Patents
Literature
74results about How to "High operating freedom" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Vehicle and traffic system
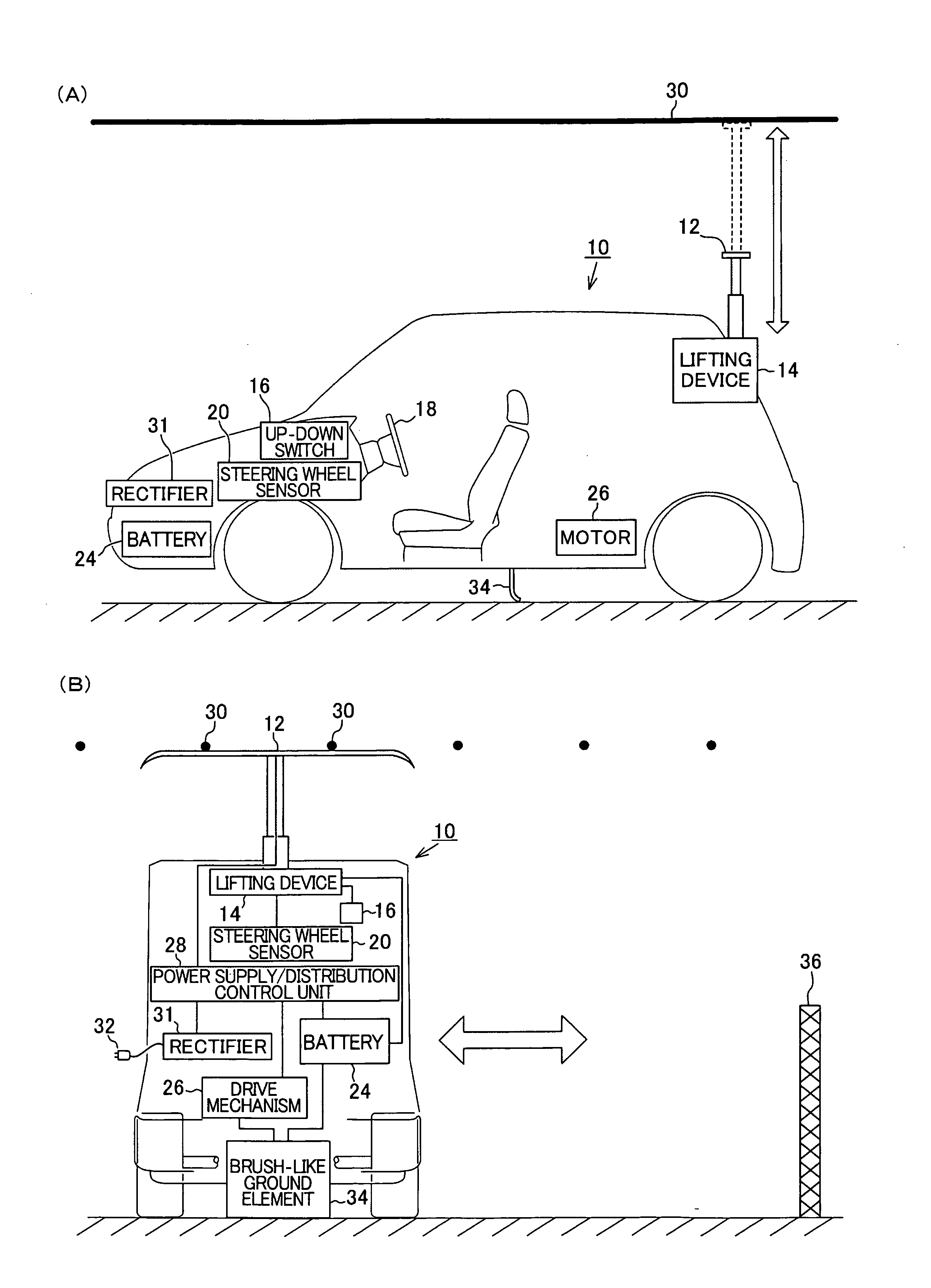
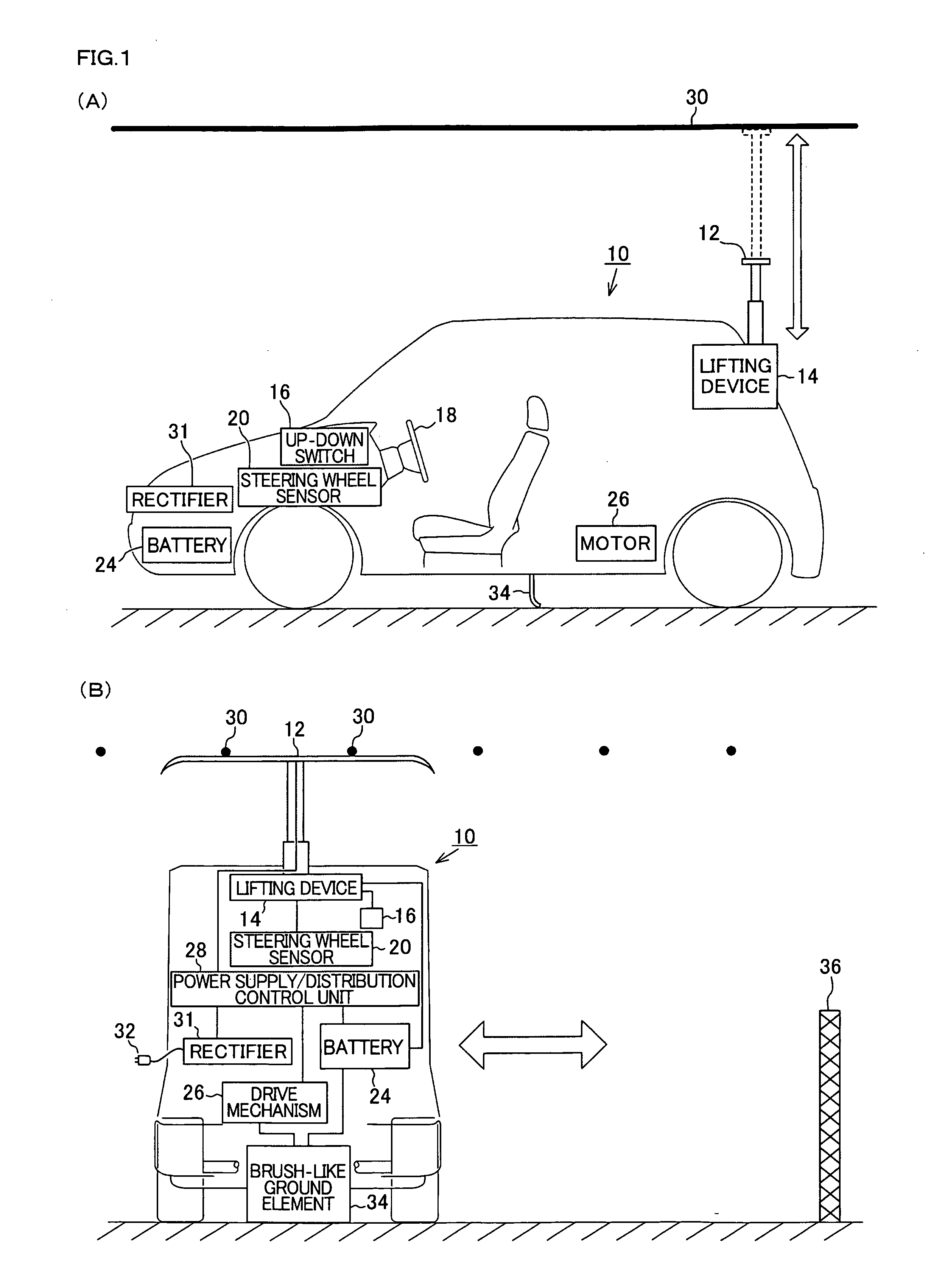
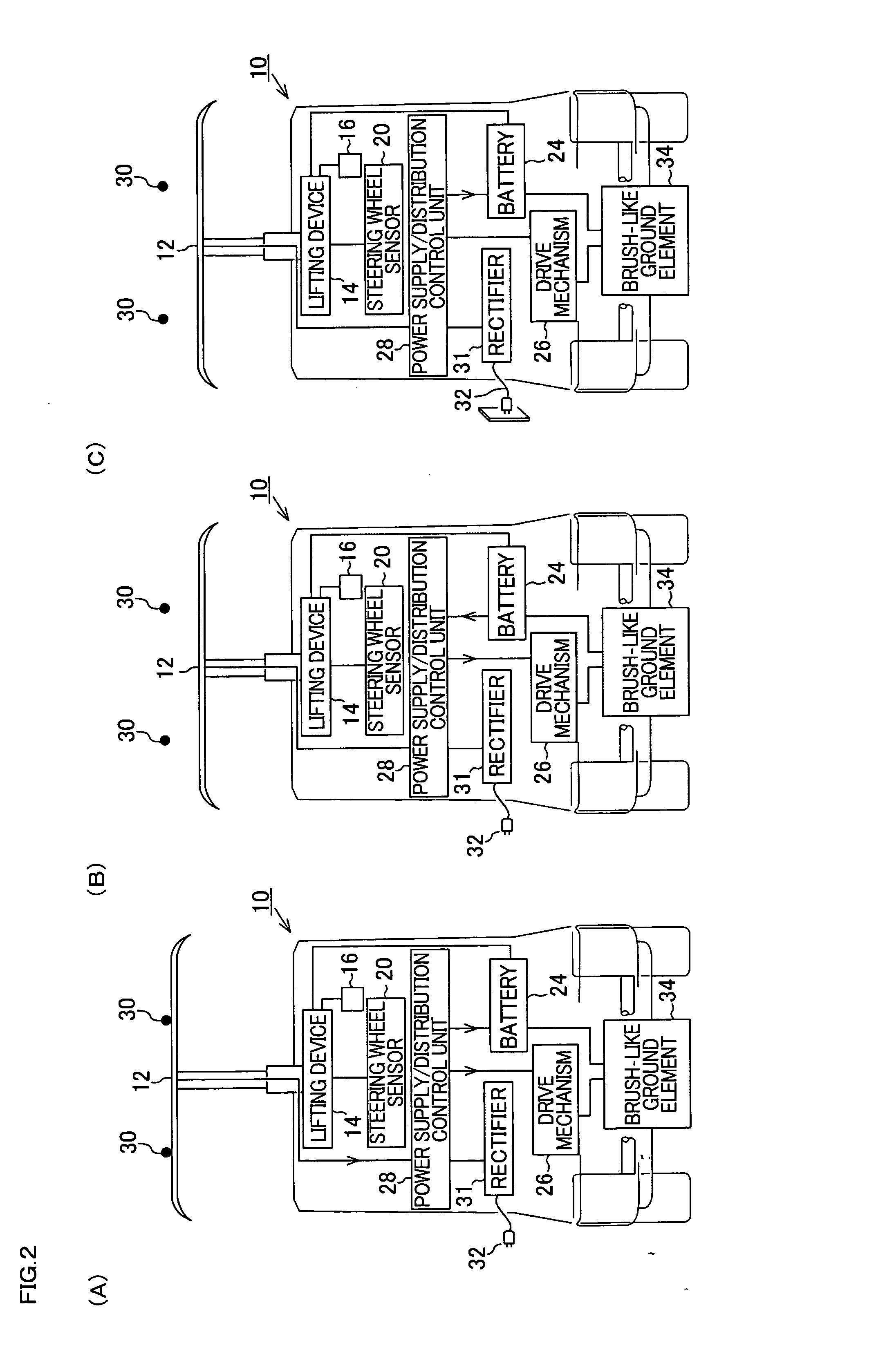
InactiveUS20100121509A1High operating freedomExcellent eco-friendly effectRail devicesRoadwaysElectrical batteryElectric power
Provided are a vehicle having high degree of operation freedom due to electric power being able to be supplied to the vehicle during its travel and due to the vehicle being able to drive on normal roads, and a traffic system. A large number of overhead lines are arranged over a road. An extendable electric power collector is provided at the rear of the vehicle, and a battery and a drive mechanism are mounted on the vehicle. When the power collector is in contact with an overhead line, electric power supplied from the overhead line is supplied to the battery to charge it and electric power is supplied also to the drive mechanism. When the vehicle travel on a normal road having no such overhead lines, electric power is supplied from the battery to the drive mechanism.
Owner:TAKESHIMA NAGAE +1
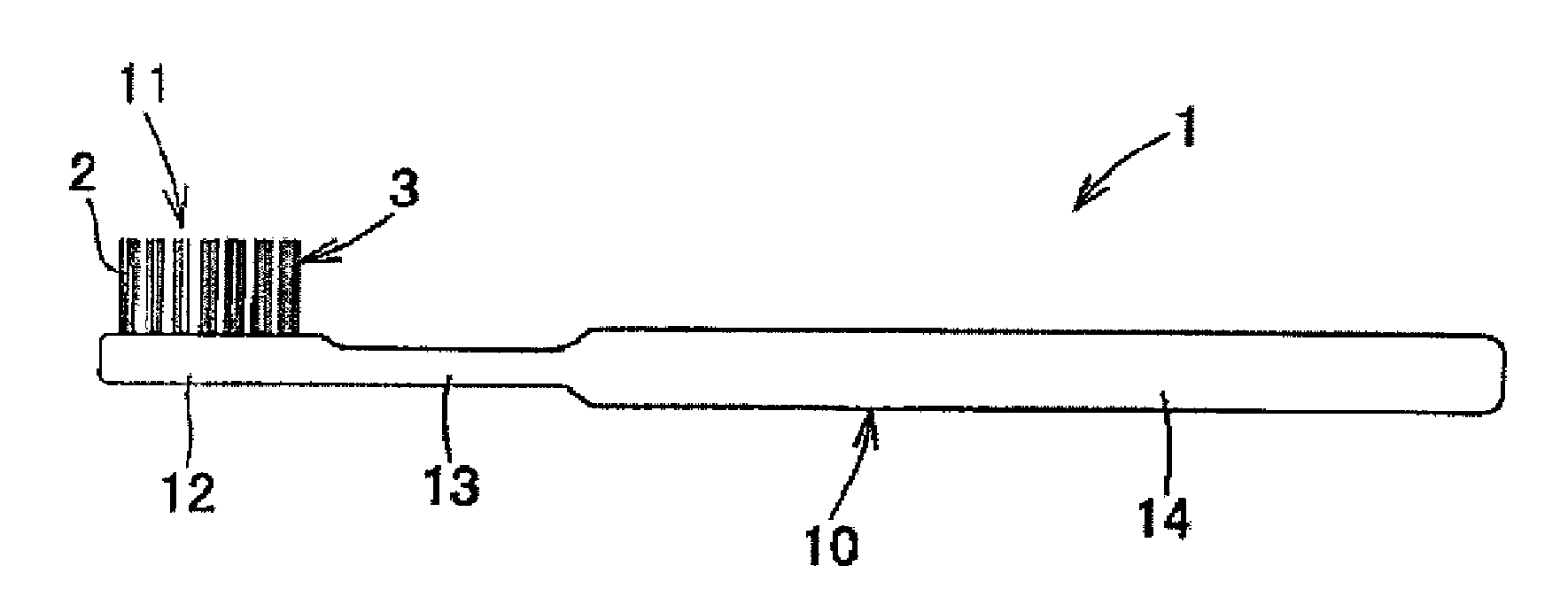
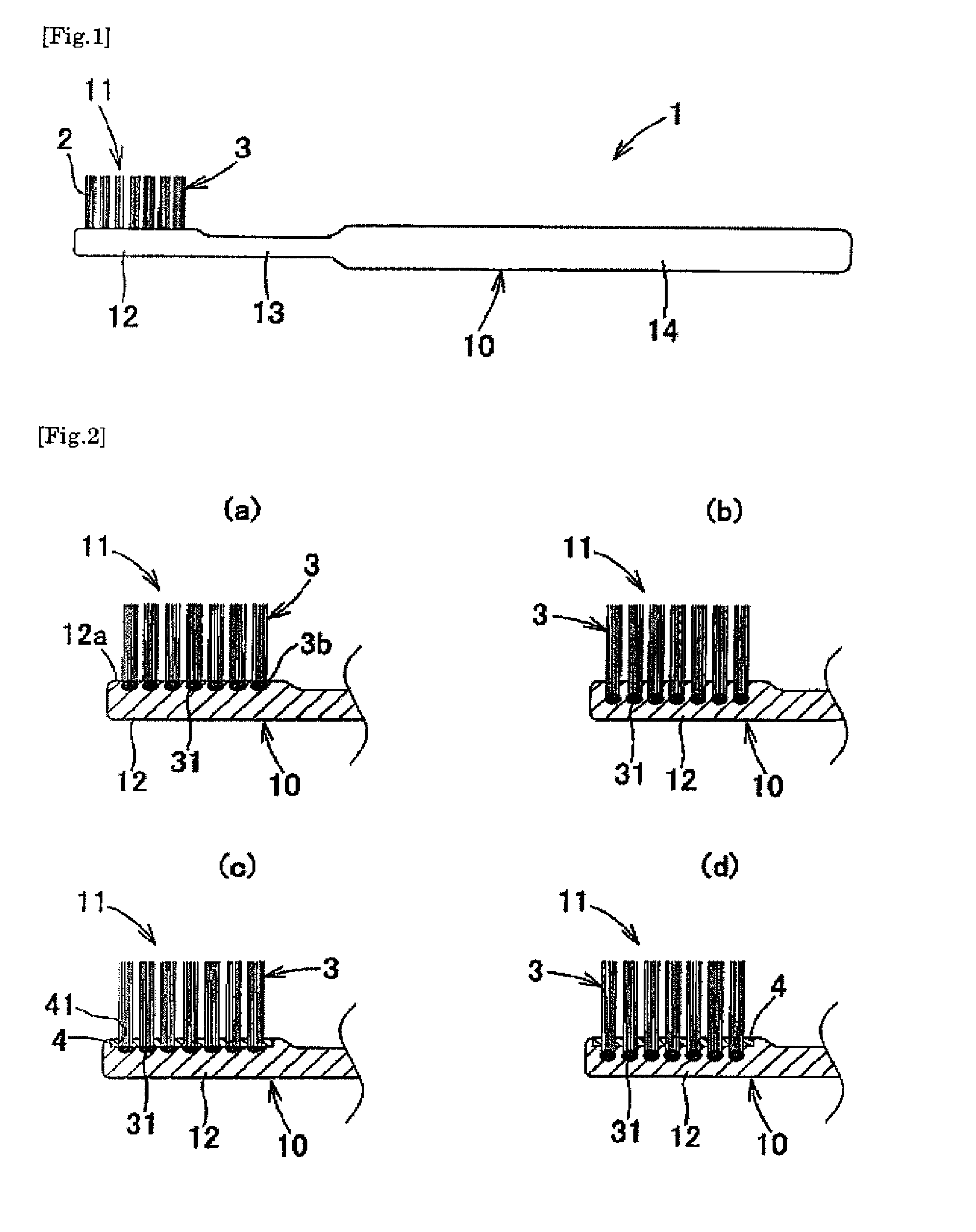
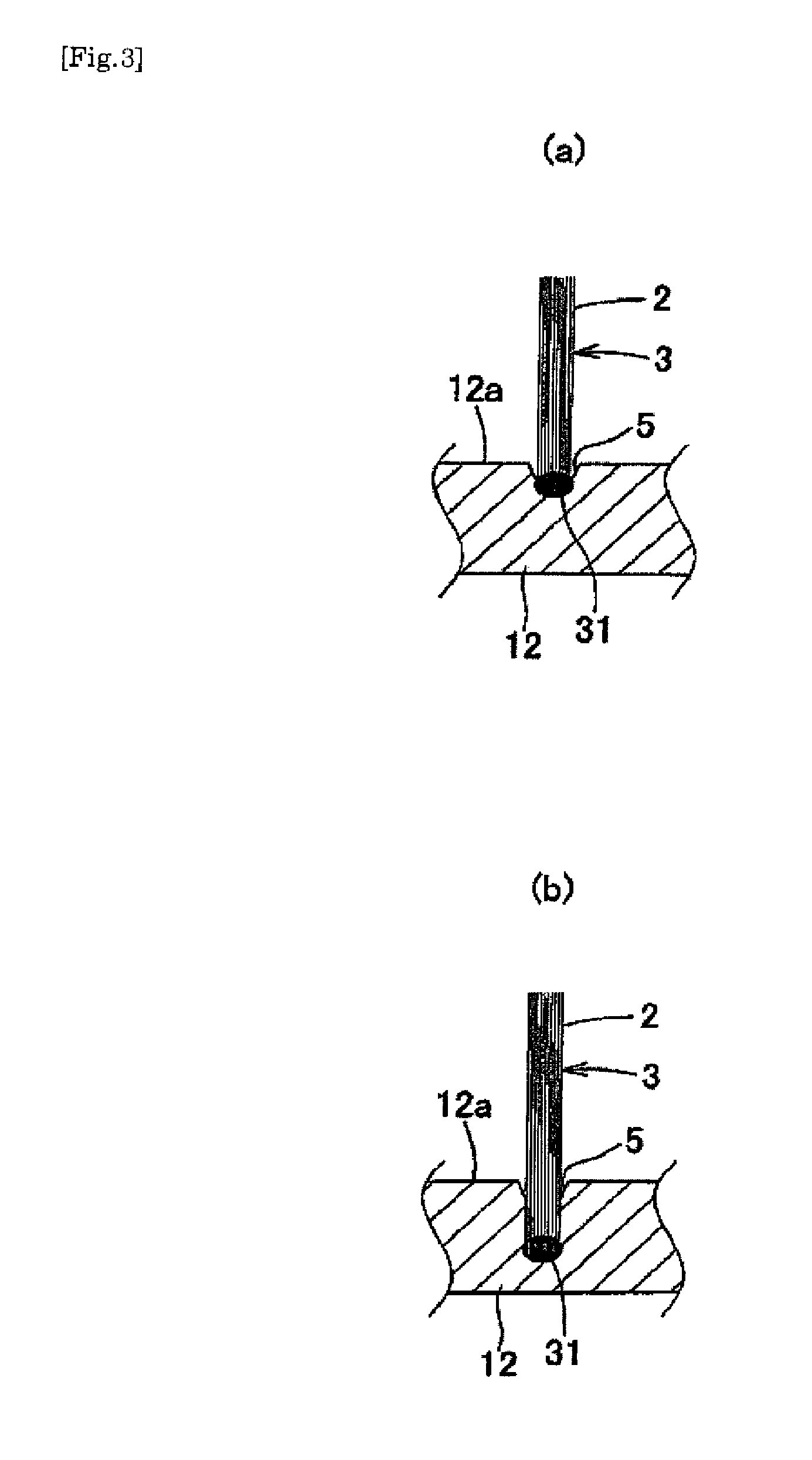
Toothbrush
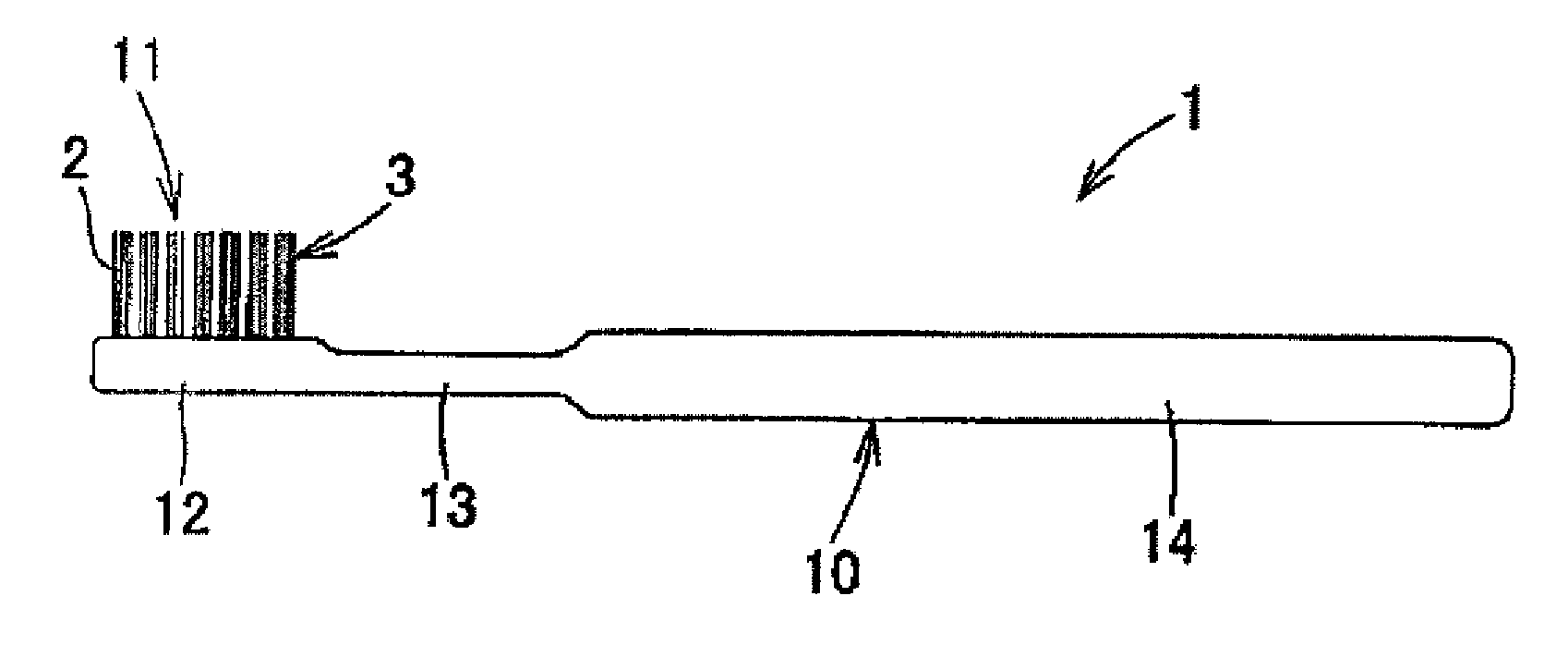
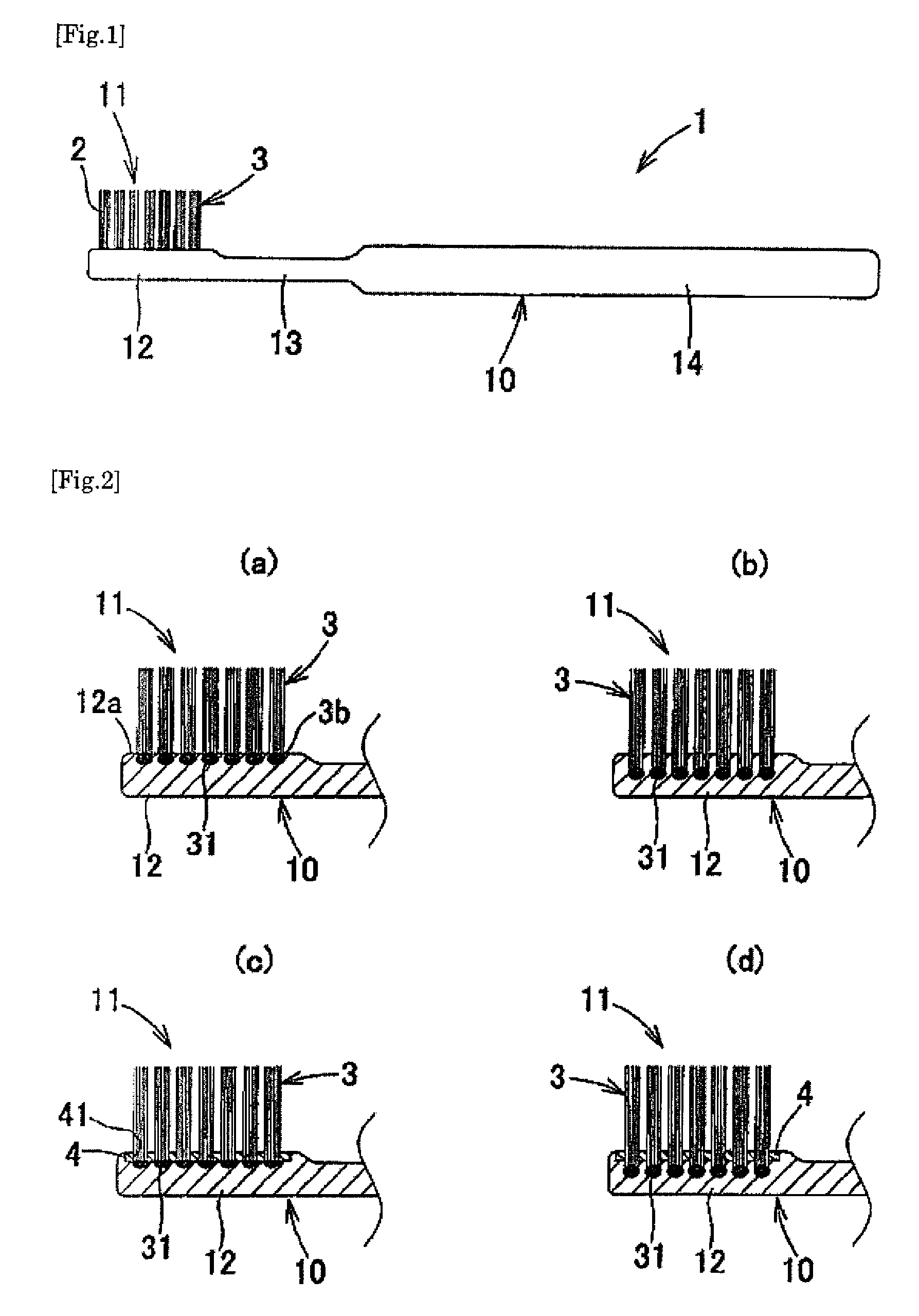
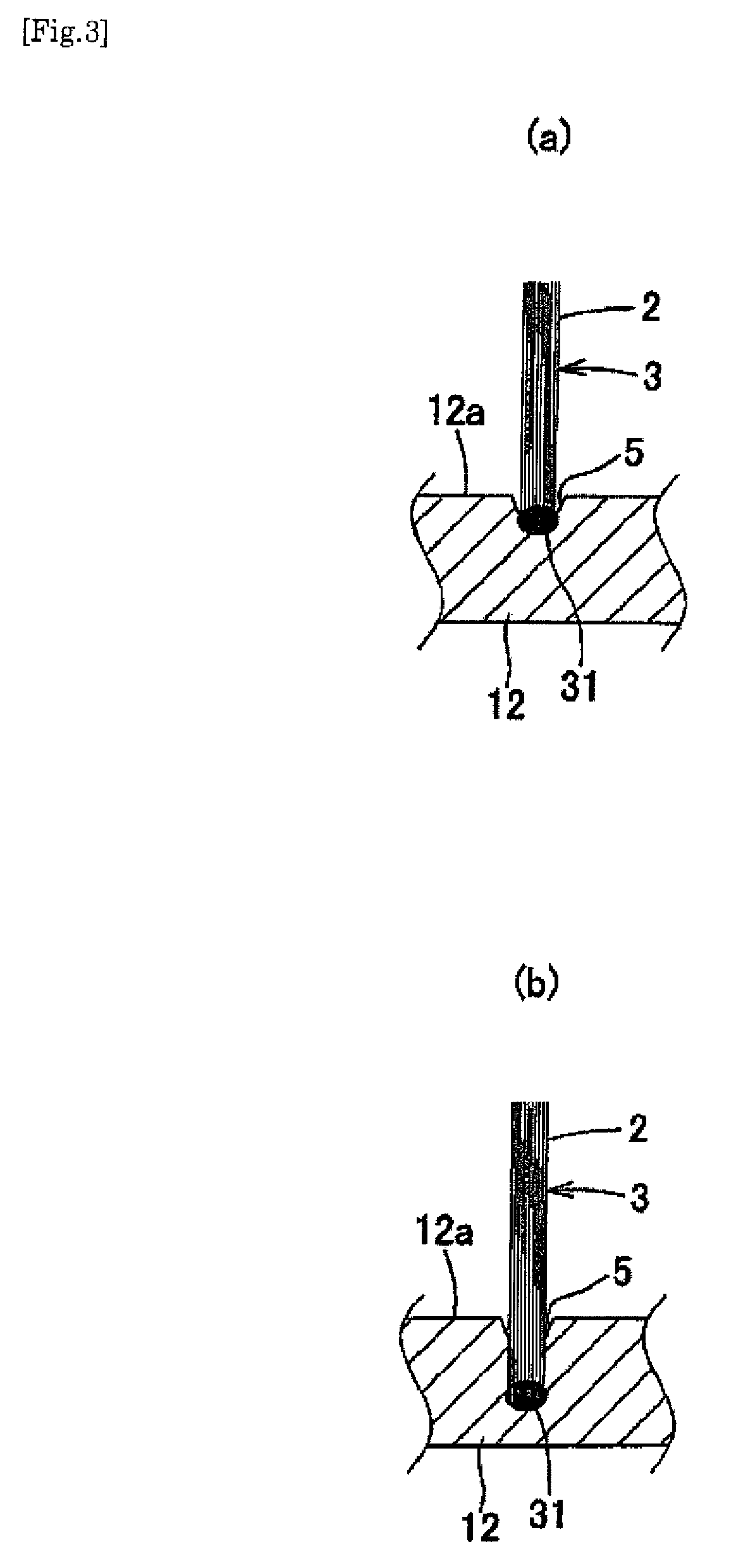
InactiveUS20090013488A1Easy to useHighly attractive appearanceBristleDomestic articlesBristleEngineering
A toothbrush which comprises a brush main body made of a synthetic resin and having a bristle base and bristles made of a thermoplastic resin which have been fusion-bonded to the bristle base to constitute a bristled part, wherein the bristles constituting the bristled part at least partly comprise: tapered bristles which are bristles having