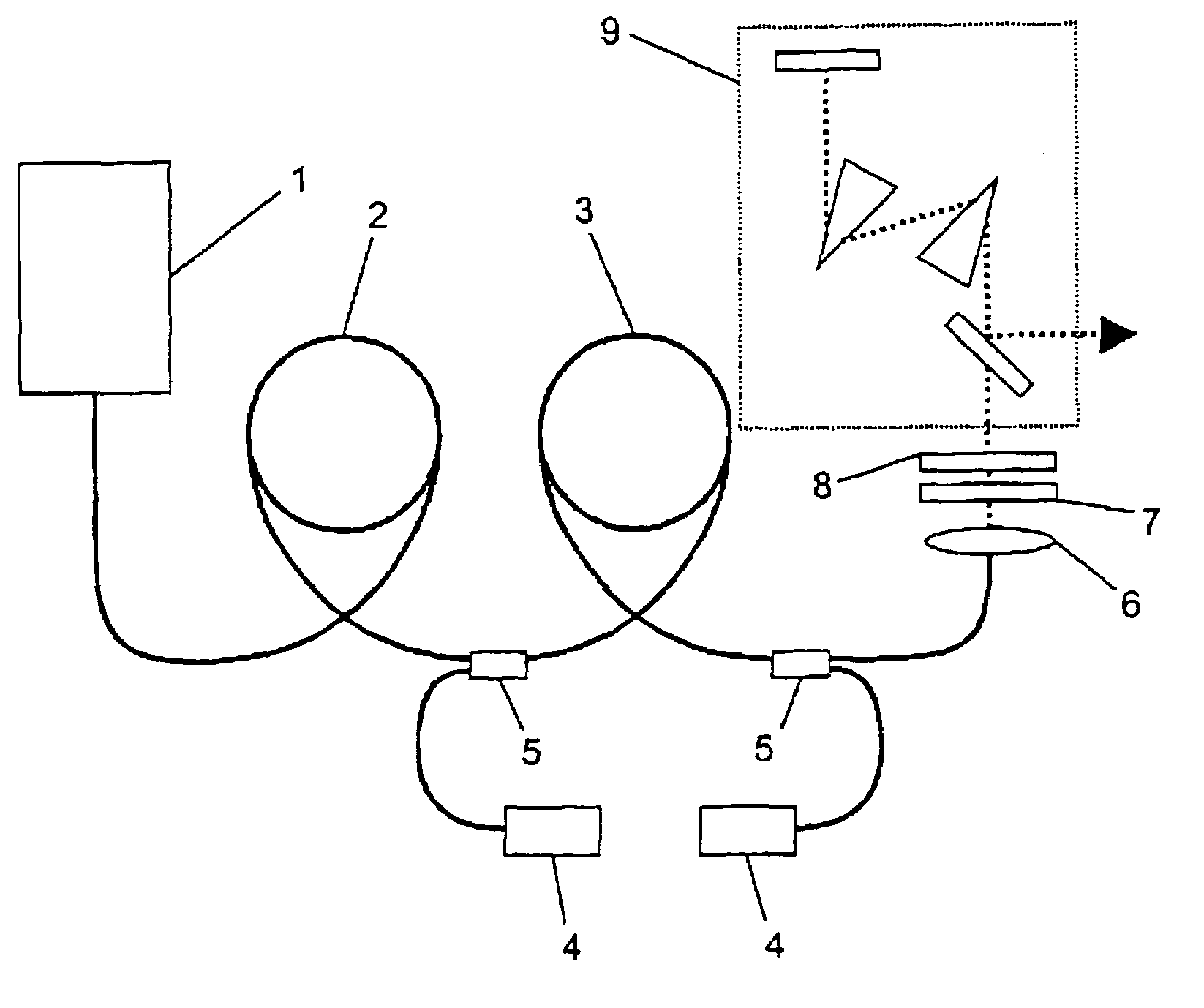
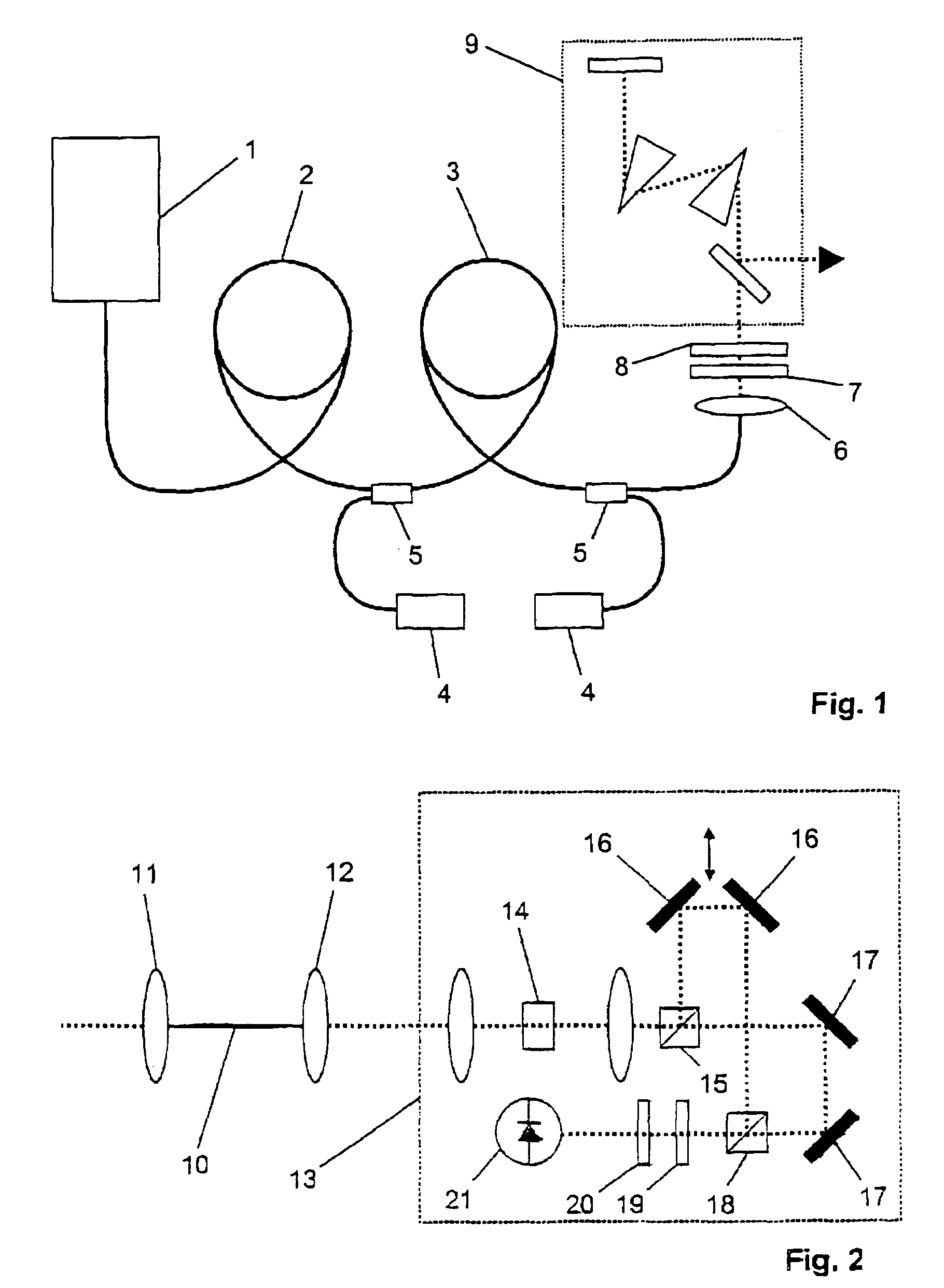
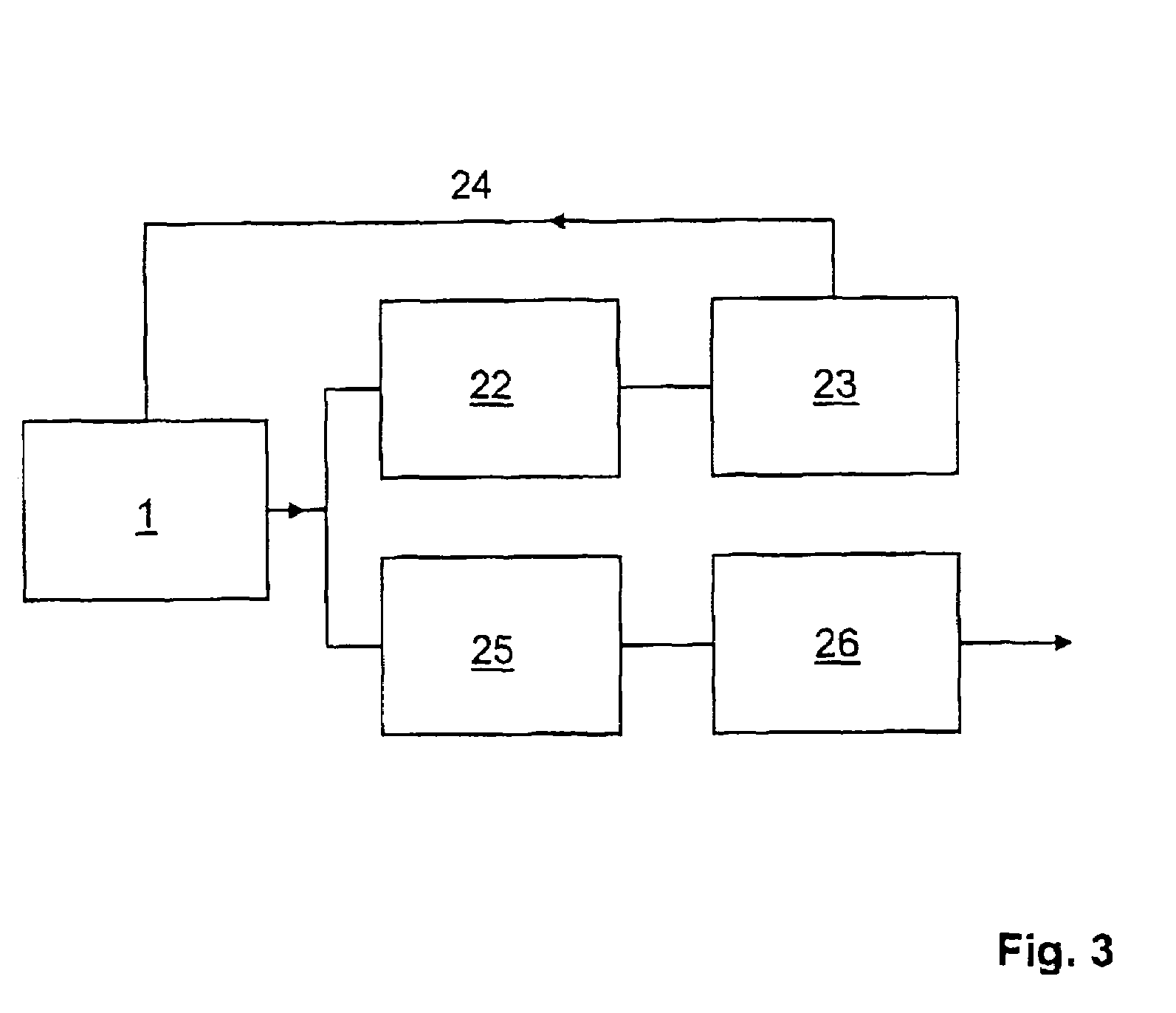
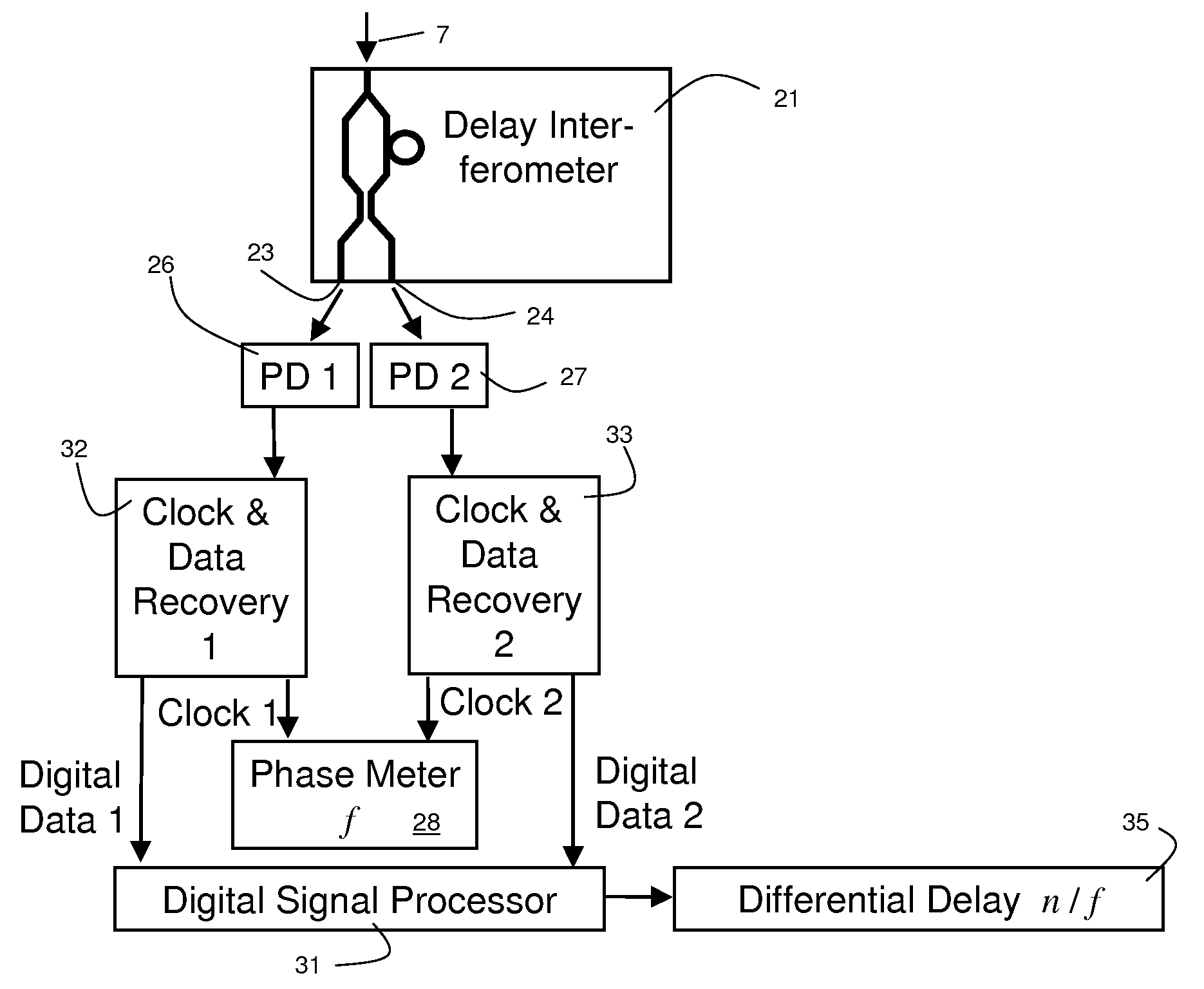
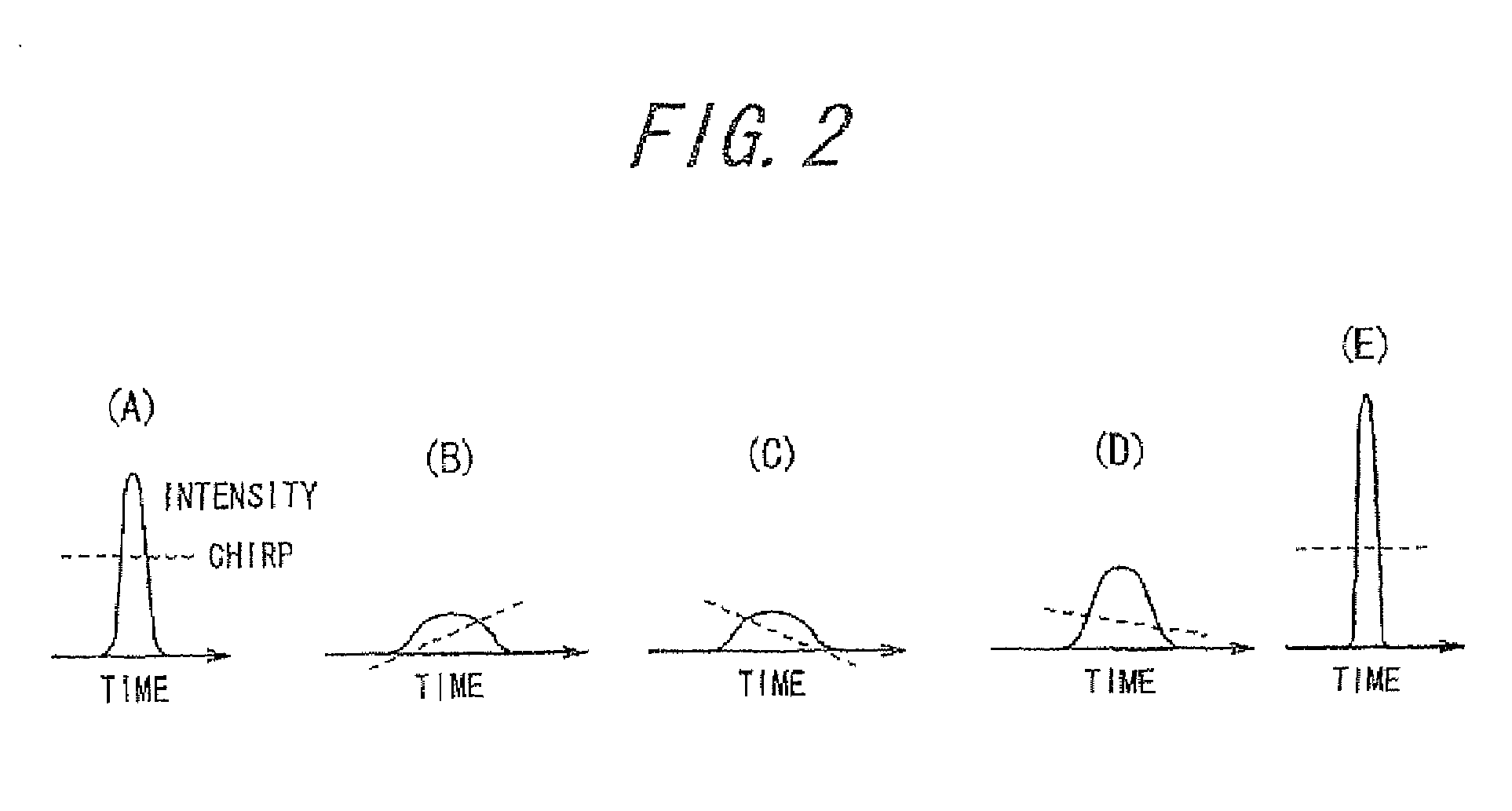
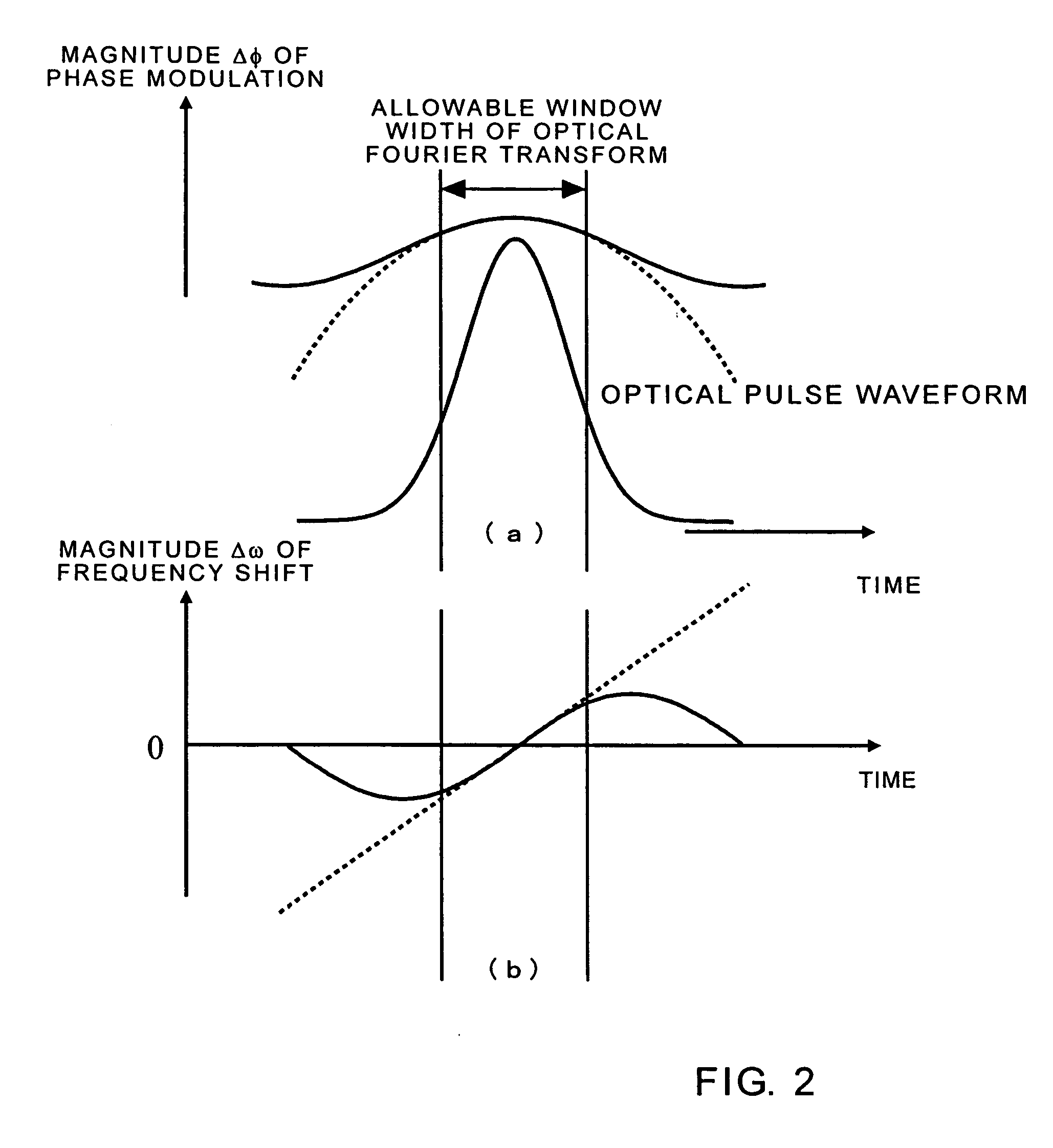
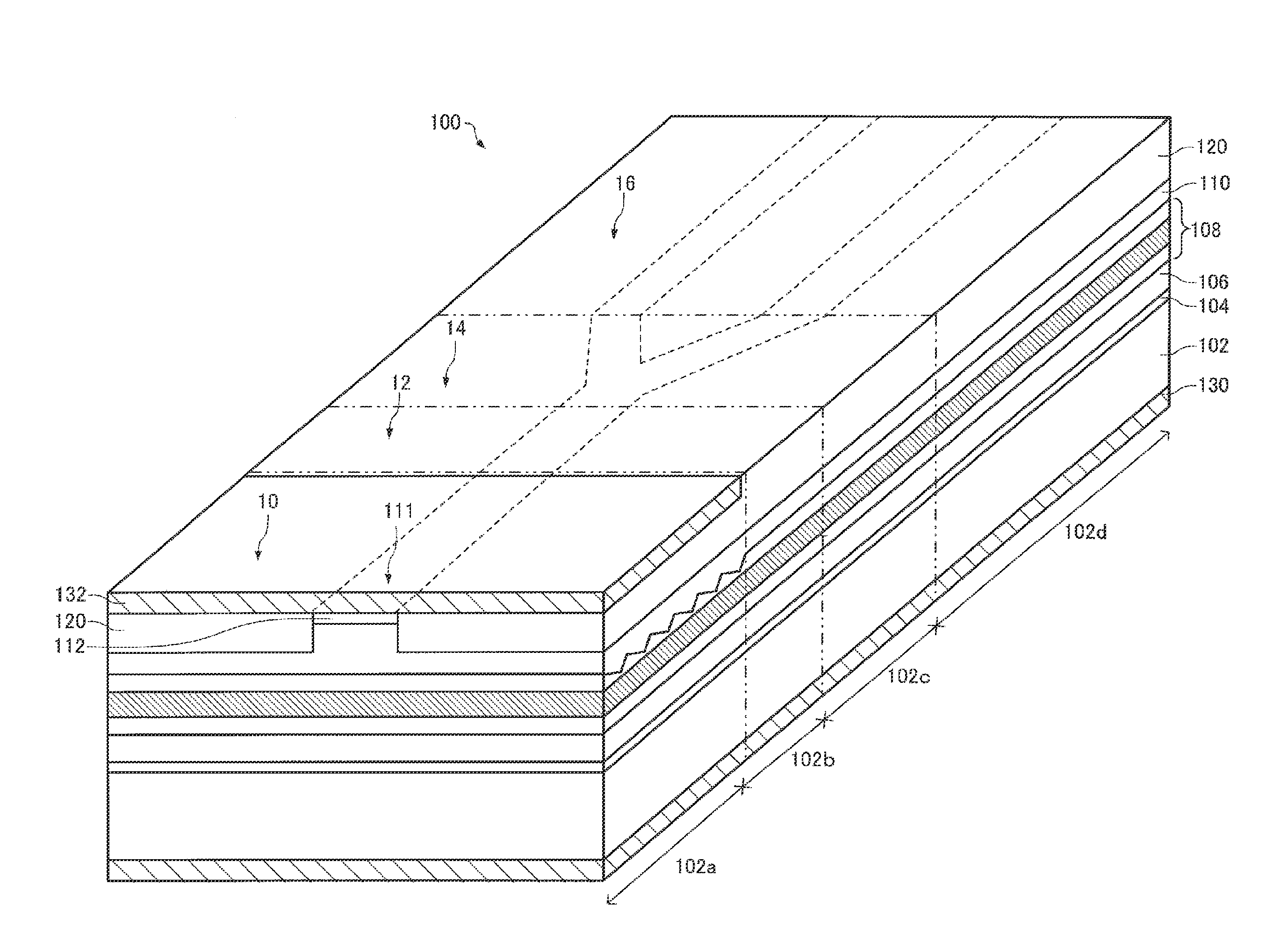
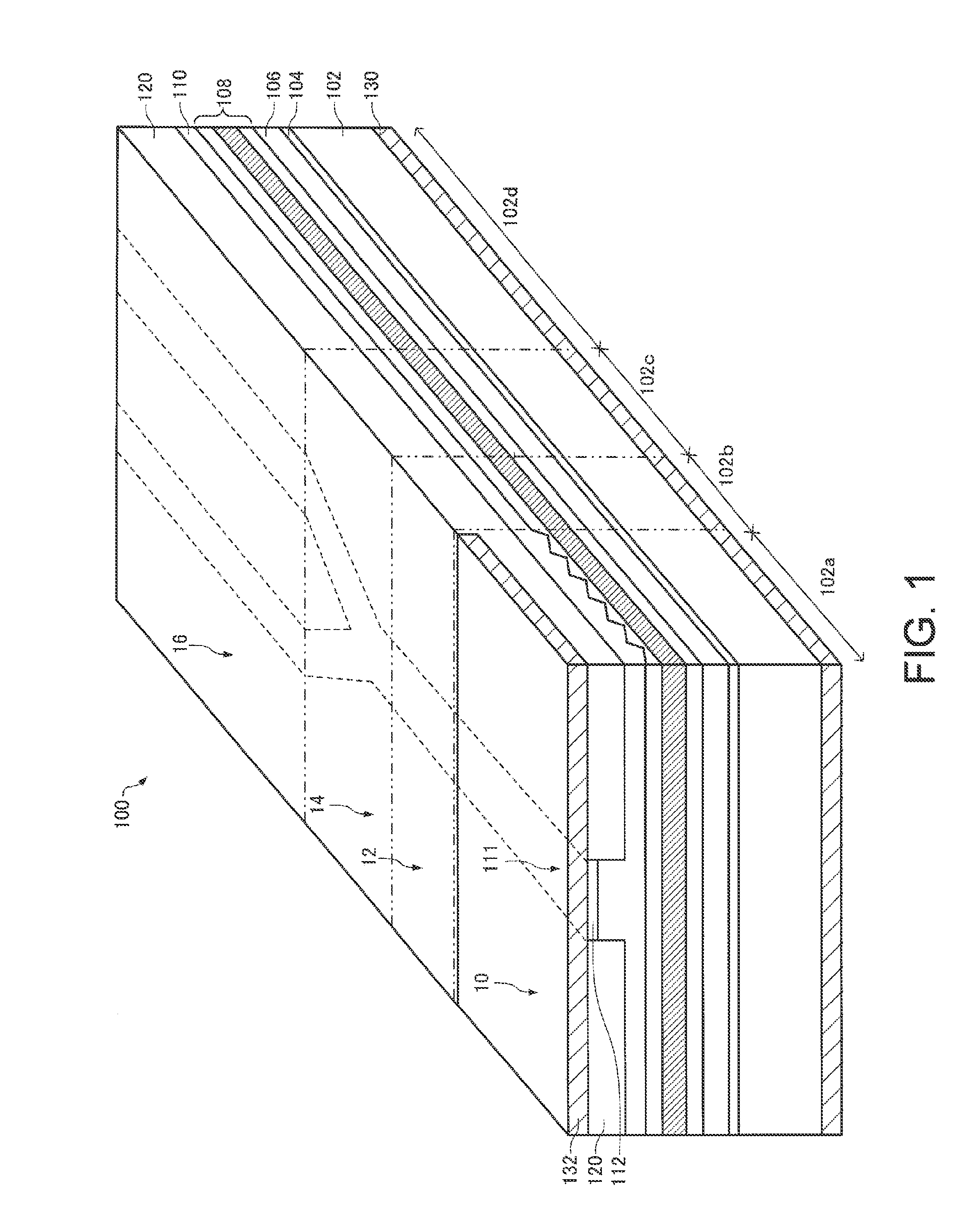
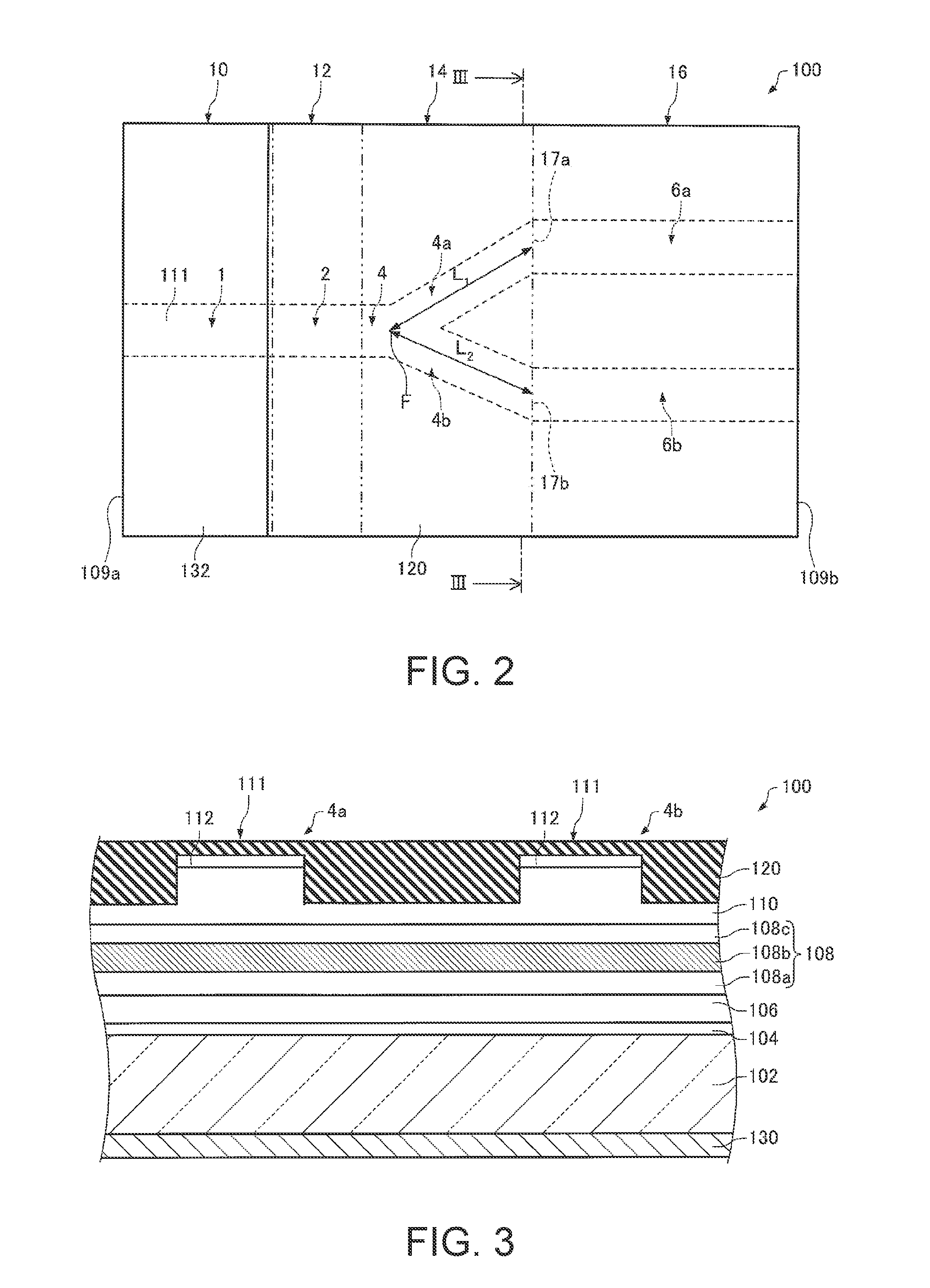
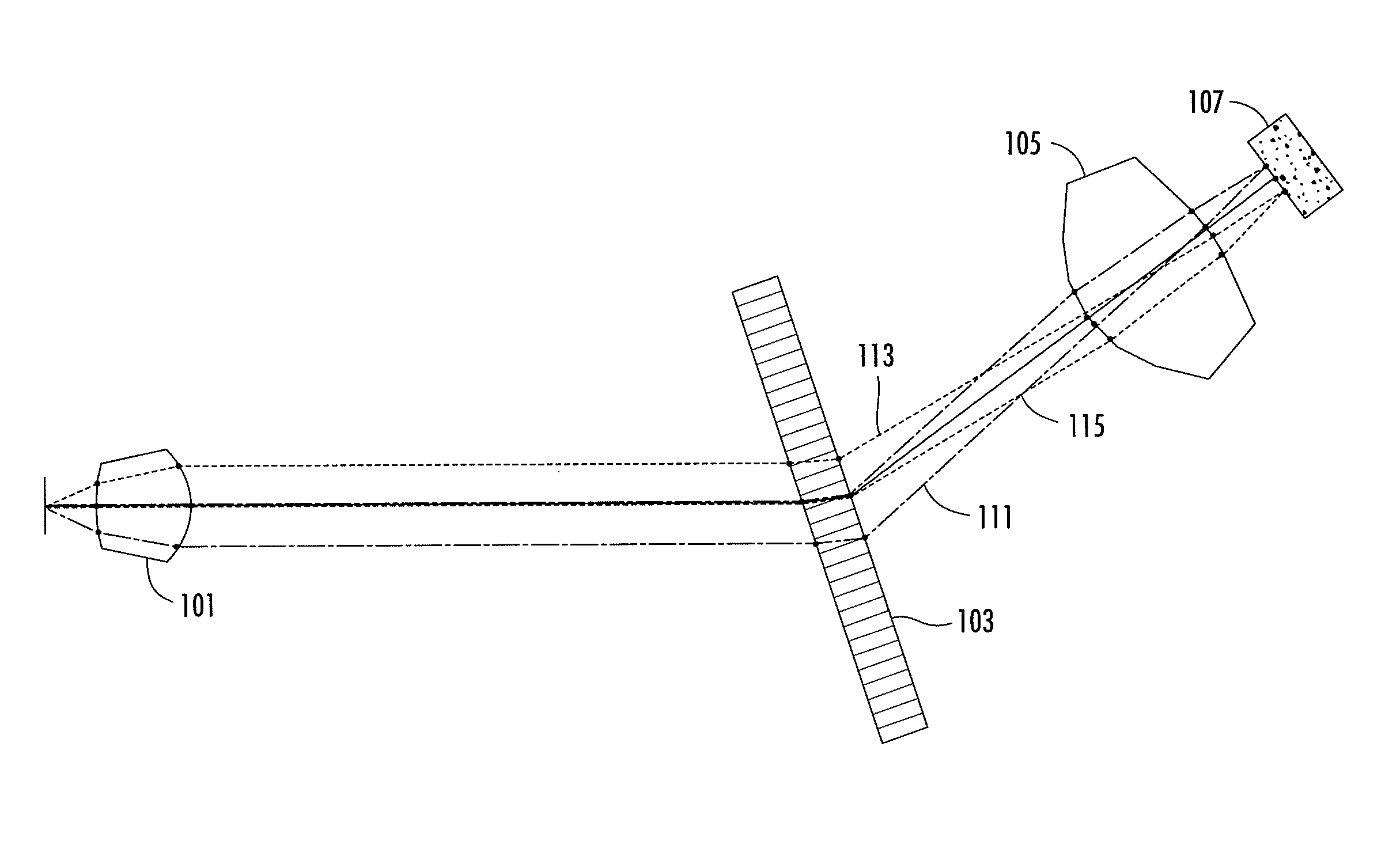
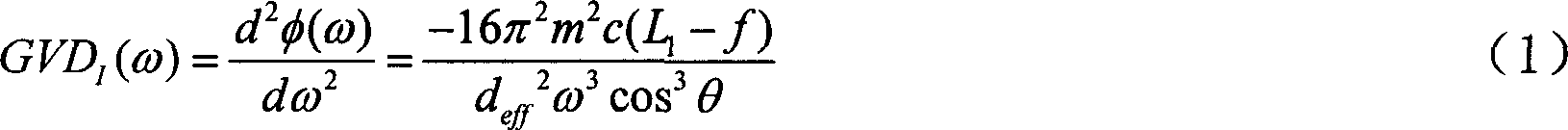Patents
Literature
142 results about "Group velocity dispersion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
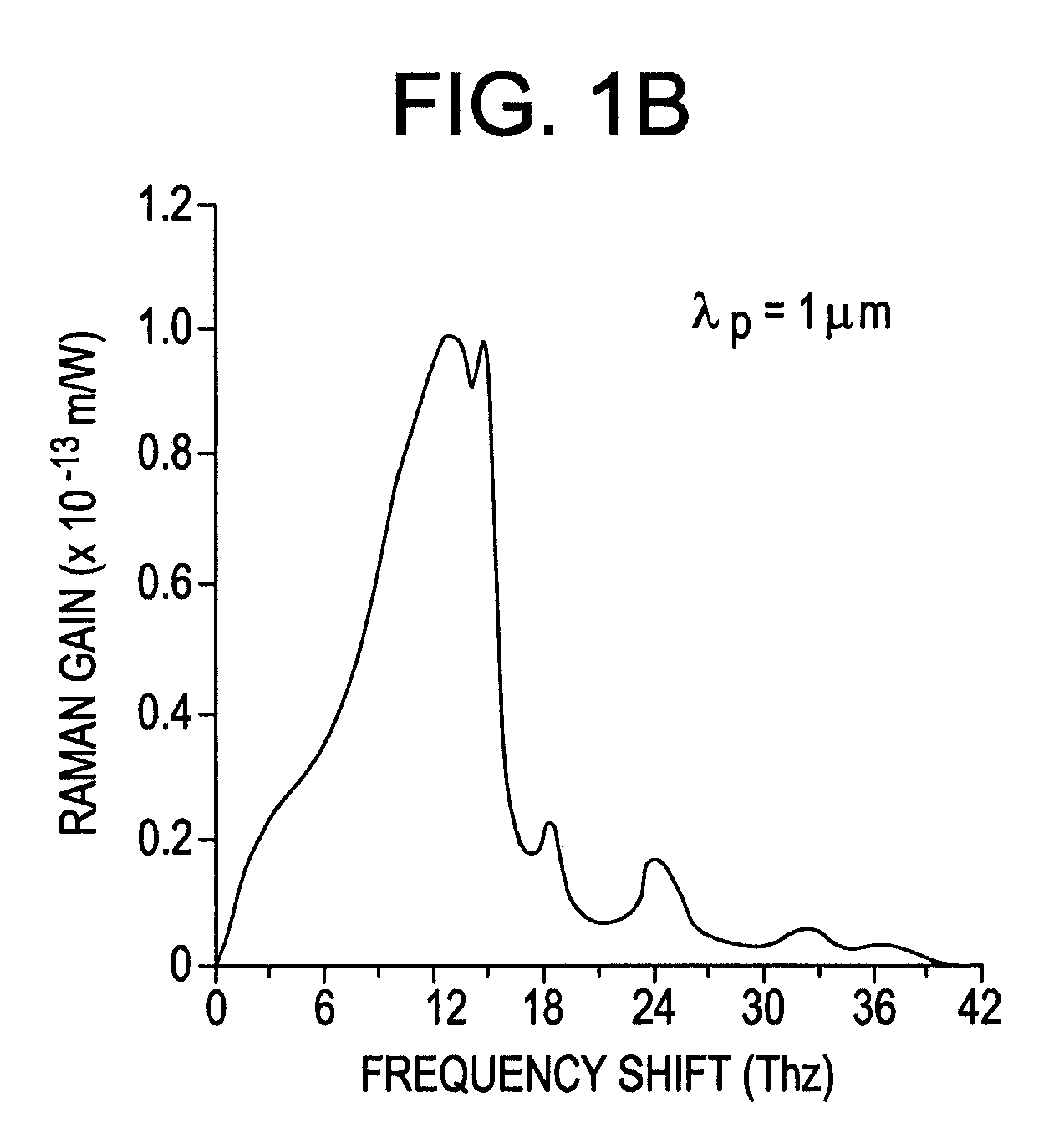
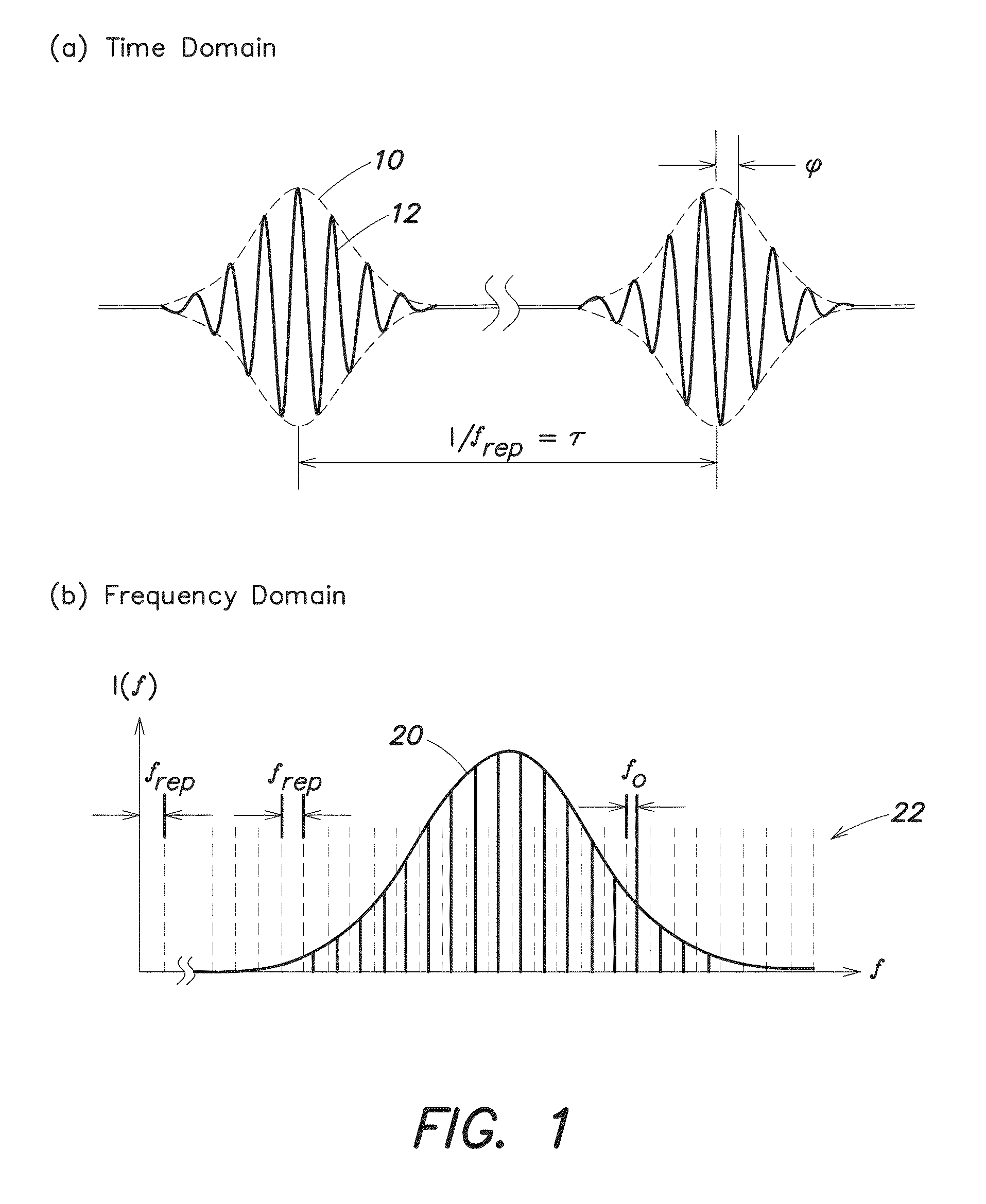
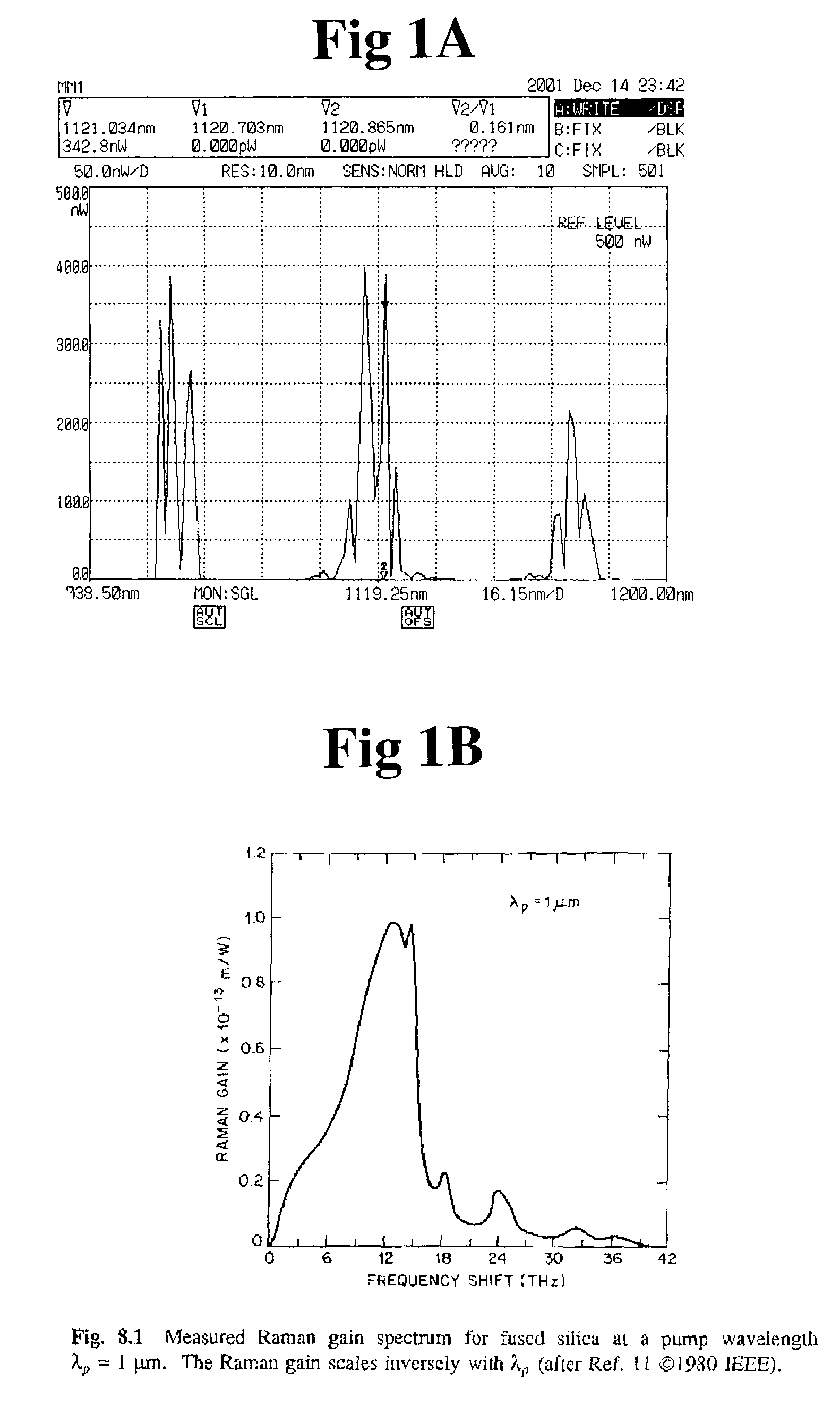
In optics, group velocity dispersion (GVD) is a characteristic of a dispersive medium, used most often to determine how the medium will affect the duration of an optical pulse traveling through it. Formally, GVD is defined as the derivative of the inverse of group velocity of light in a material with respect to angular frequency,
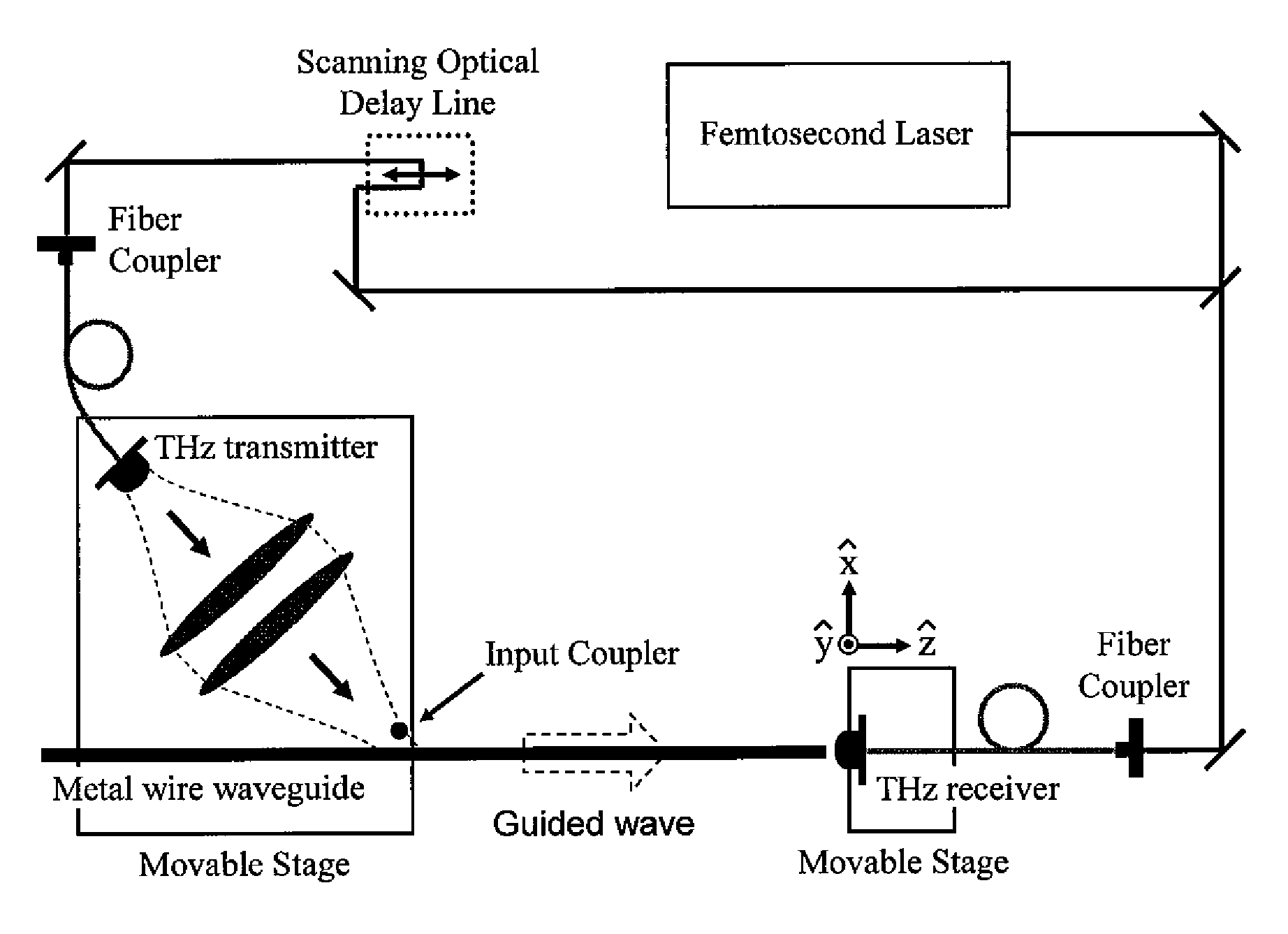
Method and system for transmitting terahertz pulses
InactiveUS7531803B2Improve performanceReduce lossRadiation pyrometryAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyGroup velocity dispersionSensing applications
Systems for THz transmission using new types of THz waveguides with low loss, negligible group velocity dispersion and structural simplicity are described herein. The THz system incorporates the use of a waveguide with two or more substantially parallel conductive elements which may enable many new THz sensing applications. It is now possible to direct the THz pulse inside of containers or around corners, where line-of-sight optics are not practical. Moreover, the systems allow use of either radially polarized or linearly polarized THz antennas. The disclosed systems are compatible with existing terahertz generation and detection techniques.
Owner:RICE UNIV
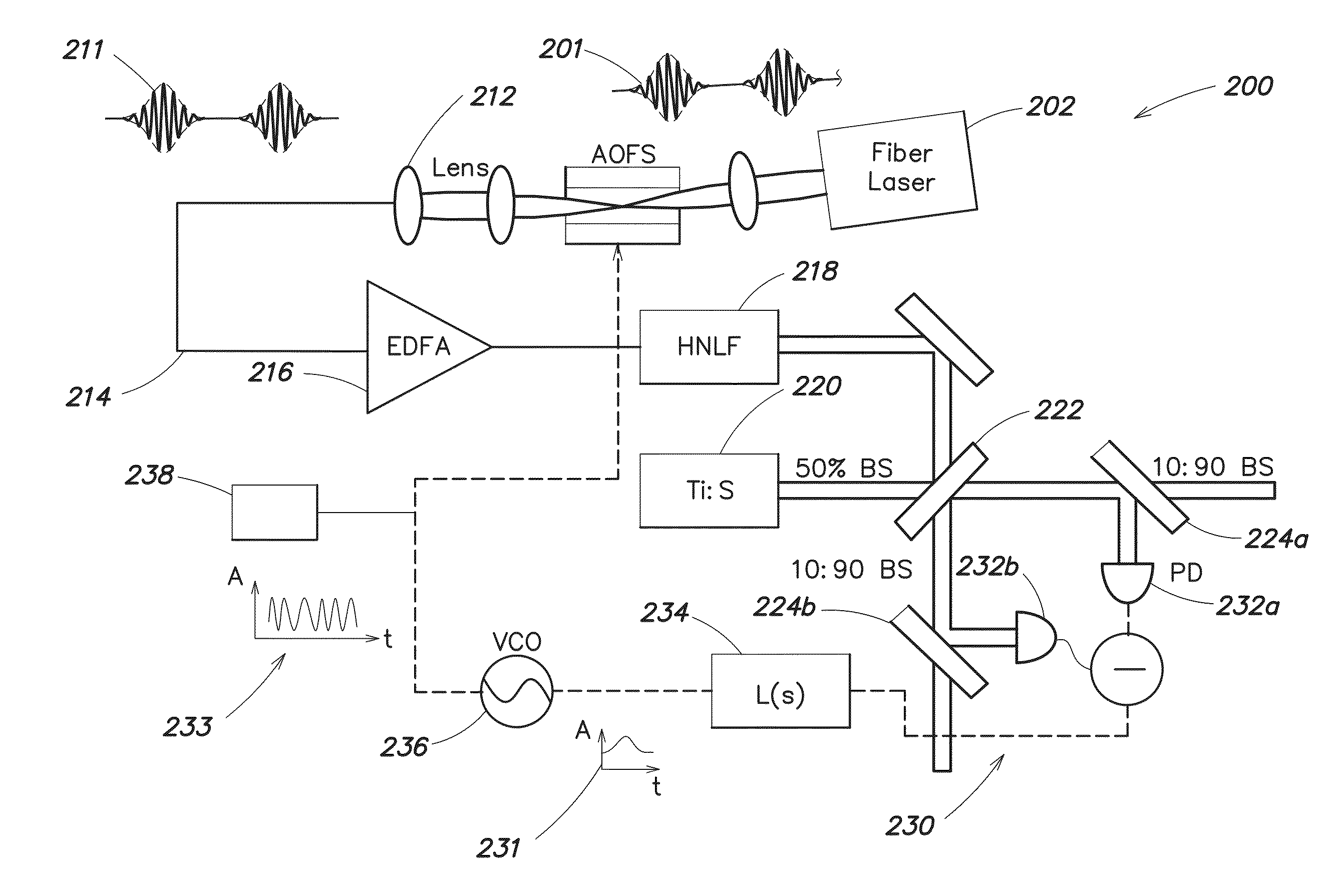
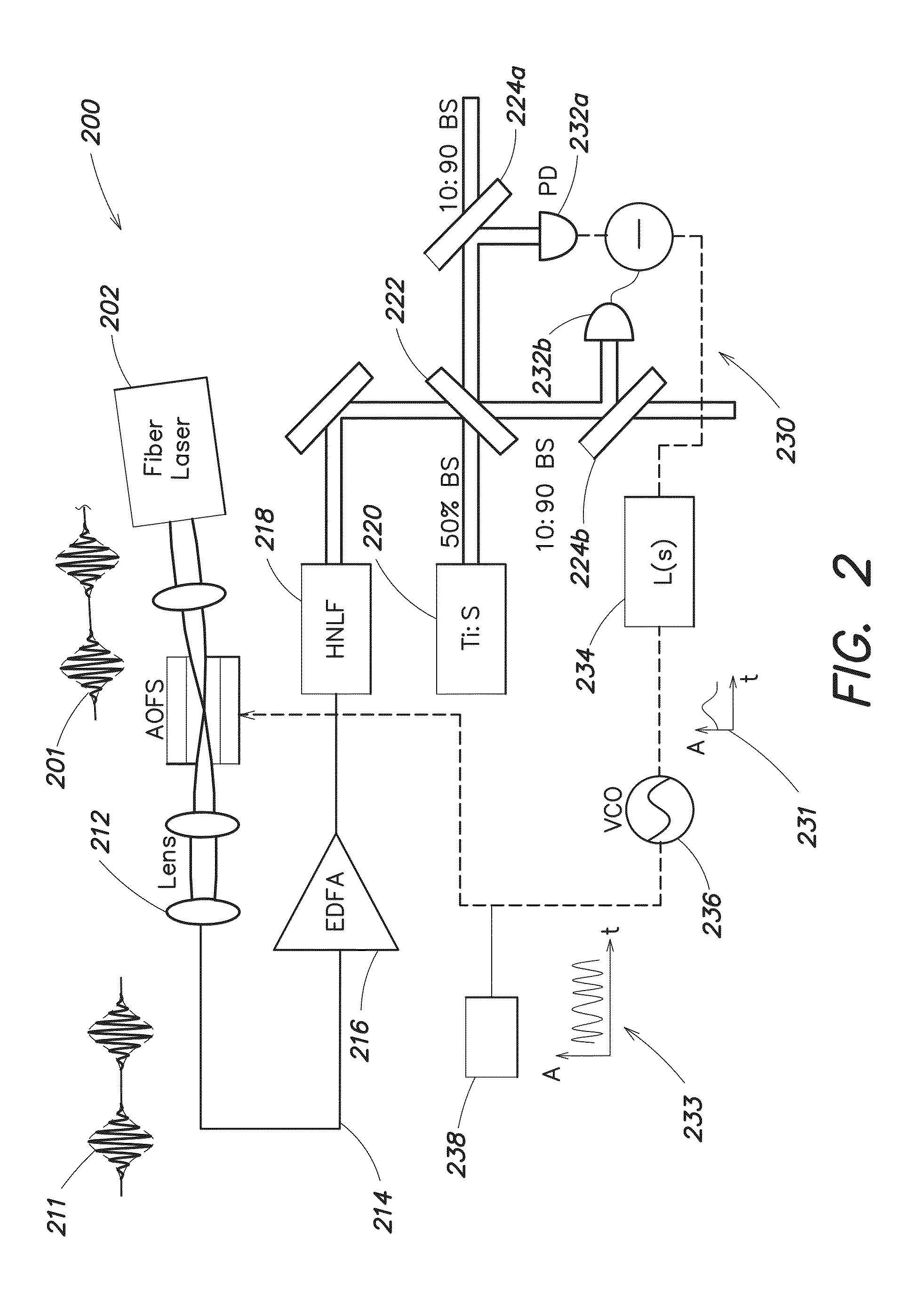
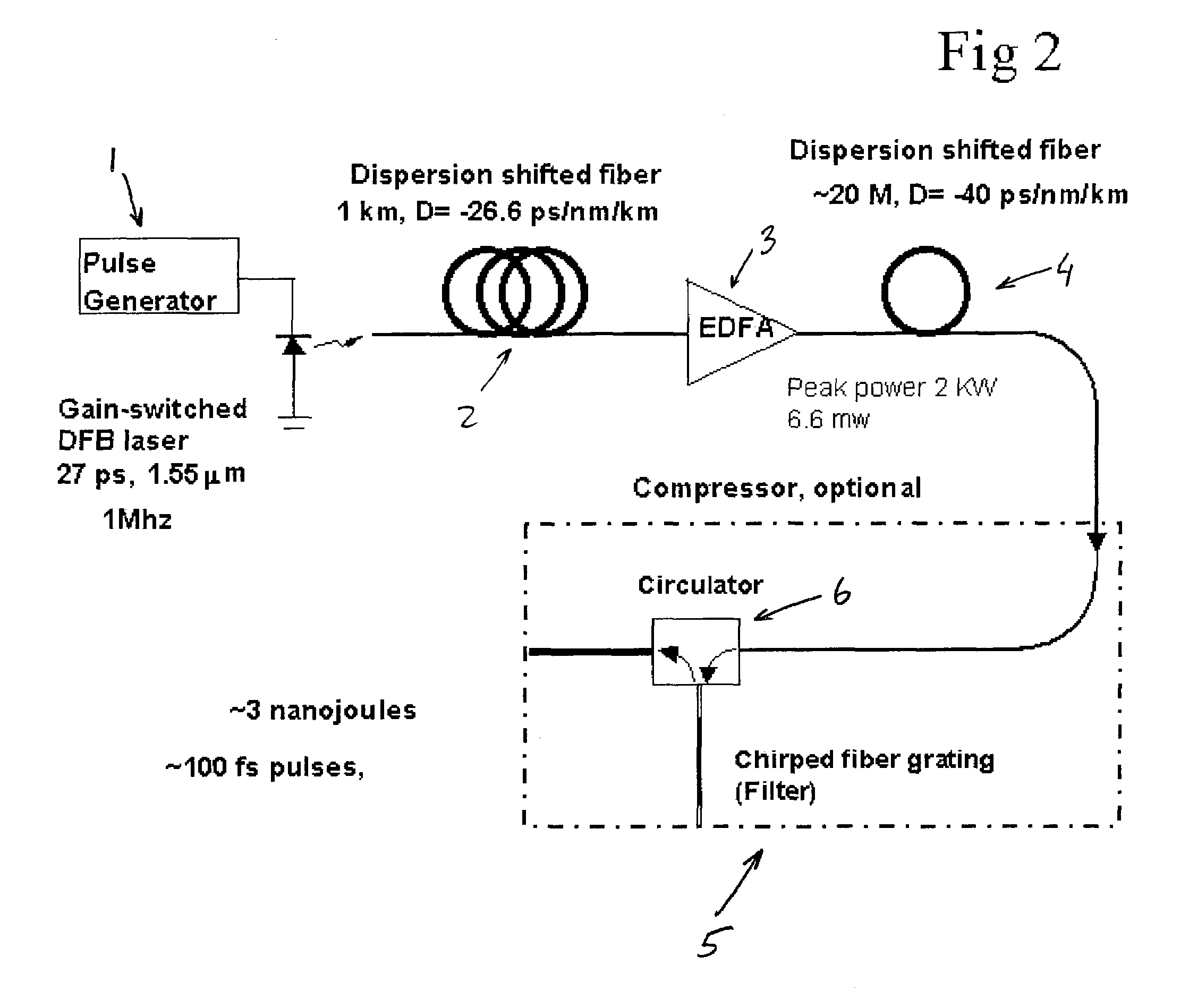
Generation of stabilized, ultra-short light pulses and the use thereof for synthesizing optical frequencies
InactiveUS6785303B1Optical measurementsMaterial analysis by optical meansLinear dispersionOptical frequencies
A process for operation of a laser device (1) is described, whereby circulating light pulses each comprising spectral components according to a plurality of longitudinal modes of a resonator configuration (3) are generated in the resonator configuration (3) and subjected to a compensation of group velocity dispersion, and a predetermined linear dispersion is introduced into the light path of the resonator configuration (3), so that at least one mode has a predetermined frequency and / or the mode distance between the modes has a predetermined value. Furthermore, regulations for stabilizing the laser device on the basis of this process and applications of the regulations for the generation for stabilized, ultra-short light pulses, generation of optical frequencies and in the frequency and / or time measuring technique as well as in the spectroscopy are described.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Method and device for creating supercontinuum light pulses
