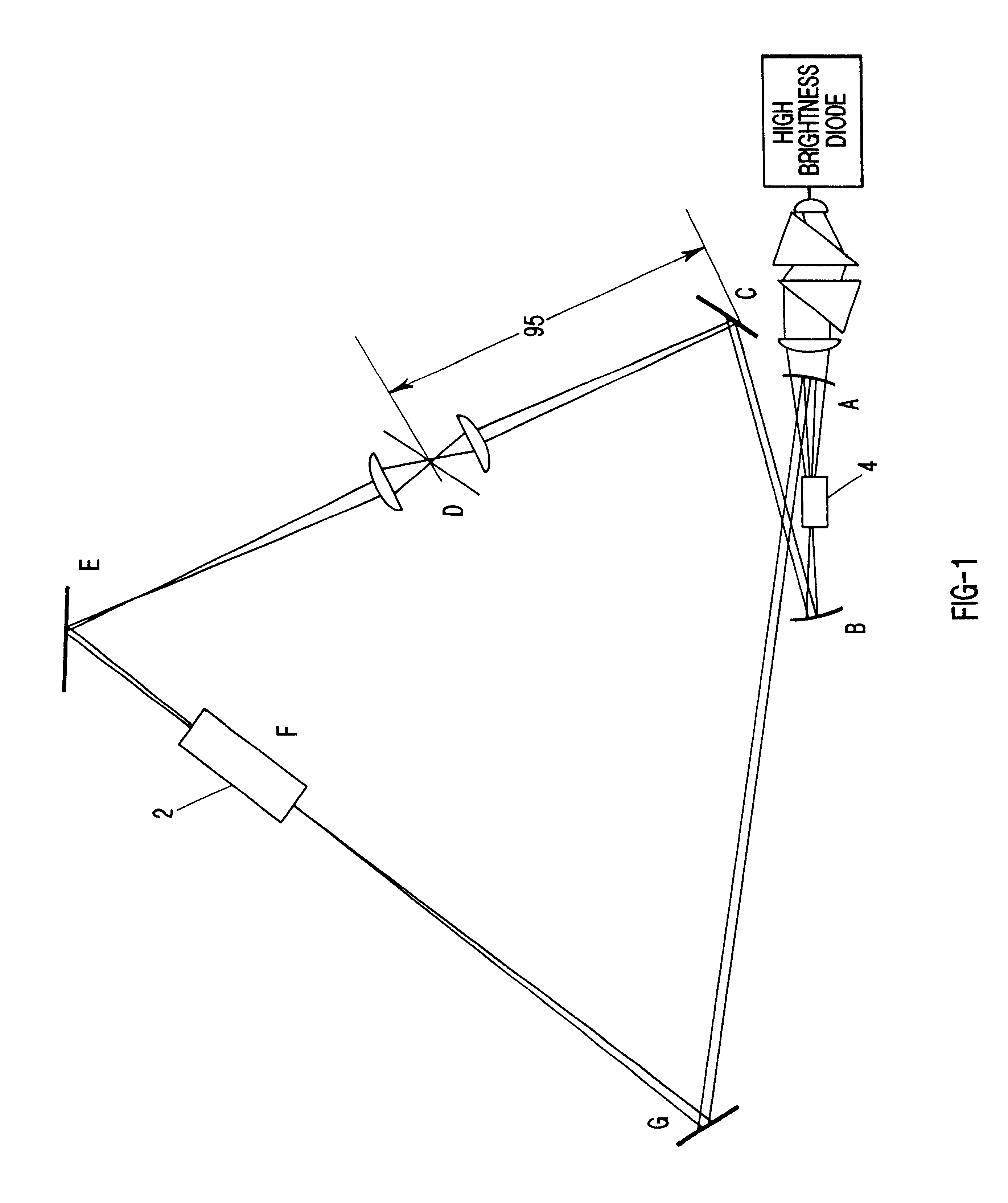
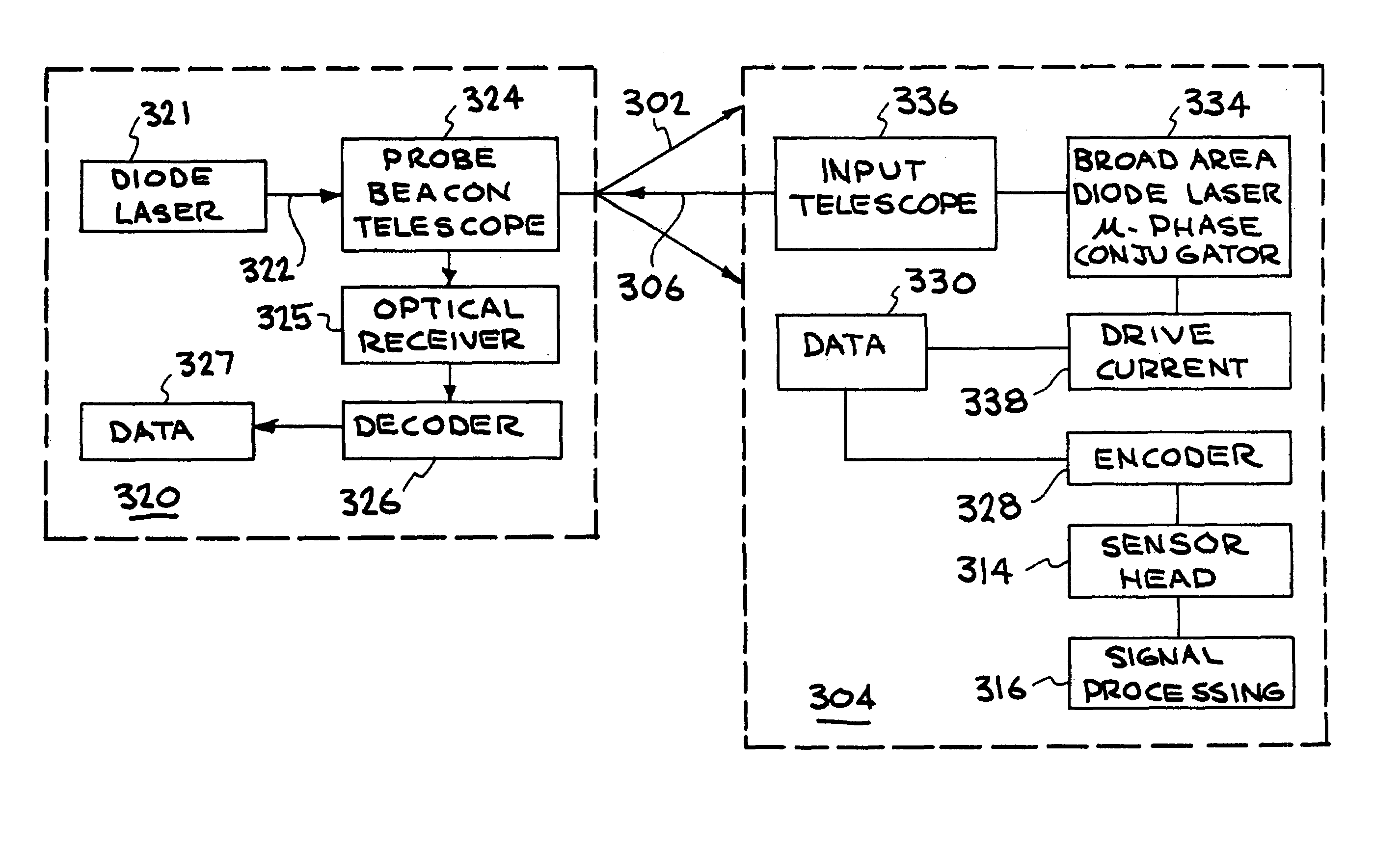
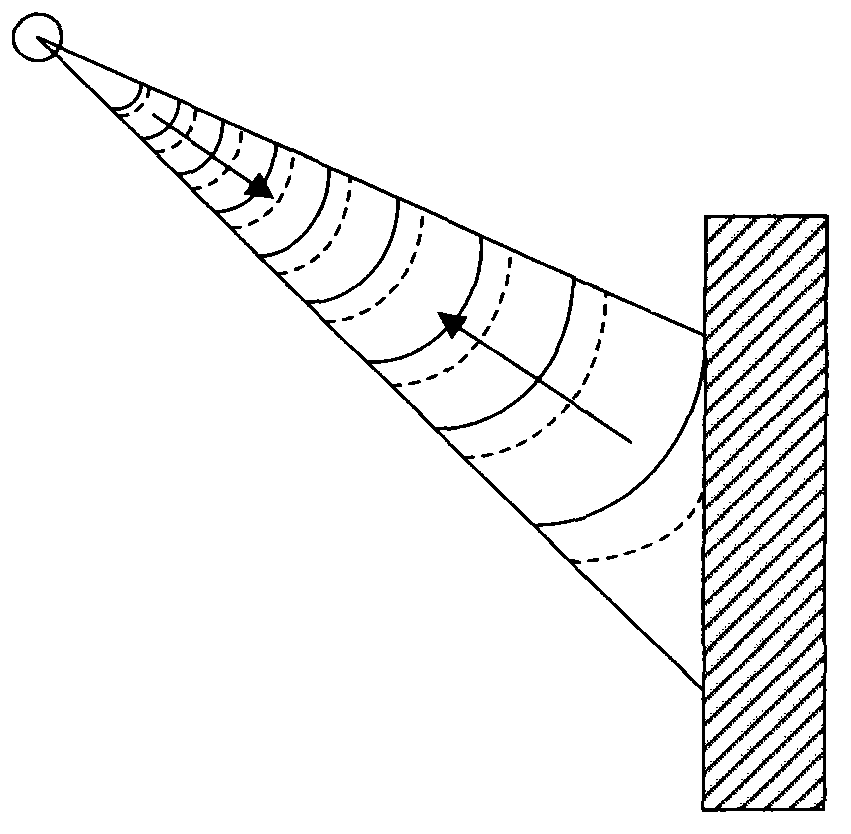
Remotely-interrogated high data rate free space laser communications link
A system and method of remotely extracting information from a communications station by interrogation with a low power beam. Nonlinear phase conjugation of the low power beam results in a high power encoded return beam that automatically tracks the input beam and is corrected for atmospheric distortion. Intracavity nondegenerate four wave mixing is used in a broad area semiconductor laser in the communications station to produce the return beam.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
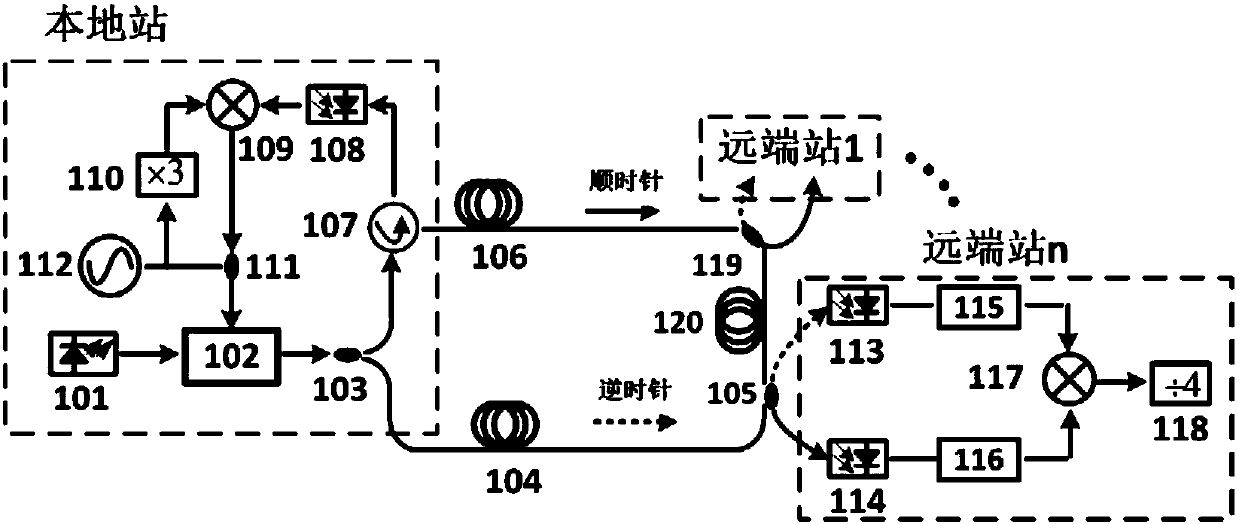
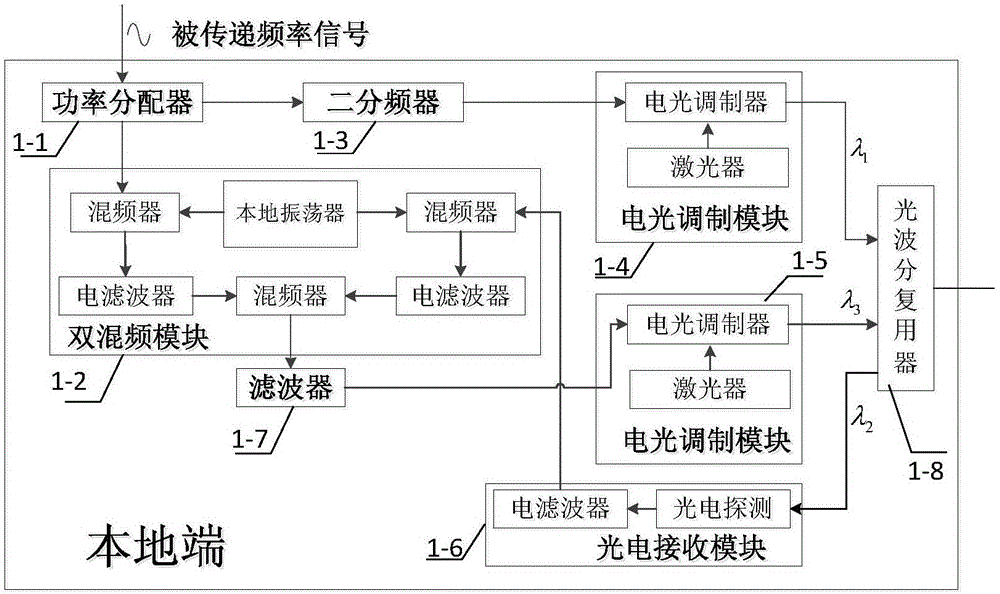
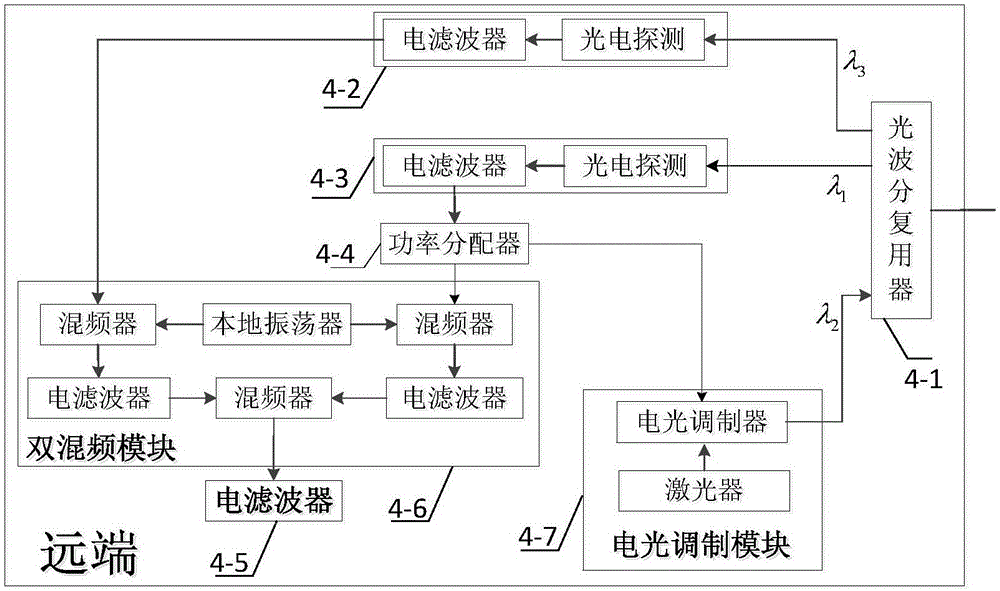
Quadruplicated frequency signal optical fiber arbitrary point steady-phase distribution system based on phase conjugation
ActiveCN108282227AEvenly distributedInhibit deteriorationDistortion/dispersion eliminationElectromagnetic transmittersCarrier signalOptical fiber coupler