split free ends, the split free ends having been tapered beforehand; tapered bristles which have a sectional shape having a core-sheath structure or islands in a sea structure; or tapered bristles in each of which a core bristle comprising a core or island part has been formed beforehand so as to be exposed at the free end. The toothbrush has excellent suitability for bristle insertion into narrow parts. It is highly effective in removing dental plaque and cleaning the teeth. It is highly easy to use in the oral cavity. It further has a highly attractive appearance.
Owner:SUNSTAR INC
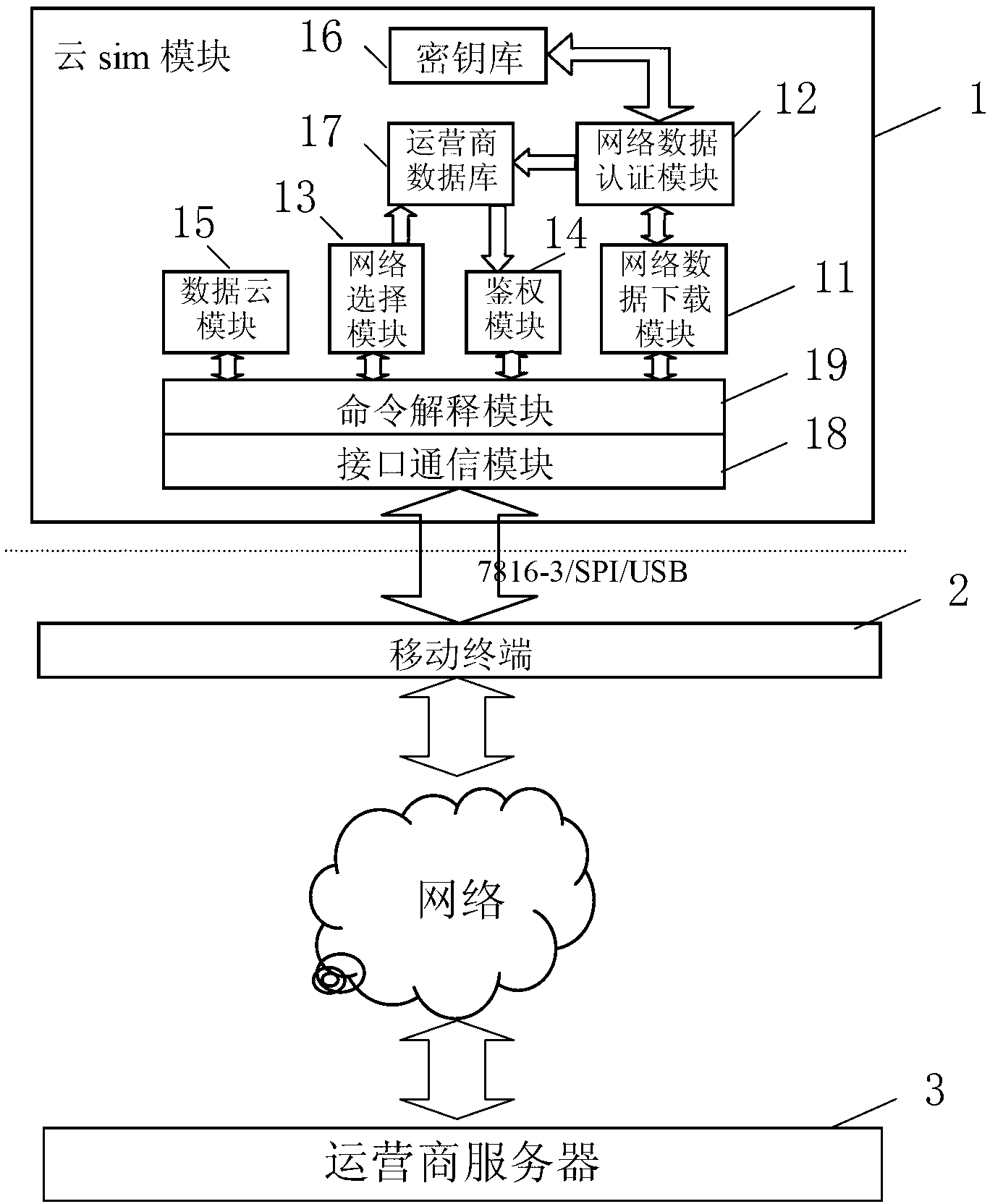
Cloud SIM (subscriber identity module) capable of freely downloading network data
InactiveCN103079193AHigh operating freedomImprove business efficiencySecurity arrangementNetwork data managementNetwork dataSubscriber identity module
The invention discloses a cloud SIM (subscriber identity module) capable of freely downloading network data. The cloud SIM comprises a network data downloading module, a key store, an operator database, a network data authentication module, an authentication module, a network selection module, a command interpretation module and an interface communication module. According to the scheme provided by the invention, subscribers can freely download network authentication data and network configuration data of an operator server, so the subscribers can use different operator networks through the same SIM card, the operation freedom degree of the subscribers is greatly improved, and in addition, the subscribers can download different network authentication data for handling different services, so the service handling efficiency of the subscribers is improved. Therefore, the cloud SIM provided by the invention has the advantages that different operator networks can be replaced for communication, so convenience is brought for users.