ActiveUS9160137B1Simple controllabilityRemissionLaser using scattering effectsNon-linear opticsGroup velocity dispersionOptoelectronics
A method of spectrally broadening light pulses includes the steps of providing the light pulses with a laser source, said light pulses having a pulse duration below 1 ps, in-coupling the light pulses into a hollow optical waveguide device, and spectrally broadening the light pulses propagating along the pulse guiding medium by subjecting them to a Raman nonlinearity via excitation of a Raman polarization having a first Raman period, wherein the optical waveguide device subjects the light pulses to anomalous group velocity dispersion which combines with the spectral broadening of the light pulses to result in a Raman-enhanced self-compression of the light pulses, and the light pulses further propagate along the optical waveguide device such that the Raman-enhanced self compression results in a further excitation of a Raman polarization having a second Raman period which is faster than the first Raman period.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Supersonic guide-wave time reversion detection apparatus and method for defect of pipeline
ActiveCN1978977AImprove readabilityImprove detection abilityPipeline systemsSonificationWave detection
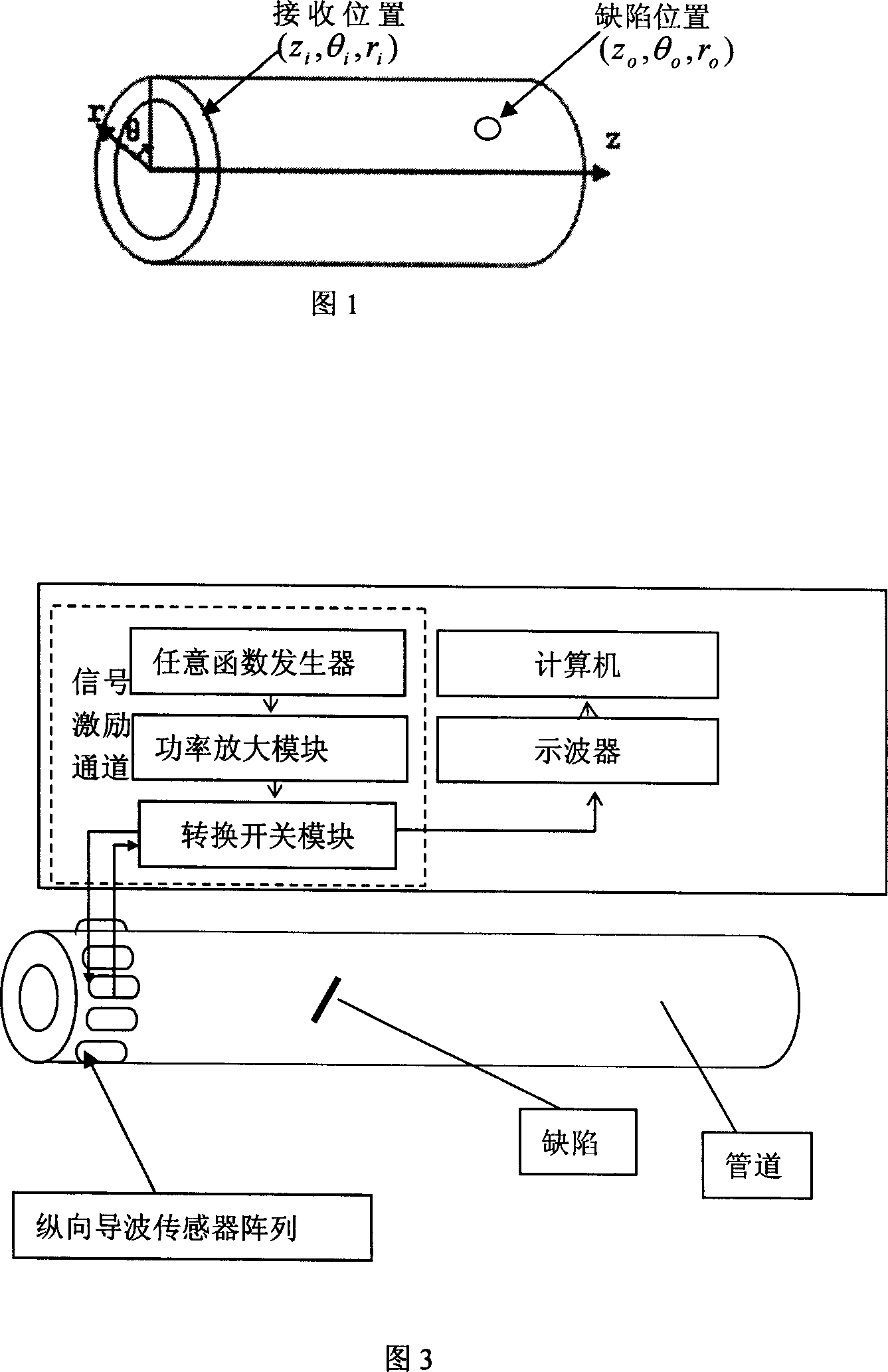
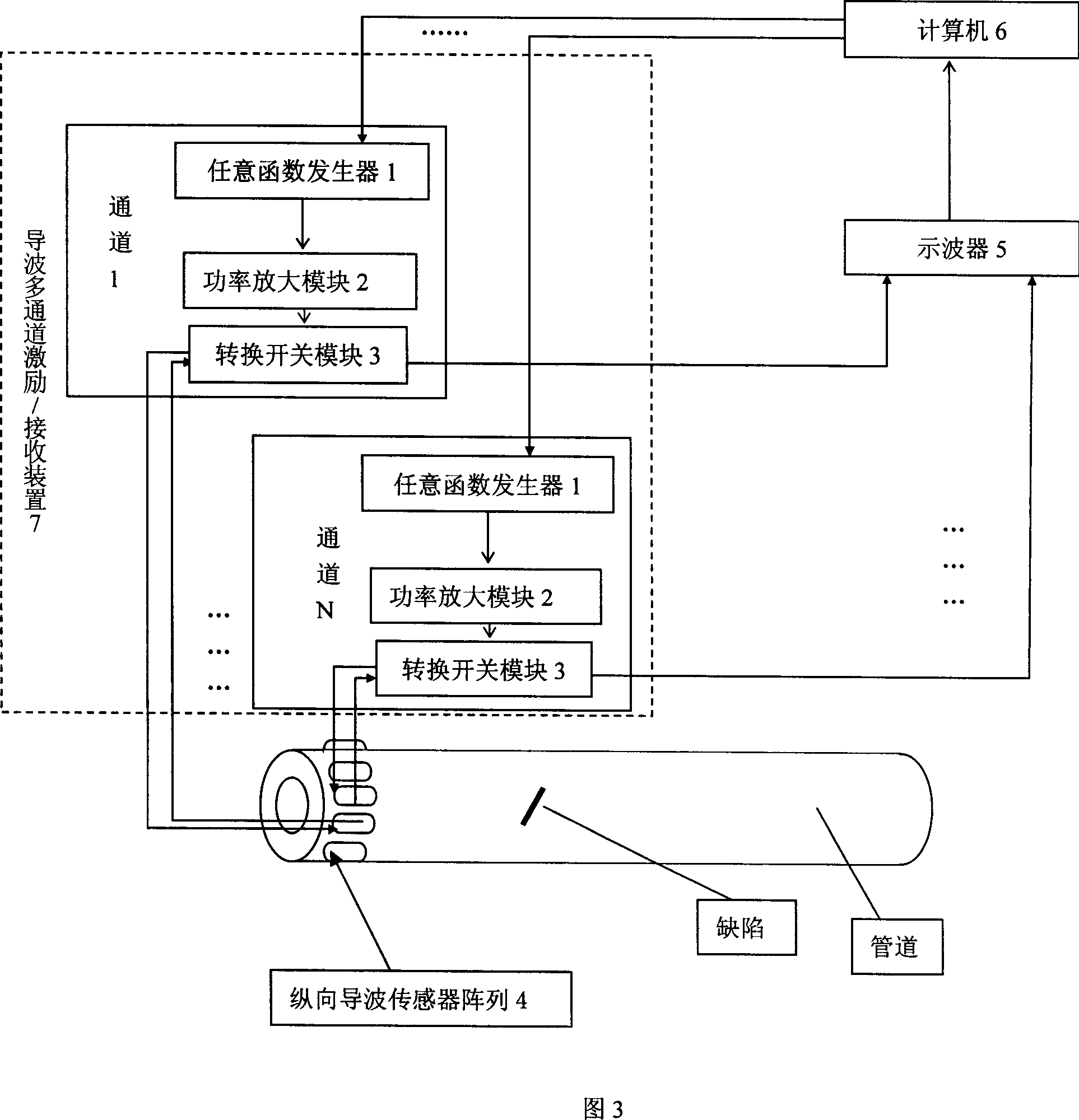
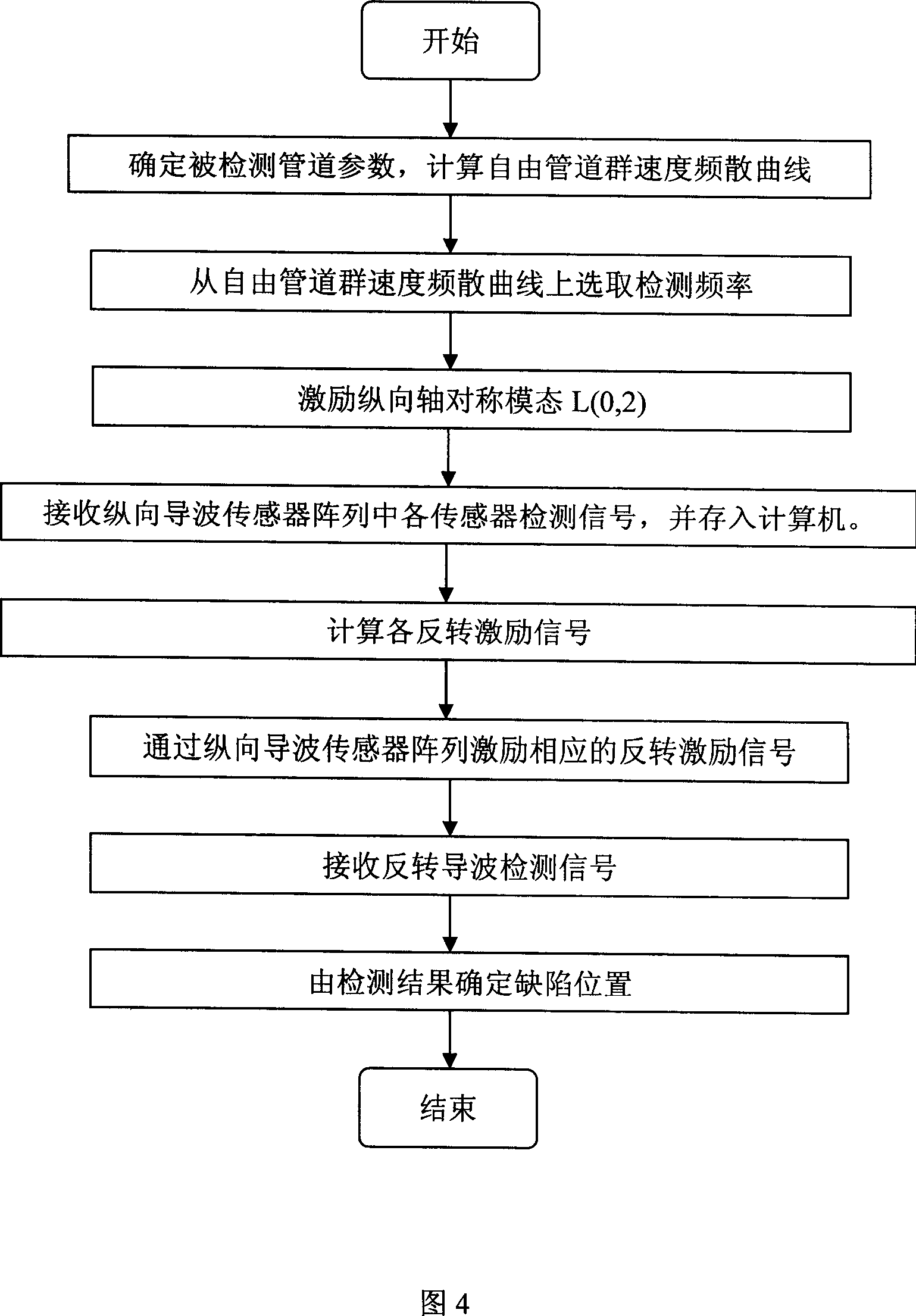
The invention relates to pipeline defect ultrasound guided wave time reversal detection device and method. The method includes the following steps: selecting detecting frequency according to the detected pipeline corresponding free hollow column structure group velocity dispersion curve; inputting the frequency into the arbitrary function generator to generate center frequency used as single sound signal; sending the signal to each passage of exciting / receiving set to transducer unit; exciting longitudinal axis symmetry guided wave modal; sending the reflected signal to the computer and gaining reversal excitation signal by time reversal; repeatedly exciting guided signal to detect. The invention realize space and time focus for guided wave detection, greatly improve detection capability for little defect.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Fiber-optic amplification of light pulses
ActiveUS7224518B2High energyAvoid disadvantagesLaser arrangementsActive medium materialFiberGroup velocity dispersion
A device for amplifying light pulses has an optical stretcher, in which the light pulses of a pulsed laser light source are temporally stretched, and an optically pumped amplifier fiber, in which the light pulses are amplified and, at the same time, temporally compressed. In order to improve such a system with regard to the pulse duration and the pulse energy that can be achieved, the amplifier fiber has a positive group velocity dispersion, whereby the amplifier fiber has non-linear optical properties, so that the optical spectrum of the light pulses is broadened during the amplification process, taking advantage of non-linear self-phase modulation.