The invention provides a quadruplicated frequency signal optical fiber arbitrary point steady-phase distribution system based on phase conjugation and belongs to the technical field of optical fiber steady-phase distribution; the system comprises an annular optical fiber link structure mainly composed of a local end, n far-end stations, n +1 sections of optical fiber links and n optical fiber couplers, wherein the local station comprises a microwave source, a dual-carrier wave optical signal generating module, a phase conjugated optical signal generating module, an optical fiber coupler, a first photoelectric detector and an optical fiber circulator; and each of the far-end stations respectively comprises an electro-optical frequency mixing module, an optical amplifier, a second photoelectric detector, an electric amplifier and an electric filter. The main device used by the system is a photonic device; due to the high-frequency broadband characteristic of the photonic device, the system can achieve optical fiber long-distance stable phase distribution of higher frequency signals; and the problem of deterioration of the phase stability precision caused by local oscillator leakage and harmonic interference introduced when an electric mixer is used is effectively avoided.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Apparatus and method for irradiating a scattering medium with a reconstructive wave
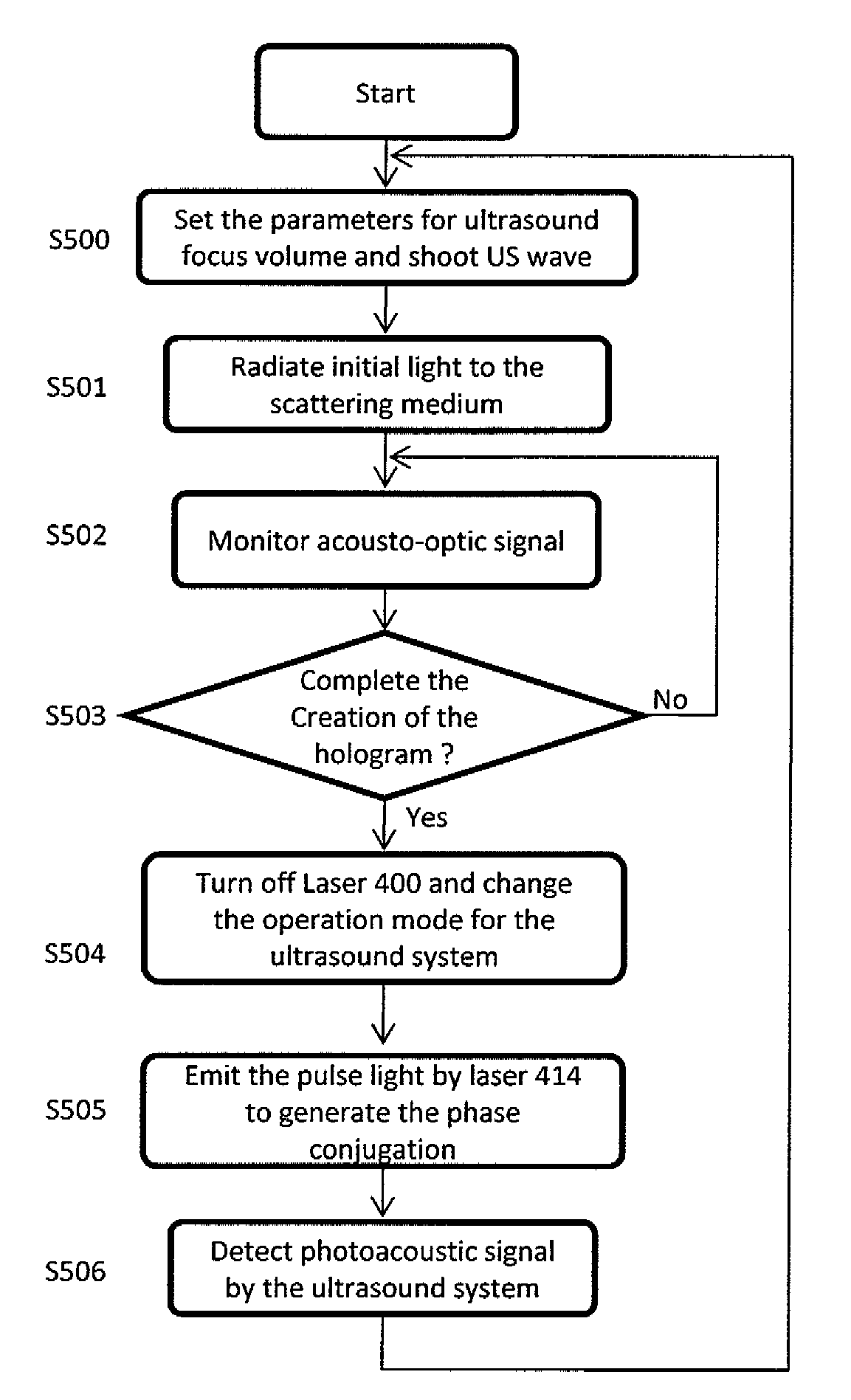
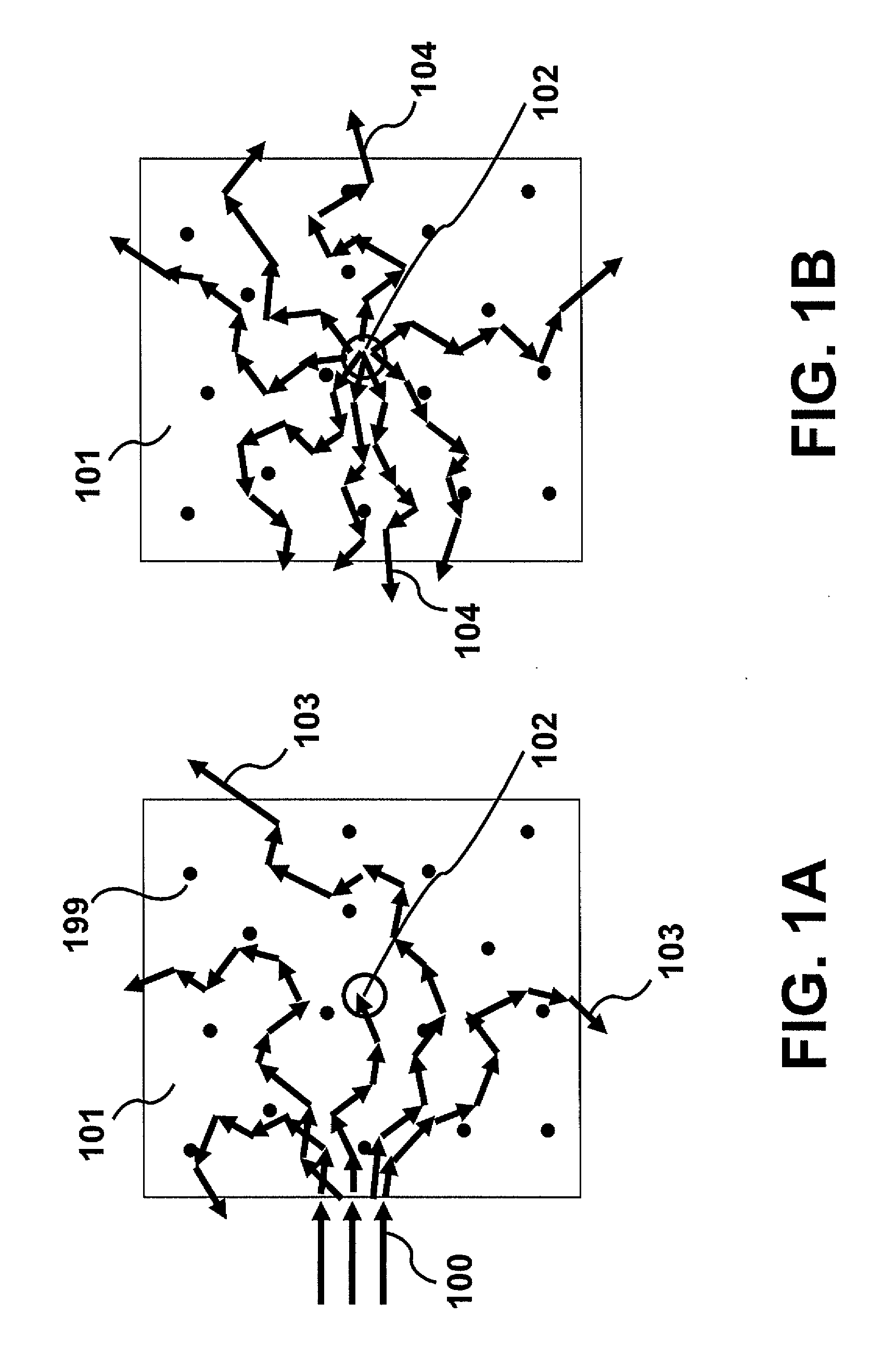
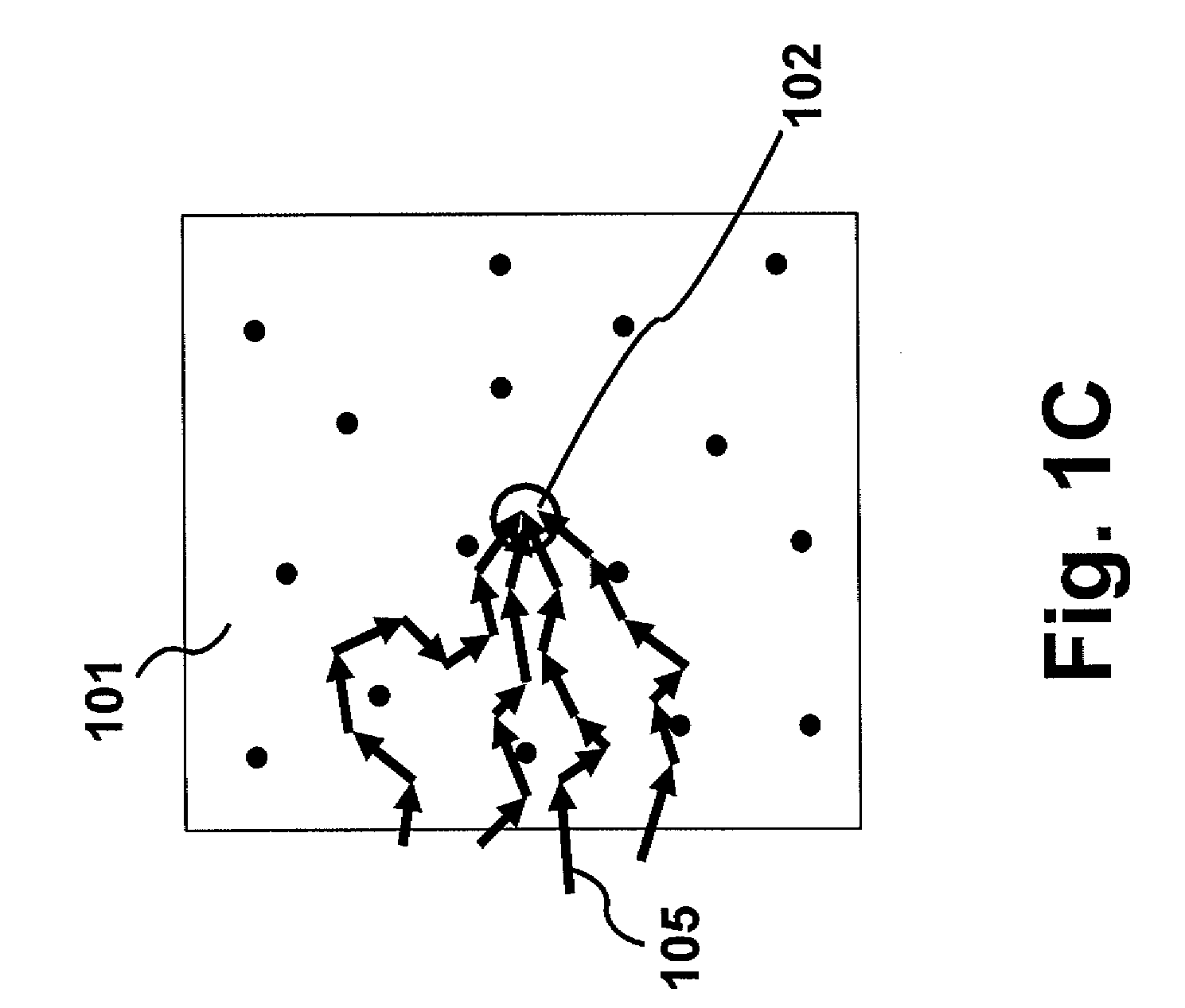
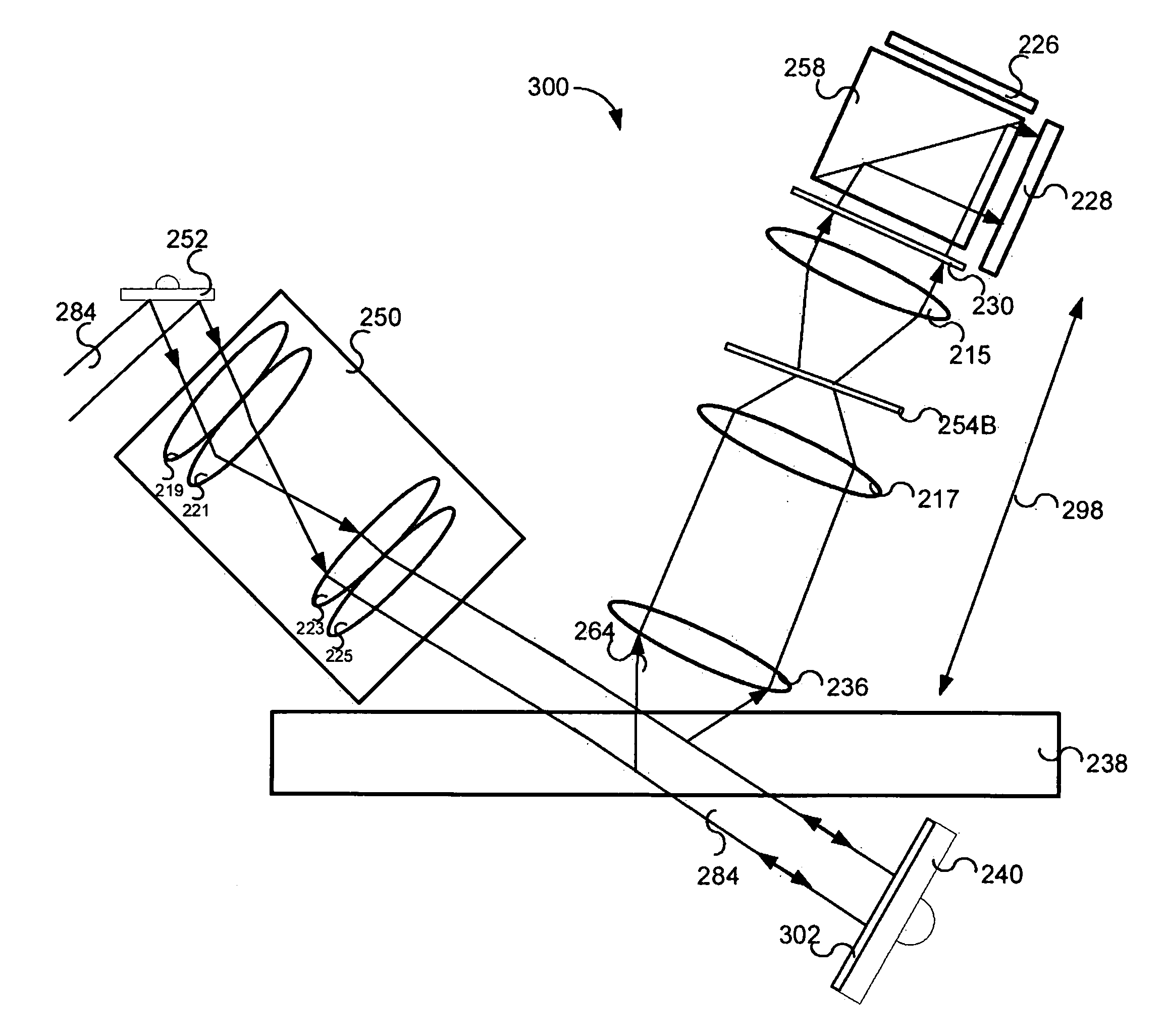
InactiveUS9057695B2Holographic light sources/light beam propertiesScattering properties measurementsReference waveOptics
A system and method for irradiating a medium including irradiating the medium with an electromagnetic wave which is scattered in the medium and modulated in frequency at a position in the medium; obtaining information corresponding to an interference pattern generated by interference between the modulated electromagnetic wave and a reference wave; and generating a phase conjugate wave, based on the obtained information, which irradiates the medium.