Owner:EASTCOMPEACE TECH
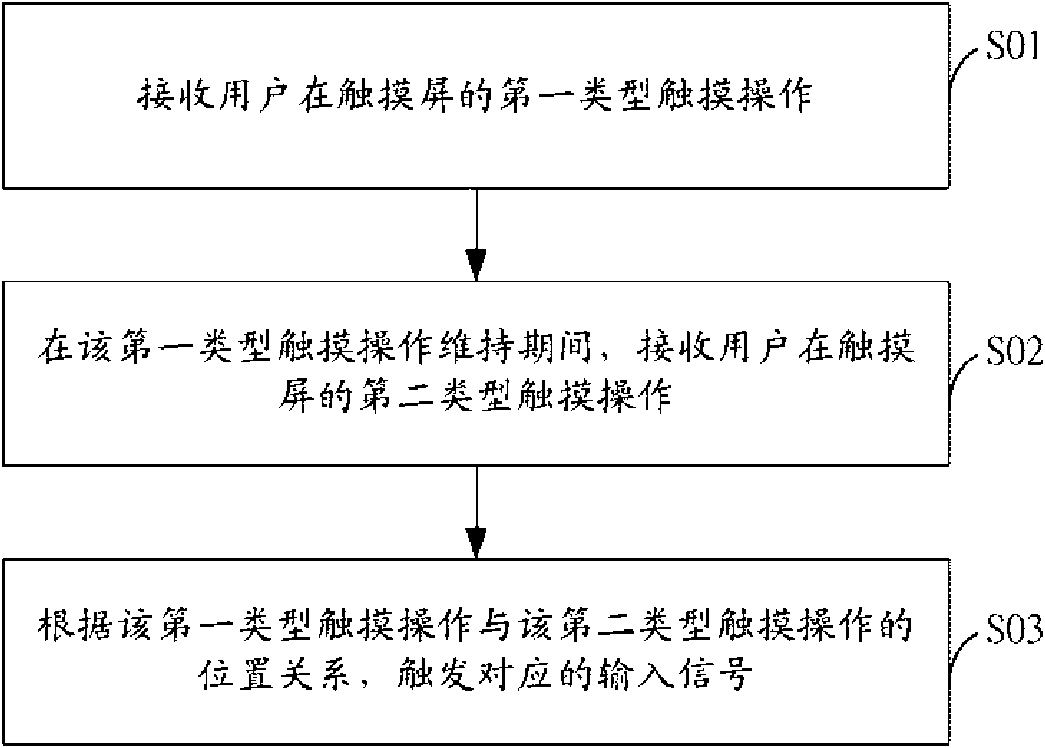
Input method based on touch screen
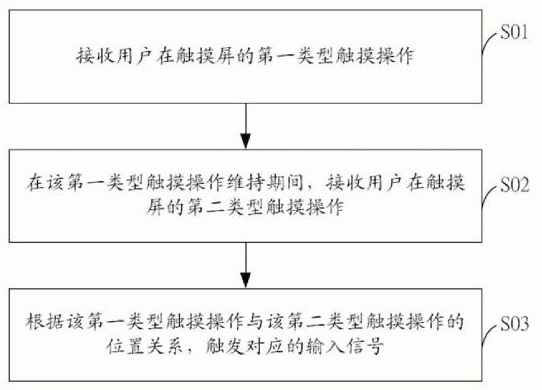
InactiveCN101847055AHigh operating freedomImprove operational efficiencyInput/output processes for data processingSignal onTouchscreen
The invention provides an input method based on a touch screen, which is convenient to use. The method comprises the following steps of: receiving a first type touch operation of user on a touch screen; during the maintenance of the first type touch operation, receiving a second type touch operation of the user on the touch screen; and trigging a corresponding input signal according to the position relationship between the first type touch operation and the second type touch operation. The input method based on the touch screen allows the user to input signals in any area of the touch screen, without identifying a specific area of a corresponding input signal on the touch screen, and therefore, the degree of freedom of operation is high. Moreover, the input method based on the touch screen can associate various position relationships between the first type touch operation and the second type touch operation as traditional bottom-layer menu input, so as to avoid complex menu operation and improve the operation efficiency.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
Vehicle-mounted multi-angle electronic device bracket
ActiveCN104999942AHigh operating freedomAvoid issues that could pose a potential safety threat to passengersArm restsIn vehiclePersonal computer
The invention relates to a vehicle-mounted multi-angle electronic device bracket. The vehicle-mounted multi-angle electronic device bracket comprises a bracket body and a rotary gear mechanism, wherein the bracket body is connected to an in-vehicle supporting structure in a front and back sliding manner through a sliding rail, and the rotary gear mechanism is contained and supported in the bracket body and connected with the sliding rail so that the bracket body can be connected to the in-vehicle supporting structure in the manner that the bracket body rotates leftwards and rightwards around the rotary gear mechanism. The operation freedom degree of the bracket body is increased, the front, back, left and right positions of the bracket body can be freely adjusted by a passenger according to the actual use condition, and the potential safety threat likely to happen to the passenger in the opening state is avoided. Meanwhile, supports are conveniently provided for light electronic devices such as a tablet personal computer and a mobile phone.
Owner:YANFENG ADIENT SEATING CO LTD
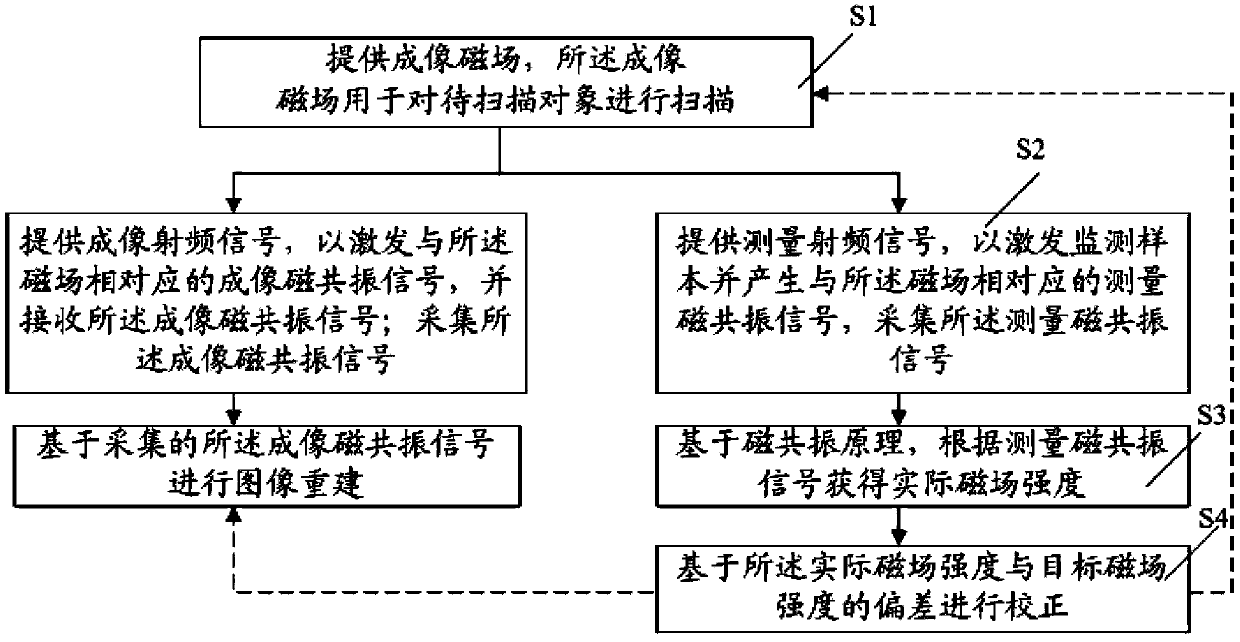
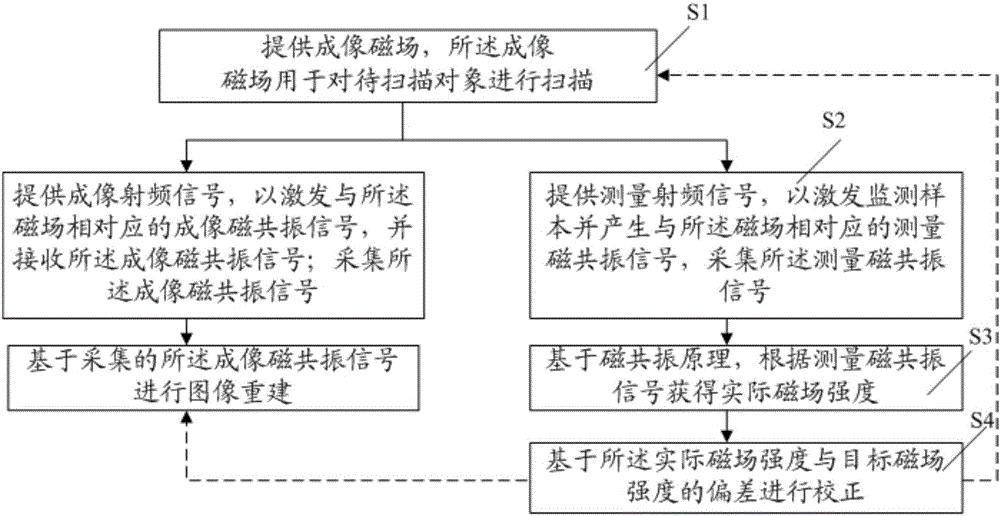
Method of measuring and correcting imaging magnetic field in magnetic resonance device and system
ActiveCN104181480ANon-ideal compensationImprove image qualityMagnetic measurementsElectrical measurementsResonanceMri image
A method and a system for measuring and calibrating an imaging magnetic field in a magnetic resonance apparatus are provided. The method includes: providing the imaging magnetic field, where the imaging magnetic field is adapted for scanning an object; sampling a signal corresponding to the imaging magnetic field; processing the signal to obtain an actual magnetic field intensity; and calibrating based on a difference between the actual magnetic field intensity and a target magnetic field intensity. The system includes: a magnetic component, adapted for scanning an object to be imaged; a sampling unit, adapted for sampling a signal corresponding to the imaging magnetic field; a processing unit, adapted for processing the signal to obtain an actual magnetic field intensity; a calibration unit, adapted for calibrating based on a difference between the actual magnetic field intensity and a target magnetic field intensity; and a control unit, adapted for controlling the system.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE CO LTD
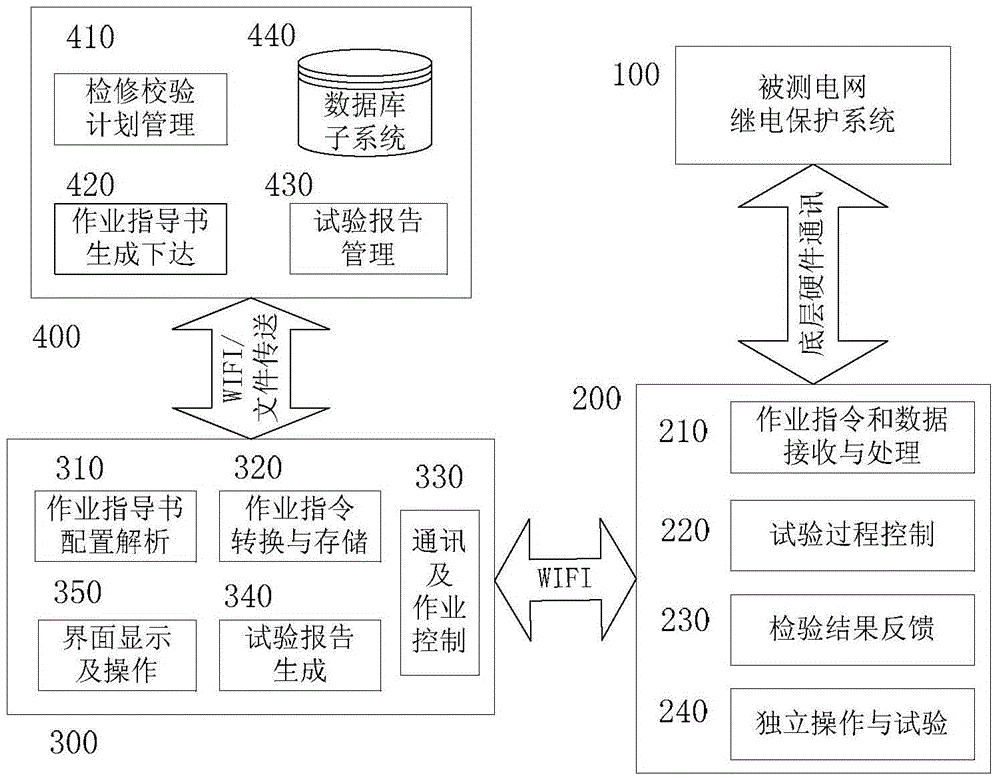
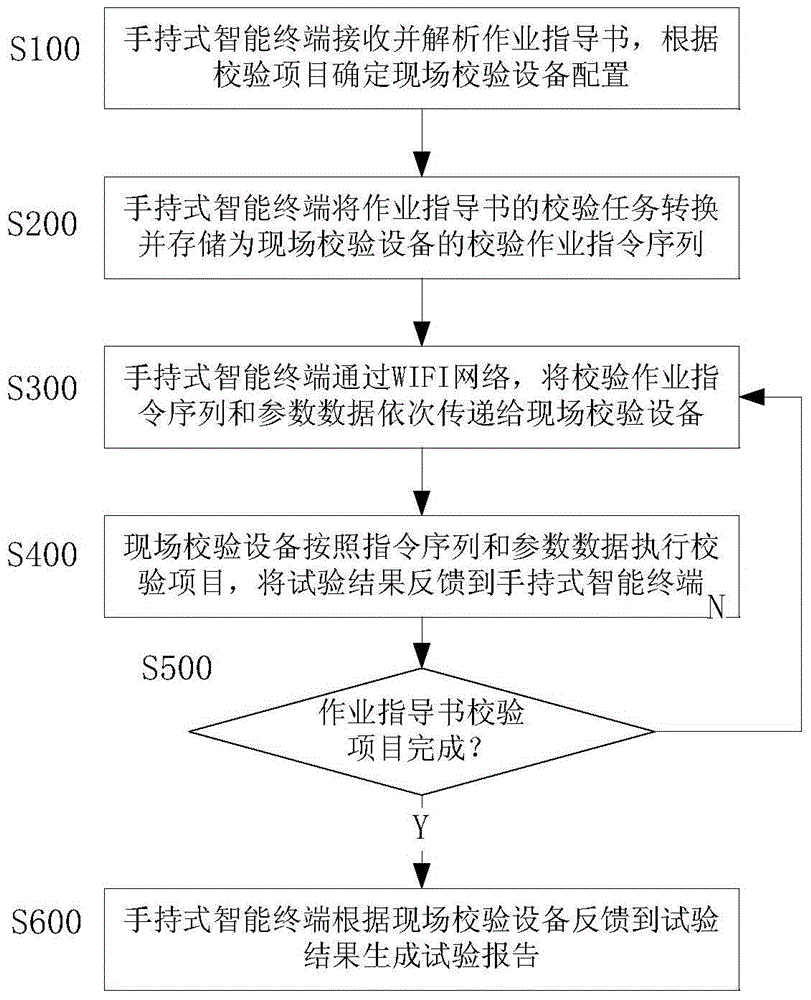
Mobile Internet-based relay protection verification device
ActiveCN105069587AIntelligently complete on-site operationsEfficiently complete on-site operationsResourcesElectric power systemMaterial resources
The utility model belongs to the technical field of emergency protection circuit devices of power grid systems and relates to a mobile Internet-based relay protection verification device, in particular, an integrated verification device used for power grid relay protection verification field operation and information management. The mobile Internet-based relay protection verification device includes a handheld intelligent terminal which is connected with a field verification device through the mobile Internet; the field verification device includes an operation instruction and data receiving processing module, a test process control module, a verification result feedback module and a verification test function module; the handheld intelligent terminal includes an operation guide book configuration parsing module, an operation instruction conversion and storage module, a communication and operation control module, a test report generation module and an interface display and operation module. According to the mobile Internet-based relay protection verification device, the handheld intelligent terminal and field verification device relay protection test instrument interaction integrated test system is adopted, and therefore, filed operation can be completed efficiently, conveniently and intelligently, and complex work of field operation can be optimized, and manpower and material resources can be saved for a power system, and a guarantee can be provided for safe and stable operation of power equipment.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ELECTRIC POWER CO
Imaging magnetic field measurement and correction system for magnetic resonance device
ActiveCN106443535ANon-ideal compensationImprove image qualityElectrical measurementsMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsResonanceMri image