Owner:TOPTICA PHOTONICS AG
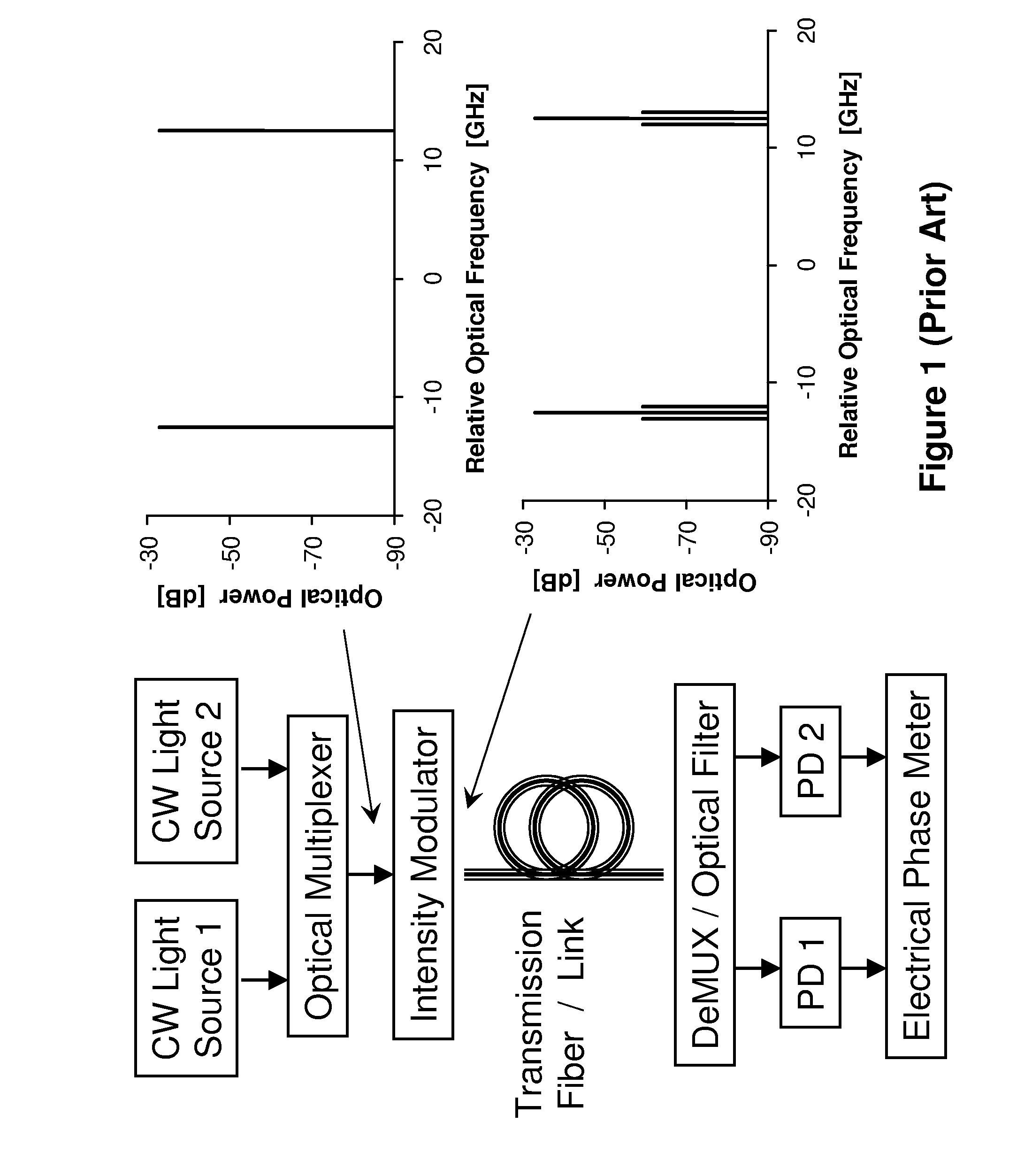
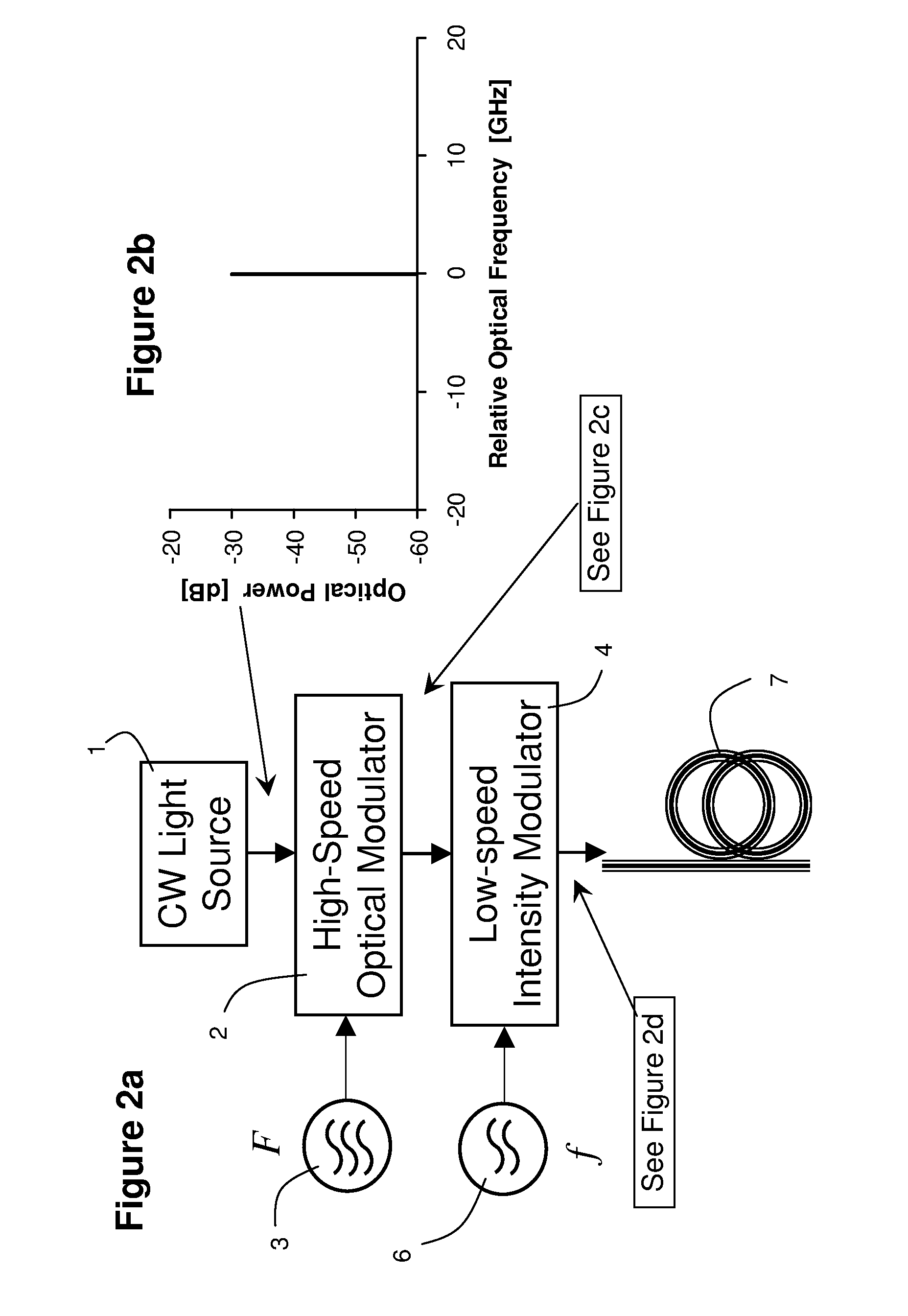
Measuring chromatic dispersion in an optical wavelength channel of an optical fiber link
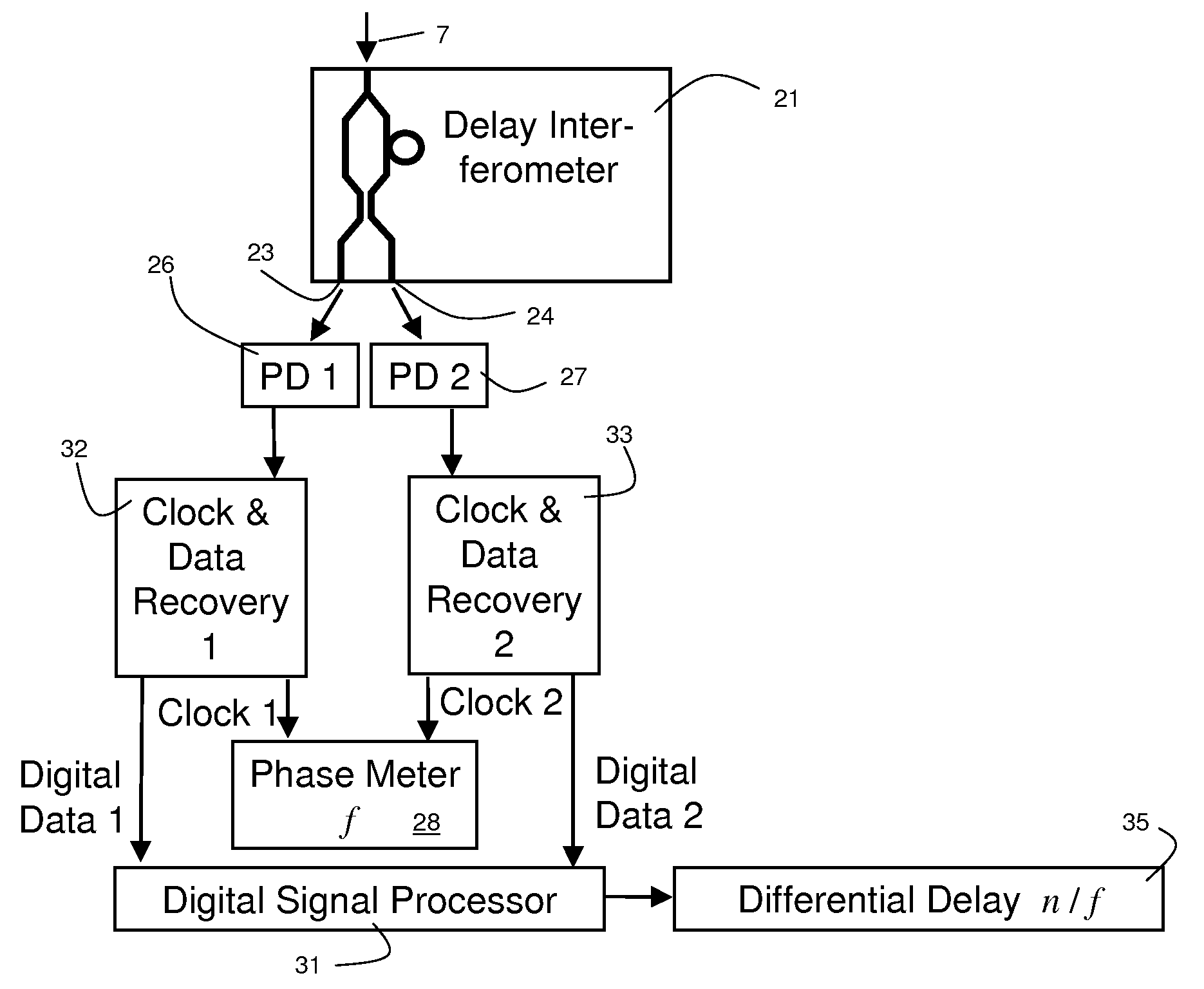
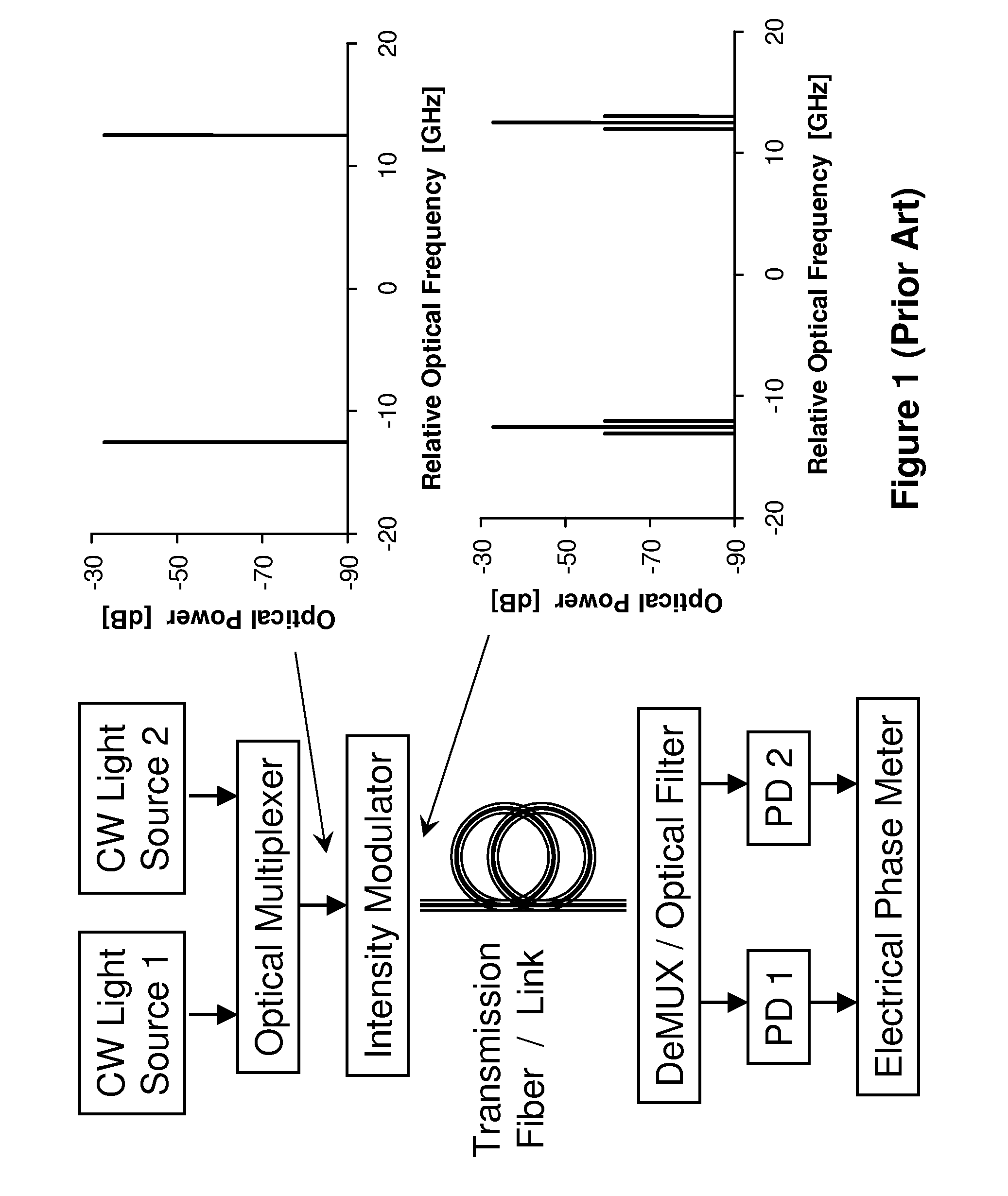
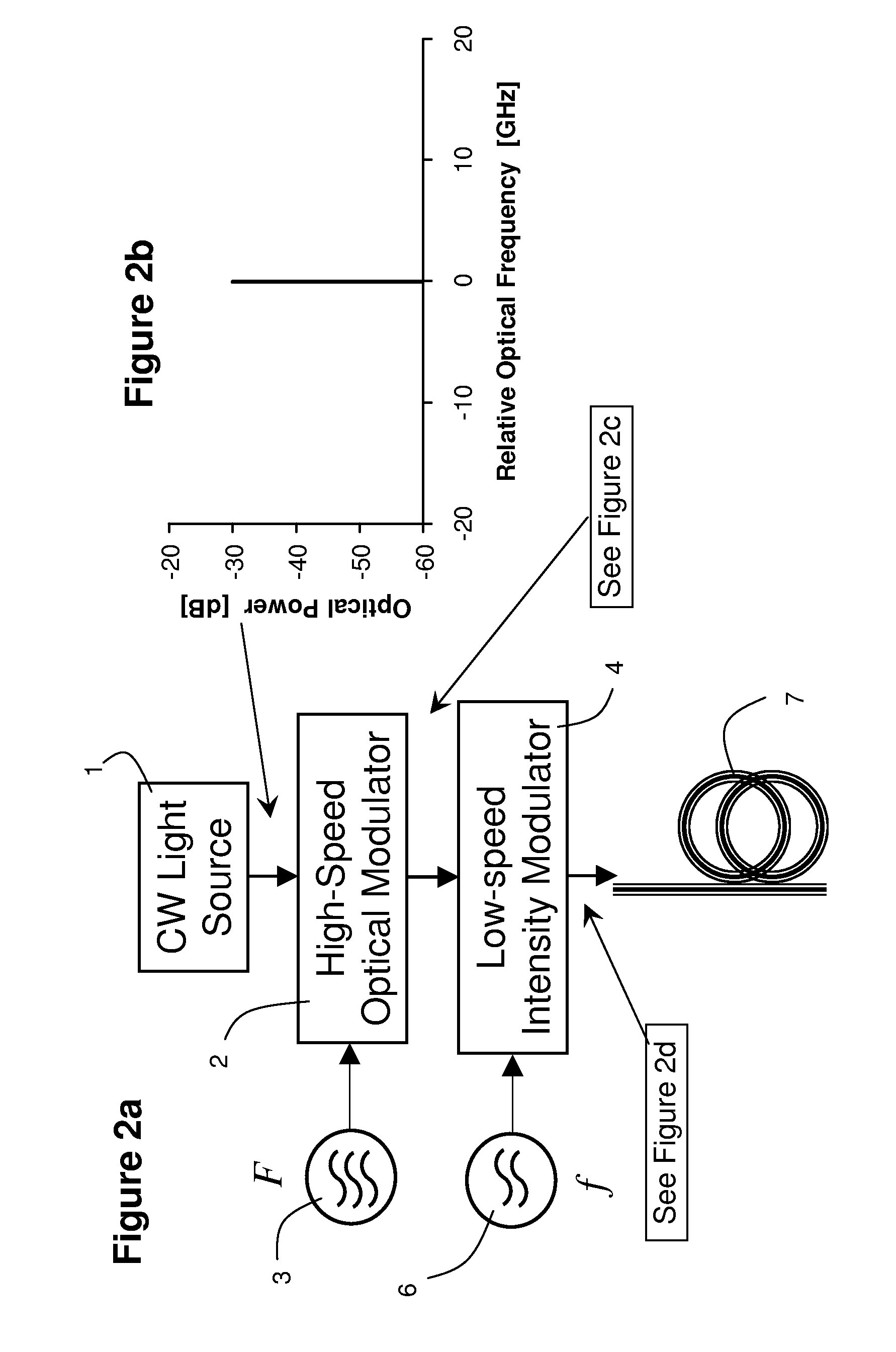
ActiveUS20090297140A1Transmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsGroup velocity dispersionIntensity modulation
Two intensity modulated test signals are generated with precise frequency offset from a single laser source, and multiplexed into a combined test signal. The two modulated signals are demultiplexed at a receiver using a fixed periodic optical filter with complementary output ports. Group velocity dispersion / chromatic dispersion is measured over a large dynamic range, using pseudo-random intensity modulation and digital demodulation techniques.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
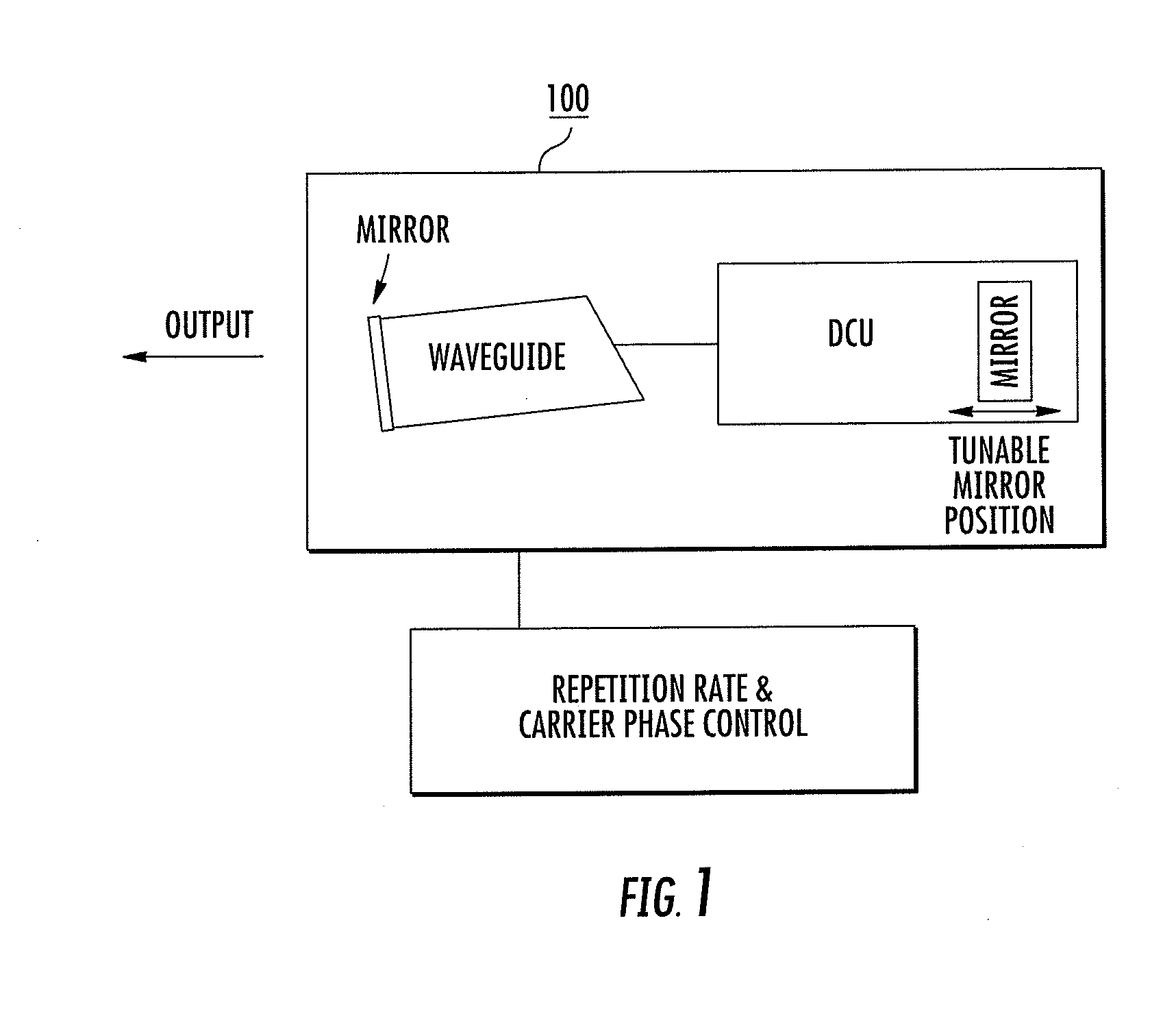
Frequency comb source with large comb spacing
InactiveUS20120133931A1Reduce lossLow-loss bandwidth controlRadiation pyrometryLaser using scattering effectsLow noisePhase noise
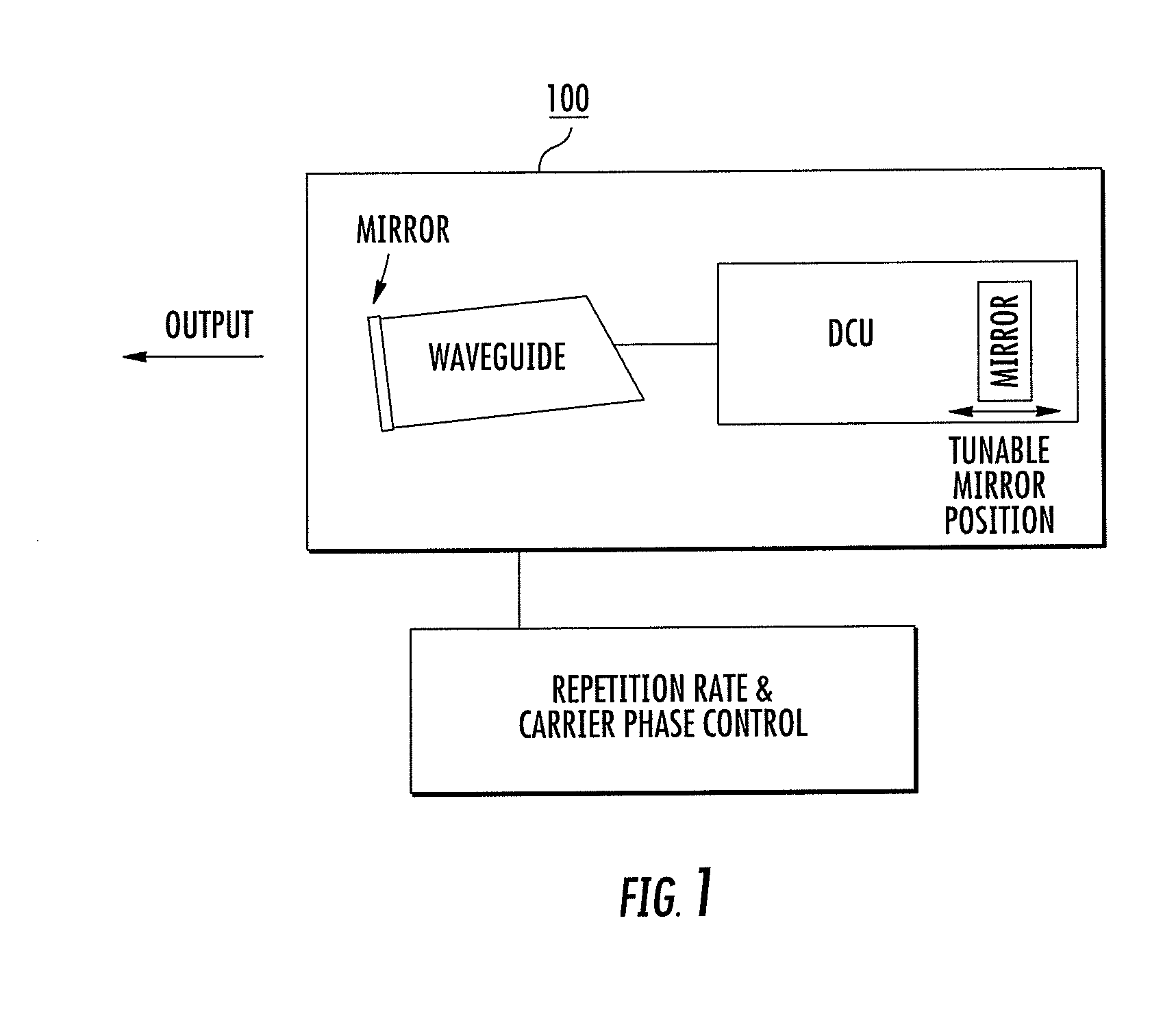
A frequency comb laser providing large comb spacing is disclosed. At least one embodiment includes a mode locked waveguide laser system. The mode locked waveguide laser includes a laser cavity having a waveguide, and a dispersion control unit (DCU) in the cavity. The DCU imparts an angular dispersion, group-velocity dispersion (GVD) and a spatial chirp to a beam propagating in the cavity. The DCU is capable of producing net GVD in a range from a positive value to a negative value. In some embodiments a tunable fiber frequency comb system configured as an optical frequency synthesizer is provided. In at least one embodiment a low phase noise micro-wave source may be implemented with a fiber comb laser having a comb spacing greater than about 1 GHz. The laser system is suitable for mass-producible fiber comb sources with large comb spacing and low noise. Applications include high-resolution spectroscopy.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Inexpensive variable rep-rate source for high-energy, ultrafast lasers
InactiveUS20080130099A1High pulse energyReduce repetition rateLaser optical resonator constructionLaser using scattering effectsFiberCost effectiveness
System for converting relatively long pulses from rep-rate variable ultrafast optical sources to shorter, high-energy pulses suitable for sources in high-energy ultrafast lasers. Fibers with positive group velocity dispersion (GVD) and self phase modulation are advantageously employed with the optical sources. These systems take advantage of the need for higher pulse energies at lower repetition rates so that such sources can be cost effective.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Methods and apparatus for broadband frequency comb stabilization
Feedback loops can be used to shift and stabilize the carrier-envelope phase of a frequency comb from a mode-locked fibers laser or other optical source. Compared to other frequency shifting and stabilization techniques, feedback-based techniques provide a wideband closed-loop servo bandwidth without optical filtering, beam pointing errors, or group velocity dispersion. It also enables phase locking to a stable reference, such as a Ti:Sapphire laser, continuous-wave microwave or optical source, or self-referencing interferometer, e.g., to within 200 mrad rms from DC to 5 MHz. In addition, stabilized frequency combs can be coherently combined with other stable signals, including other stabilized frequency combs, to synthesize optical pulse trains with pulse durations of as little as a single optical cycle. Such a coherent combination can be achieved via orthogonal control, using balanced optical cross-correlation for timing stabilization and balanced homodyne detection for phase stabilization.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Inexpensive variable rep-rate source for high-energy, ultrafast lasers
InactiveUS7330301B2High pulse energyReduce repetition rateCladded optical fibreLaser optical resonator constructionFiberCost effectiveness
System for converting relatively long pulses from rep-rate variable ultrafast optical sources to shorter, high-energy pulses suitable for sources in high-energy ultrafast lasers. Fibers with positive group velocity dispersion (GVD) and self phase modulation are advantageously employed with the optical sources. These systems take advantage of the need for higher pulse energies at lower repetition rates so that such sources can be cost effective.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Method and system for transmitting terahertz pulses
InactiveUS20080023633A1Improve performanceReduce lossRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansGroup velocity dispersionTransfer system
Systems for THz transmission using new types of THz waveguides with low loss, negligible group velocity dispersion and structural simplicity are described herein. The THz system incorporates the use of a waveguide with two or more substantially parallel conductive elements which may enable many new THz sensing applications. It is now possible to direct the THz pulse inside of containers or around corners, where line-of-sight optics are not practical. Moreover, the systems allow use of either radially polarized or linearly polarized THz antennas. The disclosed systems are compatible with existing terahertz generation and detection techniques.