Owner:CANON KK
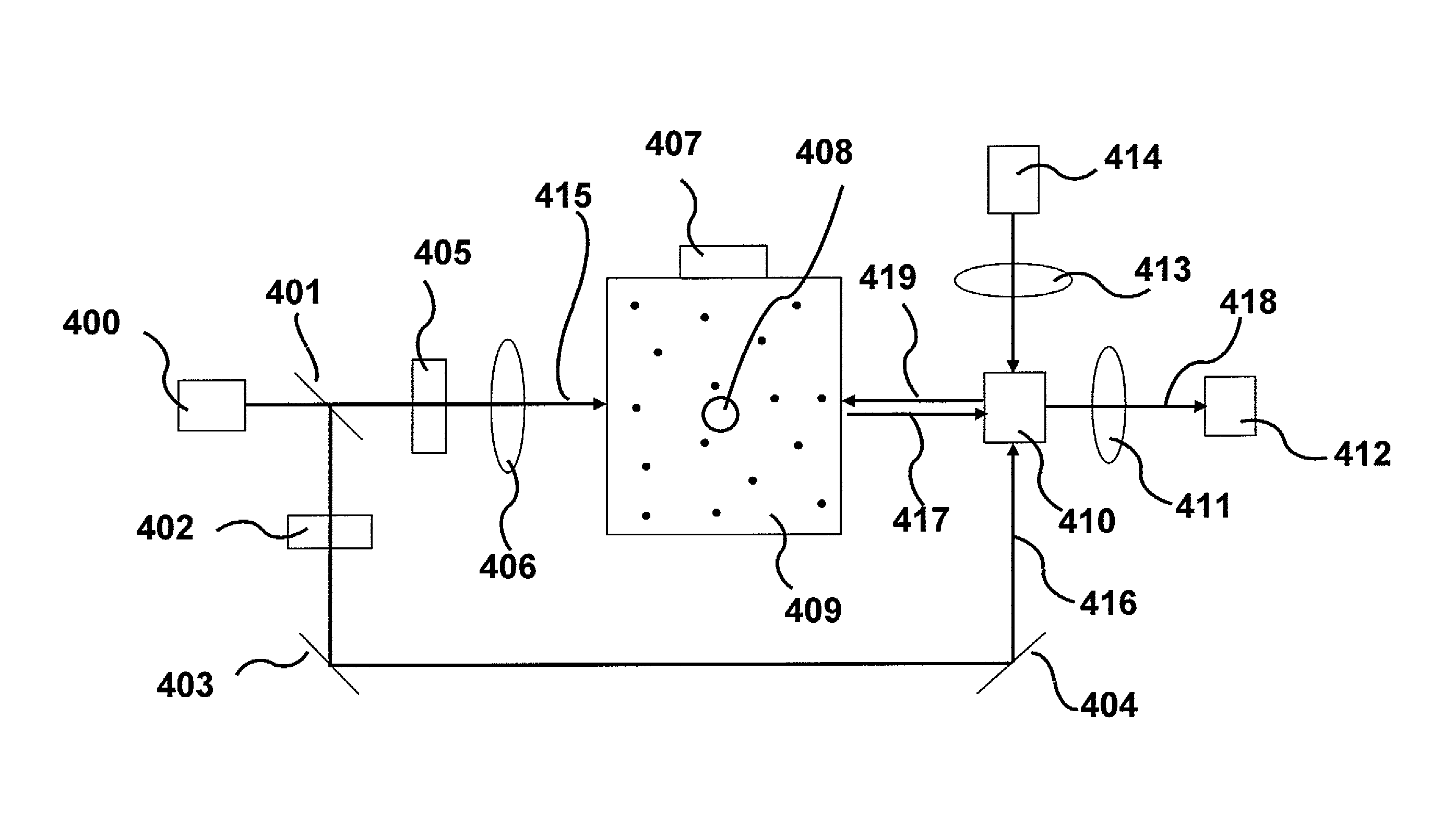
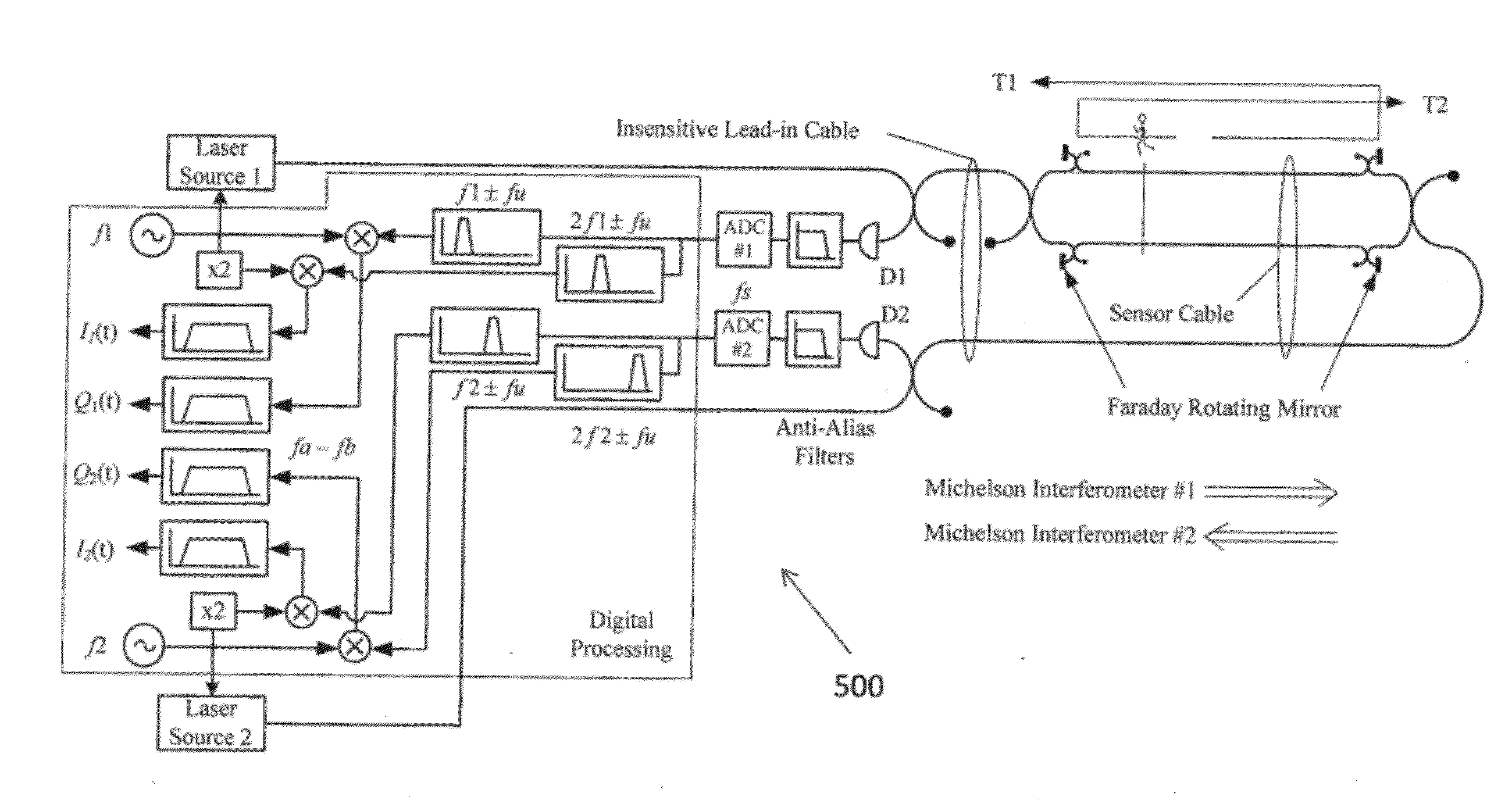
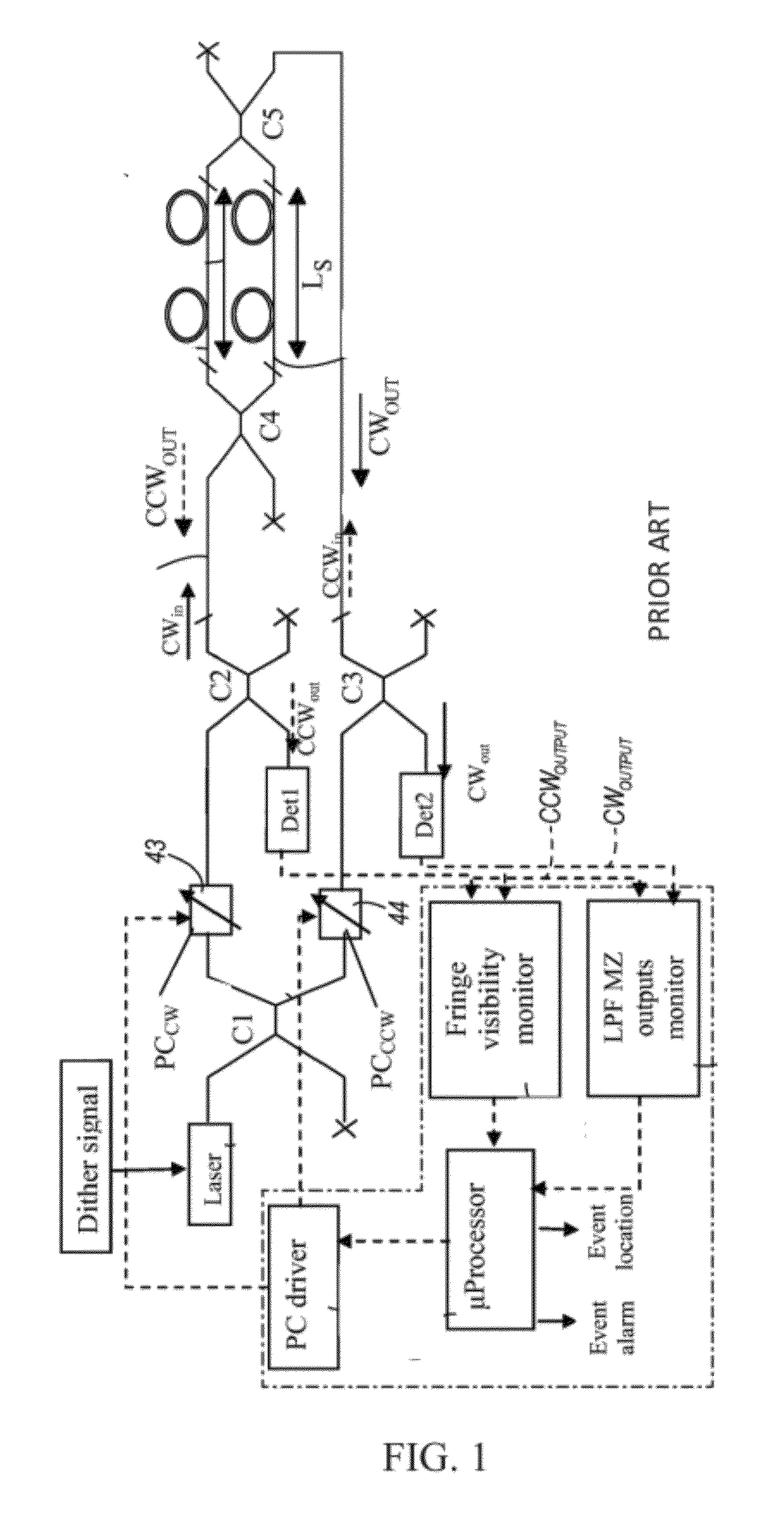
Interferometer systems
ActiveUS20120224182A1Detect presenceInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansOptoelectronicsOptic sensor
A fiber-optic sensor can have a Michelson sensor portion and a Mach-Zehnder sensor portion. A first splitter-coupler can be configured to split incoming light between a first fiber portion and a second fiber portion. A first polarization-phase conjugation device can be configured to conjugate a polarization phase of incident light corresponding to the first fiber portion, and a second polarization-phase conjugation device can be configured to conjugate a polarization phase of incident light corresponding to the second fiber portion. Each of the first and second polarization-phase conjugation devices can be configured to reflect light toward a detector and through the respective first and second fiber portions. A coupler can be configured to join light in the first fiber portion with light in the second fiber portion, and a third fiber portion can be configured to receive light from the coupler and to illuminate a second detector.