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Teaching rocker, robot teaching method and robot control system
ActiveCN109927056AEasy to controlRealize blind operationProgramme-controlled manipulatorControl systemSimulation
Owner:合肥欣奕华智能机器股份有限公司
Injection device with means for signalling the time since the last injection
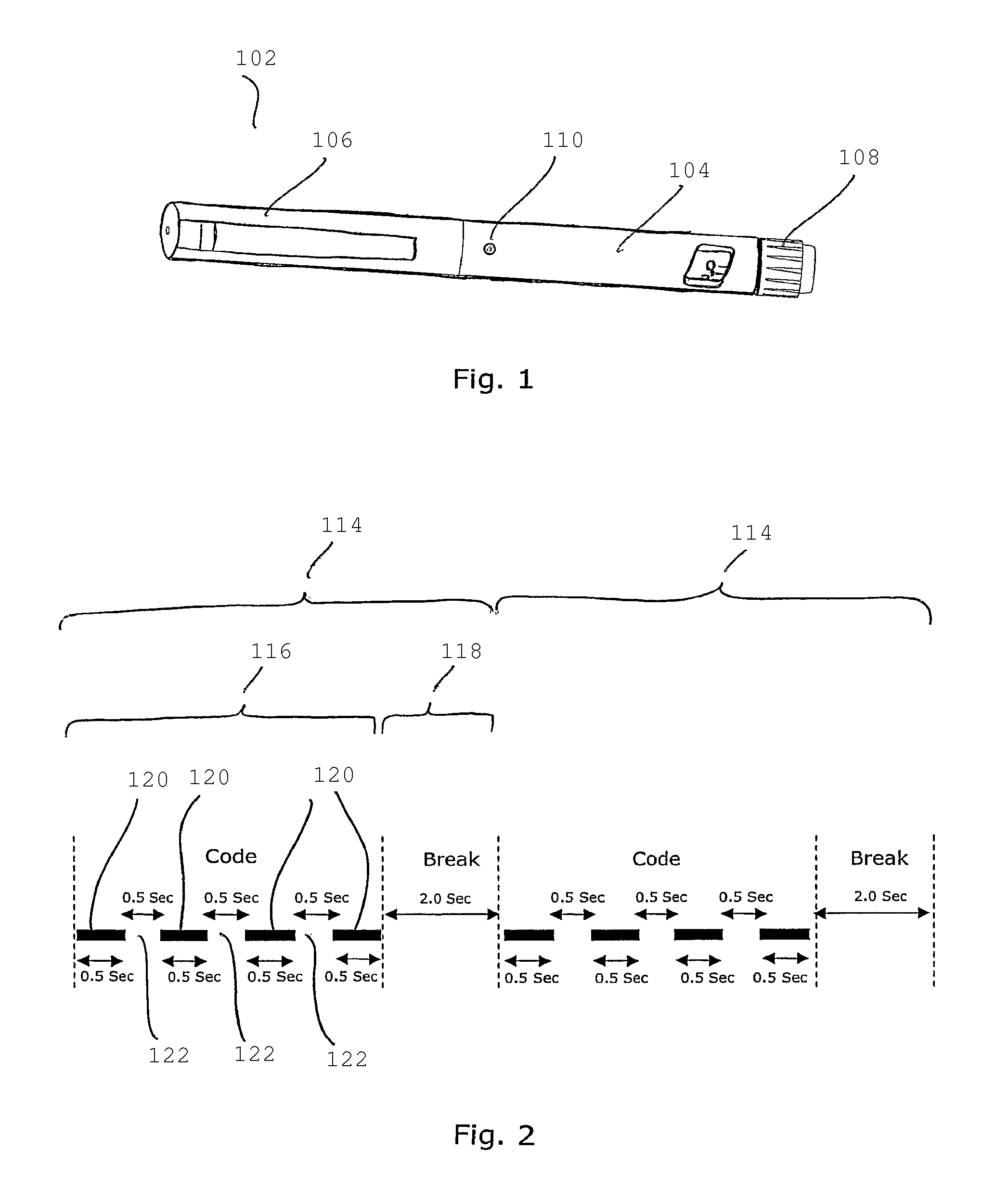
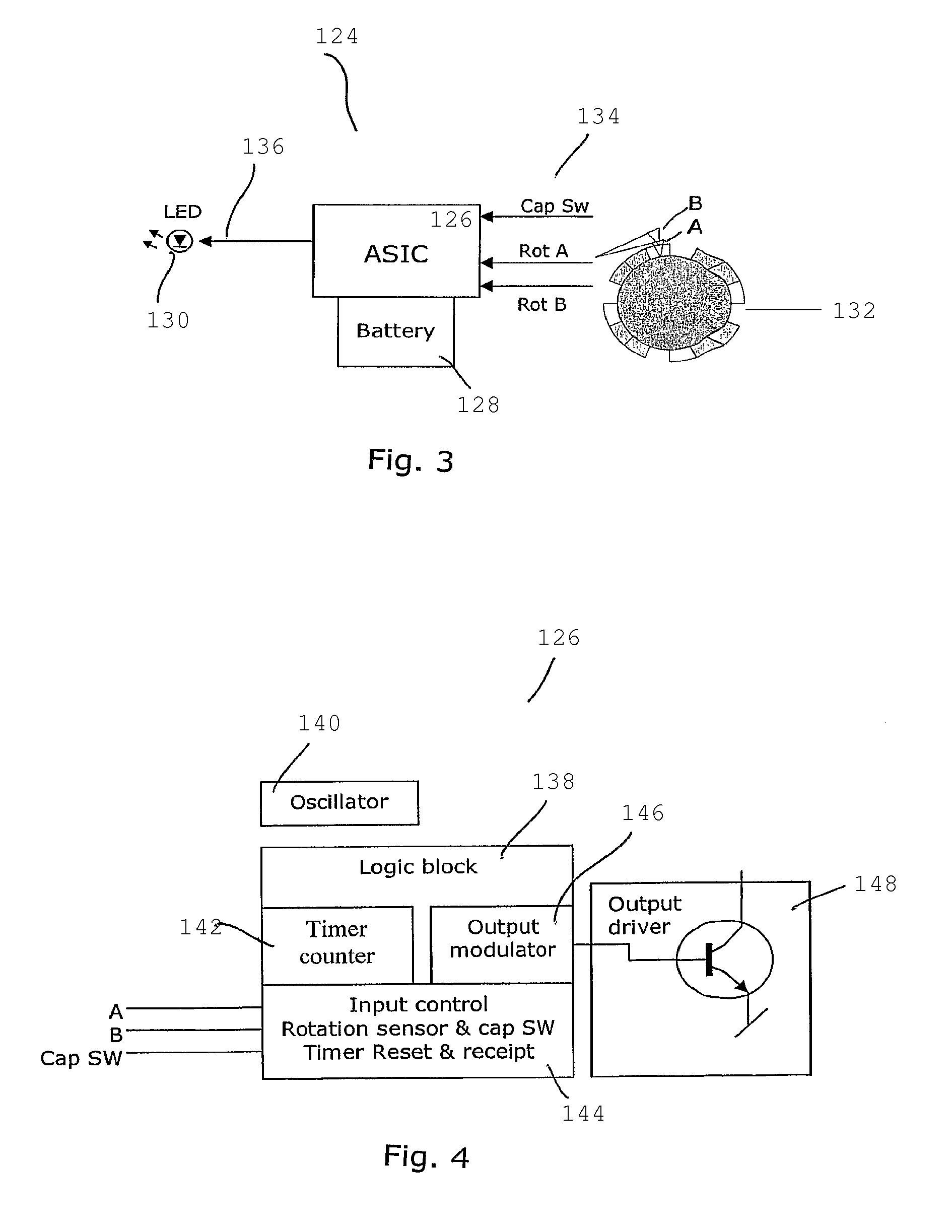
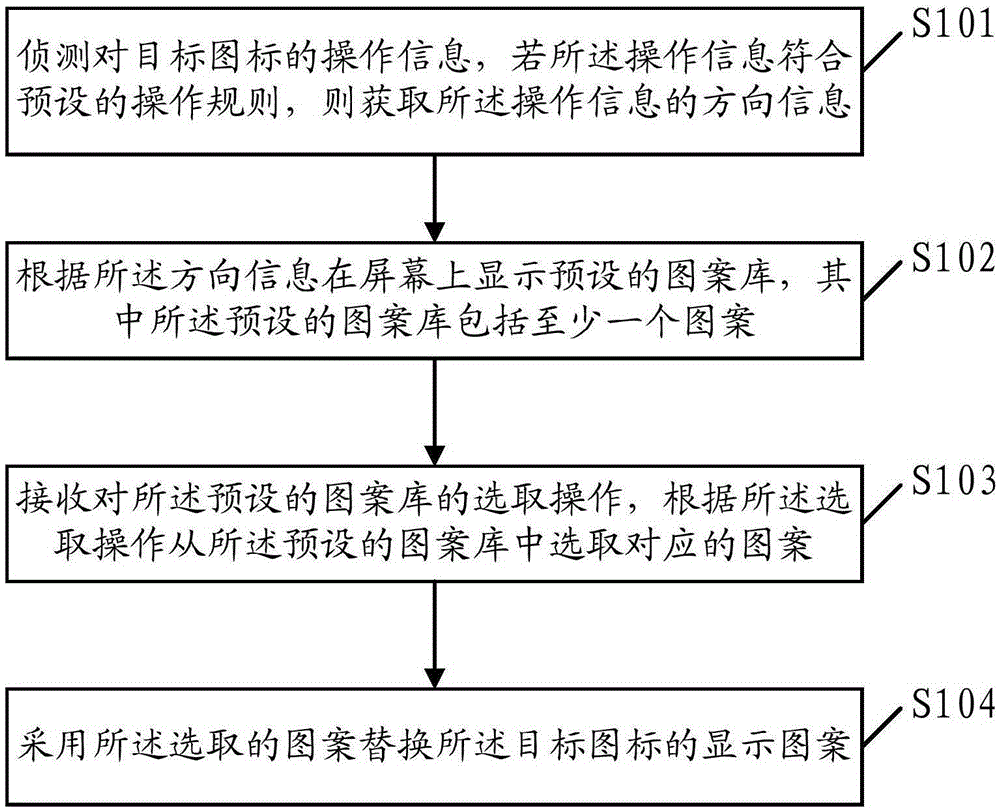
InactiveUS9314573B2High operating freedomPrevent insertionAmpoule syringesMedical devicesEngineeringLight signal
The present Invention relates to an injection device capable of emitting a flashing light signal indicating the time elapsed since last ejection and / or the size of the last ejected dosage and / or a return signal indicating the operable state of the device and / or a time out signal indicating when the pen can be removed after ejecting of a dosage. The injection device comprises an electronic control circuit comprising: a sensor unit arranged to detect the occurrence of an ejection of a drug from the injection device; a timer for determining an approximate time elapsed since last ejection; a signal emitting device being able to emit a signal, the signal emitting device being controllable by the electric control circuit, so as to emit a time signal that varies with the time elapsed since last ejection.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
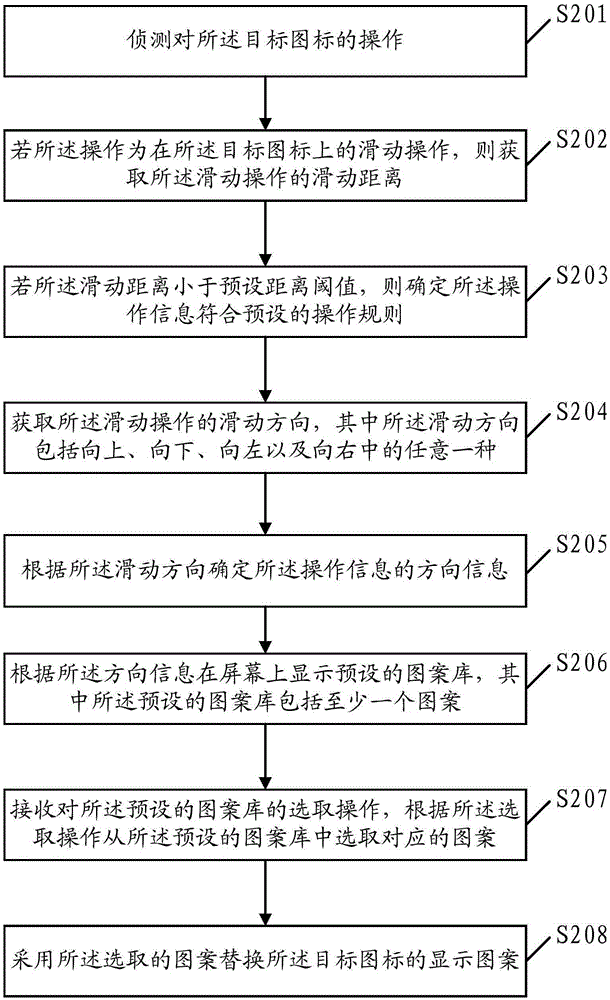
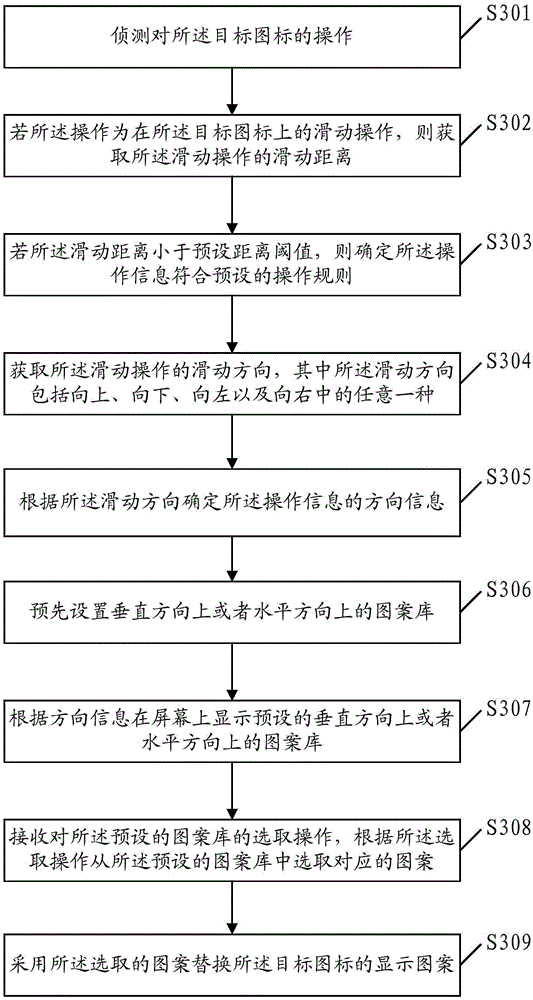
Icon processing method and apparatus
InactiveCN105260081AHigh operating freedomImprove operating experienceInput/output processes for data processingDegrees of freedomDirection information
Embodiments of the present invention disclose an icon processing method and apparatus. The icon processing method comprises: detecting information of operation on a target icon, and if the operation information complies with preset operation rules, then acquiring direction information of the operation information; according to the direction information, displaying a preset pattern library on a screen, wherein the preset pattern library comprises at least one pattern; receiving a selective operation on the preset pattern library and selecting a corresponding pattern from the preset pattern library according to the selective operation; and using the selected pattern to replace a display pattern of the target icon. According to the method and the apparatus provided by the present invention, users can not only select which icon to be replaced by themselves but also further select replaced display patterns, the operation is simple and convenient, a greater operation degree of freedom is offered to the users, and operation experience of the users is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI DROI TECH CO LTD
Multicore-fiber-based optical motor and micropump
InactiveCN102183818AEasy to fixEasy to modifyCladded optical fibreRadiation/particle handlingMicropumpMulticore fiber
The invention provides a multicore-fiber-based optical motor and a micropump. The optical motor comprises multicore fibers with wedge-shaped front end and a micro rotor; the micro rotor comprises two sphere bodies, a rotating shaft and wings, wherein the wings are positioned on the rotating shaft, and the two sphere bodies are arranged at two ends of the rotating shaft to form the micro rotor with a symmetrical structure; and the multicore fiber with the wedge-shaped front end comprises two pairs of shaft fixing fiber cores and driving fiber cores, wherein the shaft fixing fiber cores are symmetrical at two sides and play a shaft fixing role in forming dual optical tweezers for capturing the sphere bodies of the micro rotor, and the driving fiber cores emit outgoing light to drive the wings of the micro rotor; two V-shaped grooves and dual U-shaped runners are machined on a glass substrate; the wedge-shaped multicore fiber is fixed in the V-shaped grooves; the micro rotor is placed ata U-shaped bending part of the dual U-shaped runners; and the micro rotor is driven by the multicore fiber with the wedge-shaped front end to rotate to drive fluid to flow to form the micropump. Compared with the traditional optical drive device, the optical motor has the advantages of small size, light weight, simple structure, low cost, easiness in operation, saved operation space, and the likeand can be widely applied to biological and chemical fields.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
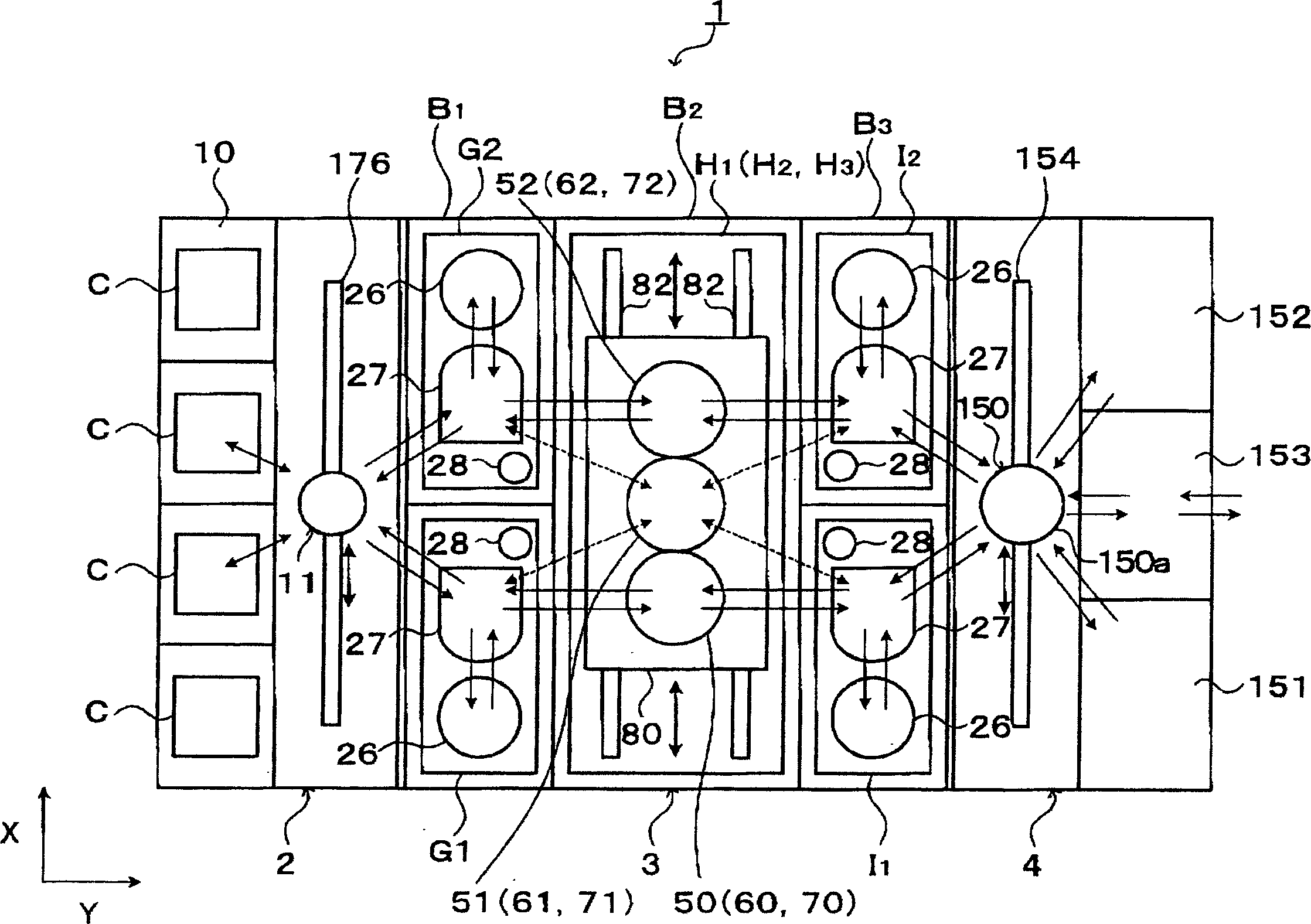
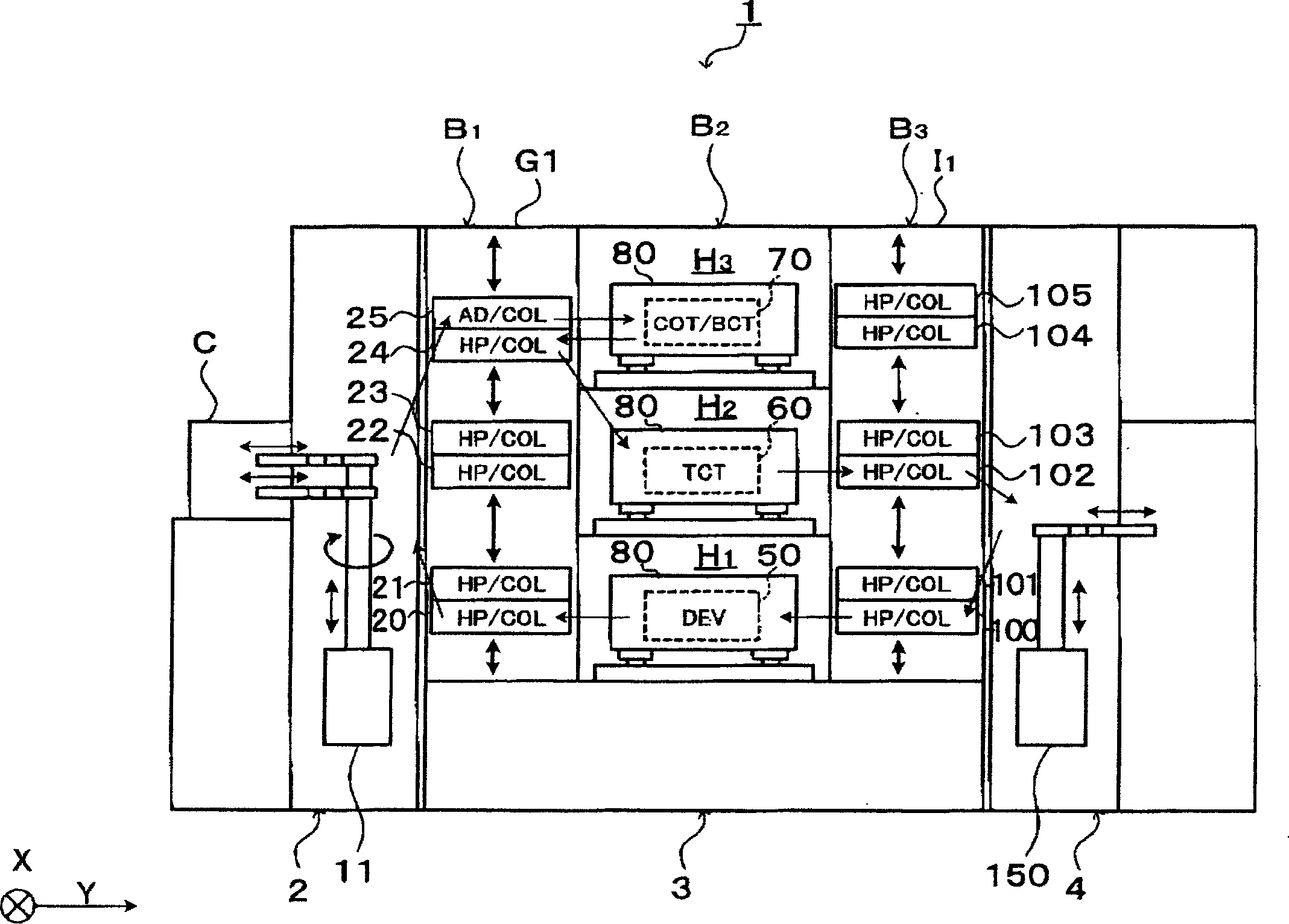
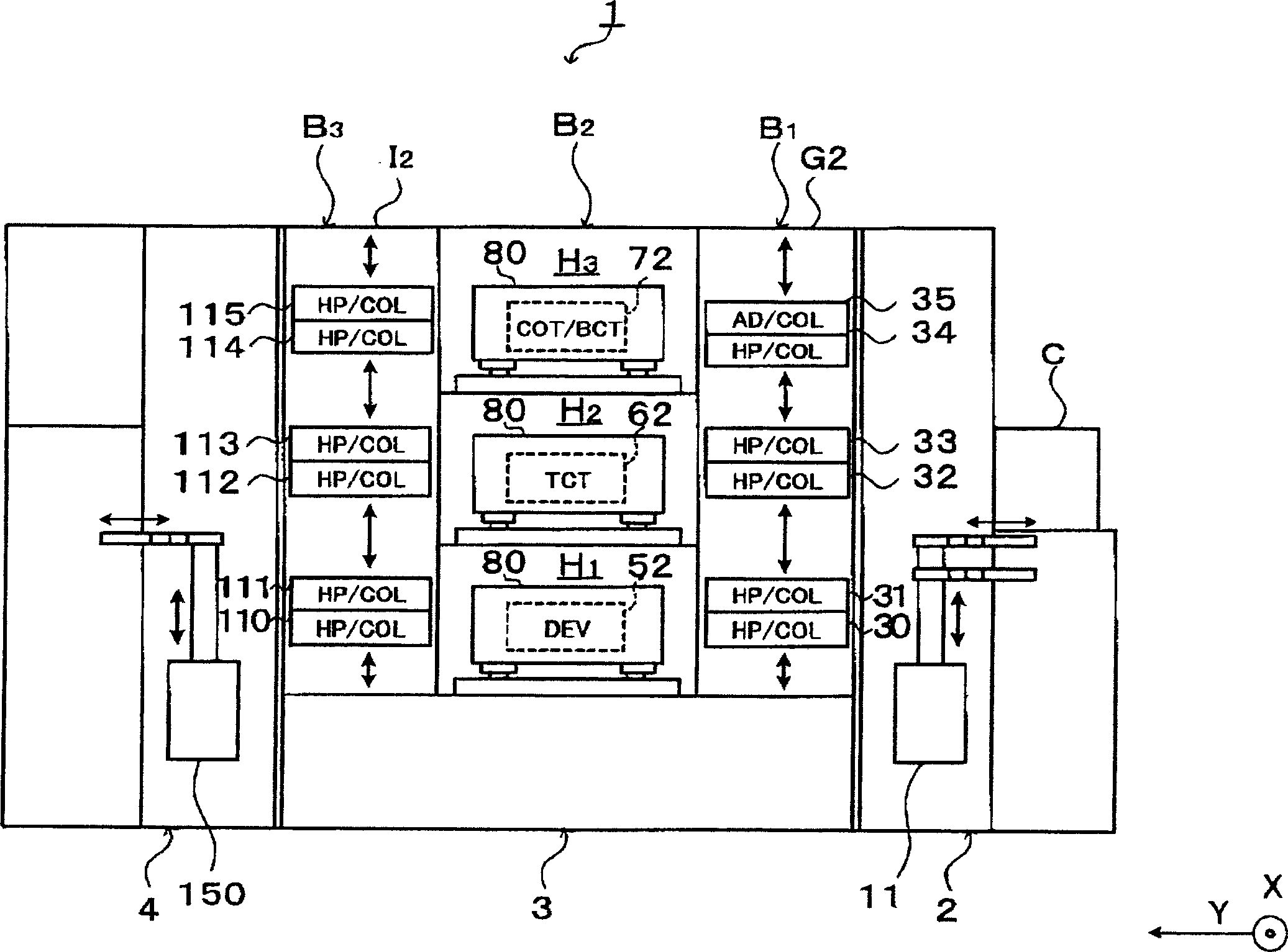
Substrate carrier
InactiveCN1905151AHigh operating freedomEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharge manipulationElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Toothbrush
Owner:SUNSTAR INC
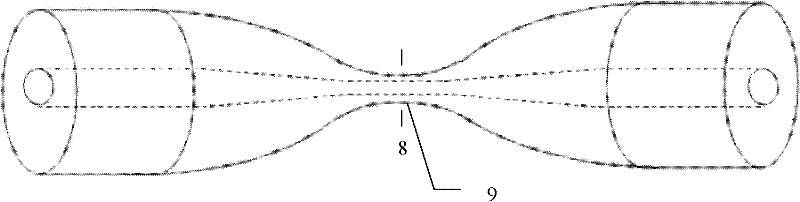
Microscopic particle rotator of bidirectional conical optical fibers
InactiveCN102231292AEasy to modifyAvoid damageCladded optical fibreRadiation/particle handlingOptical radiationFiber
The invention provides a microscopic particle rotator of bidirectional conical optical fibers, comprising two conical optical fibers and two-body microscopic particles, wherein the conical optical fibers are formed by fused biconical taper; the two conical optical fibers are arranged horizontally; the conical ends are staggeredly arranged at intervals oppositely; the opposite ends of the two conical optical fibers are connected with an optical source respectively; the two-body microscopic particles comprise a driving layer, a stirring layer ad a connecting post respectively; the driving layeris integrated with the stirring layer into a whole by the connecting post; the two-body microscopic particles are arranged in the gap which is formed by staggering the two conical ends of the two conical optical fibers; the conical optical fibers cause transmission lights in fiber cores to transmit a cladding layer and form an evanescent field on the cladding layer; the generated optical radiation forces act the driving layers of the two-body microscopic particles, so that the driving layers of the two-body microscopic particles rotate to drive the stirring layers of the two-body microscopic particles. The rotator is small in volume, light in weight, simple in structure, low in price, easy to operate, large in operating range and high in stirring efficiency; by using the rotator, the solvent activity can be avoided being damaged due to direct contact; and the rotator can be applied to biology and chemistry microflow systems.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