Owner:RICE UNIV
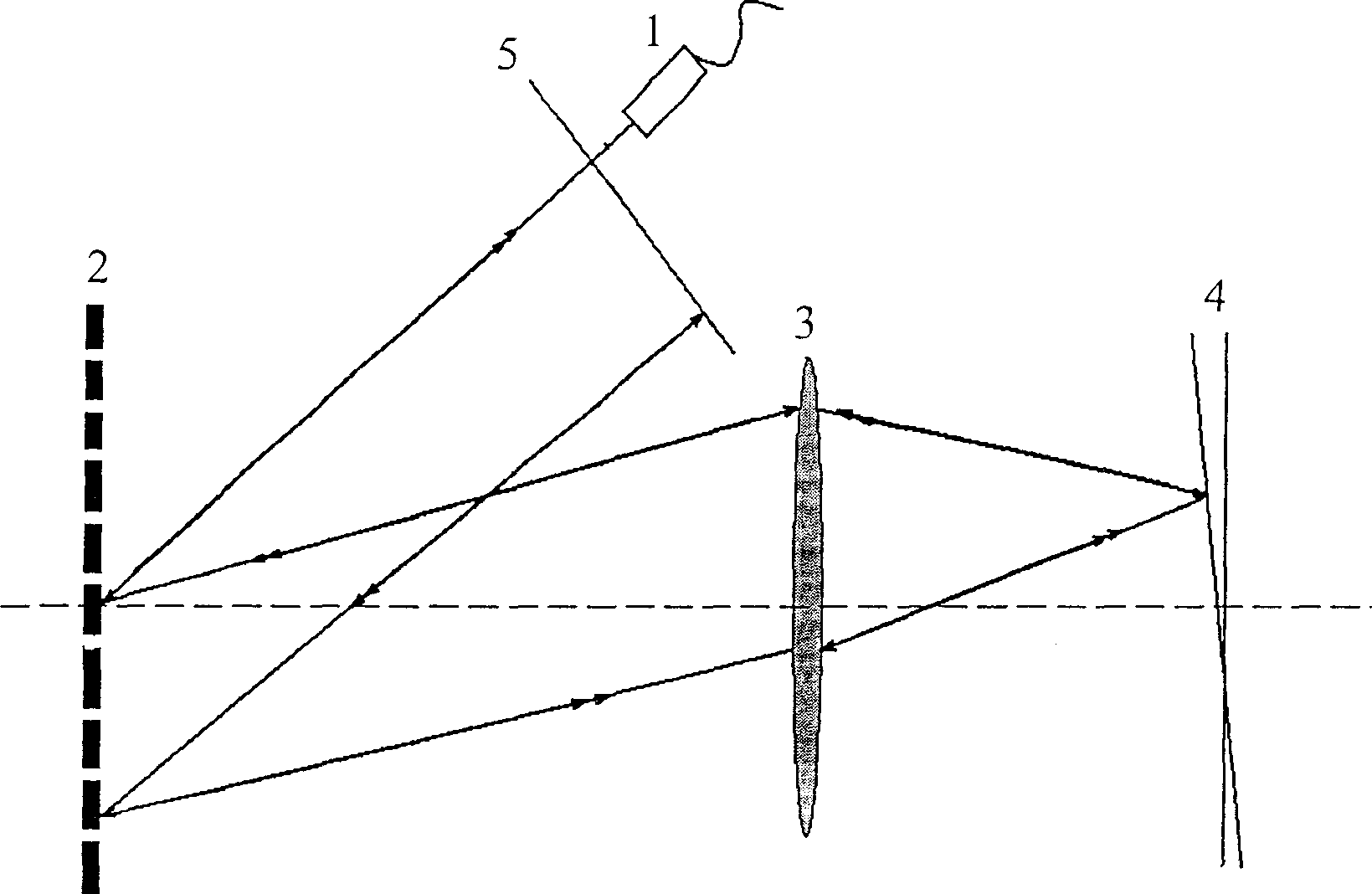
Spectral coverage OCT imaging method based on optical scanning delay line and the system
InactiveCN101040778AAvoid mistakesEliminate phase shift errorsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhase shiftedGrating
The invention discloses a spectrum OCT (optical coherent tomography) image method and relative system based on optical scanning delay line, wherein it arranges an optical scanning delay line in a reference arm of a spectrum OCT system, to realize scatter-free phase shift of reference light and system scatter compensation. And when guides in optical scanning delay line based on double gratings, the invention can generate group speed scatter and third-order scatter formed by any marks in large change range, to accurately match the scatters of reference arm and sample arm in spectrum OCT system. The scatter-free phase shift and scatter compensation can assure the axial resolution ratio of spectrum OCT system, eliminate coherent noise, and expand the image depth for one time. The invention is significant for dual-spectrum OCT system with ultra-high resolution ratio.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
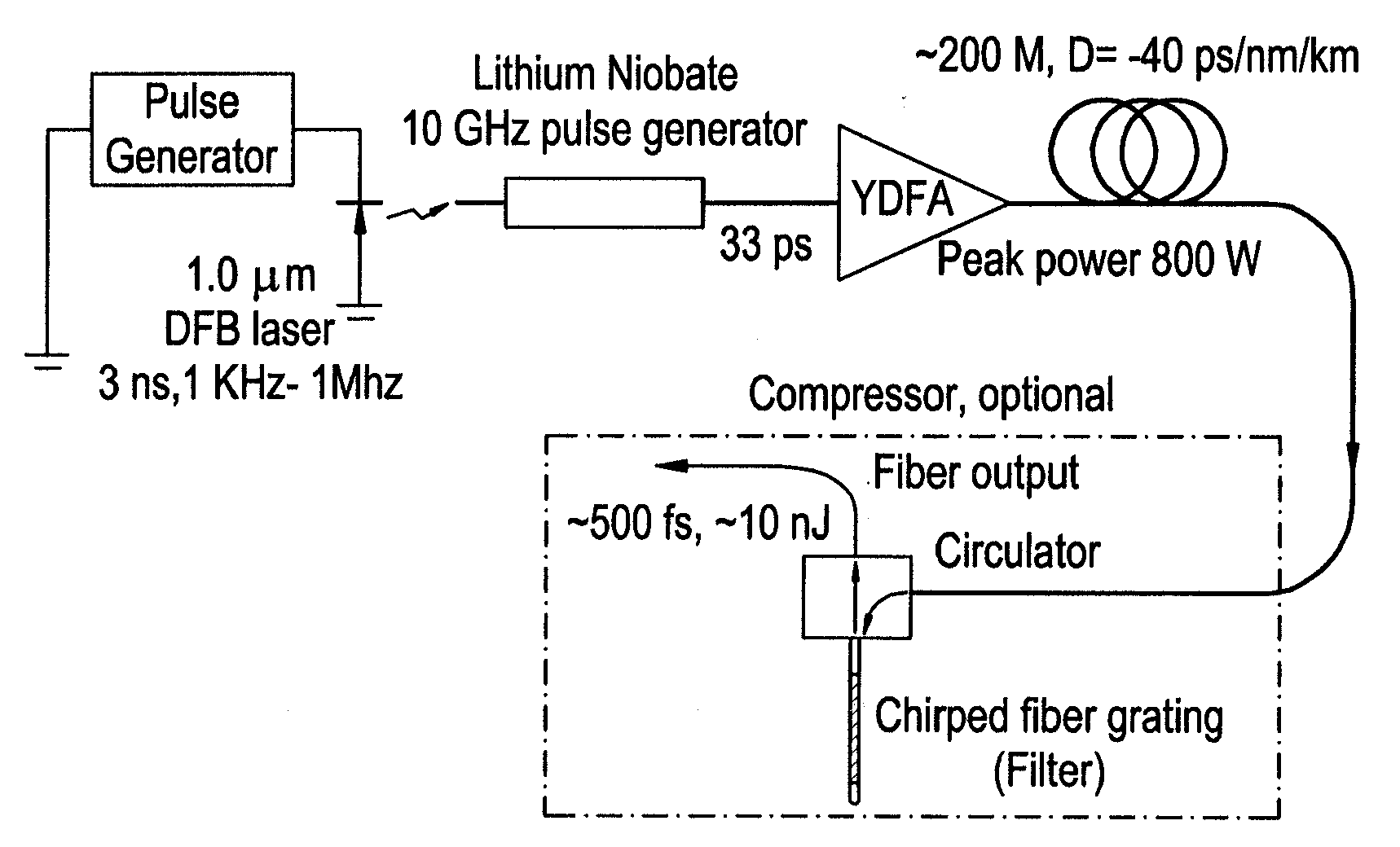
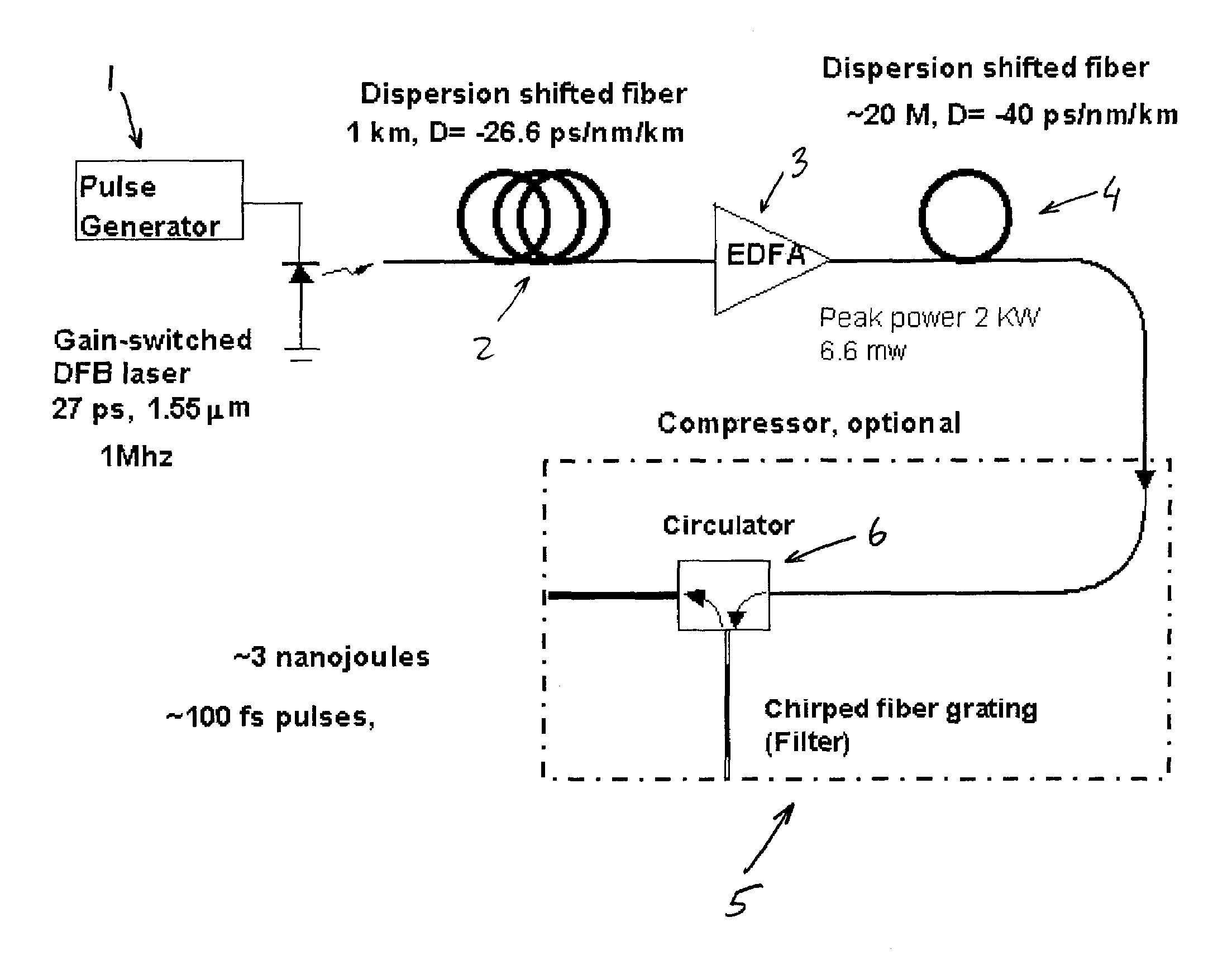
Compression design for high energy short pulse fiber laser
ActiveUS20070014317A1Quality improvementIncrease flexibilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionGratingHigh energy
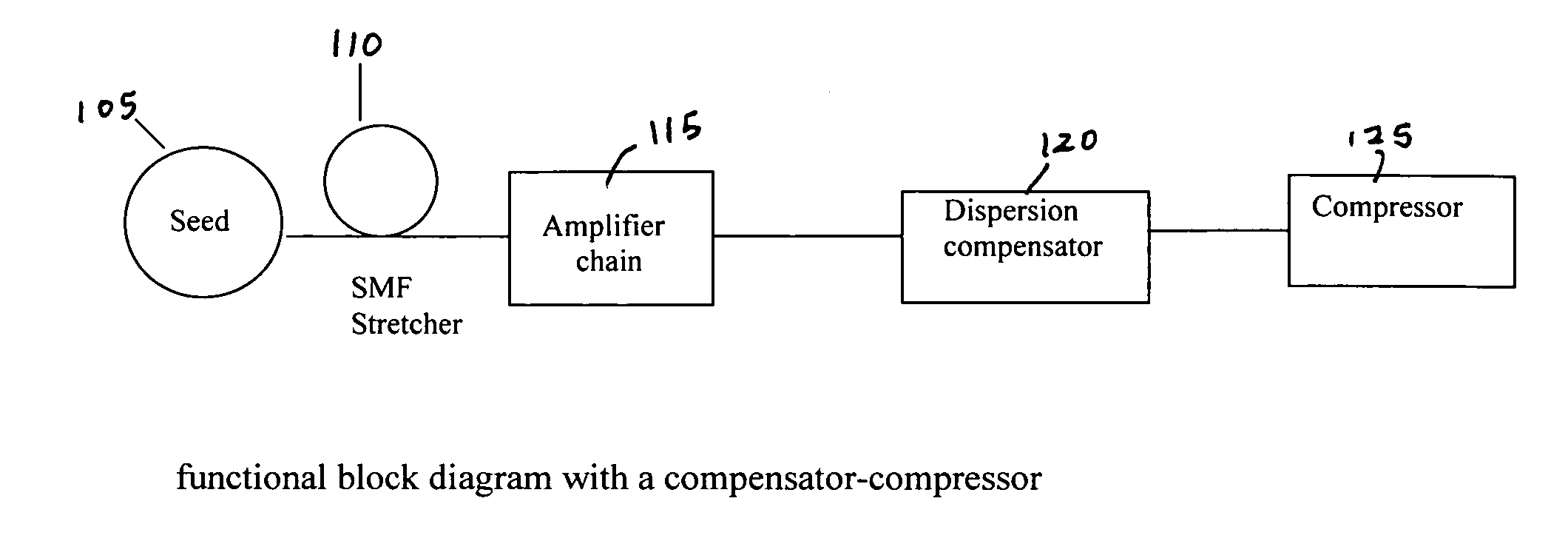
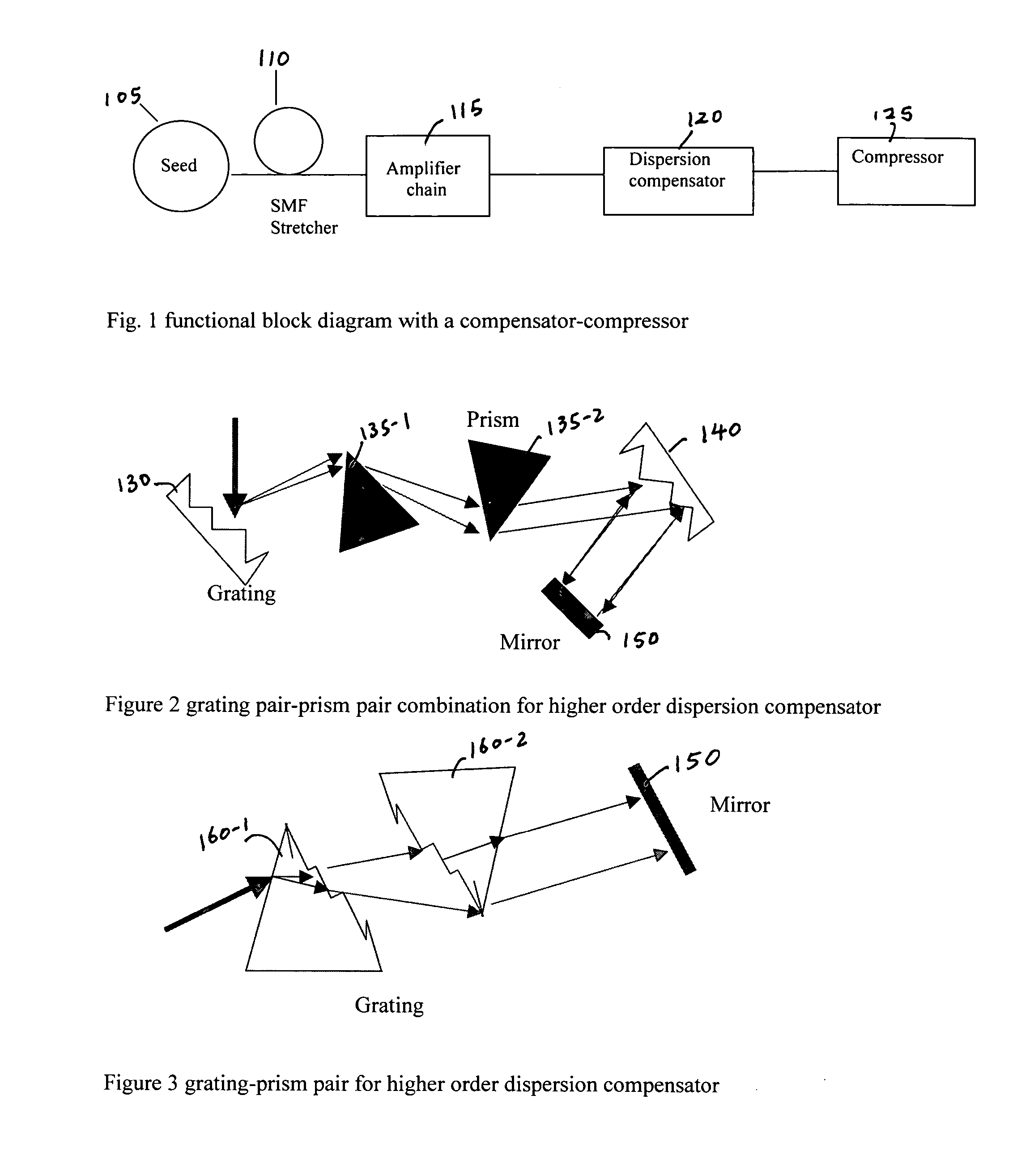
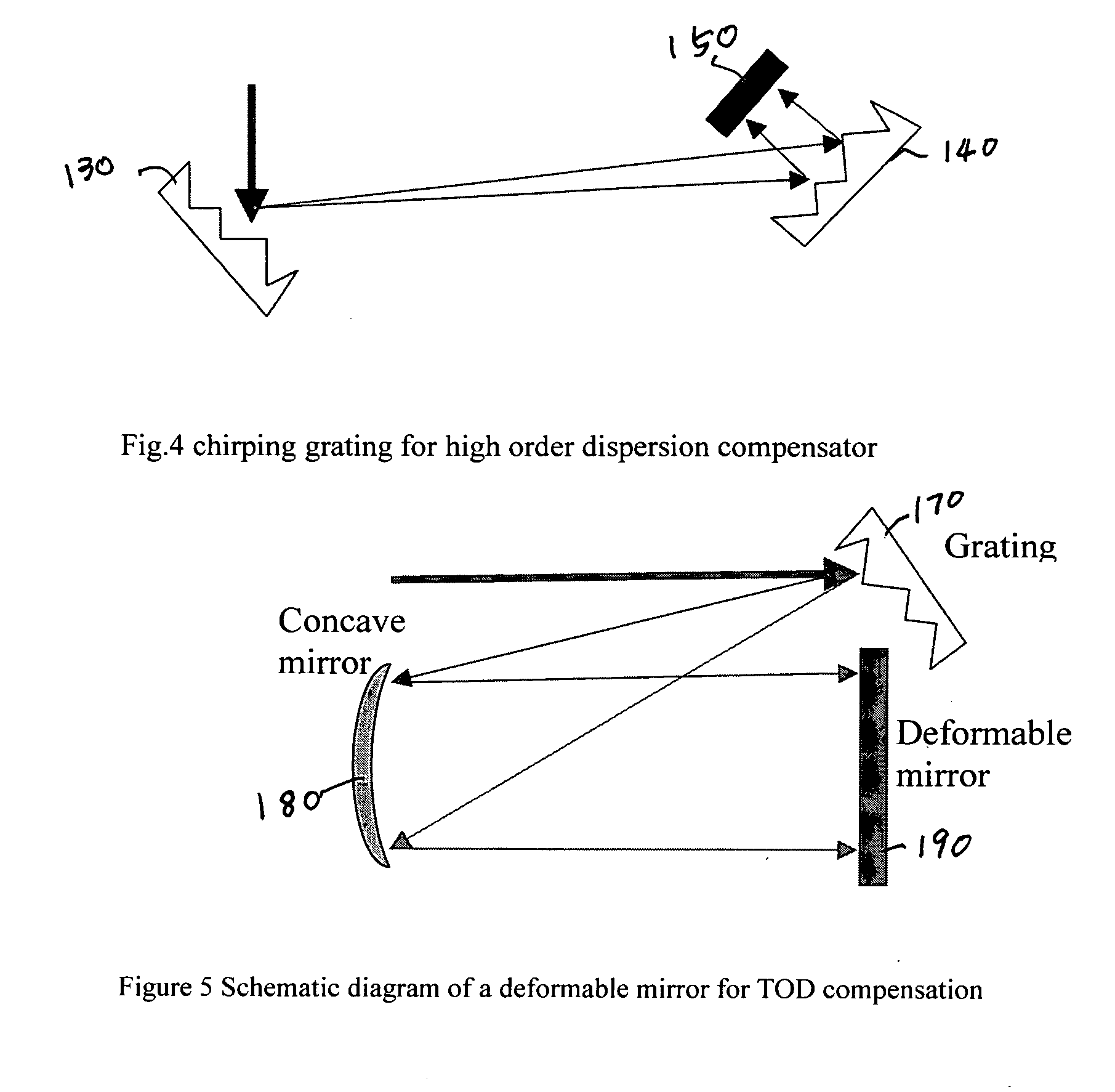
A fiber Chirped Pulse Amplification (CPA) laser system includes a fiber mode-locking oscillator for generating a laser for projecting to a fiber stretcher for stretching a pulse width of the laser. The fiber CPA laser system further includes a multistage amplifier for amplifying the laser and a high-order dispersion compensating compressor for compensating high order dispersions and compressing the pulse width of the laser. The high-order dispersion compensating compressor further includes a pair of gratings coupled with a pair of prisms, a grating pair engraved on the surfaces of a pair of prisms, a chirped grating pair and a phase modulator consists of a grating and a deformable mirror, for generating a negative group velocity dispersion (GVD) and a negative third order dispersion (TOD) for the laser.