Owner:FIBERSONICS
Wave transmission medium and waveguide circuit
ActiveUS7397977B2Effective controlImprove efficiencyCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideForward propagationPhase difference
A wave transmission medium includes an input port 3-1 and an output port 3-2. A field distribution 1 and a field distribution 2 are obtained by numerical calculations. The field distribution 1 is a field distribution of the propagation light (forward propagation light) launched into the input port 3-1. The field distribution 2 is a field distribution of the phase conjugate light (reverse propagation light) resulting from reversely transmitting from the output port side an output field that is expected to be output from the output port 3-2 when an optical signal is launched into the input port 3-1. According to the field distributions 1 and 2, a spatial refractive index distribution is calculated such that the phase difference between the propagation light and reverse propagation light is eliminated at individual points (x, z) in the medium.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Device and system for phase conjugate conversion and wavelength conversion
InactiveUS7043099B1Broadening conversion bandImprove accuracyCoupling light guidesDistortion/dispersion eliminationFiberOptical circulator
The device according to the present invention relates to phase conjugate conversion and wavelength conversion. This device includes a polarization beam splitter and a polarization maintaining fiber (PMF). The polarization beam splitter has first, second, and third ports. The first port is supplied with signal light including first and second polarization components respectively having first and second polarization planes orthogonal to each other, and with pump light. The first and second ports are coupled by the first polarization plane, and the first and third ports are coupled by the second polarization plane. The PMF has first and second ends, and has a polarization mode to be maintained between the first and second ends. The first end is optically connected to the second port so that the first polarization plane is adapted to the polarization mode, and the second end is optically connected to the third port so that the second polarization plane is adapted to the polarization mode. Converted light generated by four-wave mixing based on the signal light and the pump light in the PMF is output from the first port, so that the converted light can be taken out by an optical circulator.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