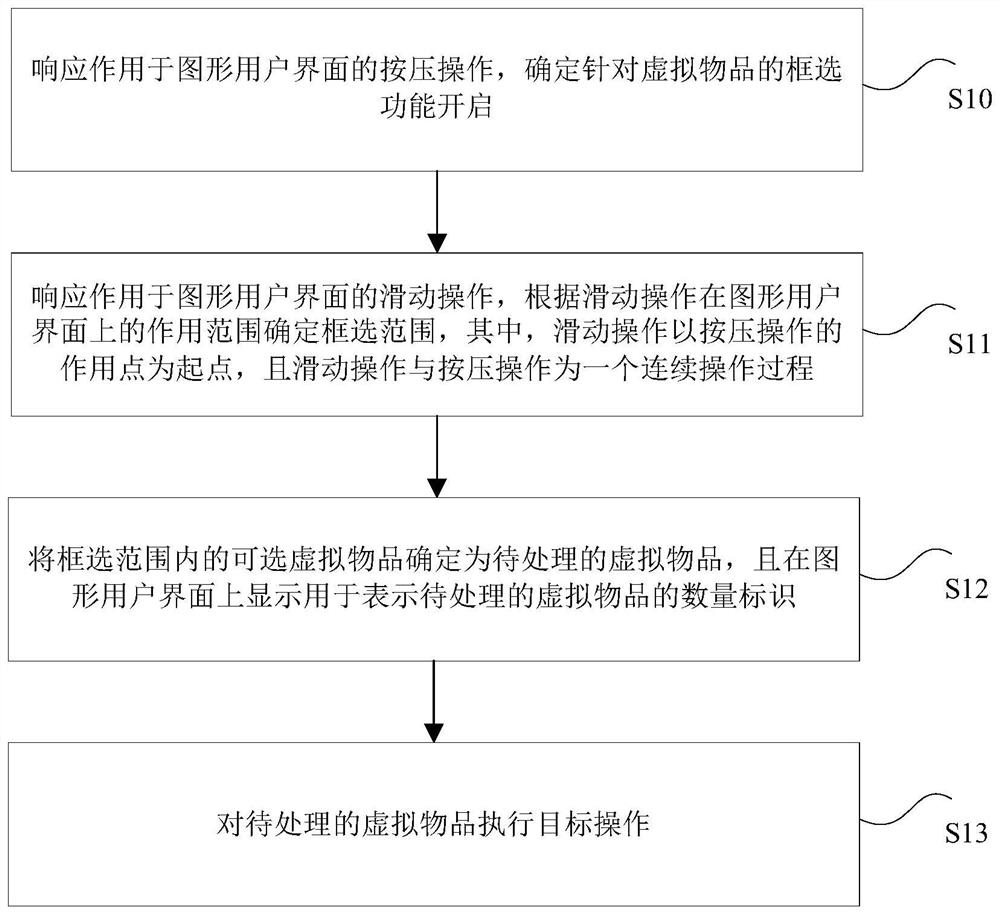
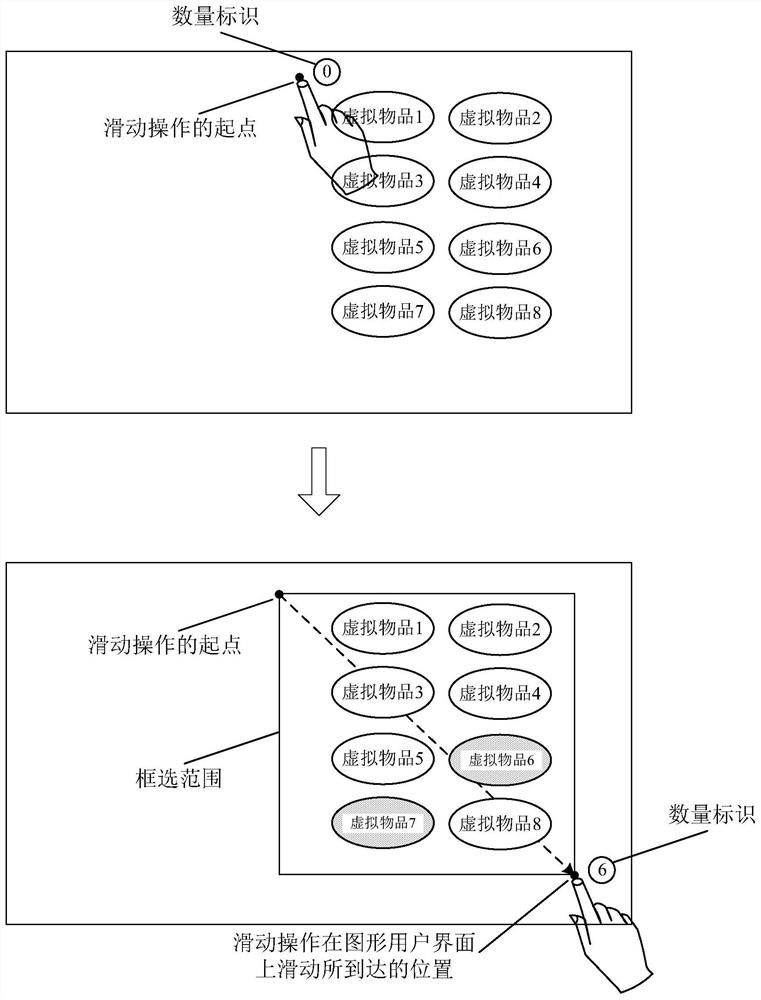
Virtual article processing method and device, storage medium and electronic device
PendingCN112190922AReduce operational complexityHigh operating freedomVideo gamesGraphical user interfaceGame player
The invention discloses a virtual article processing method and device, a storage medium and an electronic device. The method comprises the following steps: in response to a pressing operation on a graphical user interface, determining that a box selection function for a virtual article is enabled; in response to a sliding operation on the graphical user interface, determining a frame selection range according to an action range of the sliding operation on the graphical user interface, wherein the sliding operation takes an action point of the pressing operation as a starting point, and the sliding operation and the pressing operation form a continuous operation process; determining selectable virtual articles in the frame selection range as to-be-processed virtual articles, and displayinga quantity identifier used for representing the to-be-processed virtual articles on the graphical user interface; and executing a target operation on the to-be-processed virtual articles. The technical scheme of the invention overcomes the technical problem of influence on the game experience of a game player due to the fact that the operation complexity of the game player is easily increased orthe operation freedom degree of the game player is easily reduced in a mode of picking up the virtual articles in a game scene.
Owner:NETEASE (HANGZHOU) NETWORK CO LTD
Bidirectional curved surface core optical fiber micro-particle rotator
InactiveCN102183820AEasy to modifyAvoid damageCladded optical fibreRadiation/particle handlingFiberHigh density
The invention provides a bidirectional curved surface core optical fiber micro-particle rotator, which comprises two curved single-core optical fibers and micro-particles, wherein the curved single-core optical fibers are single-core optical fibers which can make an evanescent field on the surfaces of fiber cores transmit a cladding and of which the fiber cores on curved parts at least are close to the surface of the cladding; opposite ends of the two curved optical fibers are connected with a light source respectively; the two curved single-core optical fibers are symmetrically arranged and have the same curved radian; the micro-particles are positioned at a symmetrically central position of the two curved single-core optical fibers; and the micro-particles have a cylindrical upper body which is made of low-density materials and a helical bottom which is made of high-density materials and is provided with a plurality of wings. The invention has the advantages that: the rotator is small in volume, light in weight, simple in structure, low in cost, easy to operate, easy to package and fix, and the like, and the rotator is conveniently and manually operated. Moreover, the phenomenon of burning the micro-particles due to over-high power and the damage to solvent activity due to direct contact can be avoided, and the rotator has a wide application prospect in fields of biology and chemistry.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Portable electronic terminal retaining tool
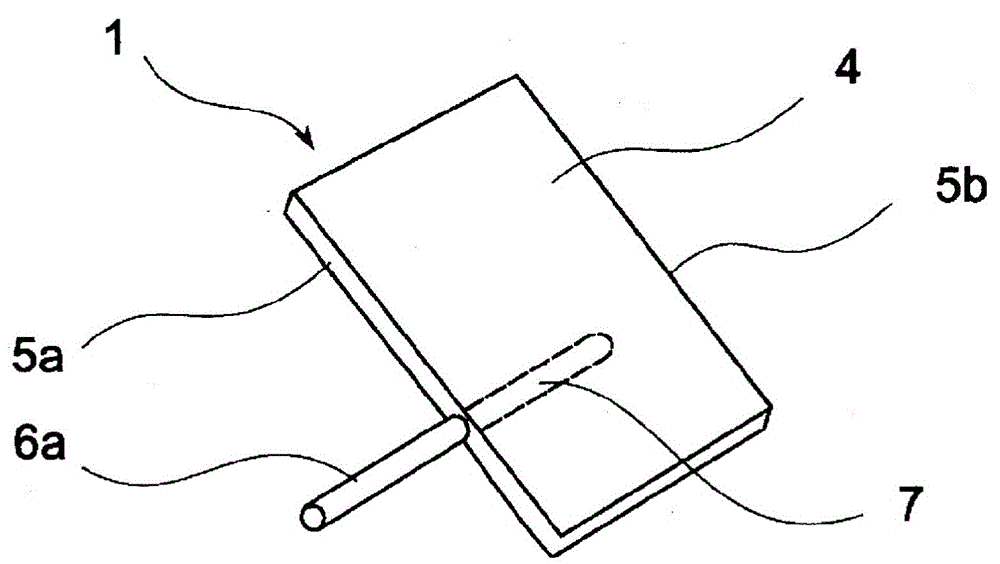
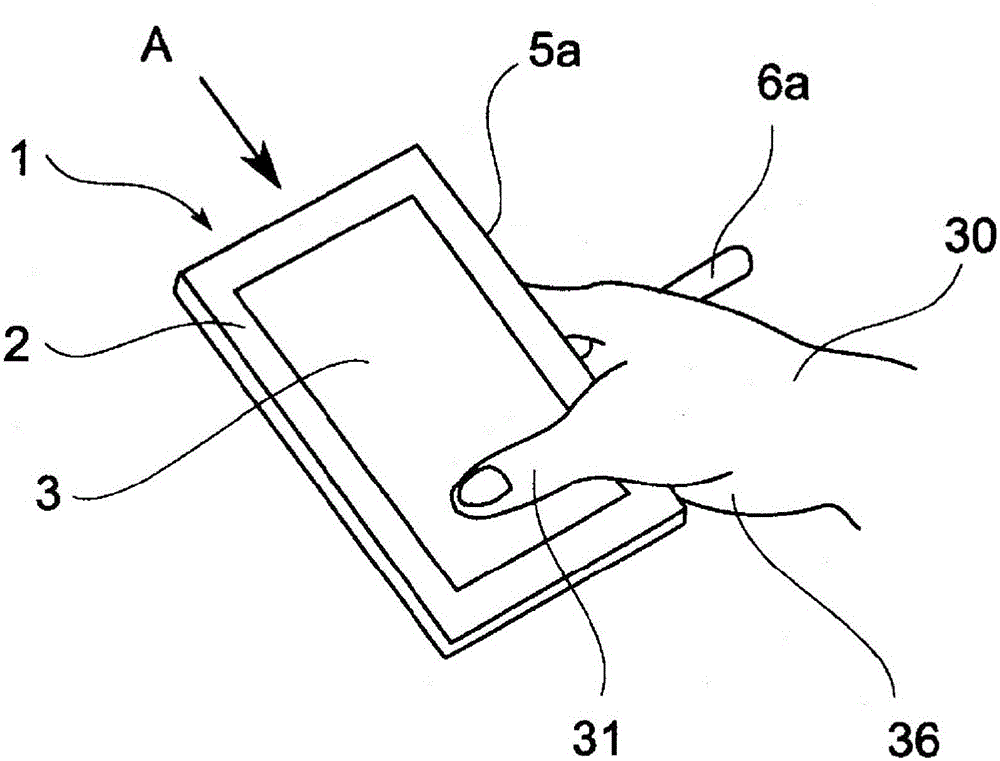
InactiveCN104956286AHigh operating freedomLarge range of motionTravelling carriersHoldersOperabilityComputer terminal
[Problem] Whereas a conventional retaining tool of a portable electronic terminal has a falling prevention function, increasing the operability of thumb input has not been considered, and it is also practically impossible to expand the actual operation range of the thumb. [Solution] By using a portable electronic terminal retaining tool wherein, while pinching, between fingers other than the thumb, a rod which is attached to the portable electronic terminal and which protrudes in a lateral face direction of the portable electronic terminal, the fingers other than the thumb are applied to the rear face of the portable electronic terminal, retaining same, it is possible, while reliably retaining the portable electronic terminal, to improve thumb input operability.
Owner:定井禅
Multifunctional electronic pointer device with motion control function
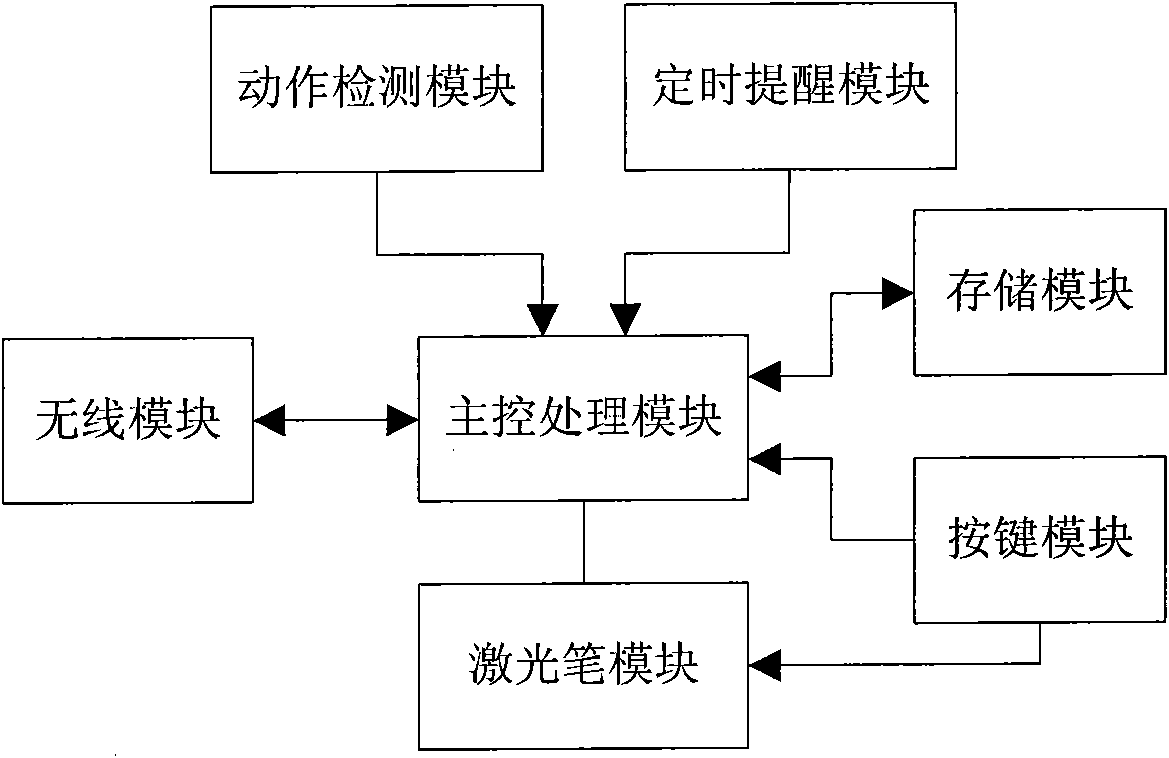
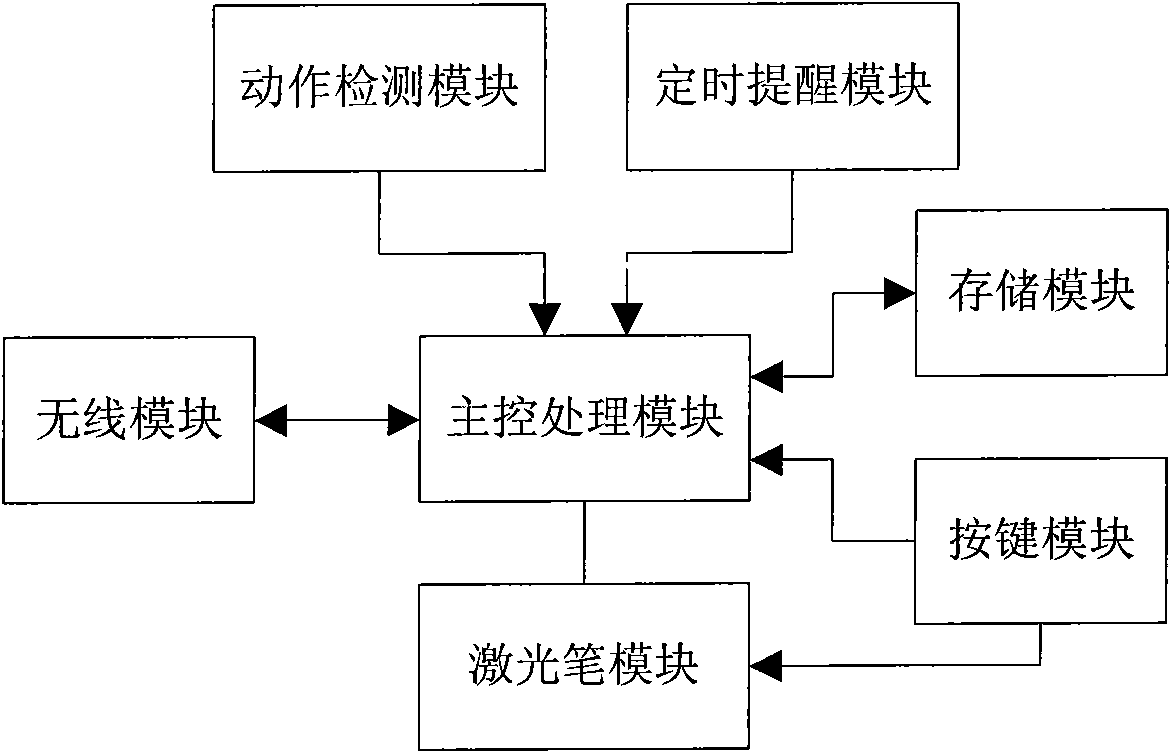
InactiveCN102103805AHigh operating freedomPowerfulReadingInput/output processes for data processingKey pressingTime control
The invention discloses a multifunctional electronic pointer device with a motion control function, by which a user can control four direction keys in the left, the right, the top and the bottom by waving arms, so that the user has higher degrees of operation freedom. The multifunctional electronic pointer device can be used as a USB flash disk when the user is not in a speech, and a regularly reminding function of the multifunctional electronic pointer device can provide functions, such as speech time control, serving as an alarm clock and the like, for the user. The multifunctional electronic pointer device is small and portable, and has powerful functions. The multifunctional electronic pointer device with the motion control function comprises a wireless module, a motion detection module, a laser pen module, a regular reminding module, a key module, a storage module and a master control processing module.