Owner:POLARONYX
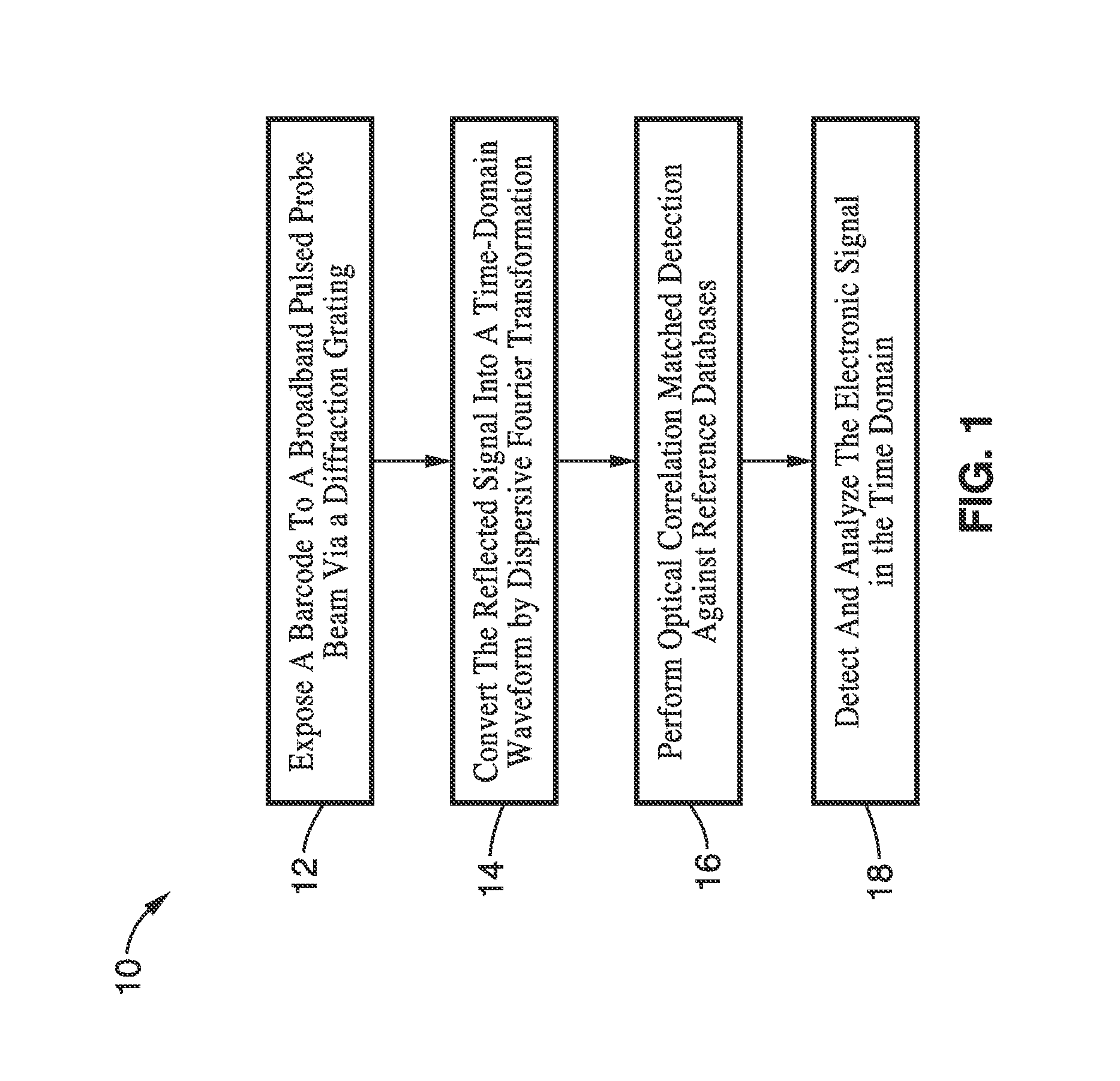
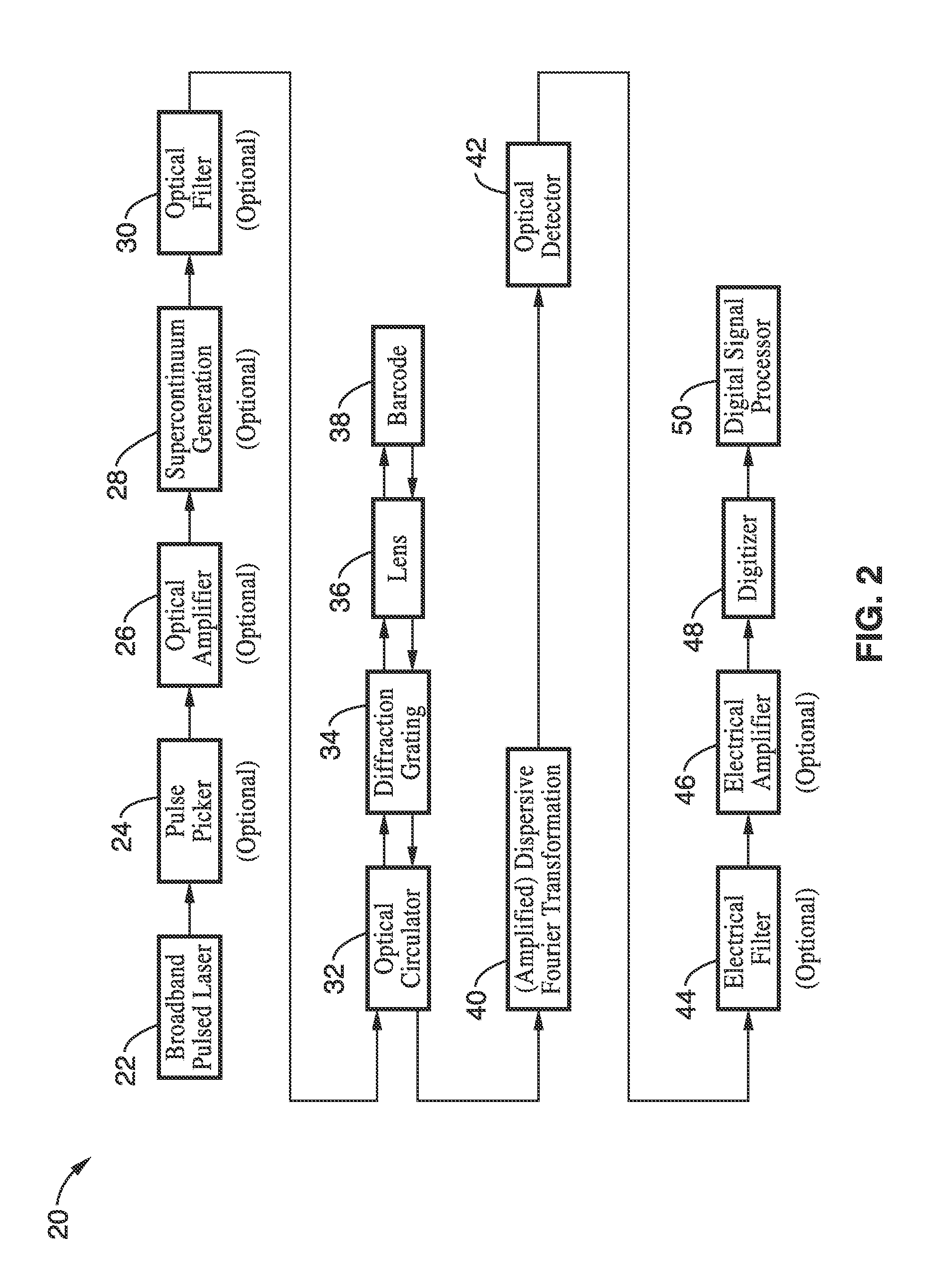
Apparatus and method for dispersive fourier-transform imaging
InactiveUS20110168776A1High strengthImprove performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionUsing optical meansFrequency spectrumPhotodetector
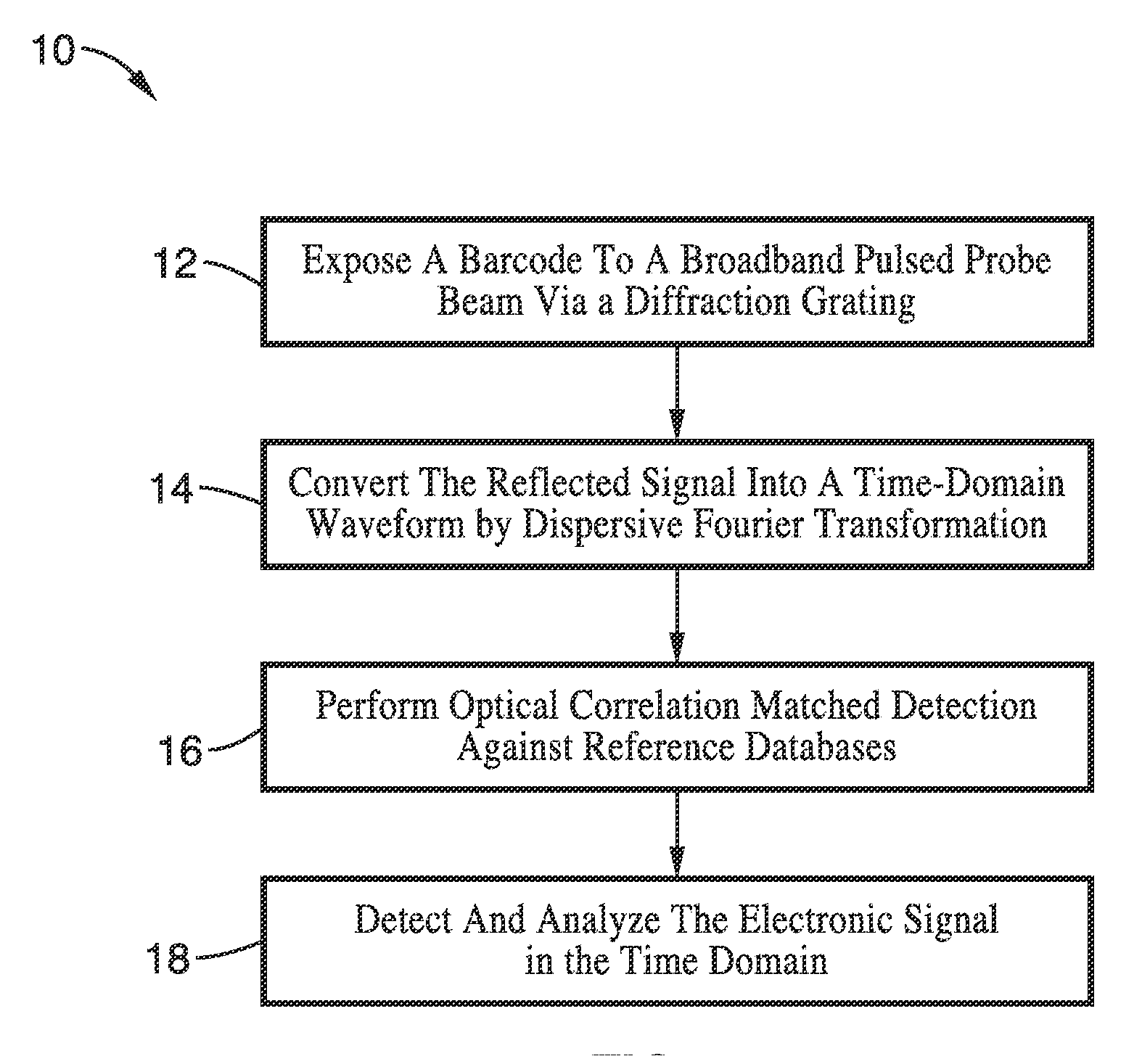
A barcode reading apparatus and method in which the spectrum of a probe light is first Fourier-transformed into space, directed upon a barcode, and then Fourier-transformed converting the spectrally encoded barcode pattern to a time domain waveform. In one implementation, the Fourier transformation from the spectrum domain into a spatial domain is performed by a dispersive element, while the Fourier transformation from the spectrally encoded barcode pattern to a time domain waveform is performed by group-velocity dispersion (GVD). The temporally encoded barcode pattern is detected by a photodetector, digitized by a digitizer, and analyzed by a digital signal processor. The invention is applicable to a number of fields which involve the reading of one- and two-dimensional barcodes, displacement sensing, surface measurements, measurement of width and gap, flow cytometry, reading of optical media, presense or absence detection, and other related fields.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
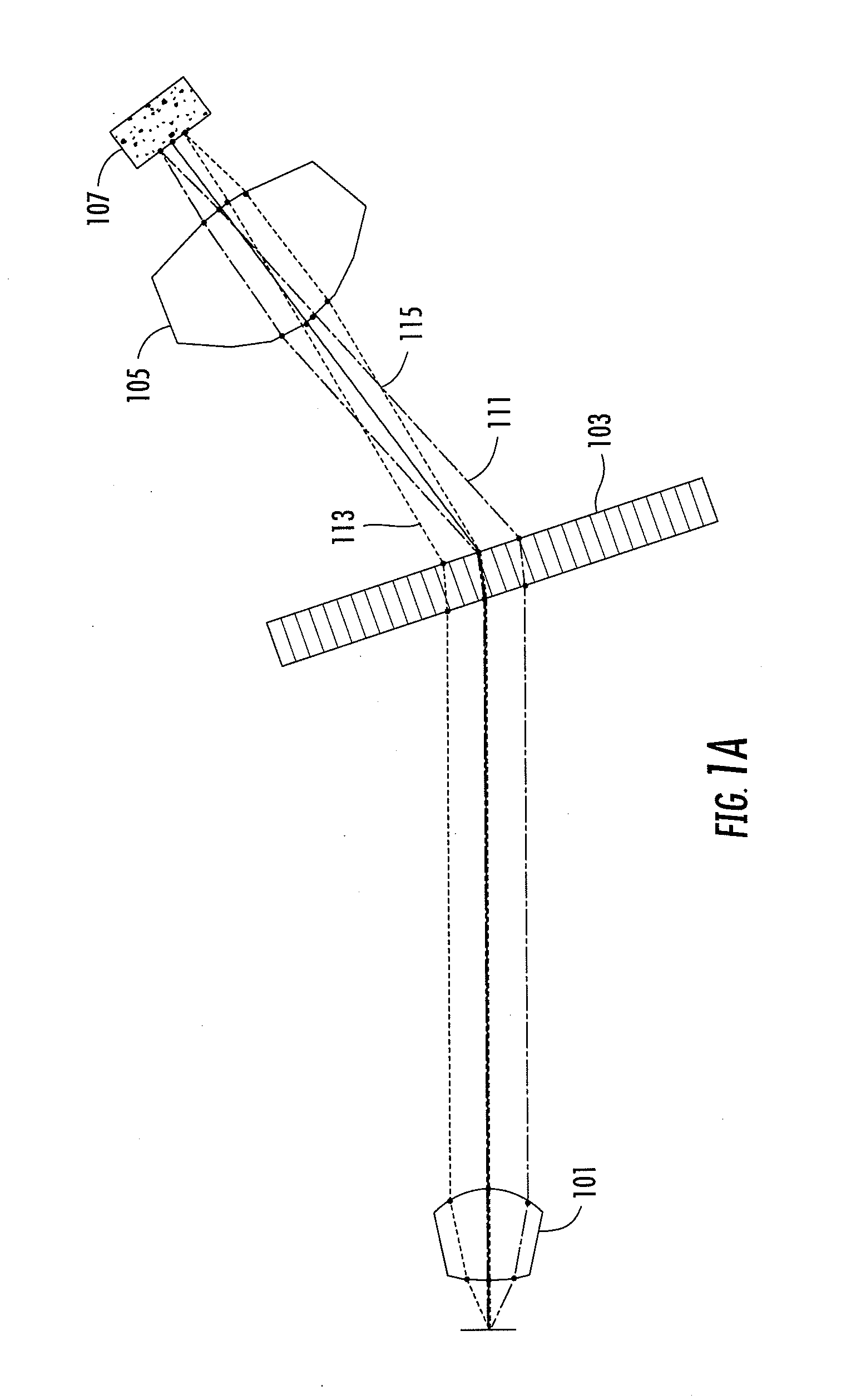
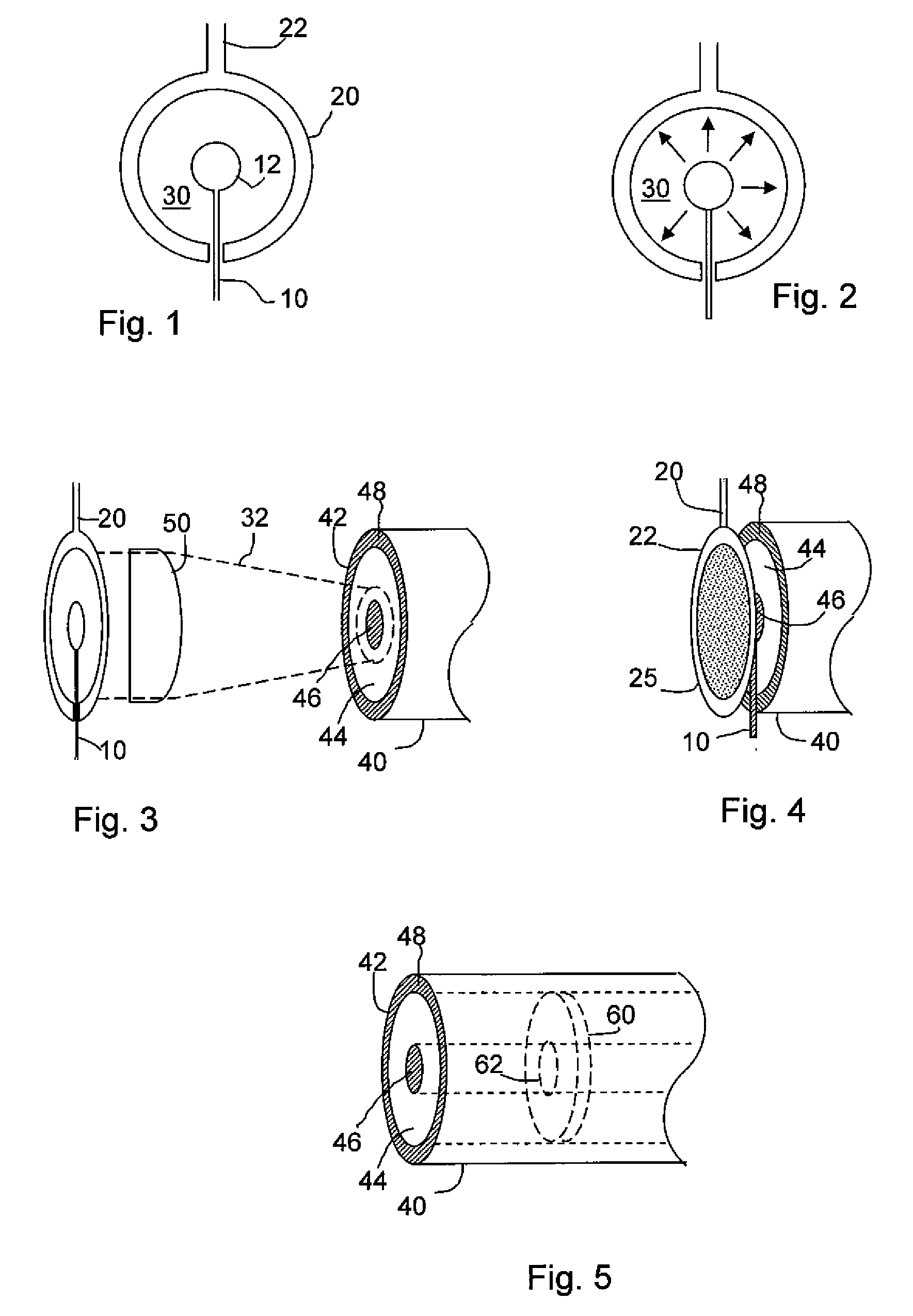
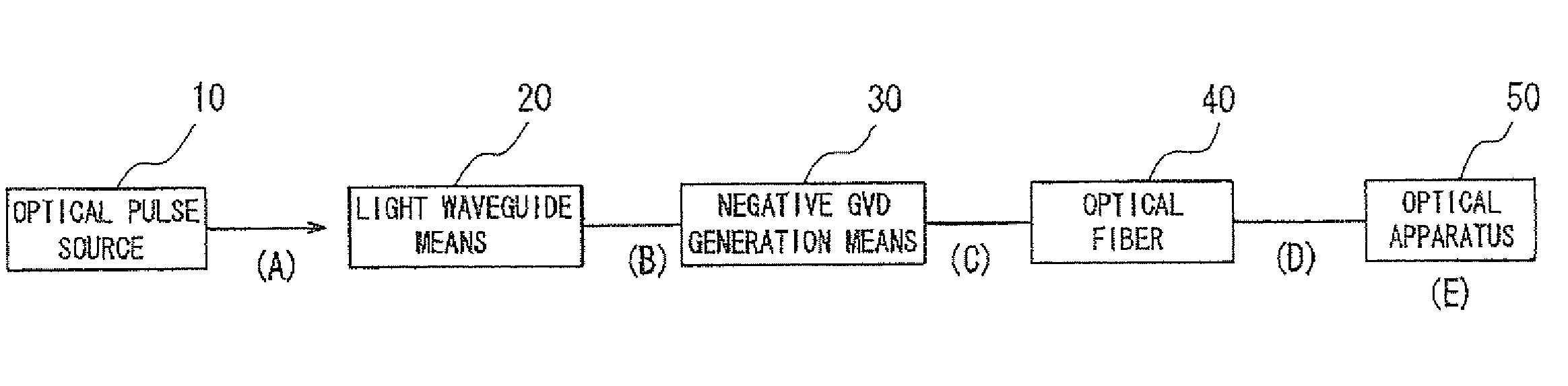
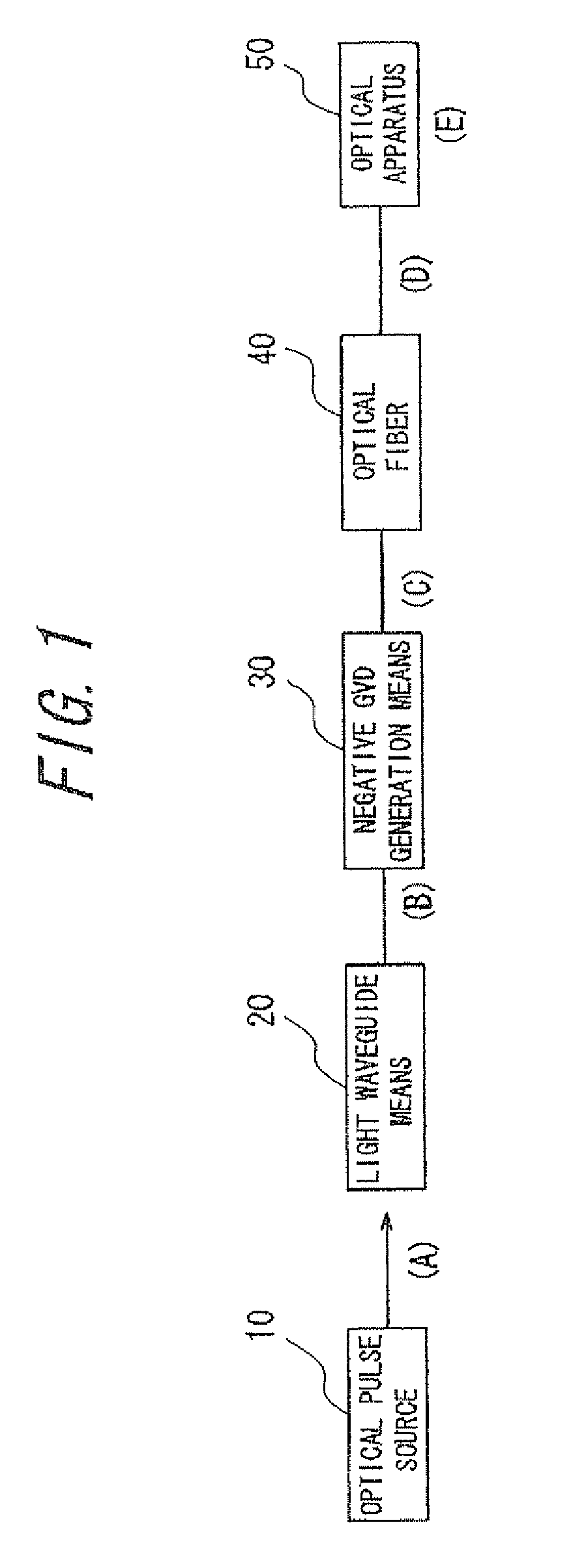
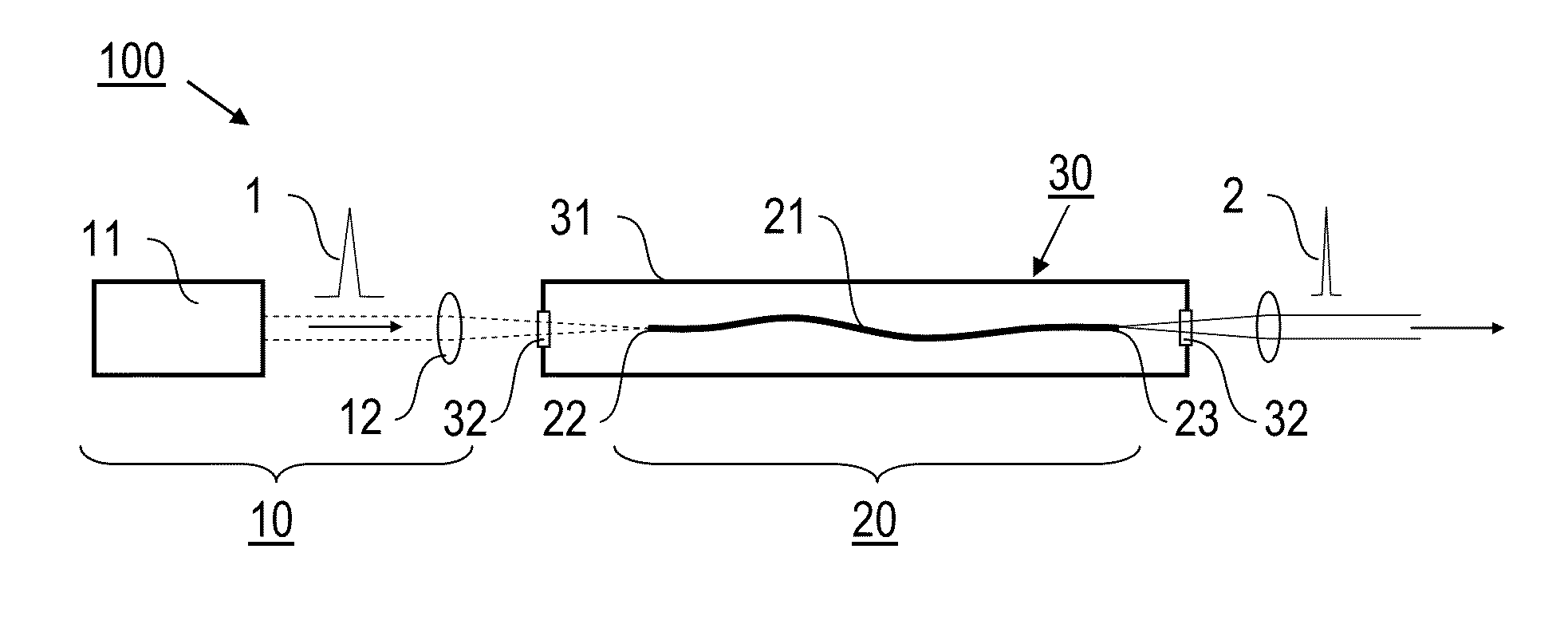
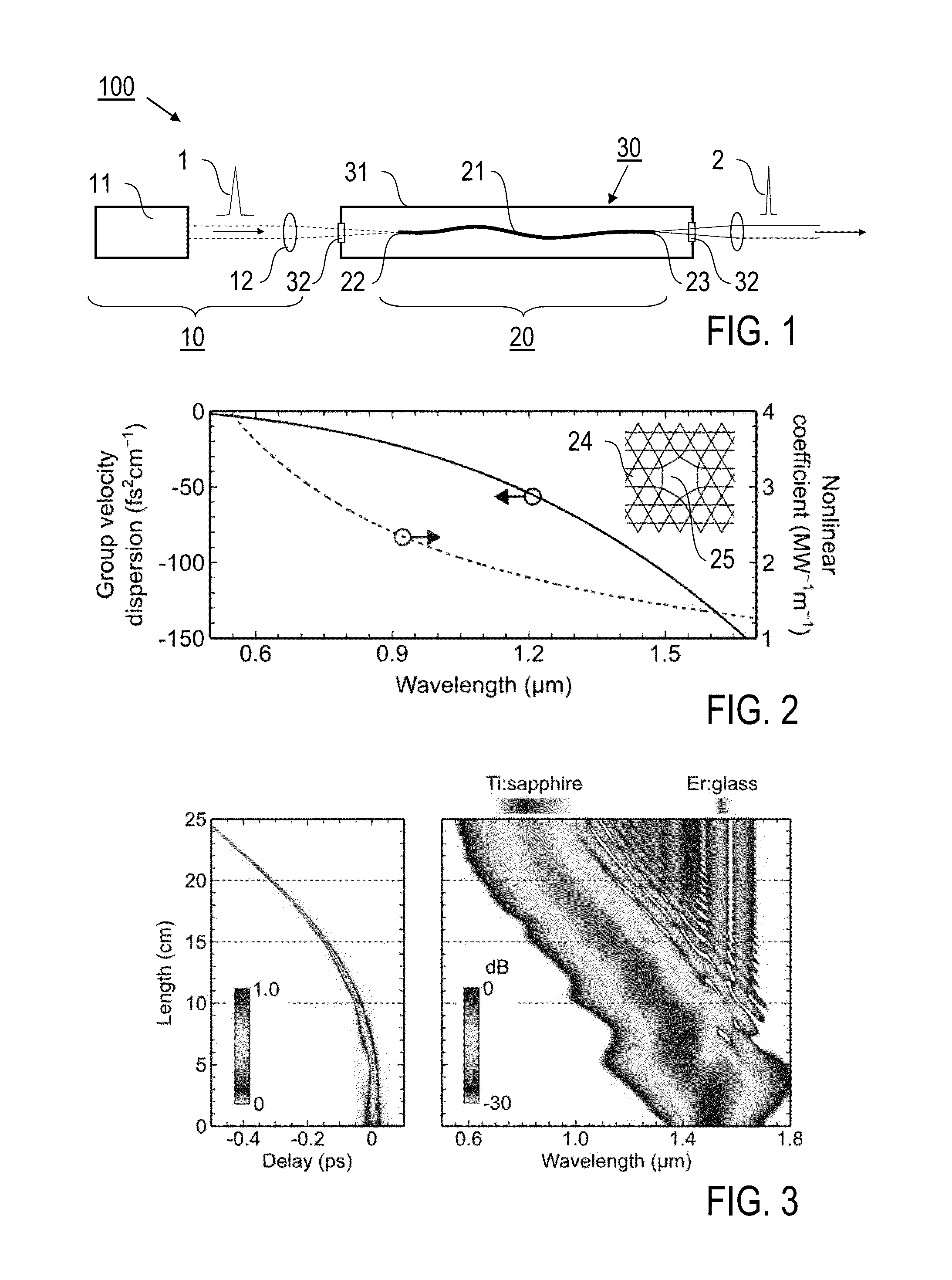
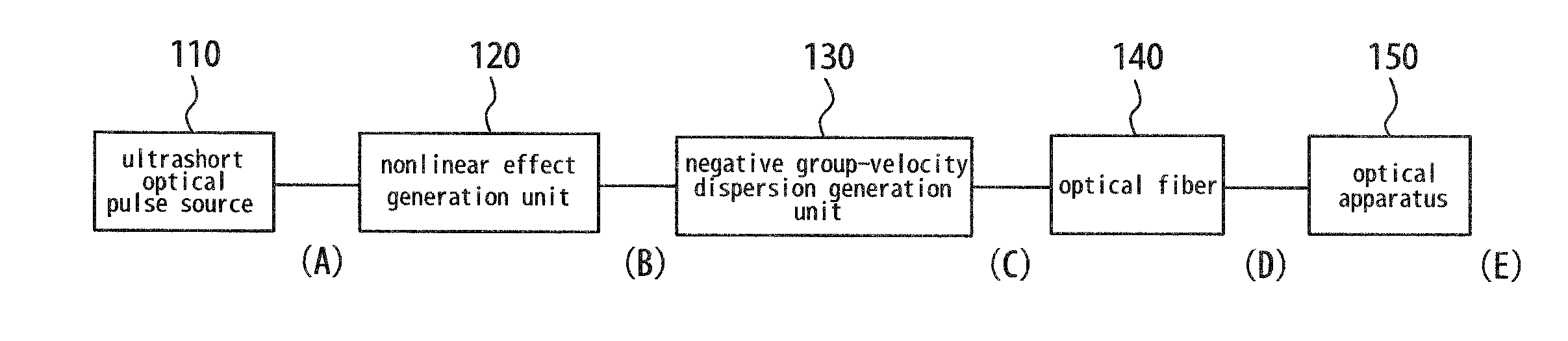
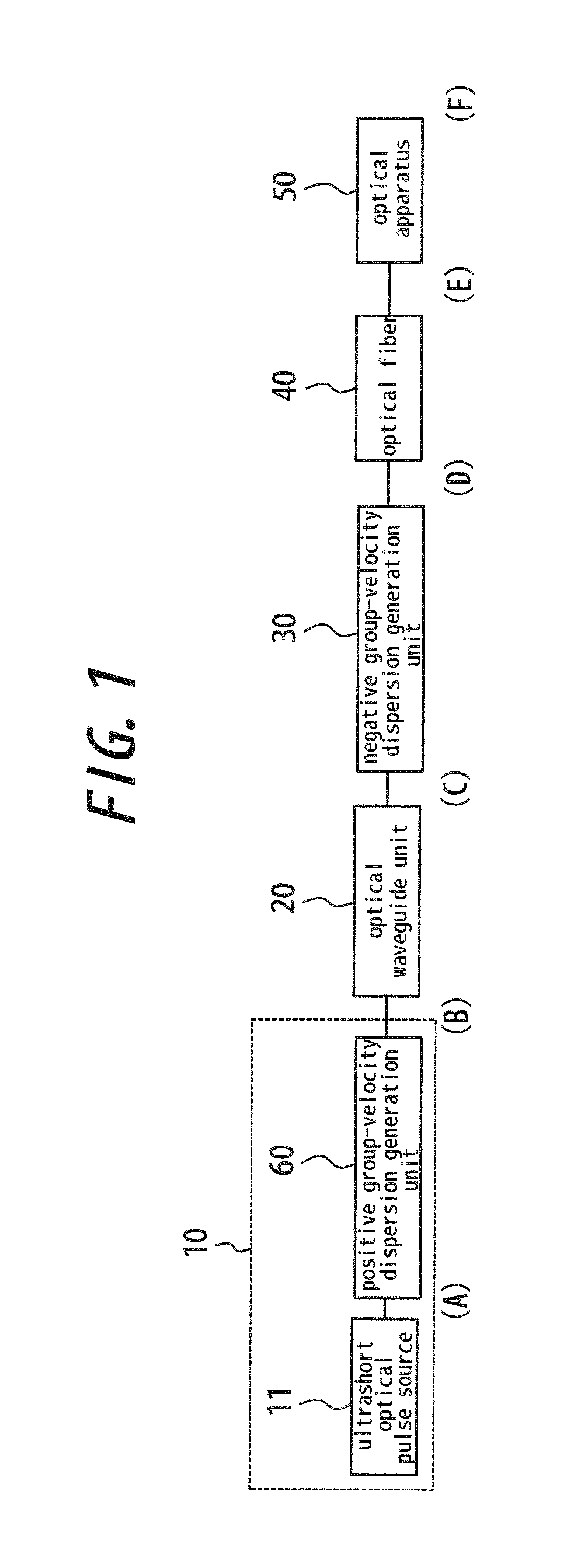
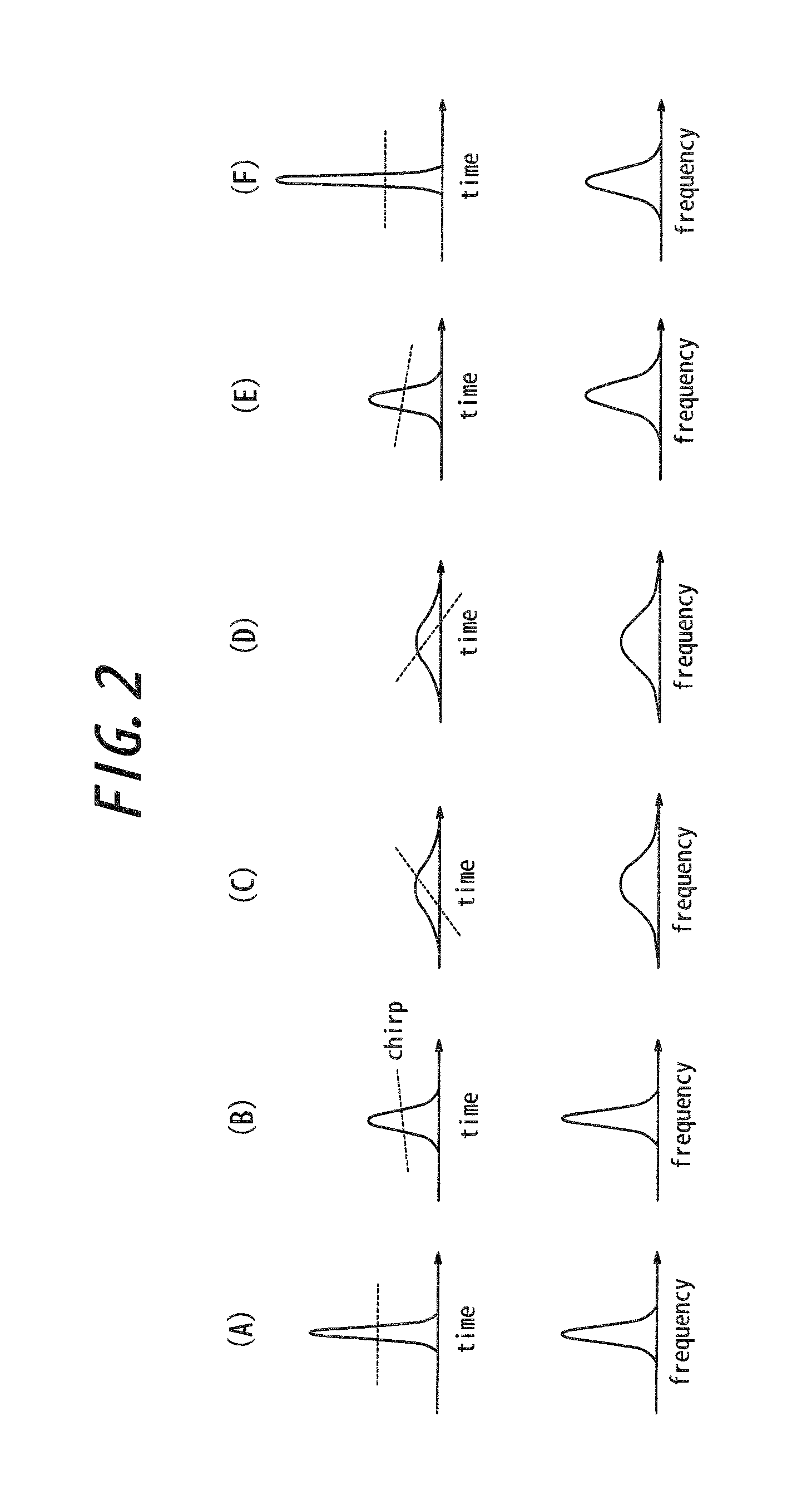
Optical fiber delivery system for delivering ultrashort optical pulses and optical system including the same
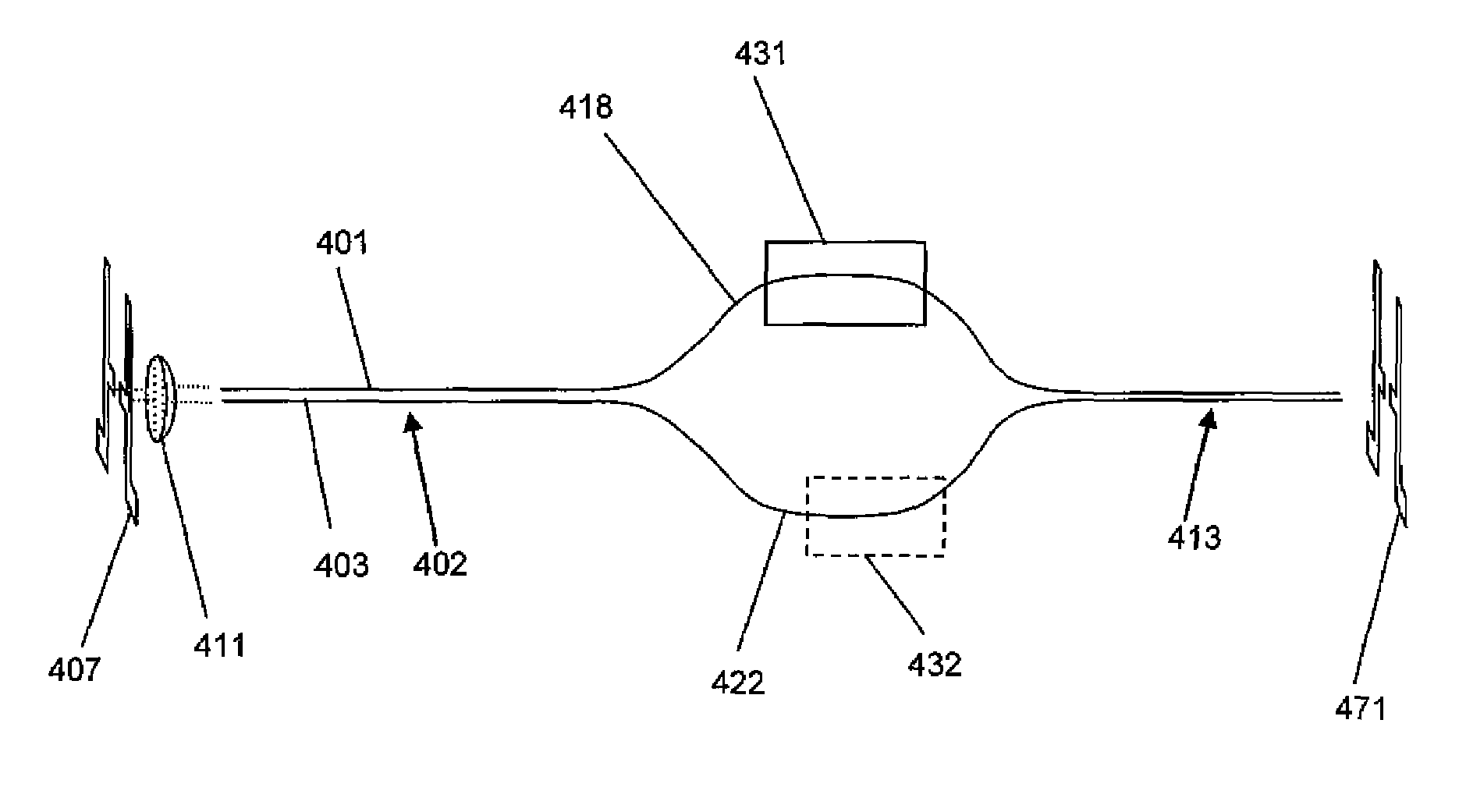
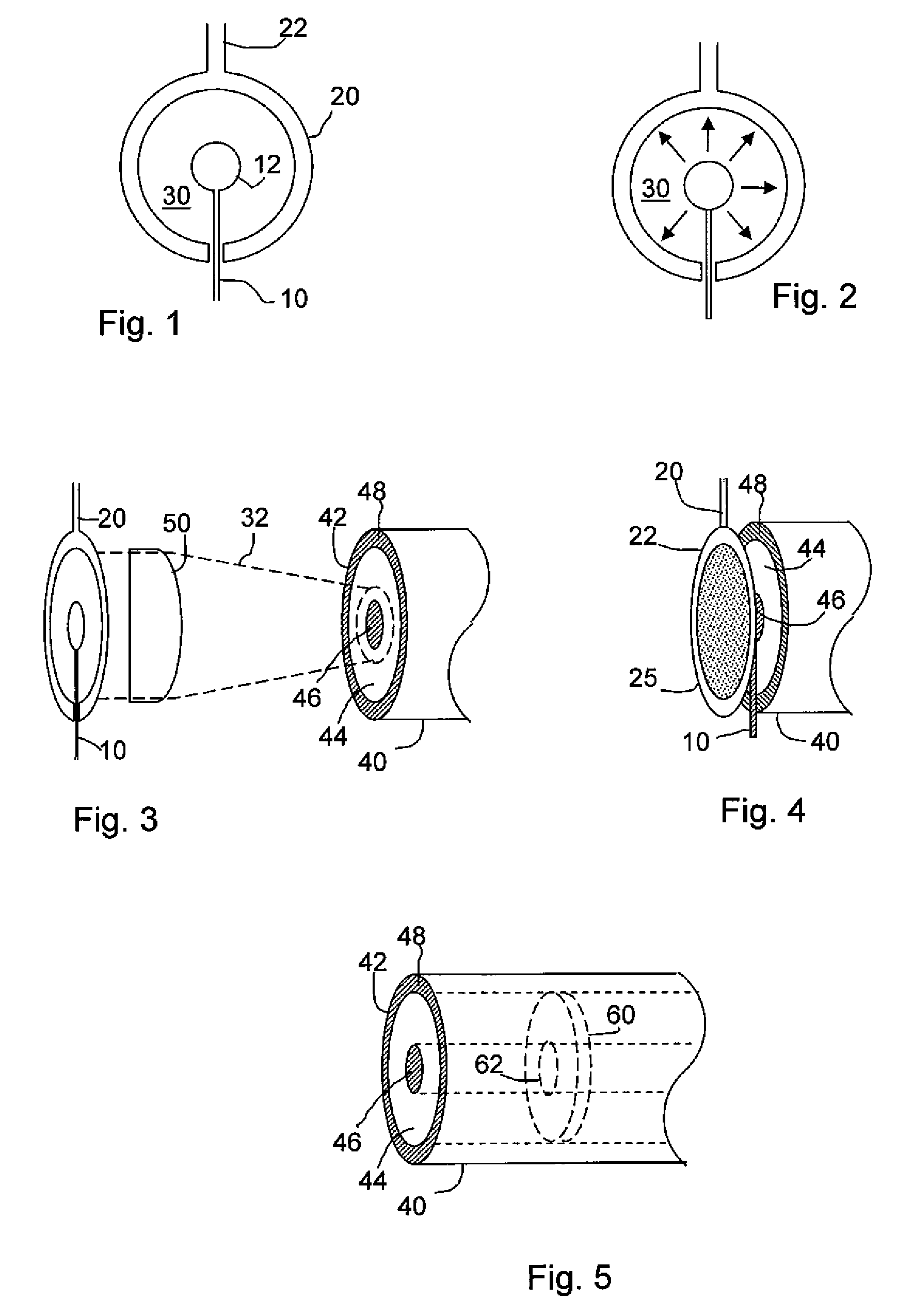
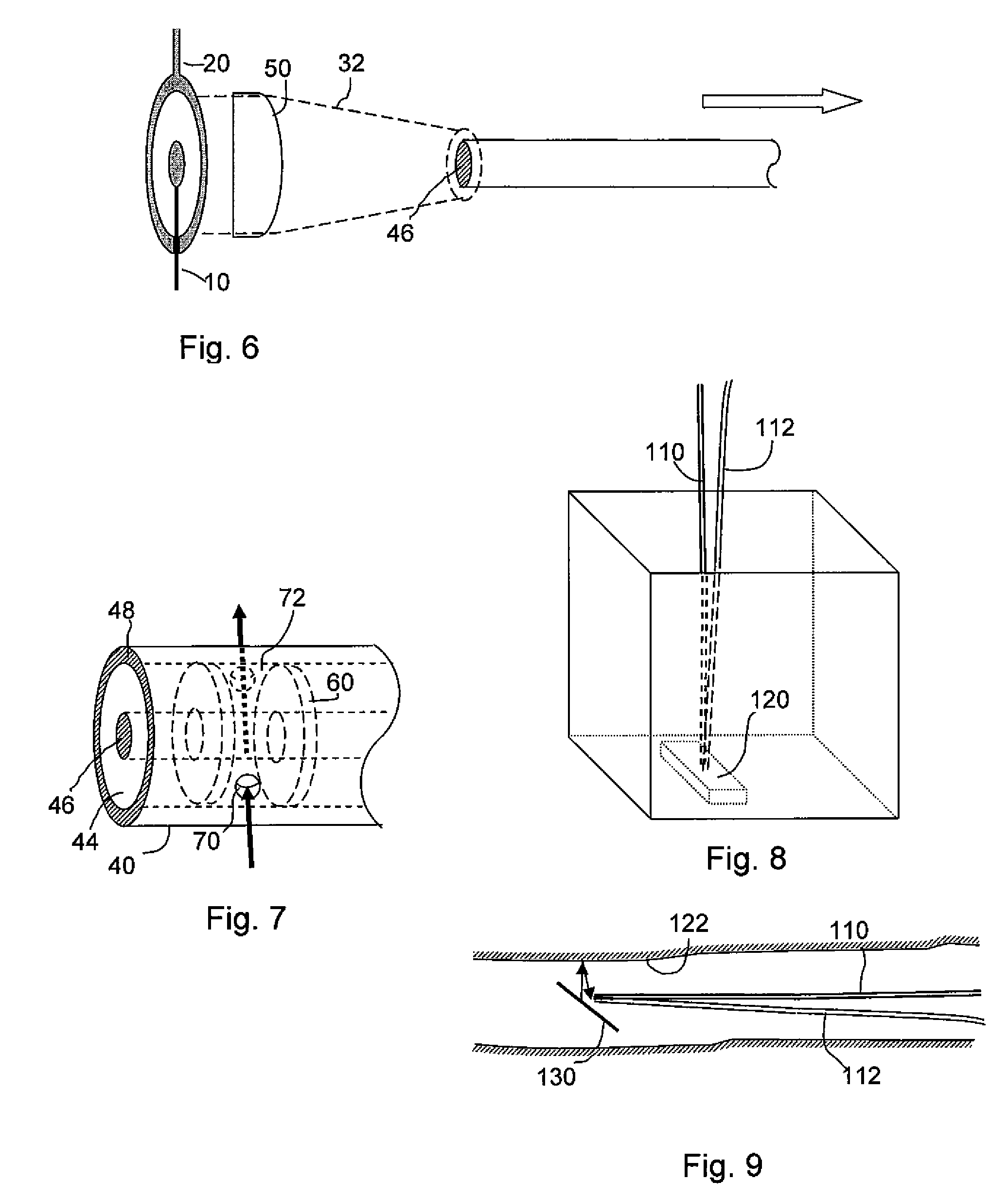
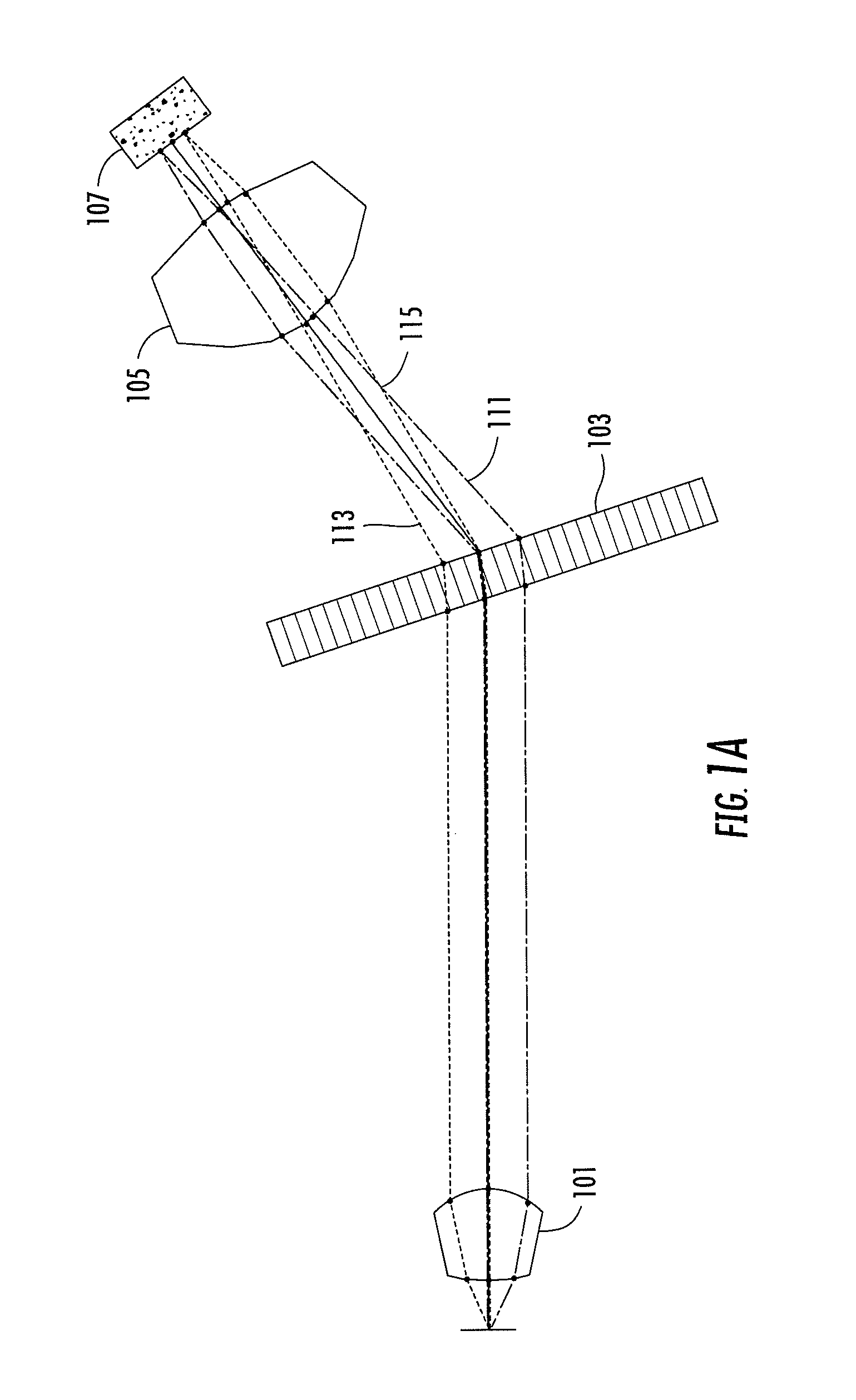
ActiveUS7551809B2Guaranteed normal transmissionLaser detailsCladded optical fibreGroup velocity dispersionPeak value
An optical fiber delivery system for delivering ultrashort optical pulses that can efficiently transmit high peak power, ultrashort optical pulses from an optical pulse source to a desired position in an optical apparatus is provided. An optical system including such an optical fiber delivery system is also provided. The optical fiber delivery system includes light waveguide means 20 for receiving high-peak power, ultrashort optical pulses and transmitting the optical pulses, negative group-velocity dispersion generation means 30 for providing negative group-velocity dispersion to the optical pulses transmitted through the light waveguide means 20, and an optical fiber 40 that transmits the optical pulses transmitted through the negative group-velocity dispersion generation means 30 along a desired distance. The incident ultrashort optical pulses that have been injected into the light waveguide means 20 are converted into down-chirped pulses.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
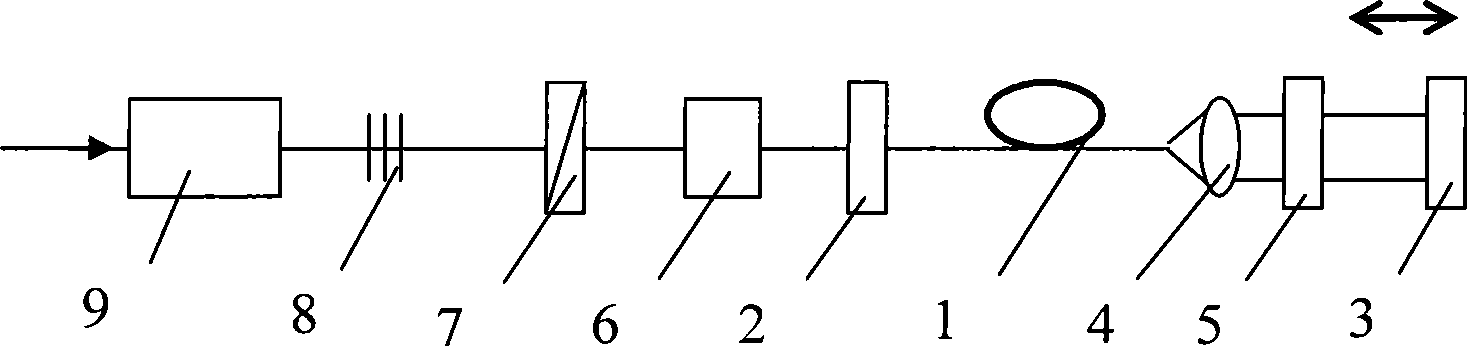
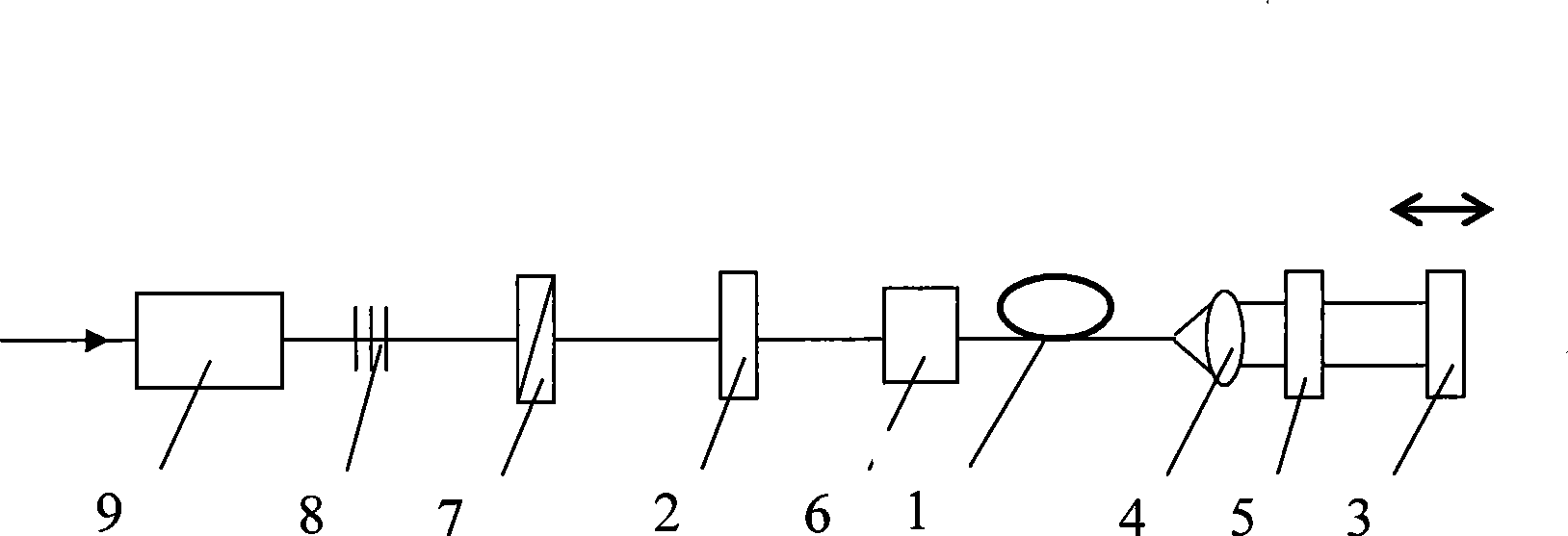
Optical fourier transform device and method
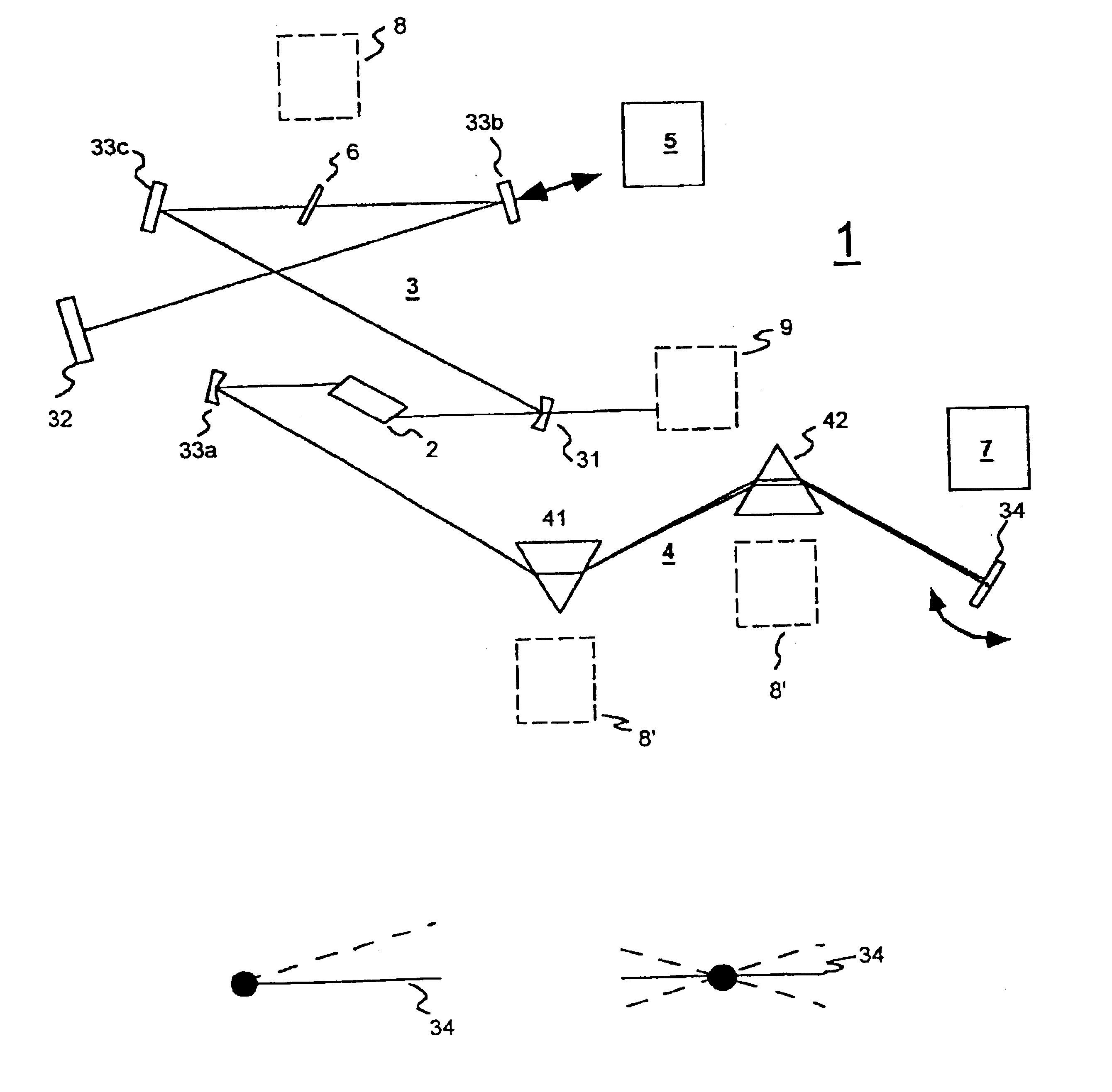
ActiveUS20070273958A1Accurate optical Fourier transformLimited applicationLight demodulationNon-linear opticsFrequency spectrumGroup velocity dispersion
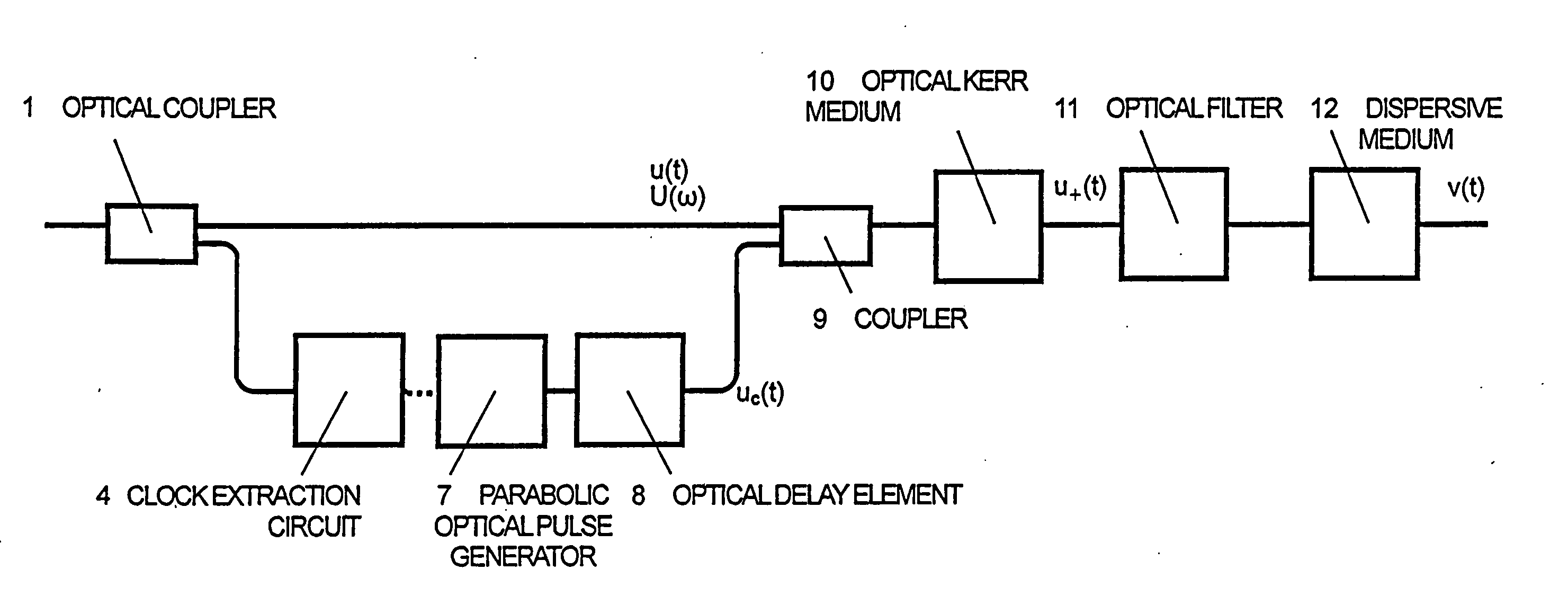
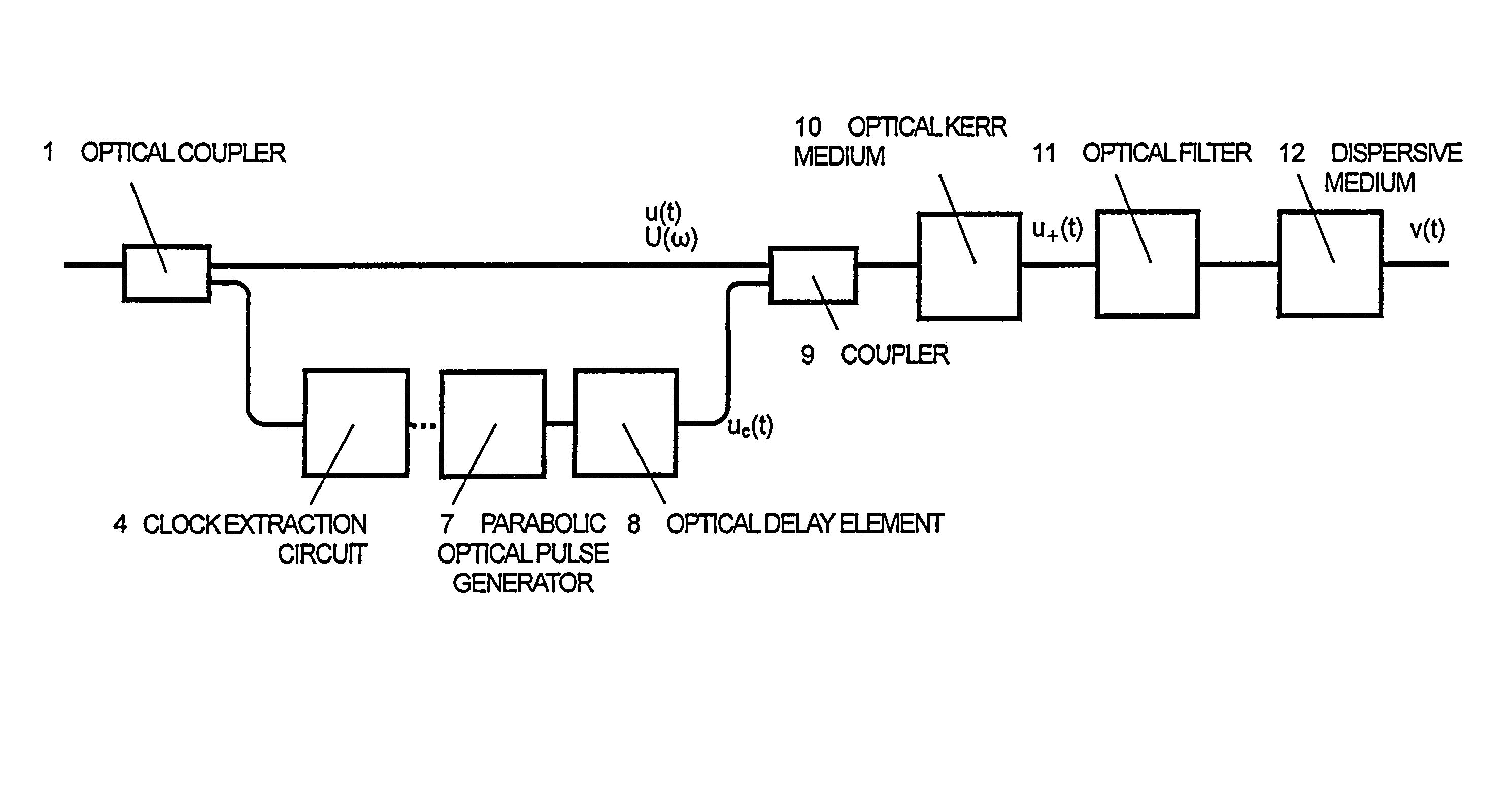
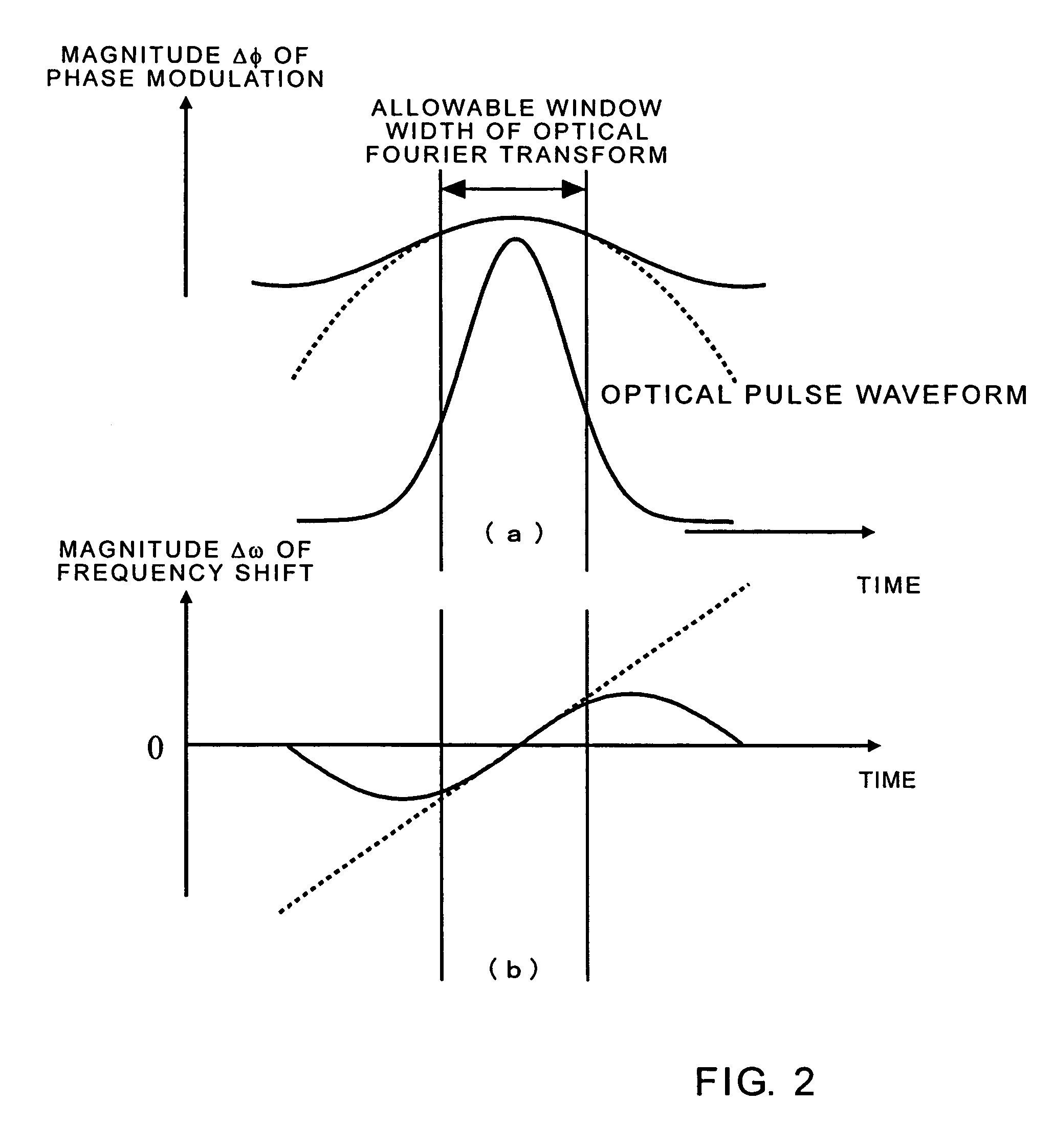
Optical Fourier transform is executed over a wide time range. A quadratic function type optical pulse generator (7) generates a control light pulse of a shape expressed by a quadratic function or a parabola according to a clock signal based on a signal light pulse from an optical coupler (1). The signal light pulse inputted is multiplexed by a multiplexer (9) with the control light pulse optically delayed by an optical delay element (8) so that the timing is matched with the signal light pulse, and introduced into an optical Kerr medium (10). In the optical Kerr medium (10), the signal light pulse inputted by the mutual phase modulation between the signal light pulse and the control light pulse is subjected to a linear phase modulation (frequency chirp) over the entire pulse or a wide time range. After that, the signal light pulse isolated by an optical filter (11) is introduced into the dispersion medium (12) having a group velocity dispersion (secondary dispersion), thereby converting the time waveform of the inputted signal light pulse into the shape of the frequency spectrum.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
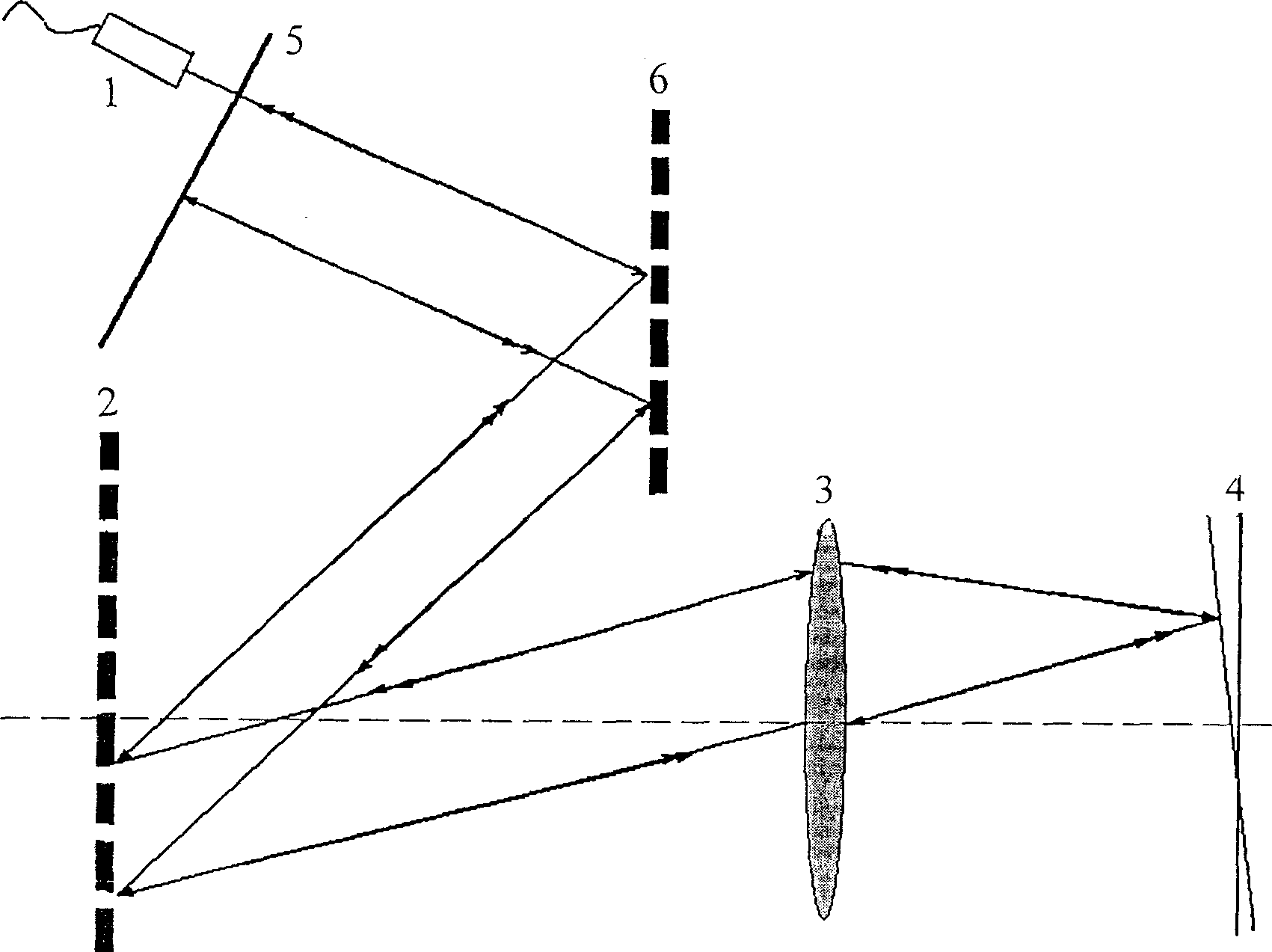
Dispersion compensating method and system for optically coherent chromatographic imaging
InactiveCN1887220ALarge dispersion adjustment rangeWide Compensation Spectral RangeSurgeryMaterial analysis by optical meansGratingPhase retardation
The present invention discloses dispersion compensating method and system for optically coherent tomographic imaging (OCT). The system has one increased blazed grating parallelly set with the original blazed grating in a single grating fast scanning optical delay line, and thus one independently regulated variable of interval between two blazed gratings and capacity of generating group velocity dispersion and third-order dispersion in great varying range and arbitrary sign combination, so that the OCT system may obtain precise matching between the dispersion of the reference arm and the dispersion of the sample arm and longitudinal resolution approaching the theoretical calculated value. The double grating system has wide dispersion regulating range, wide compensation spectrum range and small residual dispersion other than the capacity of independently controlling phase delay and group delay, and possesses three functions of depth scan, phase modulation and dispersion compensation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