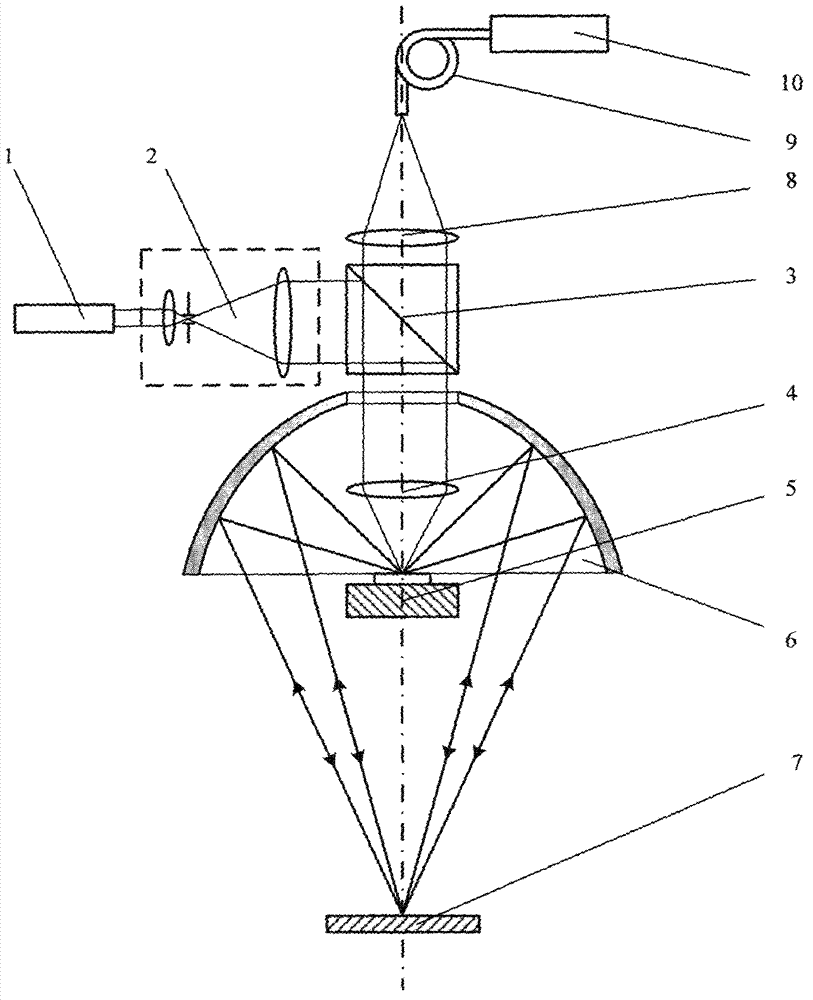
Phase conjugate reflection bi-pass lighting confocal microscopic device
InactiveCN102818522AWith detection abilityAchieve secondary lightingUsing optical meansBeam expanderPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention discloses a phase conjugate reflection bi-pass lighting confocal microscopic device, belonging to an optics measuring microtechnique. A collimation beam expander and a spectroscope are configured on a laser direct light path in sequence; a focusing objective lens and a three-dimensional micrometric displacement objective table are configured on a spectroscope reflecting light path; a collecting objective lens is configured on a spectroscope transmission light path; a collecting objective lens converging light is conducted to a photoelectric detector through conduction optical fibers; an ellipsoid reflecting lens is also configured on the spectroscope reflecting light path; a near focus of the ellipsoid reflecting lens is located on a surface of a sample put on the three-dimensional micrometric displacement objective table; and a phase conjugate reflecting lens is configured at a remote focus of the ellipsoid reflecting lens. According to the device, bi-pass lighting to a large curvature convex surface is carried out by adopting a characteristic that a reflection ray as a phase conjugate light wave of an incidence light of the phase conjugate reflecting lens can go back along an original way in combination with a characteristic that the ellipsoid reflecting lens is provided with a pair of isoplanatic image formation conjugate focuses, so that the device has a measurement ability of the large curvature convex surface and a characteristic of a high axial resolution force.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
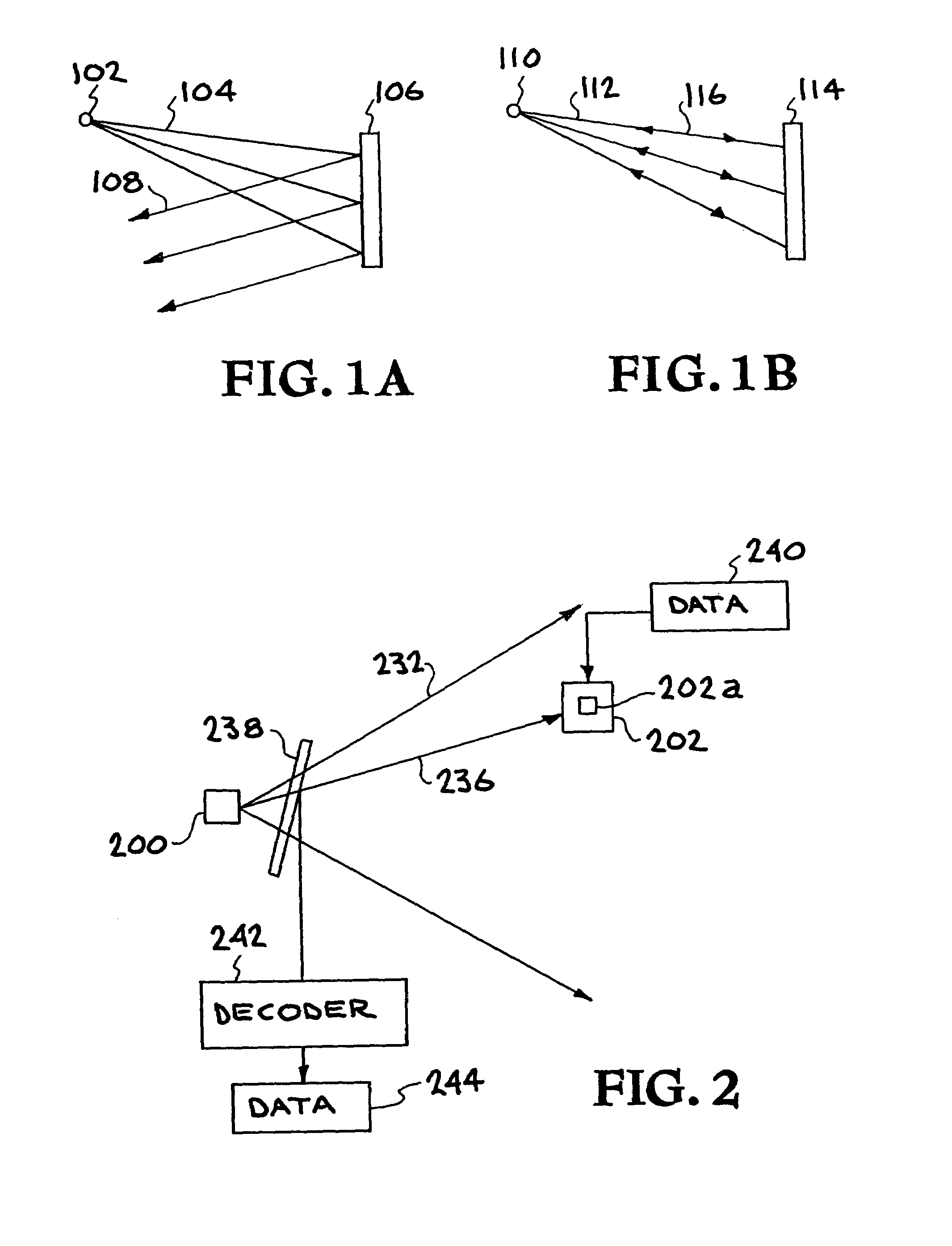
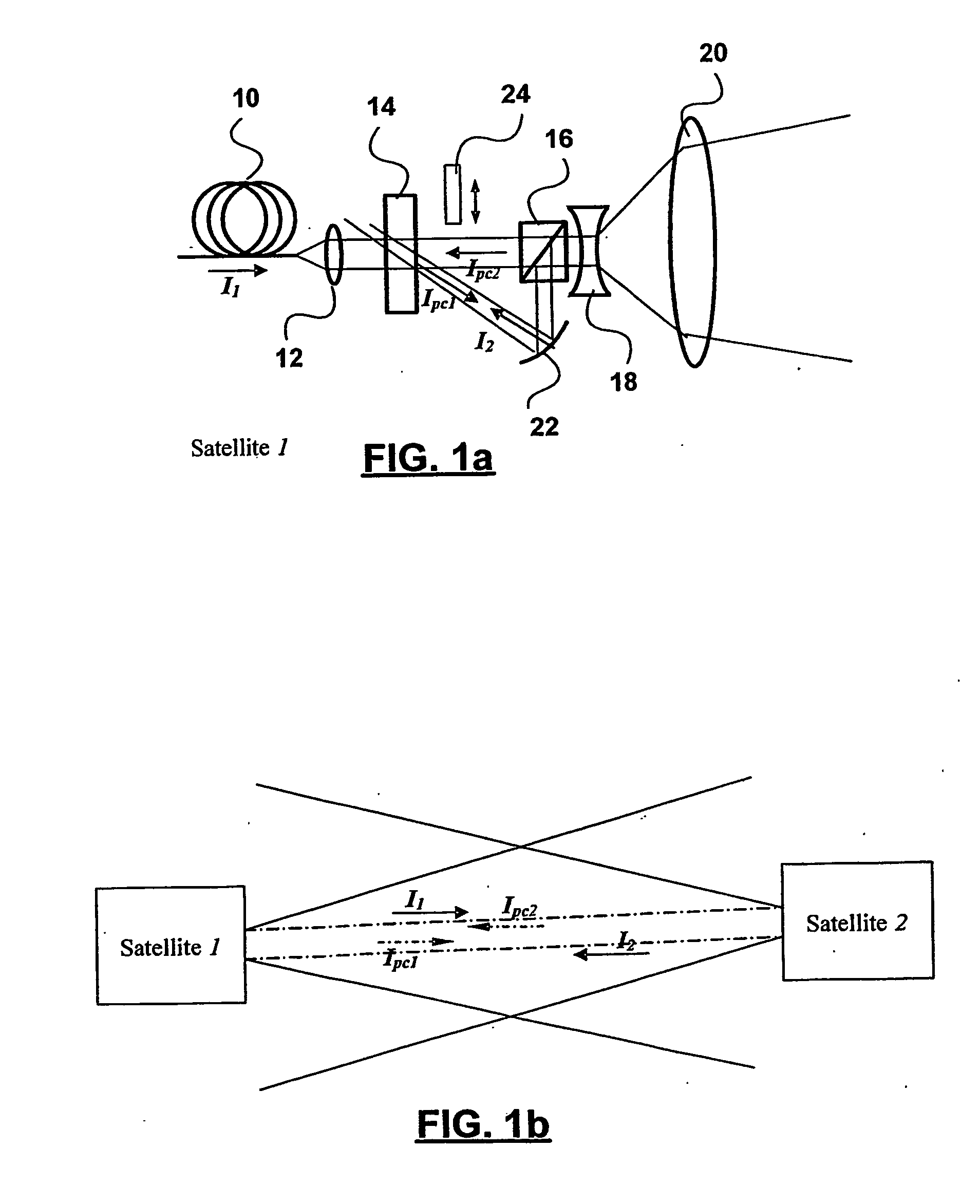
Method of establishing communication through free space between a pair of optical communication devices
InactiveUS20050259991A1Eliminate needImprove performanceDirection/deviation determining electromagnetic systemsSatellite communication transmissionLight beamOptical communication
A method is disclosed for establishing communication through free space between a pair of optical communication devices. A divergent beam is transmitted from each of the optical communication devices toward the other. A portion of the received divergent beam is used to create a phase conjugated beam that is returned to the other device. A diffraction grating is dynamically recorded at each devices so as to establish a bi-directional self-tracking optical link between the devices.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