Owner:王立禾
DD-PS strong anti-offset loose coupling transformer and parameter determination method thereof
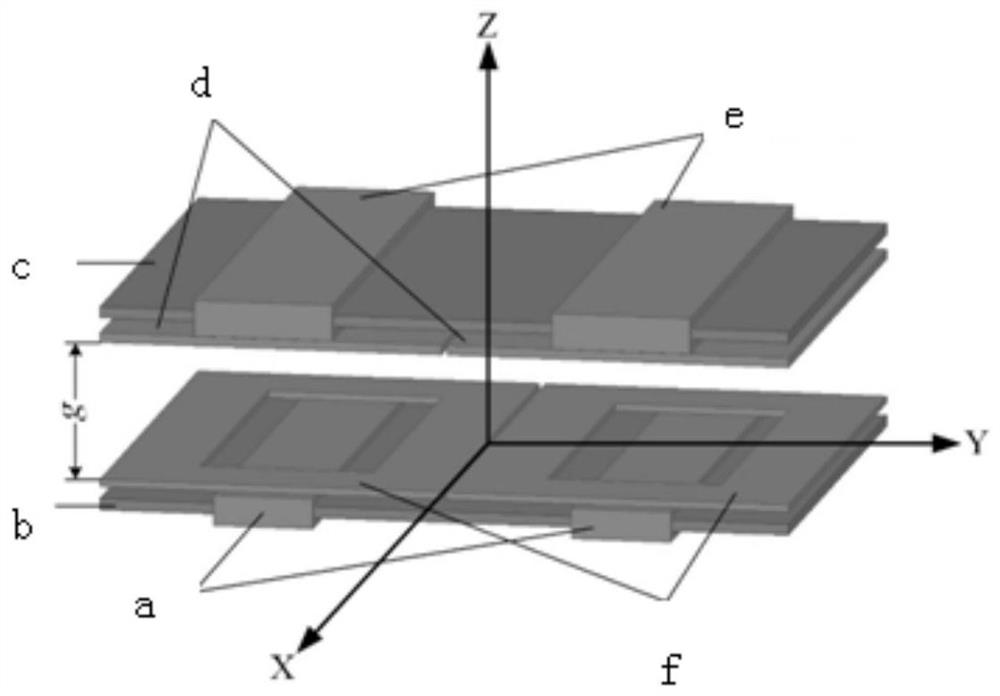
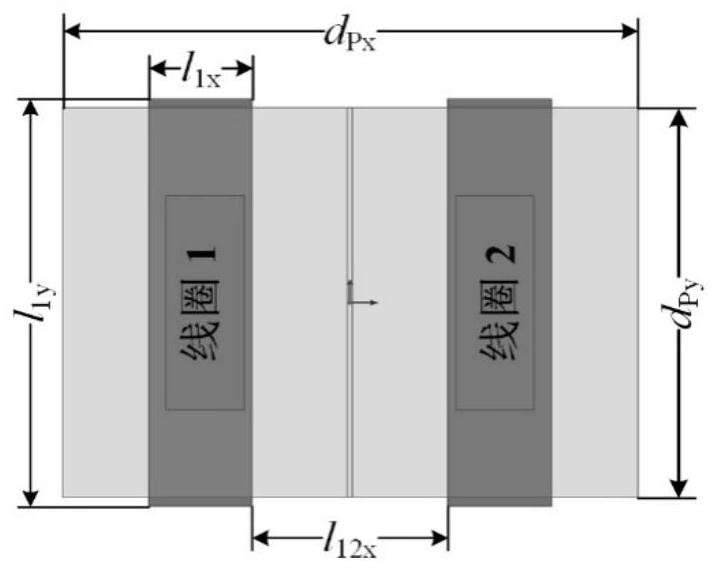
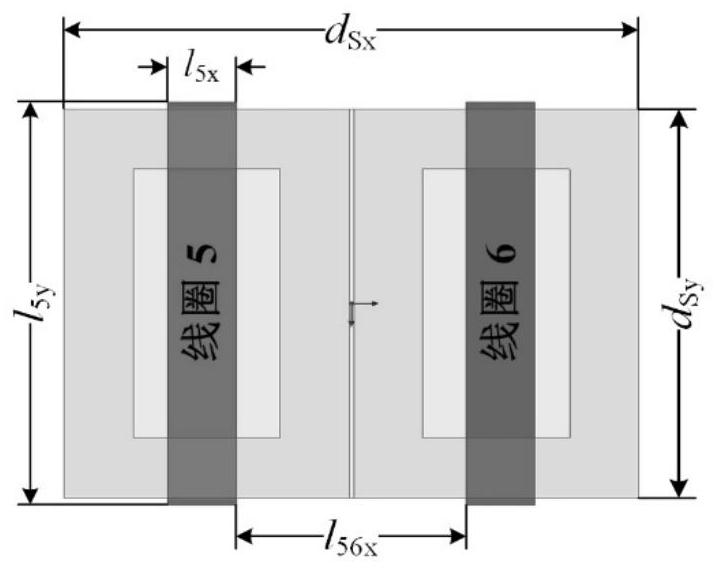
ActiveCN113053623AImprove anti-offset performanceExcellent anti-offset performanceTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsFixed transformers or mutual inductancesTransmission technologyControl theory
The invention relates to a DD-PS strong anti-offset loose coupling transformer and a parameter determination method thereof, belongs to the technical field of wireless power transmission, and solves the problem of low system efficiency caused by a weak anti-offset capability of the existing compensation topology. According to the invention, a planar solenoid coil and a DD coil are combined, and different connection modes are adopted at the primary side and the secondary side so that anti-offset performance of the DD-PS loose coupling transformer in a magnetic field direction is remarkably improved, and meanwhile the excellent anti-offset performance of the planar solenoid loose coupling transformer and the DD-shaped loose coupling transformer in the vertical magnetic field direction is reserved. According to the parameter determination method of the loose coupling transformer, the parameters of the loose coupling transformer can be rapidly determined, and an optimal solution meeting application requirements is obtained. The invention is suitable for the technical field of wireless power transmission.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
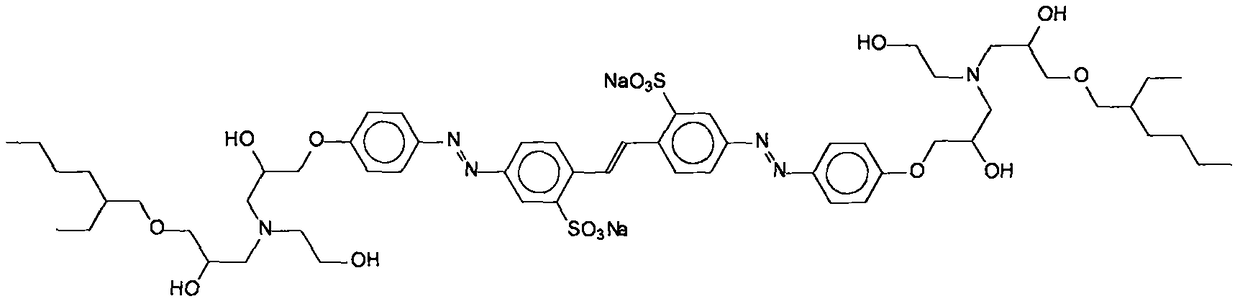
Polymerization method for toluylene bisazo dye
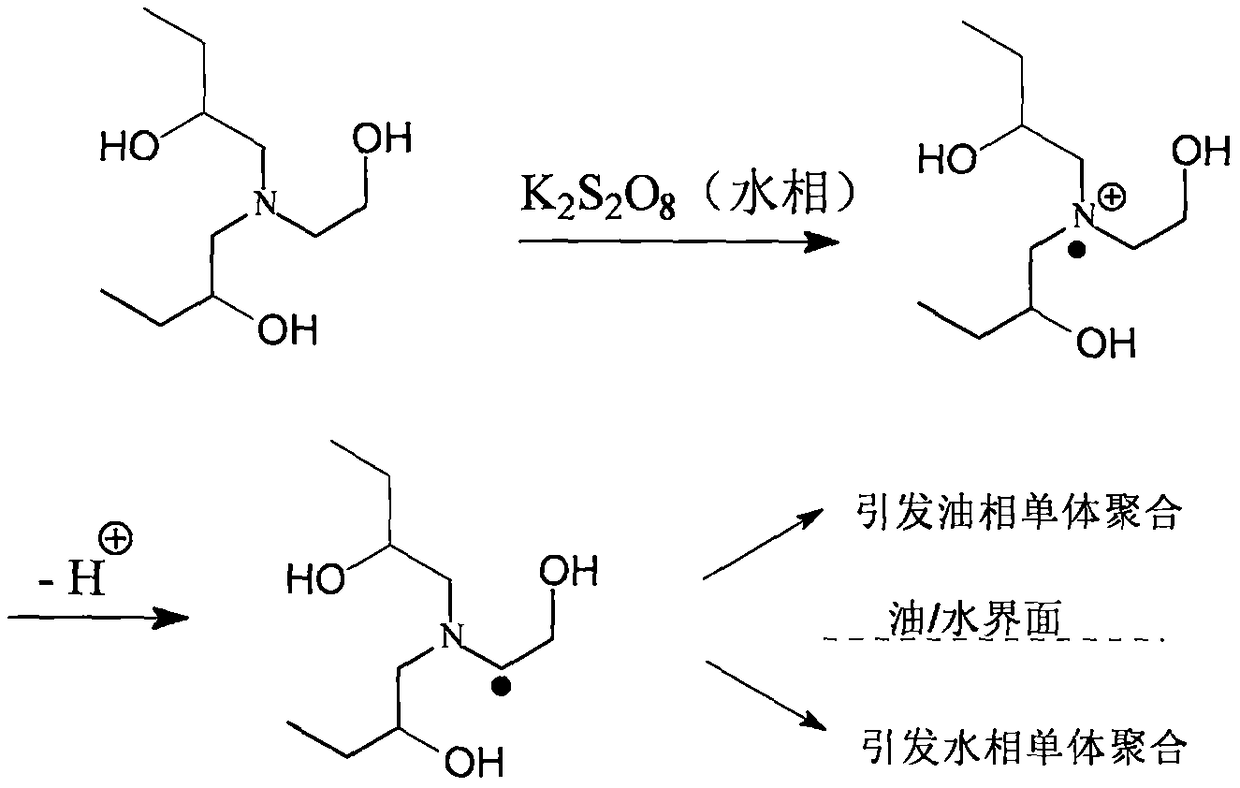
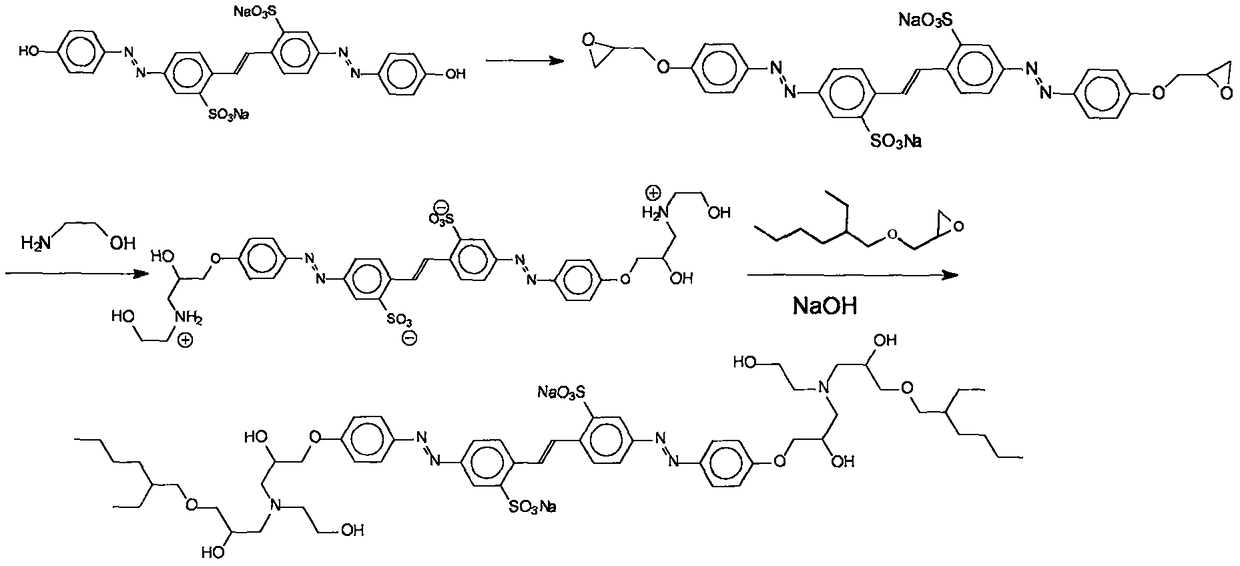
ActiveCN109134723AImprove adaptabilityEasy to operateSulfonic acids salts preparationPolyvinyl alcoholCarvacryl acetate
The invention relates to a polymerization method for toluylene bisazo dye. An amphipathy compound containing a fluorescein perssad and a tertiary amine structure is synthesized and can be used as an initiator polymerized with free radicals, tertiary amine can be subjected to a redox reaction with potassium persulfate under the normal temperature, active free radicals are produced repeatedly, oil soluble monomer vinyl acetate polymerization is initiated on a water / oil interface, the obtained product is hydrolyzed to obtain a polymer containing a hydrophilic polyvinyl alcohol chain segment, andtherefore the purpose of toluylene bisazo dye polymerization is achieved. In this mode, functionalization and polymerization reactions do not interfere with each other, the operation degree of freedomis large, the product varieties are multiple, the polymerization reaction conditions are mild, no organic solvent or emulsifier is adopted, and the requirement for green chemistry is met.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Micro stirrer driven by a multi-core fiber
InactiveCN102156326AHigh torqueEasy to modifyCladded optical fibreRadiation/particle handlingHigh densityLow density
The invention provides a micro stirrer driven by a multi-core fiber, comprising a pyramidal multi-core fiber made of a section of multi-core fibers via fused biconical taper and small particles made from composite materials, wherein the small particles are located at the pyramidal end of the pyramidal multi-core fiber; the non-pyramidal end of the pyramidal multi-core fiber is connected with a light source; a plurality of fiber core emergent lights of the pyramidal multi-core fiber simultaneously act on the small particles in a vertical suspension liquid; the upper body of each small particle is a sphere and a rotating shaft which are made from materials with lower density; and the bottom of the each small particle is of a windmill-shaped structure with a plurality of wings made from materials with higher density. The micro stirrer provided by the invention has the characteristics of small volume, light weight, simple structure, low price, easiness in operation, high mixing efficiency, benefit of the reduction of reagents, and the like and can be widely applied to the fields of biology and chemistry.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Linkage wearable sixteen-degree-of-freedom driving end mechanical arm
ActiveCN112238459AHigh operating freedomFlexible operationManipulatorPhysical medicine and rehabilitationLinkage (mechanical)
The invention relates to the field of robots, in particular to a linkage wearable sixteen-degree-of-freedom driving end mechanical arm which comprises a support, a waist assembly, a trunk base, shoulder assemblies and arm assemblies. The waist assembly can achieve two degrees of freedom of rotation and pitching, and the shoulder assemblies can achieve three degrees of freedom of abduction and adduction, outward rotation and inward rotation and forward bending and backward stretching. The left shoulder assembly and the right shoulder assembly achieve six degrees of freedom in total, the arm assemblies can achieve four degrees of freedom of forward bending and backward stretching of elbows, inward rotation and outward rotation of forearms, flexor bending and contortion of wrists, and palm bending and opisthenar bending of wrists and eight degrees of freedom of the left arm and the right arm, and action information sensing assemblies are arranged in all rotating joints. According to the linkage wearable sixteen-degree-of-freedom driving end mechanical arm, the degree of freedom of operation is greatly increased, different positions of the waist, shoulders, wrists, forearms and wristsof an operator can be sensed according to the rotating angle of each joint, and then position information is sent to the bionic robot auxiliary arm, so that the bionic robot auxiliary arm makes corresponding actions, and control is more accurate.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Microscopic particle rotator of bidirectional conical optical fibers
InactiveCN102231292BEasy to modifyReduce volumeCladded optical fibreRadiation/particle handlingOptical radiationFiber
The invention provides a microscopic particle rotator of bidirectional conical optical fibers, comprising two conical optical fibers and two-body microscopic particles, wherein the conical optical fibers are formed by fused biconical taper; the two conical optical fibers are arranged horizontally; the conical ends are staggeredly arranged at intervals oppositely; the opposite ends of the two conical optical fibers are connected with an optical source respectively; the two-body microscopic particles comprise a driving layer, a stirring layer ad a connecting post respectively; the driving layeris integrated with the stirring layer into a whole by the connecting post; the two-body microscopic particles are arranged in the gap which is formed by staggering the two conical ends of the two conical optical fibers; the conical optical fibers cause transmission lights in fiber cores to transmit a cladding layer and form an evanescent field on the cladding layer; the generated optical radiation forces act the driving layers of the two-body microscopic particles, so that the driving layers of the two-body microscopic particles rotate to drive the stirring layers of the two-body microscopic particles. The rotator is small in volume, light in weight, simple in structure, low in price, easy to operate, large in operating range and high in stirring efficiency; by using the rotator, the solvent activity can be avoided being damaged due to direct contact; and the rotator can be applied to biology and chemistry microflow systems.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Water surface garbage cleaner
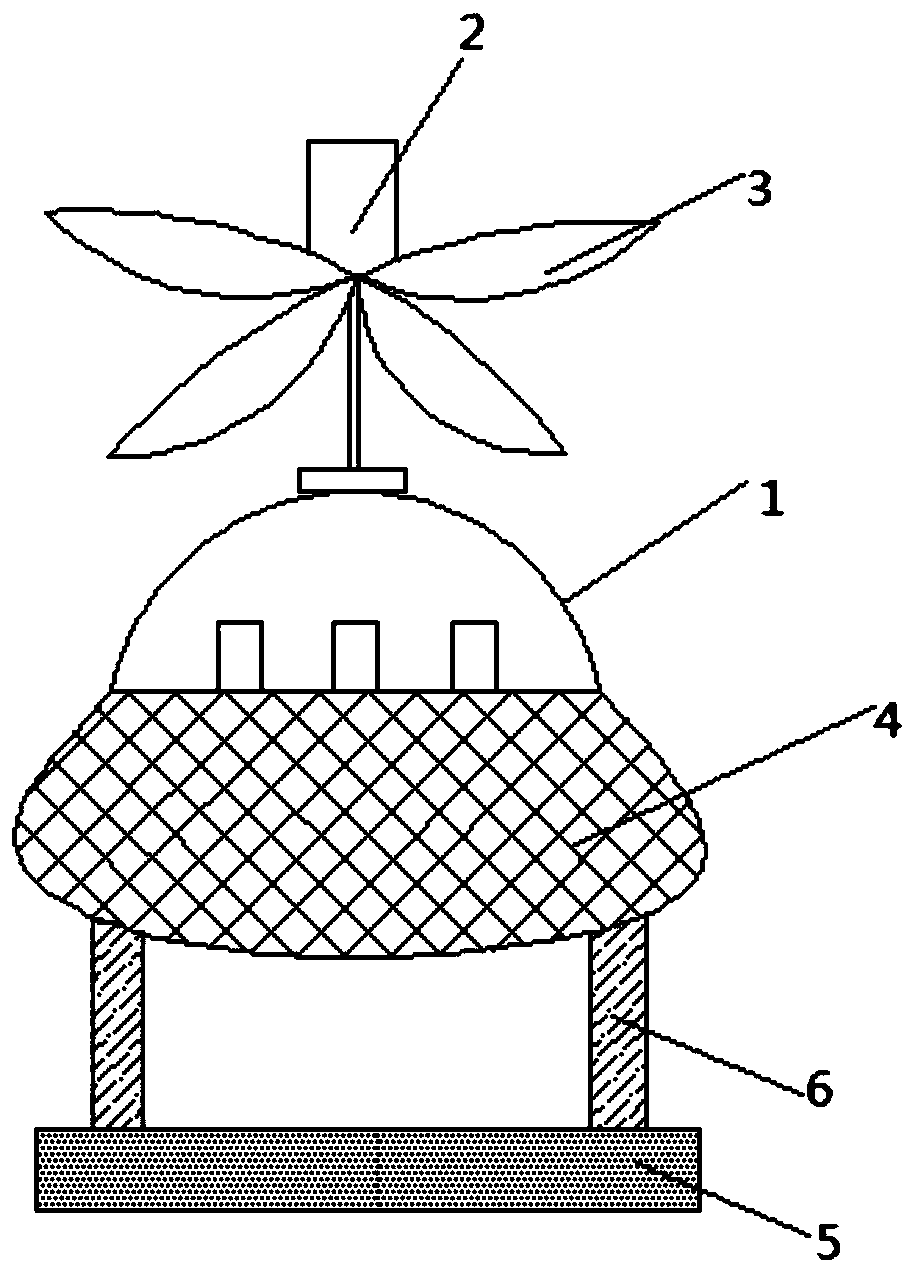
InactiveCN110697041ATake advantage of flight stabilityImprove carrying capacityWater cleaningGeneral water supply conservationFly controlRobotic arm
The invention discloses a water surface garbage cleaner. The garbage cleaner comprises a rack, the rack is sequentially provided with a flight control computer, a four-rotor aircraft and a garbage binfrom top to bottom. The flight control computer is connected with the four-rotor aircraft; the garbage bin and the rack are detachably connected together, oil absorption sponge, a telescopic device and a mechanical arm are arranged below the garbage bin, the mechanical arm and the oil absorption sponge are connected with the rack through the telescopic device, the camera and the four-rotor aircraft are further arranged on the rack to conduct automatic flight operation, the design is novel, the operation freedom degree is large, and time and labor are saved.
