Method for determining linear dispersion space-time codes for receiving antenna numberless than transmitting antenna number
A technology of receiving antenna and transmitting antenna, applied in the field of channel coding, can solve problems such as loss of application value, and achieve the effect of good coding performance and simple coding design complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] System model:
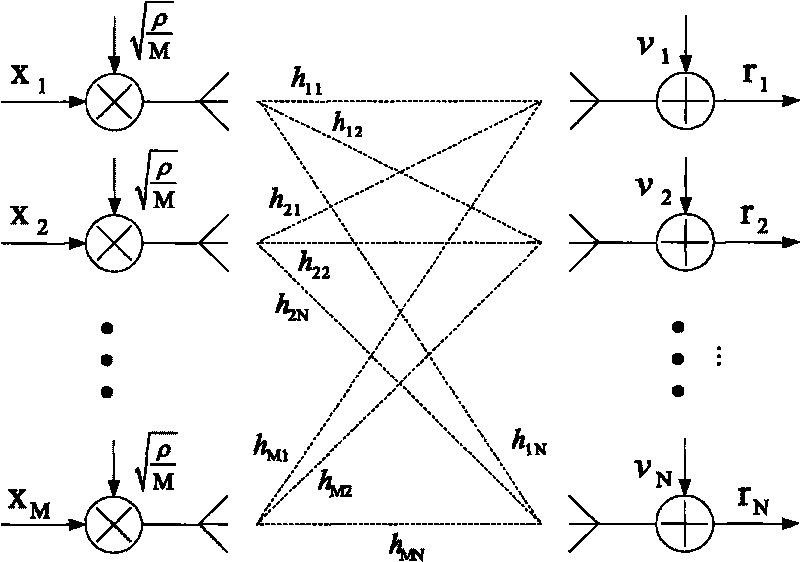
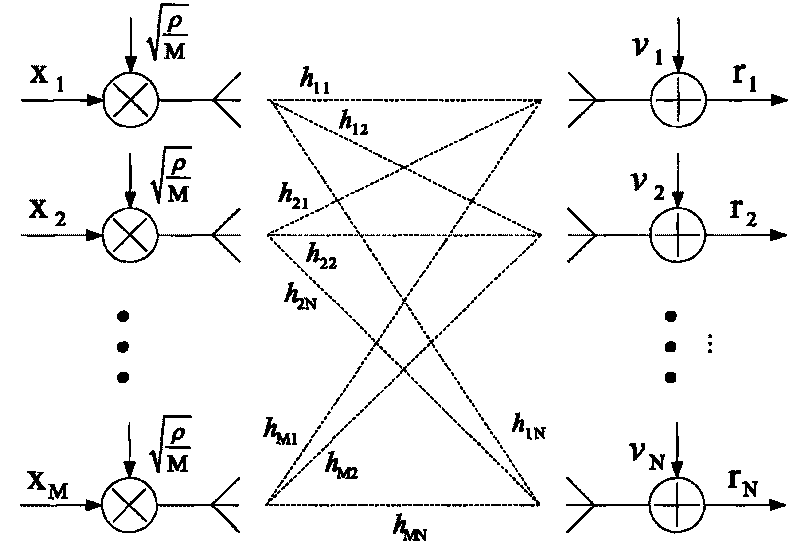
[0026] Suppose the number of transmitting antennas is M, the number of receiving antennas is N, (N≤M) MIMO channel model see figure 1 .
[0027] Consider the case of T transmission time periods (that is, the number of times the channel is used is T), and the input-output relationship is expressed as
[0028] R=HX+v (1)
[0029] Among them, R is an N×T receiving matrix, which means that the N-dimensional column vector is received for a total of T times at each time. H is an NxM channel matrix which is flat (ie constant) over time T. X is an M×T transmission matrix, which means that M-dimensional column vectors are transmitted through M transmission antennas at each time, and T times are transmitted in total. V is an N×T complex Gaussian noise matrix.
[0030] X from the q-dimensional uncoded vector s=[s 1 ...s q ] T Encoding comes, q=min(MT, NT), when N≤M, when q=NT its encoding process is
[0031] X = Σ ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com