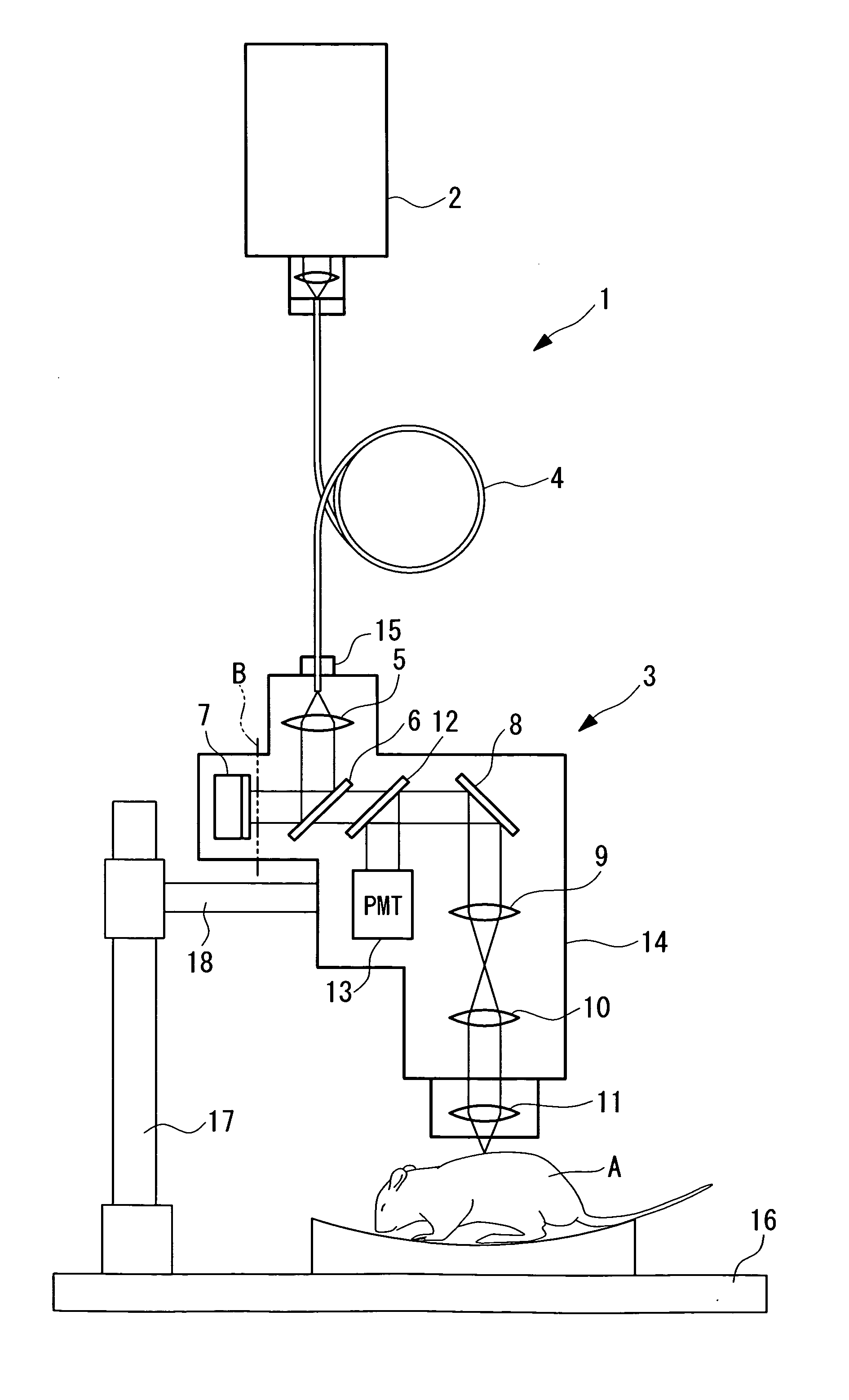
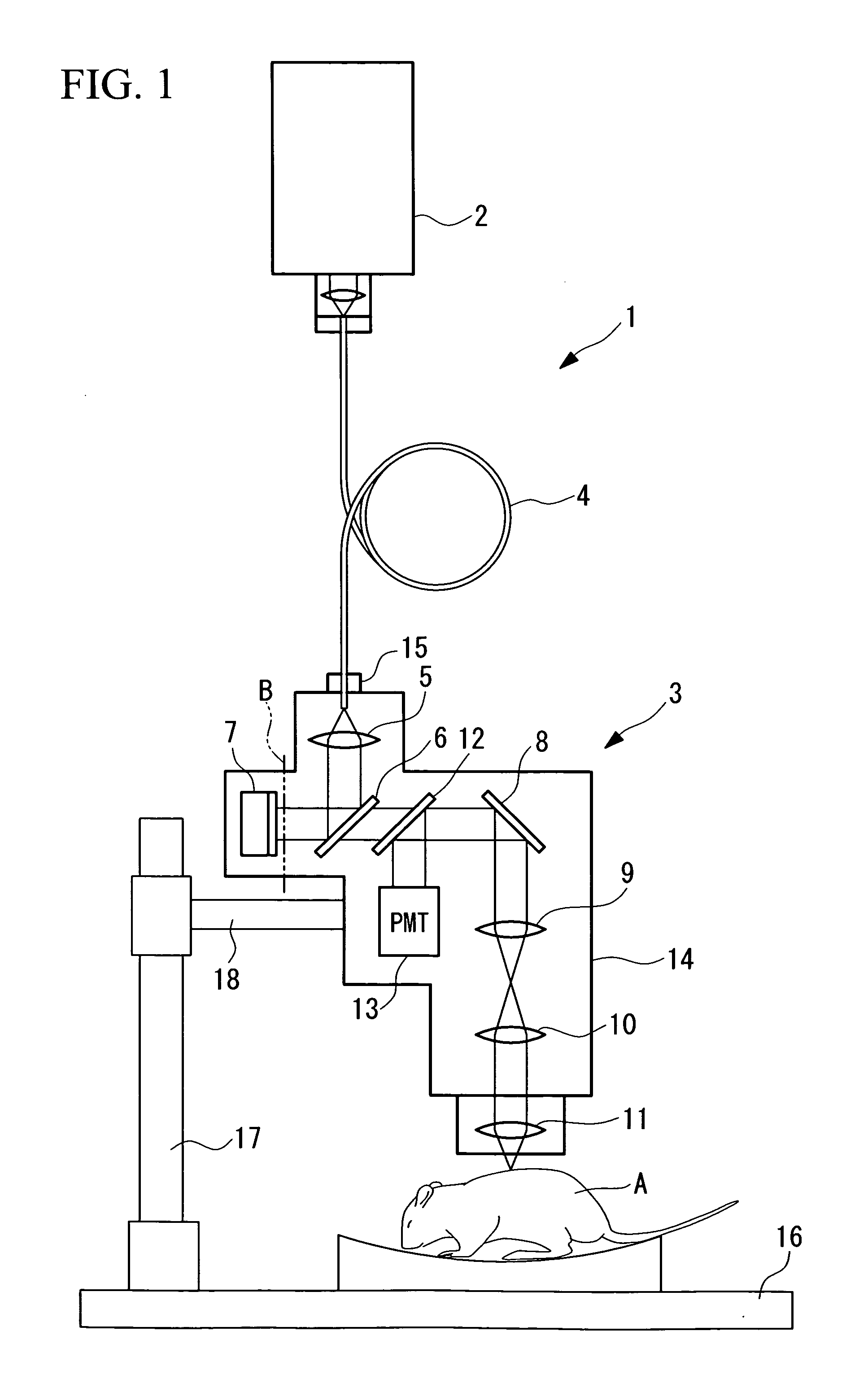
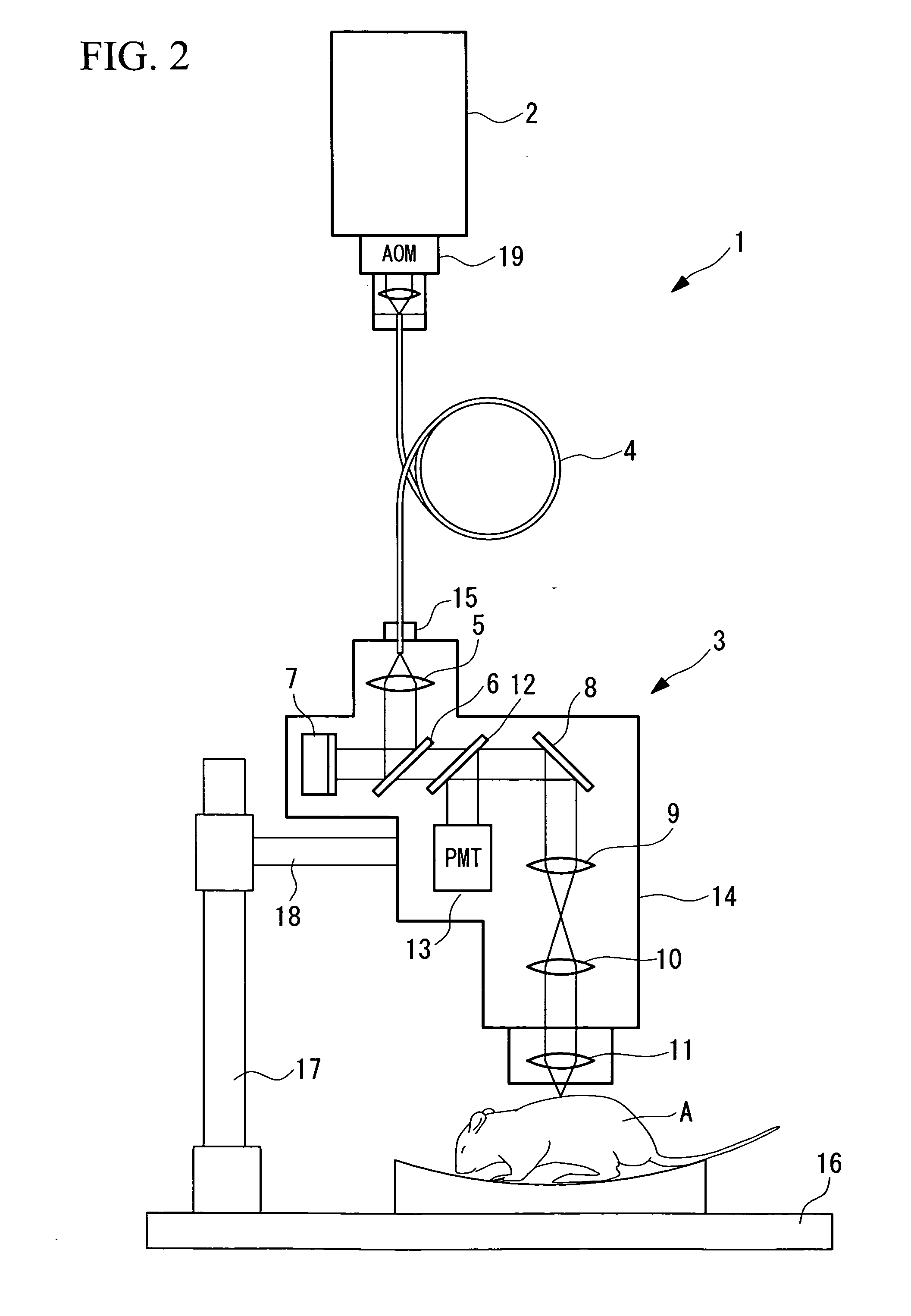
Multiphoton-excitation-type examination apparatus
InactiveUS20050279950A1Generate efficientlyEasy to adjustBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsPhotometryGroup velocity dispersionLaser light
The invention provides a multiphoton-excitation-type examination apparatus that efficiently generates a multiphoton-excitation effect, that makes the measurement head compact, and that can be easily adjusted when the measurement head is replaced. The multiphoton-excitation-type examination apparatus comprises a laser light source that oscillates ultrashort pulsed laser light; an optical fiber that transmits the ultrashort pulsed laser light from the laser light source; a support member; a measurement head supported on the support member so as to be movable upwards and downwards and at an angle, and having an optical system that irradiates a specimen with the ultrashort pulsed laser light transmitted by the optical fiber that measures fluorescence or reflected light coming from the specimen; and a dispersion-compensating member, in the measurement head, that compensates for group velocity dispersion of the ultrashort pulsed laser light irradiated onto the specimen.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Method and light pulse source for generating soliton light pulses
InactiveUS20140334763A1Stable changeIncreasing waveguide diameterLaser detailsNon-linear opticsGroup velocity dispersionOptoelectronics
A method of generating light pulses including pumping laser pulses with a pump laser source, coupling the laser pulses into a pulse guiding medium having an anomalous group-velocity dispersion and a Kerr nonlinearity, and propagating the laser pulses along the pulse guiding medium, wherein soliton-shaped light pulses are formed from the laser pulses within the pulse guiding medium and, resulting from a photoionization of the pulse guiding medium by the light pulses, the light pulses are subjected to a frequency, wherein the method further includes setting the pump laser source and the pulse guiding medium such that the light pulses are fundamental soliton light pulses propagating in the pulse guiding medium, wherein the group-velocity dispersion of the pulse guiding medium being selected such that a ratio of the dispersion and the Kerr nonlinearity decreases with increasing frequency and the fundamental soliton light pulses are compressed with the frequency shift.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
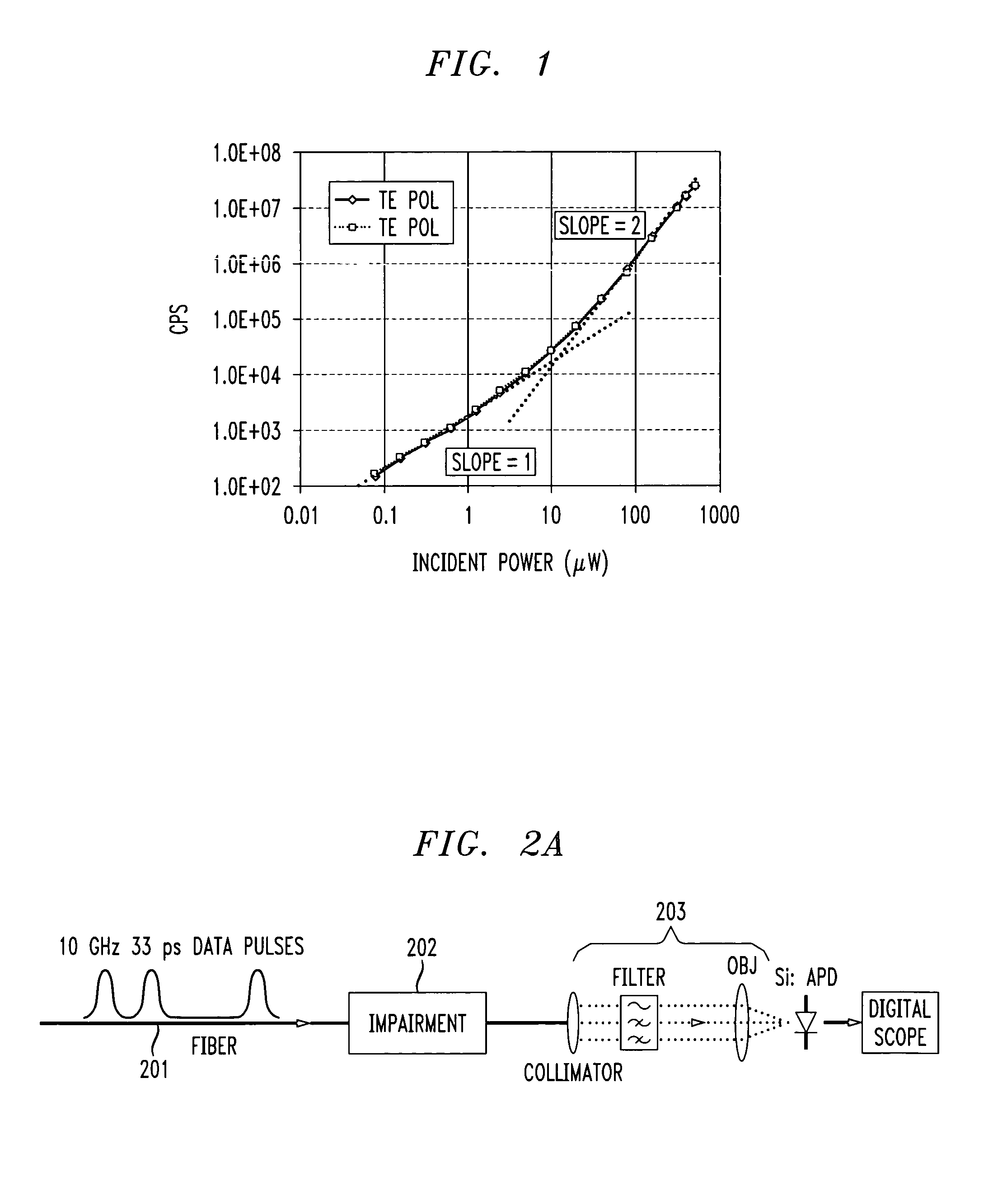
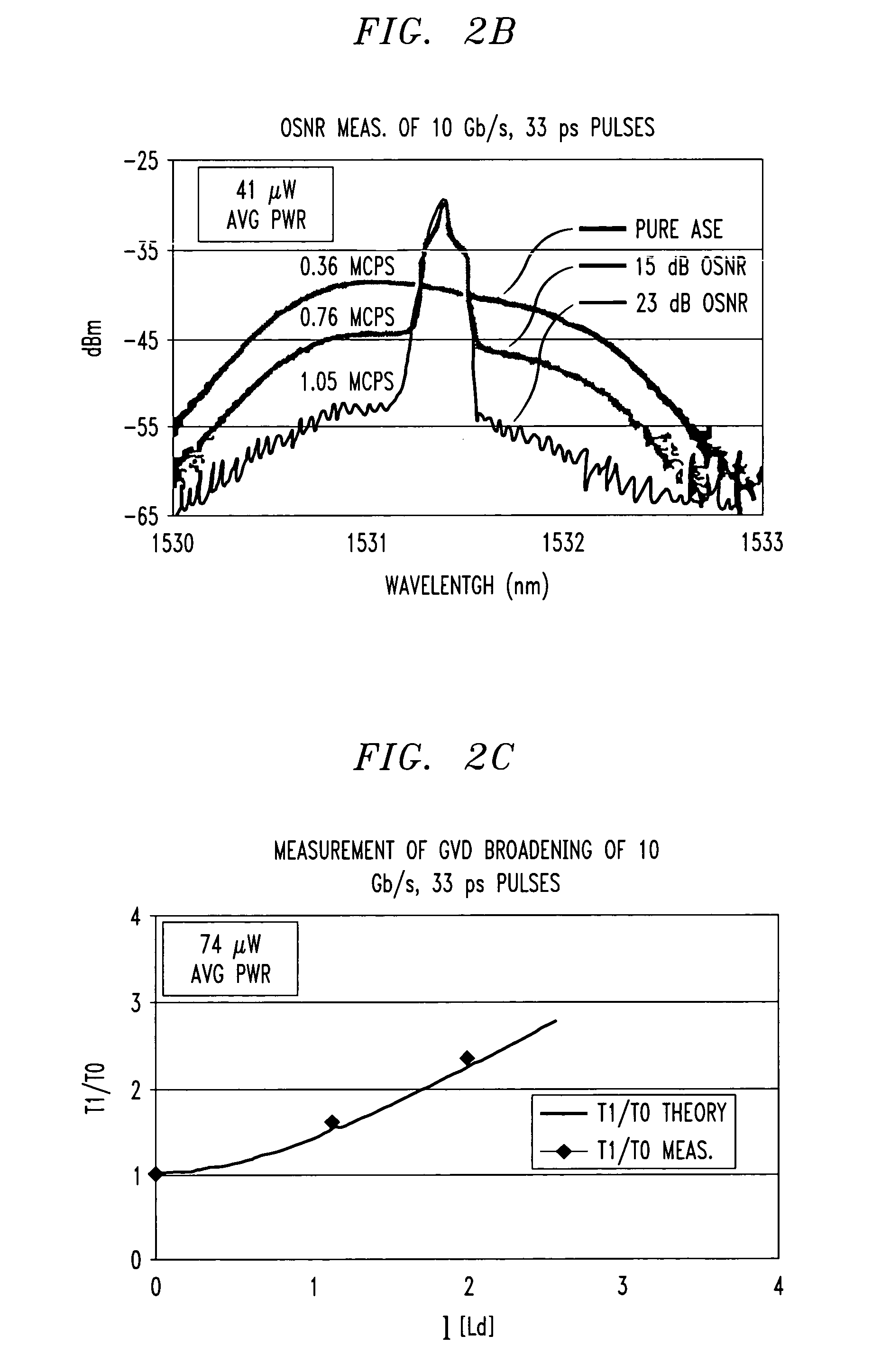
Dynamic measurement of and compensation for impairments to optical data communication pulses using photon-counting silicon avalanche photodiode
InactiveUS7024111B2Transmission monitoringElectromagnetic receiversTwo-photon absorptionGroup velocity dispersion
Apparatus and method is described for using a silicon photon-counting avalanche photodiode (APD) to detect at least two-photon absorption (TPA) of an optical signal, the optical signal having a wavelength range extending from 1.2 μm to an upper wavelength region that increases as the number of photons simultaneously absorbed by the APD increases beyond two. In one embodiment, the TPA count is used by a signal compensation apparatus to reduce dispersion of a received optical pulse communication signal subjected to group velocity dispersion, polarization mode dispersion, or other signal impairment phenomena which effect the TPA count. Another embodiment, the TPA count is used to determine the optical signal-to-noise ratio of a received optical pulse communication signal. Another embodiment uses the TPA count to determine the autocorrelation between a first and second optical pulse signals as a function of the relative delay between the first and second optical pulse signals. Another embodiment uses the TPA count to achieve synchronization of a second optical pulse signal to a first optical pulse signal.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Measuring chromatic dispersion in an optical wavelength channel of an optical fiber link
ActiveUS8135275B2Transmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsGroup velocity dispersionIntensity modulation
Two intensity modulated test signals are generated with precise frequency offset from a single laser source, and multiplexed into a combined test signal. The two modulated signals are demultiplexed at a receiver using a fixed periodic optical filter with complementary output ports. Group velocity dispersion / chromatic dispersion is measured over a large dynamic range, using pseudo-random intensity modulation and digital demodulation techniques.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
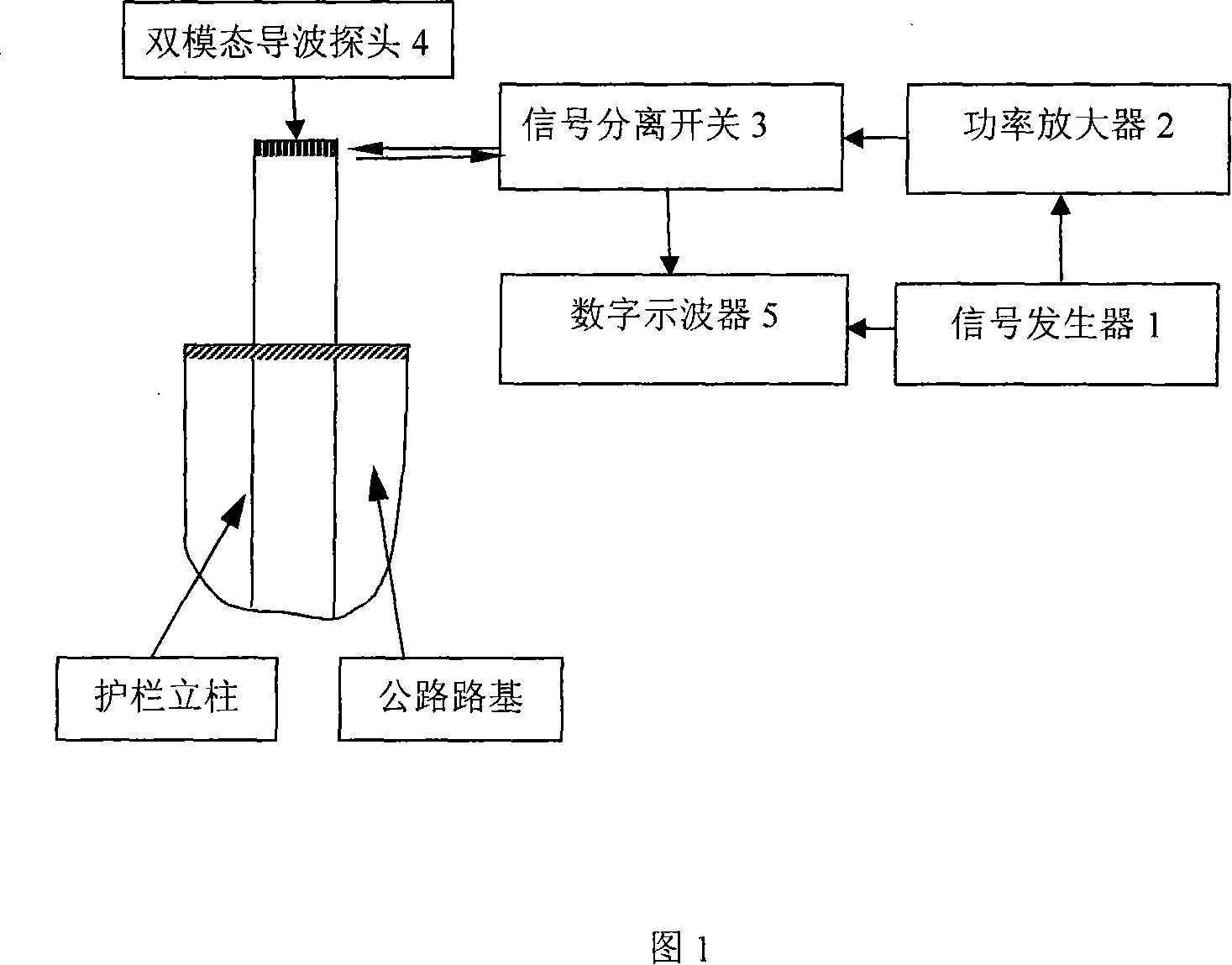
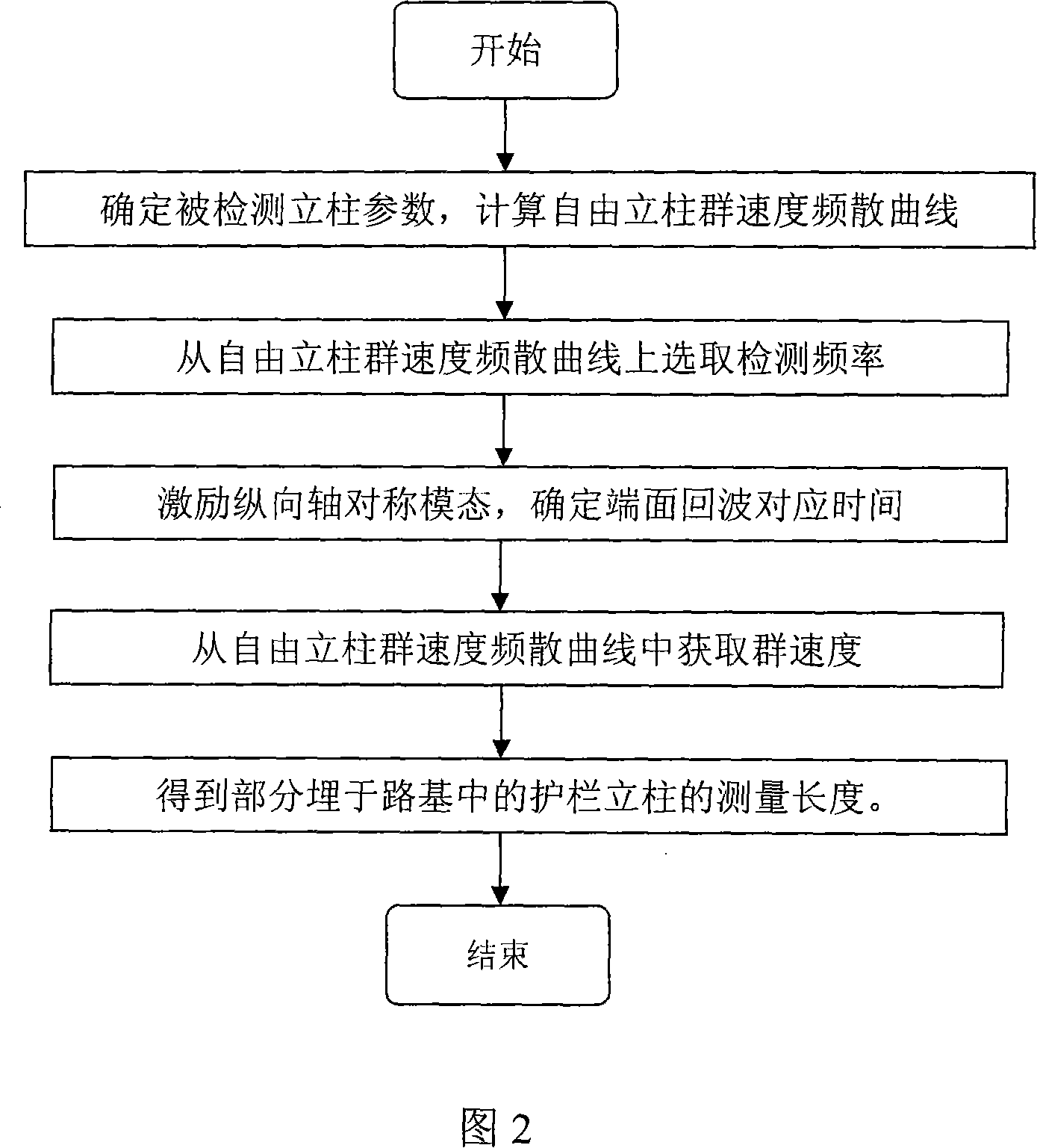
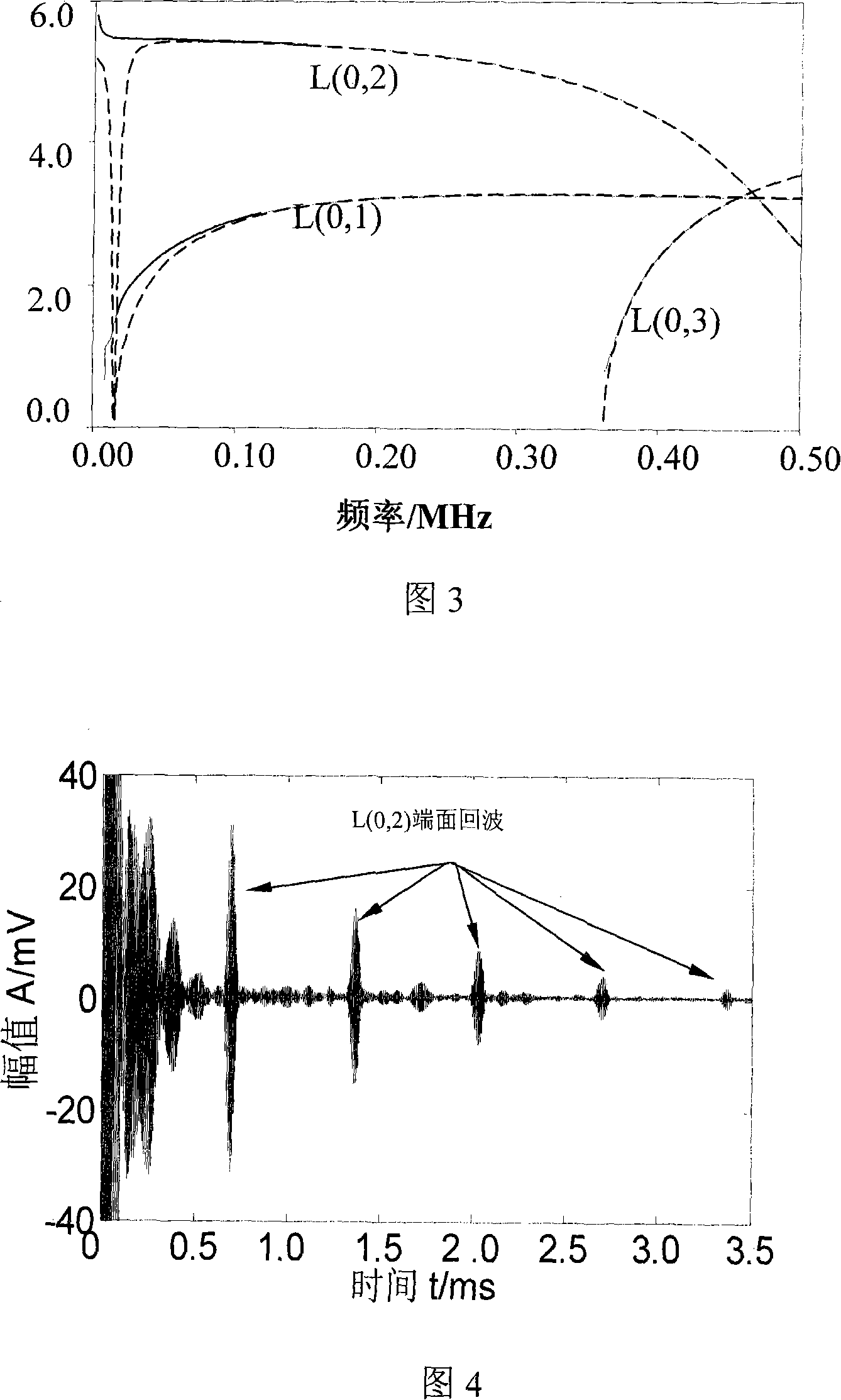
Method for nondestructive detecting length of high speed highway guardrail upright post by ultrasonic guided wave