Owner:江苏玖泰电力实业有限公司
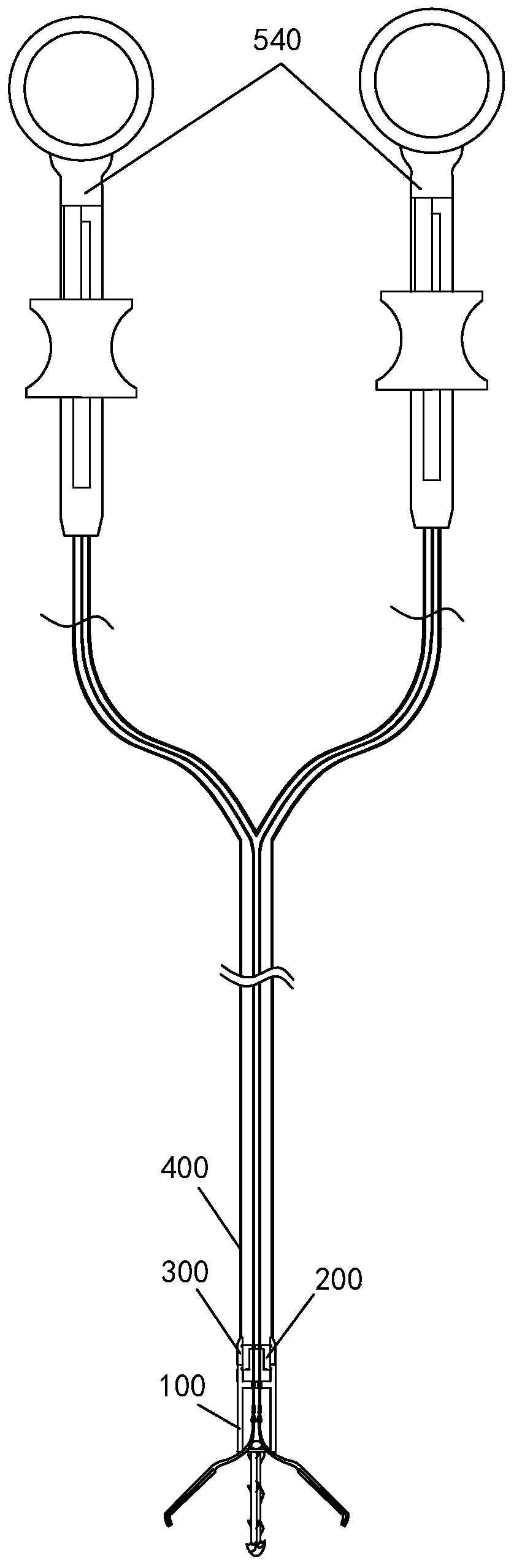
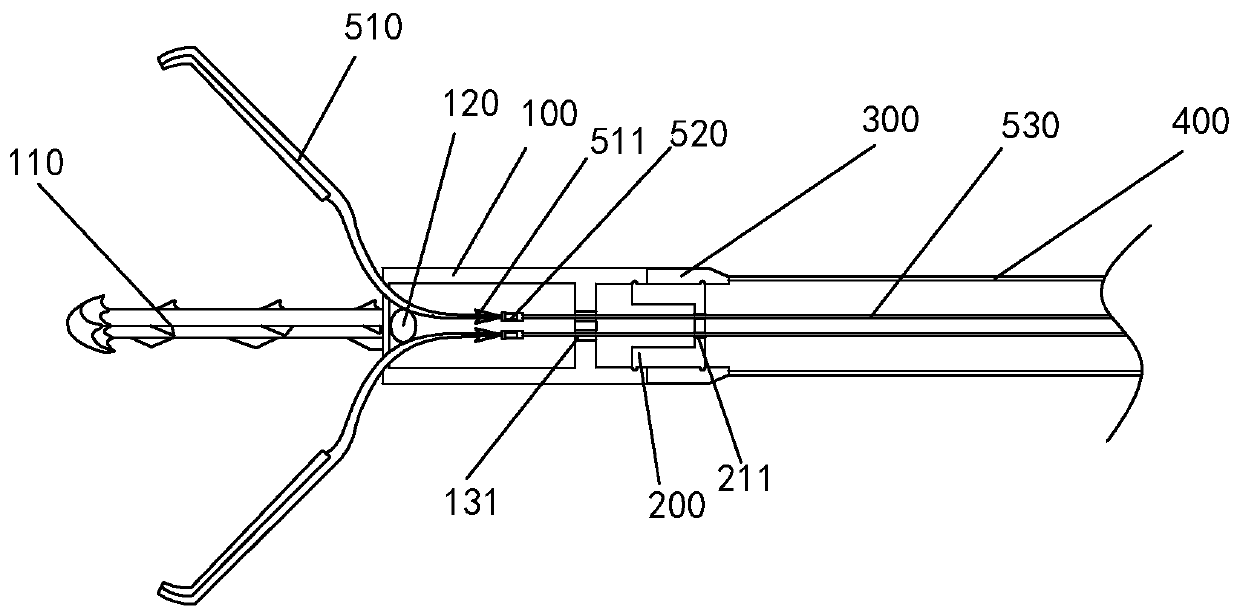
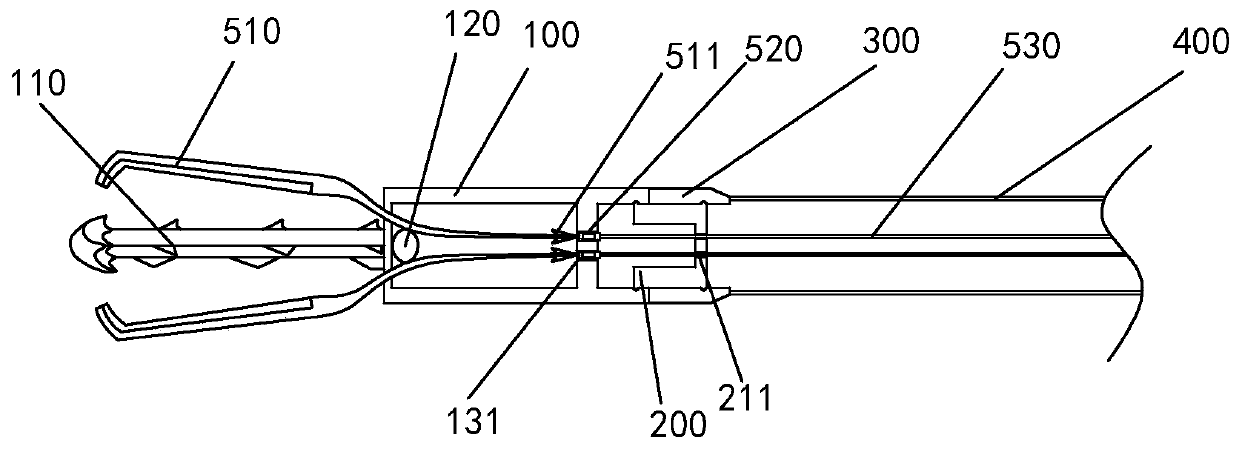
Endoscope double-arm closing clamp for closing digestive tract perforation
The invention discloses an endoscope double-arm closing clamp for closing a digestive tract perforation. The closing clamp comprises a releasable clamping head assembly, a connecting block and a releasing assembly. Through the handheld part of an sliding operating handle, a side tong head can be independently controlled, and the clamping head assembly can be released. The closing clamp can processlarge perforation, the tong head can be repeatedly opened and closed, the tong head can be independently controlled, and meanwhile misoperation is prevented.
Owner:苏军凯
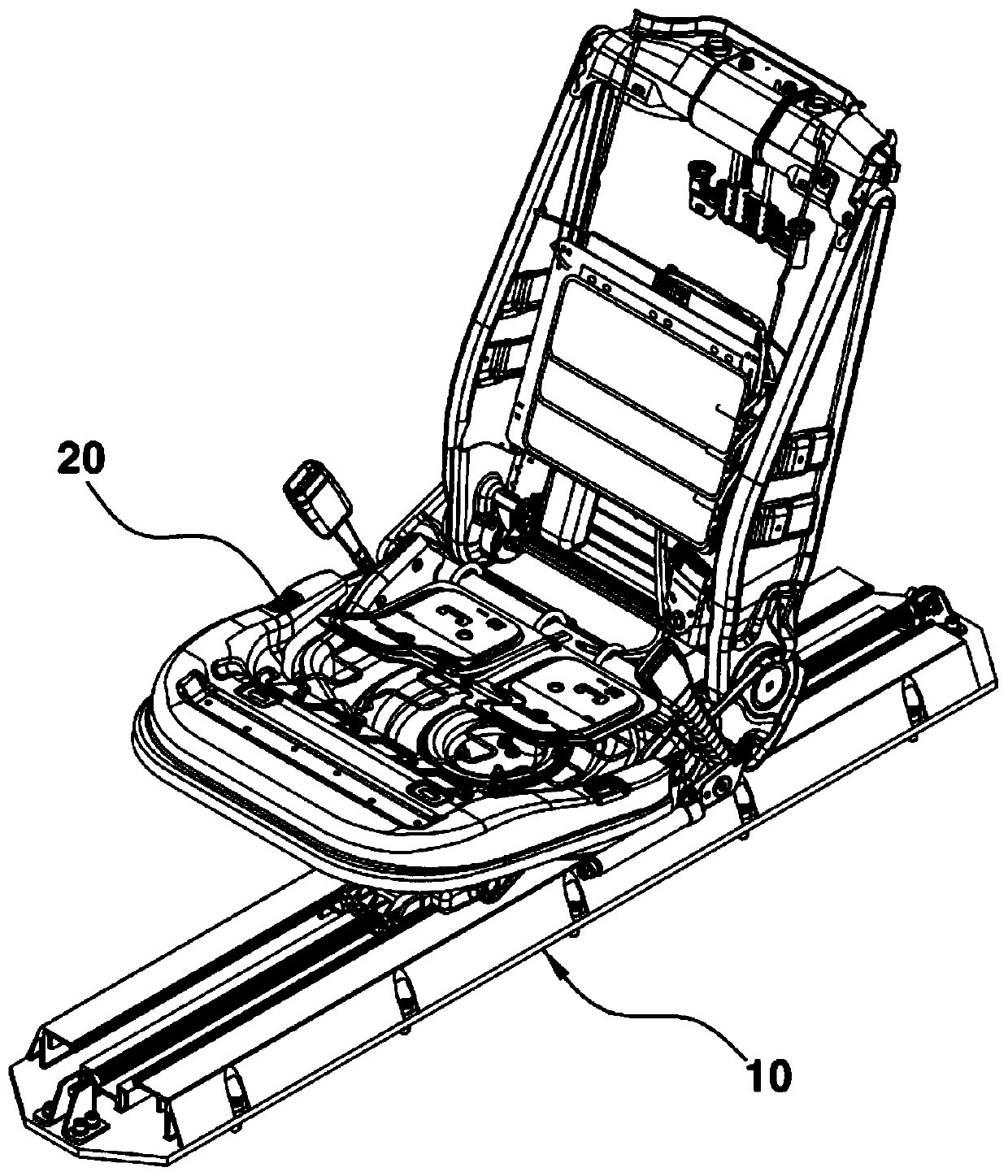
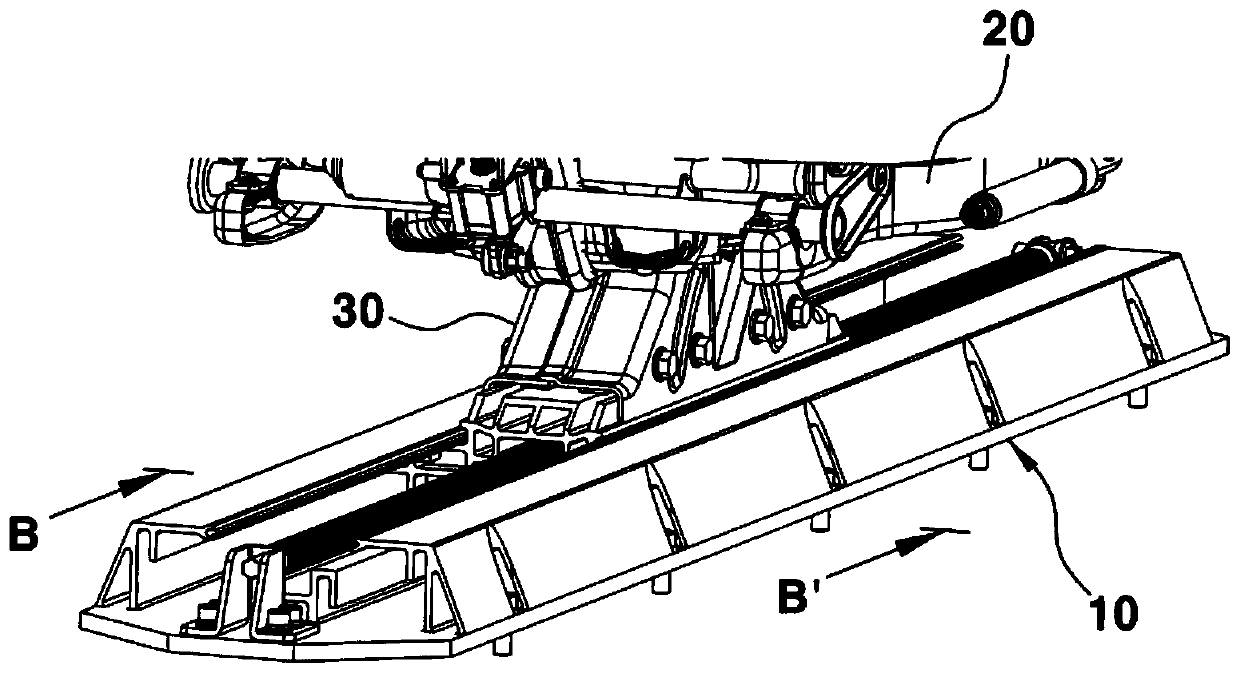
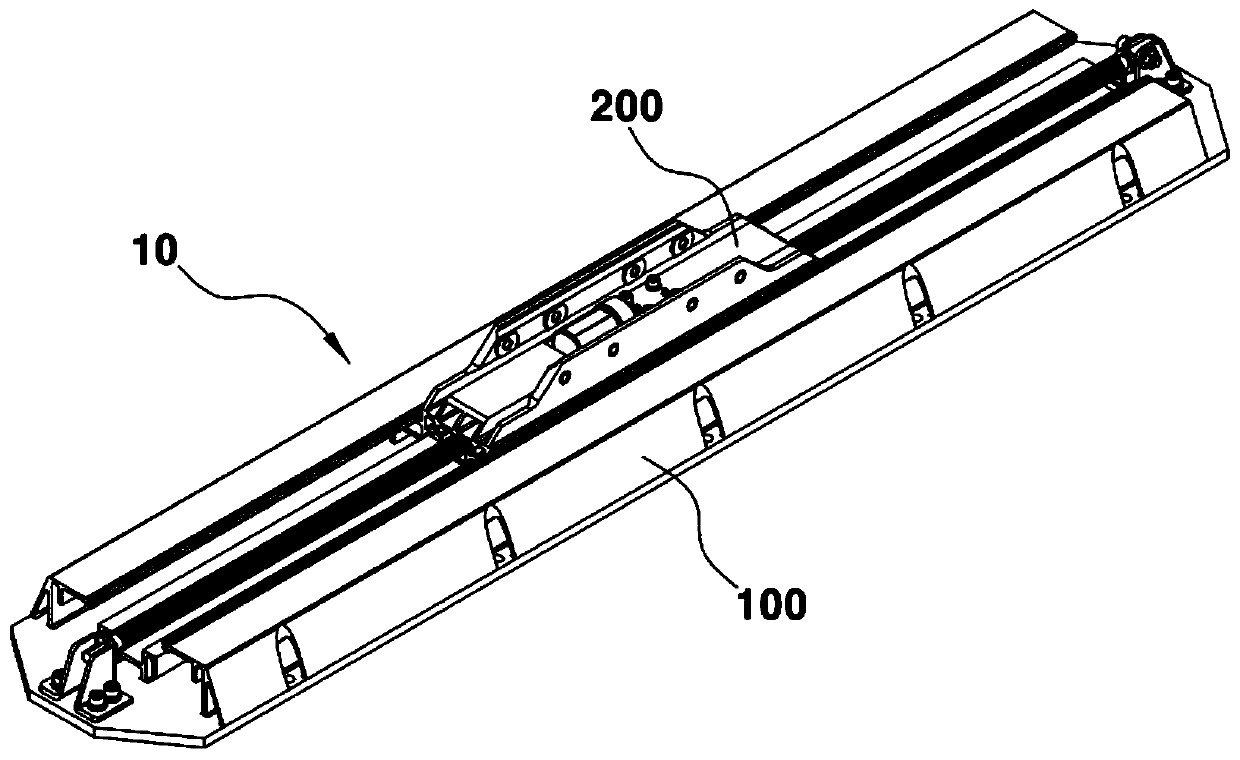
Seat track mechanism for vehicle seat
ActiveCN111319525ASimple structureSlim and sleek designBus seatsMovable seatsControl theoryMechanical engineering
Owner:HYUNDAI TRANSYS INC
VCG capacity adjustment method and VCG communication network
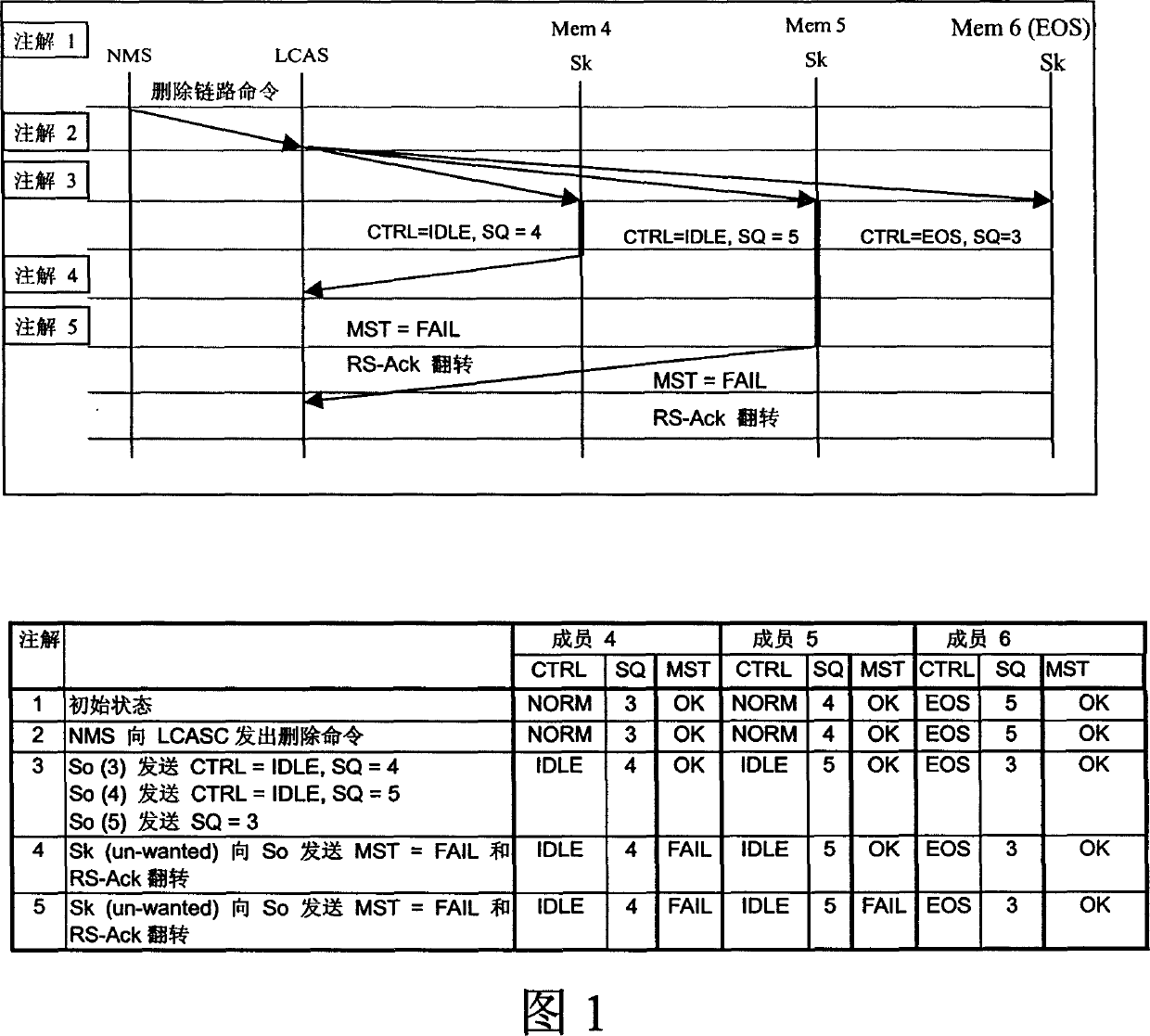
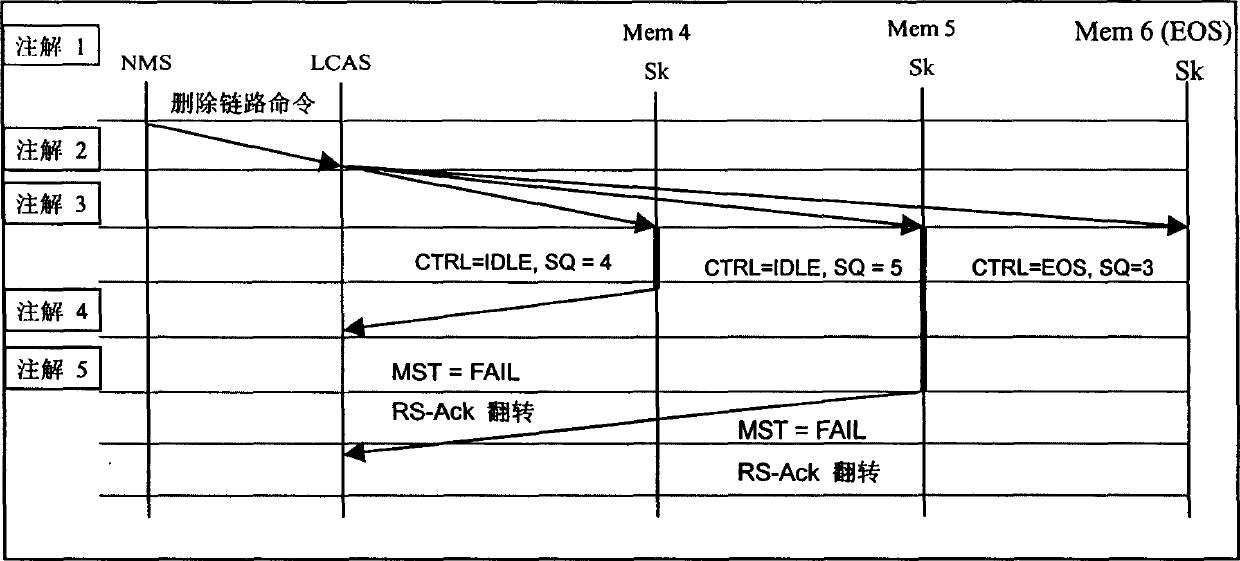
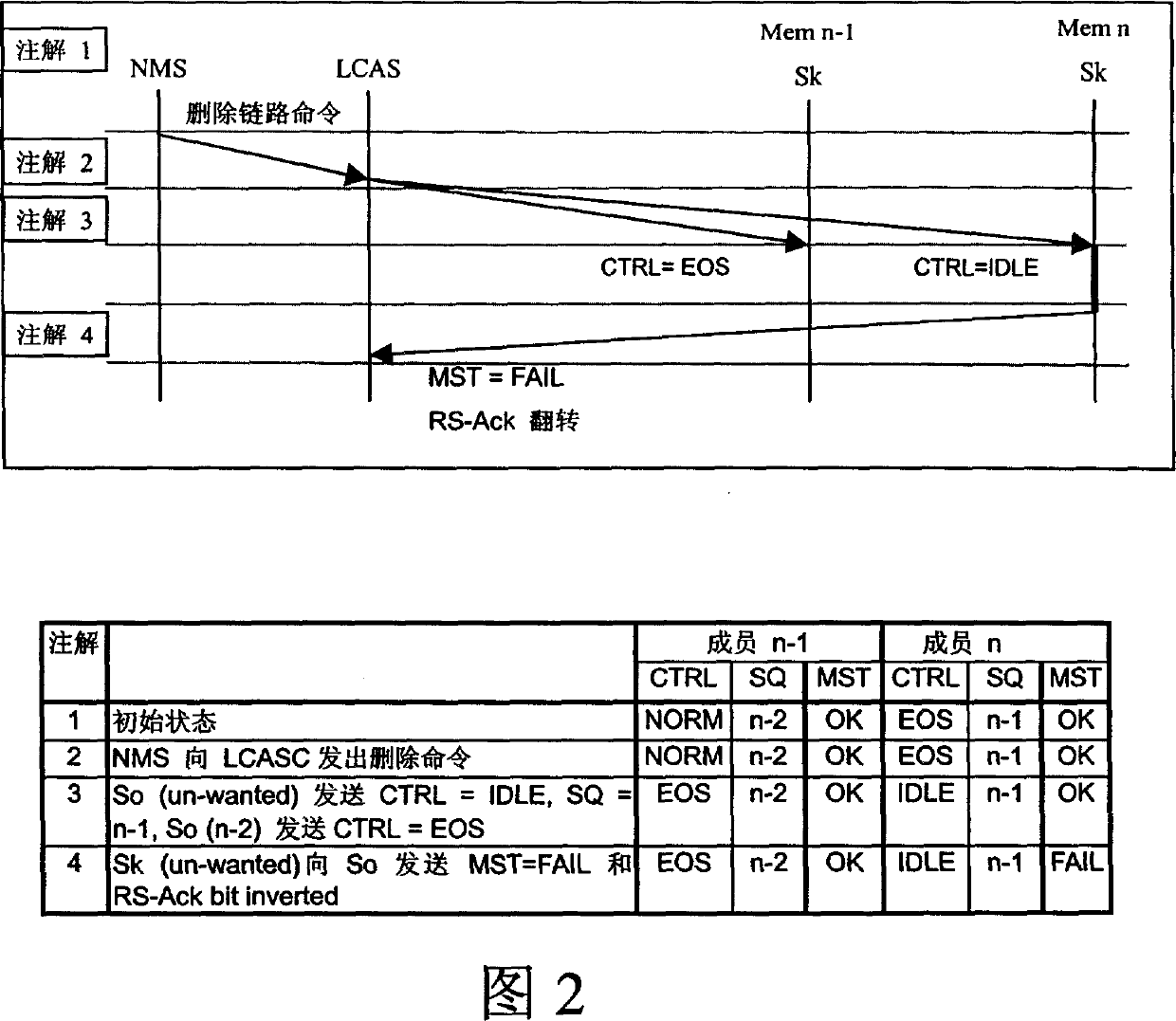
ActiveCN1731783AHigh operating freedomGuaranteed InteroperabilityTime-division multiplexTransmissionNetwork managementDistributed computing
This invention provides a method for adjusting virtue level integral capacity and communication net. Based on the invention, which provides an adjusting method for virtue integral level capacity in communication net with a plurality of devices supporting LCAS protocol and a net management device, comprising the following steps: the net management device deleting in any order it's a pair of upward chain route member and a downword chain route member.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method for direct bonding of orthodontic brackets
The invention relates to the field of orthodontic bracket bonding, and discloses a method for direct bonding of orthodontic brackets. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, constructing a three-dimensional digital occlusal model, and generating a dental arch morphology in a simulation manner; step 2, constructing virtual orthodontic brackets; step 3, importing the three-dimensional occlusal model into an orthodontic software, and automatically positioning clinical crown centers of teeth by the orthodontic software; step 4, performing imitative positioning on the orthodontic bracketsat the clinical