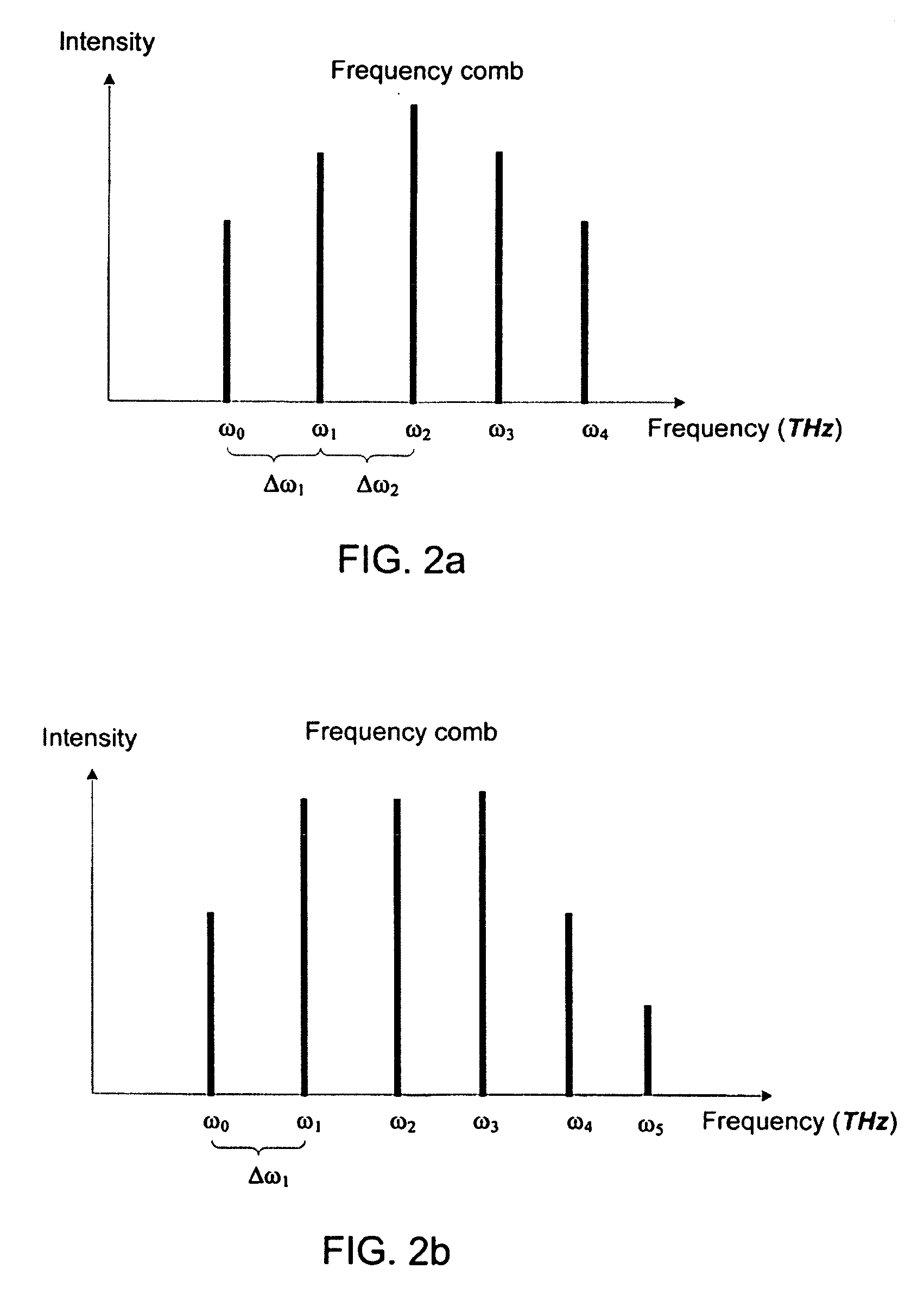
Speckle reduction in imaging applications and an optical system thereof
Speckle effect in imaging applications is reduced by generating additional speckle patterns on the screen such that the speckle patterns are overlapped and the overlapped speckle patterns average out on the screen to appear as a noise background to the viewers. The speckle patterns are generated by discrete optical signals of a visible frequency comb. A visible frequency comb having discrete optical signals is generated through modulation-instability processes, phase-conjugation processes, and Bragg-scattering processes using a non-linear optical material and a wavelength converter.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
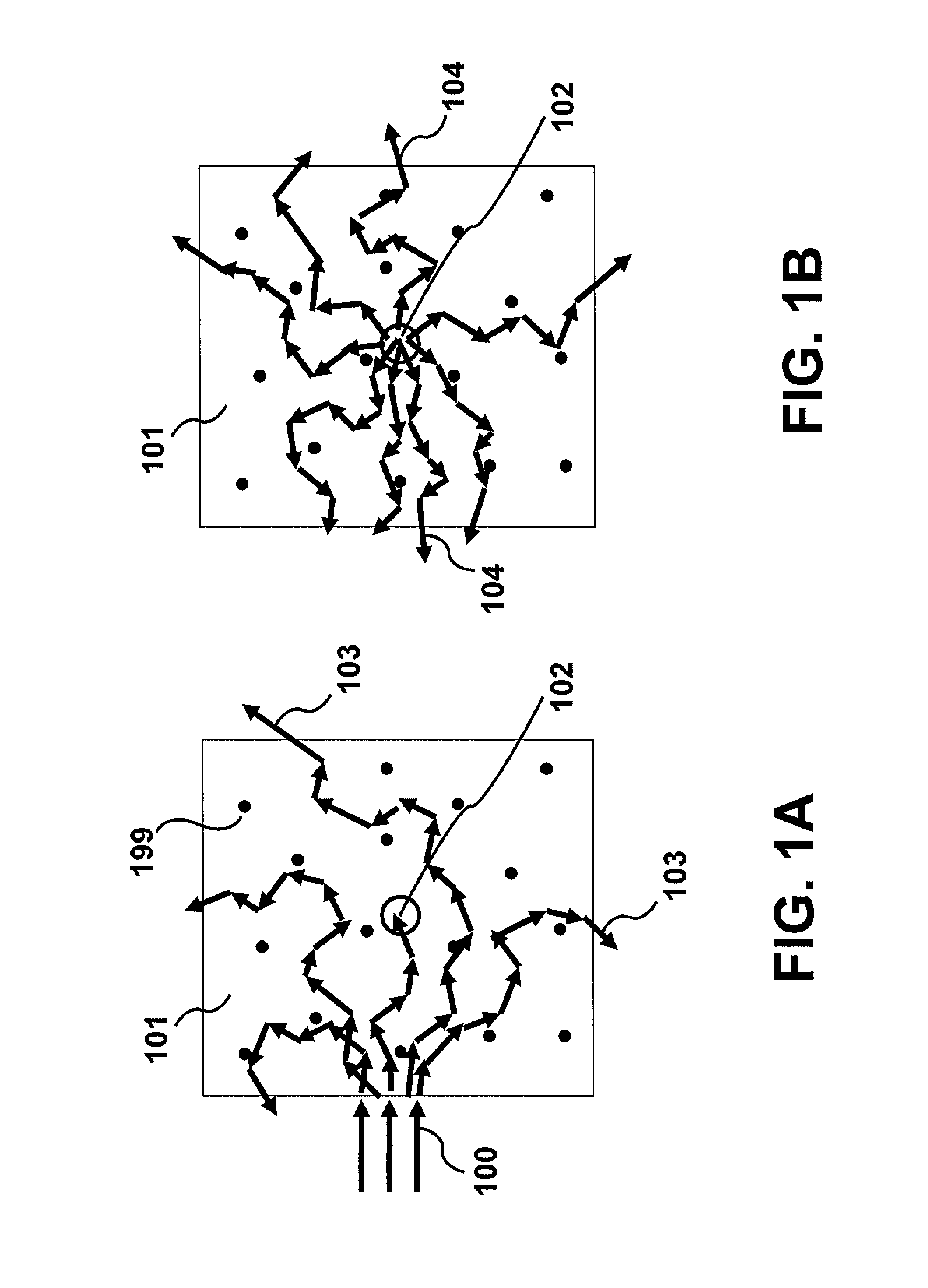
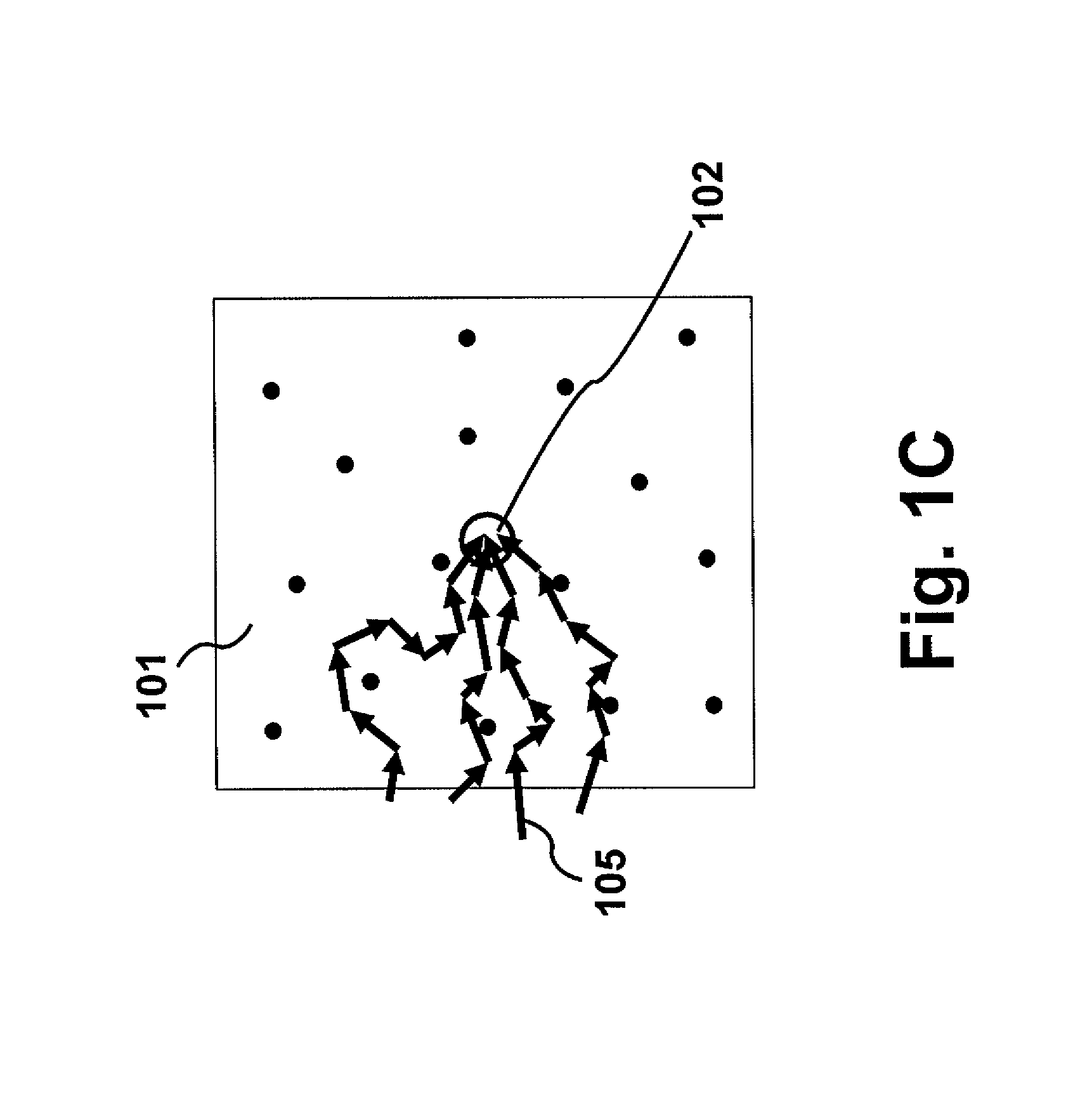
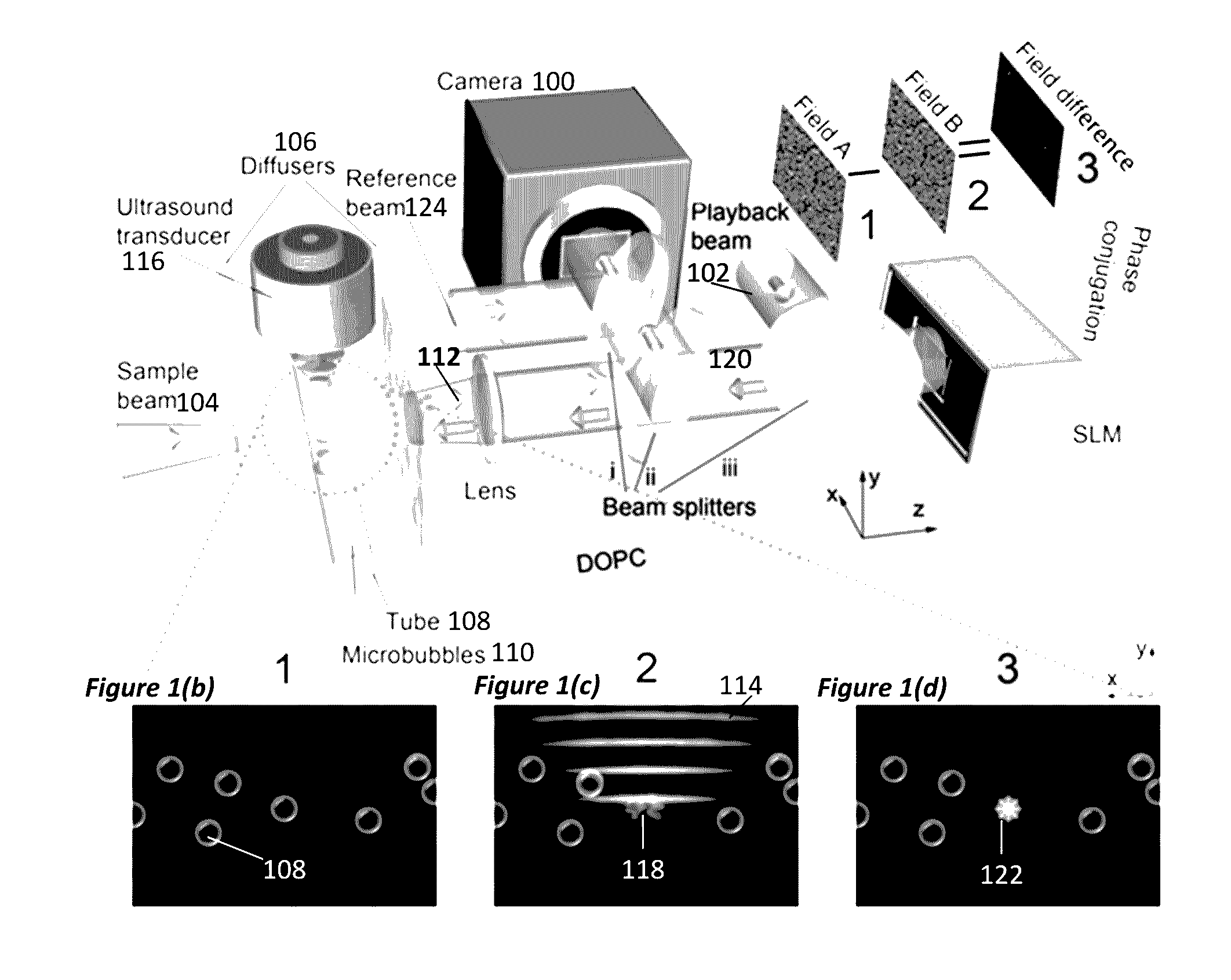
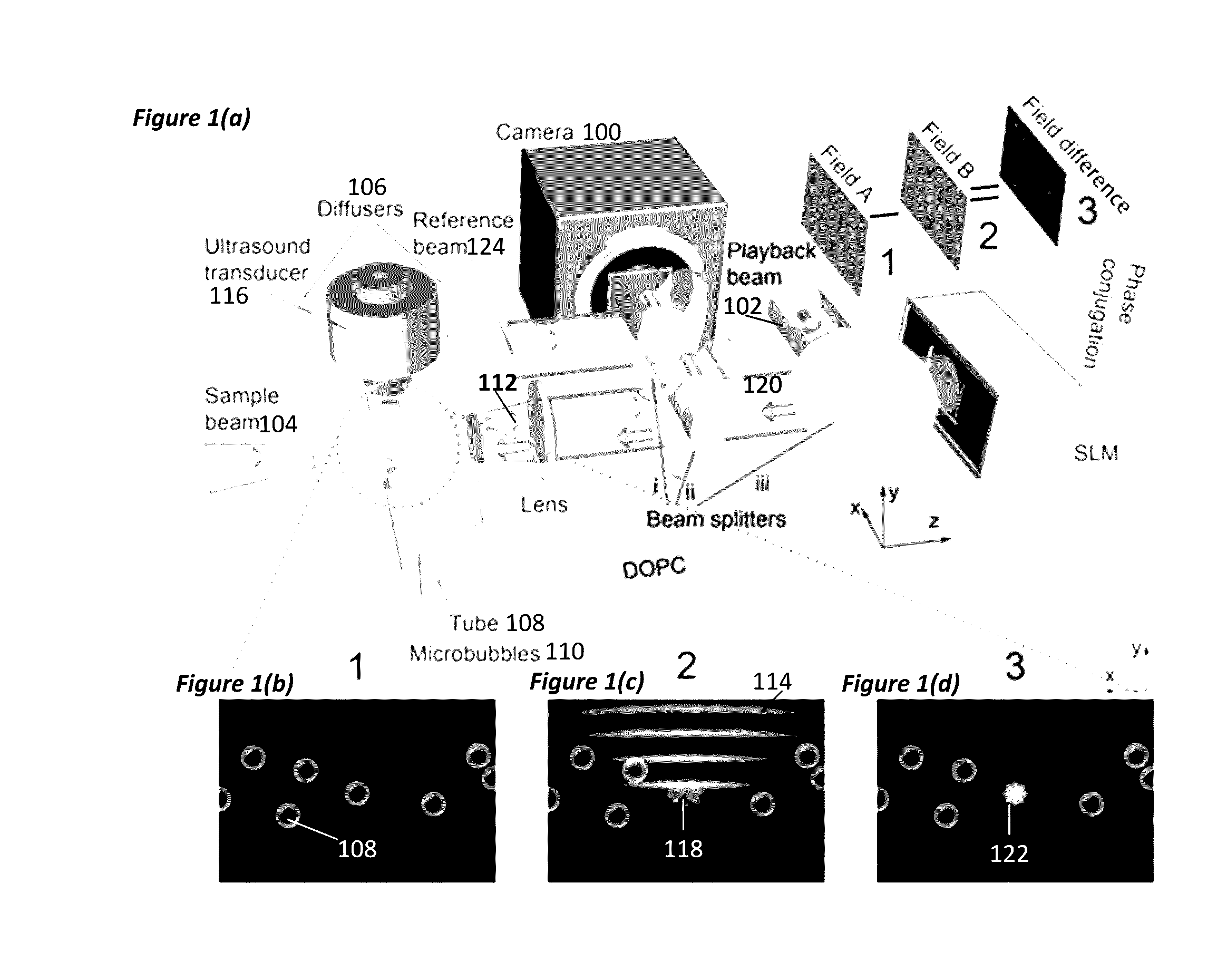
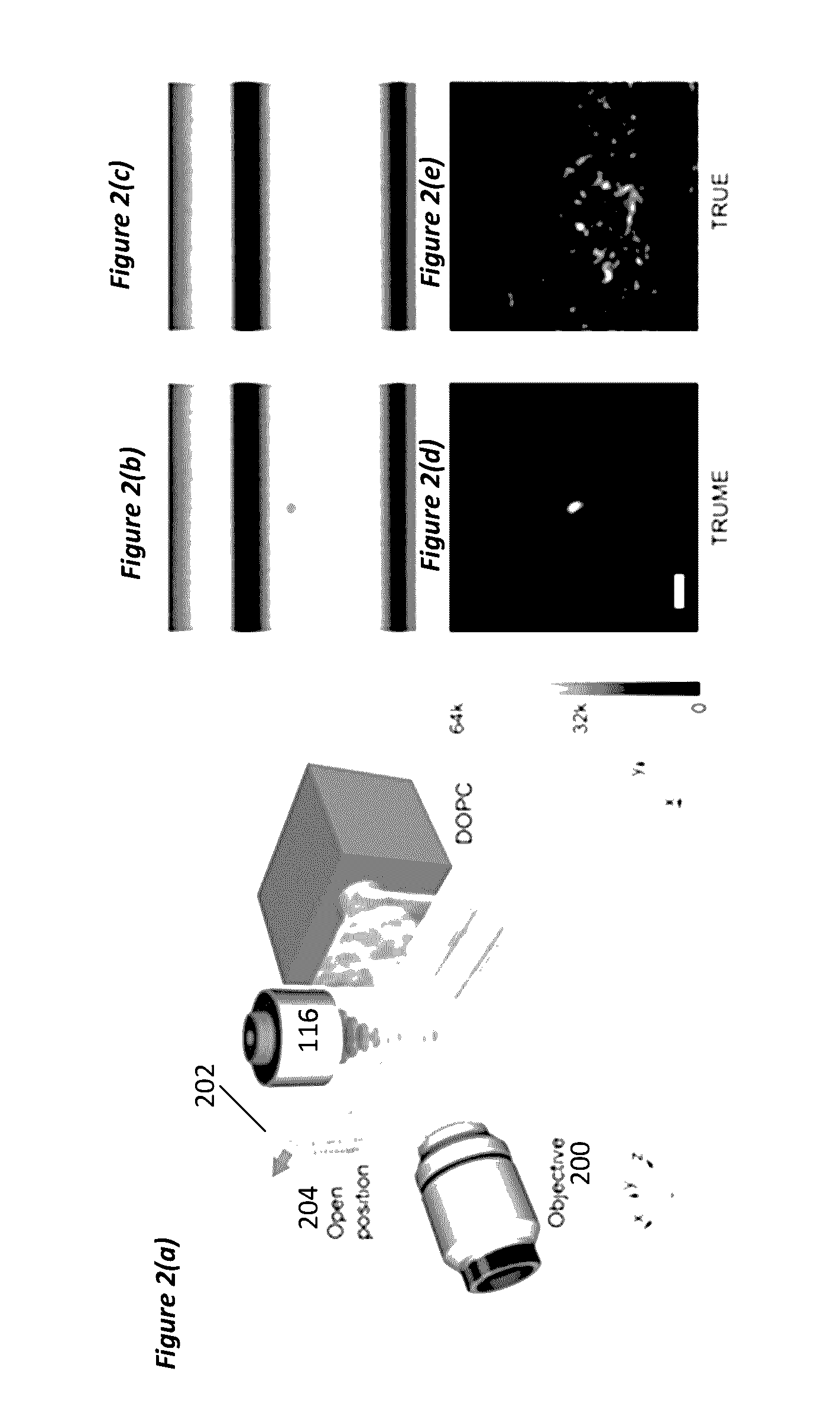
Optical focusing inside scattering media with time-reversed ultrasound microbubble encoded (TRUME) light
ActiveUS20160363527A1Improve efficiencyImprove concentrationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsScattering properties measurementsElectromagnetic radiationUse of time
A method for irradiating scattering medium, including modifying a particle's response to electromagnetic radiation irradiating the particle in a scattering medium, wherein the electromagnetic radiation is scattered by the scattering medium, and modulated by the modifying, into scattered electromagnetic radiation comprising a scattered field; forming a phase conjugate field, wherein the phase conjugate field is a phase conjugate of the scattered field; and irradiating the scattering medium with the phase conjugate field, wherein the phase conjugate field forms a focus at a target defined by the particle.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
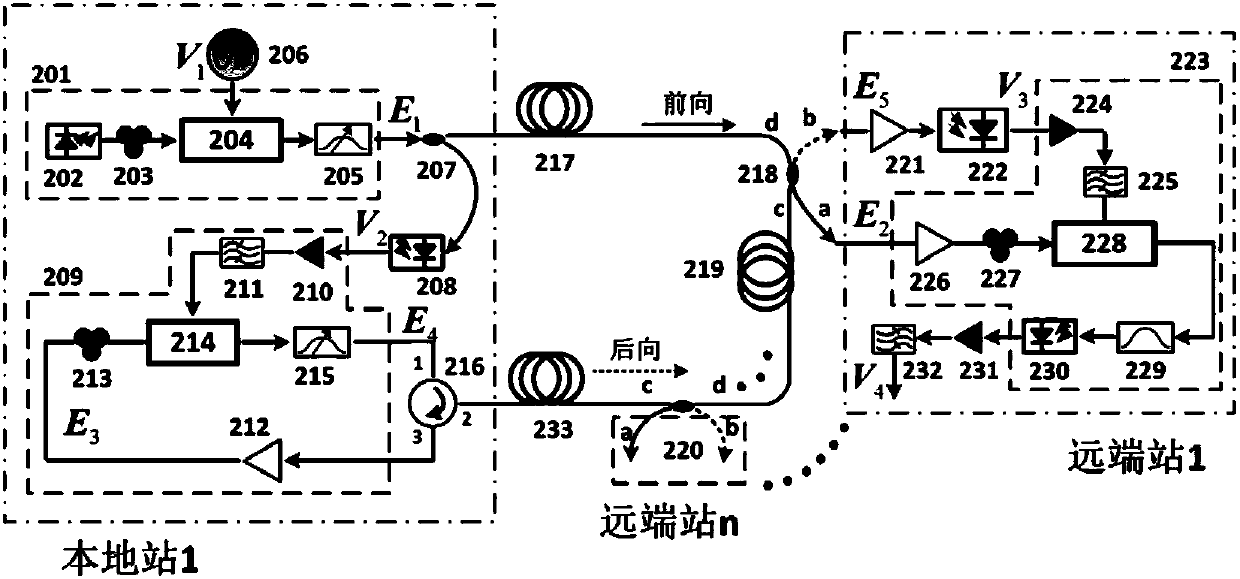
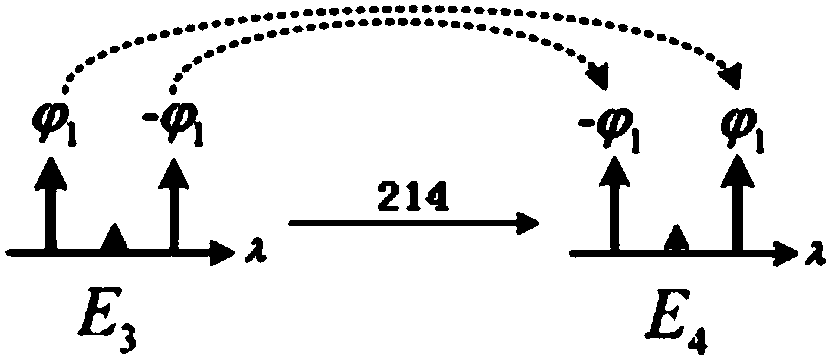
High-precision distributed optical fiber frequency transfer method
ActiveCN106603158AAvoid Short-Term Stability ImpactsEasy to solveWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionFiberPhase noise