InactiveCN101131319AFree from destructionNot affected by working conditionsUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansAcoustic wave reradiationTransceiverSonification
A method of using ultrasonic guided wave to detect the length of grate column of half buried under different highway roadbed, belongs to nondestructive testing field. The method is to determine parameters of grate column before buried calculate group velocity dispersion curve of grate column before buried; select detection frequency from the curve and input the arbitrary function generator to form a single audio signal through the power amplifier module, switch modules, guided wave transceiver components, stimulate the vertical axisymmetric guided wave mode in the vertical column; the guided wave modal generate end echo when encounter the end of the column, the end echo is sent to oscilloscope through guided wave transceiver components and switch modules, determine the corresponding time of end echo, obtain the group velocity from the group velocity dispersion curve, multiple the group velocity with the echo time, divided by 2 to obtain the length of column. The present invention has the advantages of do not need to consider surrounding medium of column, high detection accuracy and of low cost.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Methods and apparatus of entangled photon generation using four-wave mixing
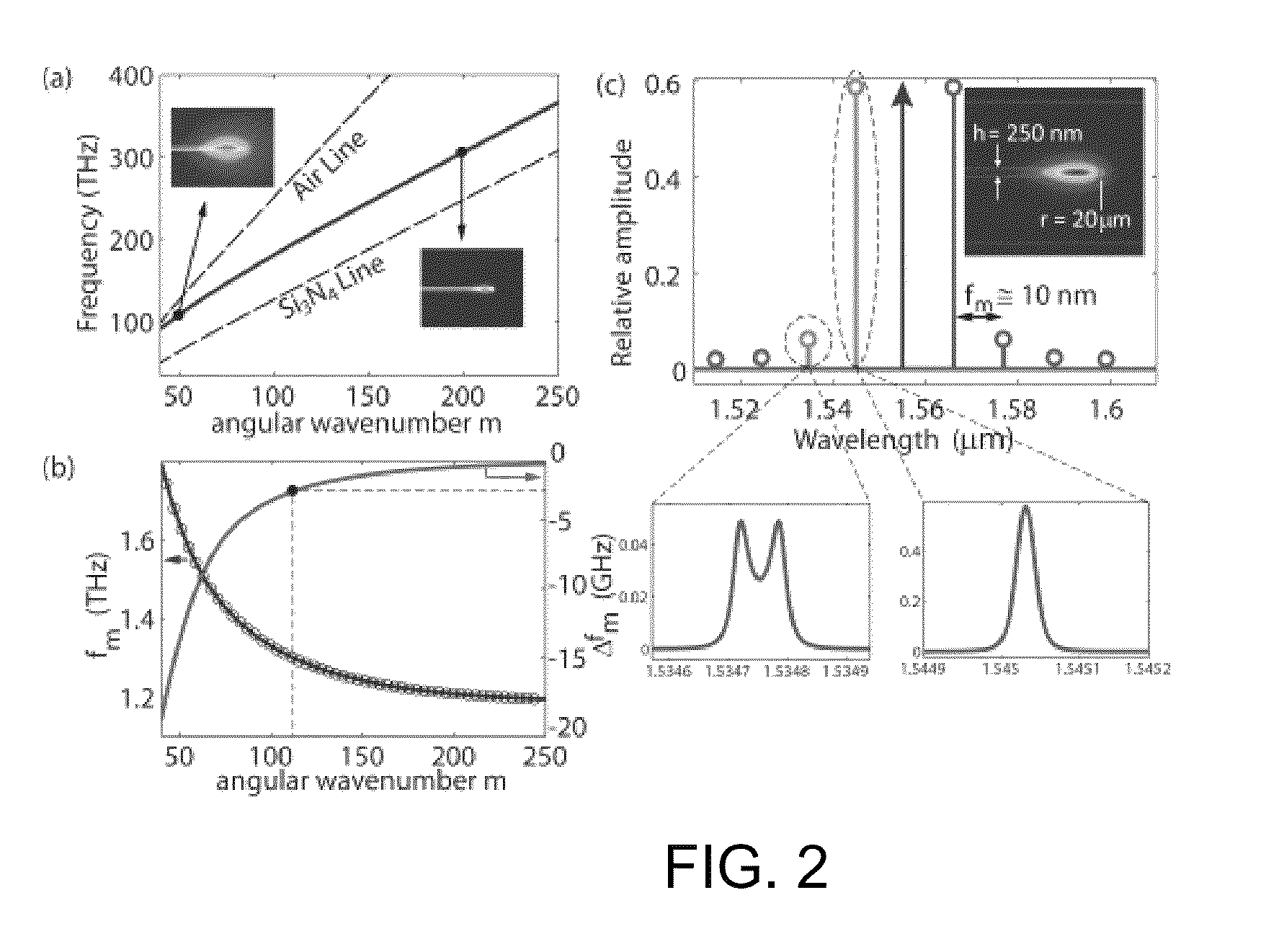
A non-linear optical device is provided. The device comprises an optical disk or ring microresonator fabricated from a material that exhibits an optical nonlinearity able to produce degenerate four-wave mixing (FWM) in response to a pump beam having a pump frequency in a specified effective range. The microresonator is conformed to exhibit an angular group velocity minimum at a pump frequency within the specified effective range such that there is zero angular group velocity dispersion at the pump frequency. We refer to such a pump frequency as the “zero dispersion frequency”. In embodiments, excitation of the resonator by a pump beam of sufficient intensity at the zero-dispersion frequency causes the resonator to emit a frequency comb of entangled photon pairs wherein the respective frequencies in each pair are symmetrically placed about the zero-dispersion frequency.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Optical fourier transform device and method
Optical Fourier transform is executed over a wide time range. A quadratic function type optical pulse generator (7) generates a control light pulse of a shape expressed by a quadratic function or a parabola according to a clock signal based on a signal light pulse from an optical coupler (1). The signal light pulse inputted is multiplexed by a multiplexer (9) with the control light pulse optically delayed by an optical delay element (8) so that the timing is matched with the signal light pulse, and introduced into an optical Kerr medium (10). In the optical Kerr medium (10), the signal light pulse inputted by the mutual phase modulation between the signal light pulse and the control light pulse is subjected to a linear phase modulation (frequency chirp) over the entire pulse or a wide time range. After that, the signal light pulse isolated by an optical filter (11) is introduced into the dispersion medium (12) having a group velocity dispersion (secondary dispersion), thereby converting the time waveform of the inputted signal light pulse into the shape of the frequency spectrum.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Optical fiber delivery system for delivering optical short pulses and optical fiber delivery method
The optical fiber delivery system for delivering optical short pulses includes: a chirped pulse source (10) for emitting an up-chirped optical short pulse having high peak power; optical waveguide unit (20) for delivering the optical short pulse emitted from the chirped pulse source (10); negative group-velocity dispersion generation unit (30) for providing negative group-velocity dispersion to the optical short pulse exited from the optical waveguide unit (20); and an optical fiber (40) for delivering the optical short pulse exited from the negative group-velocity dispersion generation unit (30), along a desired distance, in which the optical short pulse emitted from the chirped pulse source (10) is adapted to be exited, from the optical fiber (40), as a down-chirped optical short pulse that is substantially free of waveform distortion resulting from higher-order dispersion.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
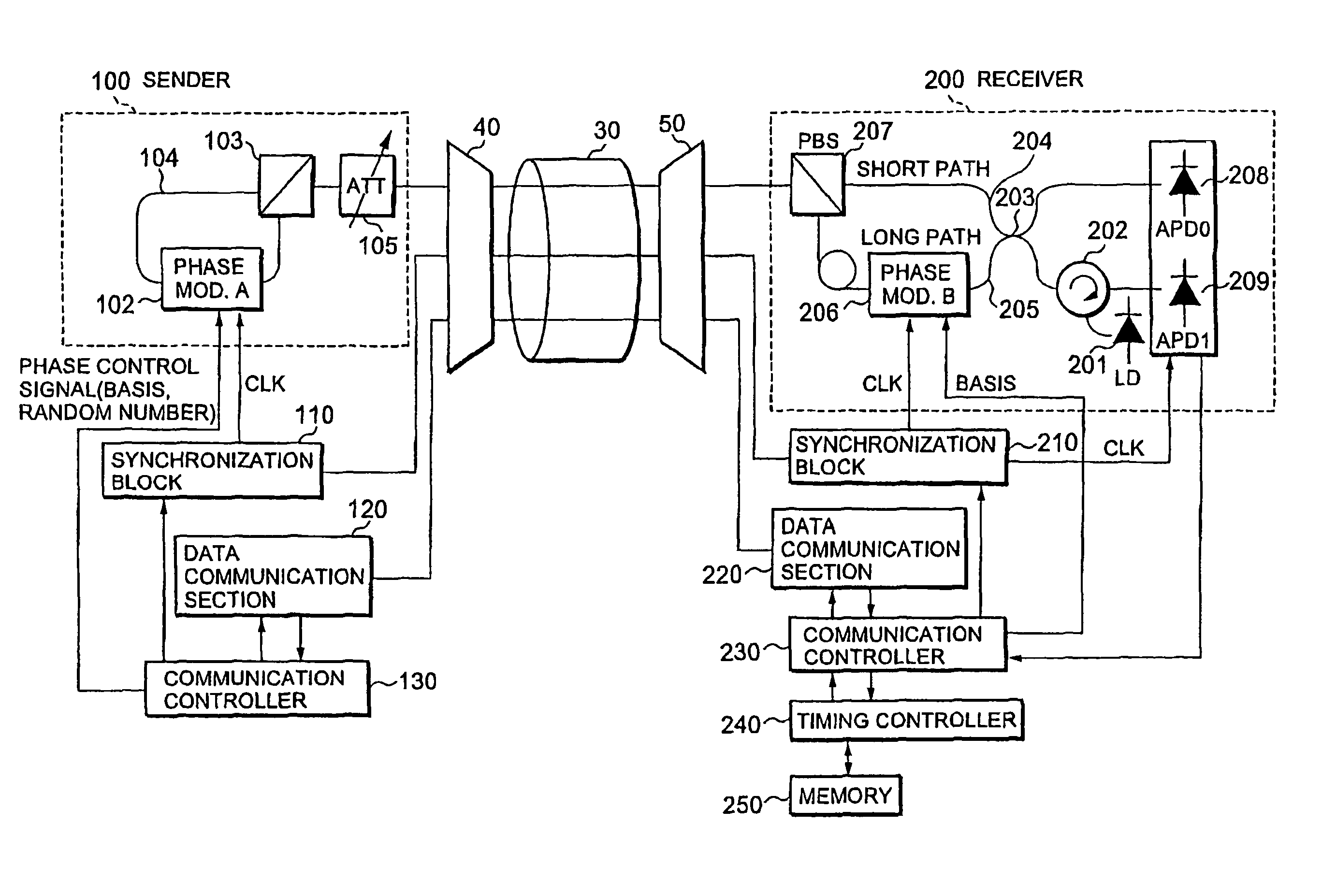
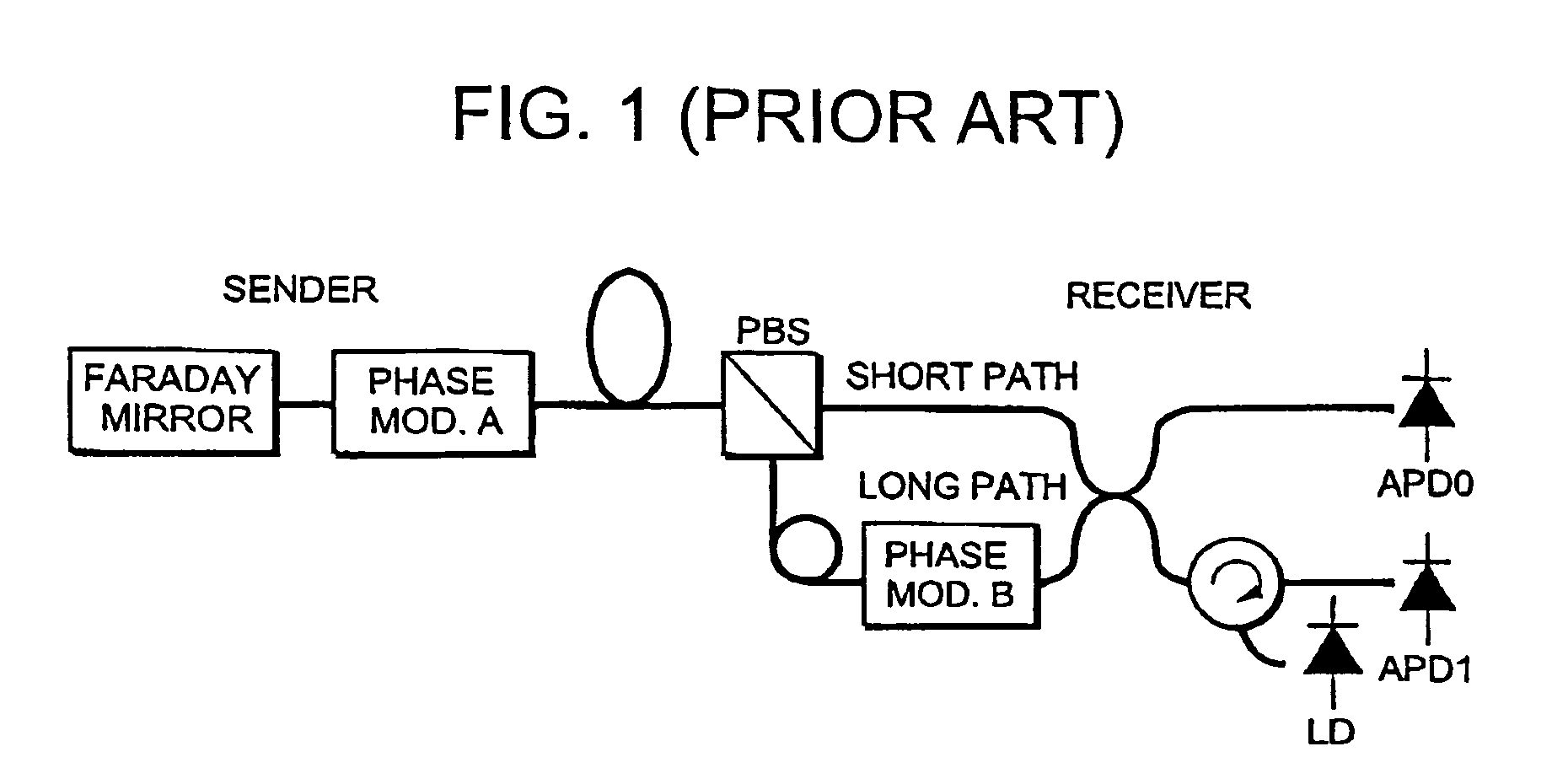
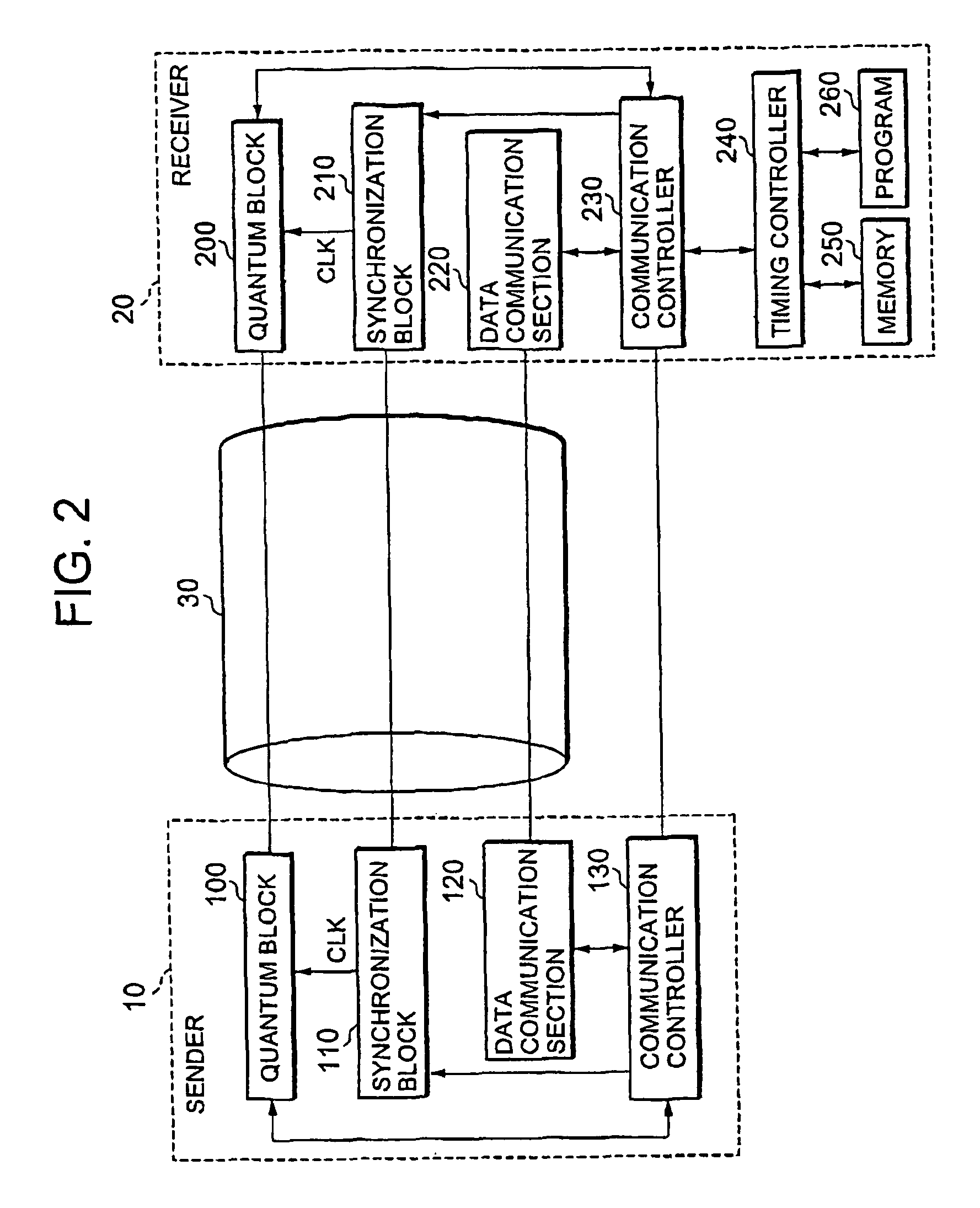
Communication system and timing control method
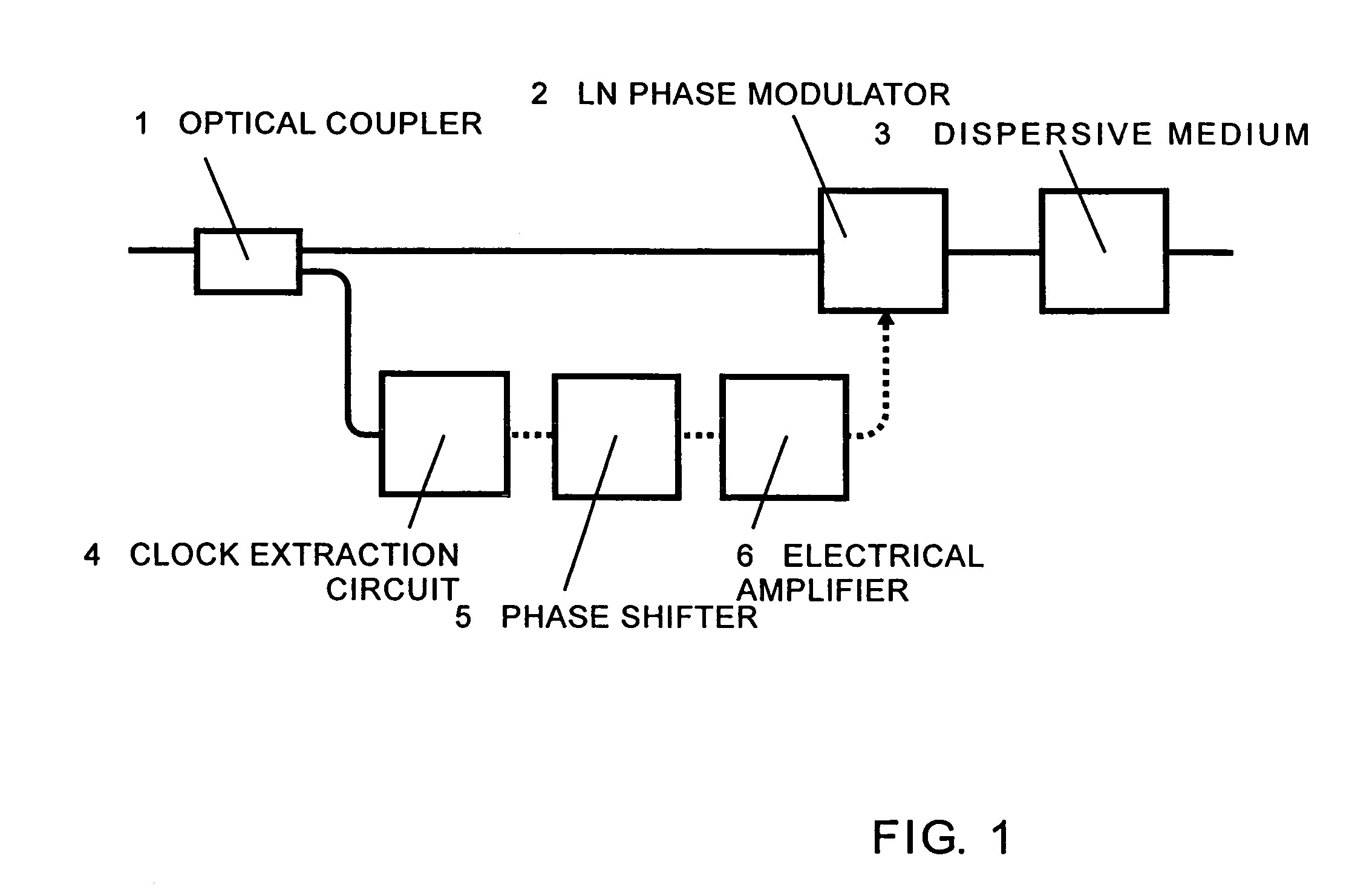
ActiveUS8184989B2Convenient timeEvenly distributedKey distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationCommunications systemGroup velocity dispersion
A communication system and a timing control method are proposed that optimize timing in a sender and thereby enable information to be stably transmitted at the right timing. Under instructions from a timing controller in a receiver, the timing of driving a phase modulator in a sender is shifted by one step after another, and the then amount of clock shift and result of interference are monitored at the receiver and stored in a memory. The optimum timing is determined based on the stored data. Thus, a clock for driving the phase modulator in the sender can be set at the right timing. This is equivalent to compensating for group velocity dispersion due to wavelength dispersion that occurs when an optical signal channel and a clock signal channel are transmitted by wavelength division multiplexing transmission.