crown centers according to requirements and a pre-designed correction plan; step 5, forming an occlusal tray model according to a tooth morphology of a three-dimensional dental cast,step 6, according to data of an installation bracket and the positions of the orthodontic brackets on the tooth surface, arranging insertion holes corresponding to each orthodontic bracket in the trayin a simulation manner; step 7, outputting a 3D print file of the tray; and step 8, performing 3D printing on the tray. The installation bracket is also arranged, the physical orthodontic brackets are installed on the installation bracket, and the installation bracket is inserted into the corresponding insertion holes of the orthodontic brackets. The bonding method provided by the invention has the characteristics of reliable bonding, high bonding efficiency and high bonding accuracy.
Owner:张正朴
Multifunctional suitcase
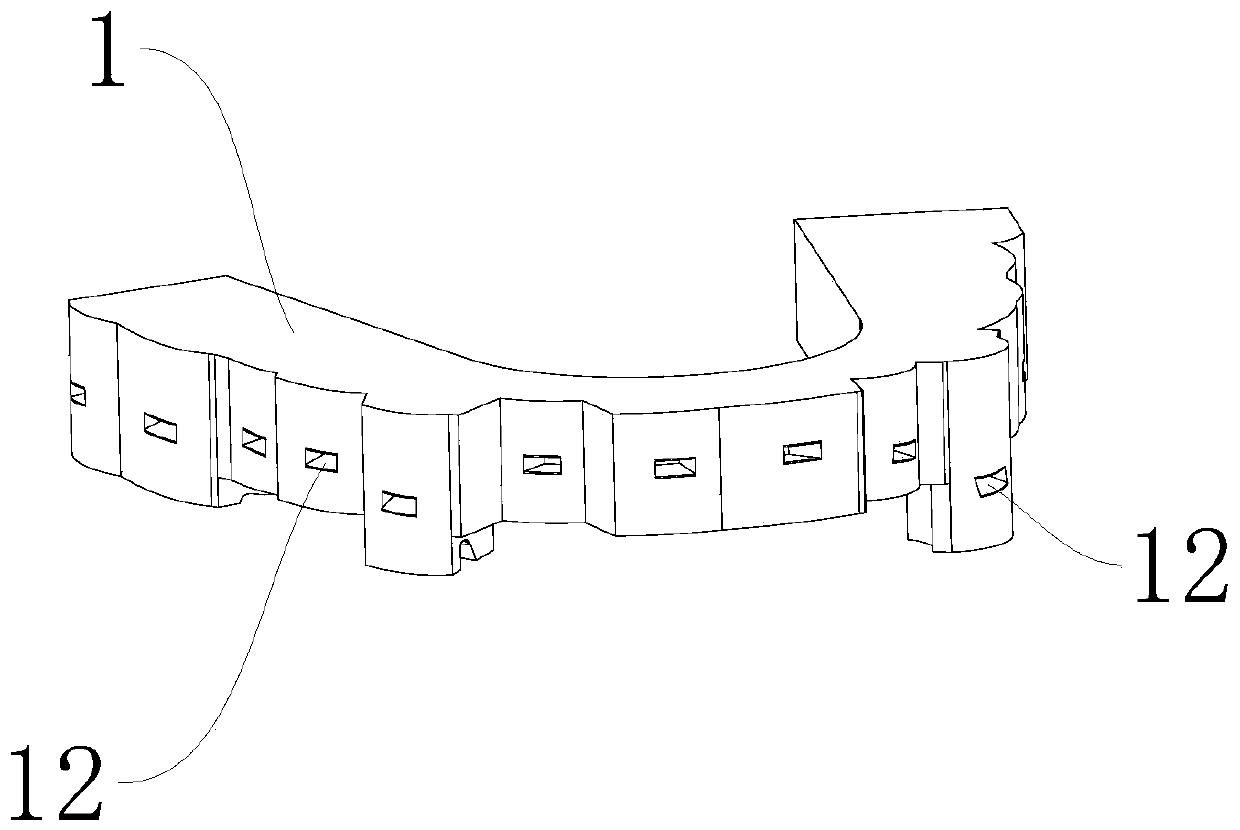
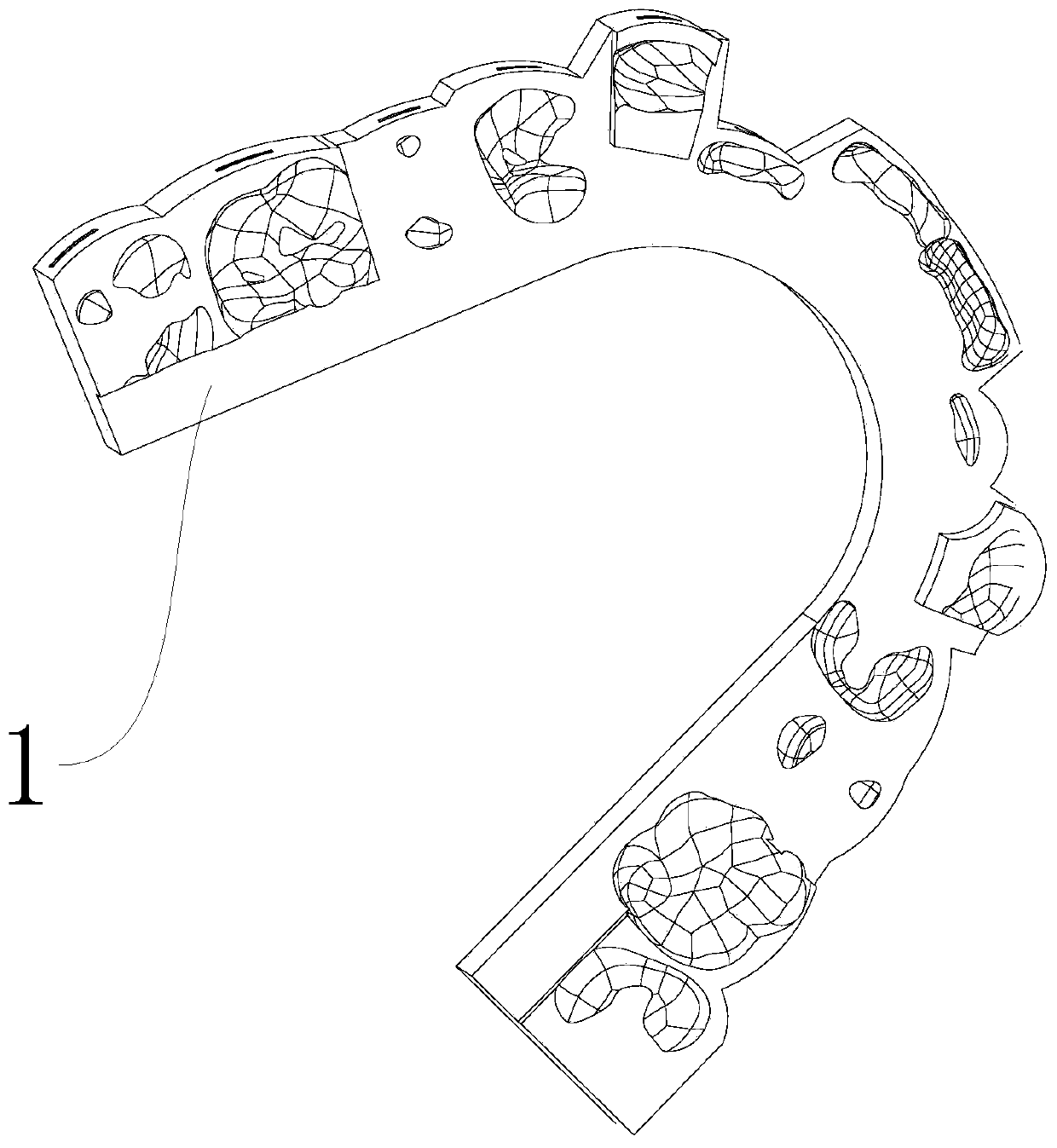
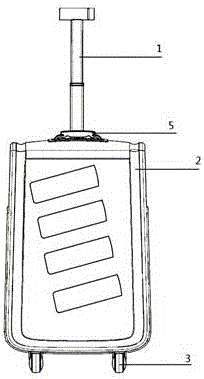
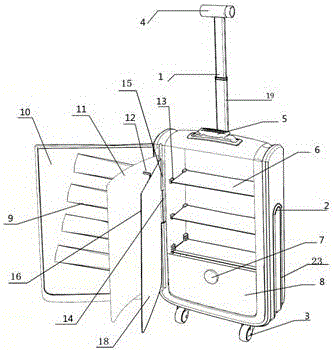
The invention discloses a multifunctional suitcase which comprises a suitcase body. A pull rod is parallelly arranged on the top of the suitcase body and comprises a pull rod handle and a telescopic rod body, a front cover capable of being opened and closed is arranged on the front face of the suitcase body, file bag partition plates are uniformly distributed inside the suitcase body, a drawer is arranged at the bottom inside the suitcase body, the drawer and the file bag partition plate at the lowest layer form a closed space, a support is arranged between the front cover and the file bag partition plates, a rotating shaft is arranged on one side of the support, a rotating shaft sleeve is arranged on a rotating rod fixed in the suitcase body in a sleeving mode to achieve rotation of the support, a soft bag plate is arranged on the front face of the support, and the soft bag plate is connected with the support through a zipper to achieve the purpose that the soft bag plate covers the support. The multifunctional suitcase is attractive in appearance and symmetrical in structure, the internal space can be divided reasonably as needed, the degree of freedom of operation is extremely high, the multifunctional suitcase has a good market prospect, and the problems that an existing suitcase is single in storage function, focuses on appearance design, neglects reasonable application of the internal space of the product and the like are solved.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com