The invention discloses a high-precision distributed optical fiber frequency transfer method. Local transferred frequency signals are subjected to frequency halving and then serve as detection signals, the signals are transmitted back and forth between the local end and a remote end through bidirectional wavelength division multiplexing, and detection signals comprising optical fiber link phase noise are obtained at the local end; the returned detection signals and the local transferred frequency signals are subjected to frequency mixing and filtering to obtain phase conjugation signals, and the phase conjugation signals are transmitted to the optical fiber link through another wavelength channel; all users detect forward conjugation signals and backward detection signals, and stable frequency signals are obtained through frequency mixing; and the remote end carries out frequency mixing on the received forward phase conjugation signals and the forward detection signals to obtain stable frequency signals. Influences on frequency transfer short-term stability by backscattering noise can be avoided; the users share the same wavelength, and the fiber frequency long-term stability influences and the cost due to increasing of users can be reduced; and by adopting passive compensation, the method has the advantages of relatively simple and unlimited dynamic range and quick compensation.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
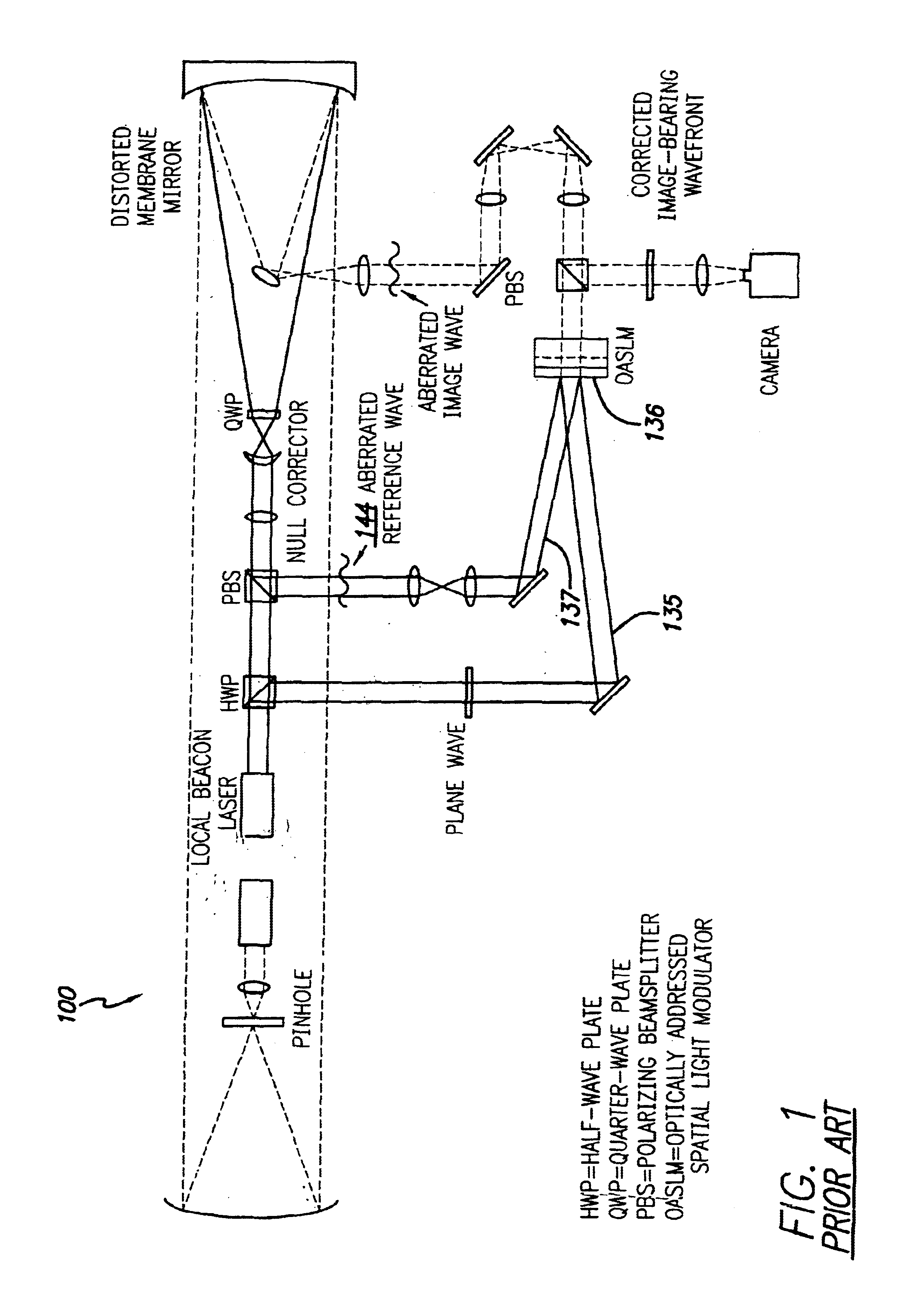
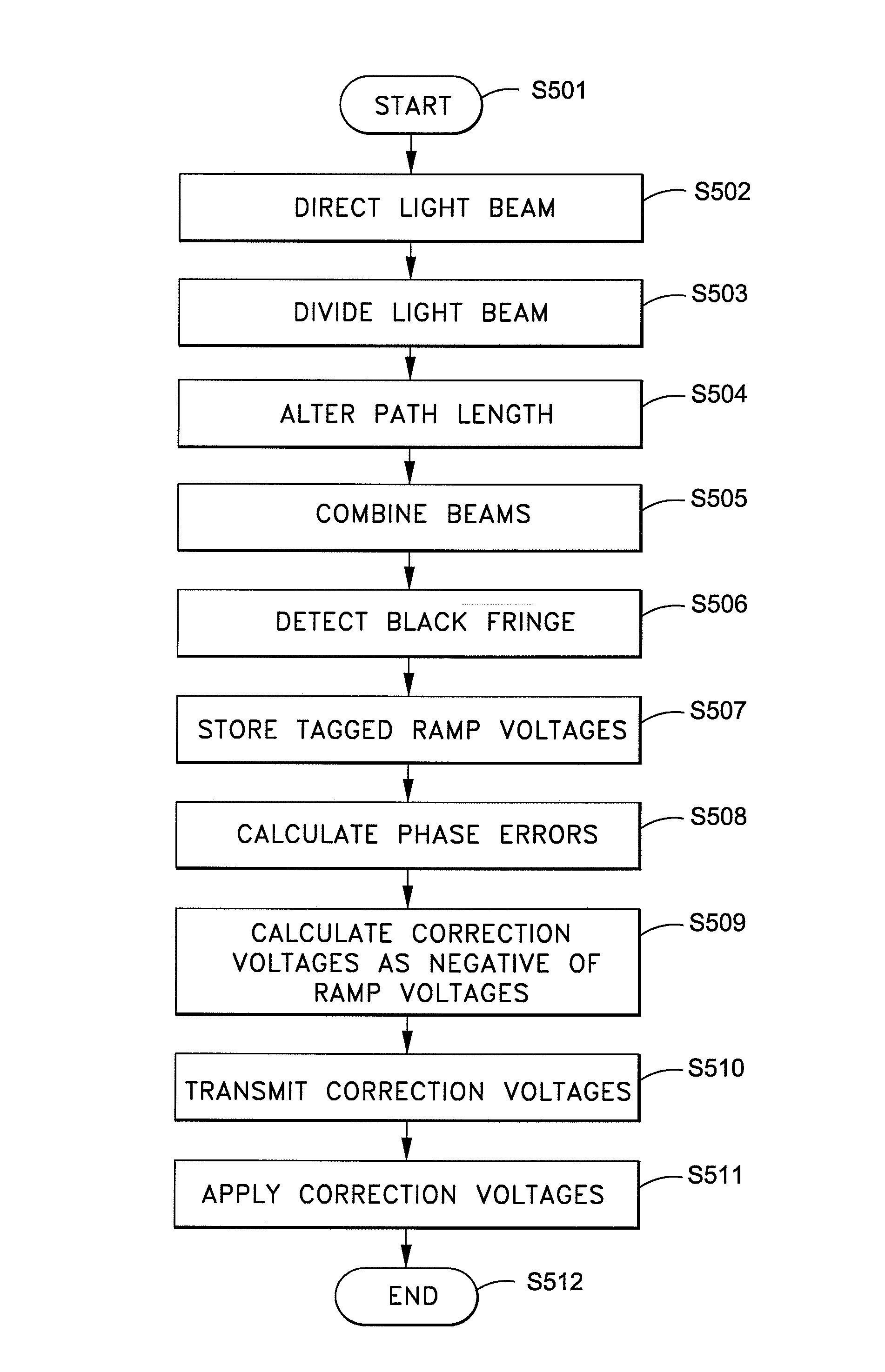
Black fringe wavefront sensor
A method of performing closed loop correction of phase aberrations, including the steps of directing an incoming light beam into a black fringe wavefront sensor via an adaptive optical device (“AOD”), dividing the incoming light beam into measurement and reference beams, altering the path length of the measurement beam and the location of the black fringe by modulating a ramp voltage of a modulator, combining the measurement and reference beams into a common output beam, detecting the black fringe in the common output beam using detectors mapped to the AOD, storing, as tagged ramp voltages, a corresponding ramp voltage for each detector when it detects black fringe, calculating phase errors based upon the tagged ramp voltages and modulator scaling, calculating adaptive optics correction voltages based upon the phase errors, transmitting and applying the correction voltages to the AOD to correct phase aberrations of the incoming light beam via phase conjugation.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com