Owner:NEC CORP
Optically parametric oscillator
ActiveCN101499608ASatisfy Phase Matching RequirementsAchieving tuned outputActive medium materialNon-linear opticsZero-dispersion wavelengthLine width
The invention relates to an optical parametric oscillator, which comprises a nonlinear optical material (1) with the double-zero dispersion wavelength, a high reflector (2), an output mirror (3), a parametric oscillation optical beam collimator (4), a parametric optical line width compressor (5), a pumped optical coupler (6), a lambda / 2 phase retarder (7), a laser power controller (8) and an optical isolator (9). The nonlinear optical material (1) has a double-zero dispersion wavelength and is arranged in a resonant cavity formed by the high reflector and the output mirror. The pumped optical wavelength is in the anomalous dispersion regime of the photonic crystal fiber, thereby ensuring the phase matching conditions and generating the highly efficient four-wave mixing effect. For the parametric oscillation formed by simplifying the four-wave mixing, the wavelengths of the two parametric lights are respectively arranged at the double-zero dispersion wavelength of the photonic crystal optical fiber, thereby realizing the group velocity dispersion compensation of the parametric light, solving the problem of the ultra-short pulse dispersion compensation, and greatly reducing the pumping threshold.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Short light pulse generation device, terahertz wave generation device, camera, imaging device, and measurement device
InactiveUS20140240509A1Positive group velocity dispersion characteristicPositive group velocity dispersion characteristicsTelevision system detailsLaser using scattering effectsPath lengthMeasurement device
A short light pulse generation device includes: a light pulse generation portion that has a quantum well structure and generates a light pulse; a frequency chirping portion that has a quantum well structure and chirps a frequency of the light pulse; a light branching portion that branches a chirped light pulse; and a group velocity dispersion portion that has a plurality of optical waveguides, on which each of a plurality of the light pulses branched in the light branching portion is incident, and produces a group velocity difference depending on a wavelength with respect to a plurality of branched light pulses, wherein light path lengths of the light pulses in a plurality of light paths before the light pulse is branched in the light branching portion and then incident on the plurality of optical waveguides of the group velocity dispersion portion are equal to each other.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Frequency comb source with large comb spacing
InactiveUS8571075B2Reduce lossEasy to adjustRadiation pyrometryLaser using scattering effectsLow noisePhase noise
A frequency comb laser providing large comb spacing is disclosed. At least one embodiment includes a mode locked waveguide laser system. The mode locked waveguide laser includes a laser cavity having a waveguide, and a dispersion control unit (DCU) in the cavity. The DCU imparts an angular dispersion, group-velocity dispersion (GVD) and a spatial chirp to a beam propagating in the cavity. The DCU is capable of producing net GVD in a range from a positive value to a negative value. In some embodiments a tunable fiber frequency comb system configured as an optical frequency synthesizer is provided. In at least one embodiment a low phase noise micro-wave source may be implemented with a fiber comb laser having a comb spacing greater than about 1 GHz. The laser system is suitable for mass-producible fiber comb sources with large comb spacing and low noise. Applications include high-resolution spectroscopy.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Method and device for compensating chromatic dispersion in optical communication system
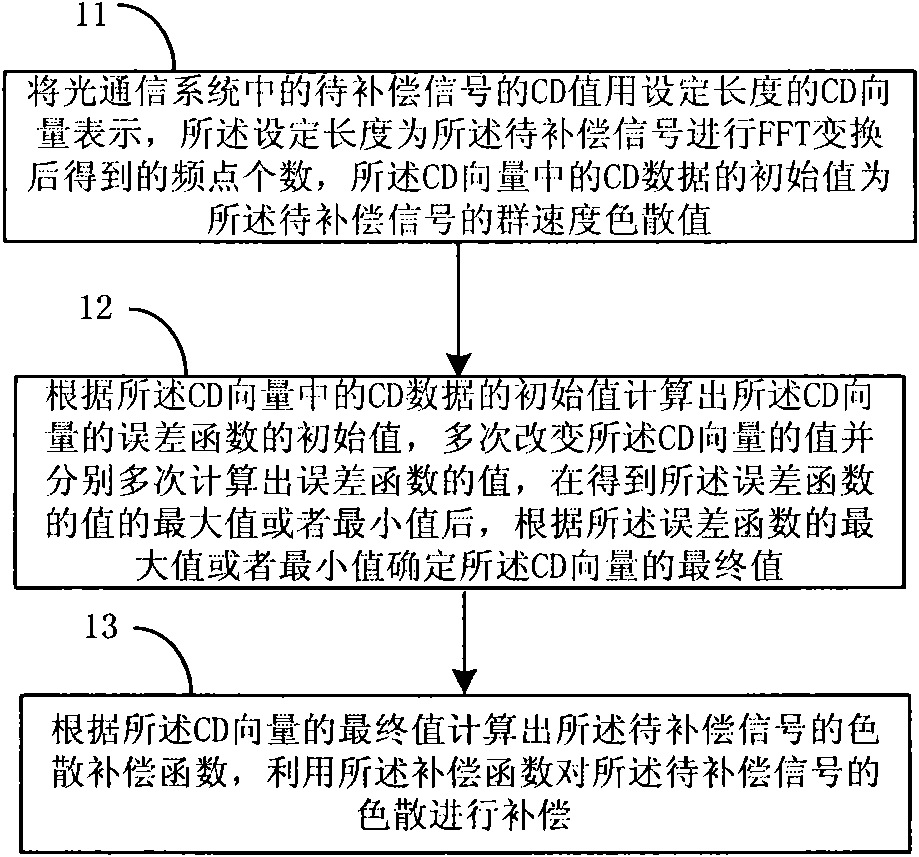
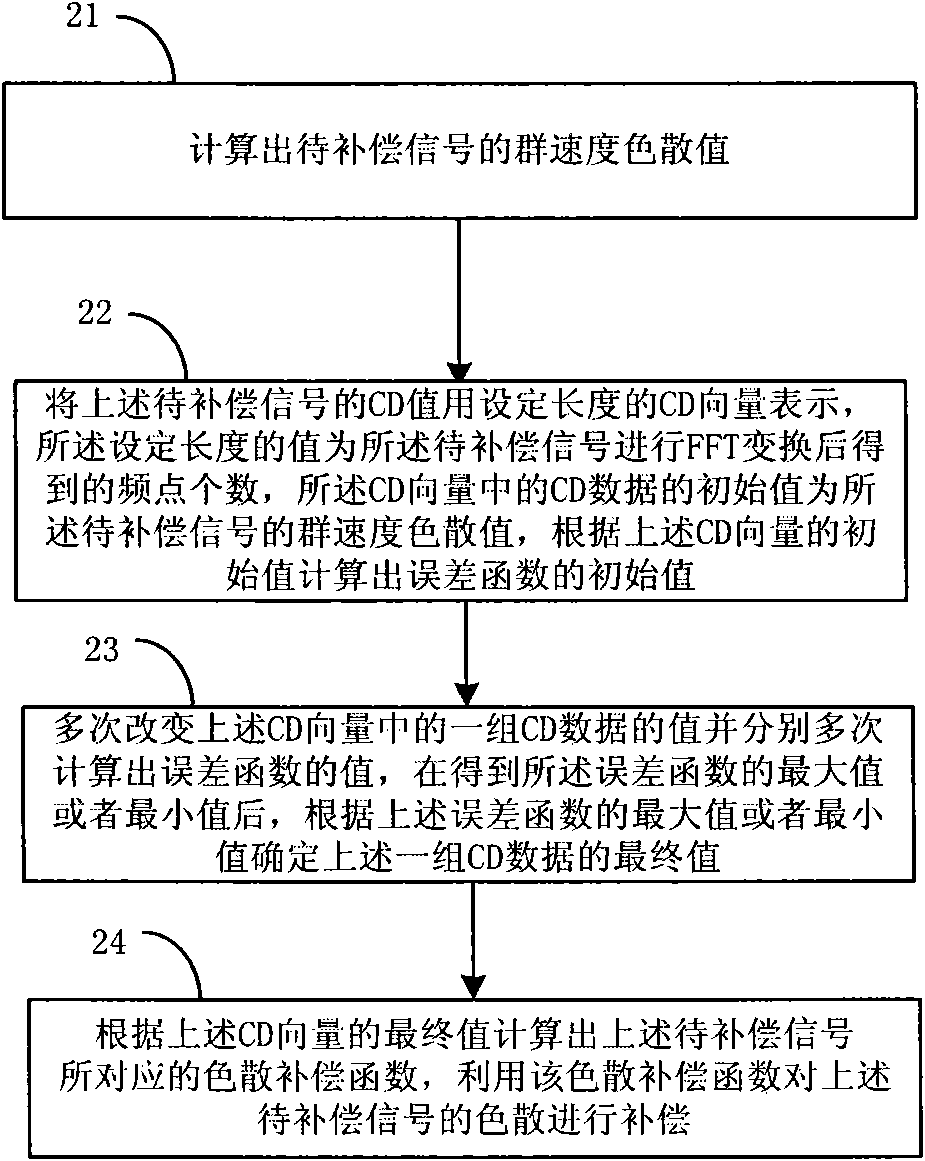
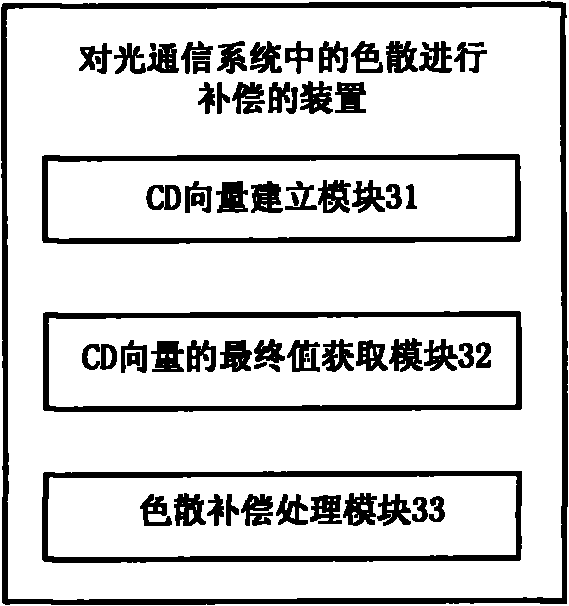
ActiveCN102142905ACompensation for Dispersion RippleCompensation for dispersionElectromagnetic transmissionFast Fourier transformCommunications system
The embodiment of the invention provides a method and a device for compensating chromatic dispersion in an optical communication system. The method comprises the following steps: representing the chromatic dispersion (CD) value of a signal to be compensated by a CD vector, wherein the CD vector is obtained after carrying out fast fourier transform (FFT) to the signal to be compensated, frequency point numbers have equal length, and the initial value of the CD data in the CD vector is a group velocity dispersion value corresponding to the signal to be compensated; according to the initial value of the CD vector, calculating the initial value of an error function corresponding to the CD vector; and according to maximum value or the minimum value of the error function, which are calculated several times, determining the final value of the CD vector so as to calculate a dispersion compensation function corresponding to the signal to be compensated. The embodiment of the invention can adapt to the scene that the CD value of each frequency component in the signal to be compensated is not equal, and dispersion ripples brought by each optical device is effectively compensated.
Owner:深圳市泽信通信息工程有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com